Optical information detecting method, optical head, and optical disc apparatus
A detection method and optical information technology, which are applied in the recording/reproducing, information storage, recording information storage and other directions by optical methods, can solve the problems of high S/N, practical difficulties, etc., and achieve the effect of high signal amplification effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
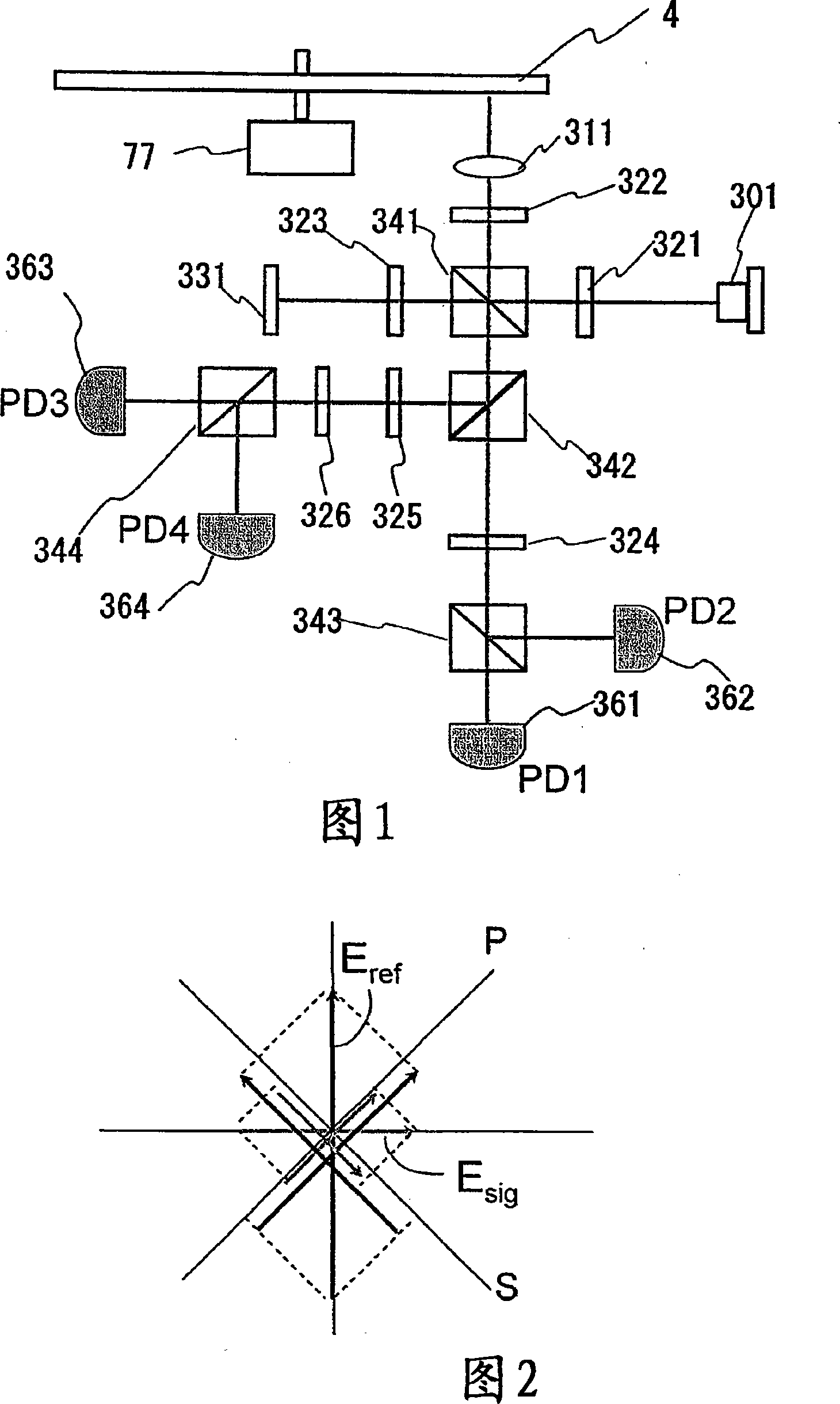
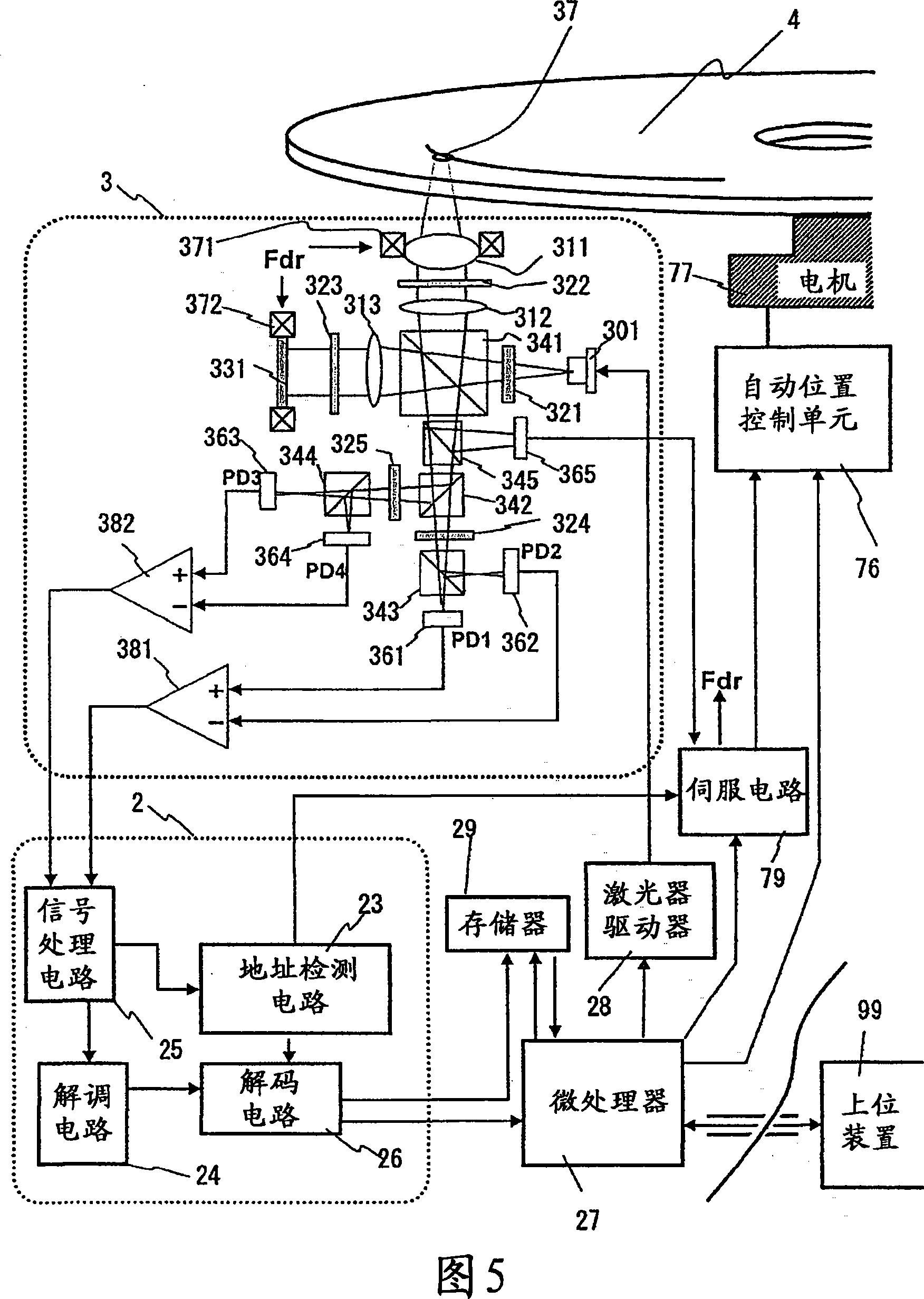
[0127]FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing an optical system for realizing the optical signal detection method of the present invention. The light emitted from the laser 301 is transmitted through the first λ / 2 plate 321, so that the polarization direction is rotated by 45 degrees. The polarization-rotated light is split into two orthogonal linearly polarized lights by the first polarization beam splitter 341, and the light of one polarized light (reproduction light) is reflected and transmitted through the first λ / 4 plate 322, thereby being transformed into a circular polarized light. The polarized light is then condensed by the objective lens 311 and irradiated on the optical disk 4 . The reflected light (hereinafter referred to as signal light) from the optical disc 4 rotated by the spindle motor 77 is changed back to parallel light with the objective lens 311, and is changed back to linearly polarized light on the first λ / 4 plate 322, but due to the Reflection, the direction...
Embodiment 2
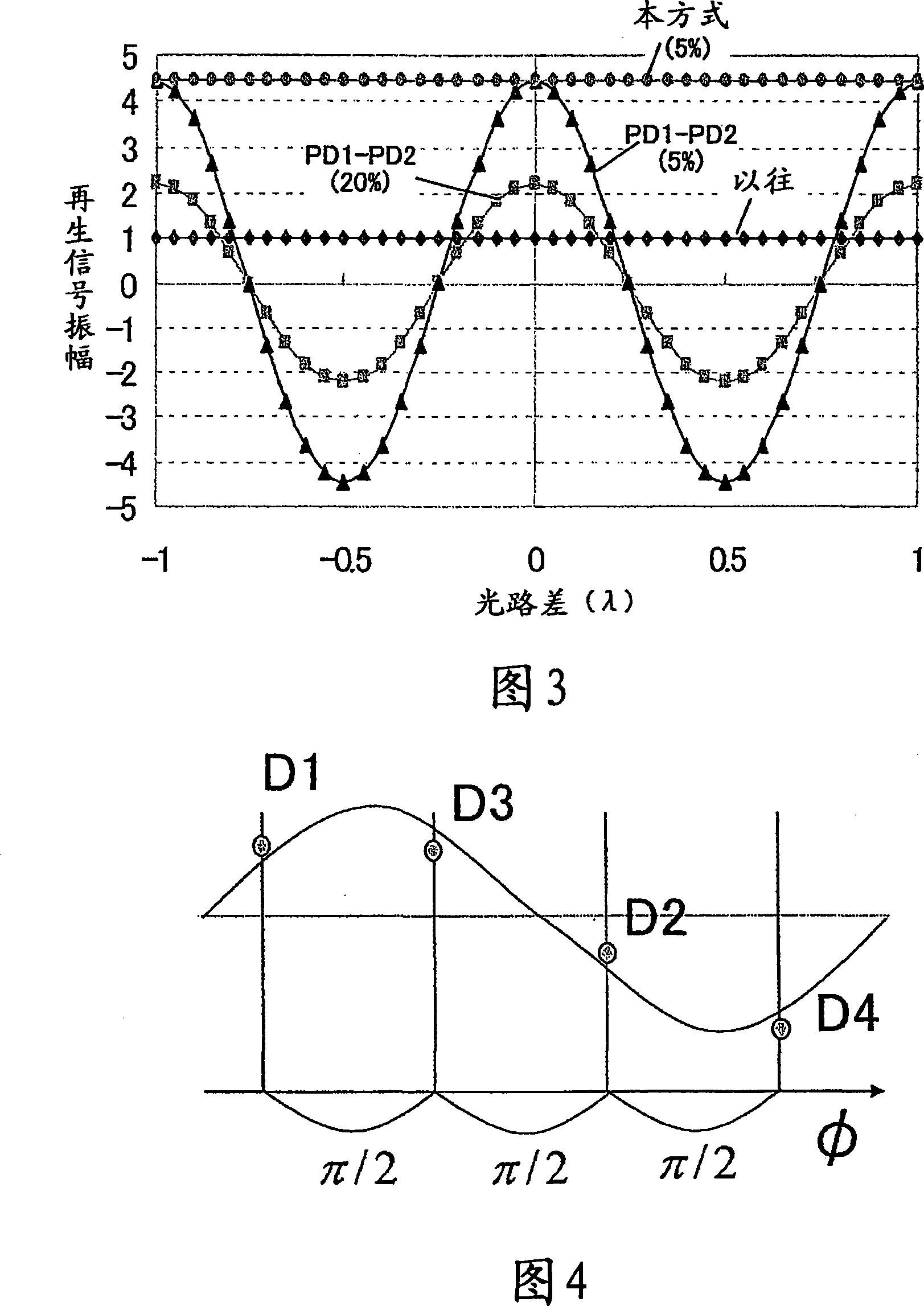
[0159] In Embodiment 1, it is assumed that the signal light and the reference light are completely coherent, but in general semiconductor lasers, the resonator length is short and the coherence length (light-interferable distance) is not too long. 8 is a graph showing changes in reproduction signal intensity when a normal blue light semiconductor laser (LD) is used in the configuration of the first embodiment. In order to track and focus against disc shake, the objective lens 311 moves up and down, and the optical path length of the signal light changes. However, since the optical path length of the reference light does not change, a difference in optical path length occurs between the reference light and the signal light. If the difference in the optical path length is larger than the coherent distance of the LD, the output of the formula (7) cannot be obtained. Usually, the output in the incompletely coherent state is multiplied by the degree of coherence (interferability) ...
Embodiment 3
[0163] In Examples 1 and 2, the reproduced signal was obtained by the calculation of Equation (7), but the reproduced signal can also be obtained without performing the square root calculation.
[0164] That is, put (Sig1) 2 +(Sig2) 2 =|Esig| 2·|Eref| 2 Used as a signal. In this calculation, since the square root calculation is not required, the circuit configuration is simplified, and there is an advantage that the energy of the signal light is proportional to the reproduction output. In the conventional optical signal detection method, the reproduced signal output is also the same as |Esig| 2 Therefore, in the method of this embodiment, there is an advantage that it is easy to use the same signal processing method as in the past.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| reflectivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| reflectivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com