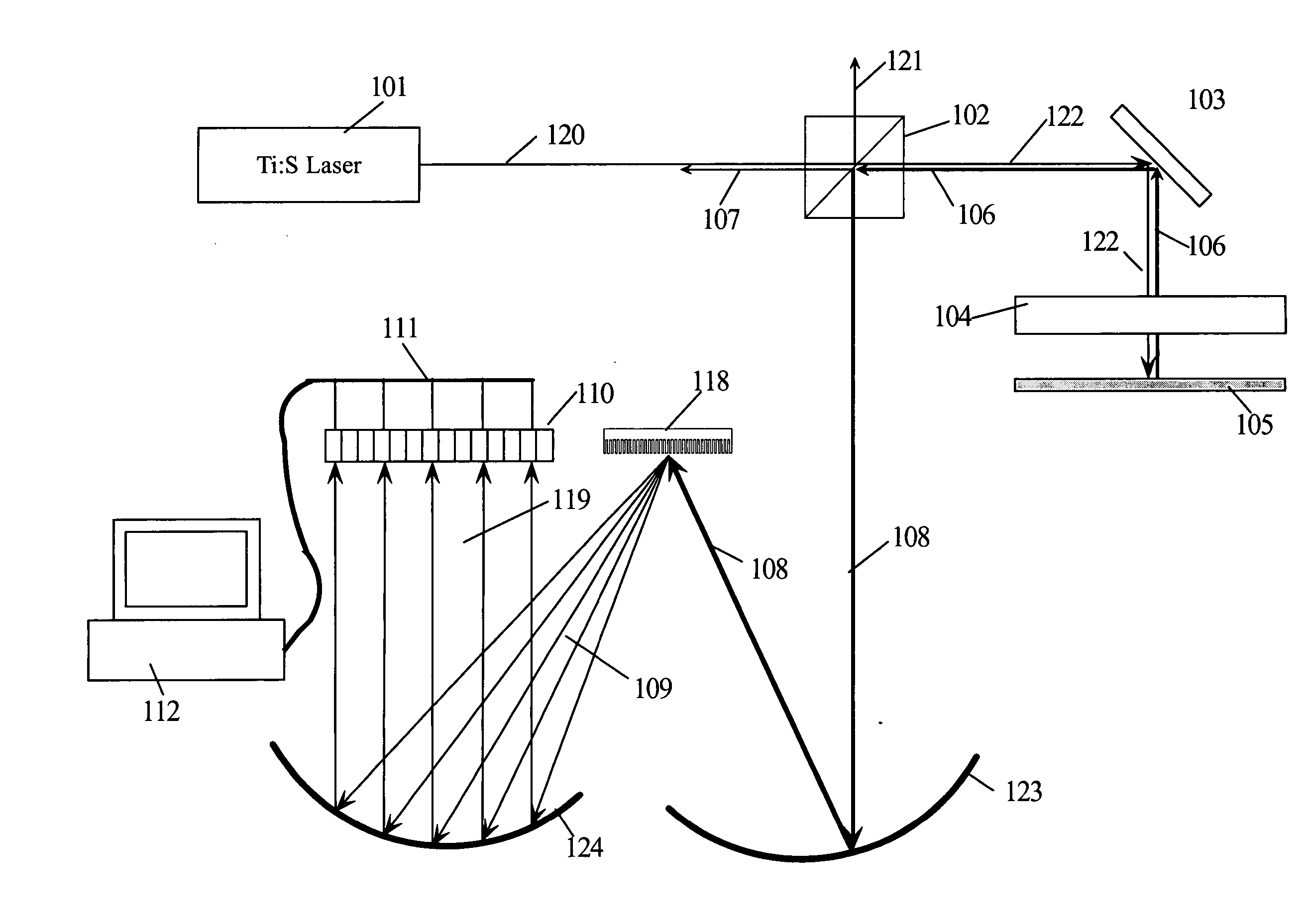
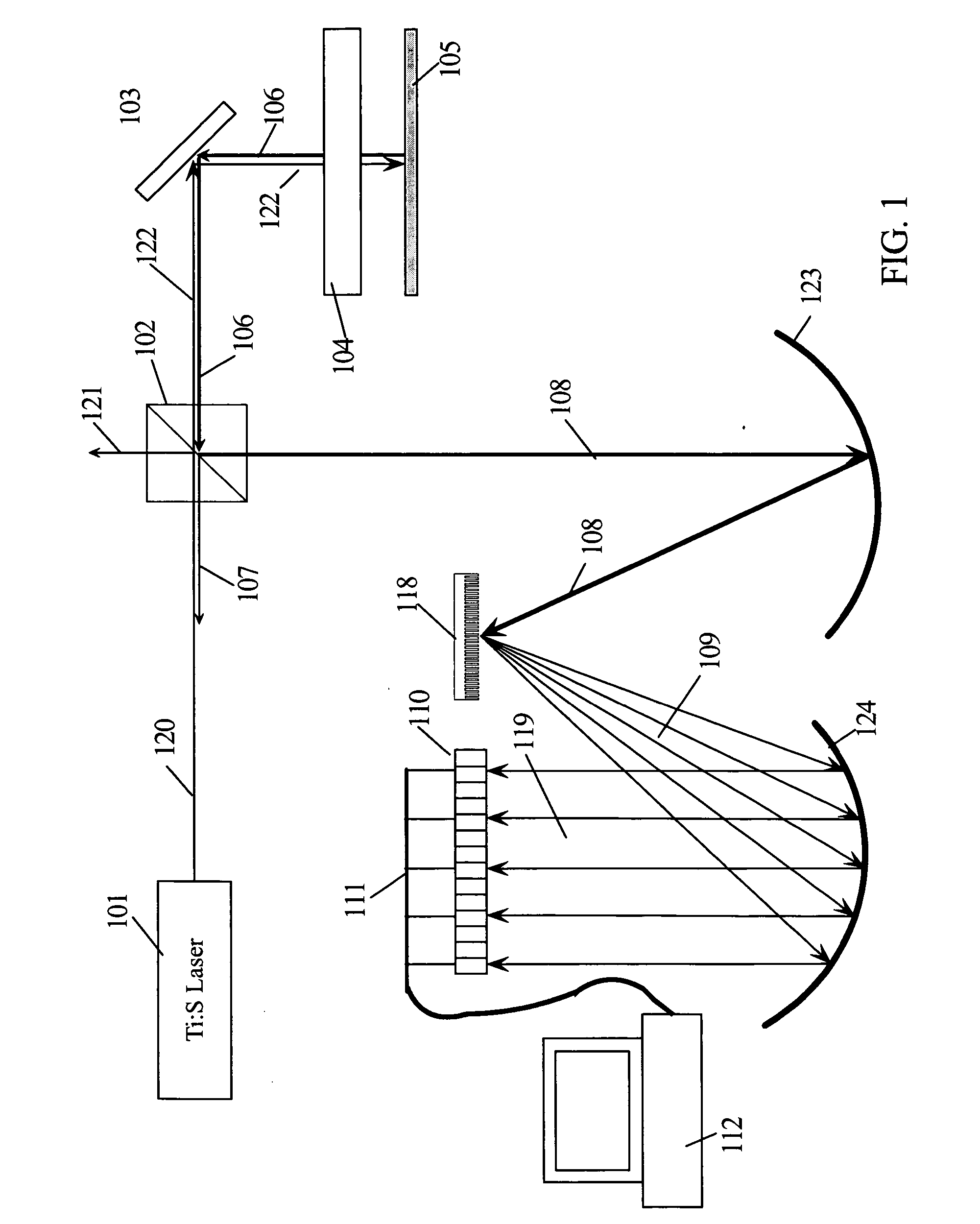
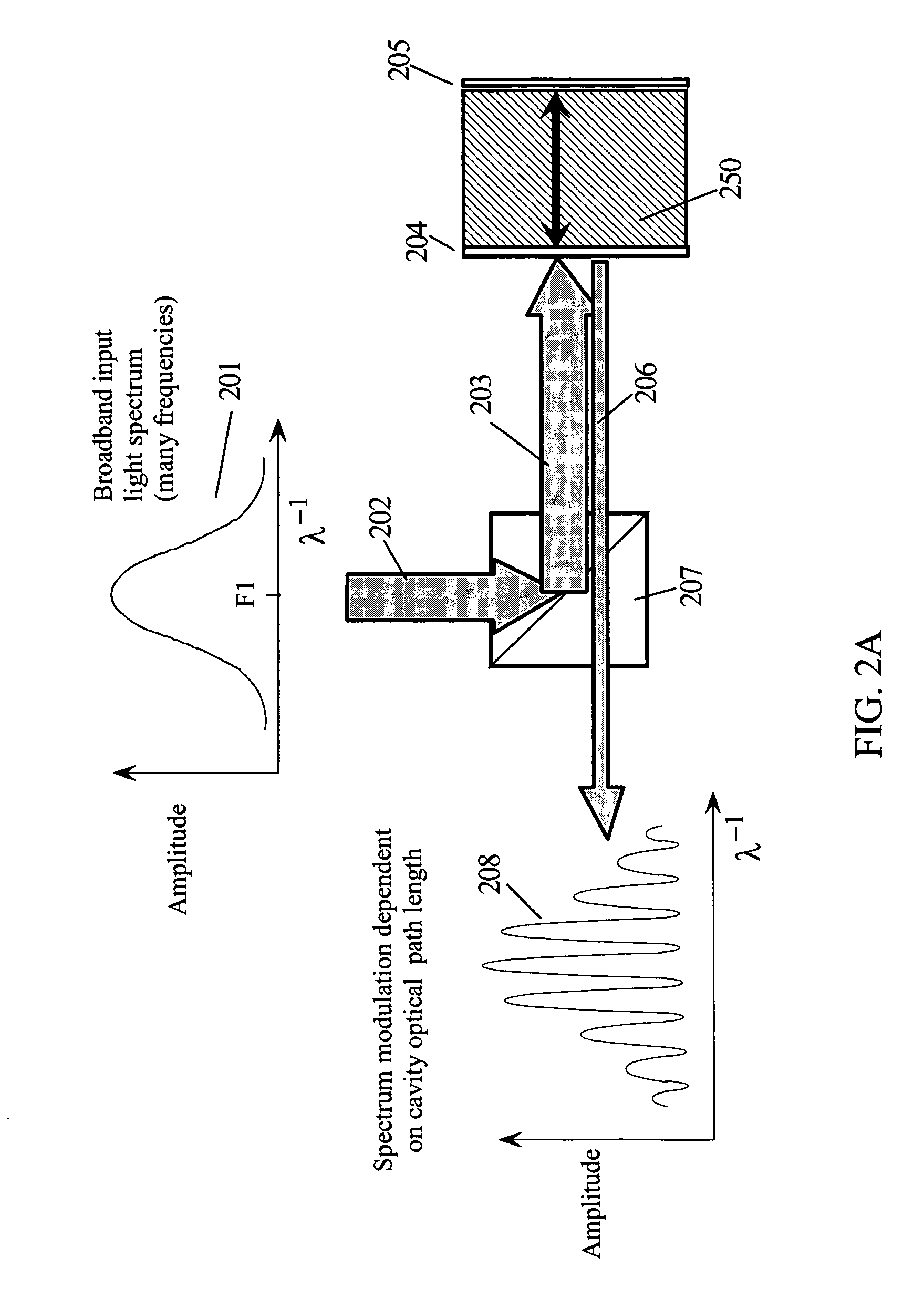
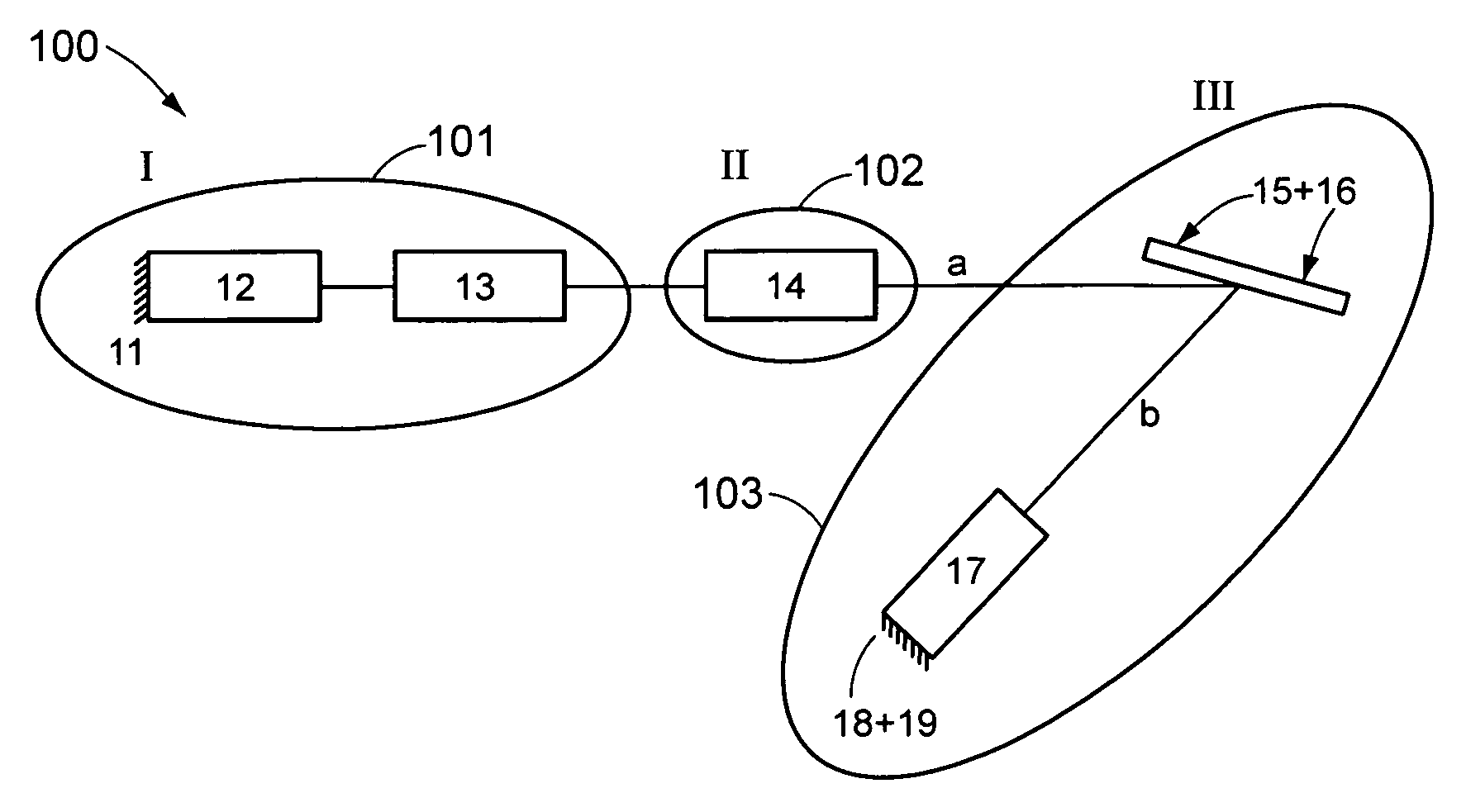
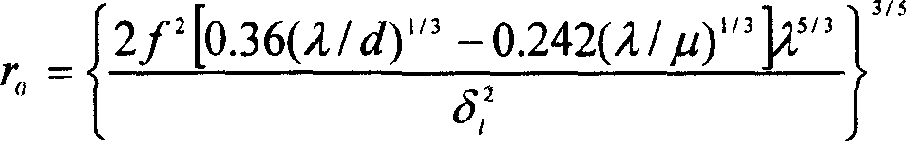Patents
Literature
385 results about "Coherence length" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics, coherence length is the propagation distance over which a coherent wave (e.g. an electromagnetic wave) maintains a specified degree of coherence. Wave interference is strong when the paths taken by all of the interfering waves differ by less than the coherence length. A wave with a longer coherence length is closer to a perfect sinusoidal wave. Coherence length is important in holography and telecommunications engineering.
Medical device with low magnetic susceptibility
InactiveUS20050079132A1Batteries circuit arrangementsElectrotherapyMagnetic susceptibilityCoherence length
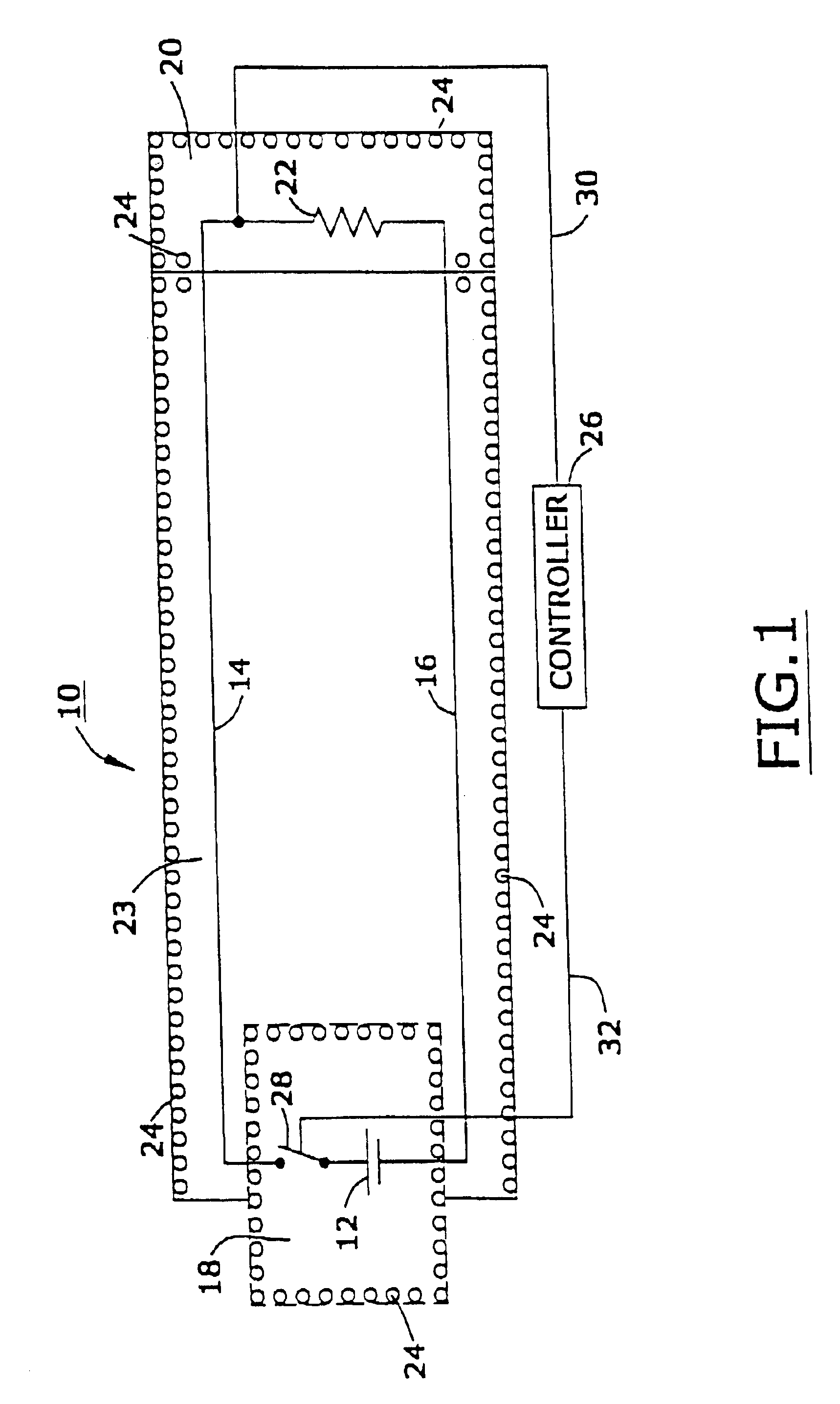
An assembly with a substrate, nanomagnetic material and magetoresistive material. The nanomagnetic material has a saturation magentization of from about 2 to about 3000 electromagnetic units per cubic centimeter; and it contains nanomagnetic particles with an average particle size of less than about 100 nanometers. The average coherence length between adjacent nanomagnetic particles is less than 100 nanometers.
Owner:BIOPHAN TECH
Nanomagnetically shielded substrate
A shielded substrate assembly that contains a magnetic shield with a layer of magnetic shielding material; the magnetic shield has a magnetic shielding factor of at least about 0.5. The magnetic shield contains nanomagnetic material nanomagnetic material with a mass density of at least about 0.01 grams per cubic centimeter, a saturation magnetization of from about 1 to about 36,000 Gauss, a coercive force of from about 0.01 to about 5,000 Oersteds, a relative magnetic permeability of from about 1 to about 500,000, and an average particle size of less than about 100 nanometers. The nanomagnetic material contains magnetic material with a coherence length of from about 0.1 to about 100 nanometers.
Owner:BIOPHAN TECH
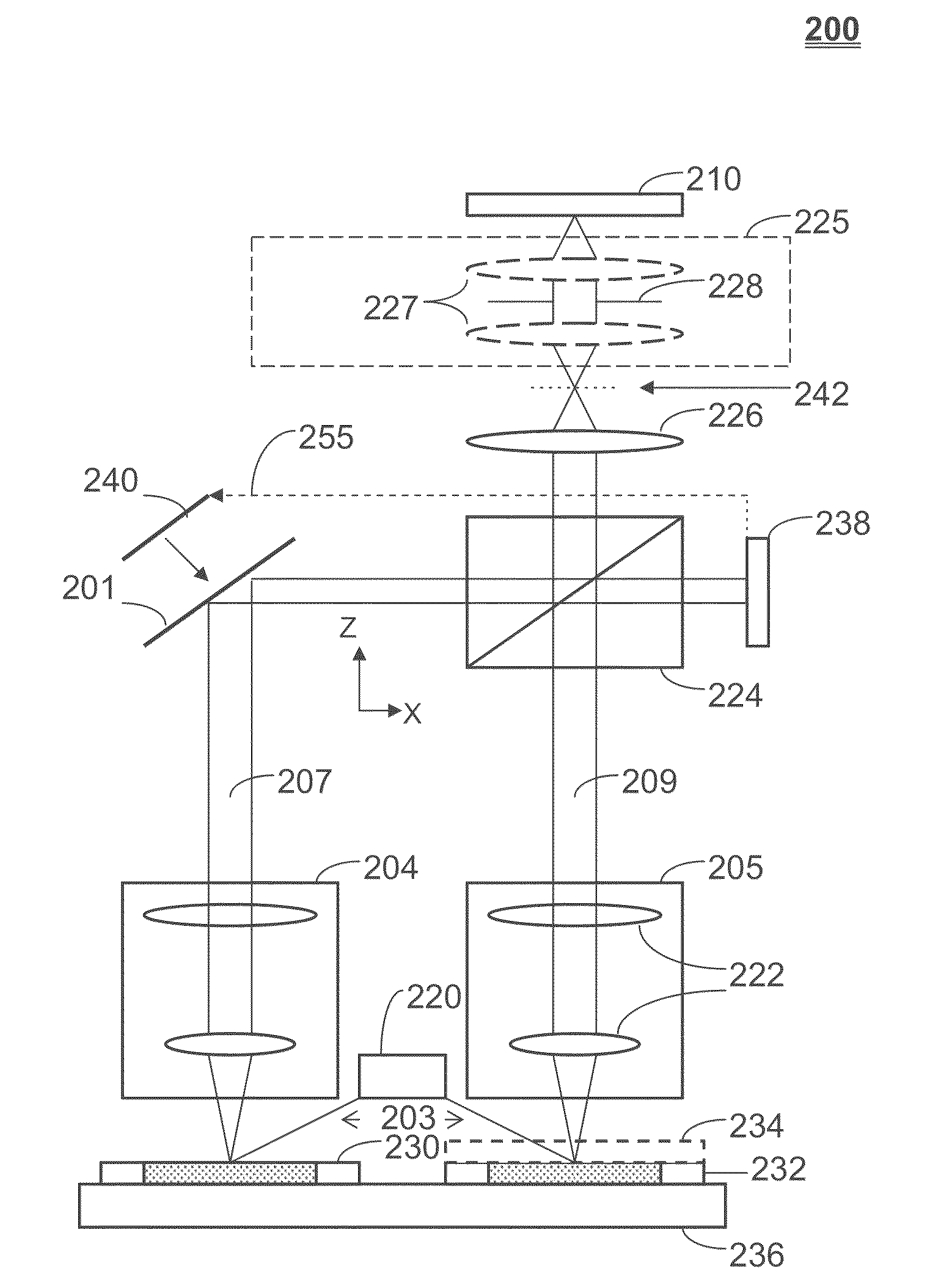
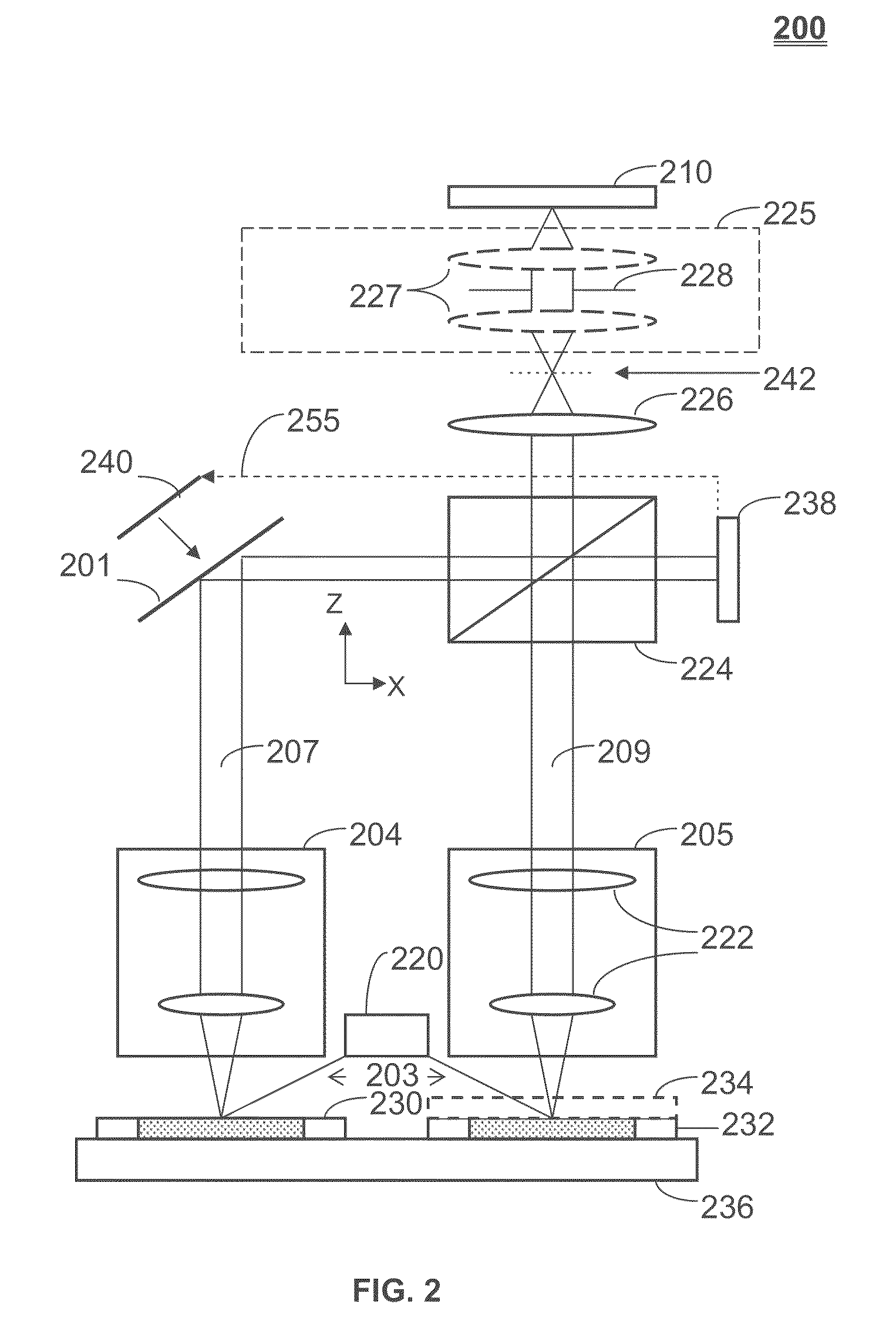
Lateral-scanning interferometer with tilted optical axis
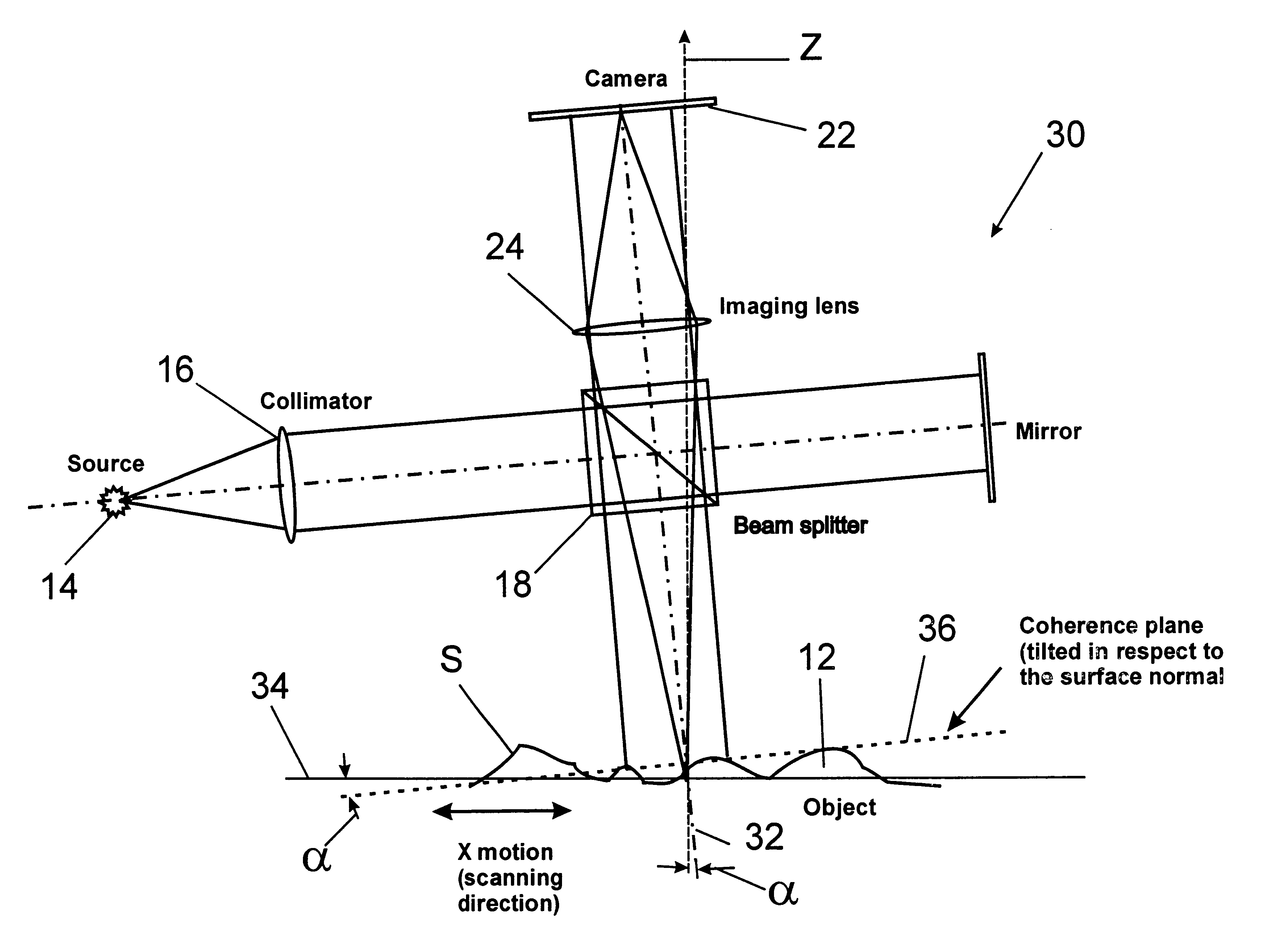
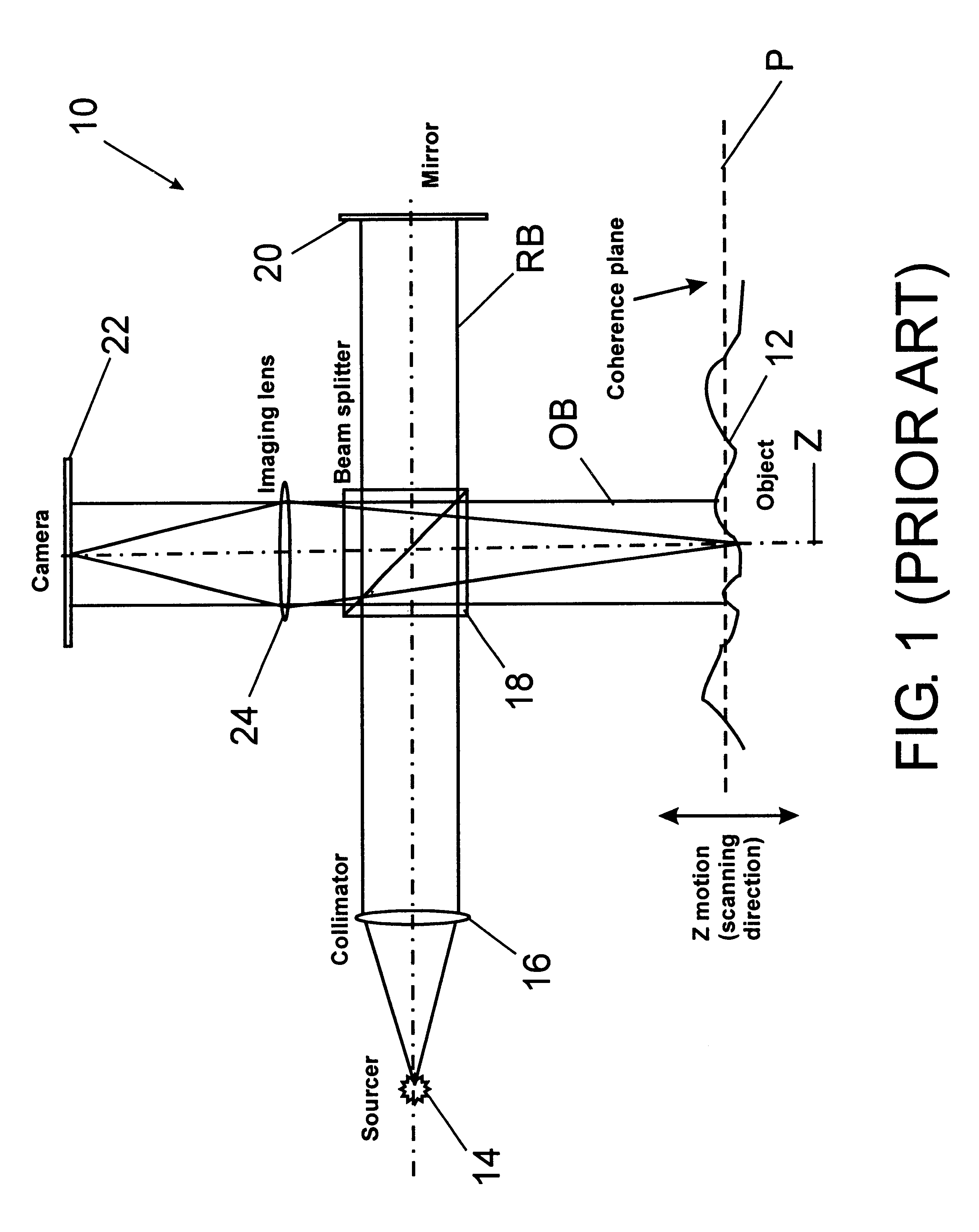
An interferometer scans the sample surface laterally with respect to the optical axis of the interferometric objective. The objective is tilted, so that the sample surface is placed at an angle with respect to the maximum coherence plane of the instrument. By moving the sample stage laterally, at an angle, through a point at a set distance from the objective on the objective's optical axis, rather than vertically along the optical axis, different parts of the object intersect the maximum coherence plane at different times as the surface passes through the coherence plane, the precise time depending on the profile of the surface. When the OPD of a point on the object's surface is greater than the coherence length of the light source, the intensity of light reflected from this point does not produce interference fringes. Therefore, the intensity registered by the detector is approximately constant. However, when the object point enters the zone of coherence, the interference effects modulate the intensity the same way as in a regular VSI procedure. As the object moves along the scanning direction, it also has a relative vertical speed with respect to the objective because of the tilt of the objective's optical axis with respect to the scanning plane; therefore, the lateral scanning motion produces an OPD variation as the vertical scan in a conventional system. As a result, light intensity data are acquired continuously as the test surface is scanned, thus elimination the need for stitching multiple sub-sets of data.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
Laser speckle reduction element
ActiveUS20120081786A1Reduce coherenceBroaden wavelength bandwidthPolarising elementsLight beamOptical pathlength
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and apparatus for reducing laser speckle using polarization averaging
InactiveUS6956878B1Speckle reductionOptical resonator shape and constructionOptical elementsBeam splitterTransducer
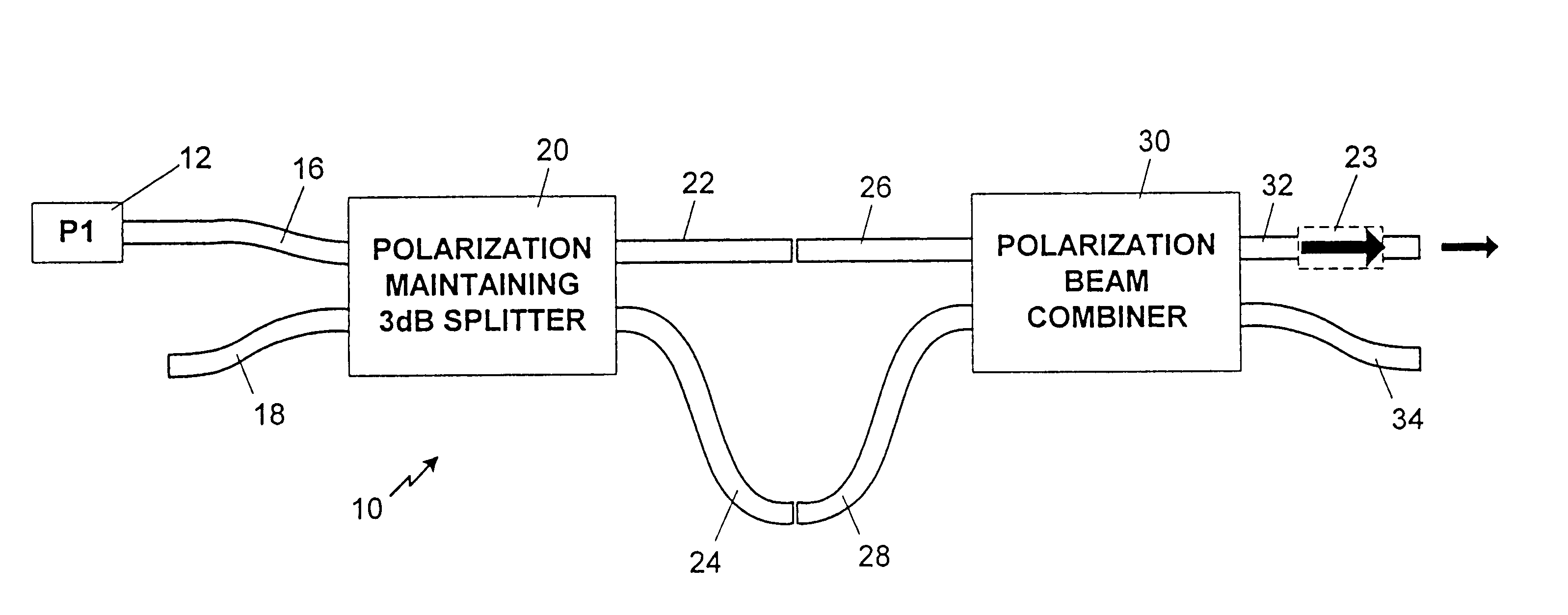
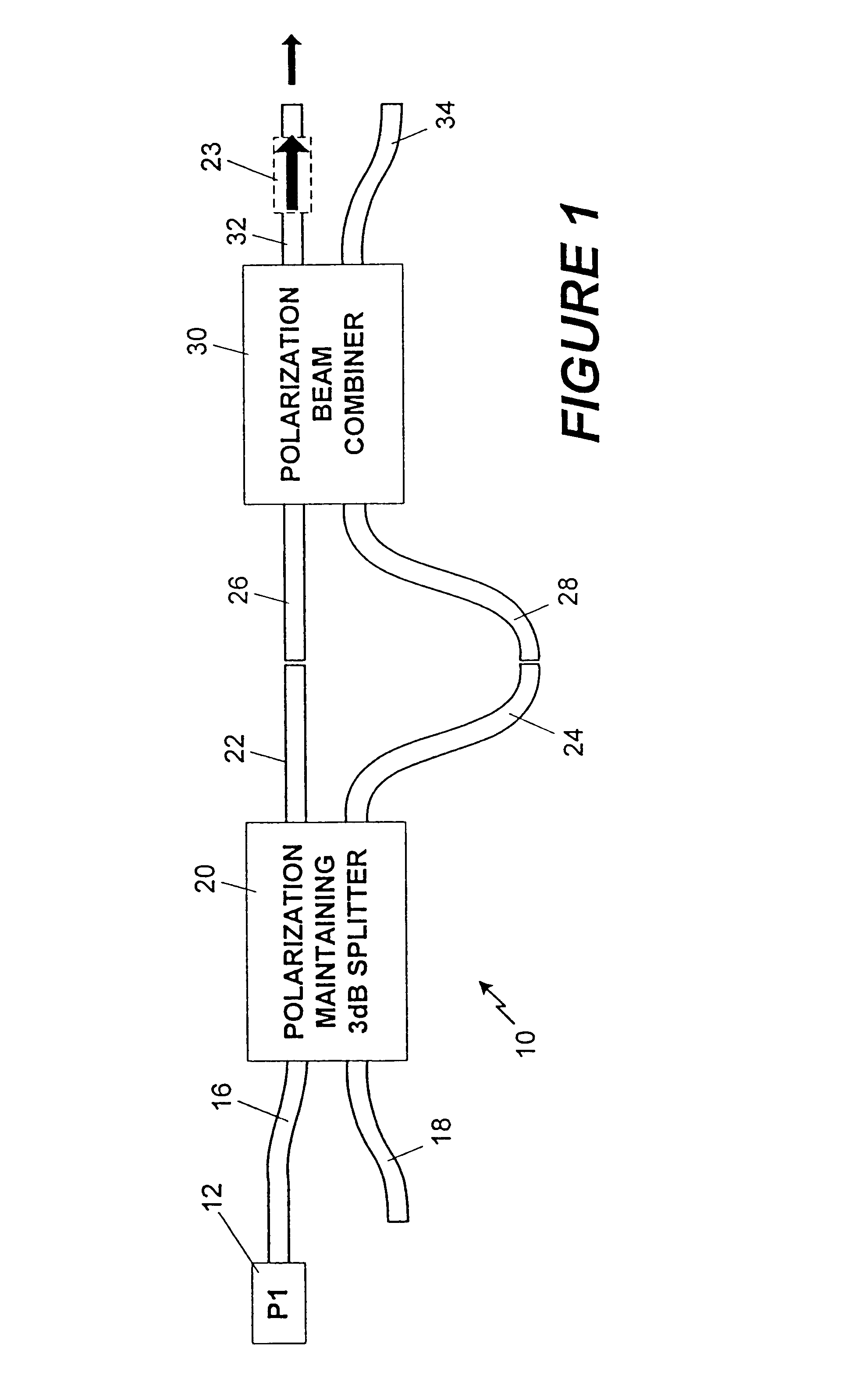
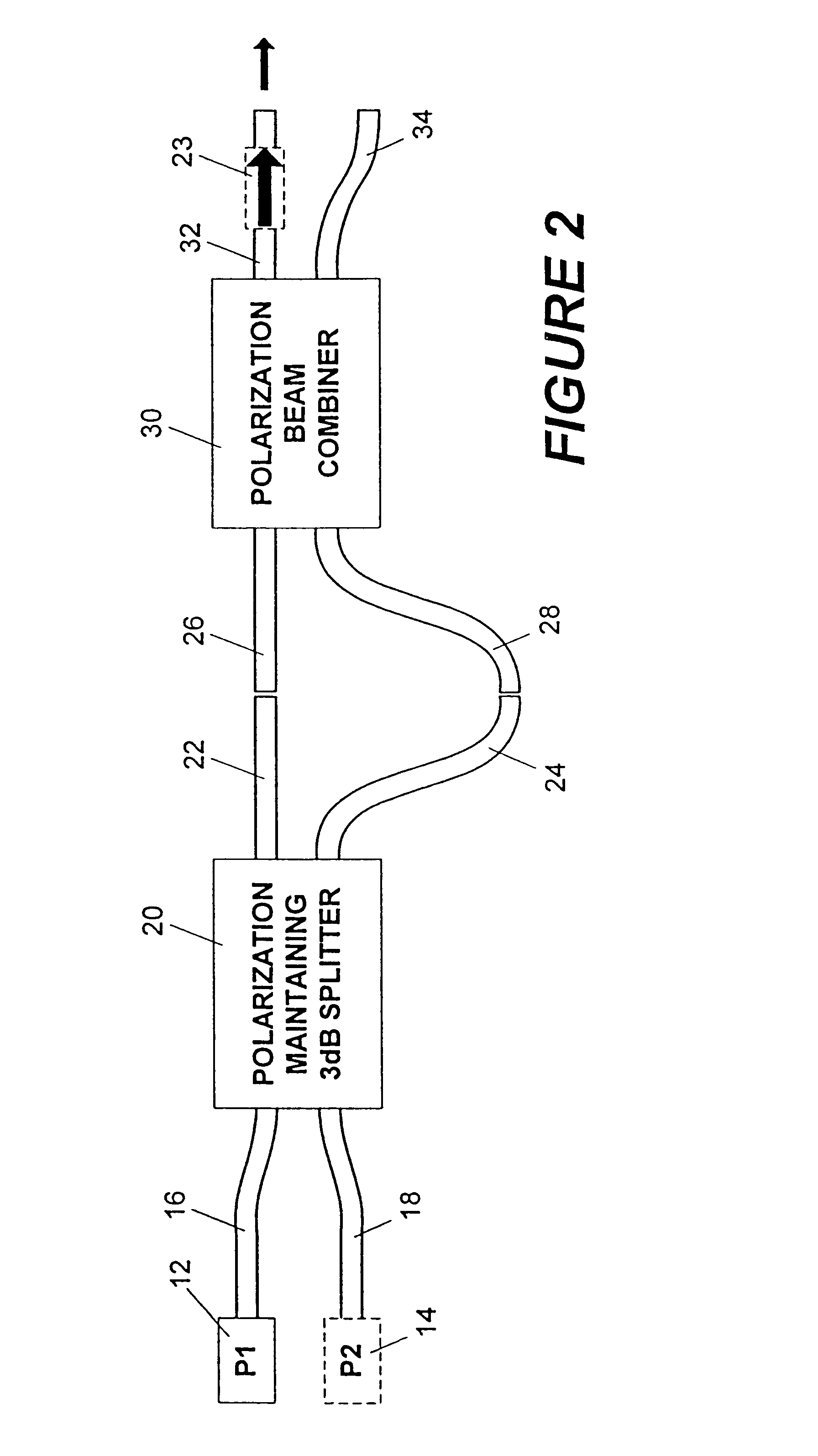
A method and apparatus for reducing speckle uses polarization averaging. A polarizing beam splitter divides a first polarized laser output into a second polarized laser output and a third polarized laser output. A plurality of mirrors creates an optical path difference between the second and third polarized laser outputs. The optical path difference is at least about a coherence length for the first polarized laser output. The second and third polarized laser outputs are combined into a fourth laser output, which illuminates a depolarizing screen. If a human eye or an optical system having a intensity detector views the depolarizing screen, the eye or the intensity detector will detect reduced speckle, which results from uncorrelated speckle patterns created by the second polarized laser output and the third polarized laser output. A first alternative embodiment of the invention functions without the optical path difference being at least about the coherence length. In the first alternative embodiment, a piezoelectric transducer varies an optical path length by at least about a half wavelength of the first polarized laser output. By varying the optical path length by a sufficient frequency, the eye or the intensity detector will detect the reduced speckle. A second alternative embodiment combines two orthogonally polarized laser outputs, from two lasers, into a combined laser output. The combined laser output illuminates the depolarizing screen. A third alternative embodiment rotates the first laser output with a rotation frequency to form a rotating polarized laser output, which illuminates the depolarizing screen.
Owner:SILICON LIGHT MACHINES CORP
Compact multimode laser with rapid wavelength scanning
InactiveUS20060203859A1Large scanning rateSufficient coherence lengthOptical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersLength waveCoherence length
In accordance with the present invention, a compact laser system with nearly continuous wavelength scanning is presented. In some embodiments, the compact laser system can be scanned over a broad range. In some embodiments, the compact laser system can be scanned at high scan rates. In some embodiments, the compact laser system can have a variable coherence length. In particular, embodiments with wavelength scanning over 140 nm with continuously variable scan rates of up to about 1 nm / μs, and discrete increase in scan rates up to about 10 nm / μs, and variable coherence lengths of from 1 mm to about 30 mm can be achieved.
Owner:THORLABS INC
Self-calibrating optical fiber pressure, strain and temperature sensors
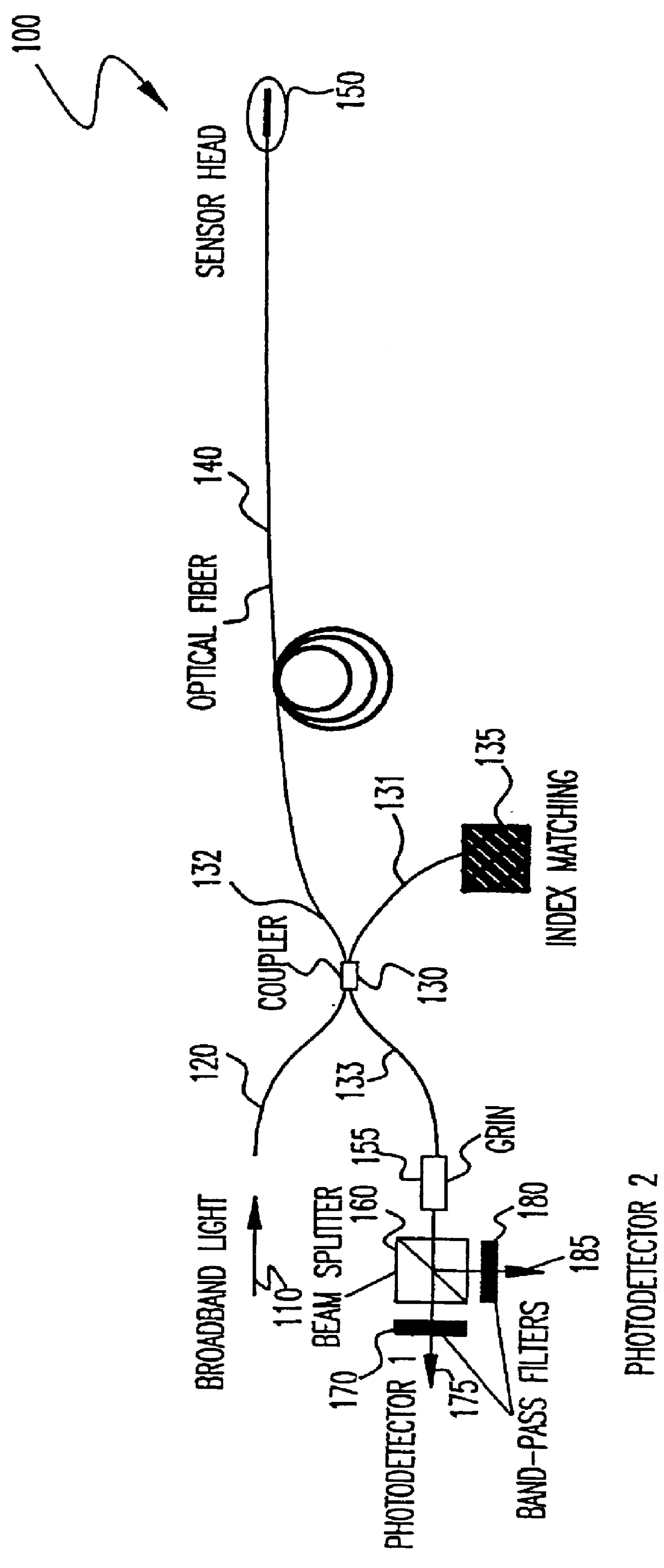
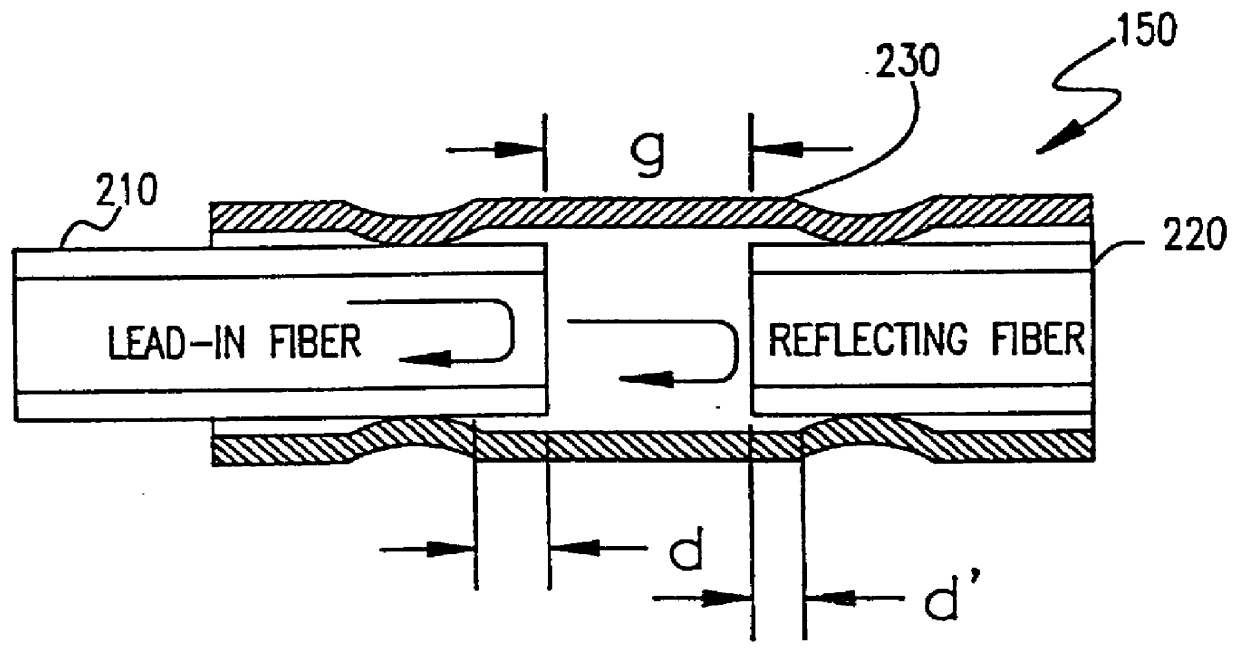
InactiveUS6069686AForce measurement by measuring optical property variationThermometers using physical/chemical changesFiberFrequency spectrum
Broadband energy incident on a transducer having partially or fully reflective surfaces separated by a gap which is greater than the coherence length of the broadband energy but smaller than one-half a coherence length of a band of energy within said broadband energy causes a portion of the spectral content of the broadband energy corresponding to a coherence length greater than twice the gap length to exhibit interference effects while the average power of the broadband energy remains unaffected. Splitting energy reflected from the transducer into two beams which are filtered at preferably similar center frequencies but with different pass bands yields beams which are radically different in sensitivity to changes in gap length. Analyzing the beams to derive a ratio of powers (since source intensity and fiber attenuation in a common fiber are thus self-cancelling) allows high accuracy and high resolution absolute measurement of temperature, pressure or strain. Effects of any of these physical parameters which are not of interest in a measurement can be fully compensated or made arbitrarily insignificant in a simple transducer structure of extremely small size. Use of broadband energy permits measurement over greater lengths of optical fiber.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Laser irradiation device
InactiveUS6563843B1Laser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight beamOptical pathlength
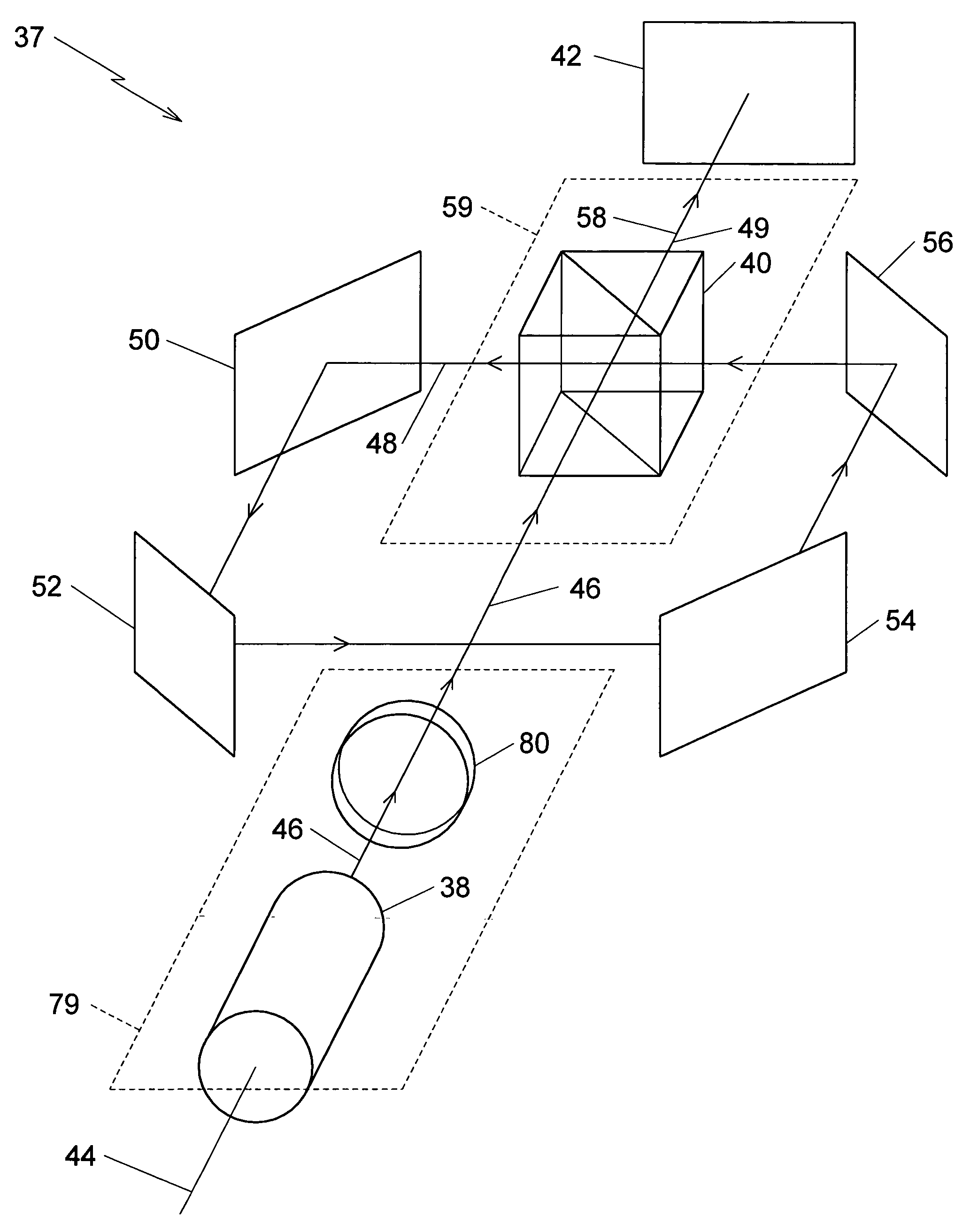
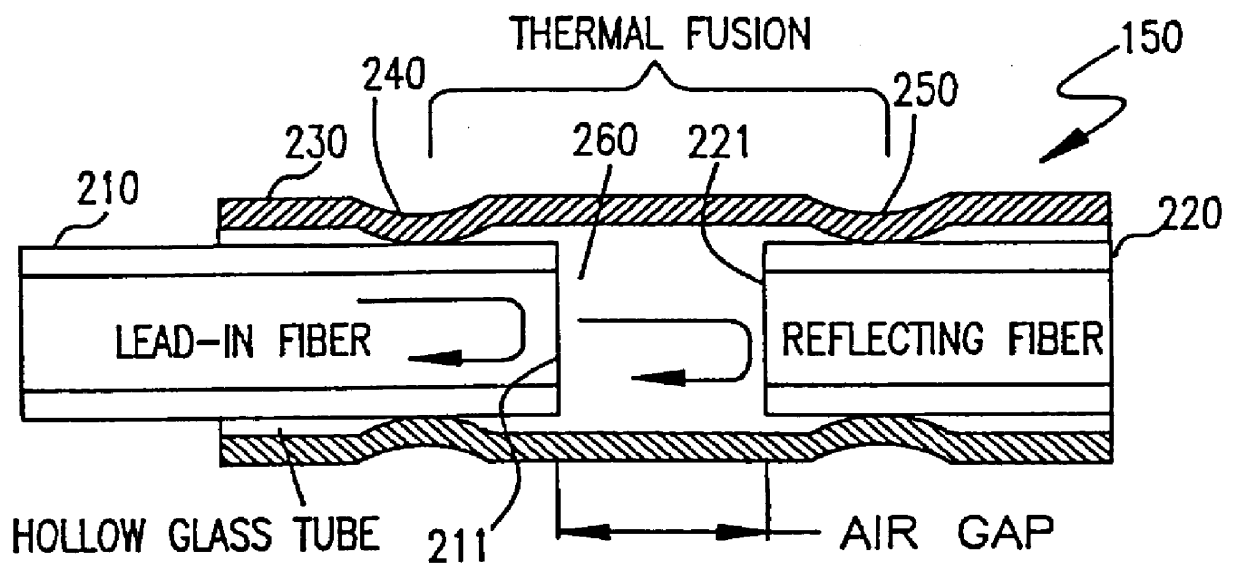
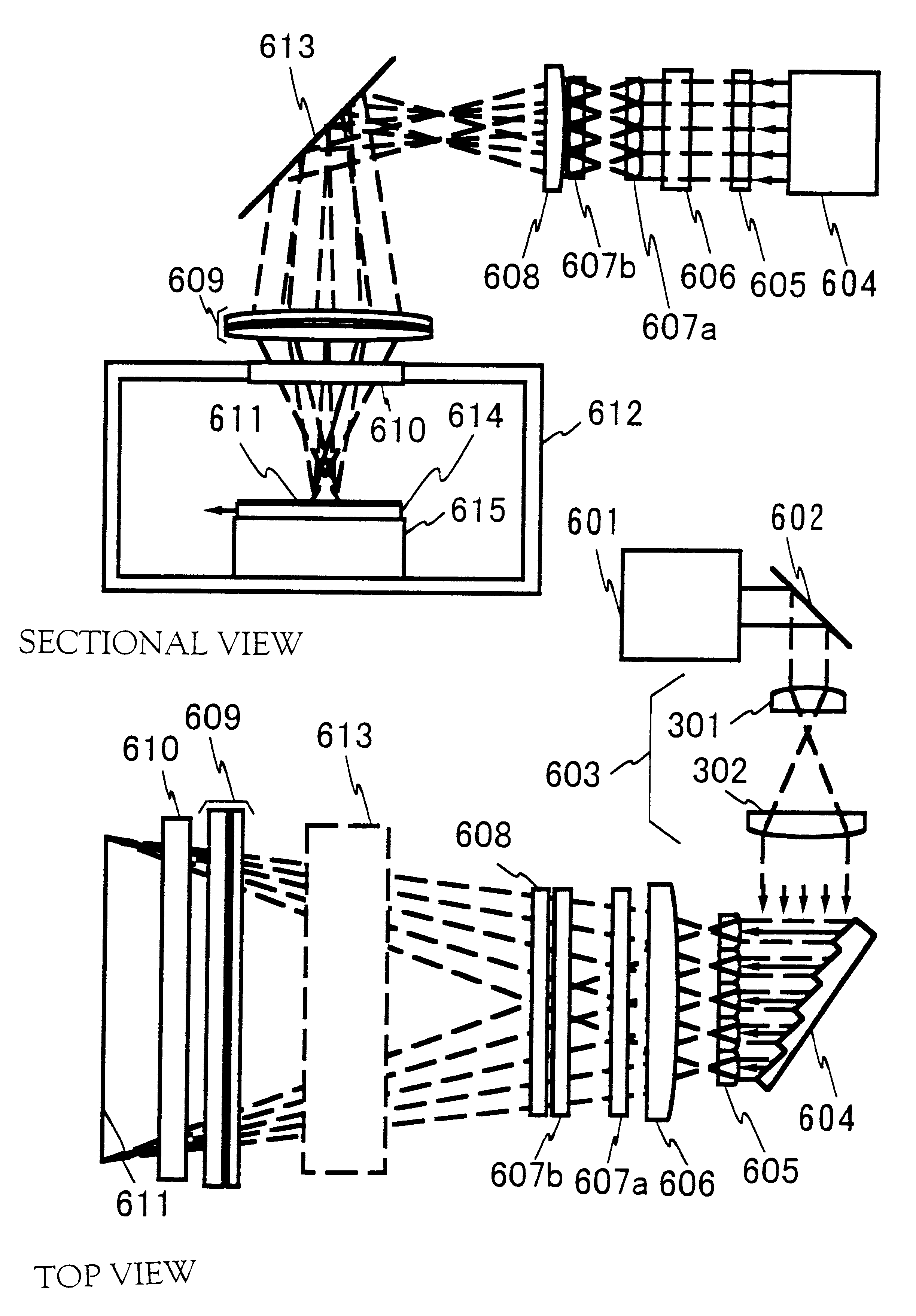
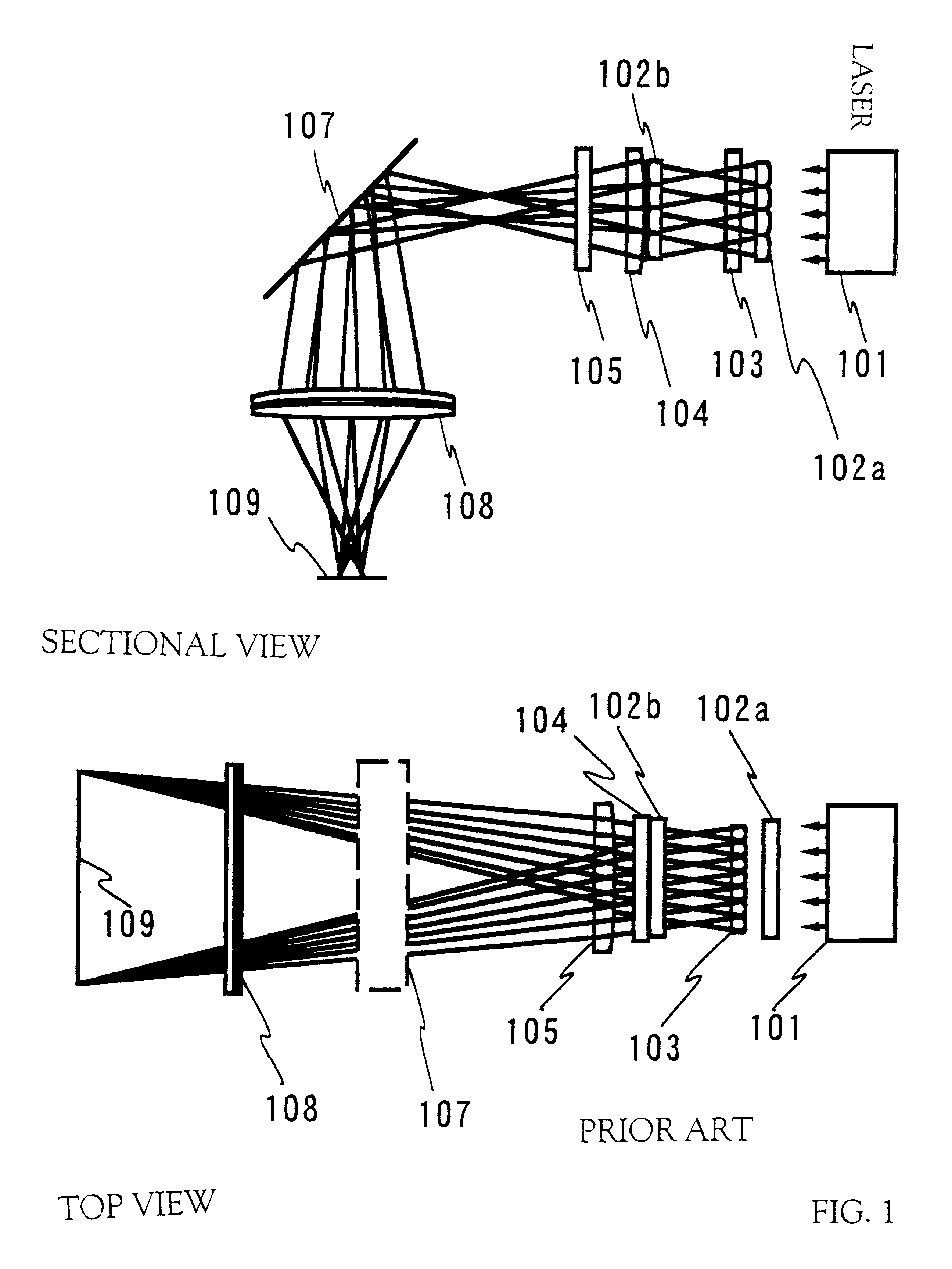
In annealing a non-single crystal silicon film through the use of a linear laser beam emitted by a YAG laser of a light source, it is the object of the present invention to prevent heterogeneity in energy caused by an optical interference produced in the linear laser beam from having an effect on the silicon film. The laser beam is divided by a mirror 604 shaped like steps into laser beams which have an optical path difference larger than the coherence length of the laser beam between them. The divided laser beams are converged on an irradiate surface 611 by the action of a cylindrical lens array 605 and a cylindrical lens 606 to homogenize the energy of the laser beam in the length direction and to determine the length of the linear laser beam. On the other hand, the laser beams divided by a cylindrical lens array 607 are converged on the irradiate surface 611 by a cylindrical lens 608 and a doublet cylindrical lens 609 to homogenize the energy in the width direction of the laser beam and to determine the width of the linear laser beam. Interference fringes parallel to the width direction of the linear laser beam disappears in the linear laser beam by the action of a mirror 604 shaped like steps. If the silicon film is annealed by the linear laser beam while the linear laser beam is being shifted in the width direction of the linear laser beam, the silicon film is remarkably homogenized as compared with a conventional silicon film.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
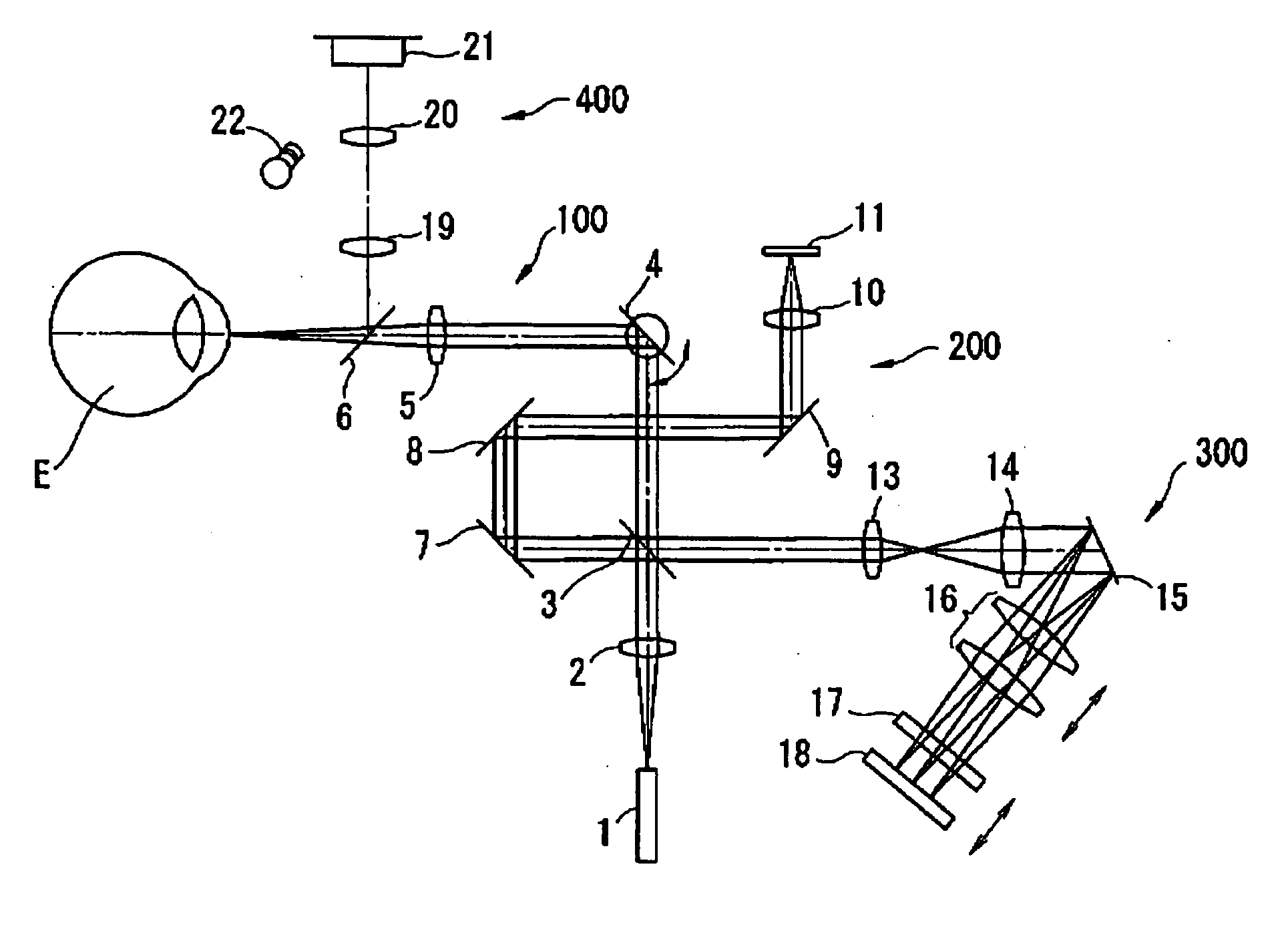
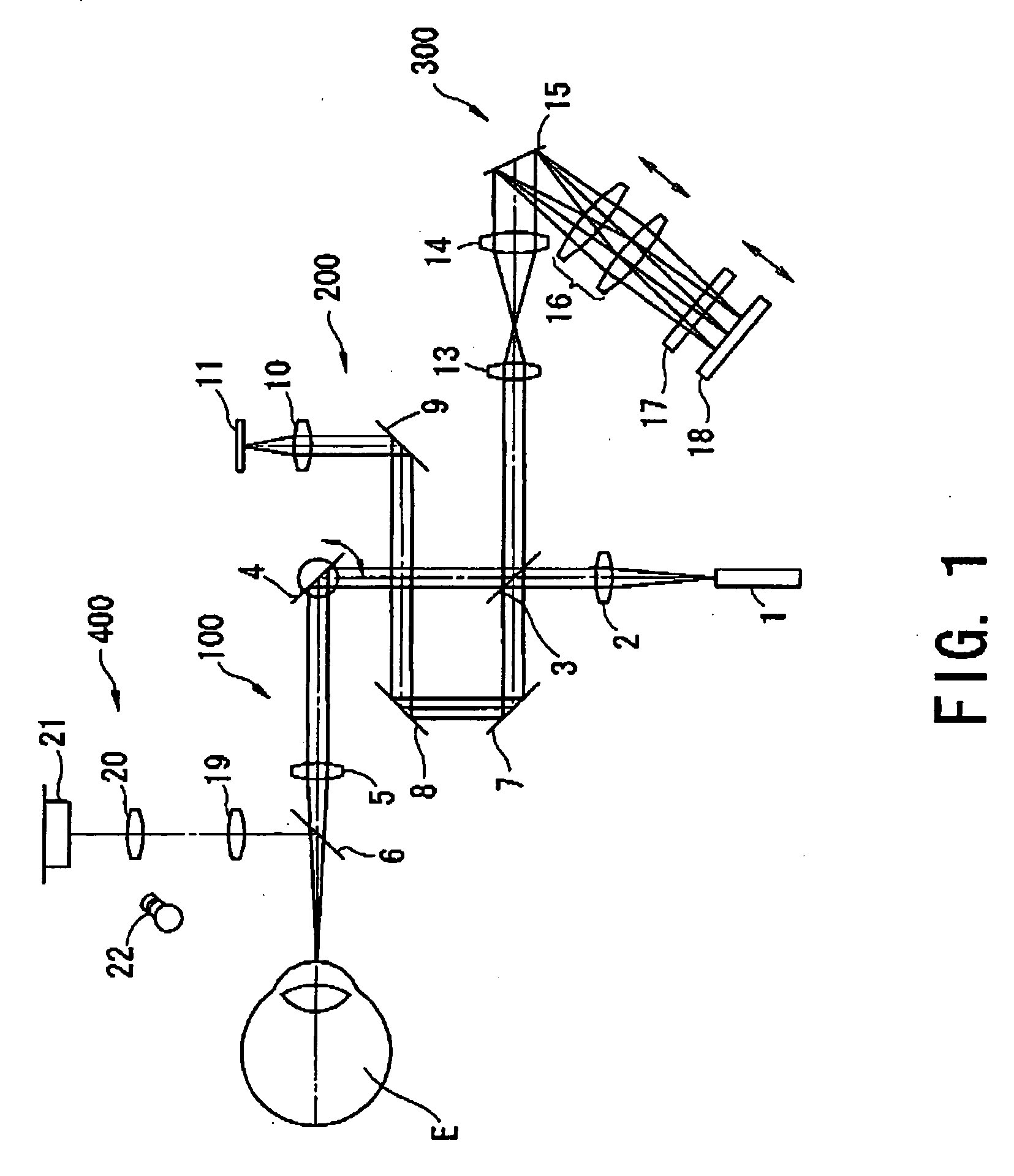
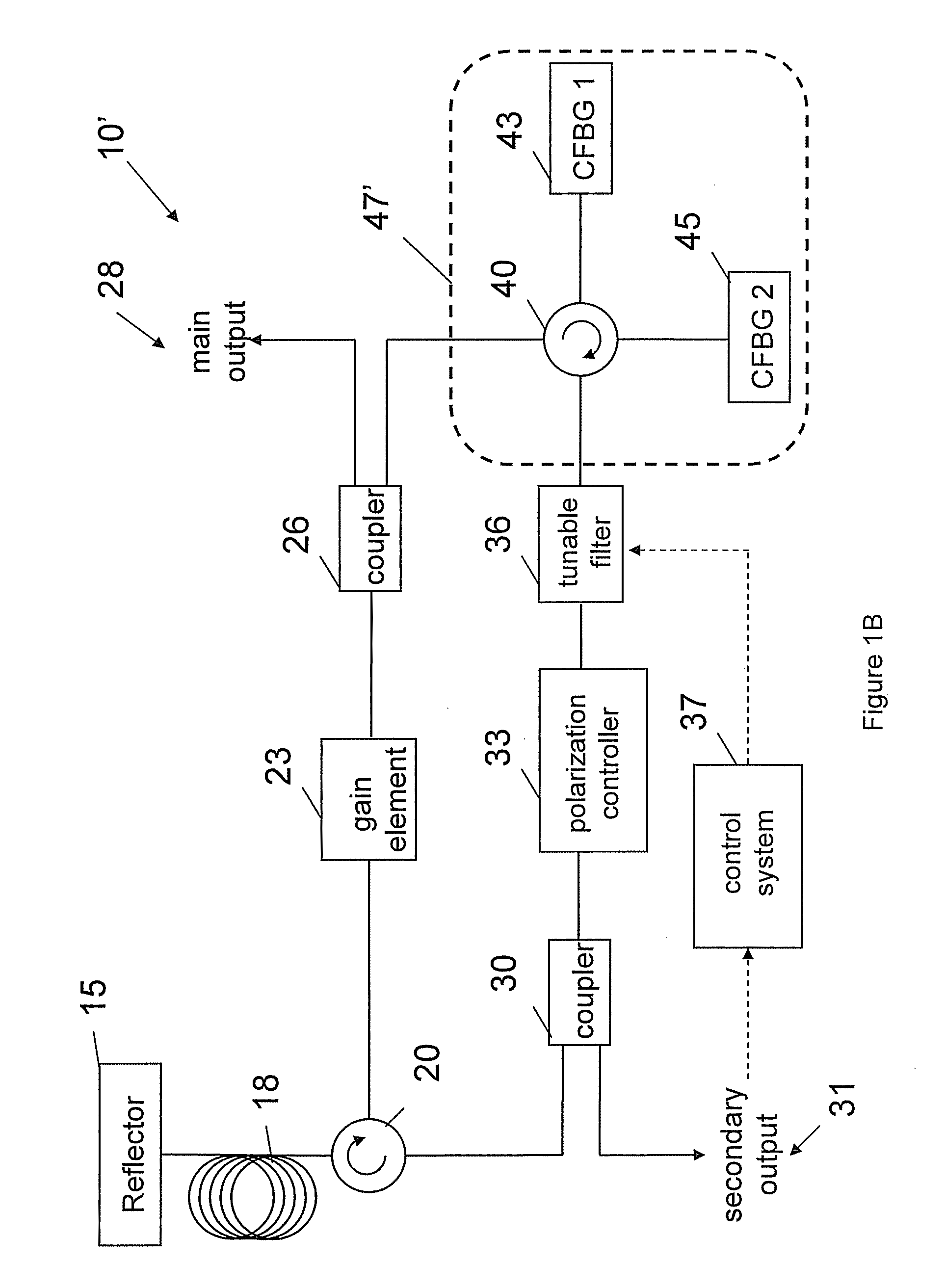
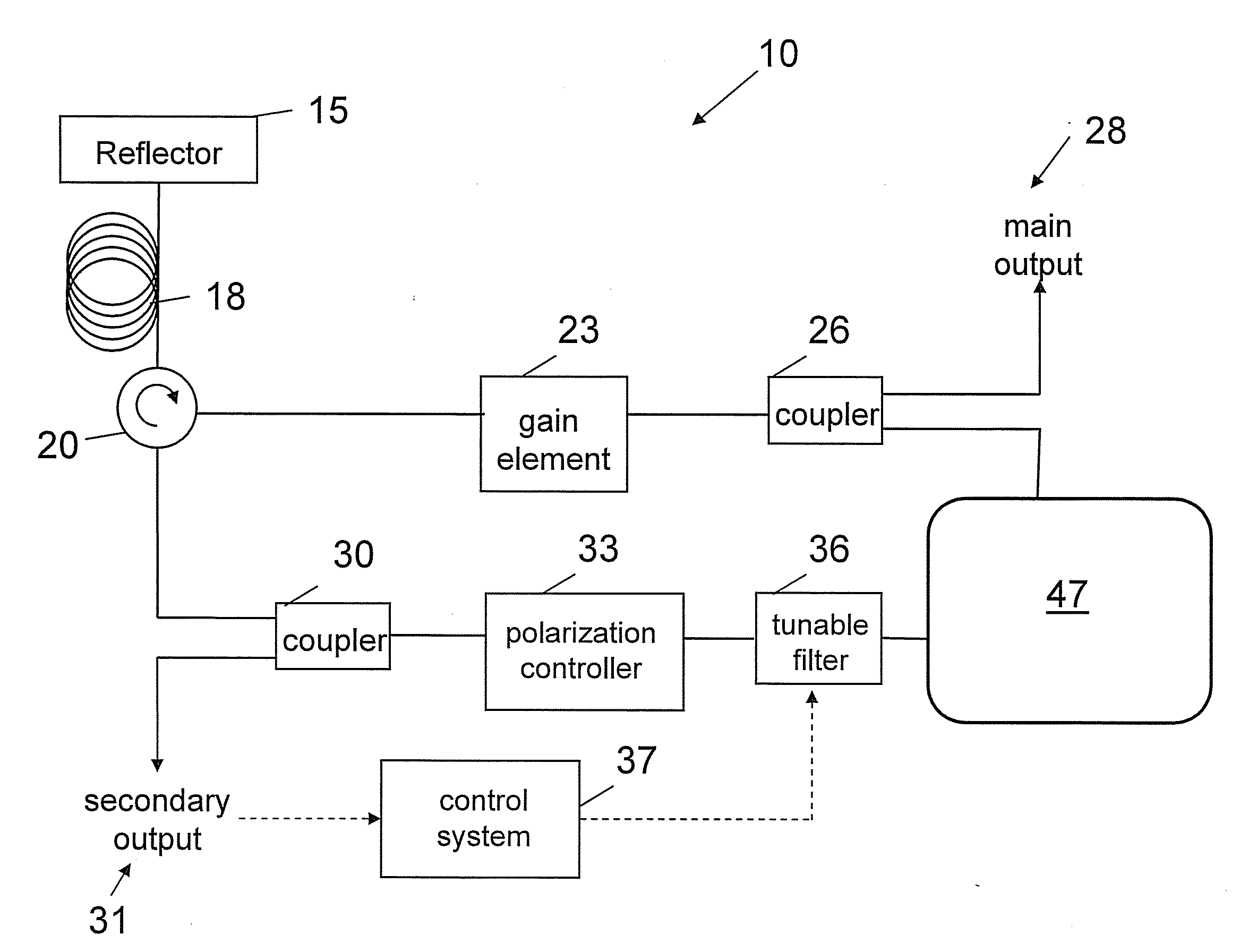
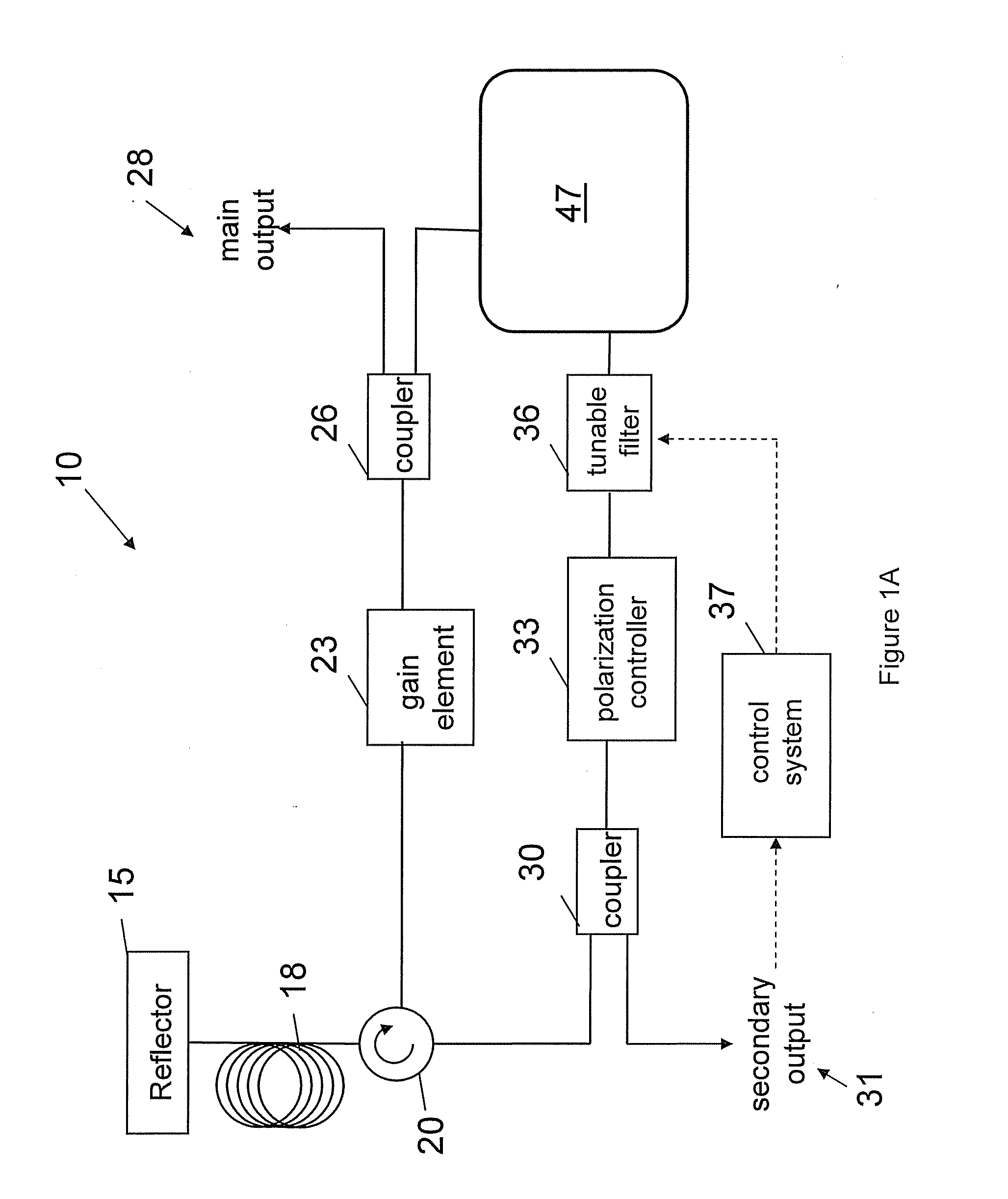
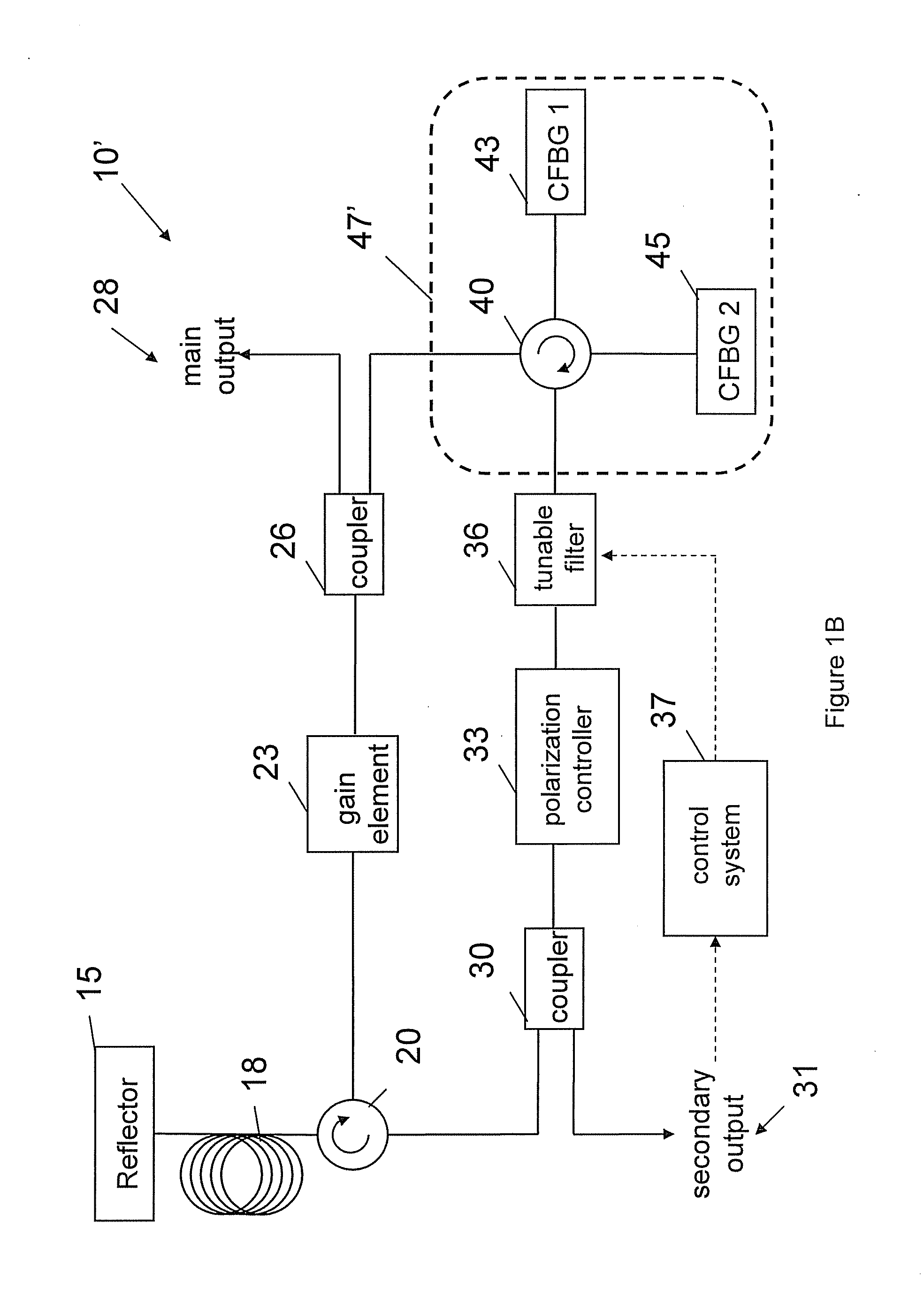
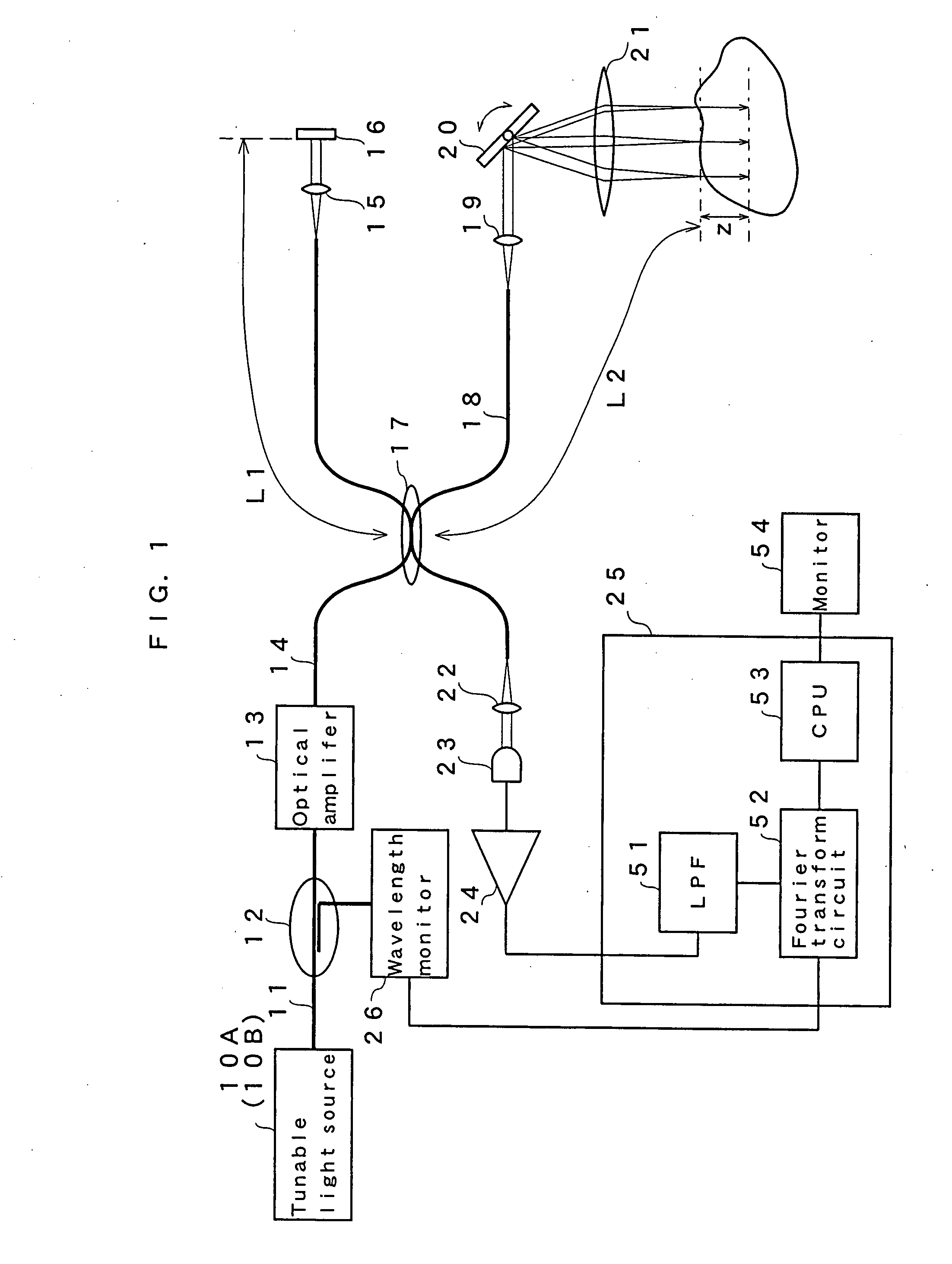
Optical coherence tomography apparatus based on spectral interference and an ophthalmic apparatus
InactiveUS20060066869A1Information acquisition range in a depth direction can be enlargedEye diagnosticsUsing optical meansOphthalmological devicePhotovoltaic detectors
An optical coherence tomography apparatus based on spectral interference where object information can be speedily obtained and an information acquisition range in a depth direction can be enlarged, and an ophthalmic apparatus. The apparatus includes a first optical system for projecting light with short coherence length onto an object to form object light which is reflection light from the object, a second optical system for projecting light with short coherence length onto a reference surface to form reference light which is reflection light from the surface, an optical system for synthesizing the object light and the reference light to be interference light, dispersing the interference light into predetermined frequency components and photo-receiving the dispersed light with a photodetector, a device varying a spectral characteristic when the interference light is dispersed by the interference / dispersion / photo-receiving optical system, and a calculation part obtaining the information based on an output signal from the photodetector.
Owner:NIDEK CO LTD
System and method for measuring an optical path difference in a sensing interferometer
ActiveUS6842254B2Robust and reliable measurementFast measurementInterferometersUsing optical meansLight beamAbsolute measurement
An apparatus and a method of measuring an optical path difference in a sensing interferometer. Light from a source is directed in the sensing interferometer. The light reflected from the sensing interferometer is splitted into first and second beams respectively directed into two reference interferometers having optical path differences greater than the coherence length of the source and such that the optical signals are in quadrature. The intensities of the light transmitted by the reference interferometers and recombined light reflected from the reference interferometers are detected for measuring the optical path difference in the sensing interferometer. Additional light sources allow for correction of internal perturbations and absolute measurement of the optical path difference in the sensing interferometer.
Owner:FISO TECH
Method and apparatus for gas discharge laser output light coherency reduction
A method and apparatus for producing with a gas discharge laser an output laser beam comprising output laser light pulses, for delivery as a light source to a utilizing tool is disclosed which may comprise a beam path and a beam homogenizer in the beam path. The beam homogenizer may comprise at least one beam image inverter or spatial rotator, which may comprise a spatial coherency cell position shifter. The homogenizer may comprise a delay path which is longer than, but approximately the same delay as the temporal coherence length of the source beam. The homogenizer may comprise a pair of conjoined dove prisms having a partially reflective coating at the conjoined surfaces of each, a right triangle prism comprising a hypotenuse face facing the source beam and fully reflective adjoining side faces or an isosceles triangle prism having a face facing the source beam and fully reflective adjoining side faces or combinations of these, which may serve as a source beam multiple alternating inverted image creating mechanism. The beam path may be part of a bandwidth measuring the bandwidths of an output laser beam comprising output laser light in the range of below 500 femtometers at accuracies within tens of femtometers. The homogenizer may comprise a rotating diffuser which may be a ground glass diffuser which may also be etched. The wavemeter may also comprise a collimator in the beam path collimating the diffused light; a confocal etalon creating an output based upon the collimated light entering the confocal etalon; and a detector detecting the output of the confocal etalon and may also comprise a scanning mechanism scanning the angle of incidence of the collimated light entering the confocal etalon which may scan the collimated light across the confocal etalon or scan the etalon across the collimated light, and may comprise an acousto-optical scanner. The confocal etalon may have a free spectral range approximately equal to the E95 width of the beam being measured. The detector may comprise a photomultiplier detecting an intensity pattern of the output of the confocal etalon.
Owner:CYMER INC
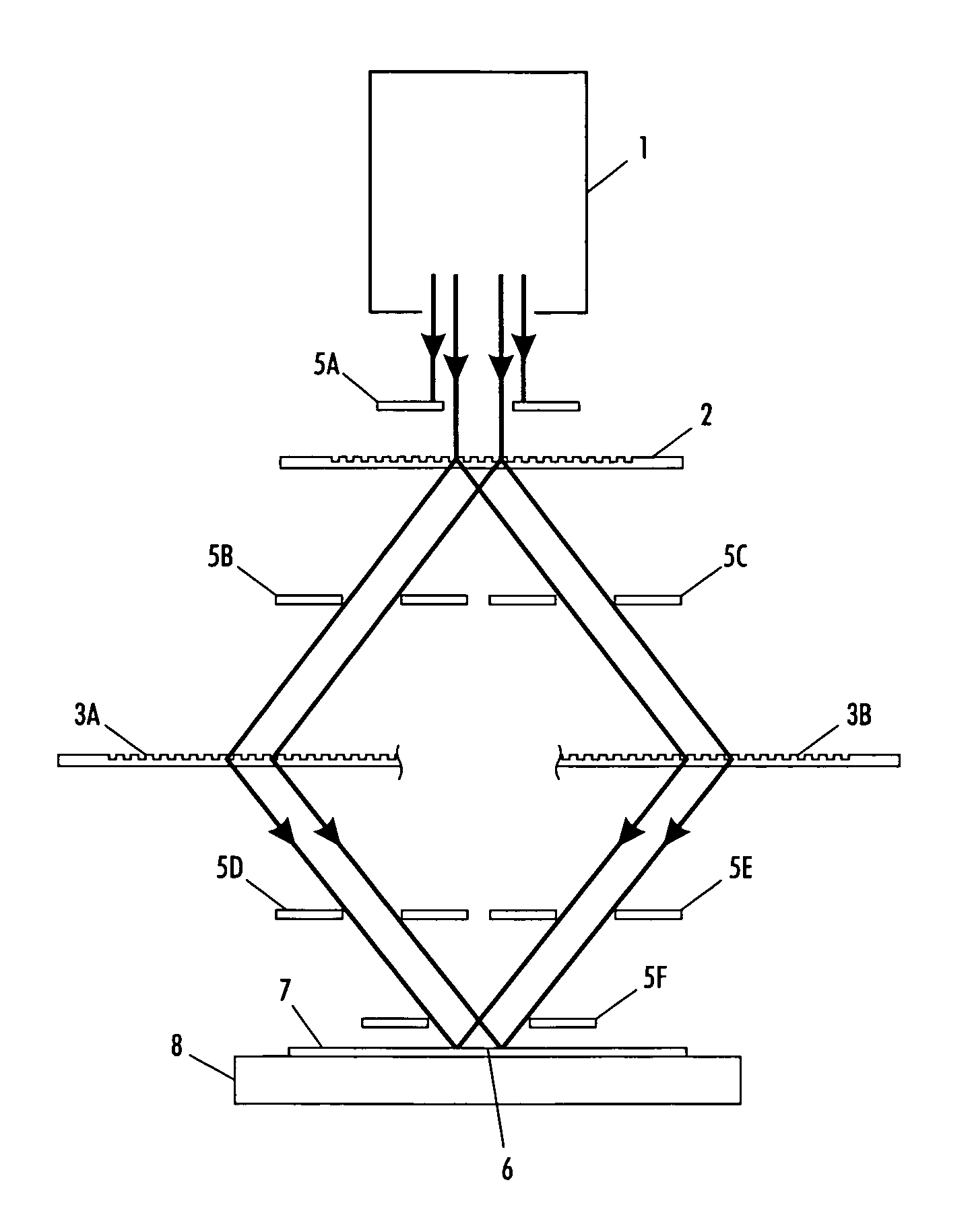
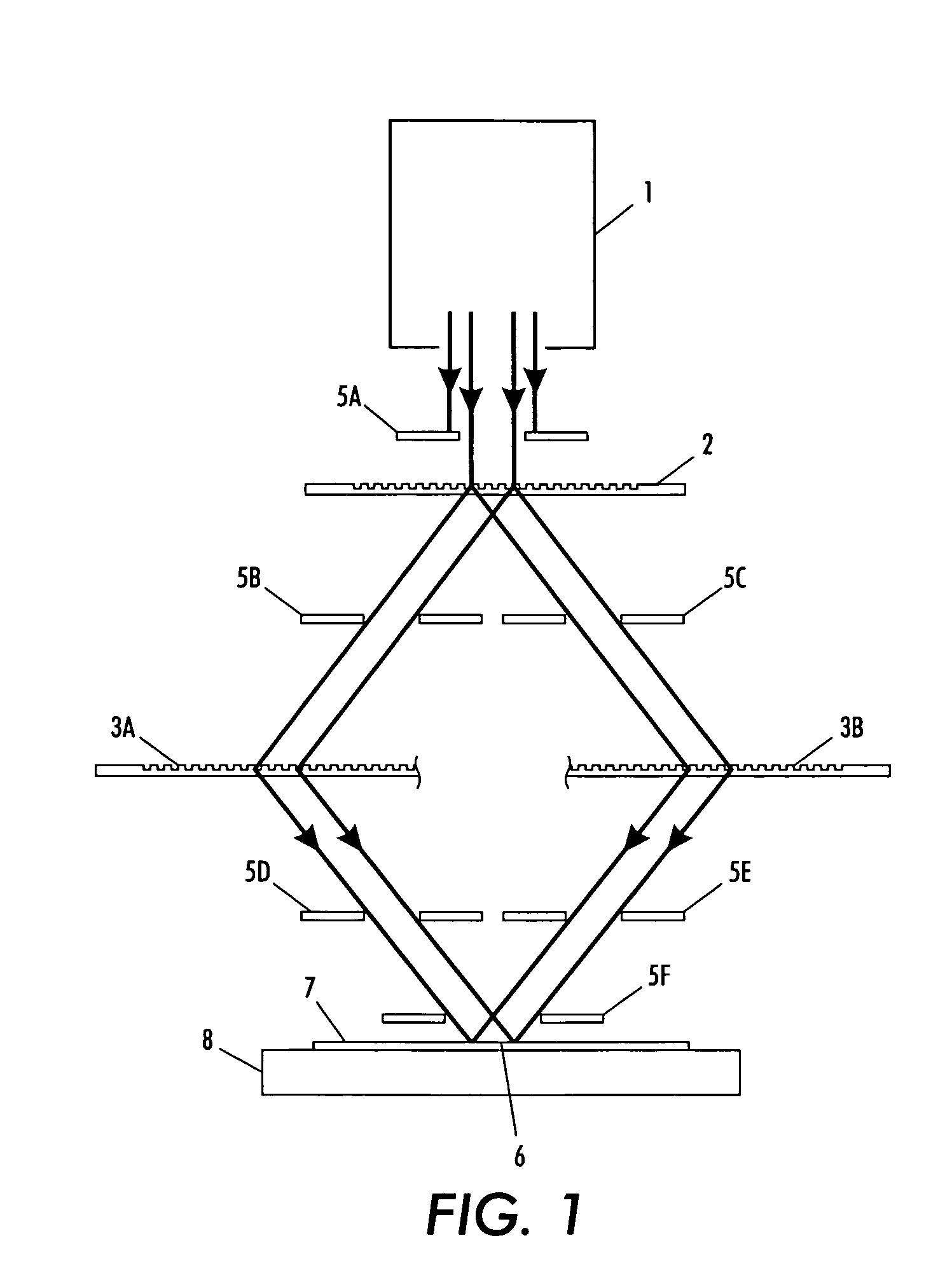
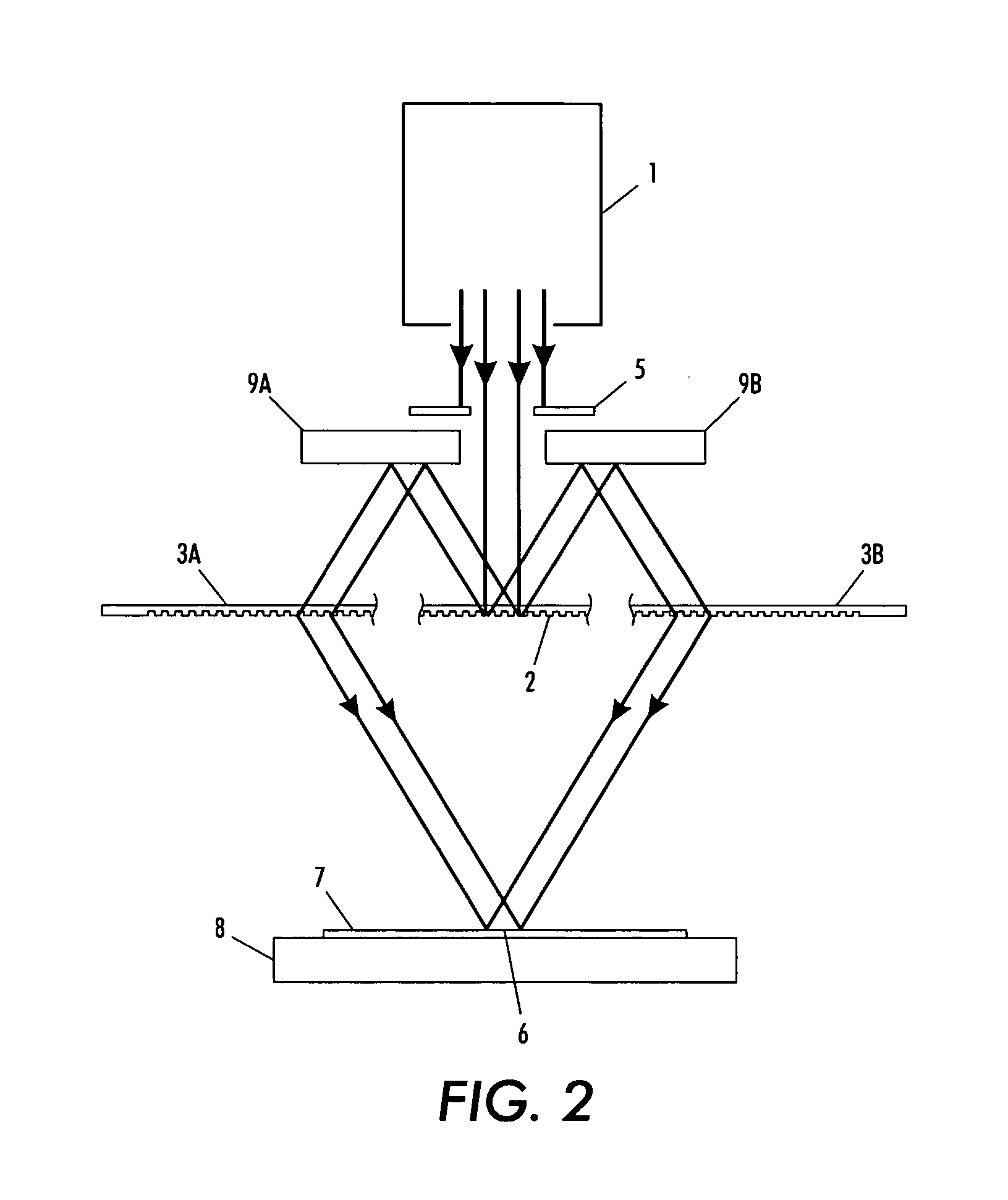
System and method for forming well-defined periodic patterns using achromatic interference lithography
InactiveUS20060109532A1Clear processHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesPhotomechanical apparatusLight beamCoherence length
A beam, from a short-coherence-length source, is split and recombined by diffraction gratings not necessarily equal in spatial period. The recombining beams overlap and expose a common area on a substrate. The exposed area on the substrate is defined or shaped by at least one aperture in the beam paths. After exposure of one shaped area, relative translation between components permits exposure of another shaped area on the substrate. Additionally or alternatively, by introducing either rotation or translation between components during each exposure, the exposed area is made larger than the original shaped area.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Forward Scanning OCT Endoscope
InactiveUS20100292539A1Compact and narrow designLikely can be usedSurgeryEndoscopesBeam splittingRefractive index
An apparatus for optical coherence tomography has a broadband light source with a short coherence length, an optical fiber that guides the light from the light source to a focusing optics, and a graded-index optics arranged between the optical fiber and the focusing optics with two opposite parallel flat sides, that is contacted on its first flat side by the optical fiber forming an irradiation point guiding light to the graded-index optics and having a pitch of N / 8, N being a natural number that cannot be divided by 4. A first structure for light reflection is arranged on the first flat side of the graded-index optics adjacent to the irradiation point, and a second structure for beam splitting is arranged on the second flat side of the graded-index optics. The focusing optics are designed for focusing the light transmitted by the second structure essentially at right angles to the flat sides of the graded-index optics.
Owner:MEDIZINISCHES LASERZENTRUM LUEBECK GMBH
Methods, systems, and devices for timing control in electromagnetic radiation sources
ActiveUS8582619B2Reduce and remove dispersionHigh gainOptical resonator shape and constructionUsing optical meansElectromagnetic radiationTime control
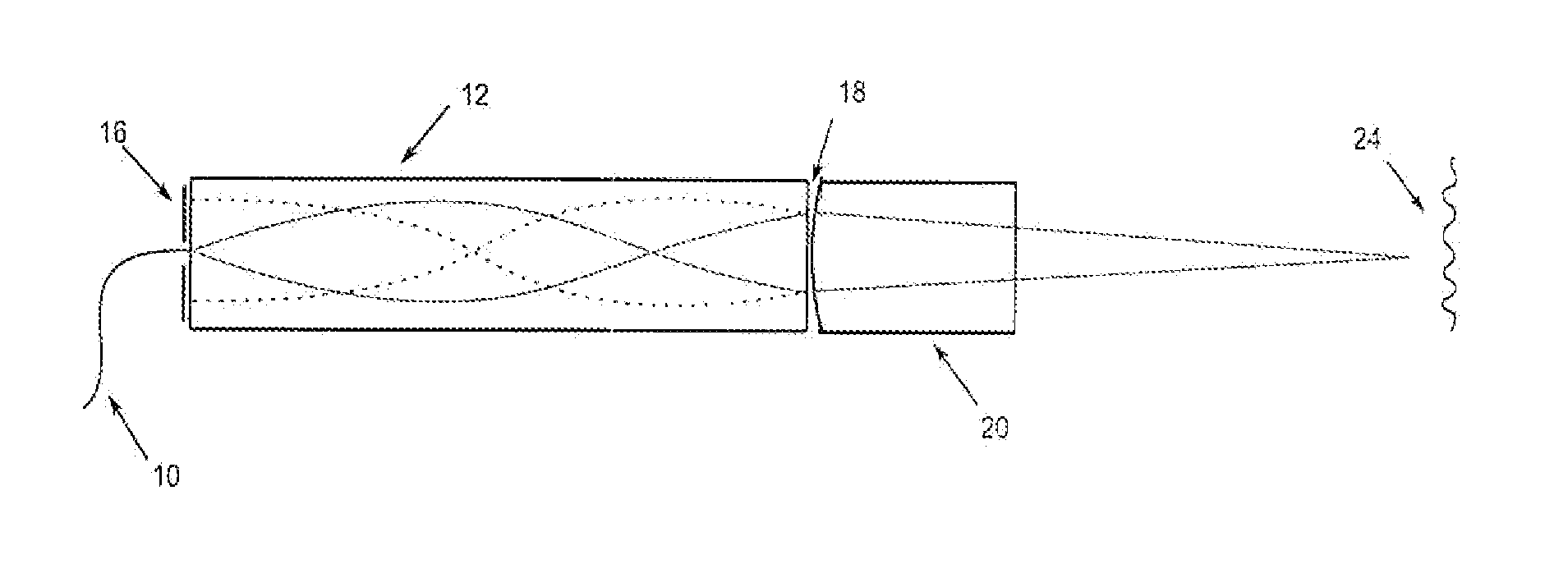
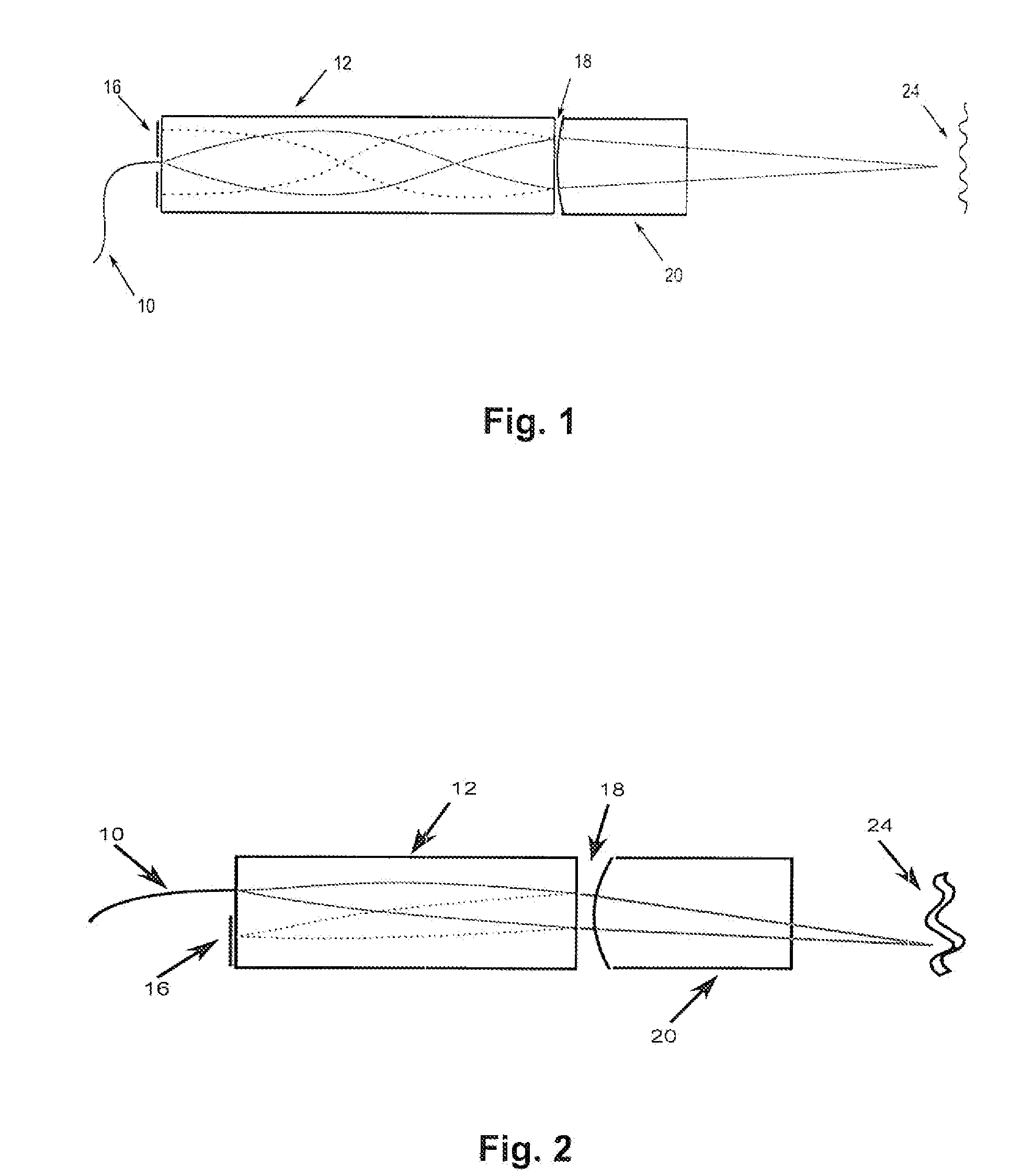
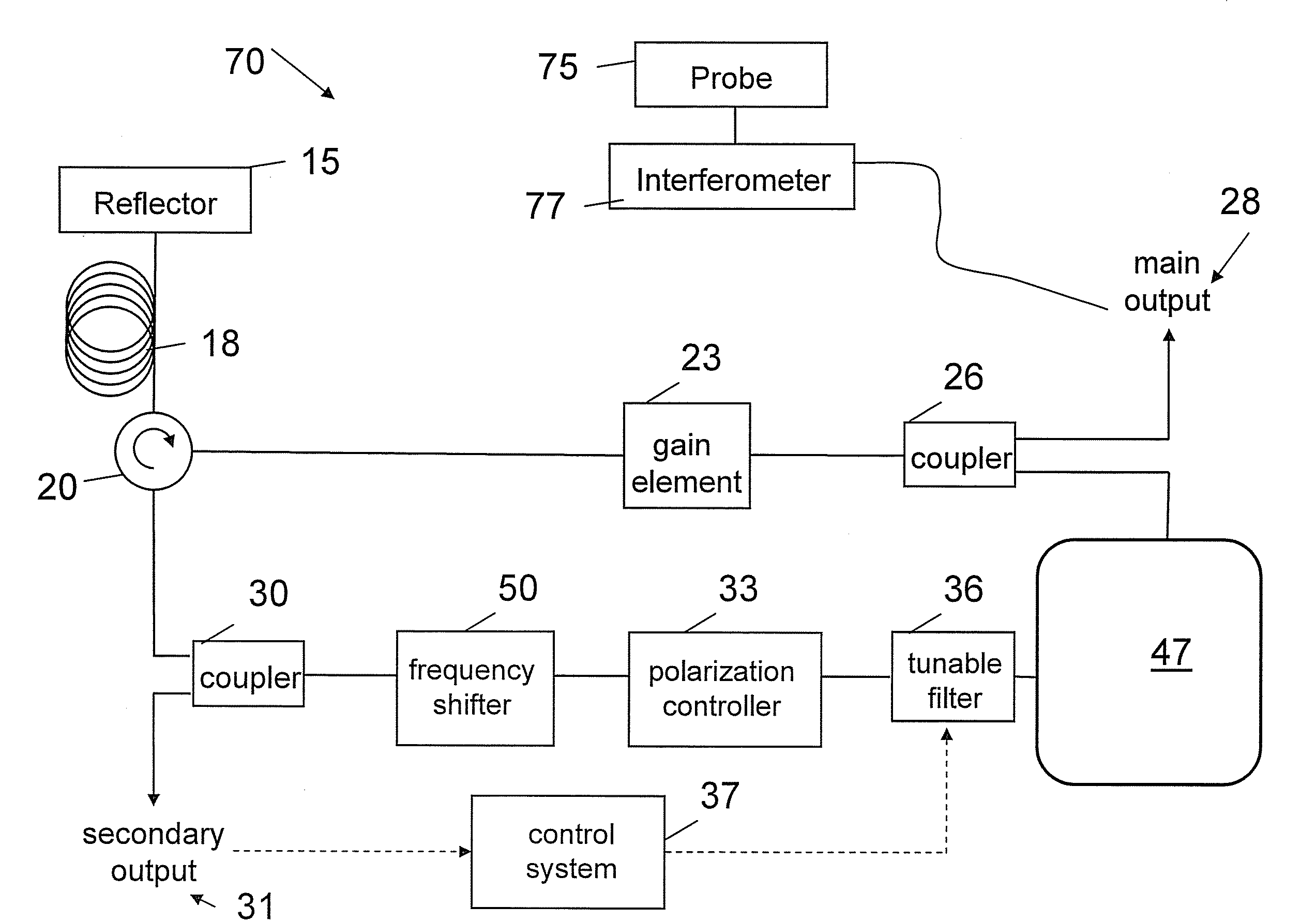
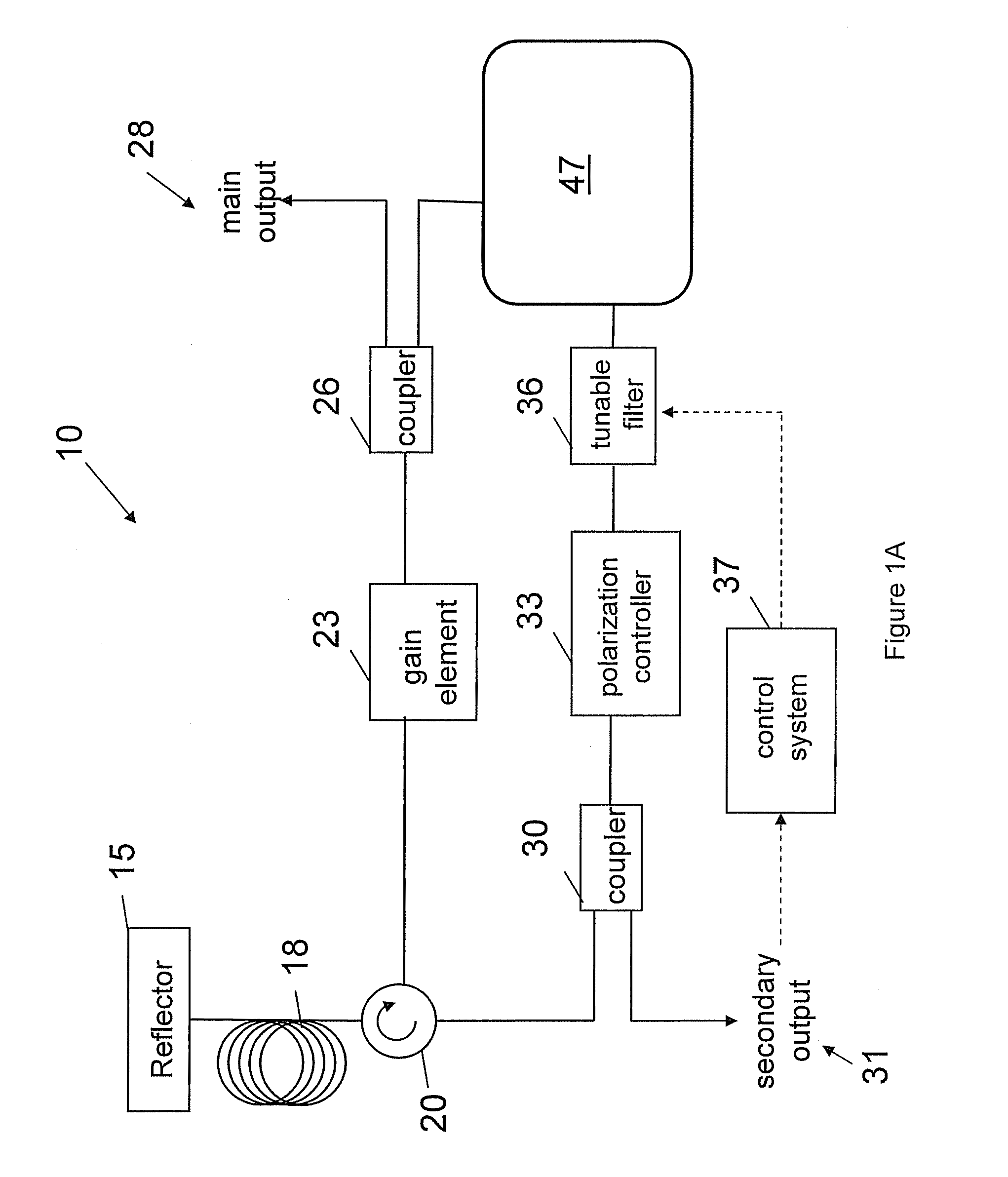
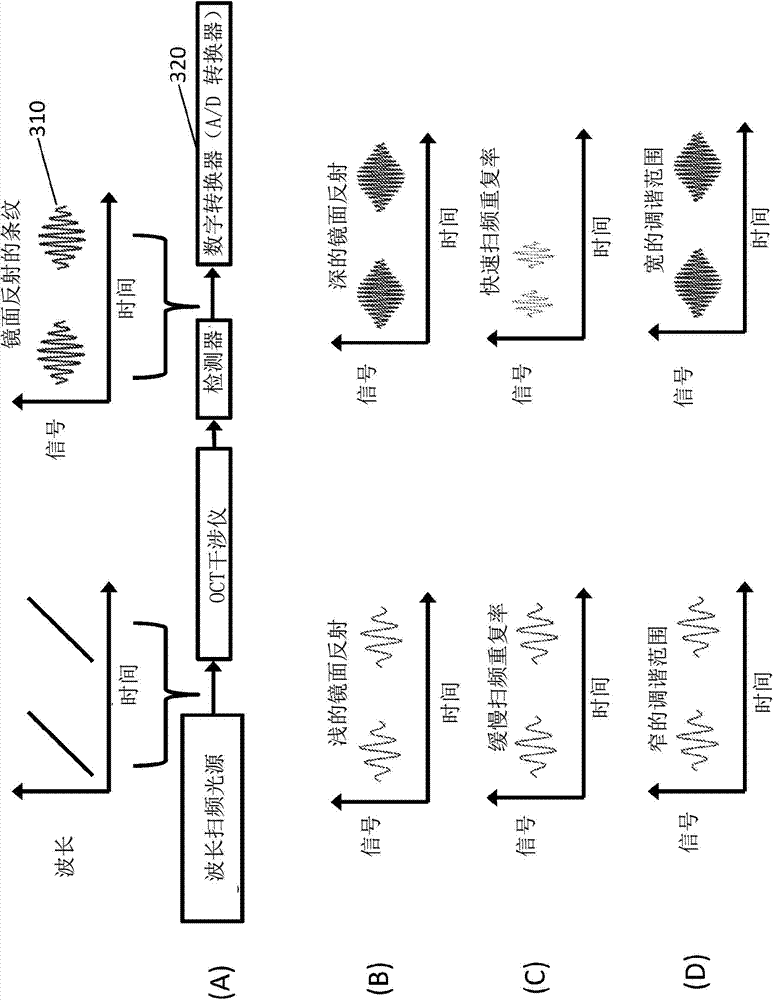
In one embodiment, the invention relates to systems, methods and devices for improving the operation of an electromagnetic radiation source or component thereof. In one embodiment, the source is a laser source. A Fourier domain mode locked laser can be used in various embodiments. The sources described herein can be used in an optical coherence tomography (OCT) system such as a frequency domain OCT system. In one embodiment, laser coherence length is increased by compensating for dispersion. A frequency shifter can also be used in one embodiment to compensate for a tunable filter induced Doppler shift.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
Methods, Systems, and Devices for Timing Control in Electromagnetic Radiation Sources
ActiveUS20120236883A1Reduce and remove dispersionHigh gainOptical resonator shape and constructionUsing optical meansTime controlElectromagnetic radiation
In one embodiment, the invention relates to systems, methods and devices for improving the operation of an electromagnetic radiation source or component thereof. In one embodiment, the source is a laser source. A Fourier domain mode locked laser can be used in various embodiments. The sources described herein can be used in an optical coherence tomography (OCT) system such as a frequency domain OCT system. In one embodiment, laser coherence length is increased by compensating for dispersion. A frequency shifter can also be used in one embodiment to compensate for a tunable filter induced Doppler shift.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
Simultaneous phase-shifting fizeau interferometer
ActiveUS20050046864A1Mitigate stray reflectionReduce measurement integration timeInterferometersUsing optical meansPhase shiftedLight beam
The tilted relationship between the reference and test mirrors of a Fizeau interferometer is used to spatially separate the reflections from the two surfaces. The separate beams are filtered through a spatial polarization element that provides different states of polarization to the beams. The beams are subsequently recombined to form a substantially collinear beam that is processed using a spatial-phase-shift interferometer that permits quantitative phase measurement in a single video frame. Alternatively, two beams with orthogonal polarization are injected into the Fizeau cavity at different angles, such that after reflection from the reference and test optics they are substantially collinear. Unwanted reflections are blocked at the focal plane through the use of a circular aperture. Short coherence length light and a delay line may be used to mitigate stray reflections, reduce measurement integration times, and implement temporal phase averaging.
Owner:ONTO INNOVATION INC
Optical coherent tomography
ActiveUS20080159468A1Increase speedContinuous changeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingFast Fourier transformOptical tomography
A surface emission laser light source is used as a tunable laser light source. Since the surface emission laser light source can realize a broad frequency scanning range at a high speed and in the single mode, a coherent length is longer than that of a multi mode light source. For this reason, when a tomography image is calculated by executing the Fourier transform for an output obtained from an interference optical device, measuring depth can be deepened.
Owner:SANTEC
Illuminating optical unit in image display unit, and image display unit
InactiveUS6897992B2Suppress speckle noiseSuppresses degradation of image qualityTelevision system detailsProjectorsLight beamOptoelectronics
Disclosed is an illuminating optical unit in an image display unit for displaying an image by irradiating a GLV (spatial modulation device) with a laser beam and modulating the laser beam based on an image signal inputted to the GLV, which includes a polarized light rotation means for equally dividing a polarized light component of the laser beam into a P polarized light component and an S polarized light component, a polarized light beam splitter for separating from each other the P polarized light component and the S polarized light component equally divided by the polarized light rotation means, and an optical path difference generation means for generating an optical path difference not less than the coherence length of the laser beam between the laser beam of the P polarized light component and the laser beam of the S polarized light component.
Owner:SONY CORP
Device for measuring linewidth of narrow linewidth laser based on optical fiber time-delay self heterodyne method as well as method for measuring thereof
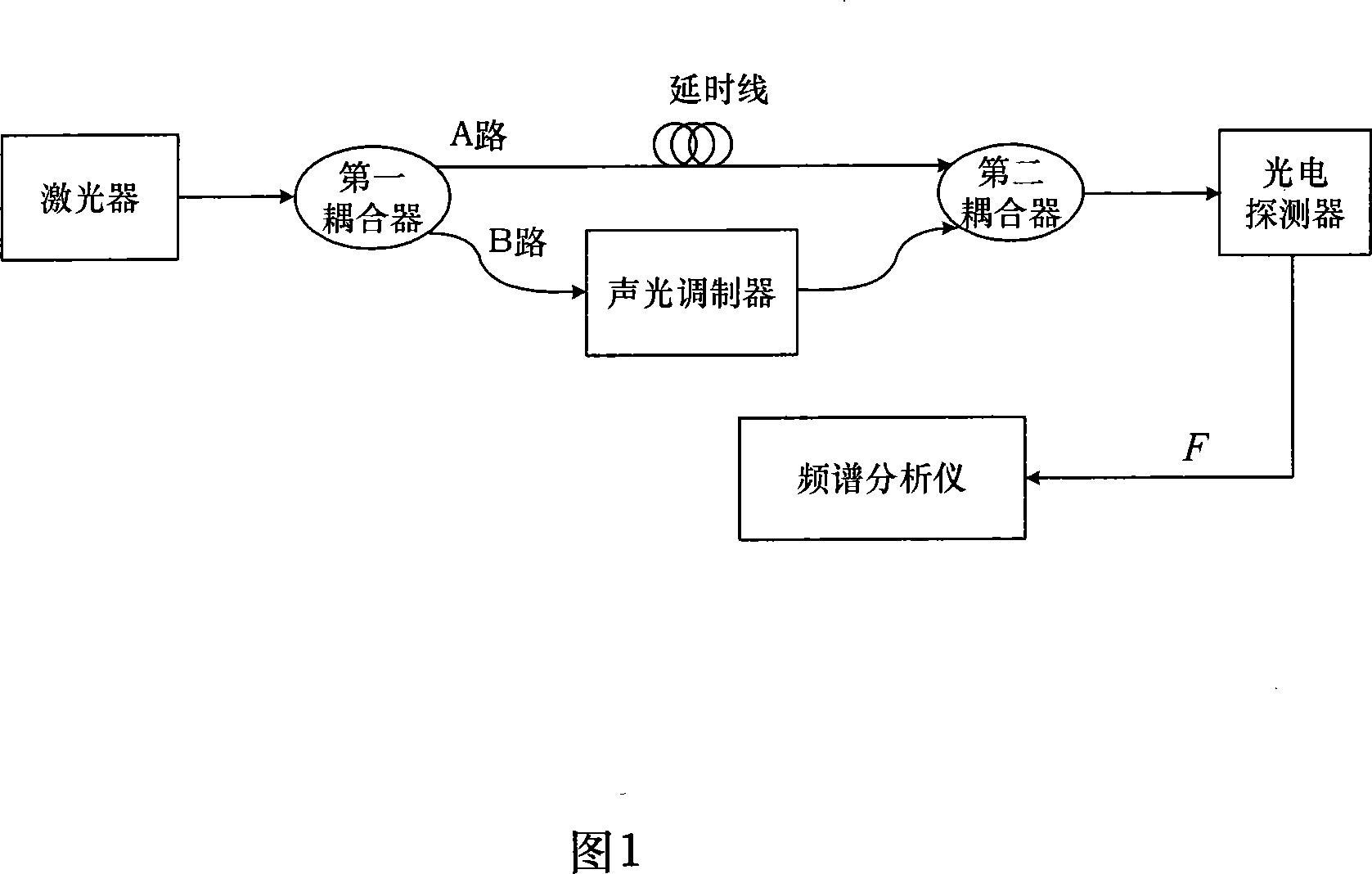
InactiveCN101201243ARealize high-precision testingReduce volumeUsing optical meansThree levelSpectrum analyzer
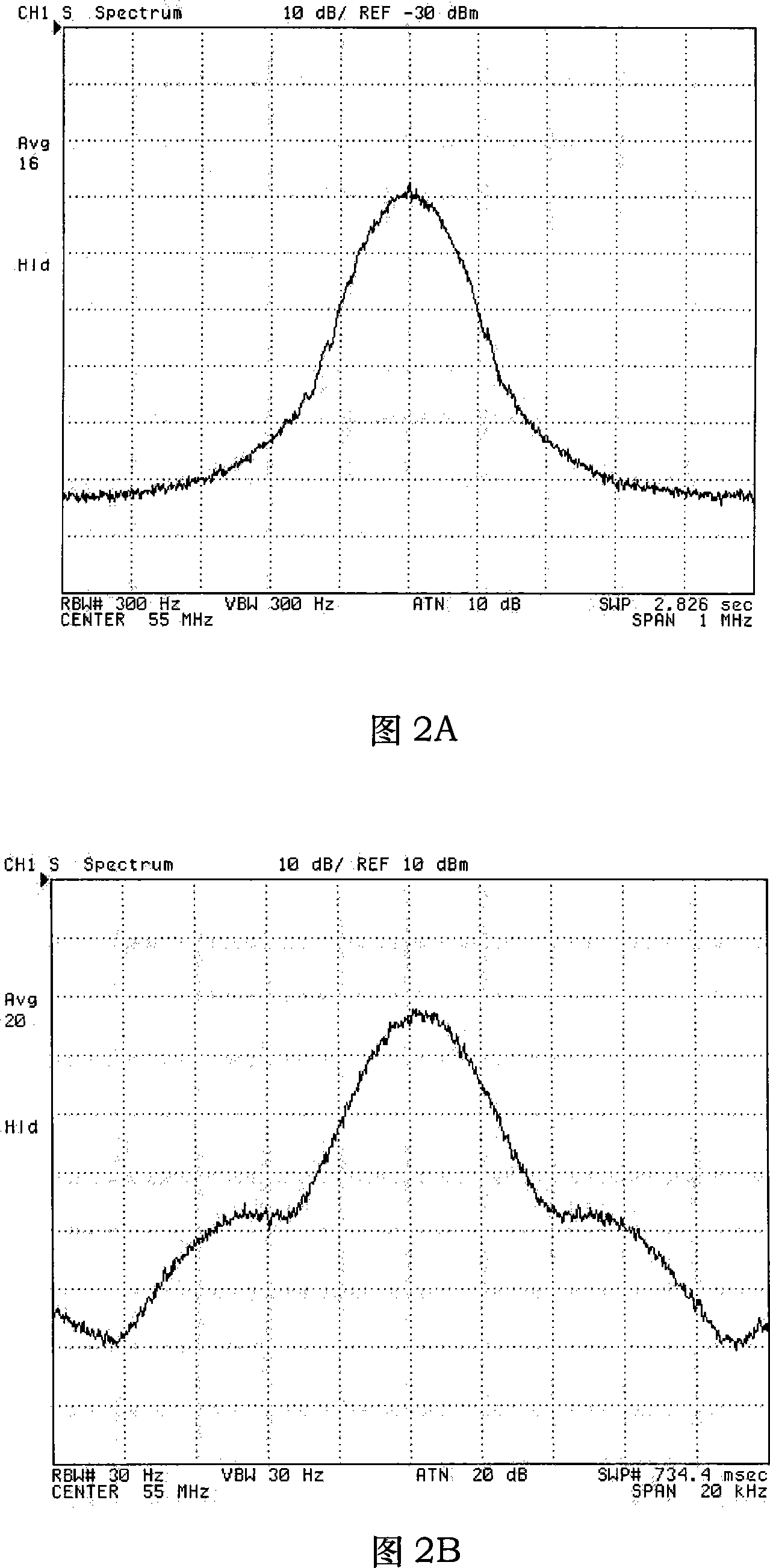
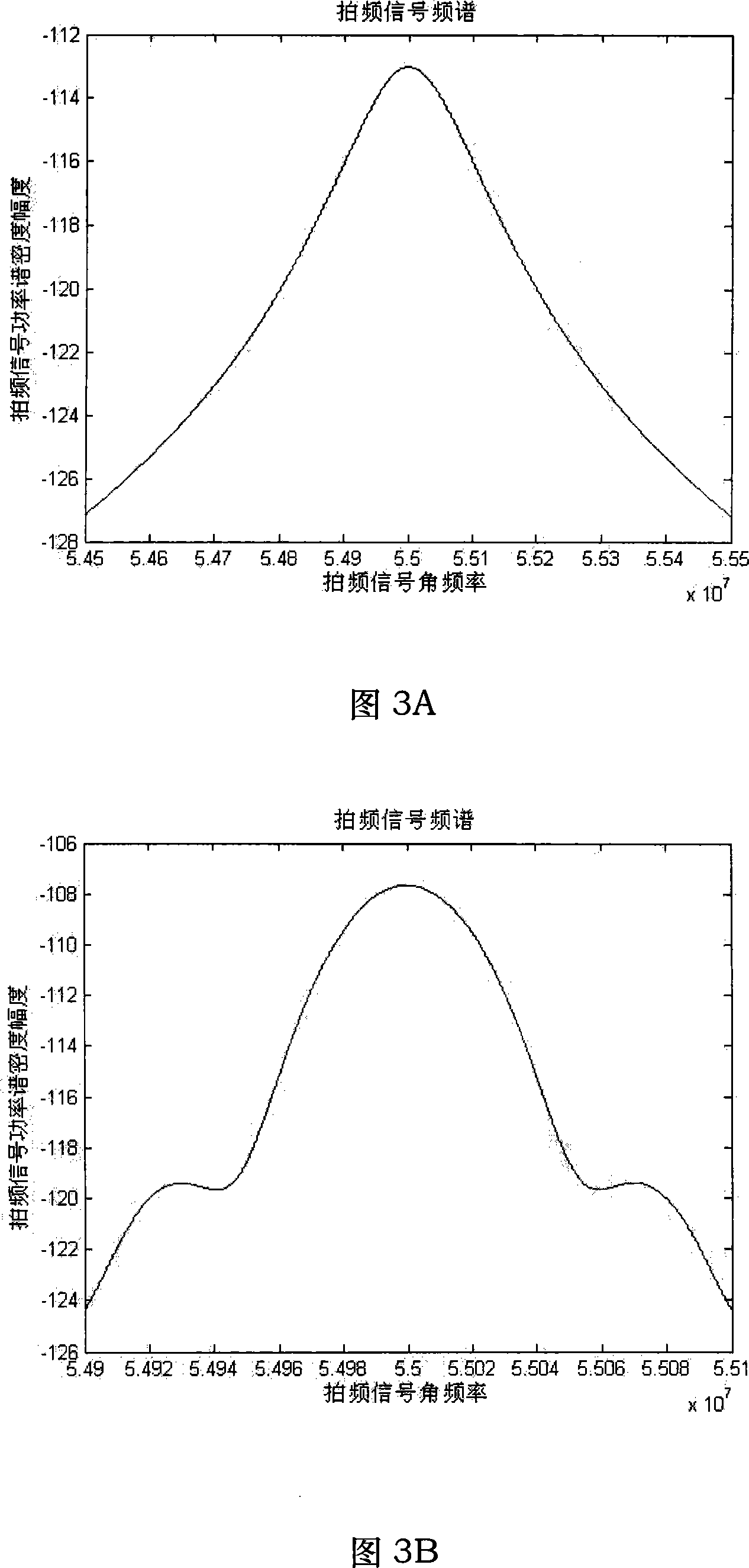
The invention discloses a device of measuring the line-width of a laser with narrow line-width and a method of measuring the line-width based on a optical fiber delay self-heterodyne method; in the hardware device, an optical fiber delay line is connected between a first and a second couplers; an acousto-optic modulator is connected between the first and the second couplers; the measured laser is connected to the input of the first coupler, and a photoelectric detector is connected to the output of the second coupler; the photoelectric detector is connected with a spectrum analyzer. In the line-width measurement, simulation models of the line-width triangle v of the laser and the spectrum-width triangle f of the photoelectric current heterodyne signal are built in the frequency shift delay self-heterodyne methodology, and the function relation between the line-width triangle v of the laser and the spectrum-width triangle f of the photoelectric current heterodyne signal is obtained fitting of the three-level proportion function model. The invention presents that with the short optical fiber delay self-heterodyne method, the device can eliminate the deficiency of greatly reduced measuring precision because of not enough delayed time in the delay self-heterodyne method when the length of the delay optical fiber is less than 6 times coherence length of the laser, so as to provide an effective method of precisely measuring the line-width of the laser with narrow line-width in projects.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
System for measuring the optical image quality of an eye in a contactless manner
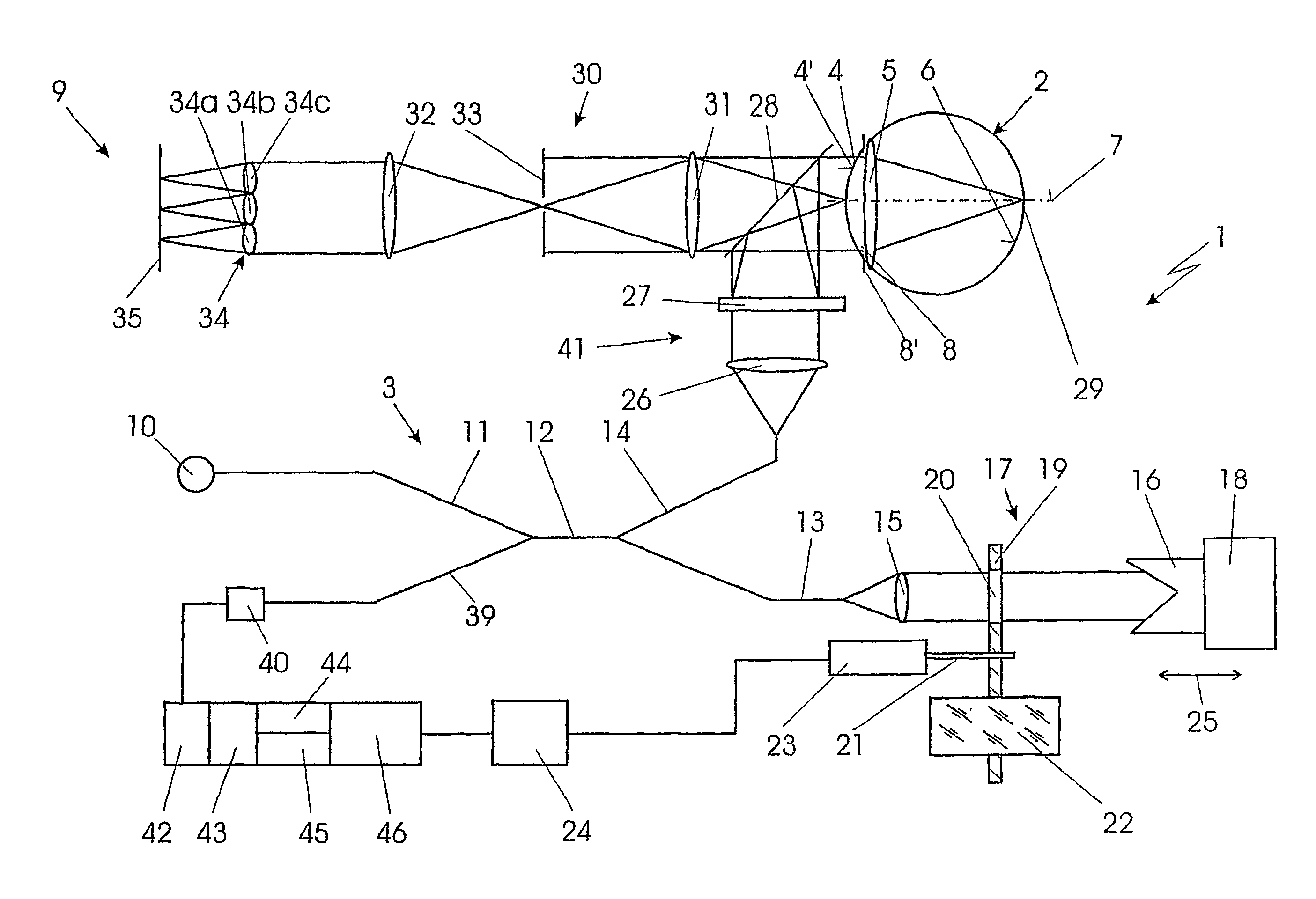
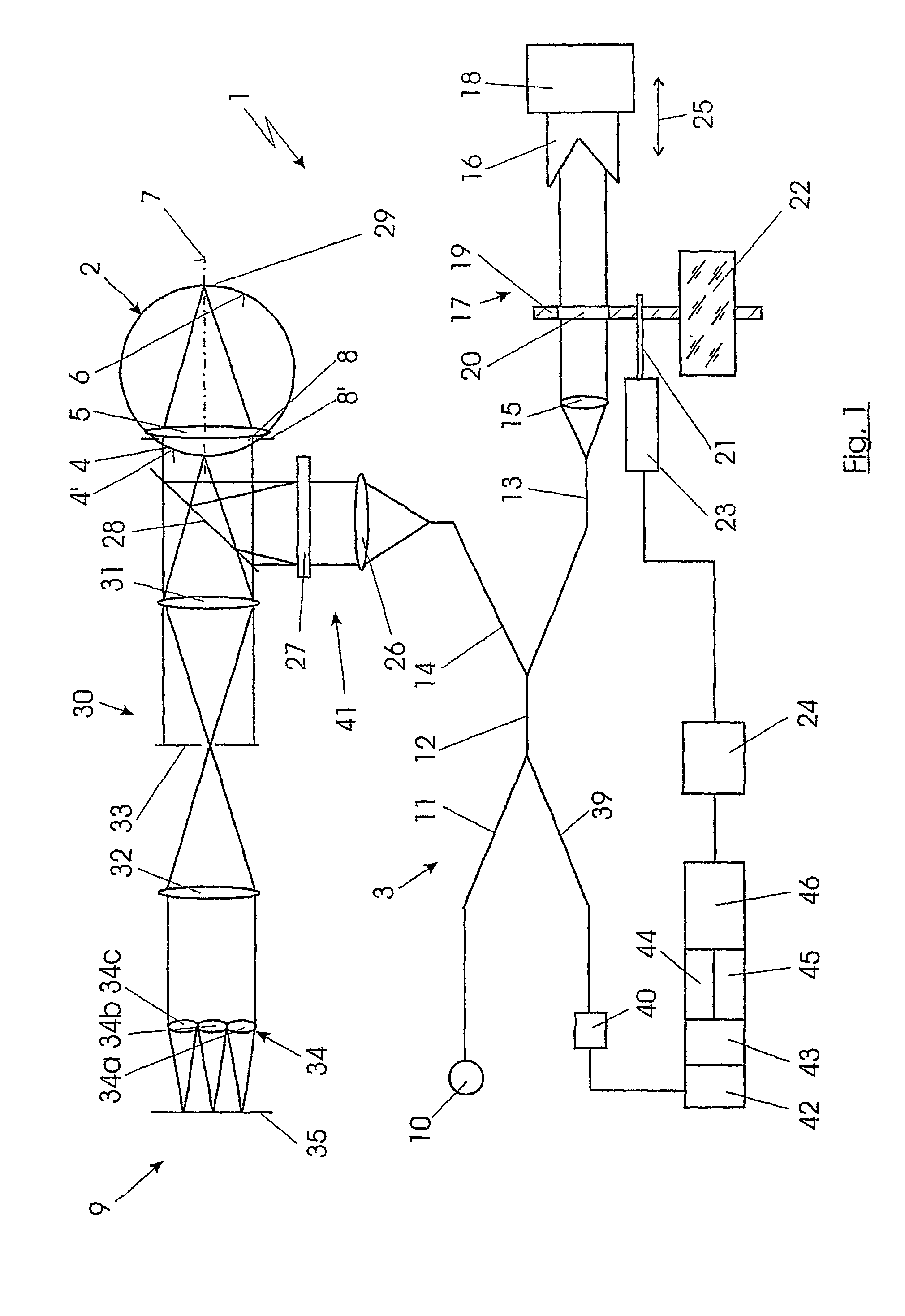
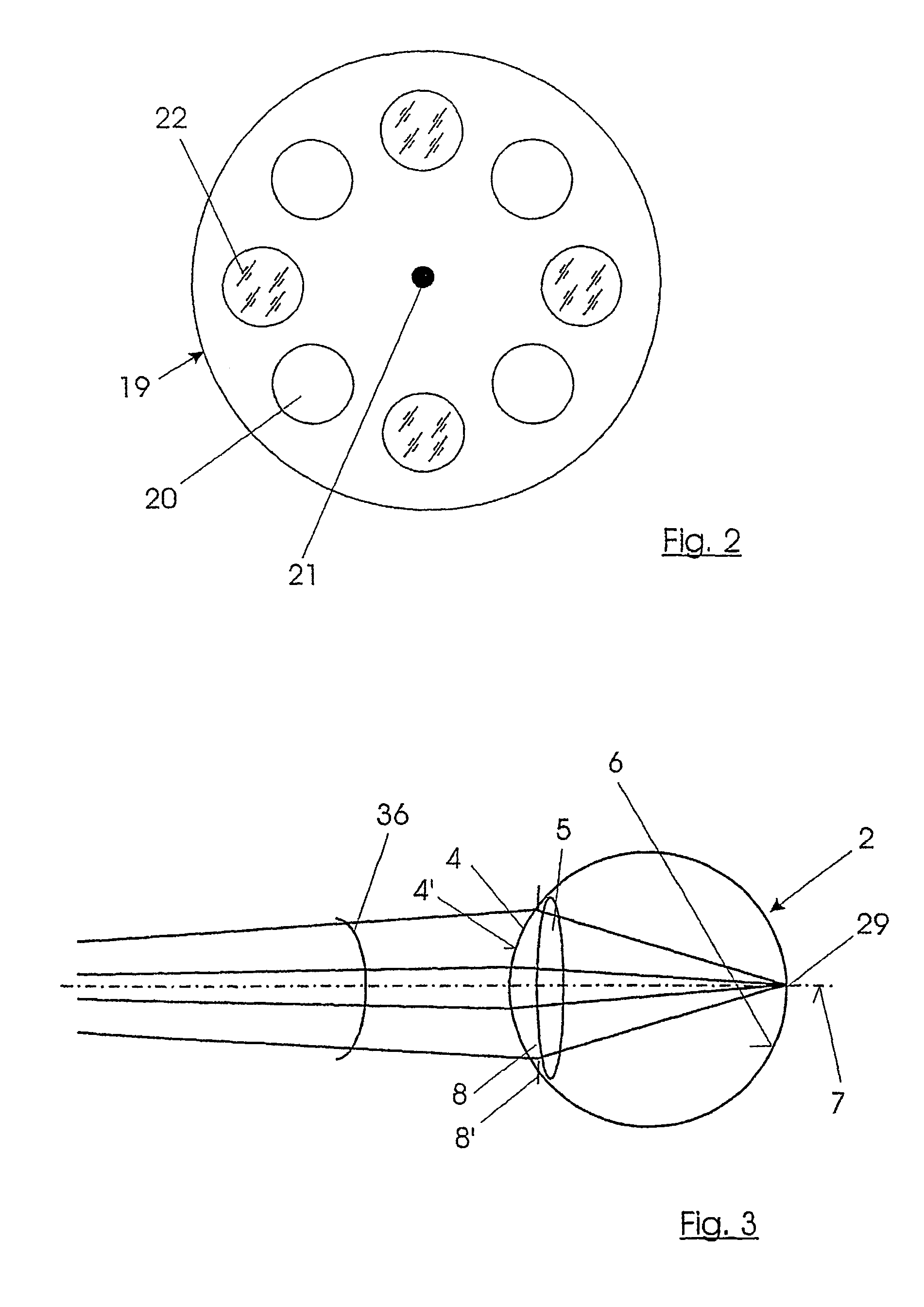
InactiveUS7084986B2Easy to useQuality improvementInterferometersUsing optical meansRetinaCoherence length
A system is used for contactless measurement of the optical imaging quality of an eye with an interferometer by which at least one light pulse with a short coherence length is coupled into the eye from a light source. The optical path length of at least one arm of the interferometer is varied for measuring the length of the eye until a typical interference pattern between a reflection of the cornea and a reflection of the retina of the eye occurs in a detector. This interference pattern together with a known path segment of the variation of the optical path length allows conclusions to be made about the length of the eye. The variation of the optical path length is carried out by introducing at least partially optically transparent elements and by at least one element of the interferometer which is movable in a defined manner in at least one of the light paths of the interferometer.
Owner:CARL ZEISS JENA GMBH
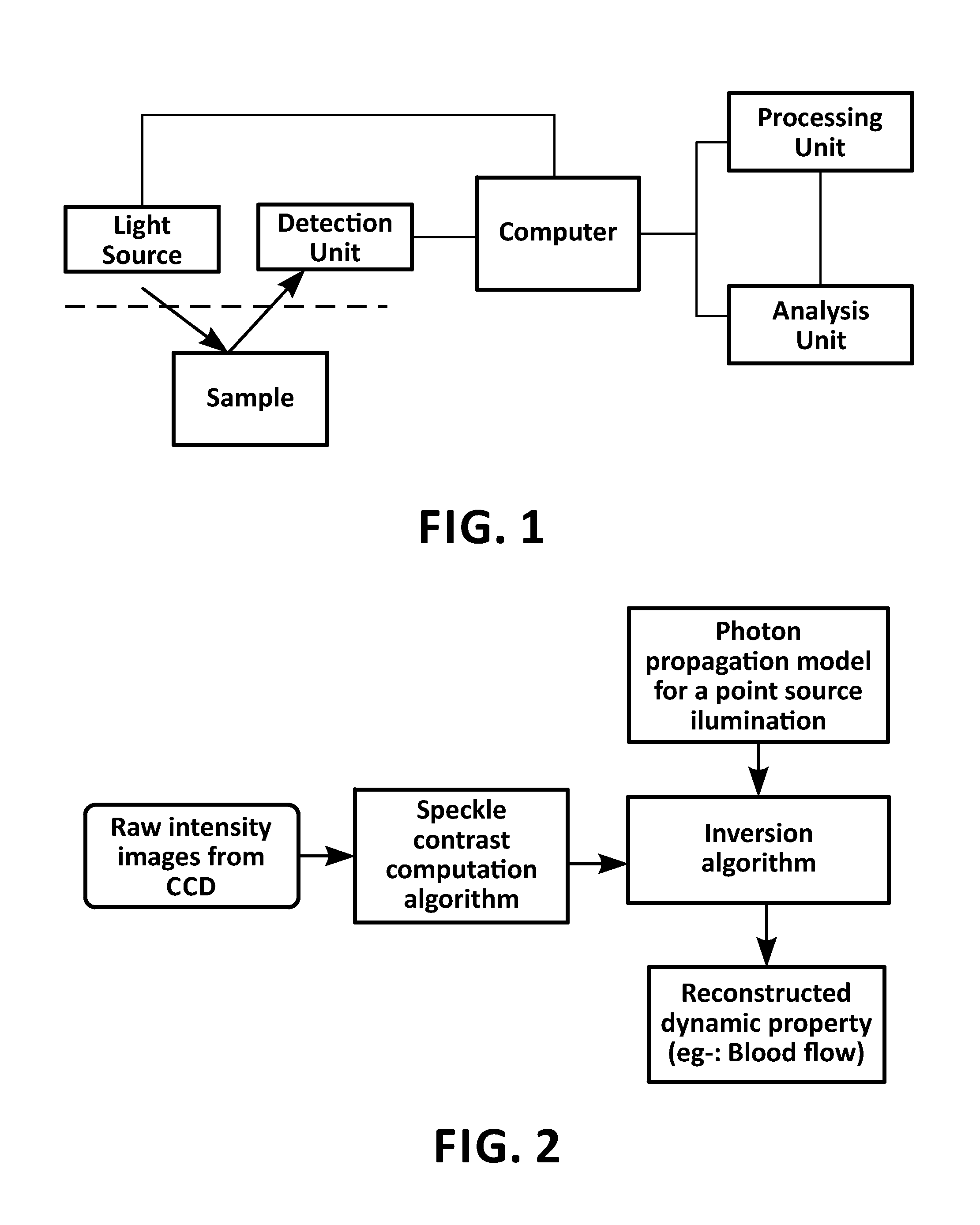
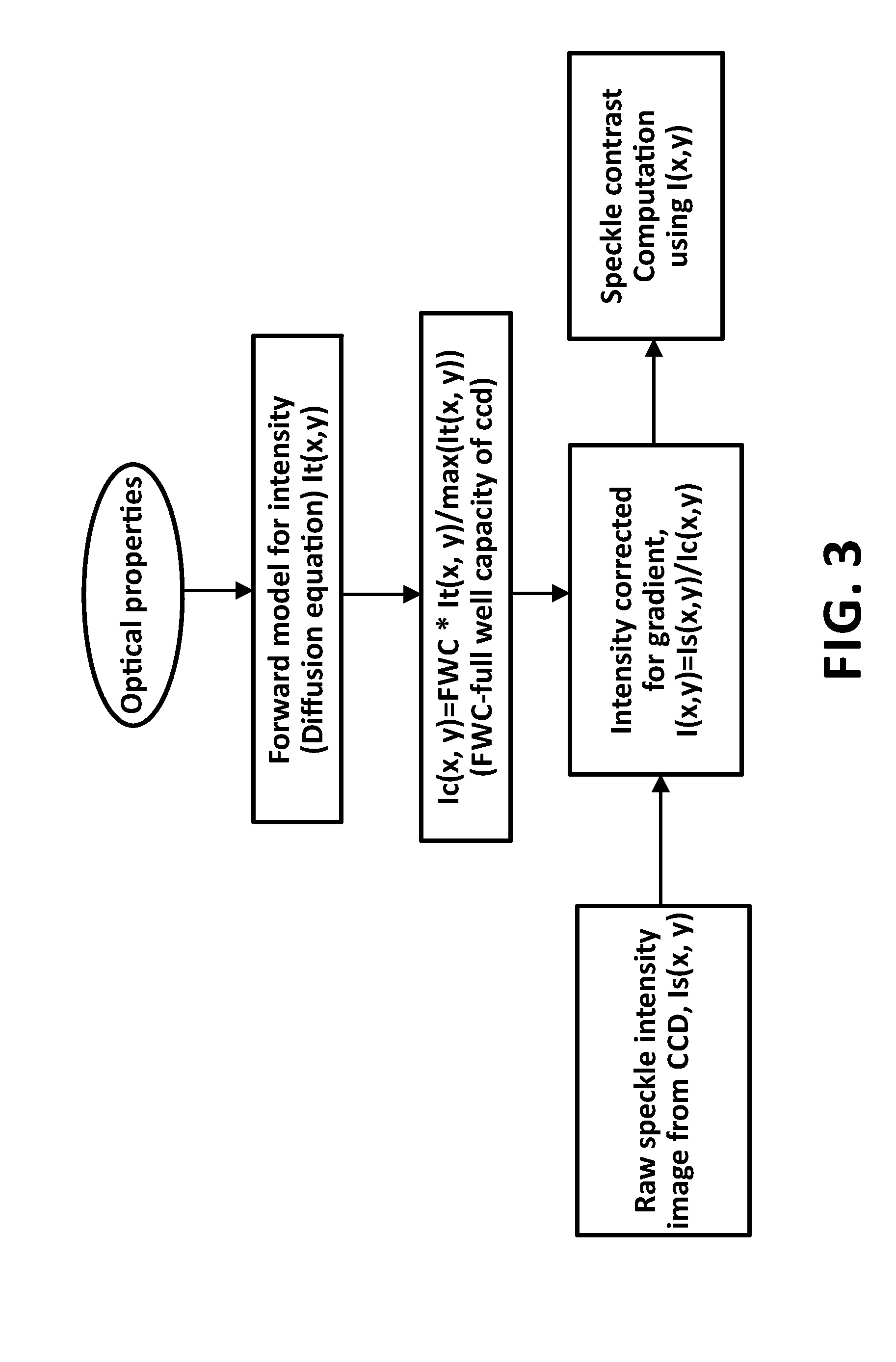
Speckle contrast optical tomography
ActiveUS20150182136A1Increase contrastIncrease the number ofDiagnostics using tomographyUsing optical meansOptical tomography3d image
Speckle contrast optical tomography system provided with at least one point source and multiple detectors, means for providing different source positions, the point source having a coherence length of at least the source position-detector distance and means for arranging the source position-detector pairs over a sample to be inspected, the system being further provided with means for measuring the speckle contrast; the speckle contrast system of the invention thus capable of obtaining 3D images.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS +1
Agile imaging system
ActiveCN104755908AEnhanced Dynamic Range Imaging CapabilitiesLaser detailsSurgeryMultiple modesLength wave
An agile optical imaging system for optical coherence tomography imaging using a tunable source comprising a wavelength tunable VCL laser is disclosed. The tunable source has long coherence length and is capable of high sweep repetition rate, as well as changing the sweep trajectory, sweep speed, sweep repetition rate, sweep linearity, and emission wavelength range on the fly to support multiple modes of OCT imaging. The imaging system also offers new enhanced dynamic range imaging capability for accommodating bright reflections. Multiscale imaging capability allows measurement over orders of magnitude dimensional scales. The imaging system and methods for generating the waveforms to drive the tunable laser in flexible and agile modes of operation are also described.
Owner:THORLABS INC +1
Optical transmission link including raman amplifier
An optical transmission system that employs a Raman amplifier including a Raman pump for introducing depolarized pump light into the fiber. The pump includes an optical source generating a polarized optical pump signal, an optical splitter that splits the pump signal into a first pump portion and a second pump portion, and a beam combiner that combines the first pump portion and the second pump portion into the depolarized pump light. Further, the pump includes a delay device, such as a length of fiber, that causes the first pump portion to propagate farther from the beam splitter to the beam combiner than the second pump portion. The length of fiber is longer than the coherence length of the pump signal.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
Reticle Inspection Systems and Method
ActiveUS20100149548A1Easy to distinguishPhase-affecting property measurementsPhotomechanical apparatusImage subtractionPhase difference
A method and systems for reticle inspection. The method includes coherently illuminating surfaces of an inspection reticle and a reference reticle, applying a Fourier transform to scattered light from the illuminated surfaces, shifting the phase of the transformed light from the reference reticle such that a phase difference between the transformed light from the inspection reticle and the transformed light from the reference reticle is 180 degrees, combining the transformed light as an image subtraction, applying an inverse Fourier transform to the combined light, and detecting the combined light at a detector. An optical path length difference between two optical paths from the illumination source to the detector is less than a coherence length of the illumination source. The image detected by the detector represents a difference in amplitude and phase distributions of the reticles allowing foreign particles, defects, or the like, to be easily distinguished.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
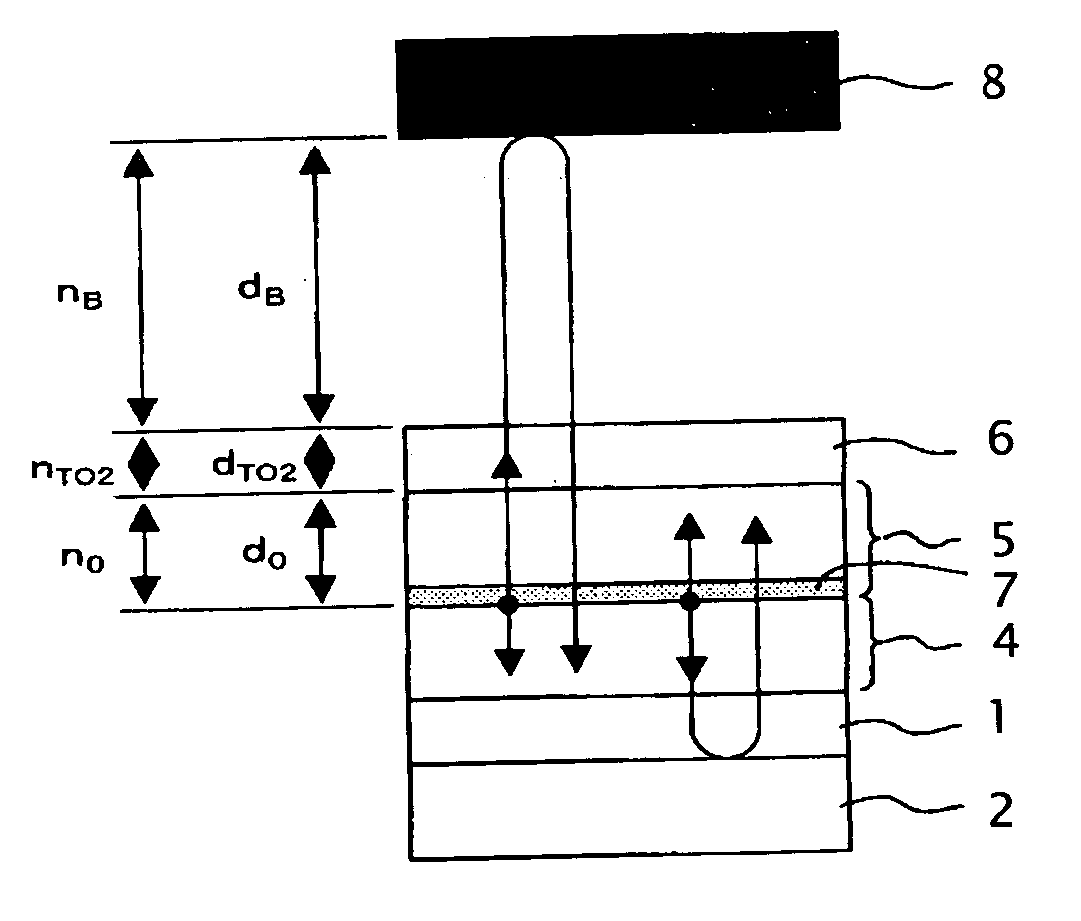
Light emitting diode device
InactiveUS20060049419A1Eliminate the effects ofEfficient extractionElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesRefractive indexCoherence length
A light emitting diode device can include a pair of opposed electrodes and a thin film multilayer structure interposed between the pair of electrodes. The device can include one or more light emitting layers each having an emission interface. In the device, there can be adjacent layers having an interfacial plane therebetween. The interfacial plane being disposed in a position where an optical path length from the emission interface to the interfacial plane is substantially equal to, or less than, the coherent length of light emitted from the emission interface. Furthermore, the difference in refractive index between the adjacent layers is substantially equal to, or less than, 0.6. This can eliminate an interference effect within the thin film multilayer structure, thereby enhancing light emitting efficiency and achieving intended light color.
Owner:STANLEY ELECTRIC CO LTD
Simultaneous phase-shifting Fizeau interferometer
ActiveUS7057738B2Reduce reflectionReduce integration timeInterferometersUsing optical meansPhase shiftedLight beam
Owner:ONTO INNOVATION INC
Atmospheric turbulance detection laser rader using position-sensitive detector
InactiveCN1945355ALow priceHigh sensitivityElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationRayleigh scatteringRefractive index
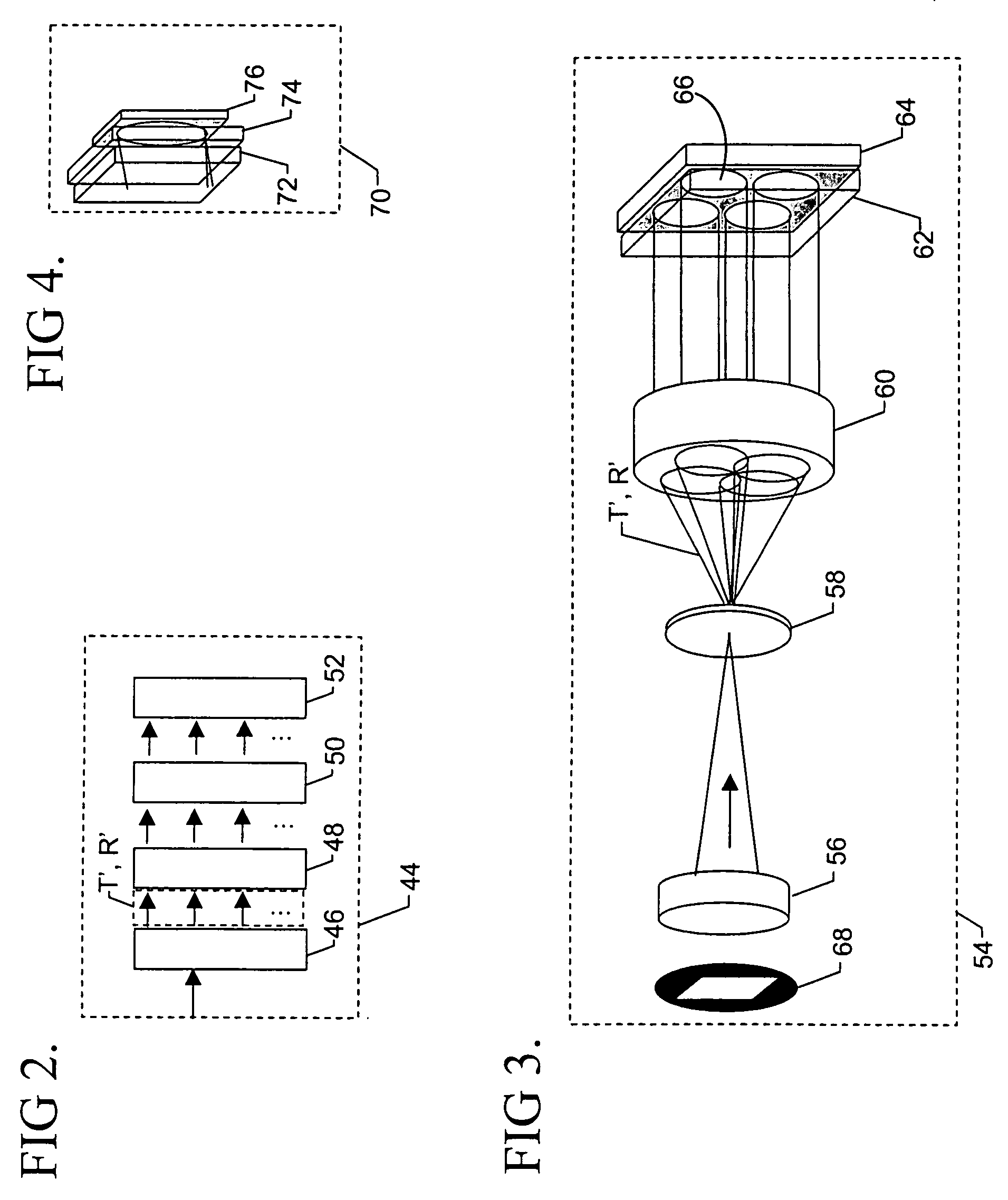
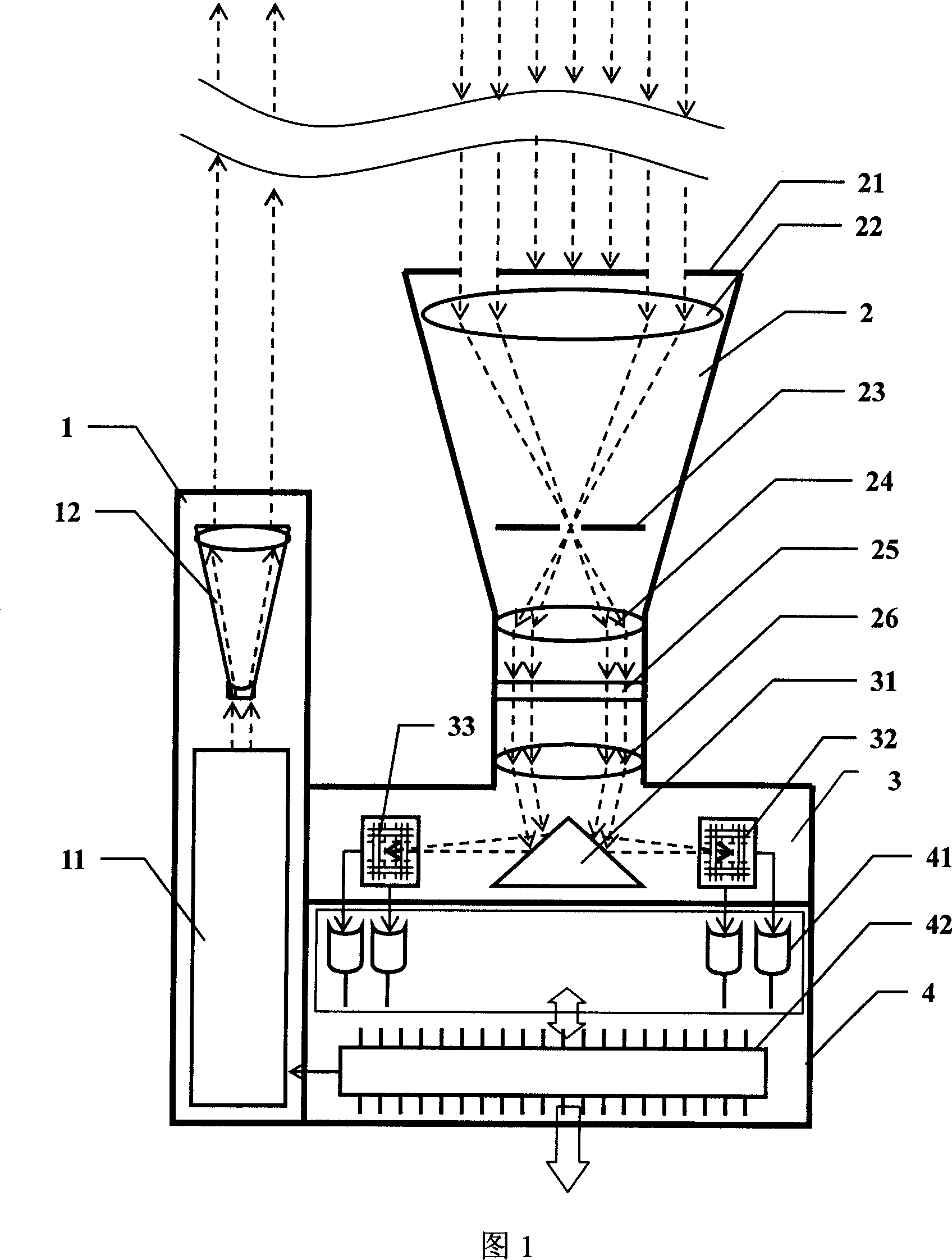
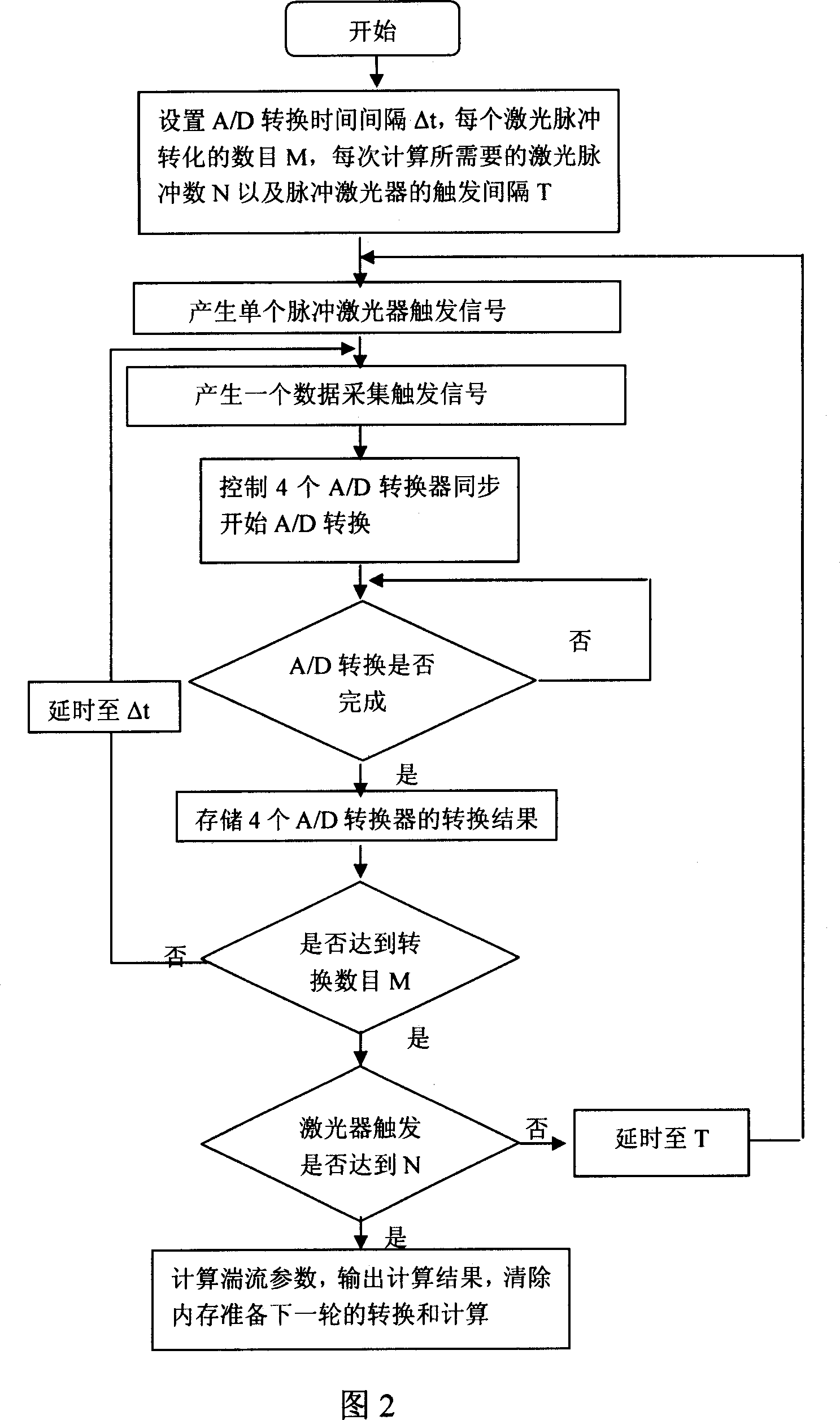
The invention discloses a laser radar for detecting the atmosphere turbulence via a positioning sensitive detector, which relates to the refractive index structure constant profile Cn2 and atmospheric coherence length r0 of the atmosphere turbulence. In the invention, the laser radar takes a pulsed laser as the emission source, and the dual-aperture Rayleigh scattering echo received by the telescopes is focused on the positioning sensitive detector through the reflection prism, and the profile Cn2 and atmospheric coherence length r0 are obtained by micro-processing after the positioning signals are transferred to the digital signals via A / D processor.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Broadband cavity spectrometer apparatus and method for determining the path length of an optical structure
InactiveUS20070086018A1Slack in trackRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryPath lengthFrequency spectrum
A broadband light source with a sufficiently long coherence length is impinged on the optical cavity. The broadband laser light reflects from the first and second surfaces of the cavity. The two light beams, either reflected or transmitted, are phase shifted from one another by an amount proportional to the optical path length of the cavity and inversely proportional to the wavelength of the light (4πnd / λ) The two light beams interfere with each other and form a modulated light beam that has a spectrum approximately like the laser's broadband spectrum multiplied by a cosine with a frequency 4πnd / λ. The modulated light beam is coupled to a spectrometer that measures the intensity of the light as a function of wavelength over a range of wavelengths. The Fourier transform of the spectrum contains a peak that is related to the OPL and is located at 2*n*d where n*d is the OPL.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HLDG 40
Compact multimode laser with rapid wavelength scanning
InactiveUS7843976B2Optical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersLength waveCoherence length
Owner:THORLABS INC
Fiber optical illumination system
InactiveUS6892013B2Reduce transmission lossIncrease illuminationOptically investigating flaws/contaminationCoupling light guidesFiberLighting system
A fiber optical illumination delivery system, which is effective in reducing the effects of source coherence. The system preferably utilizes either a single bundle of optical fibers, or serial bundles of optical fibers. In the single bundle embodiment, the differences in optical lengths between different fibers of the bundle is preferably made to be equal to even less than the coherence length of the source illumination. In the serial bundle embodiment, the fibers in the other bundle are arranged as groups of fibers of the same length, and it is the difference in lengths of these groups which is made equal to, or even more preferably, less than the overall difference in length between the shortest and the longest fibers in the other bundle. Both of these fiber systems enable construction of illumination systems delivering a higher level of illumination, but without greatly affecting the coherence breaking abilities of the system, thus enabling a generally more applicable system to be constructed.
Owner:NEGEVTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com