Patents
Literature
770 results about "Spatial modulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Spatial modulation (SM) is a multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) system that achieves a MIMO high spectral efficiency while maintaining the transmitter computational complexity and requirements as low as those of the single-input systems.
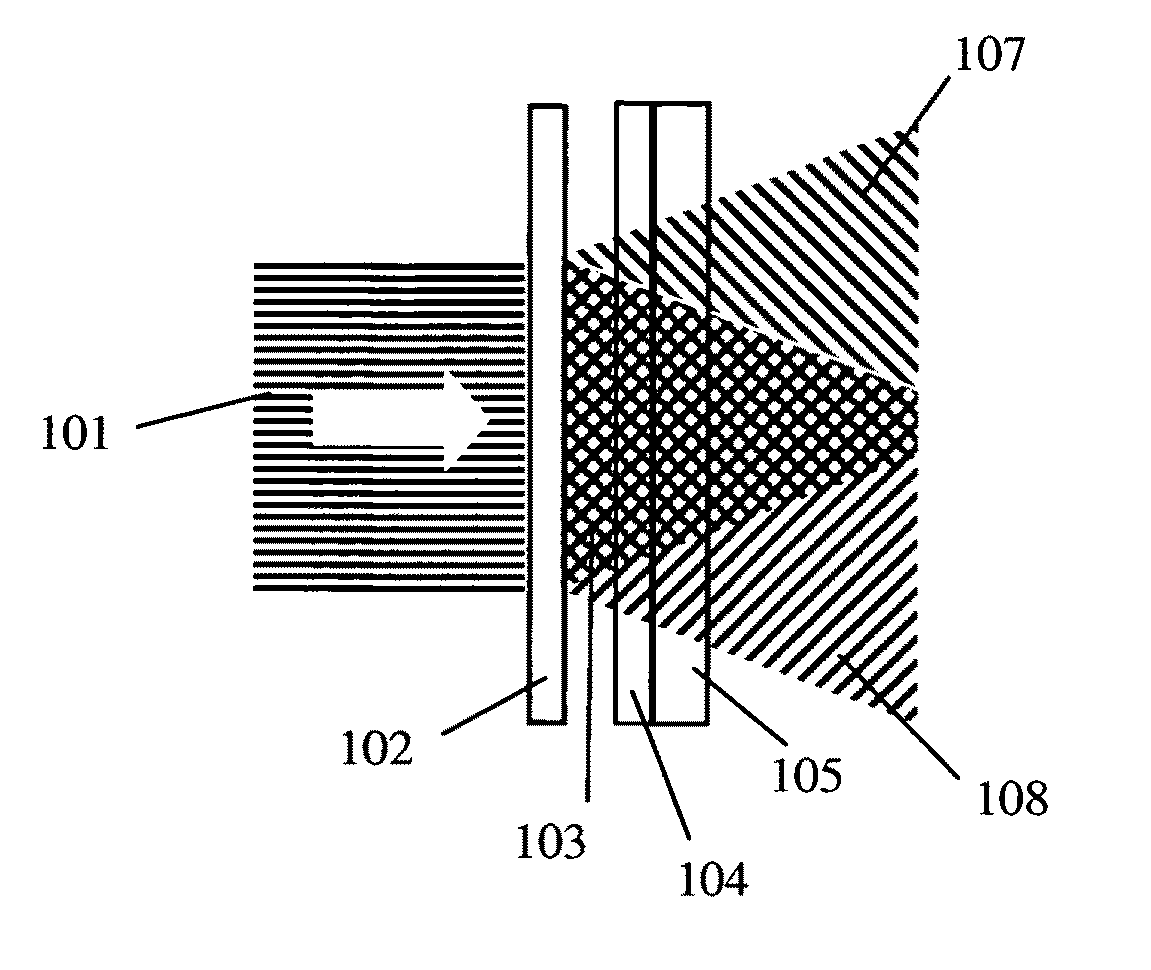
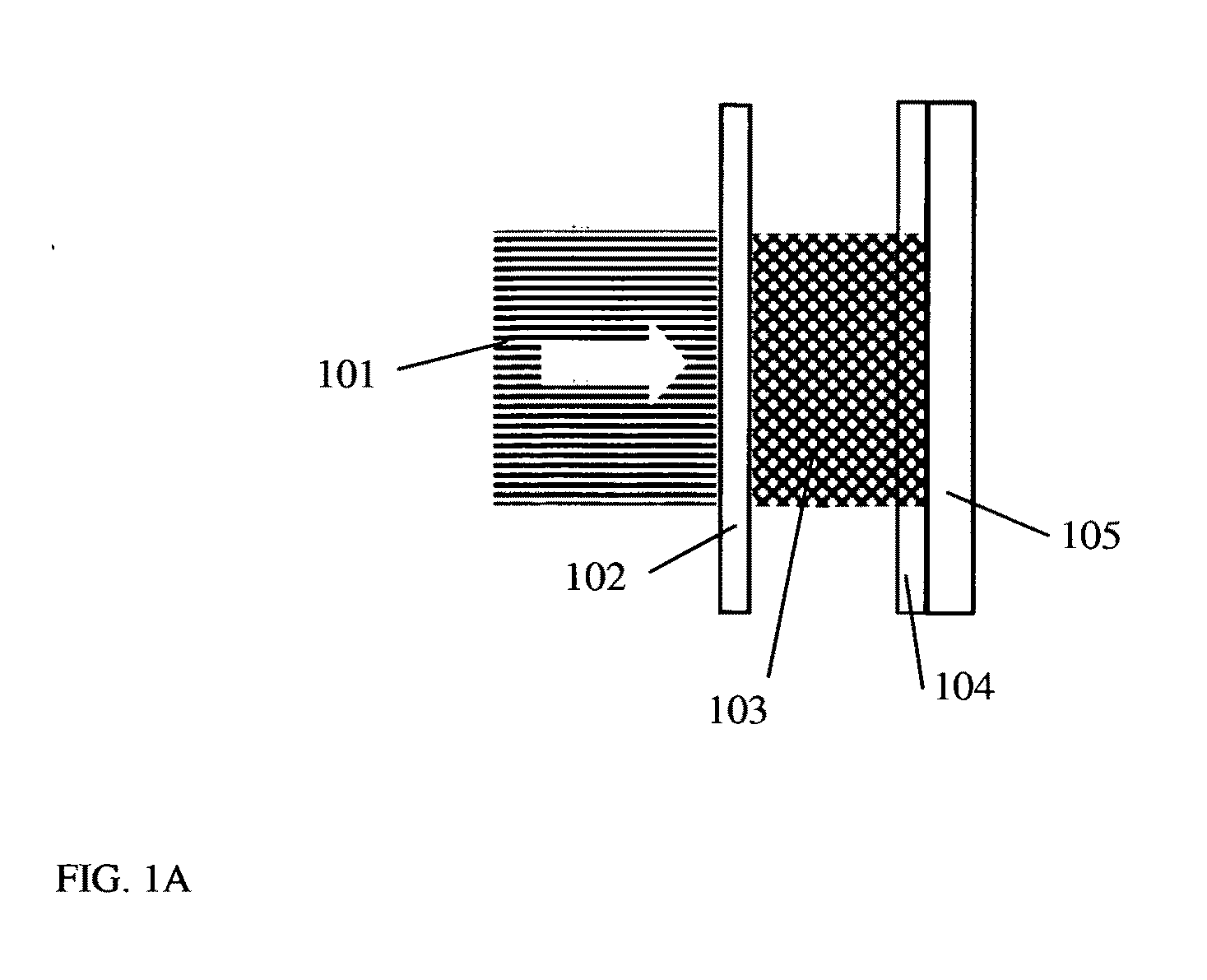
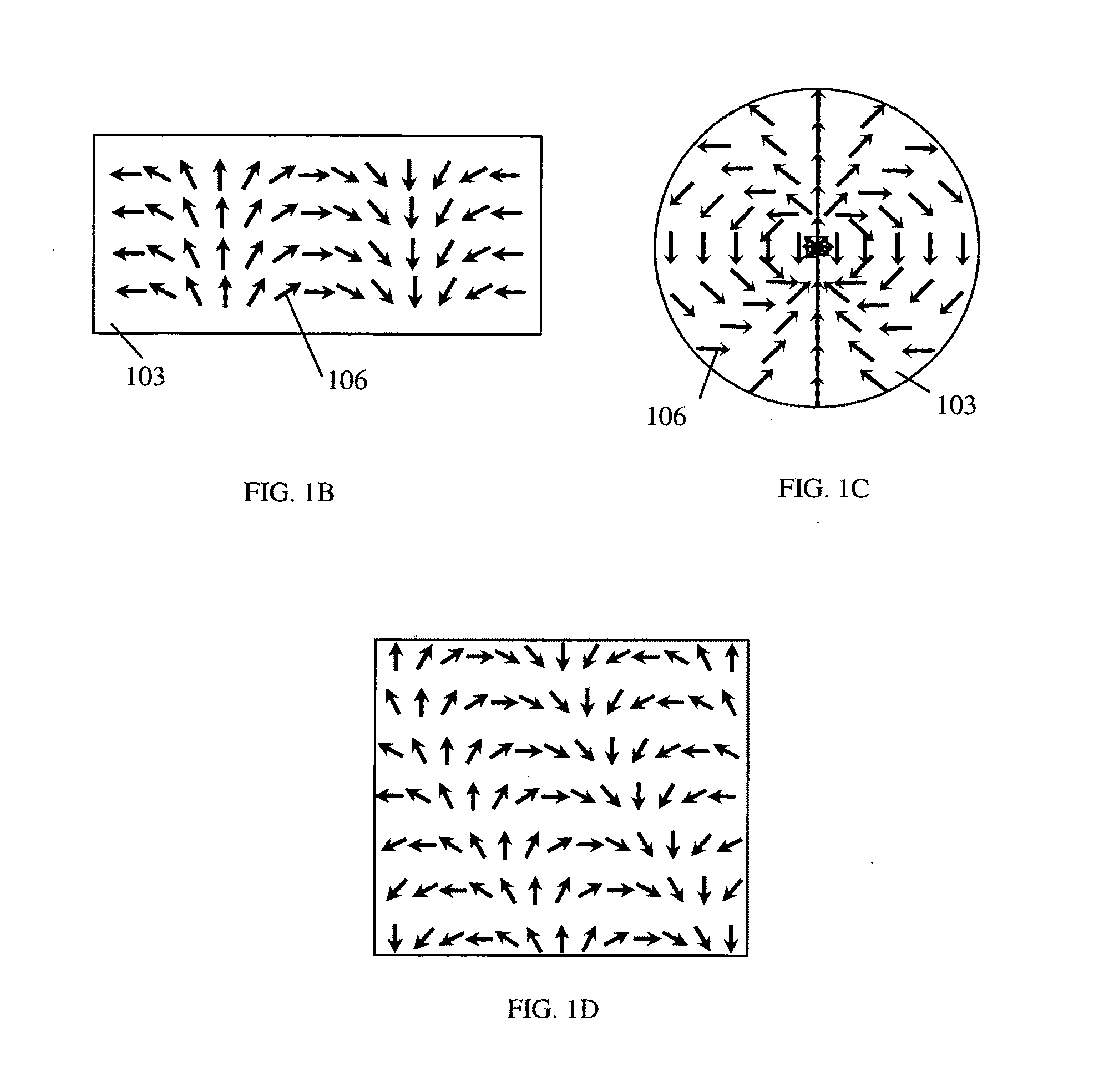
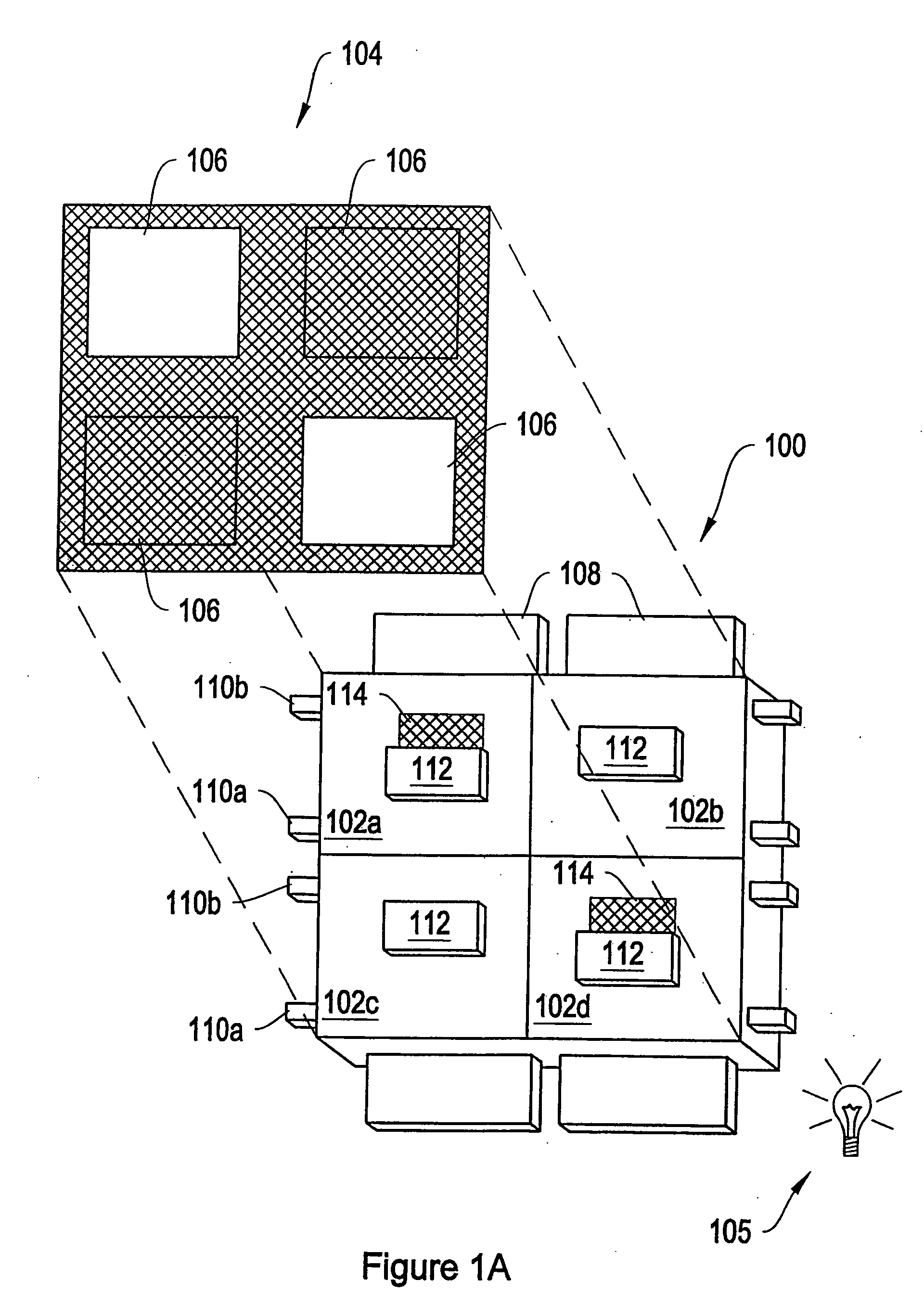
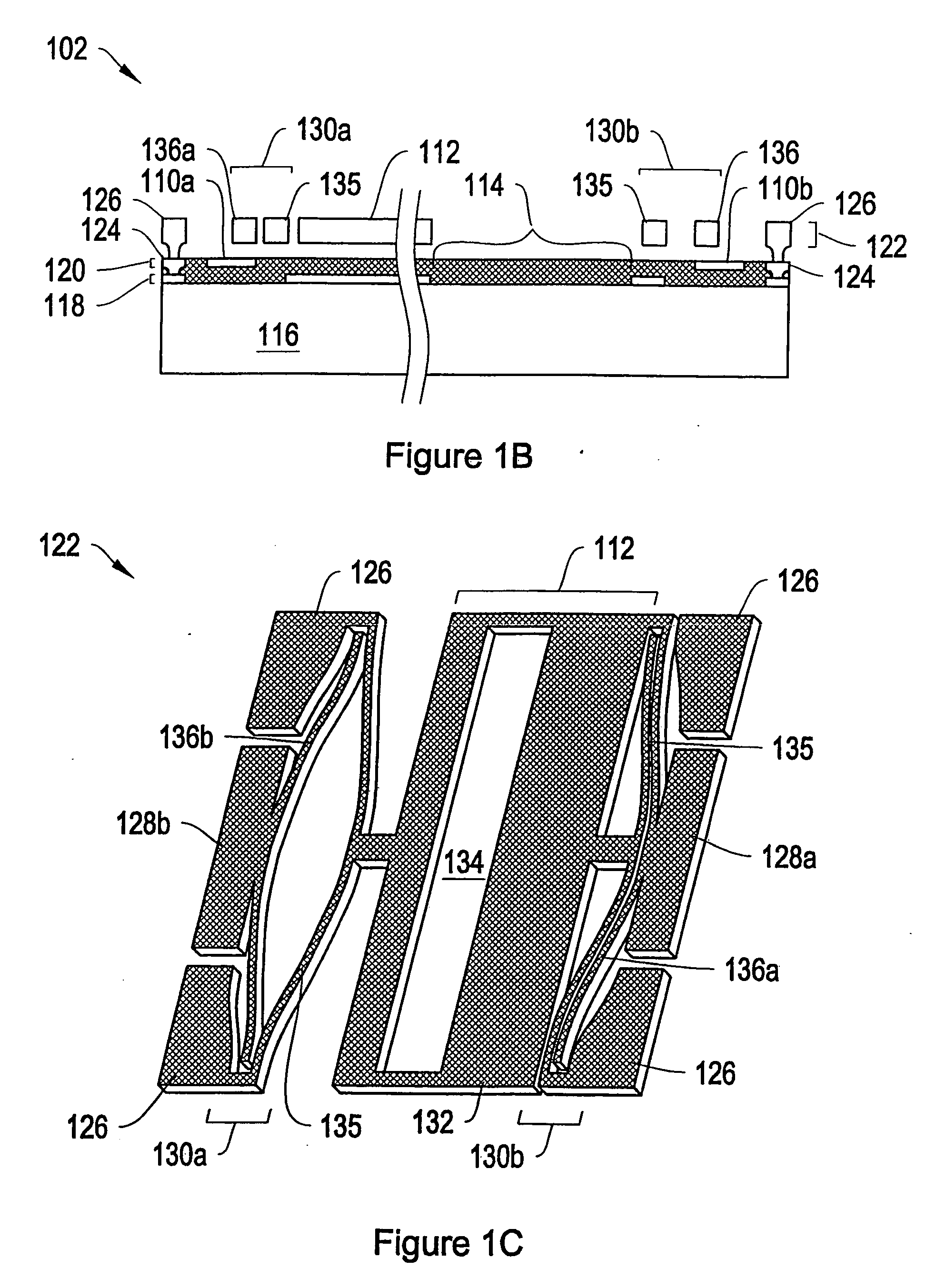
Coil array autocalibration MR imaging
InactiveUS6289232B1Shorten the timeEasy accessDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsData spaceIn vivo
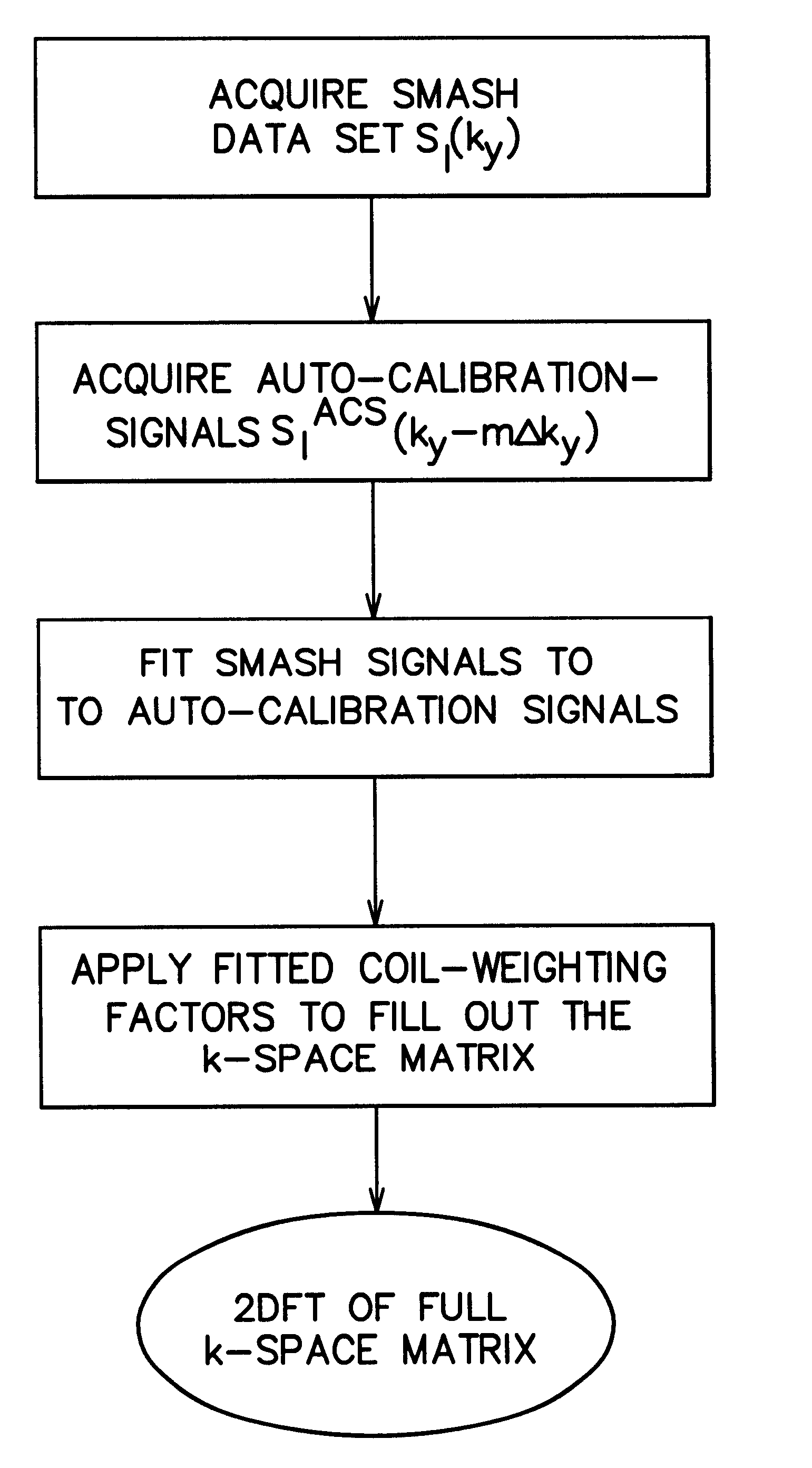
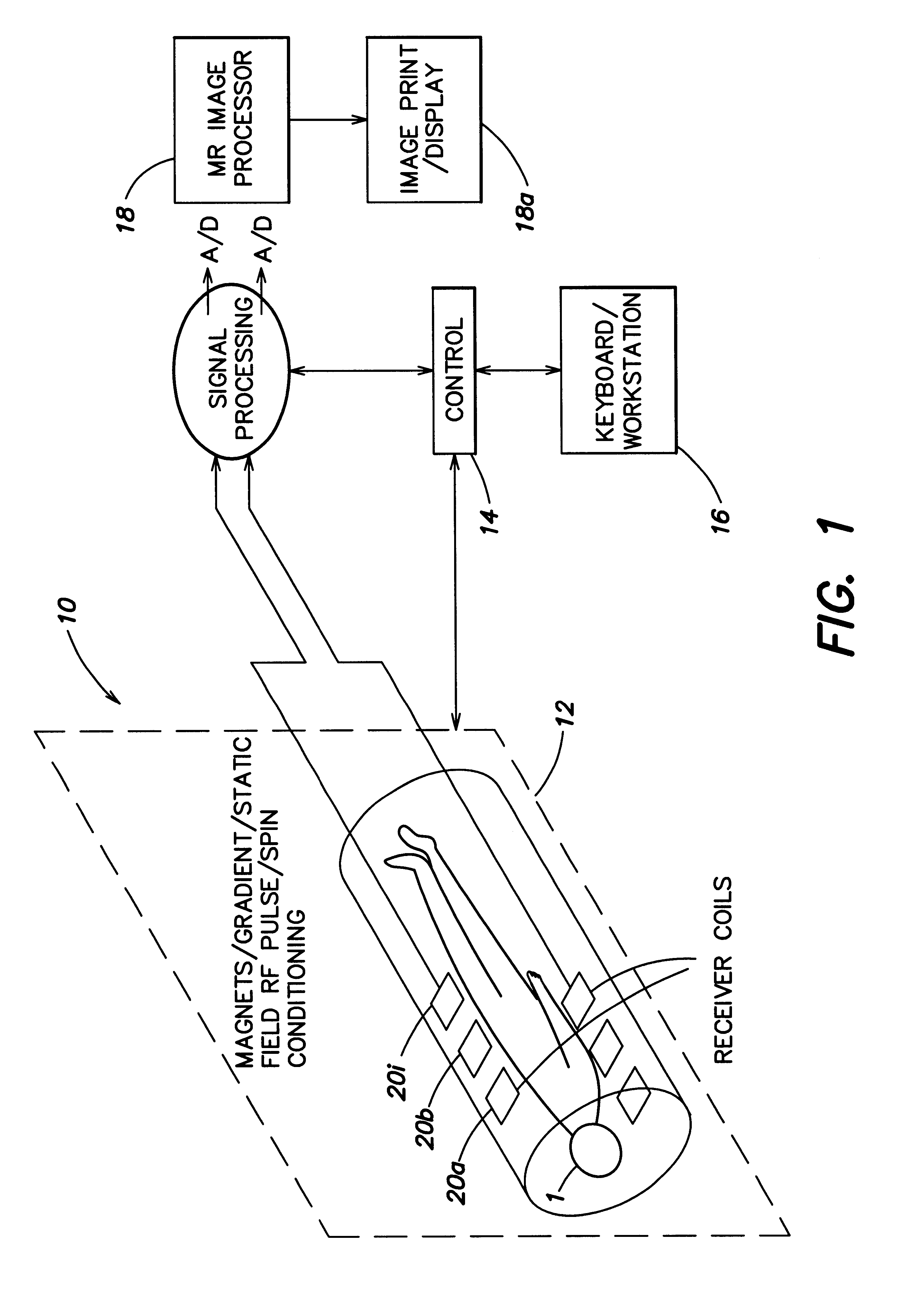
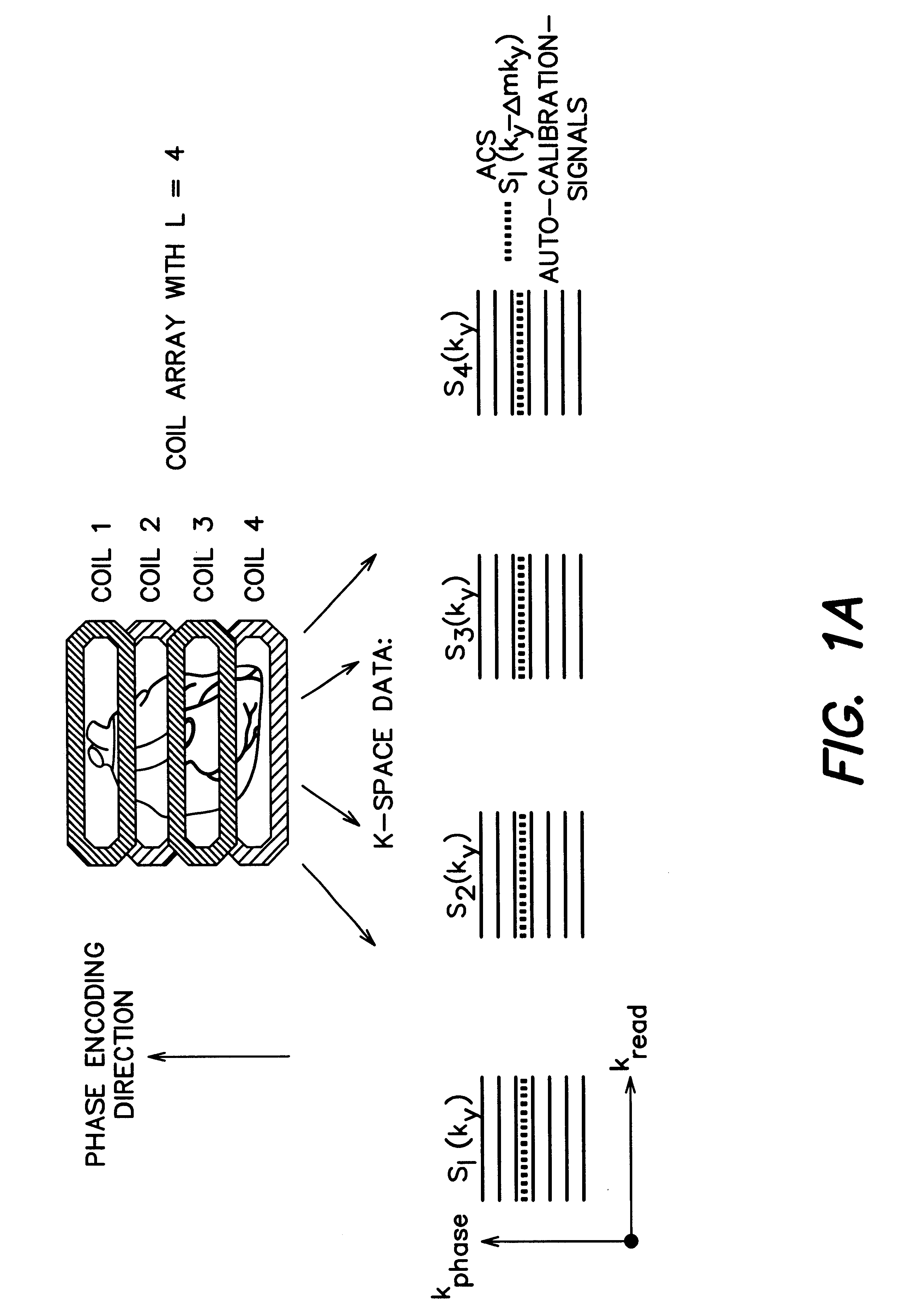
A magnetic resonance (MR) imaging apparatus and technique exploits spatial information inherent in a surface coil array to increase MR image acquisition speed, resolution and / or field of view. Magnetic resonance response signals are acquired simultaneously in the component coils of the array and, using an autocalibration procedure, are formed into two or more signals to fill a corresponding number of lines in the signal measurement data matrix. In a Fourier embodiment, lines of the k-space matrix required for image production are formed using a set of separate, preferably linear combinations of the component coil signals to substitute for spatial modulations normally produced by phase encoding gradients. One or a few additional gradients are applied to acquire autocalibration (ACS) signals extending elsewhere in the data space, and the measured signals are fitted to the ACS signals to develop weights or coefficients for filling additional lines of the matrix from each measurement set. The ACS lines may be taken offset from or in a different orientation than the measured signals, for example, between or across the measured lines. Furthermore, they may be acquired at different positions in k-space, may be performed at times before, during or after the principal imaging sequence, and may be selectively acquired to optimized the fitting for a particular tissue region or feature size. The in vivo fitting procedure is readily automated or implemented in hardware, and produces an enhancement of image speed and / or quality even in highly heterogeneous tissue. A dedicated coil assembly automatically performs the calibration procedure and applies it to measured lines to produce multiple correctly spaced output signals. One application of the internal calibration technique to a subencoding imaging process applies the ACS in the central region of a sparse set of measured signals to quickly form a full FOV low resolution image. The full FOV image is then used to determine coil sensitivity related information and dealias folded images produced from the sparse set.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
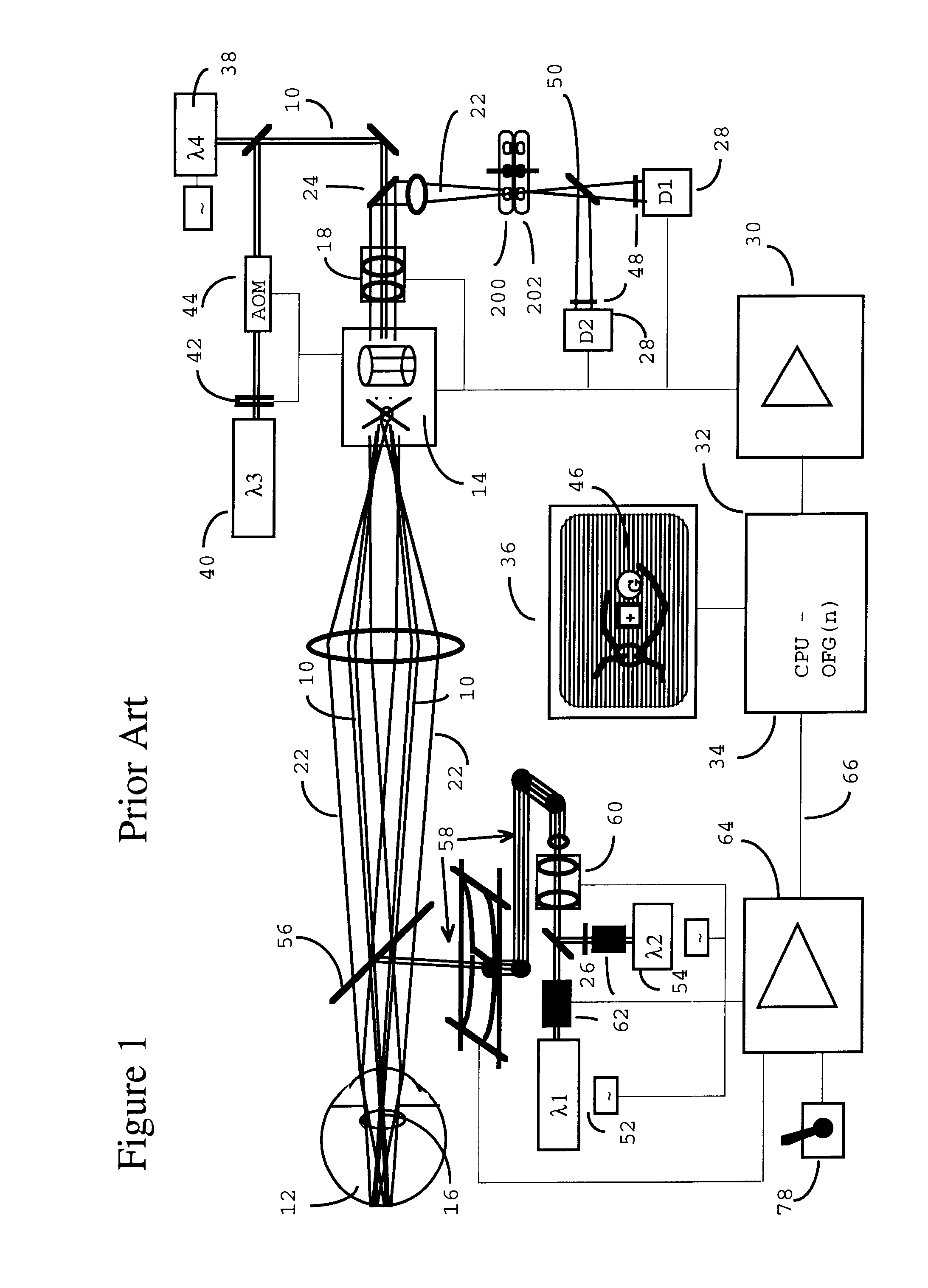
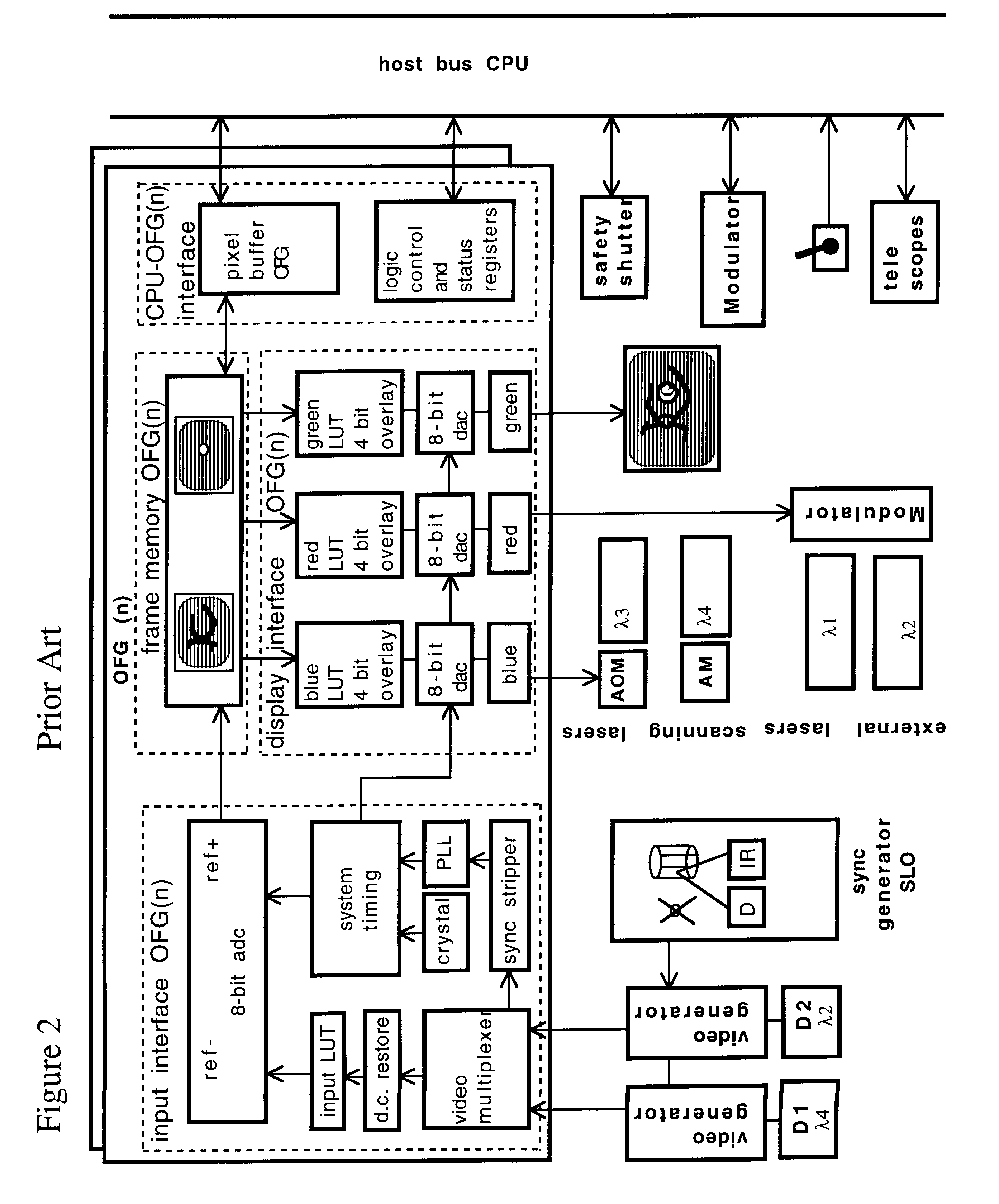
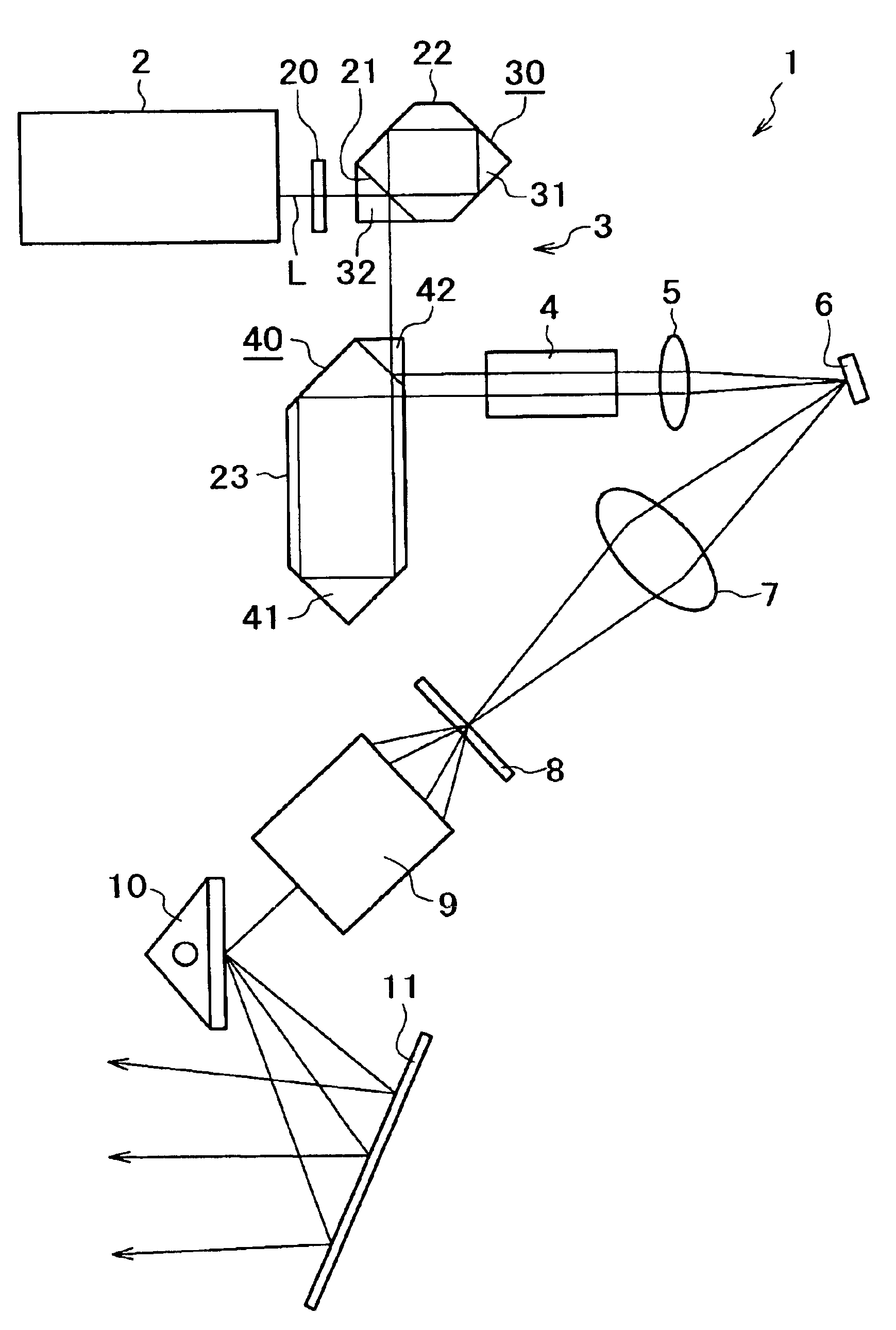
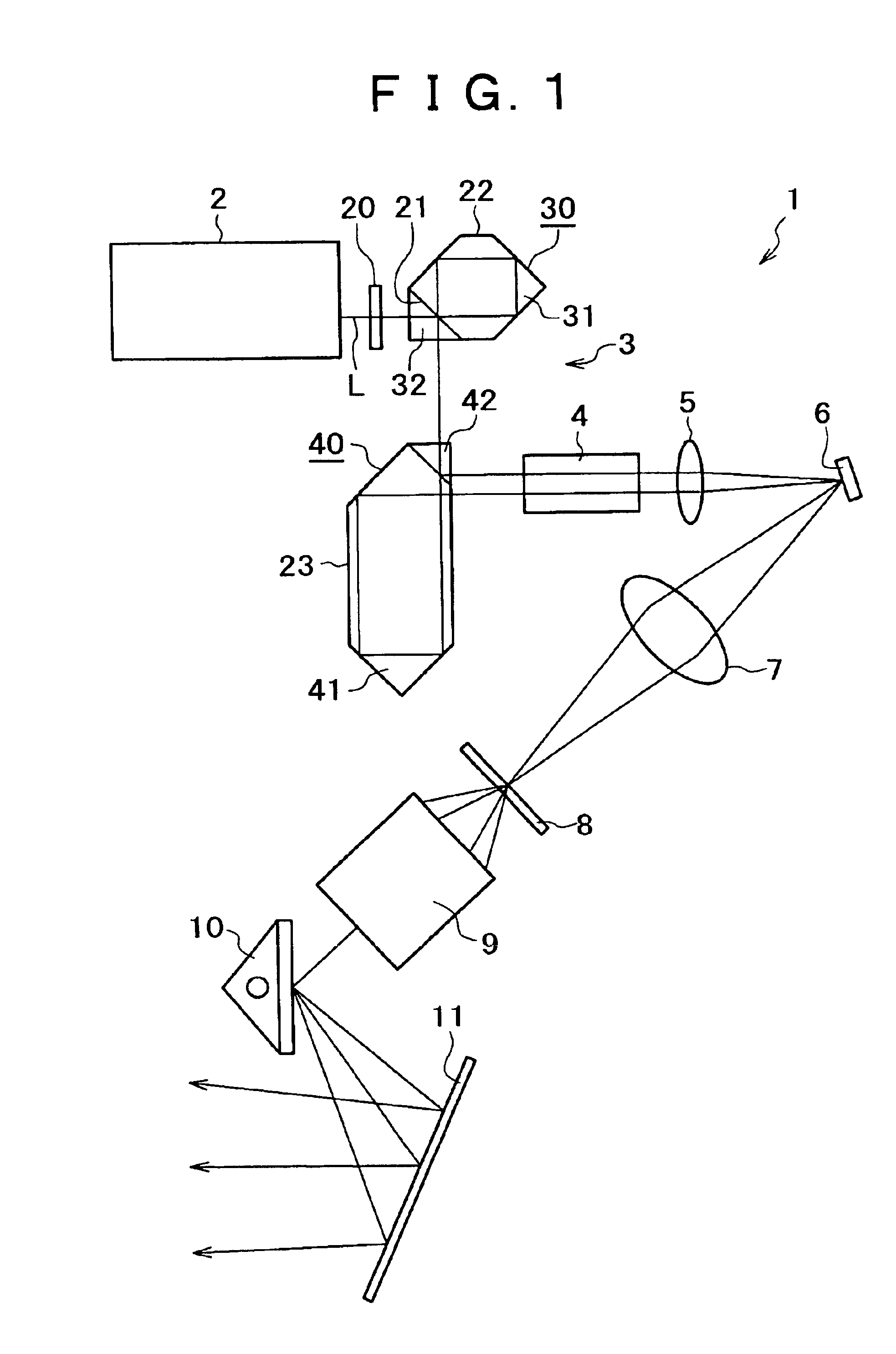
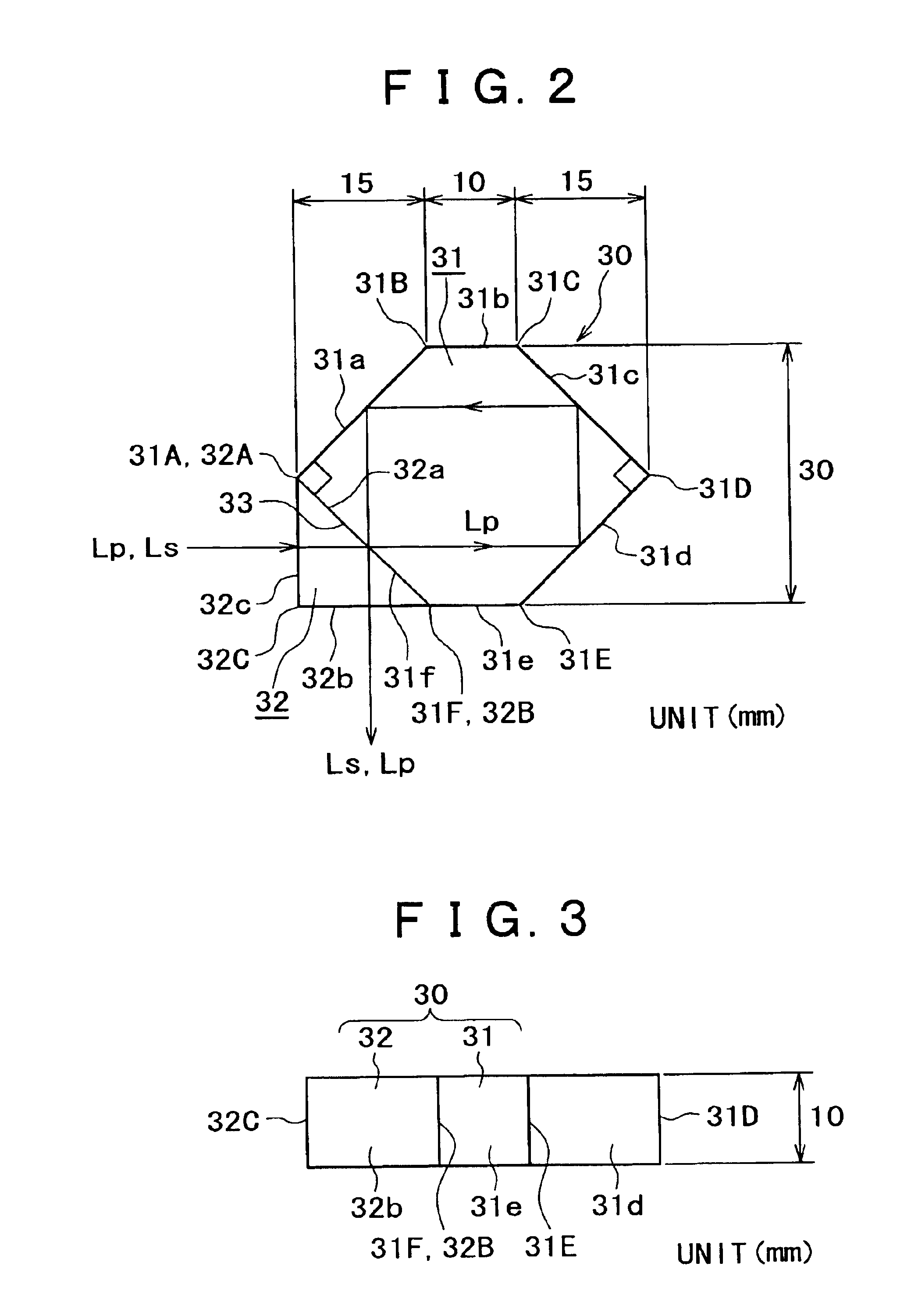
Scanning laser ophthalmoscope for selective therapeutic laser
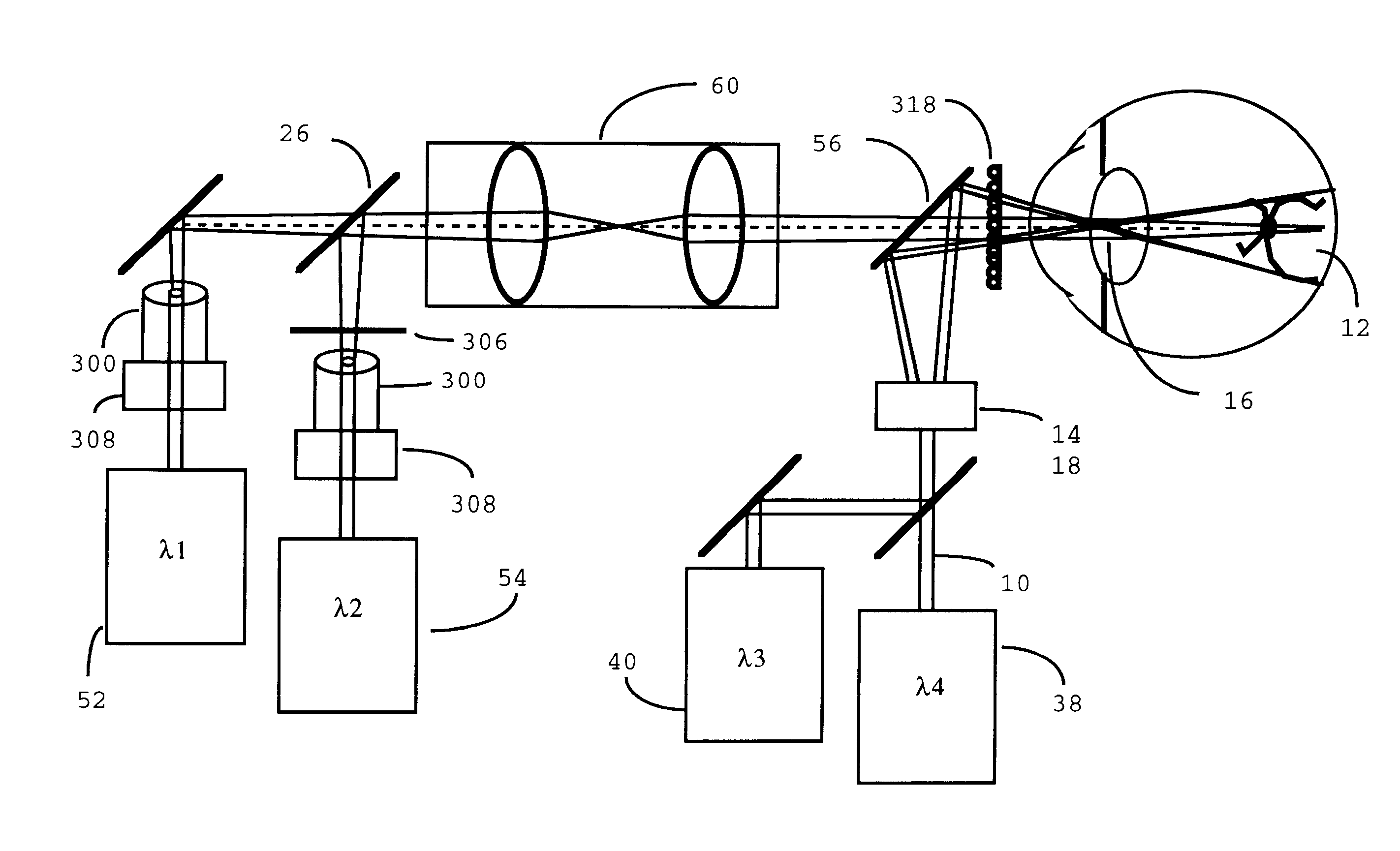
A combination of a scanning laser ophthalmoscope and external laser sources (52) is used for microphotocoagulation and photodynamic therapy, two examples of selective therapeutic laser. A linkage device incorporating a beamsplitter (56) and collimator-telescope (60) is adjusted to align the pivot point (16) of the scanning lasers (38, 40) and external laser source (52). A similar pivot point minimizes wavefront aberrations, enables precise focusing and registration of the therapeutic laser beam (52) on the retina without the risk of vignetting. One confocal detection pathway of the scanning laser ophthalmoscope images the retina. A second and synchronized detection pathway with a different barrier filter (48) is needed to draw the position and extent of the therapeutic laser spot on the retinal image, as an overlay (64). Advanced spatial modulation increases the selectivity of the therapeutic laser. In microphotocoagulation, an adaptive optics lens (318) is attached to the scanning laser ophthalmoscope, in proximity of the eye. It corrects the higher order optical aberrations of the eye optics, resulting in smaller and better focused applications. In photodynamic therapy, a spatial modulator (420) is placed within the collimator-telescope (60) of the therapeutic laser beam (52), customizing its shape as needed. A similar effect can be obtained by modulating a scanning laser source (38) of appropriate wavelength for photodynamic therapy.
Owner:VAN DE VELDE JOZEK F
Methods and apparatus for spatial light modulation
ActiveUS20060187528A1Improve luminous efficiencyReduced Power RequirementsOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsOptical cavityOptoelectronics
Improved apparatus and methods for spatial light modulation are disclosed which utilize optical cavities having both front and rear reflective surfaces. Light-transmissive regions are formed in the front reflective surface for spatially modulating light.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Method for optimizing spatial modulation in a wireless link and network element thereto
ActiveUS20080317014A1Maximize total transmission throughputHigh data transmission reliabilityMultiplex system selection arrangementsFrequency-division multiplex detailsData rateTransfer mode
Owner:ELEKTROBIT WIRELESS COMM LTD
Fabrication of high efficiency, high quality, large area diffractive waveplates and arrays
InactiveUS20110262844A1Quality improvementLow costPhotomechanical exposure apparatusHologram recording materialOptical polarizationImage quality
The objective of the present invention is providing a method for fabricating high quality diffractive waveplates and their arrays that exhibit high diffraction efficiency over large area, the method being capable of inexpensive large volume production. The method uses a polarization converter for converting the polarization of generally non-monochromatic and partially coherent input light beam into a pattern of periodic spatial modulation at the output of said polarization converter. A substrate carrying a photoalignment layer is exposed to said polarization modulation pattern and is coated subsequently with a liquid crystalline material. The high quality diffractive waveplates of the present invention are obtained when the exposure time of said photoalignment layer exceeds by generally an order of magnitude the time period that would be sufficient for producing homogeneous orientation of liquid crystalline materials brought in contact with said photoalignment layer. Compared to holographic techniques, the method is robust with respect to mechanical noises, ambient conditions, and allows inexpensive production via printing while also allowing to double the spatial frequency of optical axis modulation of diffractive waveplates.
Owner:BEAM ENG FOR ADVANCED MEASUREMENTS
2-Channel display system comprising micro electro mechanical systems
InactiveUS20050141076A1The implementation process is simpleSteroscopic systemsOptical elementsLight beamEngineering
The two channel stereo display system with micro electromechanical systems (MEMS, e.g. DMDs from Texas Instruments) simultaneously generates a right and a left image in two discrete modulation channels, which differ by the polarization of their light beams. More specifically, the invention relates to the chirality (handedness) of MEMS and uncovers solutions for some of the geometric problems associated with this handedness in stereoscopic systems. Unpolarized light is split by a first PBS (5) and directed via two TIRs (3,4) onto two MEMSs (1,2) for spatial modulation. In some embodiments, mirror symmetric, compact light paths and complete superposition of the two subimages with a second PBS (6) are realized with two different MEMSs (1) and (2) which are a pair of stereo isomers. Furthermore we uncover solutions with two identical MEMSs.
Owner:BAUSENWEIN BERNHARD RUDOLF +1
Treatment of skin by spatial modulation of thermal heating
InactiveUS8246611B2Good curative effectImproved post-treatment healingSurgical instruments for heatingTherapeutic coolingThermal injuryMedicine
Treating skin can include delivering a beam of radiation to a target region of the skin to cause a zone of thermal injury including a lateral pattern of varying depths of thermal injury distributed along the target region. The lateral pattern includes at least one first sub-zone of a first depth of thermal injury laterally adjacent to at least one second sub-zone of a second depth of thermal injury. The first depth is greater than the second depth. The at least one first sub-zone of the first depth and the at least one second sub-zone of the second depth extend from a surface of the target region of the skin to form a substantially continuous surface thermal injury. The at least one first sub-zone of the first depth and the at least one second sub-zone of the second depth are substantially heated to at least a critical temperature.
Owner:CANDELA CORP
Method for optimizing spatial modulation in a wireless link and network element thereto
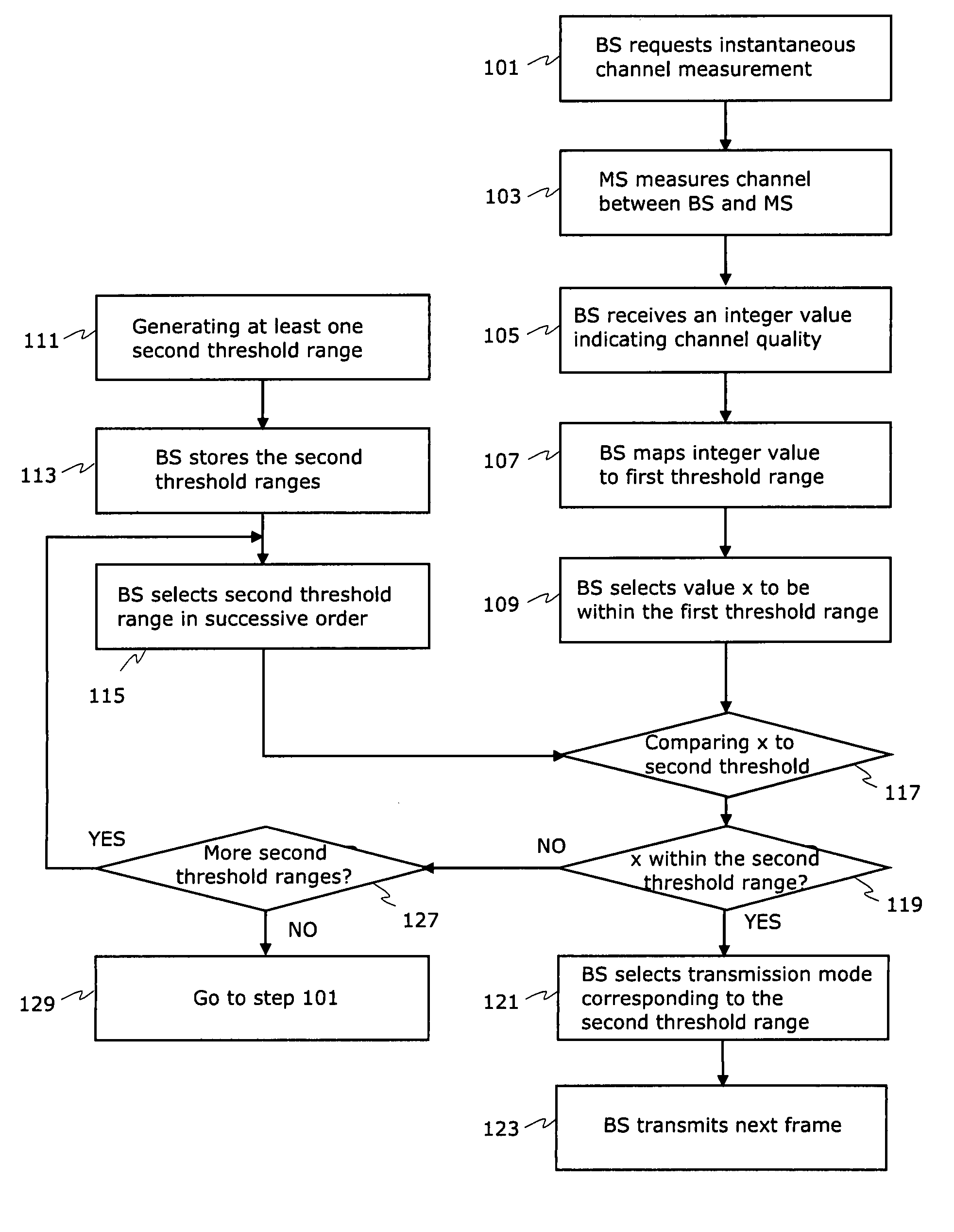
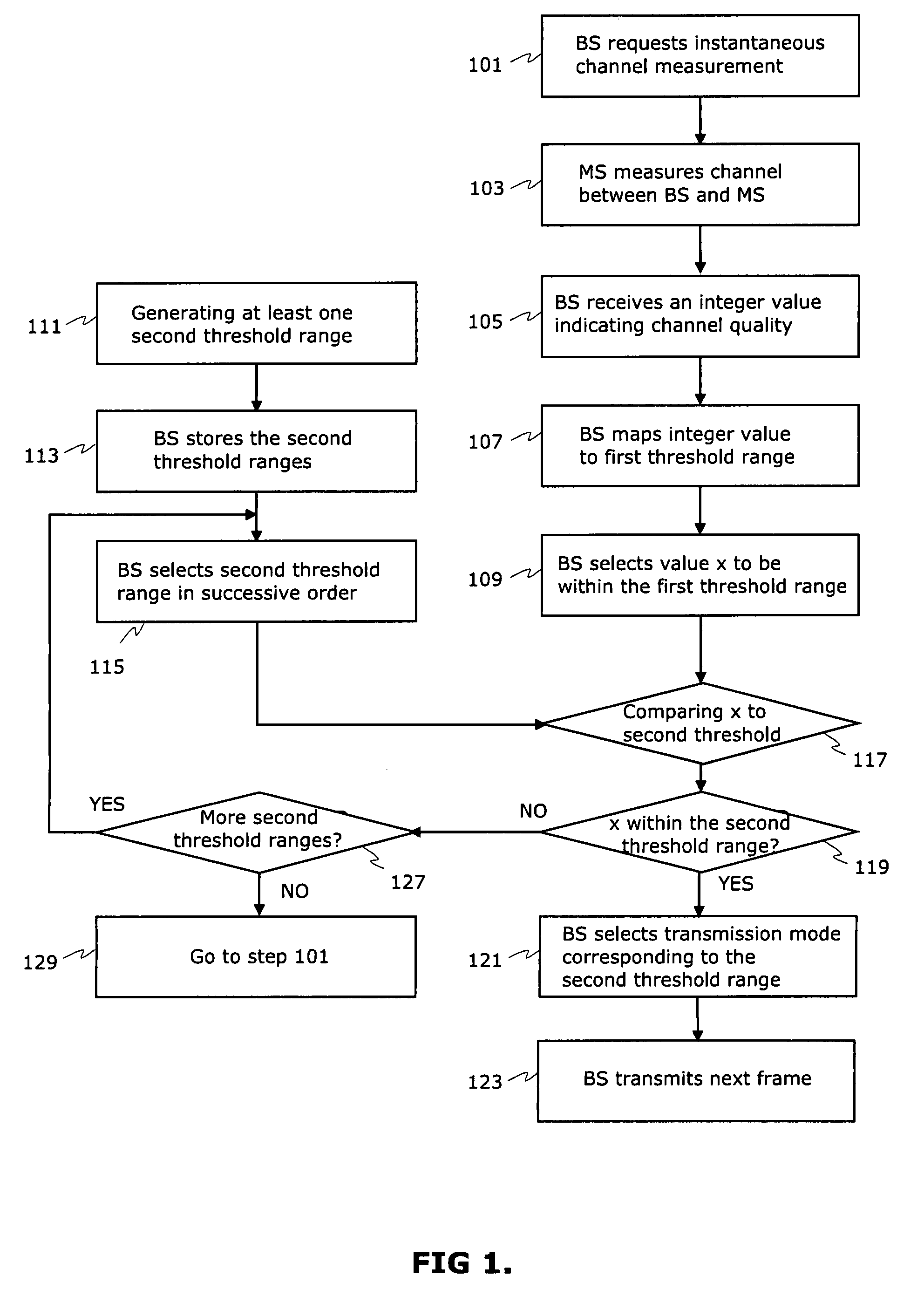
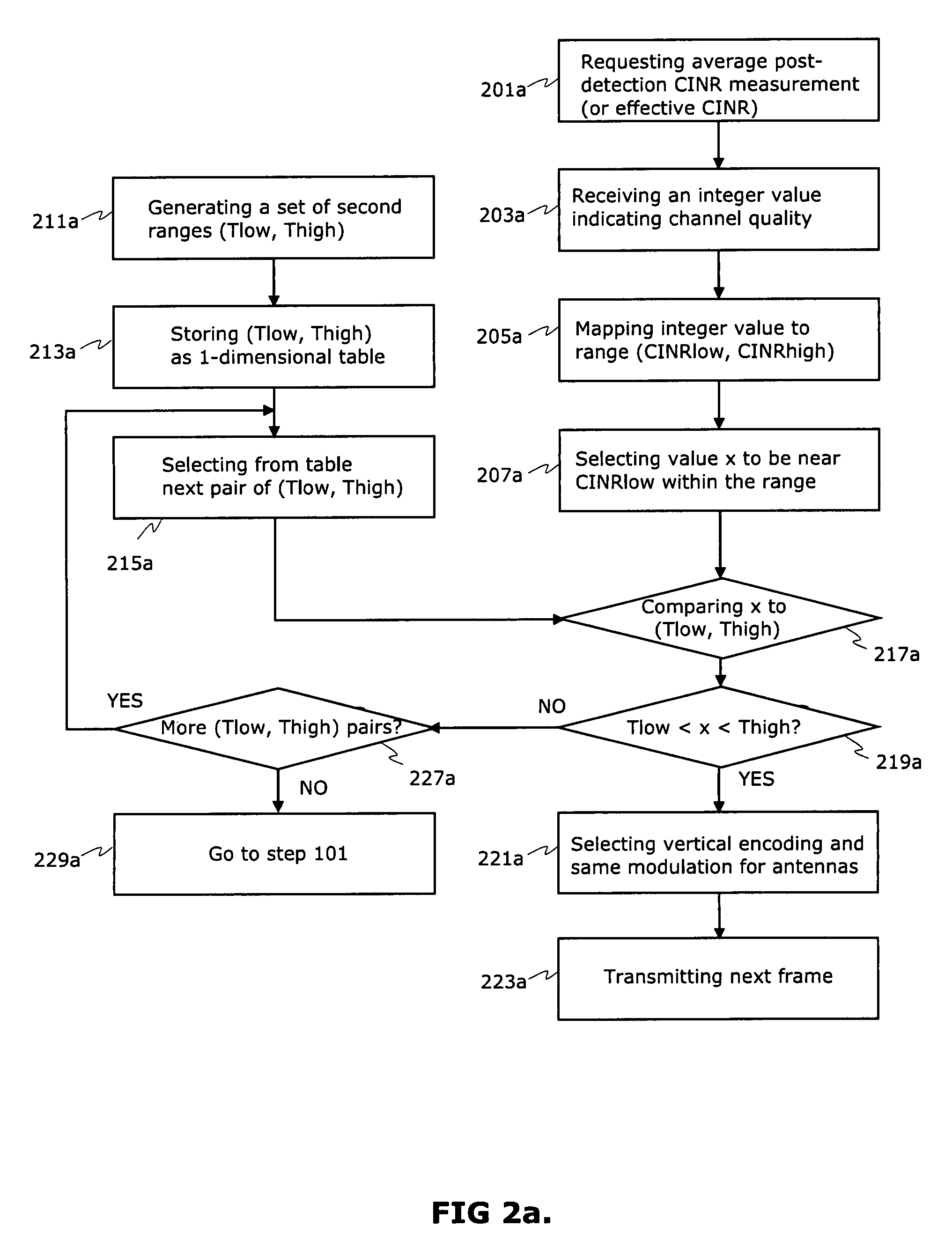
ActiveUS8160601B2High data transmission reliabilityMinimising channel capacity dropFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission systemsTransfer modeData rate
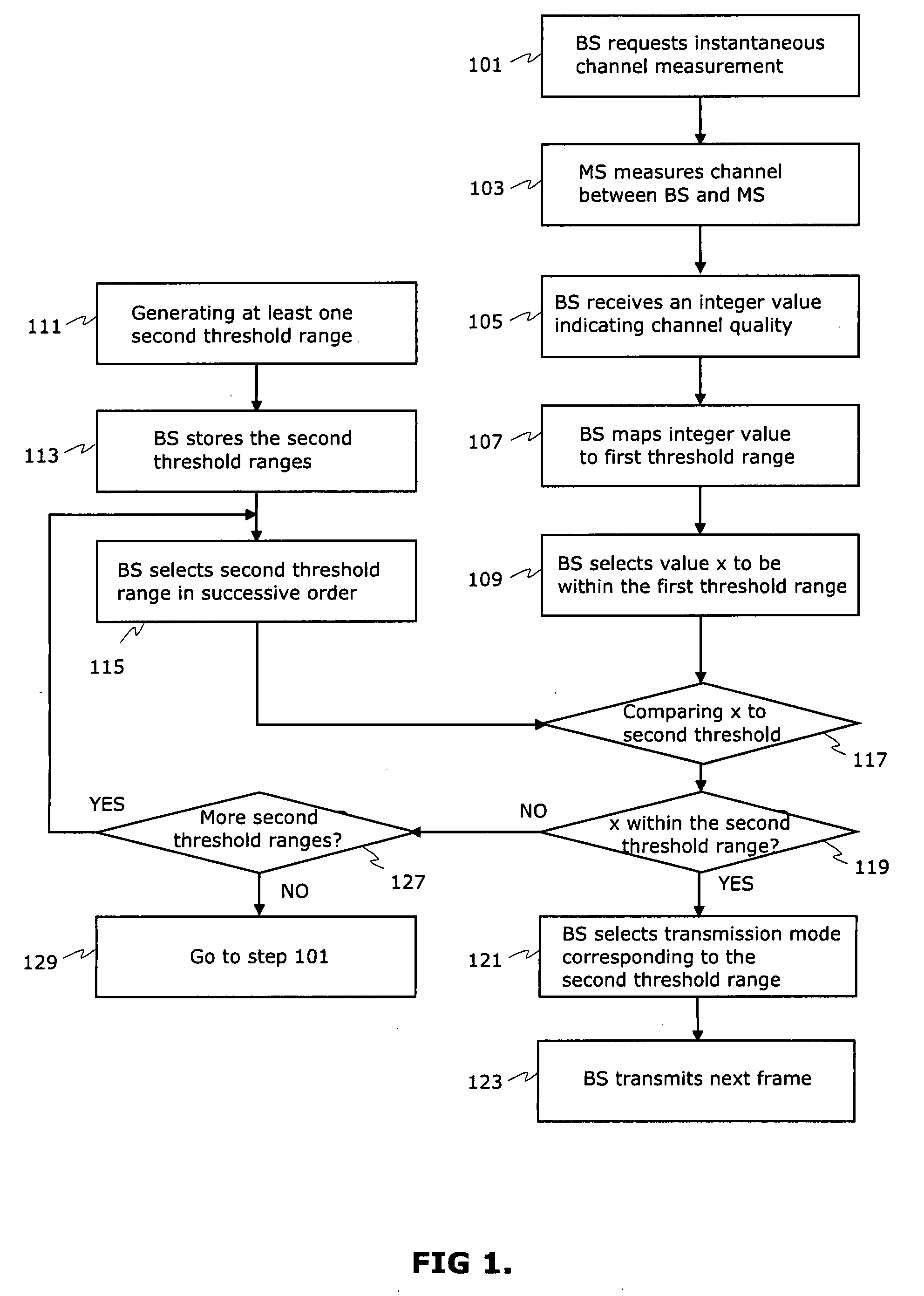
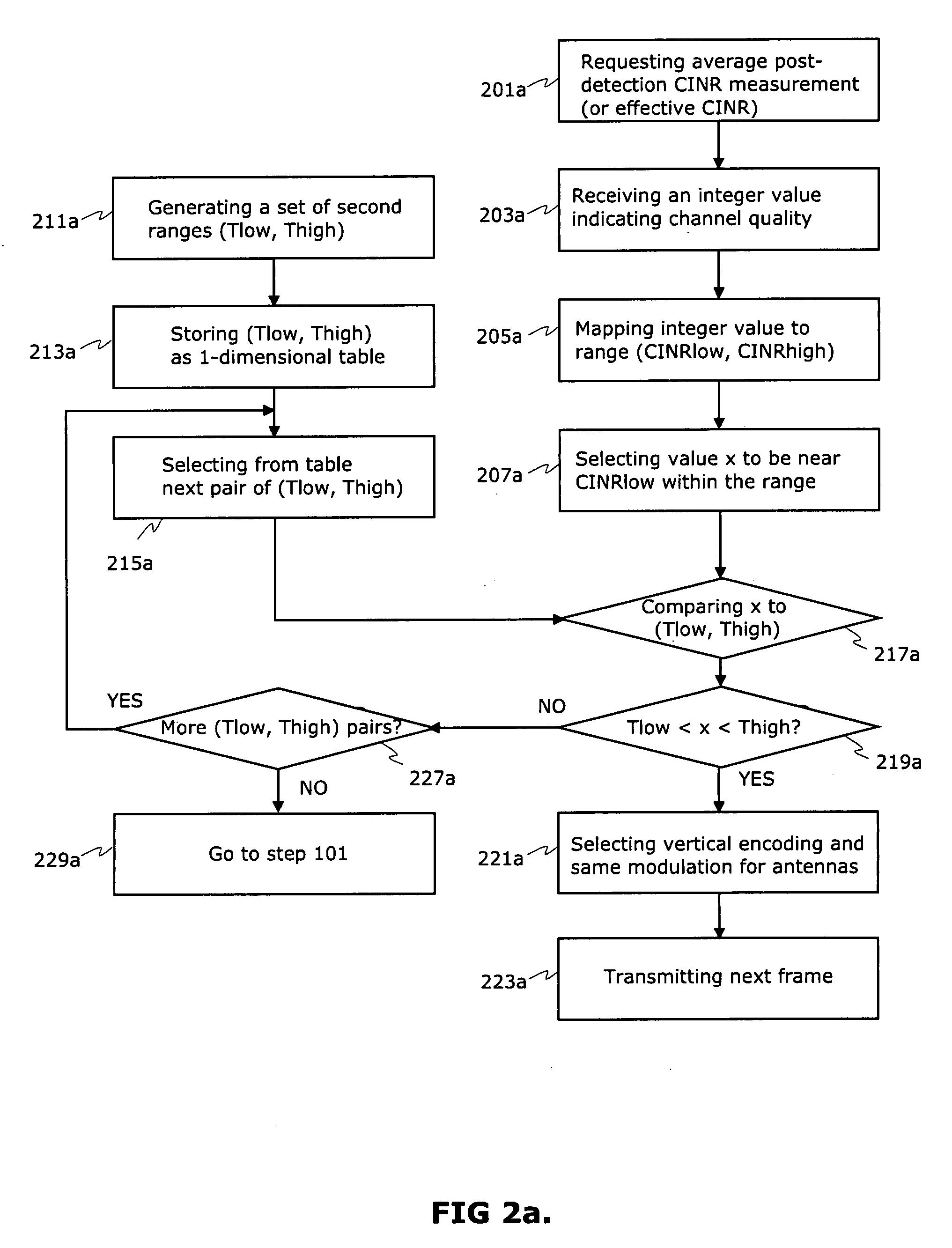
The selection of the spatial mode together with modulation and encoding schemes based on channel condition measurements requested from MS forms a basis for selecting a best transmission data rate in a wireless link in every channel conditions. A method and network element comprising multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) capable antenna technology allows the use of a best transmission data rate in the channel if selection of transmission mode has been made correctly. The thresholds for transmission mode selections are pre-determined and compared to instantaneous channel quality information. The practical MIMO solution based on correct selection procedure provides also continuous sufficient channel condition for terminal users when the user moves from LOS situation to NLOS situation.
Owner:ELEKTROBIT WIRELESS COMM LTD
Speckle reduction in laser-projector images
InactiveUS20080212034A1Reduce appearance problemsSpeckle reductionProjectorsMountingsSpatial light modulatorSpecular reflection
A laser projector having a configurable spatial light modulator (SLM) adapted to display various spatial modulation patterns and redirect illumination from a laser to form an image on the viewing screen. The laser projector drives the SLM to change spatial modulation patterns at a rate that causes the corresponding sequence of projected images to fuse to mitigate appearance of speckle in the resulting fused image. The SLM can be designed to redirect the illumination using either diffraction or specular reflection of light from the displayed spatial modulation pattern. In one embodiment, the SLM is a MEMS device having an array of individually addressable mirrors supported over a substrate and adapted to move (e.g., translate and / or rotate) with respect to the substrate.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
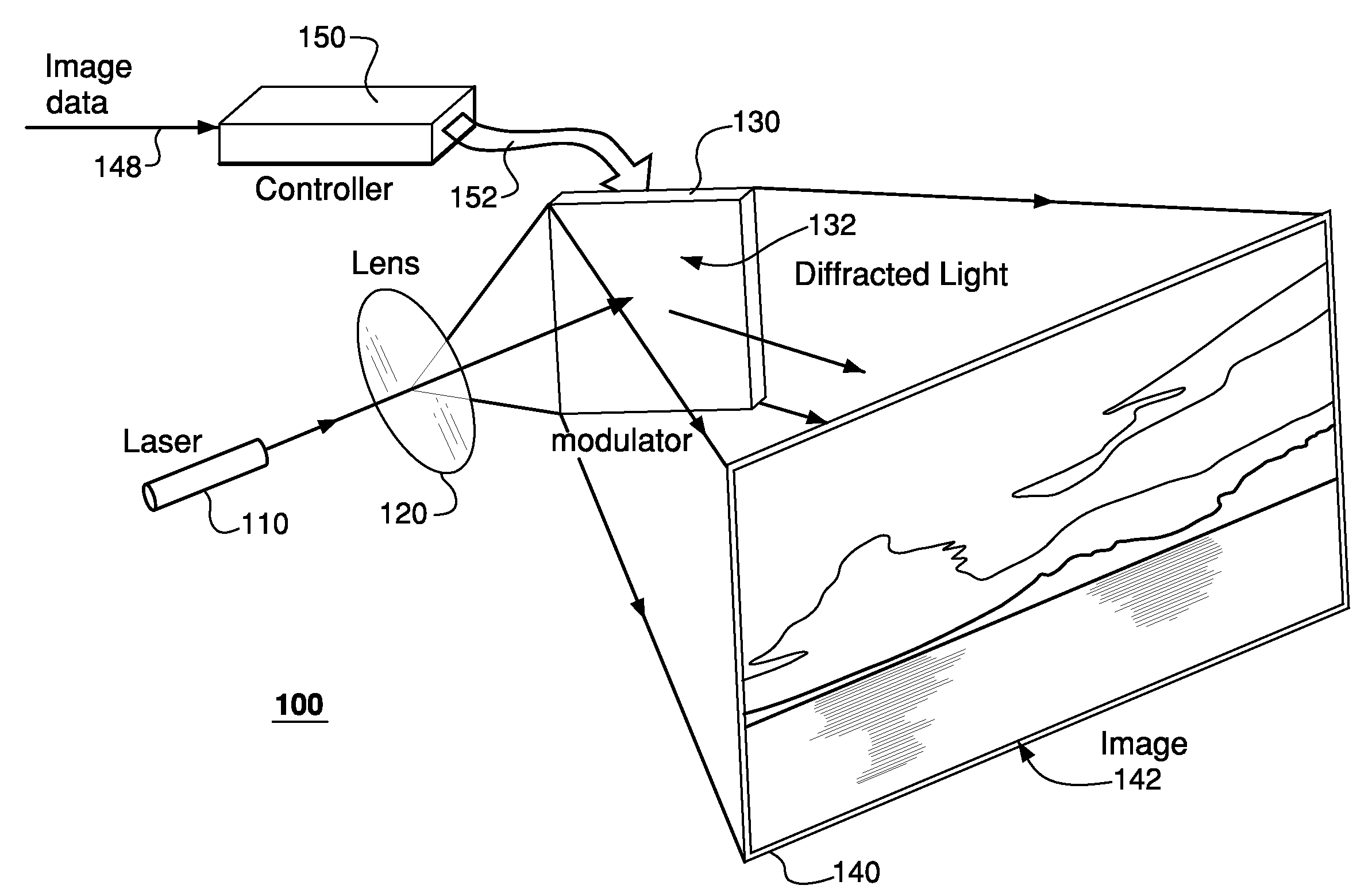
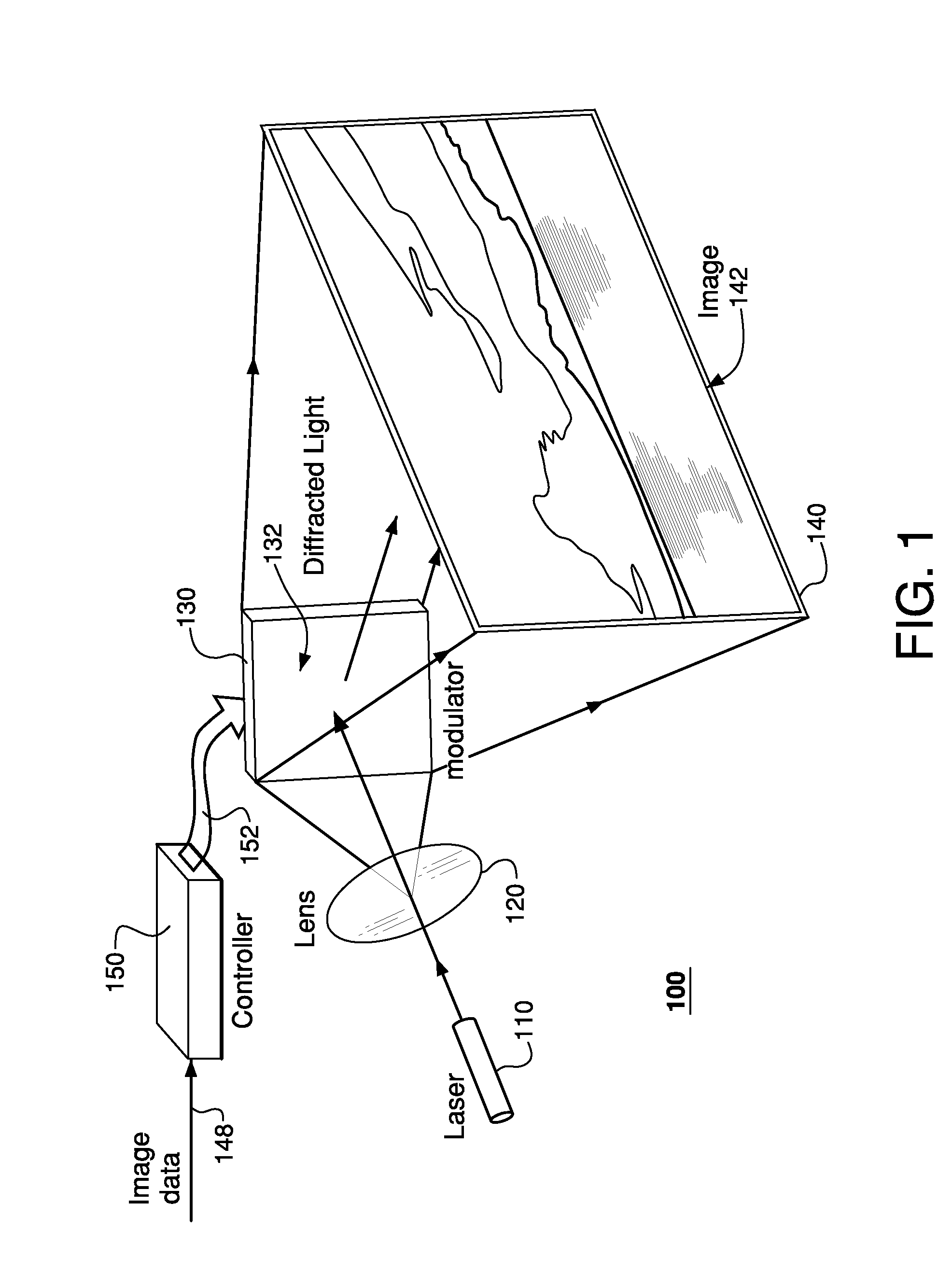
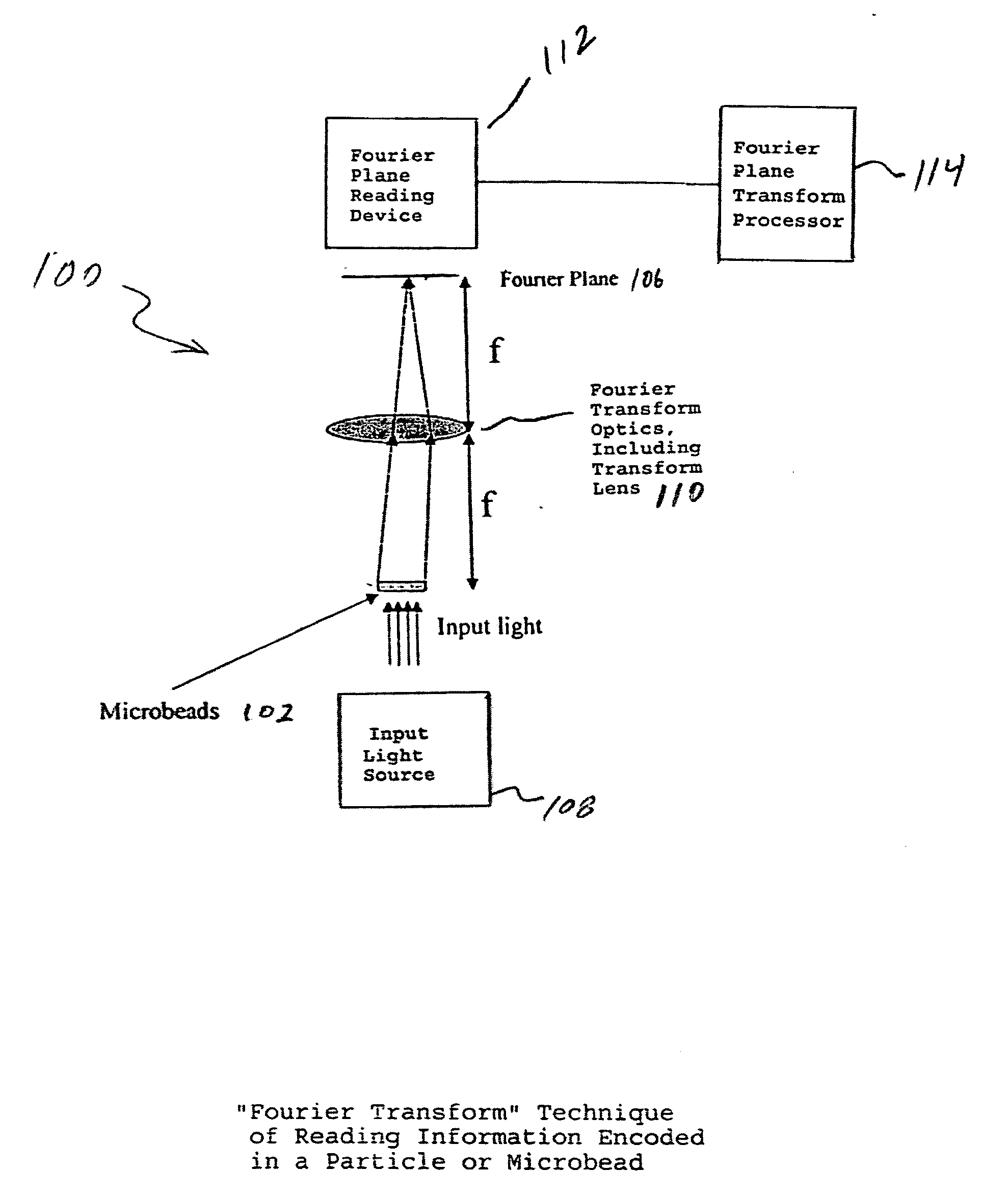
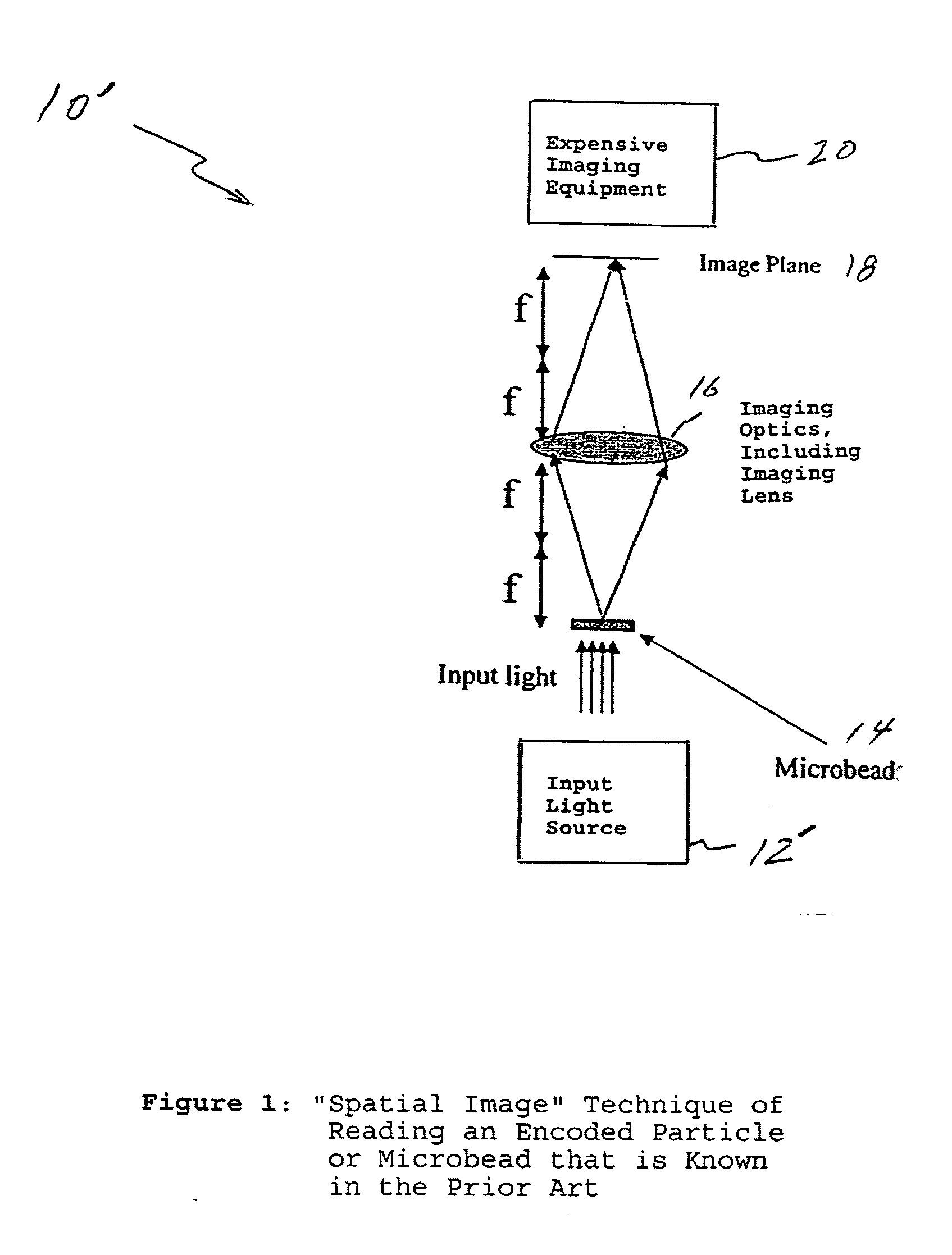
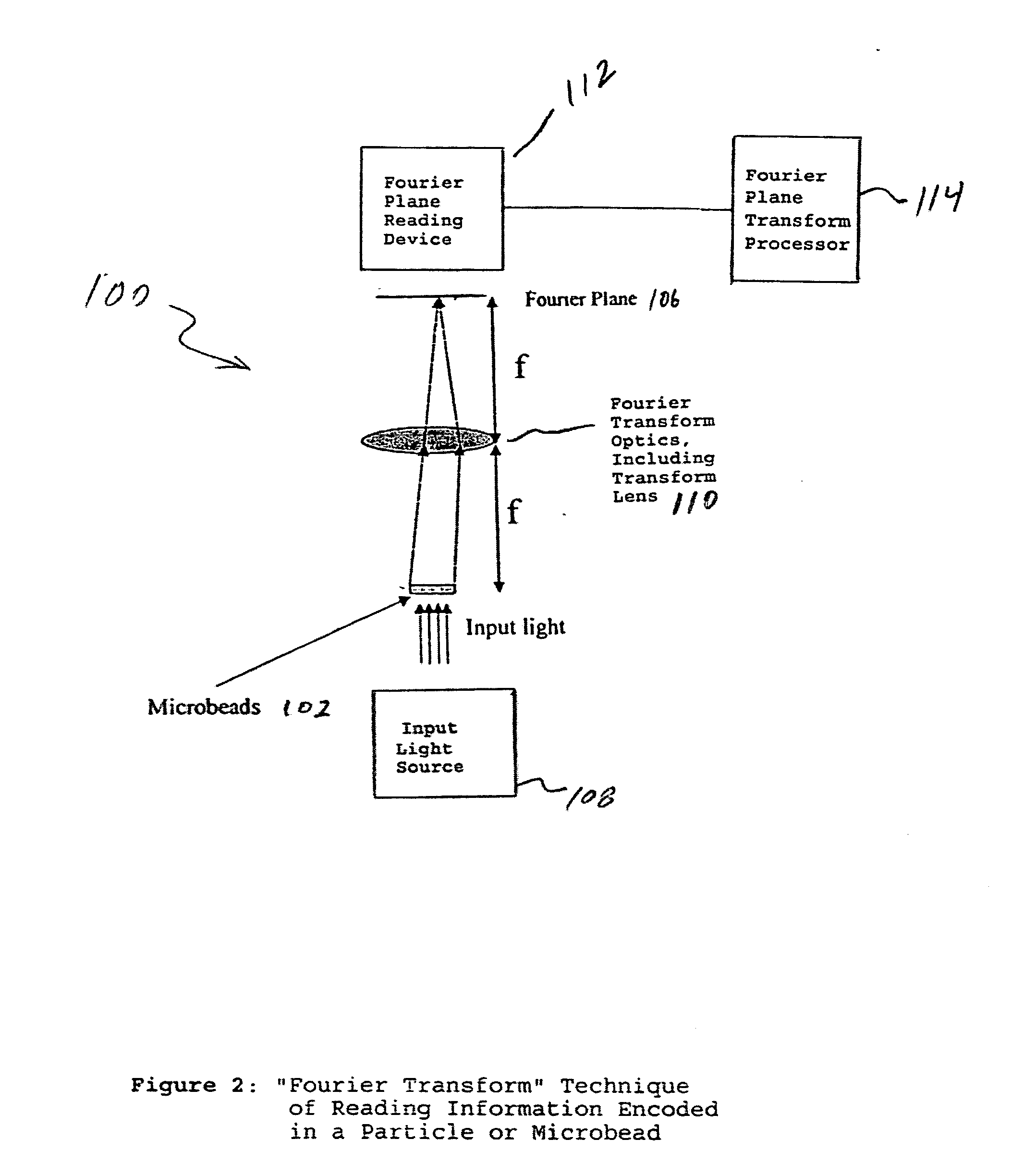
Fourier scattering methods for encoding microbeads and methods and apparatus for reading the same
ActiveUS20060119913A1Enhance the imageNanoopticsCharacter and pattern recognitionSpectral patternFluorescence
A method and apparatus for reading a microbead having a code thereon is provided wherein the code is projected on and read from a Fourier plane. The microbead may be 1-1000 microns (um) or smaller in feature size. The code is projected on the Fourier plane by scattering input light off the microbead. The scattered light from the microbead is directed through an optical arrangement having a transform lens for projecting the code on the Fourier plane, and read on the Fourier plane using a charge coupled device (CCD) or other similar device. The code may include periodic layers of material having different refractivities or phase, including index of refraction differences; periodic spatial modulations having a different phase or amplitude; a periodic binary phase change used to code information in the Fourier plane; a photonic crystal used to encode the information on the microbead, wherein a pattern of holes causes interference between incident and scattered light to form spatial and spectral patterns in the far field that are unique to the pattern of holes; or may be formed in the microbead using a single photoactive inner region, a series of longitudinal holes, different fluorescence regions, or concentric rings of material in a preform.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Hand-Held X-Ray Backscatter Imaging Device
InactiveUS20130195248A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation measurementObject basedHand held
Apparatus for imaging items behind a concealing barrier. A source of penetrating radiation is contained entirely within a housing. A spatial modulator forms the penetrating radiation into a beam and sweeps the beam to irradiate an inspected object. A detector generates a scatter signal based on penetrating radiation scattered by contents of the inspected object, and a sensor senses motion relative to a previous position of the apparatus with respect to the inspected object. A processor receives the scatter signal and generates an image of the contents of the inspected object based at least on the scatter signal. The housing may be adapted for singled-handed retention by an operator
Owner:AMERICAN SCI & ENG INC
Constrained interleaving for 5G wireless and optical transport networks
InactiveUS20160352419A1Increase data rateIncrease performance rateSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation multiplex systemsCommunications systemAlgorithm
The present invention provides a design framework that is used to develop new types of constrained turbo block convolutional (CTBC) codes that have higher performance than was previously attainable. The design framework is applied to design both random and deterministic constrained interleavers. Vectorizable deterministic constrained interleavers are developed and used to design parallel architectures for real time SISO decoding of CTBC codes. A new signal mapping technique called constrained interleaved coded modulation (CICM) is also developed. CICM is then used to develop rate matching, spatial modulation, and MIMO modulation subsystems to be used with CTBC codes and other types of codes. By way of example, embodiments are primarily provided for improved 5G LTE and optical transport network (OTN) communication systems. Detailed descriptions of embodiments are also provided that combine aspects of MIMO and spatial modulation systems to improve bandwidth efficiency. Such embodiments are applicable to multi-antenna and single antenna MIMO systems as well as multichannel systems, OFDM systems, and TDM systems.
Owner:FONSEKA JOHN P +1
Fourier domain sensing
Methods, systems, and apparatuses are provided for measuring one or more sinusoidal Fourier components of an object. A structured second radiation is generated by spatially modulating a first radiation. The structured second radiation illuminates the object, The structured second radiation is scaled and oriented relative to the object. The object produces a third radiation in response to the illuminating. A single-element detector detects a portion of the third radiation from multiple locations on the object substantially simultaneously for each spatial modulation of the first radiation and for each orientation of the second radiation. A time-varying signal is produced based on said detected portion of the third radiations. One or more characteristics of the one or more sinusoidal Fourier components of the object are estimated based on the time-varying signal.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
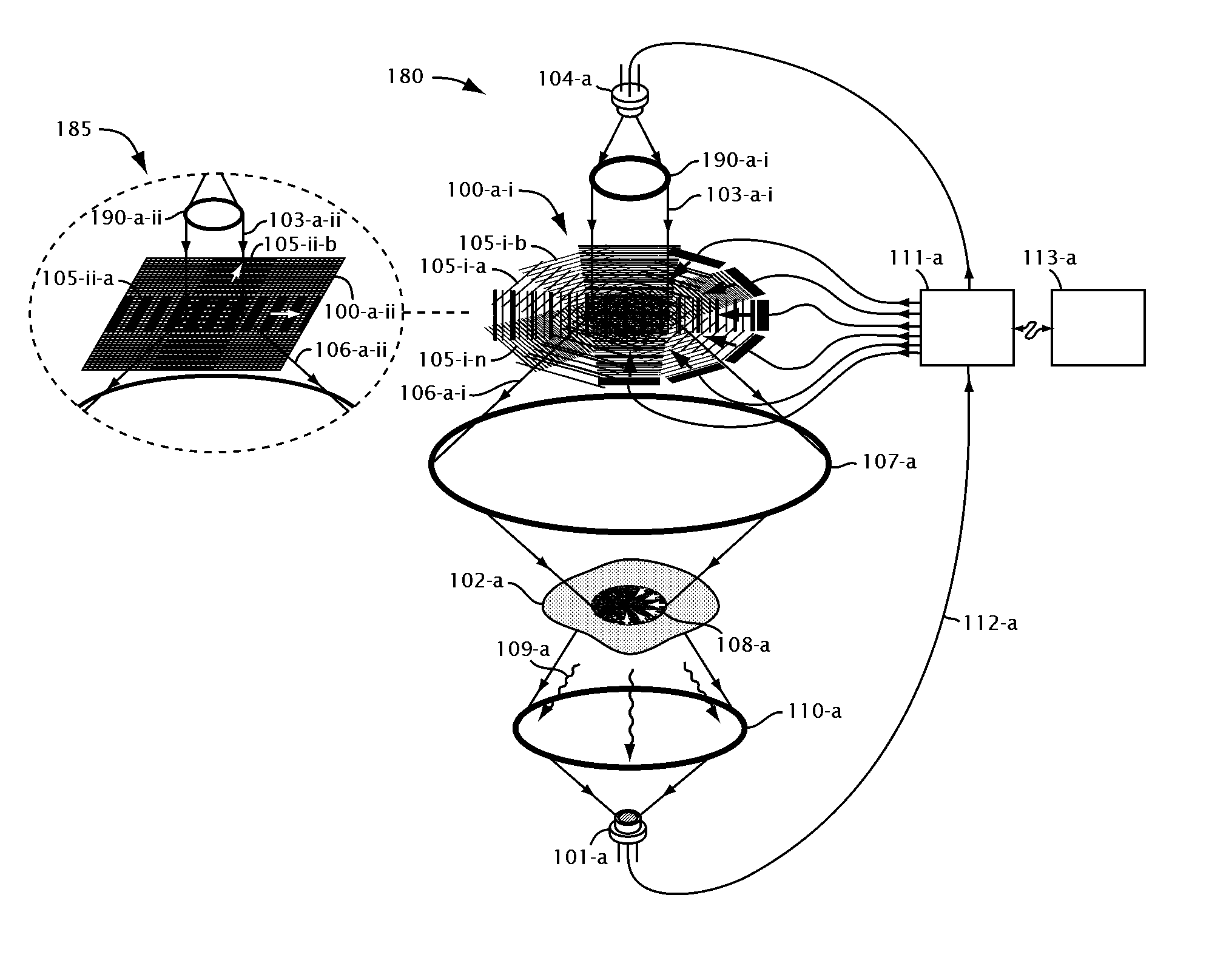
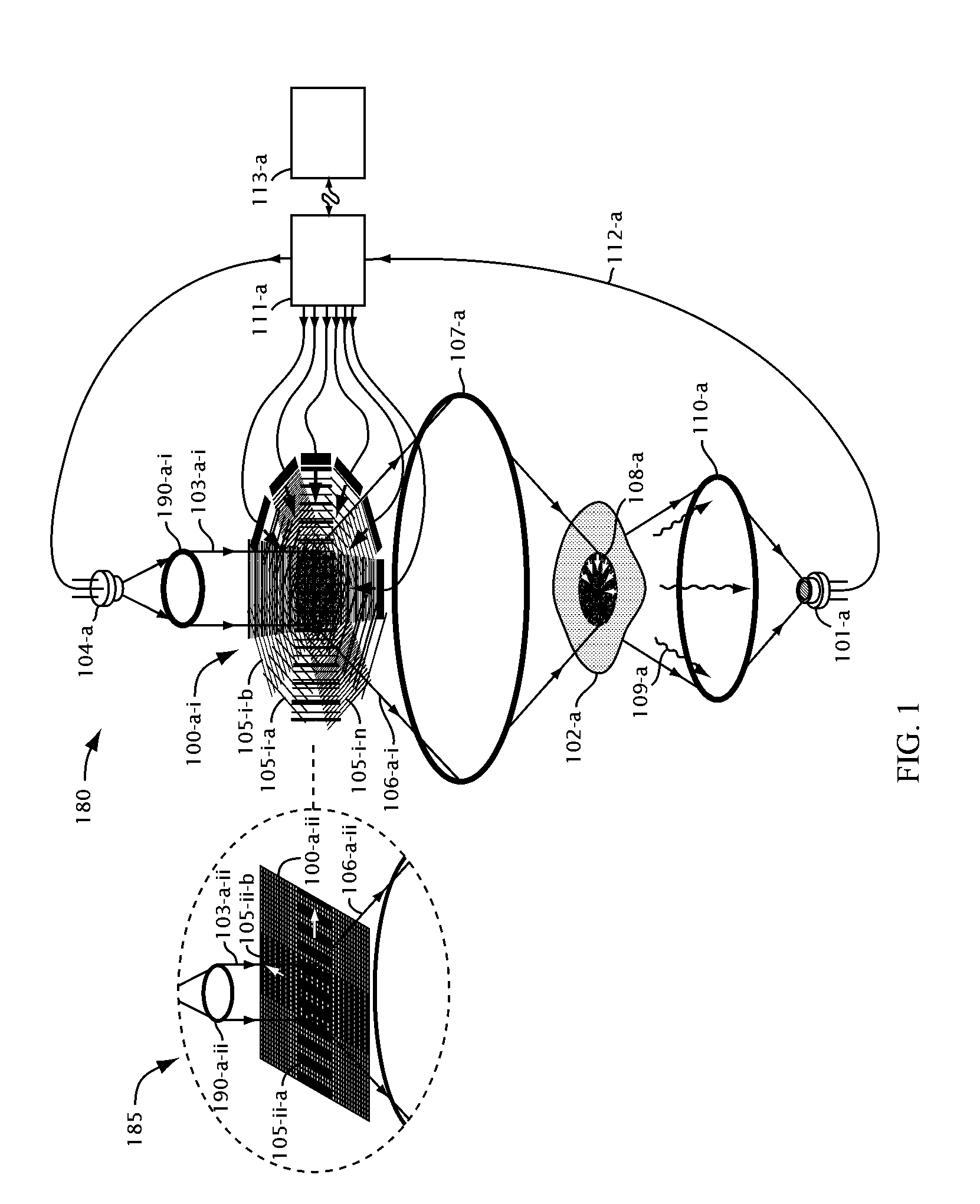
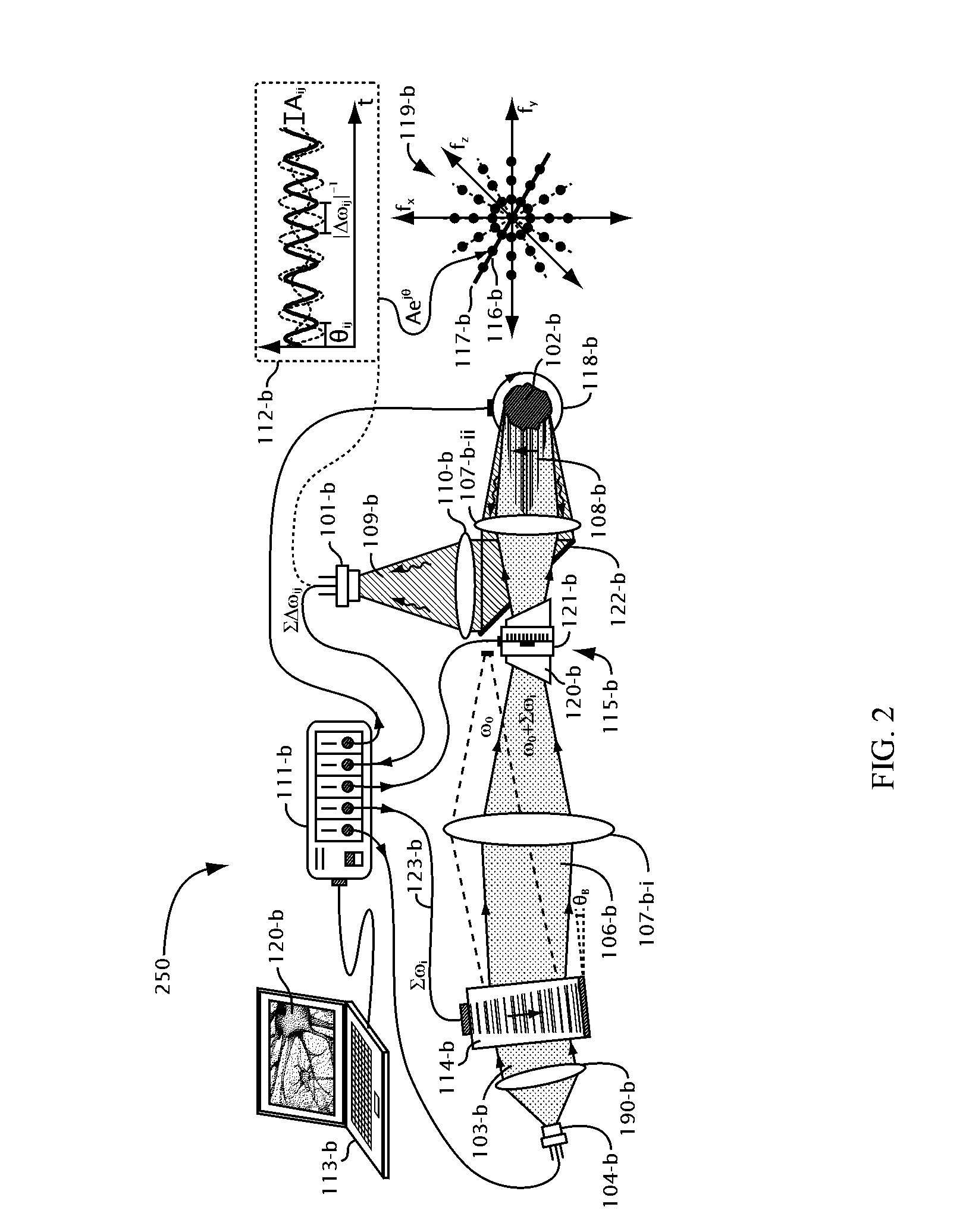
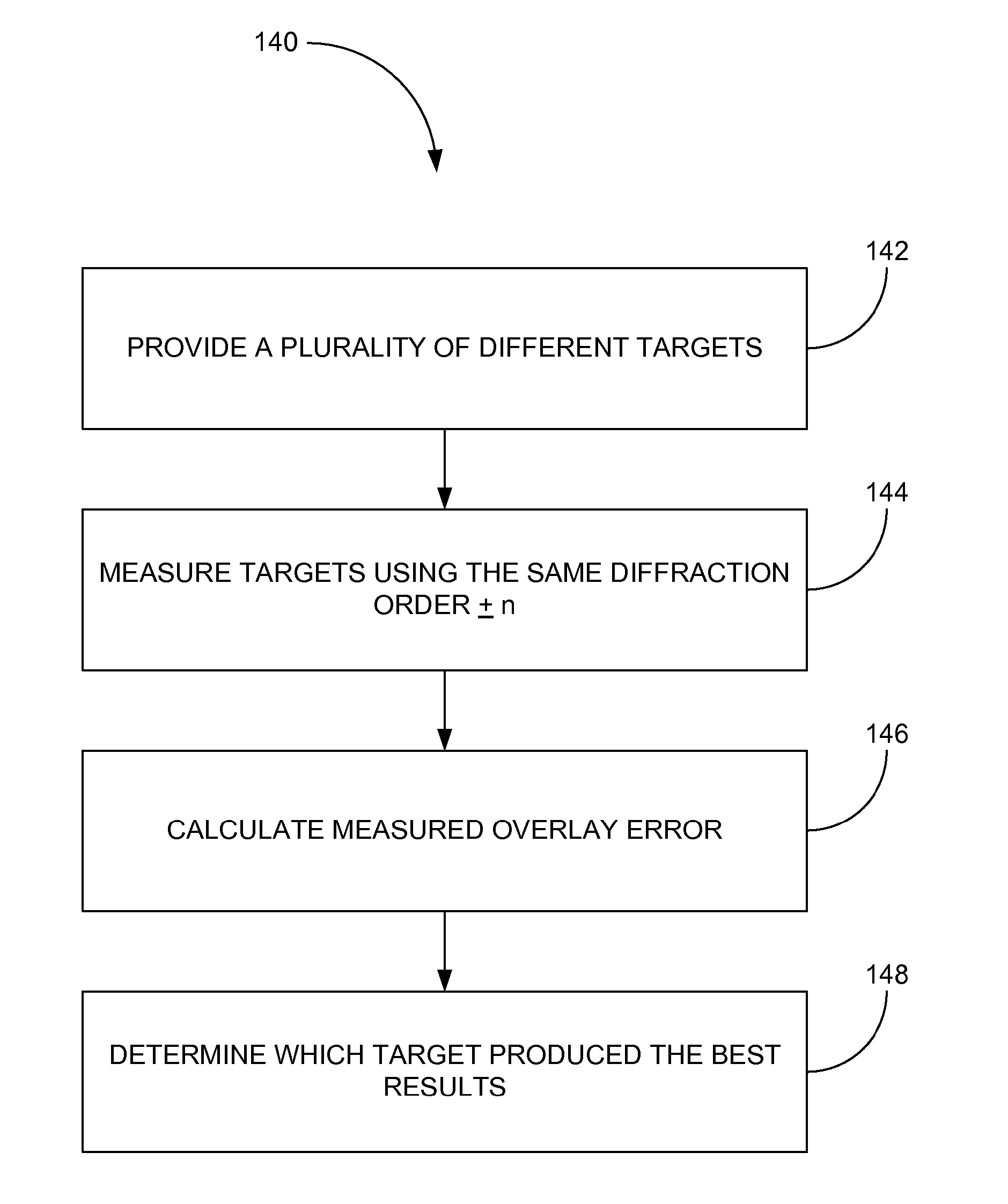
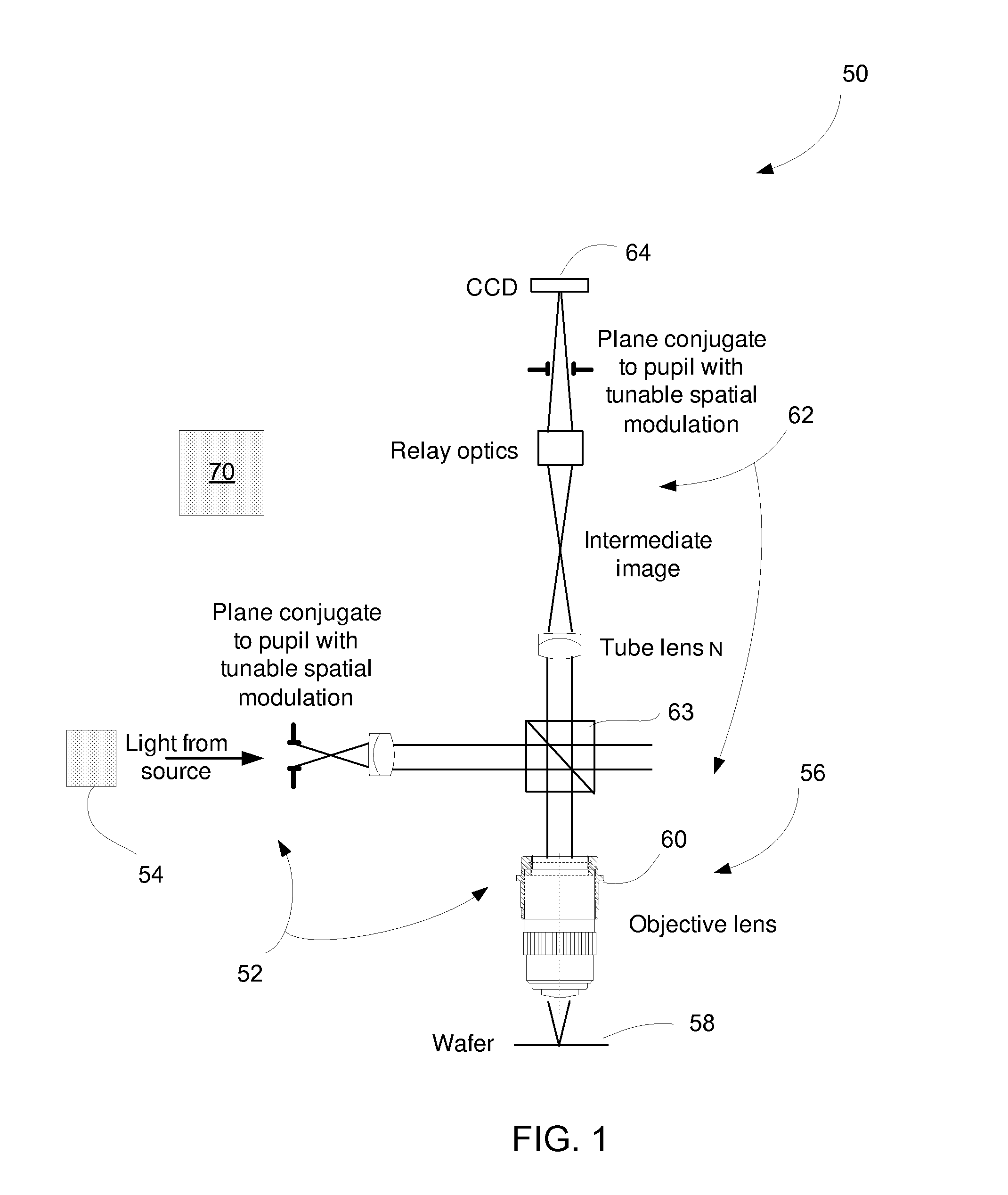
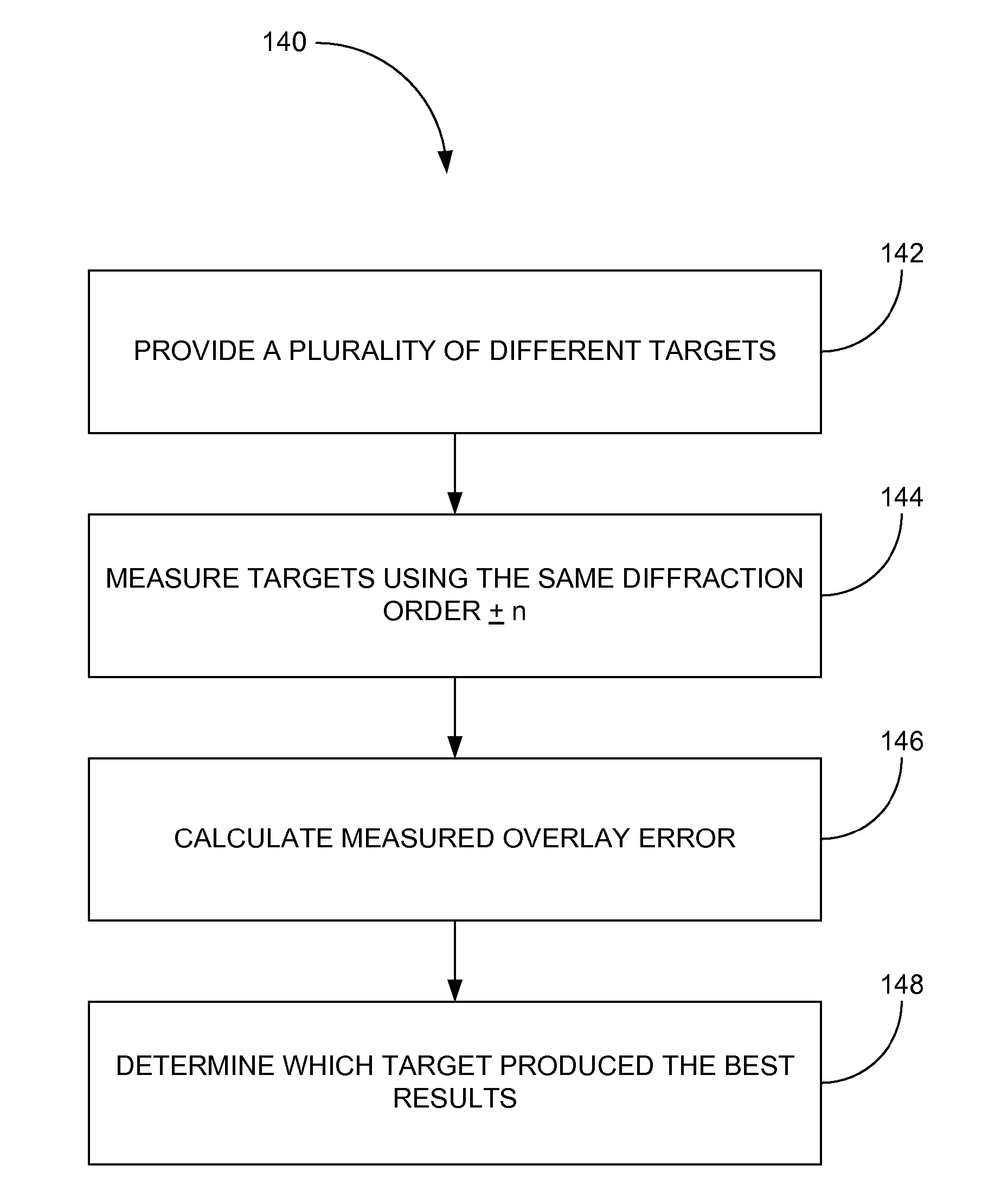
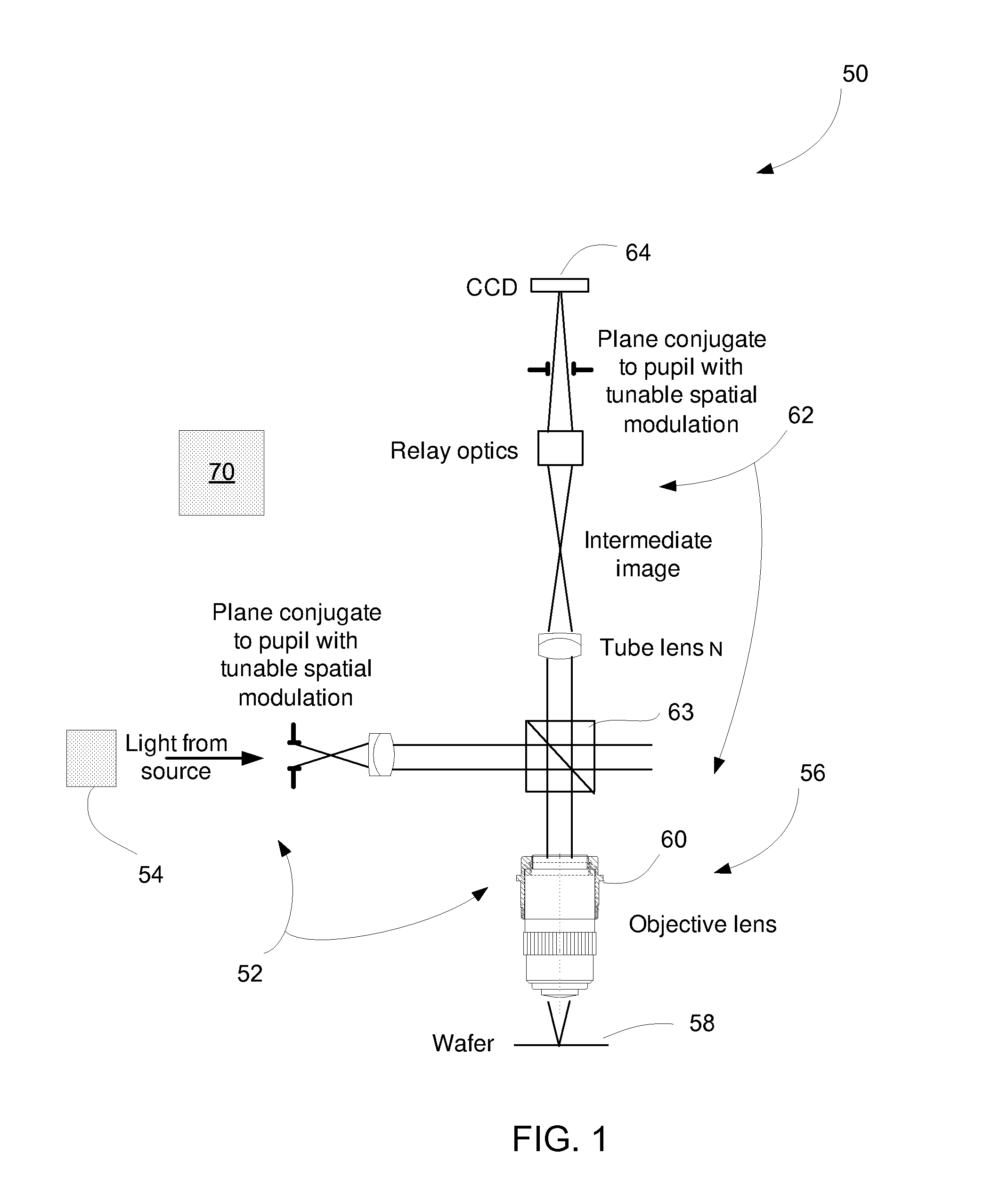
Order selected overlay metrology
ActiveUS20070279630A1Maximize contrastPhotomechanical apparatusMaterial analysis by optical meansDiffraction orderMetrology
Disclosed are apparatus and methods for measuring a characteristic, such as overlay, of a semiconductor target. In general, order-selected imaging and / or illumination is performed while collecting an image from a target using a metrology system. In one implementation, tunable spatial modulation is provided only in the imaging path of the system. In other implementations, tunable spatial modulation is provided in both the illumination and imaging paths of the system. In a specific implementation, tunable spatial modulation is used to image side-by-side gratings with diffraction orders ±n. The side-by-side gratings may be in different layers or the same layer of a semiconductor wafer. The overlay between the structures is typically found by measuring the distance between centers symmetry of the gratings. In this embodiment, only orders ±n for a given choice of n (where n is an integer and not equal to zero) are selected, and the gratings are only imaged with these diffraction orders.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
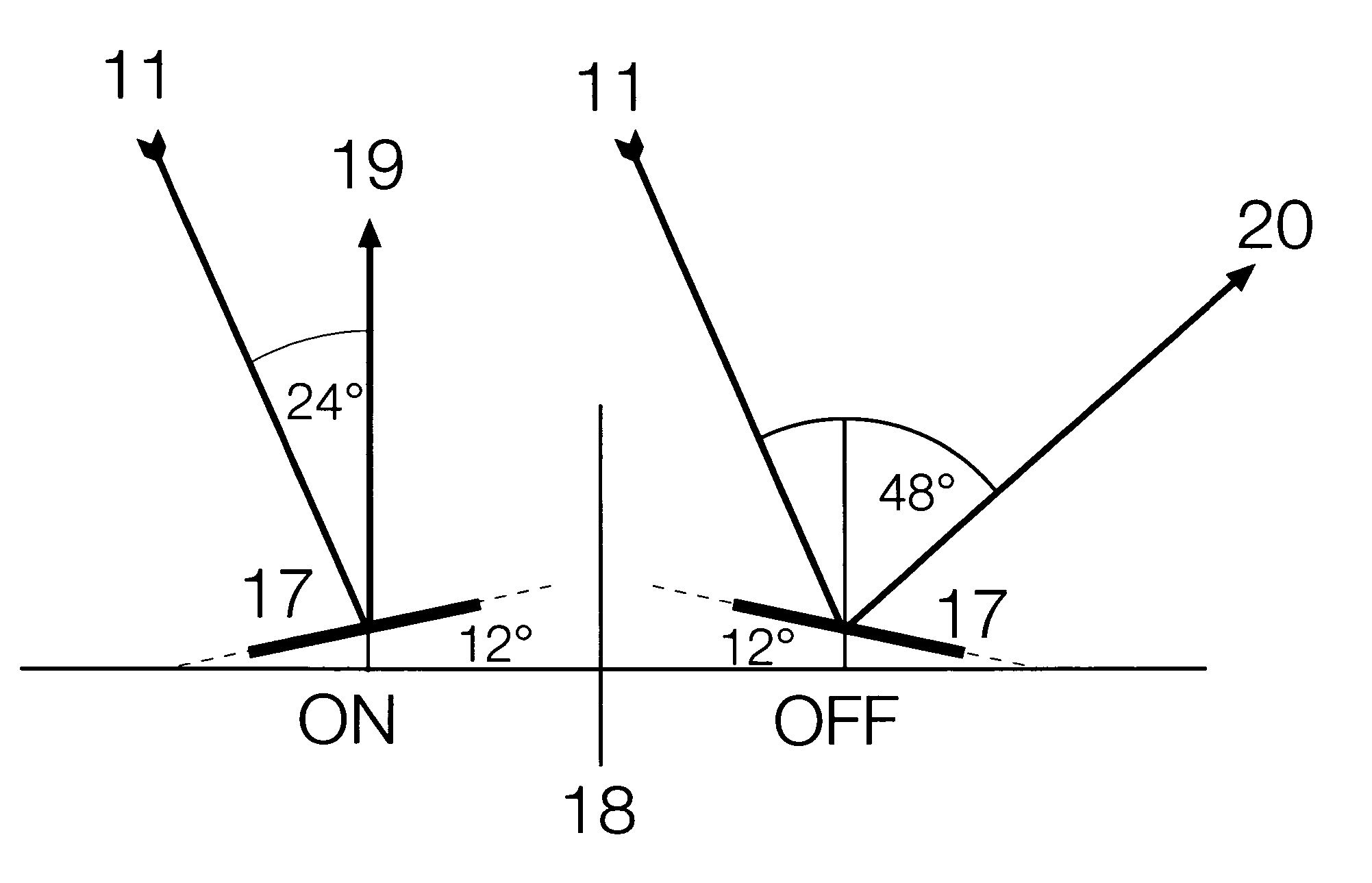
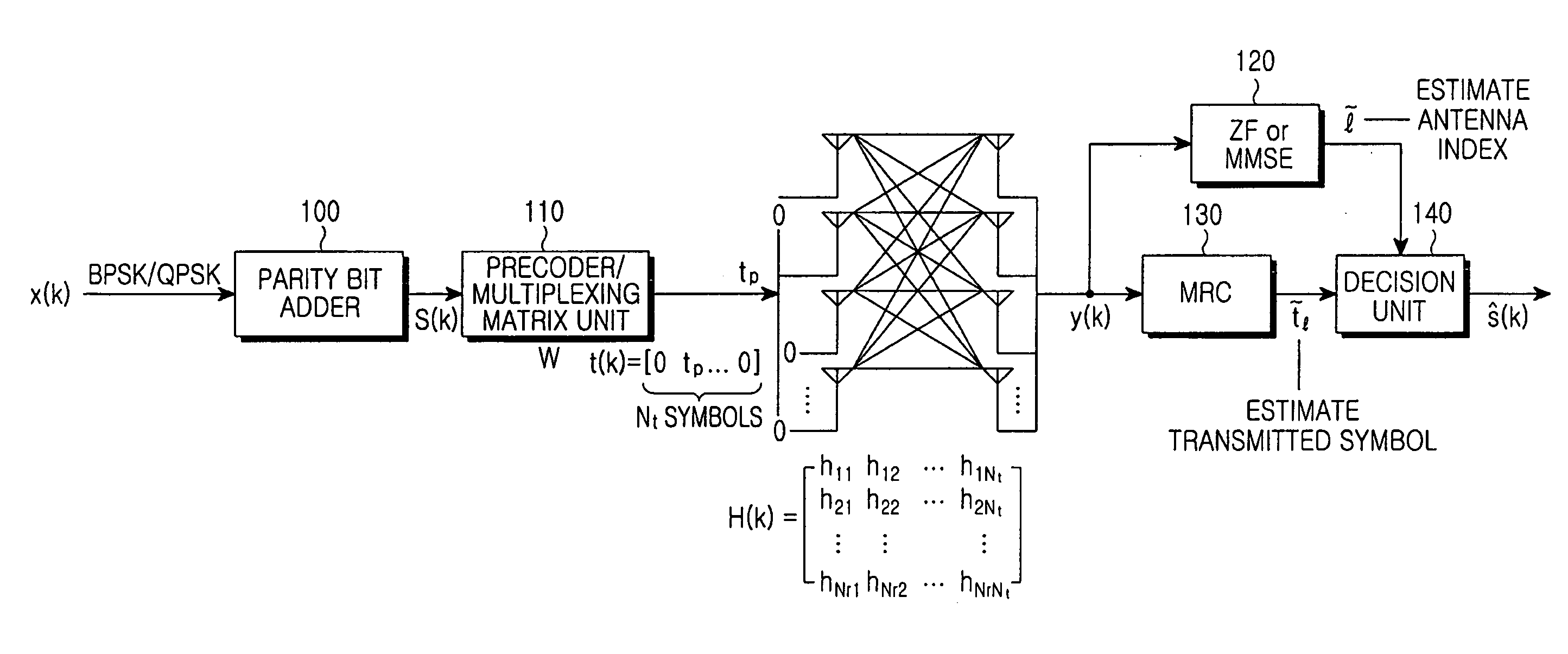
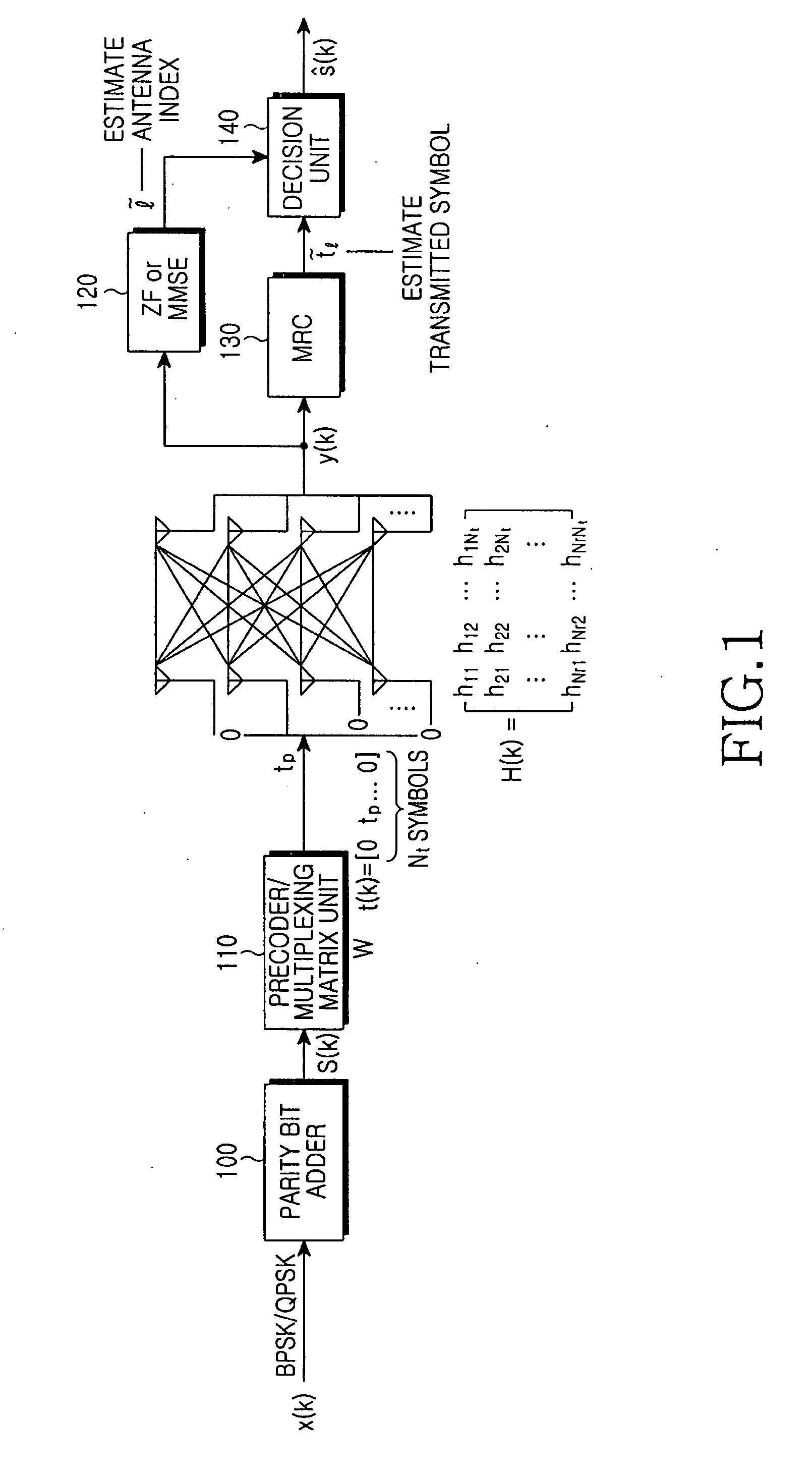
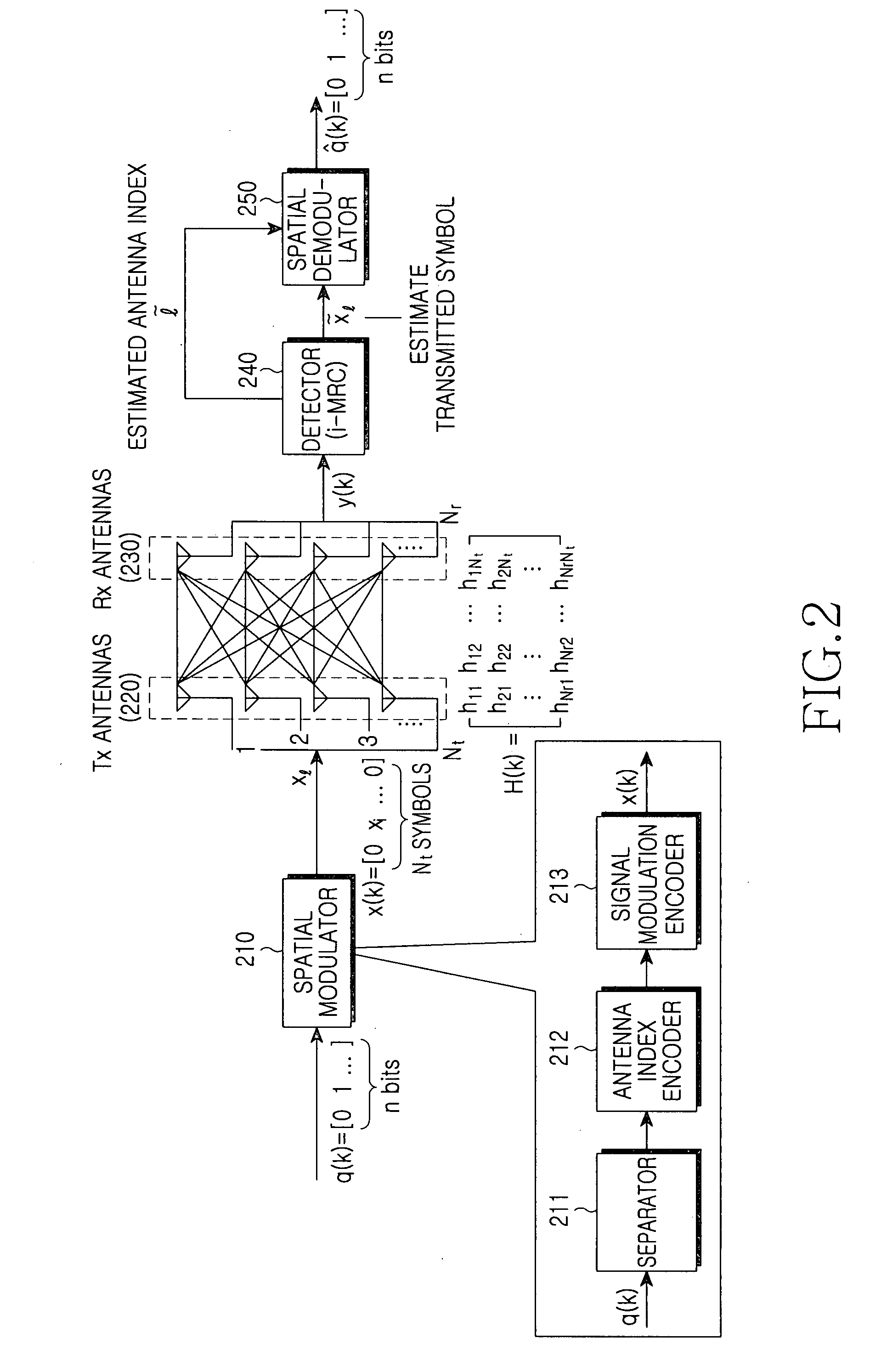
Spatial modulation method and transmitting and receiving apparatuses using the same in a multiple input multiple output system
ActiveUS20080037673A1Eliminate needImprove transmission efficiencyDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationMultiple inputSignal modulation
A spatial modulation method and transmitting and receiving apparatuses using the spatial modulation method in a MIMO system are provided. The spatial modulation method uses an index of an activated antenna and a signal modulation constellation as an information source. The spatial modulation method is applied to the transmitting apparatus. The receiving apparatus uses a spatial modulation detection method in which a channel path gain is repeatedly multiplied to detect the spatially modulated signal efficiently.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
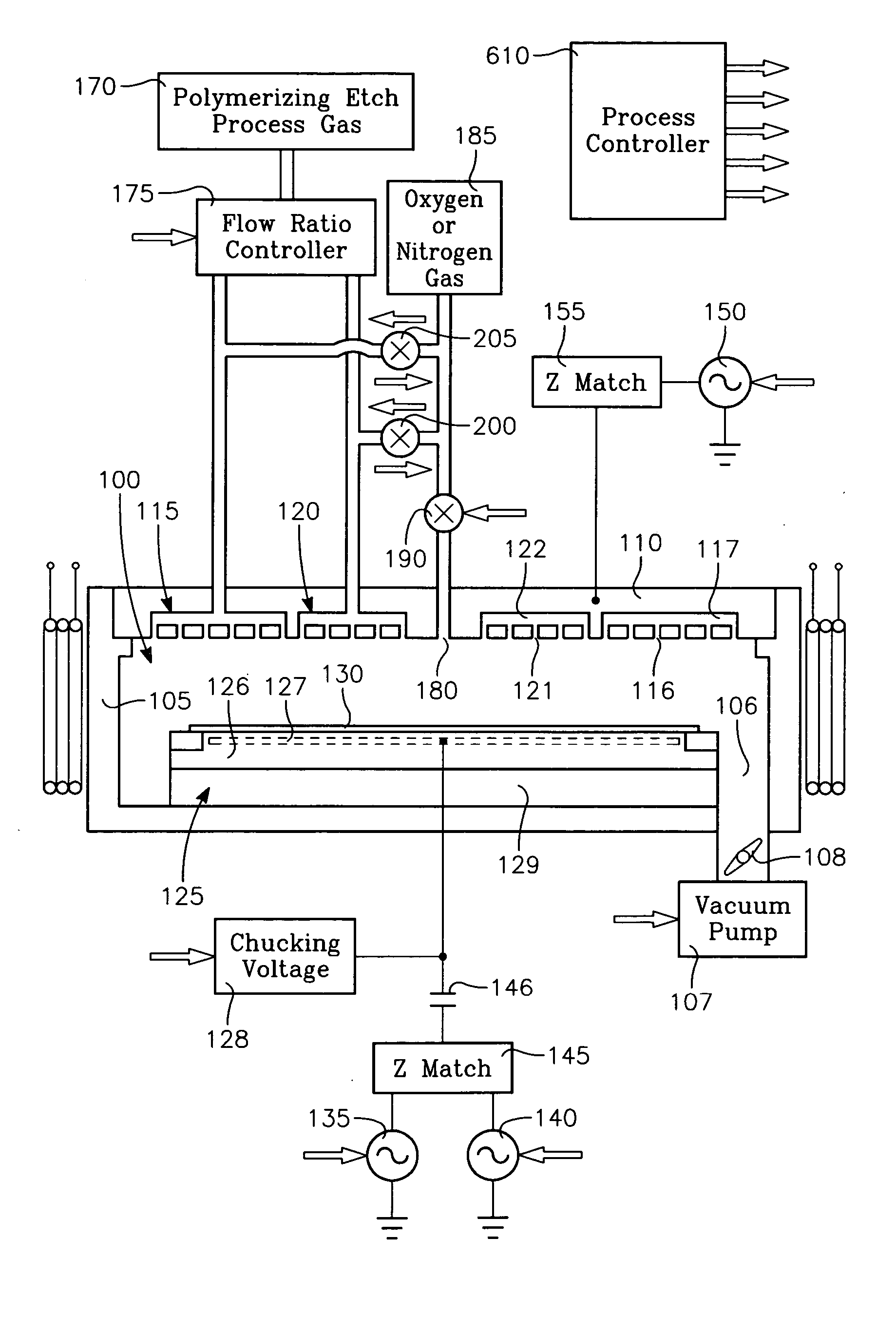
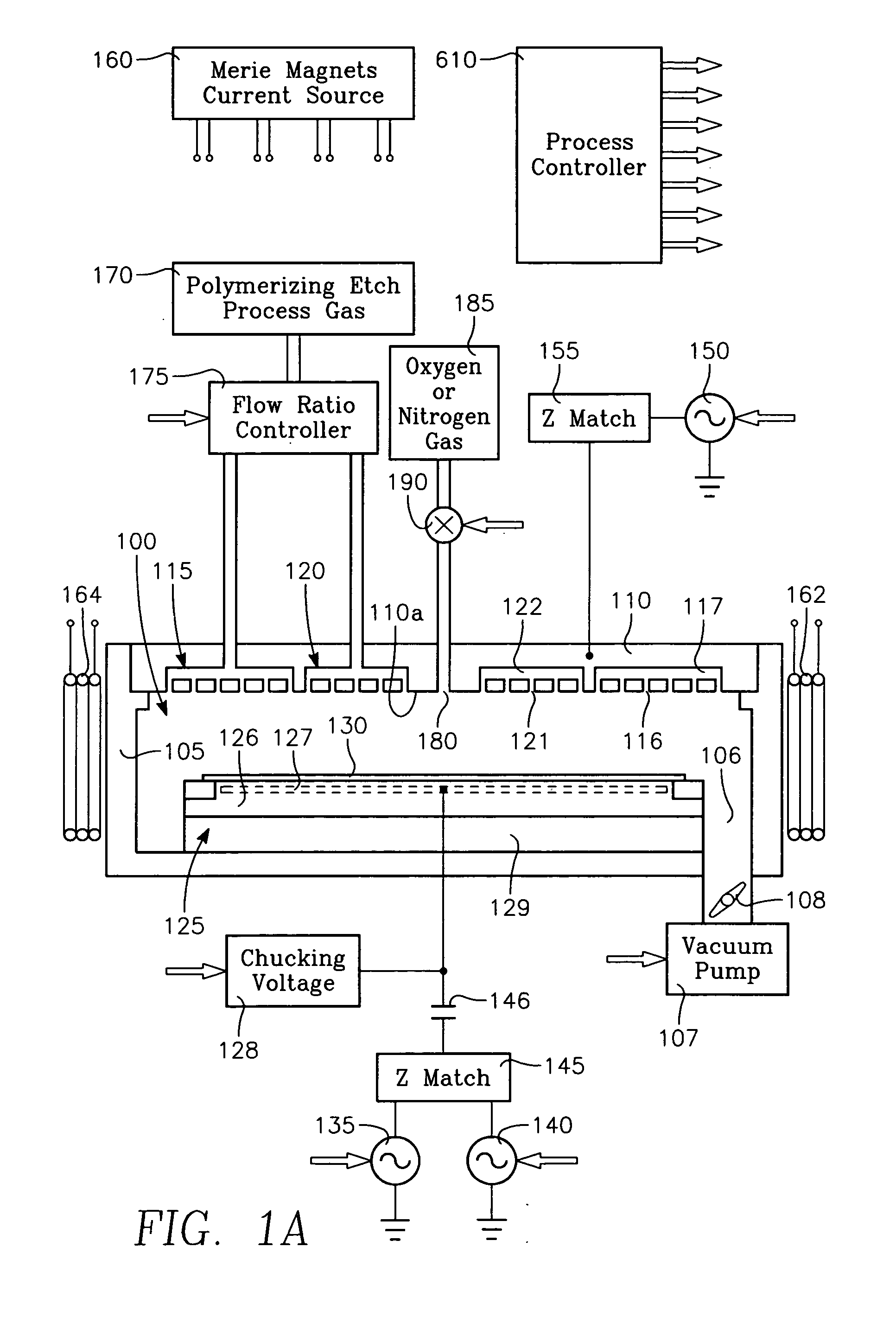
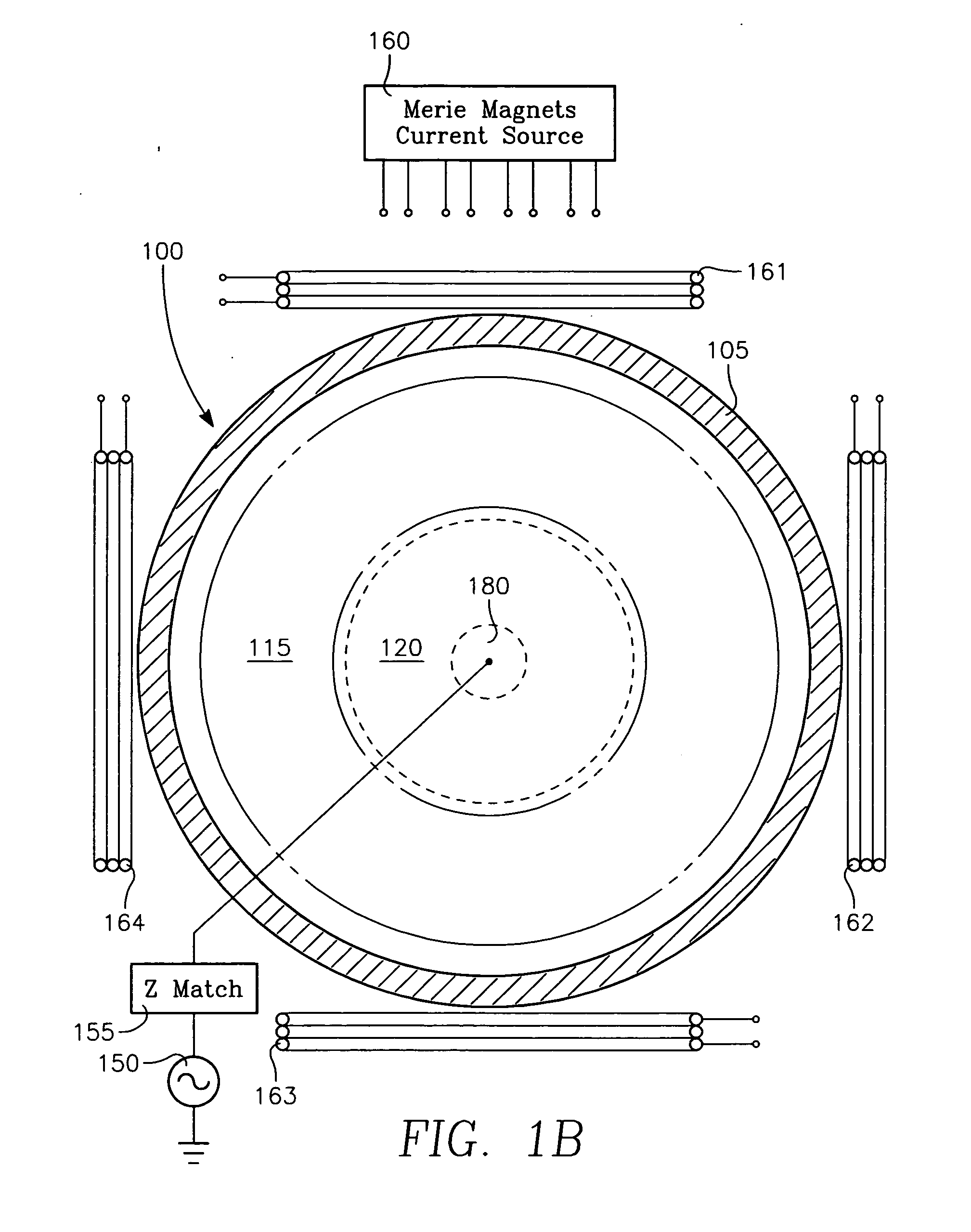
Plasma etch process using polymerizing etch gases across a wafer surface and additional polymer managing or controlling gases in independently fed gas zones with time and spatial modulation of gas content
ActiveUS20070251917A1Slow deposition rateMinimizing etch stopElectric discharge tubesVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsEngineeringOxygen
A plasma etch process etches high aspect ratio openings in a dielectric film on a workpiece in a reactor having a ceiling electrode overlying the workpiece and an electrostatic chuck supporting the workpiece. The process includes injecting a polymerizing etch process gas through an annular zone of gas injection orifices in the ceiling electrode, and evacuating gas from the reactor through a pumping annulus surrounding an edge of the workpiece. The high aspect ratio openings are etched in the dielectric film with etch species derived from the etch process gas while depositing a polymer derived from the etch process gas onto the workpiece, by generating a plasma in the reactor by applying VHF source power and / or HF and / or LF bias power to the electrodes at the ceiling and / or the electrostatic chuck. The process further includes slowing the deposition rate of the polymer, minimizing etch stop and / or increasing the etch rate in a region of the workpiece typically the center by injecting oxygen or nitrogen and / or high-fluorine containing gas through gas injection orifice in the corresponding region of the ceiling electrode, and adjusting the flow rate of the oxygen or nitrogen and / or high-fluorine containing gas through the gas injection orifice to minimize the difference between profiles and etch depths at the workpiece center and the workpiece periphery.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Order selected overlay metrology
ActiveUS7528941B2Maximize contrastPhotomechanical apparatusMaterial analysis by optical meansDiffraction orderMetrology
Disclosed are apparatus and methods for measuring a characteristic, such as overlay, of a semiconductor target. In general, order-selected imaging and / or illumination is performed while collecting an image from a target using a metrology system. In one implementation, tunable spatial modulation is provided only in the imaging path of the system. In other implementations, tunable spatial modulation is provided in both the illumination and imaging paths of the system. In a specific implementation, tunable spatial modulation is used to image side-by-side gratings with diffraction orders ±n. The side-by-side gratings may be in different layers or the same layer of a semiconductor wafer. The overlay between the structures is typically found by measuring the distance between centers symmetry of the gratings. In this embodiment, only orders ±n for a given choice of n (where n is an integer and not equal to zero) are selected, and the gratings are only imaged with these diffraction orders.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Methods and apparatus for spatial light modulation
ActiveUS20070091038A1Improve luminous efficiencyIncrease brightnessStatic indicating devicesOptical light guidesOptical cavityOptoelectronics
Improved apparatus and methods for spatial light modulation are disclosed which utilize optical cavities having both front and rear reflective surfaces. Light-transmissive regions are formed in the front reflective surface for spatially modulating light.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Microscope device and image processing method
ActiveUS20090225407A1Increase speedCharacter and pattern recognitionMicroscopesImaging processingFluorescence
A diffraction grating produces the first diffraction light in a symmetrical direction with respect to the 0-th diffraction light and the optical axis. Each light flux forms two flux interference patterns on a sample surface through a second objective lens and a first objective lens, and a sample is illuminated by spatially modulated illumination light. Fluorescence is generated on the sample by structured illumination light as excitation light. The fluorescence caught by the first objective lens forms a modulated image of the sample on a sample conjugate surface through an objective optical system comprised of the first objective lens and the second objective lens. The modulated image is further modulated through the diffractive grating. Fluorescence from the further modulated image passes through a lens and a dichroic mirror, enters into a single light path of an observation optical system, passes through a fluorescent filter, and forms an enlarged image of the further modulated image through a lens.
Owner:NIKON CORP
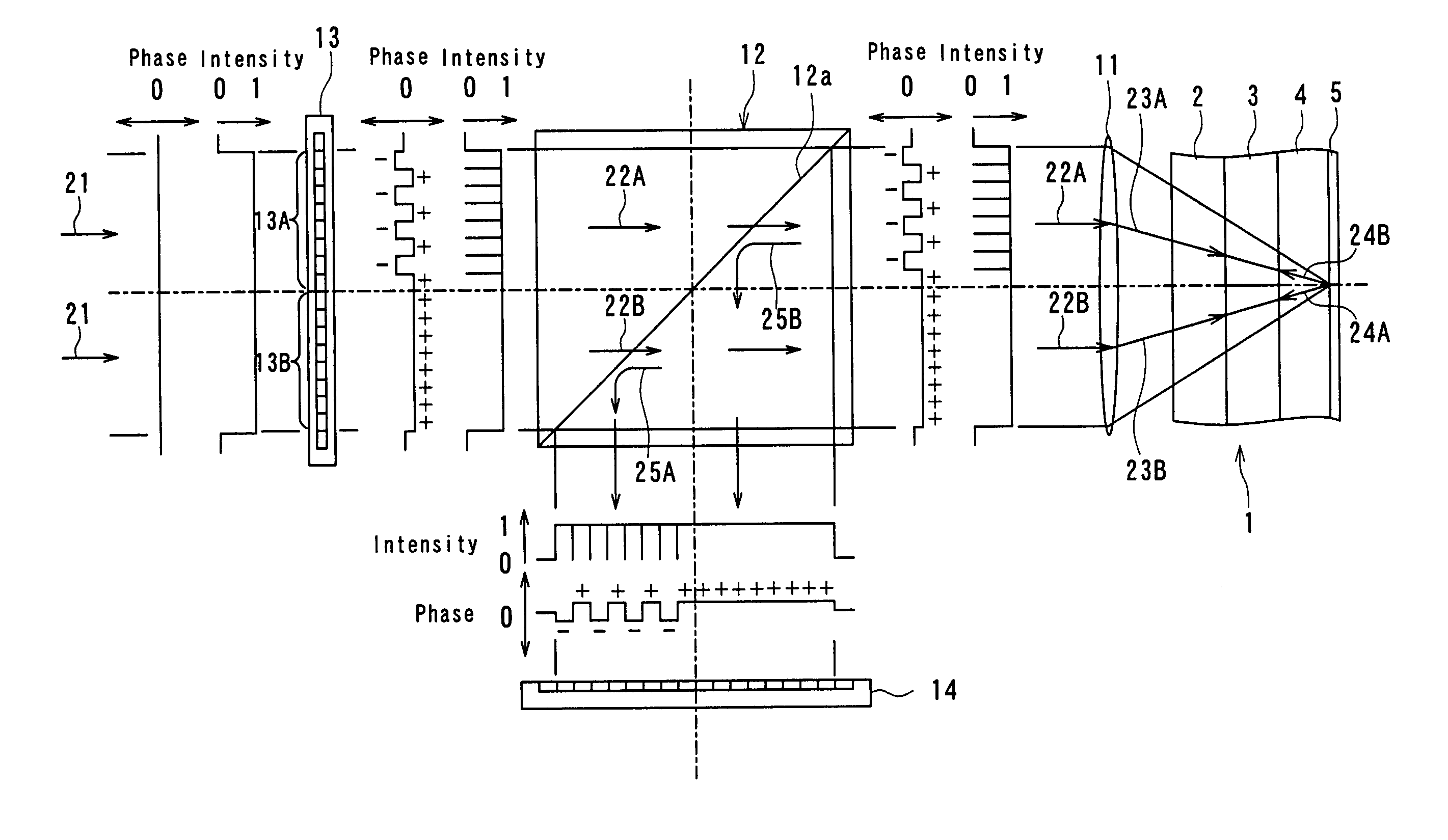
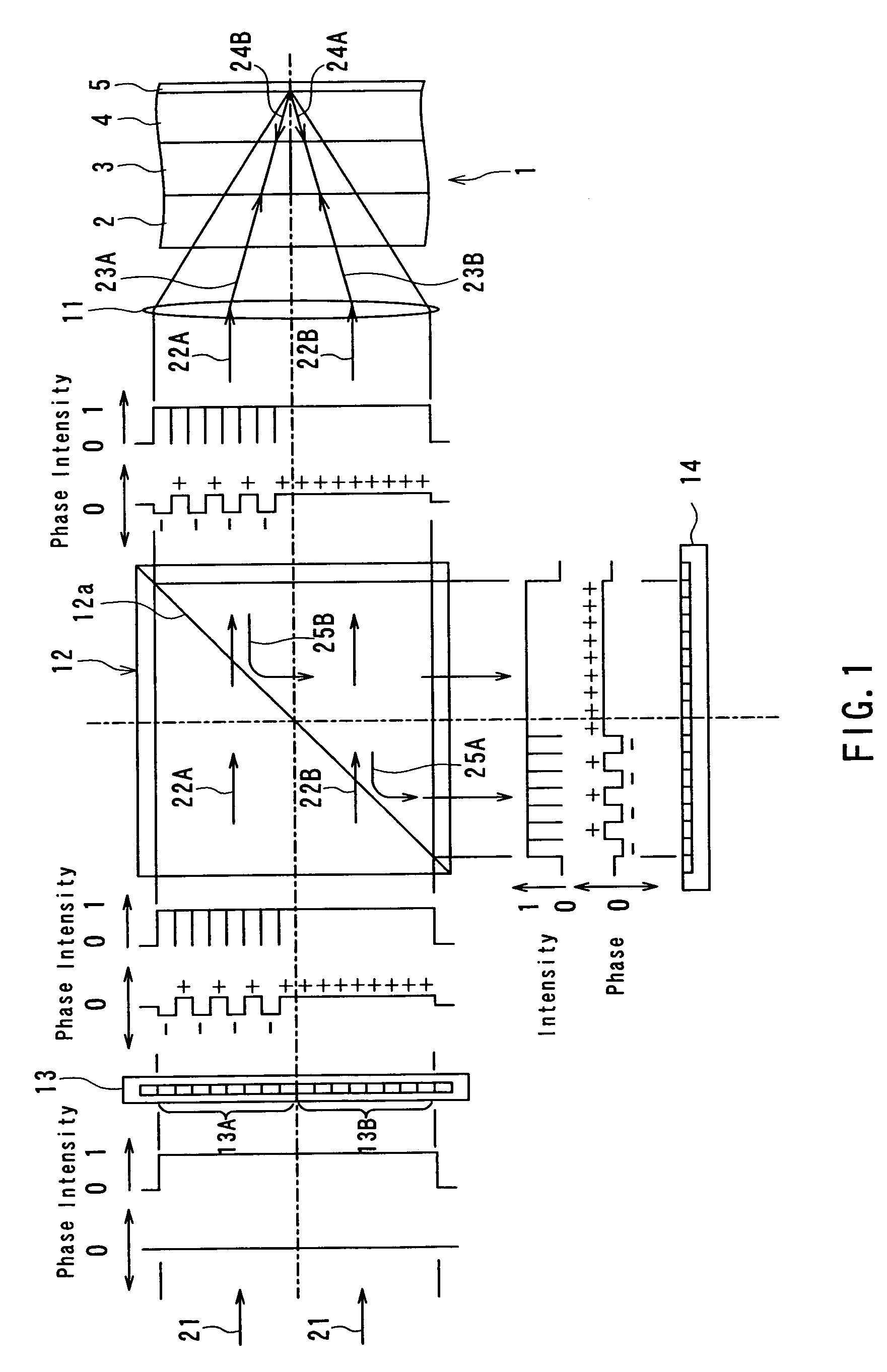
Apparatus for recording optical information
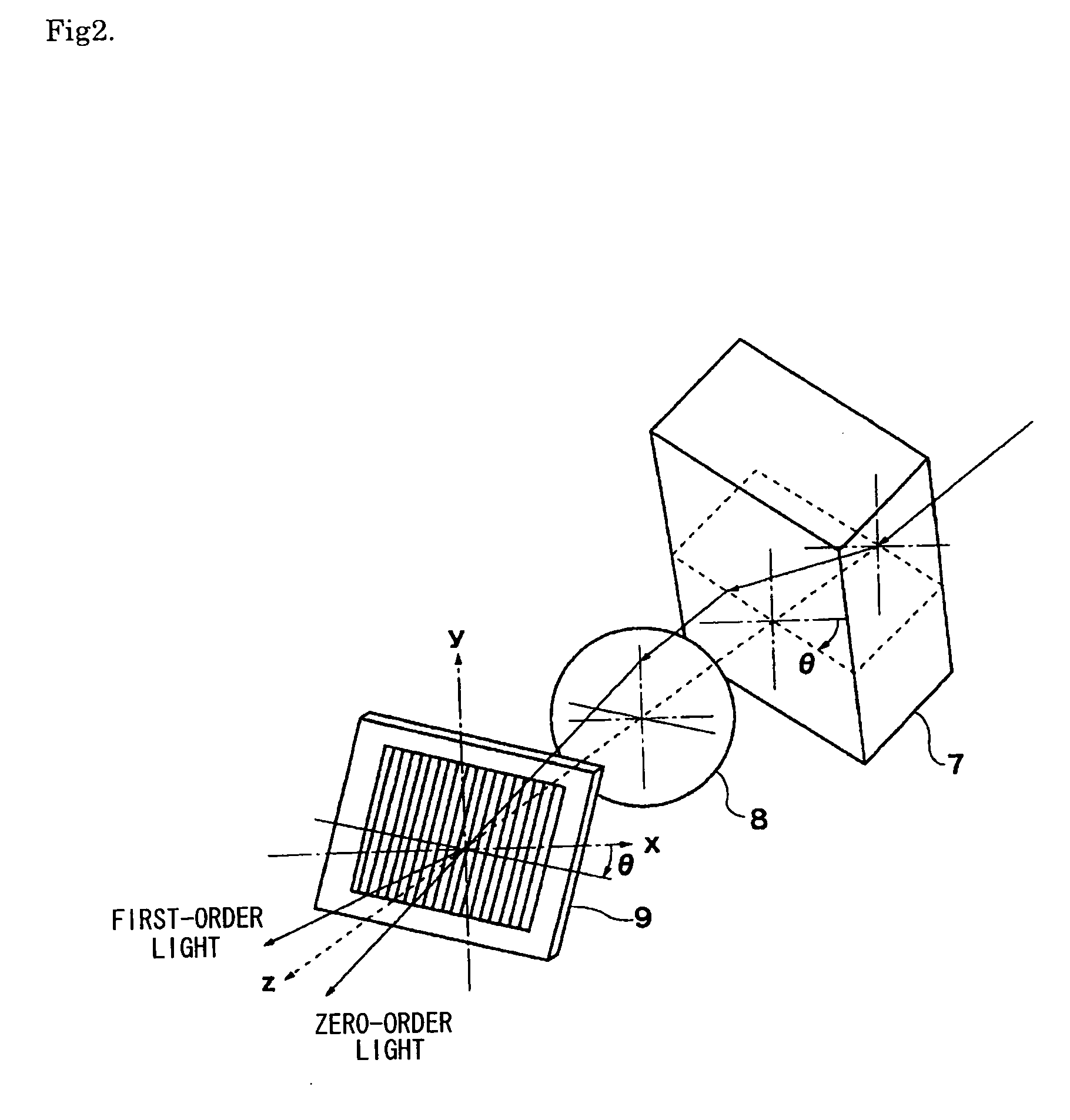
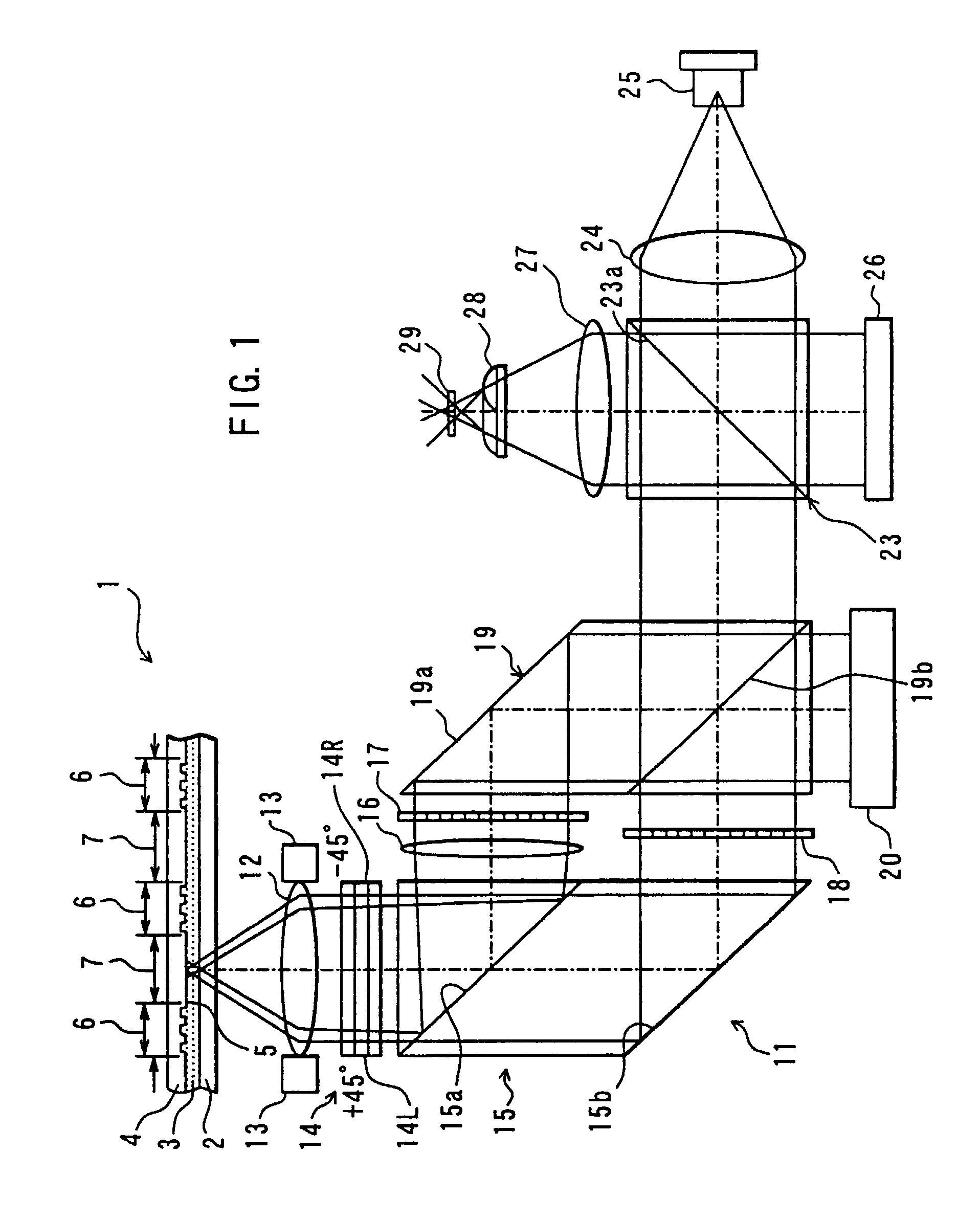
InactiveUS6995882B2Compact configurationPrecise positioningInformation arrangementOptical discsSpatial light modulatorLaser light
The present invention makes it possible to reduce the size of an optical system for multiplex recording or reproduction of information utilizing holography.A pick-up (11) of an optical information recording / reproducing apparatus generates information light by spatially modulating laser light emitted by a light source device (25) with a spatial light modulator (18) depending on the information to be recorded and generates reference light for recording having a spatially modulated phase by spatially modulating the phase of laser beam emitted by the light source device (25) with a phase-spatial light modulator (17). The information light and the reference light for recording are projected upon an optical information recording medium (1) such that they converge in different positions, and information is recorded in the hologram layer (3) in the form of an interference pattern as a result of interference between the information light reflected by a reflecting film (5) and the reference light for recording. The positioning of the information light and the reference light for recording is carried out based on information recorded in address servo areas (6).
Owner:OPTWARE
Illuminating optical unit in image display unit, and image display unit
InactiveUS6897992B2Suppress speckle noiseSuppresses degradation of image qualityTelevision system detailsProjectorsLight beamOptoelectronics
Disclosed is an illuminating optical unit in an image display unit for displaying an image by irradiating a GLV (spatial modulation device) with a laser beam and modulating the laser beam based on an image signal inputted to the GLV, which includes a polarized light rotation means for equally dividing a polarized light component of the laser beam into a P polarized light component and an S polarized light component, a polarized light beam splitter for separating from each other the P polarized light component and the S polarized light component equally divided by the polarized light rotation means, and an optical path difference generation means for generating an optical path difference not less than the coherence length of the laser beam between the laser beam of the P polarized light component and the laser beam of the S polarized light component.
Owner:SONY CORP
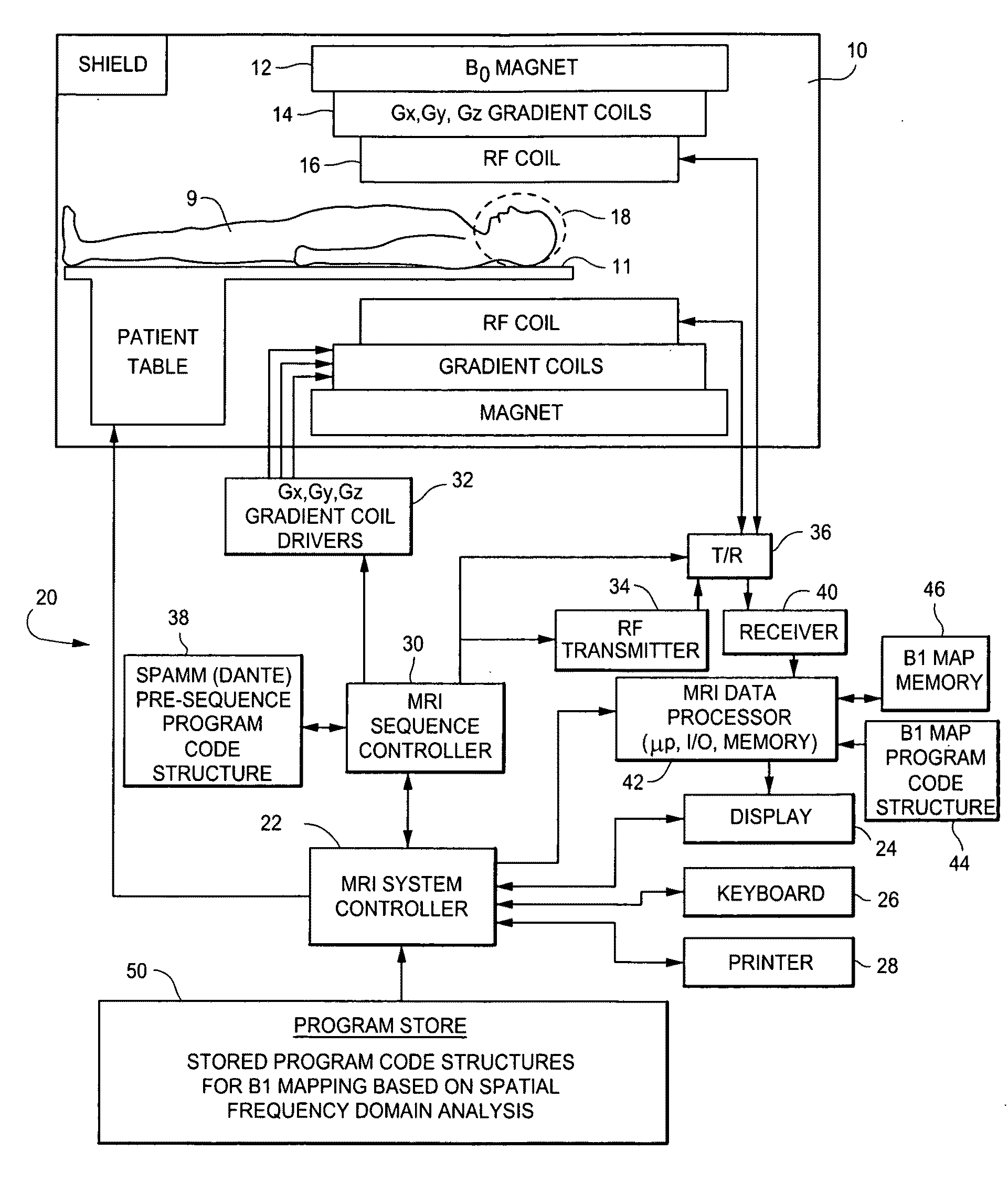
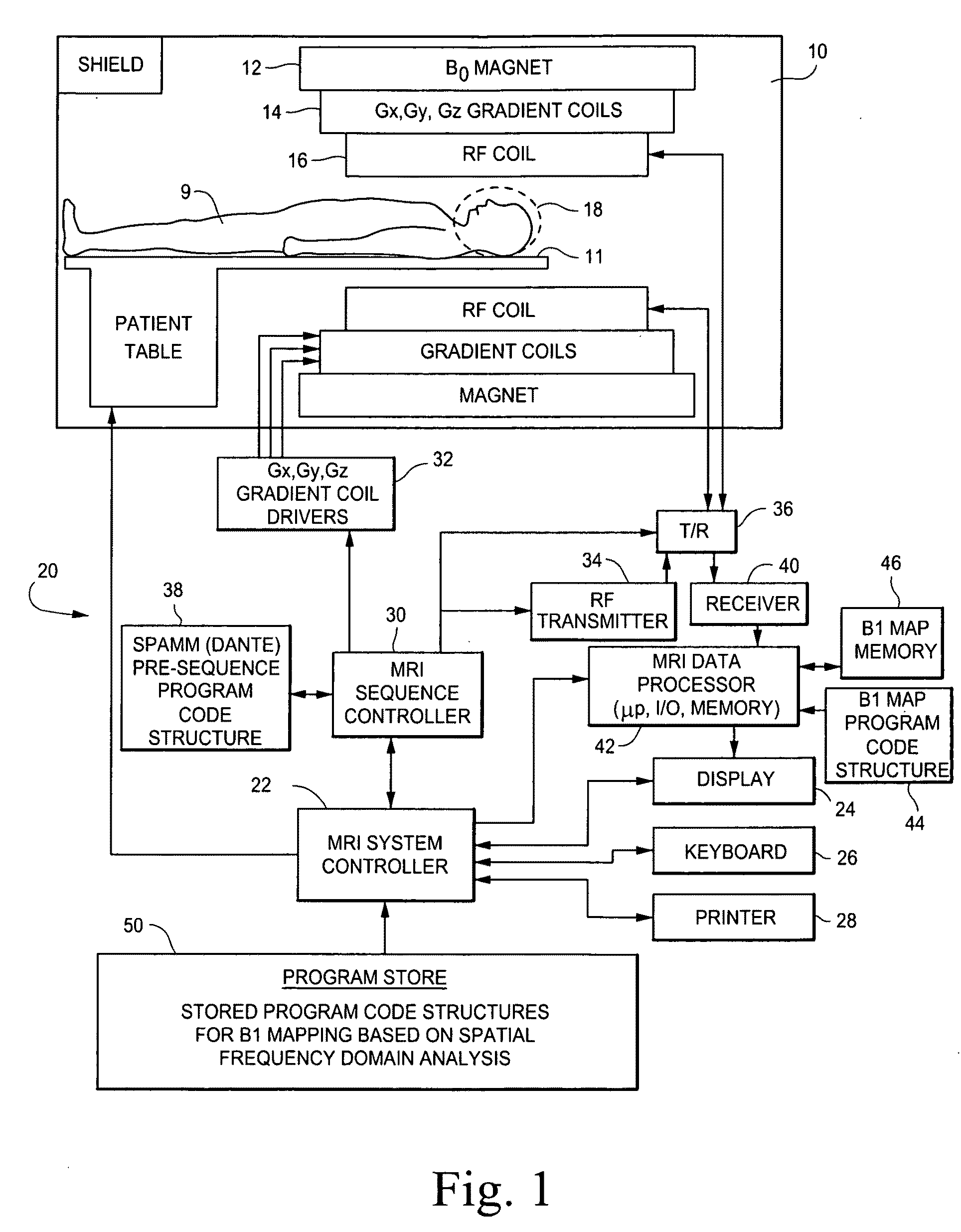
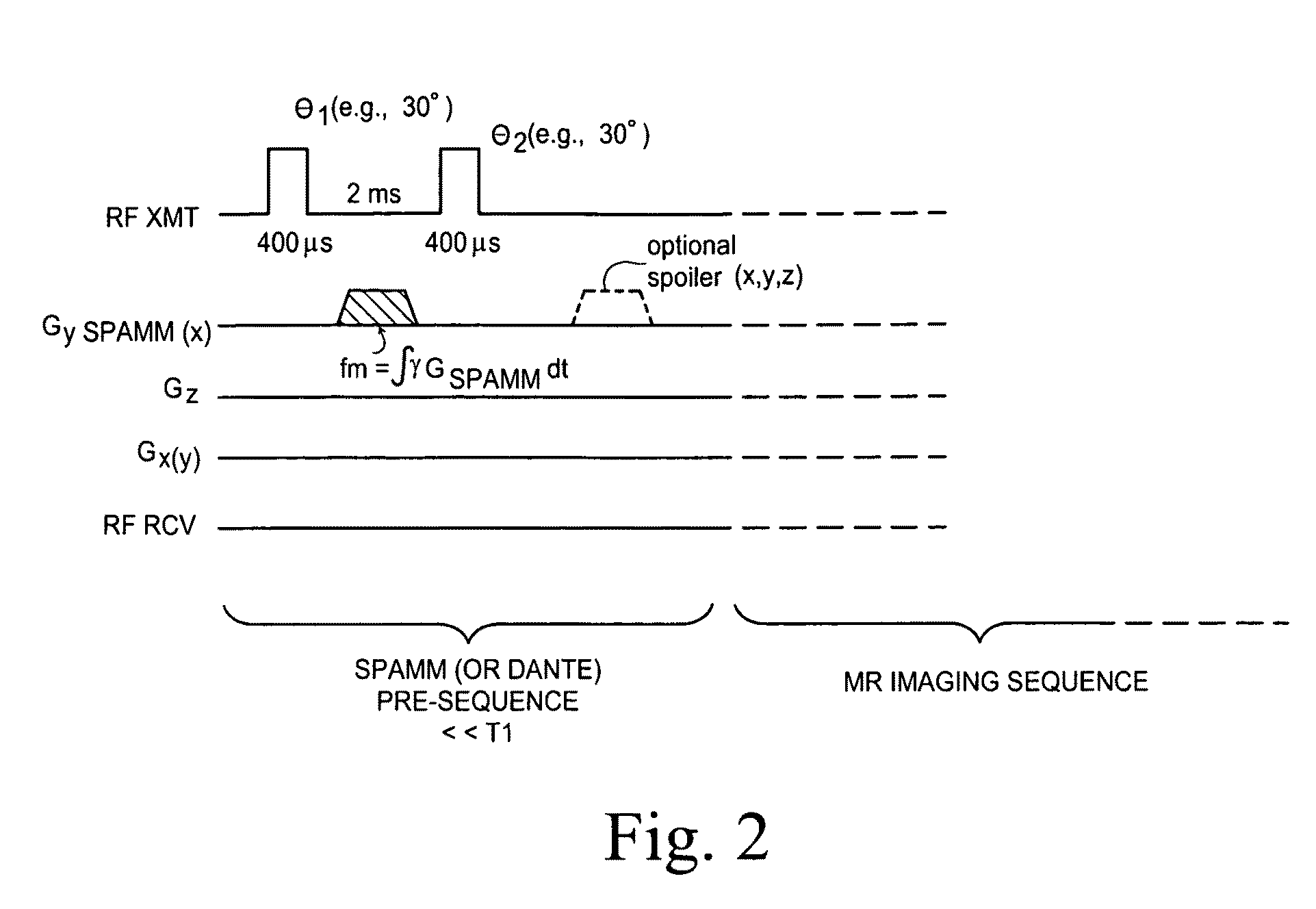
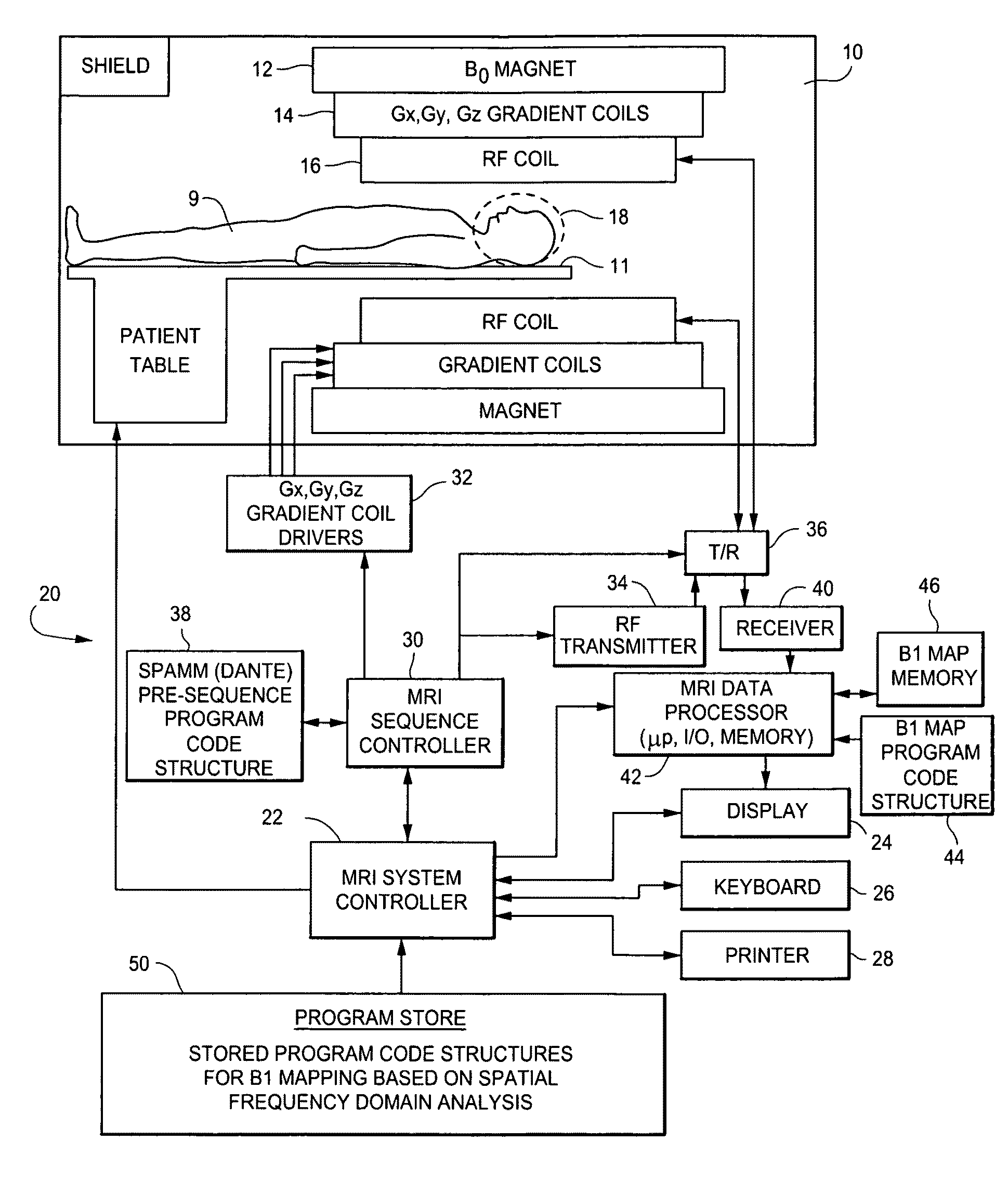
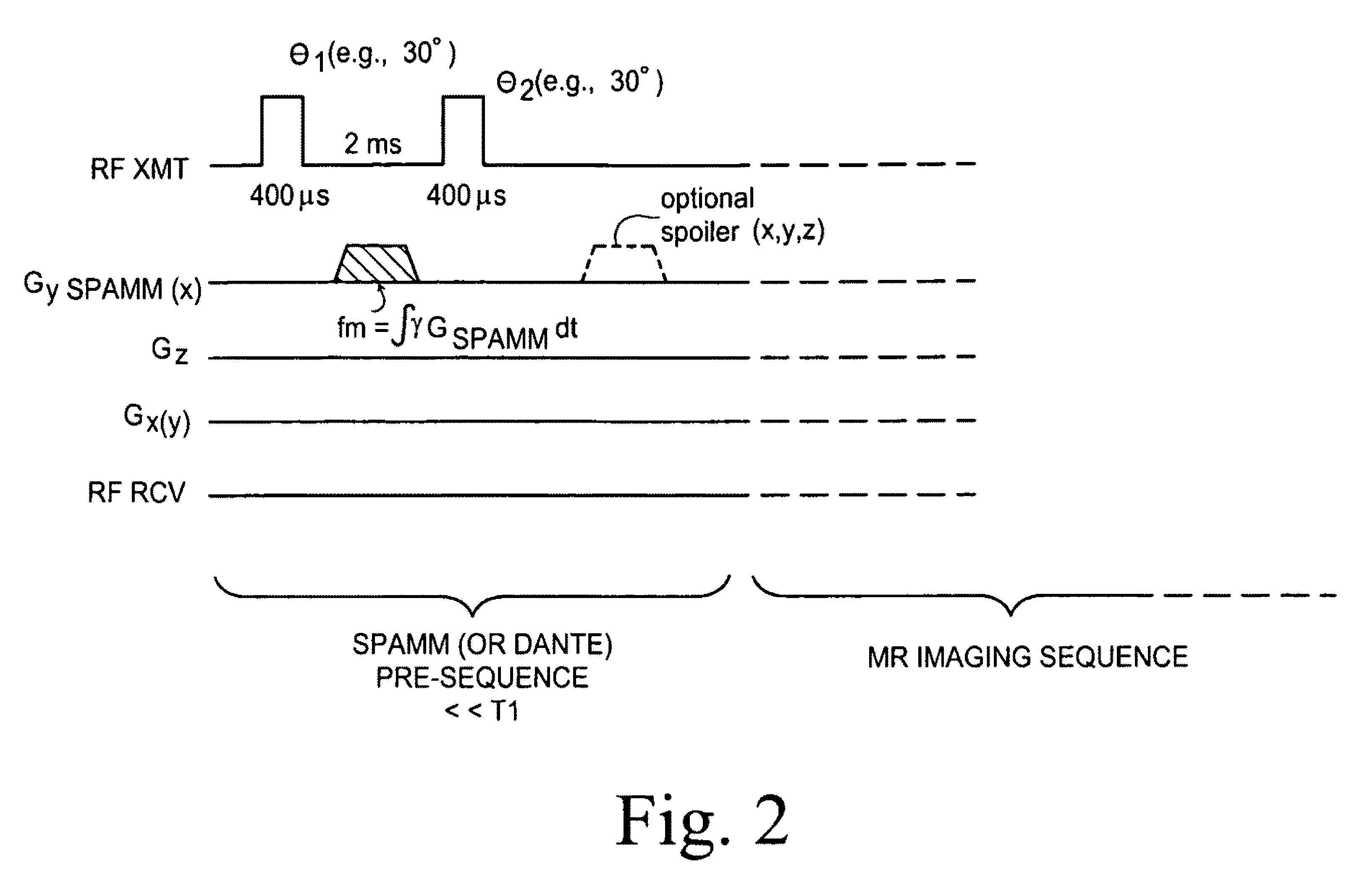
B1 mapping in MRI system using k-space spatial frequency domain filtering
ActiveUS20100239142A1High resolutionReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionFrequency filteringCondensed matter physics
Frequency filtering of spatially modulated or “tagged” MRI data in the spatial frequency k-space domain with subsequent 2DFT to the spatial domain and pixel-by-pixel arithmetic calculations provide robust ratio values that can be subjected to inverse trigonometric functions to derive B1 maps for an MRI system.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Apparatus and method for recording/reproducing optical information
InactiveUS7065032B2Small configurationImprove signal-to-noise ratioIntegrated optical head arrangementsOptical beam sourcesSpatial light modulatorPhotovoltaic detectors
Apparatus and method for recording and reproducing optical information using holography is designed to provide a small configuration and to improve the S / N ratio of reproduced information. During recording, a phase spatial light modulator generates information light spatially modulated in phase based on information to be recorded, and recording-specific reference light, that irradiate an information recording layer of an optical recording medium to record the information in the form of an interference pattern, resulting from interference between the information light and the recording-specific reference light. During reproduction, reproduction-specific reference light irradiates the information recording layer to generate reproduction light which is superimposed on the reproduction-specific reference light to generate composite light. The composite light is detected by a photodetector to reproduce the information.
Owner:OPTWARE
Spatially modulated detector for radiation
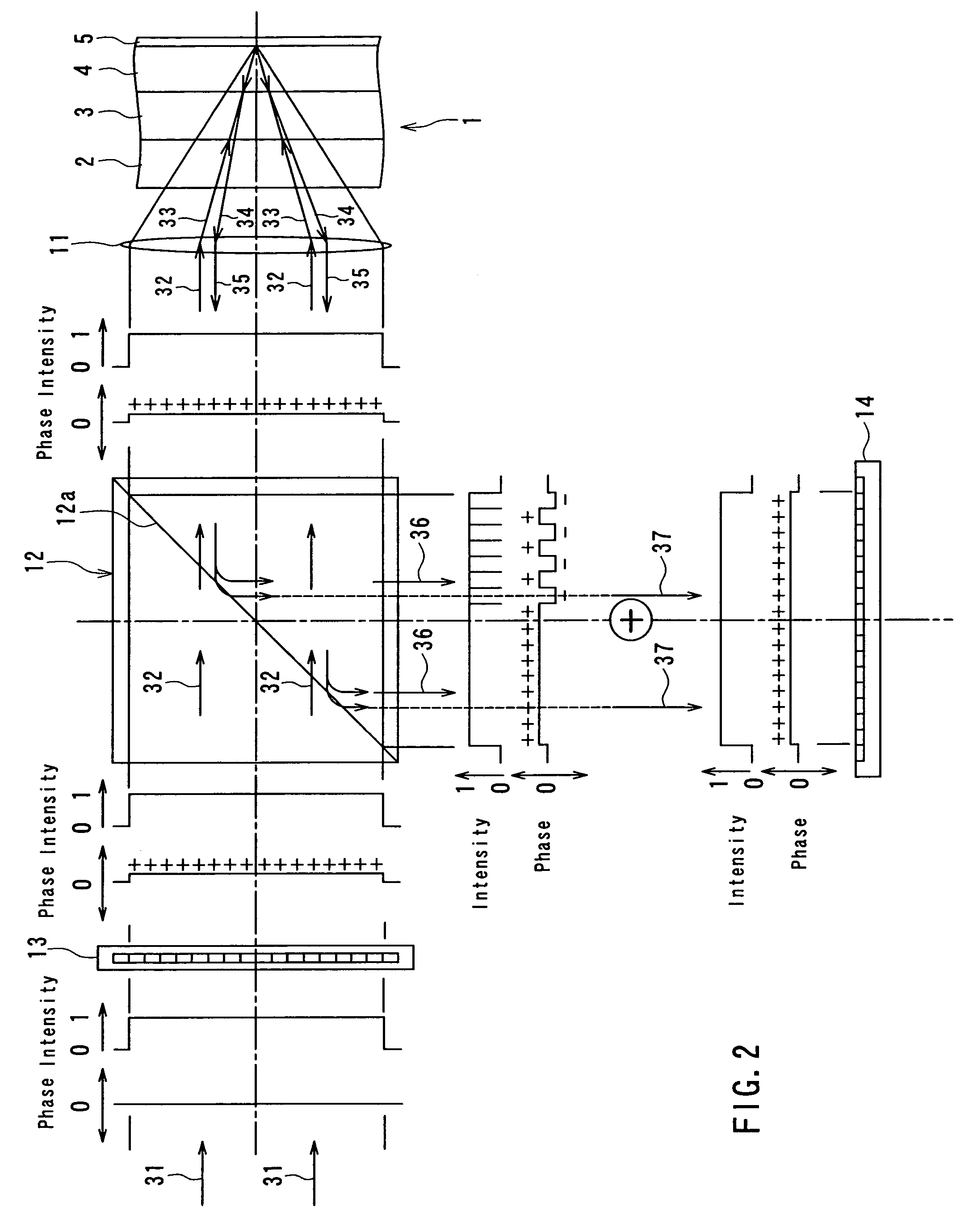
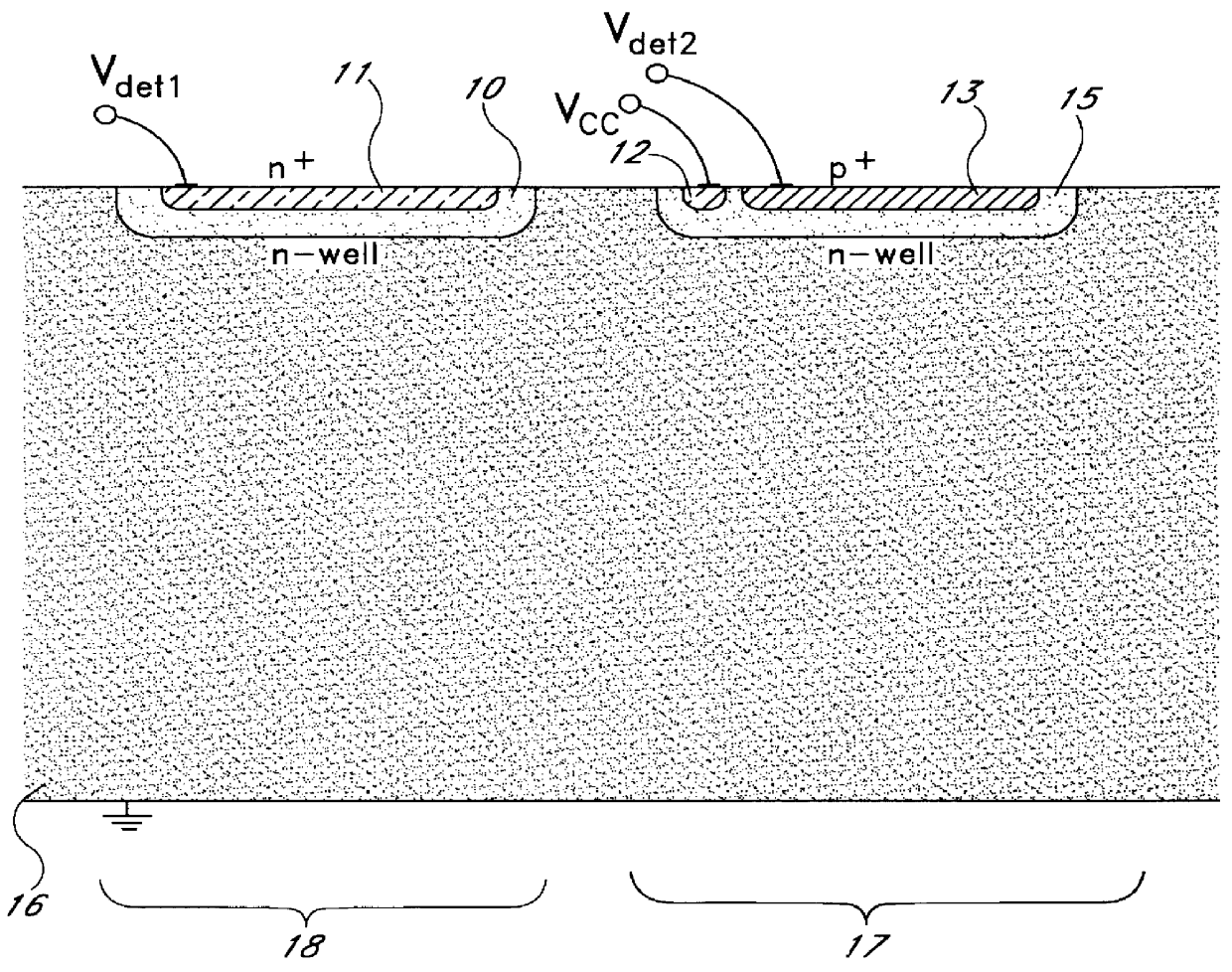
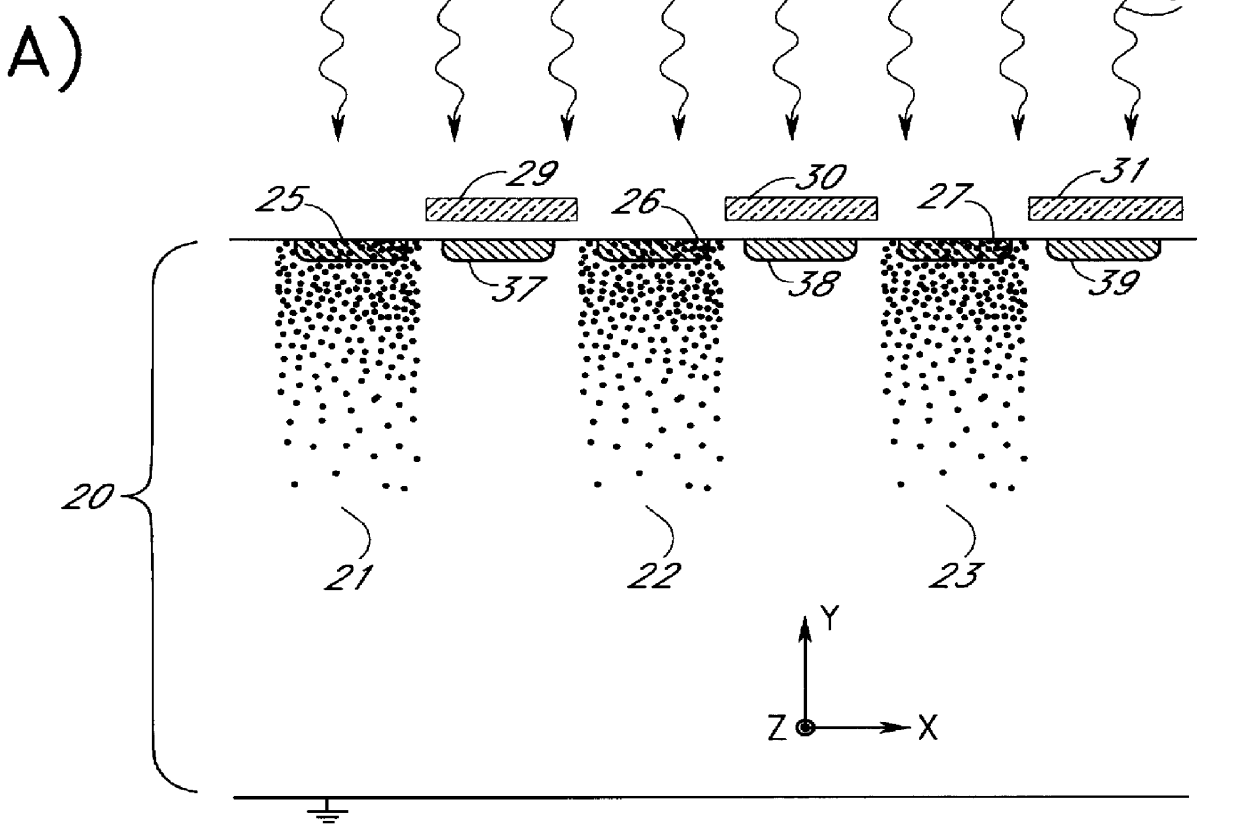
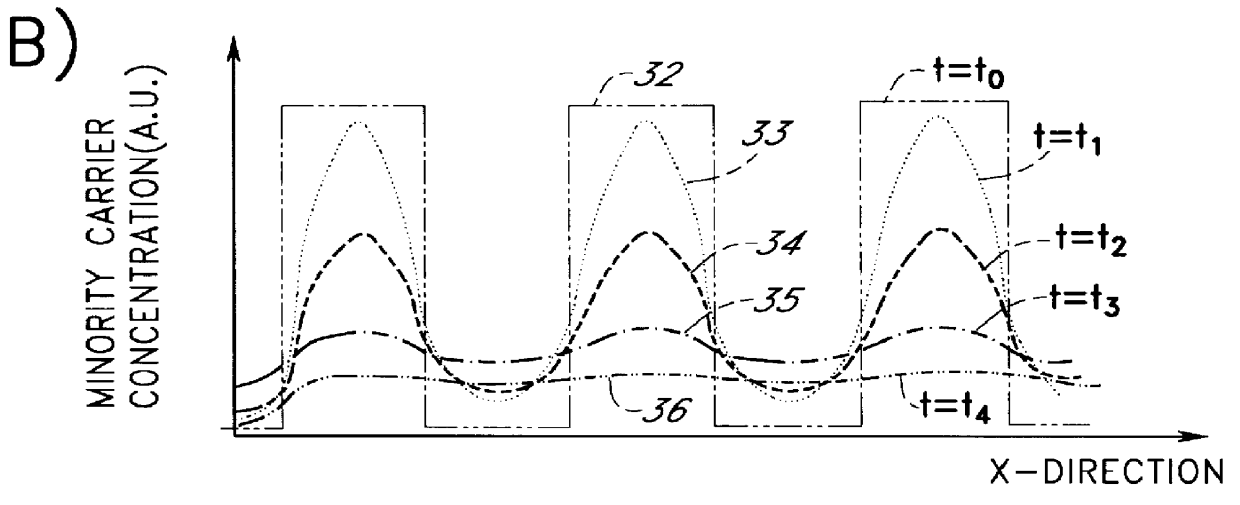
InactiveUS6157035AIncrease speedHigh speed detectionPhotometrySolid-state devicesFiberOptical detector
A novel radiation detector, a detection principle and an associated structure are provided for semiconductor substrate detectors in general and for CMOS based circuits in particular. For an optical detector, photons absorbed in the neutral zone of the substrate generate electron hole pairs that migrate by diffusion. A shadow mask gives a spatial modulation to the incident, and consequently, to the absorbed light in the semiconductor substrate. By measuring the magnitude of the spatial frequency component in the minority carrier distribution with a spatial frequency corresponding to that of the shadow mask, a fast detector is conceived. A shadow mask with higher spatial modulation frequency delivers a faster turn-off. The combination of a plurality of these detectors with an image fiber forms a basic system for constructing high-speed parallel optical interconnects between chips.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
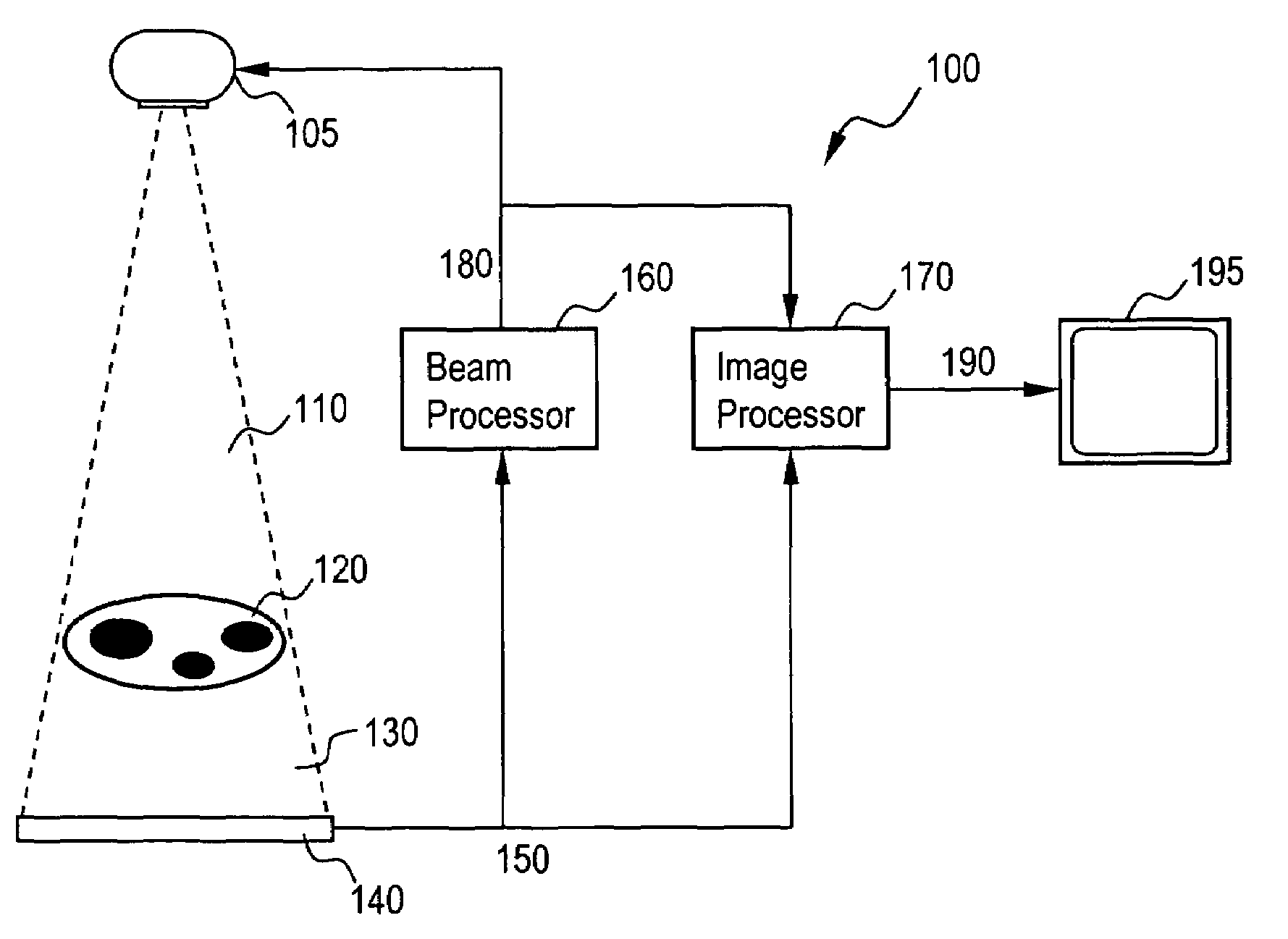
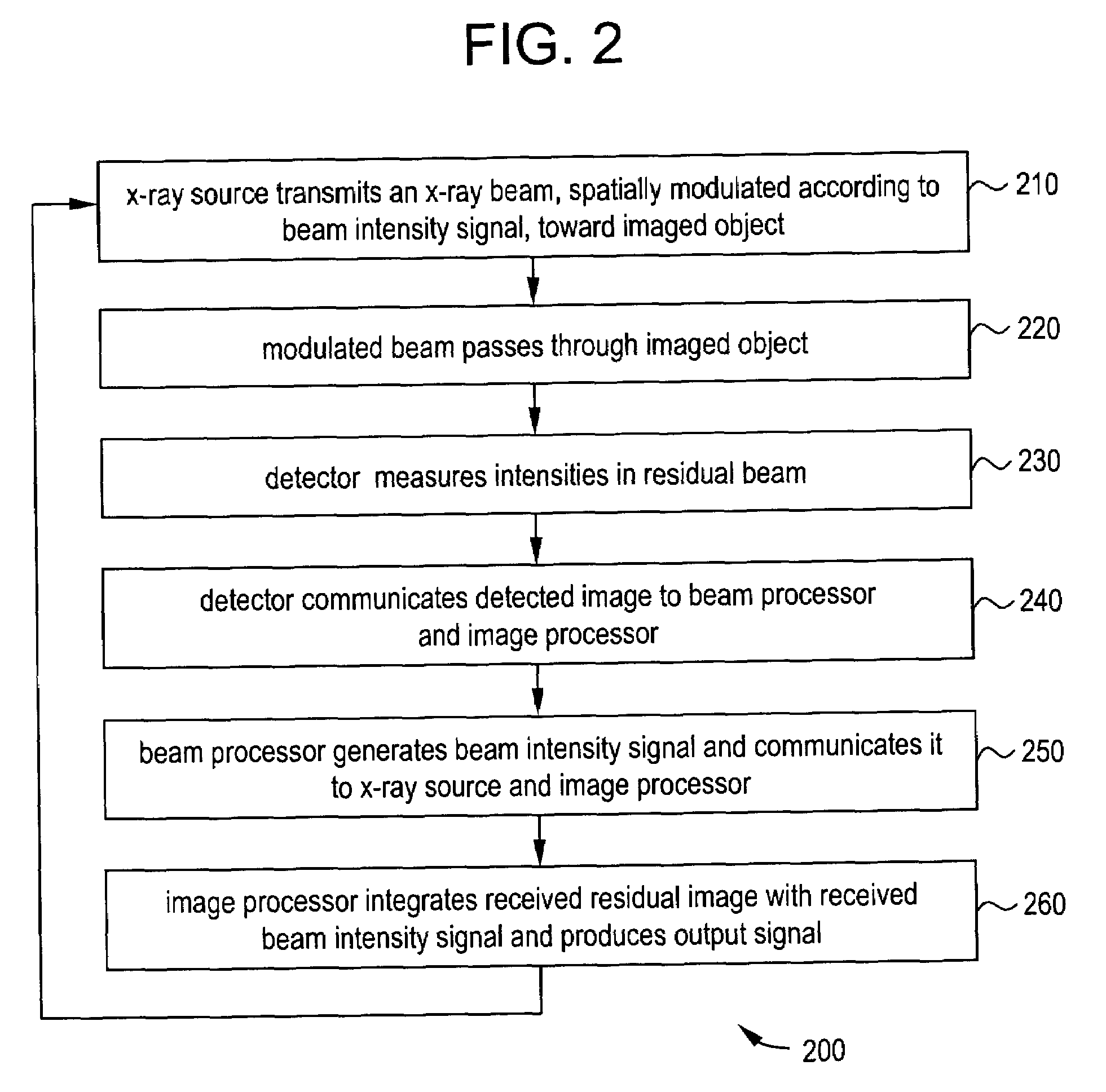
System and method for an adaptive morphology x-ray beam in an x-ray system
The present invention provides for an x-ray system and method using dynamic automated spatial modulation of an x-ray beam. The system includes an x-ray source transmitting a spatially modulated beam towards an object to be imaged, an x-ray detector receiving the beam and measuring a plurality of intensities across the beam, a beam processor controlling the beam intensity profile, and an image processor producing an output image signal. The detector produces a residual image based on at least the intensities measured at the detector. The beam intensity profile may be based on at least some of the following: (a) the residual image from the x-ray detector, (b) current beam intensities, (c) regions on interest in the image, and (d) predicted or measured object motion in the image. The system's output image is based on one or more of said residual image and said beam intensity signal.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and apparatus for spatial light modulation
ActiveUS20070030555A1Improve luminous efficiencyIncrease brightnessOptical light guidesOptical cavityOptoelectronics
Improved apparatus and methods for spatial light modulation are disclosed which utilize optical cavities having both front and rear reflective surfaces. Light-transmissive regions are formed in the front reflective surface for spatially modulating light.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
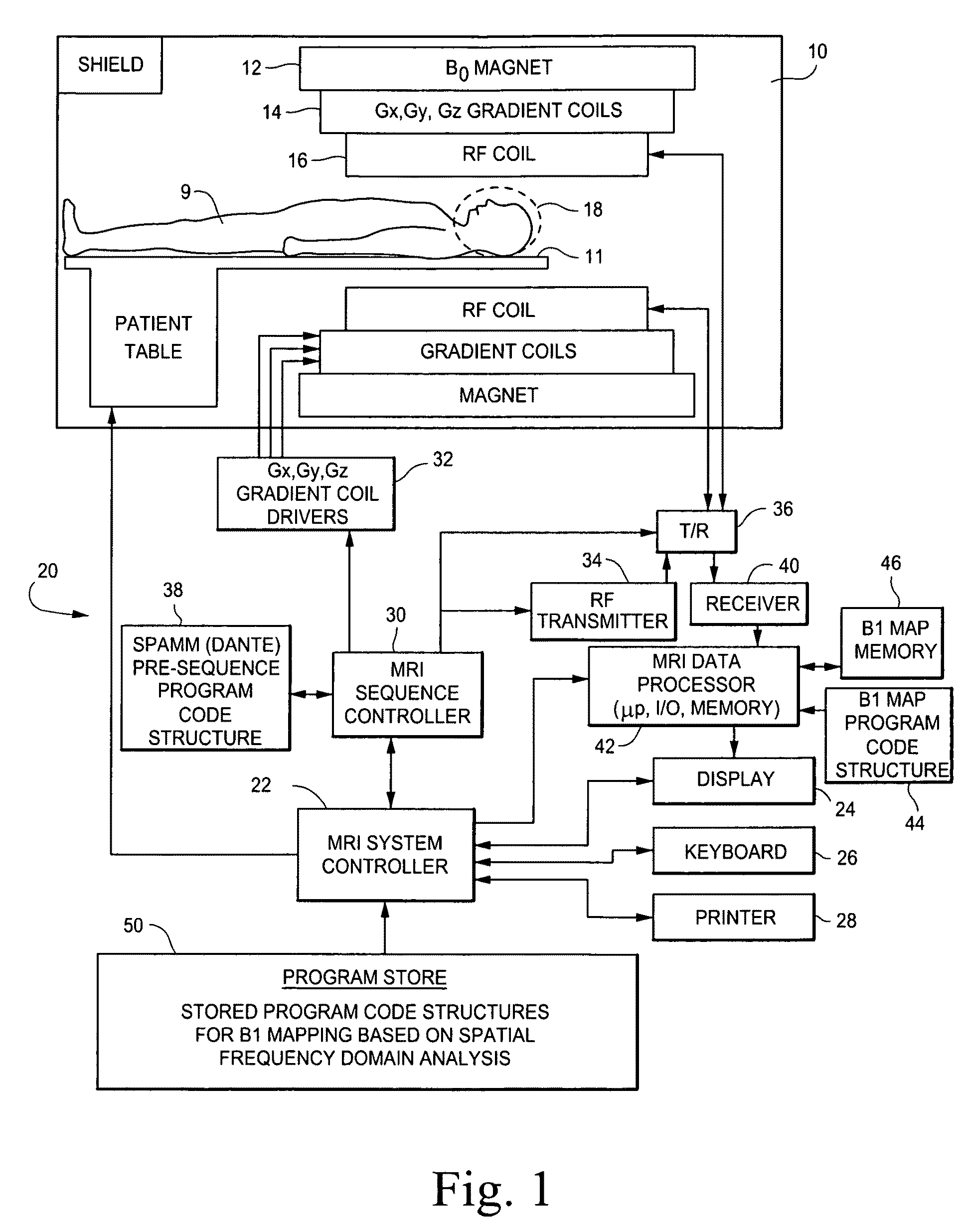
B1 mapping in MRI system using k-space spatial frequency domain filtering
ActiveUS8077955B2High resolutionReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionFrequency filteringCondensed matter physics
Frequency filtering of spatially modulated or “tagged” MRI data in the spatial frequency k-space domain with subsequent 2DFT to the spatial domain and pixel-by-pixel arithmetic calculations provide robust ratio values that can be subjected to inverse trigonometric functions to derive B1 maps for an MRI system.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Laser projection apparatus with liquid-crystal light valves and scanning reading beam
InactiveUS20050057727A1Image contrast superiorHigh resolutionProjectorsPicture reproducers using projection devicesBeam splitterLiquid crystal light valve
Laser lines at 635 nm or longer (ideally 647 nm) are preferred for red, giving energy-efficient, bright, rapid-motion images with rich, full film-comparable colors. Green and blue lines are used too—and cyan retained for best color mixing, an extra light-power boost, and aid in speckle suppression. Speckle is suppressed through beam-path displacement—by deflecting the beam during projection, thereby avoiding both absorption and diffusion of the beam while preserving pseudocollimation (noncrossing rays). The latter in turn is important to infinite sharpness. Path displacement is achieved by scanning the beam on the liquid-crystal valves (LCLVs), which also provides several enhancements—in energy efficiency, brightness, contrast, beam uniformity (by suppressing both laser-mode ripple and artifacts), and convenient beam-turning to transfer the beam between apparatus tiers. Preferably deflection is performed by a mirror mounted on a galvanometer or motor for rotary oscillation; images are written incrementally on successive portions of the LCLV control stage (either optical or electronic) while the laser “reading beam” is synchronized on the output stage. The beam is shaped, with very little energy loss to masking, into a shallow cross-section which is shifted on the viewing screen as well as the LCLVs. Beam-splitter / analyzer cubes are preferred over polarizing sheets. Spatial modulation provided by an LCLV and maintained by pseudocollimation enables imaging on irregular projection media with portions at distinctly differing distances from the projector—including domes, sculptures, monuments, buildings; waterfalls, sprays, fog, clouds, ice; scrims and other stage structures; trees and other foliage; land and rock surfaces; and even assemblages of living creatures including people.
Owner:TROYER DIANE
System and method for high-resolution with a small-format focal-plane array using spatial modulation
InactiveUS7542090B1Reduce processing loadHigh levelTelevision system detailsColor television detailsHigh resolution imageFocal Plane Arrays
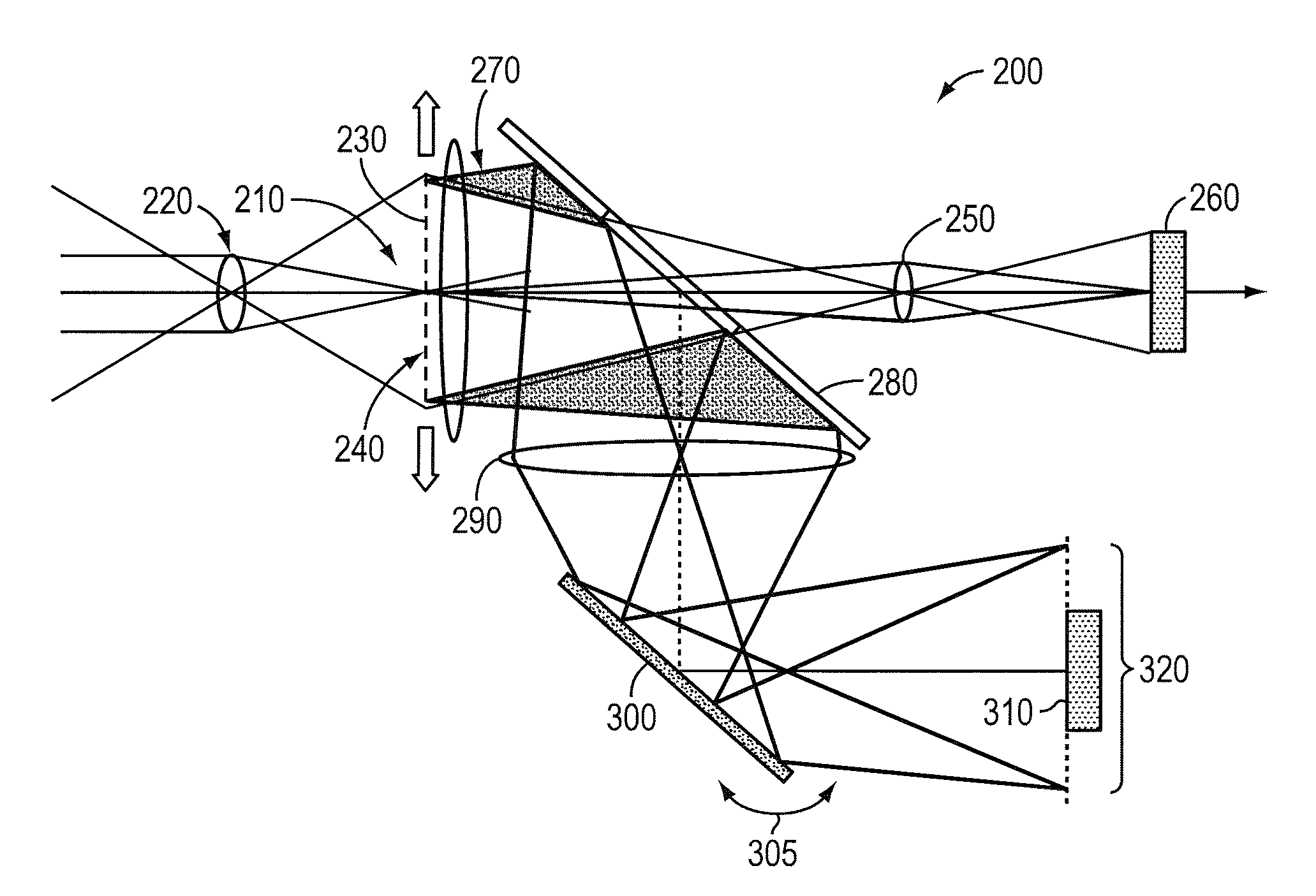
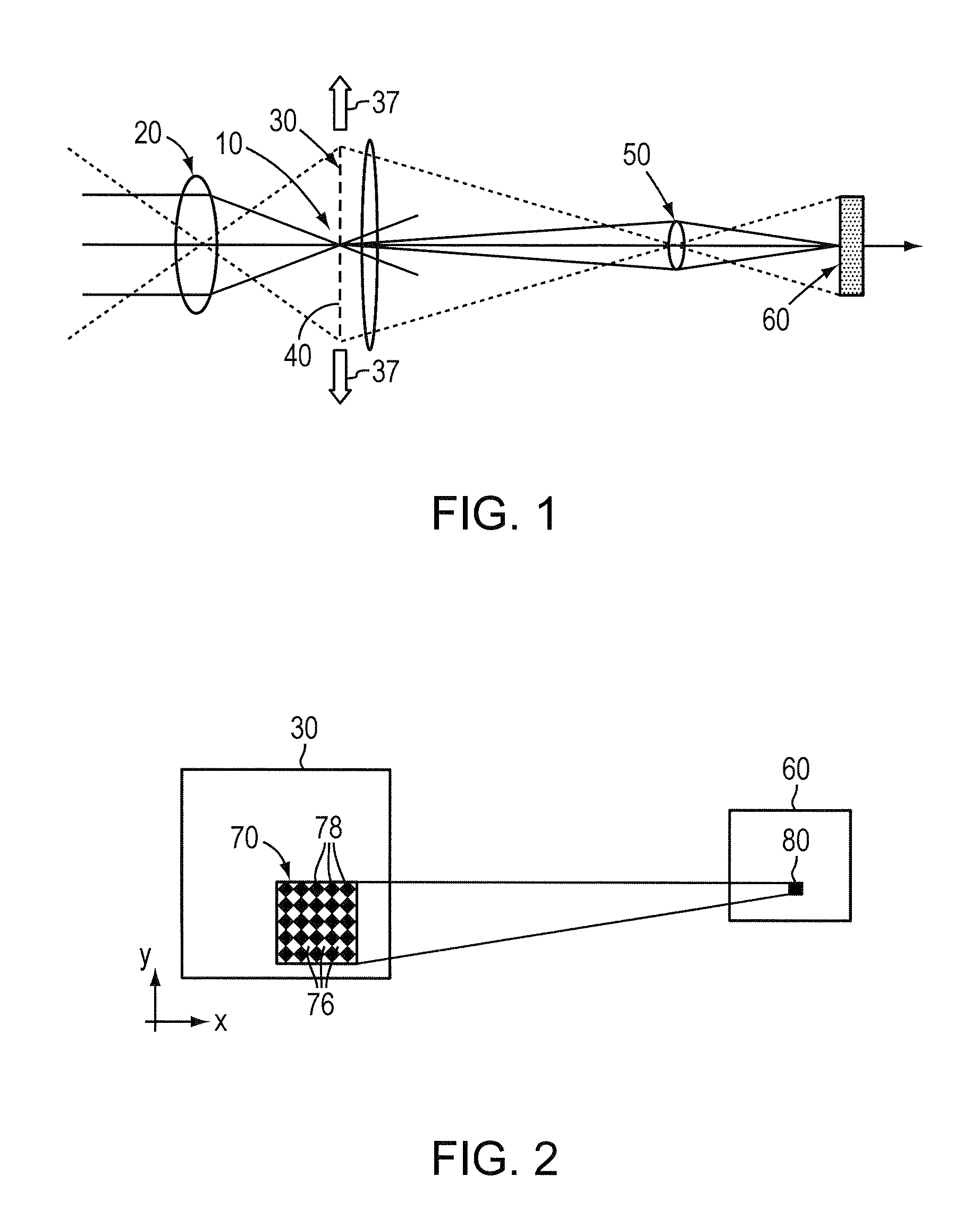
This invention provides a system and method for balanced-demodulation procedures that remove image clutter even in the presence of scene motion. A system that employs balanced demodulation moves a chopping reticle located in the intermediate focal plane where front end optics focus a high-resolution image. The chopping reticle has a checkerboard pattern of clear and opaque cells and moves in an uneven rate (e.g. Δx≠Δy) along the x-axis and y-axis. The resulting image is projected on a focal plane array from which differences are calculated to generate the desired balanced demodulation value. This invention further provides a foveal enhancement of the baseline spatial-modulation staring sensor. In this enhancement the WFOV low-resolution conventional image is displayed to the operator, but with a selectable subarea of that image replaced by a conventionally generated high-resolution image at the same scale. The operator would be able to naturally select the region for foveal enhancement by simply pointing directly at the detail of special interest which would then be displayed to the user at high-resolution. The remainder of the scene would be displayed at low-resolution, typically with marks at the locations of point sources detected by the spatial modulation.
Owner:AERODYNE RES
Apparatus for spatial modulation of an x-ray beam
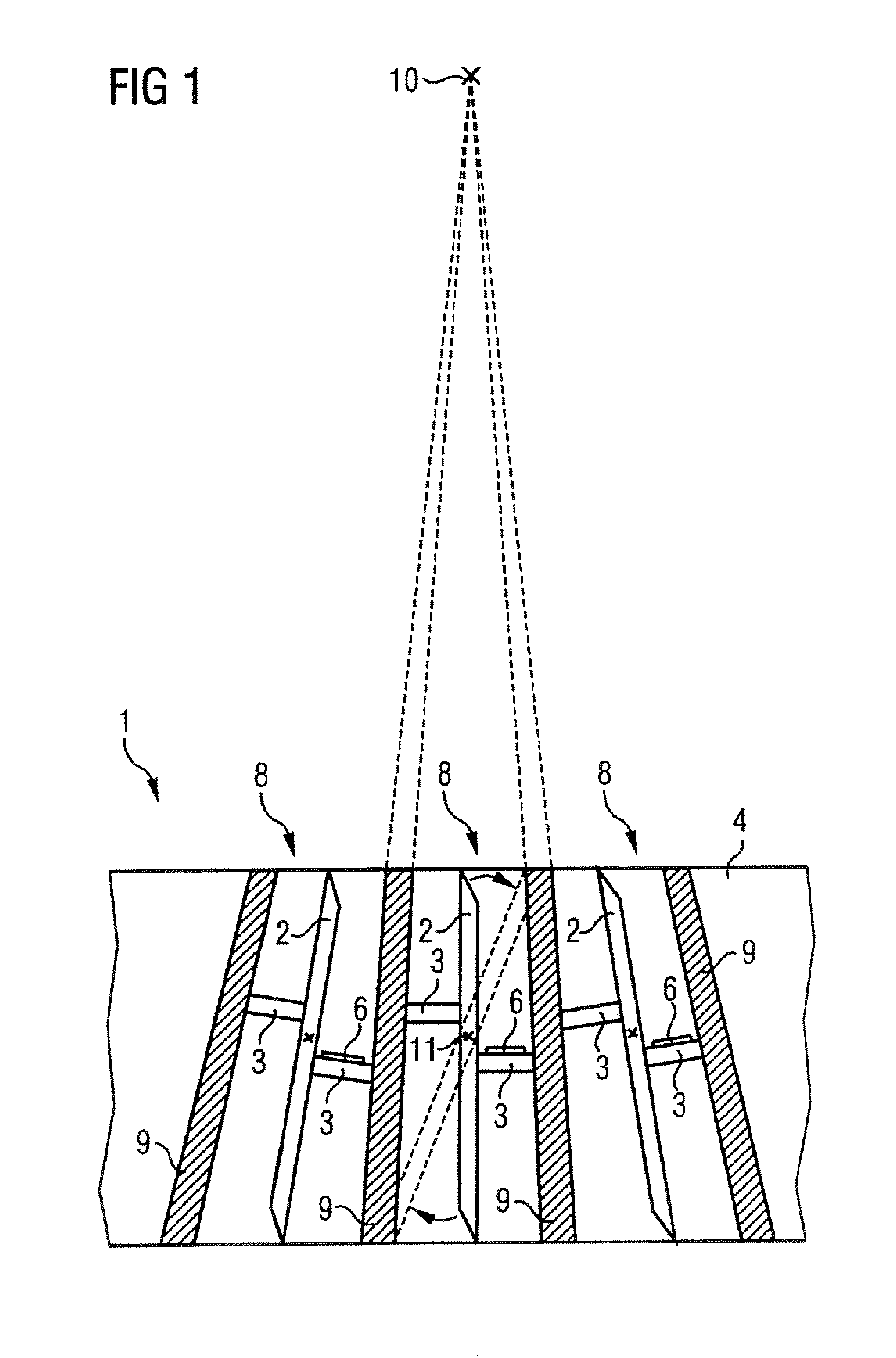
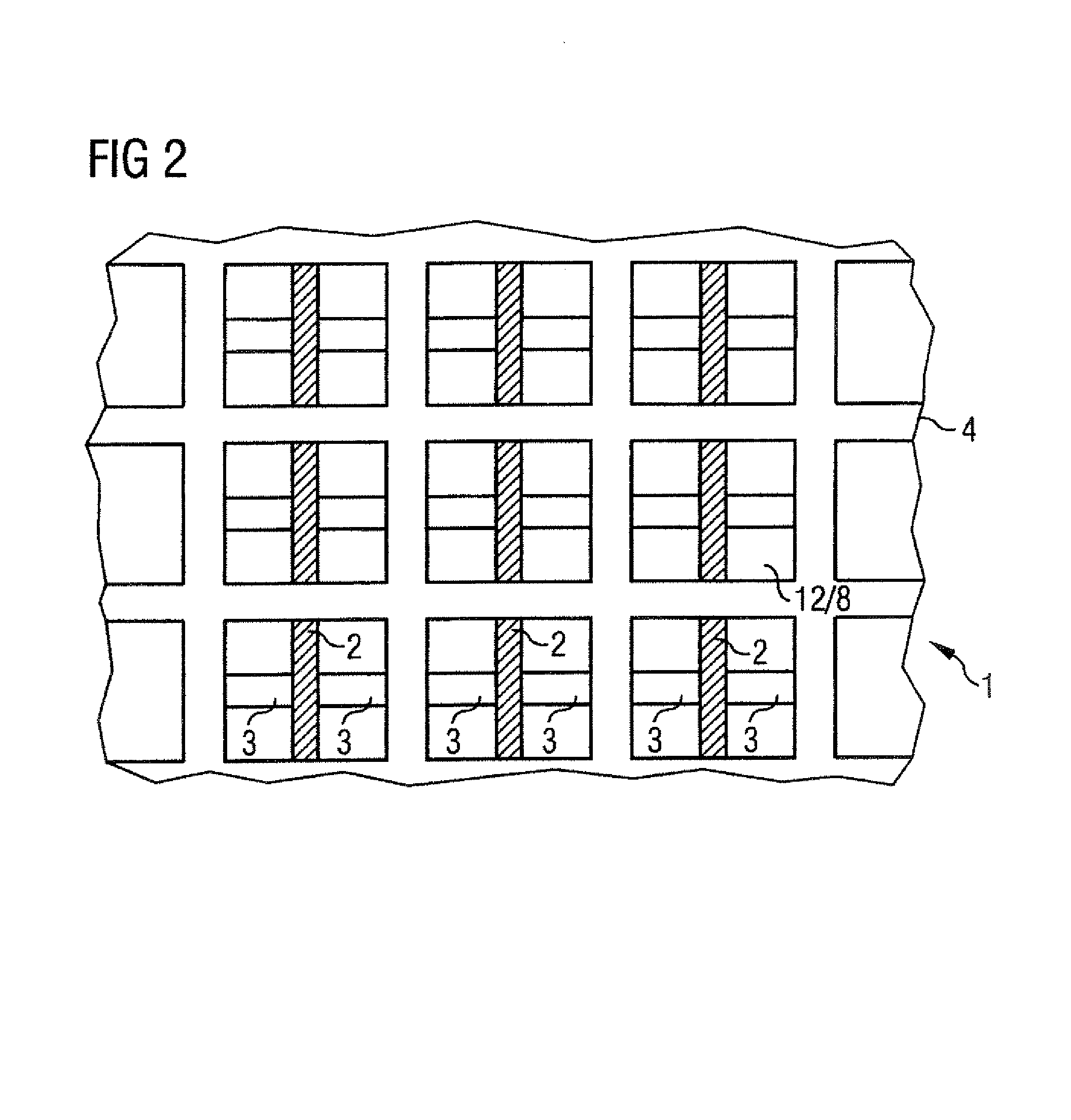
InactiveUS7209547B2Accurate measurementAdditive manufacturing apparatusMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationUltrasound attenuationElectricity
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com