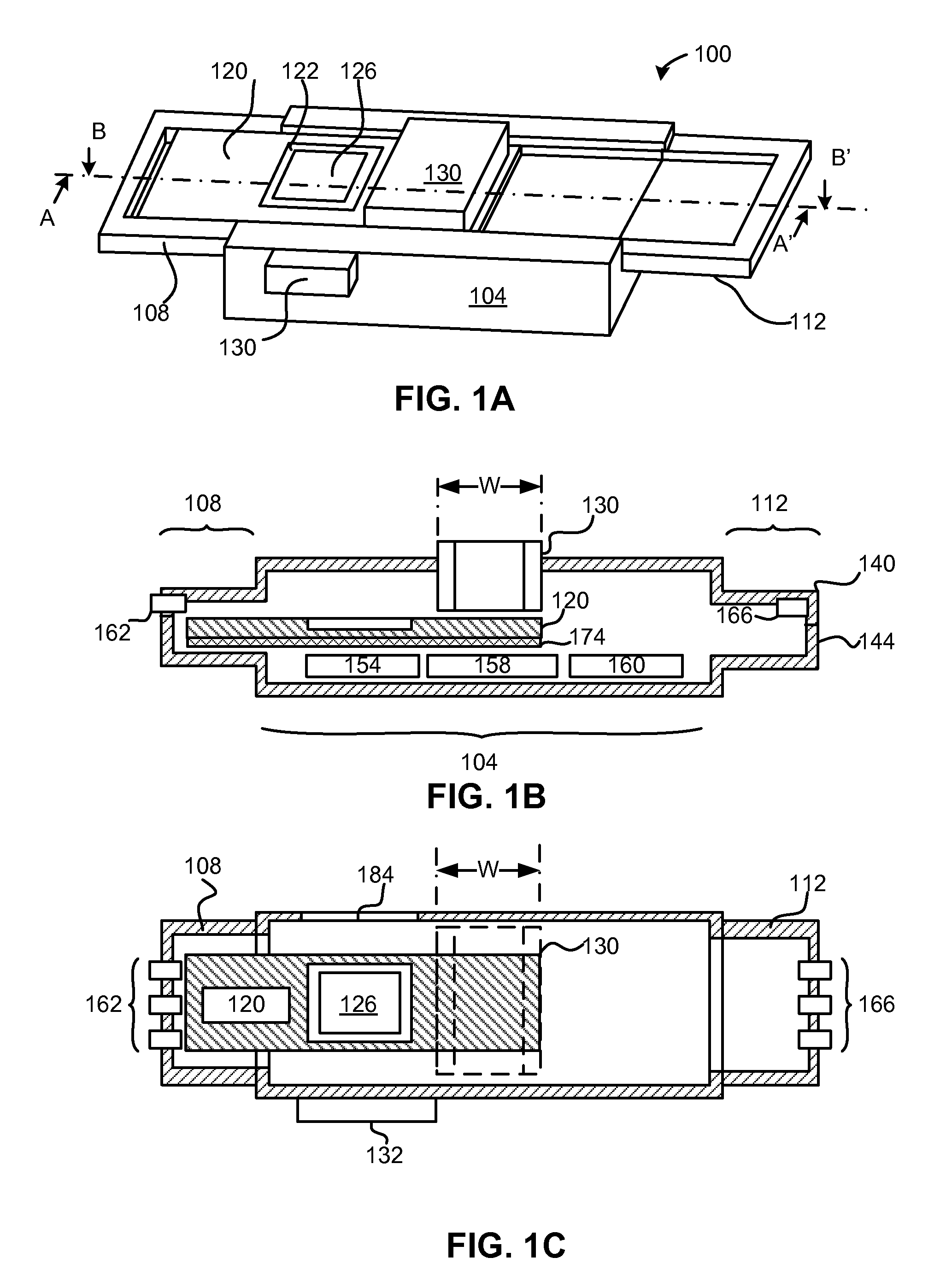
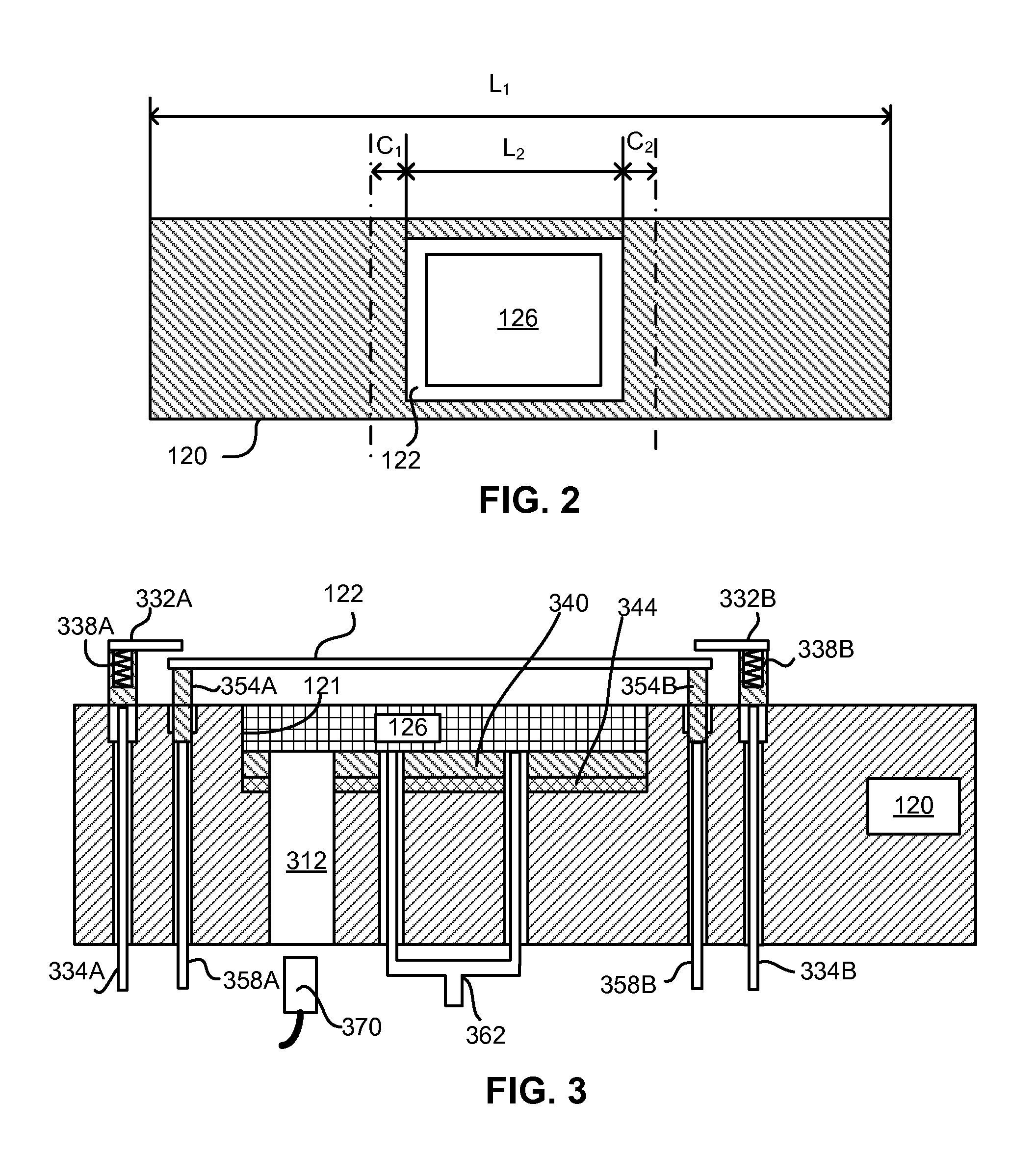
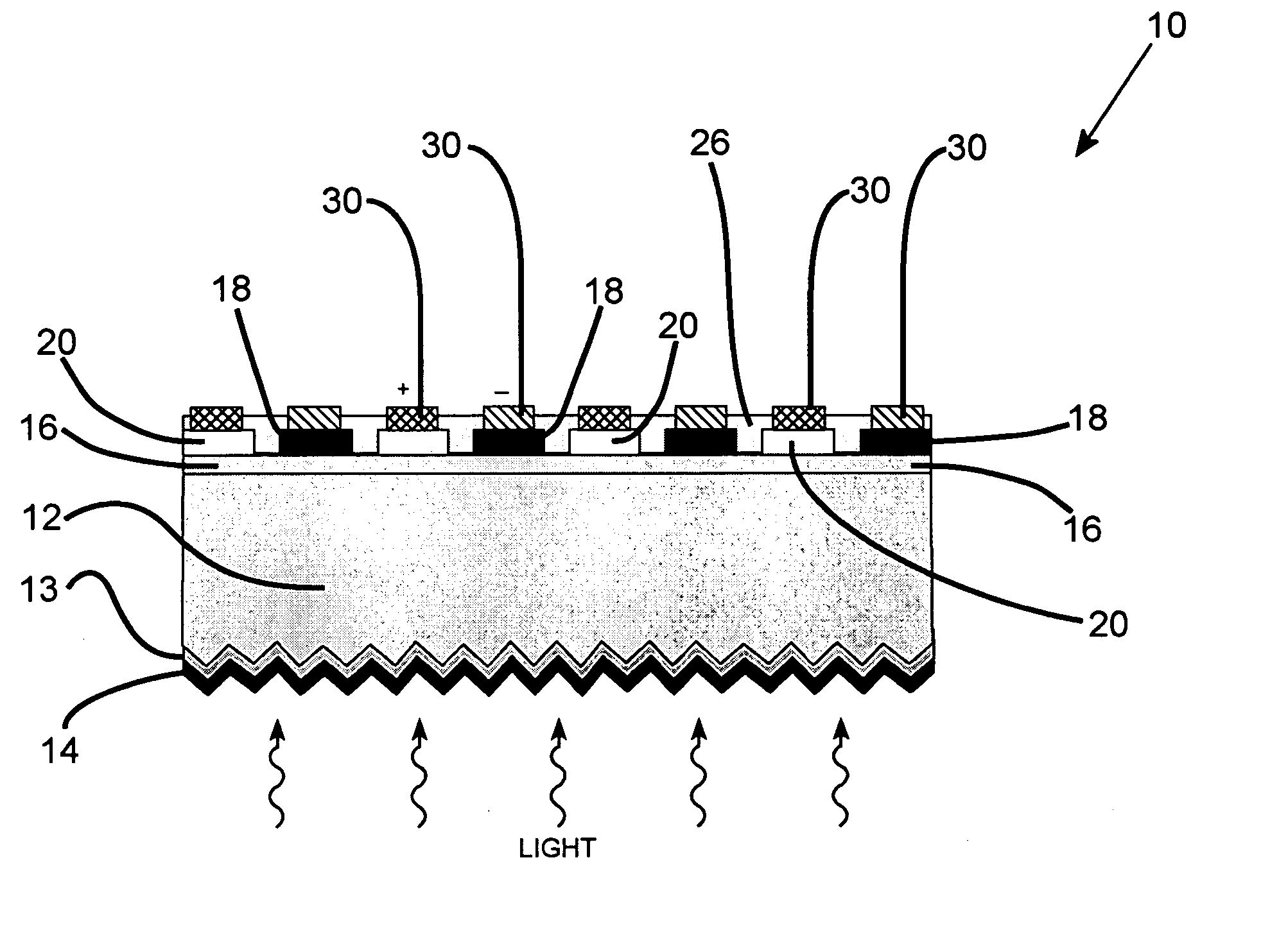
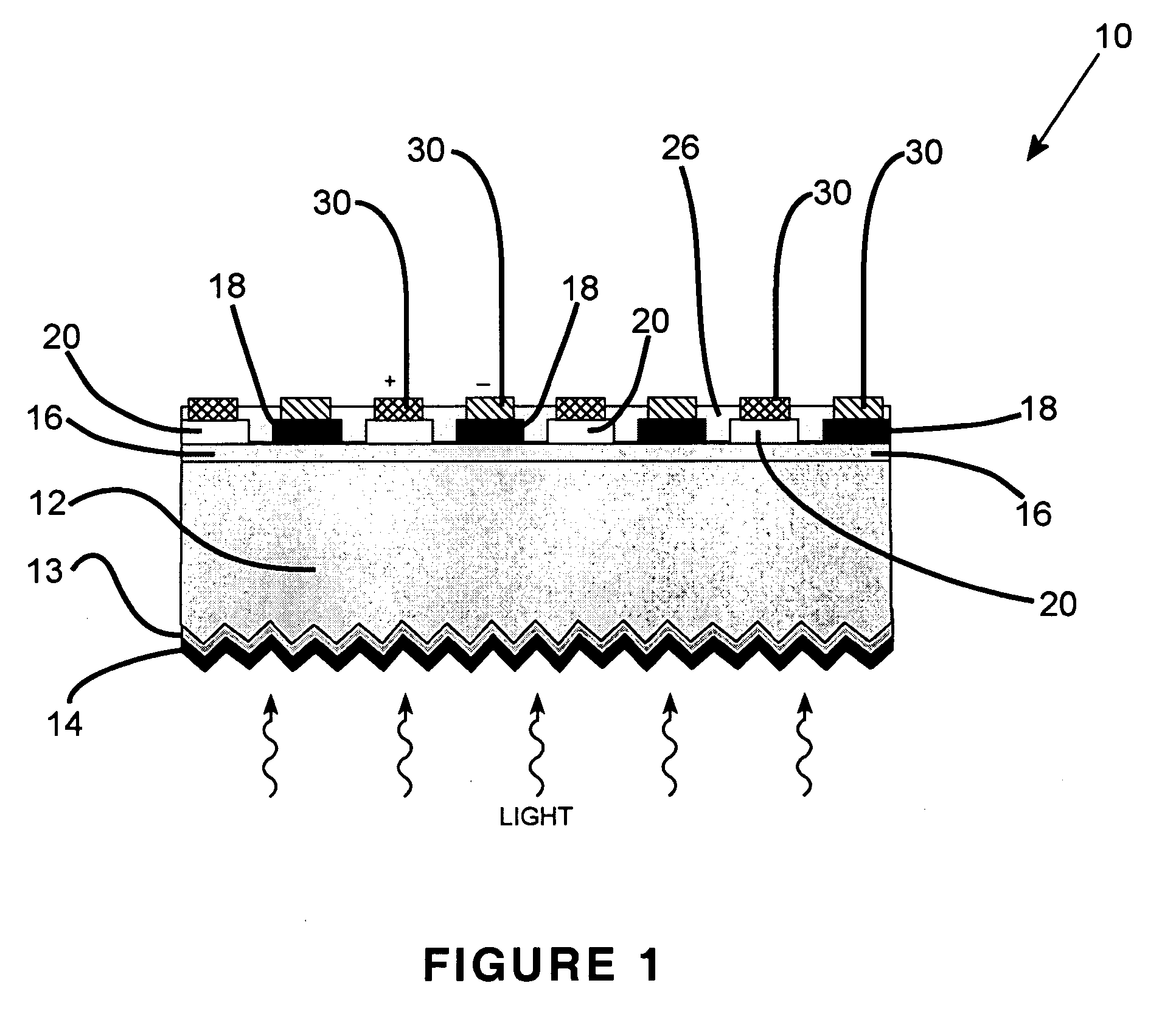
Patents
Literature
1028 results about "Shadow mask" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
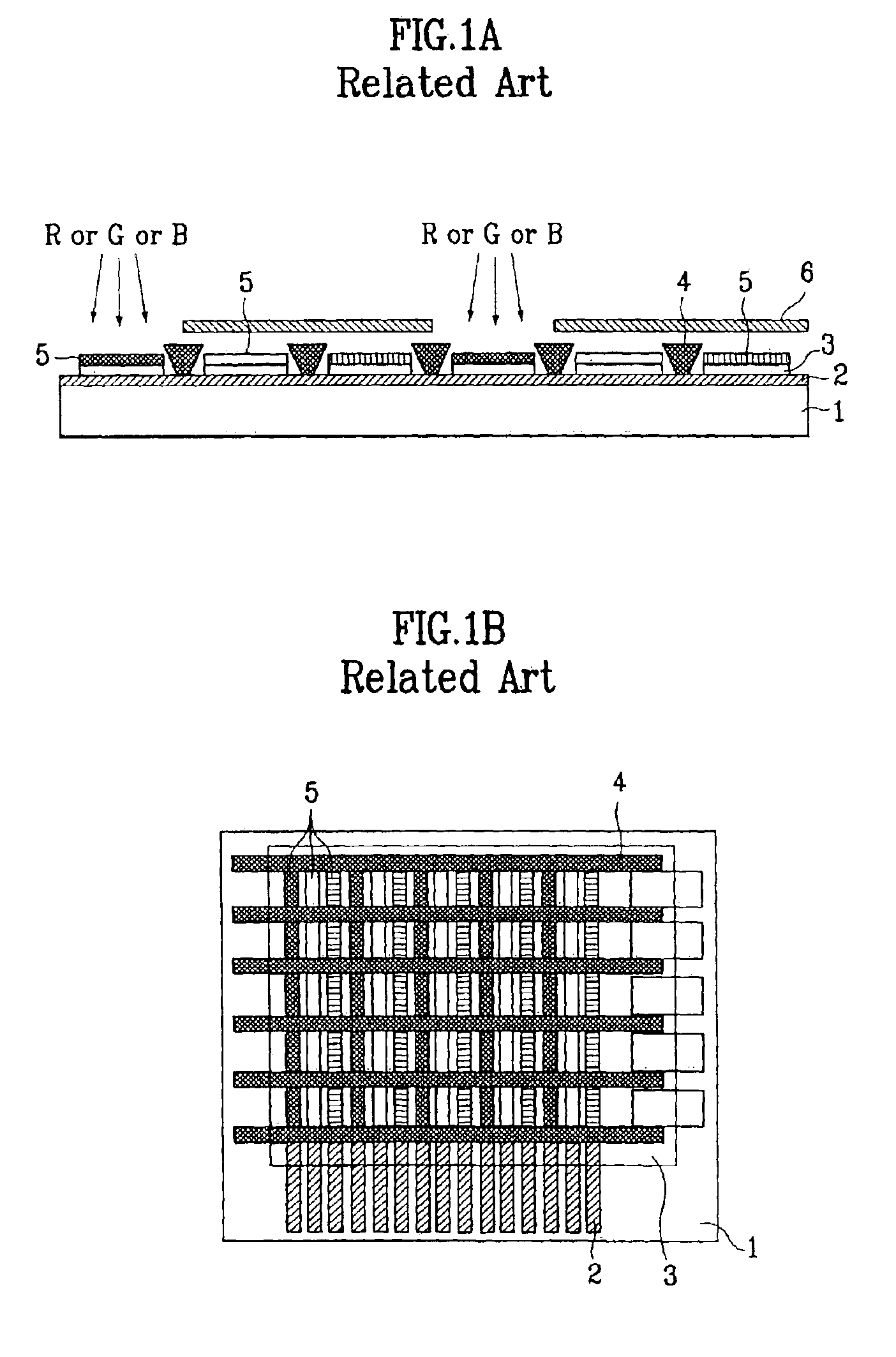
The shadow mask is one of the two technologies used in the manufacture of cathode-ray tube (CRT) televisions and computer monitors which produce clear, focused color images. The other approach is the aperture grille, better known by its trade name, Trinitron. All early color televisions and the majority of CRT computer monitors used shadow mask technology. Both of these technologies are largely obsolete, having been increasingly replaced since the 1990s by the liquid-crystal display (LCD).
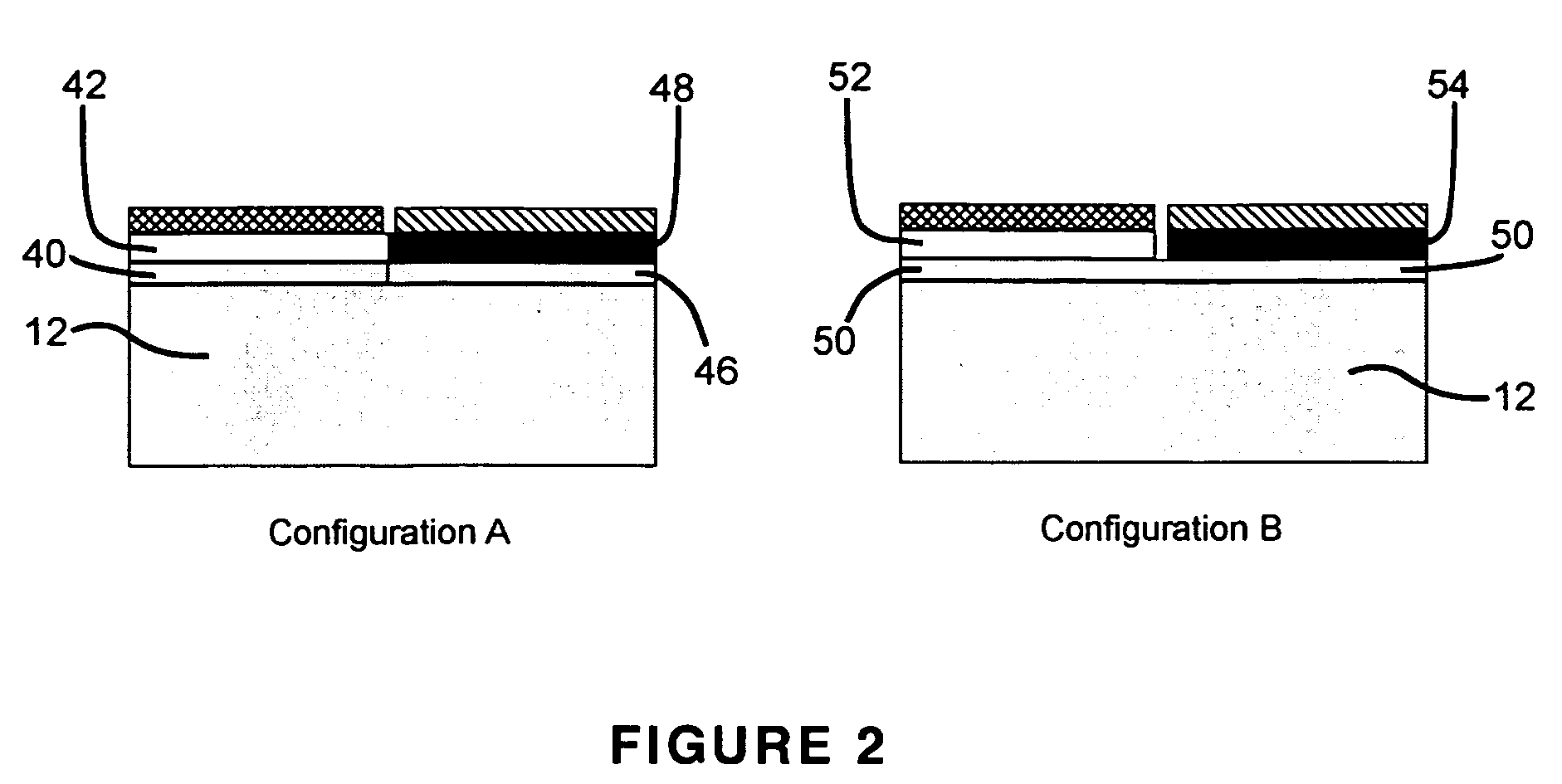
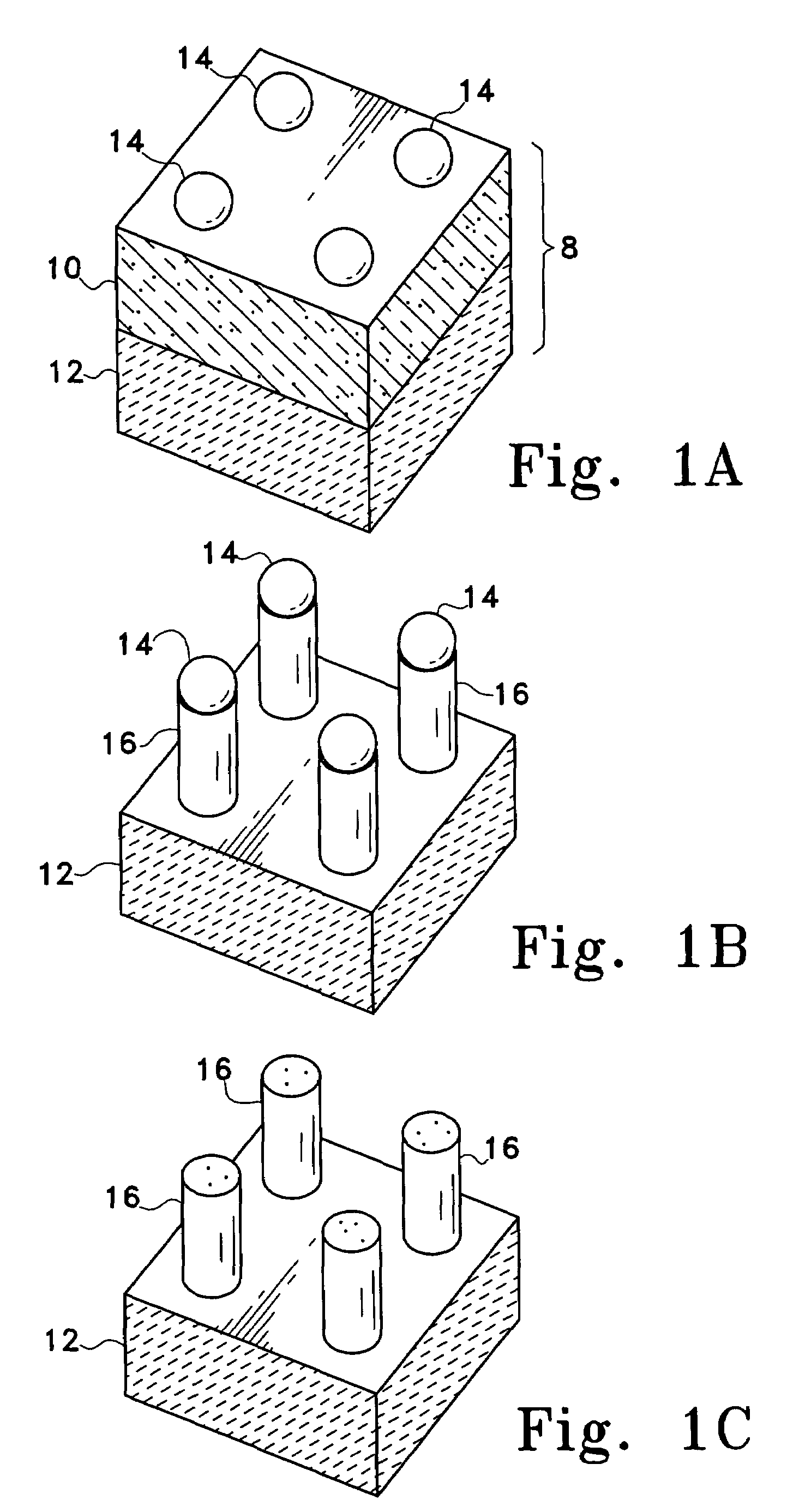
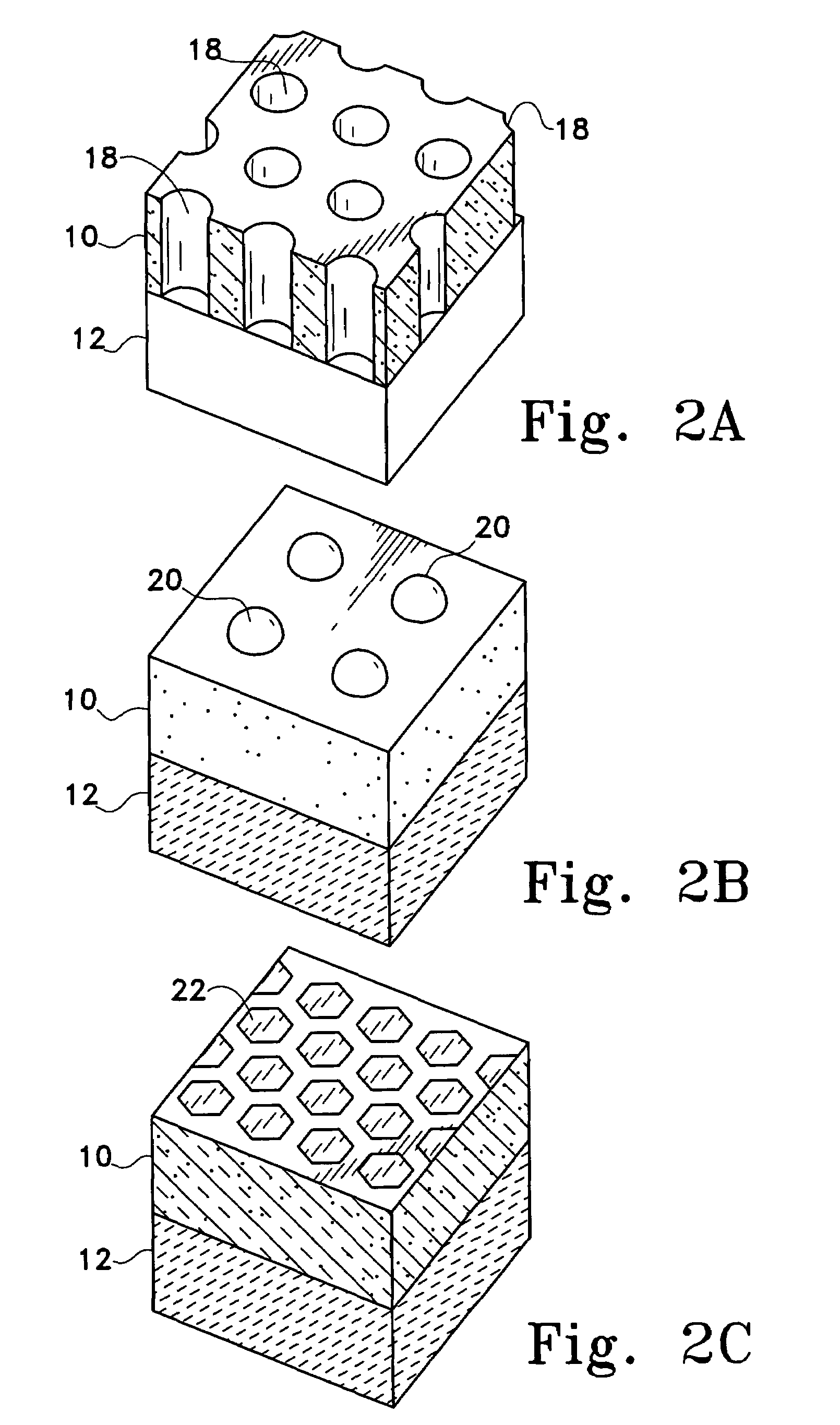
High reliability multlayer circuit substrates and methods for their formation
InactiveUS20040061234A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsElectrical conductorOptoelectronics
A multilayer circuit substrate for multi-chip modules or hybrid circuits includes a dielectric base substrate, conductors formed on the base substrate and a vacuum deposited dielectric thin film formed over the conductors and the base substrate. The vacuum deposited dielectric thin film is patterned using sacrificial structures formed by shadow mask techniques. Substrates formed in this manner enable significant increases in interconnect density and significant reduction of over-all substrate thickness.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Linear atomic layer deposition apparatus
InactiveUS20130092085A1Avoid enteringPrevent leakageLiquid surface applicatorsChemical vapor deposition coatingSusceptorComputer science
Embodiments relate to a linear deposition apparatus with mechanism for securing a shadow mask and a substrate onto a susceptor. The linear deposition apparatus includes a set of members attached to latches that are raised to unlock the shadow mask and the substrate from the susceptor. The latches are lowered to secure the shadow mask and the substrate to the susceptor. Another set of members are provided in the linear deposition apparatus to move and align the shadow mask with the substrate. The linear deposition apparatus also includes a main body and two wings provided at both sides of the main body to receive the substrate as the substrate moves linearly to expose the substrate to materials or radicals injected by reactors.
Owner:VEECO ALD
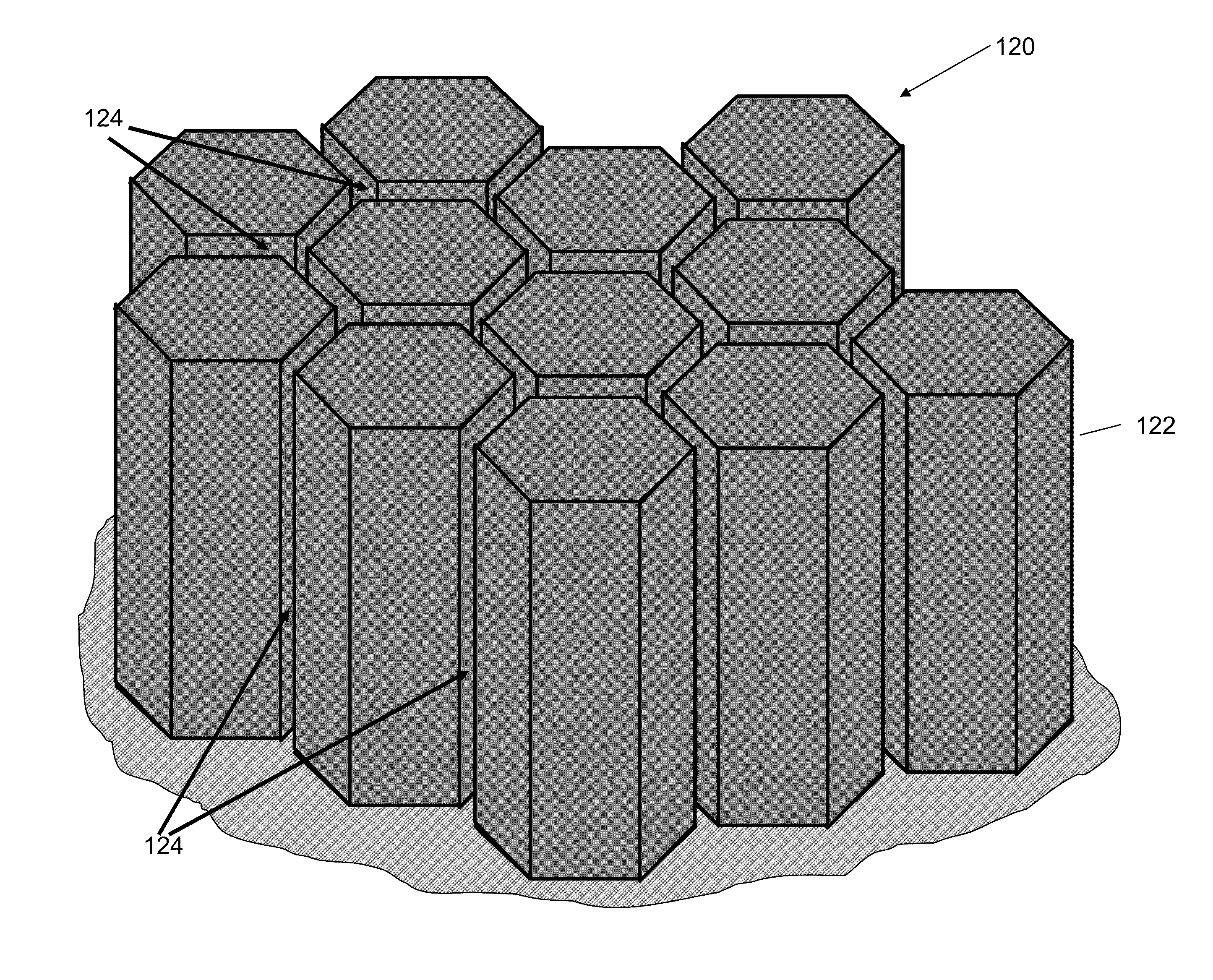
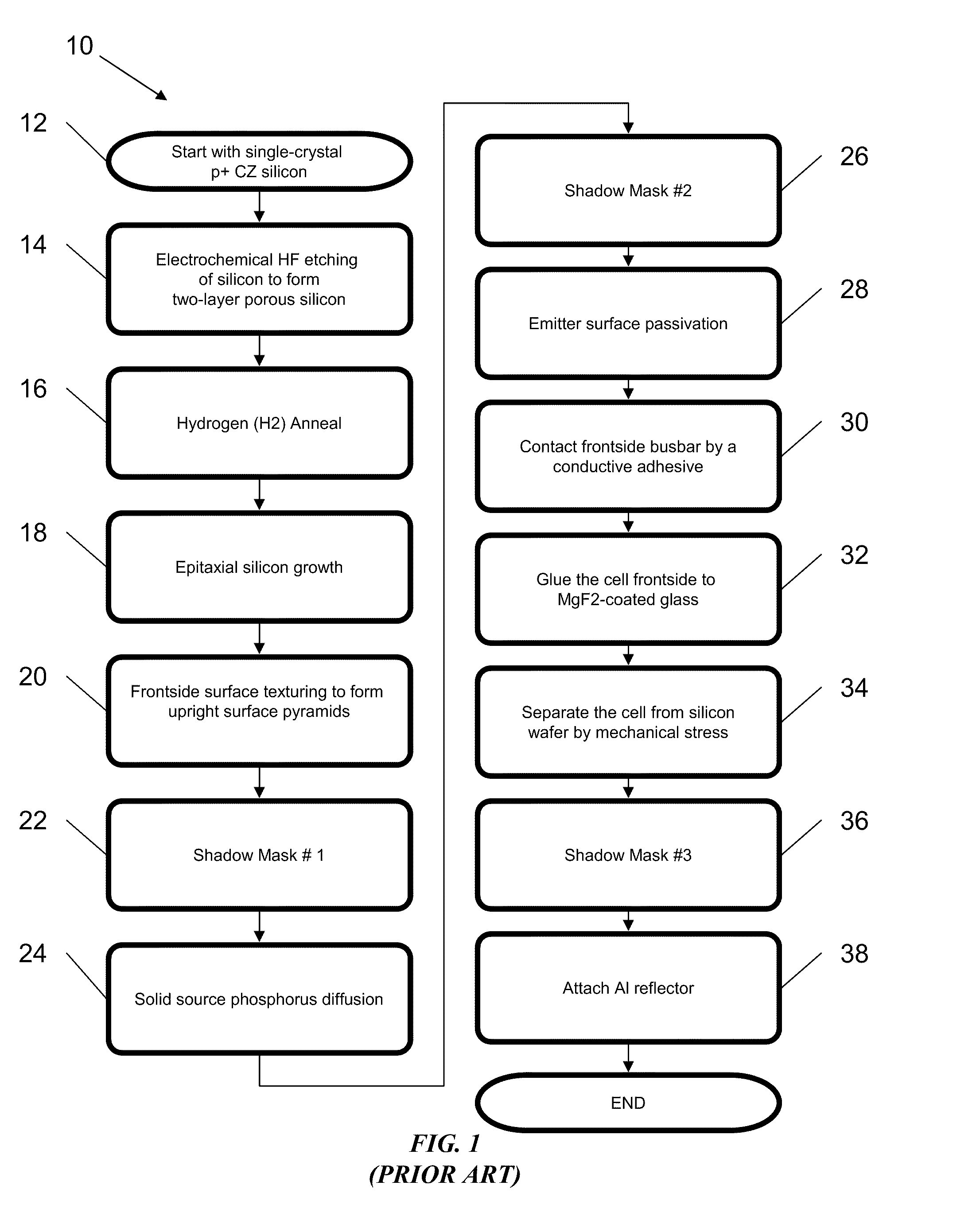
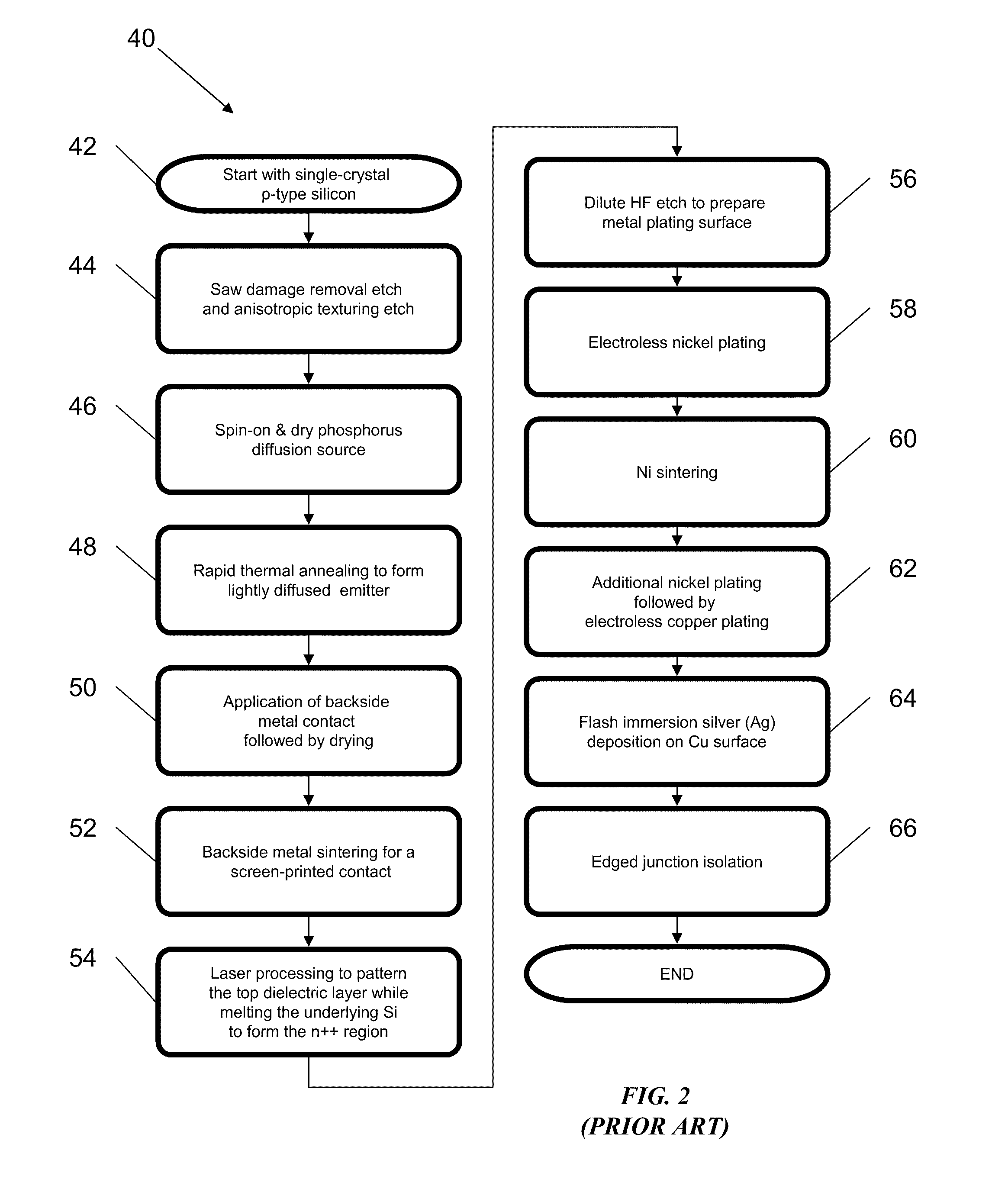
Solar cell
InactiveUS20070169808A1Low costEasy to usePhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionManufacturing technology
The present invention provides a thin film amorphous silicon-crystalline silicon back heterojunction and back surface field device configuration for a heterojunction solar cell. The configuration is attained by the formation of heterojunctions on the back surface of crystalline silicon at low temperatures. Low temperature fabrication allows for the application of low resolution lithography and / or shadow masking processes to produce the structures. The heterojunctions and interface passivation can be formed through a variety of material compositions and deposition processes, including appropriate surface restructing techniques. The configuration achieves separation of optimization requirements for light absorption and carrier generation at the front surface on which the light is incident, and in the bulk, and charge carrier collection at the back of the device. The shadowing losses are eliminated by positioning the electrical contacts at the back thereby removing them from the path of the incident light. Back contacts need optimization only for maximum charge carrier collection without bothering about shading losses. A range of elements / alloys may be used to effect band-bending. All of the above features result in a very high efficiency solar cell. The open circuit voltage of the back heterojunction device is higher than that of an all-crystalline device. The solar cell configurations are equally amenable to crystalline silicon wafer absorber as well as thin silicon layers formed by using a variety of fabrication processes. The configurations can be used for radiovoltaic and electron-voltaic energy conversion devices.
Owner:KHERANI NAZIR P +1
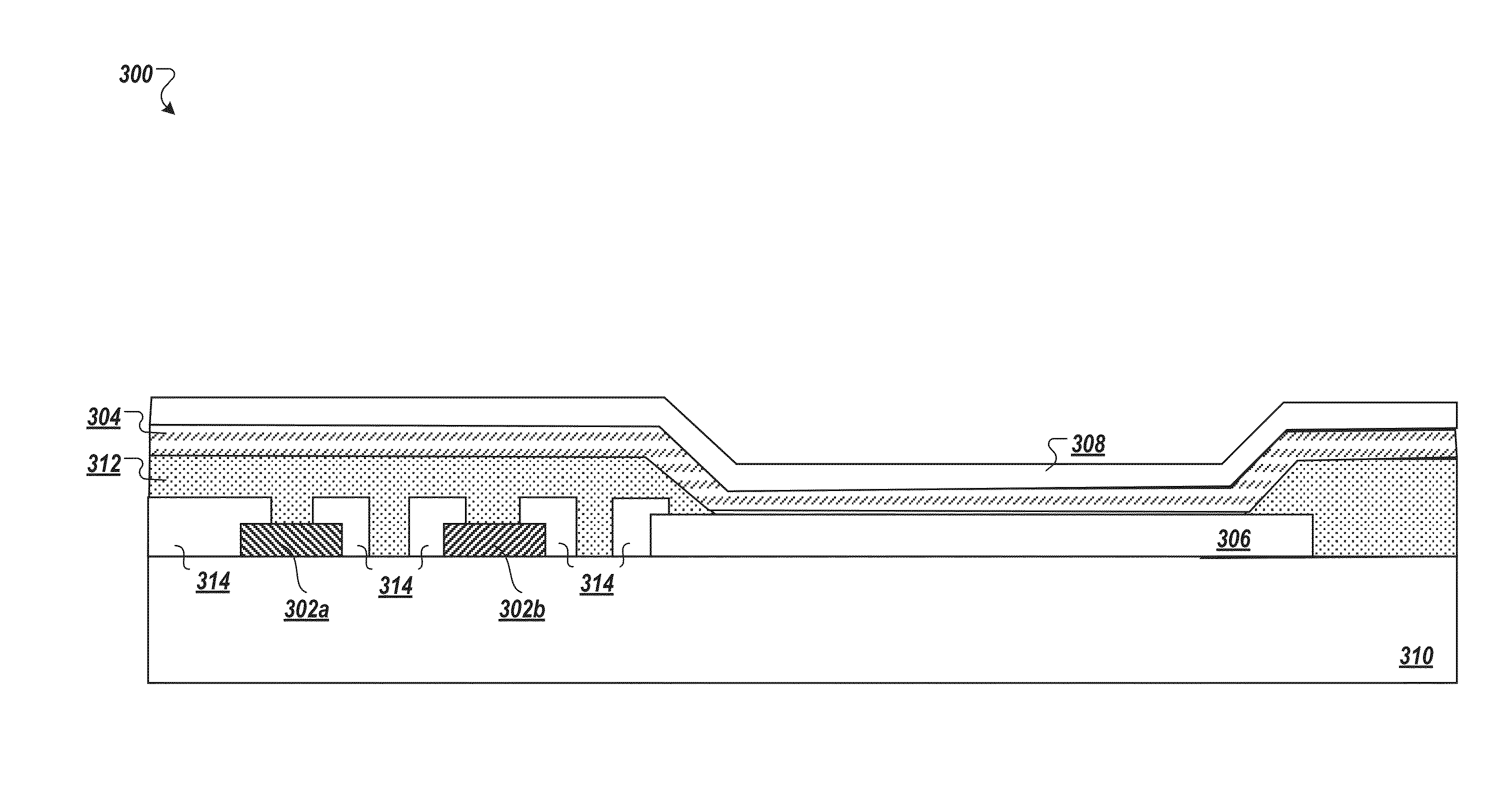
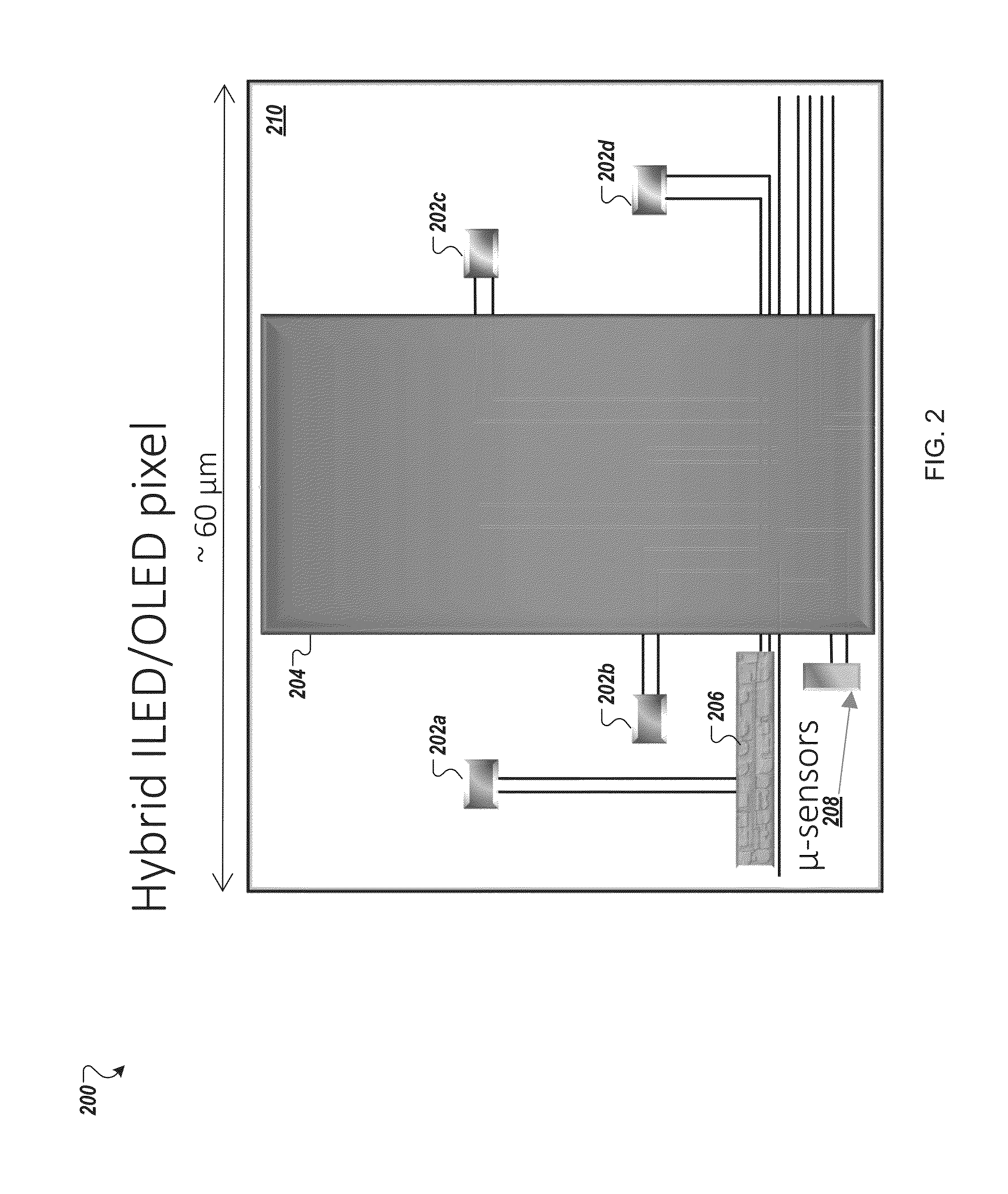
Micro assembled hybrid displays and lighting elements
ActiveUS20160064363A1Improve efficiencyImprove manufacturabilityFinal product manufactureElectroluminescent light sourcesLithographic artistDisplay device
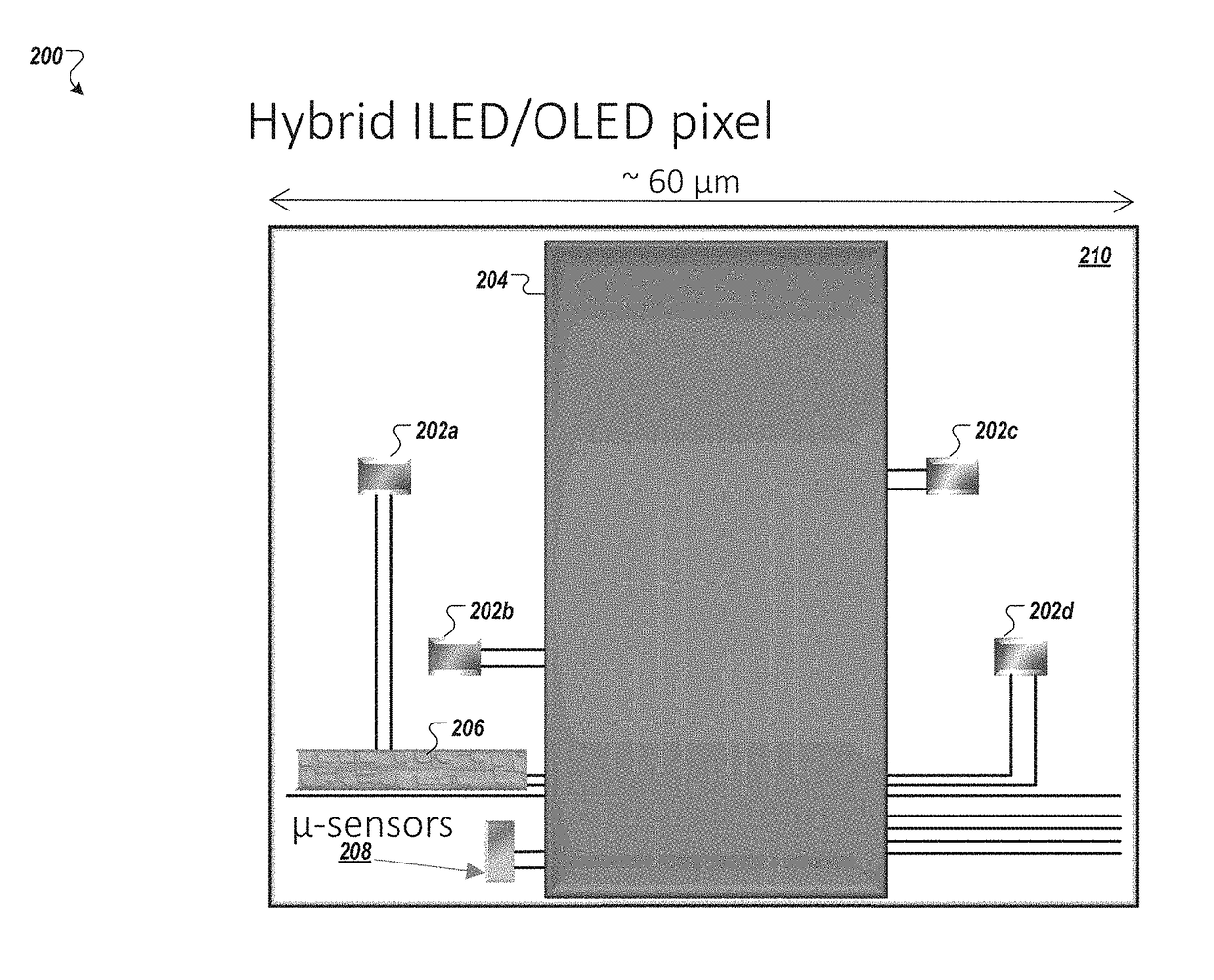
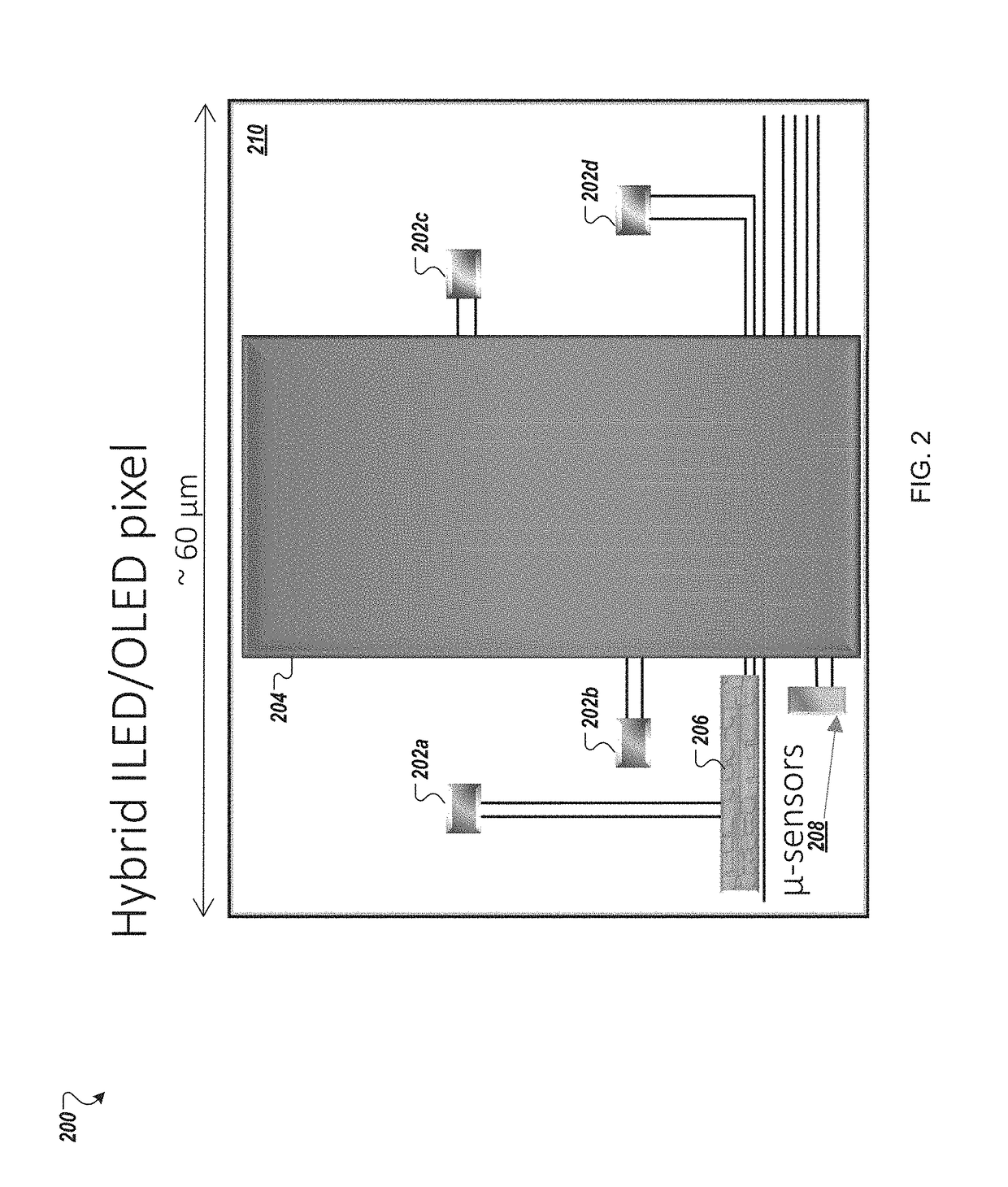
The disclosed technology relates generally hybrid displays with pixels that include both inorganic light emitting diodes (ILEDs) and organic light emitting diodes (OLEDs). The disclosed technology provides a hybrid display that uses a mixture of ILEDs and OLEDs in each pixel. In certain embodiments, each pixel in the hybrid display includes a red ILED, a blue ILED, and a green OLED. In this instance, the OLED process would not require a high resolution shadow mask, thereby enhancing the manufacturability of OLEDs for larger format displays. Additionally, the OLED process in this example would not require any fine lithography. The OLED subpixel (e.g., green subpixel) can be larger and the ILEDs can be small (e.g., micro-red and micro-blue ILEDs). The use of small ILEDs allows for other functions to be added to the pixel, such as micro sensors and micro integrated circuits.
Owner:X DISPLAY CO TECH LTD
Micro assembled hybrid displays and lighting elements
ActiveUS9716082B2Improve efficiencyImprove manufacturabilityFinal product manufactureElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceLight-emitting diode
The disclosed technology relates generally hybrid displays with pixels that include both inorganic light emitting diodes (ILEDs) and organic light emitting diodes (OLEDs). The disclosed technology provides a hybrid display that uses a mixture of ILEDs and OLEDs in each pixel. In certain embodiments, each pixel in the hybrid display includes a red ILED, a blue ILED, and a green OLED. In this instance, the OLED process would not require a high resolution shadow mask, thereby enhancing the manufacturability of OLEDs for larger format displays. Additionally, the OLED process in this example would not require any fine lithography. The OLED subpixel (e.g., green subpixel) can be larger and the ILEDs can be small (e.g., micro-red and micro-blue ILEDs). The use of small ILEDs allows for other functions to be added to the pixel, such as micro sensors and micro integrated circuits.
Owner:X DISPLAY CO TECH LTD
Color picture tube
InactiveUS20050269930A1Satisfactory visibilityReduce degradationCathode-ray/electron-beam tube vessels/containersElectrode and associated part arrangementsVisibilityLong axis
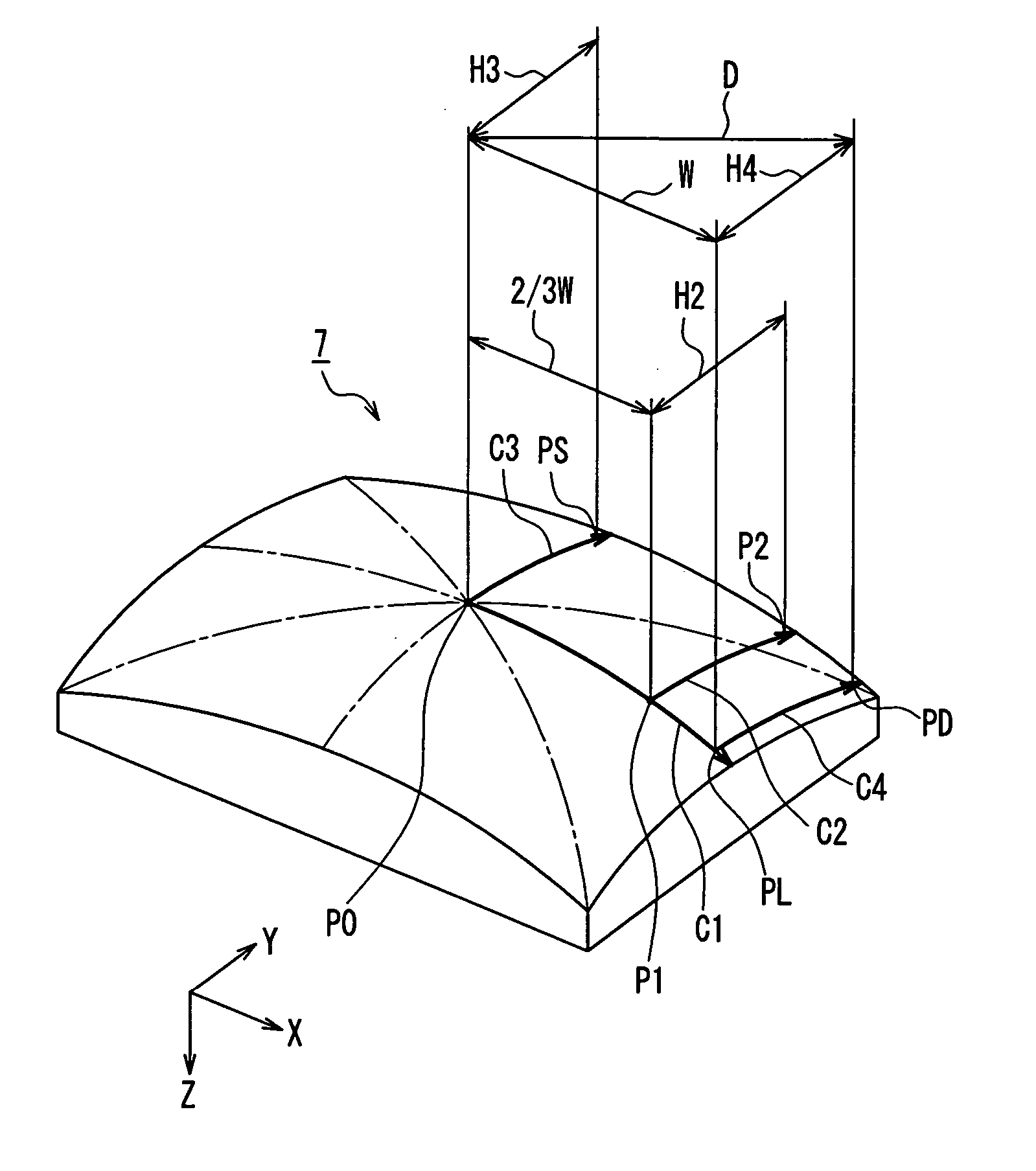
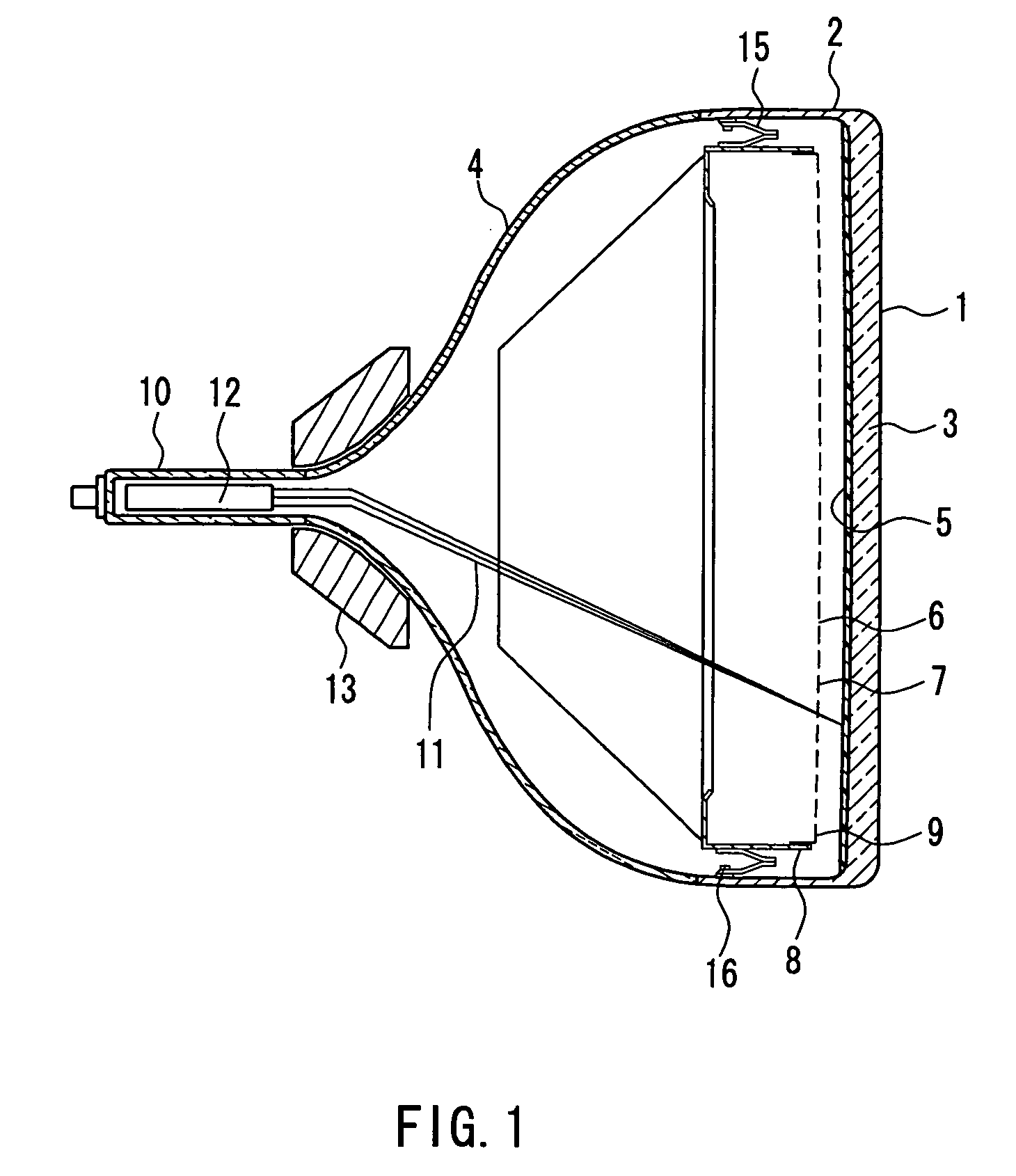
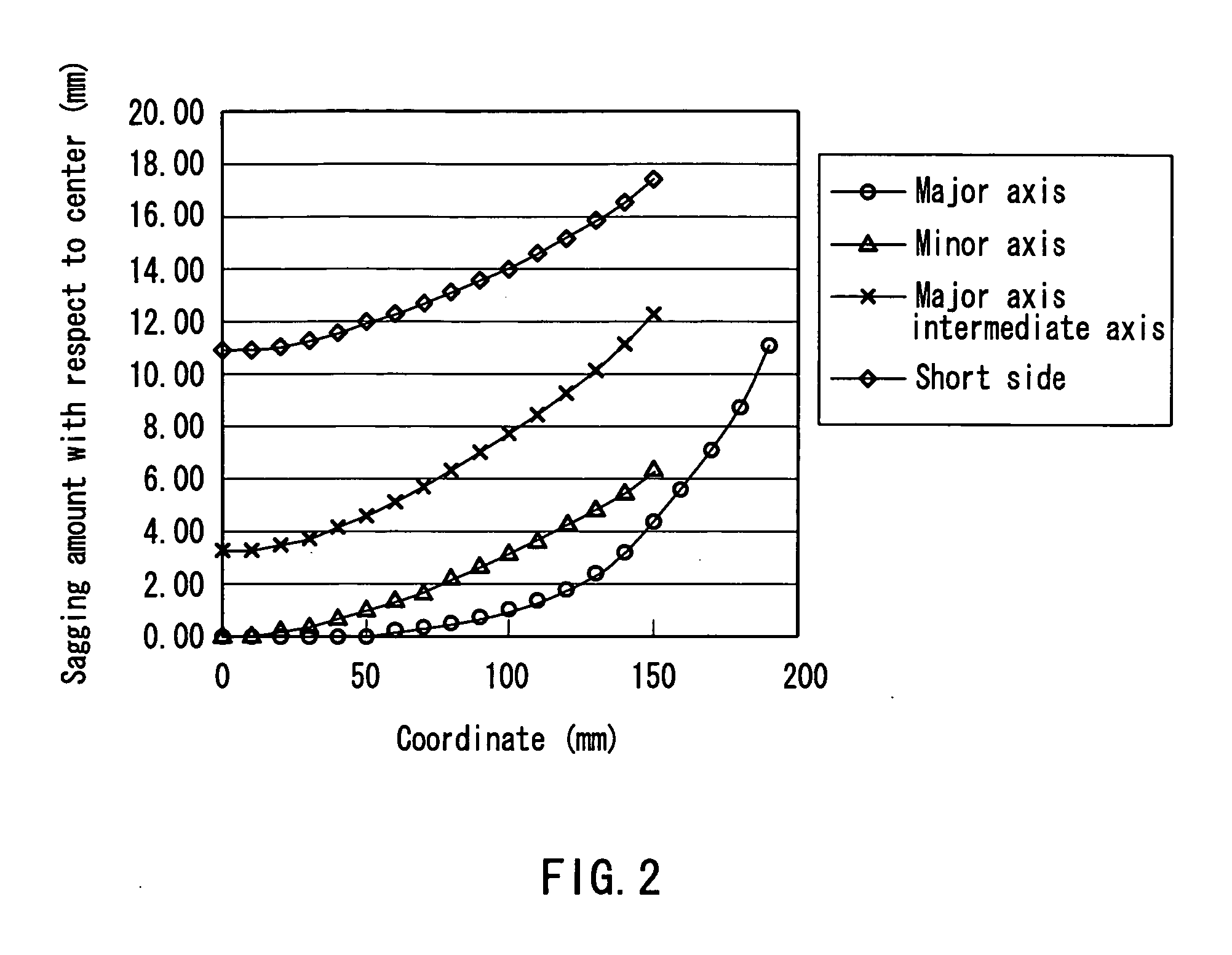
The radius of curvature of the outer surface of a panel is 10,000 mm or more, and a shadow mask is made of a material containing 95% or more of iron. A sagging amount change curve along a curve C1 on the surface of the shadow mask, which a plane passing through a center P0 of a useful area of the shadow mask and parallel to a tube axis and a major axis crosses, satisfies a particular Condition 1. Assuming that an intersection between the curve C1 and a useful area end of the shadow mask is a major axis end PL, a distance from the center P0 to the major axis end PL along a major axis is W, and a point on the curve C1 away from the center P0 by ⅔×W in the major axis direction is P1, a sagging amount change curve along a curve C2 on the surface of the shadow mask, which a plane passing through the point P1 and parallel to the tube axis and the minor axis crosses, satisfies a particular Condition 2. Consequently, a color picture tube can be realized, which has satisfactory visibility, and less degradation in color purity caused by doming while having a shadow mask made of an inexpensive material with satisfactory moldability.
Owner:MATSUSHITA TOSHIBA PICTURE DISPLAY CO LTD
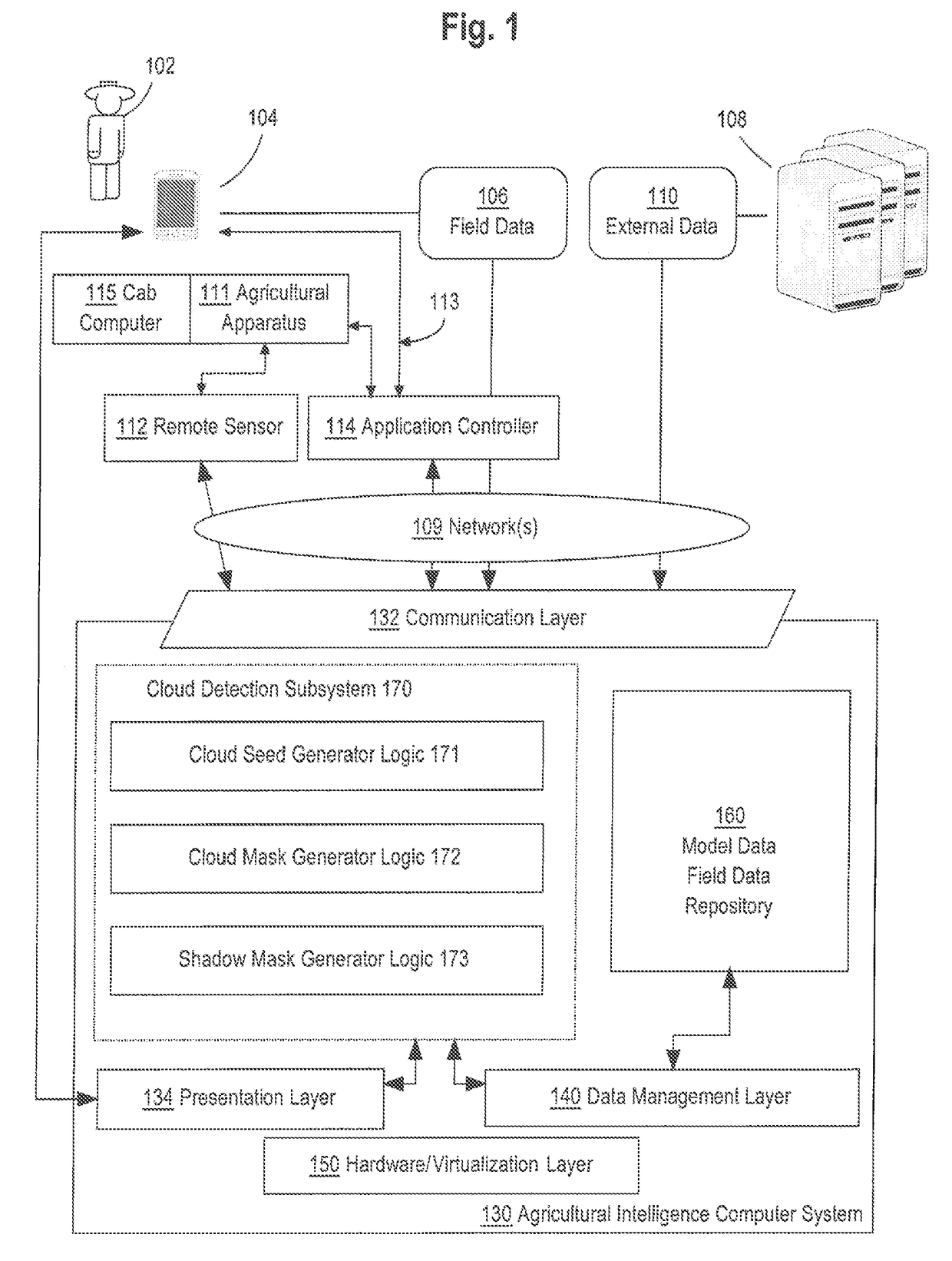
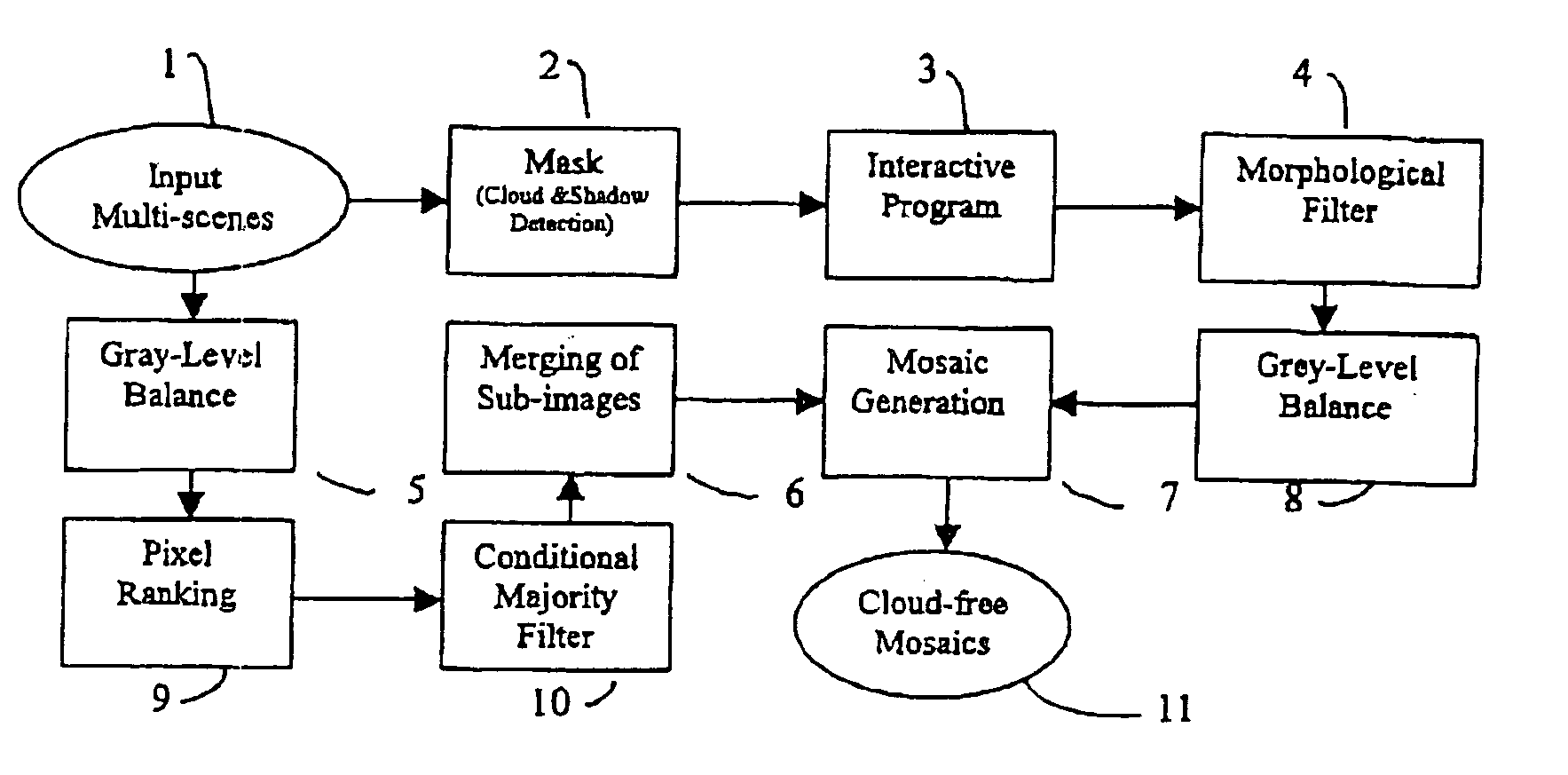
Cloud detection on remote sensing imagery
A system for detecting clouds and cloud shadows is described. In one approach, clouds and cloud shadows within a remote sensing image are detected through a three step process. In the first stage a high-precision low-recall classifier is used to identify cloud seed pixels within the image. In the second stage, a low-precision high-recall classifier is used to identify potential cloud pixels within the image. Additionally, in the second stage, the cloud seed pixels are grown into the potential cloud pixels to identify clusters of pixels which have a high likelihood of representing clouds. In the third stage, a geometric technique is used to determine pixels which likely represent shadows cast by the clouds identified in the second stage. The clouds identified in the second stage and the shadows identified in the third stage are then exported as a cloud mask and shadow mask of the remote sensing image.
Owner:CLIMATE LLC
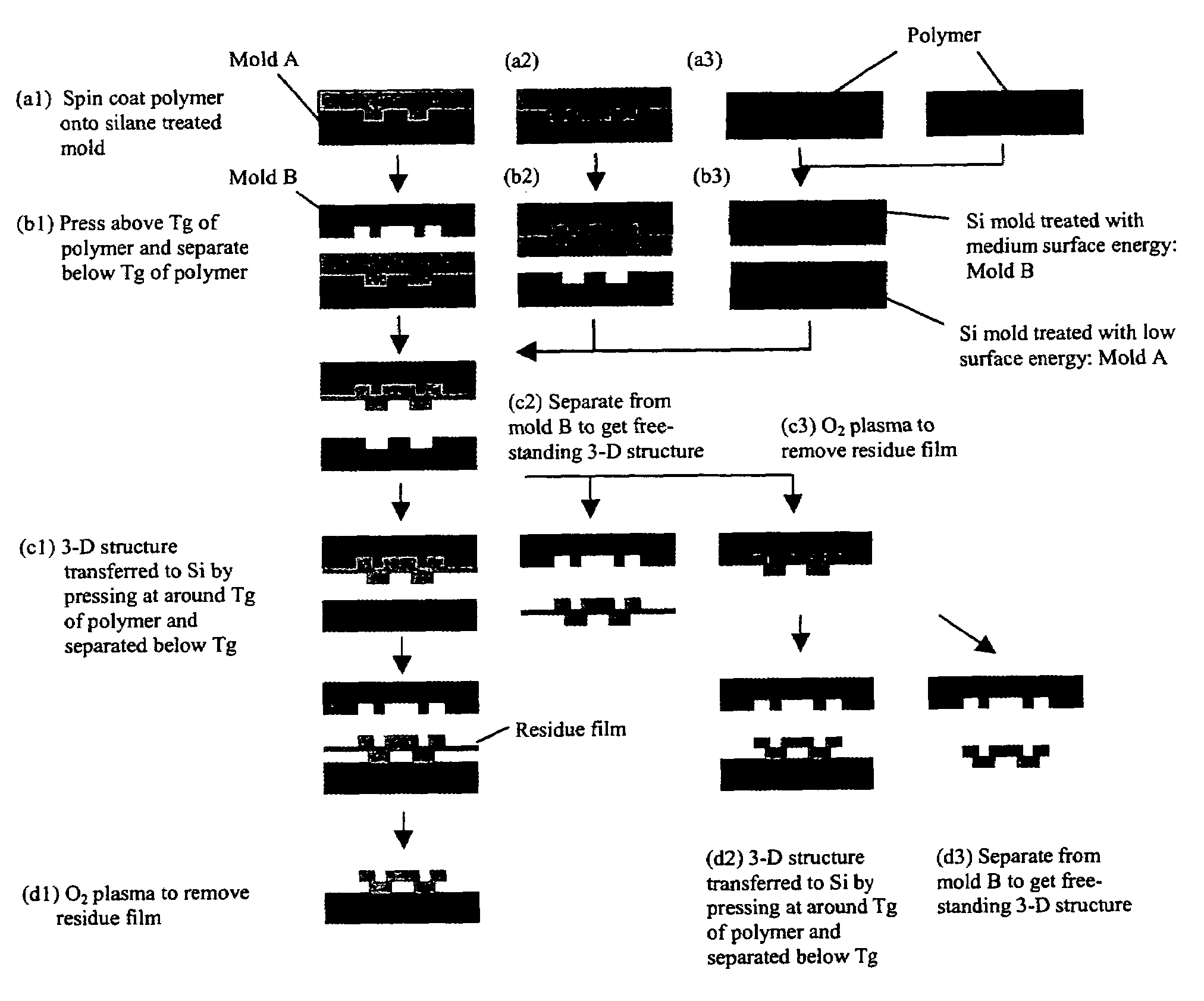
Method of imprinting shadow mask nanostructures for display pixel segregation
InactiveUS20050258571A1Easy to separateRemove heatNanostructure manufactureDecorative surface effectsVitrificationDisplay device
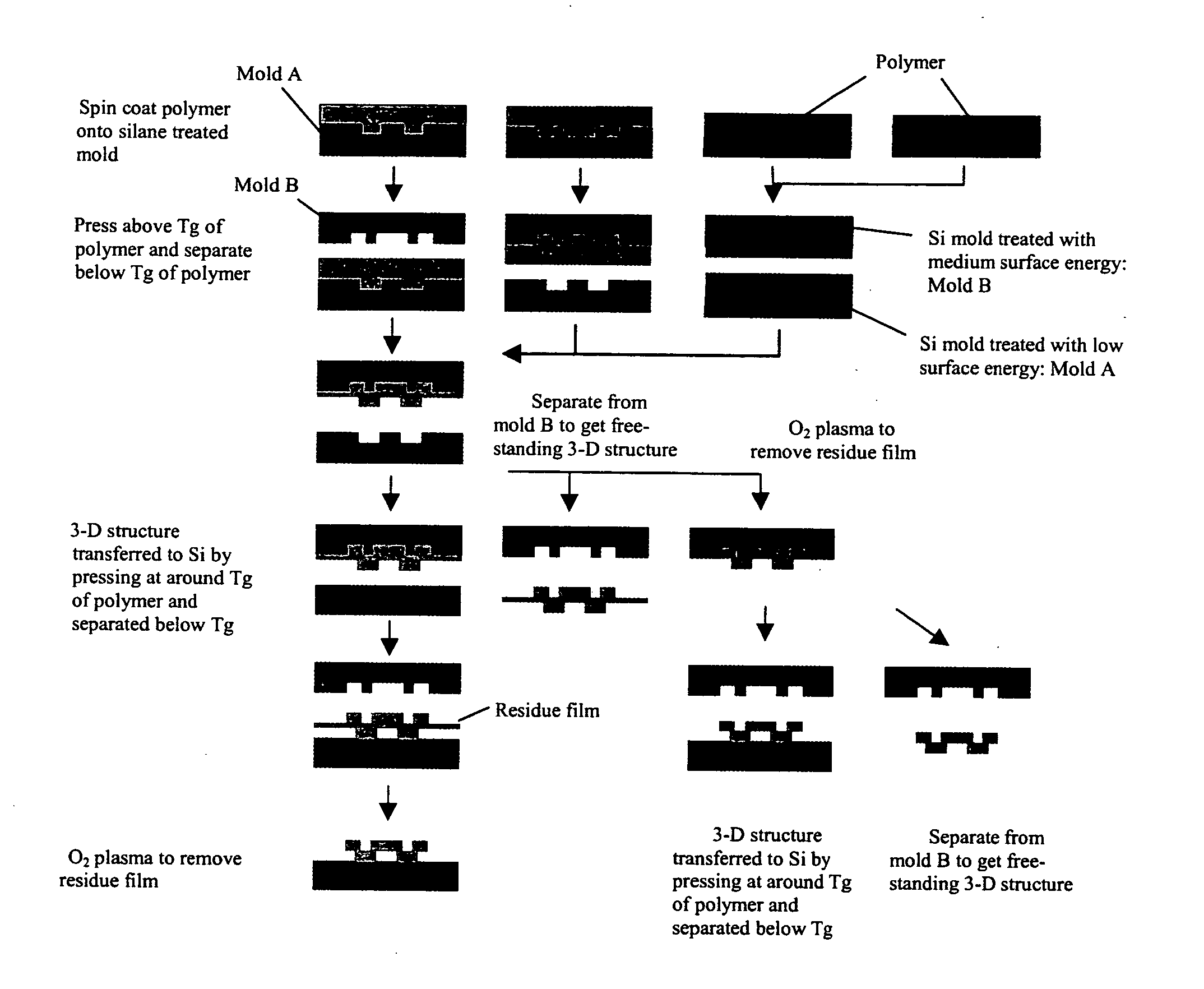
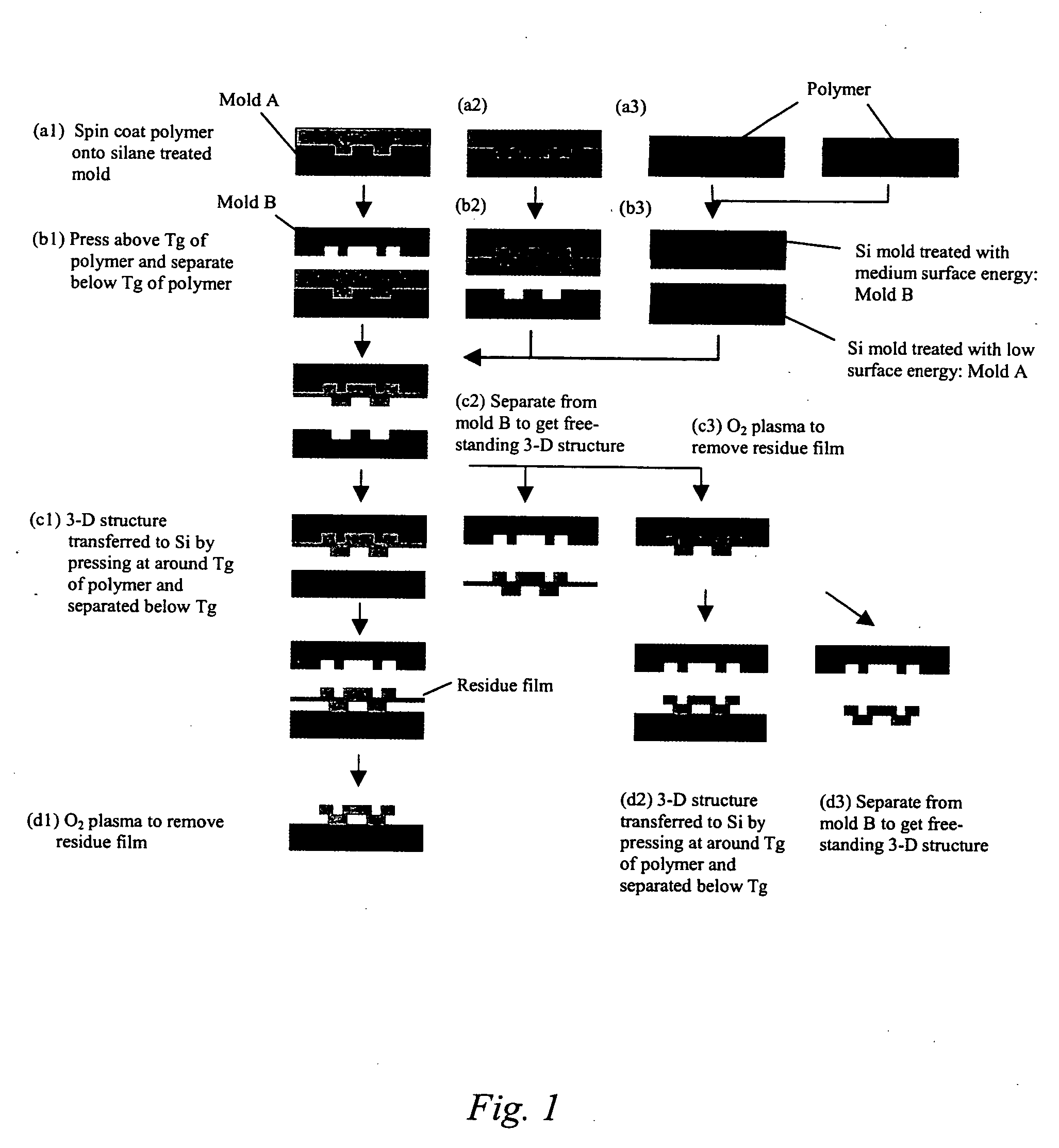
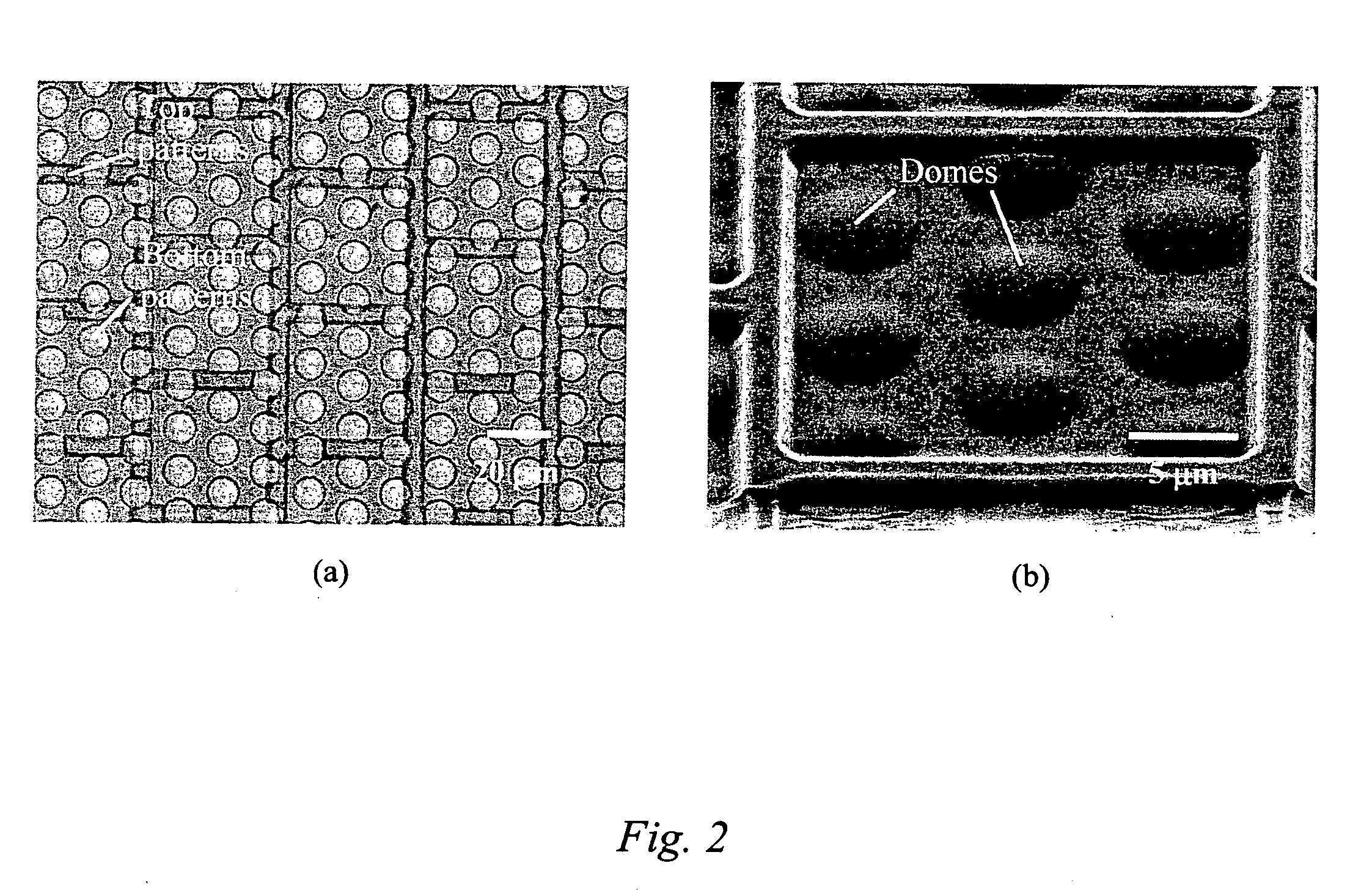
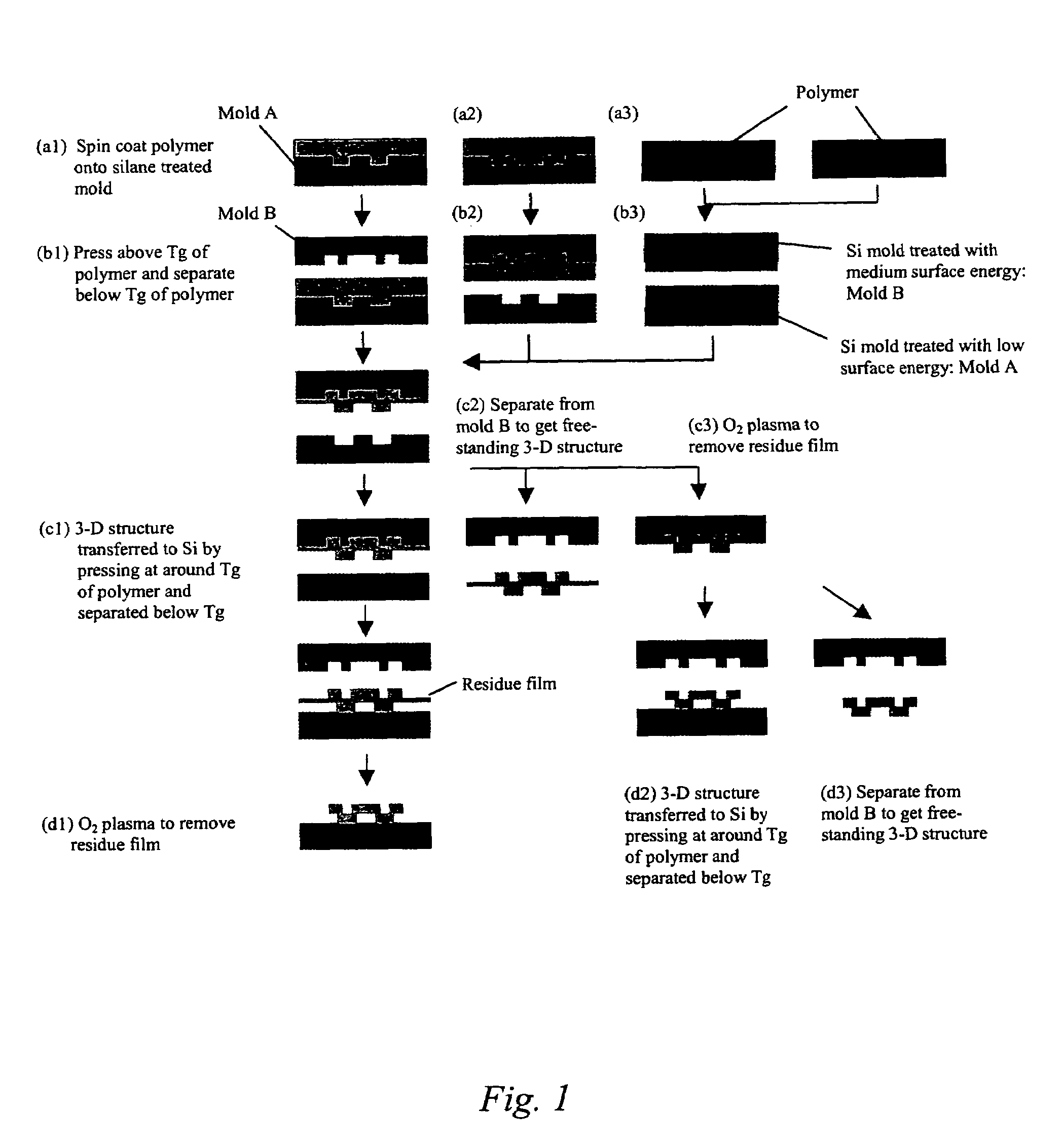
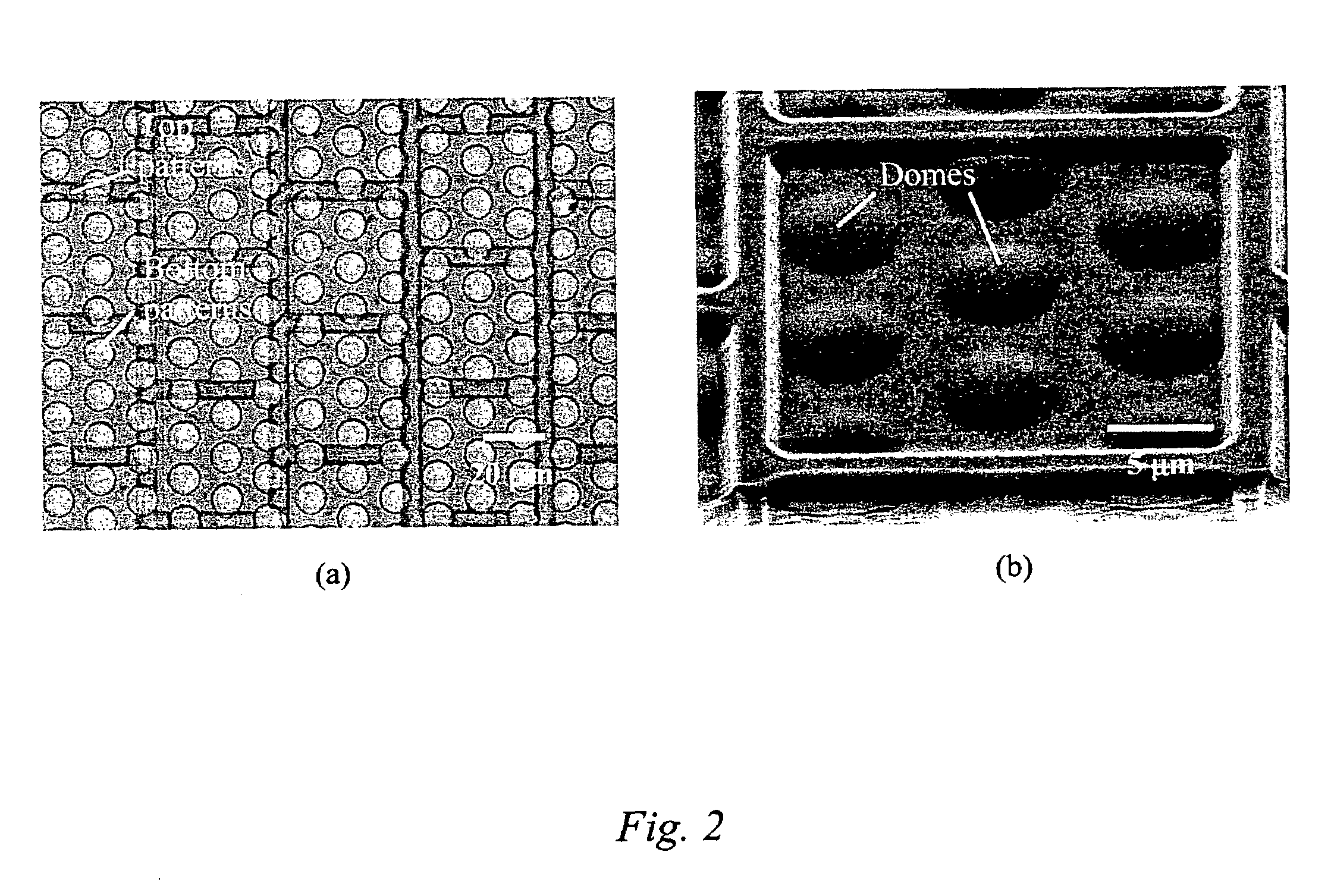
The present invention is directed to micro- and nano-scale imprinting methods and the use of such methods to fabricate supported and / or free-standing 3-D micro- and / or nano-structures of polymeric, ceramic, and / or metallic materials, particularly for pixel segregation in OLED-based displays. In some embodiments, a duo-mold approach is employed in the fabrication of these structures. In such methods, surface treatments are employed to impart differential surface energies to different molds and / or different parts of the mold(s). Such surface treatments permit the formation of three-dimensional (3-D) structures through imprinting and the transfer of such structures to a substrate. In some or other embodiments, such surface treatments and variation in glass transition temperature of the polymers used can facilitate separation of the 3-D structures from the molds to form free-standing micro- and / or nano-structures individually and / or in a film. In some or other embodiments, a “latch-on” assembly technique is utilized to form supported and / or free-standing stacked micro- and / or nano-structures that enable the assembly of polymers without a glass transition temperature and eliminate the heating required to assemble thermoplastic polymers.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Organic electroluminescent device
InactiveUS6878209B2Highly precise fine patterningImprove stabilityLiquid surface applicatorsSolid-state devicesGas phaseOptoelectronics
A method for producing an organic electroluminescent device, which is provided with first electrodes formed on a substrate, a thin film layer formed on the first electrode containing at least an emitting layer composed of an organic compound and a plurality of second electrodes formed on the thin film layer, and has a plurality of luminescent regions on said substrate, comprising the steps of forming spacers having a height at least partially exceeding the thickness of said thin film layer on the substrate, and vapor-depositing a deposit for patterning while the shadow mask having reinforcing lines formed across its apertures is kept in contact with said spacers.Highly precise fine patterning can be effected under wide vapor deposition conditions without degrading the properties of organic electroluminescent elements, and high stability can be achieved by a relatively simple process without limiting the structure of the electroluminescent device.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
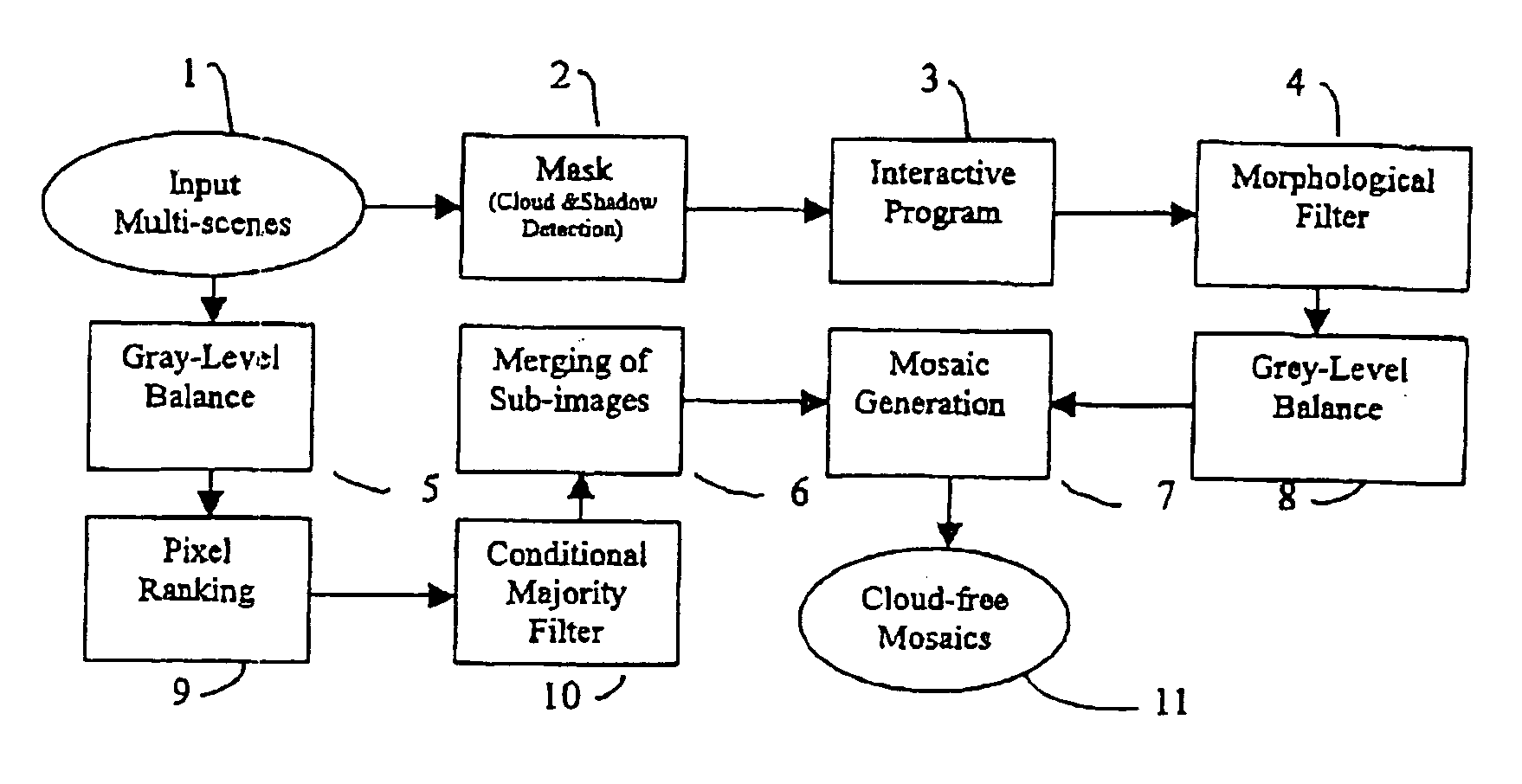
Method for producing cloud free and cloud-shadow free images
A method for generating a cloud free and cloud-shadow free image from a plurality of images of a region, the method including the steps of ranking pixels in order of cloudiness and shadowness, generating cloud and shadow masks by classifying a group of pixels as cloud, shadow, or noncloud-nonshadow, and creating a mosaic from the plurality of images to form the cloud free and cloud-shadow free image.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Solar cell
InactiveCN101401215APhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionBack surface field
The invention provides a thin film amorphous silicon-crystalline silicon back heterojunction and back surface field device configuration for a heterojunction solar cell. The configuration is attained by the formation of heterojunctions on the back surface of crystalline silicon at low temperatures. Low temperature fabrication allows for the application of low resolution lithography and / or shadow masking processes to produce the structures. The heterojunctions and interface passivation can be formed through a variety of material compositions and deposition processes, including appropriate surface restructing techniques. The configuration achieves separation of optimization requirements for light absorption and carrier generation at the front surface on which the light is incident, and in the bulk, and charge carrier collection at the back of the device. The shadowing losses are eliminated by positioning the electrical contacts at the back thereby removing them from the path of the incident light. Back contacts need optimization only for maximum charge carrier collection without bothering about shading losses. A range of elements / alloys may be used to effect band-bending.
Owner:ARISE TECH CORP
Methods of processing of gallium nitride
InactiveUS7015117B2Polycrystalline material growthFrom solid stateThermal energyElectrical conductor
A method for improving thermal dissipation in large gallium nitride light emitting diodes includes replacing sapphire with a better thermal conductor resulting in more efficient removal of thermal energy. A method for achieving a reliable and strong temporary bond between a GaN epitaxial layer and a support wafer. A method for transferring an epitaxial film from a growth substrate to a secondary substrate. An excimer laser initiates film delamination from the growth substrate. The laser beam is shaped by a shadow mask and aligned to an existing pattern in the growth substrate. A method for fabricating a LED that radiates white spectrum light. A phosphor that radiates a white spectrum after excitation in the blue or UV spectrum onto the GaN epitaxial wafer prior to die separation and packaging. A method for depositing a metal substrate onto a GaN epitaxy layer.
Owner:ALLEGIS TECH
Method of manufacturing patterned subtrate for culturing cells, patterned subtrate for culturing cells, patterning method of culturing cells, and patterned cell chip
InactiveUS20110053800A1Preparing sample for investigationPretreated surfacesCulture cellPatterned substrate
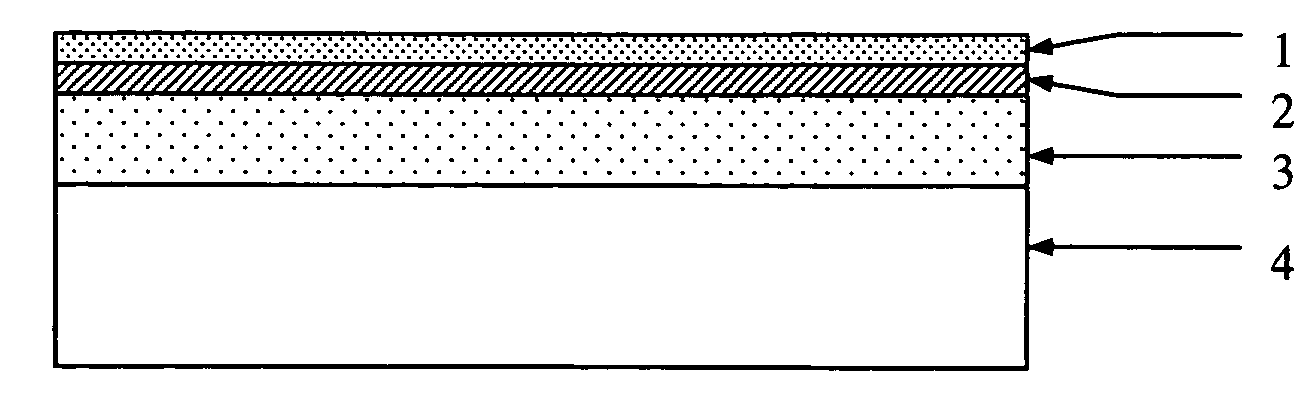
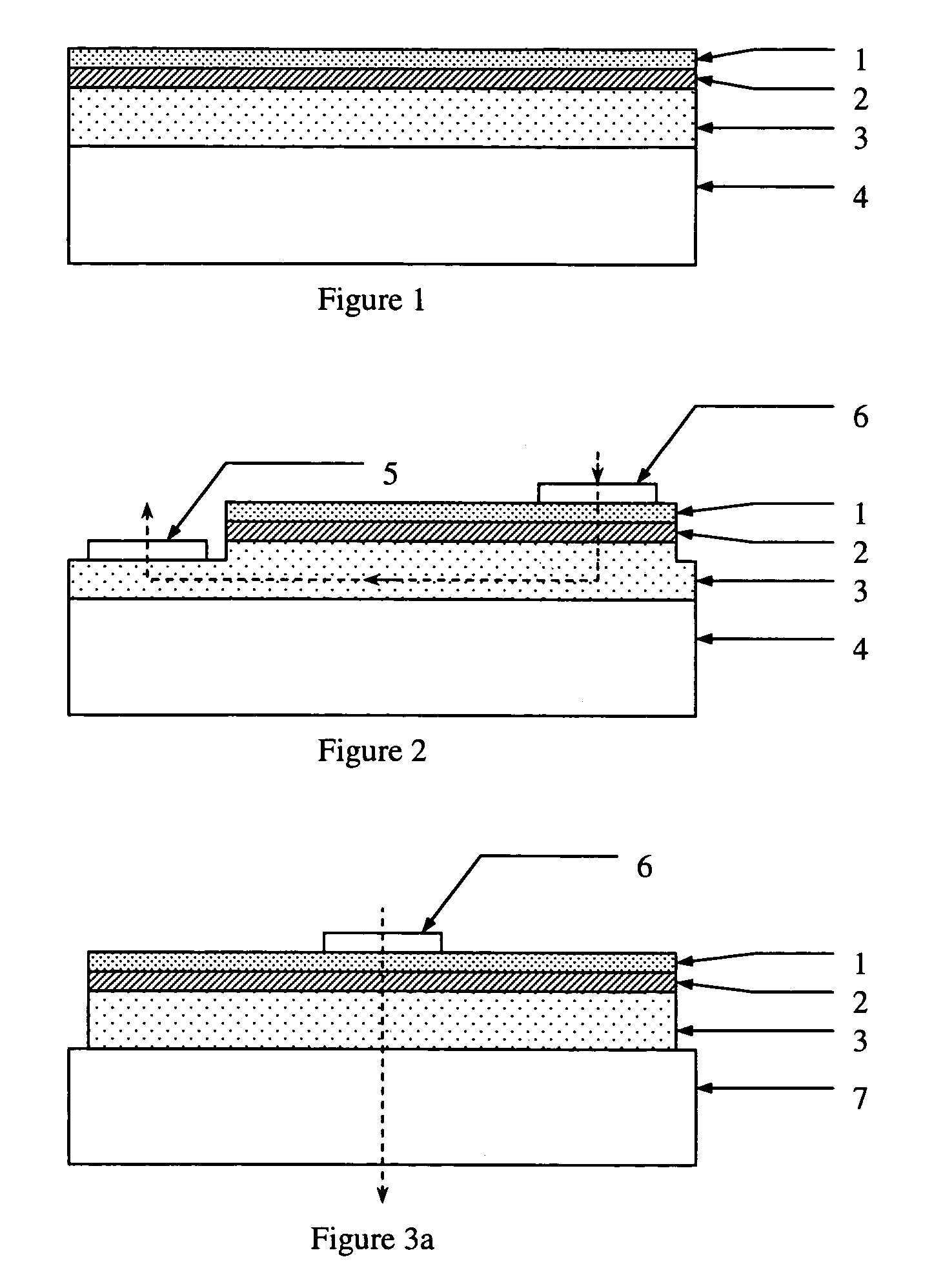
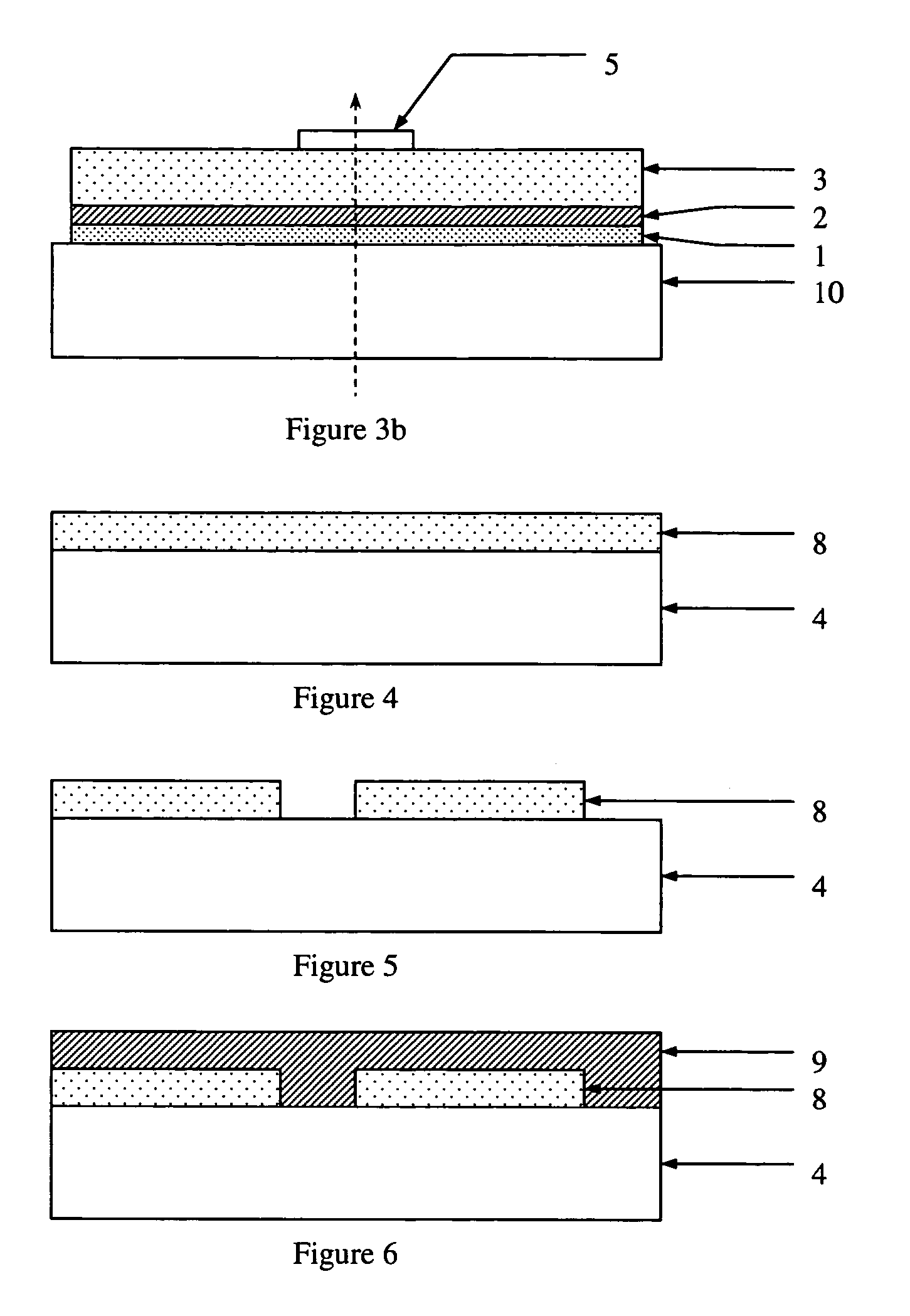
The present invention relates to a method of manufacturing a patterned substrate for culturing cells, comprising the steps of: (1) preparing a substrate; (2) forming a first plasma polymer layer by integrating a first precursor material using a plasma on the substrate; (3) placing a shadow mask having a predetermined pattern on the first plasma polymer layer; and (4) forming a second patterned plasma polymer layer by integrating a second precursor material using a plasma.
Owner:SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIVERSITY
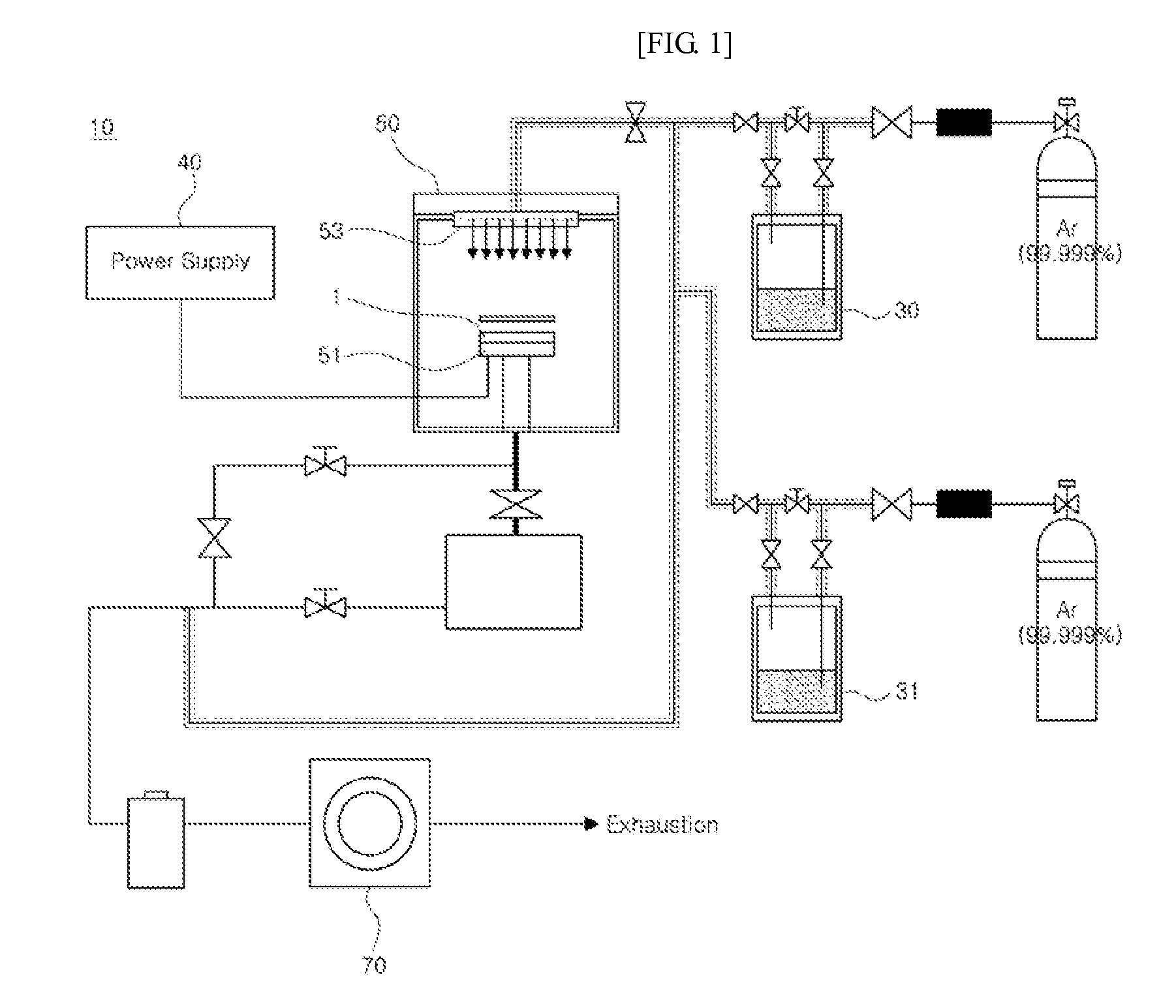
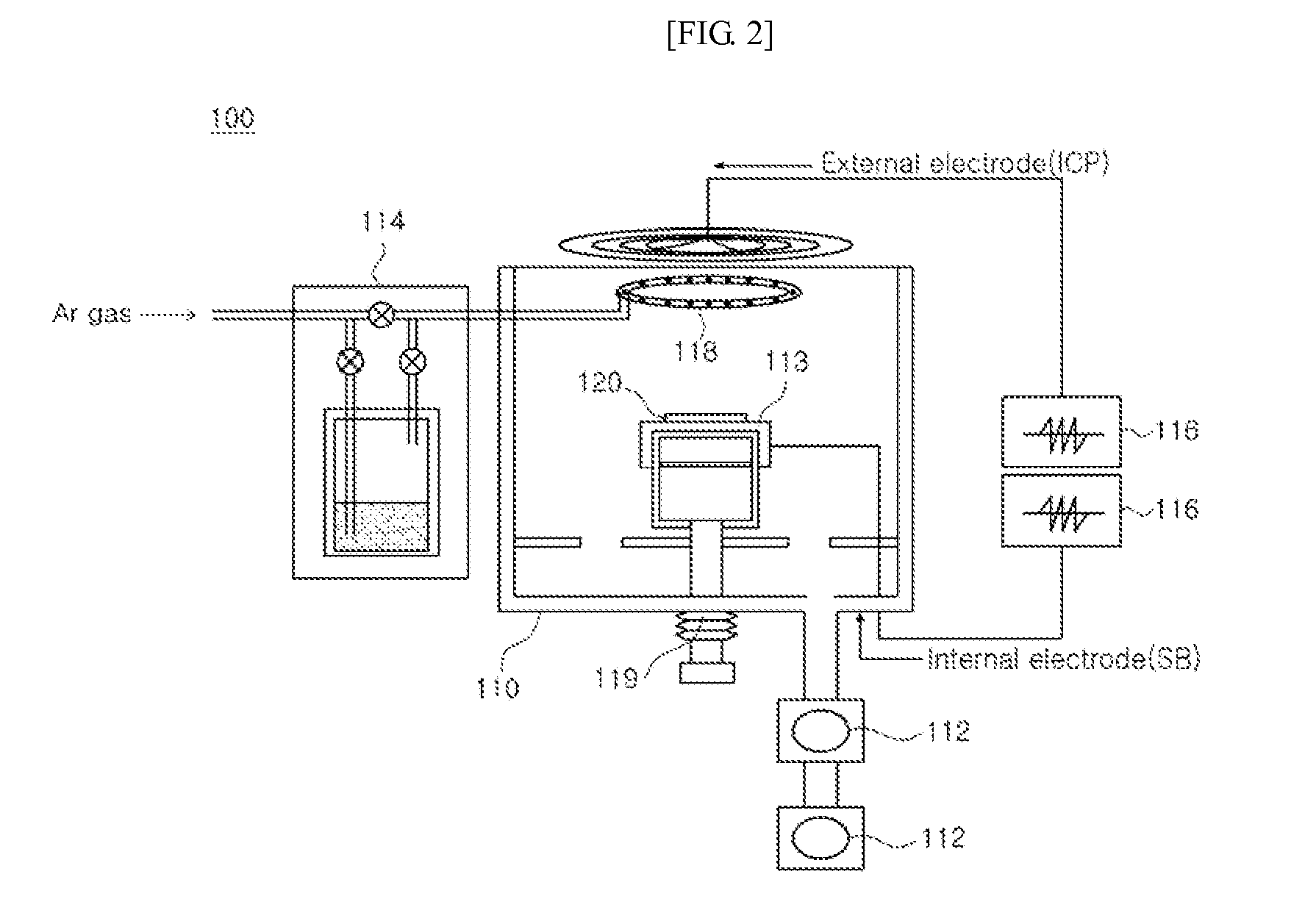
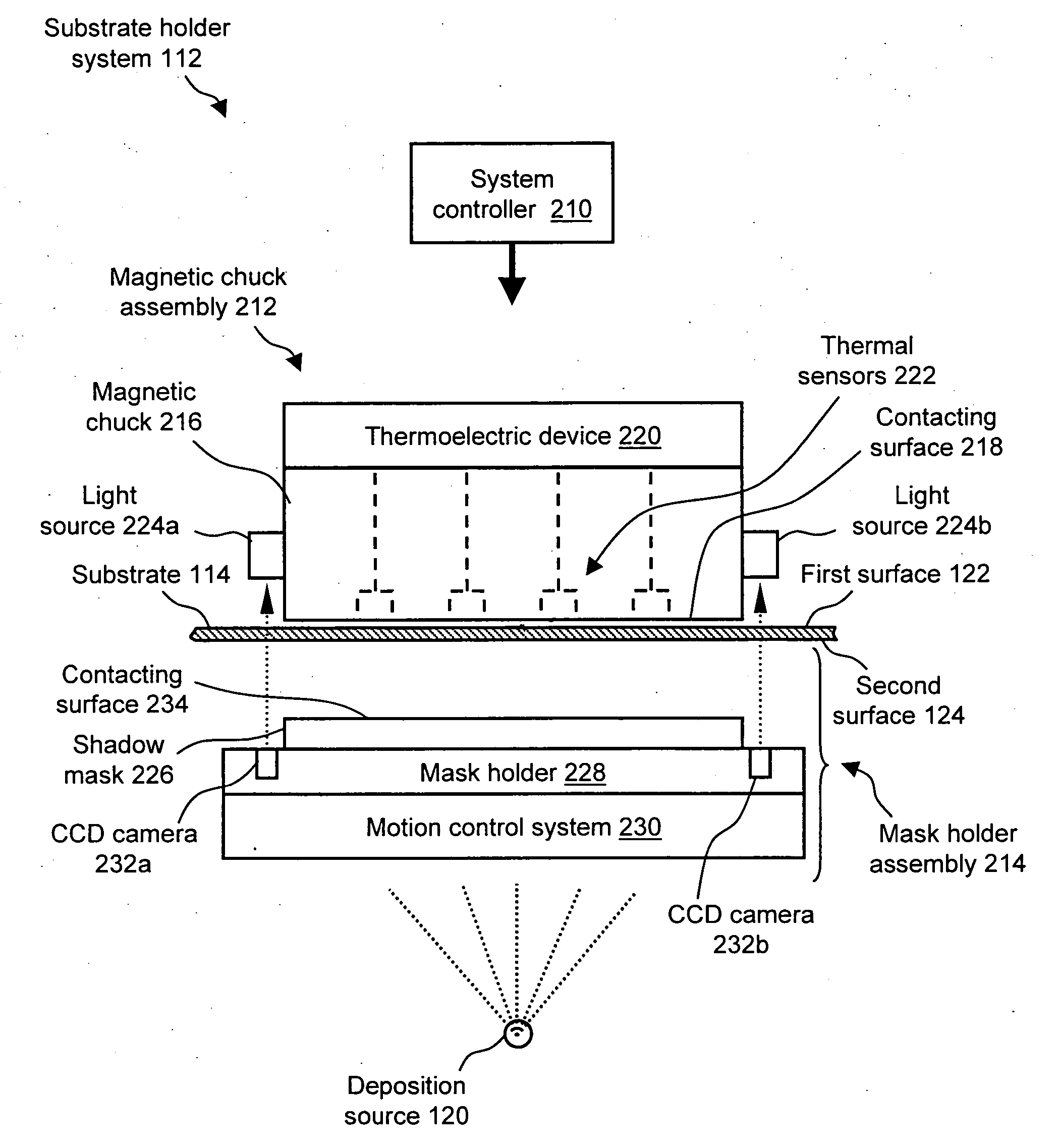
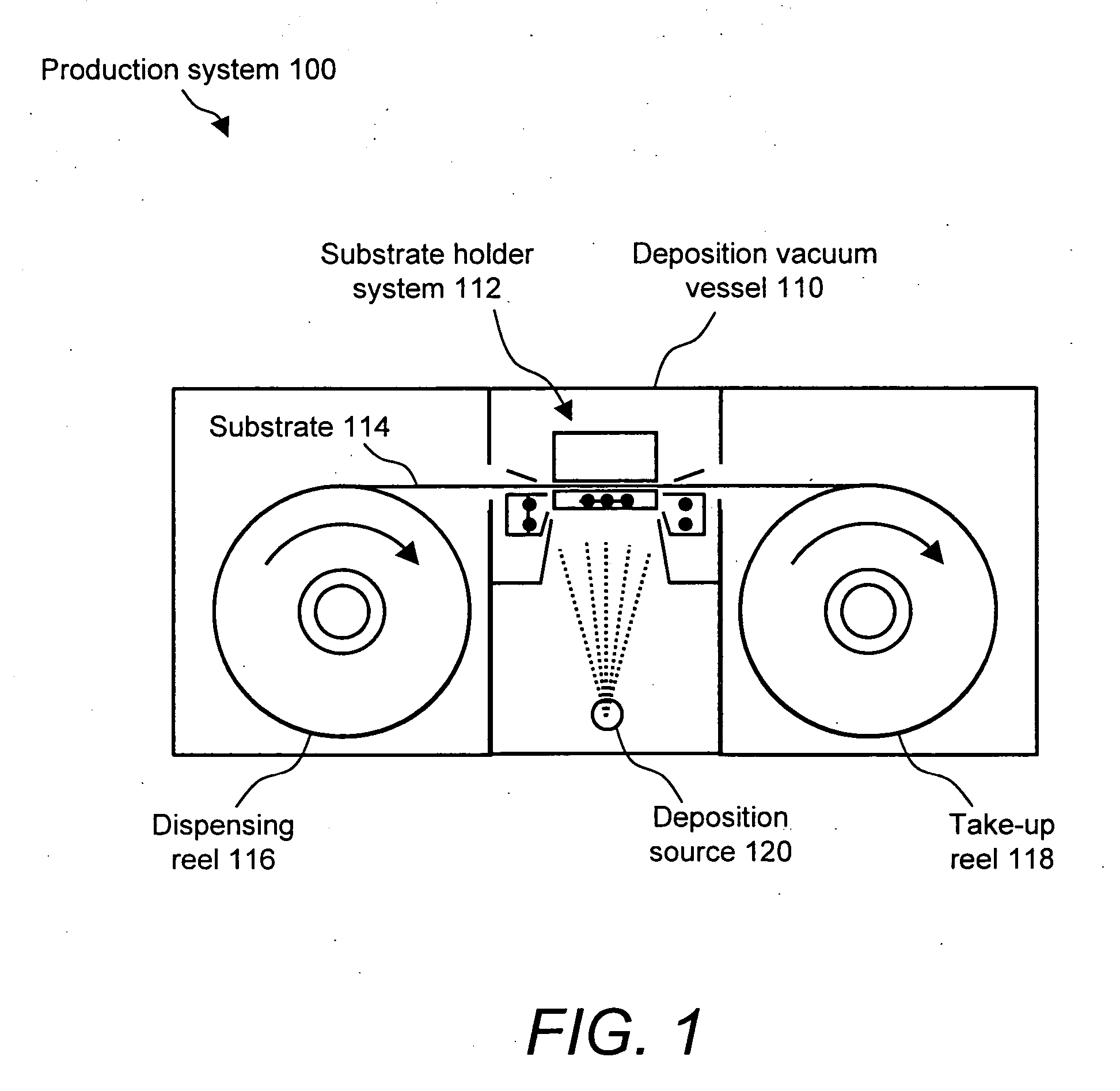
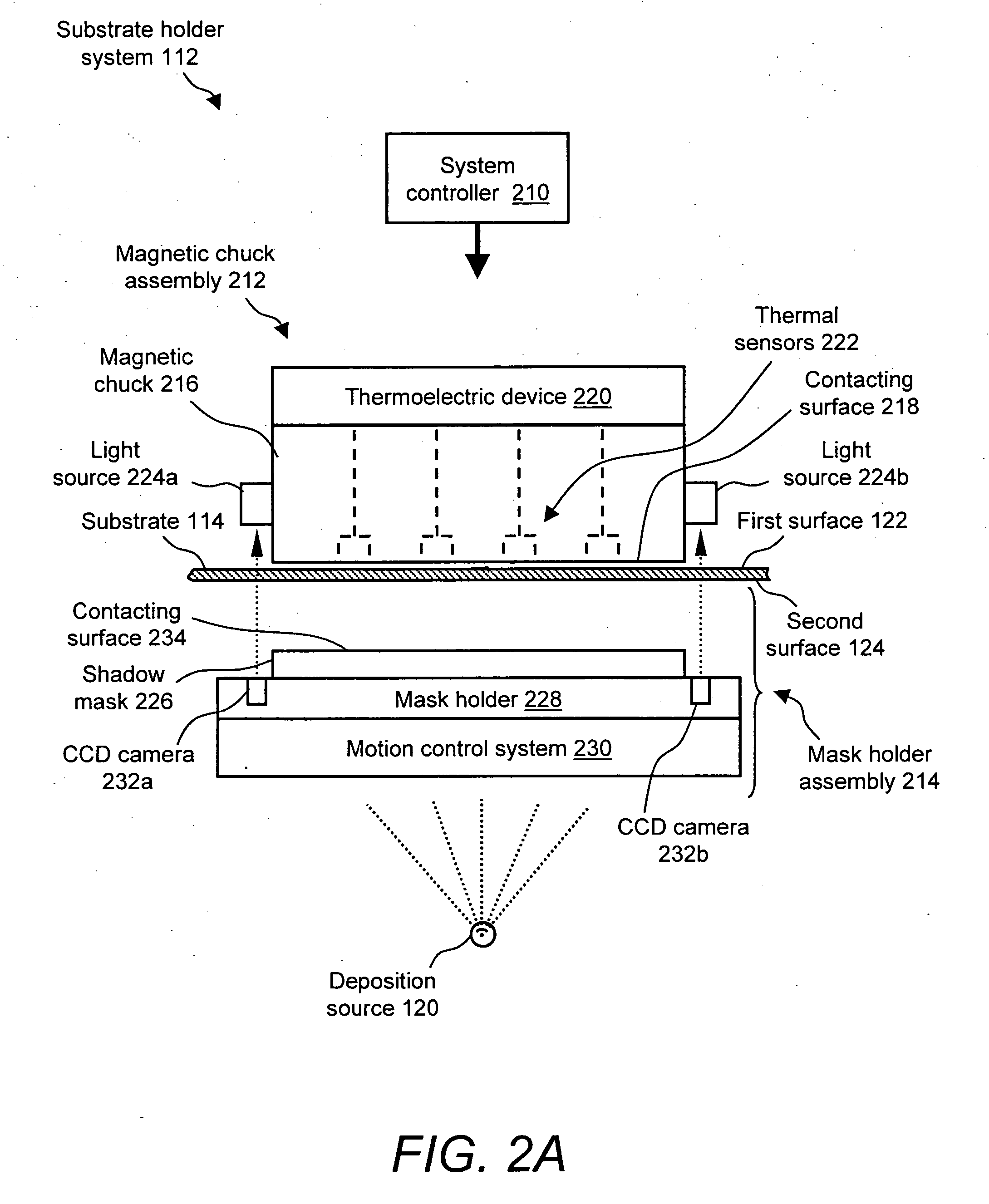
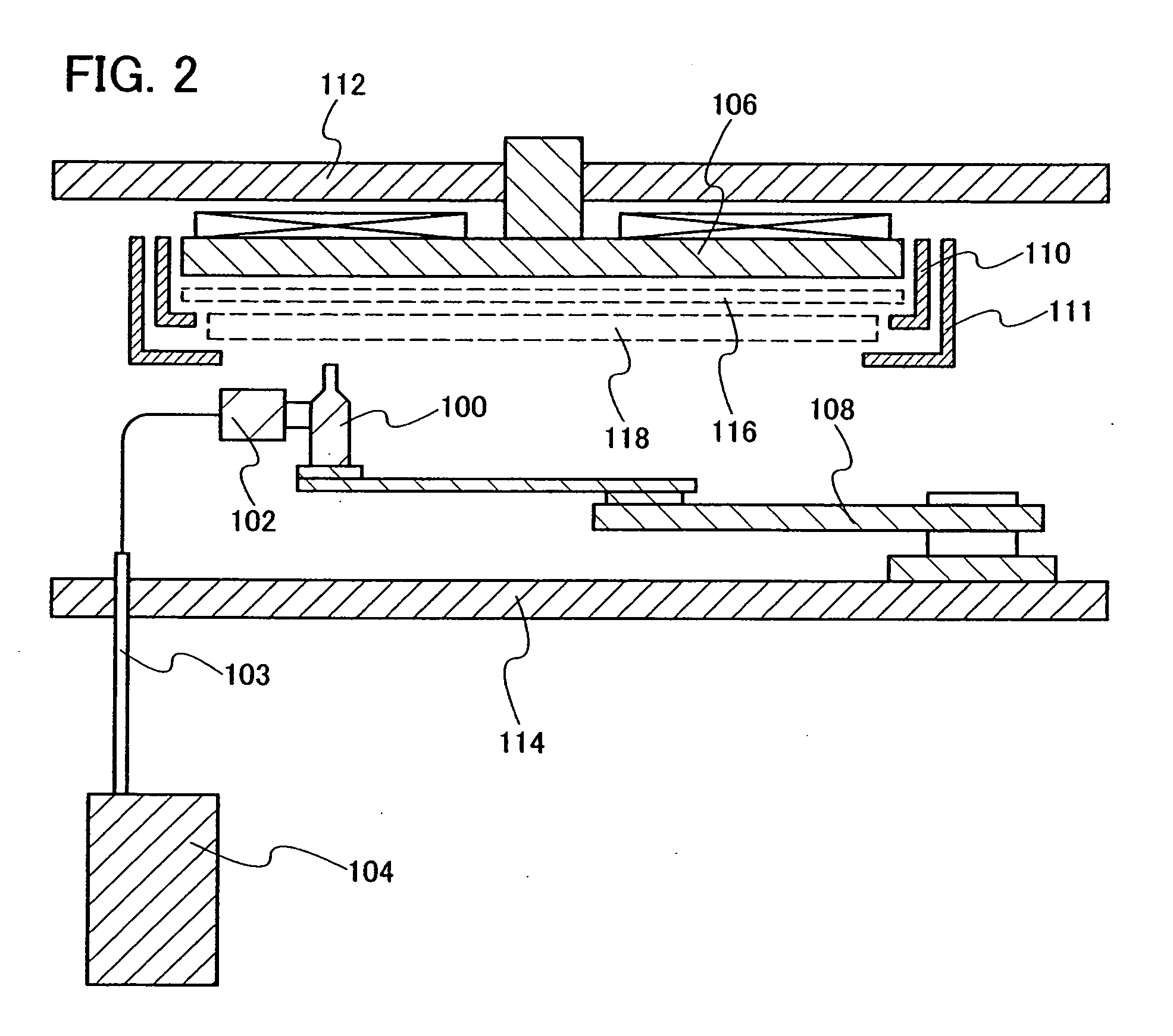
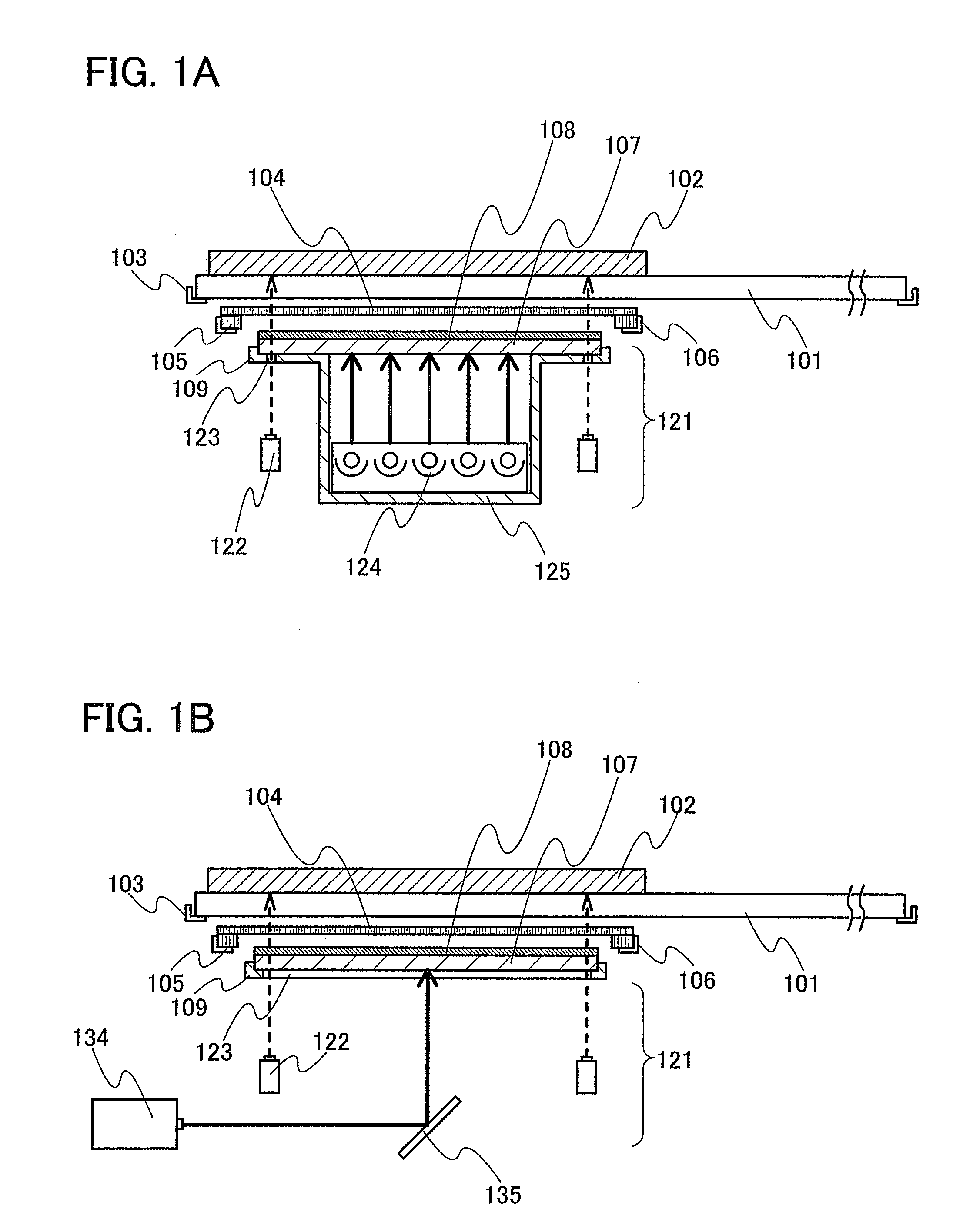
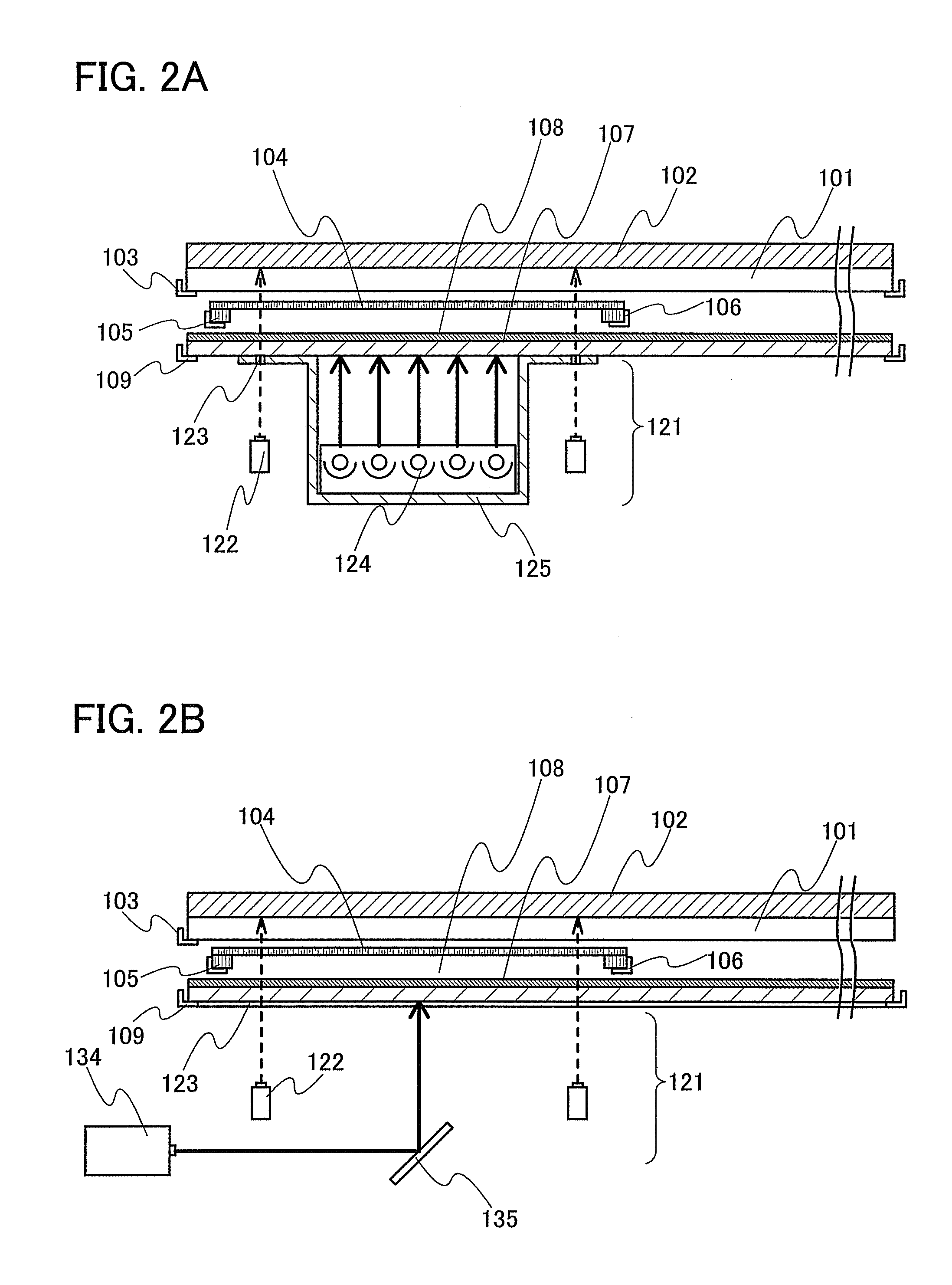
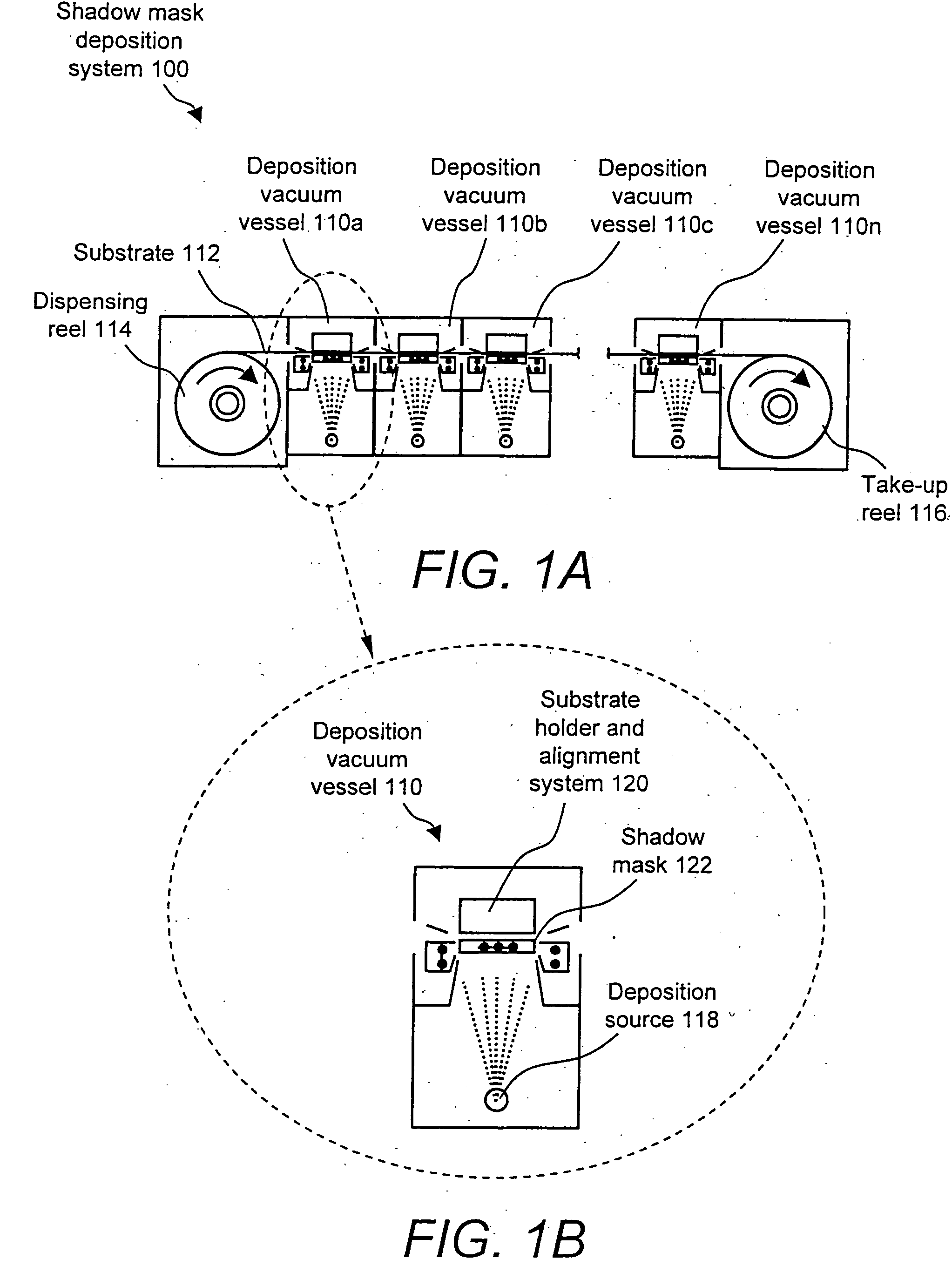
Substrate-to-mask alignment and securing system with temperature control for use in an automated shadow mask vacuum deposition process
InactiveUS20060086321A1Vacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingTemperature controlControl system
The present invention is a substrate holder system for and method of providing a substrate-to-mask alignment mechanism, securing mechanism and temperature control mechanism. The substrate holder system is suitable for use in an automated shadow mask vacuum deposition process. The substrate holder system includes a system controller, and a substrate arranged between a magnetic chuck assembly and a mask holder assembly. The magnetic chuck assembly includes a magnetic chuck, a thermoelectric device, a plurality of thermal sensors and a plurality of light sources. The mask holder assembly includes a shadow mask, a mask holder, a motion control system and a plurality of cameras. The substrate holder system of the present invention provides close contact between the substrate and the shadow mask thereby avoiding the possibility of evaporant material entering into a gap therebetween.
Owner:ADVANTECH GLOBAL LTD
Light emitting device and fabrication method thereof
ActiveUS20100012969A1Improved light emissionEfficient light emissionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOhmic contactReflective layer
There is provided a method of fabricating a vertical light emitting diode. The method comprises the steps of: growing a low doped first conductive semiconductor layer on a sacrificial substrate; forming an aluminum layer on the low doped first conductive semiconductor layer; forming an AAO layer having a large number of holes formed therein by performing anodizing treatment of the aluminum layer; etching and patterning the low doped first conductive semiconductor layer using the aluminum layer with a large number of the holes as a shadow mask to expose a portion of the low doped first conductive semiconductor layer, thereby forming a large number of grooves; removing the aluminum layer remaining on the low doped first conductive semiconductor layer; sequentially forming a high doped first conductive semiconductor layer, an active layer and a second conductive semiconductor layer on the low doped first conductive semiconductor layer with a large number of the grooves; forming a metal reflective layer and a conductive substrate on the second conductive semiconductor layer; separating the sacrificial substrate; and forming an electrode pad on the other surface of the low doped first conductive semiconductor layer, the electrode pad being filled in a large number of the grooves to be in ohmic contact with the high doped first conductive semiconductor layer
Owner:SEOUL VIOSYS CO LTD
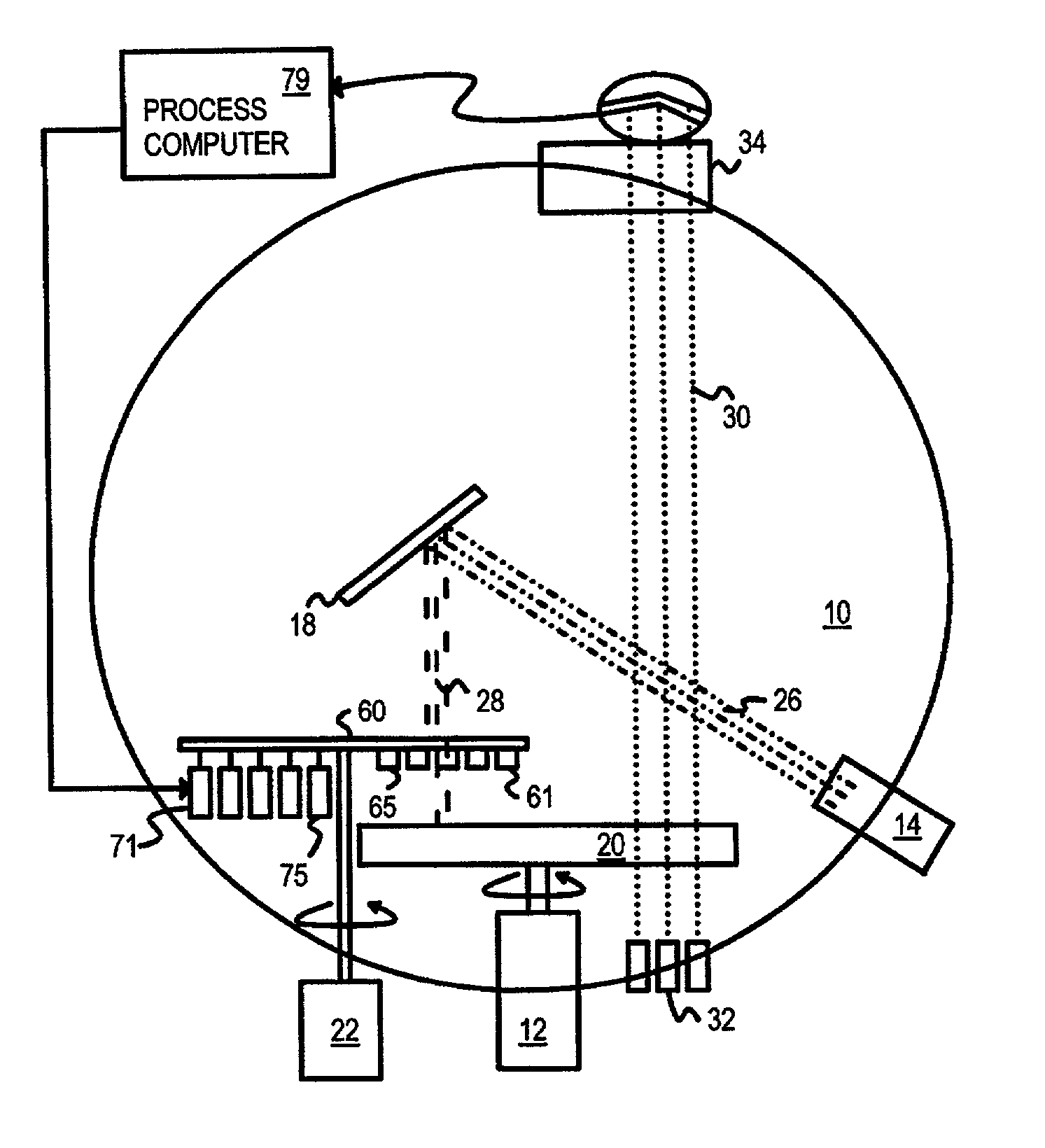
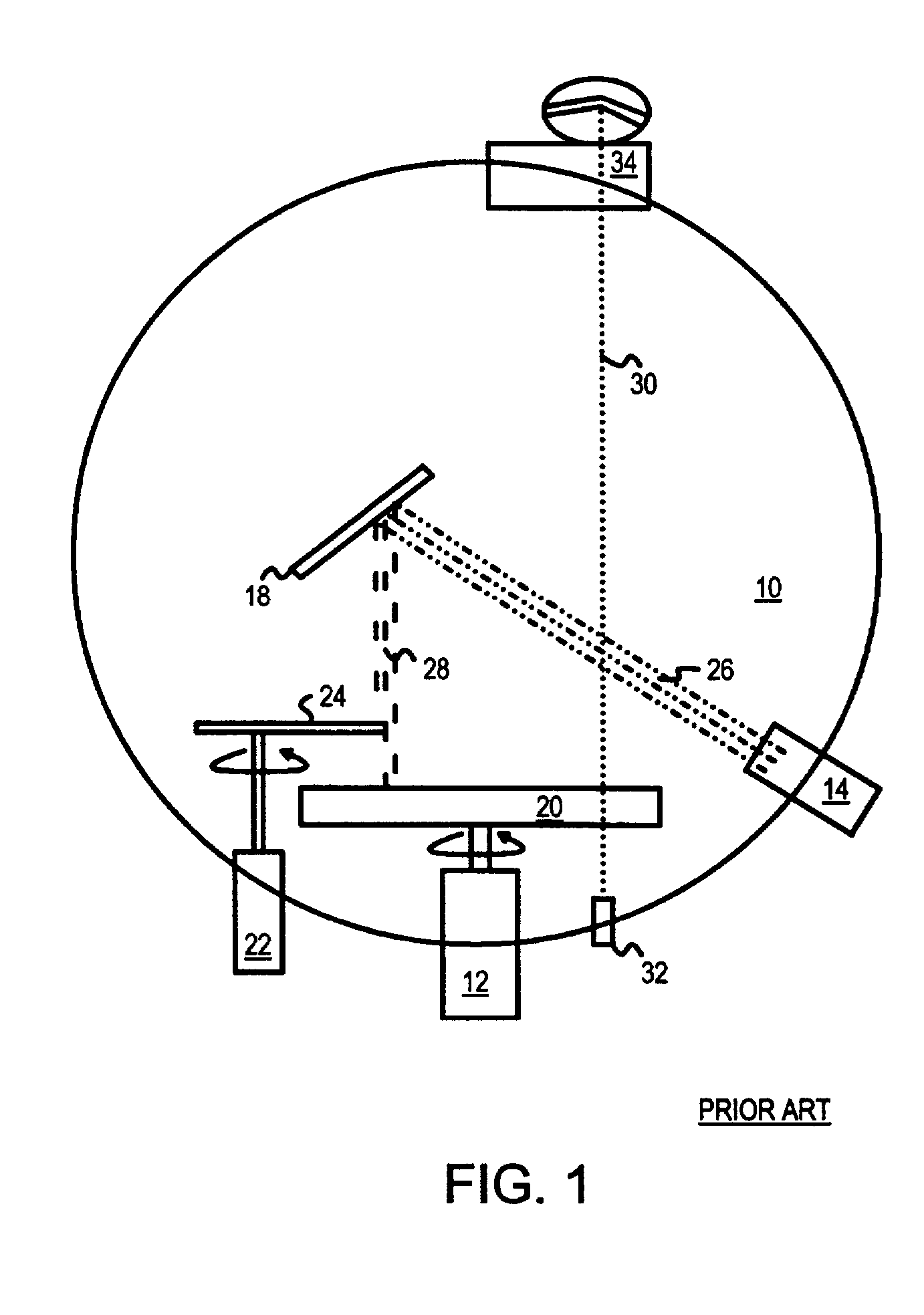
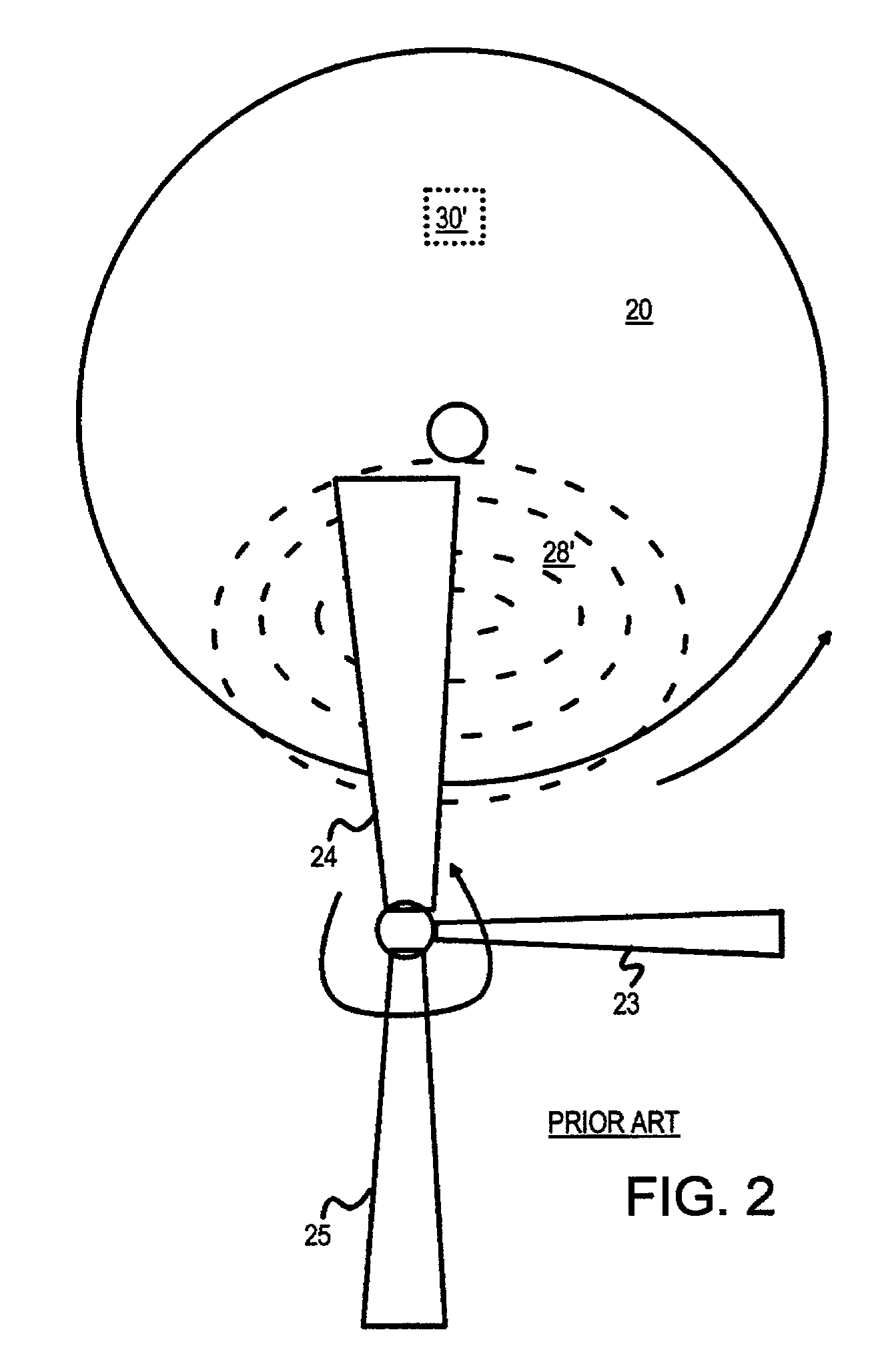
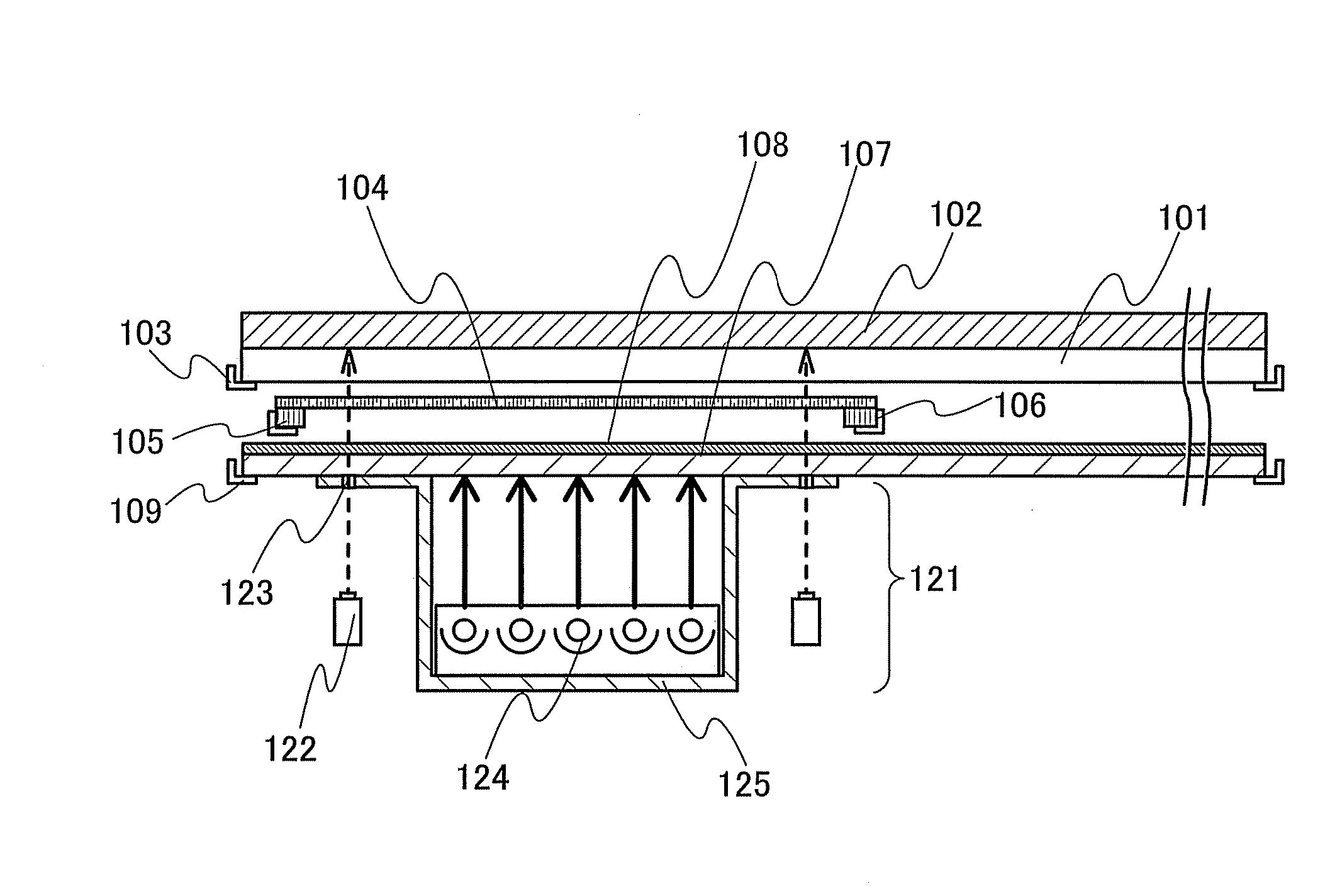
Adjustable shadow mask for improving uniformity of film deposition using multiple monitoring points along radius of substrate
A vacuum chamber deposits thin films on a substrate by sputtering a target. The beam of atoms or ions from the target is partially blocked by a shadow or adjustable uniformity mask, reducing the deposition rate onto the substrate. The adjustable uniformity mask has several adjustable fingers. The fingers extend or retract to enlarge or reduce the size of the mask. Each finger covers a different annular region or radius of the substrate. The deposition rate at different substrate radii is thus adjustable by the fingers. Several optical beams monitor the film transmittance at different substrate radii. A transmittance profile is continually generated during deposition. As deposition proceeds, radii with a thicker film have their fingers extended to reduce their deposition rate, producing a more uniform film thickness across all radii. Motors extend or retract the individual fingers.
Owner:SUPER TALENT ELECTRONICS
Method of imprinting shadow mask nanostructures for display pixel segregation
InactiveUS7615179B2Easy to separateRemove heatNanostructure manufactureDecorative surface effectsVitrificationDisplay device
The present invention is directed to micro- and nano-scale imprinting methods and the use of such methods to fabricate supported and / or free-standing 3-D micro- and / or nano-structures of polymeric, ceramic, and / or metallic materials, particularly for pixel segregation in OLED-based displays. In some embodiments, a duo-mold approach is employed in the fabrication of these structures. In such methods, surface treatments are employed to impart differential surface energies to different molds and / or different parts of the mold(s). Such surface treatments permit the formation of three-dimensional (3-D) structures through imprinting and the transfer of such structures to a substrate. In some or other embodiments, such surface treatments and variation in glass transition temperature of the polymers used can facilitate separation of the 3-D structures from the molds to form free-standing micro- and / or nano-structures individually and / or in a film. In some or other embodiments, a “latch-on” assembly technique is utilized to form supported and / or free-standing stacked micro- and / or nano-structures that enable the assembly of polymers without a glass transition temperature and eliminate the heating required to assemble thermoplastic polymers.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
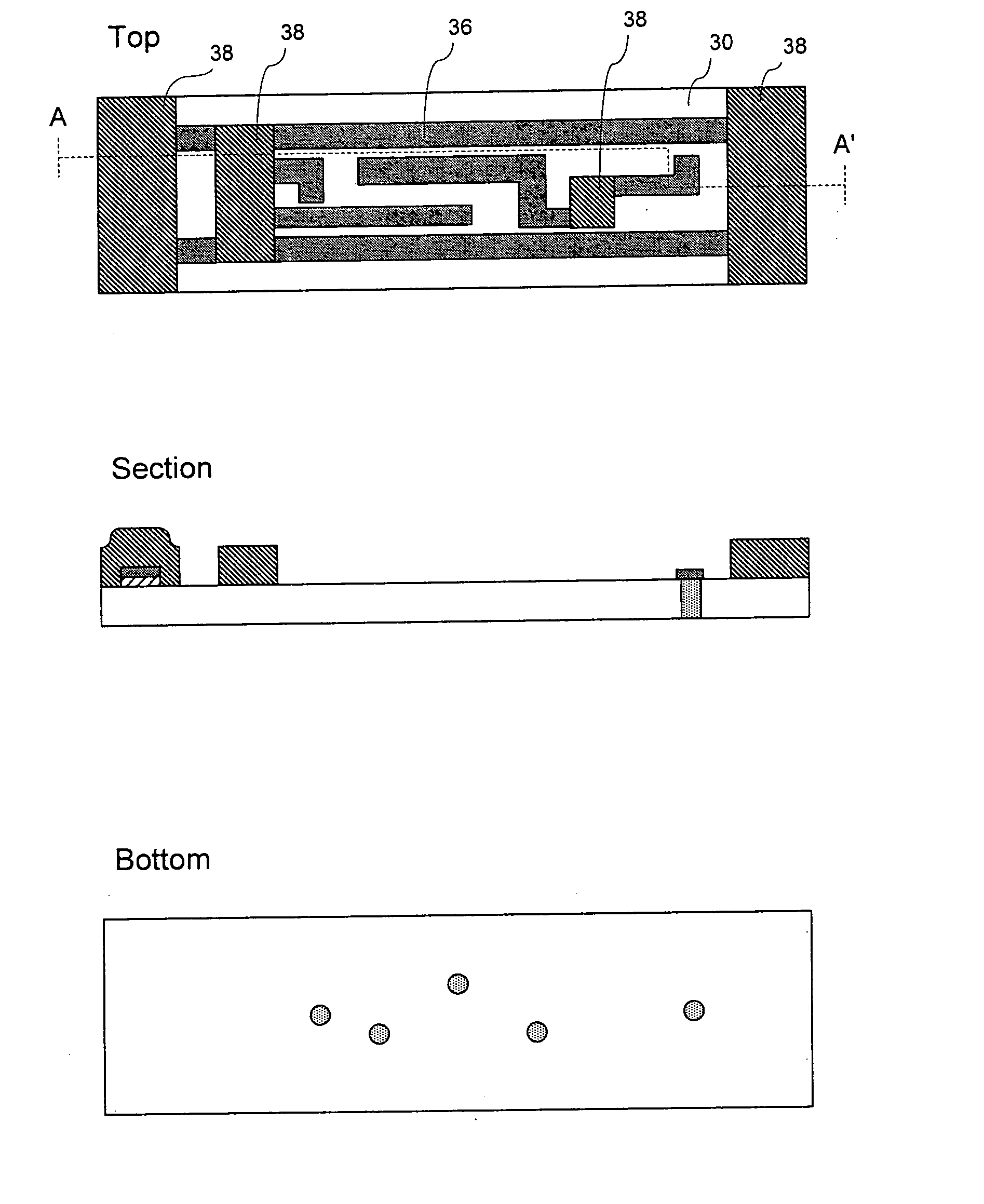
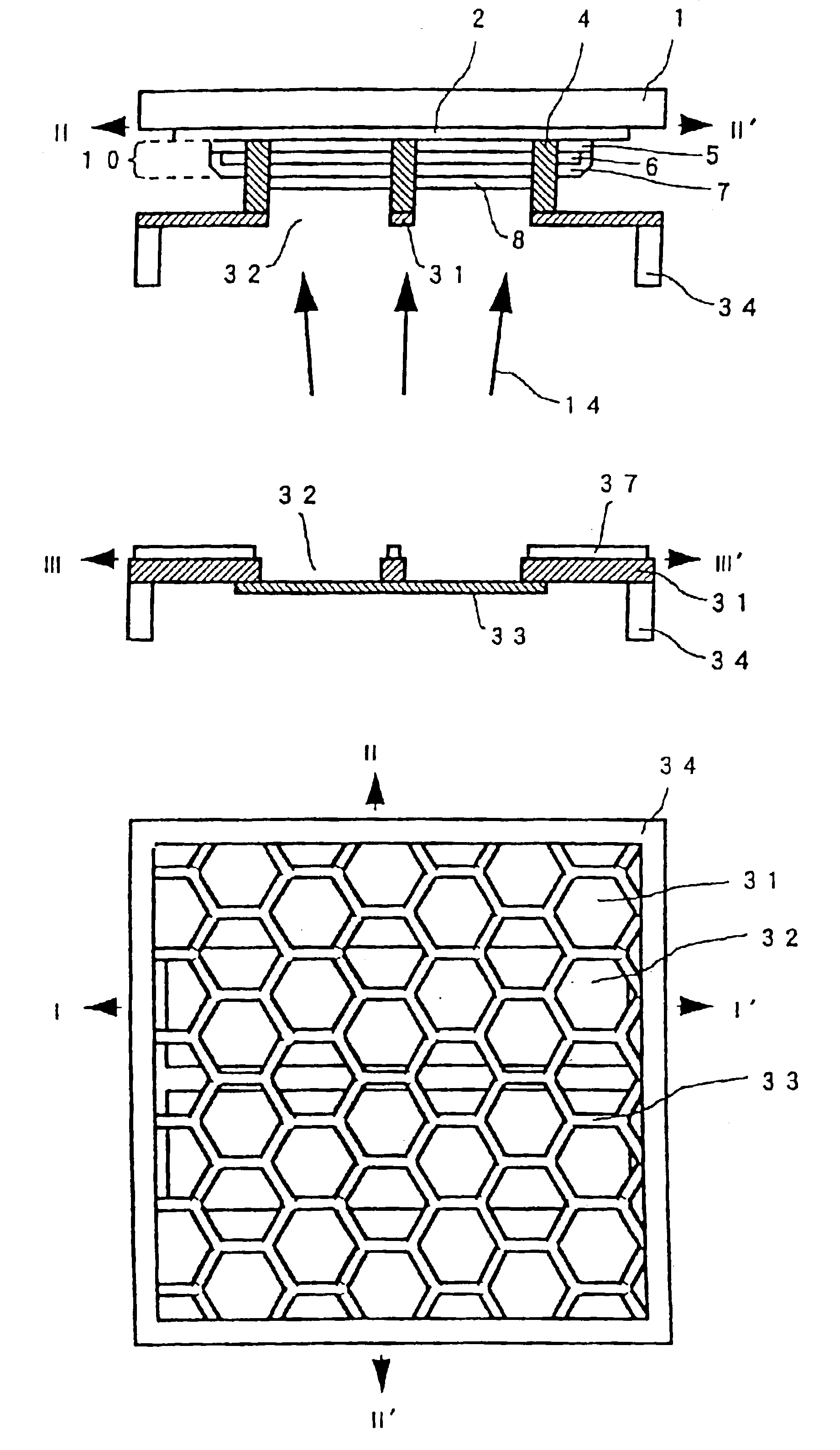
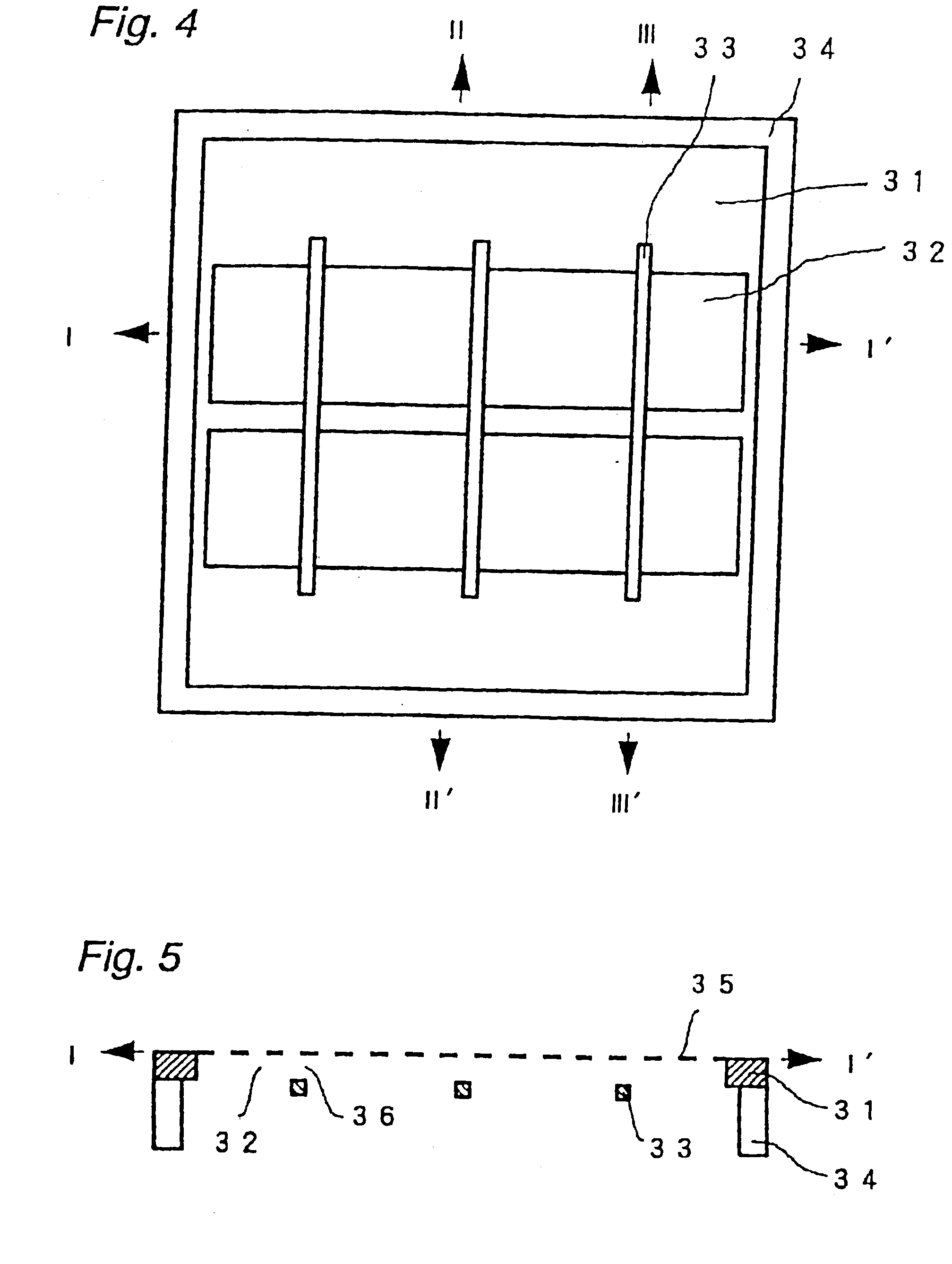
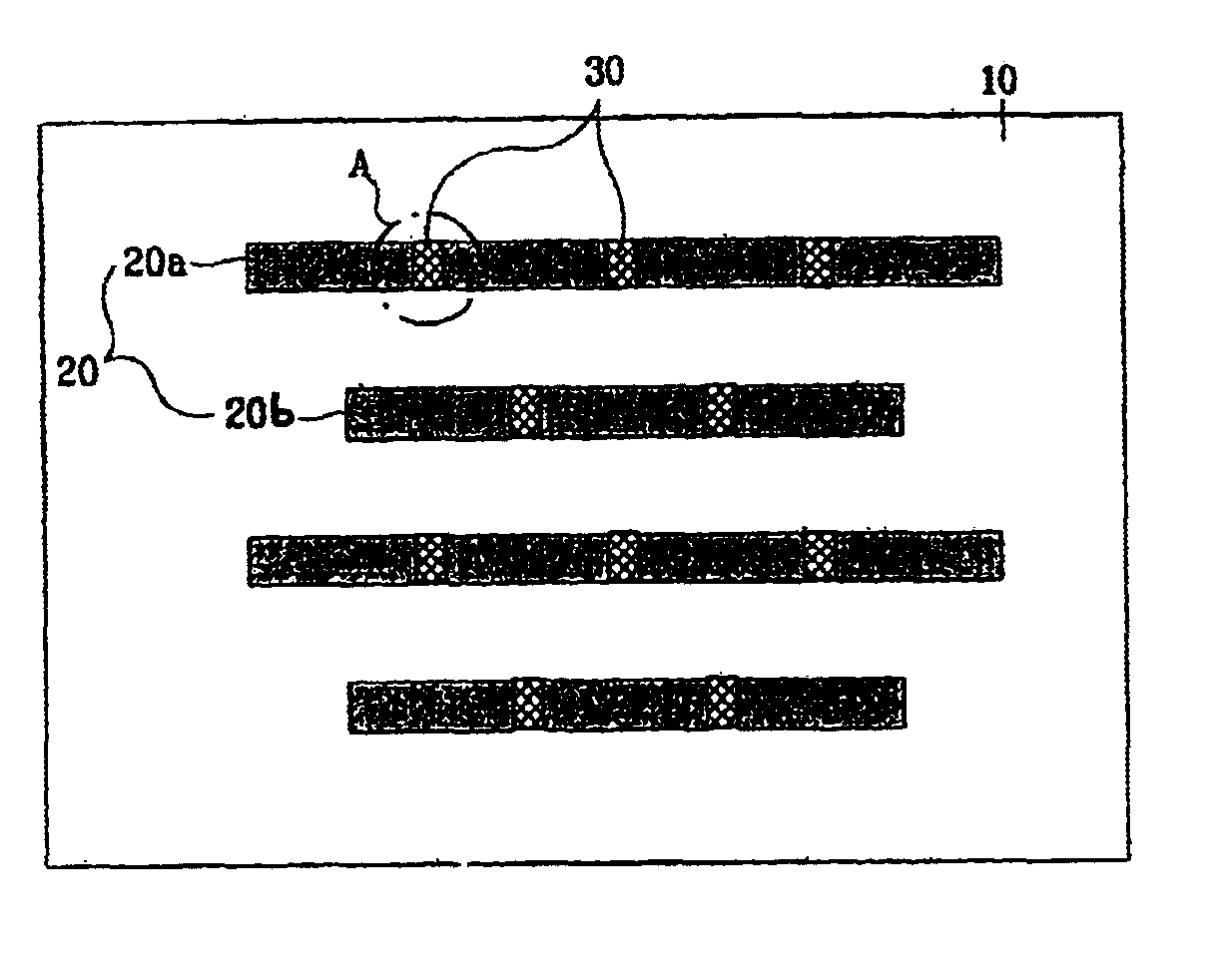
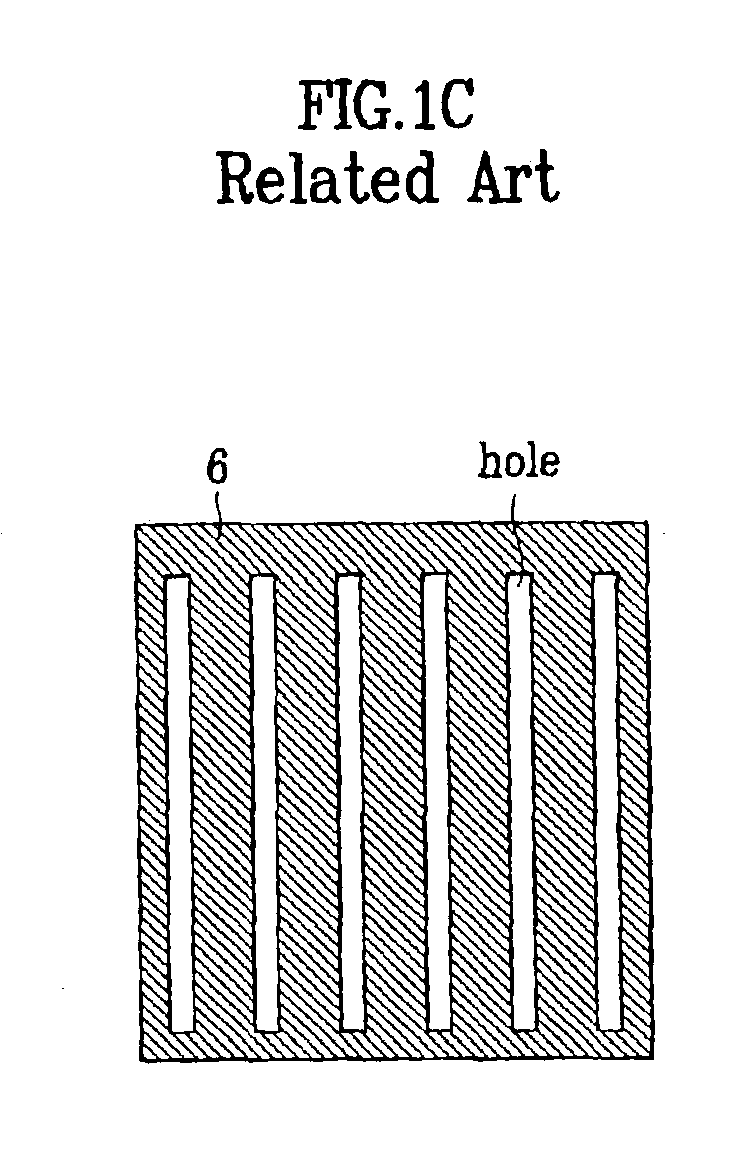
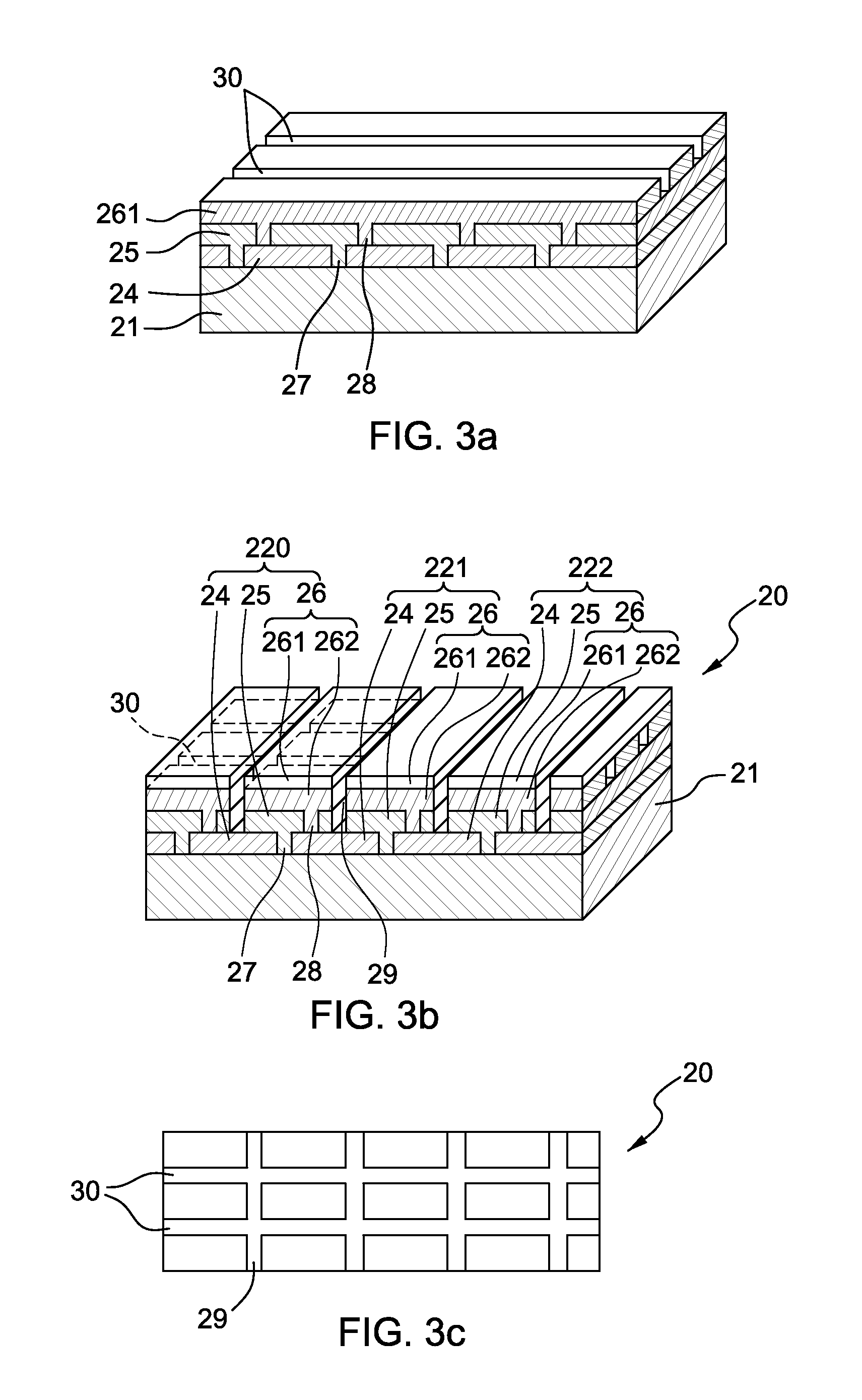
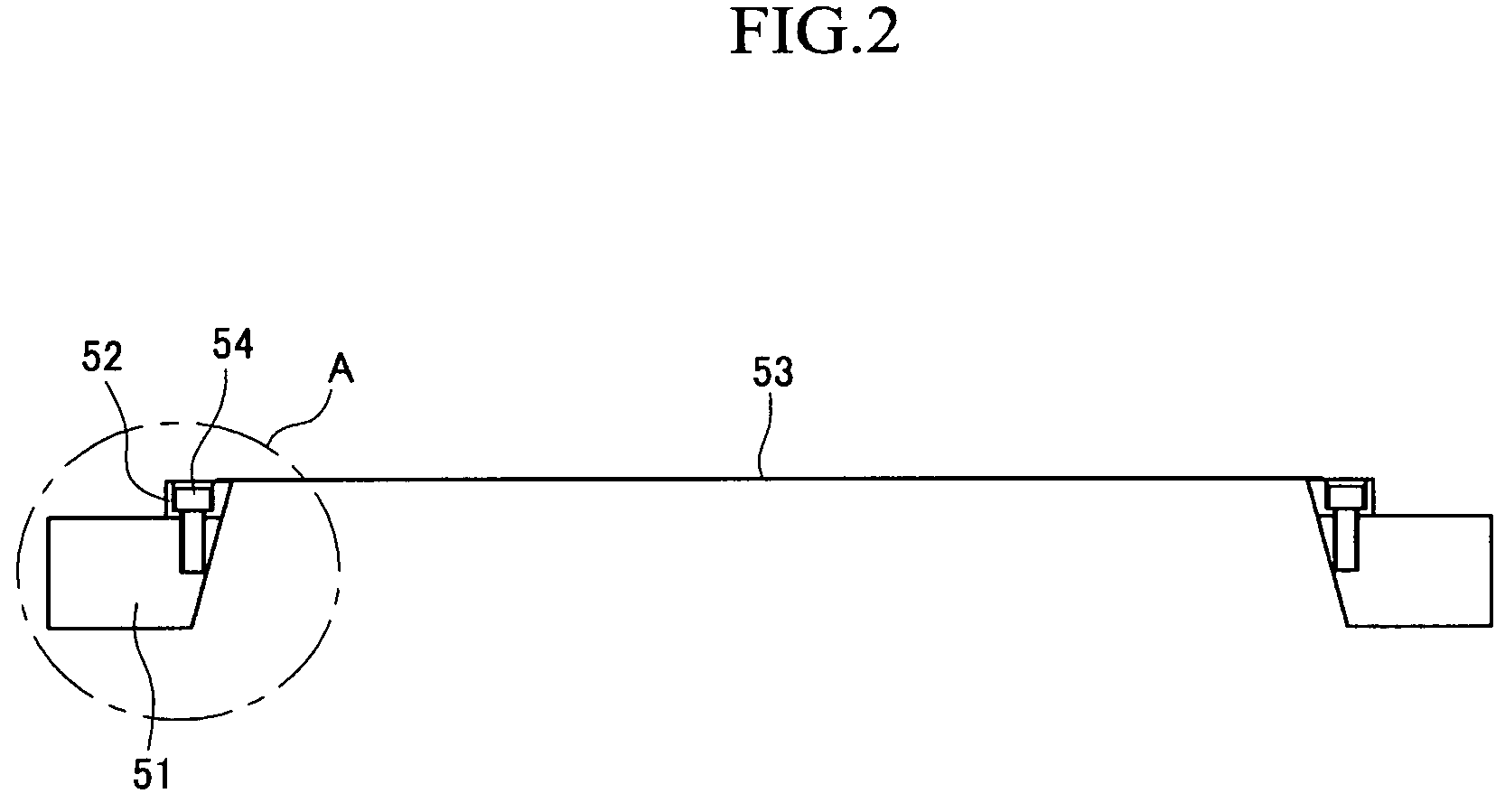
Shadow mask and flat display fabricated by using the same and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS6946783B2Avoid deformationFine apertureElectroluminescent light sourcesElectrode and associated part arrangementsDisplay deviceFlat panel display
Shadow mask, flat display fabricated by using the same, and method for fabricating the flat display, the shadow mask including a substrate, a plurality of via holes formed in the substrate on a plurality of rows, inclusive of first via holes on odd numbered rows, and second via holes on even numbered rows, wherein the first via holes are arranged to straddle the second via holes, and bridges formed between the first via holes, and between the second via holes, thereby improving an aperture.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Deposition device
InactiveUS20070087130A1Improve throughputWell formedVacuum evaporation coatingSolid-state devicesEvaporationEngineering
It is an object of the present invention to provide a deposition device that can selectively form a thin film without using a shadow mask with respect to a substrate having a large size. In the deposition device, an evaporation source is provided with a cylinder cell, a heater for heating a lower part of the cylinder cell, and a heater for heating an upper part of the cylinder cell. A hot plate can control a temperature by a heater provided inside thereof. The hot plate heats an evaporation material supplied into the cylinder cell from a material supply portion that is connected to the cylinder cell, and vaporizes the evaporation material by evaporation or sublimation. A rotating mechanism for rotating the hot plate in the cylinder cell may be provided to achieve uniformity of a temperature. A heater for heating the material supply potion may be provided to raise a temperature of the evaporation material supplied into the cylinder cell. By such an evaporation source, deposition can be uniformly and continuously performed with respect to a substrate having a large size.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Shadow Mask Methods For Manufacturing Three-Dimensional Thin-Film Solar Cells
InactiveUS20100304521A1Eliminate and reduce disadvantageEliminate and reduce and problemSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationDopantSemiconductor
Methods for manufacturing three-dimensional thin-film solar cells using a template. The template comprises a template substrate comprising a plurality of three-dimensional surface features. The three-dimensional thin-film solar cell substrate is formed by forming a sacrificial layer on the template, subsequently depositing a semiconductor layer, selectively etching the sacrificial layer, and releasing the semiconductor layer from the template. Select portions of the three-dimensional thin-film solar cell substrate are then doped with a first dopant, while other select portions are doped with a second dopant. Next, selective emitter and base metallization regions are formed using a PECVD shadow mask process.
Owner:BEAMREACH SOLAR INC
Deposition Method and Method for Manufacturing Light Emitting Device
InactiveUS20090104721A1Improve productivityAccurate shapeElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesProduction rateEvaporation
An object is to provide a deposition method by which a film having a desired shape can be formed with high productivity. Further, a method for manufacturing a light emitting device by which a light emitting device having high definition can be manufactured with high productivity is provided. Specifically, even in the case of using a large-sized substrate, a method for manufacturing a light emitting device having high definition is provided. By using a deposition target substrate and a shadow mask having a smaller area than the deposition target substrate, the deposition target substrate and the shadow mask are aligned with each other, and an evaporation material is deposited on at least part of the deposition target substrate through a plurality of deposition steps. As an evaporation source, a light absorption layer and a supporting substrate having the evaporation material is preferably used.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Process for making partially transparent photovoltaic modules
InactiveUS20100279458A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationScreen printingRoll-to-roll processing
A process for making a partially transparent photovoltaic cell or a partially transparent photovoltaic module comprising series-connected or parallel-connected photovoltaic cells comprises the step of forming a patterned back electrode(s) by screen printing, jet printing, roll-to-roll processing or depositing through a shadow mask with openings. The pattern of the back electrode is determined at the same time when the back electrode is disposed, such that the complexity and cost of the process can be reduced.
Owner:DU PONT APOLLO
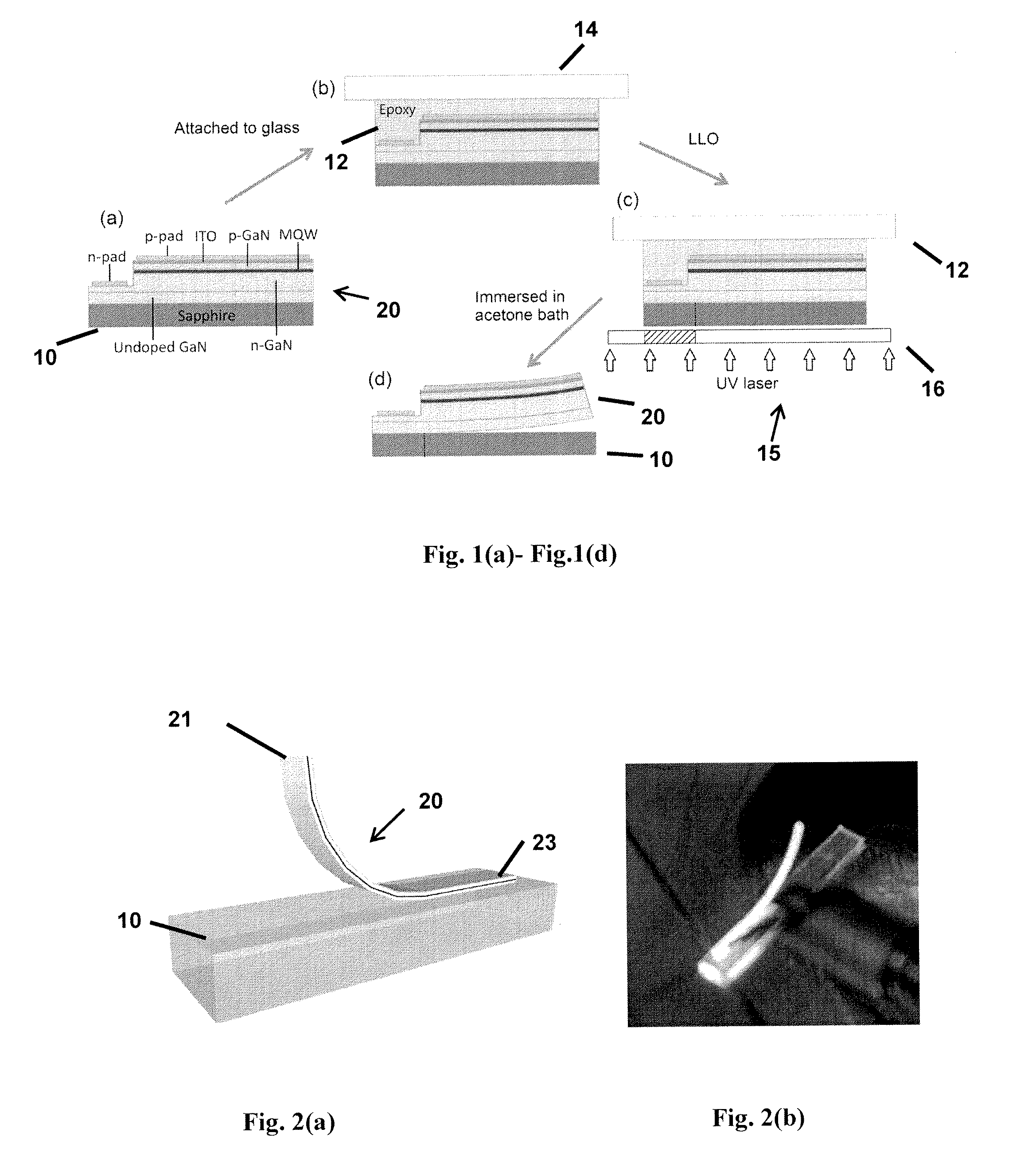
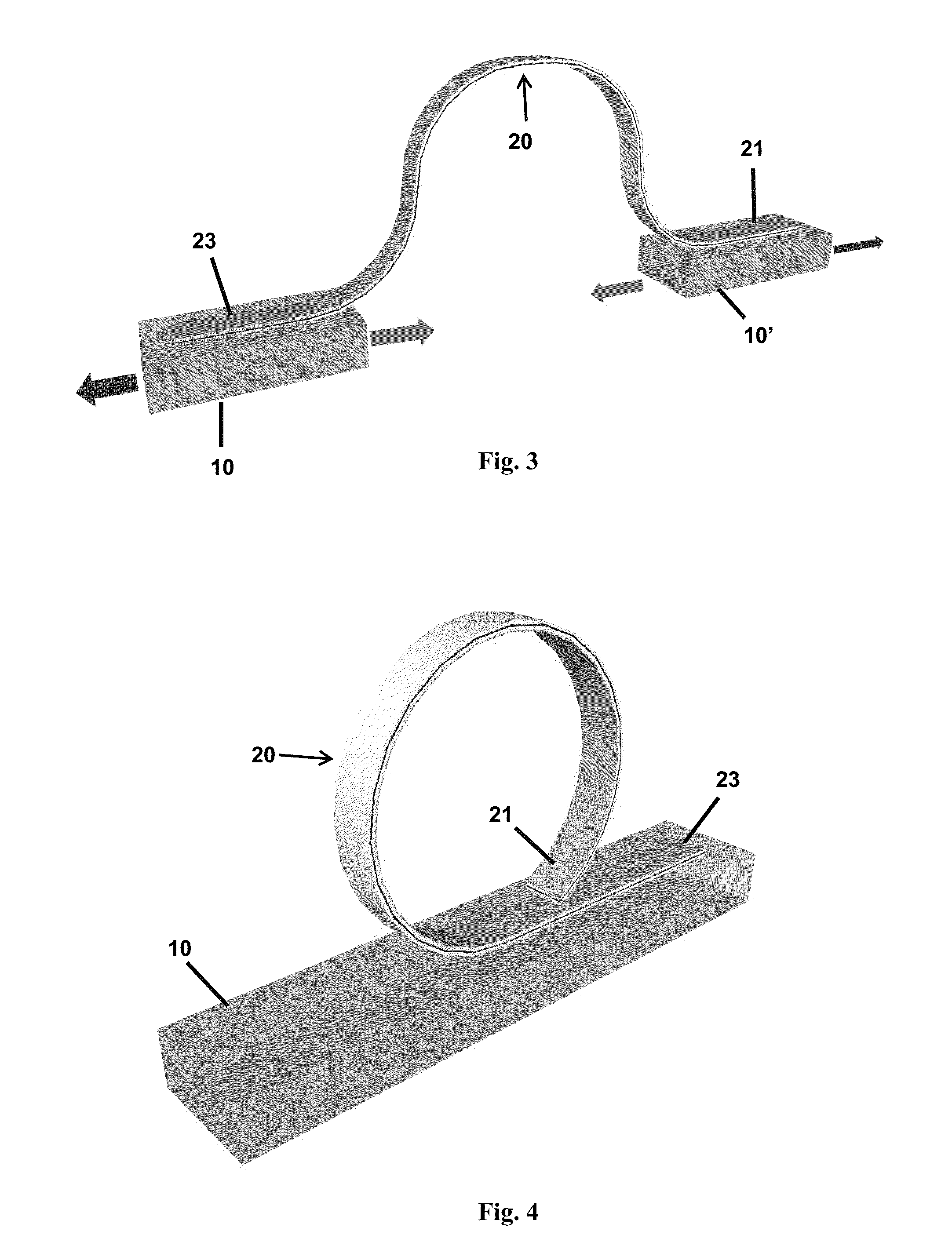
Flexible GAN light-emitting diodes
Methods of fabricating flexible, free-standing LED structures are provided. An LED structure can be formed on a sapphire substrate, and the surface of the LED structure can then be coated with epoxy and attached to a rigid supporting substrate. A laser lift-off process can be performed using an ultraviolent beam from a high-power pulsed-mode laser and a shadow mask, causing at least a portion of the LED structure to separate from the sapphire substrate. The structure can then be immersed in an acetone bath to dissolve the epoxy and separate the structure from the supporting substrate.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
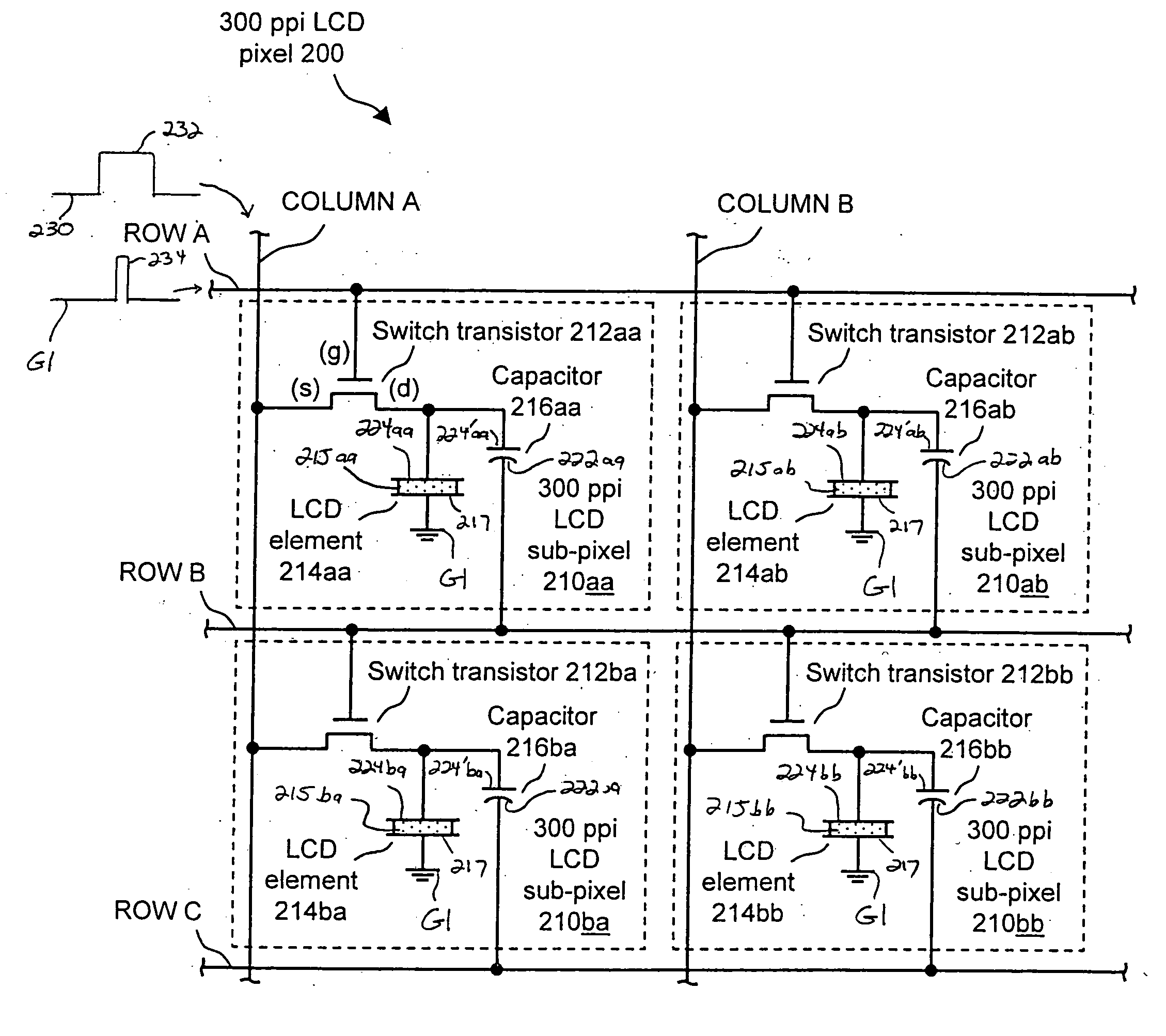
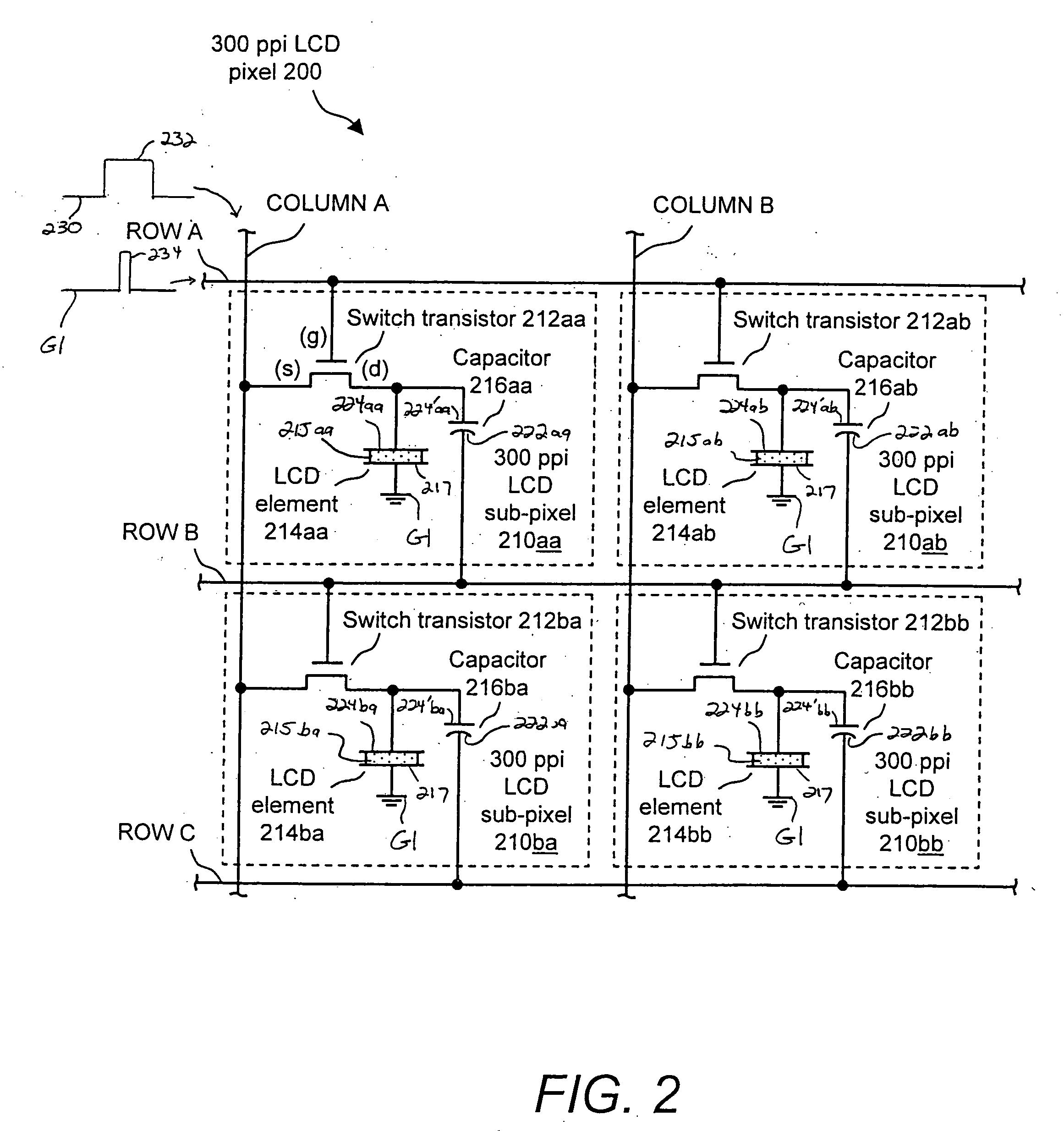
Shadow mask deposition system for and method of forming a high resolution active matrix liquid crystal display (LCD) and pixel structures formed therewith
InactiveUS20060152641A1Solid-state devicesNon-linear opticsActive-matrix liquid-crystal displayLiquid-crystal display
An LCD pixel includes a first conductive segment connected to a first bus, a first insulator segment on the first conductive segment, a second conductive segment on the first insulator segment, a liquid crystal material on the second conductive segment, a third conductive segment on the liquid crystal material, and a thin film transistor having a control terminal, a first power terminal and second power terminal connected to a second bus, a third bus and the second conductive segment, respectively. In response to application of a suitable signal on the second bus when reference voltages are present on the first bus and on the third conductive segment, and a voltage is applied to the third bus, the thin film transistor is operative for charging a capacitor formed by the first conductive segment, the first insulator segment and the second conductive segment and for activating the liquid crystal material.
Owner:ADVANTECH GLOBAL LTD
Imprinting nanoscale patterns for catalysis and fuel cells
ActiveUS7445742B2Improve battery efficiencyEfficient andMaterial nanotechnologyElectrode manufacturing processesElectrochemistryNanostructure
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Mask and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20070190889A1Electroluminescent light sourcesVacuum evaporation coatingEngineeringShadow mask
A mask that facilitates OLED processing and is capable of being made cost-effectively is presented. The mask includes a mask frame, a connection frame fastened to the mask frame, a mask plate welded to the connection frame, and a plurality of fastening members that fasten the connection frame to the mask frame. The connection frame, which is capable of being welded to the mask plate, is interposed between the mask plate and the mask frame to create a tension in the mask plate. Thus, it is possible to manufacture a shadow mask that does not sag. The mask frame may be formed with a light metal such as aluminum.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Fabrication of nanometer size gaps on an electrode
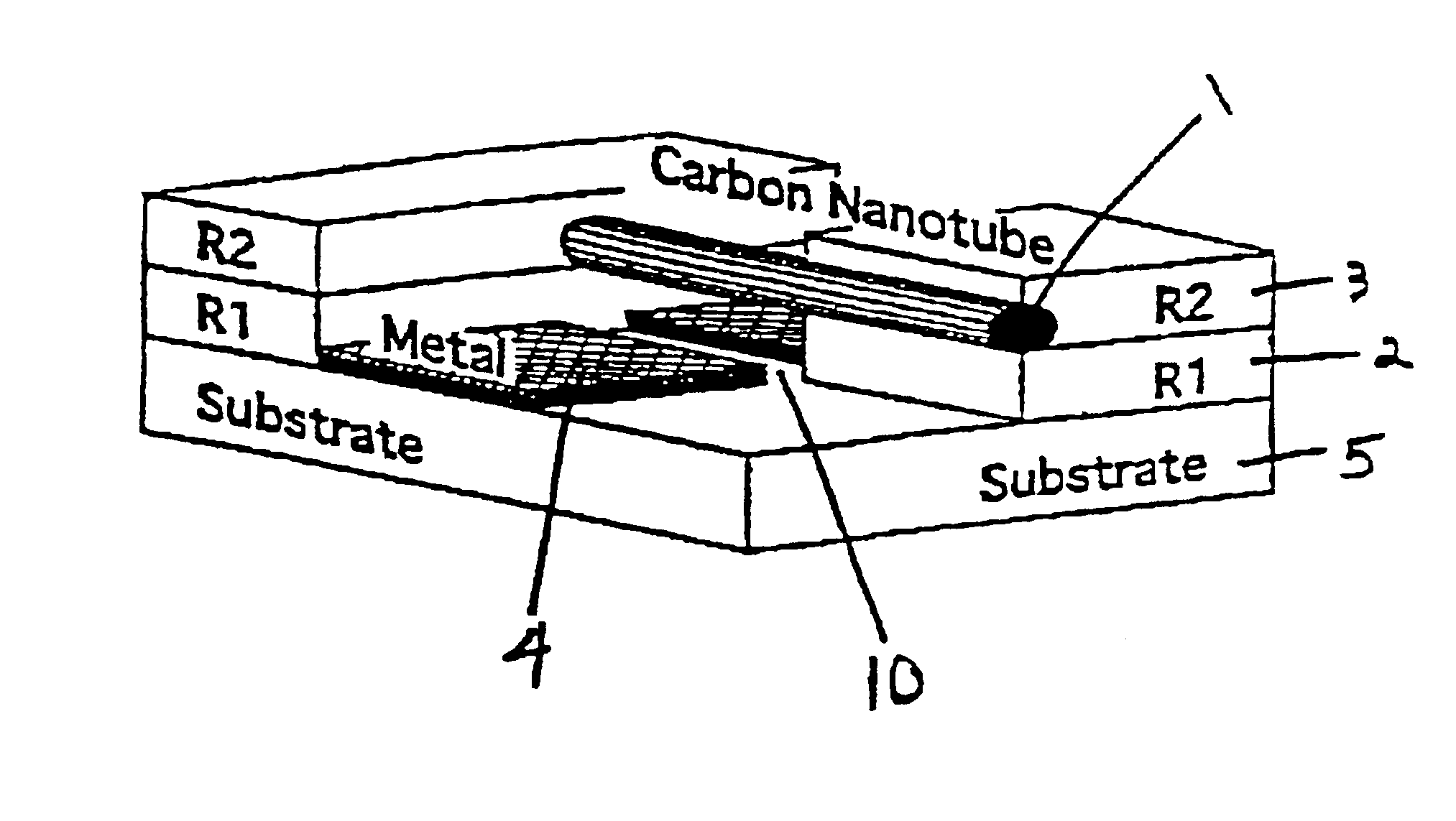
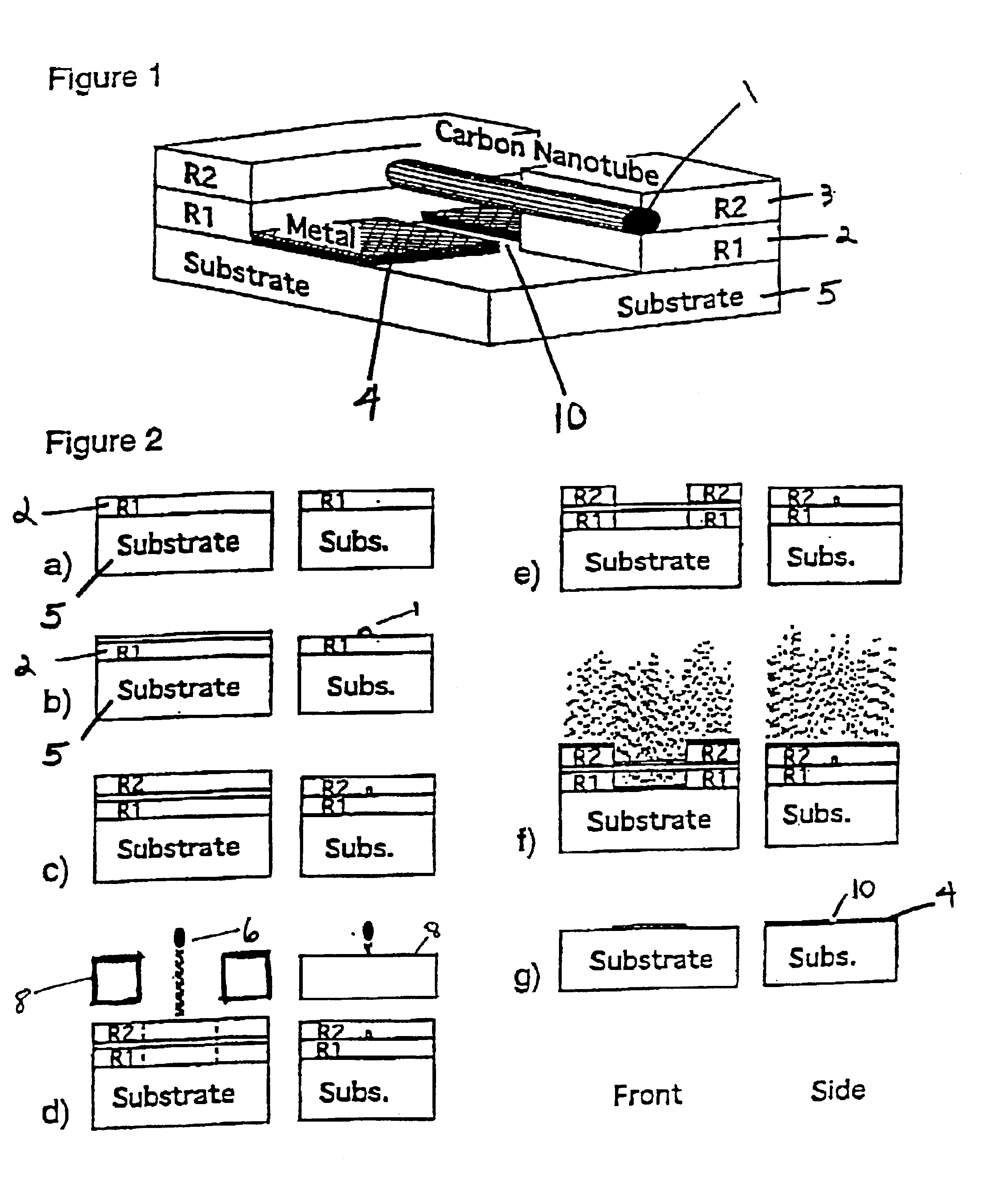
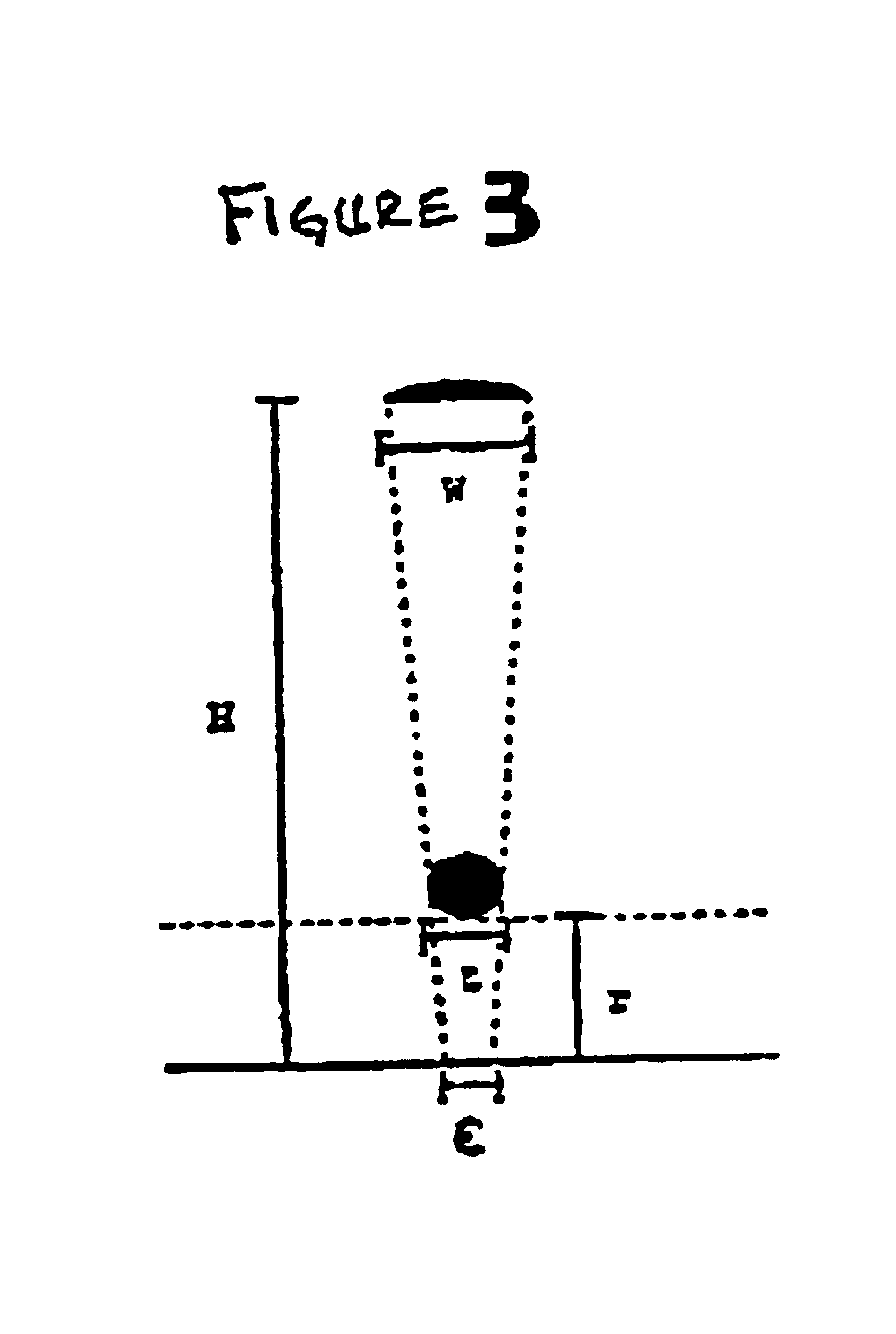
InactiveUS6897009B2Photo-taking processesNanoinformaticsField-effect transistorElectron-beam lithography
A shadow mask method to fabricate electrodes with nanometer scale separation utilizes nanotubes (NTs). Metal wires with gaps are made by incorporating multi-wall carbon nanotubes (MWNTs) or single-wall carbon nanotubes (SWNTs) (or bundles thereof) into a tri-layer electron beam lithography process. The simple, highly controllable, and scaleable method can be used to make gaps with widths between 1 and 100 nm. Electronic transport measurements performed on individual SWNTs bridge nanogaps smaller than 30 nm. Metallic SWNTs exhibit quantum dot behavior with an 80 meV charging energy and a 20 meV energy level splitting. Semiconducting SWNTs show an anomalous field effect transistor behavior.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Method and device for producing a coupling grating for a waveguide
InactiveUS20040042724A1Reduce contrastAdequate averagingCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideDiffraction effectEffective solution
The invention relates to a method and a device for producing a coupling grating (5) for a waveguide. The method relies on the technique of interference lithography, whereby an interference pattern on a light-sensitive layer (2) is exposed by superimposing two coherent light beams (3, 4) on said light-sensitive layer (2). Said pattern is then transferred onto the surface of the substrate (1) that lies underneath by subsequent developing and an etching process. The method is characterized in that it uses a shadow mask (6) that is mounted at minimum clearance relative to the surface of the light-sensitive layer (2). By observing said minimum clearance, the Fresnel diffraction images of both light beams (3, 4) are separated on the edge(7). The thickness of the light-sensitive layer (2) is selected in such a way that the superimposition of the Fresnel diffraction pattern of one light beam with the other undisturbed light beam suffices to uncover areas of the substrate (1) during subsequent developing of the layer (2). The method makes it possible to avoid transfer of unwanted diffraction effects on the edge of the shadow mask to the substrate. The method provides a cost-effective solution for the production of large-surface coupling grating matrices.
Owner:GOMBERT ANDREAS +2
Spatially modulated detector for radiation
InactiveUS6157035AIncrease speedHigh speed detectionPhotometrySolid-state devicesFiberOptical detector
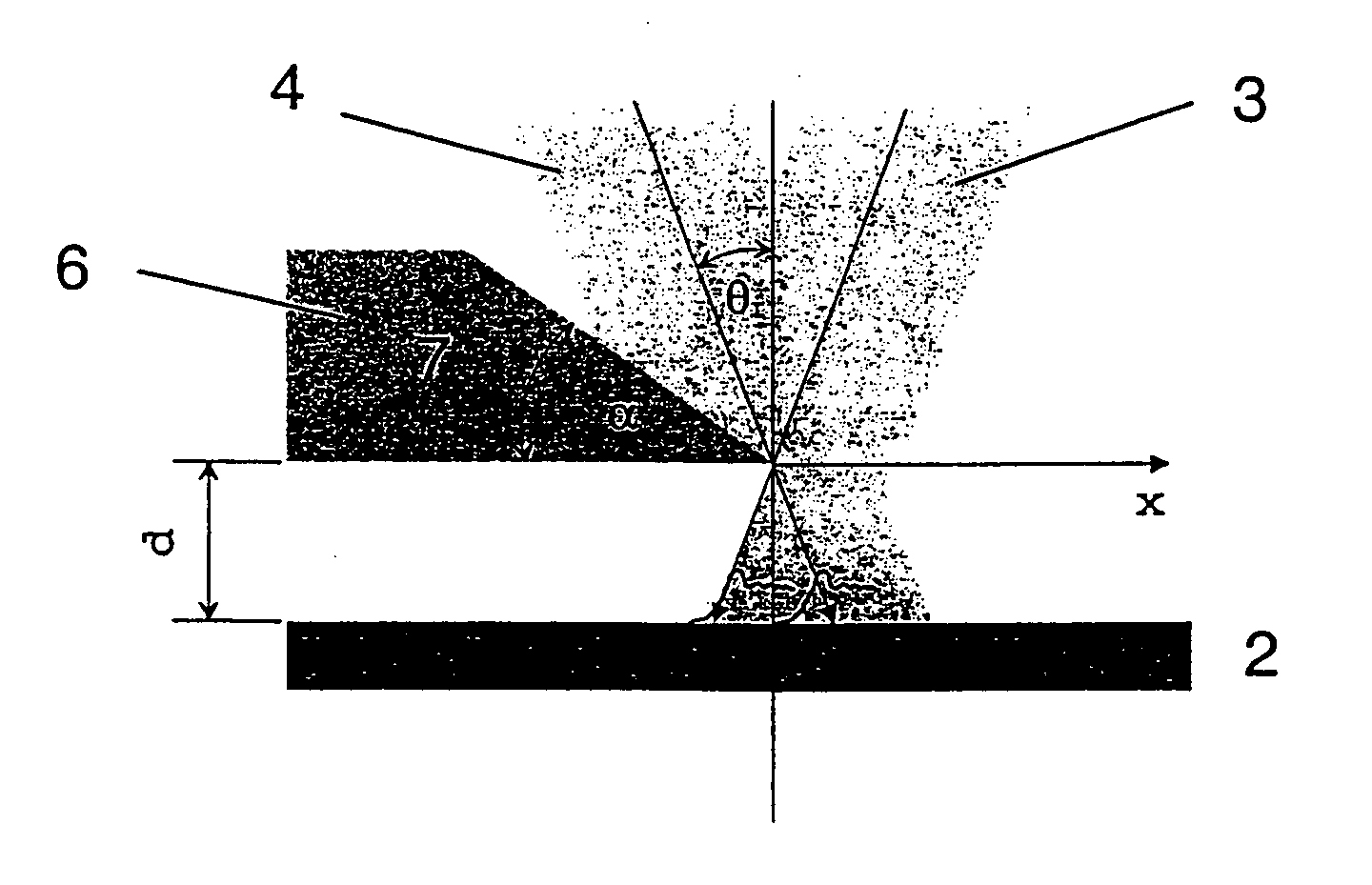
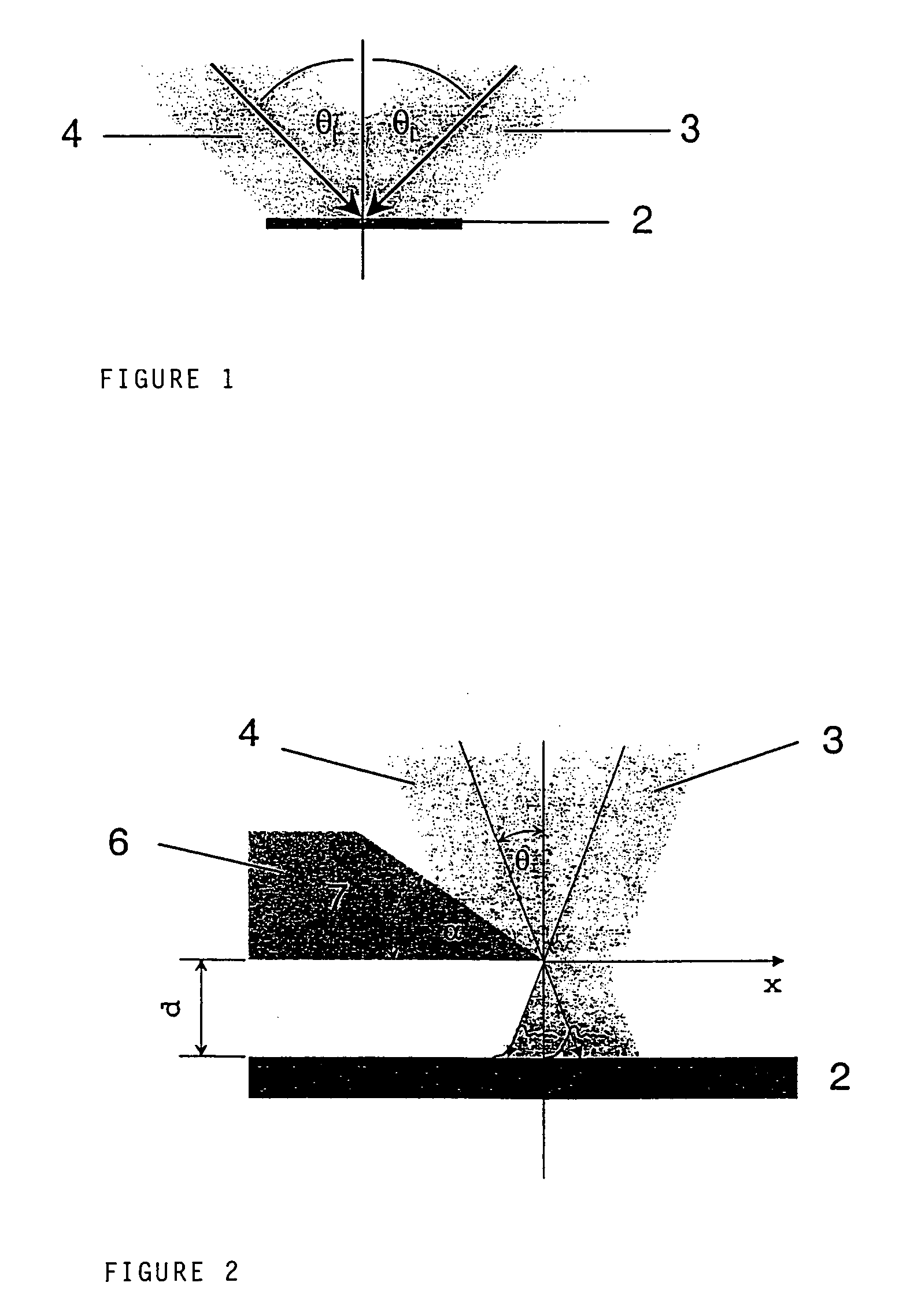
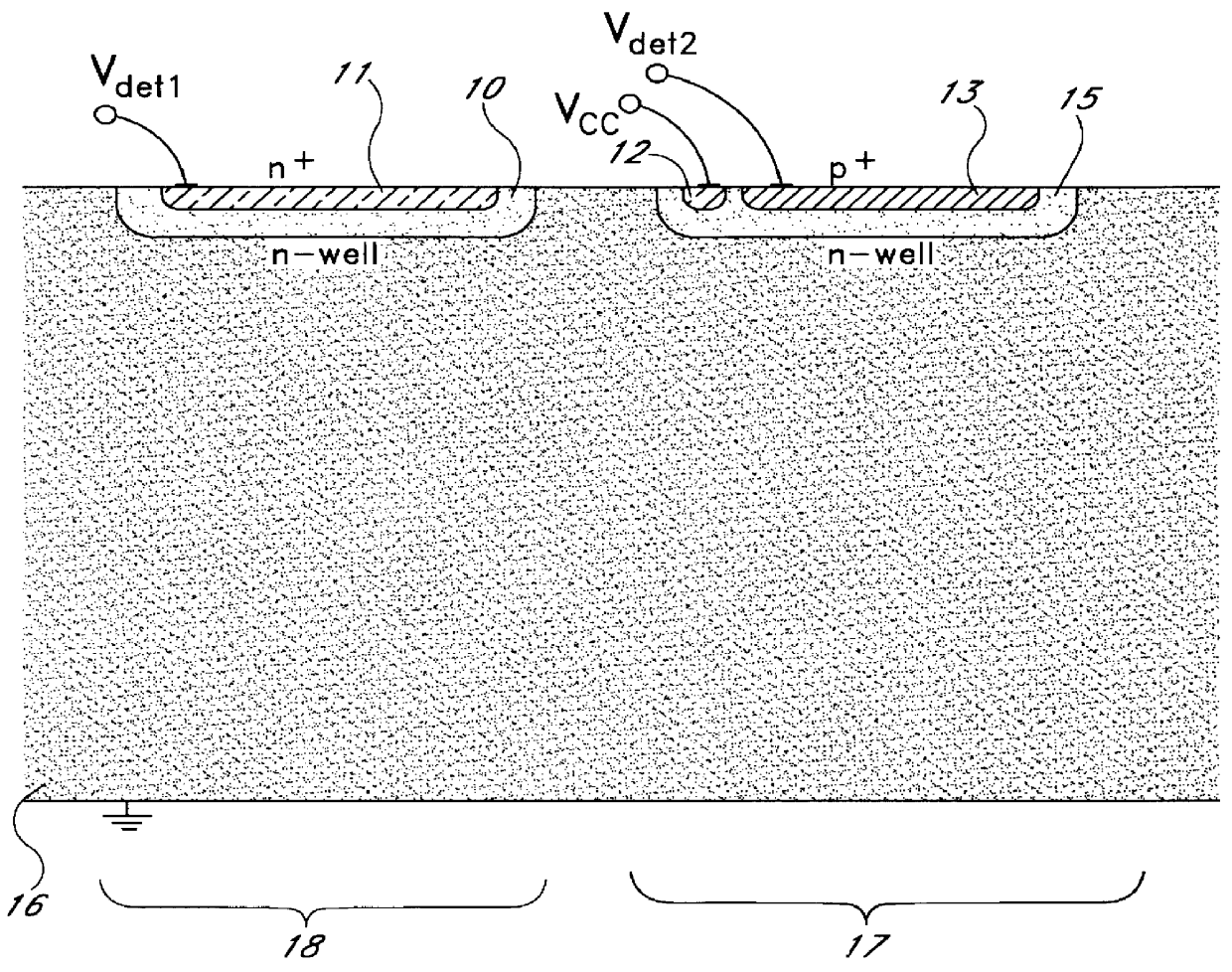
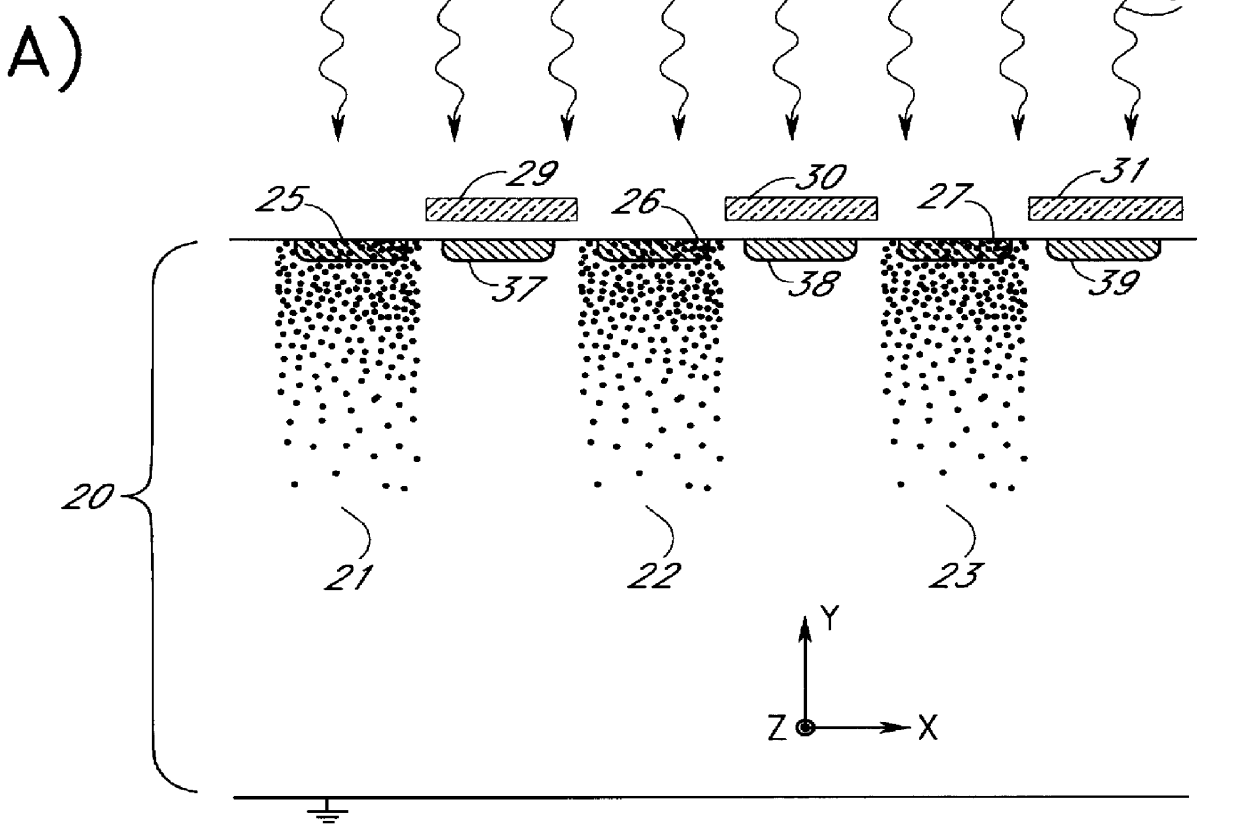
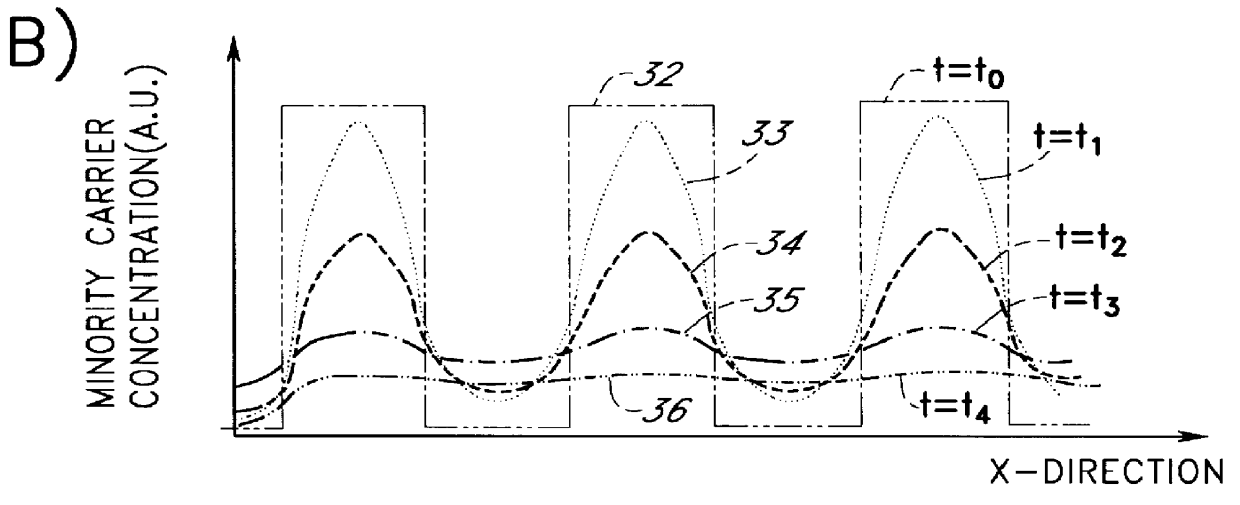
A novel radiation detector, a detection principle and an associated structure are provided for semiconductor substrate detectors in general and for CMOS based circuits in particular. For an optical detector, photons absorbed in the neutral zone of the substrate generate electron hole pairs that migrate by diffusion. A shadow mask gives a spatial modulation to the incident, and consequently, to the absorbed light in the semiconductor substrate. By measuring the magnitude of the spatial frequency component in the minority carrier distribution with a spatial frequency corresponding to that of the shadow mask, a fast detector is conceived. A shadow mask with higher spatial modulation frequency delivers a faster turn-off. The combination of a plurality of these detectors with an image fiber forms a basic system for constructing high-speed parallel optical interconnects between chips.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
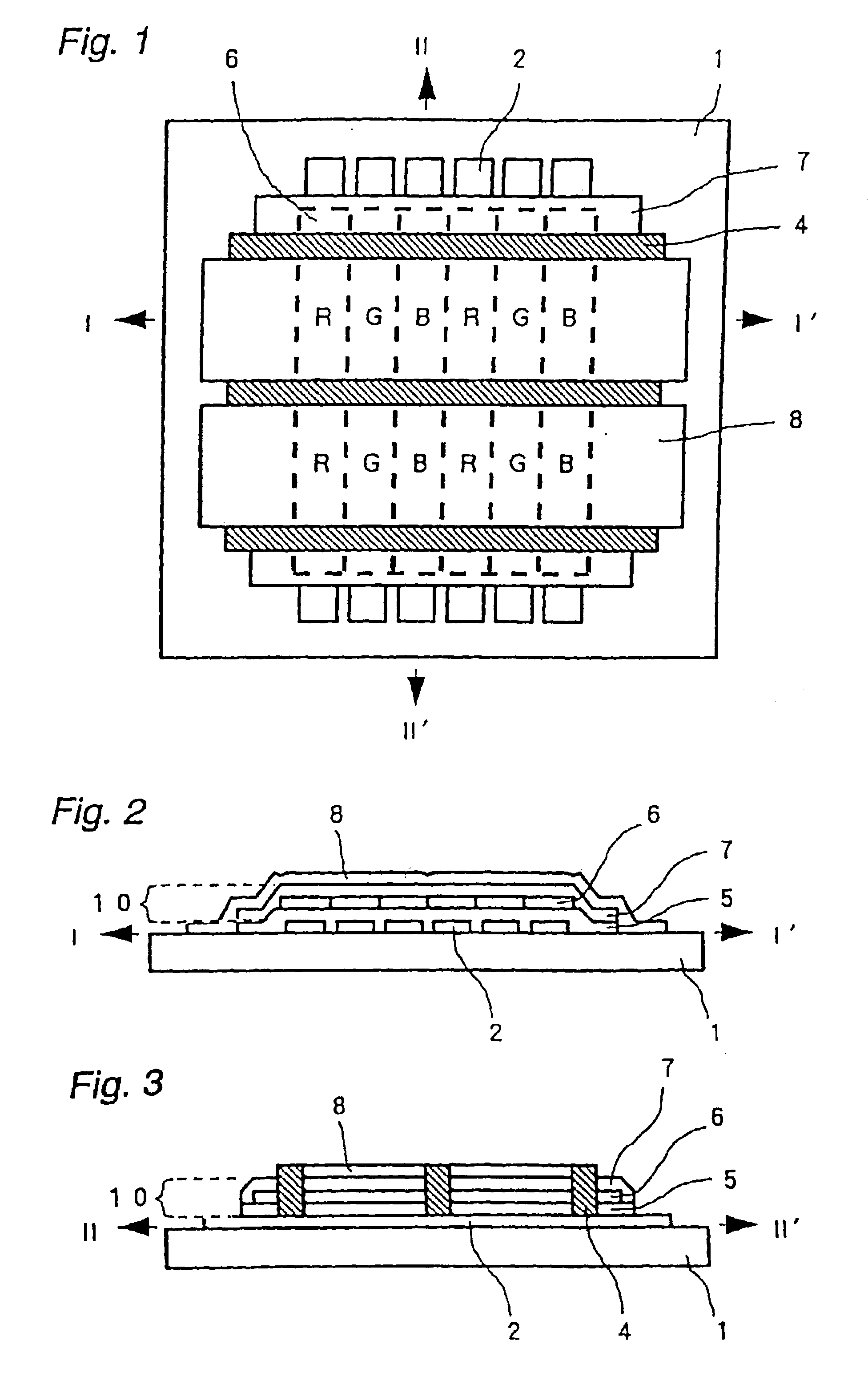
Full-color organic light emitting display and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20060060870A1Complicated processEasy alignmentIncadescent screens/filtersDischarge tube luminescnet screensOrganic layerDisplay device
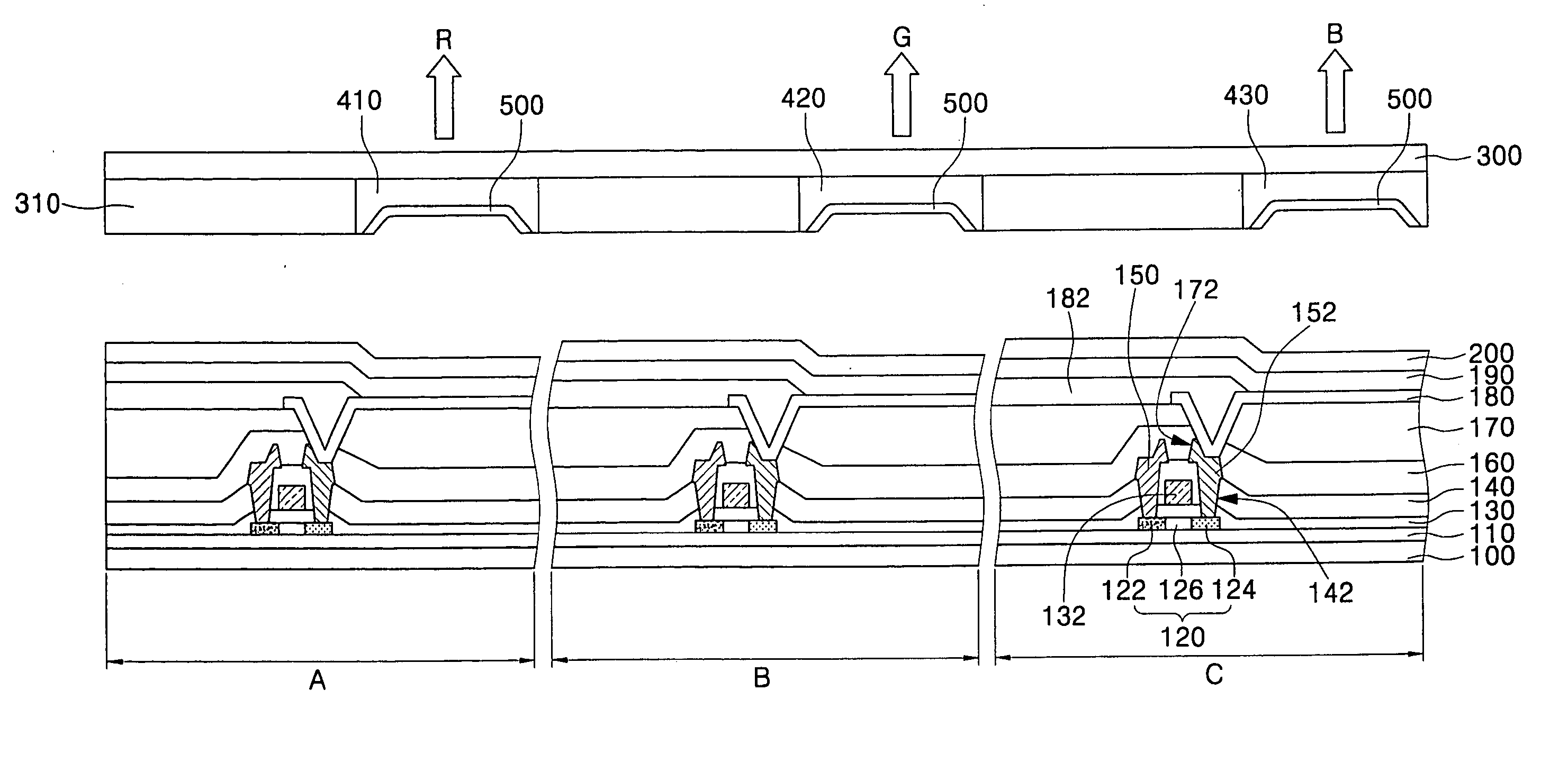
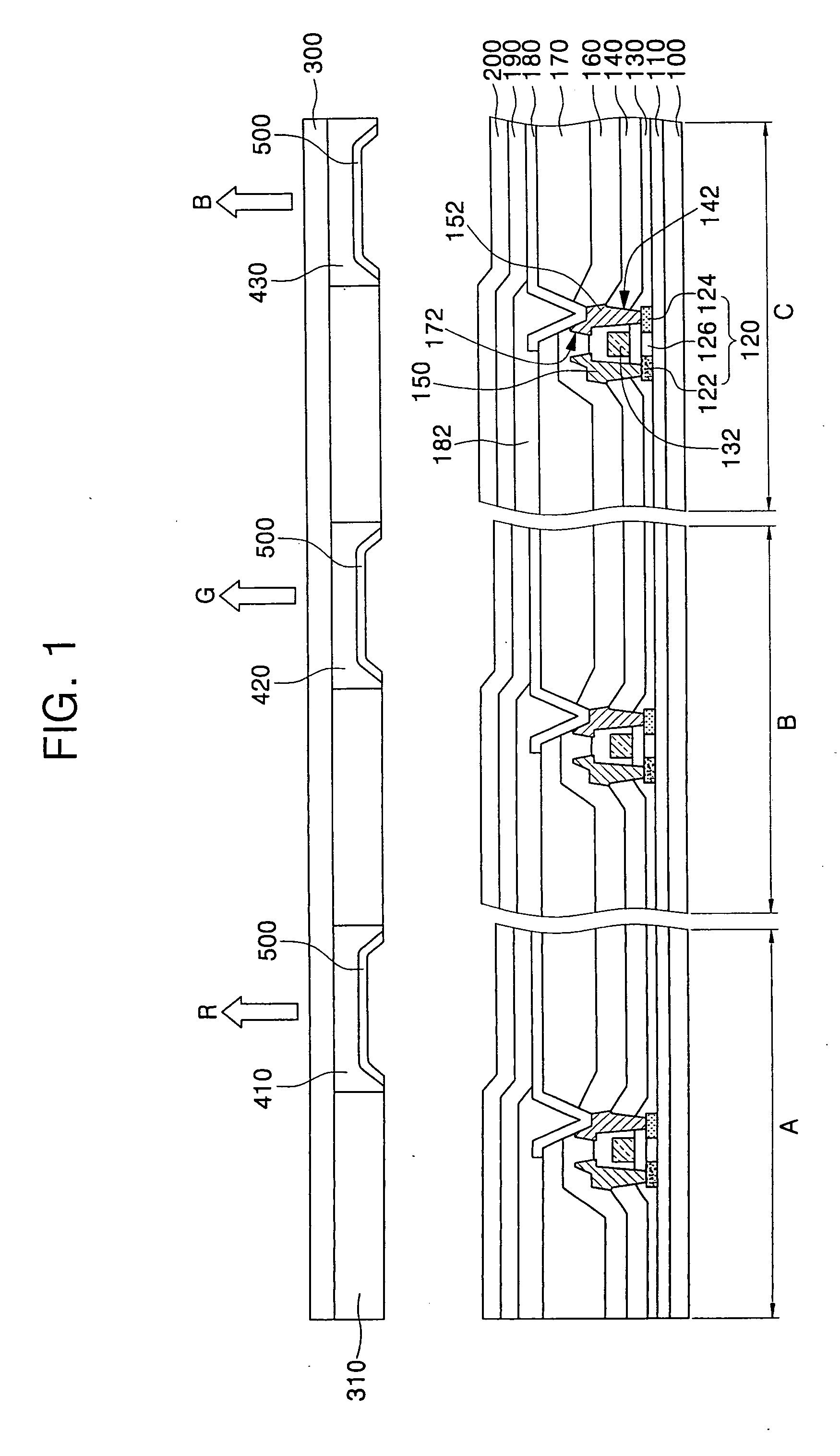
A full-color organic light emitting display (OLED) and method of fabricating the same. The display includes a substrate with a pixel electrode, an organic layer having at least an emission layer, and an opposite electrode formed thereon. An encapsulation substrate has formed thereon an organic emission layer that emits light of a single color and a black matrix that defines emission regions. A moisture absorbent material and one of color filter layers and color change mediums are formed between the black matrixes to correspond to the emission layer. The method of making alleviates the need for a separate processes for treating the moisture absorbent material and for forming the color filter layers or the color change mediums using a shadow mask.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com