Patents
Literature
711 results about "Thermal dissipation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
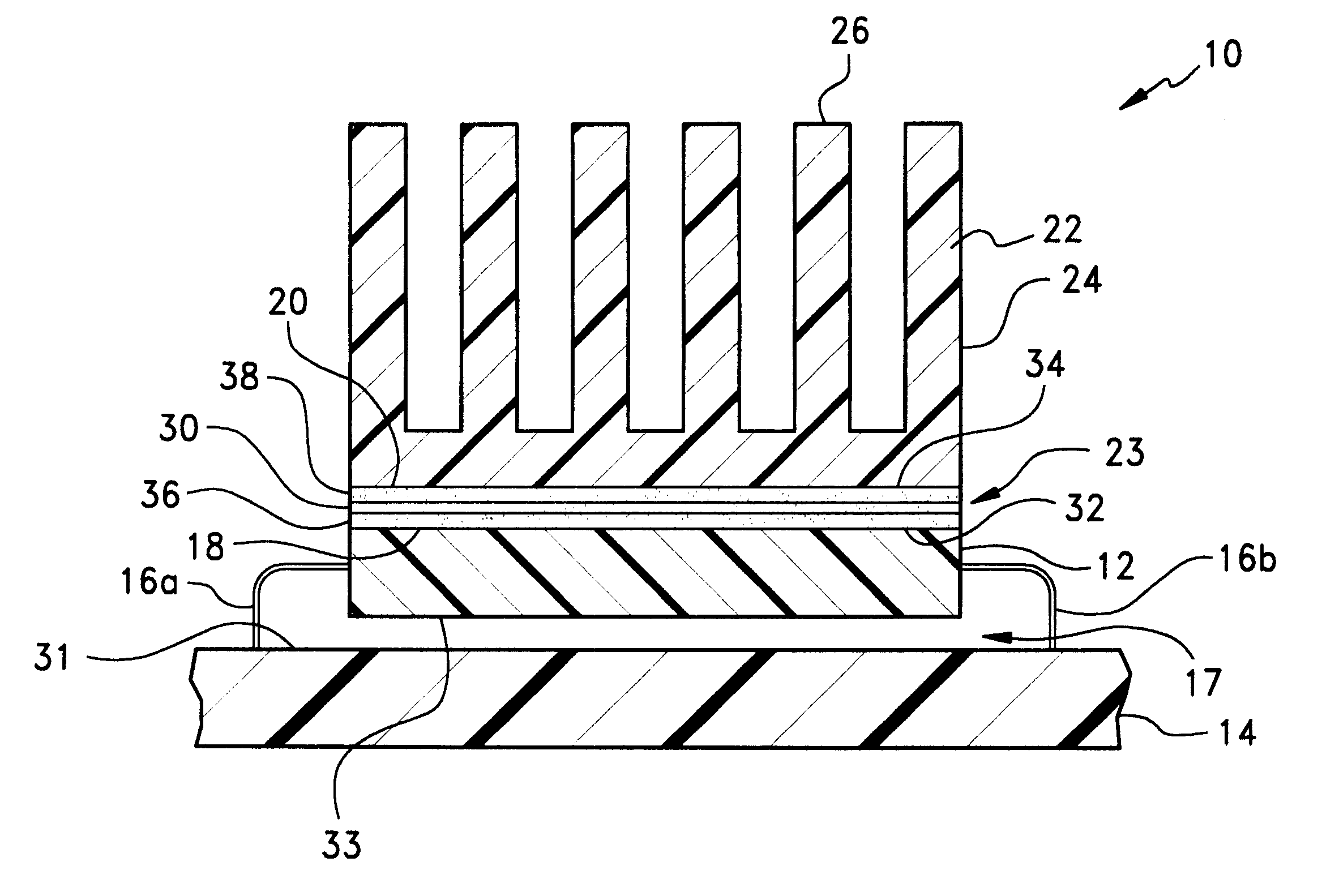
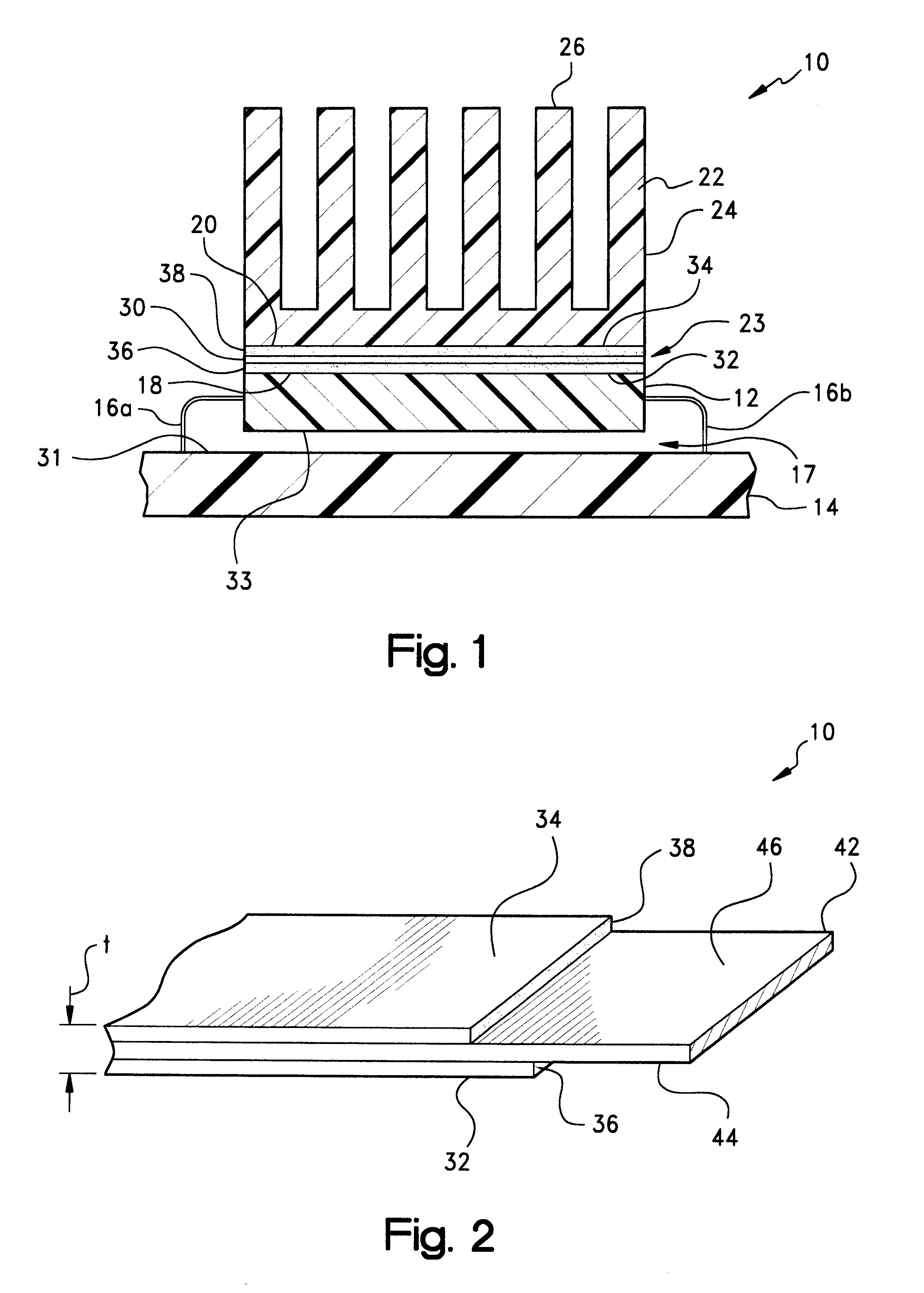
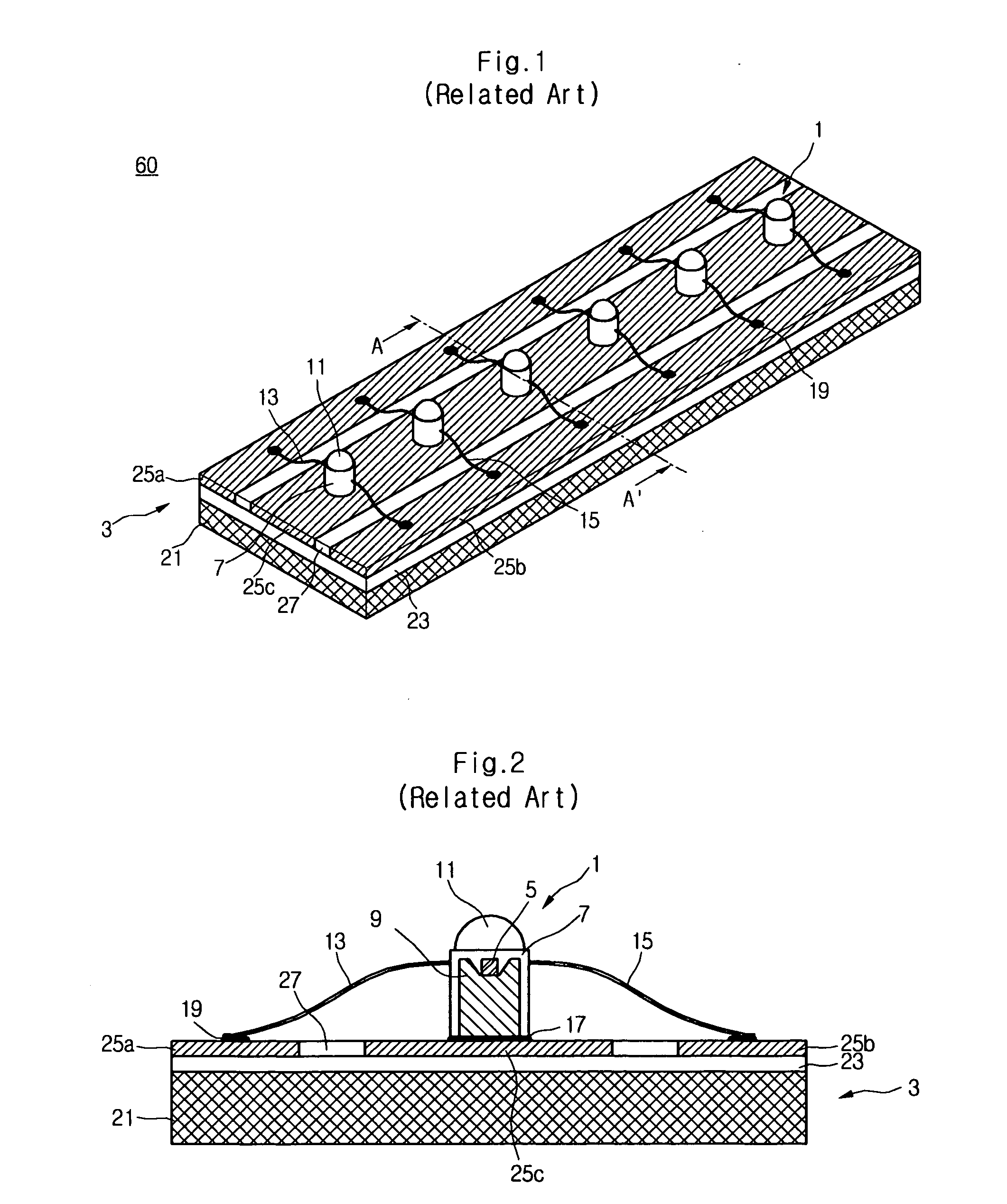
Conformal thermal interface material for electronic components
InactiveUS6054198AOptimize allocationReadily apparentSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesRoom temperatureConductive materials
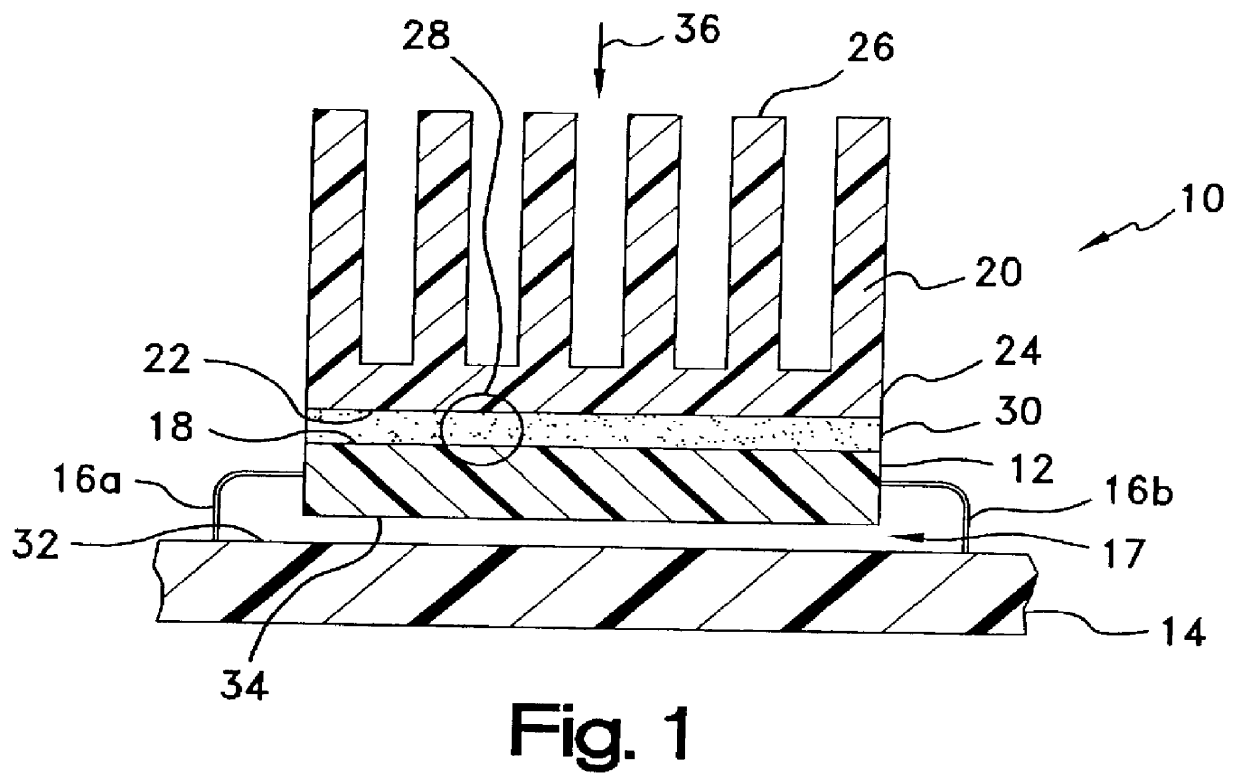
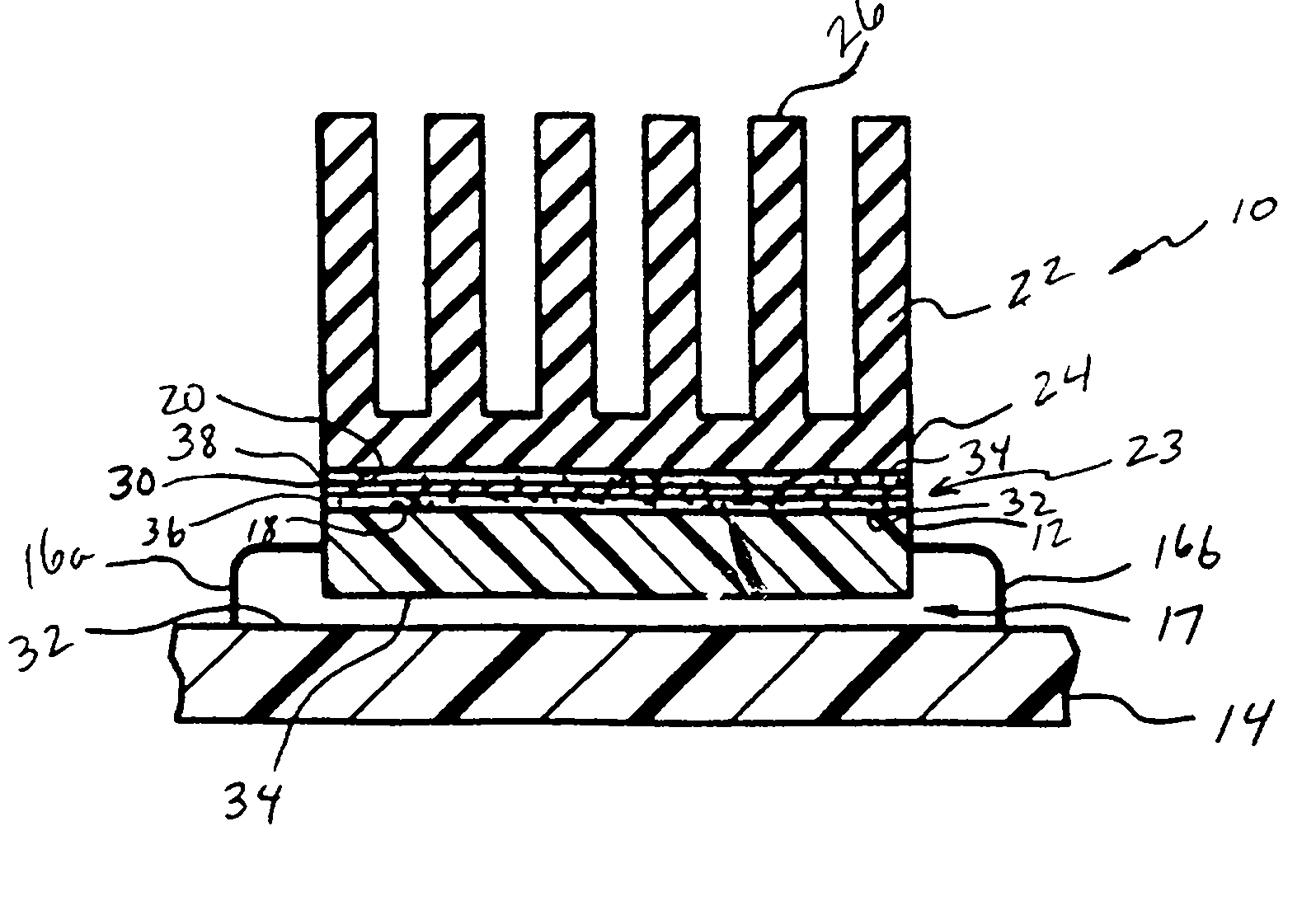
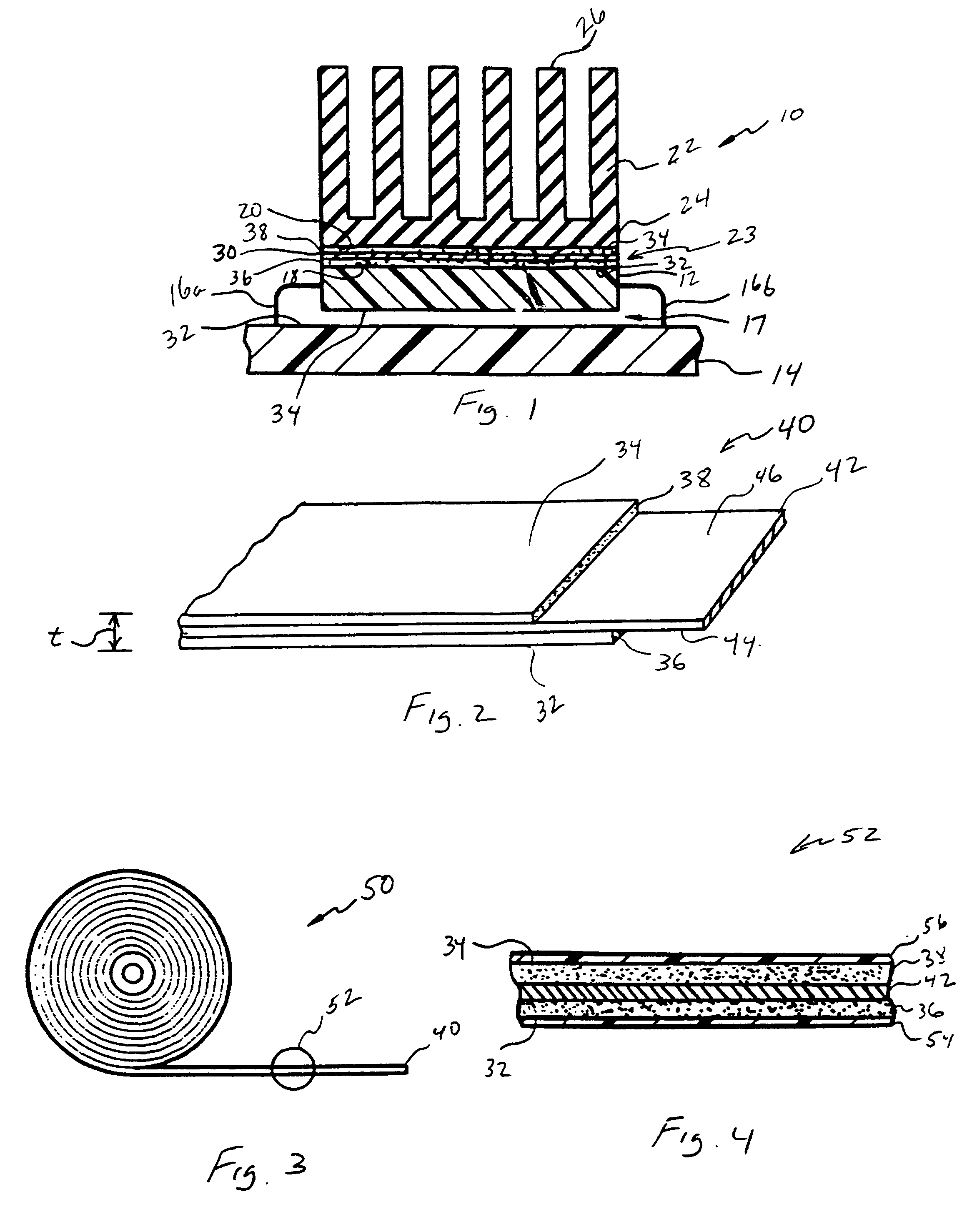
A thermally-conductive interface for conductively cooling a heat-generating electronic component having an associated thermal dissipation member such as a heat sink. The interface is formed as a self-supporting layer of a thermally-conductive material which is form-stable at normal room temperature in a first phase and substantially conformable in a second phase to the interface surfaces of the electronic component and thermal dissipation member. The material has a transition temperature from the first phase to the second phase which is within the operating temperature range of the electronic component.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
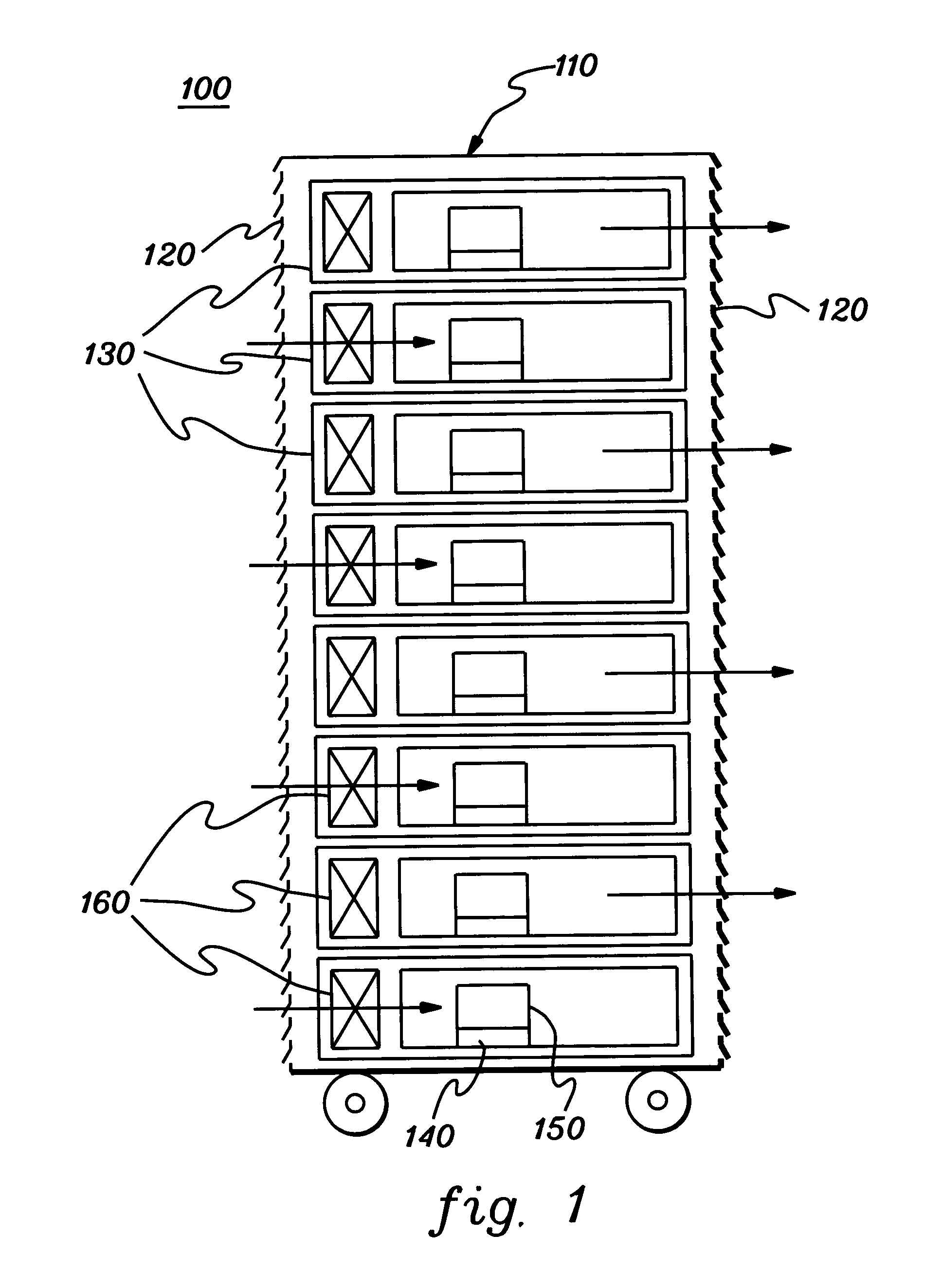
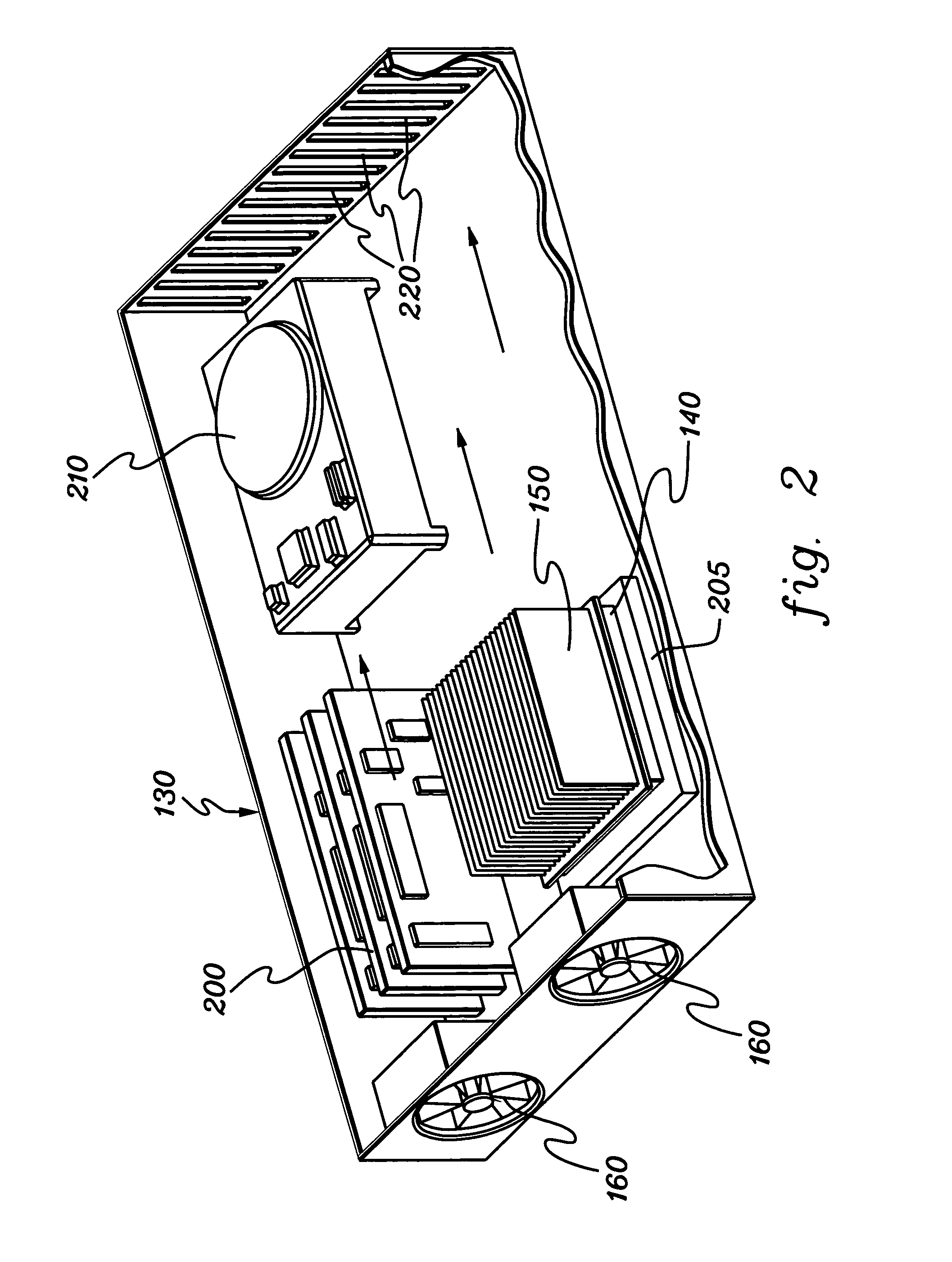
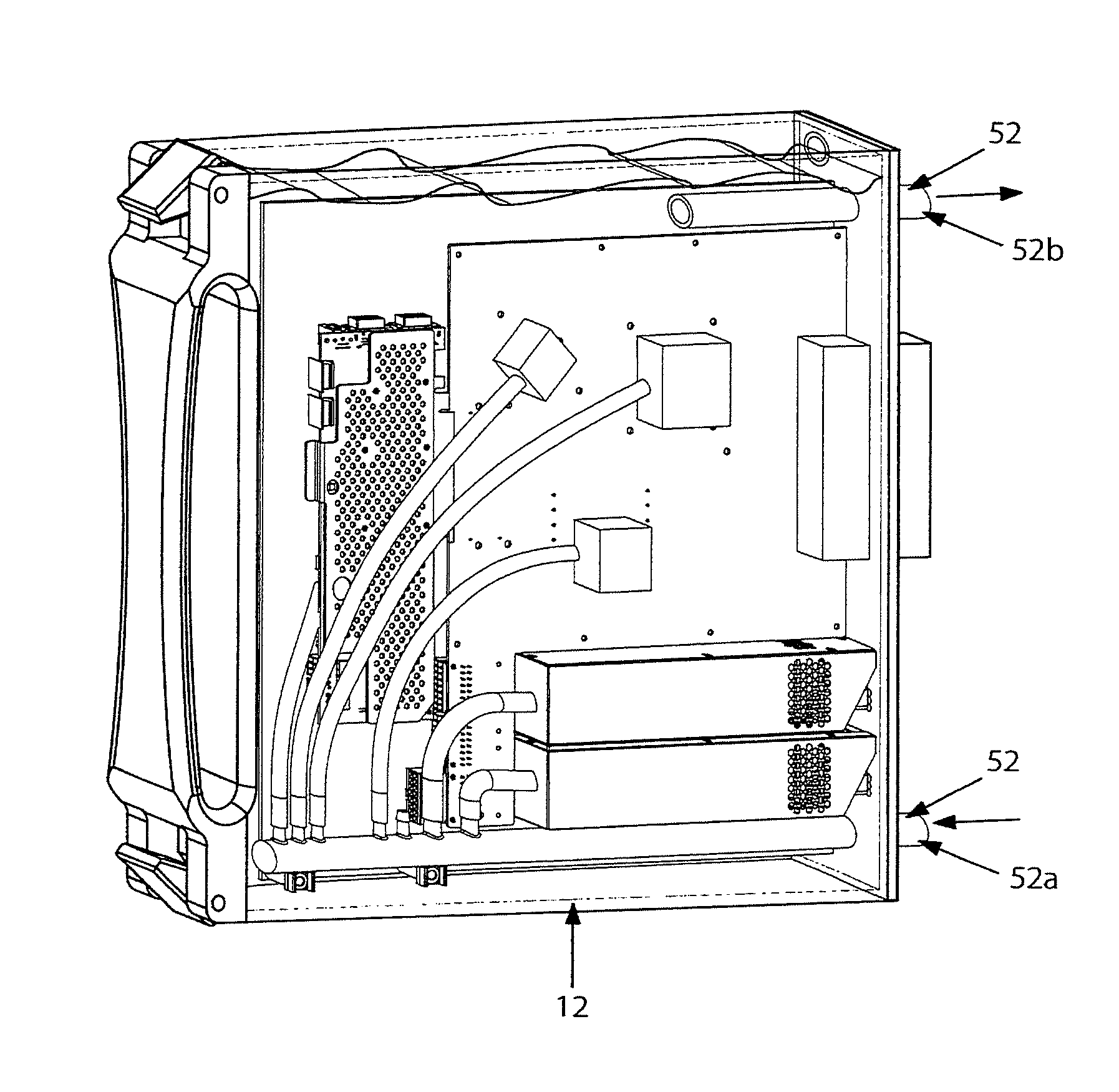
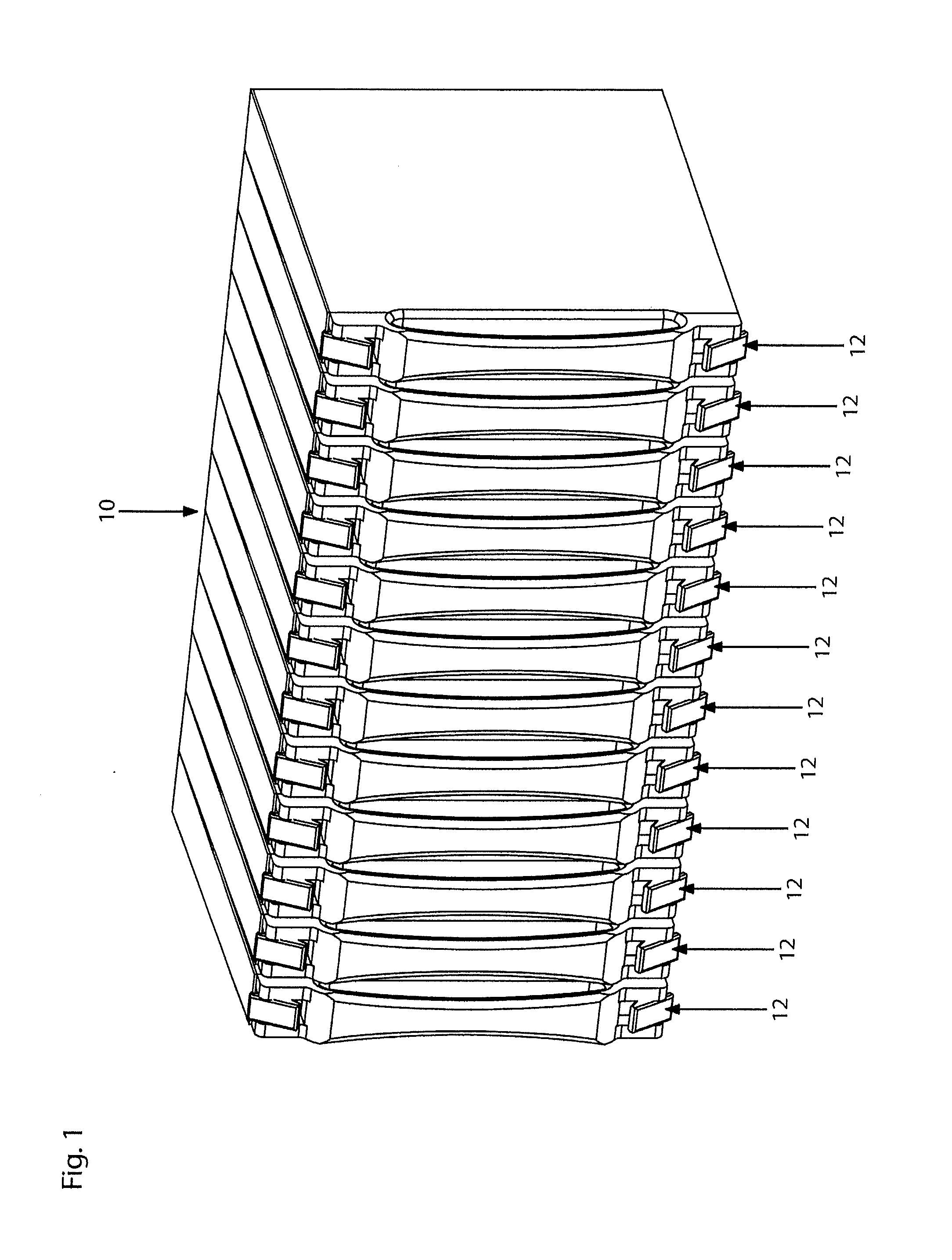
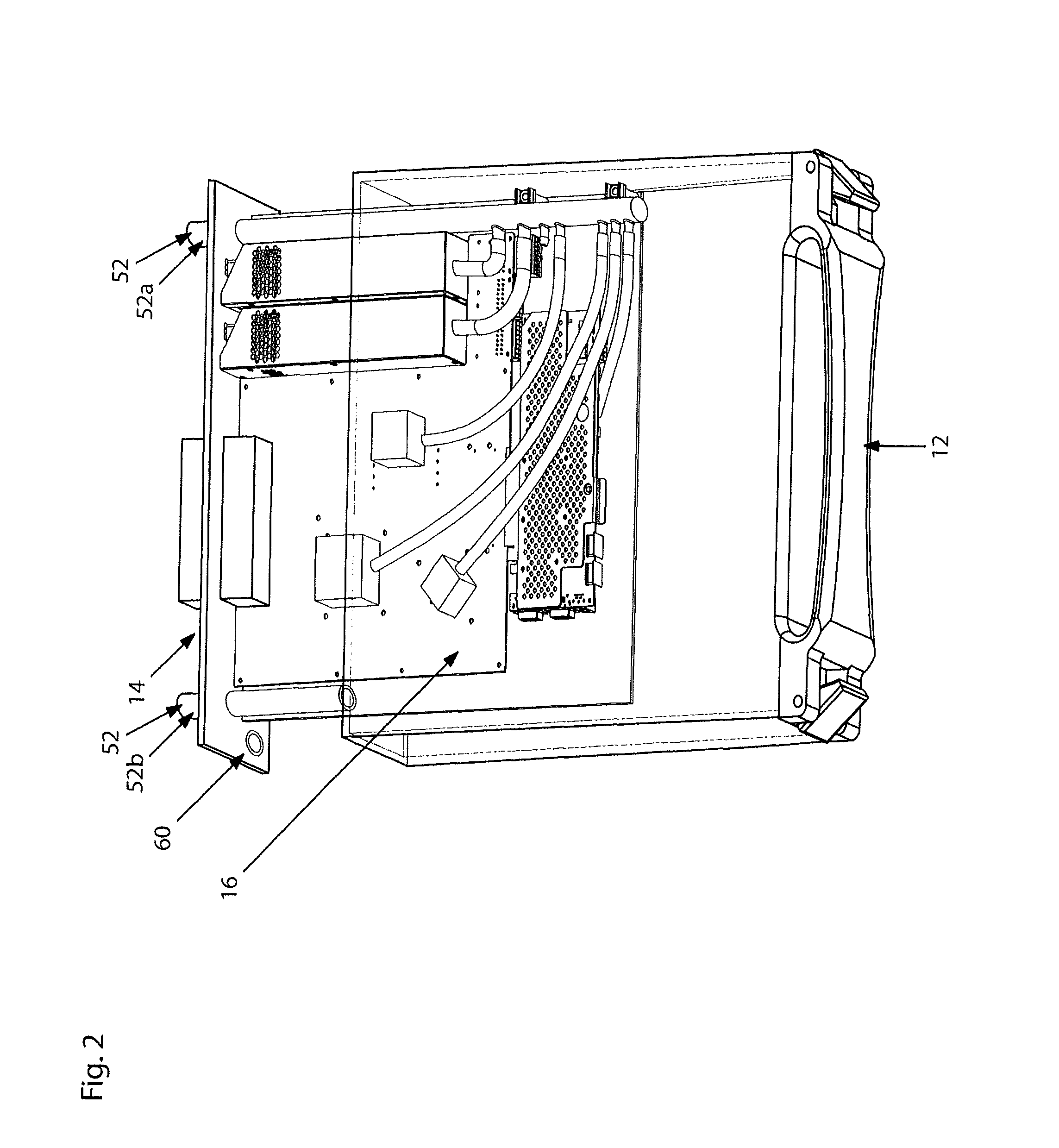
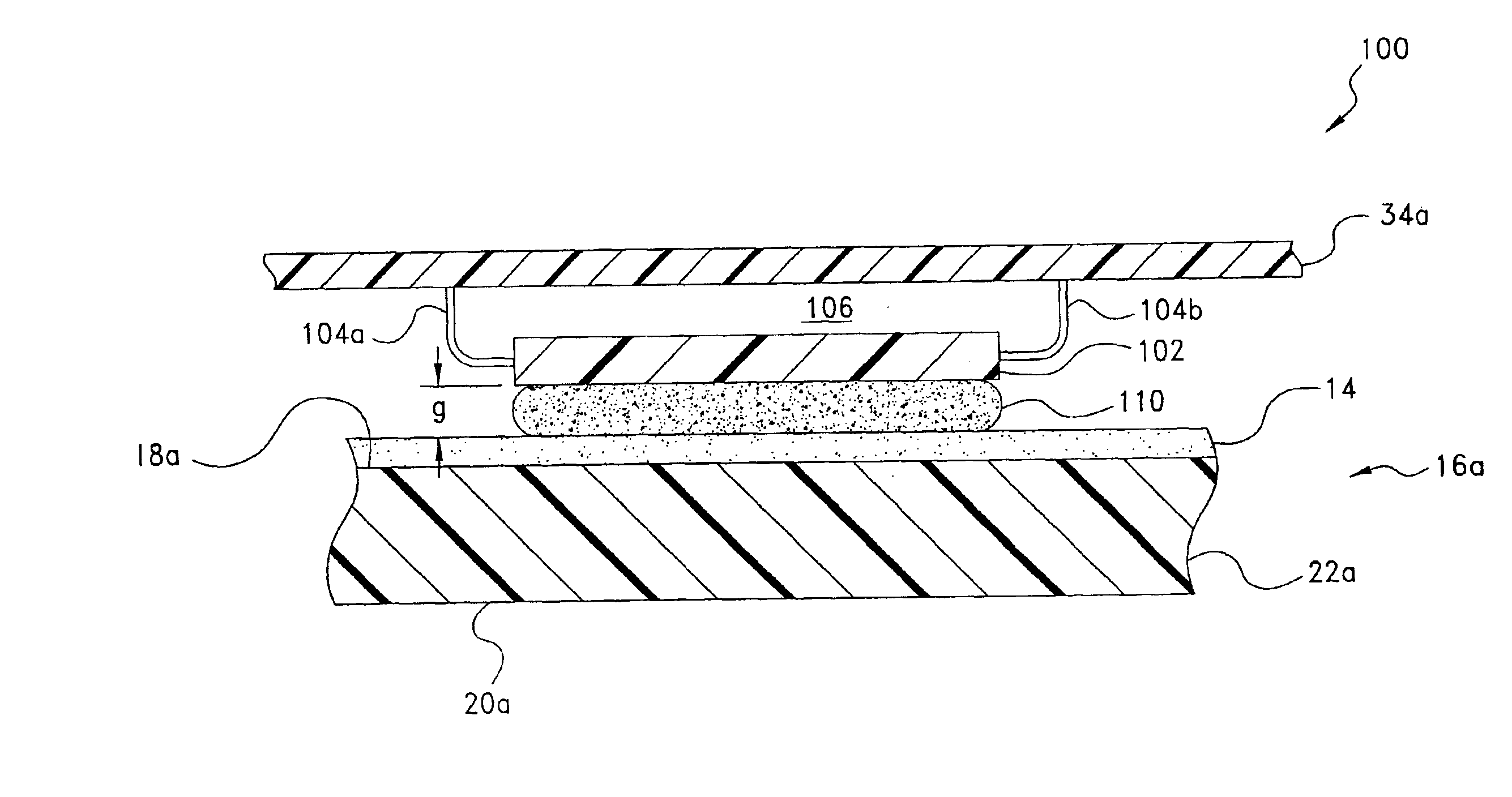
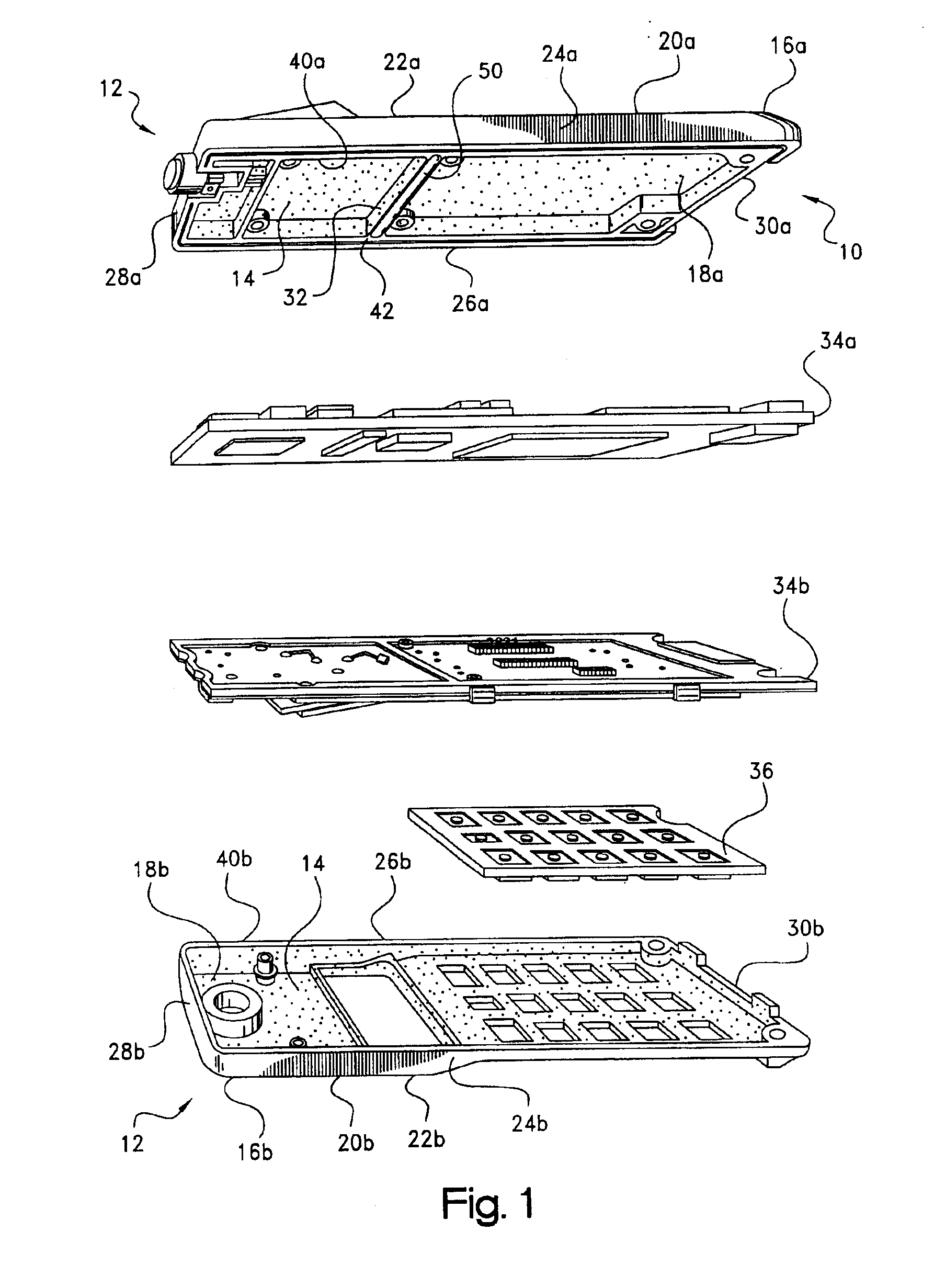
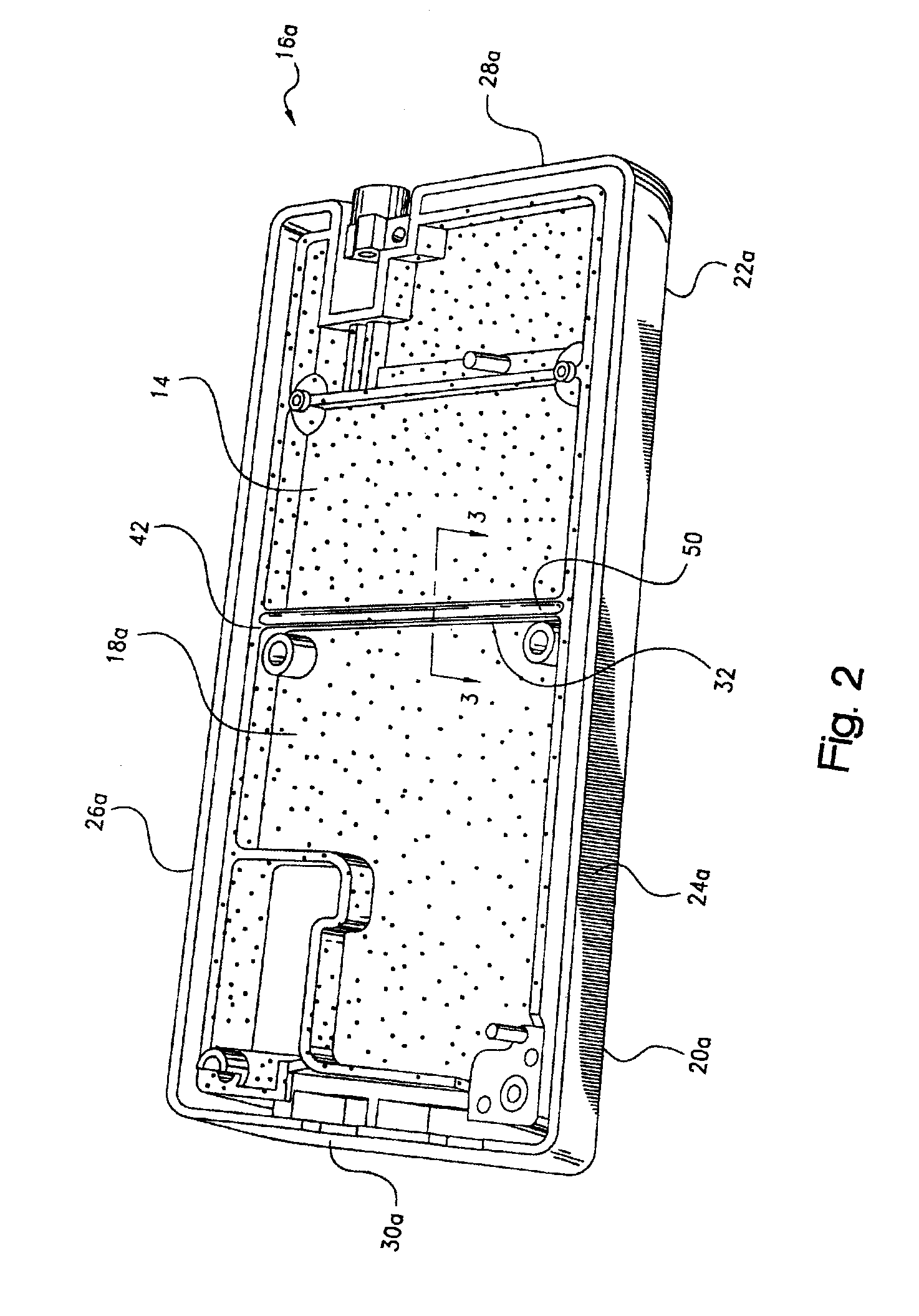
Thermal dissipation assembly and fabrication method for electronics drawer of a multiple-drawer electronics rack
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
Double-side thermally conductive adhesive tape for plastic-packaged electronic components
InactiveUS6432497B2Easy `` peel and stick '' installationPrecise thermal and adhesive propertiesInsulating substrate metal adhesion improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringHeat sink
A thermally conductive interface, which may be in the form of a double-sided, pressure sensitive adhesive tape, disposable intermediate a heat-generating source having a first heat transfer surface formed of a first material having a low surface energy, and a thermal dissipation member having a second heat transfer surface which is formed of a second material having a surface energy substantially higher than the surface energy of the first material, and which is disposable opposite the first heat transfer surface of the heat-generating source in a spaced-apart, heat transfer adjacency therewith. The interface includes a first pressure sensitive adhesive (PSA) surface which is bondable under pressure to at least a portion of the first heat transfer surface of the heat-generating source, and an opposing second pressure sensitive adhesive (PSA) surface bondable under pressure to at least a portion of the second heat transfer surface of the heat-generating source. The first PSA surface is presented from a layer of a thermally-conductive, first pressure sensitive adhesive composition, preferably silicone-based, having an affinity to the first heat transfer surface of the heat generating source. In turn, the second PSA surface is presented from a layer of a second pressure sensitive adhesive composition, preferably acrylic-based, different from the first composition and having an affinity to the second heat transfer surface of the thermal dissipation member. The interface is particularly adapted for bonding a plastic packaged electronic component to a metal heat sink.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
LED fixture
InactiveUS20090141500A1Easy to assembleImprove cooling effectLighting heating/cooling arrangementsSemiconductor devices for light sourcesEngineeringLED lamp
An LED fixture of heat-dissipating type includes a lampshade, an LED lamp set and a power source connector. The lampshade is made of materials, such as aluminum, capable of thermal dissipation, and its interior is horizontally arranged a divider for being divided into a first space and a second space. The LED lamp set is thus arranged in the first space, while the power source connector is arranged in the second space. A fixing pole shown as a hollow configuration is arranged on the power source connector and projected into the second space with a fixing element arranged into its interior. In the present invention, the fixing element penetrates through the divider of the lampshade for being fixed to a light-reflecting shade of the LED lamp set, thus that an assembly can be achieved quickly with a significantly enhanced contact between the lampshade and the LED lamp set.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
LED light source assembly
ActiveUS7093958B2IntensiveImprove cooling effectPoint-like light sourceLighting support devicesElectricityHigh concentration
A compact LED light source providing intensive LED positioning along with thermal dissipation can be made with a heat conductive plate supporting a plurality of LEDs mounted on the plate and in thermal contact with the plate. The plate further supports electrical circuitry providing electrical connection to the LEDs. A heat conductive stem mechanically supports the plate and may provide a thermal conduction path from the plate away from the LEDs. A high concentration of LED can then be conveniently mounted and held in close proximity for increased optical system intensity, while providing a thermal exit path for the associated increase in heat concentration.
Owner:SUZHOU LEKIN SEMICON CO LTD
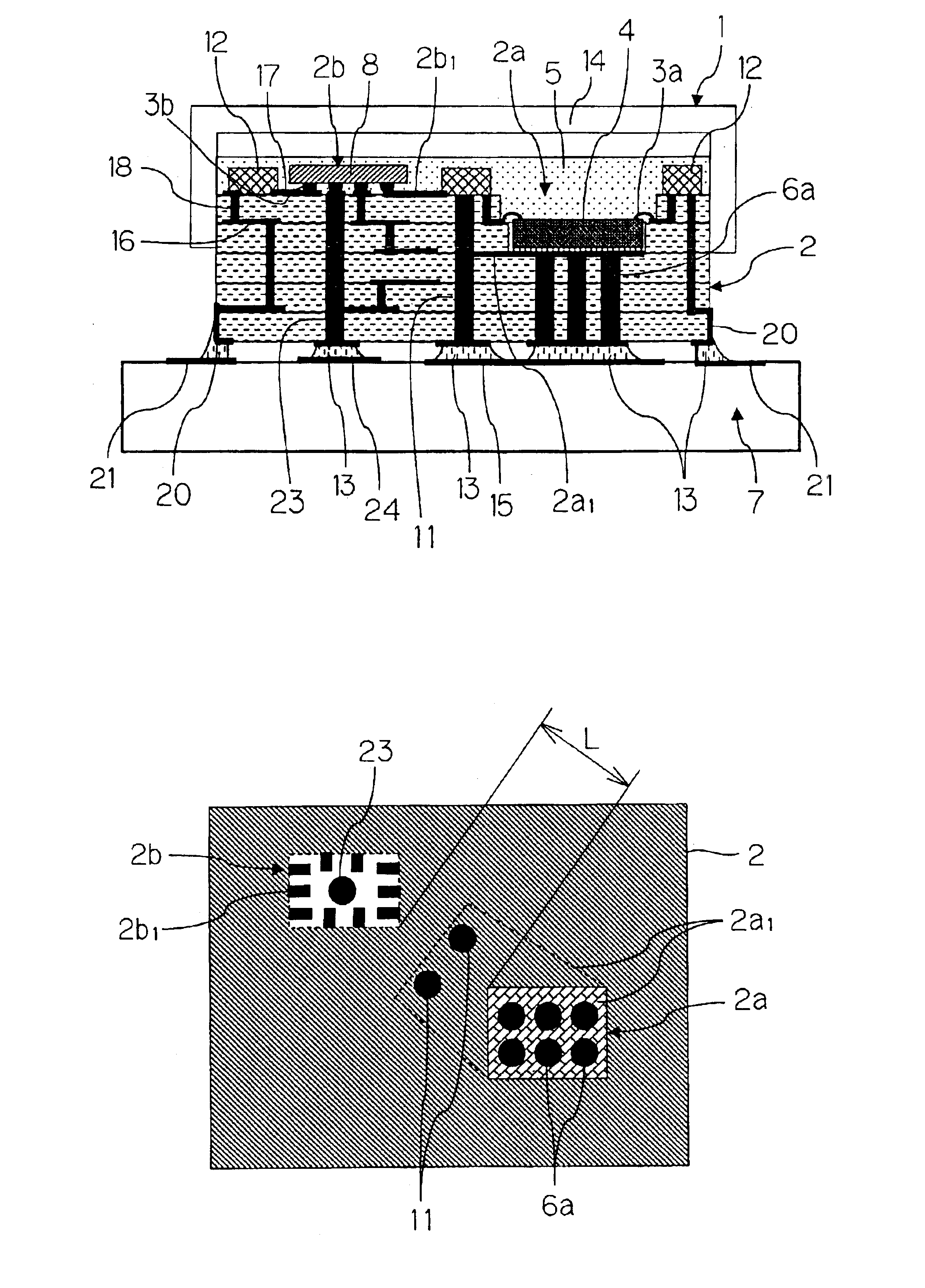
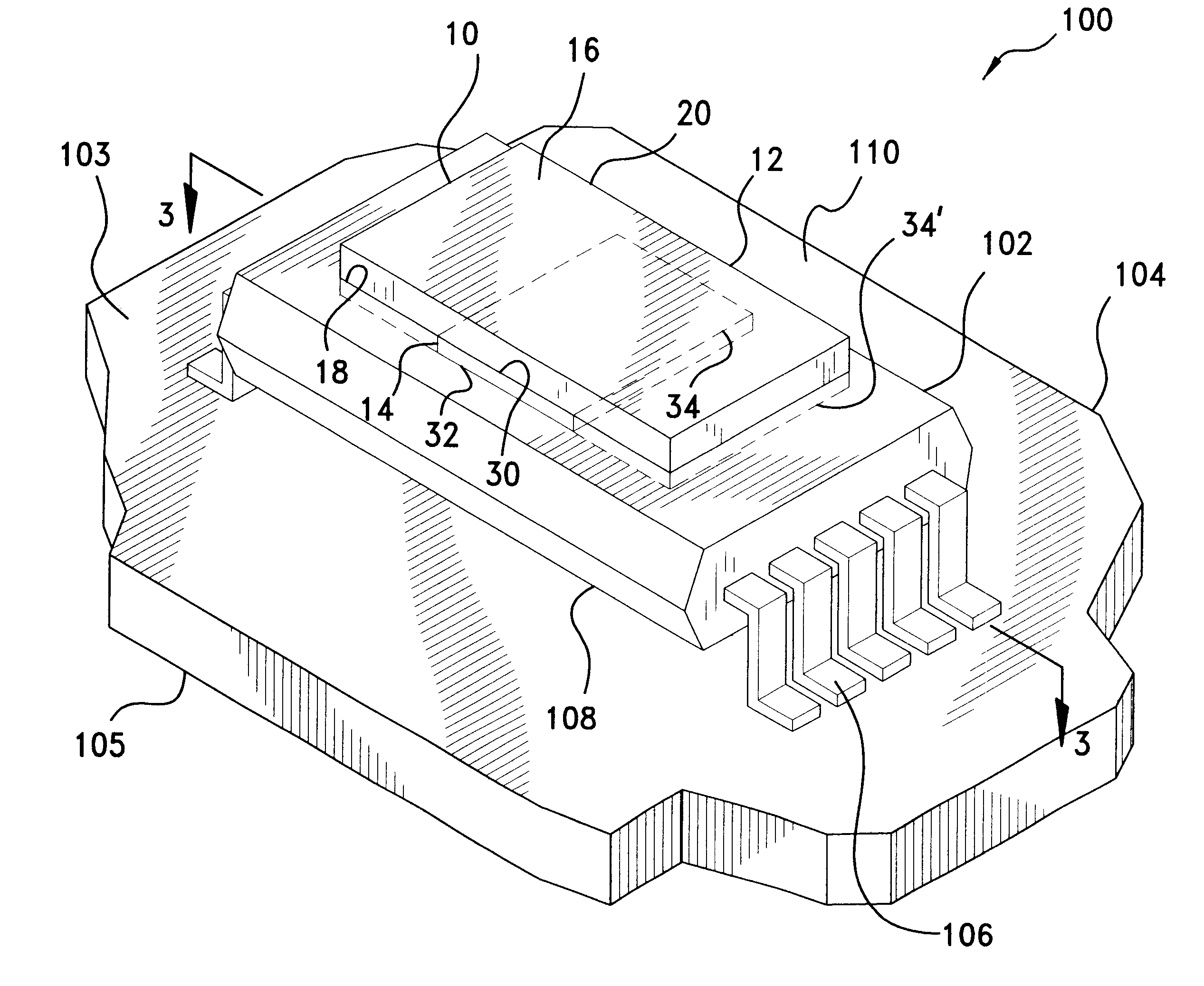
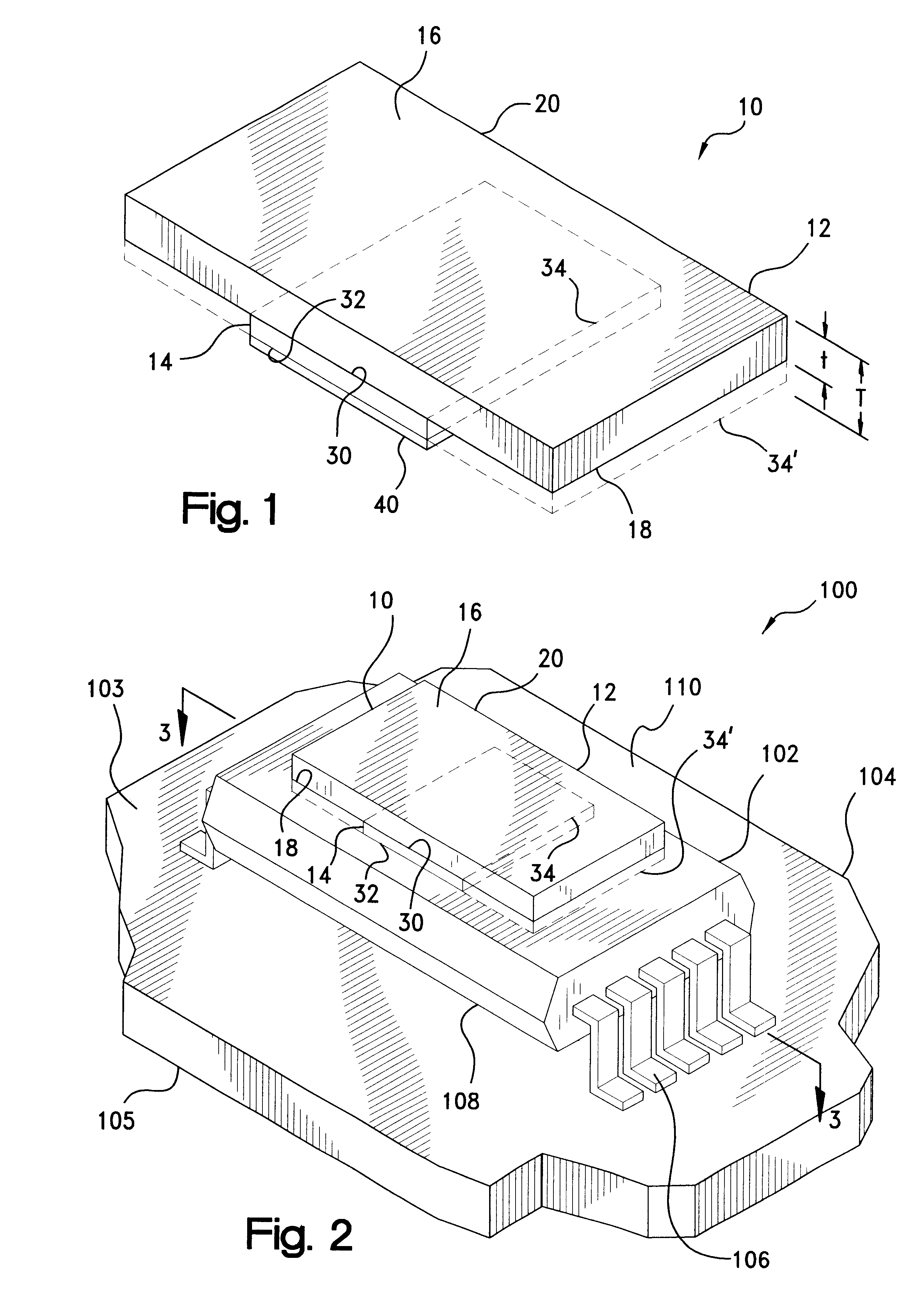
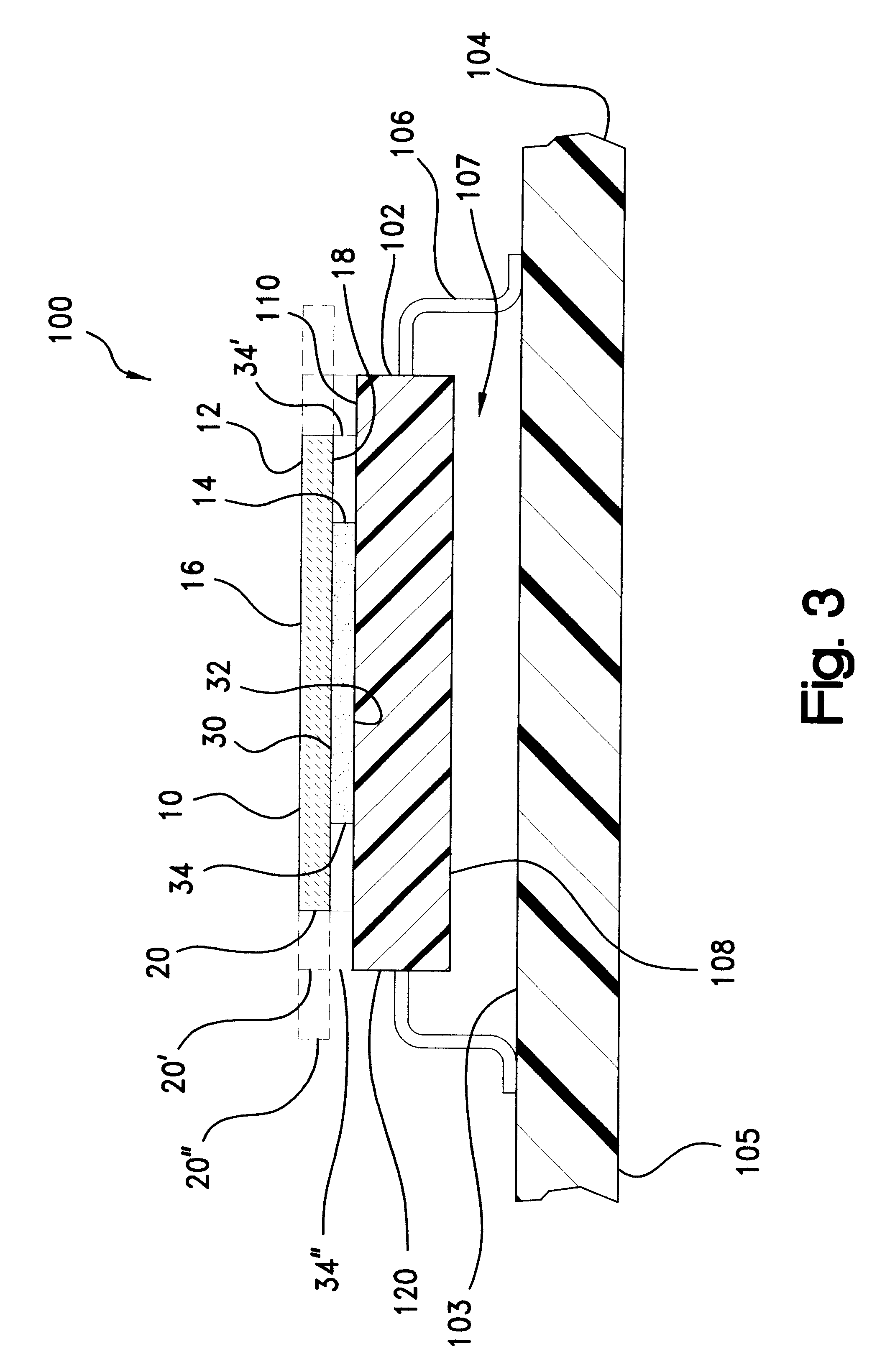
High frequency module
InactiveUS6873529B2Low costImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringSurface acoustic wave
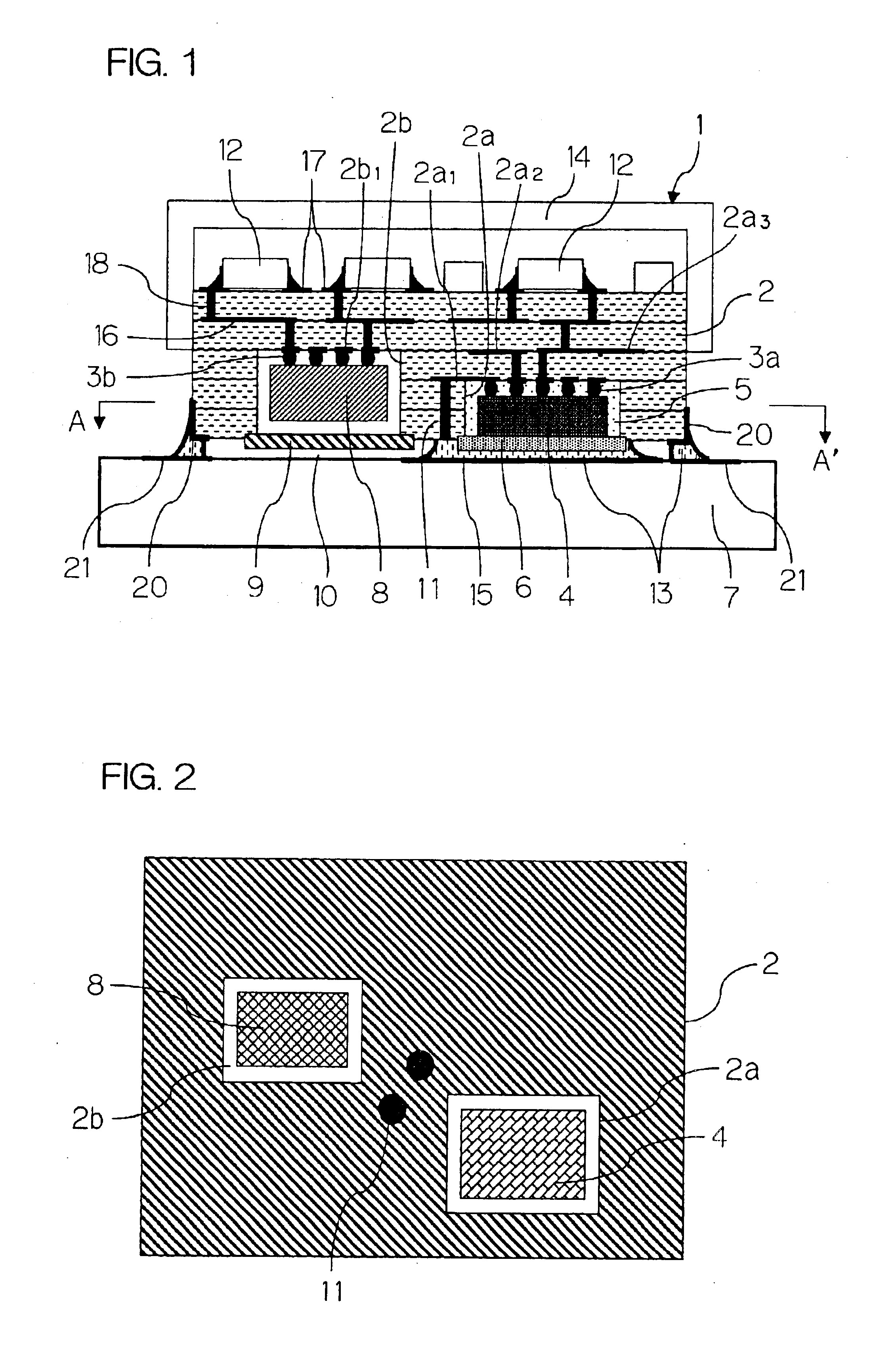
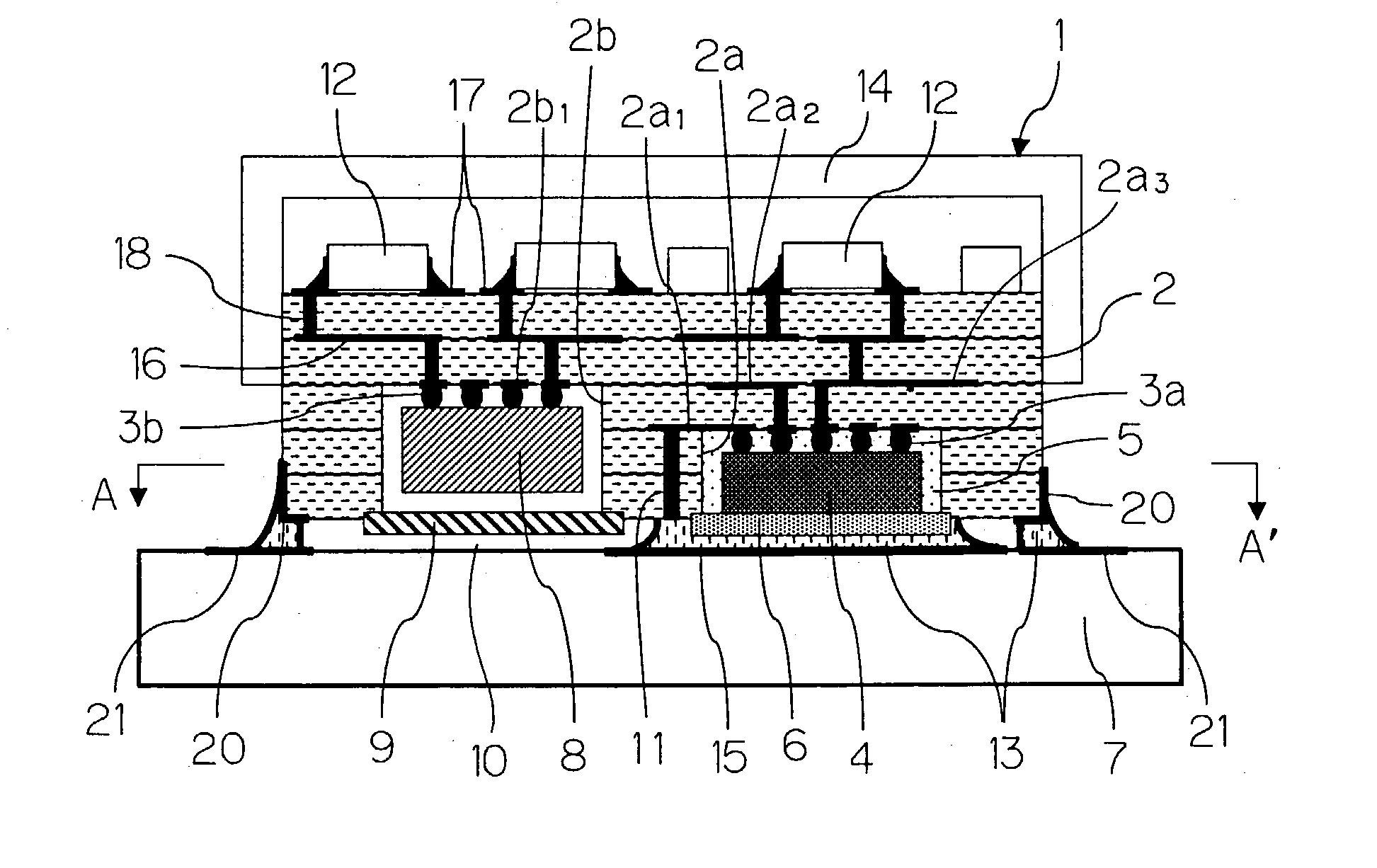
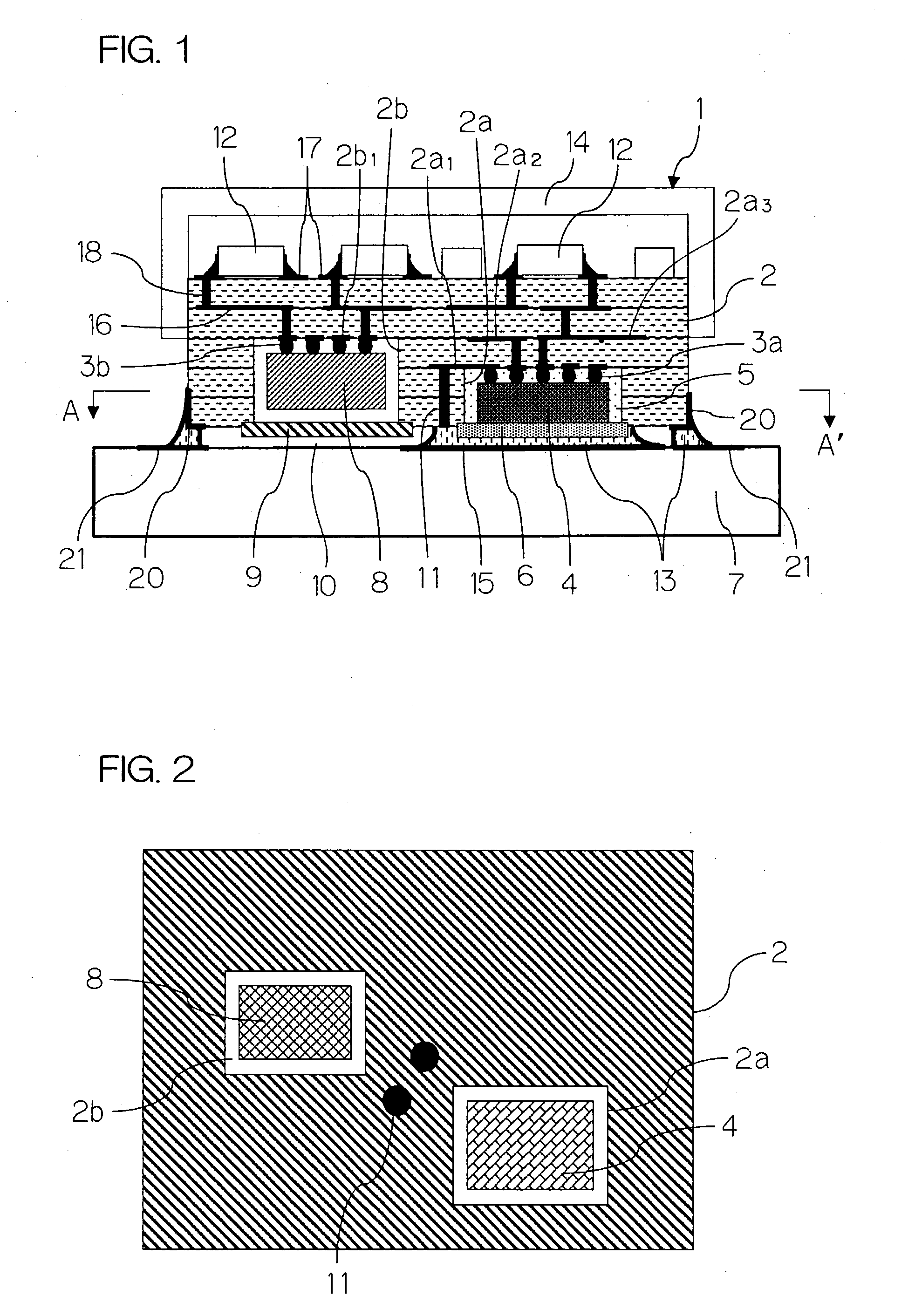
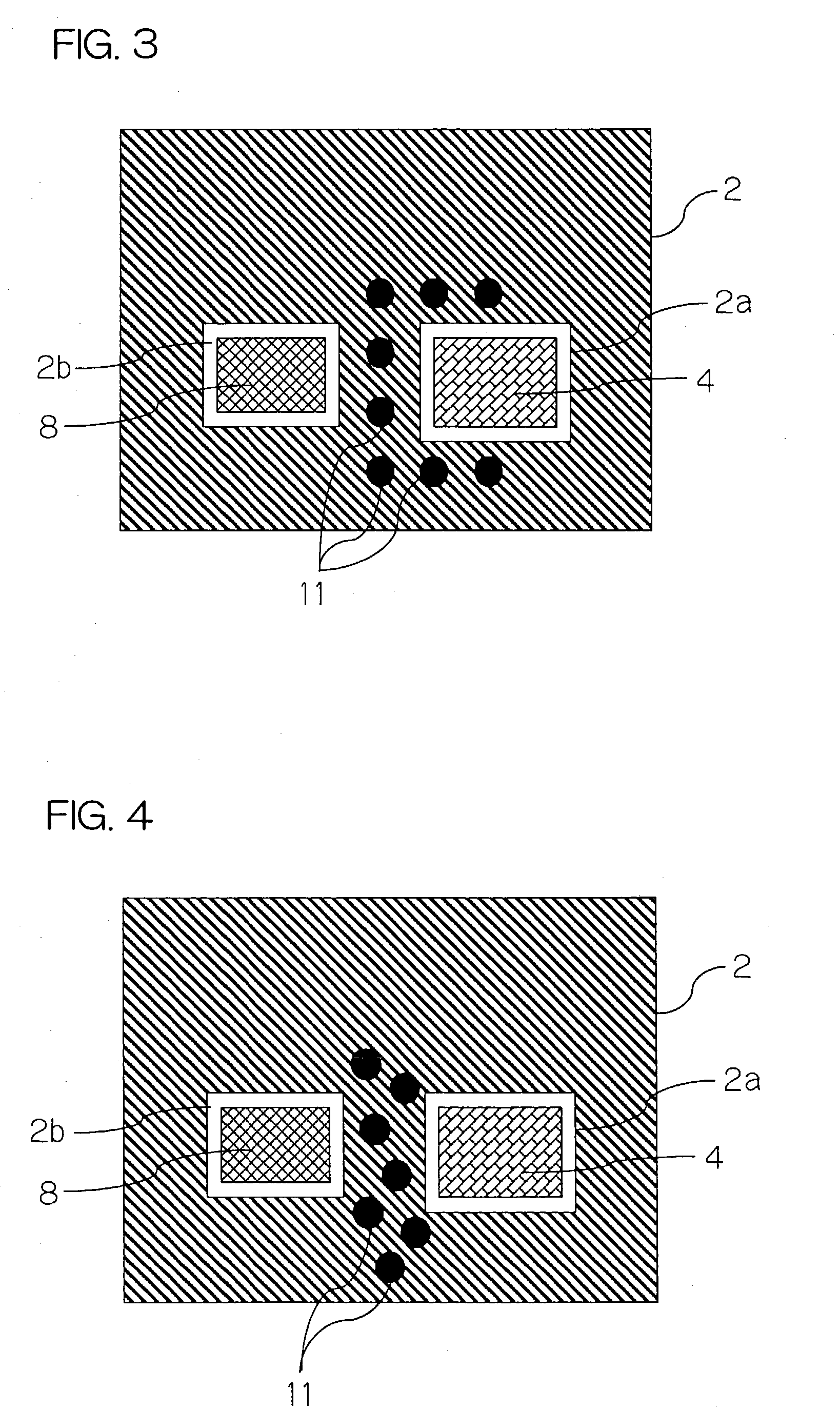
There is presented a high frequency module, in which a recess 2a for mounting power amplifier device is formed on a lower surface of a dielectric substrate 2, and a recess 2b for mounting surface acoustic wave filter is formed on an upper surface of the dielectric substrate 2, and a power amplifier device 4 and a surface acoustic wave filter 8 are mounted through conductive bumps 3a and 3b on the recesses 2a and 2b, respectively. In addition, a through-hole conductor 11 whose one end is exposed at the lower surface of the dielectric substrate 2 is provided between the recesses 2a and 2b. The exposed end of the through-hole conductor 11 is attached to a thermal dissipation conductor 15 on an upper surface of an external electric circuit board 7 through a brazing material 13.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Thermal interface material having a zone-coated release linear
InactiveUS6644395B1Reduce generationIncrease physical strengthFilm/foil adhesivesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringConductive materials
A release liner particularly adapted for use with a layer of a thermal interface material having a first surface and a second surface which is bondable to the heat transfer surface of a thermal dissipation member. The liner has an exterior surface and an interior surface disposable in adhering contact with the first surface of the thermally-conductive material. The liner interior surface has one or more first zones defined thereon which exhibit a first release value relative to the first surface of the thermally-conductive material, and one or more second zones bordered by the first zones which exhibit a second release value relative to the first surface of the thermally-conductive material which is lower than the first release value of the first zones. With the second surface of the thermally-conductive material being bonded to the heat transfer surface of the thermal dissipation member, the release liner is removable from the first surface of the thermally-conductive material without substantial cohesive or adhesive failure thereof.
Owner:PARKER HANNIFIN CORP
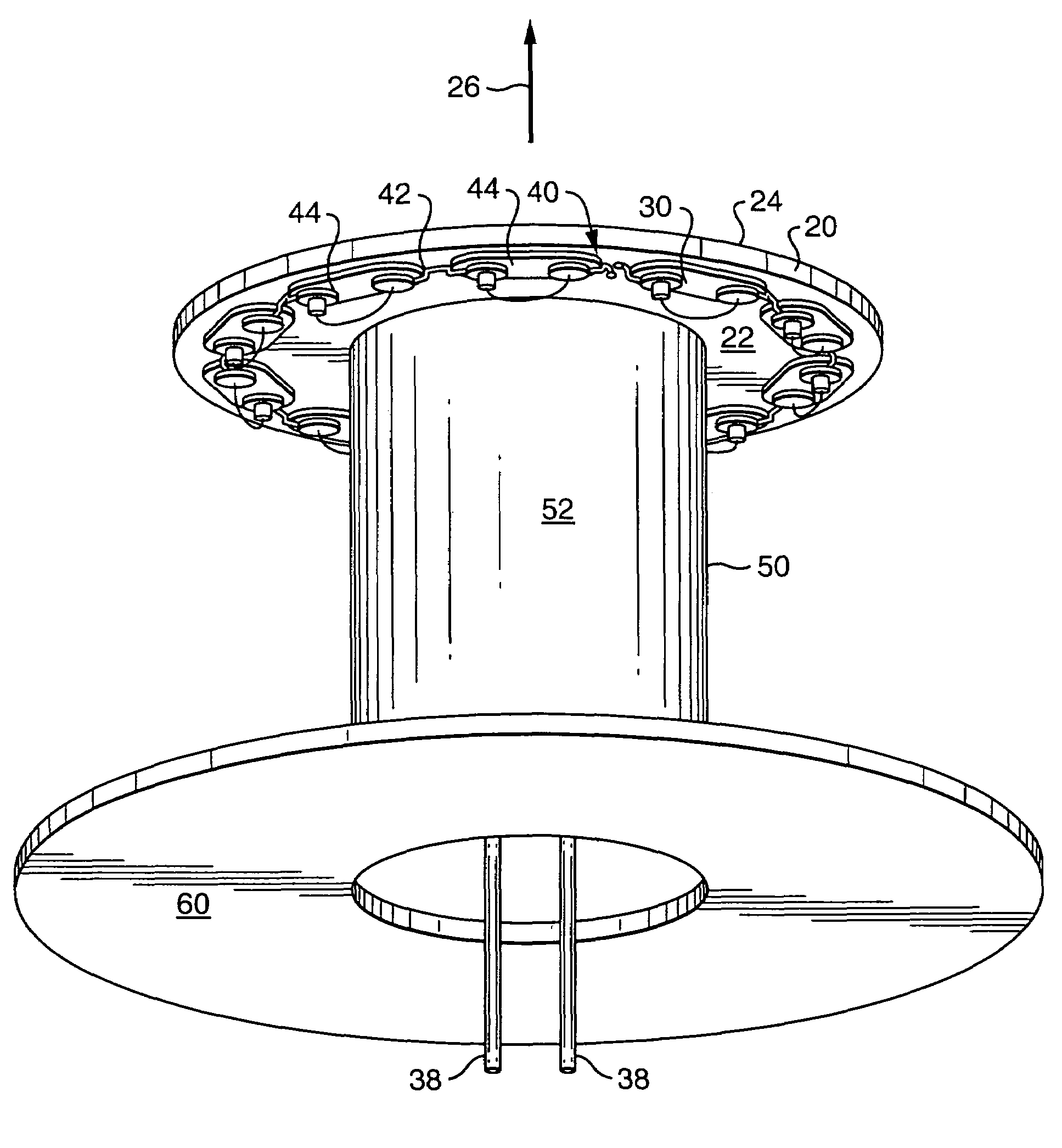
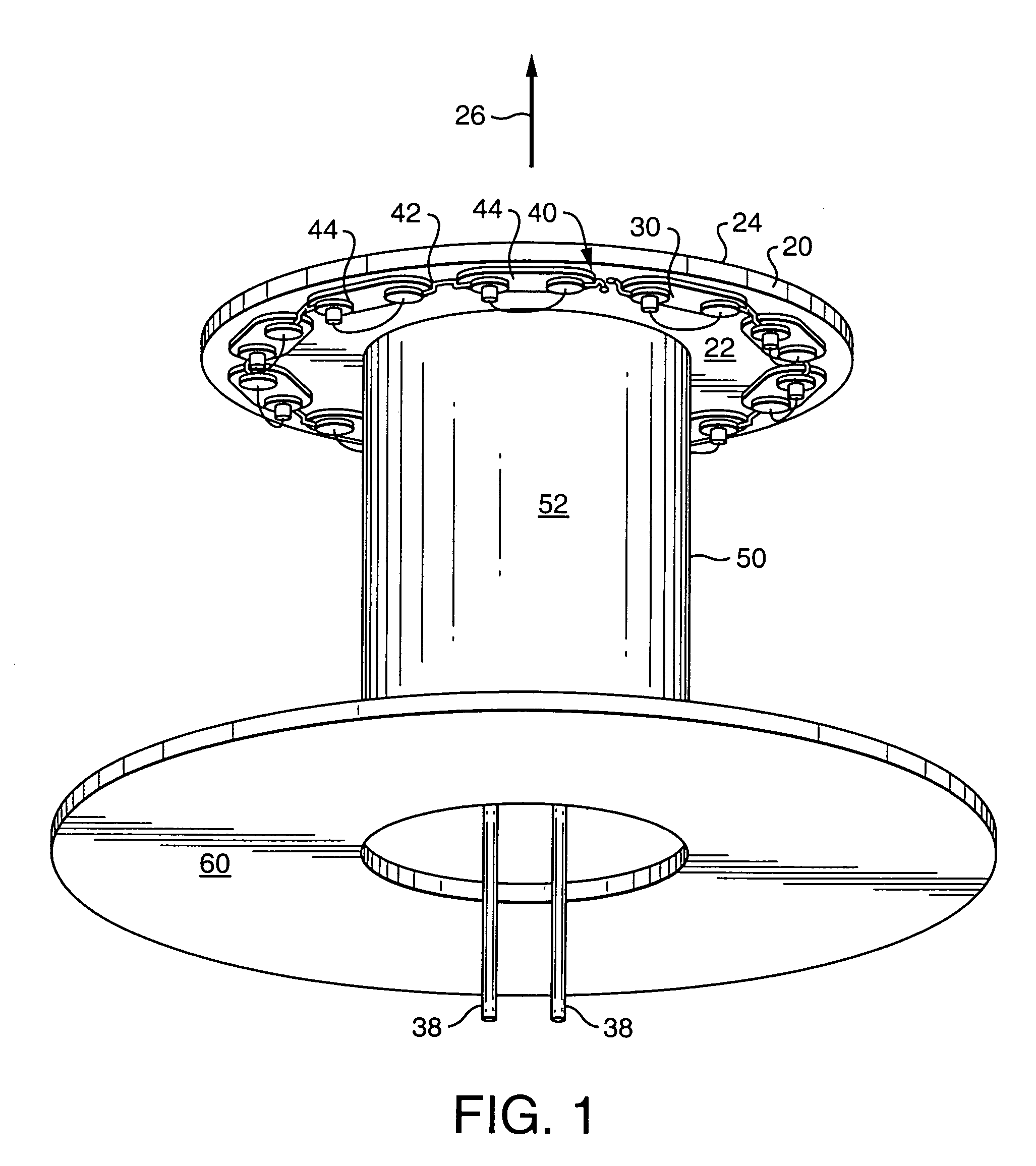
Apparatus and method for thermal dissipation in a light
A device is disclosed for producing light that may include one or more printed circuit boards (PCBs), an electronics package may be disposed about the first surface of one or more of the PCBs and a housing. The PCBs may include a metal layer and a core, and, in some aspects, may include multiple cores interposed between multiple metal layers, and in some embodiments a backplane may be disposed along the core(s). A plurality of PCB's may be set apart and connected by pins to dissipate heat from one PCB to another, and / or to convey electrical connectivity. Pins may be configured to pass through or into one or both the PCBs including the cores to conduct heat generated by the electronics package away for dispersion. In some embodiments, the pins may pass into the backplane. The PCBs may include LEDs, lights, computer devices, memories, telecommunications devices, or combinations of these. The device may also include a housing to contain the plurality of PCBs such that air flow may enter the housing and pass by the pins for cooling of the PCBs and electronics thereof. The housing may also be configured to permit external power to be applied to the PCBs within the apparatus.
Owner:NEXXUS LIGHTING
High frequency module
InactiveUS20030169575A1Efficiently dissipatedLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAudio power amplifierElectrical conductor
There is presented a high frequency module, in which a recess 2a for mounting power amplifier device is formed on a lower surface of a dielectric substrate 2, and a recess 2b for mounting surface acoustic wave filter is formed on an upper surface of the dielectric substrate 2, and a power amplifier device 4 and a surface acoustic wave filter 8 are mounted through conductive bumps 3a and 3b on the recesses 2a and 2b, respectively. In addition, a through-hole conductor 11 whose one end is exposed at the lower surface of the dielectric substrate 2 is provided between the recesses 2a and 2b. The exposed end of the through-hole conductor 11 is attached to a thermal dissipation conductor 15 on an upper surface of an external electric circuit board 7 through a brazing material 13.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Flip-chip light emitting diode with resonant optical microcavity
InactiveUS6969874B1Improve efficiencyAccelerate emissionsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesDielectric substrateGallium nitride
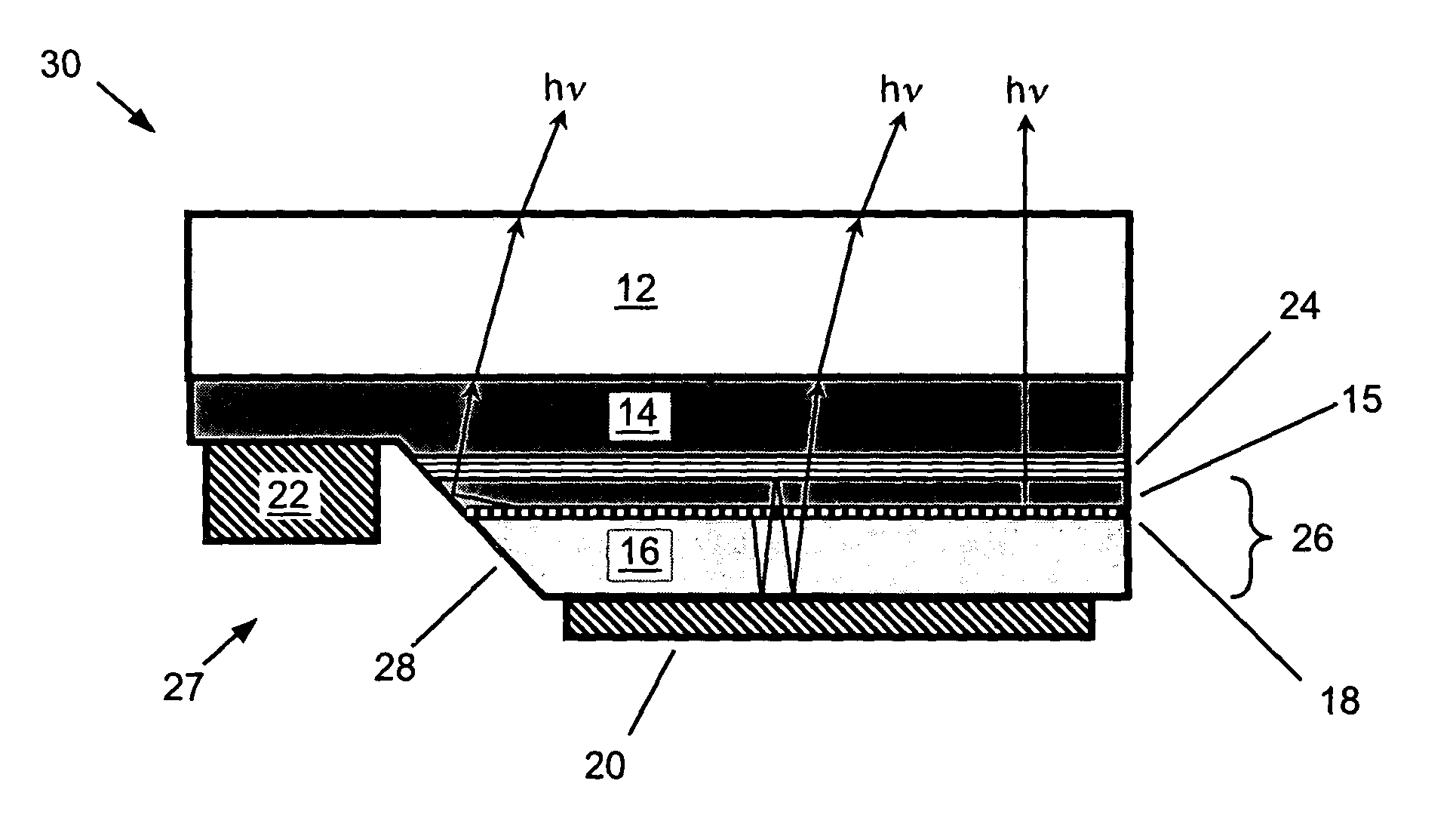
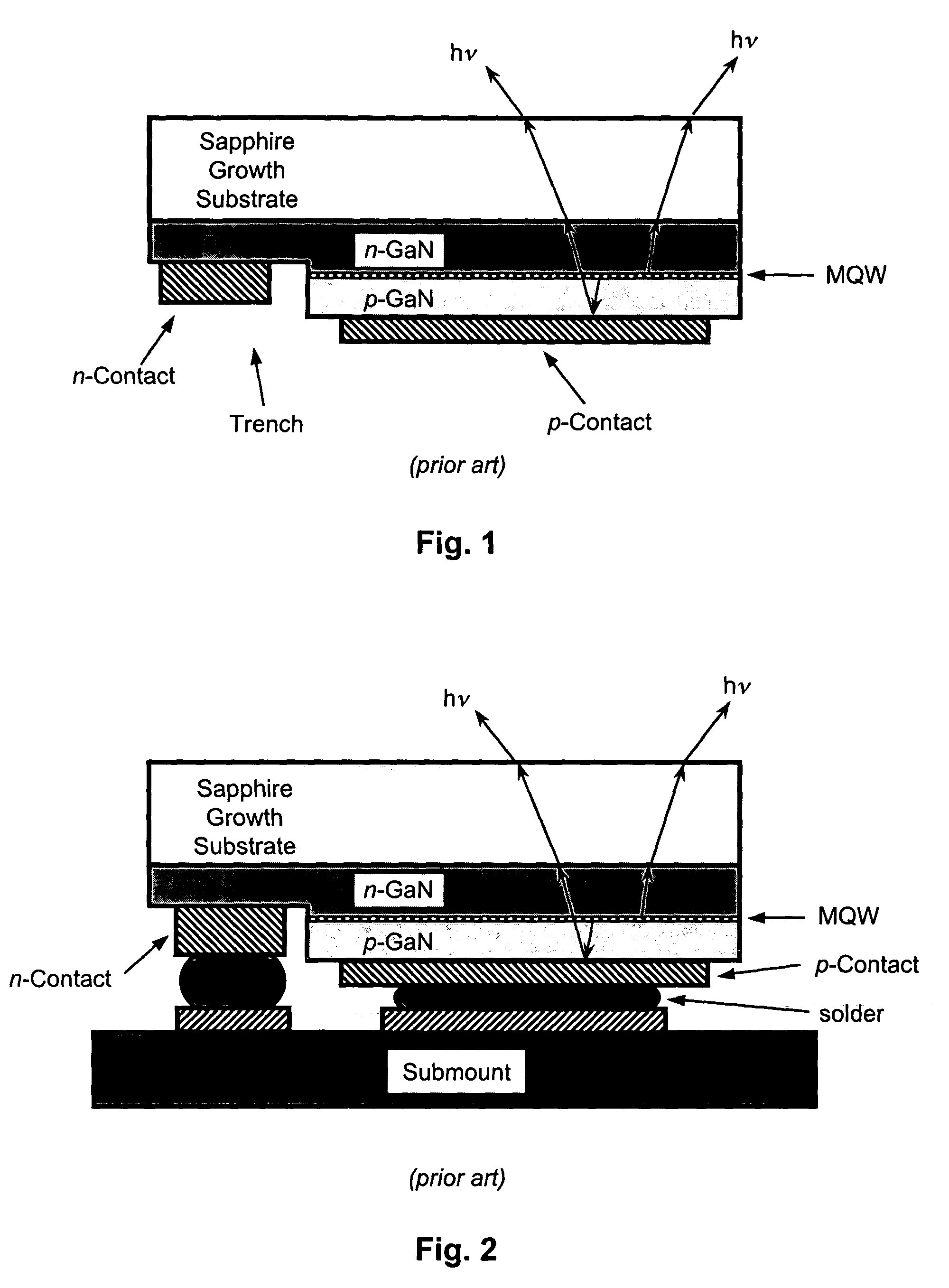
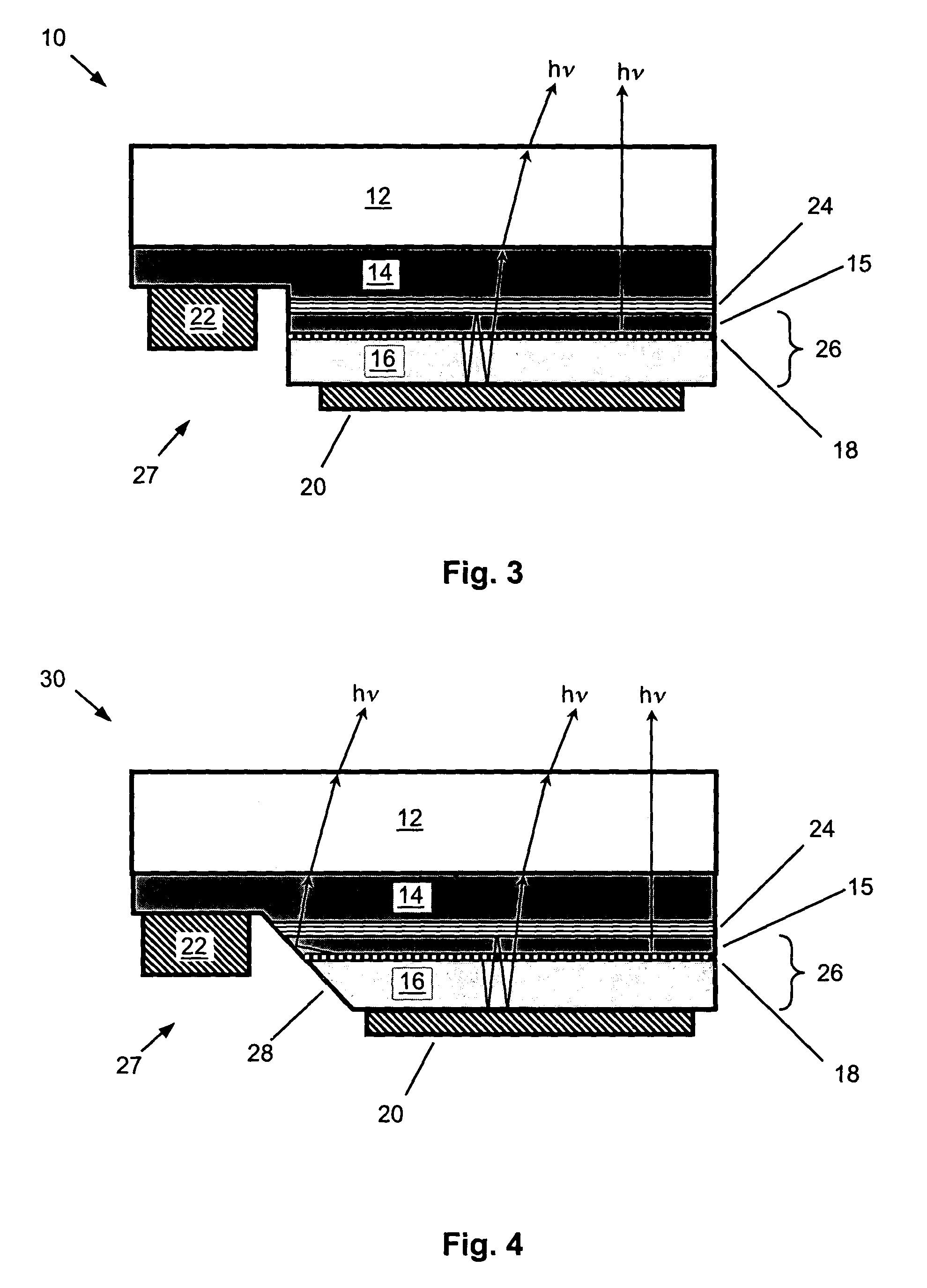
A flip-chip light emitting diode with enhanced efficiency. The device structure employs a microcavity structure in a flip-chip configuration. The microcavity enhances the light emission in vertical modes, which are readily extracted from the device. Most of the rest of the light is emitted into waveguided lateral modes. Flip-chip configuration is advantageous for light emitting diodes (LEDs) grown on dielectric substrates (e.g., gallium nitride LEDs grown on sapphire substrates) in general due to better thermal dissipation and lower series resistance. Flip-chip configuration is advantageous for microcavity LEDs in particular because (a) one of the reflectors is a high-reflectivity metal ohmic contact that is already part of the flip-chip configuration, and (b) current conduction is only required through a single distributed Bragg reflector. Some of the waveguided lateral modes can also be extracted with angled sidewalls used for the interdigitated contacts in the flip-chip configuration.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Thermal-sprayed metallic conformal coatings used as heat spreaders
InactiveUS20030066672A1Eliminate needHeat dissipationMolten spray coatingScreening gaskets/sealsMolten stateThermal spraying
Heat dissipation and electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding for an electronic device having an enclosure. An interior surface of the enclosure is covered with a conformal metallic layer which, as disposed in thermal adjacency with one or more heat-generating electronic components or other sources contained within the enclosure, may provide both thermal dissipation and EMI shielding for the device. The layer may be sprayed onto the interior surface in a molten state and solidified to form a self-adherent coating.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
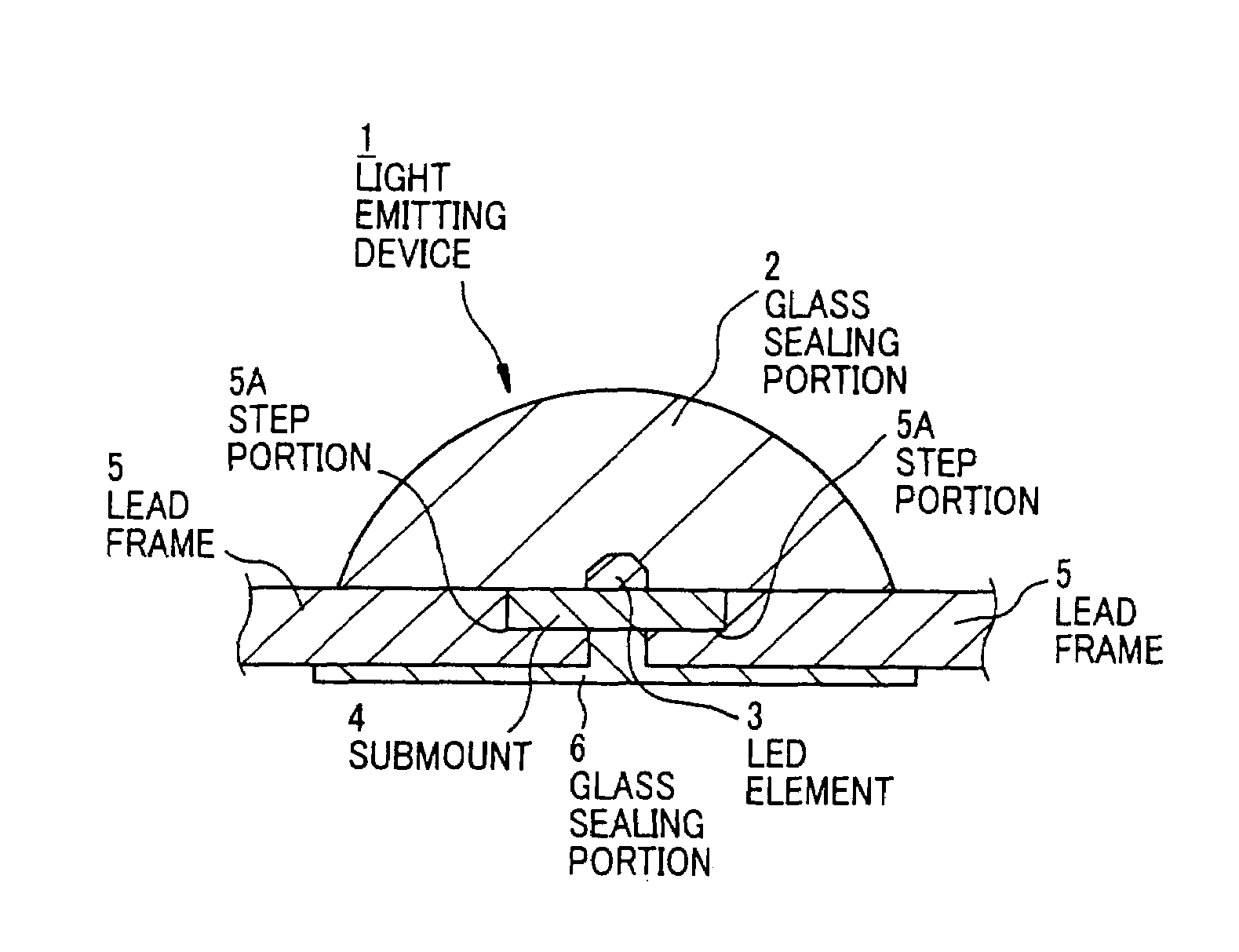
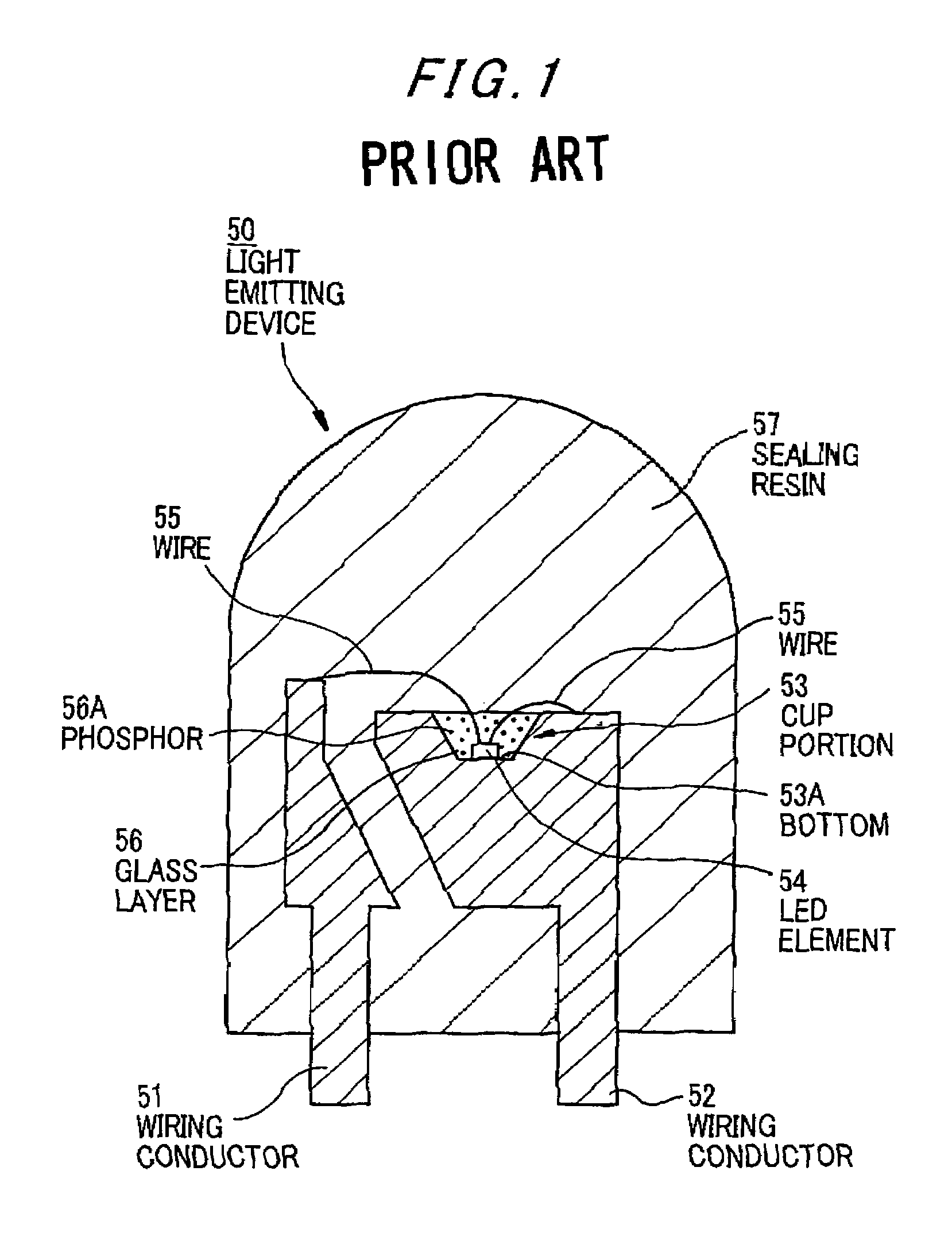
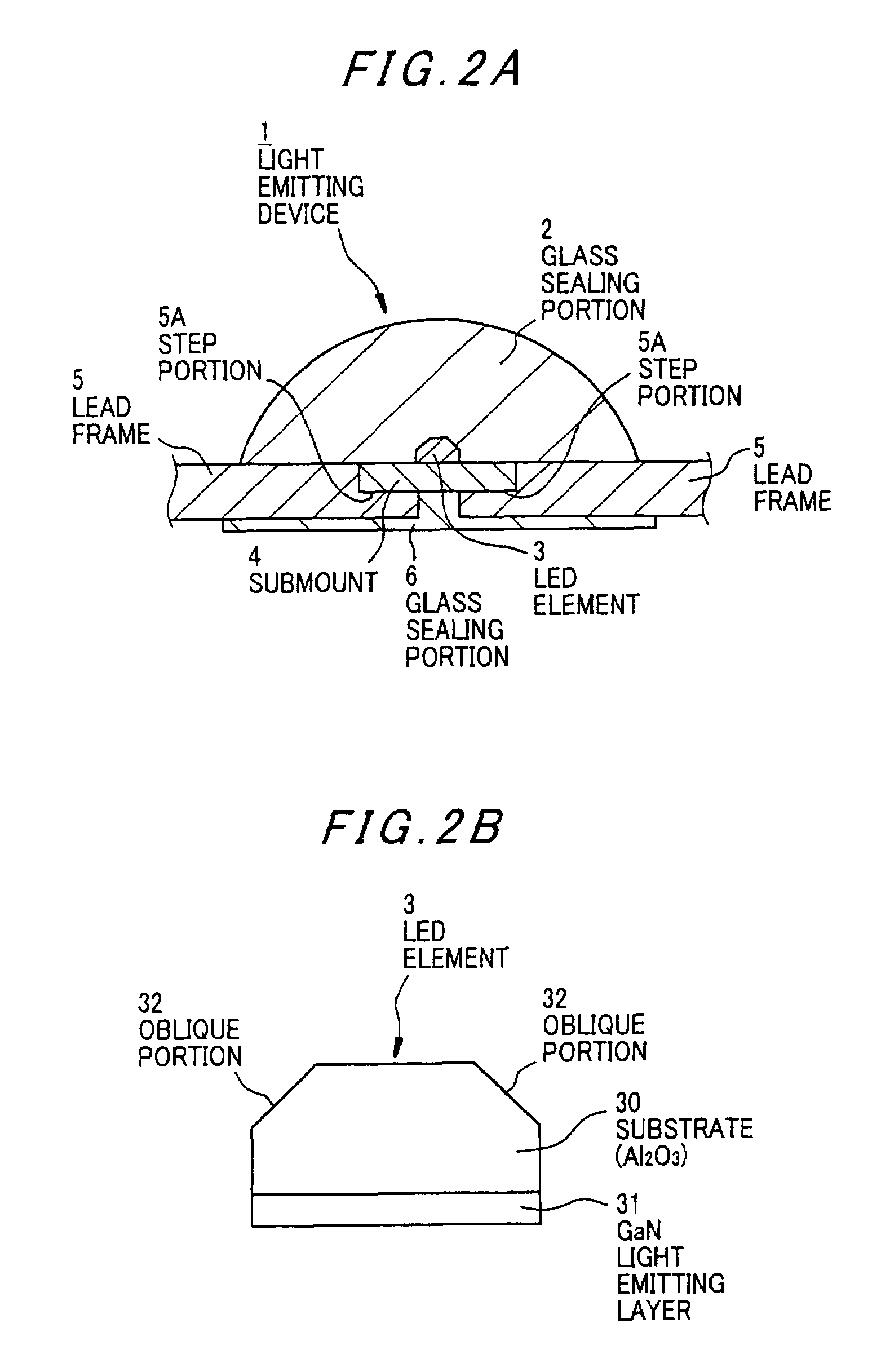
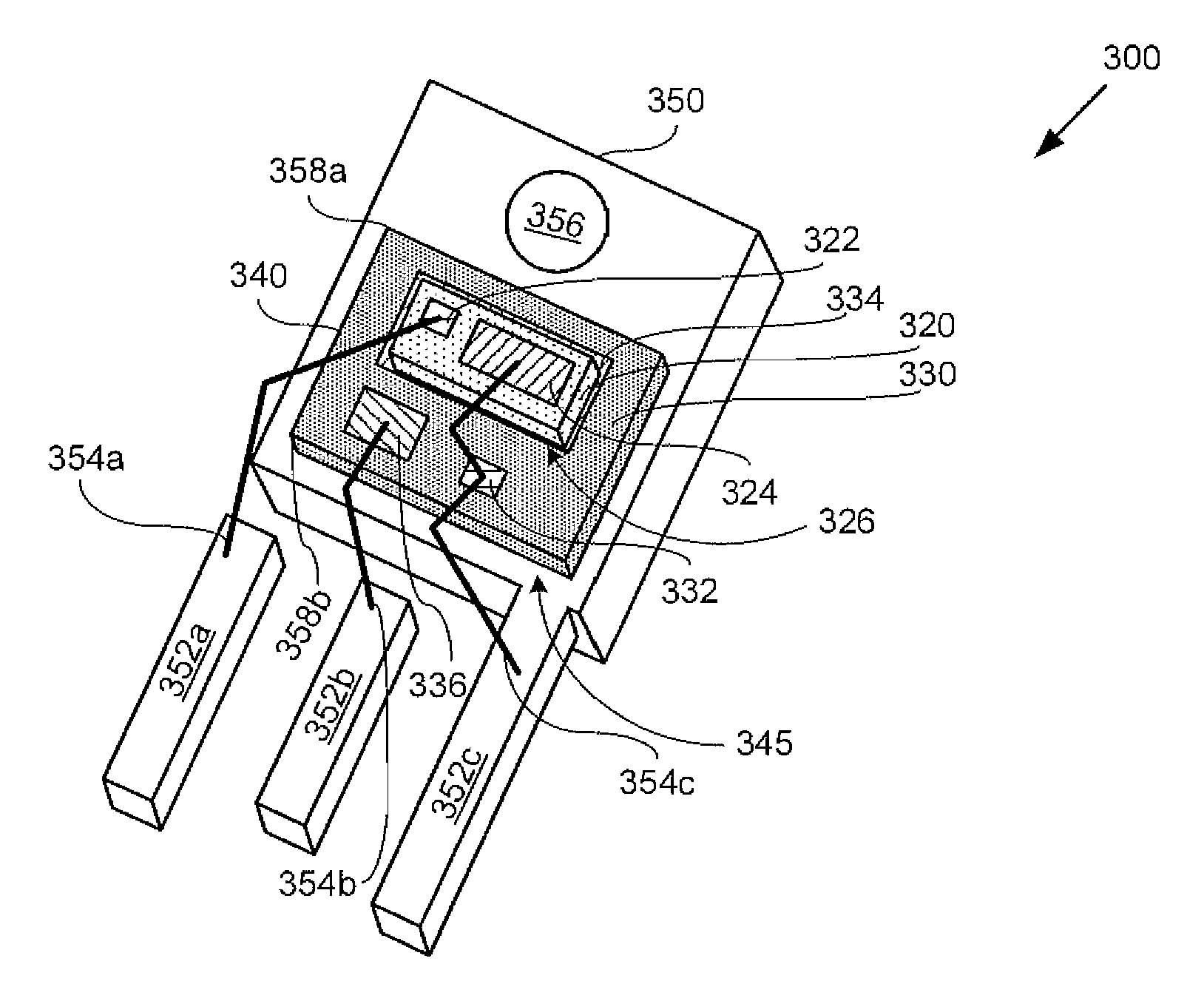
Light emitting device provided with a submount assembly for improved thermal dissipation
ActiveUS7391153B2Lowing of residual bubbleReduce internal stressDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesThermal expansionLight emitting device
A light emitting device has: a light emitting element; a lead that is electrically connected to the light emitting element at its one end and serves as a terminal to supply a power source to the light emitting element; a metal base that the light emitting element is mounted thereon and radiates heat of the light emitting element; and a sealing member that is of transparent resin or glass and covers the light emitting element. The lead is secured to the metal base by a heat-resisting insulating member with a thermal expansion coefficient nearly equal to that of the metal base.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Double-side thermally conductive adhesive tape for plastic-packaged electronic components
InactiveUS20020012762A1Easy `` peel and stick '' installationPrecise thermal and adhesive propertiesInsulating substrate metal adhesion improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringElectronic component
A thermally conductive interface, which may be in the form of a double-sided, pressure sensitive adhesive tape, disposable intermediate a heat-generating source having a first heat transfer surface formed of a first material having a low surface energy, and a thermal dissipation member having a second heat transfer surface which is formed of a second material having a surface energy substantially higher than the surface energy of the first material, and which is disposable opposite the first heat transfer surface of the heat-generating source in a spaced-apart, heat transfer adjacency therewith. The interface includes a first pressure sensitive adhesive (PSA) surface which is bondable under pressure to at least a portion of the first heat transfer surface of the heat-generating source, and an opposing second pressure sensitive adhesive (PSA) surface bondable under pressure to at least a portion of the second heat transfer surface of the heat-generating source. The first PSA surface is presented from a layer of a thermally-conductive, first pressure sensitive adhesive composition, preferably silicone-based, having an affinity to the first heat transfer surface of the heat generating source. In turn, the second PSA surface is presented from a layer of a second pressure sensitive adhesive composition, preferably acrylic-based, different from the first composition and having an affinity to the second heat transfer surface of the thermal dissipation member. The interface is particularly adapted for bonding a plastic packaged electronic component to a metal heat sink.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
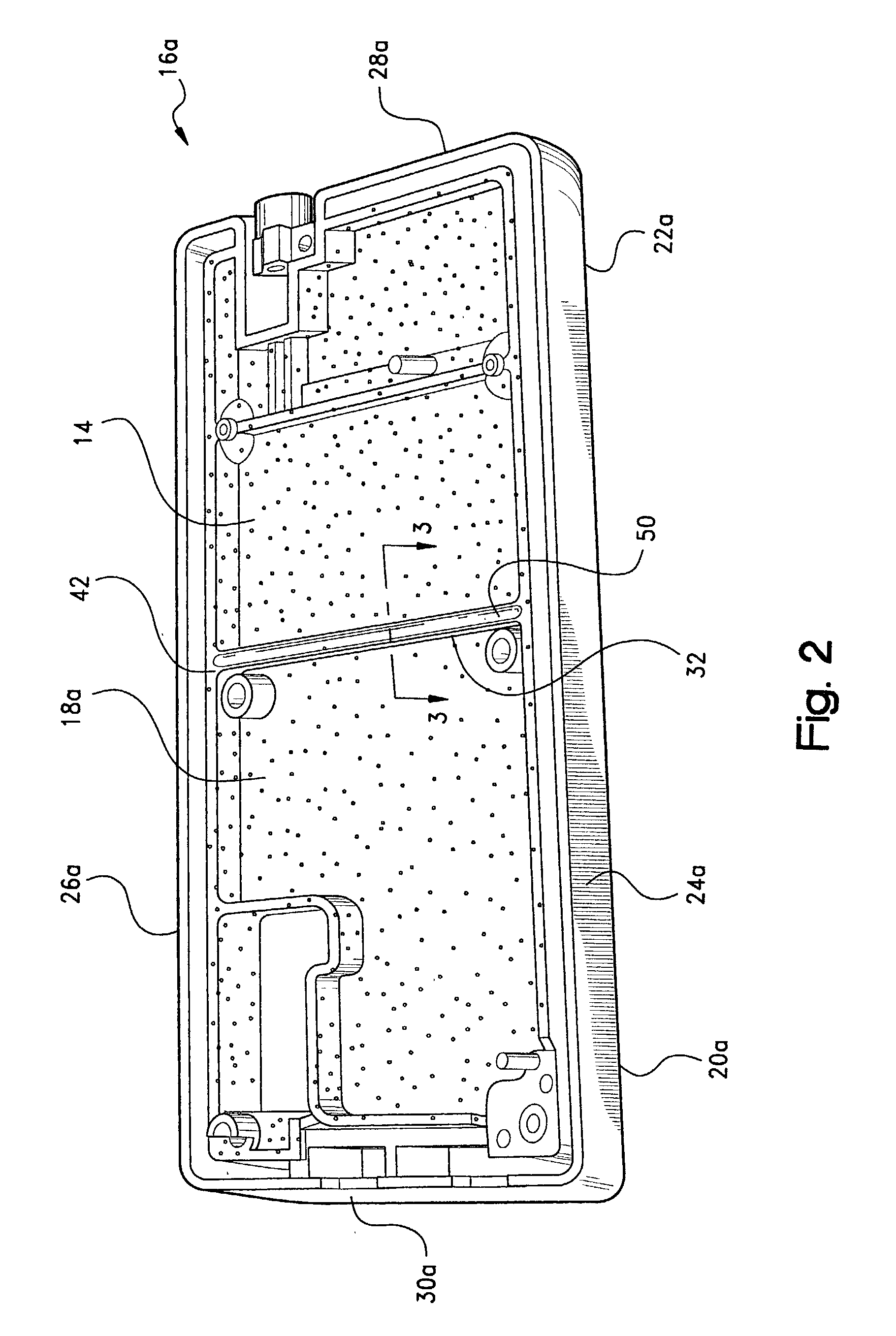
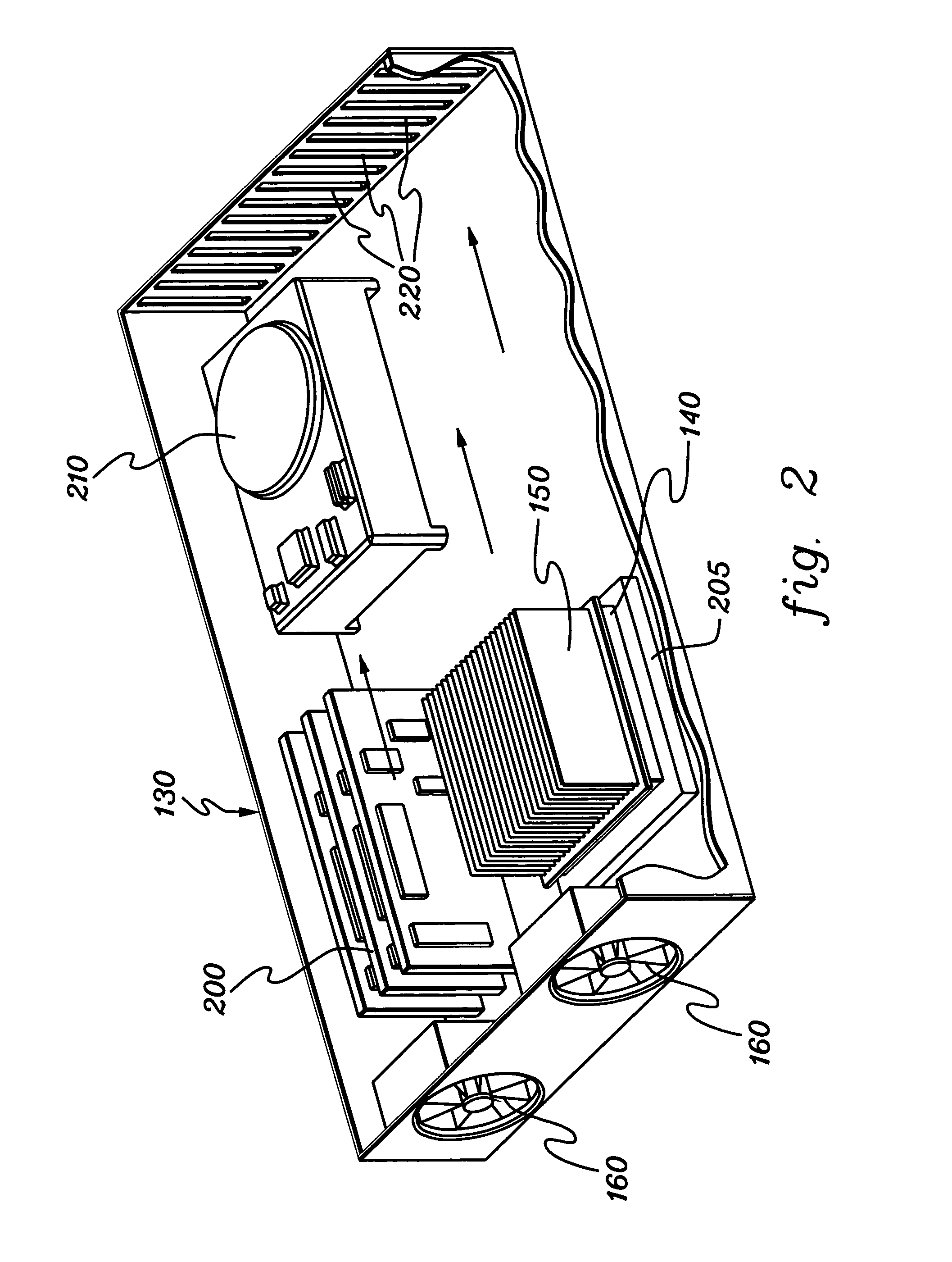
Thermal dissipation assembly and fabrication method for electronics drawer of a multiple-drawer electronics rack
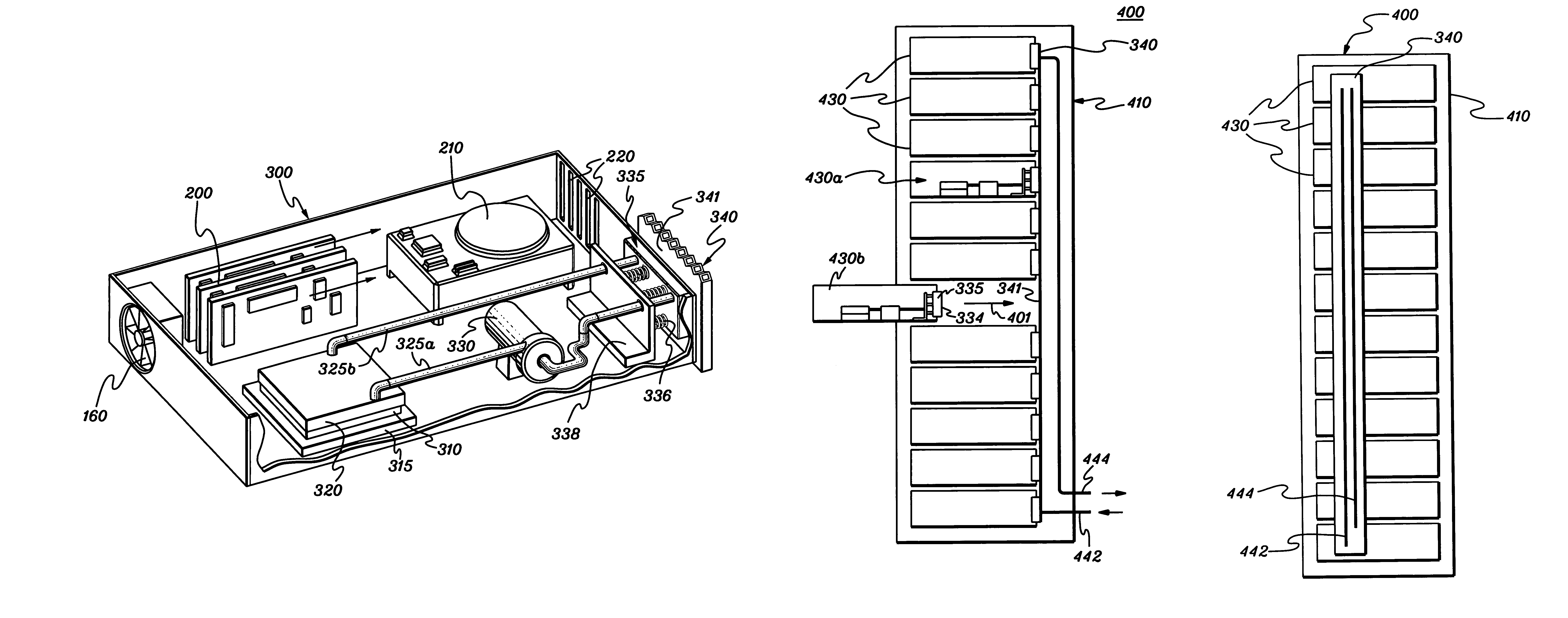
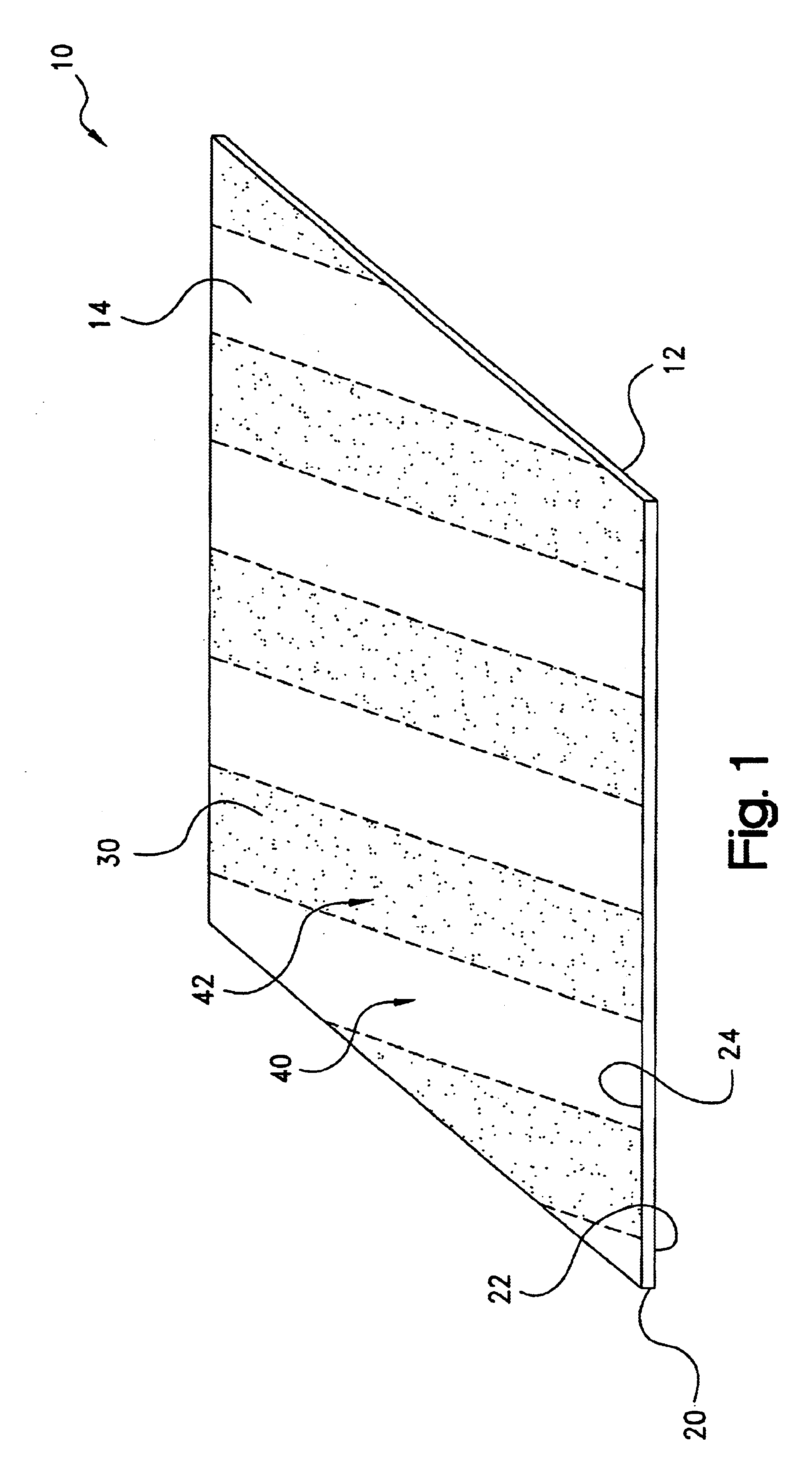
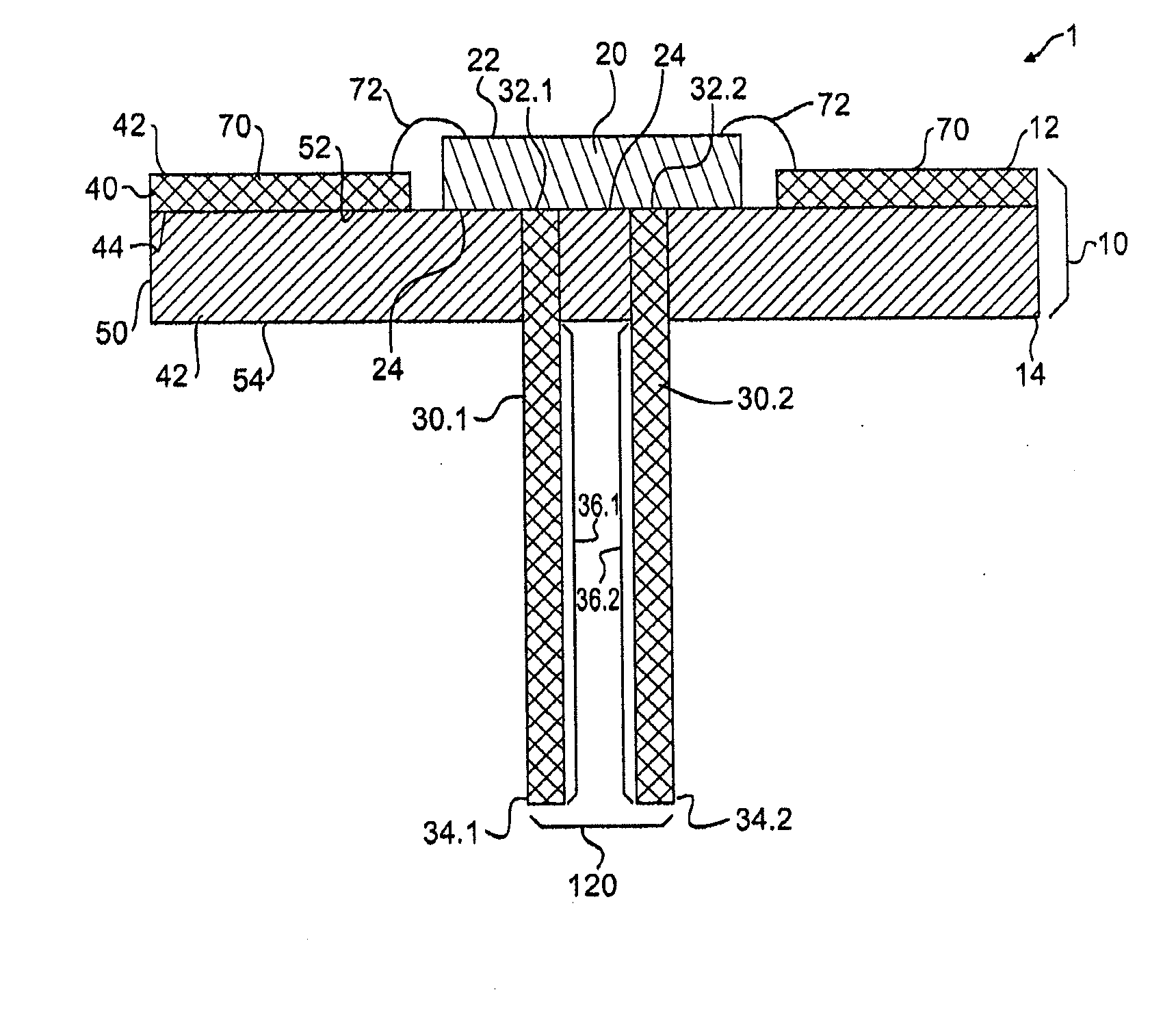
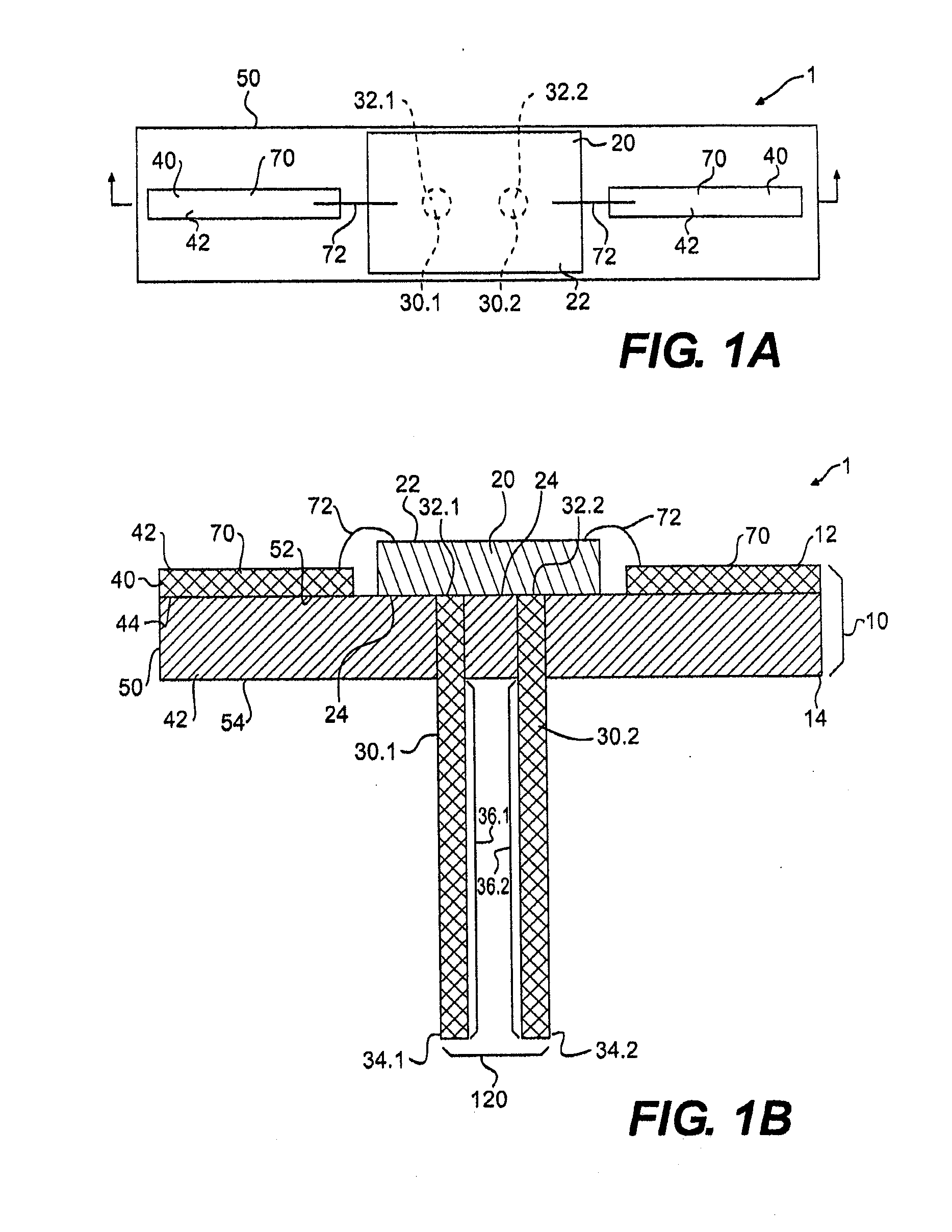
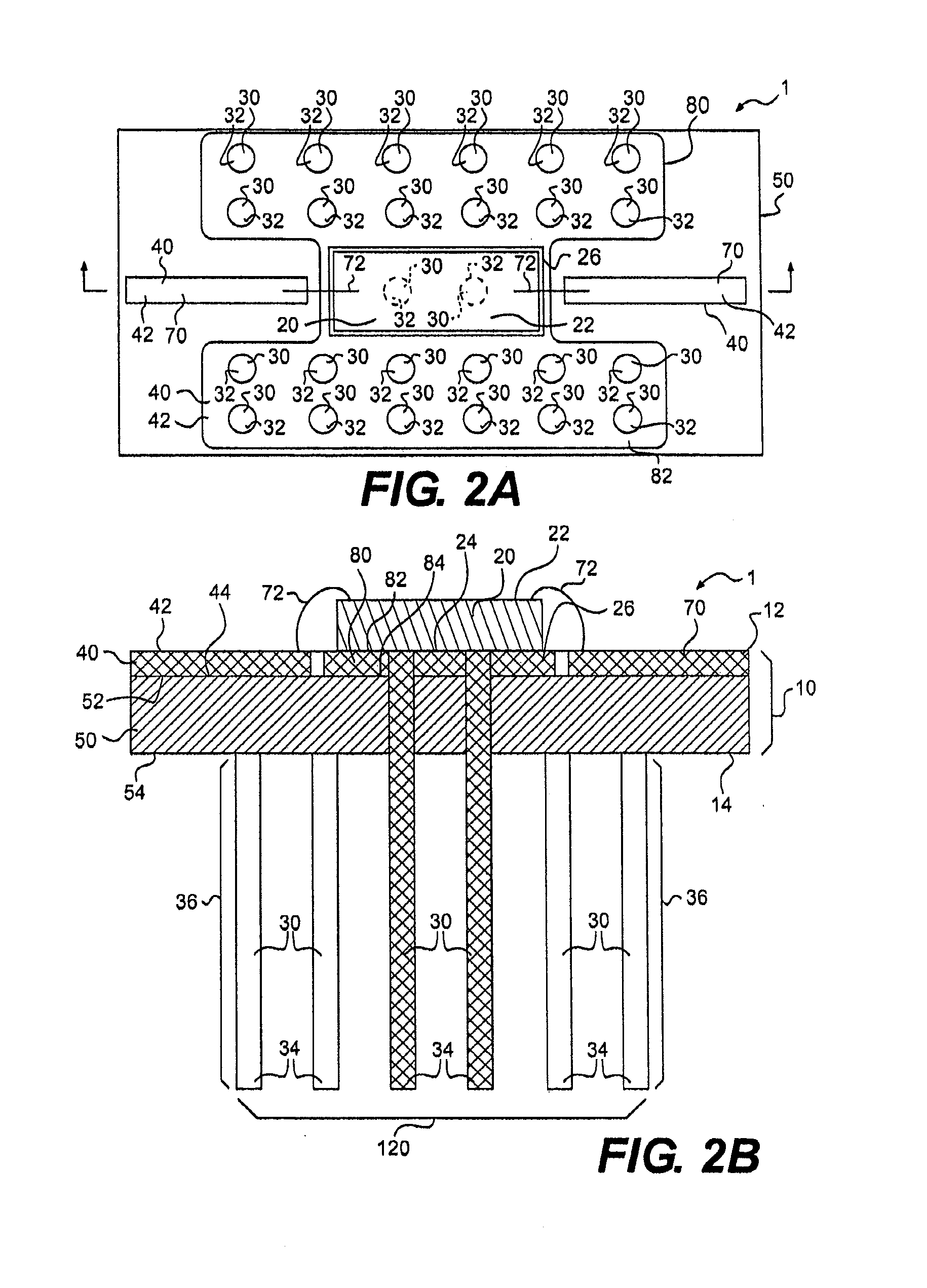
ActiveUS20050068728A1Digital data processing detailsIndirect heat exchangersEngineeringThermal dissipation
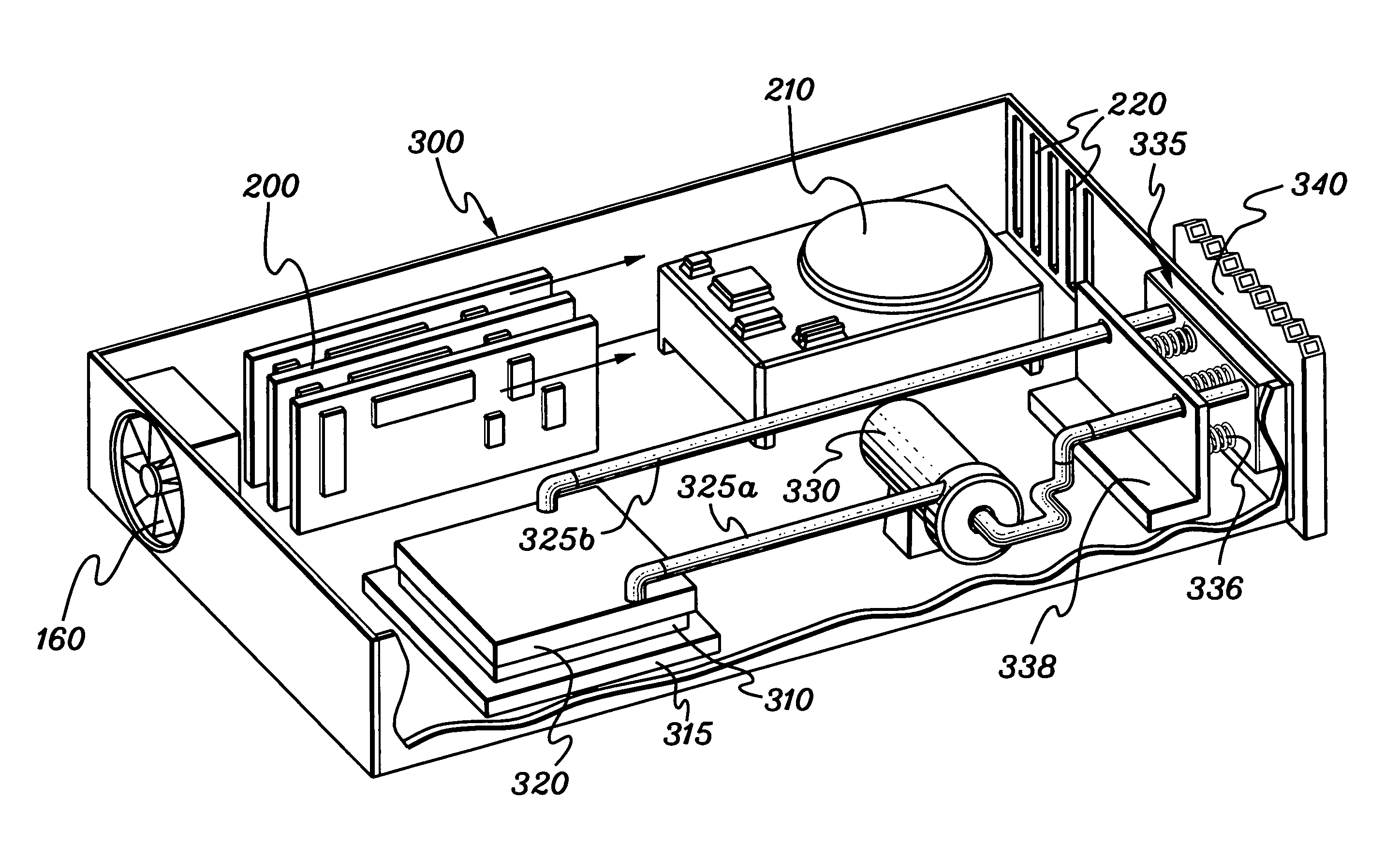
A thermal dissipation assembly and method, and a cooled multi-drawer electronics rack are provided having a first cooling loop and a second cooling loop. The first cooling loop is disposed substantially within an electronics drawer and positioned to extract heat from an electronics module within the drawer. The first cooling loop further includes a first planar heat transfer surface. The second cooling loop is disposed substantially external to the electronics drawer and includes a second planar heat transfer surface. A biasing mechanism mechanically forces the first planar heat transfer surface and the second heat transfer surface coplanar when the electronics drawer is in a docked position in the electronics rack to facilitate the transfer of heat from the first cooling loop to the second cooling loop.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
Non-electrically conductive thermal dissipator for electronic components
InactiveUS6705388B1Improve consistencyEasy to disassembleSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectronic componentPrinted circuit board
A thermal dissipator disposable in a heat transfer relationship with a heat-generating source, such as an electronic component, which is mounted on a substrate, such as a printed circuit board. The dissipator includes a thermal dissipation member having a top and bottom surface, and a pressure sensitive adhesive layer disposed on the thermal dissipation member to cover at-least a portion of the bottom surface thereof. The dissipation member is formed of a thermally-conductive, electrically-nonconductive ceramic material. The pressure sensitive adhesive layer has an inner surface adhered to the bottom surface of the thermal dissipation member, and an outer surface bondable to a heat transfer surface of the source for attaching the dissipator to the source in a heat transfer relationship therewith.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
Case and rack system for liquid submersion cooling of electronic devices connected in an array
ActiveUS7911793B2Reduce the amount requiredReduce weightDigital data processing detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsInterior spaceMultiple case
A liquid submersion cooling system that is suitable for cooling a number of electronic devices in parallel using a plurality of cases connected to a rack system. The system cools heat-generating components in server computers and other devices that use electronic, heat-generating components and are connected in parallel systems. The system includes a housing having an interior space, a dielectric cooling liquid in the interior space, a heat-generating electronic component disposed within the space and submerged in the dielectric cooling liquid. The rack system contains a manifold system to engage and allow liquid transfer for multiple cases and IO connectors to engage electrically with multiple cases / electronic devices. The rack system can be connected to a pump system for pumping the liquid into and out of the rack, to and from external heat exchangers, heat pumps, or other thermal dissipation / recovery devices.
Owner:LIQUIDCOOL SOLUTIONS
Thermal-sprayed metallic conformal coatings used as heat spreaders
InactiveUS6965071B2Eliminate needReduce device temperatureMolten spray coatingScreening gaskets/sealsElectromagnetic interferenceEngineering
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
Light-emitting unit with enhanced thermal dissipation and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS7192163B2Improve cooling effectImprove heat transfer performanceLighting applicationsPoint-like light sourceEngineeringLight-emitting diode
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Light-emitting unit with enhanced thermal dissipation and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20060139932A1Improve cooling effectImprove heat transfer performanceLighting applicationsPoint-like light sourceEngineeringLight-emitting diode
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Photovoltaic receiver for solar concentrator applications
InactiveUS20090000662A1Impact performanceMaintaining dielectricFinal product manufactureLaminationDielectricThermal energy
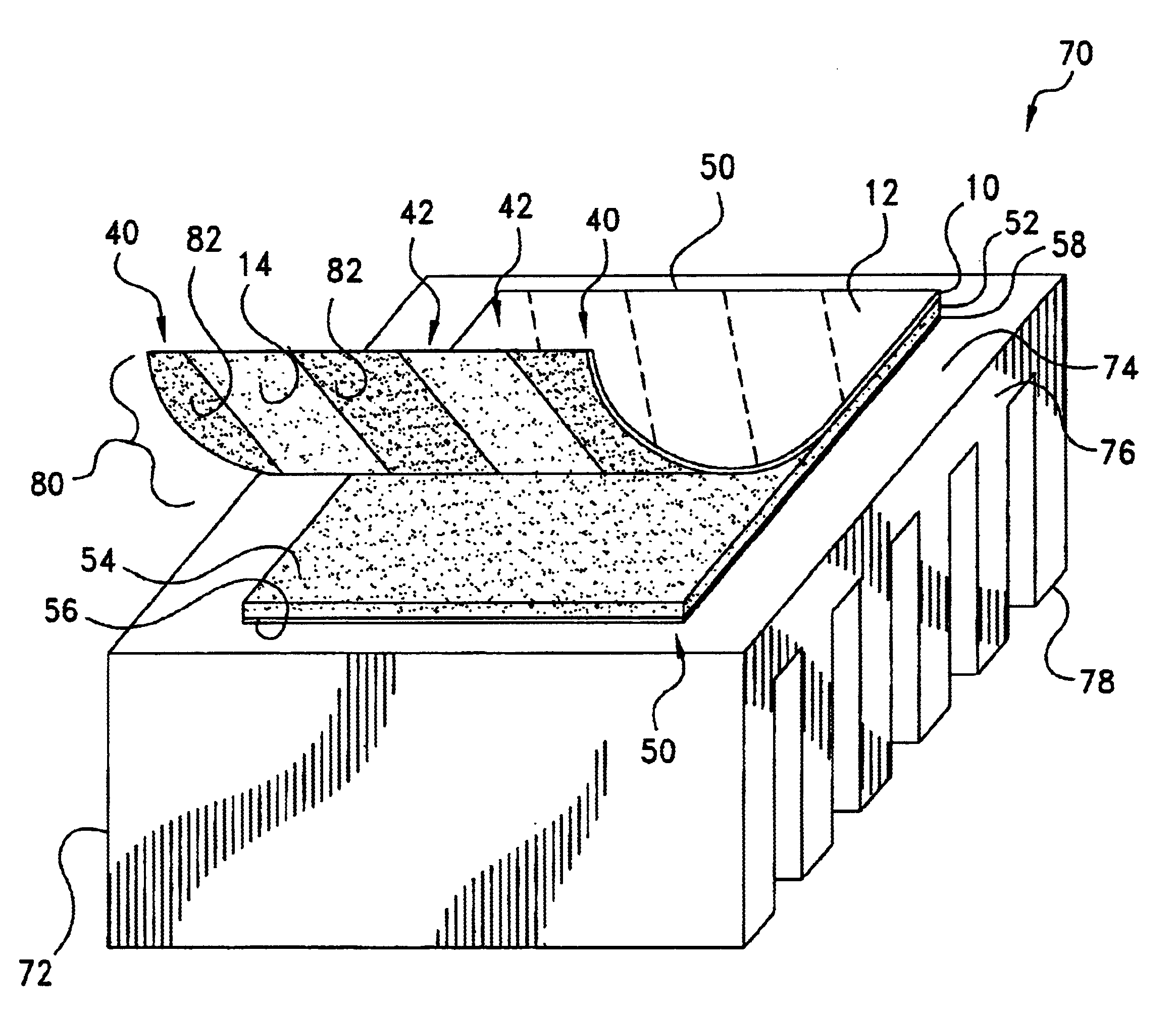
The present invention provides solar concentrators incorporating photovoltaic receiver assemblies with improved thermal dissipation, dielectric, encapsulation, and cell / wiring protection characteristics. The concentrators are particularly useful for photovoltaic power systems such as rooftop mounted systems. The present invention teaches that the geometry of the substrate used to support receiver assemblies can have a dramatic impact upon thermal / dielectric performance. In particular, the present invention teaches how contours incorporated into such substrates can improve thermal performance (i.e., dissipation of thermal energy from photovoltaic cells through the substrate) while still maintaining dielectric and encapsulation objectives. In the past, dielectric and encapsulation objectives have been obtained at the expense of such thermal dissipation. Also, material choice and form also impacts thermal, dielectric, and encapsulation performance. In preferred embodiments, components of receiver assemblies are provided in sheet form and laminated together in the course of making the receiver assemblies.
Owner:SOLIANT ENERGY INC
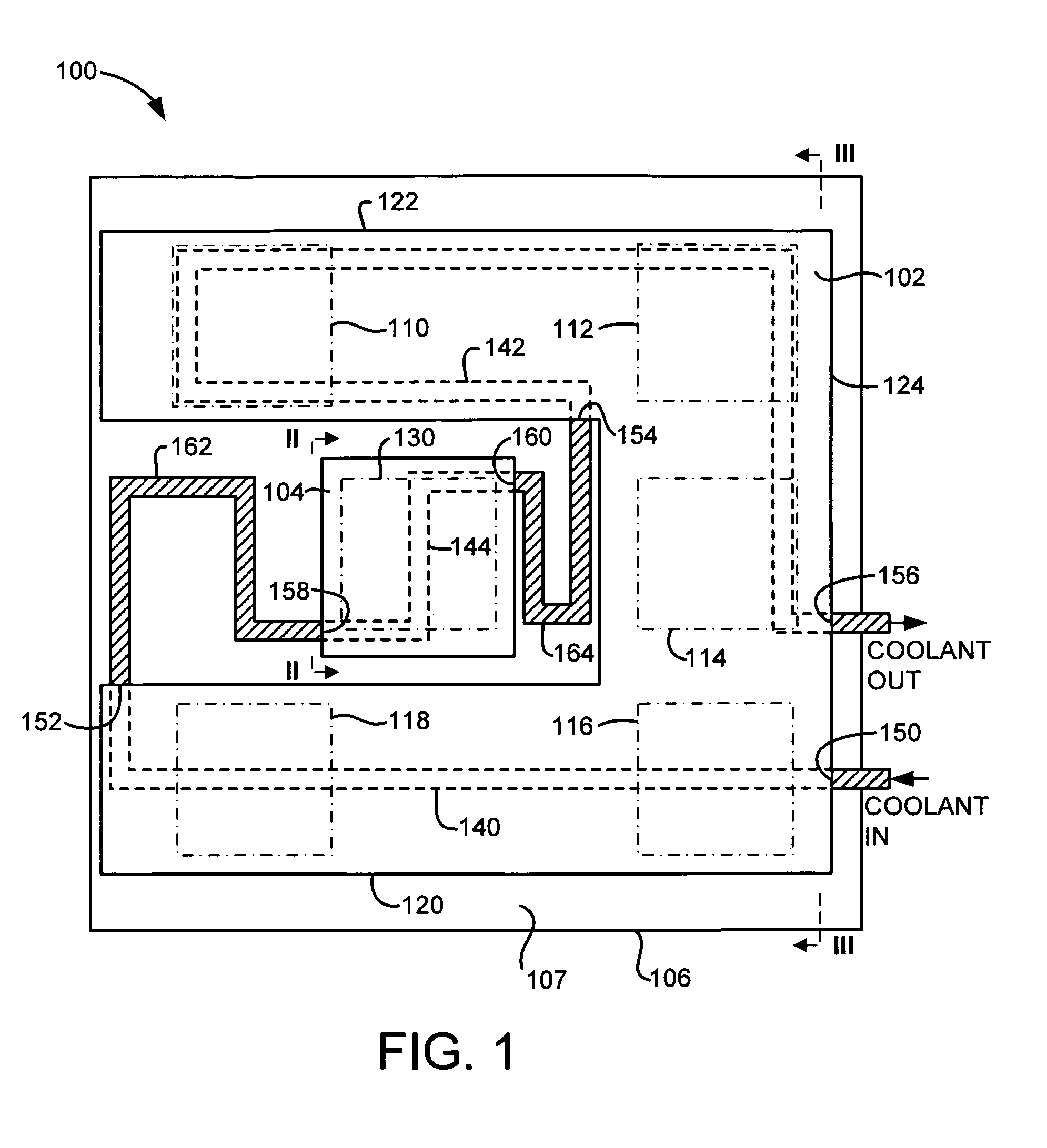
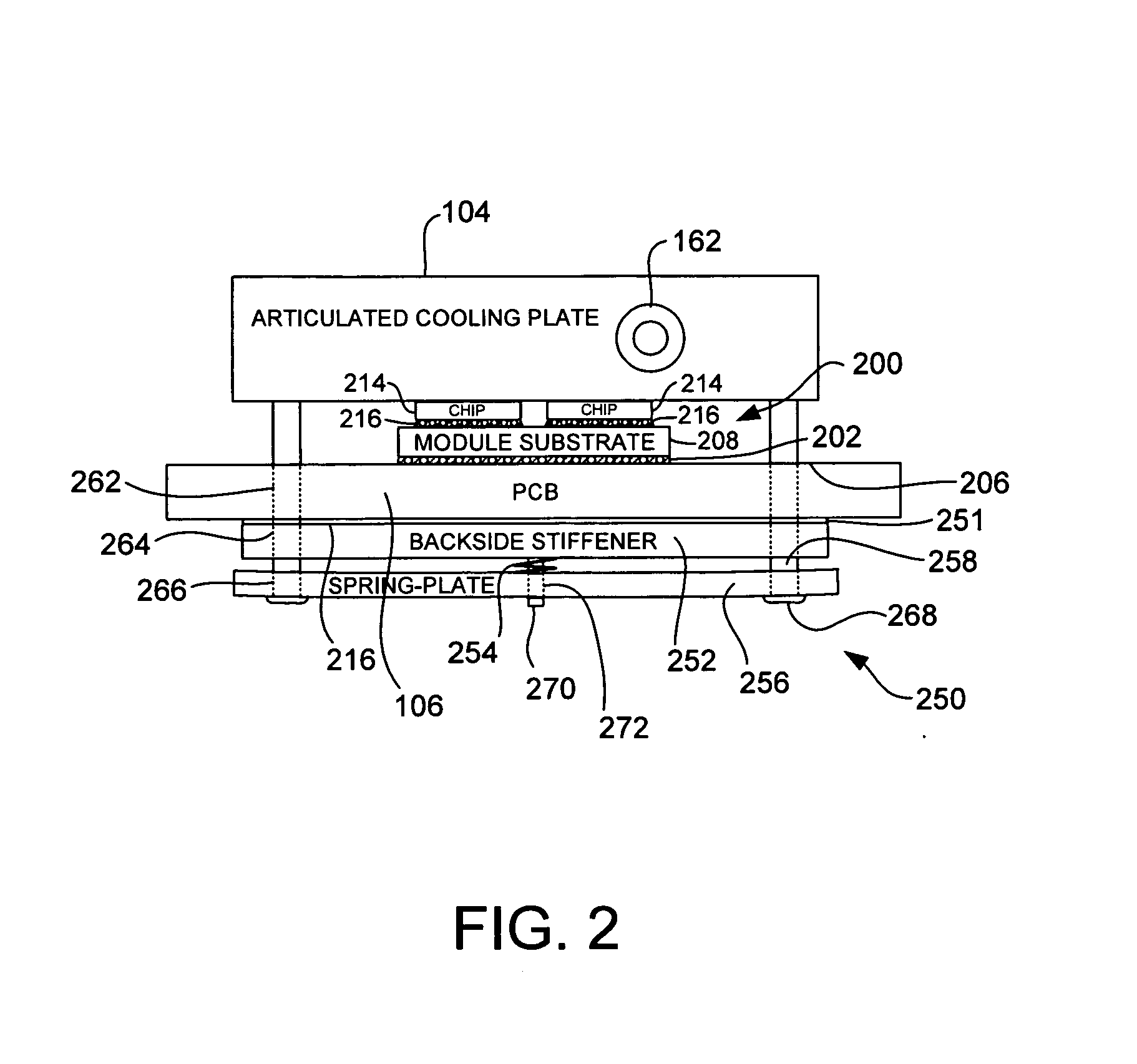
Cooling Plate Assembly with Fixed and Articulated Interfaces, and Method for Producing Same
InactiveUS20090213541A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElastic compressionFree expansion
A cooling plate assembly for transferring heat from electronic components mounted on a circuit board includes both fixed and articulated interfaces. A fixed-gap coldplate is positioned over and in thermal contact with (e.g., through an elastomerically compressive pad thermal interface material) electronic components mounted on the circuit board's top surface. An articulated coldplate is positioned over and in thermal contact with at least one electronic component mounted on the circuit board's top surface. In the preferred embodiments, the articulated coldplate is spring-loaded against one or more high power processor components having power dissipation greater than that of the electronic components under the fixed-gap cooling plate. Thermal dissipation channels in the coldplates are interconnected by flexible tubing, such as copper tubing with a free-expansion loop. In the preferred embodiments, the coldplates and the flexible tubing are connected to define a portion of a single flow loop used to circulate cooling fluid through the coldplates.
Owner:IBM CORP
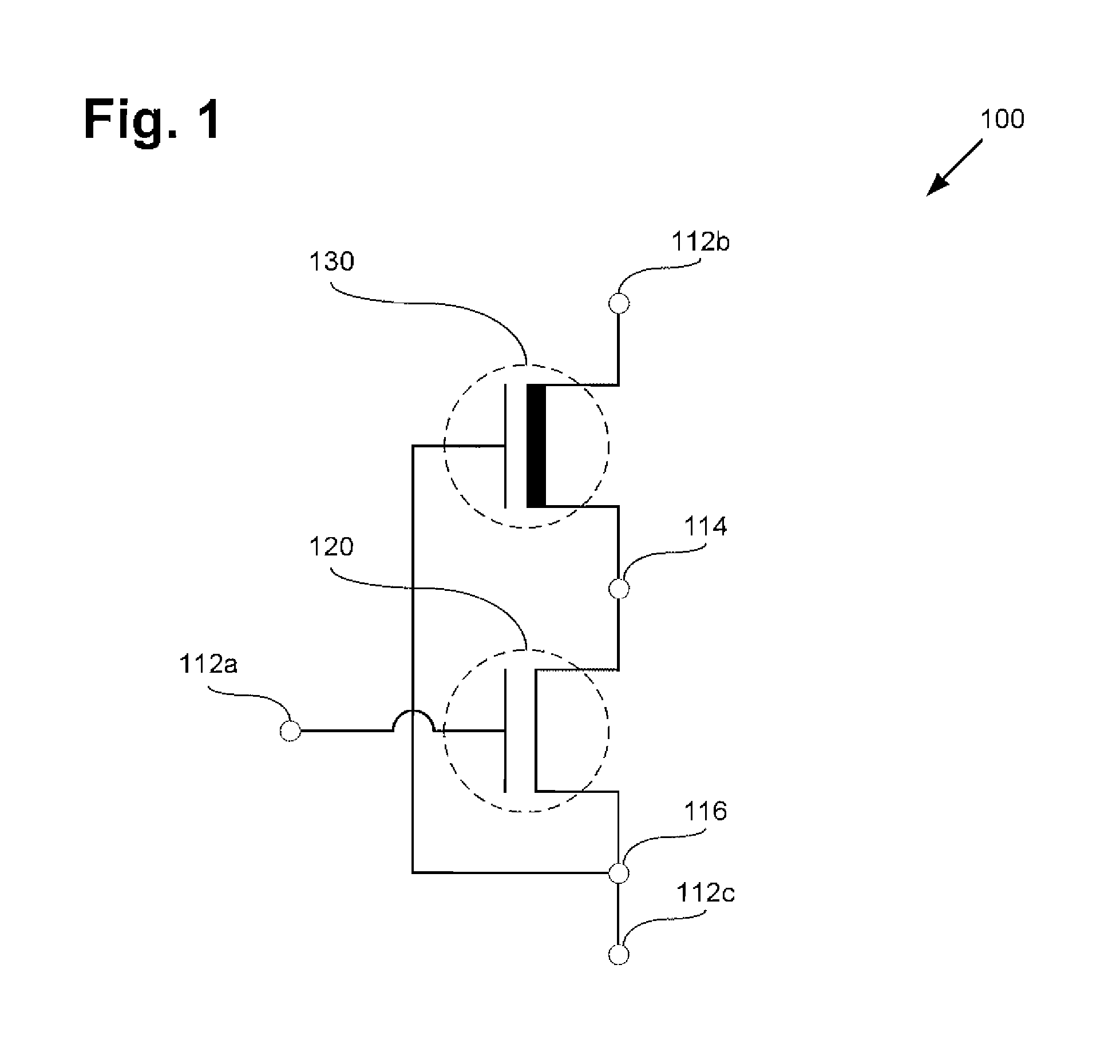
III-Nitride Transistor Stacked with FET in a Package
ActiveUS20120223321A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSmall form factorField-effect transistor
One exemplary disclosed embodiment comprises a three-terminal stacked-die package including a field effect transistor (FET), such as a silicon FET, stacked atop a III-nitride transistor, such that a drain of the FET resides on and is electrically coupled to a source of the III-nitride transistor. A first terminal of the package is coupled to a gate of the FET, a second terminal of the package is coupled to a drain of the III-nitride transistor. A third terminal of the package is coupled to a source of the FET. In this manner, devices such as cascoded switches may be packaged in a stacked-die form, resulting in reduced parasitic inductance and resistance, improved thermal dissipation, smaller form factor, and lower manufacturing cost compared to conventional packages.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
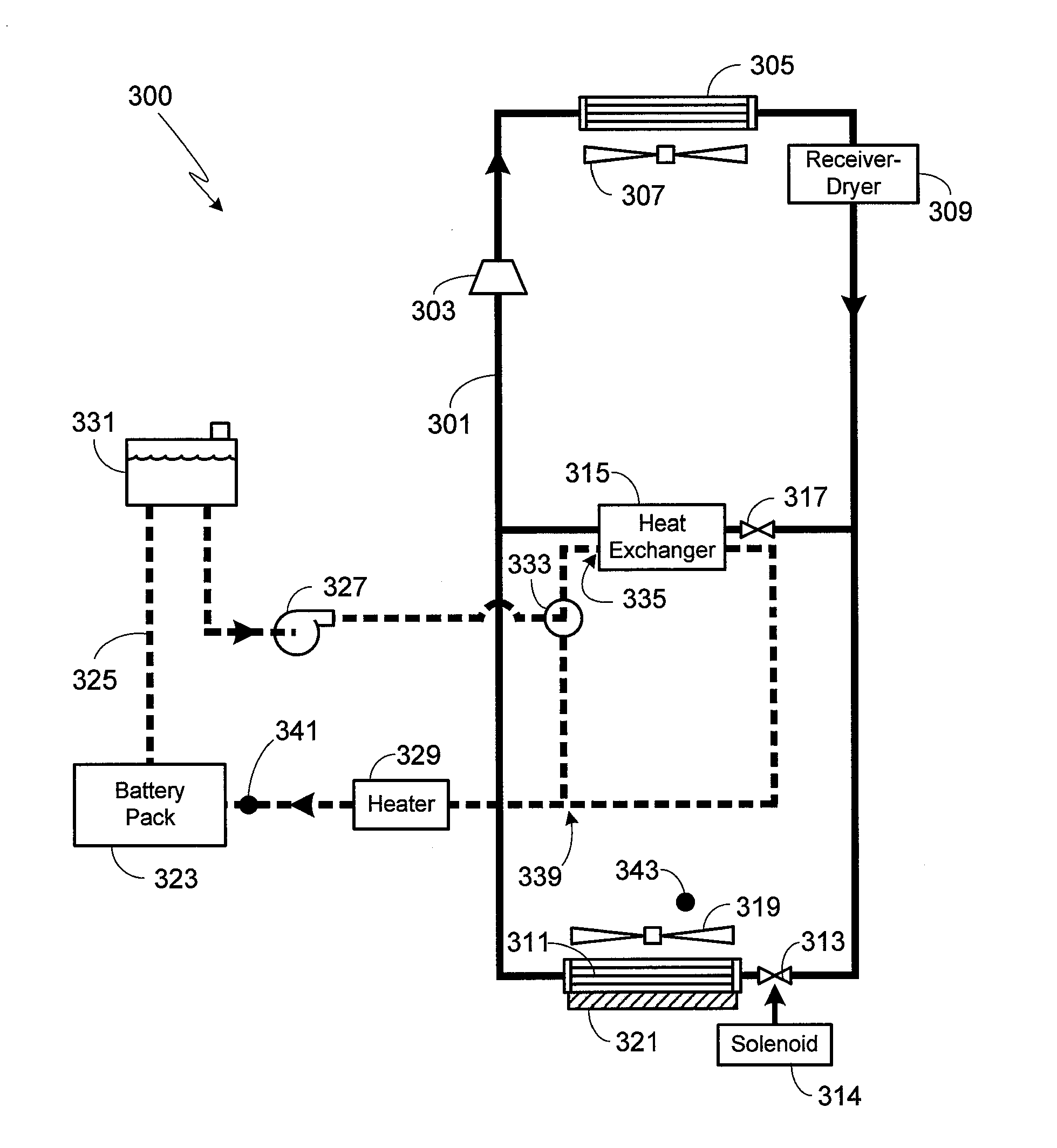
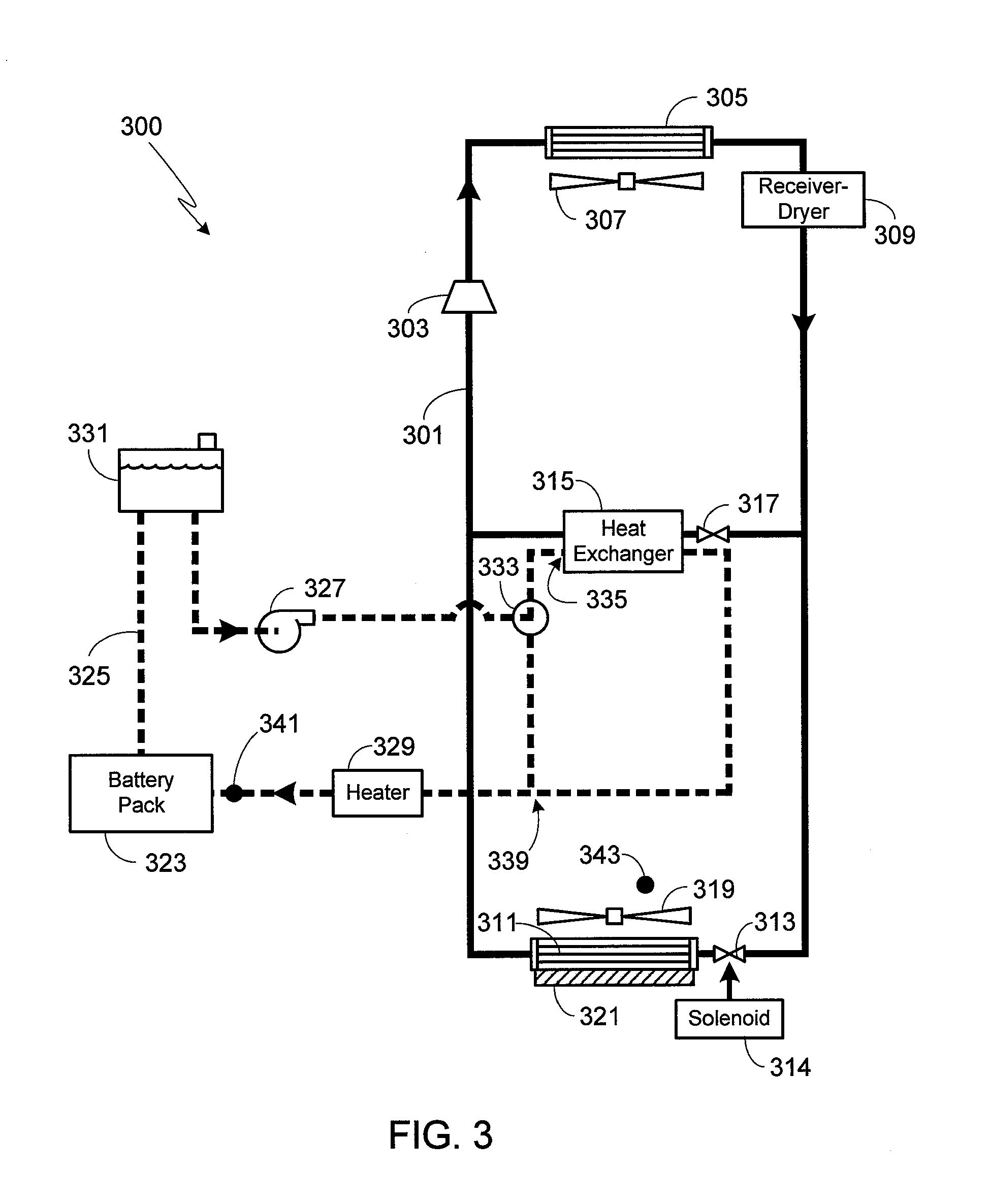
Battery Centric Thermal Management System Utilizing a Heat Exchanger Blending Valve
ActiveUS20130298583A1Compression machines with non-reversible cycleCells cooling/heatingThermal management systemEngineering
A method of regulating thermal dissipation from a vehicle battery pack is provided in which a by-pass valve is used to control the amount of battery pack coolant either passing through, or by-passing, a heat exchanger, where the coolant passing through the heat exchanger is cooled by a refrigeration system. The vehicle's HVAC system is controlled to insure that HVAC operation does not compromise maintaining the battery pack within an acceptable range of temperatures.
Owner:TESLA INC
Methods of processing of gallium nitride
InactiveUS7015117B2Polycrystalline material growthFrom solid stateThermal energyElectrical conductor
A method for improving thermal dissipation in large gallium nitride light emitting diodes includes replacing sapphire with a better thermal conductor resulting in more efficient removal of thermal energy. A method for achieving a reliable and strong temporary bond between a GaN epitaxial layer and a support wafer. A method for transferring an epitaxial film from a growth substrate to a secondary substrate. An excimer laser initiates film delamination from the growth substrate. The laser beam is shaped by a shadow mask and aligned to an existing pattern in the growth substrate. A method for fabricating a LED that radiates white spectrum light. A phosphor that radiates a white spectrum after excitation in the blue or UV spectrum onto the GaN epitaxial wafer prior to die separation and packaging. A method for depositing a metal substrate onto a GaN epitaxy layer.
Owner:ALLEGIS TECH
Integrated LED-based luminare for general lighting
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
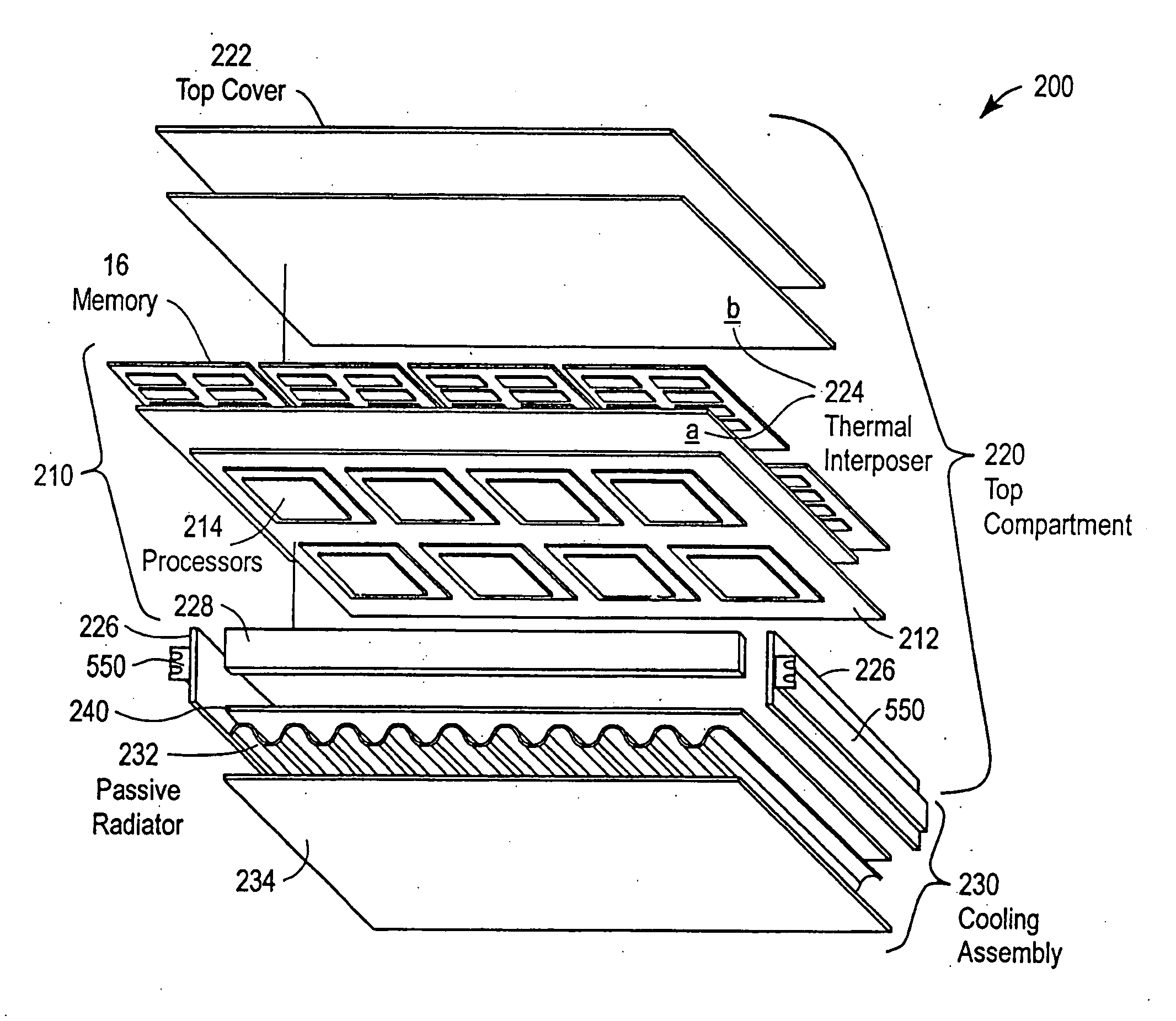
Thermal management for a ruggedized electronics enclosure
InactiveUS20070041160A1High strength to weight ratioEfficient heat dissipationCooling/ventilation/heating modificationsEngineeringElectronic component
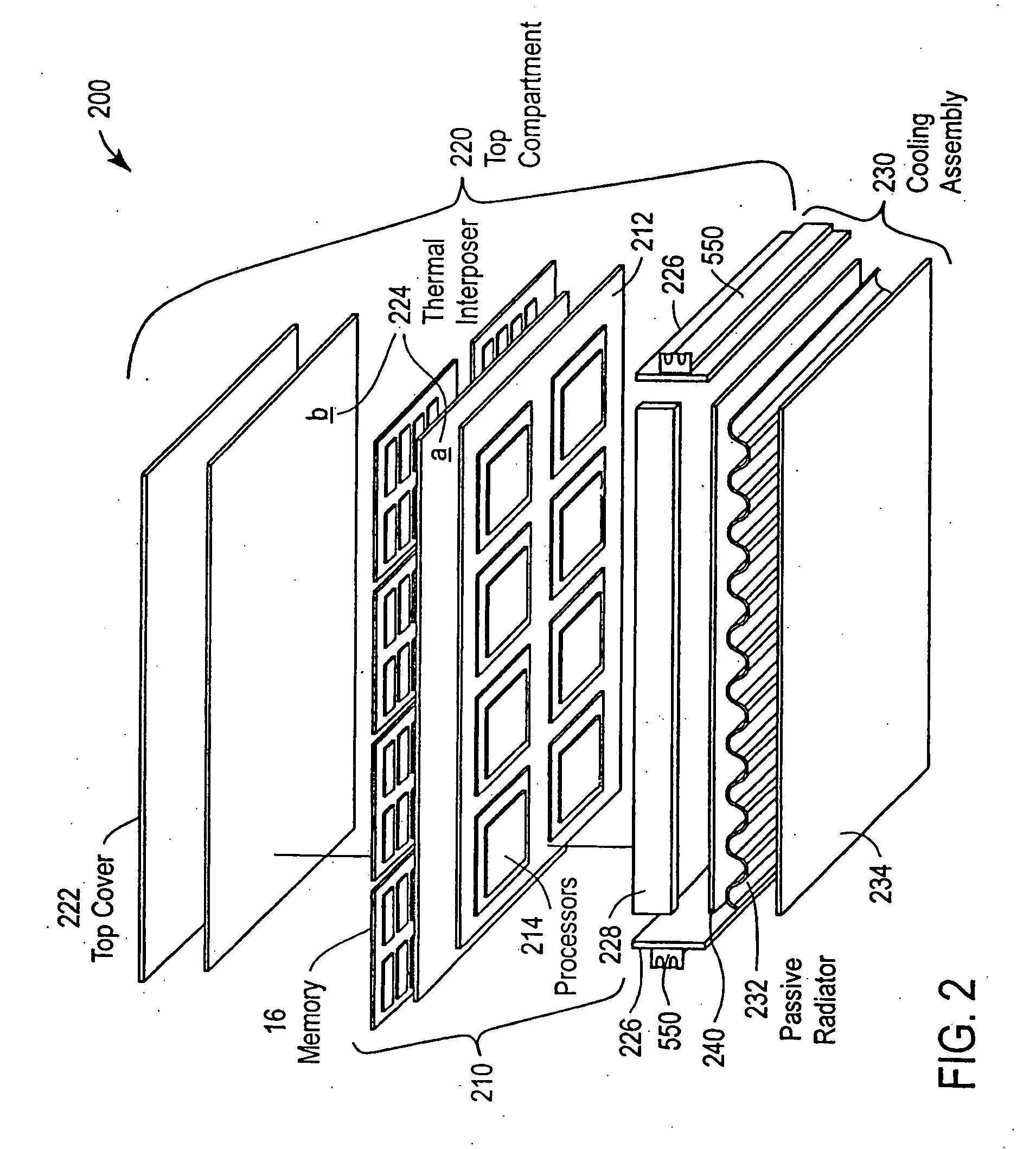
The present invention relates to a liquid cooling assembly for cooling electronic components. The liquid cooling assembly contains a heat spreader plate rigidly coupled to a structural foam layer for providing mechanical support and thermal dissipation for the electronic components. A fluid channel, rigidly coupled to the structural foam, is provided for directing a cooling fluid in the plane of the heat spreader and a bottom plate rigidly coupled to the structural foam to protect the electronic components against one or more destructive shock events and to provide thermal dissipation of heat generated by the electronic components. The present invention also provides a maze structure in the liquid cooling assembly to increase structural stability against destructive shock events. The present invention relates to a ruggedized electronics enclosure for housing electronic components containing a top compartment configured to house the electronic components. The top compartment contains a first electronics layer and a second electronics layer adjacent to said first electronics layer and a cooling assembly, rigidly coupled to the top compartment. A thermal shunt is configured to channel heat from the first and second electronics layers to the cooling assembly and to provide additional mechanical support to protect against potentially destructive shock events.
Owner:THEMIS COMP
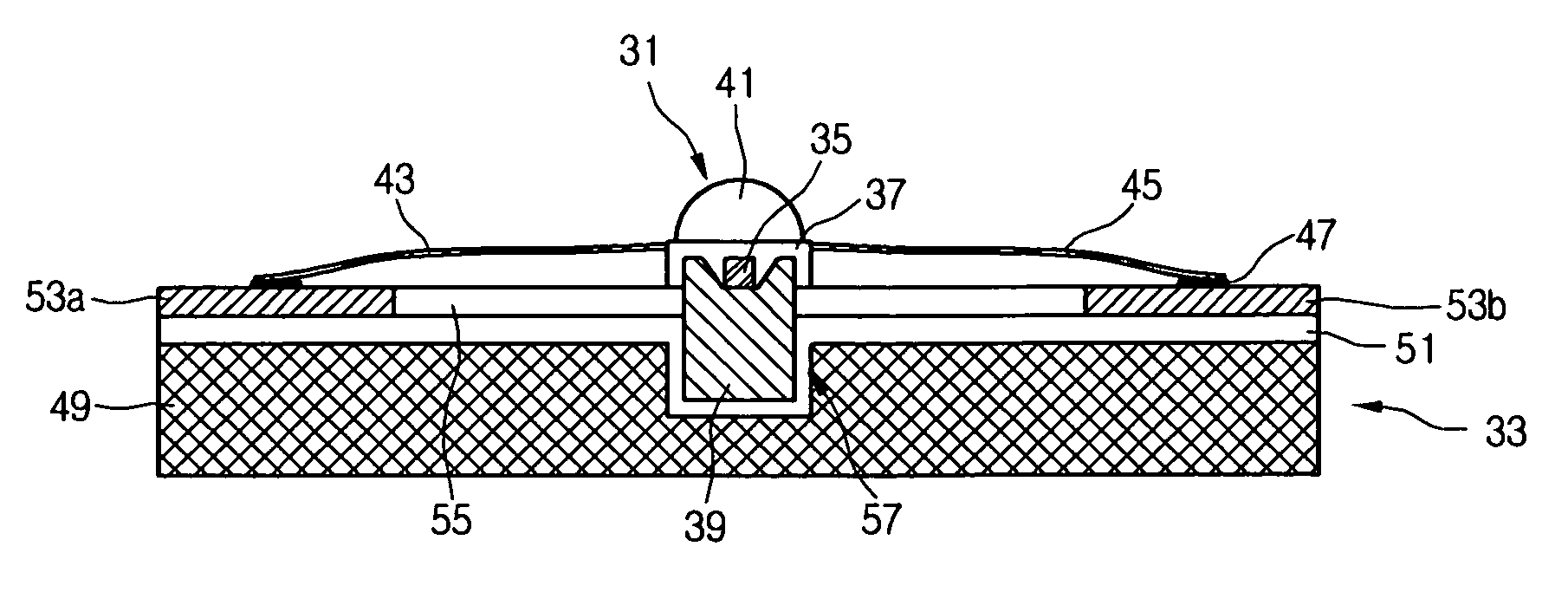
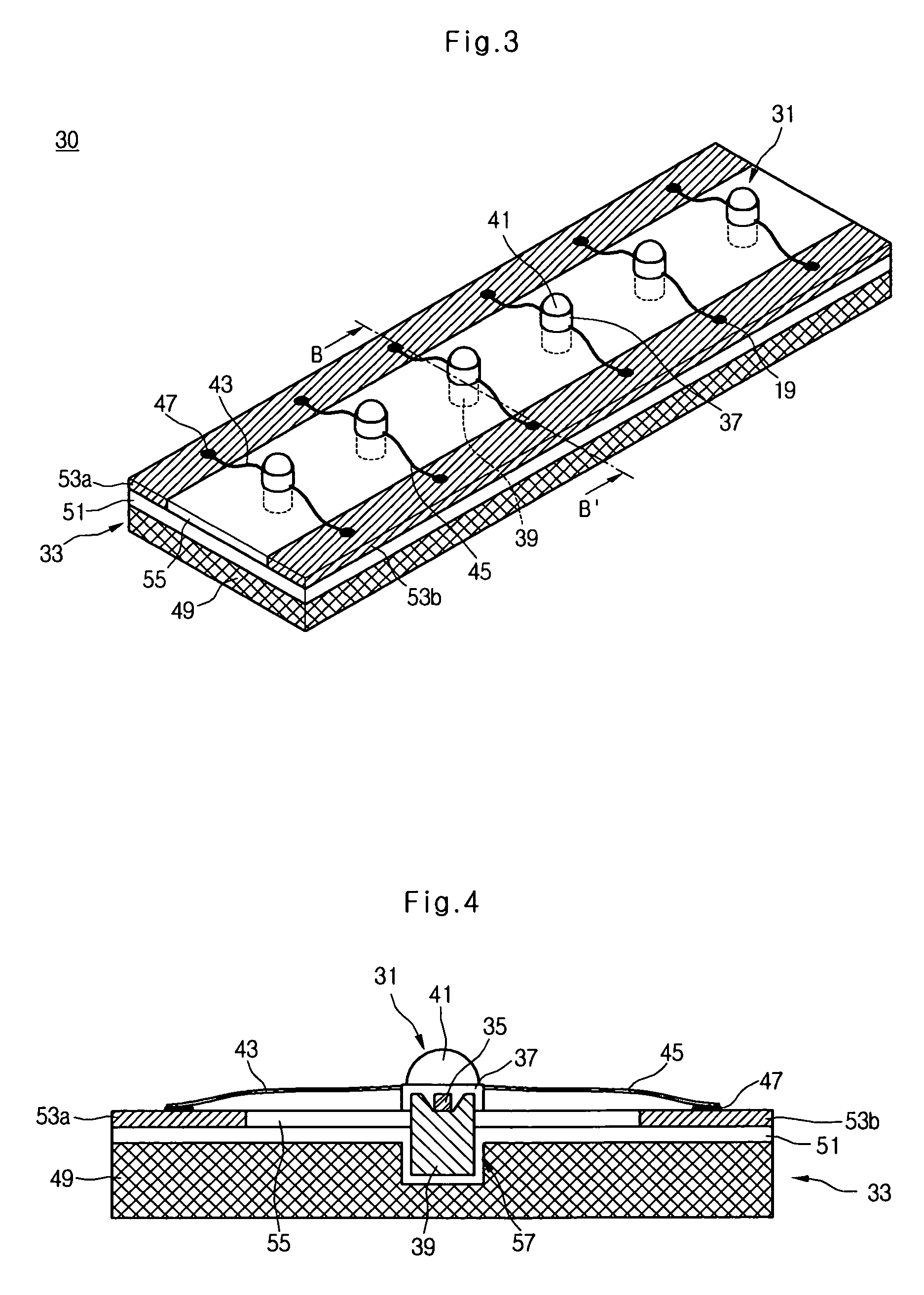
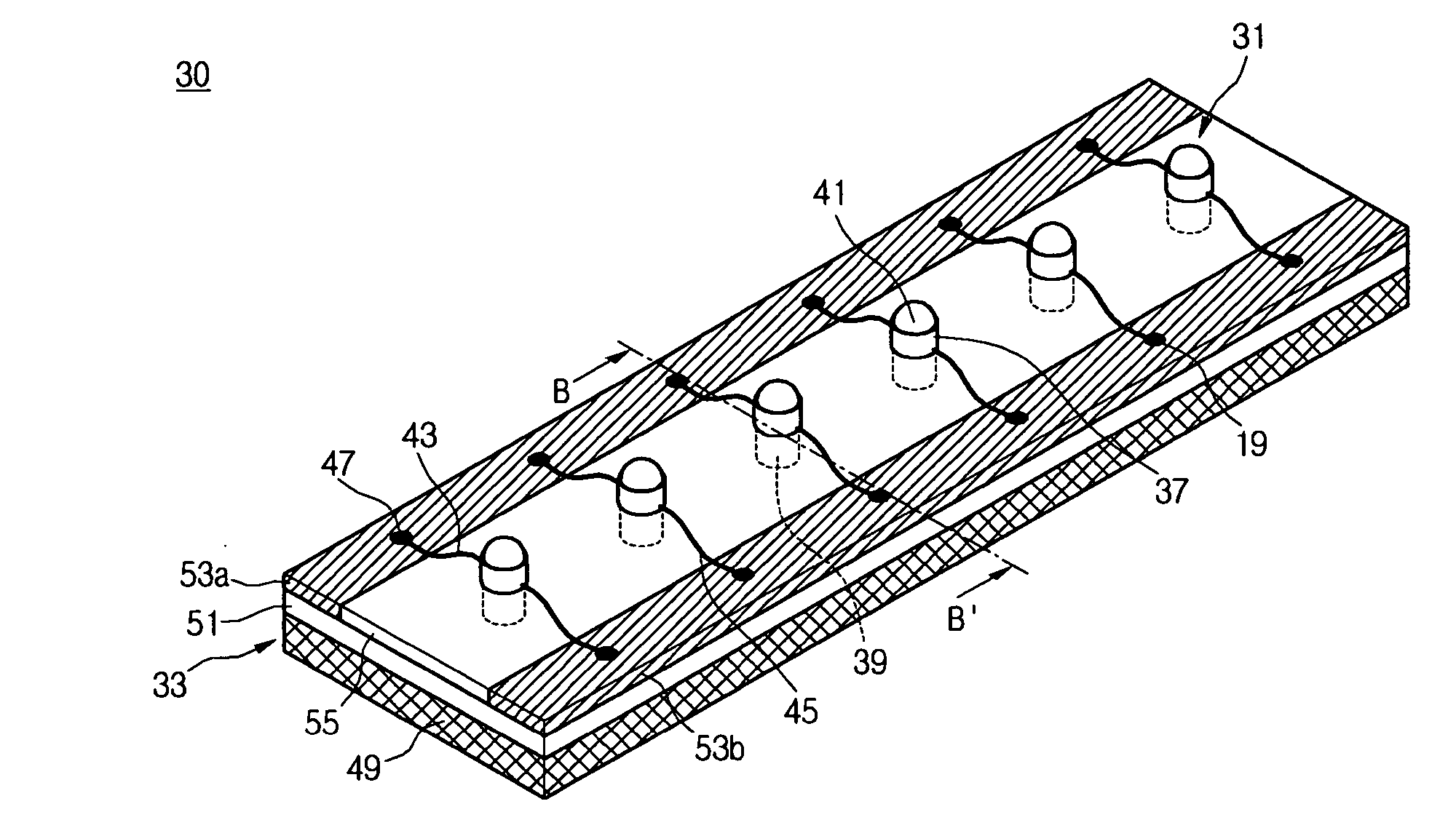
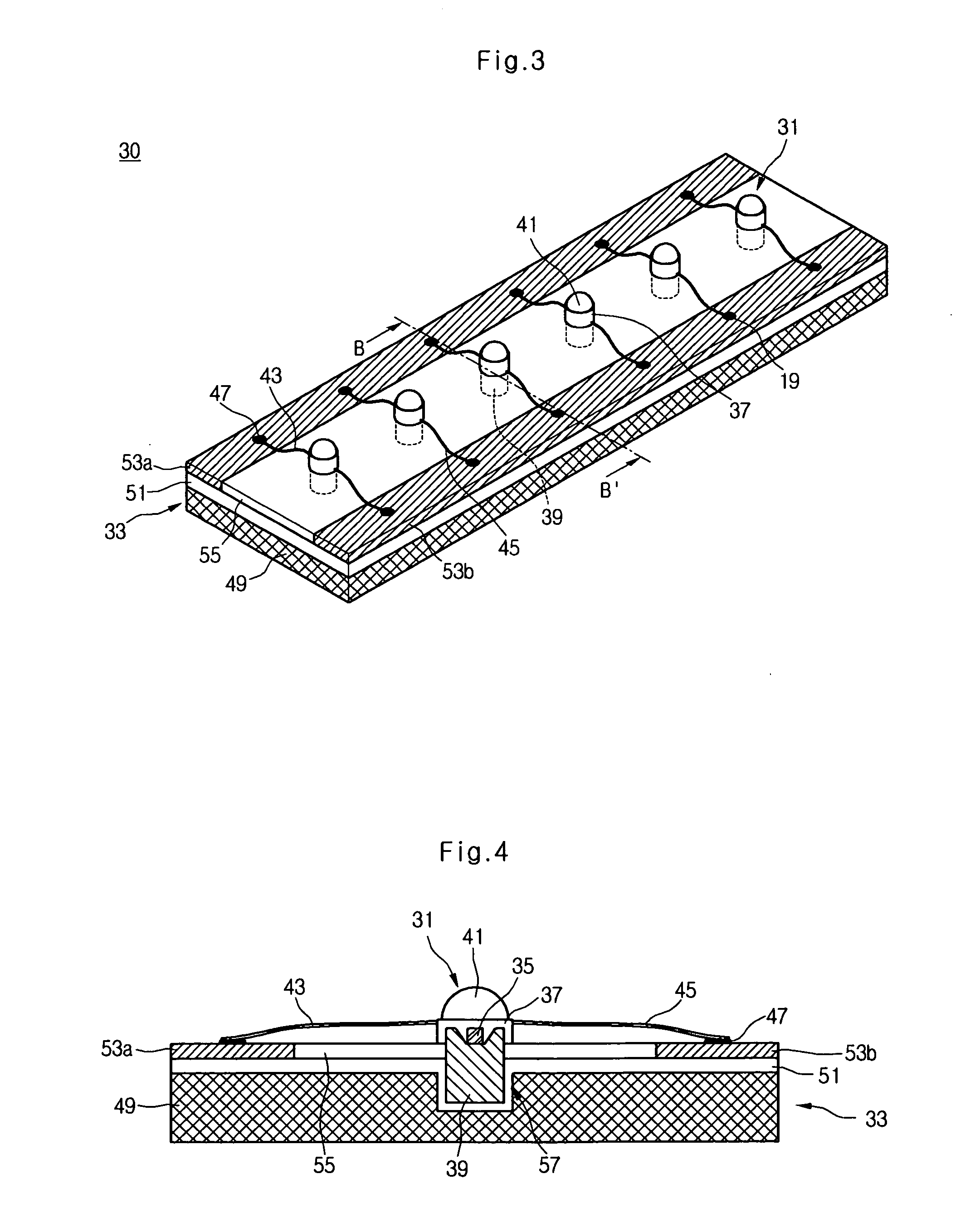
Flexible circuits having improved reliability and thermal dissipation
InactiveUS20080067526A1Flexible propertiesReliability of flexiblePrinted circuit aspectsSolid-state devicesFlexible circuitsElectrical connection
A flexible circuit that includes mounted electrical components, where bonding wires providing an electrical connection to the electrical components are aligned perpendicularly to the primary plane in which the flexible circuit bends and multiple redundant vias for electrical and thermal connections. The flexible circuit may include an array of light emitting diodes “(LEDs”) that are positioned length-wise in a flexile LED strip as well as flexible printed circuits having a plurality of electrical components attached thereto, where the electrical components may include LEDs. Methods of improving the reliability and thermal dissipation of a flexible circuit and producing a flexible circuit with re-aligned bonding wires and multiple vias for electrical and thermal connections are also provided.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Lighting and/or signaling device for a motor vehicle incorporating a material having thermal anisotropy
InactiveUS20070076422A1Improve featuresHigh thermal anisotropyVehicle headlampsPoint-like light sourceAir cycleGraphite
The device comprises at least one power light emitting diode light source and other means able to constitute one or more heat sources of such a nature as to affect the thermal environment of the light emitting diode light source. In accordance with the invention, the device also comprises a support piece formed at least partially from a material based on anisotropic graphite supporting the light emitting diode light source and opposing an effect of the other means on the thermal environment of the light emitting diode light source. According to other characteristics, the support piece comprises at least one thermal dissipation heat sink and the device can comprise a fan able to force a circulation of air through the heat sink.
Owner:VALEO VISION SA
Thermal enhanced low profile package structure
ActiveUS7511365B2Printed electric component incorporationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectronic componentDielectric layer
A thermal enhanced low profile package structure and a method for fabricating the same are provided. The package structure typically includes a metallization layer with an electronic component thereon which is between two provided dielectric layers. The metallization layer as well as the electronic component is embedded and packaged while the substrates are laminated via a lamination process. The fabricated package structure performs not only a superior electric performance, but also an excellent enhancement in thermal dissipation.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Solid state lighting apparatus utilizing axial thermal dissipation
InactiveUS7740380B2Improve cooling effectHeat dissipationPoint-like light sourceLighting support devicesLight equipmentHighly oriented pyrolytic graphite
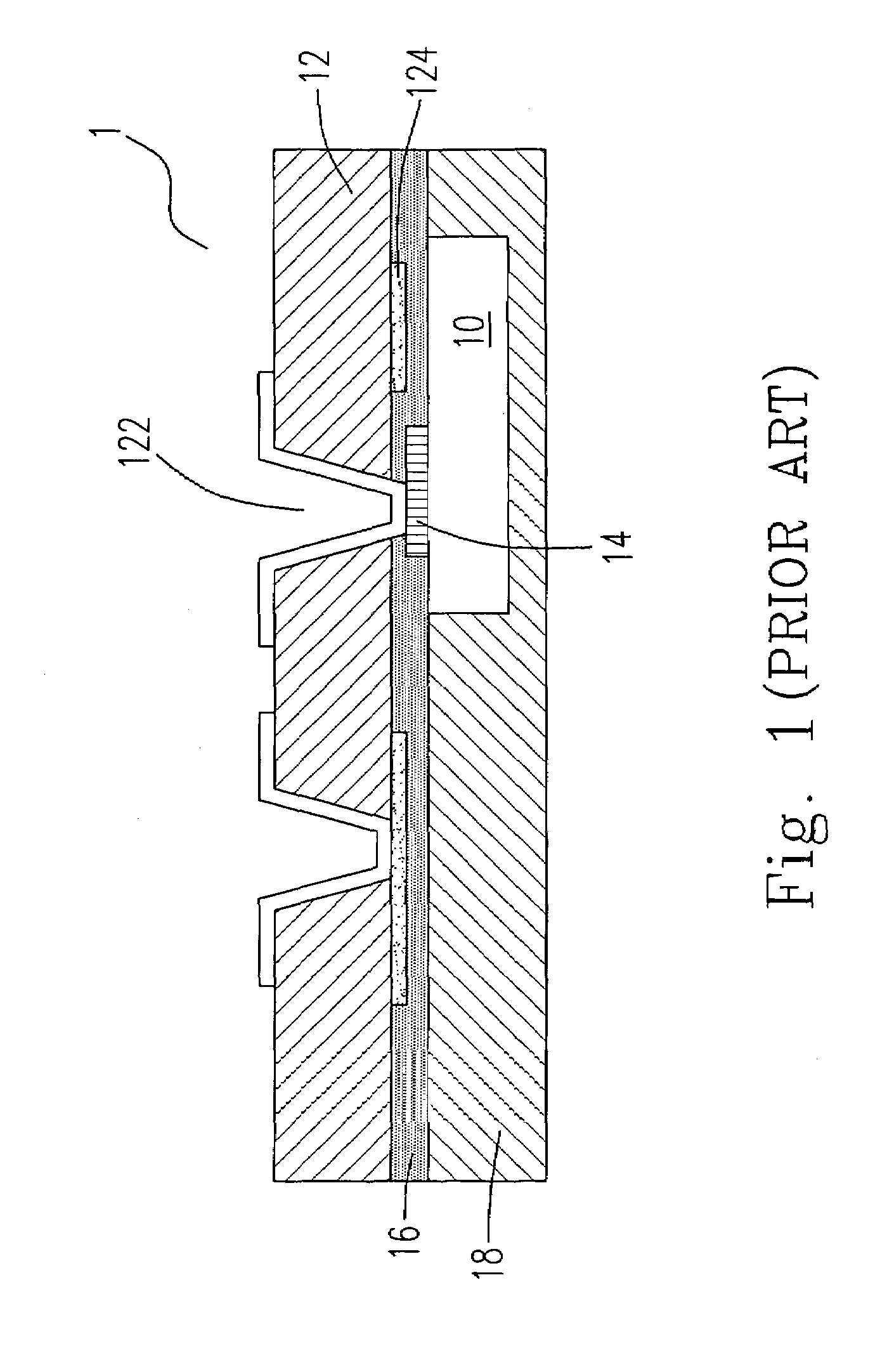
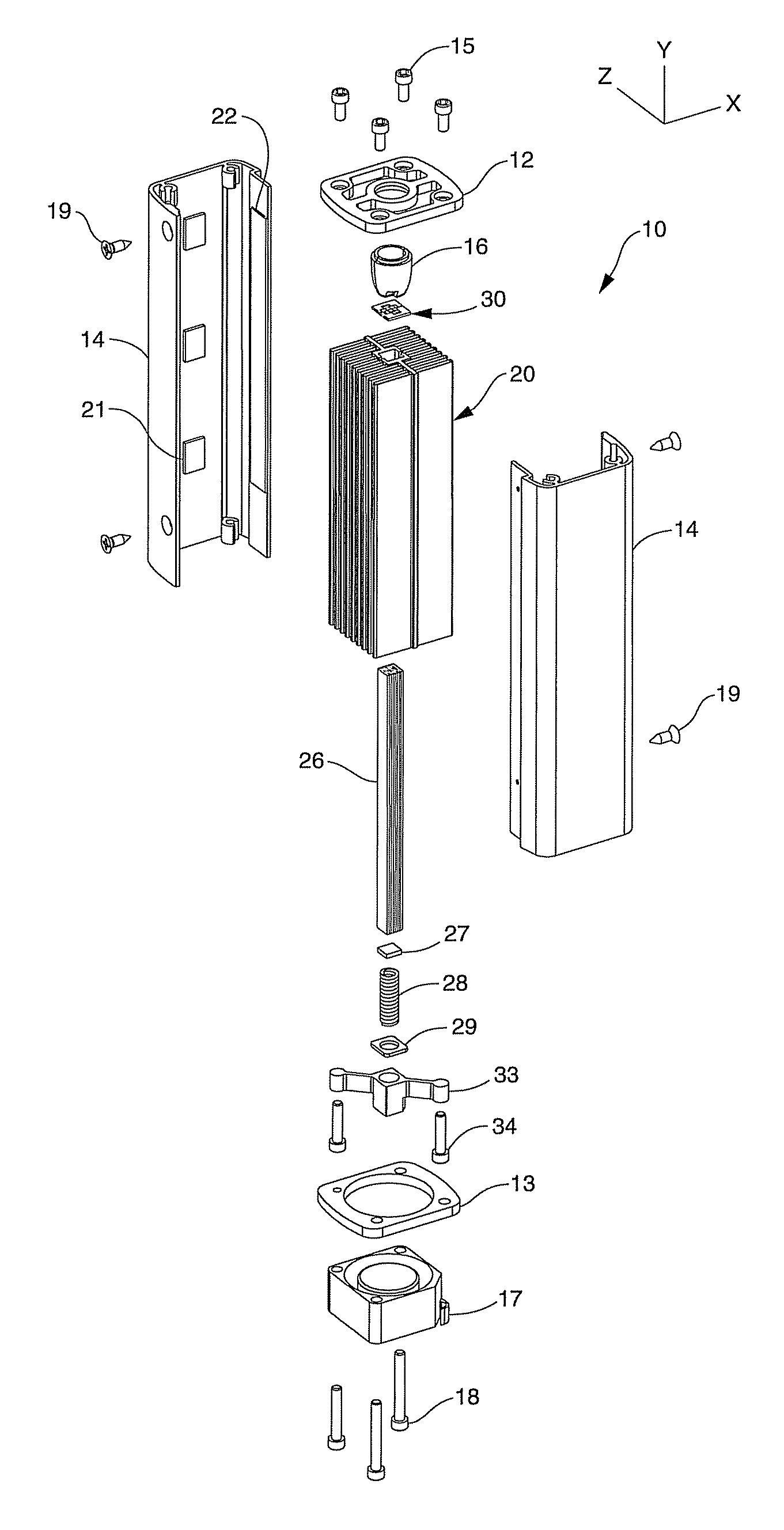
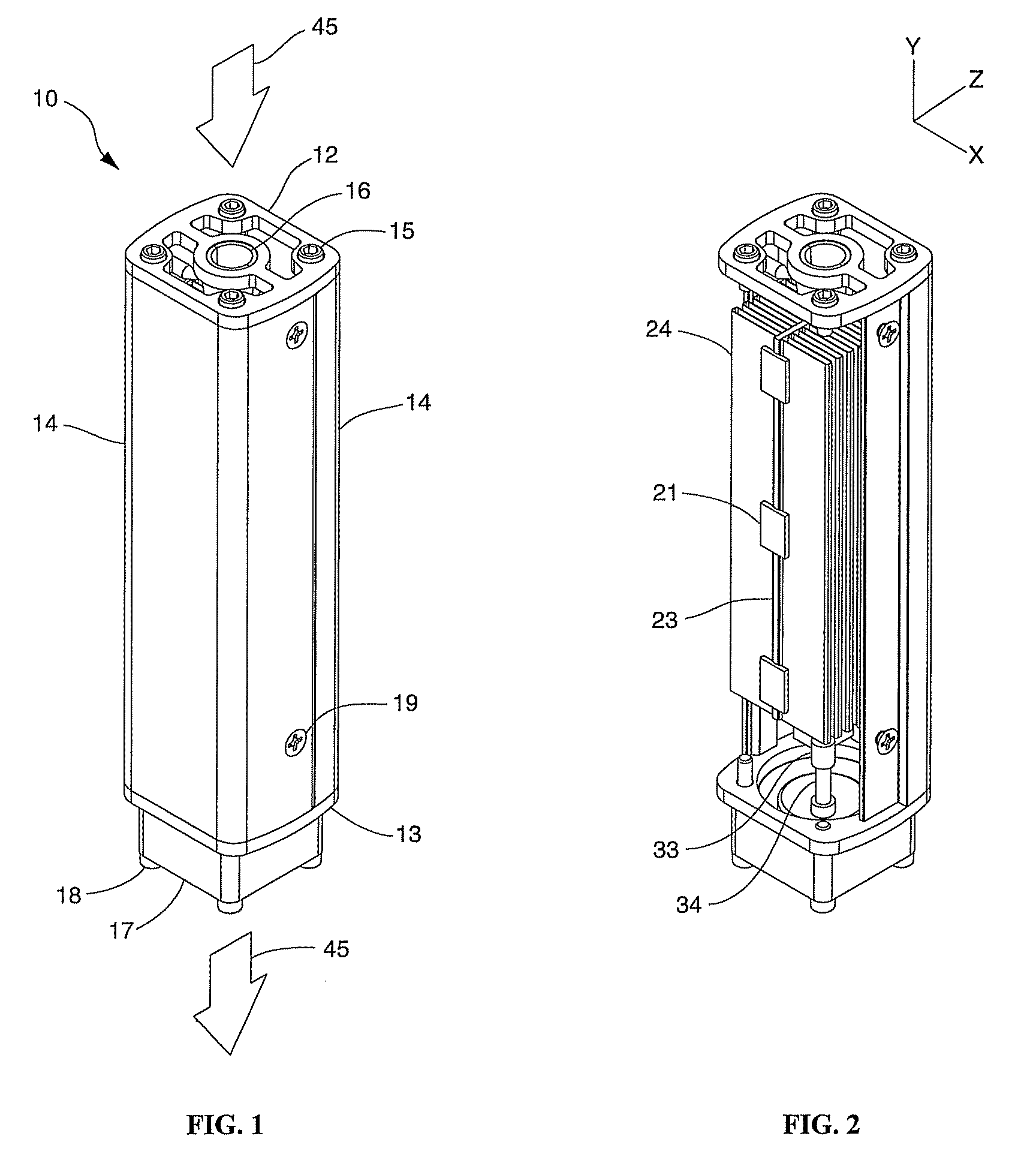
A solid state lighting apparatus characterized by its compact, predominately axial form factor, utilizes an axial thermal transfer member constructed of Highly Oriented Pyrolytic Graphite (HOPG) to aid in the dissipation of waste heat generated during its operation. The lighting apparatus is chiefly comprised of a Light Emitting Diode (LED) die array and circuit structure assembly affixed to one end of the axial thermal transfer member and further includes a transversely mounted heat sink structure, running the length of, and being affixed to, opposite sides of the axial member. The axial member serves to distribute waste heat down its length, and simultaneously, into a transverse plane where the waste heat is dissipated into the transversely mounted heat sink structure. A fan may be utilized to evacuate the waste heat out of the lighting apparatus and into the ambient environment.
Owner:THRAILKILL JOHN E
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com