Patents
Literature
318 results about "Conduction cooling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Conduction cooling is the method of using thermally conductive material to transfer heat from the PCB to a cold wall or heat sink.
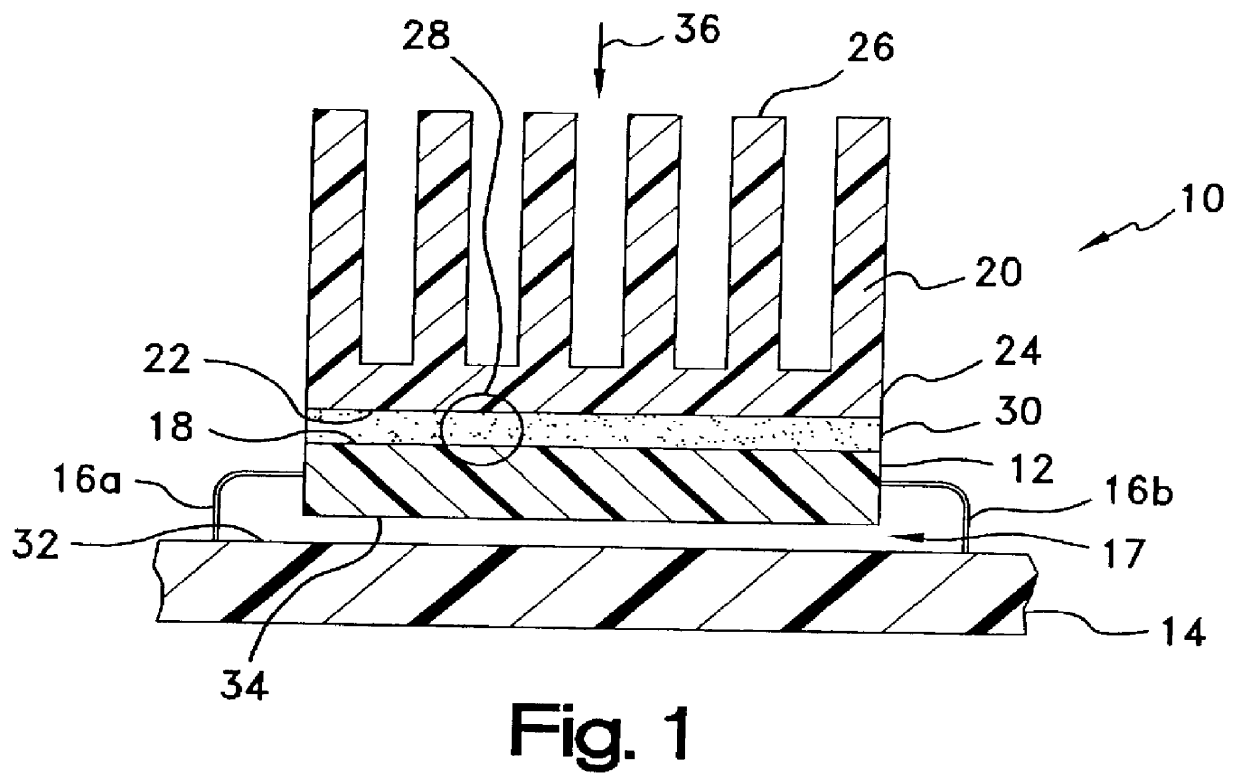
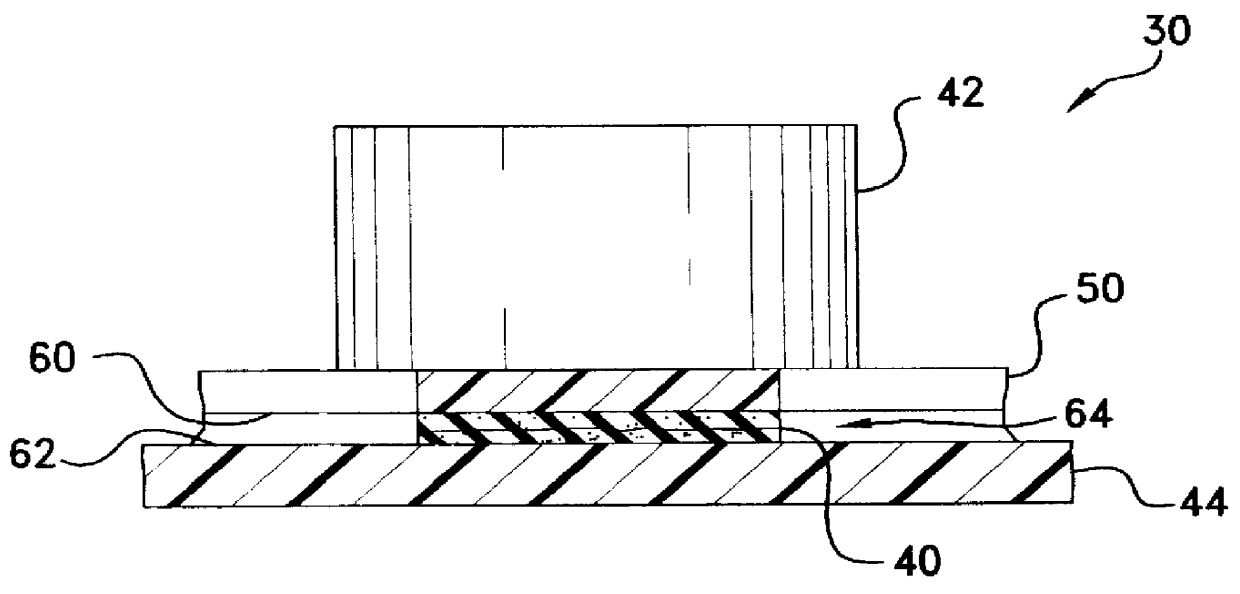
Conformal thermal interface material for electronic components
InactiveUS6054198AOptimize allocationReadily apparentSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesRoom temperatureConductive materials
A thermally-conductive interface for conductively cooling a heat-generating electronic component having an associated thermal dissipation member such as a heat sink. The interface is formed as a self-supporting layer of a thermally-conductive material which is form-stable at normal room temperature in a first phase and substantially conformable in a second phase to the interface surfaces of the electronic component and thermal dissipation member. The material has a transition temperature from the first phase to the second phase which is within the operating temperature range of the electronic component.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
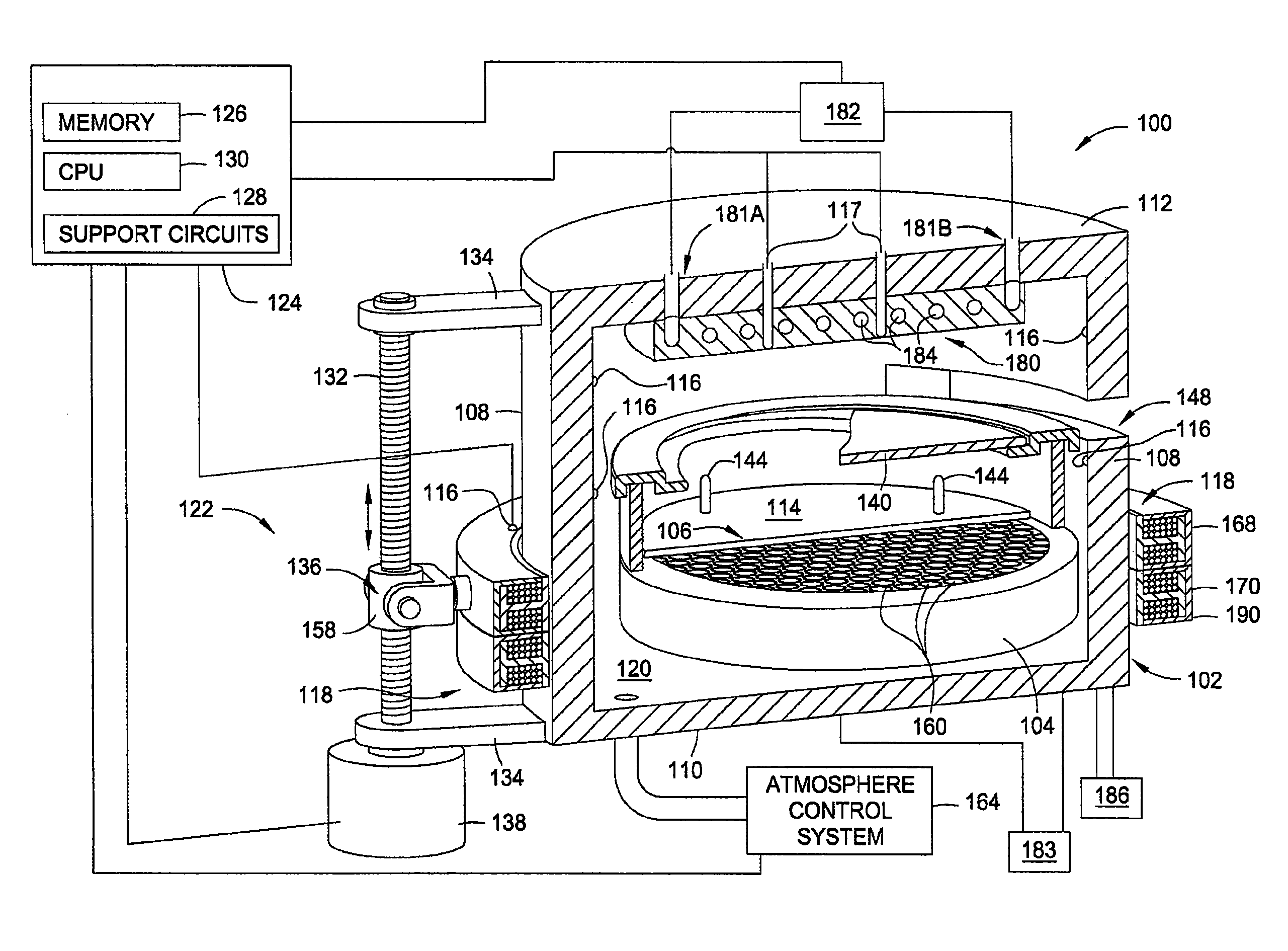
Rapid conductive cooling using a secondary process plane
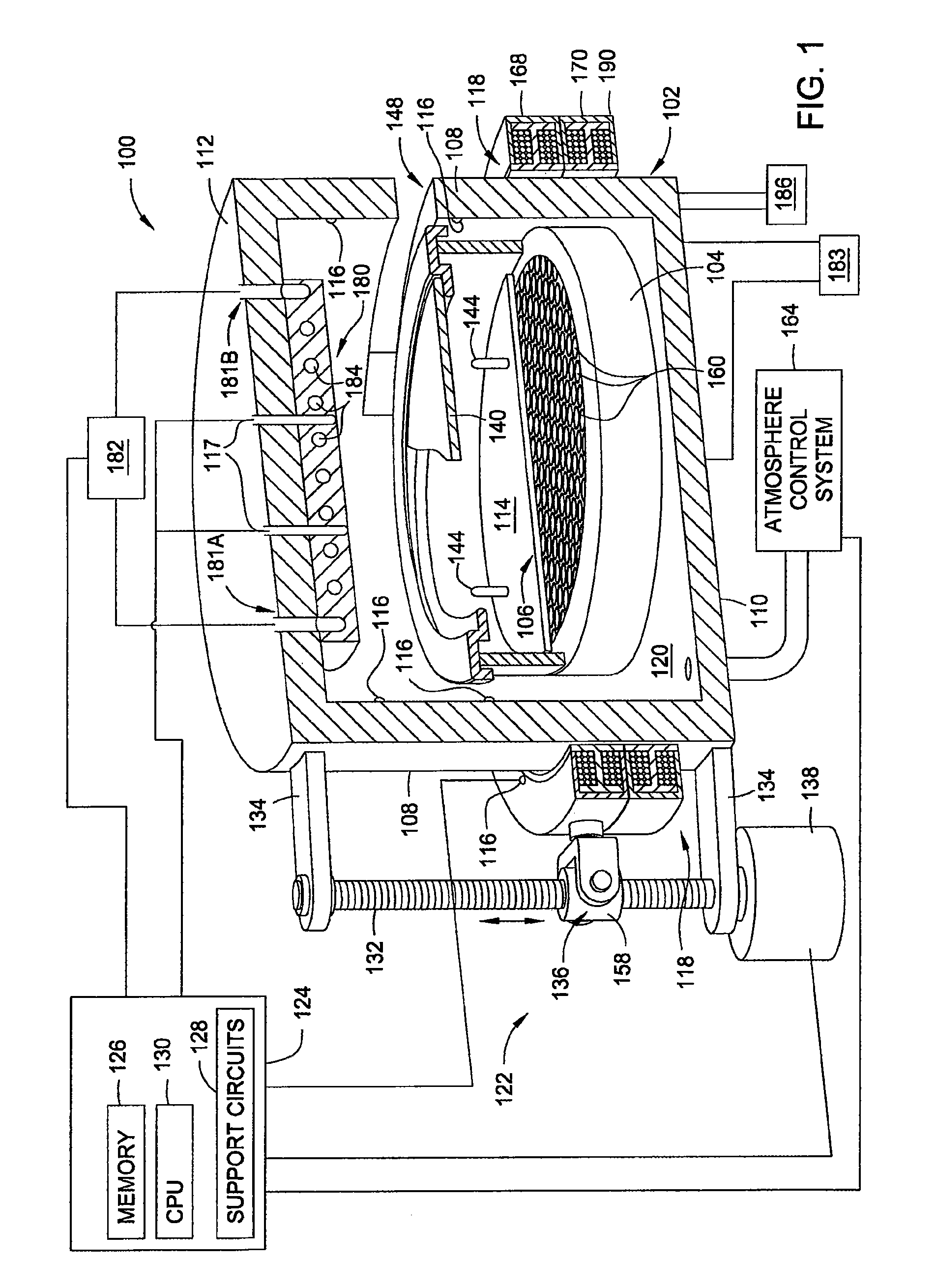
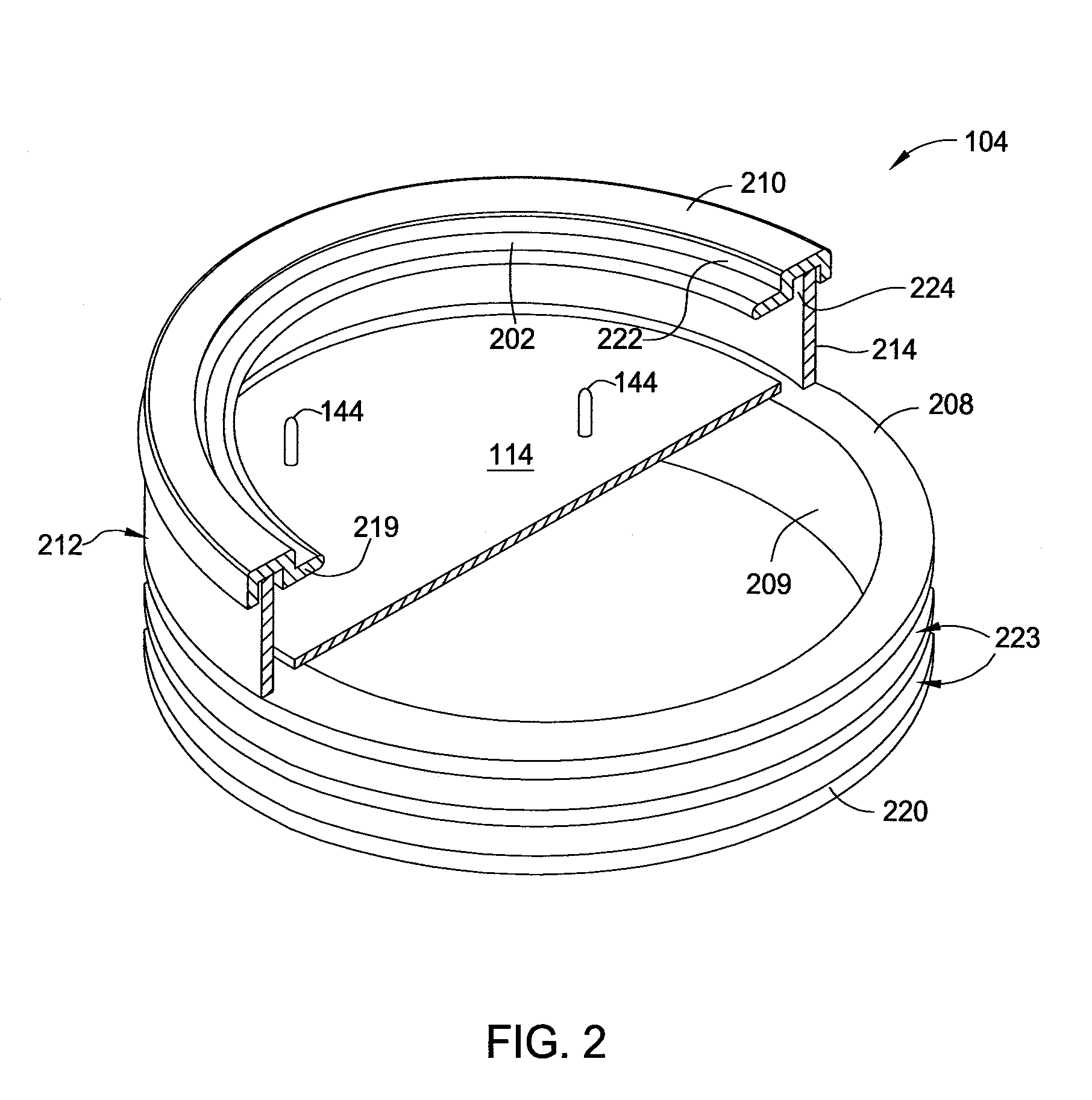
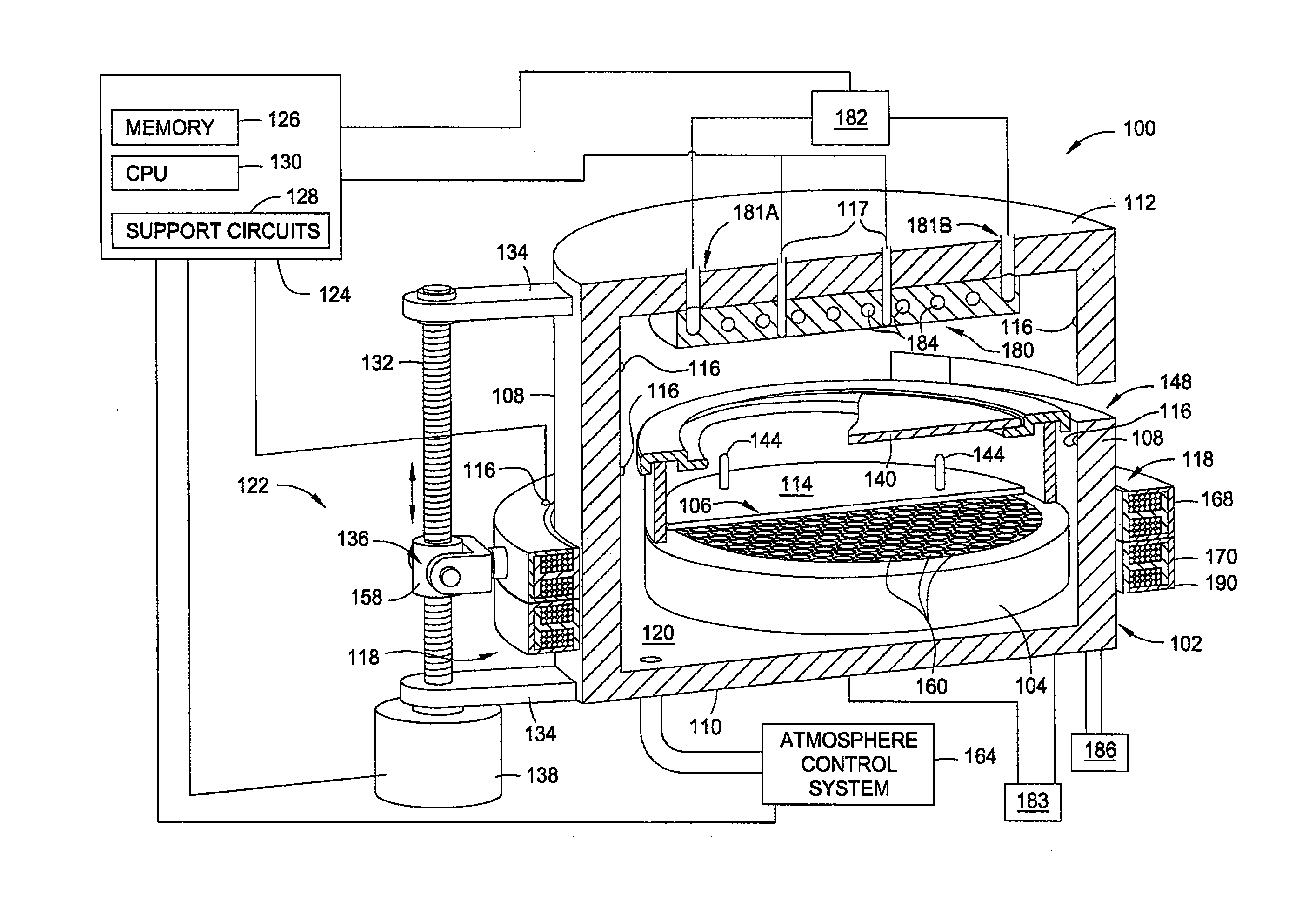
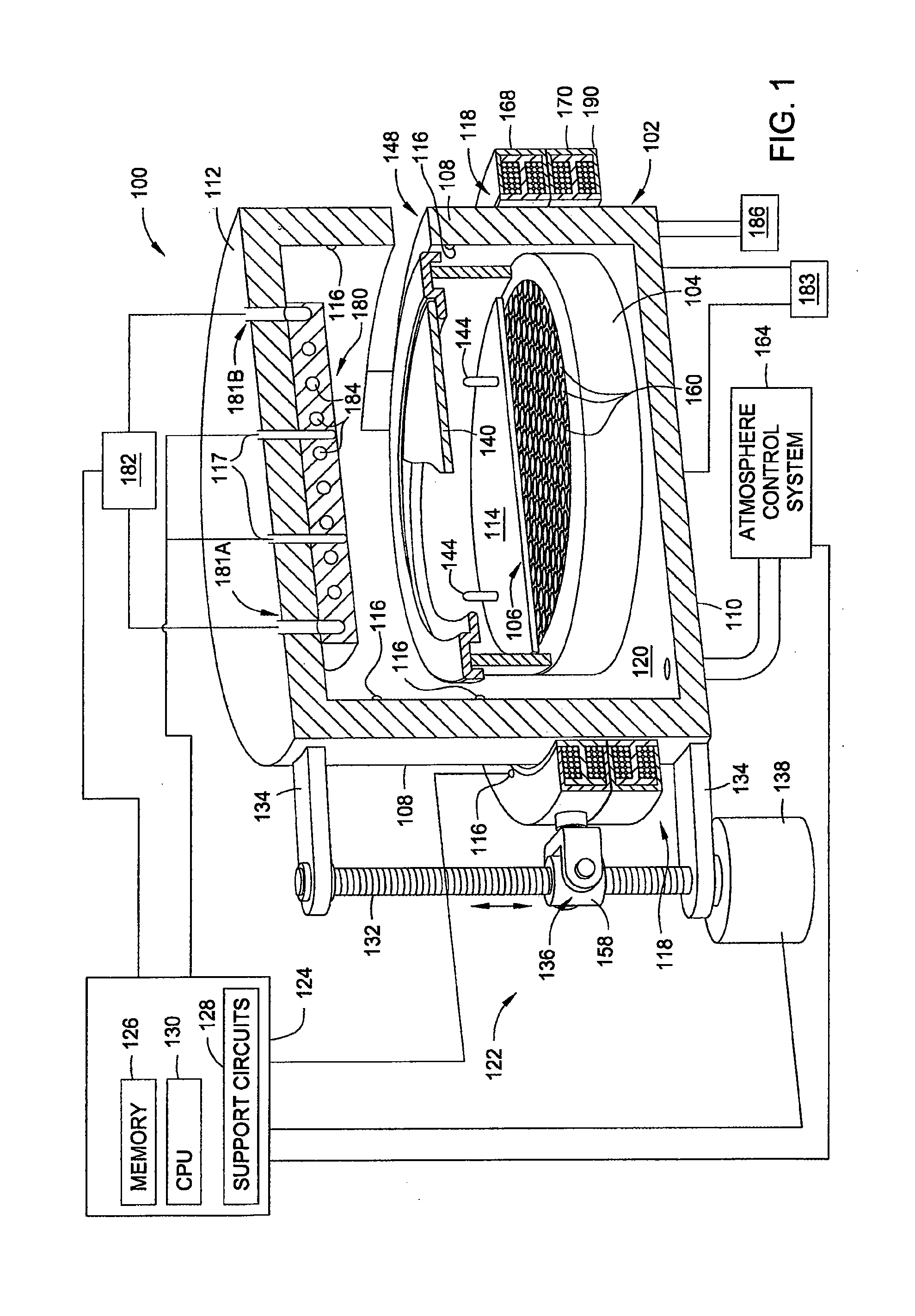
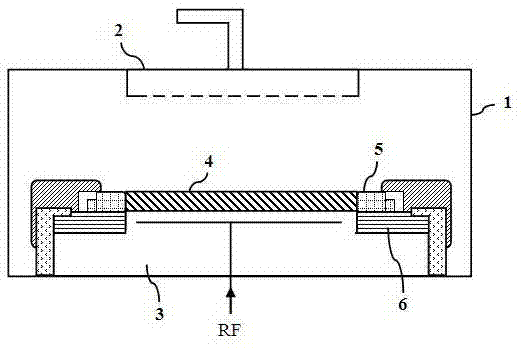
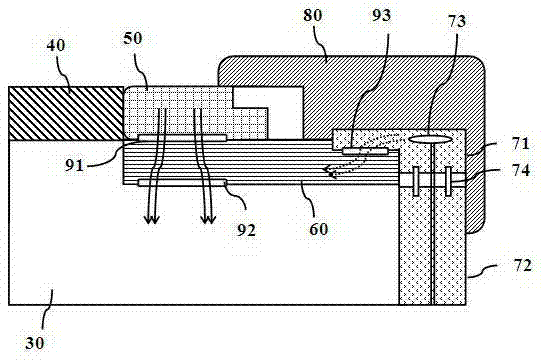
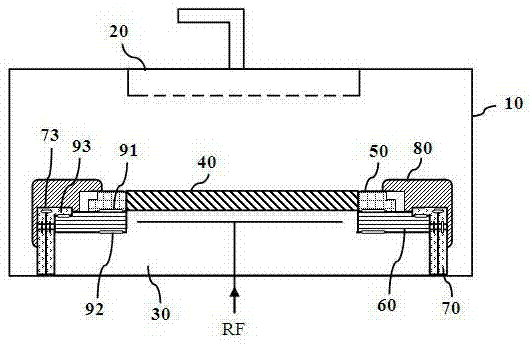
A method and apparatus for thermally processing a substrate is described. The apparatus includes a substrate support configured to move linearly and / or rotationally by a magnetic drive. The substrate support is also configured to receive a radiant heat source to provide heating region in a portion of the chamber. An active cooling region comprising a cooling plate is disposed opposite the heating region. The substrate may move between the two regions to facilitate rapidly controlled heating and cooling of the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
High dielectric strength thermal interface material
InactiveUS6096414AImprove performanceMaintain good propertiesOther chemical processesSynthetic resin layered productsThermal conductivityThermal transmittance
A thermally-conductive, electrically insulative interface for conductively cooling a heat-generating source, such as an electronic component, having an associated thermal dissipation member such as a heat sink. The interface is provided as a cured sheet of a curable material formulated as a blend of a curable silicone binder, and a particulate alumina, i.e., aluminum oxide (Al2O3), filler. The interface is observed to exhibit a thermal conductivity of at least about 0.8 W / m-K and a wet dielectric breakdown strength of at least about 475 Vac / mil.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
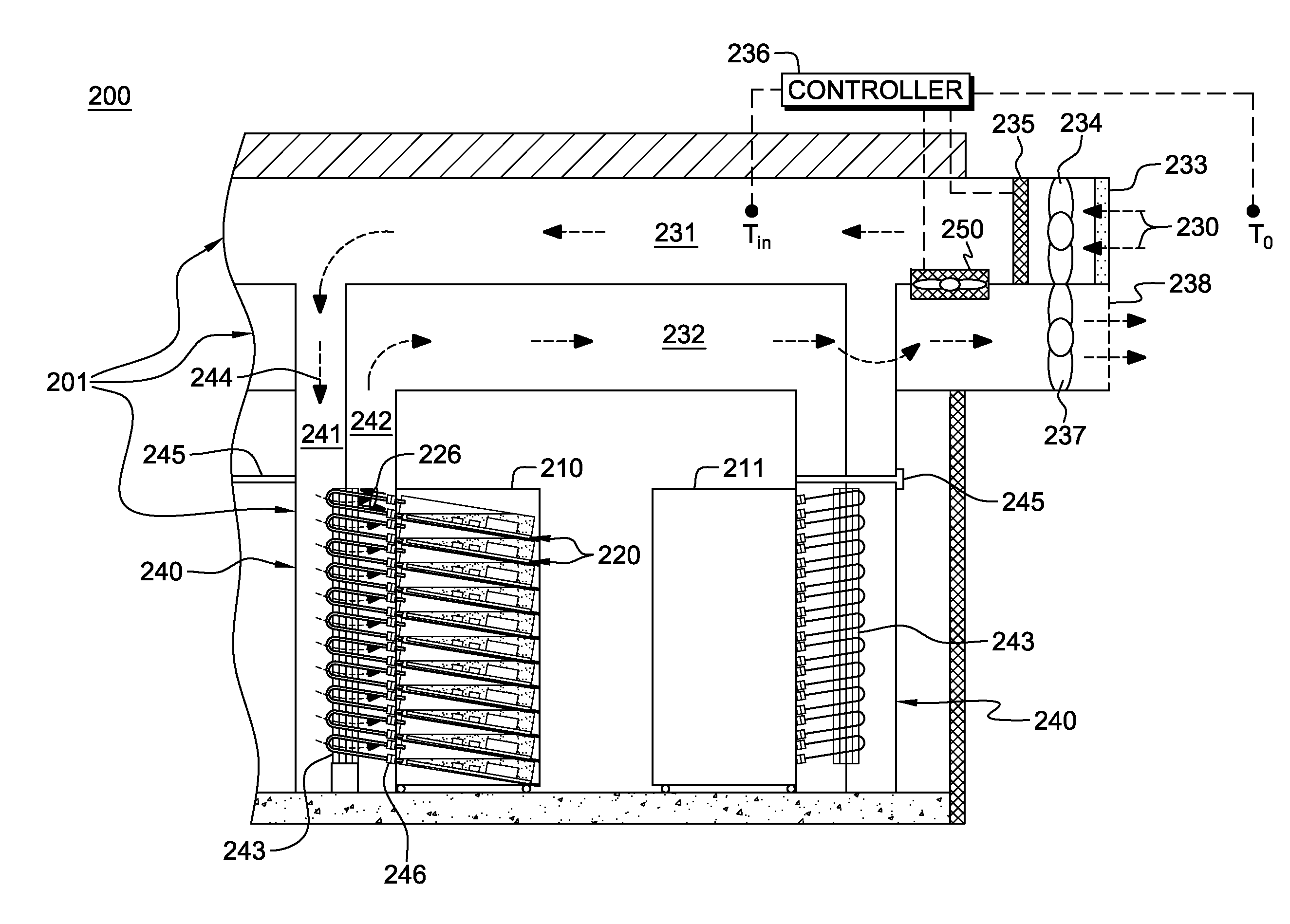
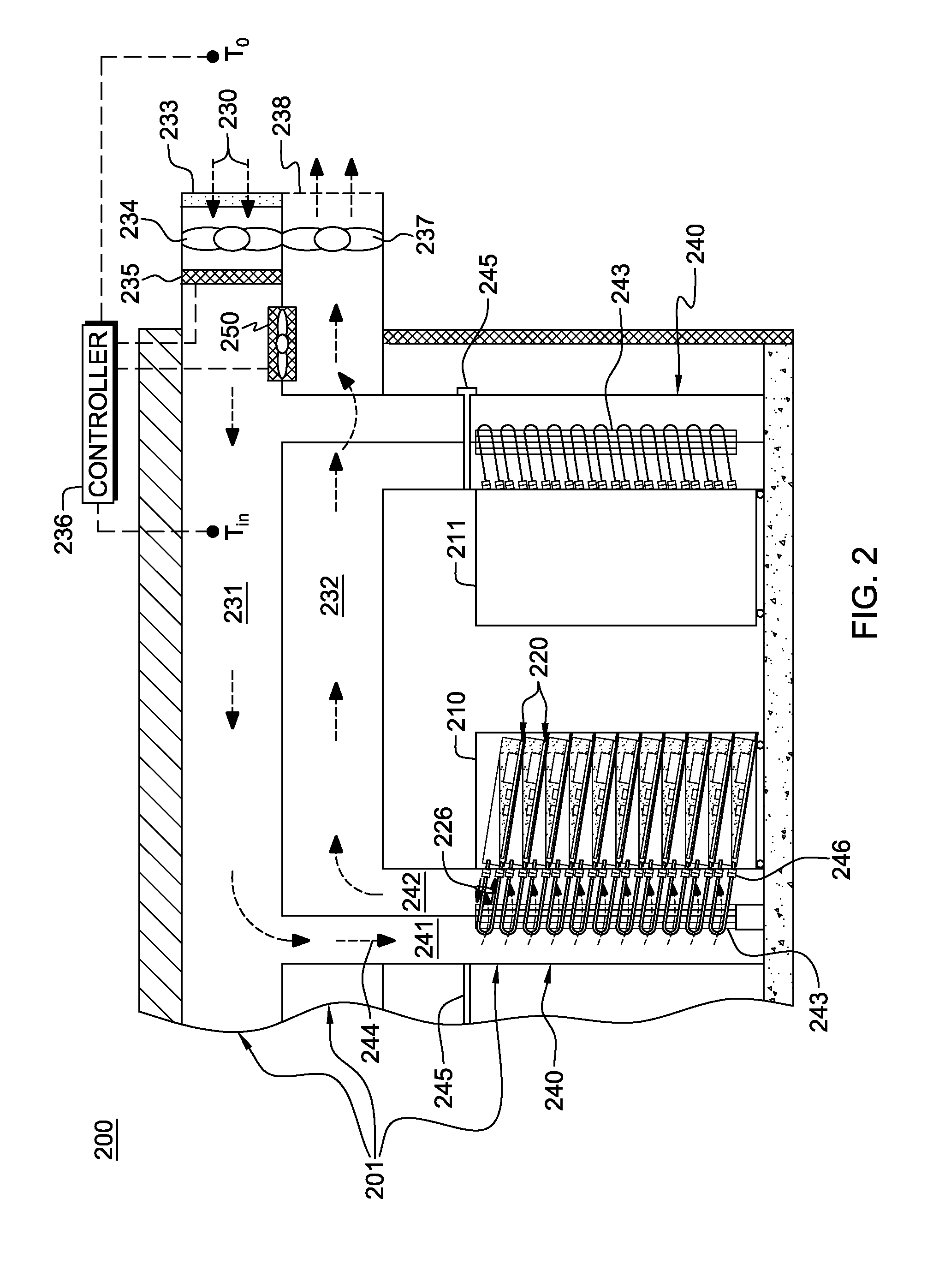
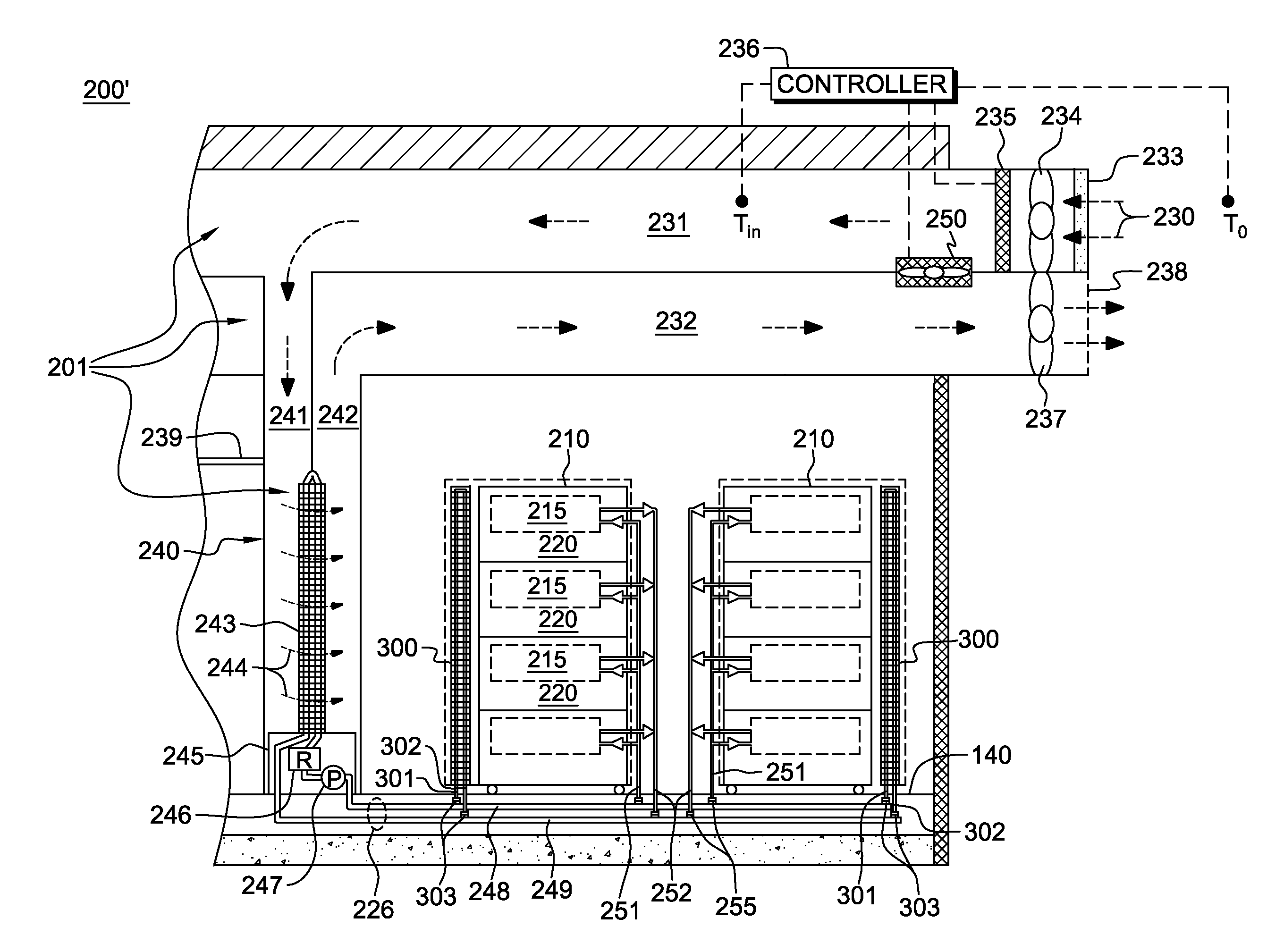
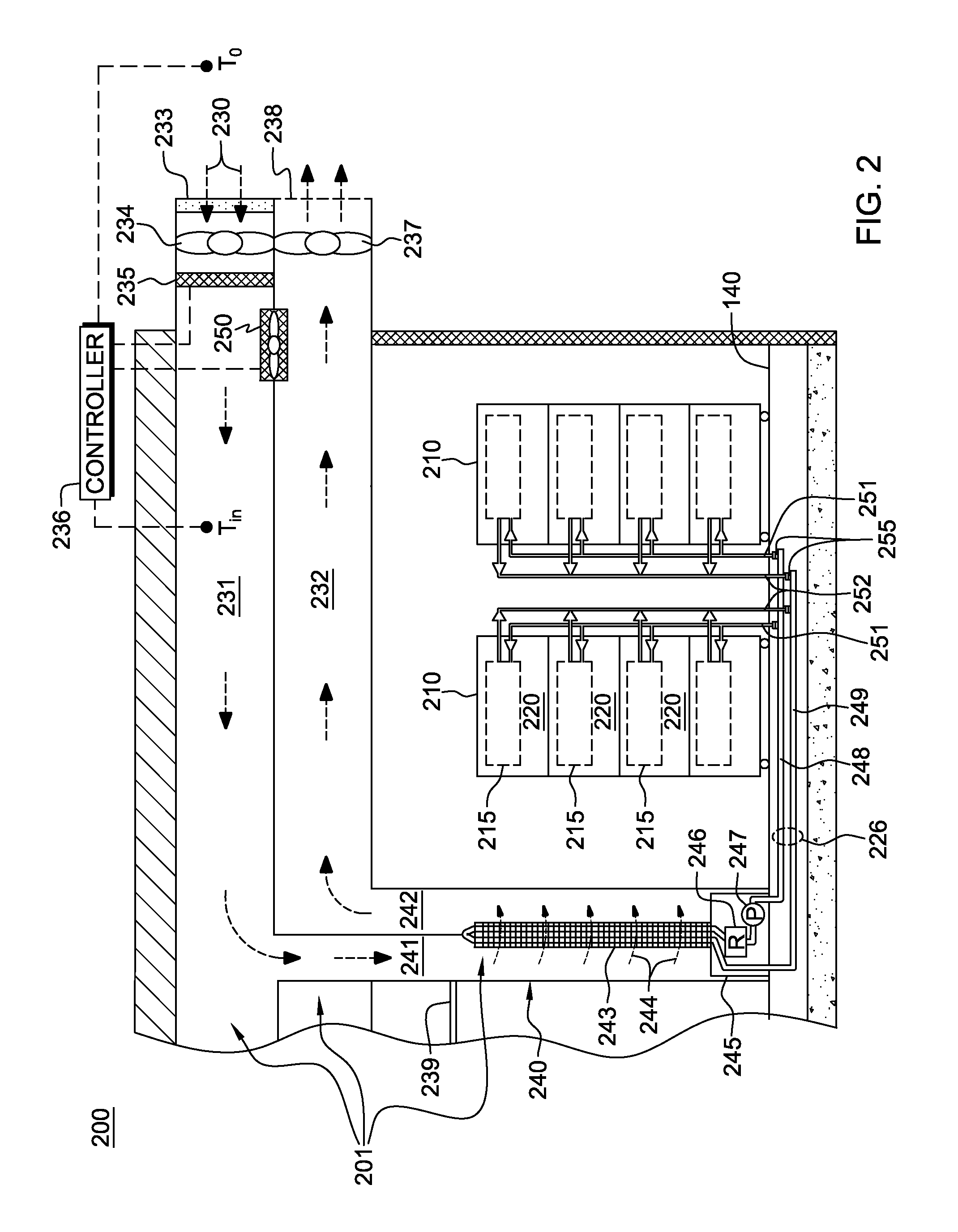
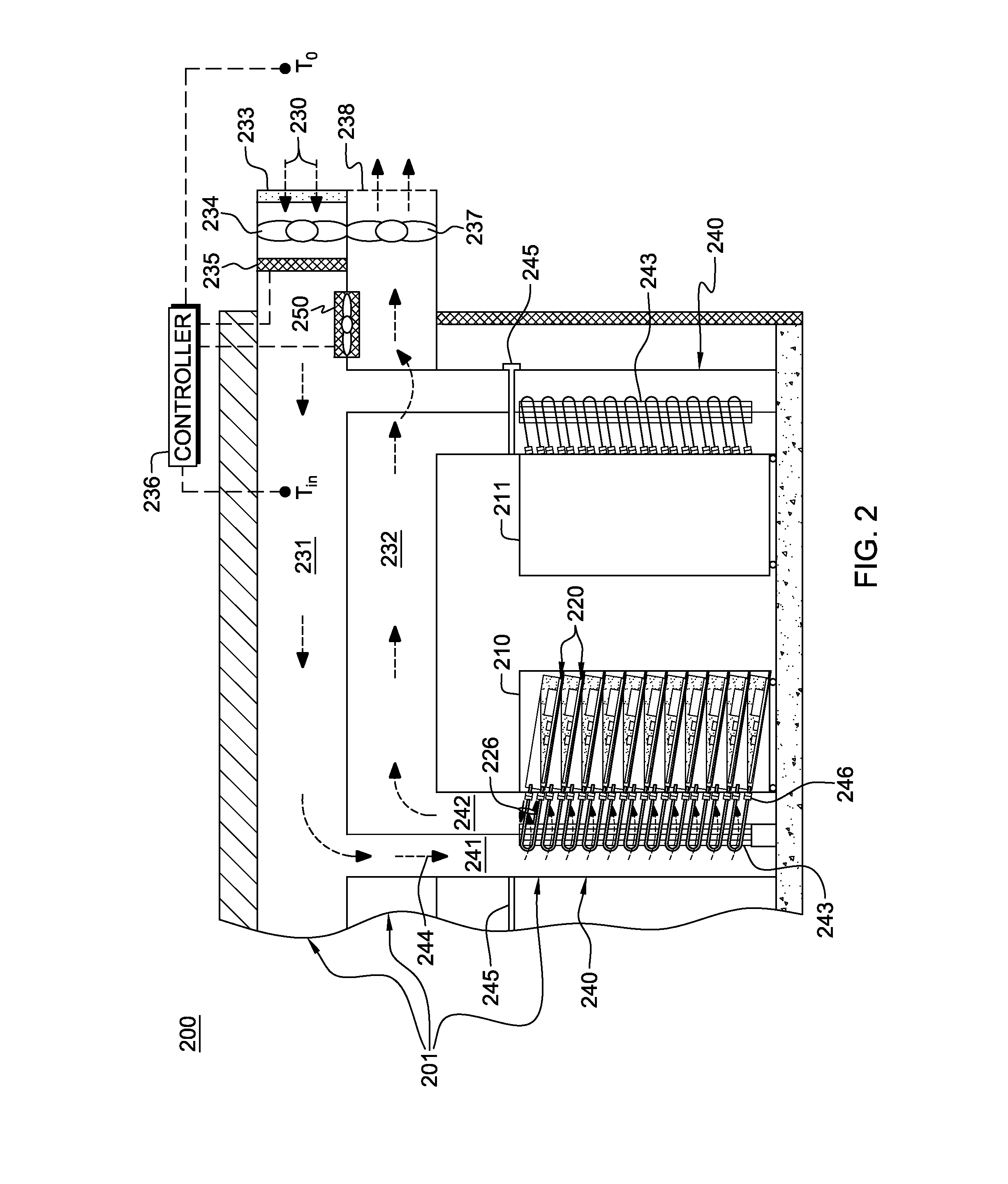
Data center cooling with an air-side economizer and liquid-cooled electronics rack(s)
InactiveUS20130021746A1Promote circulationFacilitate immersion-coolingDigital data processing detailsStationary conduit assembliesData centerNuclear engineering
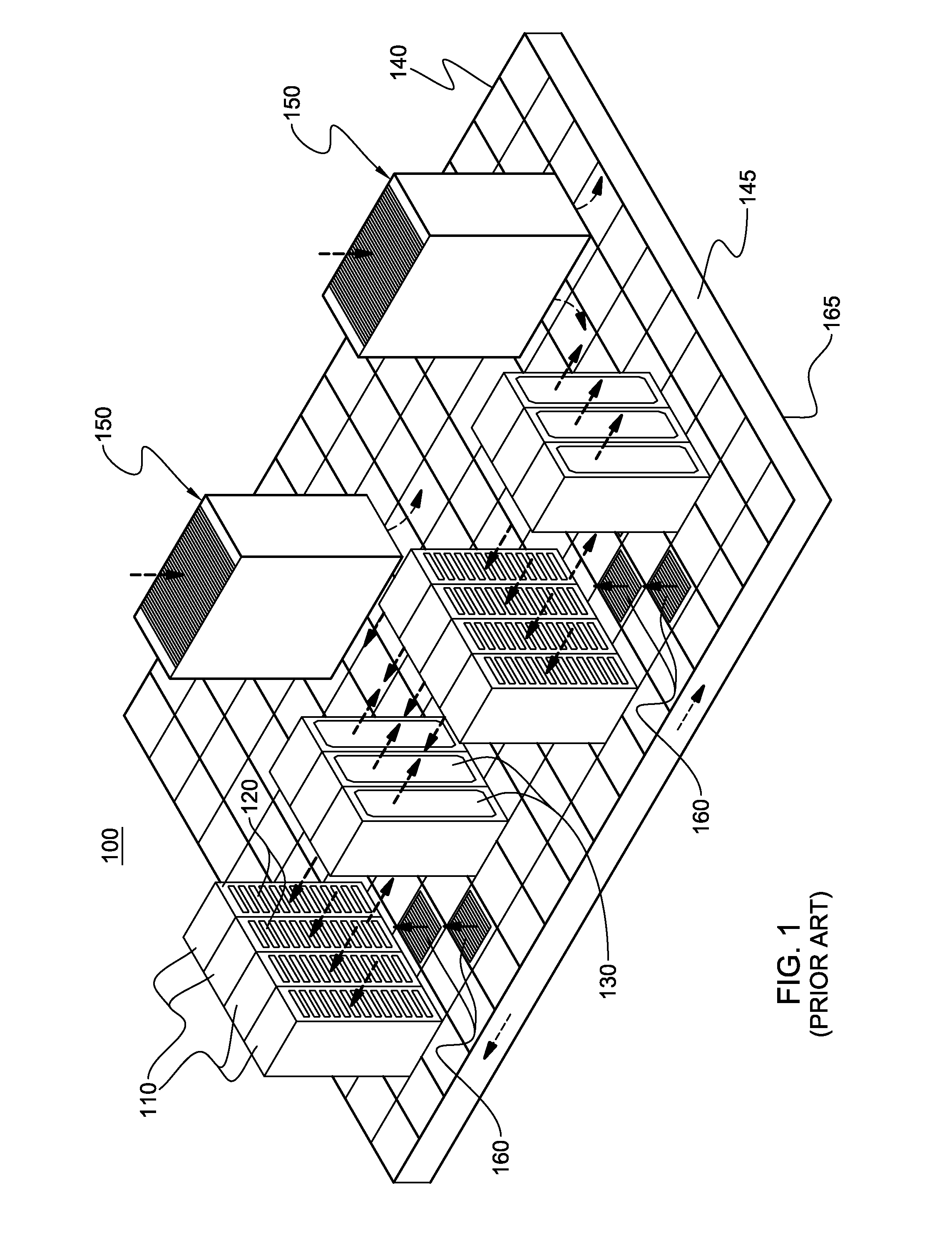
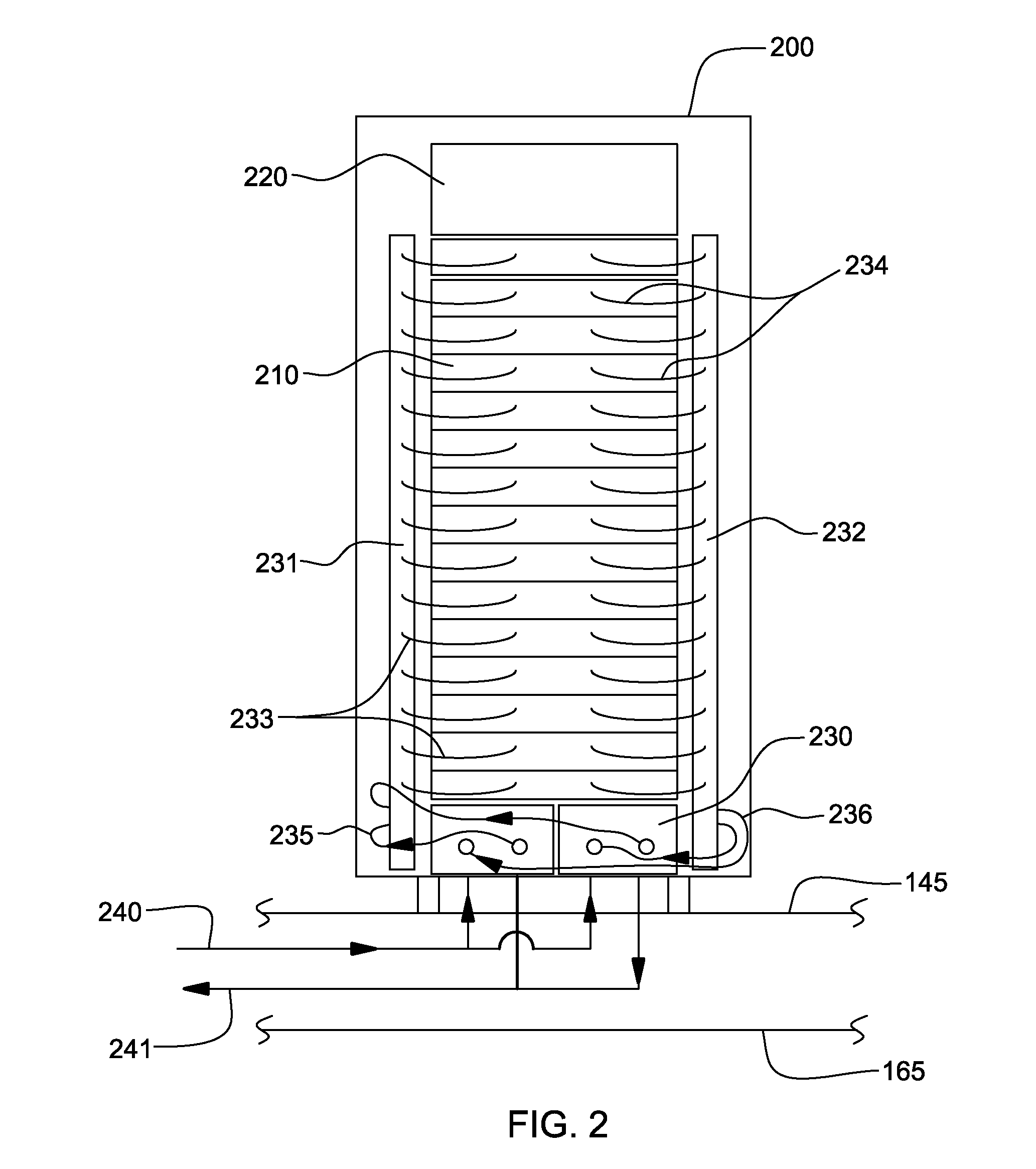
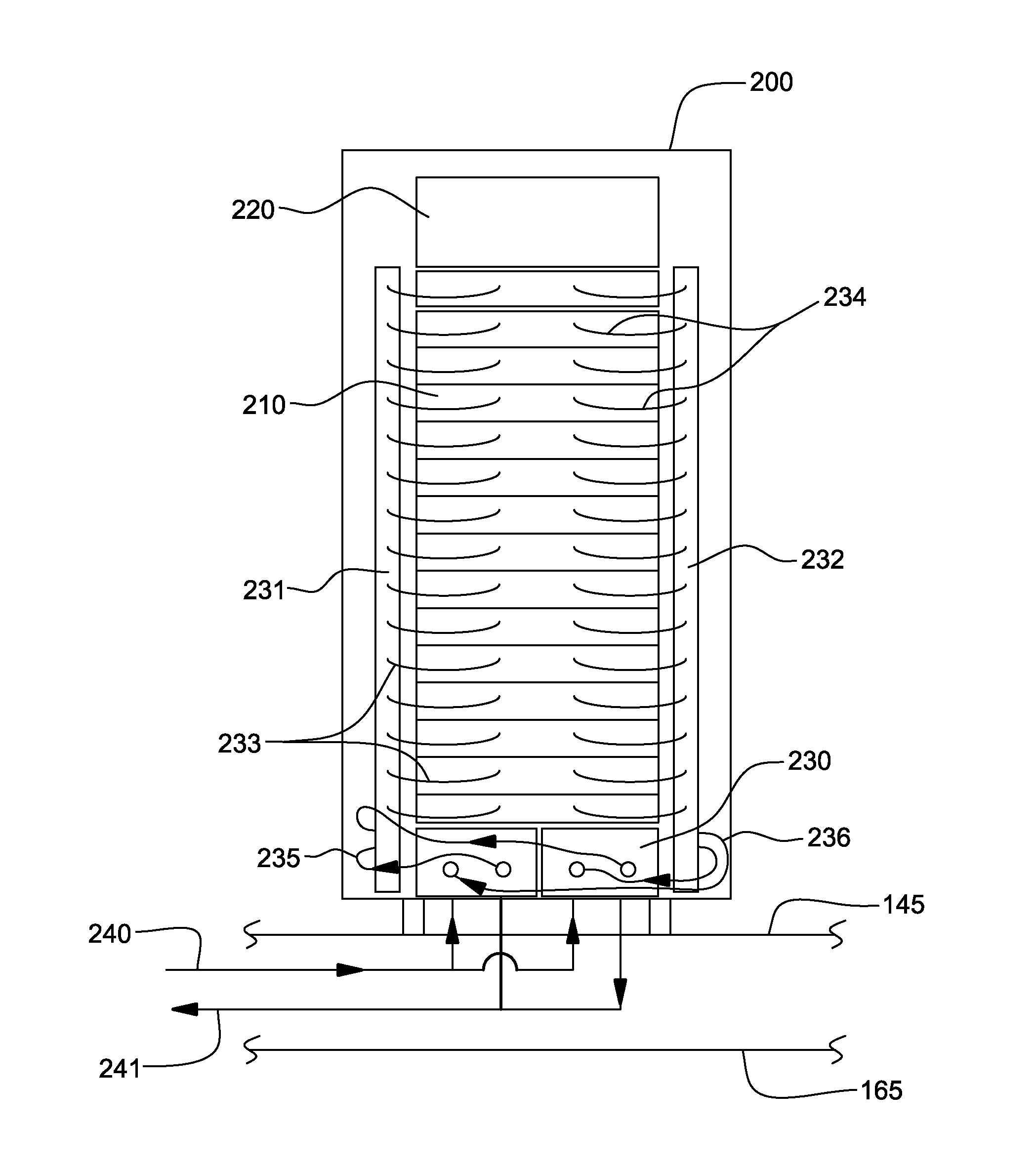
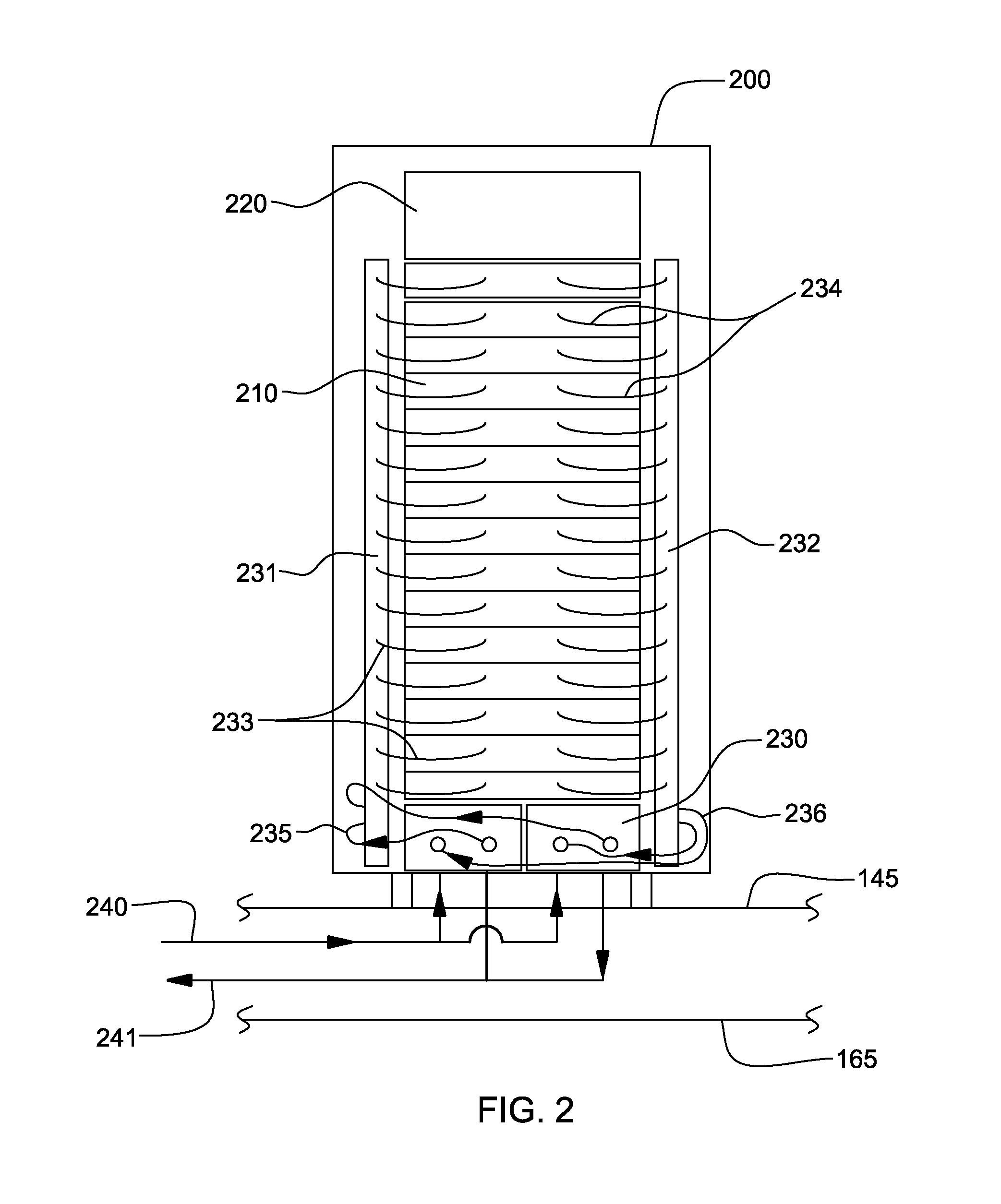
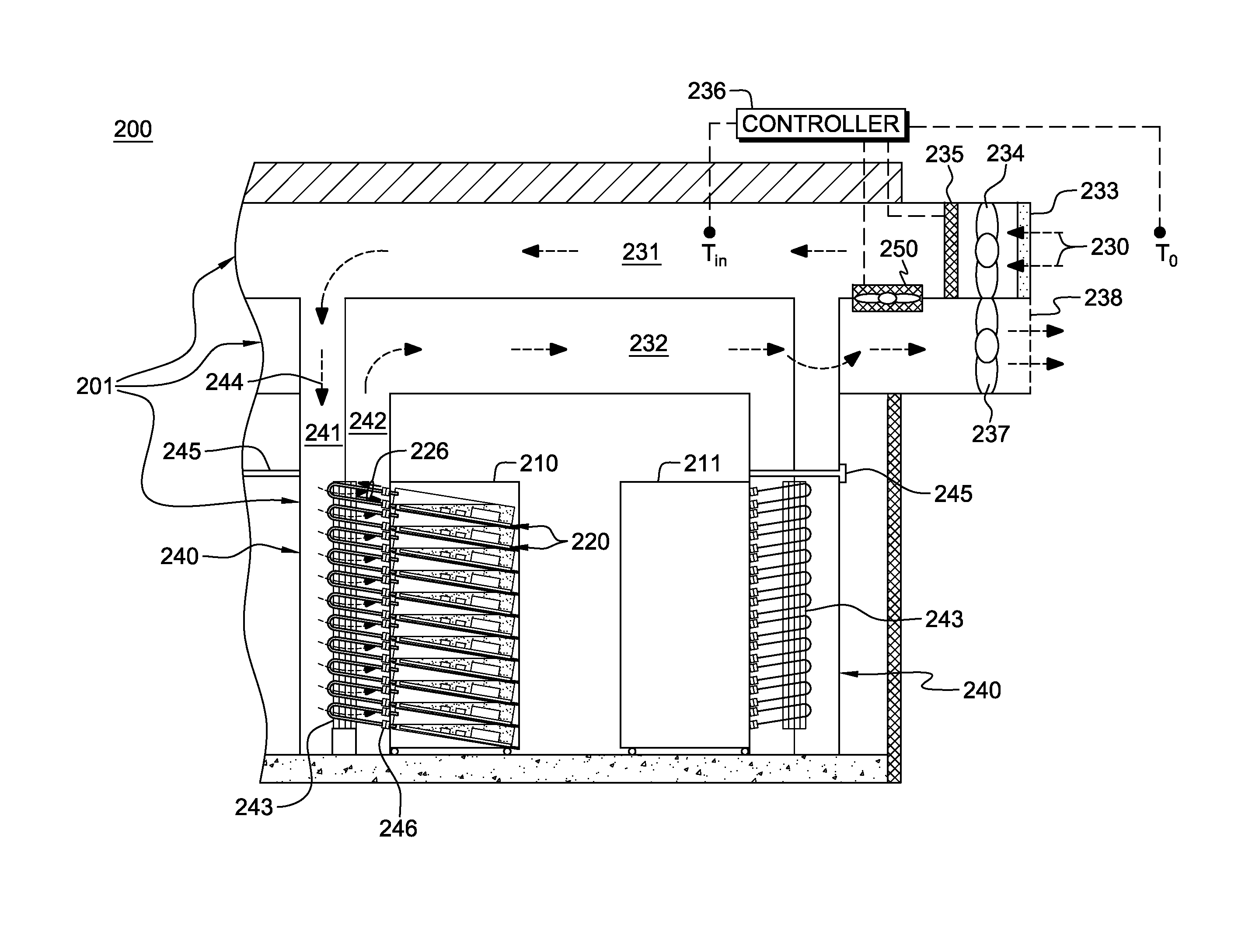
A cooling apparatus and method are provided for cooling an electronics rack. The cooling apparatus includes an air-cooled cooling station, which has a liquid-to-air heat exchanger and ducting for directing a cooling airflow across the heat exchanger. A cooling subsystem is associated with the electronics rack, and includes a liquid-cooled condenser facilitating immersion-cooling of electronic components of the electronics rack, a liquid-cooled structure providing conductive cooling to electronic components of the electronics rack, or an air-to-liquid heat exchanger associated with the rack and cooling airflow passing through the electronics rack. A coolant loop couples the cooling subsystem to the liquid-to-air heat exchanger. In operation, heat is transferred via circulating coolant from the electronics rack, and rejected in the liquid-to-air heat exchanger of the cooling station to the cooling airflow passing across the liquid-to-air heat exchanger. In one embodiment, the cooling airflow is outdoor air.
Owner:IBM CORP
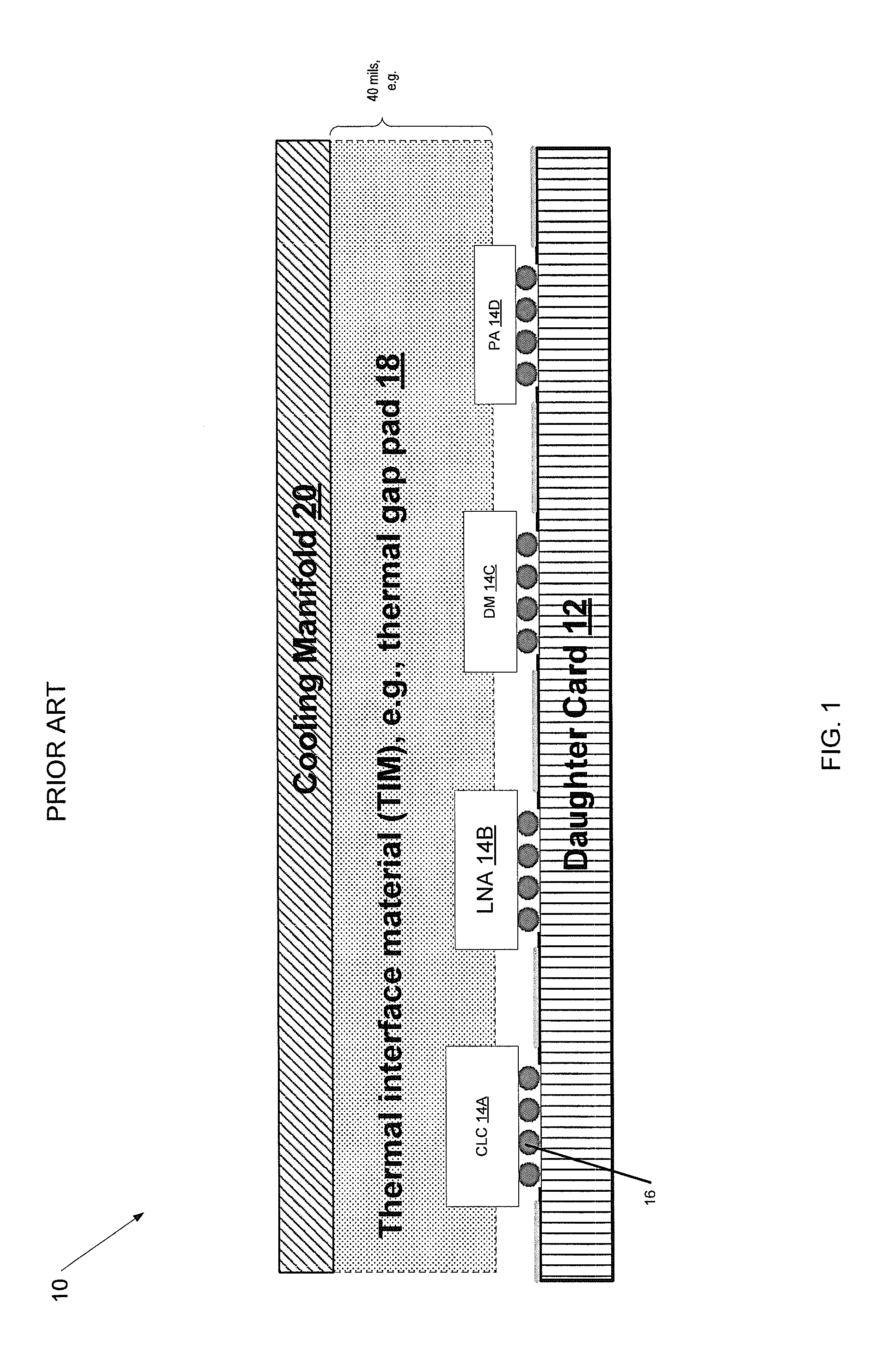
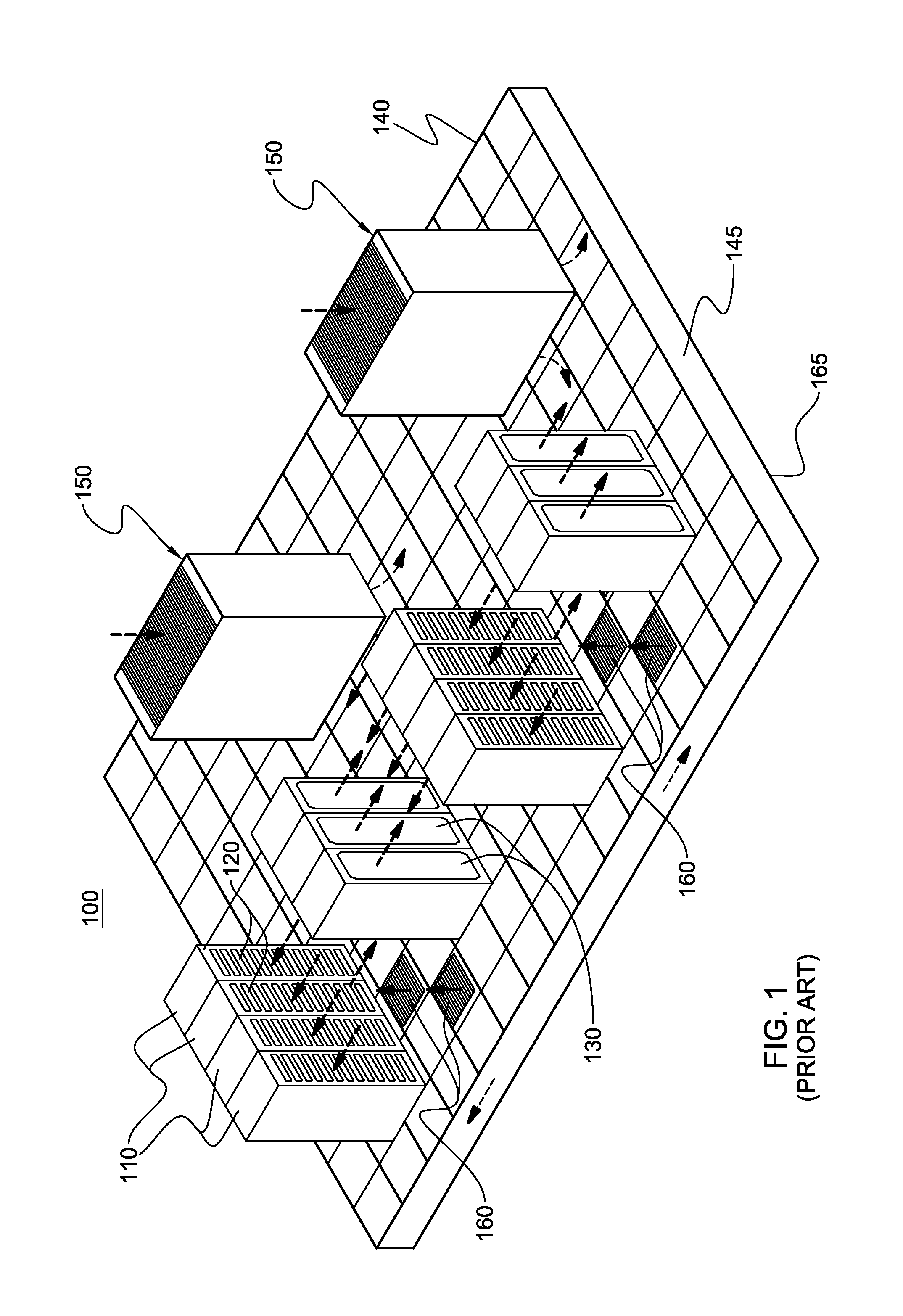
Method and system for dissipating thermal energy from conduction-cooled circuit card assemblies which employ remote heat sinks and heat pipe technology
InactiveUS7460367B2Maximum flexibilityIncrease the lengthDomestic cooling apparatusDigital data processing detailsThermal energyEngineering
Method and System for dissipating thermal energy from conduction-cooled circuit card assemblies in which thermal energy is directed into proximate heat sink assemblies and additionally is conveyed by heat pipes to one or more remote heat sink assemblies configured for the transfer of thermal energy to a flow of air and located within a chassis at a position remote from the system thermal load.
Owner:TRACEWELL SYST
Method and system for dissipating thermal energy from conduction-cooled circuit card assemblies which employ remote heat sinks and heat pipe technology
InactiveUS20080218980A1Increase the lengthMaximum flexibilityDomestic cooling apparatusDigital data processing detailsThermal energyEngineering
Method and System for dissipating thermal energy from conduction-cooled circuit card assemblies in which thermal energy is directed into proximate heat sink assemblies and additionally is conveyed by heat pipes to one or more remote heat sink assemblies configured for the transfer of thermal energy to a flow of air and located within a chassis at a position remote from the system thermal load.
Owner:TRACEWELL SYST
System including a heat exchanger with different cryogenic fluids therein and method of using the same
A system can include a heat transfer structure and a heat exchanger. The heat transfer structure is to cool an object, and the heat exchanger is to cool a portion of the heat transfer structure. The system can be cooled significantly faster than a conventional system that uses conductive cooling. The system has no or less liquid cryogen that would be vaporized as compared to a conventional system that immerses the object to be cooled within a bath of liquid cryogen or has a substantial mass of liquid cryogen within a cooling loop.
Owner:PHILIPS MEDICAL SYST MR
Embedded heat pipe for a conduction cooled circuit card assembly
InactiveUS6839235B2Improve signal integrityReduce electromagnetic radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCollector deviceConduction cooling
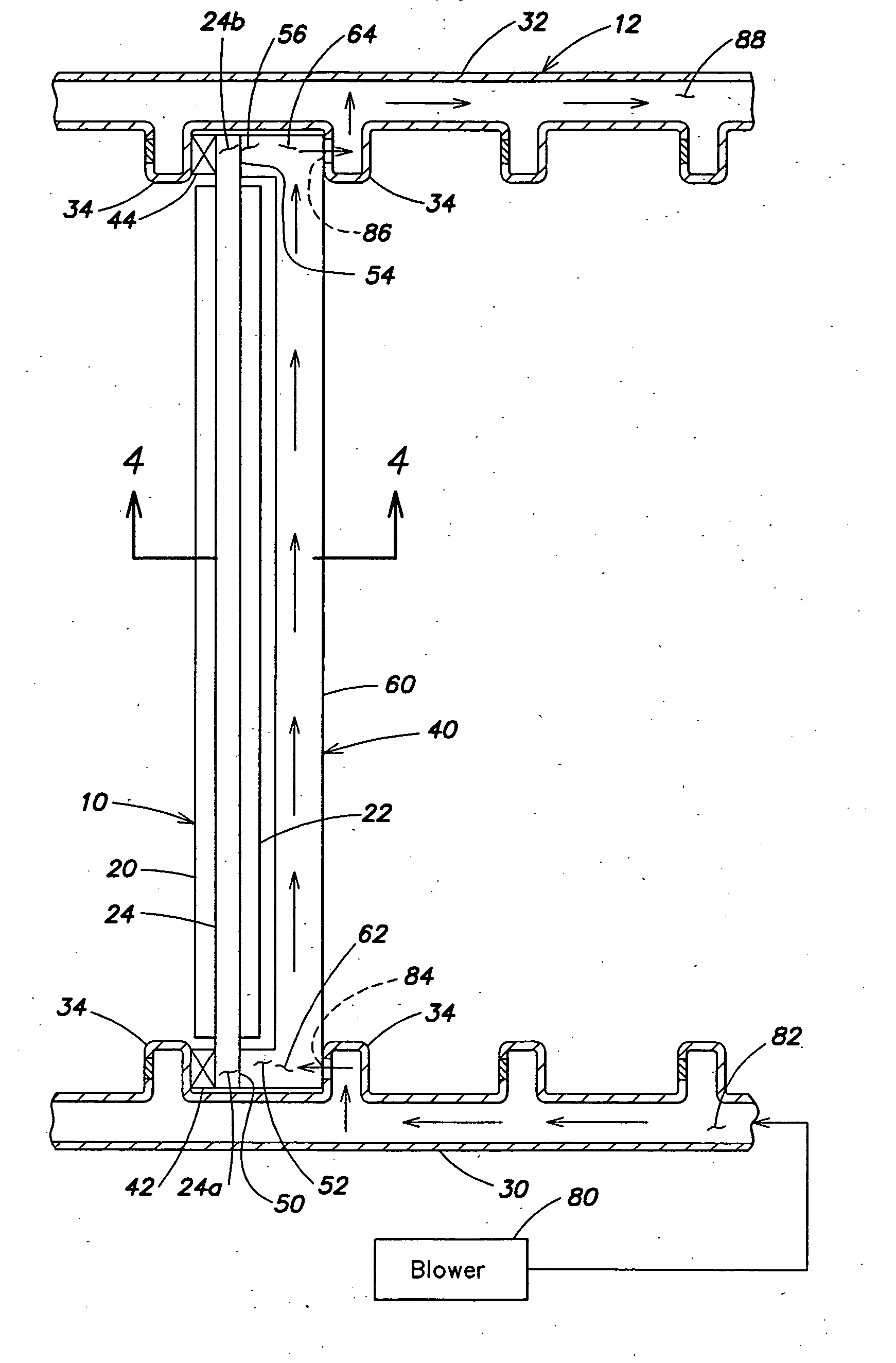
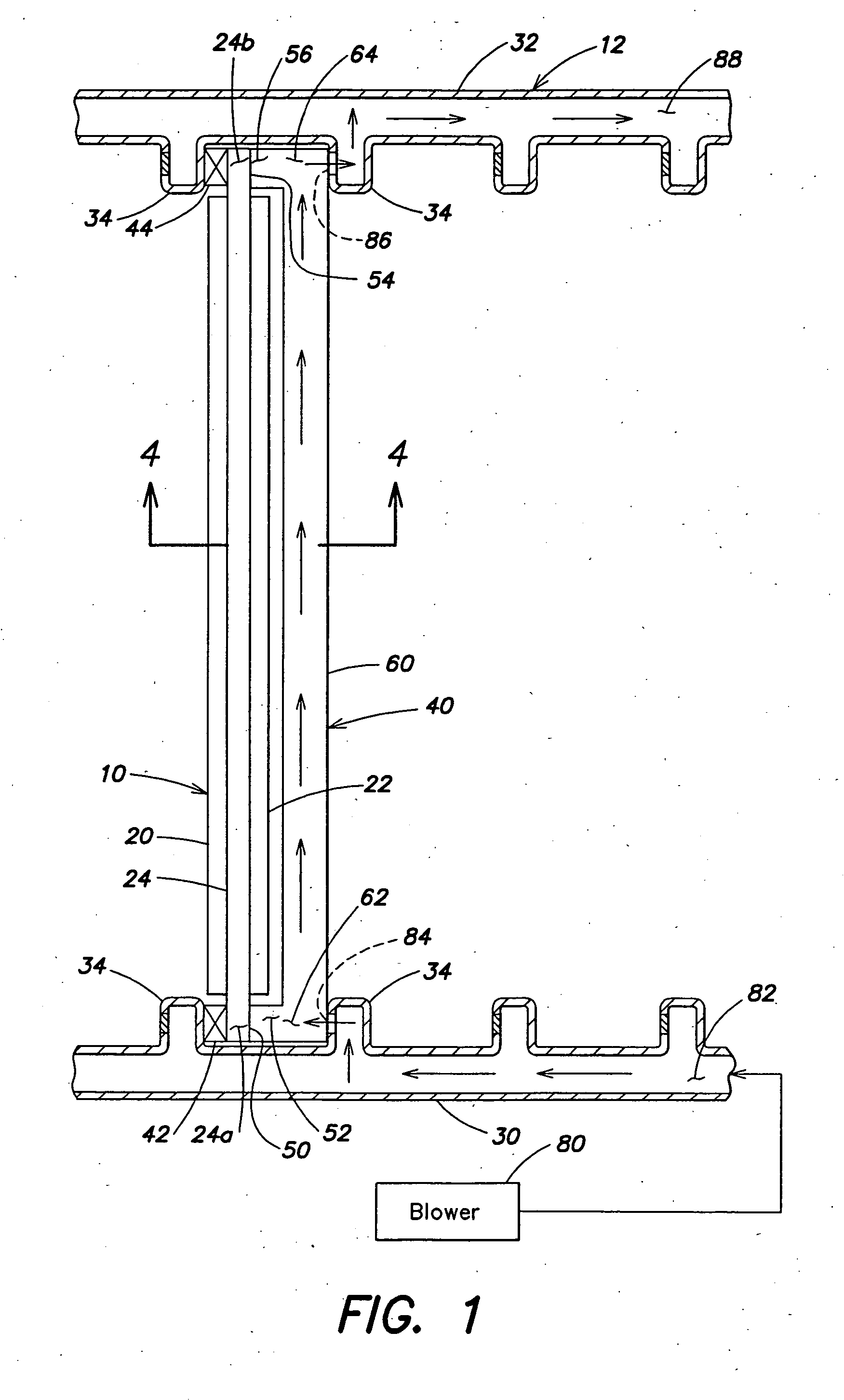
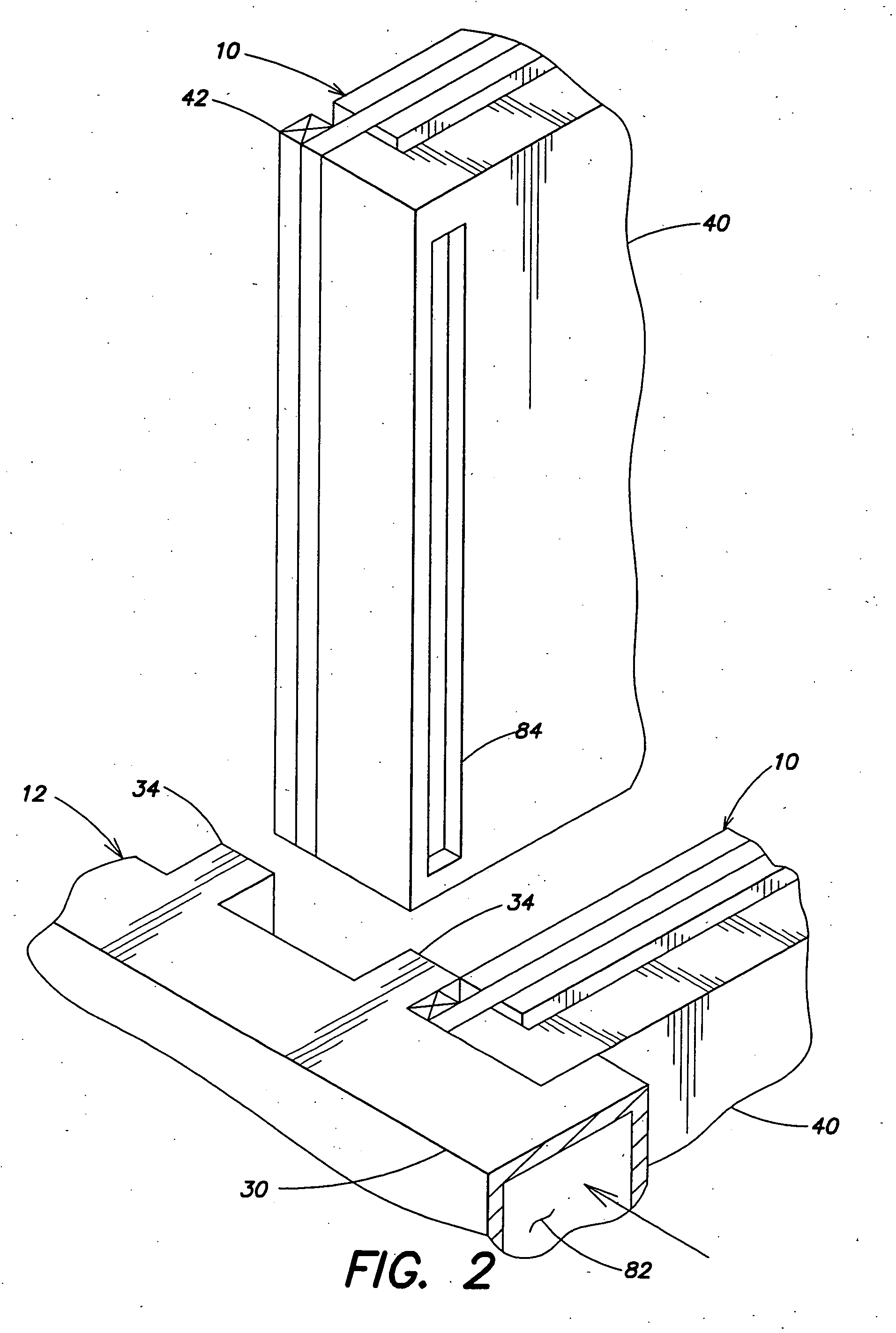
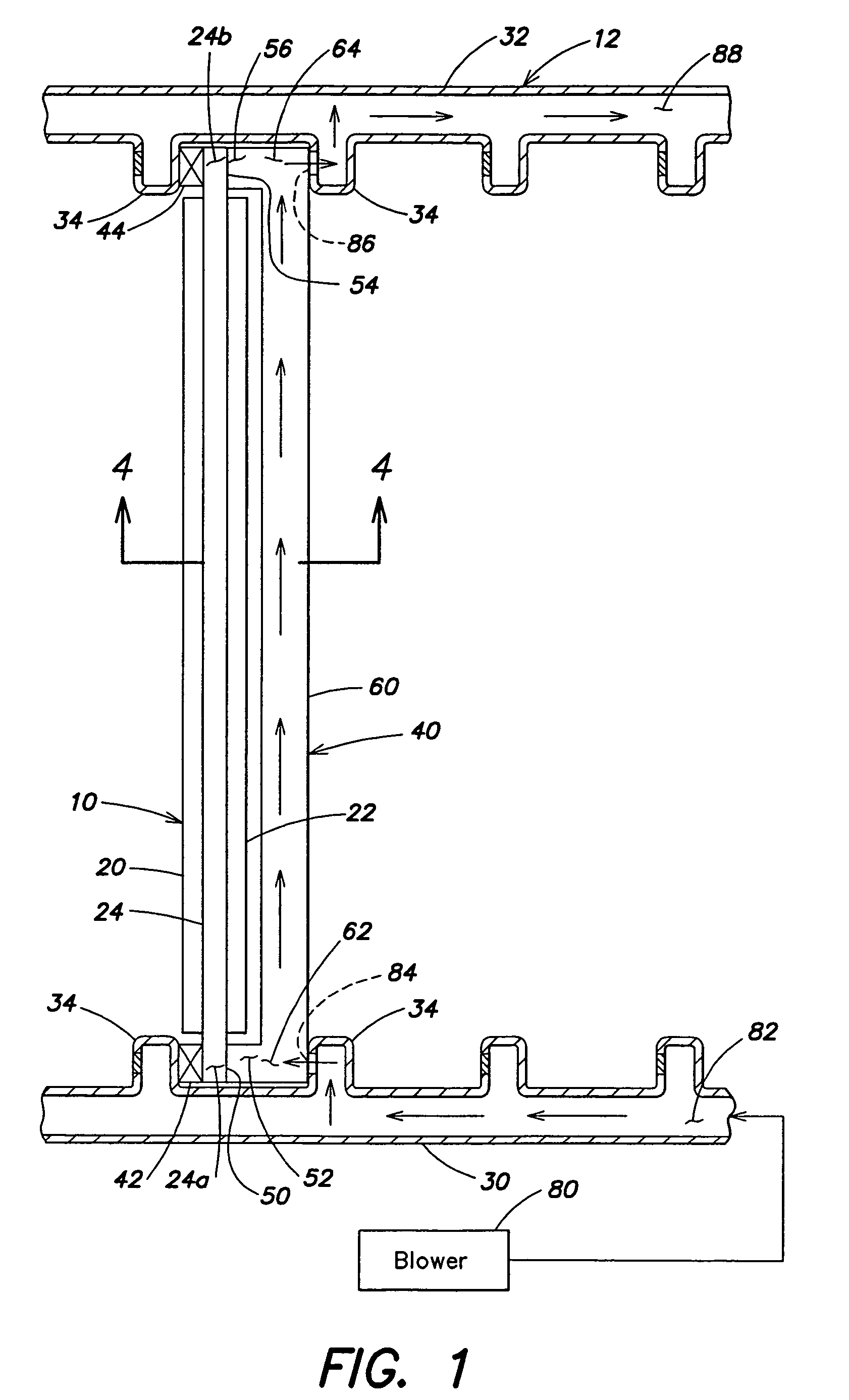
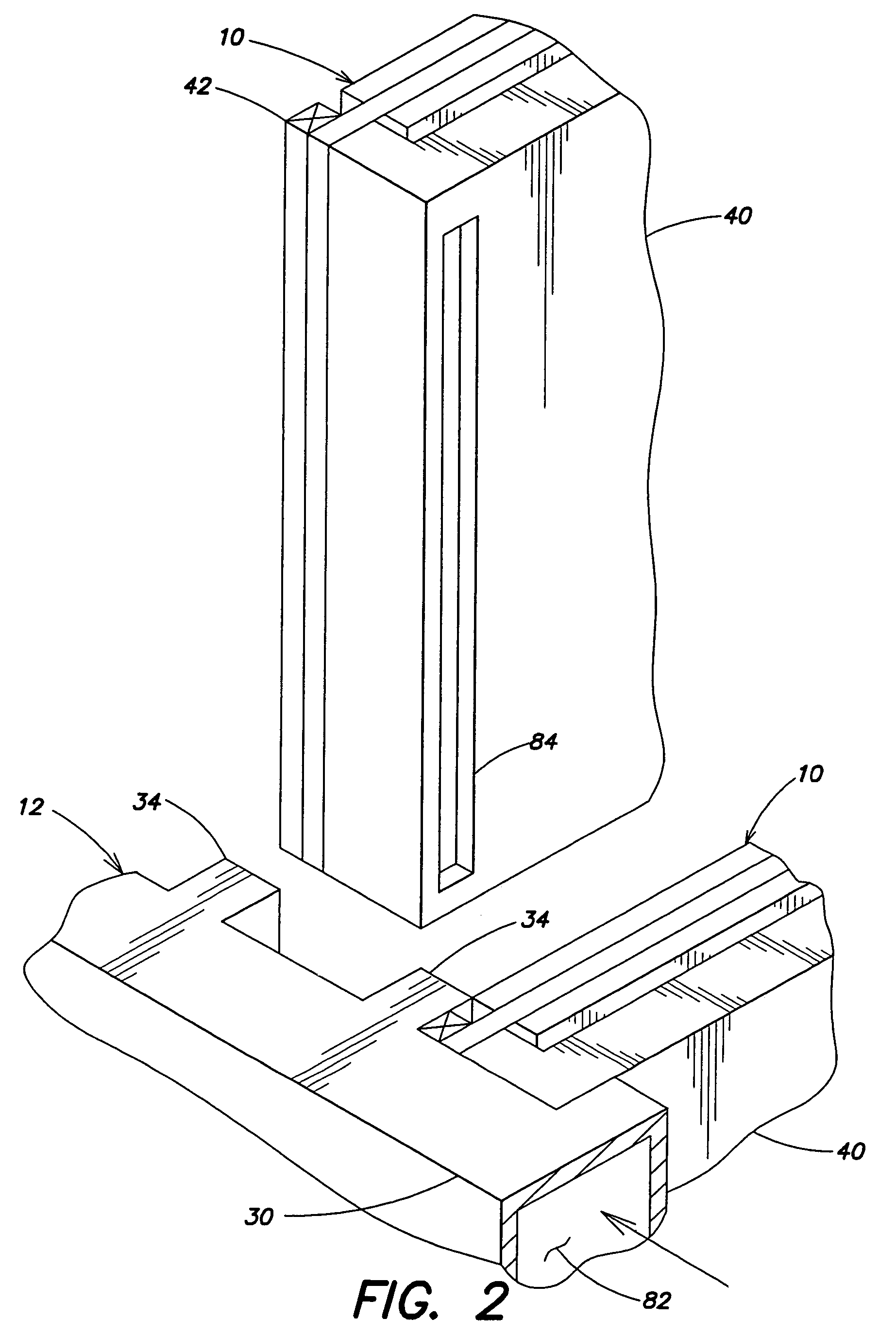
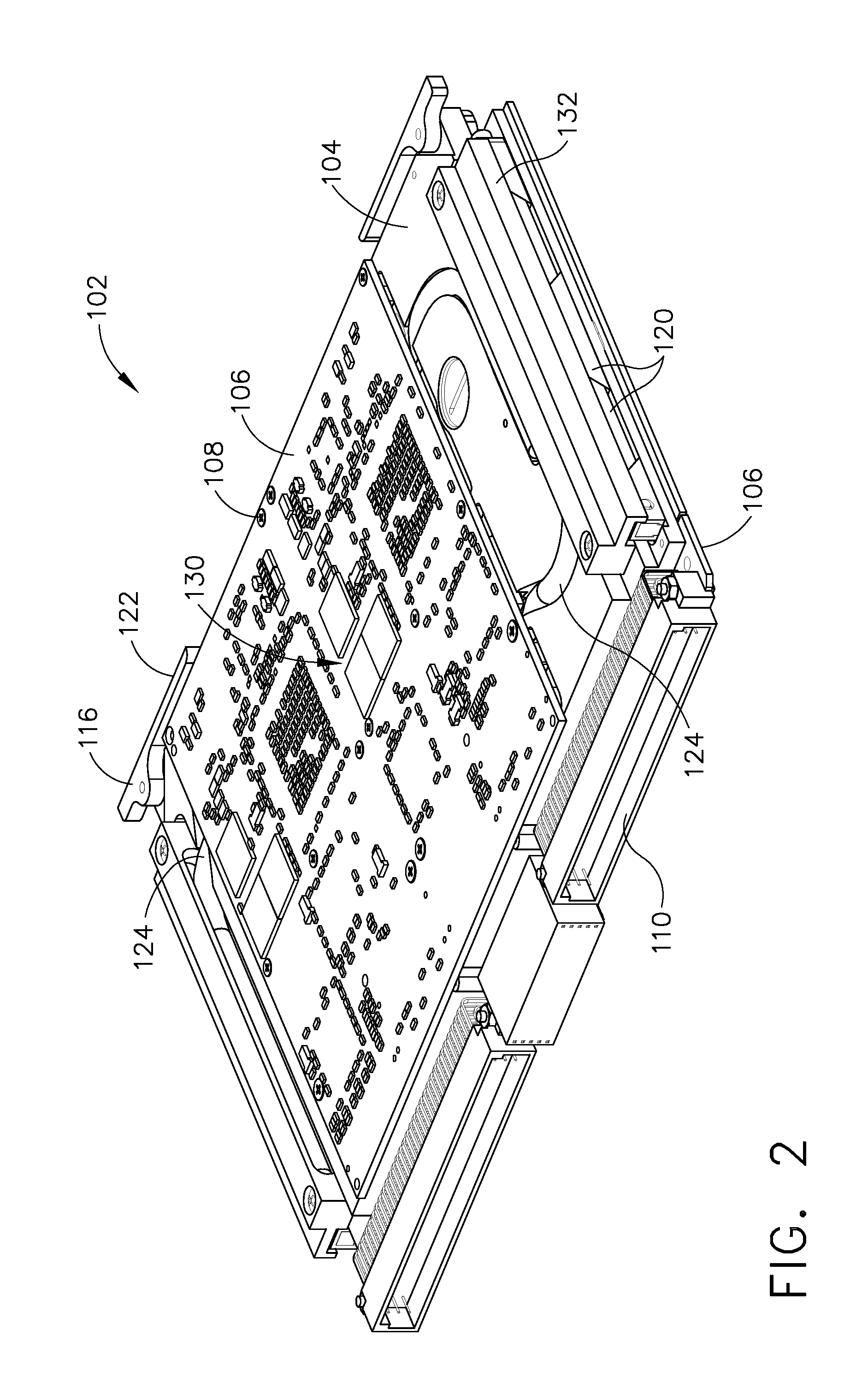
One or more heat pipes are connected between a component on a circuit card and the frame of a circuit card assembly for transfer of heat to the frame of the circuit card assembly. Circuit cards are typically held in place in channels in a chassis by an expansion type retention device. The circuit cards also include a heat frame for collecting the heat produced by the card components and channeling the heat from the card through the heat frame to the chassis. The retention device presses the heat frame in to thermal contact with one side of the channel. Heat collector can be attached to the heat generating components of a circuit card between the heat pipe and the component to provide improved thermal transfer. A number of heat collectors with pairs of heat pipes extending in opposite directions from the collector to the frame can be used to allow the heat pipes to effectively dissipate heat form the circuit card assembly regardless of the orientation of the circuit card assembly.
Owner:DY 4 SYST
Flow through cooling assemblies for conduction-cooled circuit modules
A cooling assembly is located in a chassis with a conduction-cooled circuit module and permits the conduction-cooled circuit module to be utilized in an air-flow-through or liquid-flow-through circuit module chassis assembly. The cooling assembly may be a removable cooling adapter or may be integral with the chassis. The cooling assembly includes a housing having a first end and a second end and defining one or more fluid passages. The housing further includes a thermal contact surface to contact the conduction-cooled circuit module. The cooling assembly may be configured for air-flow-through or liquid-flow-through cooling of the conduction-cooled circuit module.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
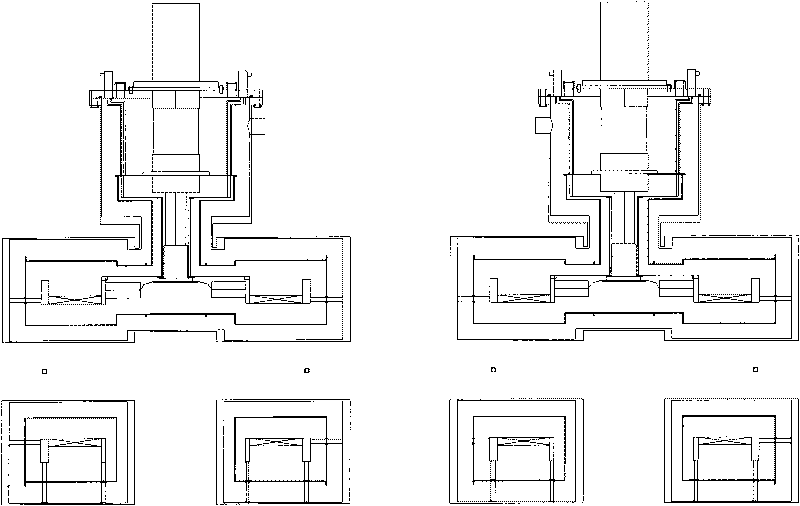
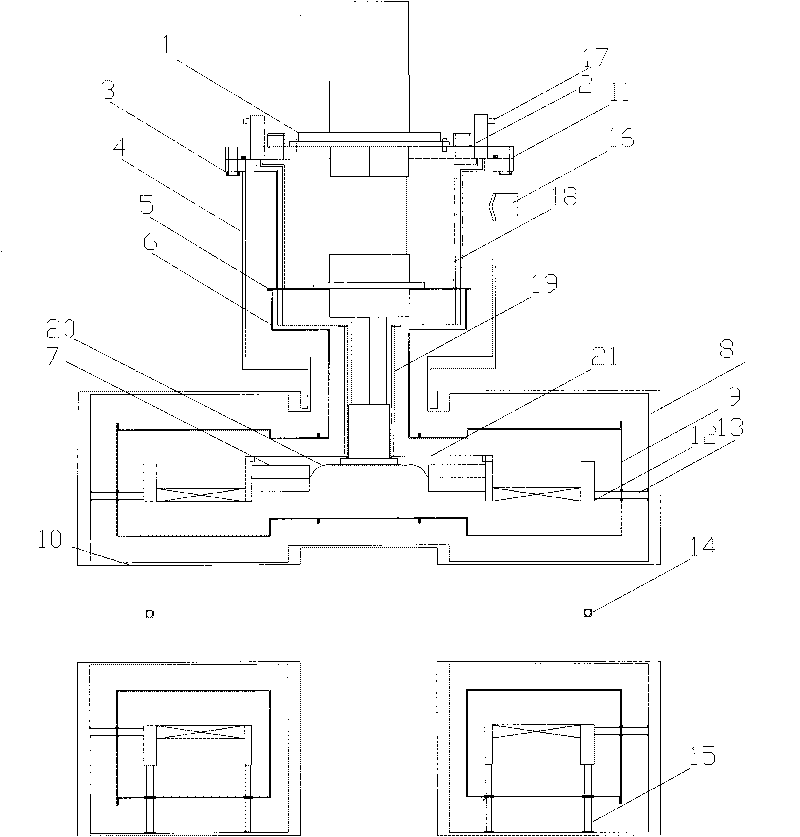
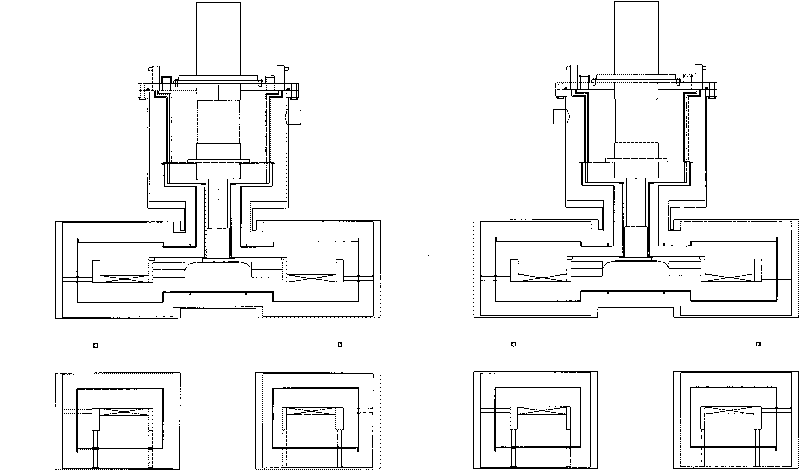
Conduction cooling superconducting magnet dewar convenient for loading and unloading
The invention relates to a conduction-cooled superconducting magnet Dewar with easy loading-unloading, comprising a Dewar cylinder. The conduction-cooled superconducting magnet Dewar is characterized in that the Dewar cylinder is a hollow annular cylinder, the middle of the annular cylinder is provided with a room temperature hole, an annular copper cold shield is arranged in the Dewar cylinder, a refrigerator and a superconducting magnet are arranged in the copper cold shield, a vacuum pumping port is arranged on the Dewar cylinder, a measuring device is arranged on an upper cover of the Dewar cylinder and the Dewar cylinder is in a vacuum state. Compared with the prior Dewar container, the conduction-cooled superconducting magnet Dewar is simpler, has small conduction heat leakage, and has the advantages of easy installation and disassembly; the refrigerator is used for conducting and cooling without a low temperature liquid (such as liquid helium and so on) cooling system; because of simple and safe system, a first-level cold junction of the refrigerator is operated under a temperature of 77K, thereby realizing heat sink of the copper cold shield, an electric lead and a support device; the first-level cold junction of the refrigerator adopts soft connection, thereby reducing temperature increment of the magnet due to vibration of the refrigerator; and the conduction-cooled superconducting magnet Dewar has the advantages of easy operation of manufacture, processing and installation, and is applicable to scale production.
Owner:INST OF PLASMA PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Fused filament fabrication using liquid cooling
InactiveUS20160271880A1Reduce incidenceReduce of of materialApplying layer meansFused filament fabricationNuclear engineering
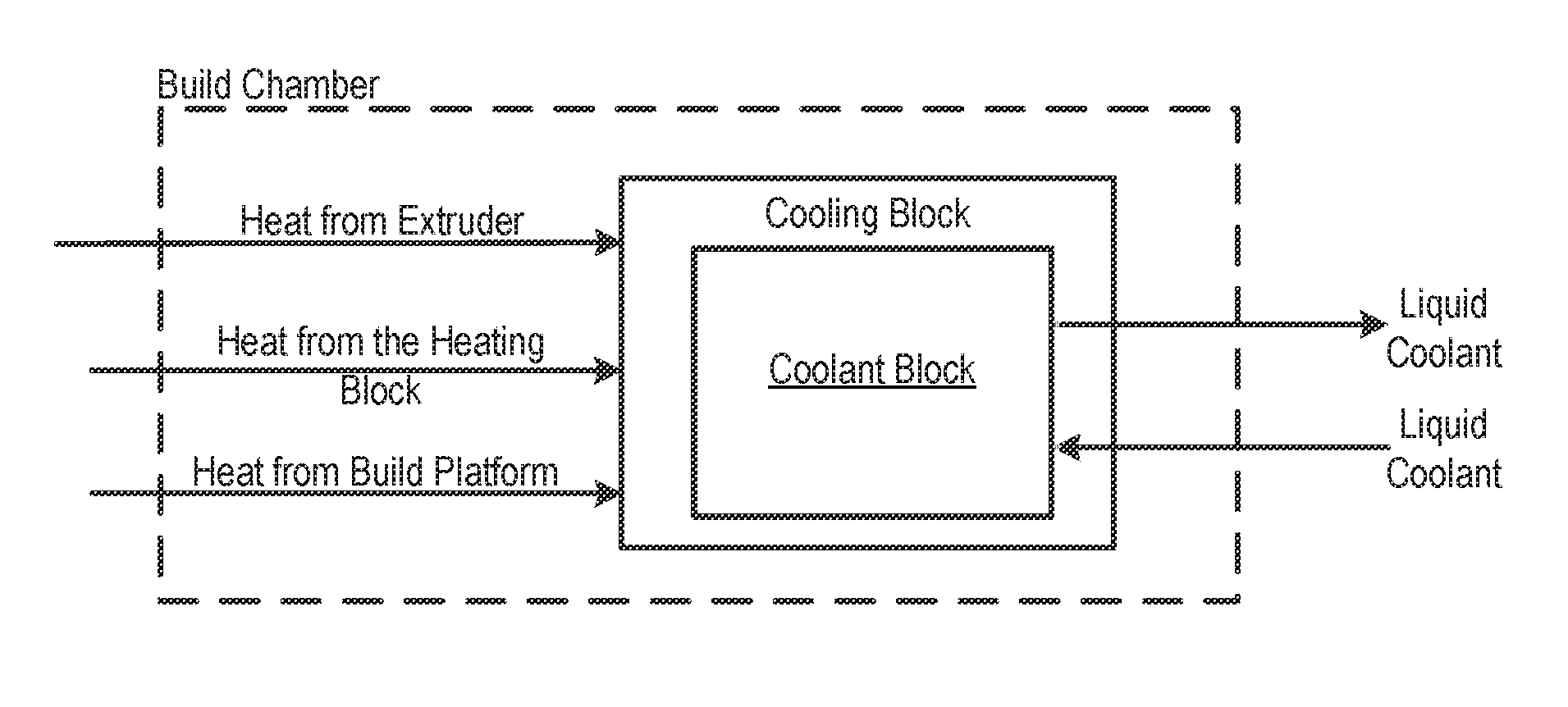
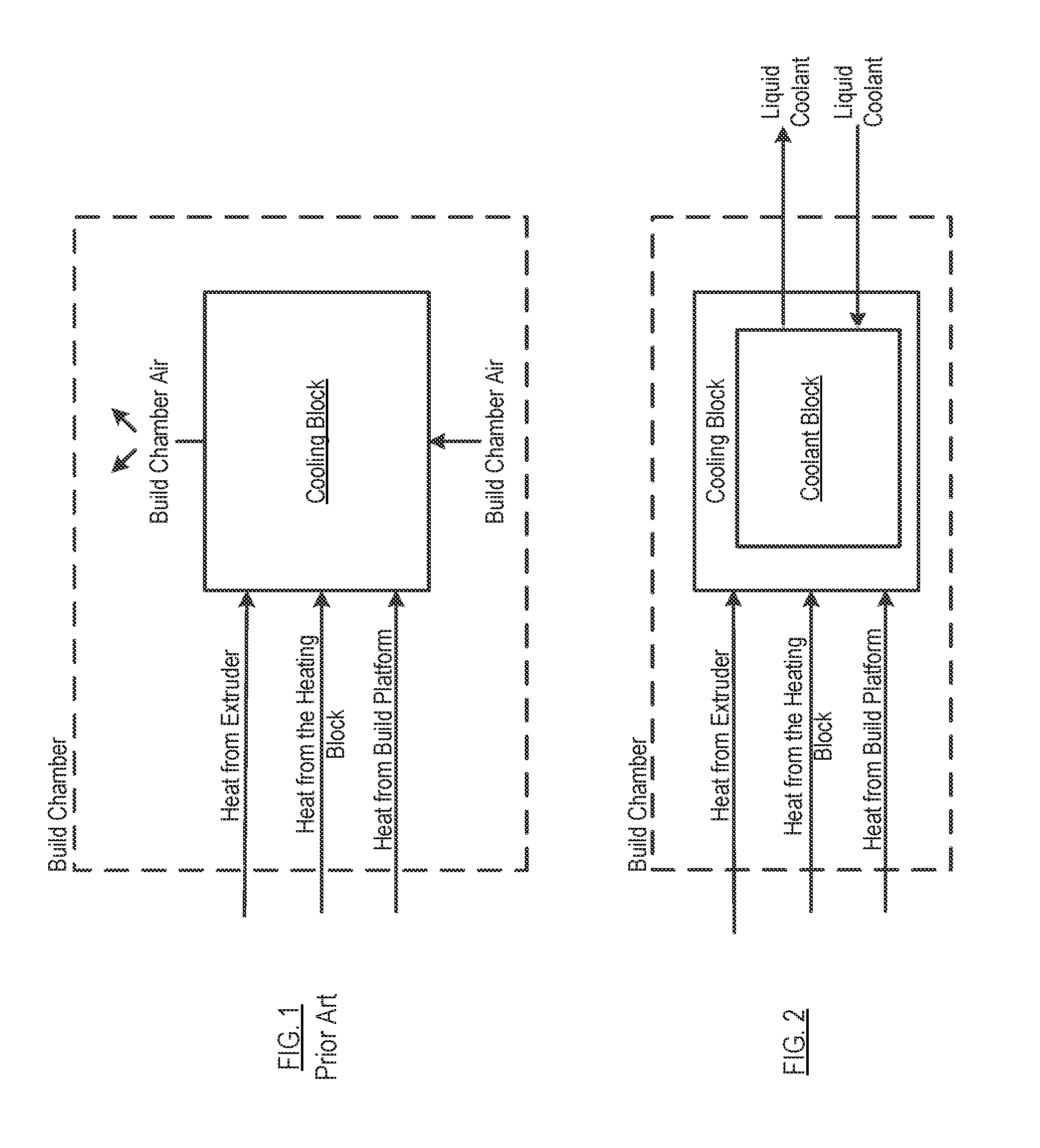
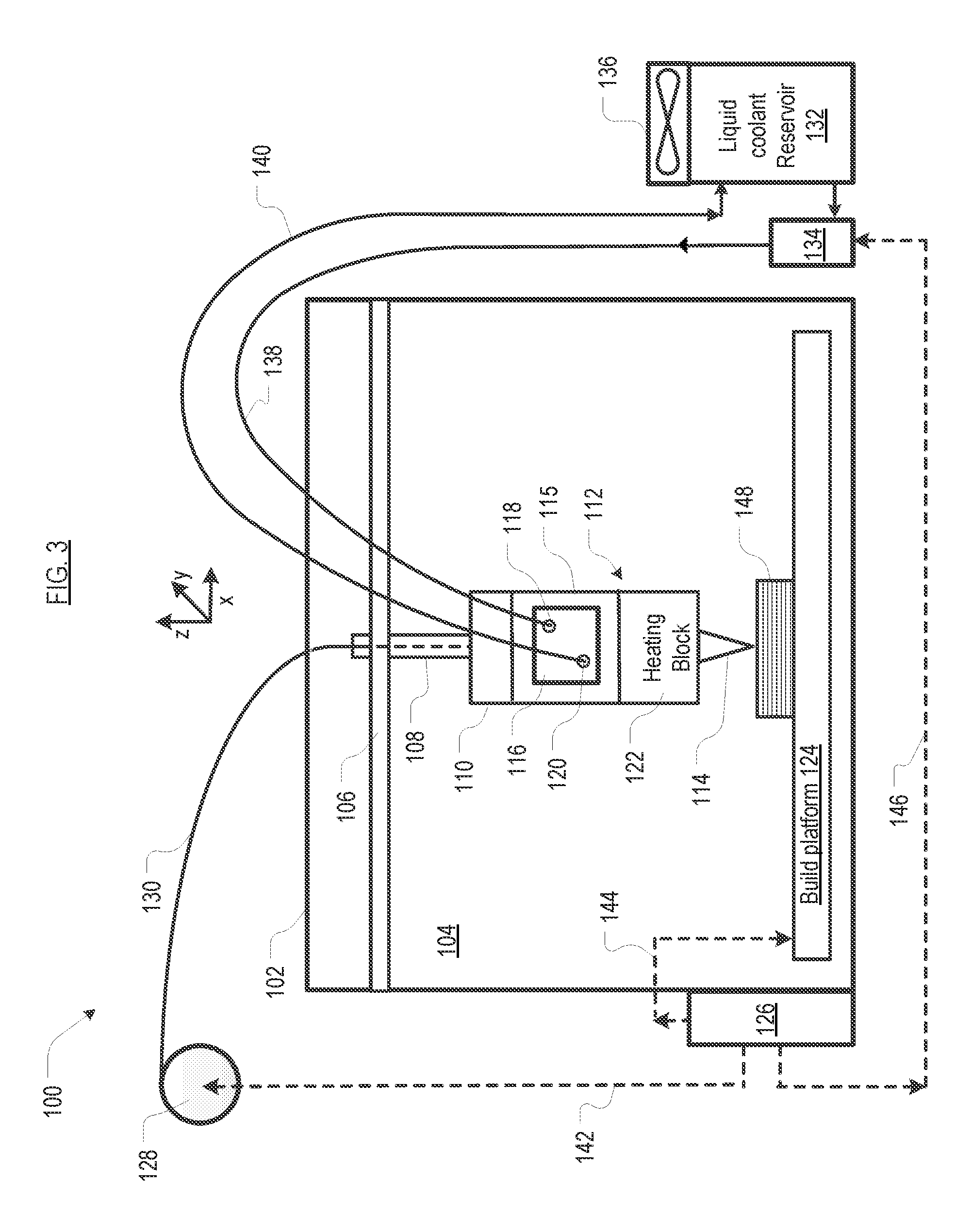
A FFF-based 3D printer includes a thermal management system that incorporates liquid cooling for the cooling block. In the illustrative embodiment, the thermal management system includes a coolant block that couples to the surface of the existing cooling block, a liquid-coolant reservoir, a fan for cooling the reservoir, a pump for pumping the coolant, and conduits for conducting the coolant to and from the coolant block. Embodiments of the invention provide a way to prevent or substantially reduce the incidence of clogging as otherwise occurs when attempting to print high-temperature, high-viscosity materials using FFF-based 3d printers.
Owner:AREVO INC
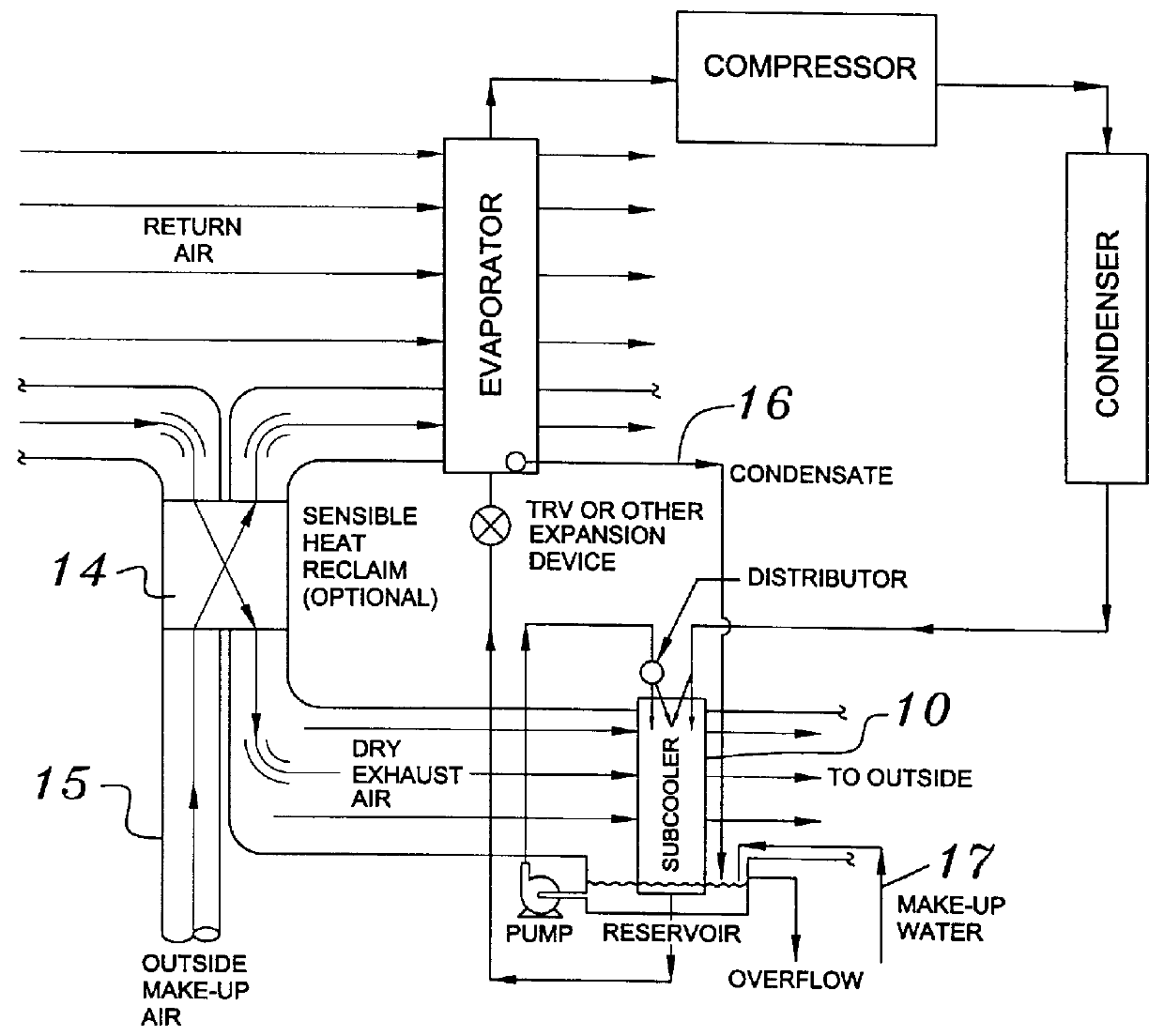
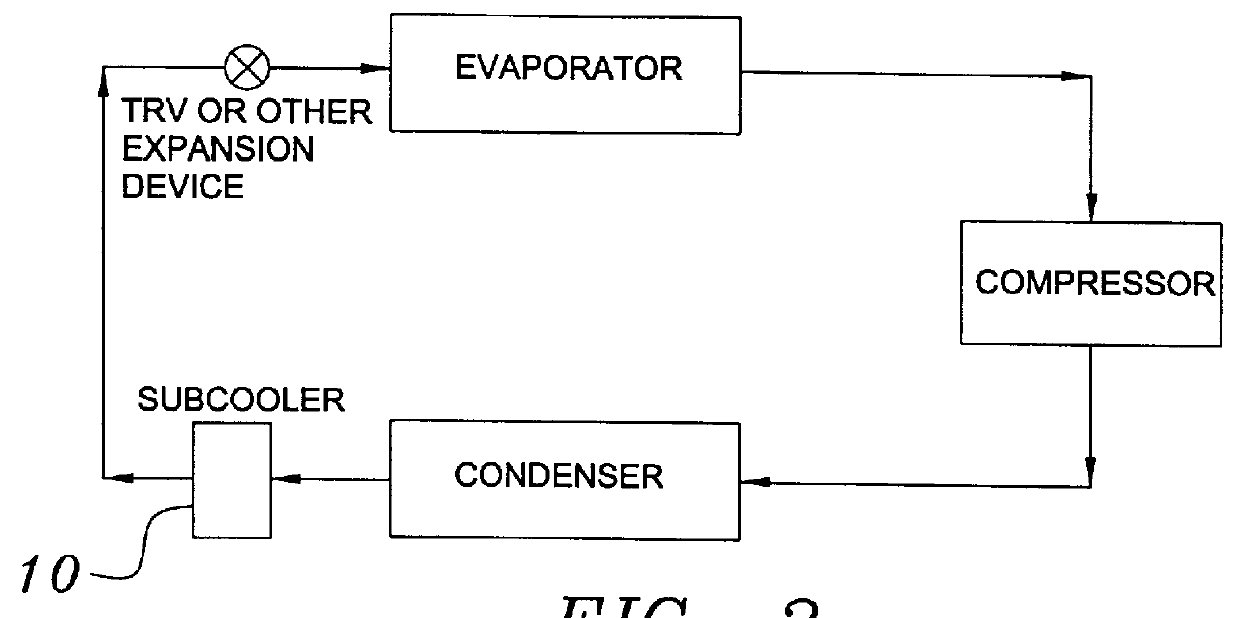
Building exhaust and air conditioner condenstate (and/or other water source) evaporative refrigerant subcool/precool system and method therefor
InactiveUS6070423AComprehensive understandingReduce the temperatureEnergy recovery in ventilation and heatingHeat recovery systemsWater wetIndoor air quality
First, a system for providing liquid refrigerant subcooling, subsequent to that subcooling accomplished by the primary condenser of an air conditioner or heat pump, by means of evaporative cooling utilizing the condensate water of said air conditioner or heat pump system and / or some other water supply to wet the surface of the subcool heat exchanger and then passing the cold, dry building exhaust air required for good indoor air quality across the wetted surface of the subcool heat exchanger. Said exhaust air could be used after first undergoing a sensible heat exchange with the incoming make up air. Said subcooling providing for an increased refrigeration capacity, and efficiency of the system. Secondly, a system for providing hot gas discharge refrigerant precooling before said hot gas passes into the primary condenser of an air conditioner or heat pump, by means of evaporative cooling utilizing the condensate water of said air conditioner or heat pump system and / or some other water supply to wet the surface of the precool heat exchanger and then passing the cold, dry building exhaust air required for good indoor air quality across the wetted surface of the precool heat exchanger. Said precooler providing lower power consumption of the compressor, lower head pressure, increased mass flow of the refrigerant and improved efficiency of the primary condenser of the air conditioning or heat pump system. Said exhaust air could be used after first undergoing a sensible heat exchange with the incoming make up air on either the subcooler or precooler. Finally, a combination subcooler and precooler system where the cold dry exhaust air is first used to evaporatively subcool the liquid refrigerant in the water wetted subcooler and then subsequently used to conductively cool the hot gas refrigerant passing through a dry surface precooler or alternately used to evaporatively cool the wetted surface of the precooler thereby evaporatively precooling the hot gas refrigerant passing through the precooler.
Owner:GLOBAL ENERGY & ENVIRONMENT RES INC +1
Rapid conductive cooling using a secondary process plane
ActiveUS20080142497A1Drying solid materials with heatMuffle furnacesActive coolingConduction cooling
A method and apparatus for thermally processing a substrate is described. The apparatus includes a substrate support configured to move linearly and / or rotationally by a magnetic drive. The substrate support is also configured to receive a radiant heat source to provide heating region in a portion of the chamber. An active cooling region comprising a cooling plate is disposed opposite the heating region. The substrate may move between the two regions to facilitate rapidly controlled heating and cooling of the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
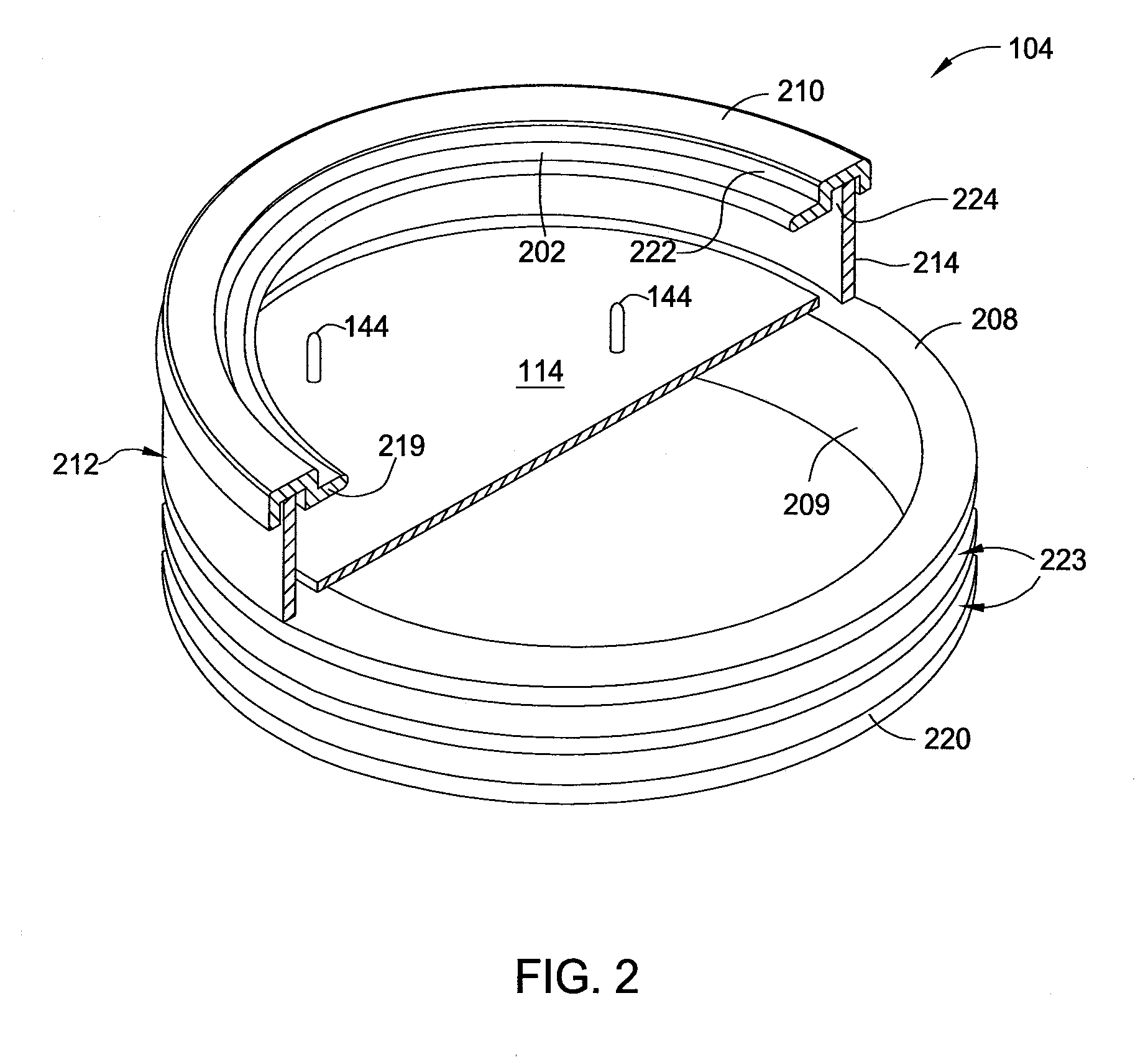
Light-weight, conduction-cooled inductor
ActiveUS20090146769A1Reduce power consumptionLess heatTransformers/inductances coolingTransformers/inductances casingsInductorMotor controller
A lightweight inductor for the motor controller of an aircraft starter includes a toroidal inductor core divided into multiple sections that are separated by a thermally conductive, but electrically insulating, material. The inductor core is wound with wire and positioned inside of an electrically and thermally conductive container, which acts as a heat sink and EMI shield, while also reducing eddy currents within the inductor core.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Flow through cooling assemblies for conduction-cooled circuit modules
A cooling assembly is located in a chassis with a conduction-cooled circuit module and permits the conduction-cooled circuit module to be utilized in an air-flow-through or liquid-flow-through circuit module chassis assembly. The cooling assembly may be a removable cooling adapter or may be integral with the chassis. The cooling assembly includes a housing having a first end and a second end and defining one or more fluid passages. The housing further includes a thermal contact surface to contact the conduction-cooled circuit module. The cooling assembly may be configured for air-flow-through or liquid-flow-through cooling of the conduction-cooled circuit module.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
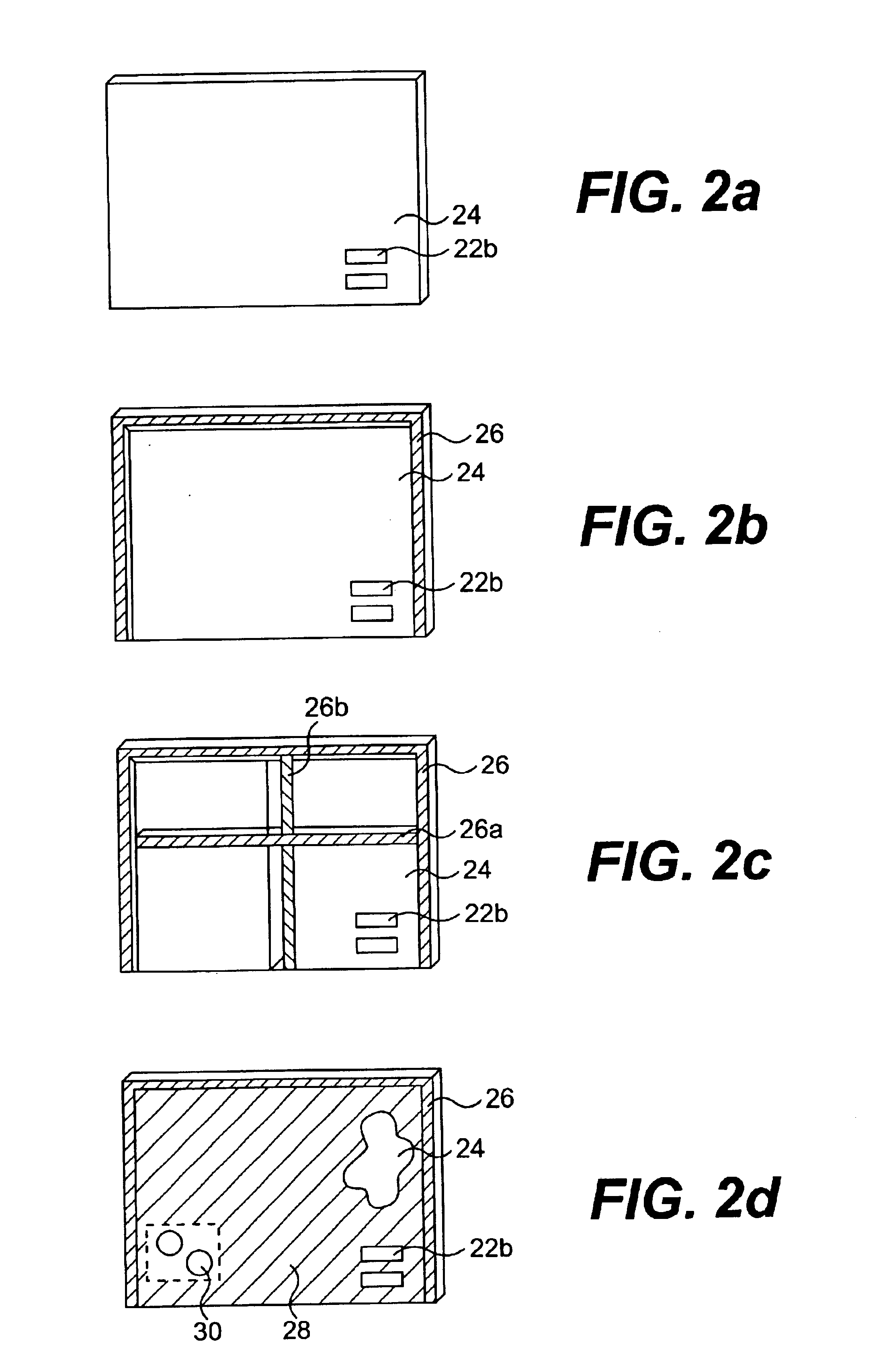
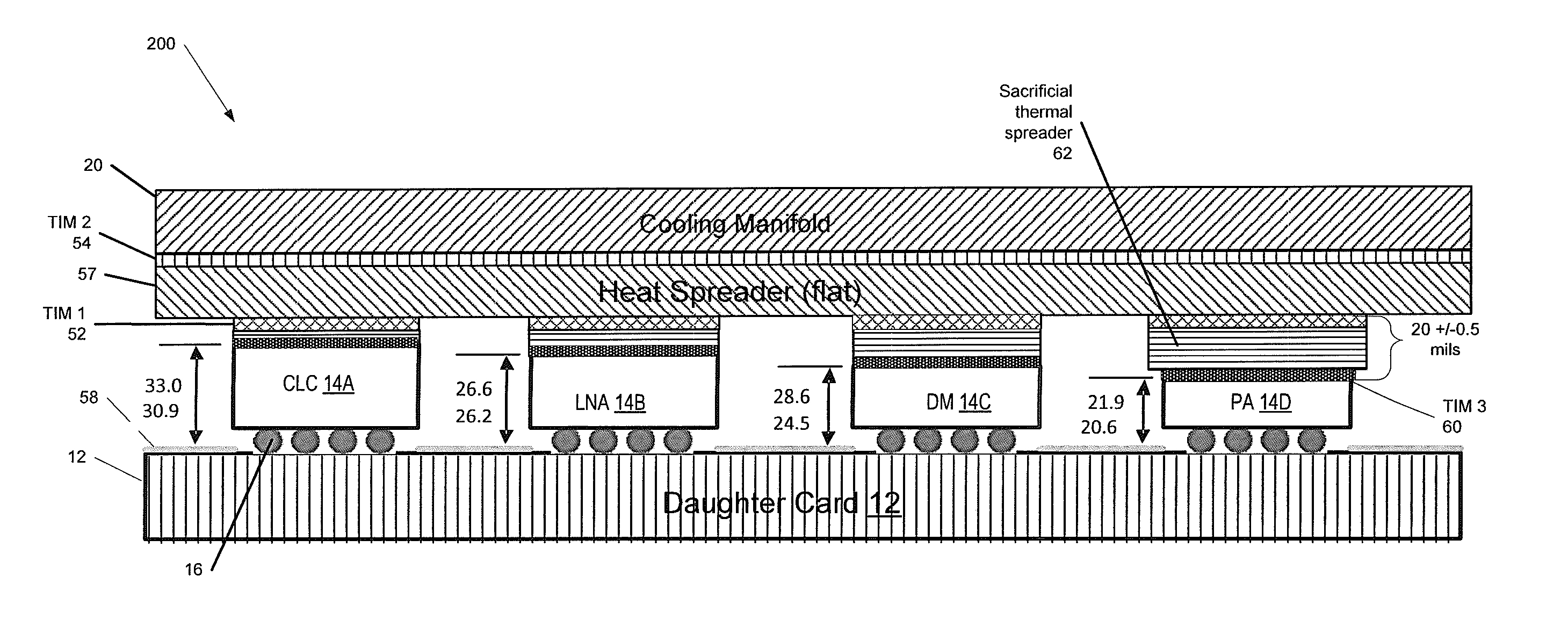
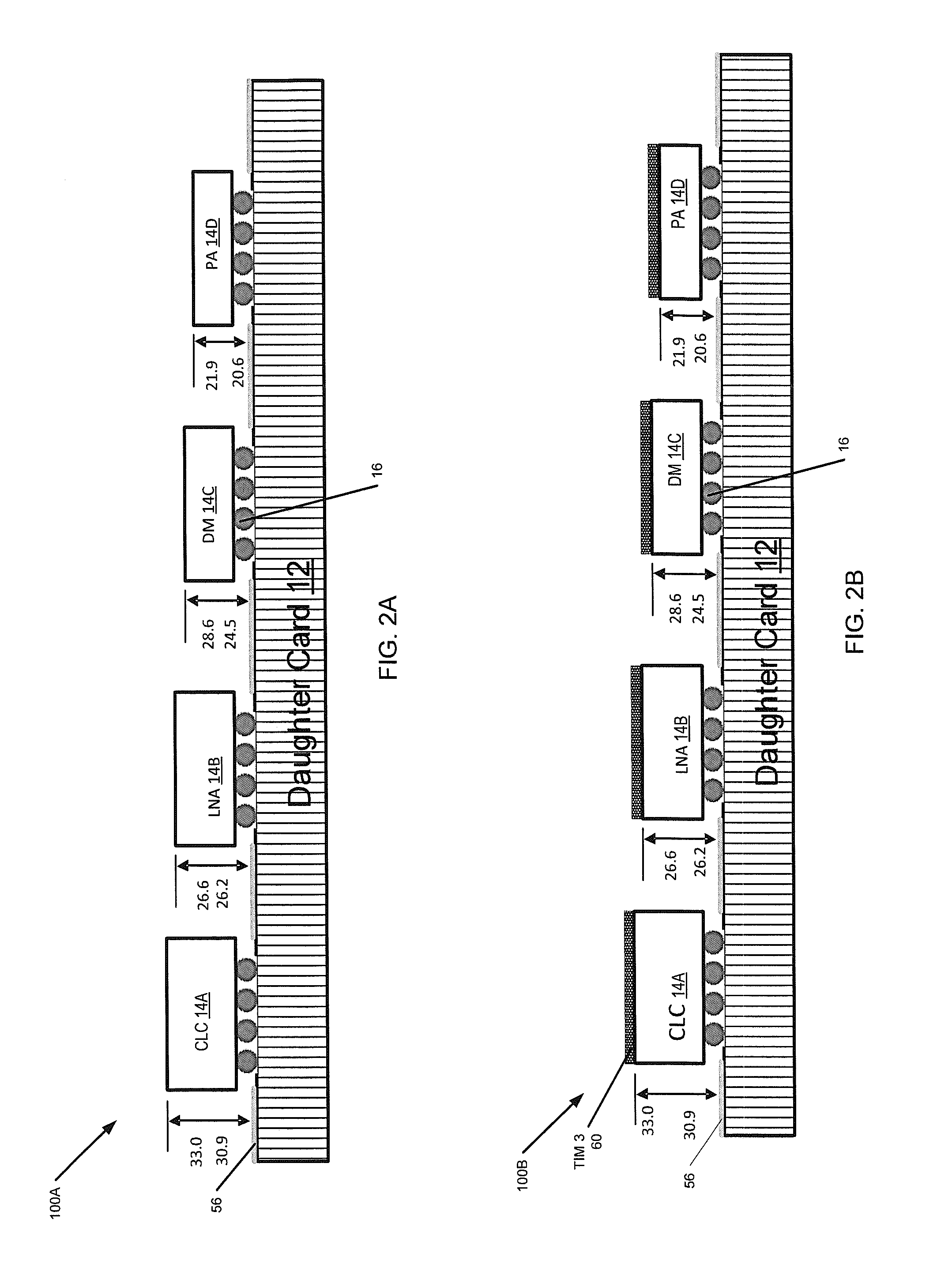
Conduction cooling of multi-channel flip chip based panel array circuits
ActiveUS20130258599A1Minimize thermal gapImprove thermal conductivitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor chipConduction cooling
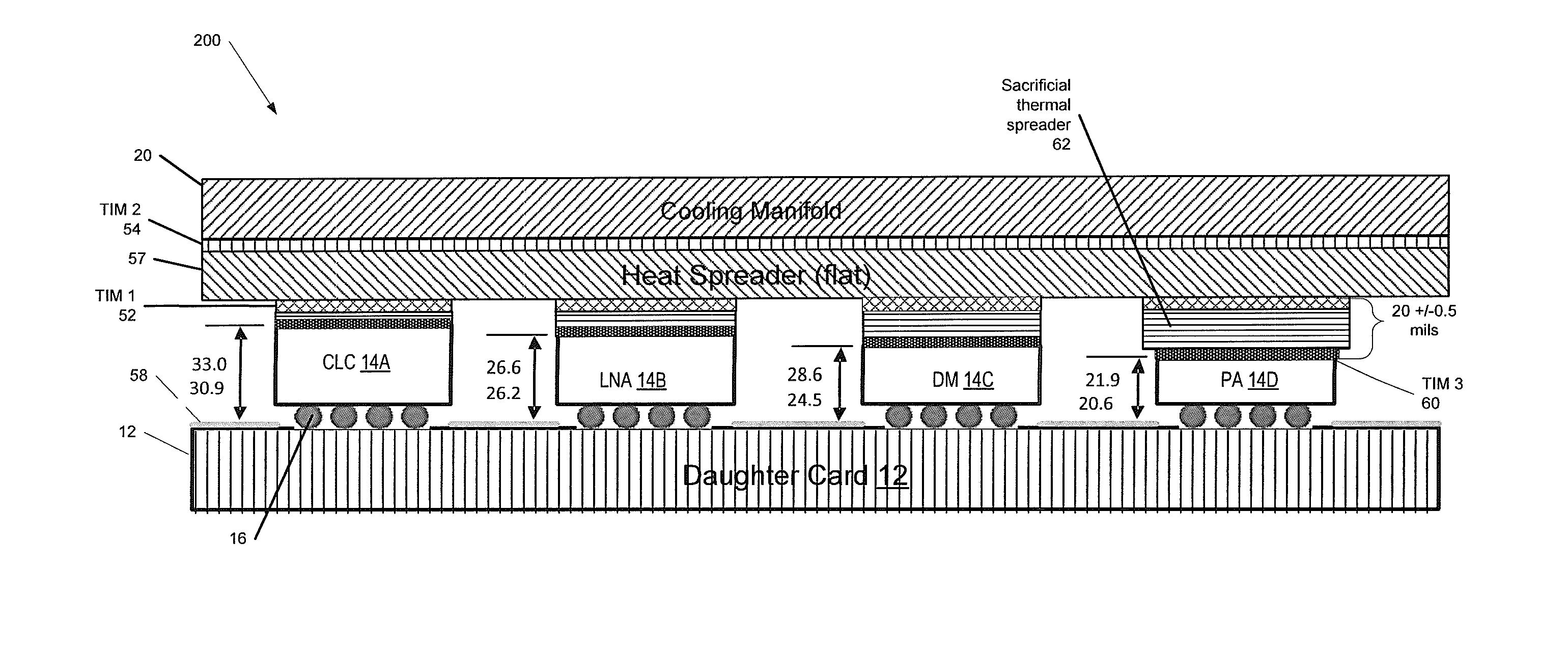
A method of forming a heat-dissipating structure for semiconductor circuits is provided. First and second semiconductor integrated circuit (IC) chips are provided, where the first and second semiconductor chips each have first and second opposing sides, wherein the first and second semiconductor IC chips are configured to be fixedly attached to a top surface of a substantially planar circuit board along their respective first sides. The respective second opposing sides of each of the first and second semiconductor IC chips are coupled to first and second respective portions of a sacrificial thermal spreader material, the sacrificial thermal spreader material comprising a material that is thermally conductive. The first and second portions of the sacrificial thermal spreader material are planarized to substantially equalize a respective first height of the first semiconductor chip and a respective second height of the second semiconductor chip.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Conduction cooled circuit board assembly
ActiveUS20110141692A1Clamping/extracting meansIndirect heat exchangersConduction coolingMechanical engineering
A conduction cooled circuit board assembly may include a frame and at least one circuit board attached to the frame, having at least one area to be cooled. The assembly may also include at least one rail attached to the frame, and at least one heat pipe having a first end and a second end, the first end disposed near the area and the second end in contact with the rail so as to transfer heat from the area to the rail.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Immersion-cooled and conduction-cooled electronic system
ActiveUS20140146467A1Facilitate immersion-coolingOvercomes shortcomingDigital data processing detailsCooling/ventilation/heating modificationsElectronic systemsConduction cooling
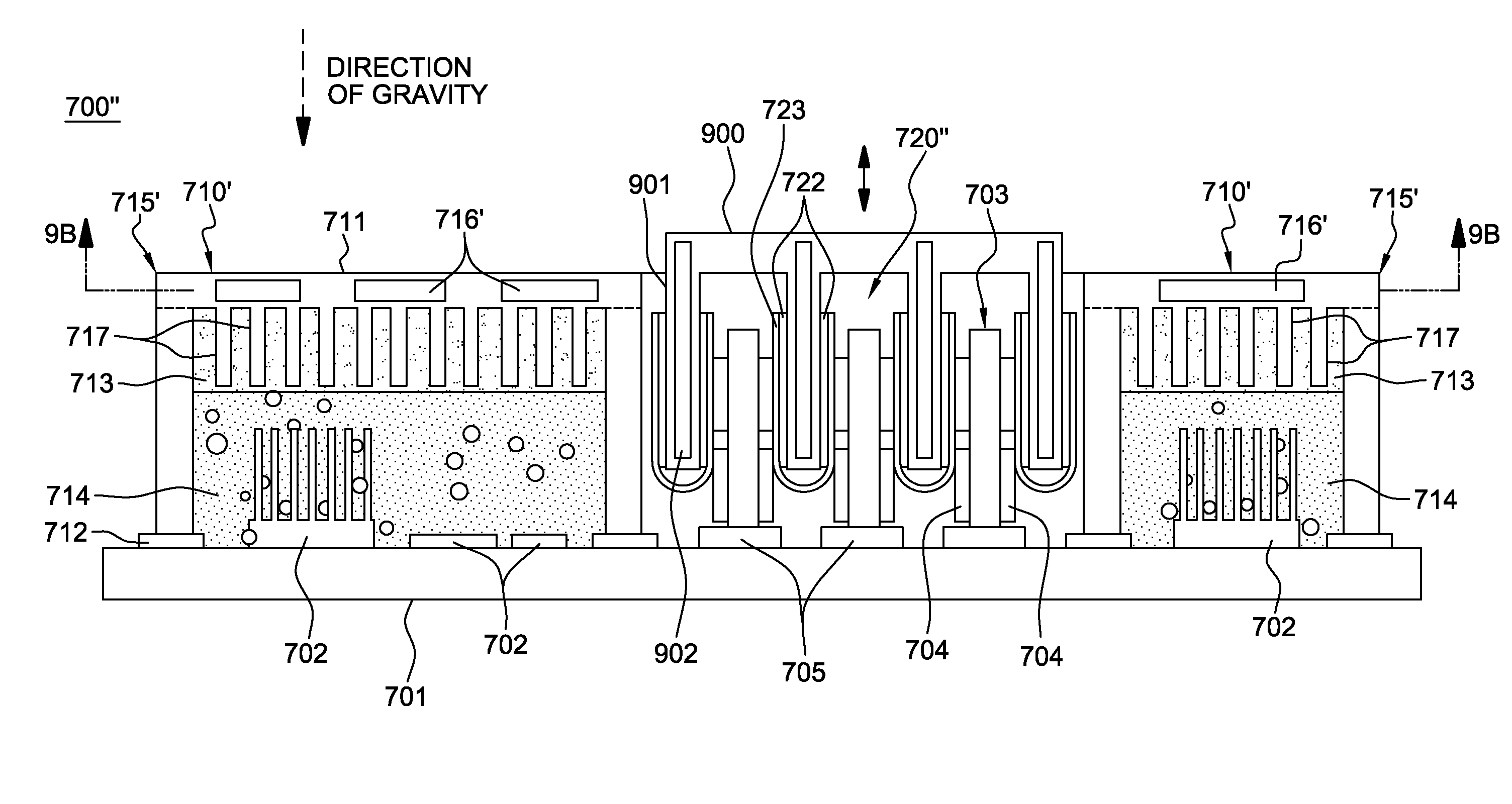
A cooled electronic system and cooling method are provided, where an electronics board having a plurality of electronic components mounted to the board is cooled by an apparatus which includes an immersion-cooled electronic component section and a conduction-cooled electronic component section. The immersion-cooled section includes an enclosure at least partially surrounding and forming a compartment about multiple electronic components of the electronic components mounted to the electronics board, and a fluid disposed within the compartment. The multiple electronic components are, at least in part, immersed within the fluid to facilitate immersion-cooling of those components. The conduction-cooled electronic component section includes at least one electronic component of the electronic components mounted to the electronics board, and the at least one electronic component is indirectly liquid-cooled, at least in part, via conduction of heat from the at least one electronic component.
Owner:IBM CORP
Air-side economizer facilitating liquid-based cooling of an electronics rack
InactiveUS20130068423A1Indirect heat exchangersHeat exchange apparatusNuclear engineeringConduction cooling
A cooling apparatus and method are provided for cooling an electronic subsystem of an electronics rack. The cooling apparatus includes a local cooling station, which has a liquid-to-air heat exchanger and ducting for directing a cooling airflow across the heat exchanger. A cooling subsystem is associated with the electronic subsystem of the rack, and includes either a housing facilitating immersion cooling of electronic components of the electronic subsystem, or one or more liquid-cooled structures providing conductive cooling to the electronic components of the electronic subsystem. A coolant loop couples the cooling subsystem to the liquid-to-air heat exchanger of the local cooling station. In operation, heat is transferred via circulating coolant from the electronic subsystem and rejected in the liquid-to-air heat exchanger of the local cooling station to the cooling airflow passing across the liquid-to-air heat exchanger. In one embodiment, the cooling airflow is outdoor air.
Owner:IBM CORP
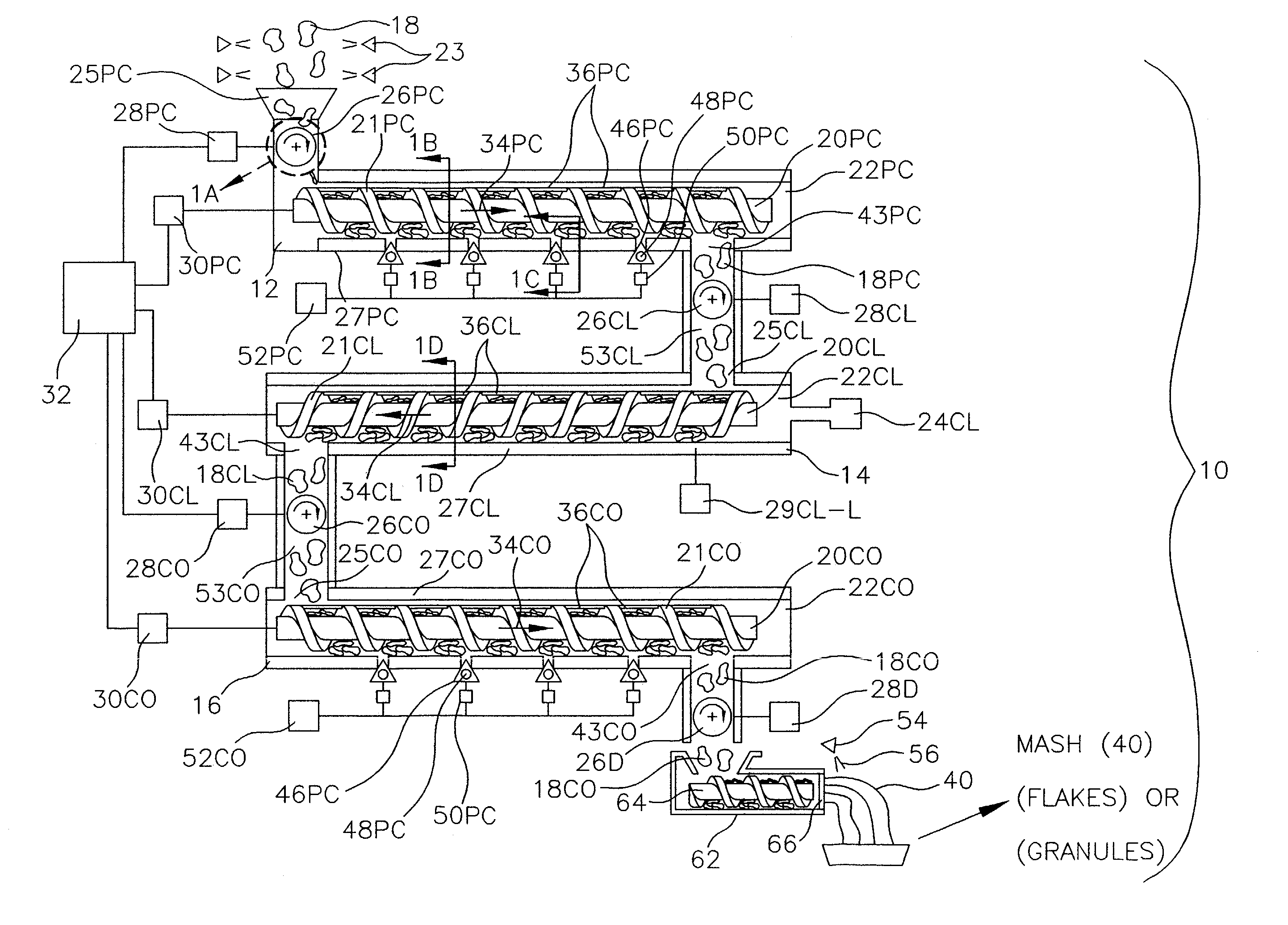
Sealed system and continuous process for making food products
InactiveUS6994016B1Minimizes damage and leachingProduction of water becomes so profuseAir-treating devicesMilk preservationWater productionEngineering
A system and a process for making food products, such as dehydrated potato products, with reduced water usage, and reduced waste water production, are provided. The system includes a precooker, a cooler and a cooker having sealed process chambers in flow communication with one another, and augers for moving the food product through the process chambers. In addition, valves seal the process chambers, and transfer the food product between the process chambers at a controlled rate. The process includes the steps of precooking the food product using steam, cooling the food product using vacuum cooling and conduction cooling in combination, and then cooking the food product using steam. The process also includes the steps of moving the food product at the controlled rate using the valves, and mixing the food product during the precooking, cooling and cooking steps.
Owner:MILES WILLARD TECH
VME circuit host card with triple mezzanine configuration
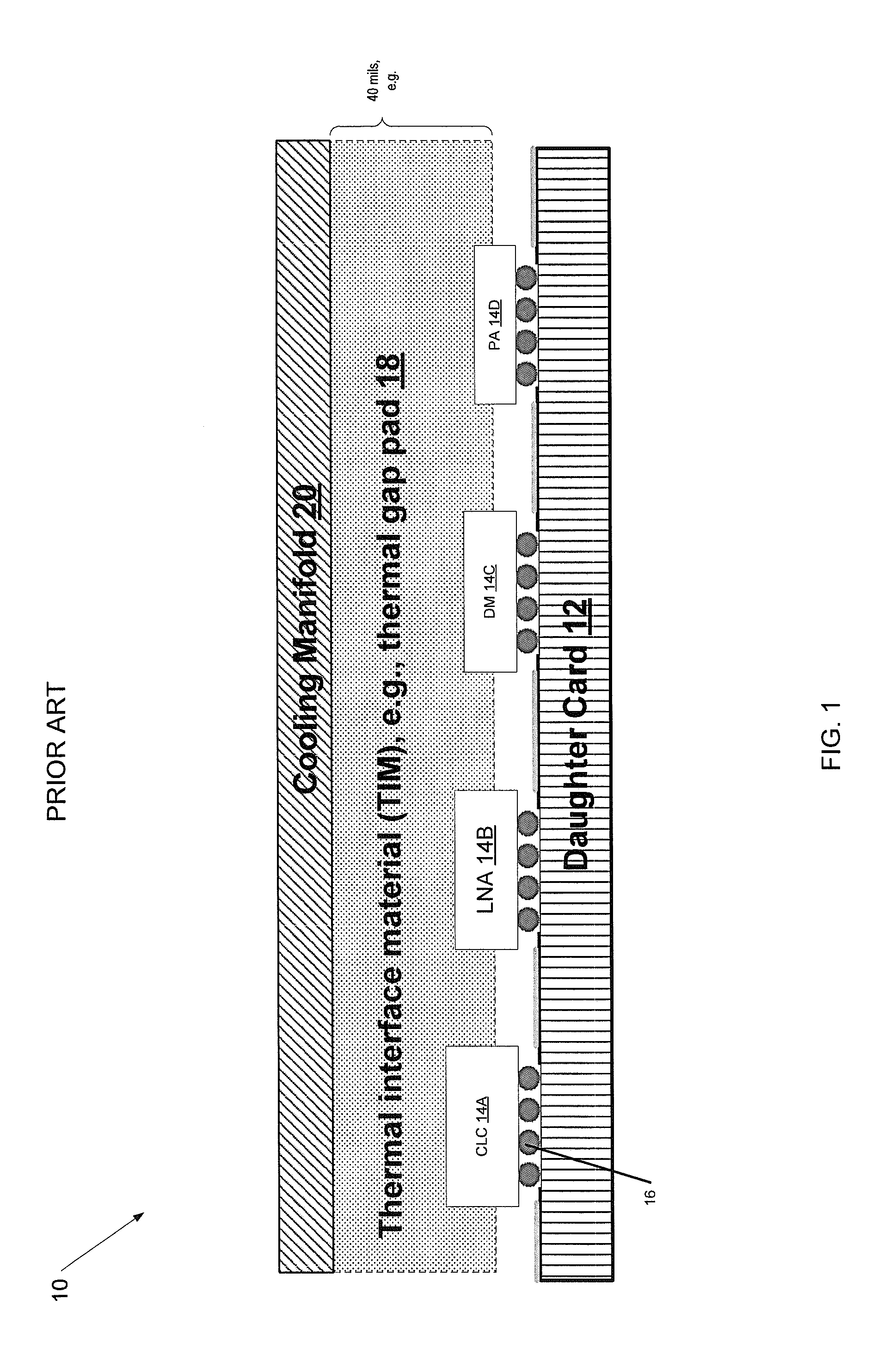
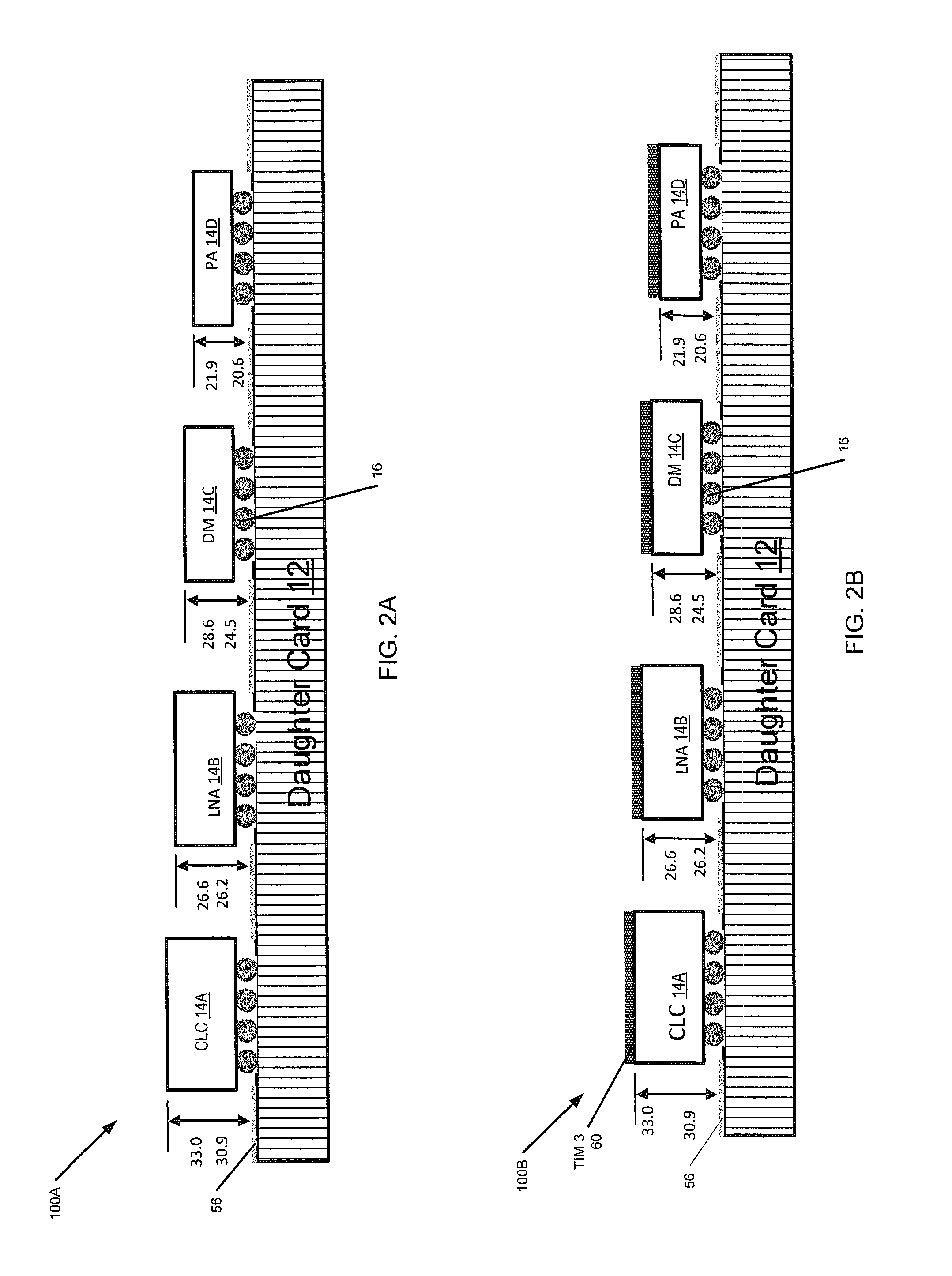
InactiveUS6768642B2Coupling device detailsPrinted circuit board receptaclesConduction coolingEngineering
A circuit card assembly includes a host card having connector assemblies and a conduction-cooling path. A first and second mezzanine card each having electronic circuitry defining a component field is mounted to the conduction-cooling path of the host card and connected to the connector assemblies. A third mezzanine card is mounted to the host card and over at least a portion of the component field of the first and second mezzanine cards. A cooling path is provided between the third mezzanine card and the host card and mechanical interference is prevented between the third mezzanine card and the component field due to the profile of the conduction-cooling path. The conduction-cooling path may also be located on the third mezzanine card or on both the host card and the third mezzanine card. The third mezzanine card is connected to the connector assemblies outside of the connector area of the other mezzanine cards.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Conduction cooling of multi-channel flip chip based panel array circuits
ActiveUS8780561B2Gap minimizationImprove thermal conductivityPrinted circuit assemblingDigital data processing detailsSemiconductor chipConduction cooling
A method of forming a heat-dissipating structure for semiconductor circuits is provided. First and second semiconductor integrated circuit (IC) chips are provided, where the first and second semiconductor chips each have first and second opposing sides, wherein the first and second semiconductor IC chips are configured to be fixedly attached to a top surface of a substantially planar circuit board along their respective first sides. The respective second opposing sides of each of the first and second semiconductor IC chips are coupled to first and second respective portions of a sacrificial thermal spreader material, the sacrificial thermal spreader material comprising a material that is thermally conductive. The first and second portions of the sacrificial thermal spreader material are planarized to substantially equalize a respective first height of the first semiconductor chip and a respective second height of the second semiconductor chip.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Data center cooling with an air-side economizer and liquid-cooled electronics rack(s)
InactiveUS20130068441A1Space heating and ventilation safety systemsSpace heating and ventilation control systemsData centerNuclear engineering
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
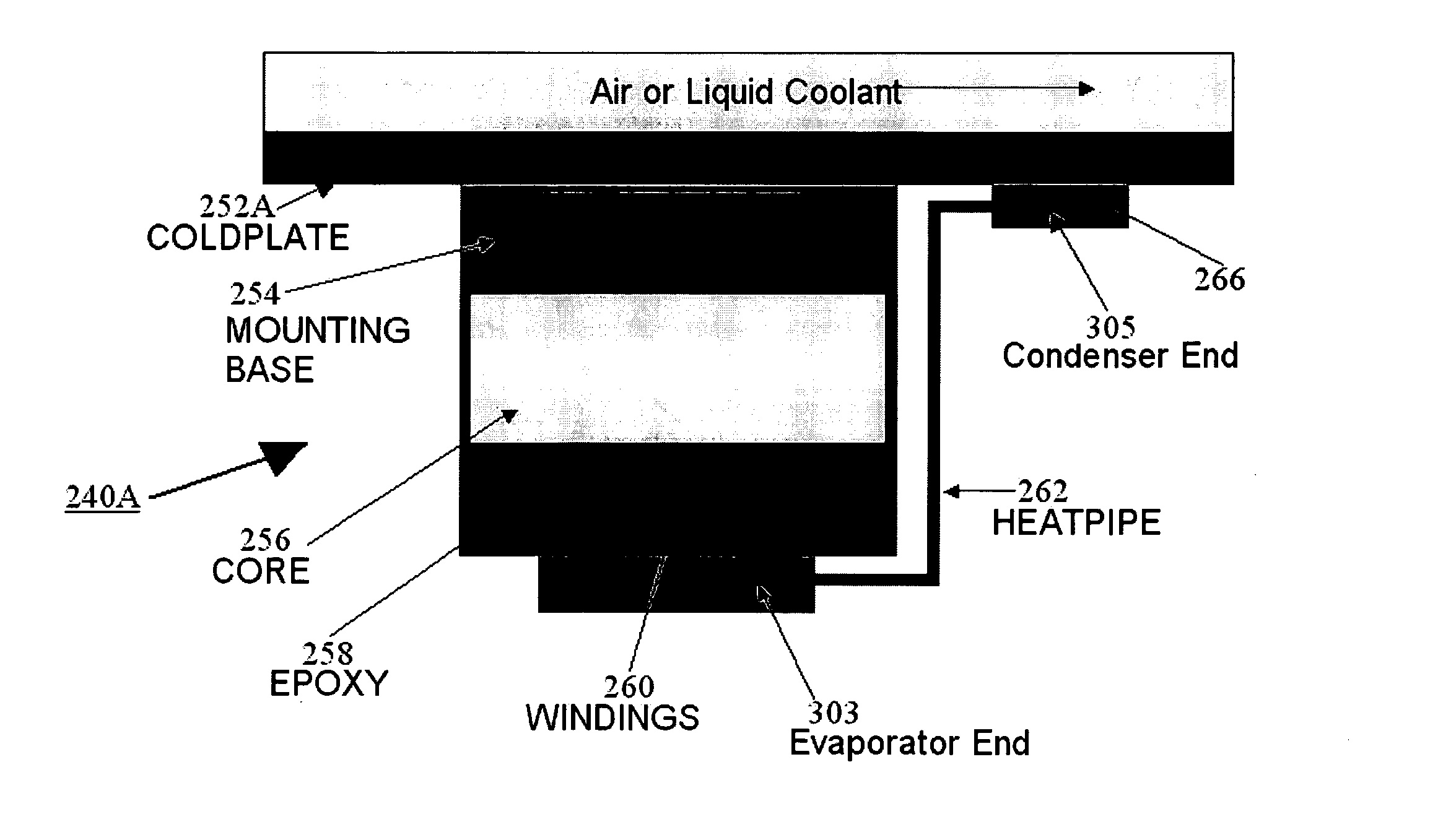
Heat pipe supplemented transformer cooling
InactiveUS20080122566A1Improve cooling effectTransformers/inductances coolingTransformers/inductances casingsTransformerClosed loop
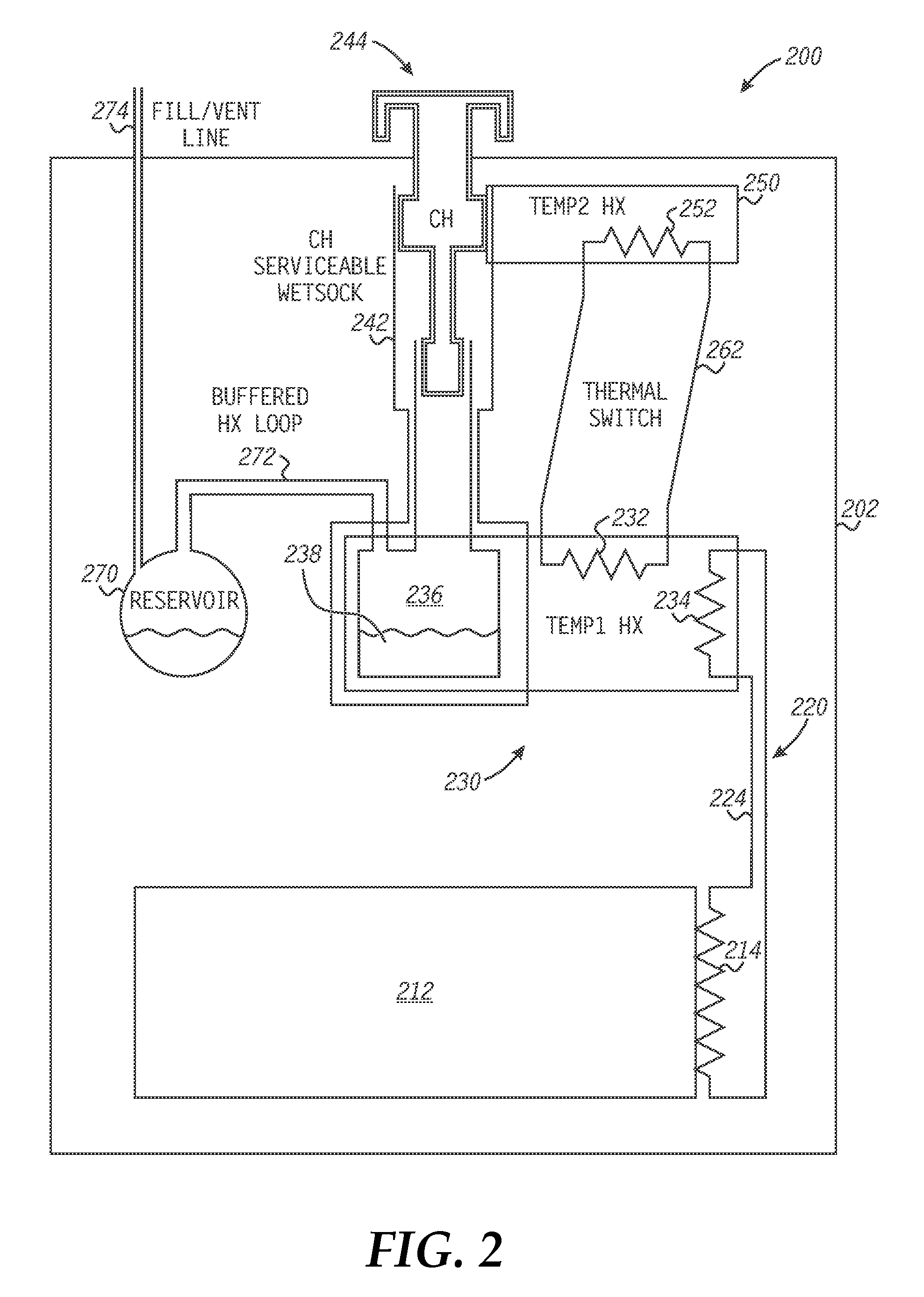
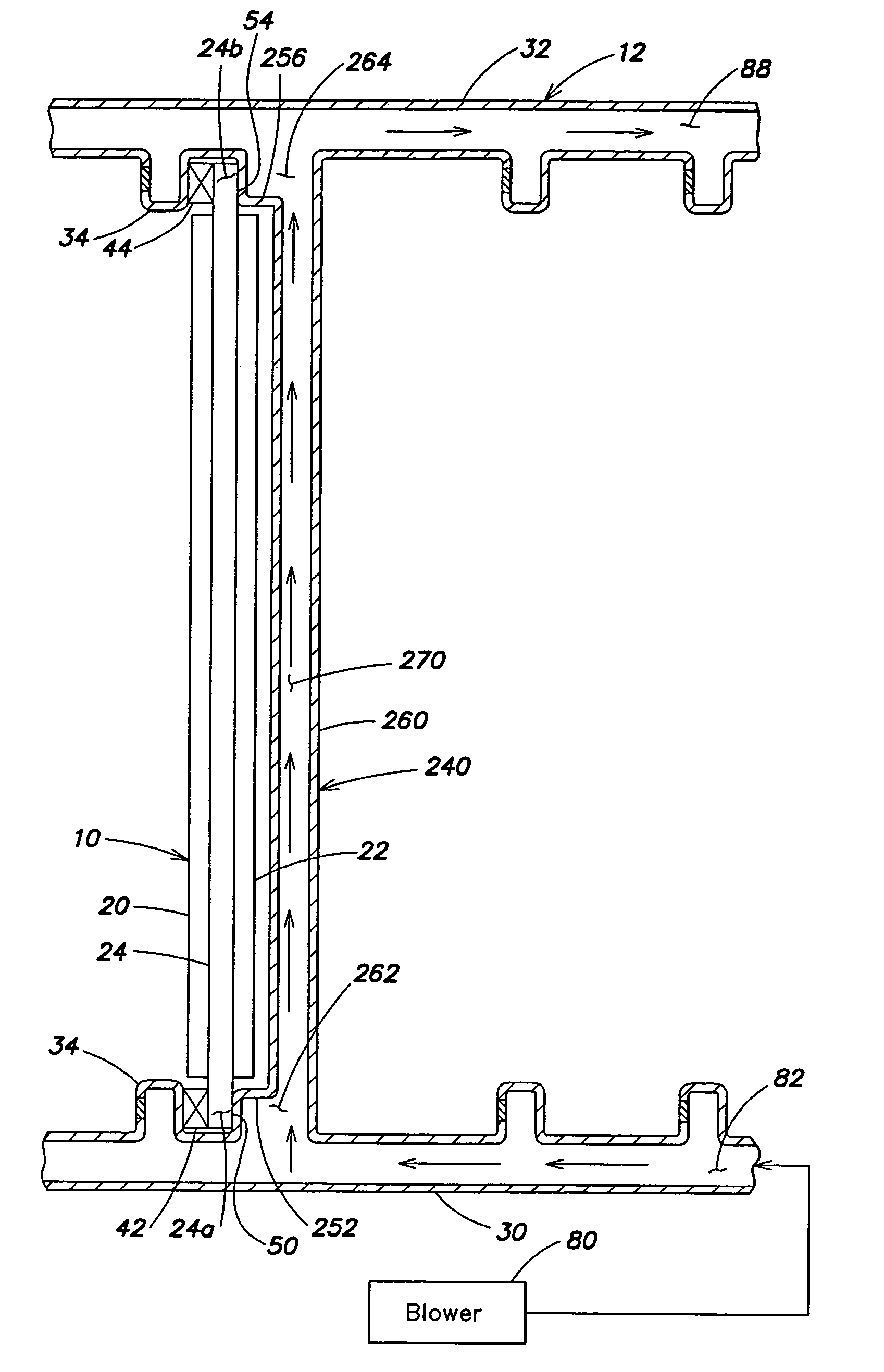
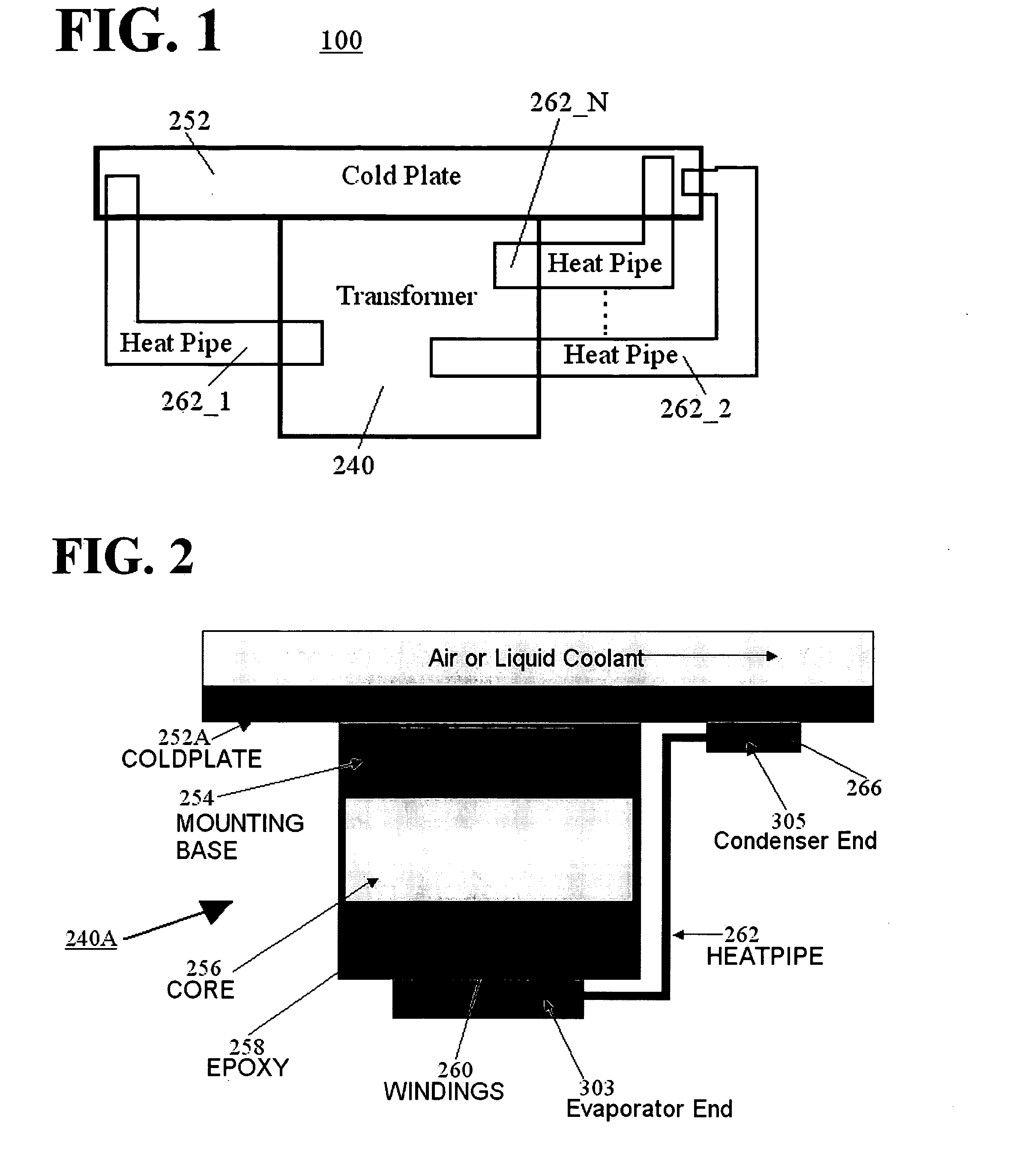
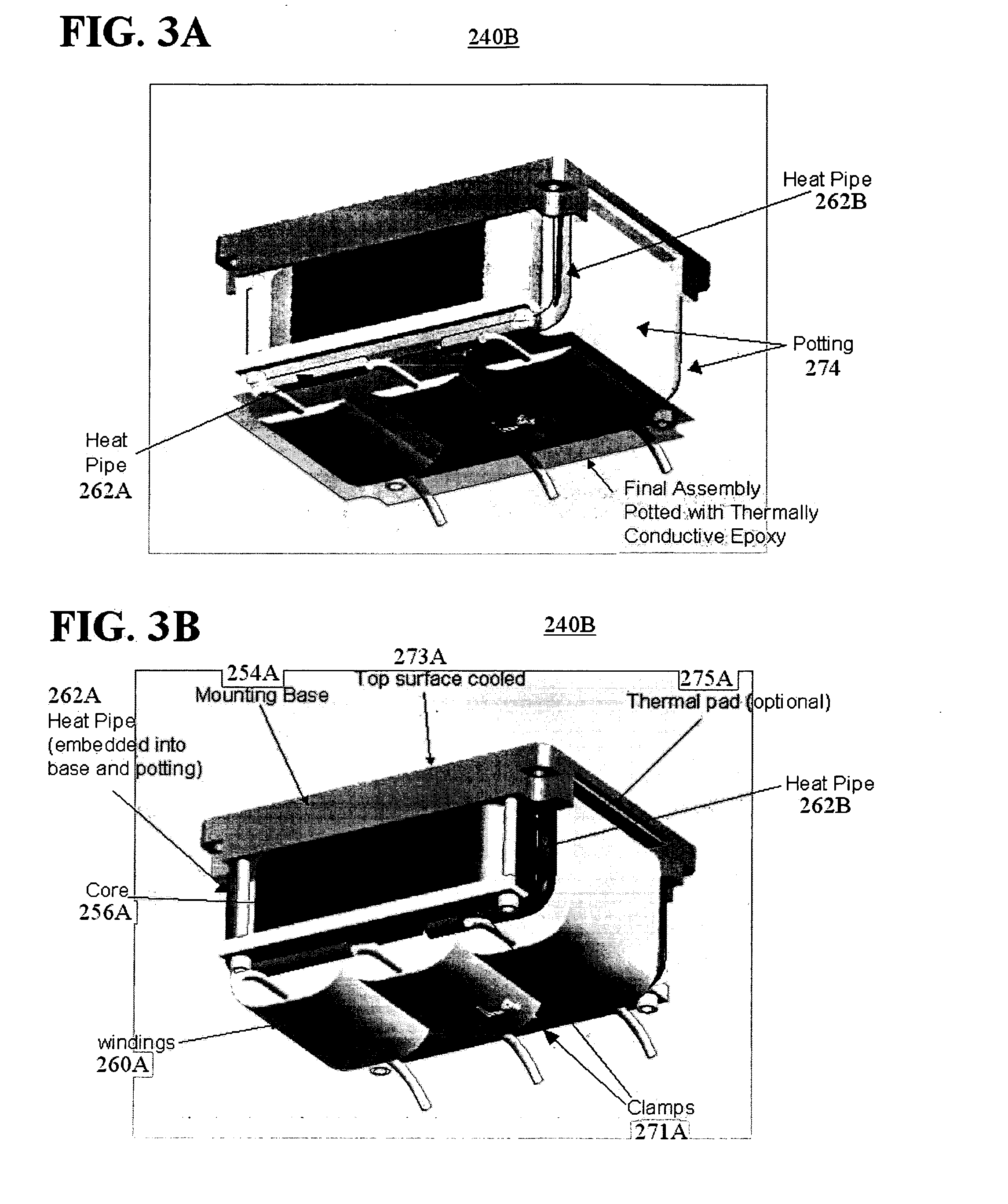
A method for cooling a transformer and transformer apparatuses are implemented. A transformer apparatus, according to one embodiment, comprises: a conduction cooled electrical transformer (240) mounted to a cold plate (252); and a heat pipe (262) for supplementing cooling of the transformer (240), the heat pipe (262) comprising a first end (303), a second end (305), and a sealed low pressure cavity containing an amount of a fluid (311), wherein the first end (303) of the heat pipe (262) is located in a hot region of the transformer (240), the second end (305) is maintained colder than the first end (303) by contact with the cold plate (252), and heat produced at the first end (303) by operation of the transformer (240) is moved to the second end (305) by a closed loop vapor cycle in the sealed low pressure cavity using the fluid (311) of the heat pipe (262).
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Device For Producing A Single Crystal Composed Of Silicon By Remelting Granules
InactiveUS20110095018A1Polycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsSide lyingConduction cooling
A device for producing a silicon single crystal by remelting granules has a rotating plate of silicon having a central opening and having a silicon tubular extension which encloses the opening and extends below the plate; a first induction heating coil above the plate for melting granules; and a second induction heating coil below the plate for crystallizing the molten granules, wherein the second induction heating coil has, on its side lying opposite the silicon plate, a lower layer composed of a magnetically permeable material and an upper layer in which there is at least one cooling channel for conducting a coolant.
Owner:SILTRONIC AG
Immersion-cooled and conduction-cooled electronic system
ActiveUS8947873B2Digital data processing detailsCooling/ventilation/heating modificationsElectronic systemsEngineering
A cooled electronic system and cooling method are provided, where an electronics board having a plurality of electronic components mounted to the board is cooled by an apparatus which includes an immersion-cooled electronic component section and a conduction-cooled electronic component section. The immersion-cooled section includes an enclosure at least partially surrounding and forming a compartment about multiple electronic components of the electronic components mounted to the electronics board, and a fluid disposed within the compartment. The multiple electronic components are, at least in part, immersed within the fluid to facilitate immersion-cooling of those components. The conduction-cooled electronic component section includes at least one electronic component of the electronic components mounted to the electronics board, and the at least one electronic component is indirectly liquid-cooled, at least in part, via conduction of heat from the at least one electronic component.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Immersion-cooled and conduction-cooled method for electronic system
ActiveUS20140146468A1Digital data processing detailsCooling/ventilation/heating modificationsElectronic systemsConduction cooling
A method of facilitating cooling of an electronics board having a plurality of electronic components mounted to the board by providing an apparatus which includes an immersion-cooled electronic component section and a conduction-cooled electronic component section. The immersion-cooled section includes an enclosure at least partially surrounding and forming a compartment about multiple electronic components of the electronic components mounted to the electronics board, and a fluid disposed within the compartment. The multiple electronic components are, at least in part, immersed within the fluid to facilitate immersion-cooling of those components. The conduction-cooled electronic component section includes at least one electronic component of the electronic components mounted to the electronics board, and the at least one electronic component is indirectly liquid-cooled, at least in part, via conduction of heat from the at least one electronic component.
Owner:IBM CORP
Temperature adjustment device and method of focusing ring
ActiveCN106920725AOptimal treatment processRealize the function of grounding conductionParticle separator tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWorking temperatureEngineering
The invention provides a temperature adjustment device and method of a focusing ring. Energy is radiated onto the focusing ring by plasma and is downwards transferred to a base by a first thermal conduction pad, an insulation ring and a second thermal conduction pad, the first thermal conduction pad is in contact with a lower surface of the focusing ring, the insulation ring is in contact with a lower surface of the first thermal conduction pad, the second thermal conduction pad is in contact with a lower surface of the insulation ring, the base is in contact with the second thermal conduction pad, cooling and temperature reduction are performed by a cooling system arranged at the base, a heater which is arranged in a shielding ring is started to generate a controllable external heating source, the shielding ring is connected with the ground, energy of the external heating source is transferred to the focusing ring by the shielding ring, a third thermal conduction pad, an insulation ring and the first thermal conduction ring, the third thermal conduction pad is in contact with the shielding ring, the insulation ring is in contact with the third thermal conduction pad, and controllable temperature rise is performed on the focusing ring. By providing a good heat conduction cooling path and by combining a heating mode of a controllable parameter, fine control on a working temperature of the focusing ring is achieved, the focusing ring is tunable during etching, so that the process demand is satisfied.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO FAB EQUIP INC CHINA
Air-side economizer facilitating liquid-based cooling of an electronics rack
InactiveUS20130019614A1Promote circulationImprove immersionLighting and heating apparatusModifications using gaseous coolantsNuclear engineeringConduction cooling
Owner:IBM CORP
High-temperature superconductive magnet system for magnetically confined plasma propeller
InactiveCN101692368AEliminate dangerIncrease the critical currentMagnetic induction acceleratorsSuperconducting magnets/coilsEvaporationConduction cooling
The invention discloses a high-temperature superconductive magnet system for a magnetically confined plasma propeller, which comprises two magnetic mirror units in the same structure, wherein each magnetic mirror unit comprises a Dewar barrel and two high-temperature superconductive magnets; and a refrigerator is used for cooling the two high-temperature superconductive magnets in each magnetic mirror unit. mode by a conductive cooling mode and uses the refrigerator to cool the two superconductive magnets in a conductive manner, so that the high-temperature superconductive magnet system for the magnetically confined plasma propeller greatly simplifies the structure, realizes high vacuum, reduces dependence on liquid nitrogen and high-cost operations, avoids a large-size low-temperature system and equipment used in the low-temperature liquid cooling mode, eliminates risks caused by the evaporation of a low-temperature liquid, cools the magnet to a temperature below 77 K and realizes a high field by increasing the critical current of the magnets, thus a superconductive low-temperature system is compact, efficient, safe and convenient, and is beneficial for integrating a superconductive apparatus with a low-temperature device.
Owner:INST OF PLASMA PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com