Patents
Literature
1018 results about "Active cooling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An active cooling system is one that involves the use of energy to cool something, as opposed to passive cooling that uses no energy. Such systems circulate a coolant to transfer heat from one place to another. The coolant is either a gas, such as in air cooling of computers, or a liquid such as in a car engine. In the latter case, liquid is pumped to transfer heat from the engine to the radiator, which in turn is cooled by passing air over it. Other active cooling systems make use of a refrigeration cycle.
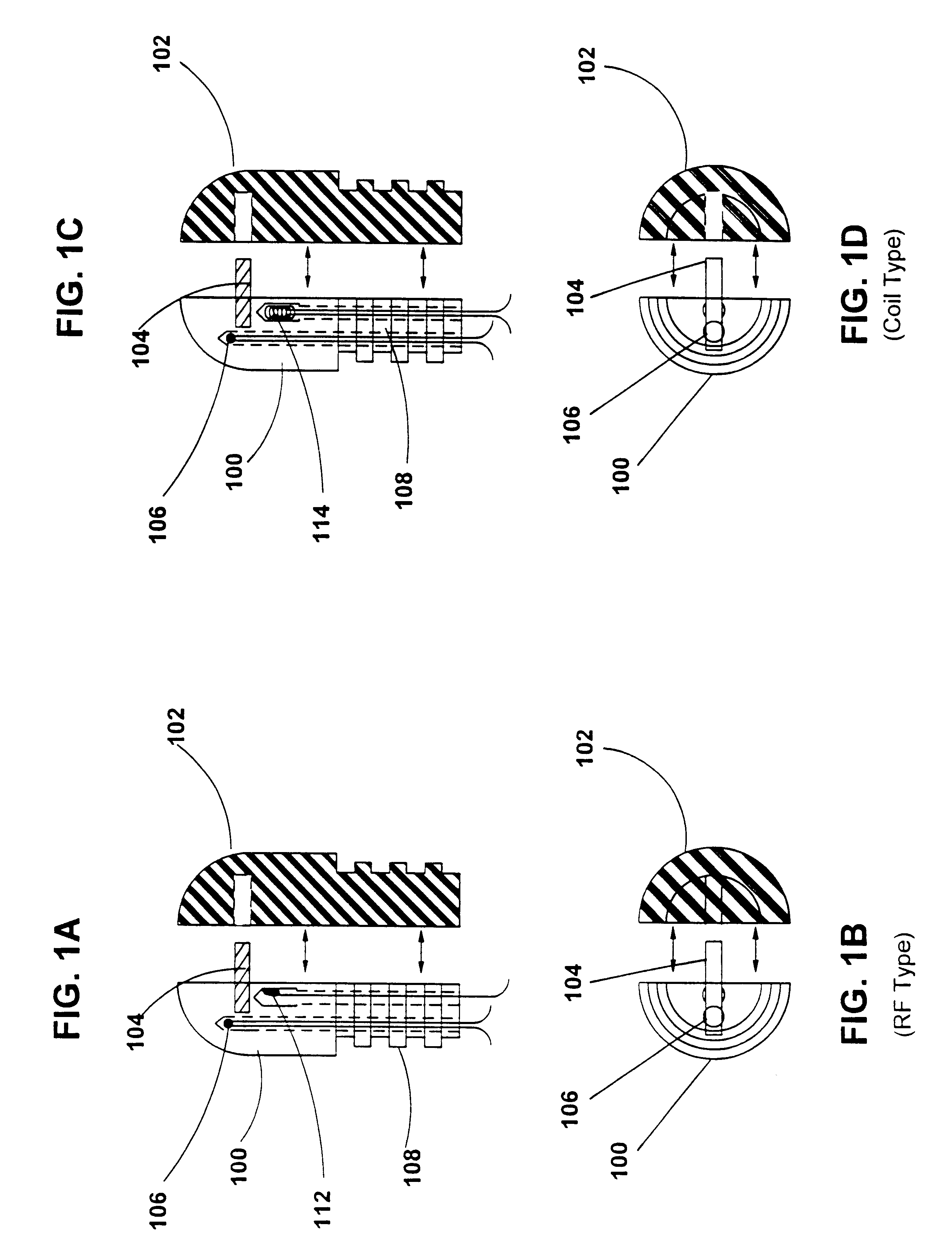
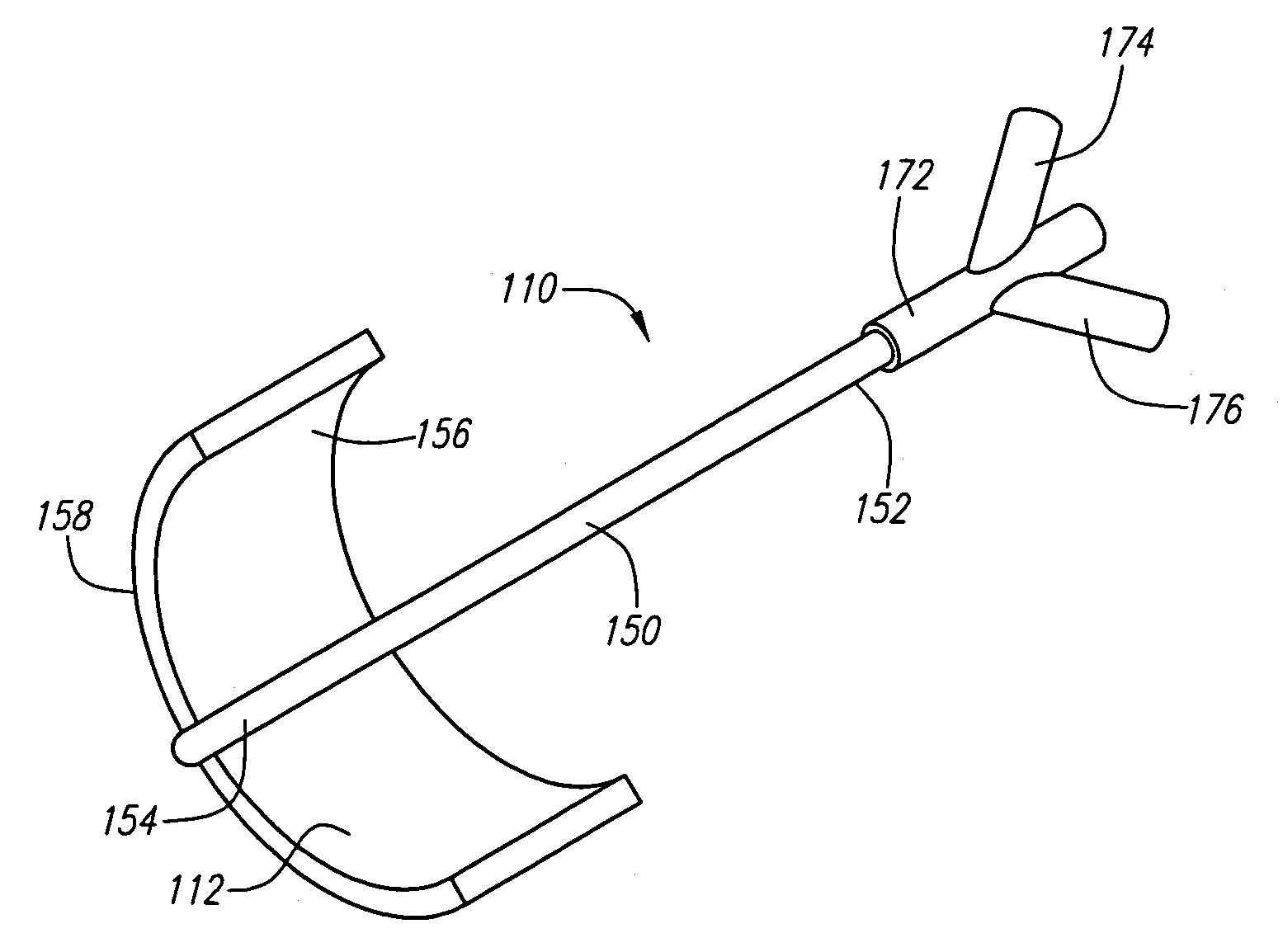
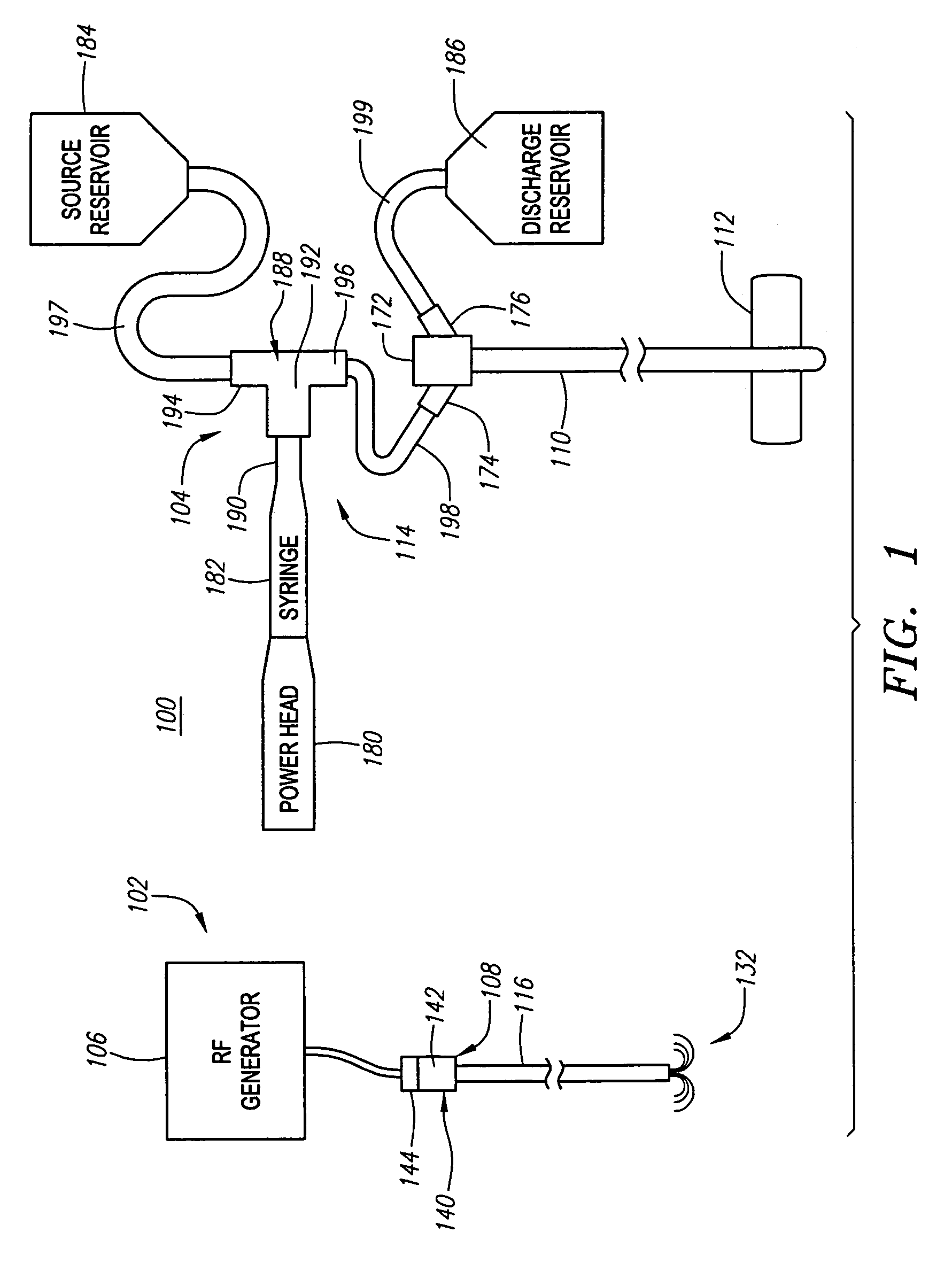
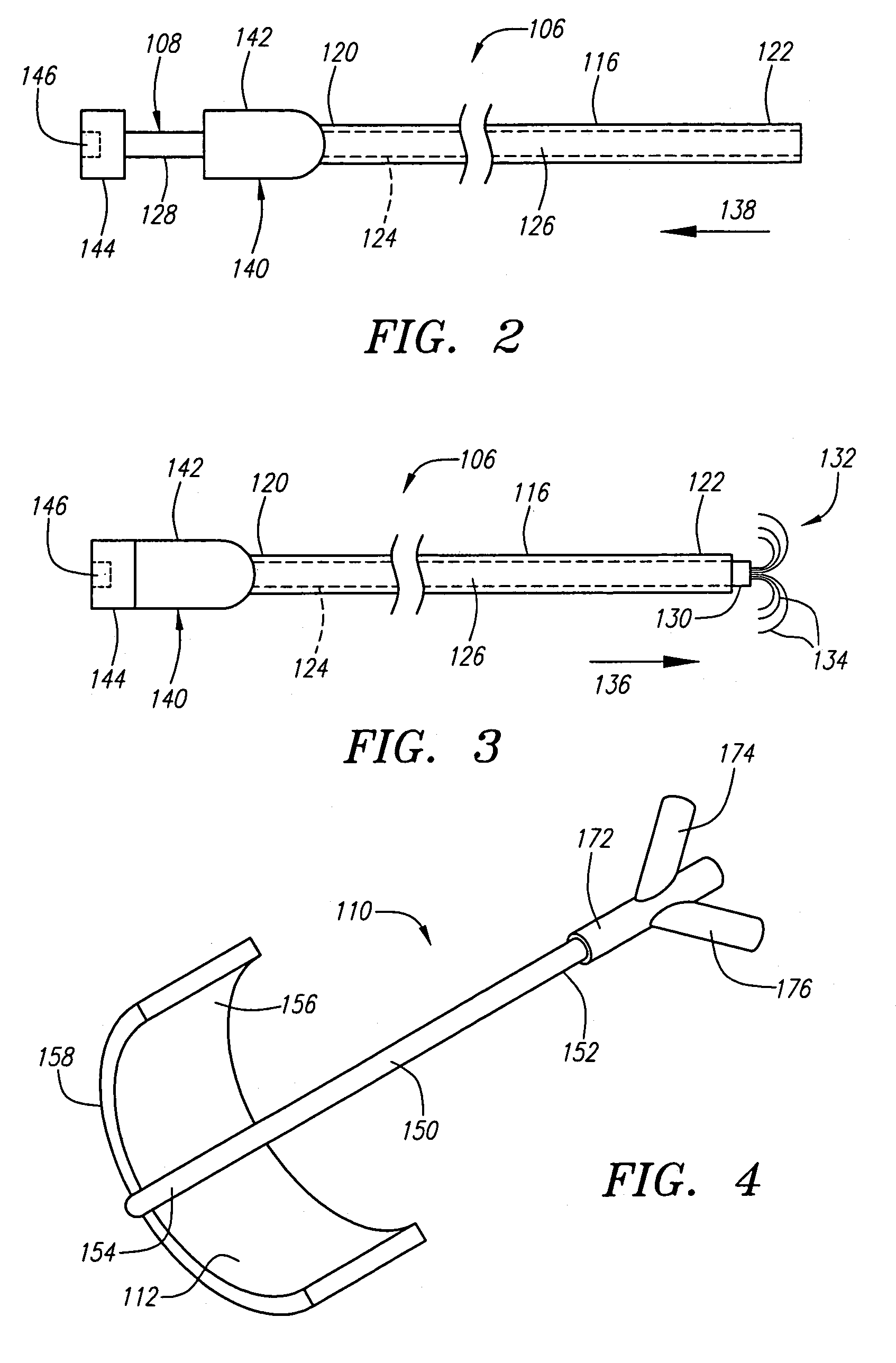
Method and apparatus for applying thermal energy to tissue asymmetrically
Systems and methods are described for treating tissue with thermal energy while minimizing the amount of thermal energy to which adjacent tissue is exposed. A surgical instrument for delivering thermal energy to a section of tissue during percutaneous surgery, includes: an elongated shaft having a proximal end and a distal end; and a split tip electrode coupled to the distal end, the split tip electrode i) including a first component and a second component coupled to the first component, and ii) defining a principle axis. The thermal energy is delivered to the section of tissue so as to heat the section of tissue asymmetrically with regard to the principle axis of the split tip electrode. The systems and methods provide advantages in that thermal energy can be directed to one side of the split tip so that a first of two juxtaposed areas of a surgical site can be heated while a second of the two juxtaposed layers is substantially not heated. In alternate embodiments a portion of the site may be actively cooled while an adjacent portion of the site may be actively cooled.
Owner:ORATEC INTERVENTIONS
Method and apparatus for applying thermal energy to tissue asymmetrically
Systems and methods are described for treating tissue with thermal energy while minimizing the amount of thermal energy to which adjacent tissue is exposed. A surgical instrument for delivering thermal energy to a section of tissue during percutaneous surgery, includes: an elongated shaft having a proximal end and a distal end; and a split tip electrode coupled to said distal end, said split tip electrode i) including a first component and a second component coupled to said first component, and ii) defining a principle axis. The thermal energy is delivered to said section of tissue so as to heat said section of tissue asymmetrically with regard to said principle axis of said split tip electrode. The systems and methods provide advantages in that thermal energy can be directed to one side of the split tip so that a first of two juxtaposed areas of a surgical site can be heated while a second of the two juxtaposed layers is substantially not heated. In alternate embodiments a portion of the site may be actively cooled while an adjacent portion of the site may be actively cooled.
Owner:ORATEC INTERVENTIONS
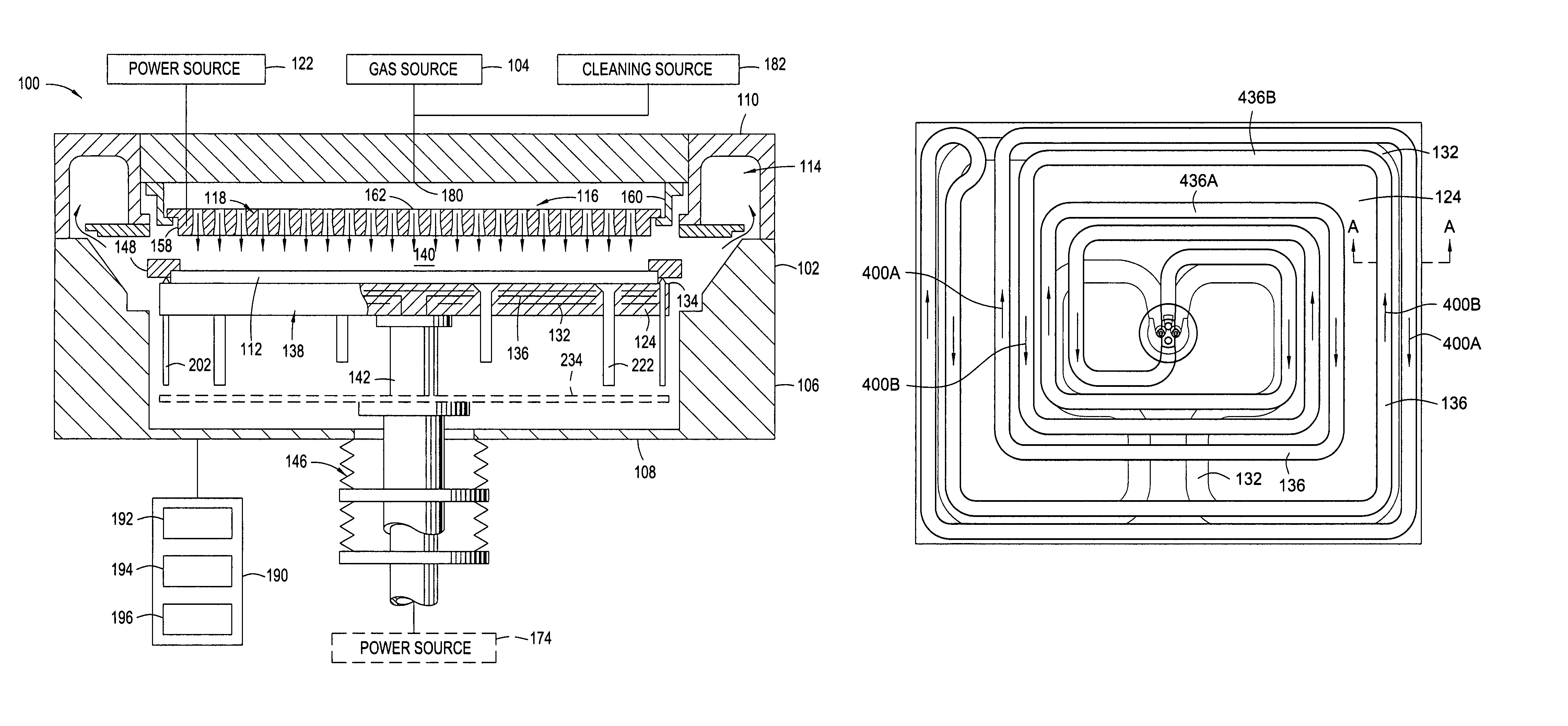
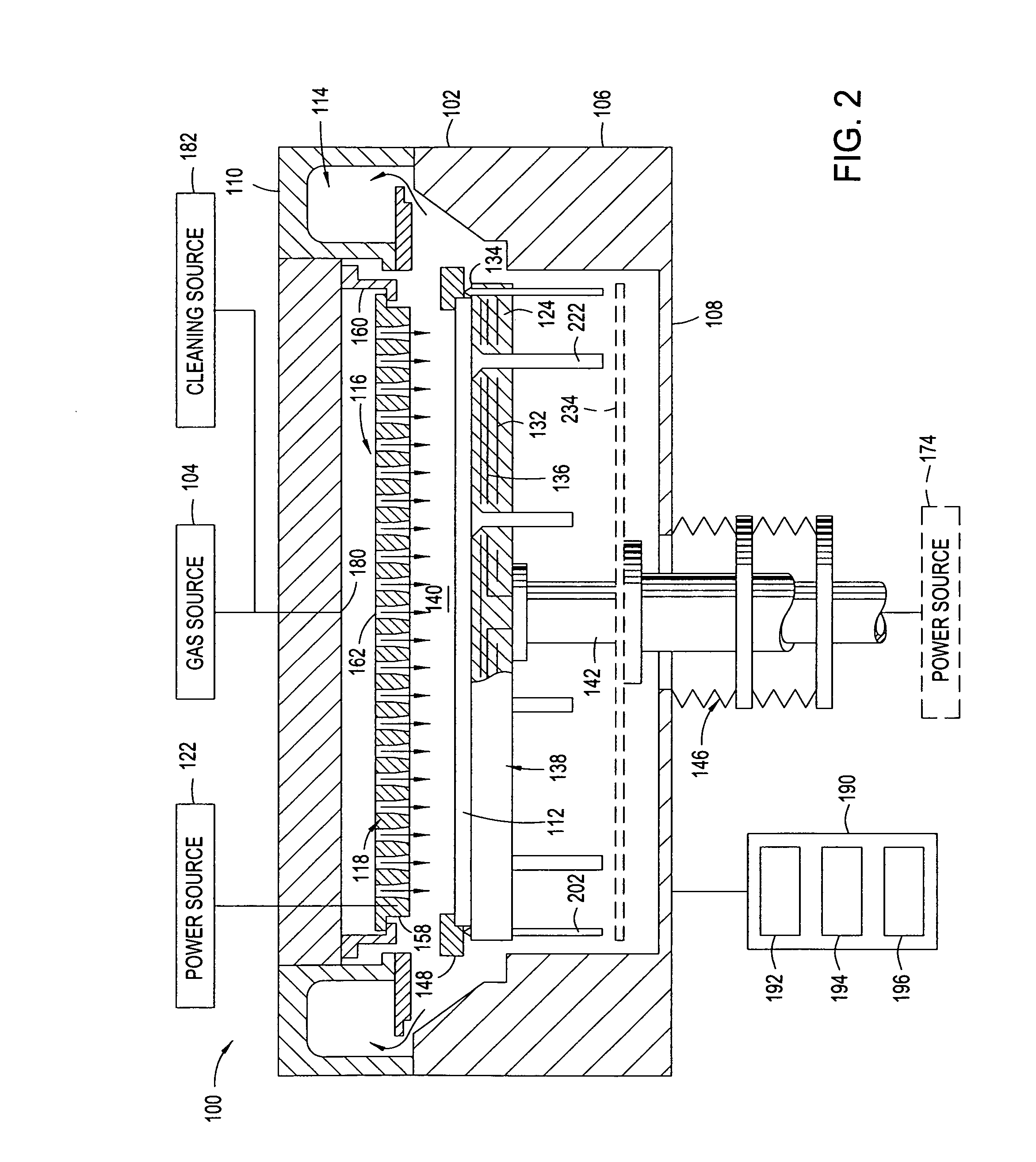
Rapid conductive cooling using a secondary process plane
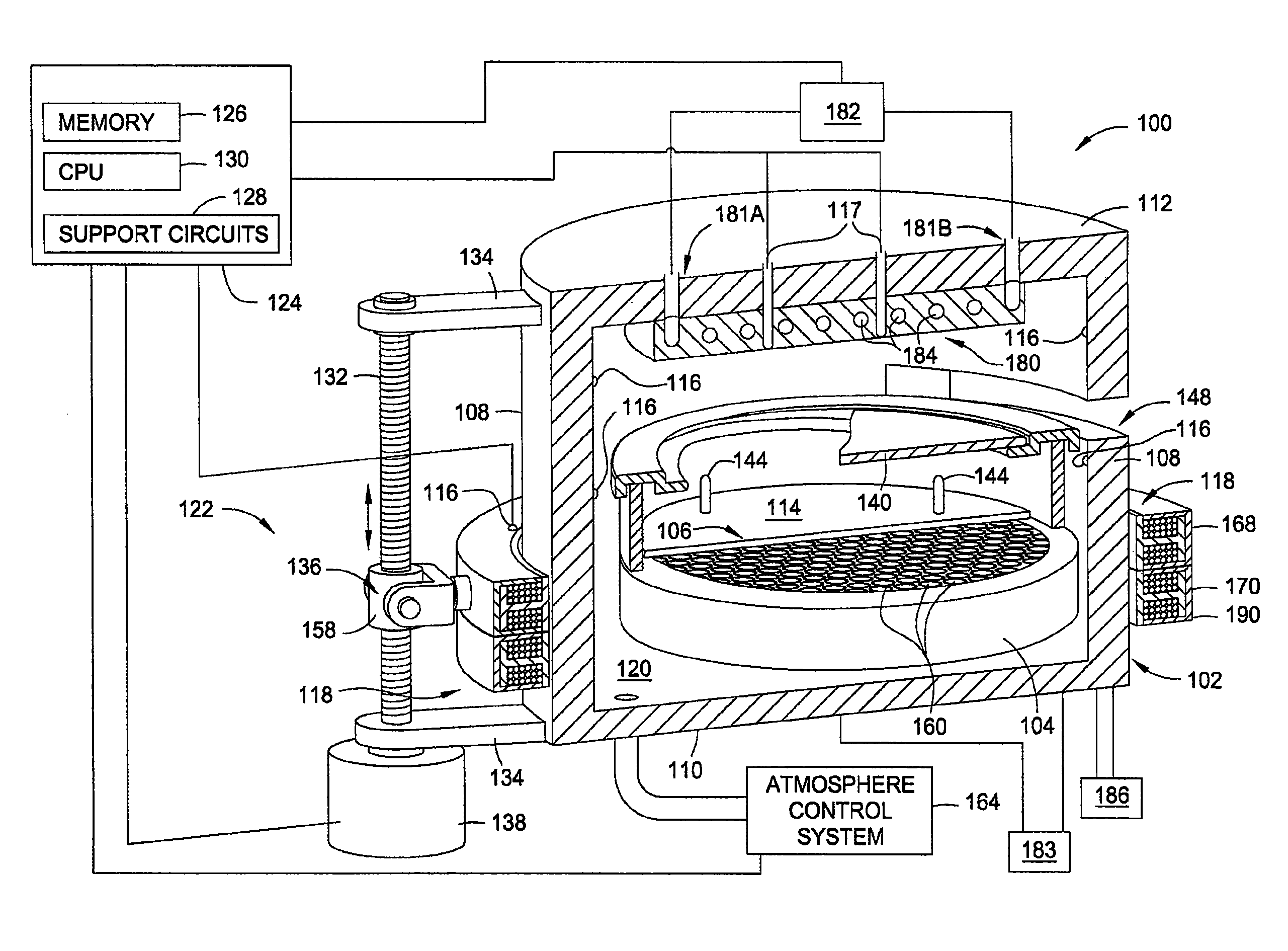
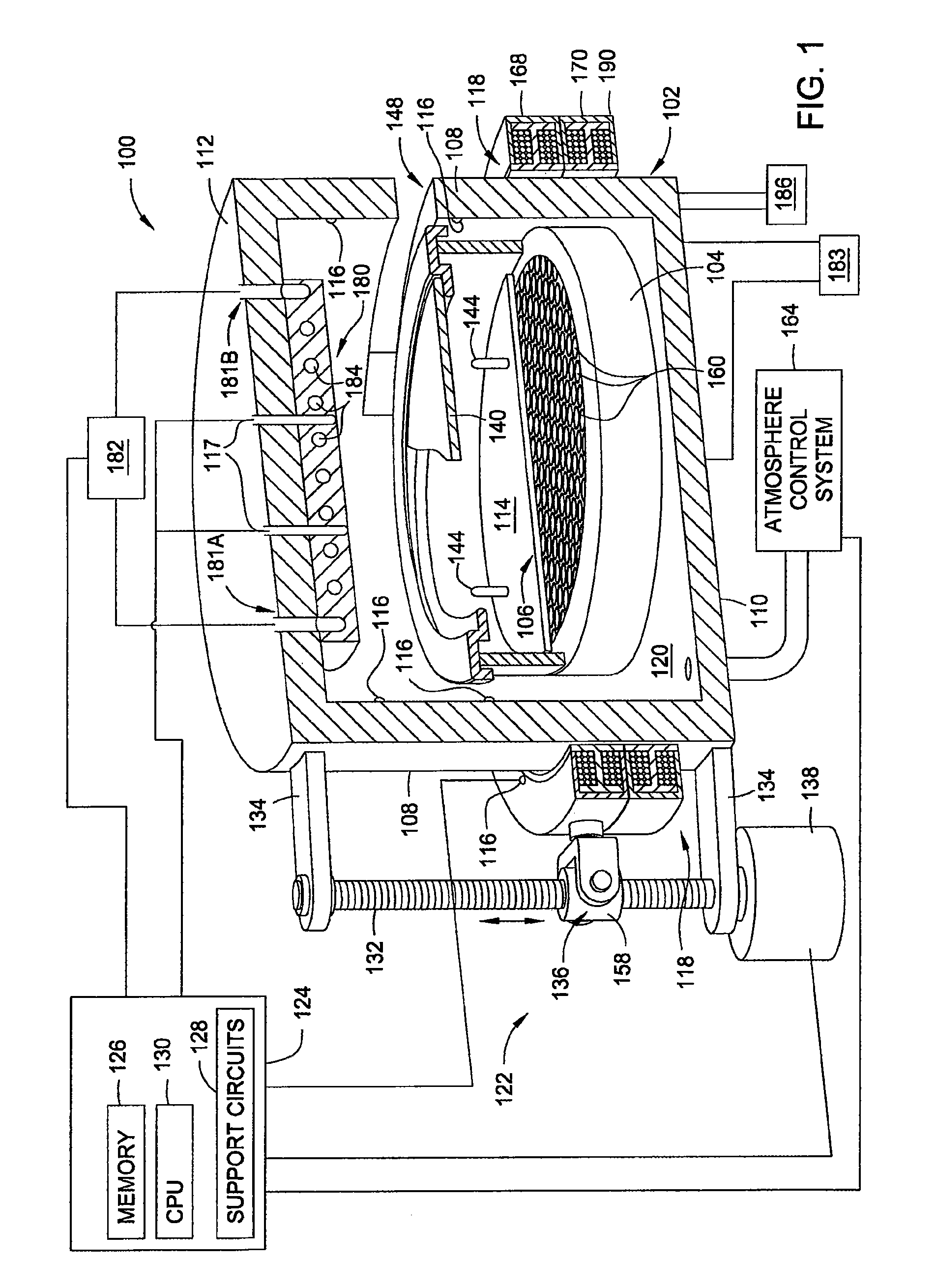
A method and apparatus for thermally processing a substrate is described. The apparatus includes a substrate support configured to move linearly and / or rotationally by a magnetic drive. The substrate support is also configured to receive a radiant heat source to provide heating region in a portion of the chamber. An active cooling region comprising a cooling plate is disposed opposite the heating region. The substrate may move between the two regions to facilitate rapidly controlled heating and cooling of the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
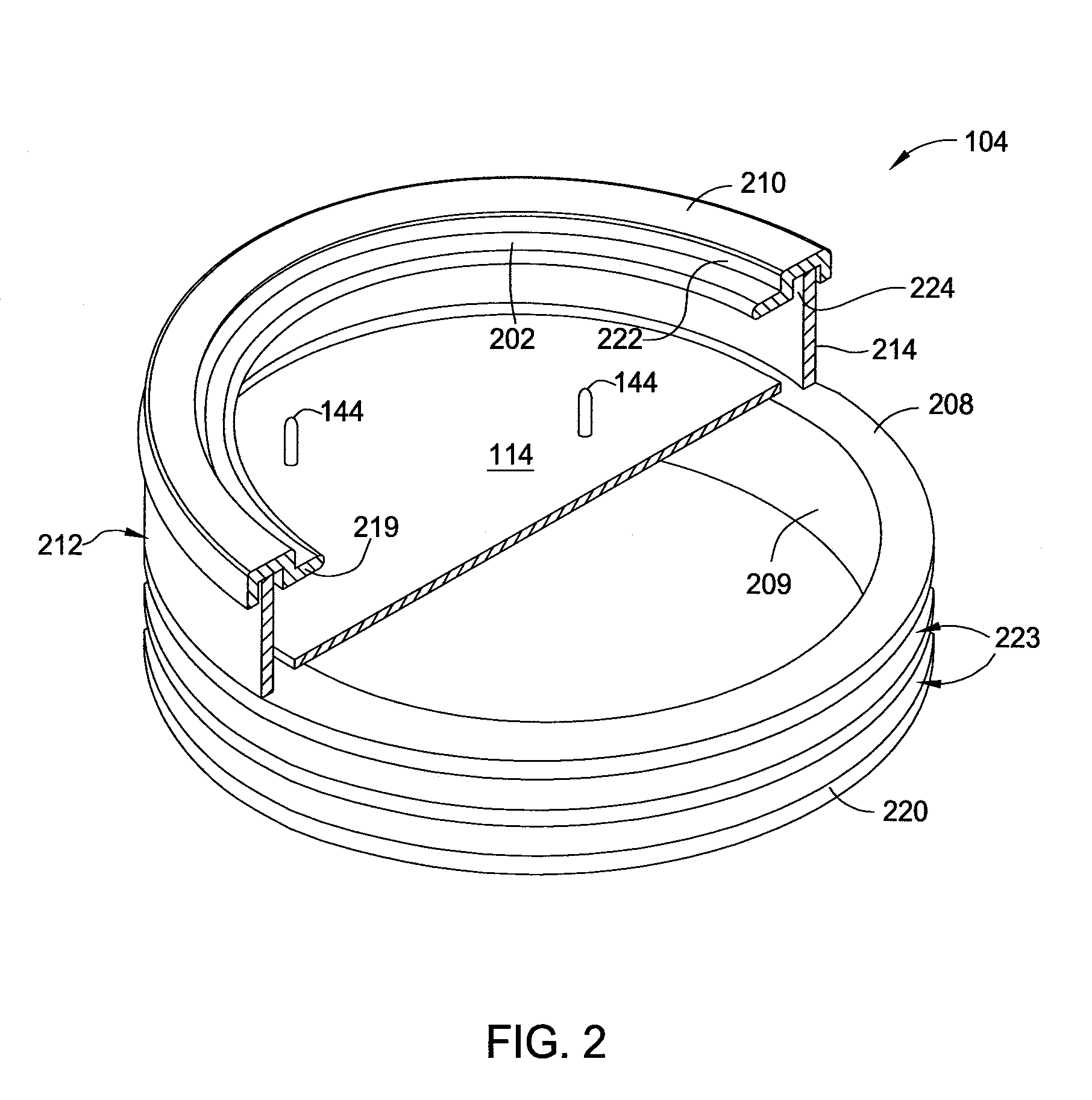
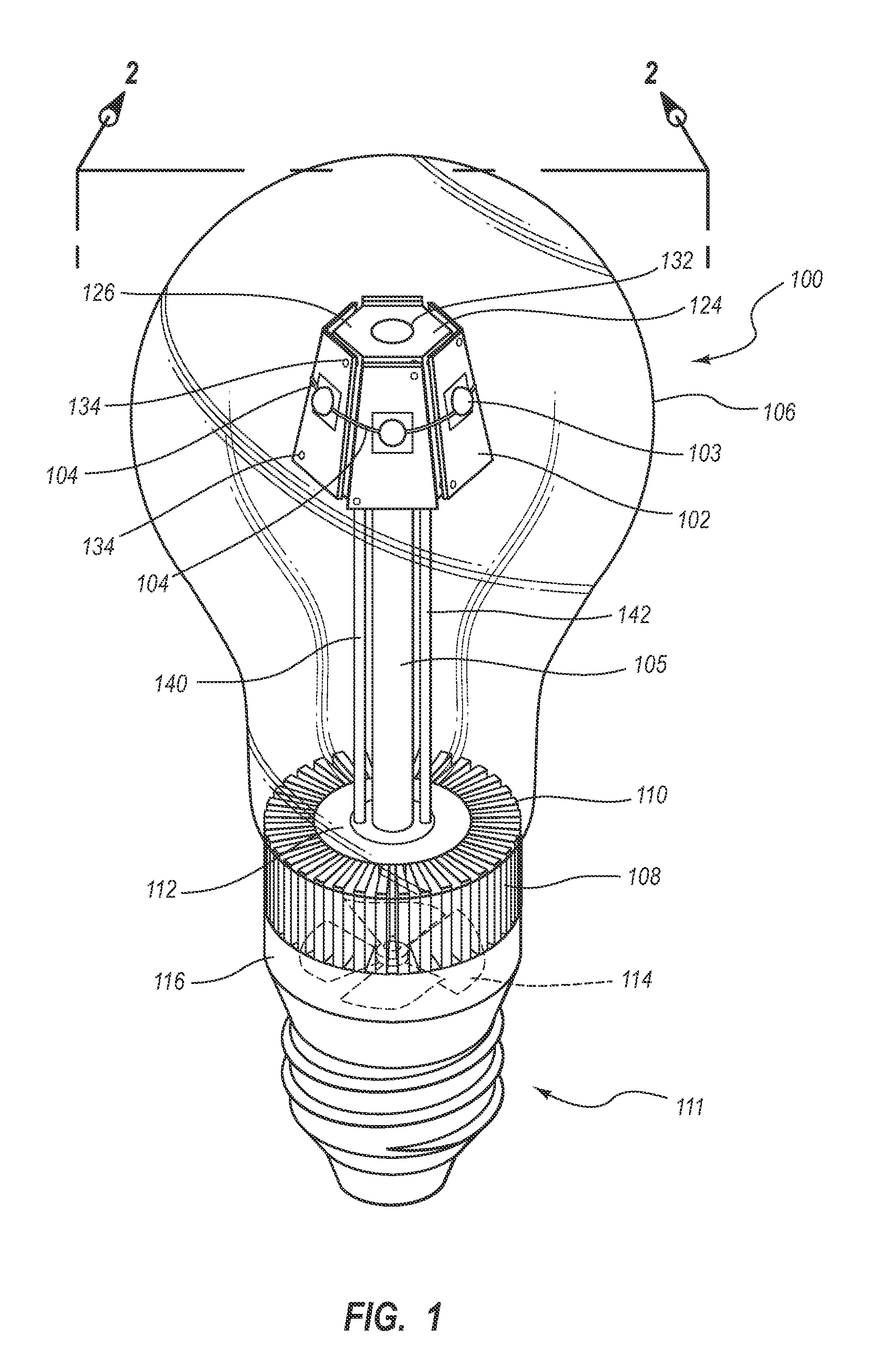
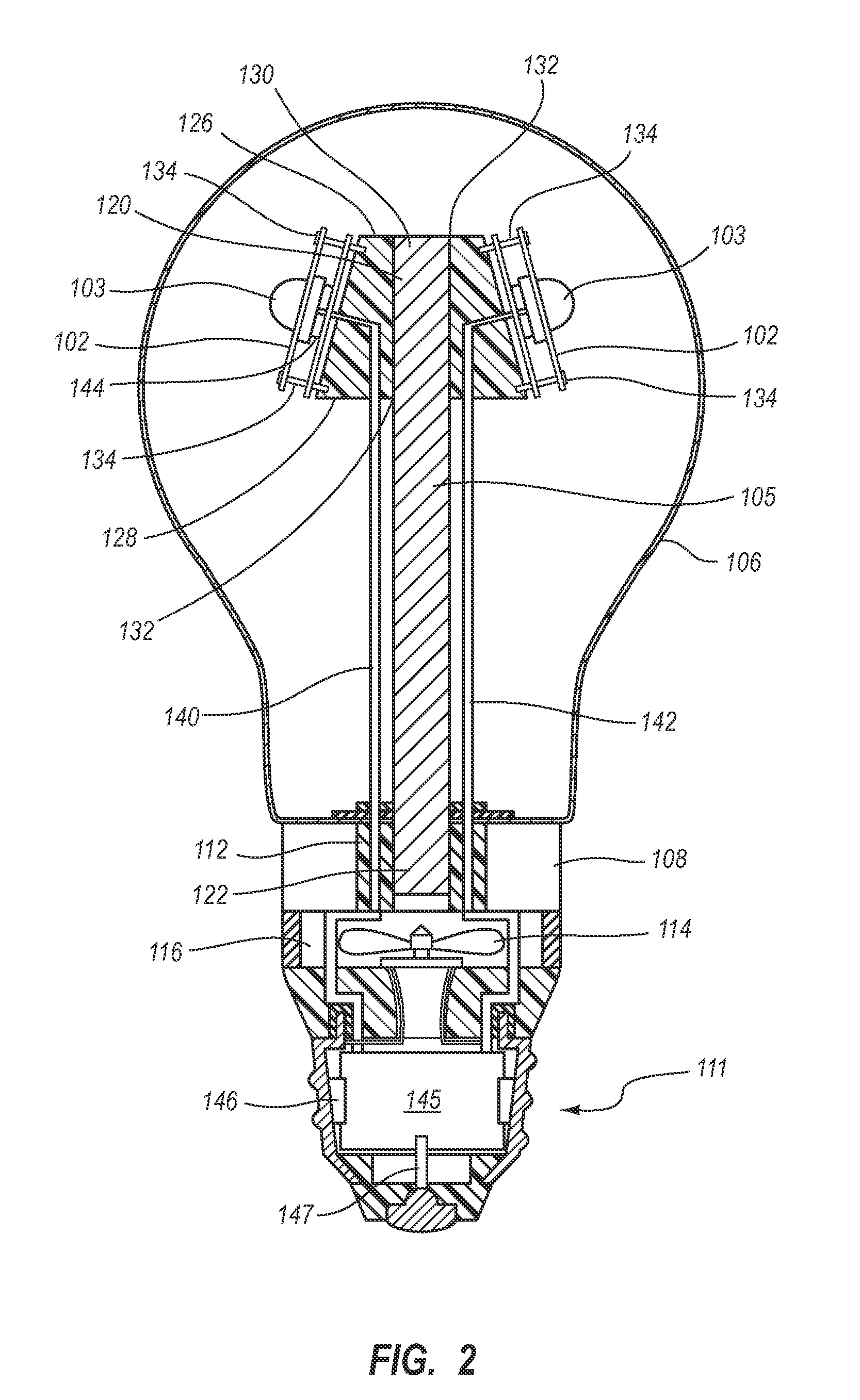
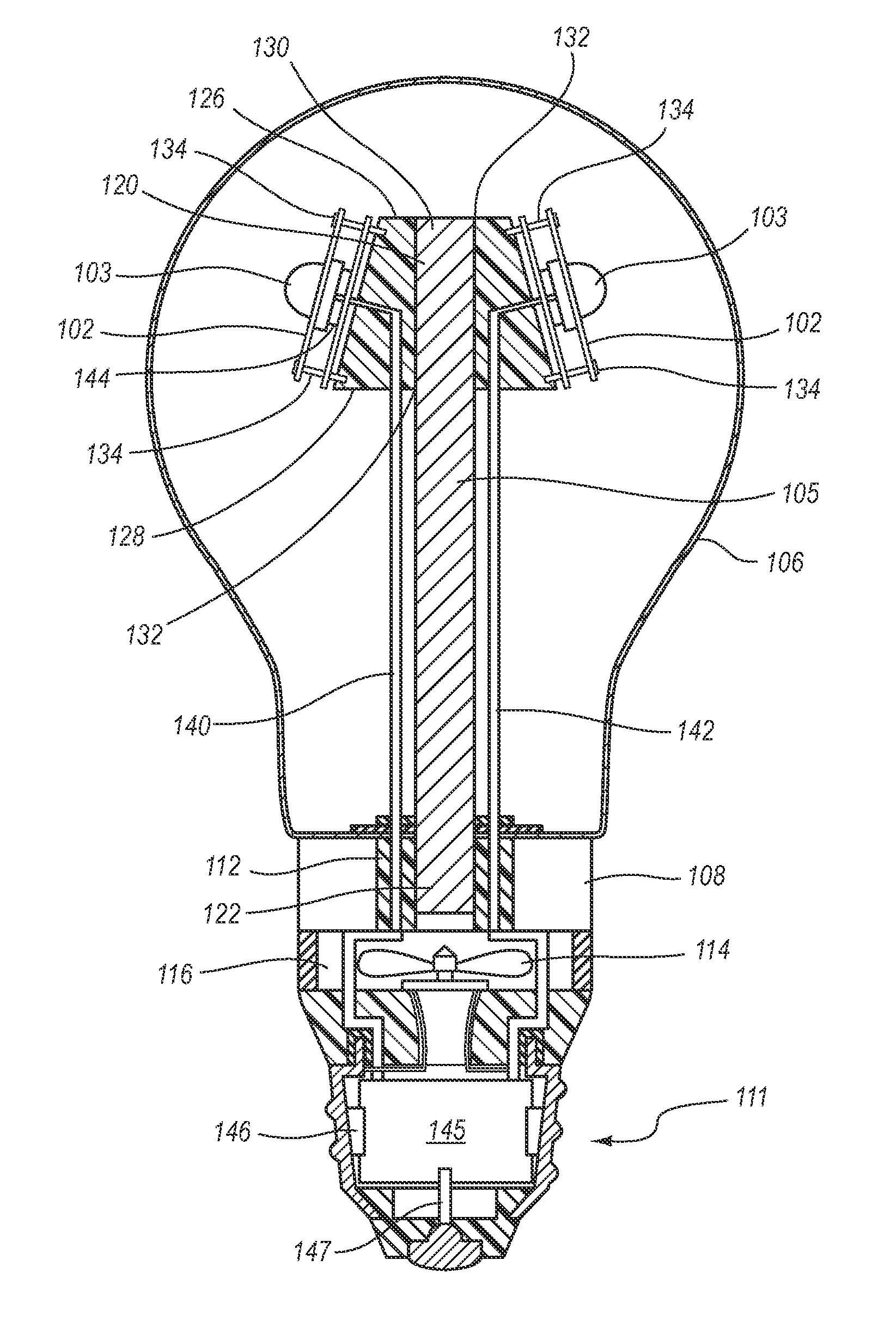
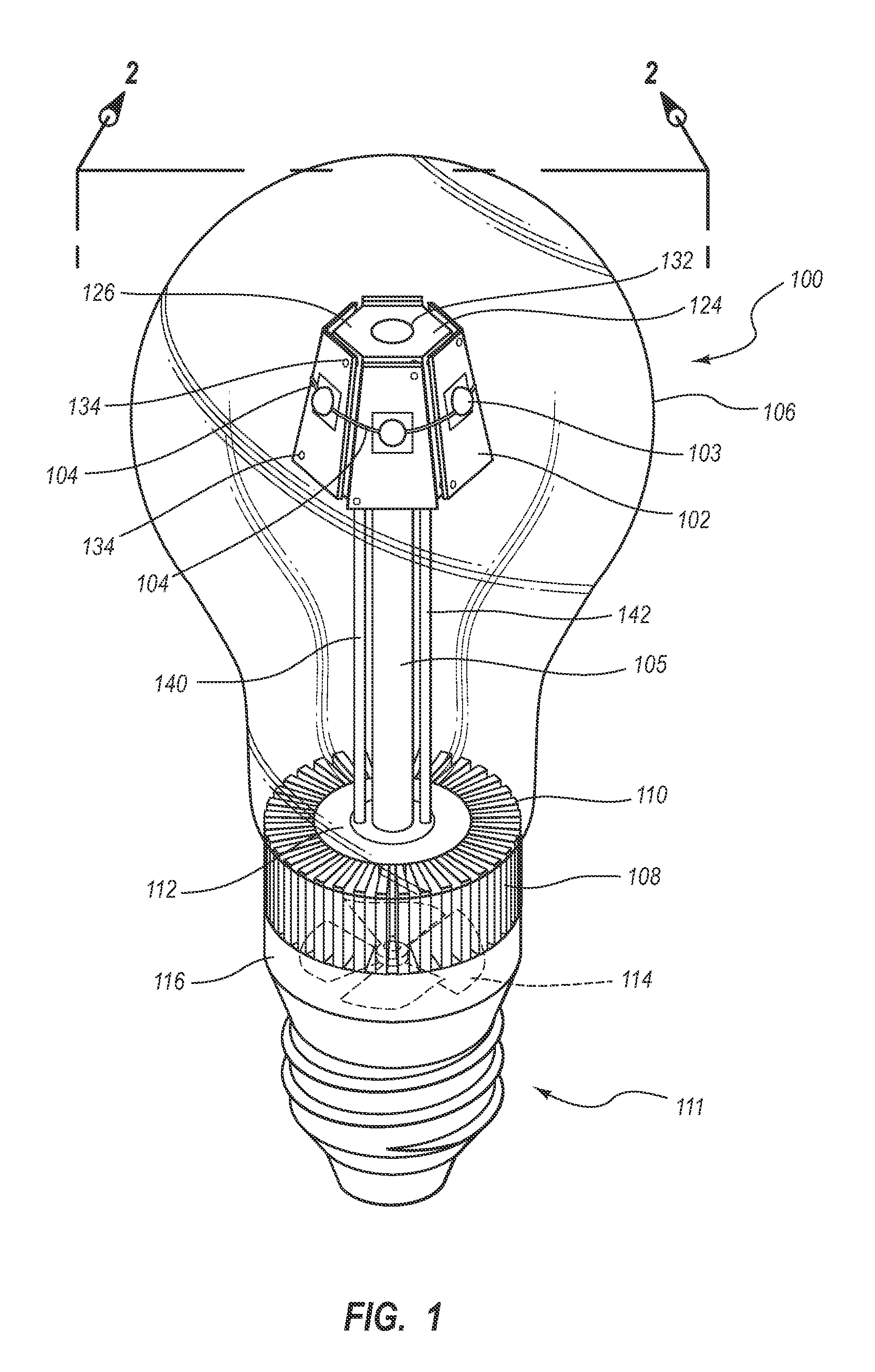
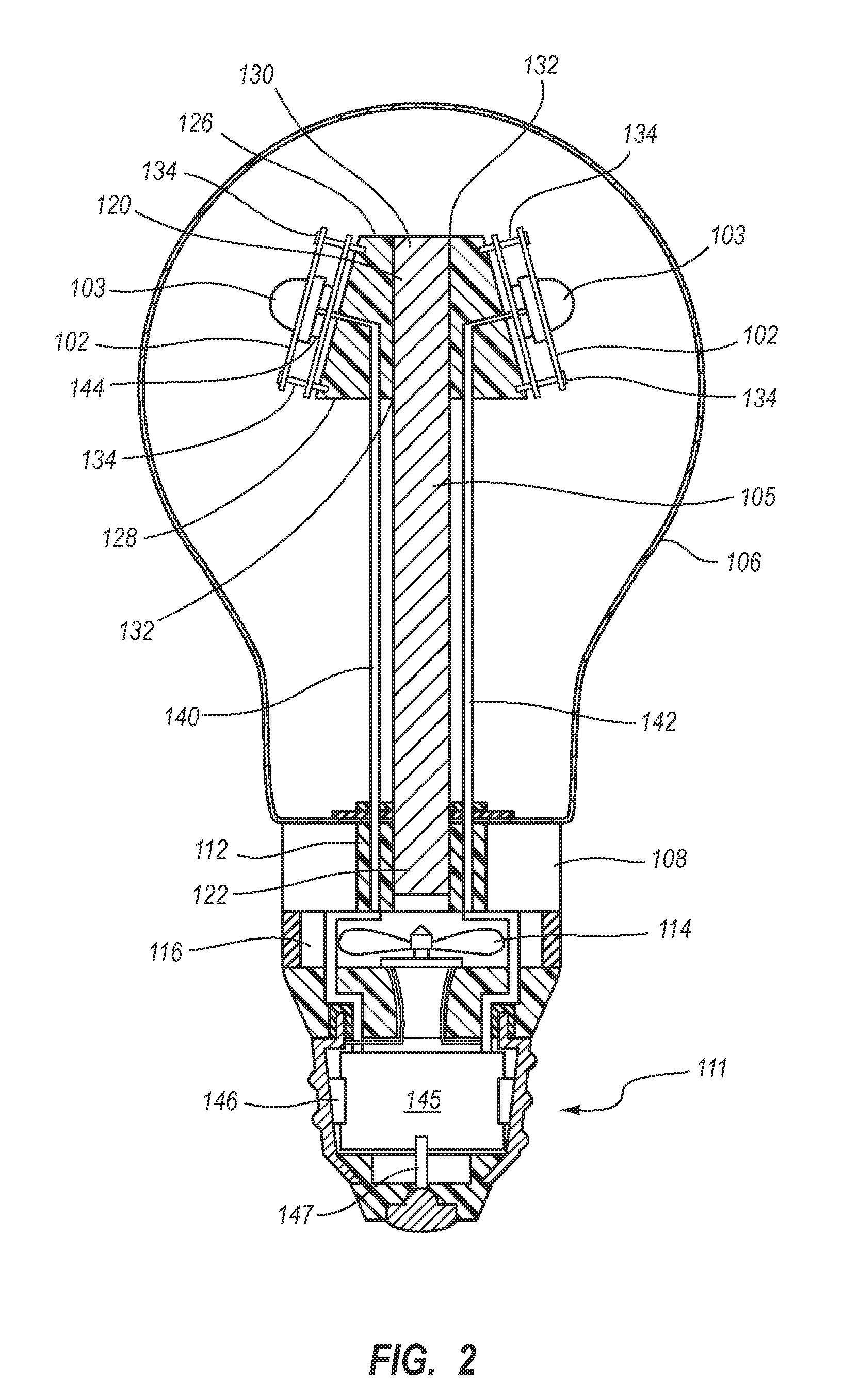
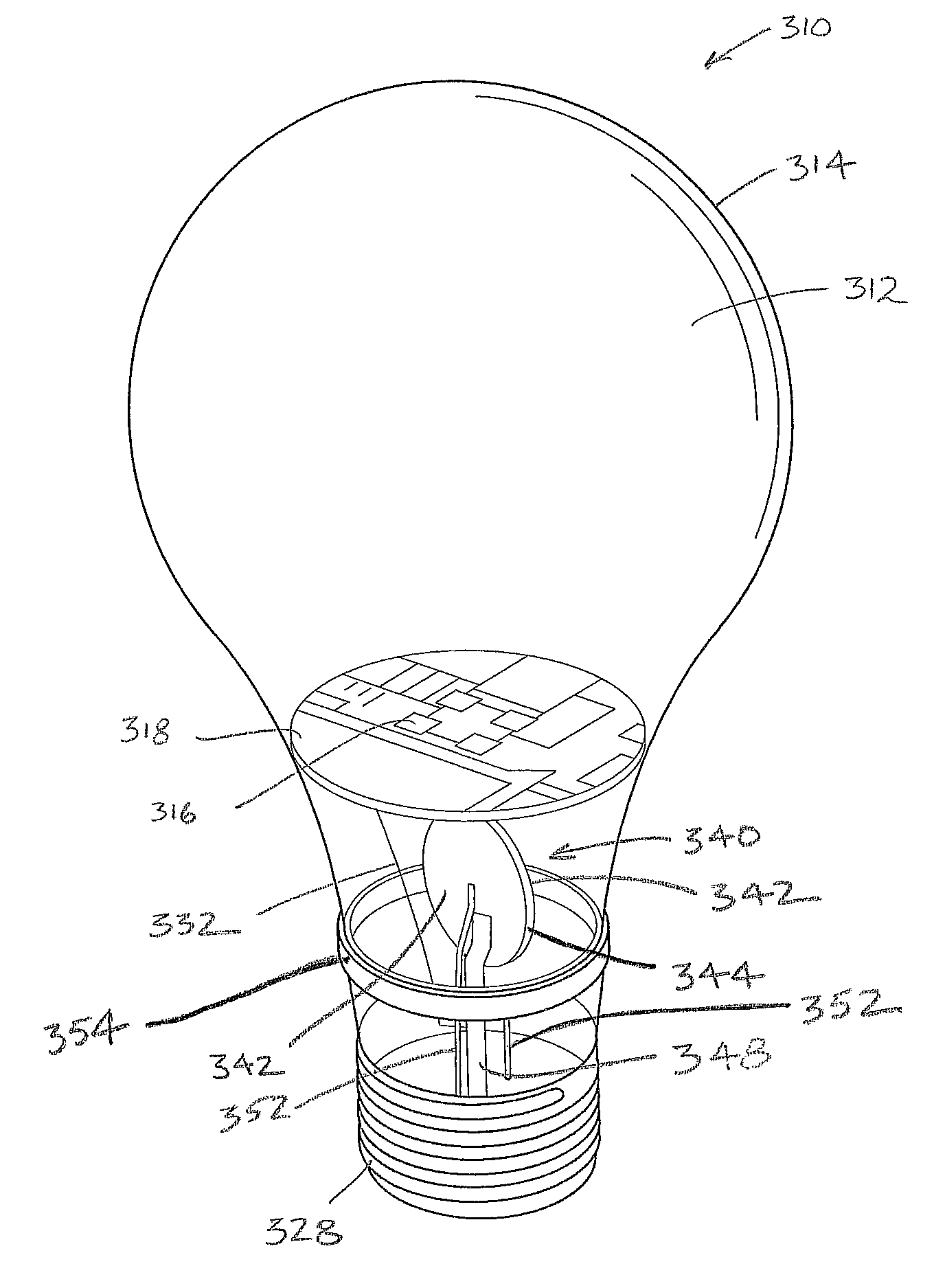
LED Light Bulbs for Space Lighting
ActiveUS20100207502A1Fast heat transferFast transferPoint-like light sourceElectric discharge tubesHeat managementActive cooling
The invention discloses a three dimensional LED arrangement and heat management method using a heat transfer or conduction pipe to enable rapid heat transfer from a three dimensional cluster of LEDs to a heatsink with or without active cooling, the light emitted from the three dimensional cluster not being obstructed by a heat sink arrangement such that the light beam profile generated by the light appears similar to that generated by traditional incandescent bulbs.
Owner:SATCO PRODS
Active cooling substrate support
ActiveUS8709162B2Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingActive coolingEngineering
A substrate support assembly and method for controlling the temperature of a substrate within a process chamber with a temperature uniformity of + / −5° C. are provided. A substrate support assembly includes a thermally conductive body comprising an aluminum material, a substrate support surface on the surface of the thermally conductive body and adapted to support the large area glass substrate thereon, one or more heating elements embedded within the thermally conductive body, and one or more cooling channels embedded within the thermally conductive body and positioned around the one or more heating elements. A process chamber comprising the substrate support assembly of the invention is also provided.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
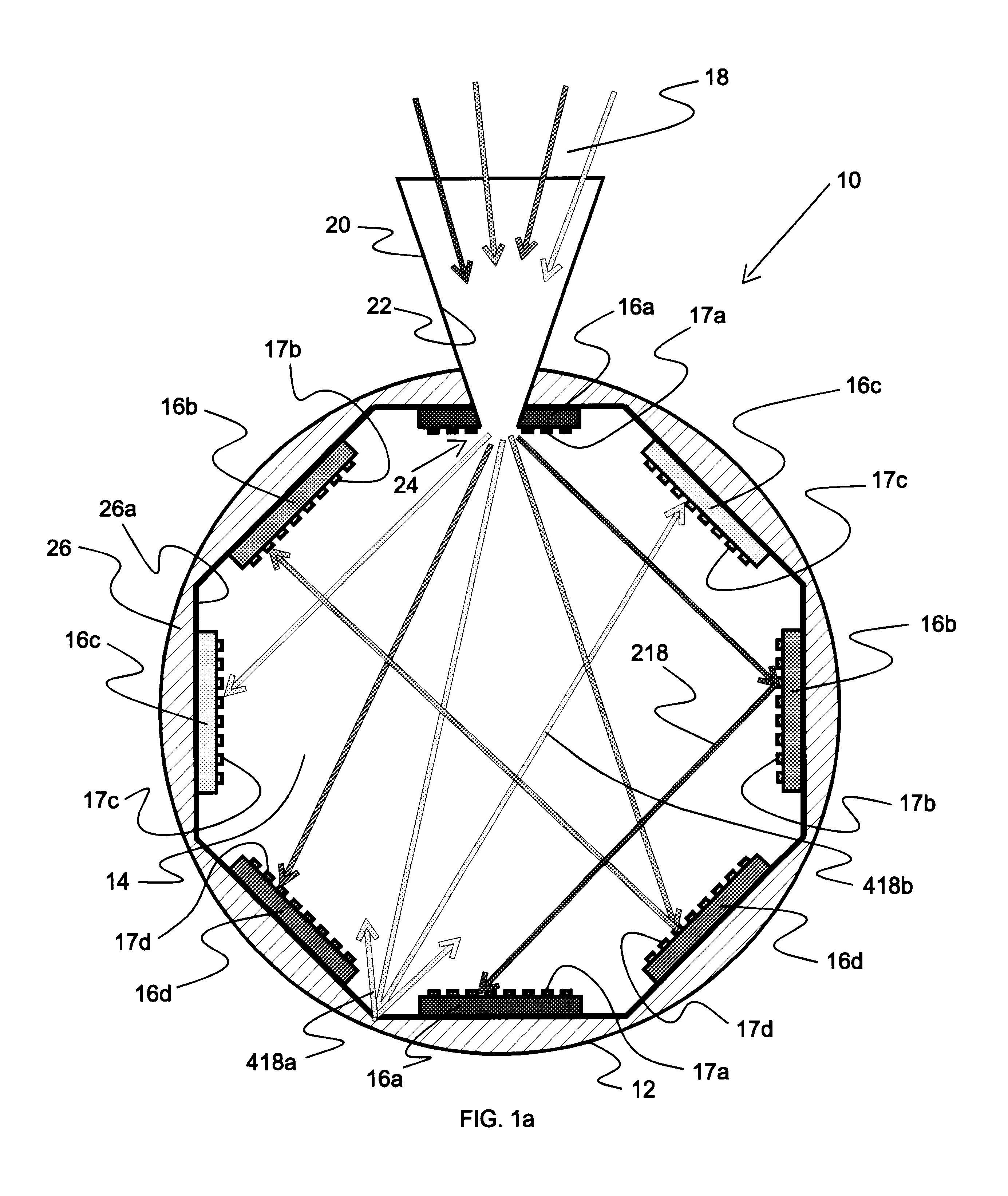
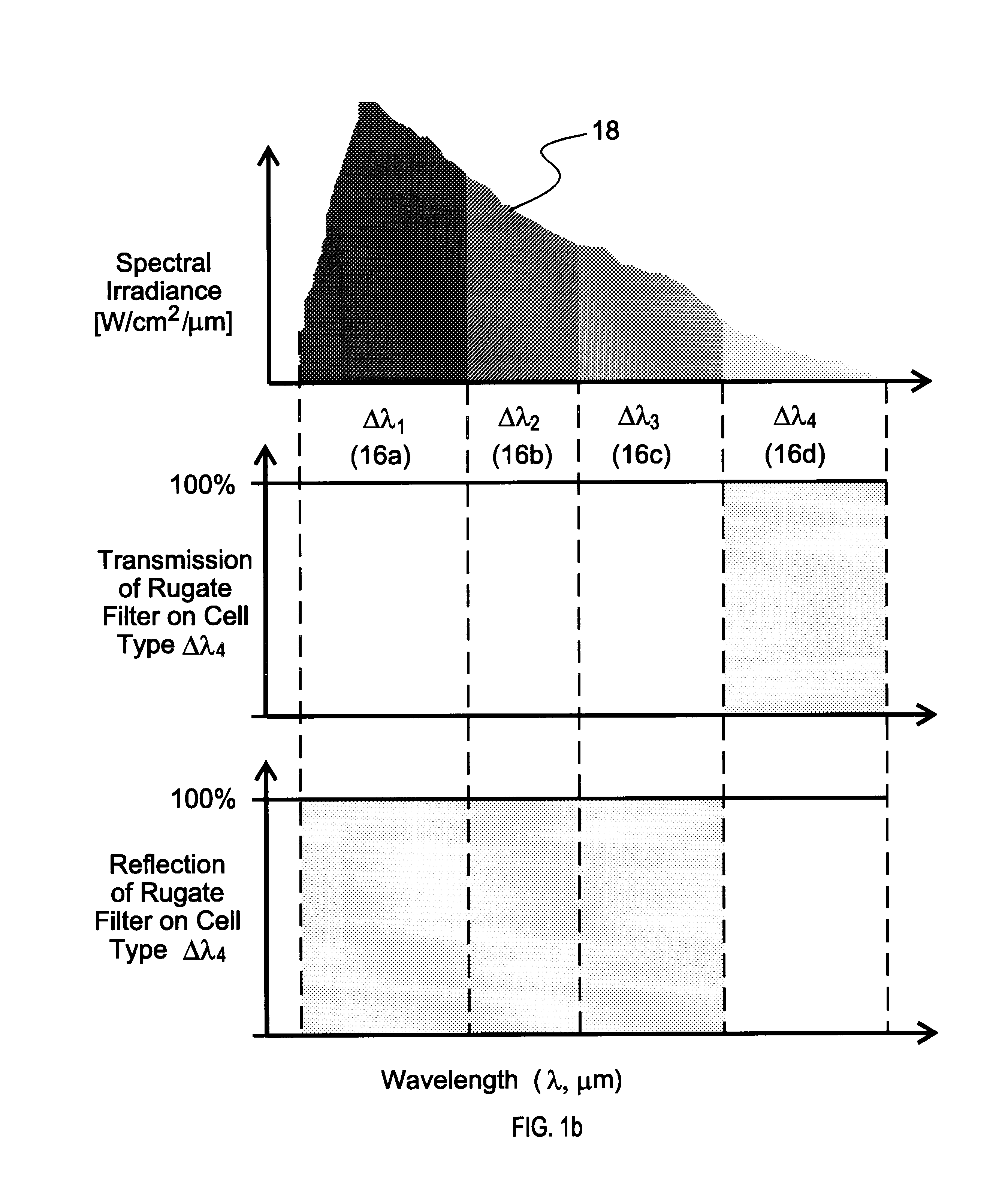
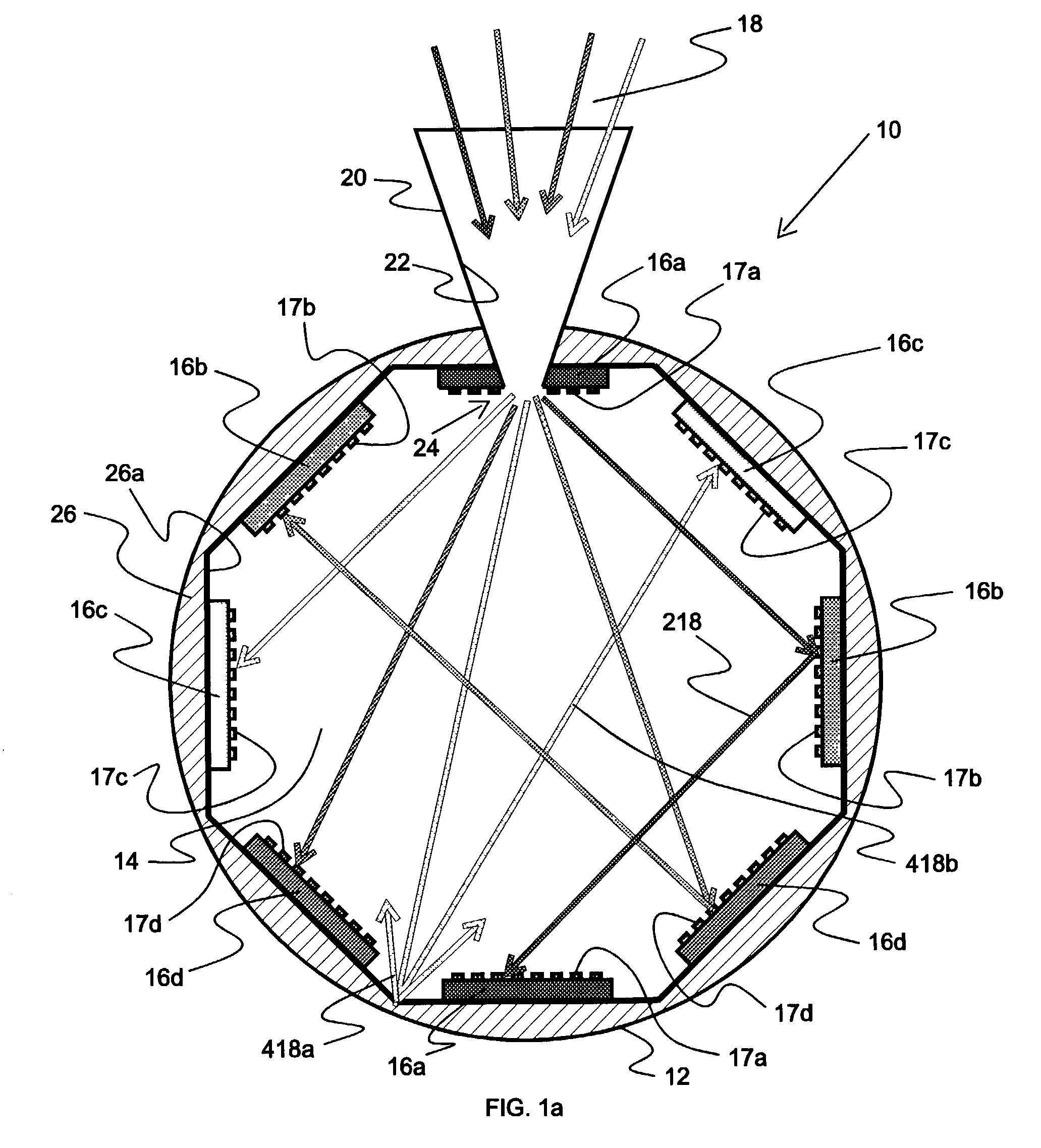
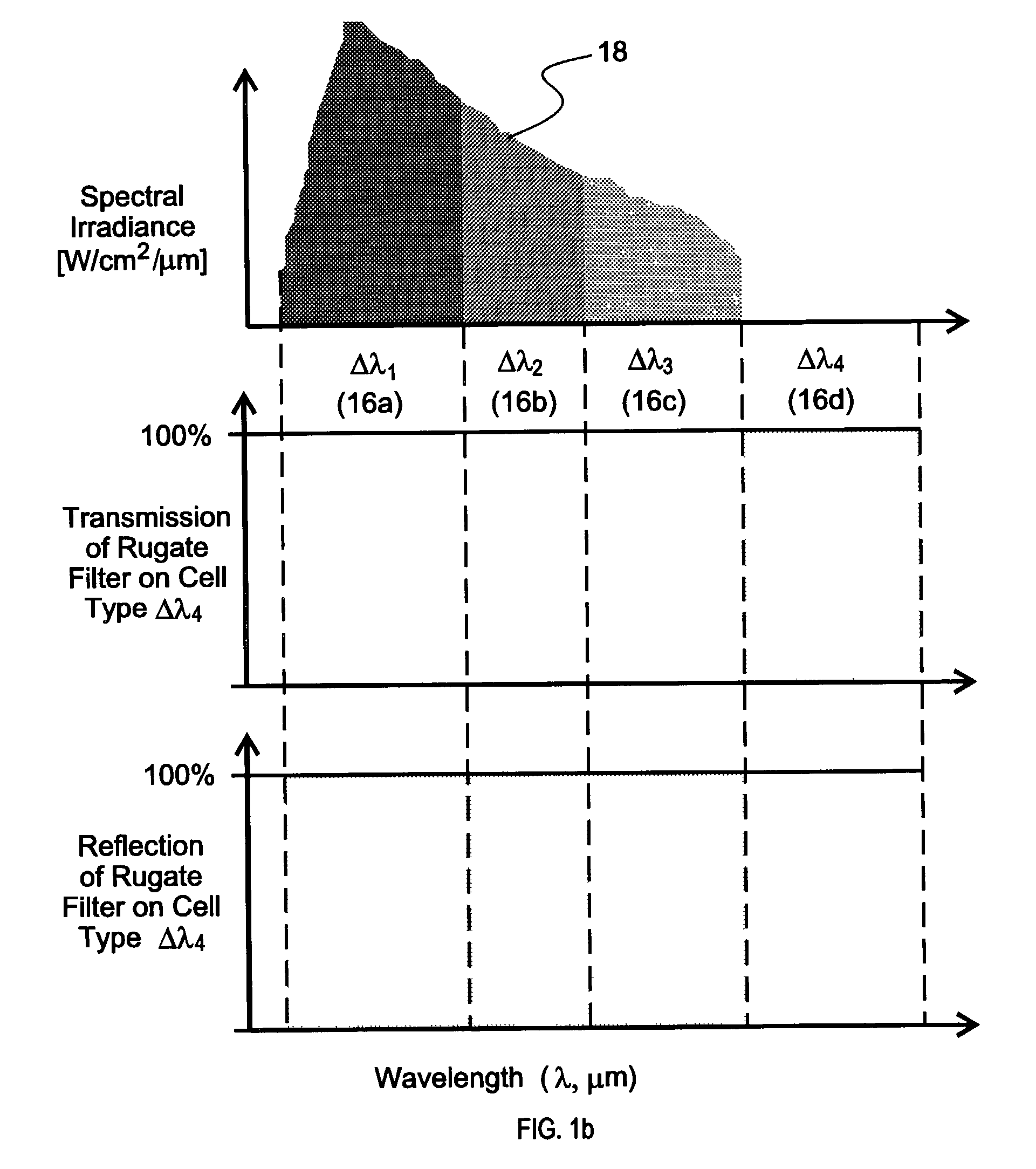
Concentrating photovoltaic cavity converters for extreme solar-to-electric conversion efficiencies
InactiveUS6689949B2Maximize utilizationAuxillary drivesFrom solar energyEngineeringEnergy conversion efficiency
A concentrating photovoltaic module is provided which provides a concentration in the range of about 500 to over 1,000 suns and a power range of a few kW to 50 kW. A plurality of such modules may be combined to form a power plant capable of generating over several hundred megaWatts. The concentrating photovoltaic module is based on a Photovoltaic Cavity Converter (PVCC) as an enabling technology for very high solar-to-electricity conversions. The use of a cavity containing a plurality of single junction solar cells of different energy bandgaps and simultaneous spectral splitting of the solar spectrum employs a lateral geometry in the spherical cavity (where the cell strings made of the single junction cells operate next to each other without mutual interference). The purpose of the cavity with a small aperture for the pre-focused solar radiation is to confine (trap) the photons so that they can be recycled effectively and used by the proper cells. Passive or active cooling mechanisms may be employed to cool the solar cells.
Owner:UNITED INNOVATIONS
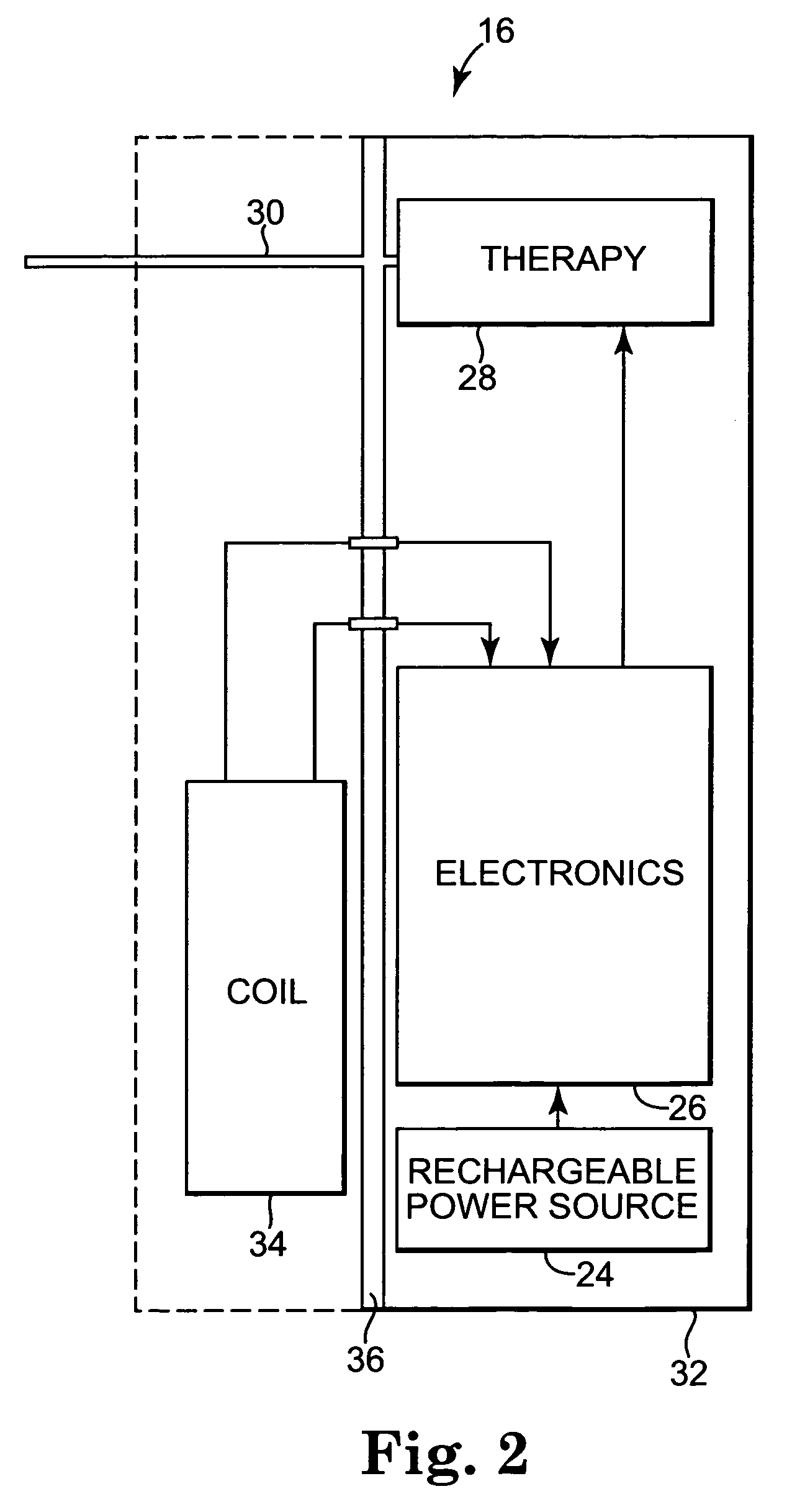
Actively cooled external energy source, external charger, system of transcutaneous energy transfer, system of transcutaneous charging and method therefore
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
LED light with active cooling
InactiveUS20070139938A1Point-like light sourceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPiezoelectric fanActive cooling
An LED lamp that includes a piezoelectric fan or synthetic jet to cool component of the lamp is disclosed.
Owner:LUMINATION
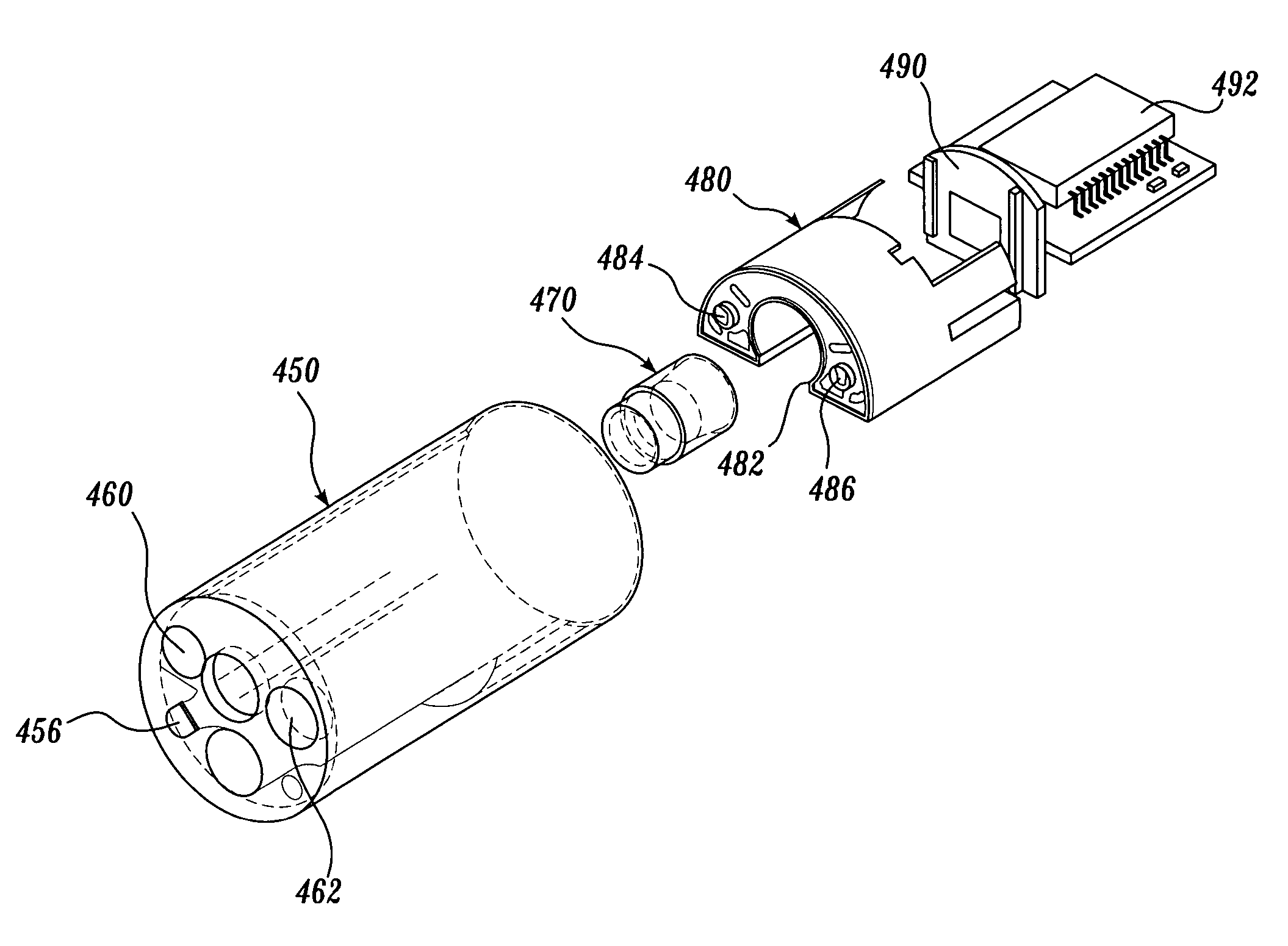
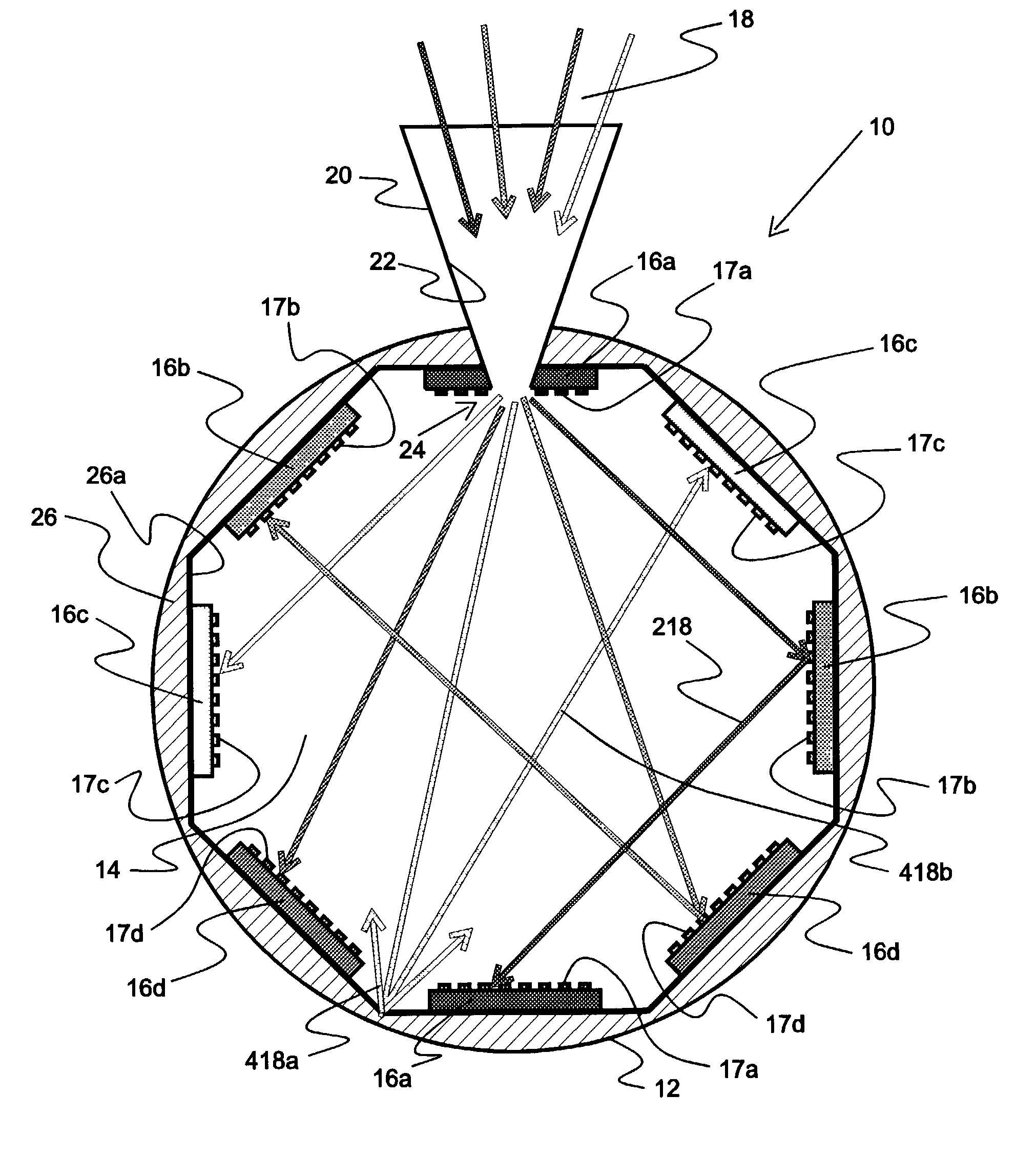
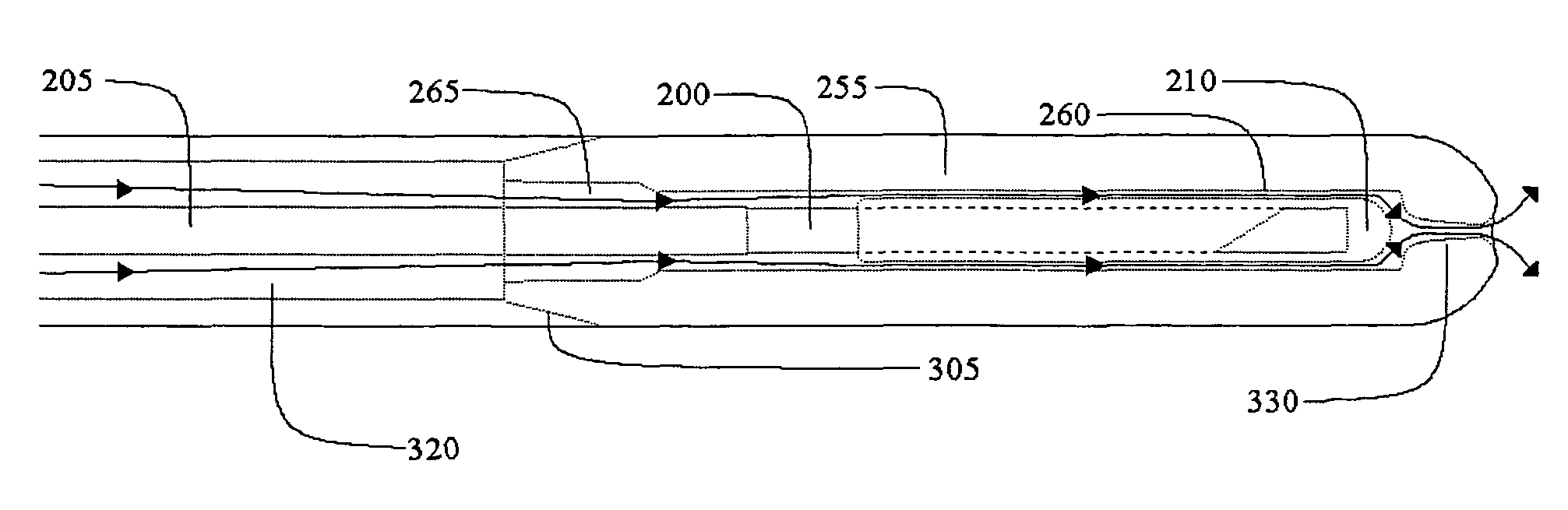
Endoscope with actively cooled illumination sources
ActiveUS7413543B2Inexpensive and easy to assembleRemove heatSurgeryEndoscopesHydrophilic coatingActive cooling
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST
Concentrating photovoltaic cavity converters for extreme solar-to-electric conversion efficiencies
InactiveUS20030213514A1Improve conversion efficiencyMaximize utilizationAuxillary drivesFrom solar energyElectricityPower station
A concentrating photovoltaic module is provided which provides a concentration in the range of about 500 to over 1,000 suns and a power range of a few kW to 50 kW. A plurality of such modules may be combined to form a power plant capable of generating over several hundred megawatts. The concentrating photovoltaic module is based on a Photovoltaic Cavity Converter (PVCC) as an enabling technology for very high solar-to-electricity conversions. The use of a cavity containing a plurality of single junction solar cells of different energy bandgaps and simultaneous spectral splitting of the solar spectrum employs a lateral geometry in the spherical cavity (where the cell strings made of the single junction cells operate next to each other without mutual interference). The purpose of the cavity with a small aperture for the pre-focused solar radiation is to confine (trap) the photons so that they can be recycled effectively and used by the proper cells. Passive or active cooling mechanisms may be employed to cool the solar cells.
Owner:UNITED INNOVATIONS
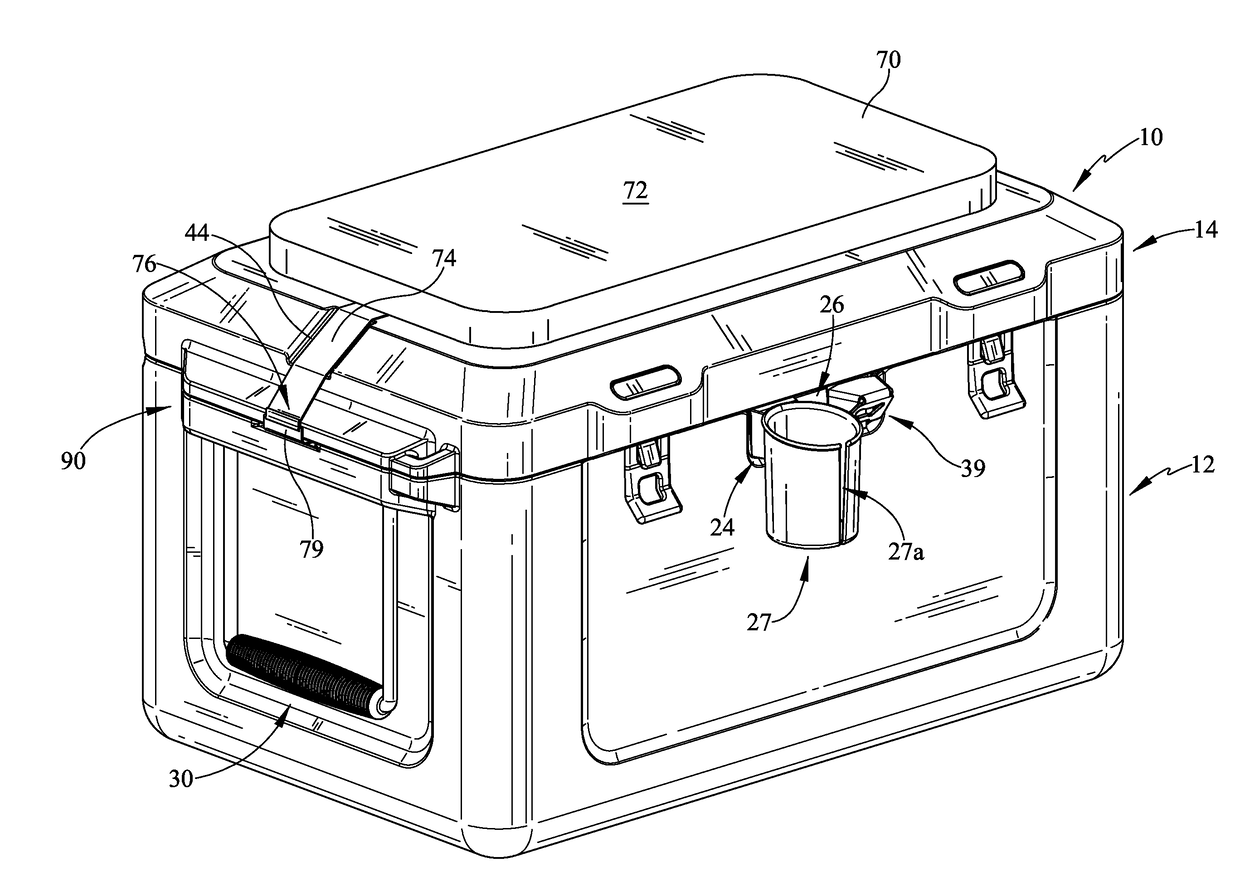
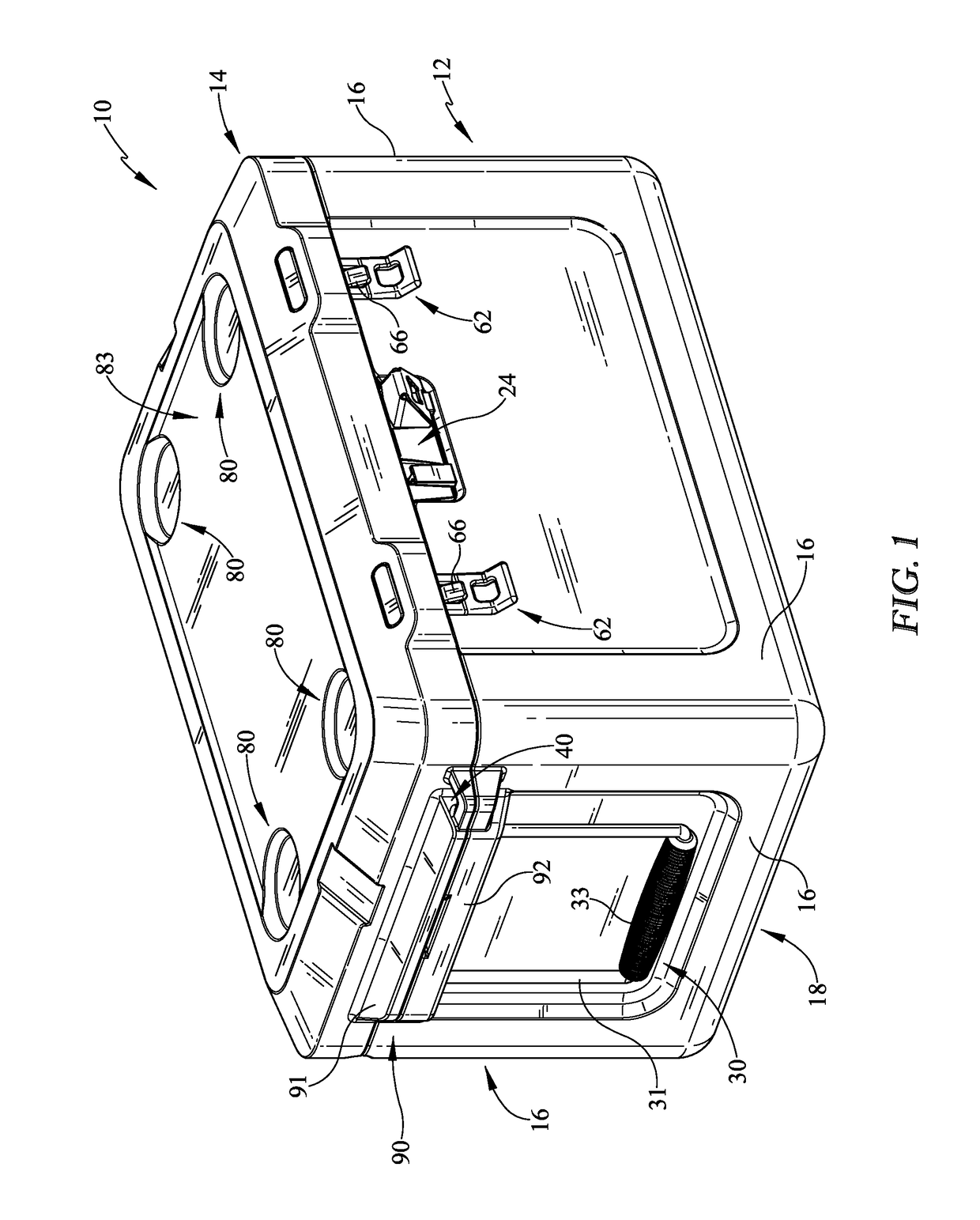
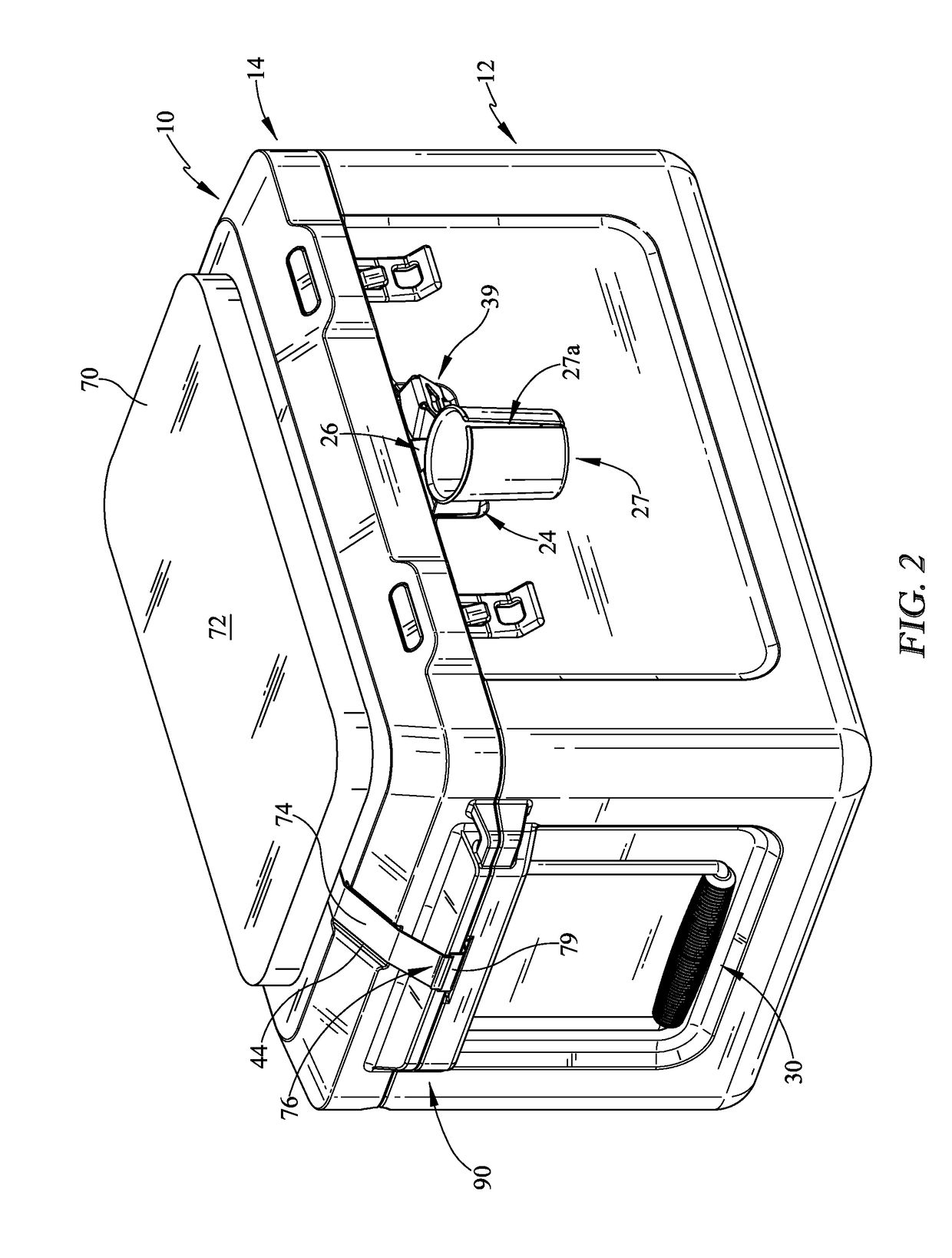
Cooler
A cooler is provided which has various improvements. The cooler may be a passive cooler or may be actively cooled for providing desirable cooling effects. The cooler may include an accessory system, for example, with bottle or can holders or a post holder which utilizes the weight of the cooler to support a sunshade. The accessory system may be positioned in various locations of the cooler, one location being in a recess which is utilized to open the cooler lid. The smart cooler may also comprise a cushion assembly which may be placed on an upper surface of the lid and may have straps to retain the cushion on the lid. The lid may be formed to accept and retain a cushion retaining feature so that the cushion does not excessively move from the top surface of the lid.
Owner:DOMETIC APPLIANCES
Led light with active cooling
InactiveUS7556406B2Point-like light sourceElectric circuit arrangementsPiezoelectric fanActive cooling
An LED lamp that includes a piezoelectric fan or synthetic jet to cool component of the lamp is disclosed.
Owner:LUMINATION
LED light with active cooling
InactiveUS20070147046A1Point-like light sourceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsActive coolingEngineering
Owner:LUMINATION
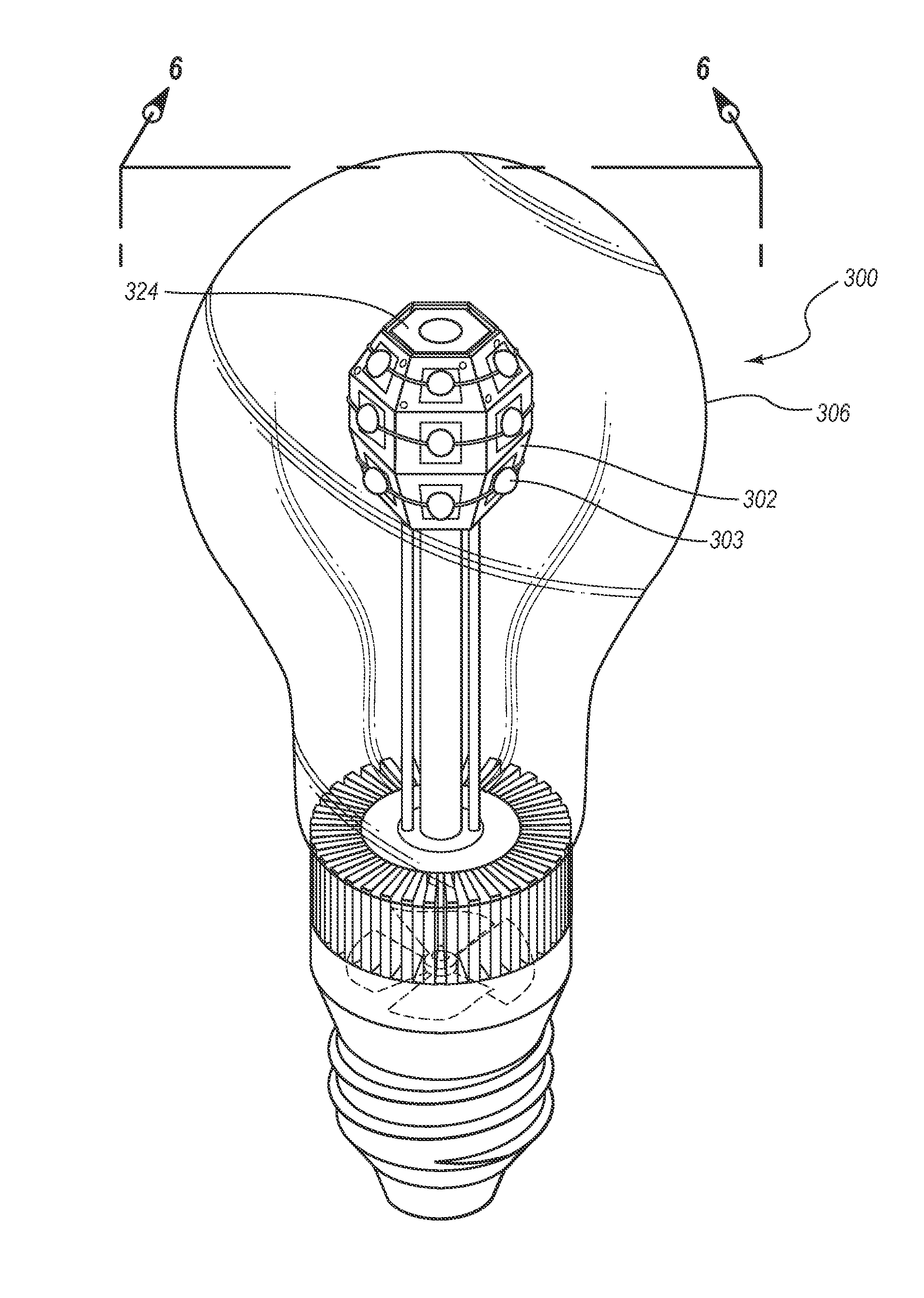
LED light bulbs for space lighting
ActiveUS8653723B2Fast transferPoint-like light sourceElectric discharge tubesHeat managementActive cooling
The invention discloses a three dimensional LED arrangement and heat management method using a heat transfer or conduction pipe to enable rapid heat transfer from a three dimensional cluster of LEDs to a heatsink with or without active cooling, the light emitted from the three dimensional cluster not being obstructed by a heat sink arrangement such that the light beam profile generated by the light appears similar to that generated by traditional incandescent bulbs.
Owner:SATCO PRODS
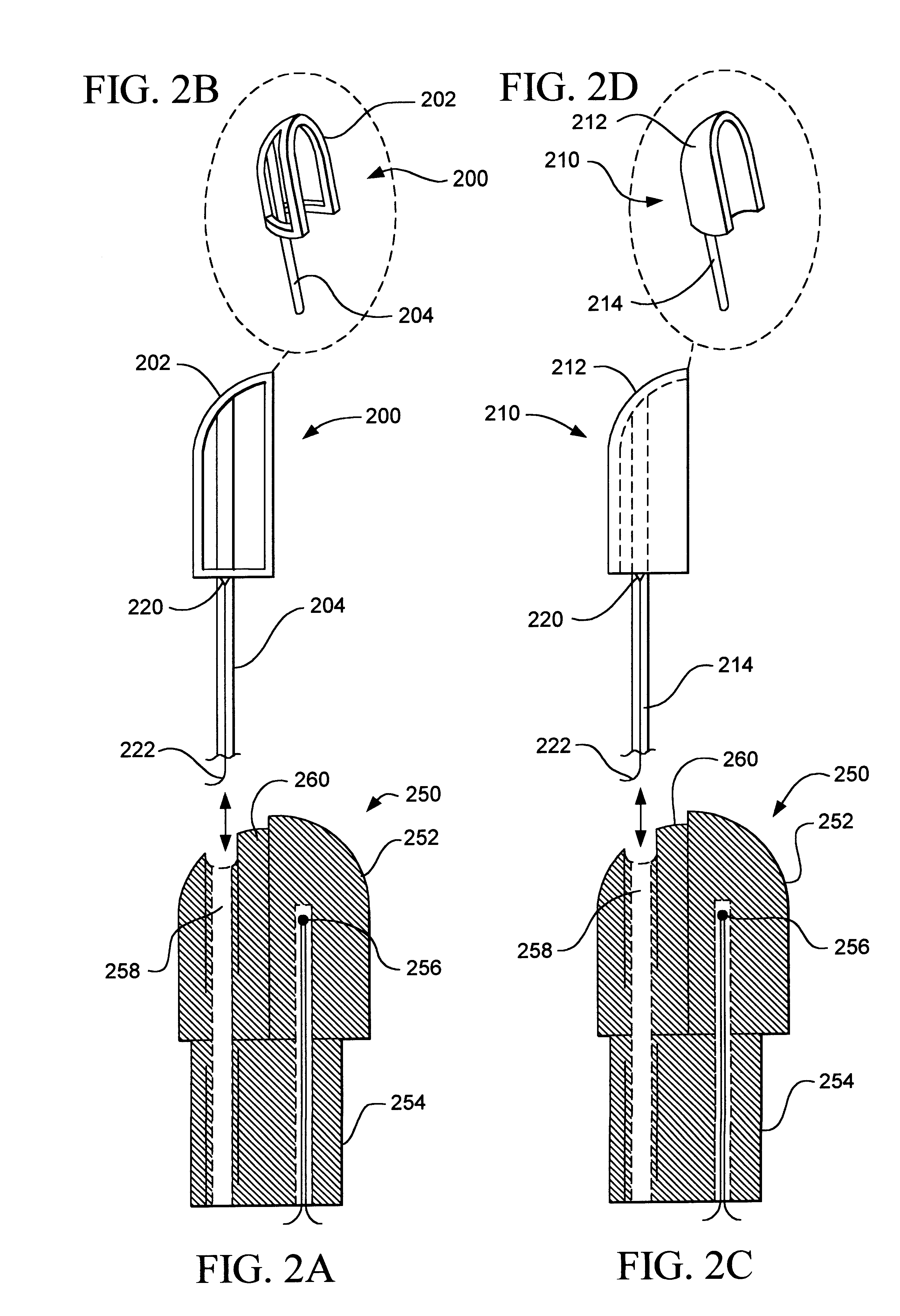
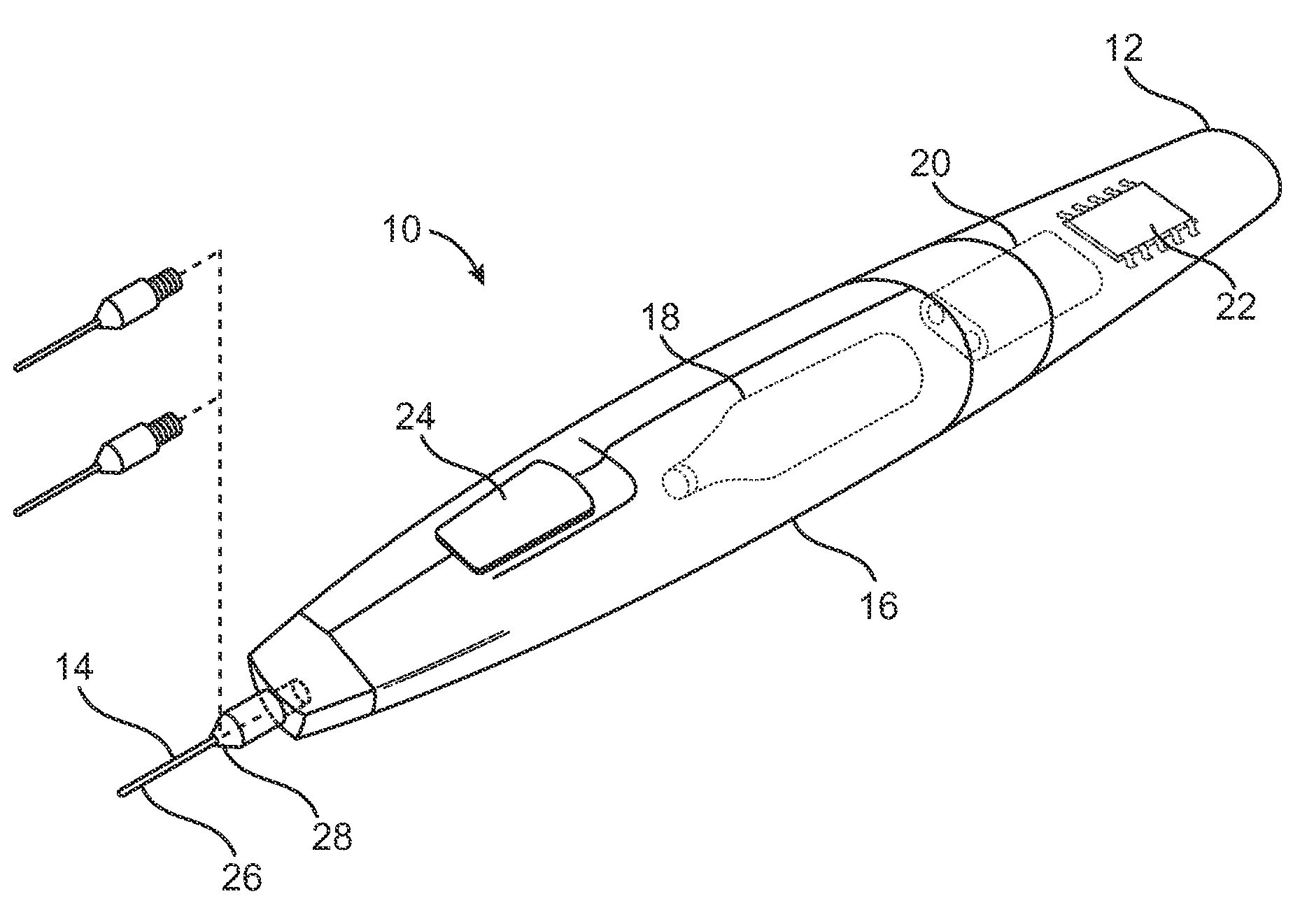
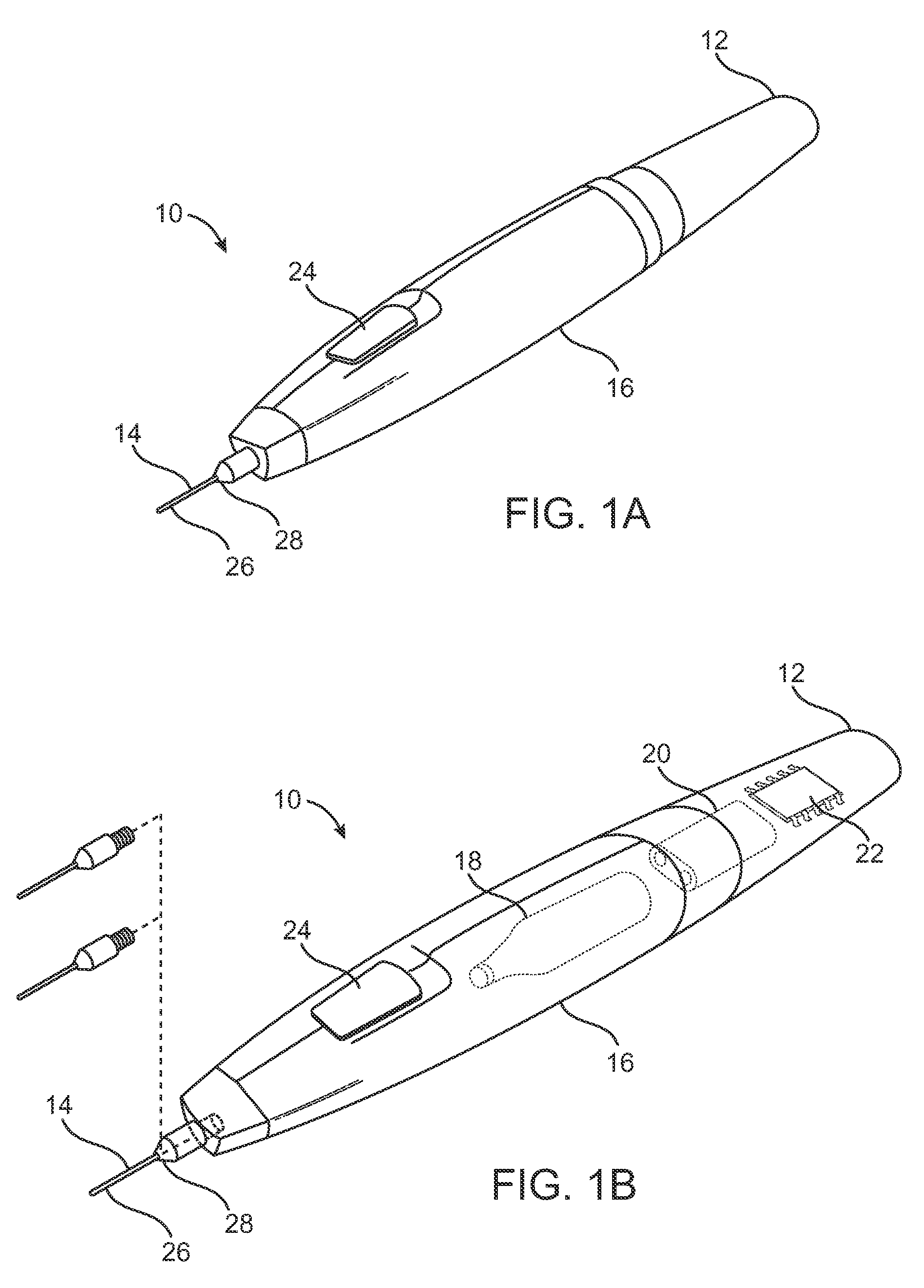
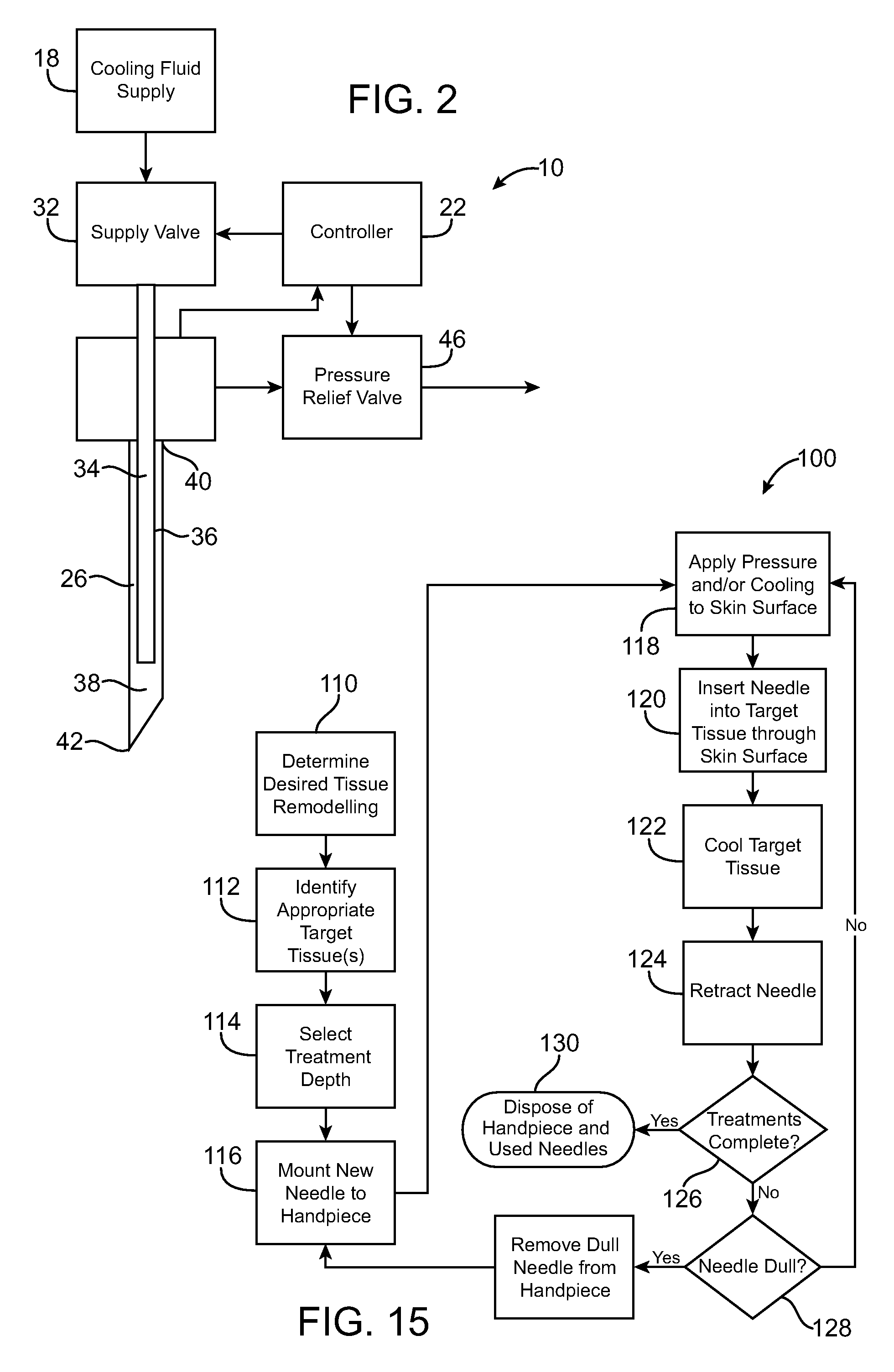
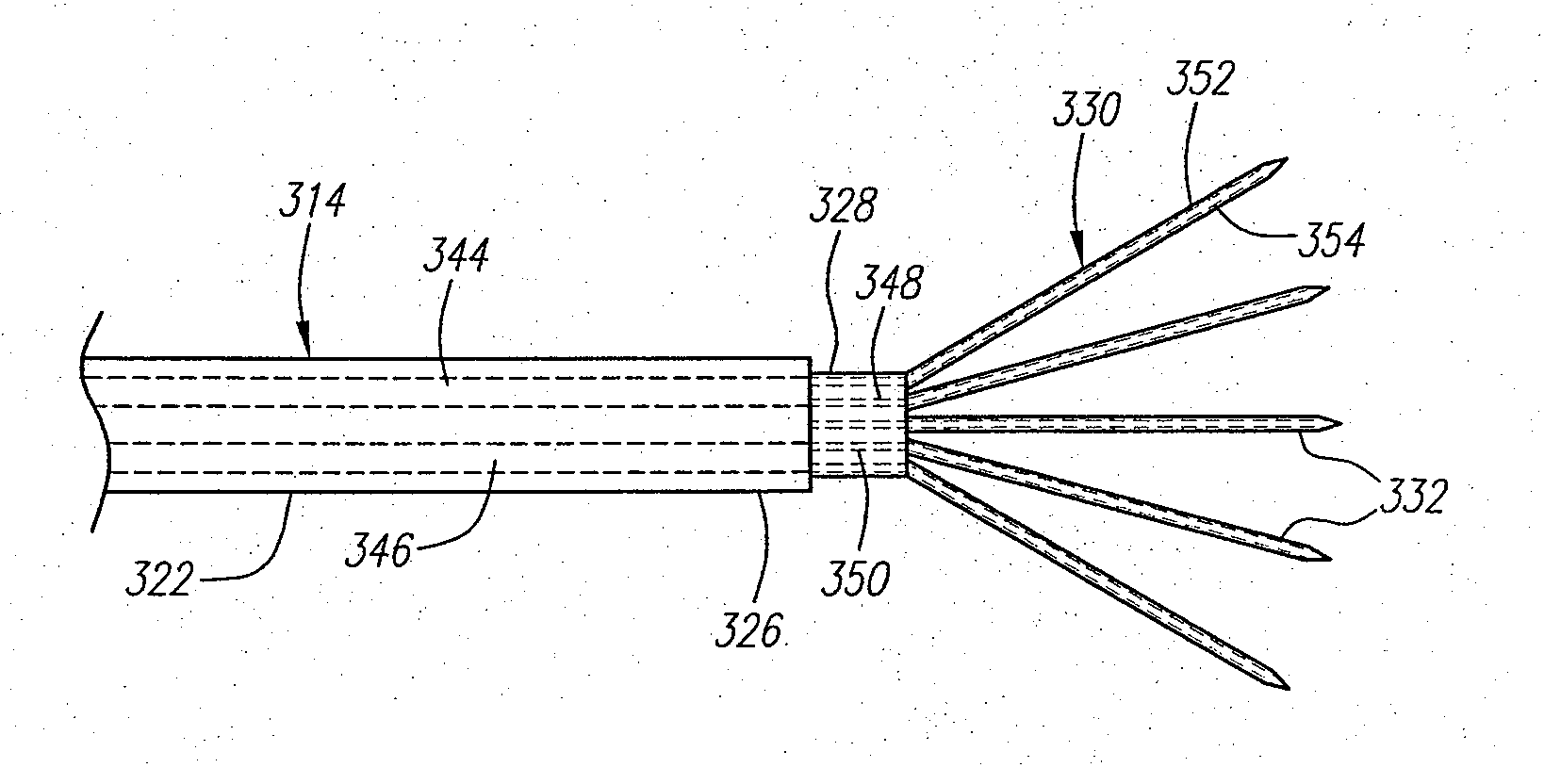
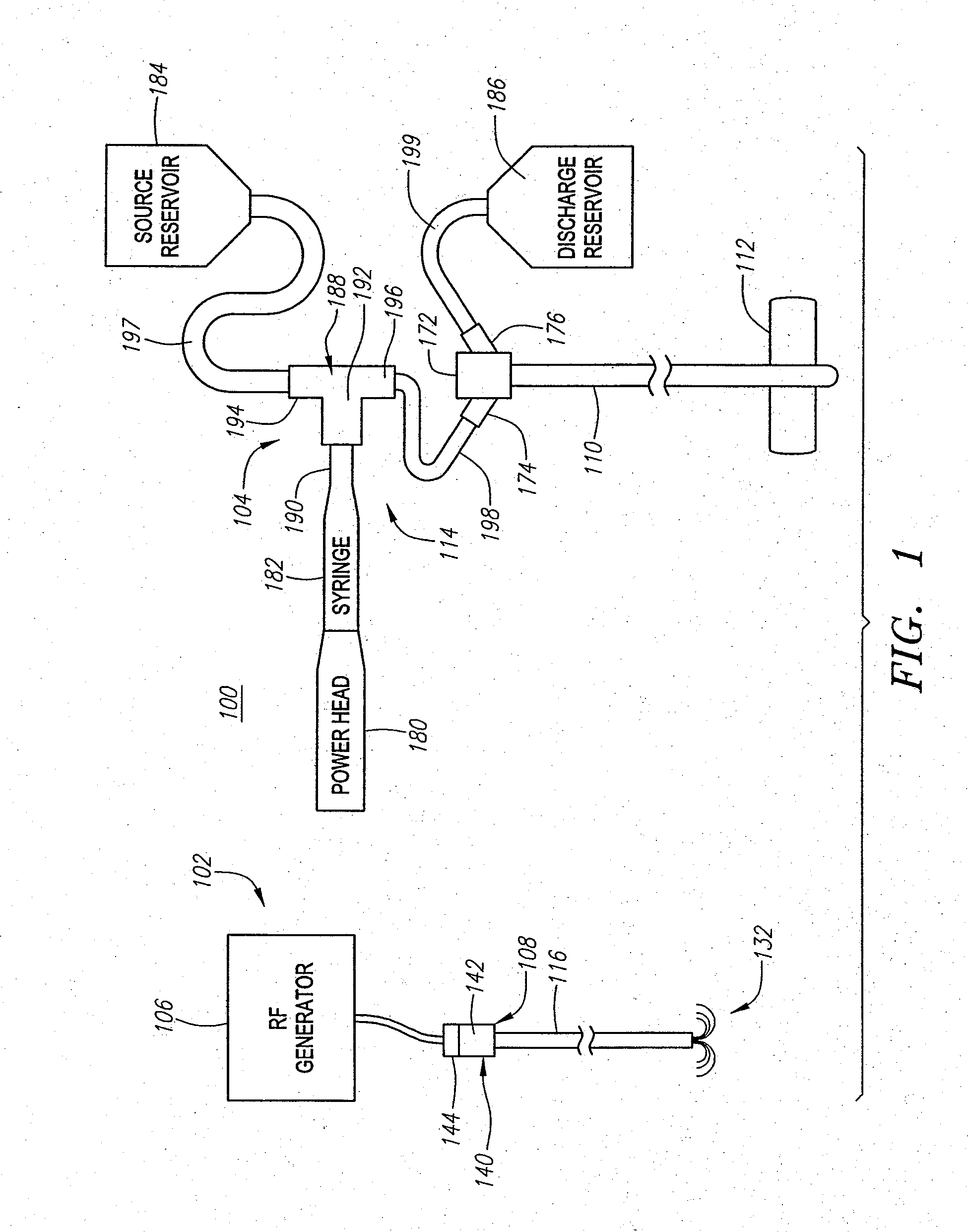
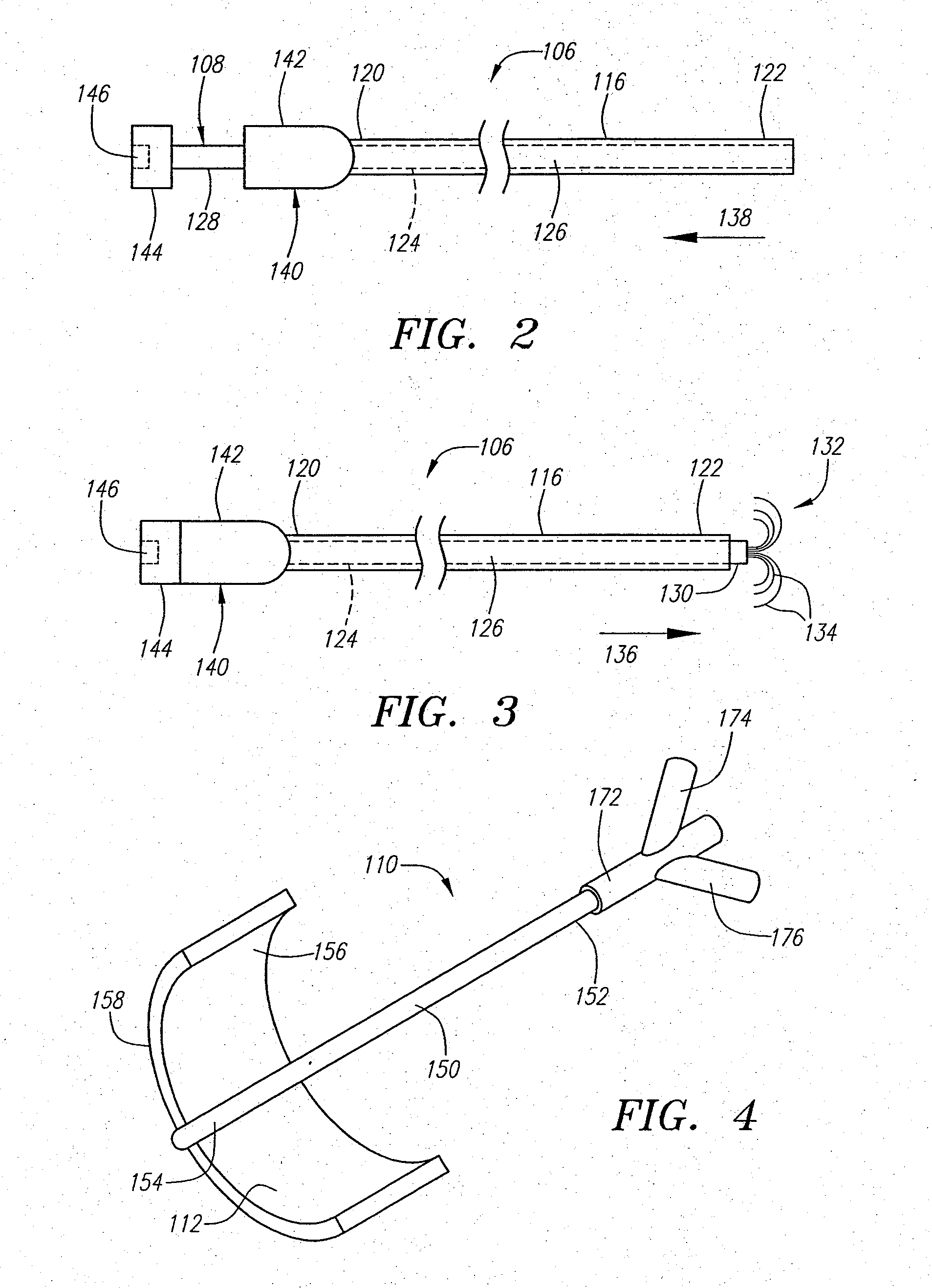
Replaceable and/or Easily Removable Needle Systems for Dermal and Transdermal Cryogenic Remodeling
ActiveUS20080200910A1Shorten the timeSmall sizeInfusion syringesSurgical instruments for coolingFluid controlActive cooling
The present invention generally provides improved medical devices, systems, and methods. Embodiments may be particularly well suited for the treatment of dermatological and / or cosmetic defects, and alternative embodiments may be configured for treatment of a wide range of target tissues. Some embodiments of the present invention apply cooling with at least one small, tissue-penetrating probe, the probe often comprising a needle having a size suitable for inserting through an exposed surface of the skin of a patient without leaving a visible scar. The cooling may remodel one or more target tissue so as to effect a desired change in a composition of the target tissue and / or a change in its behavior. Exemplary embodiments make use of replaceable needle probes supported by a probe body handle, with small needle probes often being replaced during treatment of a single patient. Unlike the large format cryogenic cooling systems of the past, small cryogenic cooling needle probes may dull or be damaged by insertion. Careful control over the control of cryogenic cooling fluid into a needle probe can allow the length of the active cooling to be controlled through depletion of liquid from an evaporating cryogenic cooling flow. Hence, even needles having similar external structures may provide differing lengths of an iceball along the needle axis. Surprisingly, small cryogenic cooling needles and / or other cryogenic cooling probes having a lubricious coating will allow safe removal of the probe from the treatment region while at a least a portion of the tissue remains frozen, significantly decreasing the overall time for a procedure involving many insertion / freeze / removal cycles.
Owner:PACIRA CRYOTECH INC
Cooling system for a semiconductor device and method of fabricating same
ActiveUS7029951B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesActive coolingConductive materials
A cooling system for a semiconductor substrate incudes a plurality of trenches formed from a backside of the semiconductor substrate, and thermally conductive material deposited in the plurality of trenches. A method of forming cooling elements in a semiconductor substrate, includes coating a backside of the semiconductor substrate with a first mask layer, forming a plurality of trench patterns in the first mask layer, etching the semiconductor substrate to form a plurality of trenches along the plurality of trench patterns, and depositing thermally conductive material in the plurality of trenches. Trenches constructed from the backside of a wafer improve efficiency of heat transfer from a front-side to the backside of an integrated-circuit chip. The fabrication of trenches from the backside of the wafer allows for increases in the depth and number of trenches, and provides a means to attach passive and active cooling devices directly to the backside of a wafer.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
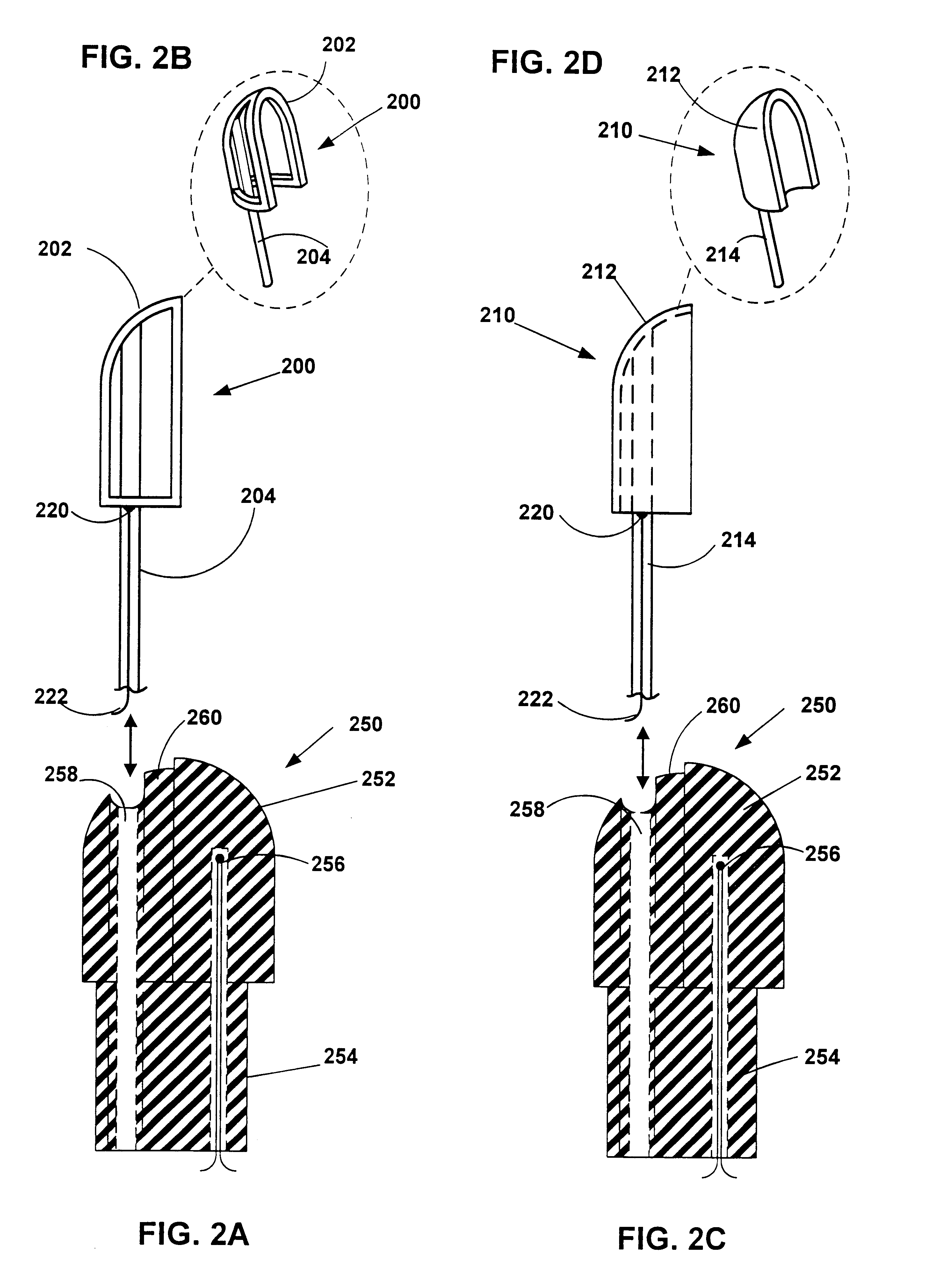
Radio frequency ablation cooling shield
A medical assembly and method are provided to effectively treat abnormal tissue, such as, a tumor. The target tissue is thermally ablated using a suitable source, such as RF or laser energy. A cooling shield is placed in contact with non-target tissue adjacent the target tissue, and actively cooled to conduct thermal energy away from the non-target tissue. In one method, the cooling shield can be placed between two organs, in which case, one of the two organs can comprise the target tissue, and the other of the two organs can comprise the non-target tissue. In this case, the cooling shield may comprise an actively cooled inflatable balloon, which can be disposed between the two organs when deflated, and then inflated. The inflatable balloon can be actively cooled by pumping a cooling medium through it. In another method, the cooling shield can be embedded within the non-target tissue. In this case, the cooling shield can comprise one or more needles. If a plurality of needles is used, they can be embedded into the non-target tissue in a series, e.g., a rectilinear or curvilinear arrangement. The needle(s) can be actively cooled by pumping a cooling medium through them.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
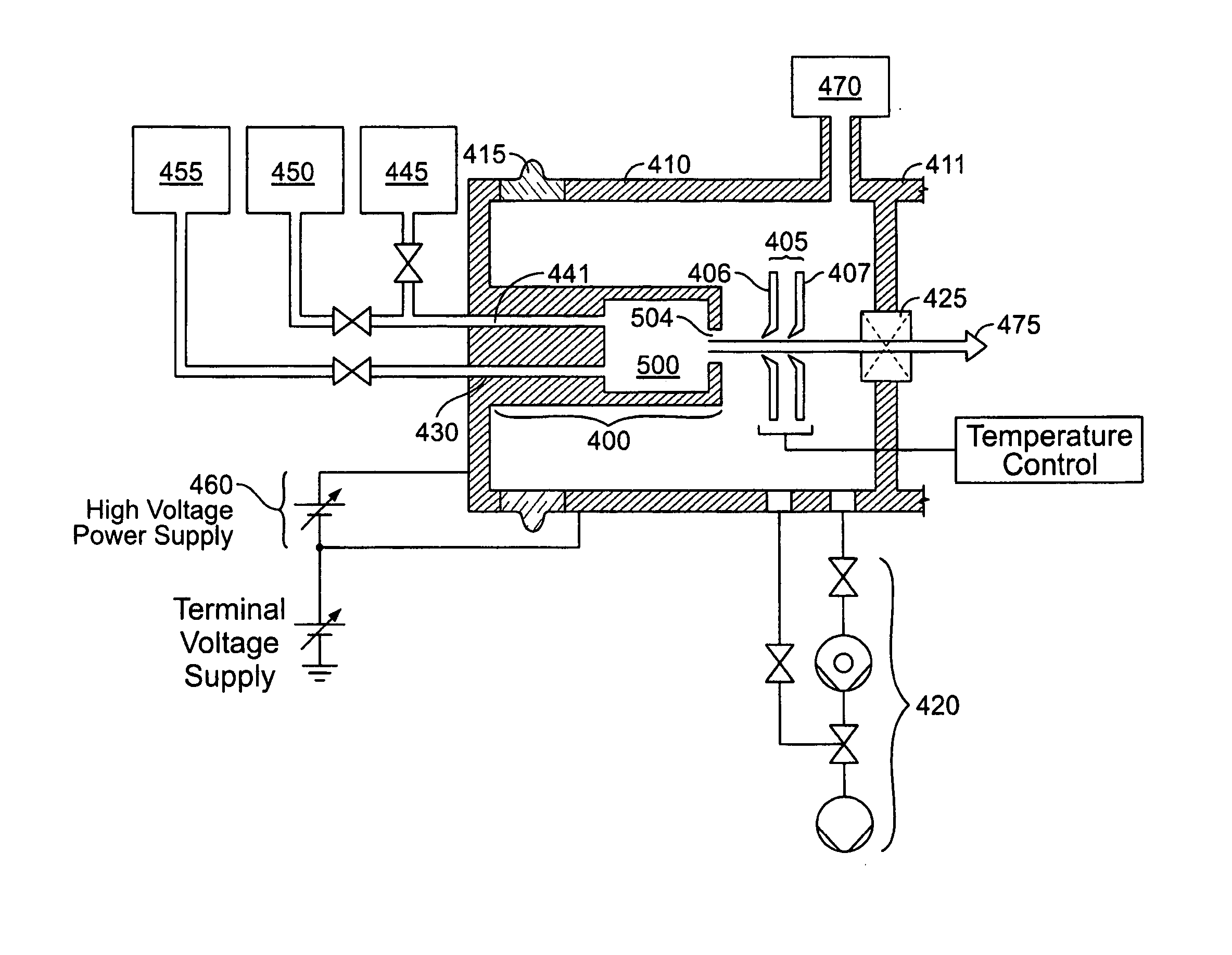
Method and apparatus for extracting ions from an ion source for use in ion implantation
InactiveUS20060272775A1Avoid unstable operationMaintain dimensional stabilityVacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRemote plasmaActive cooling
Thermal control is provided for an extraction electrode of an ion-beam producing system that prevents formation of deposits and unstable operation and enables use with ions produced from condensable vapors and with ion sources capable of cold and hot operation. Electrical heating of the extraction electrode is employed for extracting decaborane or octadecaborane ions. Active cooling during use with a hot ion source prevents electrode destruction, permitting the extraction electrode to be of heat-conductive and fluorine-resistant aluminum composition. The service lifetime of the system is enhanced by provisions for in-situ etch cleaning of the ion source and extraction electrode, using reactive halogen gases, and by having features that extend the service duration between cleanings, including accurate vapor flow control and accurate focusing of the ion beam optics. A remote plasma source delivers F or Cl ions to the de-energized ion source for the purpose of cleaning deposits in the ion source and the extraction electrode. These techniques enable long equipment uptime when running condensable feed gases such as sublimated vapors, and are particularly applicable for use with so-called cold ion sources and universal ion sources. Methods and apparatus are described which enable long equipment uptime when decaborane and octadecaborane are used as feed materials, as well as when vaporized elemental arsenic and phosphorus are used, and which serve to enhance beam stability during ion implantation.
Owner:SEMEQUIP
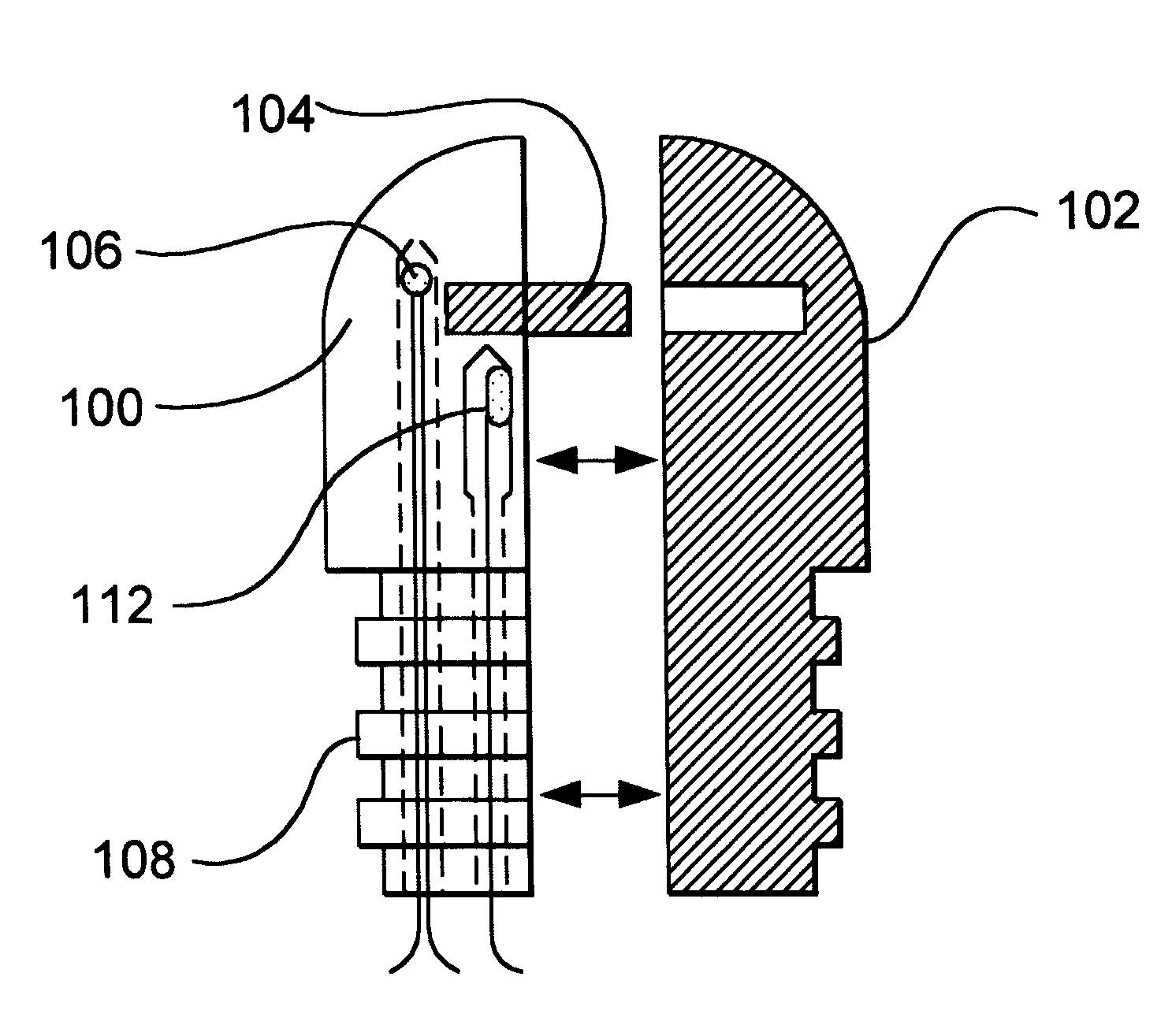
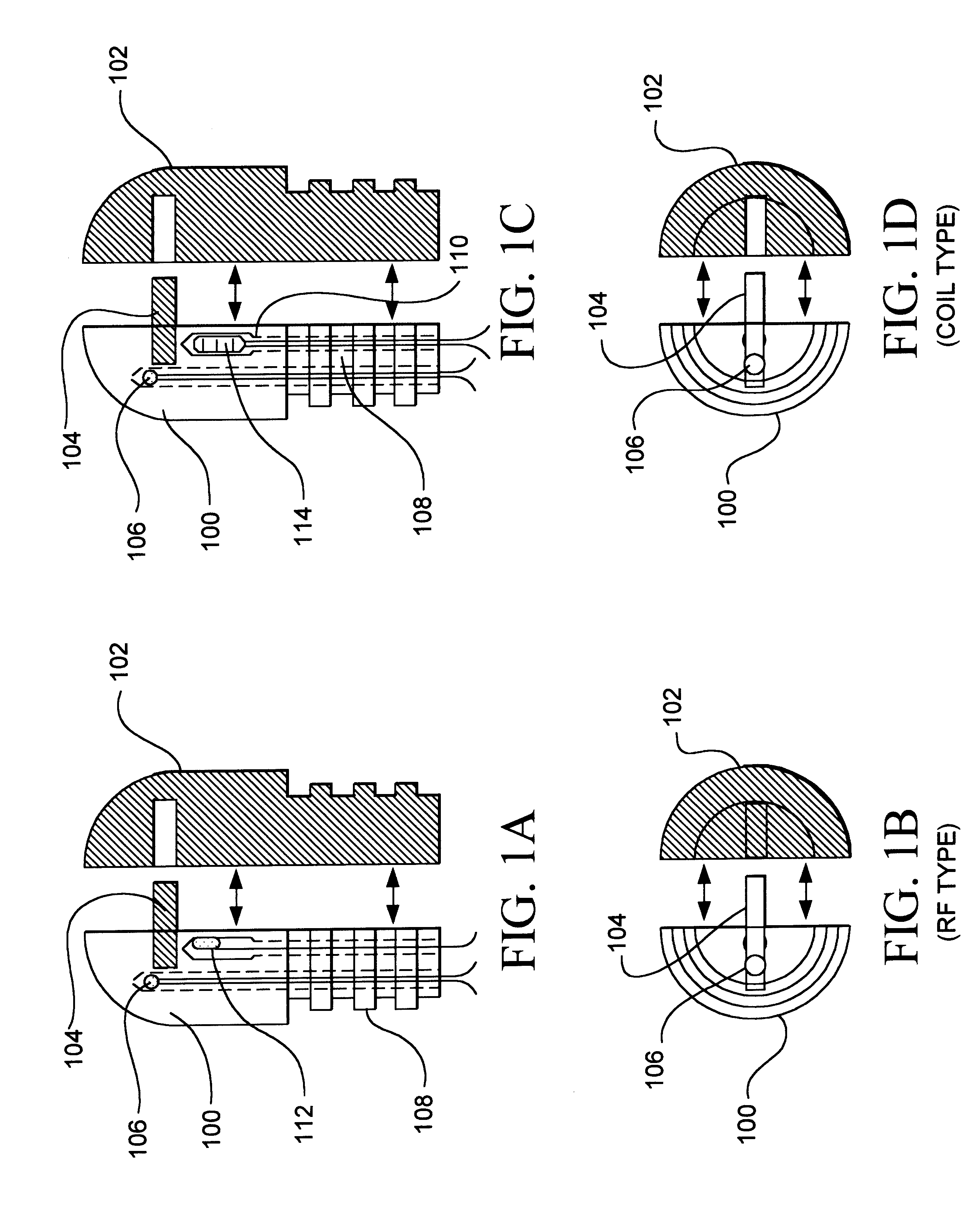
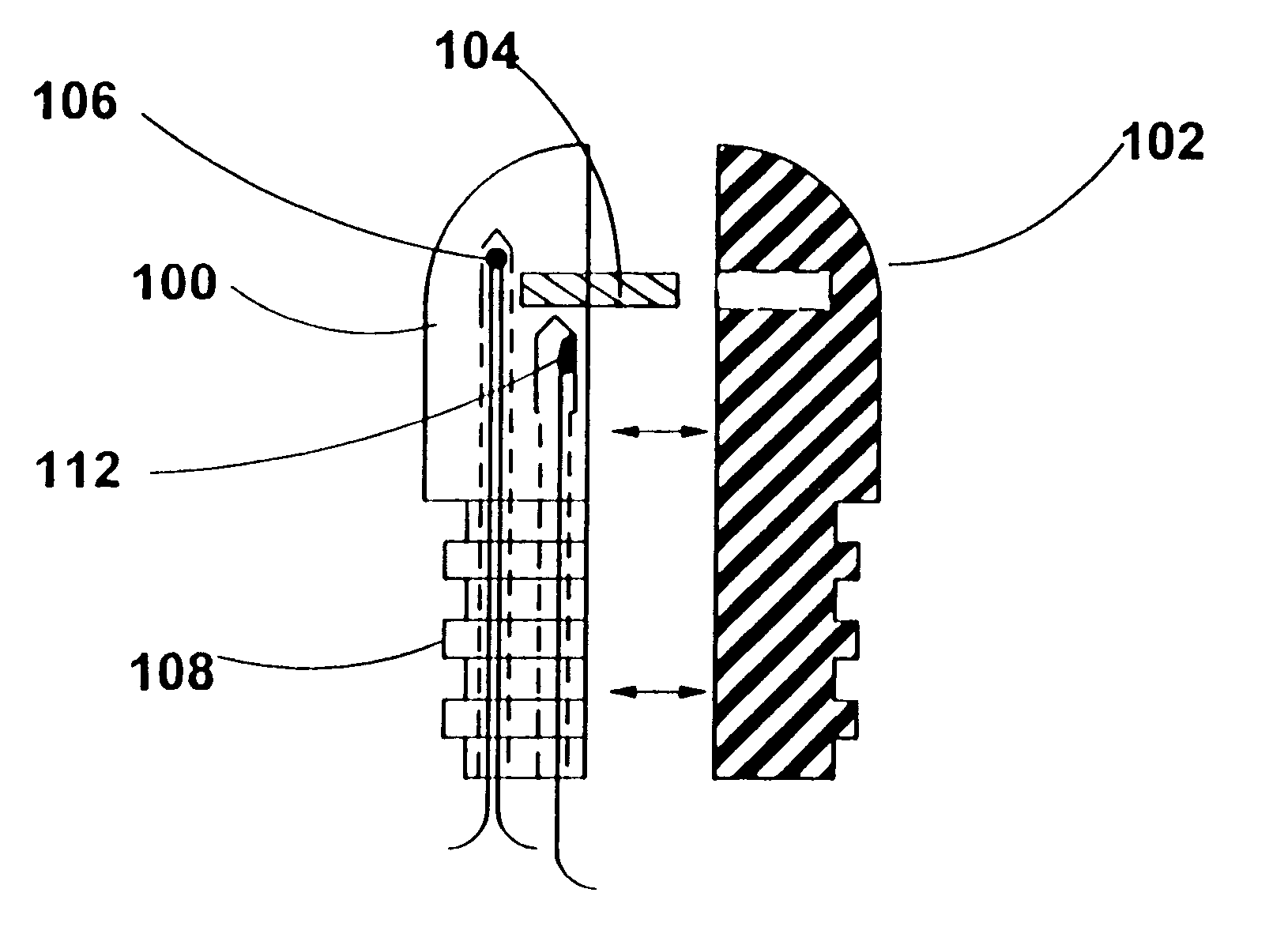
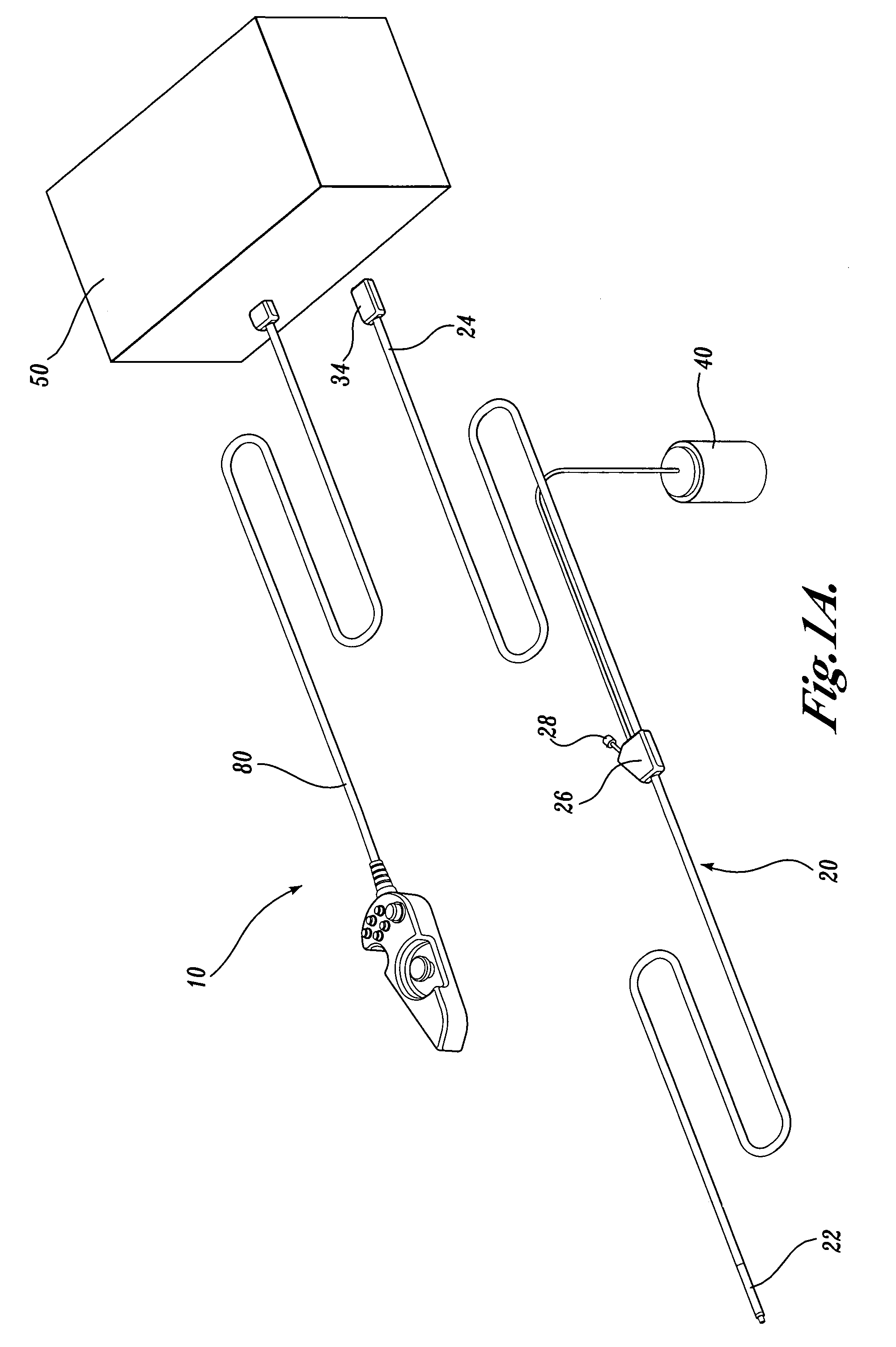
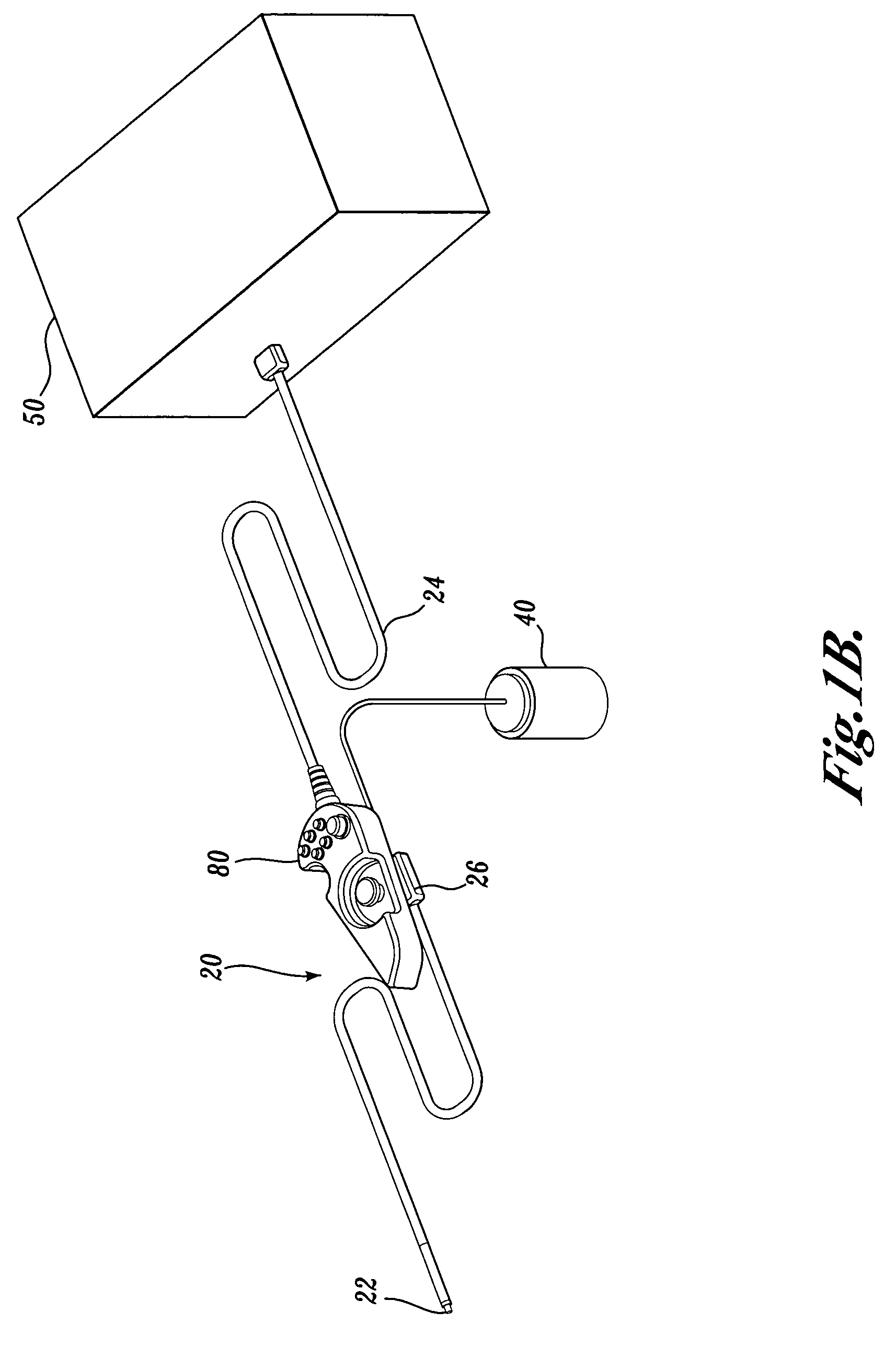
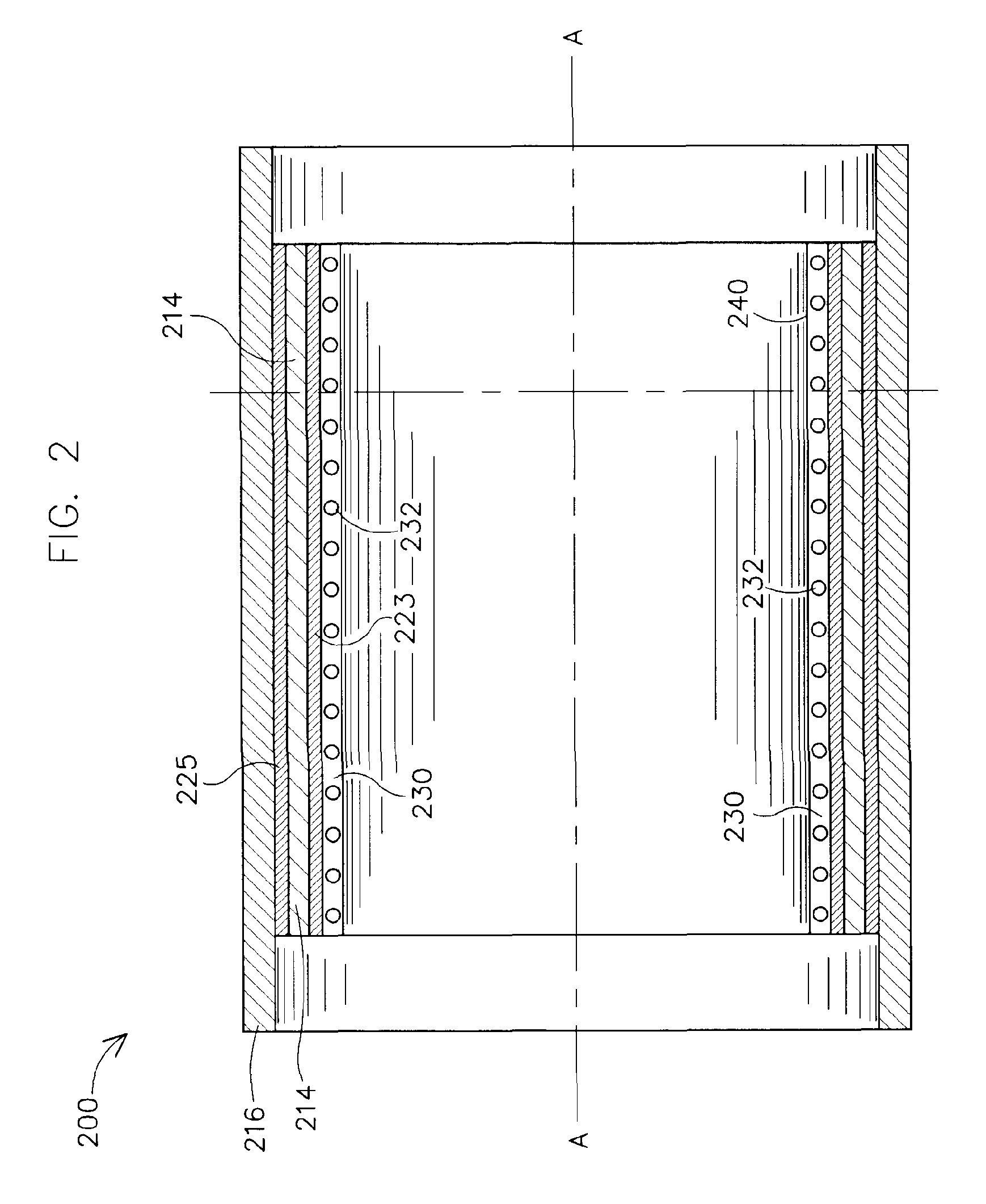
Apparatus for active cooling of an MRI patient bore in cylindrical MRI systems
InactiveUS20050030028A1Increase patient comfortReduce heat loadElectromagnets without armaturesTransformers/inductances coolingActive coolingEngineering
The present invention provides for a cooling system for circulating a coolant to cool the patient bore. In one embodiment, that patient bore consists of two concentric cylinders separated by spacers running either longitudinally or helically. In another embodiment of the present invention, fluid may be passed either helically or longitudinally through tubes bonded to the outer diameter of the patient bore such that the parts of the bore that are exposed to the patient are directly cooled. In a third embodiment, the RF coil could form part of the patient bore, with the helical or longitudinal fluid channels surrounding the patient bore.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Lateral laser fiber for high average power and peak pulse energy
ActiveUS7909817B2Minimize reflectionAvoid seizuresSurgical instrument detailsFree rotationRefractive index
An improved optical fiber comprising a waveguide with an input for coupling focused laser energy into the waveguide and communicating electromagnetic radiation in a propagation direction to an internally reflective tip of the waveguide, a tissue contacting surface wherein the light path from the reflecting surface to the transmitting surface in substantially homogenous in refractive index and cooled by fluid flow. In minimizing the variations in refractive index within the lateral light path, while providing active cooling directly below the tissue contact surface, the invention prevents internal reflections and beam distortion and greatly improves the efficiency and durability of the laterally directing probe. Free rotation of the tissue contact surface, about the lateral tip, may be provided and tissue vaporization efficiency may be improved by providing a morcellating tool on the tissue contact surface.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
LED light with active cooling
InactiveUS7543961B2Point-like light sourceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsActive coolingEngineering
Owner:LUMINATION
Radio frequency ablation cooling shield
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
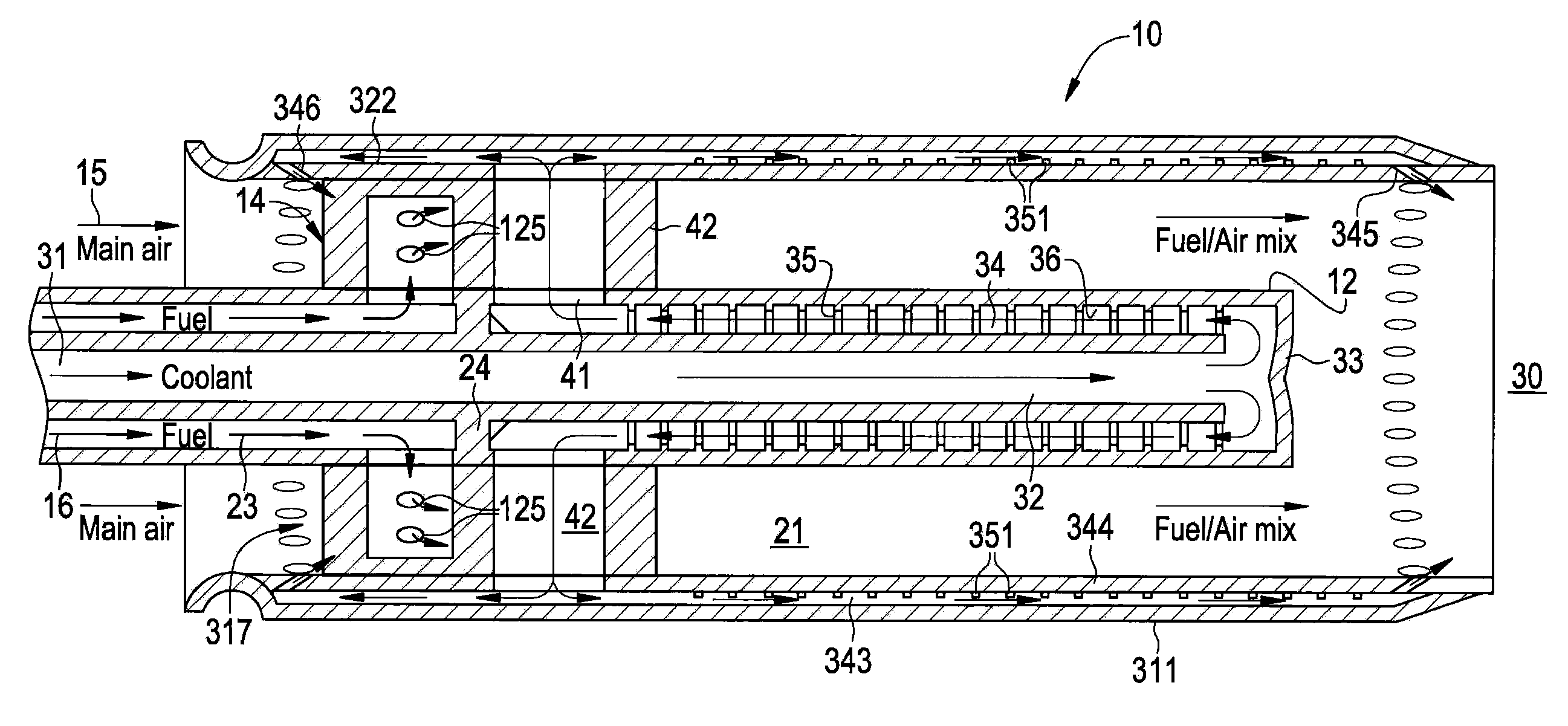
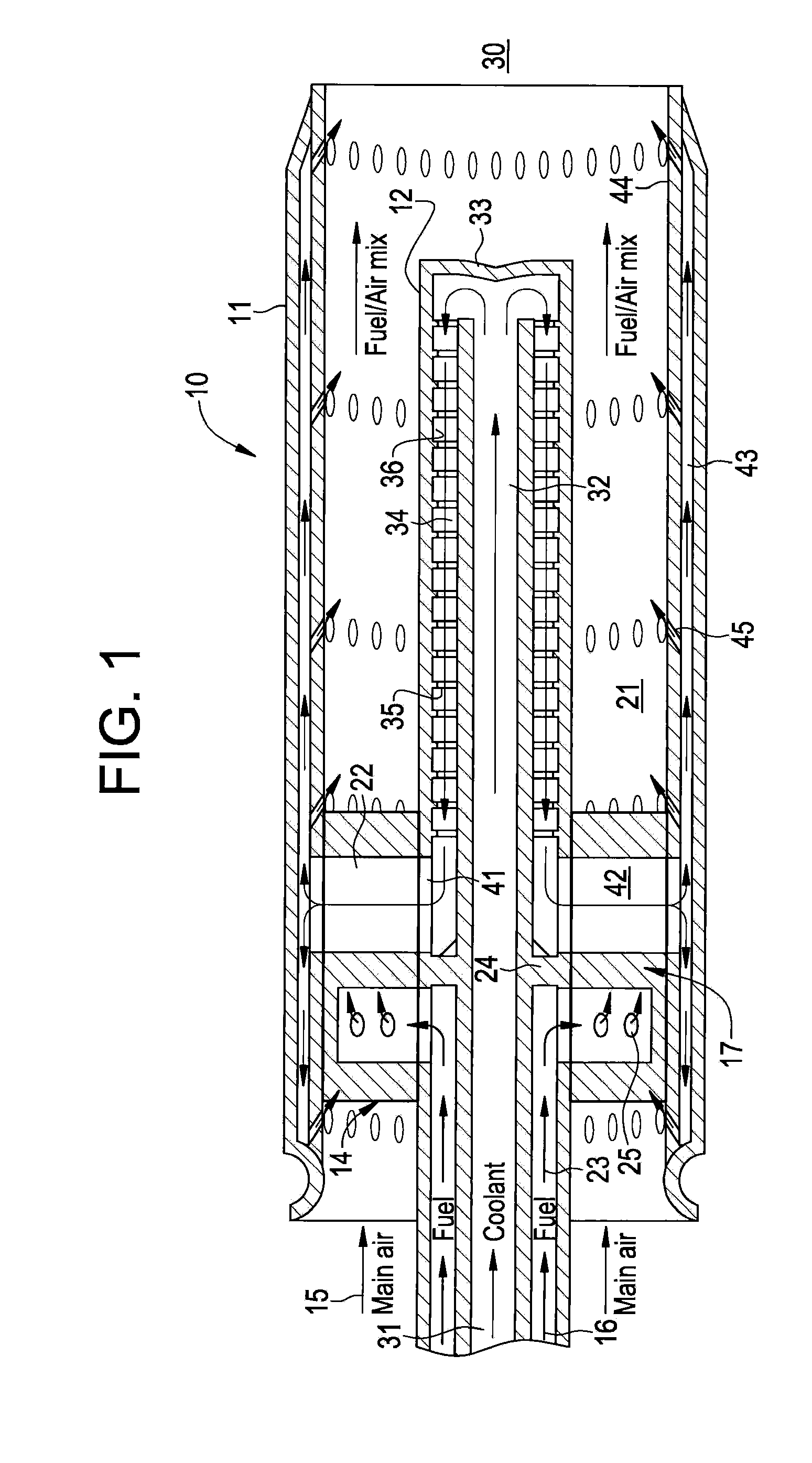
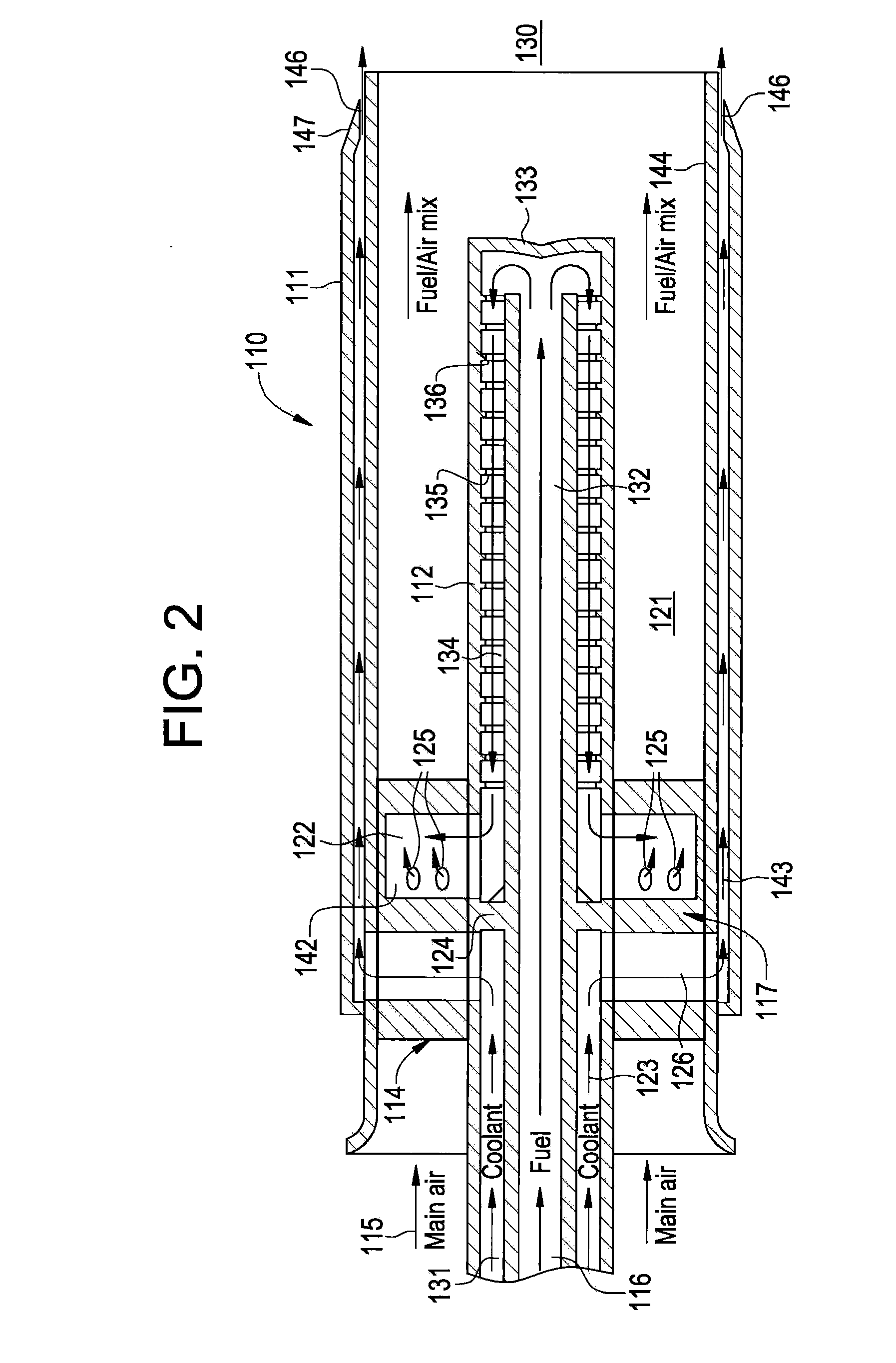
Flame Holding Tolerant Fuel and Air Premixer for a Gas Turbine Combustor
InactiveUS20100101229A1Reduce riskEnough timeContinuous combustion chamberTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsCombustorCombustion chamber
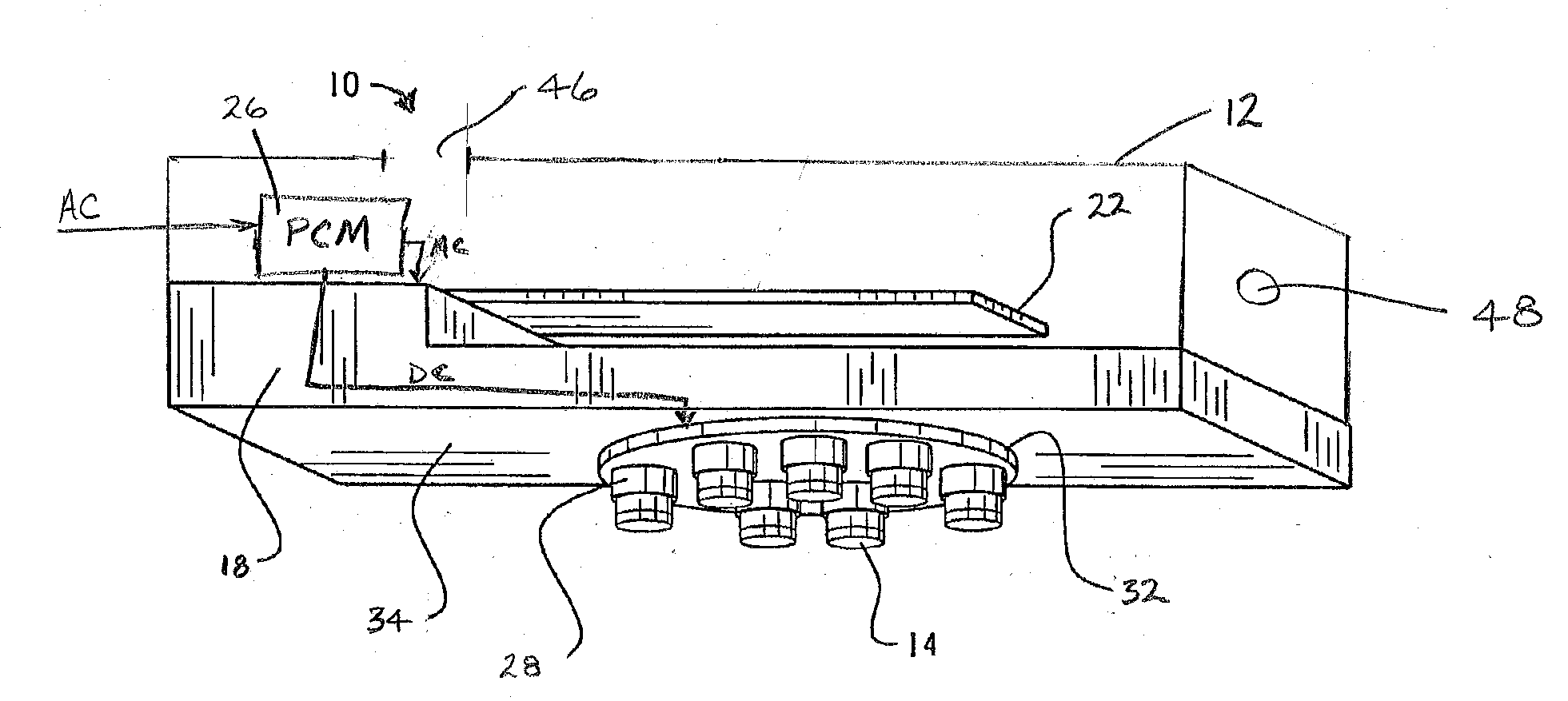
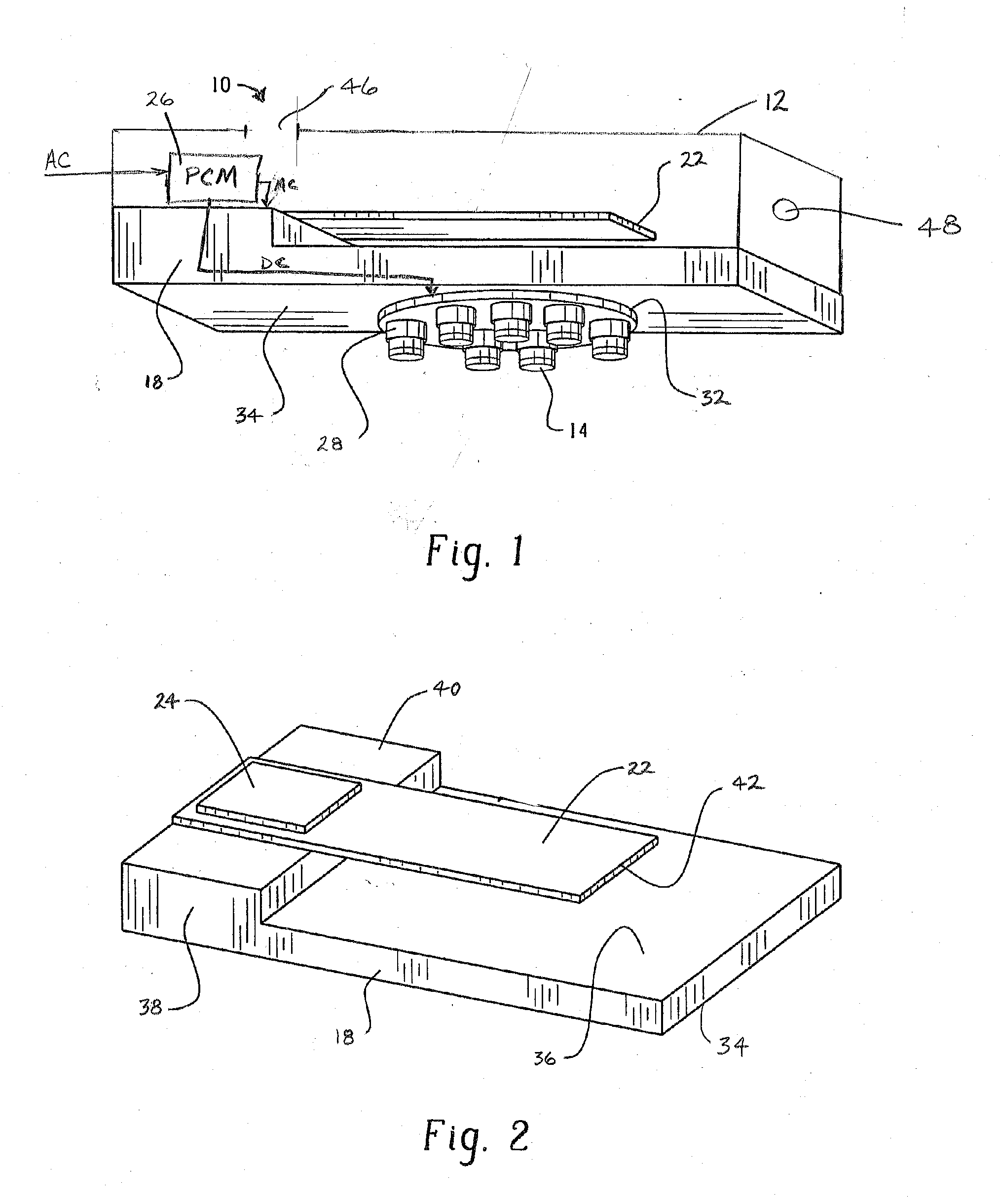
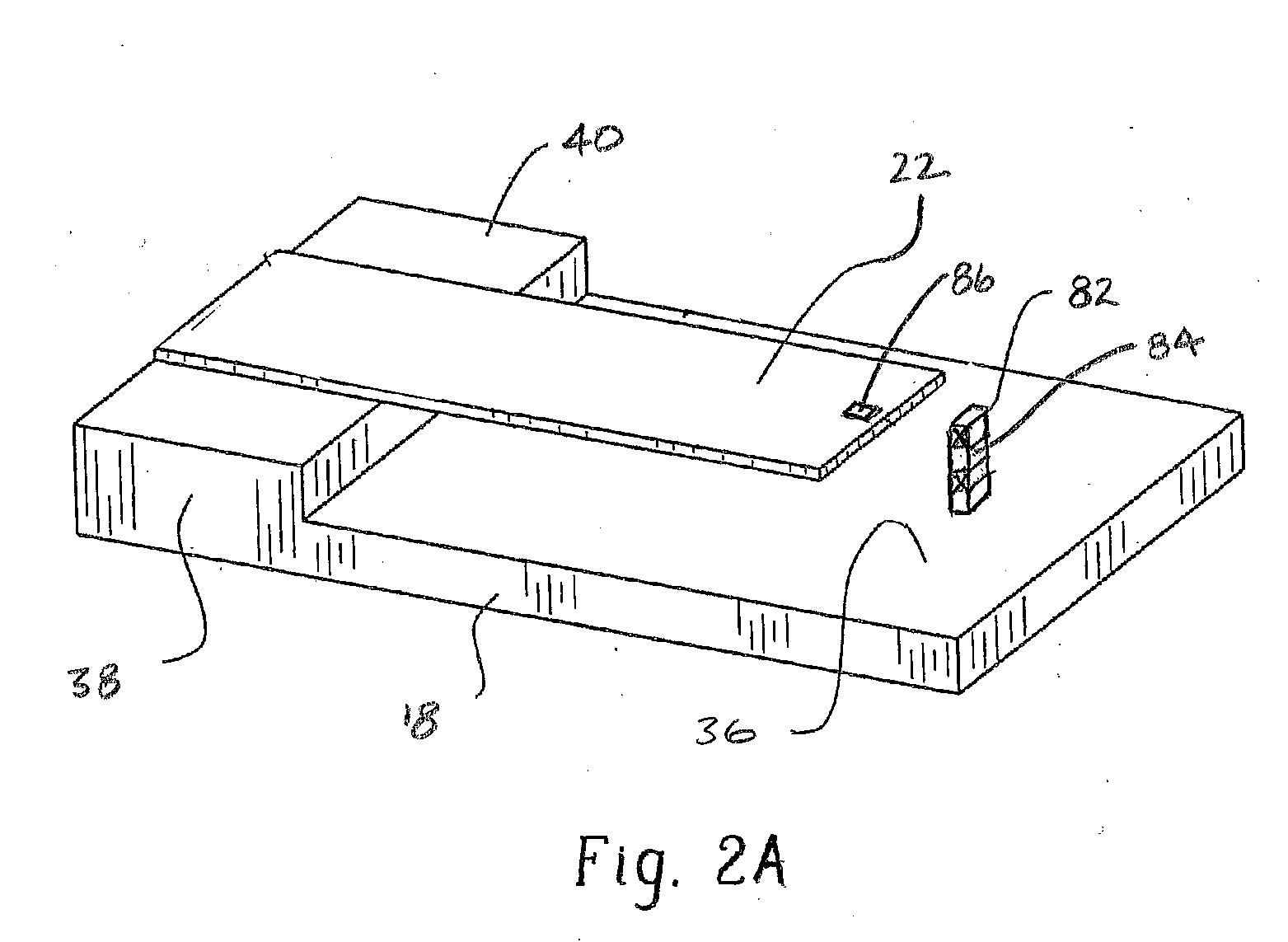
A fuel nozzle with active cooling is provided. It includes an outer peripheral wall, a nozzle center body concentrically disposed within the outer wall in a fuel and air pre-mixture. The fuel and air pre-mixture includes an air inlet, a fuel inlet and a premixing passage defined between the outer wall in the center body. A gas fuel flow passage is provided. A first cooling passage is included within the center body in a second cooling passage is defined between the center body and the outer wall.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
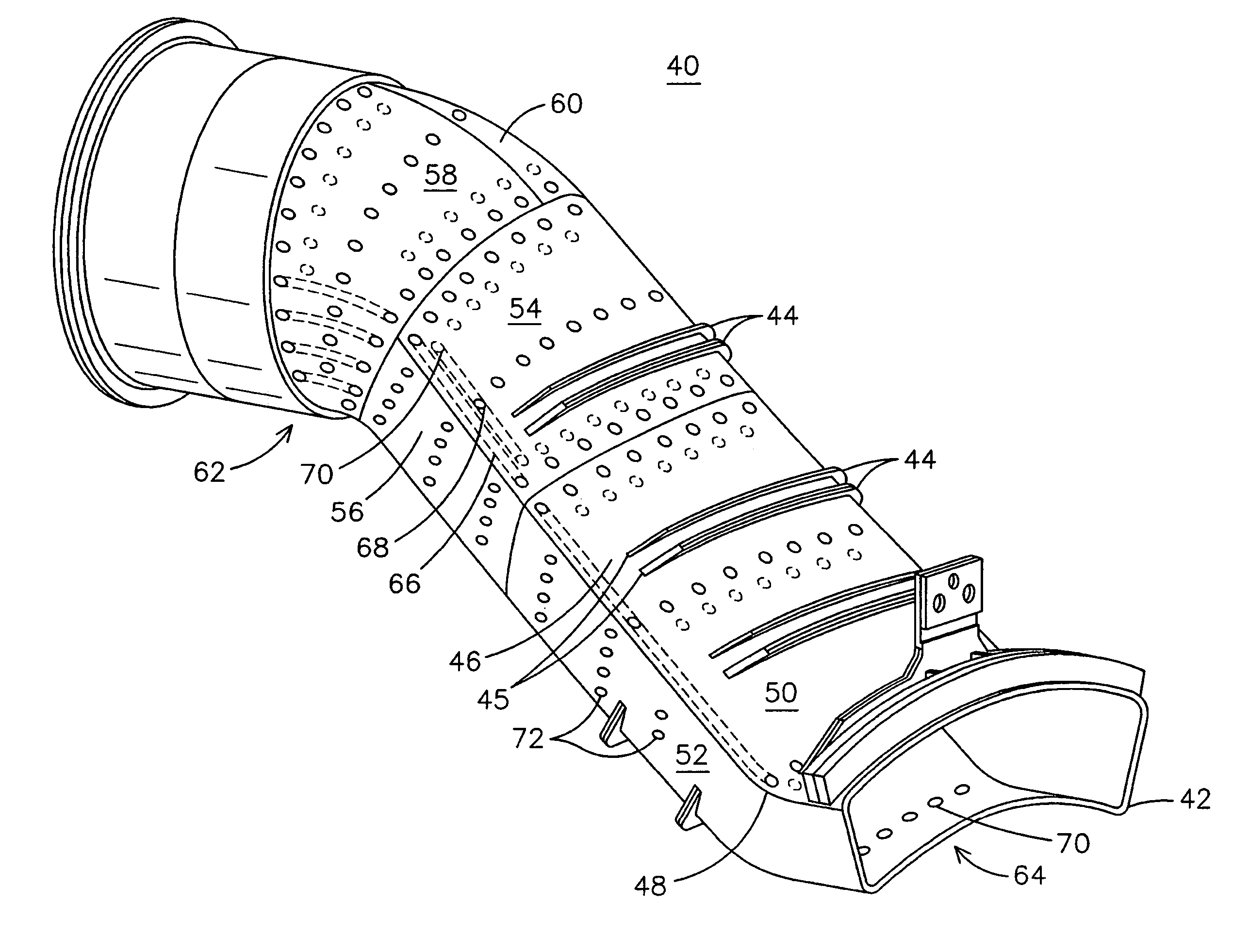
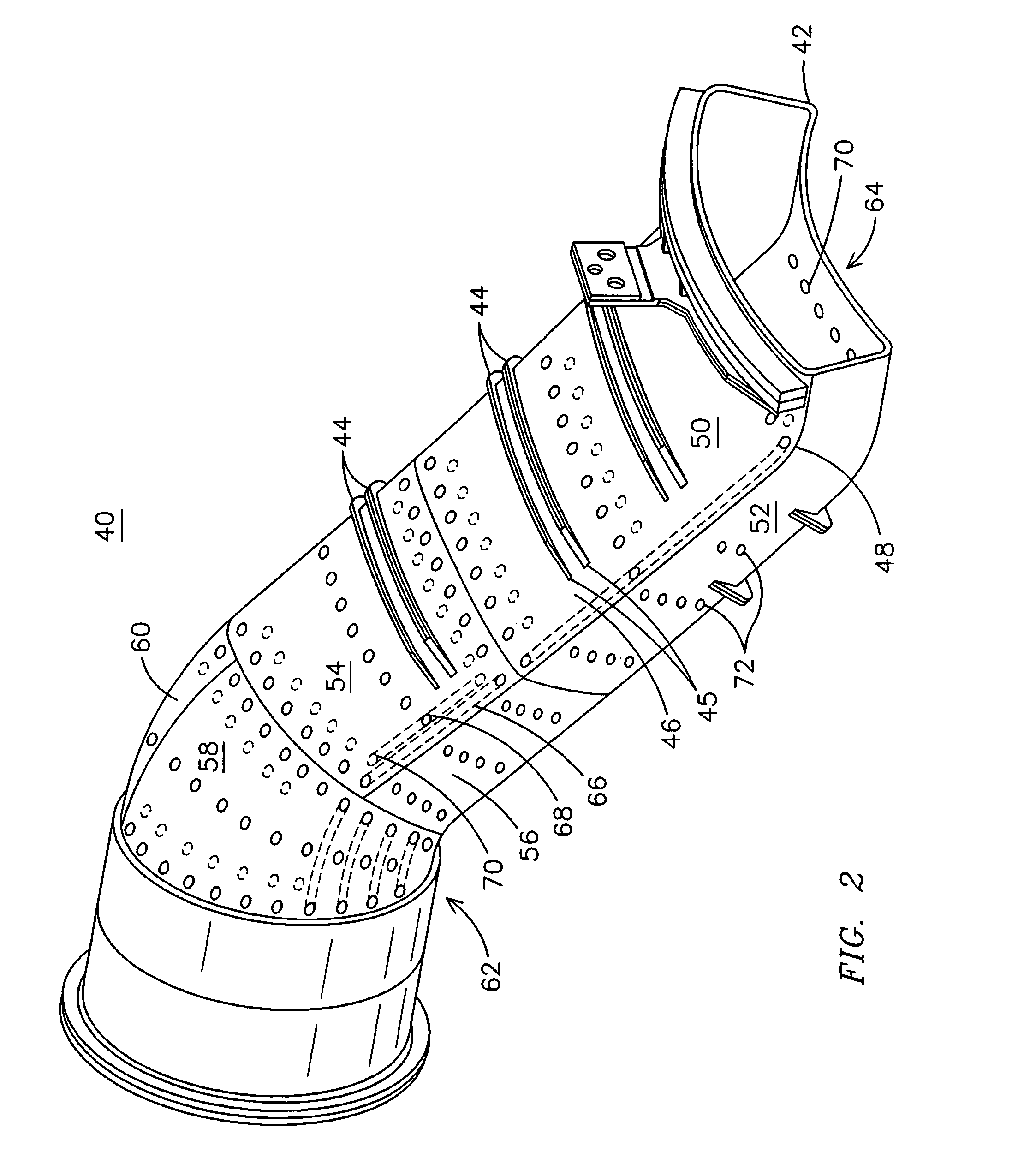
Cooled gas turbine transition duct
ActiveUS7310938B2Increase working temperatureSimple materialContinuous combustion chamberEngine fuctionsSurface coolingActive cooling
A transition duct (40) for a gas turbine engine (10) incorporating a combination of cooling structures that provide active cooling in selected regions of the duct while avoiding cooling of highly stressed regions of the duct. In one embodiment, a panel (74) formed as part of the transition duct includes some subsurface cooling holes (92) that extend under a central portion of a stiffening rib (90) attached to the panel and some subsurface cooling holes (94) that have a truncated length so as to avoid extending under a rib end (45). Effusion cooling holes (88) used to cool a side subpanel (48) of the panel may have a distribution that reduces to zero approaching a double bend region (48) of the panel. An upstream subpanel (76) of the panel may be actively cooled only when the panel is located on an extrados of the transition duct.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Low power, high density server and portable device for use with same
A high density server including a plurality of portable devices is disclosed. The portable devices may be arranged in drawers, which may be assembled into shelves for mounting within the high density server. The server rack of the high density server has a substantially open bottom and open top to permit passive airflow in and around the portable devices housed therein. Because of the configuration of the portable devices within the server, the computing power density is increased over a traditional server. Also, the design of the portable devices and their placement within the high density server minimizes the need for active cooling and in some embodiments removes the need for active cooling mechanisms altogether. The portable devices are encased in a protective coating that facilitates heat dissipation away from the portable device. The portable devices include components found in traditional servers.
Owner:ARNOUSE DIGITAL DEVICES
Apparatus for active cooling of an MRI patient bore in cylindrical MRI systems
InactiveUS7015692B2Increases patient comfortReduce heat loadElectromagnets without armaturesTransformers/inductances coolingActive coolingEngineering
The present invention provides for a cooling system for circulating a coolant to cool the patient bore. In one embodiment, that patient bore consists of two concentric cylinders separated by spacers running either longitudinally or helically. In another embodiment of the present invention, fluid may be passed either helically or longitudinally through tubes bonded to the outer diameter of the patient bore such that the parts of the bore that are exposed to the patient are directly cooled. In a third embodiment, the RF coil could form part of the patient bore, with the helical or longitudinal fluid channels surrounding the patient bore.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
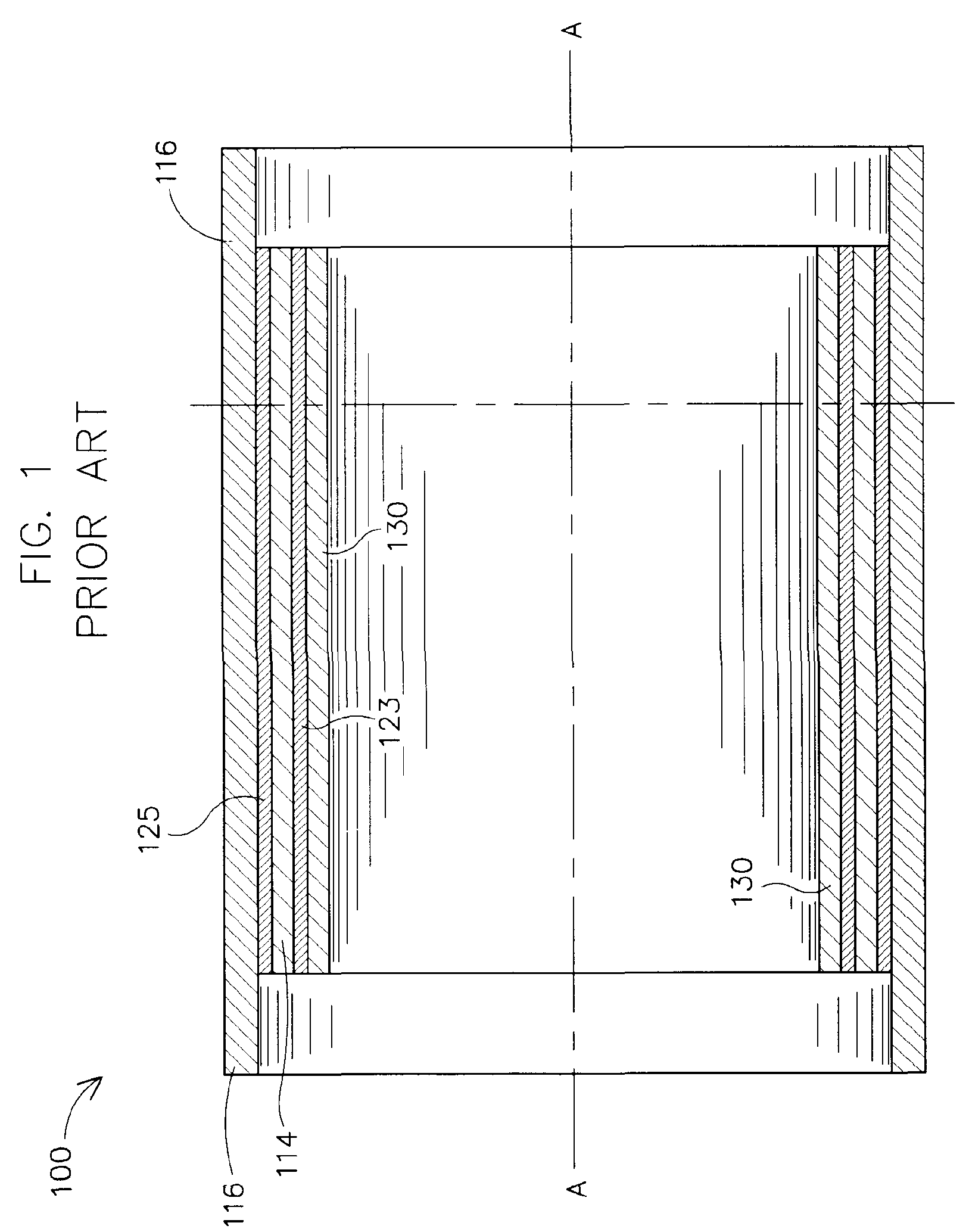
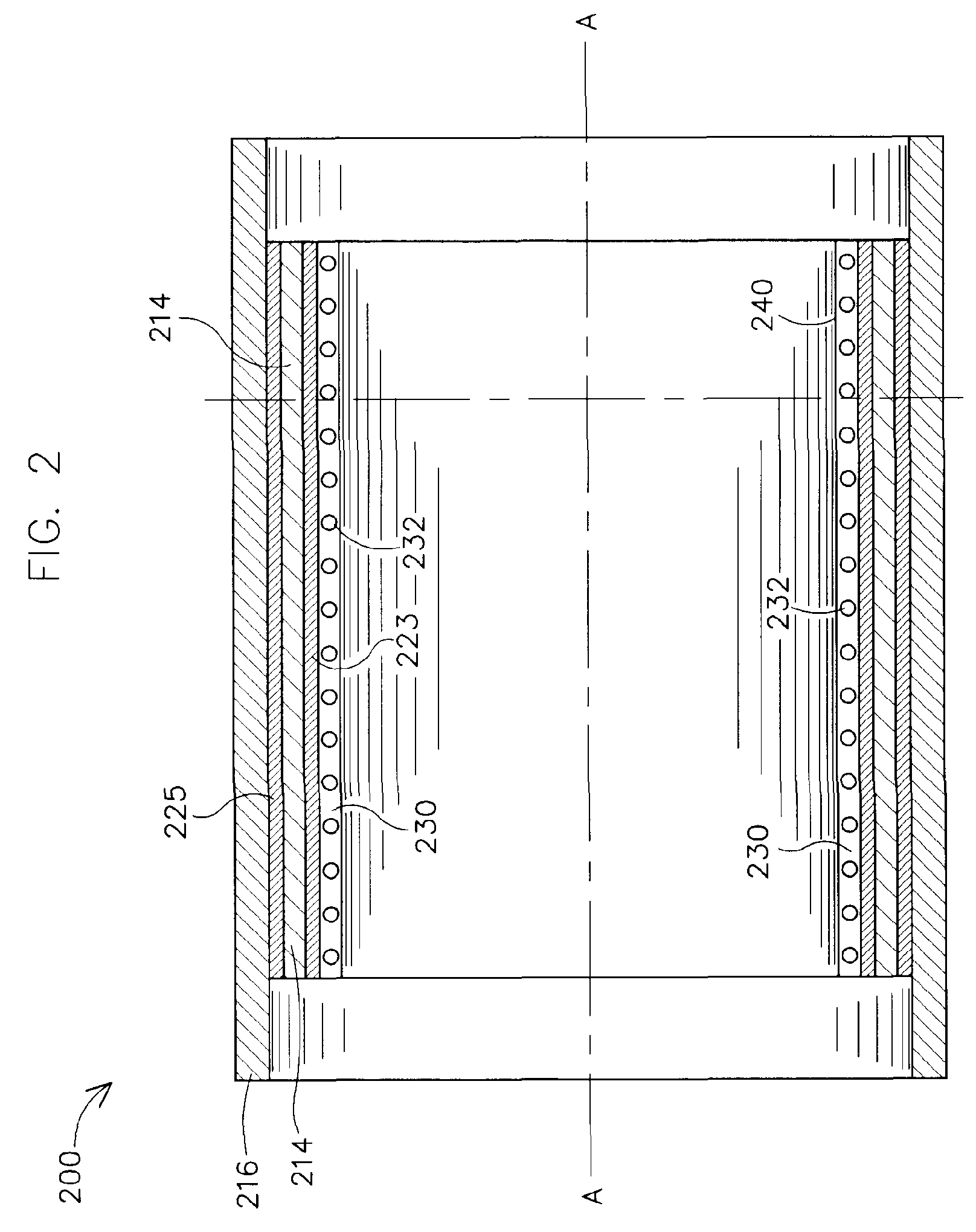
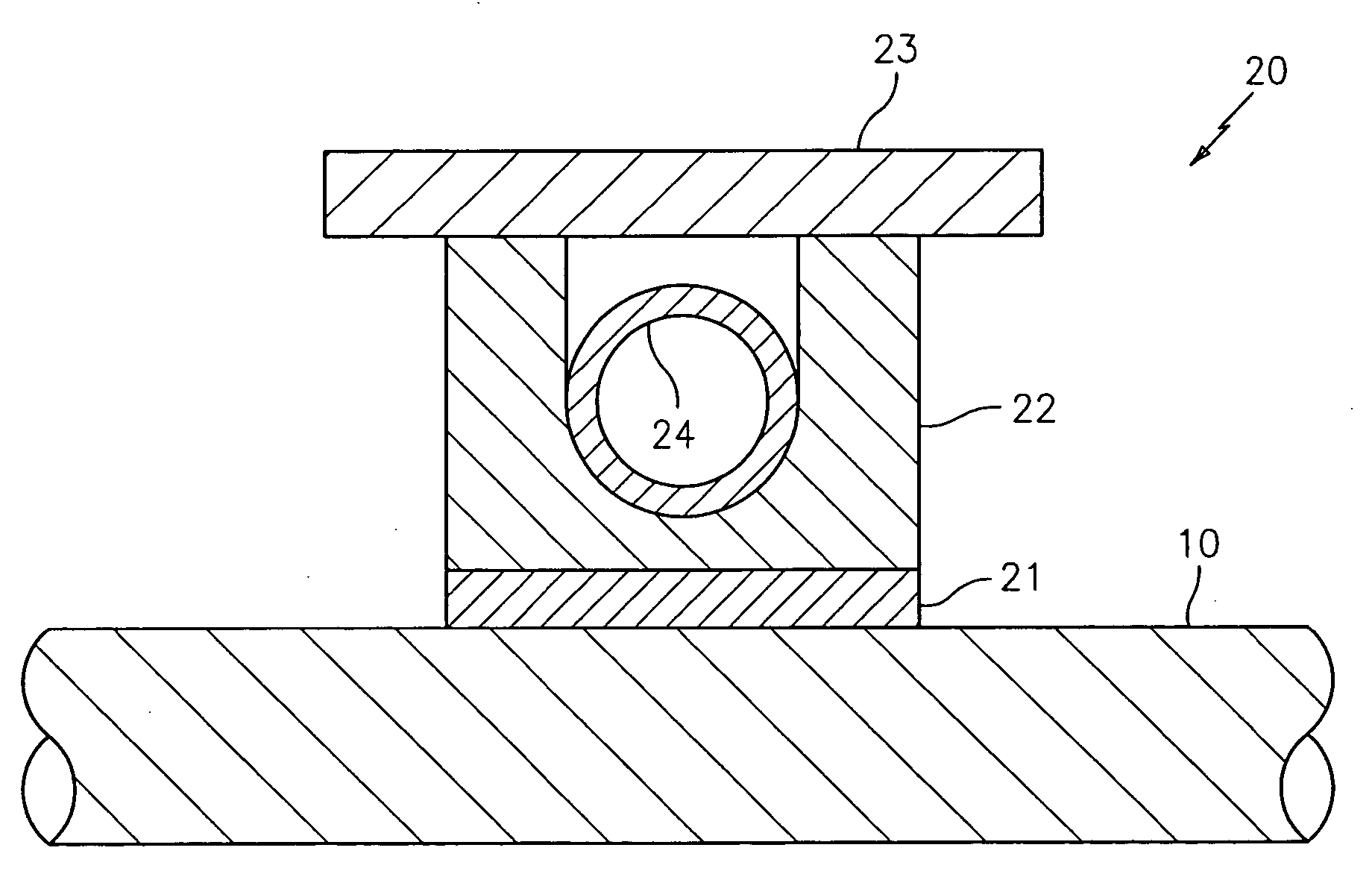
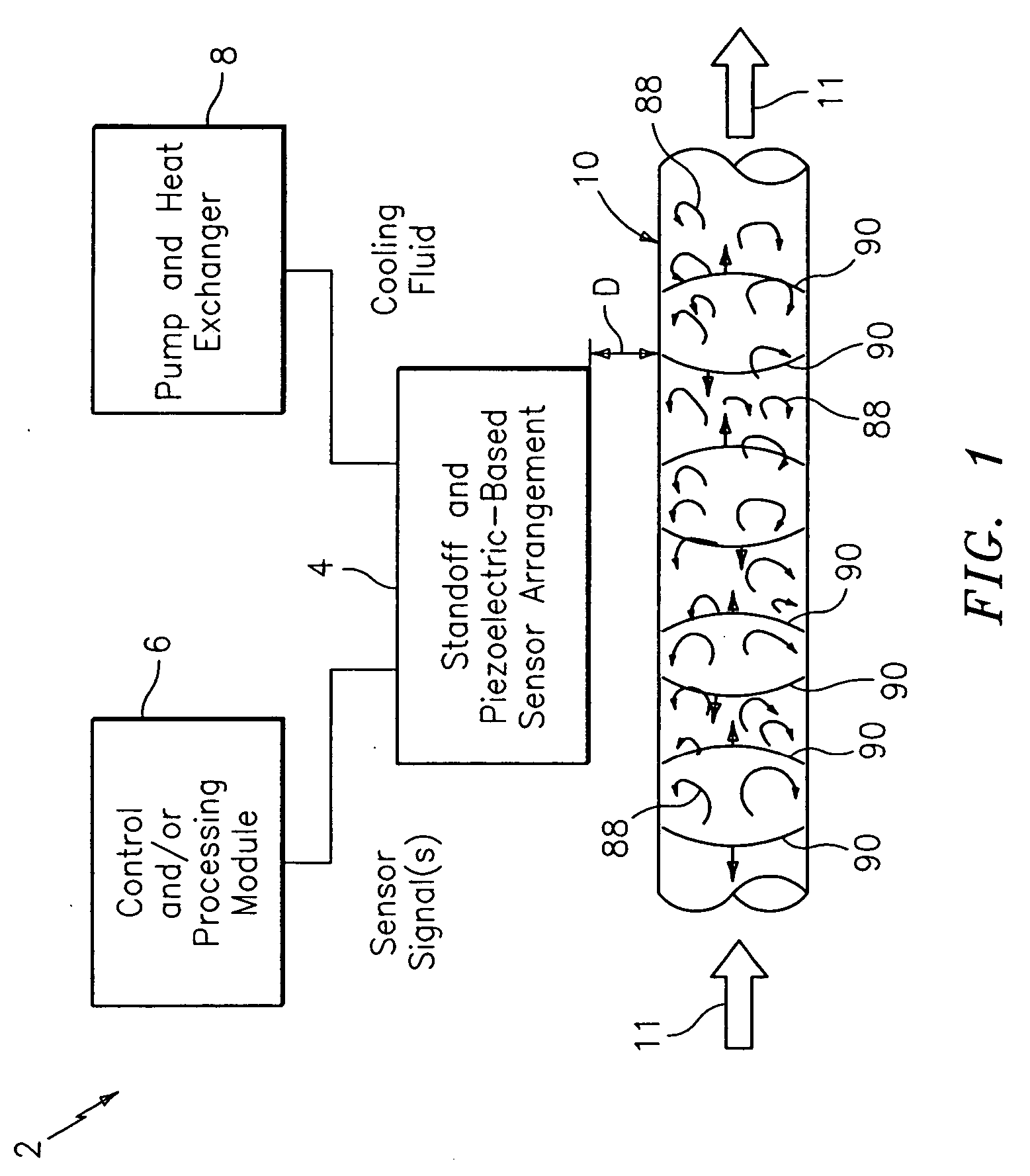
Method and apparatus for measuring a parameter of a high temperature fluid flowing within a pipe using an array of piezoelectric based flow sensors
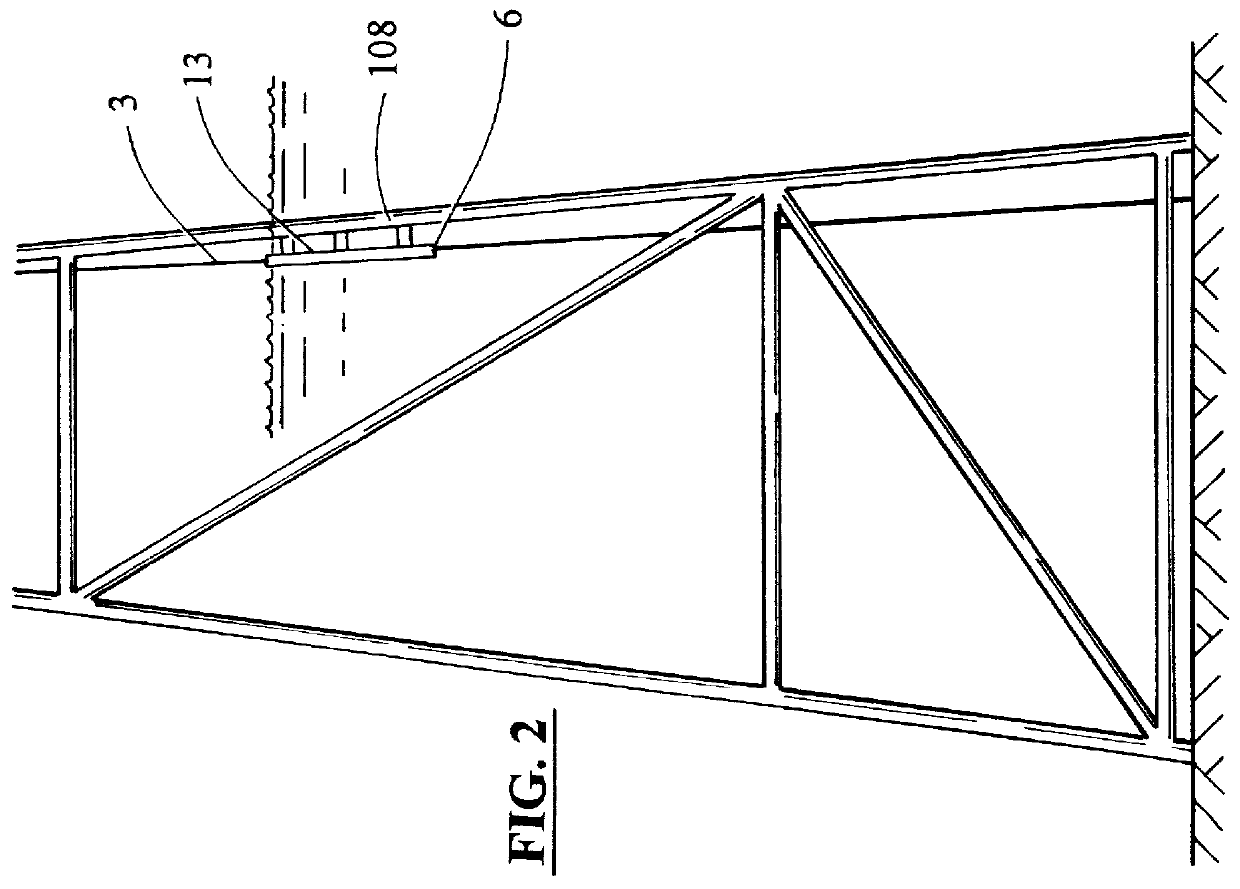
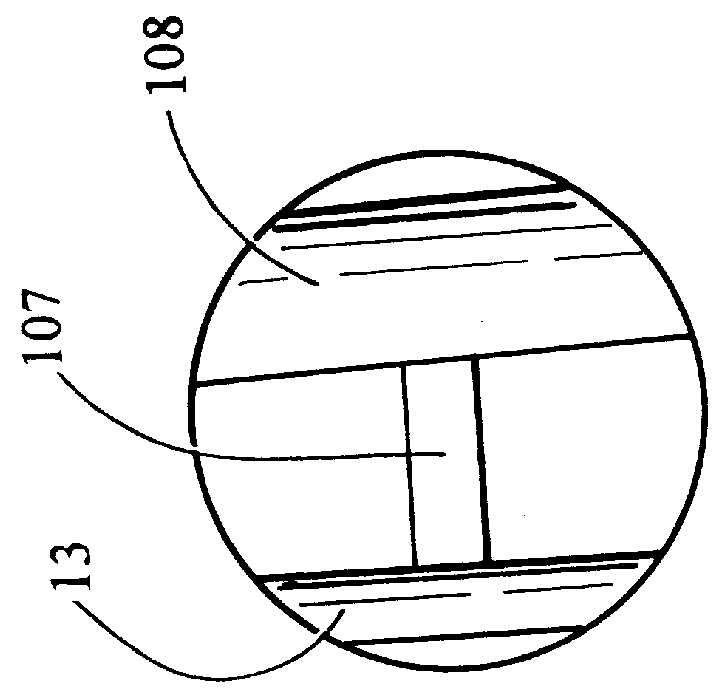
ActiveUS20050044966A1Sufficient mechanical couplingMinimizing introductionVolume/mass flow measurementSensor arrayElectricity
A method, apparatus and system are provided to measure the process flow of a fluid or medium traveling in a pipe. The system and apparatus feature a standoff and piezoelectric-based sensor arrangement having a plurality of standoffs arranged on a pipe and a plurality of sensor bands, each arranged on a respective plurality of standoffs, each having at least one sensor made of piezoelectric material arranged thereon to detect unsteady pressure disturbances in the process flow in the pipe which in turn can be converted to the velocity of and / or speed of sound propagating within the pipe, and a cooling tube arranged in relation to the plurality of standoffs for actively cooling the sensor band; and further comprise a processing module for converting one or more sensor signals into a measurement containing information about the flow of the fluid or medium traveling in the pipe, as well as a pump and heat exchanger for processing the cooling fluid flowing through the cooling tube. The processing includes maintaining the cooling fluid at a desired operating temperature.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
Water-Cooled LED Lighting System for Indoor Farming
ActiveUS20170146226A1High intensity lightReducing and eliminating heat loadElongate light sourcesClimate change adaptationActive coolingEffect light
A lighting system for indoor farming for delivering high intensity light while reducing or eliminating heat loads in a growing environment is provided. The lighting system comprises a lighting housing having a first end, a second end, a first side, a second side opposite the first side, a third side between the first side and the second side, and a fourth side opposite the third side. A first LED board is mounted to the first side and a second LED board is mounted to the second side. A first shroud covers the first LED board and a second shroud covers the second LED board. A coolant passage is formed completely through the lighting housing. A coolant liquid is receivable through the coolant passage. The coolant liquid provides active cooling, of the lighting housing from heat created by the first and second LED boards.
Owner:MJNN LLC
Passive, thermocycling column heat-exchanger system
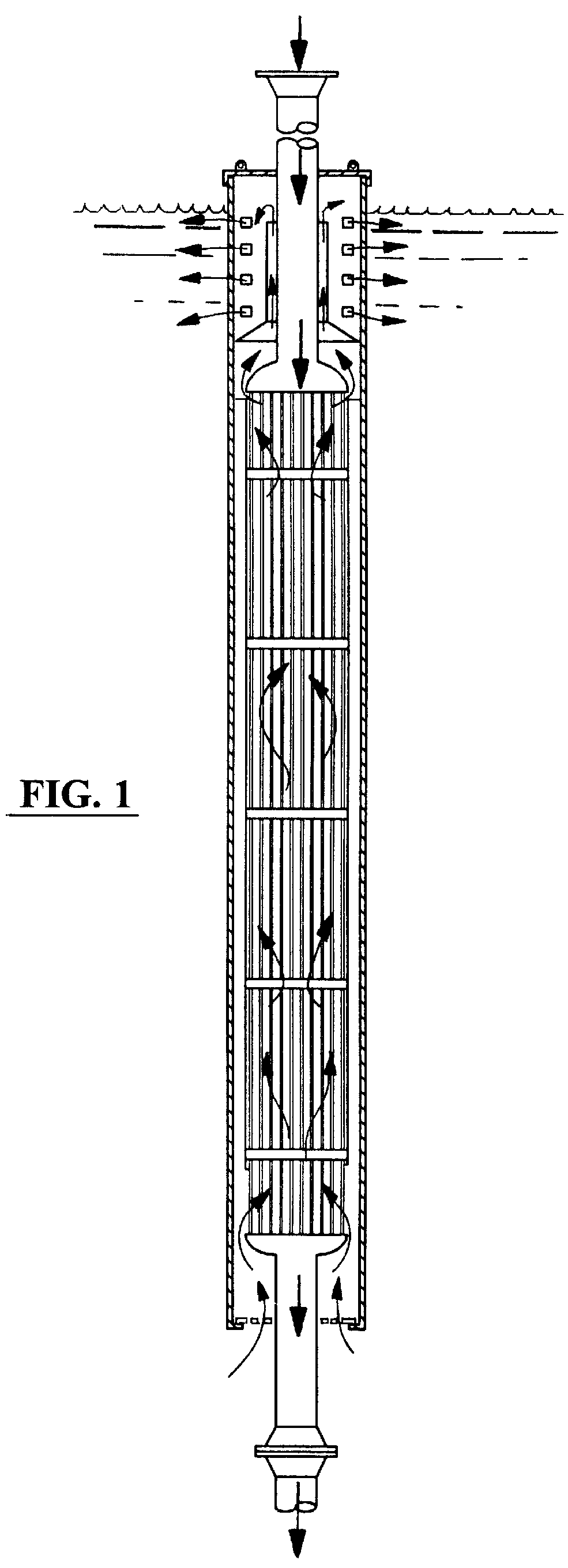
InactiveUS6142215AImprove permeabilityEasy maintenanceOther heat production devicesAir heatersActive coolingTitanium
A heat exchanger system suitable for facilitating the economical cooling of hot fluids in the vicinity of a body of water. The preferred embodiment of the present invention contemplates a vertical, or combination vertical and horizontal thermosyphonic, passive, heat exchanger column situated in a body of water and enveloped by a caisson or the like, and configured to facilitate, through percolation, enhanced circulation of seawater therethrough and effecting significant cooling of a hot, hydrocarbon well stream, or other hot fluid in the vicinity of a body of water. A vertically situated bundle of tubes forms the heat exchanger, which may include a system of staggered baffles to direct the flow of cooling seawater to effect even temperature distribution throughout the tube bundle. The present system further teaches a system for cooling high pressure, hot fluids as may be found in a deep hydrocarbon reserve offshore, utilizing a the vertical heat exchange column of the present invention. Upon passing through the system, a gaseous fluid stream, significantly cooled, should experience a commensurate pressure reduction and allow the use of conventional pipeline materials. The present system dispenses with the necessity of providing expensive, pro-active cooling, generally expending significant fuel, or the necessity of constructing an expensive, high pressure, non-corrosive pipeline of, for example, titanium or the like.
Owner:EDG
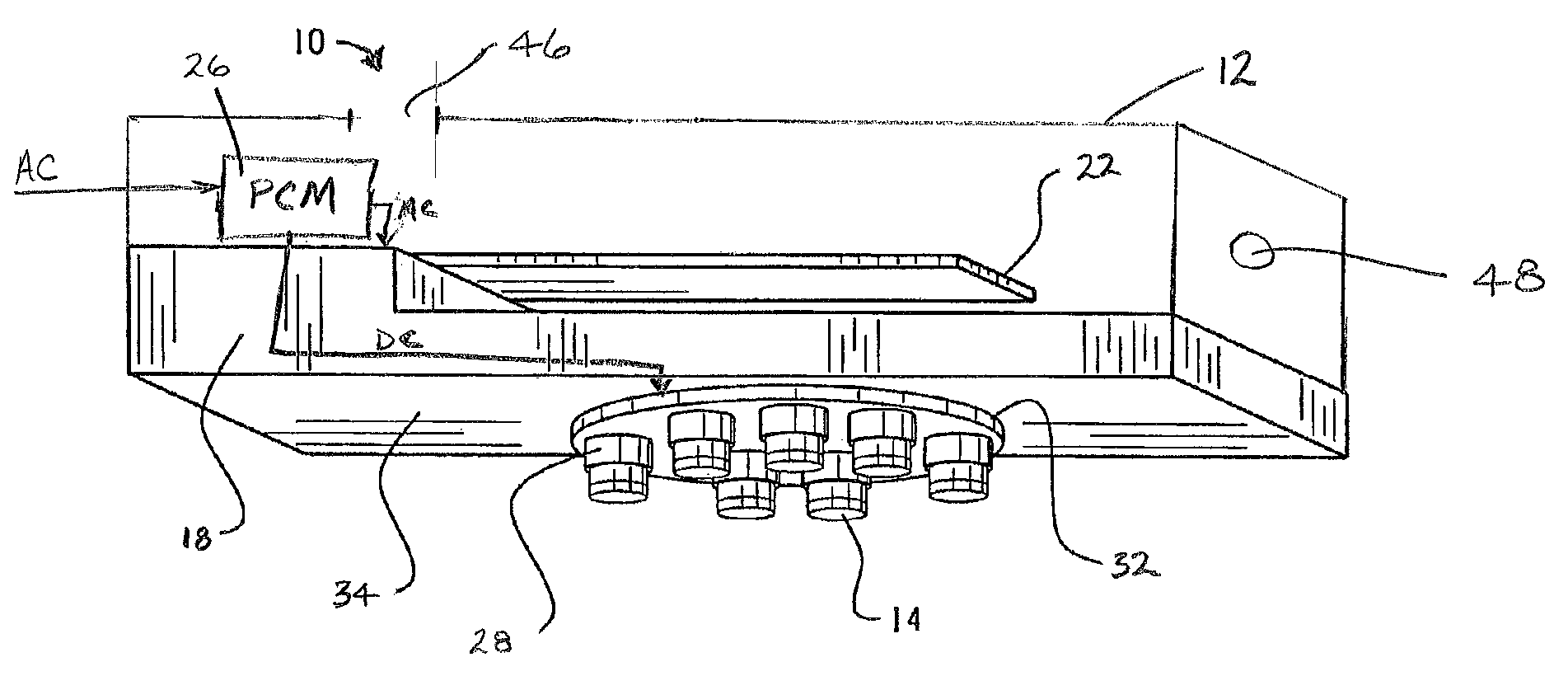
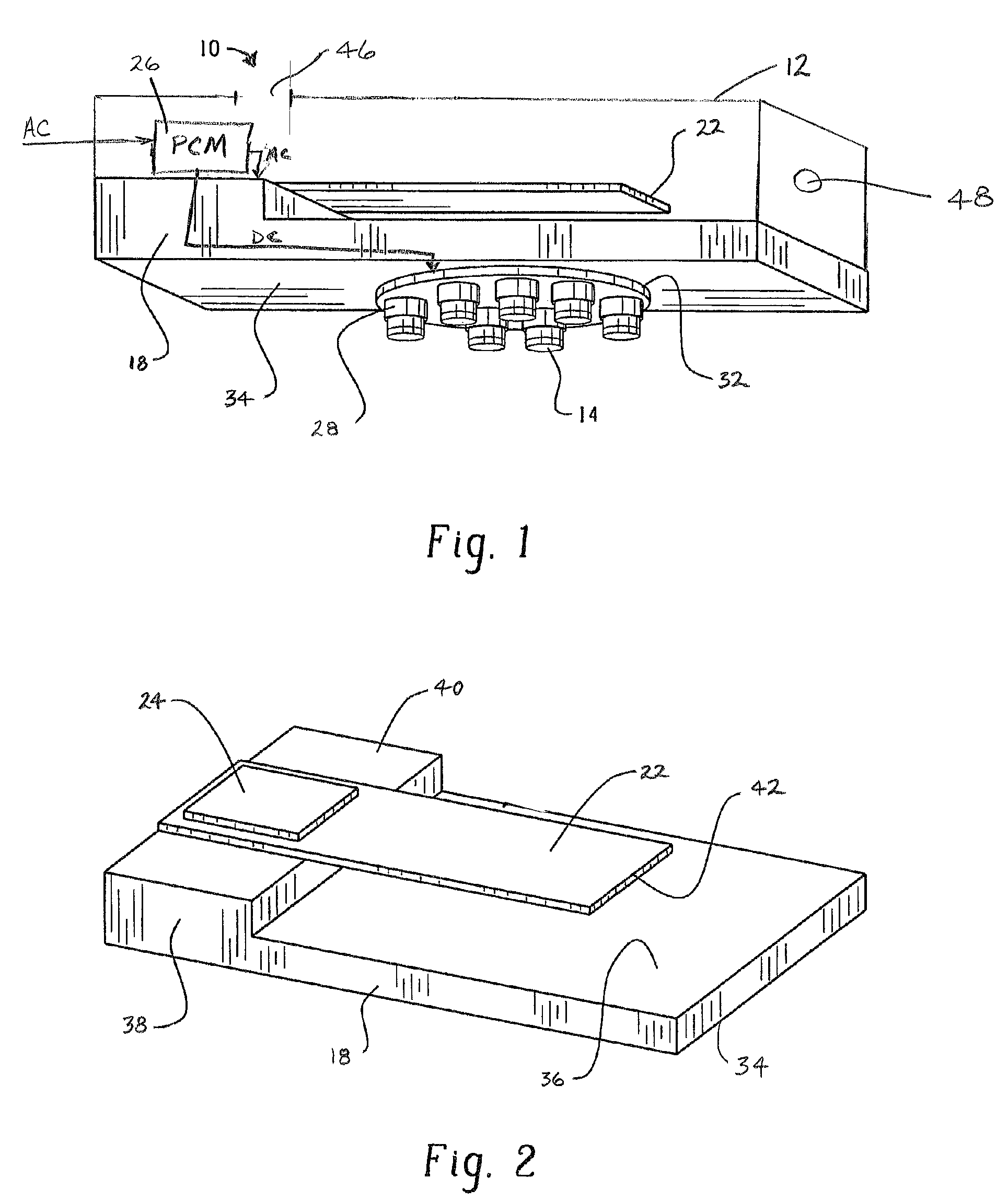
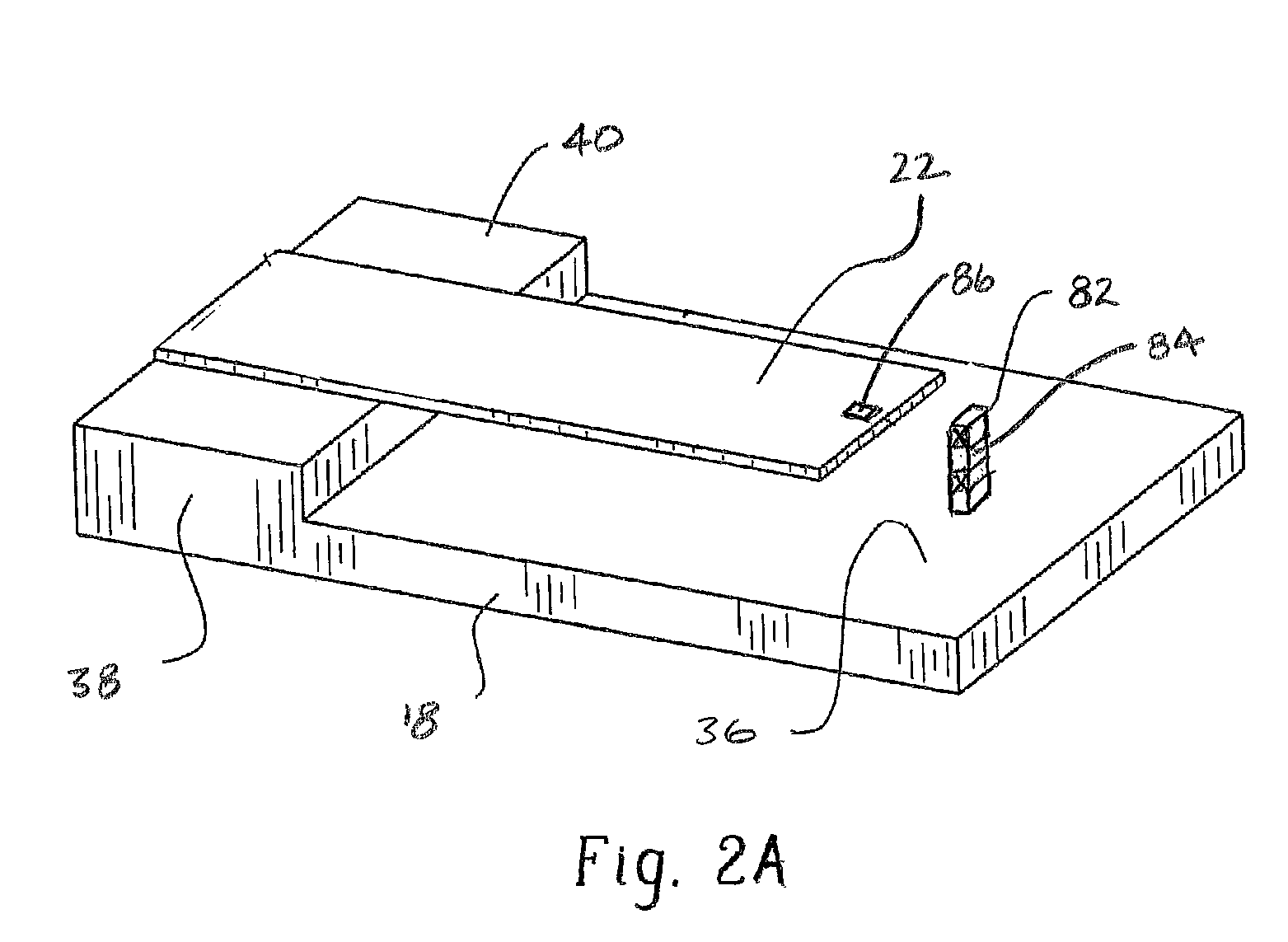
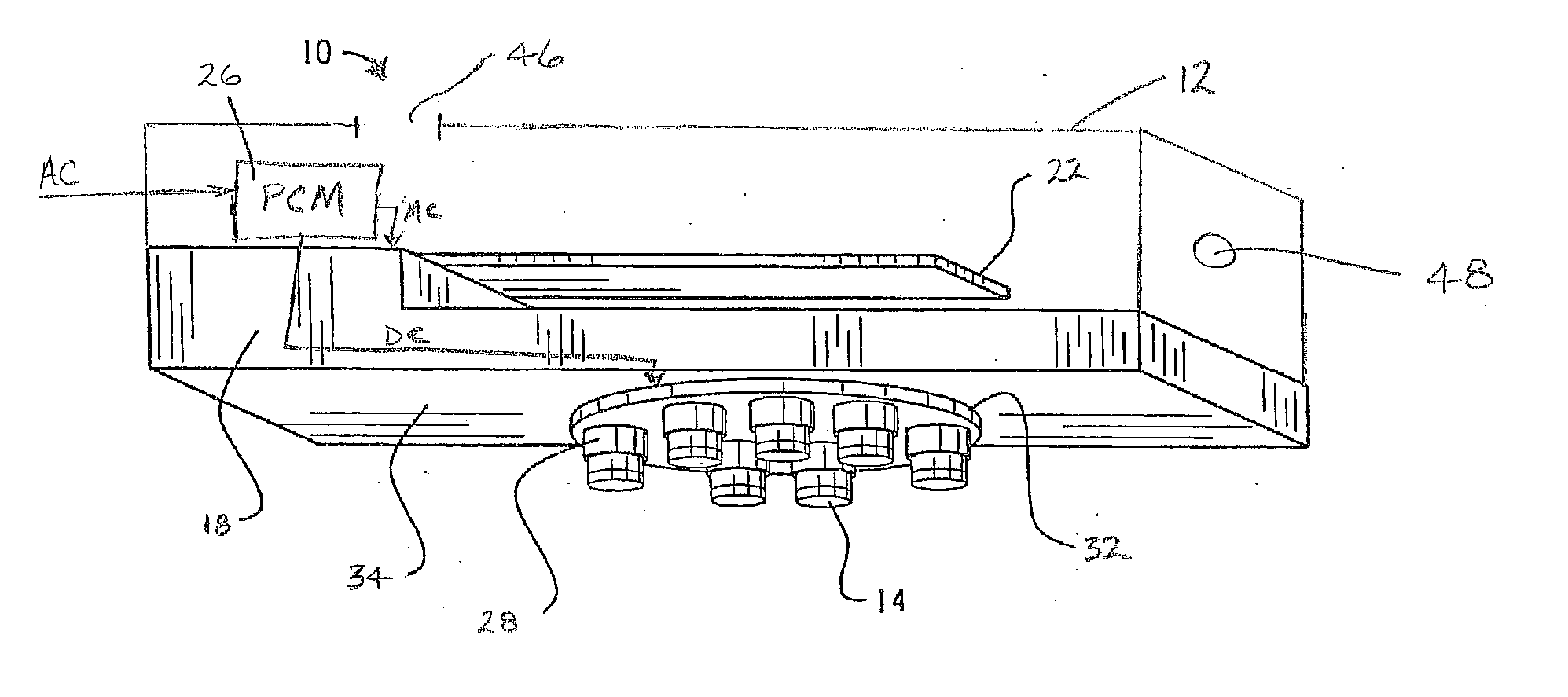
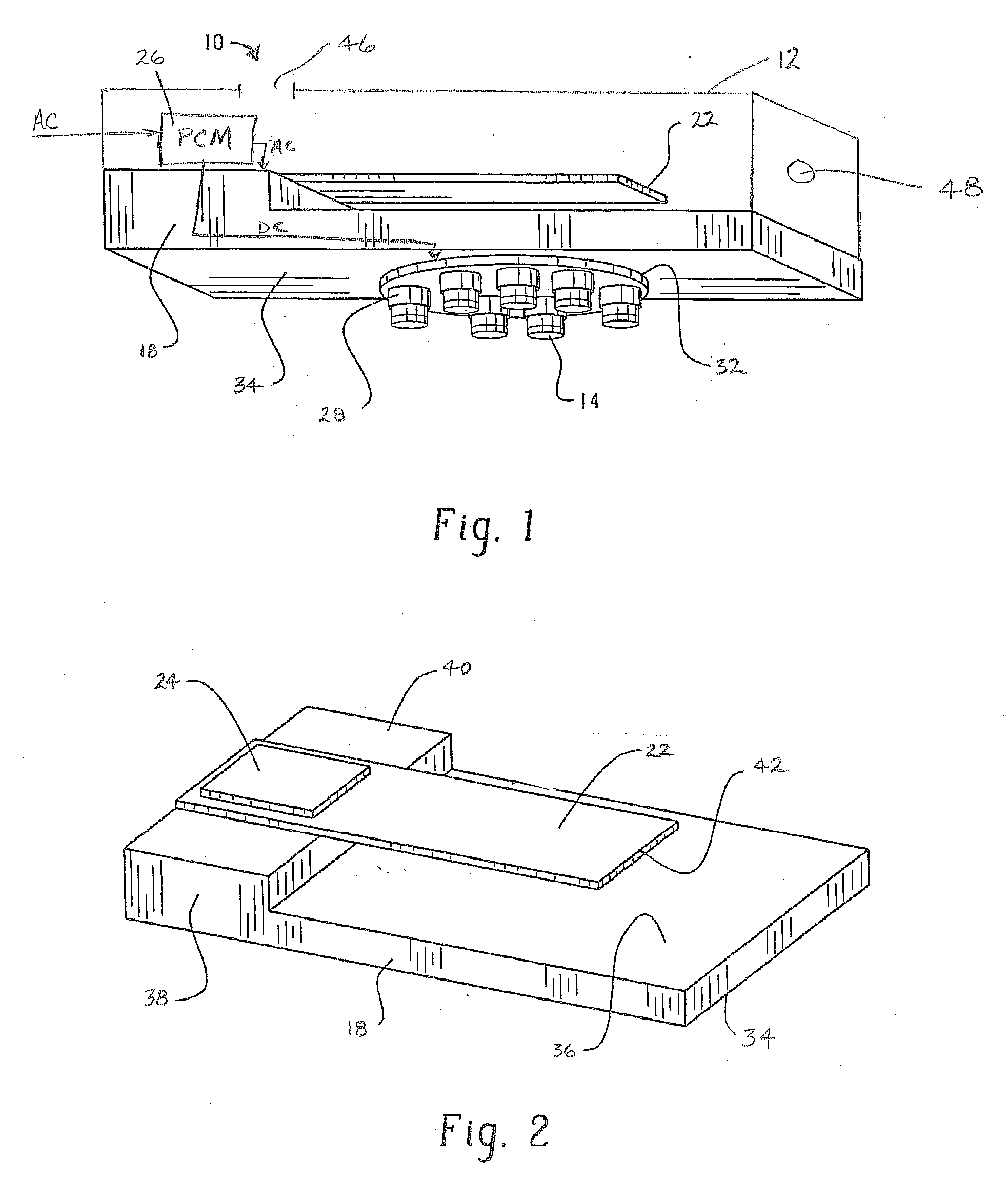
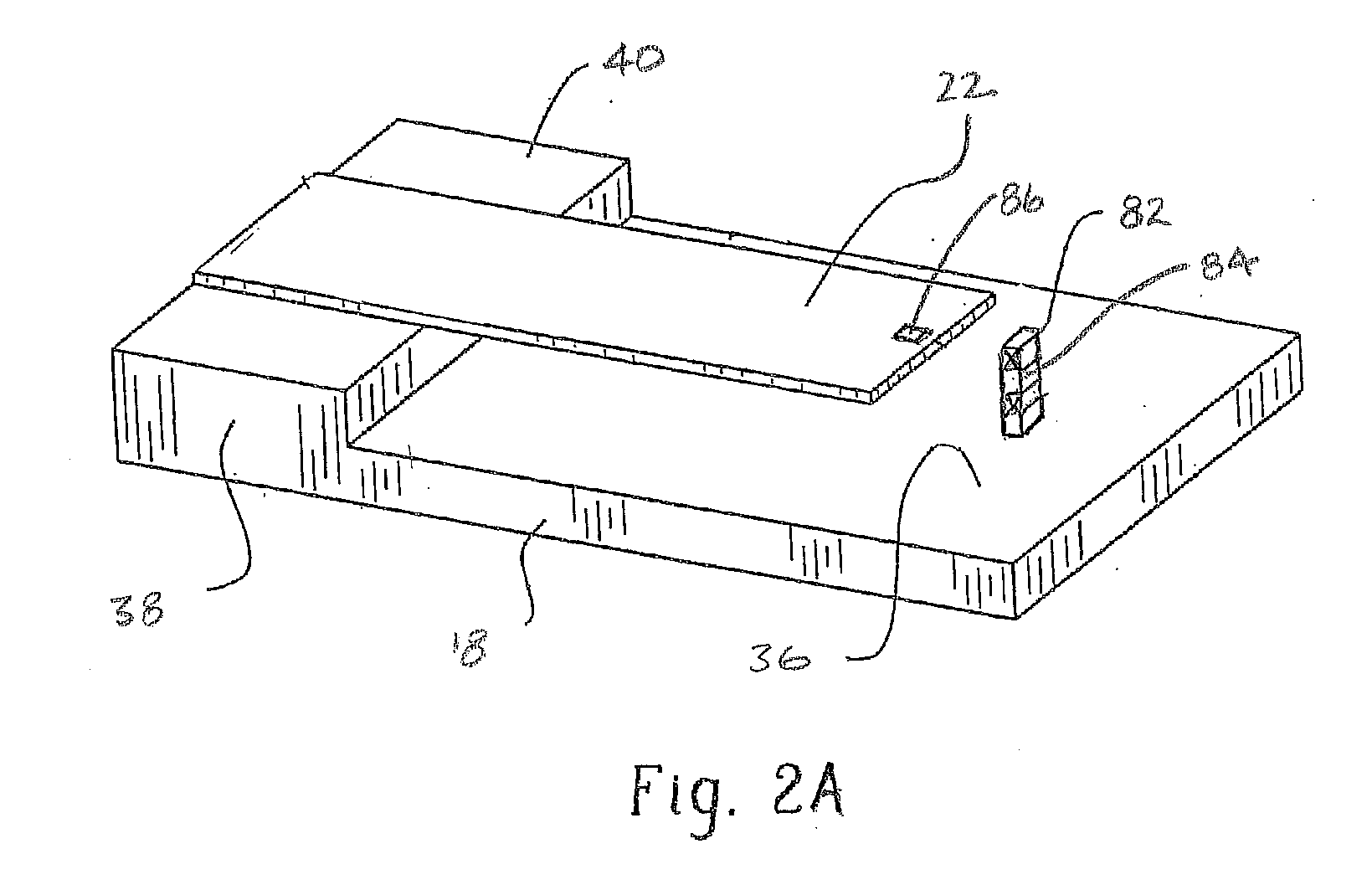
Active and passive cooling for an energy storage module
InactiveUS20140158340A1Protecting/adjusting hybrid/EDL capacitorElectrolytic capacitorsControl systemCoolant flow
The present disclosure relates to cooling an energy storage module using passive and active cooling techniques. Passive cooling is provided by storing heat in a phase change material that is contact with the energy storage cells of the energy storage module. Active cooling is provided by circulating coolant through coolant passages that are in thermal contact with the energy storage cells. A control system for determining the temperature of the energy storage module and controlling coolant flow when the temperature reaches a predetermined threshold is disclosed.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com