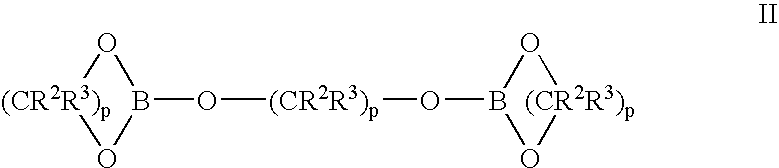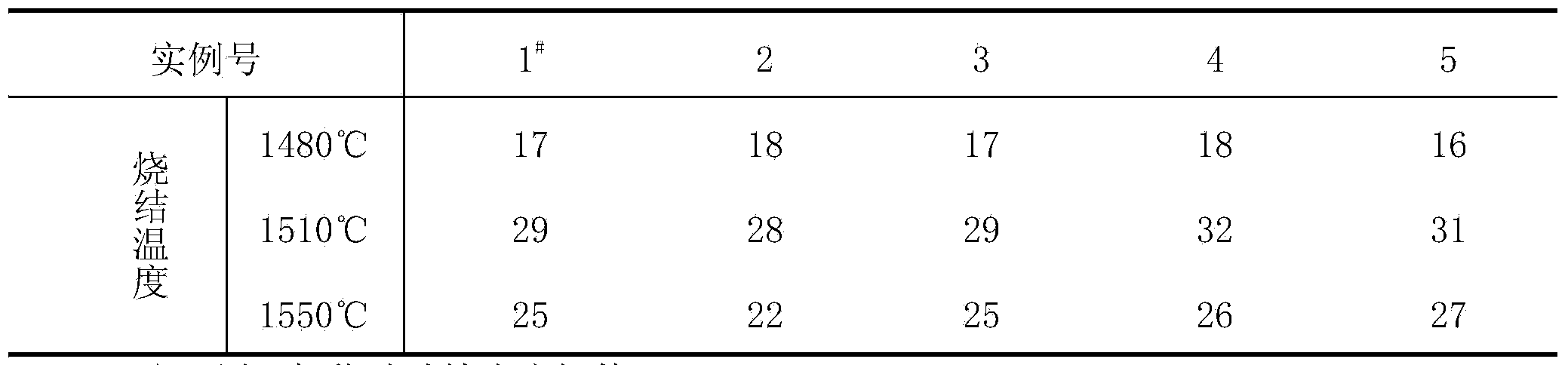Patents
Literature
45 results about "Decaborane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
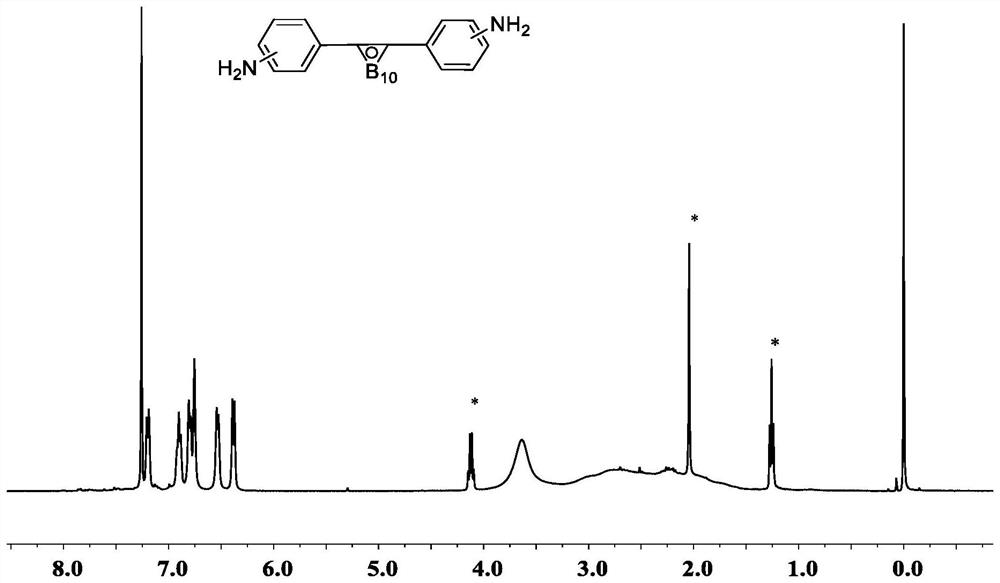
Decaborane, also called decaborane(14), is the borane with the chemical formula B₁₀H₁₄. This white crystalline compound is one of the principal boron hydride clusters, both as a reference structure and as a precursor to other boron hydrides. It is toxic and volatile, with a foul smelling odor.
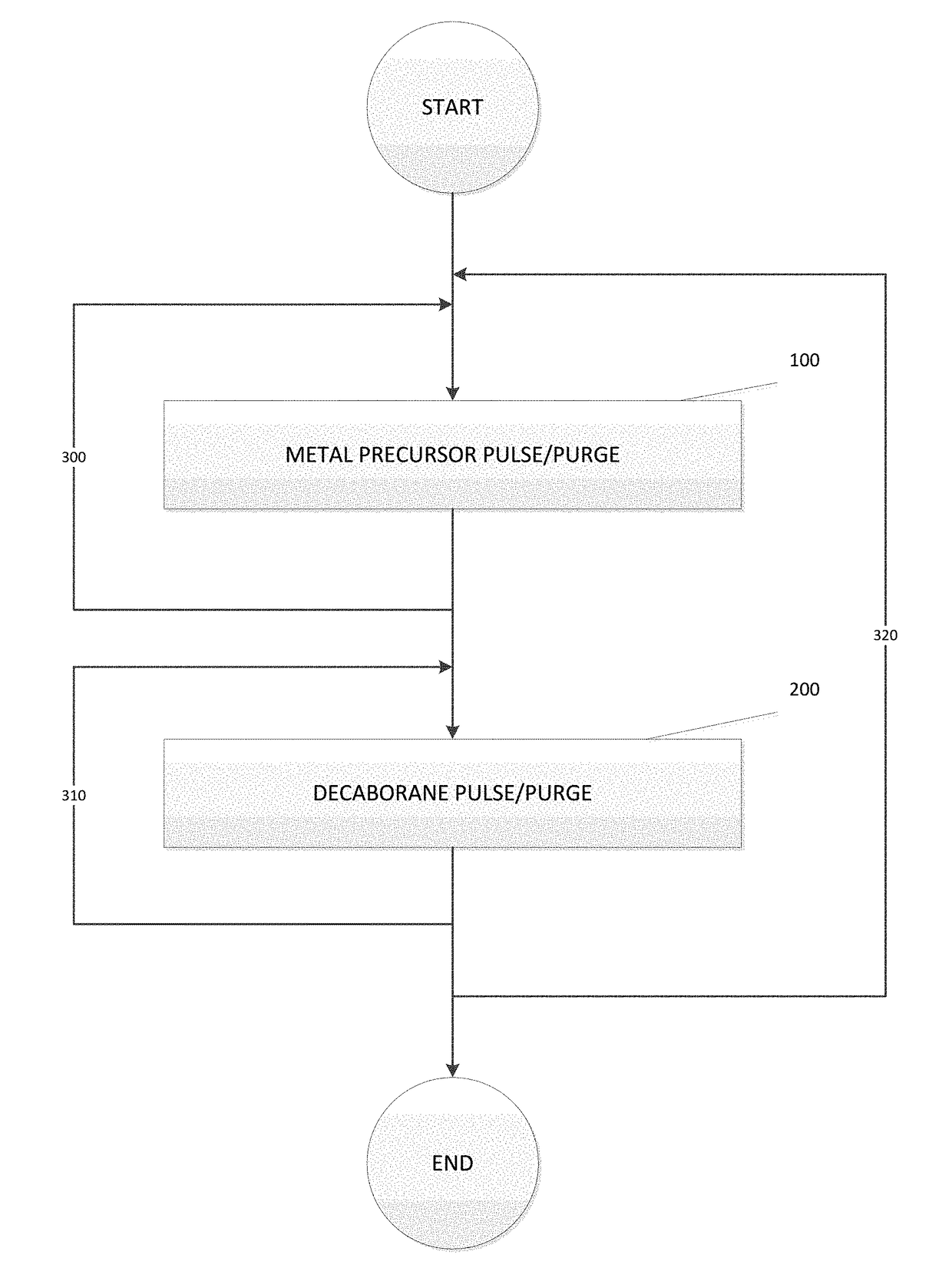
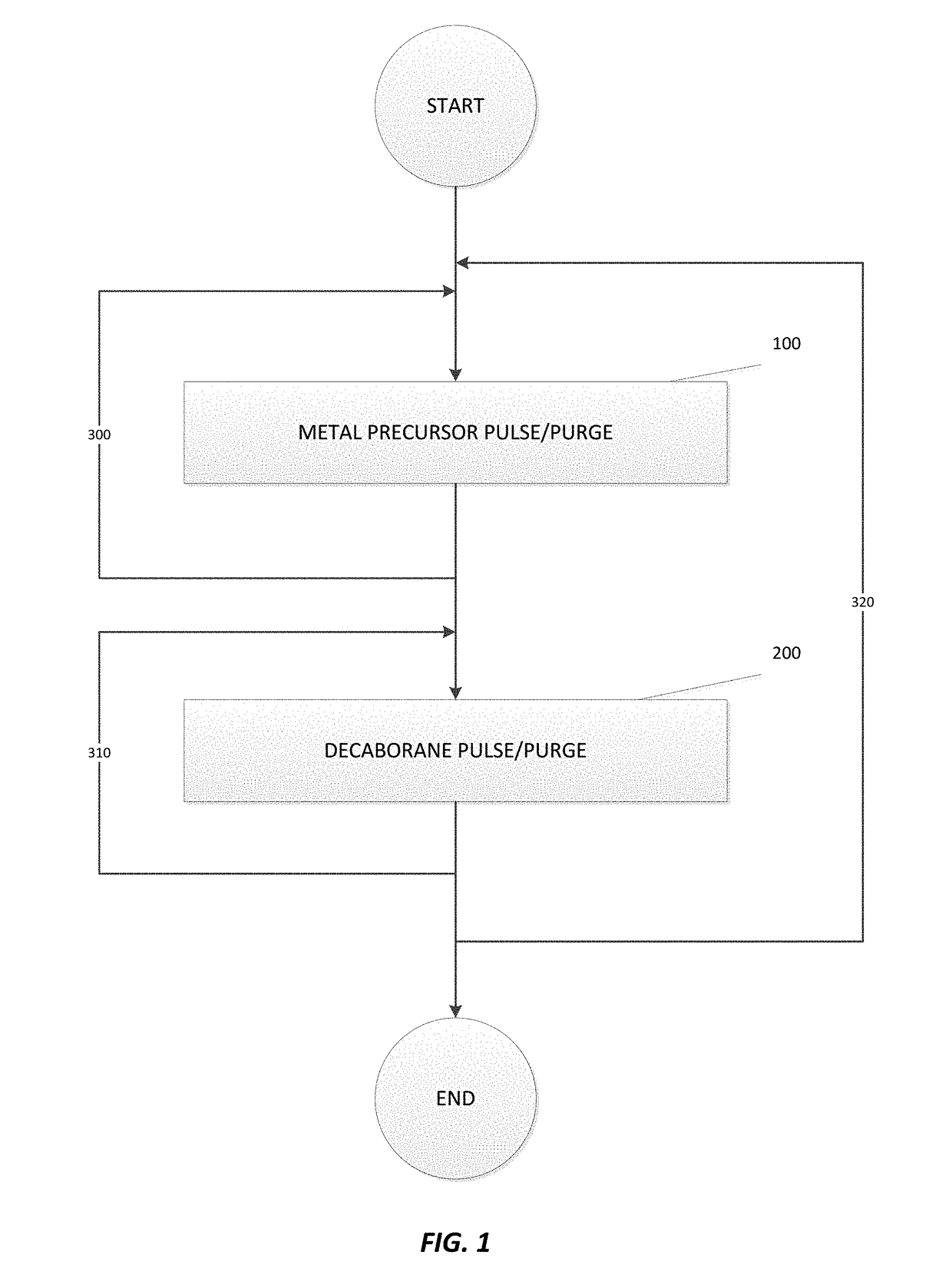
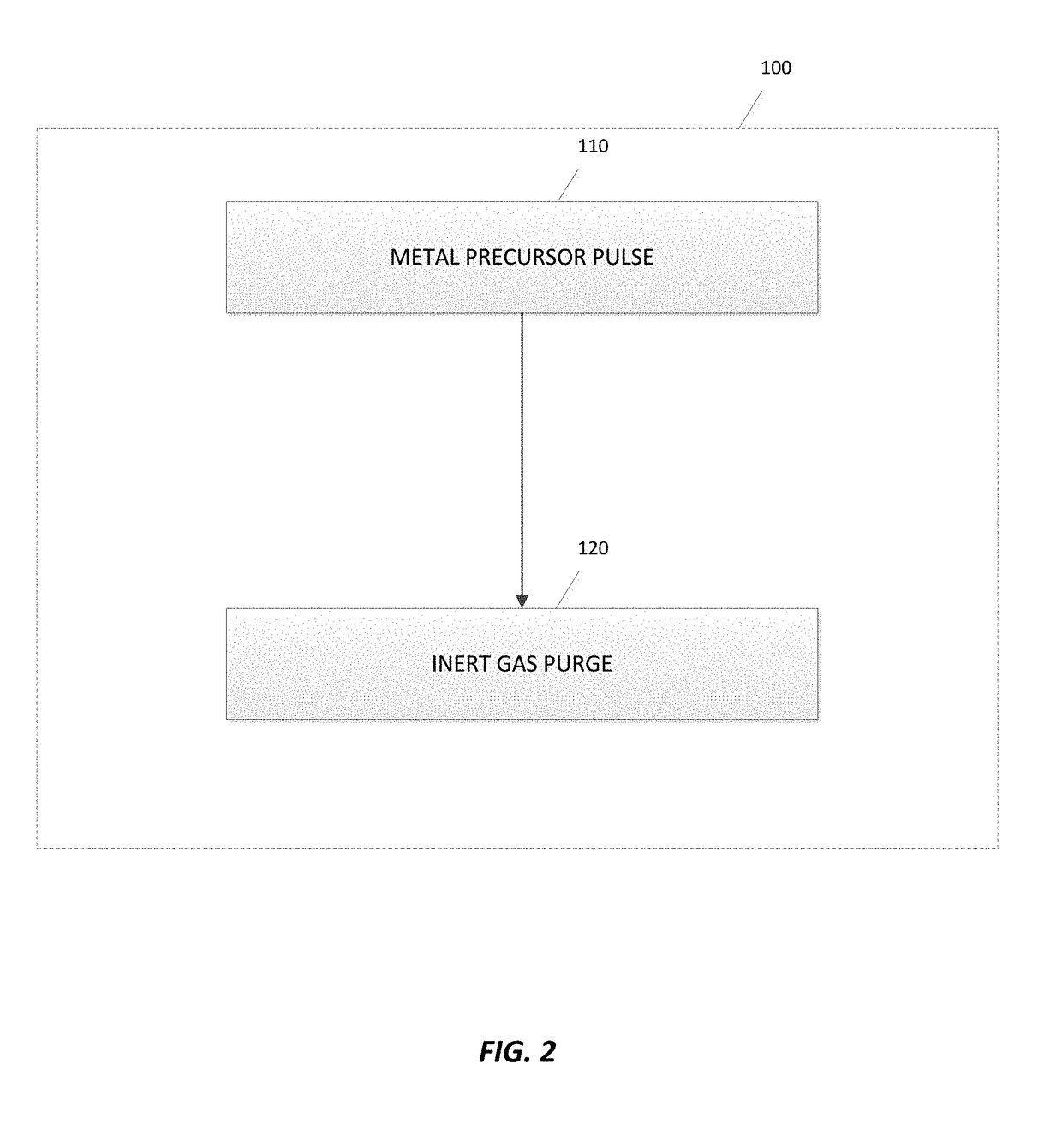
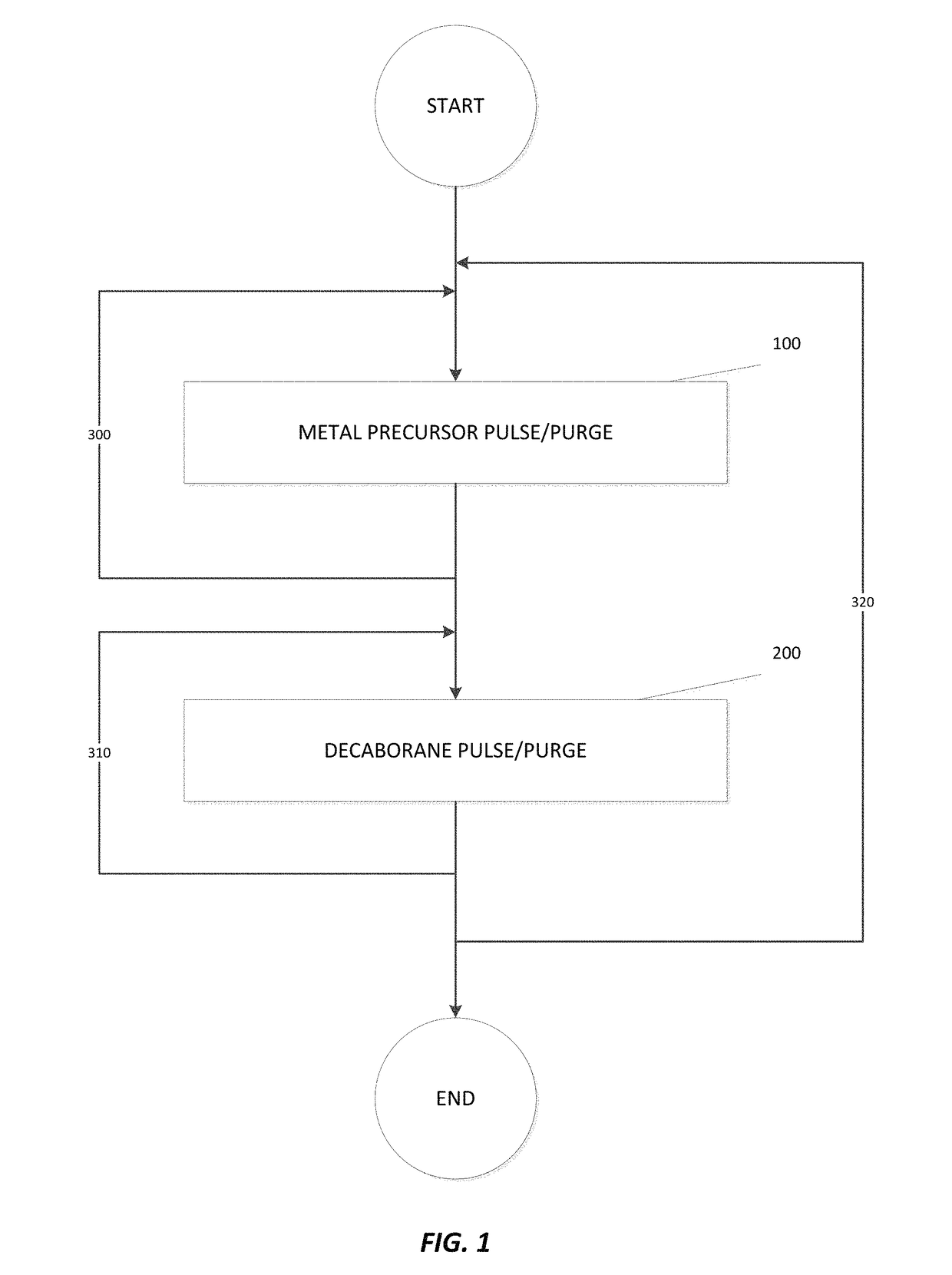
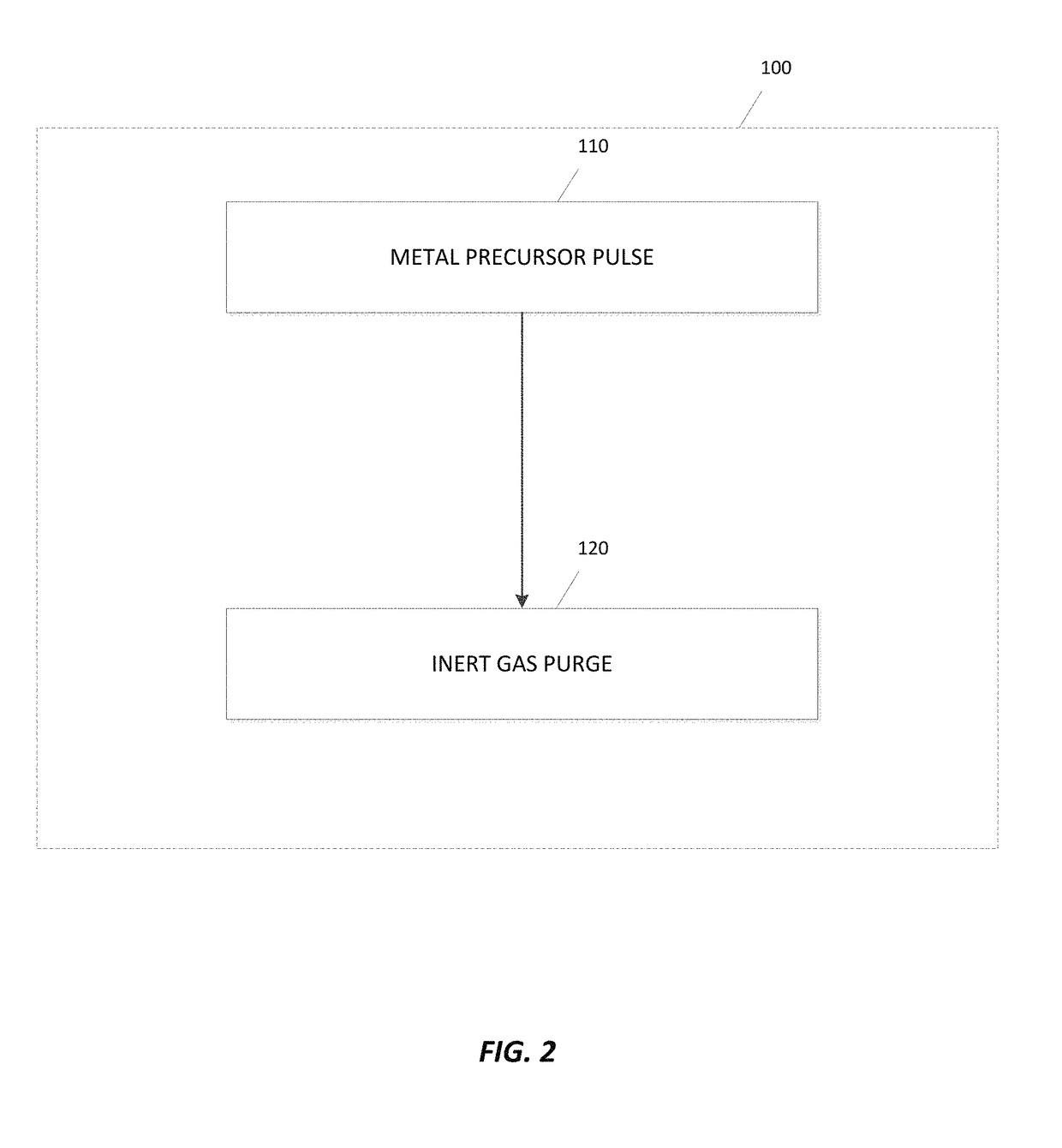
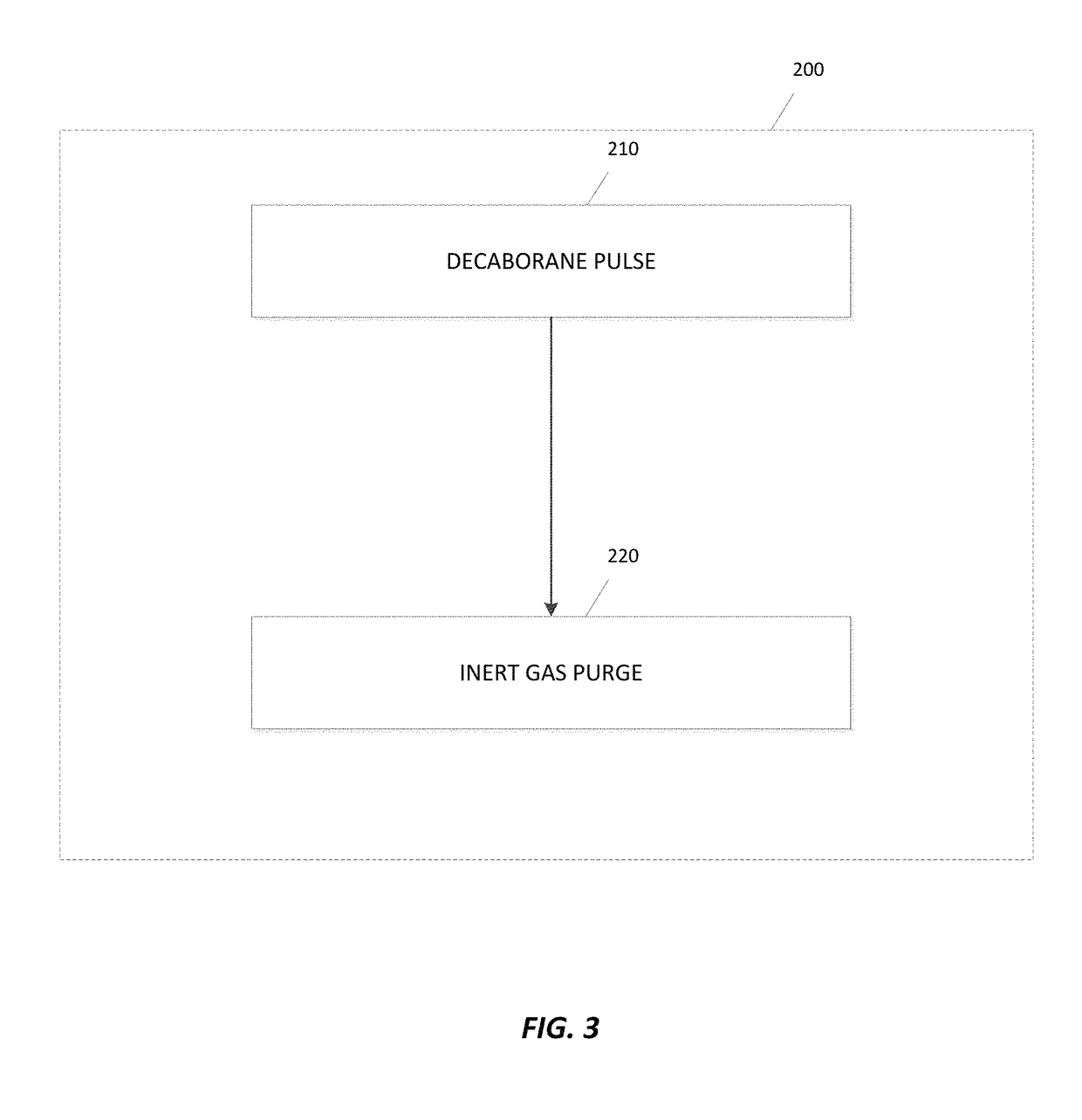
Deposition of metal borides
ActiveUS20170306480A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingMetal halidesMaterials science
A method for depositing a metal film onto a substrate is disclosed. In particular, the method comprises pulsing a metal halide precursor onto the substrate and pulsing a decaborane precursor onto the substrate. A reaction between the metal halide precursor and the decaborane precursor forms a metal film, specifically a metal boride.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Deposition of metal borides
ActiveUS10190213B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingMetal halidesMaterials science
A method for depositing a metal film onto a substrate is disclosed. In particular, the method comprises pulsing a metal halide precursor onto the substrate and pulsing a decaborane precursor onto the substrate. A reaction between the metal halide precursor and the decaborane precursor forms a metal film, specifically a metal boride.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
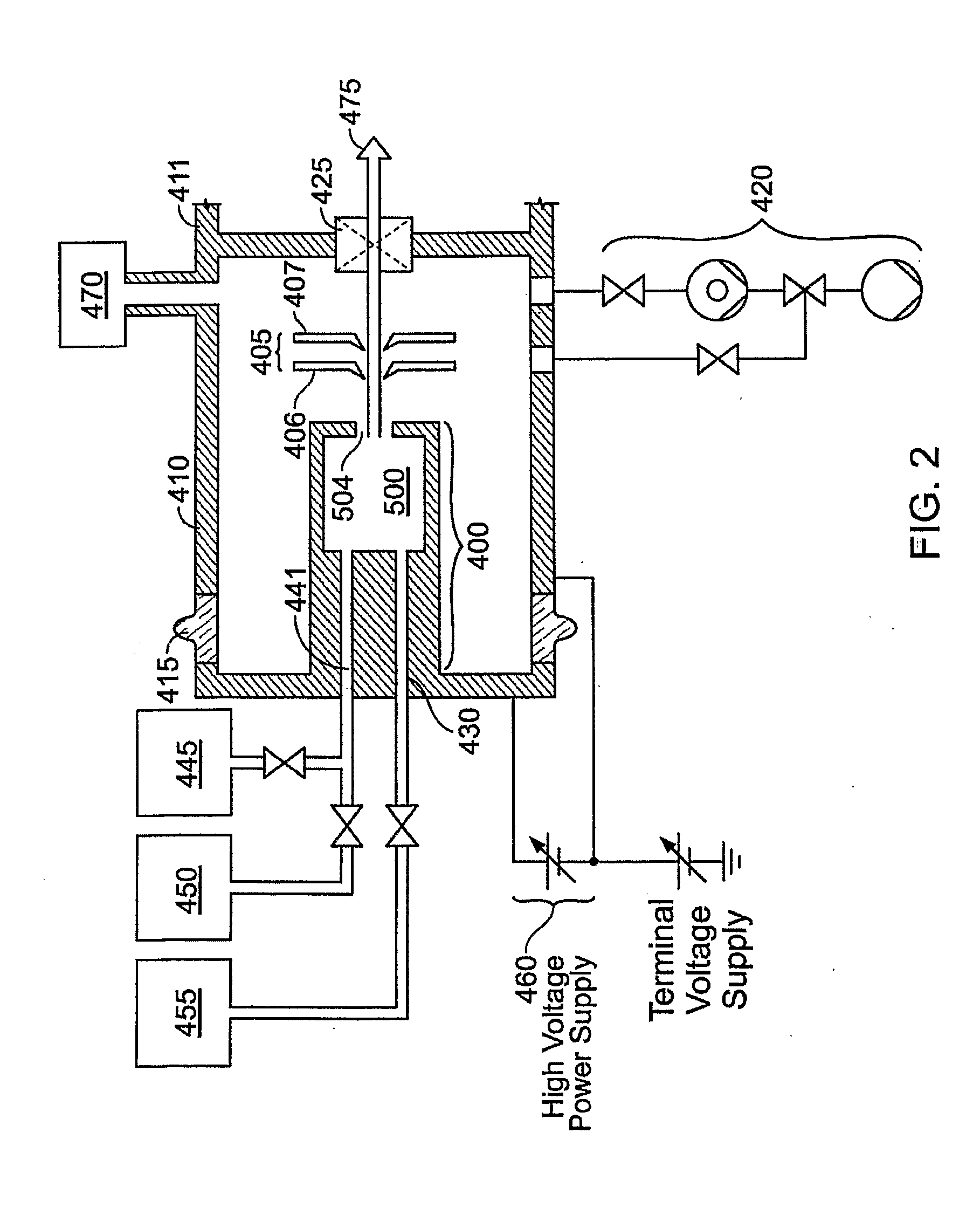
Method and apparatus for extracting ions from an ion source for use in ion implantation
InactiveUS20060272775A1Avoid unstable operationMaintain dimensional stabilityVacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRemote plasmaActive cooling
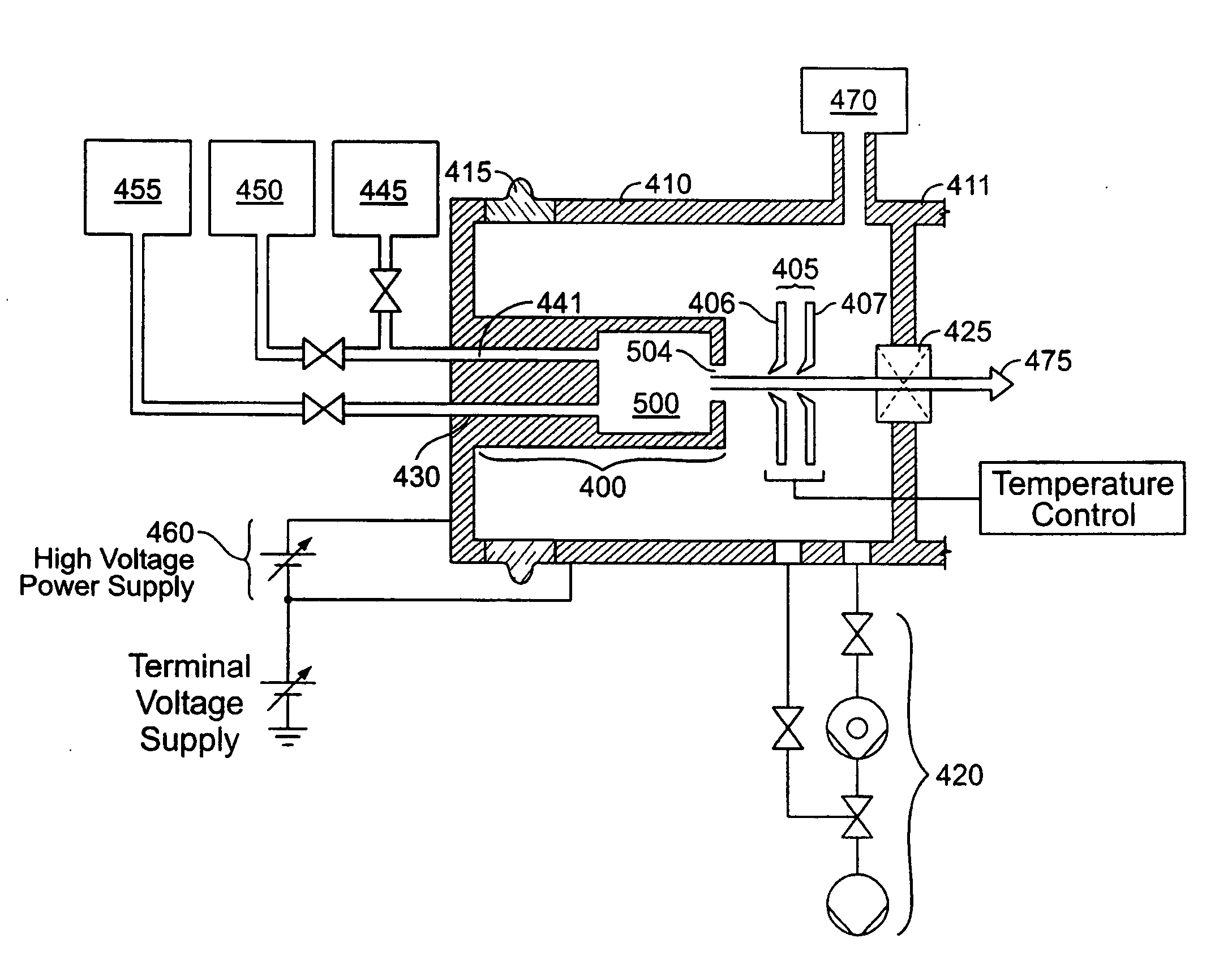
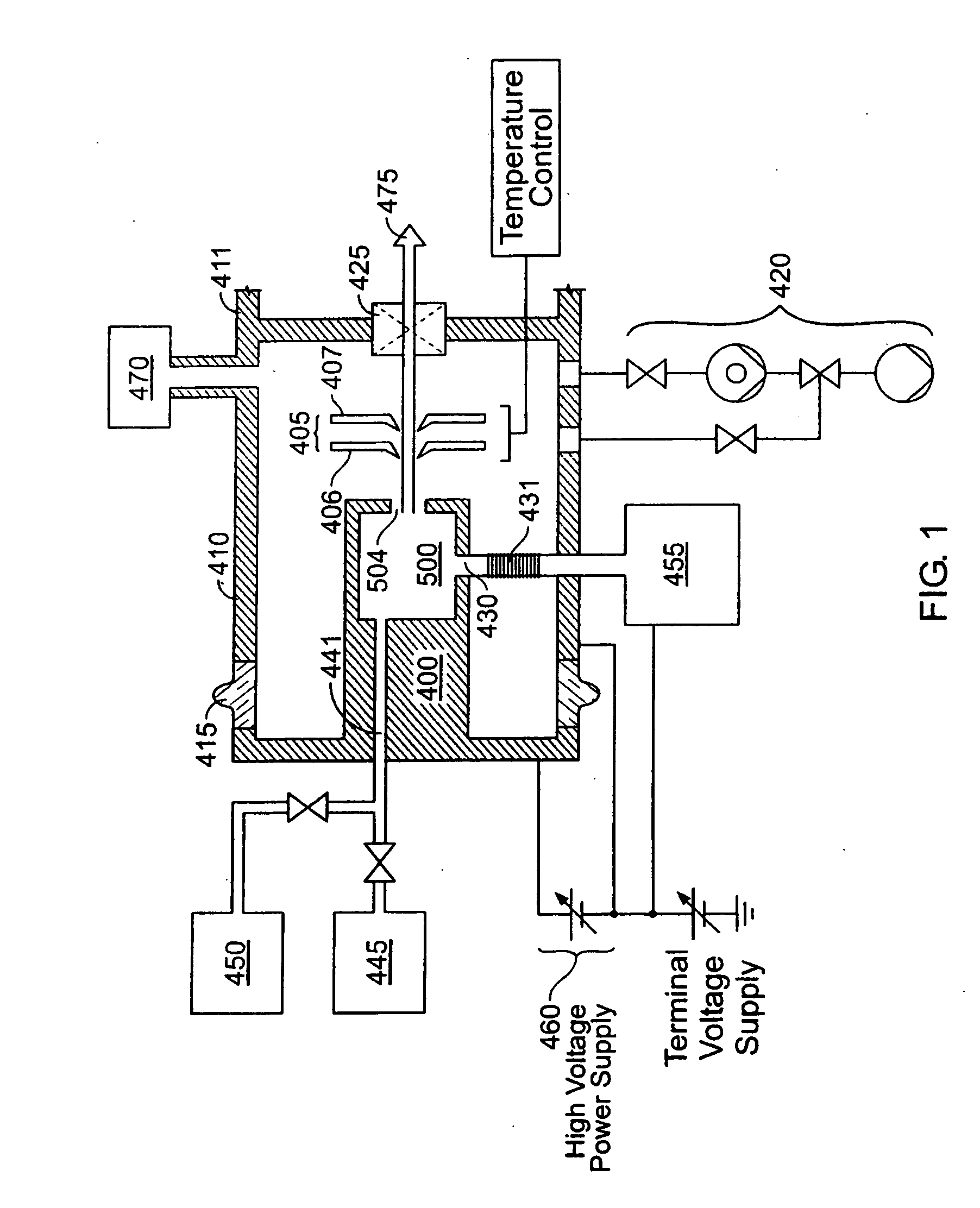
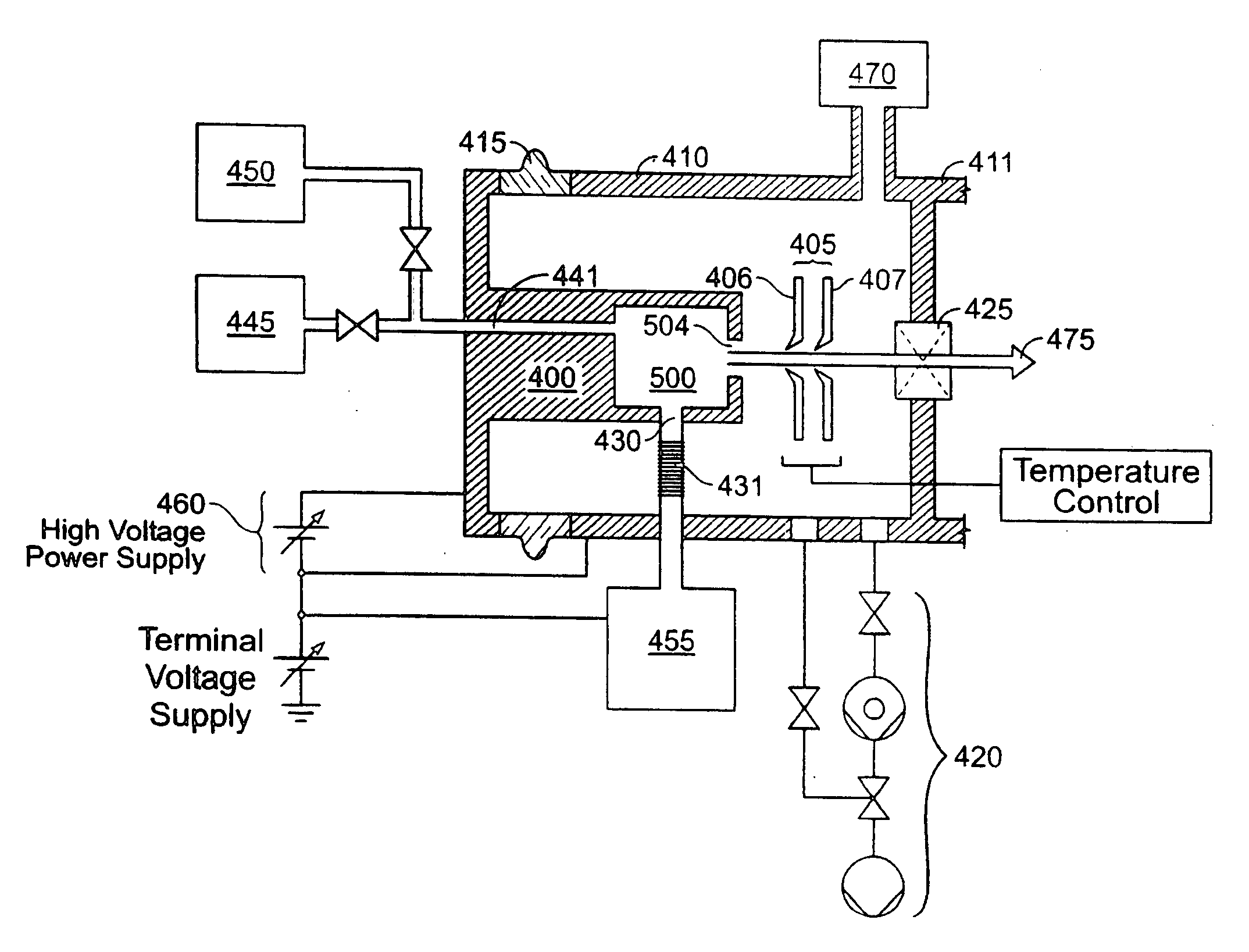
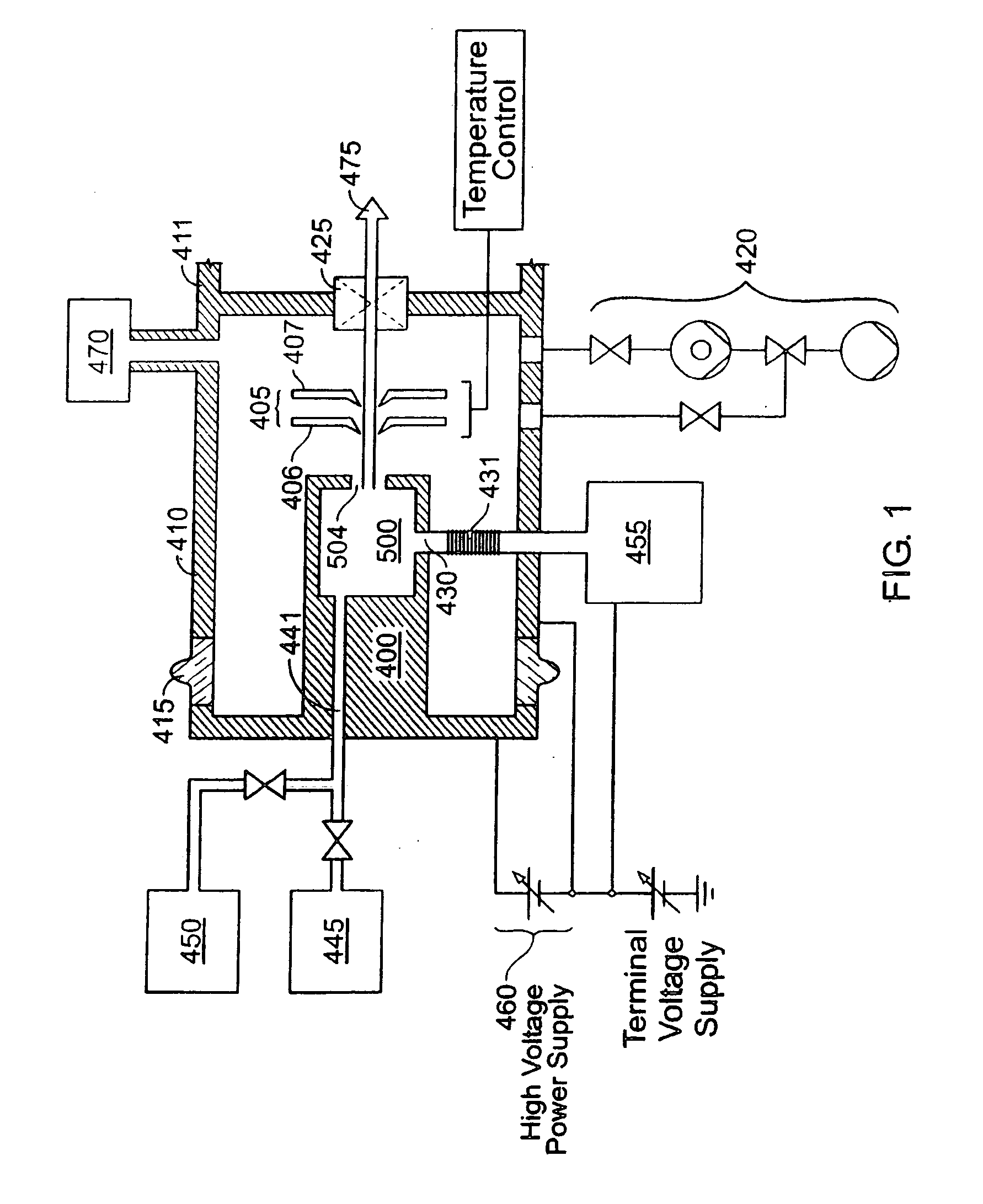
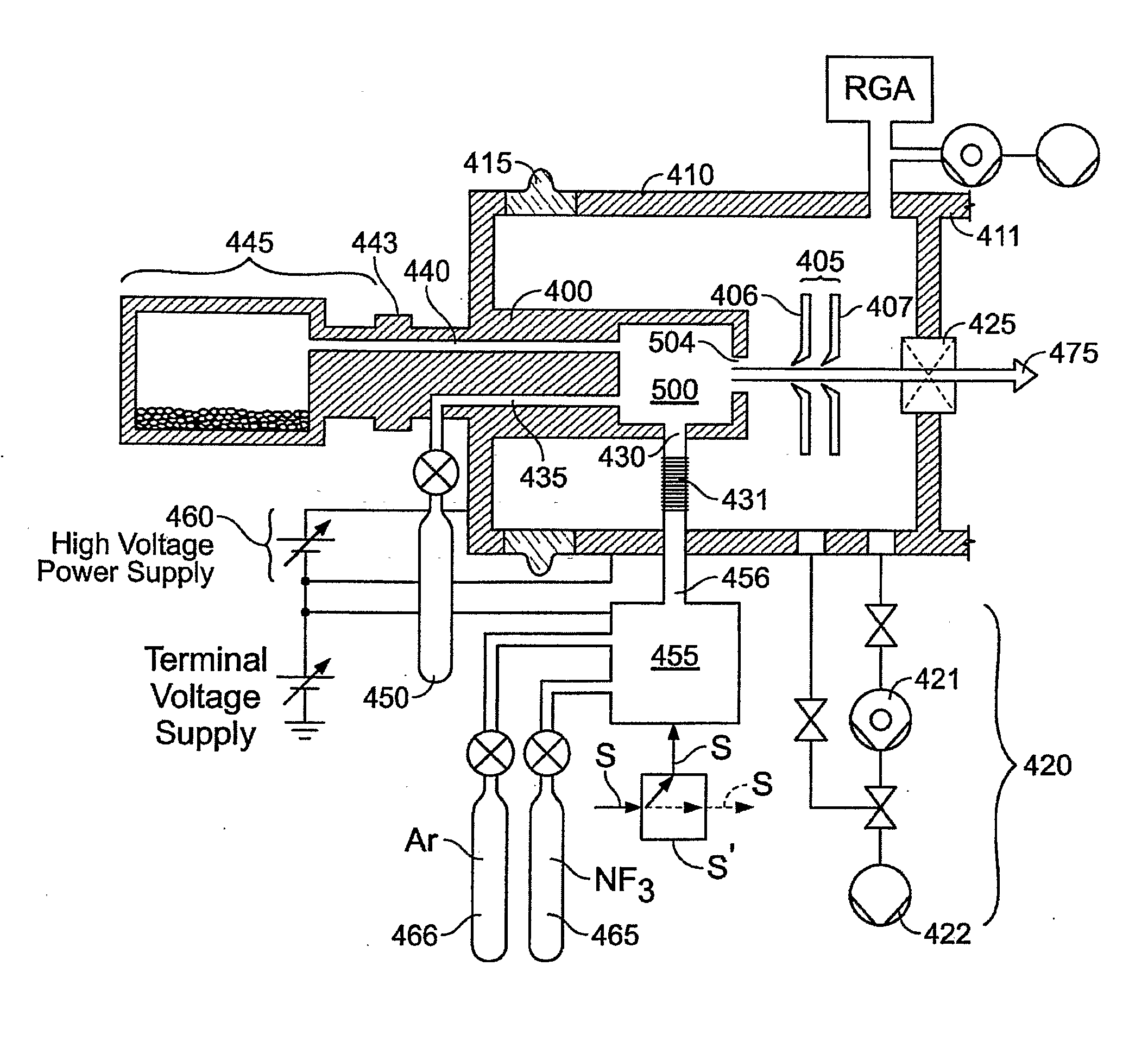
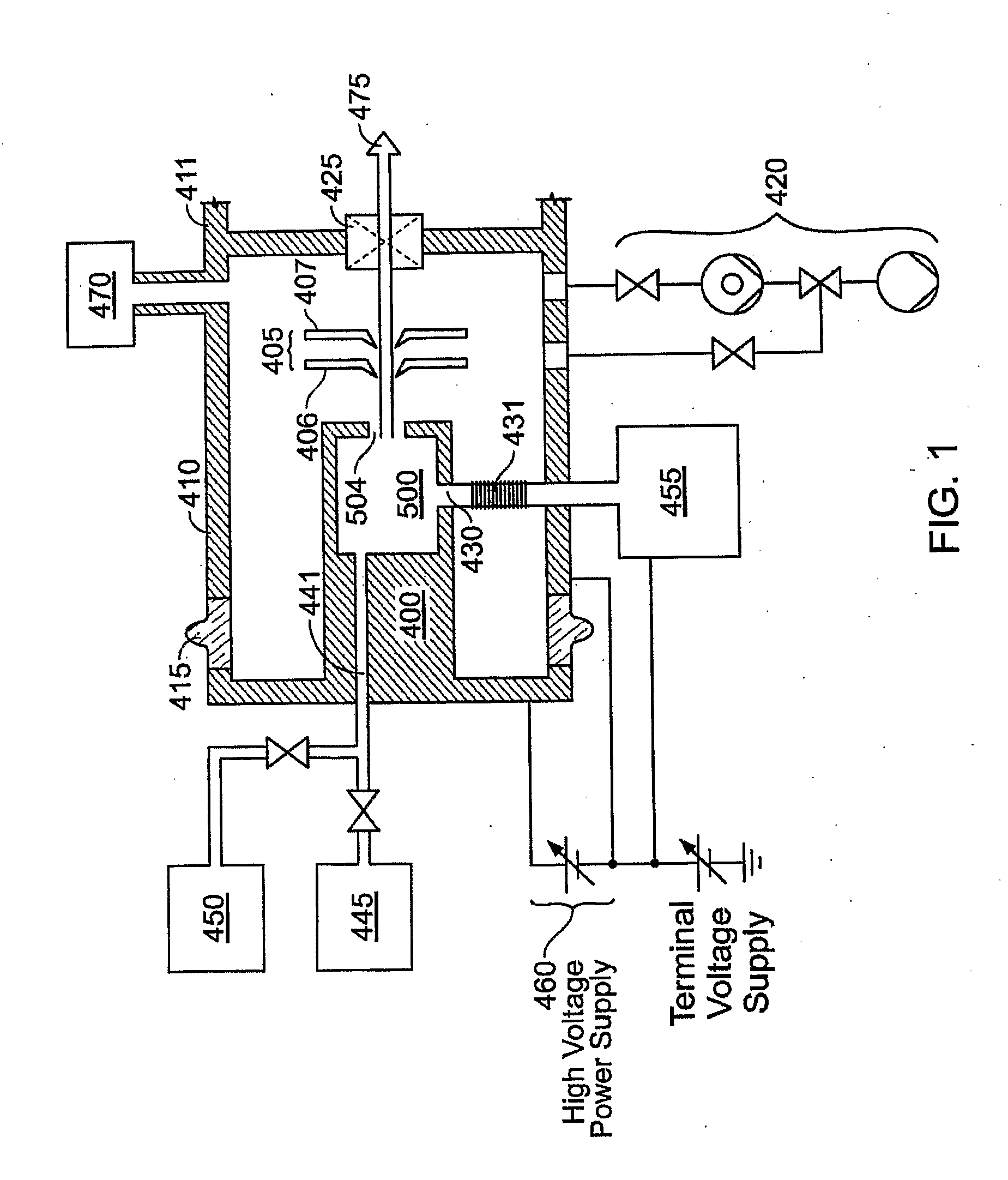
Thermal control is provided for an extraction electrode of an ion-beam producing system that prevents formation of deposits and unstable operation and enables use with ions produced from condensable vapors and with ion sources capable of cold and hot operation. Electrical heating of the extraction electrode is employed for extracting decaborane or octadecaborane ions. Active cooling during use with a hot ion source prevents electrode destruction, permitting the extraction electrode to be of heat-conductive and fluorine-resistant aluminum composition. The service lifetime of the system is enhanced by provisions for in-situ etch cleaning of the ion source and extraction electrode, using reactive halogen gases, and by having features that extend the service duration between cleanings, including accurate vapor flow control and accurate focusing of the ion beam optics. A remote plasma source delivers F or Cl ions to the de-energized ion source for the purpose of cleaning deposits in the ion source and the extraction electrode. These techniques enable long equipment uptime when running condensable feed gases such as sublimated vapors, and are particularly applicable for use with so-called cold ion sources and universal ion sources. Methods and apparatus are described which enable long equipment uptime when decaborane and octadecaborane are used as feed materials, as well as when vaporized elemental arsenic and phosphorus are used, and which serve to enhance beam stability during ion implantation.
Owner:SEMEQUIP
Ion implantation ion source, system and method
InactiveUS20050051096A1Preventing thermal dissociationReduce presenceVacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight beamHeat sensitive
An ion implantation device for vaporizing decaborane and other heat-sensitive materials via a novel vaporizer and vapor delivery system and delivering a controlled, low-pressure drop flow of vapors, e.g. decaborane, into the ion source. The ion implantation device includes an ion source which can operate without an arc plasma, which can improve the emittance properties and the purity of the beam and without a strong applied magnetic field, which can improve the emittance properties of the beam. The ion source is configured so that it can be retrofit into the ion source design space of an existing Bernas source-based ion implanters and the like or otherwise enabling compatibility with other ion source designs.
Owner:SEMEQUIP +1
Method and apparatus for extracting ions from an ion source for use in ion implantation
InactiveUS20060272776A1Extended service lifeReduce downtimeVacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRemote plasmaActive cooling
Thermal control is provided for an extraction electrode of an ion-beam producing system that prevents formation of deposits and unstable operation and enables use with ions produced from condensable vapors and with ion sources capable of cold and hot operation. Electrical heating of the extraction electrode is employed for extracting decaborane or octadecaborane ions. Active cooling during use with a hot ion source prevents electrode destruction, permitting the extraction electrode to be of heat-conductive and fluorine-resistant aluminum composition. The service lifetime of the system is enhanced by provisions for in-situ etch cleaning of the ion source and extraction electrode, using reactive halogen gases, and by having features that extend the service duration between cleanings, including accurate vapor flow control and accurate focusing of the ion beam optics. A remote plasma source delivers F or Cl ions to the de-energized ion source for the purpose of cleaning deposits in the ion source and the extraction electrode. These techniques enable long equipment uptime when running condensable feed gases such as sublimated vapors, and are particularly applicable for use with so-called cold ion sources and universal ion sources. Methods and apparatus are described which enable long equipment uptime when decaborane and octadecaborane are used as feed materials, as well as when vaporized elemental arsenic and phosphorus are used, and which serve to enhance beam stability during ion implantation.
Owner:SEMEQUIP
Method and apparatus for extracting ions from an ion source for use in ion implantation
InactiveUS20070108395A1Extended service lifeReduce downtimeVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingRemote plasmaActive cooling
Thermal control is provided for an extraction electrode of an ion-beam producing system that prevents formation of deposits and unstable operation and enables use with ions produced from condensable vapors and with ion sources capable of cold and hot operation. Electrical heating of the extraction electrode is employed for extracting decaborane or octadecaborane ions. Active cooling during use with a hot ion source prevents electrode destruction, permitting the extraction electrode to be of heat-conductive and fluorine-resistant aluminum composition. The service lifetime of the system is enhanced by provisions for in-situ etch cleaning of the ion source and extraction electrode, using reactive halogen gases, and by having features that extend the service duration between cleanings, including accurate vapor flow control and accurate focusing of the ion beam optics. A remote plasma source delivers F or Cl ions to the de-energized ion source for the purpose of cleaning deposits in the ion source and the extraction electrode. These techniques enable long equipment uptime when running condensable feed gases such as sublimated vapors, and are particularly applicable for use with so-called cold ion sources and universal ion sources. Methods and apparatus are described which enable long equipment uptime when decaborane and octadecaborane are used as feed materials, as well as when vaporized elemental arsenic and phosphorus are used, and which serve to enhance beam stability during ion implantation.
Owner:SEMEQUIP
Method And Apparatus For Extending Equipment Uptime In Ion Implantation
InactiveUS20070210260A1Extended service lifeReduce equipment downtimeVacuum evaporation coatingElectric arc lampsIon implantationThermal control
The service lifetime of an ion source is enhanced or prolonged by the source having provisions for in-situ etch cleaning of the ion source and of an extraction electrode, using reactive halogen gases (F or Cl), and by having features that extend the service duration between cleanings. The latter include accurate vapor flow control, accurate focusing of the ion beam optics, and thermal control of the extraction electrode that prevents formation of deposits or prevents electrode destruction. An apparatus comprised of an ion source for generating dopant ions for semiconductor wafer processing is coupled to a remote plasma source which delivers F or Cl ions to the first ion source for the purpose of cleaning deposits in the first ion source and the extraction electrode. These methods and apparatus enable long equipment uptime when running condensable feed gases such as sublimated vapor sources, and are particularly applicable for use with so-called cold ion sources. Methods and apparatus are described which enable long equipment uptime when decaborane and octadecarborane are used as feed materials, as well as when vaporized elemental arsenic and phosphorus are used, and which serve to enhance beam stability during ion implantation.
Owner:SEMEQUIP
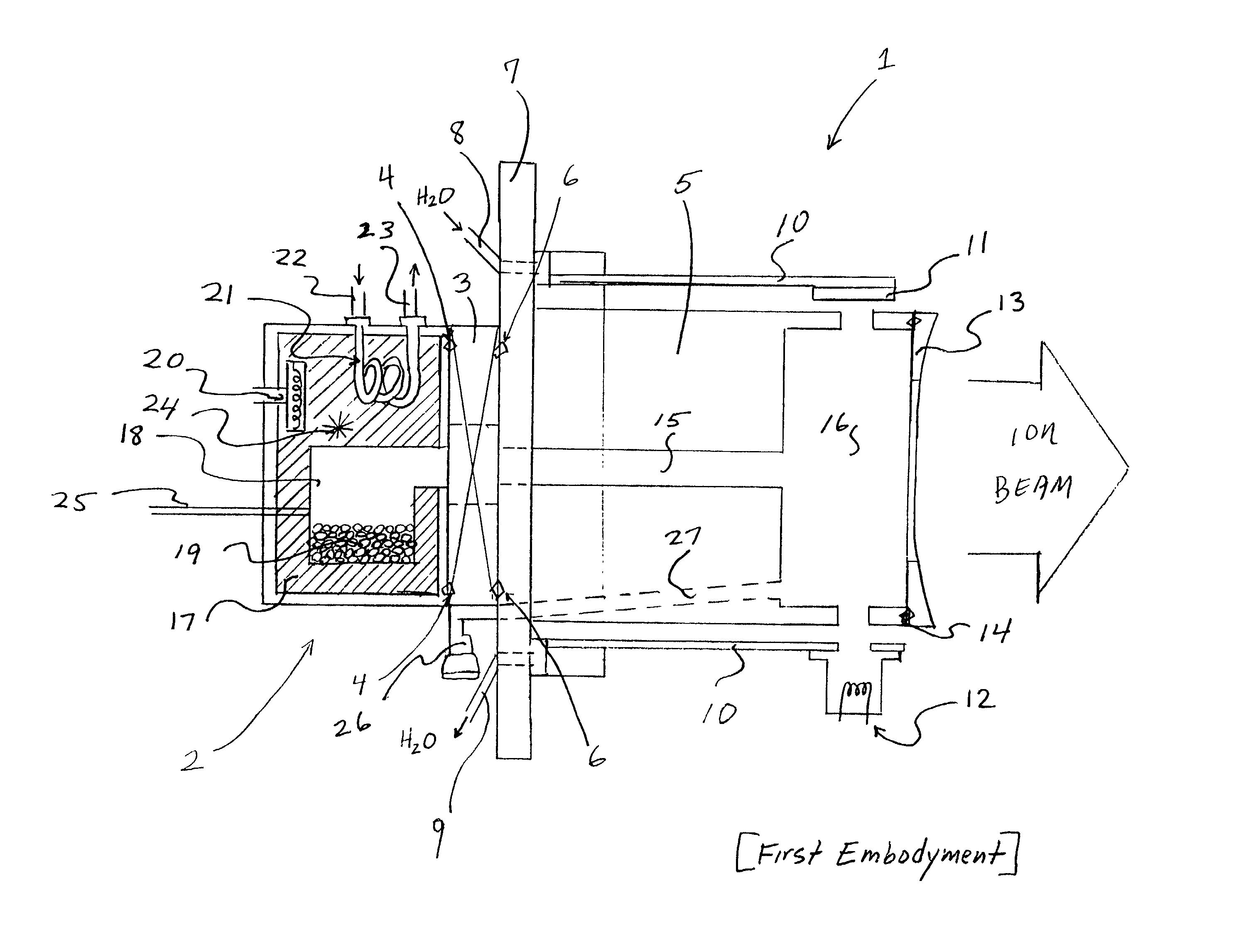
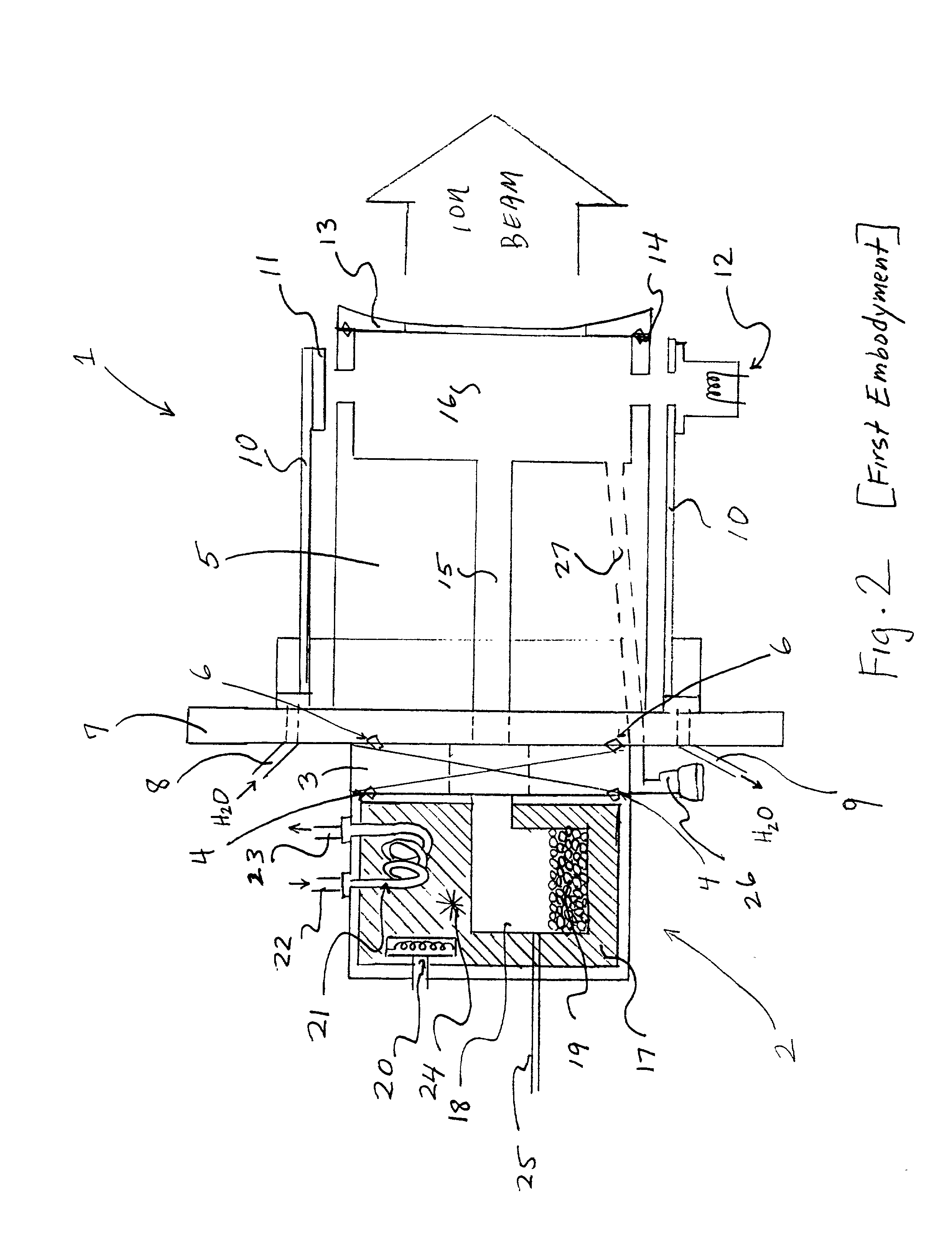
Electron beam ion source with integral low-temperature vaporizer
InactiveUS20020070672A1Maximizes conductanceMinimizes conductanceElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh energy beamIon implantation
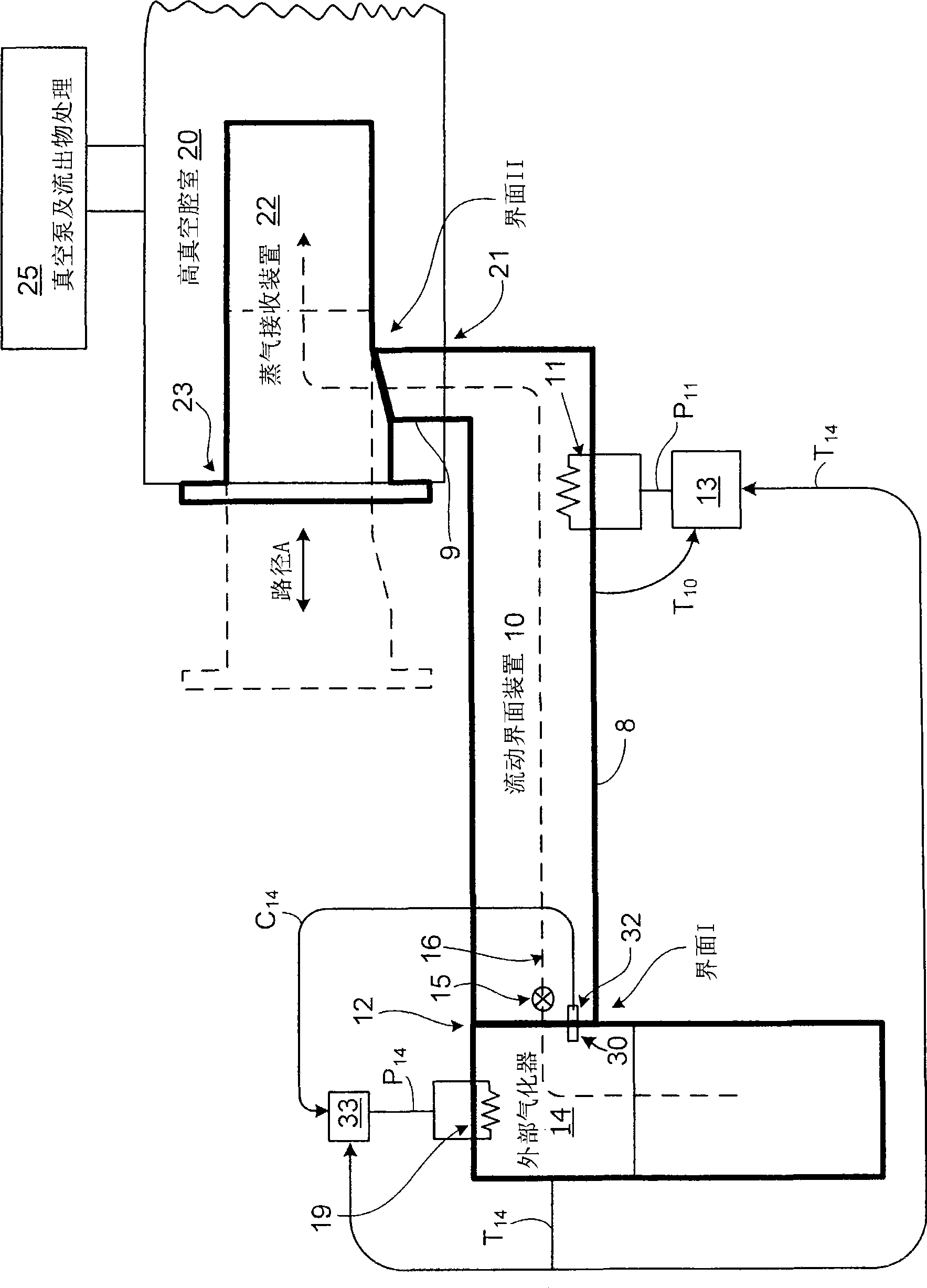
An ion source for ion implantation system and a method of ion implantation employs a controlled broad, directional electron beam to ionize process gas or vapor, such as decaborane, within an ionization volume by primary electron impact, in CMOS manufacturing and the like. Isolation of the electron gun for producing the energetic electron beam and of the beam dump to which the energetic beam is directed, as well as use of the thermally conductive members for cooling the ionization chamber and the vaporizer, enable use with large molecular species such as decaborane, and other materials which are unstable with temperature. Electron optics systems, facilitate focusing of electrons from an emitting surface to effectively ionize a desired volume of the gas or vapor that is located adjacent the extraction aperture. The components enable retrofit into ion implanters that have used other types of ion sources. Demountable vaporizers, and numerous other important features, realize economies in construction and operation. Achievement of production-worthy operation in respect of very shallow implants is realized.
Owner:SEMEQUIP
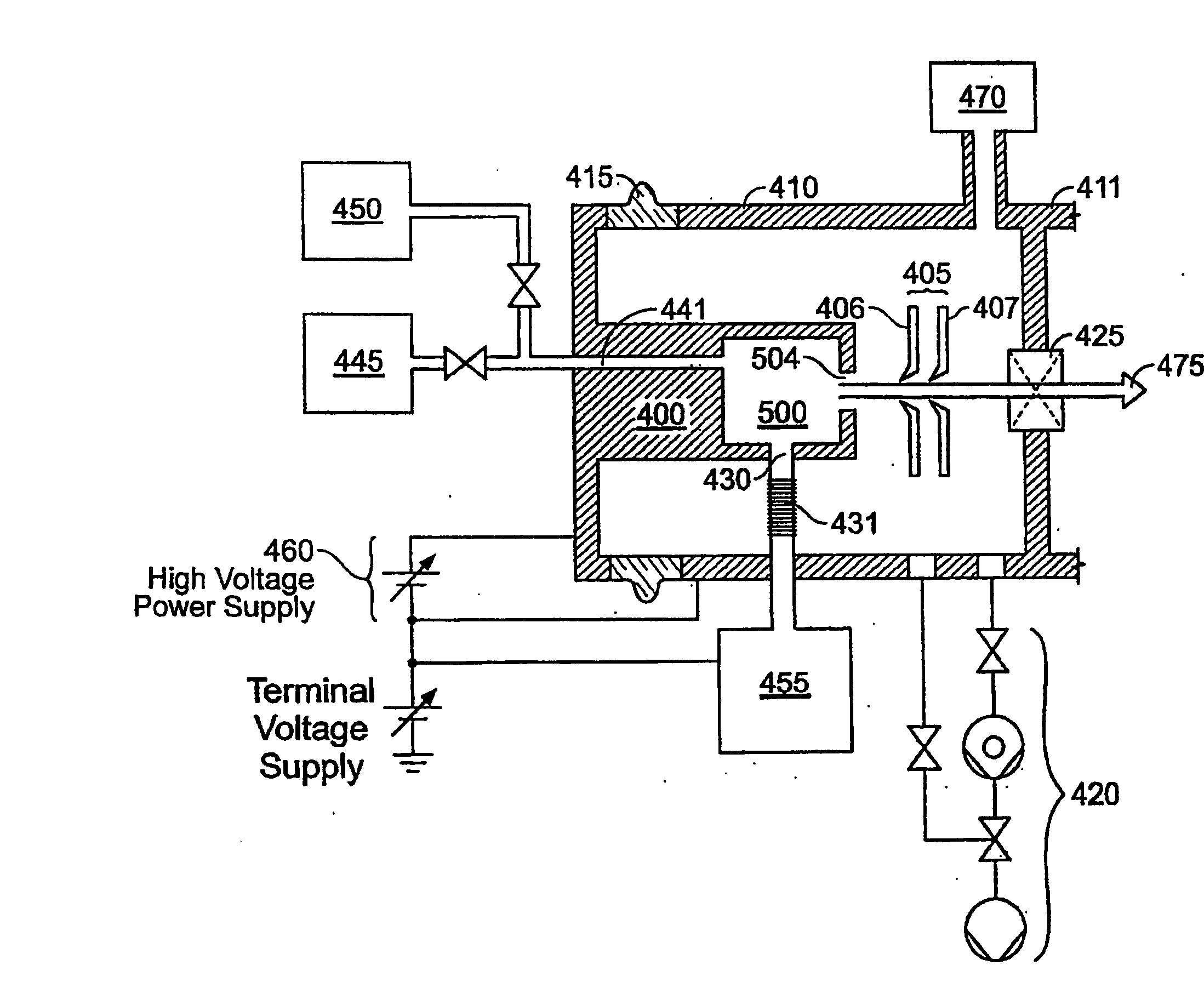
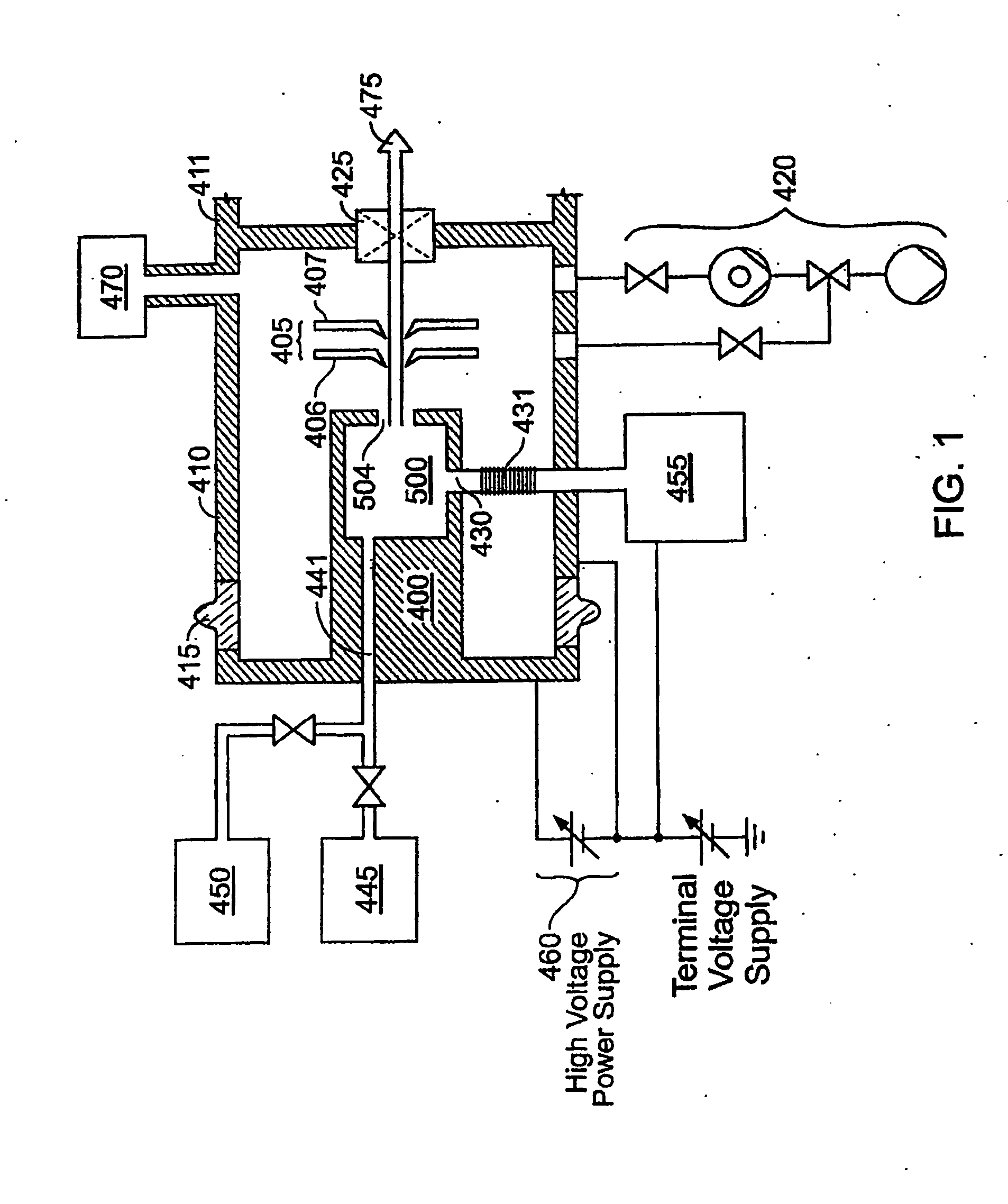
Decaborane ion source
InactiveUS6958481B2Minimize plasma densityAvoid dissociationMaterial analysis by optical meansIon beam tubesPlasma densitySource material
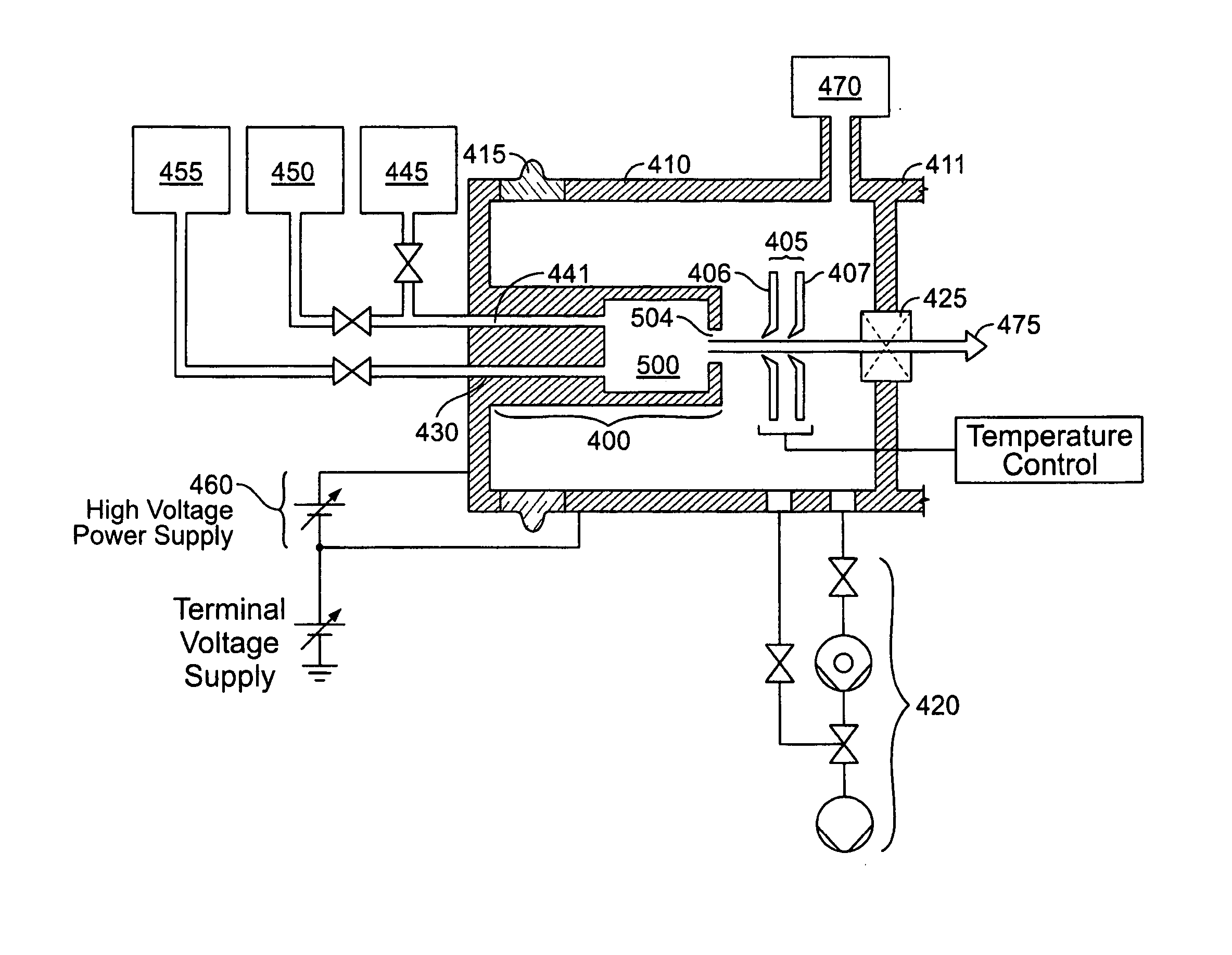
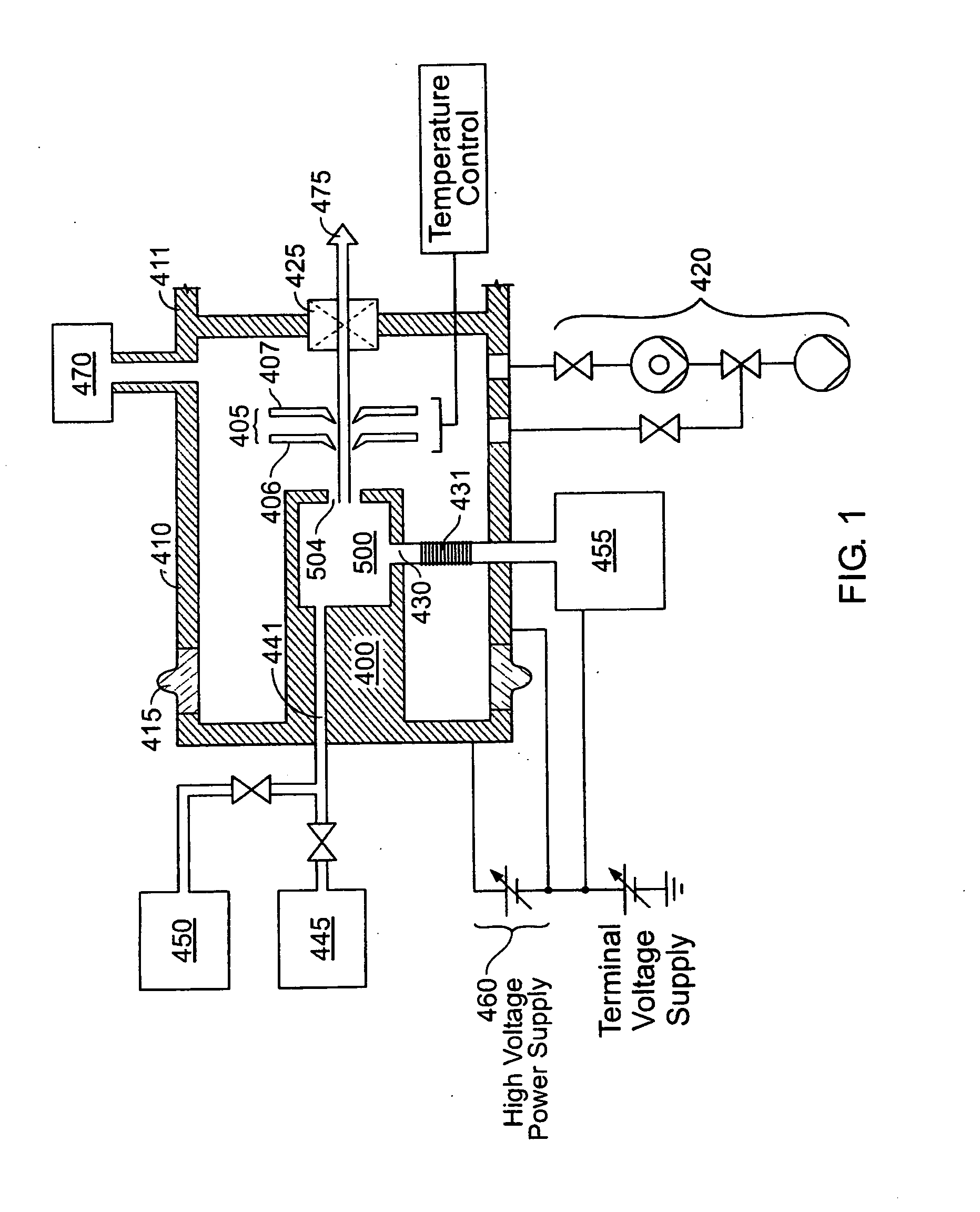
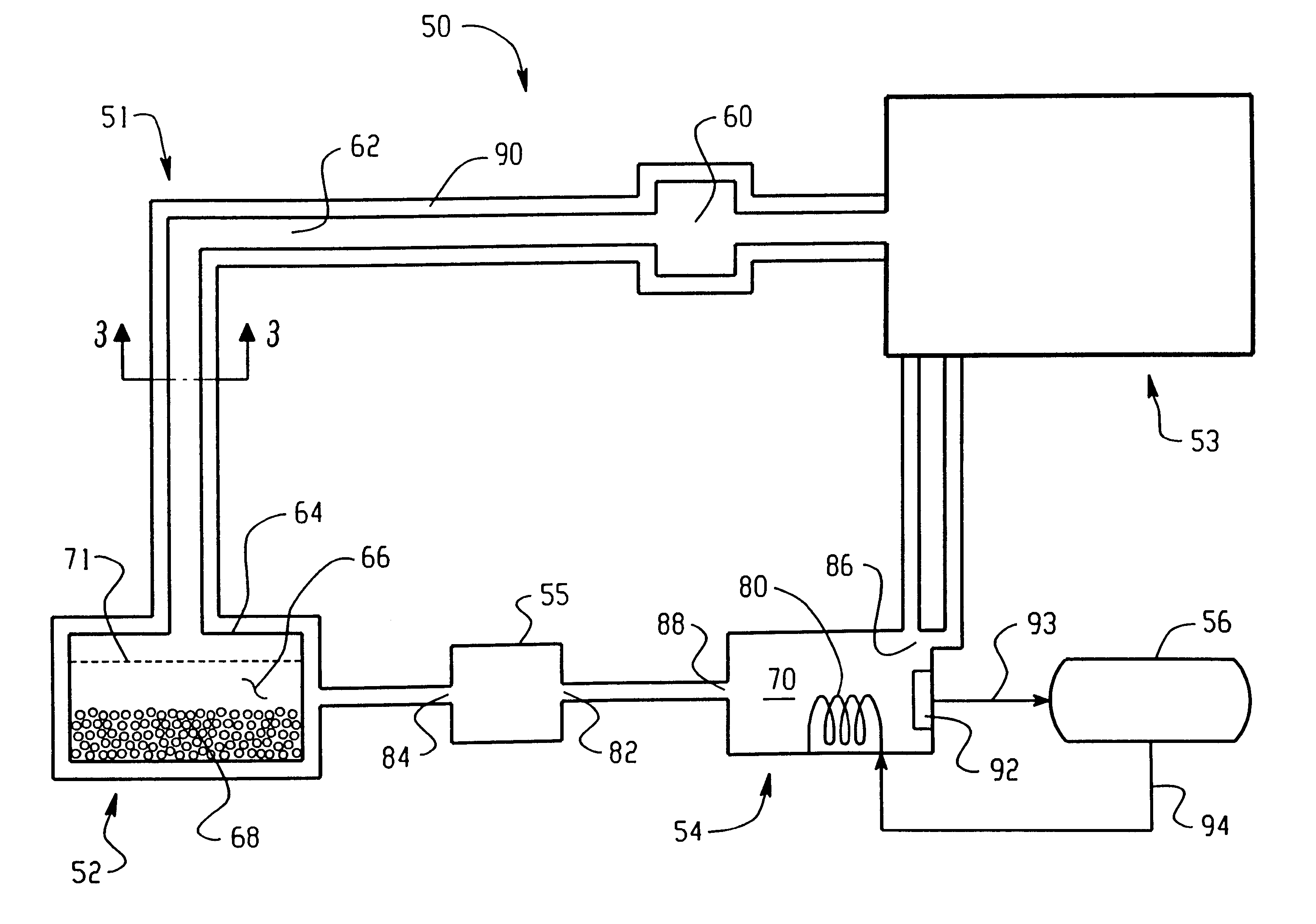
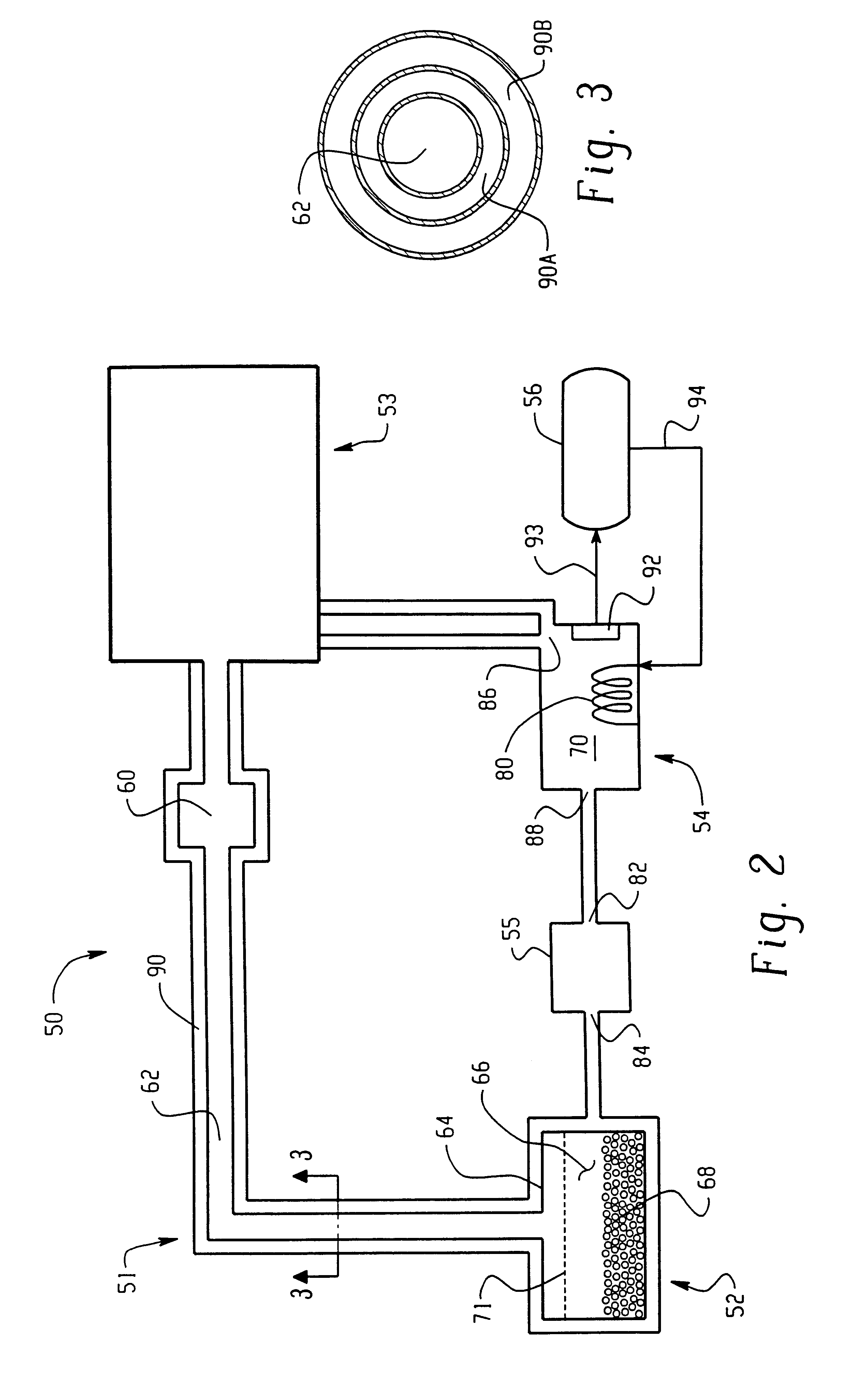
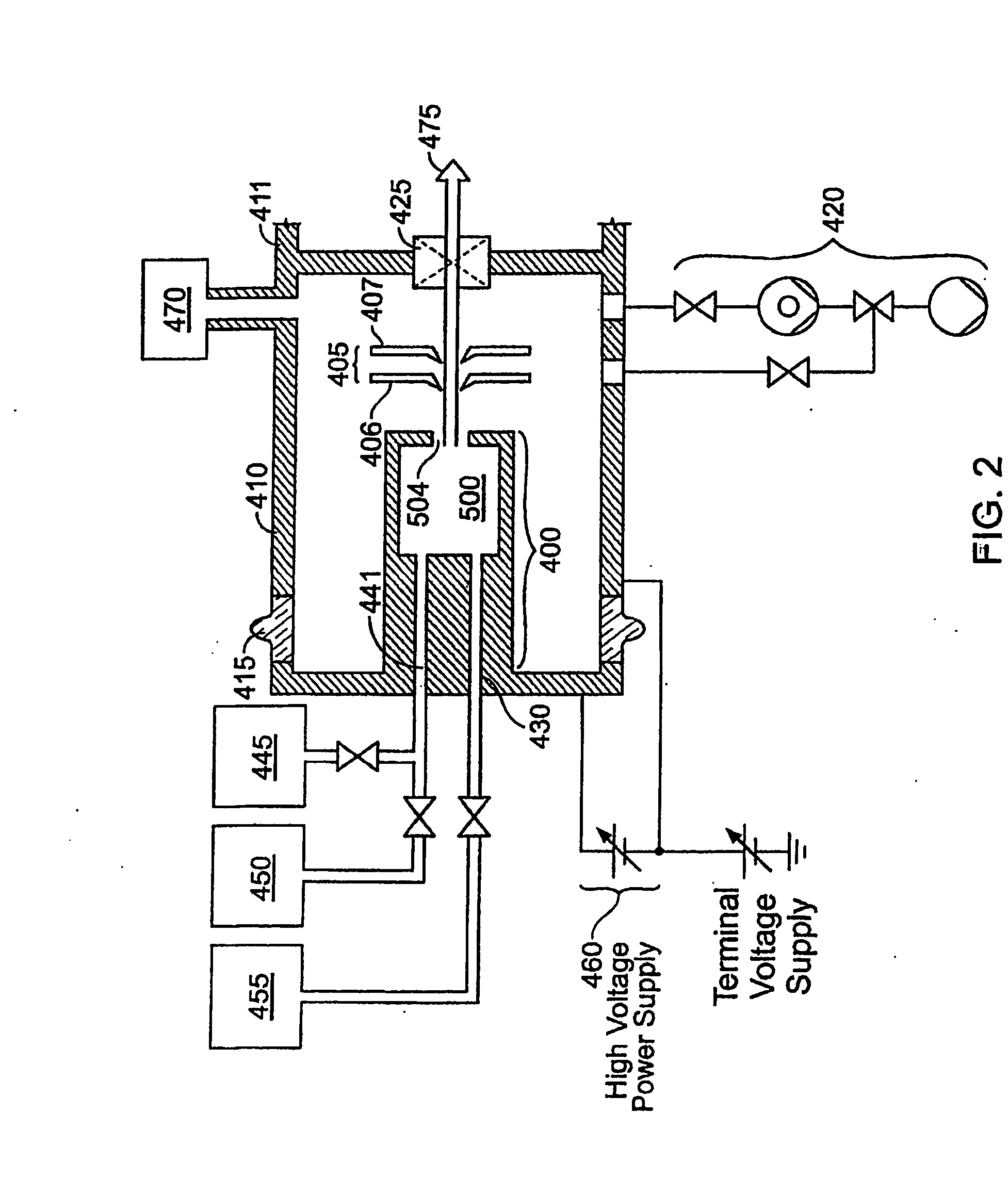
An ion source (50) for an ion implanter is provided, comprising a remotely located vaporizer (51) and an ionizer (53) connected to the vaporizer by a feed tube (62). The vaporizer comprises a sublimator (52) for receiving a solid source material such as decaborane and sublimating (vaporizing) the decaborane. A heating mechanism is provided for heating the sublimator, and the feed tube connecting the sublimator to the ionizer, to maintain a suitable temperature for the vaporized decaborane. The ionizer (53) comprises a body (96) having an inlet (119) for receiving the vaporized decaborane; an ionization chamber (108) in which the vaporized decaborane may be ionized by an energy-emitting element (110) to create a plasma; and an exit aperture (126) for extracting an ion beam comprised of the plasma. A cooling mechanism (100, 104) is provided for lowering the temperature of walls (128) of the ionization chamber (108) (e.g., to below 350° C.) during ionization of the vaporized decaborane to prevent dissociation of vaporized decaborane molecules into atomic boron ions. In addition, the energy-emitting element is operated at a sufficiently low power level to minimize plasma density within the ionization chamber (108) to prevent additional dissociation of the vaporized decaborane molecules by the plasma itself.
Owner:AXCELIS TECHNOLOGIES
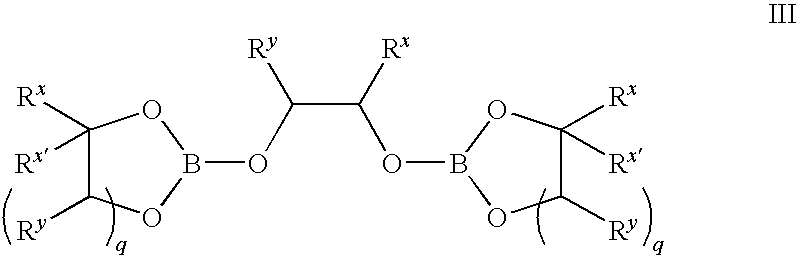
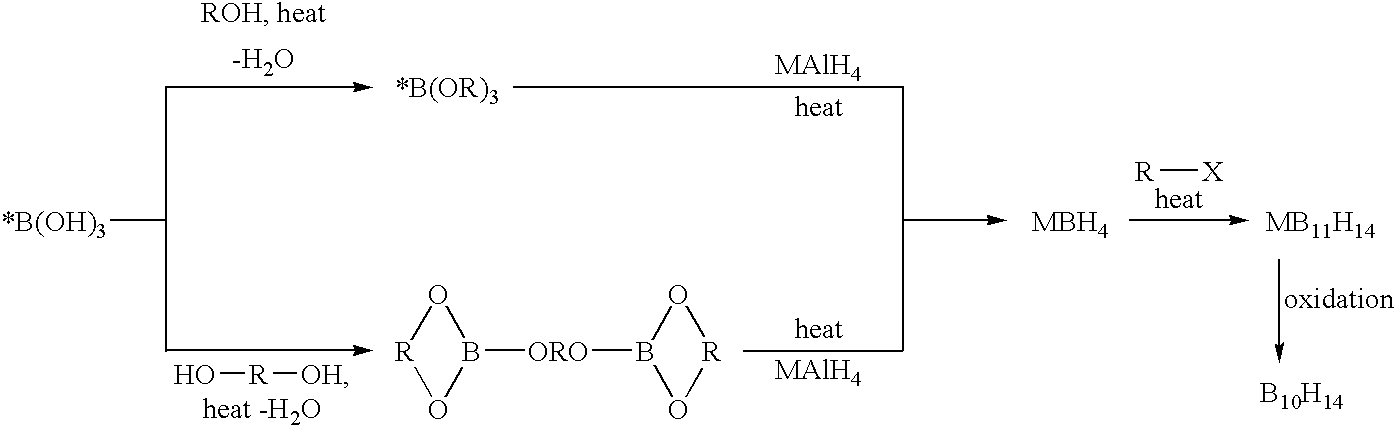
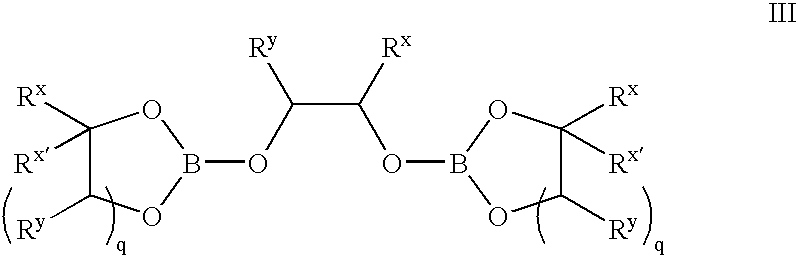
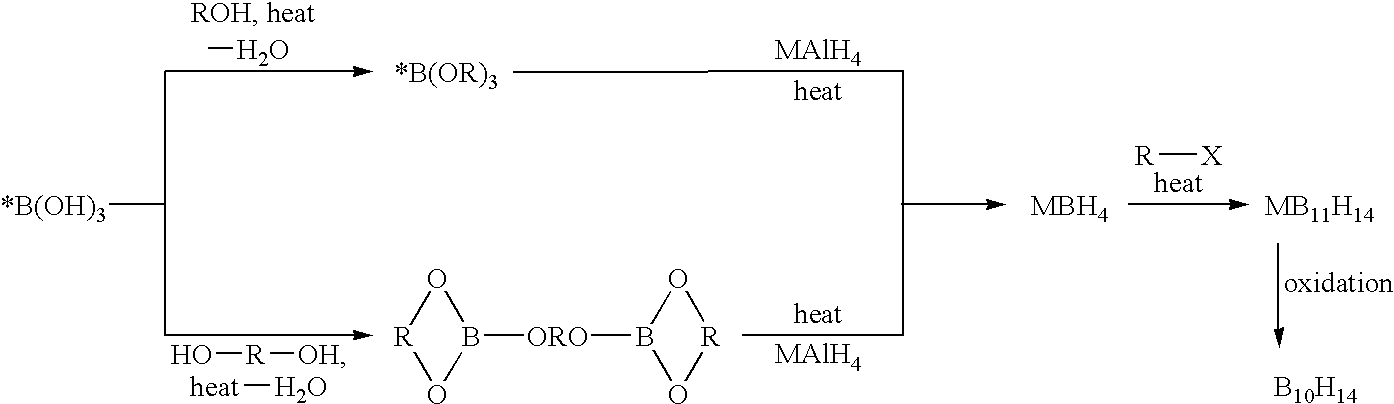
Methods of synthesis of isotopically enriched borohydride and methods of synthesis of isotopically enriched boranes
InactiveUS7641879B2High yieldPeroxides/peroxyhydrates/peroxyacids/superoxides/ozonidesMonoborane/diborane hydridesIsotopeBoric acid
The invention provides new methods for the synthesis of isotopically enriched metal borohydrides, metal tetrahydroundecaborate salts, and decaborane from isotopically enriched 10B-boric acid or 11B-boric acid. The invention is particularly useful for synthesis of isotopically enriched sodium or lithium borohydride, MB11H14 (where M is Li, Na, K, or alkylammonium), and decaborane.
Owner:SEMEQUIP
Method and apparatus for extending equipment uptime in ion implantation
InactiveUS20070241689A1Extended service lifeReduce downtimeVacuum evaporation coatingElectric arc lampsDopantRemote plasma
The service lifetime of an ion source is enhanced or prolonged by the source having provisions for in-situ etch cleaning of the ion source and of an extraction electrode, using reactive halogen gases, and by having features that extend the service duration between cleanings. The latter include accurate vapor flow control, accurate focusing of the ion beam optics, and thermal control of the extraction electrode that prevents formation of deposits or prevents electrode destruction. An apparatus comprised of an ion source for generating dopant ions for semiconductor wafer processing is coupled to a remote plasma source which delivers F or Cl ions to the first ion source for the purpose of cleaning deposits in the first ion source and the extraction electrode. These methods and apparatus enable long equipment uptime when running condensable feed gases such as sublimated vapor sources, and are particularly applicable for use with so-called cold ion sources. Methods and apparatus are described which enable long equipment uptime when decaborane and octadecaborane are used as feed materials, as well as when vaporized elemental arsenic and phosphorus are used, and which serve to enhance beam stability during ion implantation.
Owner:SEMEQUIP
Methods of synthesis of isotopically enriched borohydride and methods of synthesis of isotopically enriched boranes
InactiveUS20050169827A1High yieldMonoborane/diborane hydridesPeroxides/peroxyhydrates/peroxyacids/superoxides/ozonidesIsotopeBoric acid
The invention provides new methods for the synthesis of isotopically enriched metal borohydrides, metal tetrahydroundecaborate salts, and decaborane from isotopically enriched 10B-boric acid or 11B-boric acid. The invention is particularly useful for synthesis of isotopically enriched sodium or lithium borohydride, MB11H14 (where M is Li, Na, K, or alkylammonium), and decaborane.
Owner:SEMEQUIP
Method for manufacturing boron nitride toughened polycrystalline diamond
InactiveCN103883257AStrong reductionSimplified vacuum annealing process stepsDrill bitsUltra-high pressure processesMicrometerHeat resistance
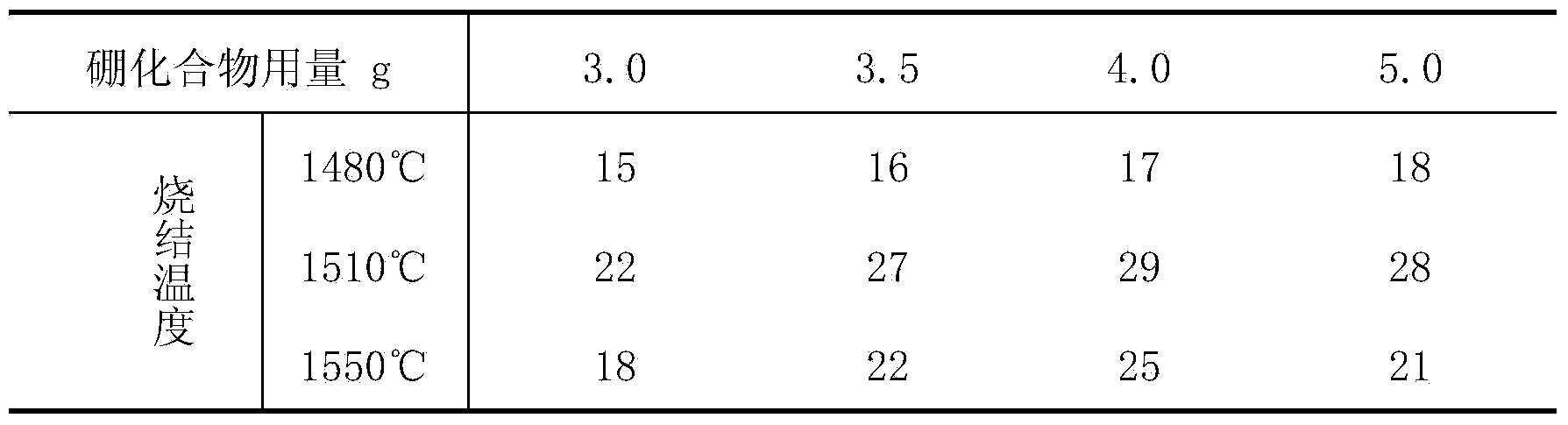
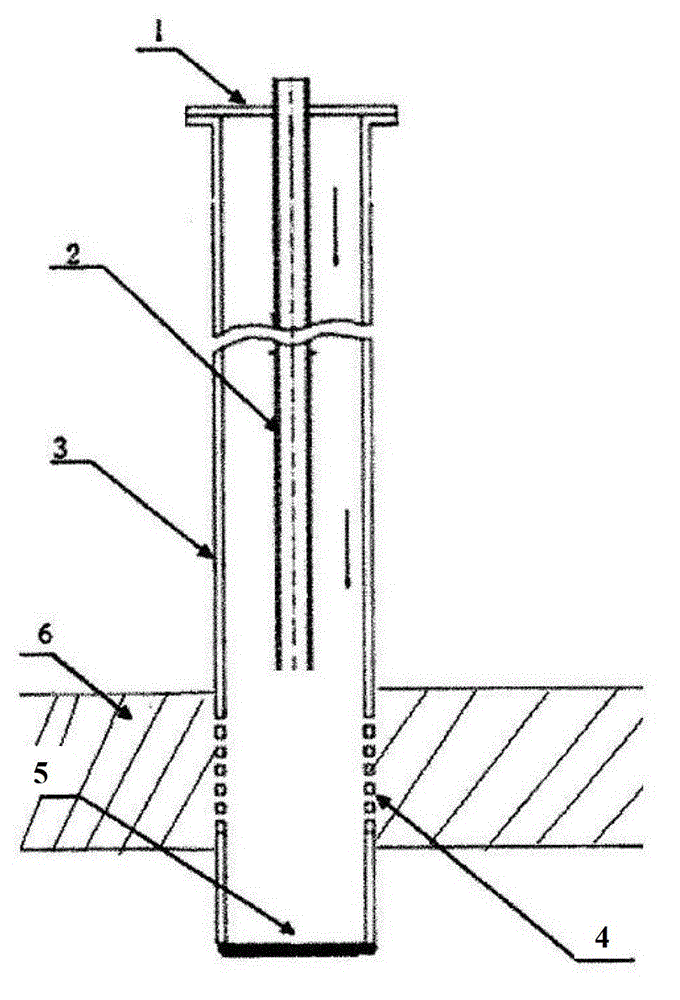
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing boron nitride toughened polycrystalline diamond. The method includes dissolving boron compounds (B<5>H<9> or B<6>H<10> or B<9>H<15> or B<10>H<14> or carbon decaborane) in solvents; adding a calculated amount of diamond micro-powder into the solvents, uniformly stirring the diamond micro-powder and removing the solvents; filling zirconium cups with the coated diamond micro-powder, compacting the diamond micro-powder in the zirconium cups, placing the diamond micro-powder and carbon tungsten alloy sheets into molybdenum cups, compacting the diamond micro-powder and the carbon tungsten alloy sheets in the molybdenum cups, and weighting the calculated amount of coated diamond micro-powder, filling the coated diamond micro-powder in the zirconium cups, paving, compacting, covering the coated diamond micro-powder with the carbon tungsten alloy sheets, placing all in the molybdenum cups, and secondarily compacting through a mold to form a pre-compaction block; filling the pre-compaction block, table salt tubes, insulating tubes, graphite tube heating elements, conductive tablets, end caps and the like into a powder compression block to form complete assembly; placing the assemblies in a six-surface diamond presser, and performing isostatic pressing sintering on the assemblies at the temperature of 1480-1550 DEG C under the pressure of 5-5.5GPa to obtain polycrystalline diamond composite sheets. Two types of micro-powder with two different grain sizes are mixed to form the diamond micro-powder, the grain size of the coarse powder is 8-14 micrometers, the grain size of the fine powder is 0.5-2.5 micrometers, and a proportion of the coarse powder to the fine powder is 3 / 1-5 / 1. The method has the advantage that the diamond crystalline composite sheets manufactured by the aid of the method are high in heat resistance and abrasion resistance.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Hydrogenation heat gas chemical yield increasing solution component applied to shallow well
ActiveCN102942913AHigh porosityImprove permeabilityFluid removalDrilling compositionPorosityAmmonium nitrate
The invention belongs to the technical field of oil exploitation, and relates to a hydrogenation heat gas chemical yield increasing solution component capable of increasing permeability of a shallow well and a near wellbore region. The solution component comprises first solution and second solution, the mass ratio of the first solution to the second solution is 1:1, the first solution comprises 37-43% of ammonium nitrate NH4NO3, 23-26% of urea CO(NH2)2, 5-8% of decaborane B10H14, 1-2% of glucose C6H12O6, 0.5-1.5% of methenamine (CH2)6N4 and 19.5-33.5% of water. The second solution comprises 44-48% of sodium nitrate NaNO3, 15-20% of sodium nitrite NaNO2, 17-21% of sodium aluminum hydride NaAlH4 and 15-19% of tetrachloroethylene C2Cl4. By the aid of the solution component, porosity of an ore bed can be increased, accordingly, permeability is increased, and the yield can be increased by 2-10 times.
Owner:吉林贯通能源科技有限责任公司
Carborane and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102140105AStrong responsivenessSimple production processOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsSynthesis methodsPlasticizer
The invention discloses a carborane and a synthesis method thereof. In the method, propiolic halide is adopted as a raw material to synthesize propargyl ether containing unsaturated carbon-carbon double bond through nucleophile substitution reaction, and the alkynyl in the propargyl ether is adducted with decaborane to obtain reactive carborane in which a carbon-carbon double bond is bonded on a cage type carborane structure through an ether bond. The synthesized reactive carborane, which is liquid at normal temperature, can have an effect of a plasticizer while being used as a composite solid burning-rate catalyst of a propellant. The unsaturated group carbon-carbon double bond, which has disconjugacy and strong reactivity, contained in the carborane is expected to overcome migration through taking part in the crosslinking curing reaction with the composite solid propellant. The carborane containing unsaturated carbon-carbon double bond has low synthesis cost and simple and convenient production technique, and is beneficial for industrial production.
Owner:天元航材(营口)科技股份有限公司
Diamine monomer containing carborane structure, dianhydride monomer containing carborane structure and preparation method and application of diamine monomer and dianhydride monomer containing carborane structure
PendingCN113135950AEasy to operateWide applicabilityGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsImidePolymer science
The invention discloses a diamine monomer containing a carborane structure, a dianhydride monomer containing a carborane structure and a preparation method and application of the diamine monomer and the dianhydride monomer. The invention also discloses high-temperature-resistant polyimide containing the carborane structure. The polyimide is prepared by condensation polymerization of the diamine monomer containing the carborane structure and a dianhydride monomer containing the carborane structure. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking decaborane and alkyne as initial raw materials, preparing a carborane structural unit through addition reaction of the decaborane and the alkyne, and then preparing the diamine monomer containing the carborane structure through nitration reaction and reduction reaction, or preparing the dianhydride monomer containing the carborane structure through oxidation and dehydrating reaction of methyl. The method for preparing the diamine monomer or dianhydride monomer containing the carborane structure has the advantages of simple operation, wide universality, convenient and easily available raw materials, high yield and the like, and is convenient for large-scale production.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
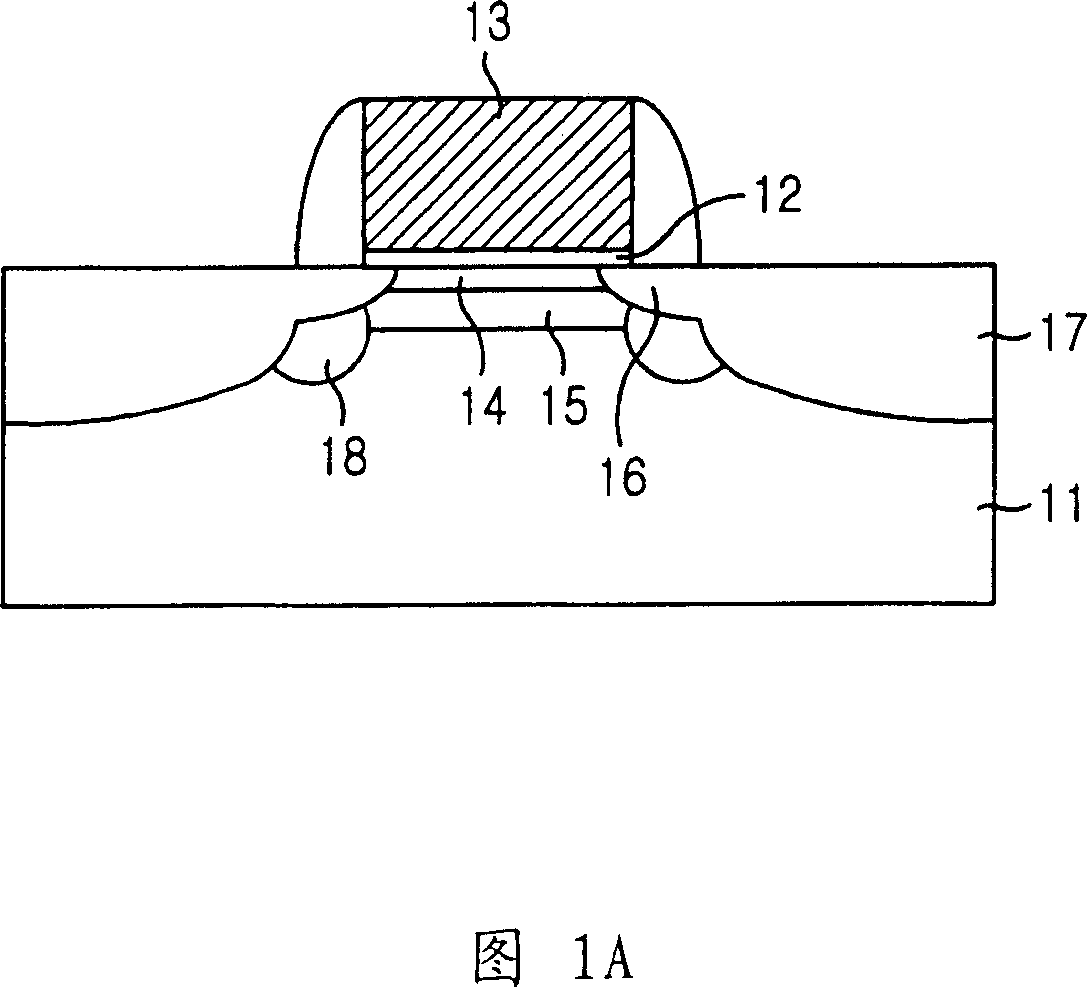
Method for preparing semiconductor device with super shallow and super steep backward surface groove
The present invention provides a method for fabricating a semiconductor device with ultra-shallow super-steep-retrograde epi-channel that is able to overcome limitedly useable energies and to enhance manufacturing productivity than using ultra low energy ion implantation technique that has disadvantage of difficulties to get the enough ion beam current as well as that of prolonged processing time. The inventive method includes the steps of: a method for fabricating a semiconductor device with ultra shallow super-steep-retrograde (hereinafter referred as to SSR) epi-channel, comprising the steps of: forming a channel doping layer below a surface of a semiconductor substrate by implanting decaborane; forming an epi-layer on the channel doping layer; forming sequentially a gate dielectric layer and a gate electrode on the epi-layer; forming source / drain extension areas shallower than the channel doping layer by being aligned at edges of the gate electrode; forming a spacers on lateral sides of the gate electrode; and forming source / drain areas deeper than the channel doping layer by being aligned at edges of the spacer through ion implantation onto the substrate.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Vapor delivery system useful with ion sources and vaporizers for use in such system
The present invention discloses a vapor conveying system and a method thereof, which controls the heating and flowing of vapor that comes from the solid feed-in material (especially the material comprising cluster module) for semiconductor manufacturing. The system and the method convey the vapor to the using point safely and effectively, especially to the ion source for ion implantation. The exhibition of ion beam implantation uses the ion from the cluster material. The vapor conveying system comprises the reactive gas cleaning and control system of the ion source and a protocol thereof, an abroad dynamic range flow control system and an effective and safe gasifier selection. The borane, decaborane, carborane, carbon cluster and other macromolecules are gasified for ion implantation. The system of the invention is exhibited for cooperating with the novel gasifier, the ion source and the reactive cleaning system.
Owner:SEMEQUIP
Preparation method of boron carbide precursor with high boron content
A preparation method of a boron carbide precursor with high boron content comprises the steps of: (1) adding a solvent in a reactor, then adding decaborane and diene organic compound, and vacuumizing and drying the reactor; (2) adding a catalyst to the reactor; (3) heating, stirring continuously for reaction under nitrogen atmosphere protection, evaporating the reaction products to remove the solvent, to obtain a viscous liquid; (4) rinsing with n-hexane or petroleum ether and removing residual catalyst and solvent in the obtained viscous liquid, to obtain a monomer; (5) placing the monomer in the reactor, and adding a solvent and a catalyst; (6) repeatedly vacuumizing the reactor; (7) heating and continuously stirring for reaction under a nitrogen atmosphere protection; and (8) removing the solvent in the reaction products. The boron carbide precursor prepared by the invention has high ceramic yield and high boron content, and is applicable to the preparation of boron carbide capsule for nuclear fusion, as well as the preparation of high performance carbide matrix composite.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
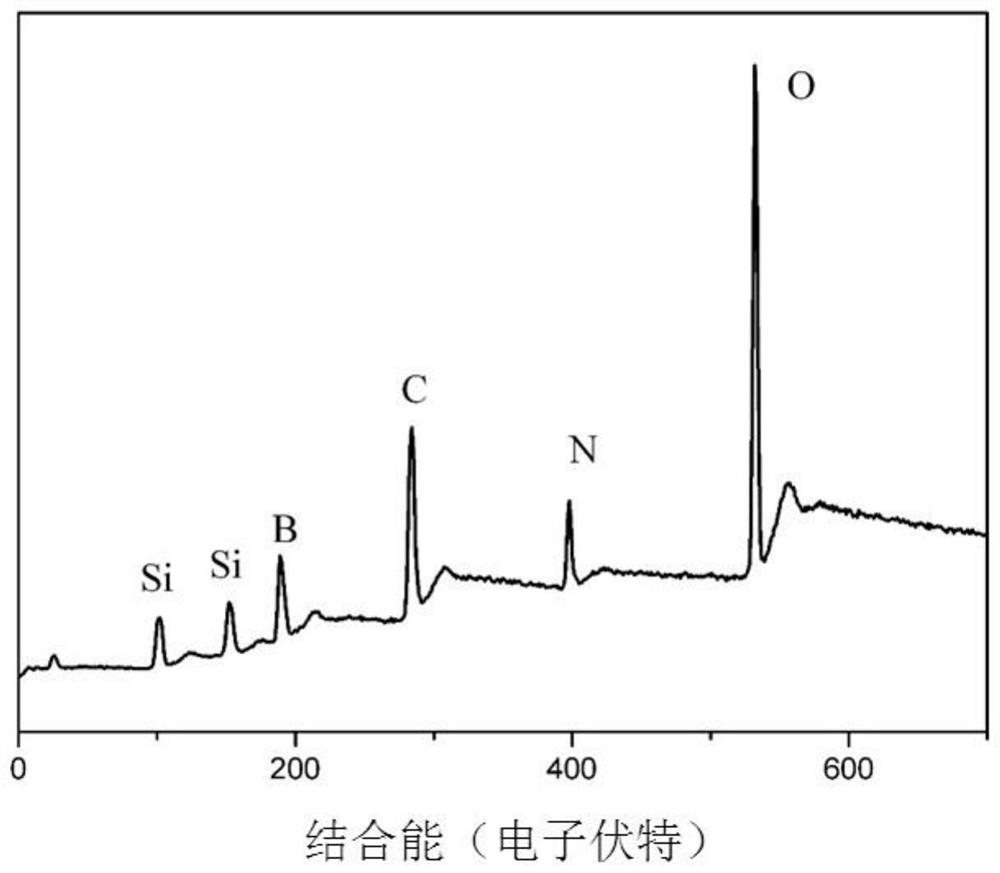
SiBCN ceramic precursor and synthesis method thereof
The invention discloses a SiBCN ceramic precursor and a synthesis method thereof.According to the synthesis method of the SiBCN ceramic precursor, decaborane and an organosilicon compound serve as raw materials, the dehydrogenation condensation reaction of the decaborane and the organosilicon compound is utilized, the new SiBCN ceramic precursor is simply and efficiently synthesized, the reaction can be conducted at the room temperature, and the synthesis yield reaches 82 wt% or above. The method has the advantages of no by-product except hydrogen, high atom utilization rate, convenience in large-scale production, good solubility of the synthesized Si-C-N-B multi-element ceramic precursor, high ceramic yield and suitability for various solution processing technologies to prepare ceramic materials with complex shapes.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
High-temperature-resistant polymer containing m-carborane group and preparation method of high-temperature-resistant polymer
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Resonance method for production of intense low-impurity ion beams of atoms and molecules
ActiveUS7365340B2Particle separator tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansSpectroscopyMass spectrometry
The present invention comprehends a compact and economical apparatus for producing high intensities of a wide variety of wanted positive and negative molecular and atomic ion beams that have been previously impossible to previously produce at useful intensities. In addition, the invention provides a substantial rejection of companion background ions that are frequently simultaneously emitted with the wanted ions. The principle underlying the present invention is resonance ionization-transfer where energy differences between resonant and non-resonant processes are exploited to enhance or attenuate particular charge-changing processes. This new source technique is relevant to the fields of Accelerator Mass Spectroscopy; Molecular Ion Implantation; Generation of Directed Neutral Beams; and Production of Electrons required for Ion Beam Neutralization within magnetic fields. An example having commercial importance is ionization of the decaborane molecule, B10H14 where an almost perfect ionization resonance match occurs between decaborane molecules and arsenic atoms.
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
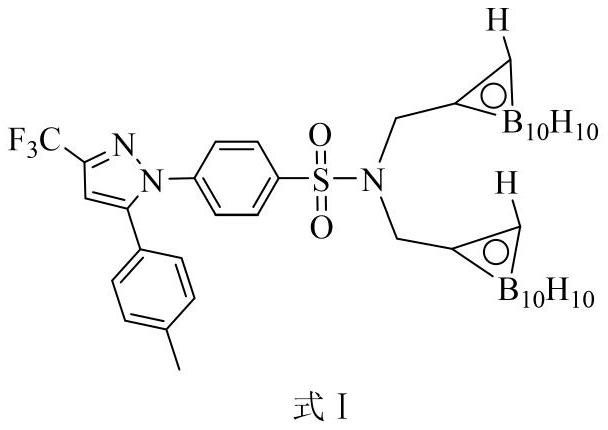
Carborane celecoxib, preparation thereof and application thereof in head and neck cancer boron neutron capture therapy drugs
ActiveCN112358492AStrong selective uptakeGood killing effectEnergy modified materialsGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsSide effectCancer cell
The invention discloses preparation of carborane celecoxib and application of carborane celecoxib in head and neck cancer boron neutron capture therapy drugs, and relates to the field of medicinal chemistry and radiological medicine. The compound can be prepared from celecoxib, 3-propargyl bromide and decaborane in a toluene solution through substitution and addition reactions step by step. The preparation process is simple and easy to operate, and the product is high in yield and purity. Head and neck cancer cell experiment results prove that the compound has high selectivity on head and neckcancer cells and has an obvious apoptosis induction effect on the head and neck cancer cells in boron neutron capture therapy. Compared with an existing clinical medicine applied to boron neutron capture therapy, the compound is high in boron loading capacity and high in tumor selectivity, the anti-inflammatory effect can be achieved while the radiotherapy effect is achieved, and the toxic and side effects of therapy are reduced.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
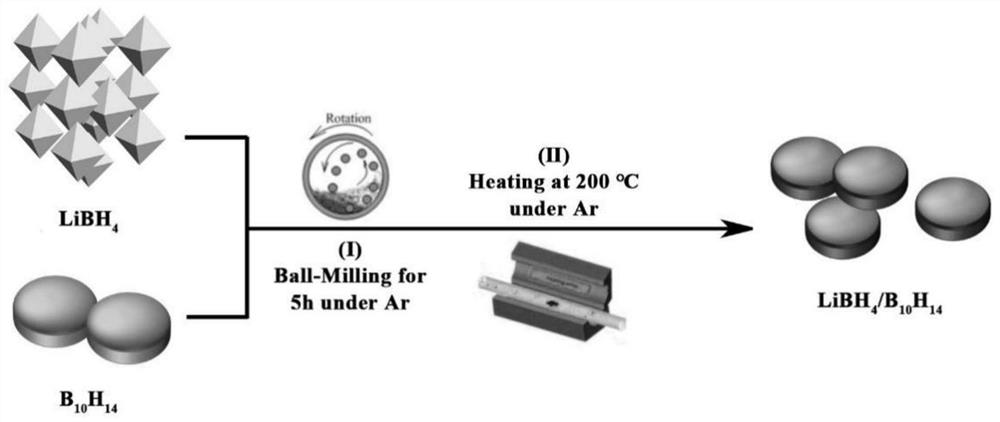
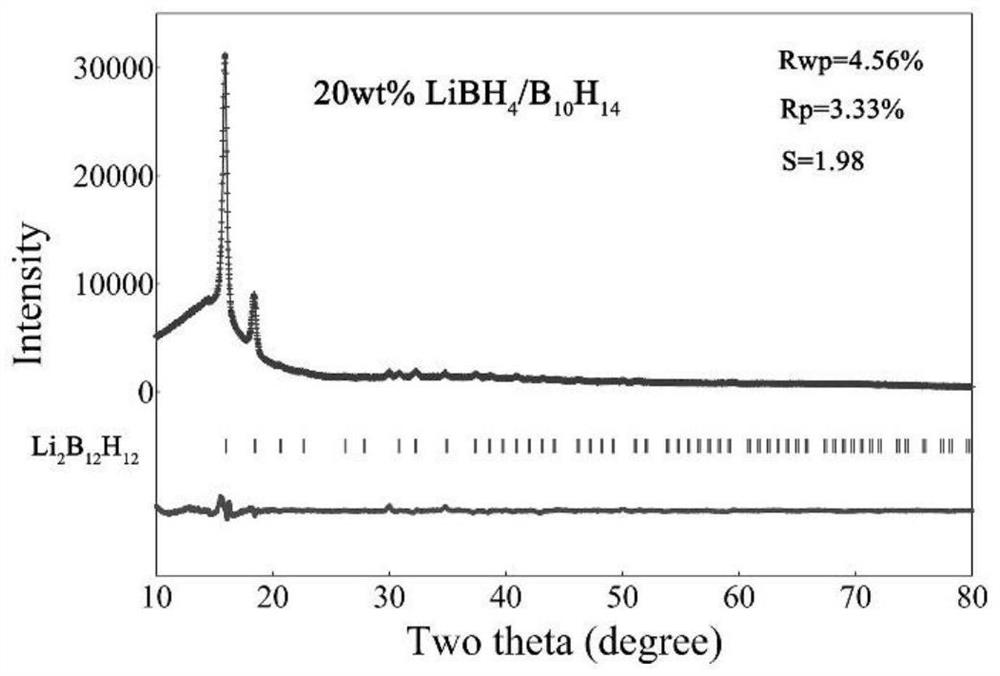
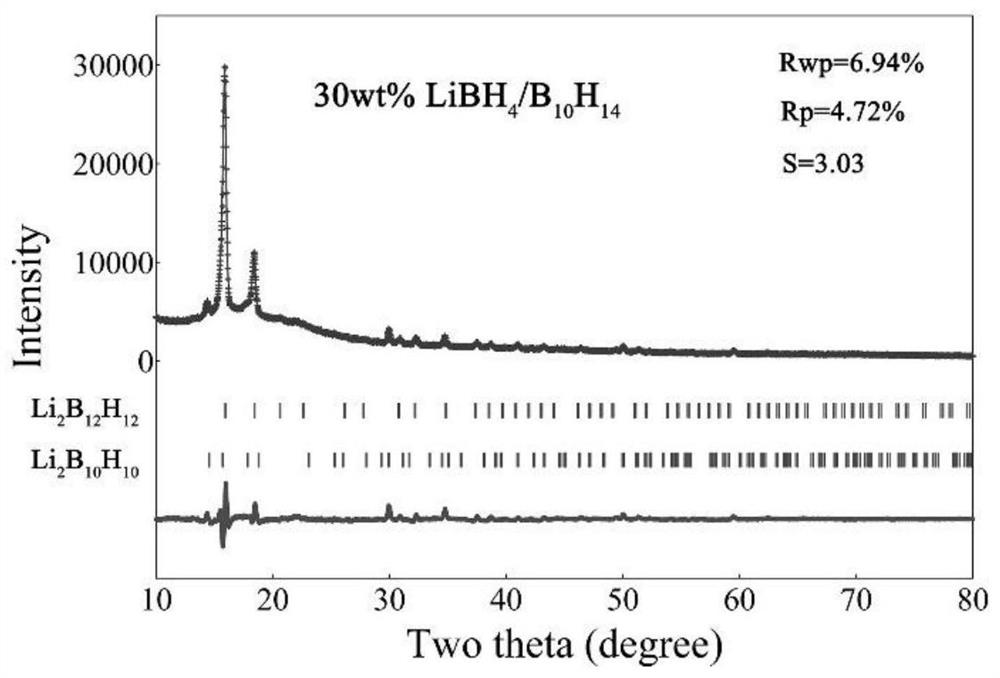
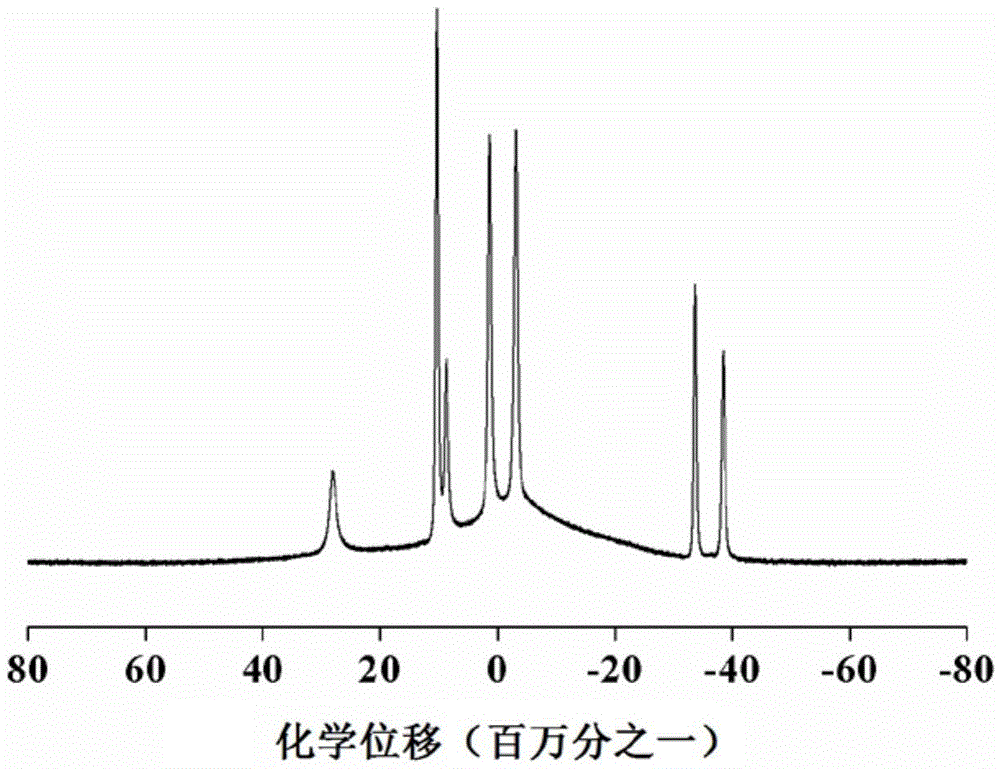
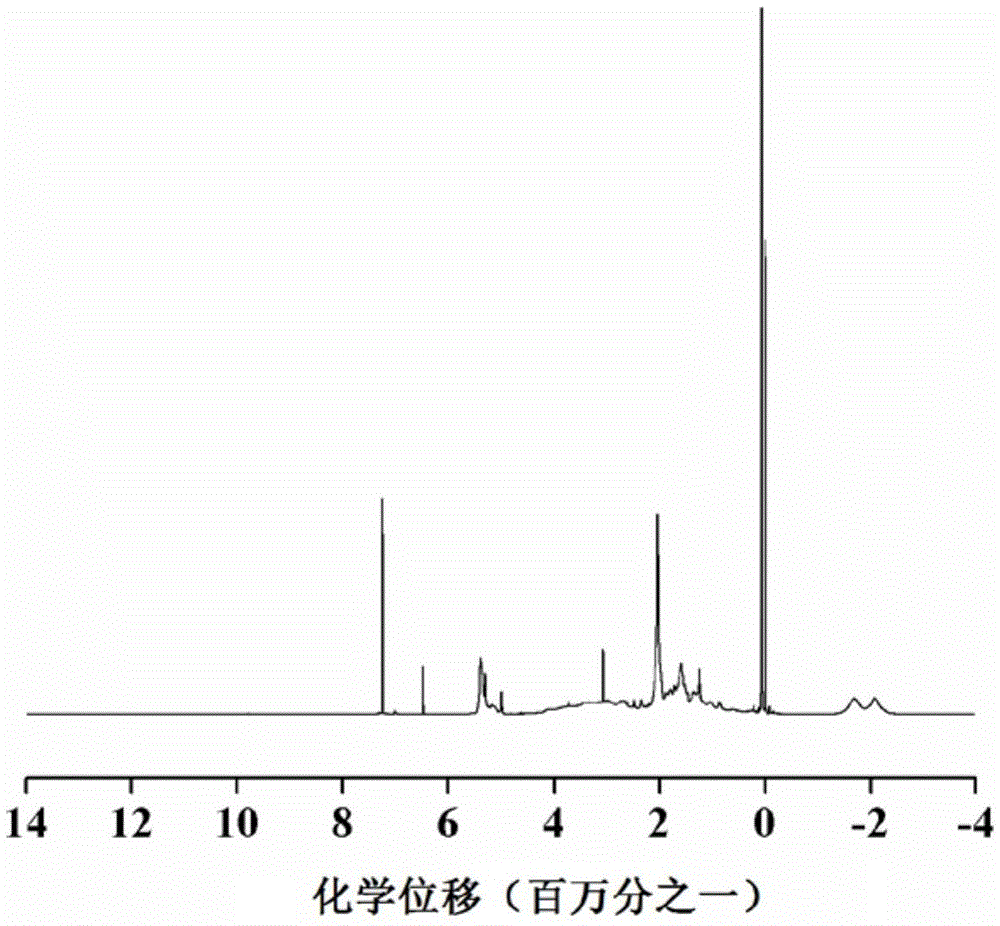
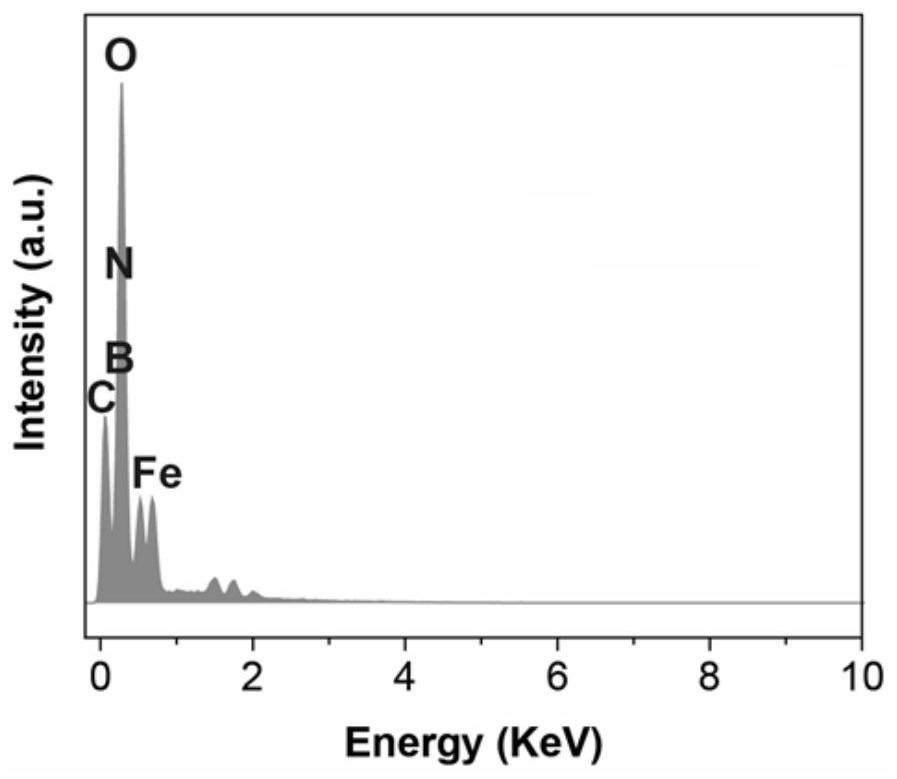
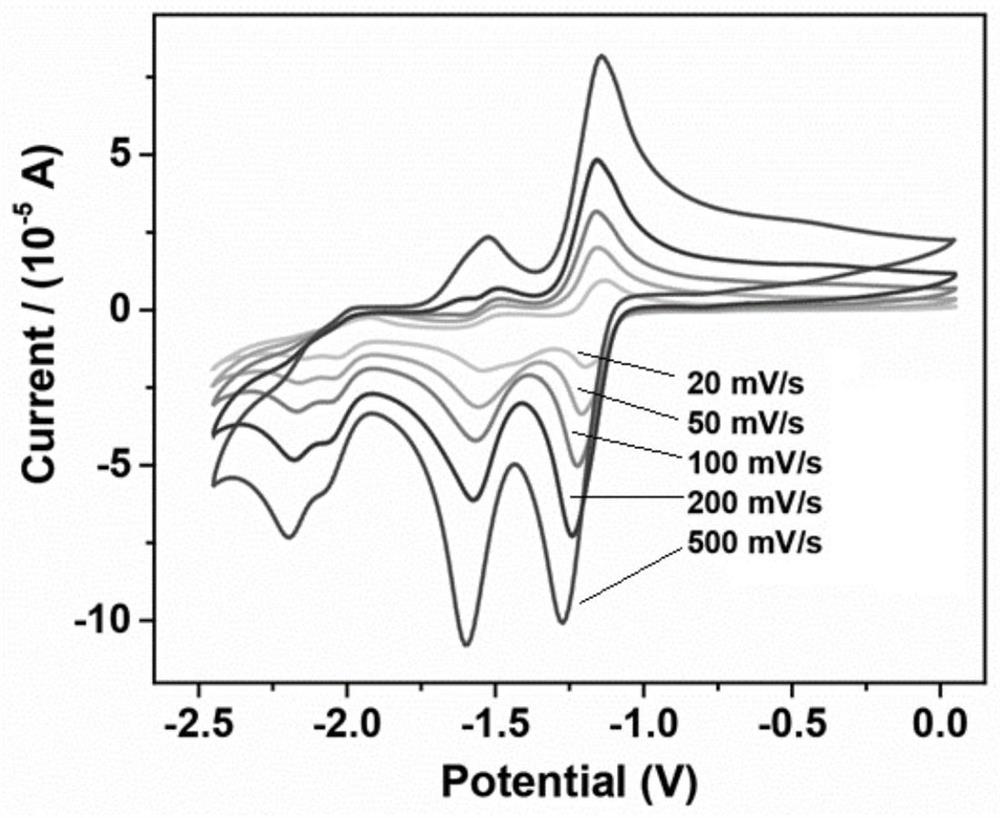
Lithium borohydride/decaborane solid electrolyte and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112467197ALarge anion sizeImprove ionic conductivitySolid electrolytesBoron/boridesSolid state electrolytePhysical chemistry
The invention relates to the technical field of solid electrolyte, in particular to lithium borohydride / decaborane solid electrolyte and a preparation method thereof. The lithium borohydride / decaborane solid electrolyte is a lithium borohydride / decaborane solid electrolyte Li2B12H12 or a mixture of the Li2B12H12 and the Li2B10H10 or a mixture of the Li2B12H12, the Li2B10H10 and the LiBH4. According to the preparation method, lithium borohydride and decaborane are used as raw materials, and the lithium borohydride / decaborane solid electrolyte is prepared through two-step reaction of hydrogen-filled ball milling and one-step heat treatment. The preparation method of the lithium borohydride / decaborane solid electrolyte is simple, environment-friendly and easy for large-scale preparation, andis a preparation method of the LiBH4-based superion conductor solid electrolyte which has popularization value and can realize batch production. The polyanion solid electrolyte prepared by the preparation method is excellent in ion transmission characteristic and excellent in electrochemical performance.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Hydrogenation heat gas chemical yield increasing solution component applied to shallow well
ActiveCN102942913BHigh porosityImprove permeabilityFluid removalDrilling compositionPorosityAmmonium nitrate
The invention belongs to the technical field of oil exploitation, and relates to a hydrogenation heat gas chemical yield increasing solution component capable of increasing permeability of a shallow well and a near wellbore region. The solution component comprises first solution and second solution, the mass ratio of the first solution to the second solution is 1:1, the first solution comprises 37-43% of ammonium nitrate NH4NO3, 23-26% of urea CO(NH2)2, 5-8% of decaborane B10H14, 1-2% of glucose C6H12O6, 0.5-1.5% of methenamine (CH2)6N4 and 19.5-33.5% of water. The second solution comprises 44-48% of sodium nitrate NaNO3, 15-20% of sodium nitrite NaNO2, 17-21% of sodium aluminum hydride NaAlH4 and 15-19% of tetrachloroethylene C2Cl4. By the aid of the solution component, porosity of an ore bed can be increased, accordingly, permeability is increased, and the yield can be increased by 2-10 times.
Owner:吉林贯通能源科技有限责任公司
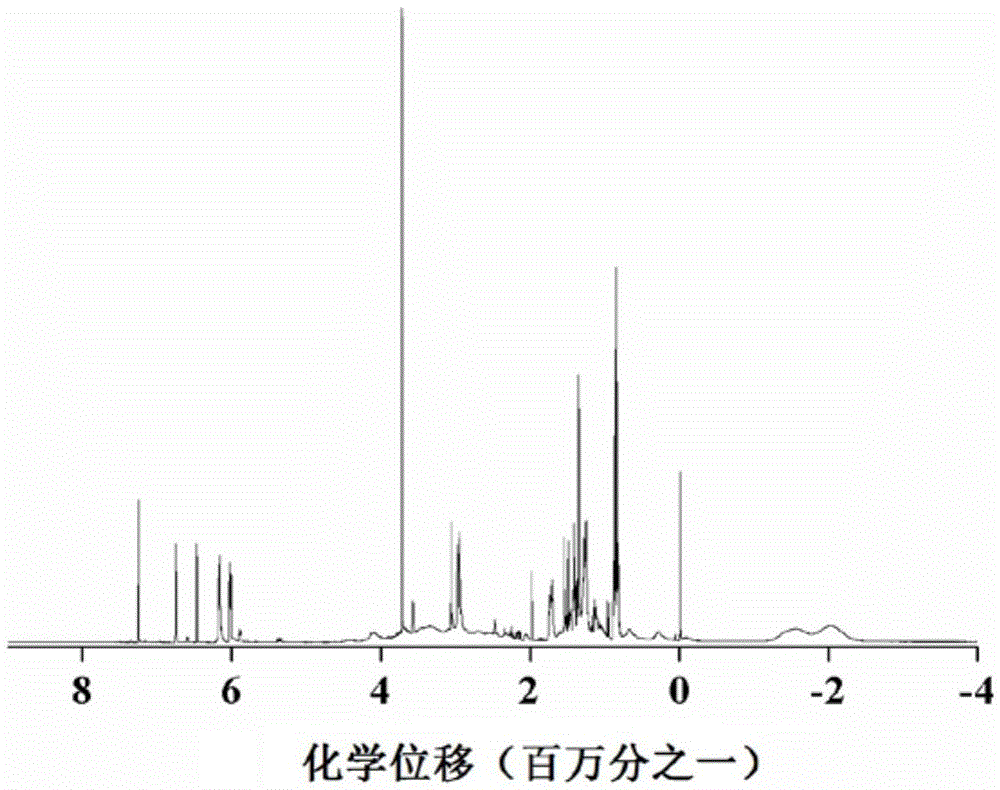
Preparation method of superfine-diameter SiBCN ceramic fibers
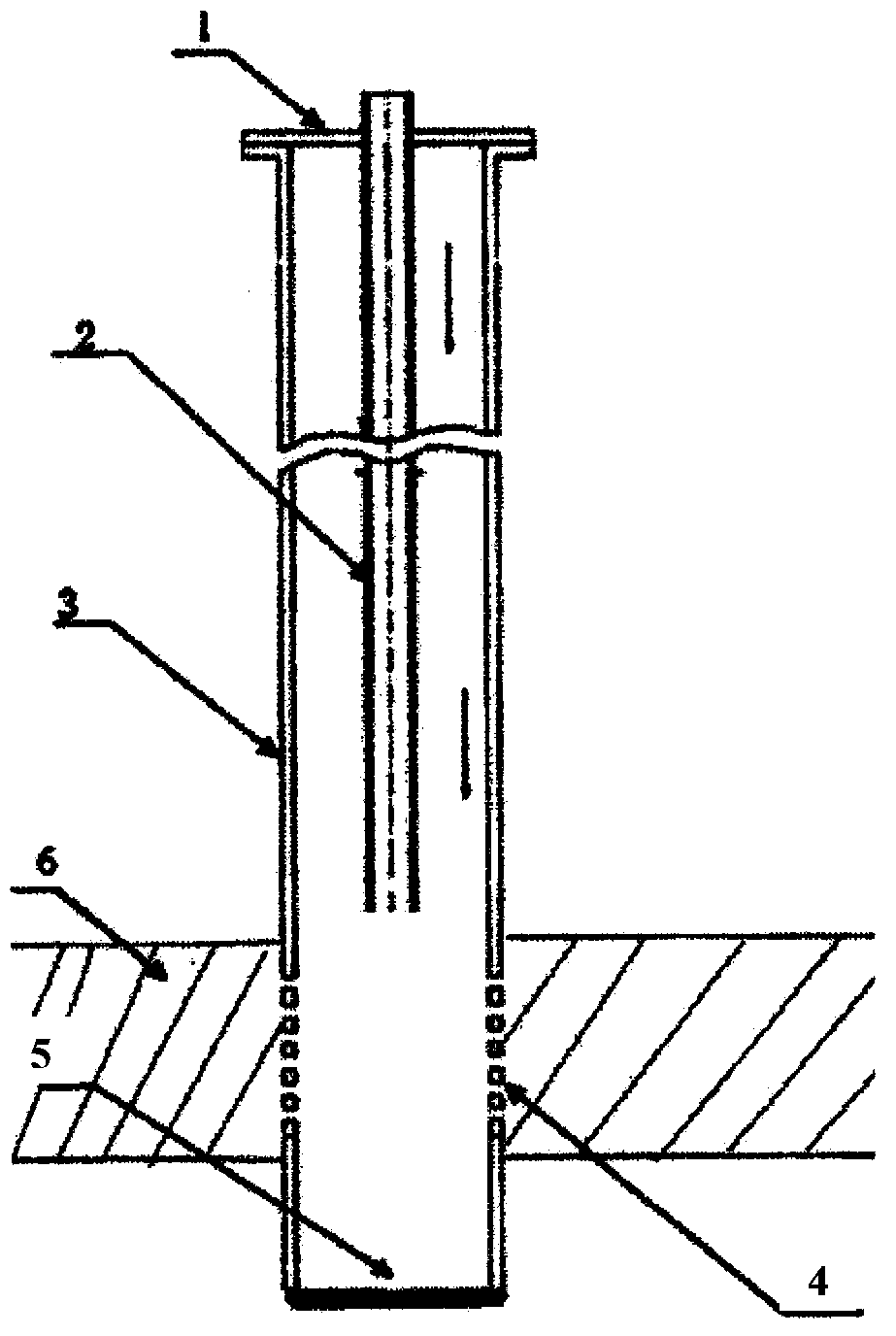
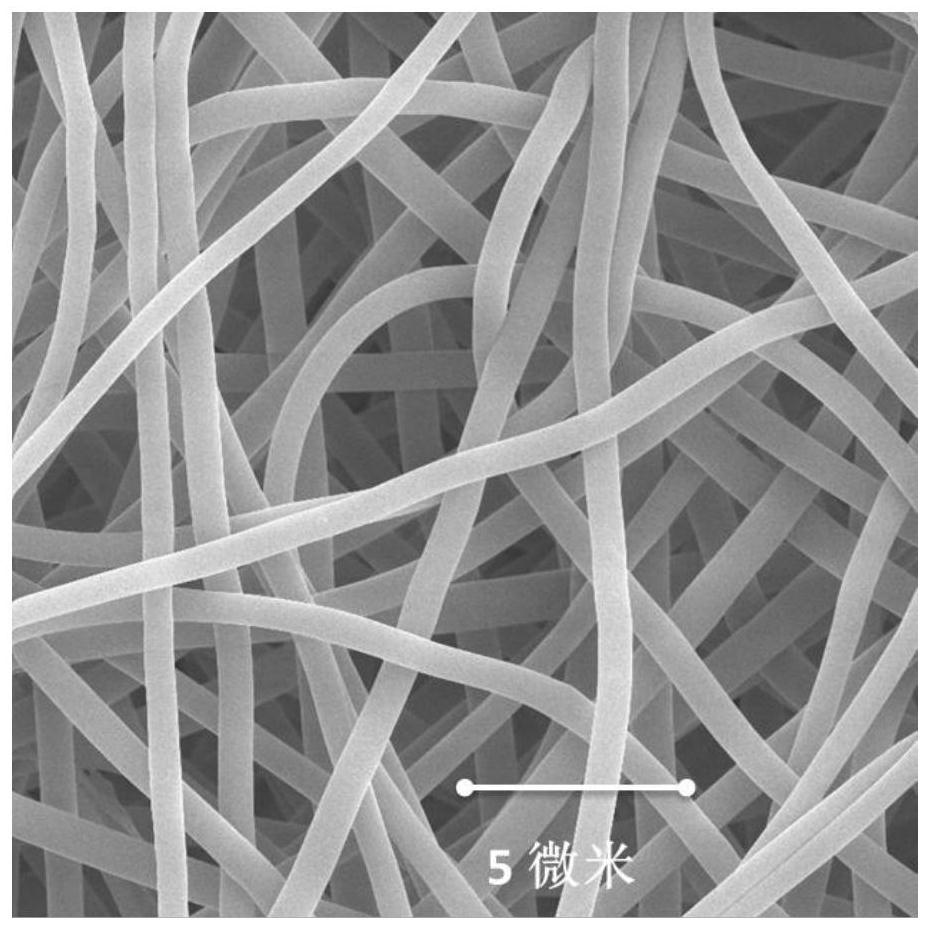
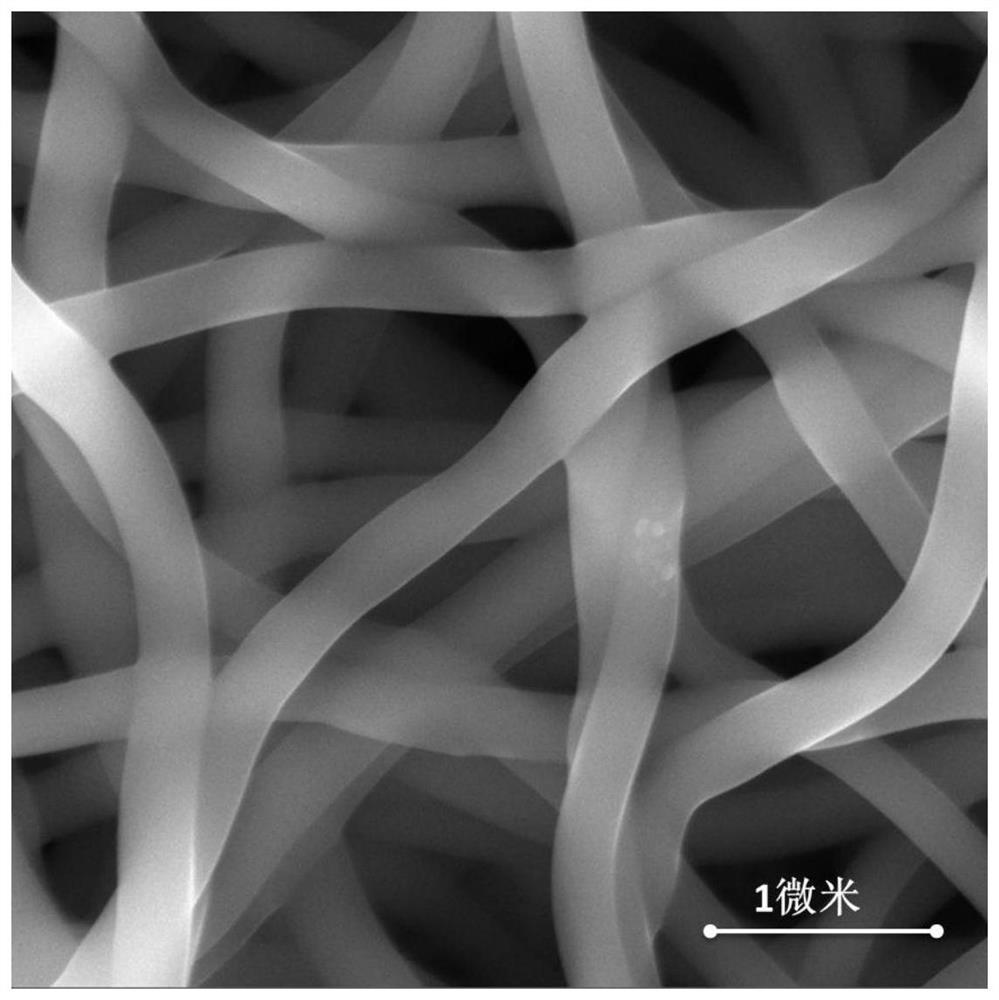
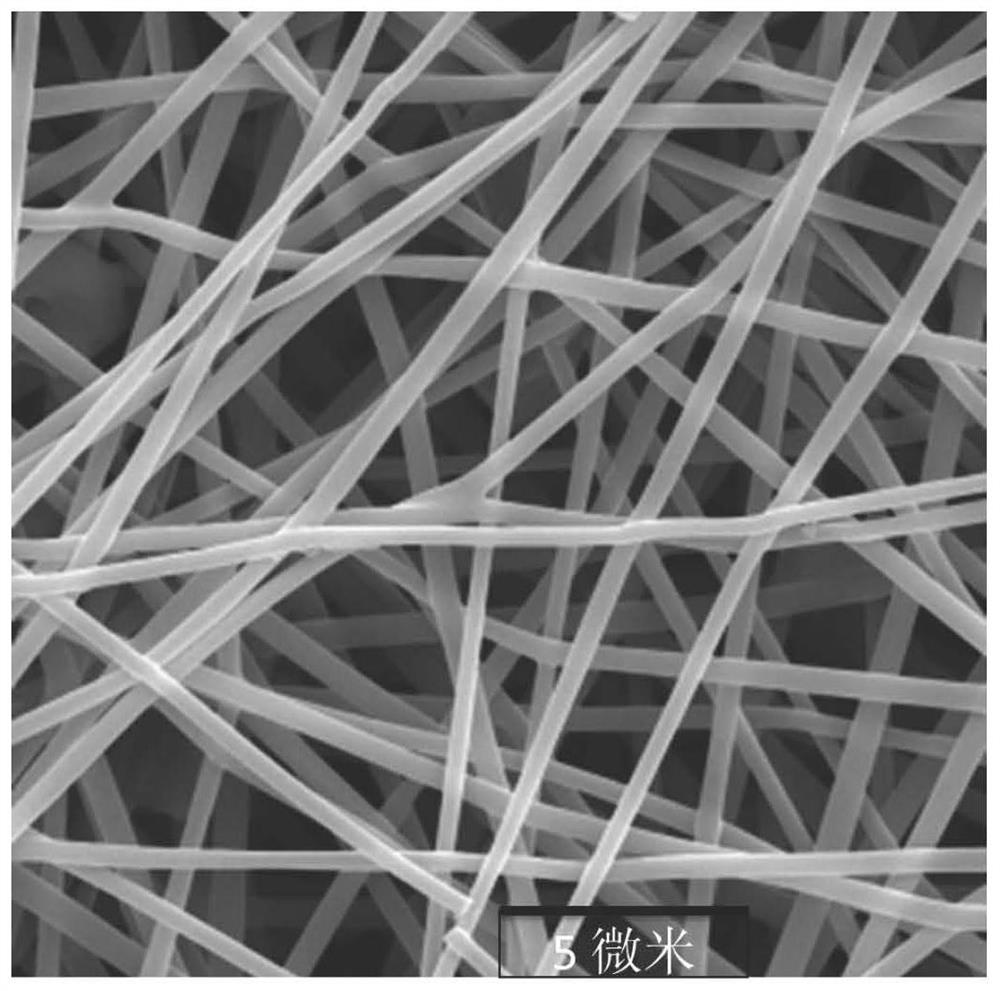
ActiveCN113151934AHigh synthetic yieldHigh ceramic yieldFibre chemical featuresSpinningElectrospinning
The invention provides a preparation method of superfine-diameter SiBCN ceramic fibers. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a decaborane solution, a diamine solution and a polyvinyl pyrrolidone solution; dropwise adding the diamine solution into the decaborane solution, reacting for more than 10 hours at room temperature, and then carrying out vacuum distillation for 8-12 hours under the 55-65 DEG C constant-temperature water bath condition to obtain silicon-containing polyborazine; adding a polyvinyl pyrrolidone solution into the silicon-containing polyborazine, and carrying out ultrasonic treatment to obtain a transparent spinning solution; performing electrostatic spinning treatment on the spinning solution to obtain superfine fibers; and placing the superfine fibers in a sintering furnace, heating to 1400-1600 DEG C from room temperature at a heating rate of 1-5 DEG C / min in an inert atmosphere, and cooling to 100 DEG C or below along with the furnace to obtain the superfine-diameter SiBCN ceramic fibers. The synthesis method is simple and easy to implement, and is suitable for the application field of preparing flexible, high-temperature-resistant and heat-insulating multifunctional materials.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
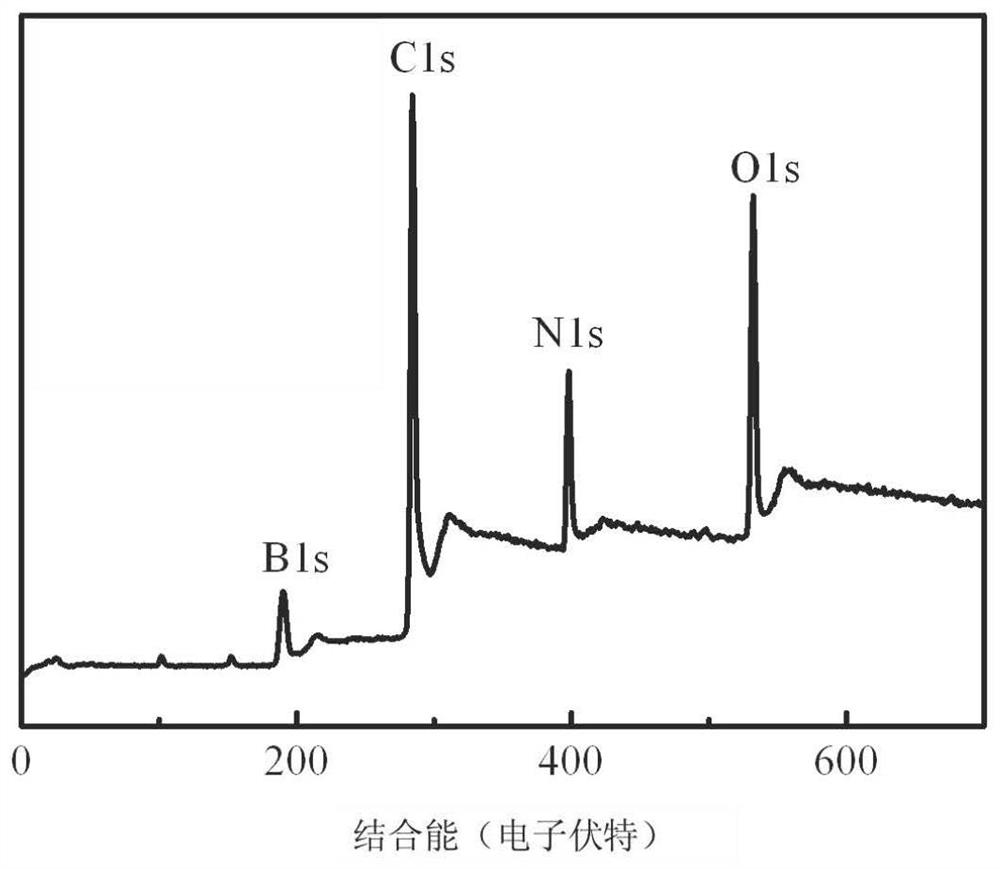
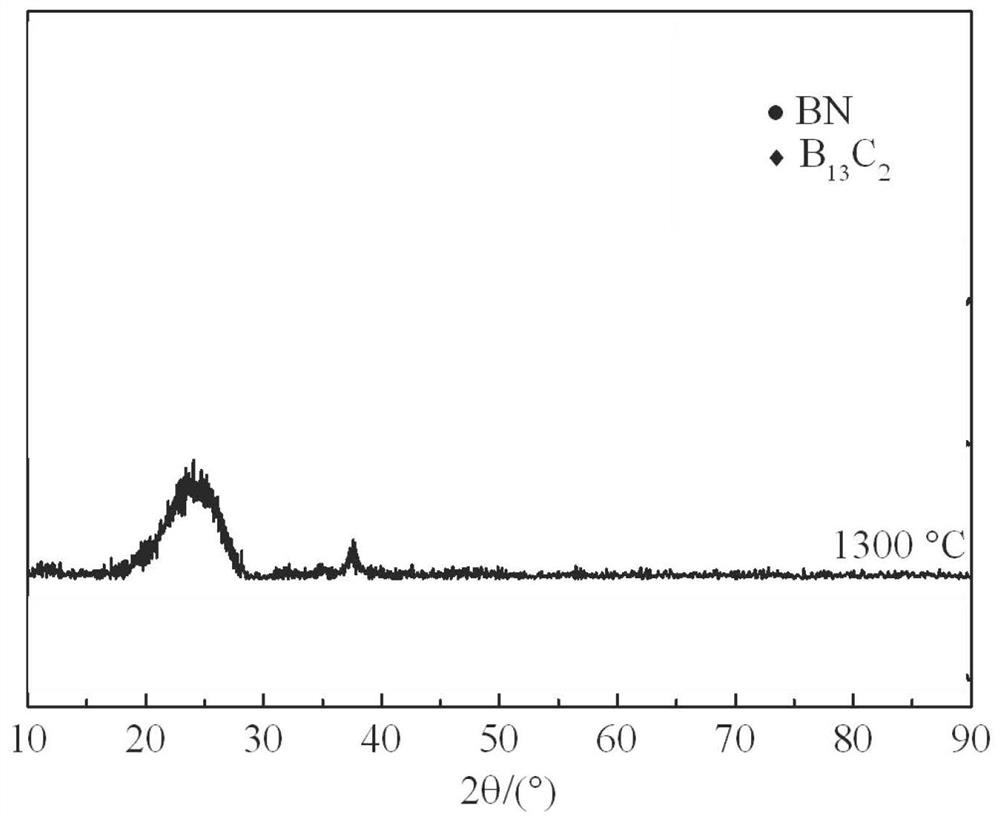
Preparation method of superfine-diameter BCN and BN ceramic fibers
ActiveCN113046862AThe synthesis method is simpleMeet different application needsInorganic material artificial filamentsSpinningPolystyrene
The invention provides a preparation method of superfine-diameter BCN and BN ceramic fibers. The preparation method comprises the following steps: reacting the same amount of decaborane and nitrogen source molecules in tetrahydrofuran at room temperature for 10-14 hours, and then distilling at 90-110 DEG C for 5-8 hours to remove a solvent to obtain a BCN ceramic precursor; dissolving the BCN ceramic precursor and polystyrene in N,N-dimethylformamide or a mixed solution of N,N-dimethylformamide and tetrahydrofuran to prepare a spinning solution; carrying out solution spinning treatment on the spinning solution to obtain superfine fiber felt; and placing the superfine fiber felt in a vacuum sintering furnace, introducing protective gas, raising the temperature to 1200-1400 DEG C at the speed of 60-100 DEG C per minute, keeping the temperature for 2 h, and cooling to the room temperature, wherein when the introduced gas is nitrogen, BCN ceramic fibers with the superfine diameter is obtained; and when the introduced gas is the mixed gas of nitrogen and ammonia gas, superfine-diameter BN ceramic fibers are obtained.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Synthetic method for boron-containing precursor copolymer
The invention provides a synthetic method for a boron-containing precursor copolymer. The synthetic method adopts a decaborane and a dienes organic compound as raw materials for reaction. A boron carbide precursor prepared by the synthetic method has high ceramic yield and boron content and favorable solubility, and can be used for preparing boron carbide pellets for nuclear fusion and other boron carbide ceramic materials.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Carborane viologen derivative as well as metal supramolecular polymer, synthesis method and application
ActiveCN112209955ALower energy gapRich redox propertiesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsAceric acidPolymer chemistry
The invention discloses a carborane viologen derivative, a metal supramolecular polymer, a synthesis method and application. Viologen is used as a central core structure, 1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)acetylene is synthesized through a Sonagashira coupling reaction, and then alkynyl is attacked by decaborane to synthesize a carborane viologen precursor A; or alkynyl in bis(4-bromophenyl)acetylene is attackedwith decaborane to synthesize bis(4-bromophenyl)carborane, then a carborane viologen precursor B is synthesized through a Still coupling reaction, and finally the carborane viologen derivative is further obtained through the carborane viologen precursor A or the carborane viologen precursor B. Then, viologen is used as a central core structure, the carborane viologen derivative, ruthenium trichloride, cobalt dichloride or ferrous acetate are used as reaction raw materials, acetic acid is used as a solvent for reflux reaction, and finally, a product in reaction liquid is separated and dried tosynthesize the carborane viologen metal supramolecular polymer.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Carboryl celecoxib and its preparation and application in boron neutron capture therapy for head and neck cancer
ActiveCN112358492BStrong selective uptakeGood killing effectEnergy modified materialsGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsCancer cellApoptosis
The invention discloses a preparation of carboryl celecoxib and its application in boron neutron capture therapy drugs for head and neck cancer, and relates to the fields of medicinal chemistry and radiation medicine. The compound can be prepared by stepwise substitution and addition reaction of celecoxib with 3-bromopropyne and decaborane in toluene solution. The invention has simple preparation process, easy operation, high product yield and high purity. The compound of the present invention has been proved by head and neck cancer cell experiment results that the compound has high selectivity to head and neck cancer cells, and has obvious apoptosis-inducing effect on head and neck cancer cells in boron neutron capture therapy. Compared with the existing clinical drugs used in boron neutron capture therapy, the compound not only has high boron loading capacity and strong tumor selectivity, but also can exert anti-inflammatory effect while exerting the curative effect of radiotherapy, and reduce the toxic and side effects of treatment.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com