Method and apparatus for extracting ions from an ion source for use in ion implantation
a technology of ion beam and ion source, which is applied in the manufacture of electrode systems, electric discharge tubes/lamps, separation processes, etc., can solve the problems of serious contamination effect, interference with the successful operation of the source, and severe impact on the precise qualities of the ion beam, so as to avoid unstable operation and maintain the effect of dimensional stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
Novel Ion Beam-Generating System
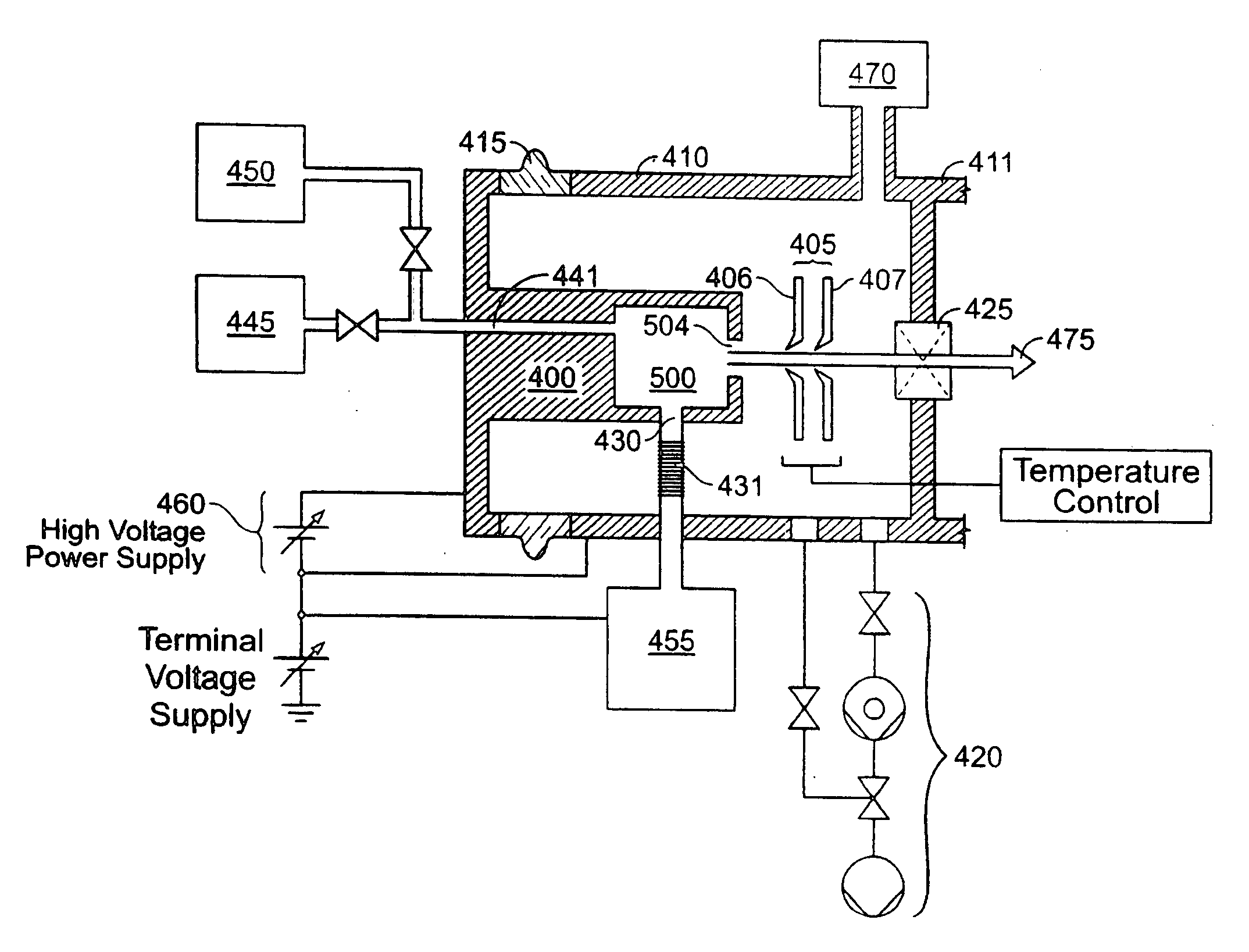
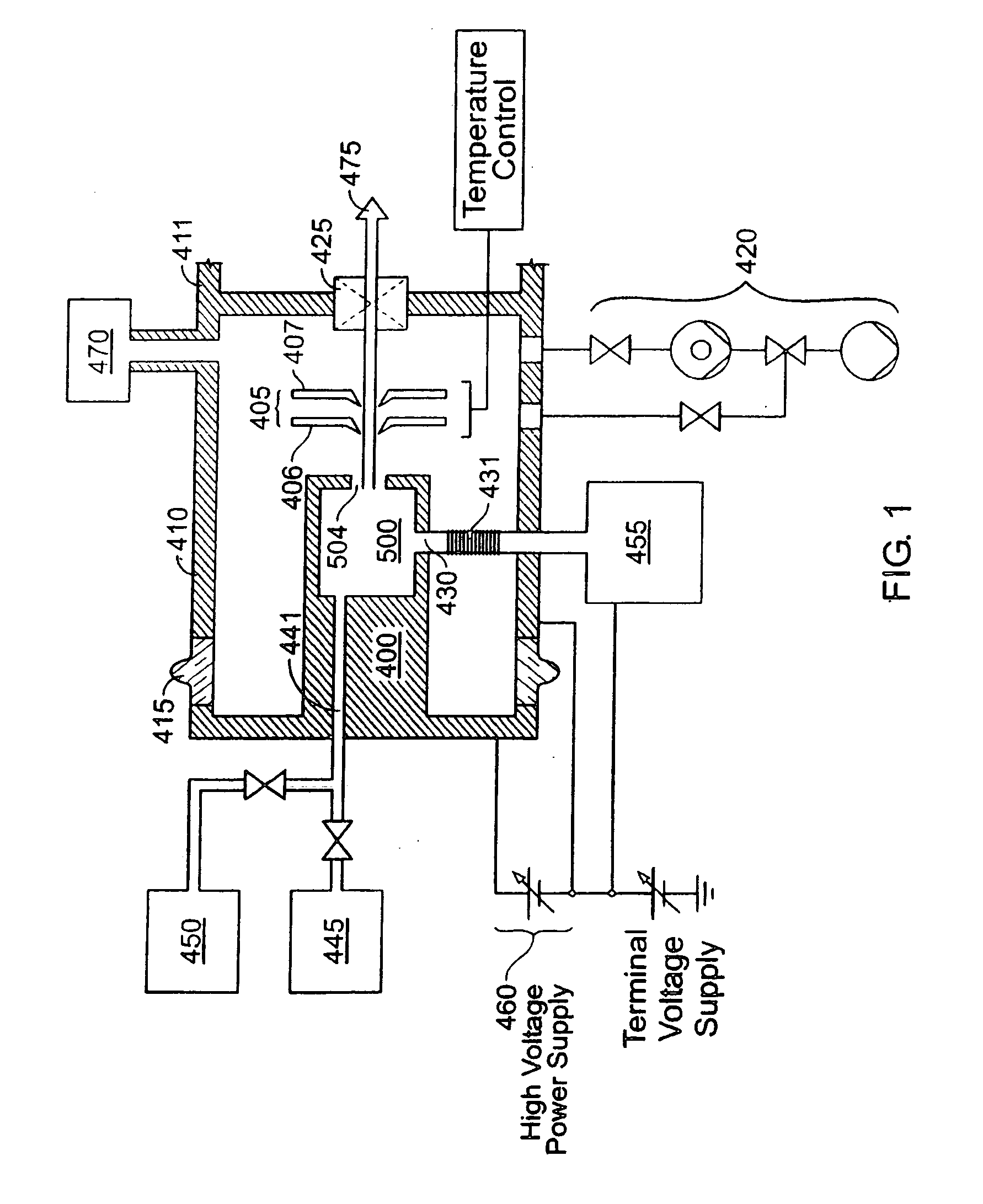
[0151]FIG. 1 shows an ion beam-generating system. As shown in this example, it is adapted to produce an ion beam for transport to an ion implantation chamber for implant into semiconductor wafers or flat-panel displays. Shown are ion source 400, extraction electrode 405, vacuum housing 410, voltage isolation bushing 415 of electrically insulative material, vacuum pumping system 420, vacuum housing isolation valve 425, reactive gas inlet 430, feed gas and vapor inlet 441, vapor source 445, feed gas source 450, reactive gas source 455, ion source high voltage power supply 460, and resultant ion beam 475. An ion beam transport housing is indicated at 411. The ion source 400 is constructed to provide cluster ions and molecular ions, for example the borohydride ions B10Hx+, B10Hx−, B18Hx+, and B18Hx− or, or in addition, more conventional ion beams such as P+, As+, B+, In+, Sb+, Si+, and Ge+. Ion source 400 may be a Bernas-style arc-discharge ion source, ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| vapor pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| internal surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com