Patents
Literature
1473results about "Drum brakes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
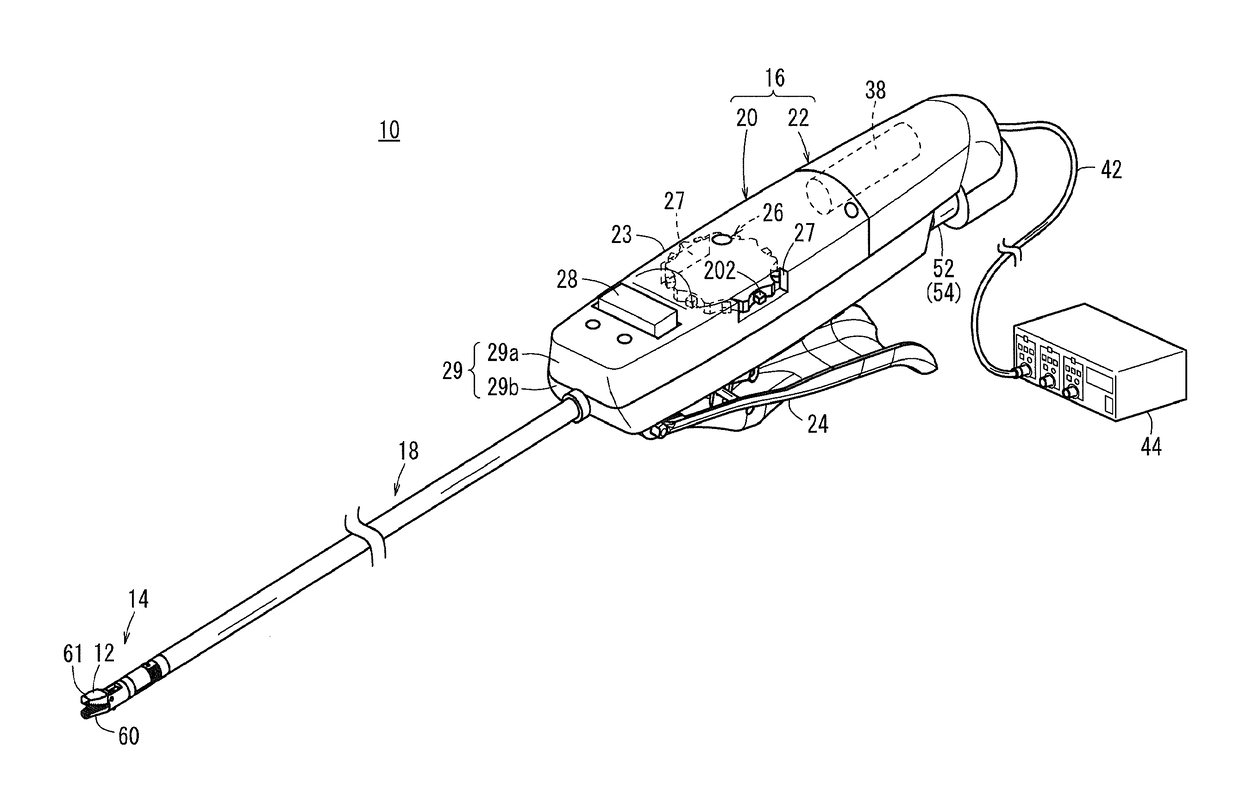
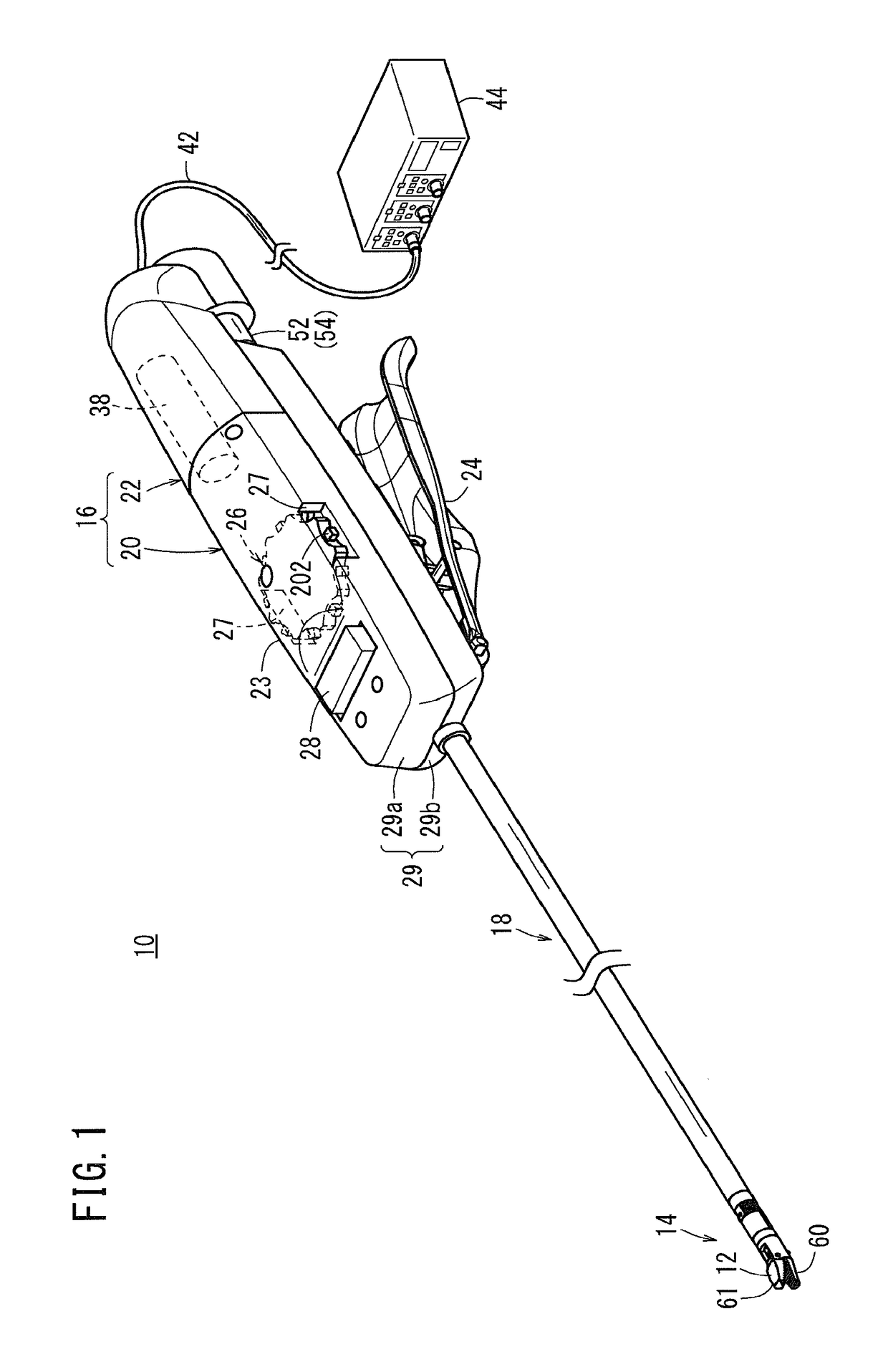
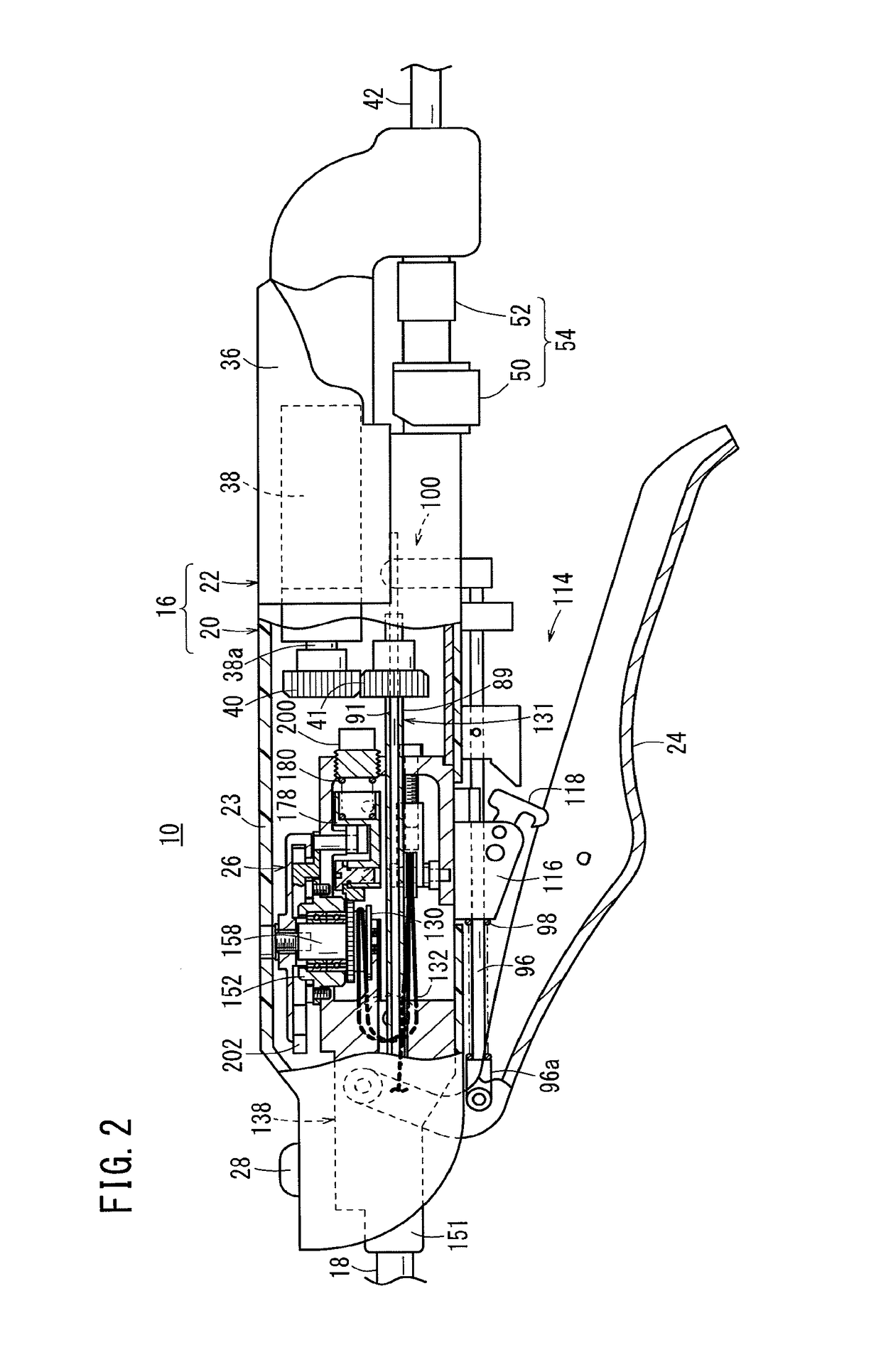
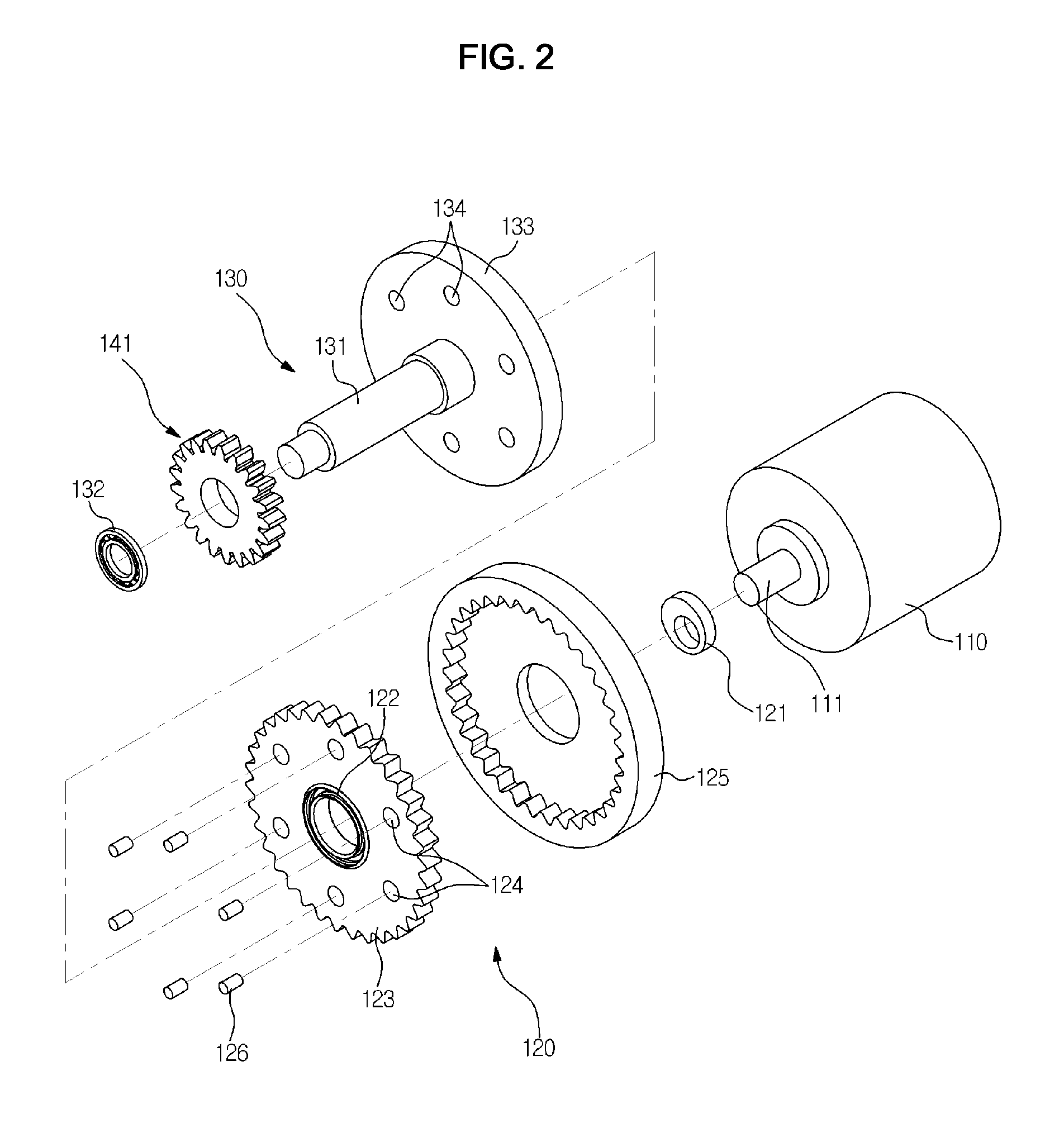
Brake release mechanism and medical manipulator provided with same
ActiveUS10064639B2Easily and swiftly releasingFacilitated releaseSurgical needlesDrum brakesEngineeringManipulator
A medical manipulator is provided with a brake release mechanism. The brake release mechanism is provided with a release button which is provided on a tilt wheel, and a lever mechanism which has at least one portion arranged on the inside of the tilt wheel and which is pressed when the release button moves inwards. By the action of the lever mechanism when the release button is operated, braking by a brake mechanism is released.
Owner:KARL STORZ GMBH & CO KG
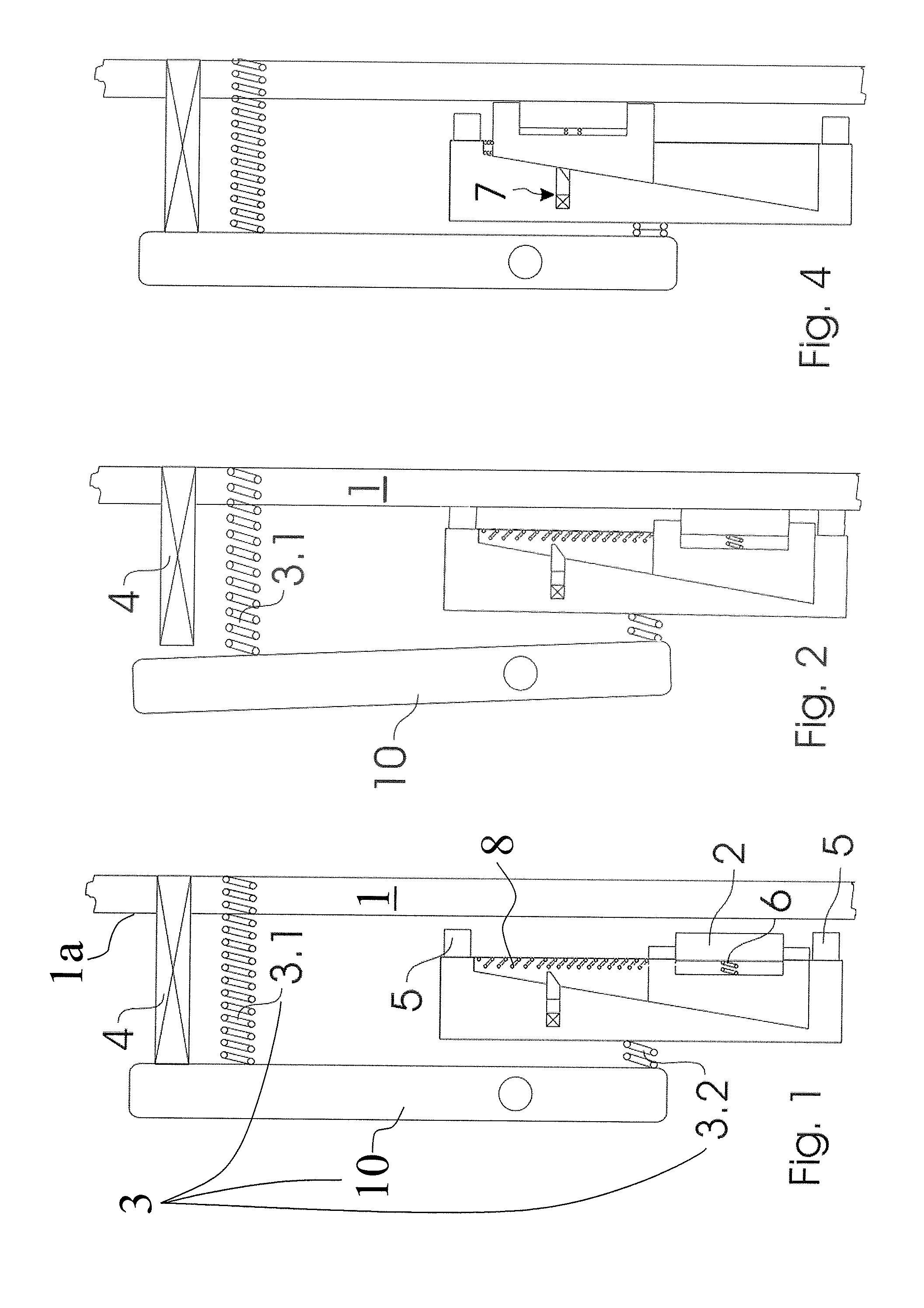
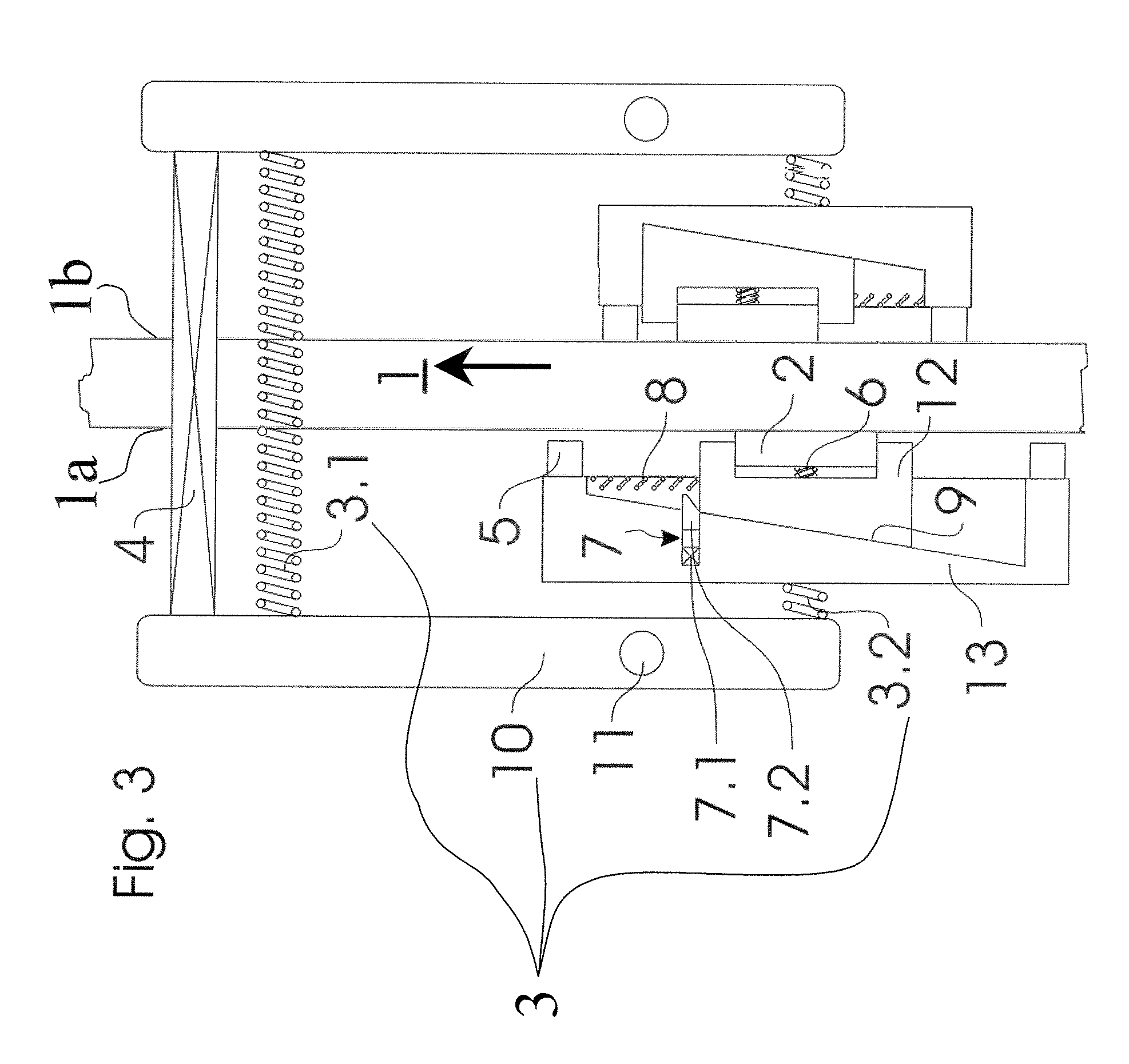
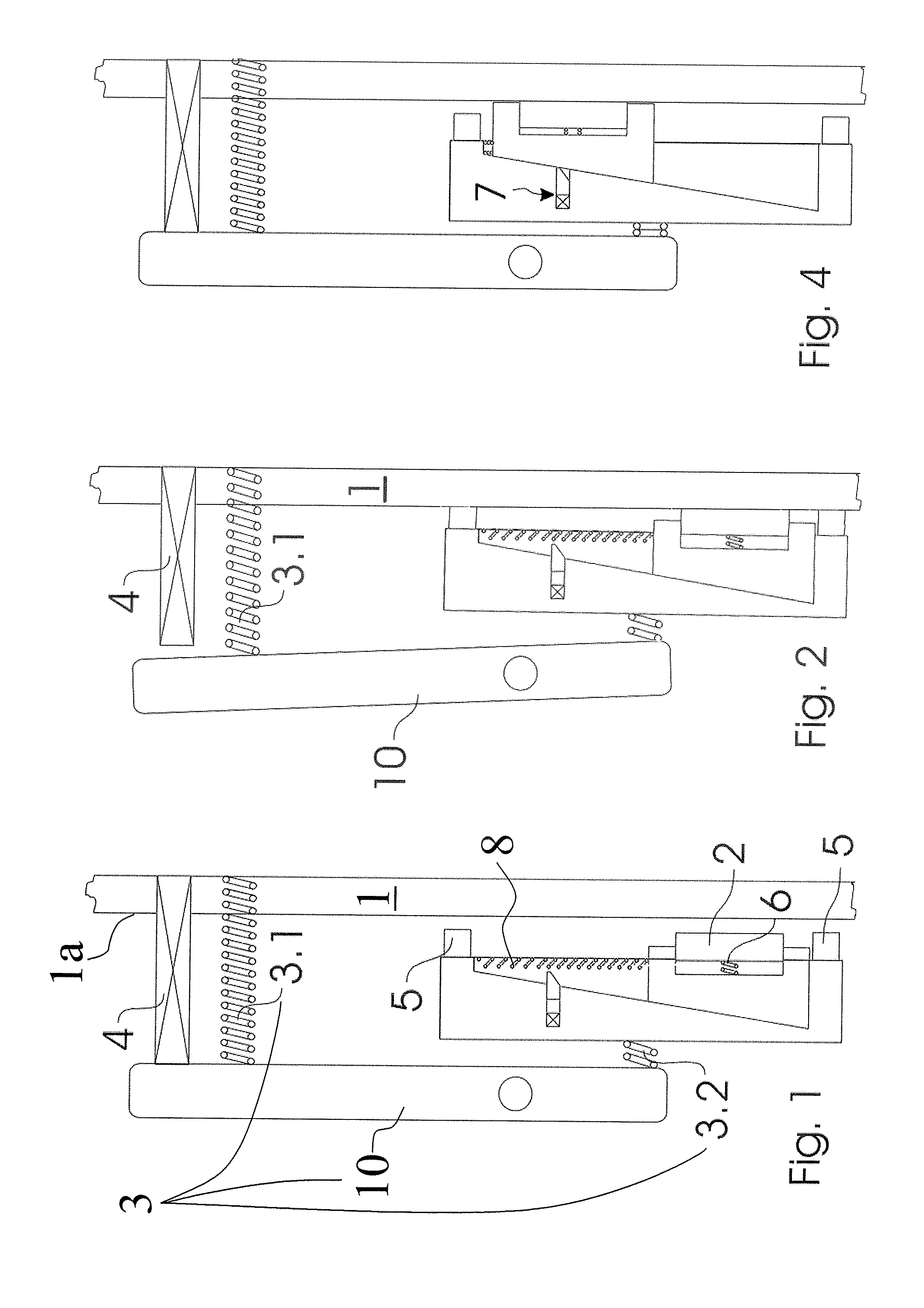
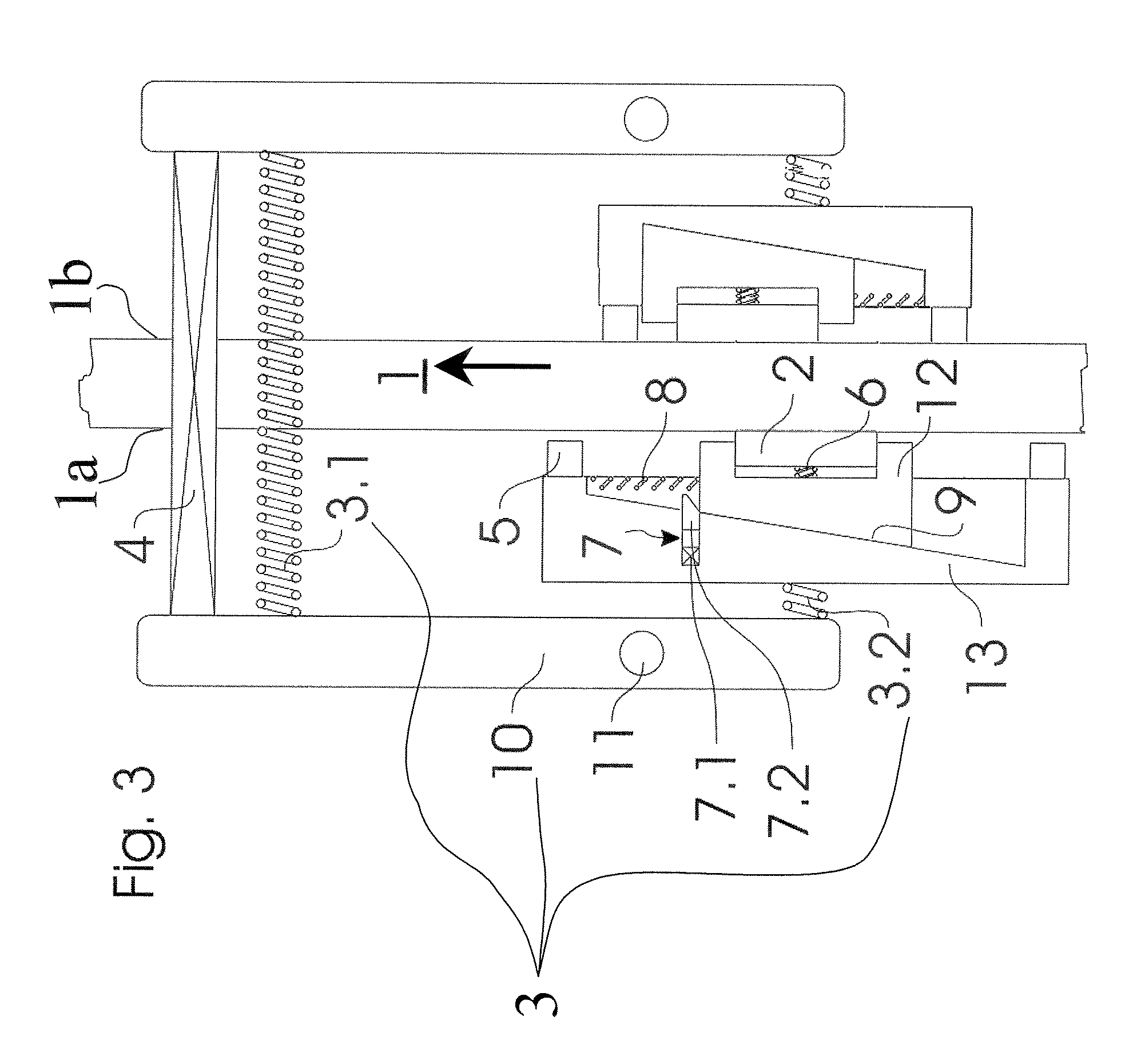
Brake equipment for holding and braking an elevator car in an elevator installation and a method of holding and braking an elevator installation
Brake equipment for holding and braking an elevator car in an elevator installation, which is arranged to be movable along a brake track in two directions of travel, includes a mount with a brake lining which automatically adjusts under friction couple with the brake track on movement of the elevator car relative to the rail and in that case tightens a first tightening means, which can be released by an actuator. The first tightening means tightens the mount together with the brake lining against the brake track by a biasing force. The brake equipment produces, with unmoved brake equipment and an unreleased state of the actuator, a holding force acting in both directions of travel. The holding force is determined substantially by the biasing force acting on the mount.
Owner:INVENTIO AG
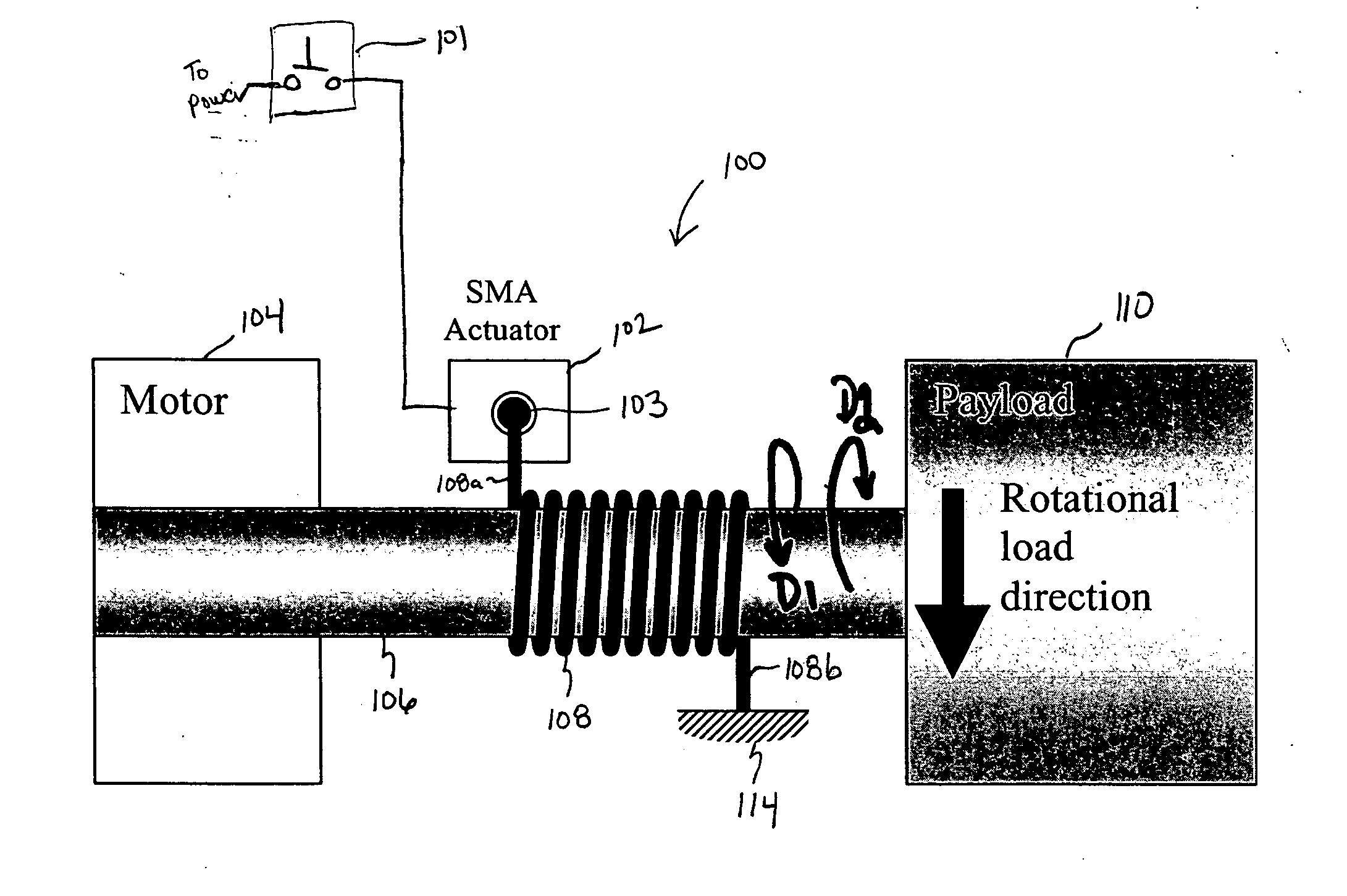
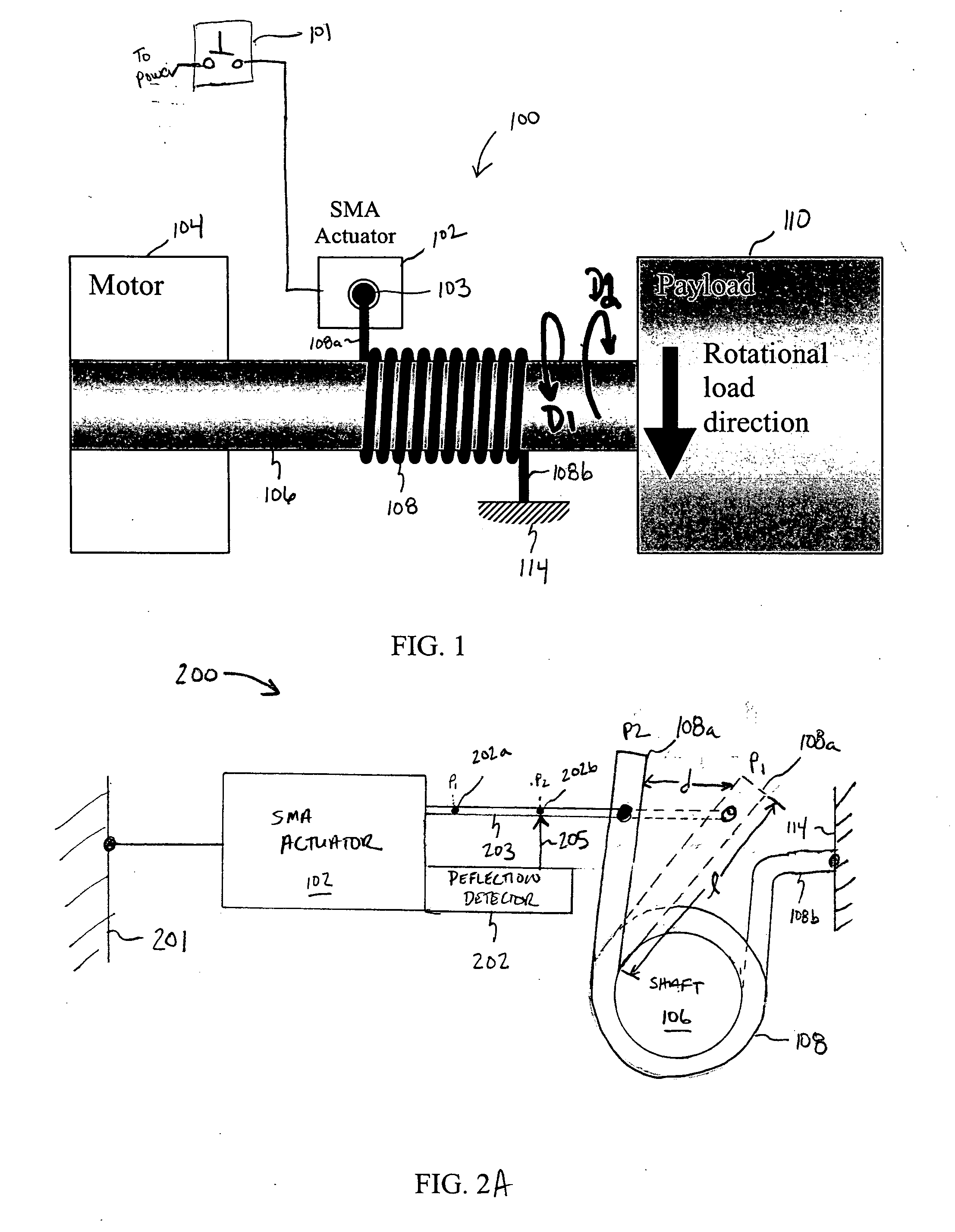
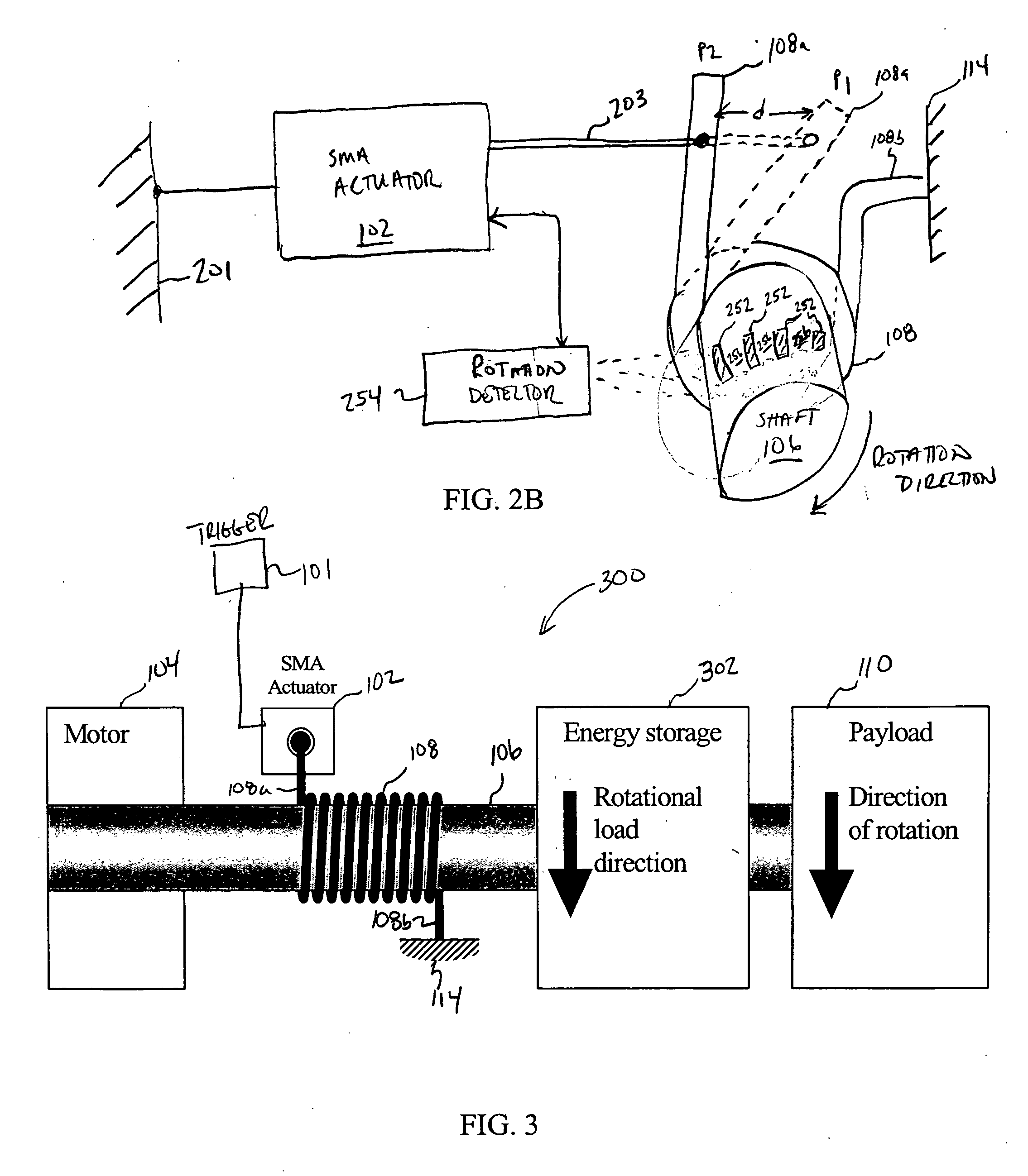
Shape memory alloy-actuated and bender-actuated helical spring brakes
In one embodiment of the present invention, a shape memory alloy (“SMA”)-actuated helical spring brake comprises a rotatable member and a helical wrap spring arranged concentrically about the rotatable member. The spring has a first spring end and a second spring end and includes a number of turns that are based radially inward and are configured to frictionally engage the rotatable member. The turns permit rotation of the rotatable member in a first direction and inhabit rotation in a second direction. The SMA-actuate helical spring brake also include an anchor point coupled to the second spring end, and an SMA actuator having an output drive member coupled to the first spring end. The SMA actuator is configured to, for example, deflect the first spring end to permit the rotatable member to rotate.
Owner:ALFMEIER PRAZISION BAUGRUPPEN & SYSTLOSUNGEN
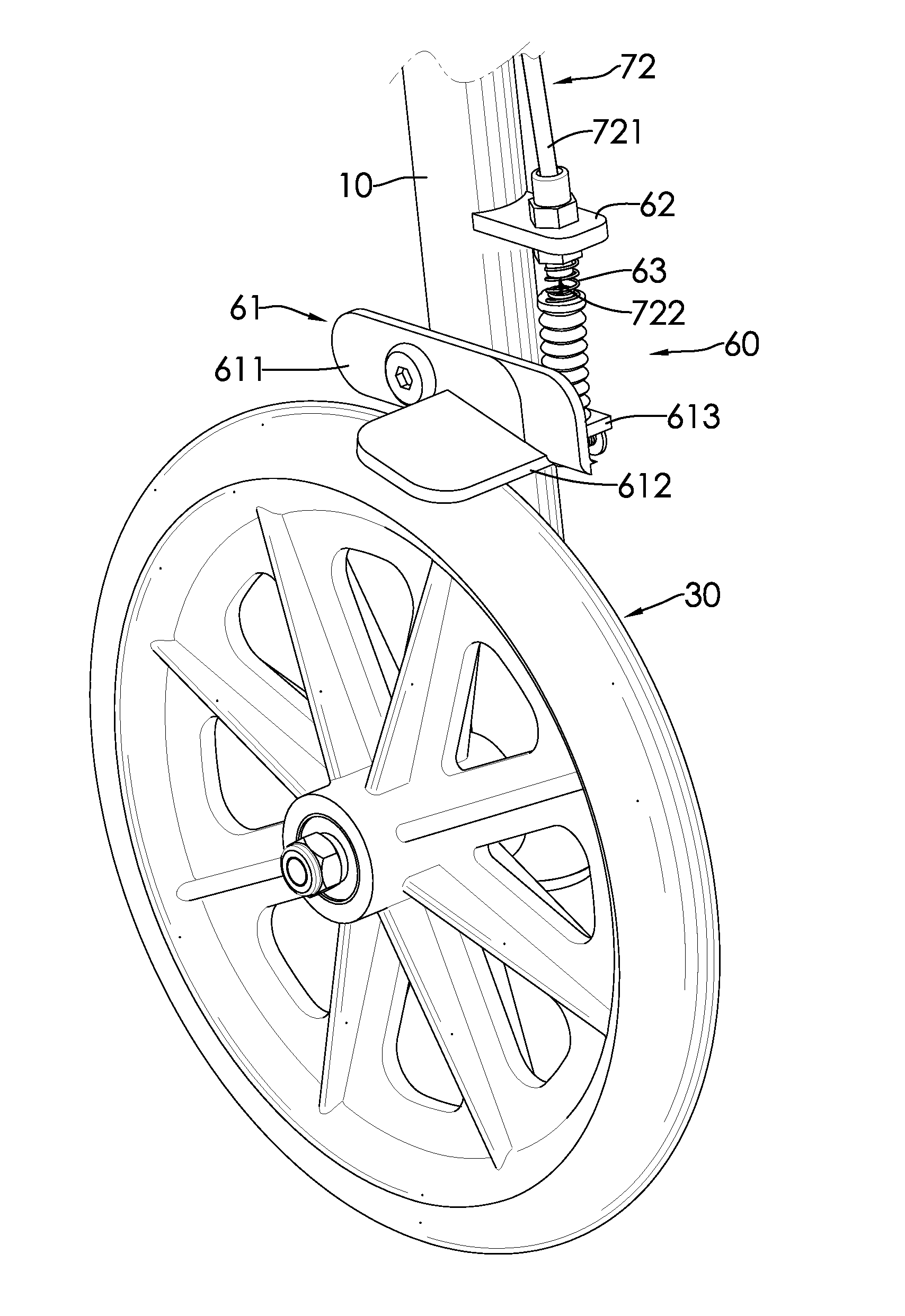
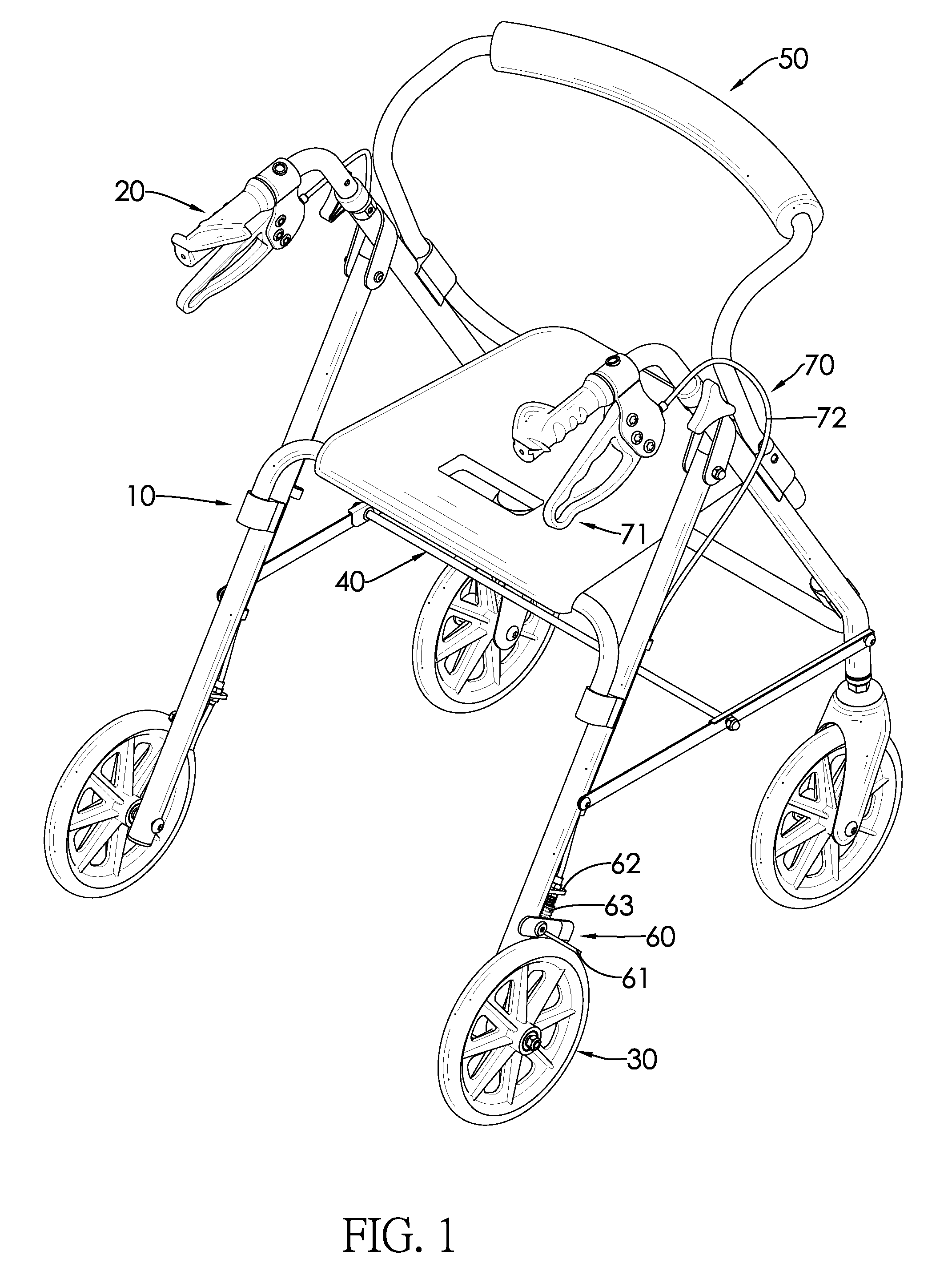
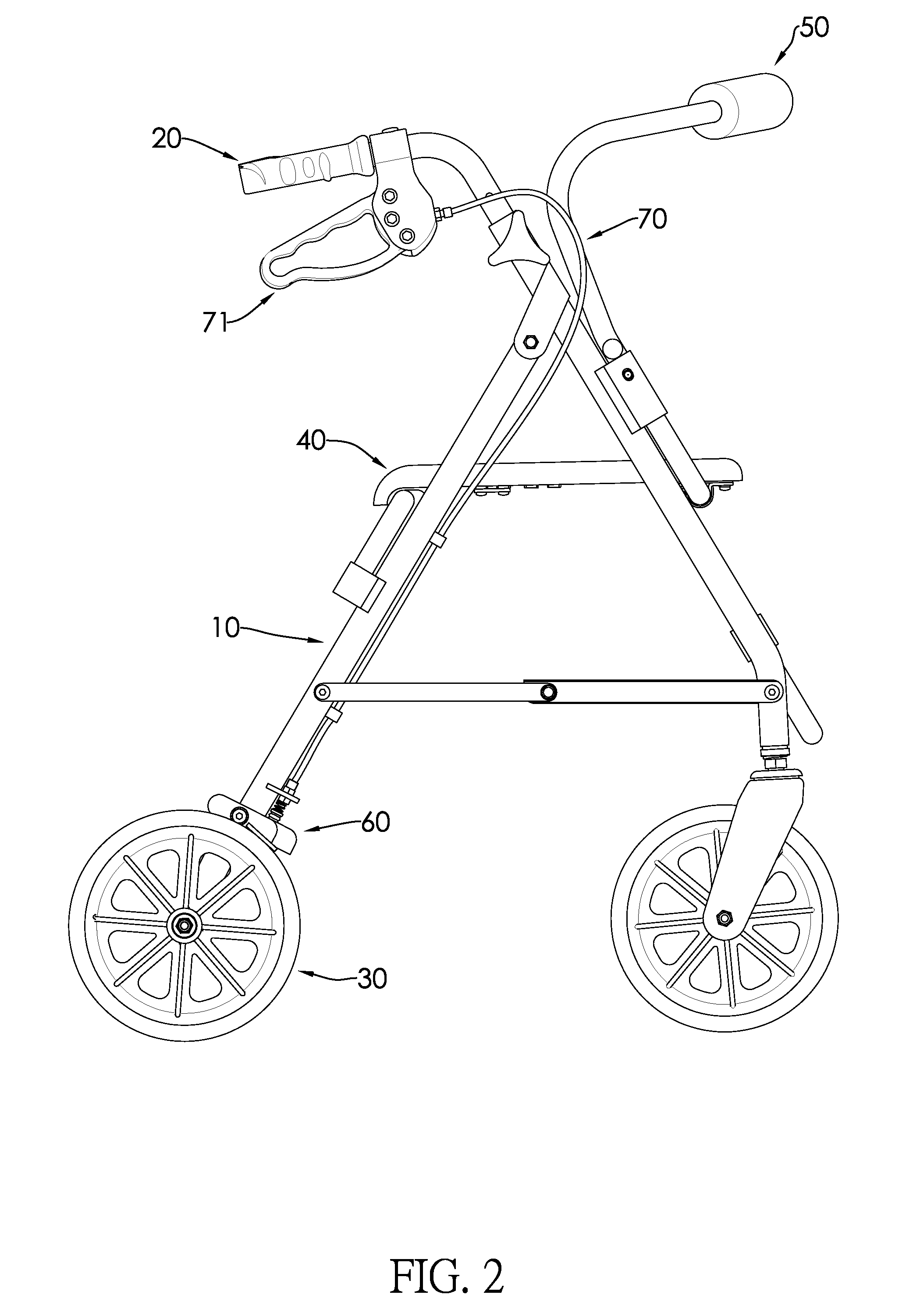
Braking system, rollator and transport chair with the same
ActiveUS8998223B2Prevent rotationCarriage/perambulator accessoriesBraking element arrangementsEngineeringBraking system
A braking system is mounted on a rollator or a transport chair and includes a braking part and an operating system. The braking part is mounted adjacent to a wheel of a rollator or a transport chair. When the operating system is unactuated, the braking part abuts a corresponding wheel to avoid a rotation of the corresponding wheel. When a user wants to walk and move the rollator or the transport chair, the user can press the operating system such that the braking part departs from the wheels and releases a brake. When the user wants to sit on the seat cushion and rest, the user can keep the braking system actuated without pressing the operating system, and accordingly the rollator or the transport chair would not be slidable when sat on, thereby avoiding danger. In addition, when the user walks on a slope, the user can release their hands from the rollator or the transport chair without making the rollator or the transport chair slide down the slope.
Owner:FLYING EAGLE TECH
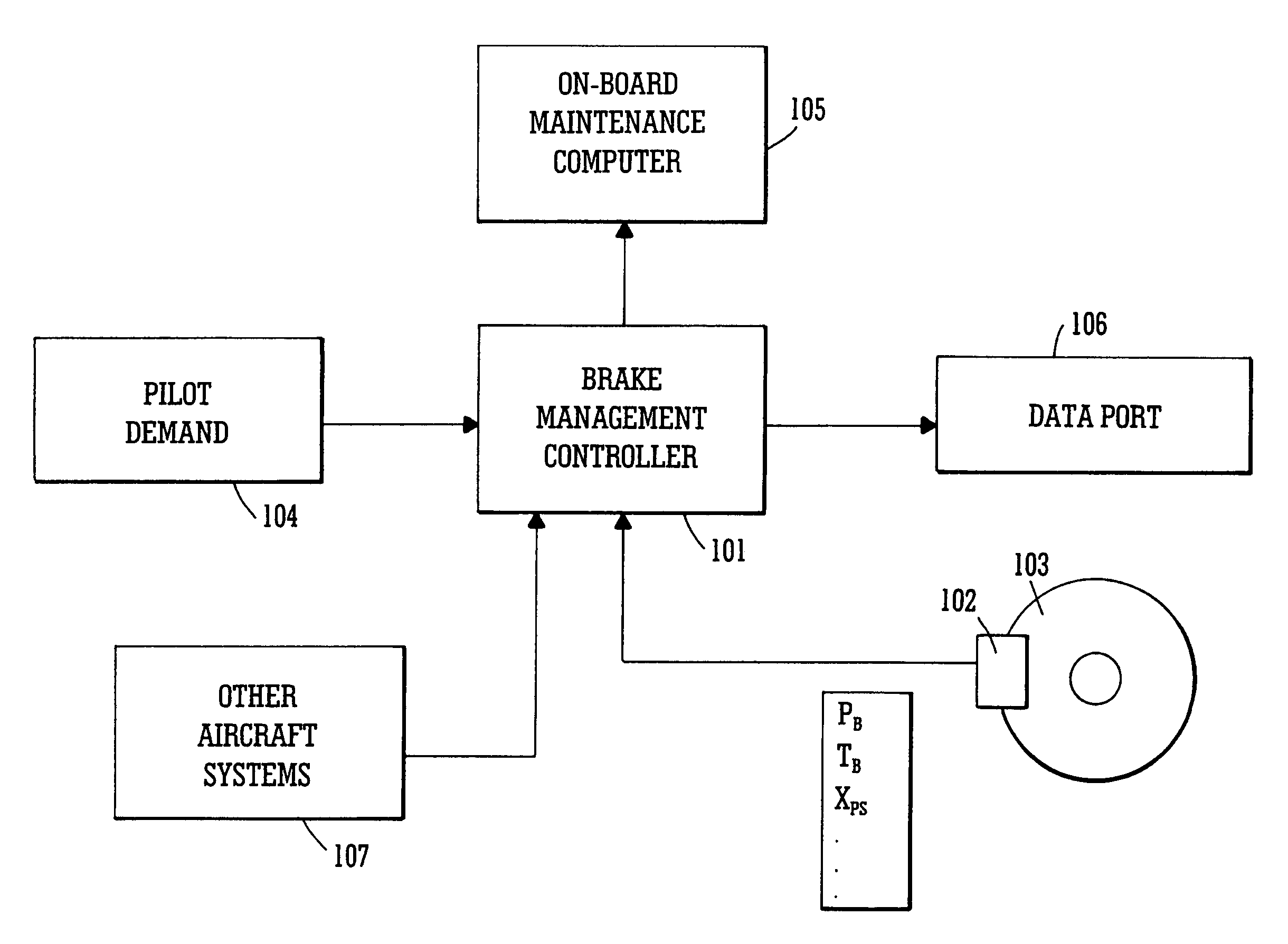
Brake condition monitoring
InactiveUS7086503B2Less-rapid decelerationBrake fluid pressure increaseFinanceAircraft braking arrangementsRelative motionBraking system
System and method for monitoring the applications of the brakes, e.g. of an aircraft to determine brake condition and operate a brake maintenance programme or charge a brake system user. It is desirable to have accurate information for determining the condition and predicting the life of carbon-carbon brake discs. This is important for safety as well as commercial reasons. The number of landings of an aircraft is often used as a determinant for such as lifetime warranties for brake discs and recommended maintenance periods. However, at least for carbon disc brakes, this may not be entirely accurate. For example such brake discs also wear during taxiing. The system and method herein includes monitoring each actuation of the brakes and making a separate record of each actuation of the brakes in which there is relative movement of the facing friction surfaces that cause wear, and from that separate record determining brake usage. The monitoring may include measuring changes and processing the signals to distinguish between those which fall below and those which are above a threshold value. Herein there is also described, a method and apparatus for monitoring a braking system comprising sensing a plurality of braking parameters having values dependent upon wear in the system and different faults of the system, and identifying and recording wear and faults based on combinations of values of said parameters.
Owner:MEGGITT AEROSPACE
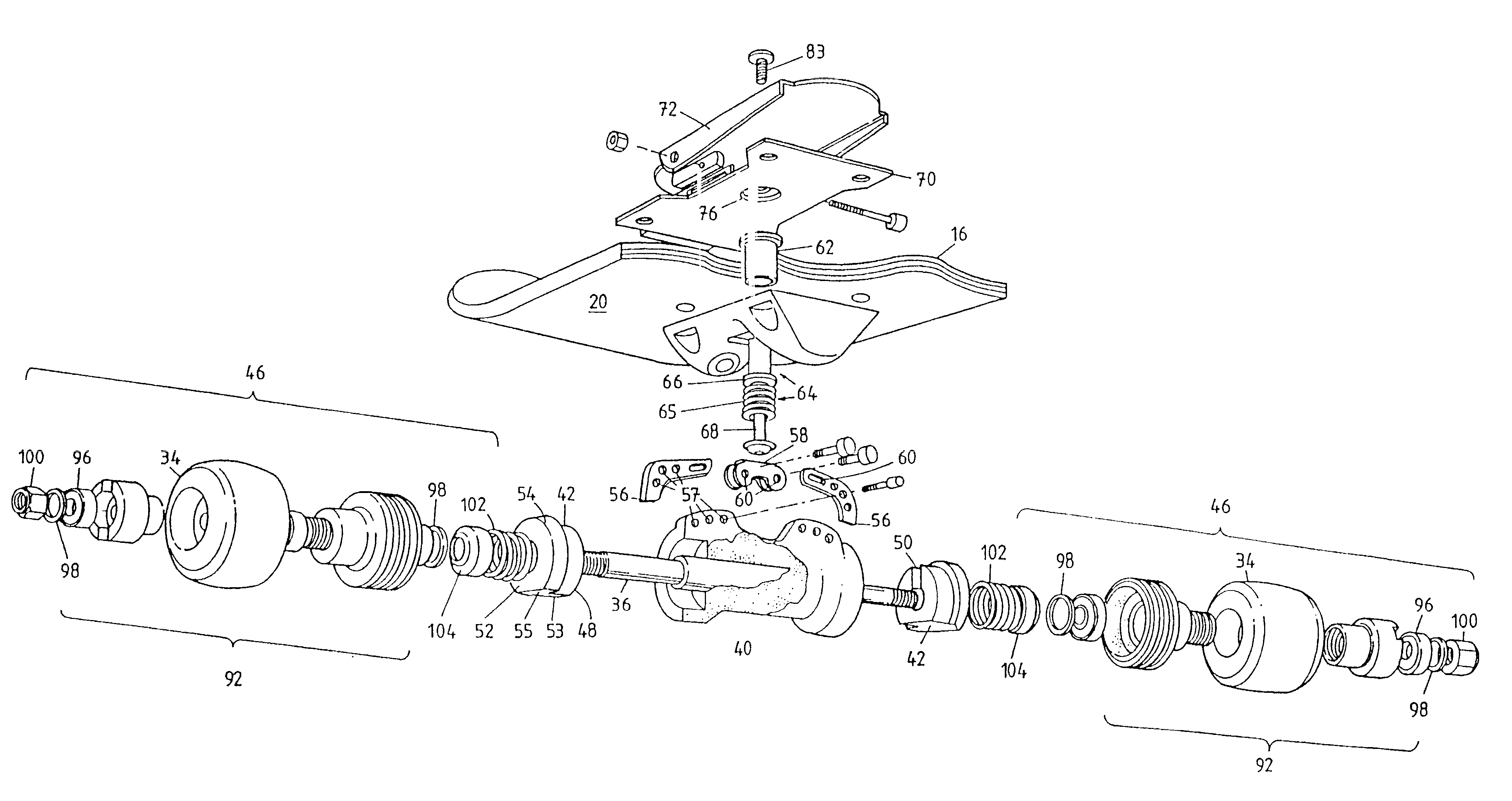
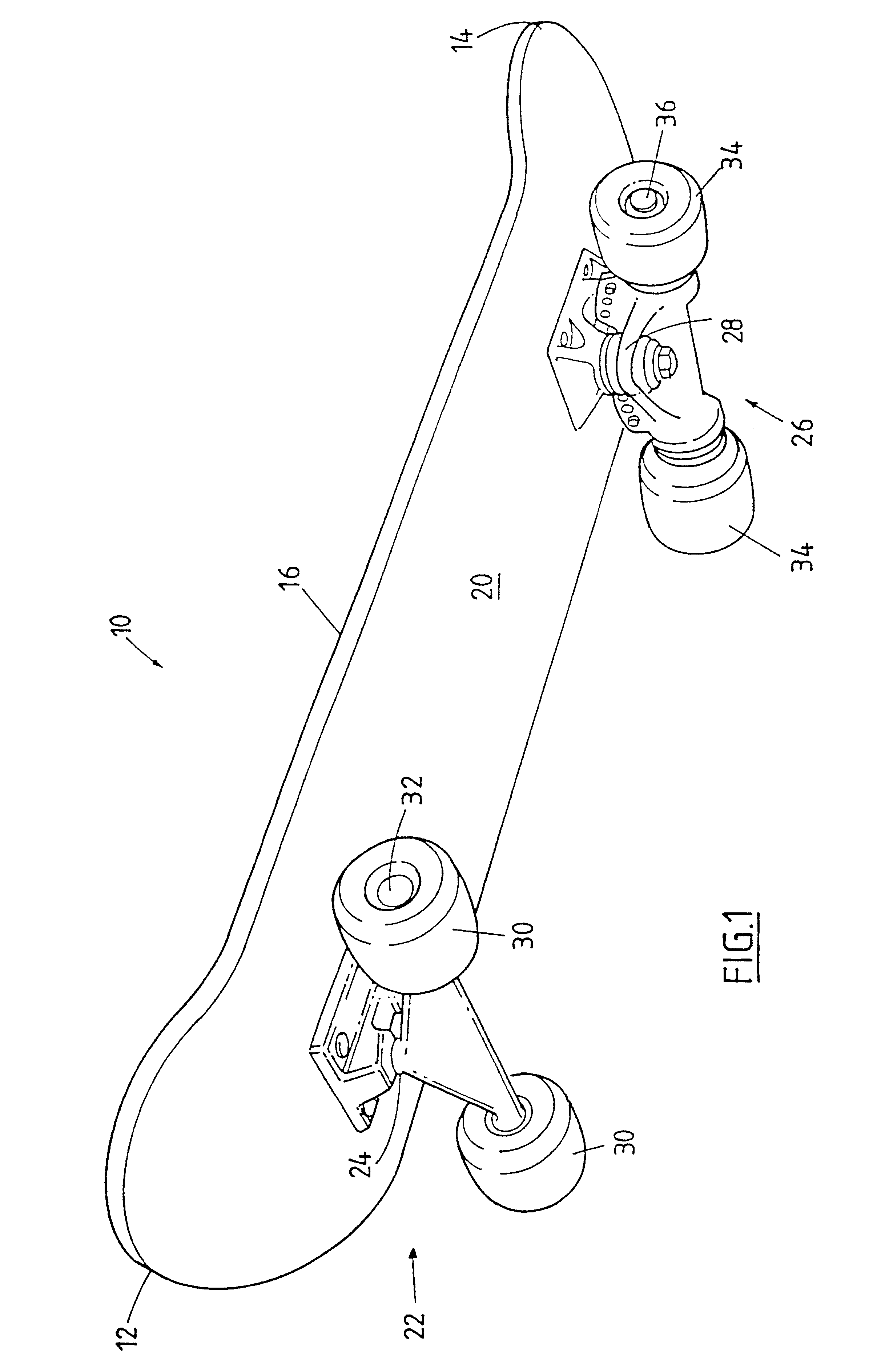
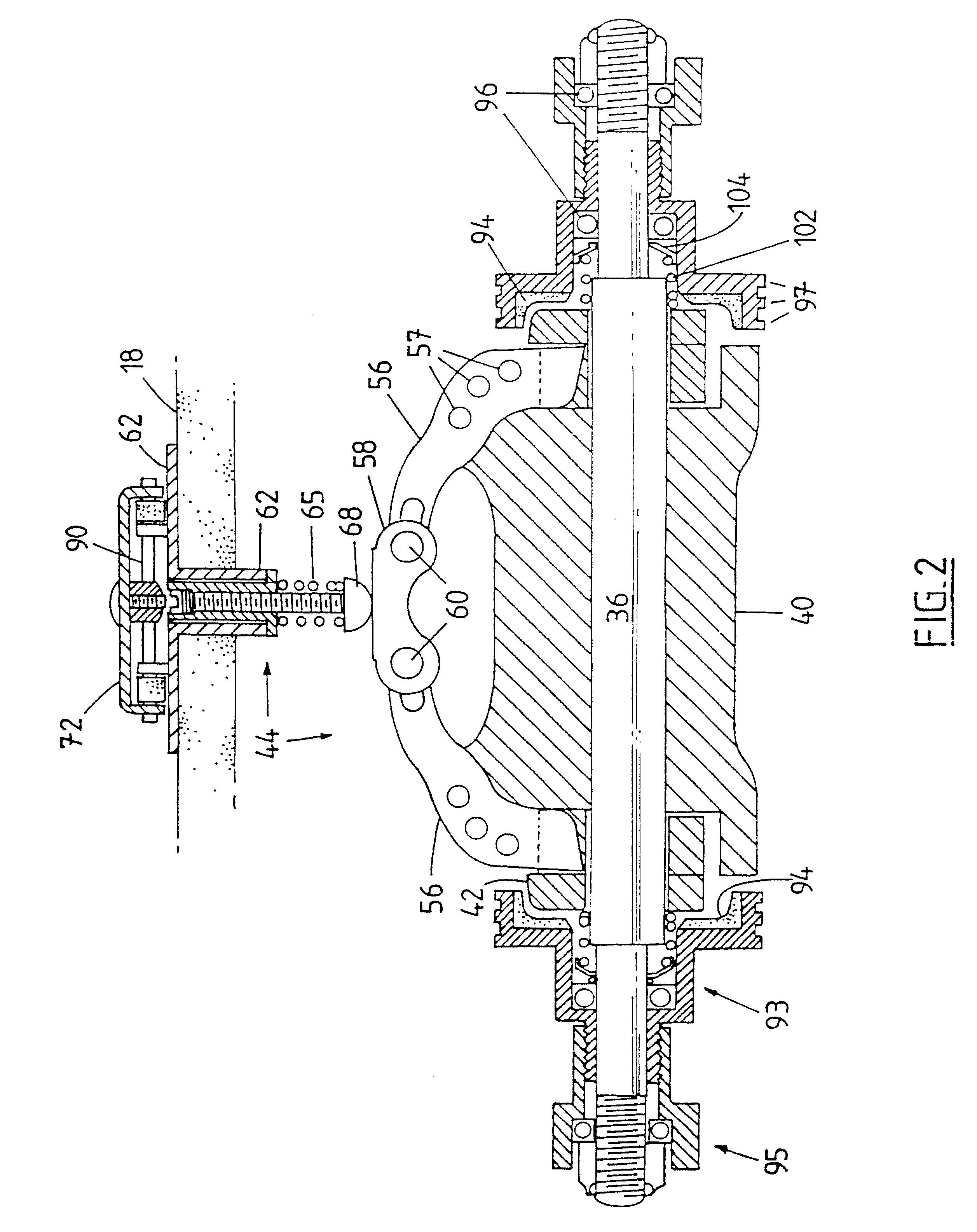
Skate board brake
A braking apparatus for a skateboard (10) having an axle (36), wherein a braking member (42) is disposed about the axle (36), and is actuated by an actuating device (44) to engage with a wheel mounting assembly (92) of the skateboard (10) so as to effect braking of the skateboard (10).
Owner:NEWMAN BENJAMIN JOHN
Electronic parking brake
ActiveUS20130087422A1Reduce rotational forceLength minimizationBraking element arrangementsBraking action transmissionReducerEngineering
Disclosed herein is an electronic parking brake which is installed in a vehicle and is operated by a motor. The electronic parking brake having a drum rotating together with a wheel and first and second brake shoes includes a motor rotated in normal and reverse directions and generating driving force for braking, a cycloid reducer connected to a rotary shaft of the motor and amplifying the driving force generated from the motor, a spindle member connected to the cycloid reducer and rotated, a spur gear assembly rotated by rotary force transmitted from the spindle member, a piston rotated and provided with the outer circumferential surface on which one gear of the spur gear assembly is integrally formed, and a push rod unit installed at both ends of the piston in the longitudinal direction, rectilinearly moved according to rotation of the piston and supported by the first and second brake shoes.
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
Universal support and vibration isolator
InactiveUS7500642B2Decrease stockGood adhesionNon-rotating vibration suppressionPipe elementsEngineeringVibration isolation
A pipe support is provided that includes a frame capable of being placed around an existing pipe and a plurality of support members within the frame. The frame is a hollow cylinder that includes two connectable halves divided along the diameter of the hollow cylinder. The pipe support includes two bearing rings connected to the frame for supporting each of the plurality of members at a minimum of two contact points. Each of the two bearing rings include bearing points for each support member arranged in a cylindrical pattern concentric with the hollow cylinder frame. The pipe support includes means for rotating each of the support members at a first contact point with respect to a second contact point so that the support members engage a pipe placed within the pipe support. The support members are rods that provide vibration isolation to a pipe placed within the pipe support.
Owner:SEICON
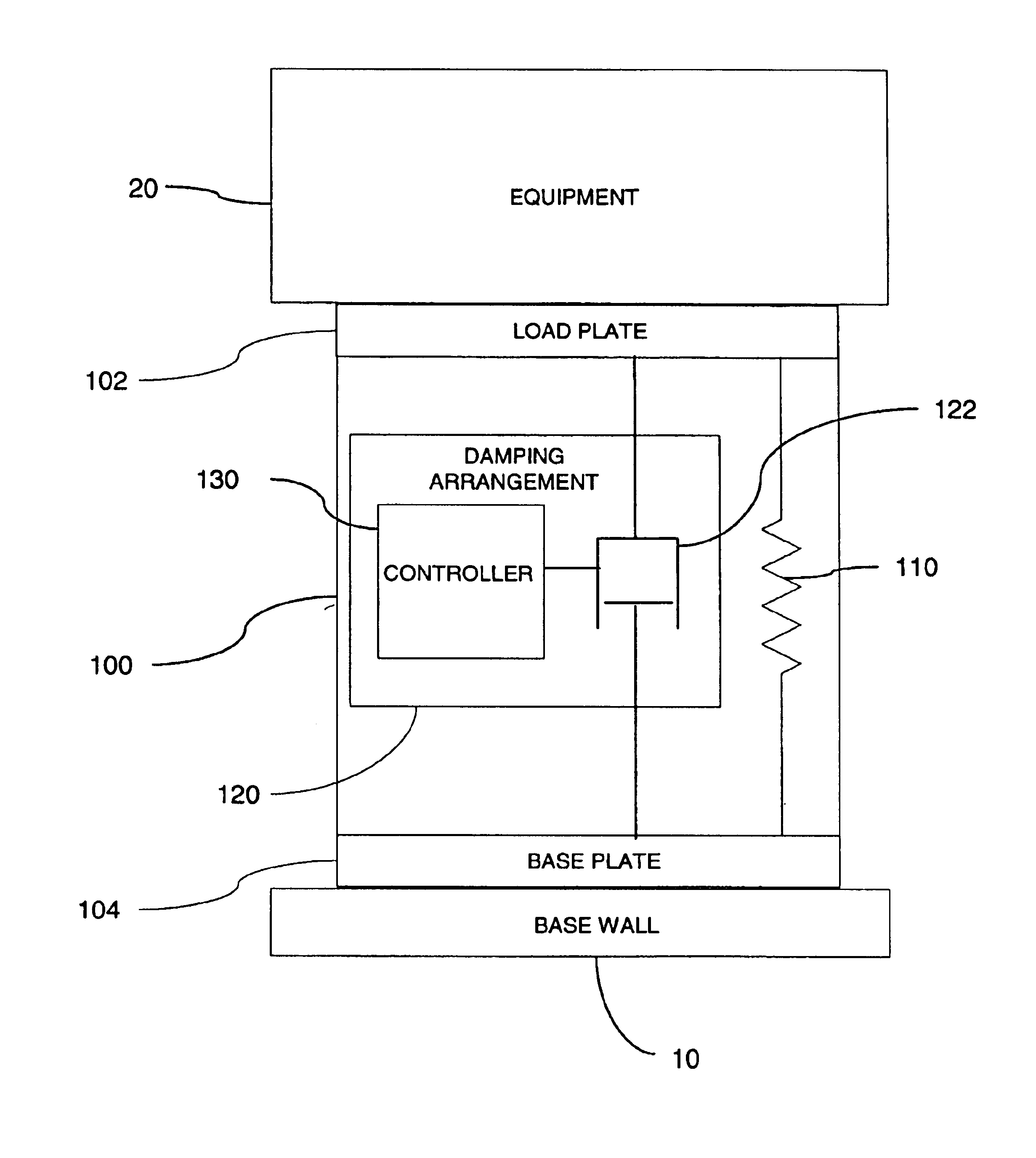
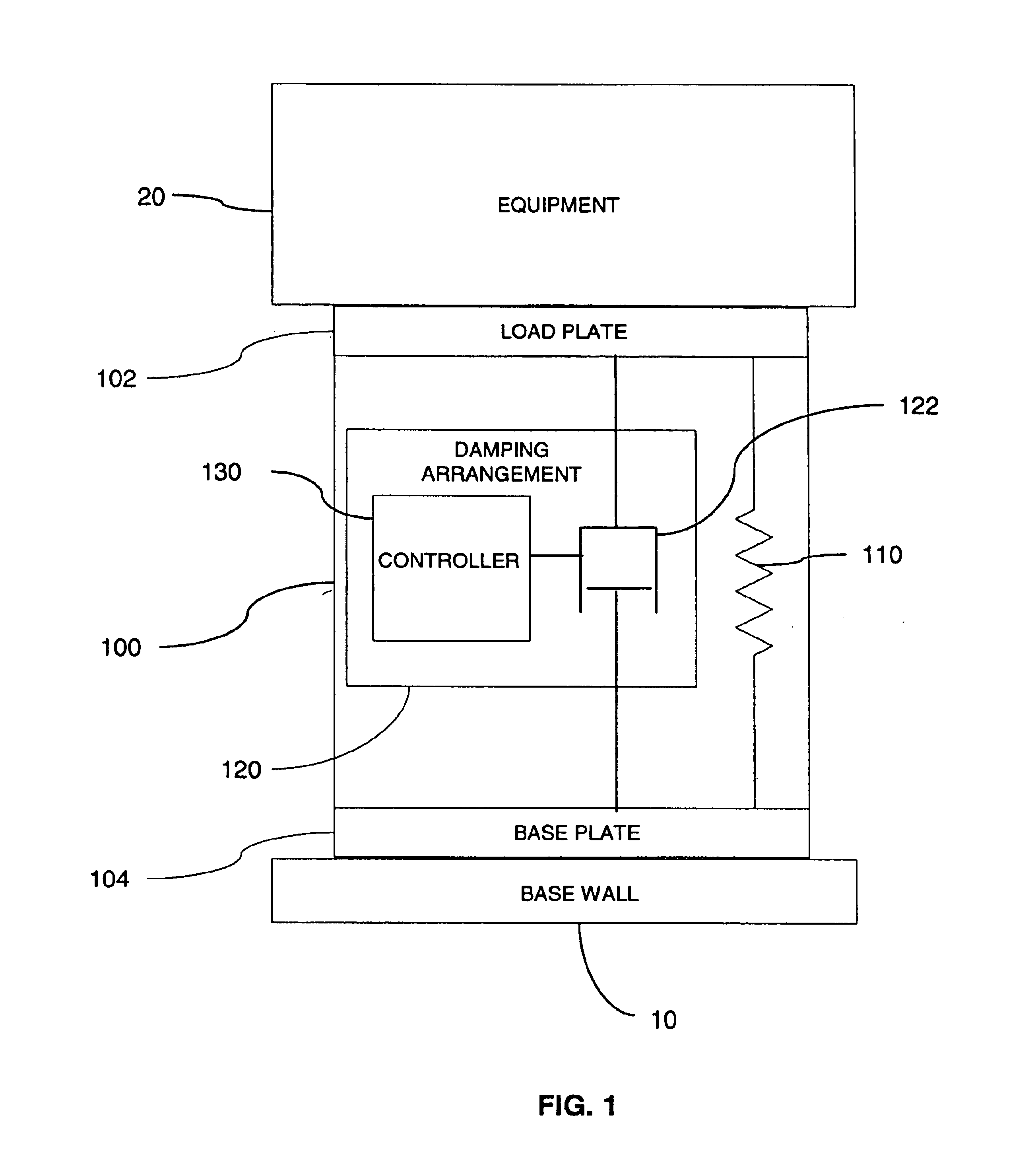
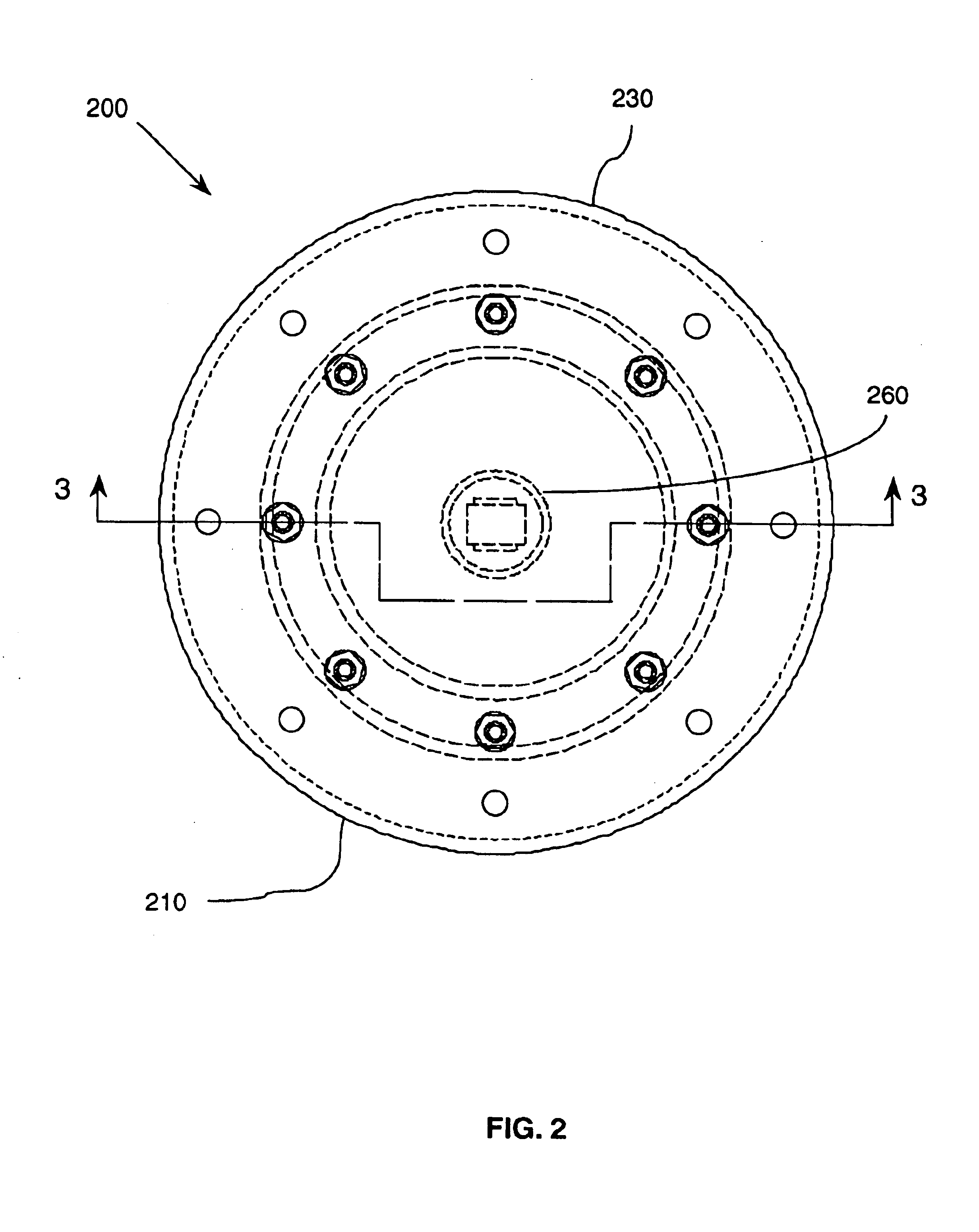
Shock, vibration and acoustic isolation system
InactiveUS6923298B2Auxillary drivesNon-rotating vibration suppressionRelative displacementSemi active
A shock and vibration isolation system for mounting equipment to a base wall uses a semi-active damper in parallel with a spring arrangement to provide optimum isolation with respect to both shock and vibration. The system comprises a load plate configured for attachment of the equipment thereto and a base plate configured for attachment to the base wall. The base plate is substantially parallel to the load plate with a spring arrangement disposed intermediate the load plate and the base plate. The spring arrangement engages the load plate and the base plate to bias the load plate and the base plate in a separated relationship. The system also comprises a damping arrangement disposed intermediate the load plate and the base plate. The damping arrangement is adapted for providing a selectively variable reaction force to the load plate and the base plate responsive to a relative displacement of the load plate with respect to the base plate.
Owner:HUNTINGTON INGALLS
Concepts for defining travel paths in parking areas
Computer program products, methods, systems, apparatus, and computing entities are provided for defining travel paths in parking areas. In one embodiment, travel paths in parking areas can be defined by connecting street networking connection points within the parking areas. In another embodiment, such defined travel paths can be merged with actual paths traveled by vehicles in the parking areas.
Owner:UNITED PARCEL SERVICE OF AMERICAN INC
Axle end wheel sensor for a vehicle, such as a truck or a trailer
InactiveUS20010052258A1Precise positioningAxially engaging brakesMachine bearings testingEngineeringTruck
Owner:WABASH NATIONAL
Brake assembly and coating
InactiveUS20060272909A1Reduce the possibilityMaintaining torqueMolten spray coatingAxially engaging brakesWear resistantCorrosion
A brake assembly is provided that includes a wear-resistant surface, or a surface prone to corrosion, wherein the surface is coated with a coating that optimizes wear-resistance, corrosion-resistance, adhesiveness, and friction factors of the coating. The coating includes a sacrificial corrosion constituent and a second constituent that is relatively harder than the sacrificial corrosion constituent wherein typical metals often employed as sacrificial anodes for example are contemplated. These include aluminum, zinc, and alloys thereof. The second constituent is potentially formed from a carbide, nitride, oxide, transitional metals and alloys thereof, and mixtures thereof.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC +1
Braking device for a personal mobility vehicle
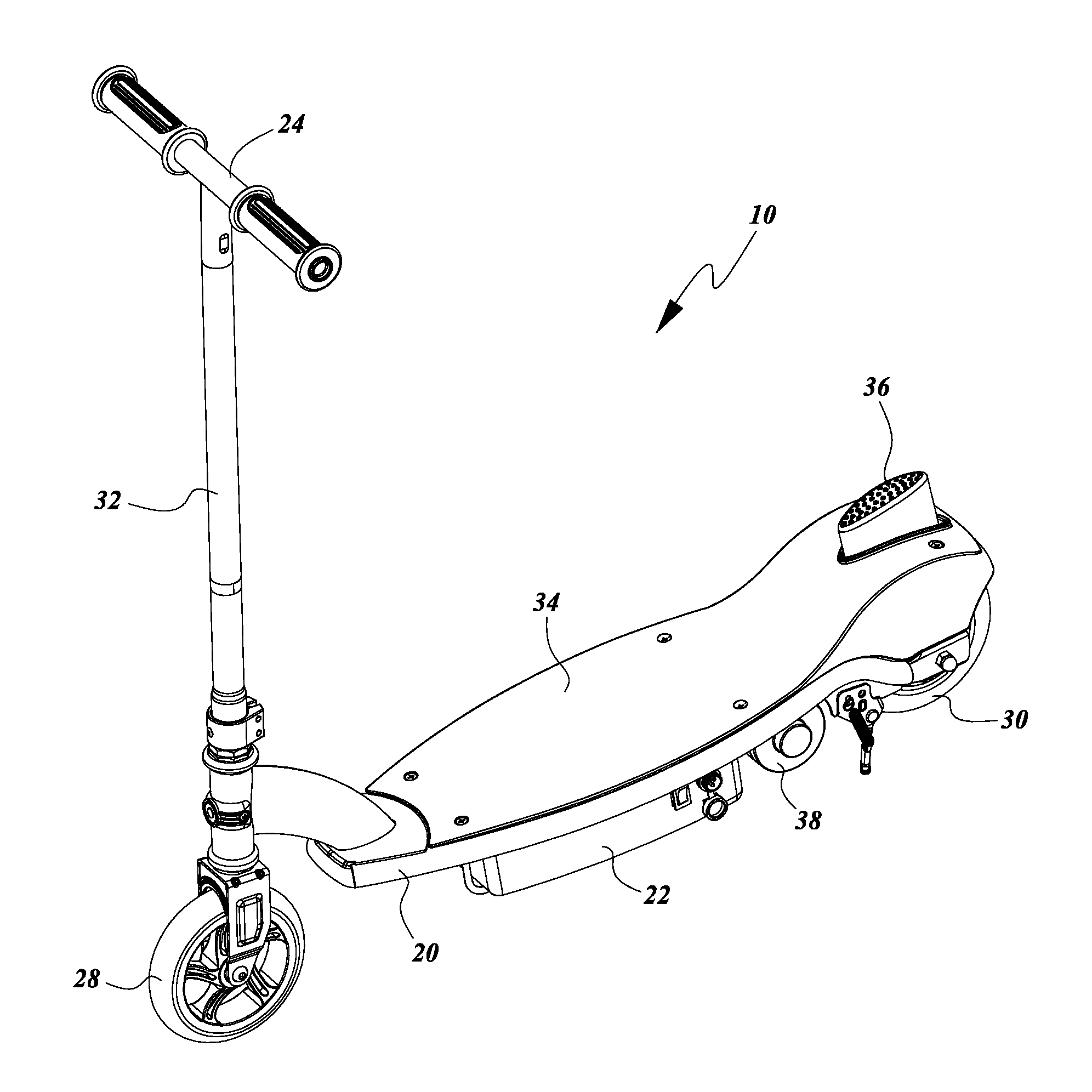
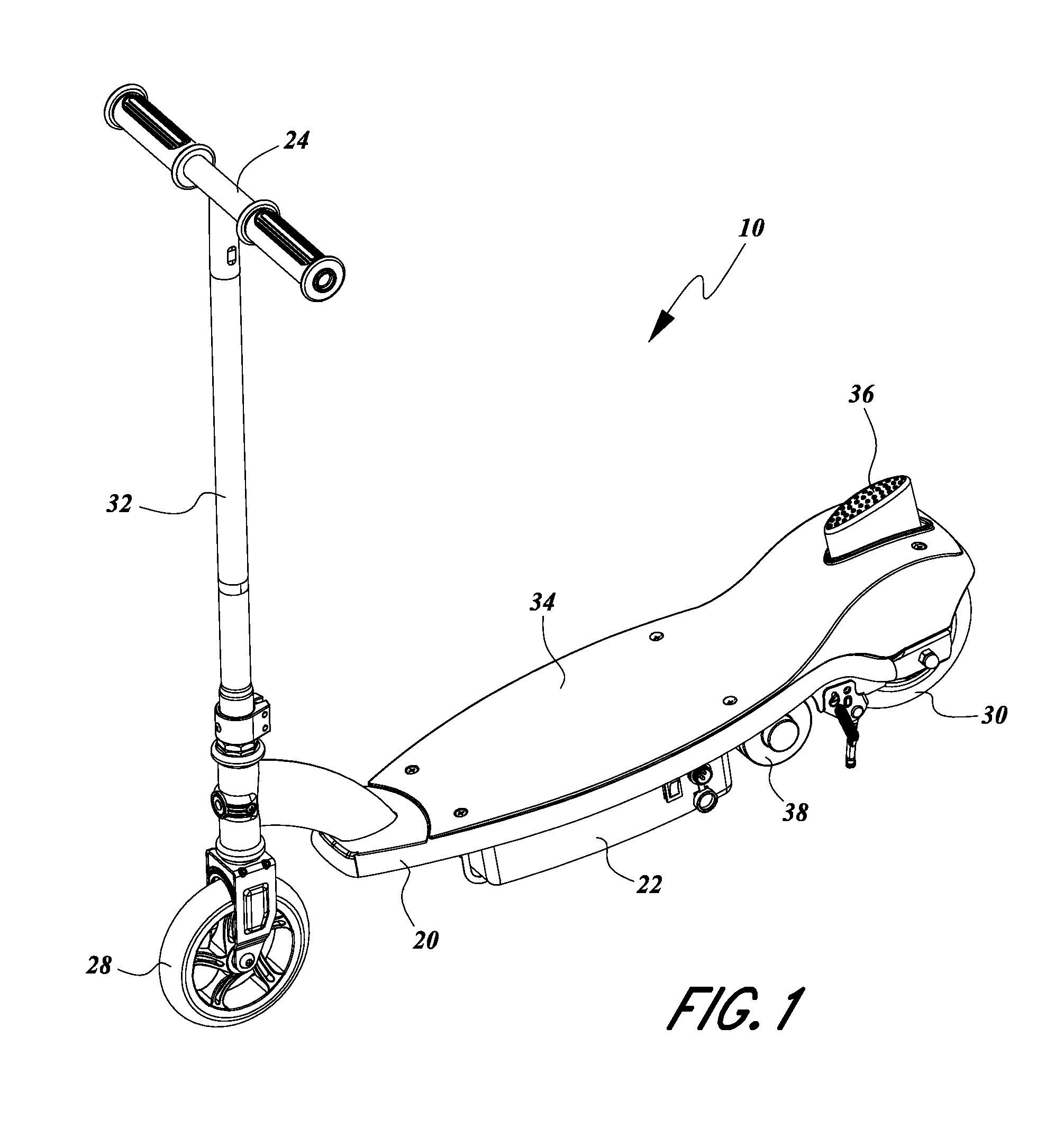
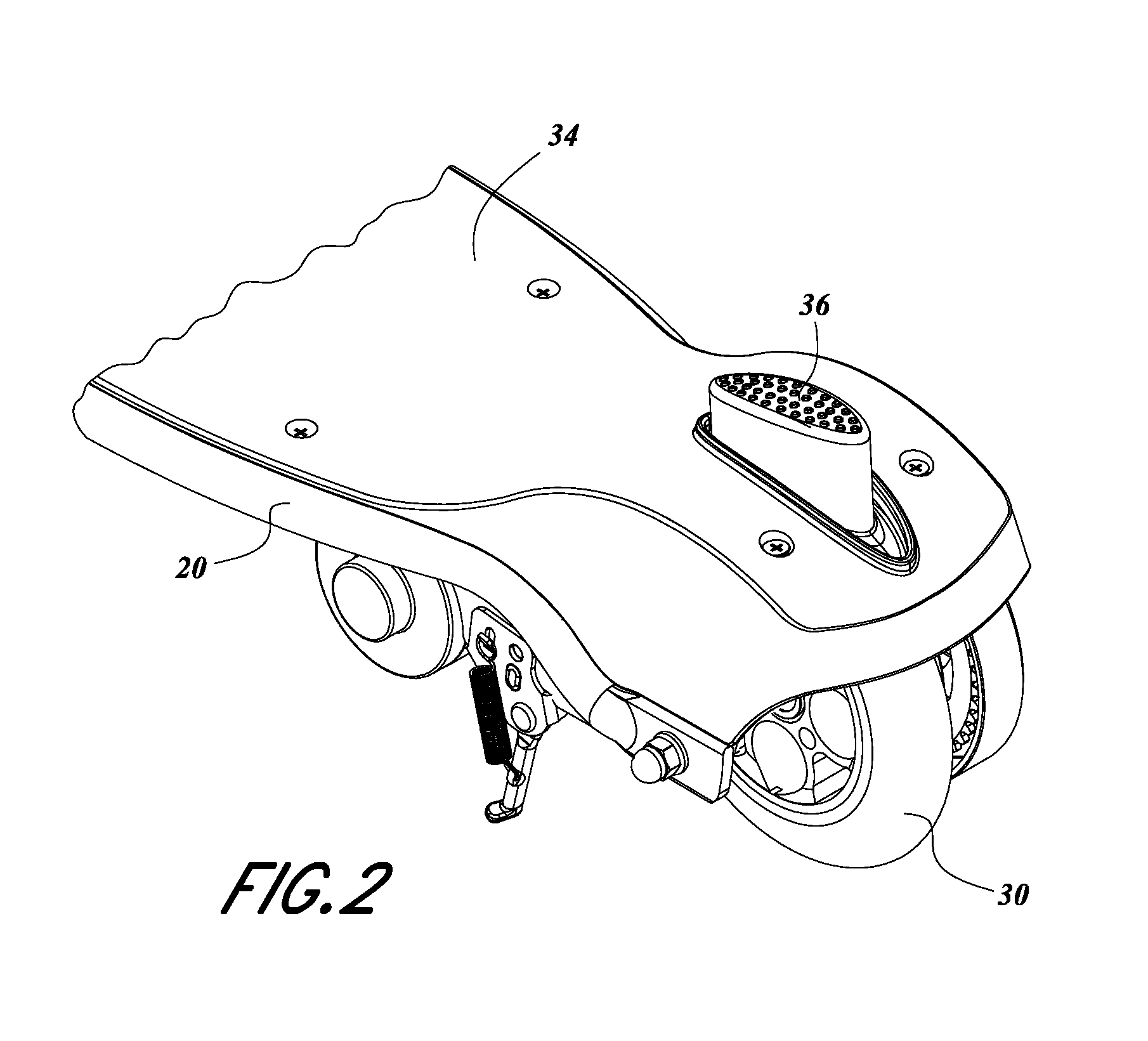
ActiveUS8813892B2Increased complexityLow priceMotorised scootersCycle control systemsDrive wheelPersonal mobility
A personal mobility vehicle, such as a scooter, includes at least one battery and motor for powering at least one driven wheel. The vehicle also includes a braking assembly configured to isolate the motor from the at least one driven wheel such that power is terminated from the motor to the at least one wheel in response to a user engaging a braking assembly of the vehicle. The vehicle can include a switch or position sensor that interacts with the braking assembly to initiate the isolation of the motor from the at least one driven wheel and the switch or position sensor preferably is inaccessible to the foot of the user.
Owner:RAZOR USA
Shaft brake mechanism of wind power generator
InactiveUS20110169268A1Energy saving effectLess electric powerPropellersWind motor controlWind forceElectric generator
A shaft brake mechanism of wind power generator, including a first brake assembly and a second brake assembly independent from each other. The first brake assembly serves to provide braking effect for the shaft of the wind power generator against rotation. The second brake assembly serves to naturally restrain the rotational speed of the shaft from exceeding a nominal upper limit of rotational speed. Accordingly, the wind power generator can still safely operate in a situation that the wind speed exceeds a nominal upper limit of wind speed. Therefore, the wind speed range for the operation of the wind power generator is widened to increase the total power generation capacity thereof.
Owner:HIWIN MIKROSYST
Bearing condition monitor for a vehicle, such as a truck or a trailer
InactiveUS20010030466A1Axially engaging brakesMachine bearings testingWheel speed sensorMonitoring system
Owner:WABASH TECH
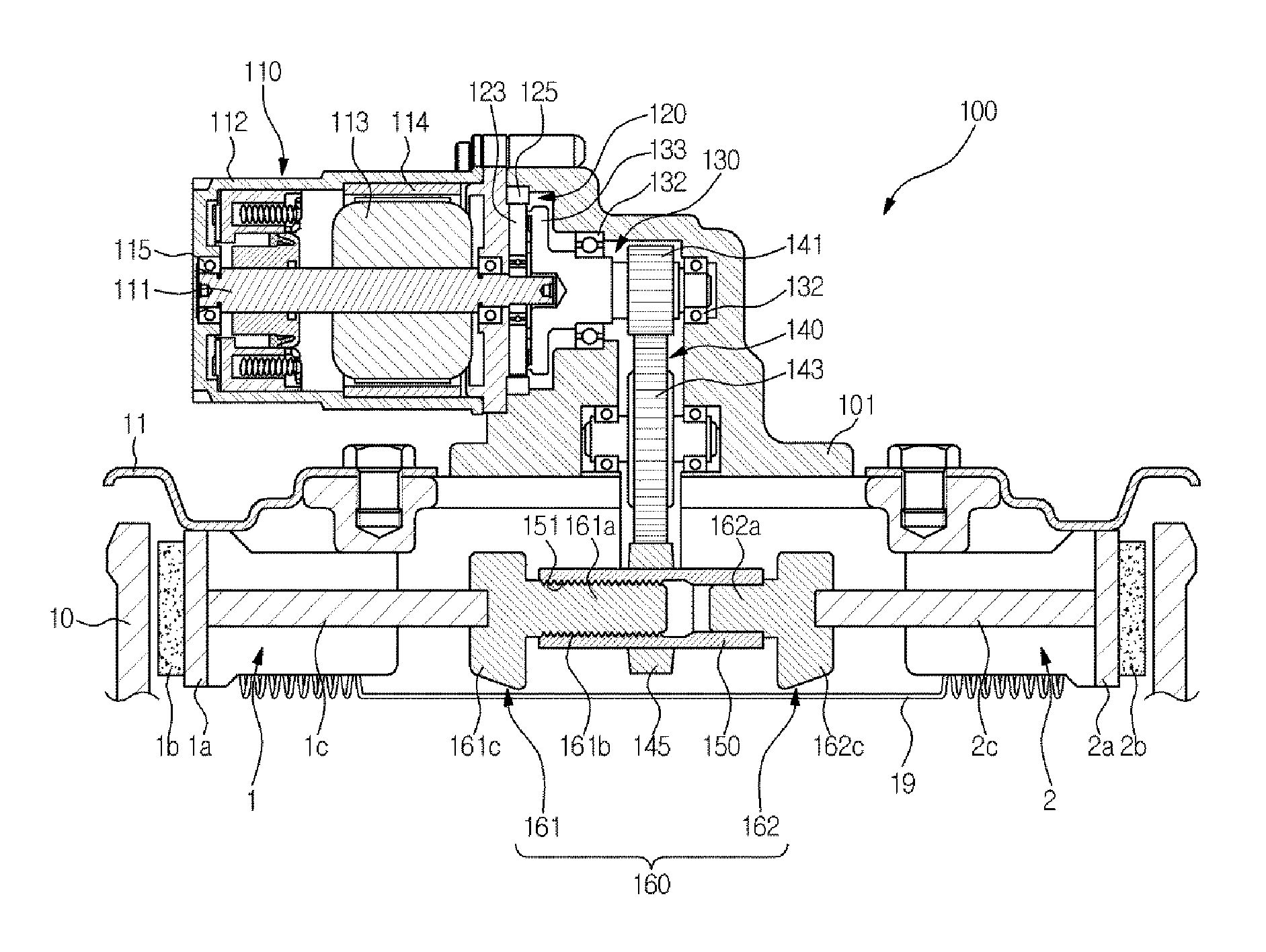
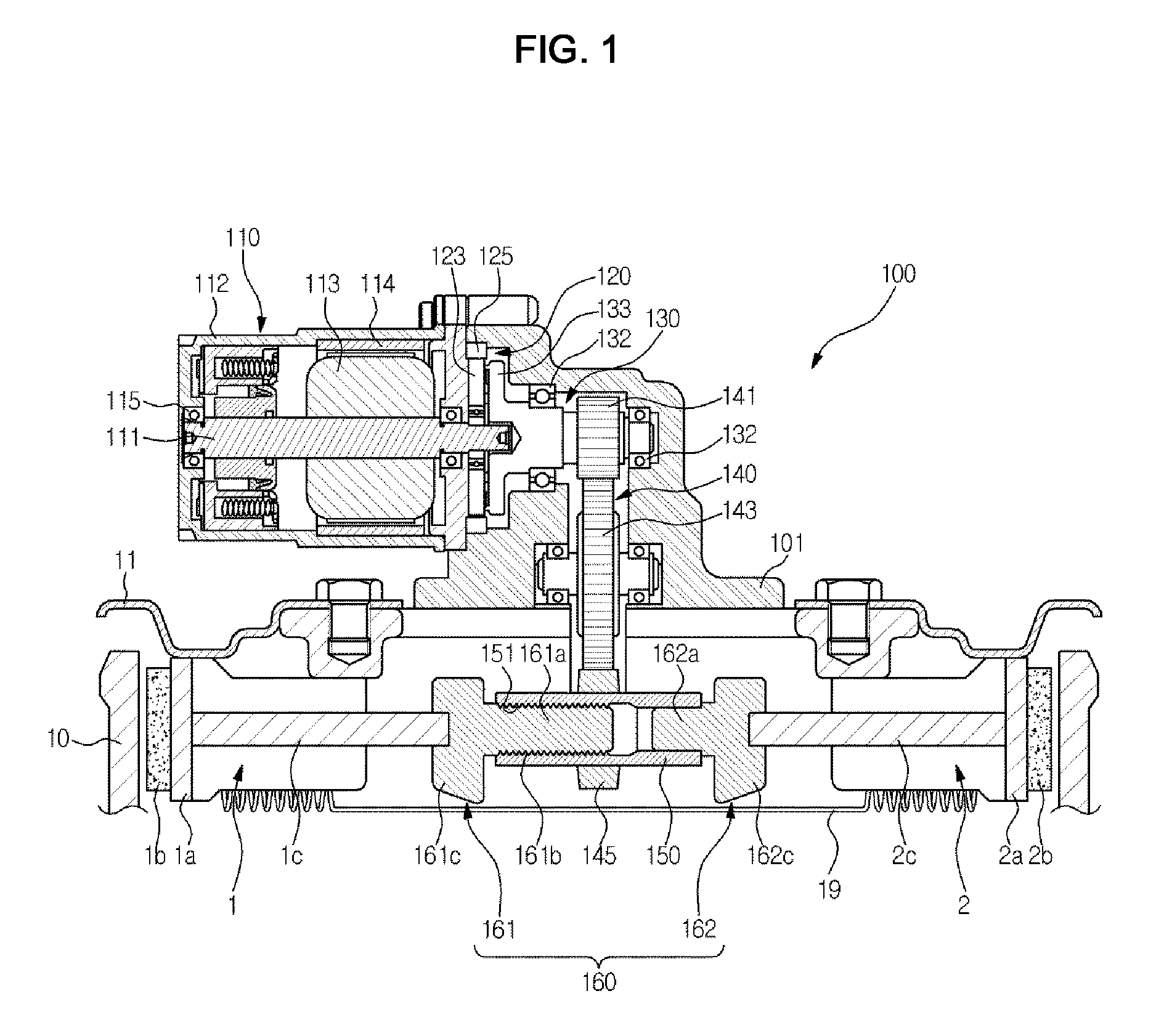
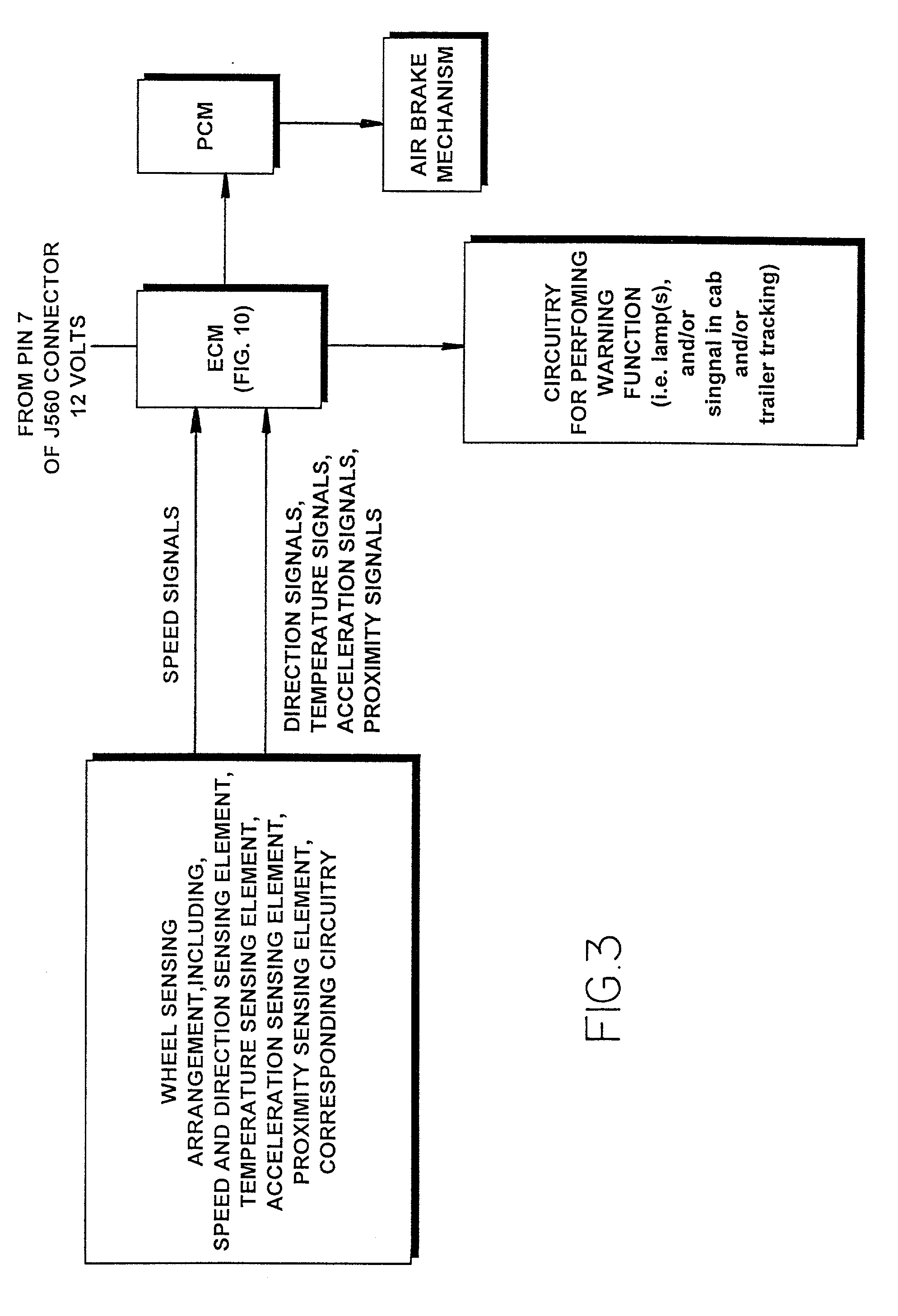
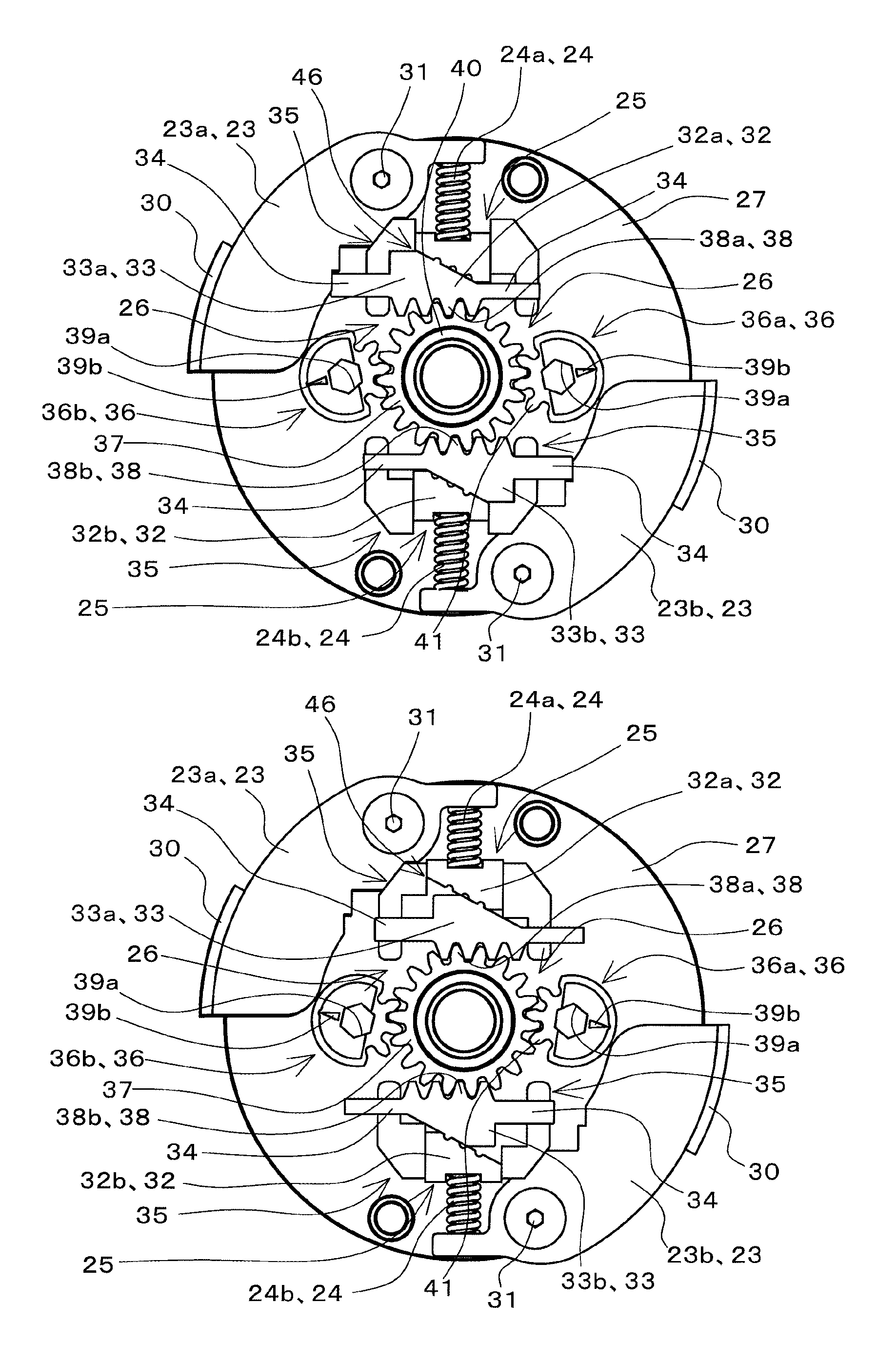
Vehicle speed control device and vehicle equipped with vehicle speed control device
ActiveUS20140224597A1Easy to changeBraking element arrangementsSelf acting brakesEngineeringBrake shoe
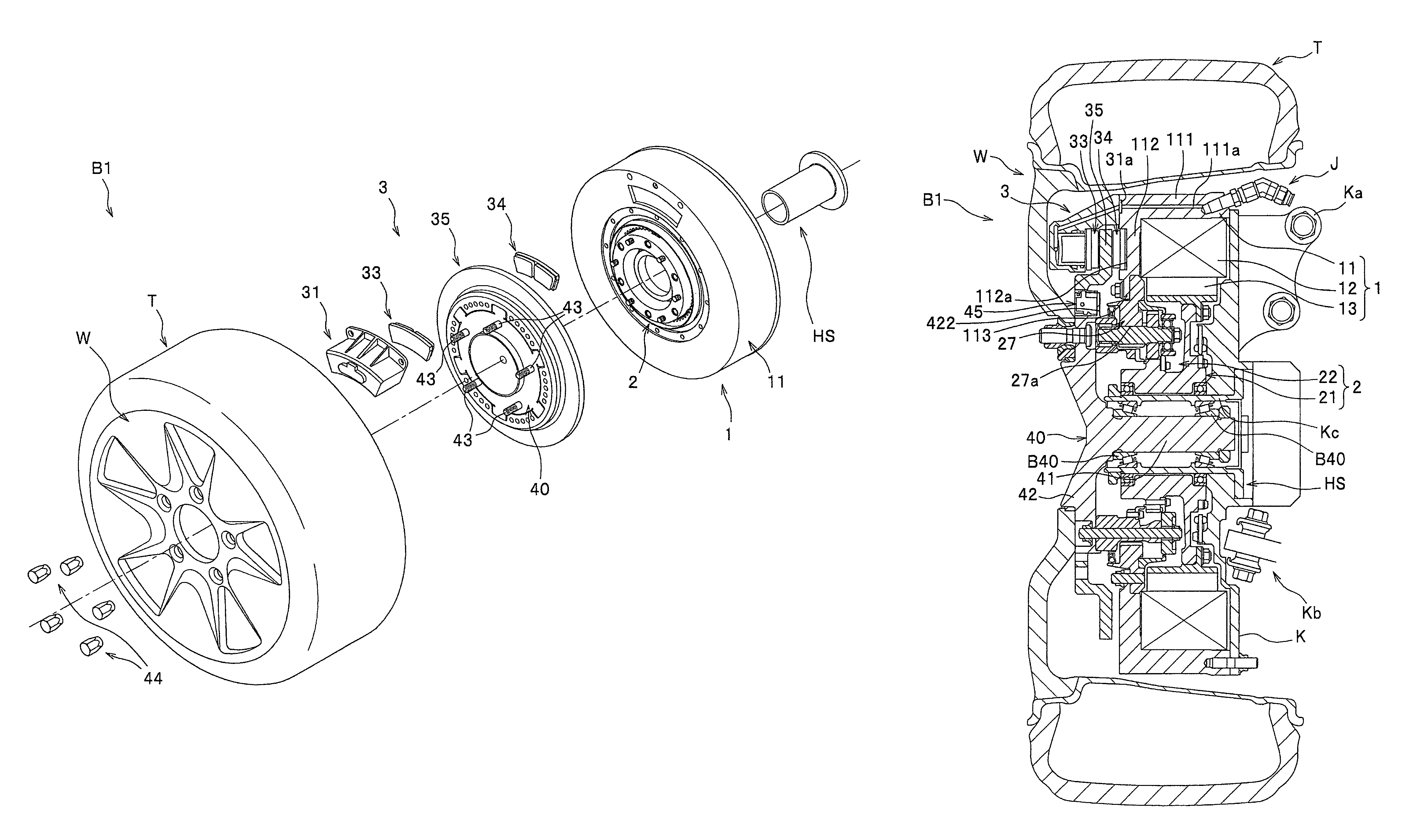
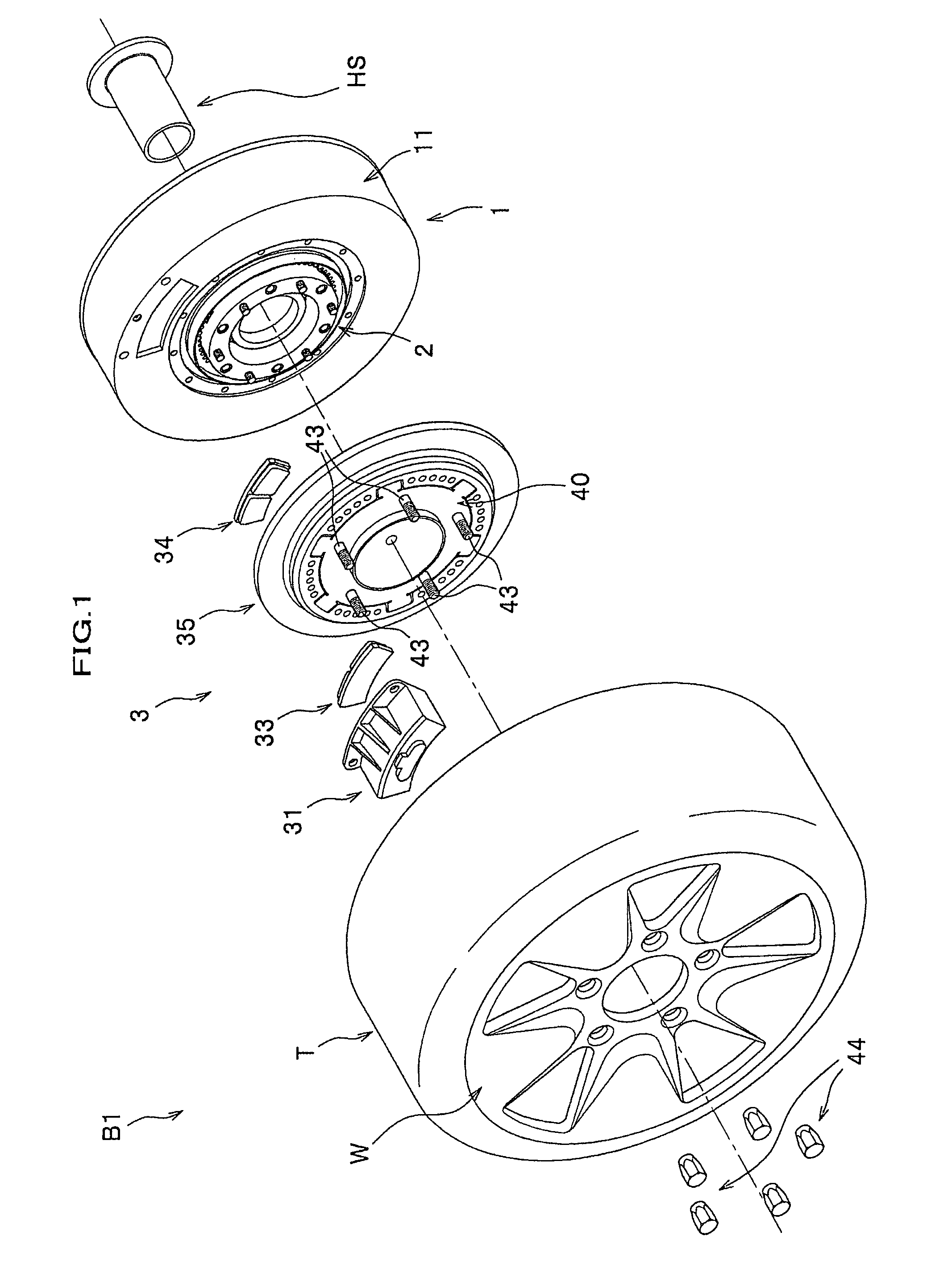
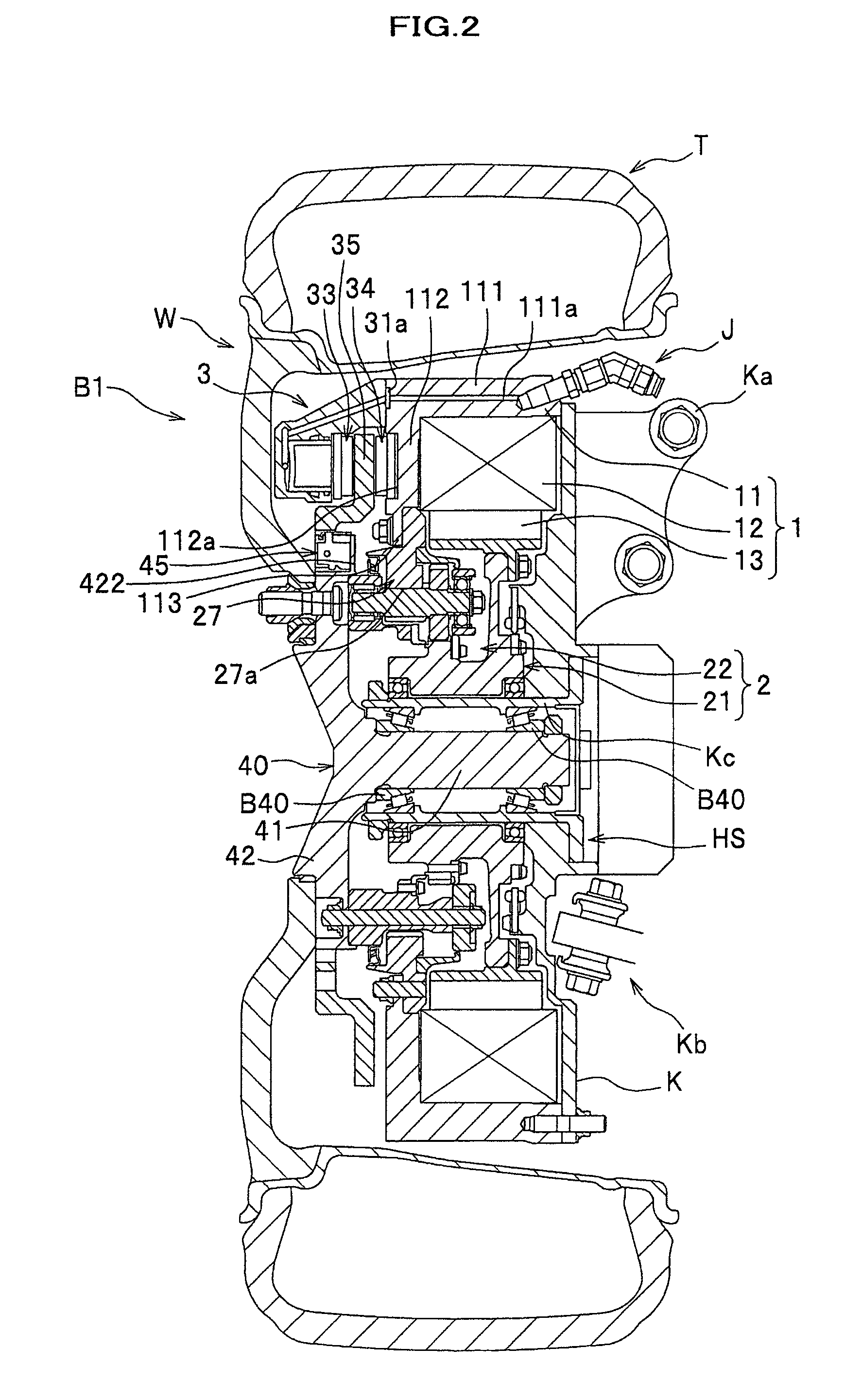
Provided is a vehicle speed control device with respect to which the speed at which a centrifugal brake operates can be easily changed from the outside without disassembling the device. A brake drum 11 is fixed to a vehicle body 101a. A brake shoe 23 rotates around a rotary shaft 20 of the wheel 101c, and reduces the rotation speed of the wheel 101c as a result of coming into contact with an inner circumferential side face of the brake drum 11. A spring 24 prevents contact between the brake drum 11 and the brake shoe 23 when the rotation speed of the wheel 101c is lower than or equal to a predetermined speed, and permits contact between the brake drum 11 and the brake shoe 23 when the rotation speed of the wheel 101c exceeds the predetermined speed. A position change mechanism 25 is installed within the brake drum 11, and changes the position of an end of the spring 24 on one end side. A transmission mechanism 26 transmits a force that is input by an external operation to the position change mechanism 25 and drives the position change mechanism.
Owner:NABLESCO CORP +1
Cam tube bracket
ActiveUS7537224B2Improve the immunityReduce frettingShrinkage connectionsRigid suspensionsHeavy dutyBraking system
A cam shaft support / enclosure assembly for brake systems of heavy-duty vehicles is mounted on a beam of an axle / suspension system and includes a cam tube. A bracket for mounting the cam tube on the beam includes a pair of plates that are mounted on the beam. Each one of the plates is formed with an opening for receiving the cam tube and includes at least three tabs, and preferably four tabs, that extend outwardly from each respective plate adjacent the opening and contact the outer surface of the cam tube. Each tab includes a generally arched and optionally textured face for mating with an outer surface of the cam tube, which may also be optionally textured, so that when the plates are mounted the tabs engage the cam tube in a press-type fit, minimizing movement of the cam tube.
Owner:HENDRICKSON USA L L C
Reciprocating saw
InactiveUS20050183271A1Easy to lockInhibition releaseMetal sawing devicesMetal sawing accessoriesMechanical engineeringEngineering
Owner:MAKITA CORP
Brake structure for a roll-up door
InactiveUS7281612B2Avoid fireDoor/window protective devicesElectrodynamic brake systemsCapacitanceDrive shaft
A brake structure for a roll-up door includes a brake drum fixed to a transmission shaft of a speed reducer. The brake drum receives a pair of brake shoes in opposite inner sides thereof. The brake shoes are pivotably connected to each other at an end of each brake shoe. A linking resilient member is connected between the free ends of the brake shoes. A brake pad is attached to a surface of each brake shoe facing the inner surface of the brake drum. A controlling lever is disposed at the top of the speed reducer corresponding to the free ends of the brake shoes. One end of the controlling lever is connected to an end of a fixing resilient member. The other end of the fixing resilient member is connected to a moving iron of a first solenoid. A clasping block is connected to the moving iron of the first solenoid. The other end of the controlling lever is connected to a moving iron of a second solenoid. A controlling block is disposed at the controlling lever between the free ends of the brake shoes and in contact to the free ends of the brake shoes. A brake control solenoid is disposed at the top of the speed reducer. The brake control solenoid is connected to a power supply with capacitance character. A moving iron of the brake control solenoid is connected to a connecting rod mechanism. The clasping block is connected to the connecting rod mechanism.
Owner:ANCHUAN CORP
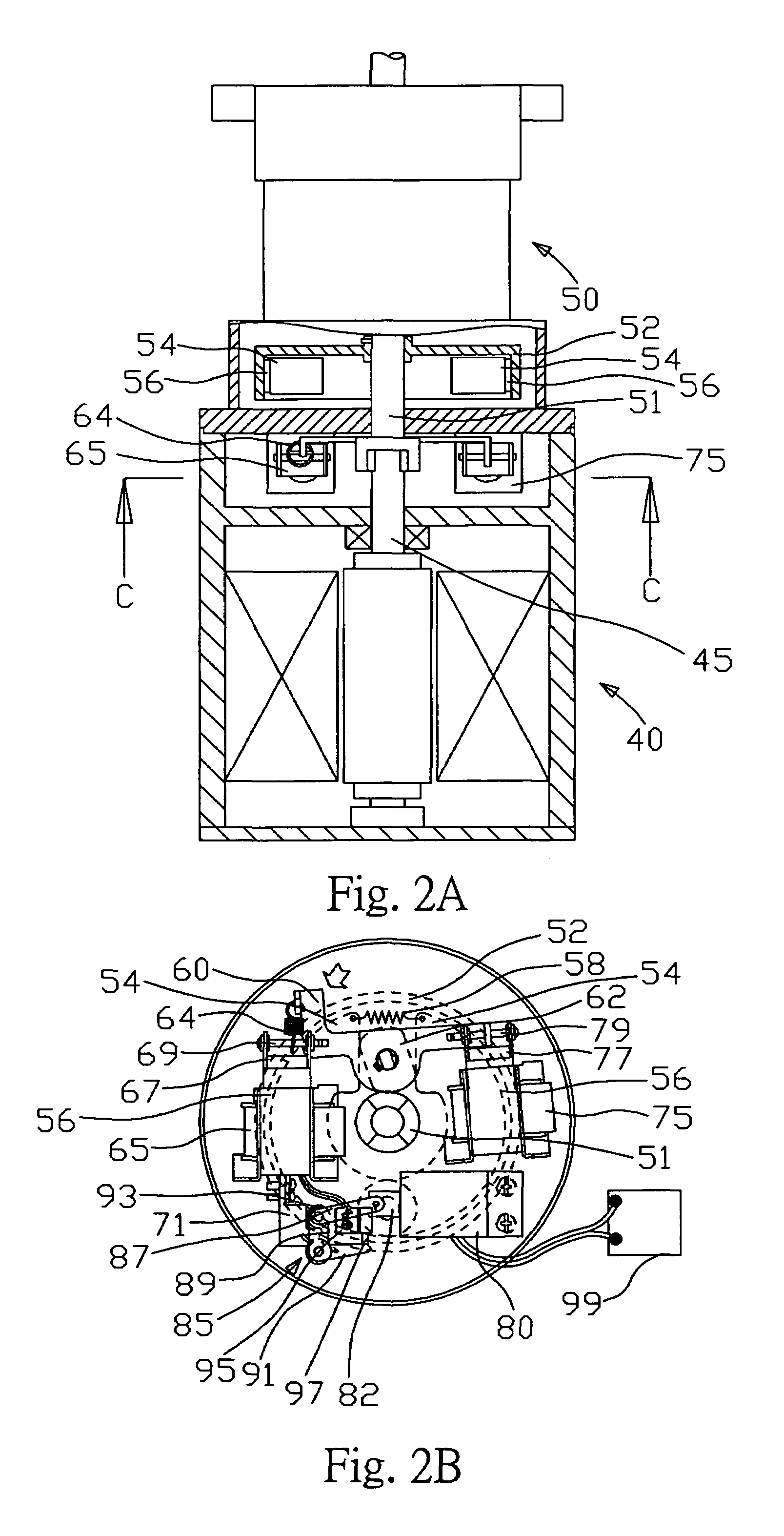
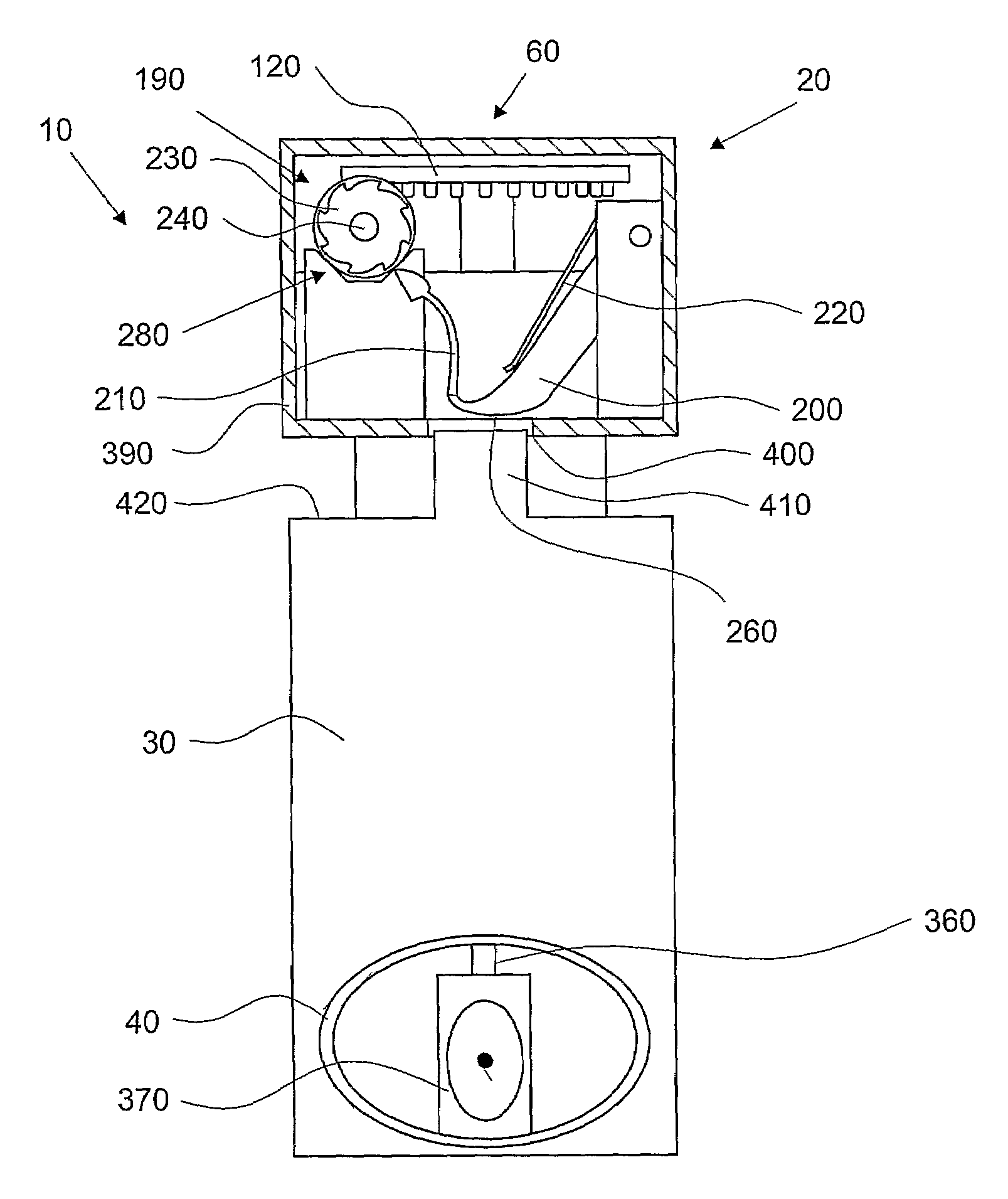
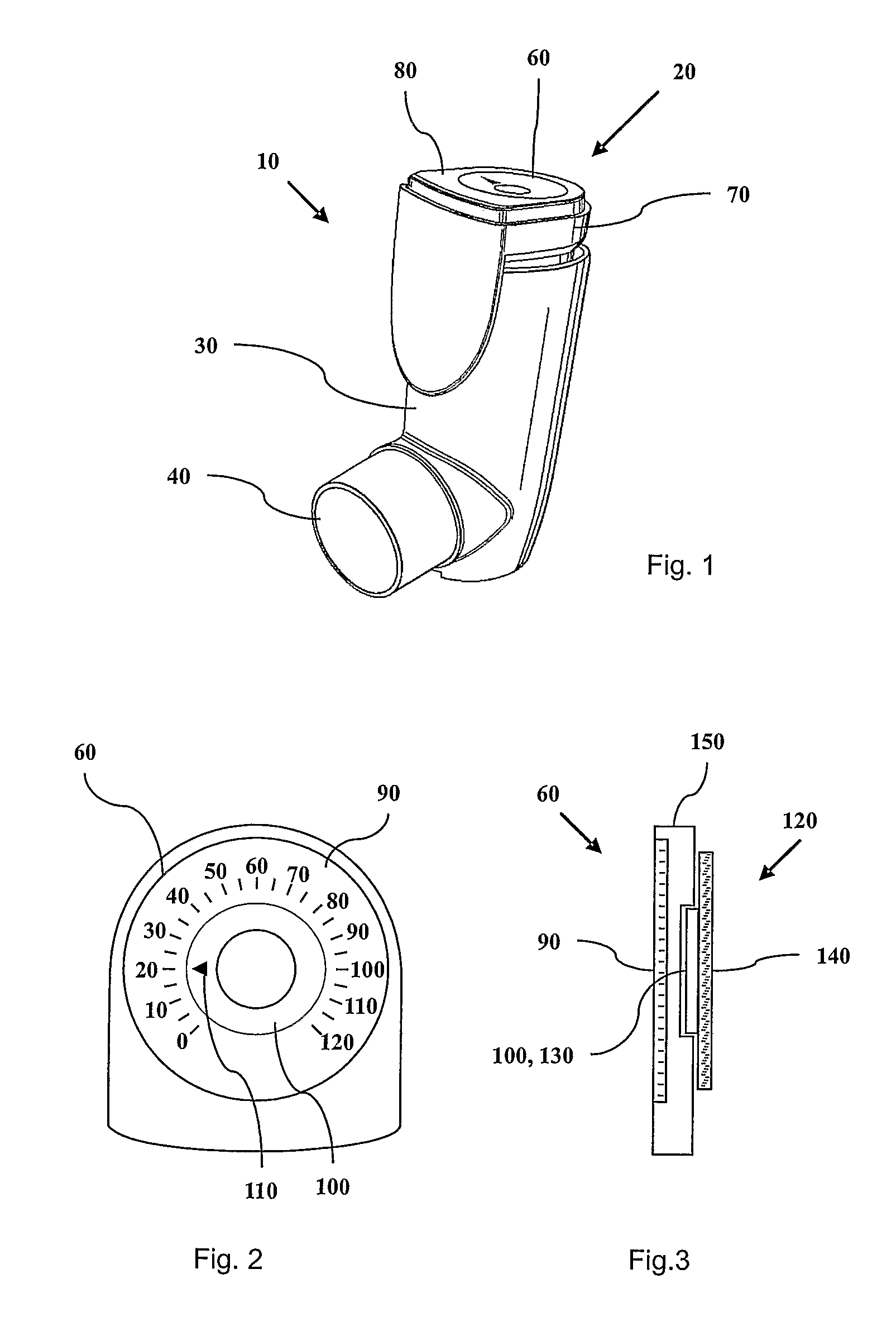
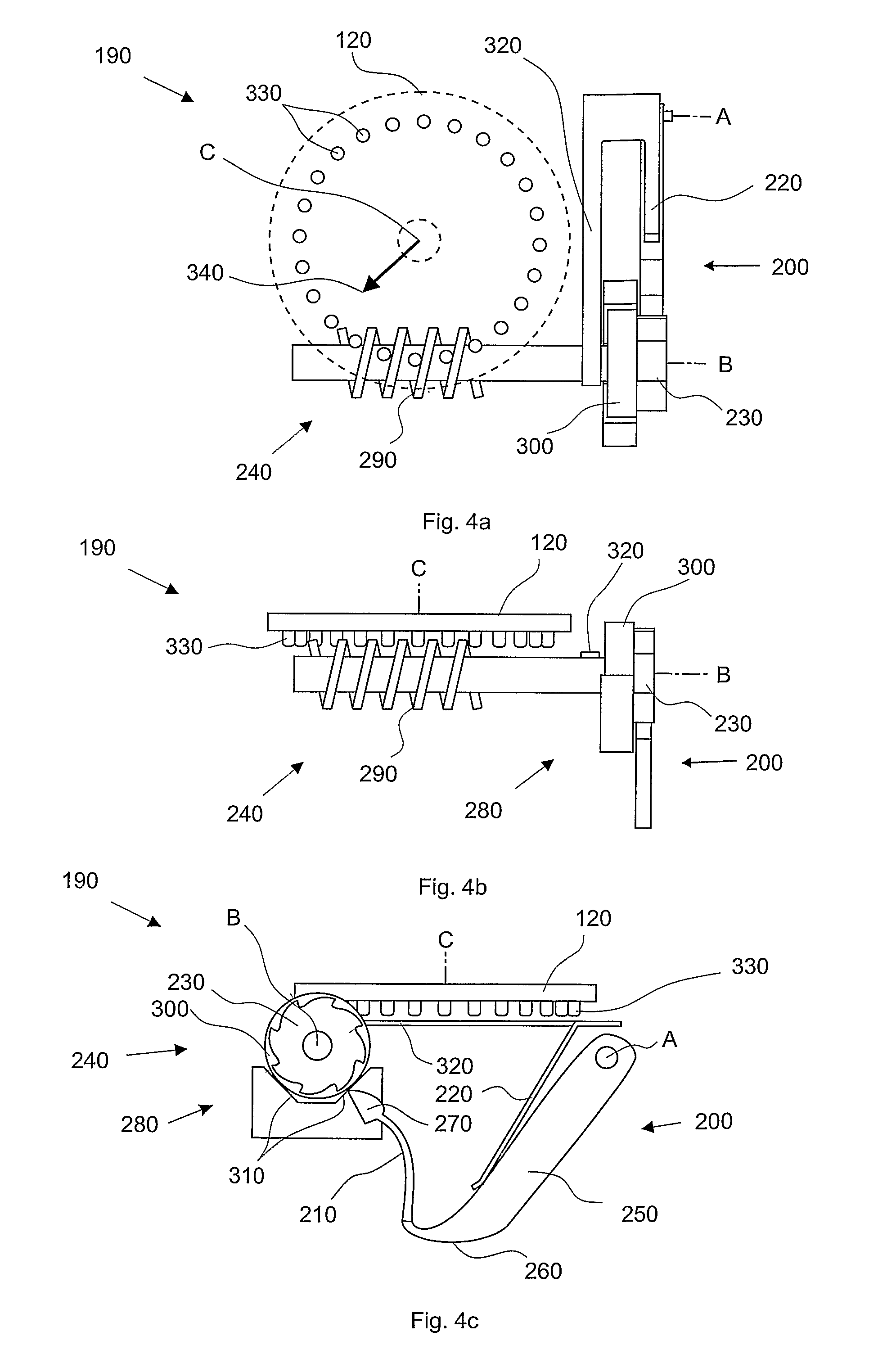
Inhaler device counter
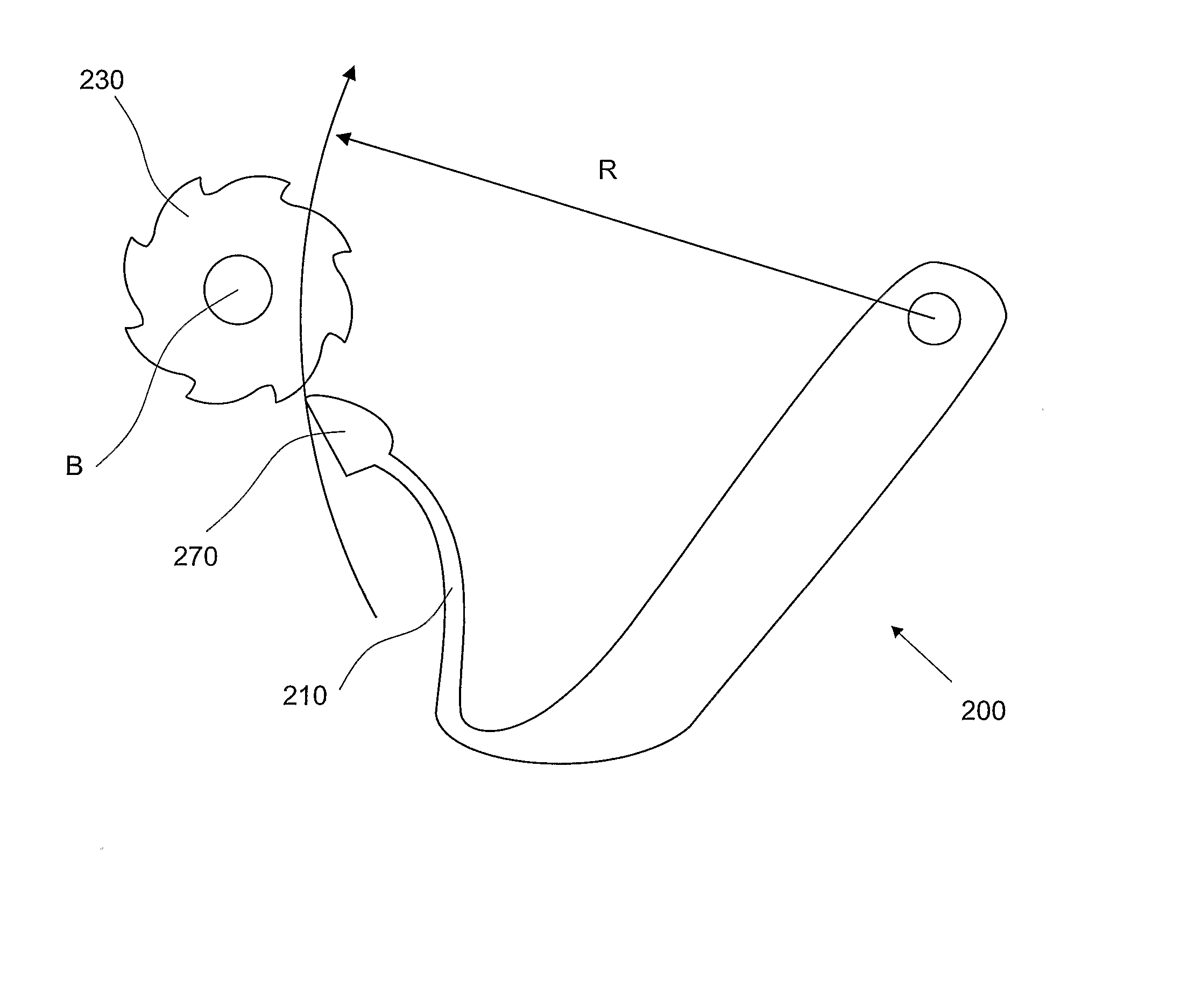
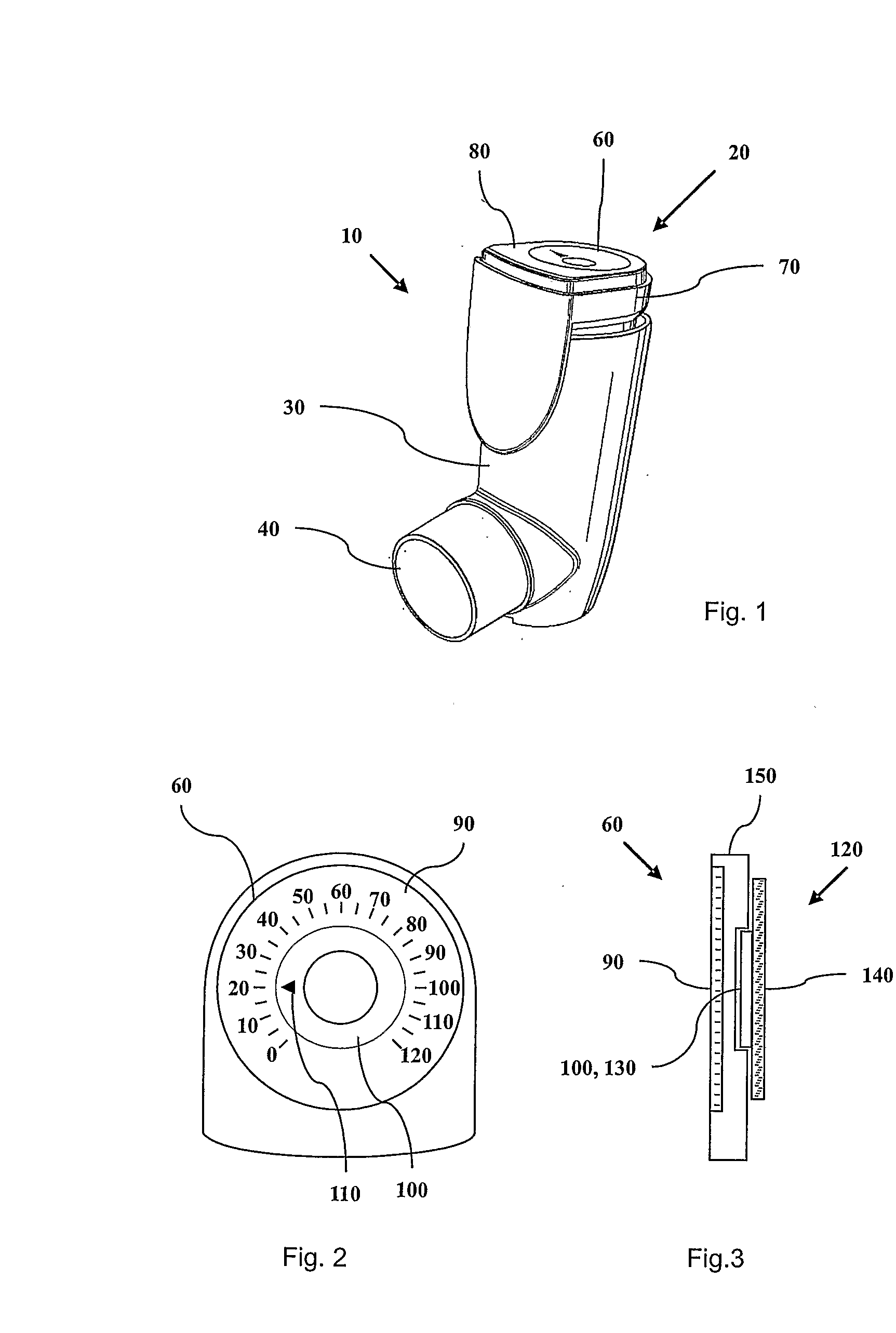
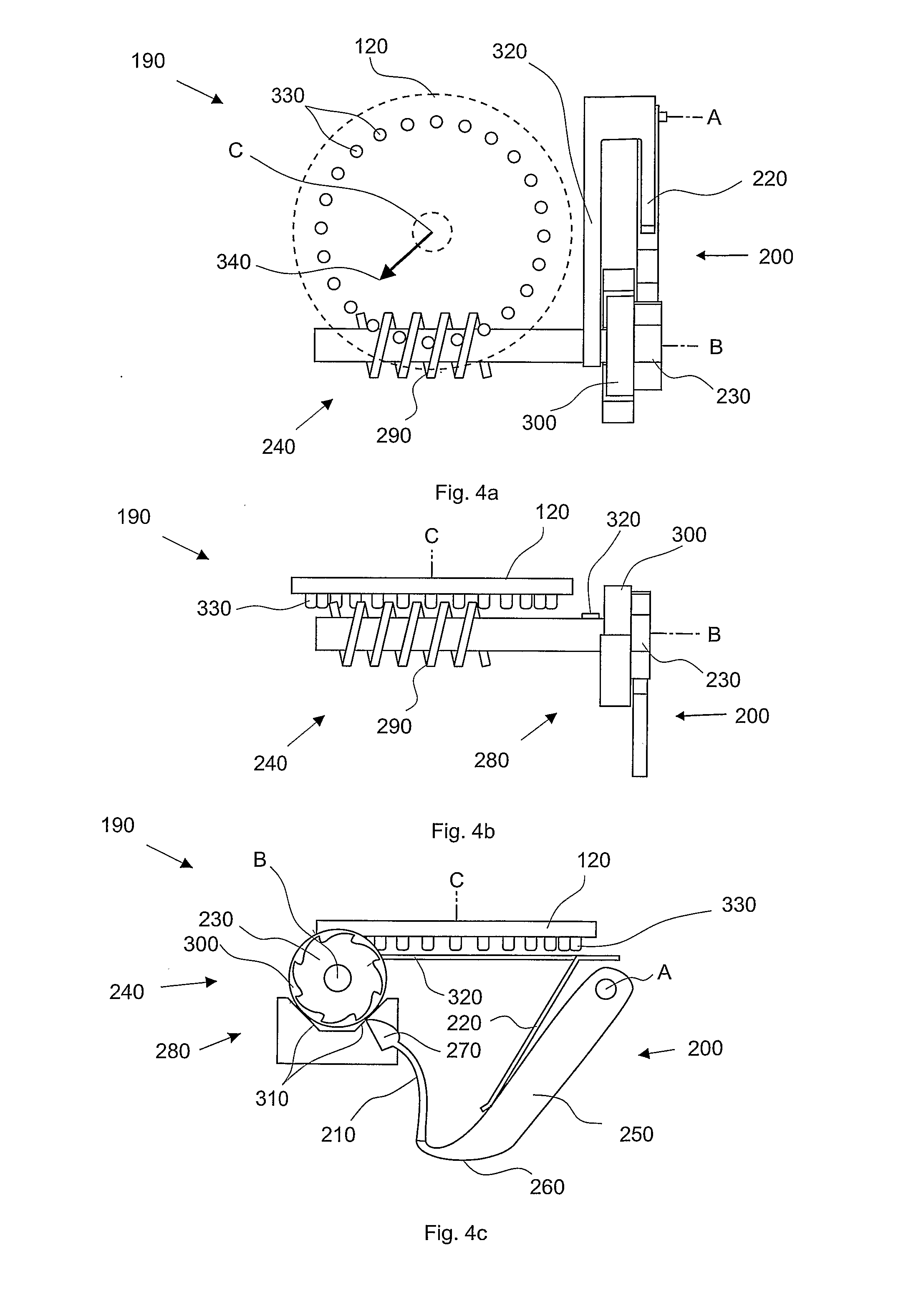
ActiveUS7587988B2Easy readable large displayLow production costFire rescueLiquid transferring devicesEngineeringRocker arm
Inhaler counter (20) comprising a counter housing (390), a rocker arm (200) with a pawl (210), the rocker arm being pivotally supported by the housing and arranged to perform a rocker movement in response to a linear actuation motion, a return spring (220) for resetting the rocker arm, a ratchet wheel (230) engagable with the pawl to convert the movement of the rocker arm into an incremental rotational motion of an axle arrangement (240) advancing a display means (60), the axle arrangement further comprising a back rotation prevention means (280) in the form of a spring loaded friction brake and a worm gear, the display means comprising rotatable indicator means (120) with teeth that engage the worm-gear and a stationary scale.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Heavy-duty axle-to-beam connection
ActiveUS20120080862A1Eliminate weldsImproves life and durabilityLaminationLamination apparatusHeavy duty
An axle-to-beam connection for a vehicle axle / suspension system includes an axle having at least one depression formed therein. A sleeve is formed with at least one depression and disposed about the axle so that the axle depression and the sleeve depression matingly engage one another to form a mated pair of depressions. A method of forming the axle-to-beam connection includes providing an axle and disposing a sleeve about the axle. At least one mated pair of depressions is simultaneously formed in the axle and the sleeve. The sleeve is immovably mounted to a vehicle axle / suspension system.
Owner:HENDRICKSON USA L L C
Emergency braking system for machine tools
ActiveUS20110048197A1Improve protectionShort braking timeEngineering safety devicesMeasurement/indication equipmentsCentrifugal forceBrake shoe
An emergency braking system for a machine tool for abruptly braking a revolving shaft includes at least one brake drum and at least one brake shoe which are engaged with one another in order to brake the shaft. The braking intervention between the brake drum and the brake shoe takes place under the influence of a centrifugal force resulting from the rotation of a shaft as soon as a locking device is released. Also provided in the braking system is a diagnostic system which allows the functionality of the locking device to be checked.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
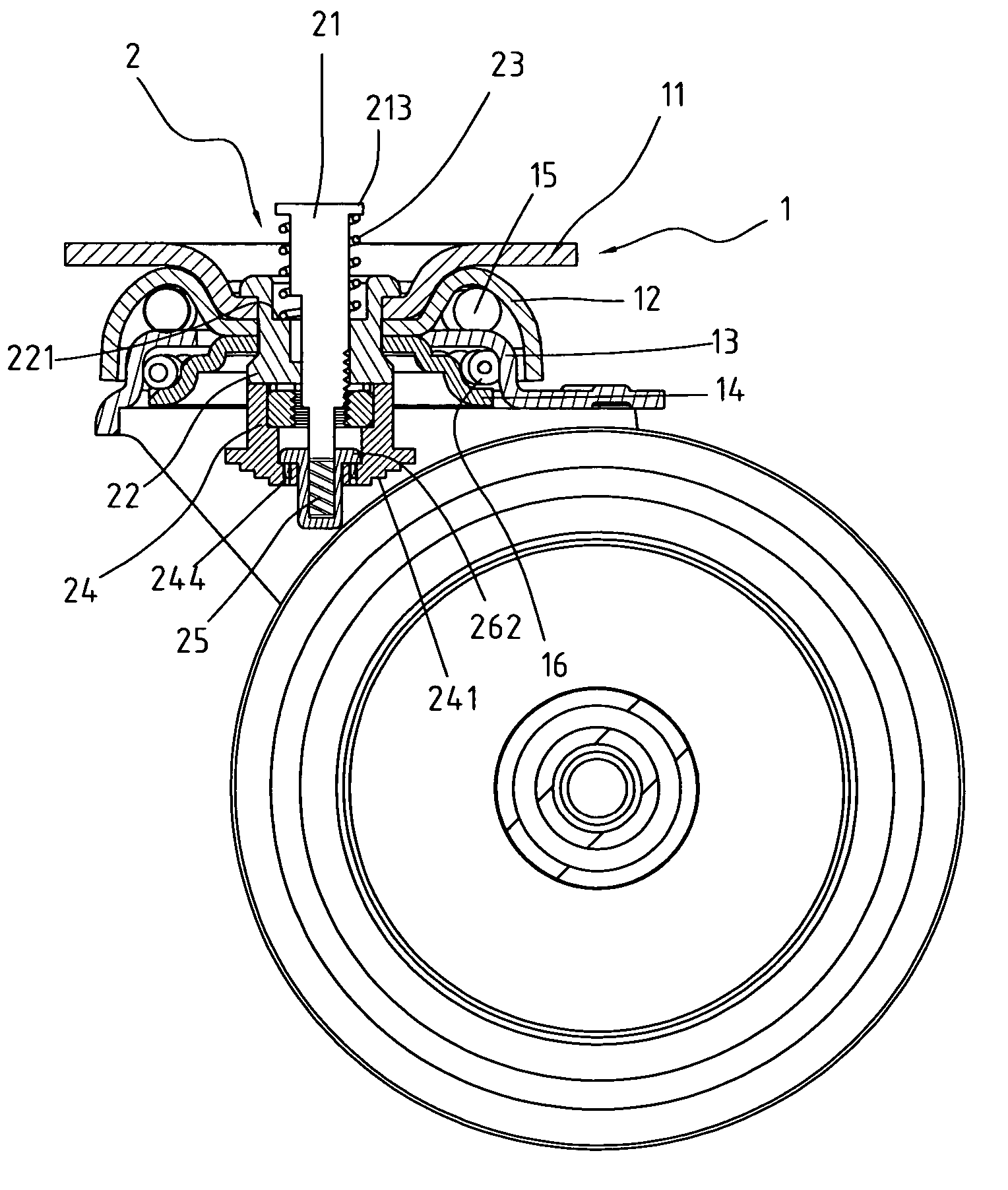
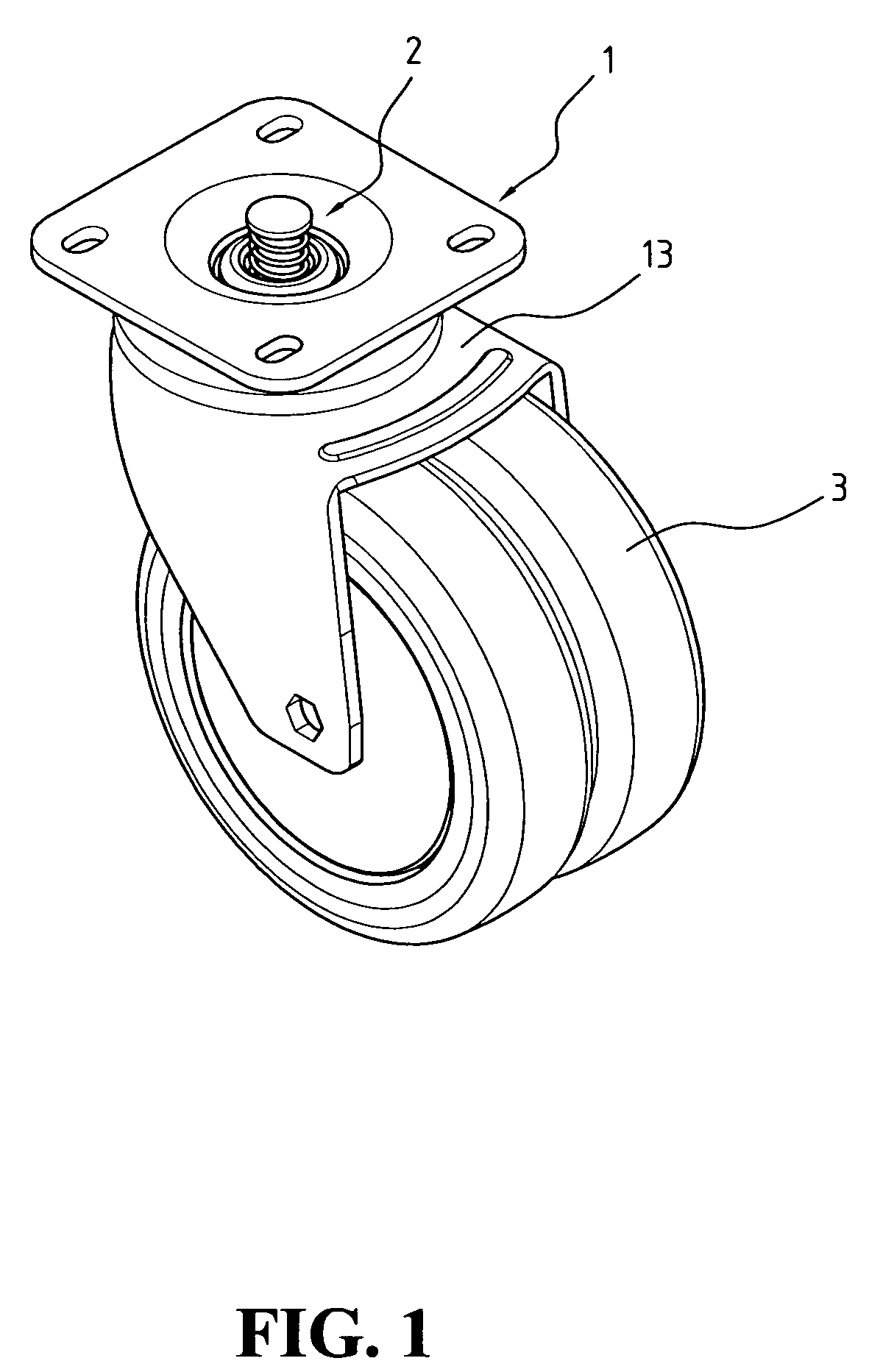
Brake caster with stroke adjustment mechanism
InactiveUS7182178B2Extended service lifeReduce operating costsBraking element arrangementsCastorsScrew threadBrake pad
Owner:LIN CHING SUNG
Brake structure for wheel rotating device
InactiveUS20080053719A1Small sizeIncrease the diameterMechanically actuated brakesElectric propulsion mountingEngineeringBrake fluid
A brake structure for a wheel rotating device is disclosed, which comprises a motor provided in a wheel and is driven for rotating the wheel, and a braking mechanism for actuating brake to brake the wheel. The motor includes: a motor housing; a stator positioned in and fixed to the motor housing; and a rotor positioned in the motor housing and facing to the stator. The braking mechanism includes: a brake rotor to rotate with the wheel; frictional members to be in contact with the brake rotor for generation of braking force; a pressing force generating unit for generating pressing force of the frictional members so that the frictional members are urged to and pressed against the brake rotor by supplying brake fluid through a brake fluid passage to transmit fluid pressure; and a housing for the pressing force generating unit. The brake fluid passage is formed inside a wall of the motor housing, and is connected to a brake fluid supply port provided in the housing for the pressing force generating unit.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Inhaler Device Counter
ActiveUS20080035144A1Easy readable large displayLow production costRespiratorsLiquid surface applicatorsEngineeringRocker arm
Inhaler counter (20) comprising a counter housing (390), a rocker arm (200) with a pawl (210), the rocker arm being pivotally supported by the housing and arranged to perform a rocker movement in response to a linear actuation motion, a return spring (220) for resetting the rocker arm, a ratchet wheel (230) engagable with the pawl to convert the movement of the rocker arm into an incremental rotational motion of an axle arrangement (240) advancing a display means (60), the axle arrangement further comprising a back rotation prevention means (280) in the form of a spring loaded friction brake and a worm gear, the display means comprising rotatable indicator means (120) with teeth that engage the worm-gear and a stationary scale.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
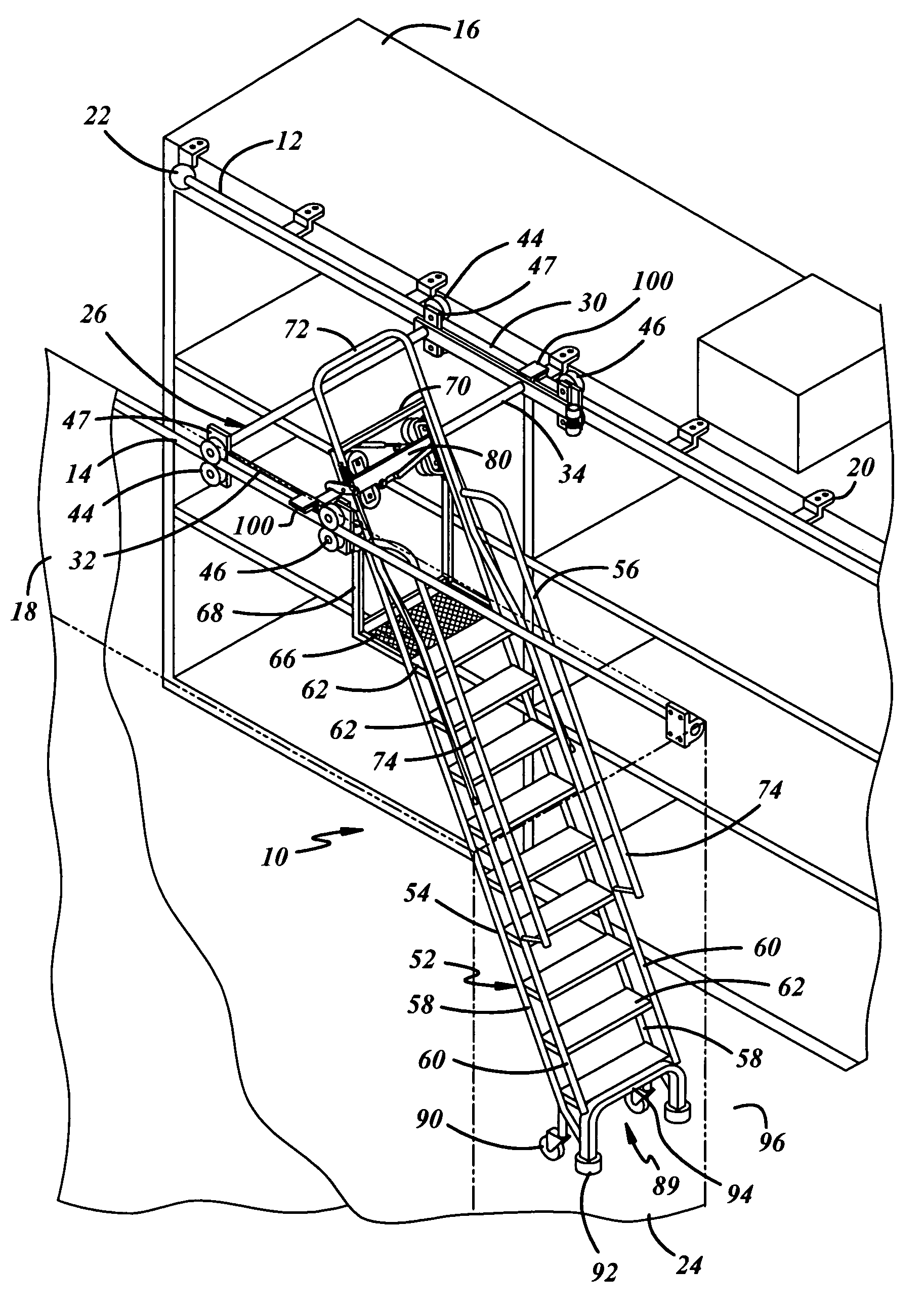
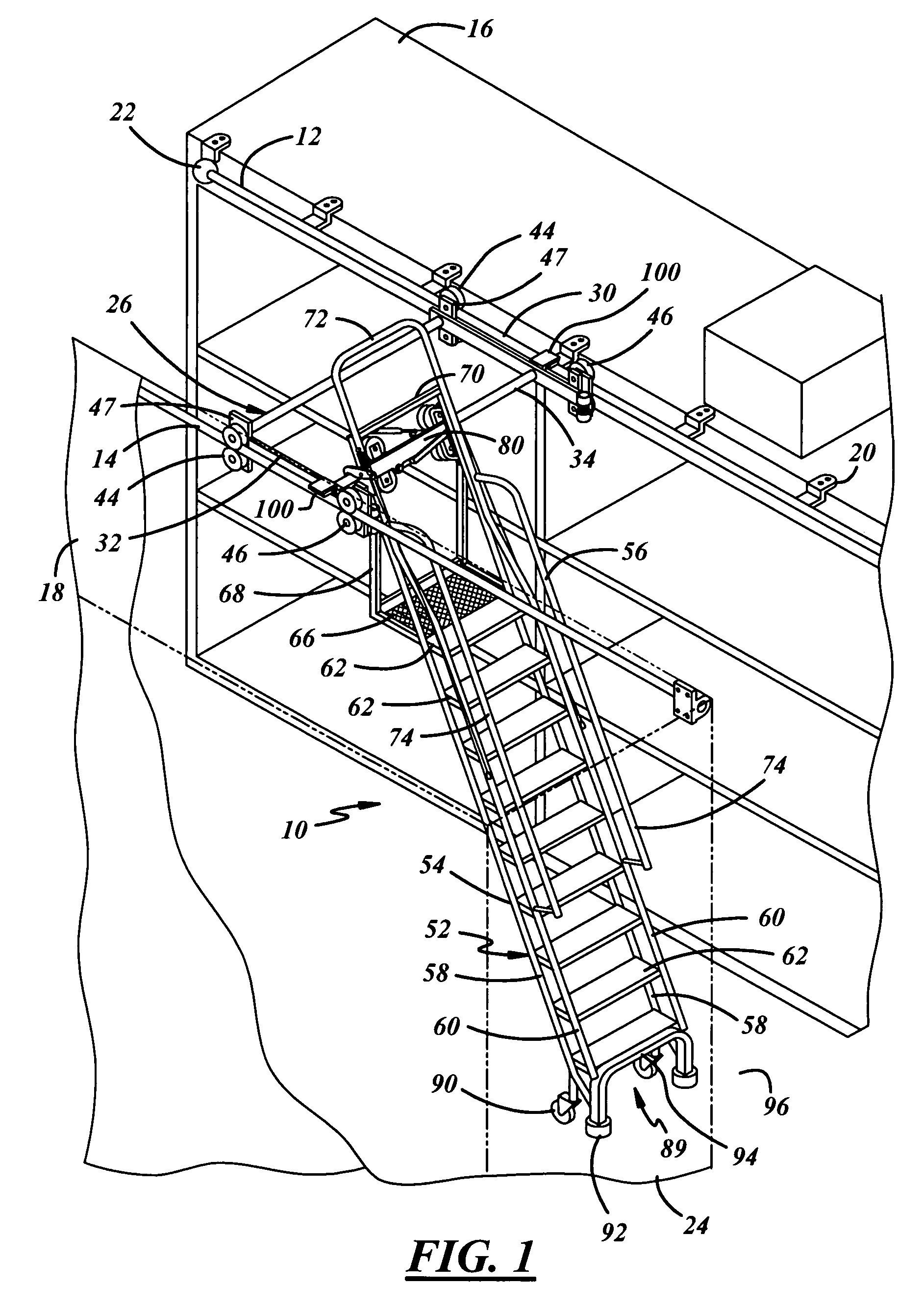
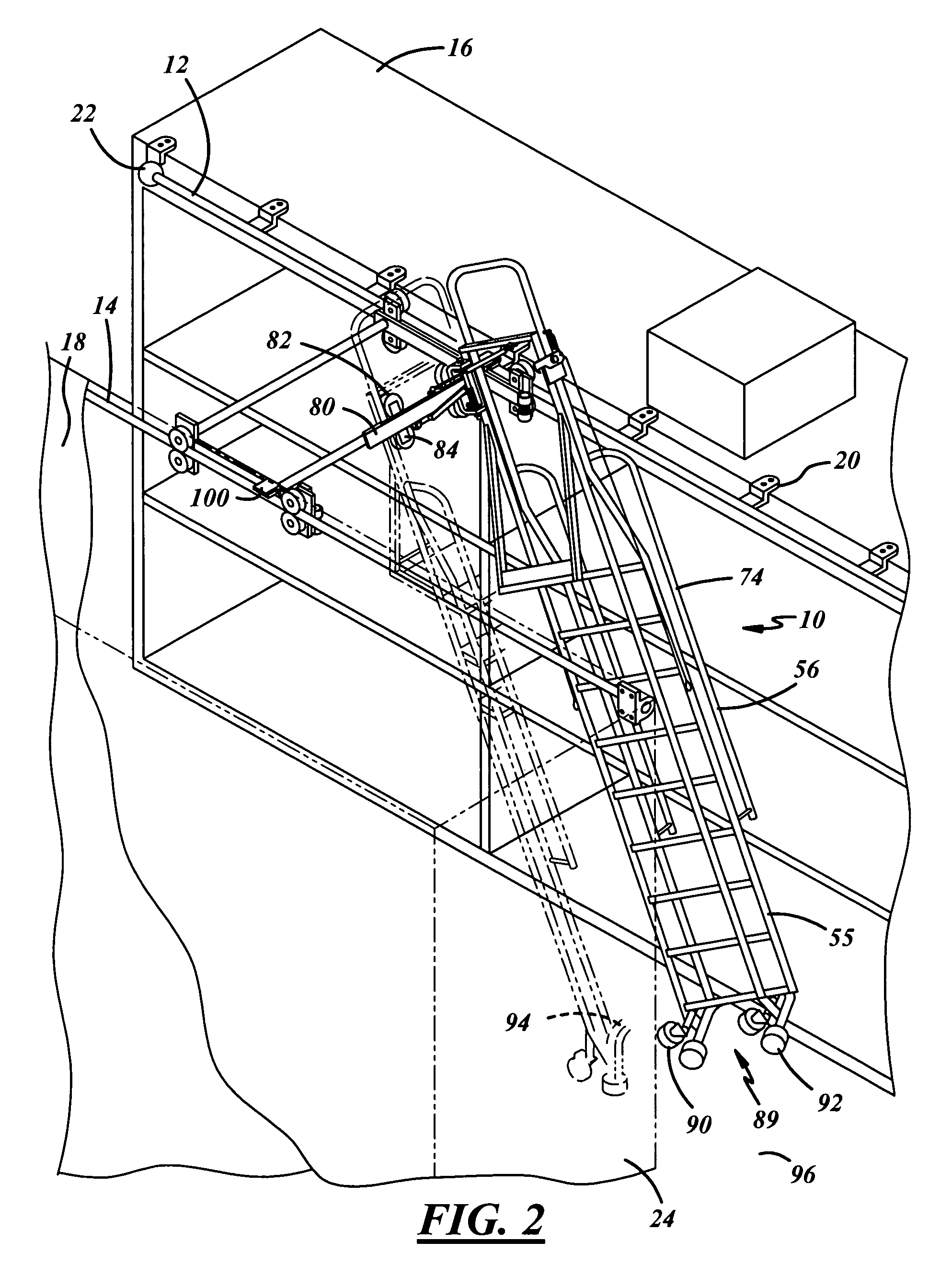
Dual track ladder with brake mechanism that is automatically applied to the upper tracks to hold the ladder in place during use
The ladder system is disposed between two spaced storage shelves of the types found in crowded warehouses. The ladder is mounted on overhead guide tracks and may be moved longitudinally along the shelves and laterally between the shelves. Locating means are provided for immobilizing the ladder against movement laterally and longitudinally. The locating means includes a pair of spring-loaded casters and rubber pads at the lower end of the ladder and a pair of braking mechanisms overlying and engageable with the guide tracks when subjected to the weight of the user to prevent movement of the ladder at the top thereof either intentionally or unintentionally. Finally, a lateral brake is carried by the ladder which prevents the roller carriage from moving laterally. The brake is applied when the ladder is in use.
Owner:MATERIAL CONTROL
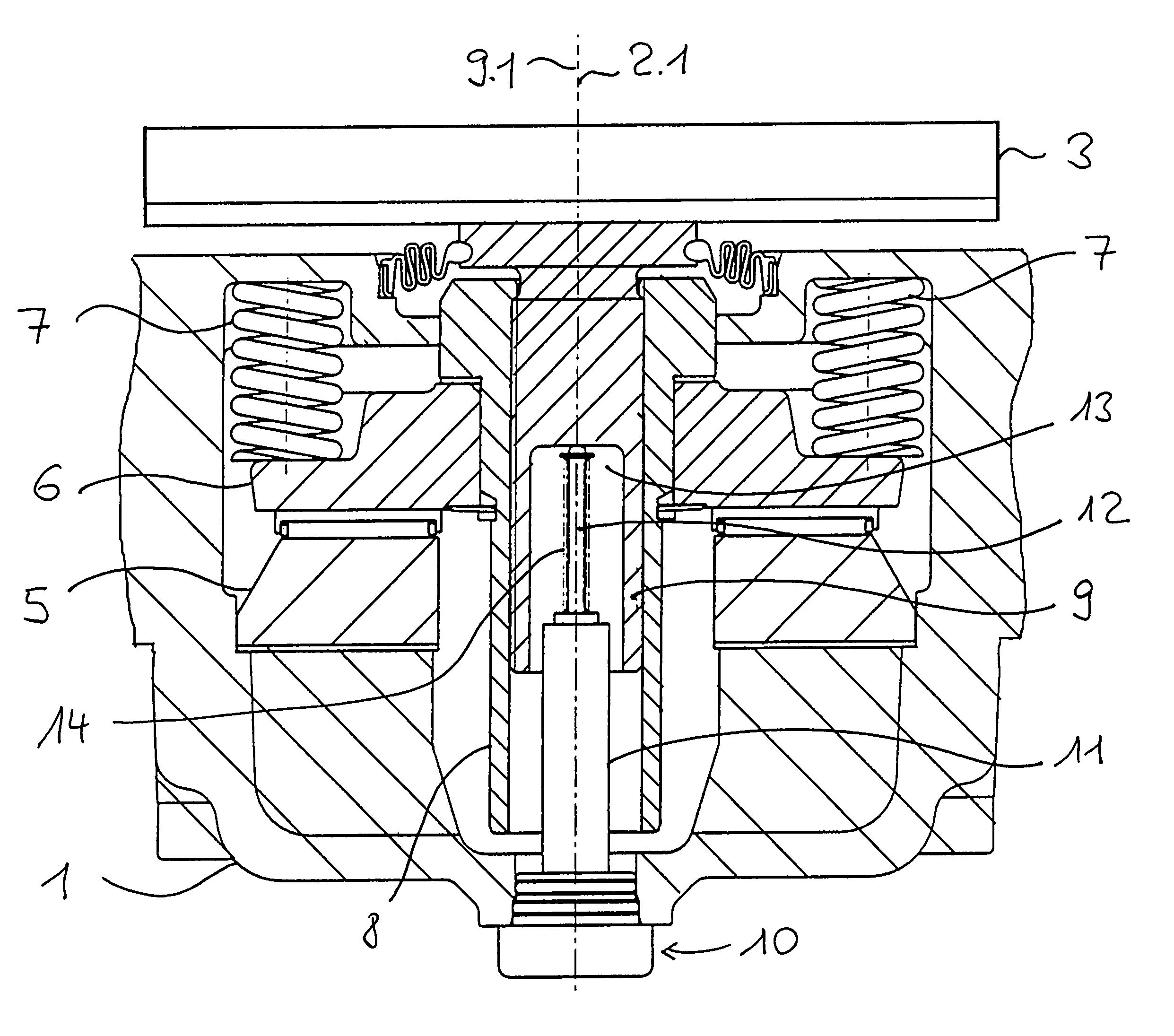
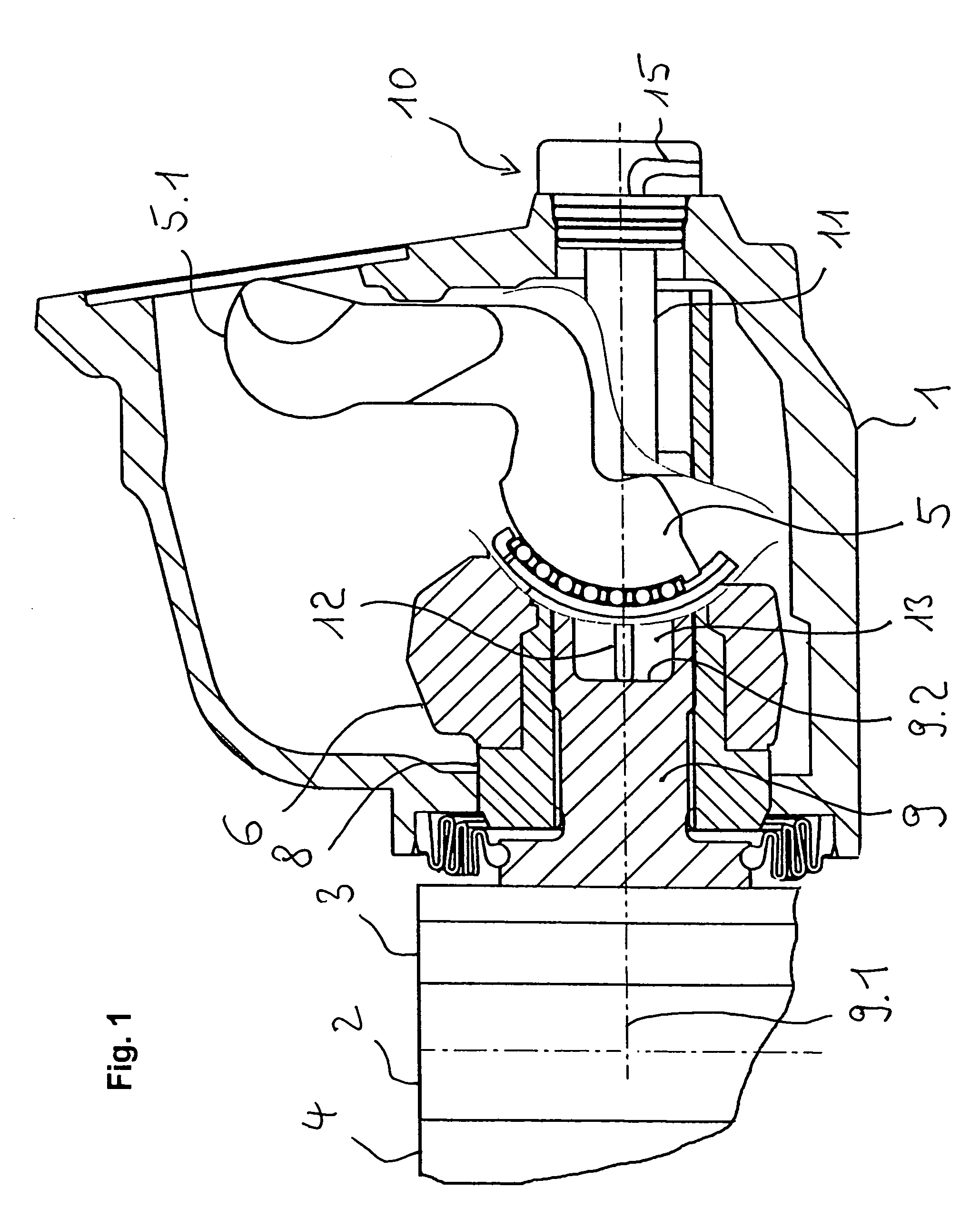
Disc brake and monitoring device for such a disc brake
ActiveUS7322447B2Simple configurationLess mounting spaceMechanically actuated brakesDrum brakesCalipersDisc brake
A disc brake has a brake disc and a brake caliper spanning the brake disc. A brake applicator shaft is supported on the brake caliper and arranged transversely to an axis of rotation of the brake disc. The brake applicator shaft has a rotary lever for actuating the brake applicator shaft. An adjusting device provided with a thrust spindle having an end face facing away from the brake disc is provided. The brake applicator shaft transmits upon brake application a brake force through the thrust spindle onto the brake disc. A monitoring device is provided that has a measuring element moveable relative to the brake caliper and resting against the end face of the thrust spindle.
Owner:WABCO EURO BVBA SPRL
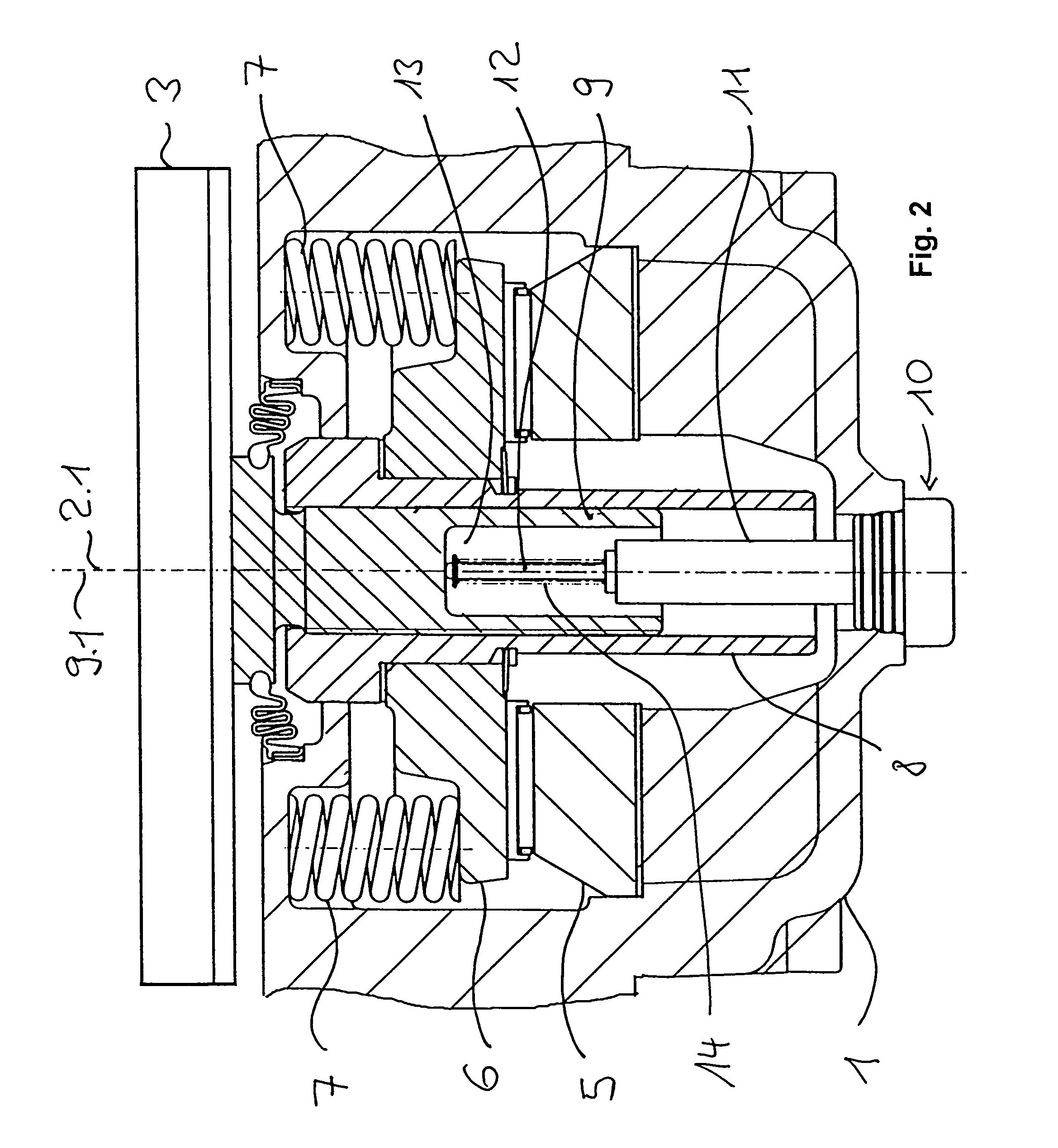
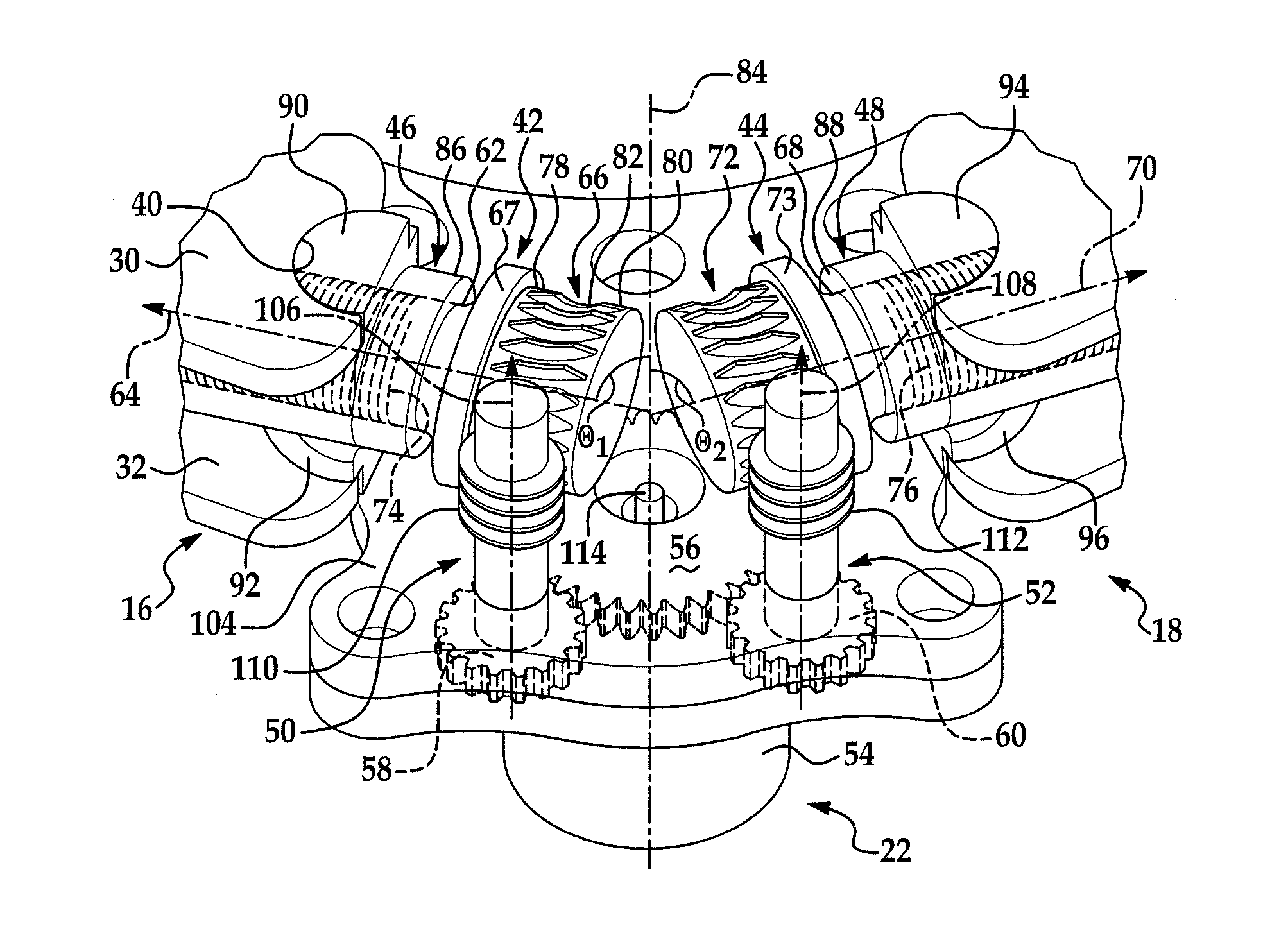
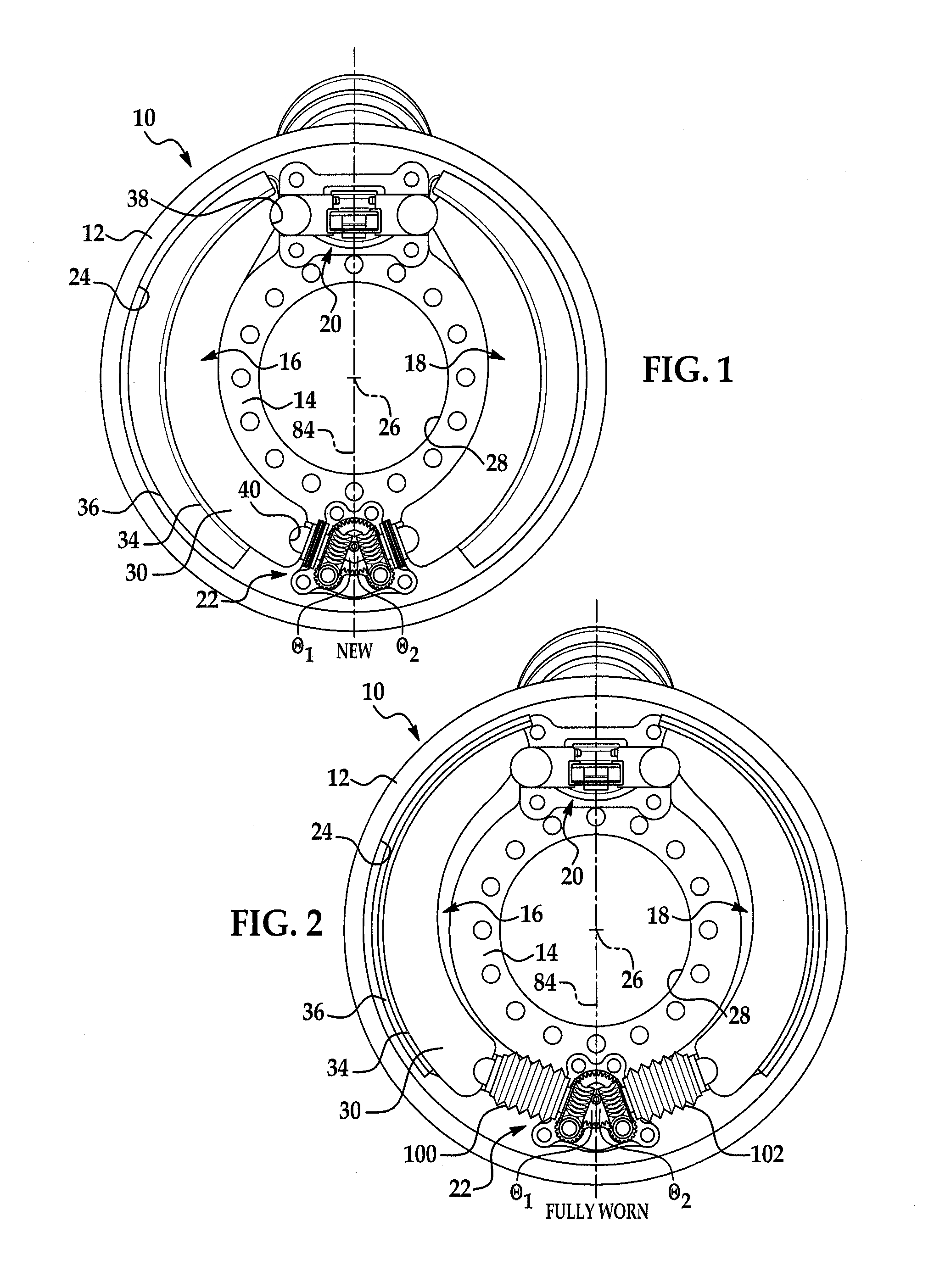
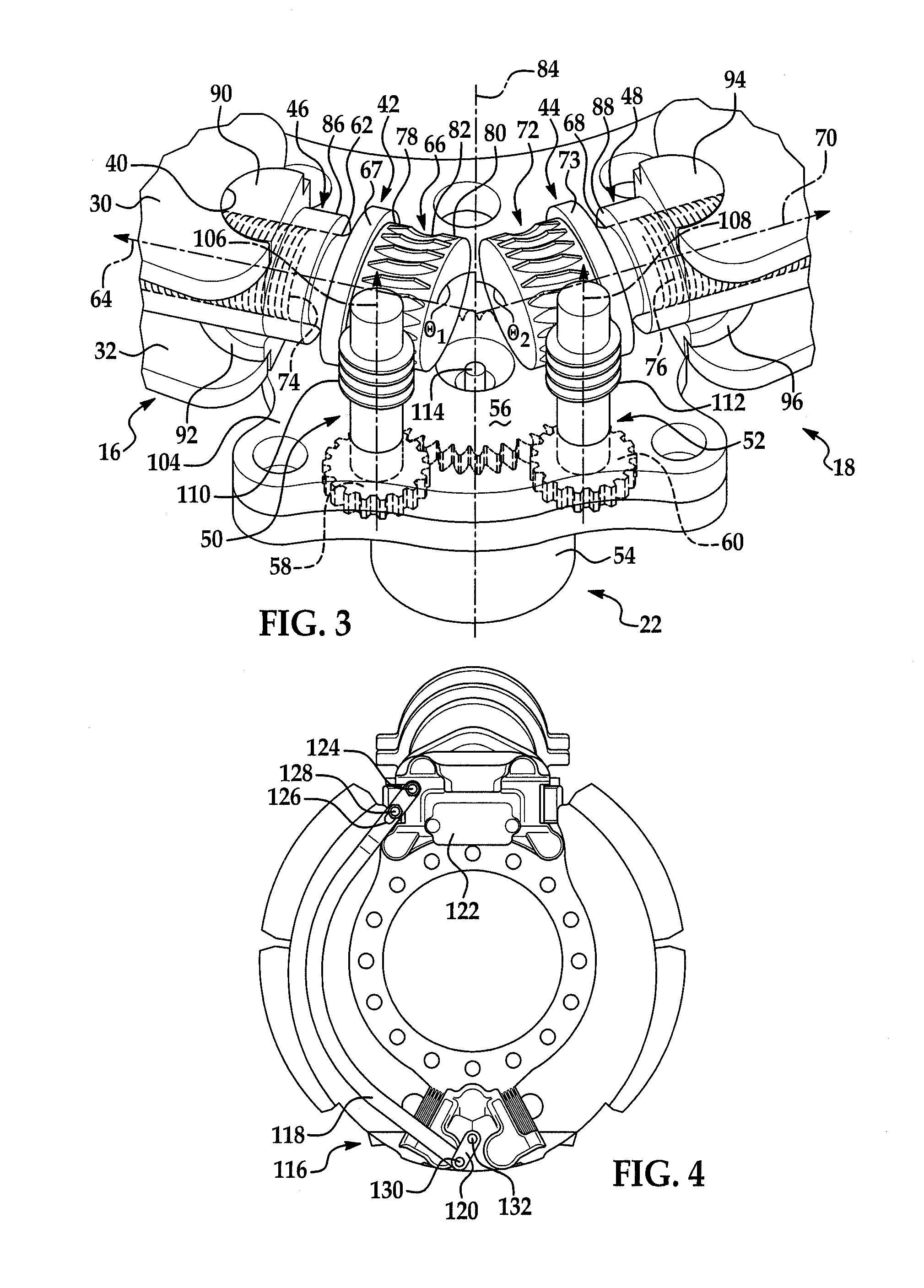
Variable position anchor assembly for adjusting brake shoes in a drum brake
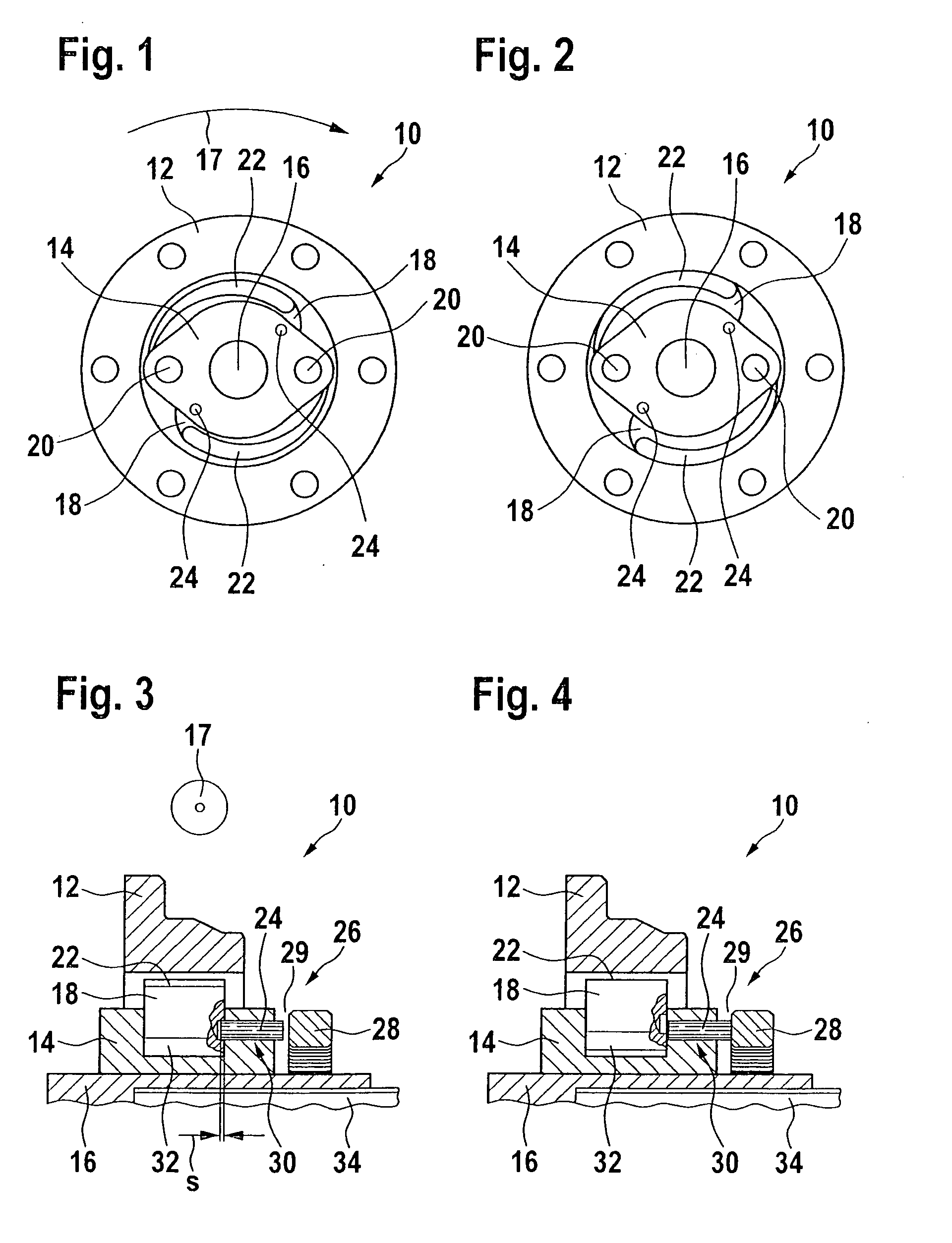
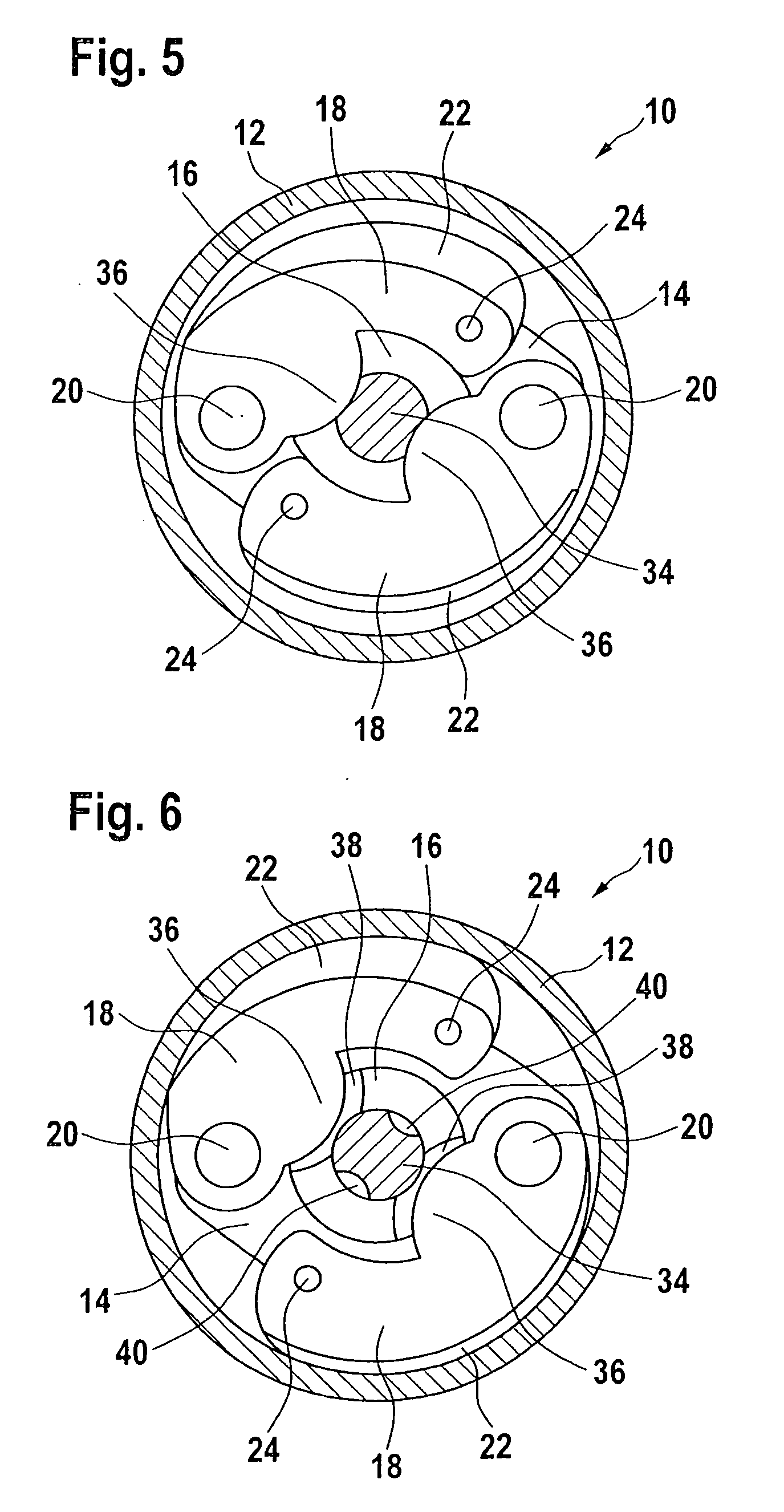
InactiveUS20120031716A1Fine adjustment rangeReduce operating costsDrum brakesBrake actuating mechanismsEngineeringMechanical engineering
An anchor assembly is provided that permits adjustment of the brake shoes in a drum brake to account for wear. The assembly includes first and second adjuster shafts each having a plurality of threads and first and second pilot connectors. The pilot connectors each have a plurality of threads in engagement with the threads of a corresponding adjuster shaft. The pilot connectors each engage one end of a corresponding brake shoe. Rotation of each adjuster shaft causes longitudinal movement of a corresponding pilot connector in engagement with a corresponding brake shoe along an axis to adjust a position of the brake shoe.
Owner:BENDIKS SPAJSER FAUNDEJSHN BREJK LLK
Brake structure for wheel rotating device
InactiveUS7938211B2Small sizeIncrease the diameterMechanically actuated brakesElectric propulsion mountingEngineeringBrake fluid
A brake structure for a wheel rotating device is disclosed, which comprises a motor provided in a wheel and is driven for rotating the wheel, and a braking mechanism for actuating brake to brake the wheel. The motor includes: a motor housing; a stator positioned in and fixed to the motor housing; and a rotor positioned in the motor housing and facing to the stator. The braking mechanism includes: a brake rotor to rotate with the wheel; frictional members to be in contact with the brake rotor for generation of braking force; a pressing force generating unit for generating pressing force of the frictional members so that the frictional members are urged to and pressed against the brake rotor by supplying brake fluid through a brake fluid passage to transmit fluid pressure; and a housing for the pressing force generating unit. The brake fluid passage is formed inside a wall of the motor housing, and is connected to a brake fluid supply port provided in the housing for the pressing force generating unit.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Brake equipment for holding and braking an elevator car in an elevator installation and a method of holding and braking an elevator installation
Brake equipment for holding and braking an elevator car in an elevator installation, which is arranged to be movable along a brake track in two directions of travel, includes a mount with a brake lining which automatically adjusts under friction couple with the brake track on movement of the elevator car relative to the rail and in that case tightens a first tightening means, which can be released by an actuator. The first tightening means tightens the mount together with the brake lining against the brake track by a biasing force. The brake equipment produces, with unmoved brake equipment and an unreleased state of the actuator, a holding force acting in both directions of travel. The holding force is determined substantially by the biasing force acting on the mount.
Owner:INVENTIO AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com