Patents
Literature
2342 results about "Brake shoe" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
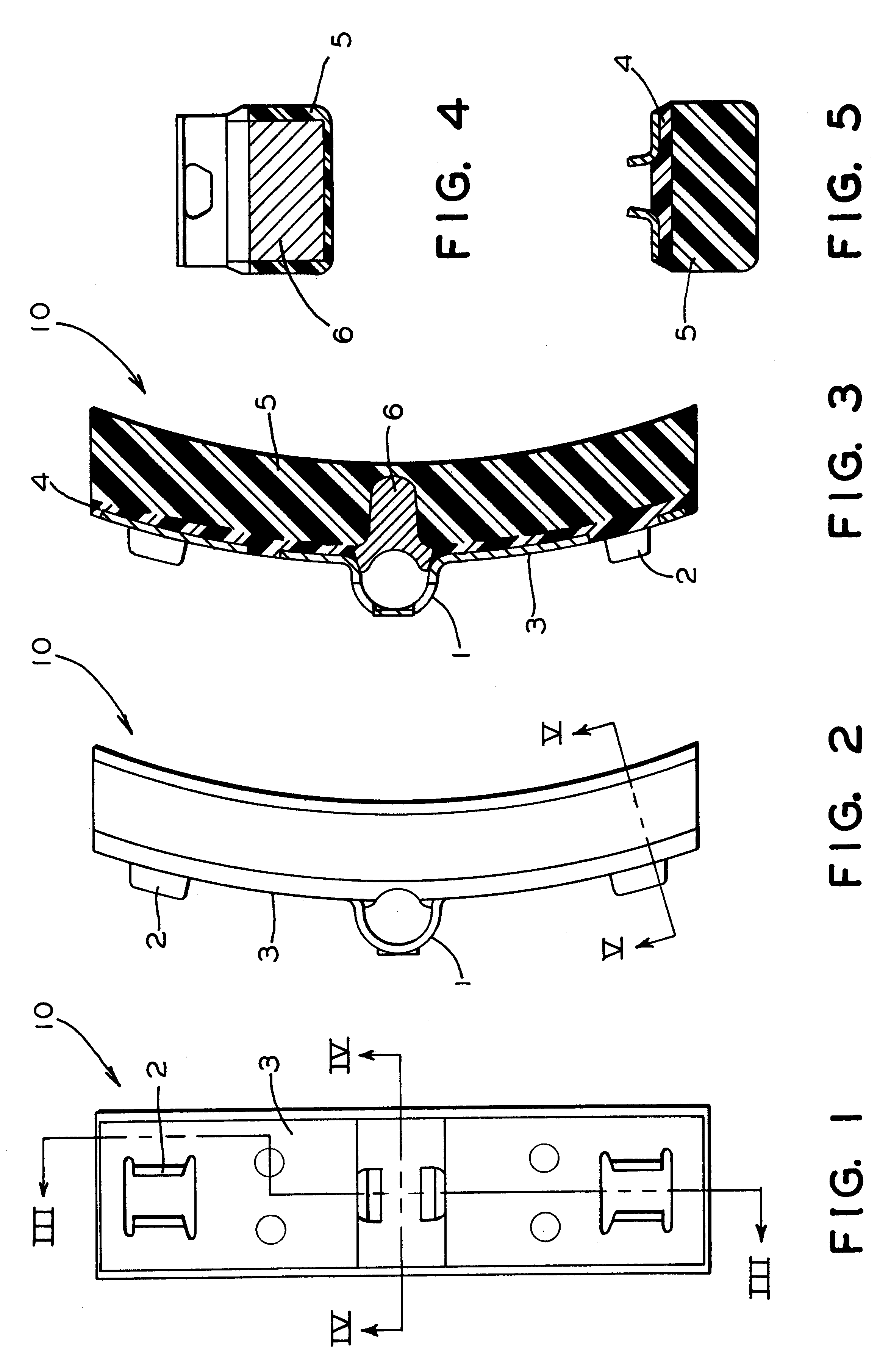
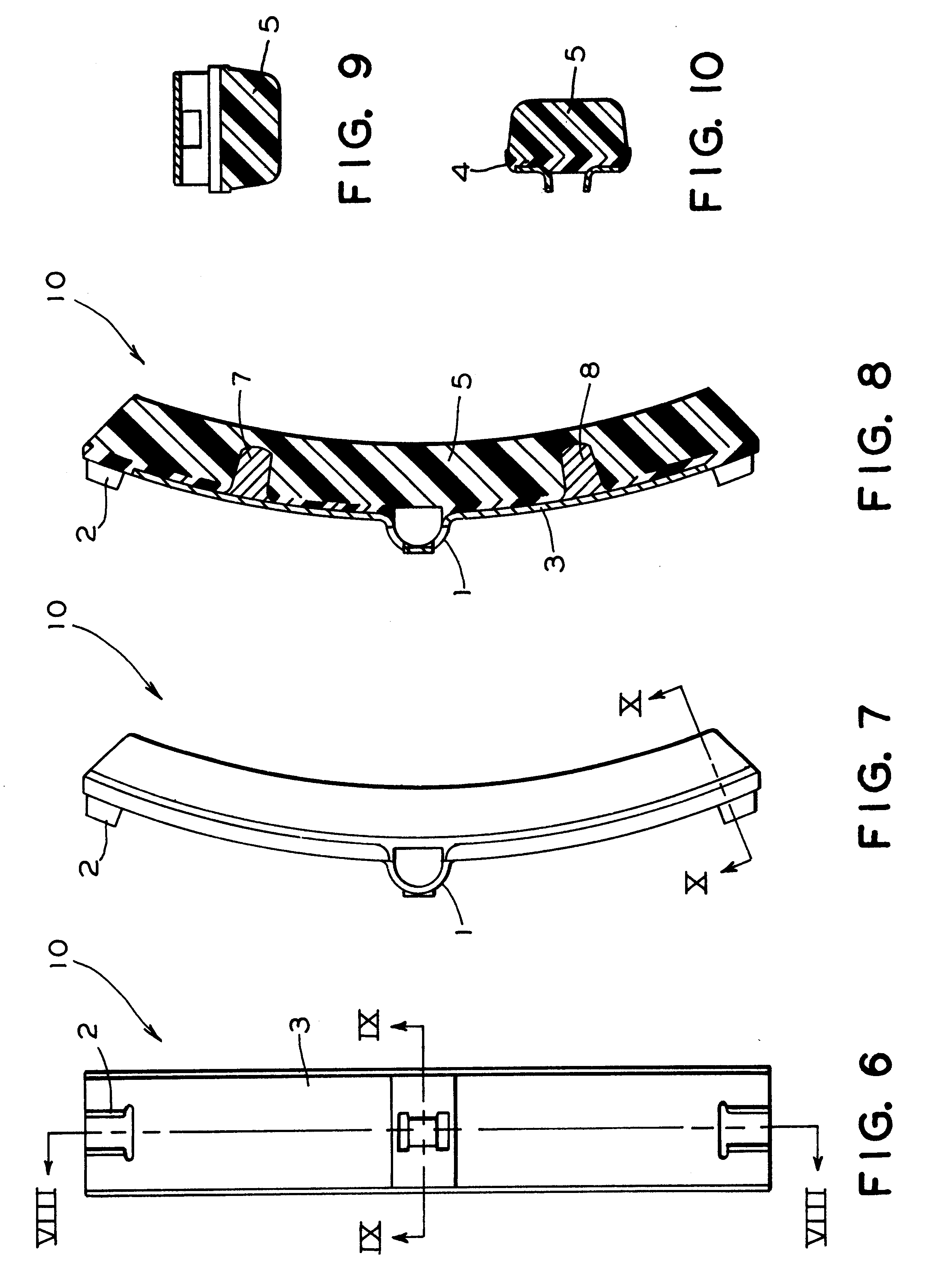
A brake shoe is the part of a braking system which carries the brake lining in the drum brakes used on automobiles, or the brake block in train brakes and bicycle brakes.
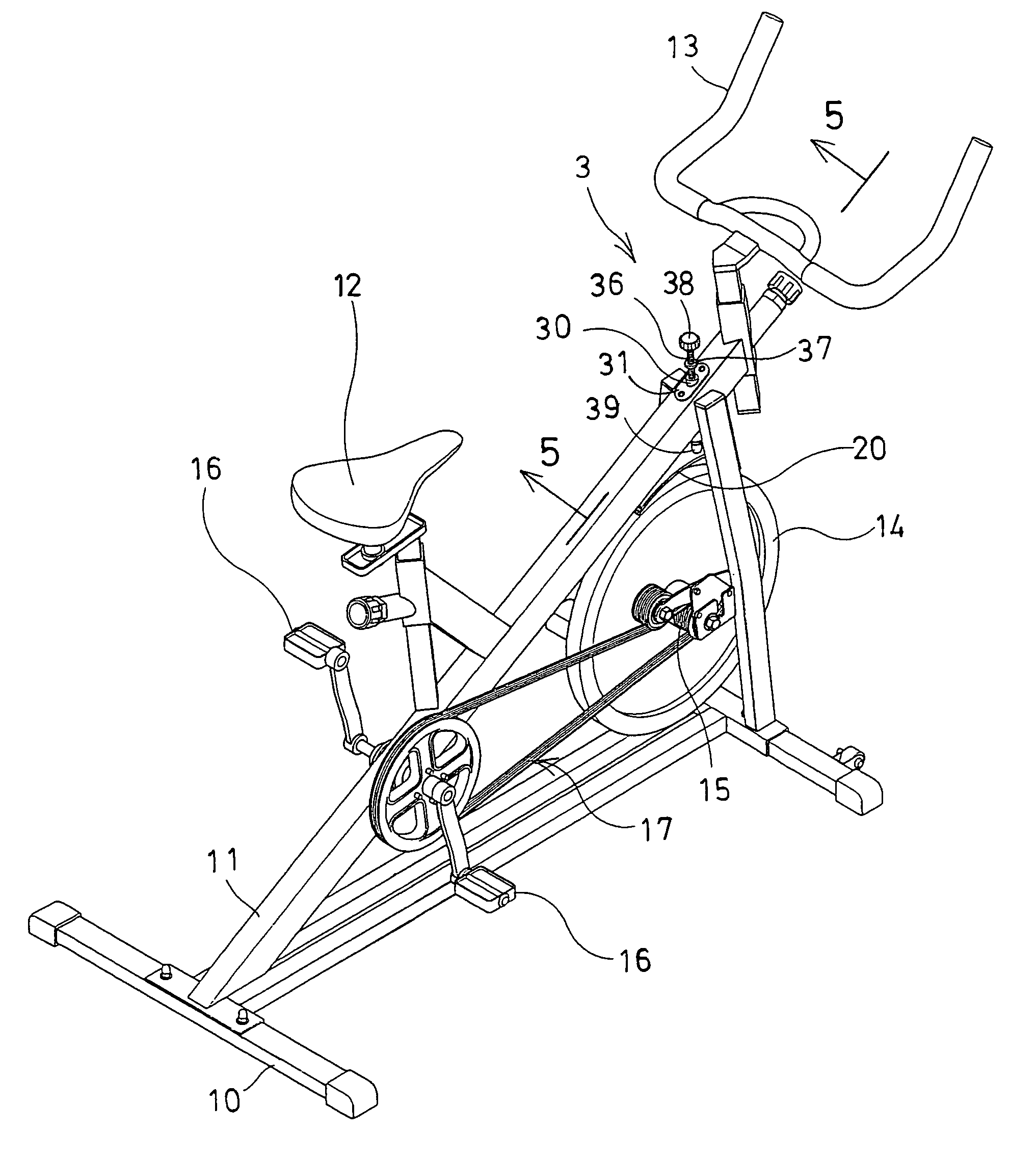
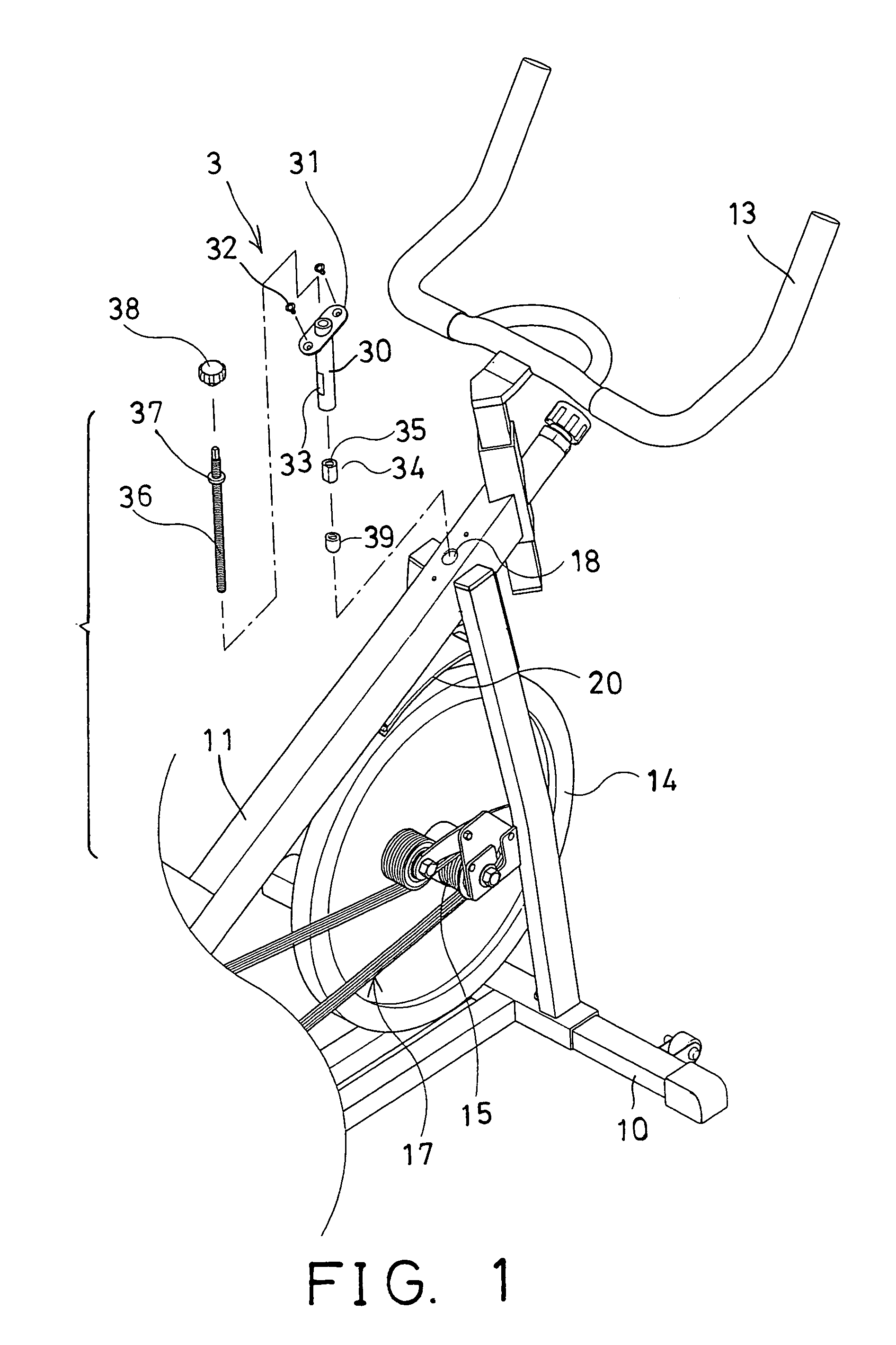
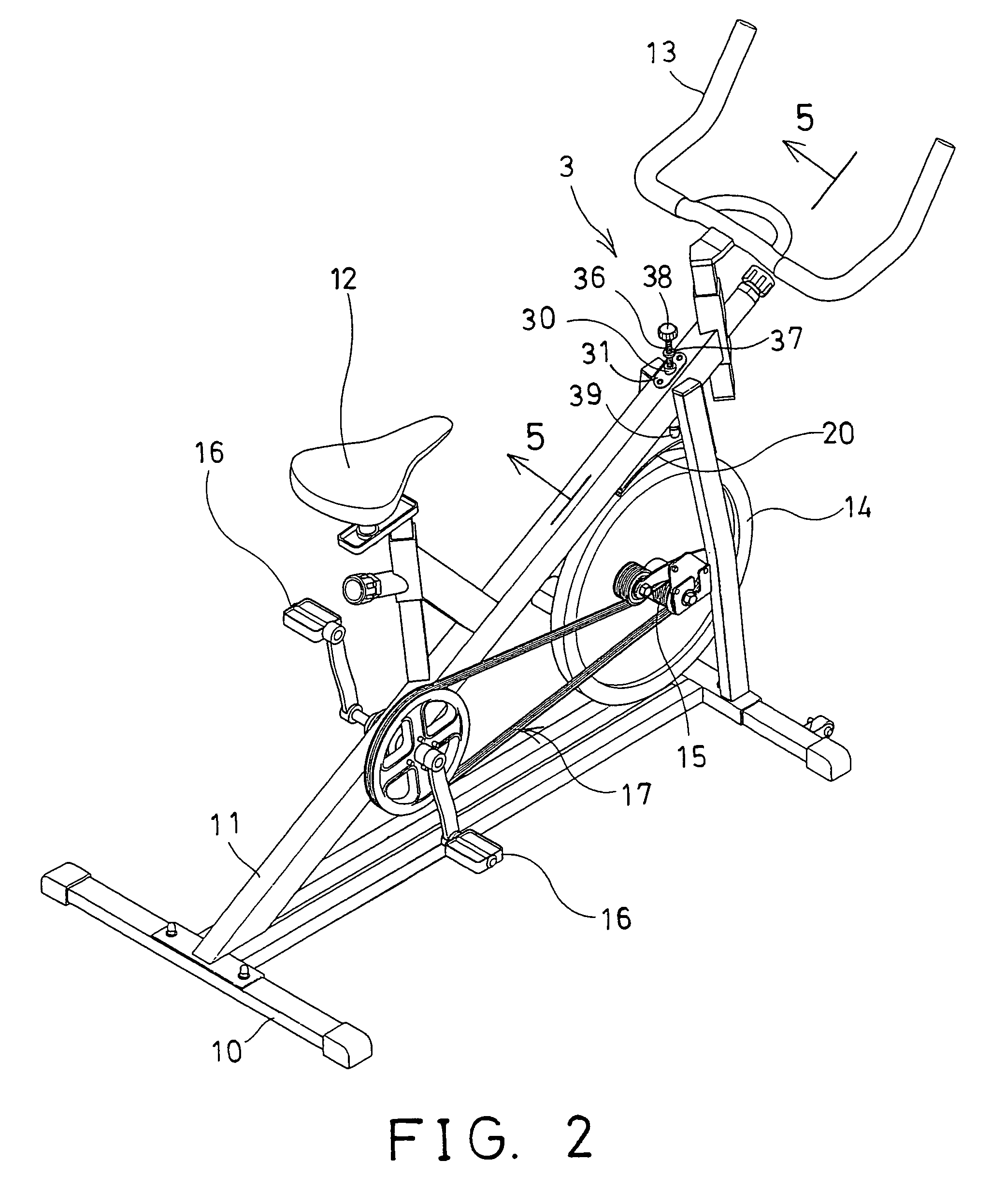
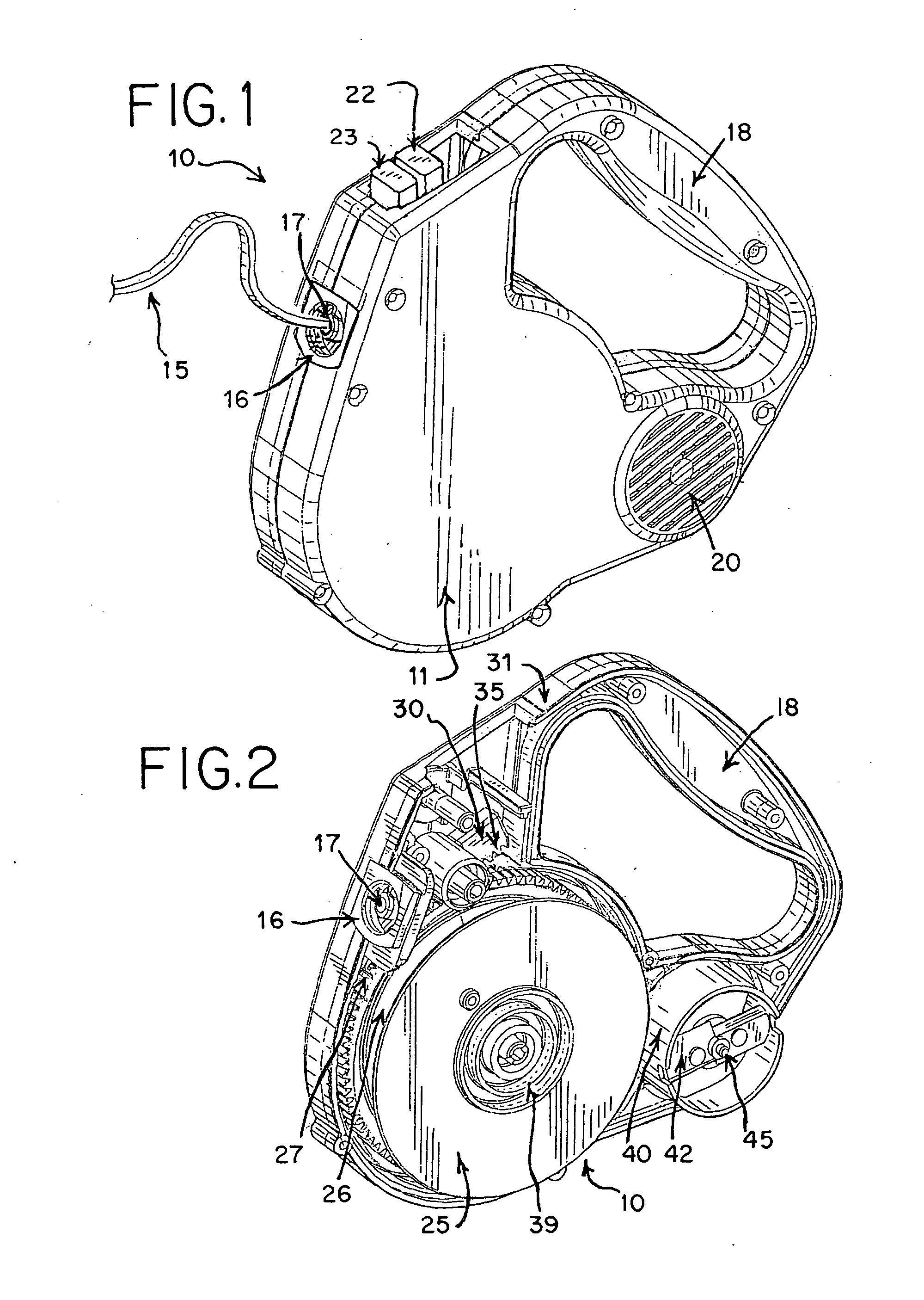
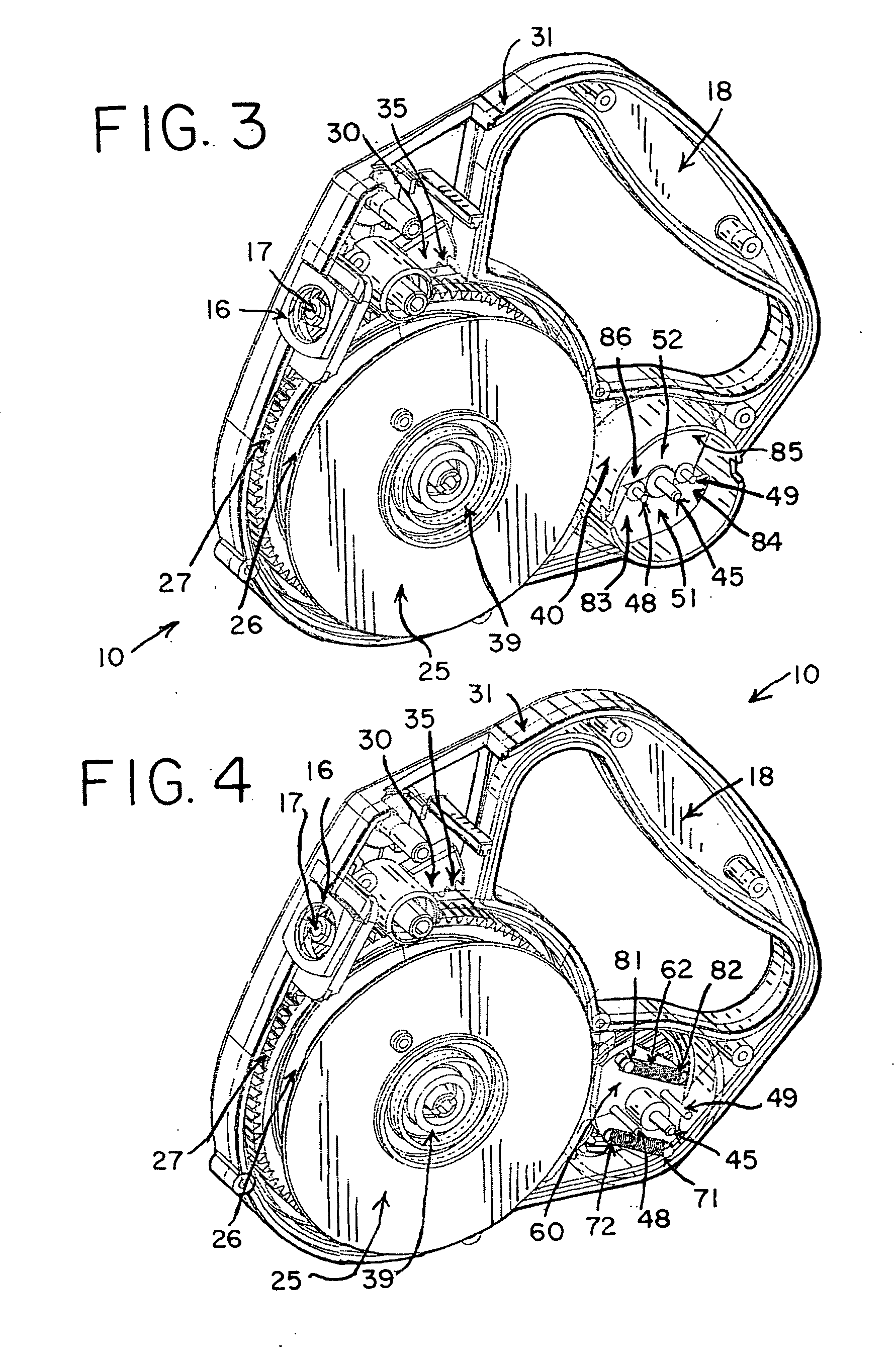
Exerciser having magnetic retarding device
InactiveUS7004888B1Different strengthSuitable for operationFrictional force resistorsMovement coordination devicesFlywheelBrake shoe
An exerciser includes a flywheel rotatably attached onto a frame and coupled to a pair of foot pedals with a transmission device, an arch having one end rotatably coupled to the frame, one or more magnetic members attached to the arch and moveable toward or away from the flywheel, to adjust the magnetic retarding force to the flywheel. A brake shoe is attached to the other end of the arch, and movable to engage with and to brake the flywheel. A spring may bias the arch and the brake shoe away from the flywheel, to allow the brake shoe to be moved toward and against the flywheel and to brake the flywheel selectively. An actuating device may force the brake shoe of the arch to engage with and to brake the flywheel.
Owner:LUNG TUNG HAI +2
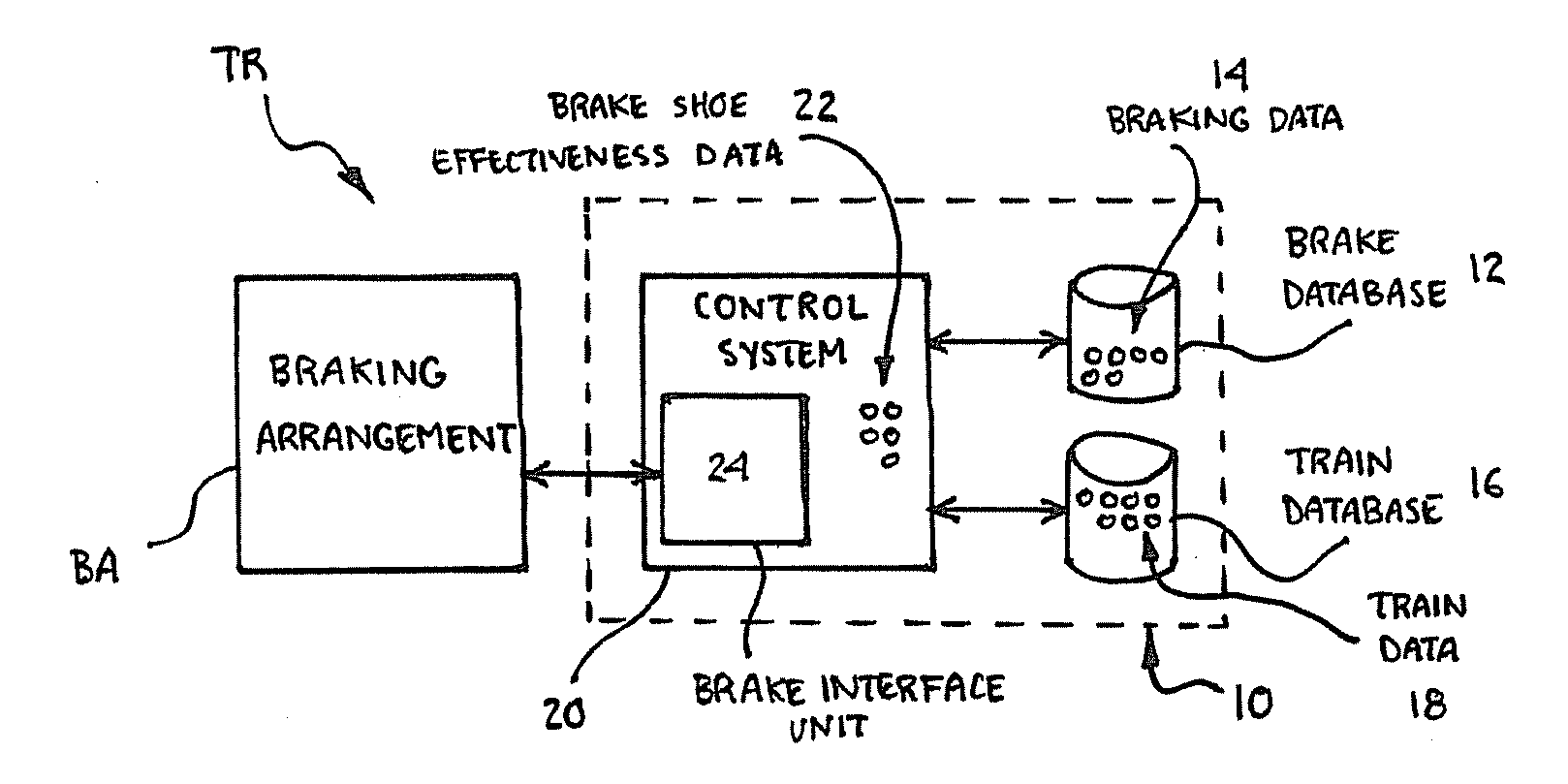
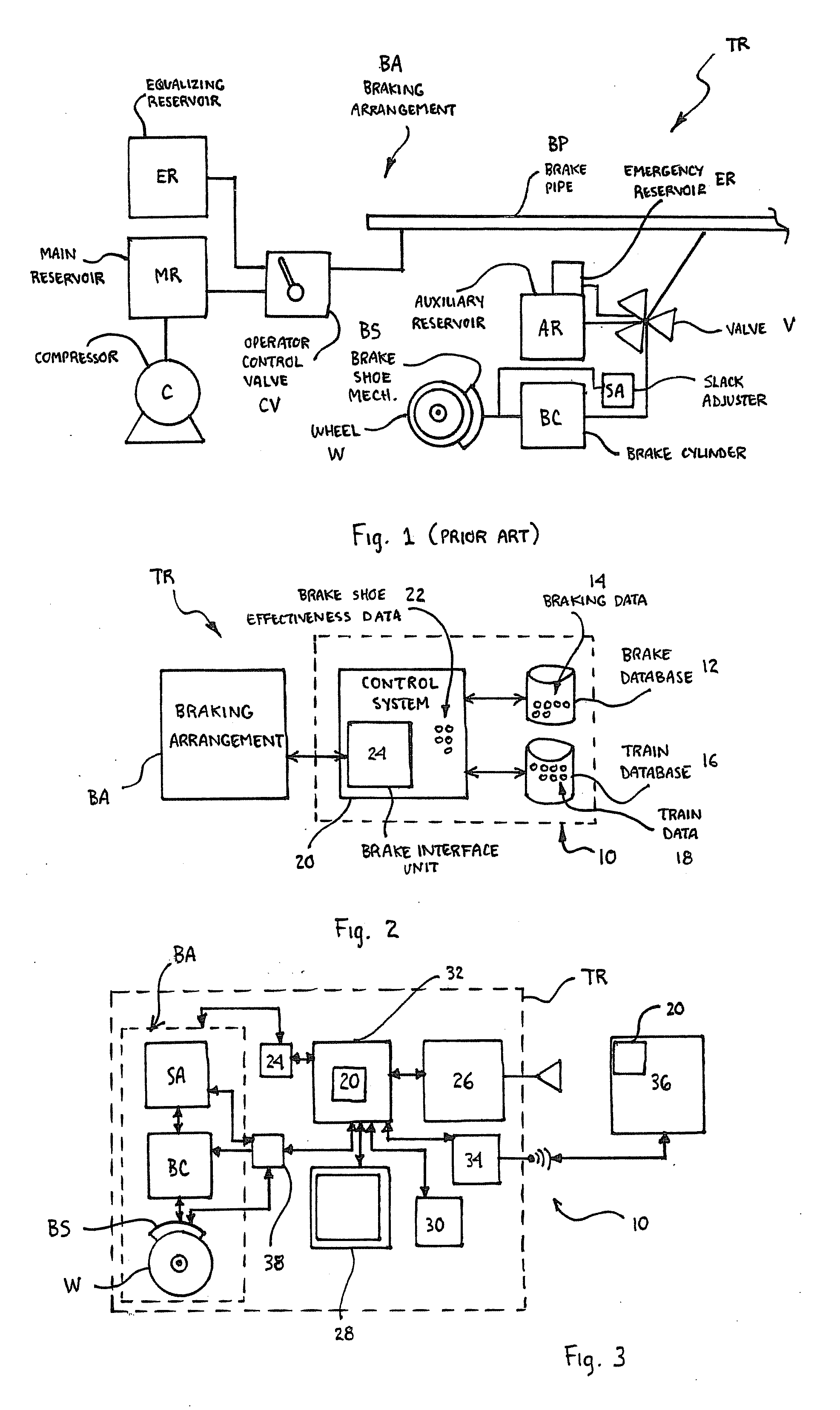
Method and System for Determining Brake Shoe Effectiveness
A system for determining brake shoe effectiveness of a braking arrangement of a train during operation of the train including at least one brake database including braking data and at least one train database including train data. A control system is in communication with the at least one brake database and the at least one train database, and the control system dynamically determines brake shoe effectiveness data based upon the braking data and the train data, where the brake shoe effectiveness data includes the ability of the braking arrangement to retard the train to a specified level.
Owner:WABTEC HLDG CORP
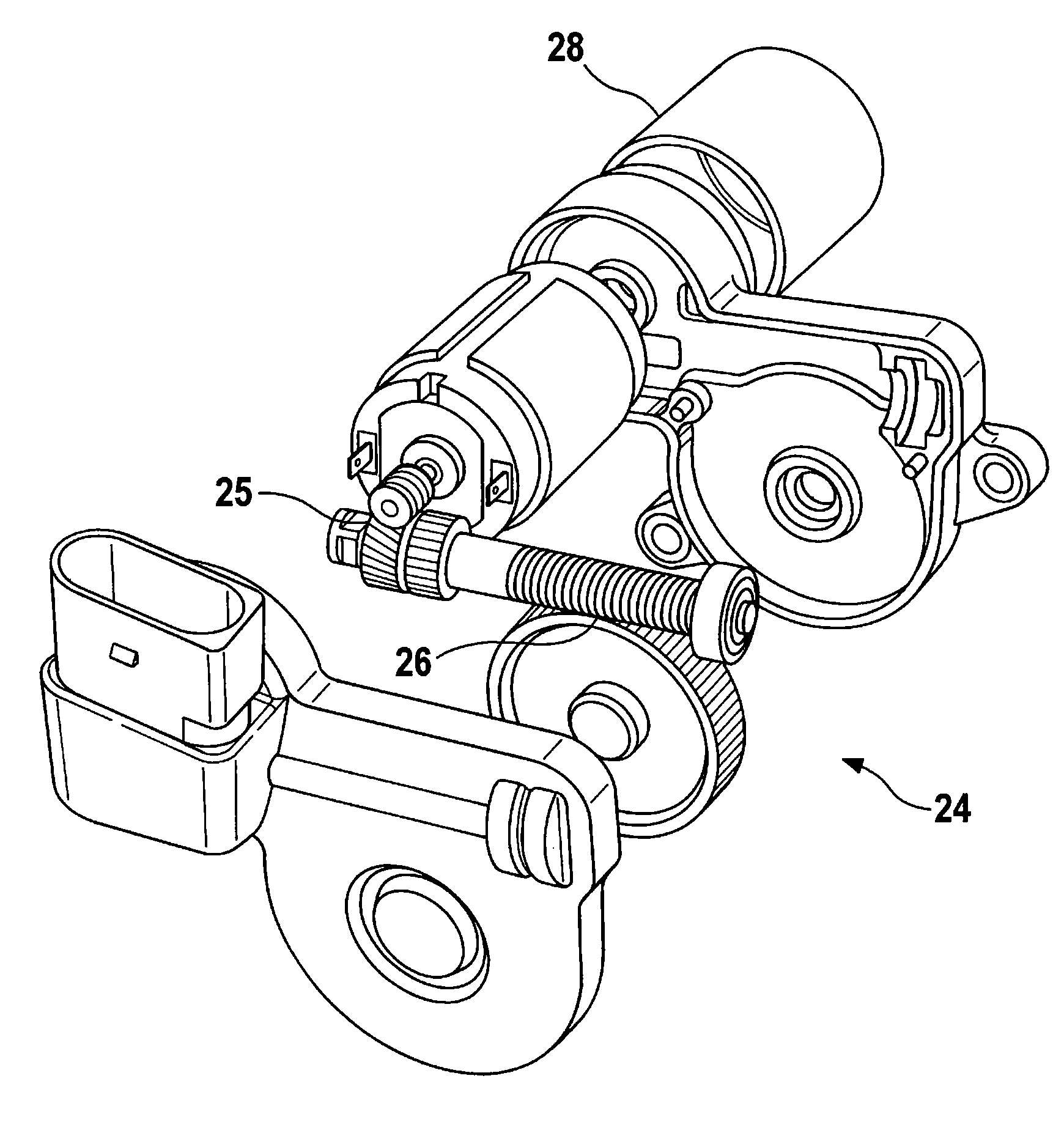
Progressive safety device
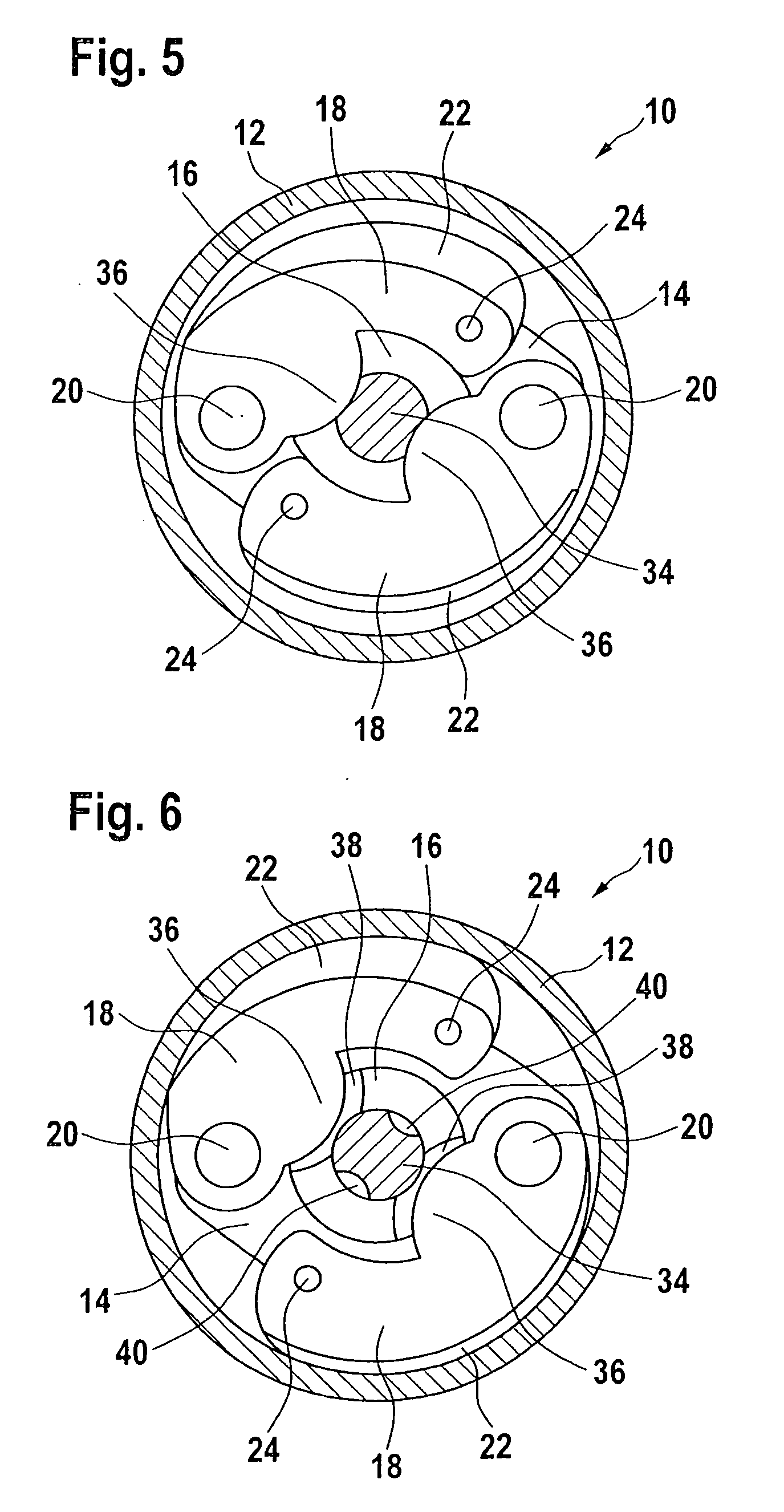
A progressive safety device for an elevator includes a brake unit and an actuating unit. The brake unit has a first brake shoe with first spring assemblies and a triangular rotatable support with second and third brake shoes. The actuating unit has an electromagnetic actuator with a locking bolt, a guide bolt with a coaxial compression spring and an actuating arm. On actuation, the compression spring moves the actuating arm against a guide rail whereby grooves on the actuating arm create a frictional engagement with the guide rail turning the actuating arm about a swivel bearing and through a follower turning the support. With the turning motion and the engagement of one of the second and third brake shoes with the guide rail, the first brake shoe is guided against the guide rail and generates the necessary braking force on the guide rail.
Owner:INVENTIO AG
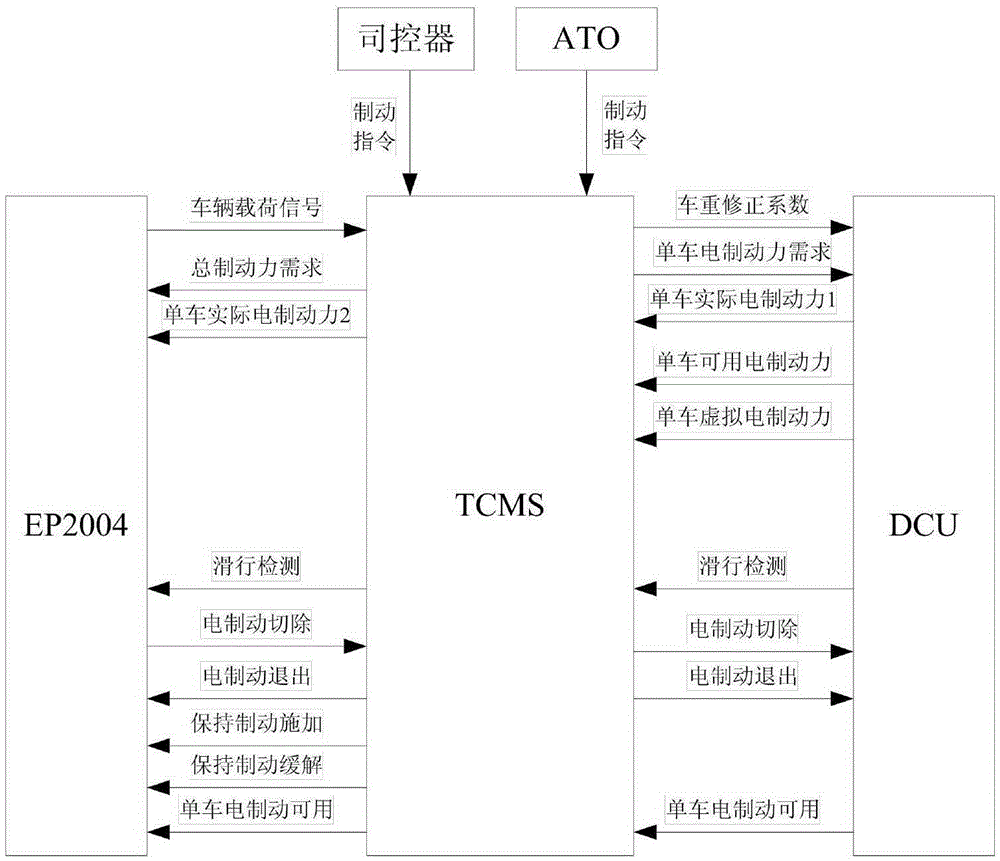
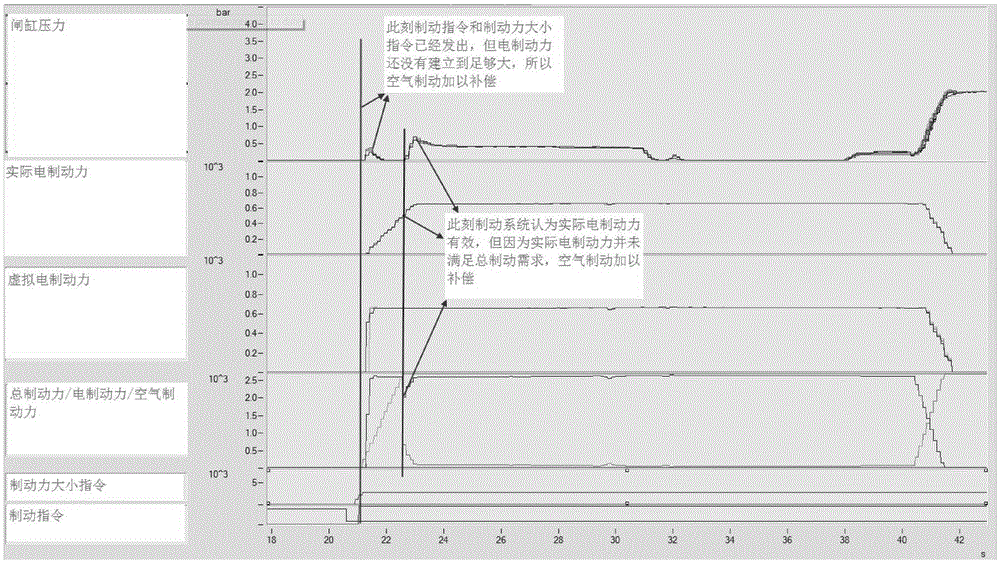
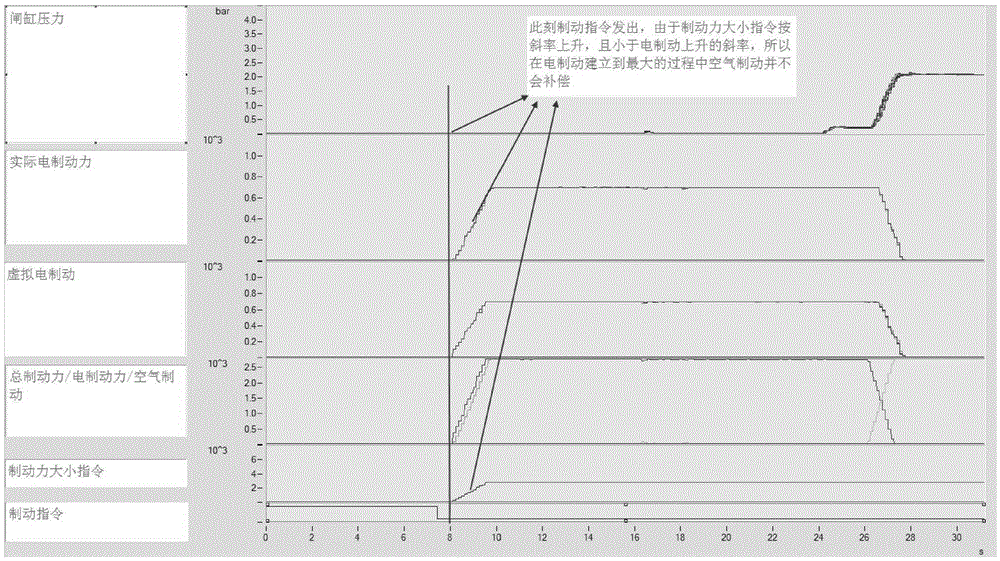
Urban railway vehicle braking force management method distributing braking force based on TCMS
ActiveCN105346556AGood energy saving effectExtend your lifeRailway hydrostatic brakesRailway hydrodynamic brakesElectricityPower grid
The invention belongs to the technical field of urban railway vehicle control, and relates to an urban railway vehicle braking force management method distributing braking force based on TCMS. According to the management method, electric braking force is used preferably, air braking serves as the supplementary for insufficient braking force, electric braking is in real-time coordinated matching with air braking, air braking is not used under the situation that the electric braking capability is enough, and the purposes that energy is fed back to a power grid to the maximum degree, and abrasion of a shoe is greatly reduced are achieved. When the electric braking capability is not enough, the air braking is preferably supplemented to a trailer and a motor vehicle with the electric braking fault, and after the maximum adhesion is reached, the purposes that the air braking is averagely supplemented on the motor vehicle with the normal electric braking, the average distribution of braking force for all vehicles is achieved, the interaction force among the vehicles is reduced, and the service life of the vehicles is prolonged are achieved. In the braking process and the starting process, the applying of the braking force is linearly controlled according to the whole vehicle impulsion limiting requirement, the vehicle impulsion is reduced, and conversion among traction force, electric braking and air braking is smooth.
Owner:CRRC CHANGCHUN RAILWAY VEHICLES CO LTD
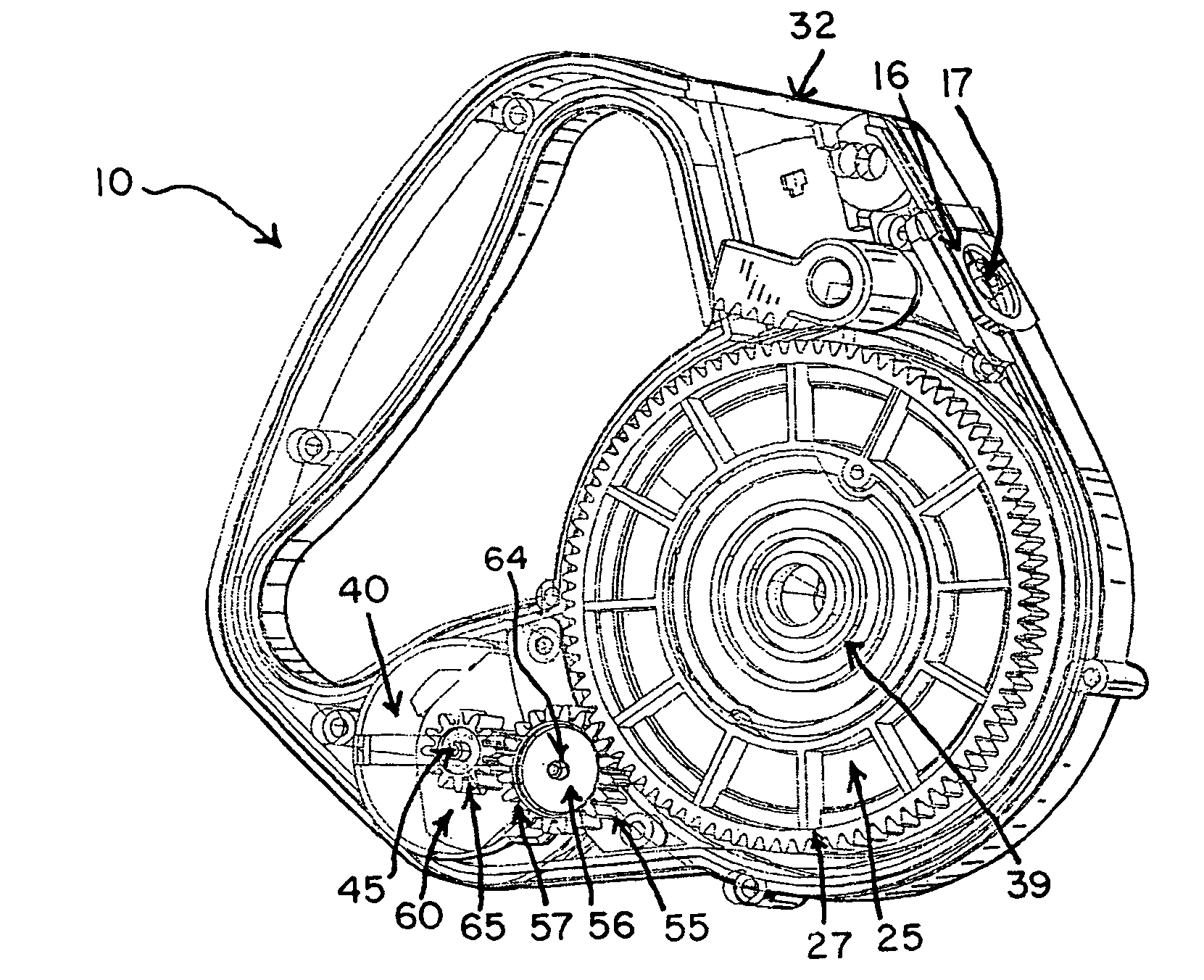
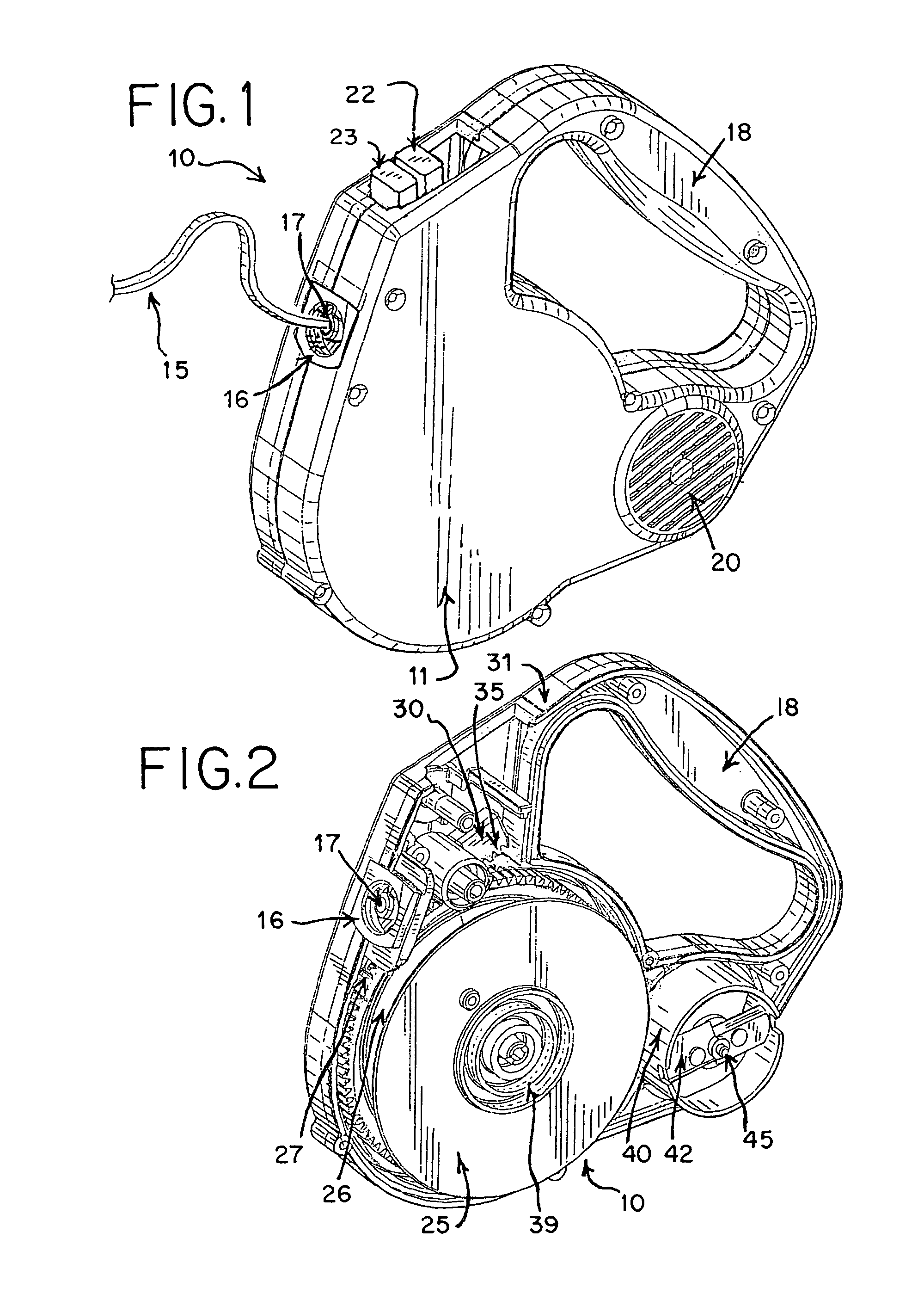
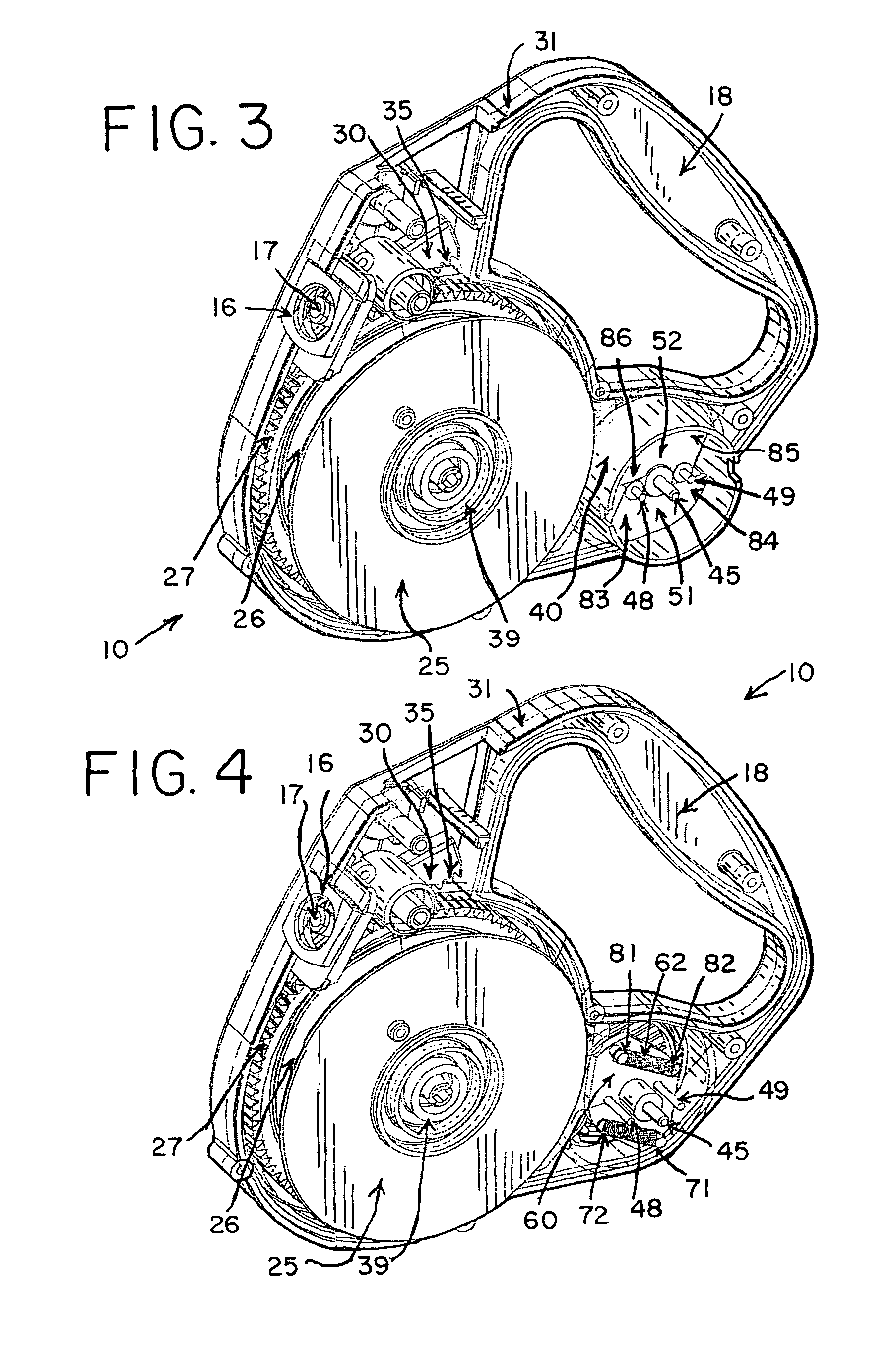
Brake shoe with insert bonded to backing plate
InactiveUS6241058B1Reduce defectsLightweight productionBraking membersFriction liningBrake shoeTread
A composition brake shoe for use on a railway vehicle for reconditioning a wheel tread surface during a normal braking application on such railway vehicle is provided. The composition brake shoe includes a backing plate having a stirrup and a brake surface having a predetermined configuration and a predetermined surface area. It further includes a first friction type composition material extending over the surface area of such brake surface of such composition brake shoe. The composition brake shoe further contains a second friction type material, formed as at least one discrete insert, having a predetermined shape and molded into such first friction type composition material. Such second friction type material initially being completely embedded within such first friction type composition material. One surface of such at least one discrete insert being incrementally exposed as such first friction type composition material is eroded away due to frictional engagement with such wheel tread surface during normal braking operations, such second friction type material exhibiting greater abrasive properties than such first friction type composition material. Such at least one discrete insert of such second friction type material is bonded to such backing plate.
Owner:RFPC HLDG CORP
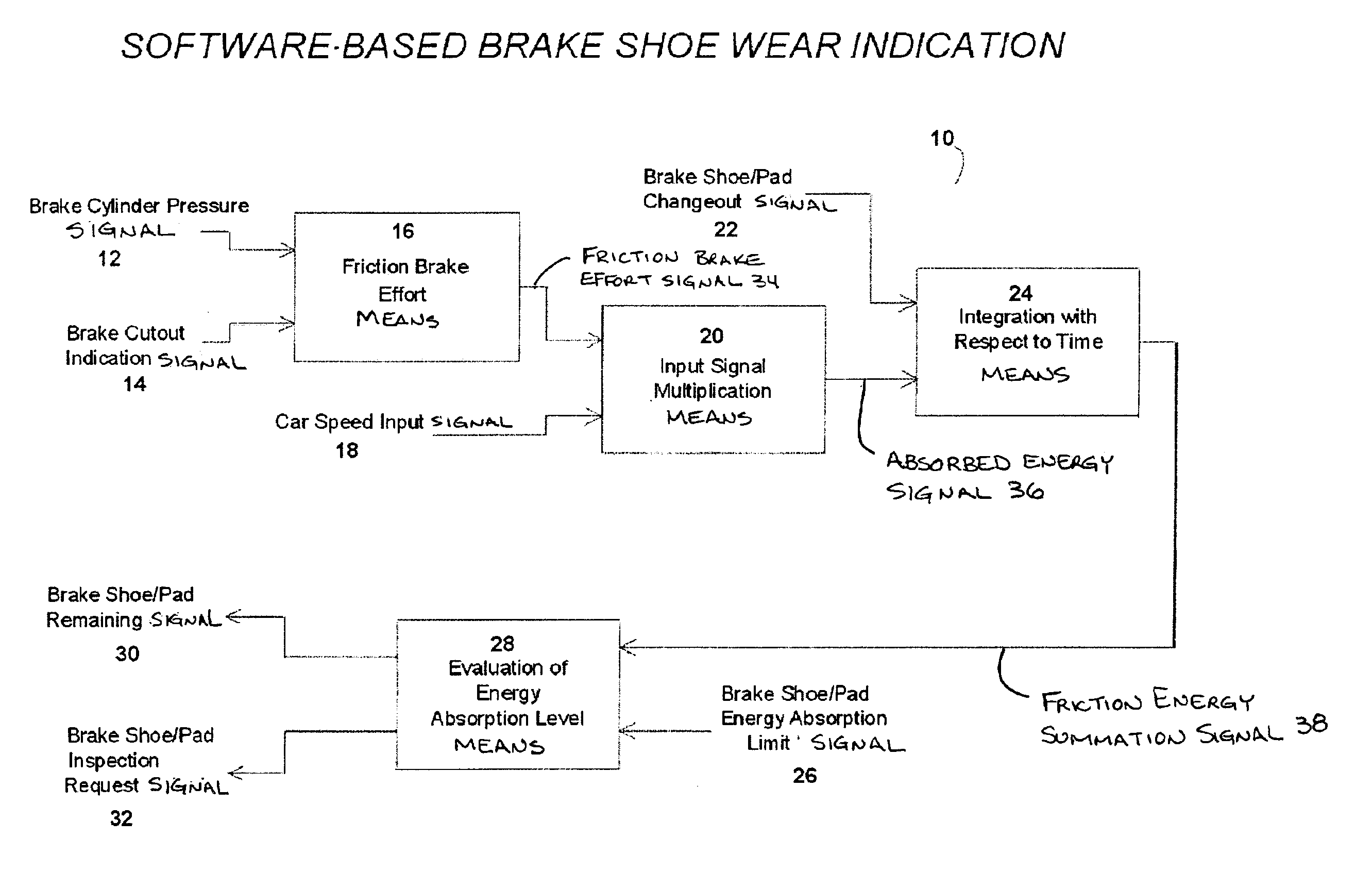
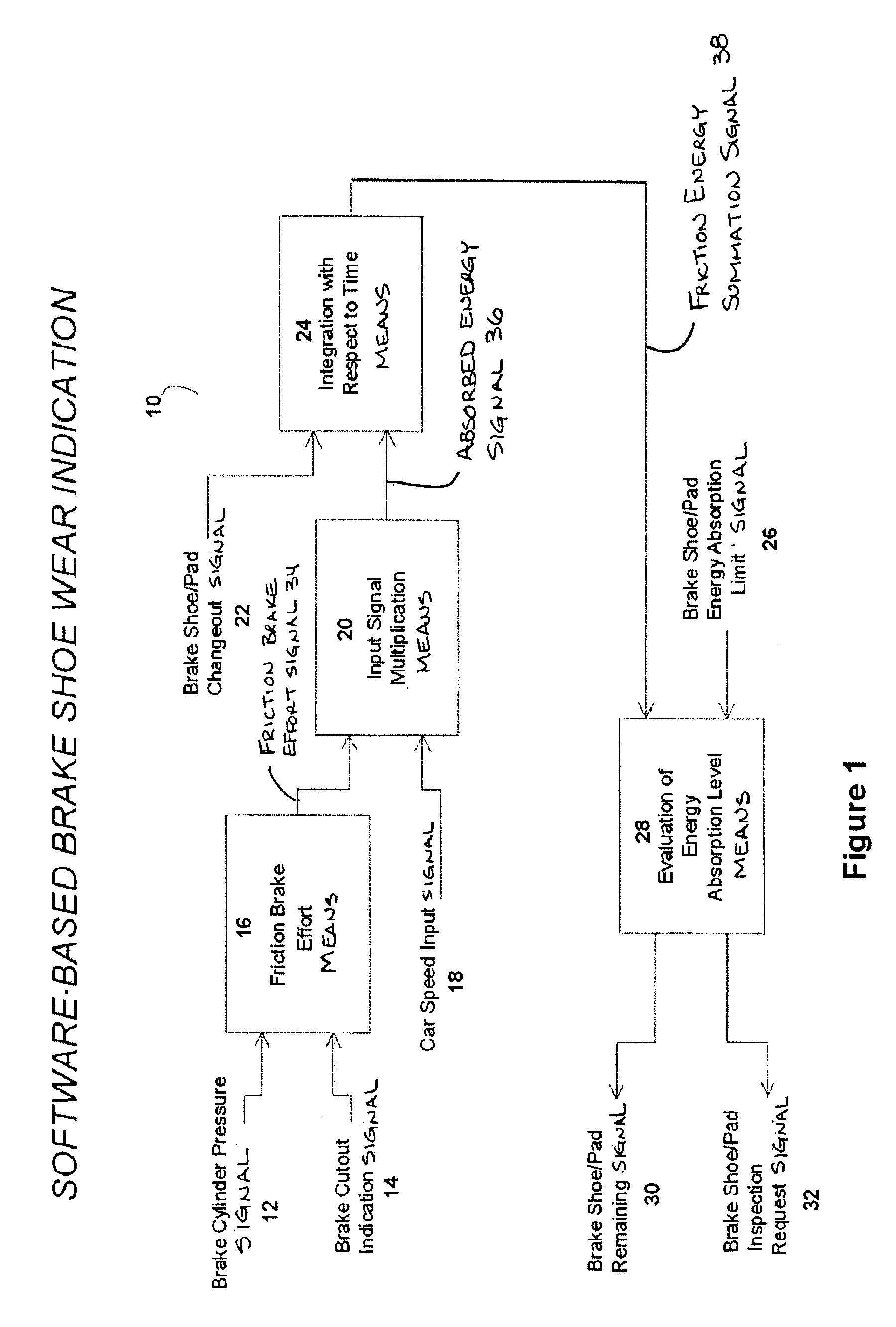
Software based brake shoe wear determination
InactiveUS6847869B2Reduce harmReduce amount of friction brake effort suppliedVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesEngineeringEnergy supply
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE AIR BRAKE TECH CORP
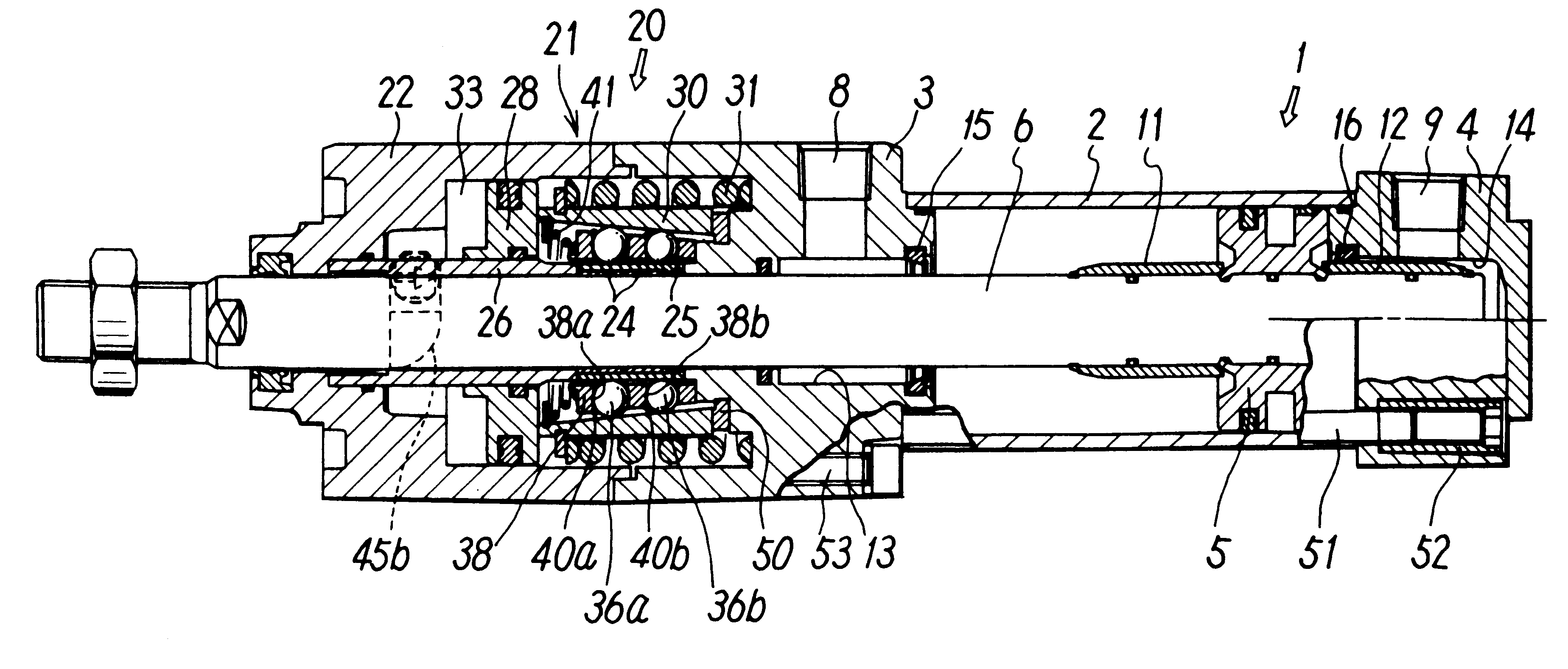
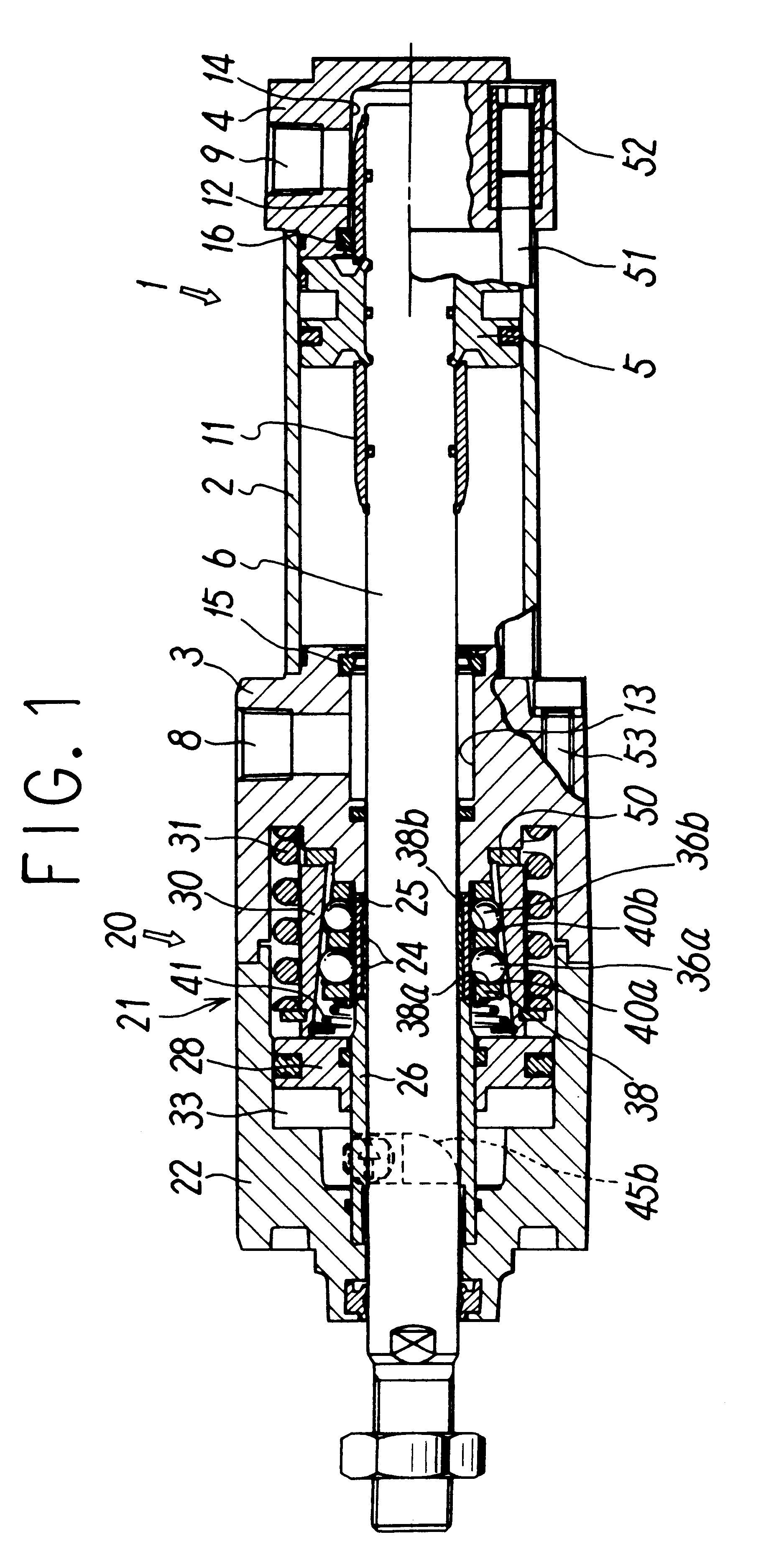
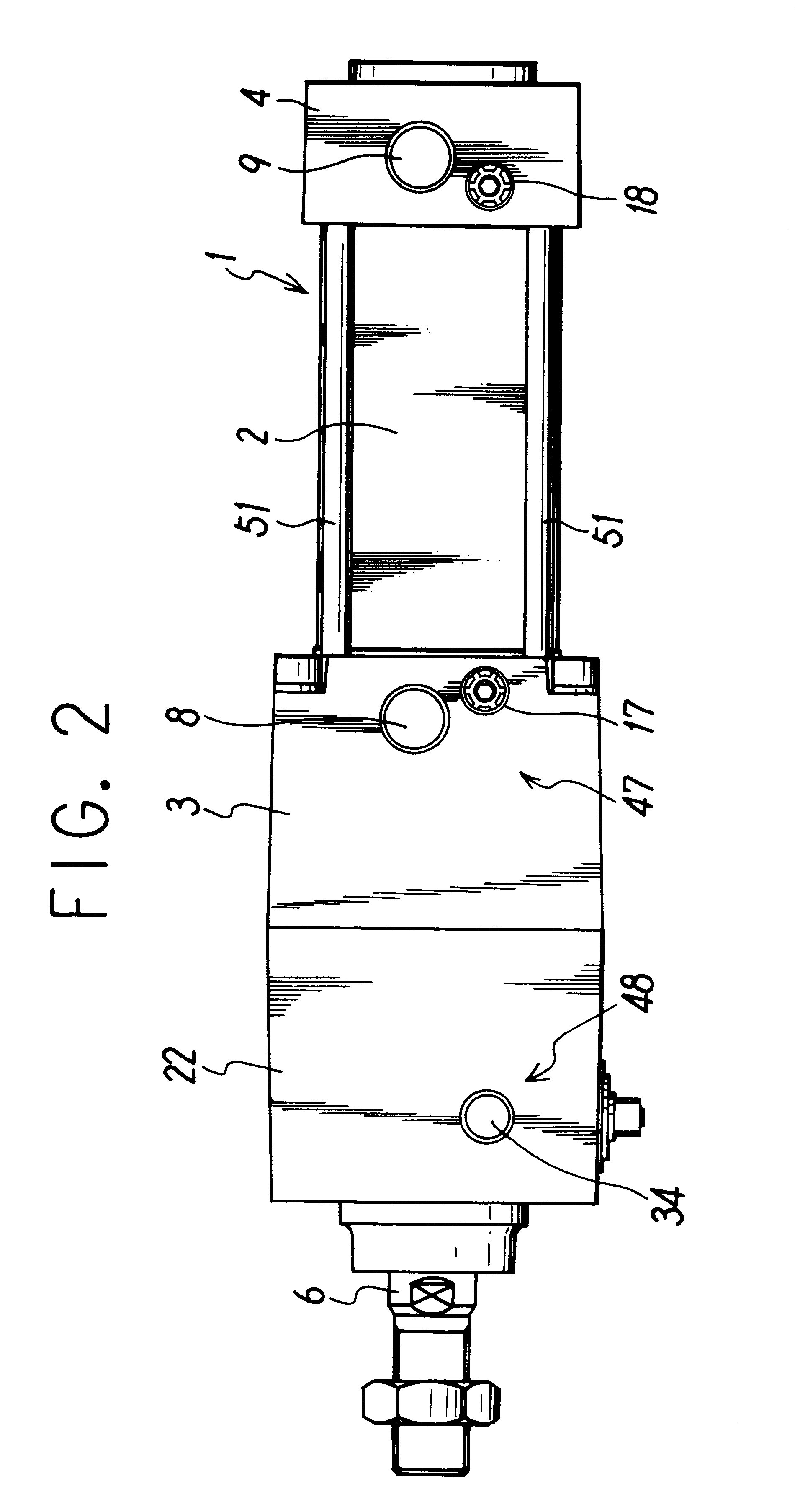
Fluid pressure cylinder with a lock mechanism
InactiveUS6178870B1Improve responseSteady braking forceFluid-pressure actuatorsLocking mechanismEngineering
This fluid pressure cylinder with a lock mechanism is adapted to provide, on the lock mechanism cover, an area where valves for controlling the cylinder and lock mechanism can be installed. In the cylinder, a brake shoe grips a piston rod 6 via balls held by a retainer inside a lock mechanism cover 21 using a tapered ring which is driven by a brake spring and returned to its original position by a release piston. A cylinder port 8 that supplies or discharges compressed air to drive the piston is provided on the side of a cylinder 1 inside the lock mechanism cover 21. On the opposite side an unlocking port 34 which leads to a pressure chamber driving a release piston is disposed and a manual opening actuator 45 is provided. This arrangement is intended to ensure a flat area 48 where valves can be installed to control compressed air fed through the ports.
Owner:SMC CORP
Progressive safety device
A progressive safety device for an elevator includes a brake unit and an actuating unit. The brake unit has a first brake shoe with first spring assemblies and a triangular rotatable support with second and third brake shoes. The actuating unit has an electromagnetic actuator with a locking bolt, a guide bolt with a coaxial compression spring and an actuating arm. On actuation, the compression spring moves the actuating arm against a guide rail whereby grooves on the actuating arm create a frictional engagement with the guide rail turning the actuating arm about a swivel bearing and through a follower turning the support. With the turning motion and the engagement of one of the second and third brake shoes with the guide rail, the first brake shoe is guided against the guide rail and generates the necessary braking force on the guide rail.
Owner:INVENTIO AG
Electronic parking brake
ActiveUS20130087422A1Reduce rotational forceLength minimizationBraking element arrangementsBraking action transmissionReducerEngineering
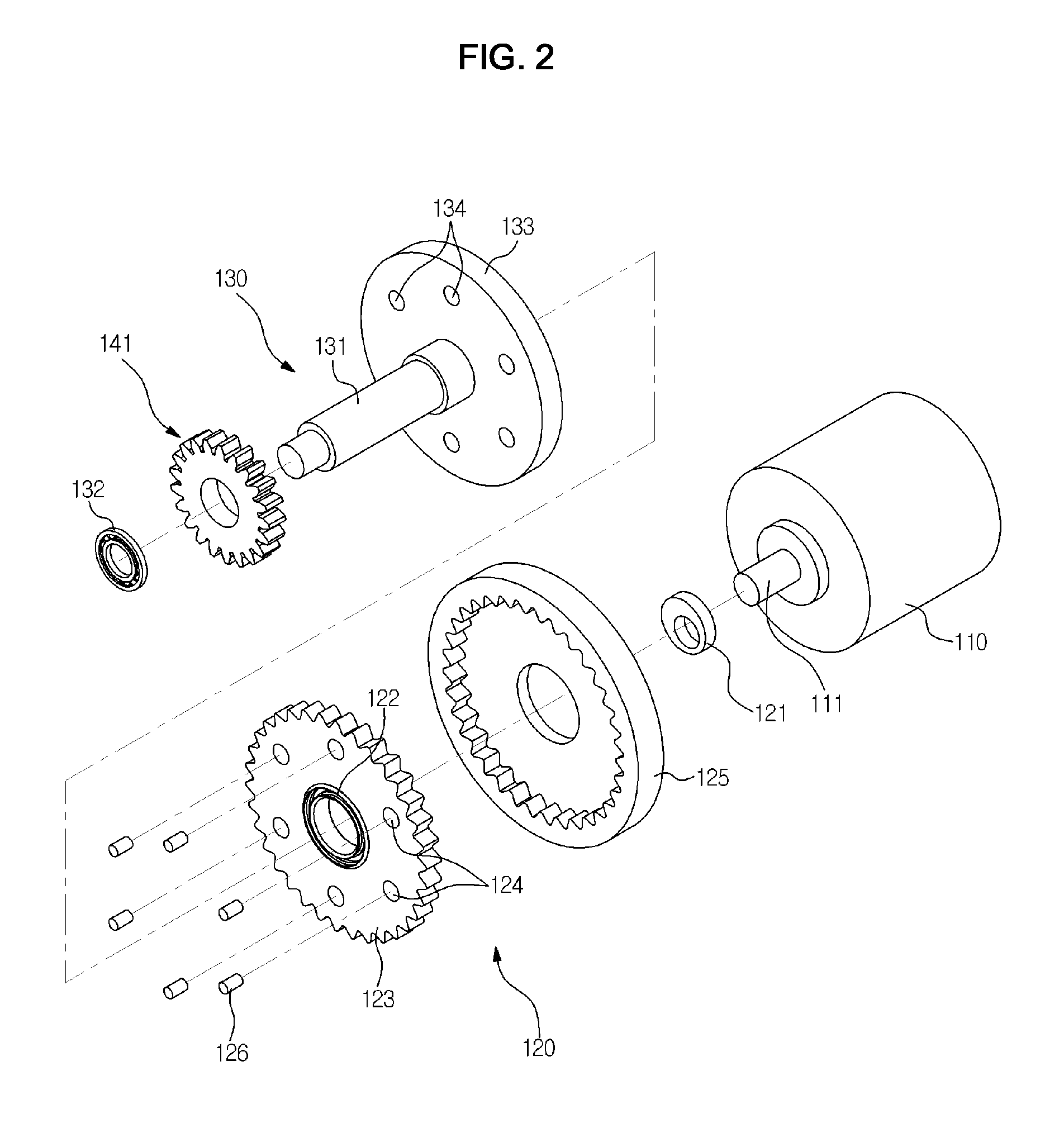
Disclosed herein is an electronic parking brake which is installed in a vehicle and is operated by a motor. The electronic parking brake having a drum rotating together with a wheel and first and second brake shoes includes a motor rotated in normal and reverse directions and generating driving force for braking, a cycloid reducer connected to a rotary shaft of the motor and amplifying the driving force generated from the motor, a spindle member connected to the cycloid reducer and rotated, a spur gear assembly rotated by rotary force transmitted from the spindle member, a piston rotated and provided with the outer circumferential surface on which one gear of the spur gear assembly is integrally formed, and a push rod unit installed at both ends of the piston in the longitudinal direction, rectilinearly moved according to rotation of the piston and supported by the first and second brake shoes.
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
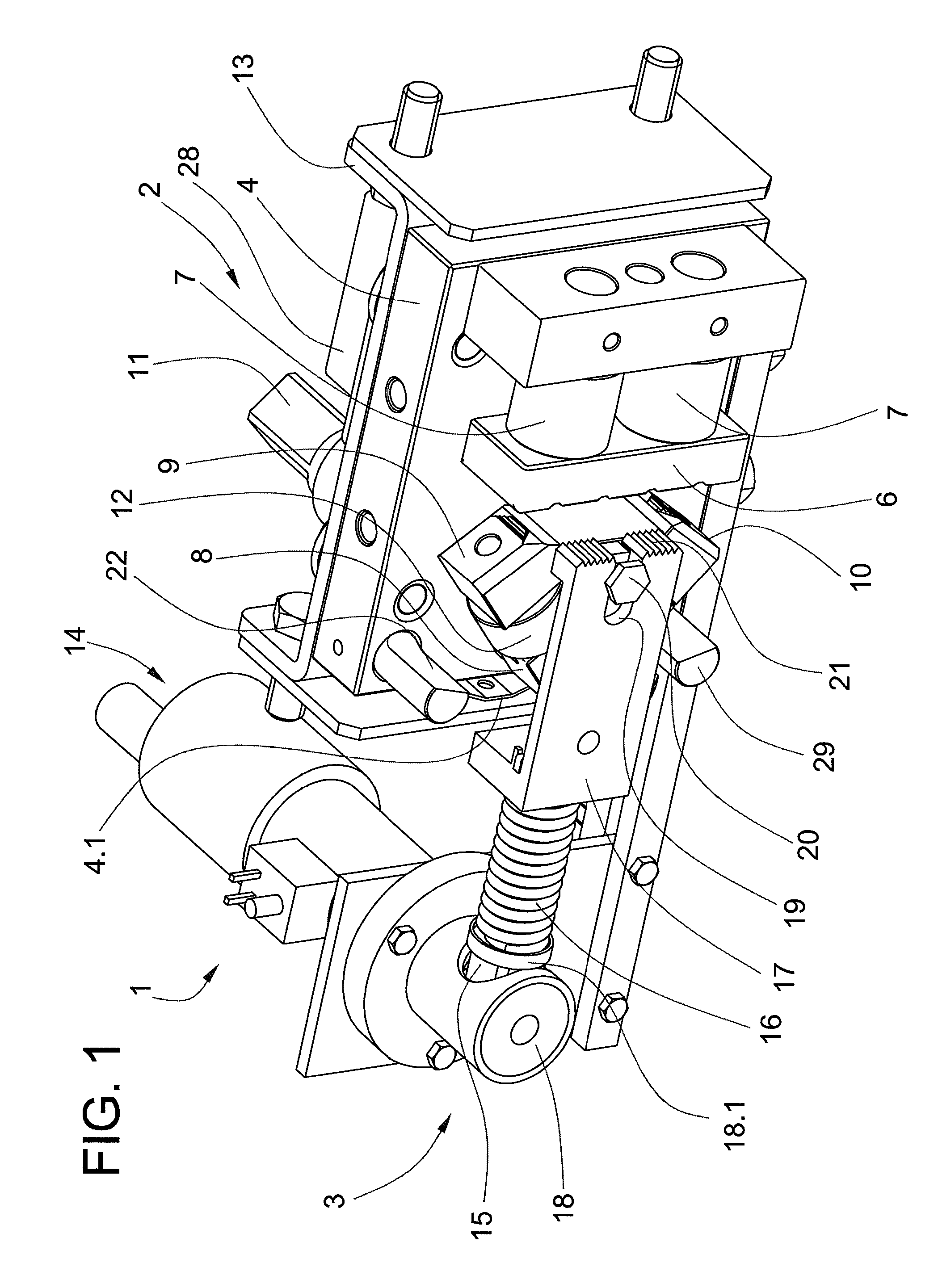
Parking brake and method for operating same
ActiveUS20100308645A1Accurate settingImprove accuracyAnalogue computers for trafficElectrodynamic brake systemsClosed loopSelf locking
A parking brake having an actuator, wherein the actuator is driven with a direct current motor which can be operated in two directions and which moves a piston of the actuator and, via a self-locking gear mechanism of the actuator, at least one brake shoe for applying or releasing the parking brake. A control unit for performing open-loop or closed-loop control of the movement of the direct current motor is also provided. During open-loop or closed-loop control of the movement of the direct current motor for applying and / or releasing the parking brake, the control unit takes into account a hydraulic admission pressure which is currently present at the piston if the brake is applied or was present at the piston if the brake has been released when it had previously been applied. A corresponding method for operating such a parking brake is also disclosed.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
High friction composite brake shoe for railway freight car and manufacture method thereof
ActiveCN101391611AHigh compressive strengthHigh impact strengthBraking membersBrake arrangement with braking memberFiberEngineering
The invention discloses a high friction composite brake shoe for a railway wagon and a manufacturing method thereof. The composite brake shoe comprises: a steel back and a brake shoe body which is fixed on the steel back, wherein, the brake shoe body is prepared by materials which are synthesized by various components with the following weight ratio: 8 to13 parts of nitrile butadiene rubber, 2 to10 parts of styrene butasiene rubber, 5 to10 parts of cresol modified A-stage phenolic resin, 15 to 30 parts of steel fiber, 10 to 15 parts of magnesium oxide, 5 to 10 parts of calcined petroleum coke, 2 to 5 parts of silicon carbide, 10 to25 parts of mineral fiber, 5 to 10 parts of calcium hydride, 10 to 20 parts of barium sulfate, 5 to 10 parts of graphite, 1 to 5 parts of molybdenum disulfide, 1 to 5 parts of carbon black, 1 to 3 parts of sulfur and 1 to 3 parts of enhancer. The brake shoe can be used in the railway heavy-duty high-speed wagon and has stable friction performance and better wear resistance; the brake shoe can effectively inhibit the phenomena of metal inlay, cracks, dropping blocks and the like and reduce the damages on wheels; and the brake shoe is characterized by better impact resistance performance and good weatherability.
Owner:BEIJING RAILWAY STAR FORTUNE HIGH TECH
Machine track system and machine track segment
A machine track system includes a track with track shoes each having a footprint, and a ground contact area equal to the footprint, the track shoes being coupled together by a total of two track chains. A first rail and a second rail are located between first and second outboard edges of each of the track shoes, such that track rollers roll directly on the track shoes. The track chains are spaced outboard of the rails, and a guide block configured to engage with an idler and a drive sprocket is positioned between the respective rails. A sprocket and idler for use with the track system includes removable track contacting segments having pockets configured to receive the guide blocks for driving and guiding the track.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Hybrid fiber reinforced friction material for train braking and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102191015AImprove toughnessImprove yieldOther chemical processesFriction liningFreight trainsAdhesive
The invention belongs to the technical field of materials, and particularly relates to a hybrid fiber reinforced friction material for train braking and a preparation method thereof. In the invention, a composite modified phenolic resin is used as an adhesive, and hybrid fibers, including carbon fiber, metal fiber, inorganic mineral fiber and the like, are used as the reinforcing fibers. Compared with the prior art, the invention improves the contour machining property of the organic synthetic brake, and the yield of the material is high; the brake has stable frictional property at different braking speeds, does not has obvious degradation of frictional property at high speed, and does not have the phenomena of shedding and cracking on the working surface after the braking test. The friction material provided by the invention can be widely used for manufacturing brake pads, brakes, brake shoes and the like in braking systems of passenger and freight trains, municipal rail transportation, subways and the like.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Brake device having adjustable spring member
A brake device includes a holder seat for attaching to cycle, one or more brake arms pivotally attached to the holder seat with shafts and each having a brake shoe for braking the cycle. One or more poles are attached to the holder seat, and each includes a stud, and a coil spring is engaged onto each of the shafts and has one end engaged with the brake arm and the other end engaged with the stud of the pole, to apply a spring biasing force against the brake arm and to recover the brake arm. A fastener may be threaded to the holder seat and engageable with the pole, for moving and adjusting the pole and the coil spring relative to the holder seat.
Owner:TSAI SHIH FAN
Counterbalance system for a tilt-in window having an improved shoe assembly and anchor mount
InactiveUS6990710B2Low costReduce frictionBuilding braking devicesWing openersSash windowLocking mechanism
Owner:JOHN EVANS SONS INC
Elevator rolling guide shoe with brake function
InactiveCN102897633AFunction increaseThere will be no mutual interferenceElevatorsHydraulic cylinderWear resistant
The invention provides an elevator rolling guide shoe with a brake function. The elevator rolling guide shoe is provided with a rolling guide wheel mechanism, hydraulic execution mechanisms and stop mechanisms, wherein three guide wheels of the rolling guide wheel mechanism cling to three working surfaces of a T-shaped guide rail and are used for limiting the horizontal movement of an elevator car; the hydraulic execution mechanisms are connected with the guide wheels of the guide shoe and used for determining whether pressures are applied to the guide wheels according to a detected elevator running state; and the stop mechanisms are integrated in the guide wheels and used for stopping the guide wheels when an elevator is in a post stall state and enabling the guide wheels to tightly hold the guide rail in combination with pressing forces provided by the hydraulic execution mechanisms, so that the emergency braking is achieved; and each stop mechanism is composed of the following parts: a guide shoe base, a long connecting rod, a main swing rod, a secondary swing rod, a brake bottom plate, a hydraulic wheel cylinder, a brake shoe, a brake pad and a brake drum covered by wear-resistant rubber.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Vehicle speed control device and vehicle equipped with vehicle speed control device
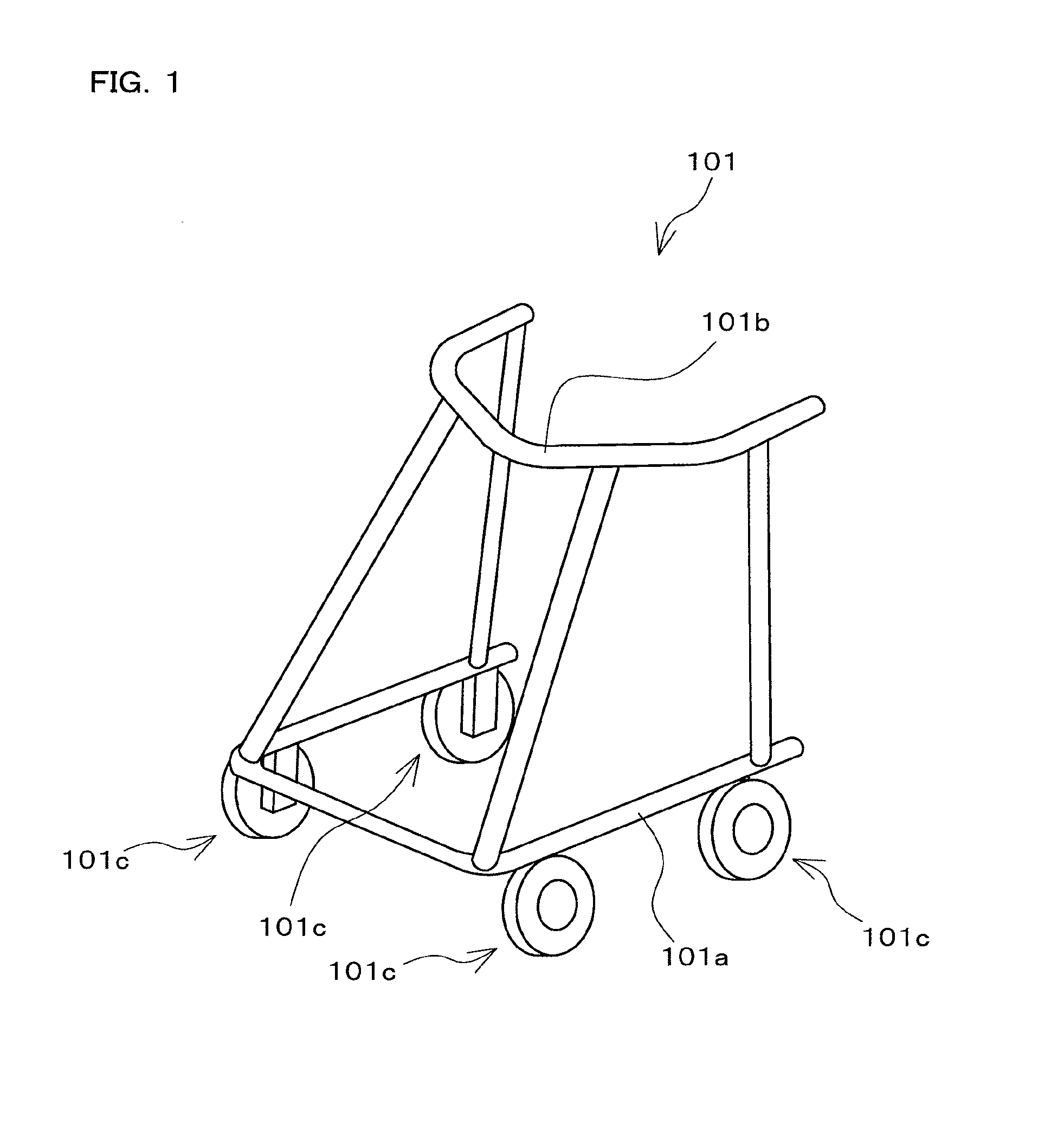
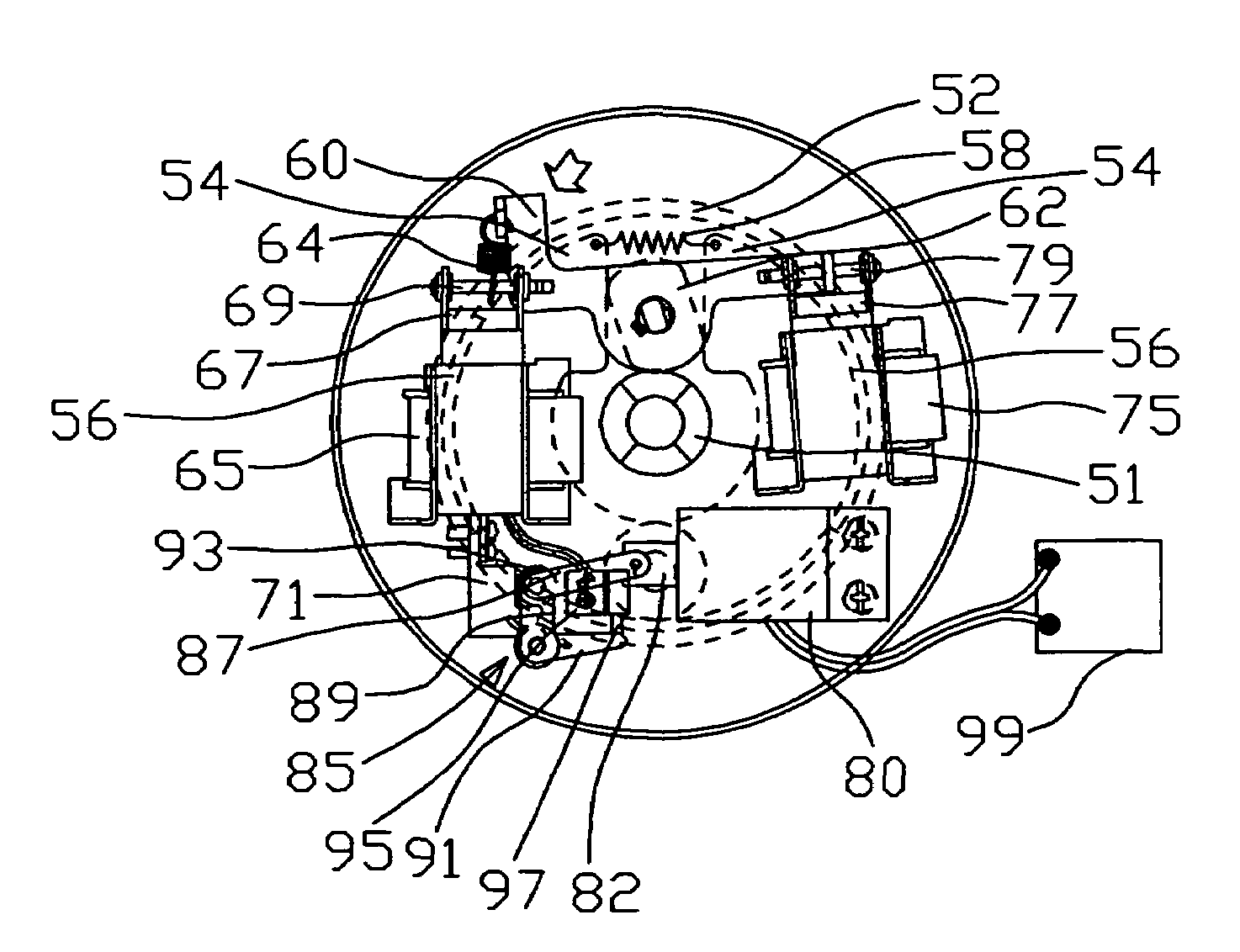
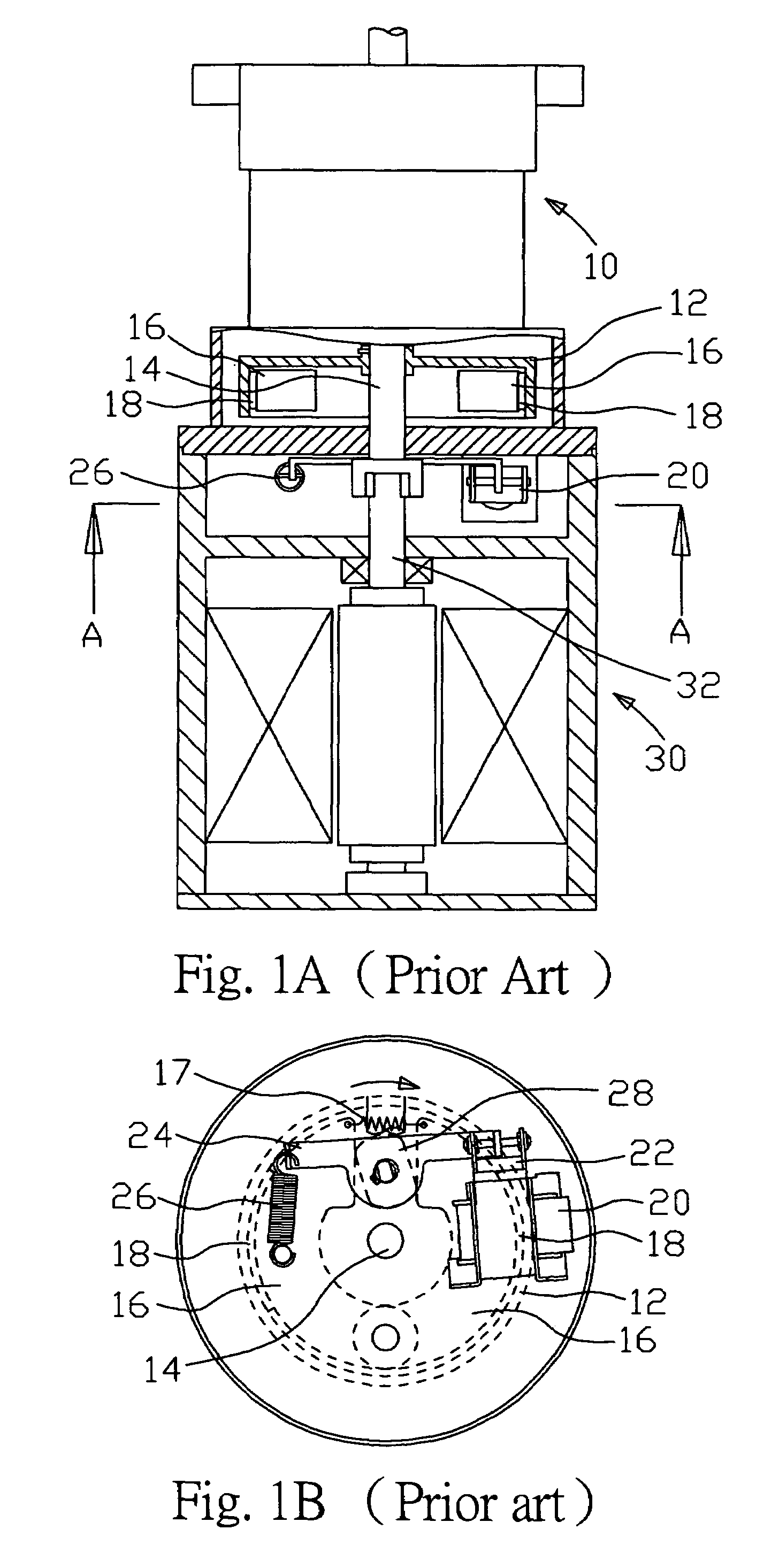
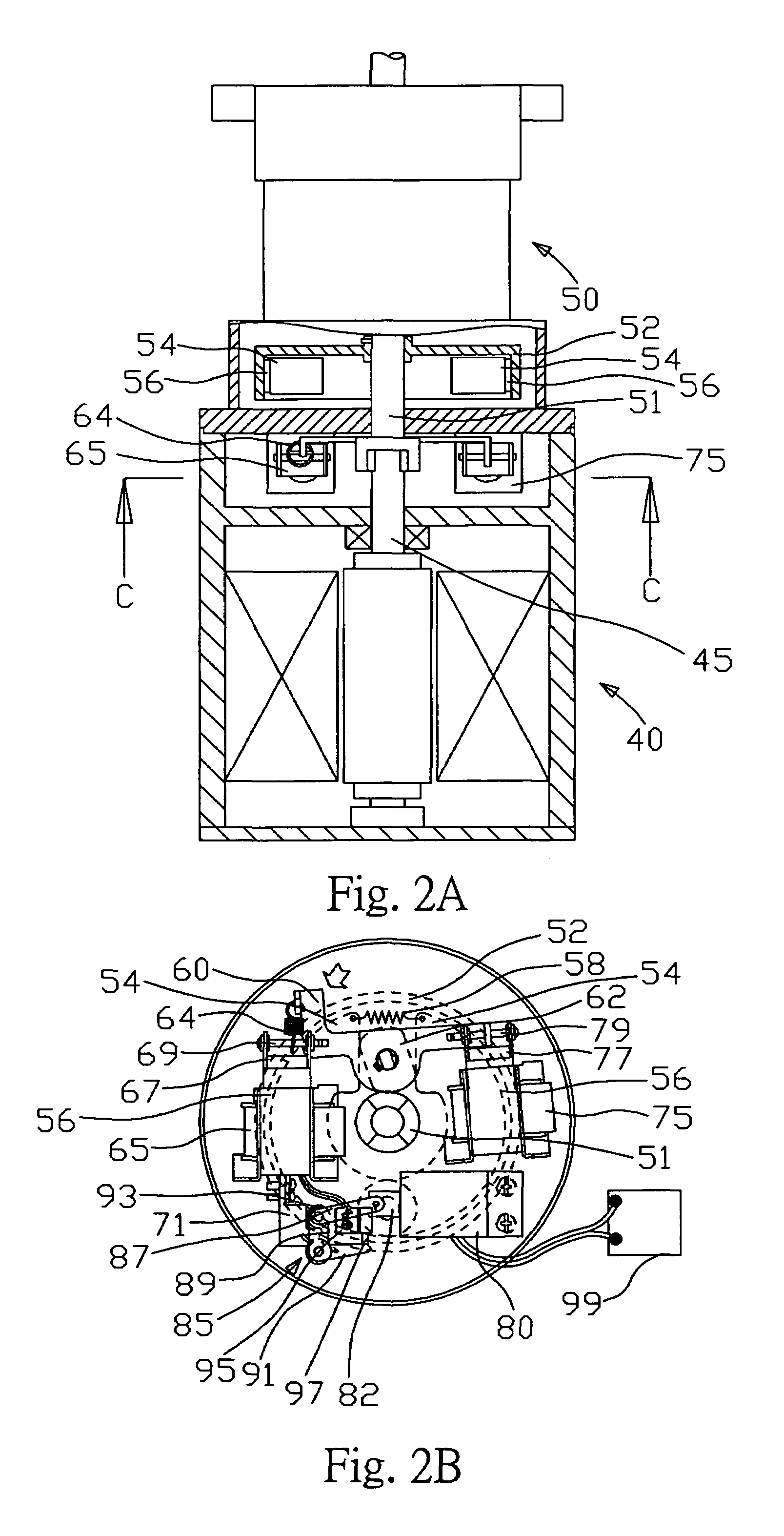
ActiveUS20140224597A1Easy to changeBraking element arrangementsSelf acting brakesEngineeringBrake shoe
Provided is a vehicle speed control device with respect to which the speed at which a centrifugal brake operates can be easily changed from the outside without disassembling the device. A brake drum 11 is fixed to a vehicle body 101a. A brake shoe 23 rotates around a rotary shaft 20 of the wheel 101c, and reduces the rotation speed of the wheel 101c as a result of coming into contact with an inner circumferential side face of the brake drum 11. A spring 24 prevents contact between the brake drum 11 and the brake shoe 23 when the rotation speed of the wheel 101c is lower than or equal to a predetermined speed, and permits contact between the brake drum 11 and the brake shoe 23 when the rotation speed of the wheel 101c exceeds the predetermined speed. A position change mechanism 25 is installed within the brake drum 11, and changes the position of an end of the spring 24 on one end side. A transmission mechanism 26 transmits a force that is input by an external operation to the position change mechanism 25 and drives the position change mechanism.
Owner:NABLESCO CORP +1
Pad retraction spring for a brake shoe assembly and a disc brake assembly
This invention relates to a pad spring for use in a disc brake assembly. According to one embodiment of the present invention, the disc brake assembly comprises an anchor bracket adapted to be secured to a vehicle component; a brake caliper adapted to be secured to the anchor bracket; an inboard friction pad and an outboard friction pad carried by the disc brake assembly and adapted to be disposed on opposite axial sides of an associated brake rotor; actuation means for selectively moving the inboard and outboard friction pads into frictional engagement with the rotor; and a pad spring carried by at least one end of one of the friction pads for moving the friction pads from engagement with the rotor when the actuation means is released; wherein the pad spring includes a first portion for applying a first retraction force and a second portion for applying a second retraction force which is different from the first retraction force.
Owner:KELSEY HAYES CO
Motorcycle wheel brake mechanism
A brake disc for a wheel constituted by a peripheral section, forming a brake band with an interior form enabling it to be fitted to its wheel, the brake band forms two lateral flat and parallel surfaces on which a brake shoe can act, said peripheral section having a series of off-sets on its inside and outside edges.
Owner:MILESI GIORGIO +2
Brake structure for a roll-up door
InactiveUS7281612B2Avoid fireDoor/window protective devicesElectrodynamic brake systemsCapacitanceDrive shaft
A brake structure for a roll-up door includes a brake drum fixed to a transmission shaft of a speed reducer. The brake drum receives a pair of brake shoes in opposite inner sides thereof. The brake shoes are pivotably connected to each other at an end of each brake shoe. A linking resilient member is connected between the free ends of the brake shoes. A brake pad is attached to a surface of each brake shoe facing the inner surface of the brake drum. A controlling lever is disposed at the top of the speed reducer corresponding to the free ends of the brake shoes. One end of the controlling lever is connected to an end of a fixing resilient member. The other end of the fixing resilient member is connected to a moving iron of a first solenoid. A clasping block is connected to the moving iron of the first solenoid. The other end of the controlling lever is connected to a moving iron of a second solenoid. A controlling block is disposed at the controlling lever between the free ends of the brake shoes and in contact to the free ends of the brake shoes. A brake control solenoid is disposed at the top of the speed reducer. The brake control solenoid is connected to a power supply with capacitance character. A moving iron of the brake control solenoid is connected to a connecting rod mechanism. The clasping block is connected to the connecting rod mechanism.
Owner:ANCHUAN CORP
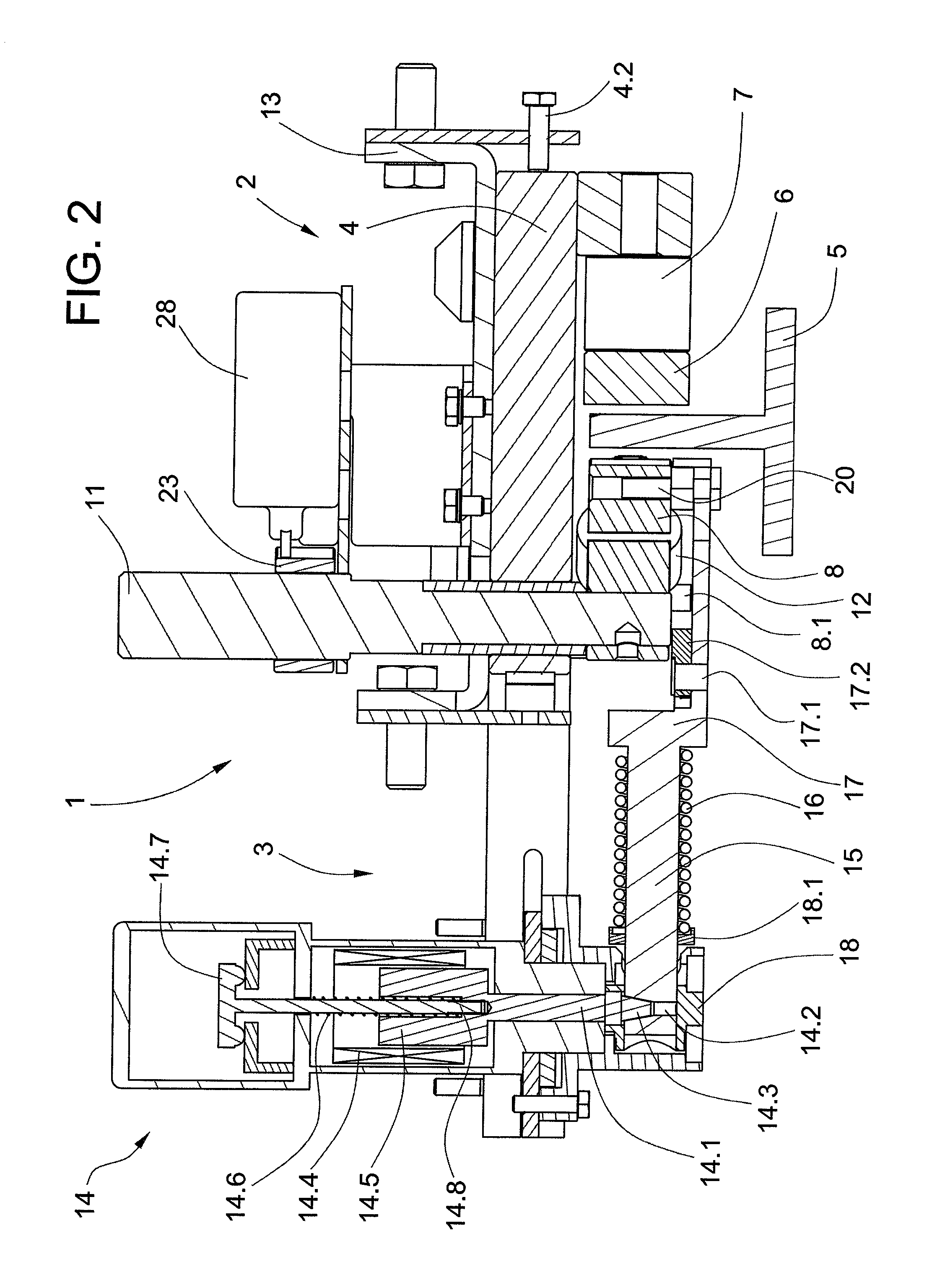
Parking brake and method for operating same
ActiveUS7992691B2Improve accuracyImprove clearanceAxially engaging brakesElectrodynamic brake systemsClosed loopSelf locking
A parking brake having an actuator, wherein the actuator is driven with a direct current motor which can be operated in two directions and which moves a piston of the actuator and, via a self-locking gear mechanism of the actuator, at least one brake shoe for applying or releasing the parking brake. A control unit for performing open-loop or closed-loop control of the movement of the direct current motor is also provided. During open-loop or closed-loop control of the movement of the direct current motor for applying and / or releasing the parking brake, the control unit takes into account a hydraulic admission pressure which is currently present at the piston if the brake is applied or was present at the piston if the brake has been released when it had previously been applied. A corresponding method for operating such a parking brake is also disclosed.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Emergency braking system for machine tools
ActiveUS20110048197A1Improve protectionShort braking timeEngineering safety devicesMeasurement/indication equipmentsCentrifugal forceBrake shoe
An emergency braking system for a machine tool for abruptly braking a revolving shaft includes at least one brake drum and at least one brake shoe which are engaged with one another in order to brake the shaft. The braking intervention between the brake drum and the brake shoe takes place under the influence of a centrifugal force resulting from the rotation of a shaft as soon as a locking device is released. Also provided in the braking system is a diagnostic system which allows the functionality of the locking device to be checked.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
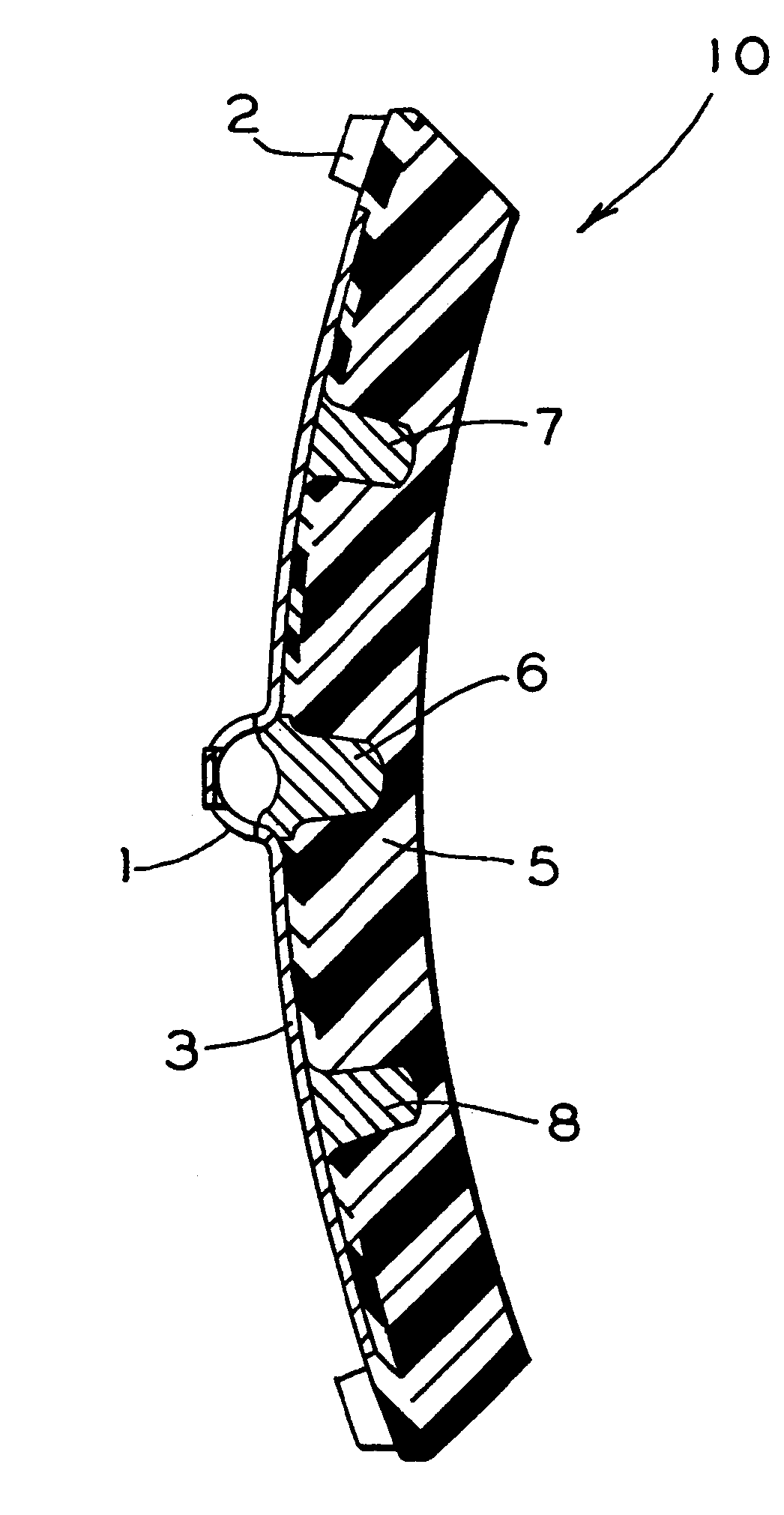
High friction brake shoe assembly
InactiveUS7320386B2Improve braking efficiencyGood friction propertiesBraking membersFriction liningEngineeringBrake shoe
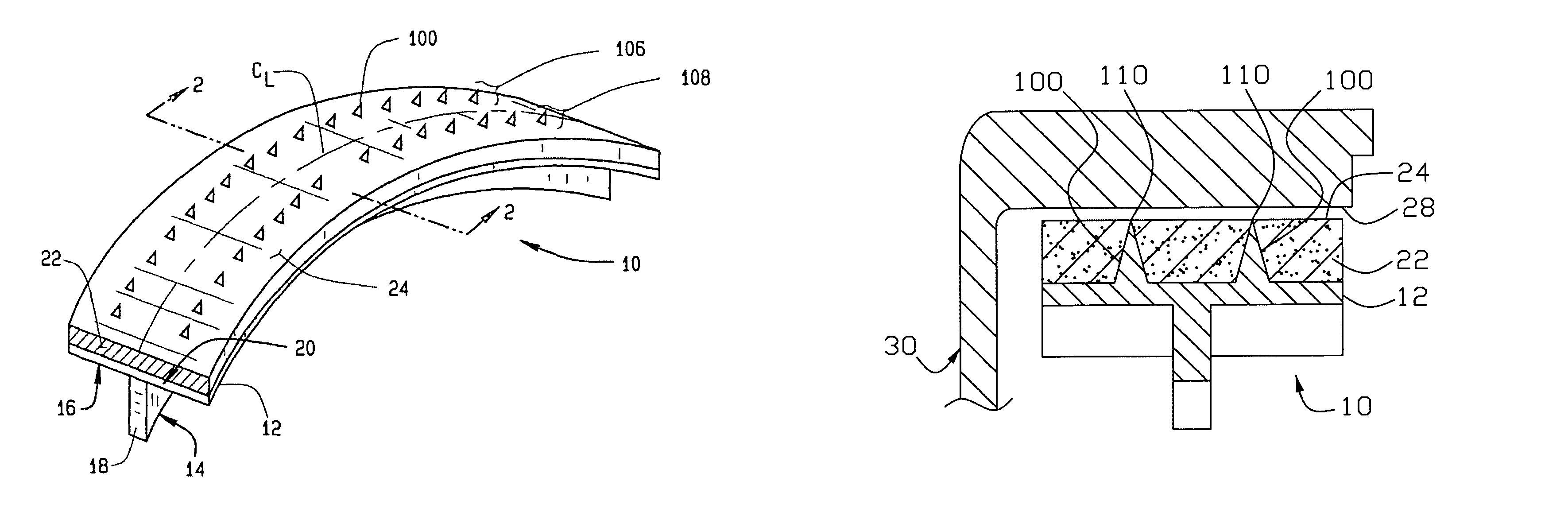
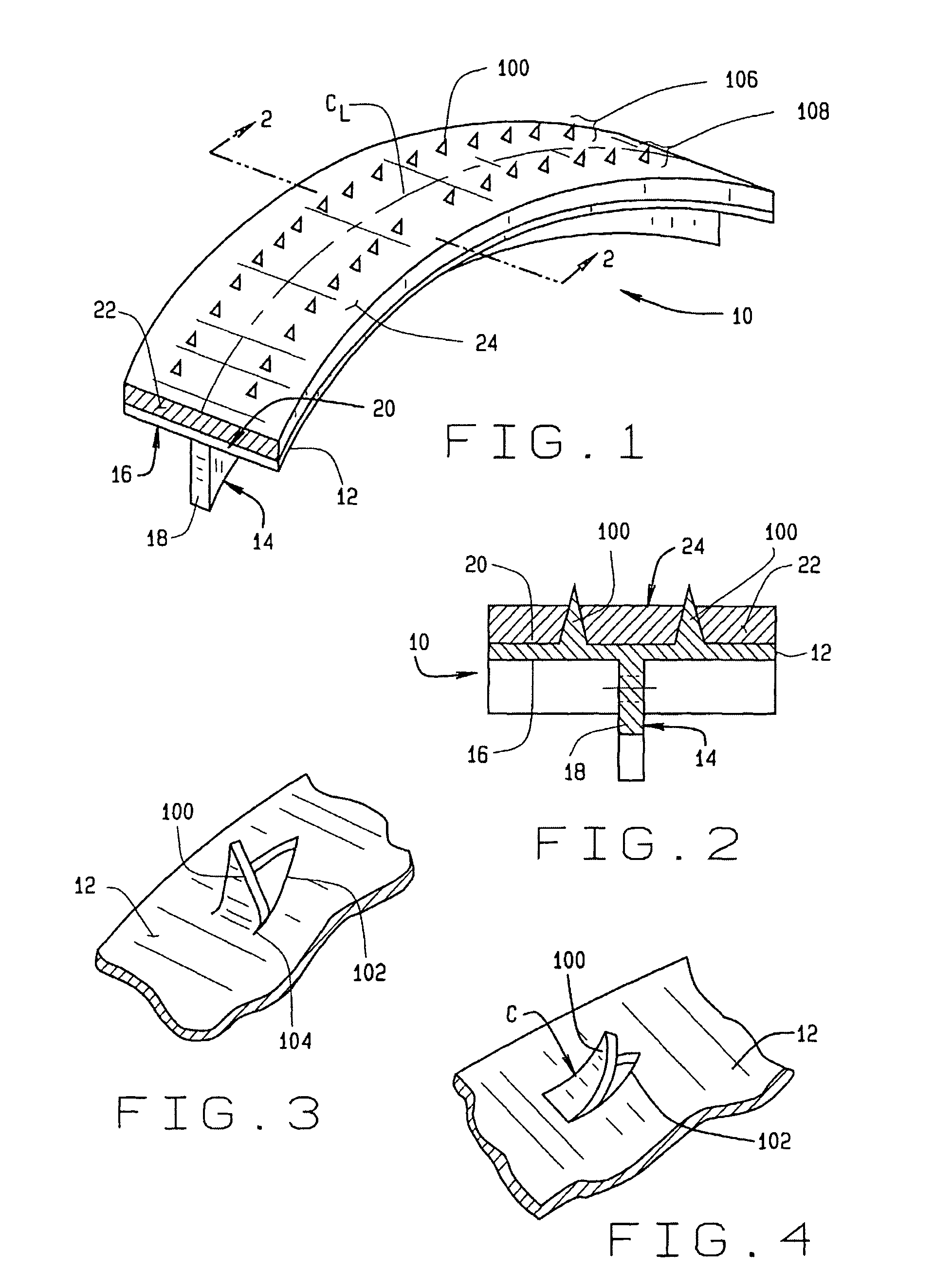
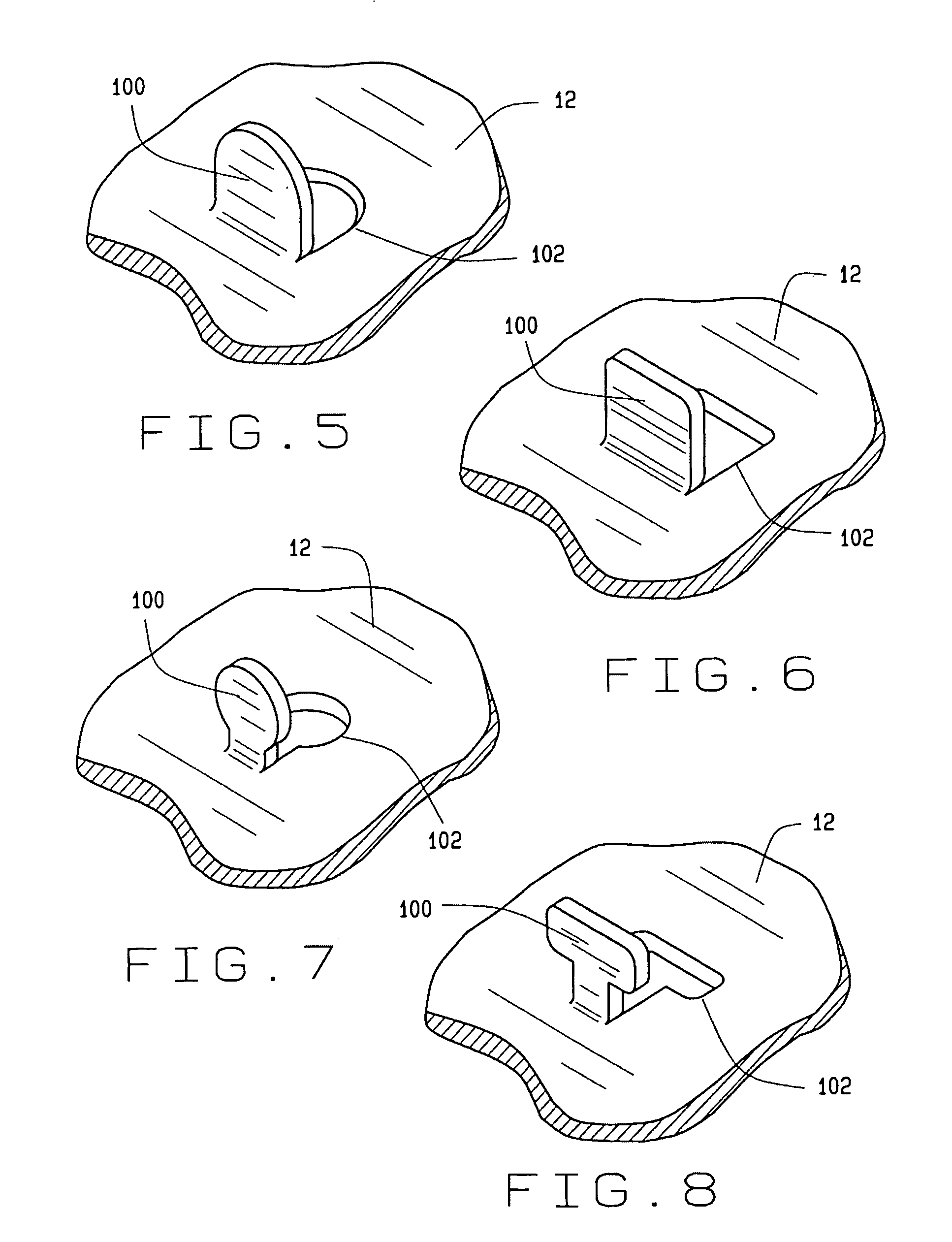
A vehicle brake shoe assembly (10) having a rigid backing plate (12) incorporating a plurality of extensions (100) which project through the brake friction material matrix (22) to the outer friction surface (24) of the brake shoe assembly (10). Each extension (100) is configured to cooperate with the brake friction material matrix (22) to engage a surface of an opposing friction element (28) simultaneously with the friction material (22), increasing the static and dynamic friction performance of the assembly (10) during initial use beyond that achieved from the application of either the brake friction material (22) or the projections (100) alone.
Owner:FEDERAL MOGUL WORLD WIDE
Leash having a speed-limiting braking mechanism and system and method for using same
An apparatus, a system and a method have a speed-limiting braking mechanism. The apparatus may use a leash to limit a velocity of movement of a pet relative to a velocity of movement of a user of the apparatus. The speed-limiting braking mechanism within the apparatus may prevent the relative velocity from exceeding a predetermined threshold without abruptly stopping unwinding of the leash. The speed-limiting braking mechanism may have a rotatable pinion component connected to one or more brake shoes. The leash may be connected to a spool. Unwinding of the leash may rotate the spool, and rotation of the spool may rotate the pinion component. If the relative velocity exceeds the predetermined threshold, the one or more brake shoes may engage a braking liner to maintain the relative velocity at the predetermined threshold.
Owner:UNLEASHED PRODS
Friction material for brake-shoe of heavy axle-load wagon and preparation method of friction material
InactiveCN104087245AMeet the friction performanceMeet the mechanicsOther chemical processesFiberKyanite
The invention discloses a friction material for a brake-shoe of a heavy axle-load wagon. The friction material is prepared from the following components in percentage by mass: 6-12 percent of nitrile rubber, 1-4 percent of butadiene styrene rubber, 3-8 percent of A-stage phenolic resin, 0.4-1 percent of insoluble sulfur, 0.1-0.6 percent of an accelerant, 0.1-0.6 part of a curing agent, 2-6 percent of carbon black, 8-18 percent of barite, 1-4 percent of kyanite, 17-40 percent of hybrid fibers, 7-14 percent of magnesium oxide, 2-6 percent of petroleum coke, 2-8 percent of calcium sulfate crystal whiskers, 1-4 percent of molybdenum disulfide, 1-5 percent of crystalline flake graphite, 1-4 percent of artificial graphite, 1-4 percent of mica iron oxide and 1-3 percent of antimony sulfide. The friction material can satisfy the friction performance and mechanical property required by the brake-shoe of the heavy axle-load wagon and can meet the high speed operating requirement on heavy load of the wagon.
Owner:BEIJING RAILWAY STAR FORTUNE HIGH TECH
Apparatus for preventing backlash of spool used in baitcasting reel
Disclosed is an apparatus for preventing backlash of a spool used in a baitcasting reel, in which the number of brake shoes can be optionally adjusted. The position of the shoe is selected between protruded guides of a shoe holder so as to apply braking force, so that the backlash of the spool is precisely controlled, without decreasing the carry distance of casting.
Owner:DOYO ENG
Novel progressive safety tongs
The invention discloses a pair of novel progressive safety tongs, which comprises a tongs body, wherein the inside of the tongs body is provided with a movable wedge; and a movable wedge pushing mechanism is arranged inside the tongs body under the movable wedge. The pushing mechanism comprises a fixed seat, two lever arms, a spring and an electromagnet, wherein the fixed seat can move up and down in the tongs body; the two lever arms are hinged on both sides of the fixed seat through a pin shaft respectively; a brake shoe is arranged on the inner surface of the front end of each lever arm, and a cushion block is arranged on the upper surface of the front end of the each lever arm; the spring is arranged between lever bodies of the two lever arms; the electromagnet is arranged on the rear end part of the two lever arms; and the switching of a circuit of the electromagnet is controlled by an elevator speed monitoring device. The invention adopts the pushing mechanism to drive the movable wedge of the progressive safety tongs to complete the elevator braking function by the structure, does not need to arrange a safety pulling device, simplifies the structure of a speed limiter, has the advantages of compact structure and convenient assembly, and is suitable to be arranged on various elevators.
Owner:HITACHI ELEVATOR CHINA
Leash having a speed-limiting braking mechanism and system and method for using same
An apparatus, a system and a method have a speed-limiting braking mechanism. The apparatus may use a leash to limit a velocity of movement of a pet relative to a velocity of movement of a user of the apparatus. The speed-limiting braking mechanism within the apparatus may prevent the relative velocity from exceeding a predetermined threshold without abruptly stopping unwinding of the leash. The speed-limiting braking mechanism may have a rotatable pinion component connected to one or more brake shoes. The leash may be connected to a spool. Unwinding of the leash may rotate the spool, and rotation of the spool may rotate the pinion component. If the relative velocity exceeds the predetermined threshold, the one or more brake shoes may engage a braking liner to maintain the relative velocity at the predetermined threshold.
Owner:UNLEASHED PRODS
Powder metallurgy iron-based high-speed brake pad
The invention relates to a powder metallurgy iron-base high-speed brake lining, composed of a brake shoe back (1), a dovetail block (2), a friction block (3) and a serging vessel (4) linked with a rivet (6) through a rivet seat (5), wherein, the friction block (3) adopts a vessel serging structure and powder metallurgy iron-base friction materials and is formed by chill pressing and compression sintering. The invention is characterized by reliable structure, stable drag friction performance, low surface temperature rise, small relative dispersion and good wearing resistance, etc., and is suited to starting or towing a car on a railway with speed at or below 300km / h.
Owner:贵州新安航空机械有限责任公司
Composition brake shoe for urban rail vehicle and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103410893AImprove brittlenessImprove heat resistanceFriction liningCarbon fibersHexamethylenetetramine
The invention relates to a composition brake shoe for an urban rail vehicle and a manufacturing method of the composition brake shoe for the urban rail vehicle. The composition brake shoe comprises the following components of, by weight, 10-15 parts of butadiene-acrylonitrile rubber, 10-20 parts of cashew nut shell oil modified phenolic resin, 6-10 parts of basalt fibers, 4-8 parts of carbon fibers, 8-15 parts of steel fibers, 5-8 parts of sepiolite fibers, 2-6 parts of hexamethylenetetramine, 5-8 parts of iron oxide powder, 5-7 parts of crystalline flake graphite, 5-7 parts of chromite, 6-9 parts of barium sulfate, 3-6 parts of potassium feldspar and 5-8 parts of frictional powder. The manufacturing method of the composition brake shoe is a dry method production technology, and comprises the steps of steel back production, abrasive blasting processing, shaping, burdening, mixing, hot compacting, heat processing, subsequent processing, finished product forming and inspection. The manufactured composition brake shoe is inspected through the 1:1 rack test, is excellent in friction and abrasion resisting performance, stable in brake performance, safe and environmentally friendly, and solves the problem that the friction coefficient drops too fast under the conditions of damascene of the composition brake shoe for the urban rail vehicle, hot cracks, hot spots and rain and snow weather.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV FOR NATITIES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com