Patents
Literature
4220 results about "Disc brake" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A disc brake is a type of brake that uses calipers to squeeze pairs of pads against a disc or "rotor" to create friction. This action slows the rotation of a shaft, such as a vehicle axle, either to reduce its rotational speed or to hold it stationary. The energy of motion is converted into waste heat which must be dispersed.
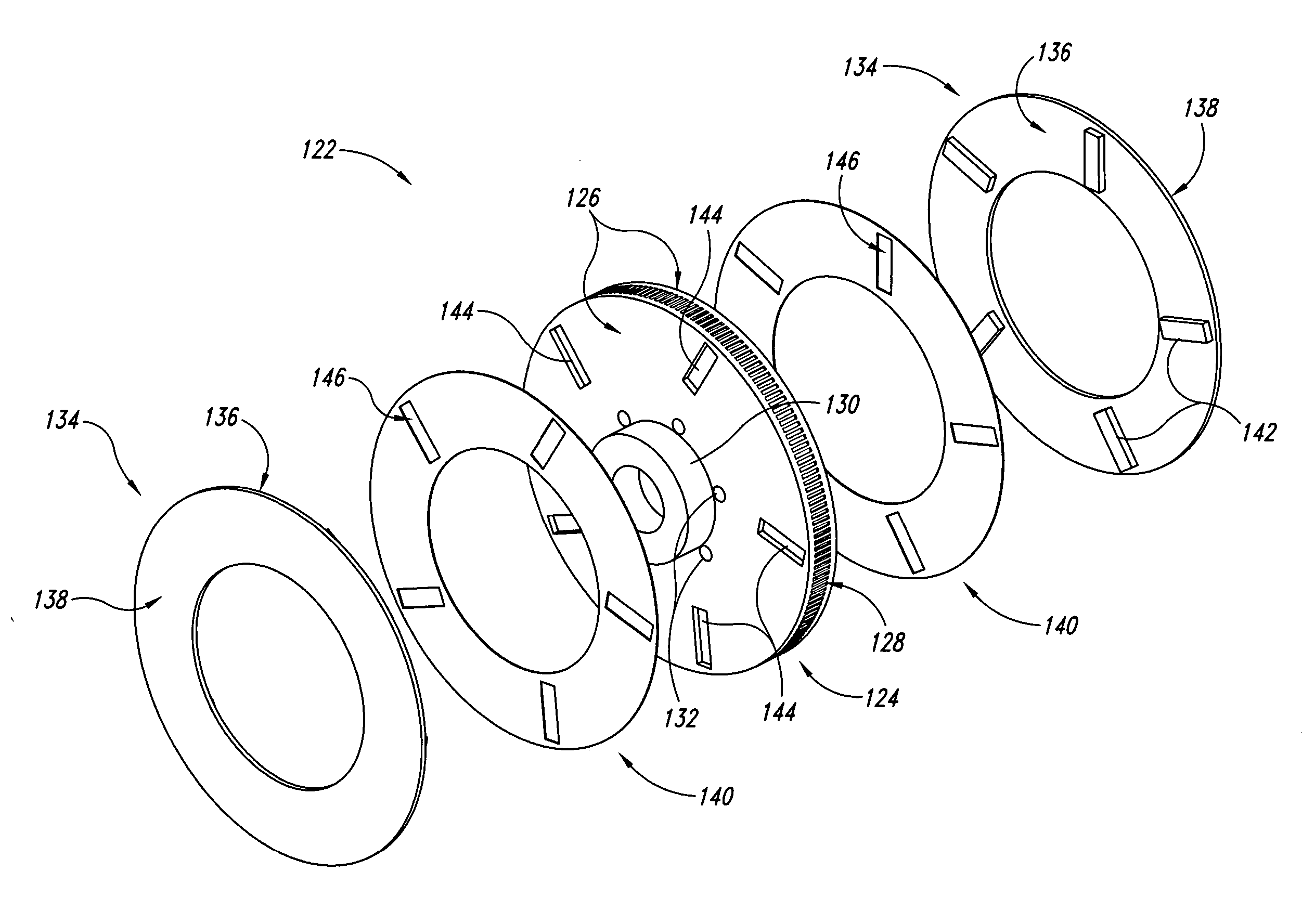
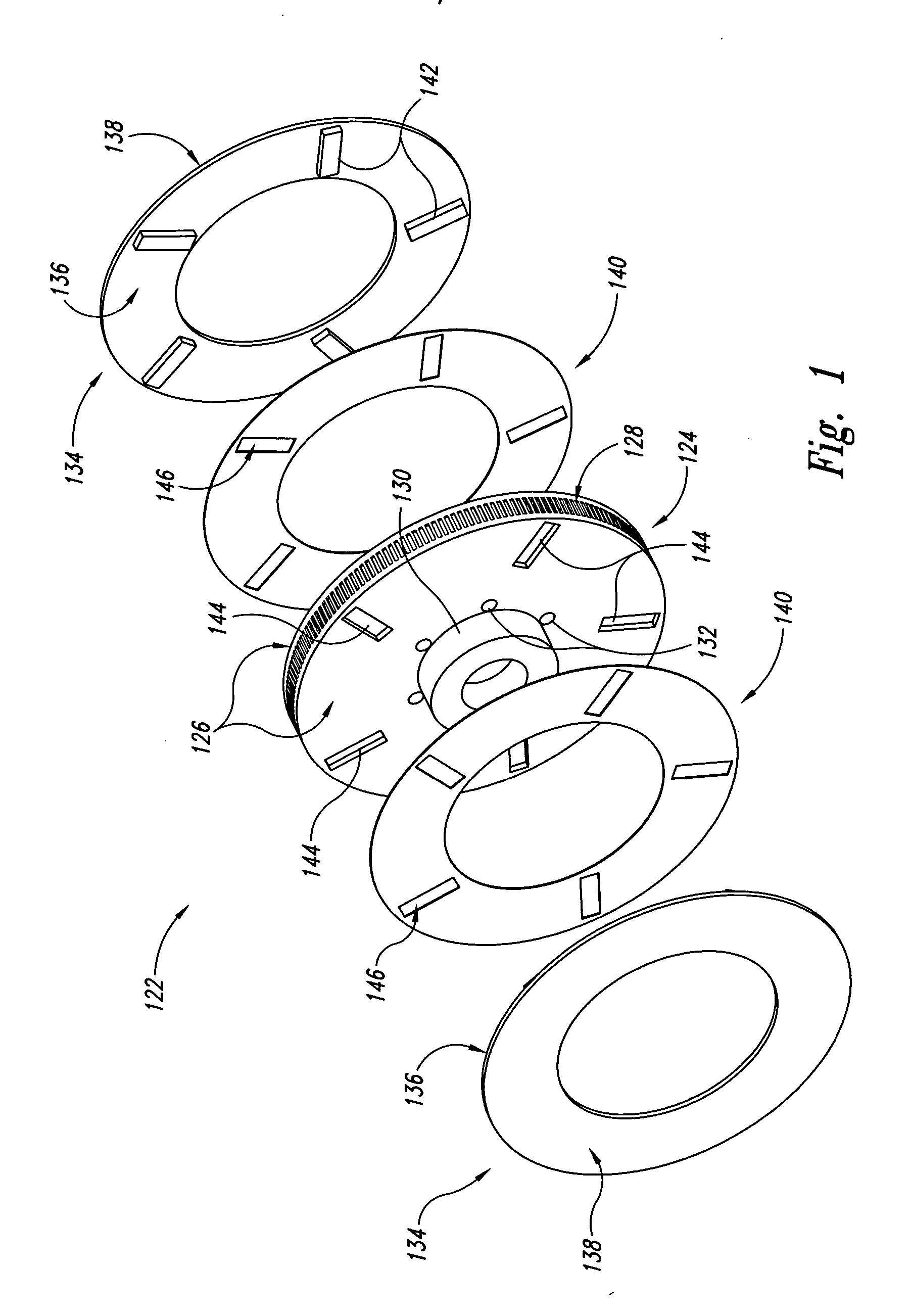
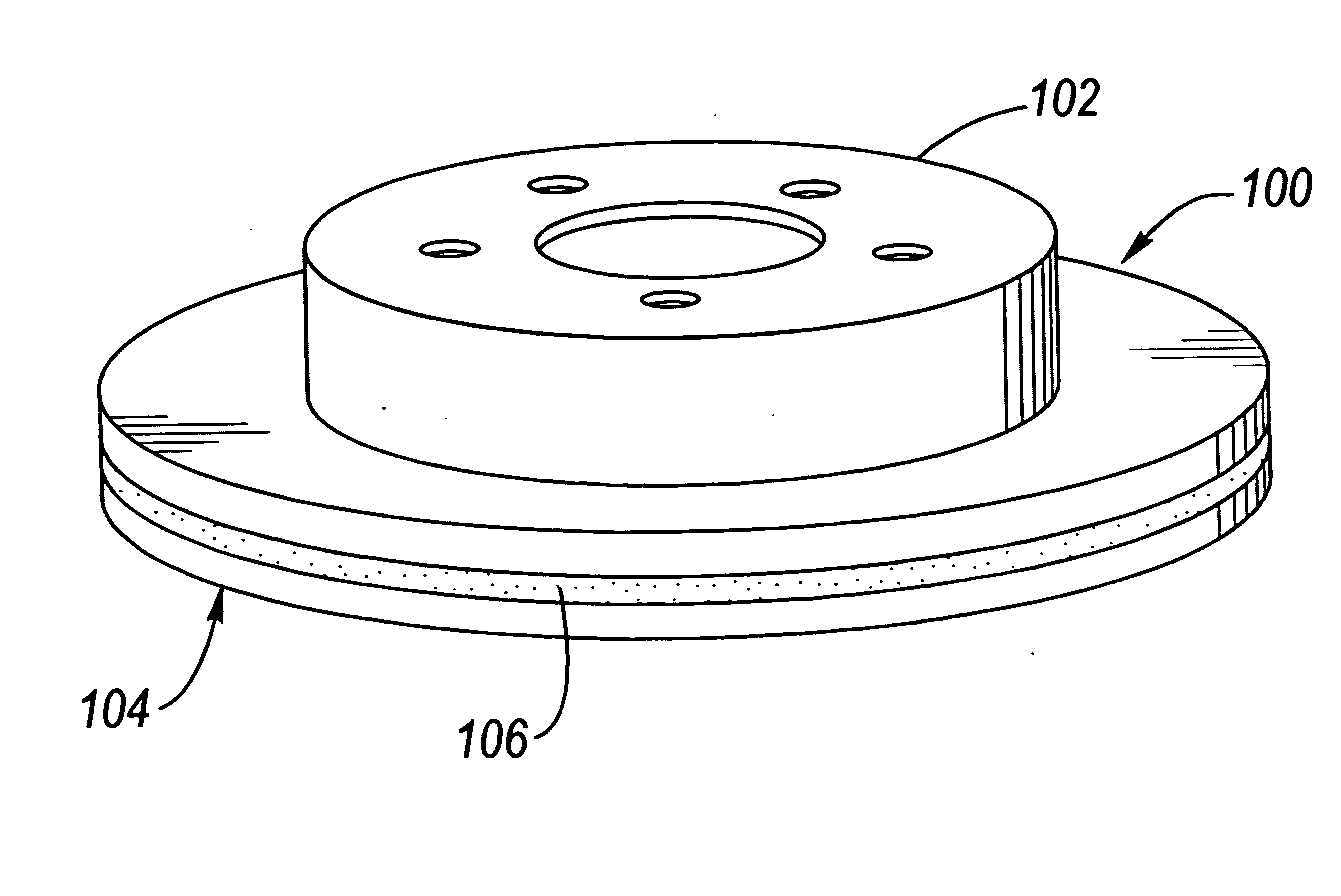
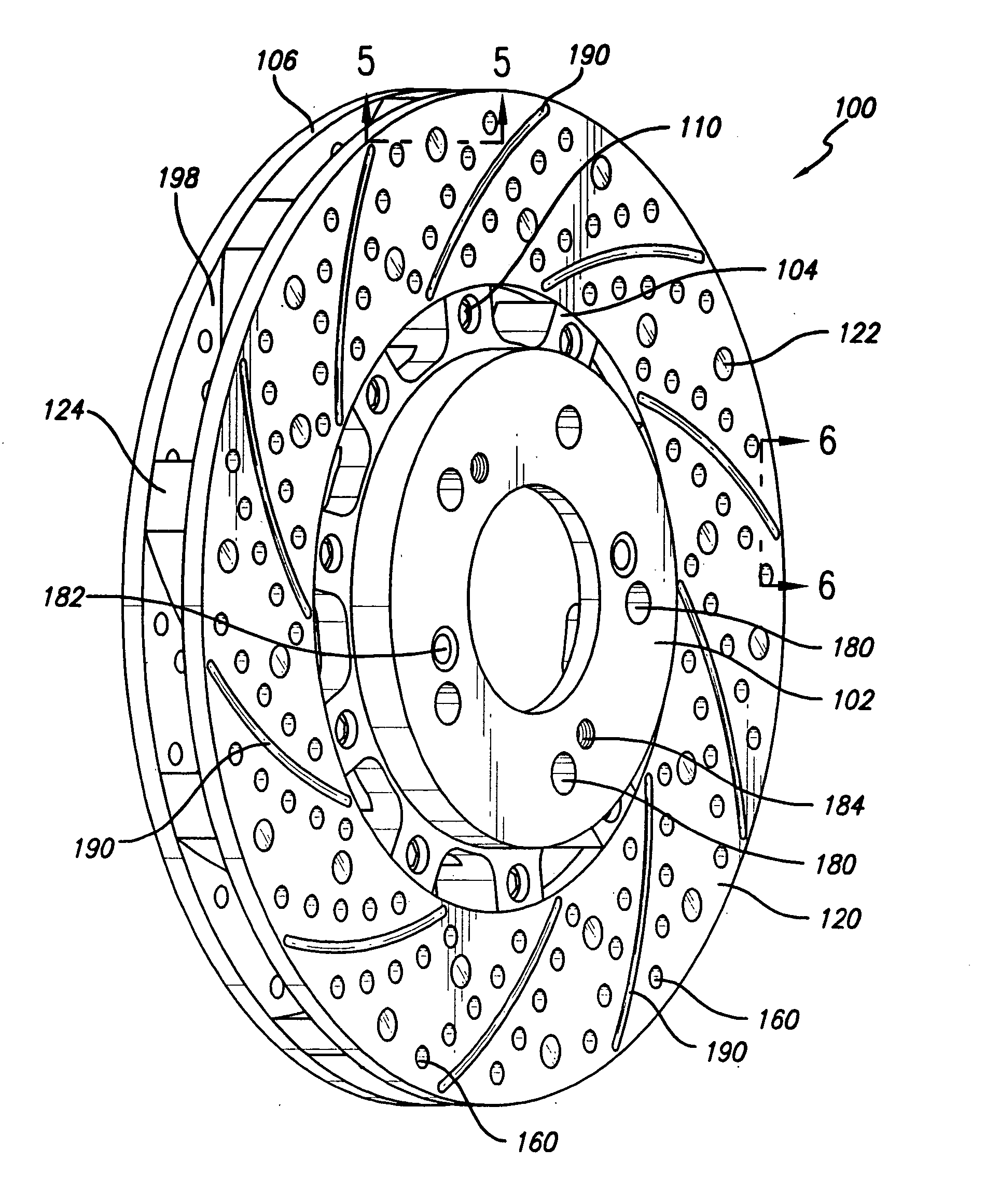
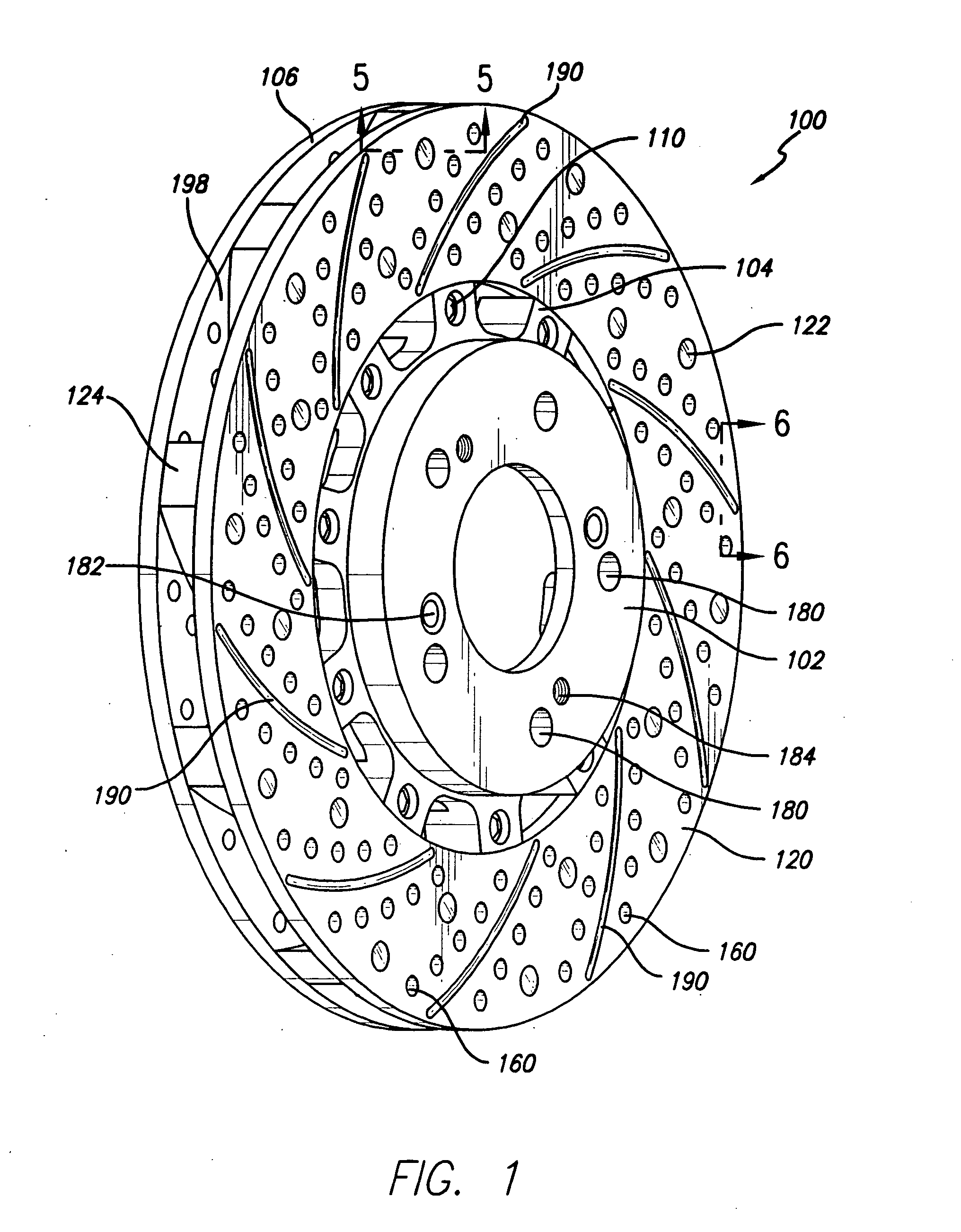
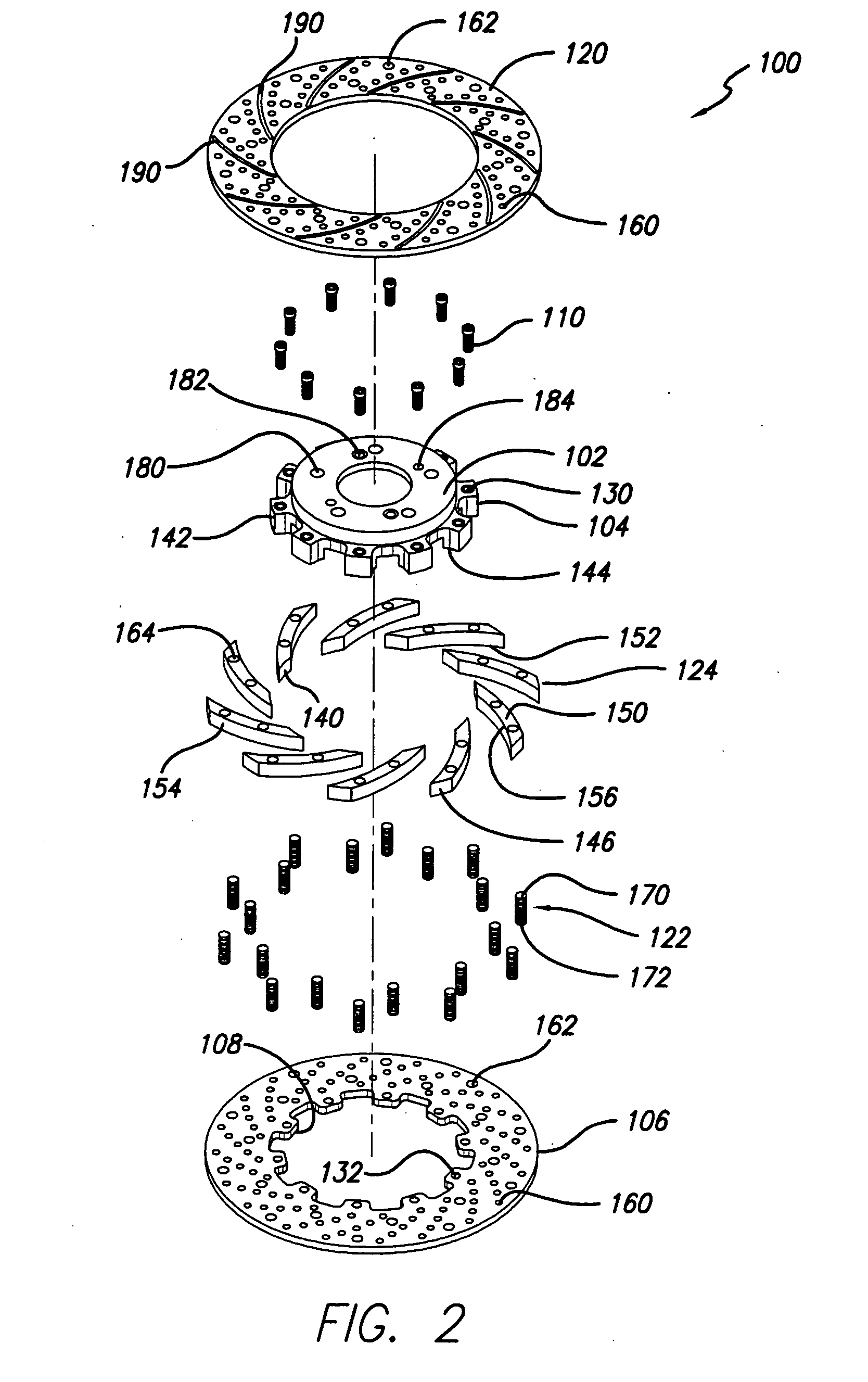
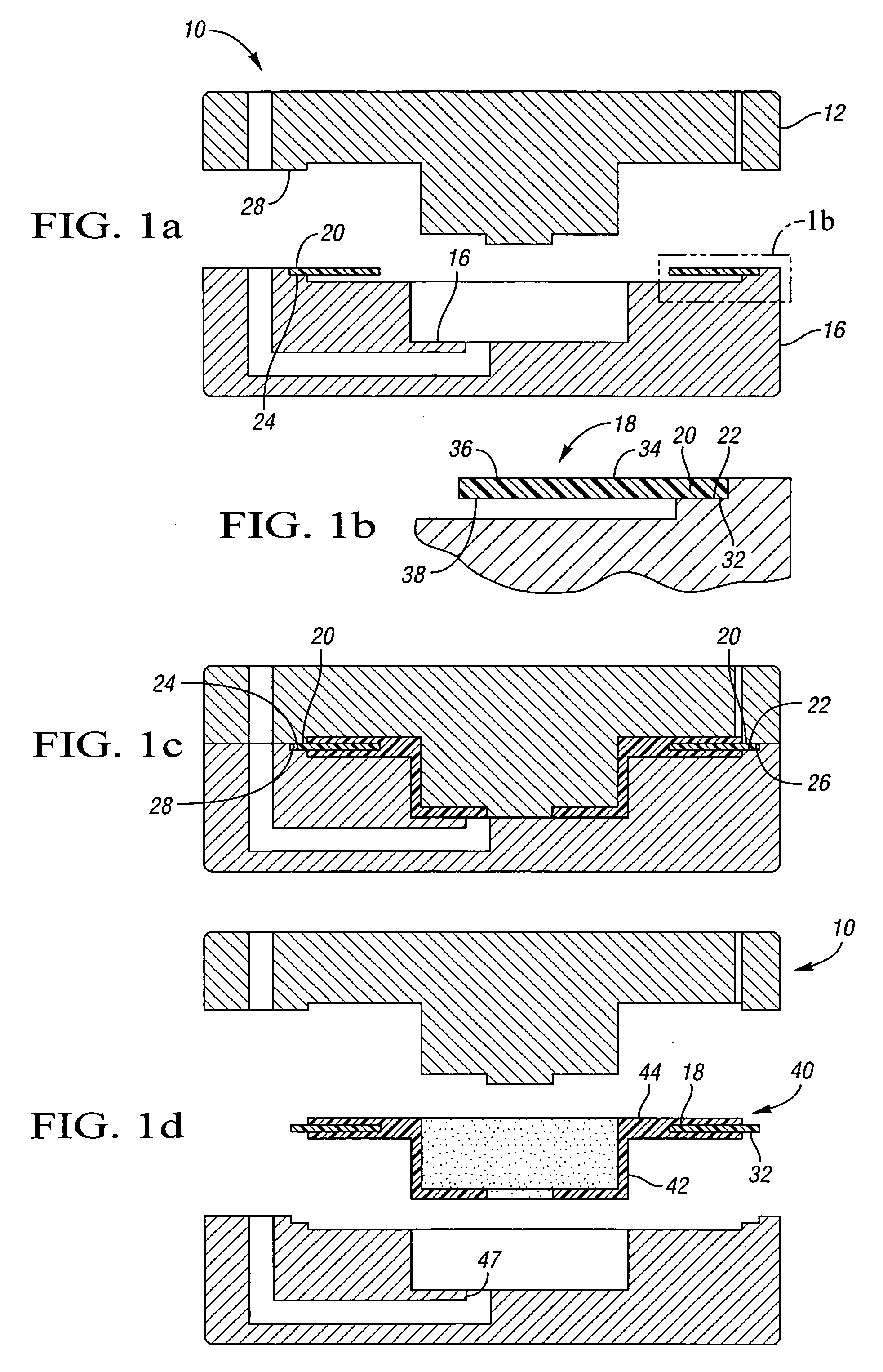
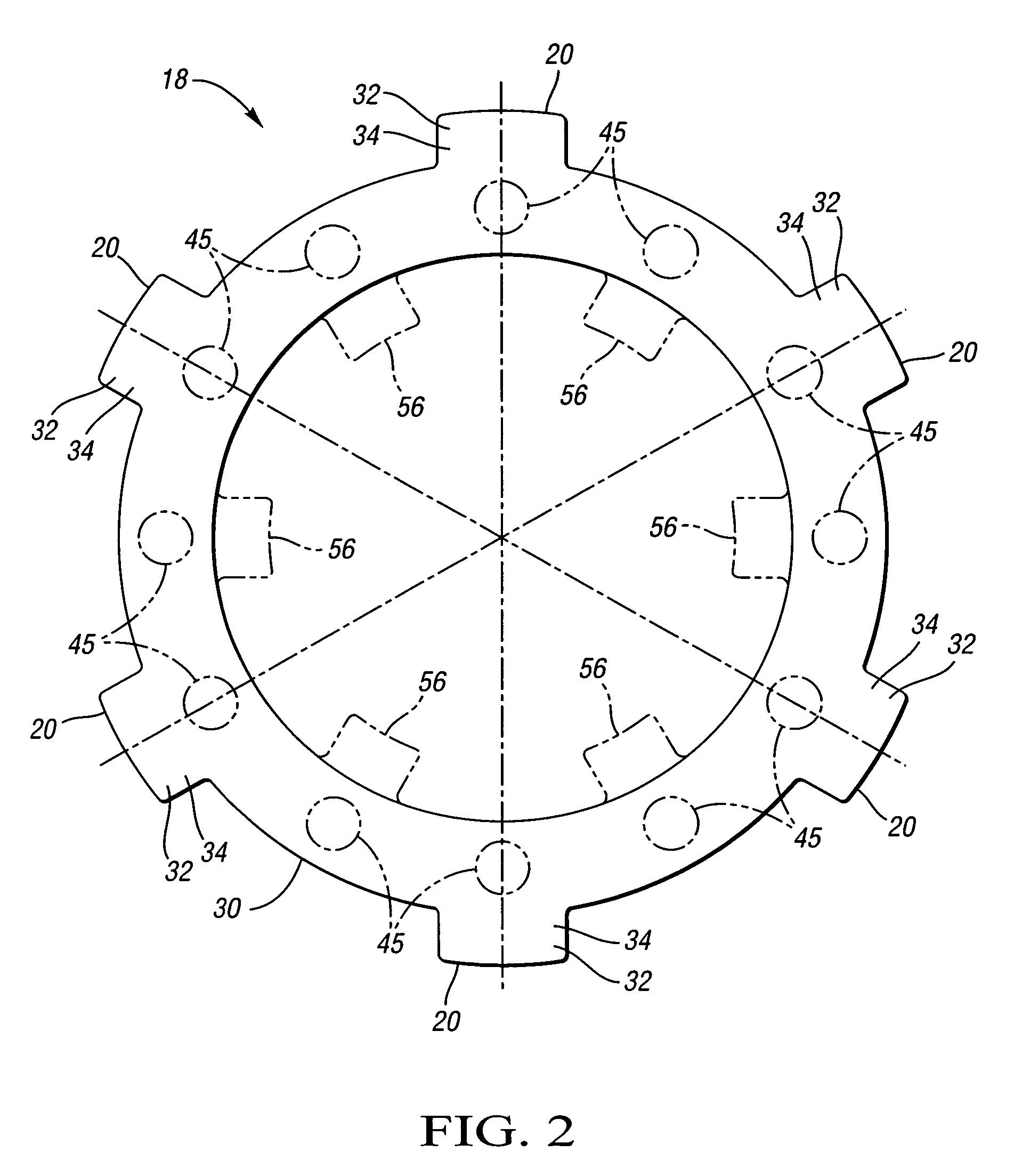
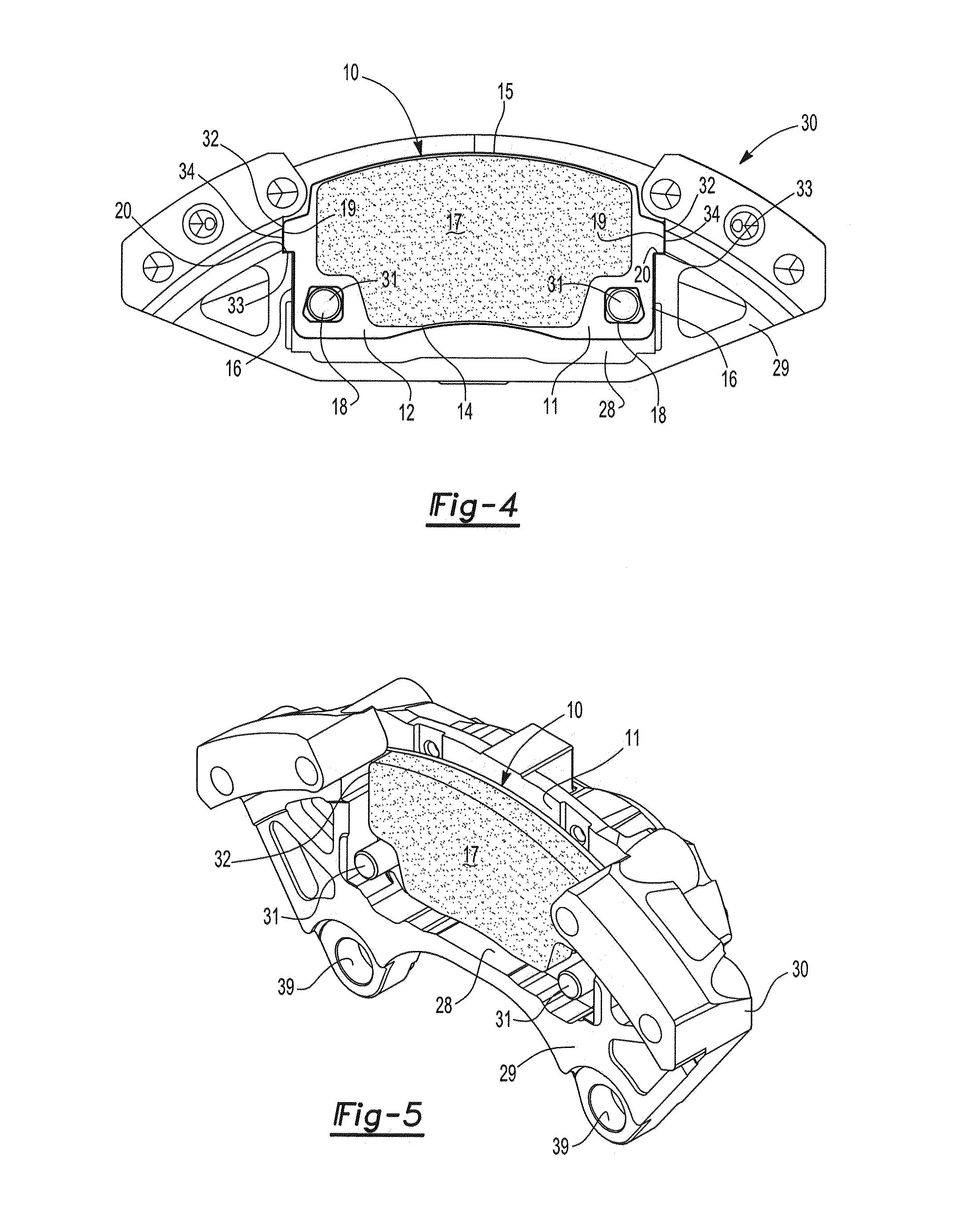
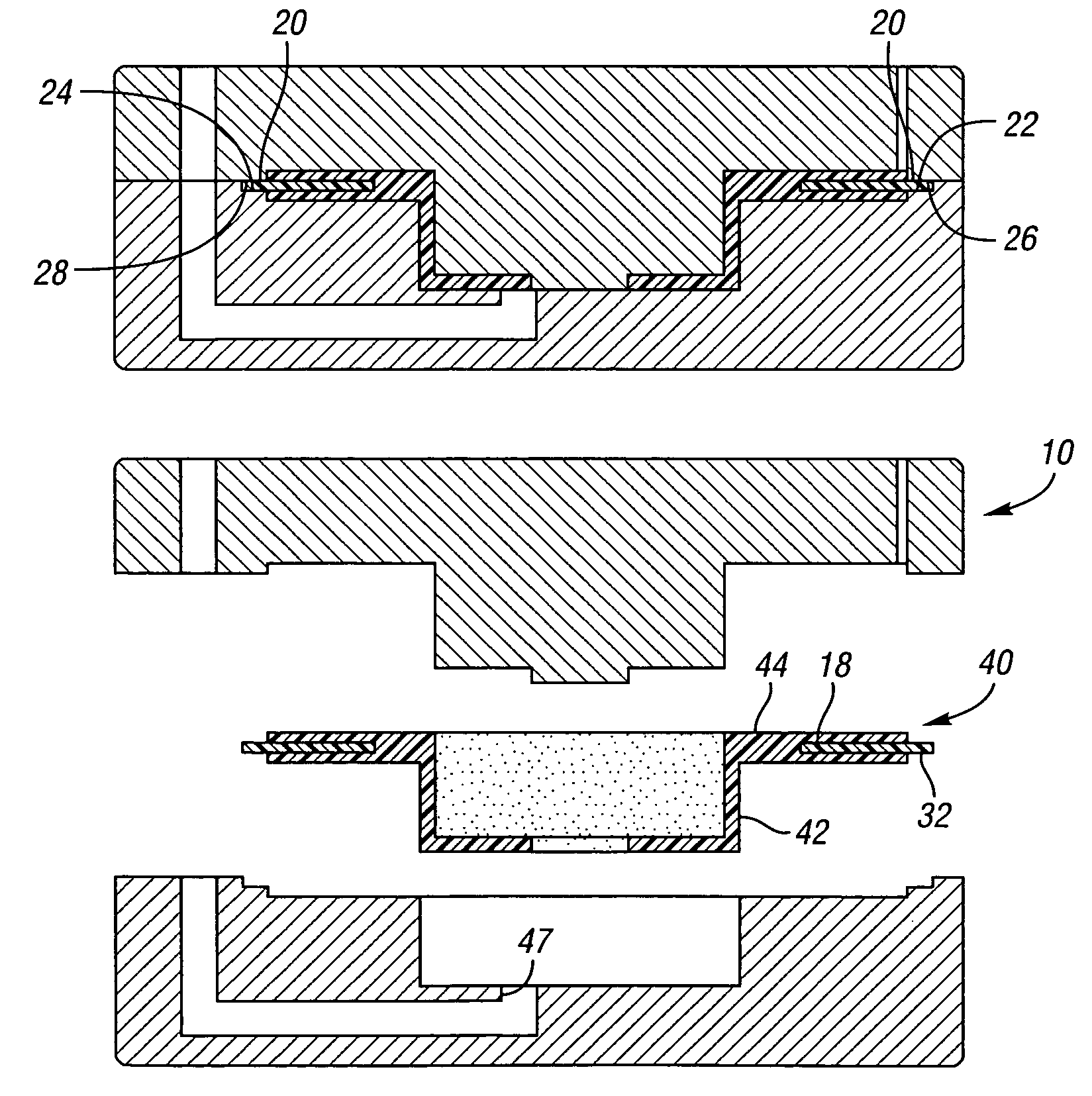
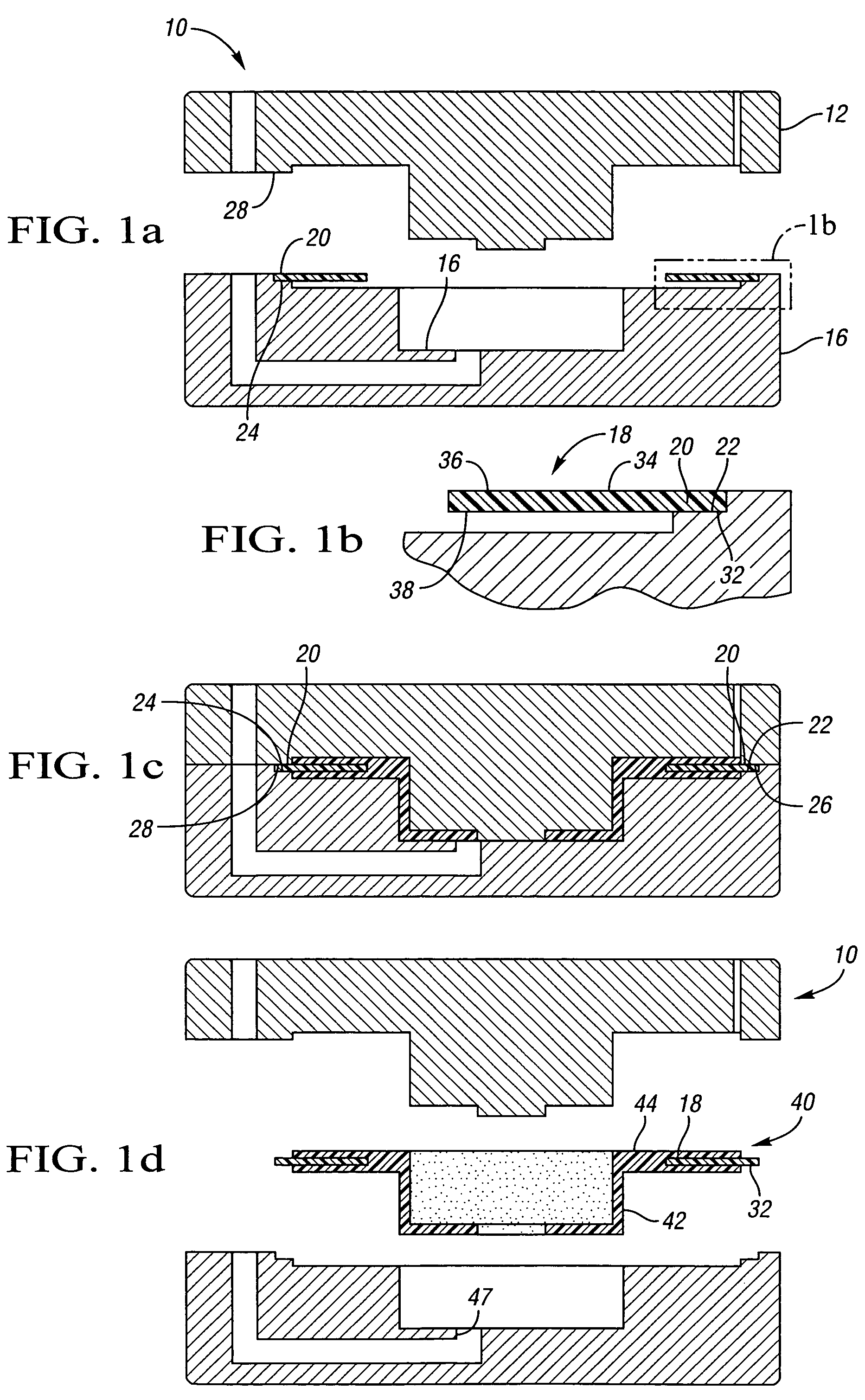
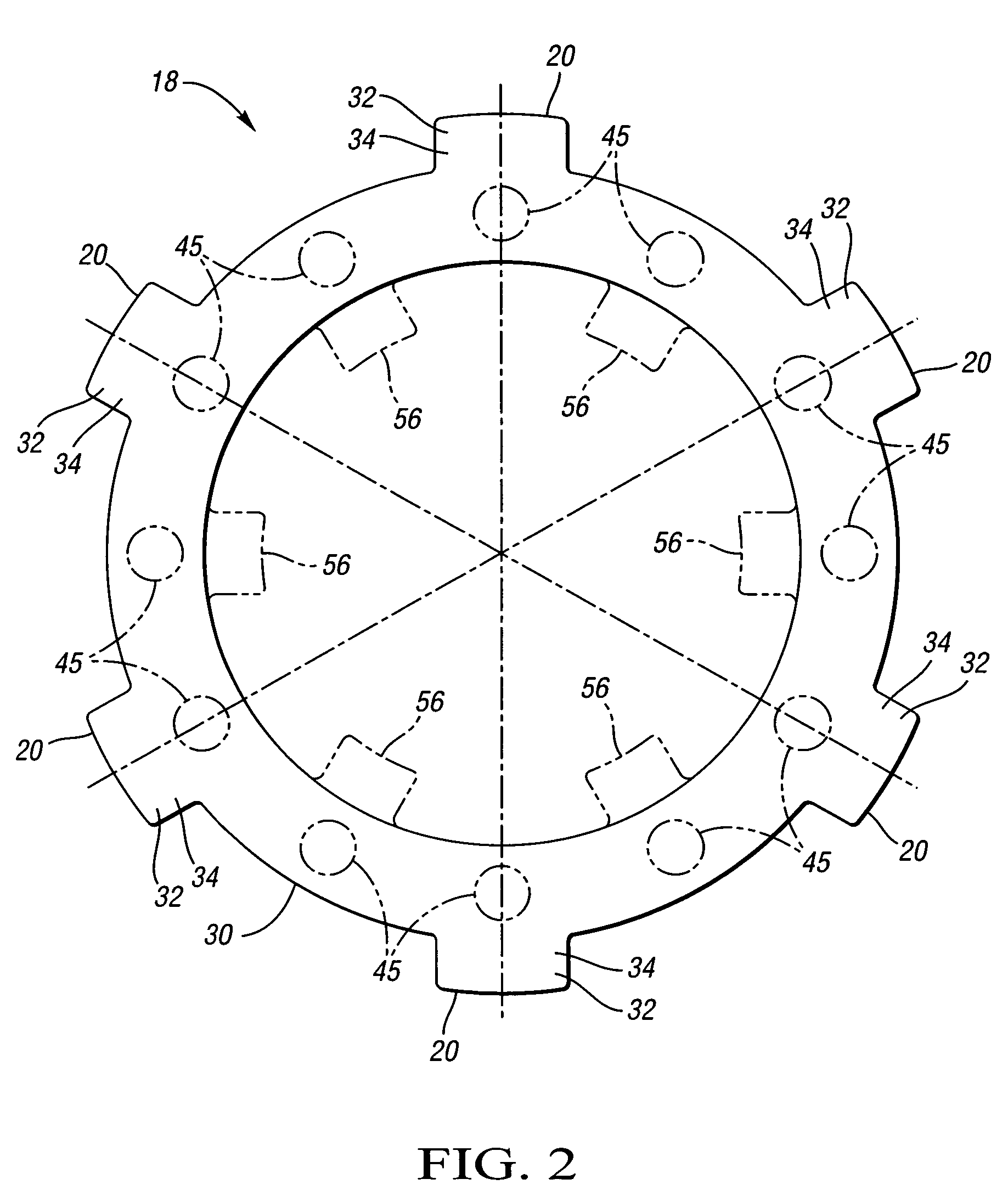
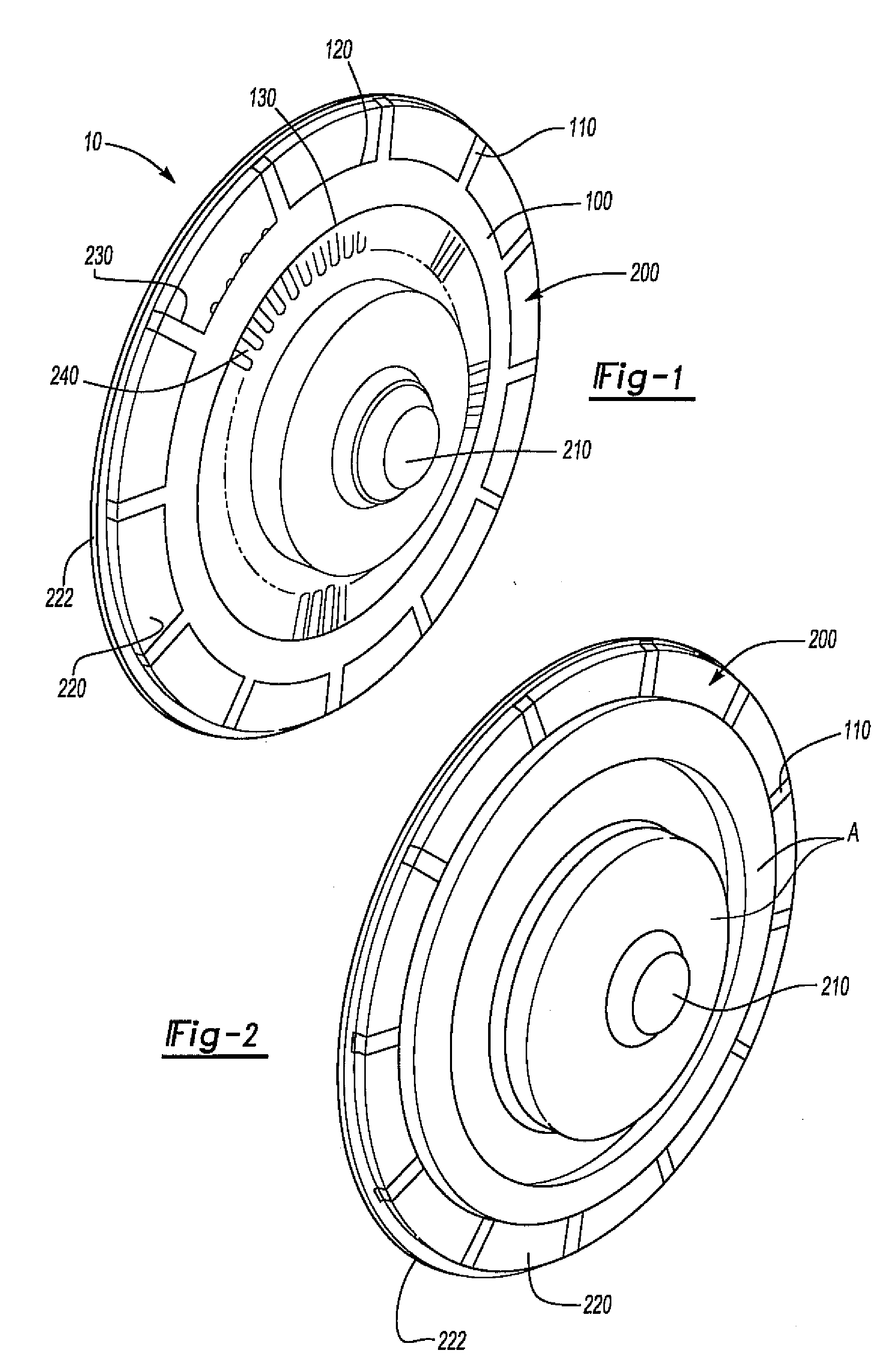
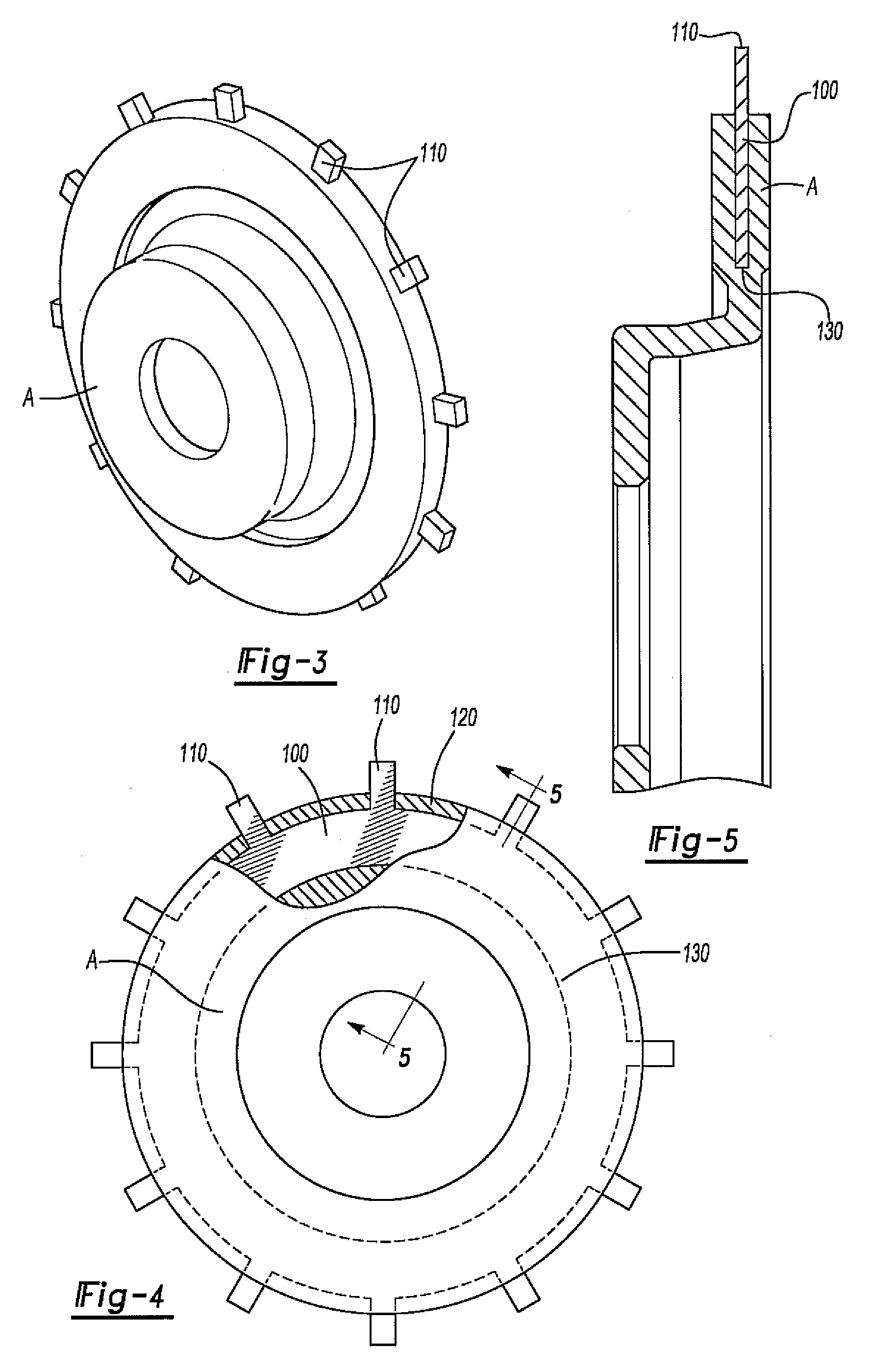
Disc brake rotor assembly and method for producing same
InactiveUS20050183909A1Improve thermal conductivityOptimize acoustic frequency transferBraking element arrangementsNoise/vibration controlAdhesiveMetal alloy
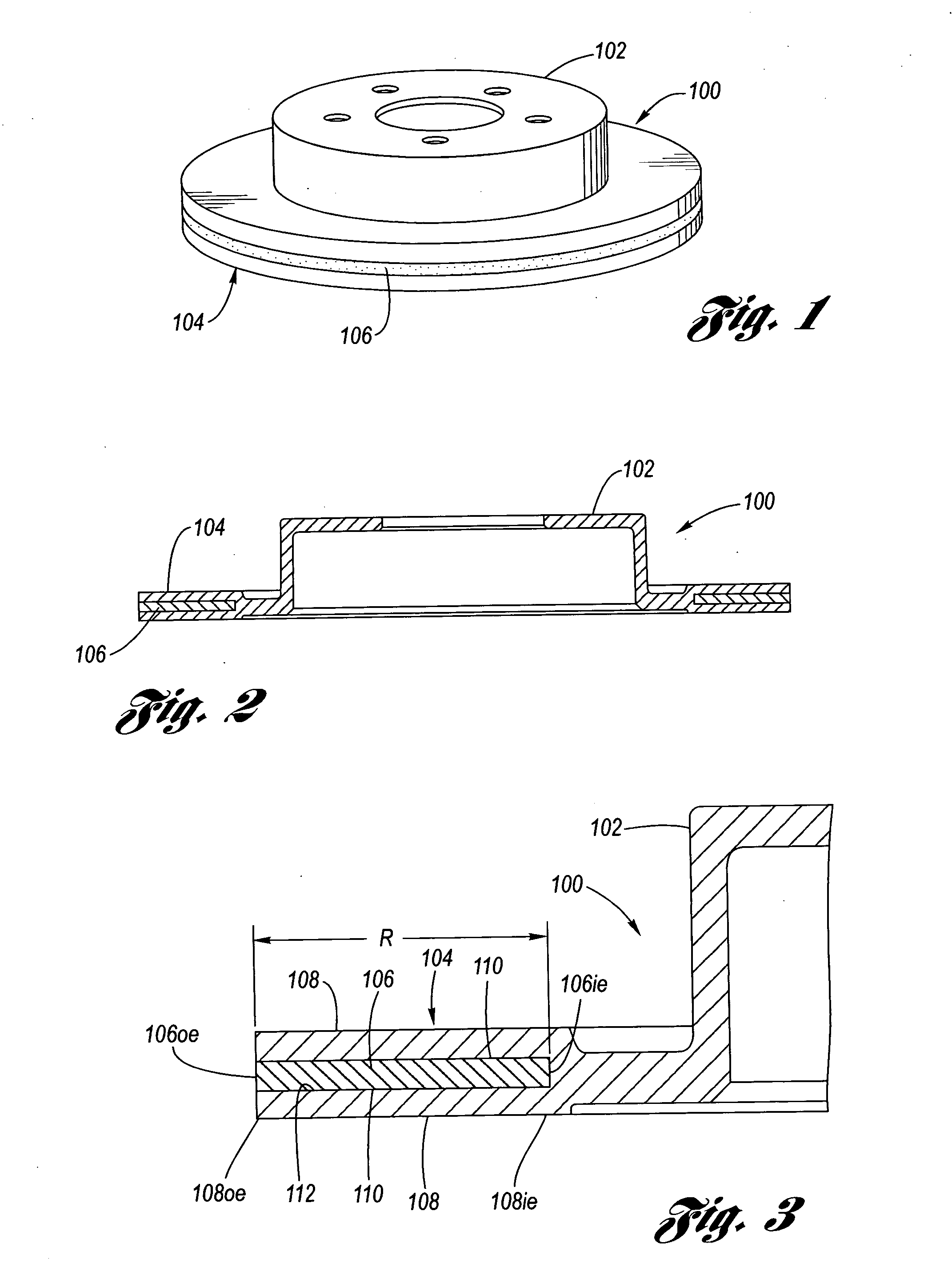
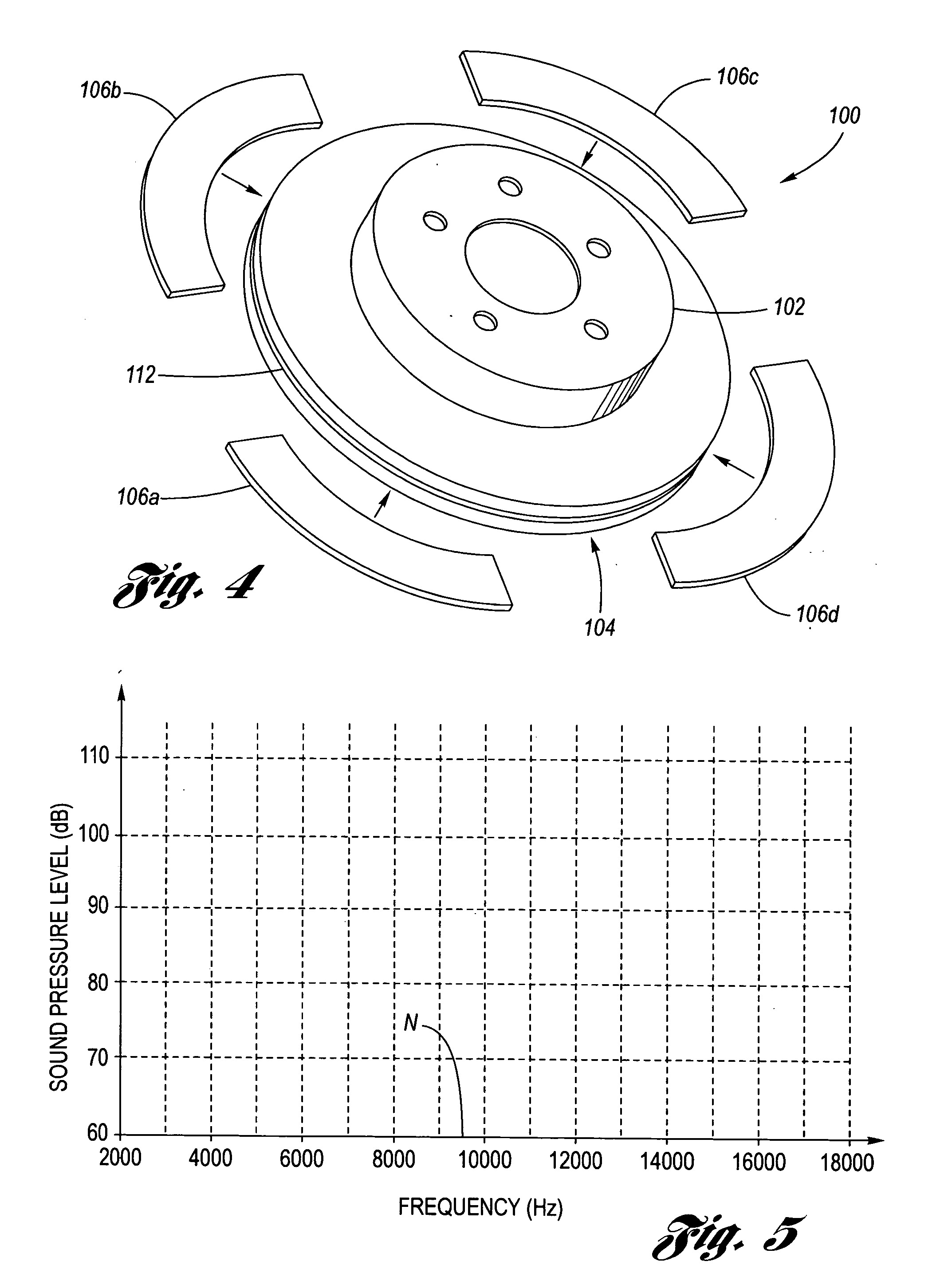
Novel composite disc brake rotor assemblies are provided, along with novel and efficient methods for manufacturing them. Preferably, the rotor assemblies comprise annular wear plates formed of particle reinforced aluminum-based metal matrix composite (MMC), ceramic matrix composite (CMC), or of ‘carbon graphite foam.’ The wear plates, made of a first material, are attached to annular surfaces of a central rotor, made of a second material, by fusing bonding layers between the wear plates and the rotor surfaces. The bonding layers are comprised of at least one of a metal alloy having a melting temperature lower than that of either the first or second materials, and a high-temperature adhesive. Preferably, the wear plates comprise projections that are positioned within adjacent receiving recesses in the center rotor. The bonding layers and projections enhance thermal and acoustical transference between the wear plates and the center rotor section. Carbon graphite foam provides for substantially enhanced heat transference. Use of the fusable binding layer, or adhesive provides for an efficient, low cost method of manufacturing for composite disc brake rotor assemblies.
Owner:BENMAXX
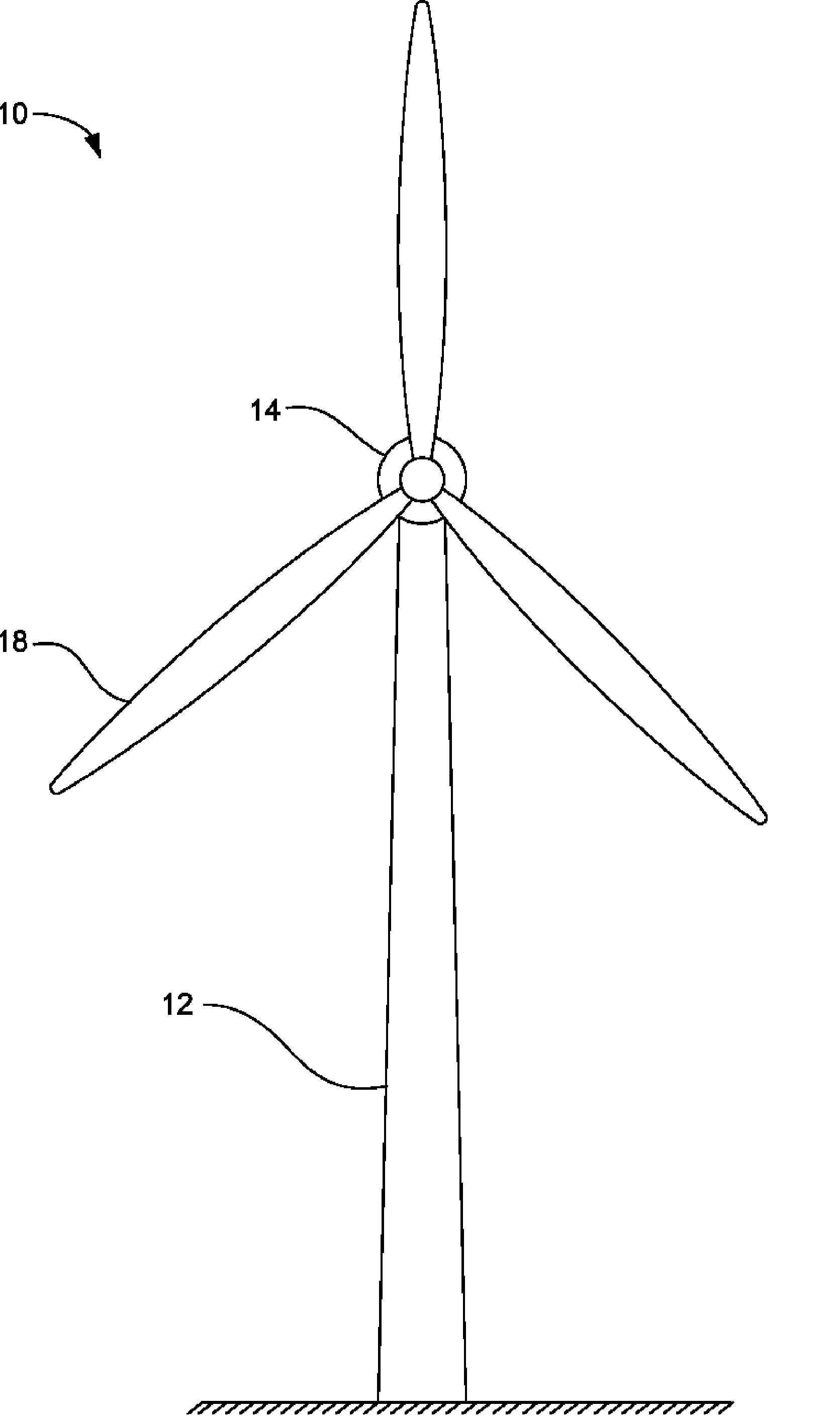
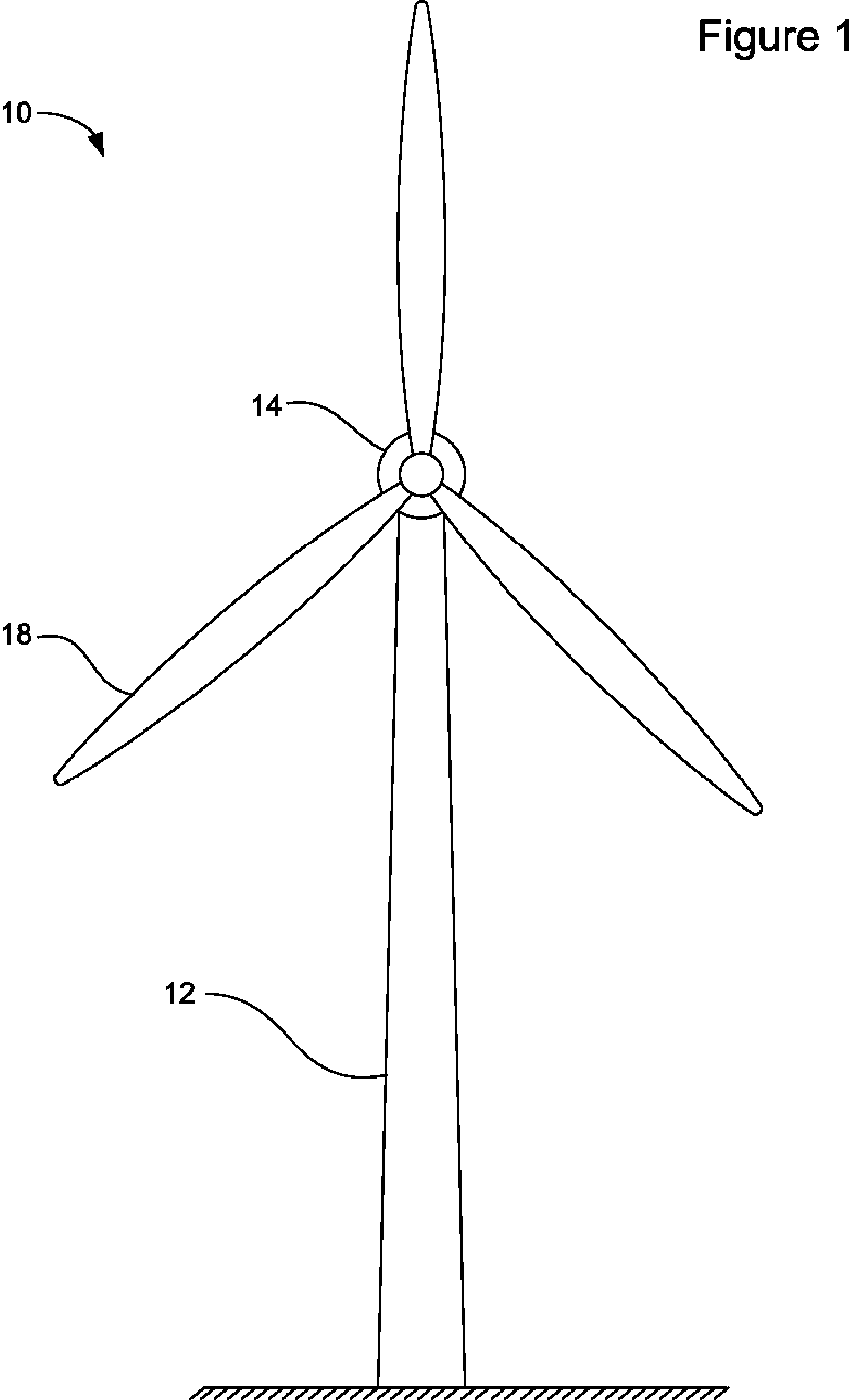
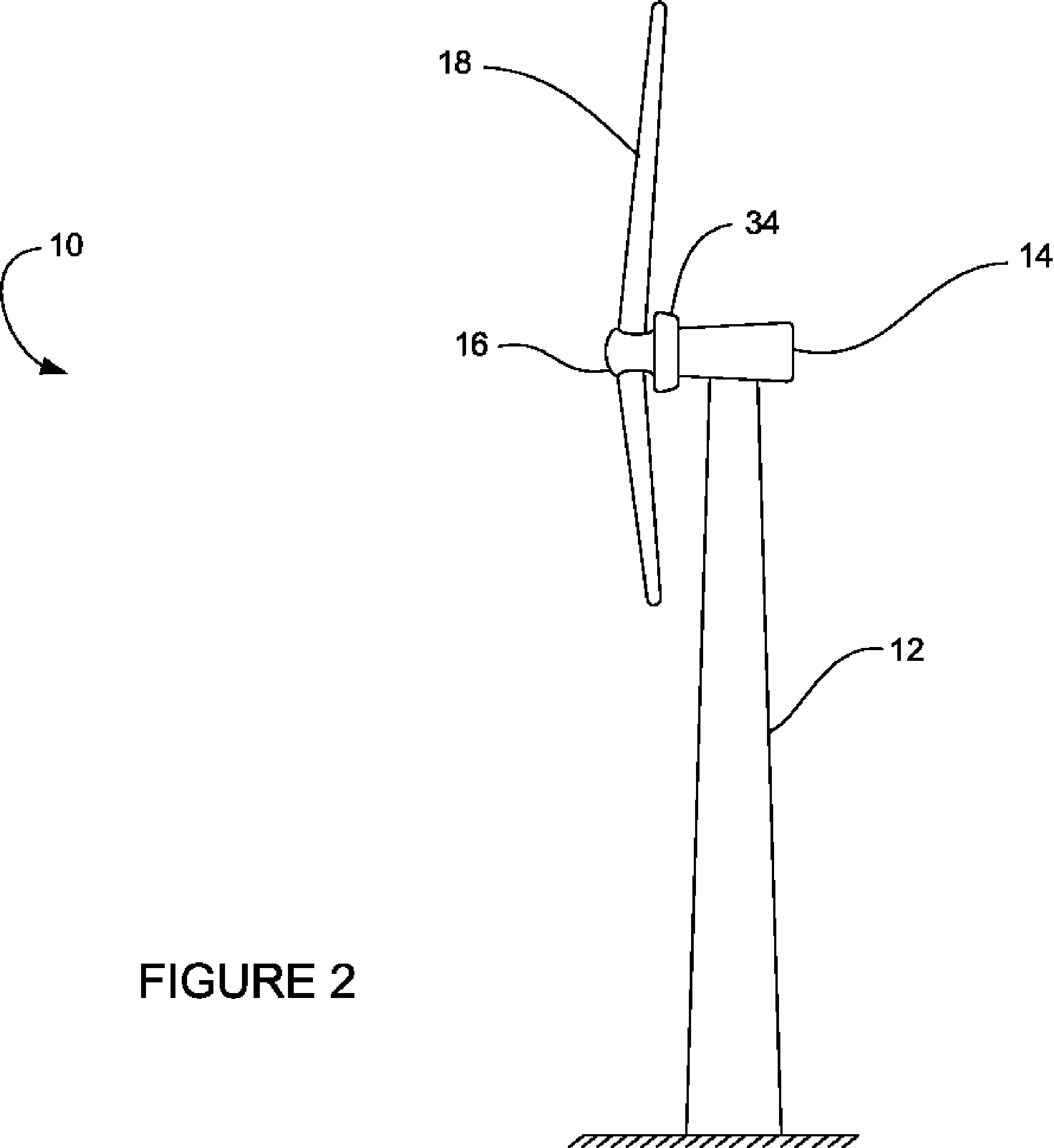
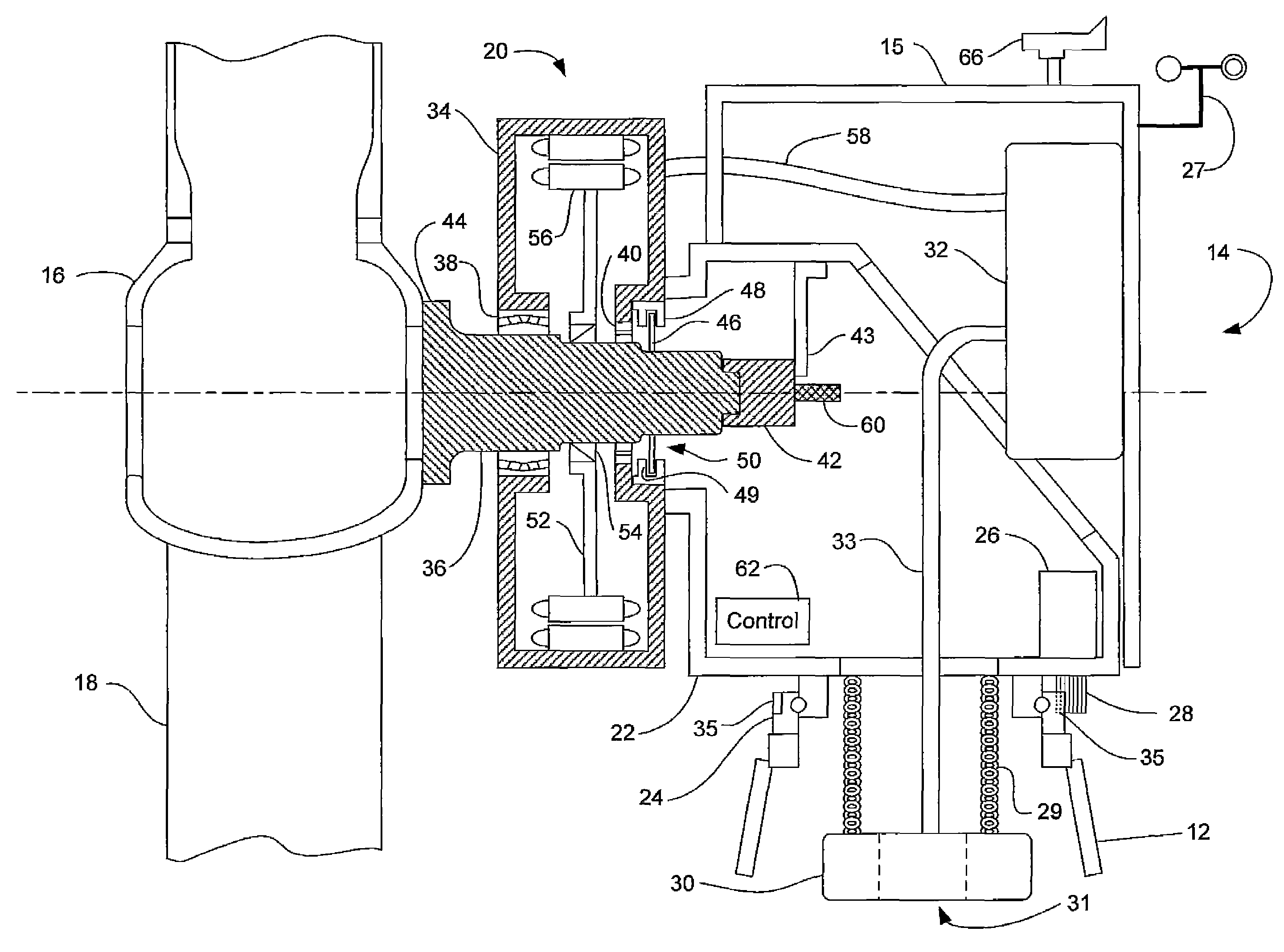
Direct Drive Wind Turbine
A wind turbine is provided that minimizes the size of the drive train and nacelle while maintaining the power electronics and transformer at the top of the tower. The turbine includes a direct drive generator having an integrated disk brake positioned radially inside the stator while minimizing the potential for contamination. The turbine further includes a means for mounting a transformer below the nacelle within the tower.
Owner:NORTHERN POWER SYSTEMS INC
Brake unit
InactiveUS6302246B1Prolong lifeImprove flatnessBraking element arrangementsNoise/vibration controlEngineeringCeramic metal
A brake unit comprising at least one brake and at least one brake pad having at least one friction lining is described. The brake has a disk brake with a brake rotor made of a ceramic-metal composite (CMC) whose outer surface or surfaces at least partially form a friction surface for the at least one friction lining, and a disk brake cup that is mounted on the disk brake by way of one or more mounting elements. The friction surface of the disk brake has a hardness of approximately 1600 to 2500 HV, and the at least one friction lining has a coefficient of friction of approximately 0.3 to 0.5. The disk brake cup and / or the mounting elements form a corrosion-inhibiting attachment to the disk brake. The brake unit can be operated in corrosion-free fashion over a service life of at least approximately eight to 10 years or approximately 200,000 to 300,000 km.
Owner:FRENI BREMBO SPA
Direct drive wind turbine
A wind turbine is provided that minimizes the size of the drive train and nacelle while maintaining the power electronics and transformer at the top of the tower. The turbine includes a direct drive generator having an integrated disk brake positioned radially inside the stator while minimizing the potential for contamination. The turbine further includes a means for mounting a transformer below the nacelle within the tower.
Owner:NORTHERN POWER SYSTEMS INC
Coulomb friction damped disc brake rotors
InactiveUS20060076200A1Average thicknessSmall thicknessNoise/vibration controlBraking discsEngineeringMechanical engineering
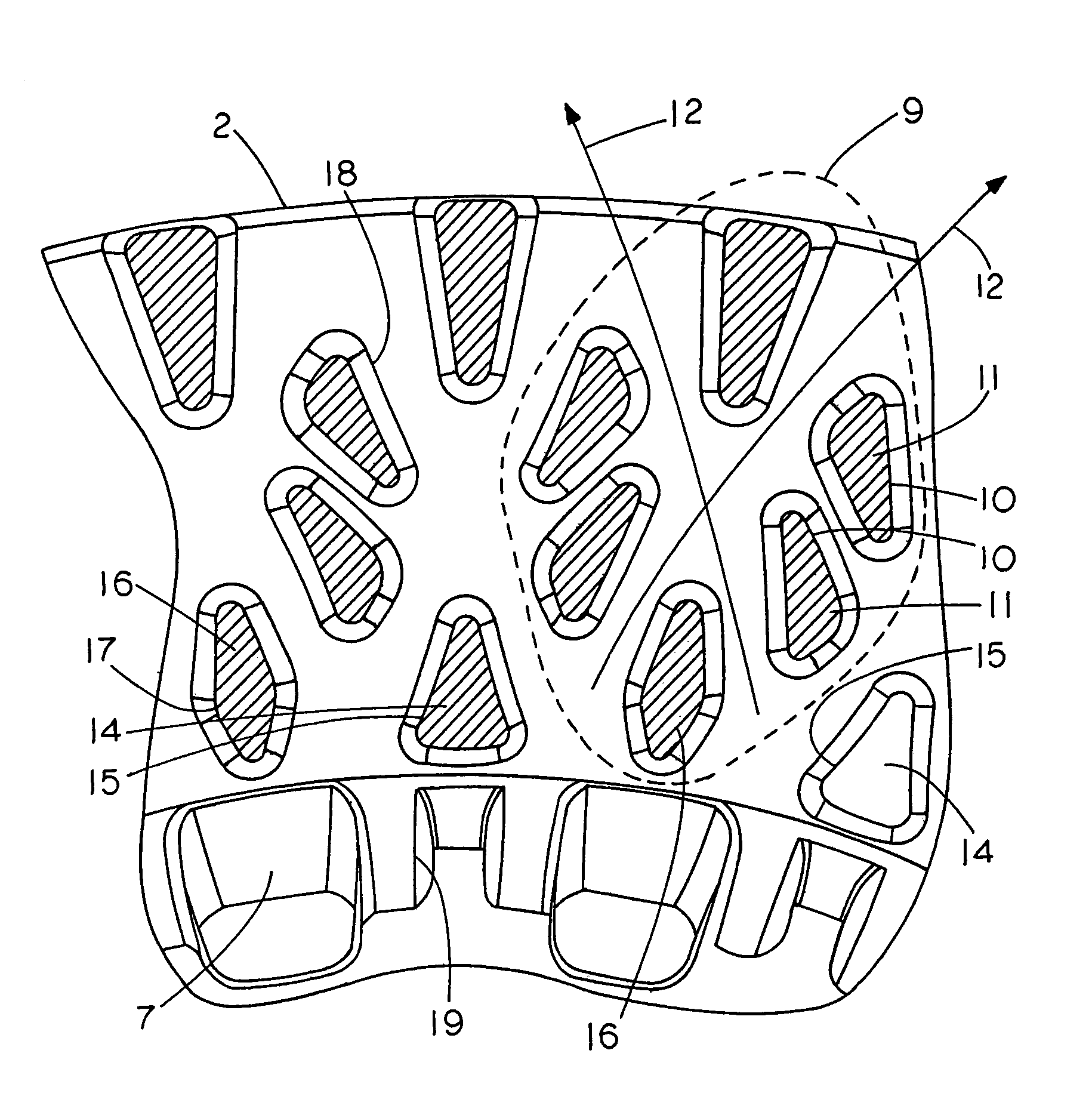
A Coulomb friction damped disc brake rotor, wherein damping is provided Coulomb friction in generally coextensive relation with the braking surfaces of the one or more rotor cheeks. The Coulomb friction damped disc brake rotor has at least one interfacial boundary formed in at least one rotor cheek disposed in generally coextensive relation to the braking surface thereof. The interfacial boundary provides a mechanically distinguishable surface boundary between two surfaces which are in mutual contact such that a state of Coulomb friction exists therebetween.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Self-ventilating disc brake rotor
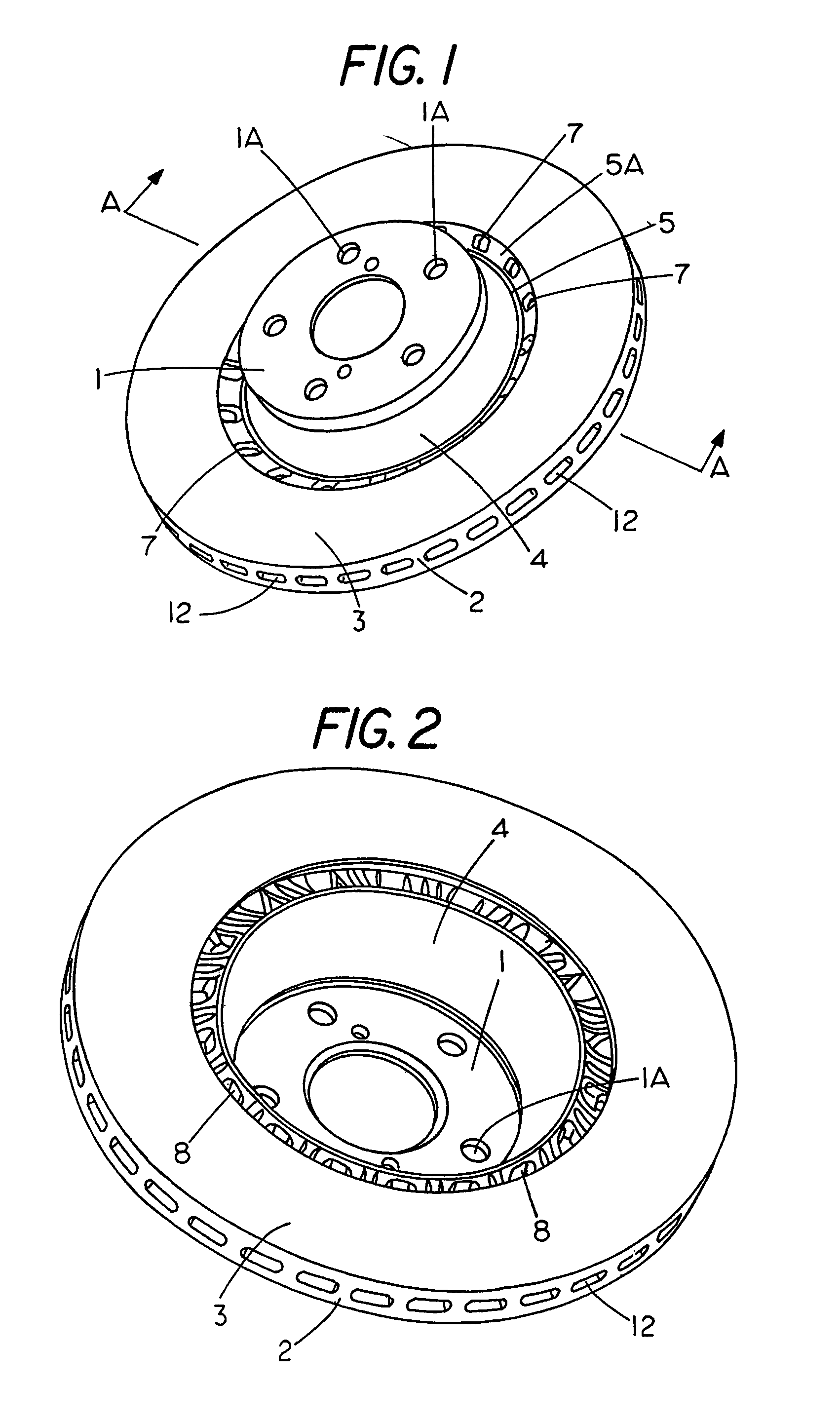
There is a brake disc rotor having a central hub (1) co-axial with surrounding rings (2) which form brake bands (3) for engagement with brake pads. The rings (3) are supported in a spaced apart parallel configuration with channels (12) therebetween whereby in use of the rotor cooling air is drawn in through vent openings formed around the inner periphery of the rings (3) and then radially outwardly through the channels (12) as the rotor turns. The vent openings include inlet vent ports (7) on the outboard side of the rotor.
Owner:DISC BRAKES AUSTRALIA
Bi-metal disc brake rotor and method of manufacturing
InactiveUS20070062768A1Avoid problemsImprove bindingNoise/vibration controlMetal rolling stand detailsCeramic coatingMaterials science
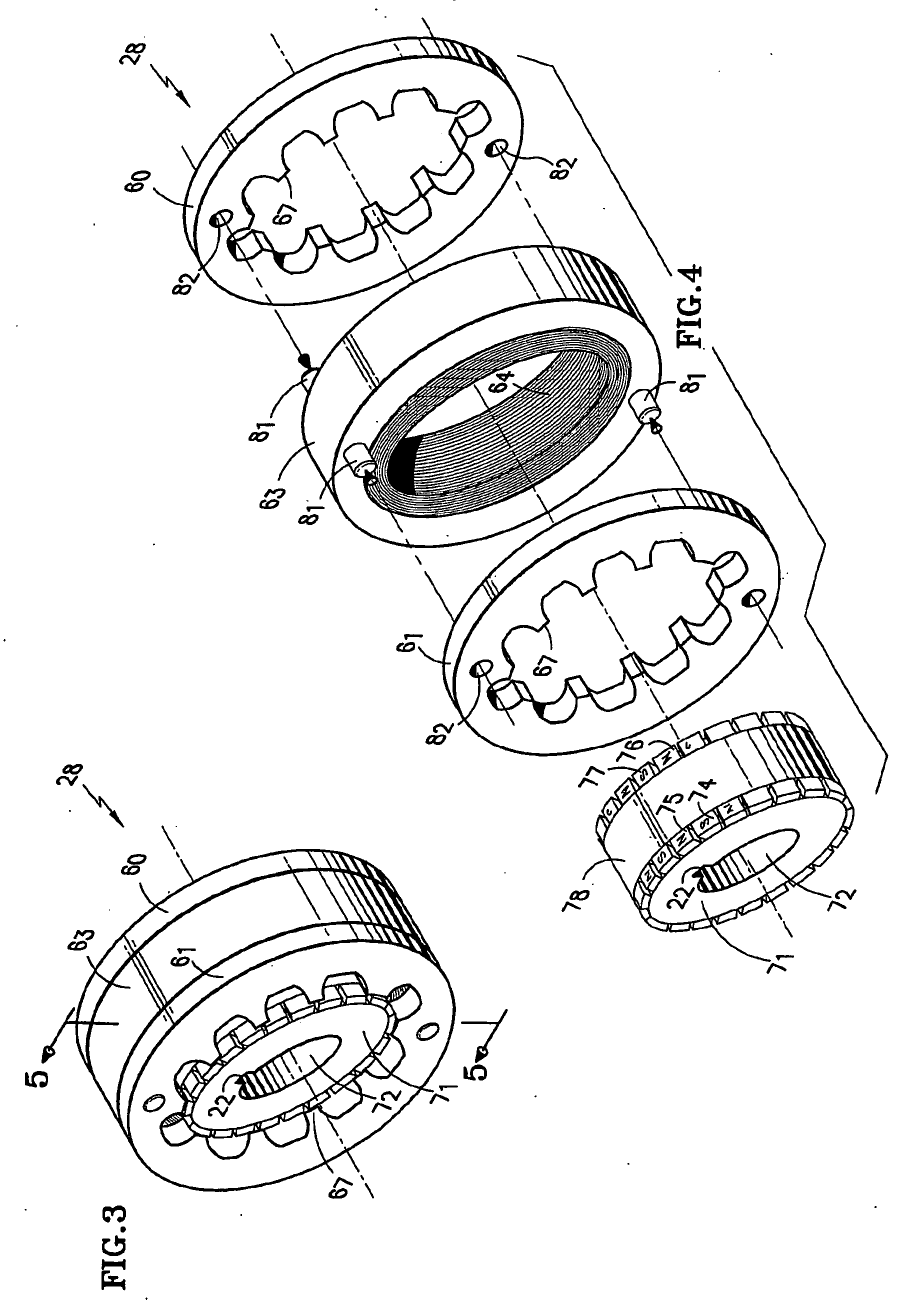
The invention provides a method for manufacturing a friction damped disc brake rotor, including the steps of: (A) providing a ceramic coating on an insert, wherein the insert has a body with tabs extending therefrom to hold the insert in a desired position within a mold; (B) washing the ceramic coating off of the tabs; (C) positioning the insert into the mold; and (D) casting a rotor cheek of the disc brake rotor in the mold around the insert such that a portion of each tab is bonded with the rotor cheek, and such that the coating is substantially non-bonded with the rotor cheek so that the coating provides a proper interfacial boundary between the body and the cheek for damping, and the at least partial bonding of each tab with the rotor cheek prevents corrosion-causing exterior elements from reaching the interfacial boundary when the friction damped disc brake rotor is in use.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Air-cooled brake rotor system
InactiveUS20070181390A1Easy to replaceImprove cooling effectBraking discsFriction liningDisc brakeEngineering
An air-cooled brake rotor system defining an inter-rotor disk slot through which spacers in the form of turbine or fan vanes propel air when the brake rotor system is turned. An inner disk brake rotor plate is attached to a hub which in turn may be attached to an axle on a vehicle such as an automobile. Pins having ends of opposite threading are used to connect the inner rotor to the outer rotor. The outer rotor is spaced apart from the inner rotor by means of spacers which are shaped to propel air through the slots defined between the two rotors. The spacers are also configured so that compression of the two rotors by a caliper system always serves to have a spacer beneath the area engaged by the brake pad to provide mechanical support for the rotor system. Each rotor generally has defined in it venting holes and inscribed debris-channeling slots in an arcuate, volute, or turbinate manner. An enhanced braking system experiencing lower heat retention is thereby attained.
Owner:KORM KEVIN
Modular transverse flux motor with integrated brake
InactiveUS20060192453A1Increased torque densityImprove efficiencySynchronous generatorsDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesTransverse fluxMotor end plates
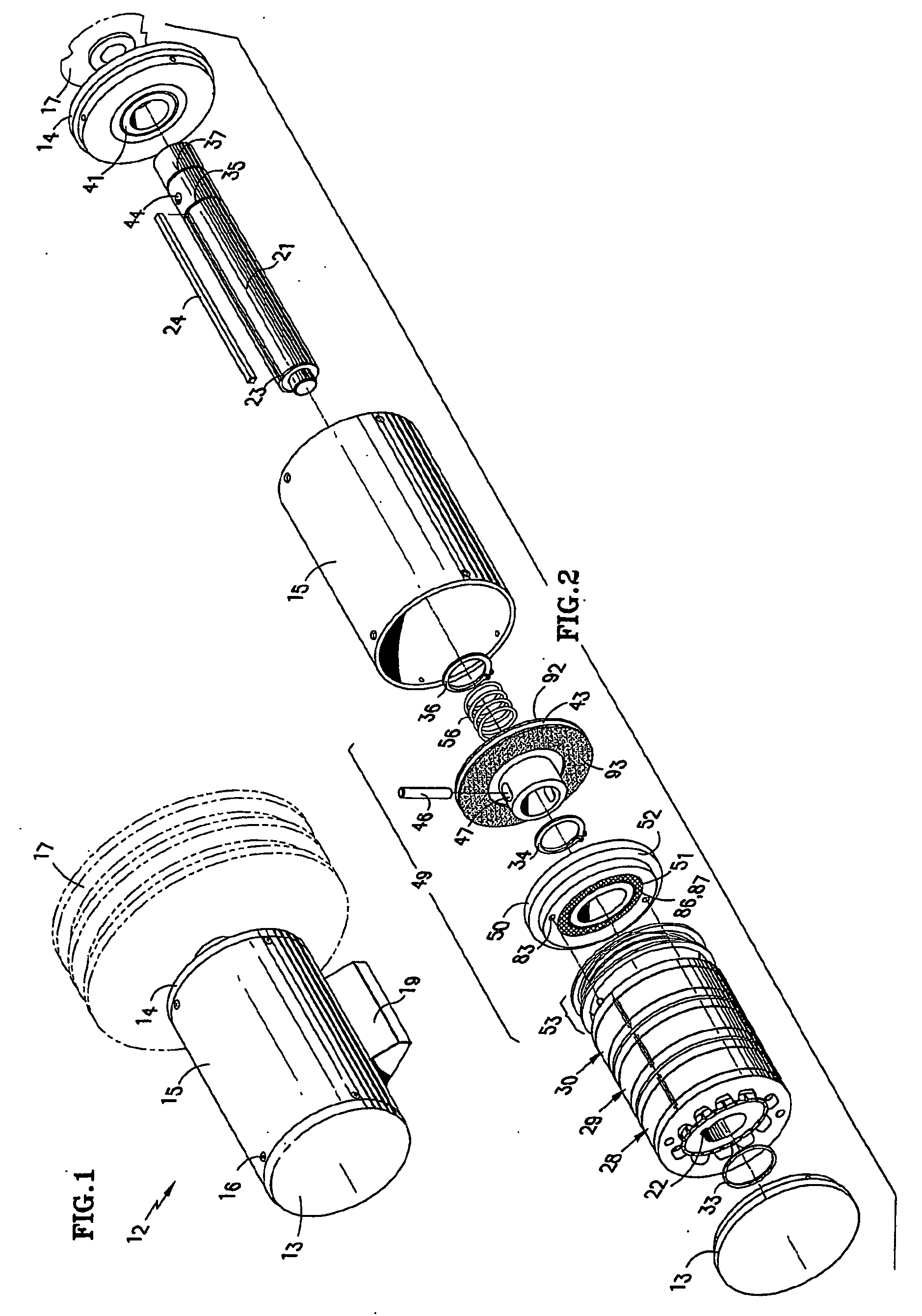
An elevator machine (12) has a plurality of identical transverse flux rotor / stator modules (28-30) of a generally cylindrical configuration arranged contiguously on a common shaft (21) to provide torque to the shaft equal to the torque capability of the modules times the number of modules. A disc brake (49) is integrated with the motor; a two-sided brake disc (49) has friction pads (92, 93) on both sides, braking force being applied to motor end plate (14) and through the brake disc to a stator (60) of one phase (30) of the motor. A process (113) forms variously-sized motors from identically sized modular components, in various configurations (12, 100, 110).
Owner:OTIS ELEVATOR CO
Mooring systems with active force reacting systems and passive damping
A mooring system including a body / arm / vessel arrangement with passive damping and / or an active force restoring system. The active force restoring system includes a sensor for generating a displacement signal representative of the displacement of the vessel from a quiescent position and an active forcing device which responds to the displacement signal to force the arm in a direction to move the vessel toward the quiescent position. The passive damping arrangement includes a device, independent of and in addition to the damping of the water on the vessel or the arm, that damps the oscillation of the vessel in response to environmental conditions which force the vessel from its quiescent position. Hydraulic cylinder arrangements are provided for active forcing and passive damping. Powered winch / cable arrangements are also provided for active force systems. Alternative devices for active and passive damping systems of torque actuators include hydraulic powered cans with internal fins, or cans with internal elastomeric elements or disk brake elements.
Owner:SOFEC
Disk Brake And Production Method For A Disk Brake
ActiveUS20130008749A1Less componentsImprove stabilityBraking element arrangementsAxially engaging brakesSpring forceEngineering
A disk brake having a brake caliper and a brake actuation mechanism being supported in it, in which the brake actuation mechanism includes an amplification mechanism for introducing a clamping force, an adjustment device for compensation of lining wear with a torque clutch, a thrust element for transmitting the clamping force onto a brake disc and a reset device, which components are arranged around a rod, in which the torque clutch, for example, is formed as a roller-ramp-mechanism. A spring force can act onto the torque clutch by means of the reset device thereby forming a torque limit. Furthermore the invention relates to an assembly method for such a disc brake.
Owner:HALDEX BRAKE PROD AB
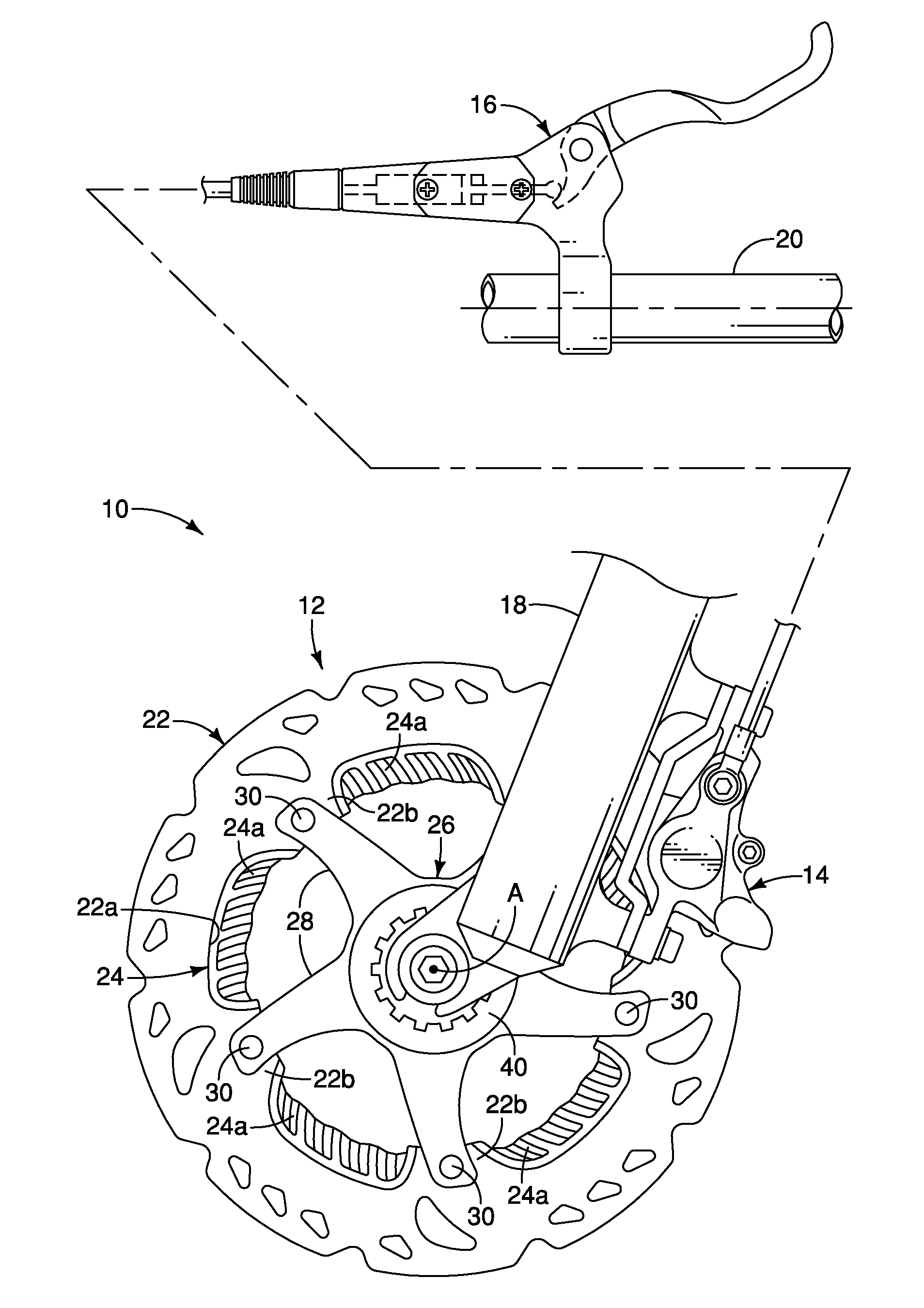
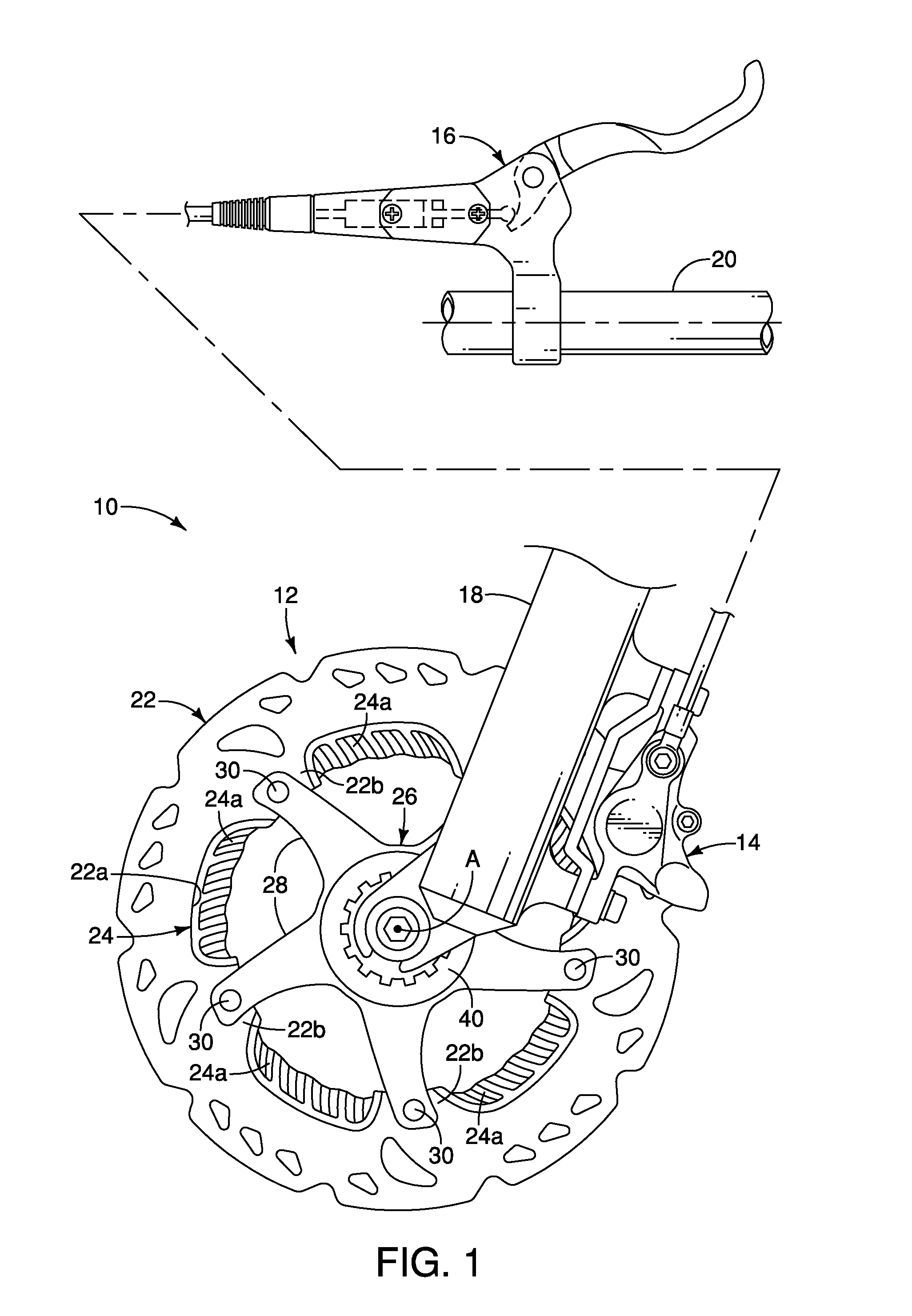
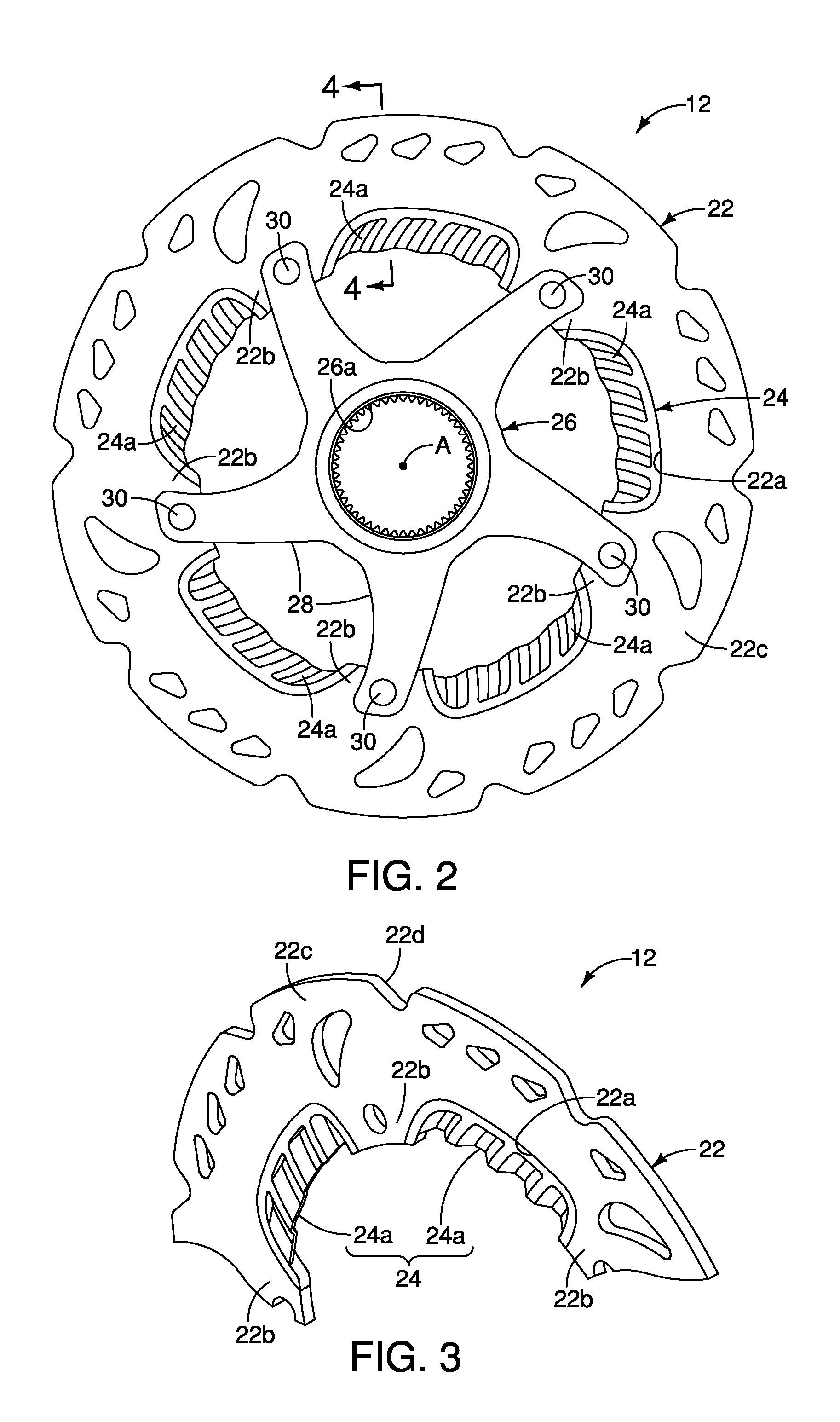
Bicycle disc brake rotor
ActiveUS20130168193A1Improve performanceEffective coolingAxially engaging brakesBraking discsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A bicycle disc brake rotor basically has an outer portion and a cooling fin. The outer portion has first and second base surfaces facing in opposite axial directions. The cooling fin is disposed radially offset from at least one of the first and second braking surfaces.
Owner:SHIMANO INC
Bi-metal disc brake rotor and method of manufacturing
InactiveUS20070056815A1Avoid problemsImprove bindingMetal rolling stand detailsBraking discsMechanical engineeringMetal
The invention provides a method for manufacturing a friction damped disc brake rotor, including the steps of: (A) positioning at least one insert into a mold, wherein the insert has a body with tabs extending therefrom to hold the insert in a desired position within the mold; and (B) casting a rotor cheek of the disc brake rotor in the mold around the insert such that a portion of each tab is bonded with the rotor cheek and the body is substantially non-bonded with the rotor cheek so that the body provides a proper interfacial boundary with the cheek for damping while the bonding of the tabs with the rotor cheek prevents corrosion-causing exterior elements from reaching the interfacial boundary.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Brake systems, caliper assemblies and pads incorporating differential abutments
InactiveUS20120043168A1Transmission of forceImprove NVH performanceMechanically actuated brakesBraking membersPush pullEngineering
The present invention is directed to a unique solution for caliper assemblies, brake pads utilized in such caliper assemblies, support structures utilized in caliper assemblies and disc brake systems containing such caliper assemblies which utilize push pull or pull push abutment designs.
Owner:AKEBONO CORP (NORTH AMERICA)
Bi-metal disc brake rotor and method of manufacturing
InactiveUS7775332B2Avoid problemsImprove bindingMetal rolling stand detailsBraking discsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention provides a method for manufacturing a friction damped disc brake rotor, including the steps of: (A) positioning at least one insert into a mold, wherein the insert has a body with tabs extending therefrom to hold the insert in a desired position within the mold; and (B) casting a rotor cheek of the disc brake rotor in the mold around the insert such that a portion of each tab is bonded with the rotor cheek and the body is substantially non-bonded with the rotor cheek so that the body provides a proper interfacial boundary with the cheek for damping while the bonding of the tabs with the rotor cheek prevents corrosion-causing exterior elements from reaching the interfacial boundary.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Coulomb damped disc brake rotor and method of manufacturing
InactiveUS20080099289A1Avoid bondingExternal exposure is reducedNoise/vibration controlBraking discsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention provides a method for manufacturing a coulomb damped disc brake rotor, including the steps of: (A) providing a mold having the general shape of the coulomb damped disc brake rotor; (B) placing a coulomb damper insert having a generally annular body and at least one tab extending generally radially from the generally annular body, wherein the at least one tab operates to locate the coulomb damper insert within the mold, and wherein the at least one tab at least partially defines an orifice with its major axis generally coincident with the periphery of the coulomb damped disc brake rotor; and (C) causing casting material to enter the mold to substantially encapsulate the coulomb damper insert with the casting material to form a rotor cheek of the coulomb damped disc brake rotor. A coulomb damper insert and coulomb damped disc brake rotor are also disclosed.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Disc brake with parking function
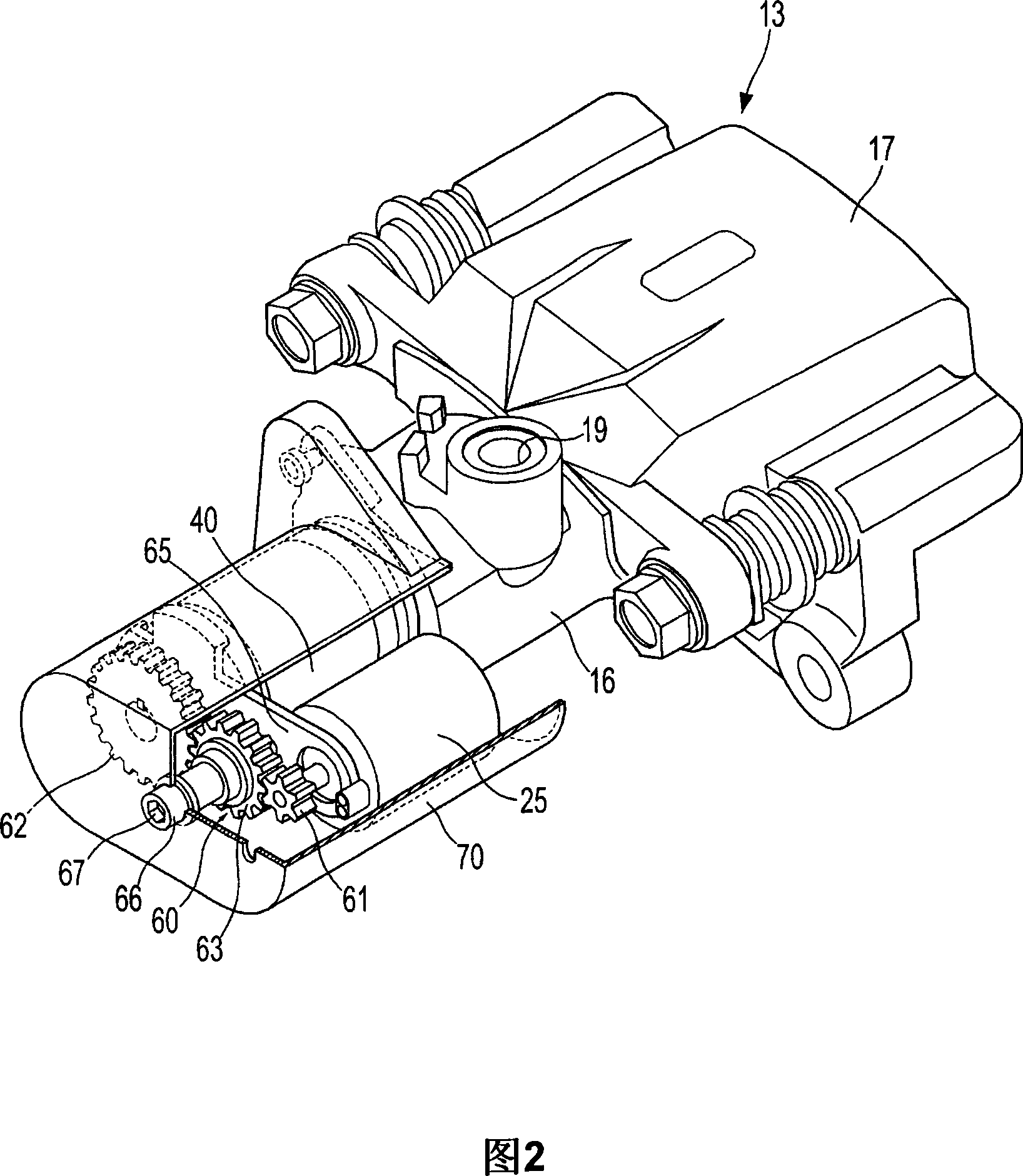
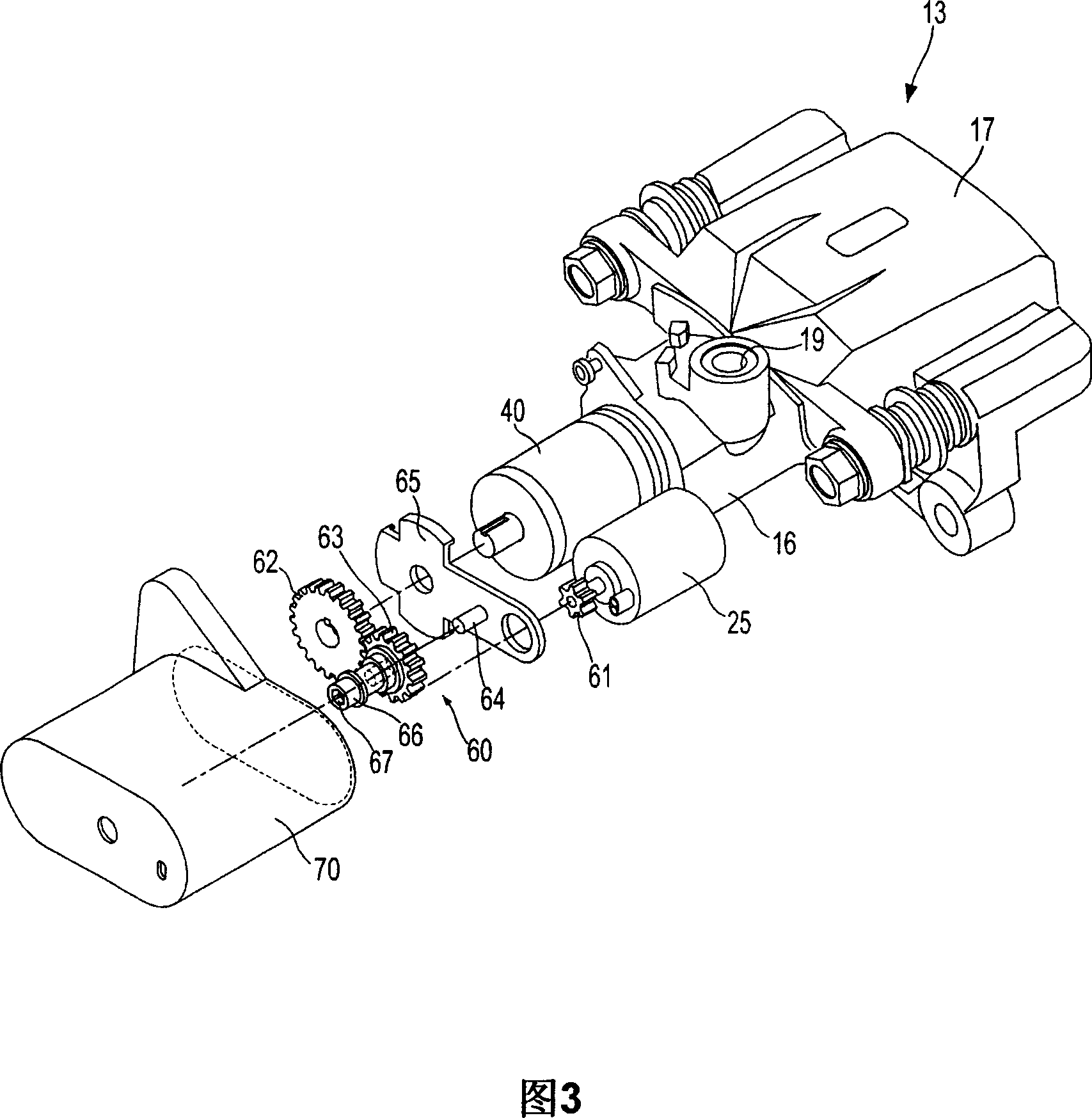
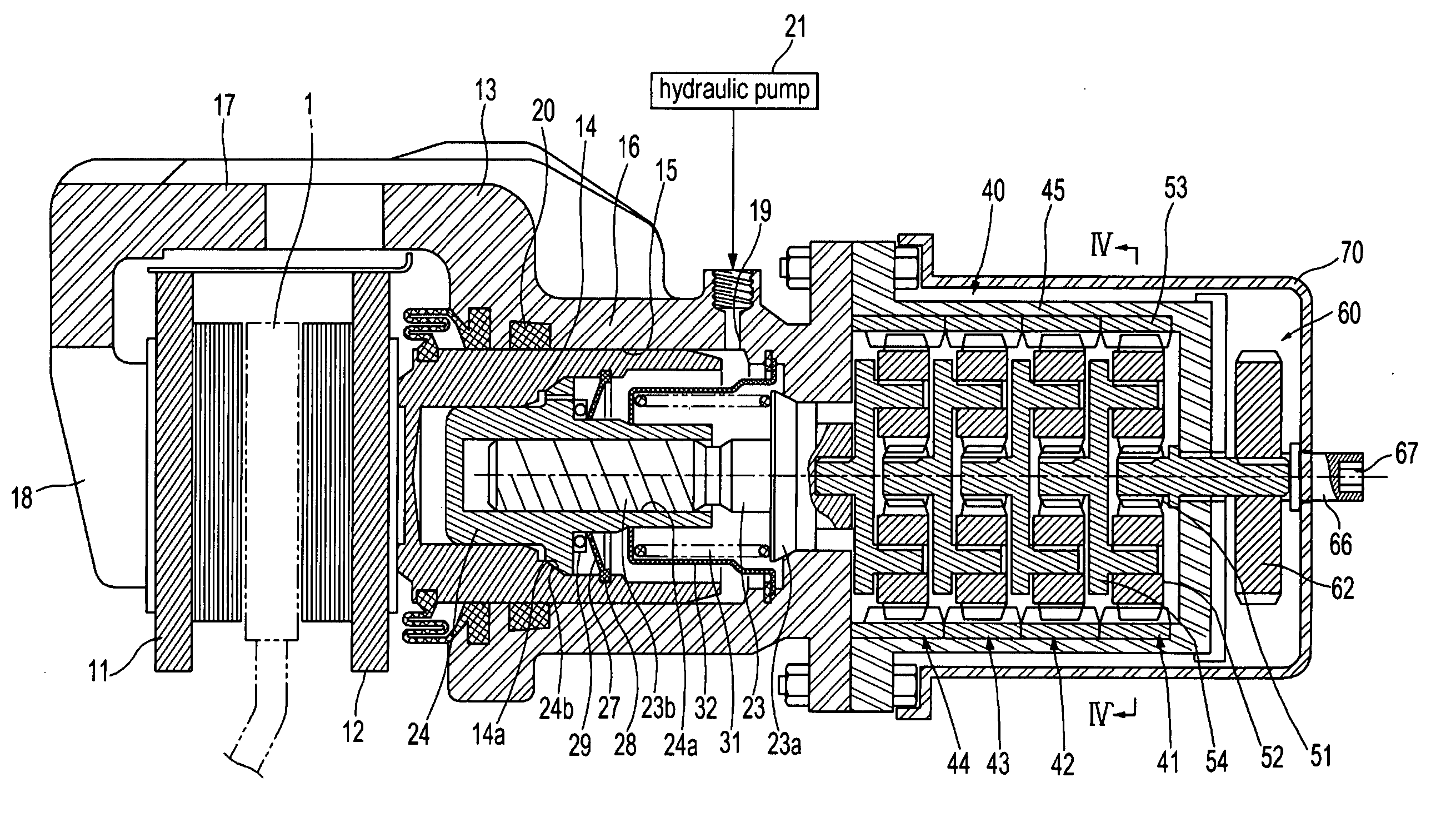
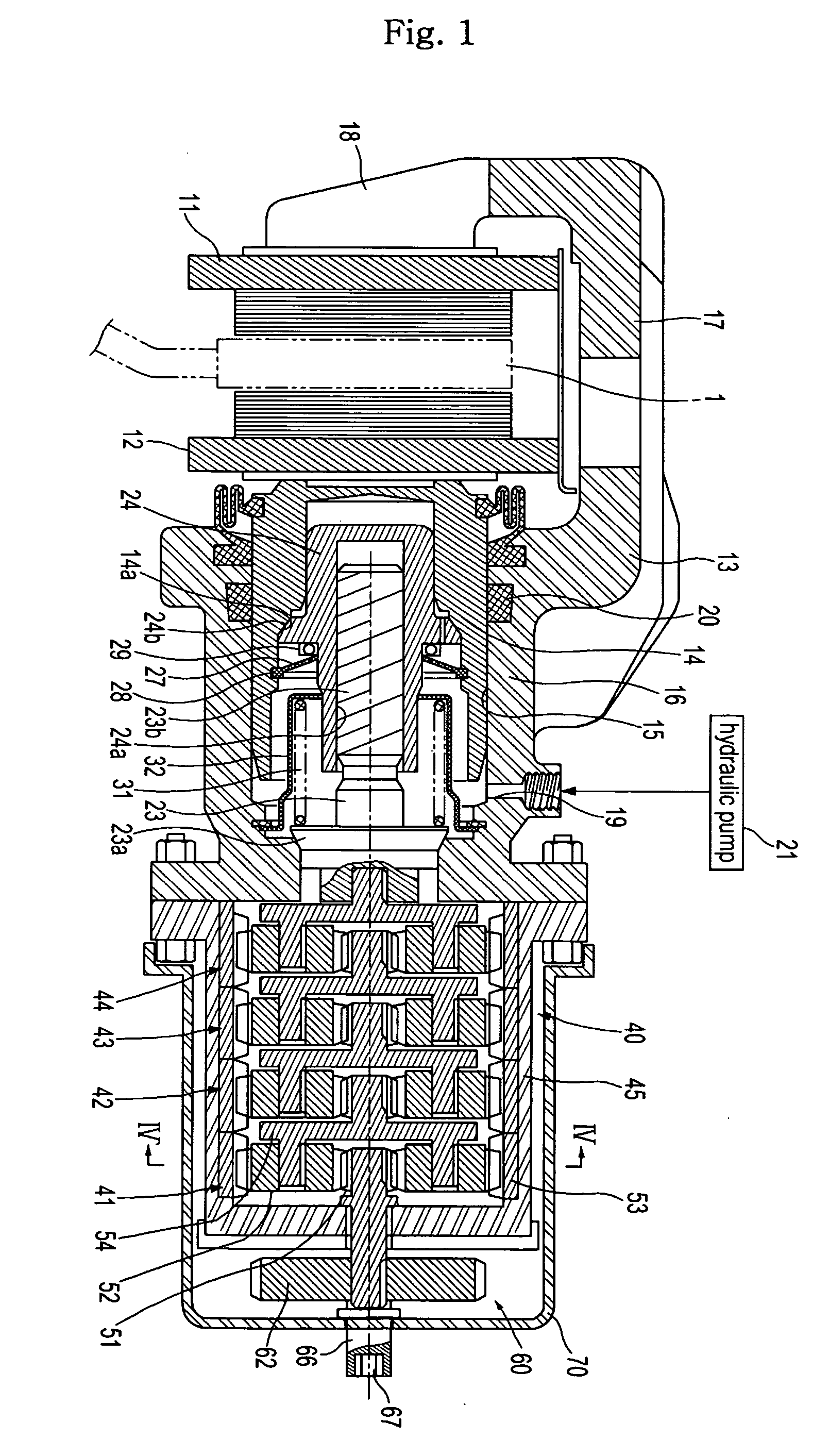
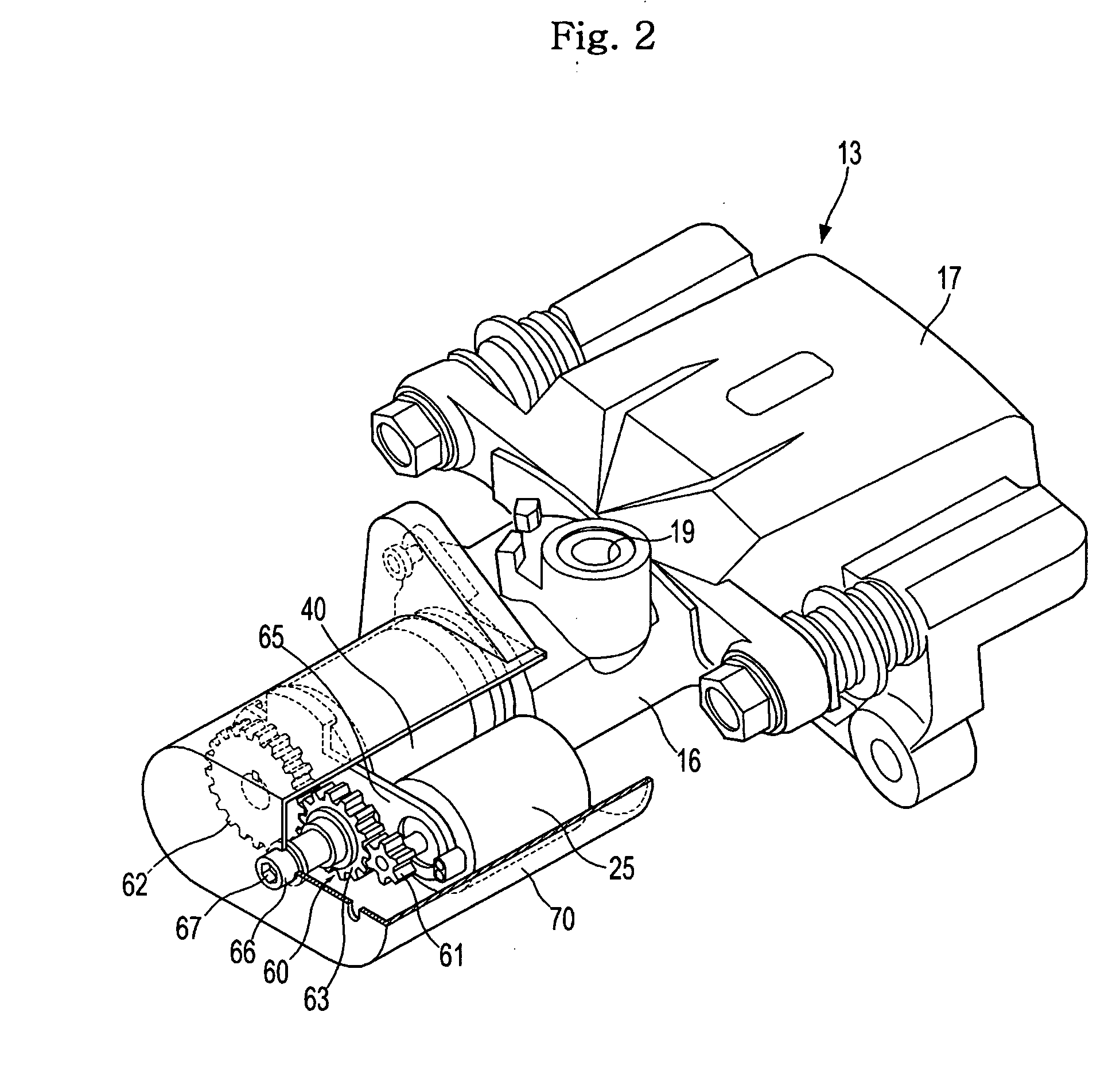
A disc brake enables a parking apparatus to be operated via actuation of an electric motor, thereby permitting easy operation of the parking apparatus. The disc brake comprises a piston to compress a friction pad used for braking of a disc, a caliper housing to receive the piston such that the piston moves linearly therein, and having a cylinder section to which a hydraulic pressure for braking is applied, an actuation shaft rotatably installed within the cylinder section, and having a male screw formed thereon, a compression sleeve installed within the piston to compress or release the piston while linearly moving therein by rotation of the actuation shaft, and having a female screw formed thereon to engage with the male screw of the actuation shaft, an electric motor to rotate the actuation shaft, a multi-stage reduction gear train to transmit rotational force of the electric motor to the actuation shaft. The multi-stage reduction gear train has a central axis deviated from that of the electric motor, and a shaft connected with a shaft of the electric motor via a power transmission unit.
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
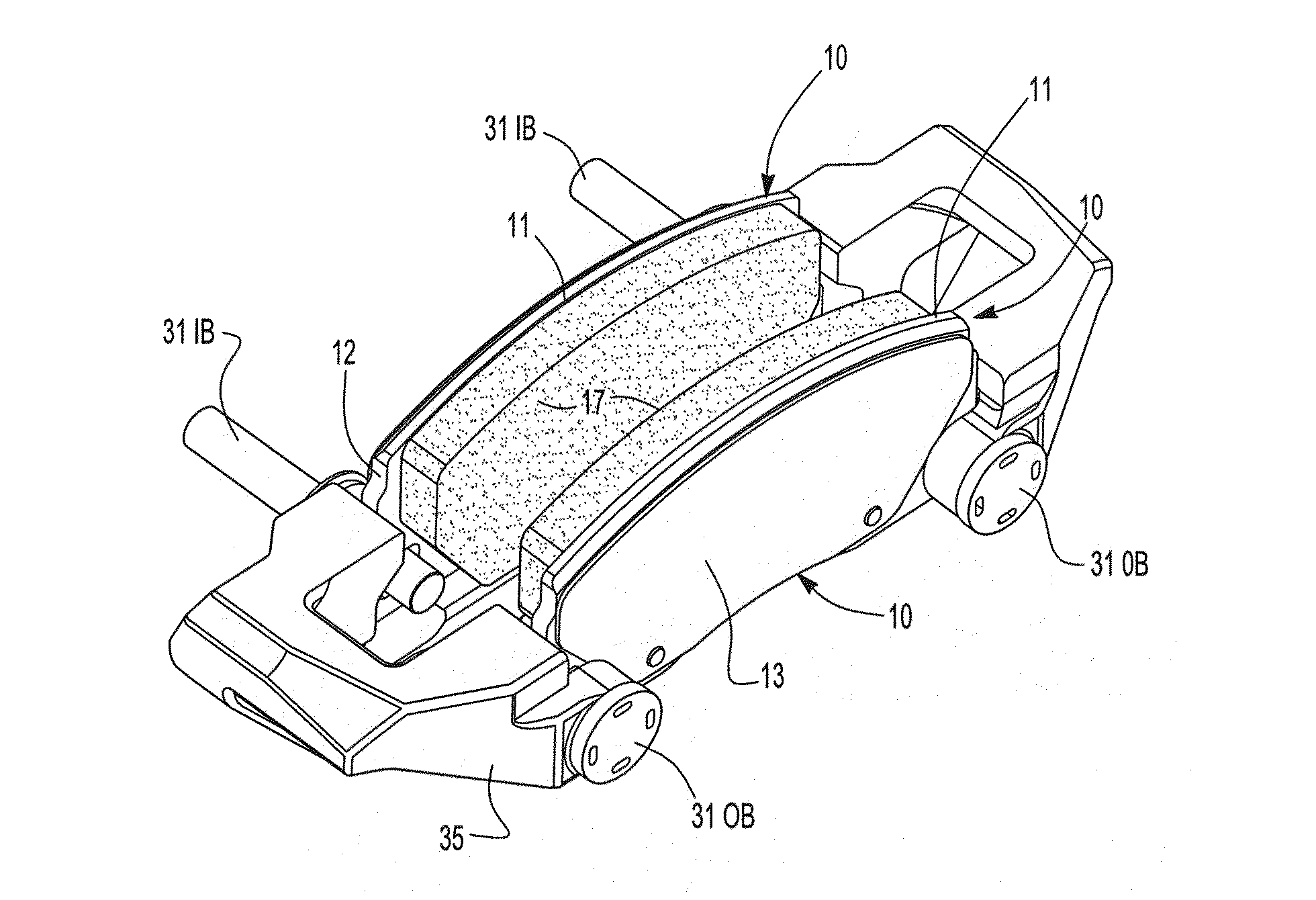
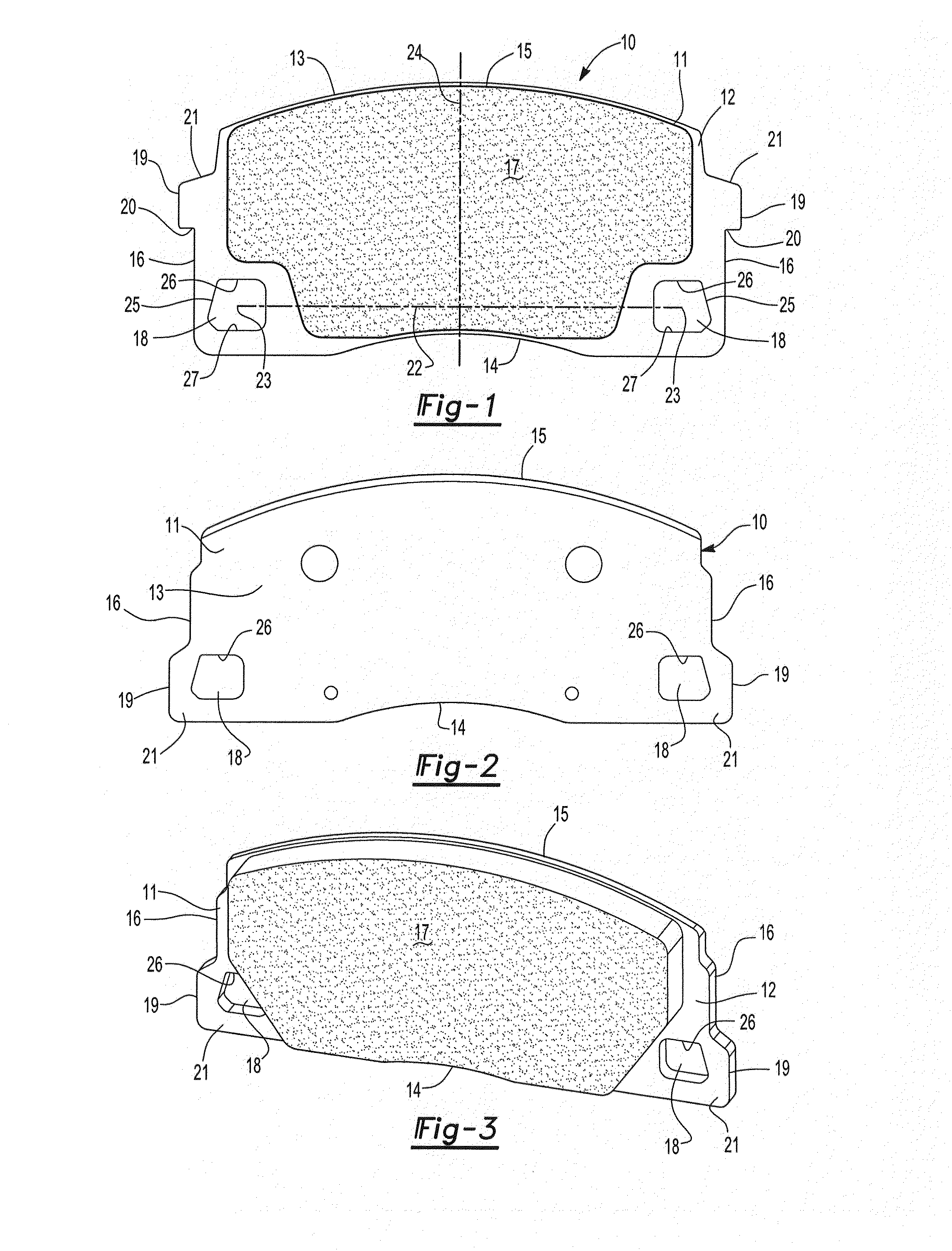
Brake Pad
The subject invention generally relates to a disc brake pad which has reduced brake squeal in response to a braking event by the incorporation of a relieved portion to the center section of a friction pad along an outer edge or inner edge thereof, or along both edges. The invention is a disc brake pad which includes a backing plate and friction pad attached to the backing plate.
Owner:FEDERAL MOGUL PROD US LLC
Disk brake
ActiveUS20070251772A1High strengthAvoid deformationAxially engaging brakesSlack adjustersMechanical engineeringDisc brake
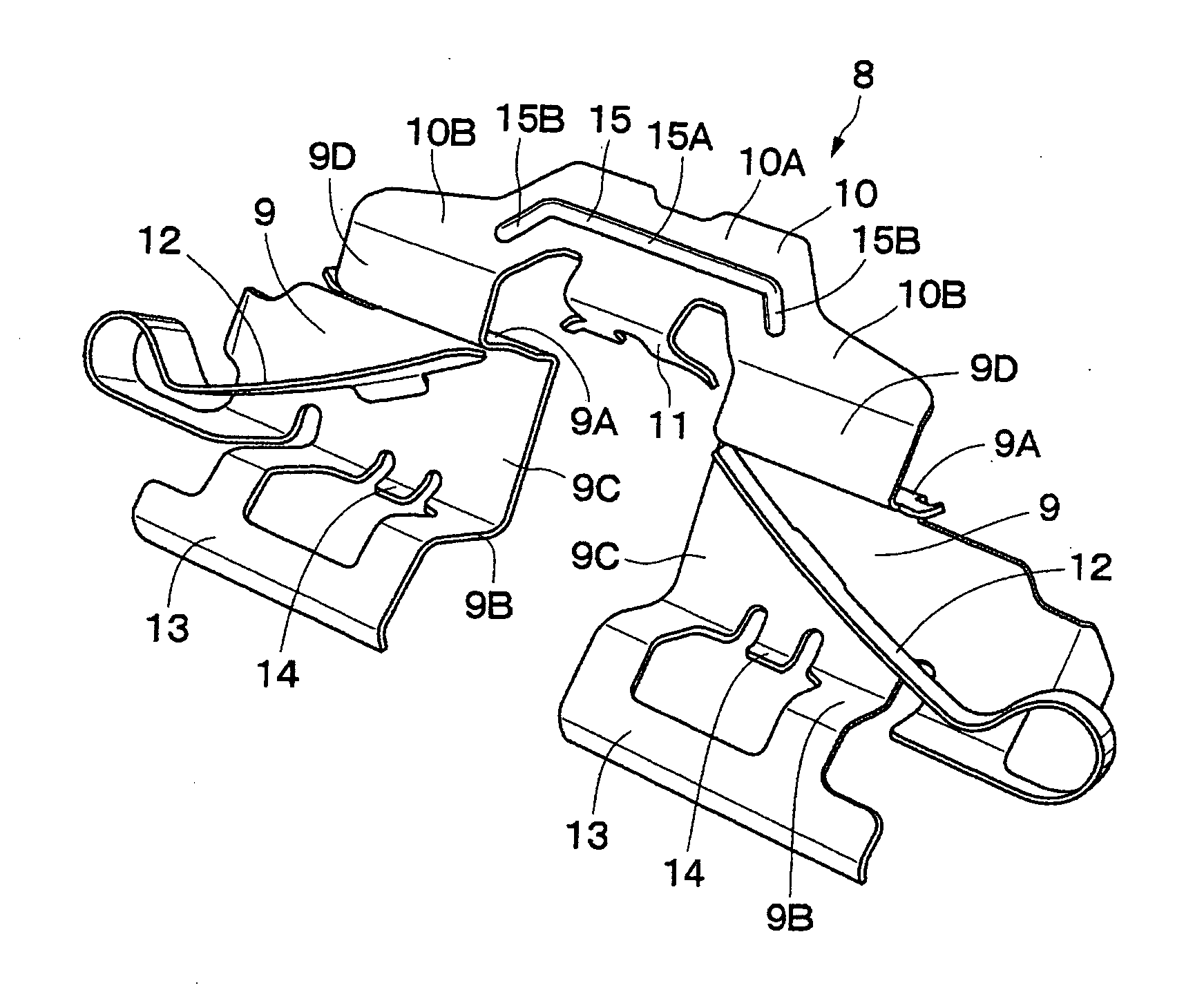
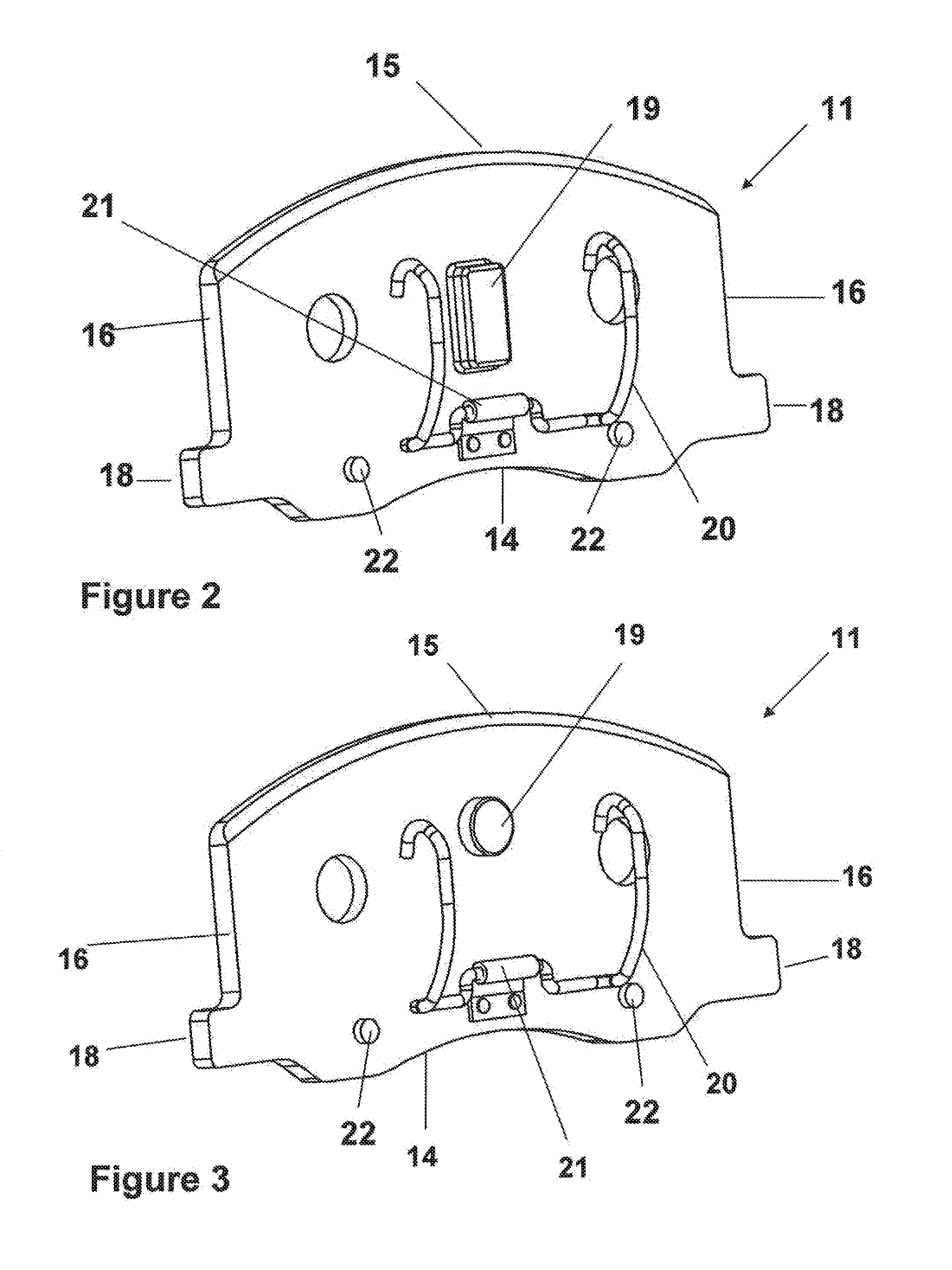
The strength and rigidity of pad springs are increased with a simple structure to prevent deformation and so forth of the pad springs caused by external force. A mounting member 1 is provided with pad springs 8 for resiliently supporting friction pads 7. Each pad spring 8 has guide plates 9, a connecting plate 10, an engagement plate 11, radially urging portions 12, circumferentially urging portions 13, reinforcement 15, etc. The reinforcement 15 includes a rectilinear reinforcement 15A formed on a flat plate portion 10A of the connecting plate 10 by embossing, for example, and oblique reinforcements 15B formed on joint portions 10B of the connecting plate 10. Thus, the joint portions 10B and so forth of the pad springs 8 can be prevented from being deformed by external force when the brake is activated or during assembling operation, for example, and hence it is possible to prevent positional displacement of the guide plates 9, etc. that would otherwise be caused by the deformation of the joint portions 10B.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
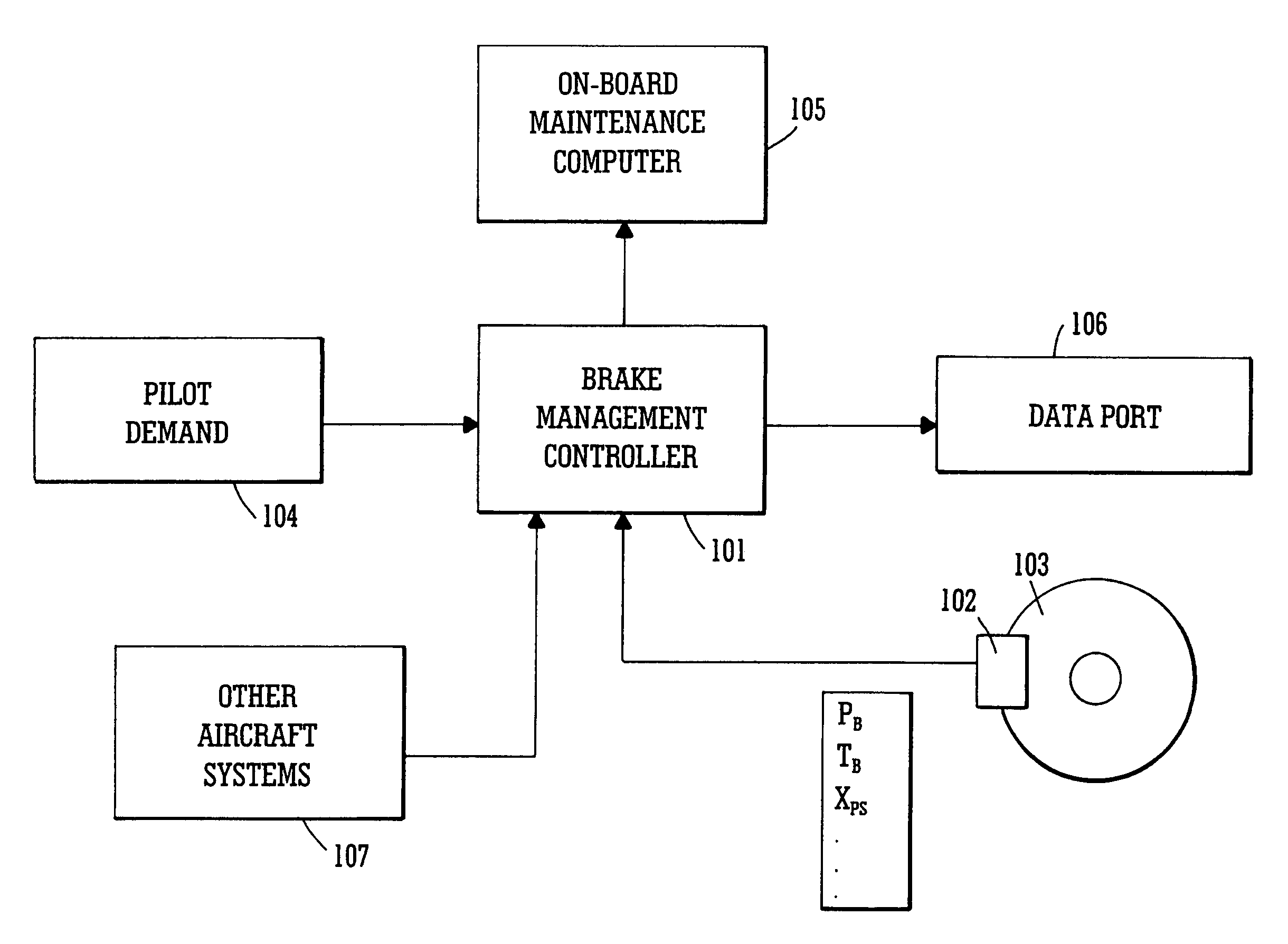
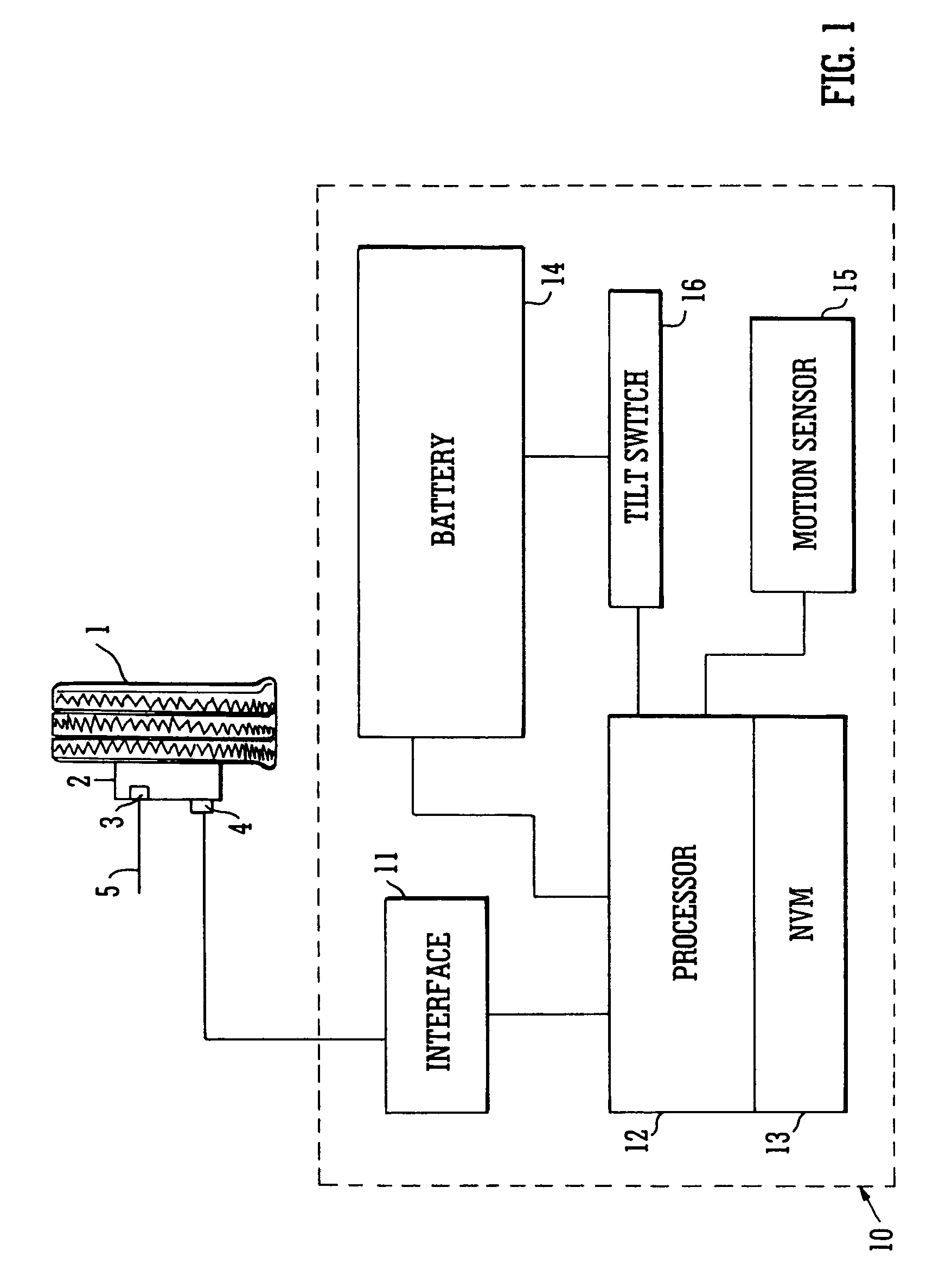
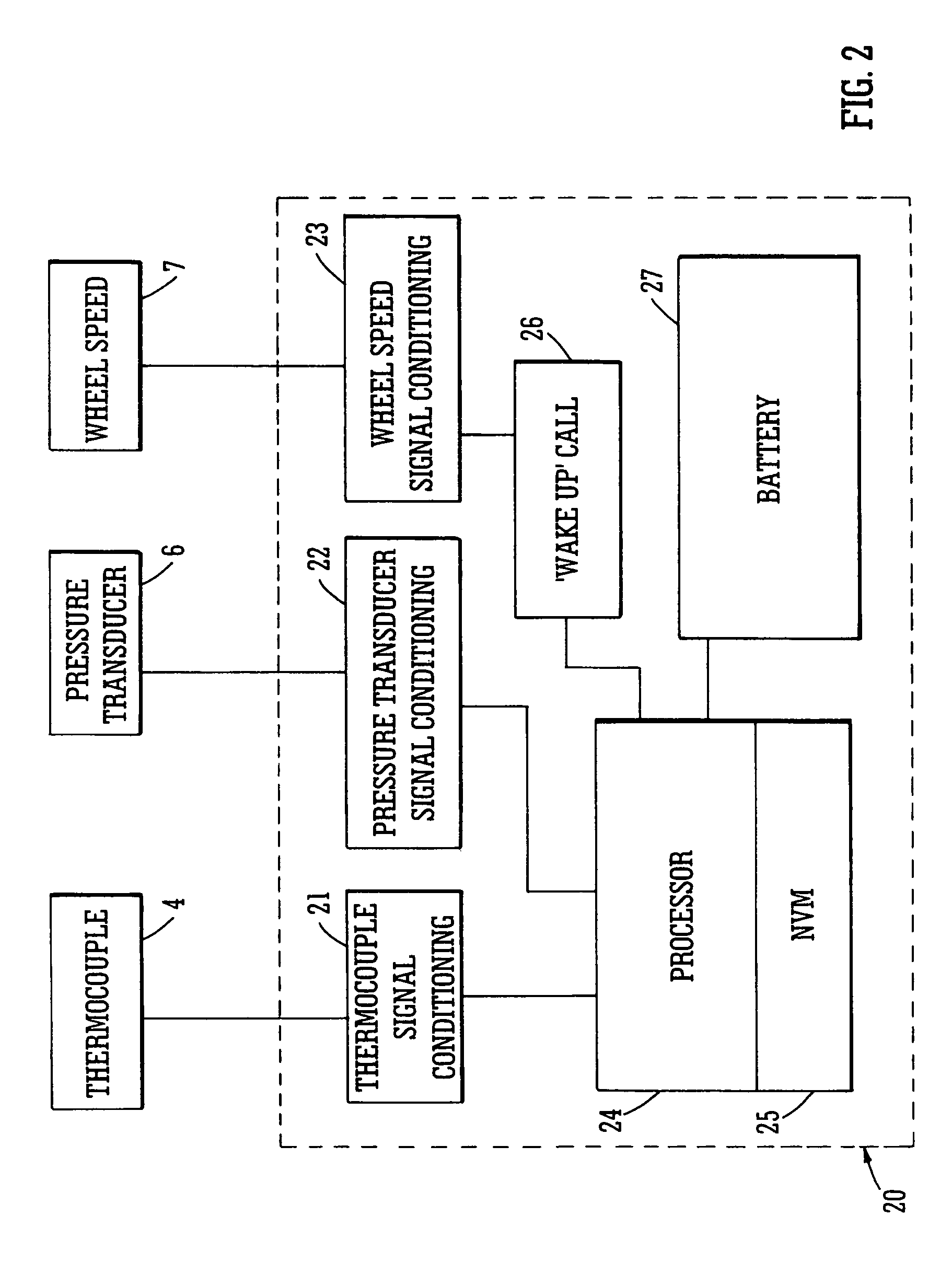
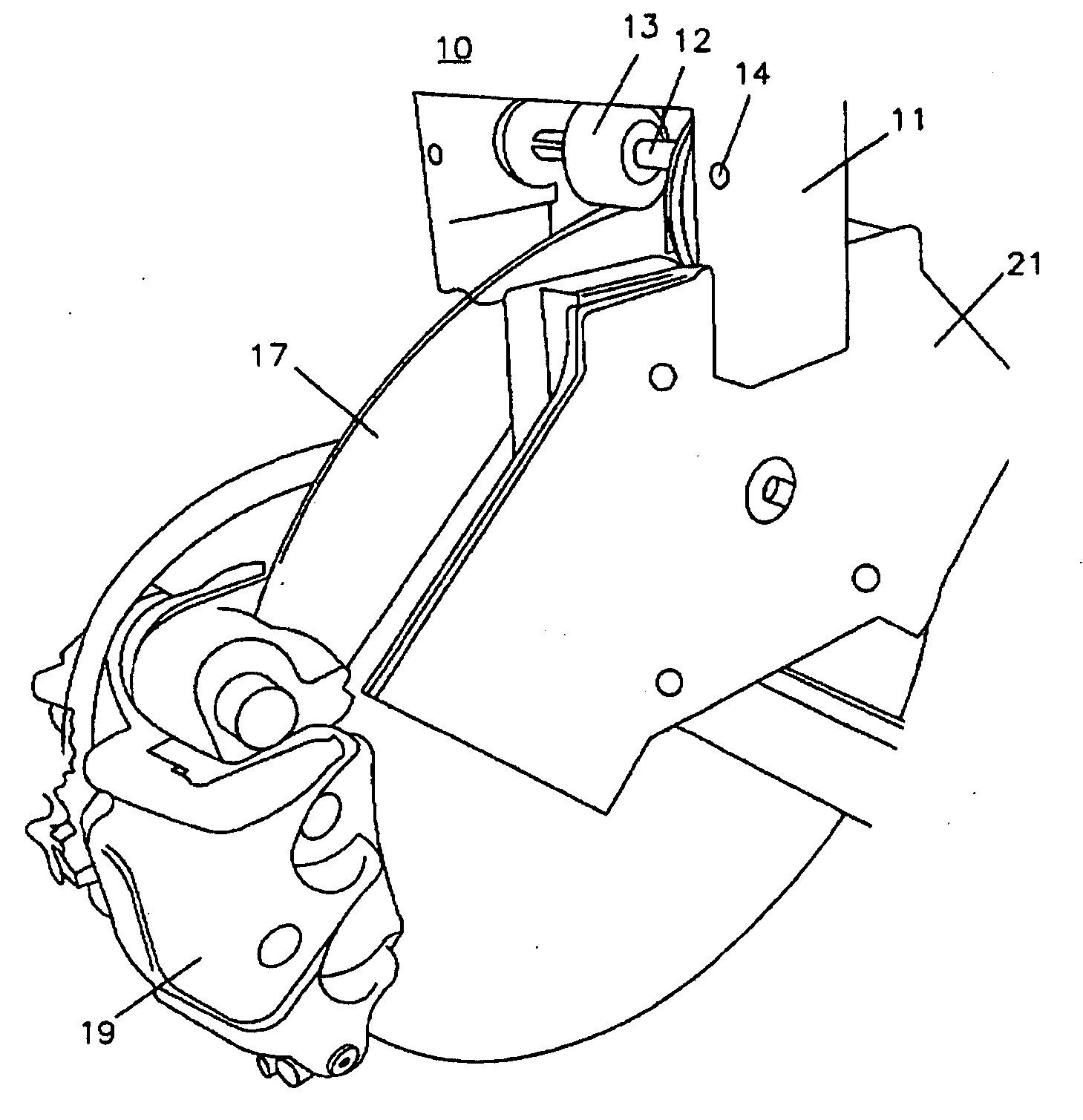
Brake condition monitoring
InactiveUS7086503B2Less-rapid decelerationBrake fluid pressure increaseFinanceAircraft braking arrangementsRelative motionBraking system
System and method for monitoring the applications of the brakes, e.g. of an aircraft to determine brake condition and operate a brake maintenance programme or charge a brake system user. It is desirable to have accurate information for determining the condition and predicting the life of carbon-carbon brake discs. This is important for safety as well as commercial reasons. The number of landings of an aircraft is often used as a determinant for such as lifetime warranties for brake discs and recommended maintenance periods. However, at least for carbon disc brakes, this may not be entirely accurate. For example such brake discs also wear during taxiing. The system and method herein includes monitoring each actuation of the brakes and making a separate record of each actuation of the brakes in which there is relative movement of the facing friction surfaces that cause wear, and from that separate record determining brake usage. The monitoring may include measuring changes and processing the signals to distinguish between those which fall below and those which are above a threshold value. Herein there is also described, a method and apparatus for monitoring a braking system comprising sensing a plurality of braking parameters having values dependent upon wear in the system and different faults of the system, and identifying and recording wear and faults based on combinations of values of said parameters.
Owner:MEGGITT AEROSPACE
Disc brake assembly
A disc brake assembly includes a rotor, a caliper, brake pads and an optional filter. The optional filter can be disposed within a shroud which covers at least about 70% of the distal side periphery on at least one of the two sides of the rotor. The disc brake also includes an impeller or other means for providing air flow to the disc brake assembly. The impeller can be provided by the rotor itself or it can be provided by a separate component which is powered either directly or indirectly by the rotor.
Owner:GELB JOSEPH
Orientated carbon nanotube composite, process for producing orientated carbon nanotube, and, produced using orientated carbon nanotube composite, pneumatic tire, wheel for vehicle, tire wheel assembly and disk brake
InactiveUS20060061011A1Improve efficiencyImprove conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyBraking discsRubber materialCarbon nanotube
A carbon nanotube orientated composite formed by orientating carbon nanotubes in a given direction in a matrix having a heat conductivity lower than that of carbon nanotube, in which at least a part of carbon nanotubes are contacted with each other to be continuous from one end to the other end between both ends in the orientated direction, is provided as a material having a heat conductivity considerably higher than that of copper, aluminum or the like or a material to be disposed in rubber material having a low heat releasing characteristic to considerably improve the heat conduction, and also there are provided a method of producing the same as well as a pneumatic tire, a wheel for a vehicle, a tire-wheel assembly and a disc brake using this material.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Reach adjustment mechanism for a master cylinder lever of a hydraulic disc brake
InactiveUS6957534B2Prevent unwanted changesIncreasing costControlling membersRotary clutchesRest positionMaster cylinder
A master cylinder for a hydraulic disc brake includes a housing defining a cylinder, the cylinder having a first and second end along its axis. A piston is received in the cylinder and has a radial seal between the piston and the cylinder. A lever is pivotably associated with the housing for pivoting between a rest position and an actuated position relative to the housing. A push rod is operatively associated with the piston and the lever to move the piston axially within the cylinder as the lever is actuated between the rest and actuated positions. A threaded engagement between a first end of the push rod and the lever is configured to cause movement of the rest position of the lever relative to the housing when a rotating force is applied to the push rod causing axial rotation of the push rod. An indexing structure is operatively associated with the push rod for providing index axial rotation of the push rod upon application of the rotating force to the push rod causing axial rotation of the push rod.
Owner:SRAM CORPORATION
Disk brake devices
ActiveUS7111709B2Effectively reduce the squealing soundsImprove distortionNoise/vibration controlBraking membersEngineeringMechanical engineering
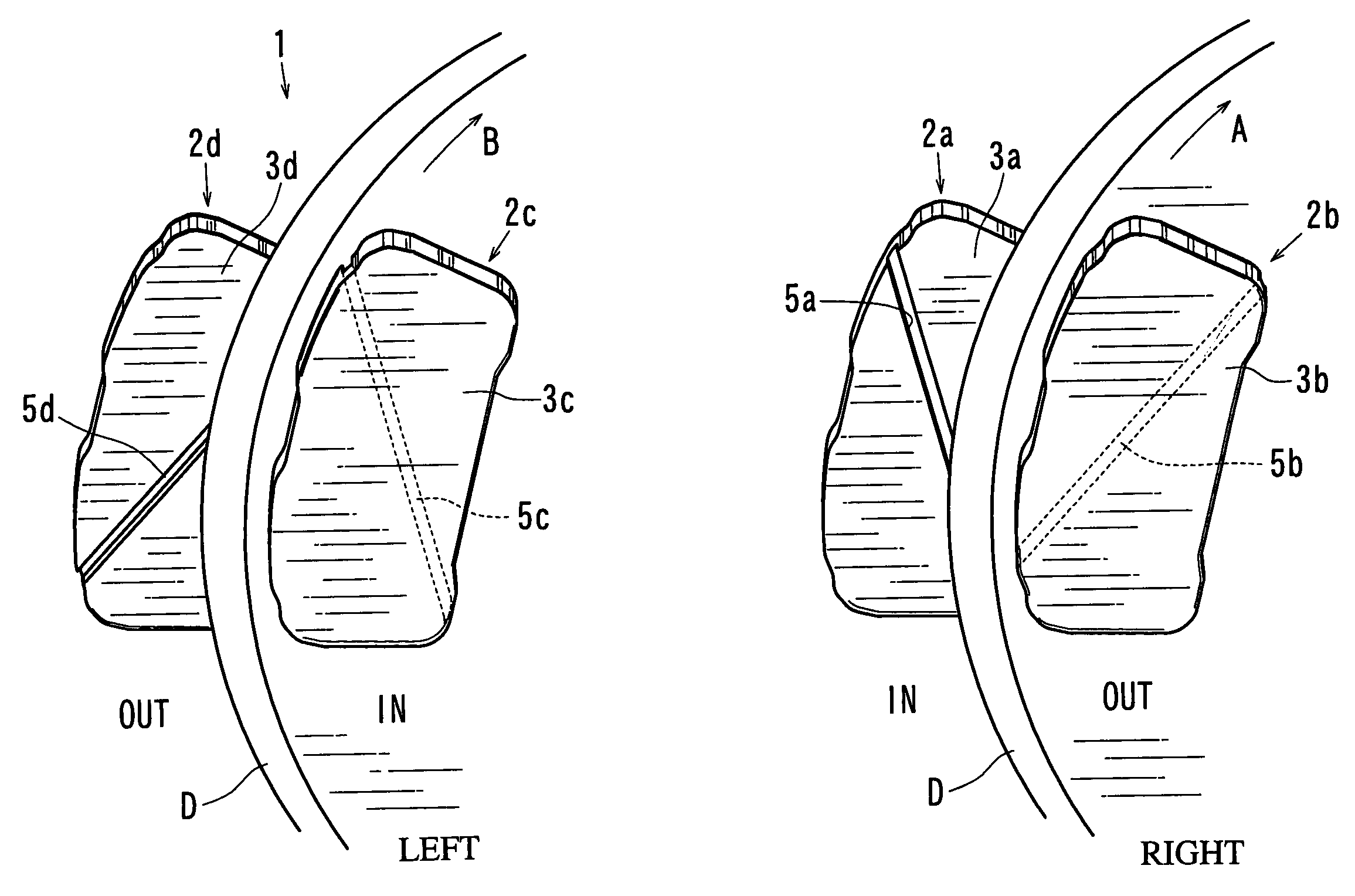
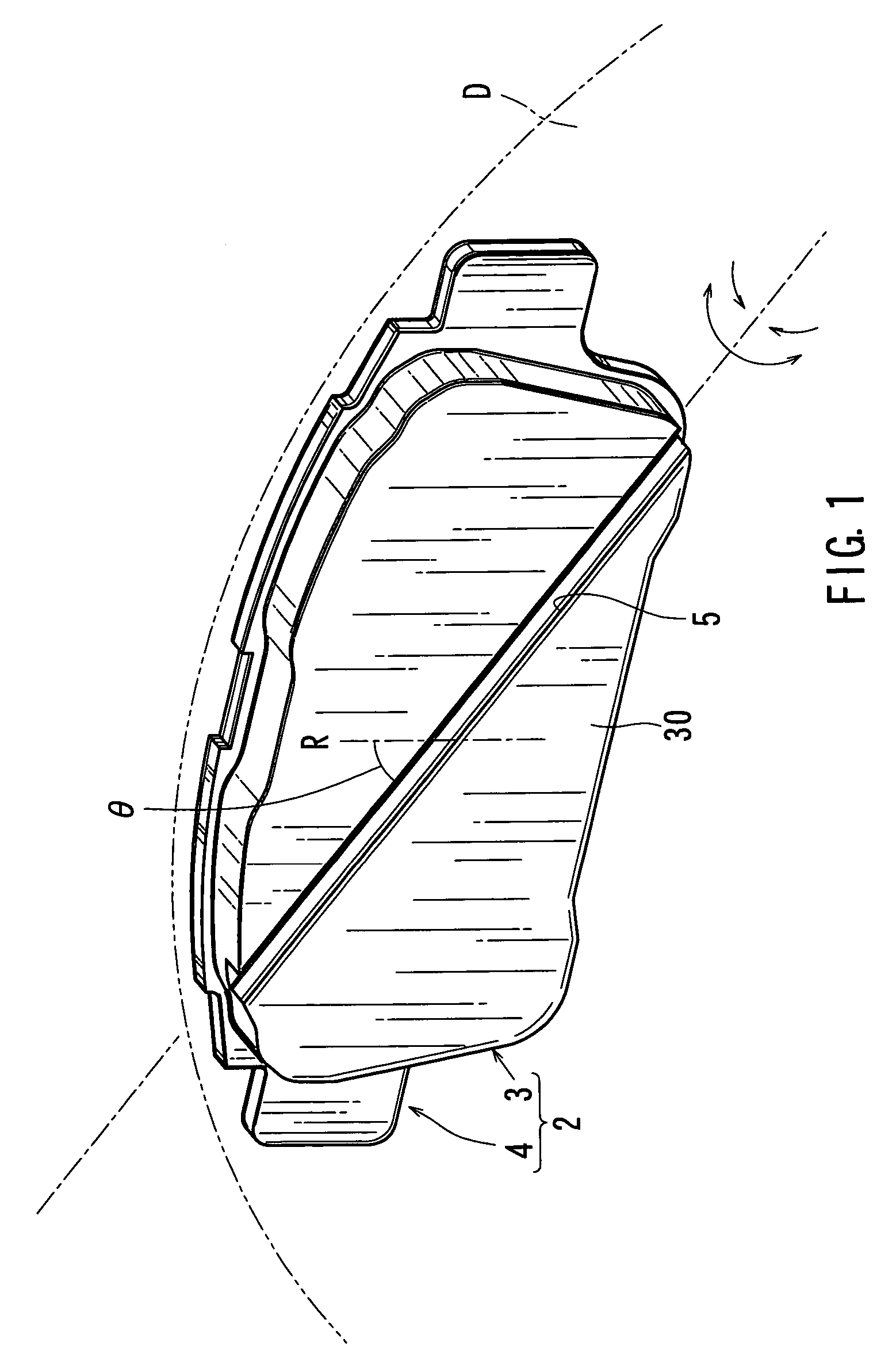
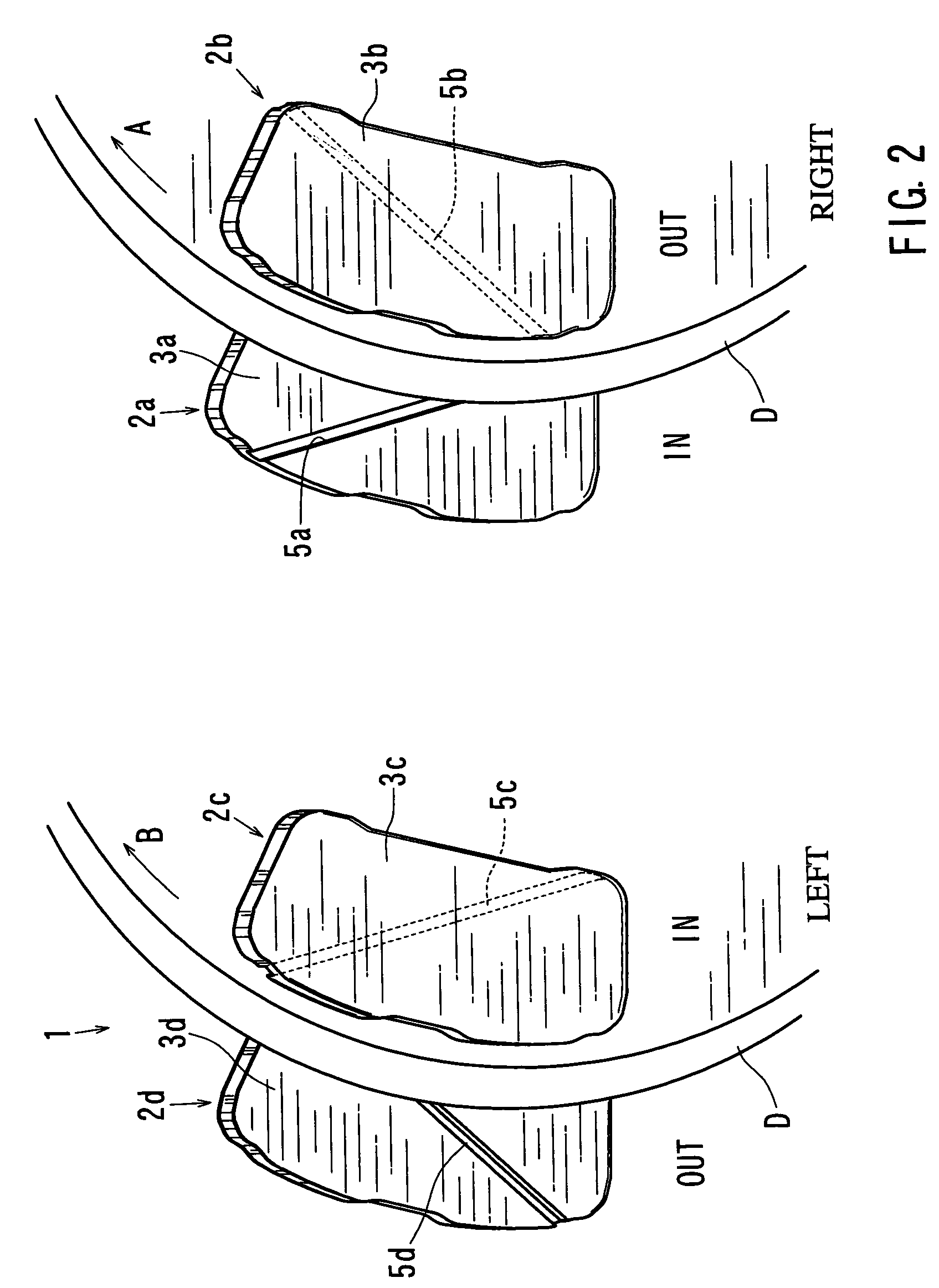
A disk brake device includes a pair of brake disks and right and left pairs of pads. Each pad includes a twisting compliant section that extends along a line inclined by an angle relative to a radial direction of the corresponding brake disk. The twisting compliant section facilitates the twisting of the pad about the compliant section. The twisting compliant sections of the right inner pad and the left inner pad are inclined in opposite directions relative to the twisting compliant sections of the right outer pad and the right inner pad. The twisting compliant sections of the right inner pad and the left inner pad are inclined in substantially the same direction with one another.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
Caliper assembly for disc brake system
InactiveUS20120085597A1Improve NVH performanceImprove component performanceMechanically actuated brakesSlack adjustersEngineeringCalipers
A caliper assembly comprising: a brake pad comprising a carrier plate having two opposing faces and a top edge a bottom edge and two opposing side edges, wherein on one face is friction material and on the opposing face is a projection adapted to seat in a matched hole or recess in a caliper body, the two opposing side edges each having an ear which is adapted to seat in pad locator indentations in a support structure; a support structure comprising a recess for housing at least one brake pad and at least two pad locator indentations adapted for receiving the ears located on the two opposing sides of the brake pad and at least two caliper body locator indentations for seating two ears defined by the caliper body; and a caliper body having a hole or recess adapted for seating the projection on the opposing face of the brake pad and having two ears on each opposing side which are adapted to seat in the caliper body locator indentations of the support structure; wherein the ears of the brake pad are seated in the pad locator indentations of the support structure, the projection on the opposing face of the brake pad is seated in the hole or recess located in the caliper body, and a clip which engages the opposing face of the brake pad and the caliper body and holds the brake pad in position with respect to the caliper body and the ears of the caliper body are seated in the caliper body locator indentations in the support structure.
Owner:AKEBONO BRAKE
Disc brake with parking function
InactiveUS20070062769A1Easy to operateShorten speedMechanically actuated brakesElectrodynamic brake systemsEngineeringCalipers
A disc brake enables a parking apparatus to be operated via actuation of an electric motor, thereby permitting easy operation of the parking apparatus. The disc brake comprises a piston to compress a friction pad used for braking of a disc, a caliper housing to receive the piston such that the piston moves linearly therein, and having a cylinder section to which a hydraulic pressure for braking is applied, an actuation shaft rotatably installed within the cylinder section, and having a male screw formed thereon, a compression sleeve installed within the piston to compress or release the piston while linearly moving therein by rotation of the actuation shaft, and having a female screw formed thereon to engage with the male screw of the actuation shaft, an electric motor to rotate the actuation shaft, a multi-stage reduction gear train to transmit rotational force of the electric motor to the actuation shaft. The multi-stage reduction gear train has a central axis deviated from that of the electric motor, and a shaft connected with a shaft of the electric motor via a power transmission unit
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
Coulomb friction damped disc brake caliper bracket
A Coulomb friction damped disc brake caliper bracket, wherein damping is provided by Coulomb friction, most preferably at the outboard tie-bar thereof. In one form, at least one clamping member applies compressive force externally to the caliper bracket, and in a second form, at least one interfacial boundary is internally disposed in the caliper bracket. Provided thereby is a mechanically distinguishable surface boundary between two surfaces which are in mutual contact such that a state of Coulomb friction exists therebetween.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
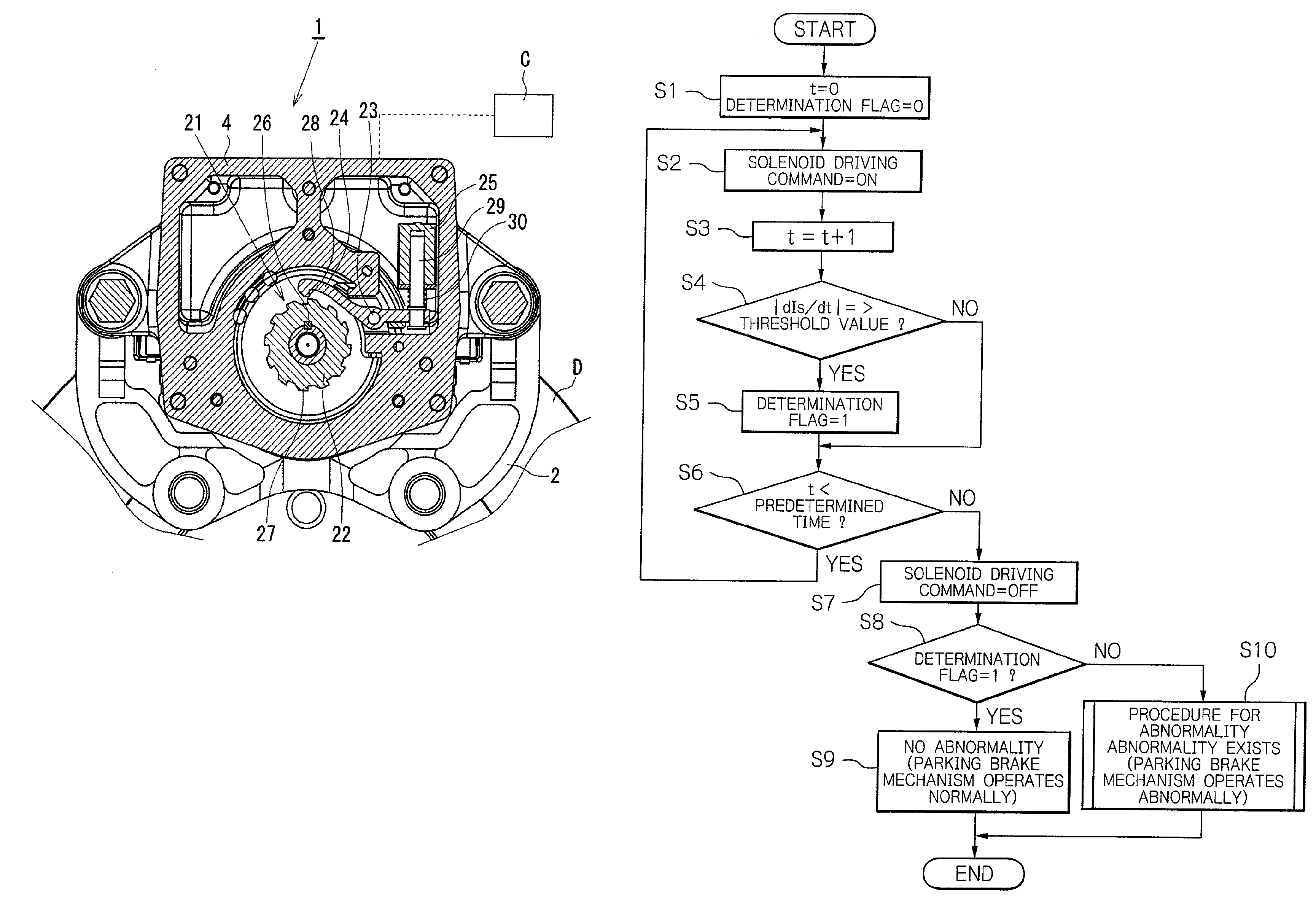
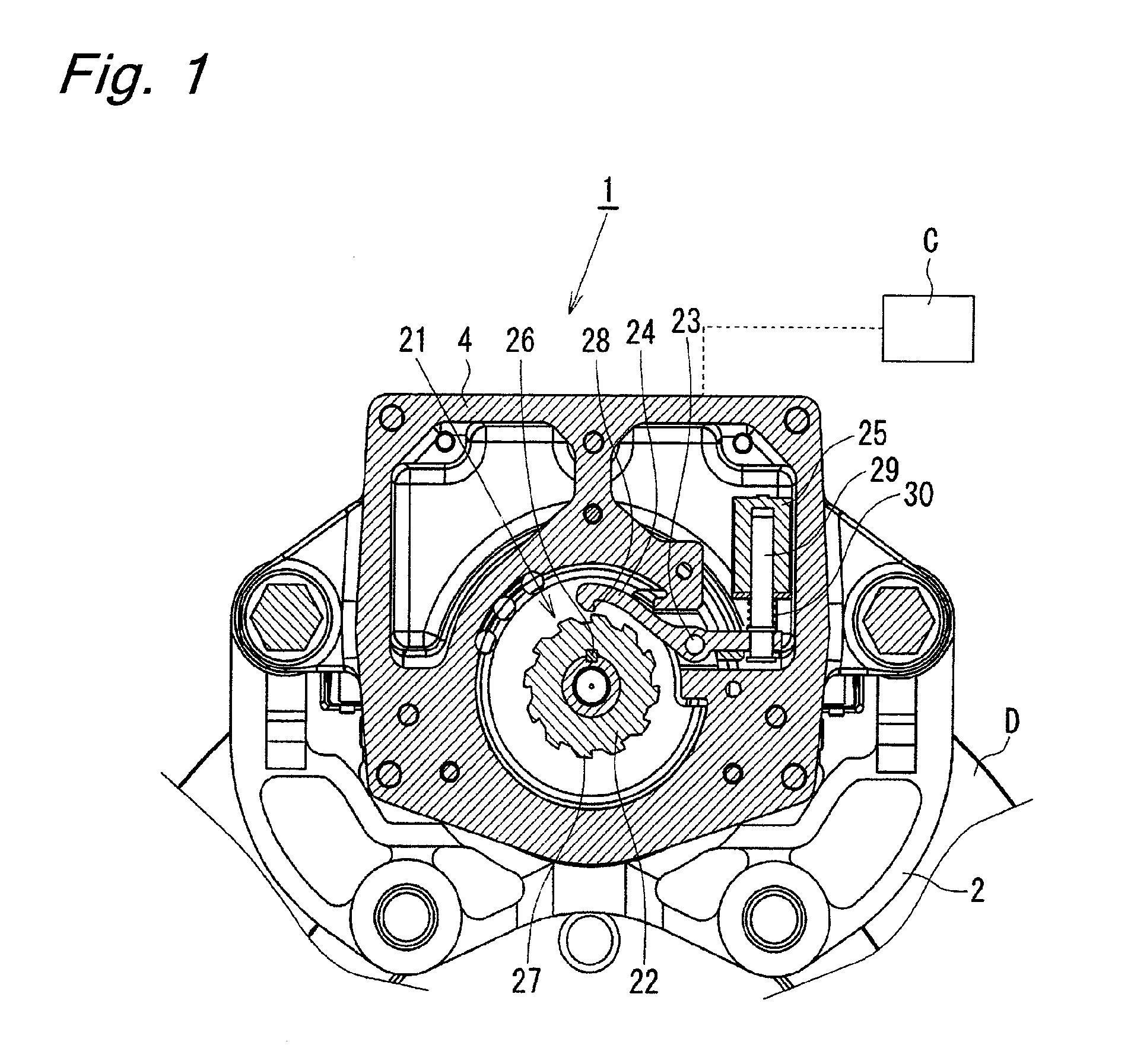
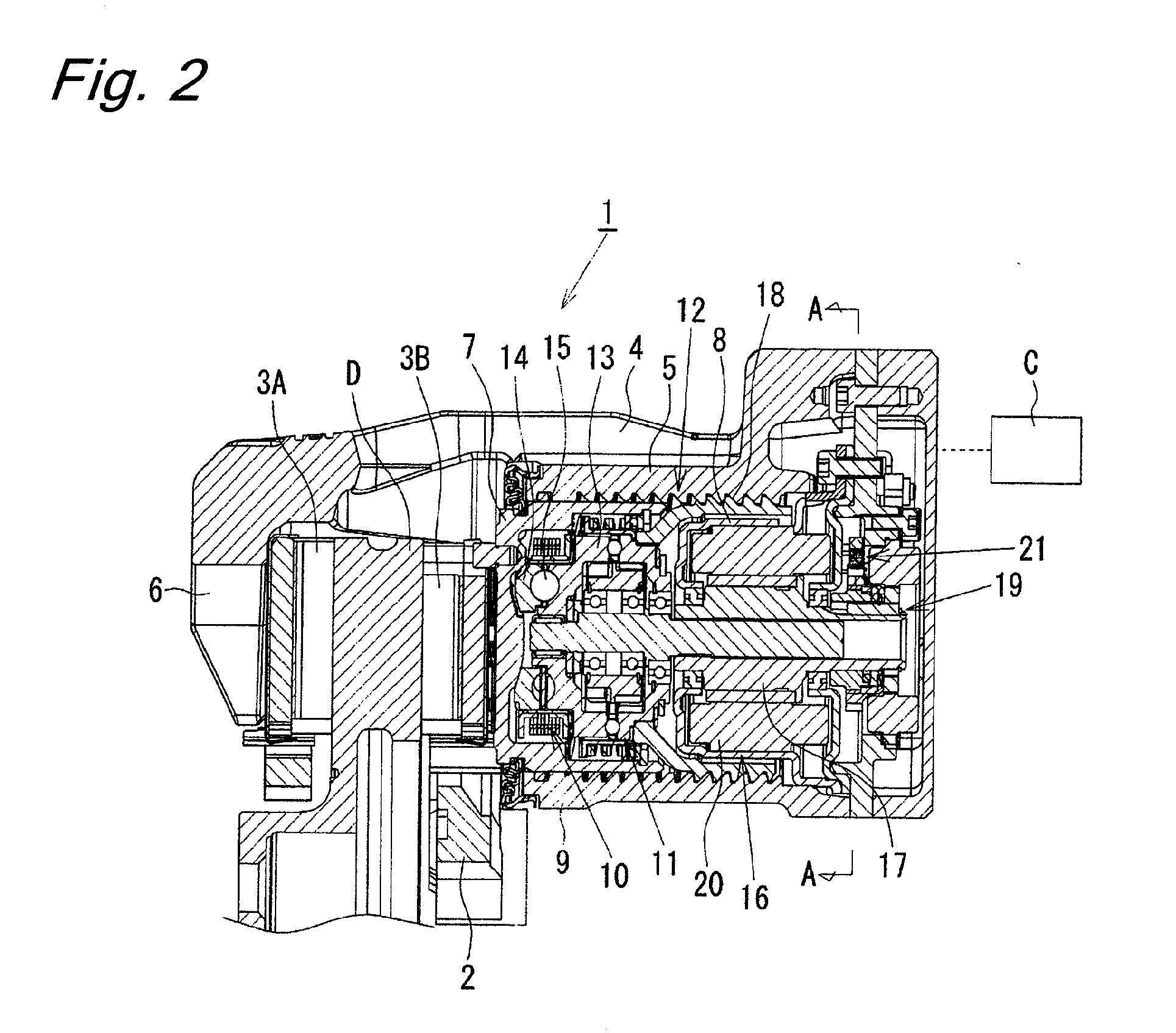
Electric disk brake
An object of the present invention is to provide an electric disk brake capable of determining an abnormality of a parking brake mechanism while the parking brake mechanism is in operation. A brake force is generated in the following manner. A rotation of an electric motor is slowed down by a differential speed reducing mechanism, and is converted into a linear motion by a ball ramp mechanism so as to advance a piston, which then presses a brake pad against a disk rotor to generate a brake force. A parking brake mechanism can lock a rotation of a rotor of the electric motor and maintain a braked state by rotating an engagement pawl through a plunger of a solenoid and causing the engagement pawl to be engaged with a ratchet wheel coupled to the rotor of the electric motor. A play is provided at a coupling portion of the engagement pawl and the plunger. The play enables the plunger to move within the range of the play while the engagement pawl is engaged with the ratchet wheel, thereby enabling determination whether the parking brake mechanism operates normally or abnormally based on whether the plunger moves or not upon application of an electric current to the solenoid while the parking brake mechanism is in an actuated state.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
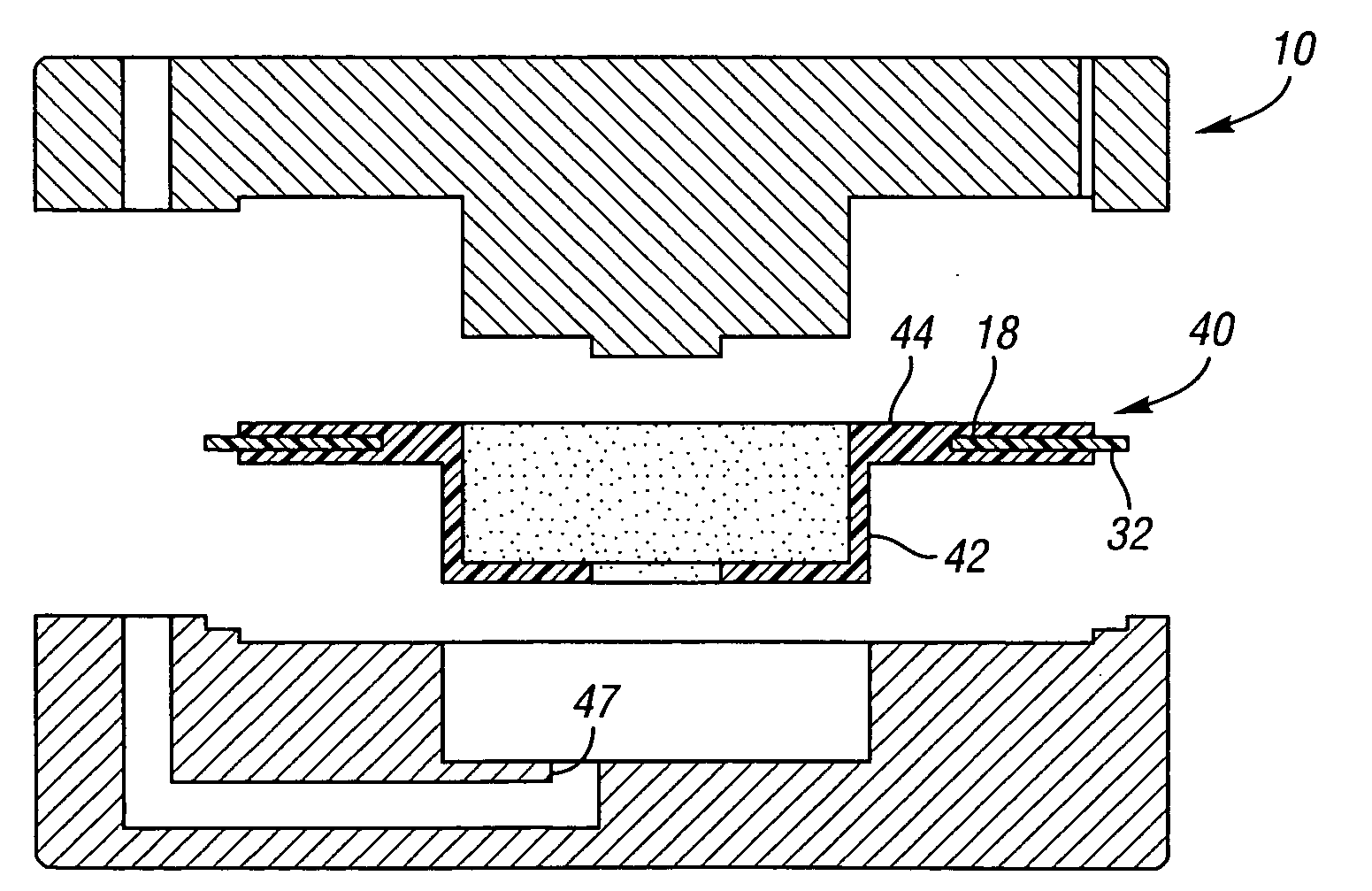
Insert for manufacture of an enhanced sound dampening composite rotor casting and method thereof
InactiveUS20070235270A1High melting pointIncrease expansionNoise/vibration controlBraking discsCasting moldCalipers
An insert for a casting mold used to produce a sound dampening rotor of a caliper disc brake is provided. The insert includes a ring having an inner diameter, an outer diameter and at least one tab. The insert also includes an inner core made from a refractory material, the inner core being adjacent to the ring. The tab of the ring is operable to position the ring relative to the inner core. Furthermore, the ring and the inner core together can be placed within the casting mold and afford for the desirable and accurate placement of the sound dampening ring within a cast sound dampening composite rotor of a caliper disc brake.
Owner:THYSSENKRUPP WAUPACA DIV
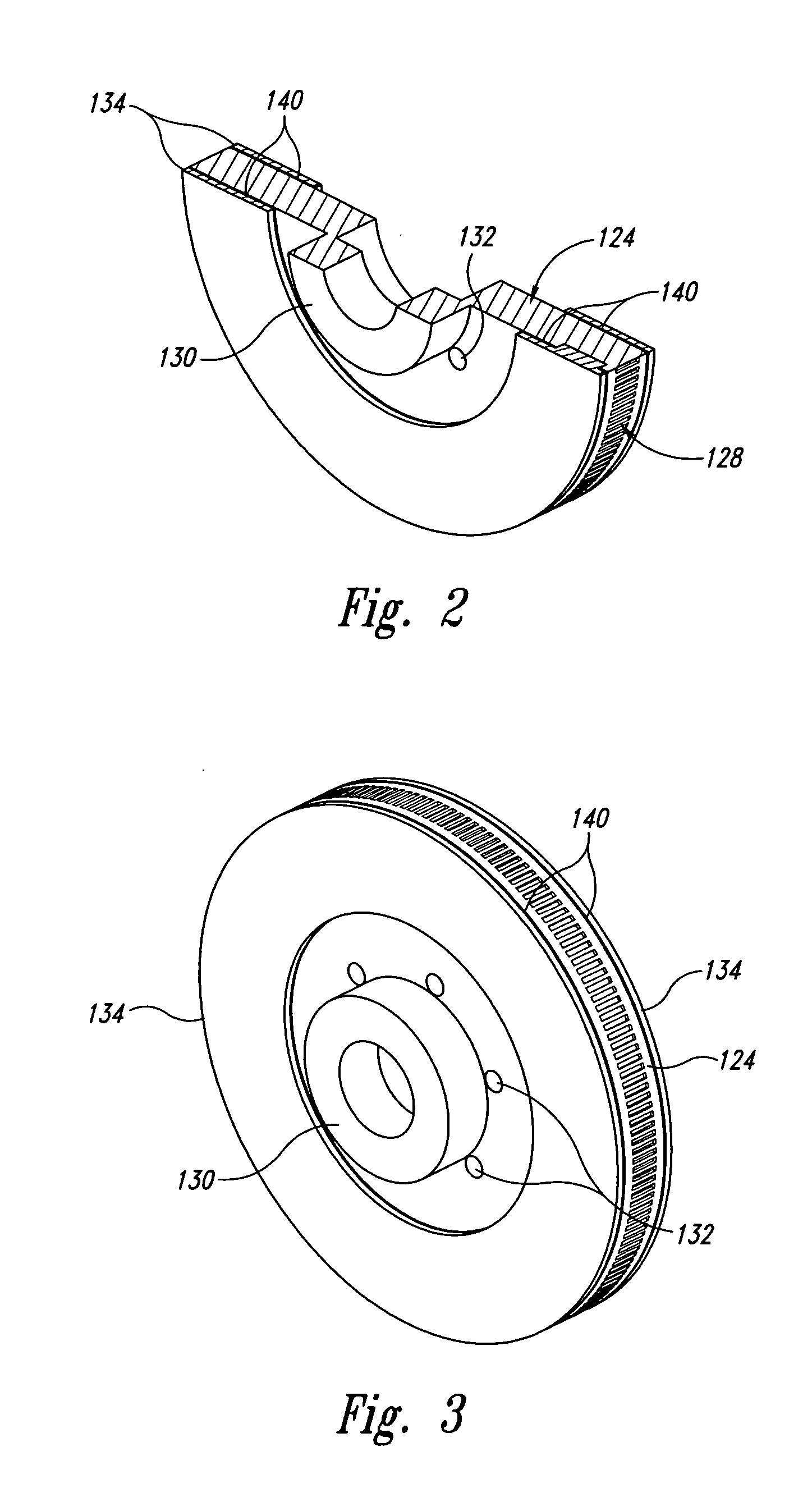
Disc brake braking band and disc for a disc brake
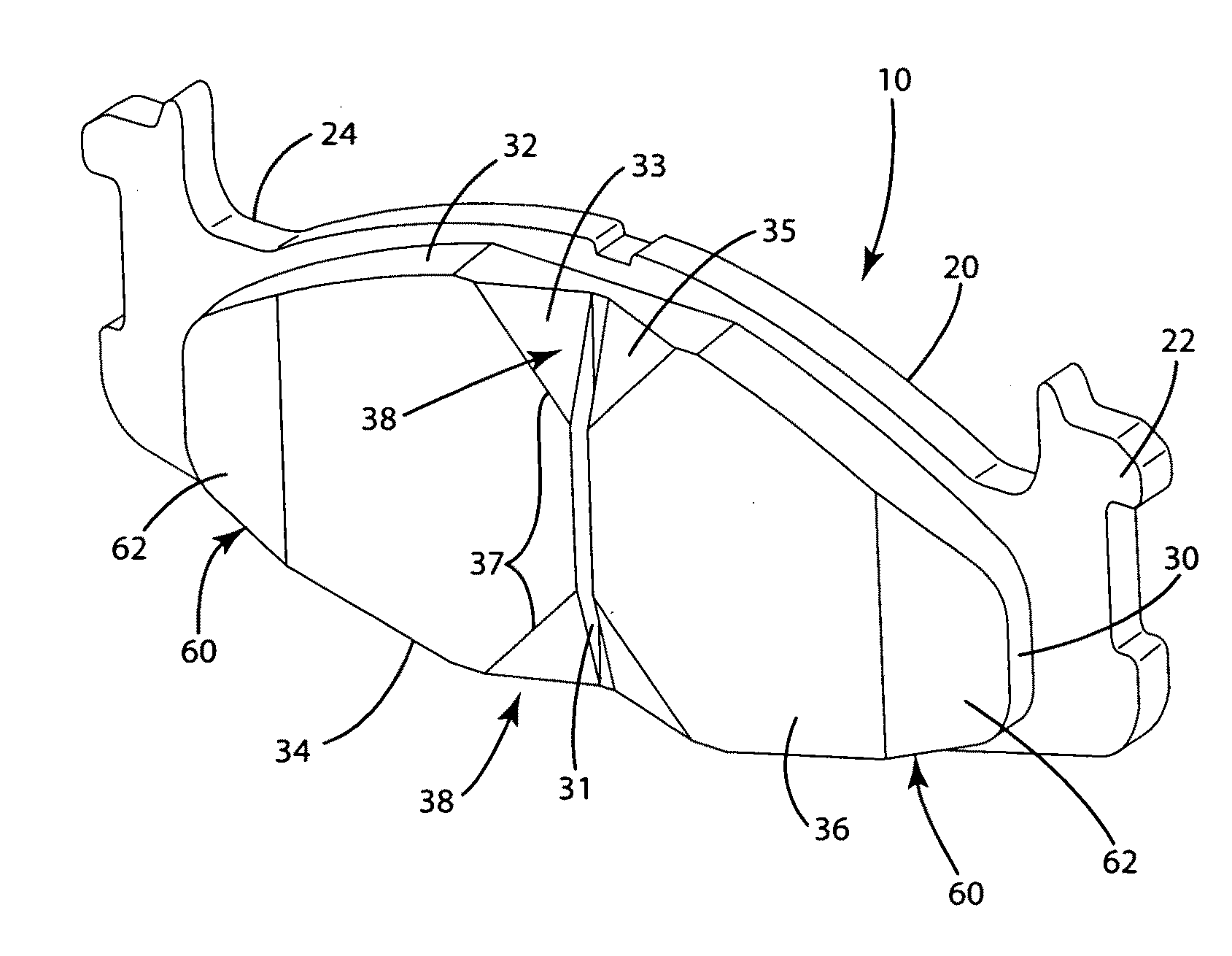
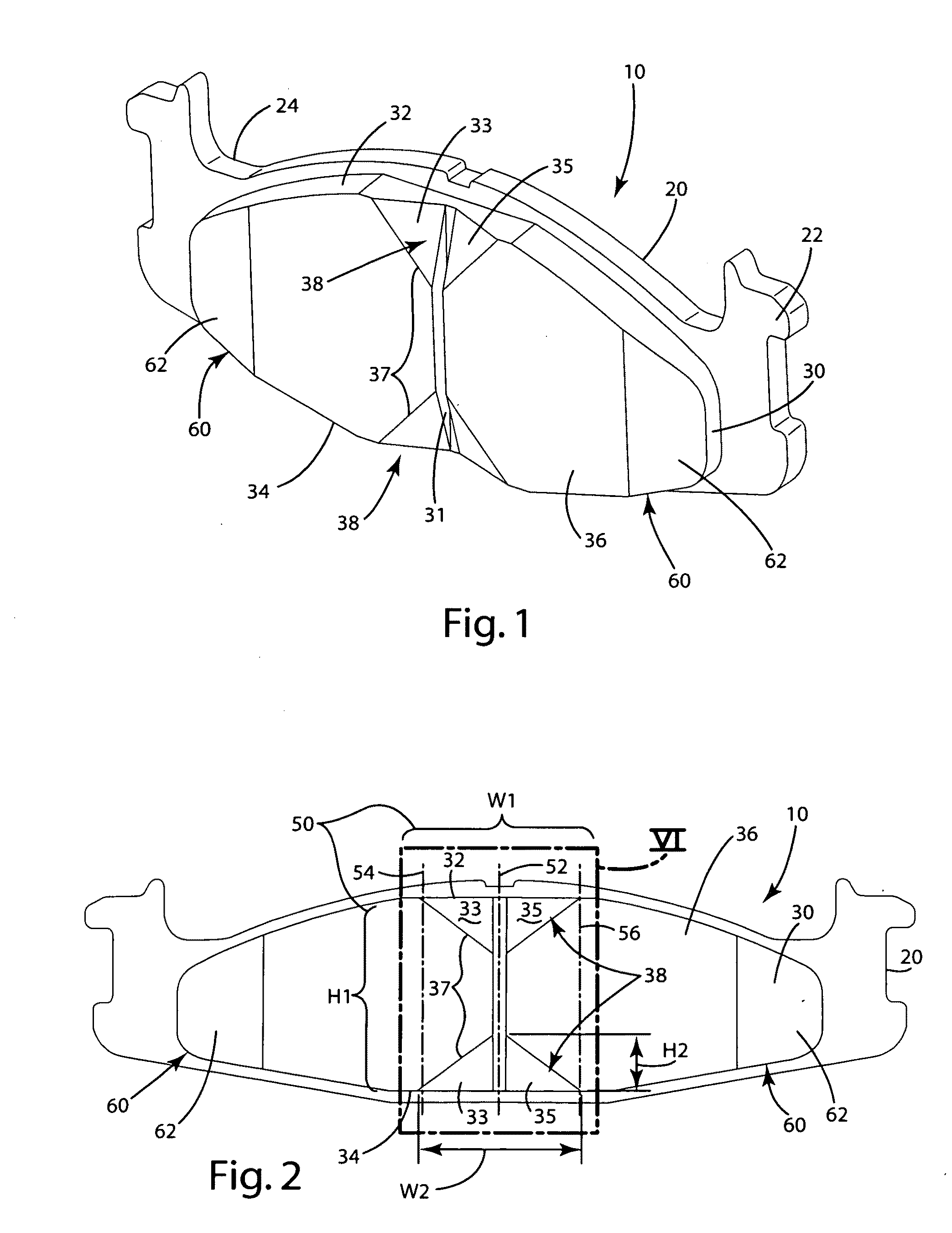
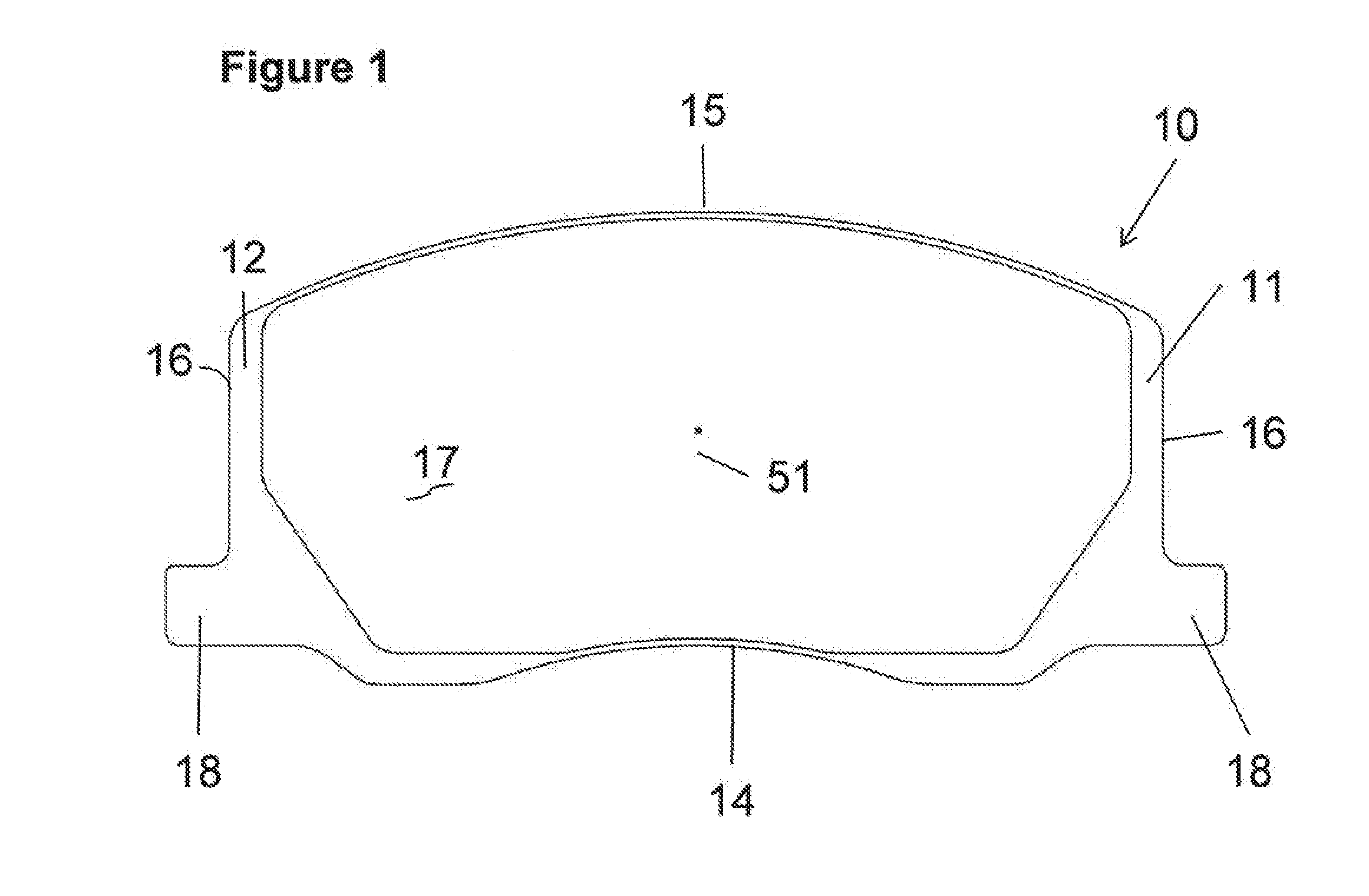
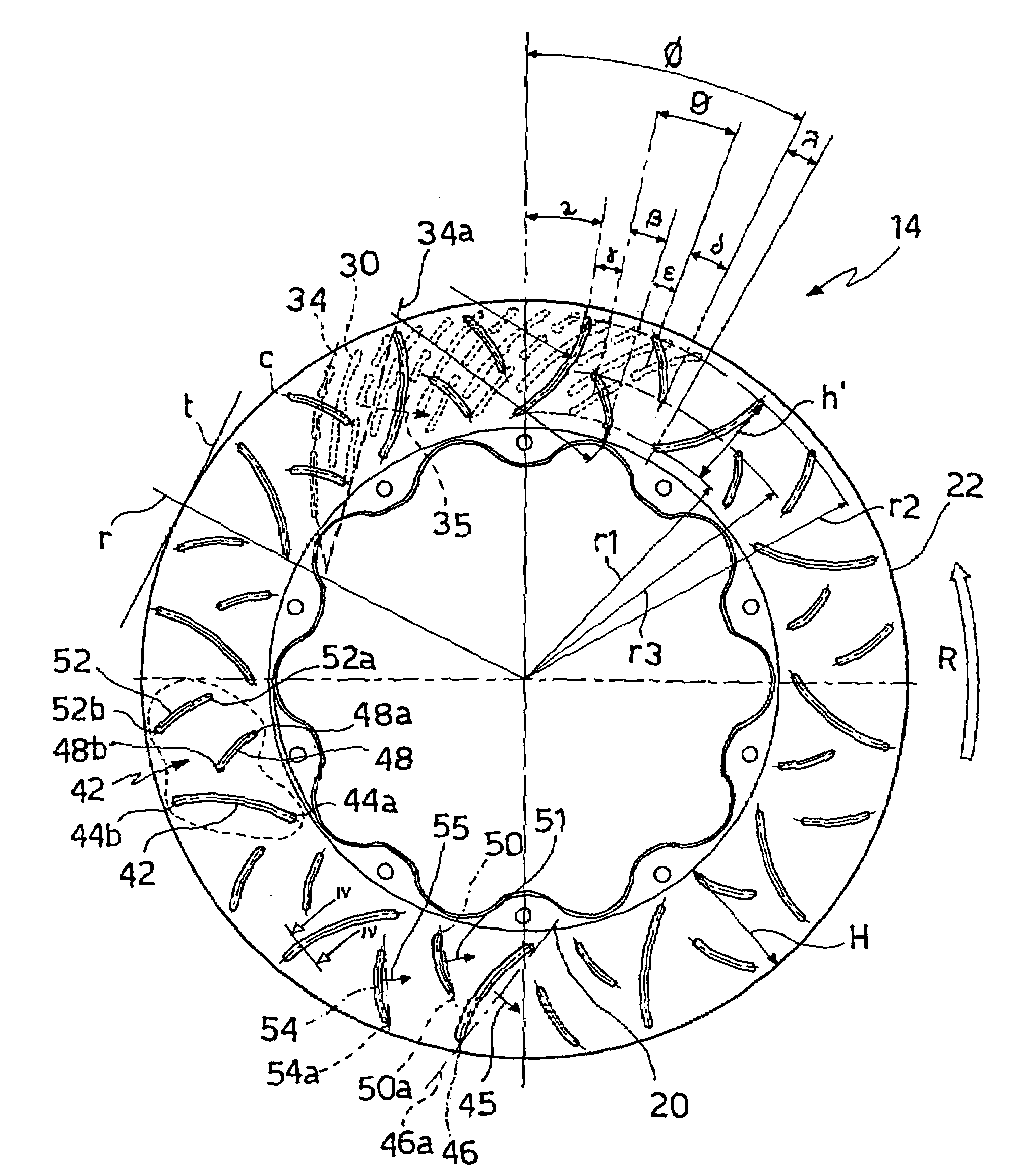
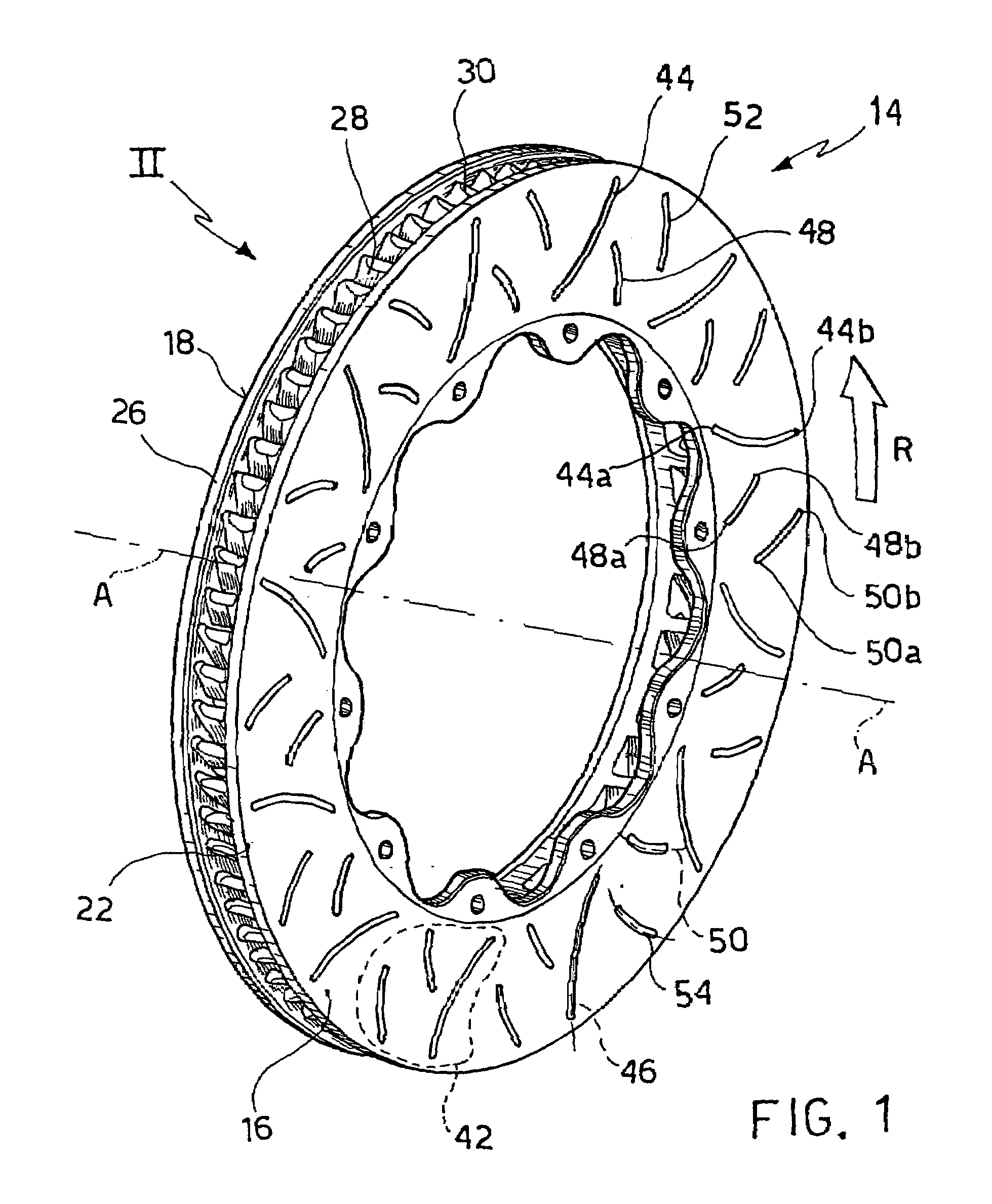
A braking band for a disc-brake disc includes opposed annular braking surfaces which extend from an inner edge facing towards the axis of rotation to an outer edge facing towards the outside of the disc. The braking band has a uniform distribution of grooves having a pattern or module that is repeated circumferentially in a manner such that the distribution is circumferentially uniform. According to an example embodiment, each of the grooves is closed and extends along a predominant line of extent defining an axis. The module extends from an inner radius to an outer radius which define an annular portion. The module further includes a first groove extending from the inner radius to the outer radius, a second groove, and a third groove that are shorter than the first groove. The axes of the second groove and of the third groove have an opposite inclination to the axis of the first groove.
Owner:FRENI BREMBO SPA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com