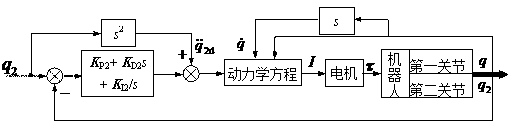
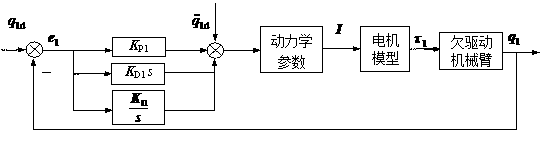
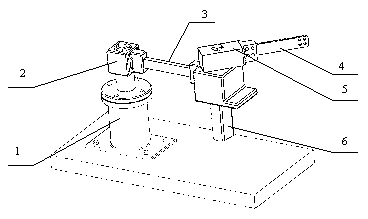
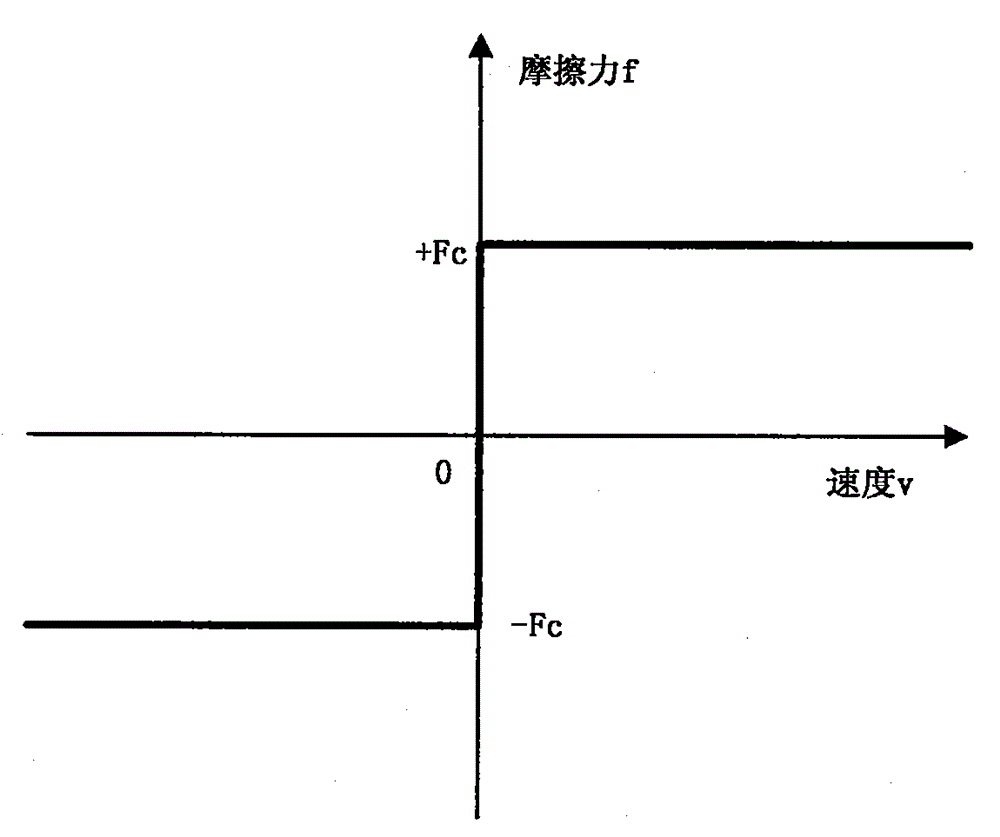
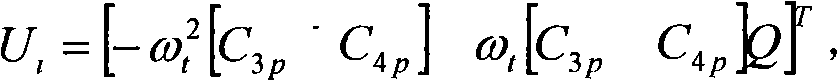Patents
Literature
84 results about "Coulomb friction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Coulomb friction is a simplified quantification of the friction force that exists between two dry surfaces in contact with each other.
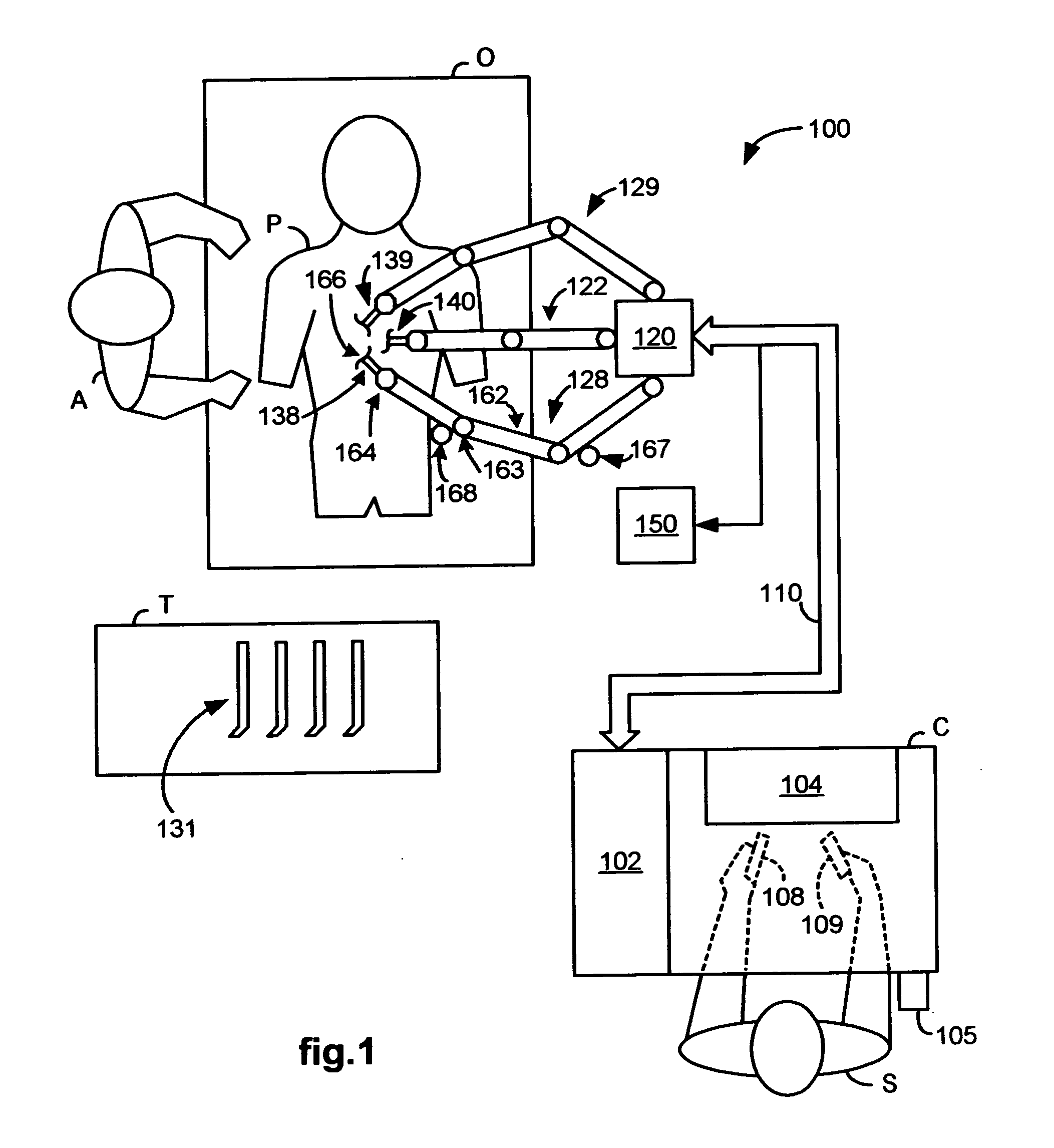
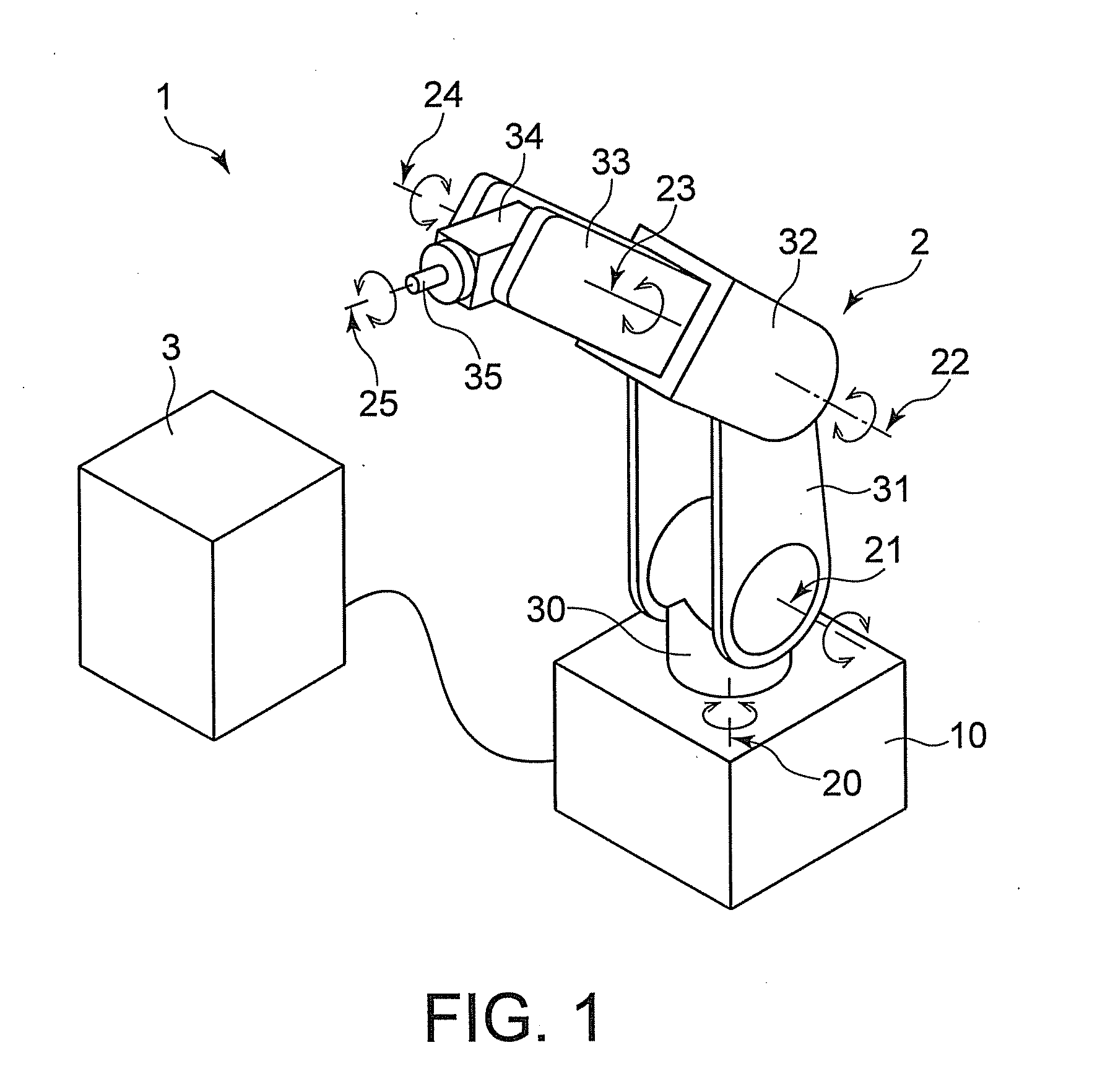
Control system for reducing internally generated frictional and inertial resistance to manual positioning of a surgical manipulator
ActiveUS7819859B2Friction is generatedReduce resistanceProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorSurgical siteAngular velocity
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Control system for reducing internally generated frictional and inertial resistance to manual positioning of a surgical manipulator
ActiveUS20070142823A1Friction is generatedReduce resistanceProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorSurgical siteAngular velocity
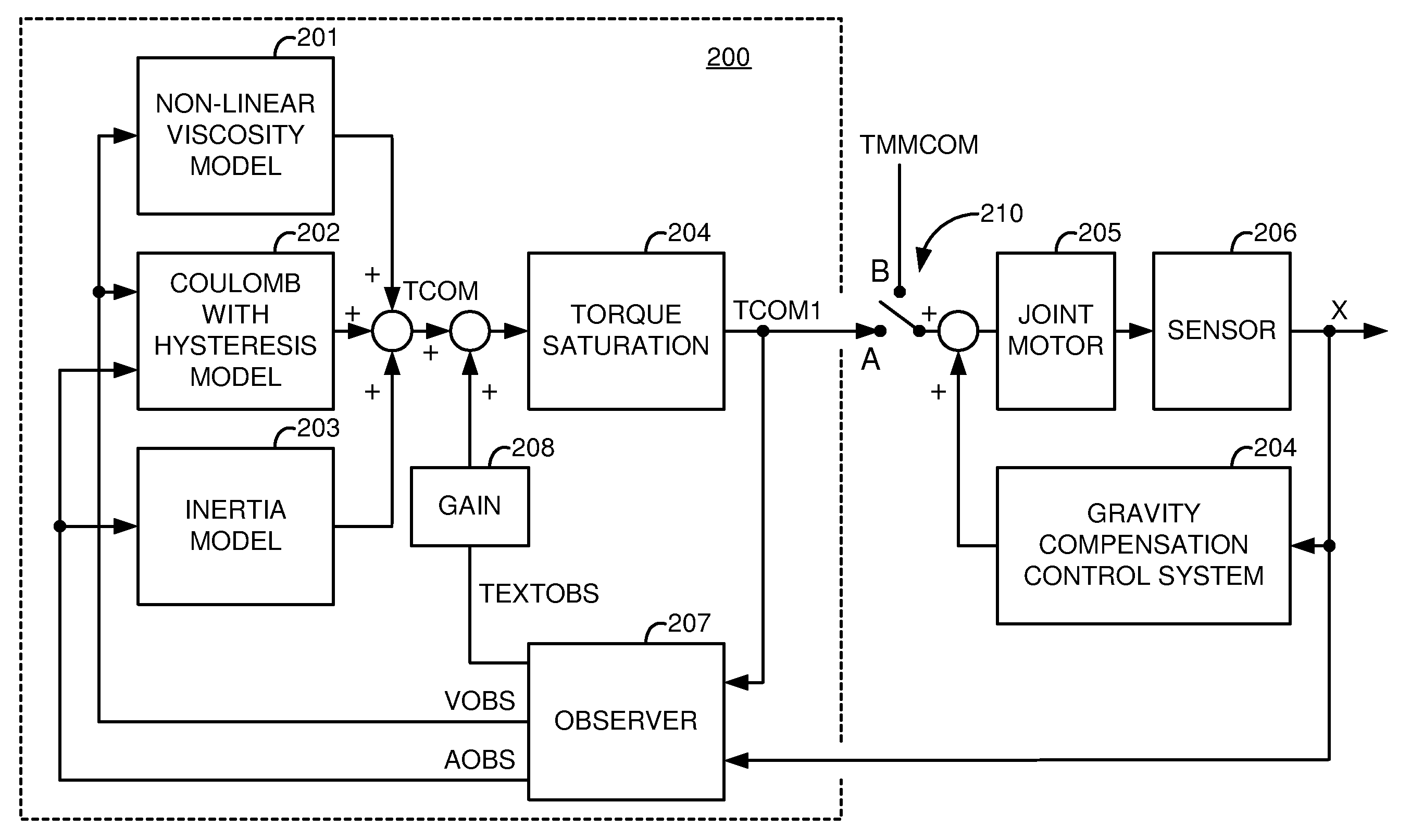
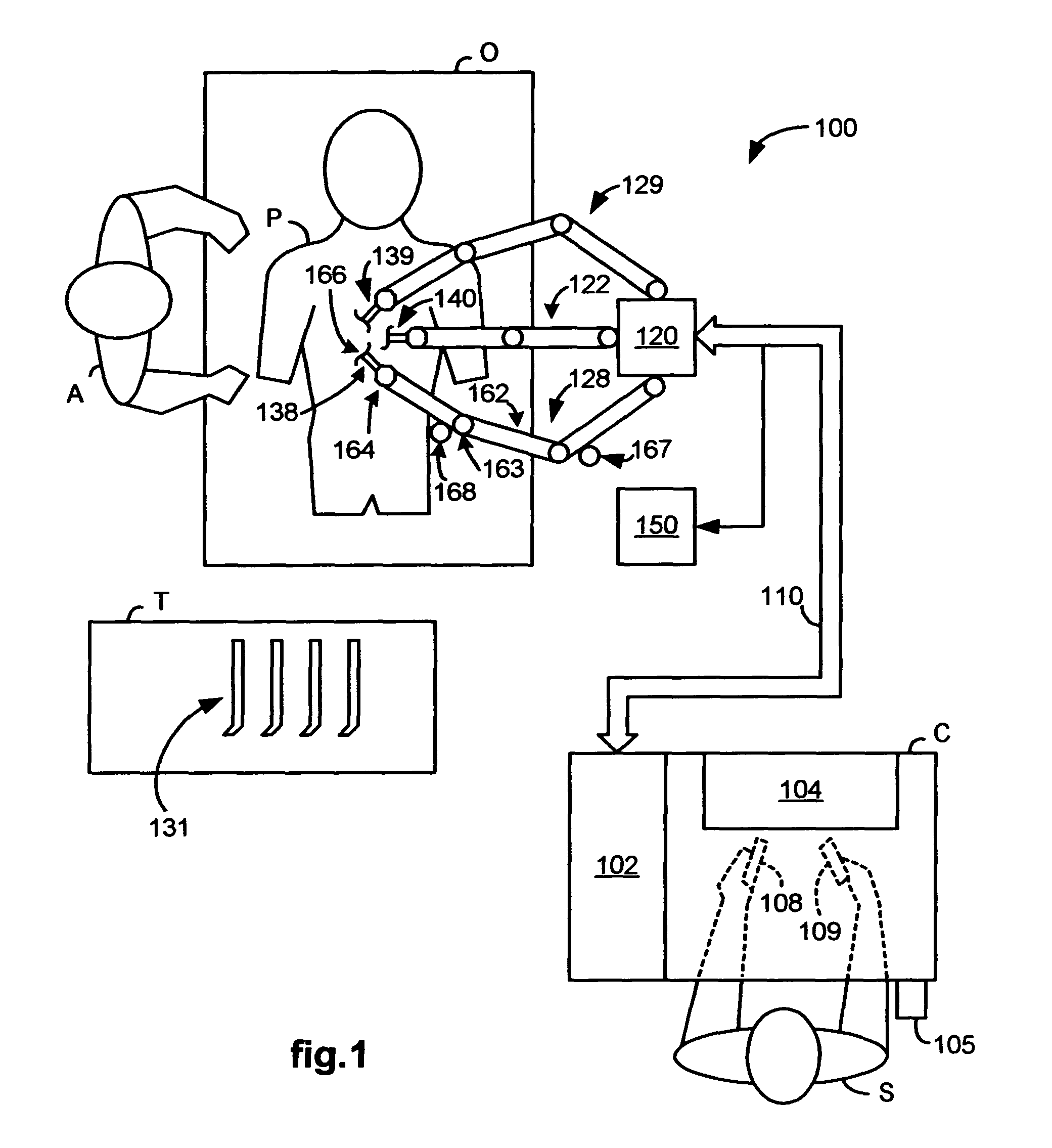
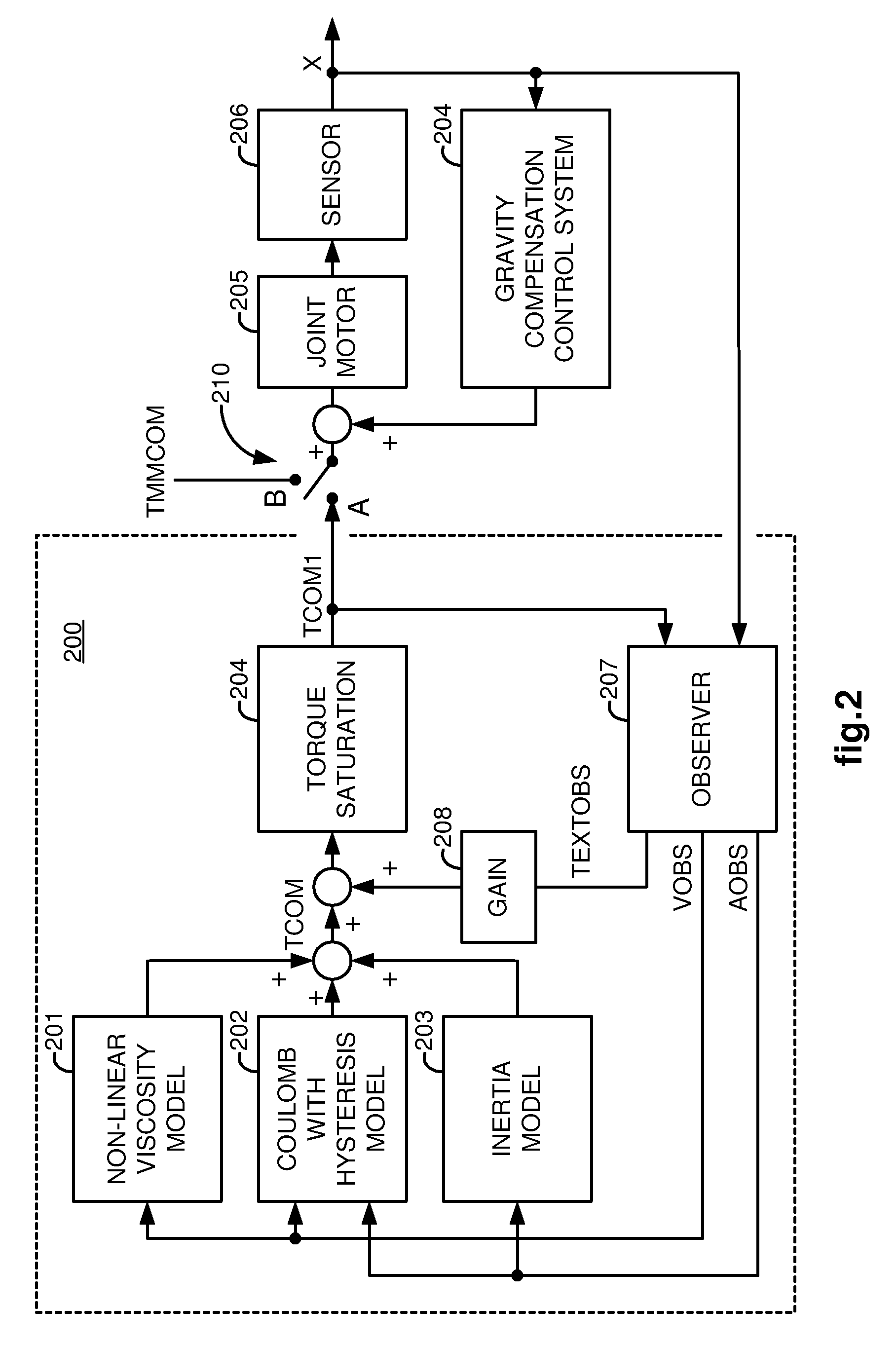
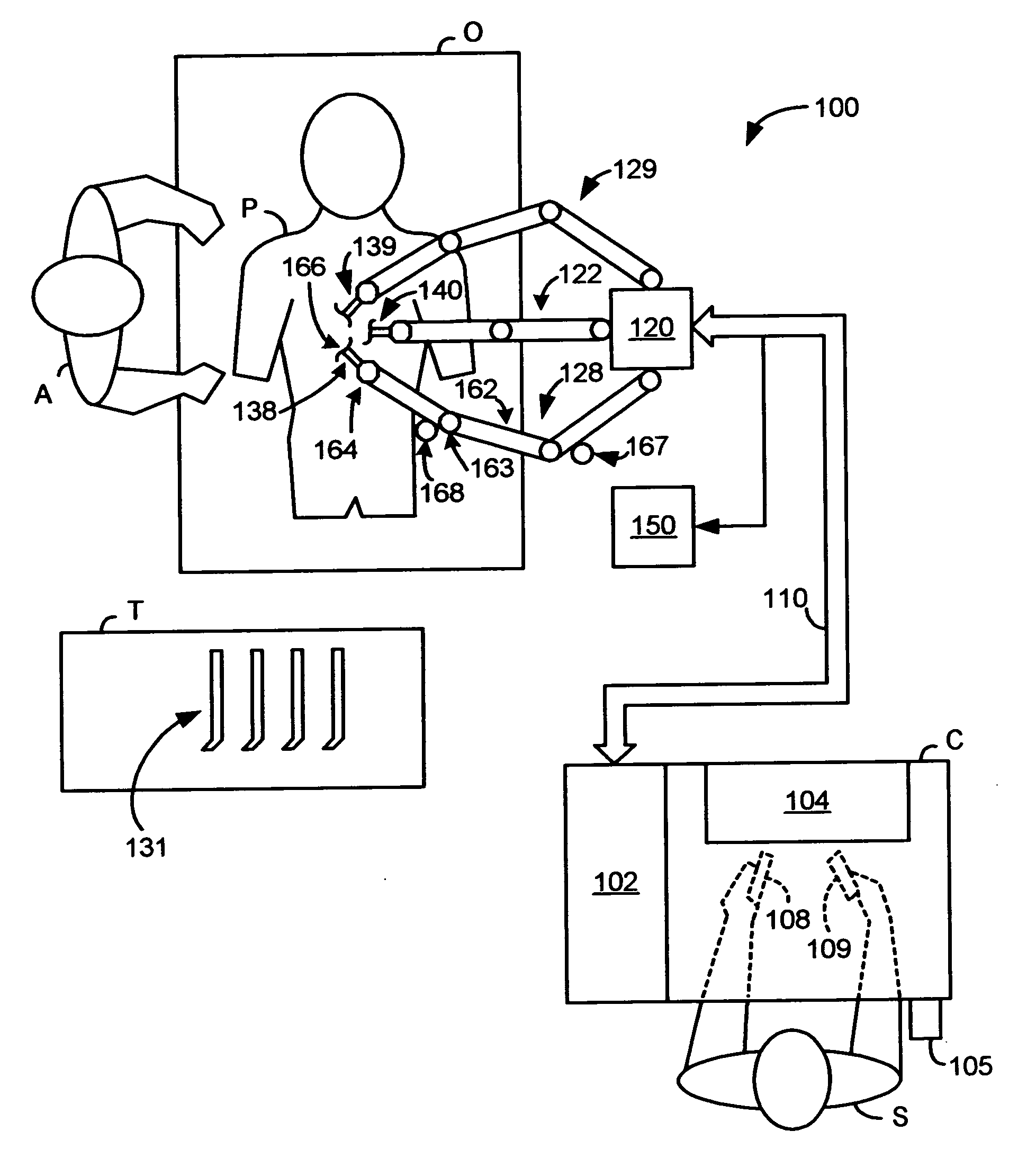
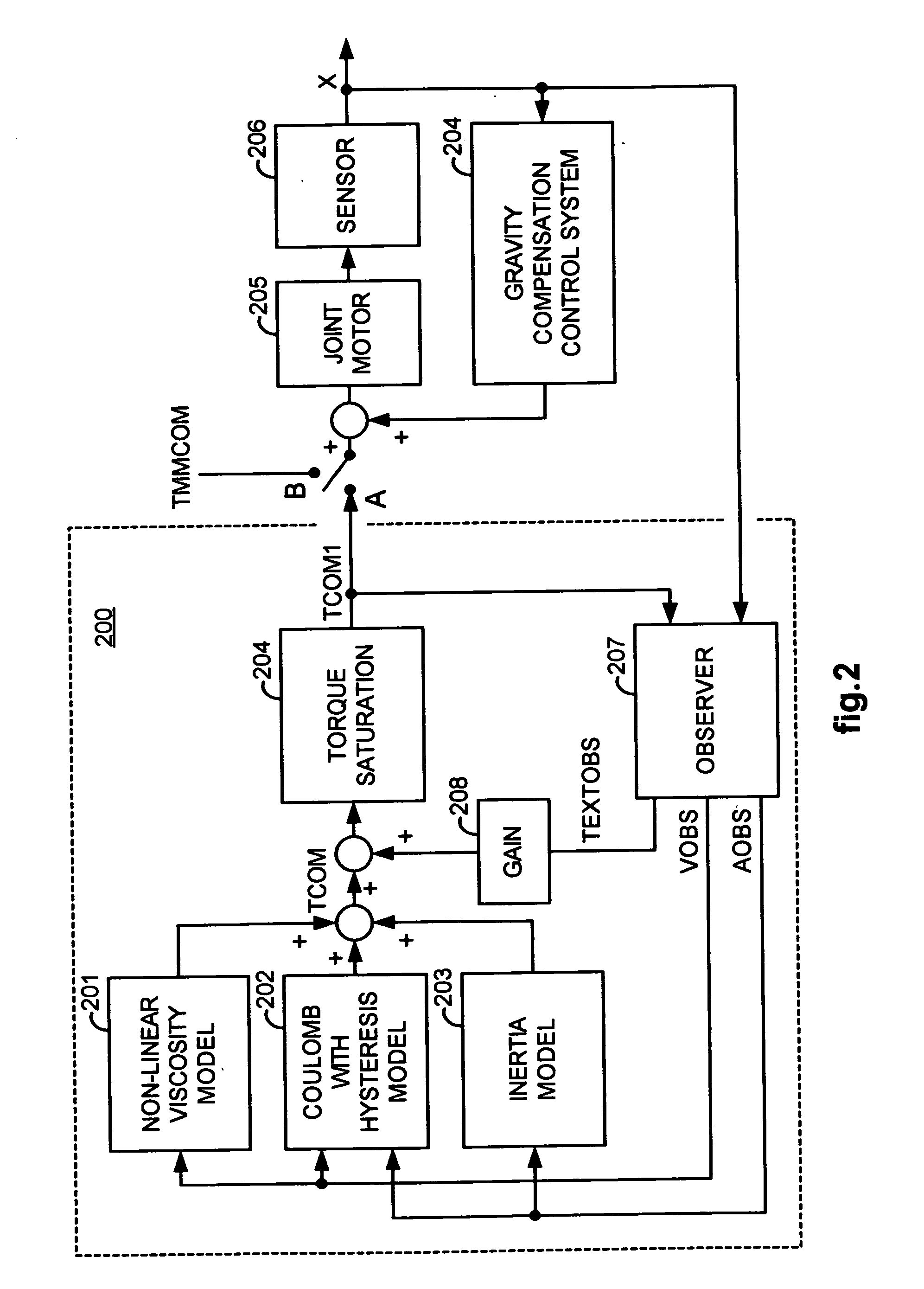
A robotic control system is placed in clutch mode so that a slave manipulator holding a surgical instrument is temporarily disengaged from control by a master manipulator in order to allow manual positioning of the surgical instrument at a surgical site within a patient. Control systems implemented in a processor compensate for internally generated frictional and inertial resistance experienced during the positioning, thereby making movement more comfortable to the mover, and stabler from a control standpoint. Each control system drives a joint motor in the slave manipulator with a saturated torque command signal which has been generated to compensate for non-linear viscous forces, coulomb friction, cogging effects, and inertia forces subjected to the joint, using estimated joint angular velocities, accelerations and externally applied torques generated by an observer in the control system from sampled displacement measurements received from a sensor associated with the joint.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
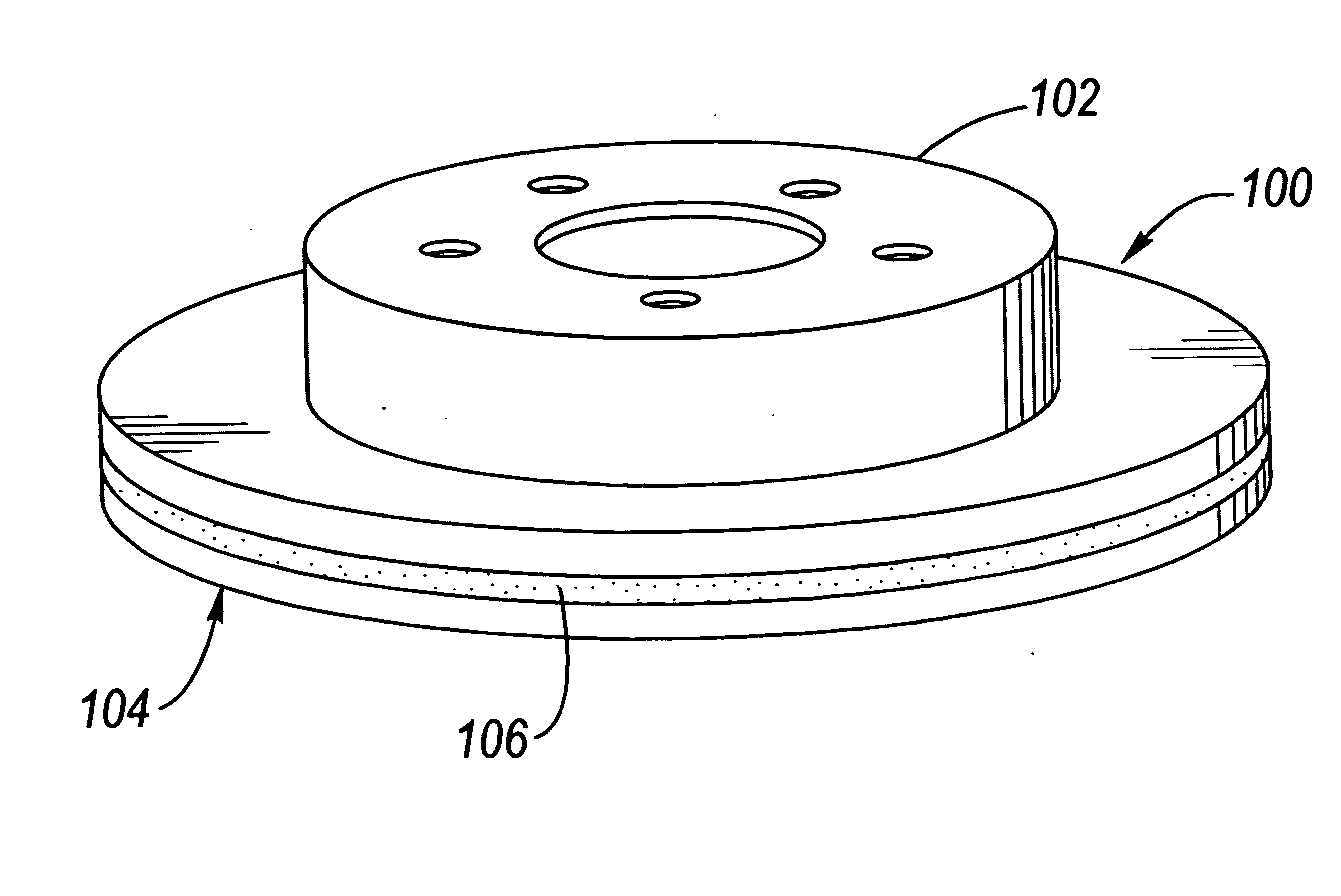
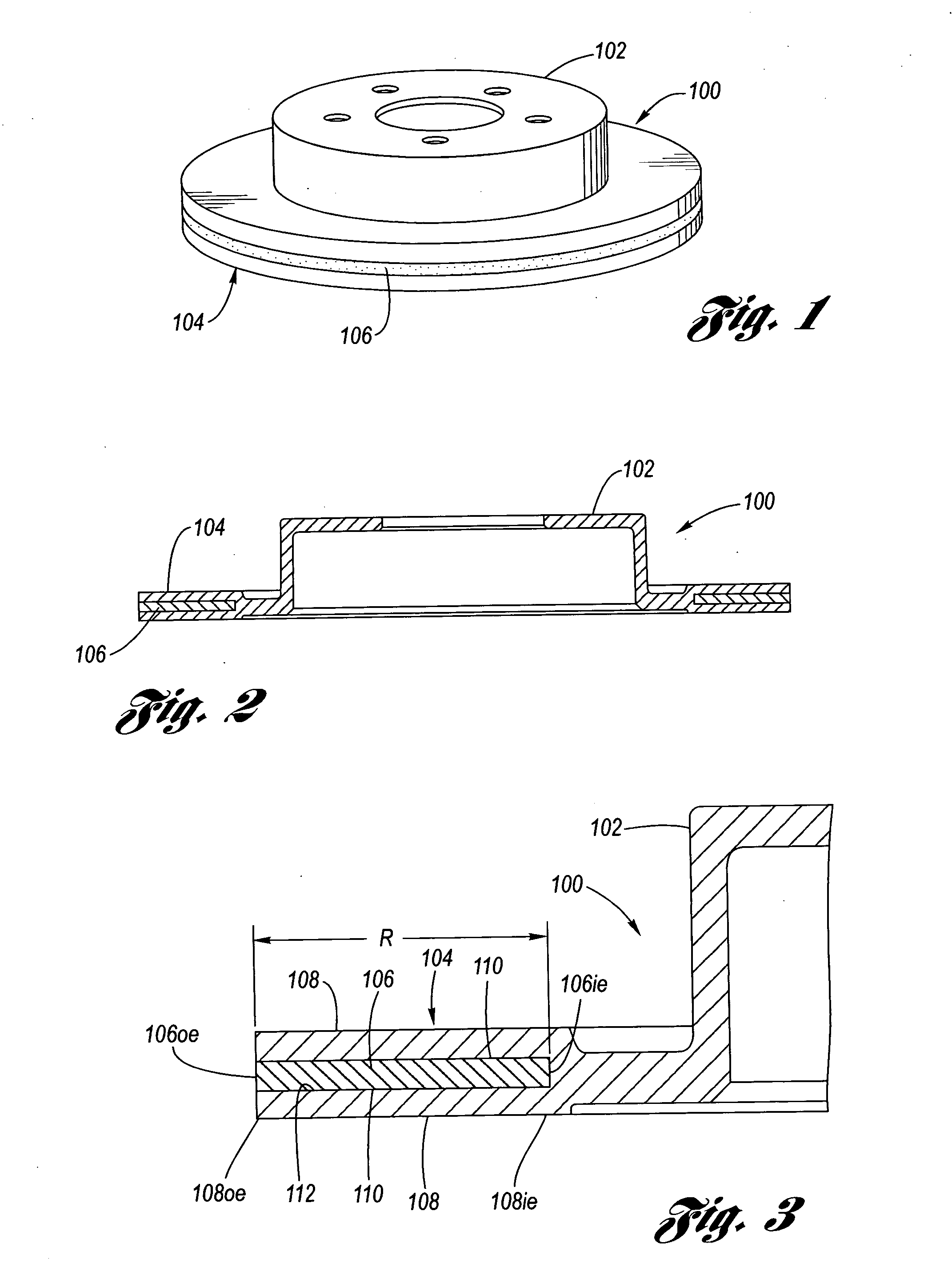
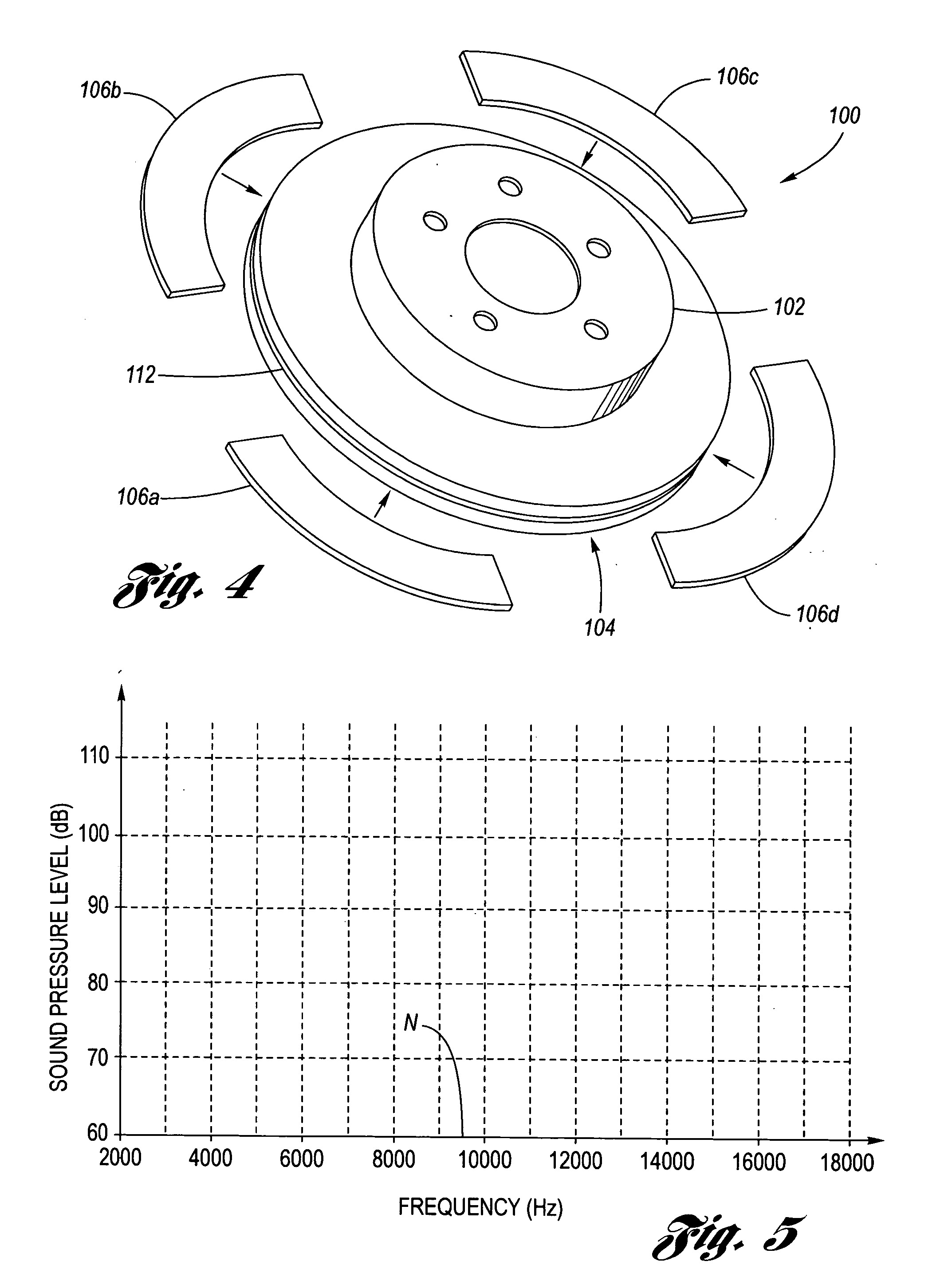
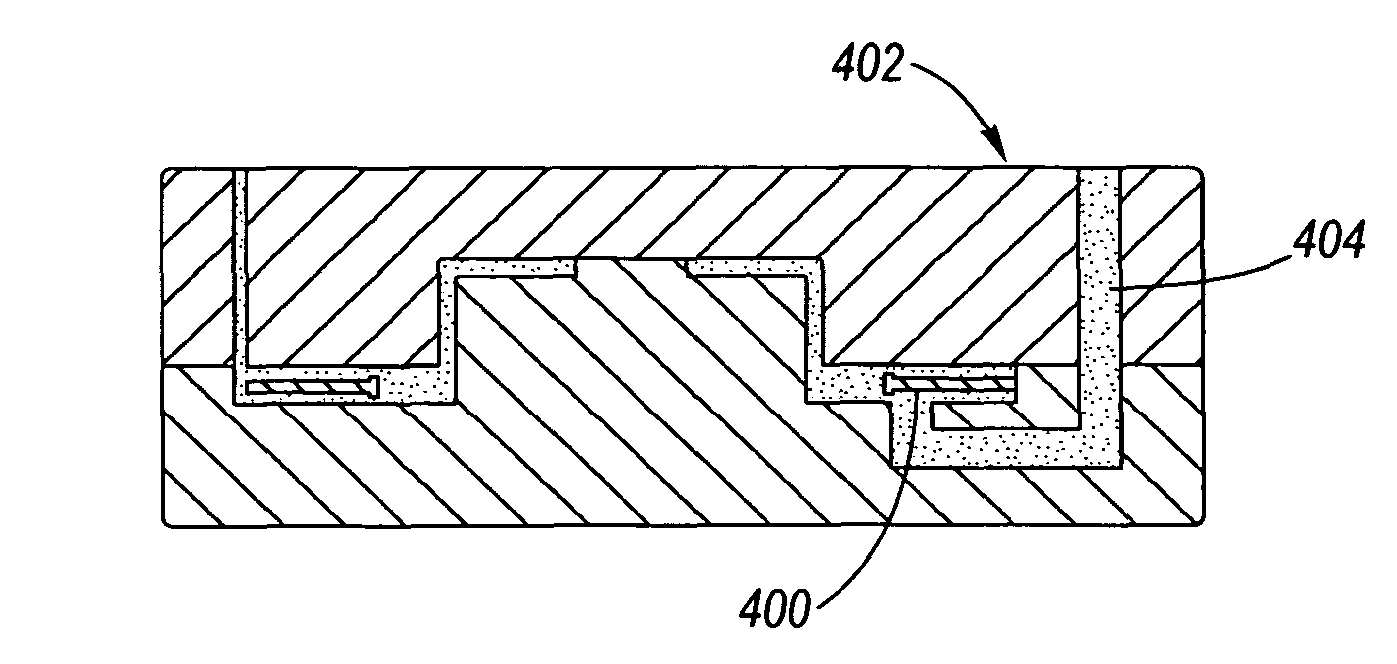
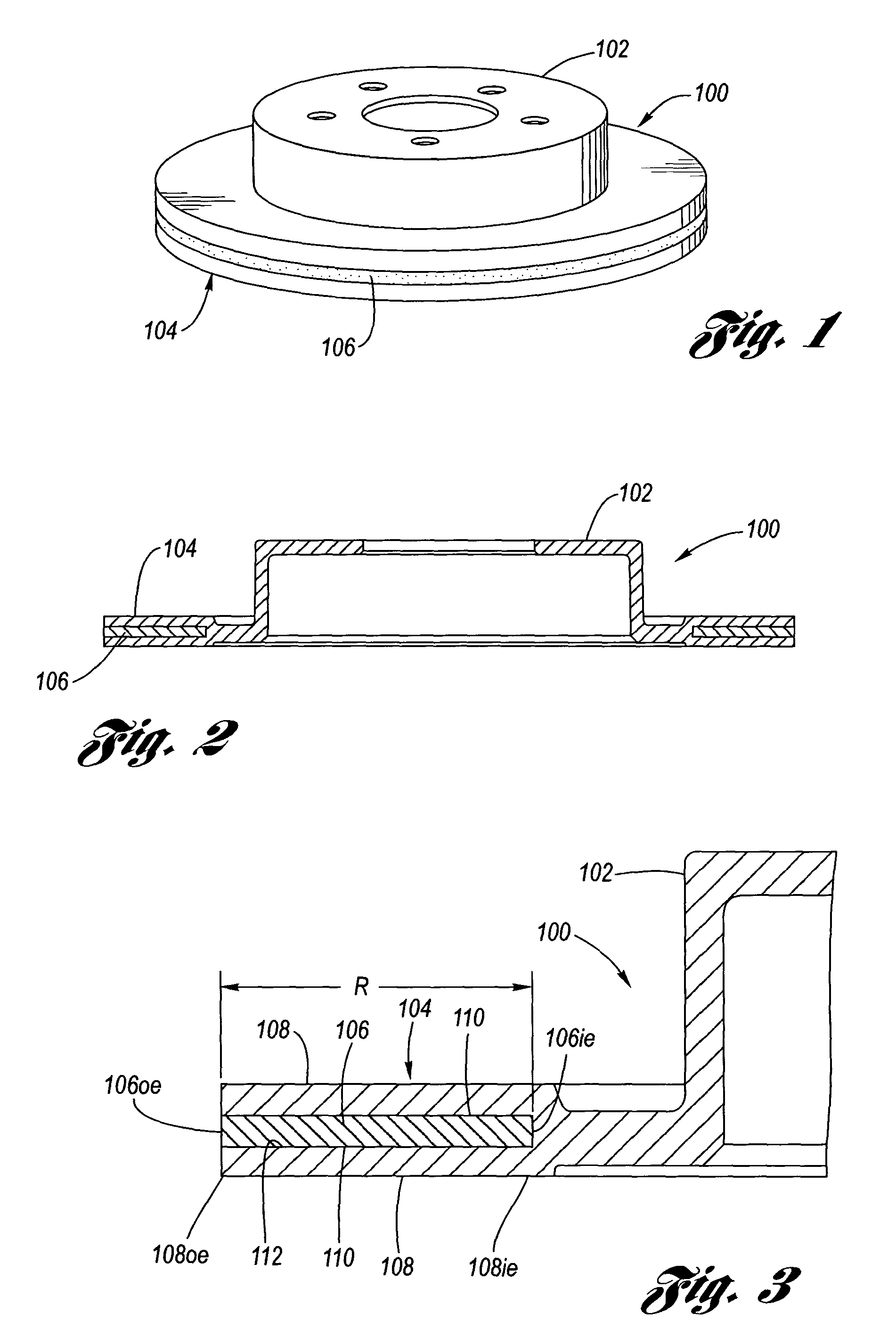
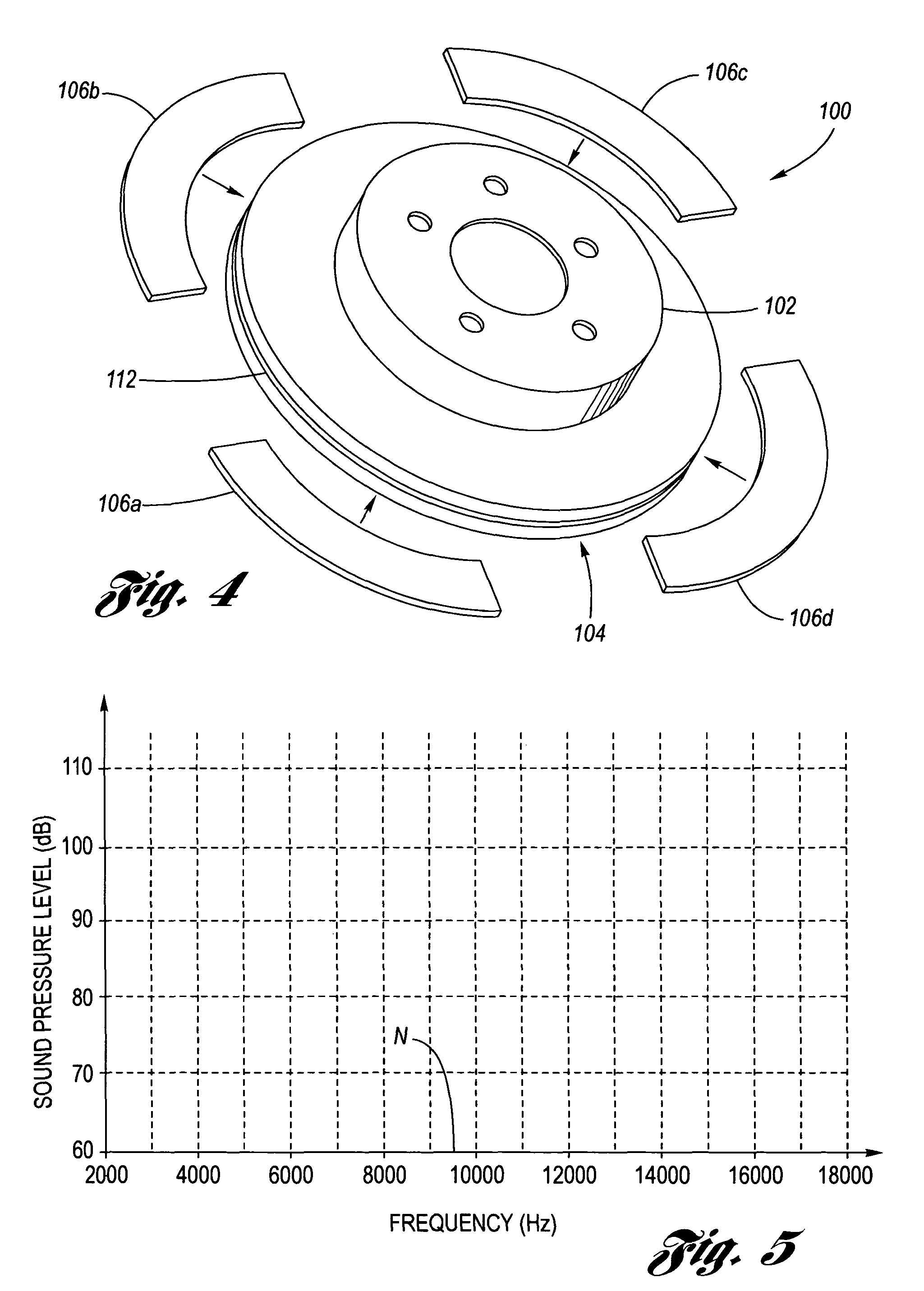
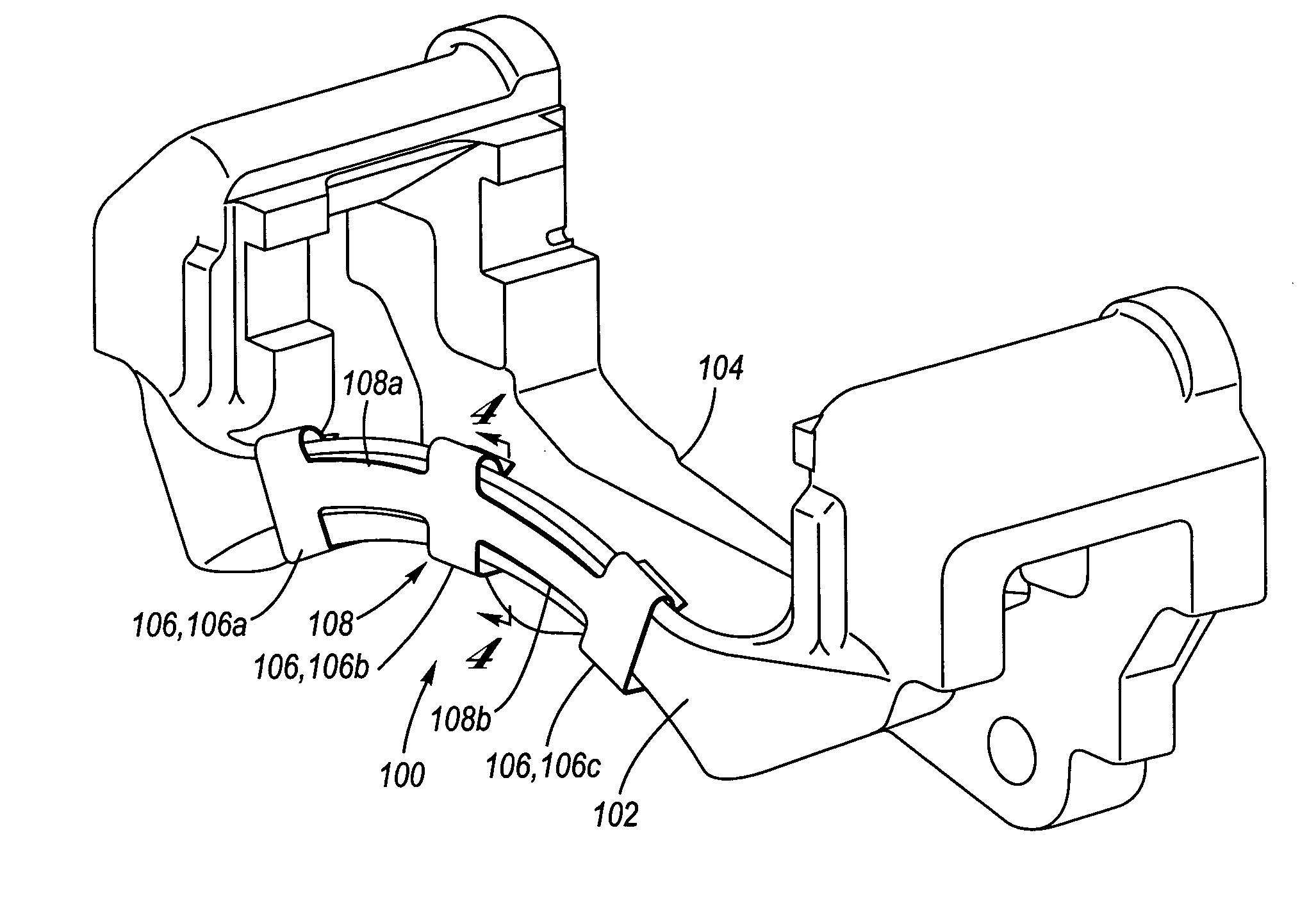
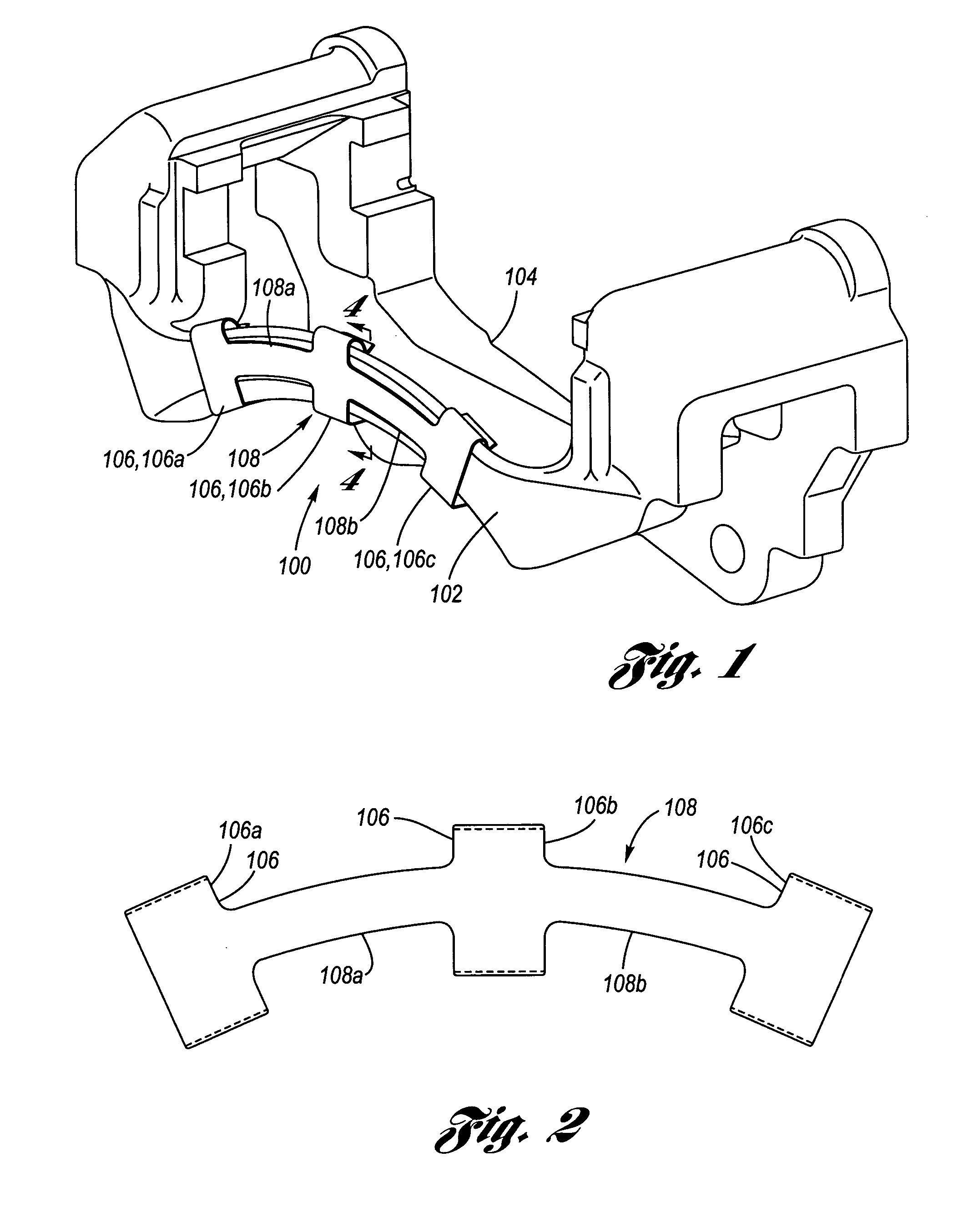
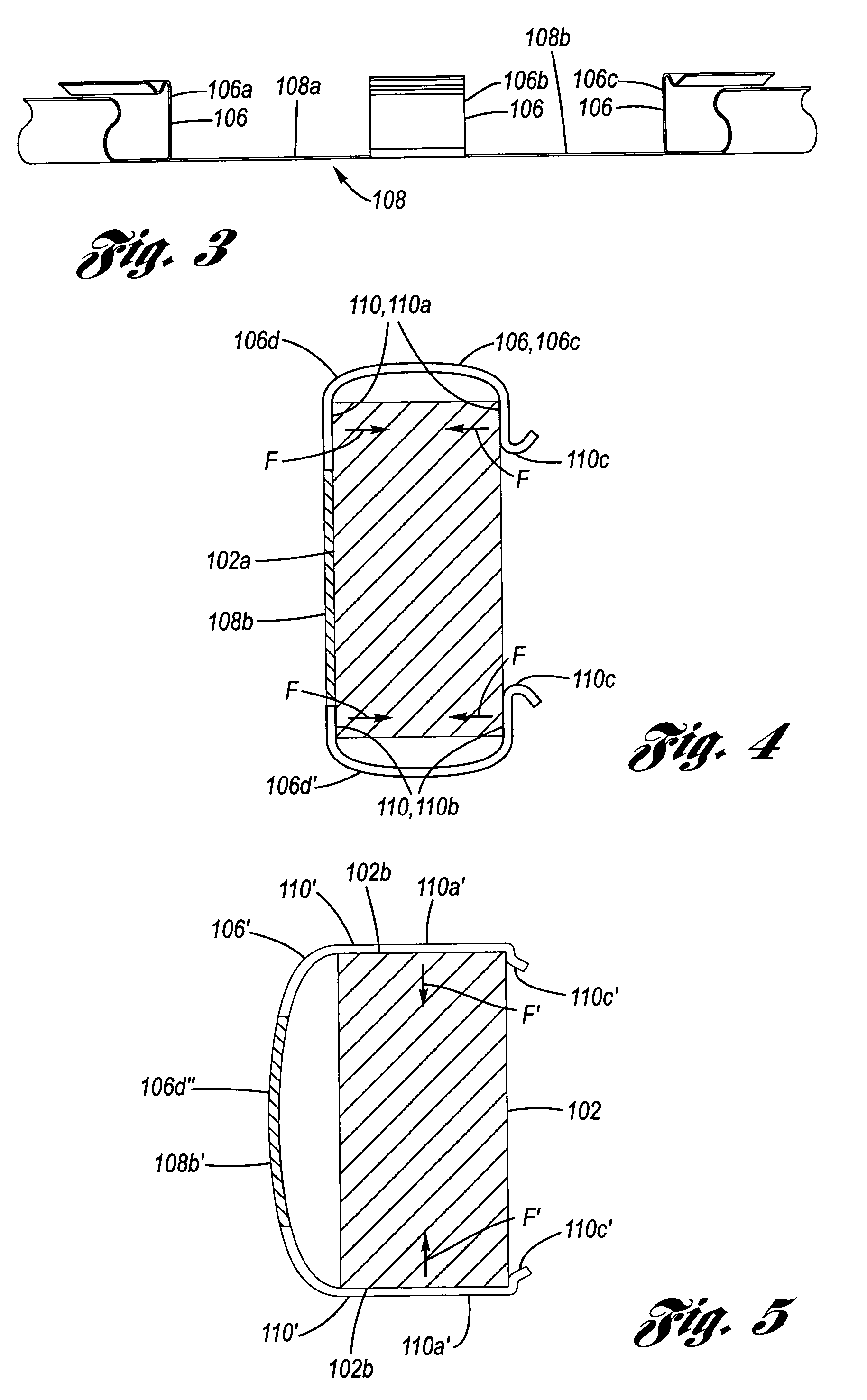
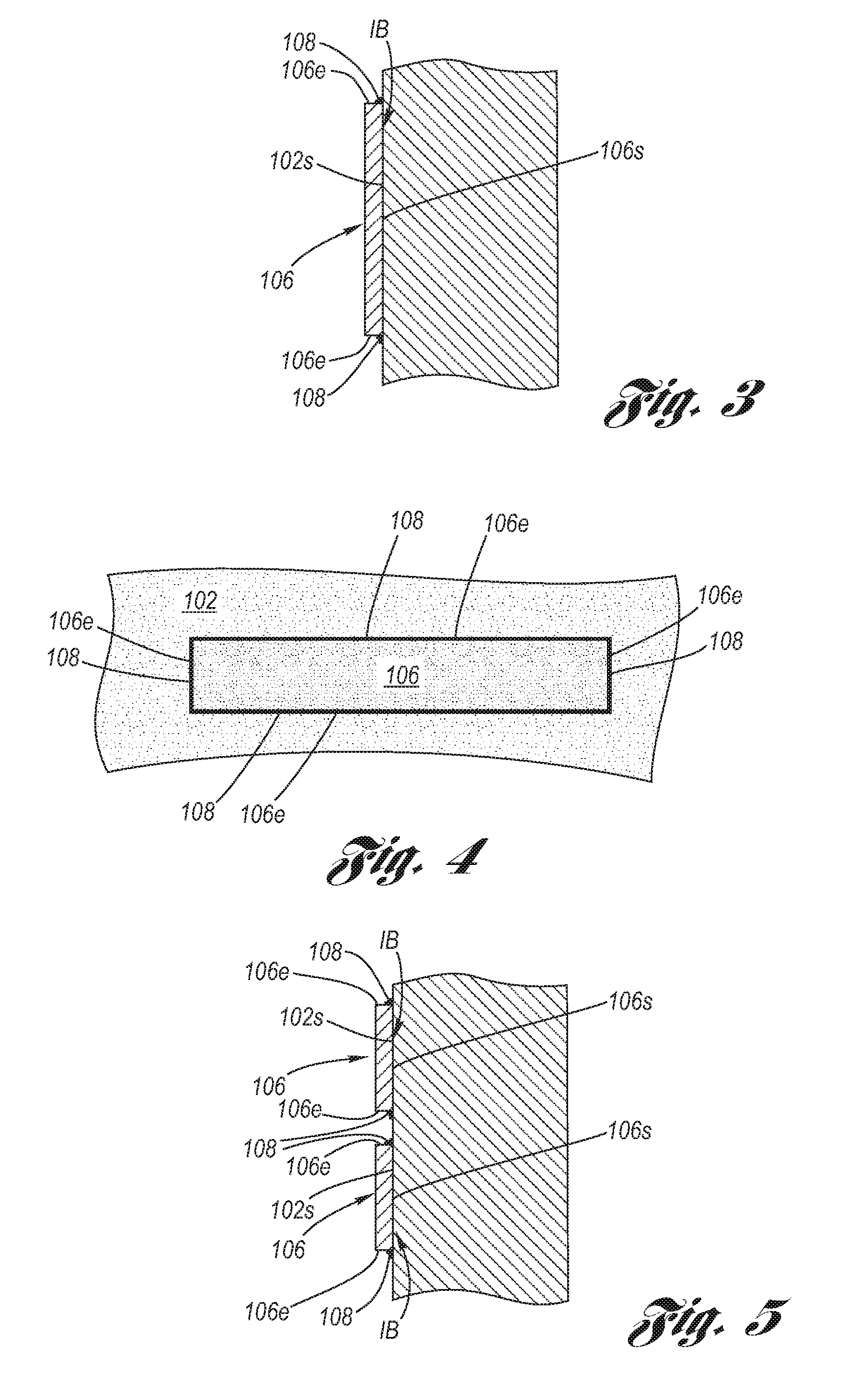
Coulomb friction damped disc brake rotors
InactiveUS20060076200A1Average thicknessSmall thicknessNoise/vibration controlBraking discsEngineeringMechanical engineering
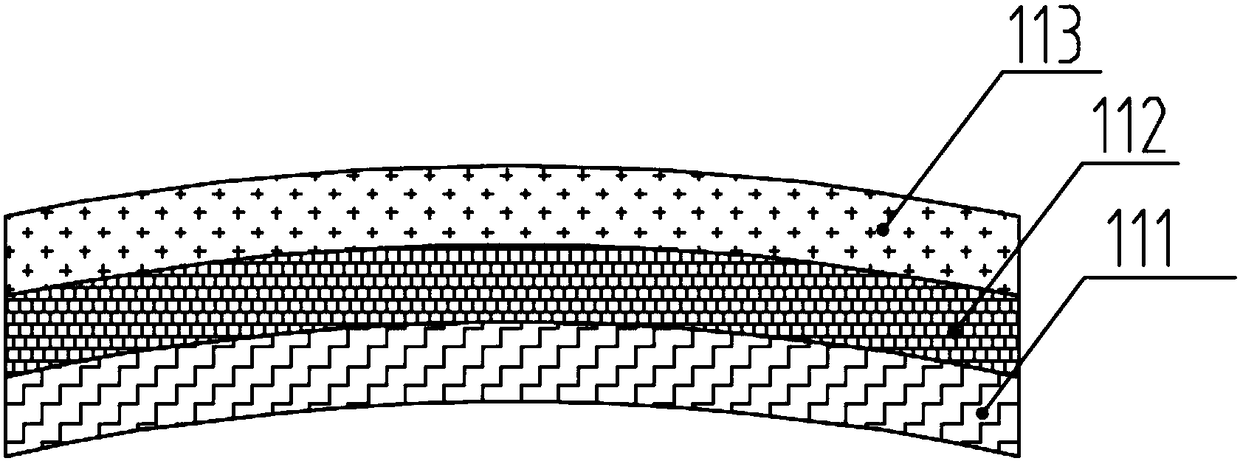
A Coulomb friction damped disc brake rotor, wherein damping is provided Coulomb friction in generally coextensive relation with the braking surfaces of the one or more rotor cheeks. The Coulomb friction damped disc brake rotor has at least one interfacial boundary formed in at least one rotor cheek disposed in generally coextensive relation to the braking surface thereof. The interfacial boundary provides a mechanically distinguishable surface boundary between two surfaces which are in mutual contact such that a state of Coulomb friction exists therebetween.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
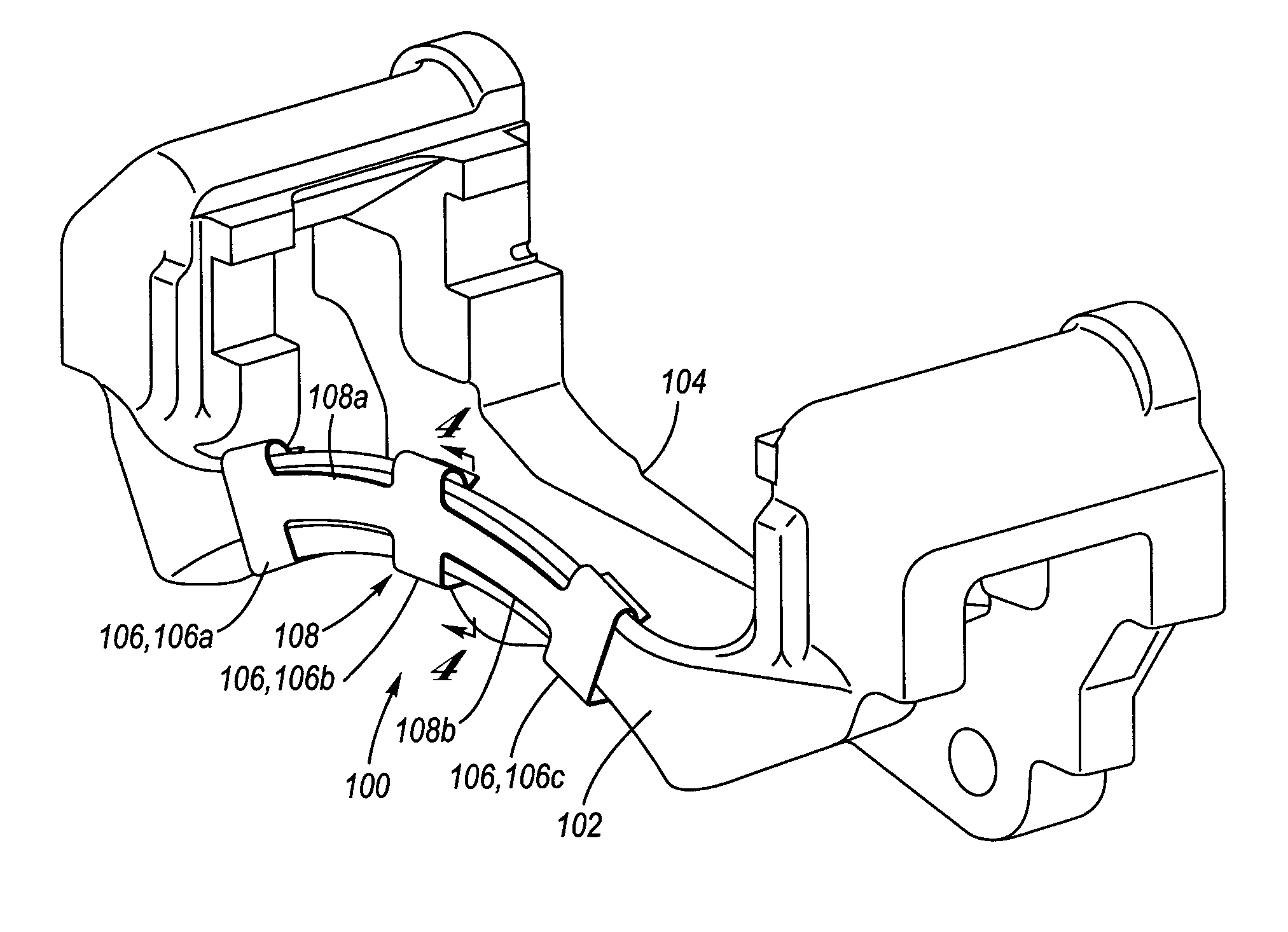
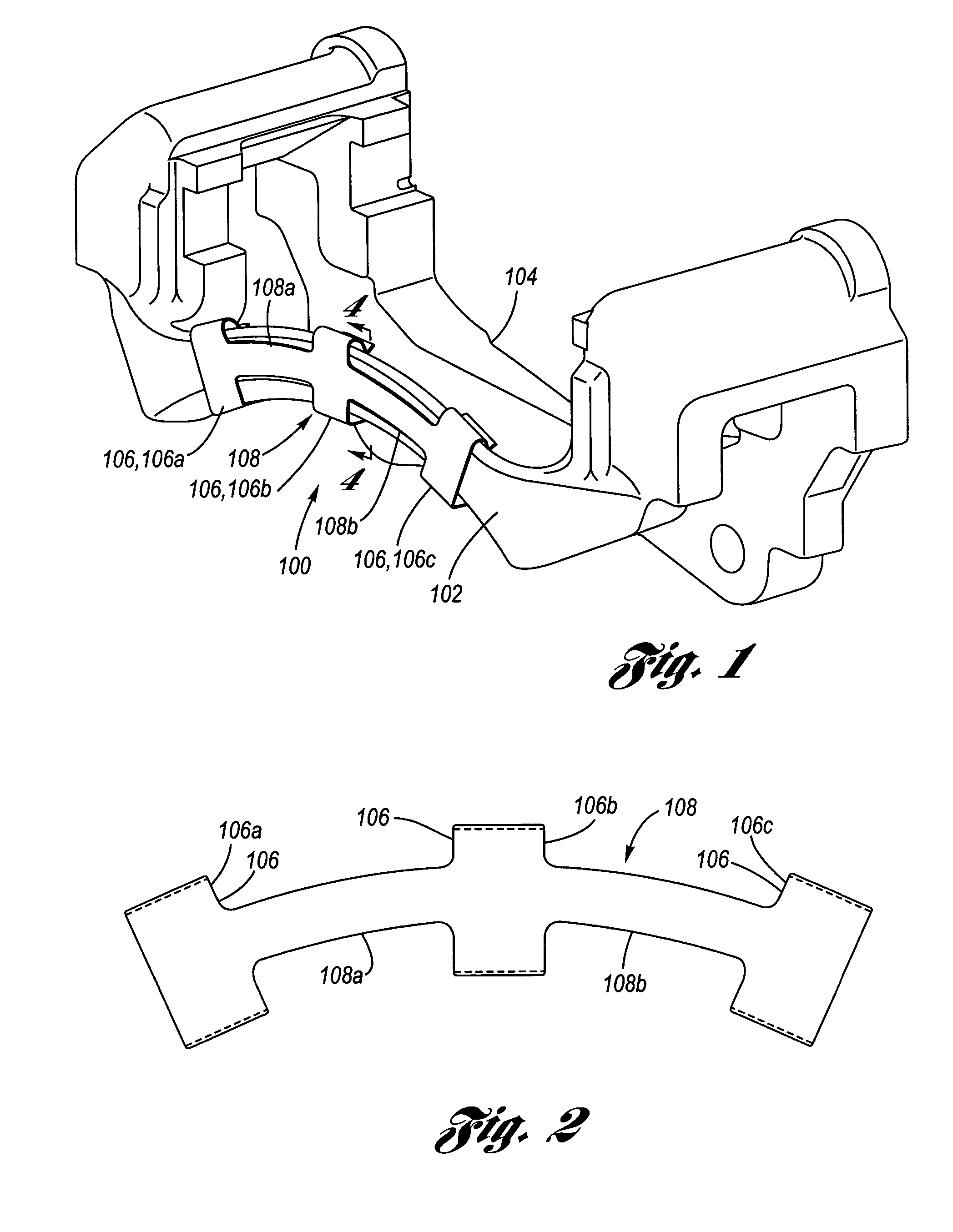
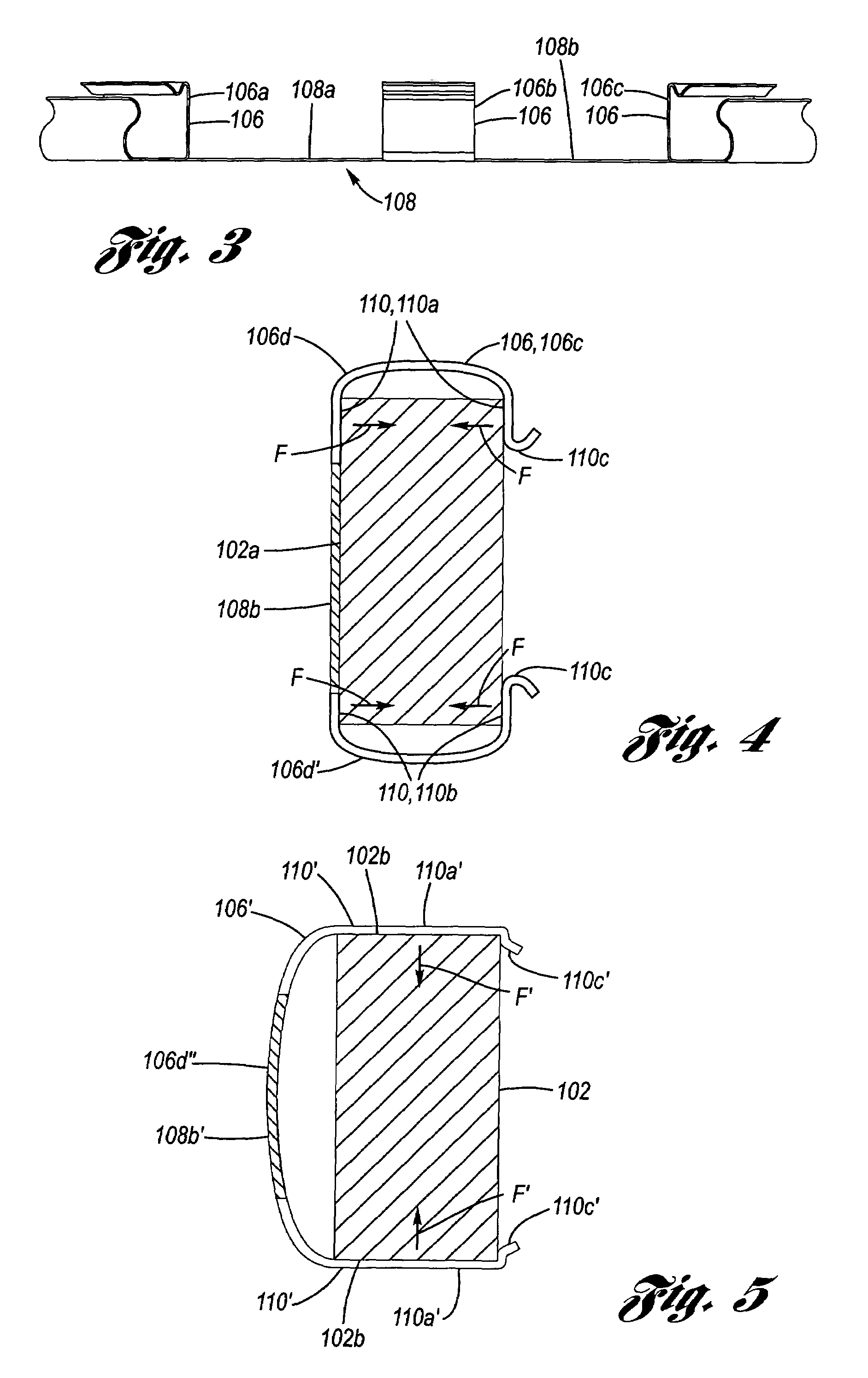
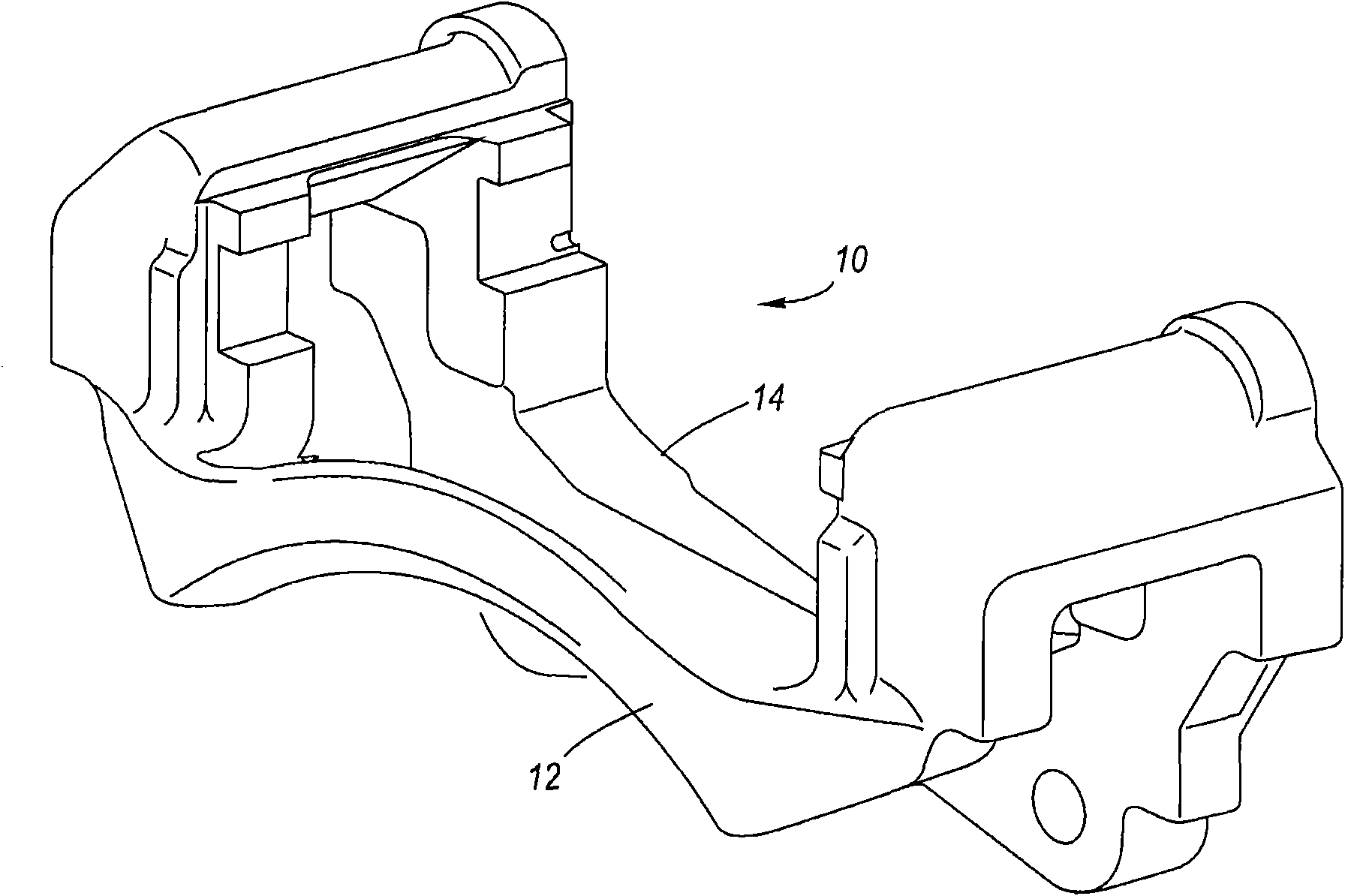
Coulomb friction damped disc brake caliper bracket
A Coulomb friction damped disc brake caliper bracket, wherein damping is provided by Coulomb friction, most preferably at the outboard tie-bar thereof. In one form, at least one clamping member applies compressive force externally to the caliper bracket, and in a second form, at least one interfacial boundary is internally disposed in the caliper bracket. Provided thereby is a mechanically distinguishable surface boundary between two surfaces which are in mutual contact such that a state of Coulomb friction exists therebetween.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Coulomb friction damped disc brake rotors
InactiveUS7975750B2Small thicknessReduce noiseNoise/vibration controlBraking discsEngineeringCoulomb friction
A Coulomb friction damped disc brake rotor, wherein damping is provided Coulomb friction in generally coextensive relation with the braking surfaces of the one or more rotor cheeks. The Coulomb friction damped disc brake rotor has at least one interfacial boundary formed in at least one rotor cheek disposed in generally coextensive relation to the braking surface thereof. The interfacial boundary provides a mechanically distinguishable surface boundary between two surfaces which are in mutual contact such that a state of Coulomb friction exists therebetween.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
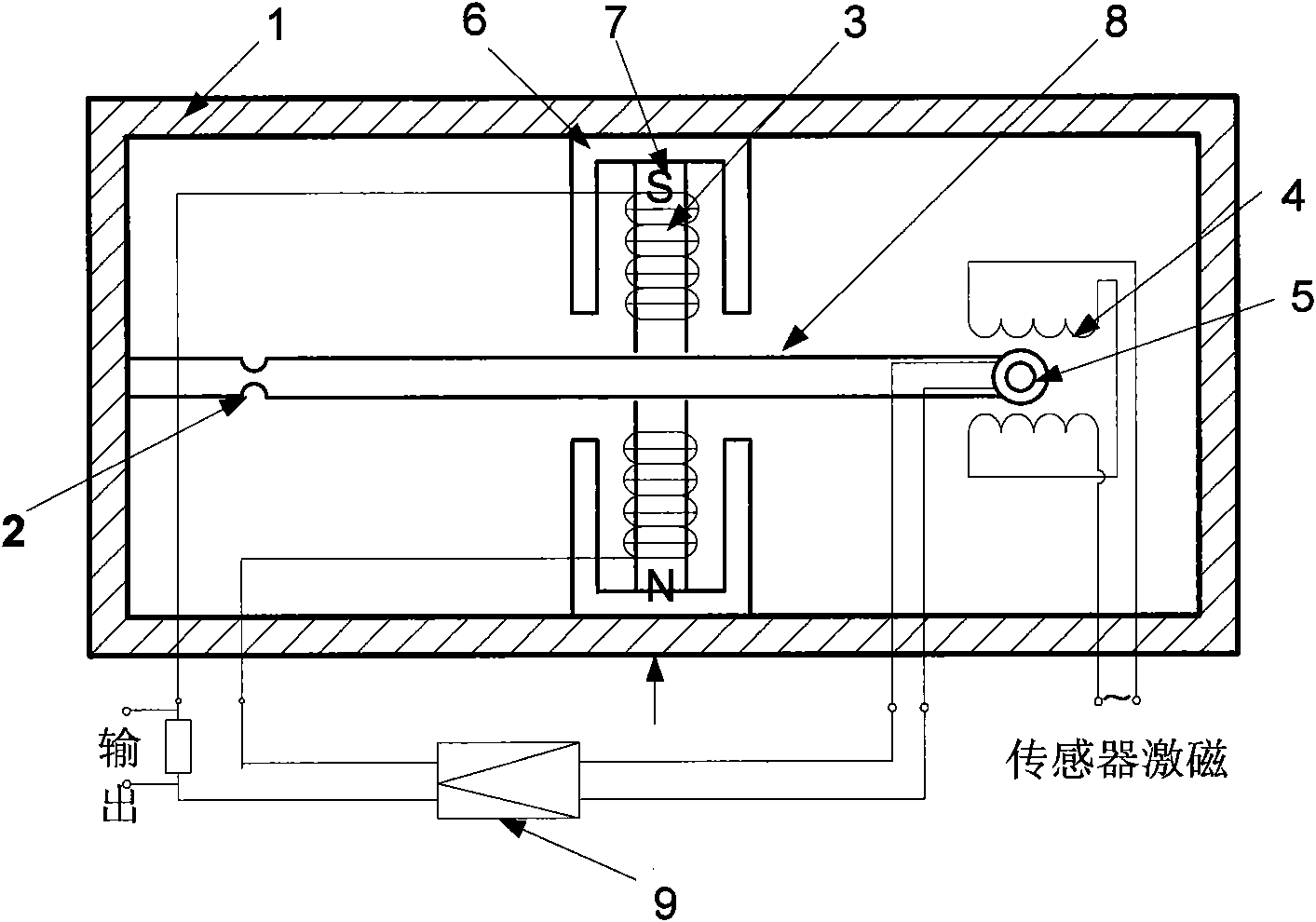
Flexible pendulous accelerometer
ActiveCN101592678AReduce stiffnessEliminate Coulomb frictionAcceleration measurement using interia forcesAccelerometerJewel bearing
The invention discloses a flexible pendulous accelerometer, which comprises a shell, a flexible rod, a torquer moving coil, a torquer stator consisting of a yoke iron and a permanent magnet, a signal sensor consisting of a signal sensor moving coil and a signal sensor stator, a triangular pendulous reed and a servoamplifier, wherein the shell is full of a damping liquid; the triangular pendulous reed, the torquer moving coil and the signal sensor moving coil form a pendulum module; the flexible rod ensures that the pendulum module and an instrument shell are elastically connected; and the torquer stator and the torquer moving coil form a torquer. The flexible pendulous accelerometer eliminates the Coulomb friction force caused by a pivot and a jewelled bearing compared with the prior jewelled bearing supporting mode due to adopting a flexible supporting mode; the flexible supporting has small rigidity in a sensitive direction of the accelerometer and has large rigidity in other directions at the same time, which improves instrument measurement precision as well as vibration-resistant and shock-resistant abilities; the flexible pendulous accelerometer adopts a liquid for damping, and has better overload capacity and shock-resistant capability compared with a quartz flexible pendulous accelerometer adopting air damping.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF AEROSPACE CONTROL DEVICES
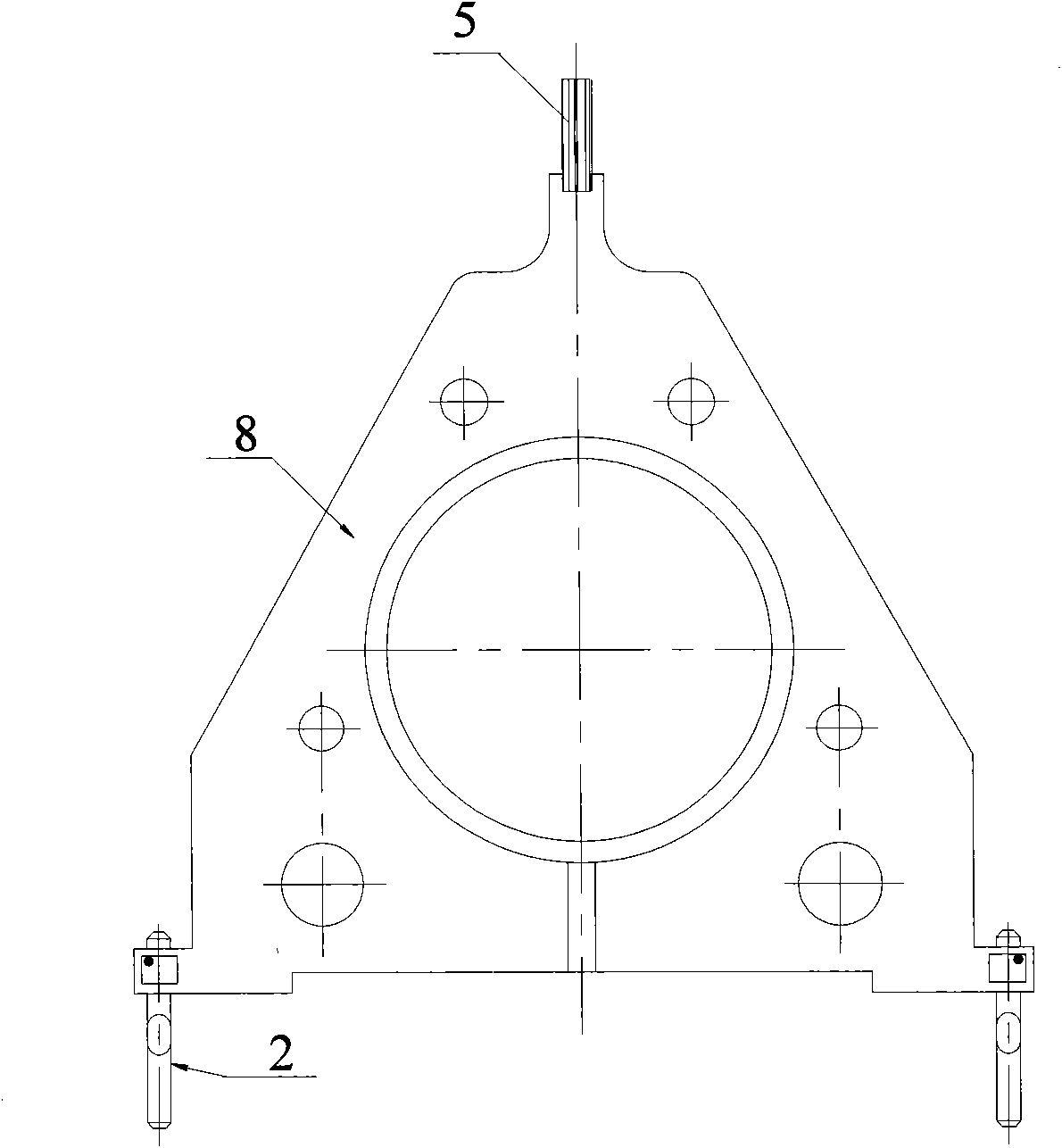
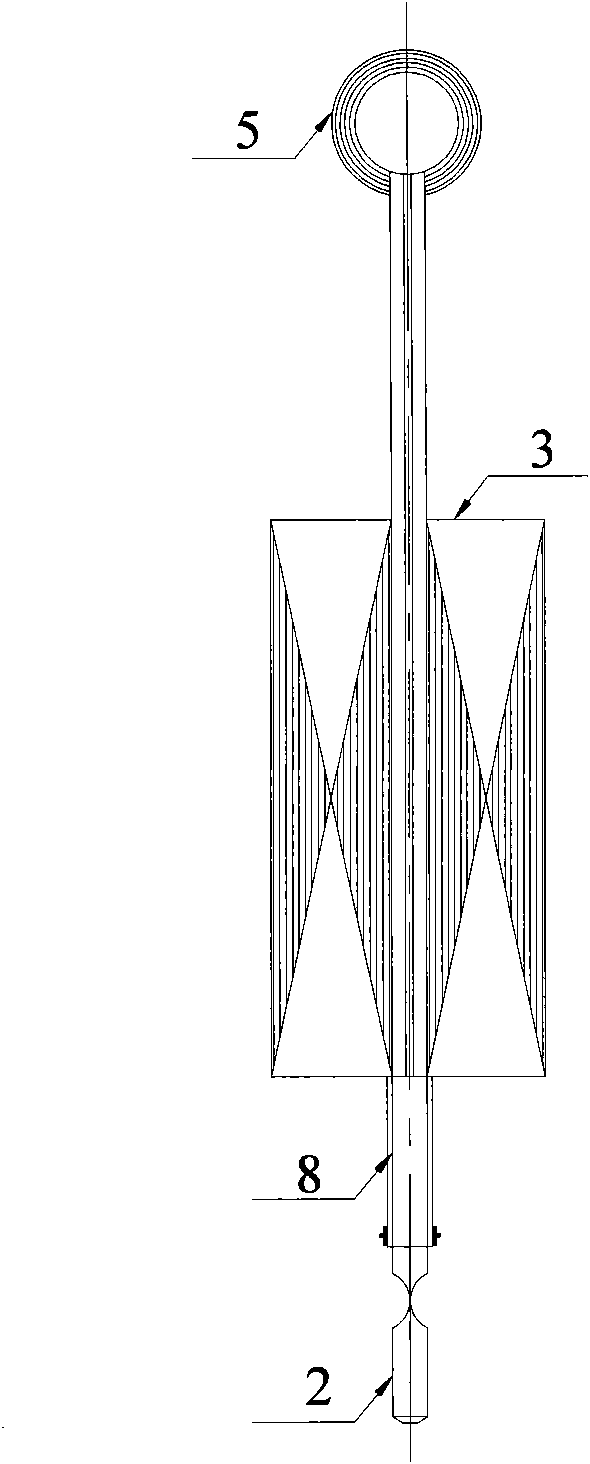
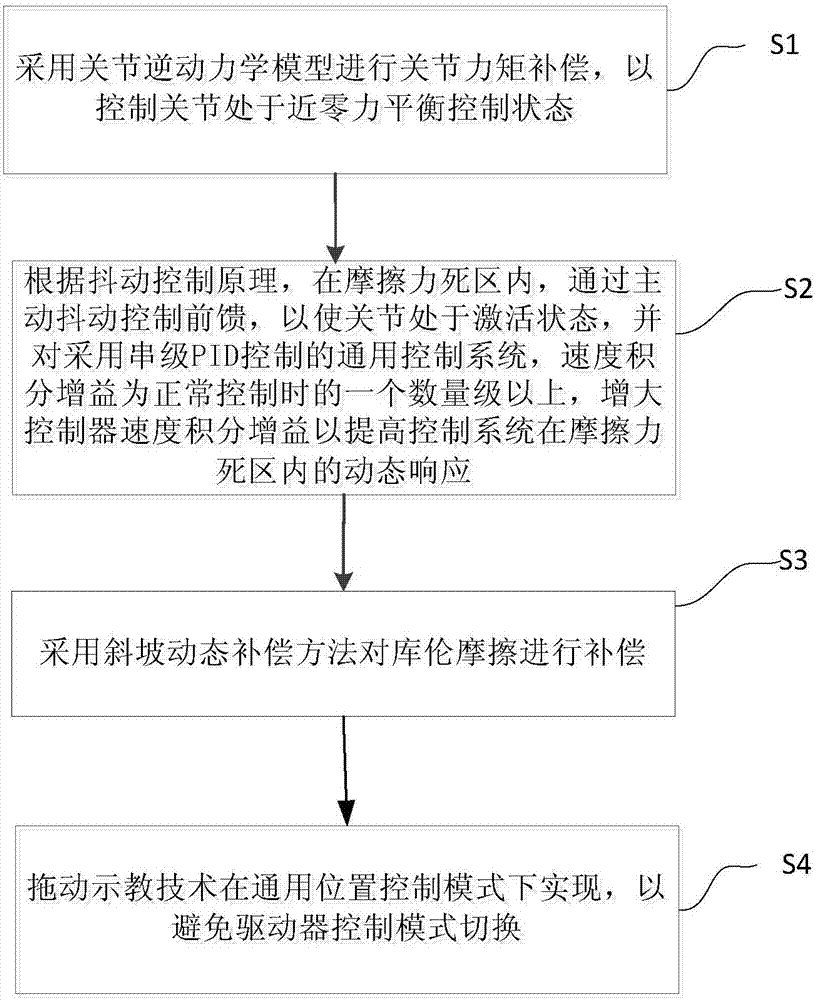
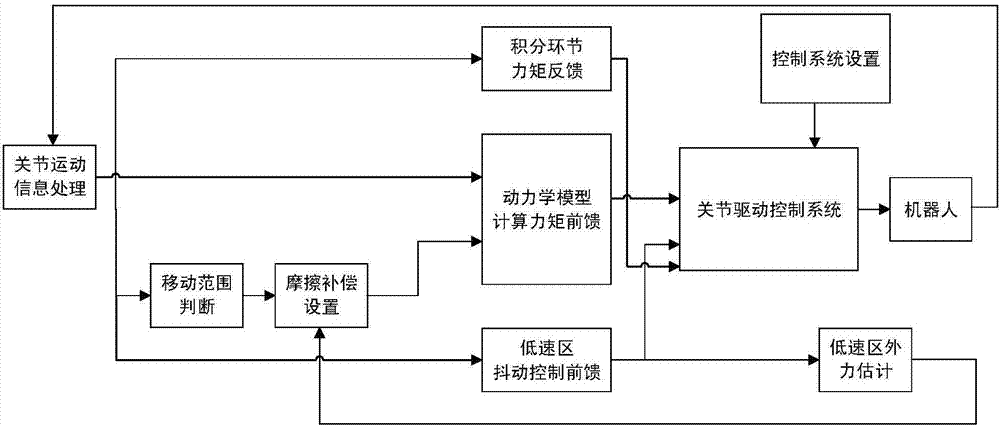
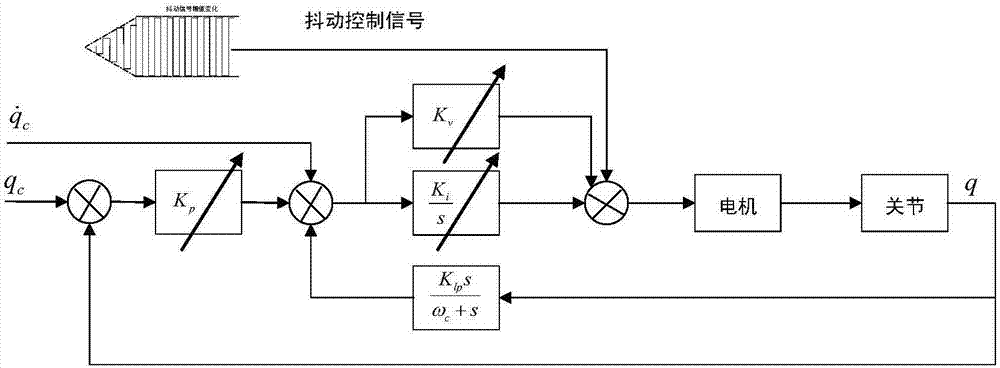
Industrial robot dragging teaching method without adopting torque sensor
The invention provides an industrial robot dragging teaching method without adopting a torque sensor. The method comprises the steps that a joint inverse dynamic model is adopted for joint moment compensation, so that a joint is controlled to be in a near-zero force balanced control state; according to a jitter control principle, feedforward is controlled through drive jitter within a dead zone of friction force, so that the joint is in an activated state, velocity integral grain of a universal control system adopting serial PID control is one order of magnitudes that of a system adopting normal control, and the controller velocity integral gain is increased to improve the dynamic response of the control system in the dead zone of the friction force; a slope dynamic compensation method is adopted for compensating coulomb friction; and a dragging teaching technology is achieved in a universal position control mode, so that switching of a control mode of a driver is avoided. According to the dragging teaching method adopted in the invention, the torque sensor is not needed, and the cost is low.
Owner:ROKAE SHANDONG INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
Coulomb friction damped disc brake caliper bracket
A Coulomb friction damped disc brake caliper bracket, wherein damping is provided by Coulomb friction, most preferably at the outboard tie-bar thereof. In one form, at least one clamping member applies compressive force externally to the caliper bracket, and in a second form, at least one interfacial boundary is internally disposed in the caliper bracket. Provided thereby is a mechanically distinguishable surface boundary between two surfaces which are in mutual contact such that a state of Coulomb friction exists therebetween.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
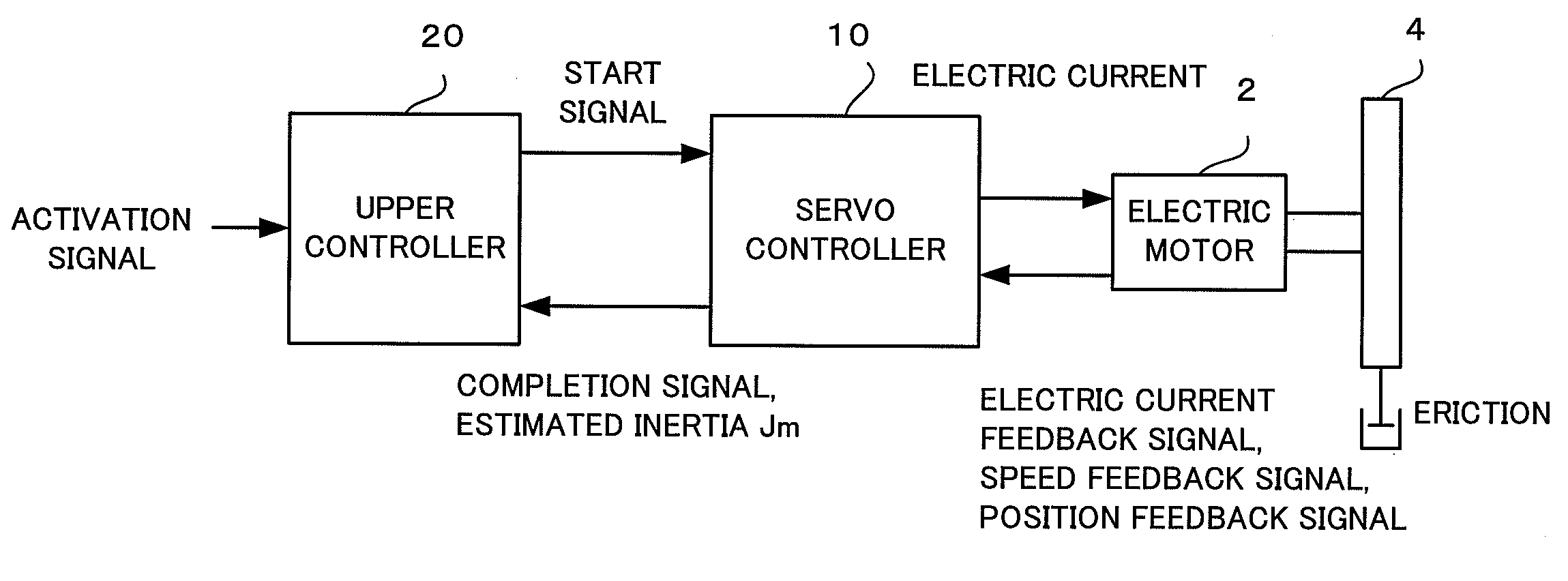
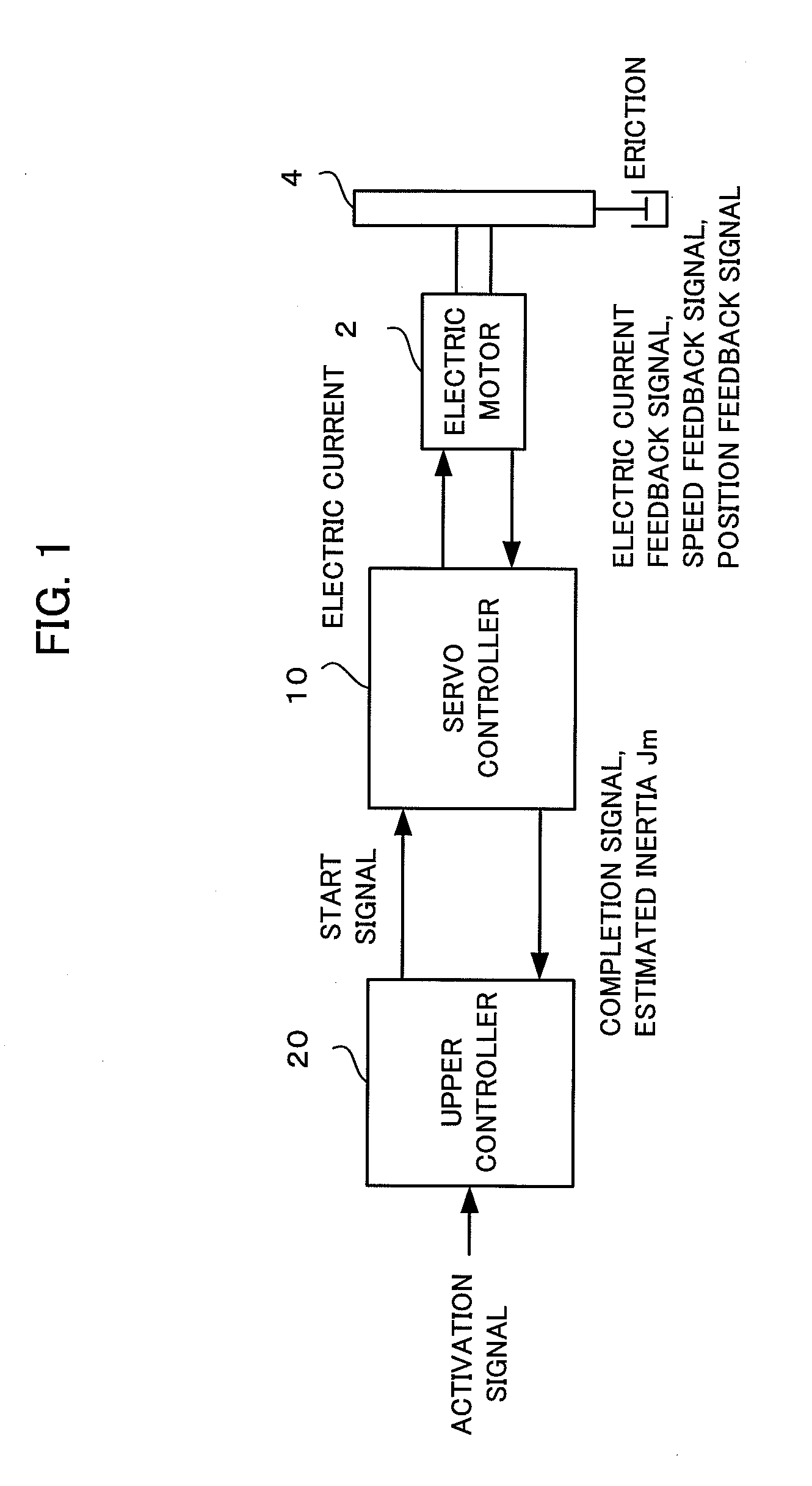
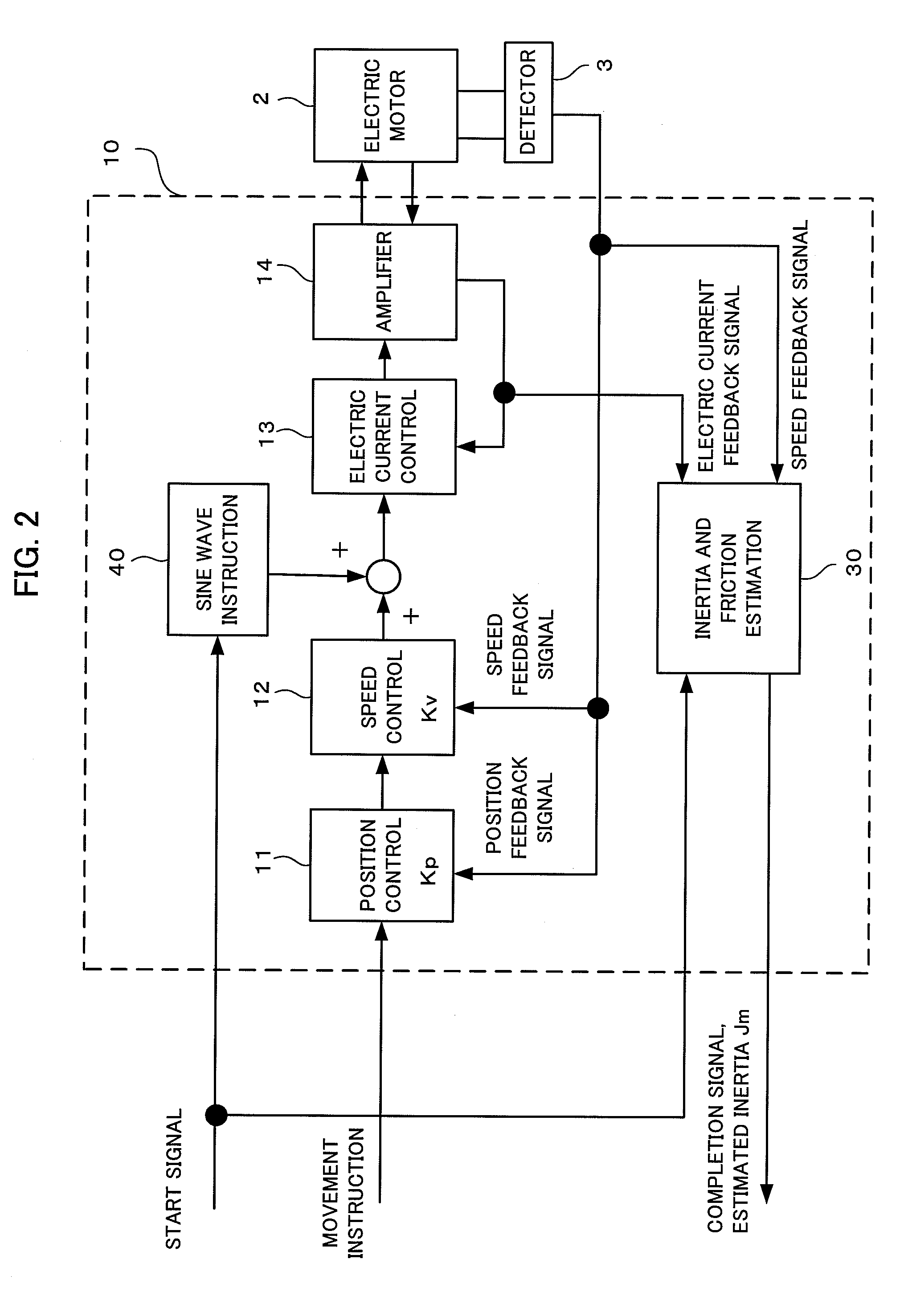
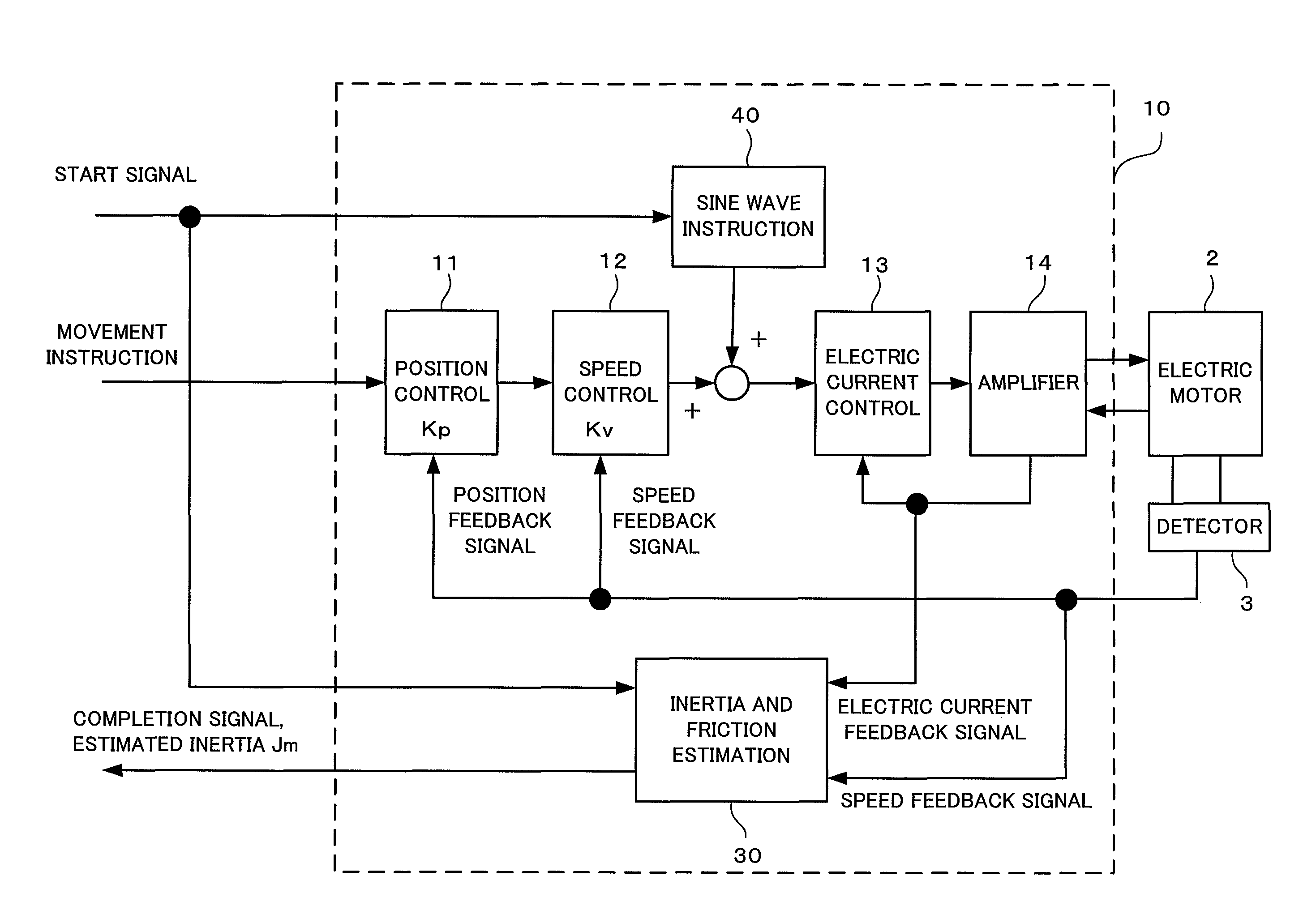
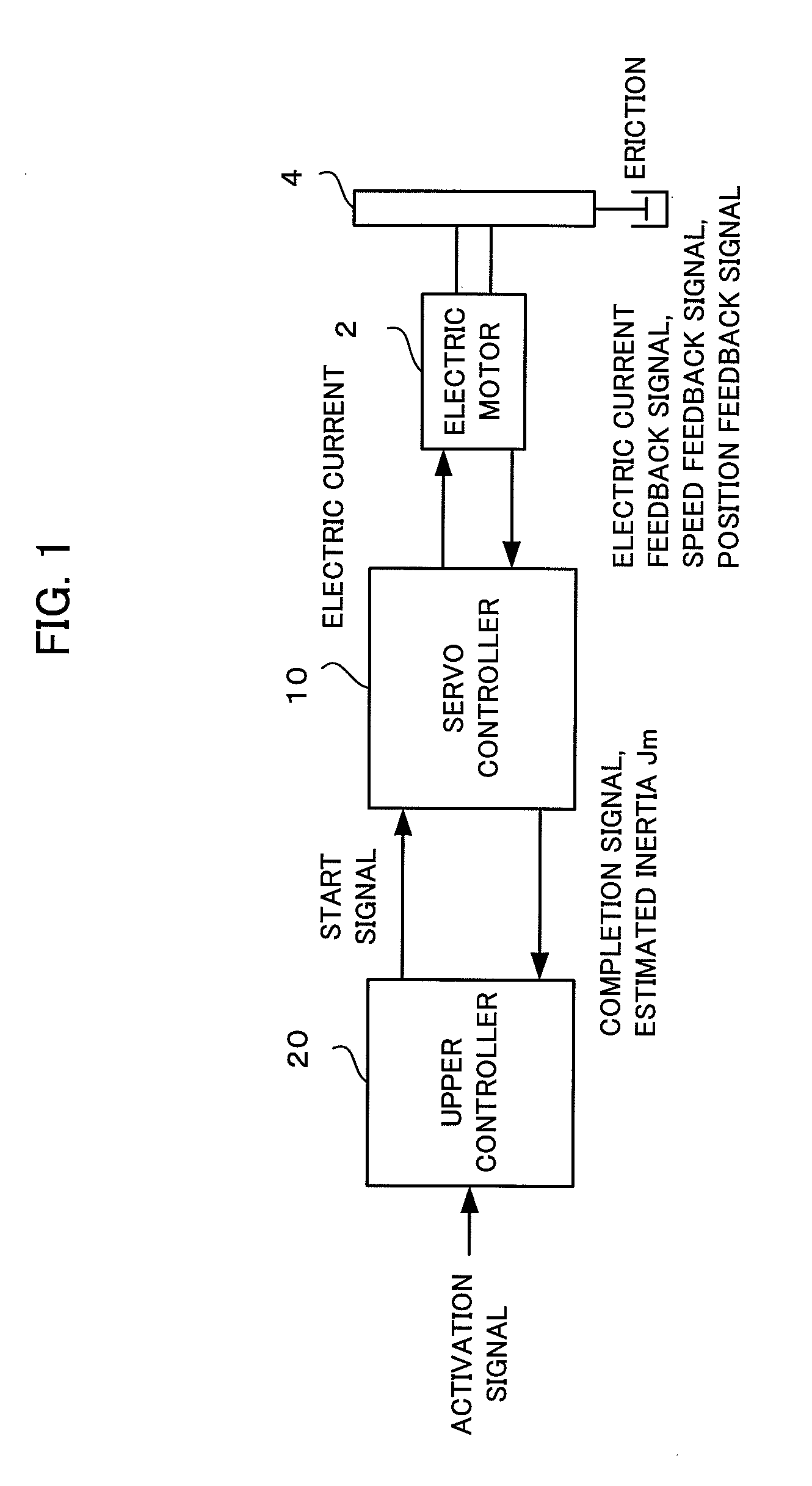
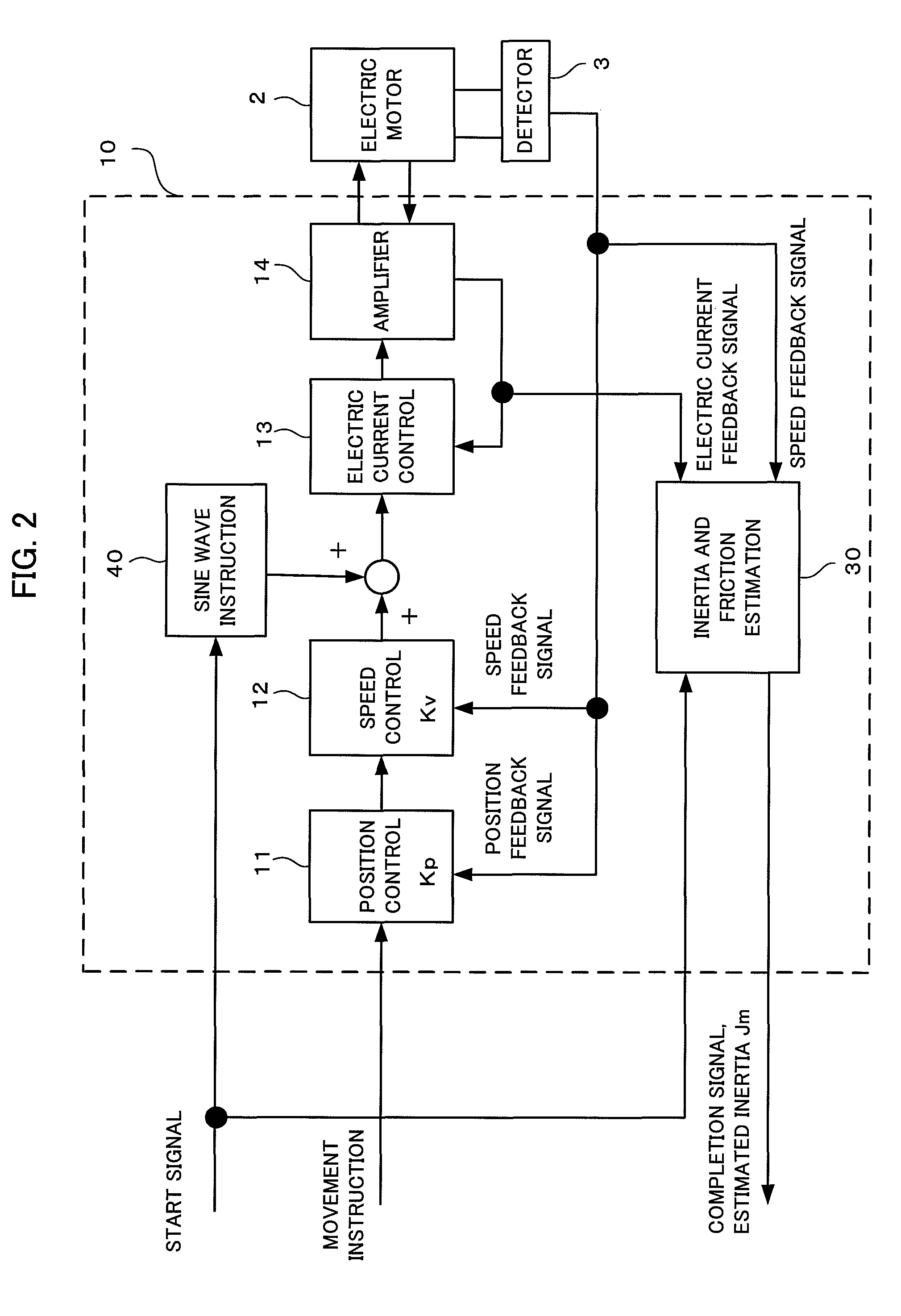
Controller of electric motor having function of estimating inertia and friction simultaneously
ActiveUS20110050146A1Improve estimation accuracyConvenient and accurateDigital data processing detailsFilamentary/web record carriersTransformerViscous friction
A controller estimates Coulomb friction itself together with inertia and viscous friction, and reduces the influence of the Coulomb friction on the accuracy of the estimated inertia. In addition, the controller estimates inertia, viscous friction and Coulomb friction simultaneously with sequential adaptation in which a Fourier transformer is not used but an inverse transfer function model is used in order to minimize the estimated error. Data sampled for a predetermined time need not be accumulated, as a result, a large amount of data memory is unnecessary.
Owner:FANUC LTD
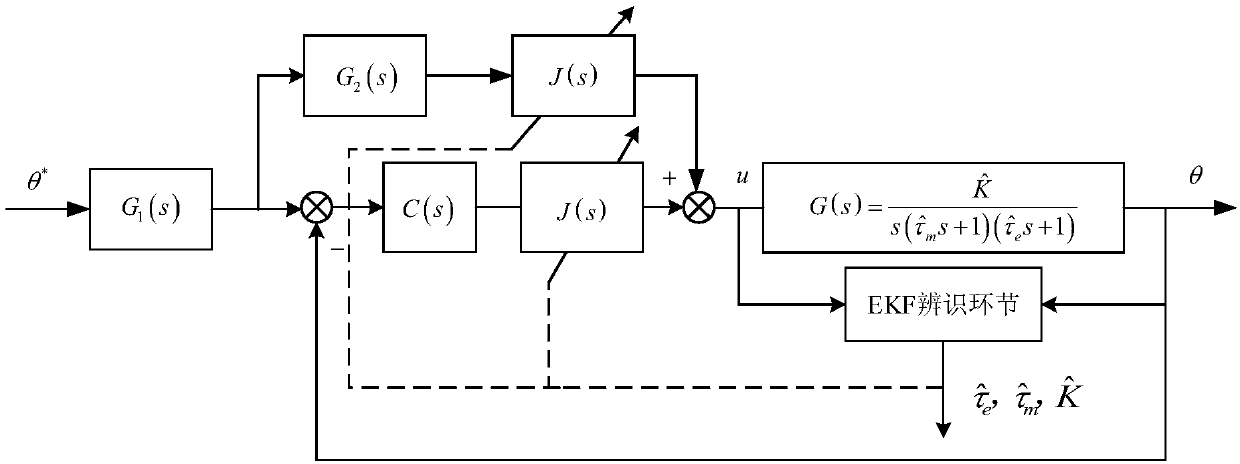
Simulation turntable self-correction control method based on model parameter accurate identification
ActiveCN107065551AIncrease dynamicsMeet the "Double Ten" targetAdaptive controlPoor adaptive skillsTransfer function model
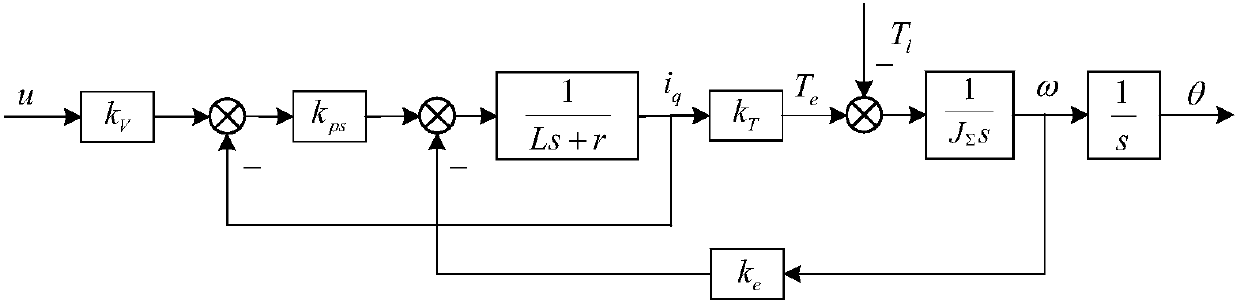
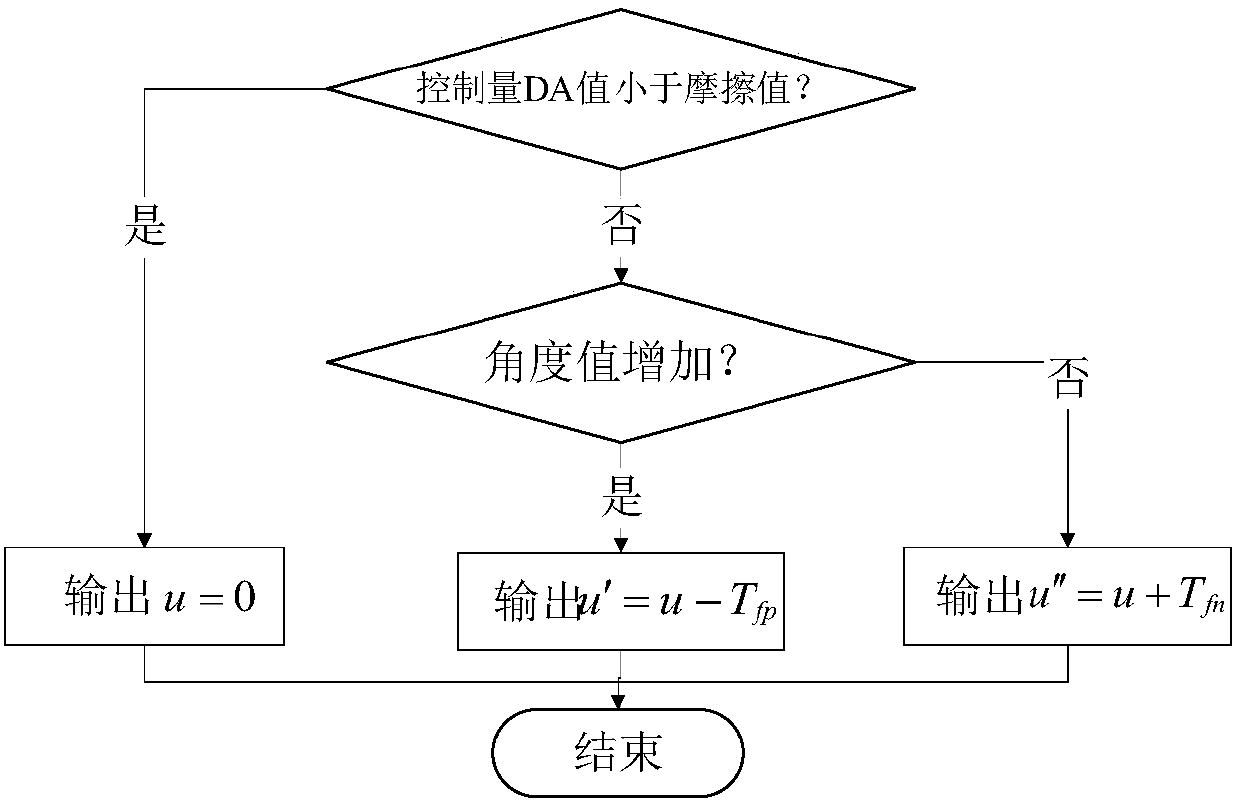
The invention provides a simulation turntable self-correction control method based on model parameter accurate identification, relates to the simulation turntable self-correction control method based on model parameter accurate identification, and is to solve the defects that an existing open-loop frequency sweep measurement method needs to consume a lot of time, a fixed parameter control method is poor in load change adaptability, and it is likely to have the problem that several sets of control method parameters cannot ensure optimum performance of a system or even cannot ensure system stability. The method comprises the following specific steps: 1) establishing a turntable servo system mechanism model according to a structure of a turntable servo system; 2) measuring a control quantity DA value needed for counteracting Coulomb friction moment Tc, and carrying out compensation on a control input signal of an open-loop transfer function model G(s) of the turntable servo system in the step 1); 3) obtaining accurate parameters taum<^>, taue<^> and K<^>; and 4) obtaining an optimal self-correction control link J(s). The method is used in the field of simulation turntable control.
Owner:哈尔滨工大航博科技有限公司
Construction method of limiting and self-resetting rubber-sliding seismic isolation bearing
InactiveCN106639024AHigh strengthImprove corrosion resistanceProtective buildings/sheltersShock proofingShape-memory alloyEngineering
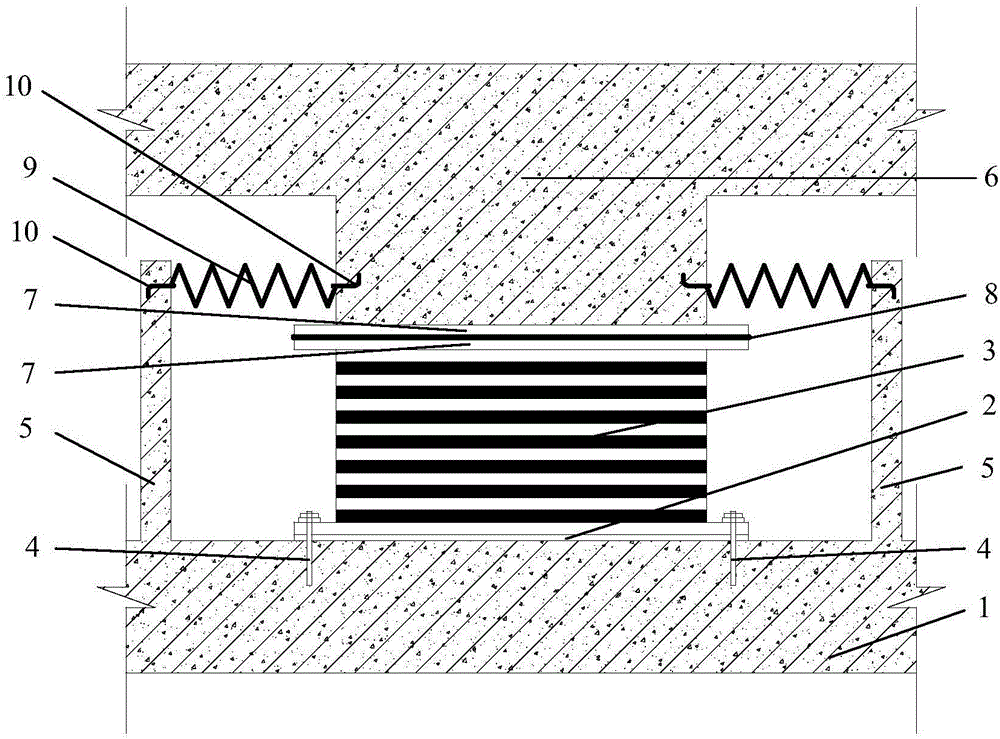
A construction method of a limiting and self-resetting rubber-sliding seismic isolation bearing comprises the steps that (1) a steel plate is embedded in the position, where a seismic isolation cushion needs to be put, of a seismic isolation layer foundation; (2) a rubber bearing is connected to the embedded steel plate through bolts; (3) reinforced concrete check blocks are formed through pouring at the portion of the seismic isolation layer foundation according to the horizontal displacement of a seismic isolation structure under the earthquake function; (4) teflon sliding materials are pasted to the top of the rubber bearing and the lower portion of the seismic isolation structure to form sliding layers, and the sliding layers adopt a coulomb friction force model; and (5) in order to reduce horizontal displacement of the structure, shape memory alloy helical springs in a large size are arranged between the check blocks and the structure and connected to concrete through embedded parts. The shape memory alloy helical springs not only have the limiting function, but also can achieve the self-resetting function after an earthquake is over due to the shape memory effect of the material, thereby greatly reducing residual displacement of the structure and ensuring post-quake normal use of the structure.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Device for testing thermal friction coefficient of sheet material in hot stamping forming process
InactiveCN103630491ATest accurateSimple structureUsing mechanical meansMaterial analysisHot stampingFrictional coefficient
A device for testing thermal friction coefficient of a sheet material in a hot stamping forming process is used for testing the friction coefficient of a high strength steel sheet at a high temperature. The device comprises an argon bottle connected with a heating furnace through a pipeline, an infrared thermometer, a pressure head, a hydraulic mechanism, a sensor, a drawing device and the like, wherein in the heating furnace with protective atmosphere, a tested sheet material sample is heated; after a corresponding temperature is reached, the tested sheet material sample is discharged from a furnace mouth under the drawing of the drawing device and penetrates through the middle part of the pressure head; a pressure is exerted by the pressure head, and the sensor records a pressure value of the pressure head and a drawing force value; and according to a Coulomb friction formula, the friction coefficient is calculated by a computer processing system. The device is simple in structure, and can accurately test the friction coefficient value of a high-strength steel sheet at high temperature, so as to provide a significant parameter for design and numerical simulation of a hot forming process.
Owner:马鸣图
Robot apparatus and control method therefor
ActiveUS20150258685A1Stable controlProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorInterval arithmeticCoulomb friction
A robot apparatus (1) includes a control apparatus (3) which carries out correction with use of an estimated value of a joint torque estimation unit (53) which estimates a joint torque acting upon each of joints (20 to 25). The joint torque estimation unit (53) includes a Coulomb frictional force torque estimation unit (70), a viscous frictional torque estimation unit (71), and a transition interval arithmetic operation unit (72) which smoothens transition from the Coulomb frictional force torque estimation unit (70) to the viscous frictional force estimation unit (71) and transition from the viscous frictional force torque estimation unit (71) to the Coulomb frictional force torque estimation unit (70).
Owner:TOSHIBA MASCH CO LTD
Numerical simulation method for analyzing structure dimensions of unequal-length working tape of extrusion die
Provided is a numerical simulation method for analyzing structure dimensions of an unequal-length working tape of an extrusion die. Simulation is carried out on the sectional material extrusion process, a die surface and the working tape are arranged to be two independent entities, a slope working tape is arranged, the inclination angle between the surface of the working tape and the extrusion direction ranges from 1 degree to 2 degrees, after three-dimensional model assembly is carried out, meshing is carried out, split friction boundary conditions are set, and a common friction model is selected for a deformation body, the inner wall of an extrusion barrel and the die surface, namely, a cutting friction model with a constant friction factor is adopted; a Coulomb friction model related to pressure is adopted for the deformation body and the surface of the working tape; extrusion technological parameters are applied to finite element software, data files are generated, and simulation analysis is carried out. According to the numerical simulation method for analyzing the structure dimensions of the unequal-length working tape of the extrusion die, due to the fact that the method of split modeling, the method of the slope working tape, the method of the split friction boundary conditions and the like are integrated, the problem that the deformation body is separated from the surface of the unequal-length working tape, or makes local contact with the surface of the unequal-length working tape is solved.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF TECH
Calculating Downhole Card in Deviated Wellbore Using Parameterized Segment Calculations
In a deviated wellbore, a pump system computes downhole data from surface data by solving a wave equation that takes both viscous damping and Coulomb friction into consideration. Mechanical friction between the rods, couplings, and tubing is considered in the calculation of downhole data in the deviated wellbore by modelling the wellbore's trajectory, parameterizing various deviated segments (build-ups, slants, drop-offs, etc.) in the trajectory, mapping the rod string to the segments, and incrementally evaluating position of the mapped string over time in order to compute drag forces and side loads experienced by the rod string during operation. These computed drag forces and side loads are then used in the solution of the wave equation to solve the surface load and position data and provide more accurate downhole position and load data.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
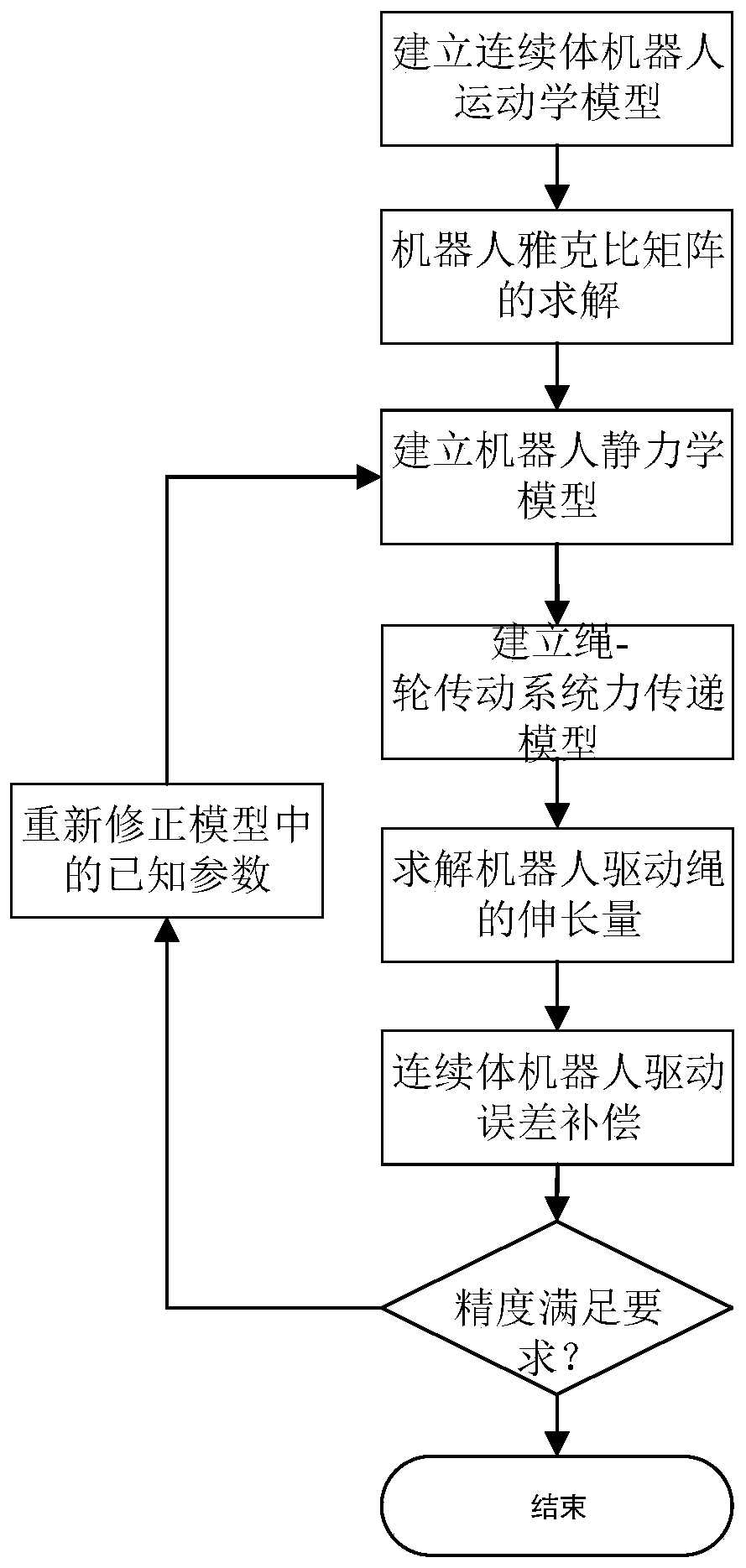
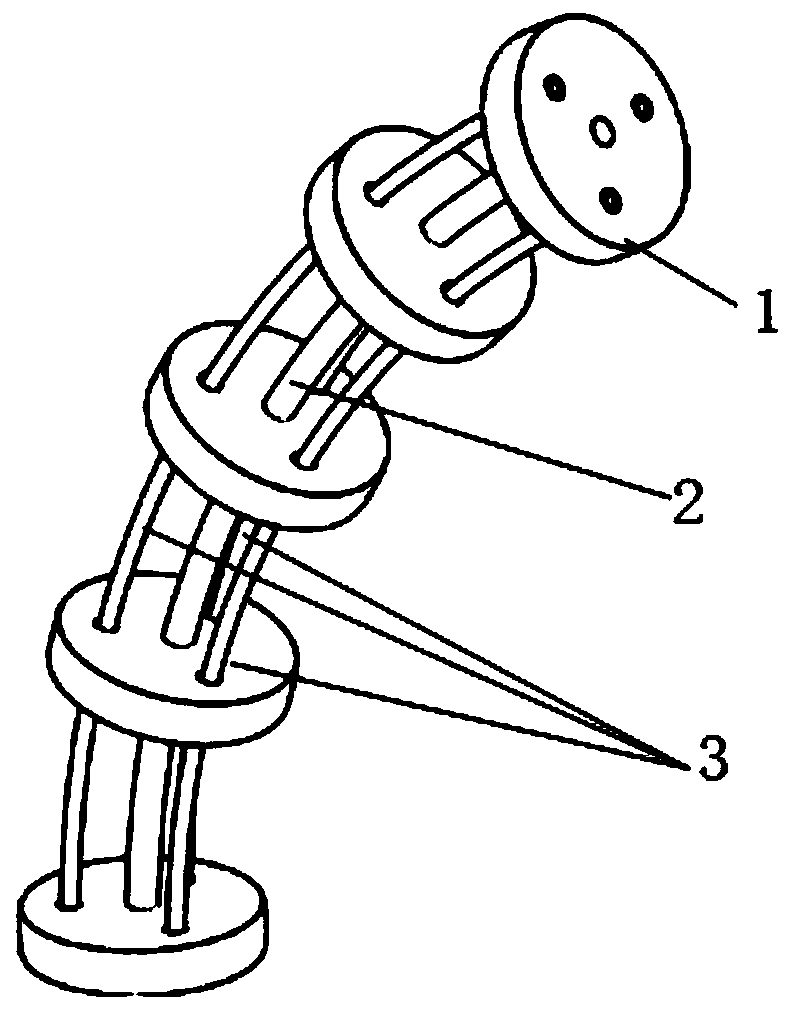
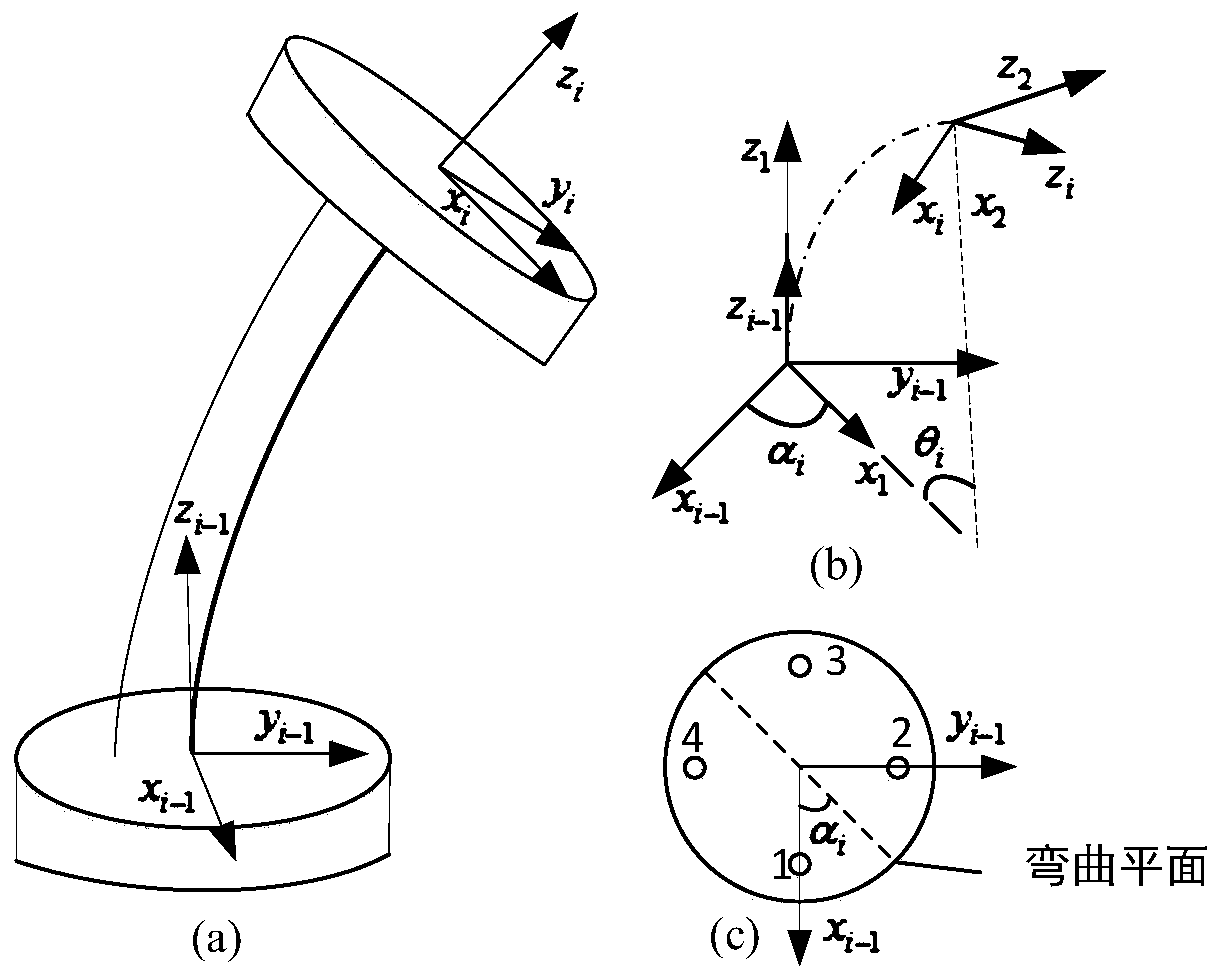
Driving compensation method for rope-driving continuum robot
ActiveCN110193827AImprove Motion Control AccuracyHigh control precisionProgramme-controlled manipulatorSimulationVirtual work
The invention discloses a driving compensation method for a rope-driving continuum robot. The method specifically comprises the following steps of establishing a kinematic model of the continuum robot by combining a segmented constant curvature arc hypothesis and a geometric analysis method; solving Jacobian matrix of the robot based on differential transformation principle; establishing a statics model of the robot based on virtual work principle; building a force transmission model of a rope-wheel drive system based on Coulomb friction; solving the elongation of a robot driving rope based on Hooke's law; and feeding back the driving rope length compensation amount to a control unit to realize error compensation of the transmission system of the continuum robot and improve the motion control precision of the robot. The method of has the characteristics of simplicity, high efficiency, low cost, good universality and the like, avoids using expensive measuring sensors, and realizes thepurpose of improving the motion control precision of the robot by establishing a driving error compensation model of the continuum robot system.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
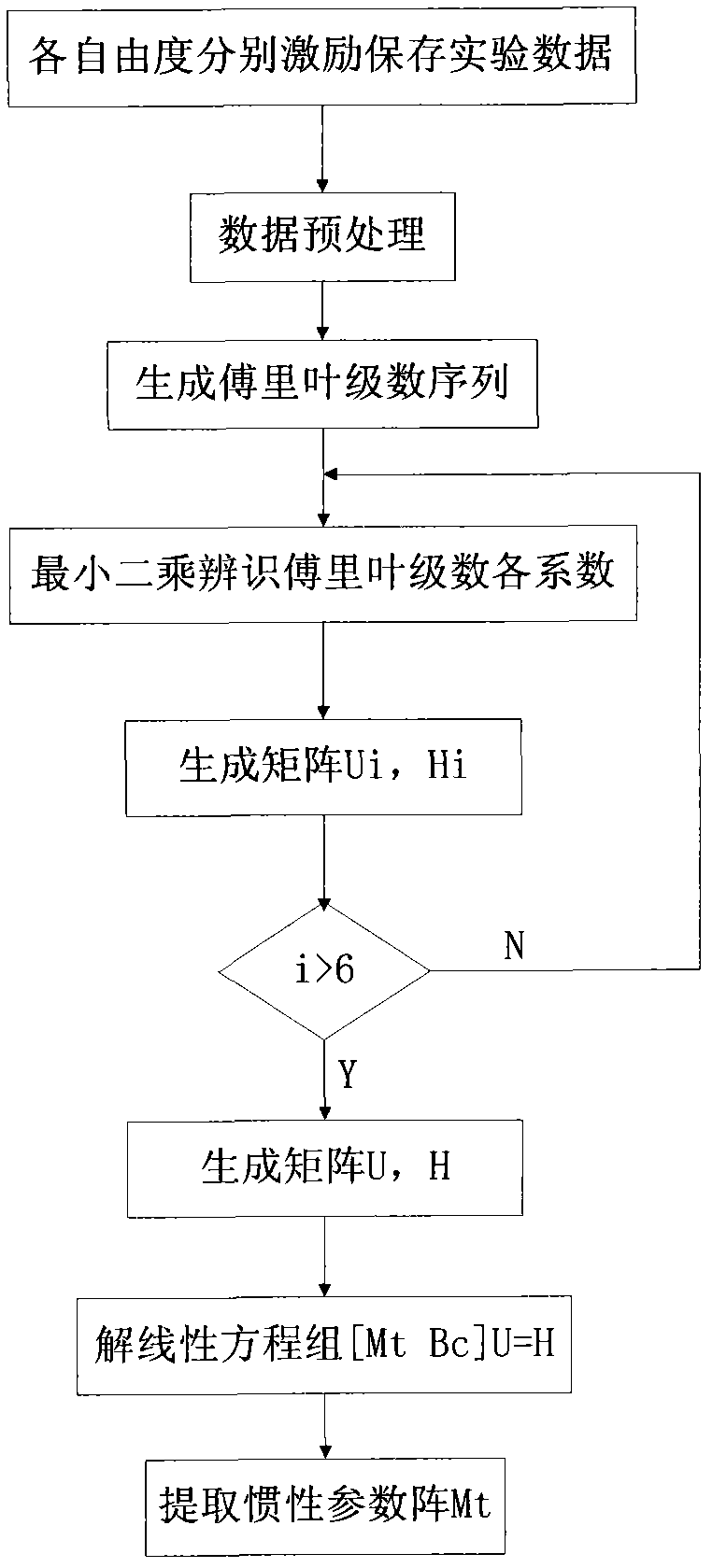
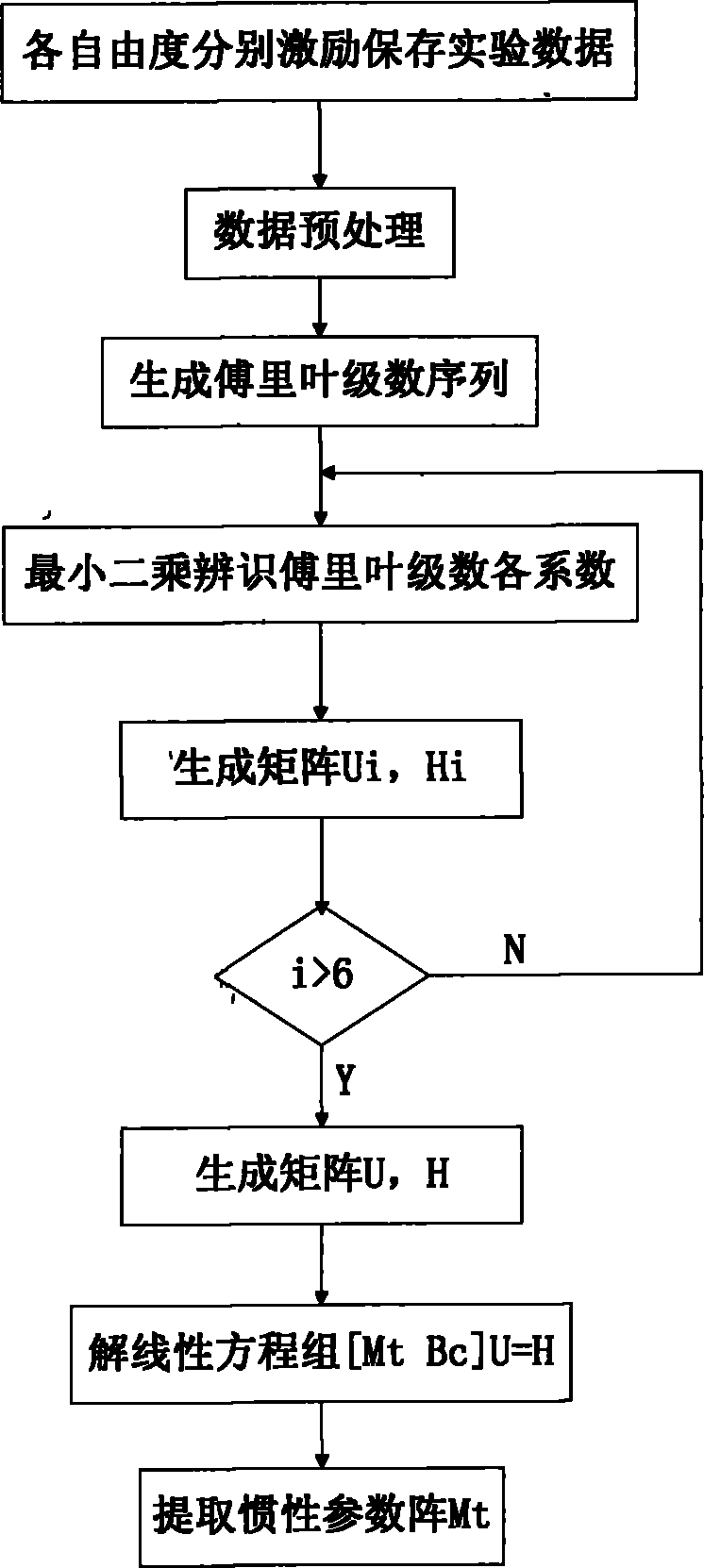
Method for identifying inertial parameters of six-degree-of-freedom parallel mechanism
InactiveCN102621891AAvoid trajectory designImprove signal-to-noise ratioAdaptive controlFundamental frequencyDegrees of freedom
The invention discloses a method for identifying the inertial parameters of a six-degree-of-freedom parallel mechanism, which comprises the following steps of: performing sine excitation with the same frequency respectively in six degree-of-freedom directions, decomposing the pose and the exciting force signal into the Fourier series form by using the least square fit principle, extracting the sine and cosine signal components of the fundamental frequency, and solving a specific linear equation set to obtain the inertial parameter matrix of the parallel mechanism. The method has the advantages of high identification accuracy, simple operation, high automation degree in identification process and small interference by system nonlinear factors (Coriolis force, Coulomb friction force and the like).
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Eddy current magnetic resistance hyperboloid friction pendulum support
PendingCN108316134ALong-term stable performanceImprove integrityVibration dampersMagnetic springsEngineeringComposite plate
The invention discloses an eddy current magnetic resistance hyperboloid friction pendulum support. The eddy current magnetic resistance hyperboloid friction pendulum support is composed of an upper support plate, an upper magnetic conductive plate, an upper eddy current plate, an upper wear-resisting plate, a permanent magnet spherical crown, a lower wear-resisting plate, a lower eddy current plate, a lower magnetic conductive plate and a lower support plate, wherein the permanent magnet spherical crown is composed of an upper friction plate, a permanent magnet, a support unit and a lower friction plate. When the eddy current magnetic resistance hyperboloid friction pendulum support is under the action of horizontal earthquake, the permanent magnet spherical crown moves reciprocatingly between the upper curved wear-resisting plate and the lower curved wear-resisting plate, and according to the principles of electromagnetism, the upper eddy current composite plate and the lower eddy current composite plate reciprocatingly cut off magnetic induction liens to produce eddy current and accordingly to generate magnetic damping, and further the magnetic damping consumes the motion energyof the eddy current magnetic resistance hyperboloid friction pendulum support together with coulomb friction damping produced by the friction plates. The eddy current magnetic resistance hyperboloid friction pendulum support has the advantages of being maintenance-free, low in manufacturing price, good in weather resistance and the like and belongs to the technical field of friction pendulum supports.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
Coulomb friction damped disc brake caliper bracket
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Location control method of 2R underactuated planar mechanical arm based on subdivision control
InactiveCN103128737ASmooth motionThe control object is universalProgramme-controlled manipulatorUnderactuated robotsResearch Object
The invention discloses a location control method of a 2R underactuated planar mechanical arm based on subdivision control. The location control method of the 2R underactuated planar mechanical arm based on subdivision control comprises the following steps: establishing an underactuated planar mechanical arm mechanics module with a driving first joint and a driven second joint, and considering Coulomb friction force and viscous friction force of joints in the module. To an underactuated robot, the friction of the driving joint can be directly compensated by a motor, but the driven joint can not be compensated, and the friction force of the driven joint is utilized. By adopting a time scale method and a proportion integration differentiation (PID) control method, the location control method of the 2R underactuated planar mechanical arm based on subdivision periodically starts joint space and location control to the 2R underactuated planar mechanical arm, and further achieves positioning control to the tail end of the robot. A research objective of the location control method is an underactuation system which includes entirely free joints, and so that the location control method of the 2R underactuated planar mechanical arm based on subdivision control has the advantages of being simplified in a mechanical device and pervasive in the control objective. The location control method of the 2R underactuated planar mechanical arm based on subdivision control utilizes a simple and feasible control method to realize the location control of the 2R underactuated planar mechanical arm, avoids to adopt complex and profound nonlinear control methods, and achieves the purposes of being distinct in train of thought, simple to programming and easy to achieve.
Owner:SHANGHAI PAXING INFORMATION TECH
Servo system friction compensation method based on time Coulomb friction model
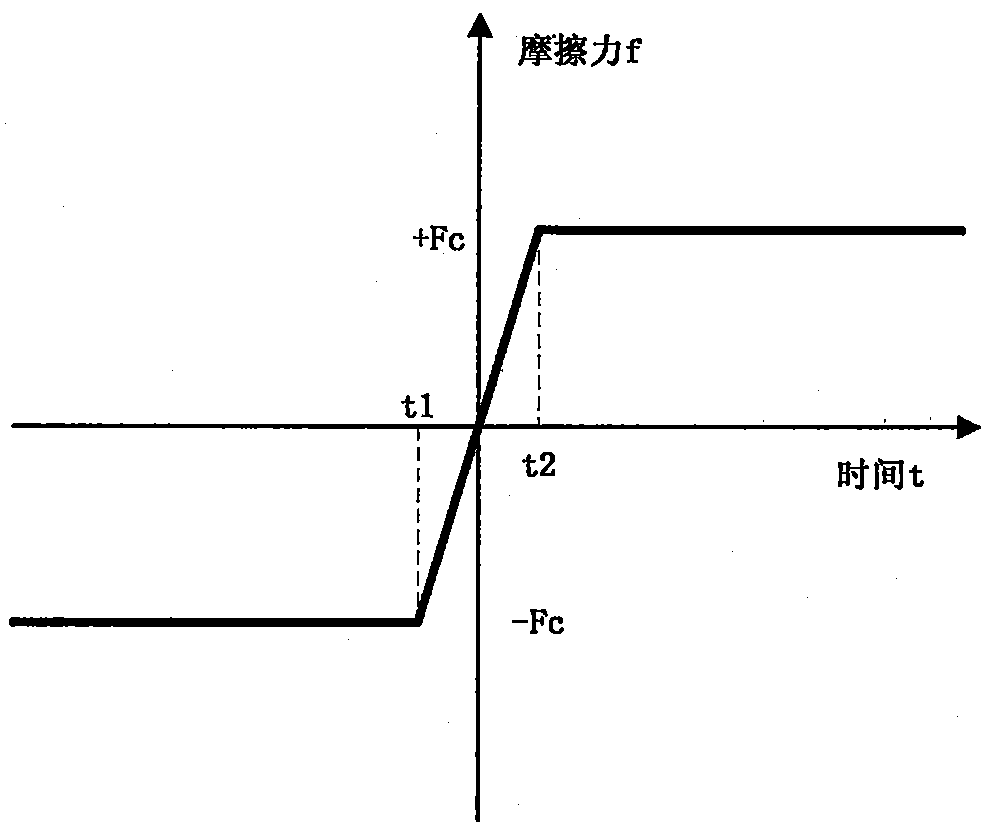
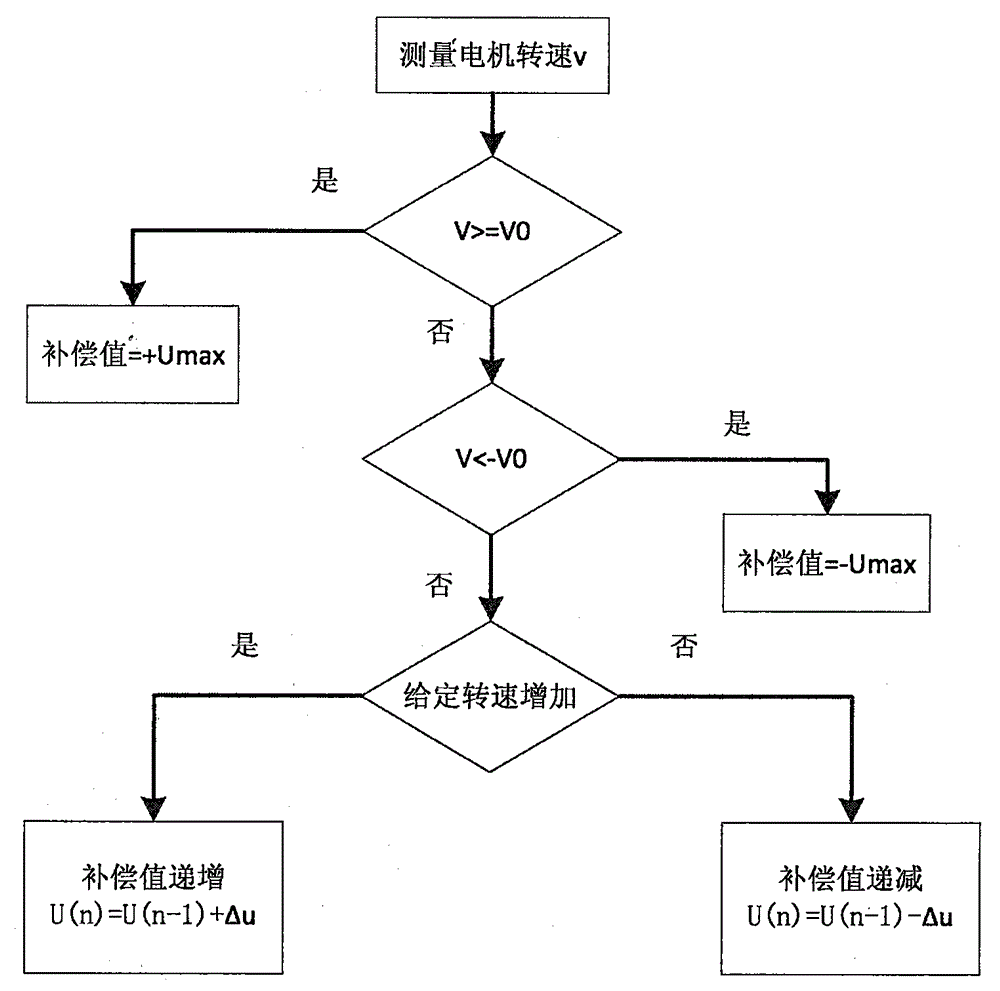
InactiveCN105022345AImprove stabilityAvoid jitterProgramme controlComputer controlFriction torqueElectric machinery
The invention provides a servo system friction compensation method based on time Coulomb friction model, and the method comprises the steps of building a model of the frictional force that changes along with time; then outputting a compensation signal by a controller according to time; then determining the compensation value according to the measured motor rotating speed based on the given signal and offsetting the friction torque. The influence of the frictional force to the servo system can be effectively overcome; because the compensation value changes along with time continuously, abrupt change of the output signal from the controller is prevented; system robust stability is raised; and jitter phenomenon caused by output abrupt change of the controller is avoided.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Coulomb Friction Damped Disc Brake Caliper Bracket
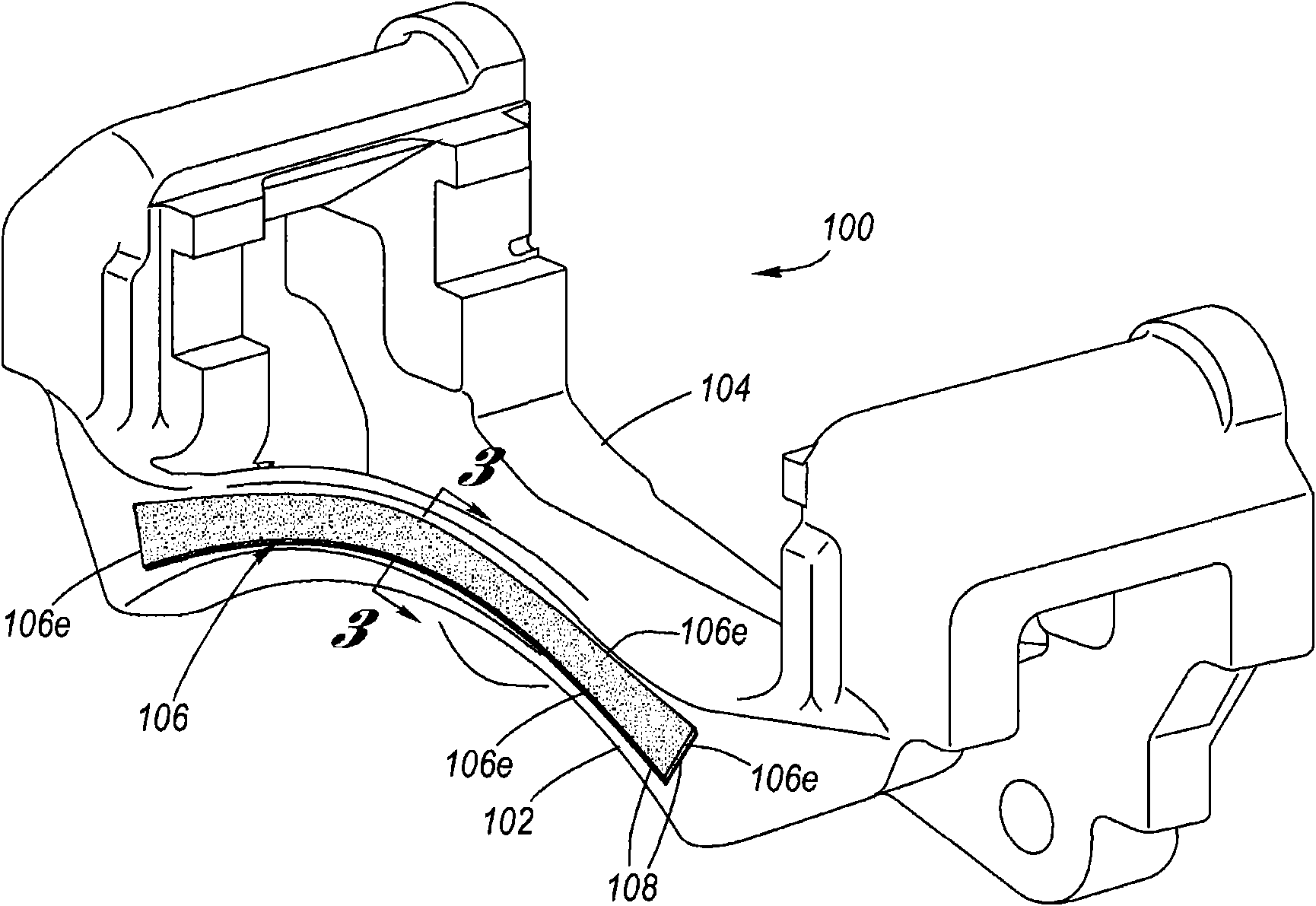
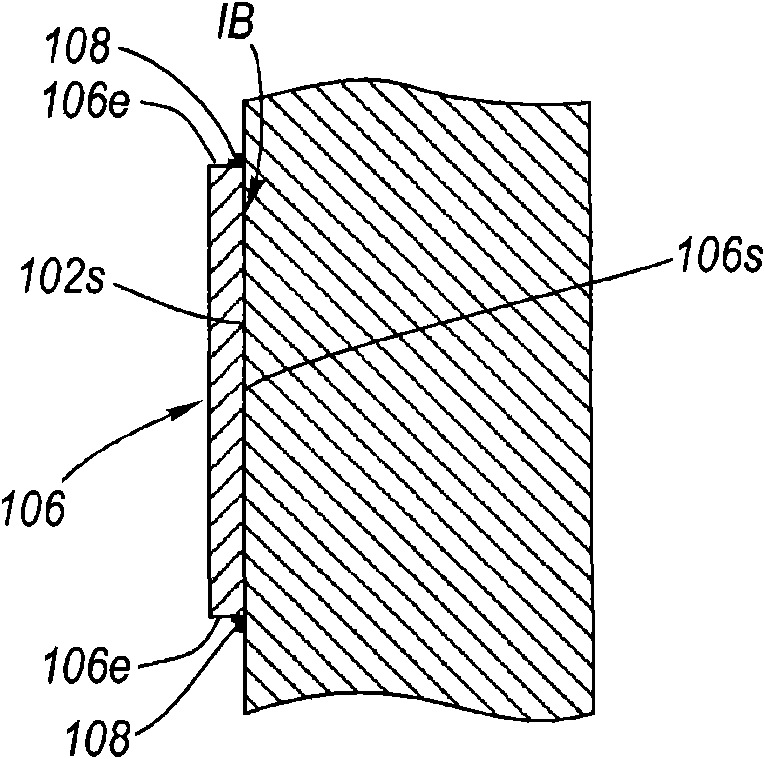
InactiveUS20110127124A1Reduce noiseNoise/vibration controlAxially engaging brakesEngineeringCalipers
A Coulomb friction damped disc brake caliper bracket, wherein damping is provided by Coulomb friction, most preferably at the outboard tie-bar thereof, by a Coulomb bar peripherally welded thereto. An inner surface of the Coulomb friction bar is in abutting contact with the external surface of the tie-bar, whereby because of the continuous peripheral edge welding, corrosion cannot find entry into the interface of the two surfaces, yet the two surfaces form are free to vibrate one as to the other in Coulomb friction fashion to thereby provide damping and reduction of brake squeal and other noise.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Novel minisize gas turbine
InactiveCN104213981AIncrease positive pressureIncreased Coulomb frictionGas turbine plantsTurbine/propulsion lubricationVibration amplitudeCombustion chamber
A disclosed novel minisize gas turbine comprises a gas compressor, a turbine and a combustion chamber; the combustion chamber is connected with an impeller and a main-shaft divided body; the impeller is connected with a main shaft via a center pull rod; and the combustion chamber is connected with the impeller and the main-shaft divided body via pipes. A 2-0-0 supporting manner is adopted in the overall structure. The gas compressor and the turbine both employ an overhung cantilever end which easily generates relatively large vibration amplitude during working. The axial-direction pre-tightening pulling force generated through cooperation of a locking nut and a turbine pull rod shaft is capable of directly improving the positive pressure of a combination surface of the end tooth, thereby improving the coulomb frictional force between contact surfaces, and further improving the radial rigidity of the shafting overhung cantilever end, so that the radial vibration amplitude of the shafting overhung cantilever end, and also asynchronous radial vibration is avoided between the gas compressor impeller and the turbine. The provided overall structure project has the advantages of simple structure, low processing cost, compact structure and high transmission efficiency.
Owner:XIAN TONGLING POWER
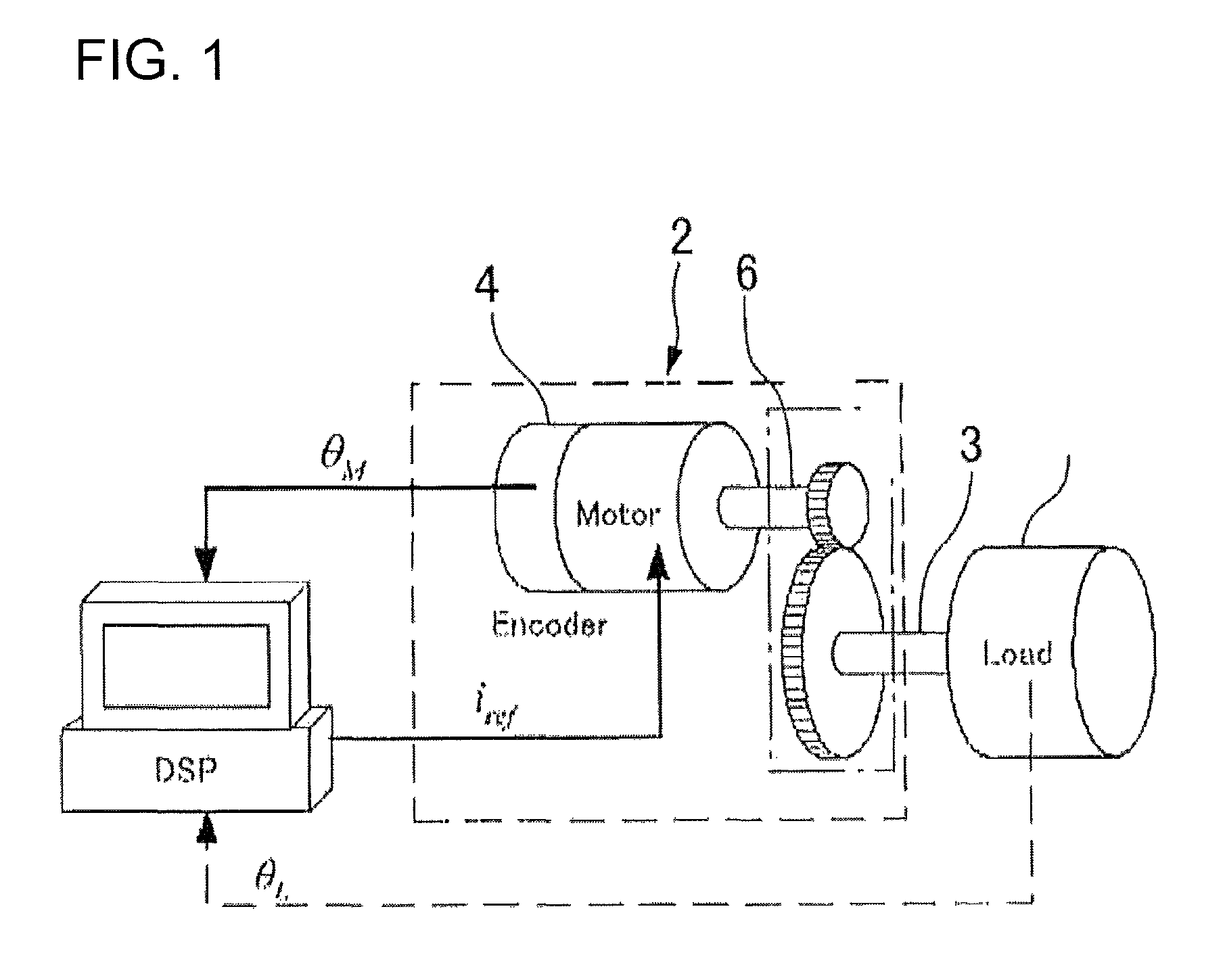
Method for identifying friction parameter for linear module
InactiveUS20170261529A1Eliminate useMuch easier and much in practiceProgramme controlMeasurement of torque/twisting force while tighteningFriction torqueReciprocating motion
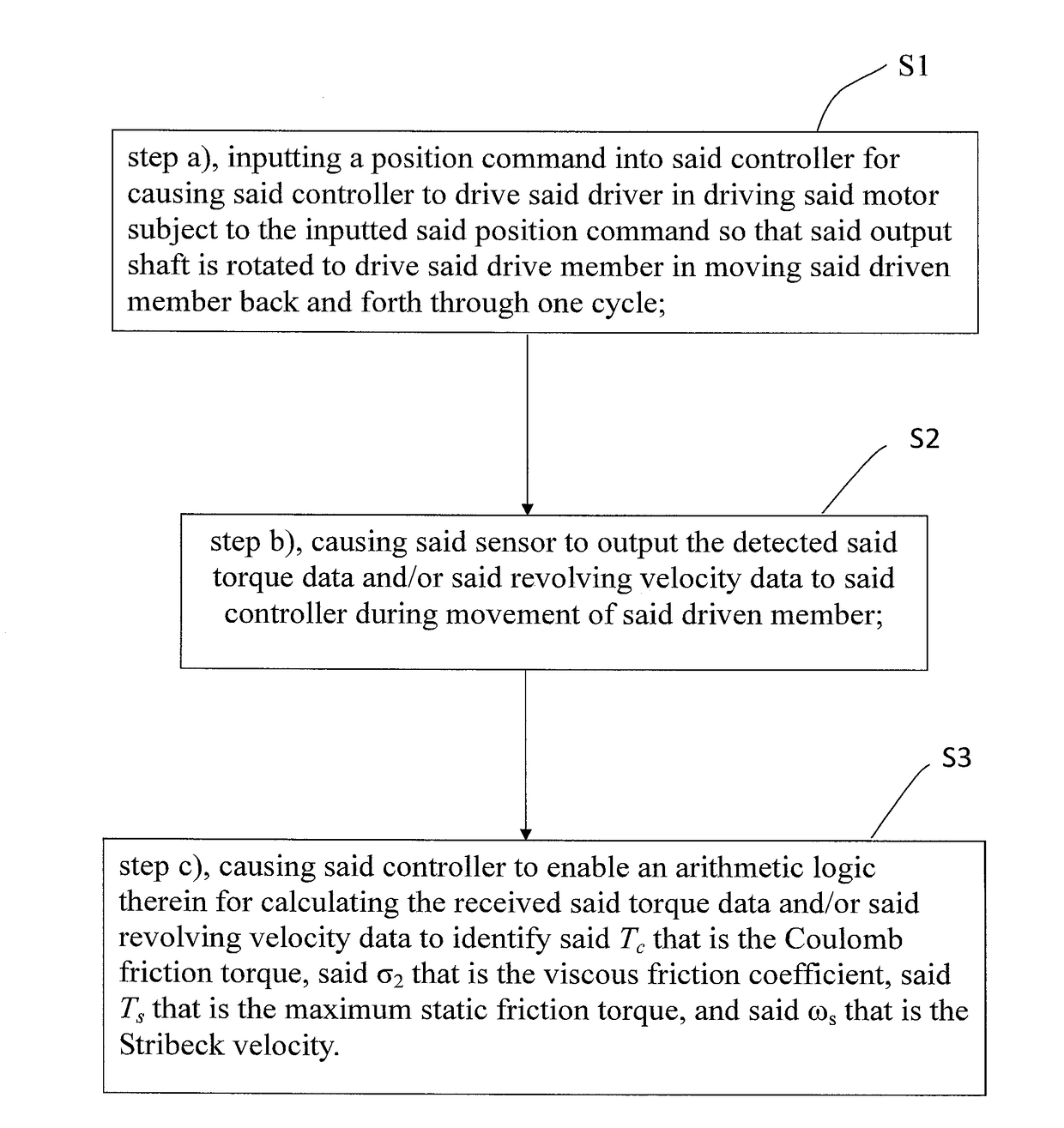
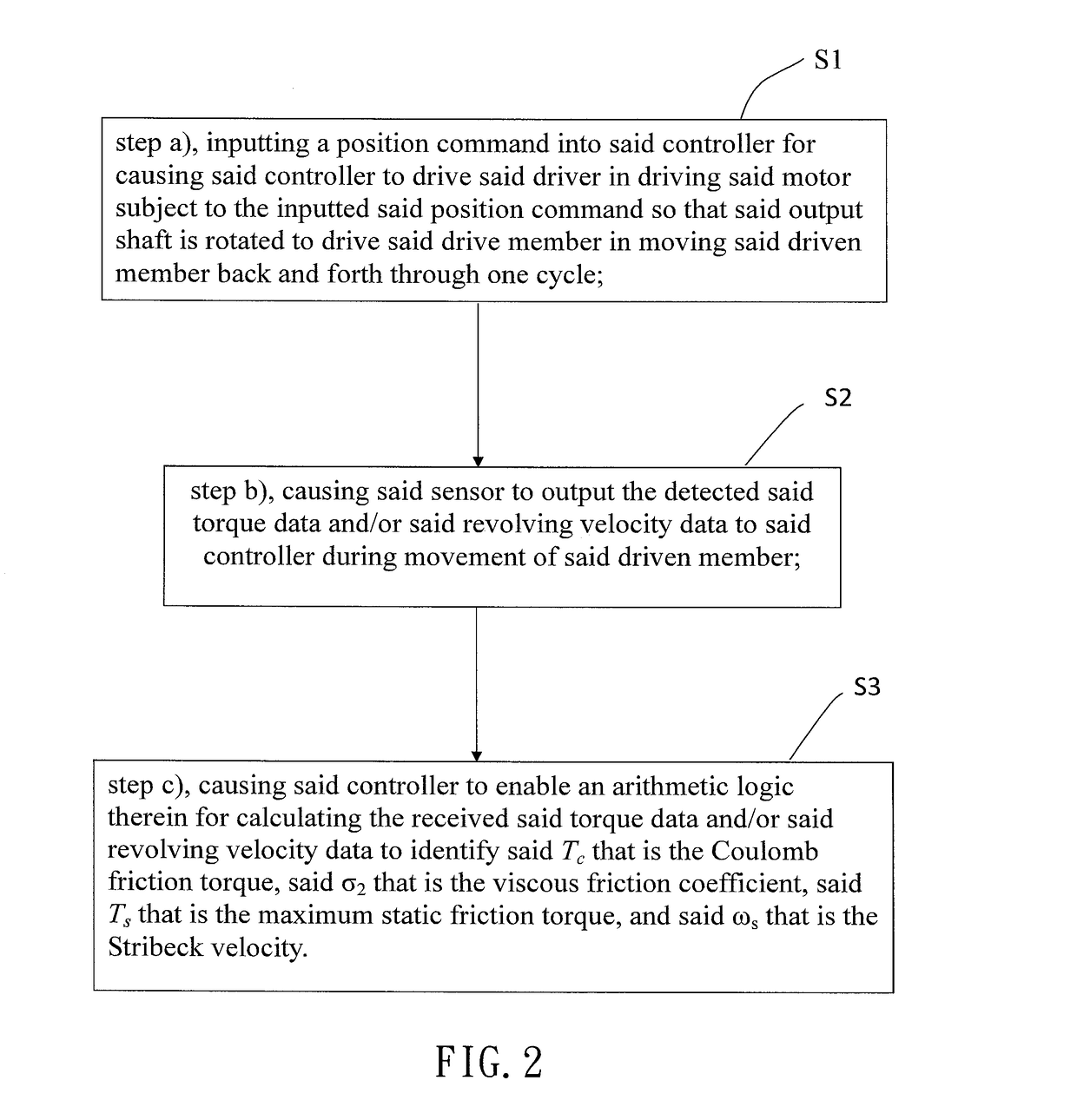
A method for identifying friction parameters for a linear module is disclosed. Since an acting interval of a friction is determined by a relative velocity between two contacting surfaces, and when the relative velocity is much greater than a Stribeck velocity, there is only a Coulomb friction and a viscous friction exist between the contacting surfaces, it is possible to use a measured torque signal of this interval to identify a Coulomb friction torque, a the linear module's friction torque, and the linear module's equivalent inertia. When the relative velocity between the two contacting surfaces is smaller than the Stribeck velocity, it is possible to identify a maximum static friction torque and the Stribeck velocity by referring to the three known parameters. Thereby, all the friction parameters can be identified within one reciprocating movement of the linear module, making the method highly feasible in practice.
Owner:HIWIN TECH
A ball socket nozzle load characteristic identification method for servo system load matching
ActiveCN109725659ALoad-matched ball-and-socket nozzle load characteristic matchingMatching Load CharacteristicsMechanical power/torque controlControl vectorViscous friction
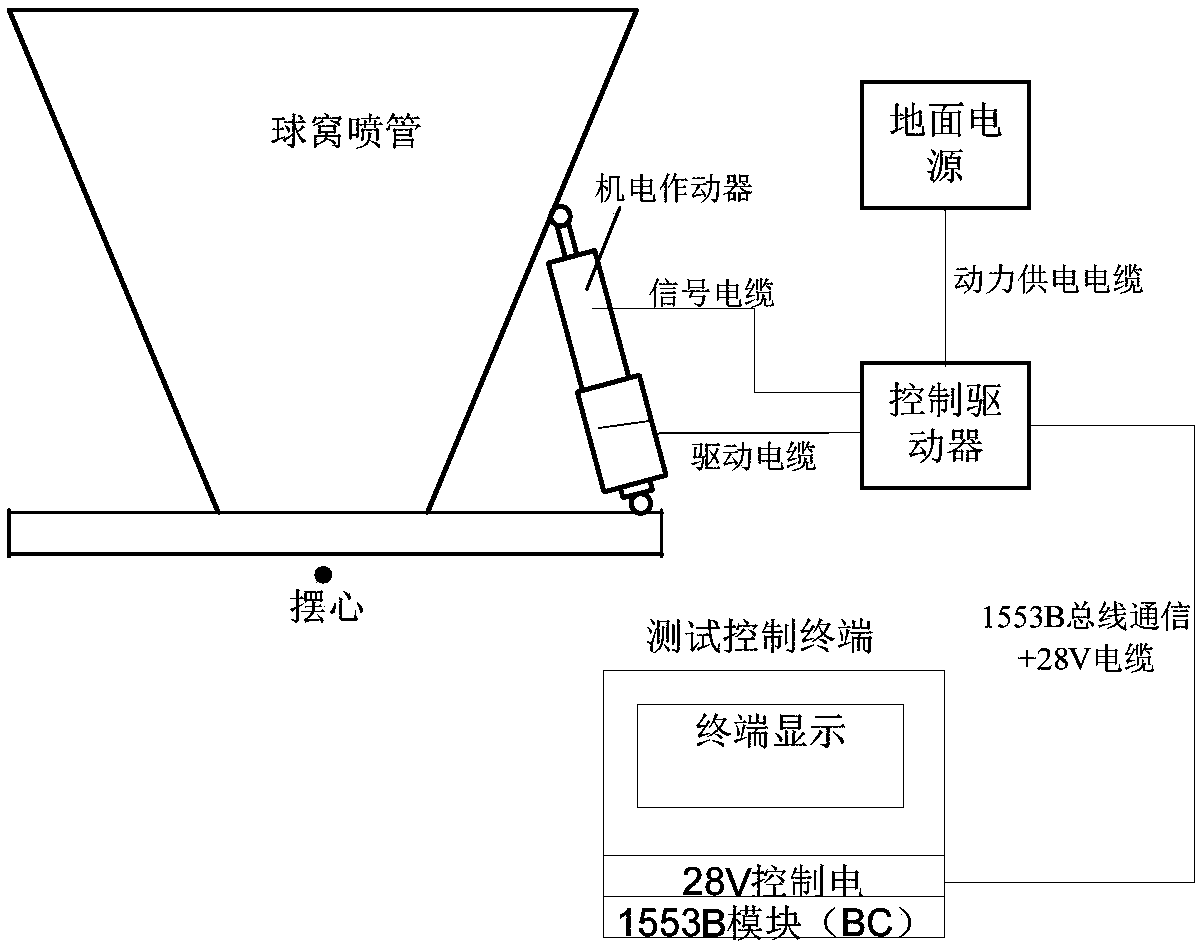
The invention belongs to the technical field of electromechanical servo systems, and particularly relates to a ball socket nozzle load characteristic identification method for servo system load matching. The method comprises a coulomb friction torque identification method, a viscous friction torque identification method, an elastic torque identification method and an inertia torque calculation method. By means of the method, accurate load characteristic parameters of a large ball socket nozzle can be identified, matching of the servo system and the load characteristics of the ball socket nozzle is achieved, and the performance requirement for thrust vector control of a solid rocket is met.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF PRECISE MECHATRONICS CONTROLS
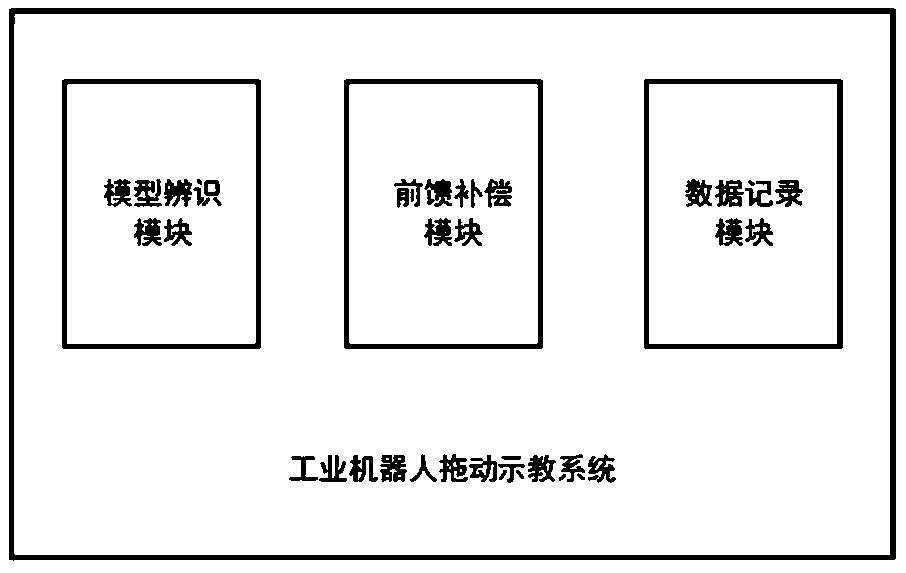
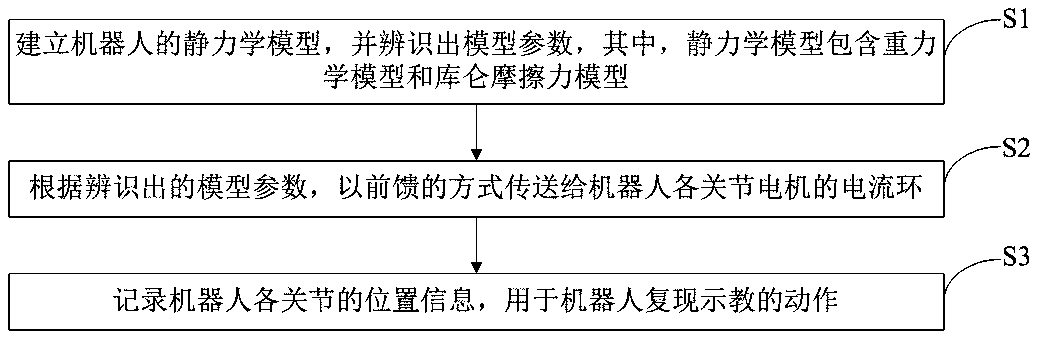
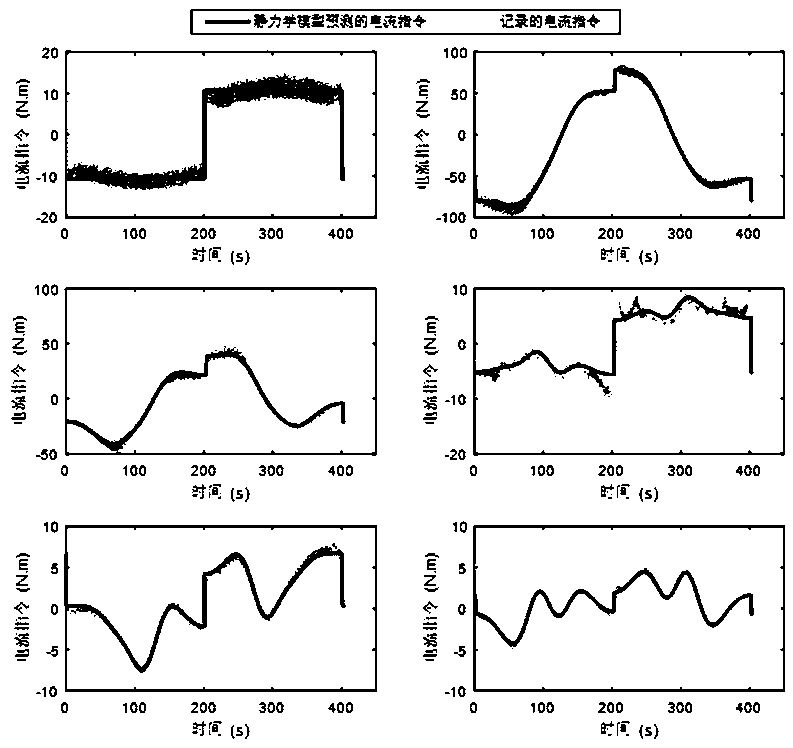
Dragging demonstration system and method
ActiveCN108839023ALow costFlexible teachingProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorPower flowSimulation
Owner:SHANGHAI JIEKA ROBOT TECH CO LTD
Controller of electric motor having function of estimating inertia and friction simultaneously
ActiveUS8232758B2Improve estimation accuracyConvenient and accurateDigital data processing detailsFilamentary/web record carriersTransformerViscous friction
A controller estimates Coulomb friction itself together with inertia and viscous friction, and reduces the influence of the Coulomb friction on the accuracy of the estimated inertia. In addition, the controller estimates inertia, viscous friction and Coulomb friction simultaneously with sequential adaptation in which a Fourier transformer is not used but an inverse transfer function model is used in order to minimize the estimated error. Data sampled for a predetermined time need not be accumulated, as a result, a large amount of data memory is unnecessary.
Owner:FANUC LTD
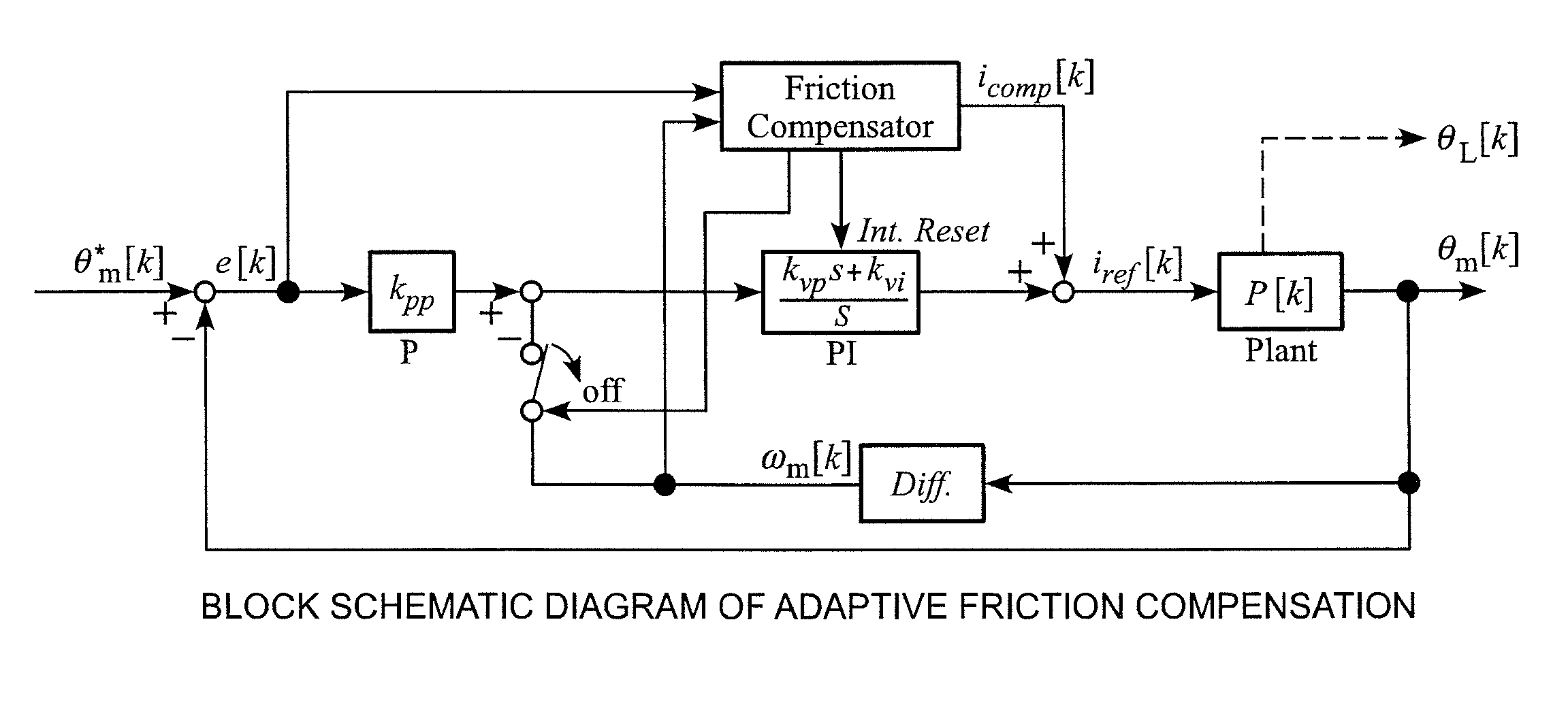
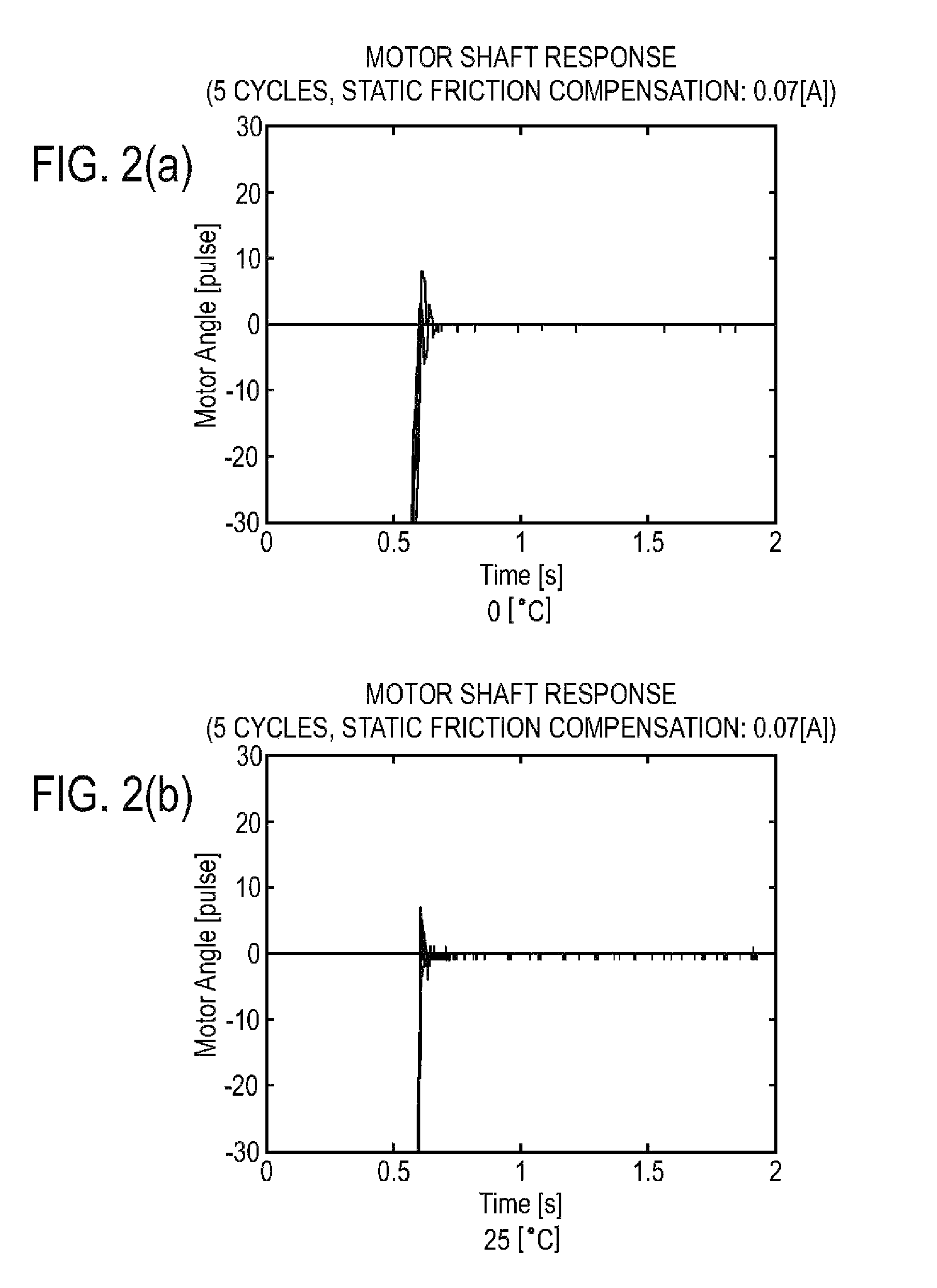
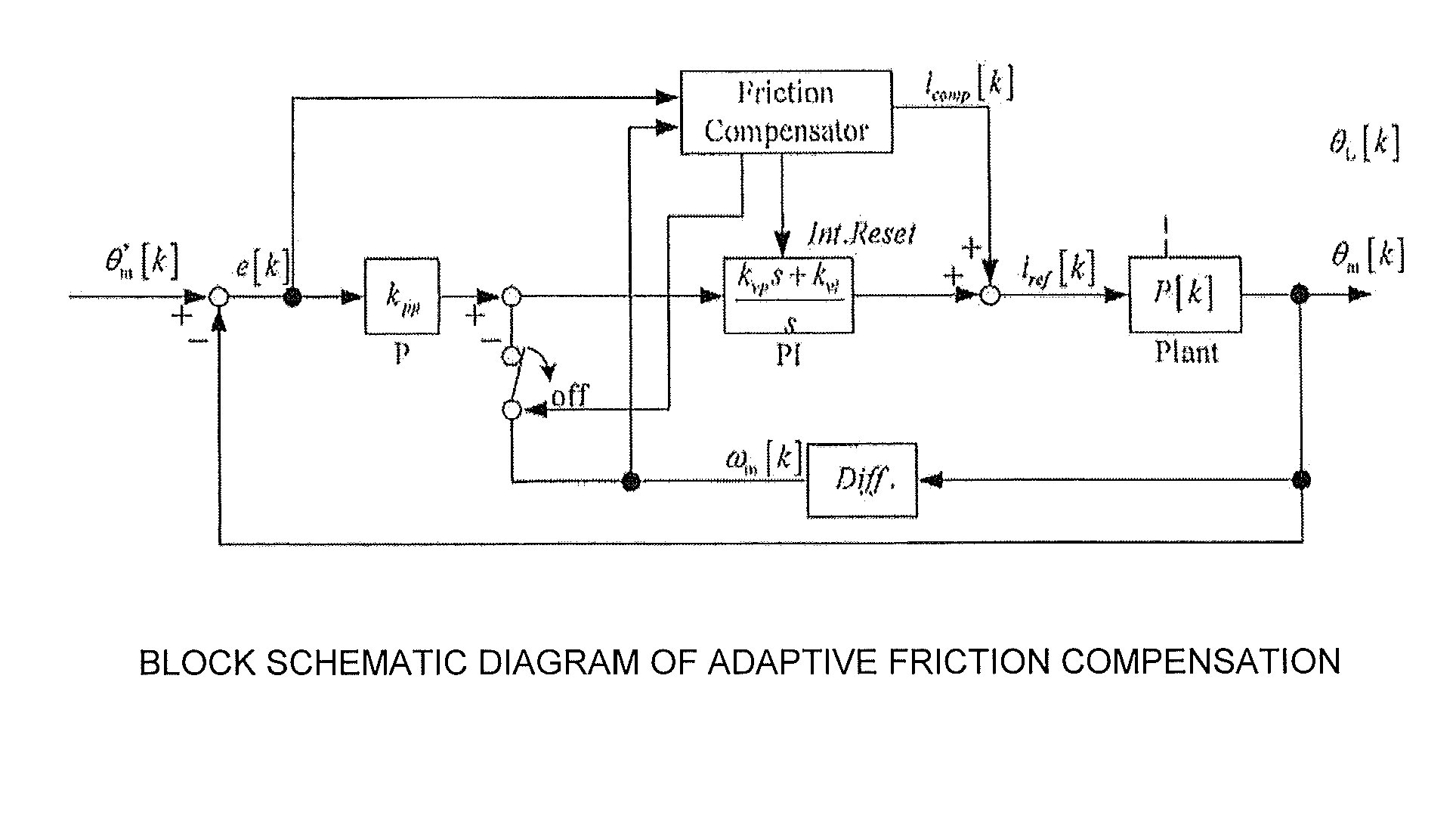
Method for performing adaptive friction compensation in an actuator accounting for variation in friction characteristics of wave gear drive accompanying change in temperature
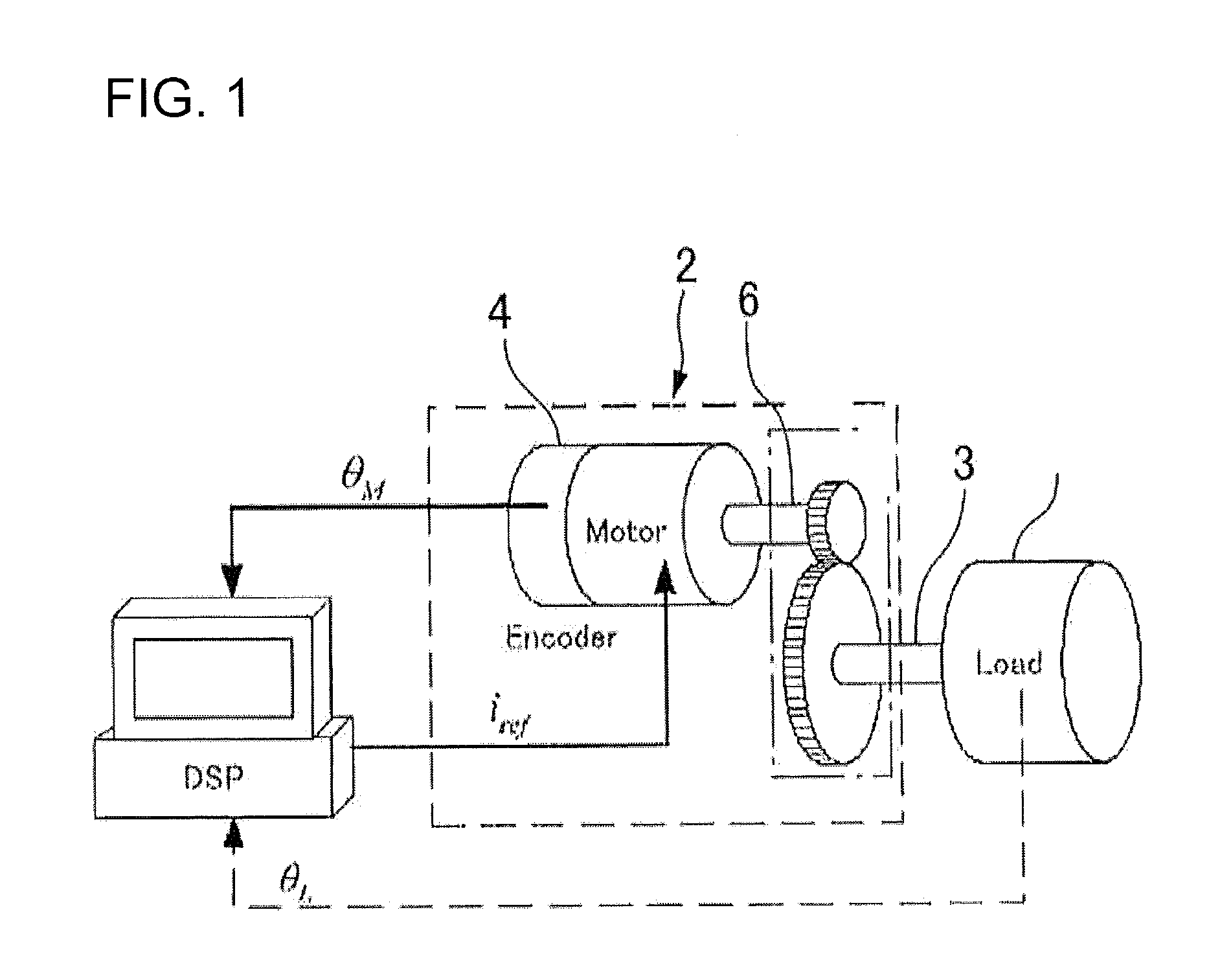
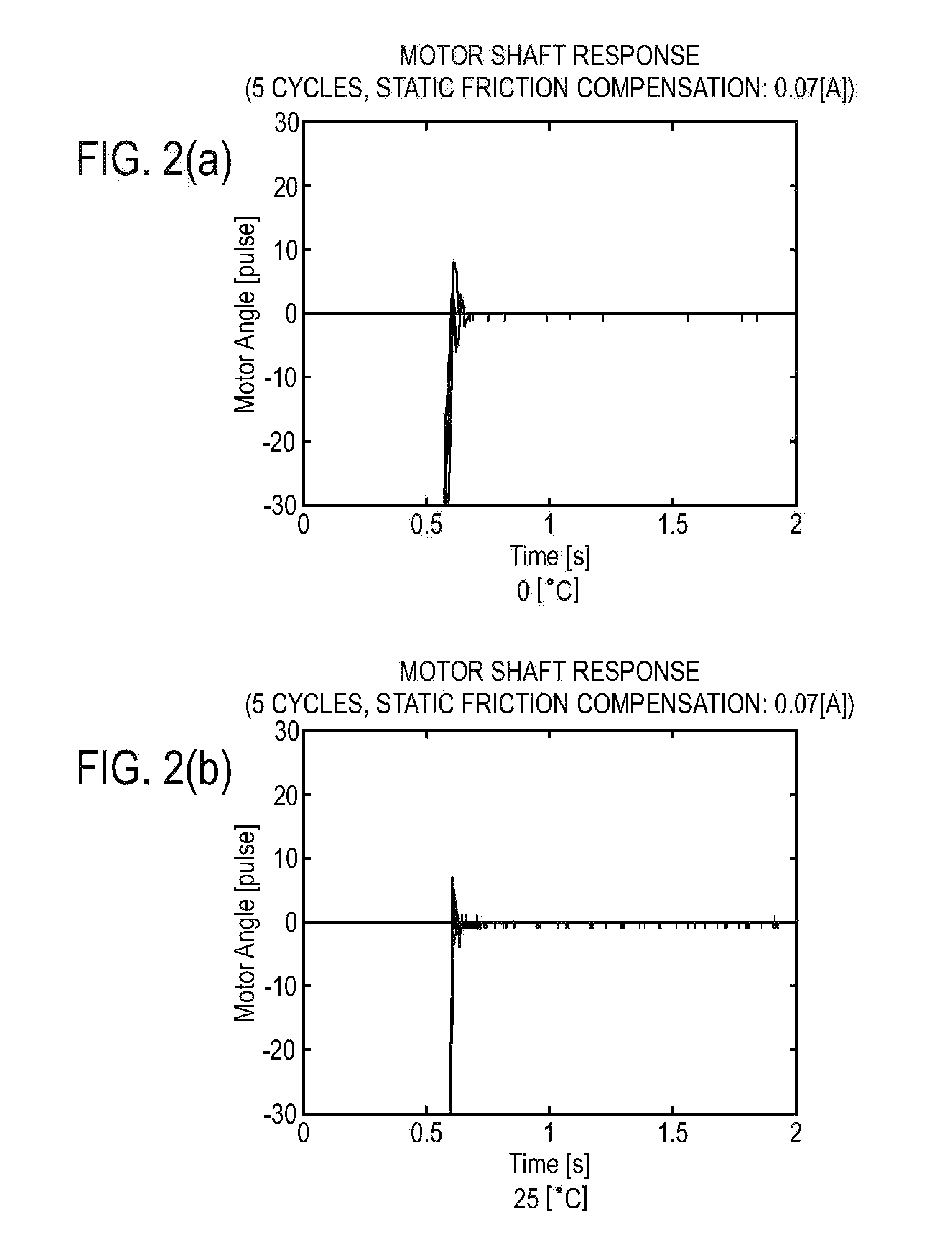
ActiveUS8442692B2Improve controlReduction in accuracySampled-variable control systemsComputer controlStatic frictionEngineering
According to a method for performing adaptive friction compensation of an actuator including a wave gear drive, there is used as a friction compensation current applied to a motor drive current a static friction compensation current is when a motor shaft stops with a deviation, and a Coulomb friction compensation current ic in other circumstances. The static friction compensation current is is obtained by adding a compensation amount isr of a monotonically increasing ramp function to a compensation amount iss of a step function, and a step-function compensation amount ics is used as the Coulomb friction compensation current ic. Since the amount of friction compensation can be changed adaptively based on the data during positioning-control response, a motor shaft can be stabilized at a target angle without prominent accompanying vibration, even if the ambient temperature changes and the friction characteristics of the wave gear drive fluctuate.
Owner:NAGOYA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Rotational inertia identification method and device of servo system
ActiveCN106998161AImprove recognition accuracyEliminate the effects ofElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsMotor speedPower flow
The invention is applicable to the technical field of a servo motor, and provides a rotational inertia identification method and device of a servo system. The method comprises the steps of acquiring an electromagnetic torque when a motor speed positively approximates to zero and an electromagnetic torque when the motor speed reversely approximates to zero, and calculating a load torque and a coulomb friction torque; sampling a speed and a current of the motor between a first initial speed and a second end speed during acceleration of the motor; sampling a speed and a current of the motor between a second initial speed and a second end speed during speed reduction of the motor; and calculating rotational inertia of the servo system according to the speed and the current which are sampled during acceleration of the motor, the speed and the current which are sampled during speed reduction of the motor, the load torque and the coulomb friction torque. By the method, the influence of a friction factor and a speed factor on calculation of the rotational inertia can be eliminated, the identification accuracy of the rotational inertia is improved, moreover, the operational quantity can be reduced, and the identification efficiency is improved.
Owner:SUZHOU WEICHUANG ELECTRICAL EQUIP TECH
Method for performing adaptive friction compensation in an actuator accounting for variation in friction characteristics of wave gear drive accompanying change in temperature
ActiveUS20110251722A1Compensation changesImprove controlSampled-variable control systemsComputer controlStatic frictionActuator
According to a method for performing adaptive friction compensation of an actuator including a wave gear drive, there is used as a friction compensation current applied to a motor drive current a static friction compensation current is when a motor shaft stops with a deviation, and a Coulomb friction compensation current ic in other circumstances. The static friction compensation current is is obtained by adding a compensation amount isr of a monotonically increasing ramp function to a compensation amount iss of a step function, and a step-function compensation amount ics is used as the Coulomb friction compensation current ic. Since the amount of friction compensation can be changed adaptively based on the data during positioning-control response, a motor shaft can be stabilized at a target angle without prominent accompanying vibration, even if the ambient temperature changes and the friction characteristics of the wave gear drive fluctuate.
Owner:NAGOYA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com