Patents
Literature
116 results about "Virtual work" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Virtual work arises in the application of the principle of least action to the study of forces and movement of a mechanical system. The work of a force acting on a particle as it moves along a displacement is different for different displacements. Among all the possible displacements that a particle may follow, called virtual displacements, one will minimize the action. This displacement is therefore the displacement followed by the particle according to the principle of least action. The work of a force on a particle along a virtual displacement is known as the virtual work.
Virtual work place
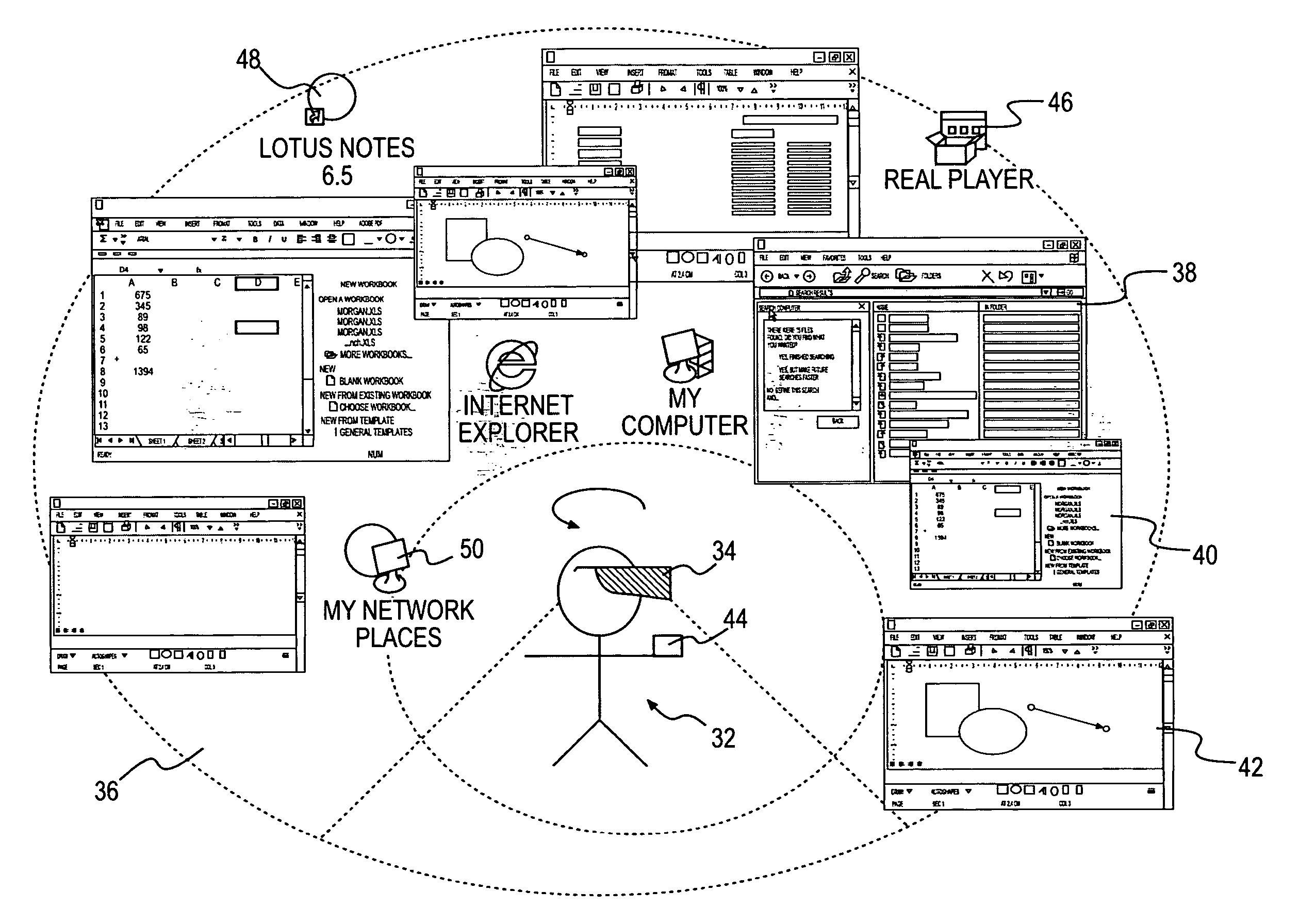
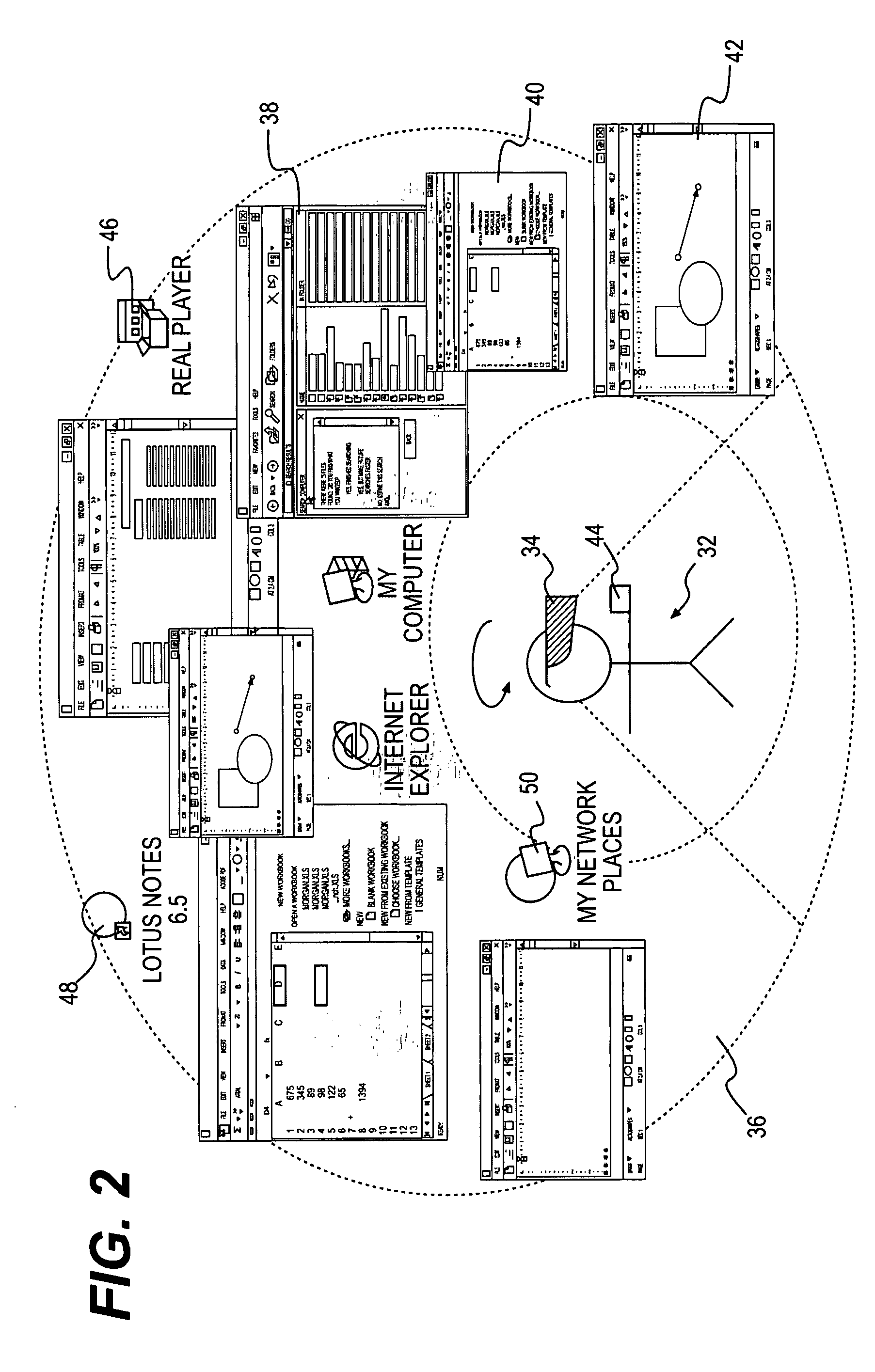
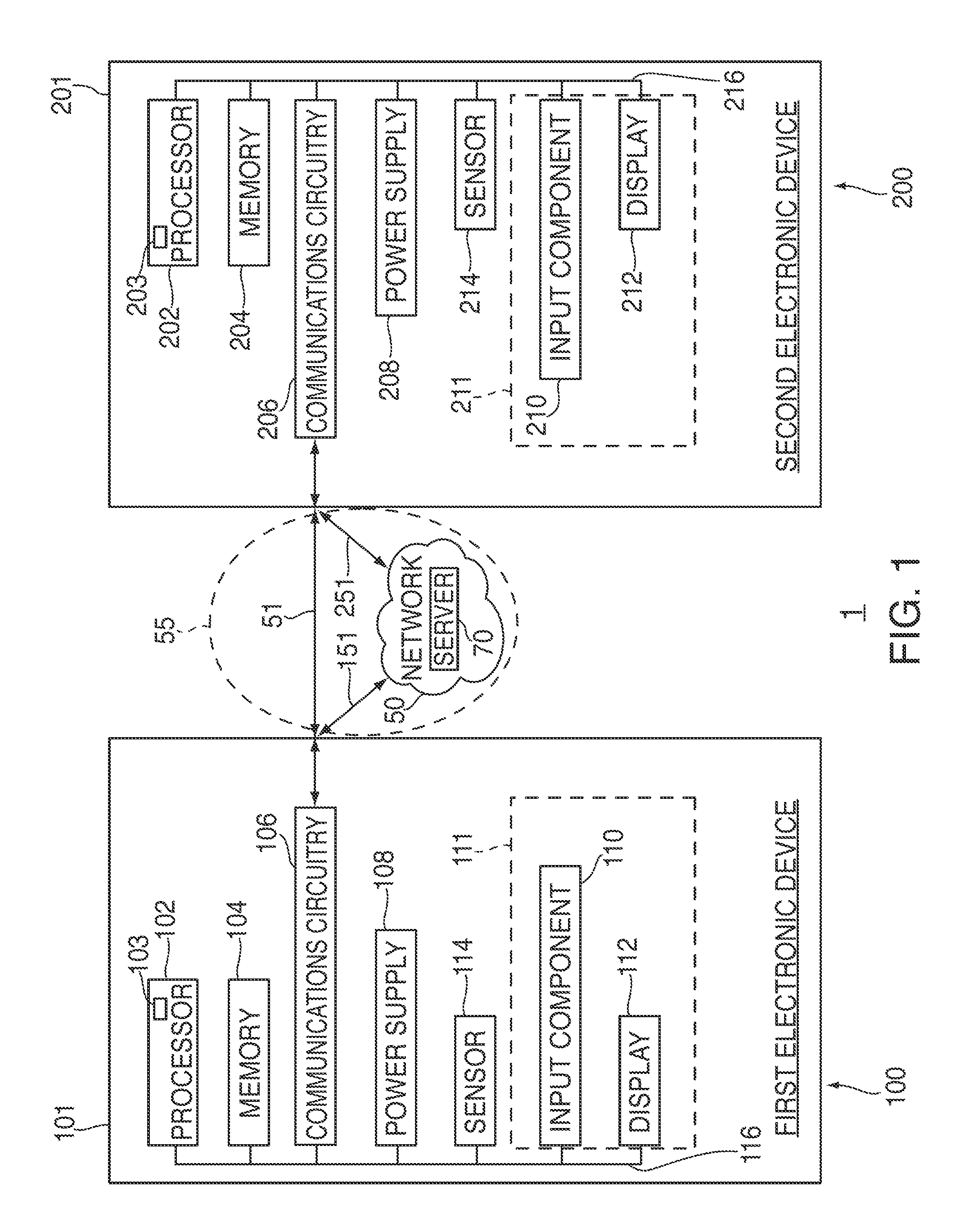
ActiveUS20080005702A1Improve working conditionsExpand accessInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsGraphical user interface
The present invention is concerned with a method and computer-based system for configuring, monitoring and / or operating a graphical user interface in two or three dimensions. In particular it is concerned with a graphical user interface used for controlling, monitoring and / or operating equipment in a control system of an industrial process or an installation for oil and gas or for an installation for electrical power generating, transmission and / or distribution.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
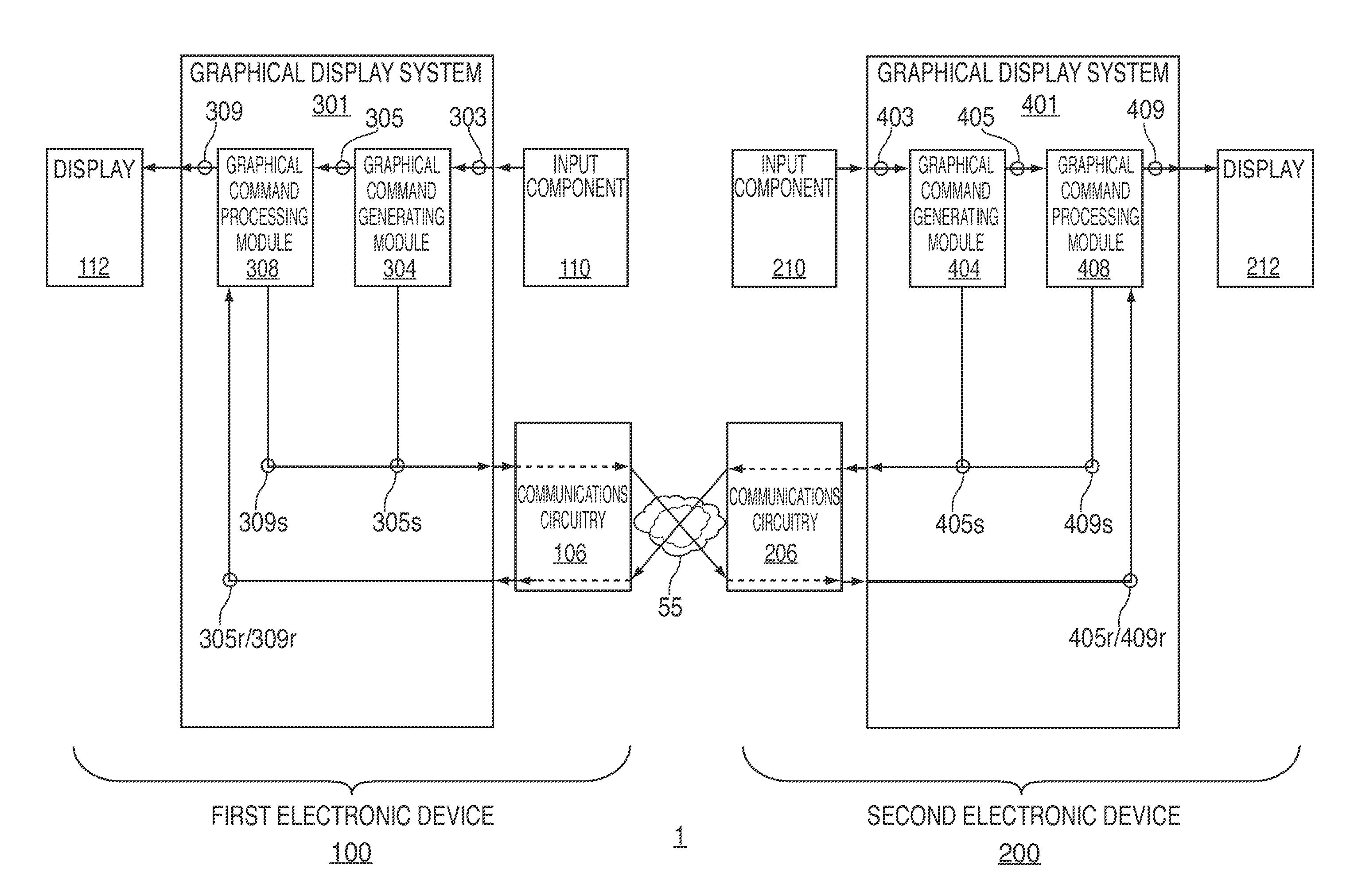
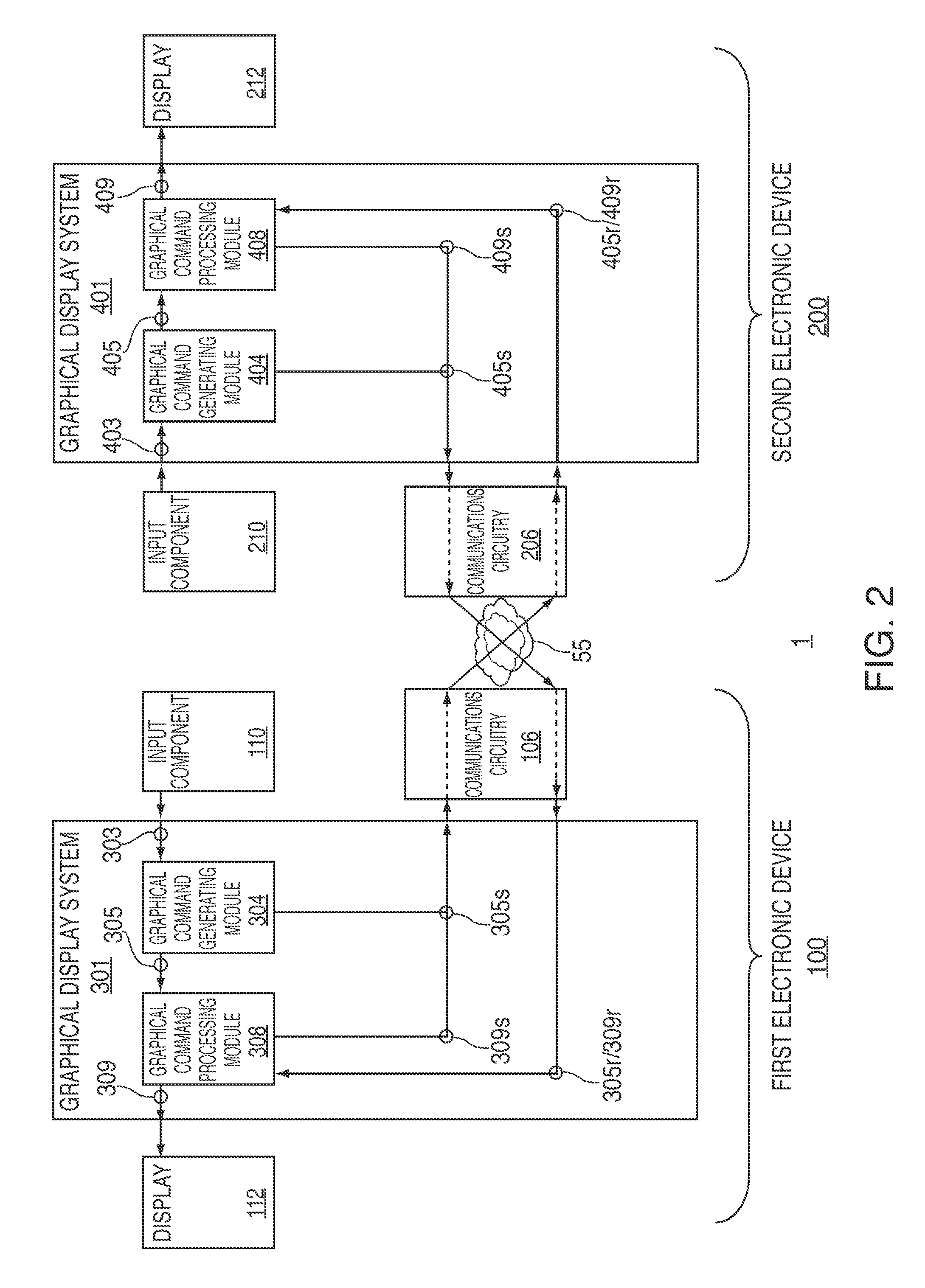
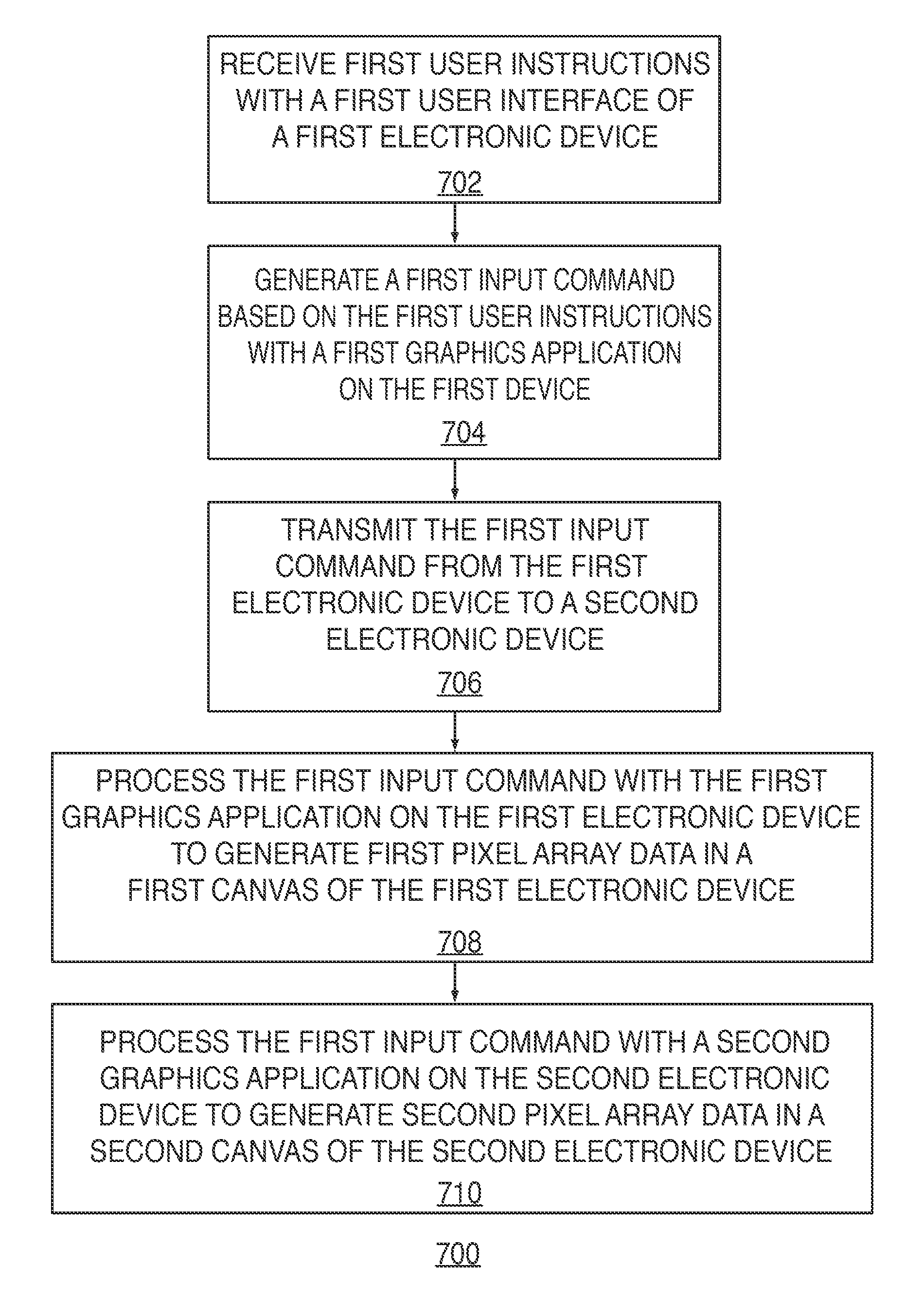
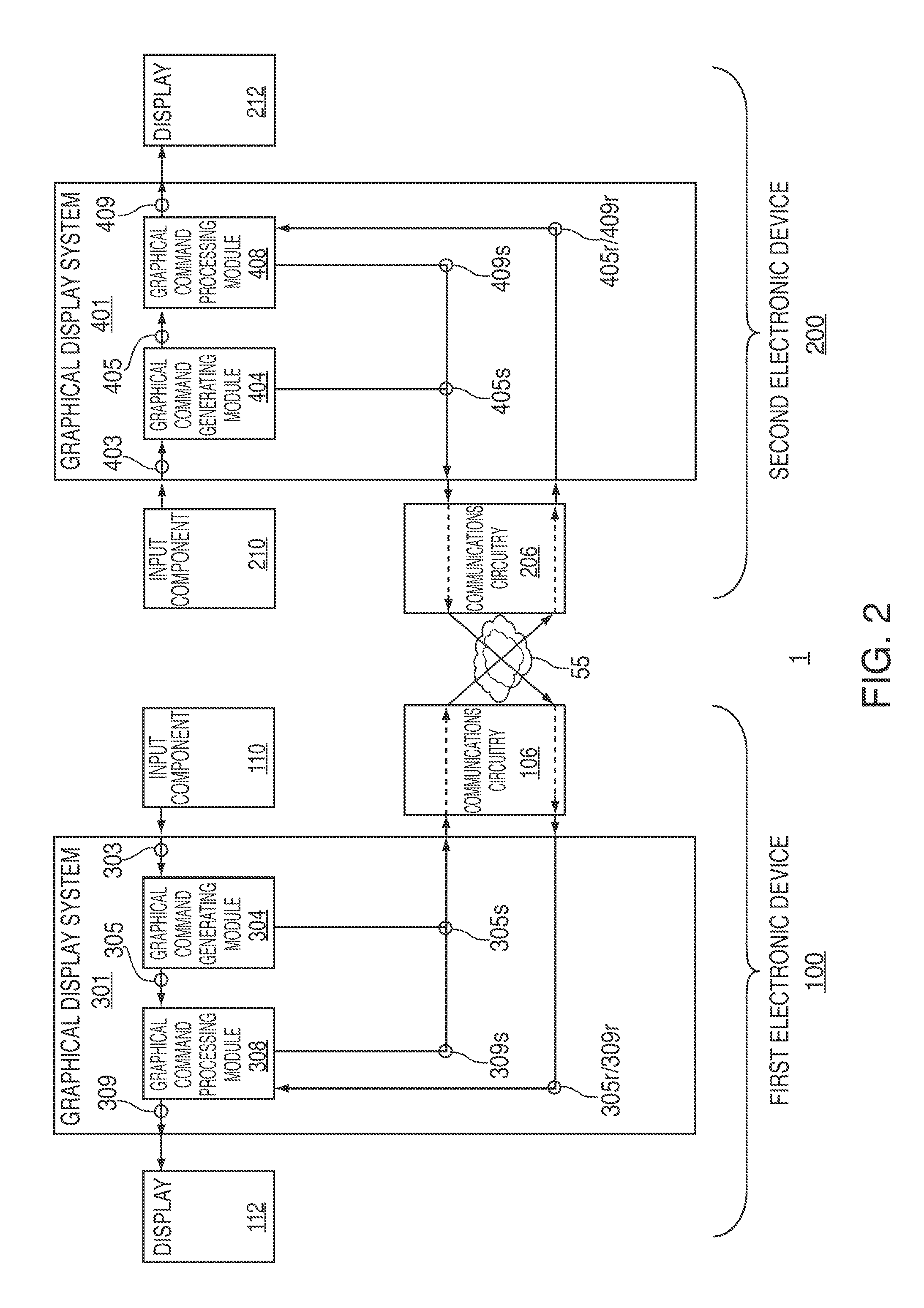
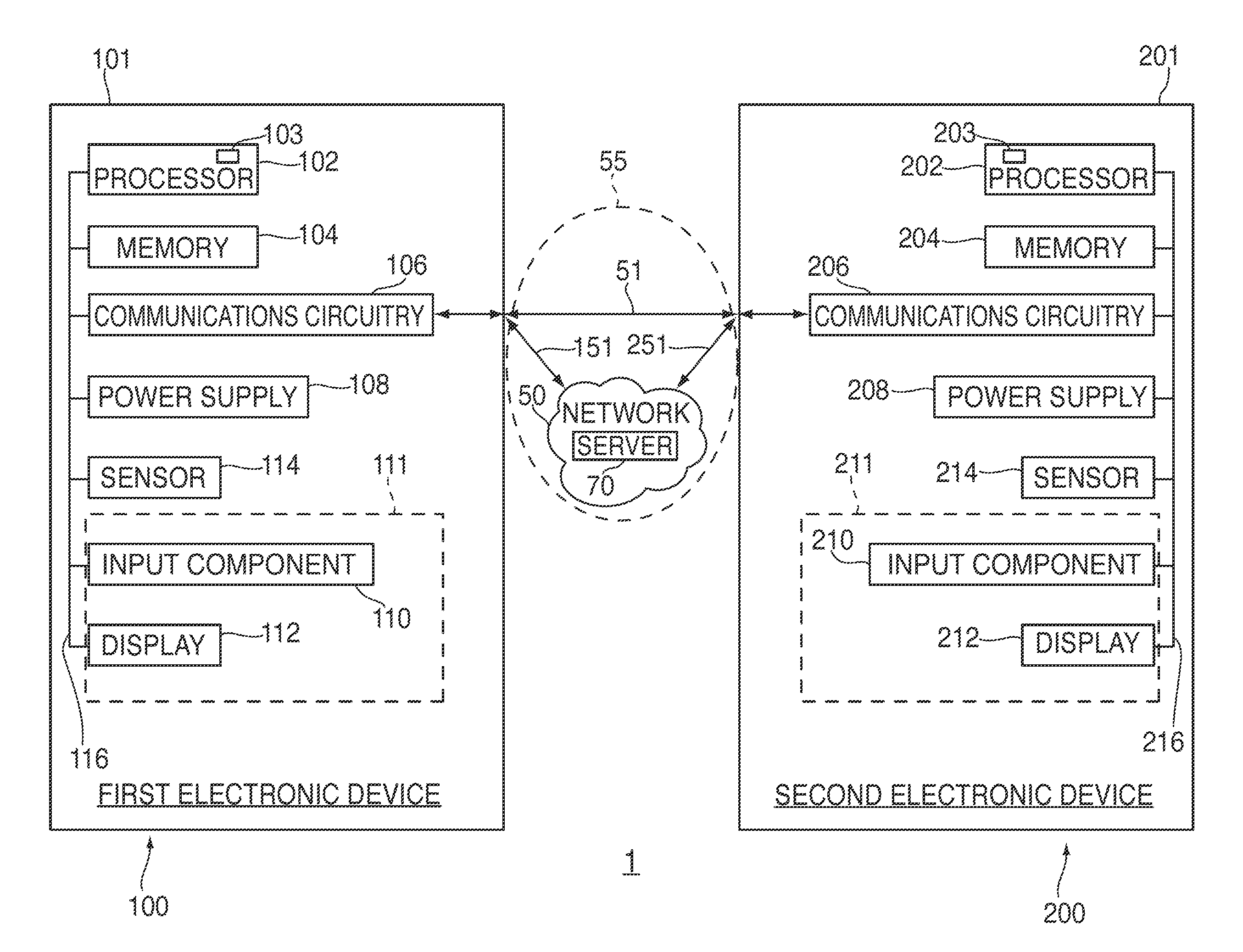
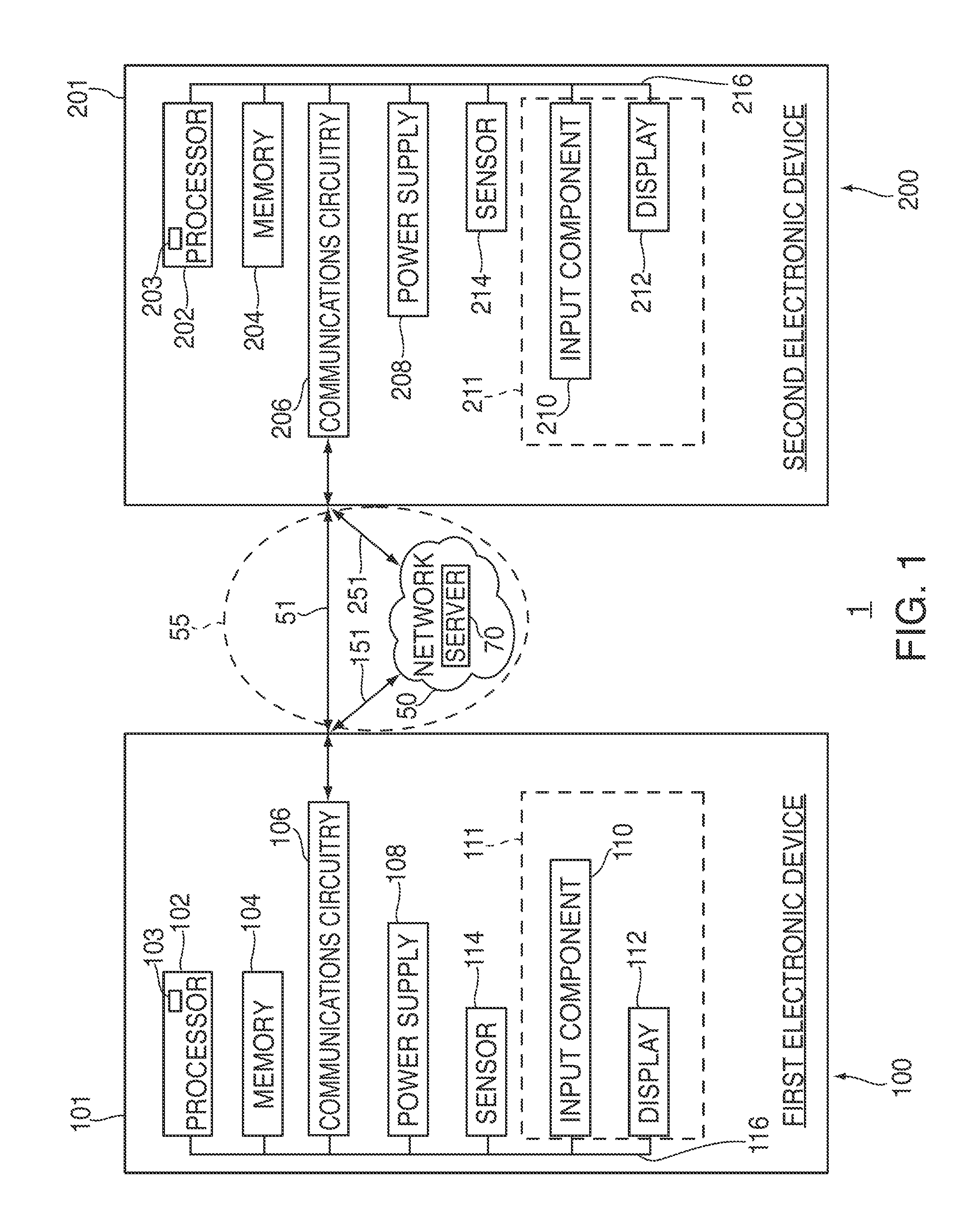
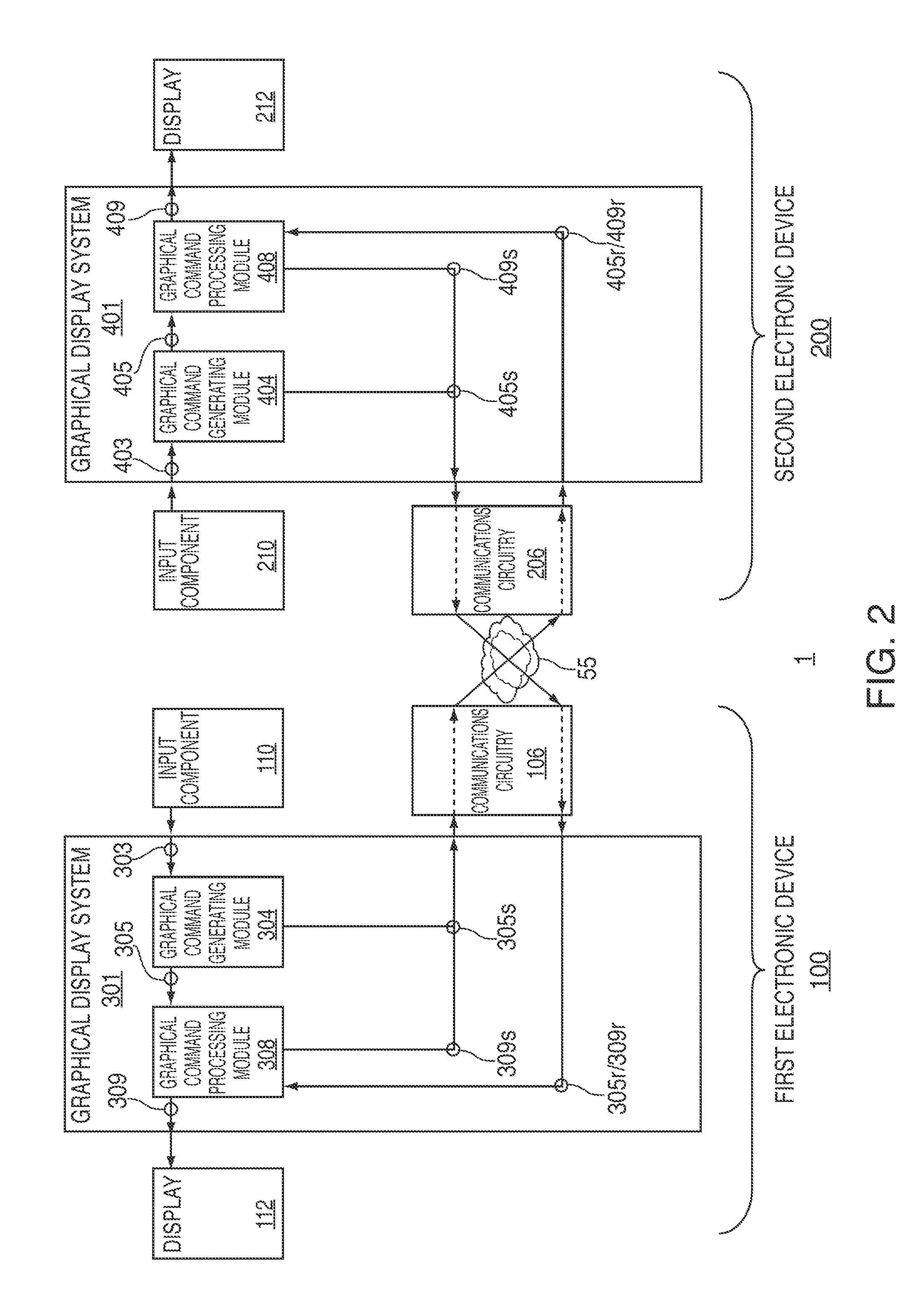
Systems, methods, and computer-readable media for managing collaboration on a virtual work of art
Systems, methods, and computer-readable media for managing collaboration on a virtual work of art between multiple electronic devices are provided. A first graphical display system of a first device may generate an input command in response to receiving user information through a user interface of the first device, and may then share this input command with a second graphical display system of a second device. The first graphical display system may process the shared input command to generate pixel array data in a canvas of the first device while the second graphical display system may process the shared input command to generate pixel array data in a canvas of the second device. By sharing input commands rather than pixel array data, system latency may be reduced. Despite operating on the same artwork, the user interfaces and graphical processing capabilities of each device may vary, thereby providing the user greater expressiveness.
Owner:APPLE INC
Systems and methods for assessing mobile asset efficiencies
InactiveUS20130030873A1Registering/indicating time of eventsRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesGraphicsWorking environment
Various embodiments of the present invention are directed to an asset management computer system for assessing operational data indicative of the movement of one or more mobile assets within a work environment. The mobile assets may be, for example, employees, packages, or vehicles moving through a work environment. According to various embodiments, the asset management computer system may be configured for analyzing the operational data and segmenting it into a plurality of position segments representing periods of time classified according to the mobile asset's position in relation to one or virtual work areas. In addition, the asset management computer system may be further configured to determine operational characteristics for each of the position segments, generate a graphical representation of the position segments, and provide operational statistics based on the position segments, which can be used to assess asset behavior and the efficiency of a work environment's design.
Owner:UNITED PARCEL SERVICE OF AMERICAN INC
Virtual work flow management method
InactiveUS6986138B1Reduce maintenance timesReduce in quantityMultiprogramming arrangementsOffice automationService flowVirtual work
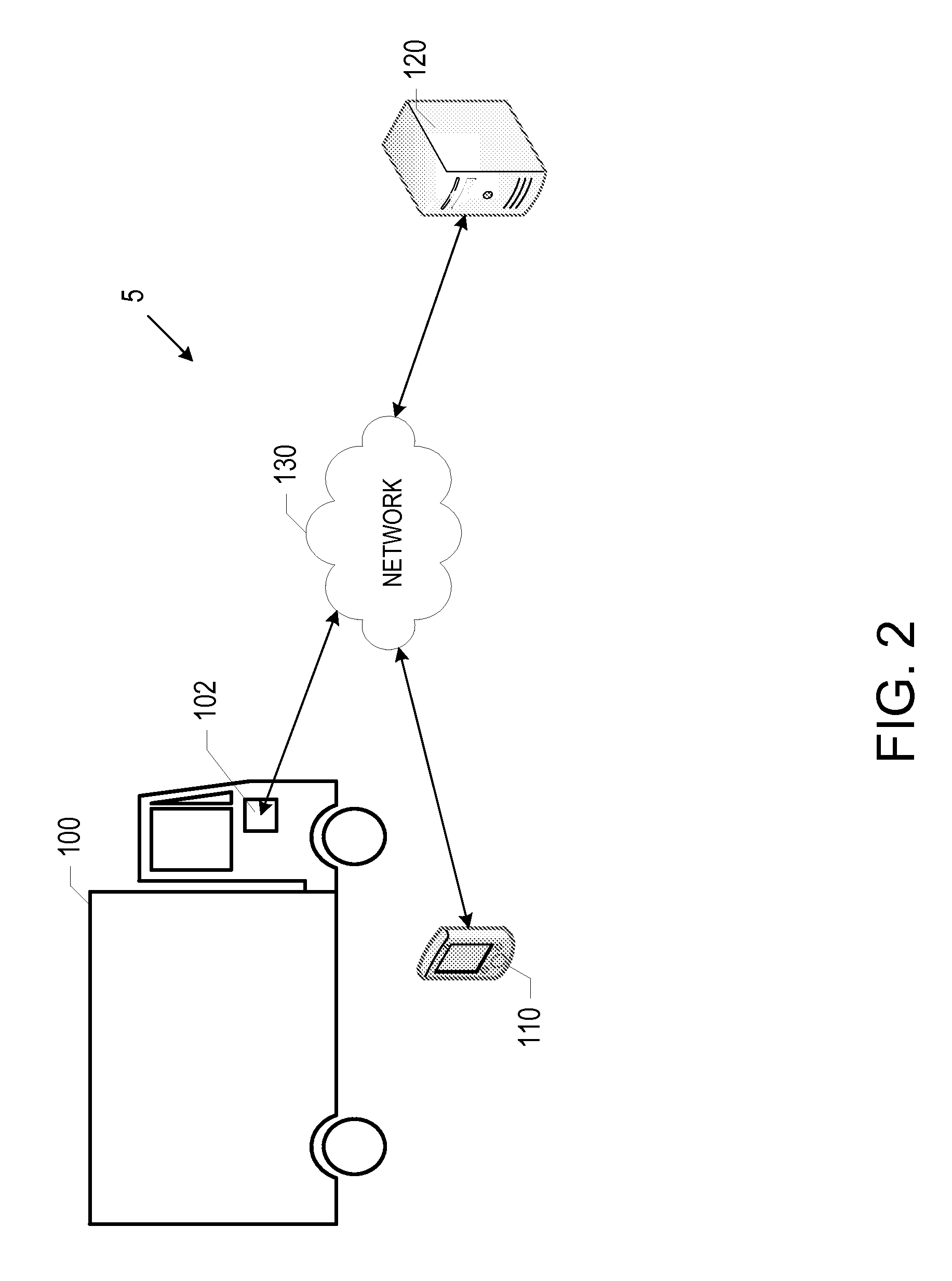
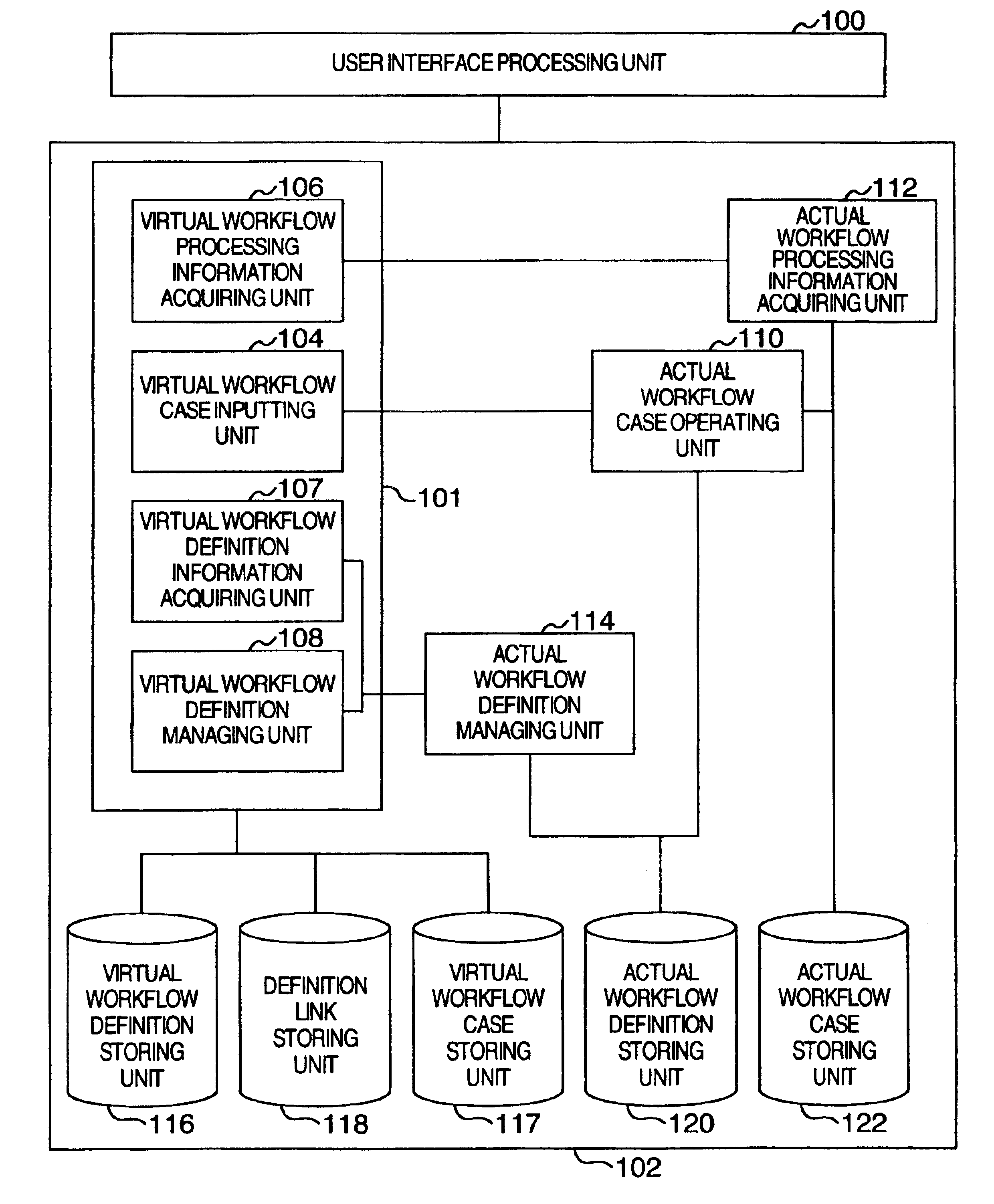
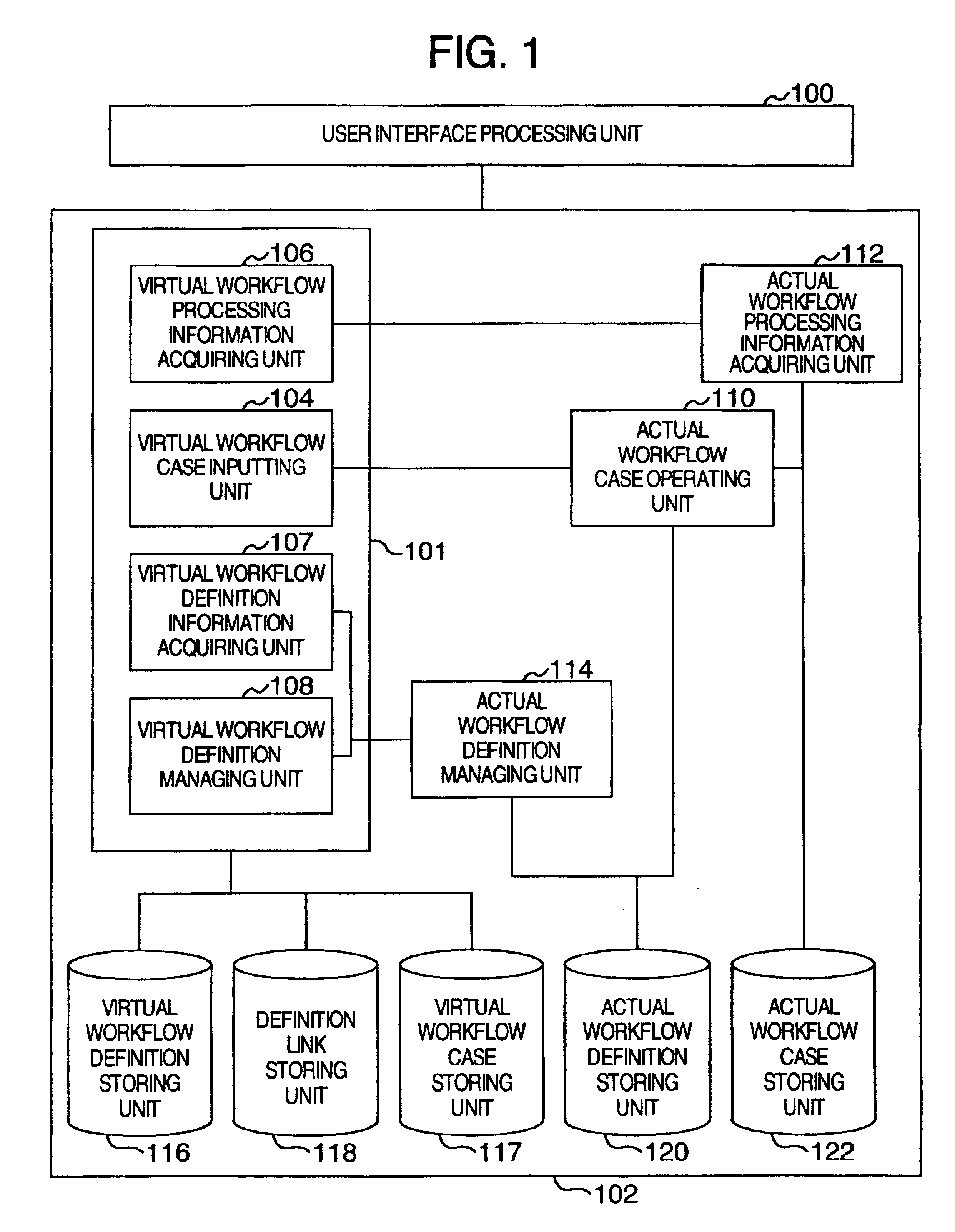
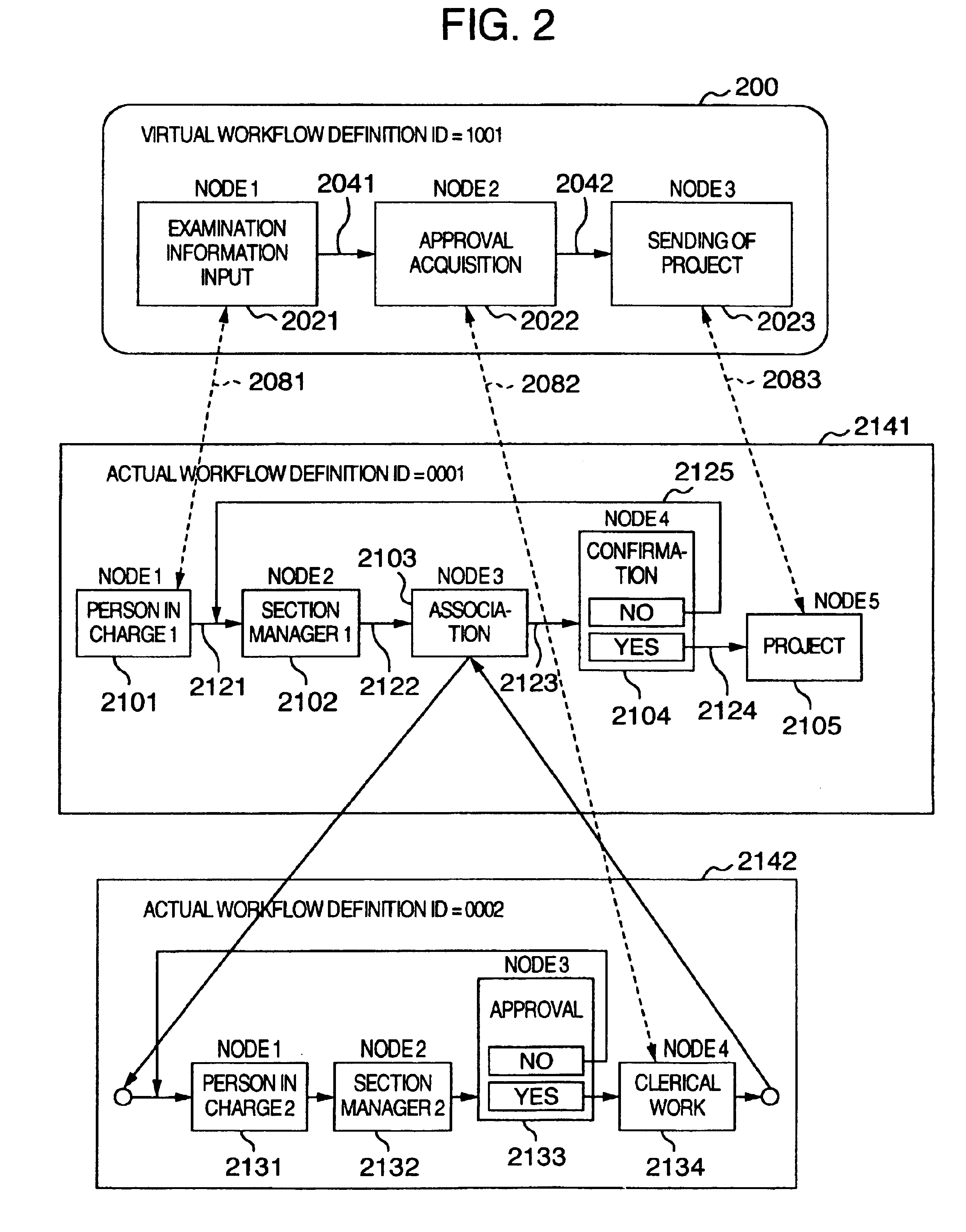
A processing node is selected from an actual workflow definition composed of the corresponding processing nodes to an actual service flow according to the purpose of use of a client. A virtual workflow definition composed of the virtual node corresponding to the selected processing node is created by a server and displayed on a screen of the client. A link is set for indicating correspondence between the virtual node of the virtual workflow and the processing node of the actual workflow. When an inquiry about the progressing state of the virtual workflow is given from a client, the server searches the processing node being current executed from the actual workflow. If the processing node does not have any link, the server tracks back the processing nodes on the actual workflow for searching the processing node having the link and an access right given from the client and then reply the progressing state of the processing node as the progress information of the virtual workflow to the client.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Virtual work place
ActiveUS8046719B2Expand the working areaFlexible and comfortable for userInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsGraphical user interface
The present invention is concerned with a method and computer-based system for configuring, monitoring and / or operating a graphical user interface in two or three dimensions. In particular it is concerned with a graphical user interface used for controlling, monitoring and / or operating equipment in a control system of an industrial process or an installation for oil and gas or for an installation for electrical power generating, transmission and / or distribution.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Application of multi-media technology to computer administered vocational personnel assessment
InactiveUS7207804B2Inhibition biasRapid and precise indicationSensorsPsychotechnic devicesVirtual workVisual perception
A multi-media method and system performs psychological assessment of an individual for suitability for particular jobs, whereby the individual is shown and provided with discrete visual and auditory stimuli on a multi-media computer screen, so that the individual's responses can be monitored in conjunction with physiological responses received by biofeedback sensors. The computer tallies the test subject's recorded responses. Virtual work environments are optionally displayed, to enable the tested individual to simulate a real work environment. Unlike other job evaluation systems, the system evaluates a job candidate's ability to maintain task focus under pressure. It directly measures performance under pressure, rather than only inferring potential performance based upon selective input from a job candidate.
Owner:HERSH MICHAEL
Application of multi-media technology to computer administered vocational personnel assessment
InactiveUS20070105080A1Minimize the differenceReliably and accurately predict real world successSensorsPsychotechnic devicesVirtual workVisual perception
A multi-media method and system performs psychological assessment of an individual for suitability for particular jobs, whereby the individual is shown and provided with discrete visual and auditory stimuli on a multi-media computer screen, so that the individual's responses can be monitored in conjunction with physiological responses received by biofeedback sensors. The computer tallies the test subject's recorded responses. Virtual work environments are optionally displayed, to enable the tested individual to simulate a real work environment. Unlike other job evaluation systems, the system evaluates a job candidate's ability to maintain task focus under pressure. It directly measures performance under pressure, rather than only inferring potential performance based upon selective input from a job candidate.
Owner:HERSH MICHAEL
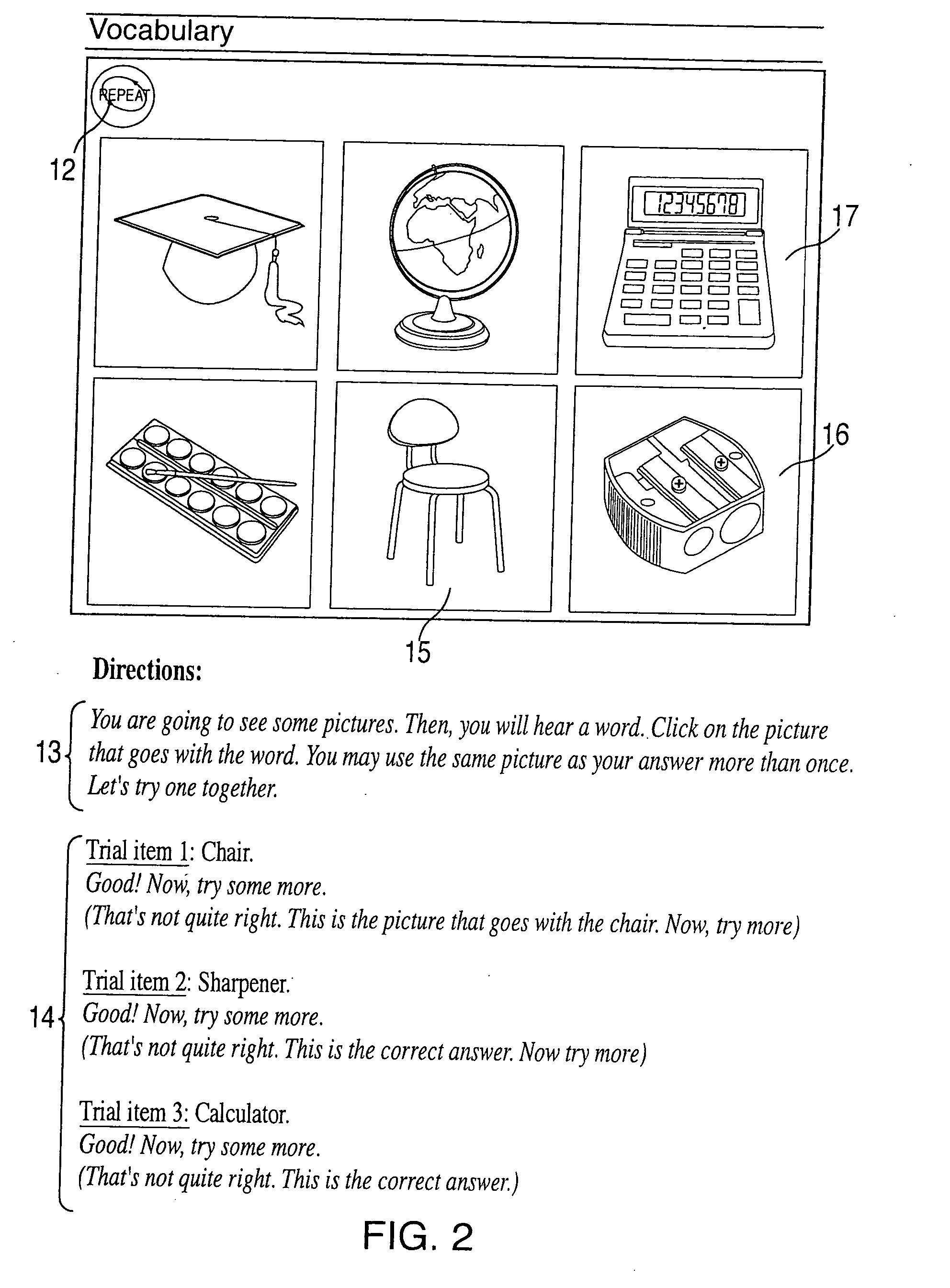
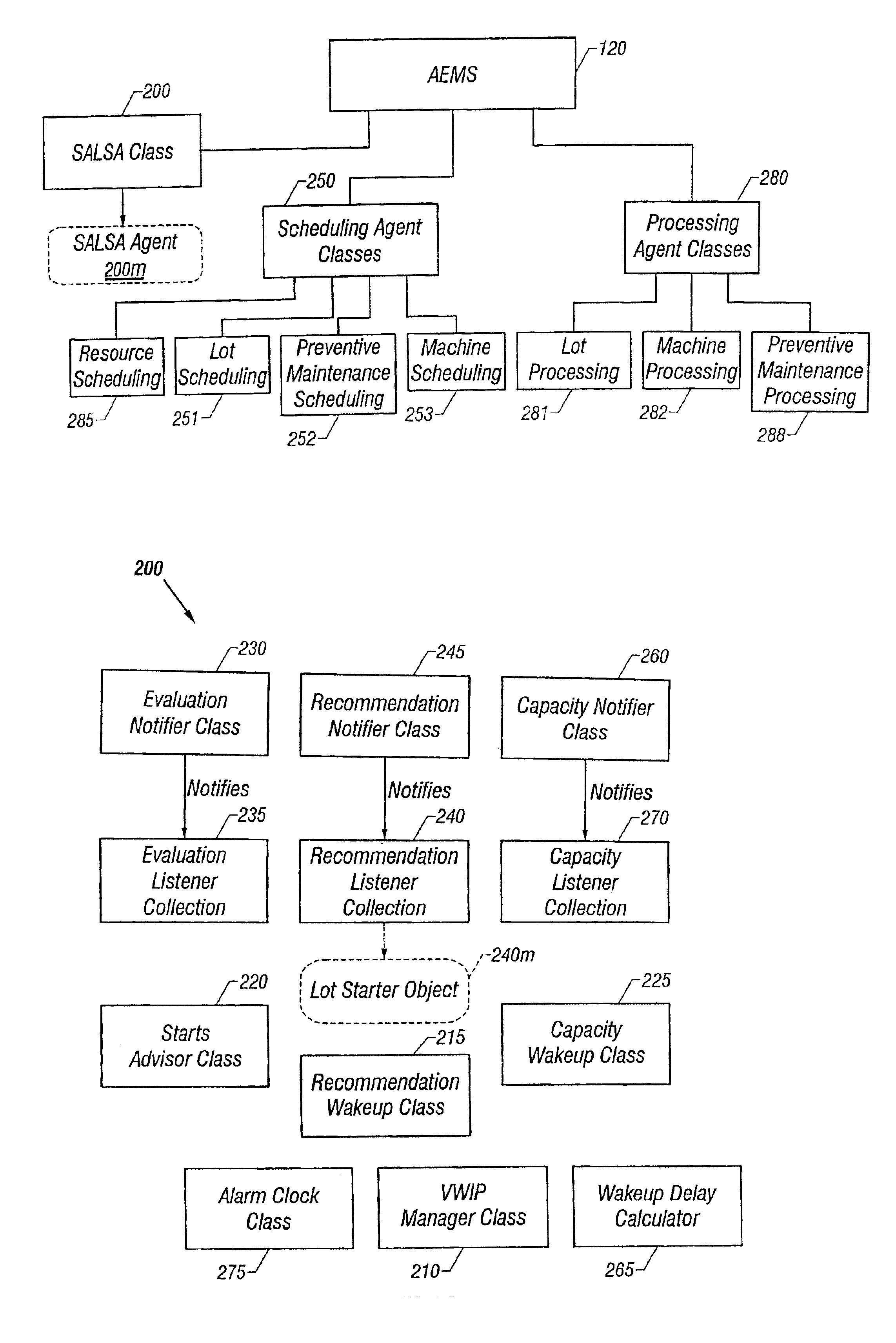
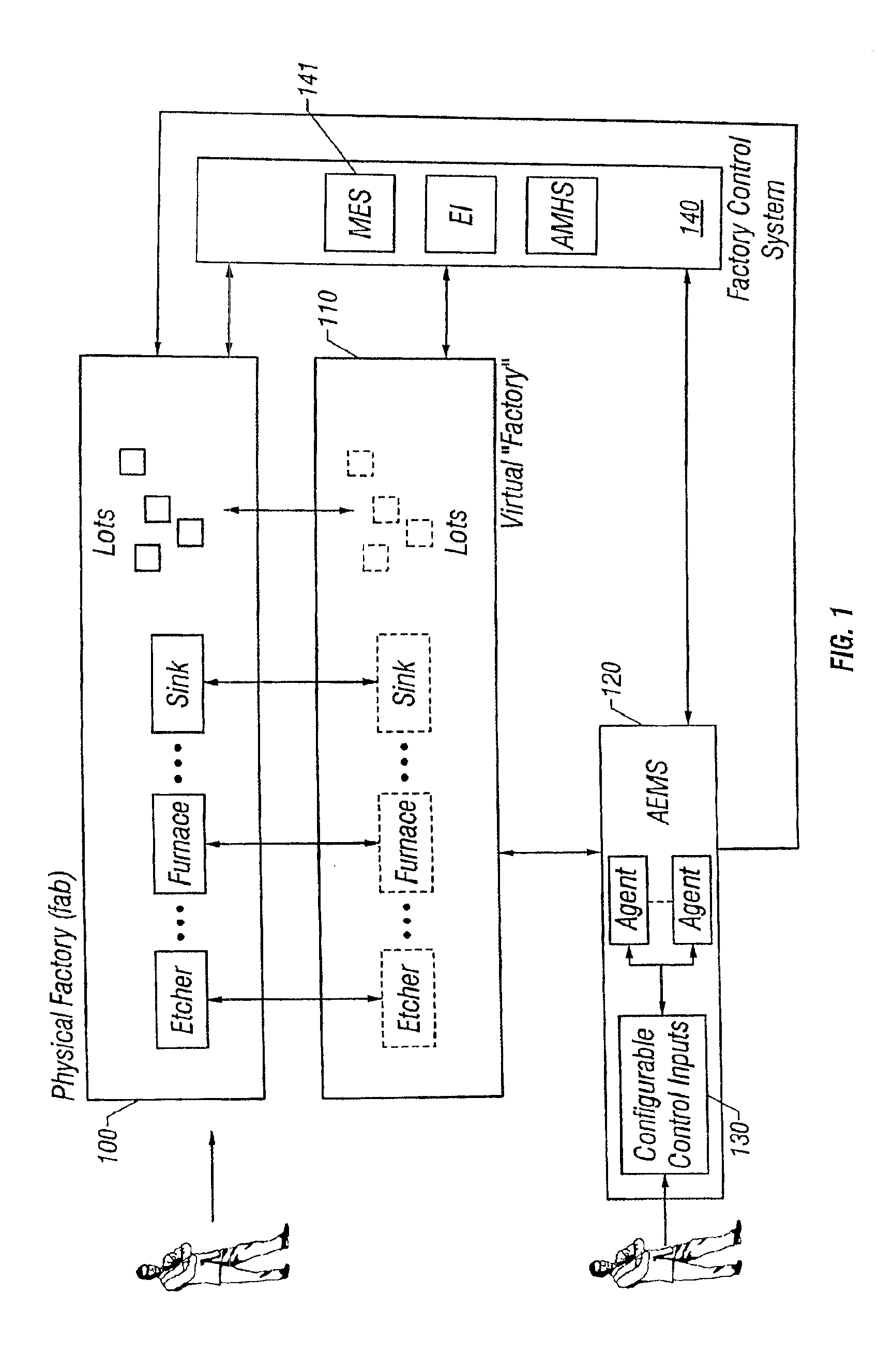
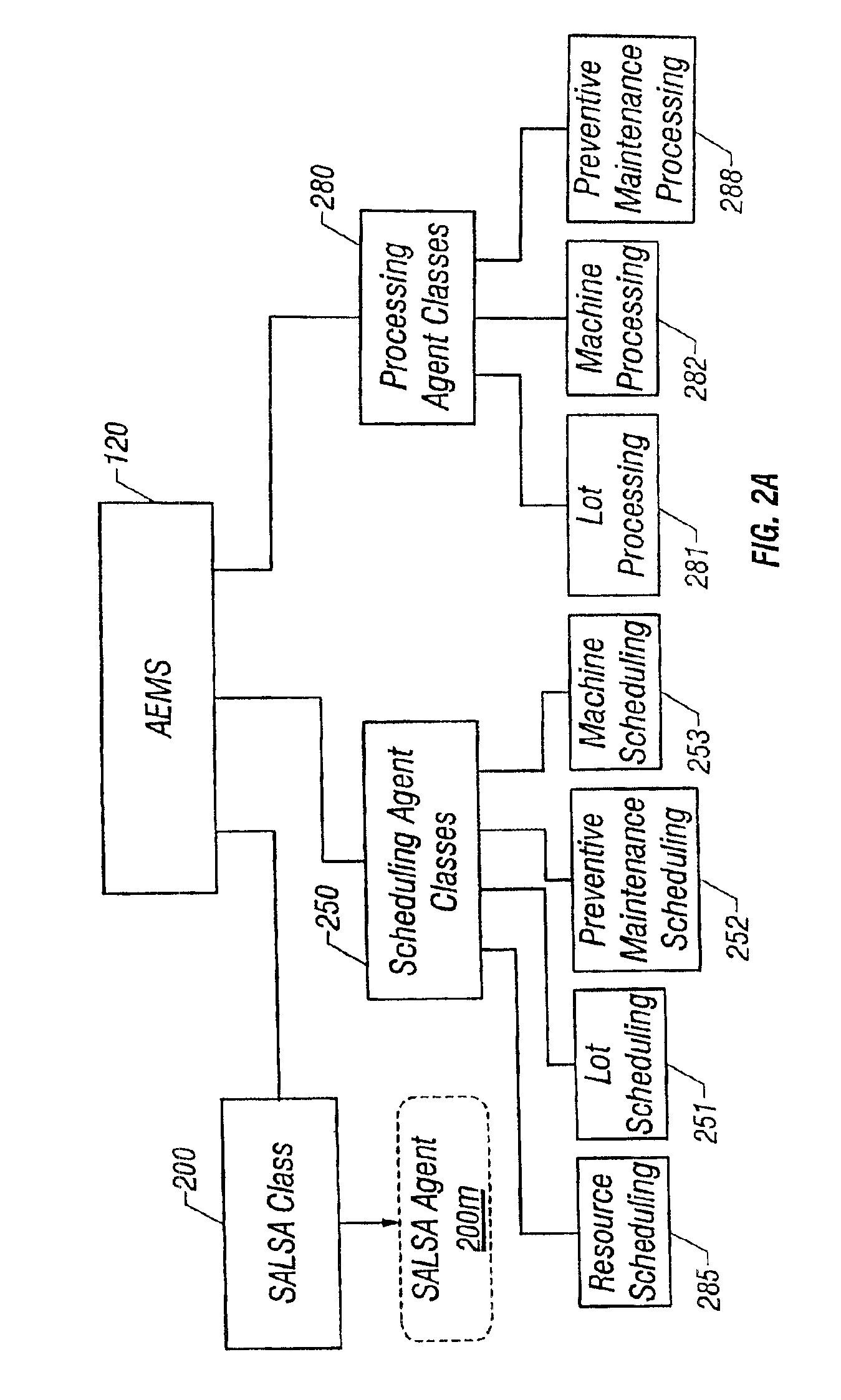
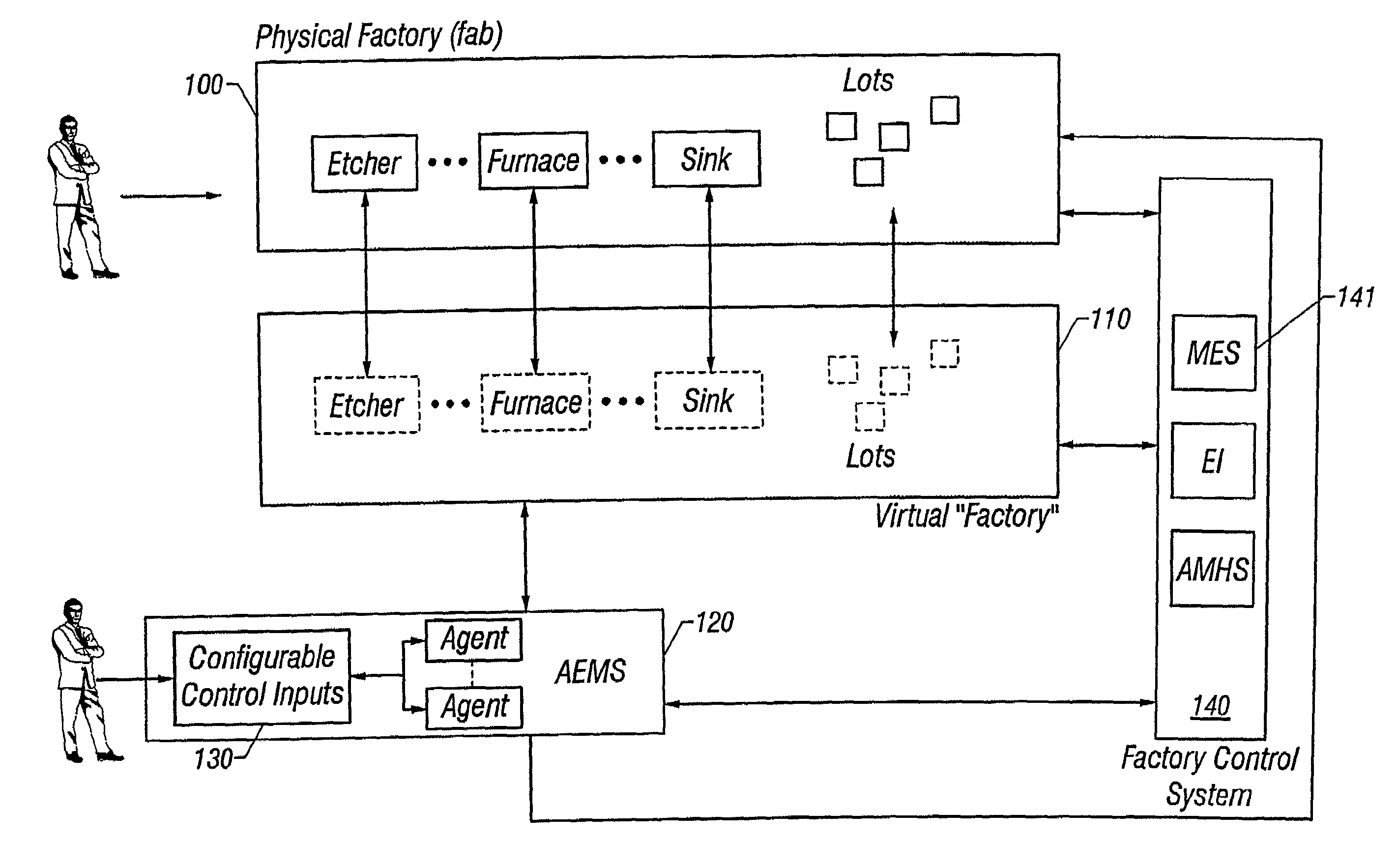
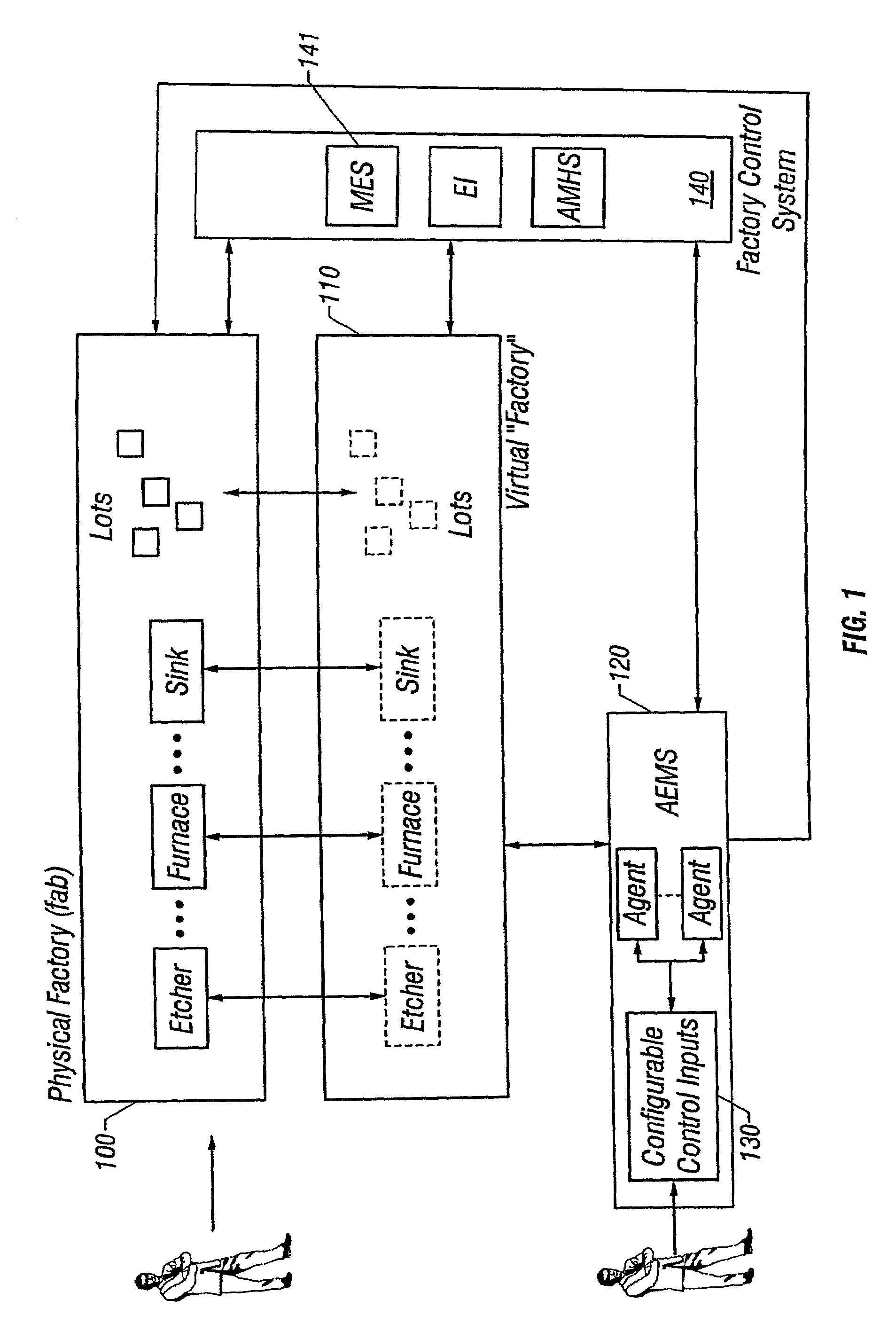
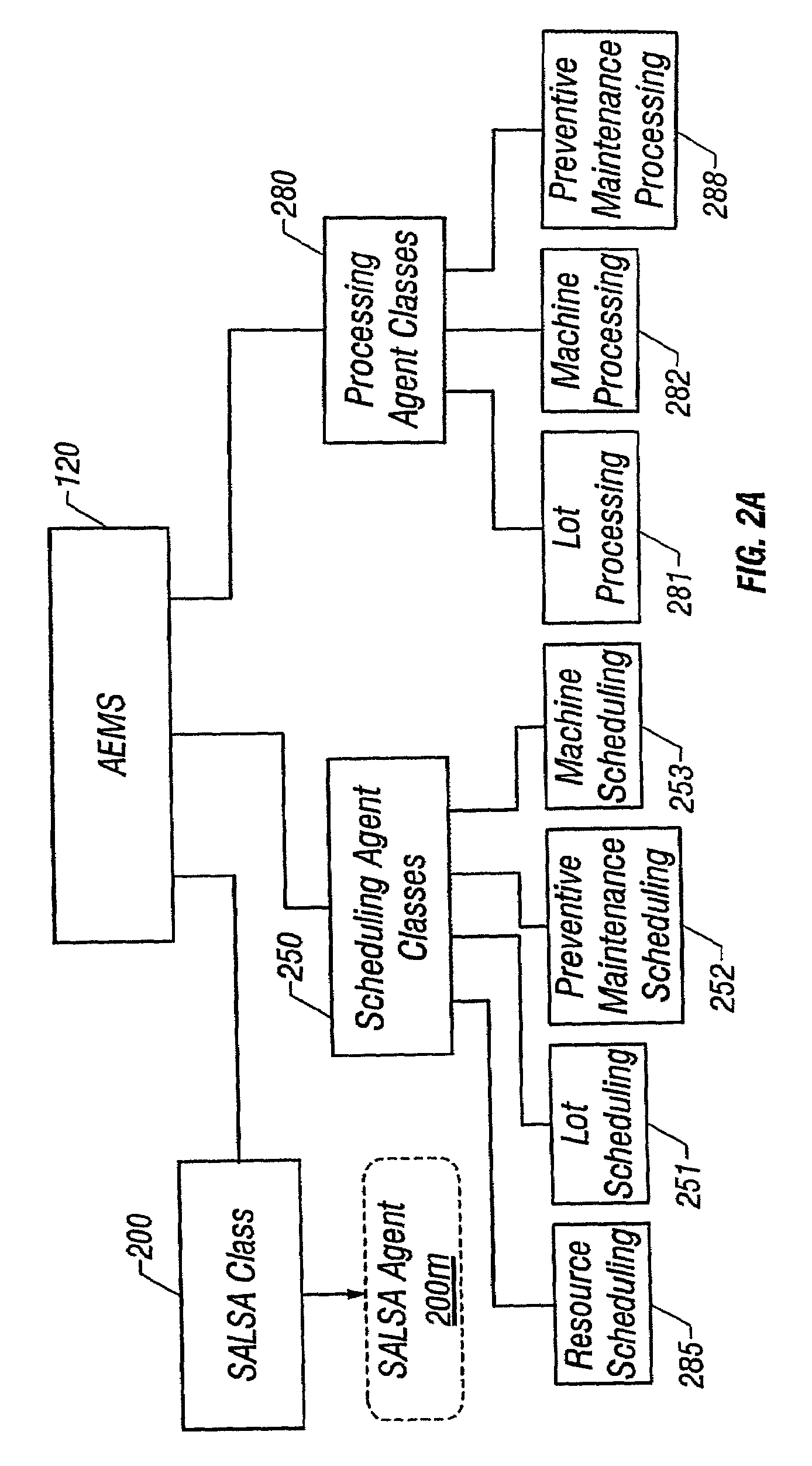
Lot start agent that determines quantity and timing for lot starts
An automated system is provided in a facility that manufactures m products, where m>0. The system comprises a software object that provides for calculation of one or more bottleneck delta virtual work in process time (“VWIP”) values. Each of the bottleneck delta VWIP values represents the amount of time until one of n bottleneck workstations begins to risk starvation, where n>0. VWIP is the amount of time a bottleneck will stay busy processing WIP that will reach the bottleneck in less time than new lot starts will reach the same bottleneck. In at least one embodiment, each of the bottleneck delta VWIP values is calculated as a mathematical function of virtual WIP time for the corresponding bottleneck workstation and a lower control limit for the corresponding bottleneck workstation. In at least one other embodiment, n>2 and the software object provides for calculation of a plurality of bottleneck delta VWIP values. The software object contains program code that provides for the foregoing functionality either directly or by invoking one or more other objects.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
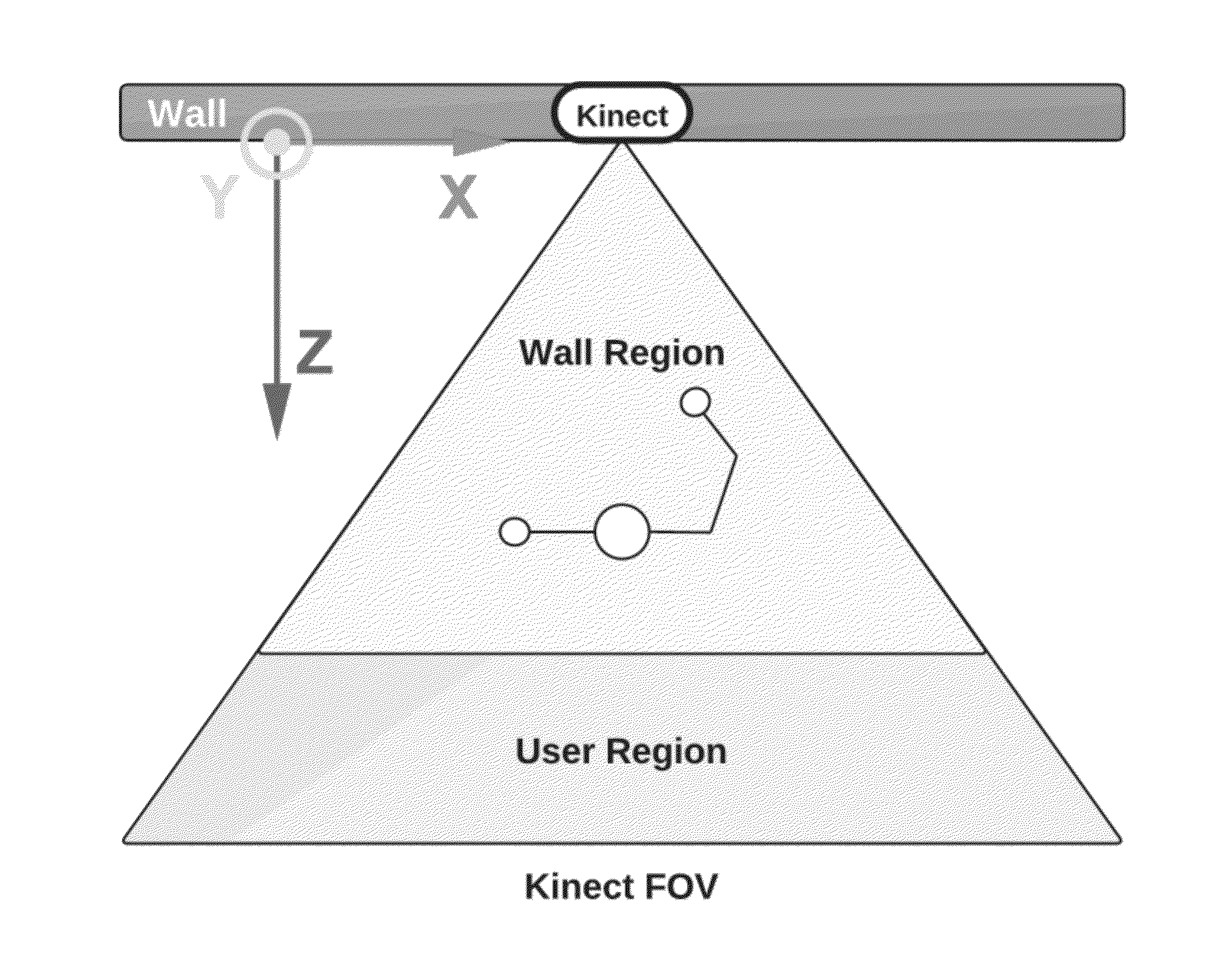
Dockable Tool Framework for Interaction with Large Scale Wall Displays
In accordance with an aspect of the present invention, a device and a method allows for body-based interaction with 3D applications on wall displays. The interface consists of virtual dockable tools which can be unholstered, used to manipulate geometry, and holstered on the user's body. The system also utilizes proprioceptive cues to allow the user to manipulate and holster tools without visual feedback. A 3D depth camera maps 3D user position to 3D coordinates in the virtual scene. Partitioning the physical work space into a region for interaction with geometry, and a region for tool management allows for intuitive mapping between the physical and virtual work space. The system can support multiple users, including simultaneous interaction with the environment, and tool exchange between users.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
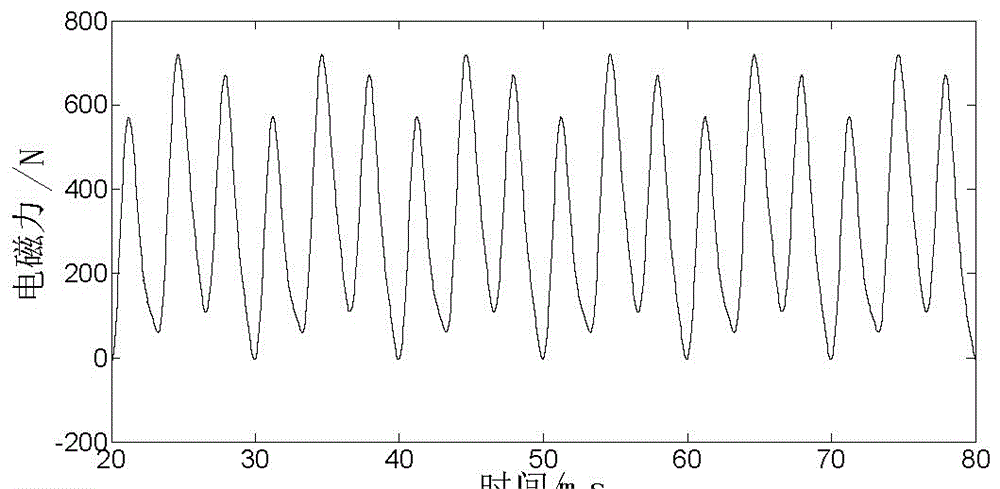
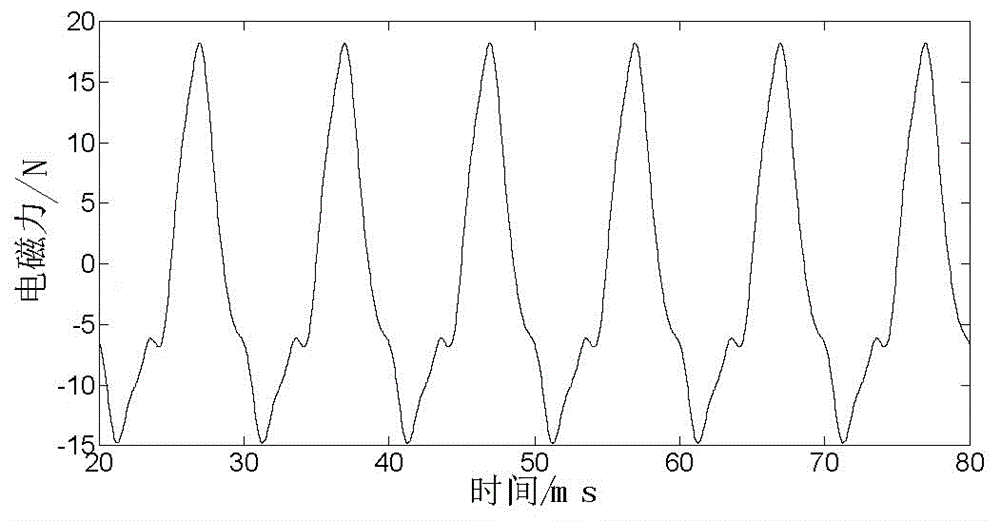
Method for computing electromagnetic force of transformer iron core based on finite element method
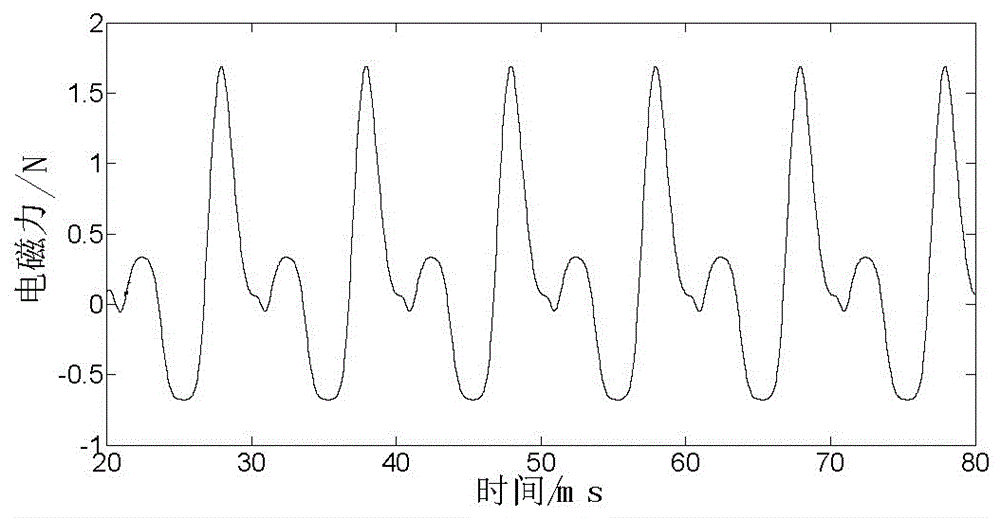
InactiveCN106570218ACalculation method directlyCalculation method is simpleDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsTransformerLow voltage
The invention discloses a method for computing electromagnetic force of a transformer iron core based on a finite element method. The method comprises the steps that structural parameters of a winding, the iron core and a fuel tank of a transformer are collected, and then a three-dimensional geometric grid model of the transformer is established; the three-dimensional geometric grid model is input into software, sinusoidal currents with a phase different of 120 DEG are applied to the cross section of the three-phase low voltage winding respectively, and Dirichlet boundary conditions are applied to the outer side of the structural grid model; and an instant electromagnetic field is solved by a virtual displacement method, magnetic field energy is computed, a virtual work method is used to compute instant electromagnetic force borne by the transformer iron core and the winding, FFT is conducted to the instant electromagnetic force, and frequency domain distribution of the electromagnetic force of the iron core can be obtained. The computation method disclosed by the invention is direct and convenient; electromagnetic vibration and force bearing situations of the transformer iron core can be analyzed from the perspective of energy; each influential factor on force bearing of the iron core is considered comprehensively; and computation results are accurate and reliable.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
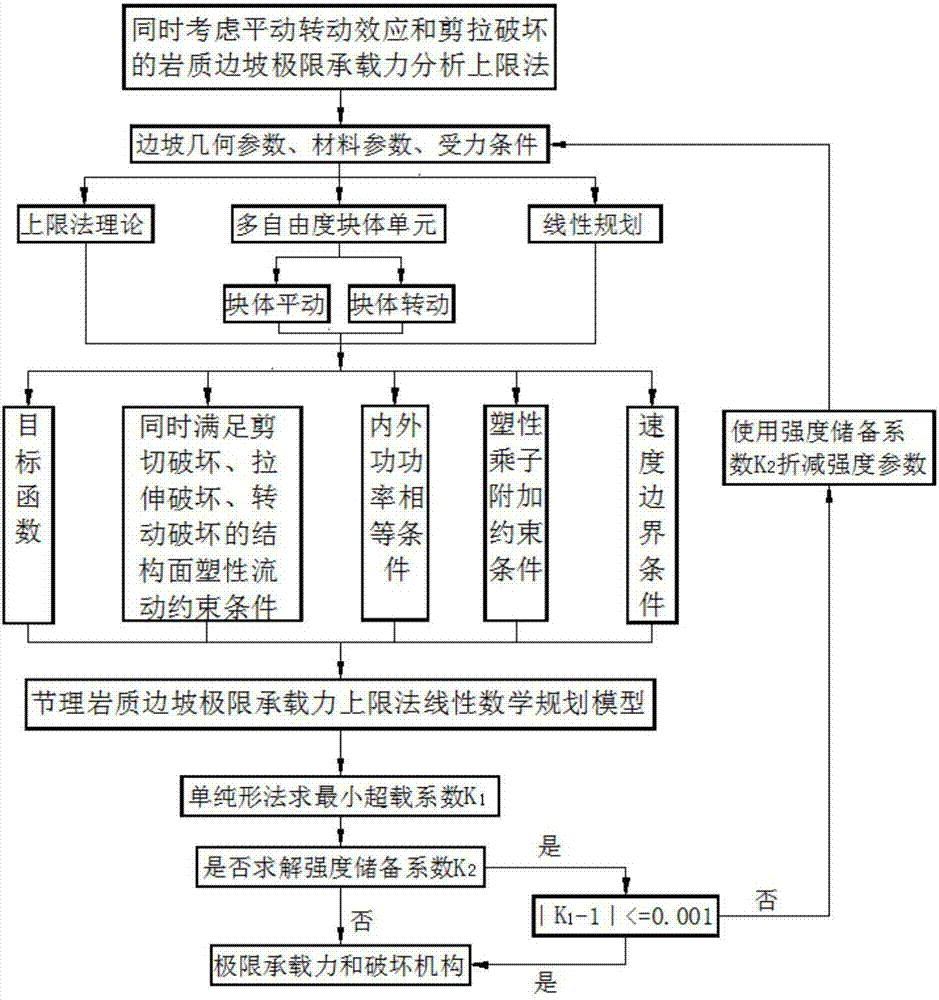
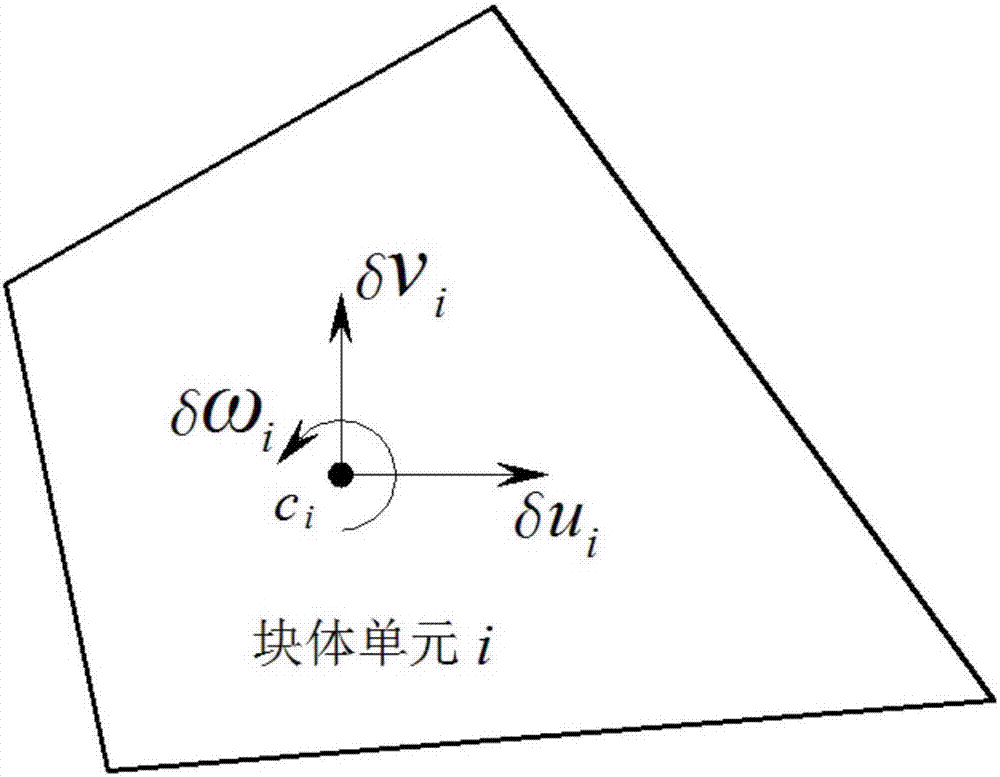
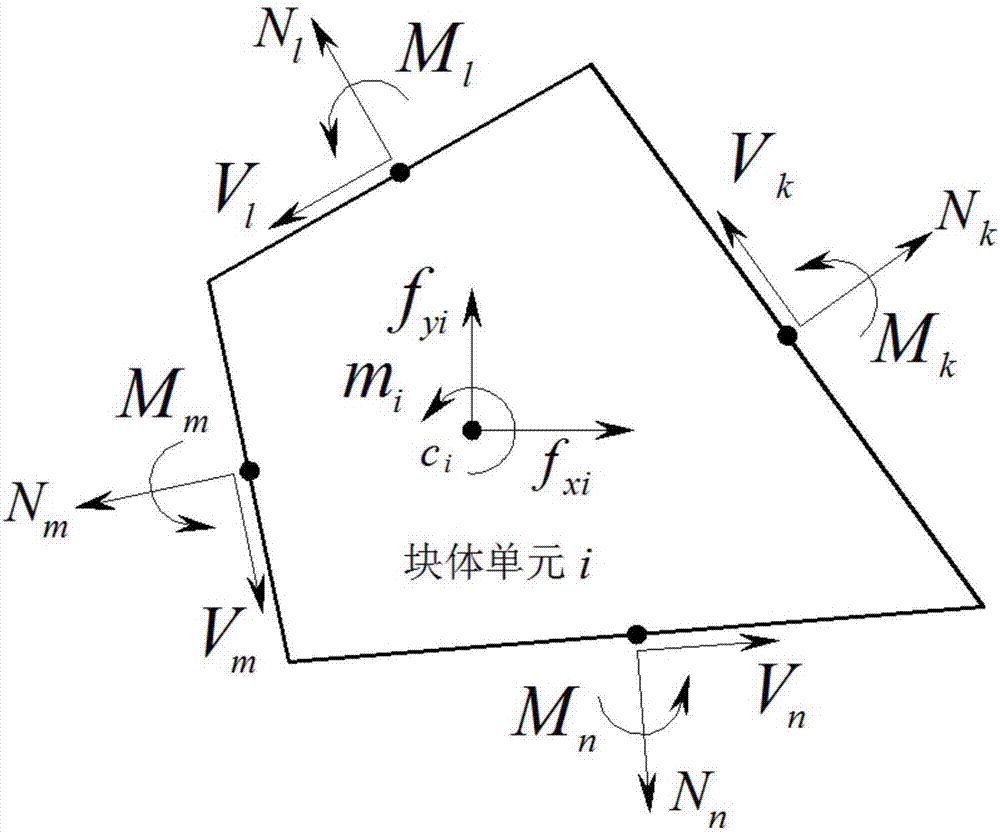
Upper-bound limit analysis method of ultimate bearing capacity of jointed rock slope considering translation and rotation effects at the same time
ActiveCN107330146AMethod concept is clearImprove calculation accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsVirtual workSimplex algorithm
The invention relates to an upper-bound limit analysis method of ultimate bearing capacity of rock slope considering rock translation and rotation effects at the same time, and belongs to the technical field of rock slope bearing capacity analysis. According to the method, based on a plastic upper-bound limit analysis theory, by means of multiple freedom degree rigid block unit discrete jointed rock slope, the translational speed and rotational speed of the rigid block unit centroid are used as unknown quantities, the translation and rotation mechanical effects of rocks are considered at the same time, the overload coefficient of the slope is used as a target function, and plastic flowing conditions satisfying shear failure, tensile failure and rotational failure of a structural plane are constructed; then combined with a virtual work principle and speed boundary conditions, a linear mathematic programming model for working out the ultimate bearing capacity of the jointed rock slope is built, the linear mathematic programming model is solved by means of a simplex method, a strength reserve coefficient is solved by means of an iterative method at the same time, and finally the upper-bound solution and corresponding failure mechanism of the ultimate bearing capacity of the jointed rock slope are acquired. The method has the advantages that the concept is clear and the computational accuracy is high.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
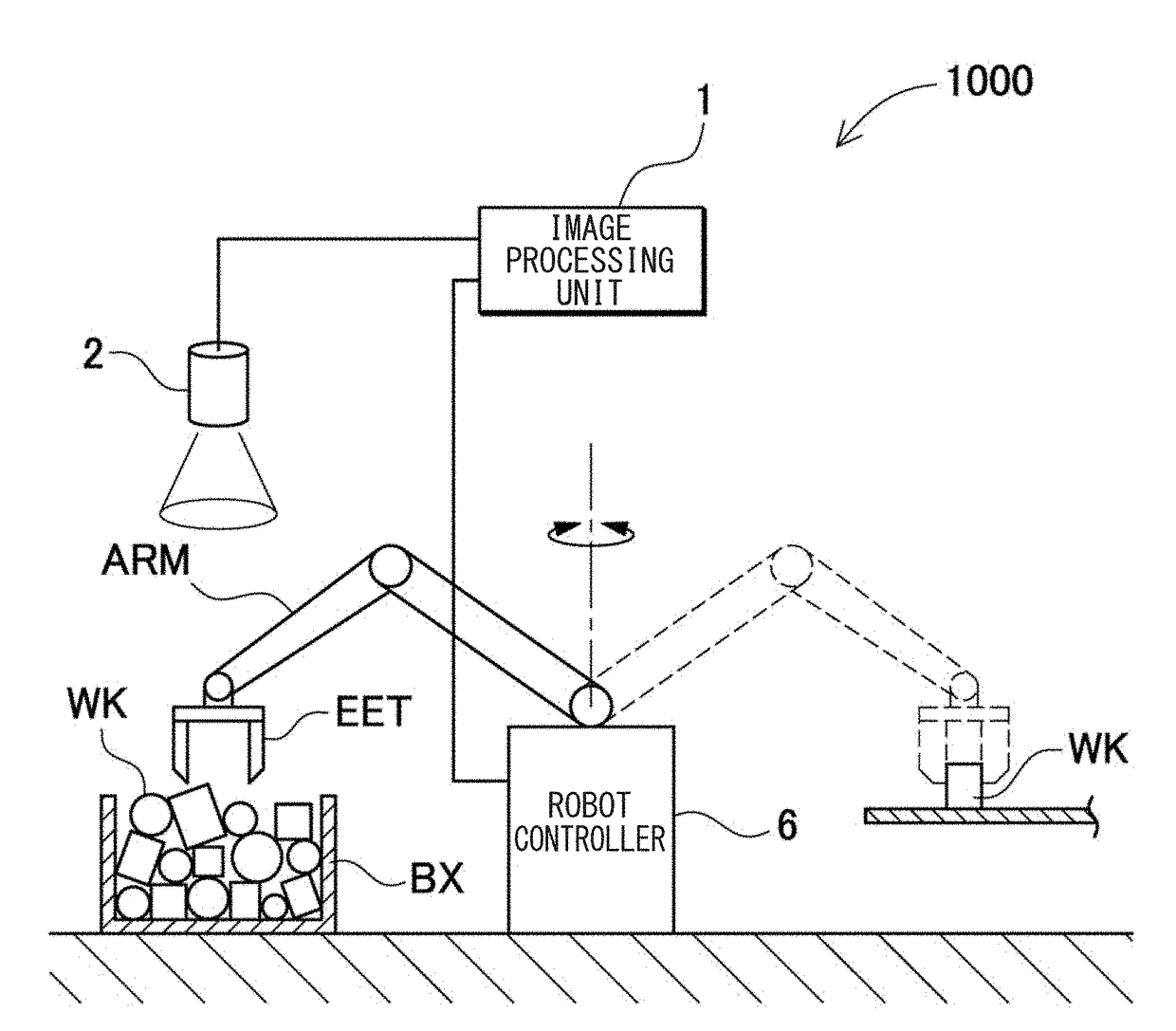
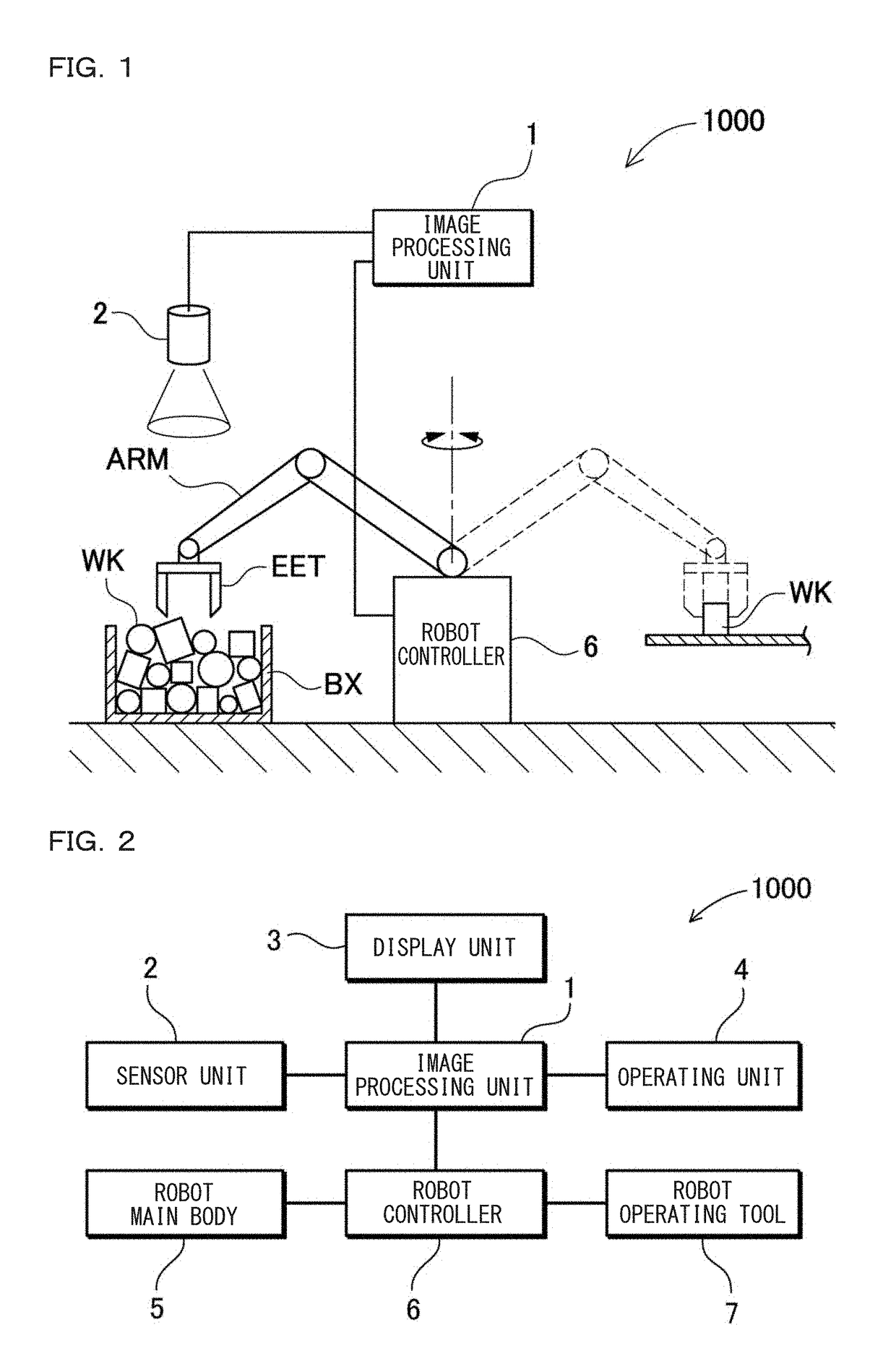
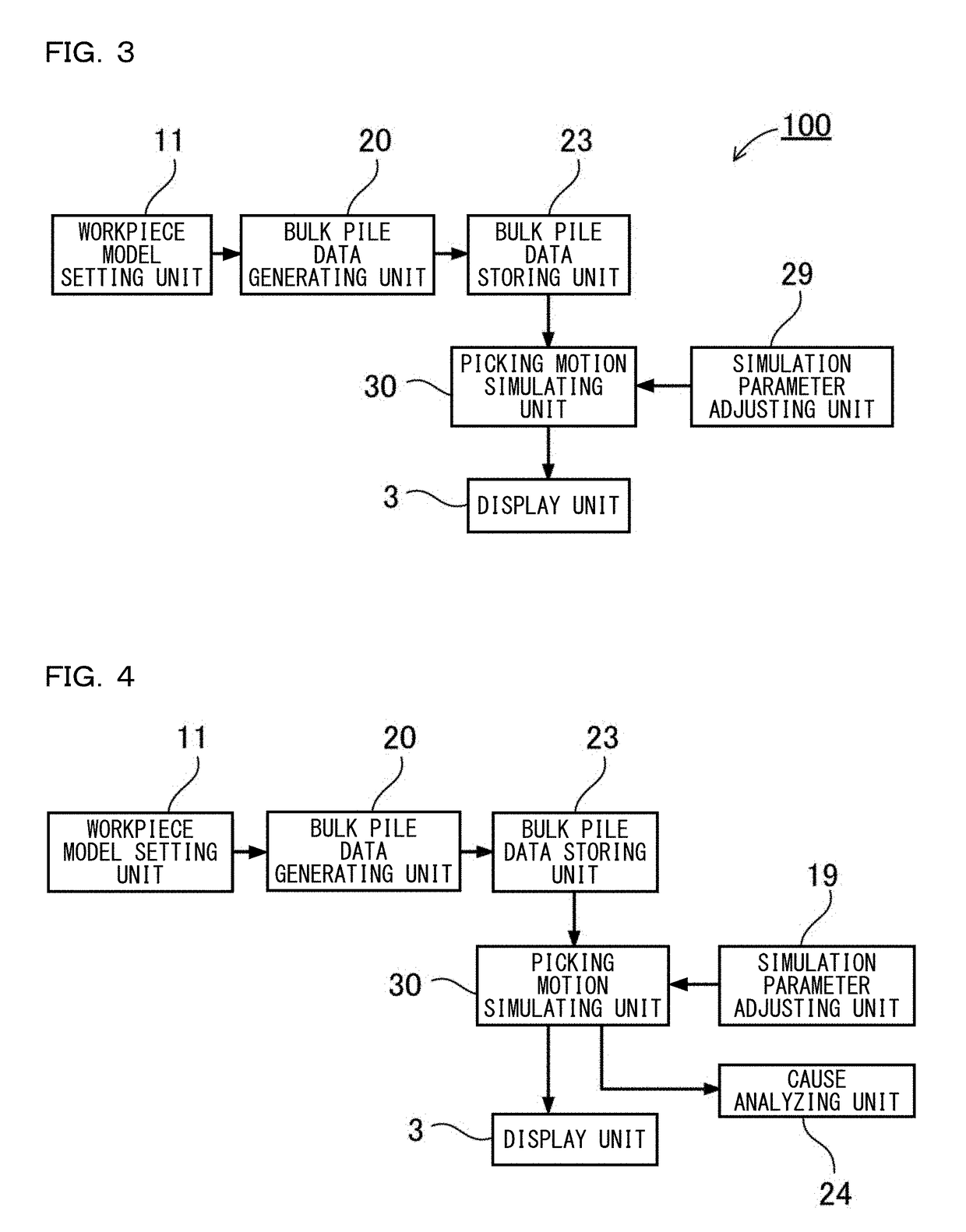
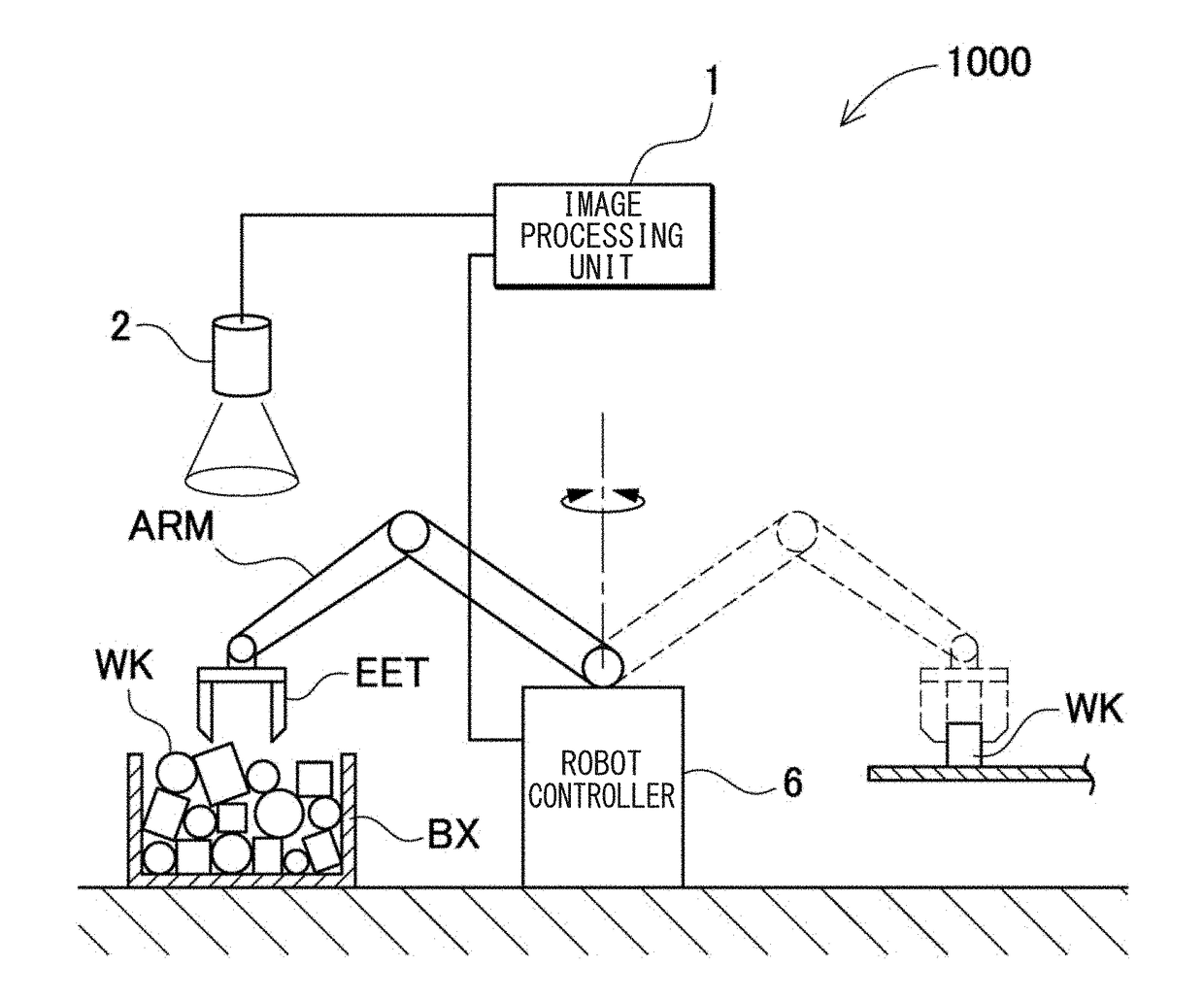
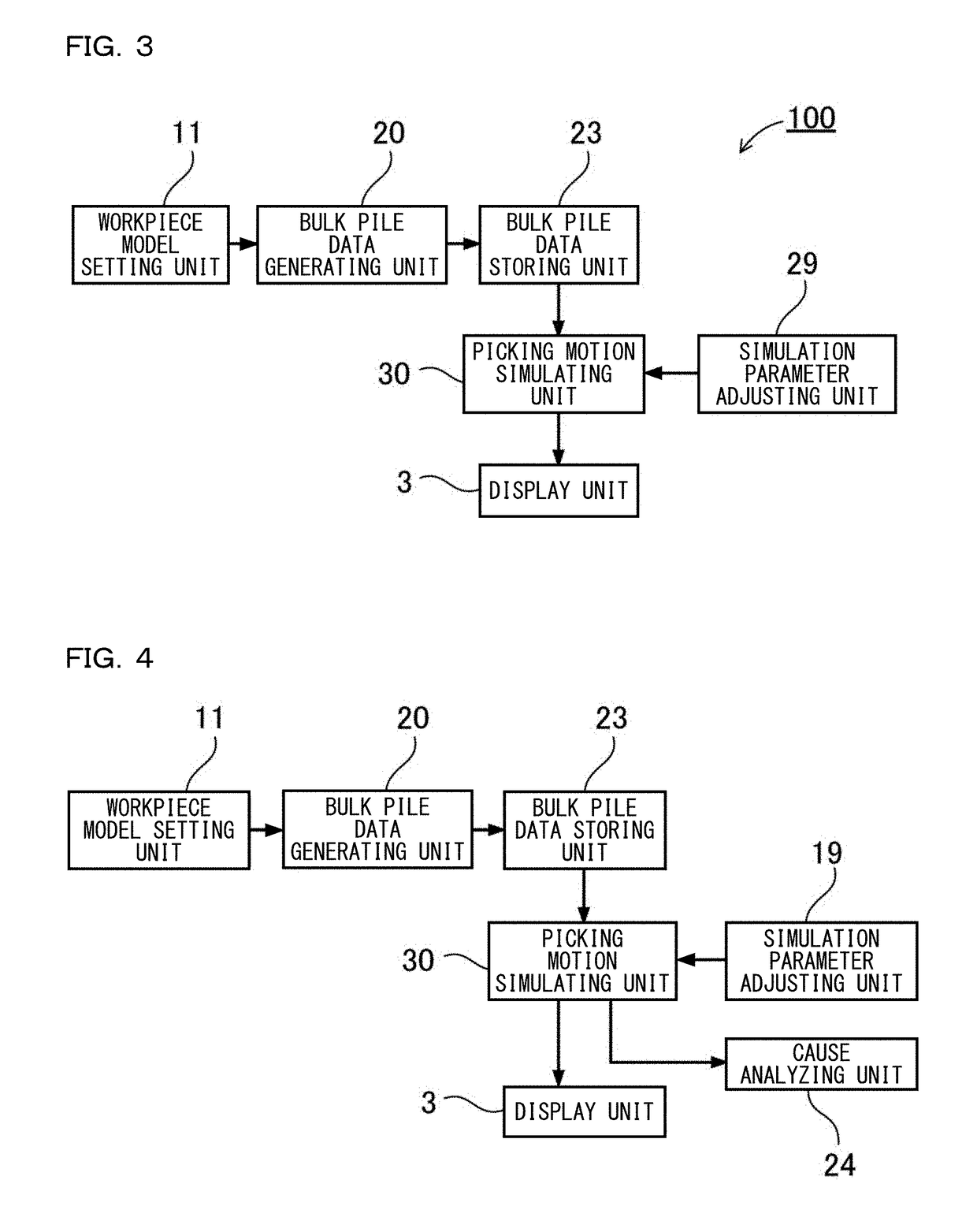
Robot Simulation Apparatus And Robot Simulation Method
InactiveUS20180253516A1Improve accuracyProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorVirtual workGenerating unit
The robot simulation apparatus includes: a picking motion simulating unit 30 that verifies a picking motion from a bulk pile of workpiece models in a virtual work space, with respect to bulk pile data generated by a bulk pile data generating unit 20. A physical simulation unit 60 is configured to re-execute a physical simulation with respect to the bulk pile data of a state obtained after one workpiece model is picked up after the picking motion simulating unit 30 grasps the workpiece model and at least a picking-up motion is started. The bulk pile data generating unit 20 is configured to update bulk pile data according to the result of the physical simulation executed by the physical simulation unit 60 during the simulation of the picking motion by the picking motion simulating unit 30.
Owner:KEYENCE
Automated Publishing Systems and Methods
InactiveUS20120150680A1Eliminate deficienciesEliminate drawbackDigital data processing detailsWebsite content managementGraphicsGraphical user interface
Provided is an automated publishing system that can include a database indexed to store contribution data that includes portions of works of authorship, a user authentication system configured to authenticate a member to the system, and a virtual work area having a graphic user interface accessible by the member. The interface can include content searching and content collating features such that a member can generate a custom work by selecting a plurality of different portions of works of authorship which are combined to generate the custom publication. The interface in addition contains an option for a member to add content at the end of each chapter, when such member is authorized by the publisher. The custom publication can be sent to the publisher for approval and is made available only after the publisher grants approval.
Owner:QBEND
Vibration control method and device for ornithopter
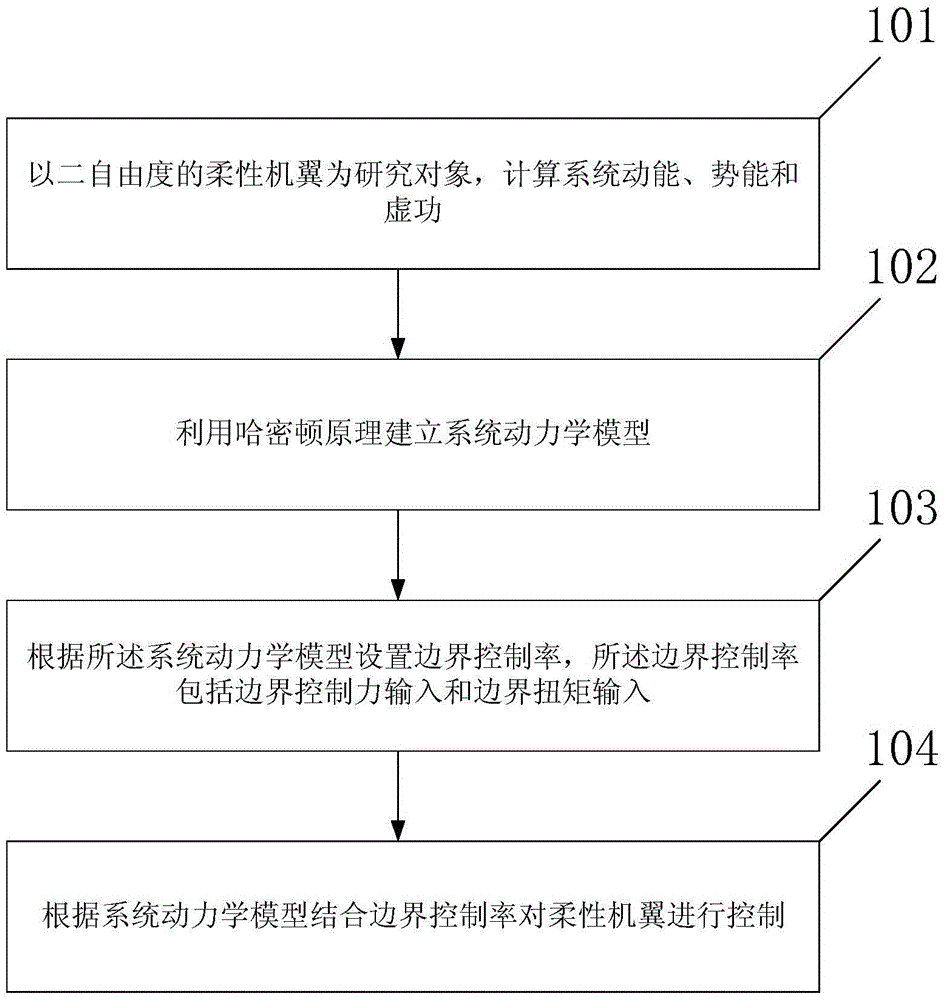
ActiveCN105644784AAvoid deformationEasy to controlActuated automaticallyOrnithoptersResearch ObjectVibration control
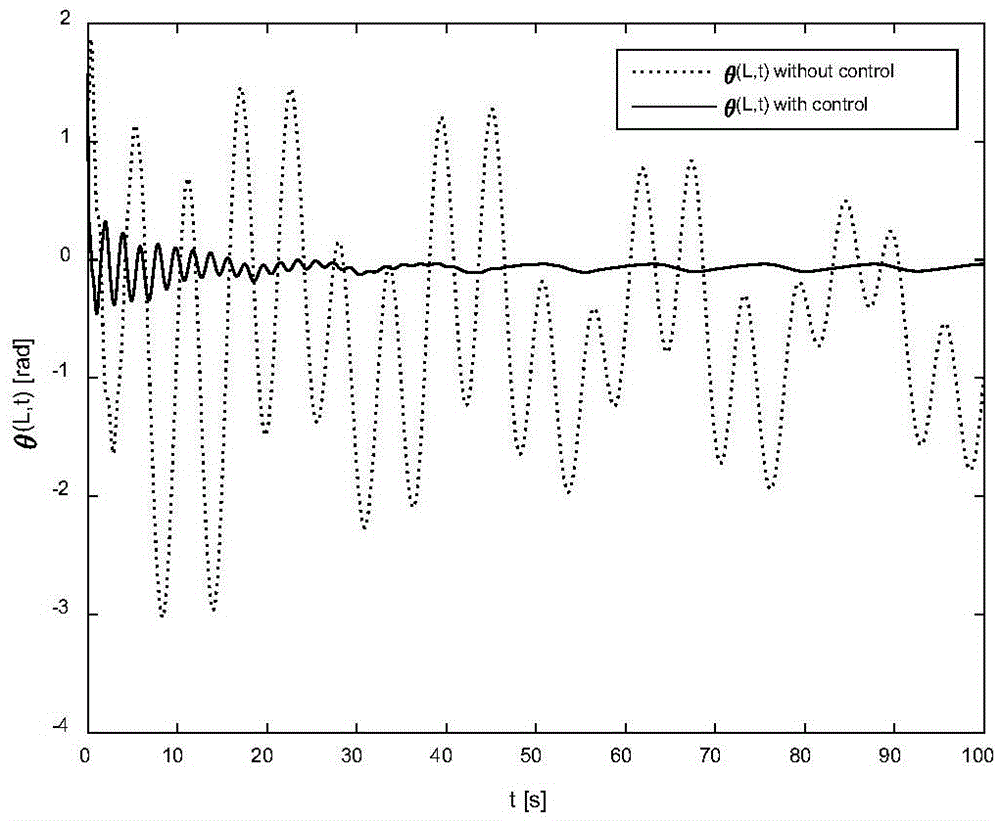
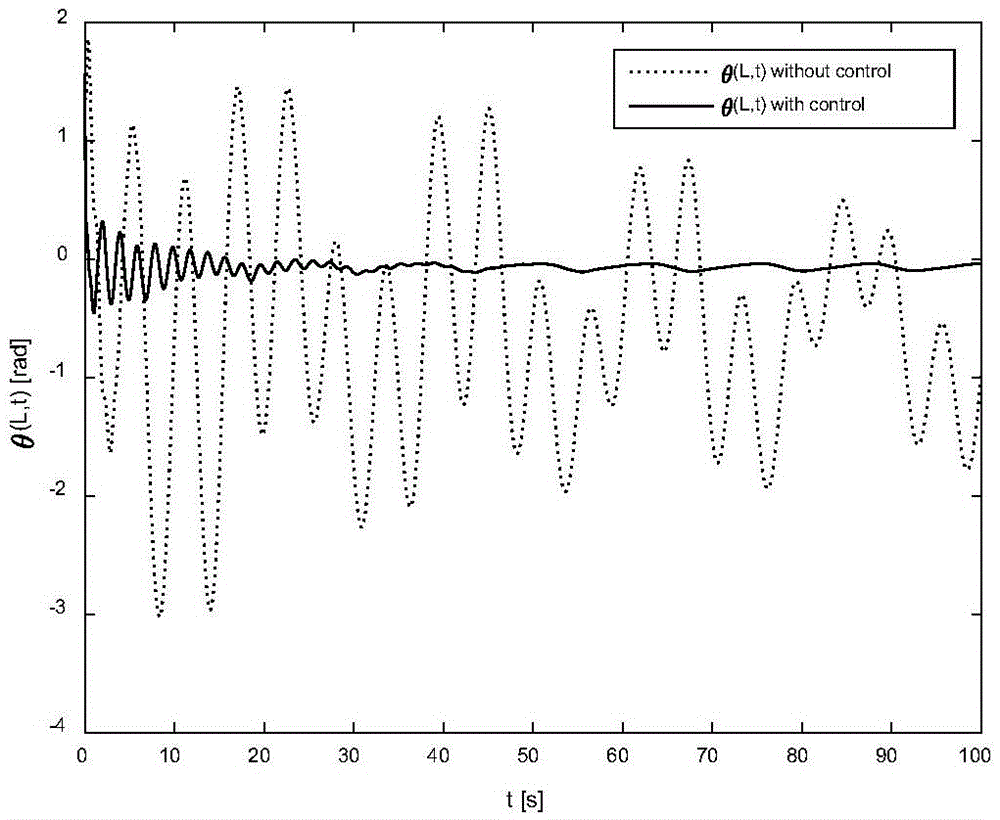
The invention provides a vibration control method and device for an ornithopter. The method comprises the following steps: by taking a flexible wing with two-degree of freedom as a research object, calculating system kinetic energy, potential energy and virtual work; constructing a system dynamics model by using a Hamilton's principle; setting a boundary control rate according to the system dynamics model, wherein the boundary control rate comprises F(t) and M(t), the F(t) is boundary control force input, and the M(t) is boundary torque input; controlling the flexible wing according to the system dynamics model and the boundary control rate. By constructing the system dynamics model by using the Hamilton's principle, and setting the boundary control rate according to the system dynamics model, a situation that distributed disturbance exists at a boundary is fully considered, and flexible wing deformation caused by external disturbance is effectively inhibited.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Lot start agent that determines delta virtual WIP time for each bottleneck station in a multi-product and multi-bottleneck manufacturing environment
ActiveUS7054702B1Function increaseProgramme controlDigital data processing detailsVirtual workWorkstation
A system and method are provided for calculating a plurality of bottleneck delta virtual work in process time (“VWIP”) values. Each of the bottleneck delta VWIP values represents the time until one of n bottleneck workstations begins to risk starvation.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
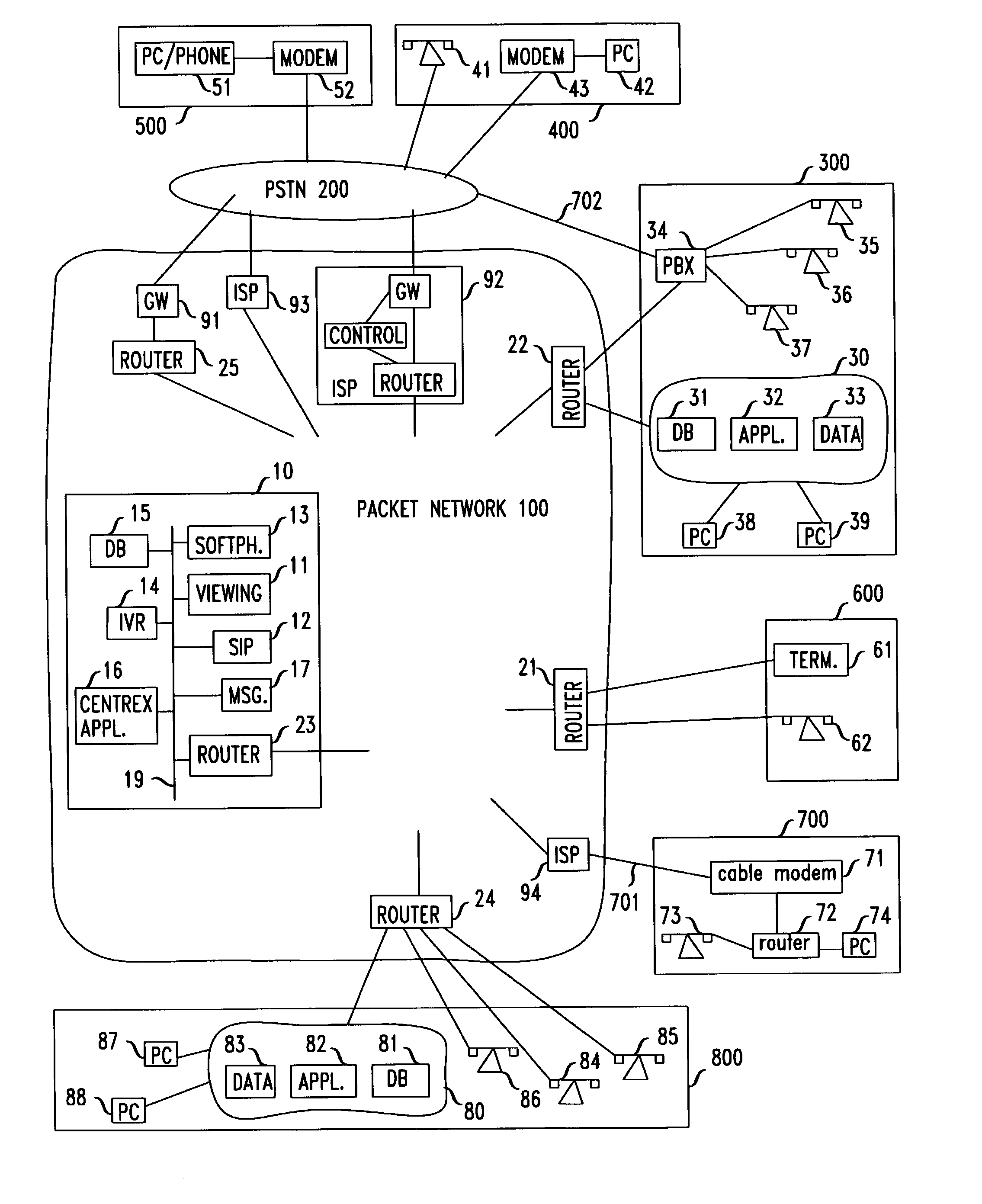
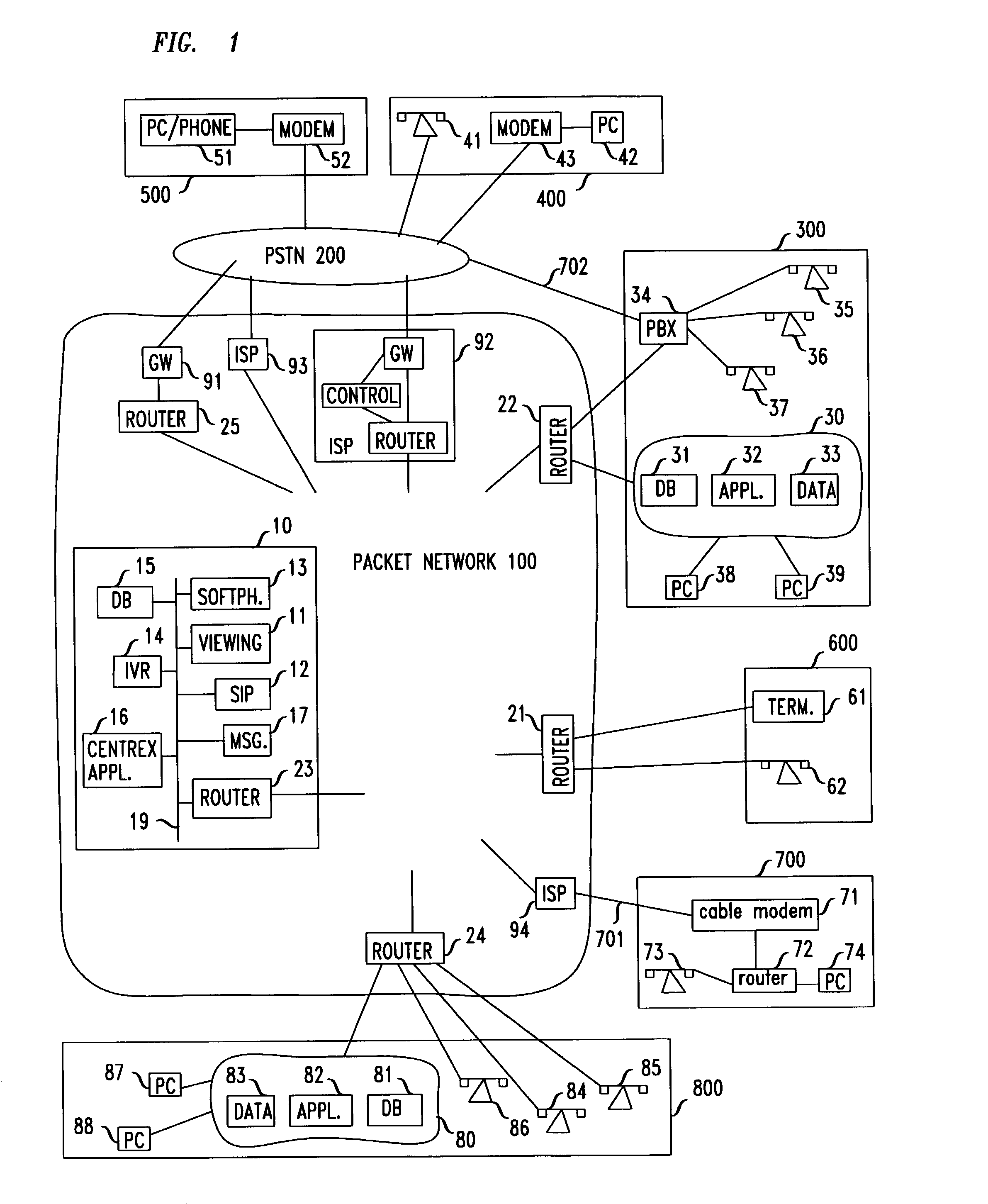
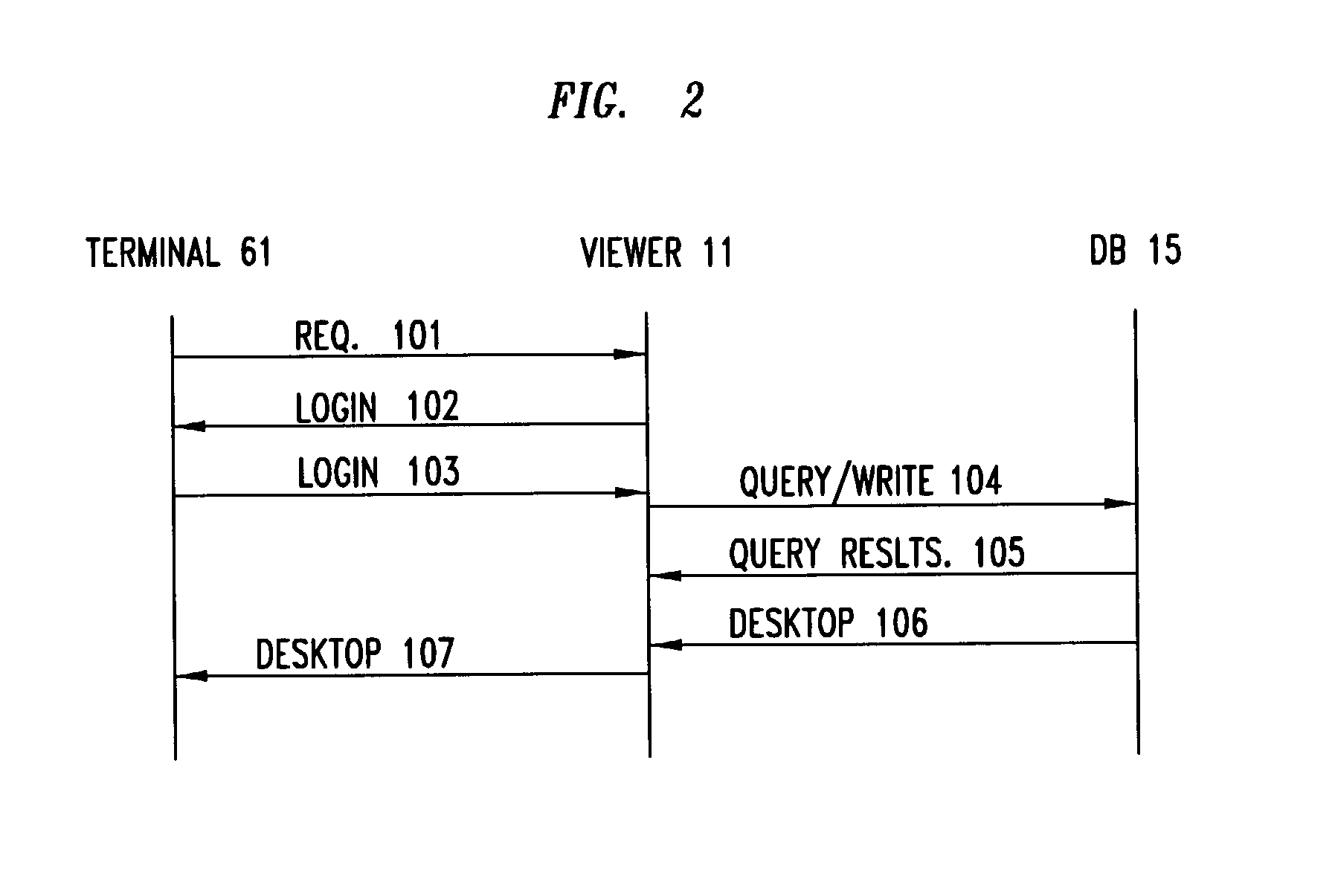
Virtual work environment for remote users
InactiveUS7062032B1Multiple digital computer combinationsManual exchangesWorking environmentVirtual work
An arrangement provides a work environment to a remote user who is logged-in as a member of an enterprise, which work environment includes both a telecommunication capability and a data processing capability, and both are concurrently associated with the logged-in user. The data processing capability is restricted to the user obtaining only views of files, rather than the files themselves, and all file processing that can potentially store data is restricted to applications that can store files only in a range of locations specified by the enterprise.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
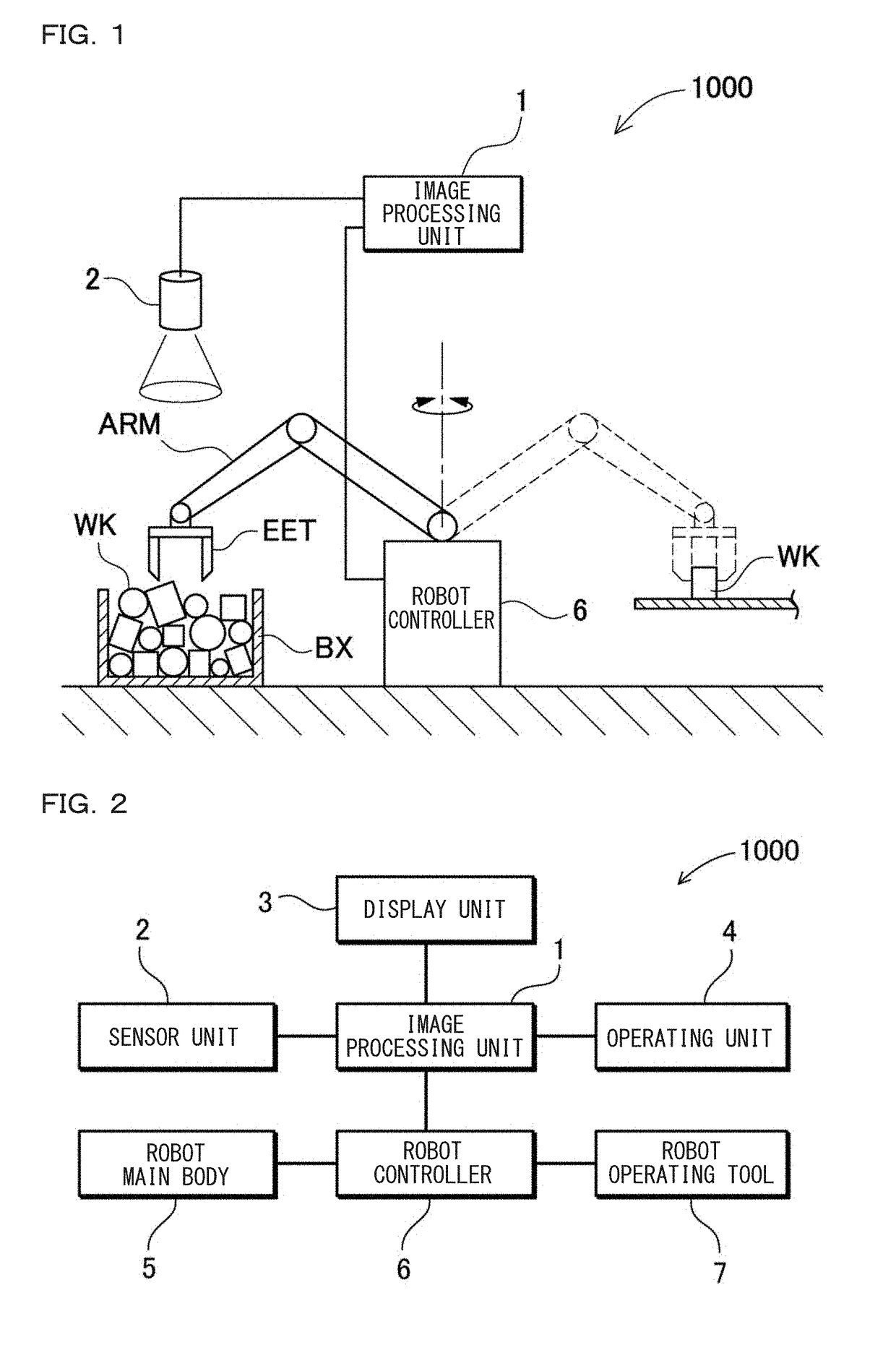
Robot Simulation Apparatus And Robot Simulation Method
ActiveUS20180250820A1Improve accuracyReduce the differenceProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorThree dimensional measurementThree dimensional shape
The robot simulation apparatus includes: a workpiece model setting unit 11 that sets a workpiece model obtained by forming a model of a three-dimensional shape of a workpiece; a bulk pile data generating unit 20 that generates virtual bulk pile data of a plurality of workpiece models piled up in a virtual work space as a virtually formed work space; a region estimating unit 22 that identifies an estimated region that is estimated to be three-dimensionally measurable by a sensor unit which is disposed above the work space, based on a position and a posture of each workpiece model in the bulk pile data; and a picking motion simulating unit 30 that executes a simulation for verifying the picking motion from the bulk pile of the workpiece models in the virtual work space, based on data of the estimated region identified by the region estimating unit 22.
Owner:KEYENCE
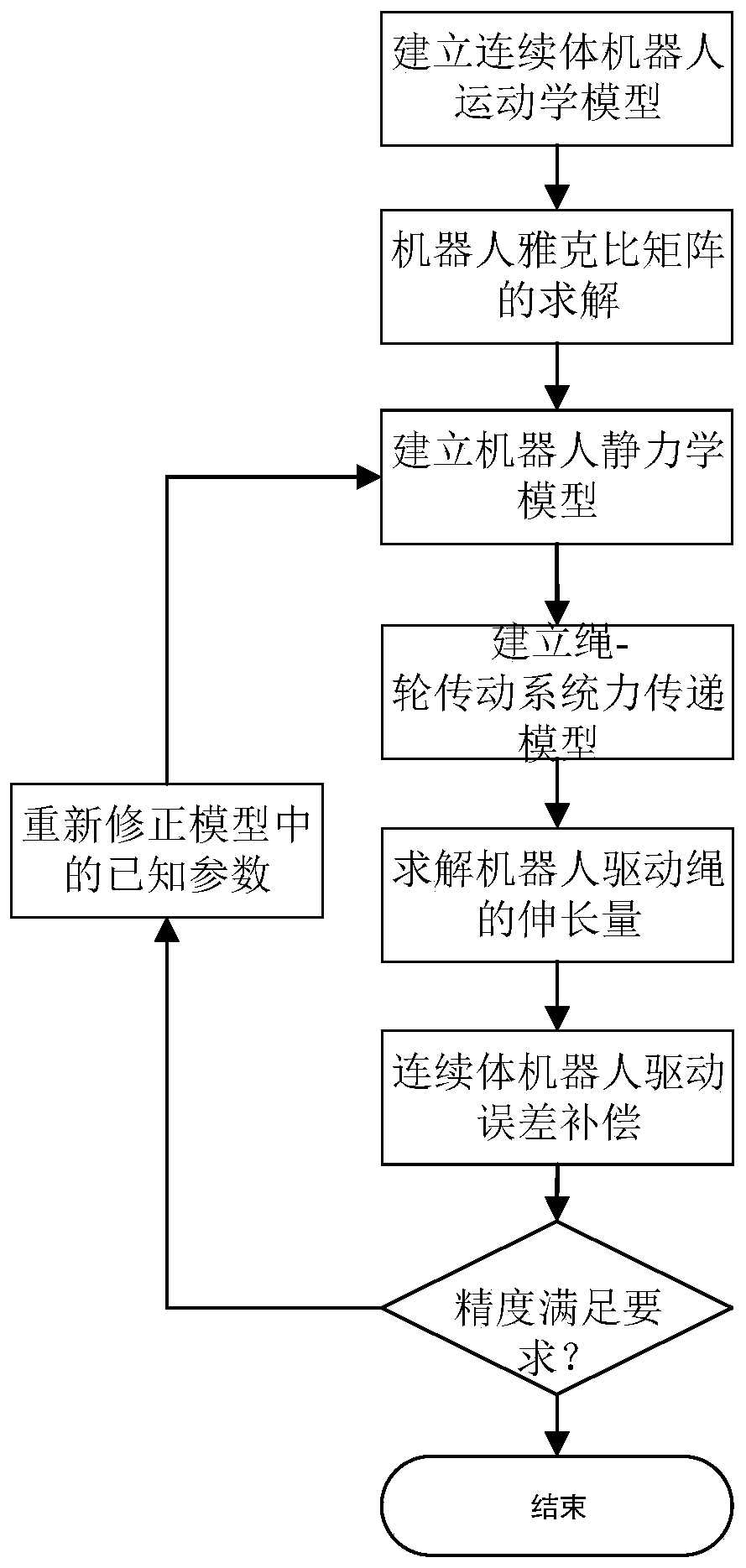
Driving compensation method for rope-driving continuum robot
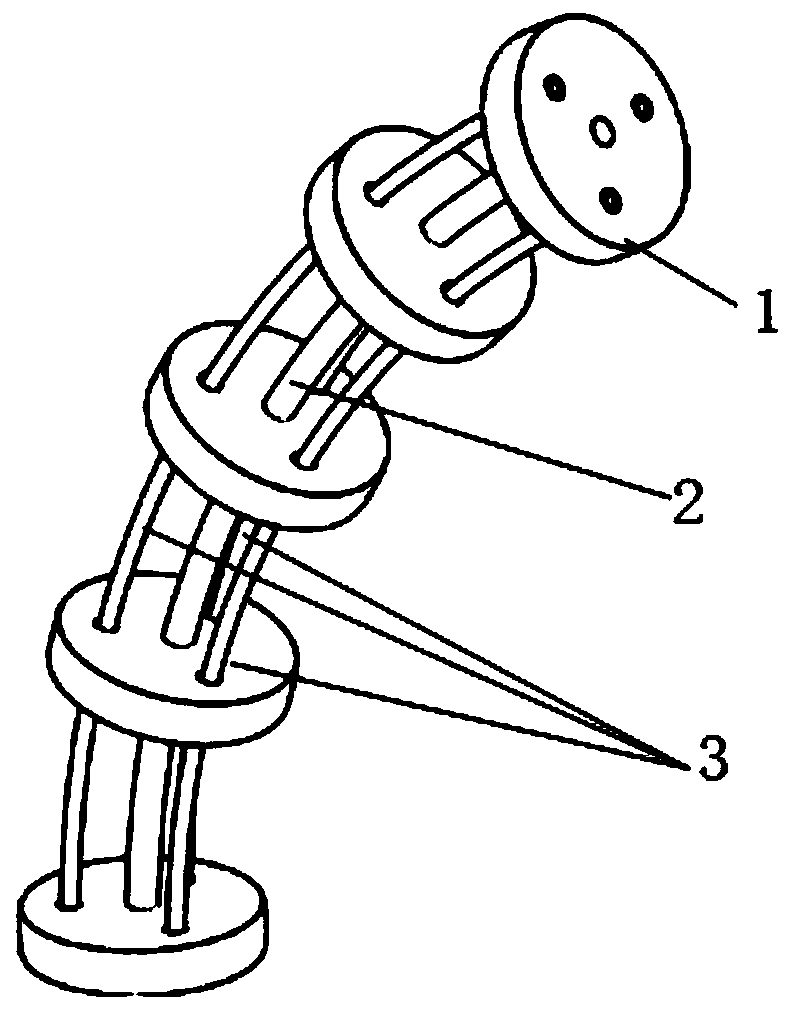
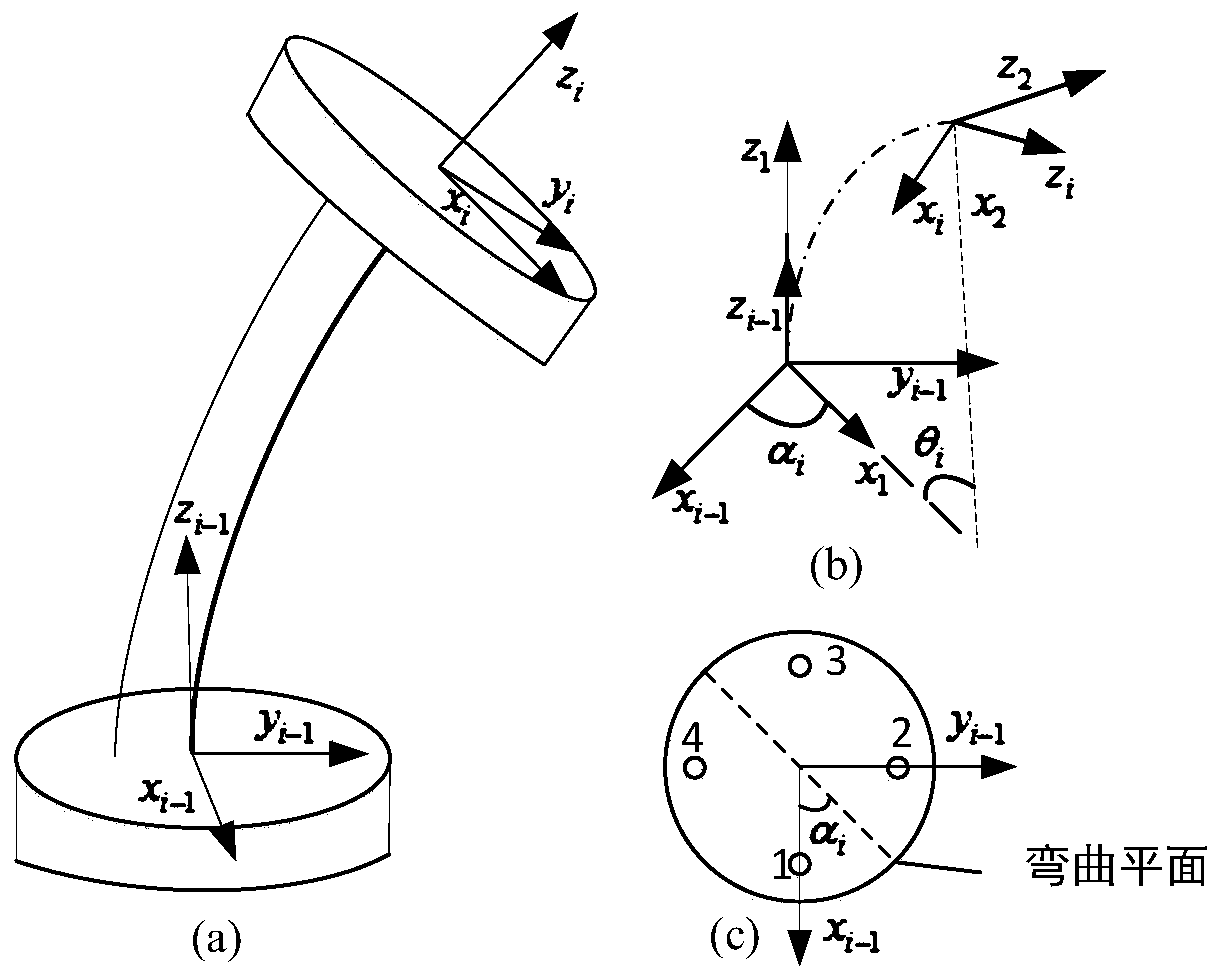
ActiveCN110193827AImprove Motion Control AccuracyHigh control precisionProgramme-controlled manipulatorSimulationVirtual work
The invention discloses a driving compensation method for a rope-driving continuum robot. The method specifically comprises the following steps of establishing a kinematic model of the continuum robot by combining a segmented constant curvature arc hypothesis and a geometric analysis method; solving Jacobian matrix of the robot based on differential transformation principle; establishing a statics model of the robot based on virtual work principle; building a force transmission model of a rope-wheel drive system based on Coulomb friction; solving the elongation of a robot driving rope based on Hooke's law; and feeding back the driving rope length compensation amount to a control unit to realize error compensation of the transmission system of the continuum robot and improve the motion control precision of the robot. The method of has the characteristics of simplicity, high efficiency, low cost, good universality and the like, avoids using expensive measuring sensors, and realizes thepurpose of improving the motion control precision of the robot by establishing a driving error compensation model of the continuum robot system.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
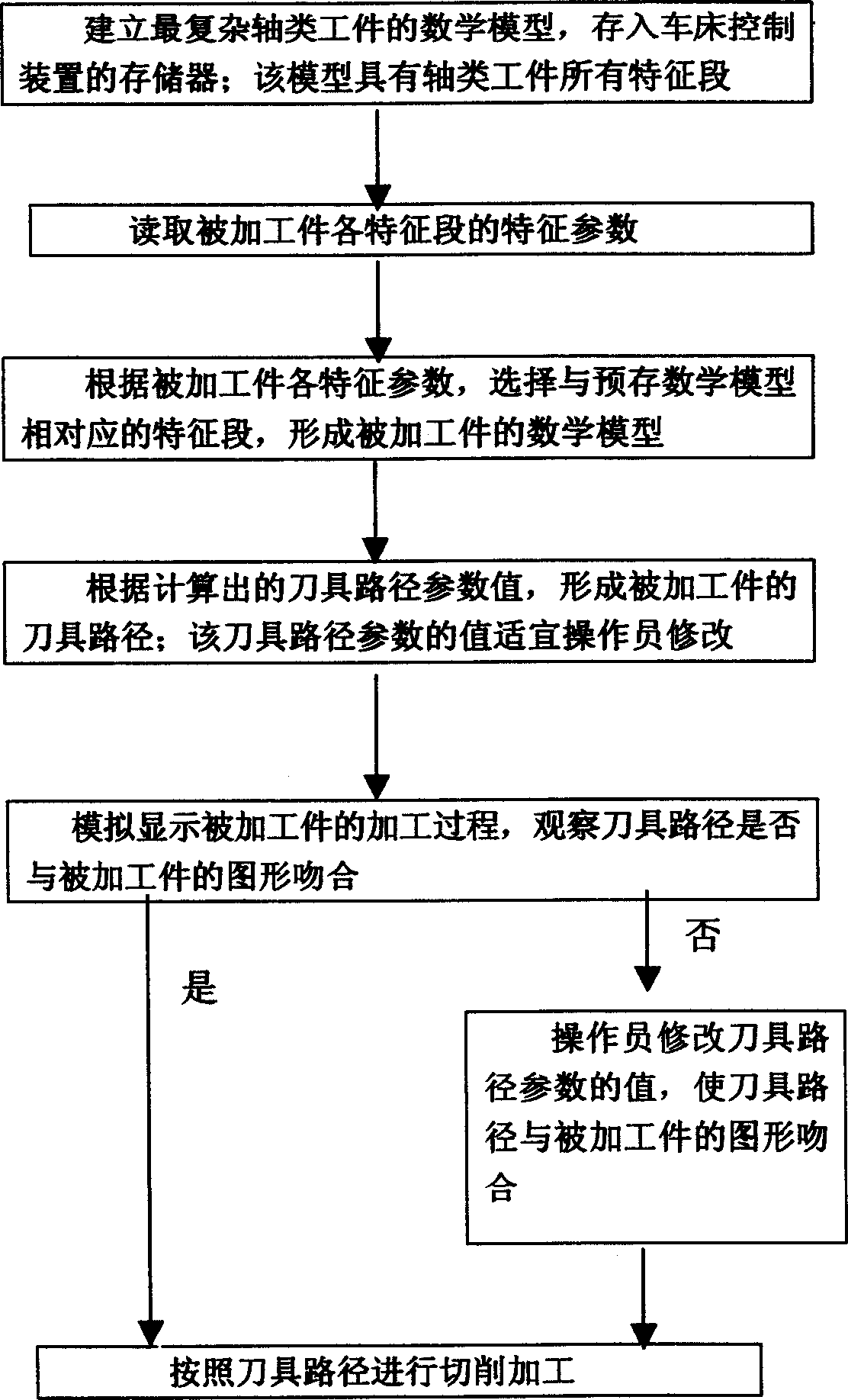
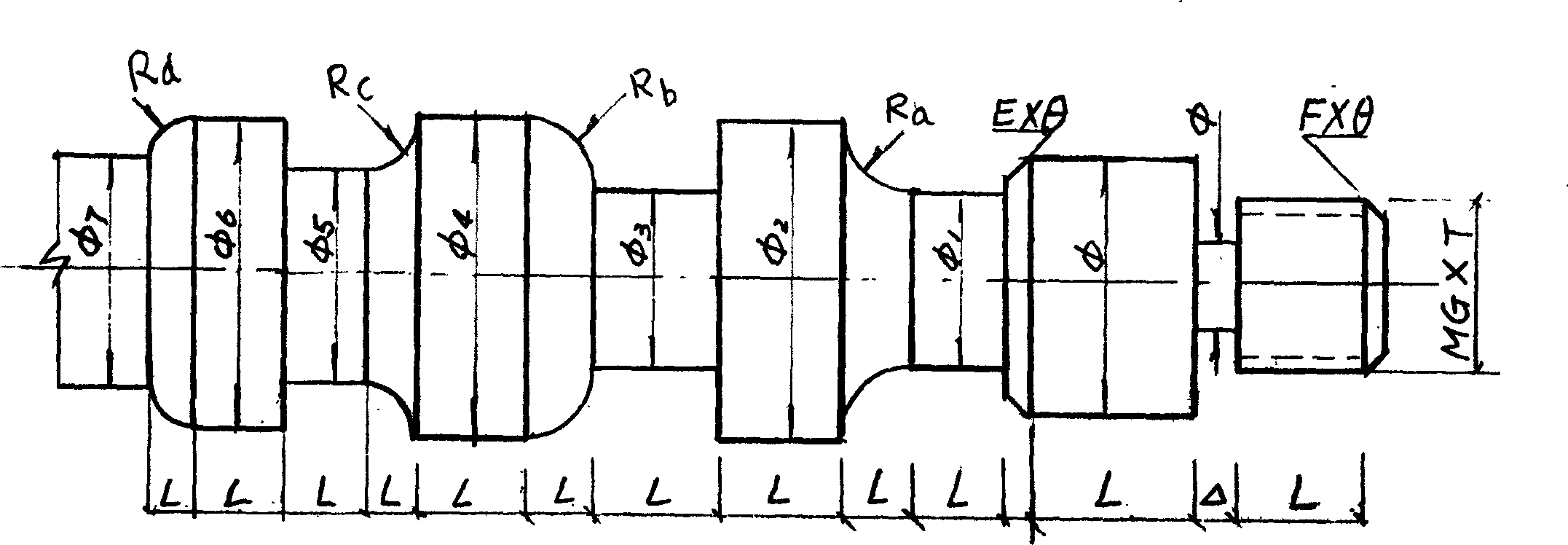
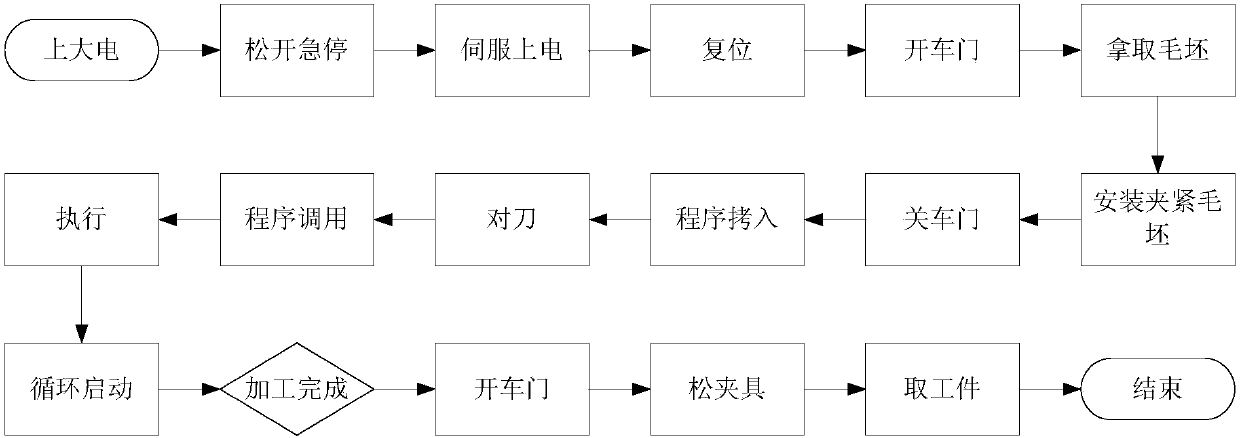
Method for working shaft-like workpiece by numerical control lathe and its control device
InactiveCN1743983AShorten the timeShorten the processing cycleNumerical controlGraphicsNumerical control
This invention refers to a method for machining axle like piece by digital controlled machine tool, which features preset mathematics model of virtual work piece in memory of lathe controller, said model having all character section of axle like work piece, the user inputting character parameter of each section of work piece, computer reading out character parameter and selecting preset corresponded character section, calculating and modifying each character section to form worked piece model and cutter route, imitating and displaying working process, modifying cutter route to fit the pattern of worked piece, then making machining.
Owner:SICHUAN ENG TECHN COLLEGE
Tail end Cartesian space rigidity modeling method for rope-driven linkage mechanical arm
ActiveCN109249428AAchieve stiffnessEasy to controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorVirtual workEngineering
The invention discloses a tail end Cartesian space rigidity modeling method for rope-driven linkage mechanical arm. The method includes: calculating integral joint equivalent rigidity of a mechanicalarm linkage rope, calculating according to a velocity-stage kinematic relation between a driving rope and a mechanical arm joint to obtain a Jacobian matrix Gq from a joint space to a driving space, acquiring integral joint equivalent rigidity of the driving rope of the mechanical arm according to a virtual work principle and a variational principle, and calculating mechanical arm joint equivalentrigidity Kq; calculating according to a velocity-stage kinematic relation between a mechanical arm joint variable and a tail end pose to obtain a Jacobian matrix Jq from the joint space to the tail end Cartesian space, and acquiring an equivalent rigidity Ke, in the tail end Cartesian space, of the mechanical arm joint equivalent rigidity Kq according to the virtual work principle and the variational principle. Rigidity analysis and control of the rope-driven linkage mechanical arm can be realized, and the method can be applied to rigidity analysis, statics analysis, force control and the like of the rope-driven linkage mechanical arm.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
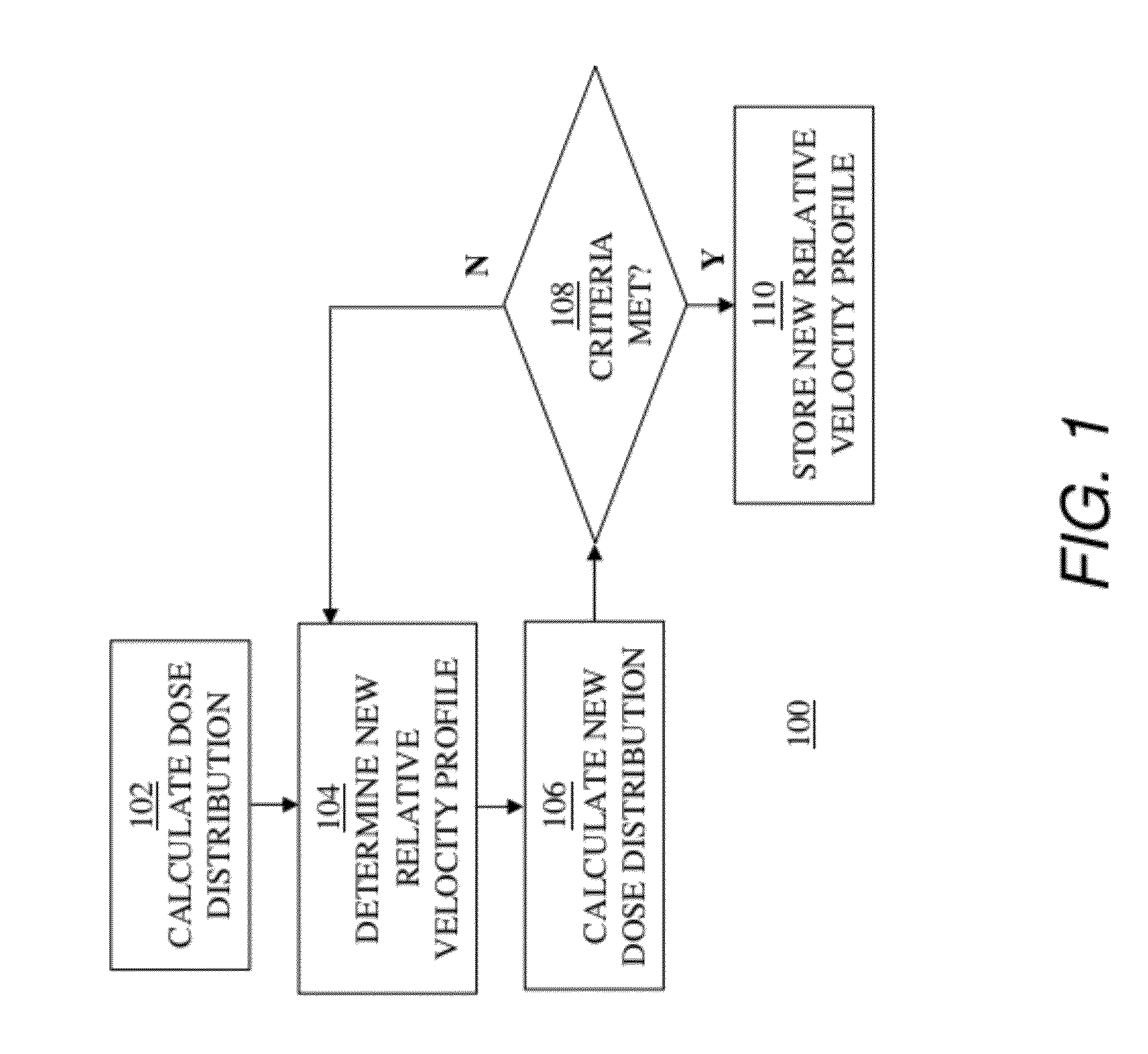
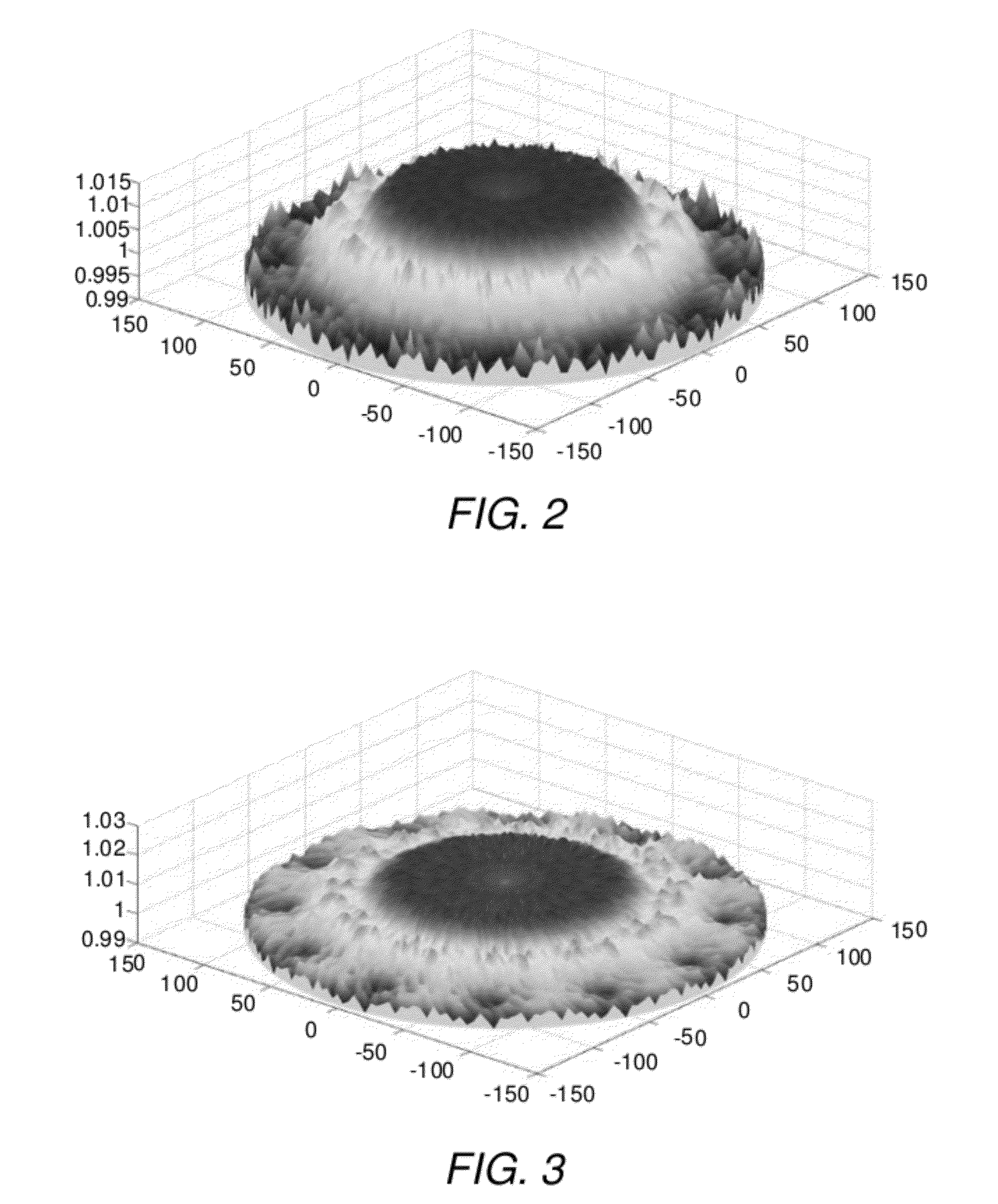
Determining relative scan velocity to control ion implantation of work piece
InactiveUS20120196047A1Liquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesVirtual workIon implantation
To select a relative velocity profile to be used in scanning an actual work piece with an ion implant beam of an ion implantation tool, the implantation of a virtual work piece is simulated. A dose distribution is calculated across the virtual work piece based on an implant beam profile and a relative velocity profile. A new relative velocity profile is then determined based on the calculated dose distribution and the relative velocity profile used in calculating the dose distribution. A new dose distribution is then calculated using the new relative velocity profile. A new relative velocity profile is determined and a corresponding new dose distribution is calculated iteratively until the new dose distribution meets one or more predetermined criteria. The new relative velocity profile is stored as the selected relative velocity profile when the new dose distribution meets the one or more predetermined criteria.
Owner:ADVANCED ION BEAM TECHNOLOGY INC
Systems, methods, and computer-readable media for managing collaboration on a virtual work of art
Systems, methods, and computer-readable media for managing collaboration on a virtual work of art between multiple electronic devices are provided. A first graphical display system of a first device may generate an input command in response to receiving user information through a user interface of the first device, and may then share this input command with a second graphical display system of a second device. The first graphical display system may process the shared input command to generate pixel array data in a canvas of the first device while the second graphical display system may process the shared input command to generate pixel array data in a canvas of the second device. By sharing input commands rather than pixel array data, system latency may be reduced. Despite operating on the same artwork, the user interfaces and graphical processing capabilities of each device may vary, thereby providing the user greater expressiveness.
Owner:APPLE INC
First-order perturbation expansion progressive homogenization method for statistical prediction of elastic constitutive matrix of random distributed composite materials
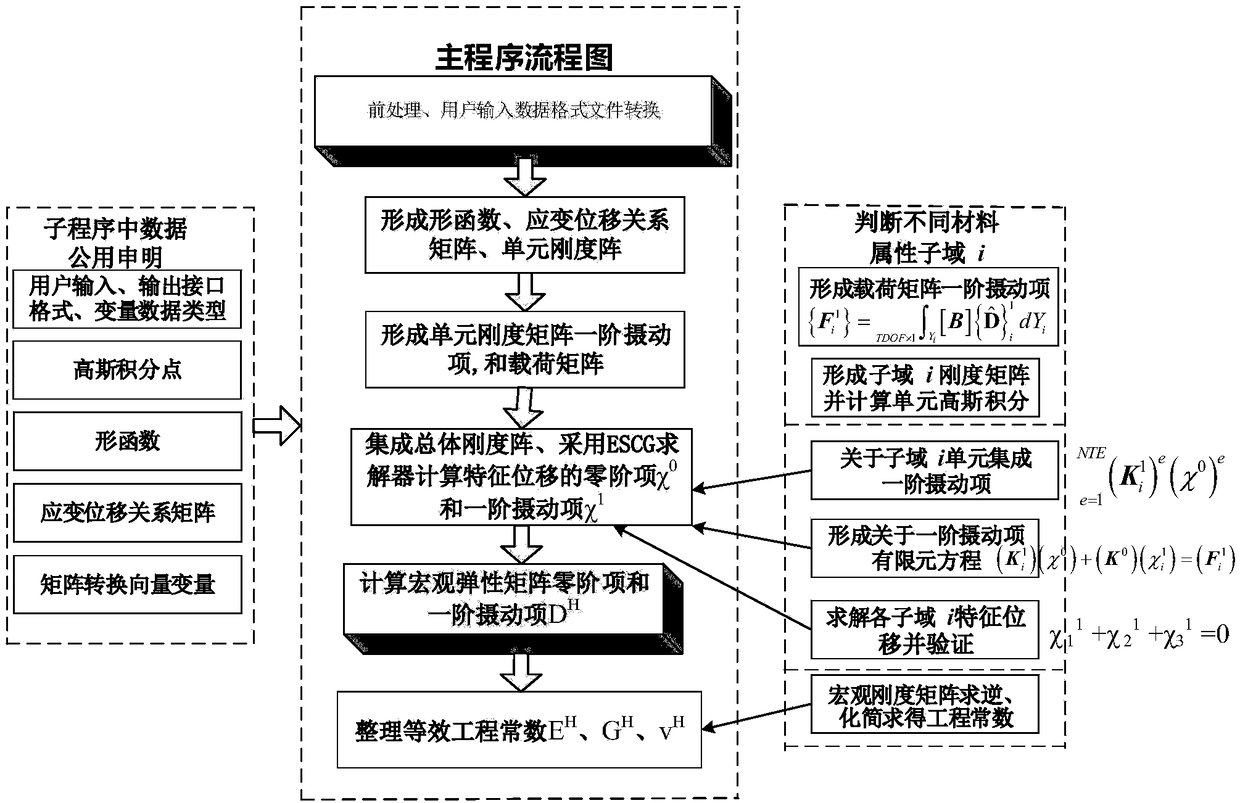
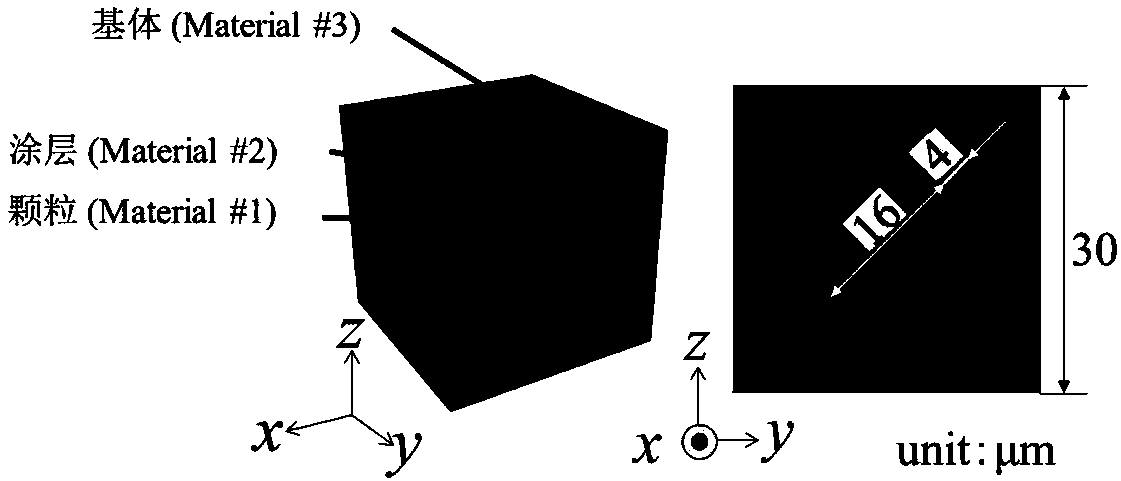
InactiveCN108153962APrediction Method of Reliable Material Structure Equivalent Elasticity MatrixAvoid repeating the tedious trial calculation processDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsVirtual workScale effects
The invention discloses a first-order perturbation expansion progressive homogenization method for statistical prediction of an elastic constitutive matrix of random distributed composite materials. The method comprises the steps that (1), according to an actual material domain, the source and range of random variables are determined, and a probability model is established; (2), the random variables are introduced by a material elastic constitutive flexibility matrix based on a first-order perturbation hypothesis, and a stiffness matrix is obtained by inversion; (3), a microscopic representative unit subdomain is intercepted in a macroscopic material structure system, and a functional scale effect relationship on a microscopic representative volume unit is hypothesized based on a progressive homogenization method to derive a virtual work principle equation and establish the equivalence relation between a macro elastic matrix and a finite element equation of a representative volume unitmaterial domain; (4), the equivalence relation between probability and statistical characteristics of the macroscopic elastic matrix and the finite element equation of the representative volume unitmaterial domain is solved; (5), probability and statistical characteristics of elastic engineering constanTS are derived from the macroscopic elastic matrix.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
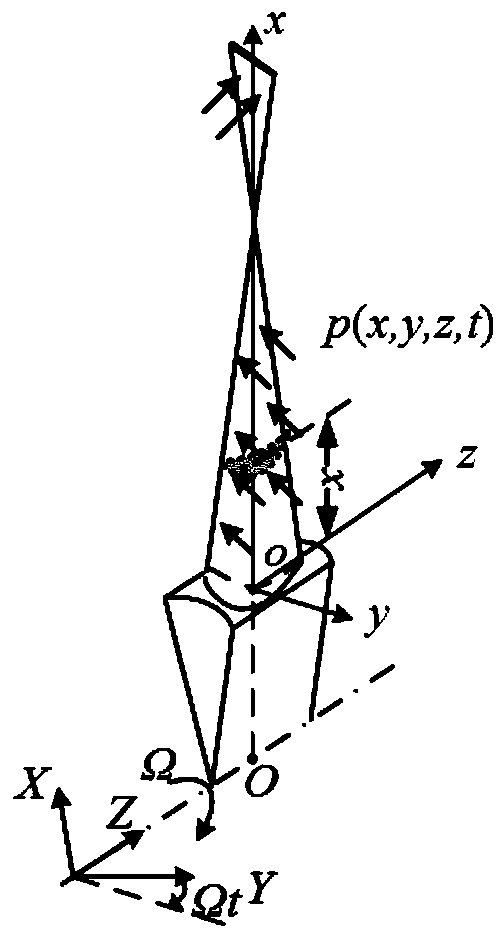
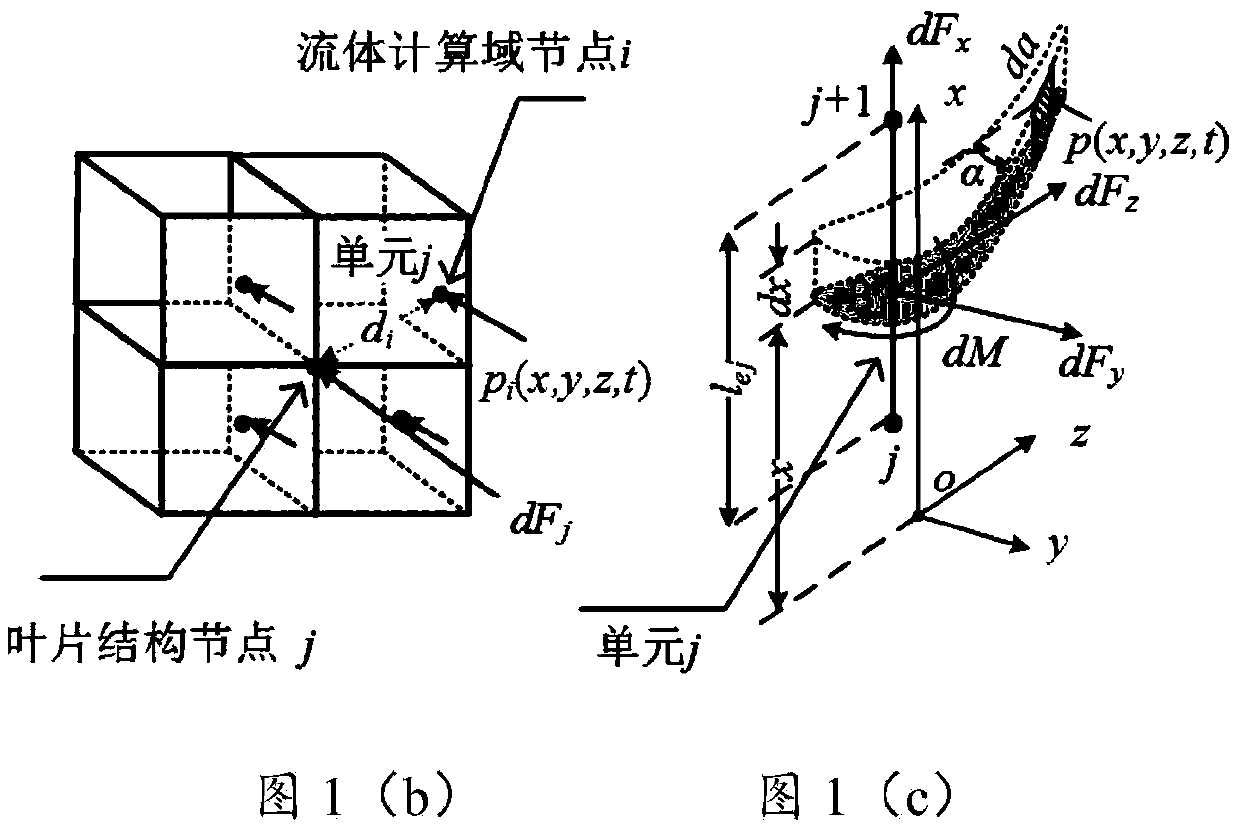
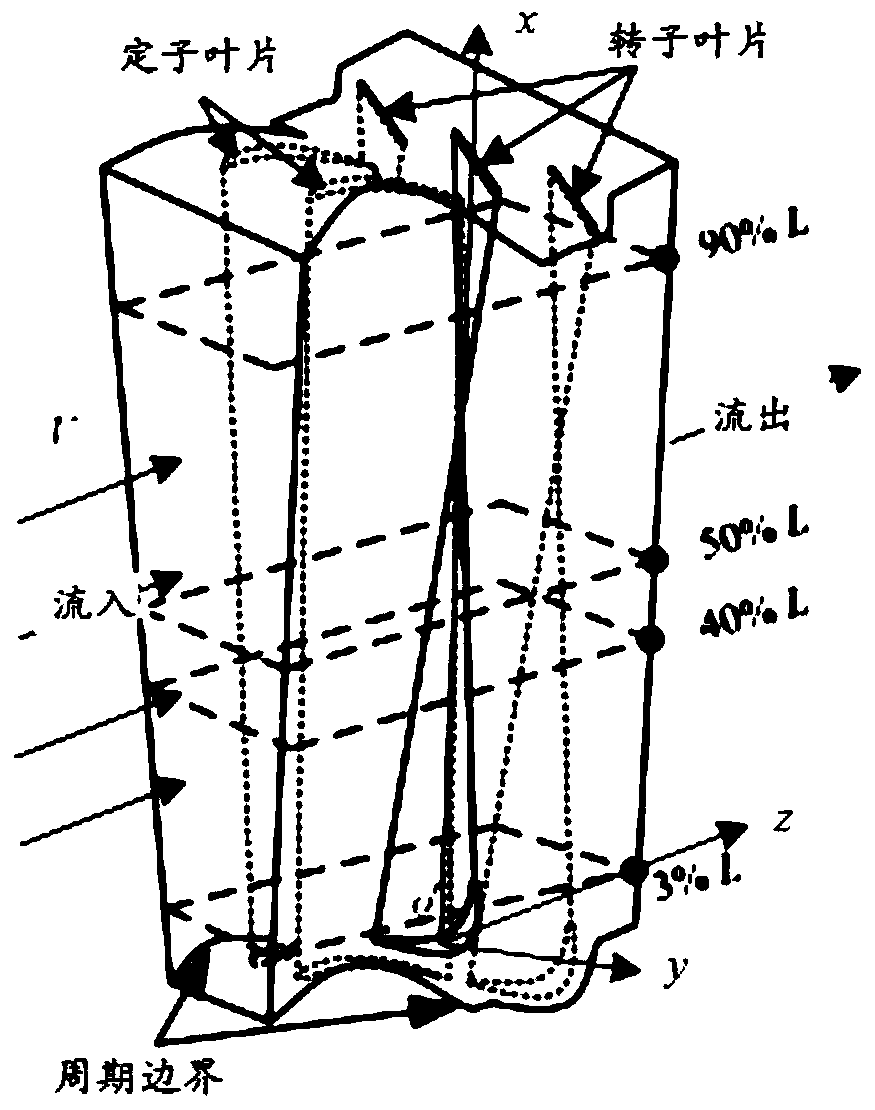
Nuclear/thermal power turbine set fluid excitation numerical calculation method and system based on flow field simulation
ActiveCN109753716ASimplified Computational DomainGuaranteed calculation accuracySpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringVirtual work
The invention provides a nuclear / thermal power turbine set fluid excitation numerical calculation method and system based on flow field simulation. The method comprises: according to set structure andoperation conditions, simplifying fluid computational domain, creating a flow channel geometric model comprising two stator blades and three rotor blades; discretizing the surface of the blade by utilizing a structured grid, introducing a discretized fluid calculation domain, setting a phase change model, a turbulence model, a boundary condition and a numerical solution parameter according to different flow working conditions, and solving transient distribution pressure of the surface of the blade under different working conditions through flow field simulation; for the blades adopting three-dimensional hexahedron unit discretization, the transient distribution pressure on the surfaces of the blades is equivalent to fluid excitation suitable for different blade structure units by utilizing an inverse distance weighted interpolation method and an equivalent method based on a virtual work principle; and for the blades adopting the spatial twisted beam units for dispersion, transient distribution pressure on the surfaces of the blades is converted into equivalent fluid excitation of the spatial twisted beam units by utilizing a virtual work principle.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
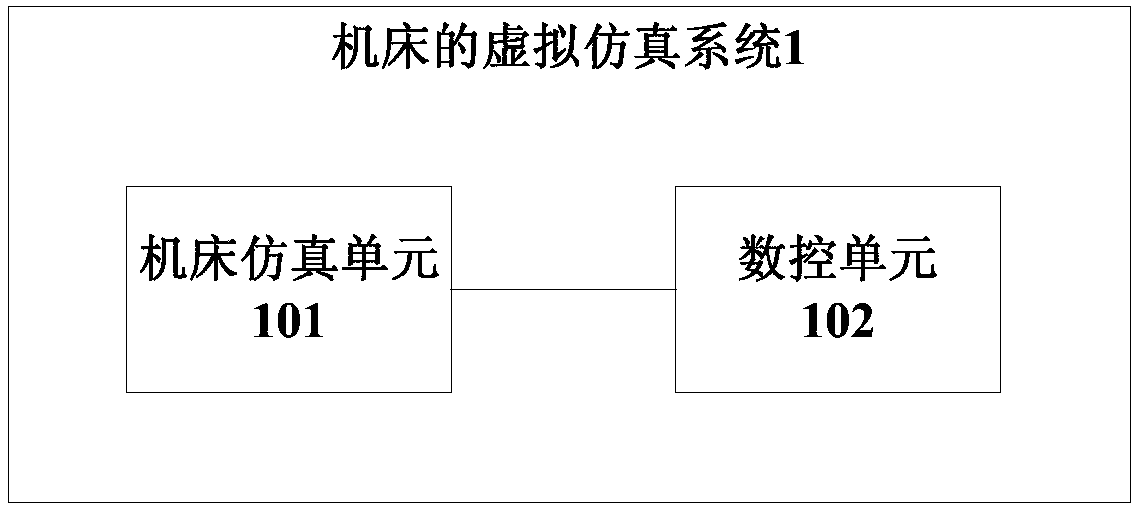
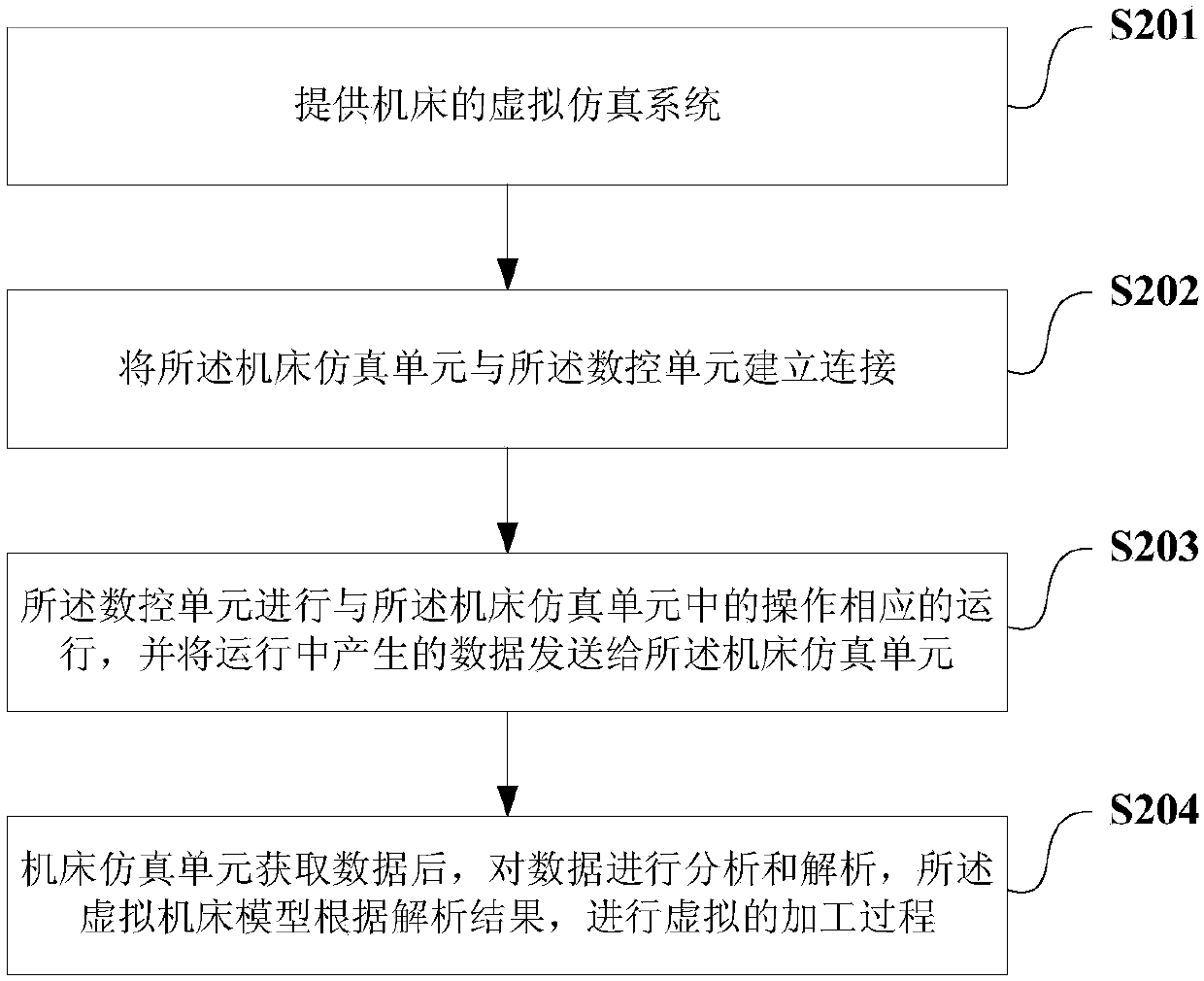
Virtual simulation system for machine tool, and virtual manufacturing method and manufacturing apparatus
InactiveCN107944067AGuarantee personal safetyIncrease costInput/output for user-computer interactionConfiguration CADNumerical controlVirtual work
The invention provides a virtual simulation system for a machine tool, and a virtual manufacturing method and manufacturing apparatus. The virtual simulation system mainly comprises a machine tool simulation unit used for providing a virtual machine tool model and obtaining machine tool operation and user operation on the virtual machine tool model, and a numerical control unit used for performingcorresponding operation according to the machine tool operation and the user operation and feeding back an operation condition to the machine tool simulation unit in real time. Moreover, the virtualmachine tool model performs corresponding virtual work in real time according to the operation condition fed back by the numerical control unit. Through analog simulation of the machine tool, a working process of the machine tool is really displayed and the personal safety of machine tool operators is effectively ensured.
Owner:SYMG SHANGHAI INTELLIGENCE SYST CO LTD
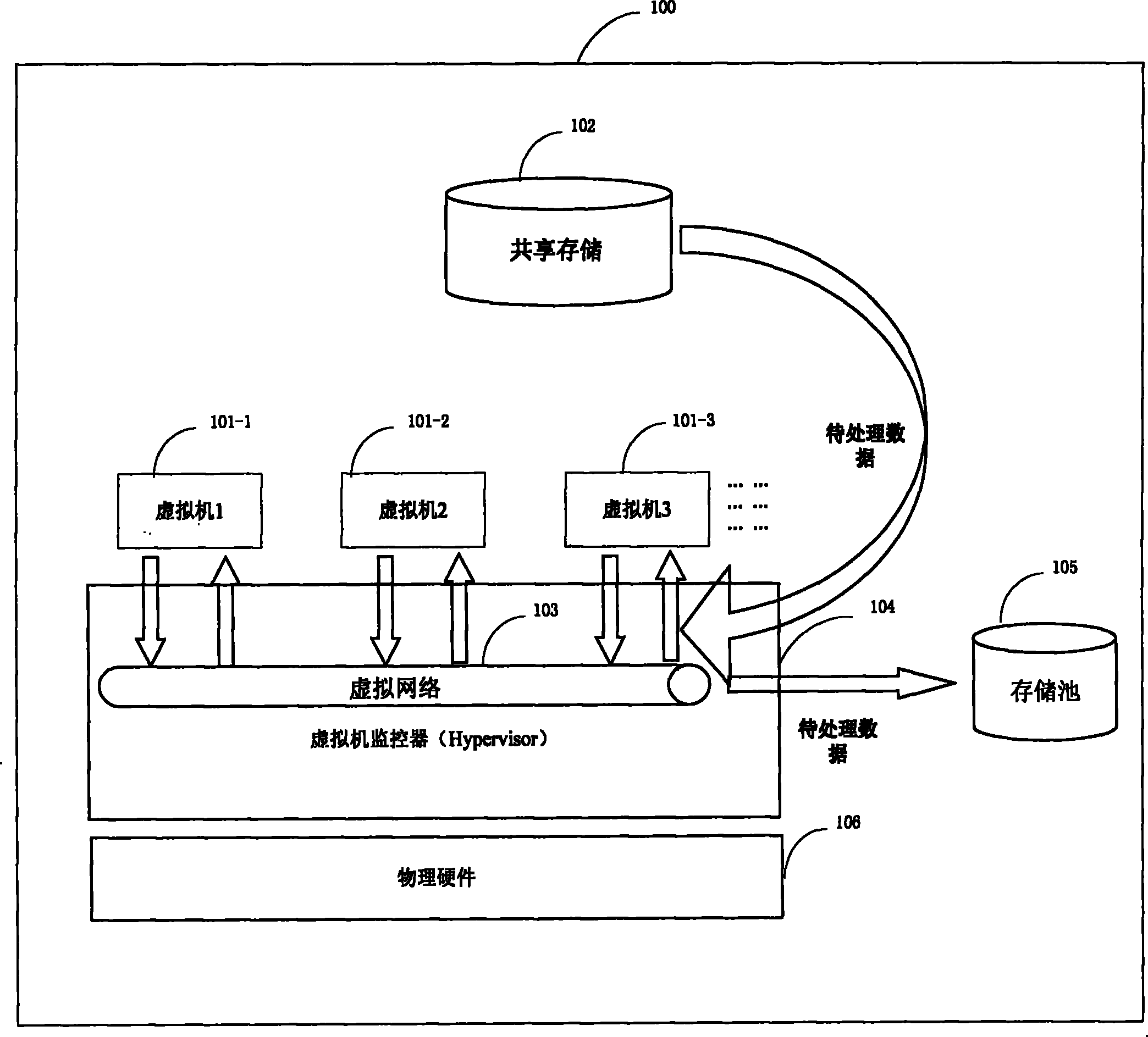
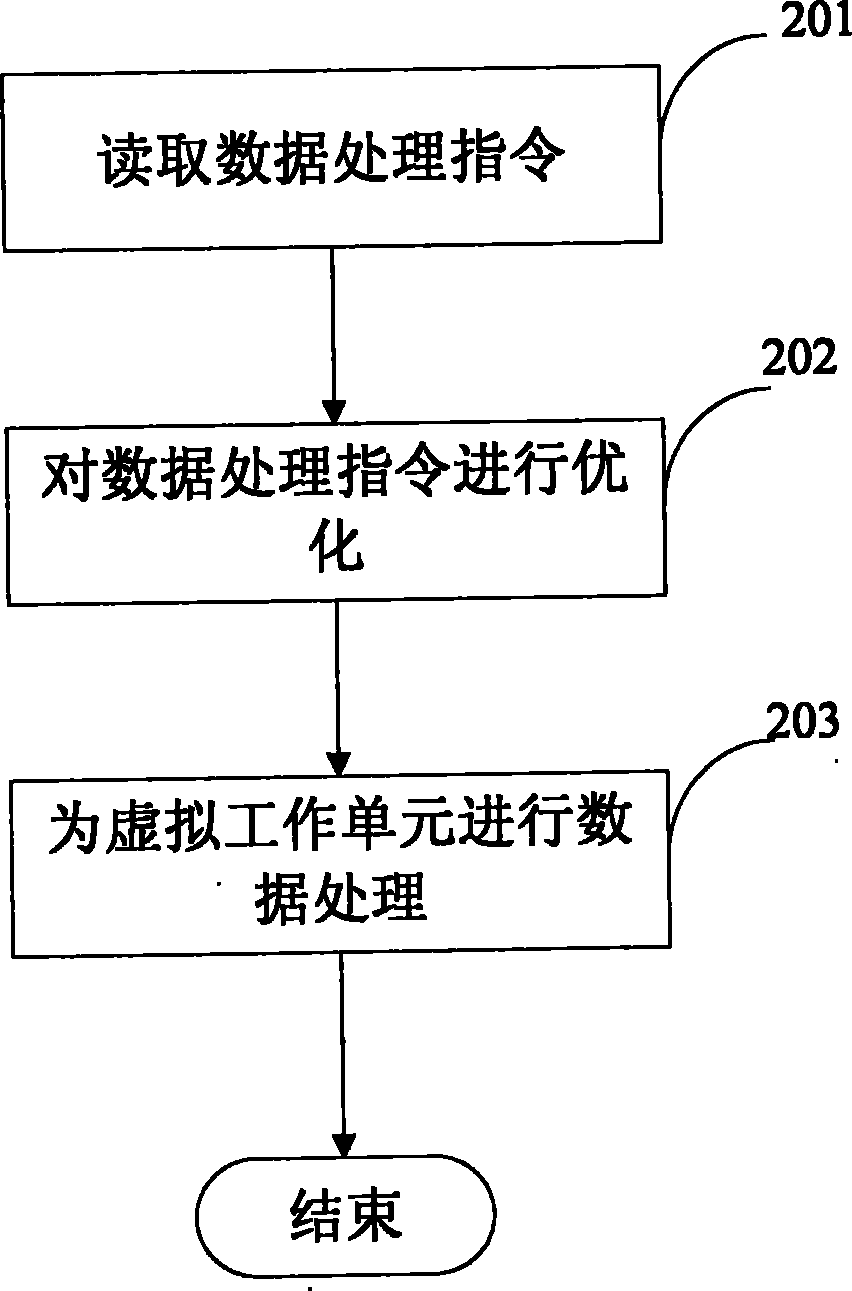
Data processing method and system in virtual environment and deployment method of system
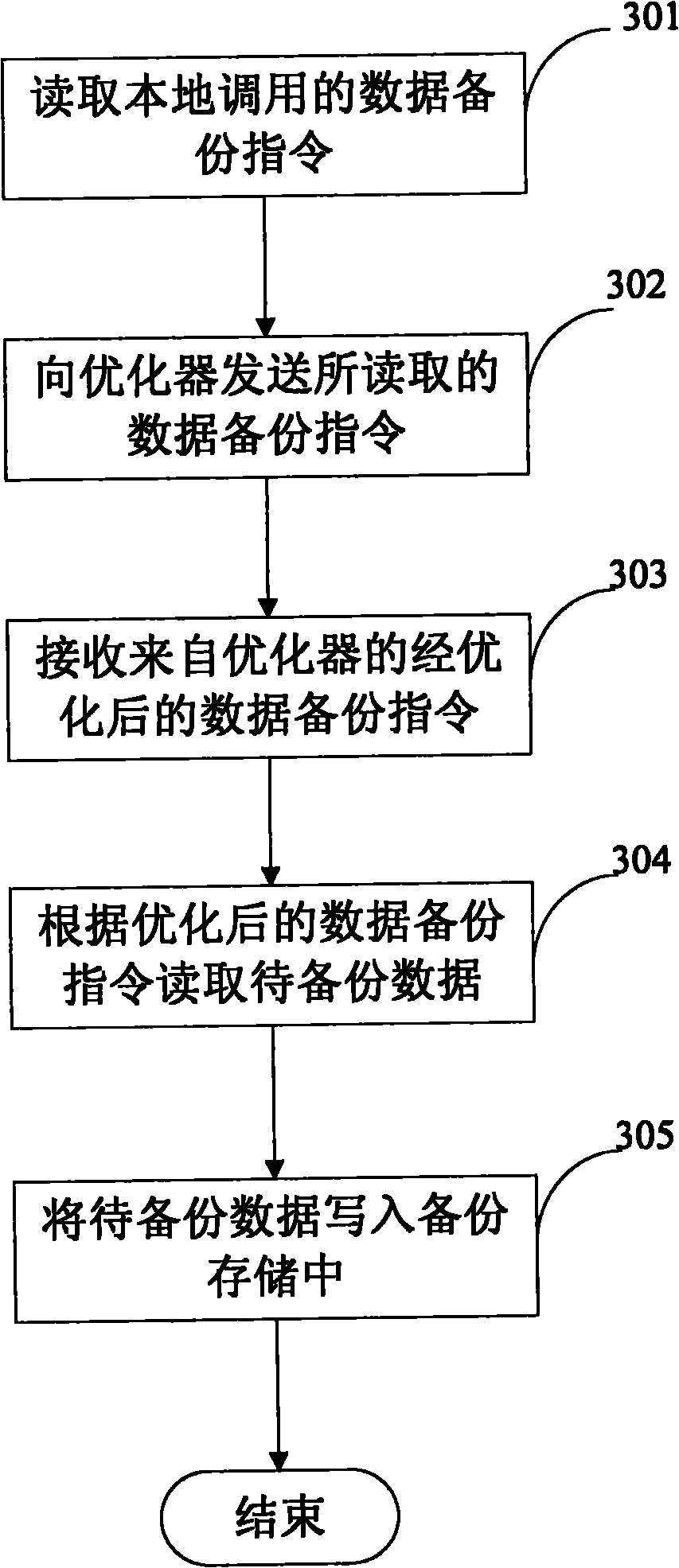
InactiveCN102141928AAvoid competitionAvoid excessive consumptionMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionParallel computingVirtual work
The invention relates to a data processing technique in a virtual environment, in particular to a technique for carrying out data backup and data recovery of a virtual machine in a virtual environment. The invention provides a data processing method in a virtual environment, and the data processing method comprises the following steps: reading a data processing command which is locally called by a virtual working unit; optimizing the read data processing command; and carrying out data processing for the virtual working unit by utilizing the optimized data processing command.
Owner:IBM CORP
Hybrid type automobile electrophoresis coating conveying mechanism dynamics modeling method
ActiveCN105159137AHas coordinate invarianceNeat and concise expressionProgramme controlSimulator controlHybrid typeDynamic models
The invention discloses a hybrid type automobile electrophoresis coating conveying mechanism dynamics modeling method. First of all, the symmetrical structure characteristic of a mechanism is fully utilized, the speed and the accelerated speed of each passive joint in the mechanism are analyzed through an analytical geometry method, and then the speed and the accelerated speed of each active joint of the mechanism are obtained by introducing a screw theory; secondly, based on this, a kinetic equation in a mechanism spinor form is established by use of virtual work principle; and finally, axial driving power of each active joint of the conveying mechanism capable of directly realizing control is obtained through calculation so that construction of a dynamics model capable of realizing high-performance control is completed. According to the invention, the analytical geometry method, the screw theory and the virtual work principle are combined together, so that the problem of coordinate transformation due to lack of coordinate invariance during dynamics modeling of a complex special mechanism is solved, the calculation complexity is reduced, and at the same time, the dynamics modeling method brought forward by the invention is quite simple, is tidy in form and is easy in programmed realization.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Creep constitutive model parameter identification method for creep test
ActiveCN108009311APredicting Creep Deformation BehaviorSatisfied with the optimal solutionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsStress conditionsMeasurement point
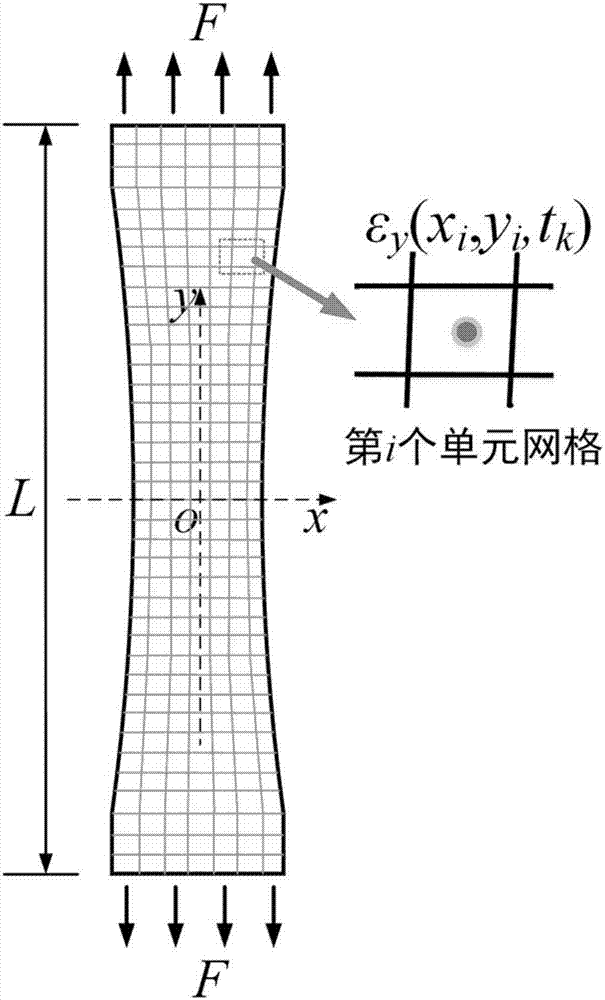
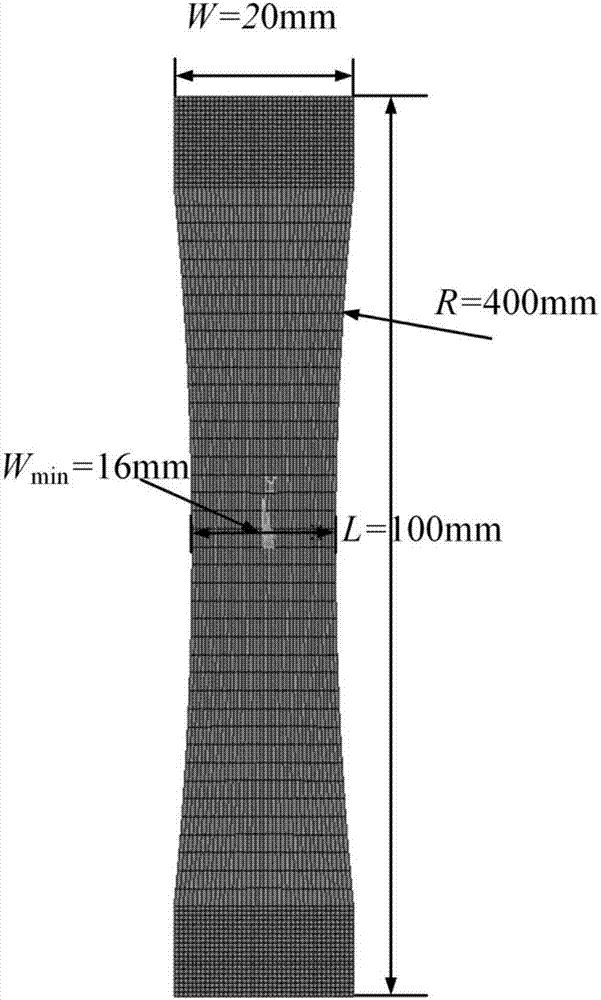
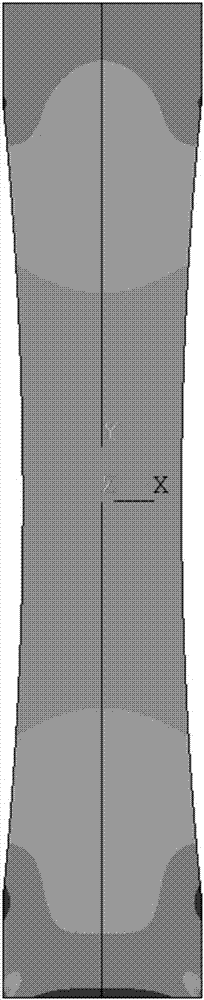
The invention discloses a creep constitutive model parameter identification method for creep test. The method includes the steps: extracting a strained measuring value epsilon y (xi, yi and tk) of ani measuring point of a sample analysis surface at a k strained measuring moment tk by a creep load F in a y direction to obtain a creep strain of the i measuring point of the sample analysis surface at the moment tk as shown in the specification; determining a grid area Ai taking the i measuring point as a center; selecting a creep constitutive model, and enabling the creep strainepsilon <cr> to express a function of stress level sigma and creep time t; acquiring virtual work under the action of the creep load F; acquiring an objective function phi (p) for identifying creep constitutive model parameters, and solving a value popt and a parameter popt of a corresponding p of a minimal value of the objective function. The corresponding parameter popt is an identified creep constitutive model parameter. The method has the advantages that sample material creep deformation behaviors can be forecasted according to stress conditions without change of materials and environmental conditions.
Owner:HEFEI GENERAL MACHINERY RES INST +1
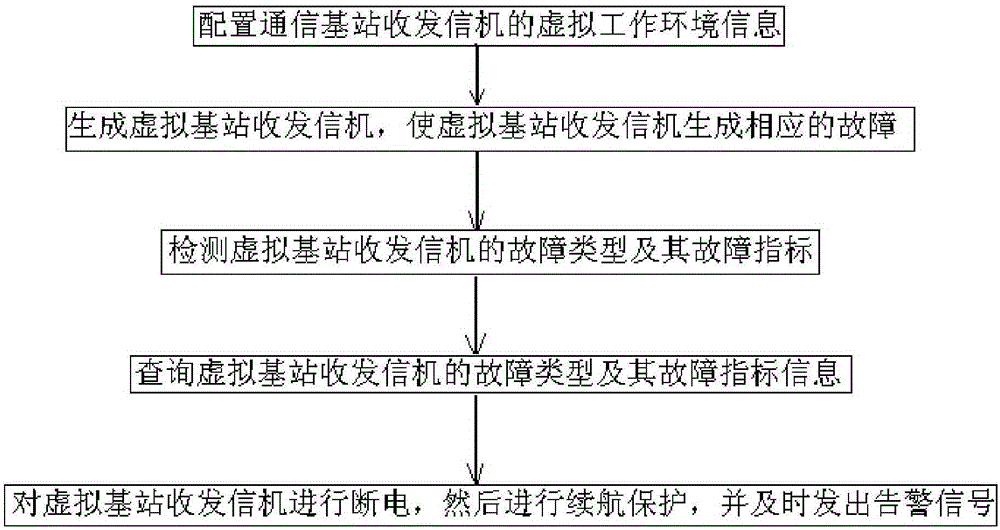
Simulation method and simulation system for fault protection of communication base station transceiver
The invention discloses a simulation method and simulation system for fault protection of a communication base station transceiver. The simulation method comprises the steps such as configuration of virtual work environment information of the communication base station transceiver. The simulation system comprises a configuration environment module and other modules. Through adoption of the simulation method, fault handling for the communication base station transceiver and protection of the communication base station transceiver during fault occurrence are simulated according to the virtual reality technology, so that not only can the waste caused by the damage to physical equipment be avoided, but also the simulation can be repeated for several times, technical personnel can accept training and learning for several times, and excellent after-sale maintenance personnel can be trained.
Owner:武汉米风通信技术有限公司
Systems, Methods, and Computer-Readable Media for Managing Collaboration on a Virtual Work of Art
Systems, methods, and computer-readable media for managing collaboration on a virtual work of art between multiple electronic devices are provided. A first graphical display system of a first device may generate an input command in response to receiving user information through a user interface of the first device, and may then share this input command with a second graphical display system of a second device. The first graphical display system may process the shared input command to generate pixel array data in a canvas of the first device while the second graphical display system may process the shared input command to generate pixel array data in a canvas of the second device. By sharing input commands rather than pixel array data, system latency may be reduced. Despite operating on the same artwork, the user interfaces and graphical processing capabilities of each device may vary, thereby providing the user greater expressiveness.
Owner:APPLE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com