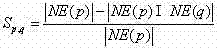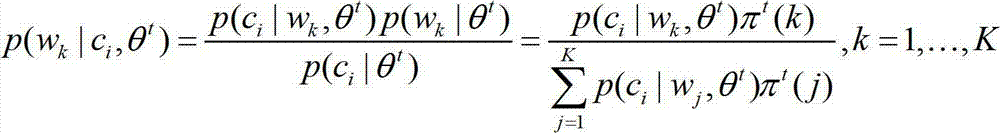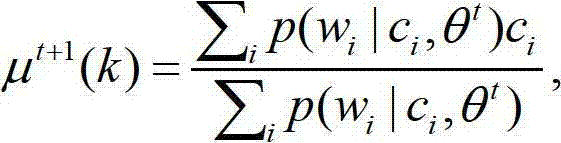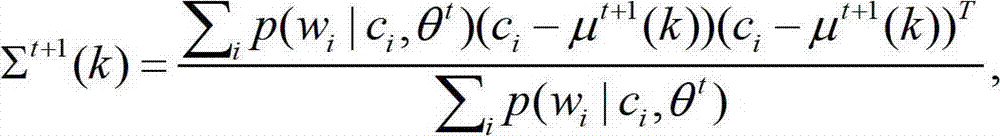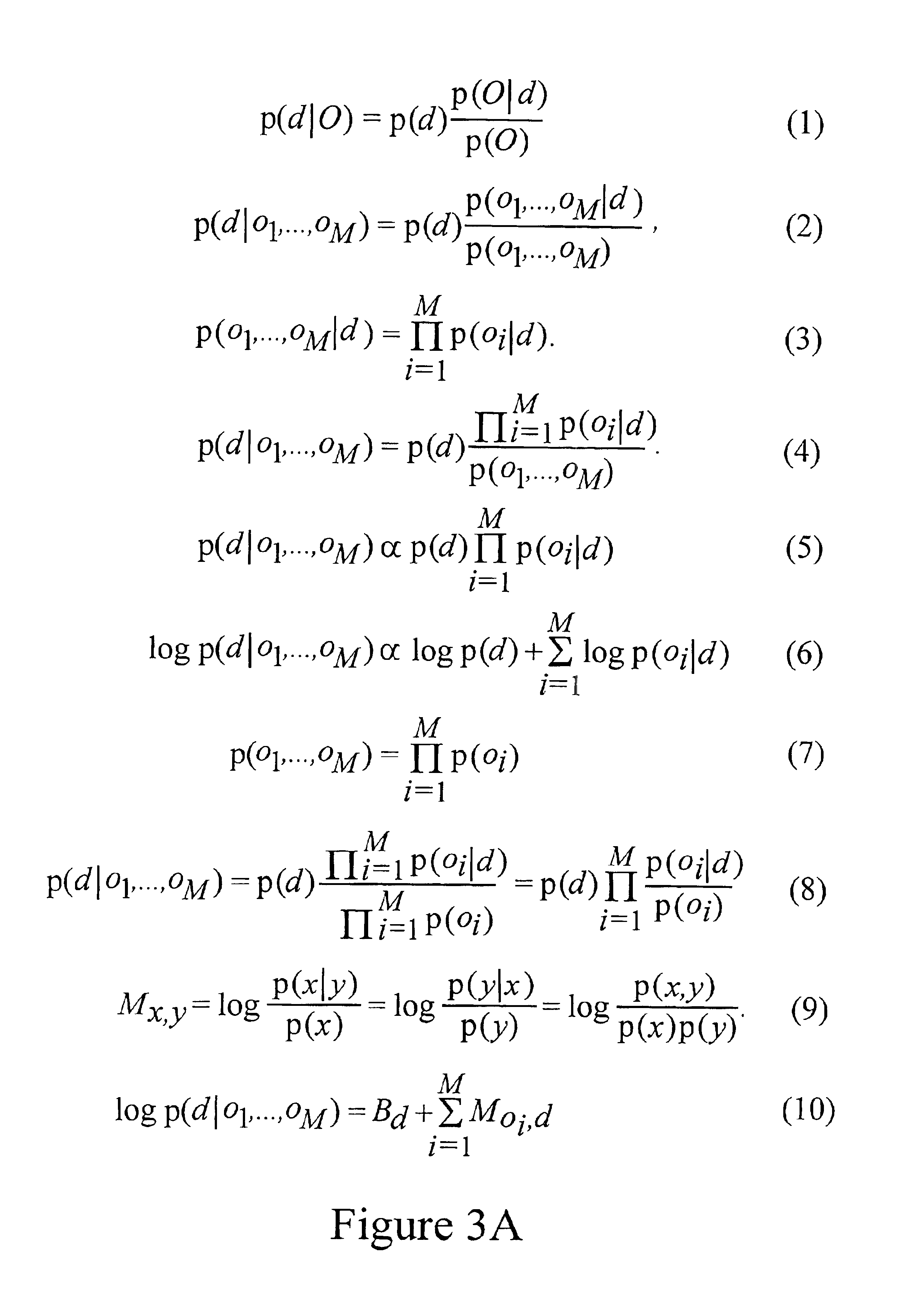Patents
Literature
1162 results about "Probability model" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
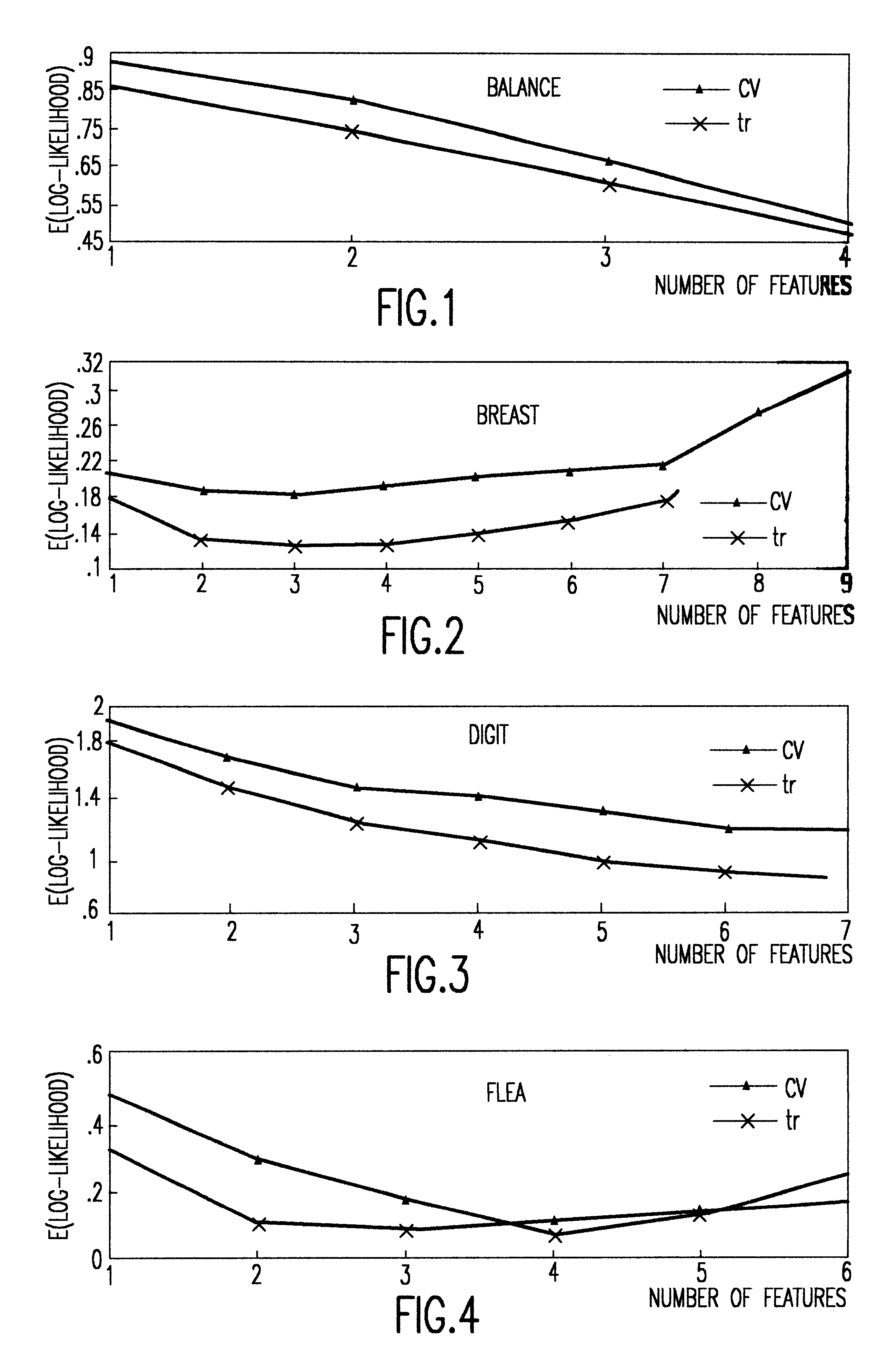
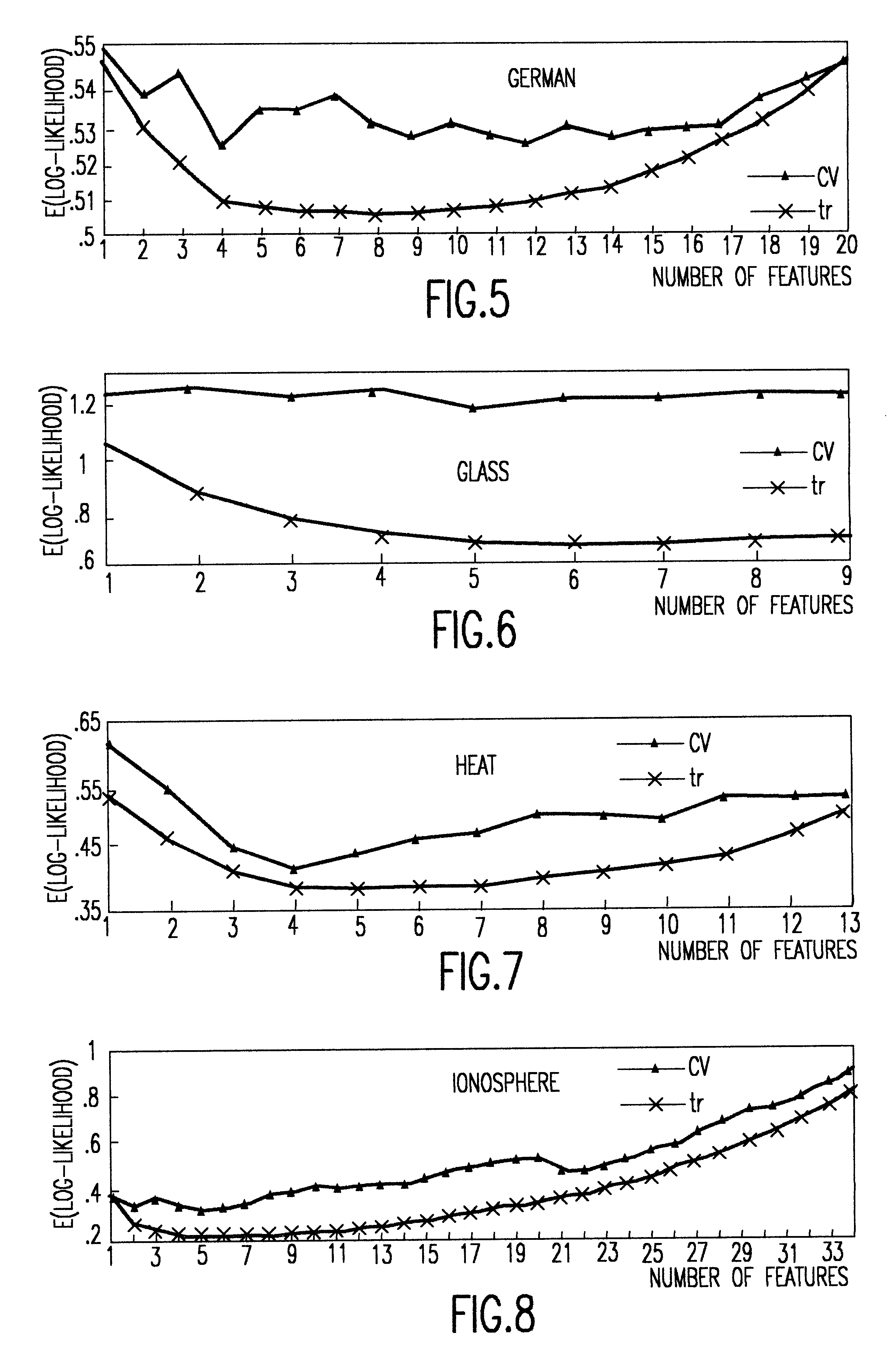
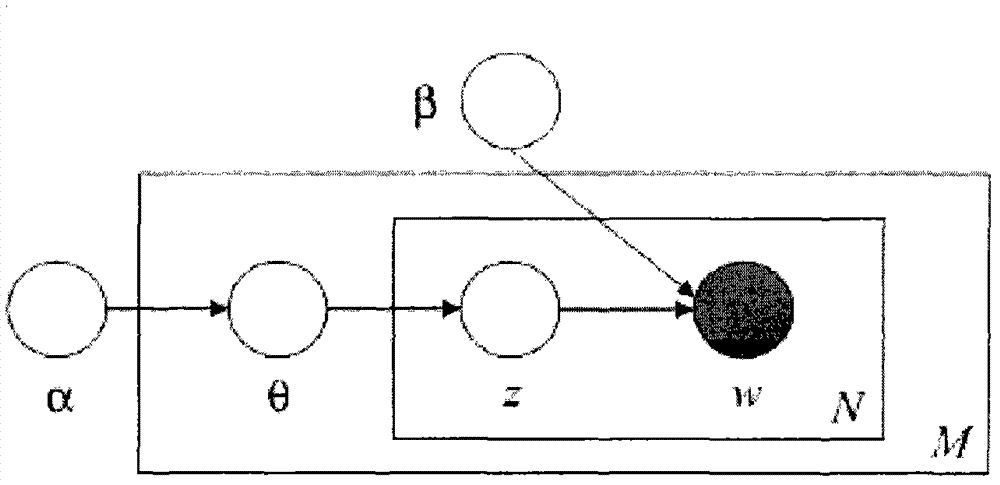
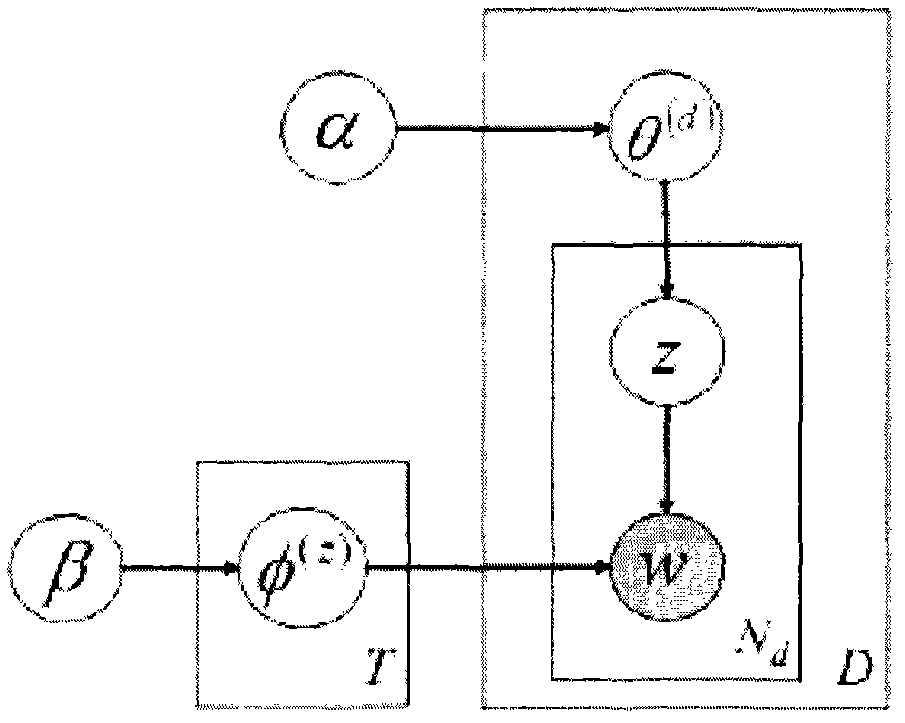
A probability model is a mathematical description of an experiment listing all possible outcomes and their associated probabilities. For instance, if there is a 1% chance of winning a raffle and a 99% chance of losing the raffle, a probability model would look much like the table below.
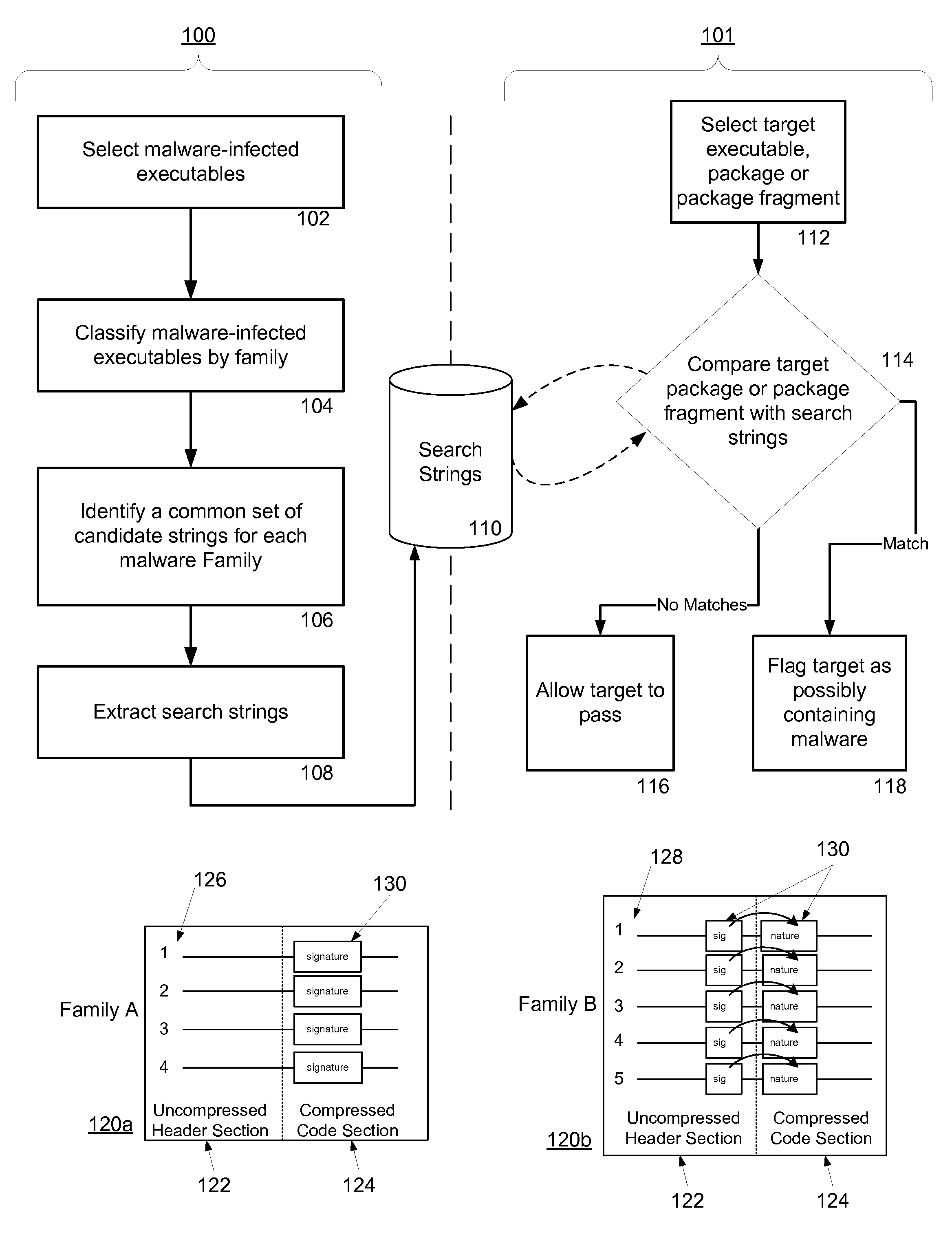
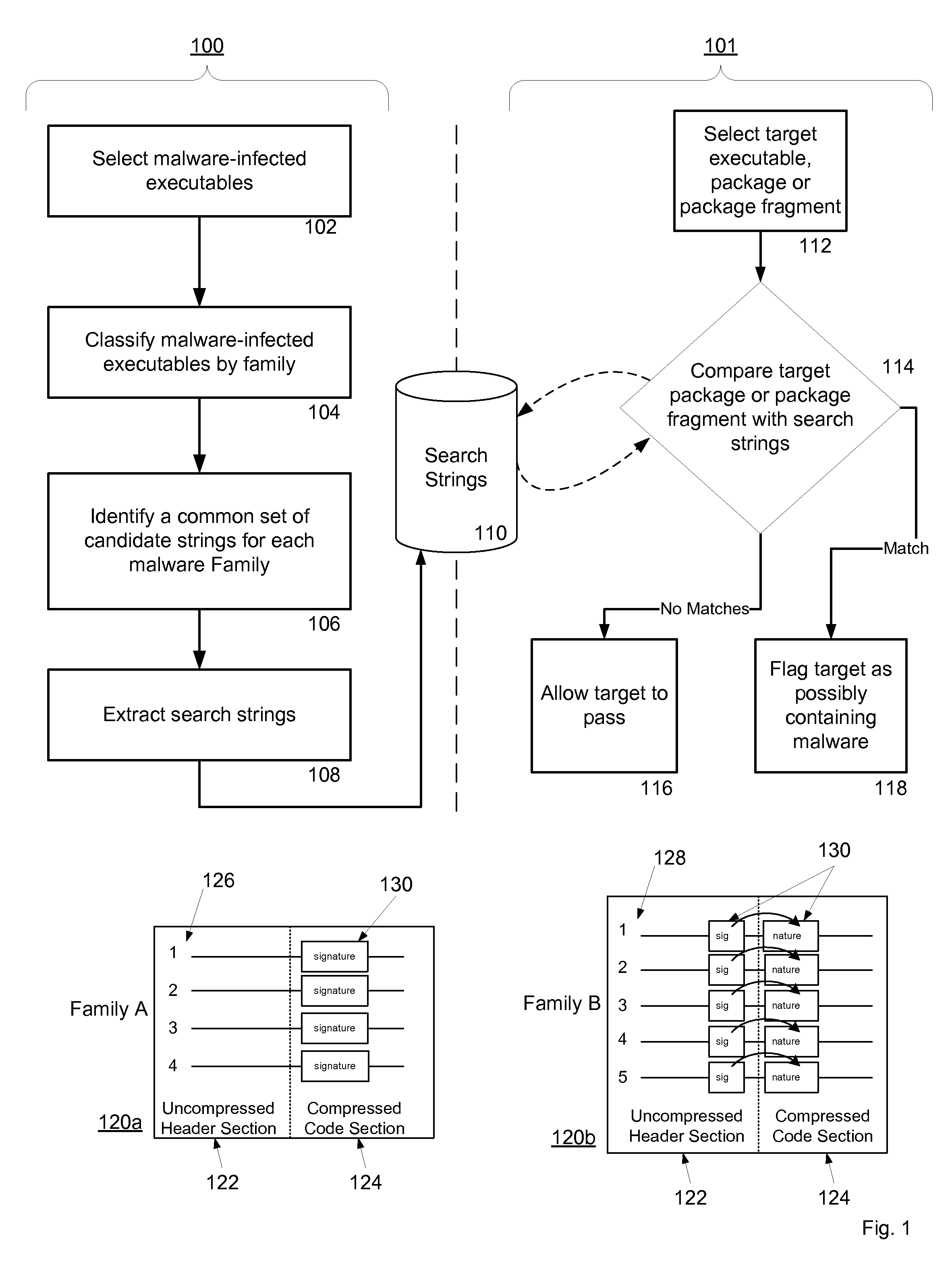
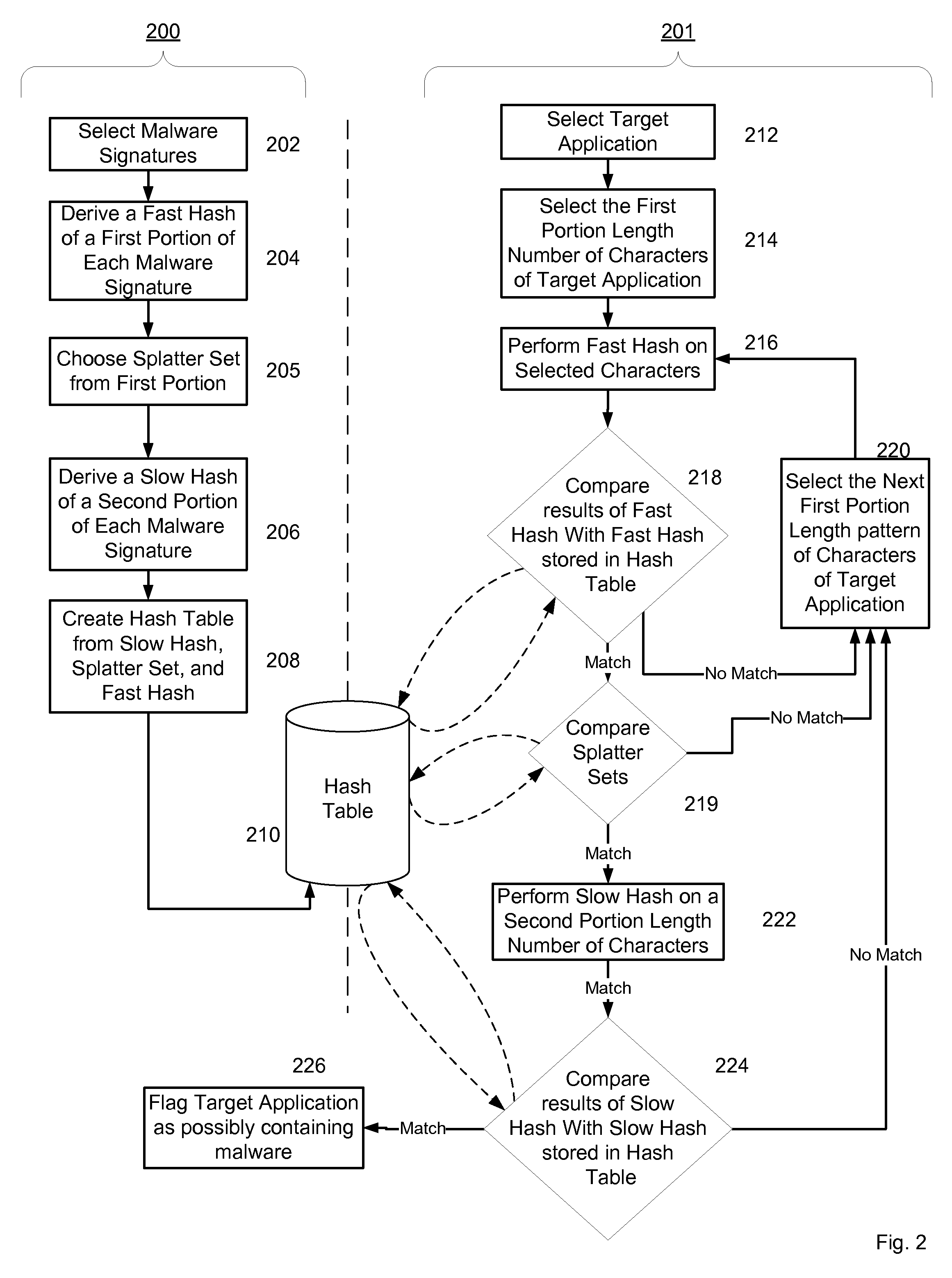
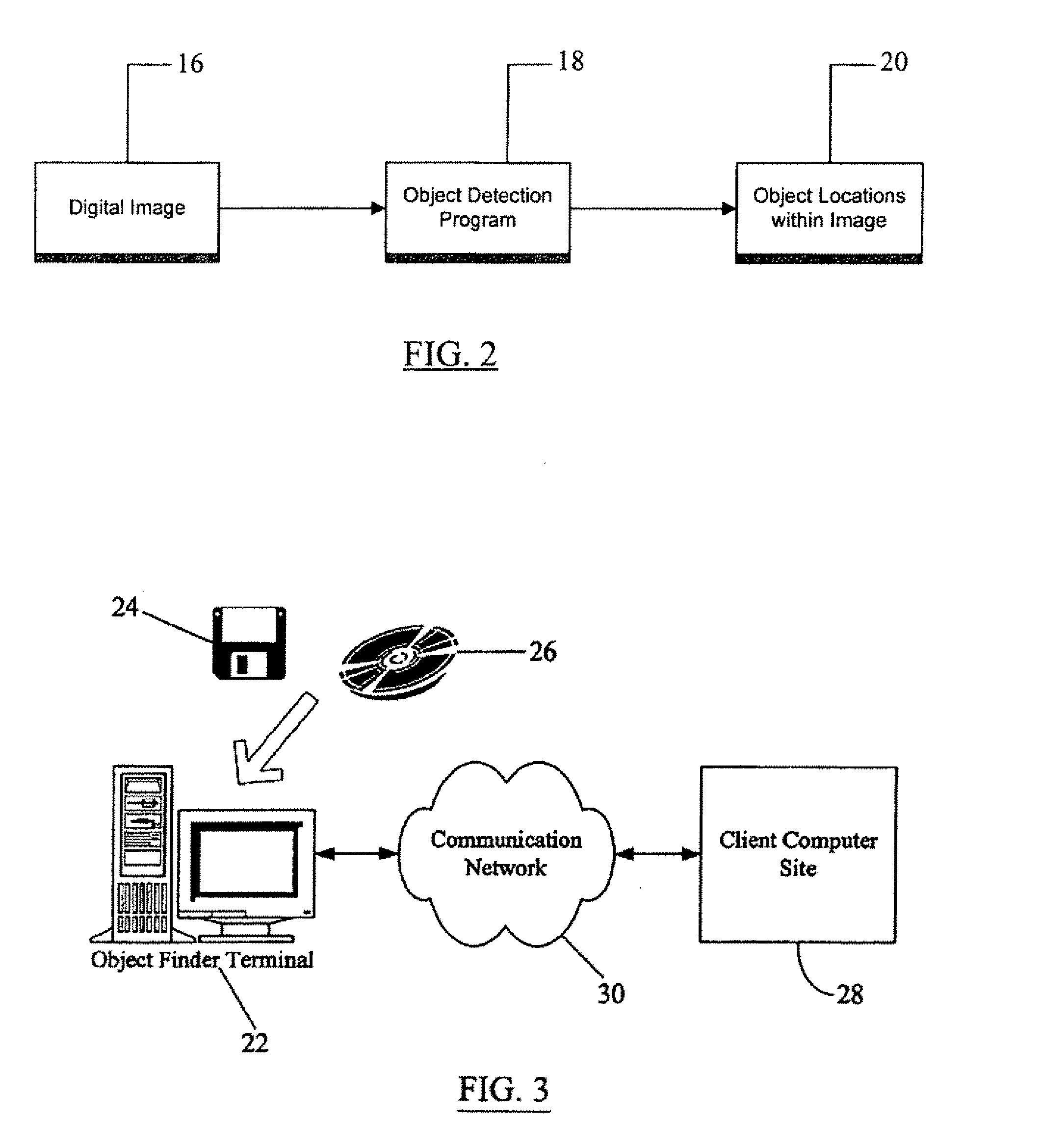
Malware Modeling Detection System And Method for Mobile Platforms
ActiveUS20070240217A1Suitable for useReliable detectionMemory loss protectionUser identity/authority verificationFeature setAlgorithm
A system and method for detecting malware by modeling the behavior of malware and comparing a suspect executable with the model. The system and method extracts feature elements from malware-infected applications, groups the feature elements into feature sets, and develops rules describing a malicious probability relationship between the feature elements. Using malware-free and malware-infected applications as training data, the system and method heuristically trains the rules and creates a probability model for identifying malware. To detect malware, the system and method scans the suspect executable for feature sets and applies the results to the probability model to determine the probability that the suspect executable is malware-infected.
Owner:PULSE SECURE
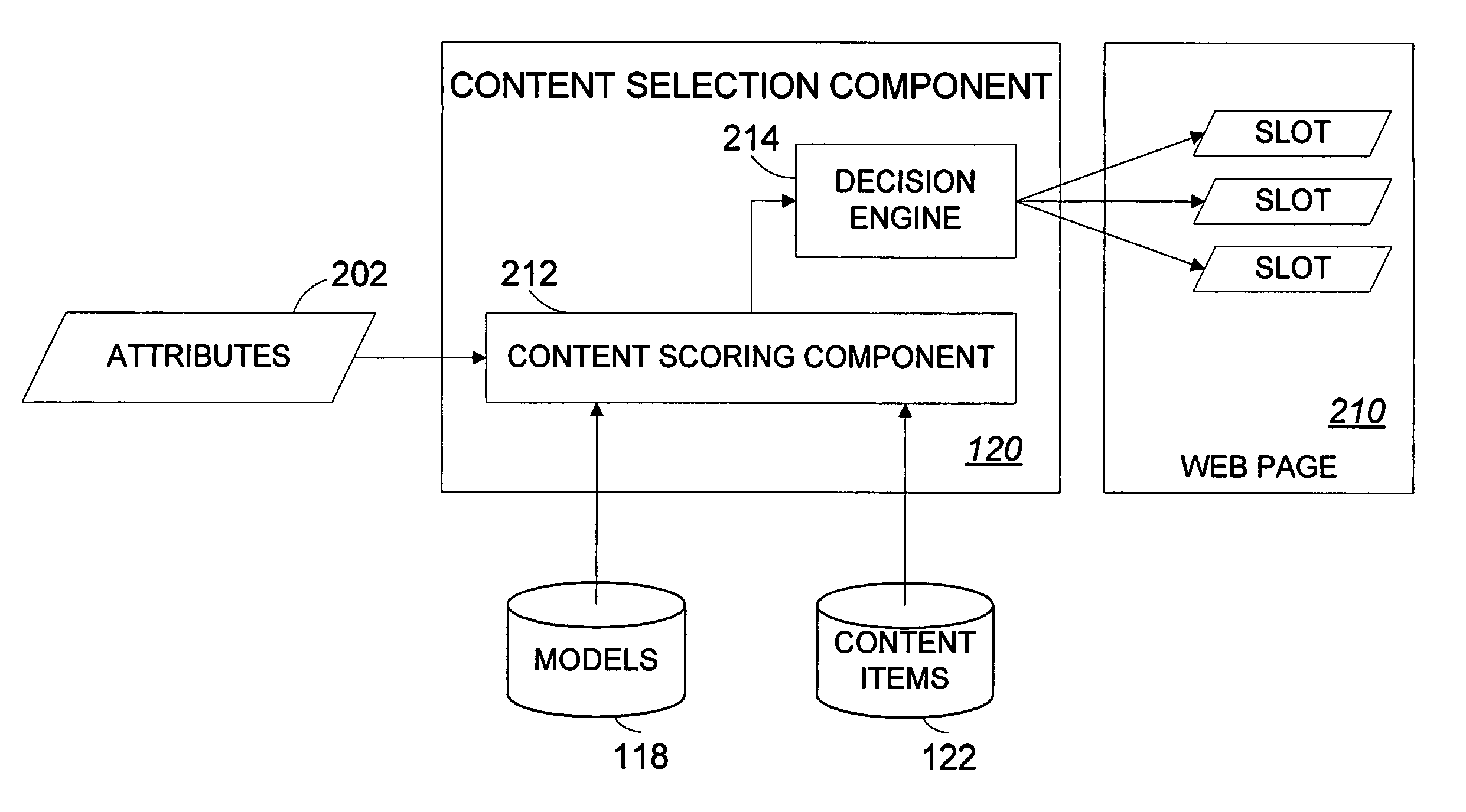
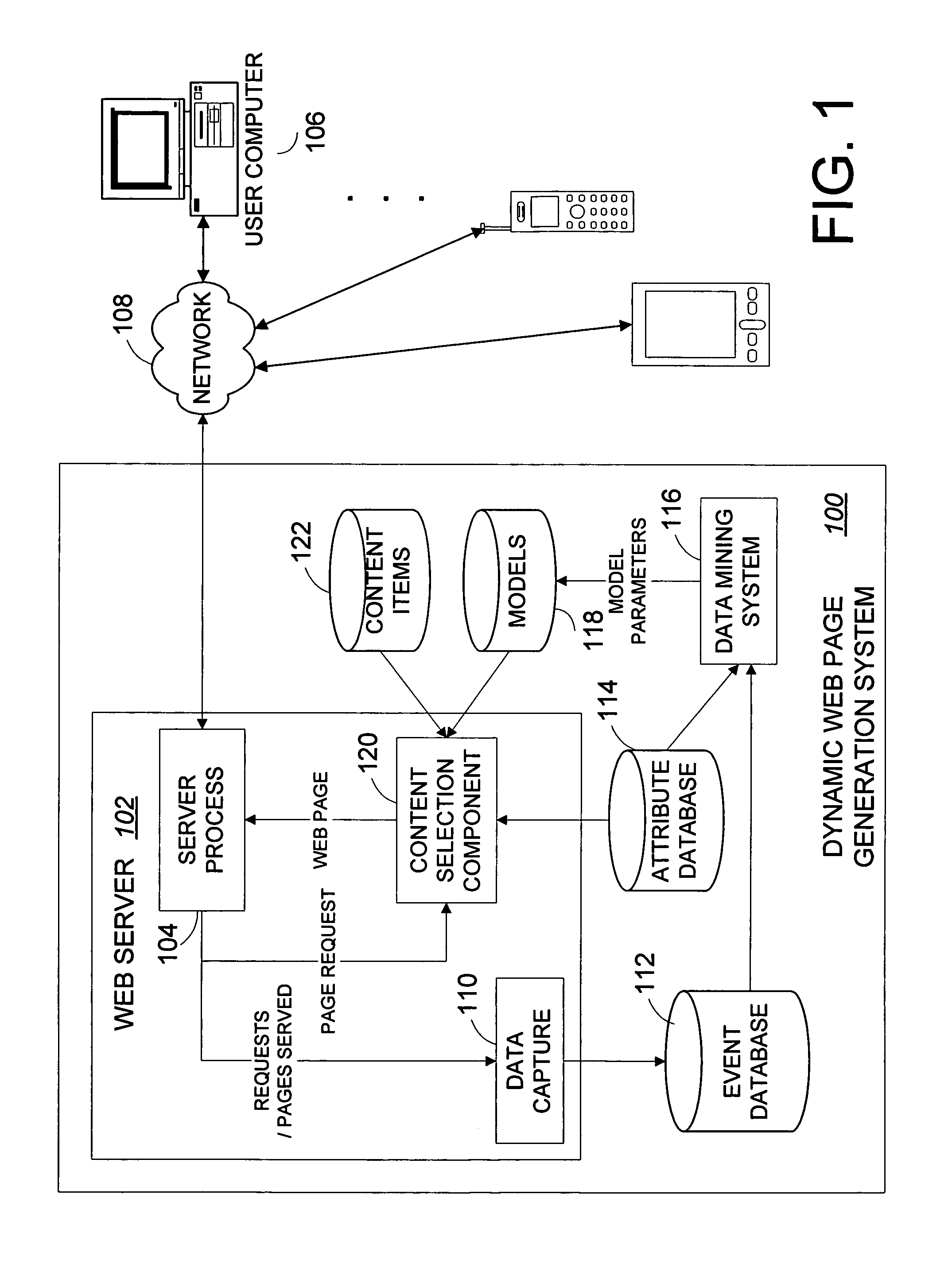
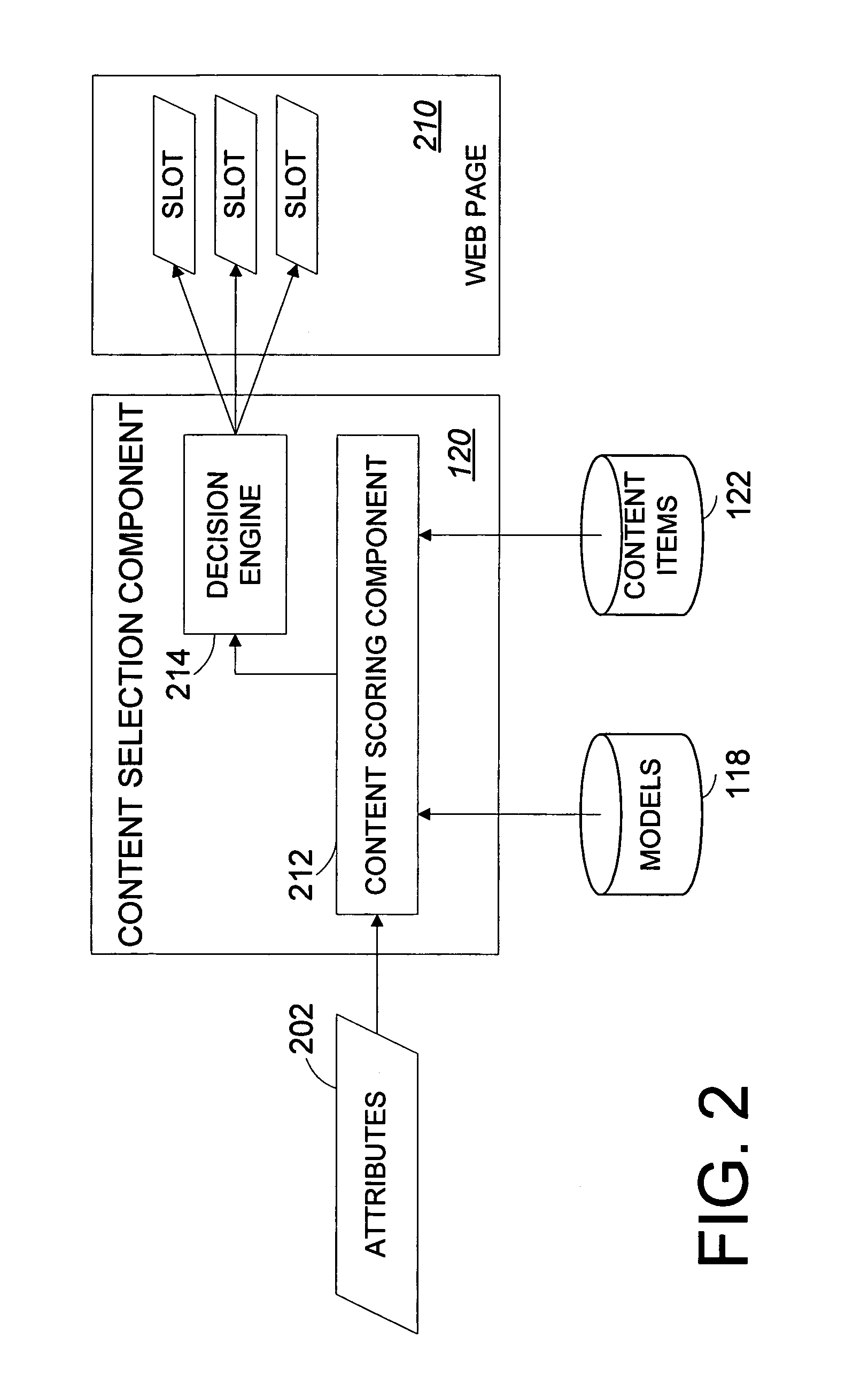
Systems and methods for statistically selecting content items to be used in a dynamically-generated display
InactiveUS7594189B1Quick responseLess time-consume and expensive manual laborDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsWeb siteWeb page
An apparatus and methods advantageously select content items for dynamically-generated web pages in an intelligent and virtually autonomous manner. This permits the operator of the web site to rapidly identify and respond to trends, thereby advantageously updating the web site relatively quickly and efficiently without or with less time consuming and expensive manual labor. User interaction for a plurality of users with the web site is collected in a database. For various content items, the database is mined to extract relationships between probability and references of select attributes in probability models. When a new web page is requested, attributes, which can include attributes associated with a user, are used as references to the applicable probability models of selected content items, combined with value weighting to generate expected values, and selected for use in the web page at least partially based on the expected values.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
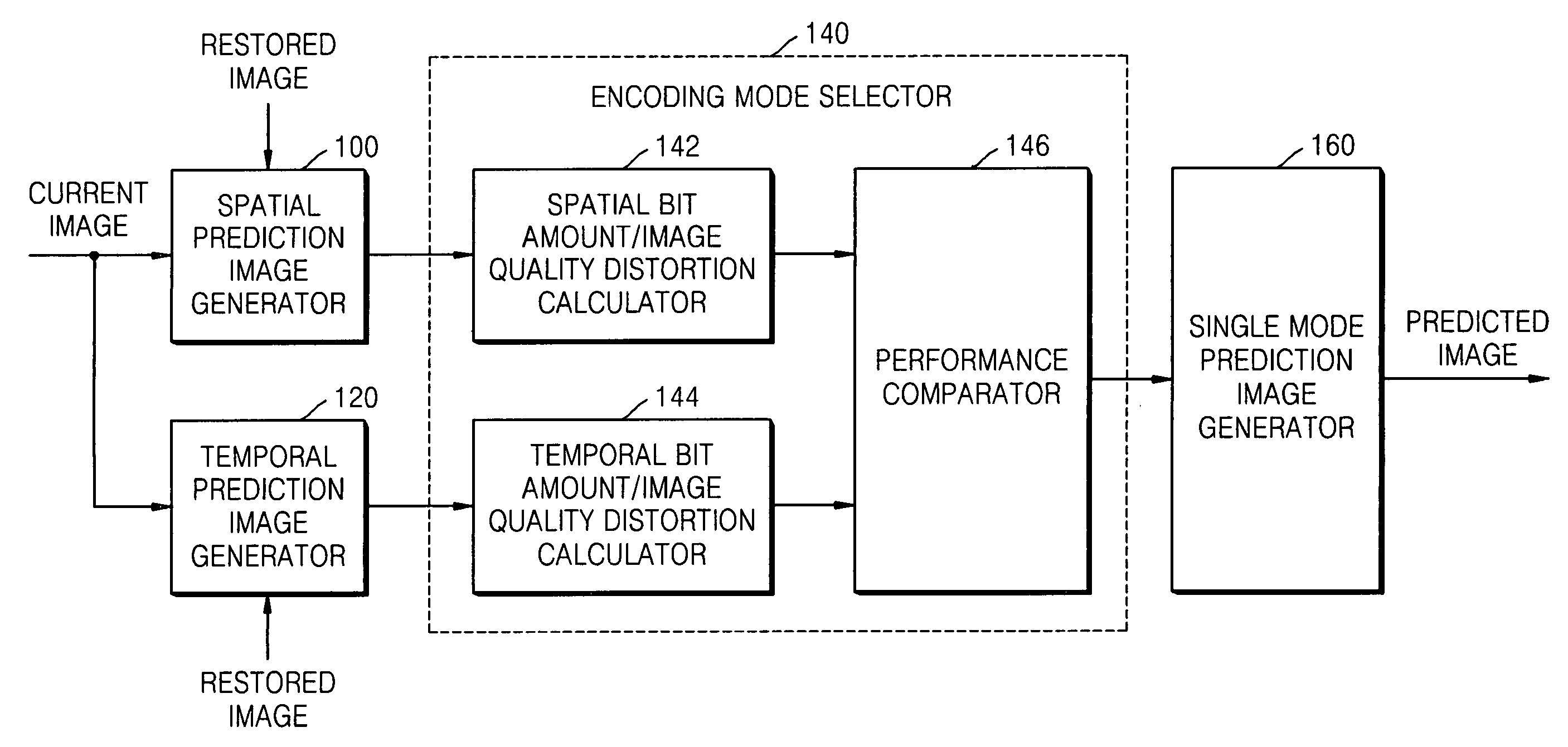
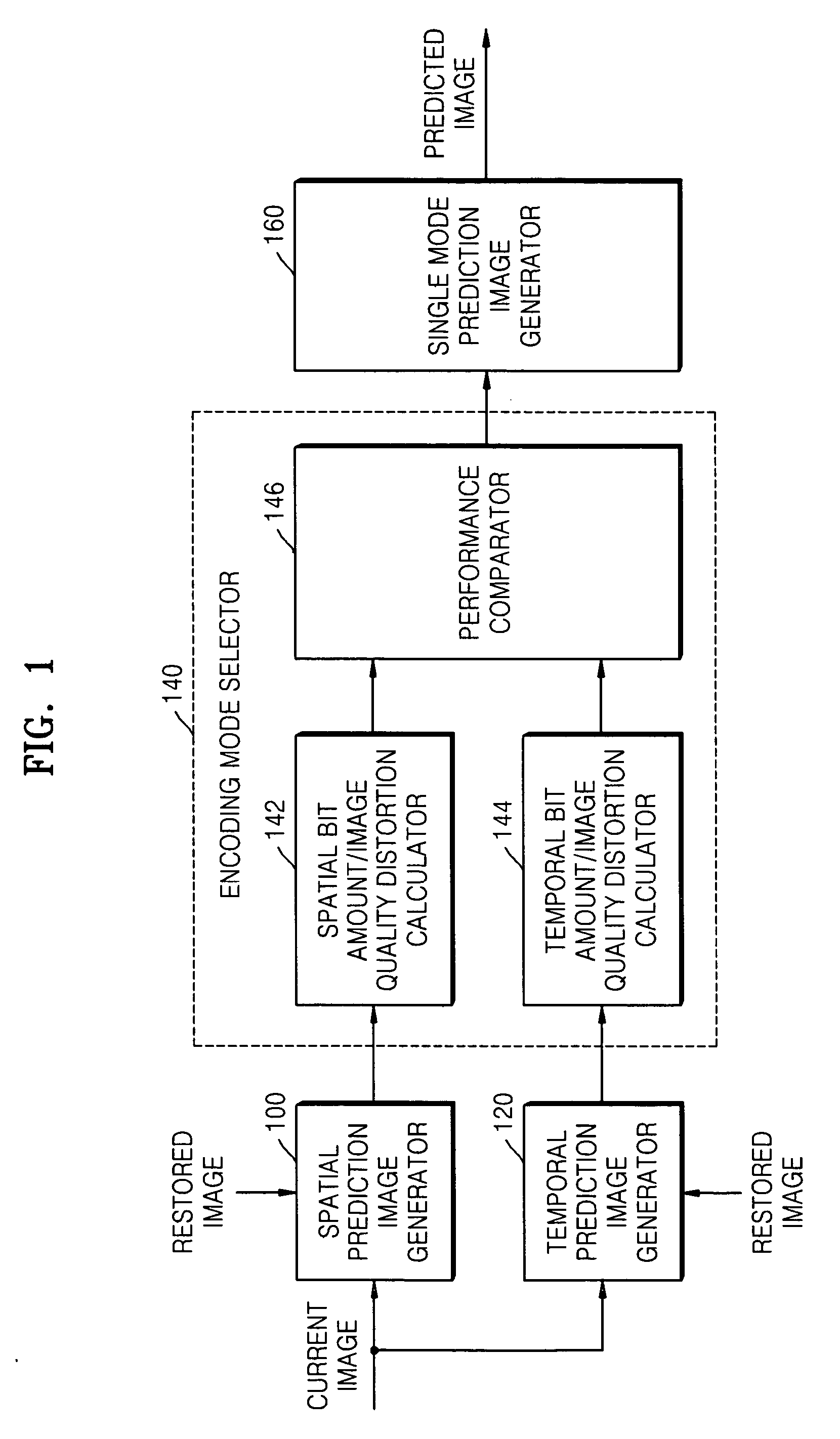
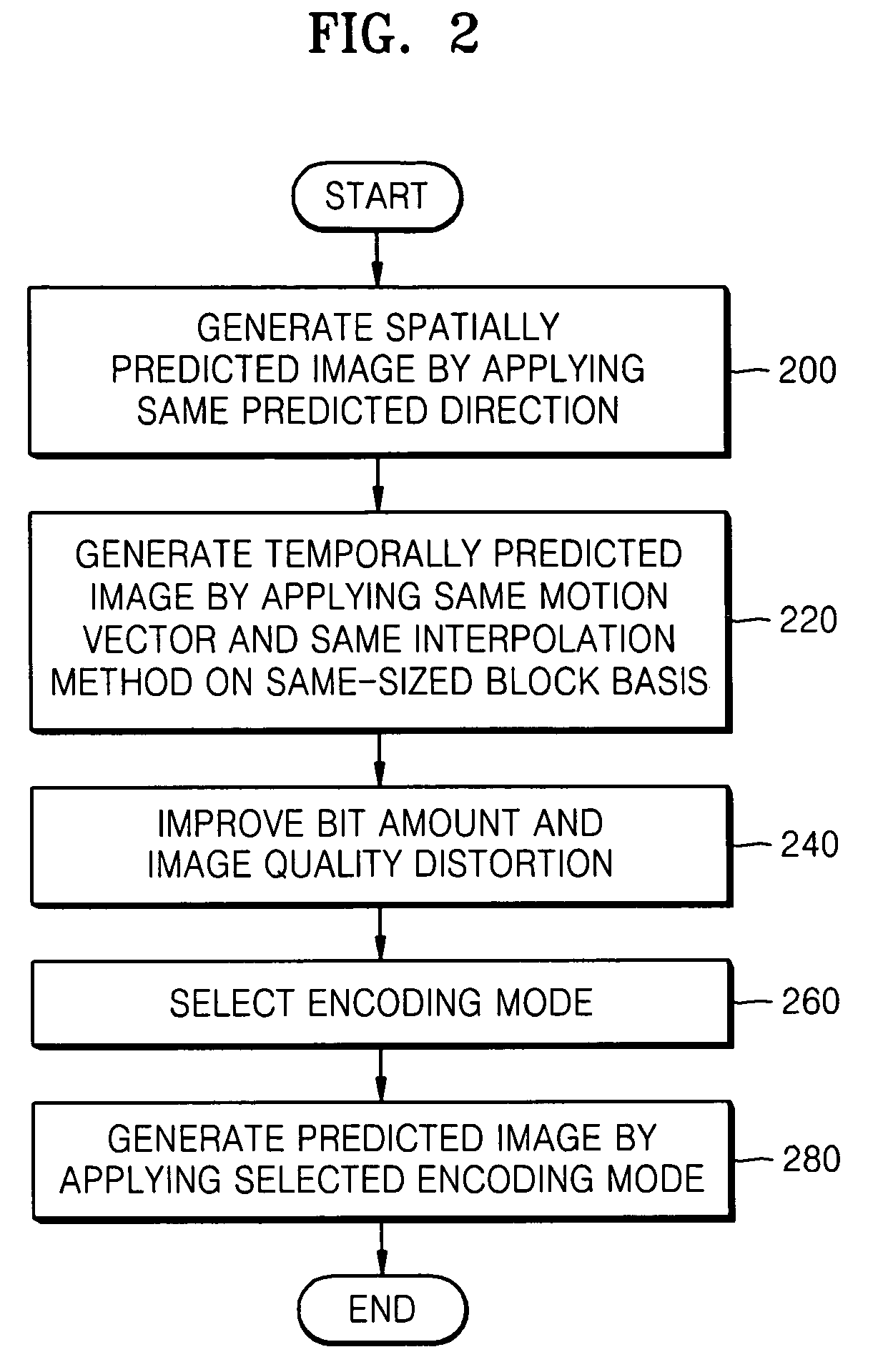
Method, medium, and apparatus encoding and/or decoding an image using the same coding mode across components
ActiveUS20070110153A1Improve efficiencyImprove image qualityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionArithmetic coding
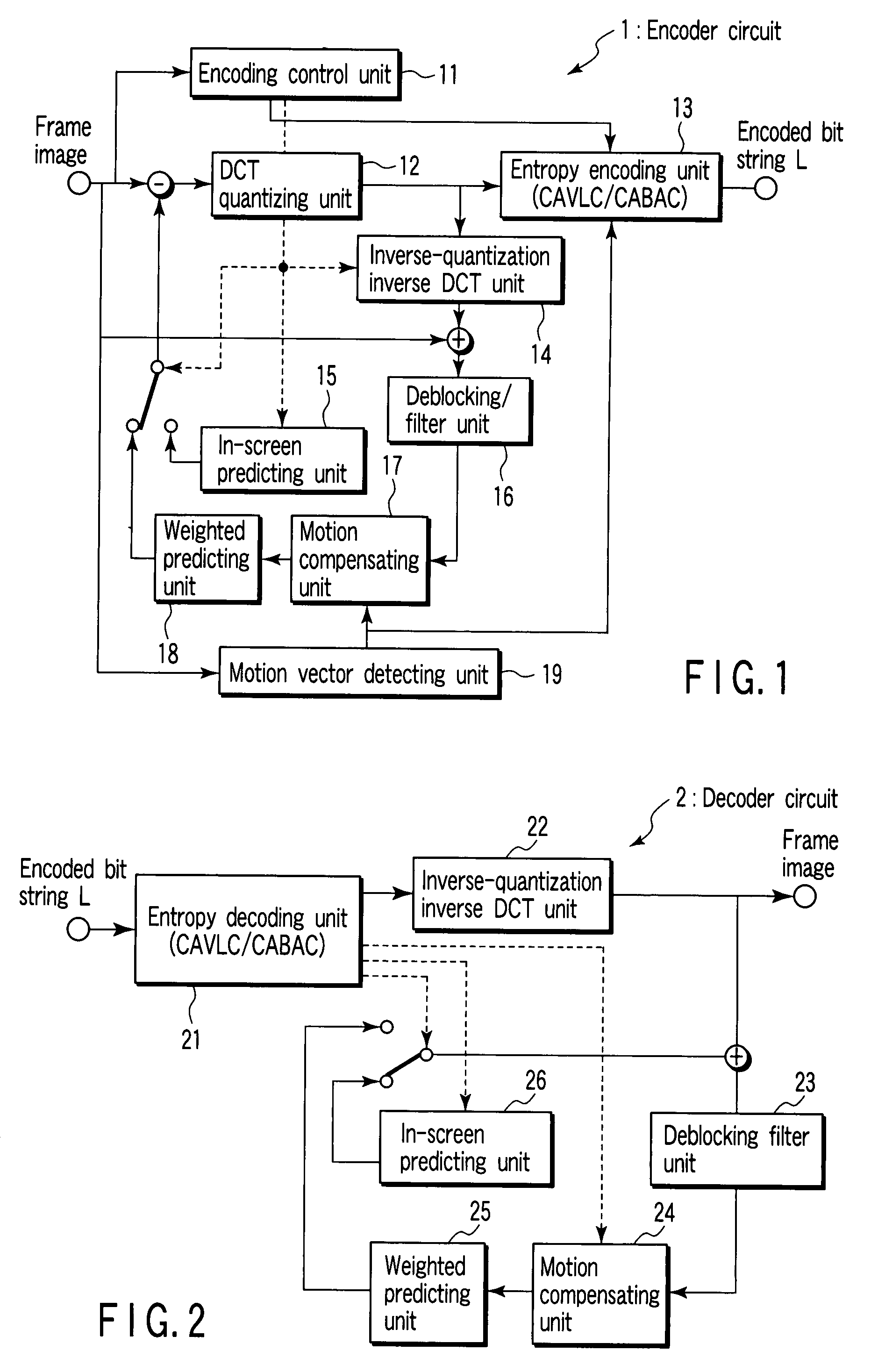
A method, medium, and apparatus encoding and / or decoding an image in order to increase encoding and decoding efficiency by performing binary-arithmetic coding / decoding on a binary value of a syntax element using a probability model having the same syntax element probability value for respective context index information of each of at least two image components.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
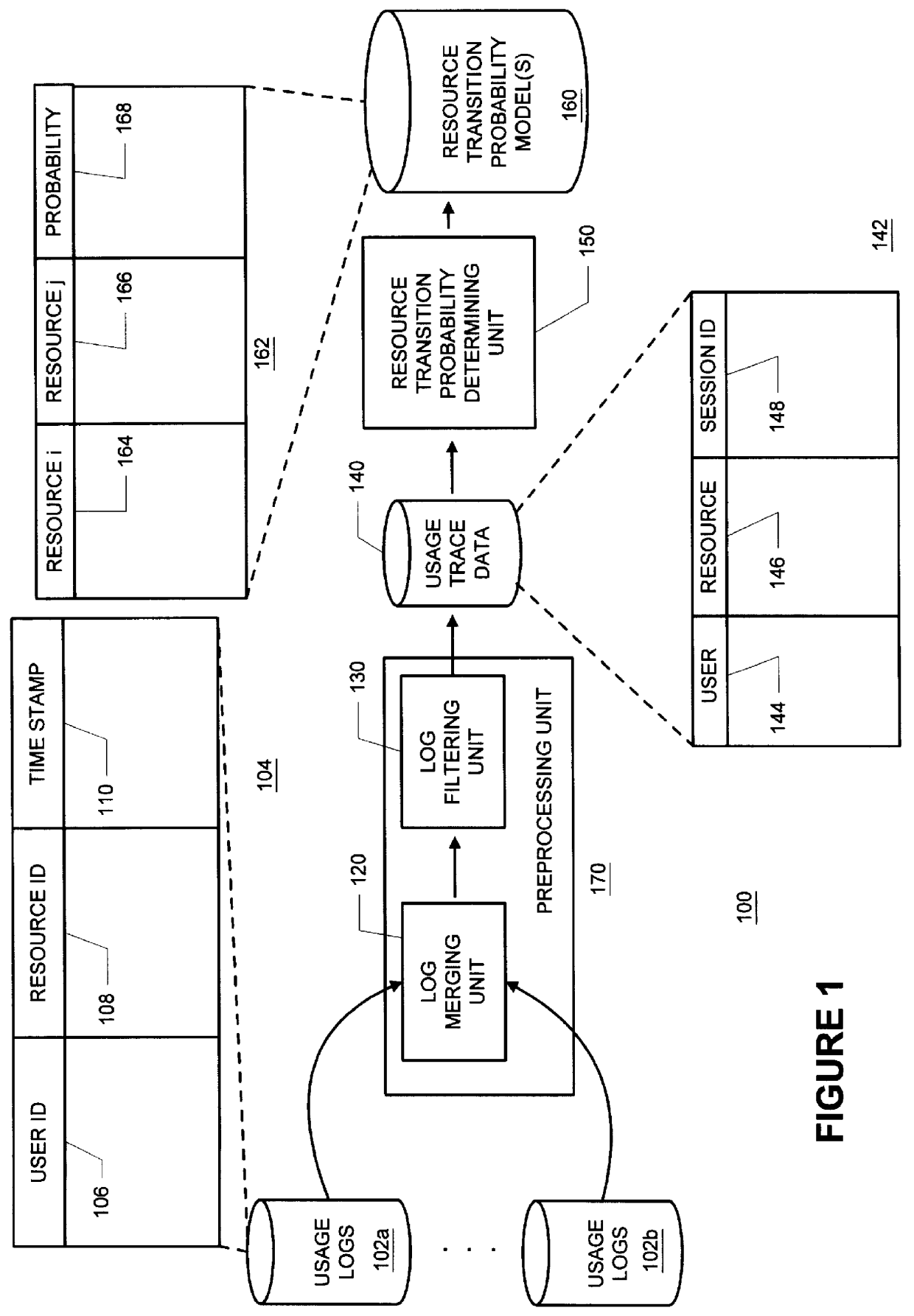
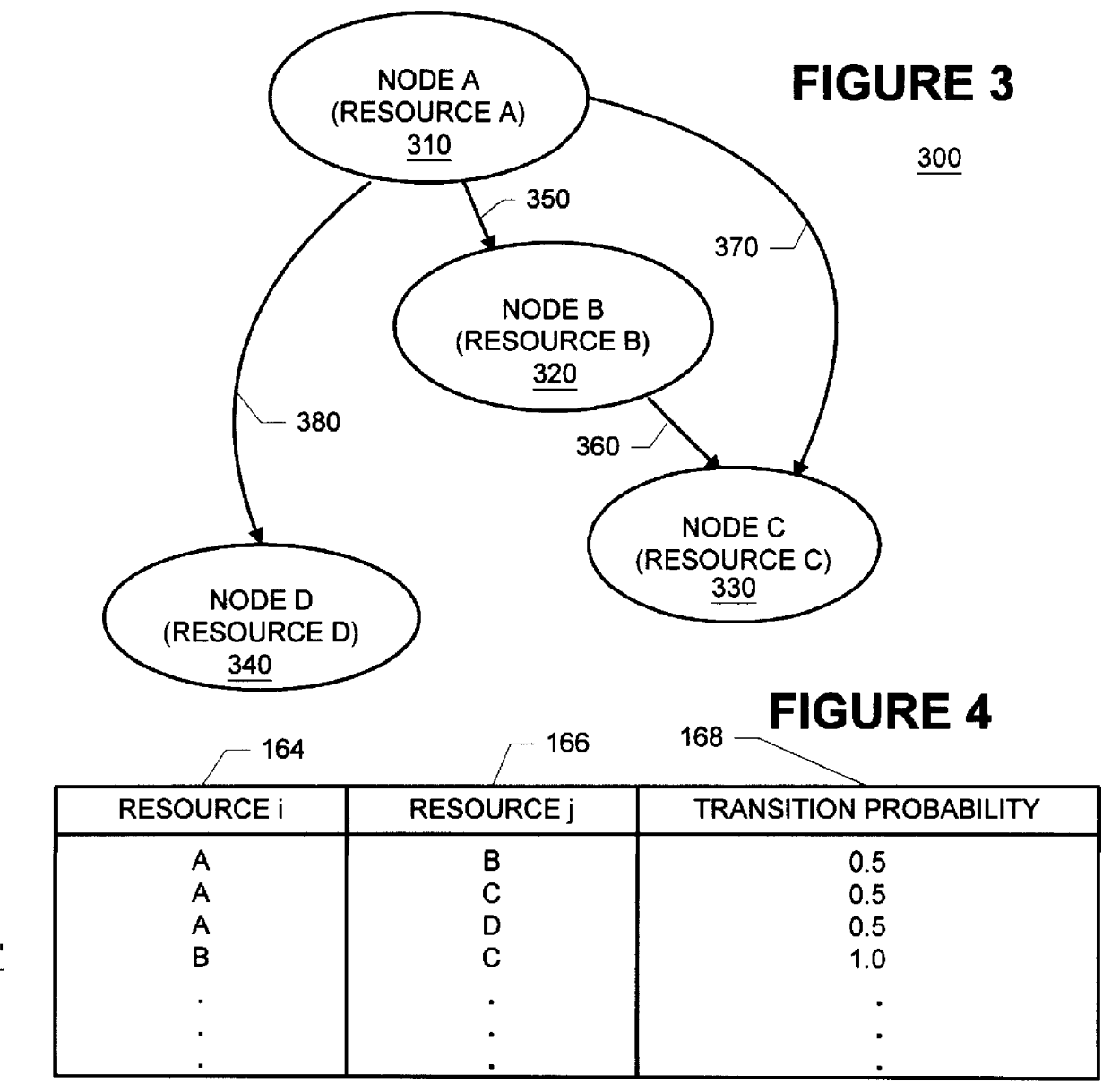
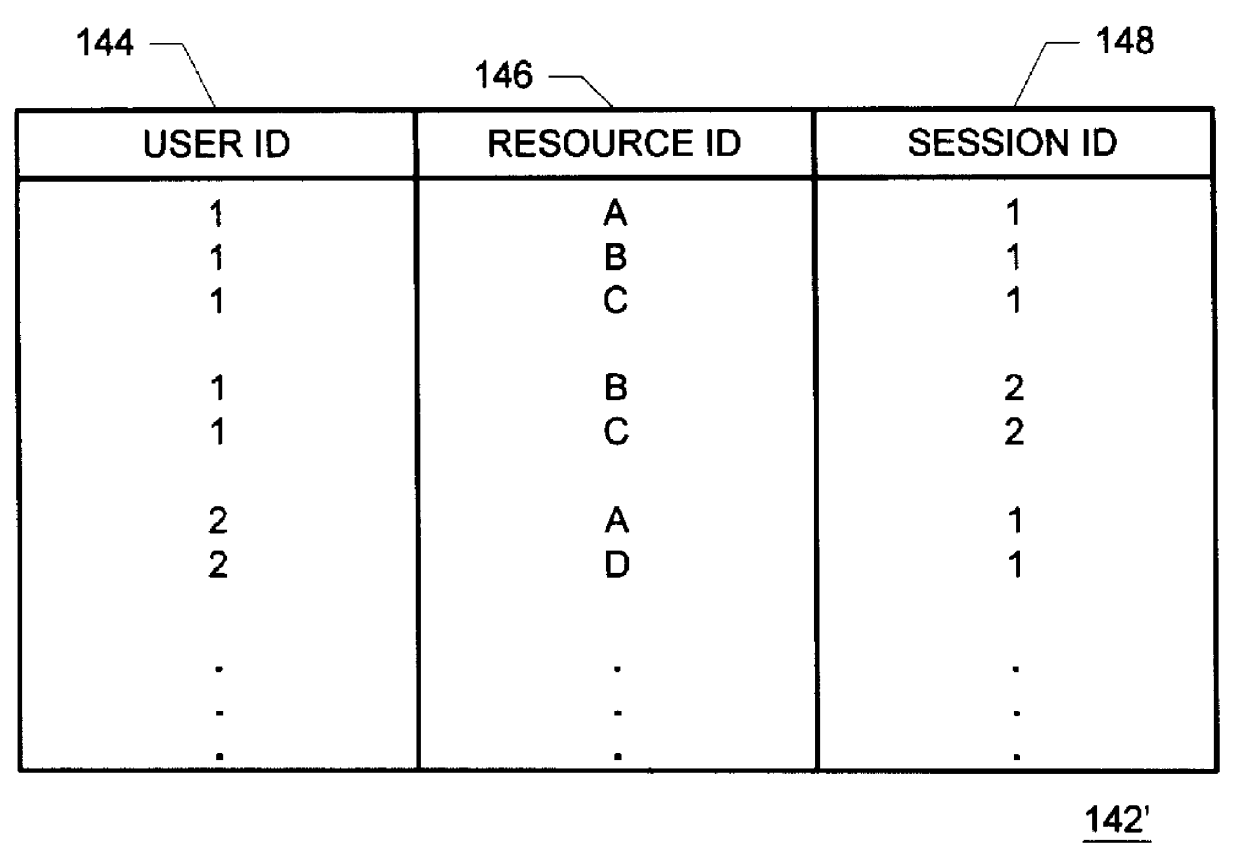
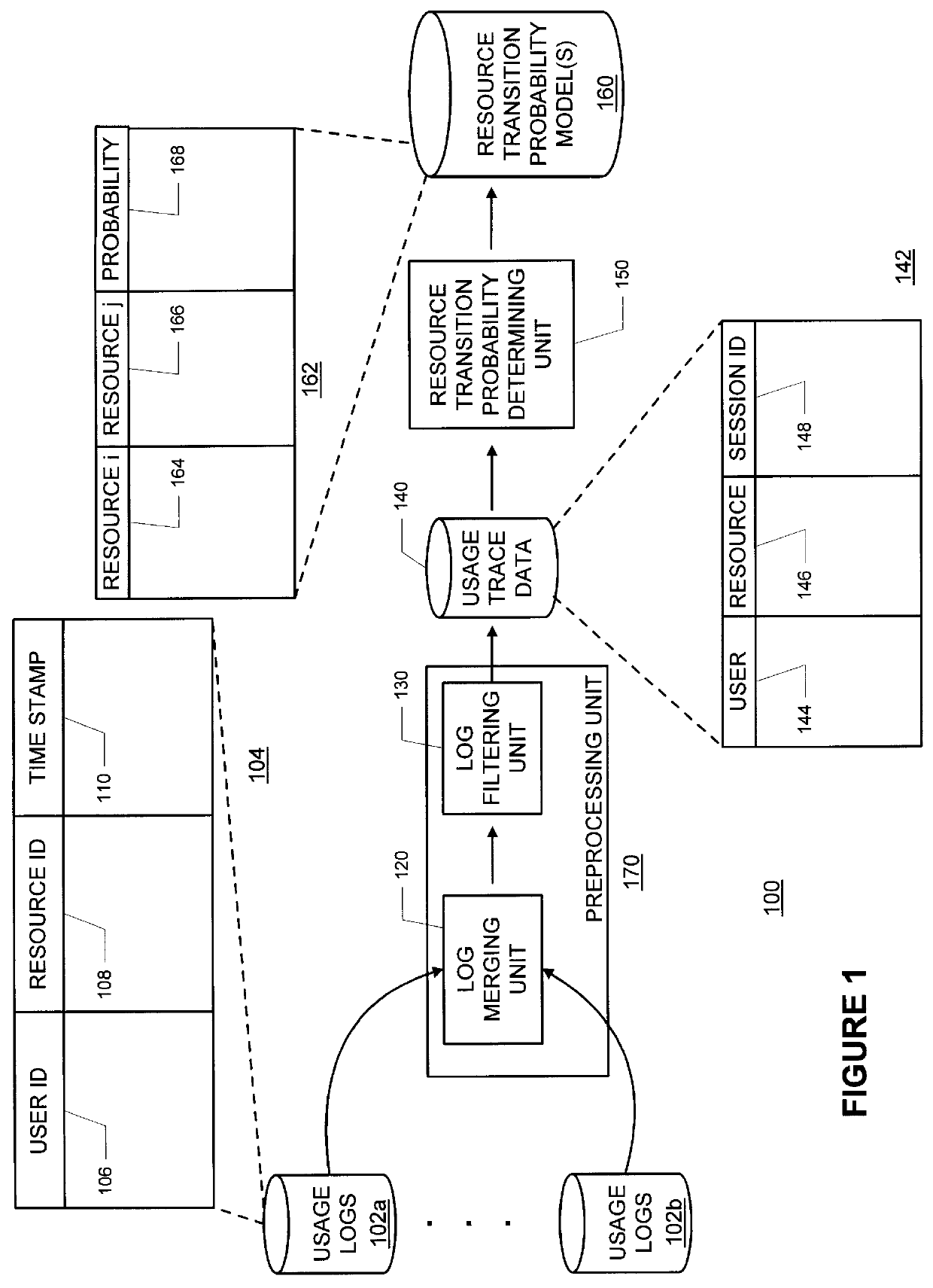
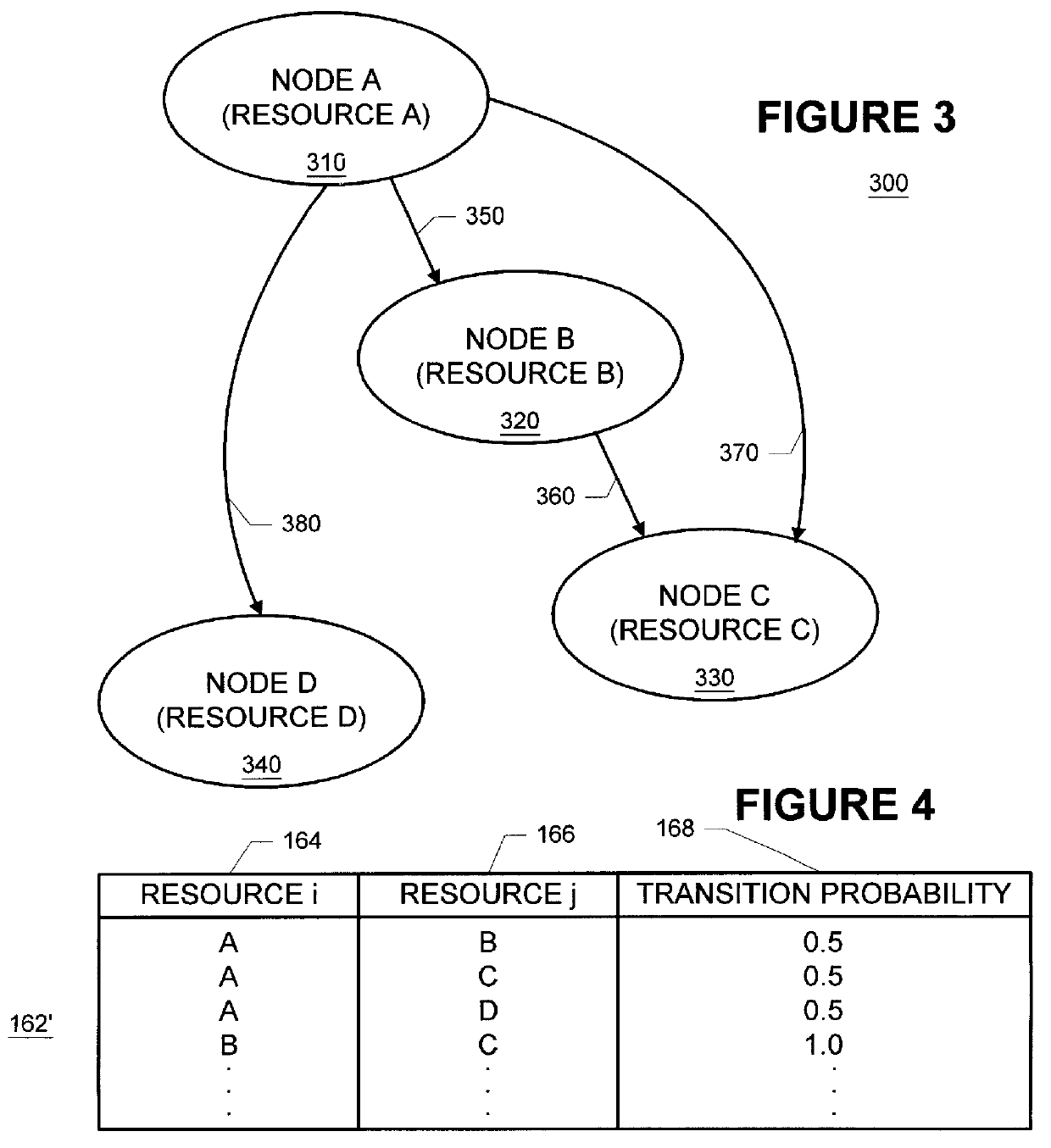
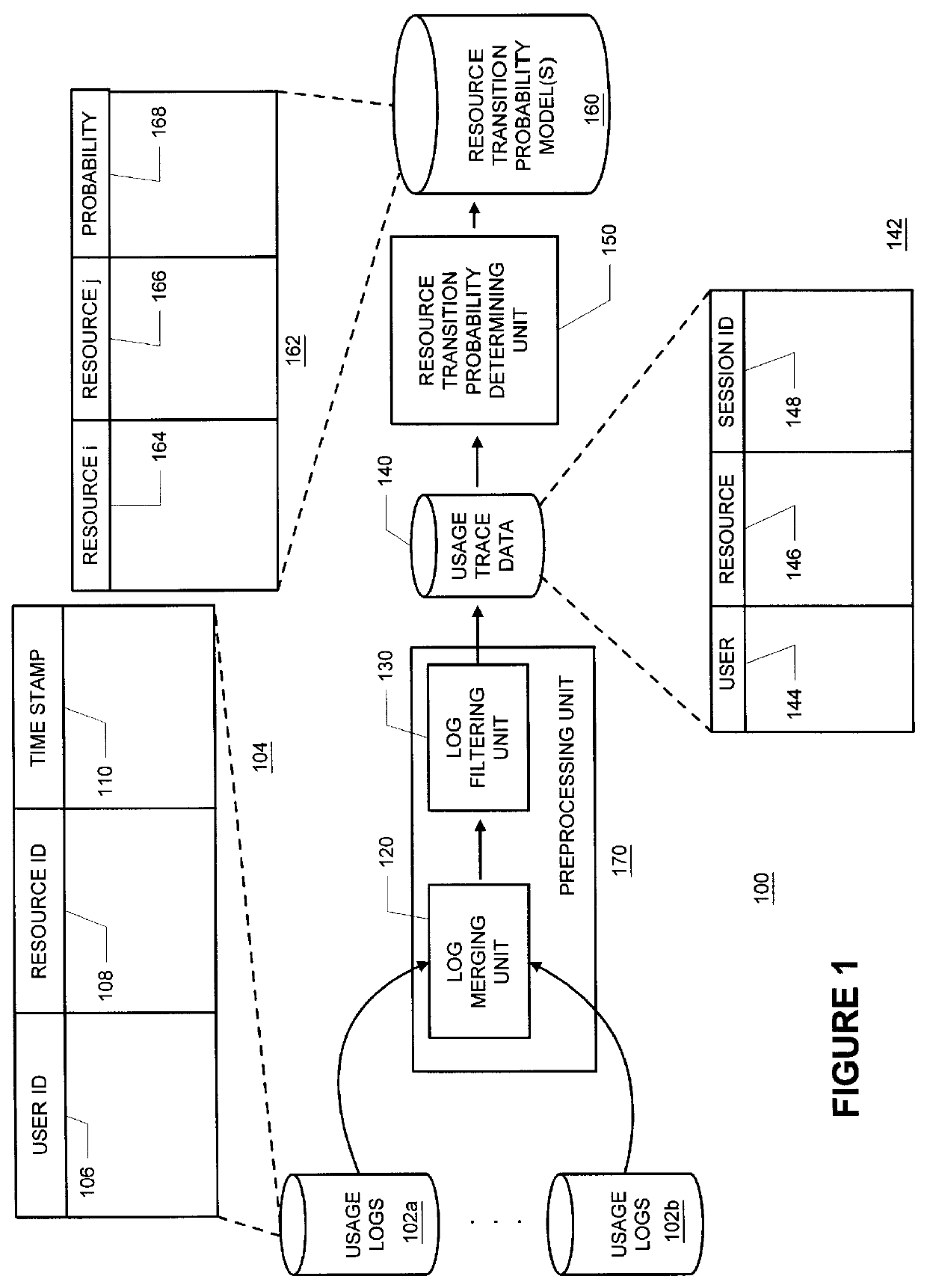
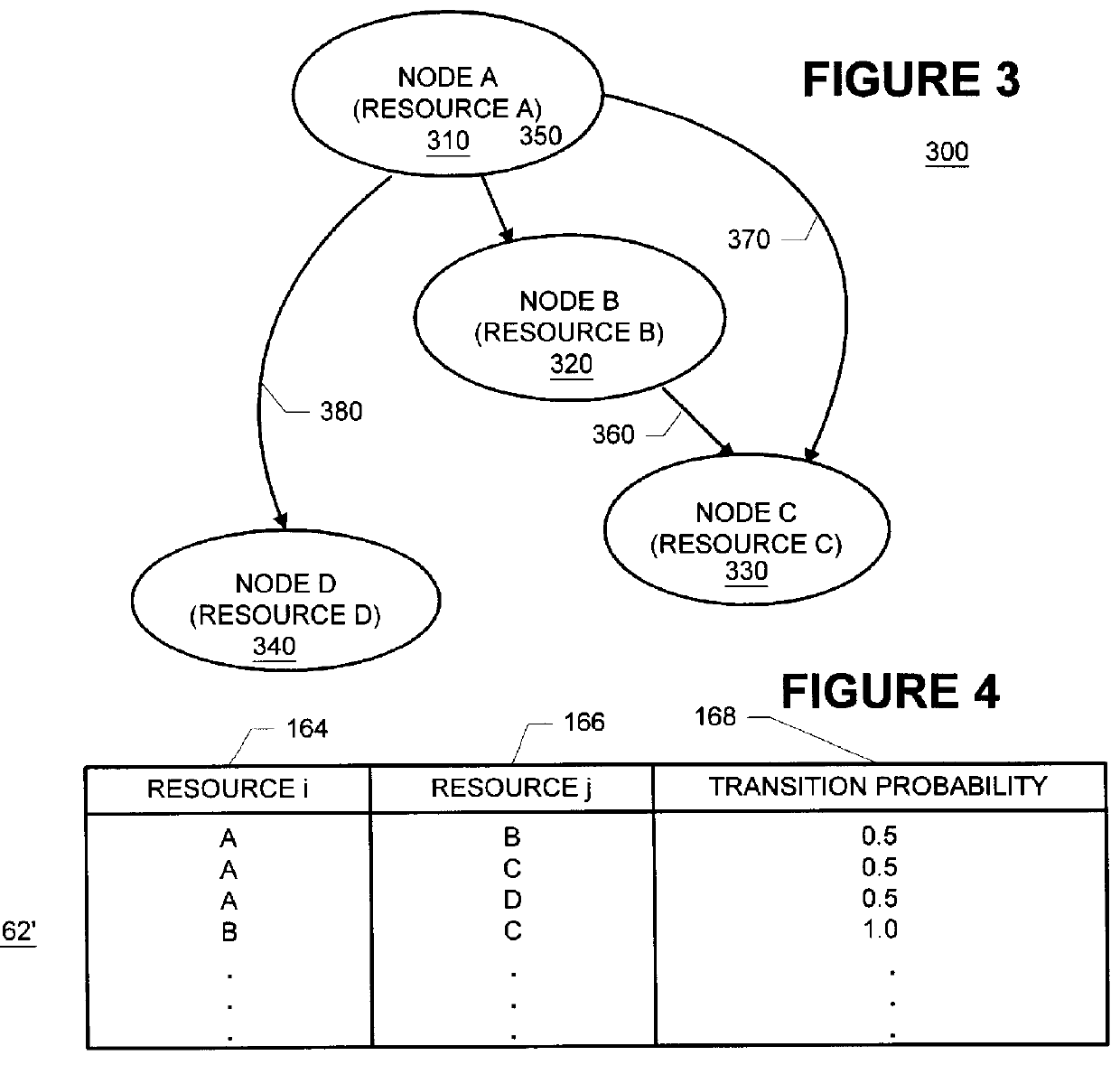
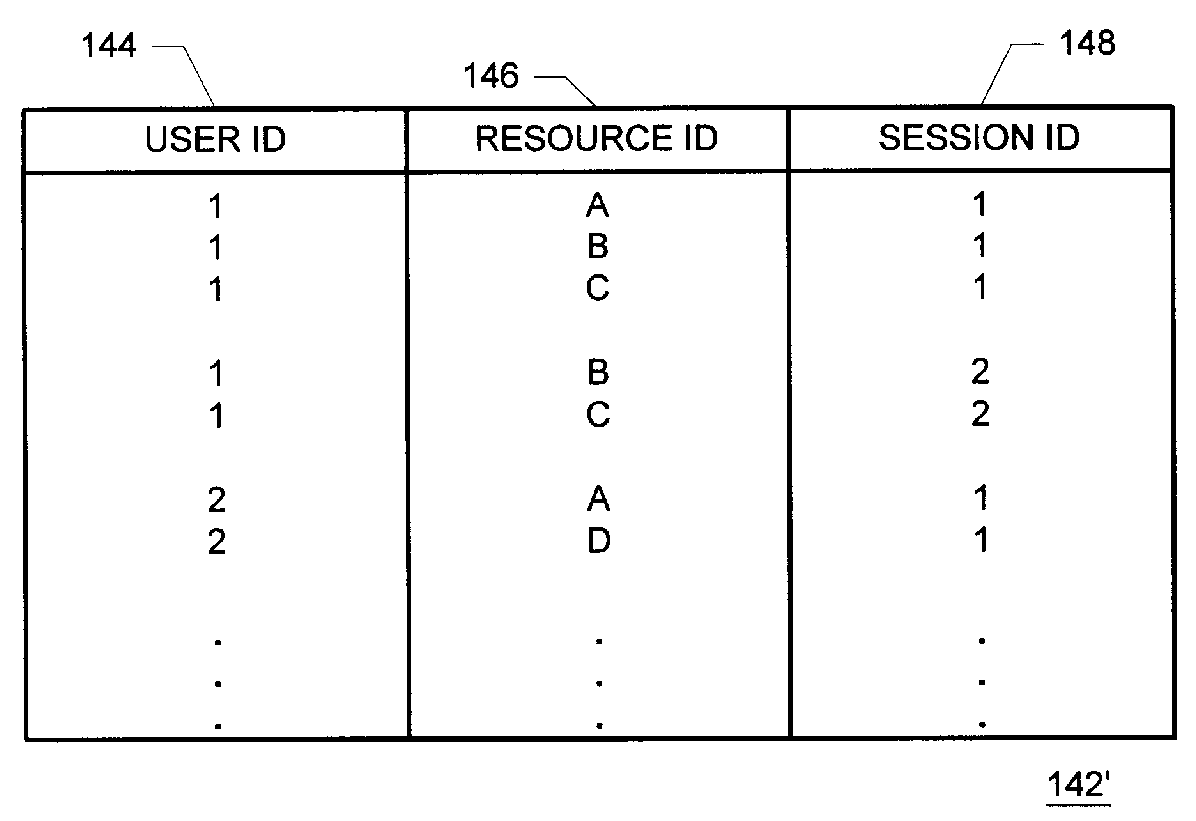
Methods and apparatus for building resource transition probability models for use in pre-fetching resources, editing resource link topology, building resource link topology templates, and collaborative filtering
InactiveUS6012052AData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalInternet contentResource transfer
Building resource (e.g., Internet content) and attribute transition probability models and using such models for pre-fetching resources, editing resource link topology, building resource link topology templates, and collaborative filtering.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
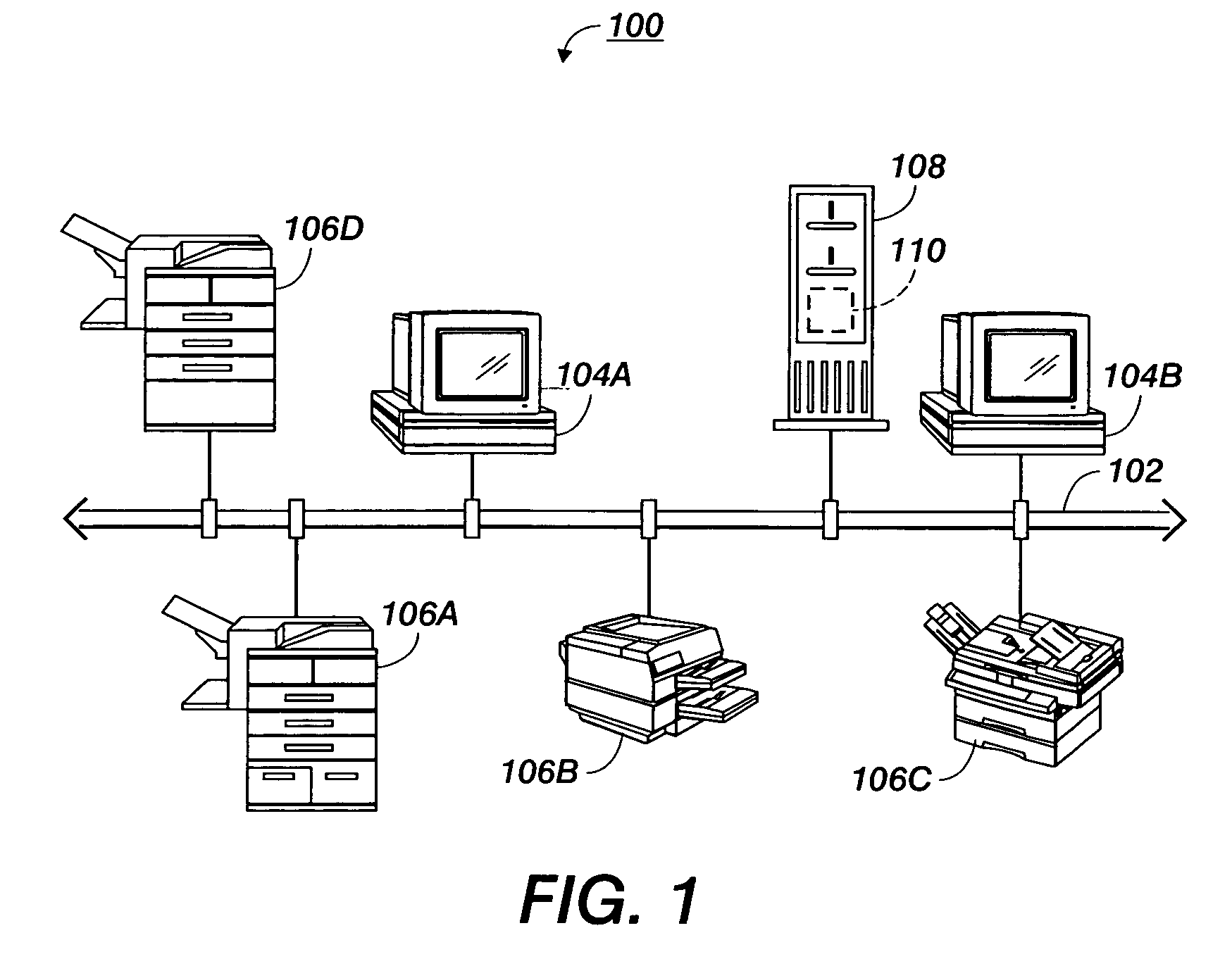
Probabilistic modeling of shared device usage
ActiveUS20060206445A1Wide rangeDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionClass of serviceModel parameters
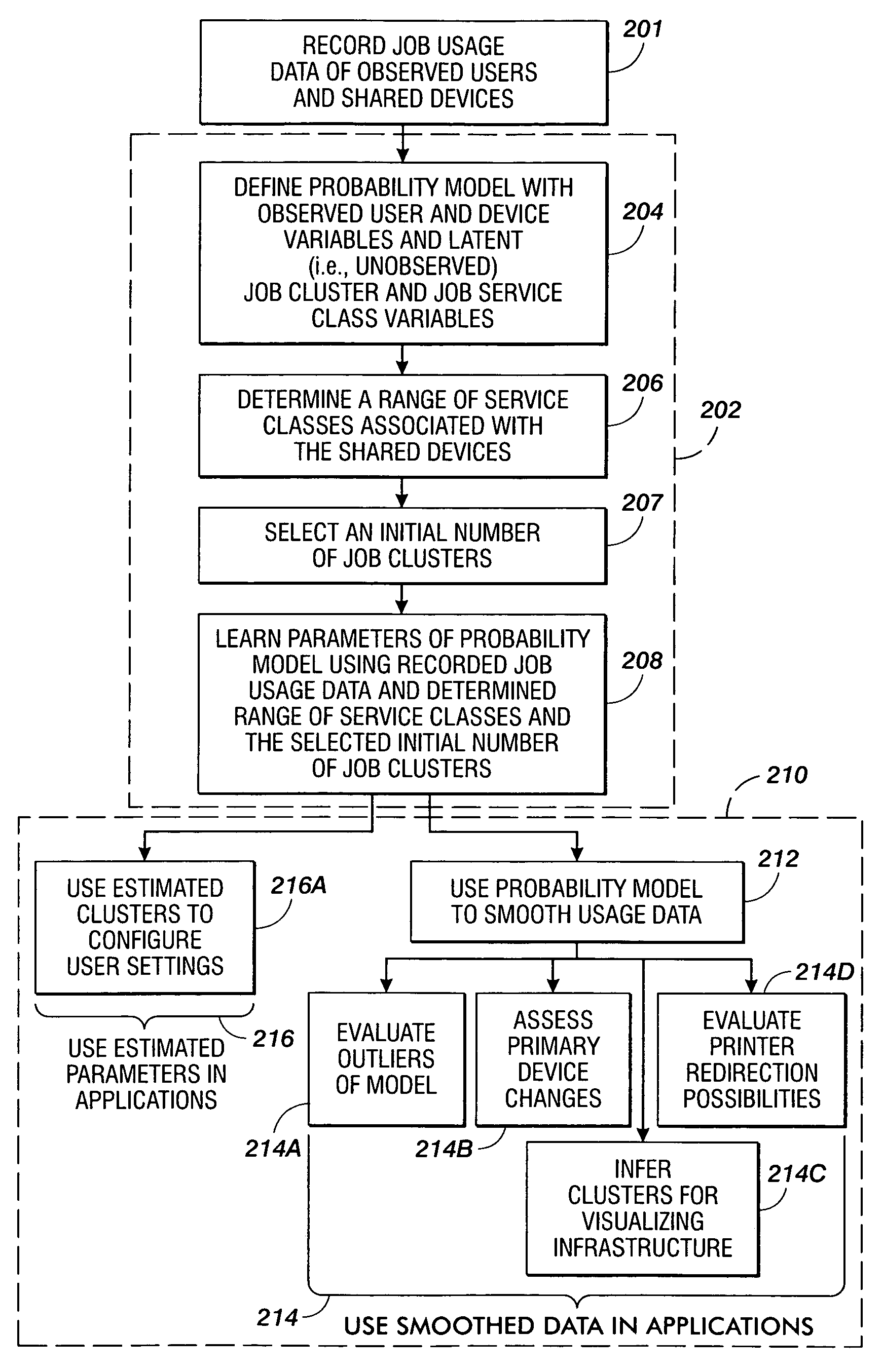
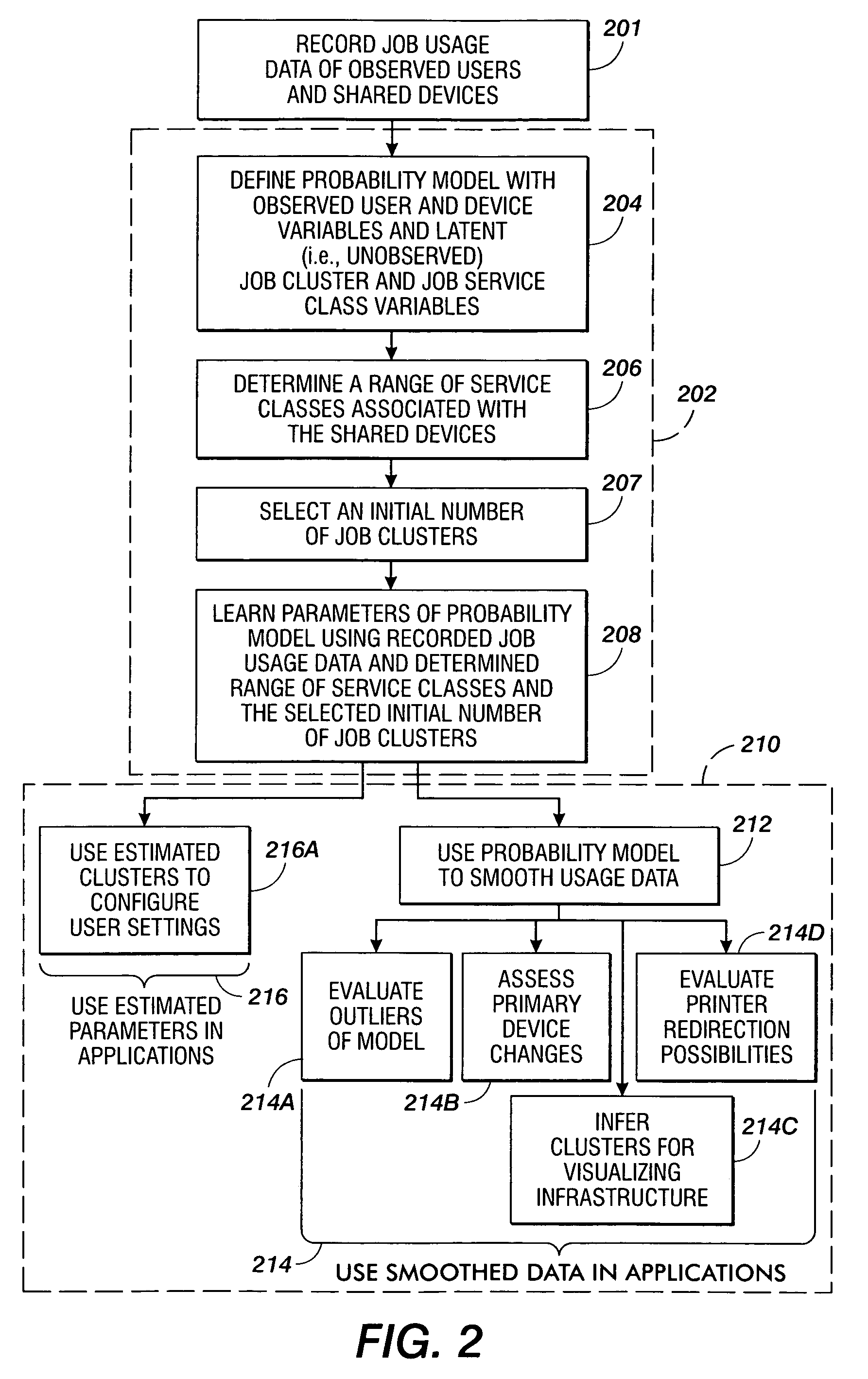
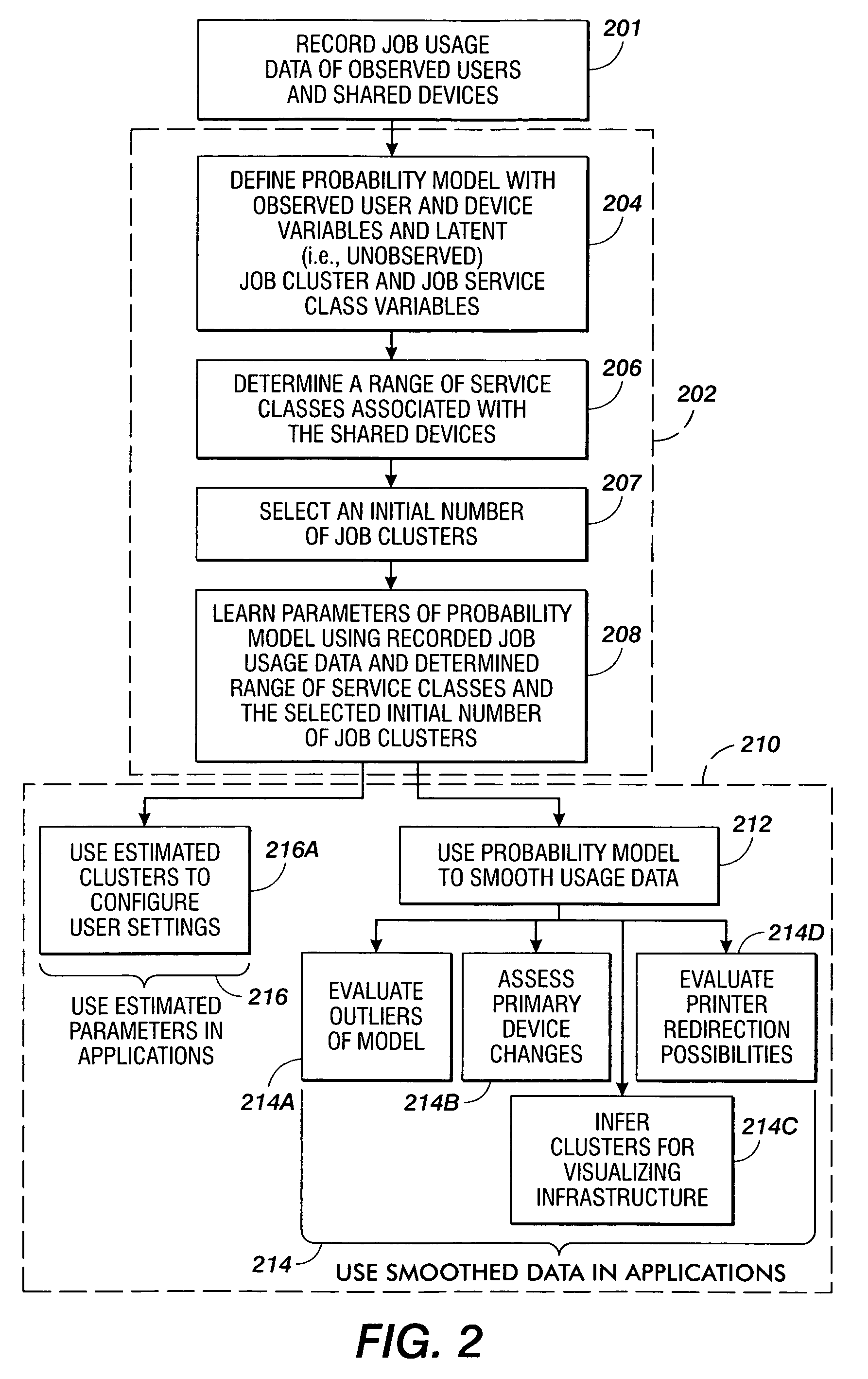
Methods are disclosed for estimating parameters of a probability model that models user behavior of shared devices offering different classes of service for carrying out jobs. In operation, usage job data of observed users and devices carrying out the jobs is recorded. A probability model is defined with an observed user variable, an observed device variable, a latent job cluster variable, and a latent job service class variable. A range of job service classes associated with the shared devices is determined, and an initial number of job clusters is selected. Parameters of the probability model are learned using the recorded job usage data, the determined range of service classes, and the selected initial number of job clusters. The learned parameters of the probability model are applied to evaluate one or more of: configuration of the shared devices, use of the shared devices, and job redirection between the shared devices.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method, apparatus, and article of manufacture for estimating parameters of a probability model on shared device usage probabilistic semantic analysis
ActiveUS7567946B2Digital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionProbabilistic semanticsAlgorithm
Methods are disclosed for estimating parameters of a probability model that models user behavior of shared devices offering different classes of service for carrying out jobs. In operation, usage job data of observed users and devices carrying out the jobs is recorded. A probability model is defined with an observed user variable, an observed device variable, a latent job cluster variable, and a latent job service class variable. A range of job service classes associated with the shared devices is determined, and an initial number of job clusters is selected. Parameters of the probability model are learned using the recorded job usage data, the determined range of service classes, and the selected initial number of job clusters. The learned parameters of the probability model are applied to evaluate one or more of: configuration of the shared devices, use of the shared devices, and job redirection between the shared devices.
Owner:XEROX CORP
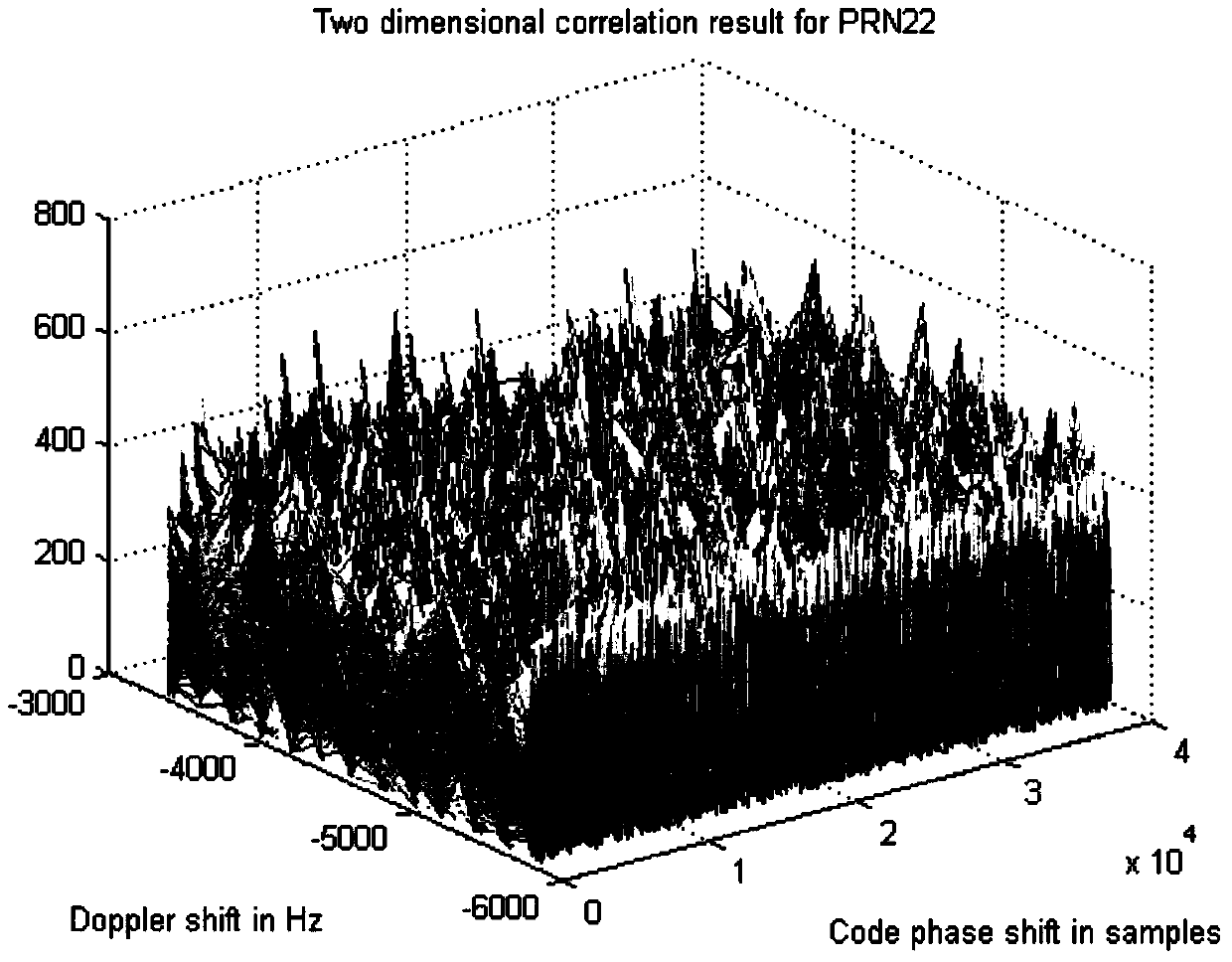
Anti-interference normal null widening method for dynamic GNSS receiver
InactiveCN104181552AImprove robustnessGuaranteed validitySatellite radio beaconingFrequency spectrumEngineering
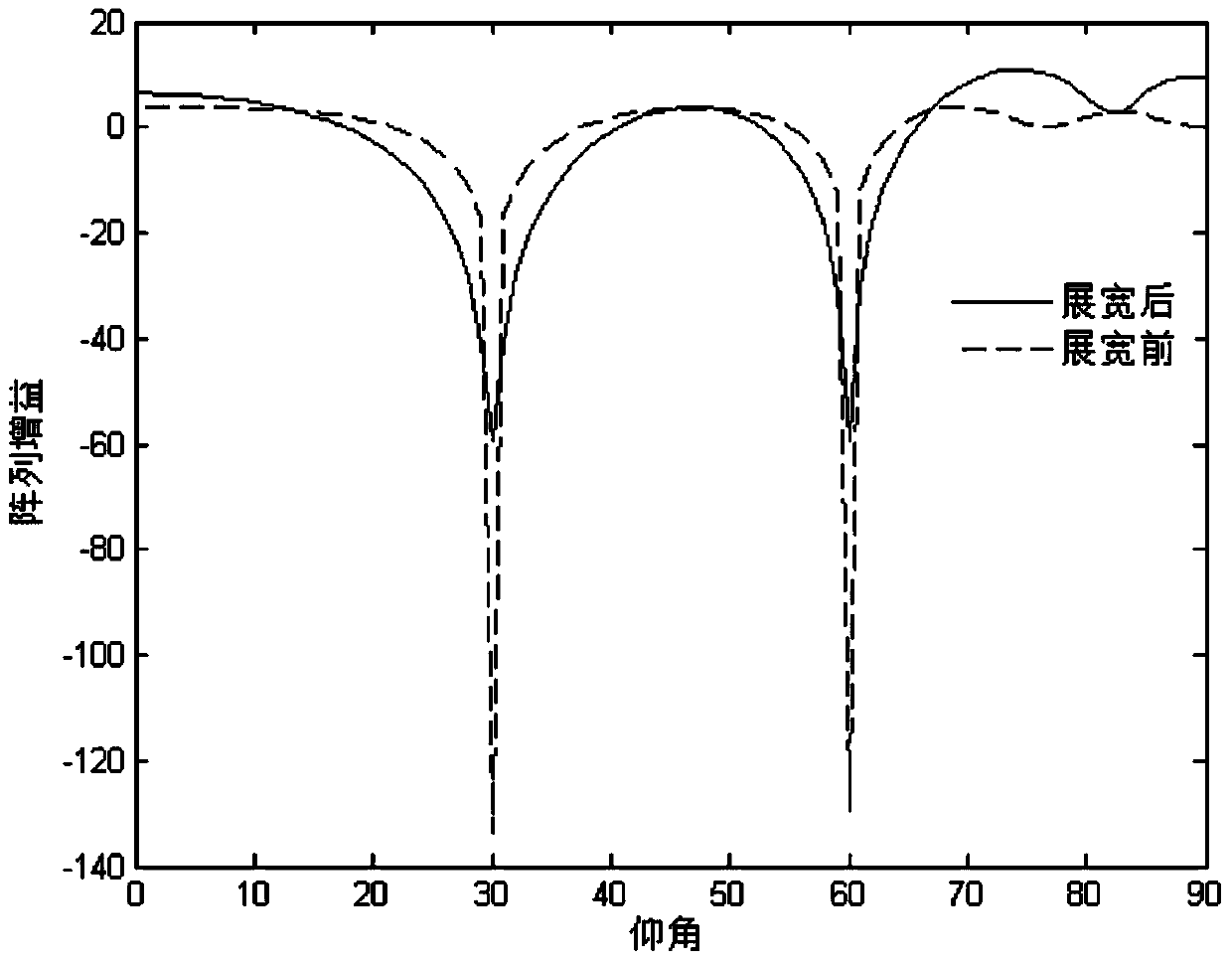
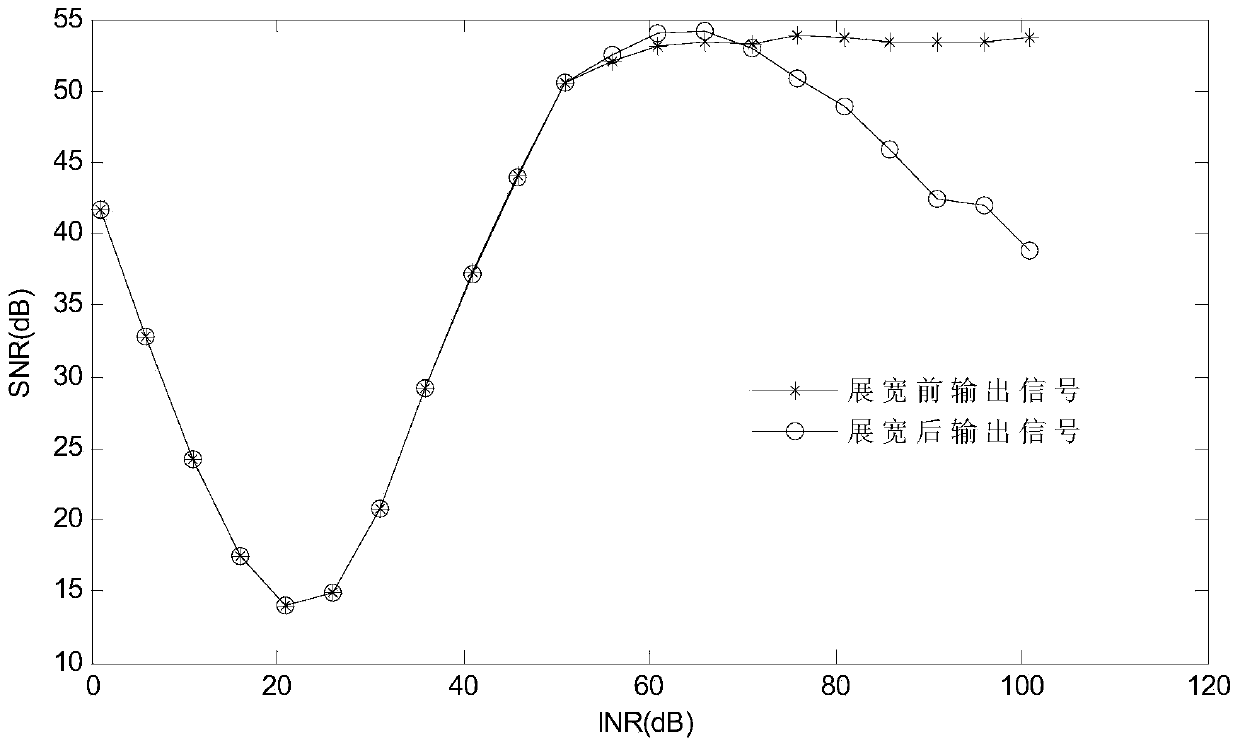
The invention belongs to the technical field of GNSS engineering safety, and relates to an anti-interference normal null widening method for a dynamic GNSS receiver. On the basis of a normal-distribution probability model, a null widening model of the dynamic GNSS receiver is provided. The model is linearized on the situation of small angle changing, and frequency spectrum gains formed before and after widening are compared by means of a Matlab simulation tool. By means of a power insertion algorithm, the relationship of an output SNR and an input INR is analyzed before and after widening, and ultimately engineering realizability of an algorithm is put forward through FPGA and DSP platform verification. As is shown by a result, widening null formed through the widening algorithm can effectively counteract interference sources changing within a certain range, the aim of preventing dynamic interferences is achieved and robustness of a self-adaptation algorithm is improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Methods and apparatus for using resource transition probability models for pre-fetching resources
InactiveUS6088718AQuickly renderedDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsInternet contentResource transfer
Building resource (e.g., Internet content) and attribute transition probability models and using such models for pre-fetching resources, editing resource link topology, building resource link topology templates, and collaborative filtering.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
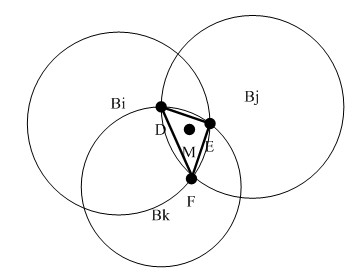
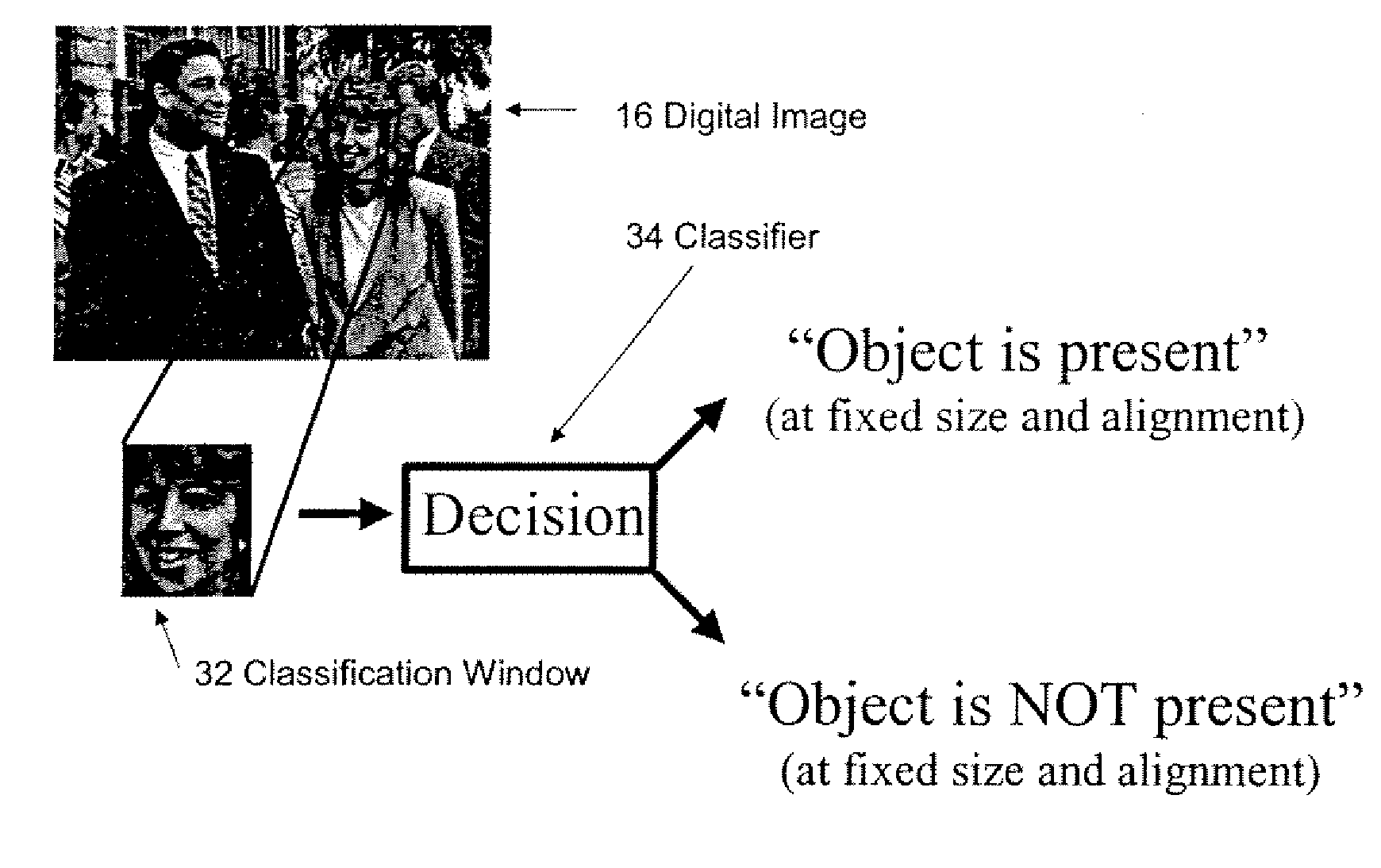
Object recognizer and detector for two-dimensional images using bayesian network based classifier
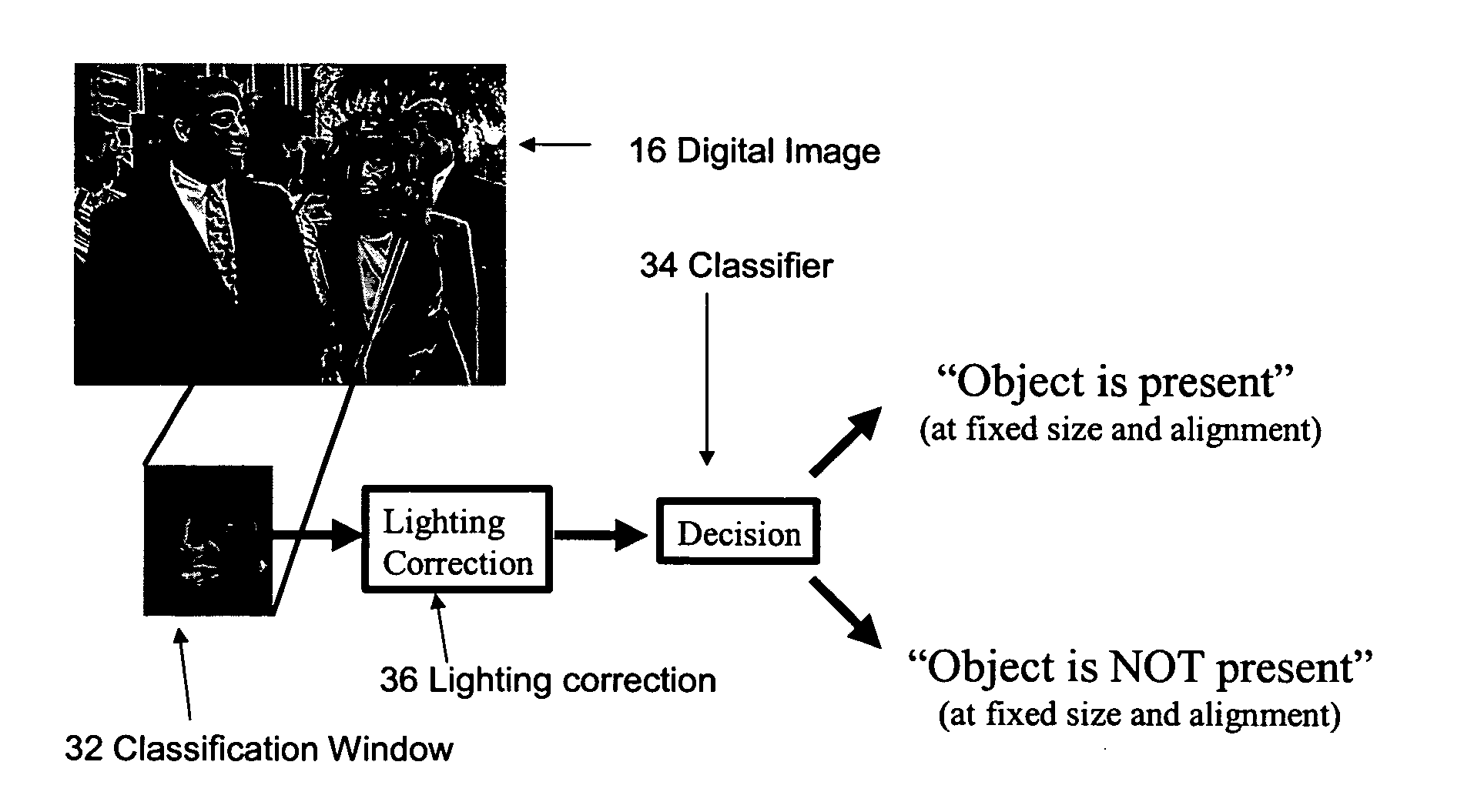
A system and method for determining a classifier to discriminate between two classes—object or non-object. The classifier may be used by an object detection program to detect presence of a 3D object in a 2D image (e.g., a photograph or an X-ray image). The overall classifier is constructed of a sequence of classifiers (or “sub-classifiers”), where each such classifier is based on a ratio of two graphical probability models (e.g., Bayesian networks). A discrete-valued variable representation at each node in a Bayesian network by a two-stage process of tree-structured vector quantization is discussed. The overall classifier may be part of an object detector program that is trained to automatically detect many different types of 3D objects (e.g., human faces, airplanes, cars, etc.). Computationally efficient statistical methods to evaluate overall classifiers are disclosed. The Bayesian network-based classifier may also be used to determine if two observations (e.g., two images) belong to the same category. For example, in case of face recognition, the classifier may determine whether two photographs are of the same person. A method to provide lighting correction or adjustment to compensate for differences in various lighting conditions of input images is disclosed as well. As per the rules governing abstracts, the content of this abstract should not be used to construe the claims in this application.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Methods and apparatus for using attribute transition probability models for pre-fetching resources
InactiveUS6154767AQuickly renderedDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsInternet contentDistributed computing
Building resource (e.g., Internet content) and attribute transition probability models and using such models for pre-fetching resources, editing resource link topology, building resource link topology templates, and collaborative filtering.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
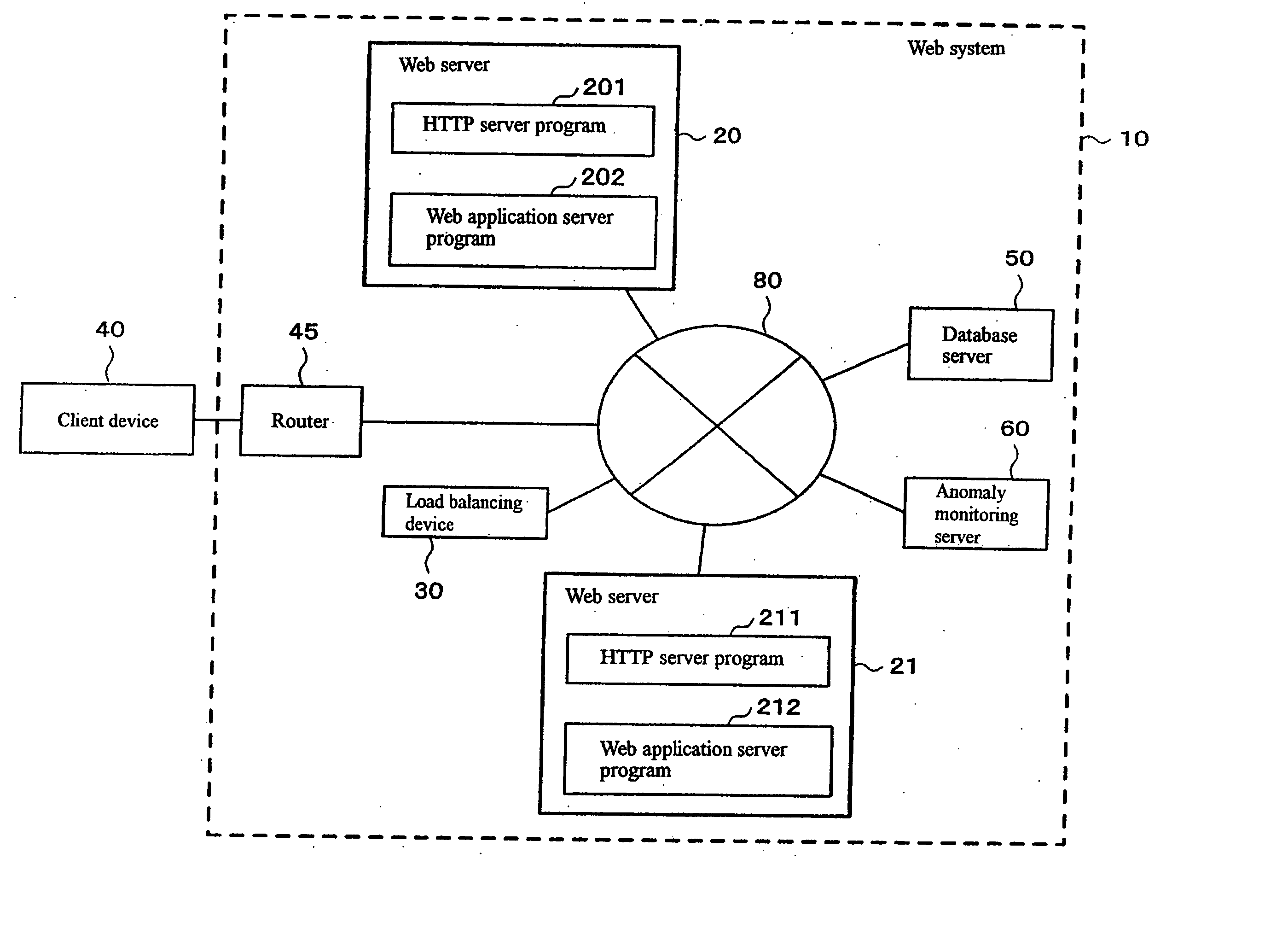
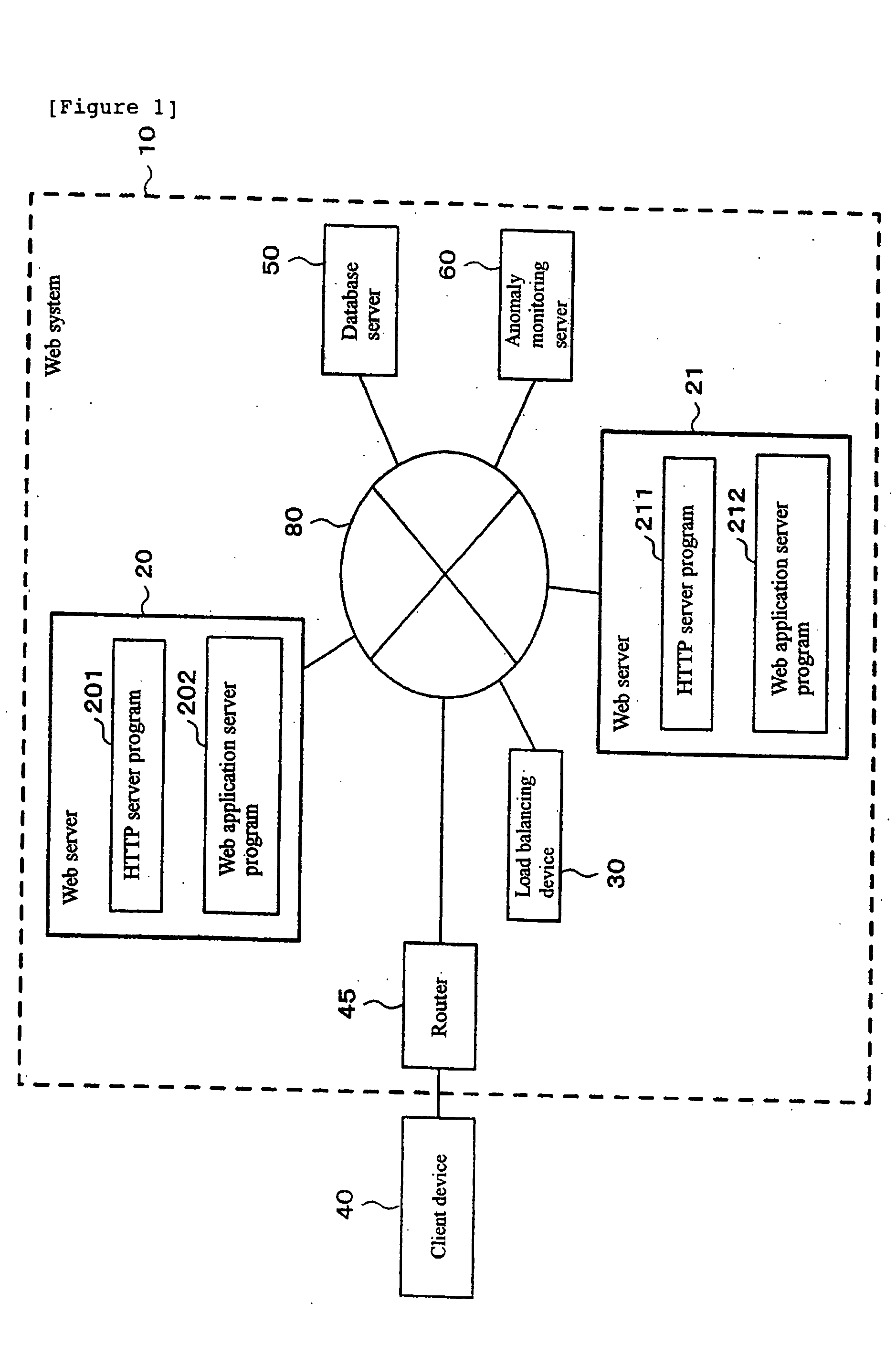
Anomaly detection
InactiveUS20050193281A1Not easy to detectDigital computer detailsHardware monitoringProbit modelFeature vector
A system such as a Web-based system in which a plurality of computers interact with each other is monitored to detect online an anomaly. Transactions of a service provided by each of a plurality of computers to another computer are collected, a matrix of correlations between nodes in the system is calculated from the transactions, and a feature vector representing anode activity balance is obtained from the matrix. The feature vector is monitored using a probability model to detect a transition to an anomalous state.
Owner:IBM CORP
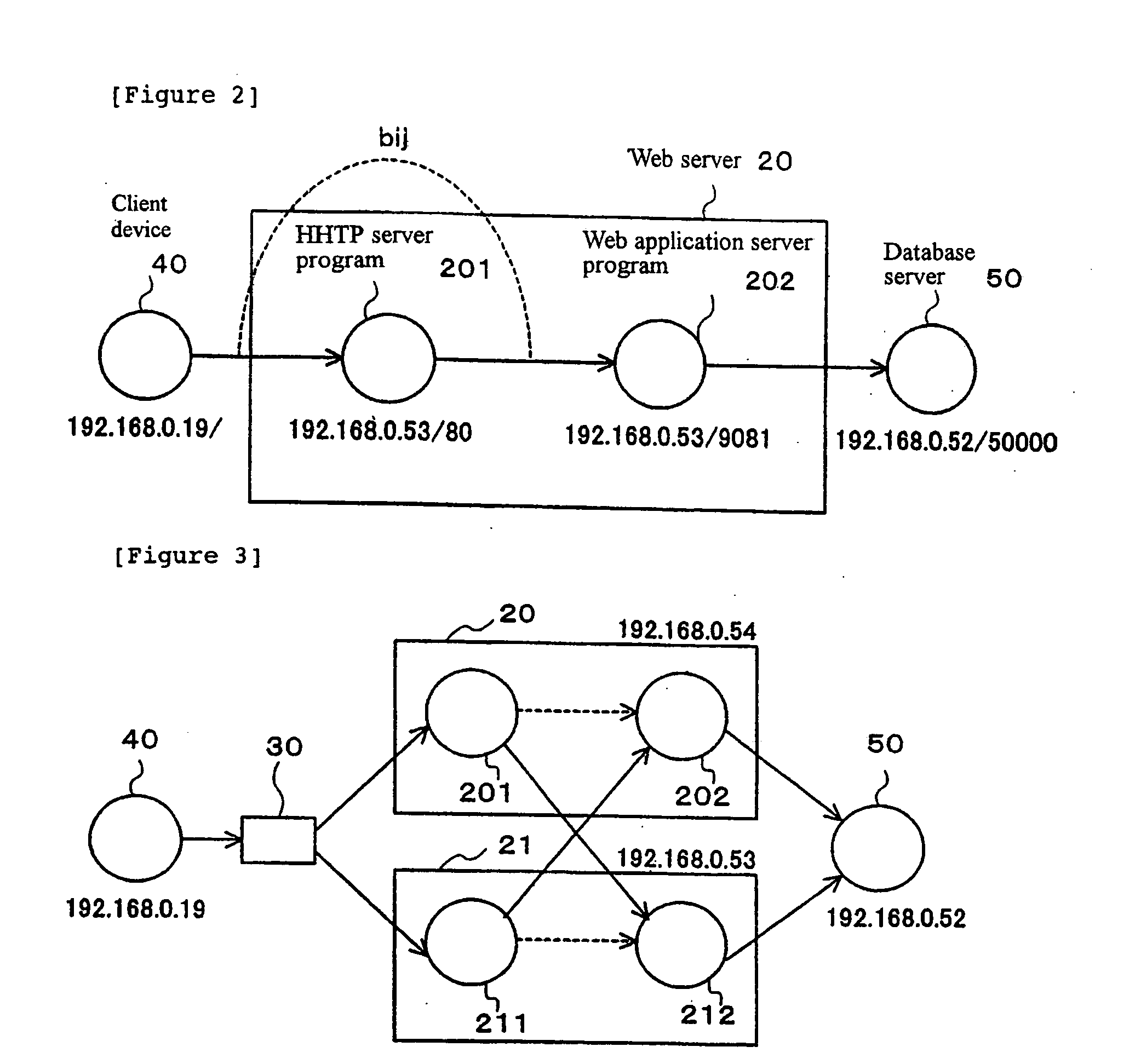
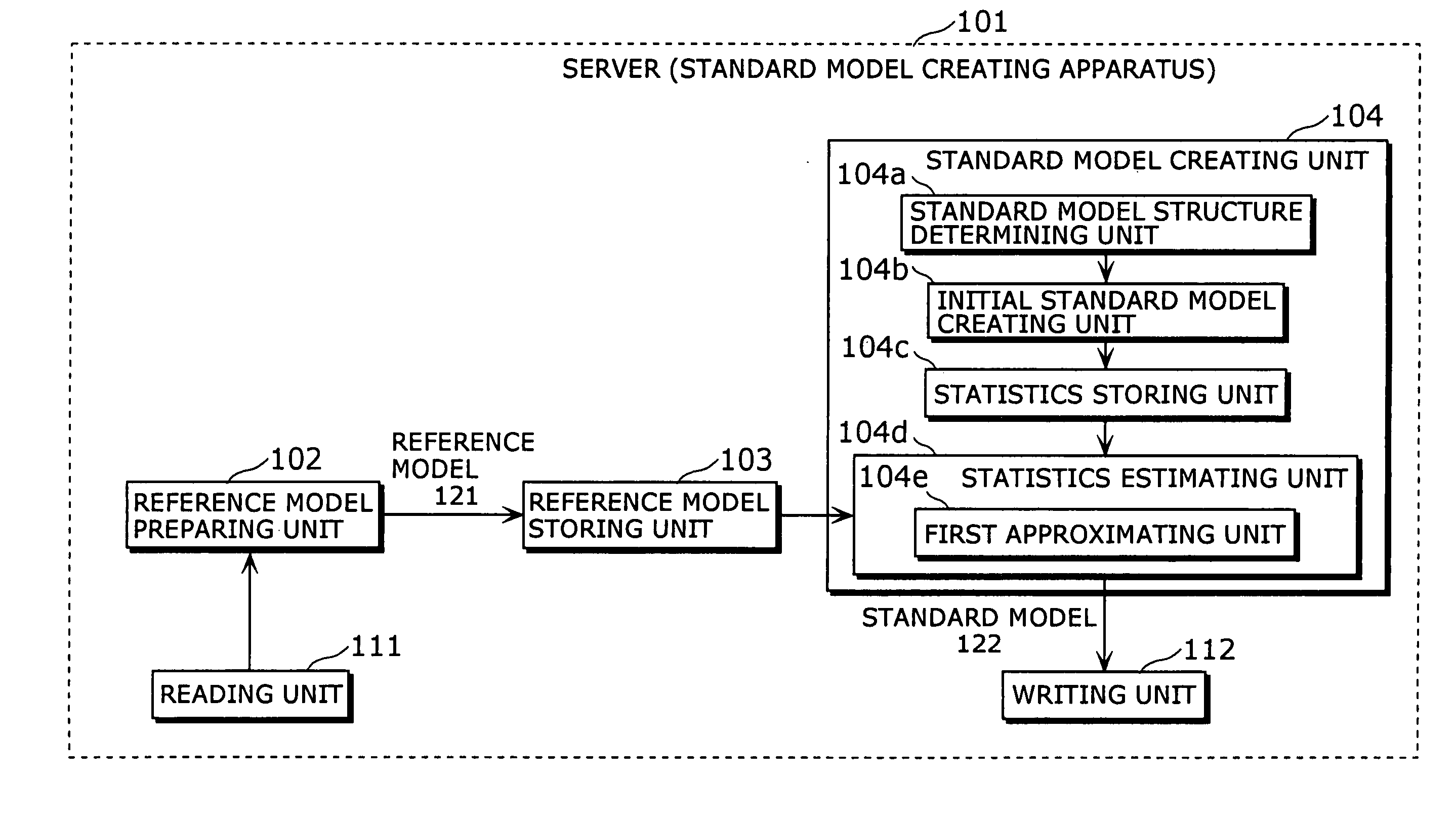
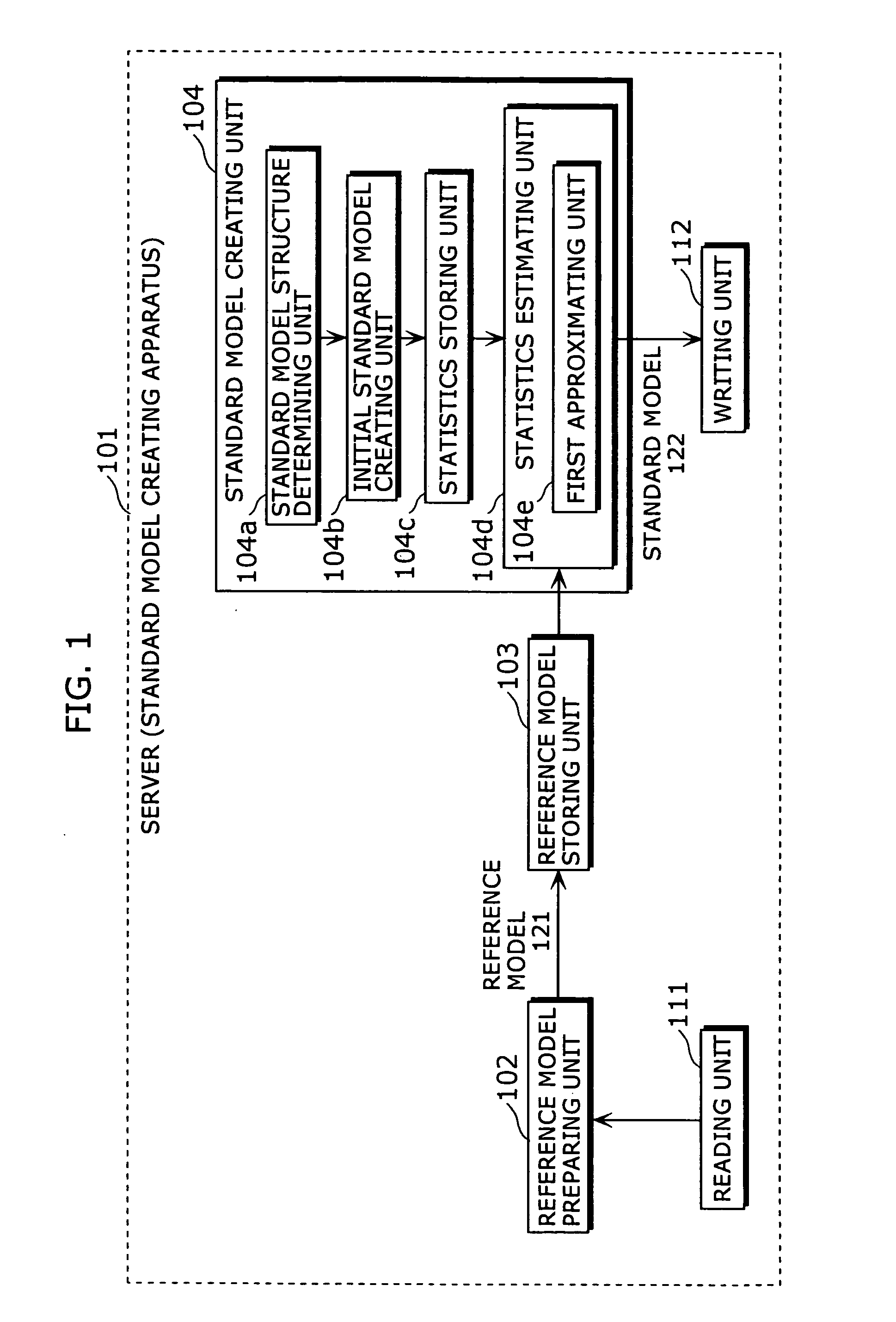
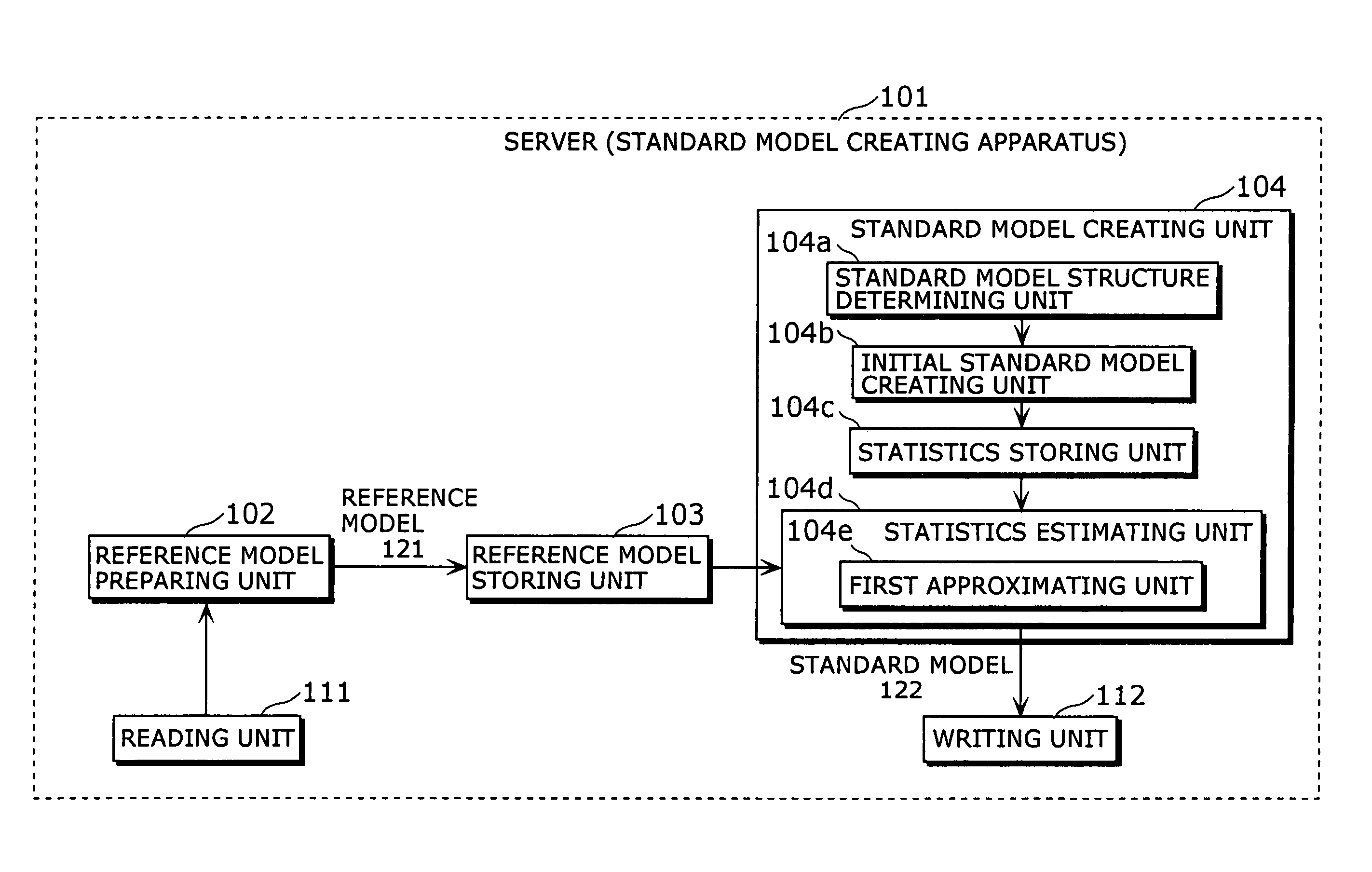
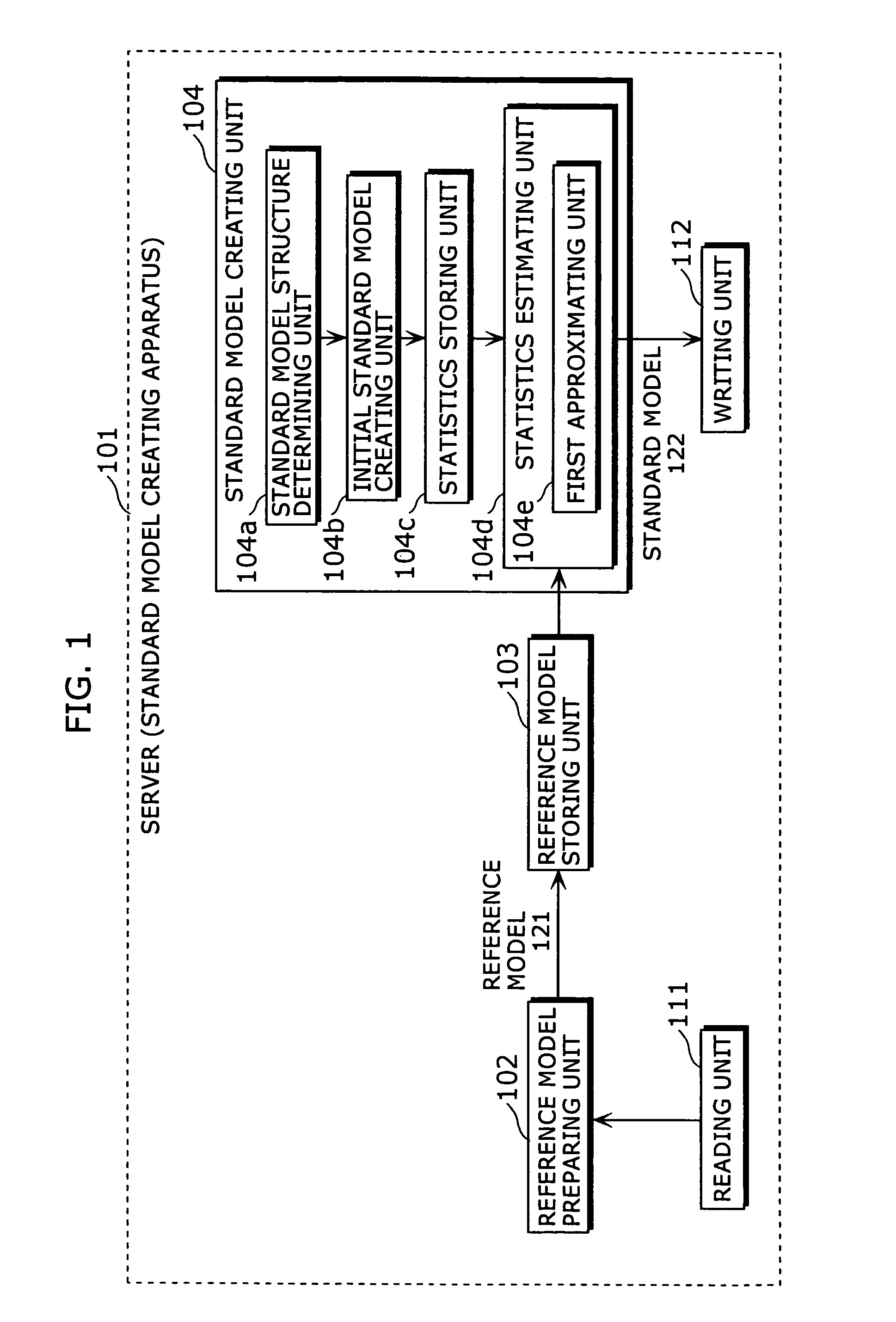
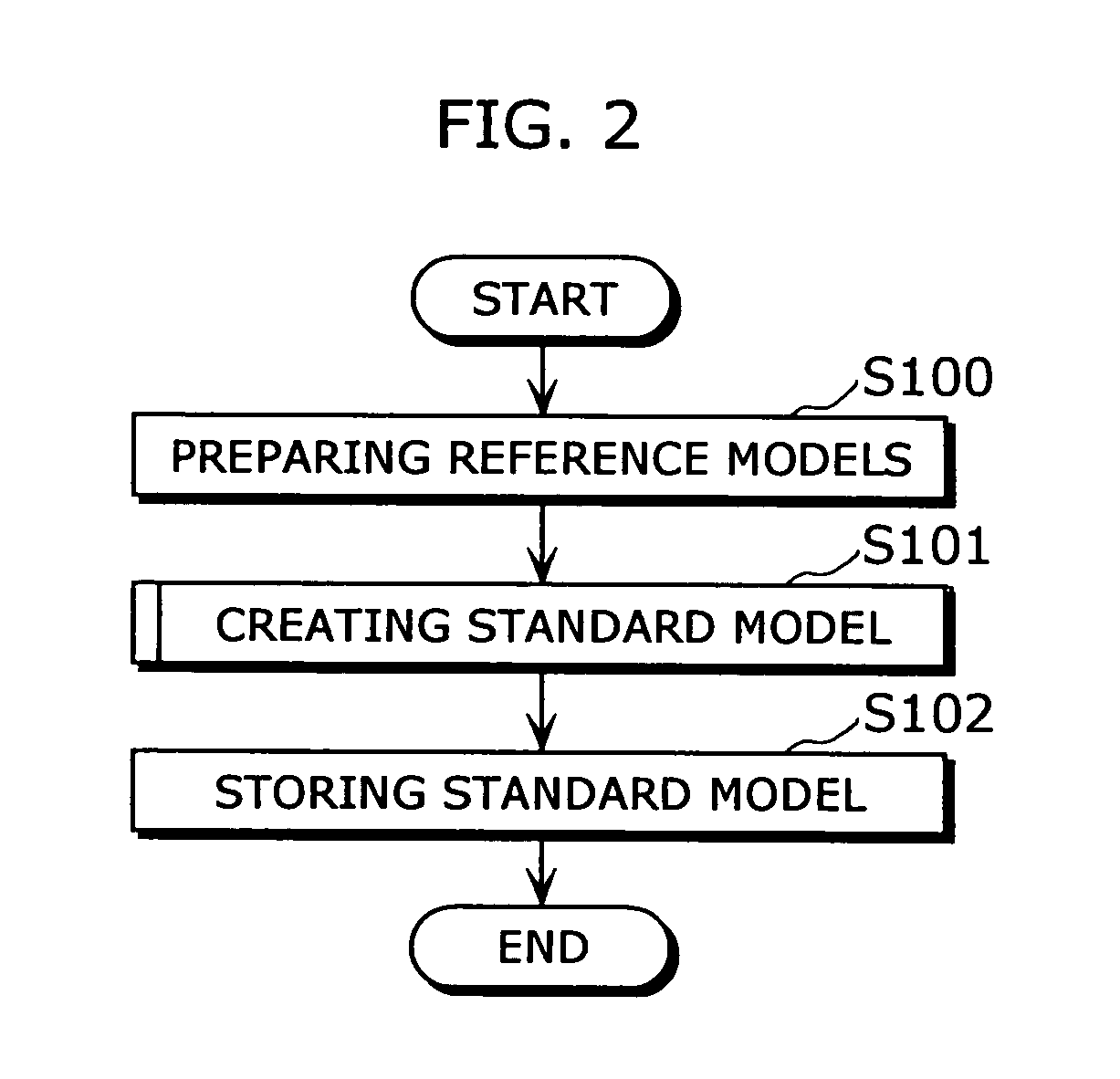
Standard model creating device and standard model creating method
ActiveUS20060053014A1Easy to createHigh practical valueSpeech recognitionReference modelHide markov model
The standard model creating apparatus which provides a high-precision standard model used for: pattern recognition such as speech recognition, character recognition, or image recognition using a probability model based on a hidden Markov model, Bayesian theory, or linear discrimination analysis; intention interpretation using a probability model such as a Bayesian net; data-mining performed using a probability model; and so forth, the apparatus comprising: a reference model preparing unit (102) operable to prepare at least one reference model; a reference model storing unit (103) operable to store the reference model (121) prepared by the reference model preparing unit (102); and a standard model creating unit (104) operable to create a standard model (122) by calculating statistics of the standard model so as to maximize or locally maximize the probability or likelihood with respect to the at least one reference model stored in the reference model storing unit (103).
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
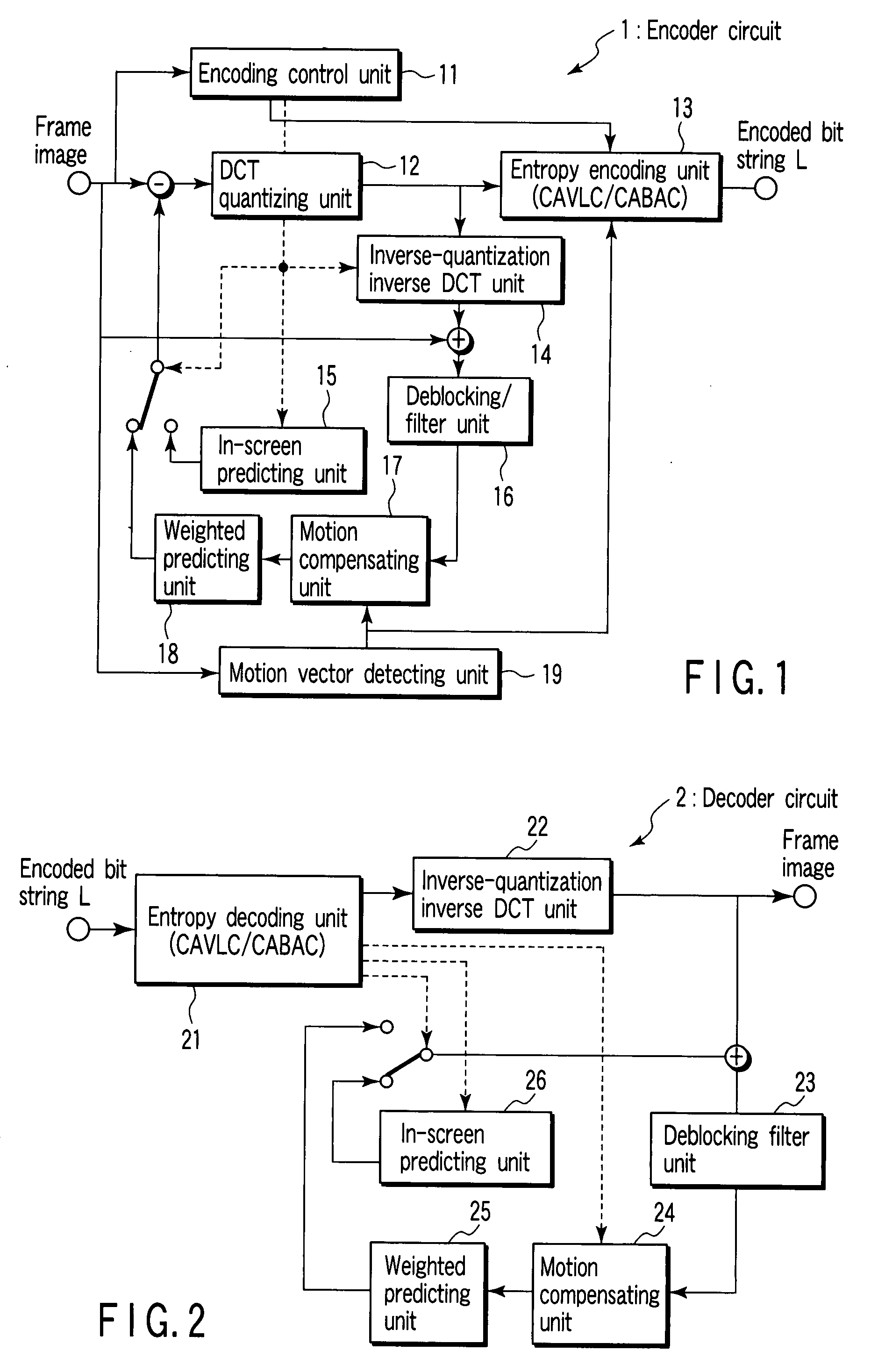
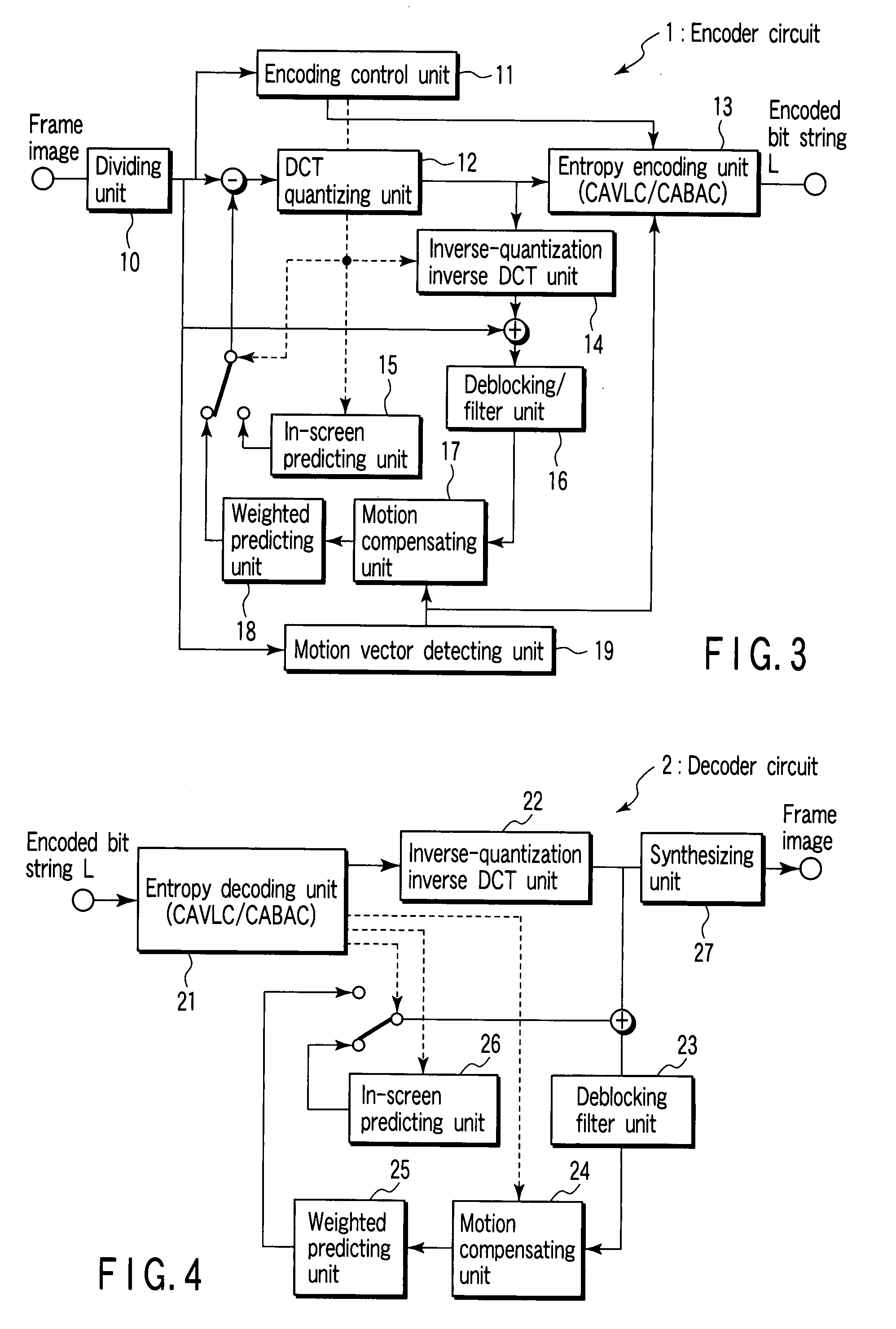
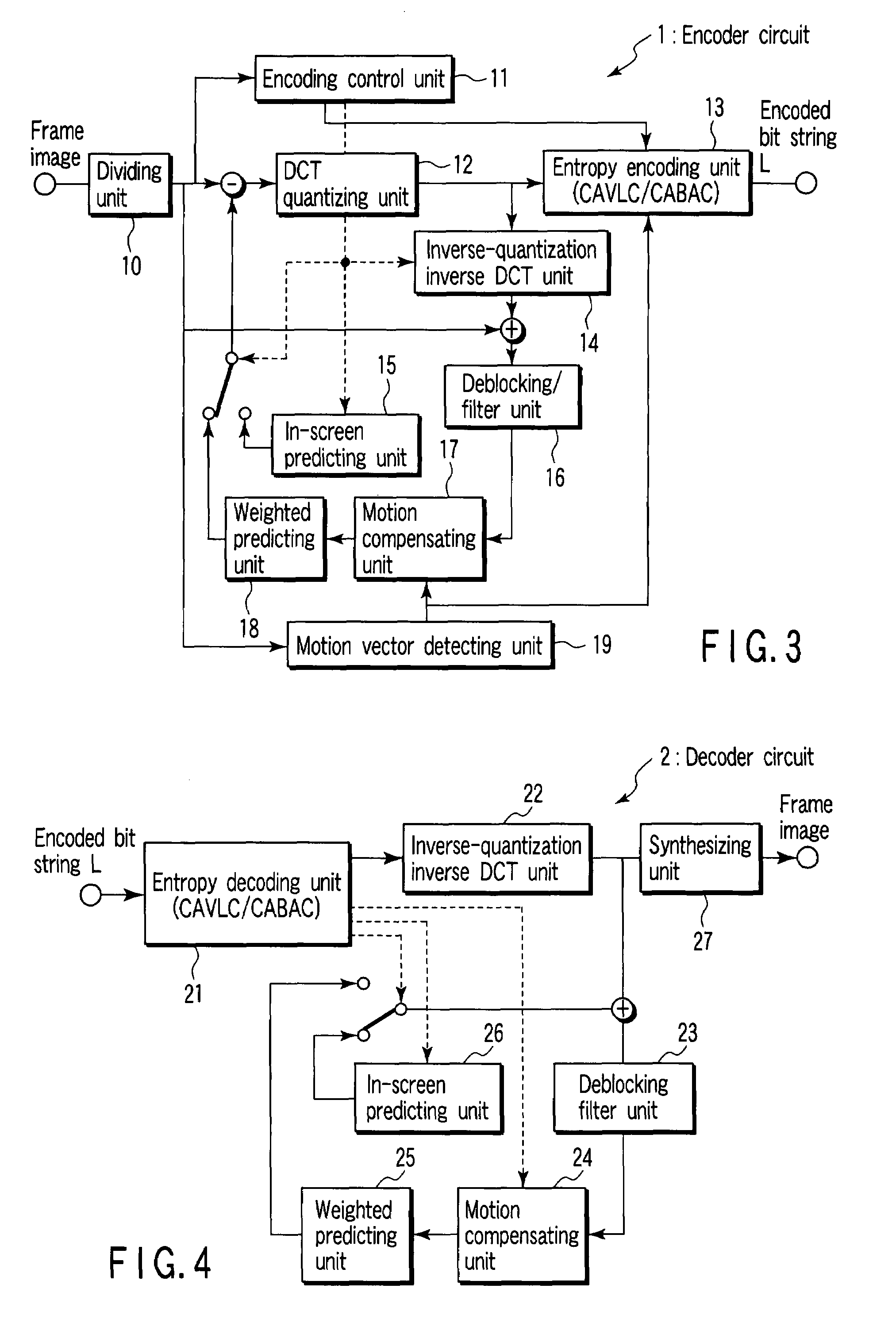
Encoding circuit, decoding circuit, encoder circuit, decoder circuit, and CABAC processing method
InactiveUS20080001796A1Code conversionDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionArithmetic coding
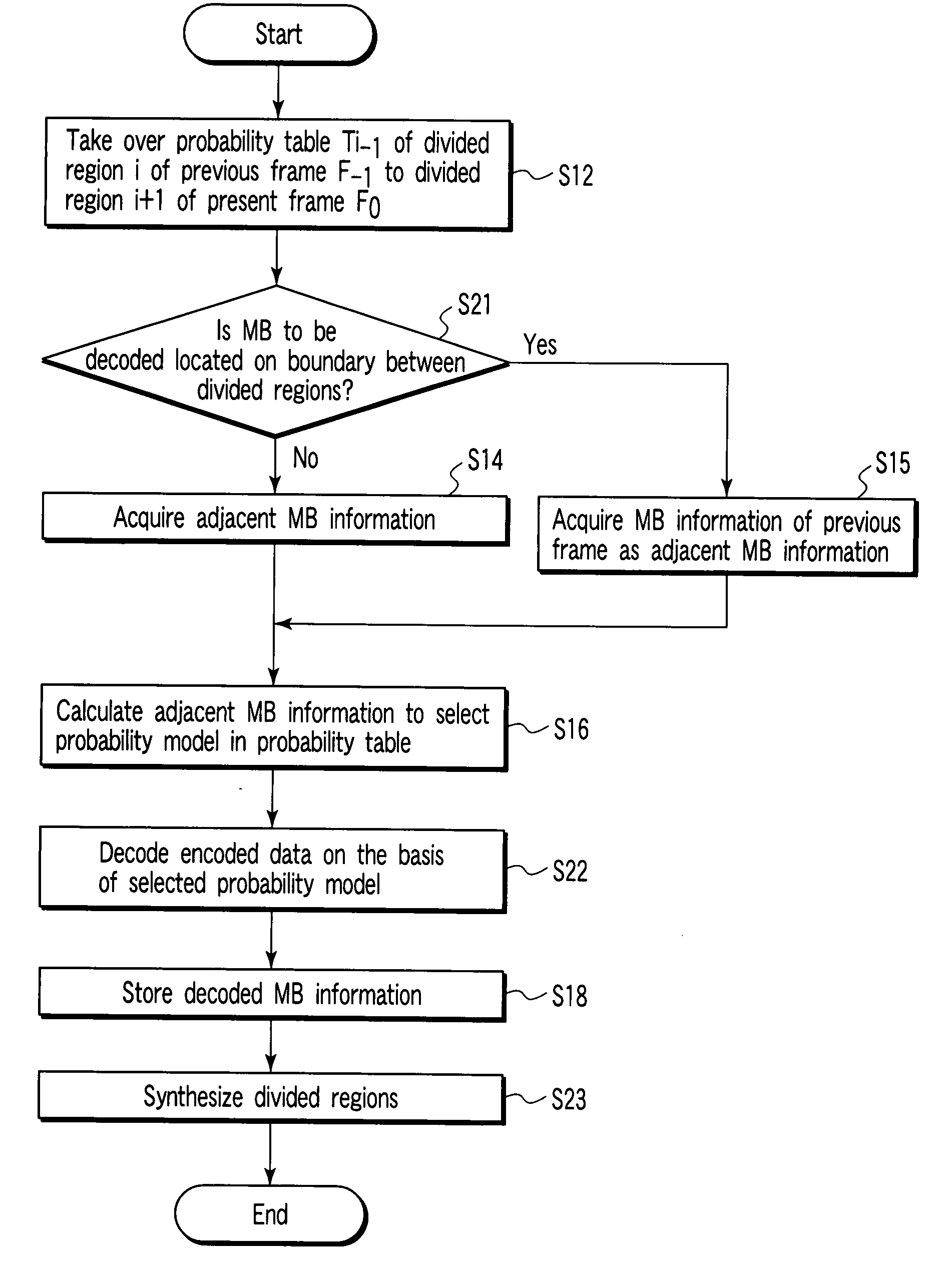
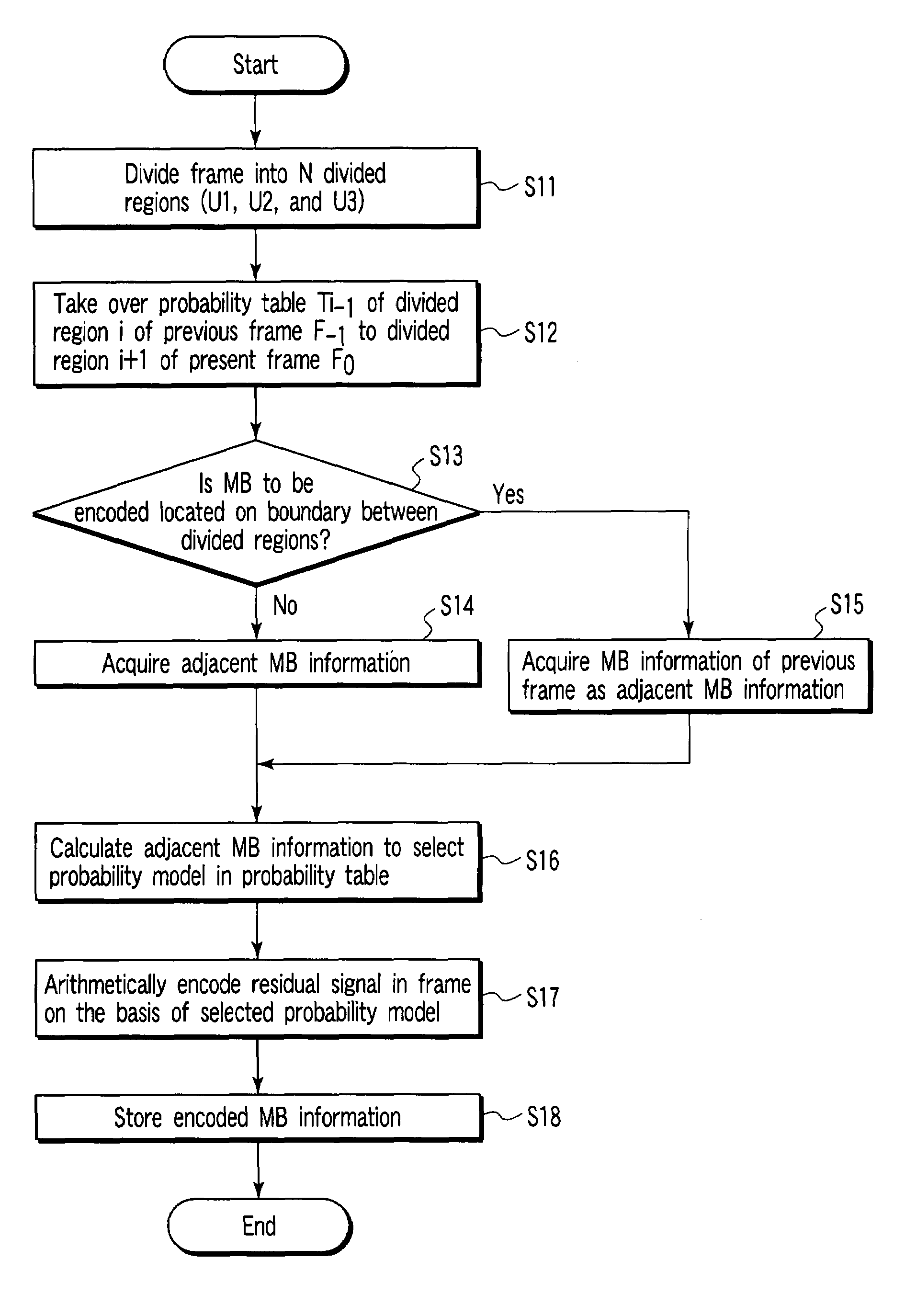
According to one embodiment, an encoding circuit includes a taking-over unit which takes over probability tables of divided regions of a previous frame image of a frame image having divided regions to divided regions of a present frame image, respectively, an acquiring unit which acquires a parameter of an adjacent macro block of the previous frame image when the macro block is located on a boundary between the divided regions, a selecting unit which calculates the parameter of the macro block to select one of probability models in the probability table, and an encoding unit which arithmetically encodes a residual signal in the frame image on the basis of the selected probability model to generate an encoded bit string.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Standard-model generation for speech recognition using a reference model
ActiveUS7603276B2Easy to createHigh practical valueSpeech recognitionReference modelHide markov model
A standard model creating apparatus which provides a high-precision standard model used for pattern recognition such as speech recognition, character recognition, or image recognition using a probability model based on a hidden Markov model, Bayesian theory, or linear discrimination analysis; intention interpretation using a probability model such as a Bayesian net; data-mining performed using a probability model; and so forth. The standard model creating apparatus includes a reference model preparing unit that prepares at least one reference model; a reference model storing unit that stores the reference model prepared by the reference model preparing unit; and a standard model creating unit that creates a standard model by calculating statistics of the standard model so as to maximize or locally maximize the probability or likelihood with respect to the reference model stored in the reference storing unit.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
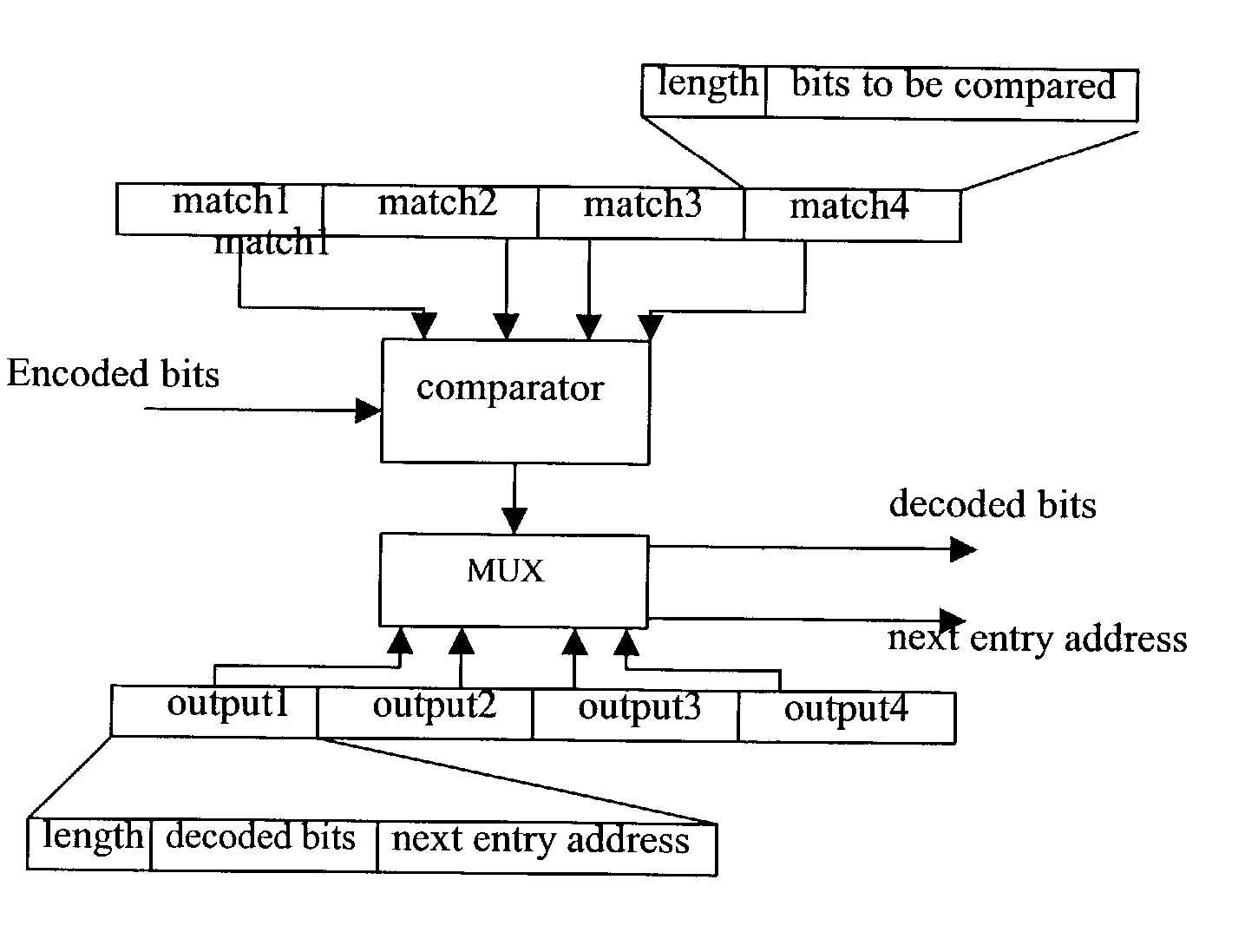
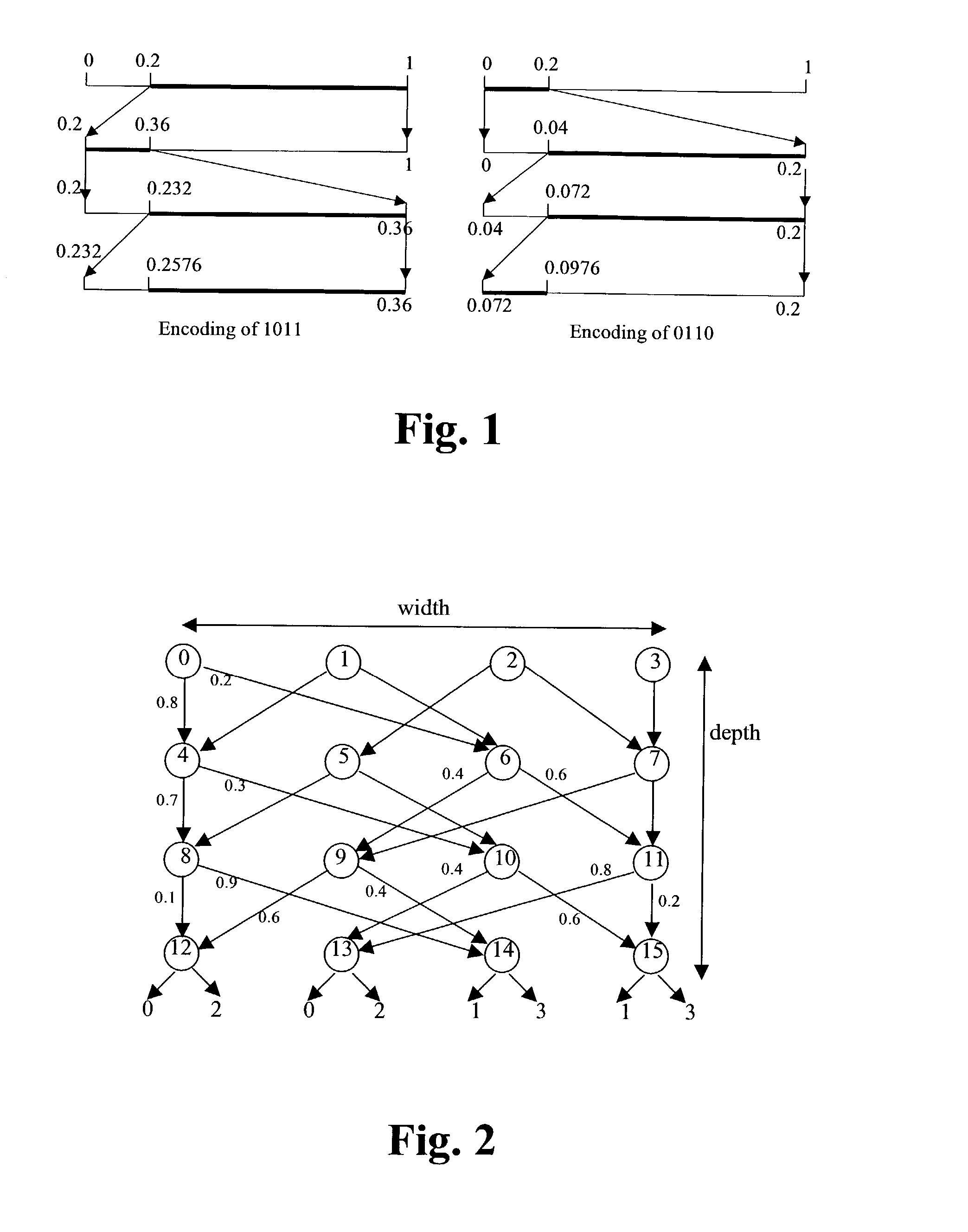
Code compression algorithms and architectures for embedded systems
InactiveUS7095343B2Increase the compression ratioSimple designCode conversionProbit modelAdaptive coding
Code compression techniques and decompression architectures for embedded systems are disclosed, providing good compression ratio while improving decompression time for VLIW instructions and reducing bus power consumption. The invention includes two fixed-to-variable (F2V) length code compression schemes based on a reduced arithmetic code compression algorithm combining arithmetic coding with probability models; a static probability model using static coding and semi-adaptive coding using a Markov model. Multi-bit decompression methods for the F2V techniques are presented, together with a parallel decompression scheme that tags and divides a compressed block into smaller sub-blocks. The Markov model provides better compression ratio, but the static model has a less complicated decompression unit design. The invention also includes two variable-to-fixed (V2F) length coding algorithms, one based on Tunstall coding and another on arithmetic coding. The V2F algorithms are also combined with a static model and a Markov model.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Probability model selection using information-theoretic optimization criterion
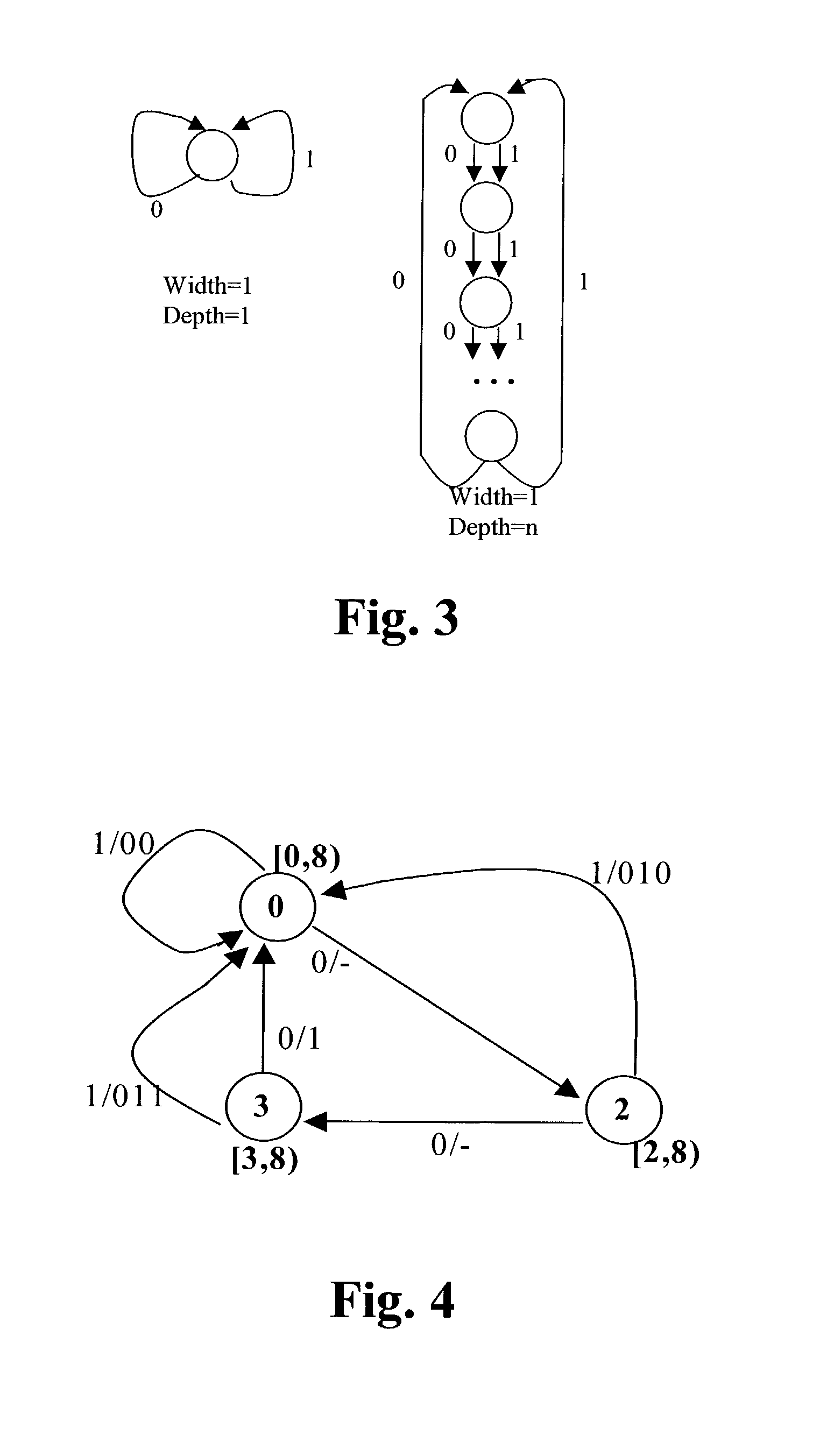
InactiveUS20020111780A1Computation using non-denominational number representationResourcesProbit modelNull vector
Owner:SY BON K
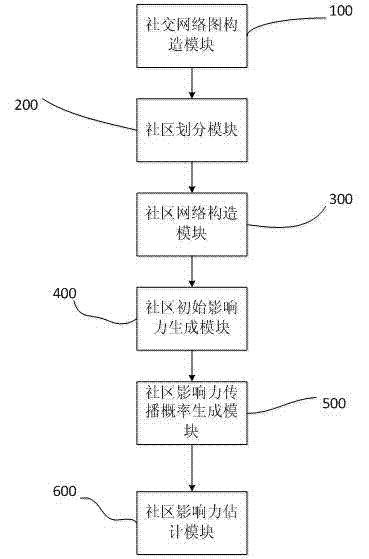
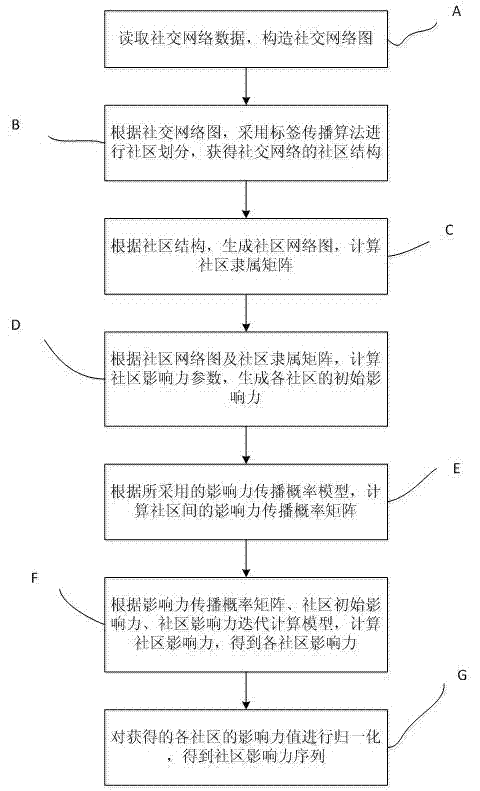
Evaluating system and method for community influence in social network
InactiveCN103678669AReasonable assessmentData processing applicationsWebsite content managementSocial graphComputational model
The invention relates to an evaluating system and method for community influence in a social network. The method comprises the steps that a social network chart with social network users as nodes and user relationships as sides is built; according to the social network chart, the community structure of the social network is obtained by carrying out community division through the label propagation algorithm; according to the social network chart and matrixes which communities belong to, the parameter of the community influence is calculated, and the initial influence of each community is generated; according to the transmission probability model of the influence, an influence transmission probability matrix is generated; according to the influence transmission probability matrix and the community influence iterative computation model, the community influence is iterated and upgraded until the iteration end condition is met, the influence value of each community is obtained, and the sequence of the community influence, namely, the influence estimation result of each community in the social network is obtained after normalization. The system and method can effectively analyze the distribution of the community influence in the social network and can be used for high-influence community mining, thereby being capable of being applied to the fields of network marketing and the like.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Segmentation method for image with deep image information
ActiveCN102903110AReduced execution timeImprove Segmentation AccuracyImage analysisImage segmentation algorithmEnergy functional
The invention discloses a segmentation method for an image with deep image information, which is high in segmentation accuracy, and capable of still achieving a good segmentation effect under the condition of a very similar front background. The segmentation method comprises the steps of: (1) obtaining the image with deep image information via Kinect; (2) performing probability modelling on the colour information of the front background and the deep image information; (3) performing parameter estimation on the model by EM (Expectation-Maximization) algorithm; and (4) performing segmentation after the first image segmentation on the image by adopting an image segmentation algorithm, wherein an energy function is formula shown in the abstract, and according to the energy function, the smallest segmentation is evaluated by a maximum flow algorithm, so as to obtain the final segmentation object.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
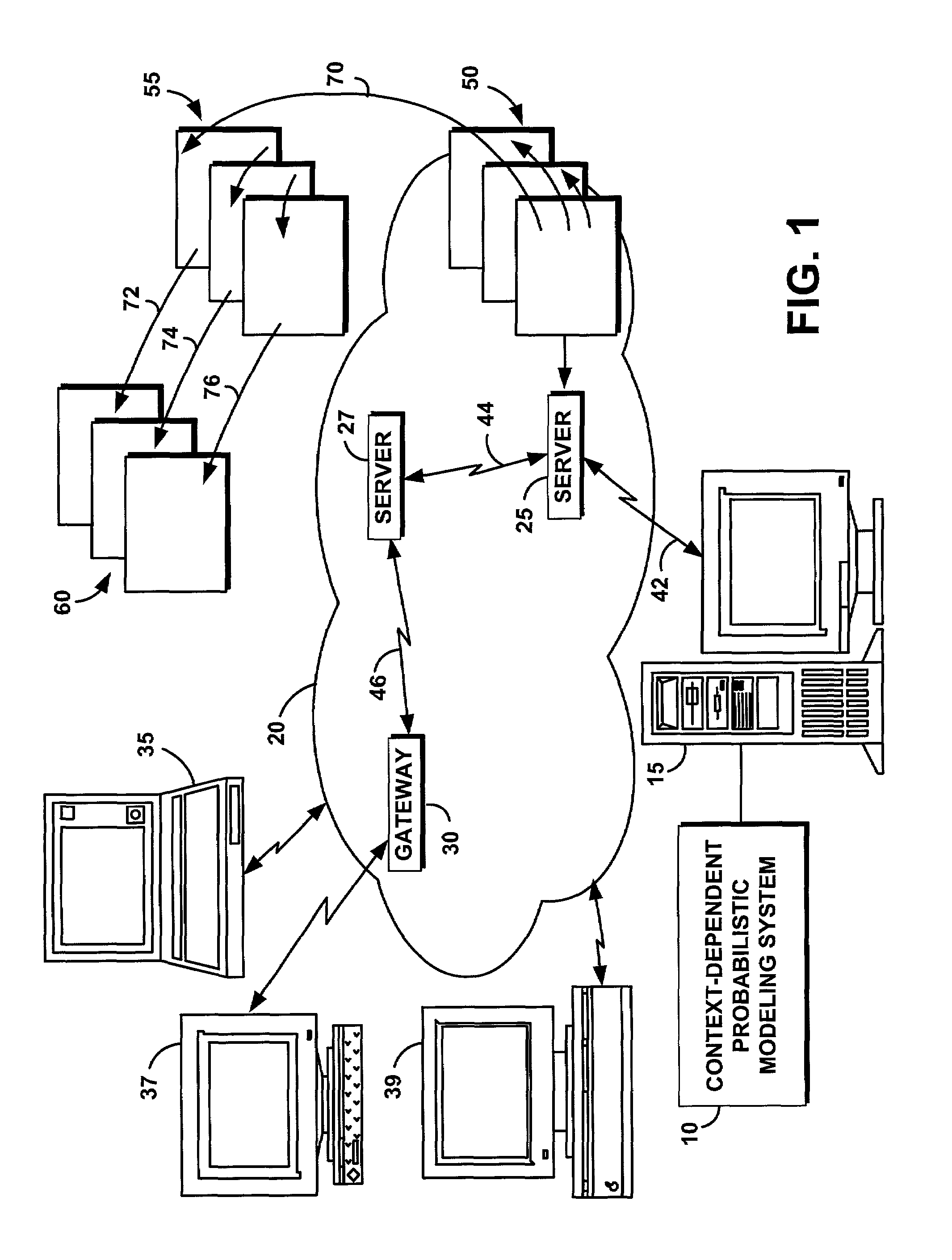
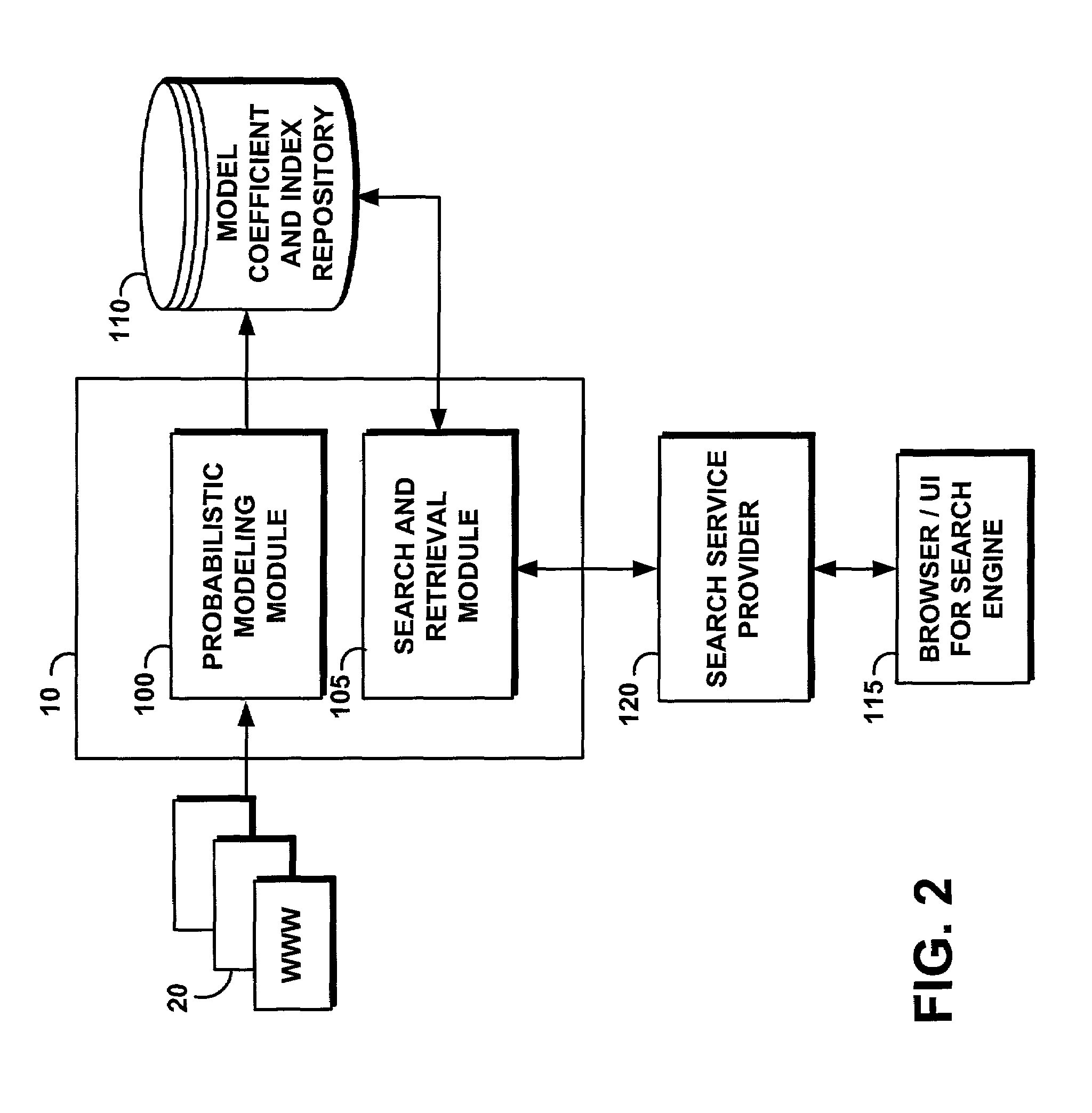
System and method for context-dependent probabilistic modeling of words and documents
InactiveUS6925433B2Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalText entryDocument preparation
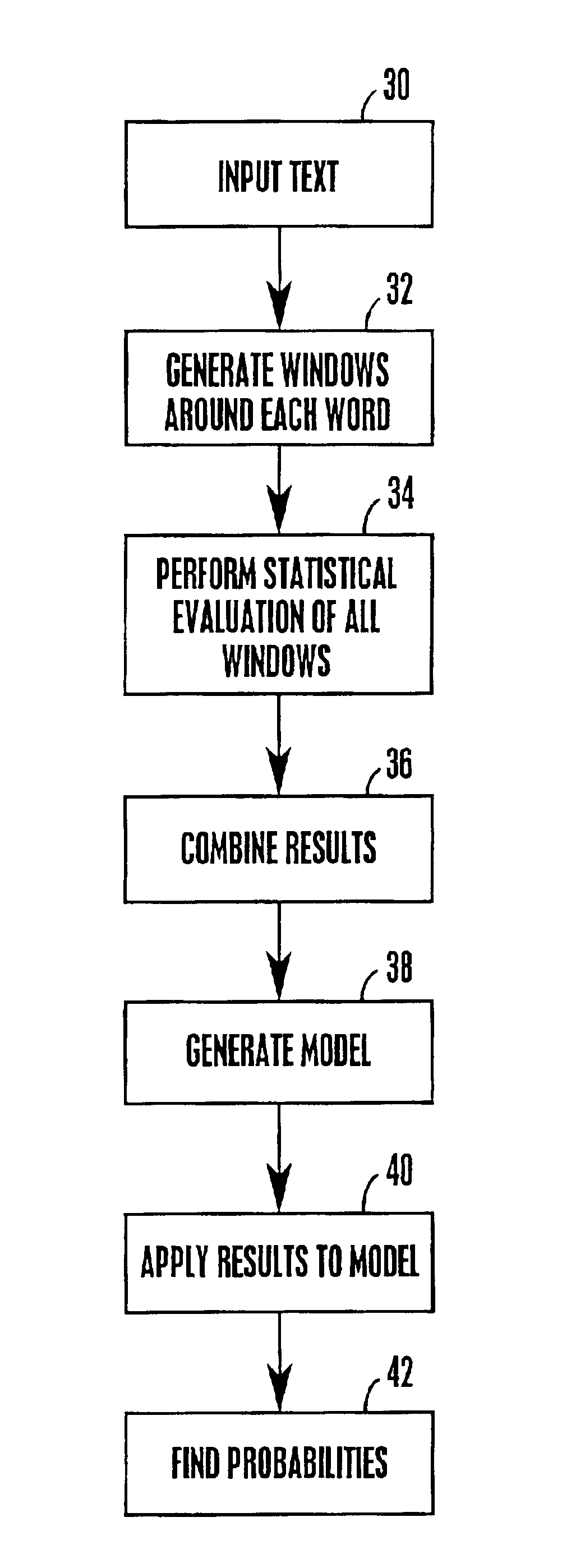
A computer-implemented system and method is disclosed for retrieving documents using context-dependant probabilistic modeling of words and documents. The present invention uses multiple overlapping vectors to represent each document. Each vector is centered on each of the words in the document, and consists of the local environment, i.e., the words that occur close to this word. The vectors are used to build probability models that are used for predictions. In one aspect of the invention a method of context-dependant probabilistic modeling of documents is provided wherein the text of one or more documents are input into the system, each document including human readable words. Context windows are then created around each word in each document. A statistical evaluation of the characteristics of each window is then generated, where the results of the statistical evaluation are not a function of the order of the appearance of words within each window. The statistical evaluation includes the counting of the occurrences of particular words and particular documents and the tabulation of the totals of the counts. The results of the statistical evaluation for each window are then combined. These results are then used for retrieving a document, for extracting features from a document, or for finding a word within a document based on its resulting statistics.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
Personalized recommendation method and system based on probability model and user behavior analysis
InactiveCN105574216AAccurately characterize acquisition needsSolve overloadSpecial data processing applicationsPersonalizationOriginal data
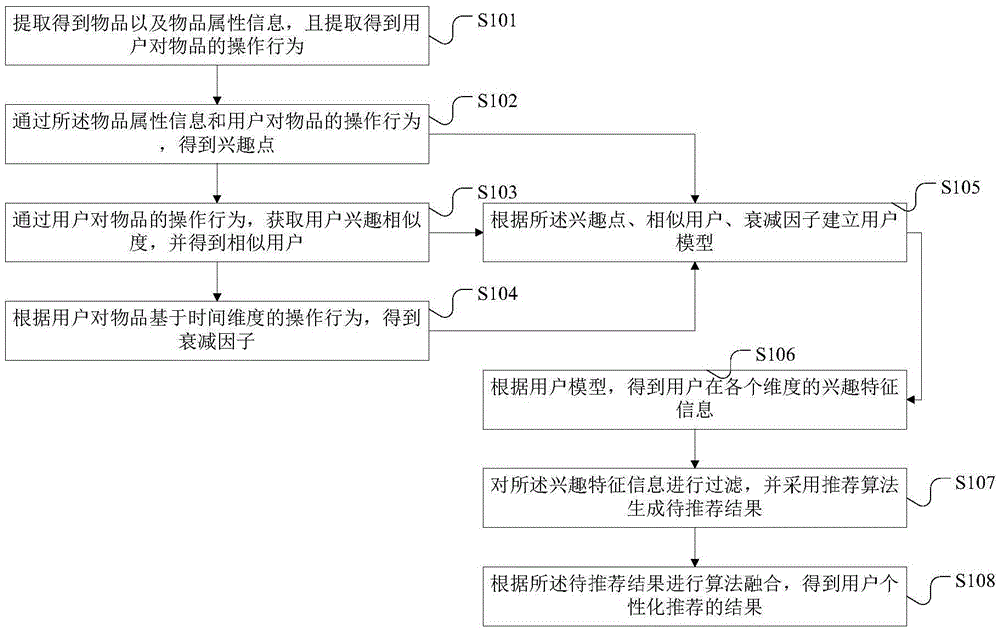
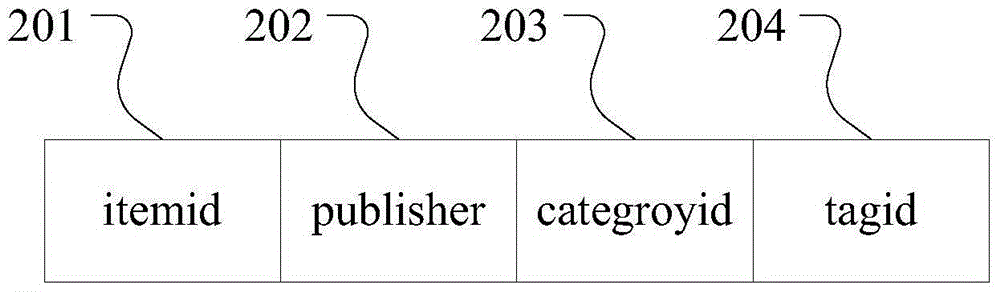
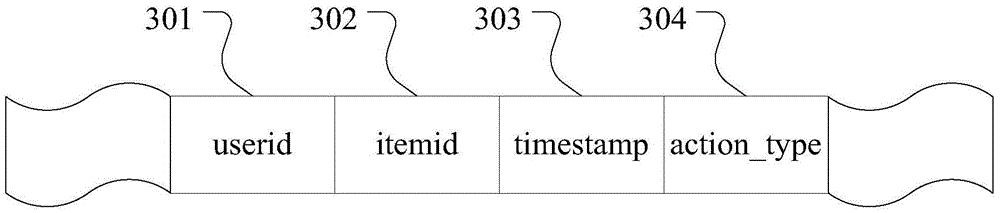
The invention discloses a personalized recommendation method and system based on a probability model and user behavior analysis. The method includes the steps that article information and article attribute information are extracted, and operation behaviors of users on articles are extracted; interest points are obtained according to the article attribute information and the operation behaviors of the users on the articles; user interest similarity is obtained according to the operation behaviors of the users on the articles, and similar users are obtained; a decay factor is obtained according to the operation behaviors of the users on the articles based on the time dimension, and a user model is set up; interest characteristic information, at all dimensions, of the users is obtained according to the user model; after filtering, a recommendation algorithm is adopted to generate results to be recommended, and algorithm fusion is conducted to obtain personalized recommendation results of the users. After original data is preprocessed, the user model is set up, the interest points of the users and essential information acquisition requirements are depicted accurately to provide accurate personalized recommendation, and therefore the problems of information overload and long-tail articles in the network are solved.
Owner:DATAGRAND TECH INC
Arithmetic unit used for context arithmetic encoding and decoding
InactiveCN102231830AReduce consumptionFast decodingTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationRandom access memoryControl data
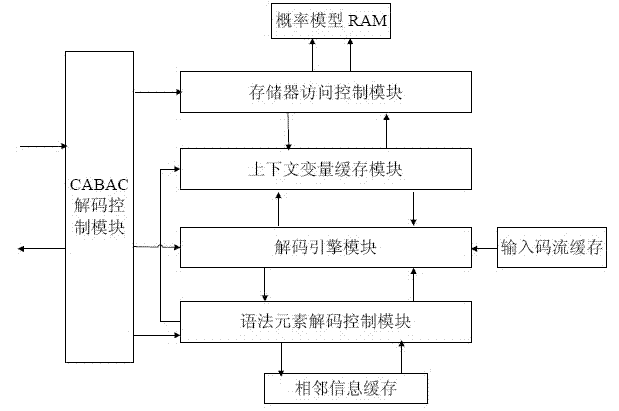
The invention discloses an arithmetic unit used for context arithmetic encoding and decoding. The arithmetic unit comprises a context-based adaptive binary arithmetic coding (CABAC) decoding control module for controlling overall CABAC decoding, a syntactic element decoding control module for controlling the decoding of various syntactic elements, a probability model cache module for caching a probability model required by current decoding, a memory access control module for controlling access to a random access memory (RAM), controlling data interaction between the RAM and the probability model cache module, , saving the data in the probability model cache module and updating the data in the probability model cache module when the probability model cache model contains no probability model required by current decoding, and a decoding engine module for performing arithmetic decoding and calculating bit number that is read in from a code stream in one bin decoding process. The arithmetic unit provided by the invention has high decoding speed, and the consumption of the memory is reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
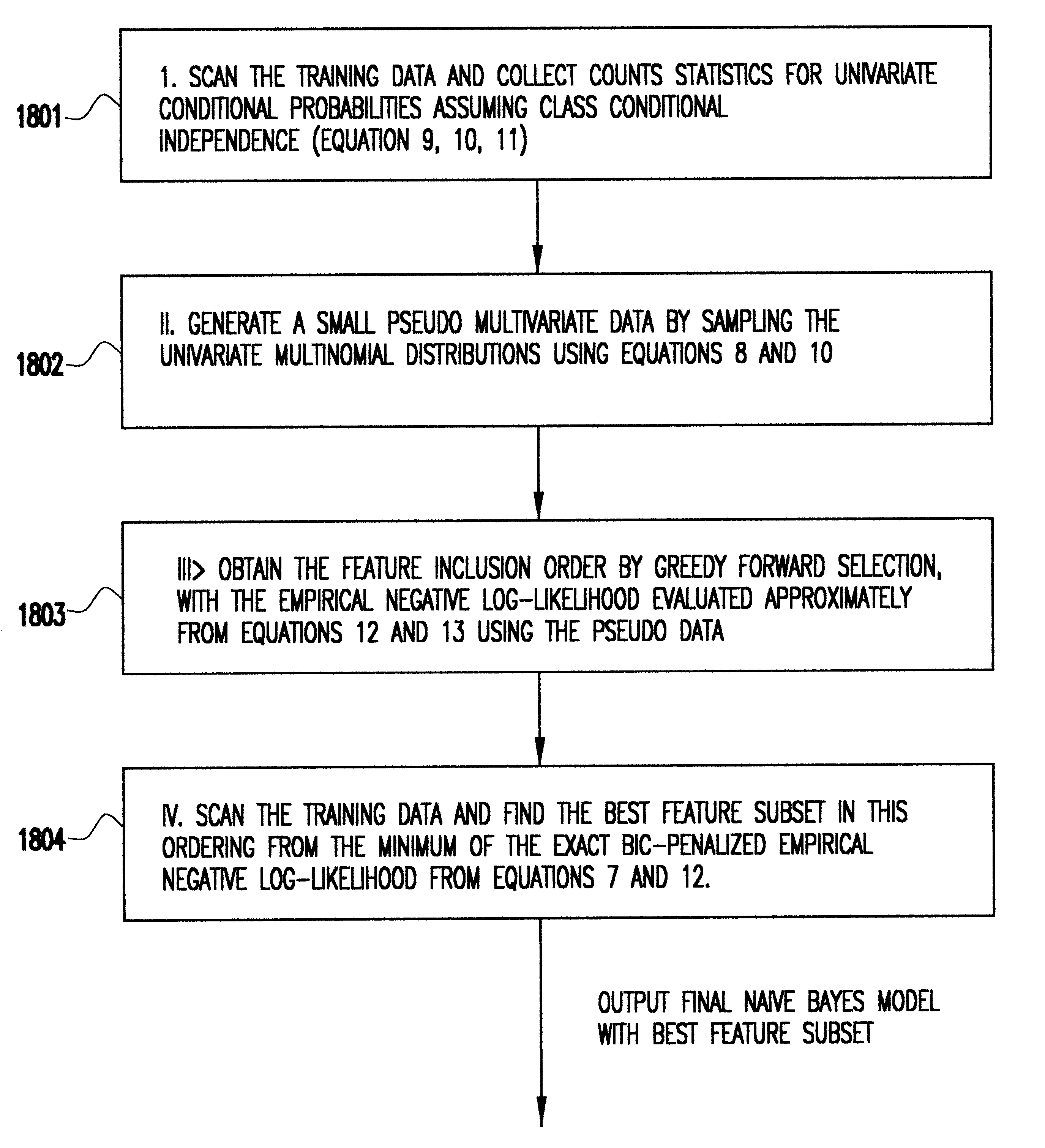
Using simulated pseudo data to speed up statistical predictive modeling from massive data sets
The computational cost of many statistical modeling algorithms is affected by the input / output (I / O) cost of accessing out-of-core training data. This is an important challenge for emerging data mining applications, where the amount of training data can be potentially enormous. A heuristic approach to this problem is described. This approach is based on constructing a simple probability model from the large training data set, and using this model to generate simulated pseudo data for some aspects of the statistical modeling procedure. This approach is illustrated in the context of building a Naive Bayes probability model with feature selection. Here, the usual algorithms would require numerous data scans over the massive training data set, but our heuristic obtains models of comparable accuracy with just two data scans.
Owner:IBM CORP
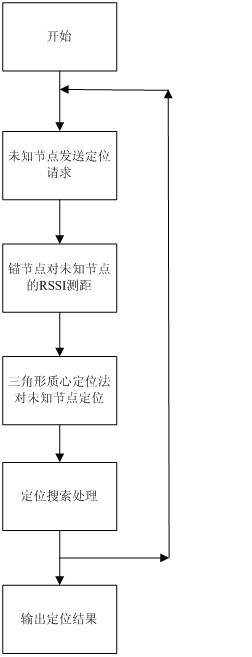
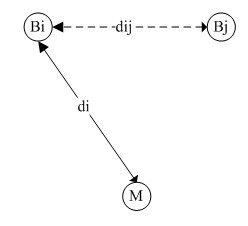
Wireless sensor network node positioning method based on received signal strength indicator (RSSI)
InactiveCN102209382AImprove ranging accuracyHigh positioning accuracyNetwork topologiesTransmission monitoringSmall probabilityModel selection
The invention relates to a wireless sensor network node positioning method based on a received signal strength indicator (RSSI). The precision of the traditional method is not high, and the traditional method is easily disturbed by environment. In the method, an effective RSSI value is selected by using a Gaussian distribution function model in the aspect of reading RSSI value, so that small probability events during RSSI measurement are removed to a certain extent, and the precision of RSSI value between nodes is improved; and the coordinates of an unknown node are obtained by a triangular positioning method, and the unknown node is circularly refined via the distribution probability model of the unknown node, so that a point with the maximum distribution probability is found and is used as the final positioning coordinate. In the method, the signal intensity and distance information between anchor nodes are introduced and are used as the reference; the unknown node coordinate is found out via the distribution probability model of the unknown node; the distance measurement precision and the positioning precision between the unknown node and the anchor node are improved; and the method is not easily disturbed by environment.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Object Recognizer and Detector for Two-Dimensional Images Using Bayesian Network Based Classifier
A system and method for determining a classifier to discriminate between two classes—object or non-object. The classifier may be used by an object detection program to detect presence of a 3D object in a 2D image (e.g., a photograph or an X-ray image). The overall classifier is constructed of a sequence of classifiers (or “sub-classifiers”), where each such classifier is based on a ratio of two graphical probability models (e.g., Bayesian networks). A discrete-valued variable representation at each node in a Bayesian network by a two-stage process of tree-structured vector quantization is discussed. The overall classifier may be part of an object detector program that is trained to automatically detect many different types of 3D objects (e.g., human faces, airplanes, ears, etc.). Computationally efficient statistical methods to evaluate overall classifiers are disclosed. The Bayesian network-based classifier may also be used to determine if two observations (e.g., two images) belong to the same category. For example, in case of face recognition, the classifier may determine whether two photographs are of the same person. A method to provide lighting correction or adjustment to compensate for differences in various lighting conditions of input images is disclosed as well. As per the rules governing abstracts, the content of this abstract should not be used to construe the claims in this application.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Online-increment evolution topic model based automatic software classifying method
ActiveCN102902700AImplement automatic classificationImprove development efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmWord list
An online-increment evolution topic model based automatic software classifying method includes acquiring relevant software texts, grouping and preprocessing by a preset time slice; generating a probability model of an online evolution topic model, computing the number of the optimum topics according to project description texts grouped according to the time slice, and incrementally computing topic word distribution and topic text distribution of the project description texts within the current time slice; acquiring a text d of an unknown classifying topic, computing topic word distribution of n topics subordinative to the text d according to the topic word distribution and the topic text distribution, classifying the text d into corresponding topics, and automatically adding semantic tags to the topics based on the word list and word inquiry method, and finally completing classification of software projects. By the online-increment evolution topic model based automatic software classifying method, new topics appearing in open source communities can be found in time, software projects can be automatically classified, a software developer can search out required open source software projects according to software topics conveniently, and accordingly, software development efficiency is improved, and quality and assurance of the open source communities are improved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Encoding circuit, decoding circuit, encoder circuit, decoder circuit, and CABAC processing method
InactiveUS7460042B2Code conversionDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionArithmetic coding
According to one embodiment, an encoding circuit includes a taking-over unit which takes over probability tables of divided regions of a previous frame image of a frame image having divided regions to divided regions of a present frame image, respectively, an acquiring unit which acquires a parameter of an adjacent macro block of the previous frame image when the macro block is located on a boundary between the divided regions, a selecting unit which calculates the parameter of the macro block to select one of probability models in the probability table, and an encoding unit which arithmetically encodes a residual signal in the frame image on the basis of the selected probability model to generate an encoded bit string.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
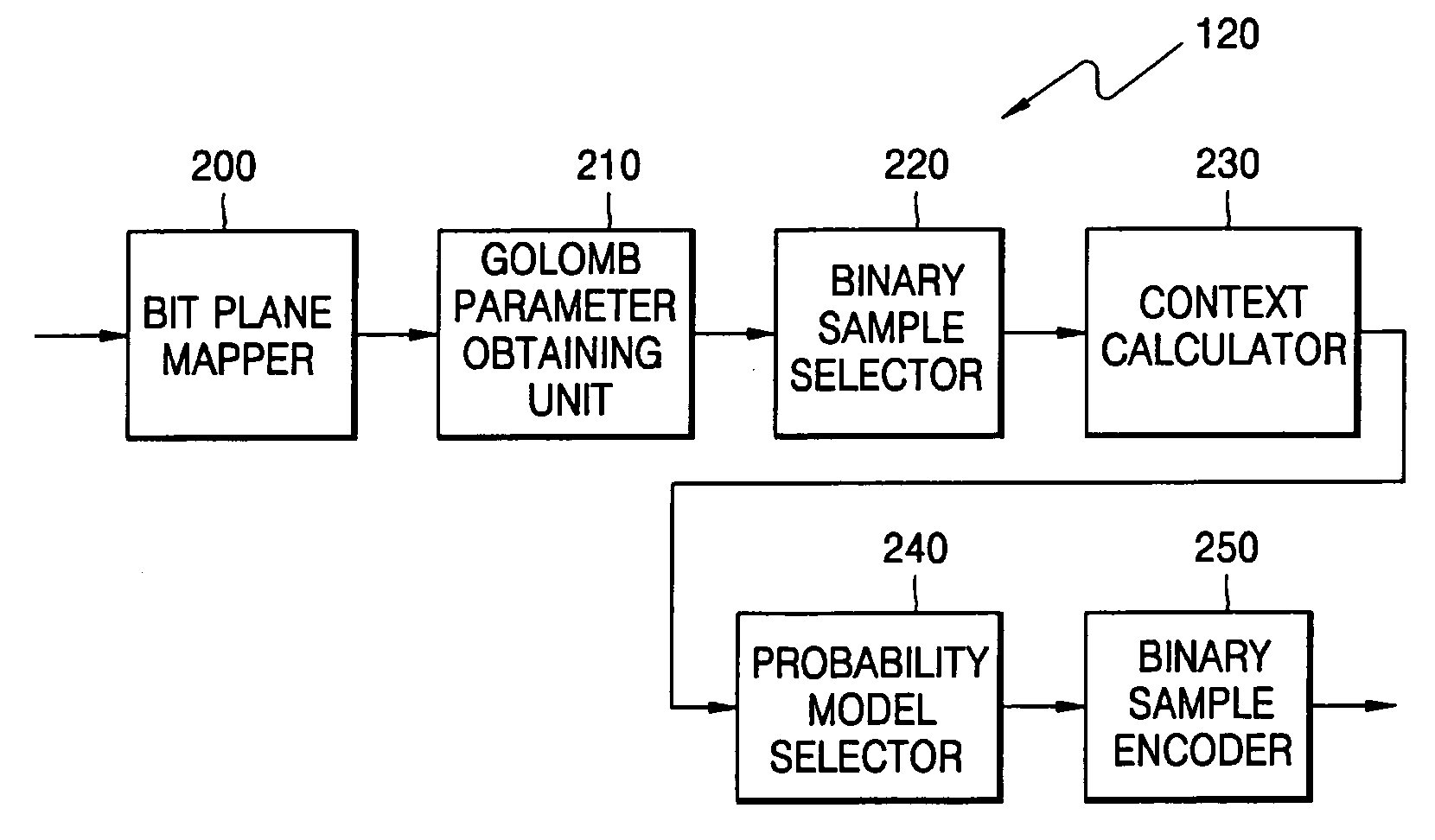
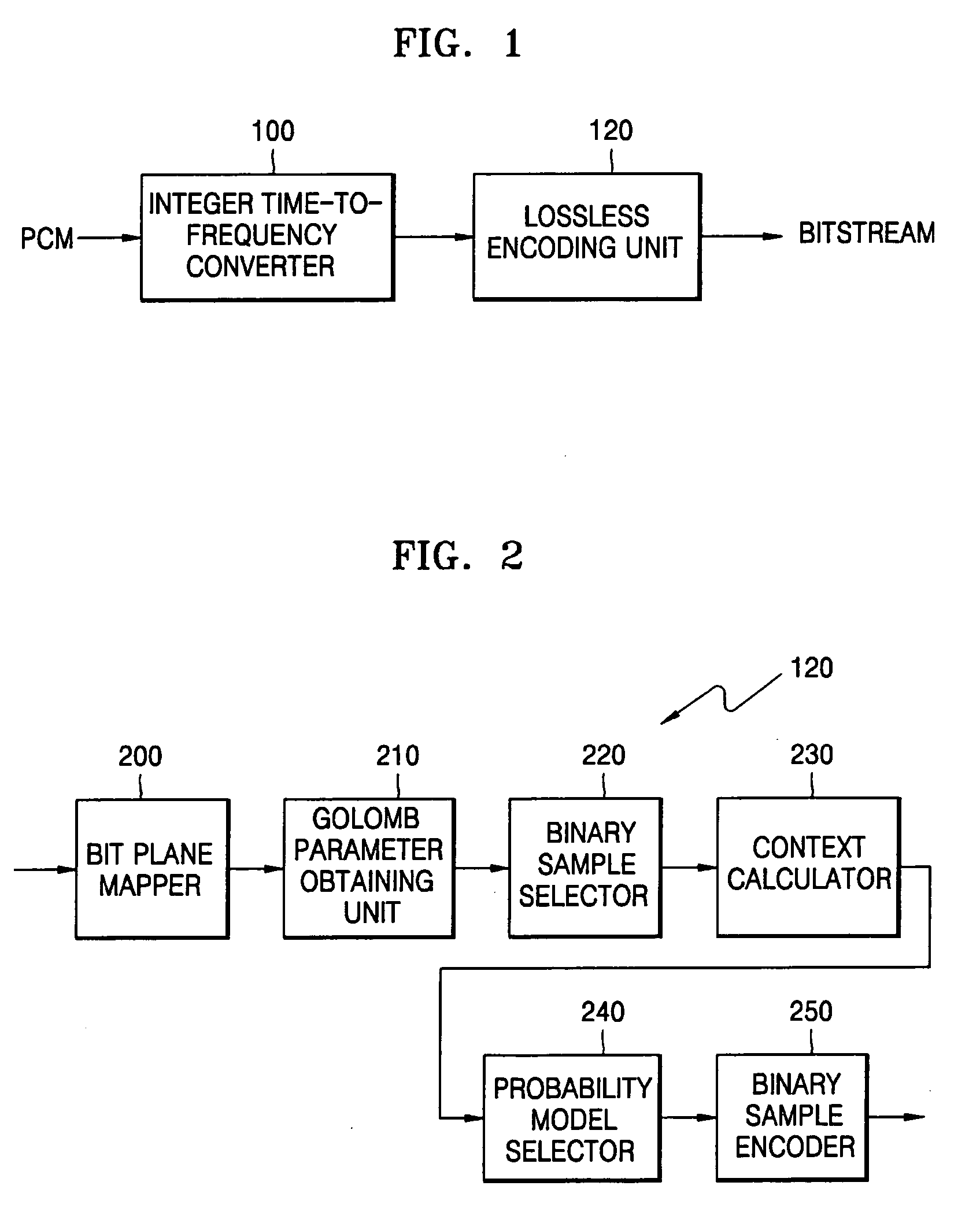
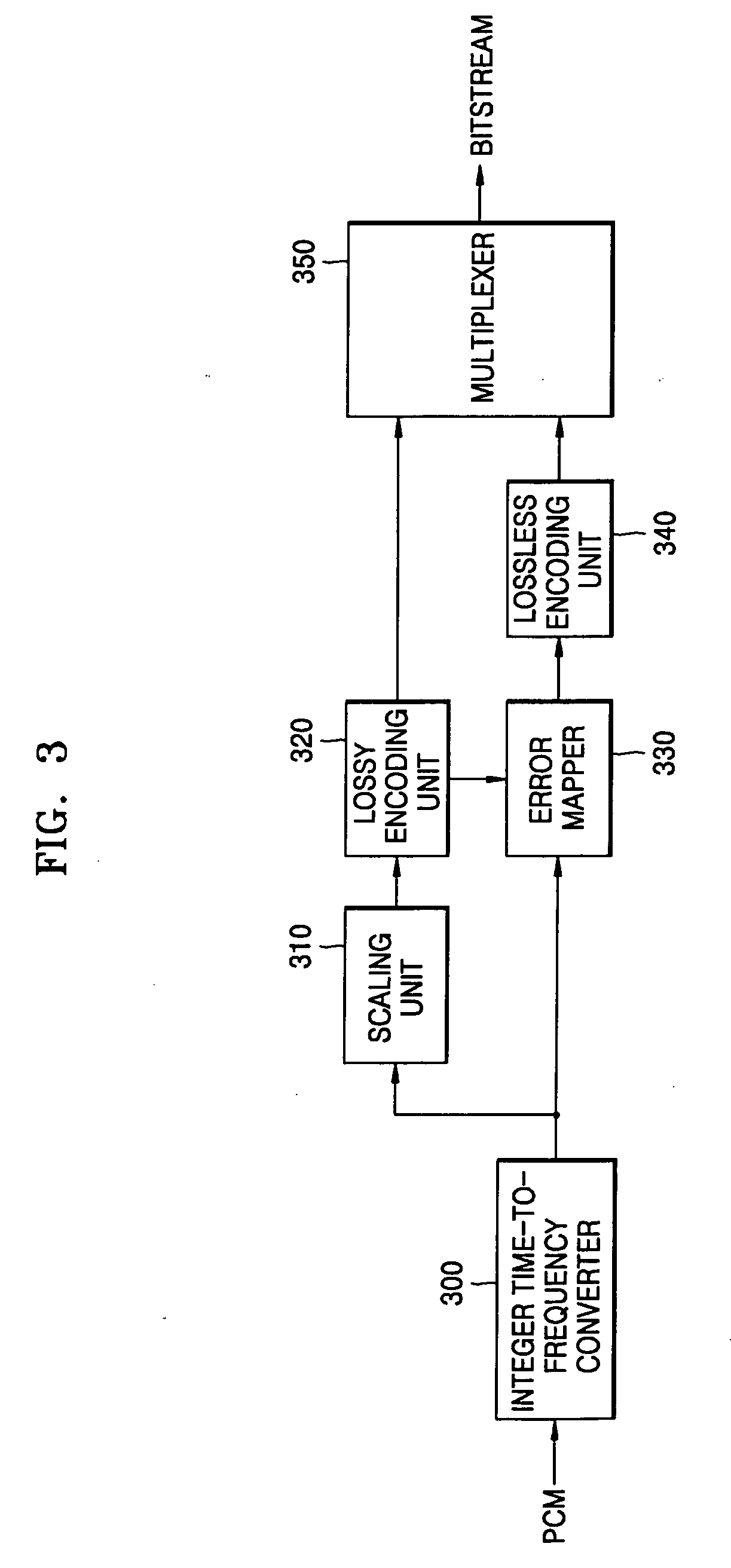
Lossless audio decoding/encoding method, medium, and apparatus
A lossless audio encoding / decoding method, medium, and apparatus. The lossless audio encoding method includes converting an audio signal in a time domain into an audio spectral signal with an integer in a frequency domain, mapping the audio spectral signal in the frequency domain to a bit plane signal according to its frequency, and losslessly encoding binary samples of bit planes using a probability model determined according to a predetermined context. The lossless audio decoding method includes extracting a predetermined lossy bitstream and an error bitstream from error data by demultiplexing an audio bitstream, the error data corresponding to a difference between lossy encoded audio data and an audio spectral signal with an integer in a frequency domain, lossy decoding the extracted encoded lossy bitstream, losslessly decoding the extracted error bitstream, and restoring the original audio frequency spectral signal using the decoded lossy bitstream and error bitstream
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
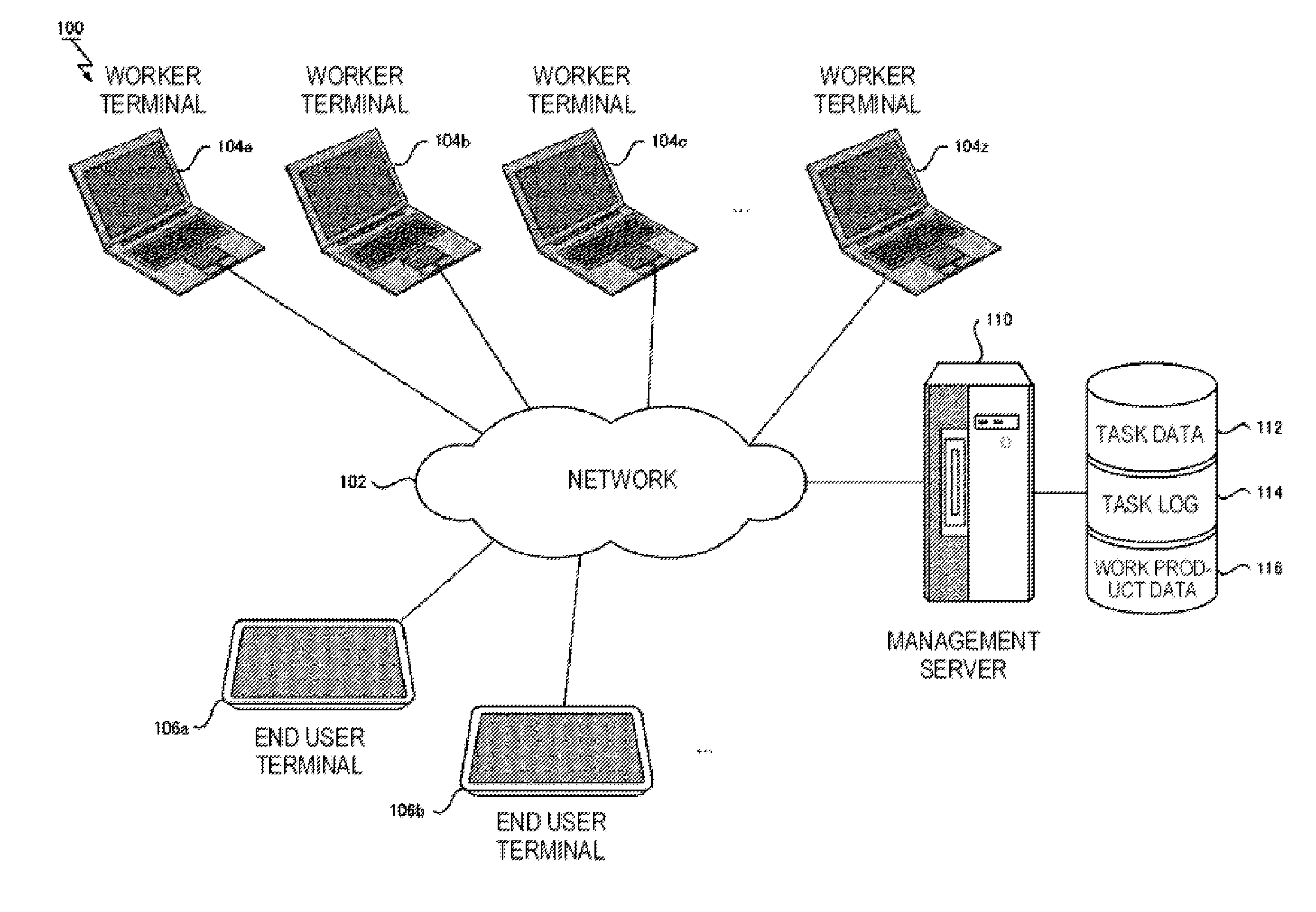
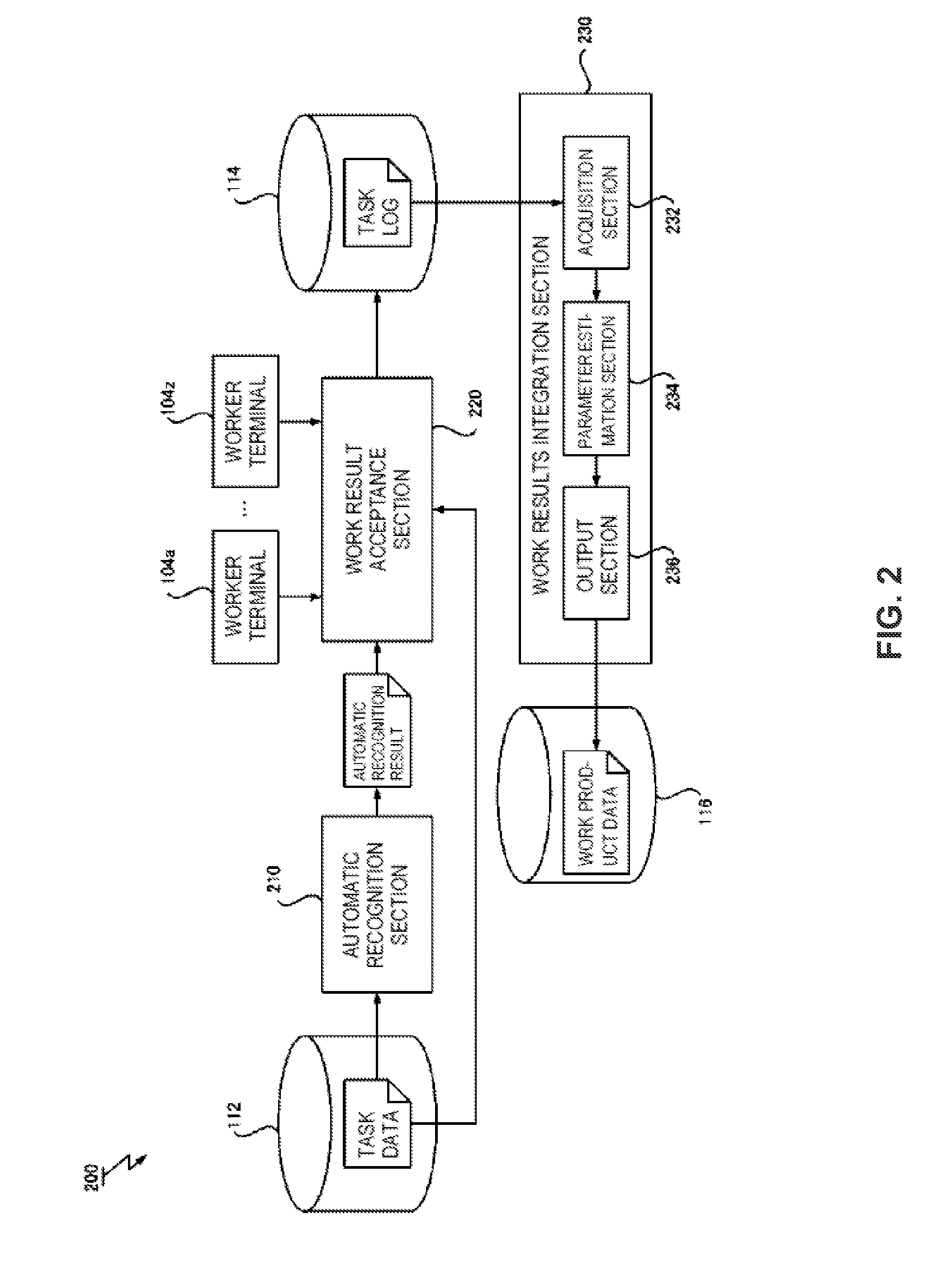
Skill estimation method in machine-human hybrid crowdsourcing
In one embodiment, a computer-implemented method for estimating an ability of a worker in a process for integrating work results of multiple workers for the same task includes acquiring, for each of one or more tasks, a work result of a preceding-stage worker and a work result of a succeeding-stage worker that works based on the work result of the preceding-stage worker. The method also includes estimating multiple parameters of a probability model in which an ability of the succeeding-stage worker conditioned by a quality of the work result of the preceding-stage worker is introduced as a conditioned ability parameter, based on the multiple work results obtained for each of the one or more tasks.
Owner:IBM CORP
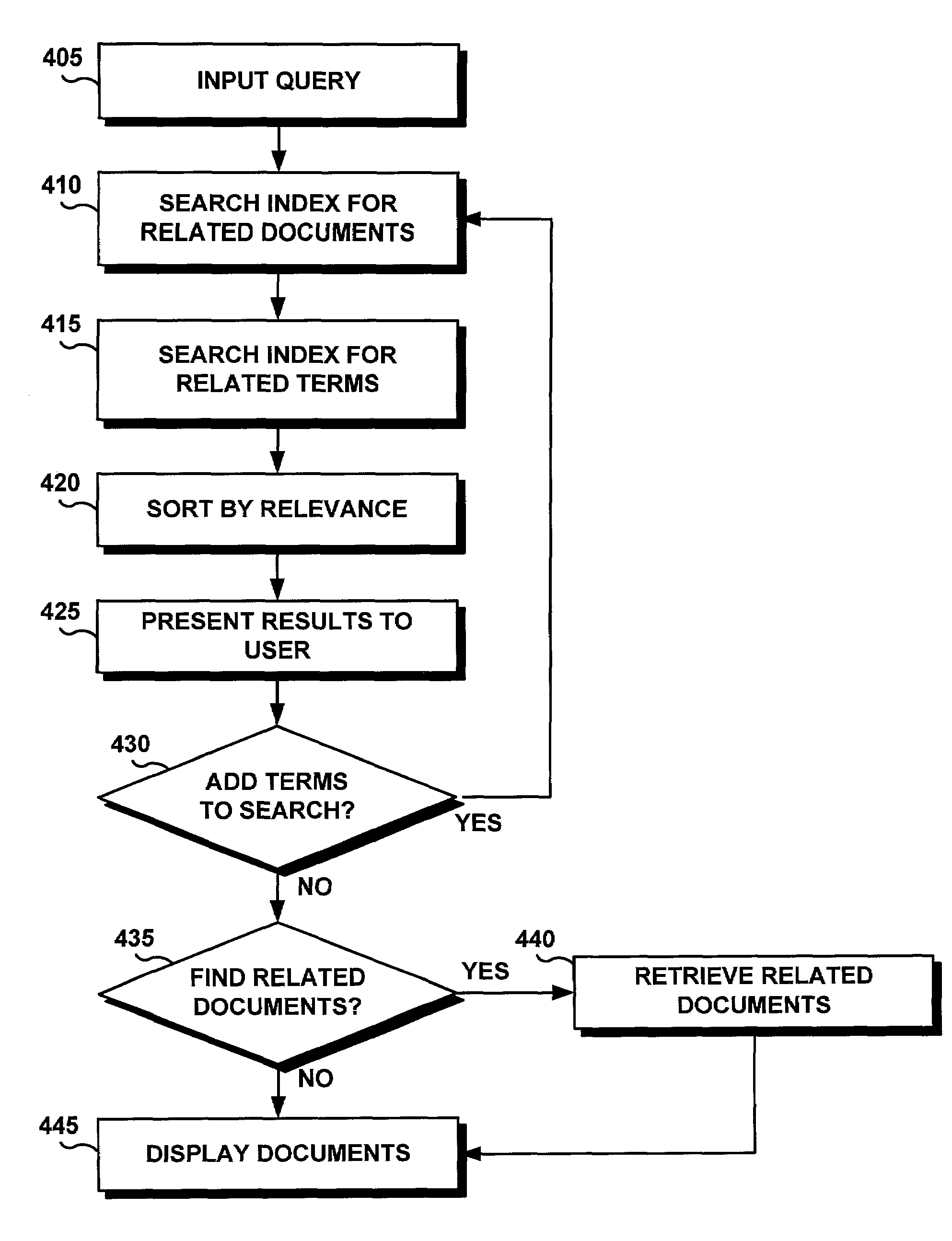
System and method of finding documents related to other documents and of finding related words in response to a query to refine a search
ActiveUS7269546B2Fast wayReduce generationData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalStatistical analysisWord list
A computer-implemented system and method is disclosed for retrieving documents using context-dependant probabilistic modeling of words and documents. The present invention uses multiple overlapping vectors to represent each document. Each vector is centered on each of the words in the document and includes the local environment. The vectors are used to build probability models that are used for predictions of related documents and related keywords. The results of the statistical analysis are used for retrieving an indexed document, for extracting features from a document, or for finding a word within a document. The statistical evaluation is also used to evaluate the probability of relation between the key words appearing in the document and building a vocabulary of key words that are generally found together. The results of the analysis are stored in a repository. Searches of the data repository produce a list of related documents and a list of related terms. The user may select from the list of documents and / or from the list of related terms to refine the search and retrieve those documents which meet the search goal of the user with a minimum of extraneous data.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
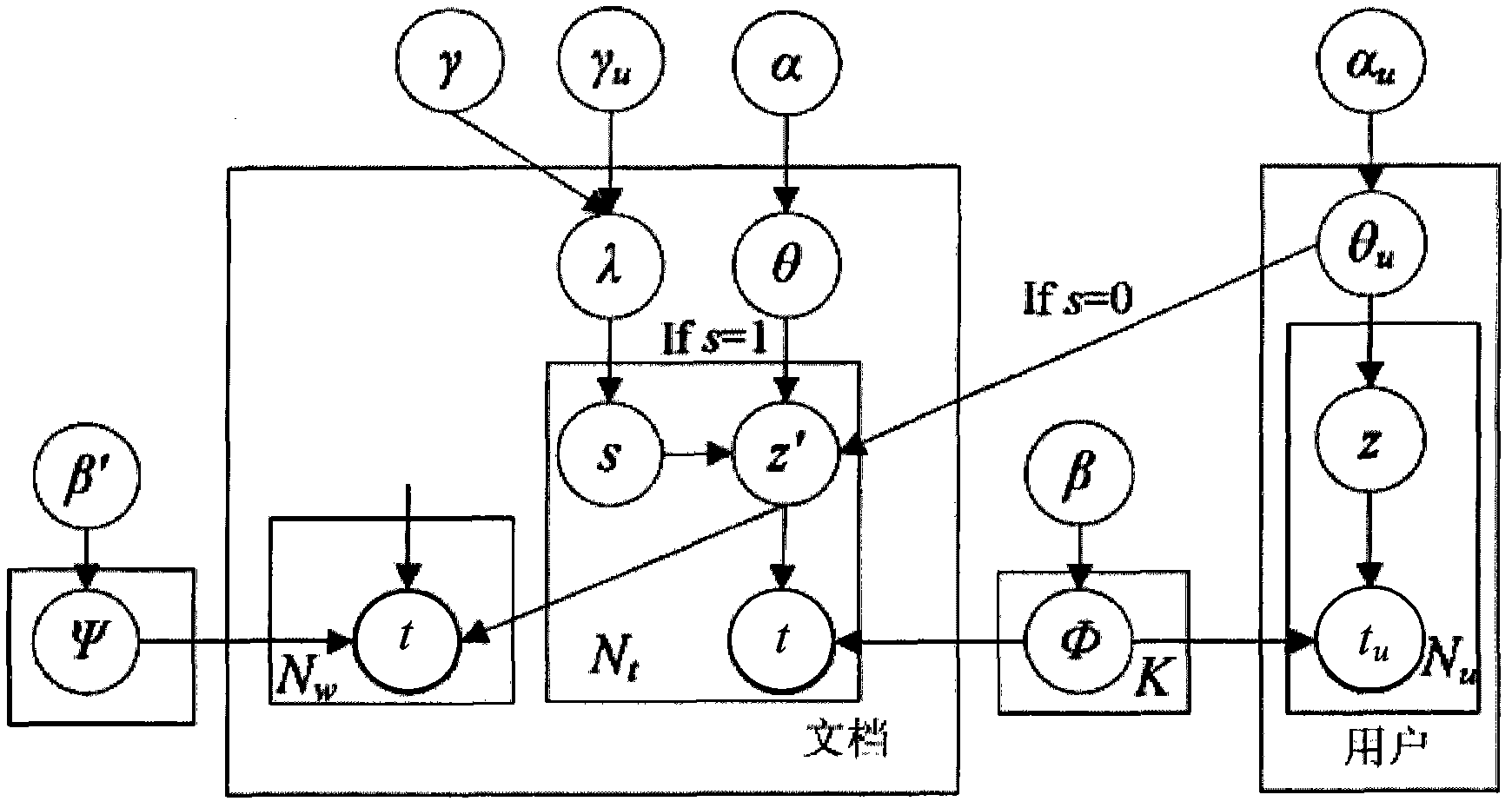
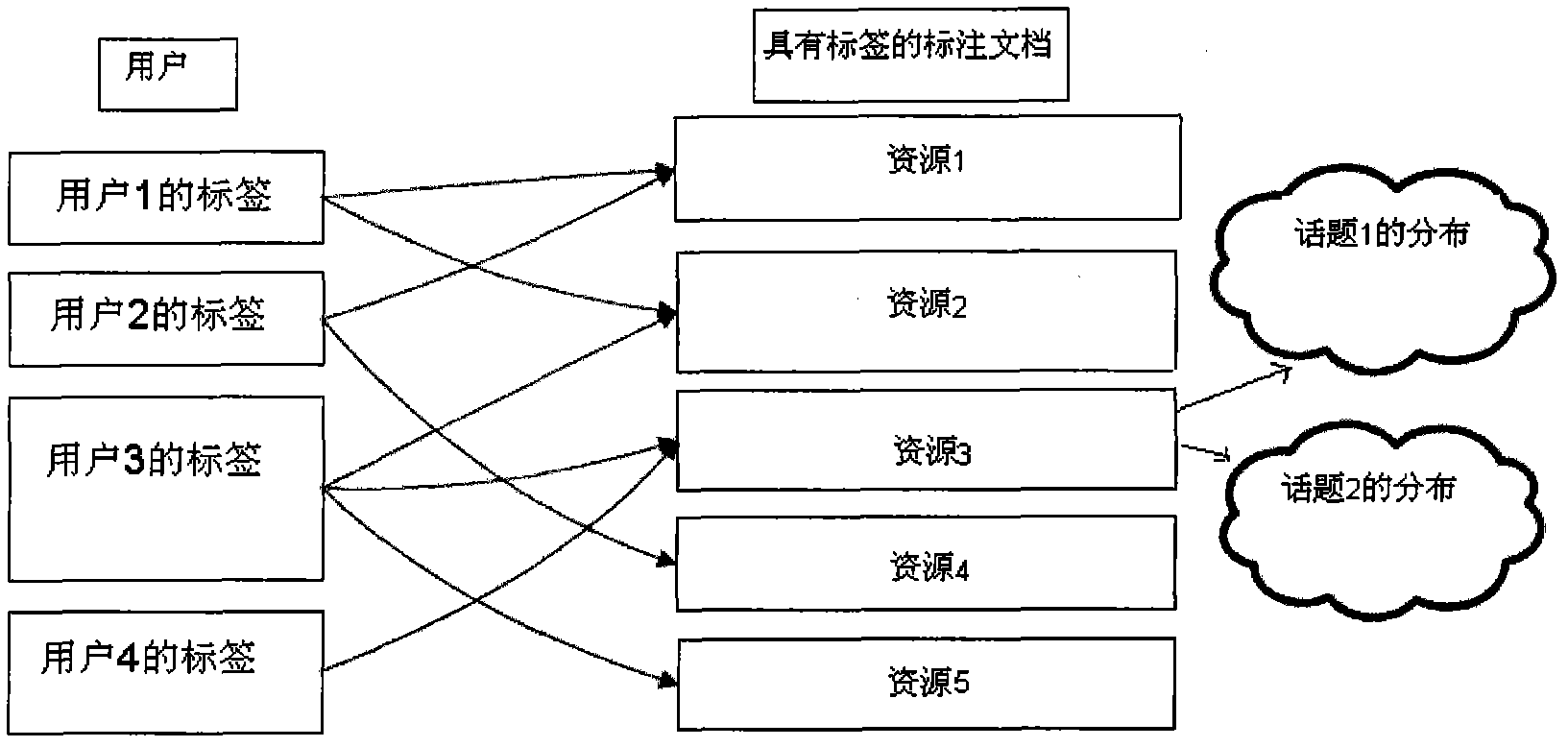
Personalized user tag modeling and recommendation method based on unified probability model
ActiveCN102004774AInterest discoveryImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsPersonalizationTopic model
The invention discloses a personalized user tag modeling and recommendation method based on a unified probability model, comprising the following steps: S1, carrying out statistics on tagging behaviors of users on a social tagging site; S2, carrying out formal definition on questions tagged by the users; S3, establishing a topic model based on user tagging, wherein the topic model is a unified probabilistic model and called a UdT model; S4, establishing a frame of a tag recommendation system based on the UdT model, wherein the frame is recommended through learning the interest of the users and according to semantic information included in the interest; and S5, verifying the frame of the tag recommendation system. Experimental results show that by using the method of the invention, user interest can be effectively explored and the accuracy of tag recommendation can be improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com