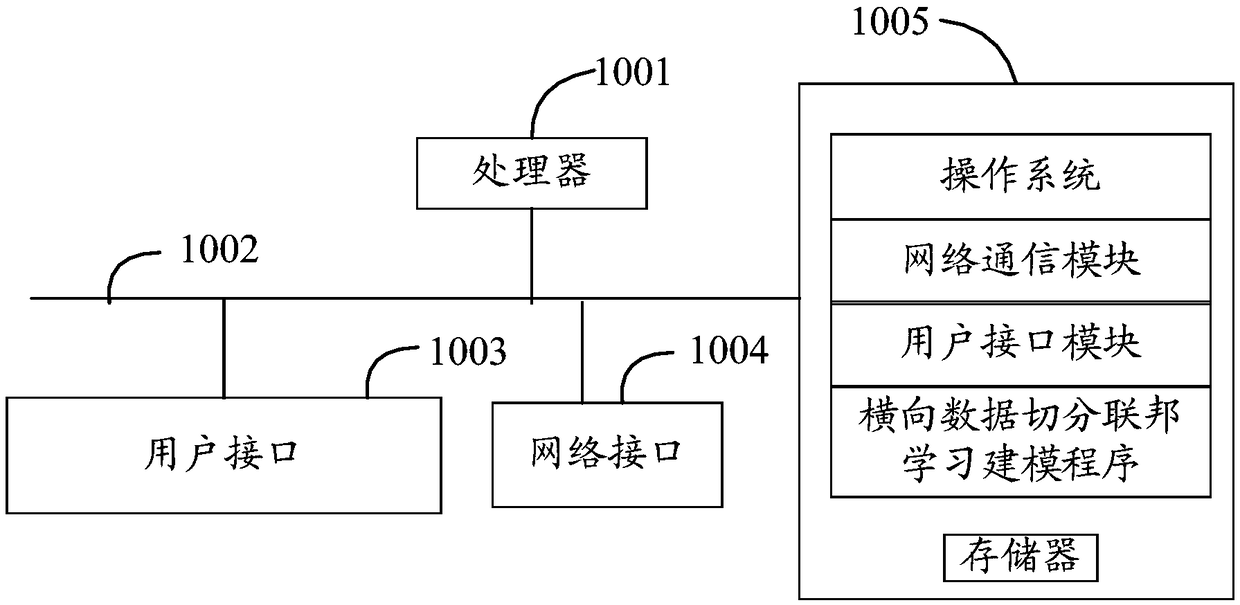
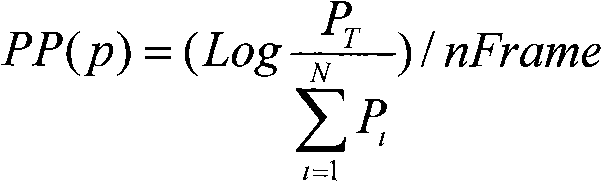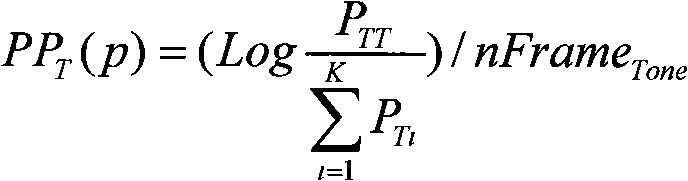Patents
Literature
494 results about "Standard Model" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Standard Model of particle physics is the theory describing three of the four known fundamental forces (the electromagnetic, weak, and strong interactions, and not including the gravitational force) in the universe, as well as classifying all known elementary particles. It was developed in stages throughout the latter half of the 20th century, through the work of many scientists around the world, with the current formulation being finalized in the mid-1970s upon experimental confirmation of the existence of quarks. Since then, confirmation of the top quark (1995), the tau neutrino (2000), and the Higgs boson (2012) have added further credence to the Standard Model. In addition, the Standard Model has predicted various properties of weak neutral currents and the W and Z bosons with great accuracy.
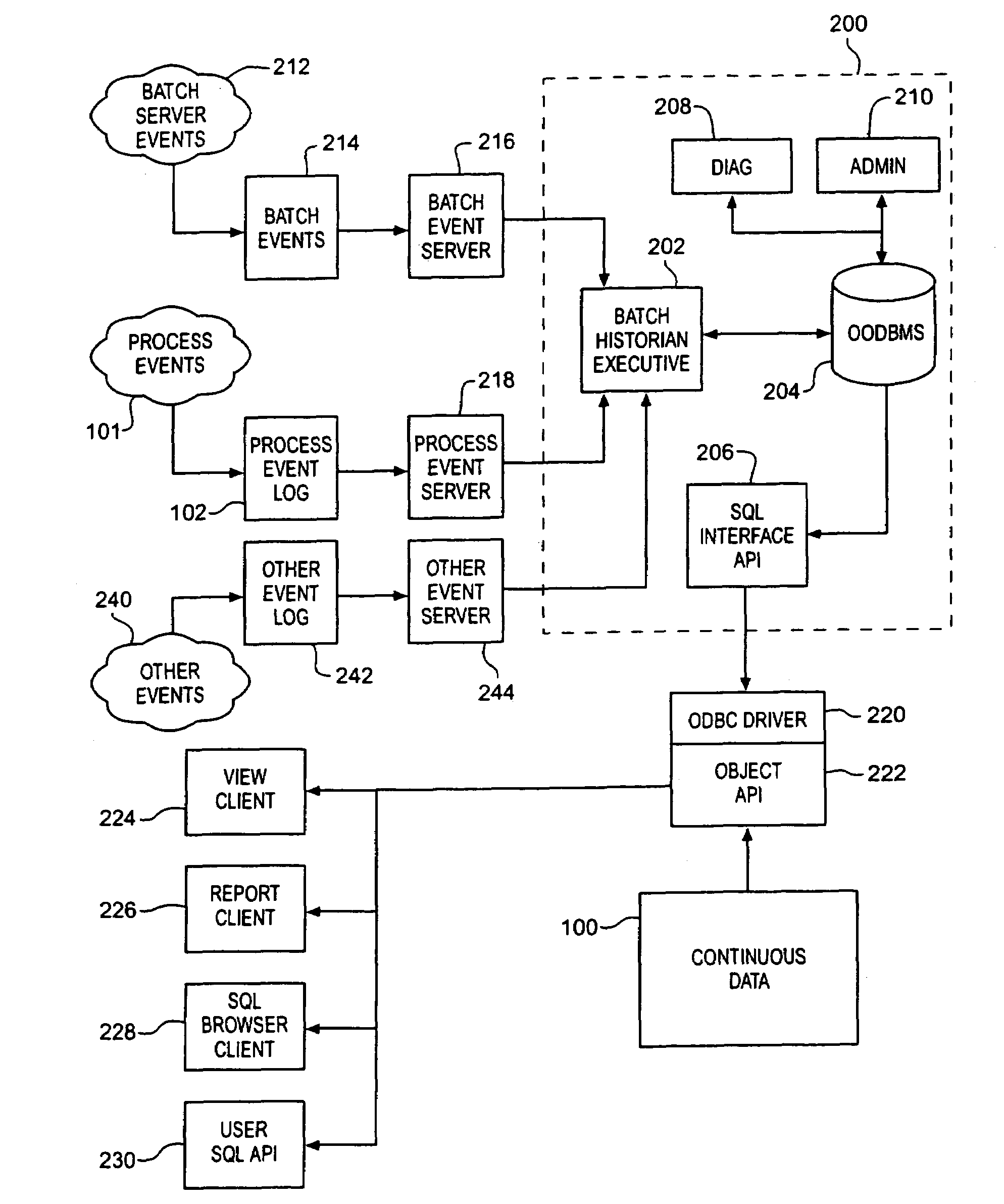
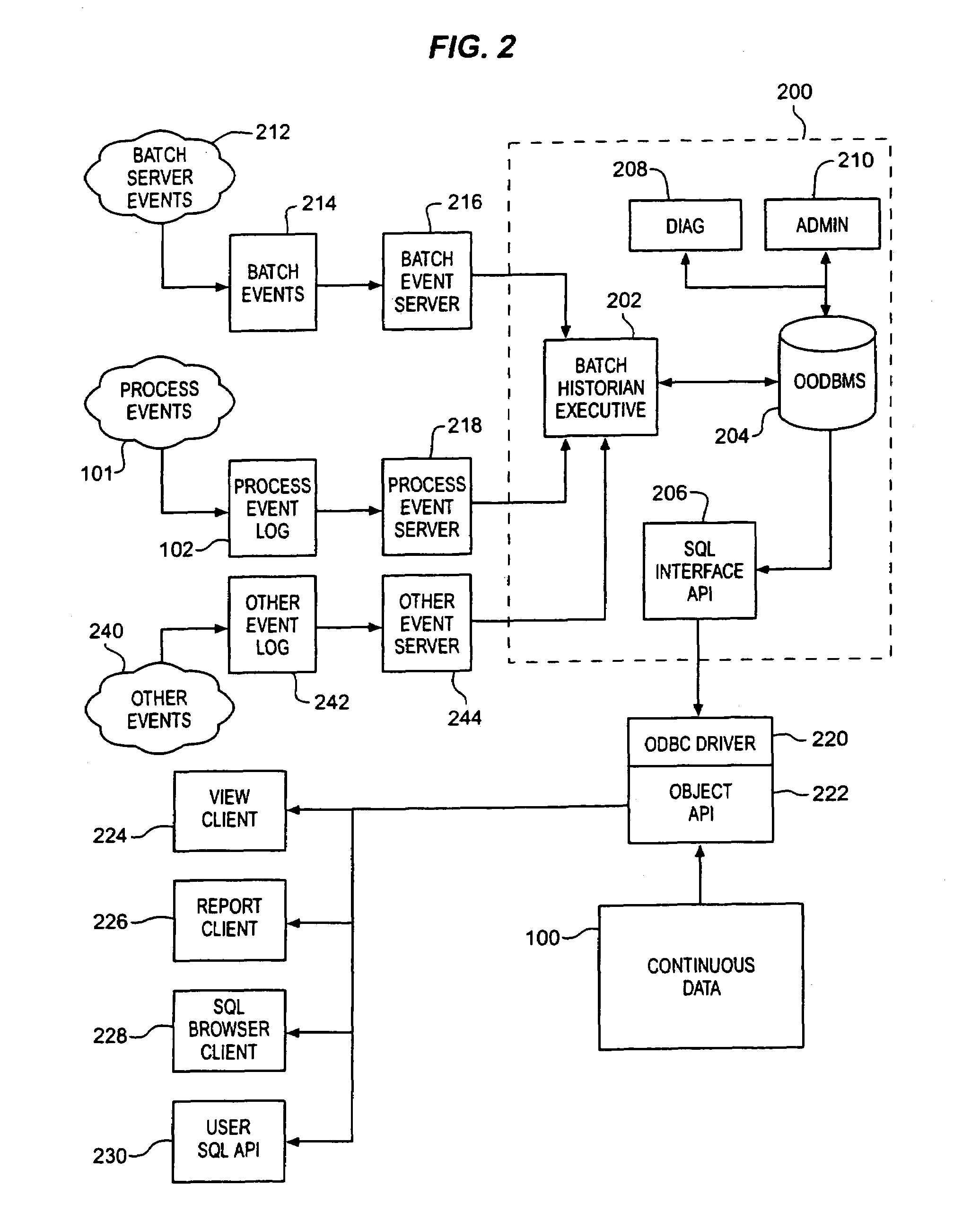
Methods and structure for batch processing event history processing and viewing
InactiveUS7249356B1Efficient captureGood conditionElectric testing/monitoringMultiprogramming arrangementsUser needsBatch processing
A batch event historian gathers, stores and presents data regarding a batch process where relationships among the various elements of data are automatically derived by an executive program. A persistent store includes structure corresponding to the relationships defined among procedural elements and equipment in accordance with batch processing industry S88.01 standards. The executive program gathers event information generated by the batch process and derives the relationships among the events in accordance with these industry standard models. Storage and corresponding retrieval and presentation of such historical data is thereby simplified for a user because the user need not manually configure the historian programs to derive the relationships. Association of any continuous data log with event information is automated thereby obviating the need for manual configuration by a user to establish such associations.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
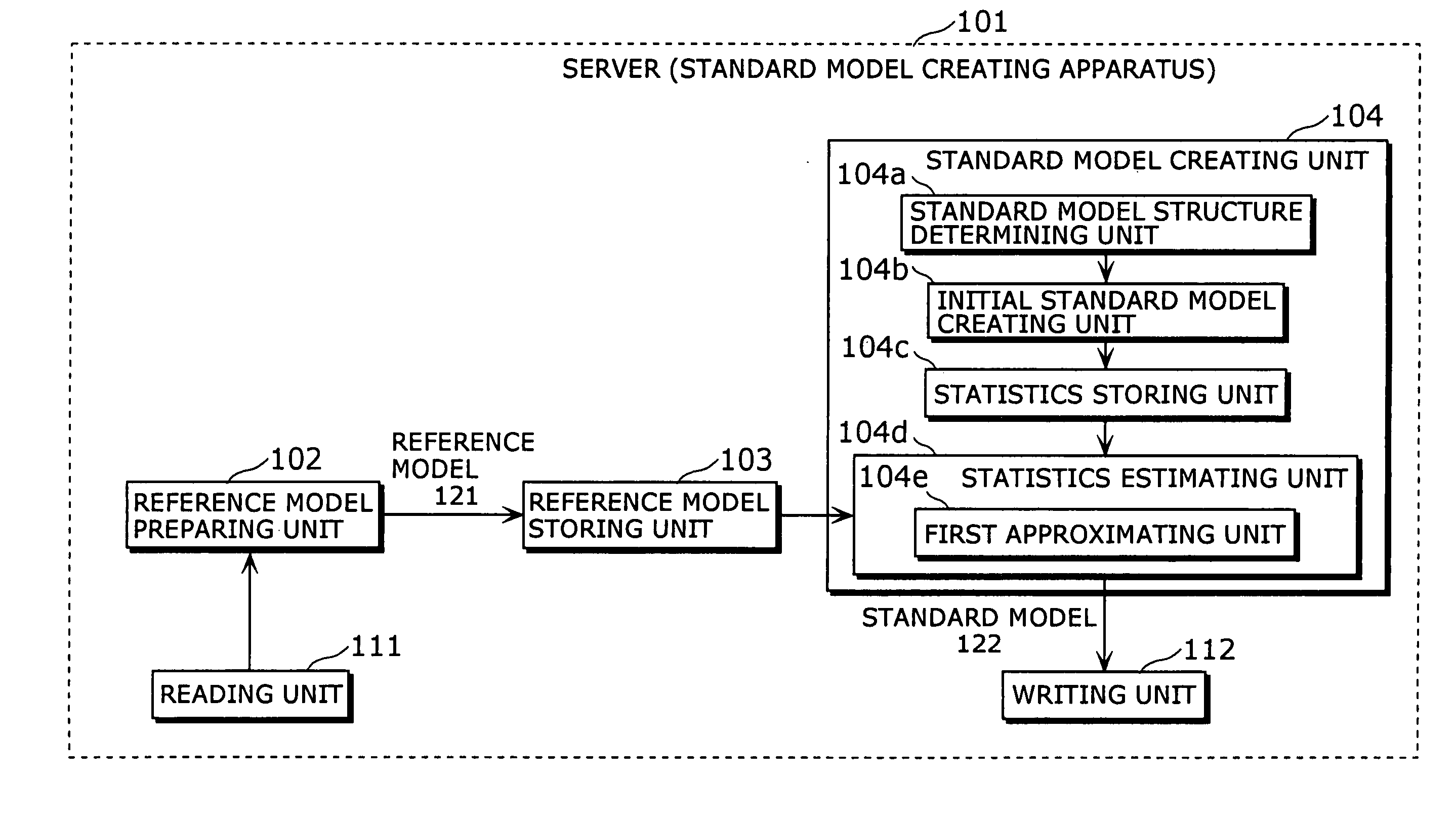
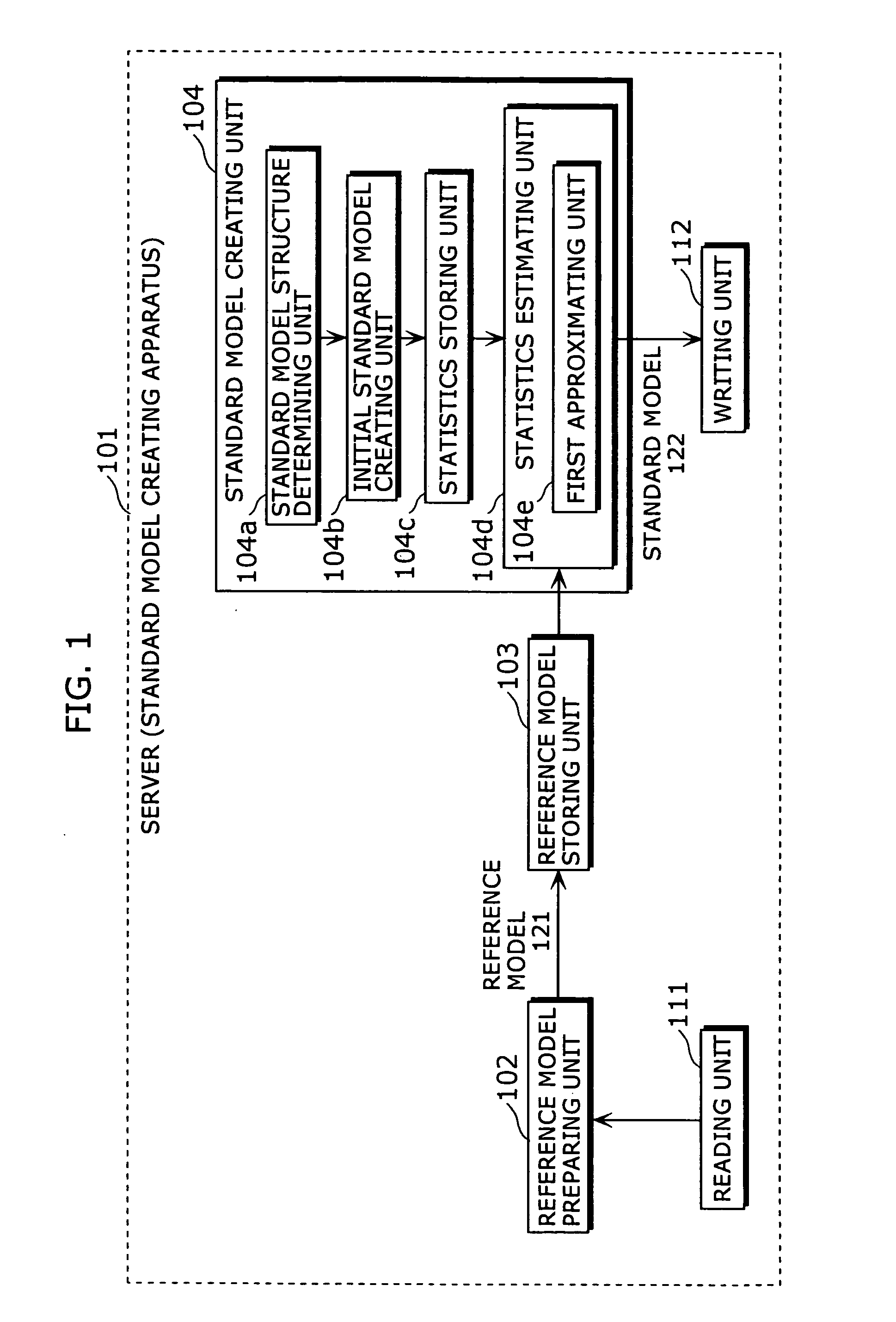
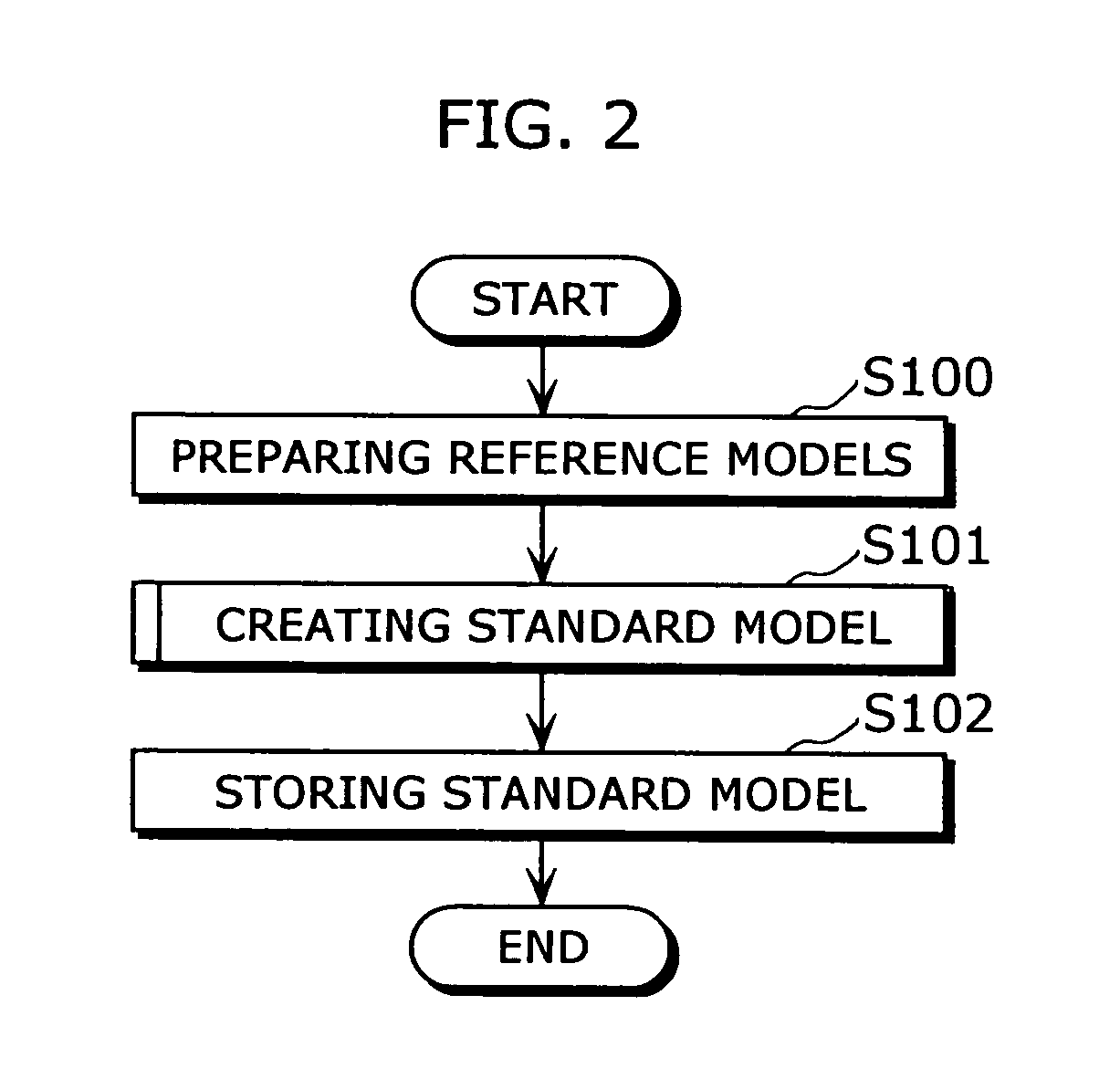
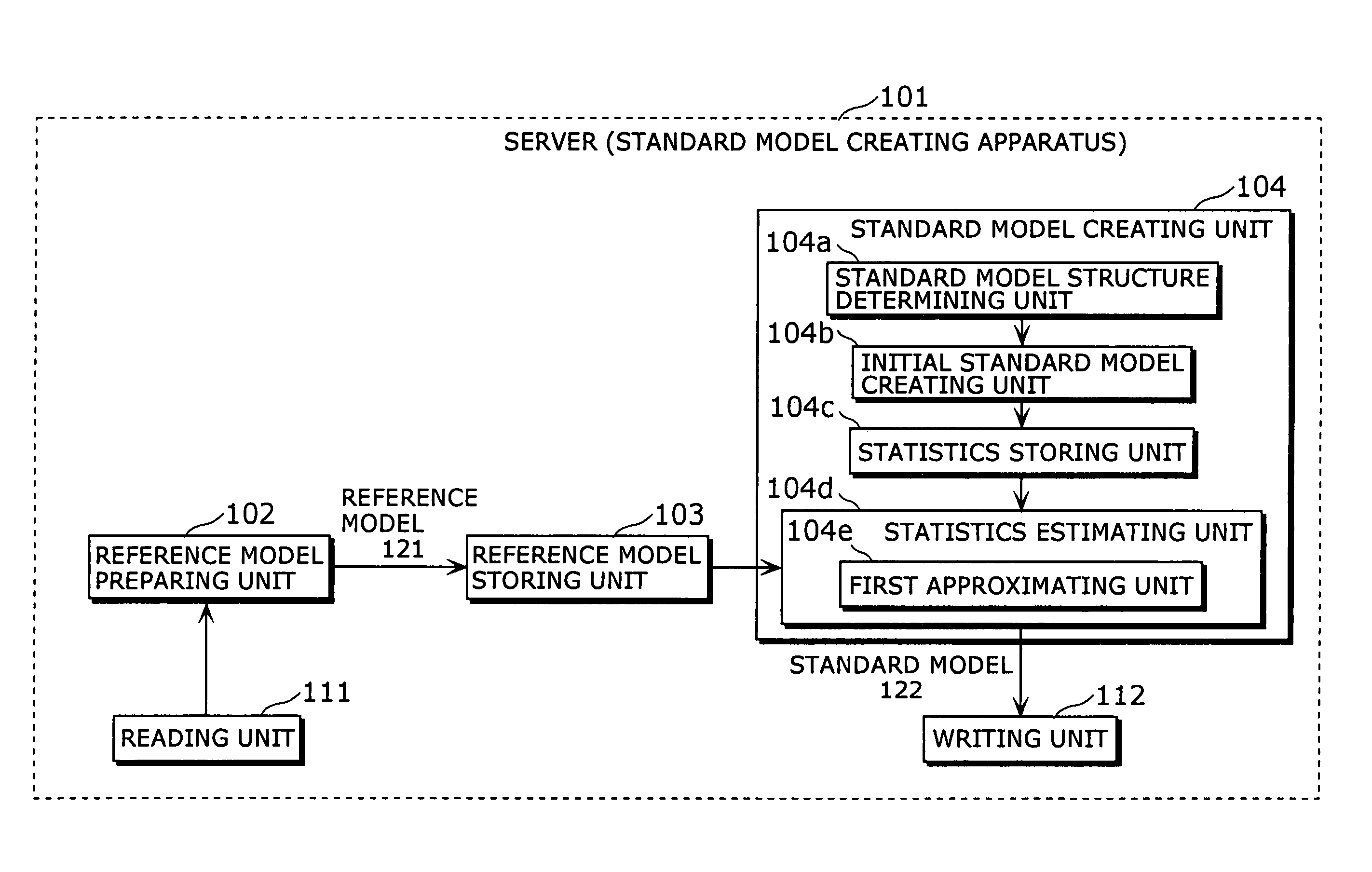
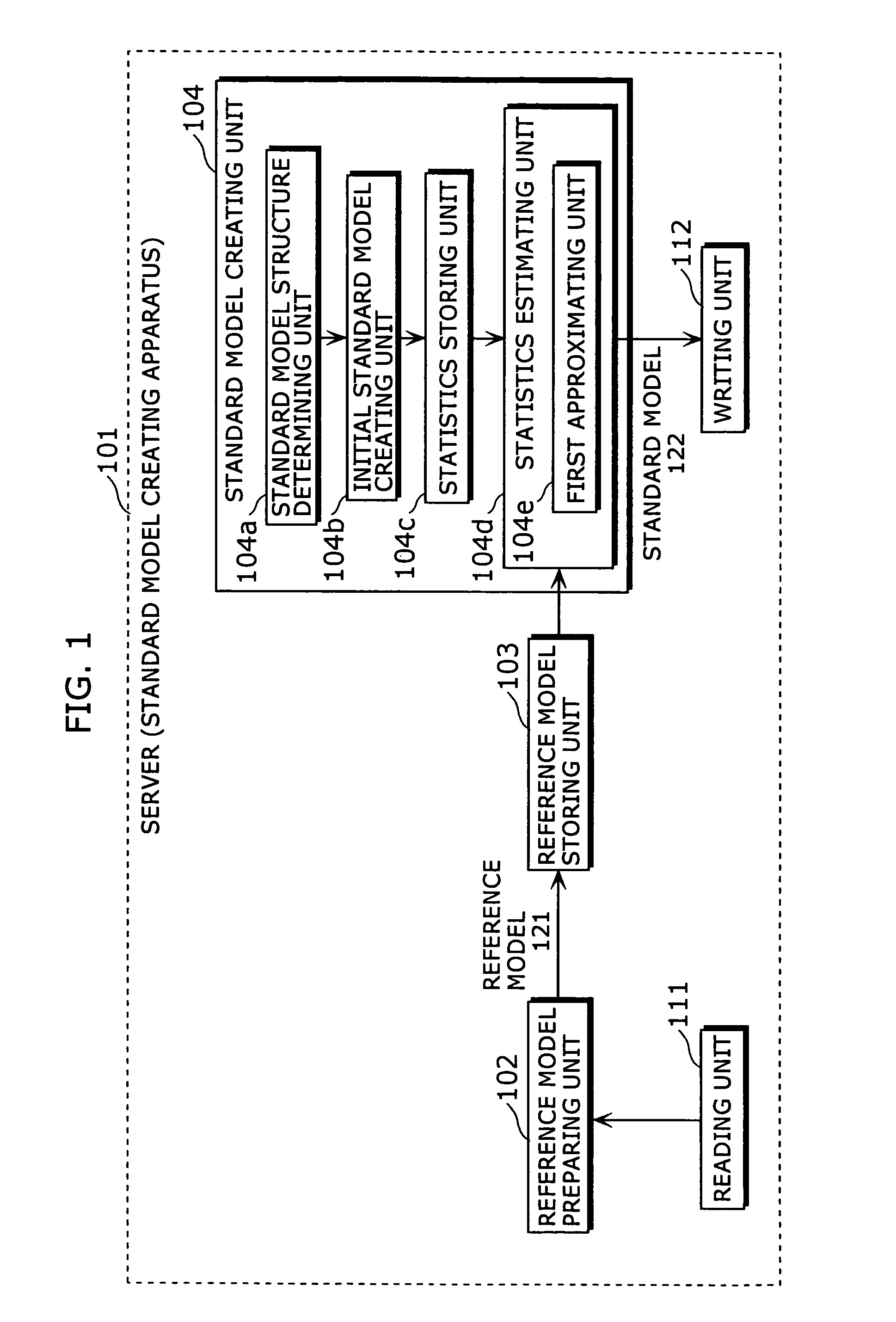
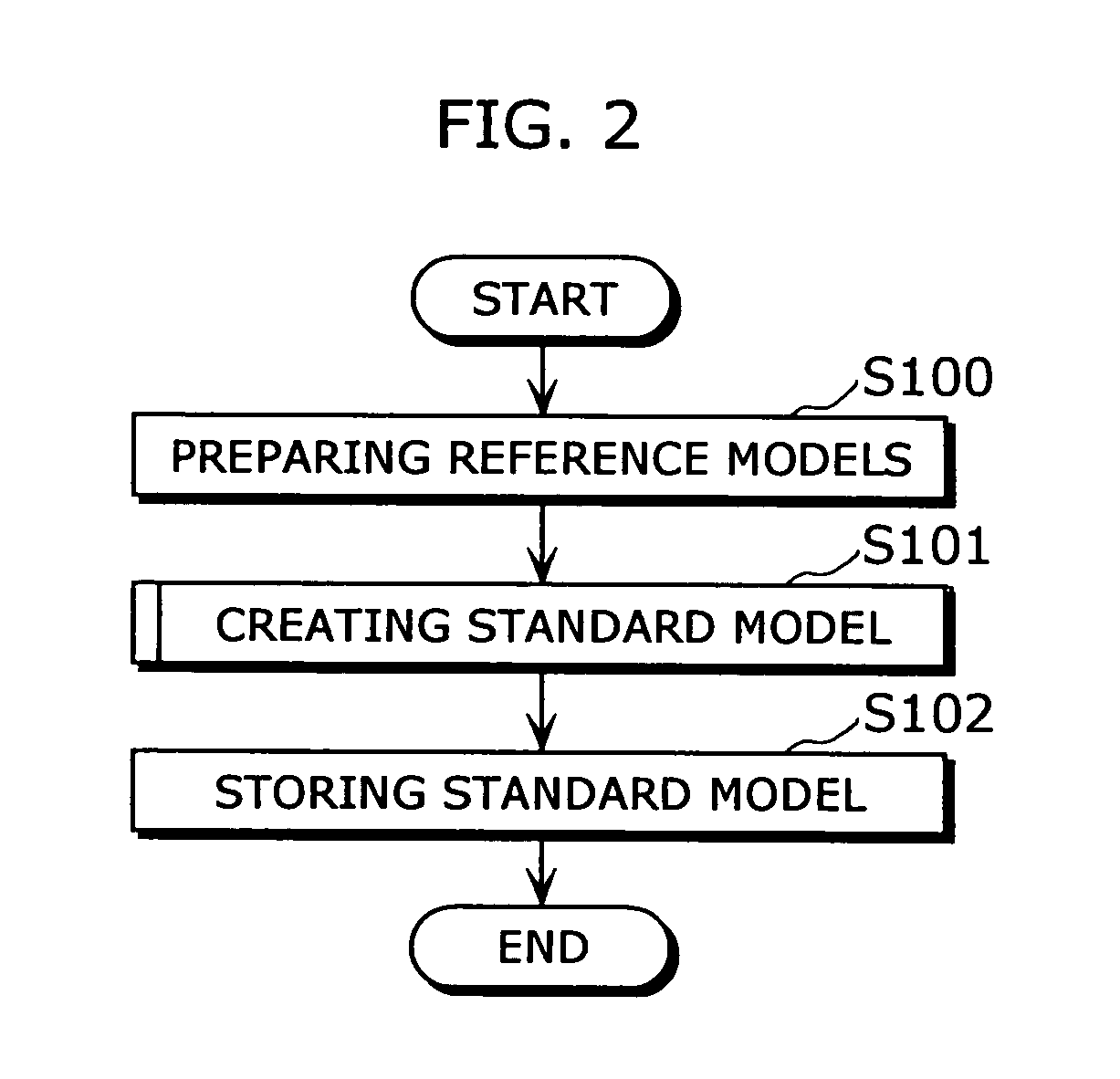
Standard model creating device and standard model creating method
ActiveUS20060053014A1Easy to createHigh practical valueSpeech recognitionReference modelHide markov model
The standard model creating apparatus which provides a high-precision standard model used for: pattern recognition such as speech recognition, character recognition, or image recognition using a probability model based on a hidden Markov model, Bayesian theory, or linear discrimination analysis; intention interpretation using a probability model such as a Bayesian net; data-mining performed using a probability model; and so forth, the apparatus comprising: a reference model preparing unit (102) operable to prepare at least one reference model; a reference model storing unit (103) operable to store the reference model (121) prepared by the reference model preparing unit (102); and a standard model creating unit (104) operable to create a standard model (122) by calculating statistics of the standard model so as to maximize or locally maximize the probability or likelihood with respect to the at least one reference model stored in the reference model storing unit (103).
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
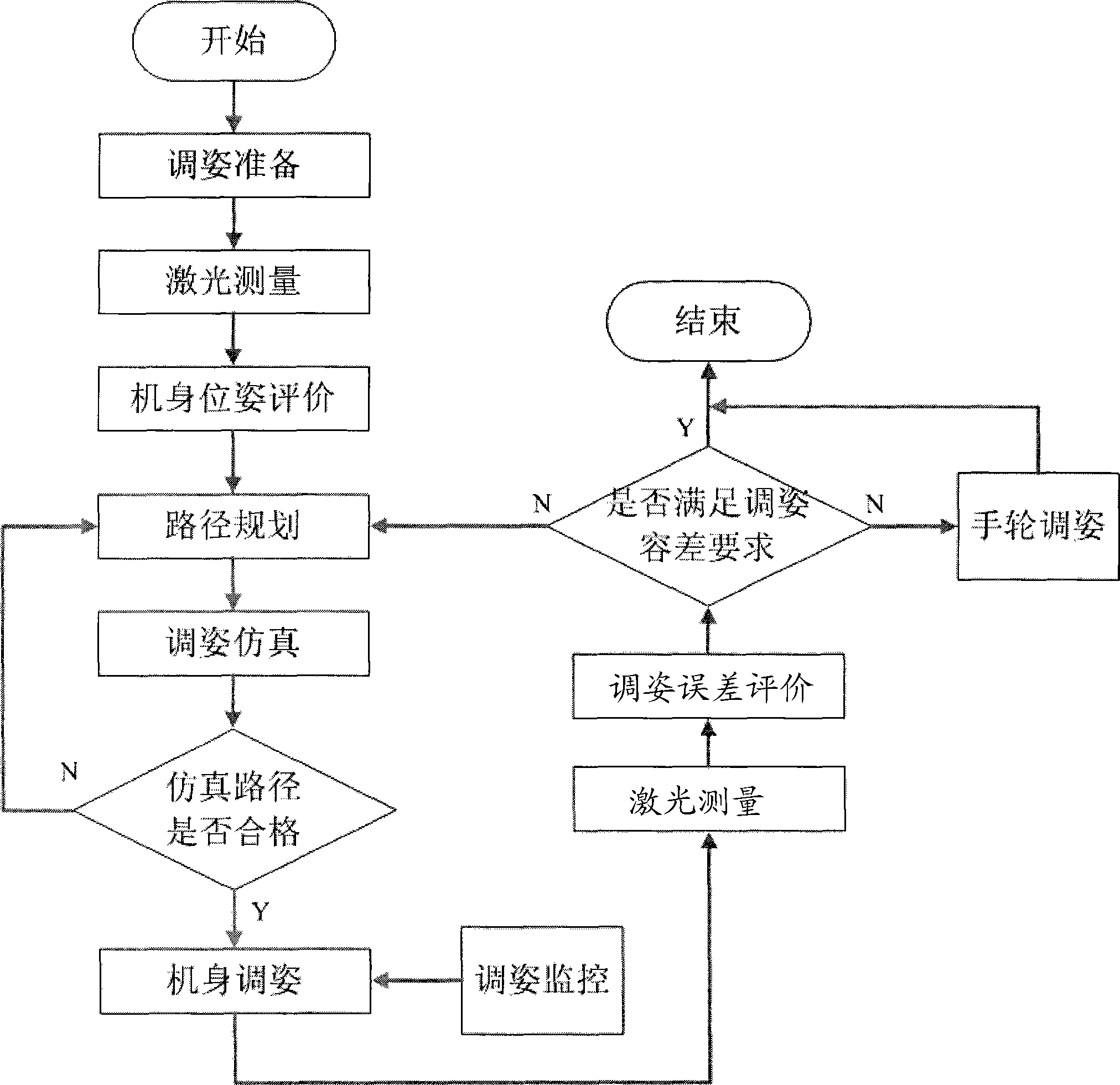
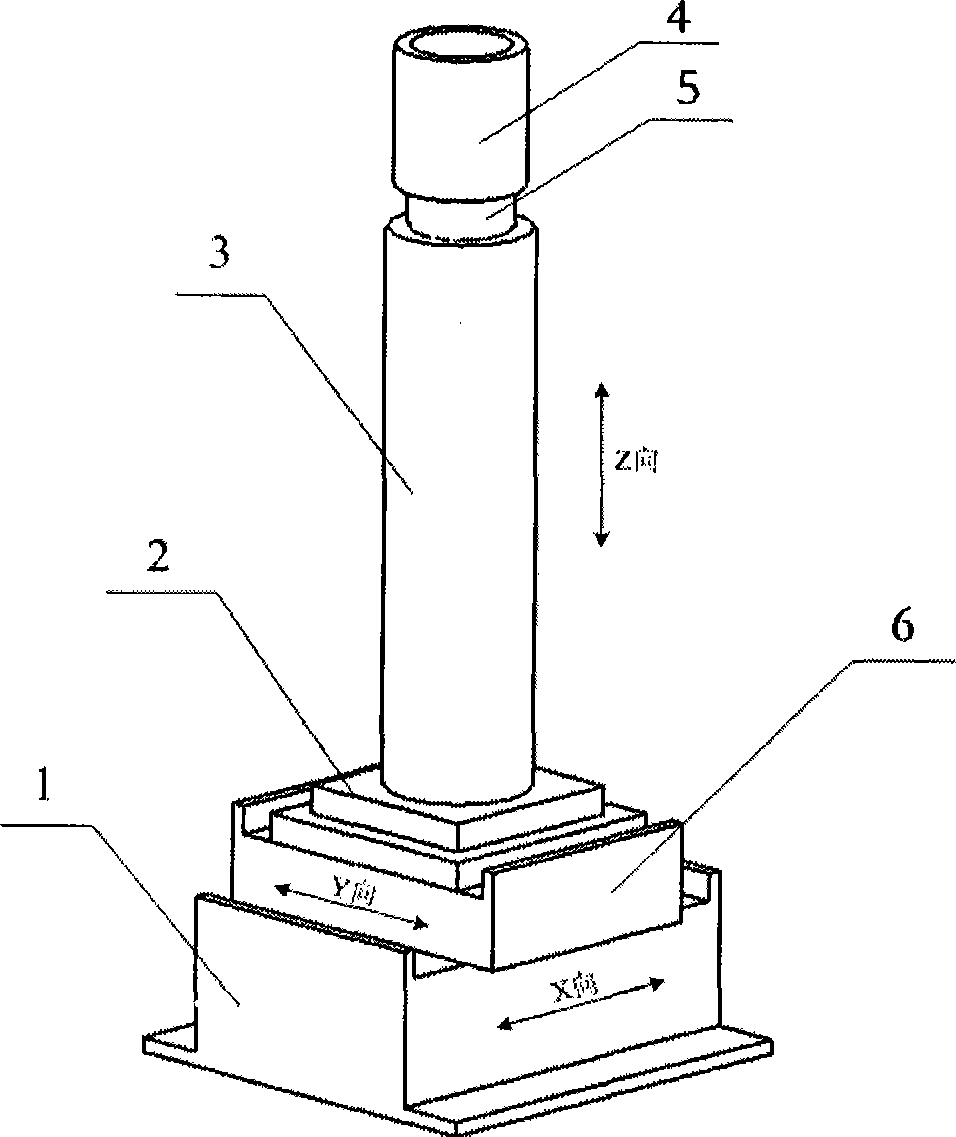
Aircraft fuselage flexible and automatic attitude-adjusting method
InactiveCN101456452ARealize digital posture adjustmentImprove flexibilityAircraft assemblyThree stageSimulation
The invention discloses a method for flexibly and automatically adjusting posture of an airframe of an airplane. The method comprises: the spatial position of a target of the airframe is measured through a laser tracking instrument; a measuring result and a digital standard model are subjected to matched analysis to calculate the posture of the airframe; and finally a plurality of three-coordinate positioner units are controlled and driven to realize adjustment of the posture of the airframe. The whole posture adjusting process comprises three stages: a posture adjusting preparation stage, an airframe posture adjusting stage and a posture adjusting result evaluation and analysis stage to realize automatic and non-stress posture adjustment of the airframe. The method has the following advantages: 1, the method can realize digital posture adjustment of the airframe; 2, the airframe is supported by the plurality of the positioner units; and in the posture adjusting process, motion cooperativity of the airframe is monitored in real time to realize non-stress posture adjustment; 3, the method has good flexibility and compatibility and can meet the requirement of posture adjustment of various airplane models; and 4, the method can carry out quantitative evaluation and analysis on the posture adjusting result and obtain the position and posture of the airframe in a scene coordinate system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Standard-model generation for speech recognition using a reference model
ActiveUS7603276B2Easy to createHigh practical valueSpeech recognitionReference modelHide markov model
A standard model creating apparatus which provides a high-precision standard model used for pattern recognition such as speech recognition, character recognition, or image recognition using a probability model based on a hidden Markov model, Bayesian theory, or linear discrimination analysis; intention interpretation using a probability model such as a Bayesian net; data-mining performed using a probability model; and so forth. The standard model creating apparatus includes a reference model preparing unit that prepares at least one reference model; a reference model storing unit that stores the reference model prepared by the reference model preparing unit; and a standard model creating unit that creates a standard model by calculating statistics of the standard model so as to maximize or locally maximize the probability or likelihood with respect to the reference model stored in the reference storing unit.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Workable solid buoyancy material for deep sea and method for preparing same
The invention provides a deep-sea machinability solid buoyancy material and its method for preparing, in which the said solid buoyancy material includes epoxide resin; flexibilizer; curing agent; accelerating agent; dispersing agent; deflocculating agent; hollow zeeosphere and coupling agent, and the hollow zeeosphere can be ceramic and / or glass zeeosphere; the hollow of the said hollow glass zeeosphere is filled with gases or vacuum; the weigh parts of the hollow zeeosphere are: 15-90; the weigh parts of the said epoxide resin are: 82-98. The method consists of adding each component into kneader, heating to 80-100 DEG C, agitating to be even; taking-up the even mixtures into the die to consolidate, then laying them into the curing press for heating and forcing, after solidified modeling, producing the needed solid buoyancy material according to the requirement. The buoyancy material can be sawed, dug, grinded, milled and adhibitted and the standard model can be produced to various shapes according to the drawing requirement to meet the application needs.
Owner:MARINE CHEM RES INST
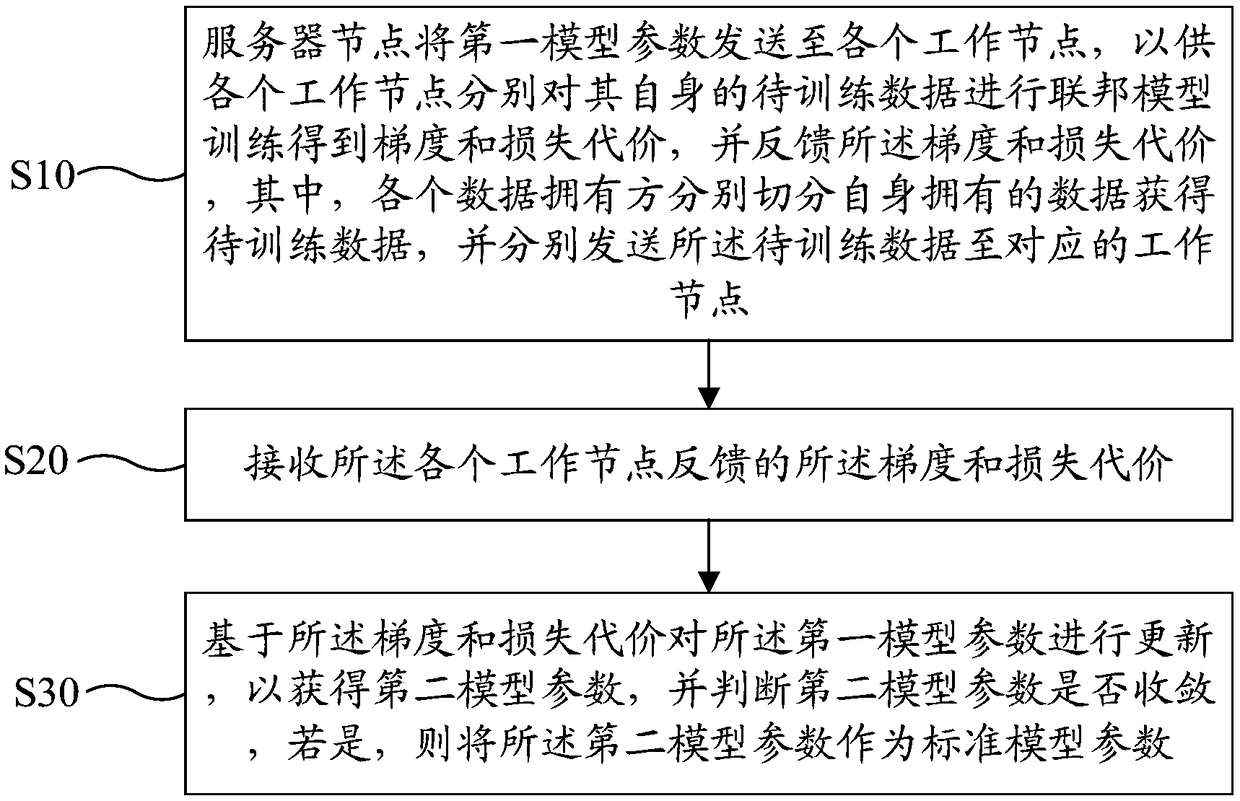
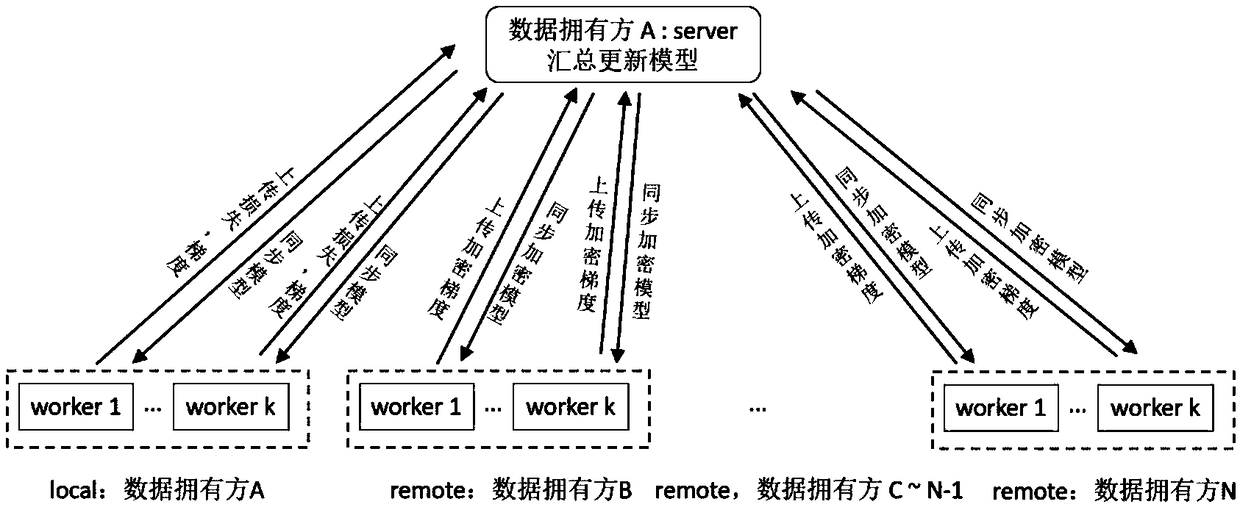
Cross data segmentation federation learning model method, server and medium
ActiveCN109189825AIncrease training rateImprove training efficiencyDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsModel methodModel parameters
A cross data segmentation federation learning modeling method, a server and a readable storage medium are provided. The method comprises the following steps: the server node sends the first model parameter to each working node, so that each working node obtains the gradient and loss cost by federated model training of its own data to be trained, and feeds back the gradient and loss cost; a gradient and a cost of loss of feedback are received from each working node; the first model parameter is updated based on the gradient and the loss cost to obtain a second model parameter, and whether the second model parameter converges or not is judged. If so, the second model parameter is taken as a standard model parameter. The invention sends model parameters, collects gradient and updates model parameters through server nodes, and the working nodes carry out federated model training at the same time, so that the problem of data leakage does not exist in the model training process according todifferent types of model parameters.
Owner:WEBANK (CHINA)
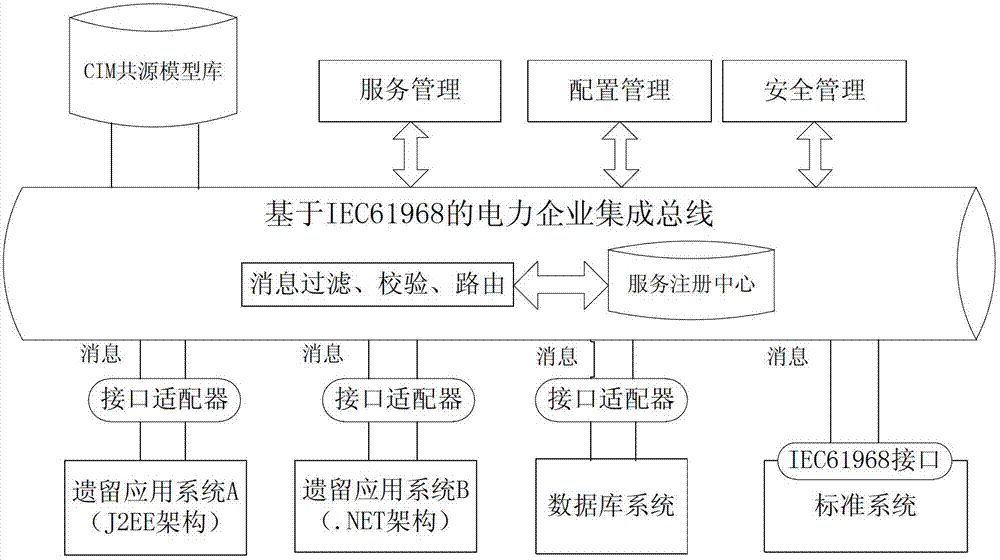
Information interaction method for heterogeneous electric power application system
ActiveCN102760184ATroubleshoot integration issuesAchieve sharingSpecial data processing applicationsData informationGoal system
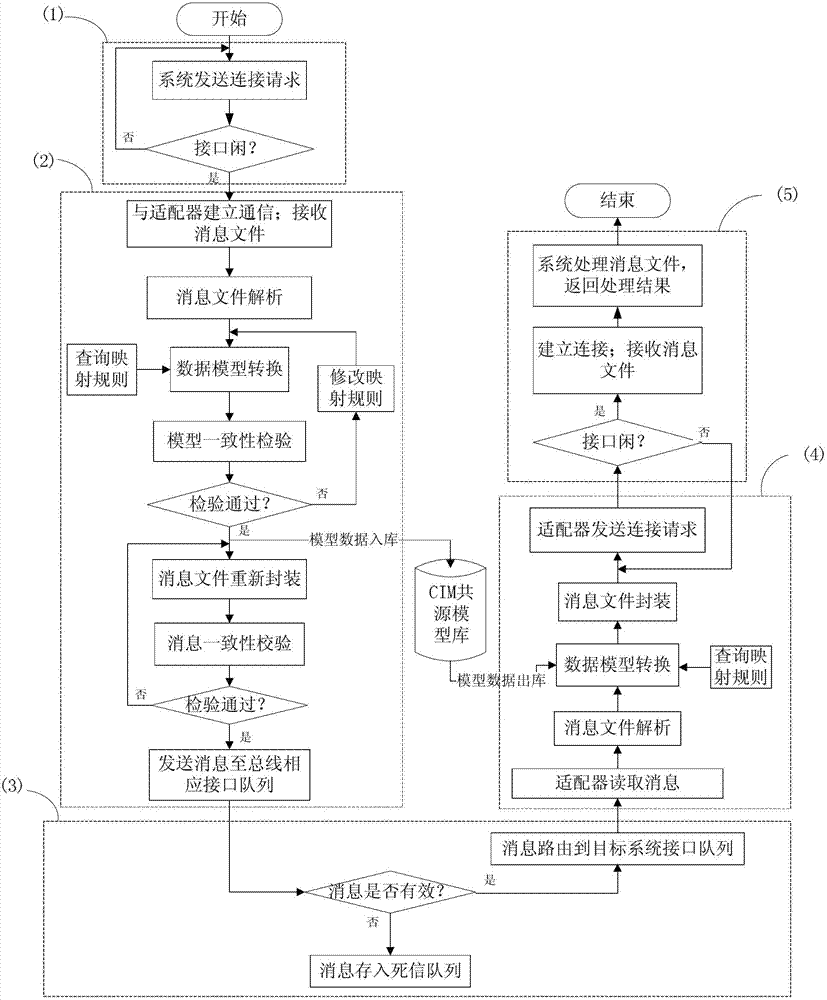
The invention discloses an information interaction method for a heterogeneous electric power application system. The information interaction method for the heterogeneous electric power application system comprises the following steps: establishing a uniform heterogeneous system data information naming and encoding standard; establishing a CIM (common information model) common source model library of a heterogeneous system and a mapping relationship between a heterogeneous system data model and the CIM model; converting the data model into a standard CIM model by an adaptor of the heterogeneous system according to the mapping relationship, and verifying and introducing the standard CIM model into the CIM common source model library for storage; packaging the converted CIM model information into IEC61968 (international electrotechnical commission 61968) information by the adaptor, and sending the IEC61968 information to a corresponding interface queue on an electric power enterprise integration bus; routing the information to an interface queue of a target system by the electric power enterprise integration bus; reading and analyzing the information by an interface adaptor of the target system, and converting the obtained CIM model information into a data form which can be recognized and processed by the target system; packing and sending the CIM model information to the target system, processing the CIM model information, and returning a result to a source system so as to realize information interaction between the heterogeneous systems.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Three-dimensional face recognition method and three-dimensional face recognition system
ActiveCN108549873ALess chance of cheatingImprove recognition accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisFeature vectorColor image
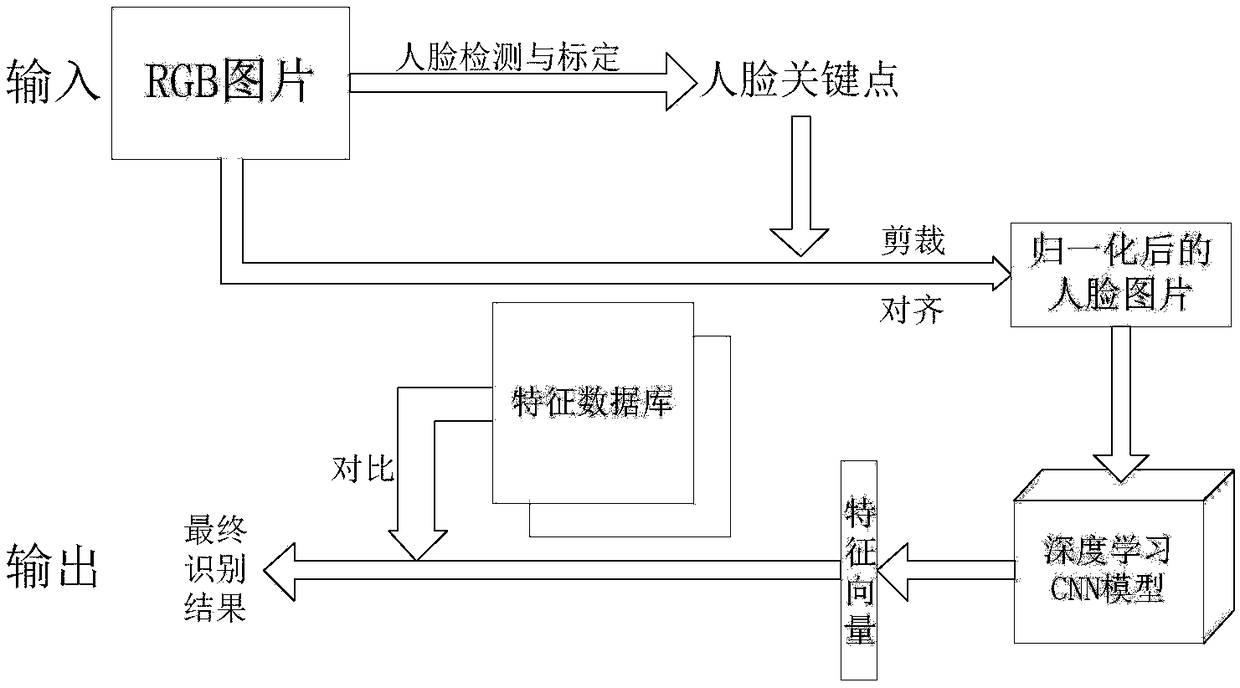
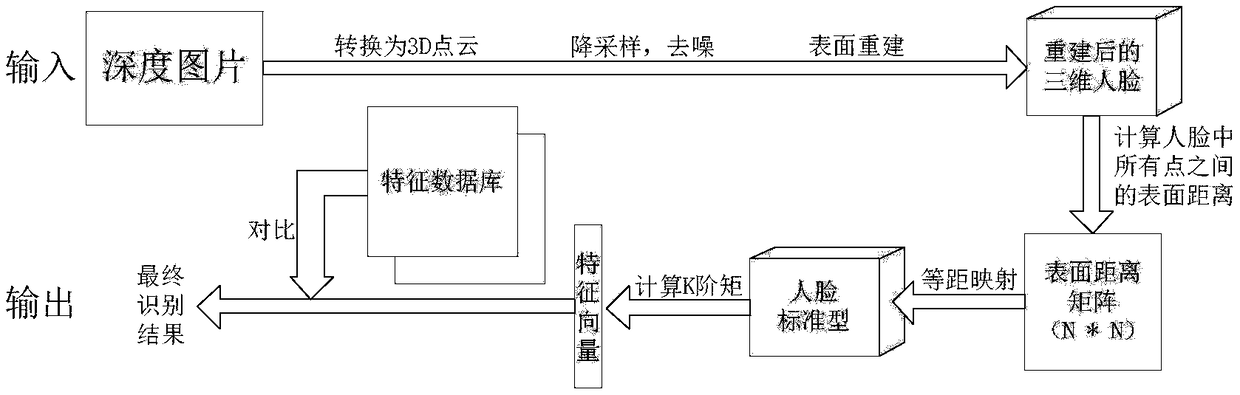
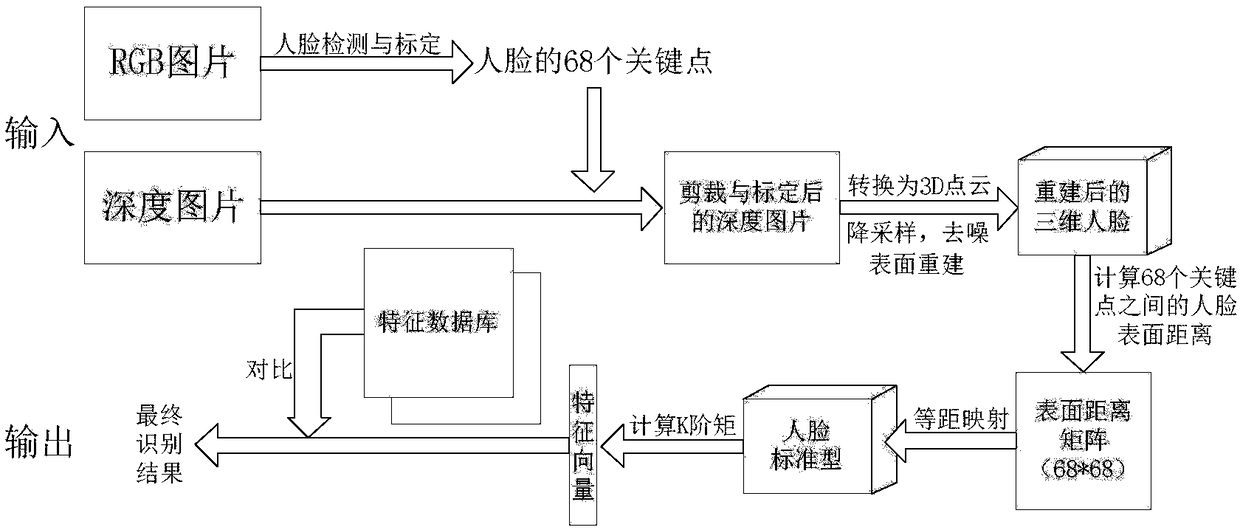
The invention discloses a three-dimensional face recognition method and system. The method includes: image data of a to-be-identified target face are collected and a face key point is calibrated, wherein the image data of the face include a depth image of the face and a color image of the face; according to the calibrated depth image of the face, three-dimensional face reconstruction is carried out to obtain a three-dimensional face reconstruction model; surface distances between a preset number of key points in the three-dimensional face reconstruction model are calculated and a surface distance matrix is generated; the surface distance matrix is transformed into a face standard model; a to-be-identified feature vector is extracted from the face standard model; and the to-be-identified feature vector is compared with existing feature vectors in the preset face feature database to realize three-dimensional face recognition. The three-dimensional face recognition method has advantages of high recognition accuracy and fast recognition speed.
Owner:BEIJING HUAJIE IMI TECH CO LTD
System for virtually trying on clothes
InactiveCN101819663AEfficient collectionImprove experienceStereoscopic photographyCommerceUser inputInteractive displays
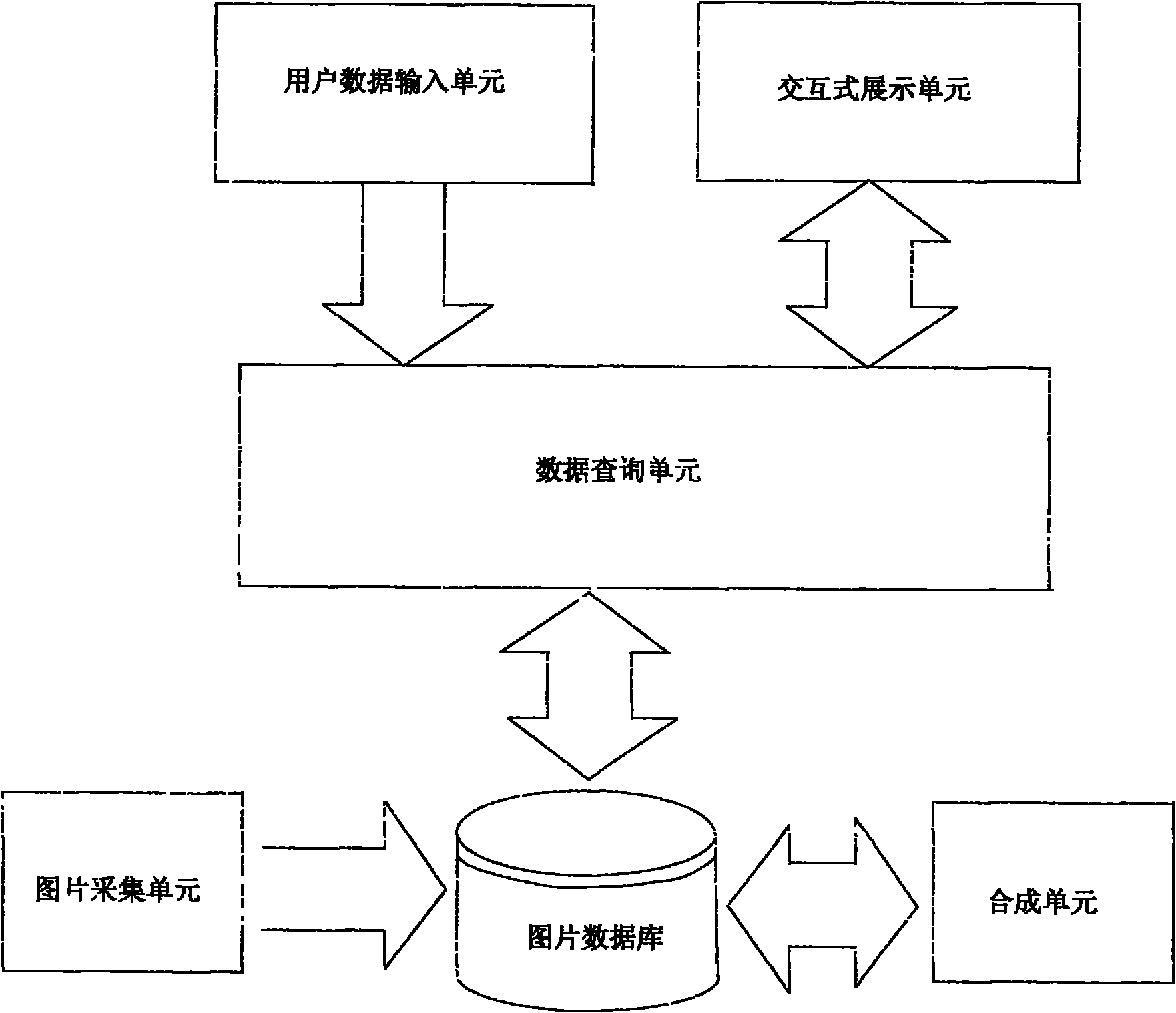
The invention discloses a system for virtually trying on clothes, which provides the cloth dressing effect with high third dimension for each independent customer and further improves the user experience of on-line shopping. The system comprises a pipelining-type picture acquisition device, a synthesis unit, a server database, a user input unit, a data inquiry unit and an interactive display unit, wherein the pipelining-type picture acquisition device is based on a mechanical manikin; the synthesis unit is used for synthesizing an acquired cloth picture and a standard model into an integrated body type picture and a rotary body video; the server database is used for storing picture information; the user input unit is used for a user to input basic body type data, head portrait and other items; the data inquiry unit is used for searching the most accurate body type number from the database; and the interactive display unit is used for the user to display a multi-angular integrated try-on picture and the rotary body video. The system is applied to the field of clothes try-on in on-line shopping.
Owner:ZHUHAI LINLANG INFORMATION TECH
Three-dimensional face modeling method and device
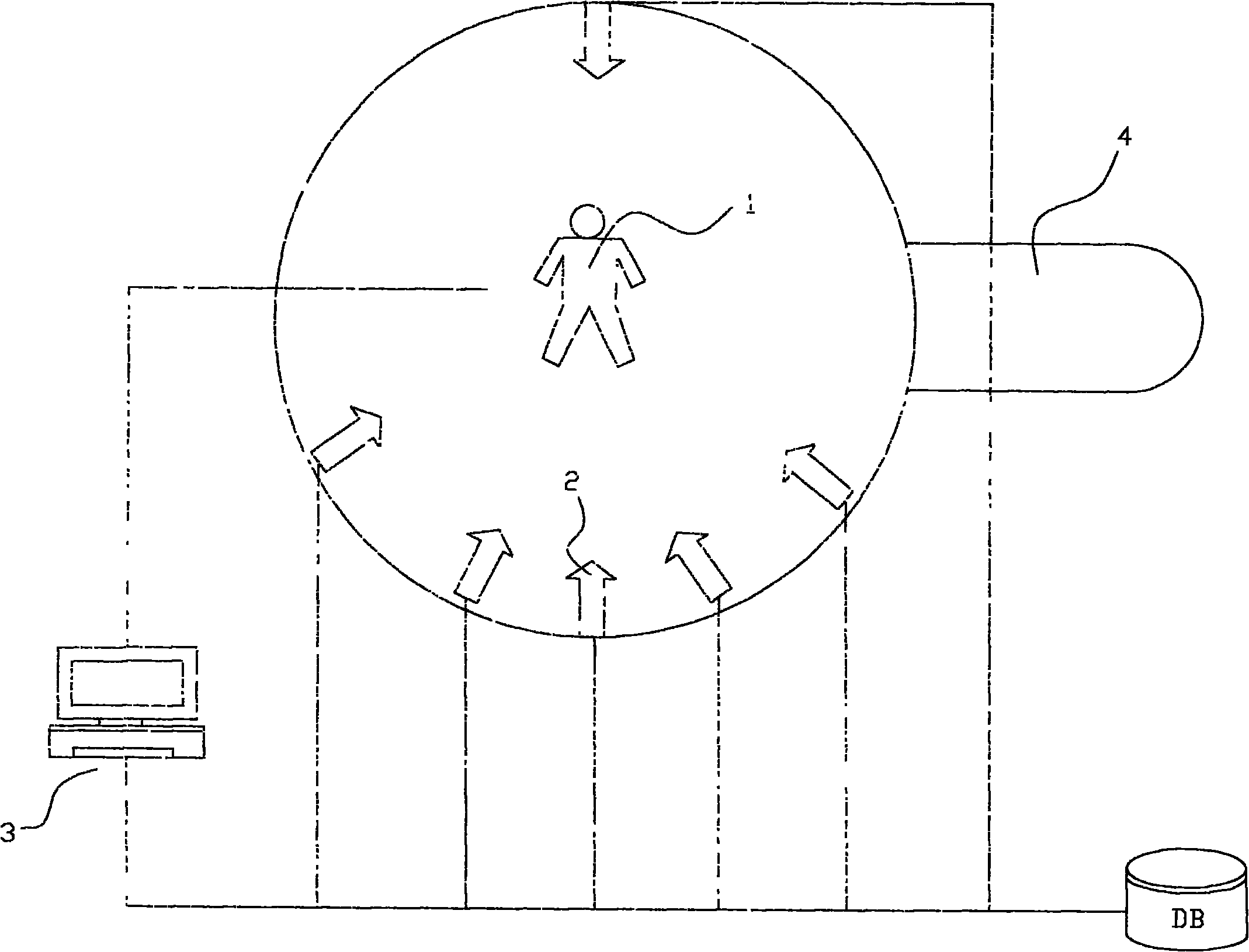
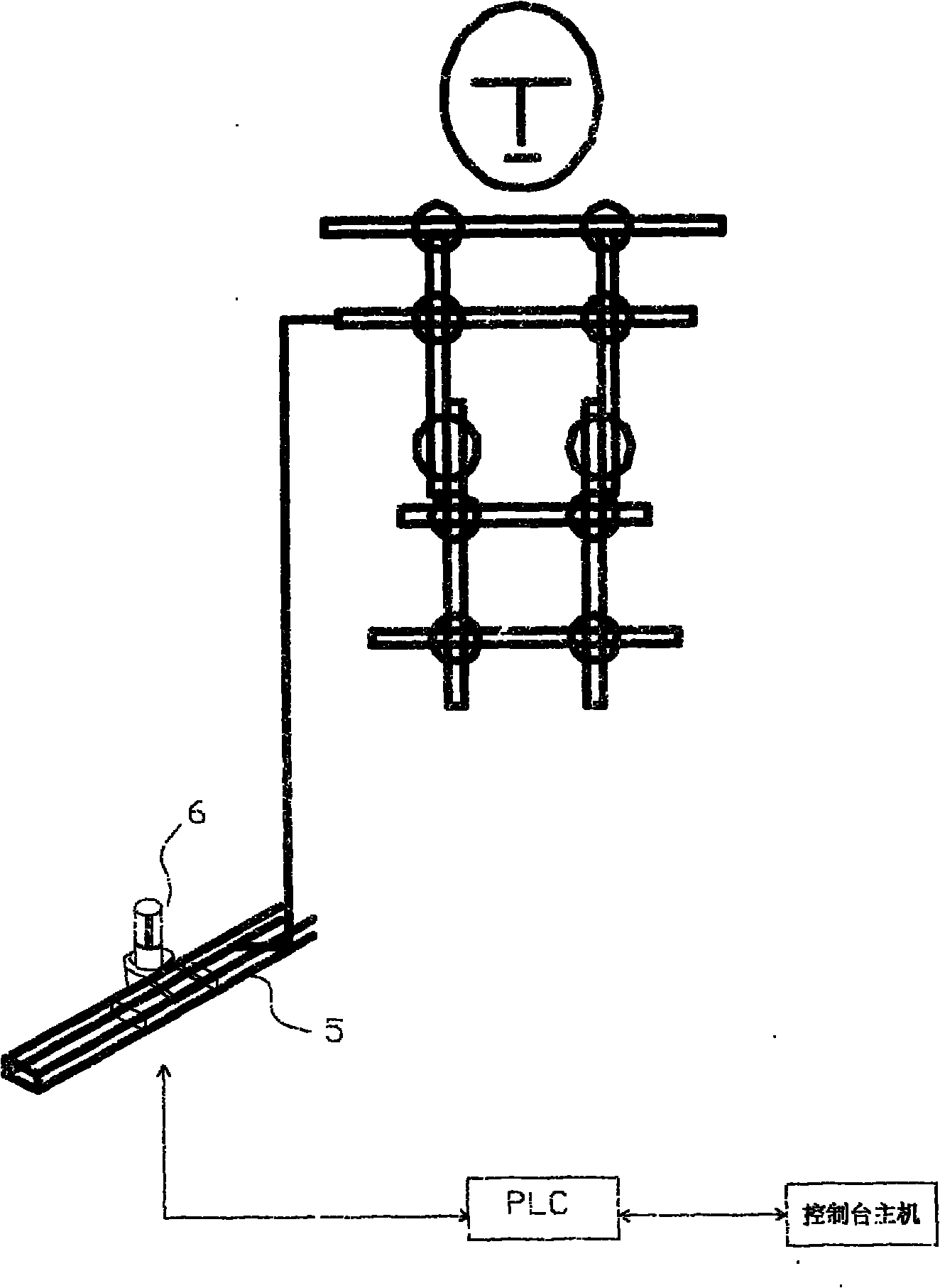
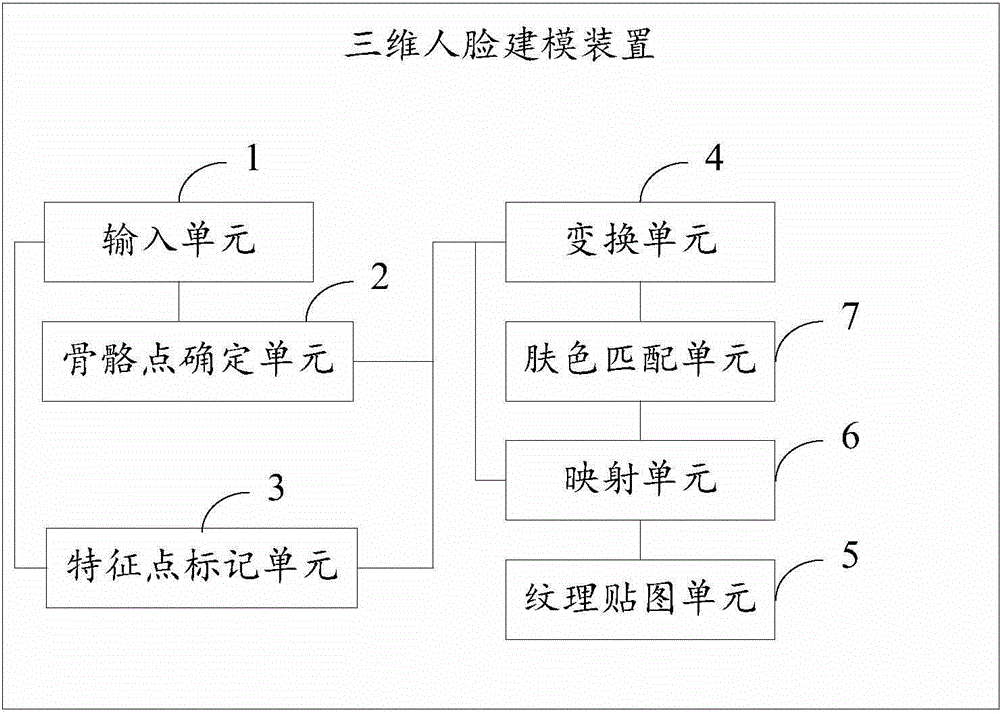
ActiveCN104376594ASimplify the collection processEasy to operate3D modellingComputer graphics (images)Data acquisition
The invention provides a three-dimensional face modeling method to achieve efficient three-dimensional face modeling. The method includes the steps that an original image and a standard model are obtained; the bone point information is obtained according to the standard model; a feature point is marked on the original portrait and the coordinate information of the feature point is recorded; first conversion is conducted on the original portrait; second conversion is conducted on the standard model; the surface of the standard model generated after the second conversion is conducted is unfolded according to the preset method to form a texture image; the original portrait generated after the first conversion is conducted is mapped to the texture image. The invention further provides a corresponding three-dimensional face modeling device for implementing the three-dimensional face modeling method. According to the technical scheme, the three-dimensional face modeling method and device are simple in operation mode, good in fitting effect and high in degree of reduction; meanwhile, the method and device are higher in implementation speed and higher in efficiency, the processes of implementation and calculation are simplified, the data collection process is simplified, practicability and adaptability of a system are improved, and the method and device have great advantages in situations of low requirement for the face depth information.
Owner:FUJIAN TQ DIGITAL
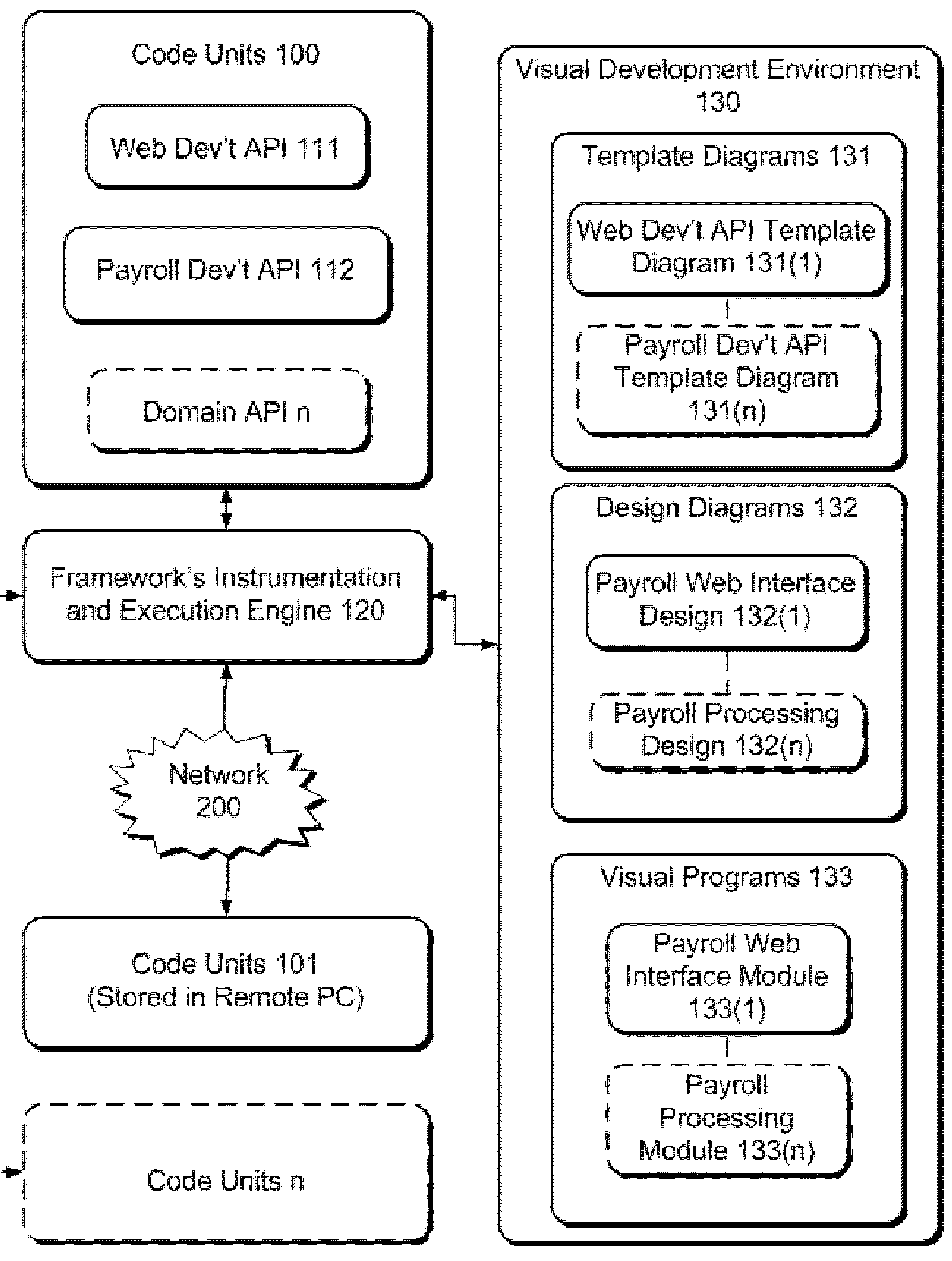
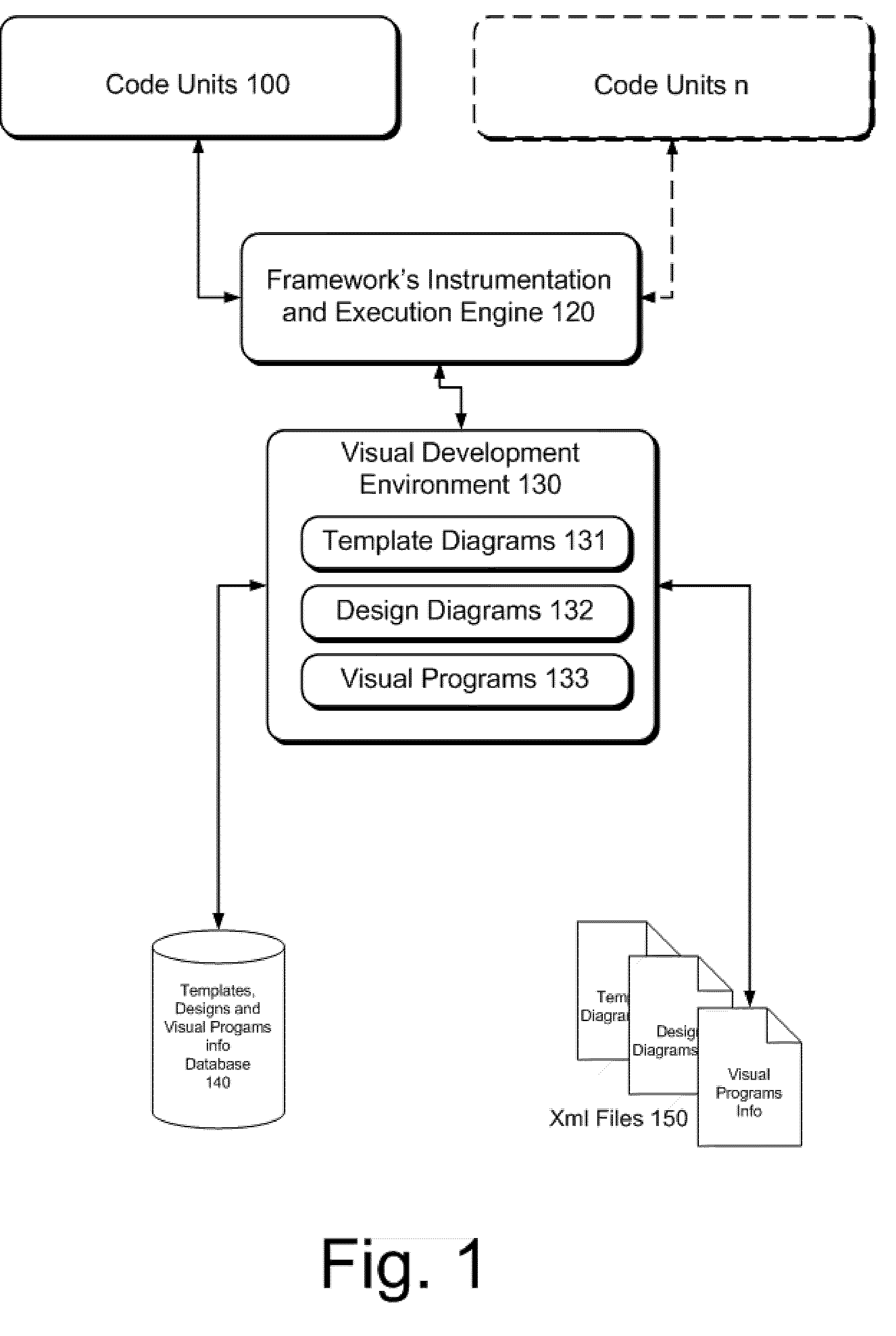
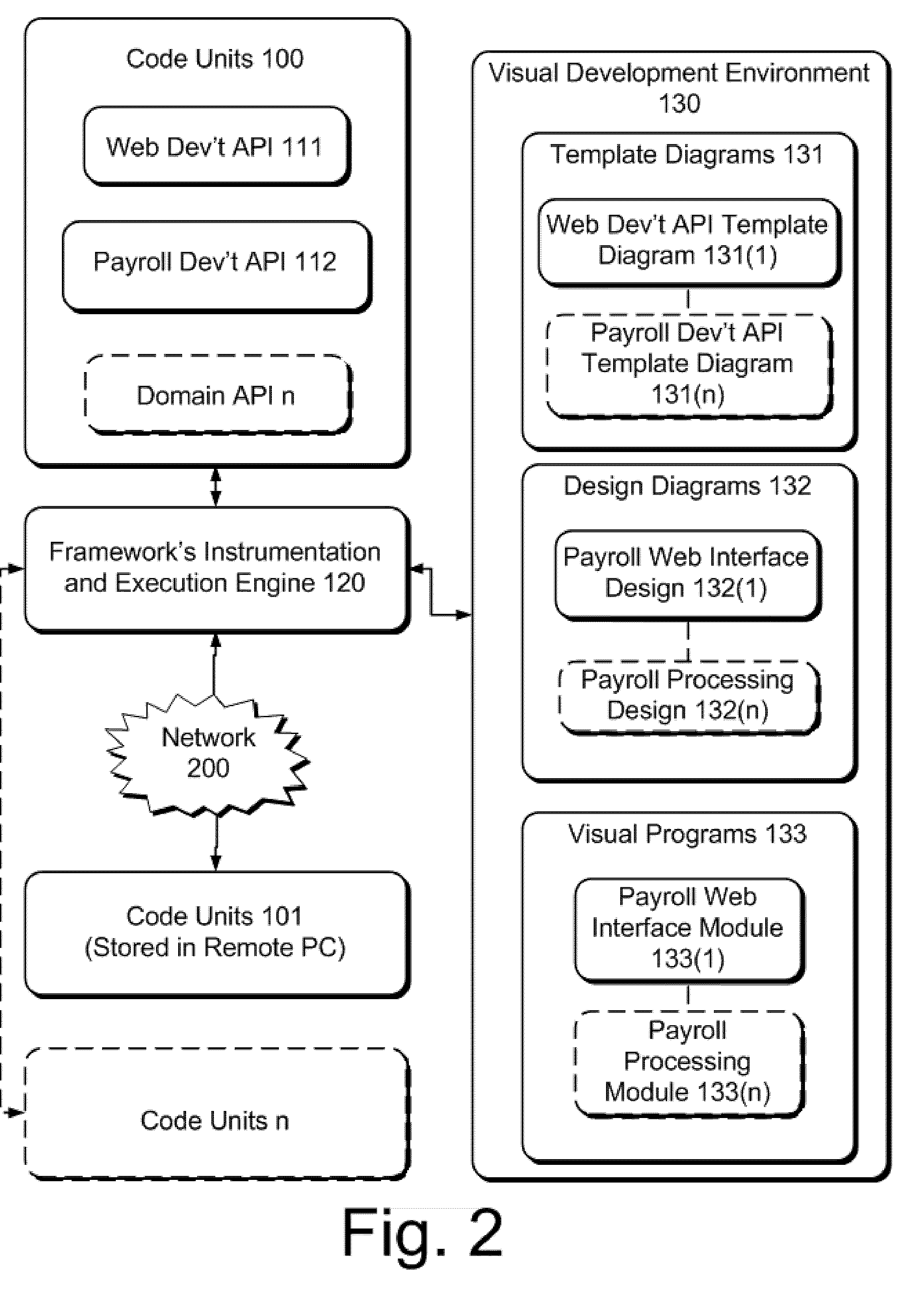
Code Units based Framework for domain- independent Visual Design and Development
InactiveUS20050044527A1Add supportVisual/graphical programmingSoftware reuseApplication programming interfaceProgramming domain
This framework provides for the creation, (re)use, and management of Domain specific Code Units as basic building block for Domain neutral Visual Programming environments. Code Units are Application Programming Interfaces (API). Users create and maintain Code Units definitions (including implementations, visual representations and / or standard Model representations for Model based development) for specific programming Domain and they or others can then use or extend the created Code Units both through the code and / or the provided visual programming on the said Domain. The semantics of “instrumented”, thus fully integrate-able to Visual environment Code Units applied to different programming Domains provide support for very rich, location transparent (i.e.—both local and remote “discovered” Code Units are supported), easy to implement and minimal “usage” footprint Visual Design and Development, two-way code generation, and generated program execution, representations of Code Units instances as Visual Entities and Models, Model Transformations and Model Analyses.
Owner:RECINTO GERARDO ARAYATA
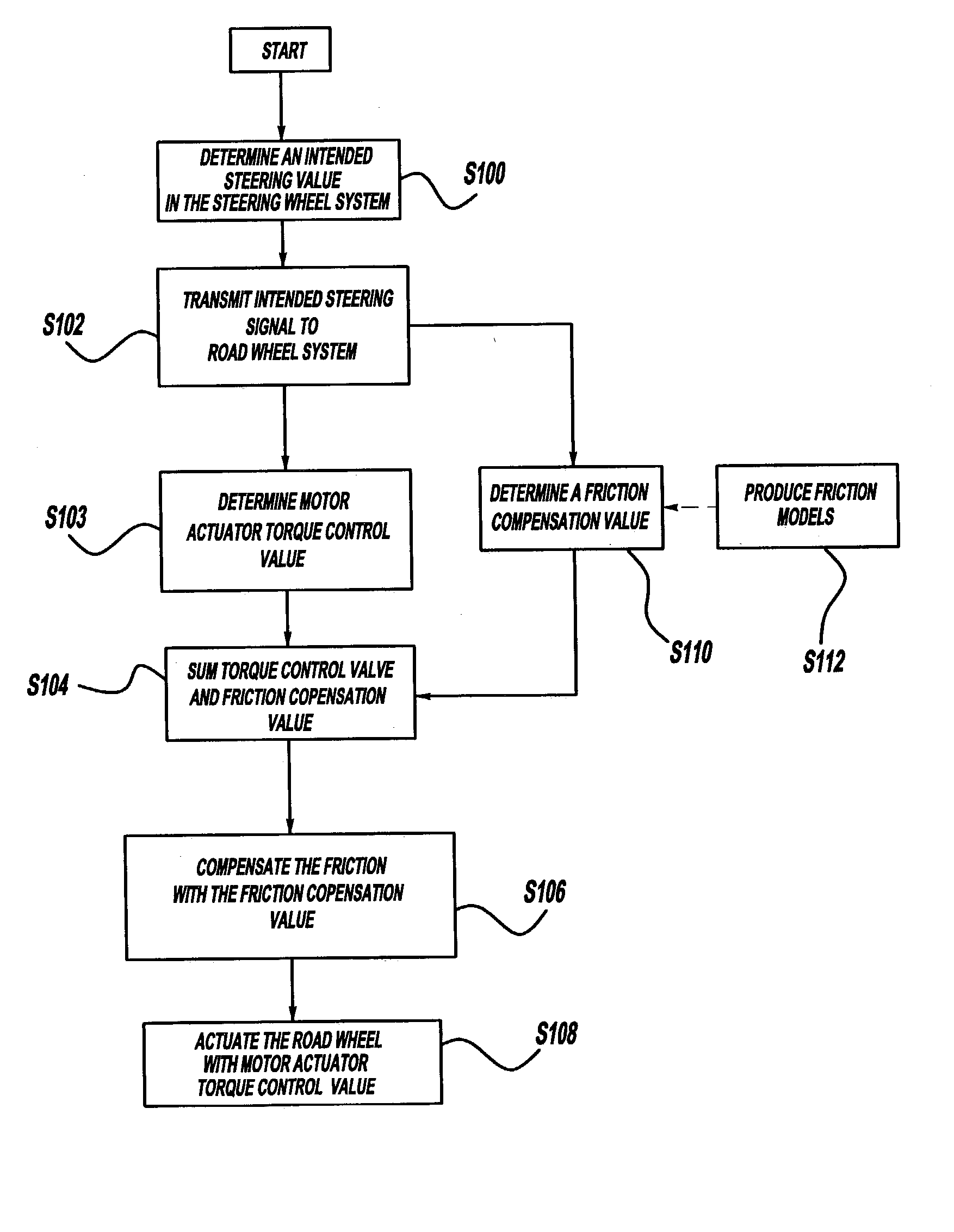
Friction compensation in a vehicle steering system
InactiveUS20040138797A1Eliminate the effects ofSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsFriction torqueControl signal
The present invention provides systems and methods of friction compensation in a steer-by-wire system or in a general electric steering system using control, estimation and modeling methodologies. A friction compensator in the steer-by-wire control system produces a friction compensating torque value equal and opposite in sign to the instantaneous friction torque. This compensating friction torque is added to the steering system control signal to eliminate the effects of friction present in the system such that the system performances are improved. The friction compensator produces the compensating friction torque according to one of two schemes: model-based or non-model based. The model-based scheme encompasses a number of different methods including a standard model-based scheme, a disturbance torque observer-based scheme, an adaptive friction compensation scheme, or a model reference adaptive control scheme. The non-model based scheme includes a fuzzy logic scheme.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Regional scale plant disease and insect pest prediction method based on multi-source information
The invention relates to the technical fields of remote sensing and spatial data analysis treatment and agronomy, and discloses a regional scale plant disease and insect pest prediction method based on multi-source information. The regional scale plant disease and insect pest prediction method based on the multi-source information comprehensively applies the satellite remote sensing data reflecting vegetation physiological status and the regional scale meteorological data reflecting the meteorological conditions to the prediction of plant diseases and insect pests, thereby overcoming the defect that a traditional disease and insect pest prediction model does not take the influence on the occurrence rate of the plant diseases and insect pests from the vegetation growth status habitat parameter differences among fields into account. The regional scale disease and insect pest prediction method based on the multi-source information takes the vegetation stress conditions and the habitat information of different planting fields into the model input, outputs the occurrence rate of the plant diseases and insect pests in different planting areas through a standard model under a certain field condition, and outputs more accurate information about the predication of the plant diseases and insect pests.
Owner:BEIJING RES CENT FOR INFORMATION TECH & AGRI
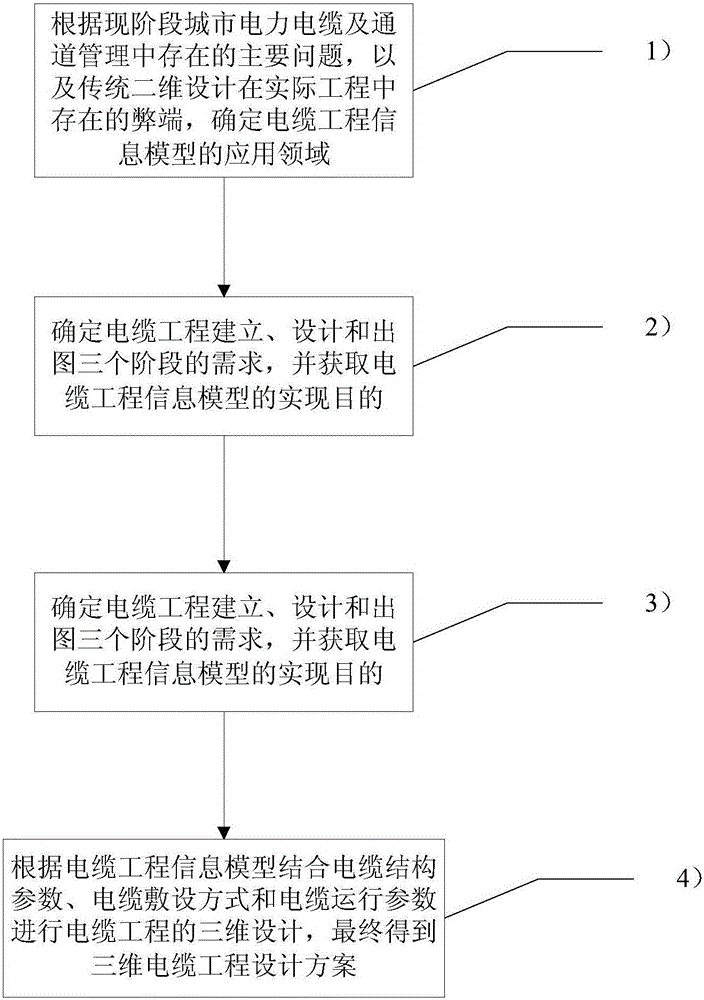
Three-dimension design method based on cable engineering information model
InactiveCN105005676ASolve the difficulty of quickly copyingSolve the problem of easy modificationSpecial data processing applicationsPower cableThree stage
The invention relates to a three-dimension design method based on a cable engineering information model. The three-dimension design method comprises the following steps: 1), according to main problems existing in city power cable and channel management at the present stage and defects of the conventional two-dimension design, which exist in actual engineering, determining an application field of the cable engineering information model; 2), determining demands in the three stages of cable engineering building, design and drawing and obtaining the achieving purpose of the cable engineering information model; 3), building the cable engineering information model by using a three-dimension design platform and according to a standard model base and regional digital model base; 4), carrying out three-dimension design on cable engineering according to the cable engineering information model and by combining cable structure parameters, a cable laying method and cable running parameters, and finally, obtaining a three-dimensional cable engineering designing scheme. Compared with the prior art, the three-dimension design method provided by the invention has the advantages of being intuitive and accurate, and advanced in platform and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
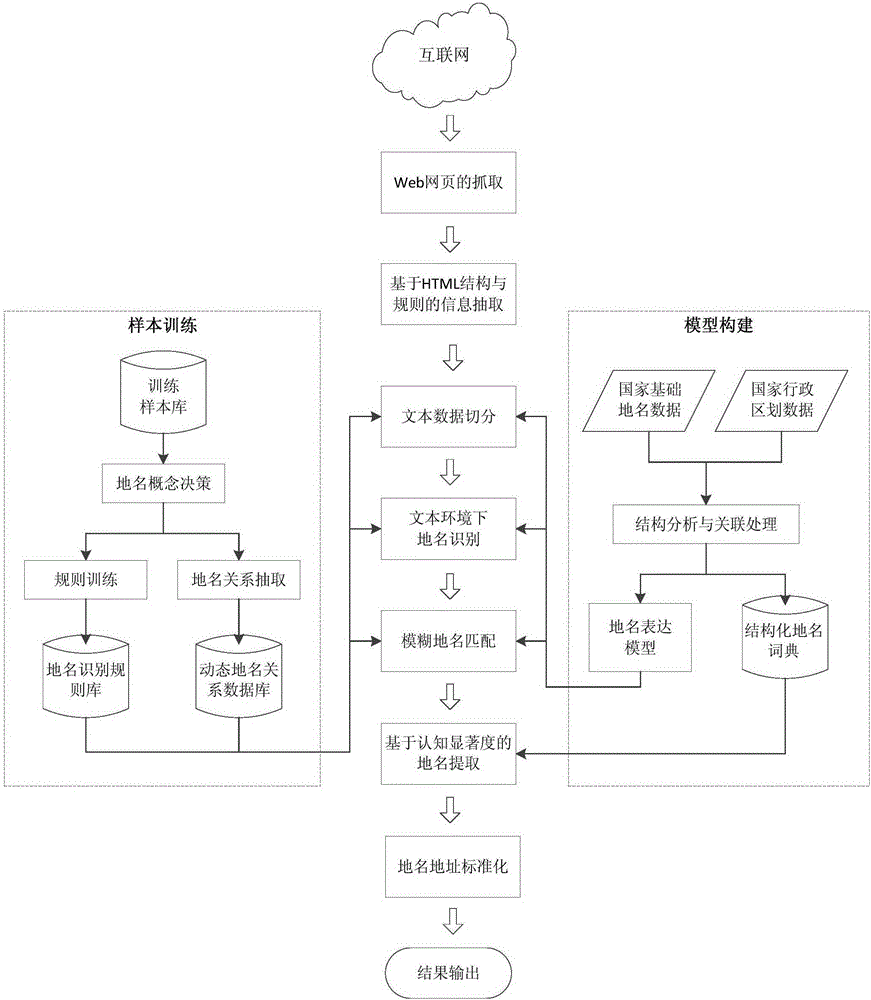
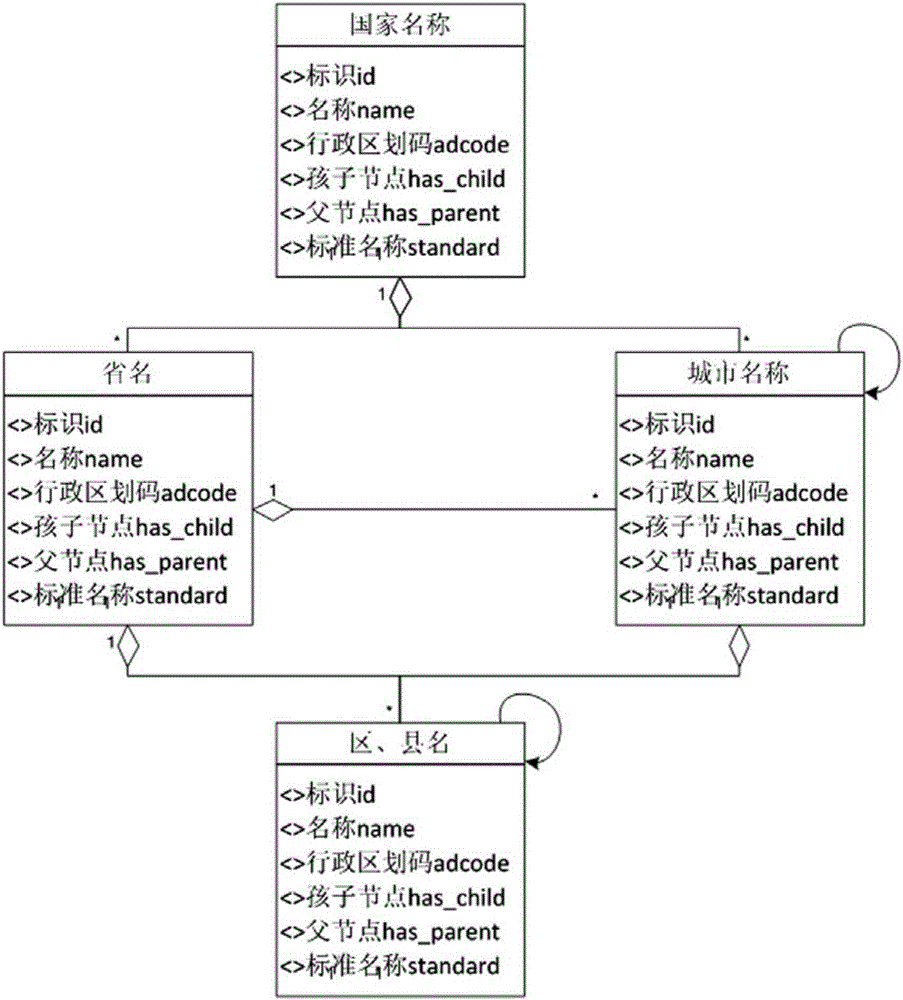
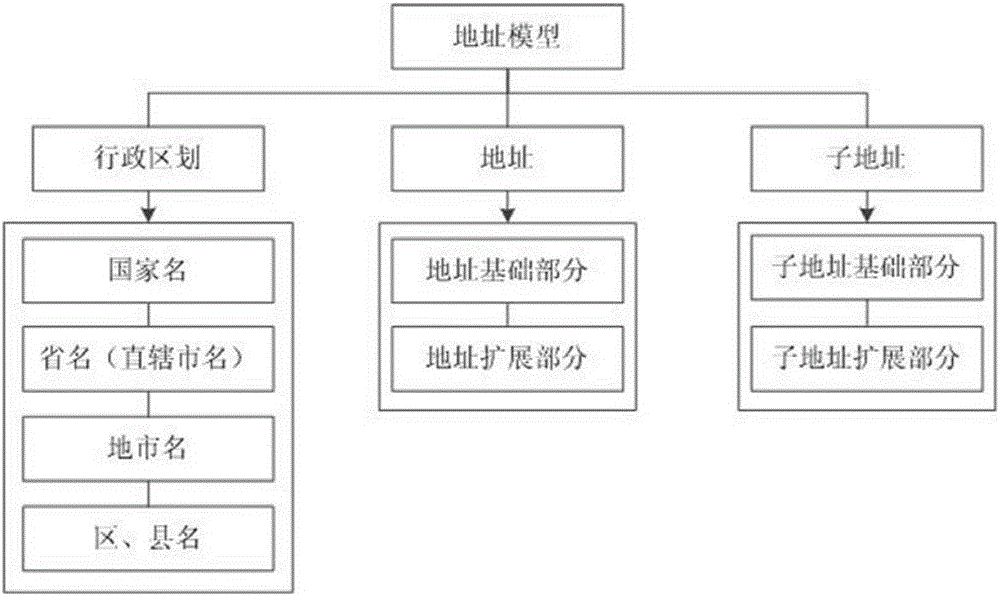
Internet-oriented place name extraction and standardization method
InactiveCN105224622AImprove accuracyRealize automatic identificationRelational databasesGeographical information databasesSpatial positioningThe Internet
The invention discloses an internet-oriented place name extraction and standardization method. According to the method, aimed at existing ways and structural features of place names and addresses in an internet page, identification is performed based on state administrative division information and a nationwide basic place name and address library by utilizing identification rules and dynamic relationships of the place names and the addresses, a multi-stage place name and address expression model and an extraction method are researched, automatic identification, extraction and standardization of Chinese place names and addresses in text information of the internet page are realized with reference to a place name and address standard model through superior-subordinate semantic relationships of the place names and the addresses in the text, and a technical basis is provided for spatial positioning of related geographic information of geographic entities, events and the like.
Owner:CHINASO INFORMATION TECH
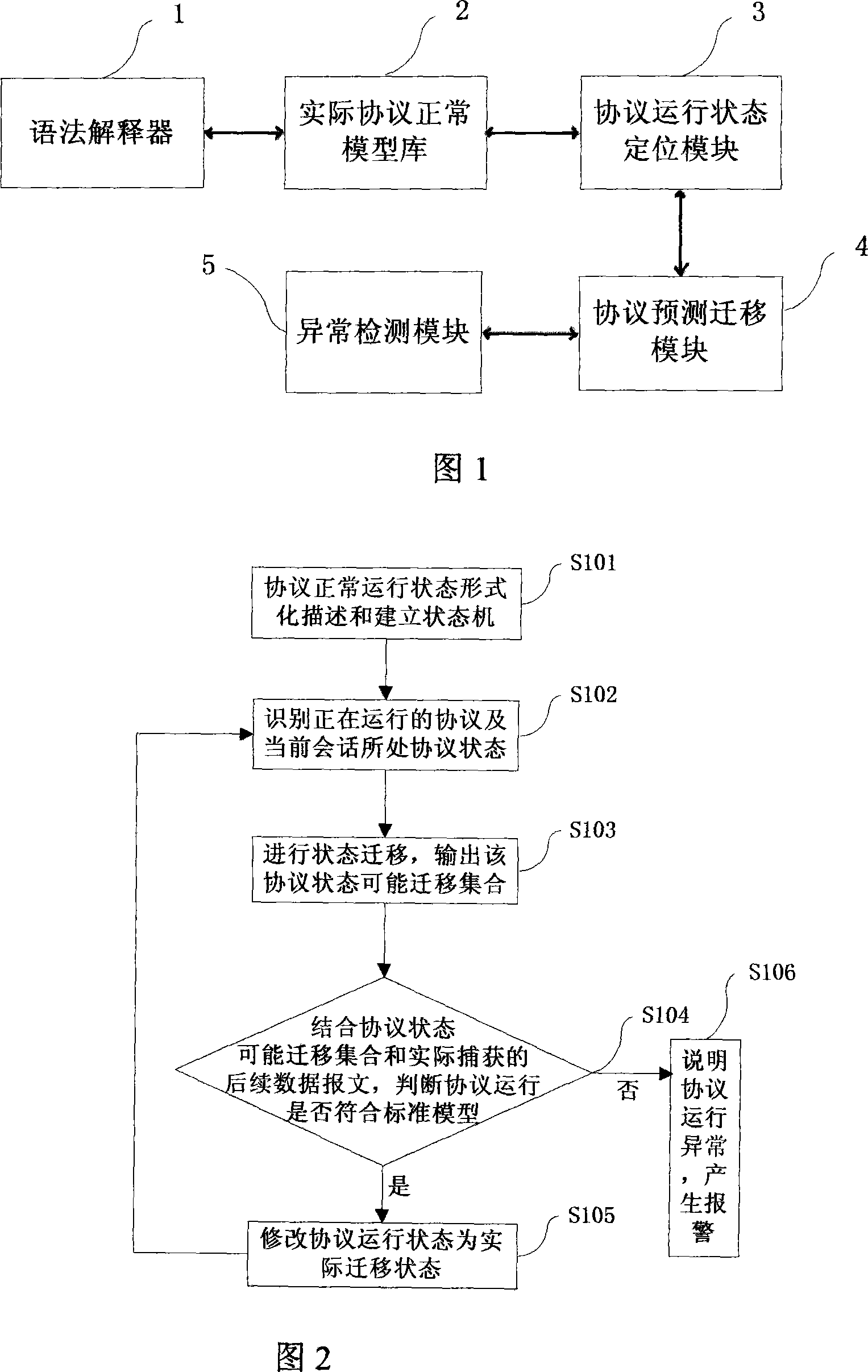
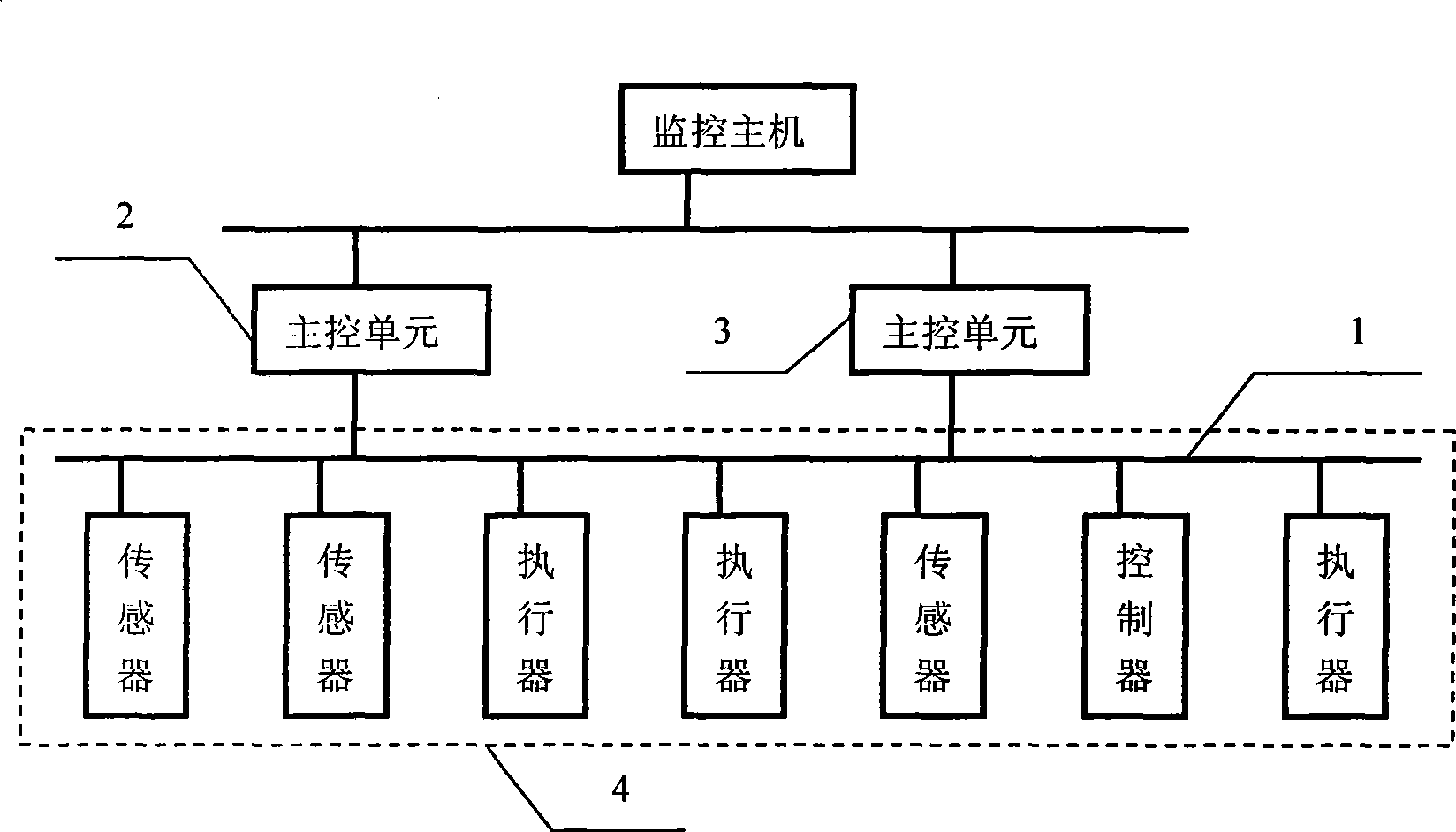
Condition detection based protocol abnormity detecting method and system
The present invention relates to a based on a status measure protocol abnormal measure method and system. The foundation of a protocol normal running state model comprises the examination of a protocol formal description expression and the making of a correlation protocol state machine; a protocol running state orientation moment realizes the exact orientation of the used protocol state in the present conversation towards the exact network communication data message; a protocol running state moving moment realizes the forecast of the next likely ongoing state moving and makes a normal state running concourse of the after-orientation protocol state; an abnormal examination moment judges whether the present protocol running accords with the protocol standard model and return the examination result by the gained subsequent message and the forecast running concourse. The present invention can check the correlative abnormal protocol in the network protocol communication process according to the exact protocol of the practically gained message and can conveniently expand the protocol normal running model according to the practical requirement.
Owner:BEIJING VENUS INFORMATION TECH +1
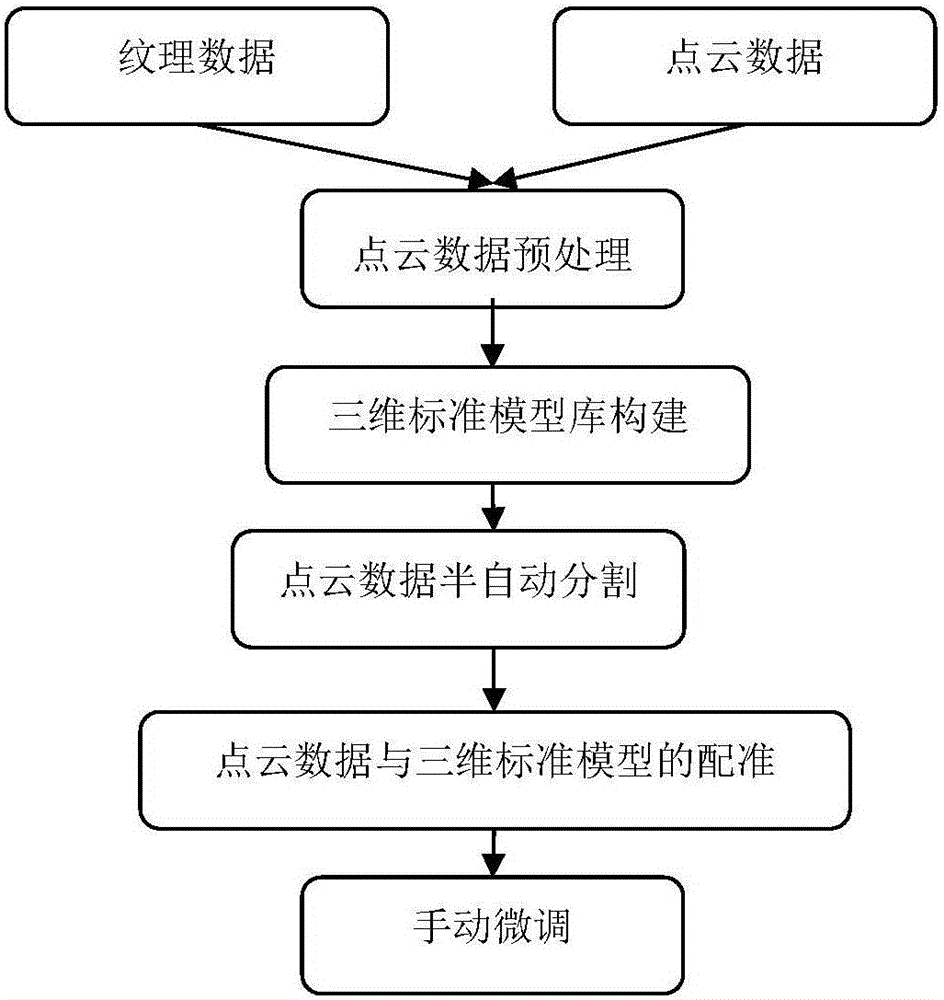
Three-dimensional transformer station semi-automatic reconstruction method based on laser point cloud data
InactiveCN105844064ARealize semi-automationReduce manual interventionDetails involving processing stepsSpecial data processing applicationsTransformerReconstruction method
Owner:XIAMEN GREAT POWER GEO INFORMATION TECH +1
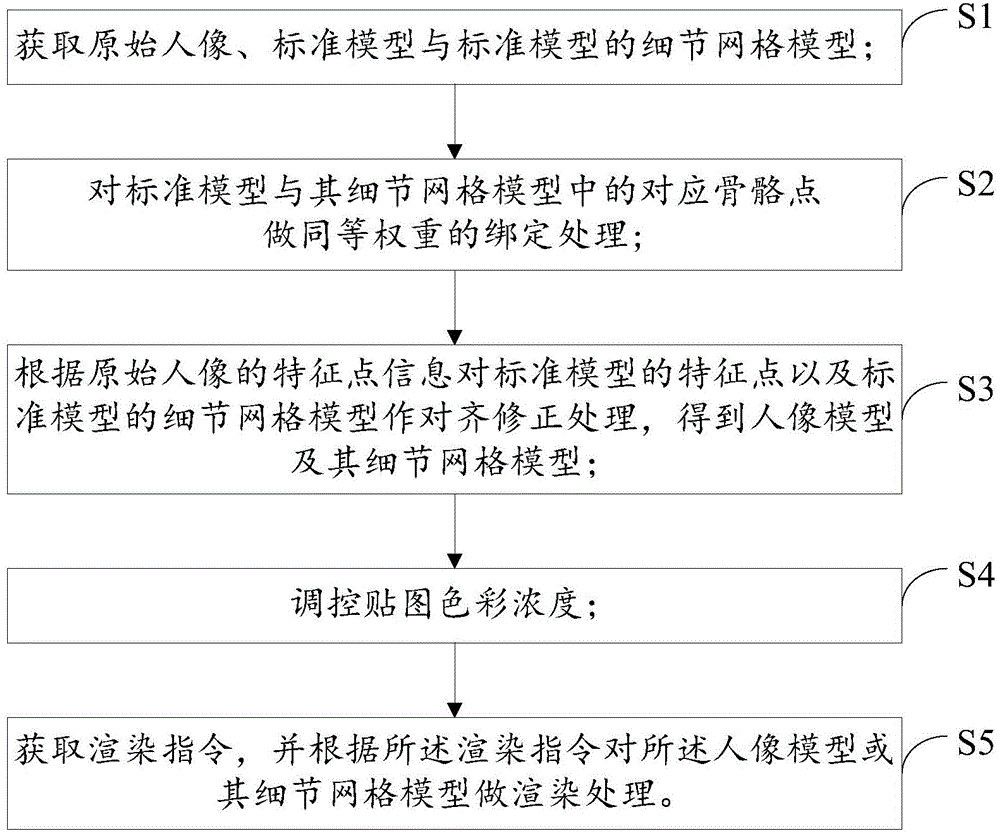
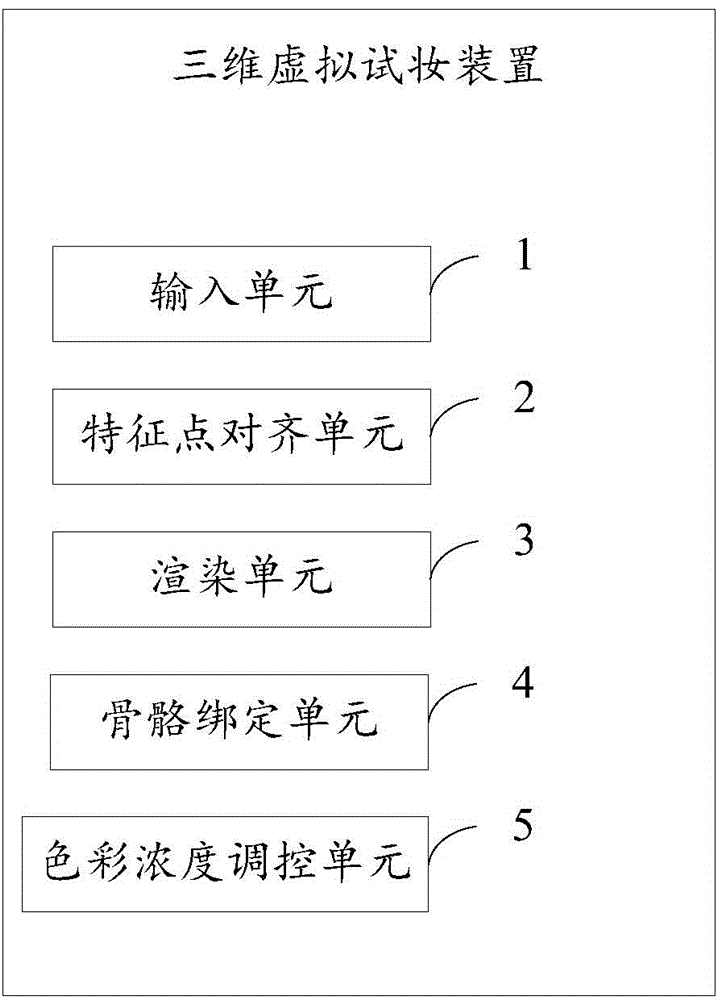
Three-dimensional virtual make-up trial method and device
InactiveCN104463938AFine makeup effectImprove operational efficiency3D-image renderingAnimationSimulation
The inventor provides a three-dimensional virtual make-up trial method in order to solve a virtual make-up trial problem. The method includes the following steps that an original person image, a standard model and a detail grid model of the standard model are obtained, the detail grid model of the standard model is built according to information of all characteristic points of the standard model, and the detail grid model of the standard model corresponds to the characteristic points one to one; the characteristic points of the standard model and the detail grid model of the standard model are subjected to aligning amendment processing according to information of characteristic points of the original person image, and a person image model and a detail grid model of the person image model are obtained; a rendering instruction is acquired, and rendering processing is performed on the person image model or the detail grid model of the person image model according to the rendering instruction. The invention further provides a corresponding three-dimensional virtual make-up trial device. The three-dimensional virtual make-up trial method and device are high in effect reality sense, information of a certain depth can be provided, and deformation of maps in the skinned animation process is avoided.
Owner:FUJIAN TQ DIGITAL
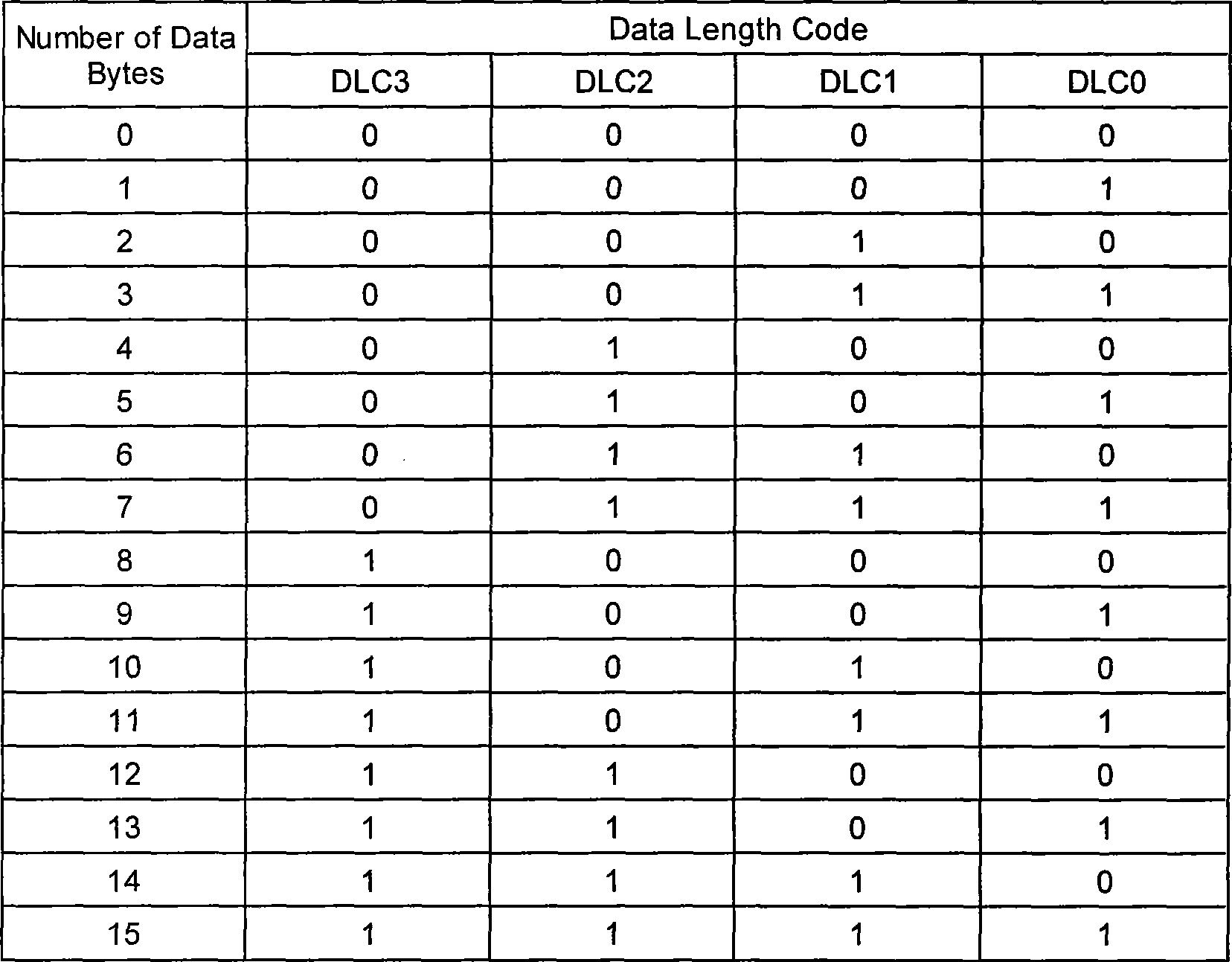
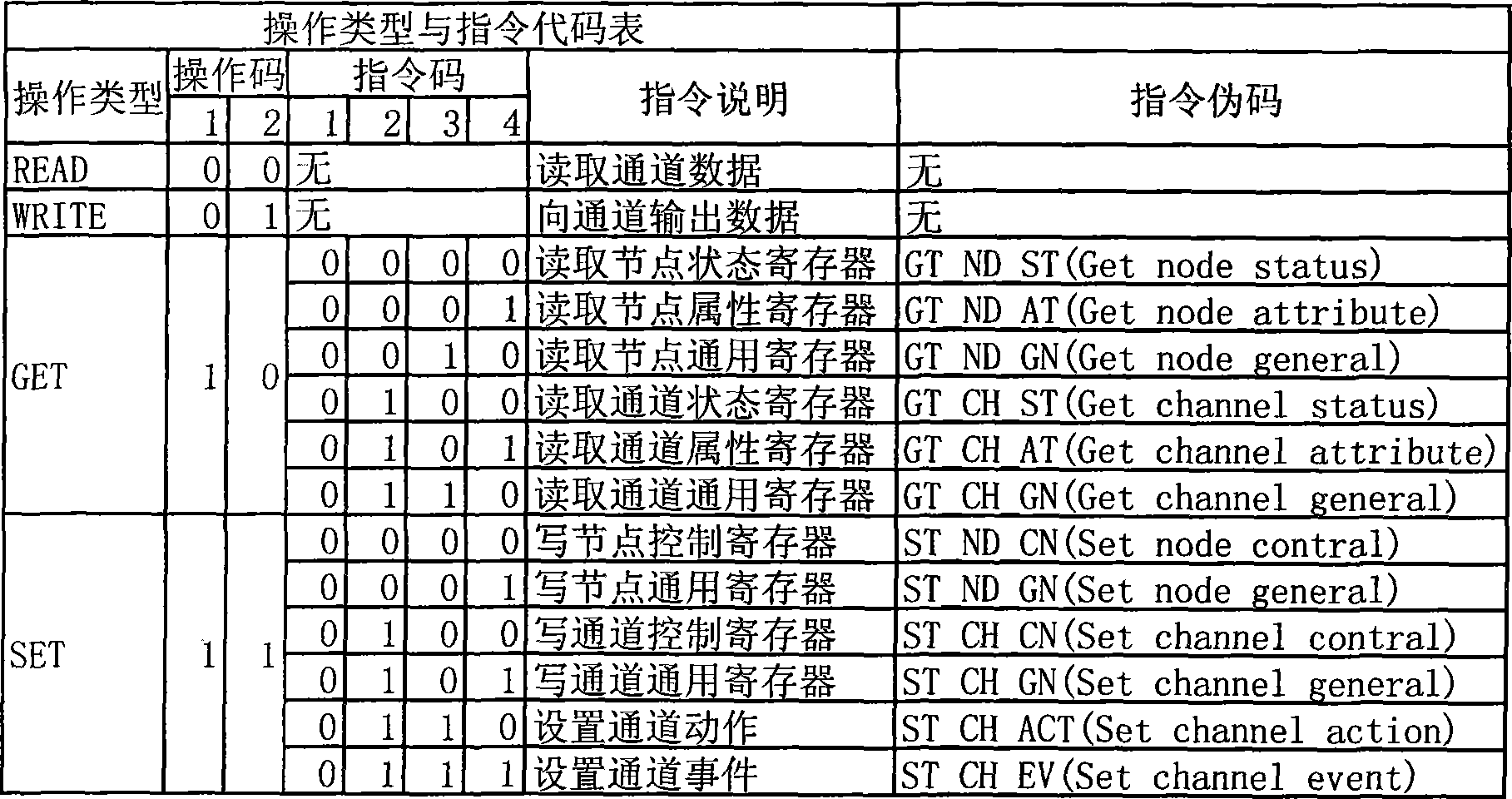
Single bus sensor network protocol
InactiveCN101374082AQuick responseKeep the master-slave communication modeBus networksLine sensorData field
The invention relates to a unibus sensor network protocol which follows the ISO / OSI standard model and provides a physical layer, a data link layer and an application layer. The physical layer defines a substrate communication medium, a driving mode and the form of a connecting terminal. The unibus sensor network protocol is characterized in that the data link layer defines the space size of the address of a node and the addressing method, the maximal transmitting data byte number, the composition method of data frames, the verification method and the arbitration method; during the compunctions process, the data of the application layer is transmitted in a manner of being packed in the data field of the link layer, the data of the application layer include the operating codes, the channel numbers, the command codes, the parameters related to the command codes, the transmitted data, the filling data, and the length, the parameters and the data total length of the parameter data of one frame. The unibus sensor network protocol supports both the master-slave communication mode and the event / action communication mode and improve the flexibility of network organization; supports a bit-based non-destructive bit-by-bit arbitration mode; meets the real-time requirement; supports the node event, the action configuration and the channel operation of the node; reduces the burdens of the host machine; facilitates the integration of the nodes; and reduces the production cost of the product.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
Printed circuit element polarity machine vision detection method and device
InactiveCN103675588AReduce personnel costsReduce chance of misconfigurationElectrical testingCapacitanceElement model
Provided is a printed circuit element polarity machine vision detection method and a device. A guide rail used for conveying a printed circuit board to be detected is arranged in a test area. The guide rail is provided with stroke switches controlled by sensors. An enclosed working case covering the test area is arranged above the guide rail. The internal part of the enclosed working case is provided with a light source capable of adjusting brightness, and multiple sensors. Different types of elements to be detected are arranged in the test area of the enclosed working case with the light source capable of adjusting brightness in turn, and element samples are acquired. Categorization is performed according to model numbers of capacitors or diodes, and detection parameters required by the elements to be detected are confirmed. Aiming at difference of positions of the printed circuit board elements, the corresponding positions of different elements on the circuit board are designated, and corresponding standard model types of different printed circuit boards are formulated via model type identification symbols, the element model numbers, the positions and detection parameter values. A machine vision mode is utilized to substitute a manual vision detection mode so that situations of staff negligence and errors of leak detection of polarity directions of the polarity elements are reduced, production cost is reduced and production quality is enhanced.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
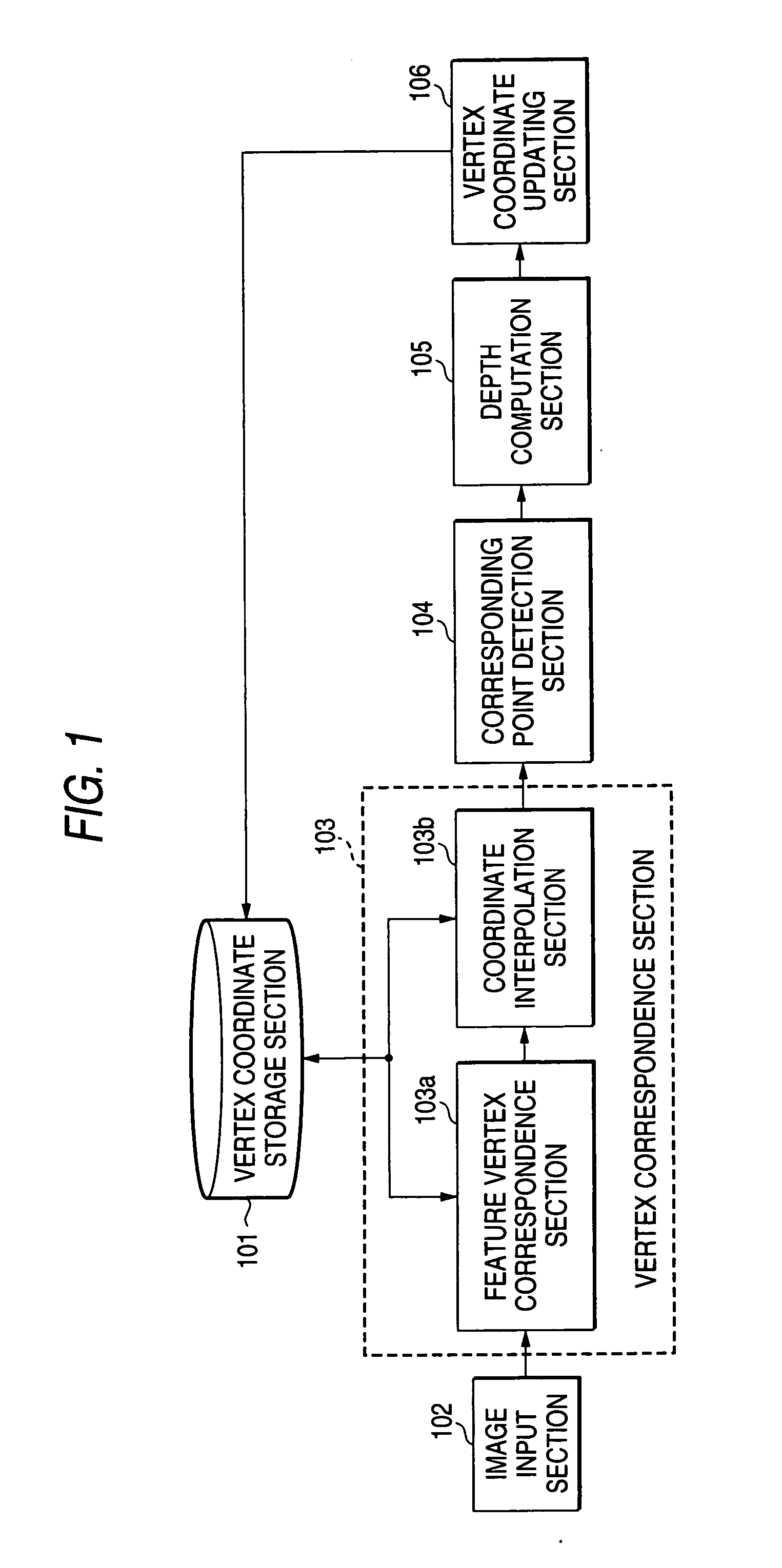
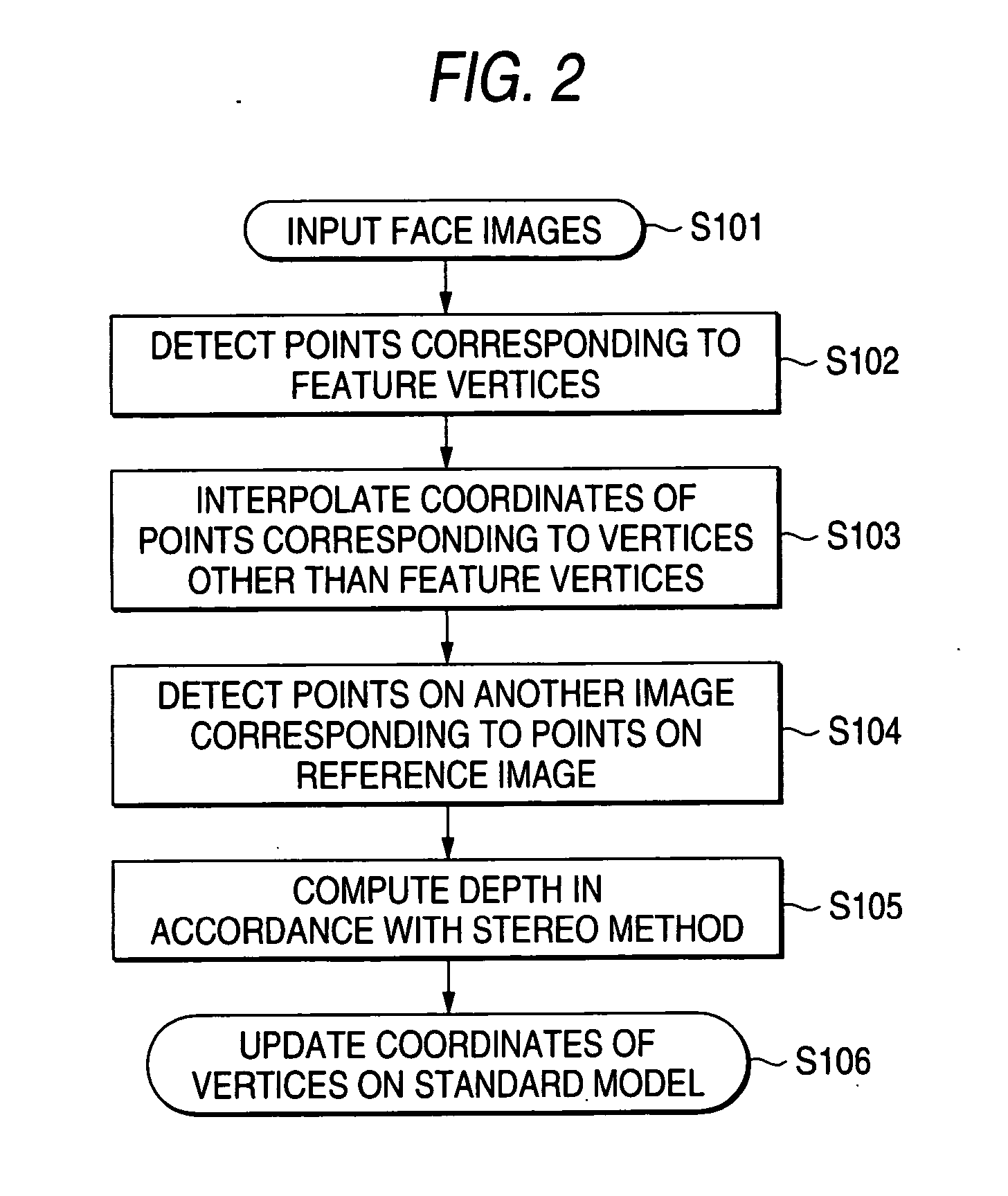
Three-dimensional model generating apparatus, method and program
InactiveUS20060210148A1Highly-accurate authenticationHighly-accurate authentication of a person3D-image renderingThree-dimensional object recognitionComputer visionThree dimensional model
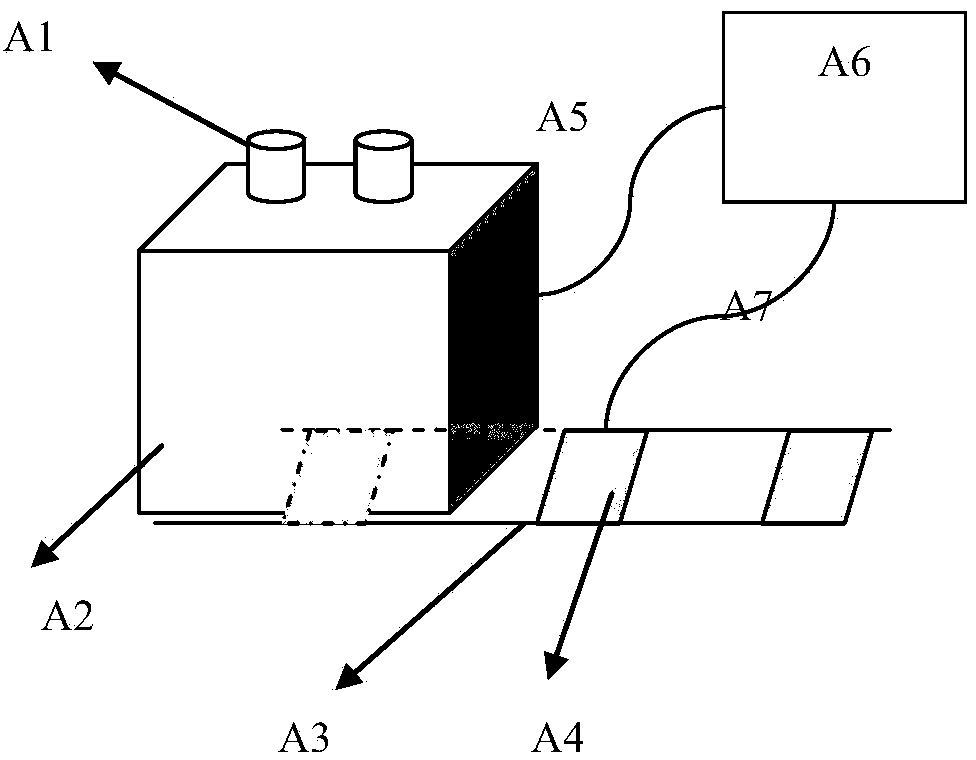
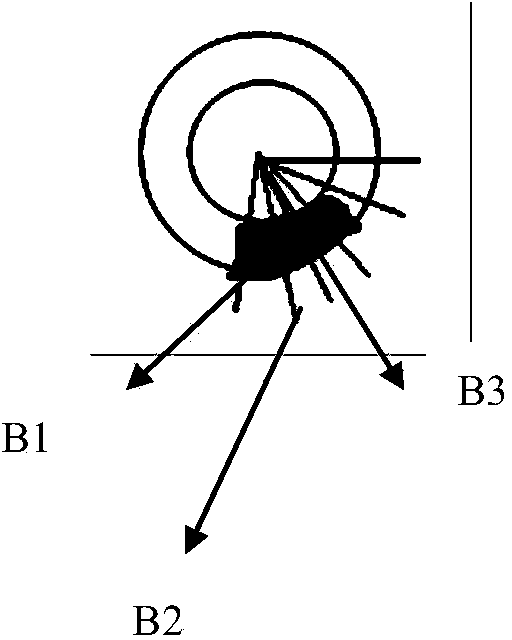
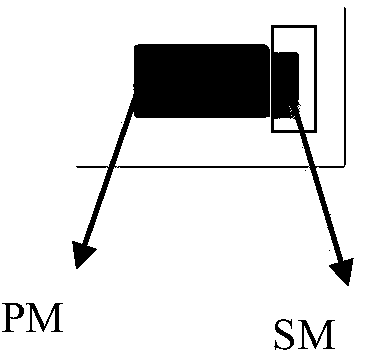
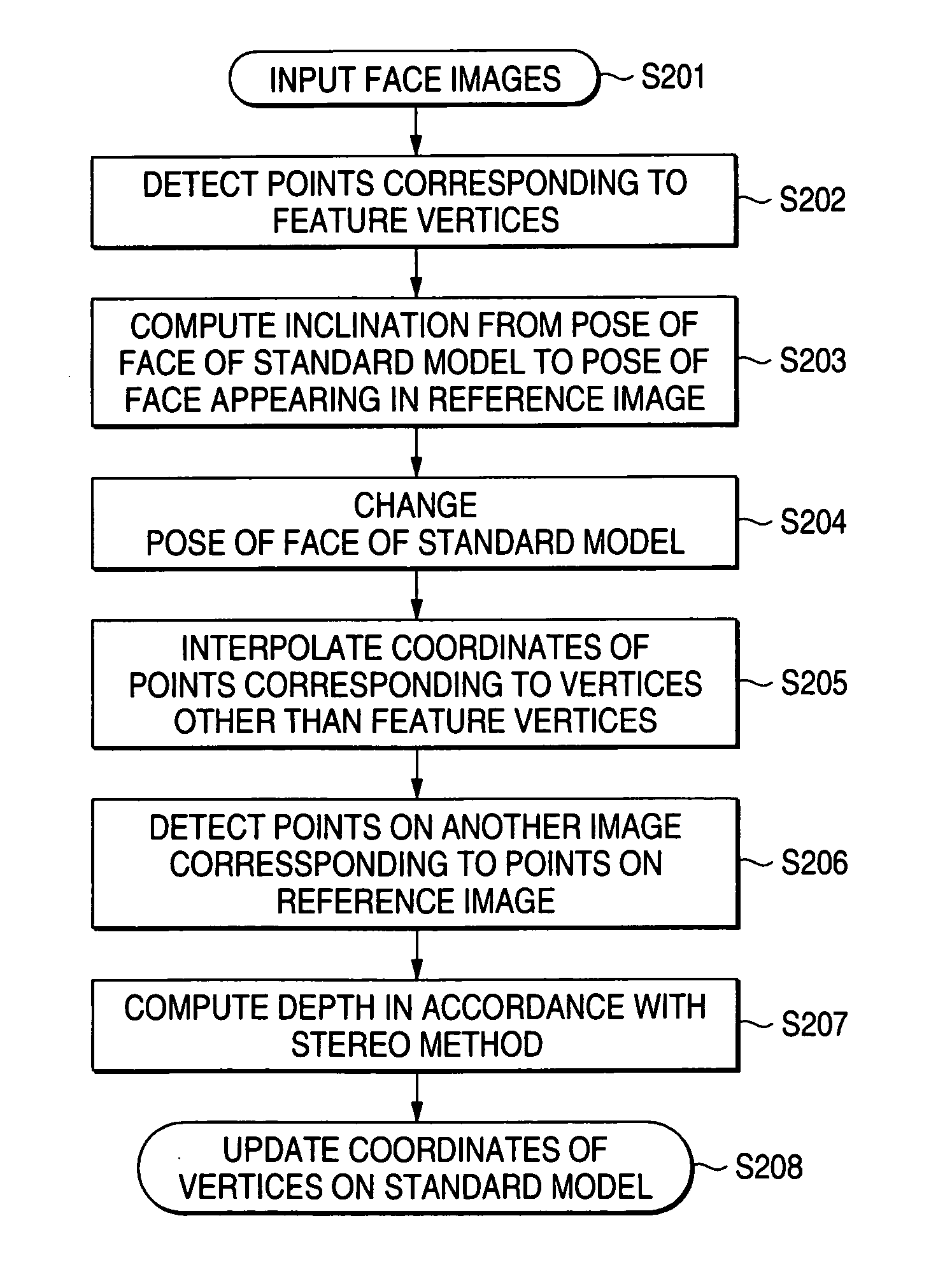
An apparatus for generating a three-dimensional model of an object includes a storage unit that stores three-dimensional coordinates of plural vertices on a standard model of the object, an image input unit that inputs plural input images acquired by photographing the object, a first detection unit that detects a coordinate of a first point corresponding to a vertex on the standard model, from a first image selected from among the plural input images, a second detection unit that detects a coordinate of a second point corresponding to the coordinate of the first point, from a second image other than the first image, a depth computation unit that computes a depth of the first point by using the coordinates of the first and second points, and a first update unit that updates the three-dimensional coordinate on the standard model based on the coordinate of the first point and the calculated depth.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
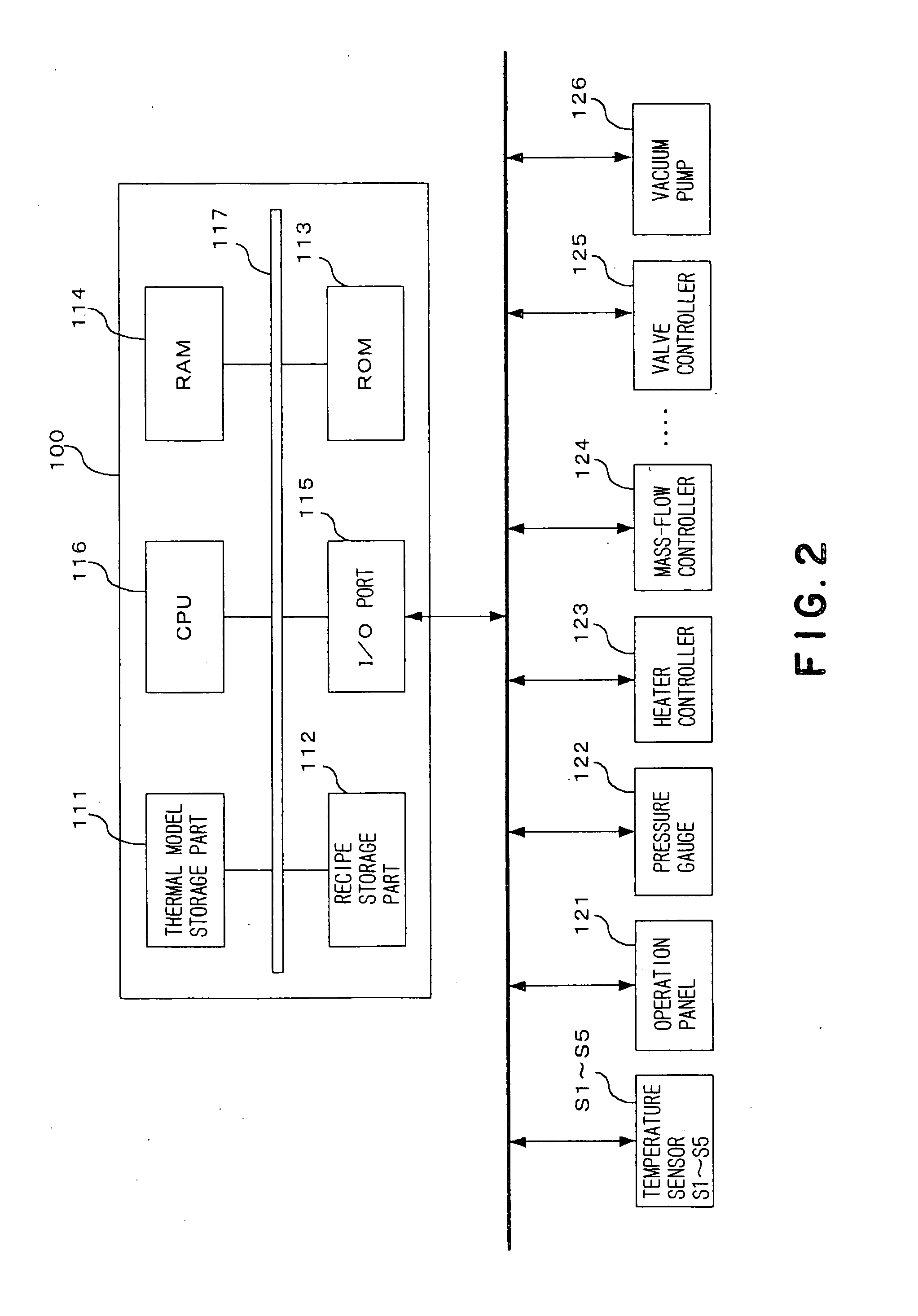
Heat treatment apparatus and method of calibrating the apparatus
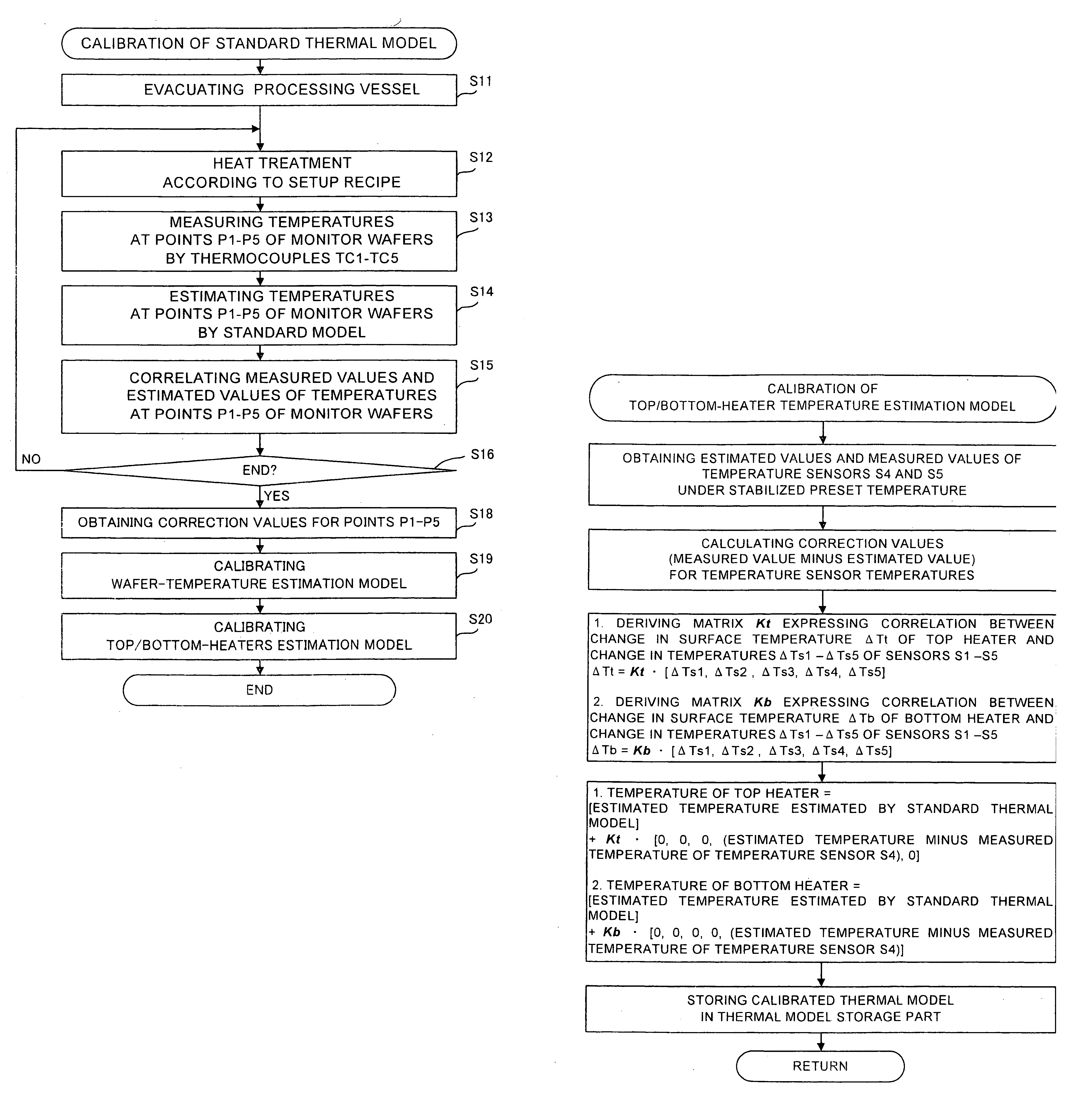
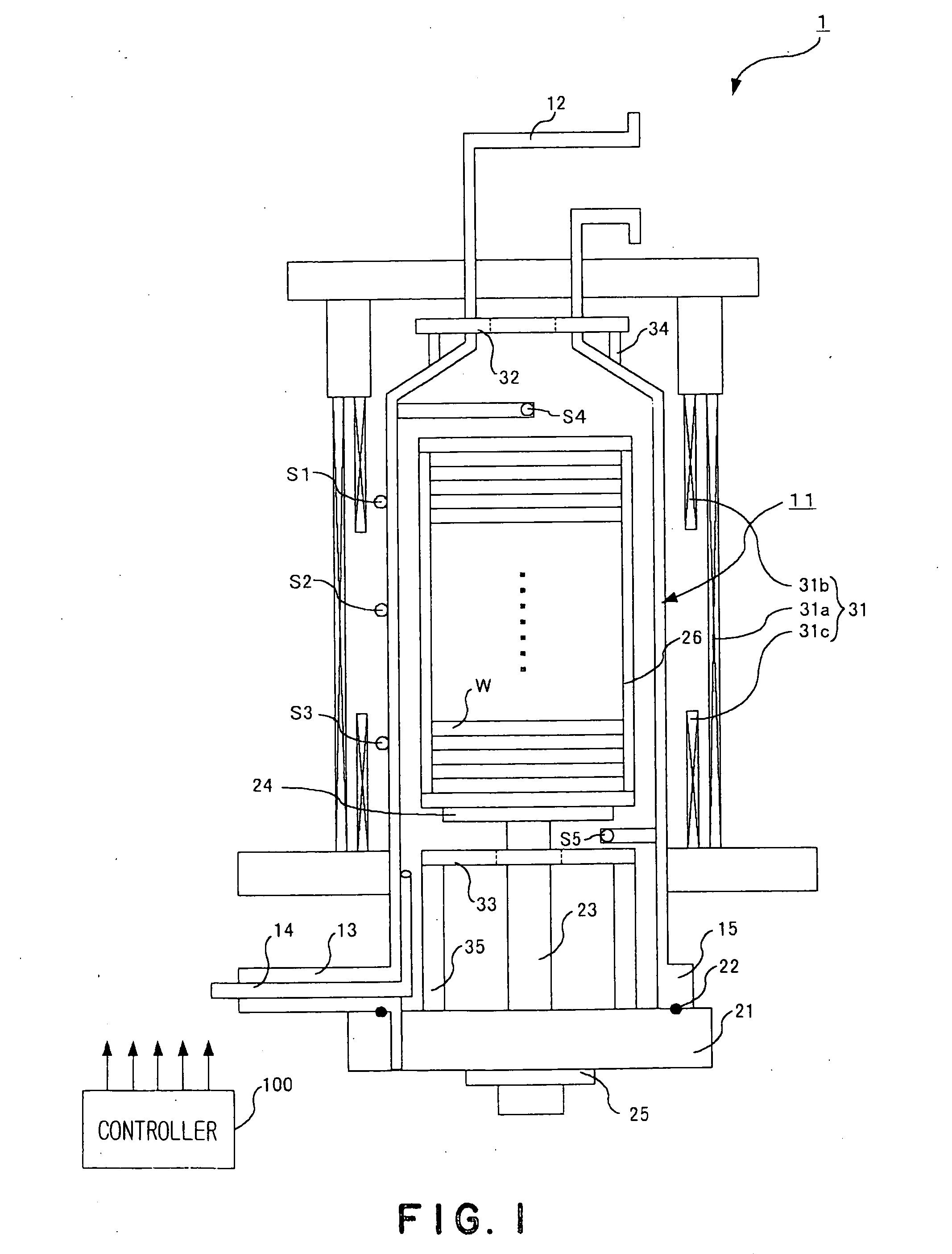
ActiveUS20070195853A1Accurate temperature estimationAccurate estimateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharge manipulationTemperature controlEngineering
The present invention provides precise temperature estimation in a heat treatment apparatus that estimates temperatures of process objects by using a thermal model and performs a heat treatment while performing a temperature control based on the estimated temperatures. The heat treatment apparatus 1 includes a processing vessel 11 accommodating plural wafers W, plural heaters 31 to 33 and plural temperature sensors S1 to S5, and stores the thermal model. The heat treatment apparatus 1 estimates temperatures of the wafers W based on outputs of the temperature sensors S1 to S5 by using the thermal model and controls the heaters 31 to 33 based on the estimated temperatures, applying a heat treatment to the wafers W. The thermal model for an individual apparatus is made by calibrating a standard thermal model designed for a standard apparatus. The standard model calibration is performed by heating an interior of the processing vessel 11, measuring the temperatures of the wafers W in the processing vessel 11, estimating the temperatures of the wafers W by using the thermal model, comparing the measured temperature and the estimated temperature, and calibrating the standard thermal model so that the measured temperature substantially coincide with the estimated temperature.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Model base for craniofacial reconstruction and craniofacial reconstruction method
ActiveCN103258349AAchieve facial restorationImprove science3D modellingPattern recognitionRelational model
The invention discloses a model base for craniofacial reconstruction and a craniofacial reconstruction method. The model base for craniofacial reconstruction comprises a craniofacial standard model base and a craniofacial PLSR shape relation model base, wherein physiological points are defined on the craniofacial standard model base. According to the craniofacial reconstruction method, a craniofacial three-dimensional surface model base, on which physiological point corresponding relations are defined, is established through a skin layer point correspondence method and a skull point correspondence method, wherein the skin layer point correspondence method combines partition deformation and multiple restrictions, and the skull point correspondence method is base on TPS overall deformation and multiple restrictions. A craniofacial partial shape relation model based on PLSR is established on the basis of the craniofacial three-dimensional surface model base, and thus the craniofacial PLSR shape relation model base is obtained. By means of a craniofacial standard model, which has the same forensic anthropological information with a to-be-reconstructed skull, in the craniofacial reconstruction model base and the craniofacial PLSR shape relation model, the face of the skull is reconstructed. The craniofacial reconstruction model base is established in the craniofacial partial shape relation modeling method based on PLSR, and the problems that samples are small and variables have multiple correlations in the craniofacial reconstruction method based on statistical theory are solved.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
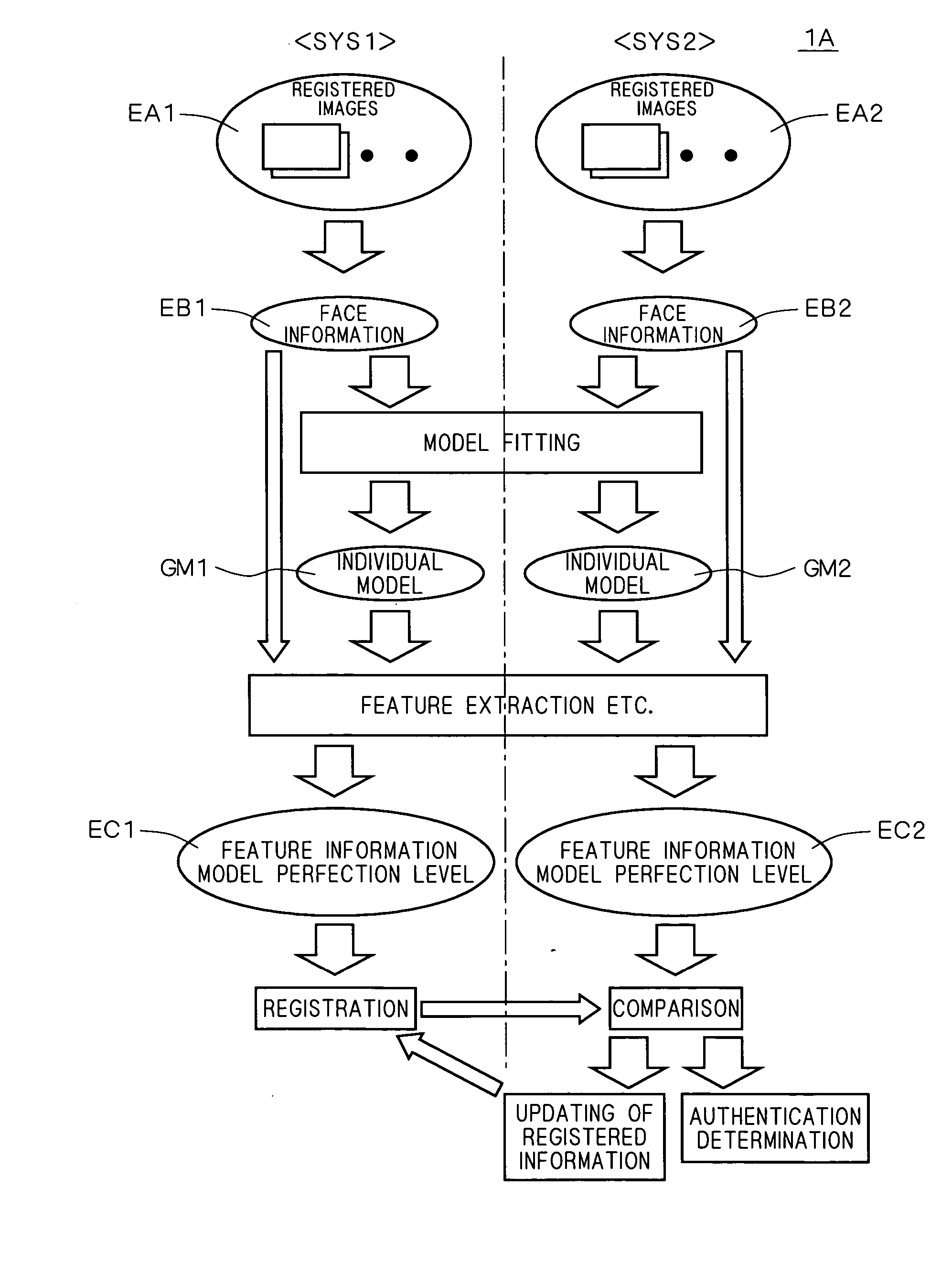
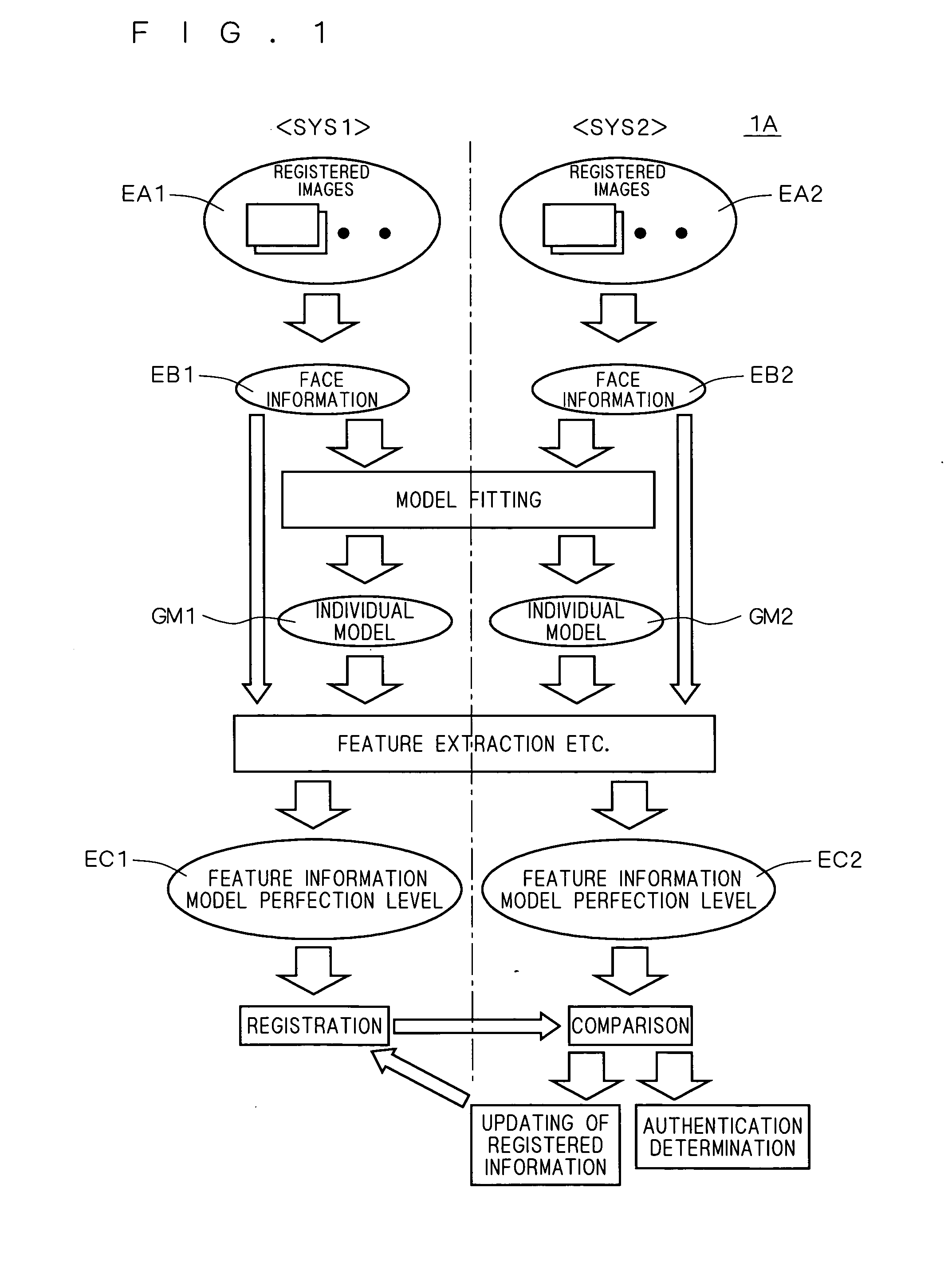
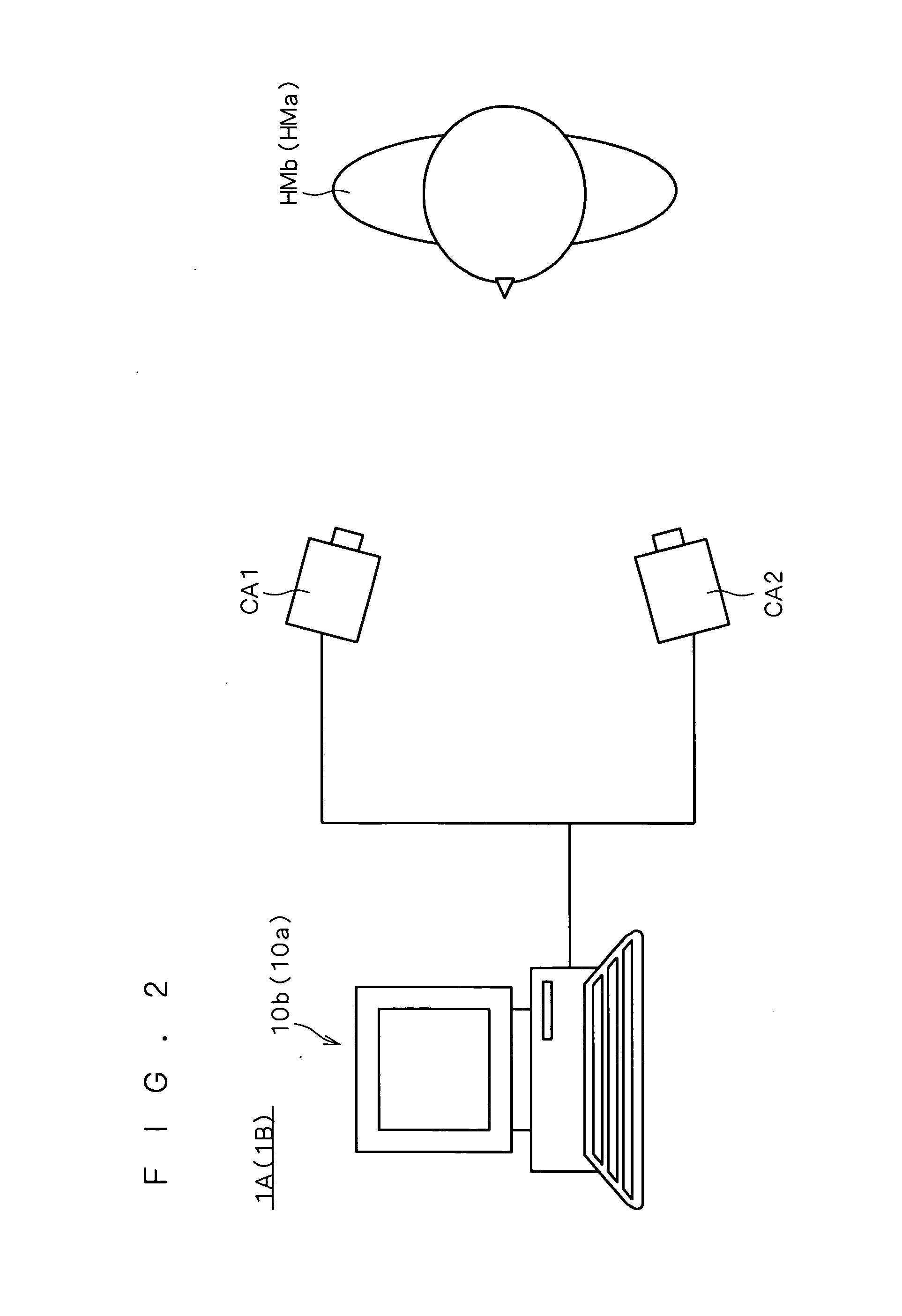
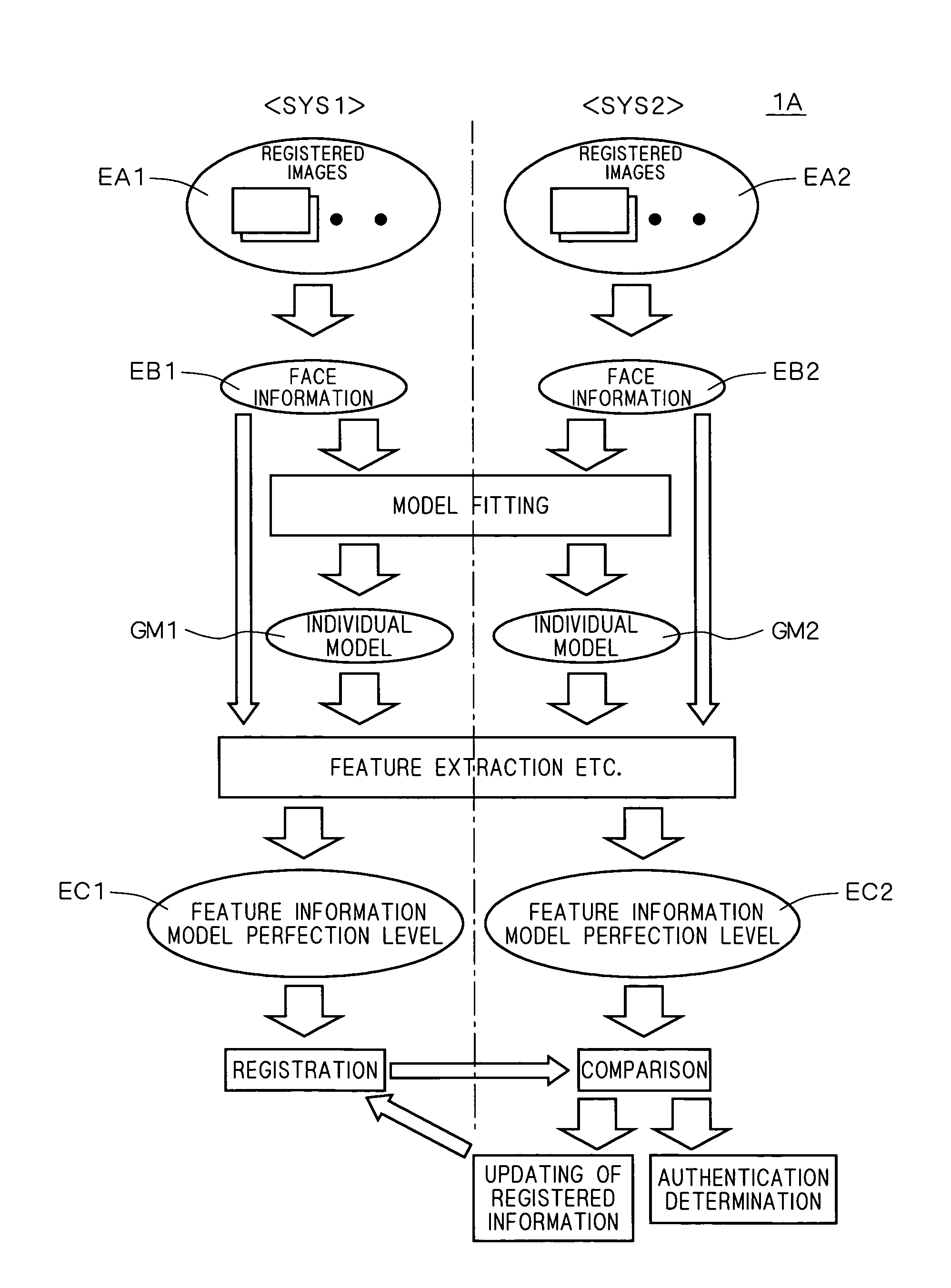
Authentication system, registration system, and program
InactiveUS20070098230A1Accurate authenticationAchieve reliabilityThree-dimensional object recognitionModel modificationThree dimensional shape
An authentication system comprises: a generating part for generating face information including at least one of three-dimensional shape information and two-dimensional information in the face of a first person to be authenticated on the basis of measurement information of the first person; a model modifying part for modifying a standard model of a human face by using the face information, thereby generating an individual model of the face of the first person; a calculating part for calculating a first model perfection level as a perfection level of the individual model on the basis of reliability of the face information; an extracting part for extracting first feature information as feature information of the first person from the individual model; an obtaining part for obtaining second feature information as feature information of a second person to be compared which is pre-registered; and an authenticating part for performing an authenticating operation on the first person by using the first model perfection level in addition to similarity between the first feature information and the second feature information.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
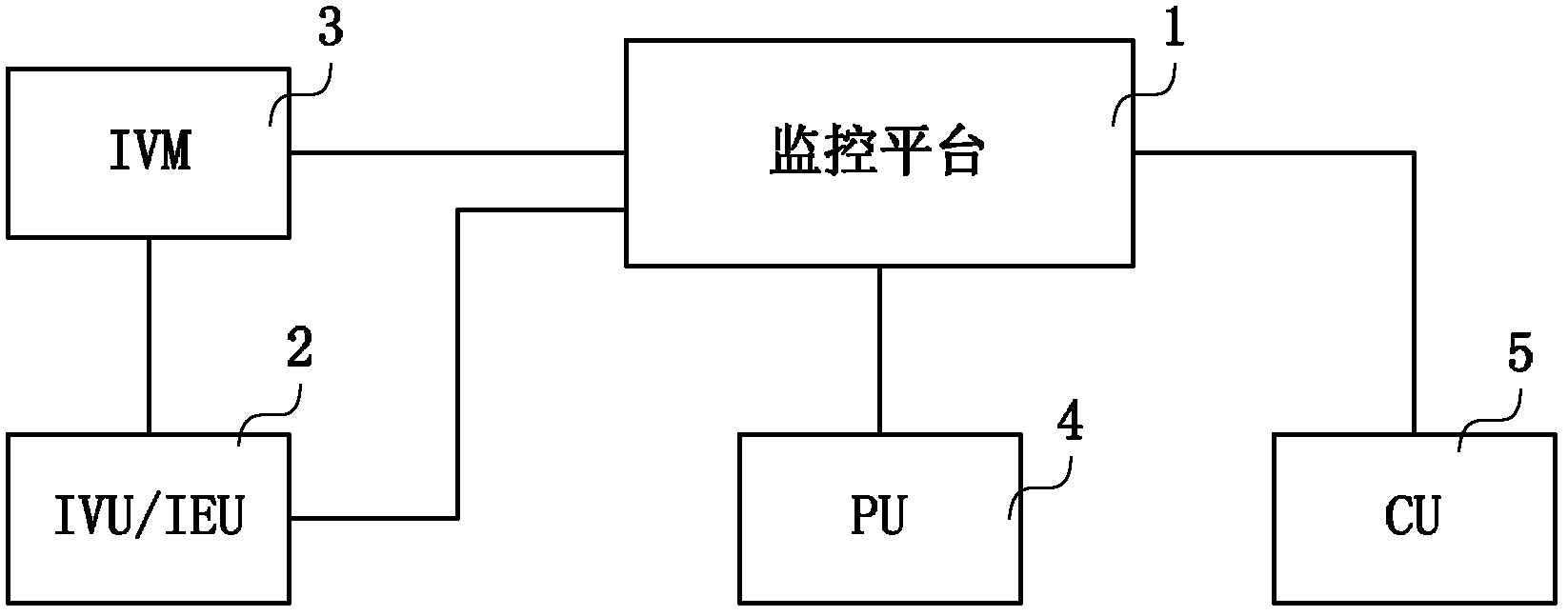
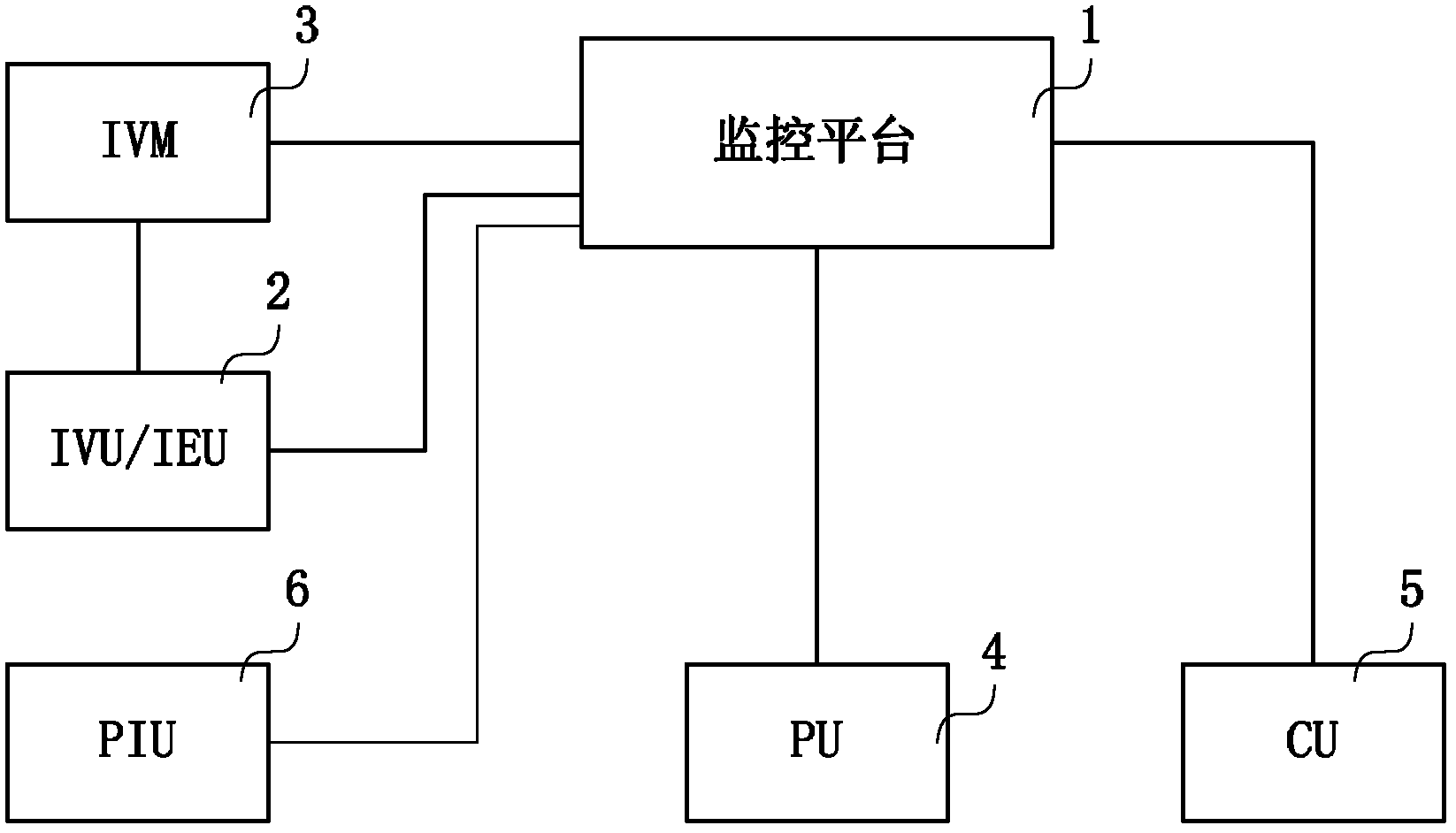
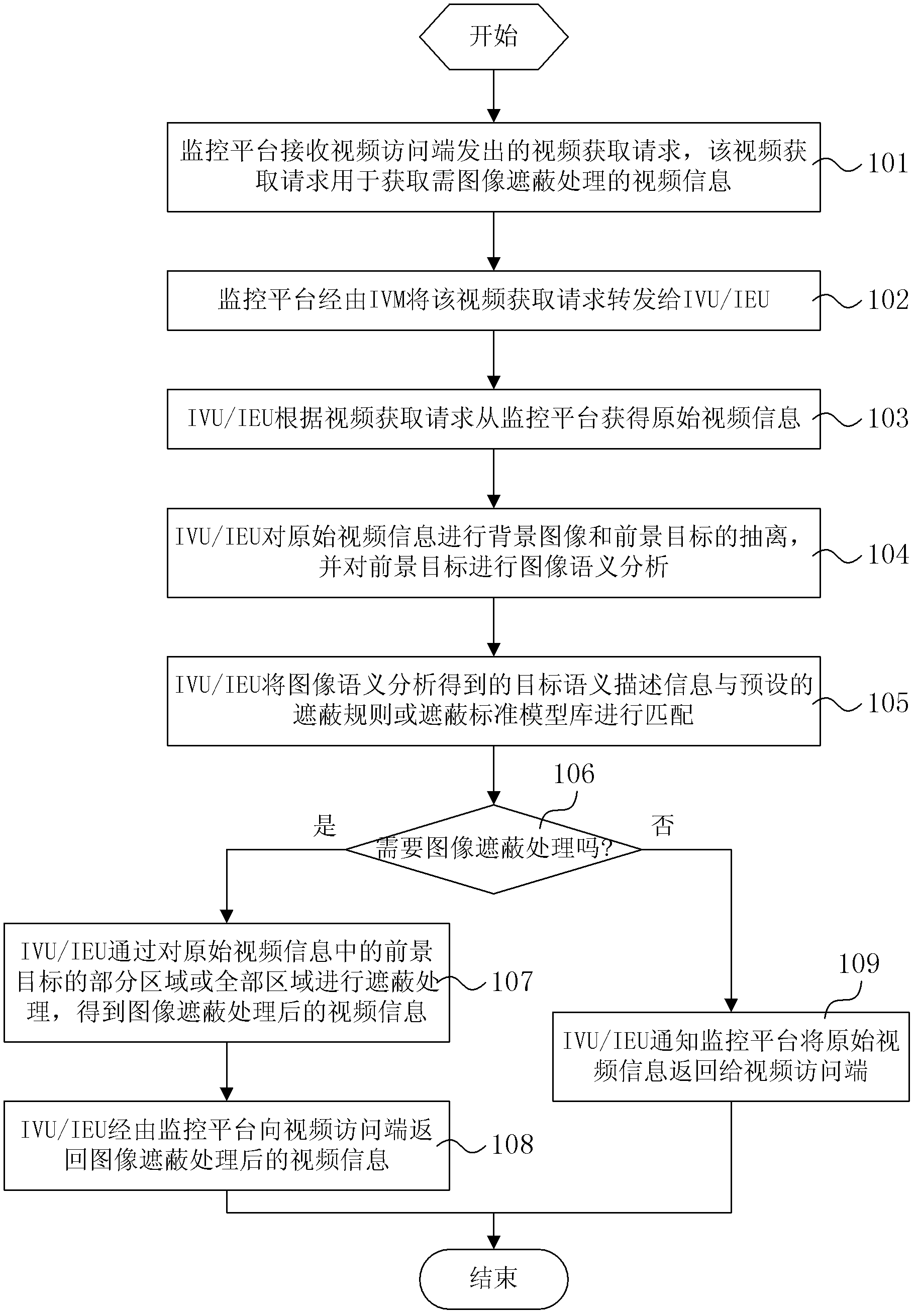
Image shielding method and system
ActiveCN103167216AAchieve protectionHigh artificial discriminationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPattern recognitionVirtualization
The invention relates to an image shielding method. The image shielding method comprises that when a monitoring platform receives a video obtaining request sent by a video access terminal, an integrated virtualization manager (IVM) forwards the video obtaining request to an intelligent video unit (IVU) / an intelligent envelop unit (IEU); the IVU / the IEU obtains corresponding original video information from the monitoring platform; the IVU / the IEU conducts extraction of background images and a foreground target to the original video information, and image semantic analysis of the foreground target is conducted; the IVU / the IEU enables obtained target semantic description information to be matched with preset shielding rules or a preset shielding standard model base, whether image shielding is required is identified, if the image shielding is required, shielding of partial areas or whole areas of the foreground target in the original video information is conducted through the IVU / the IEU, and video information after the image shielding is obtained; and the IVU / the IEU returns the video information after the image shielding to the video access terminal through the monitoring platform. According to the image shielding method and an image shielding system, intelligent object recognition technology is utilized to enable content in video images to be automatically analyzed and made out, the target is analyzed, then the image shielding is conducted, and therefore, workload of workers is reduced.
Owner:CHINA TELECOM CORP LTD
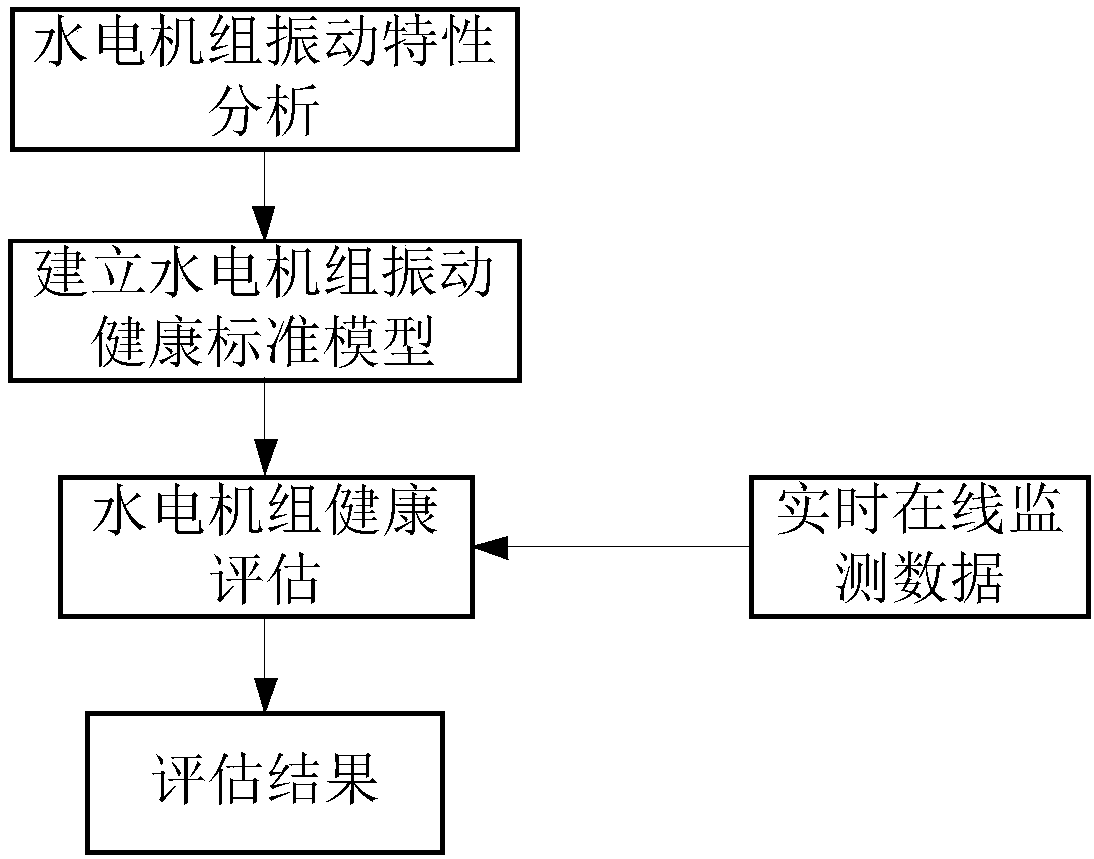
Hydropower unit health evaluation method
InactiveCN108375476AImprove practicalityData processing applicationsEngine testingState parameterComputer science
The invention relates to a hydropower unit health evaluation method. The method is characterized by comprising steps that 1), real-time online monitoring data of a hydropower unit in the present stateis acquired, and vibration characteristics of the hydropower unit are analyzed; 2), real-time online monitoring data of the hydropower unit in a healthy state under different operation conditions isacquired, correlation between the different operation conditions and state parameters of the hydropower unit in the healthy state is analyzed, and a vibration health standard model of the hydropower unit is established; and 3), according to the established vibration health standard model of the hydropower unit and the real-time online monitoring data of the hydropower unit, health state evaluationof the hydropower unit in the present state is carried out, and the health state of the hydropower unit under the present state is acquired. The method is advantaged in that visual property and strong timeliness are realized, and the method can be widely applied to the operation guarantee field of the hydropower unit.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
Authentication system and registration system related to facial feature information
InactiveUS7925060B2Achieve reliabilityThree-dimensional object recognitionPattern recognitionModel modification
An authentication system comprises: a generating part for generating face information including at least one of three-dimensional shape information and two-dimensional information in the face of a first person to be authenticated on the basis of measurement information of the first person; a model modifying part for modifying a standard model of a human face by using the face information, thereby generating an individual model of the face of the first person; a calculating part for calculating a first model perfection level as a perfection level of the individual model on the basis of reliability of the face information; an extracting part for extracting first feature information as feature information of the first person from the individual model; an obtaining part for obtaining second feature information as feature information of a second person to be compared which is pre-registered; and an authenticating part for performing an authenticating operation on the first person by using the first model perfection level in addition to similarity between the first feature information and the second feature information.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
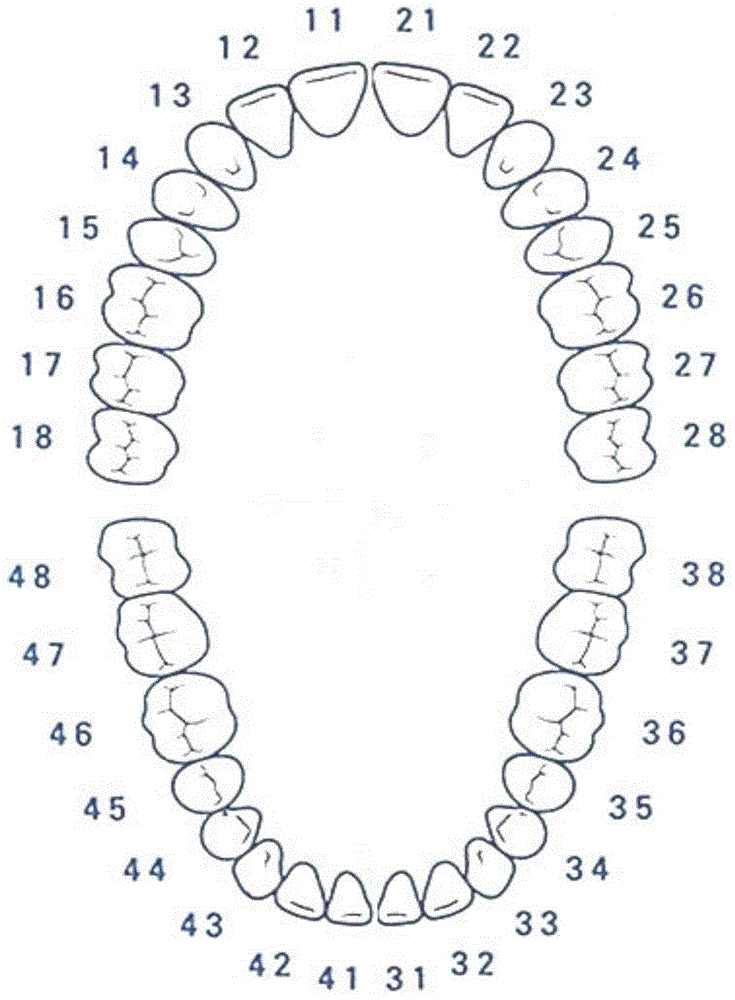
Tooth correctional system suitable for mixed dentition and manufacturing method
ActiveCN105266905ASave time and effort in the treatment processGood treatment effectOthrodonticsUnerupted dentitionEmbedded teeth
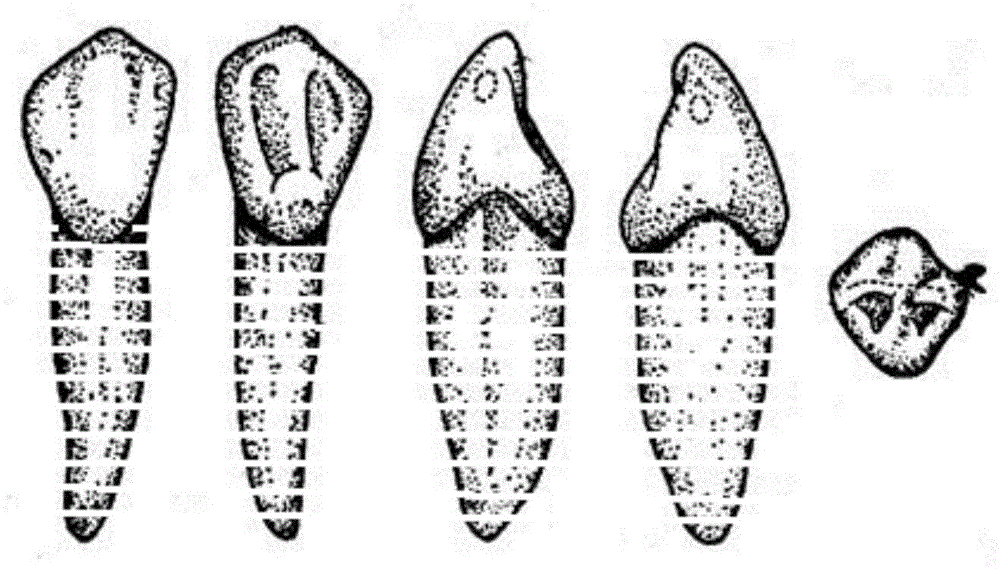
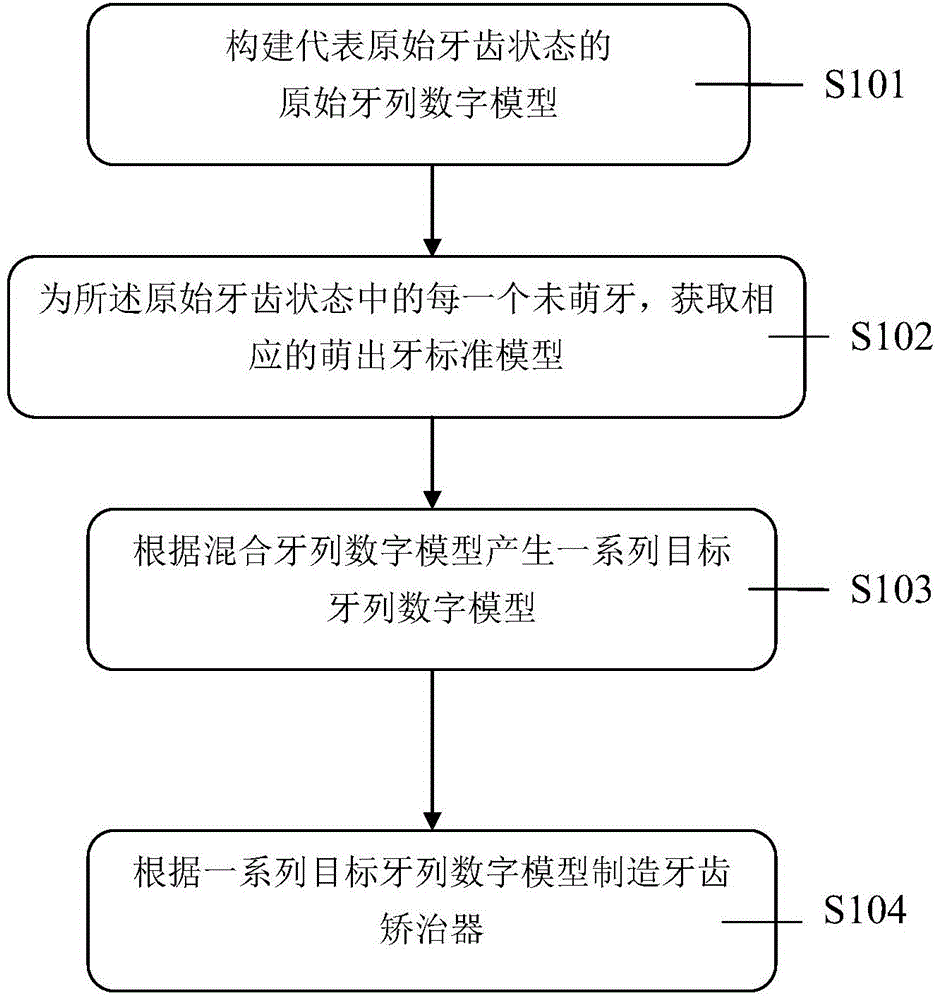
The present invention provides a tooth correctional system suitable for mixed dentition and a manufacturing method of the tooth correctional system, wherein the method comprises the following steps: building an original dentition digital model representing the original tooth state which includes at least one embedded tooth; acquiring a corresponding eruption tooth standard model for each embedded tooth in the original tooth state to obtain a mixed dentition digital model; producing a series of target dentition digital models according to the mixed dentition digital model; and manufacturing a tooth correctional device according to the produced series of target dentition digital models. The tooth correctional system can be used for correction of teeth of patients of any ages, and is especially suitable for dental transitional period adolescent patients simultaneously with deciduous teeth and permanent teeth.
Owner:SHANGHAI EA MEDICAL INSTR CO LTD
Emotion interaction based Peking Opera teaching system
InactiveCN106020440AImprove user experienceImprove recognition rateInput/output for user-computer interactionData processing applicationsEnvironmental noiseSomatosensory system
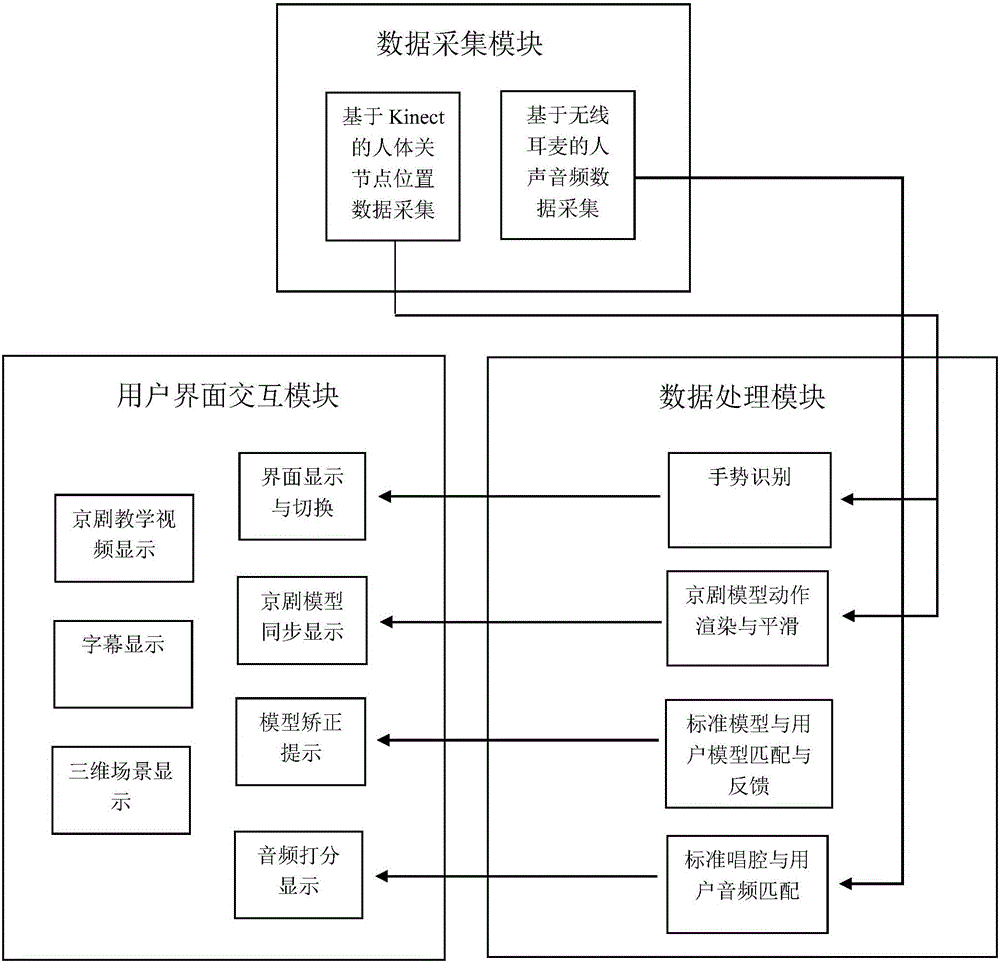
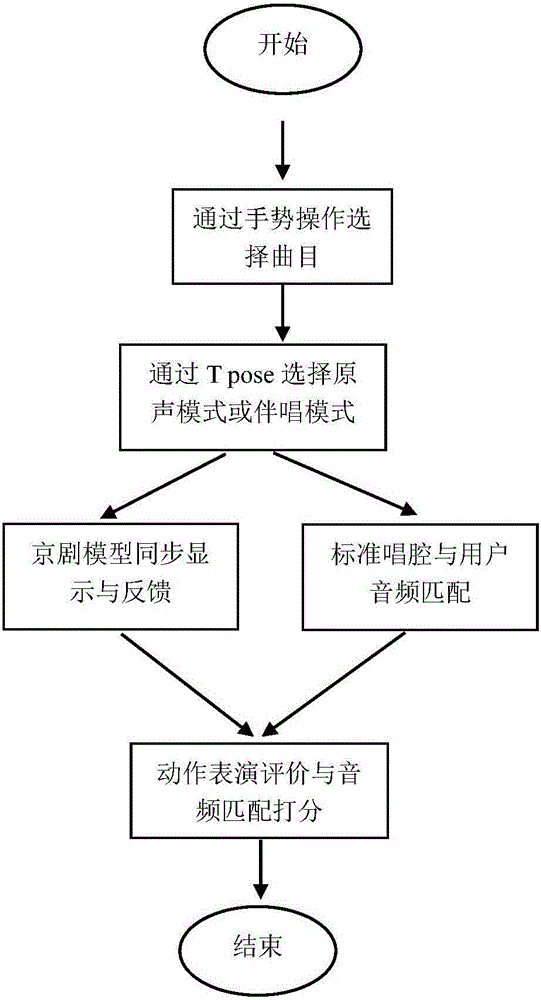
A Peking Opera teaching system based on somatosensory interaction, including a data acquisition module, a data processing module and a user interface interaction module. The data acquisition module obtains the user's joint information and sound data through the somatosensory interaction device; the data processing module realizes the user's logical control of the system Display the user model synchronized with the user's actions, perform matching and feedback between the Peking Opera standard model and the user model, obtain user voice data, and perform matching and feedback between the standard singing voice and the user's audio; the user interface interaction module performs the operation interface through the recognition of user gestures Display and switching, Peking Opera teaching video display, action performance evaluation display and audio scoring display. The Beijing opera teaching system of the present invention operates through somatosensory operation throughout, has a high recognition rate, and does not need a keyboard or a mouse as inputs. The user model has a high synchronization rate with the actual user posture, and there is no jitter, frame skipping phenomenon, and it is not affected by the hardware limitation of sensory capture and the environmental noise during bone tracking.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Self-adapting method aiming at computer language learning system pronunciation evaluation
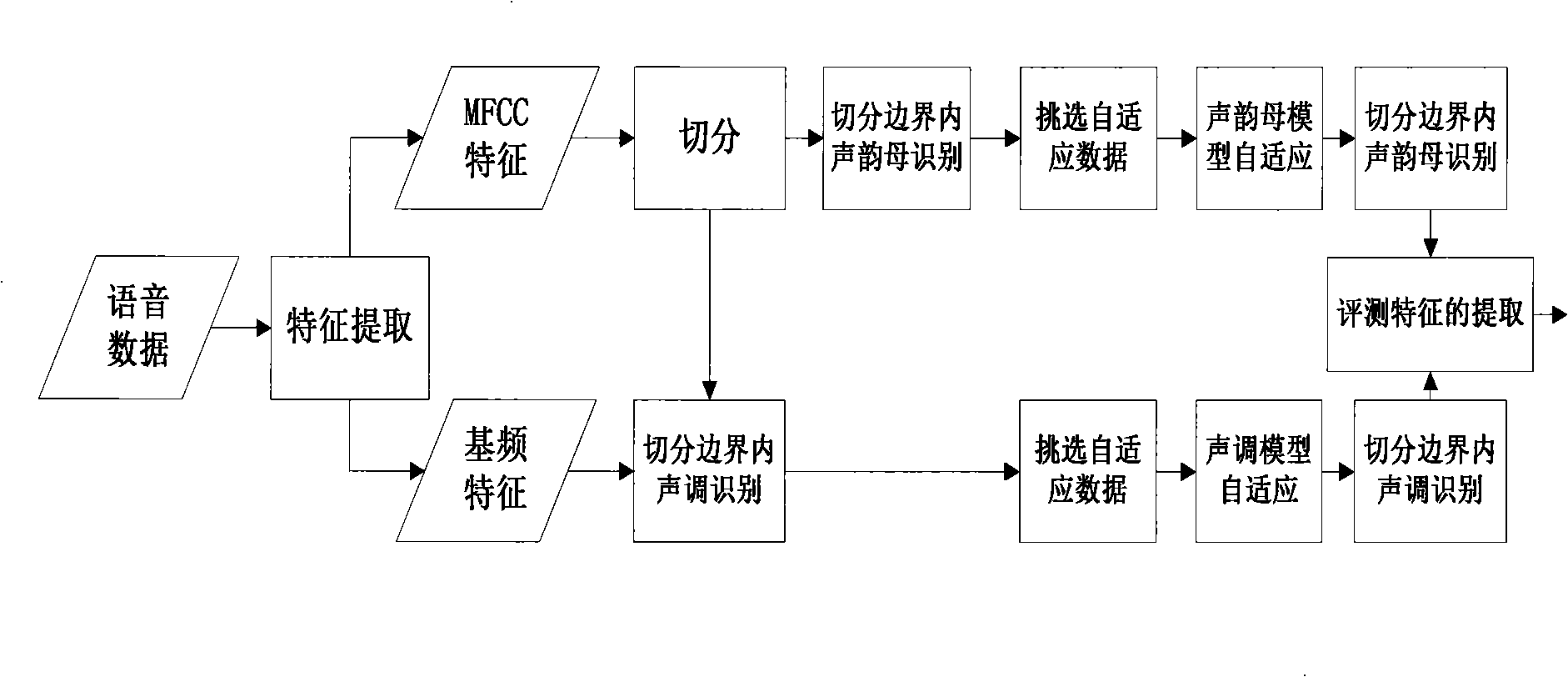
ActiveCN101315733AReduce mistakesInhibition biasSpeech recognitionTeaching apparatusSpeech identificationAcoustic model
The invention relates to a self-adaptive method for evaluating the pronunciation of a computer language learning system, comprising the following steps of: establishing a voice recognition system; carrying out the segmentation of initials and finals of voice data based on the voice recognition system and restricting the recognition of initials and finals at the boundary and the tone; calculating posterior probability of all the initials and finals and the tone according to the result of restriction of boundary recognition and the segmentation and selecting self-adaptive data according to the preset threshold; carrying out self-adaptation for an acoustic model in the recognition system according to the selected self-adaptive data; carrying out the second segmentation and recognition by using the acoustic model after the self-adaptation; using the final segmentation and recognition result to extract evaluating parameters; the invention selects a proper self-adaptive corpus by posterior probability, not only can reduce error of a recognizer caused by the differences of an actual speaker and a standard model tone, use environment and channels but also can avoid the bias of the standard model when in self-adaptation so as to be incapable of evaluating the pronunciation of the speaker accurately.
Owner:讯飞南亚东南亚信息科技(云南)有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com