Patents
Literature
1606 results about "Common source" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In electronics, a common-source amplifier is one of three basic single-stage field-effect transistor (FET) amplifier topologies, typically used as a voltage or transconductance amplifier. The easiest way to tell if a FET is common source, common drain, or common gate is to examine where the signal enters and leaves. The remaining terminal is what is known as "common". In this example, the signal enters the gate, and exits the drain. The only terminal remaining is the source. This is a common-source FET circuit. The analogous bipolar junction transistor circuit may be viewed as a transconductance amplifier or as a voltage amplifier. (See classification of amplifiers). As a transconductance amplifier, the input voltage is seen as modulating the current going to the load. As a voltage amplifier, input voltage modulates the amount of current flowing through the FET, changing the voltage across the output resistance according to Ohm's law. However, the FET device's output resistance typically is not high enough for a reasonable transconductance amplifier (ideally infinite), nor low enough for a decent voltage amplifier (ideally zero). Another major drawback is the amplifier's limited high-frequency response. Therefore, in practice the output often is routed through either a voltage follower (common-drain or CD stage), or a current follower (common-gate or CG stage), to obtain more favorable output and frequency characteristics. The CS–CG combination is called a cascode amplifier.
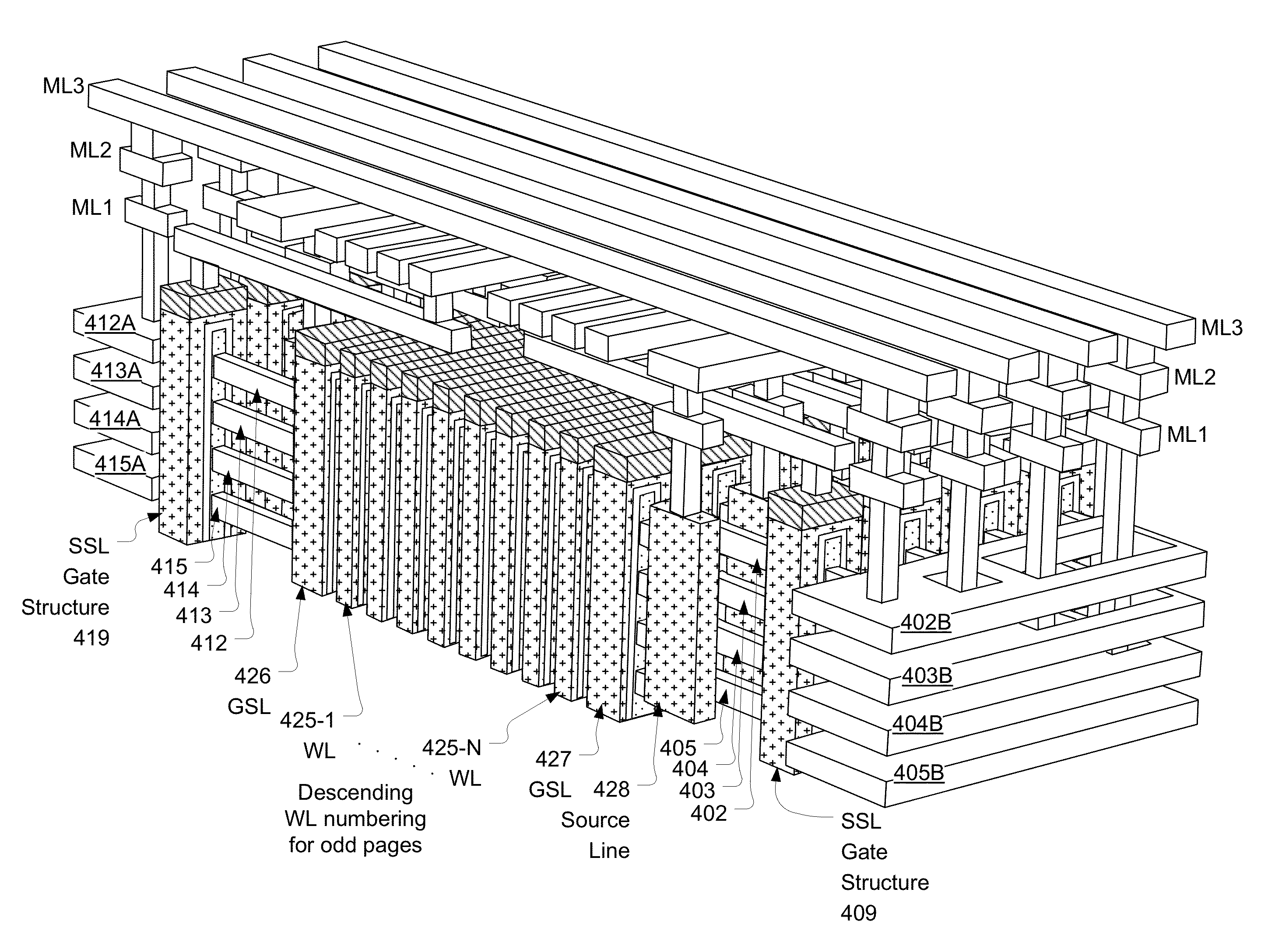
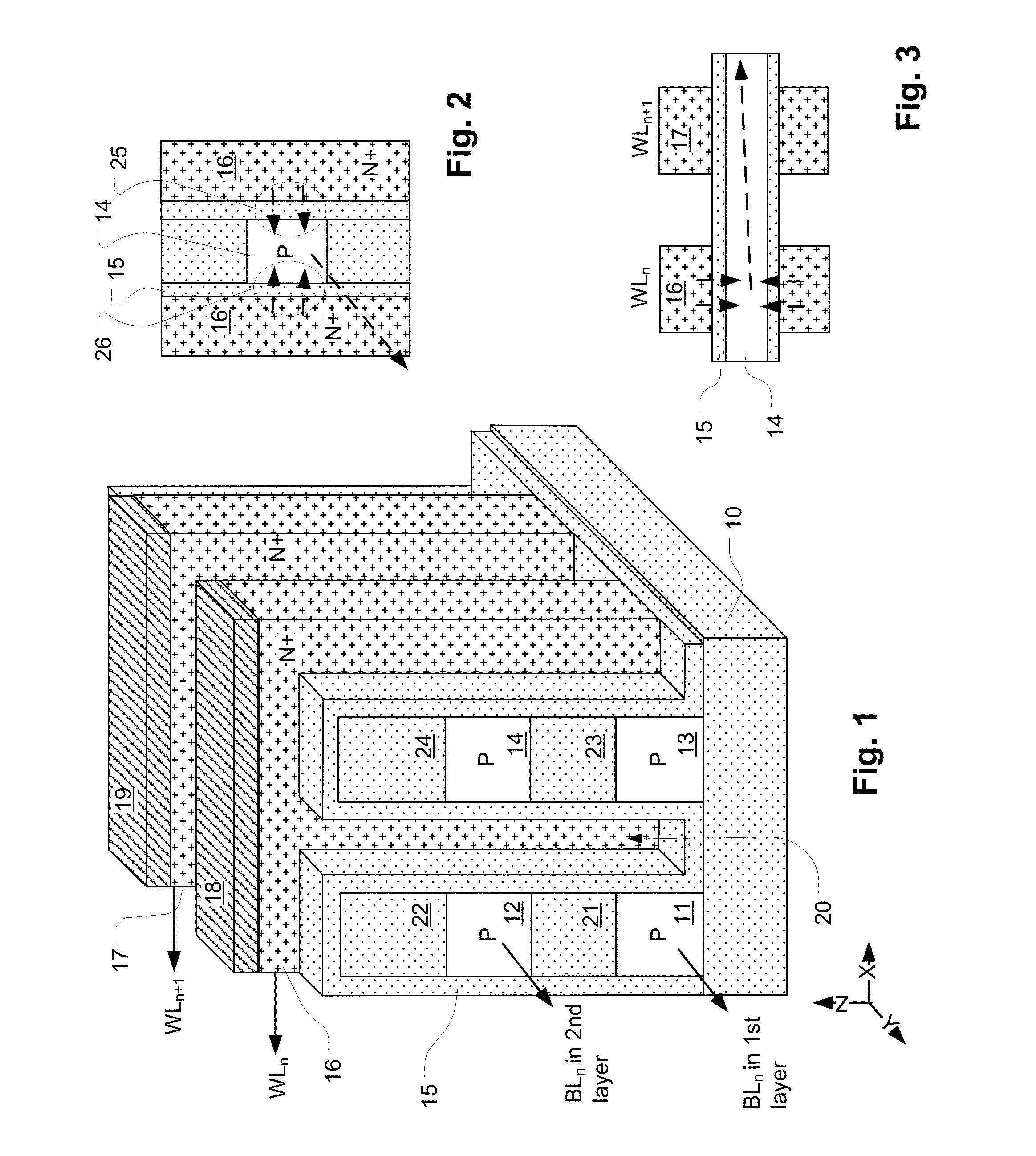
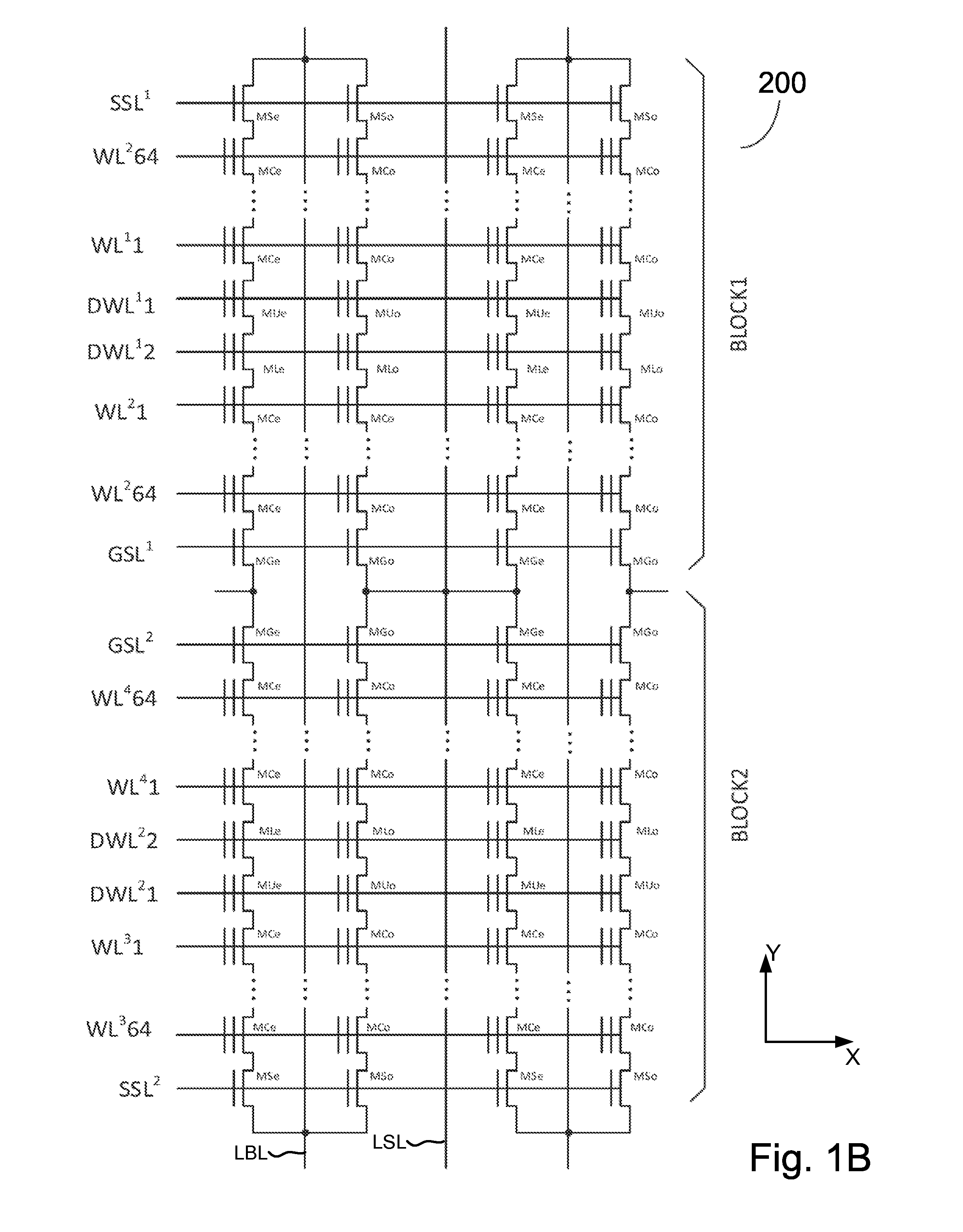
3D two-bit-per-cell NAND flash memory
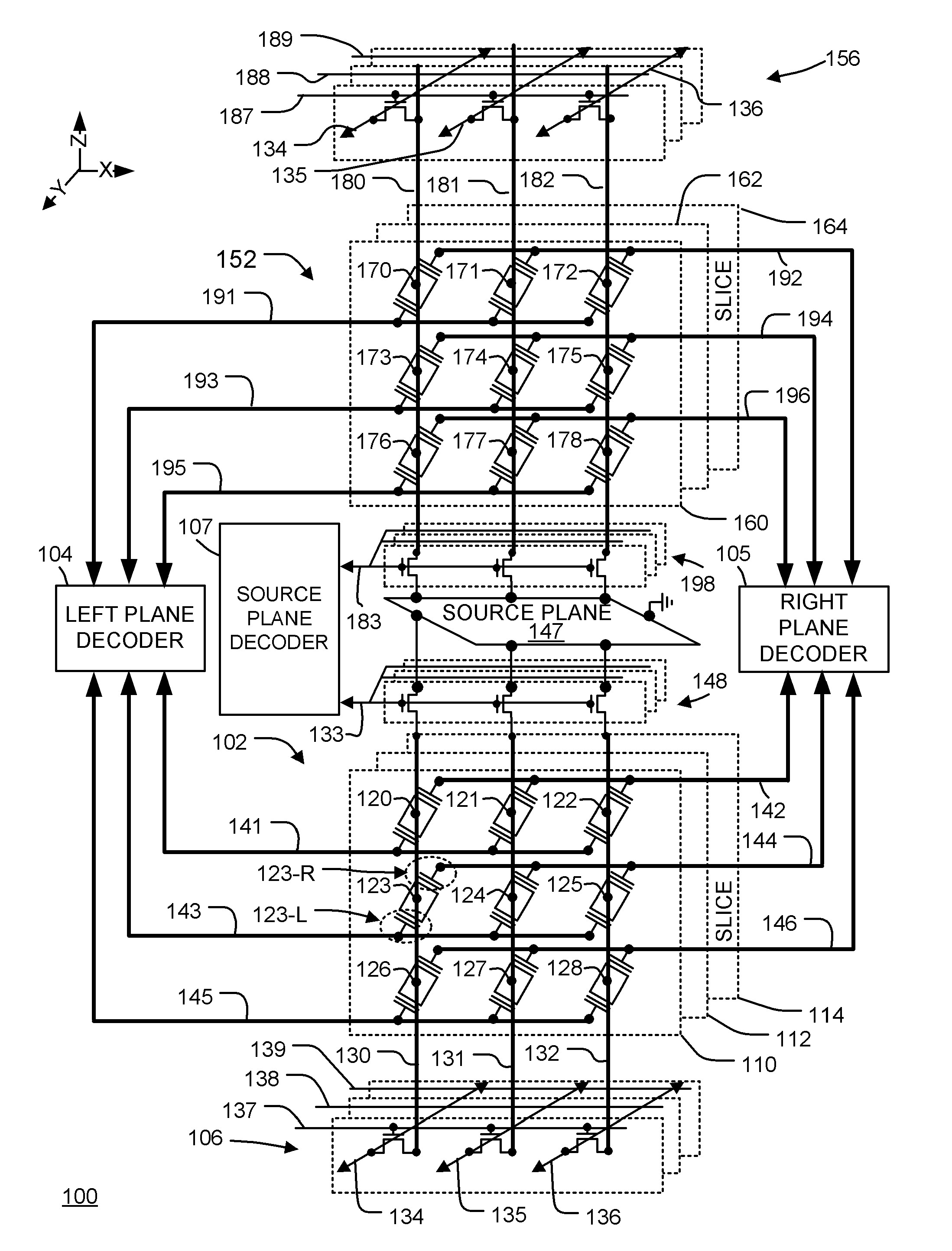
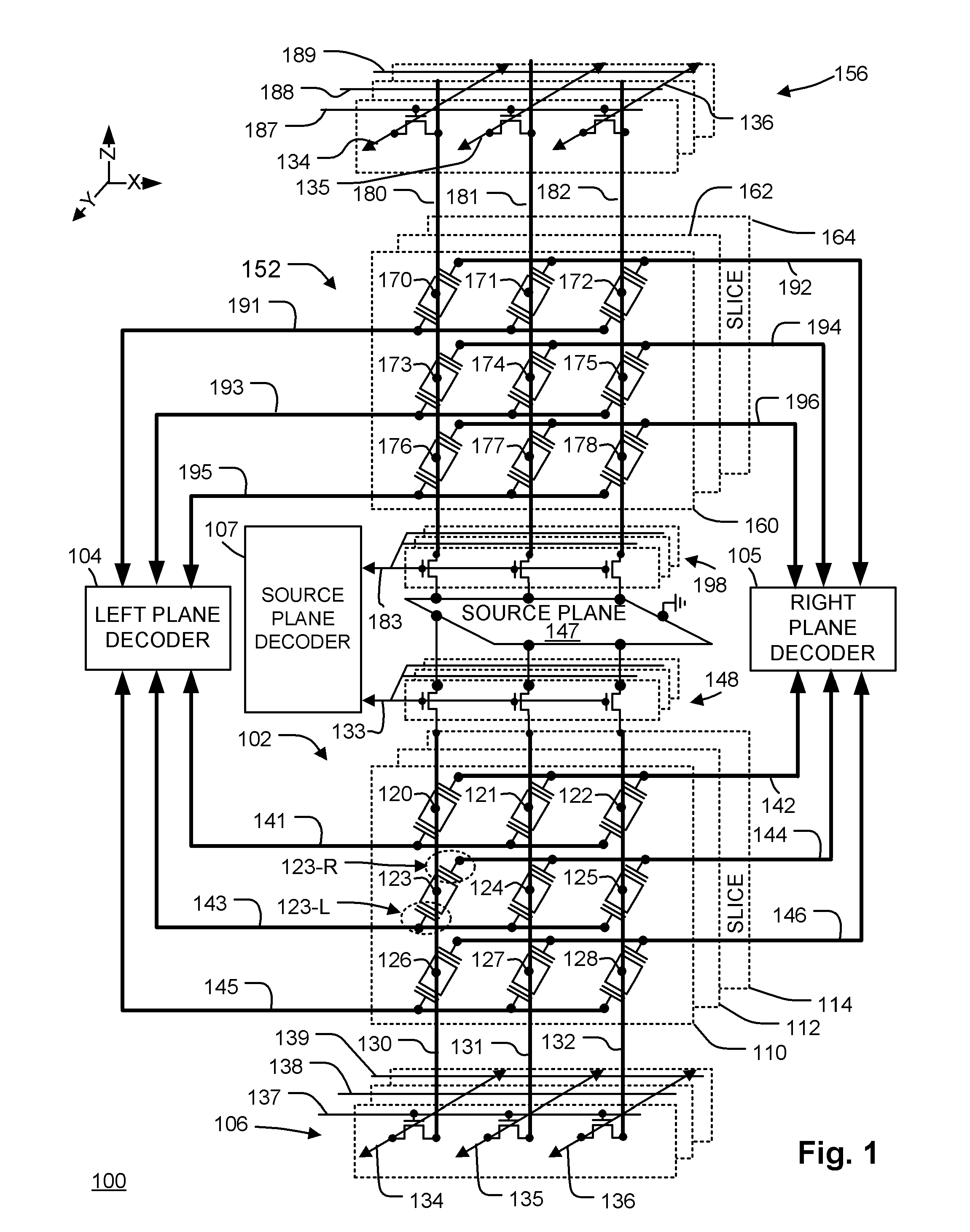
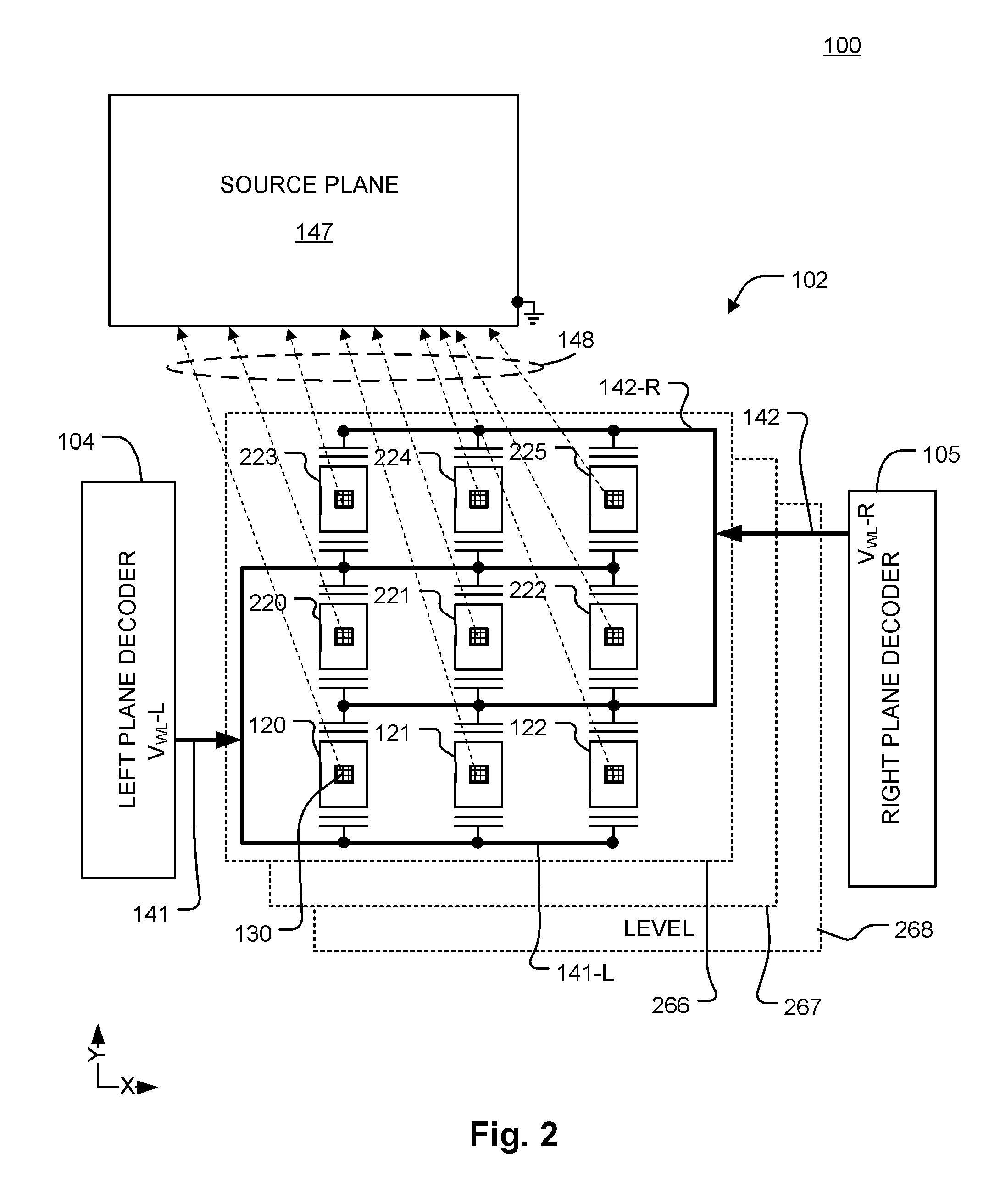
ActiveUS20110286283A1Few stepsHigh densitySolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesSource planePower flow
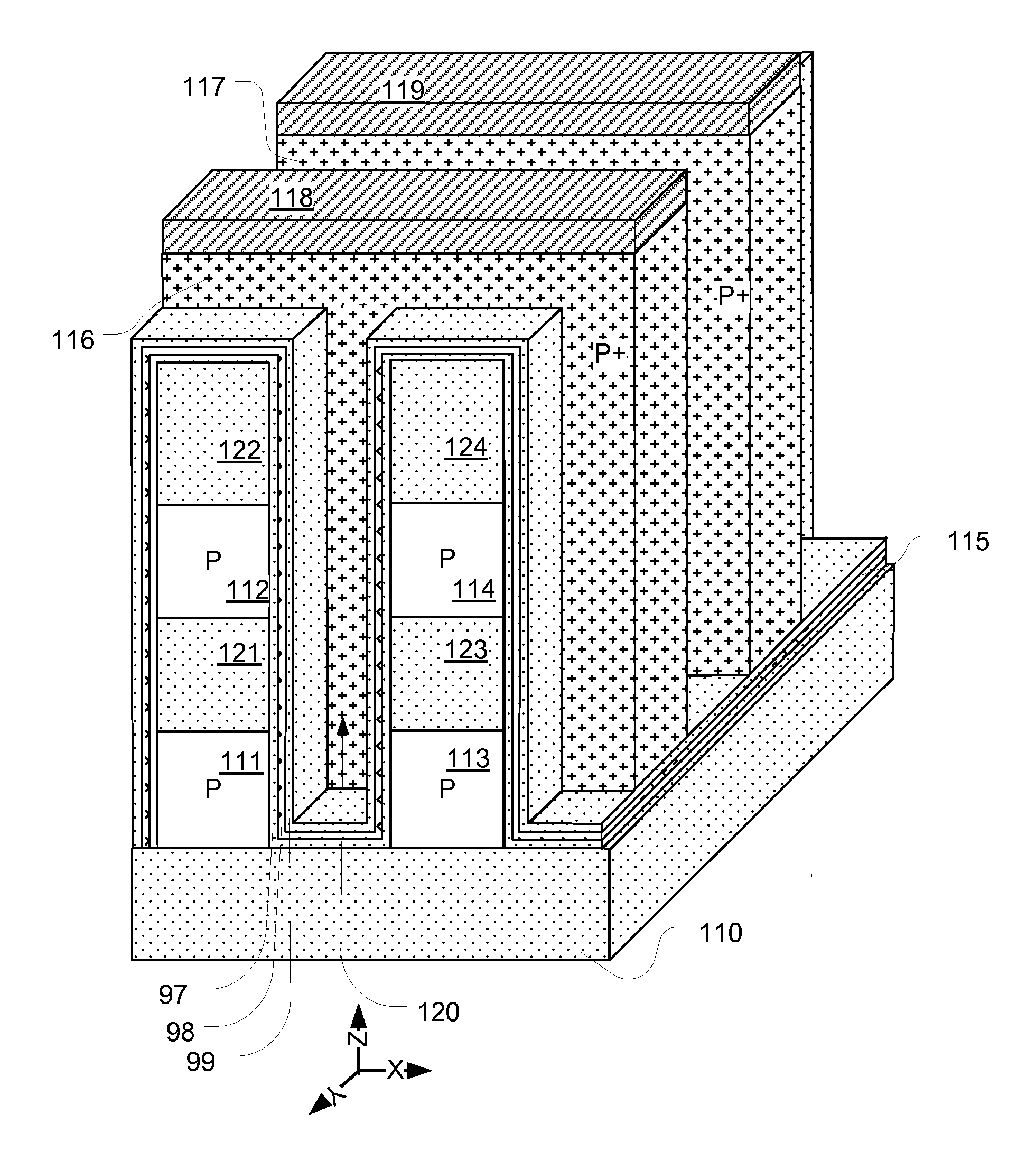
A 3D memory device is described which includes bottom and top memory cubes having respective arrays of vertical NAND string structures. A common source plane comprising a layer of conductive material is between the top and bottom memory cubes. The source plane is supplied a bias voltage such as ground, and is selectively coupled to an end of the vertical NAND string structures of the bottom and top memory cubes. Memory cells in a particular memory cube are read using current through the particular vertical NAND string between the source plane and a corresponding bit line coupled to another end of the particular vertical NAND string.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Measuring threshold voltage distribution in memory using an aggregate characteristic
ActiveUS20080285351A1Reduce errorsResistance/reactance/impedenceRead-only memoriesBit lineCapacitance
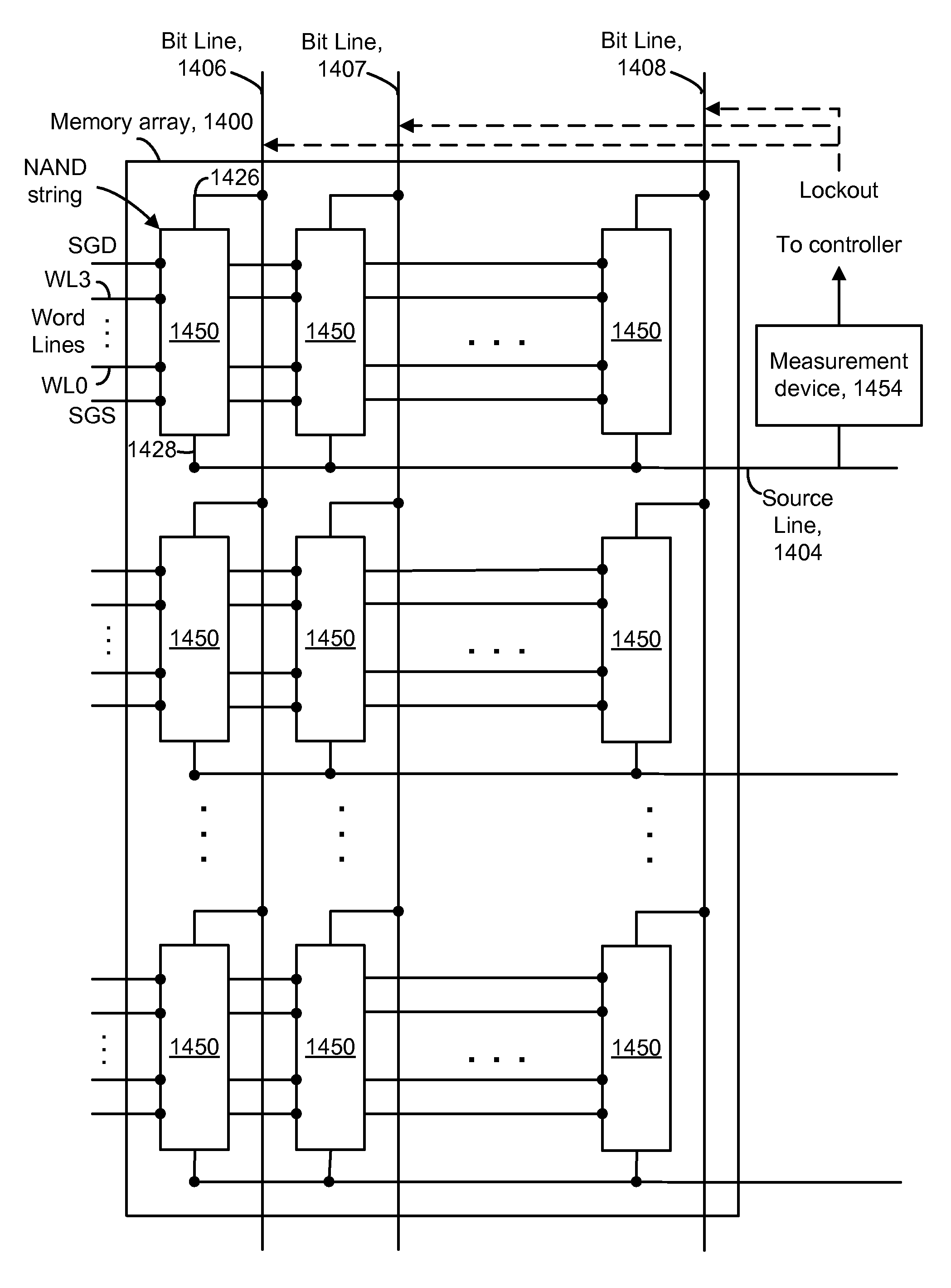
A threshold voltage distribution of a set of storage elements in a memory device is measured by sweeping a control gate voltage while measuring a characteristic of the set of storage elements as a whole. The characteristic indicates how many of the storage elements meet a given condition, such as being in a conductive state. For example, the characteristic may be a combined current, voltage or capacitance of the set which is measured at a common source of the set. The control gate voltage can be generated internally within a memory die. Similarly, the threshold voltage distribution can be determined internally within the memory die. Optionally, storage elements which become conductive can be locked out, such as by changing a bit line voltage, so they no longer contribute to the characteristic. New read reference voltages are determined based on the threshold voltage distribution to reduce errors in future read operations.
Owner:SANDISK CORP +1
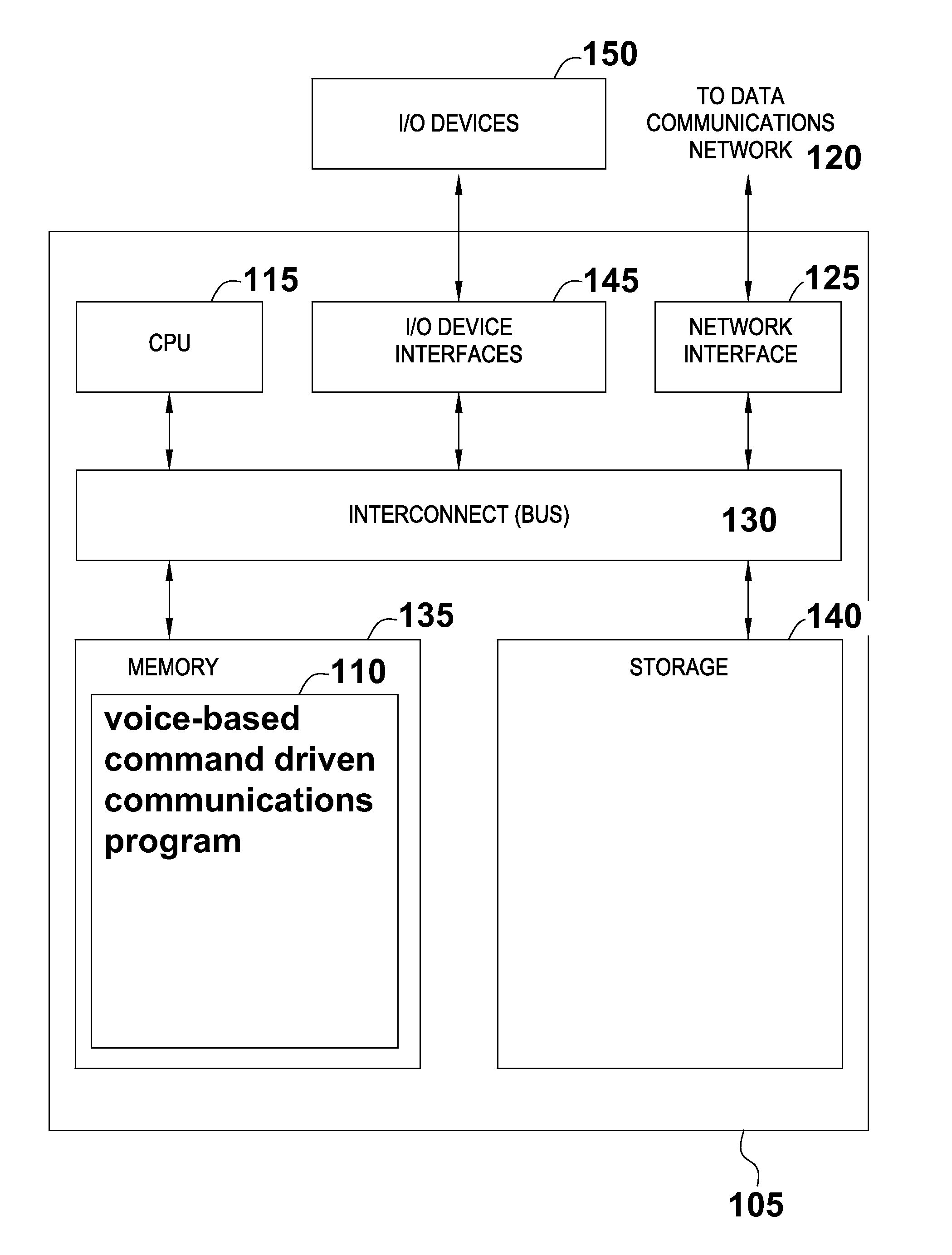
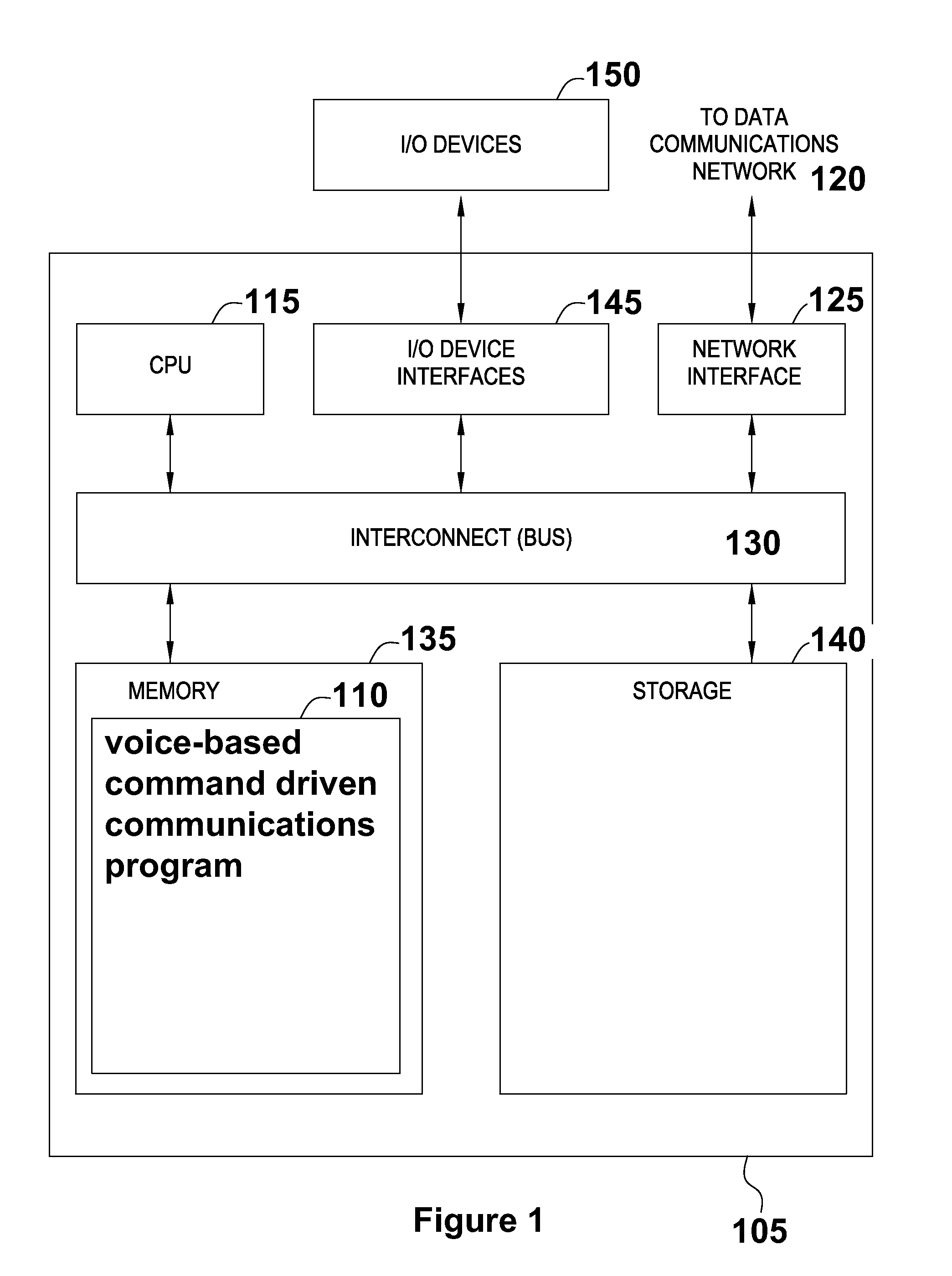
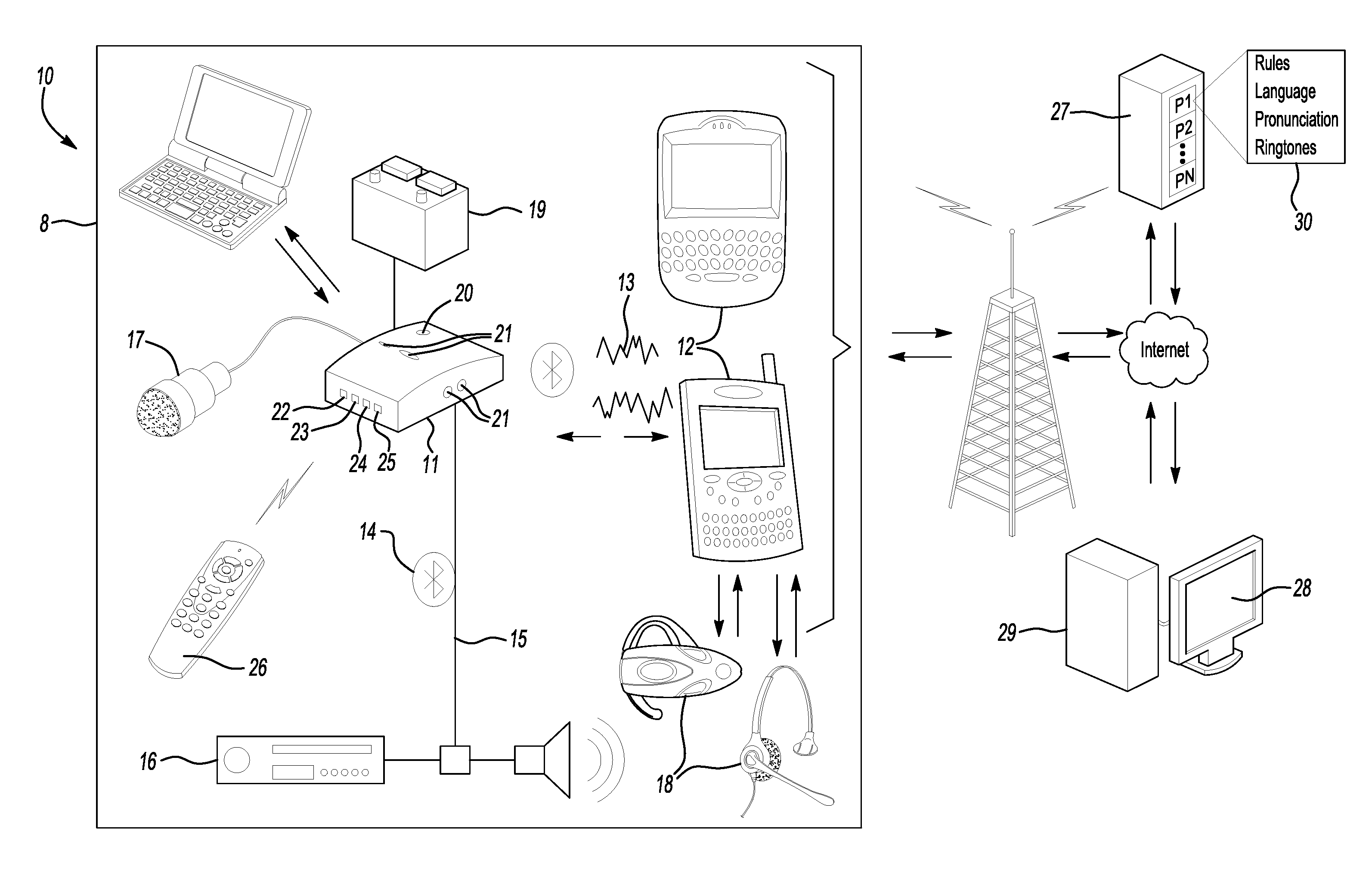
Voice-based command driven computer implemented method
InactiveUS20110201385A1Easy to mergeSubstation equipmentSpeech recognitionElectronic communicationCommon source
The present invention generally relates to a voice-based command driven computer implemented method and programmed apparatus that allows a user to easily add any open API communication product they choose to one interface. The computer implemented method filters all electronic communications selected by the user through a common source, such as the user's cell phone or computer. Each time an electronic communication is received, no matter through what program or application, the computer implemented method operates to communicate to the user that the electronic communication has been received and provides the user with the option of listening to and responding to the electronic communication, if appropriate. The user responds to the electronic communication through voice-based communication rather than physical interaction with the common source. The user may additionally initiate electronic communication through voice-based communication.
Owner:HIGGINBOTHAM CHRISTOPHER D
Three-Dimensional Semiconductor Device and Manufacturing Method Therefor
InactiveUS20170154895A1Improve control characteristicsReduce off-state leakage currentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETEtching
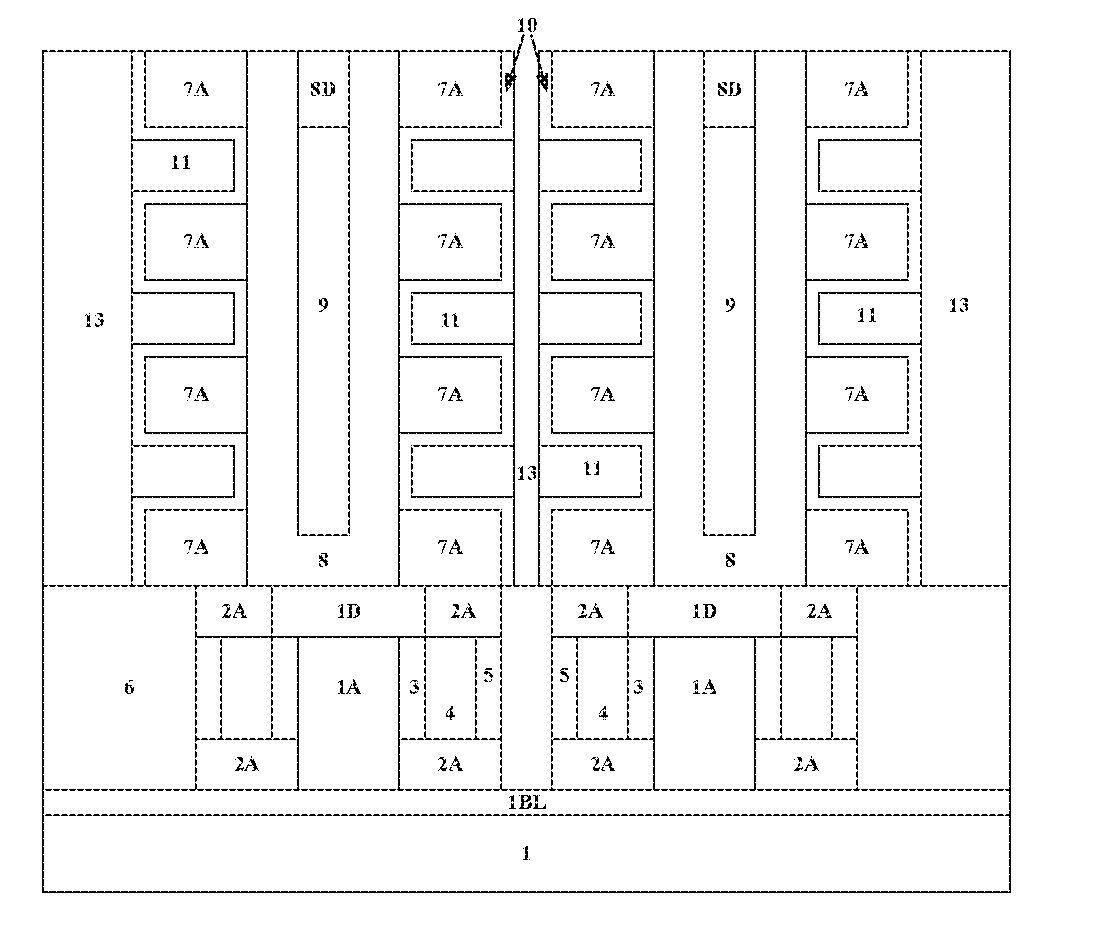
A three-dimensional semiconductor device, comprising a plurality of memory cell transistors and a plurality of select transistors at least partially overlapped in the vertical direction, wherein each select transistor comprises a first drain, an active region and a common source formed in the substrate, distributed along the vertical direction, as well as a metal gate distributed around the active region; wherein each memory cell transistor comprises a channel layer distributed perpendicularly to the substrate surface, a plurality of inter-layer insulating layers and a plurality of gate stack structures alternately stacked along the sidewalls of said channel layer, a second drain located on top of said channel layer; wherein said channel layer and said the first drain are electrically connected. In accordance with the three-dimensional semiconductor memory device and manufacturing method of the present invention, the multi-gate MOSFET is formed beneath the stack structure of the memory cell string including vertical channel to serve as the select transistor, this can improve the control characteristics of the gate threshold voltage, reduce the off-state leakage current, prevent the substrate from over-etching, and effectively improve the reliability of the device.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
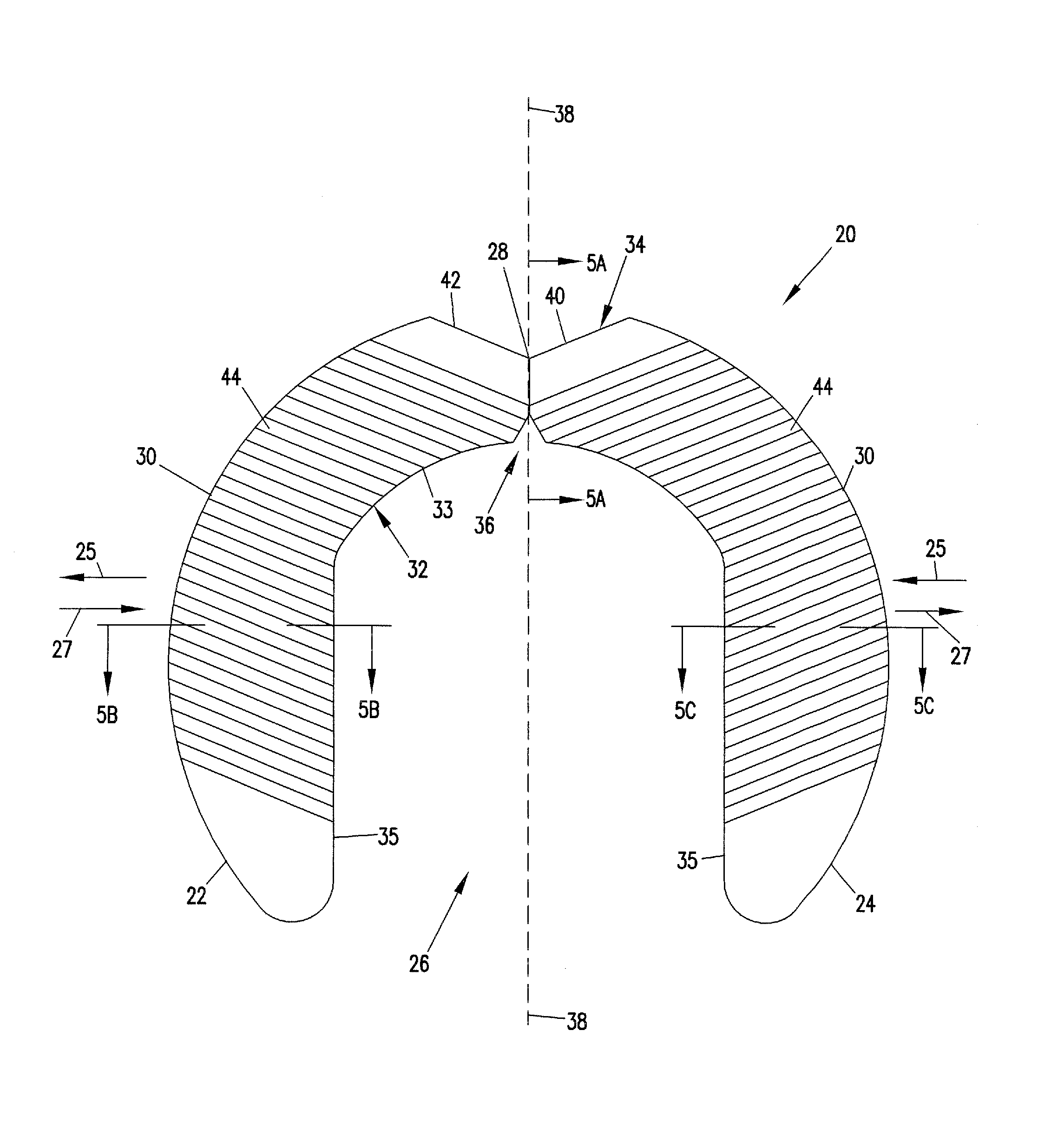
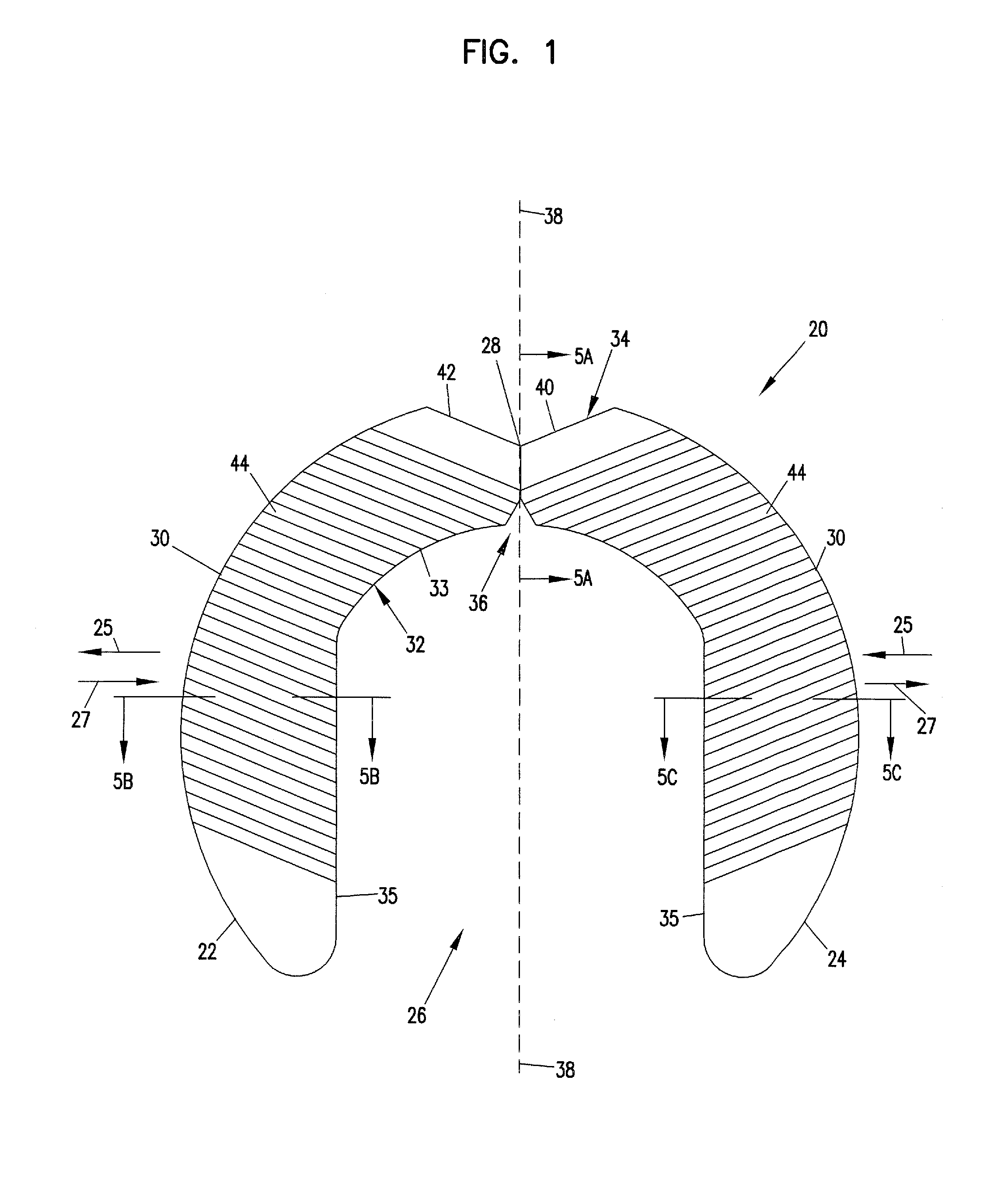
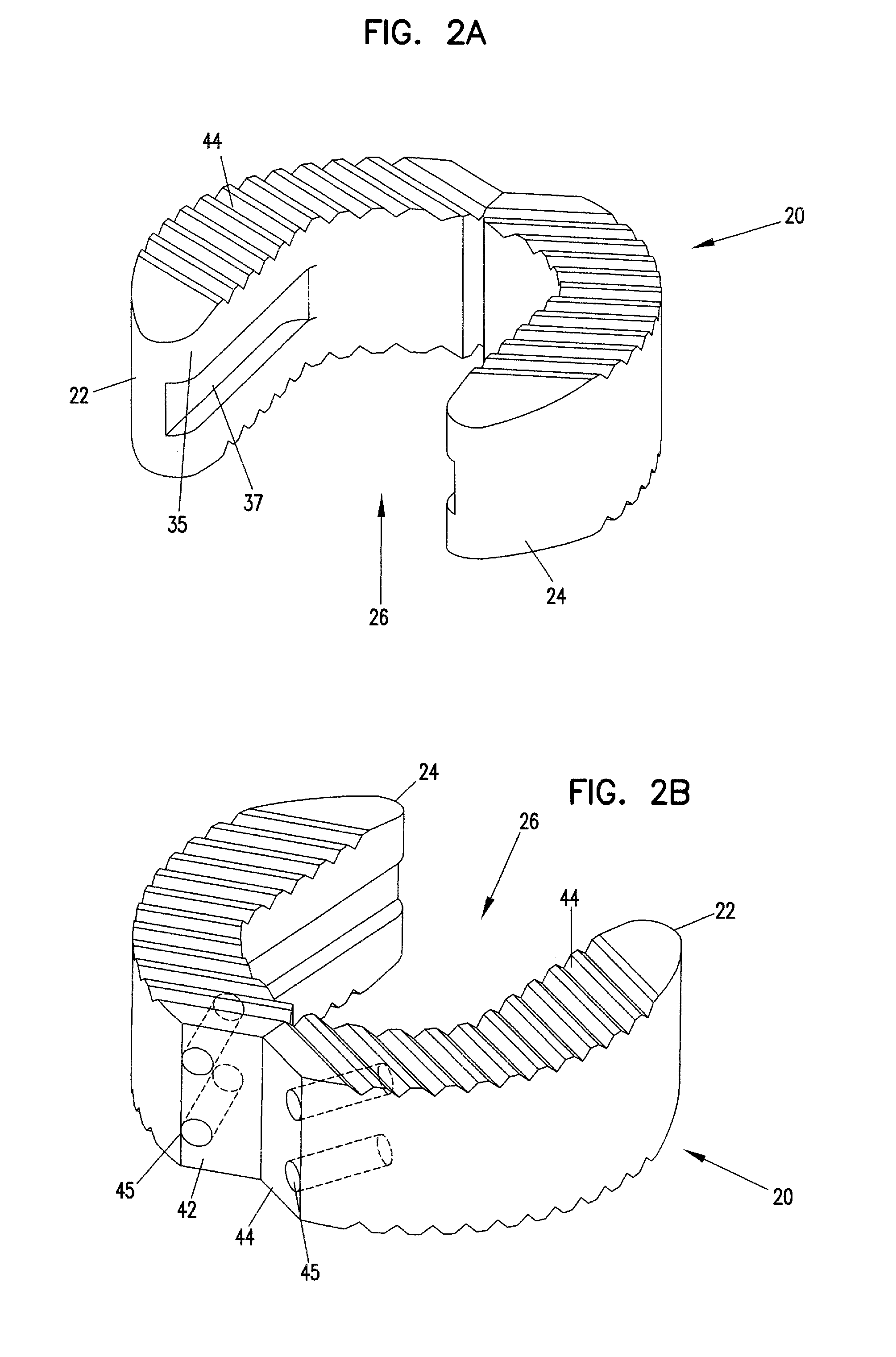
Skeletal Stabilization Implant
Owner:ZIMMER SPINE INC
Non-volatile semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS20020126532A1Wrong writing is prevented surelyTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringComputational physics
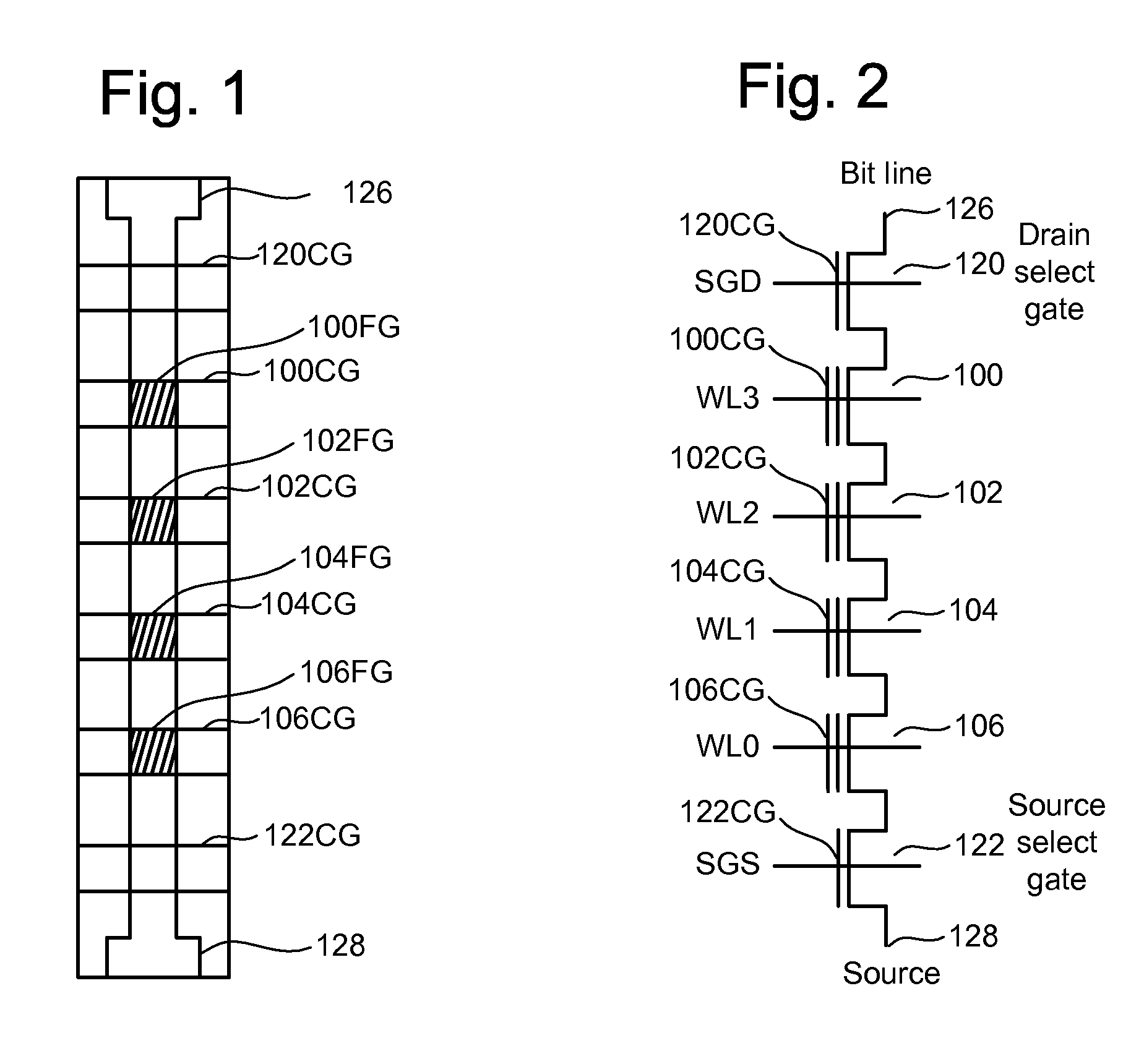
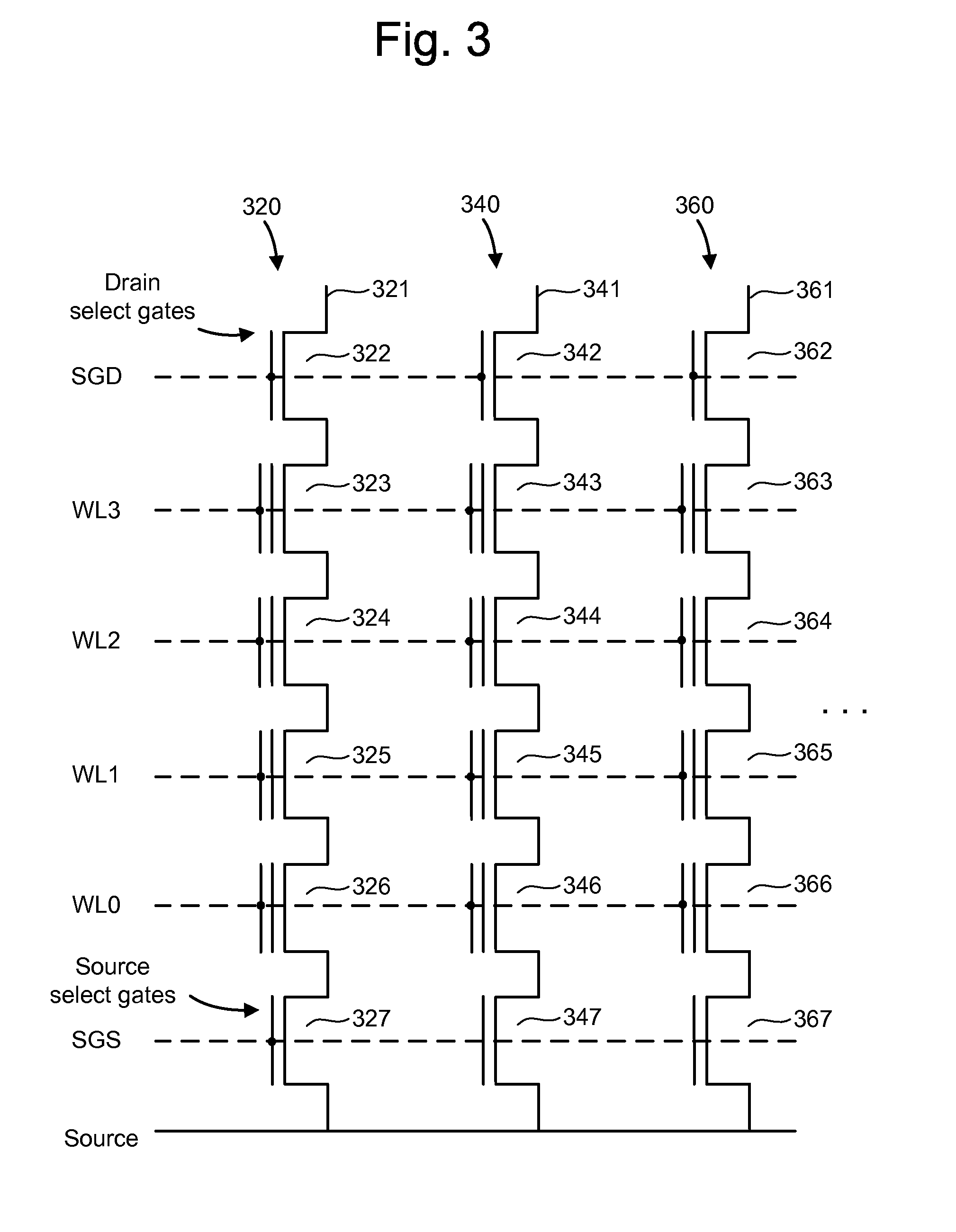
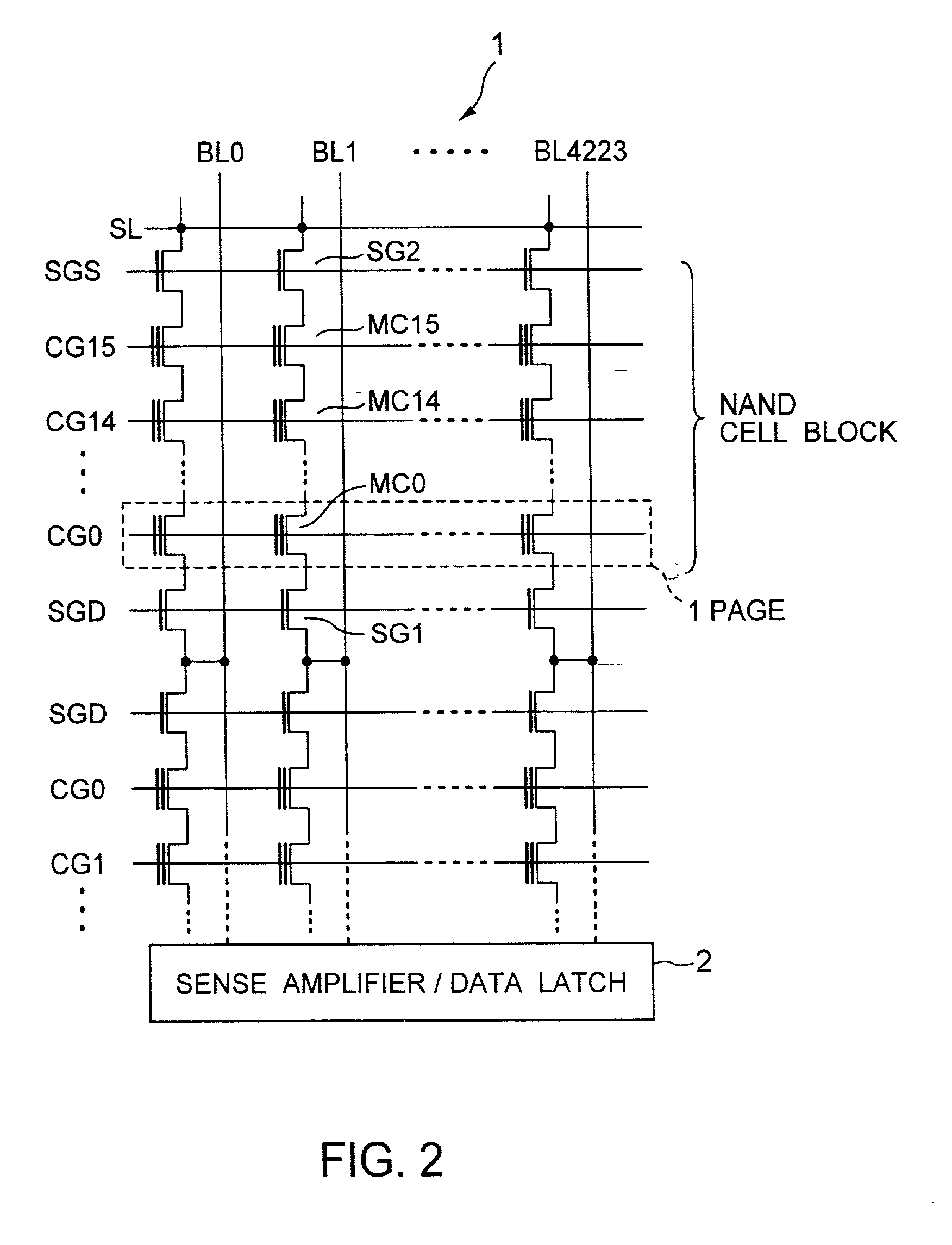
A non-volatile semiconductor memory device having a write mode in which wrong writing is prevented surely. The storage device comprises a NAND cell comprising a plurality of memory transistors connected in series and also connected at one end via a select gate transistor CG1 to a bit line BL and at the other end via a select gate transistor SG2 to a common source line SL. A write voltage Vpgm is applied to a control gate of a selected memory transistor in the NAND cell and Vss is applied to the controls gates of non-select memory transistors each adjacent to the selected memory transistor to thereby write data into the select memory transistor. When a second memory transistor from the bit line BL side is selected in the writing operation, a medium voltage Vpass is applied to the control gate of a first non-selected memory transistor from the bit line BL side, and a medium voltage Vpass is applied to the control gates of third and subsequent non-selected memory transistors from the bit line BL side.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
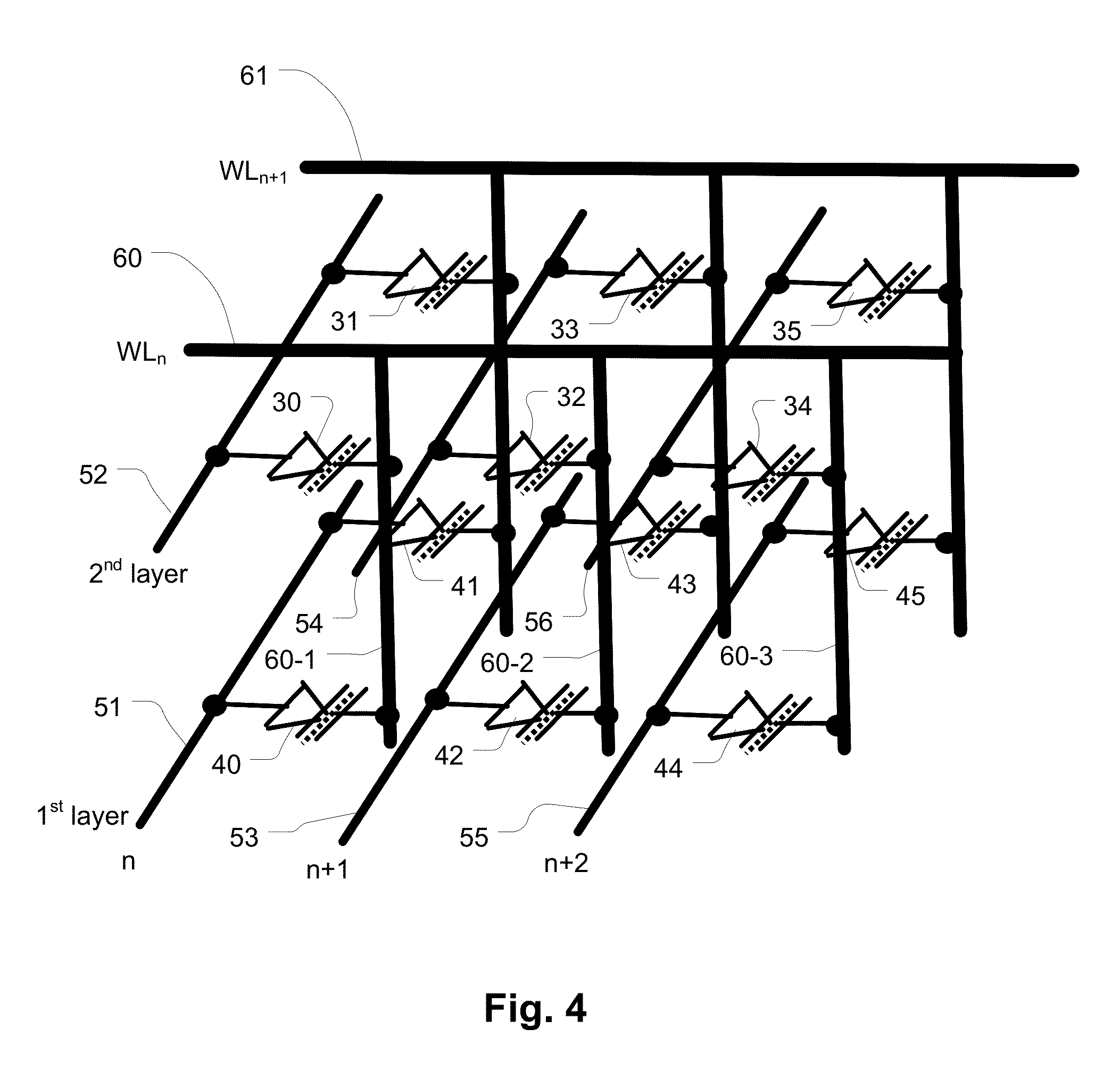
Memory Architecture of 3D Array With Alternating Memory String Orientation and String Select Structures
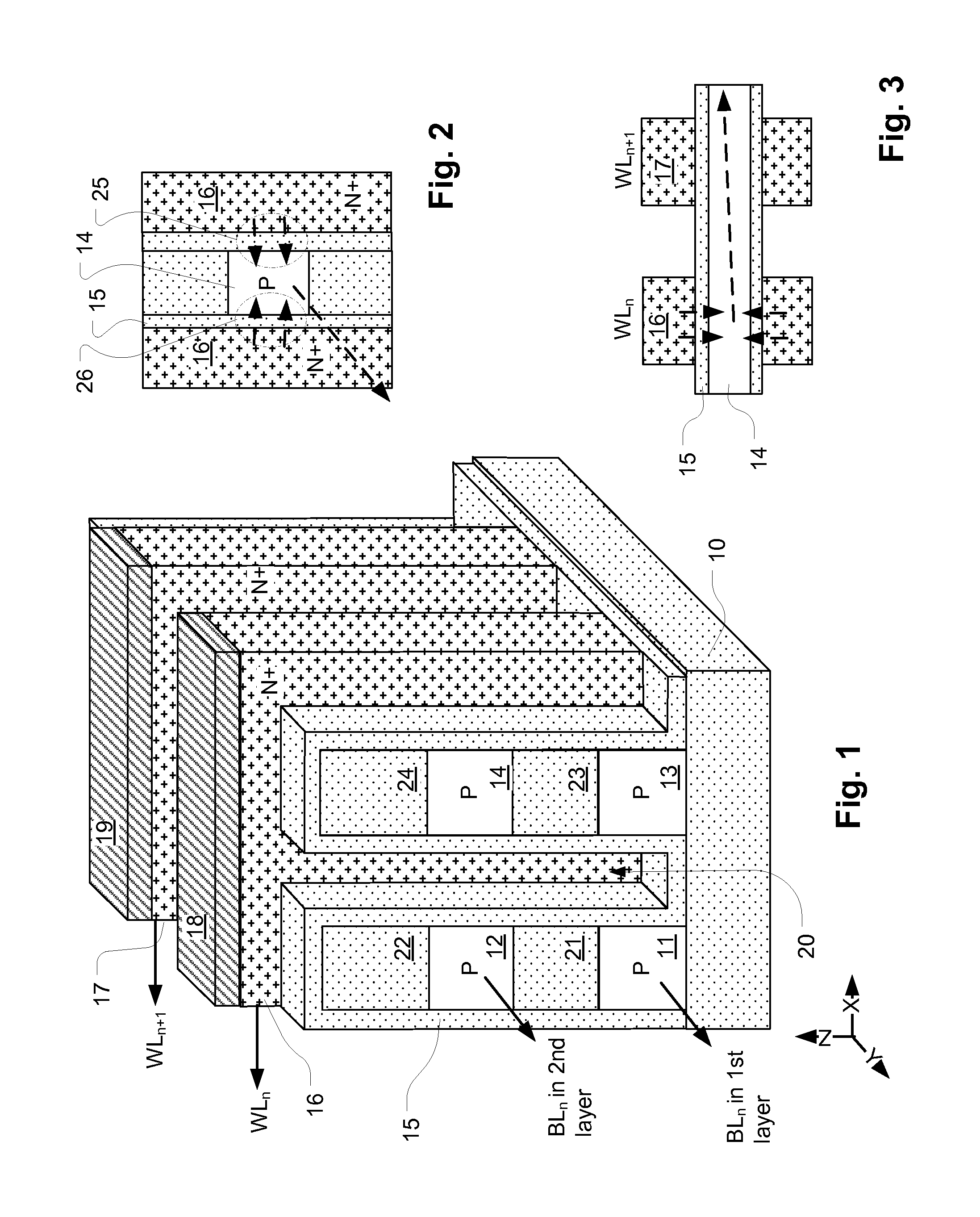
ActiveUS20120182806A1Increase pitchImproved gate structureSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesArray data structureConductive materials
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Floating gate inverter type memory cell and array
A non-volatile memory (NVM) cell and array includes a control capacitor, tunneling capacitor, CMOS inverter and output circuit. The CMOS inverter includes PMOS and NMOS inverter transistors. The control capacitor, tunneling capacitor and PMOS and NMOS inverter transistors share a common floating gate, which is programmed / erased by Fowler-Nordheim tunneling. The output circuit includes PMOS and NMOS select transistors. The PMOS inverter and select transistors share a common source / drain region. Similarly, the NMOS inverter and select transistors share a common source / drain region. This configuration minimizes the required layout area of the non-volatile memory cell and allows design of arrays with smaller footprints. Alternately, the tunneling capacitor may be excluded, further reducing the required layout area of the NVM cell. In this case, the NMOS inverter transistor functions as a tunneling capacitor for programming and erasing the cell, and the PMOS inverter transistor functions as a tunneling capacitor for erasing the cell.
Owner:TOWER SEMICONDUCTOR
Memory architecture of 3D array with alternating memory string orientation and string select structures
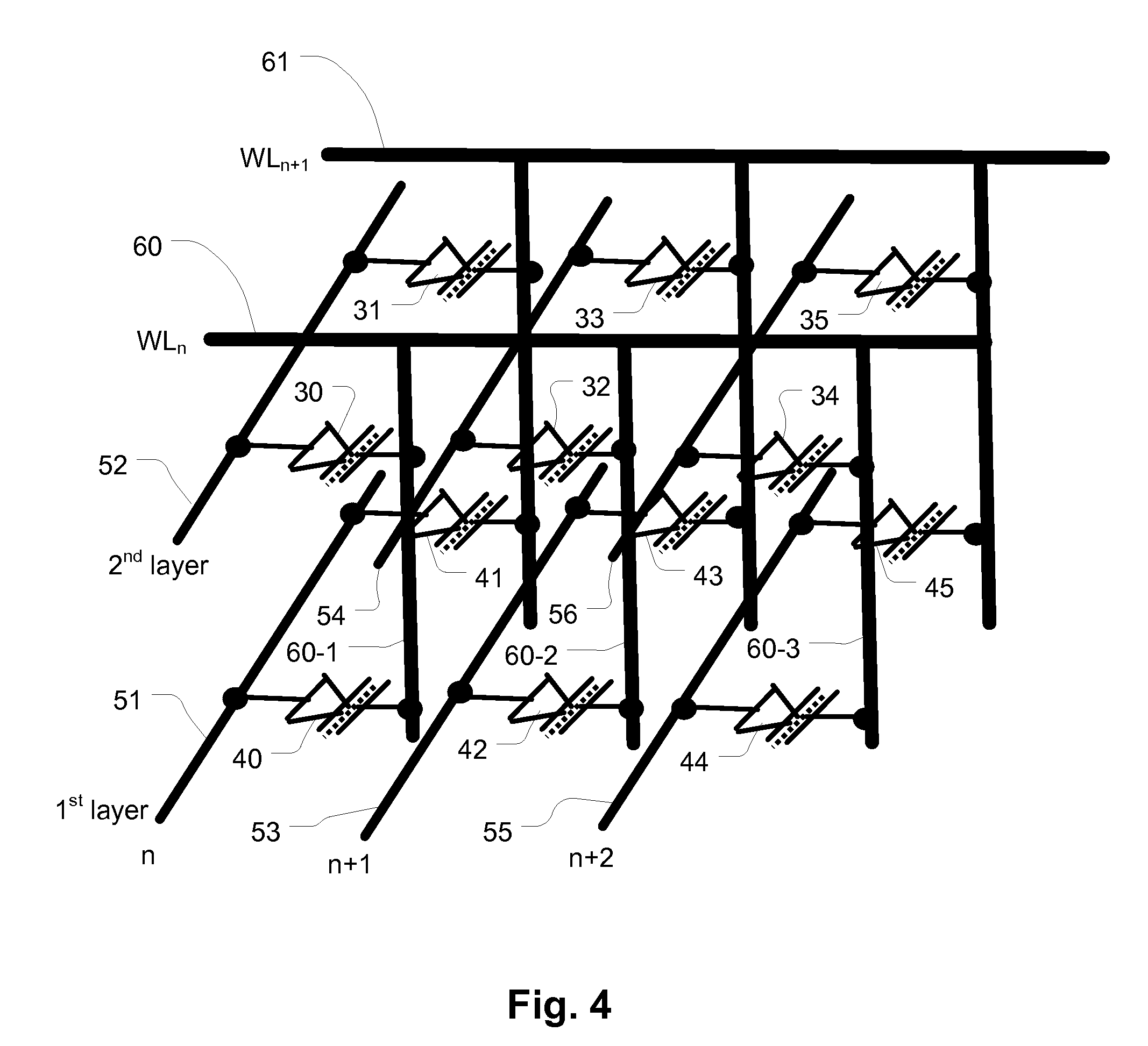
ActiveUS8503213B2Increase pitchPitch is improvedSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesAudio power amplifierConductive materials
A 3D memory device includes a plurality of ridge-shaped stacks, in the form of multiple strips of conductive material separated by insulating material, arranged as bit lines which can be coupled through decoding circuits to sense amplifiers. Diodes are connected to the bit lines at either the string select of common source select ends of the strings. The strips of conductive material have side surfaces on the sides of the ridge-shaped stacks. A plurality of word lines, which can be coupled to row decoders, extends orthogonally over the plurality of ridge-shaped stacks. Memory elements lie in a multi-layer array of interface regions at cross-points between side surfaces of the semiconductor strips on the stacks and the word lines.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
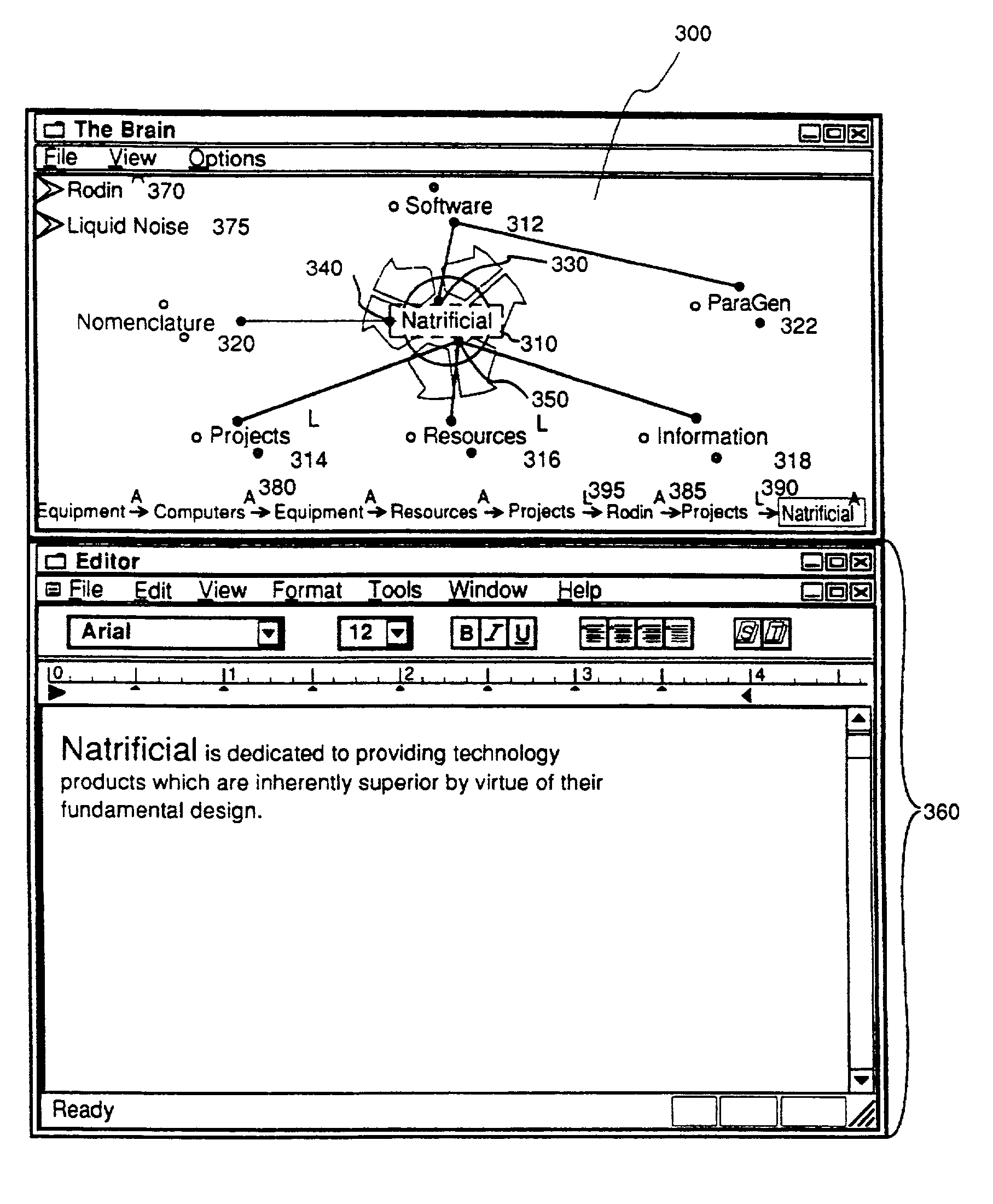
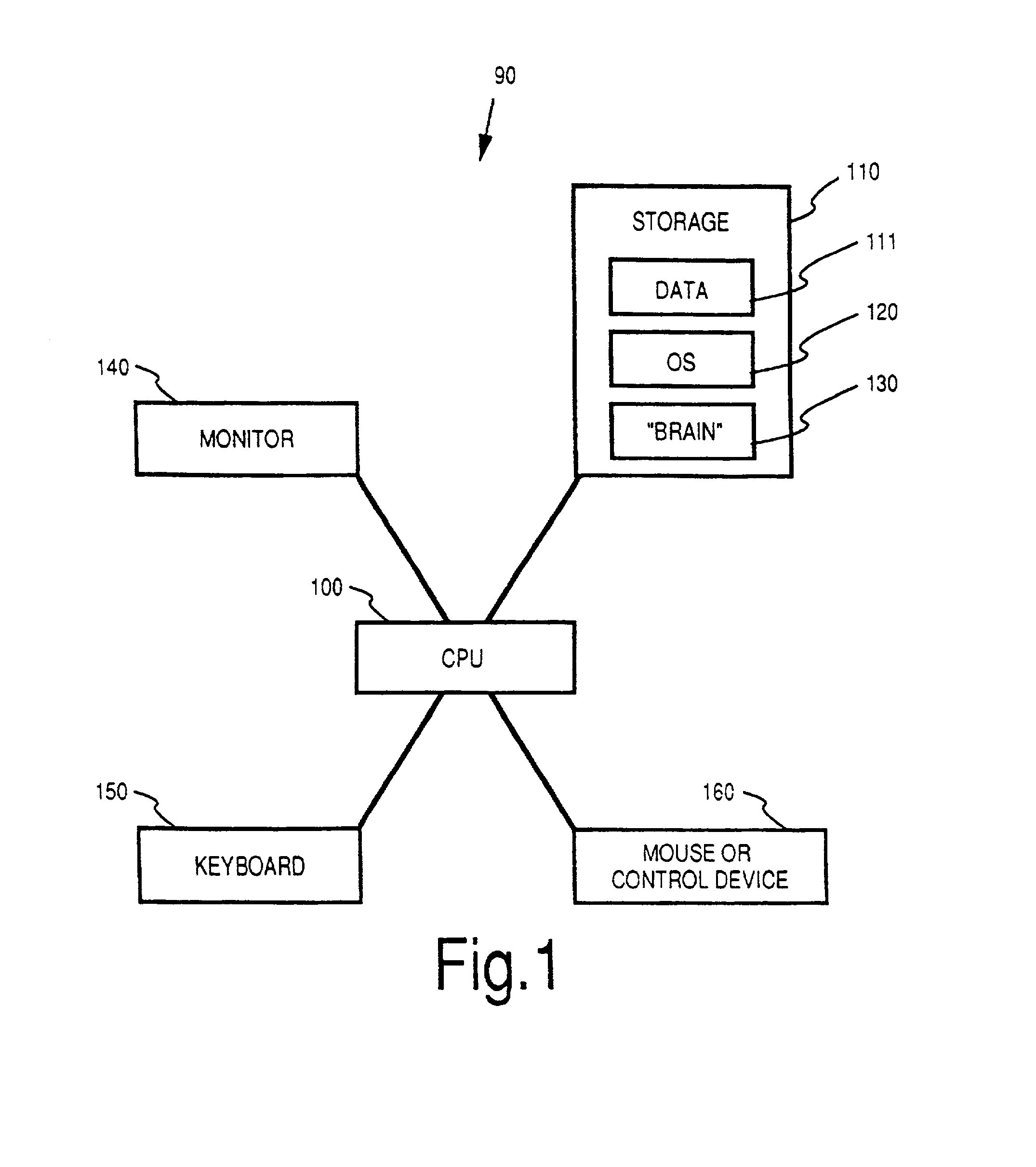
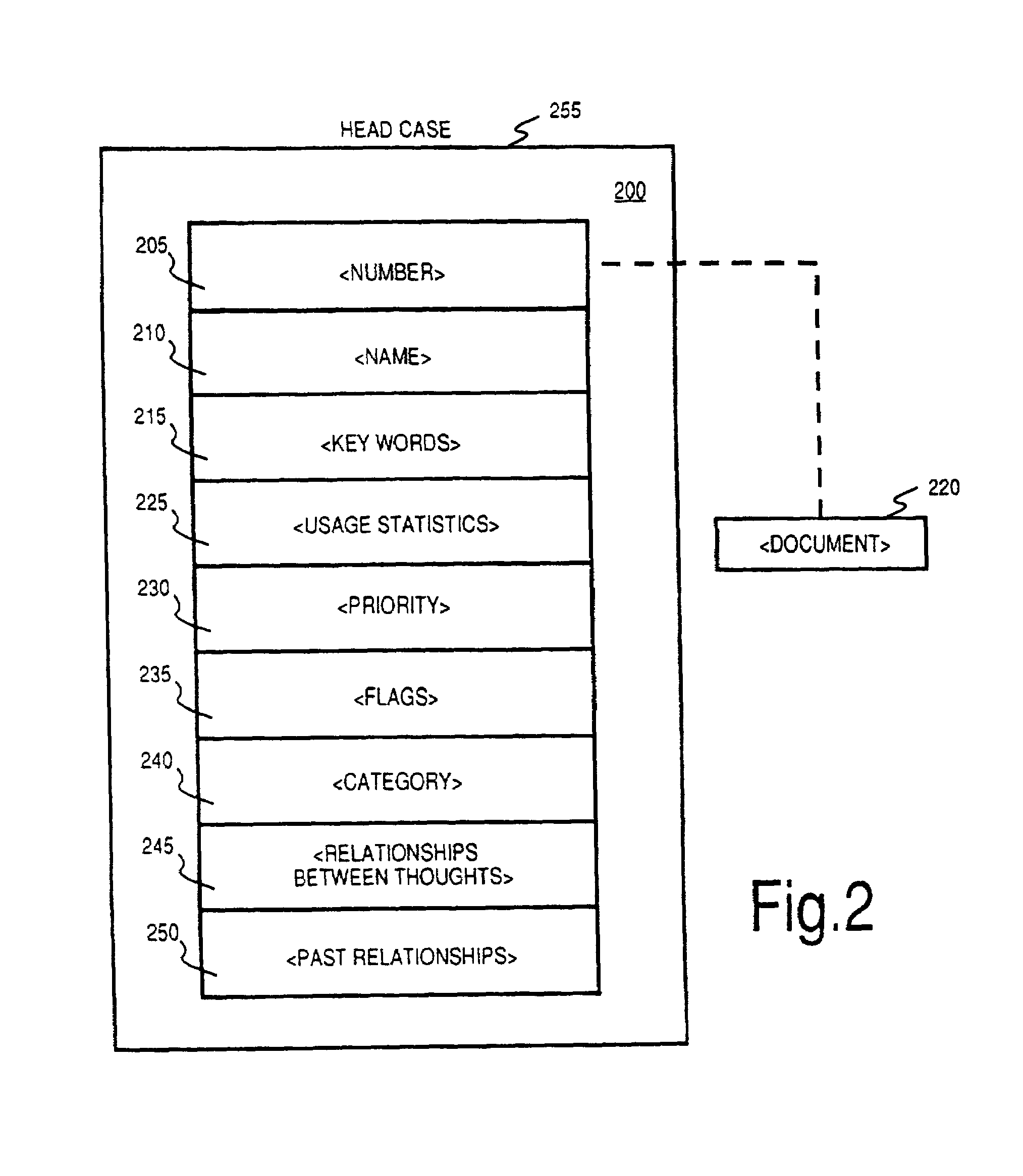
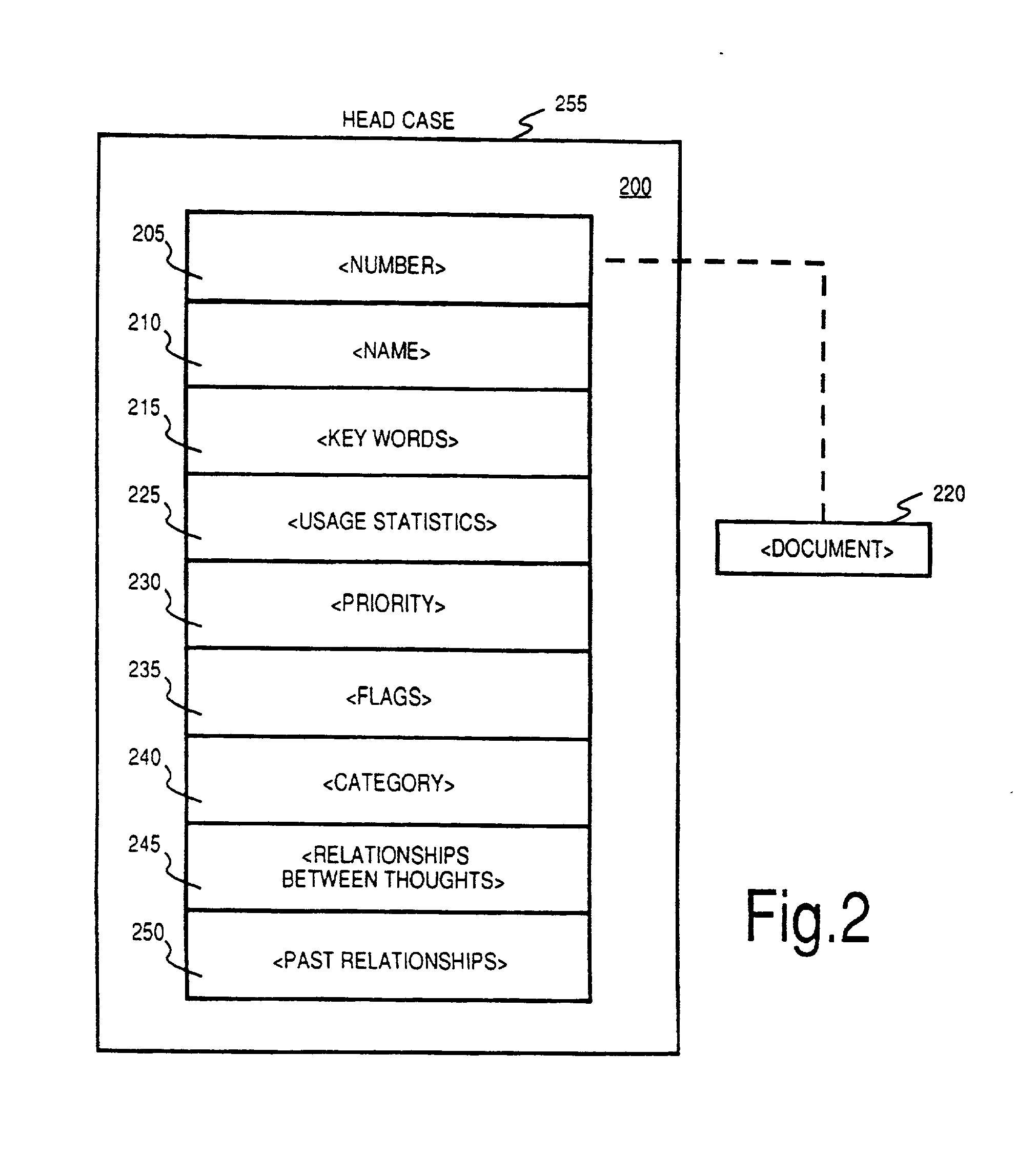
Method and apparatus for sharing many thought databases among many clients
InactiveUS7076736B2Increase flexibilityReduce loadData processing applicationsDatabase distribution/replicationDocumentation procedureDigital storage
Owner:THEBRAIN TECH LP
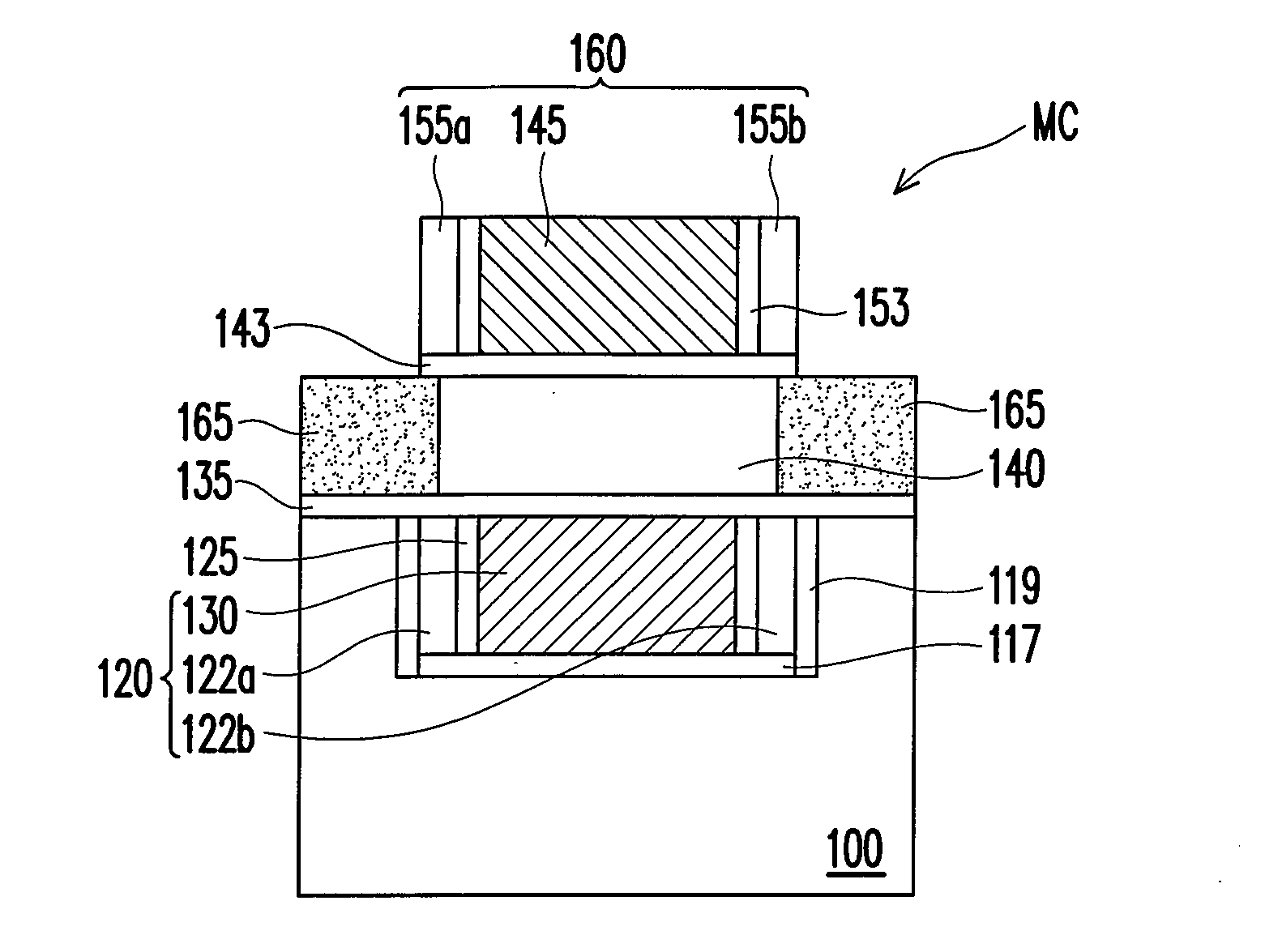
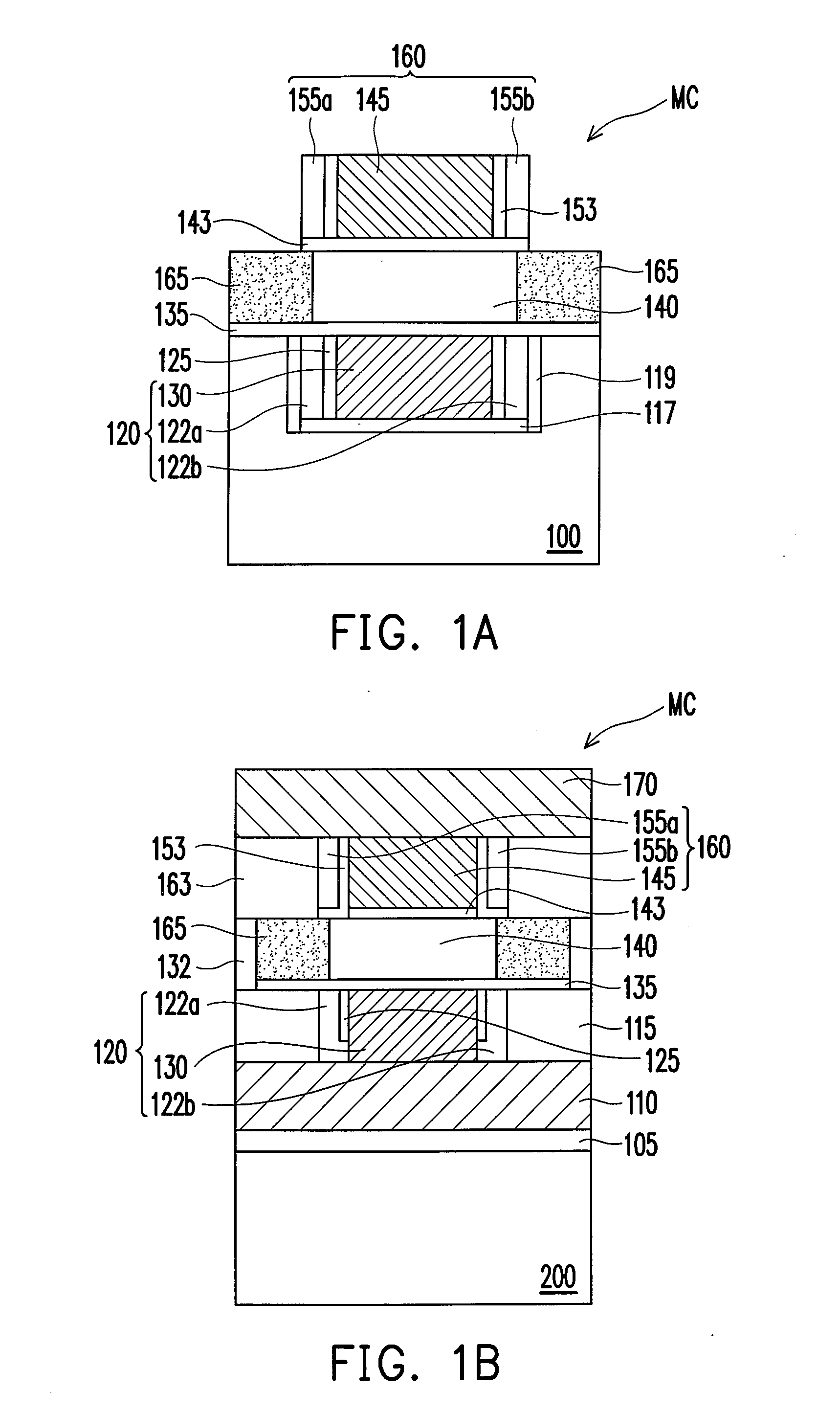
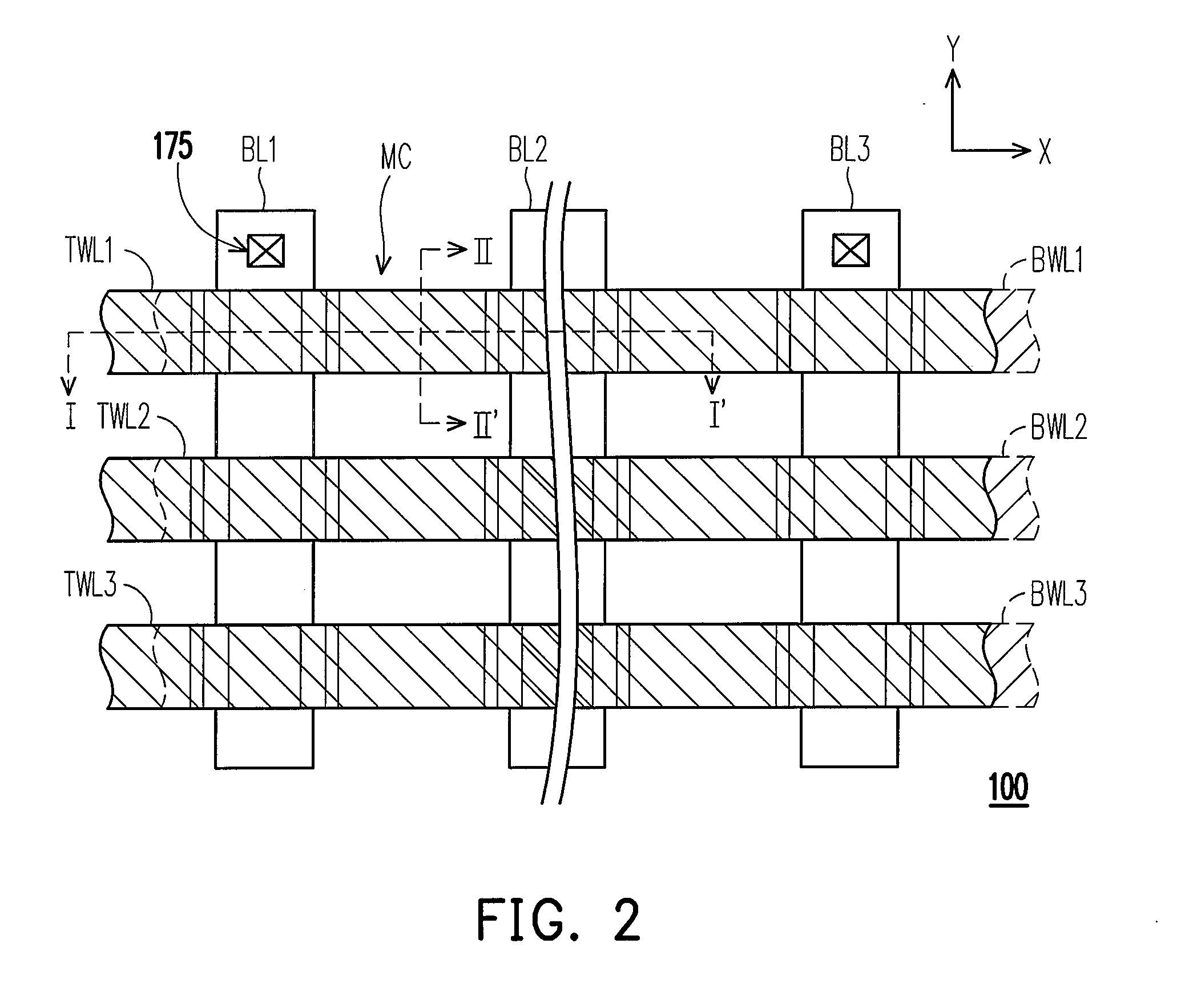
Non-volatile memory and manufacturing method and operating method thereof and circuit system including the non-volatile memory
A non-volatile memory including a memory cell is described. The memory cell includes a first unit, a semiconductor layer, a second unit, and a doped region. The first unit includes a first gate, a first charge trapping layer, and a second charge trapping layer. The first and the second charge trapping layer are respectively disposed on both sides of the first gate. The semiconductor layer is disposed on the first unit. The second unit is disposed on the semiconductor layer and is in mirror symmetry to the first unit. The second unit includes a second gate and a third and a fourth charge trapping layer respectively disposed on both sides of the second gate. The doped region is disposed at both sides of the semiconductor layer and serves as a common source / drain region of both the first and the second unit.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
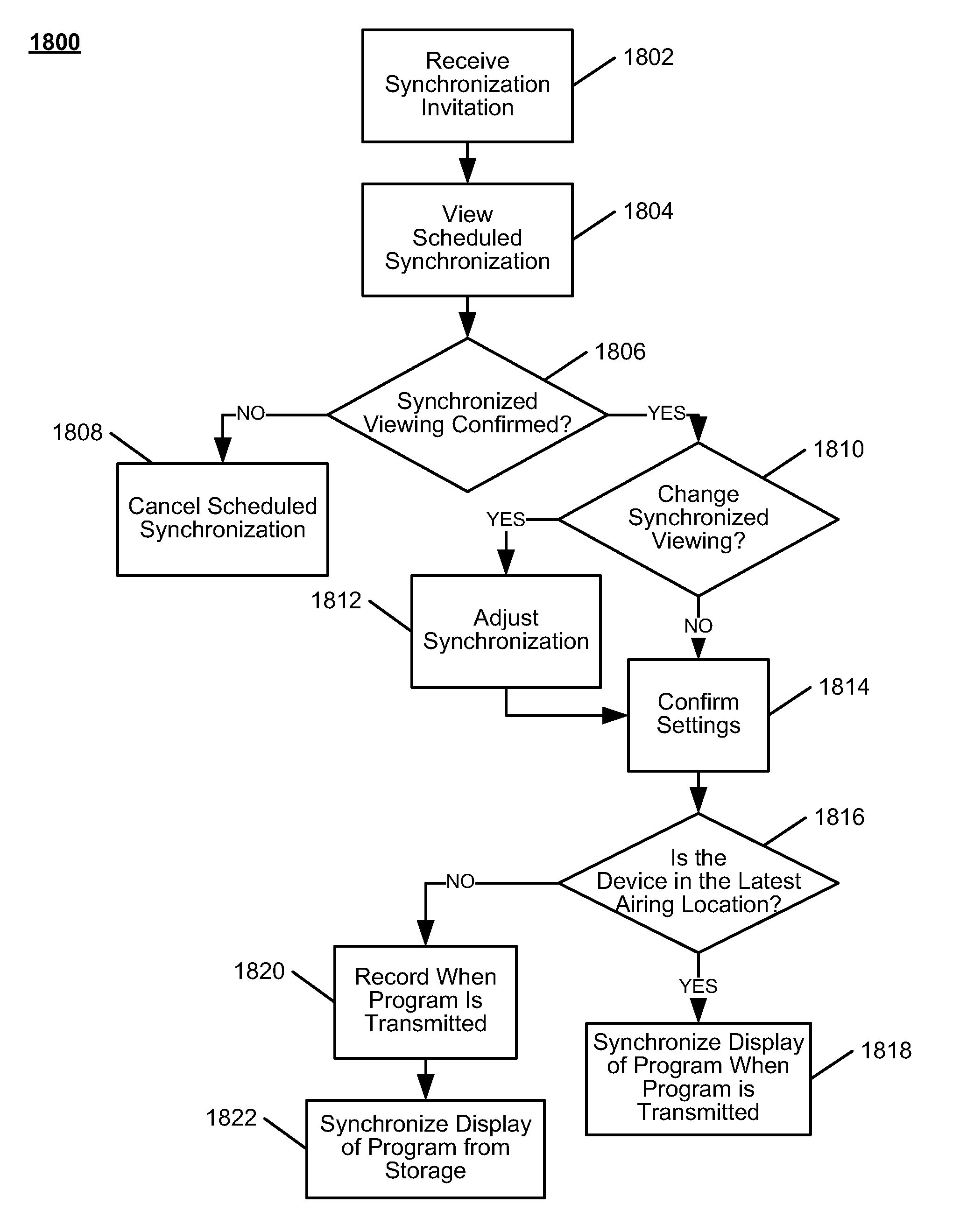
Systems and methods for latency-based synchronized playback at multiple locations
Embodiments provide methods and systems for synchronizing simultaneous media asset viewing for users at different geographical viewing locations. In some embodiments, a first user device receives a request to synchronize viewing of a media asset with a second user device. If the first user device accepts the request for synchronized viewing, the first and second user devices receive the media asset from a common source. Control circuitry at the common source may determine the latencies to the first and second user devices. The transmission of the media asset to the first and second user devices is adjusted according to the latencies.
Owner:UNITED VIDEO PROPERTIES
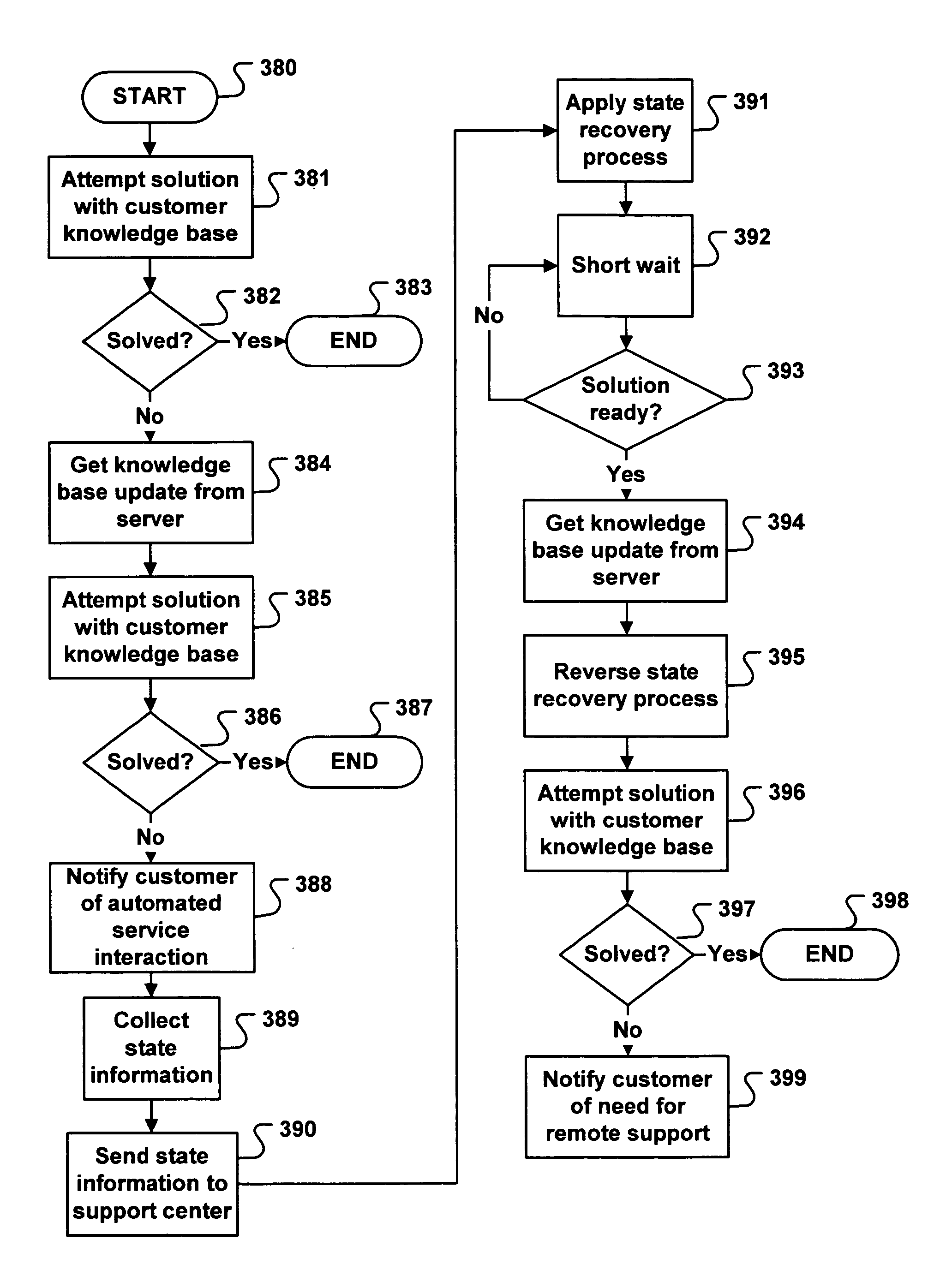
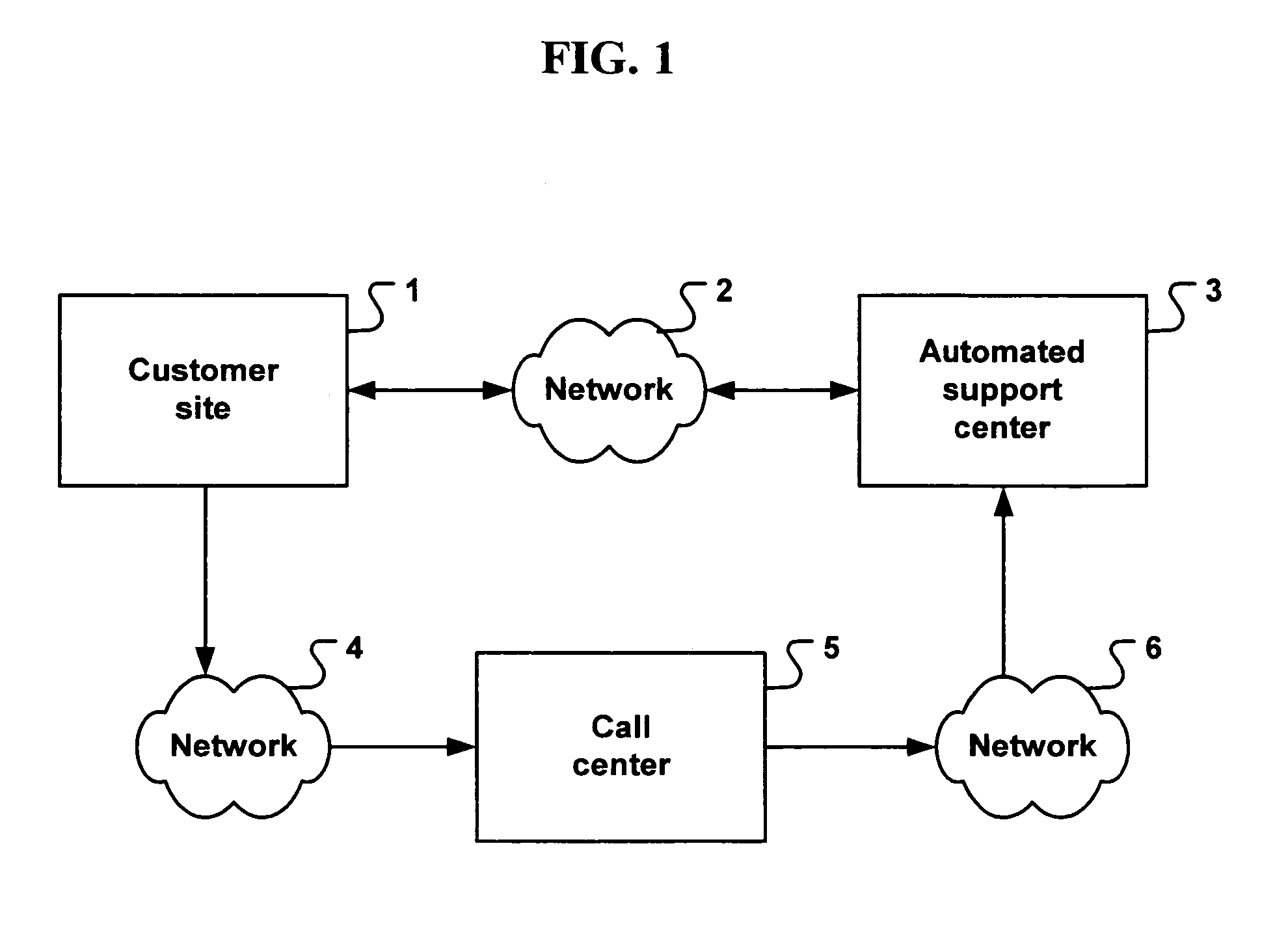
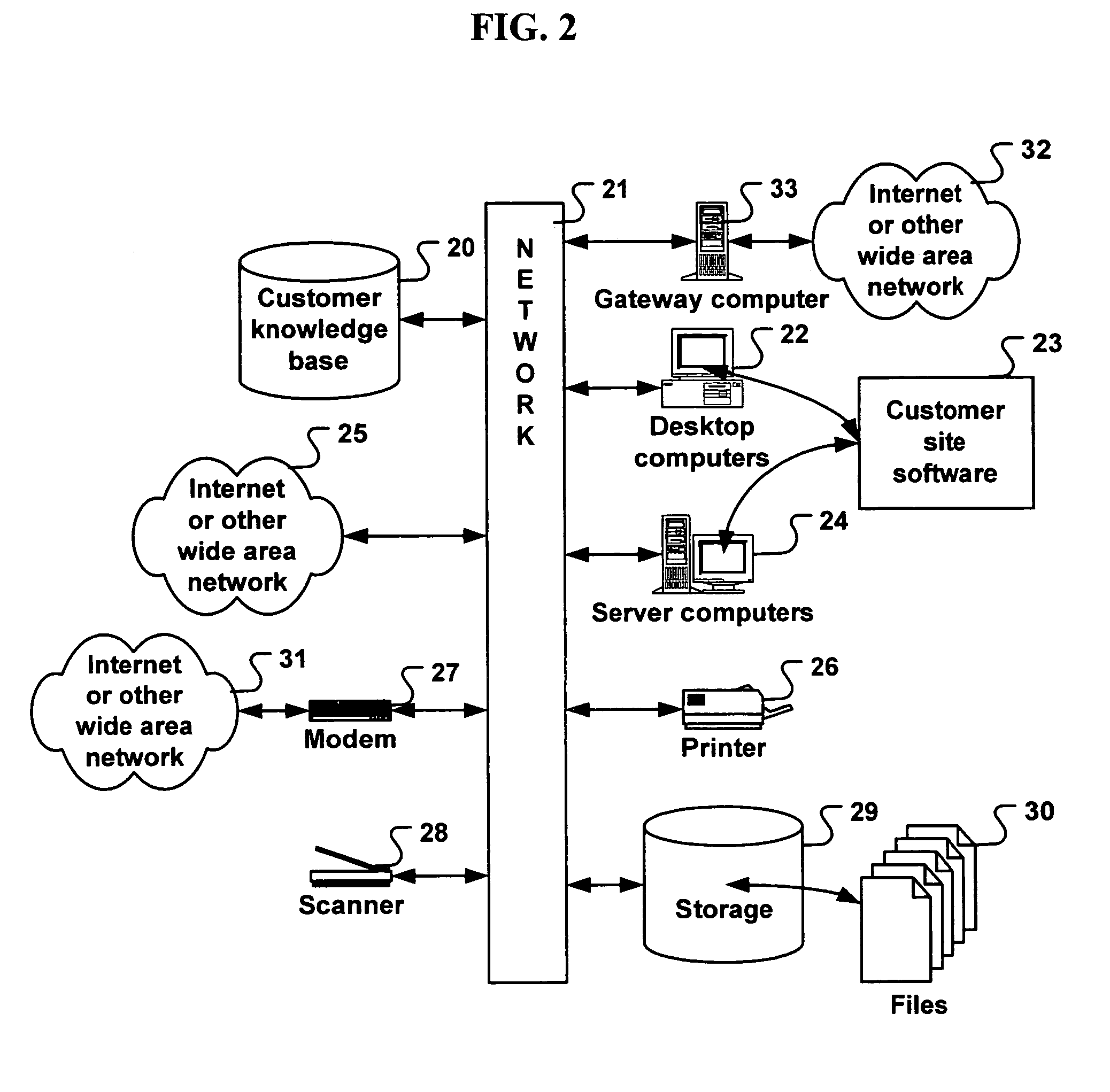
System for automated problem detection, diagnosis, and resolution in a software driven system
InactiveUS20050015678A1Guaranteed uptimeEasy to understandFault responseDetecting faulty hardware by remote testTheoretical computer scienceInstability
In many systems, computer software is a common source of failure or instability. The proliferation of multiple interacting applications from several different software vendors leads to “emergent” problems that are difficult or impossible to predict or prevent. The problems are compounded by the use of networks, which introduce the added complexity of applications on multiple machines interacting in complex scenarios. As a result, many business and home users are hindered from using software-based systems to their fullest potential. More effective use of these systems can be aided by an application which can provide services for monitoring, diagnosing, and solving problems that occur in the operation of the machines at a customer facility. In the system described herein, a database contains entries with executable code that can make use of these services in order to monitor, diagnose, and solve specific problems. Each entry in the database addresses a specific problem. The executable code is designed to isolate and recognize the problem, and then implement a fix or workaround for that problem. The executable code is designed to completely automate the entire process of detection and resolution of the problem. Further, manual intervention may be employed to complete the diagnosis or solution.
Owner:HFN LLC
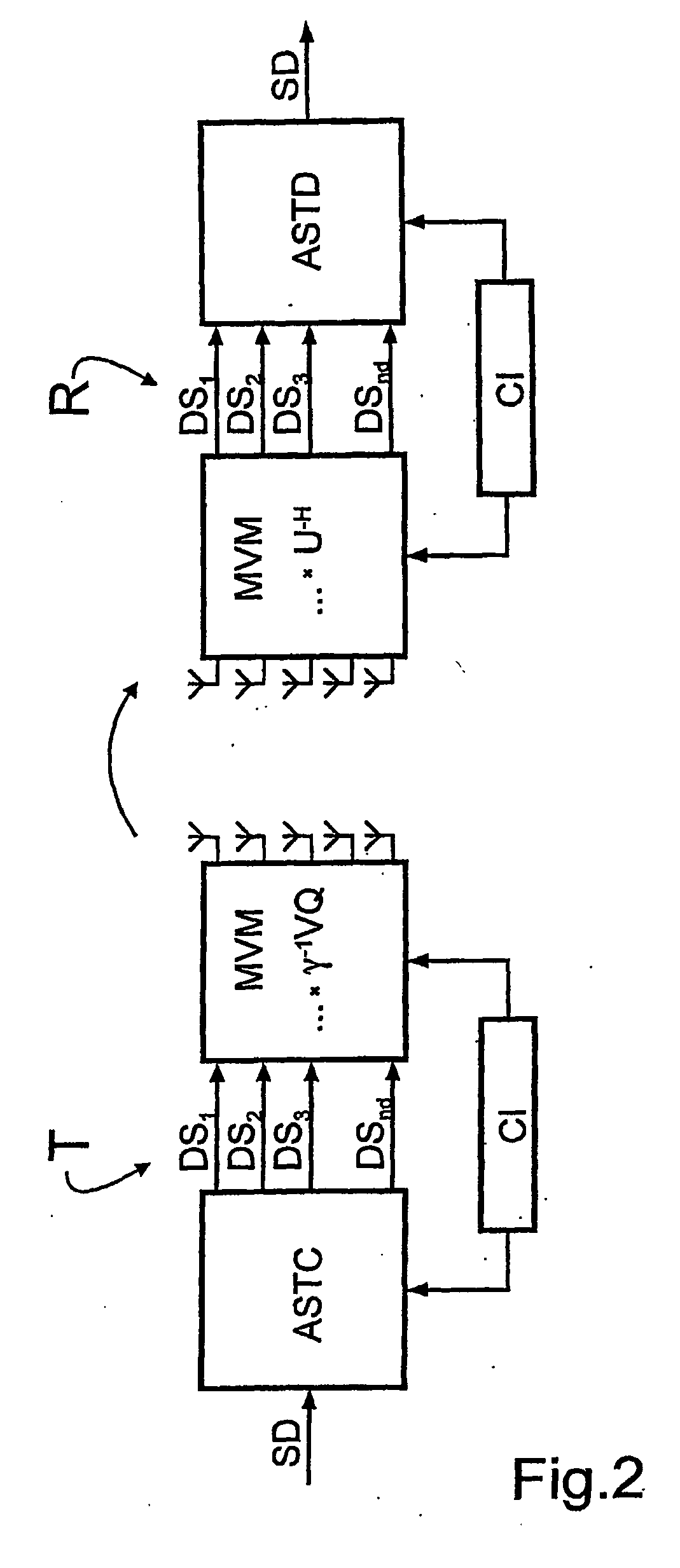
Mimo signal processing method involving a rank-adaptive matching of the transmission rate
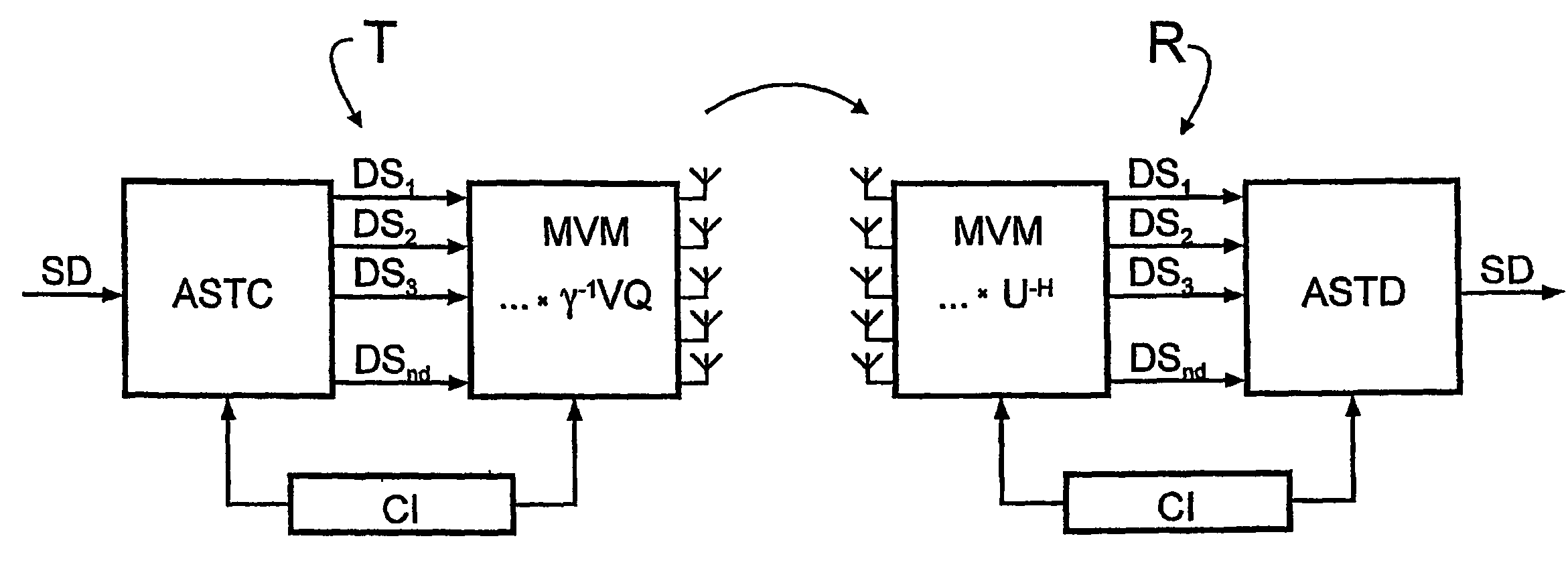
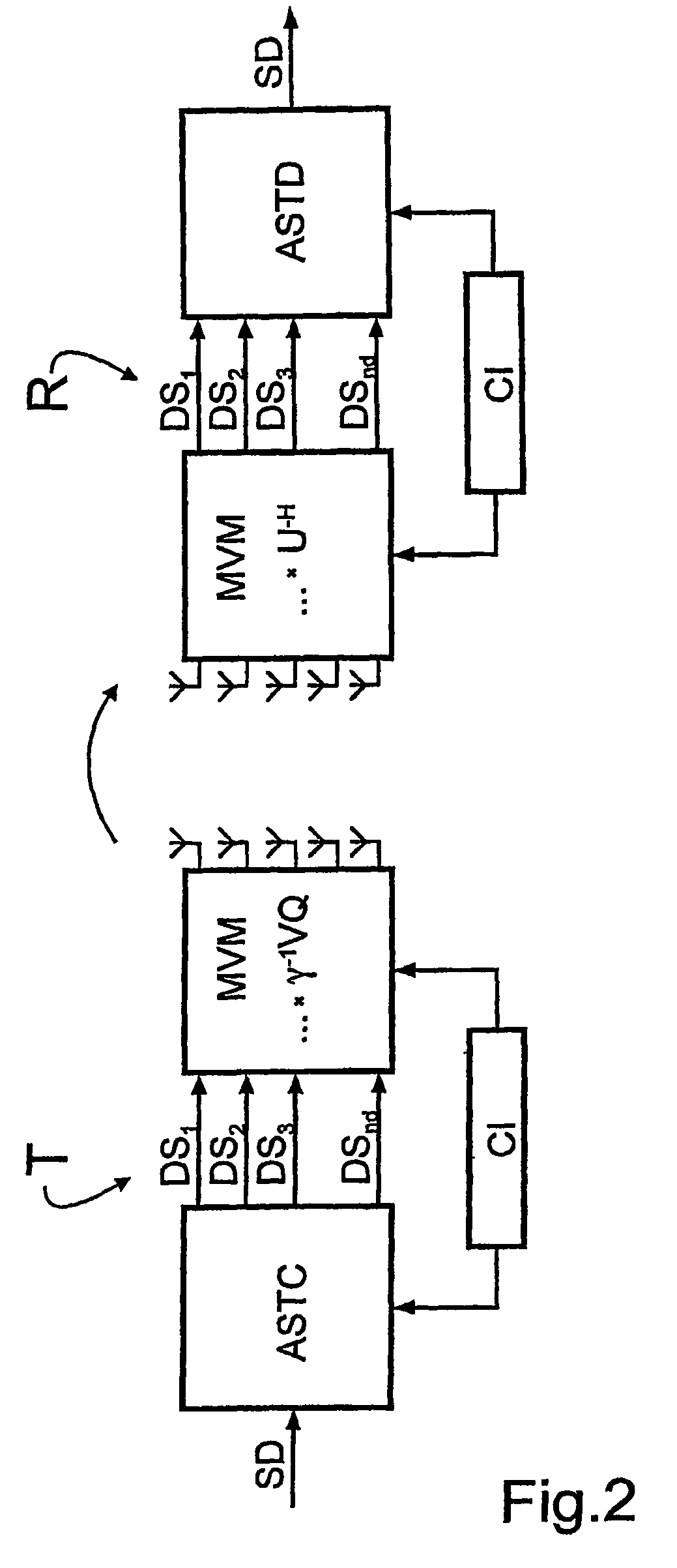
InactiveUS20060193294A1Reduce complexityReliable data transmissionPower managementTransmission control/equalisingData streamTransmitted power
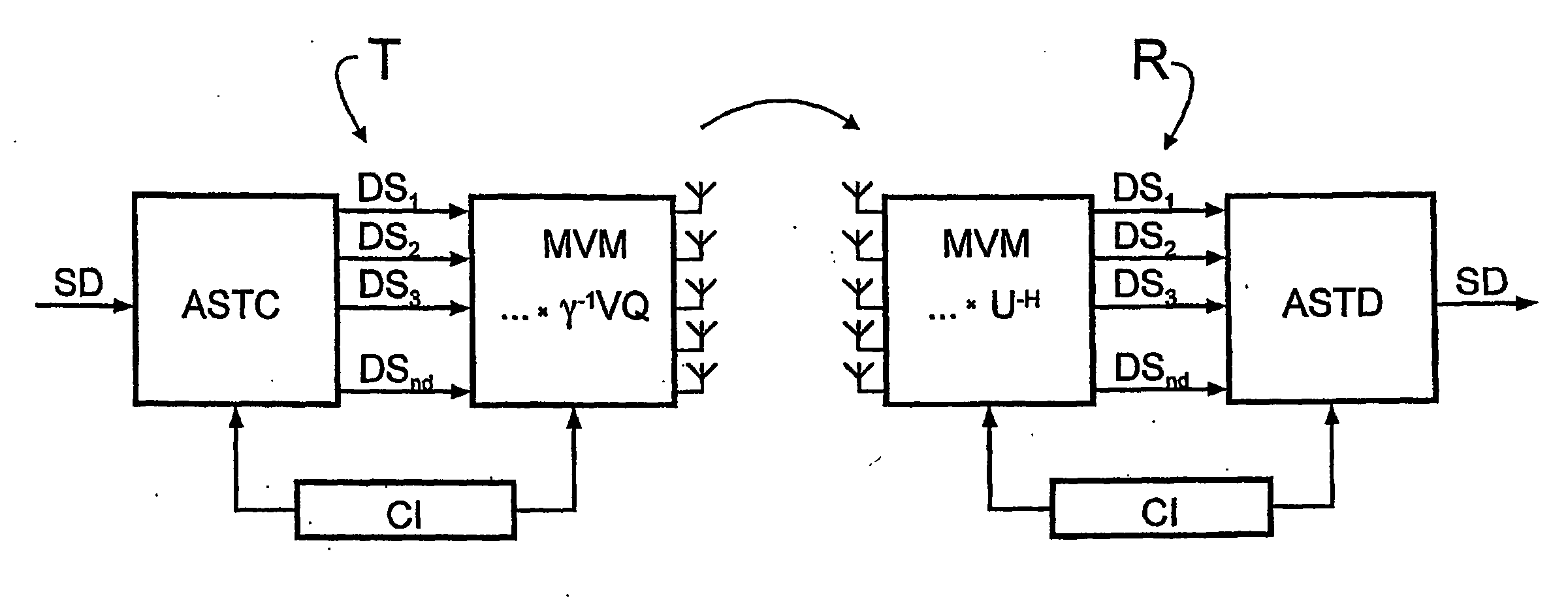
A bidirectional signal processing method uses parallel transmission of digital transmitted data streams in a multiple input-multiple output system. Related art methods generate high bit error rates mostly in singular transmission channels. For this reason, the rank-adaptive signal processing method provides that the number nd of active subchannels are varied according to the actual channel behavior in order to effect a robust data transmission even in singular radio channels based on a transmit-side and receive-side channel knowledge and a modification of the data vector by a linear matrix vector multiplication while introducing a factor gamma for limiting the maximum transmit power. The maximum transmit power is then only distributed to the currently activated subchannels so that no transmit power remains unused. Another optimization of the number of subchannels nd occurs when selecting the modulation and encoding methods. During the optimal rank-adaptation according to the water-filling principle, another power is allocated to each subchannel. Another modulation and encoding method is accordingly selected for each data stream. During the suboptimal rank-adaptation according to the channel inversion principle, all subchannels have the same power whereby enabling the data streams to be modulated and encoded in a common source
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Dynamic deep depletion field effect transistor
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Floating Gate Inverter Type Memory Cell And Array
ActiveUS20100157669A1Optimize layoutReduce layout areaTransistorSolid-state devicesCMOSFowler nordheim
A non-volatile memory (NVM) cell and array includes a control capacitor, tunneling capacitor, CMOS inverter and output circuit. The CMOS inverter includes PMOS and NMOS inverter transistors. The control capacitor, tunneling capacitor and PMOS and NMOS inverter transistors share a common floating gate, which is programmed / erased by Fowler-Nordheim tunneling. The output circuit includes PMOS and NMOS select transistors. The PMOS inverter and select transistors share a common source / drain region. Similarly, the NMOS inverter and select transistors share a common source / drain region. This configuration minimizes the required layout area of the non-volatile memory cell and allows design of arrays with smaller footprints. Alternately, the tunneling capacitor may be excluded, further reducing the required layout area of the NVM cell. In this case, the NMOS inverter transistor functions as a tunneling capacitor for programming and erasing the cell, and the PMOS inverter transistor functions as a tunneling capacitor for erasing the cell.
Owner:TOWER SEMICONDUCTOR
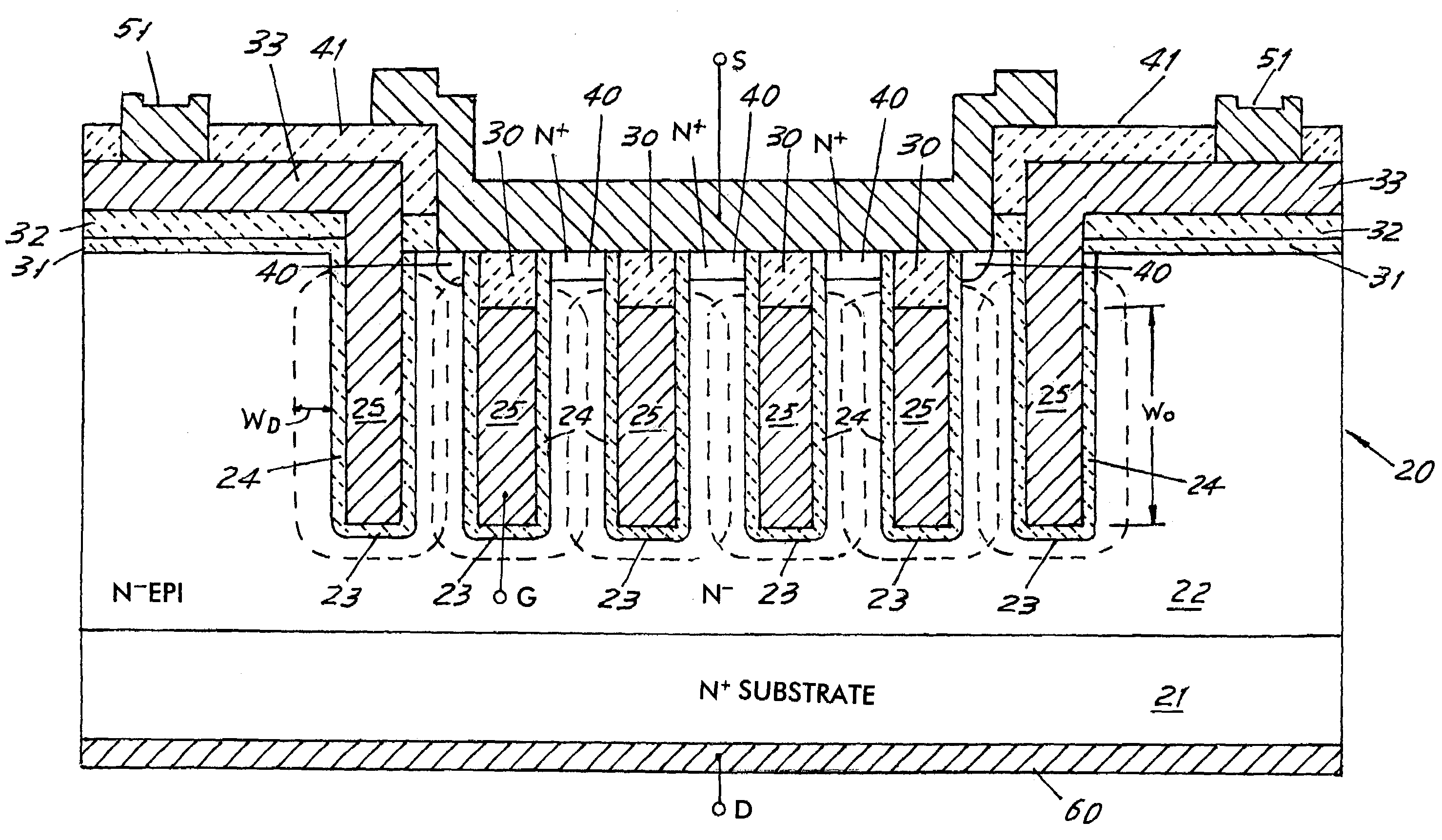
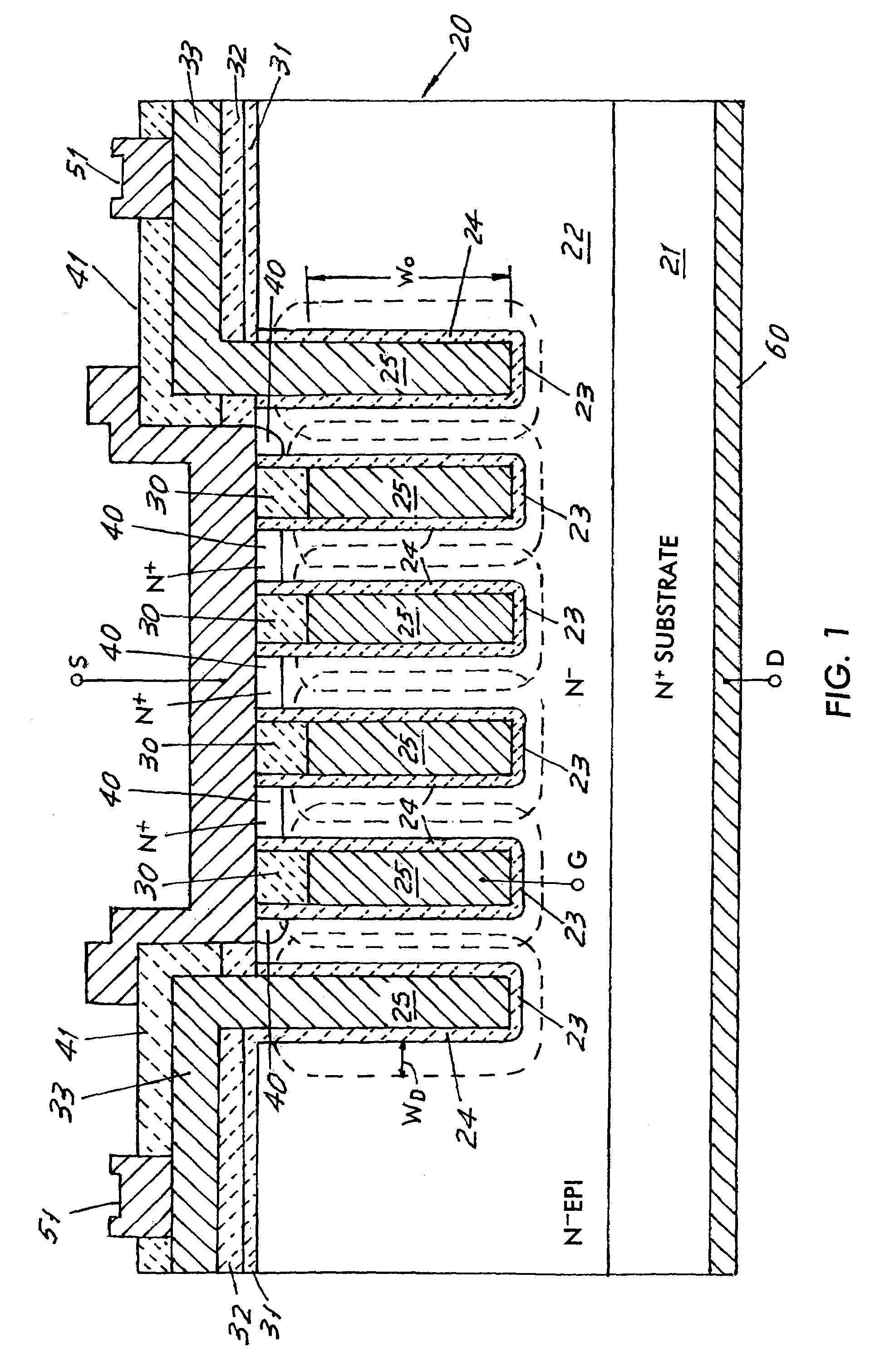
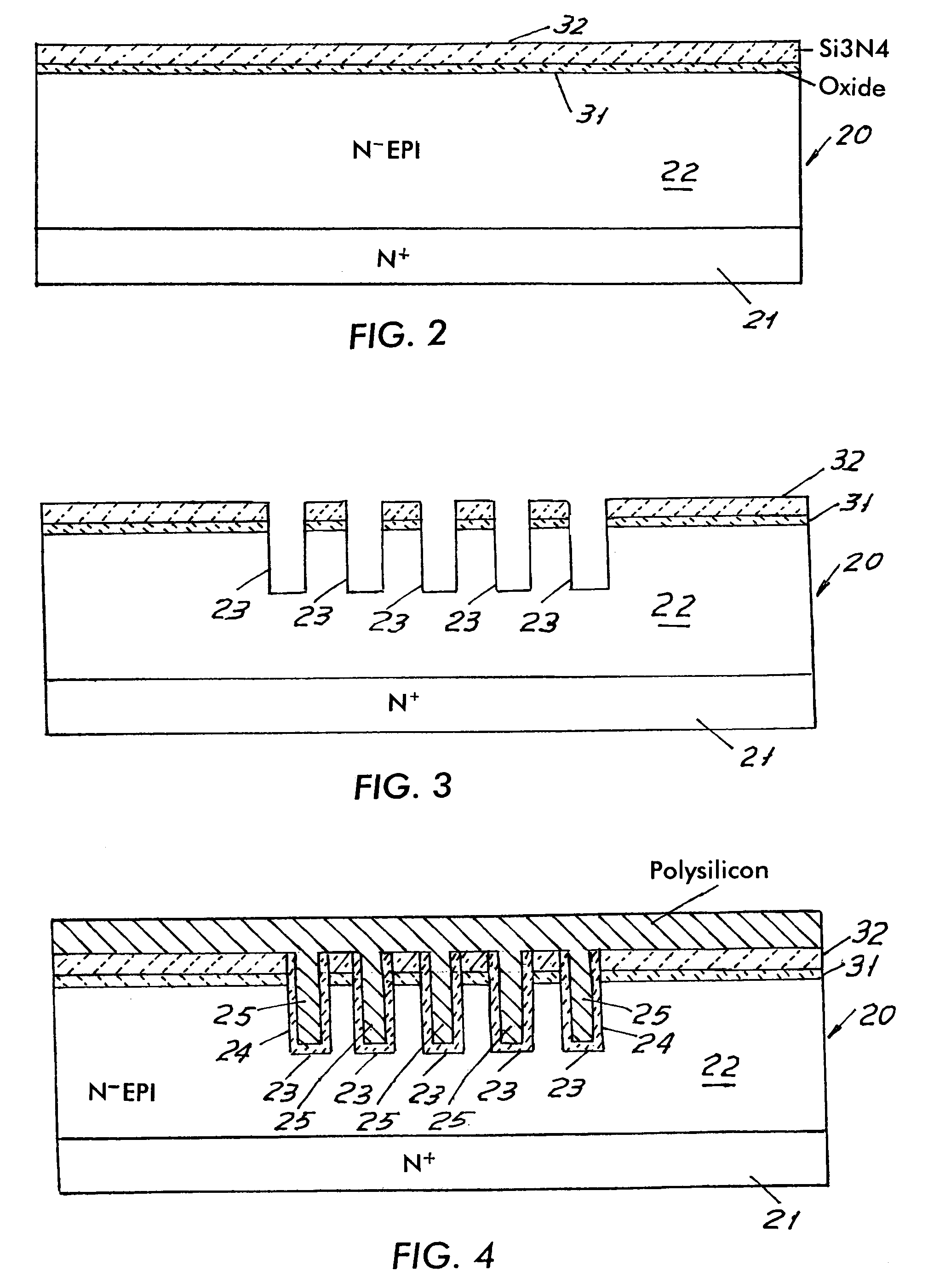
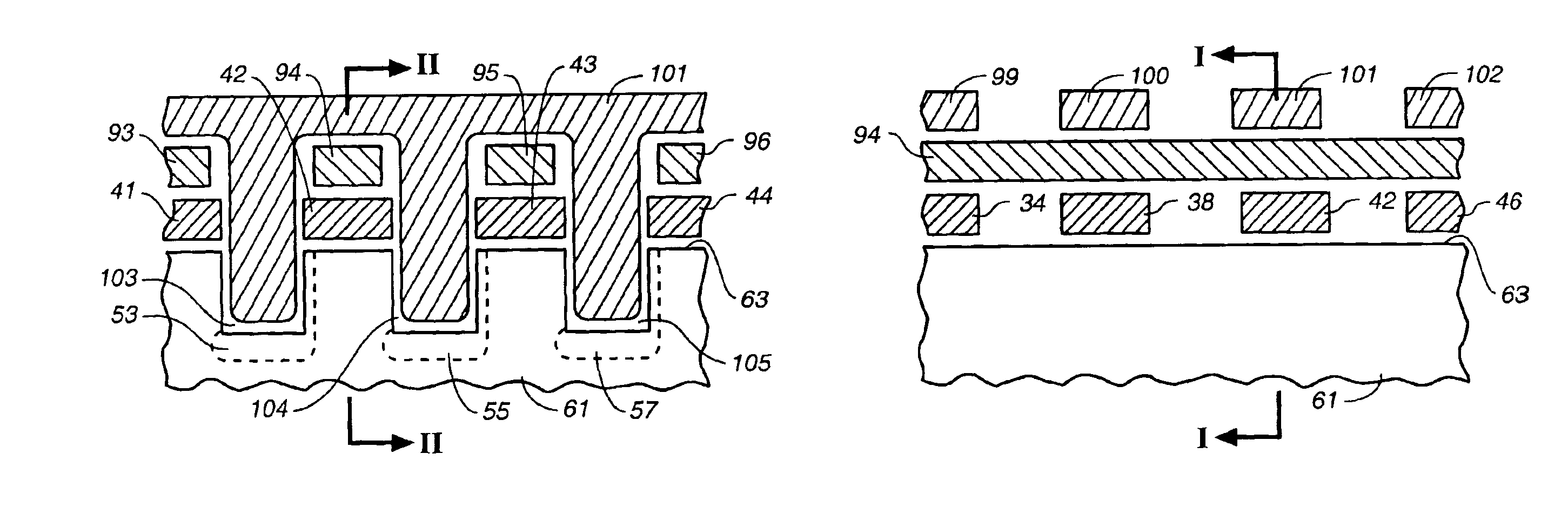
Non-volatile memory cells utilizing substrate trenches
InactiveUS6936887B2Small sizeImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceCapacitive coupling
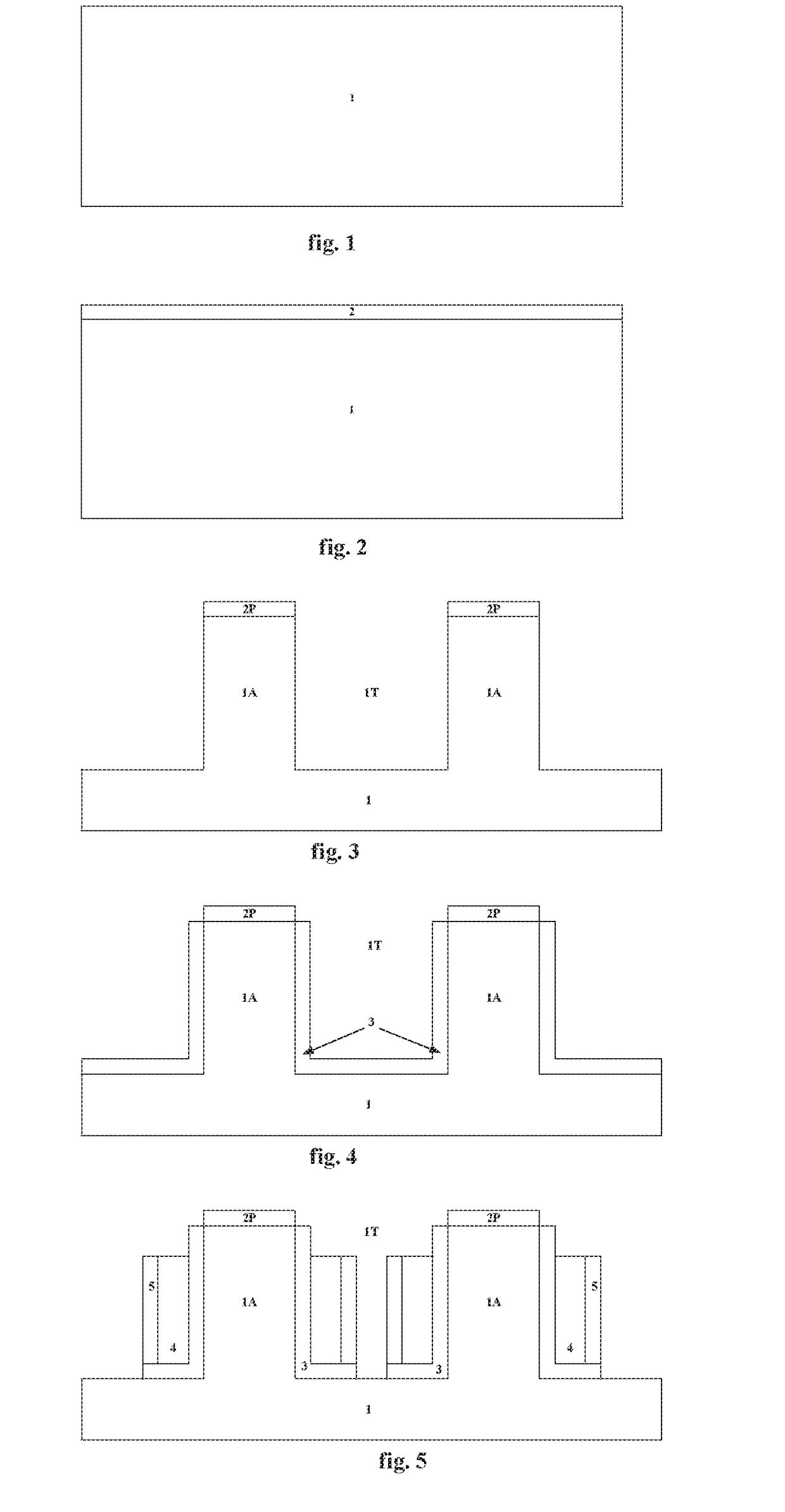
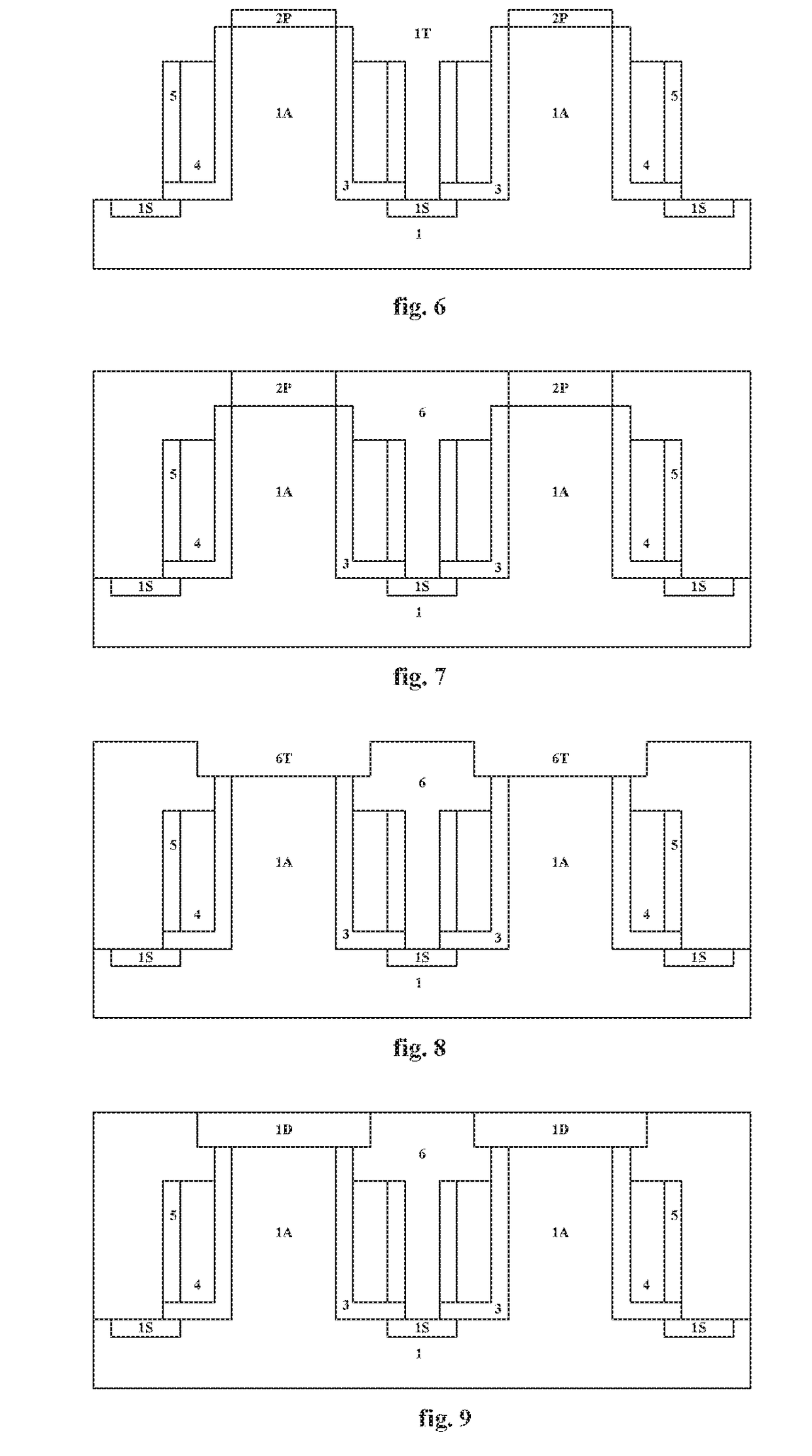
Several embodiments of flash EEPROM split-channel cell arrays are described that position the channels of cell select transistors along sidewalls of trenches in the substrate, thereby reducing the cell area. Select transistor gates are formed as part of the word lines and extend downward into the trenches with capacitive coupling between the trench sidewall channel portion and the select gate. In one embodiment, trenches are formed between every other floating gate along a row, the two trench sidewalls providing the select transistor channels for adjacent cells, and a common source / drain diffusion is positioned at the bottom of the trench. A third gate provides either erase or steering capabilities. In another embodiment, trenches are formed between every floating gate along a row, a source / drain diffusion extending along the bottom of the trench and upwards along one side with the opposite side of the trench being the select transistor channel for a cell. In another embodiment, select transistor gates of dual floating gate memory cells are extended into trenches or recesses in the substrate in order to lengthen the select transistor channel as the surface dimensions of the cell are being decreased. Techniques for manufacturing such flash EEPROM split-channel cell arrays are also included.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for sharing many thought databases among many clients
InactiveUS20030117434A1Increase flexibilityReduce loadData processing applicationsDatabase distribution/replicationDocumentation procedureDigital storage
The Brain system employs a graphical user interface to facilitate user interaction with highly flexible, associative "matrices" that enable users to conveniently organize digitally-stored "thoughts" (inter-related information) and their network of inter-relationships. The Brain system offers a solution that facilitates the capture of information from a company's repositories and showcases it in an engaging and dynamic visual interface. The Brain accomplishes this by providing a connector system that serves as an interface between the Brain server and whatever repositories are employed to store data. By use of a special type of connector, the Brain can permit a single user to collaborate with a number of different repositories at different locations and of different sorts under a single associative interface. A client can also interface directly with multiple data stores that are configured for interaction with the associative interface described herein. Multiple nodes on a network can access common sources of associative data in real-time or by way of synchronization techniques. Lastly, methods are further described permitting single items of associative data to reference multiple documents at once.
Owner:THEBRAIN TECH LP
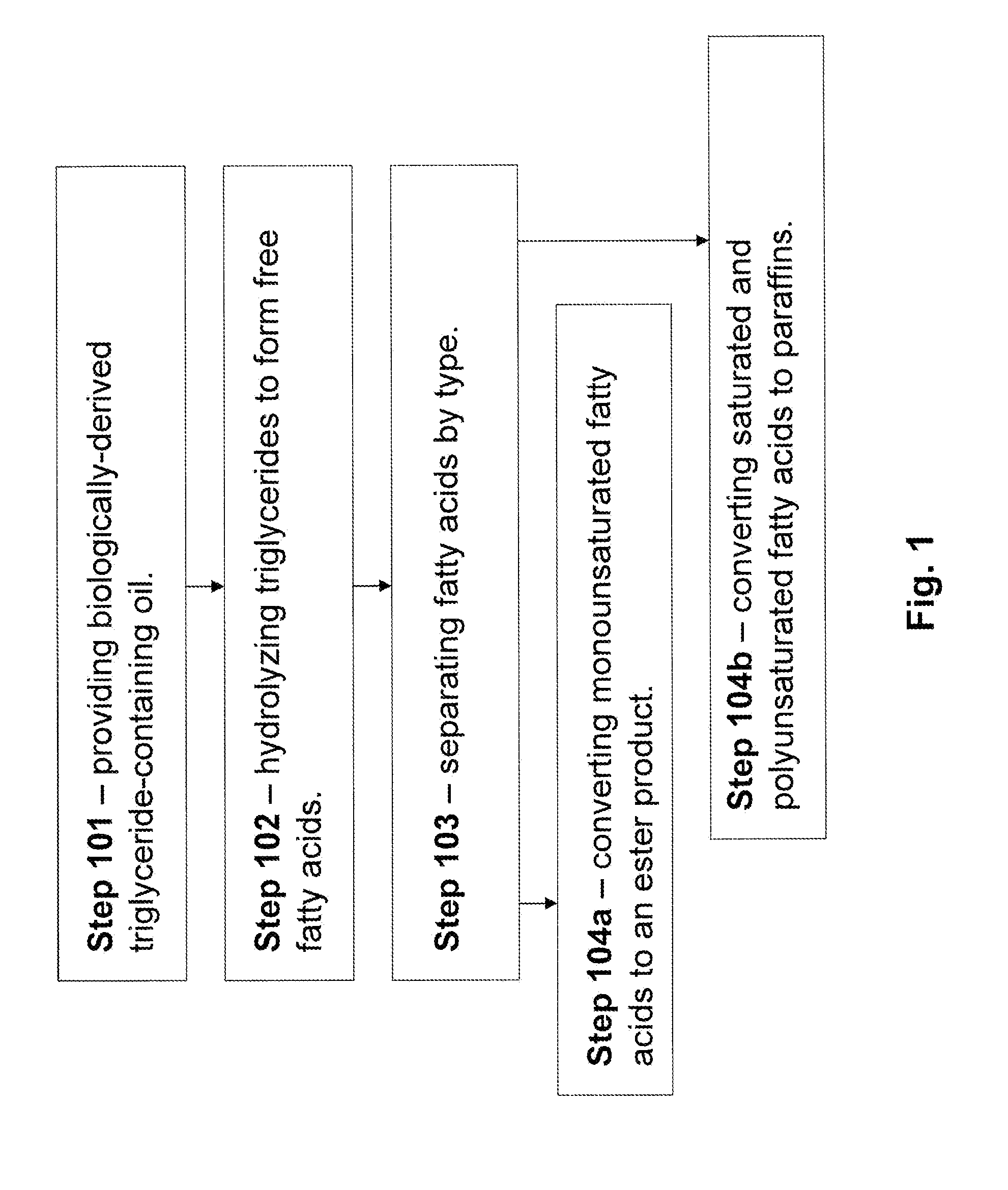
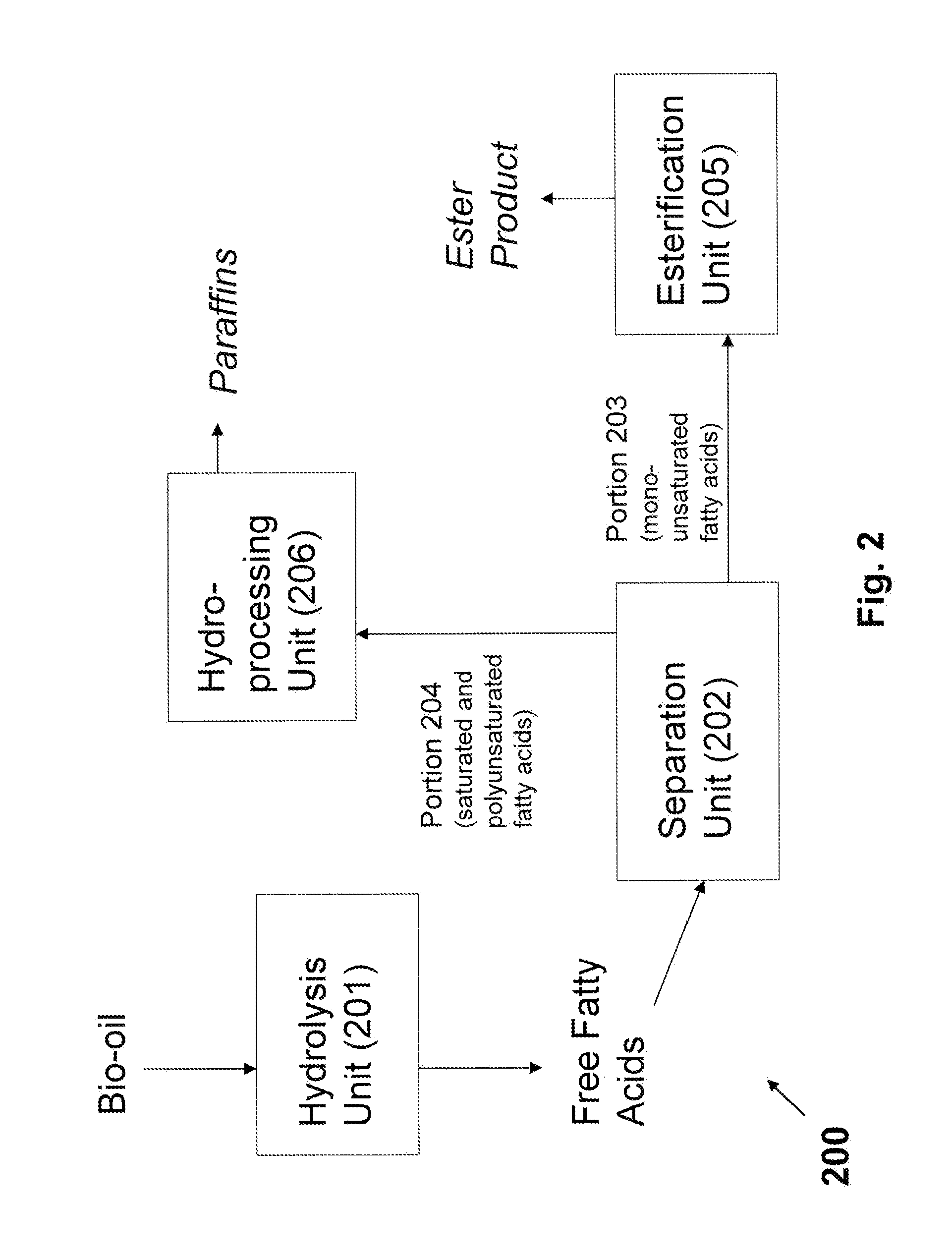
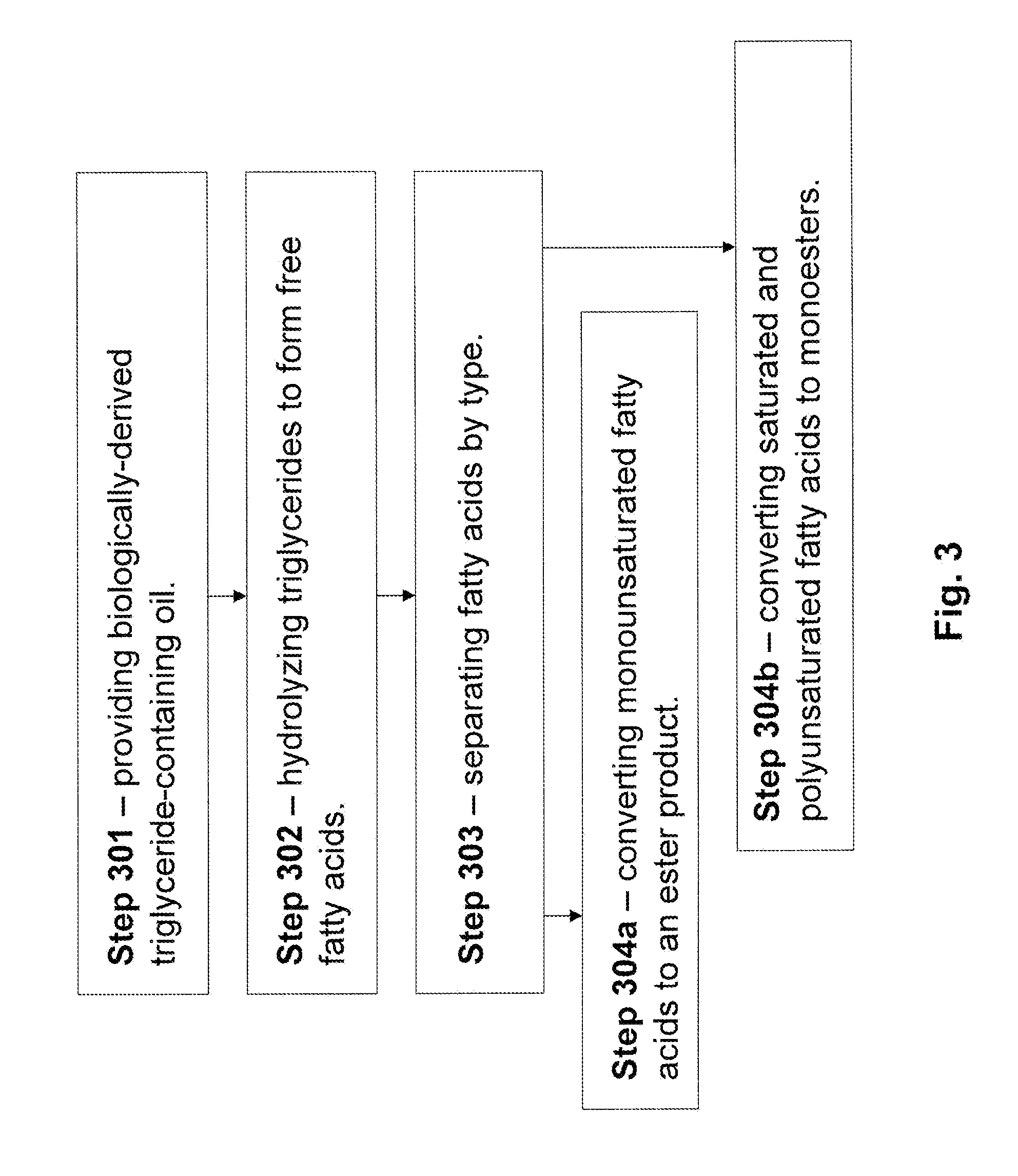
Production of Biofuels and Biolubricants From a Common Feedstock
InactiveUS20090084026A1Fatty acid esterificationRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonChemistryCommon source
The present invention is directed to methods and systems for processing triglyceride-containing, biologically-derived oils, wherein such processing comprises conversion of triglycerides to free fatty acids and the separation of these fatty acids by saturation type. Such separation by type enables the efficient preparation of both lubricants and transportation fuels from a common source using a single integrated method and / or system.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
MIMO signal processing method involving a rank-adaptive matching of the transmission rate
InactiveUS7450548B2Reduce complexityNo loss of transmit powerPower managementTransmission control/equalisingMulti inputData stream
A bidirectional signal processing method uses parallel transmission of digital transmitted data streams in a multiple input-multiple output system. Related art methods generate high bit error rates mostly in singular transmission channels. For this reason, the rank-adaptive signal processing method provides that the number nd of active subchannels are varied according to the actual channel behavior in order to effect a robust data transmission even in singular radio channels based on a transmit-side and receive-side channel knowledge and a modification of the data vector by a linear matrix vector multiplication while introducing a factor gamma for limiting the maximum transmit power. The maximum transmit power is then only distributed to the currently activated subchannels so that no transmit power remains unused. Another optimization of the number of subchannels nd occurs when selecting the modulation and encoding methods. During the optimal rank-adaptation according to the water-filling principle, another power is allocated to each subchannel. Another modulation and encoding method is accordingly selected for each data stream. During the suboptimal rank-adaptation according to the channel inversion principle, all subchannels have the same power whereby enabling the data streams to be modulated and encoded in a common source.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Differential vector storage for non-volatile memory
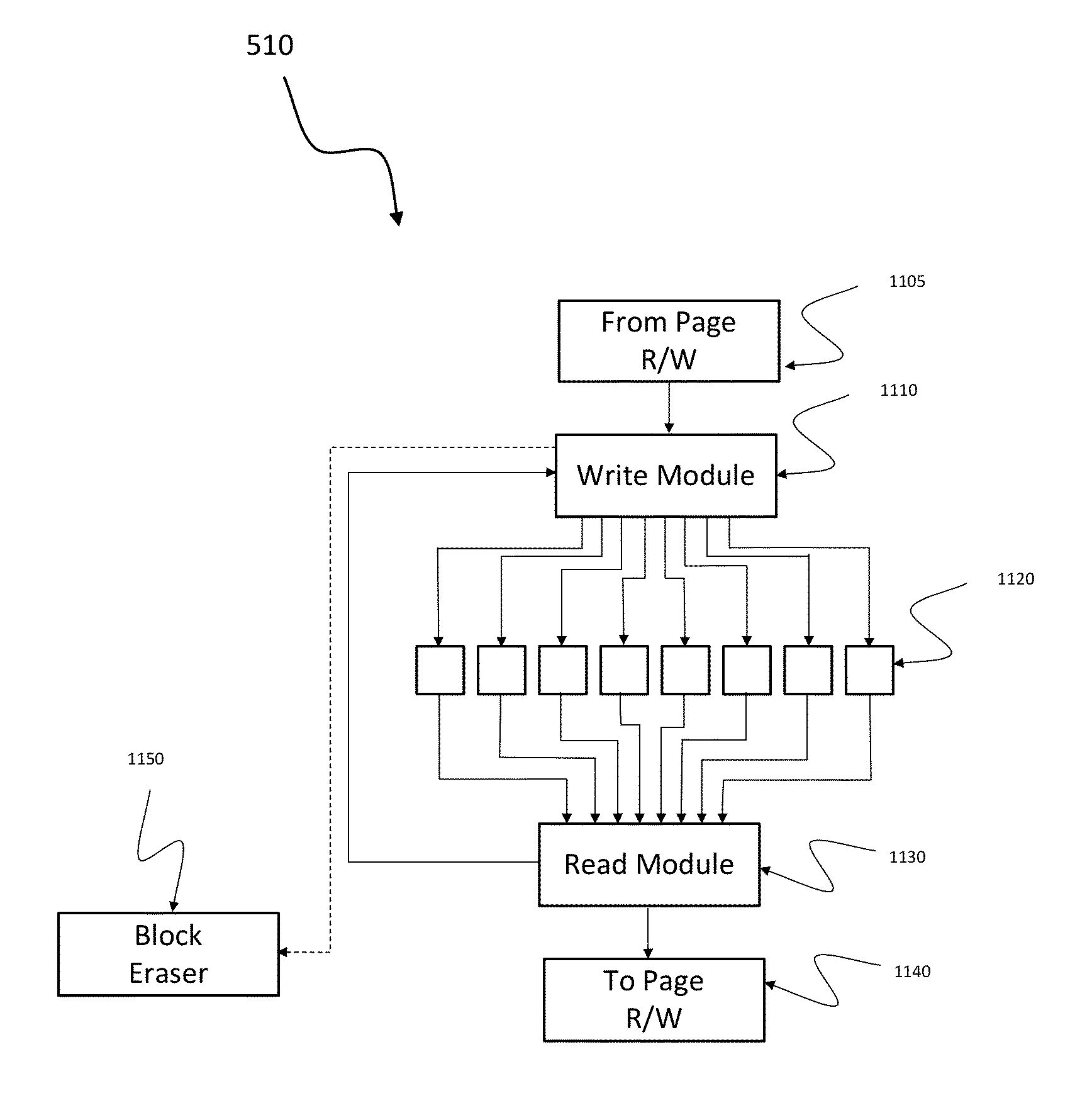
ActiveUS20130013870A1Improve reliabilityFaster write operationError detection/correctionDigital storageSources of errorVolatile memory
A method is disclosed for storing information on non-volatile memory which can rewrite memory cells multiple times before a block needs to be erased. The information to be stored is transformed into a suitable form which has better robustness properties with respect to common sources of error, such as leakage of charge, or imperfect read / write units.
Owner:KANDOU LABS
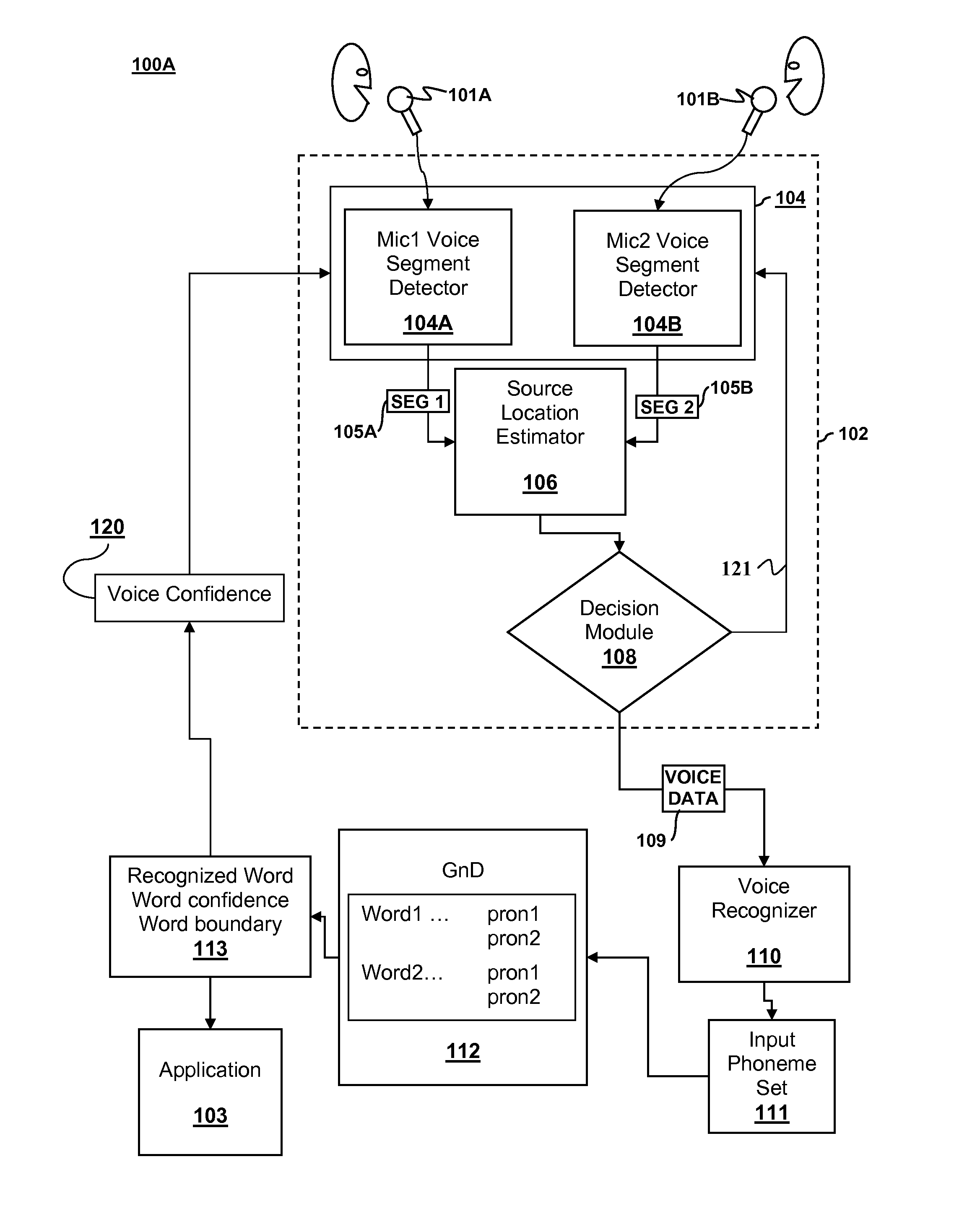
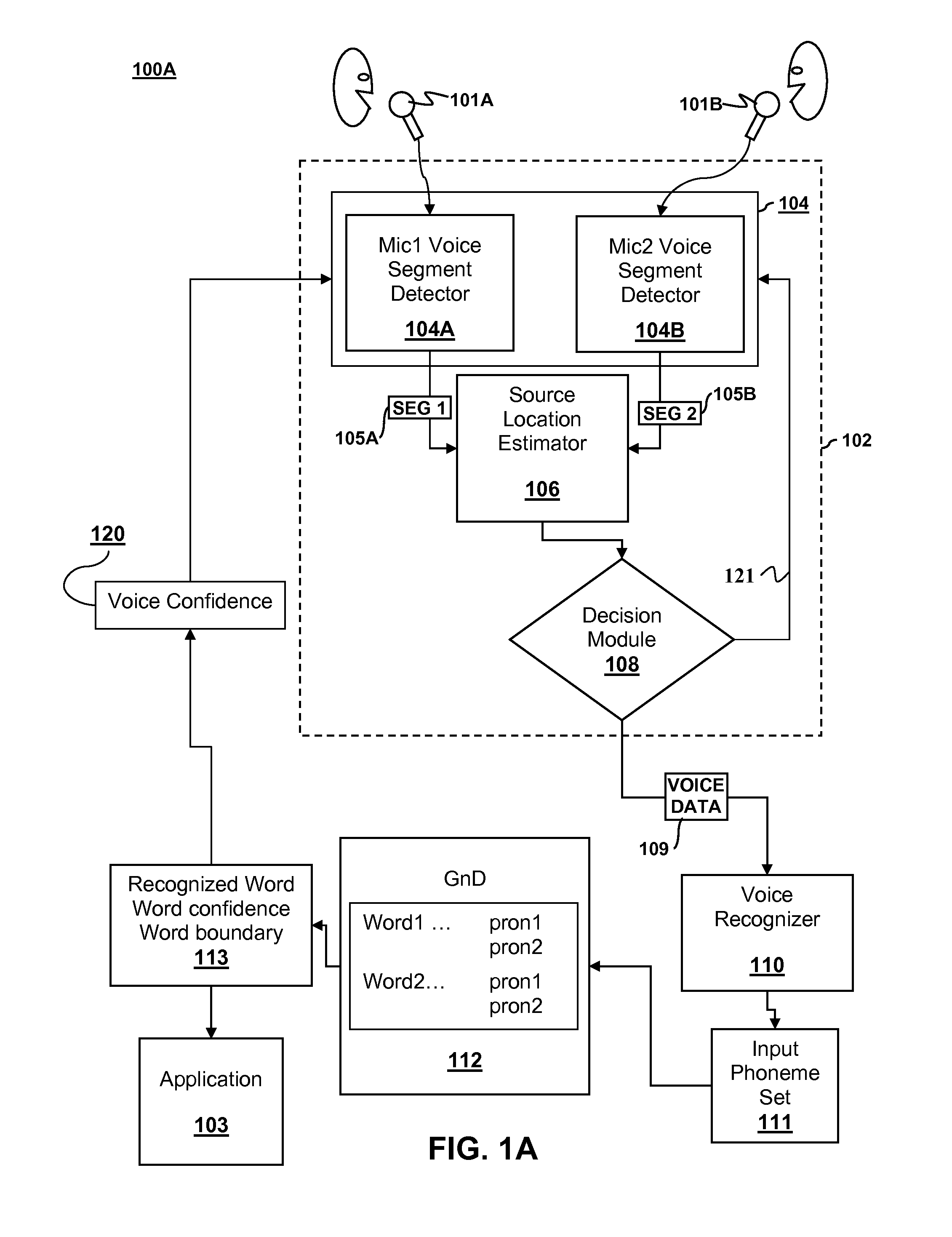
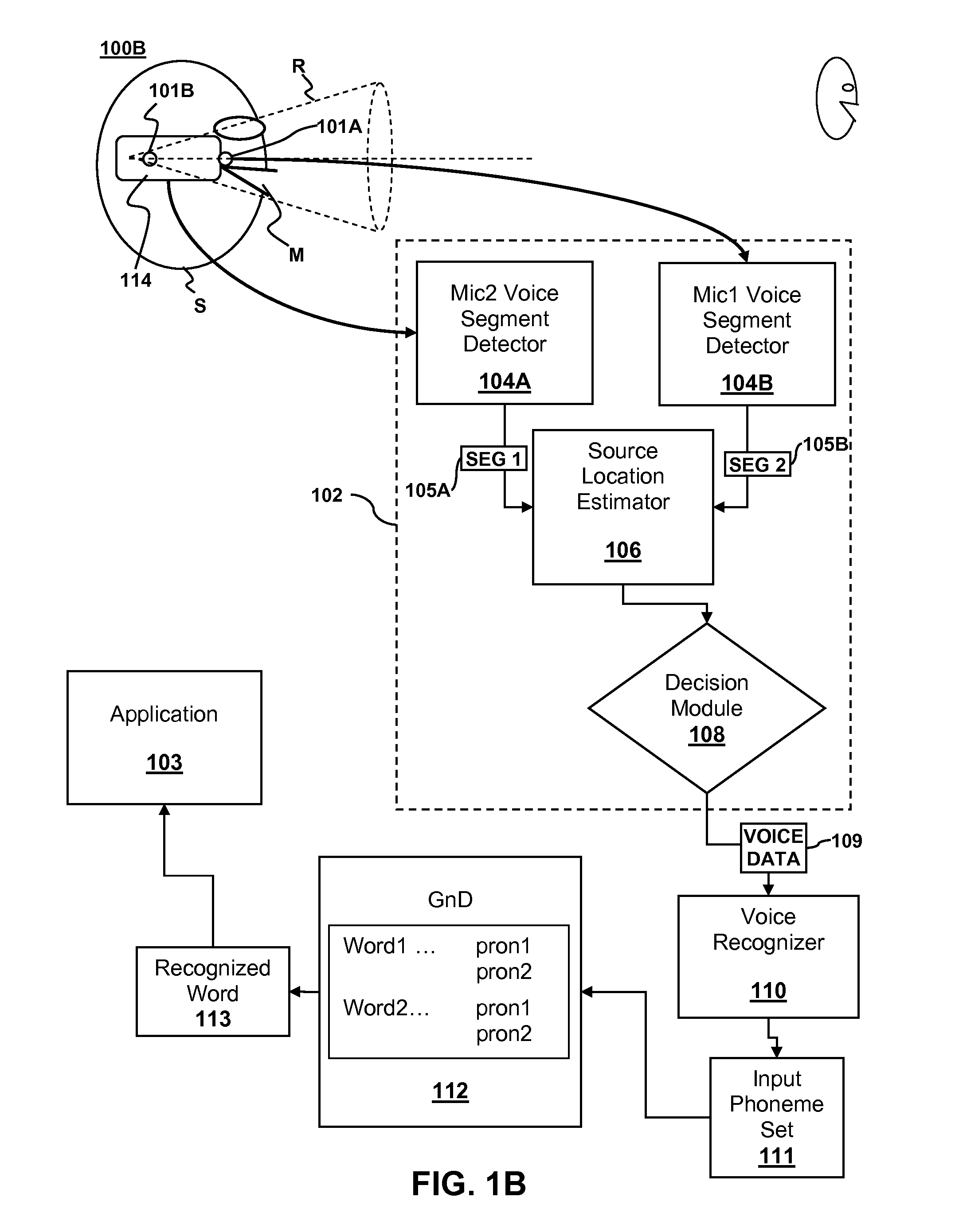
Speech processing with source location estimation using signals from two or more microphones
Computer implemented speech processing is disclosed. First and second voice segments are extracted from first and second microphone signals originating from first and second microphones. The first and second voice segments correspond to a voice sound originating from a common source. An estimated source location is generated based on a relative energy of the first and second voice segments and / or a correlation of the first and second voice segments. A determination whether the voice segment is desired or undesired may be made based on the estimated source location.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
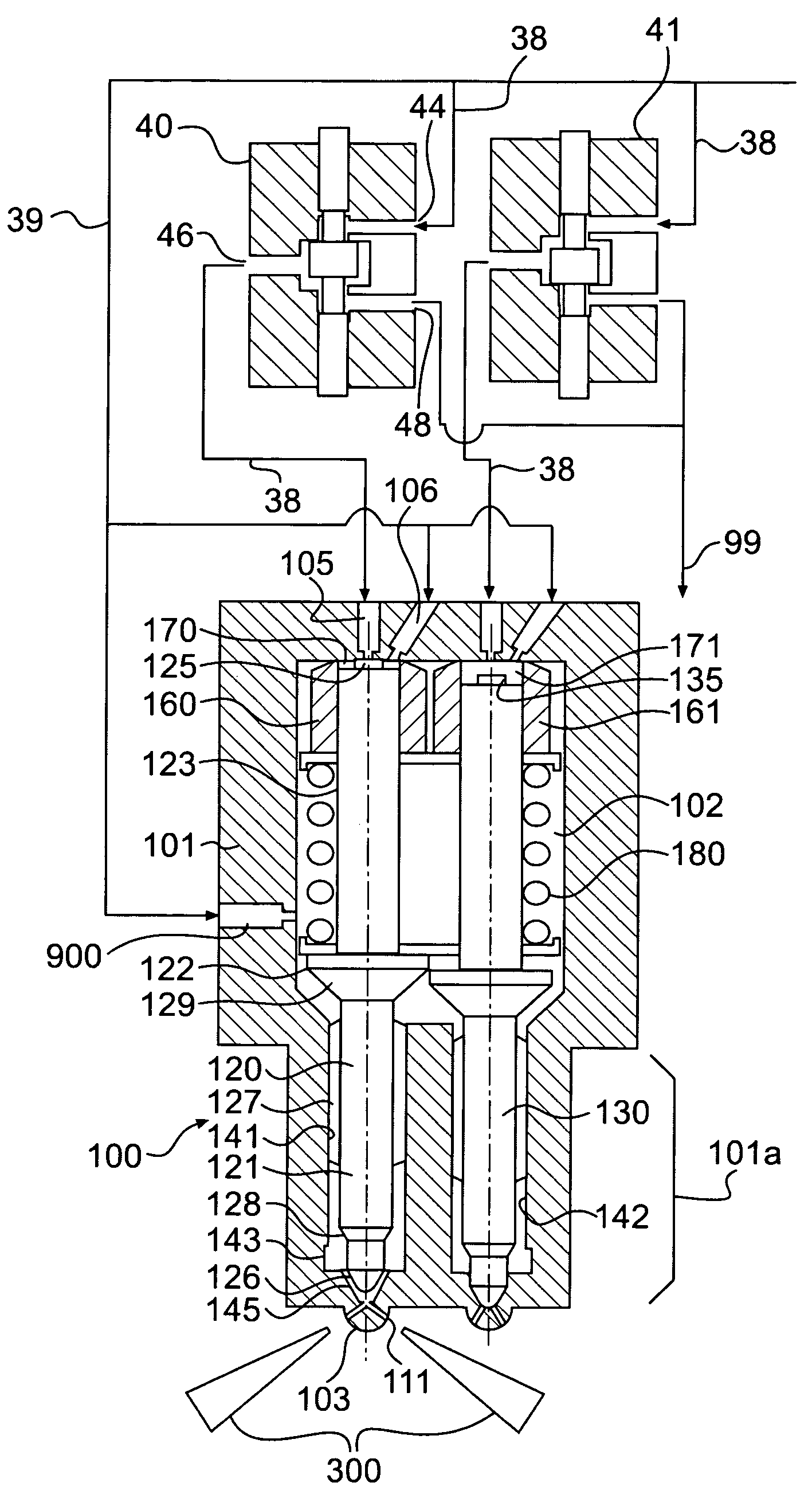
Twin needle valve dual mode injector
A fuel injector having an injector body defining a hollow interior configured to receive pressurized fuel, a first nozzle configured for providing a first fuel spray pattern, and a second nozzle configured for providing a second fuel spray pattern different from the first fuel spray pattern. The first and second nozzles may be configured to inject fuel supplied from a common source into a combustion space. The fuel injector may further include first and second needle valve members corresponding to the first and second nozzles, respectively. The first and second needle valve members may be positioned within the hollow interior of the injector body, with the second needle valve member being spaced from, but adjacent to the first needle valve member.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
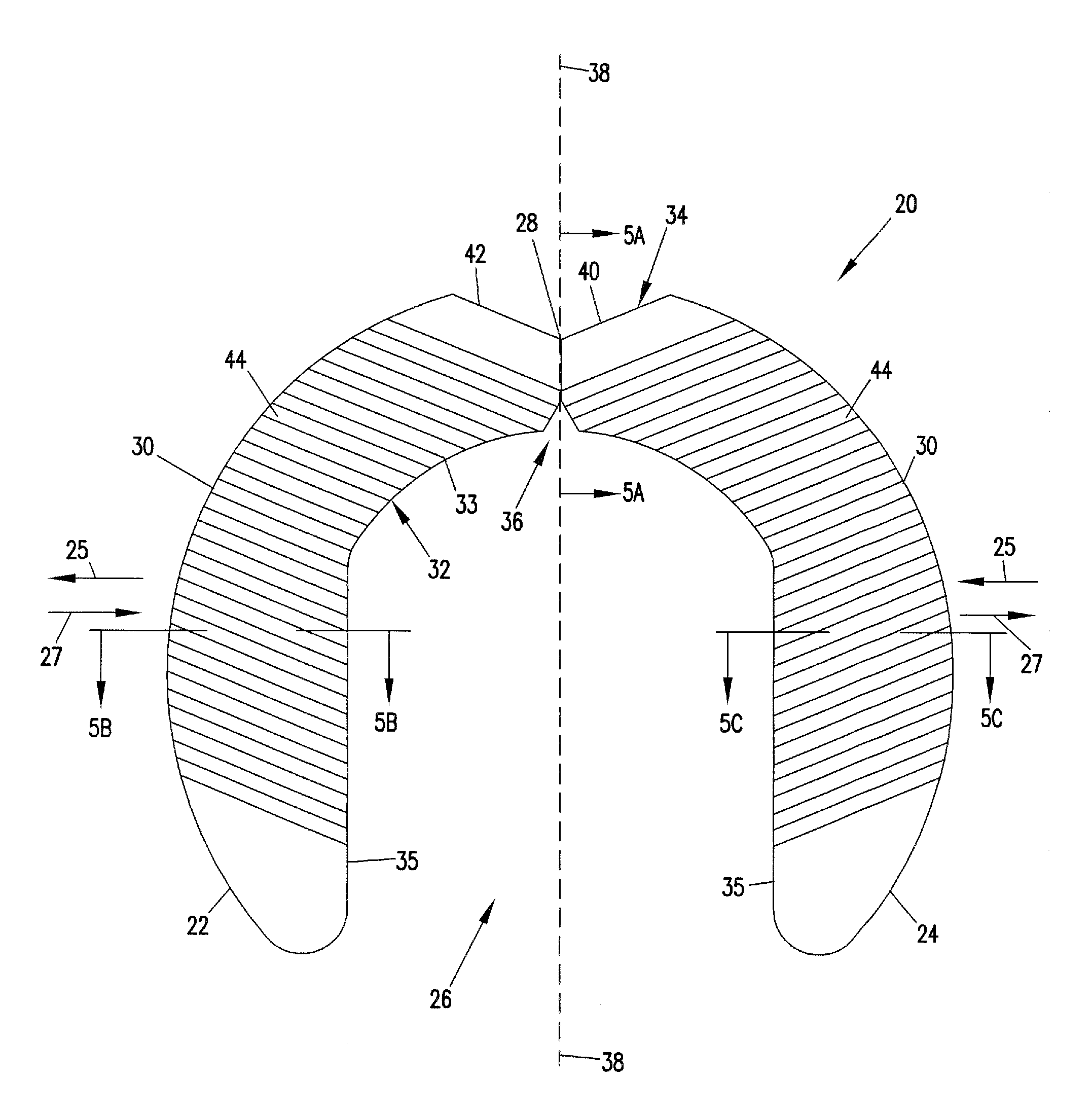
Skeletal stabilization implant
A spinal implant is described in this disclosure. The implant includes first and second pieces separated by a controlled break location. Spinal implant kits having multiple spinal implant pieces derived from a common source also are disclosed.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
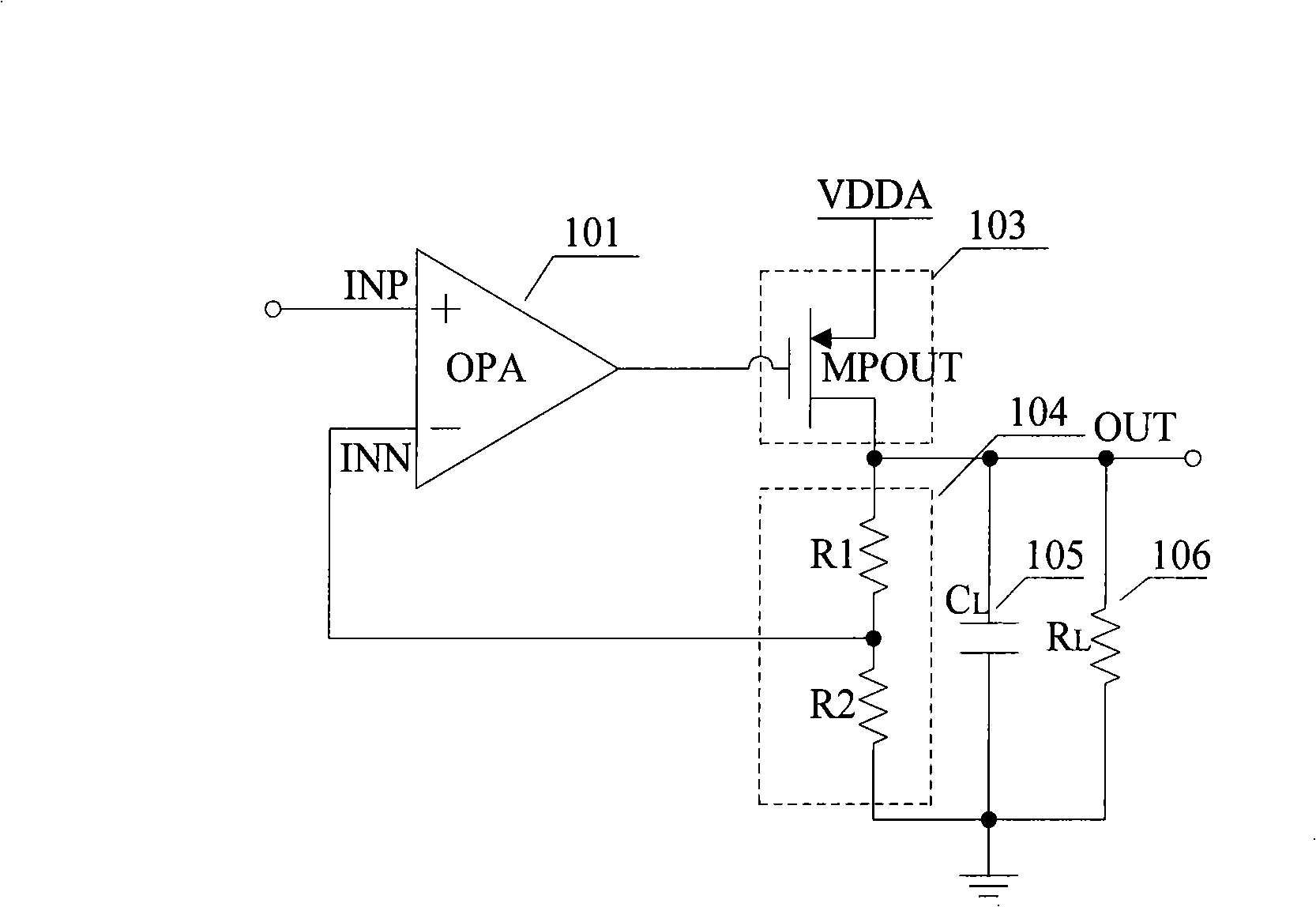
Broad output current scope low pressure difference linear manostat
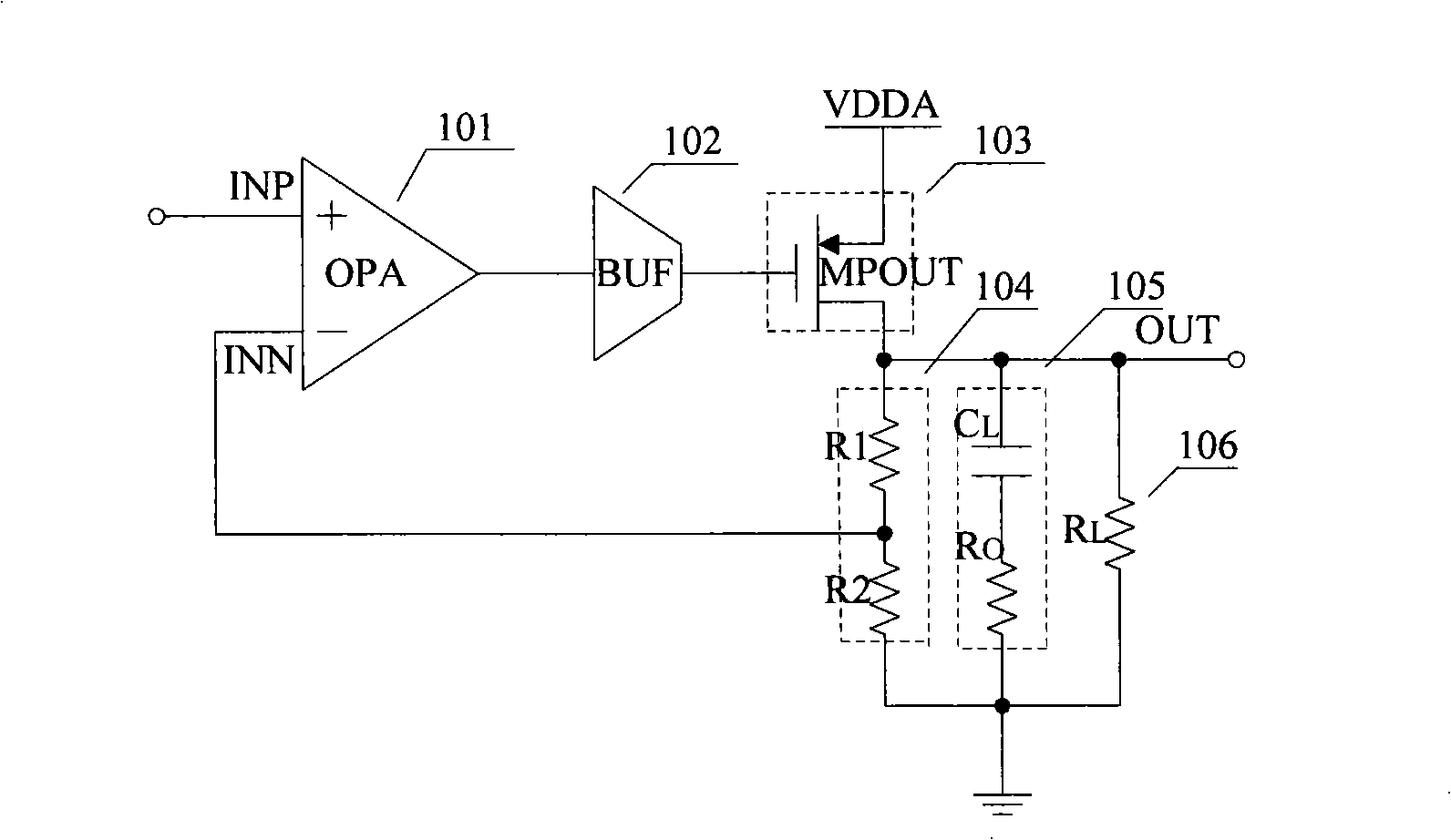
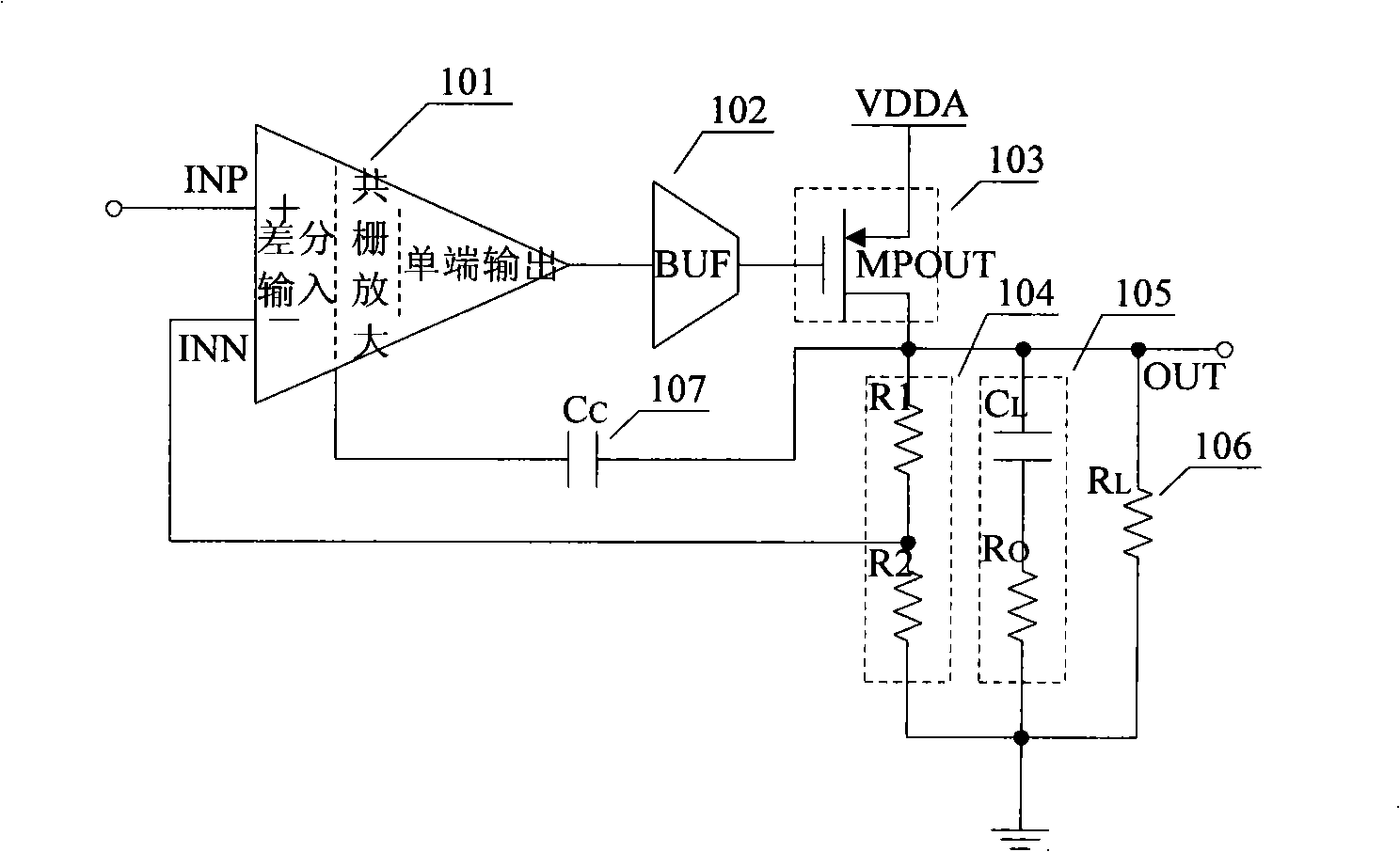
InactiveCN101339443AIncreased unity-gain bandwidthImprove stabilityLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsDifferential amplifiersCapacitanceCurrent range
A low dropout linear voltage regulator with wide output current range and low pressure difference, comprises an error amplifier in the folding common source and common gate structure, a buffer circuit, a driving element, a feedback circuit, a load capacitance equivalent series resistance compensating circuit and a multistage Miller compensation circuit, wherein the buffer circuit changes the low frequency pole into a medium frequency pole and a high frequency pole; the large load capacitance of the load capacitance equivalent series resistance compensating circuit pushes the main pole to the low frequency, causing the gain crossover point to push inwards, and generating a medium frequency zero point for counteracting the medium frequency pole connected serially with the equivalent series resistance; the stride multilevel Miller compensation circuit generates a medium high frequency pole and a medium high frequency zero point slightly smaller than the medium high frequency pole for advancing the phase margin, thereby not only adding the unity gain bandwidth, but also saving considerable chip area. When the output current has a large change range, the structure provided by the invention generates wider unity gain bandwidth, provides the phase margin of greater than 85 degrees, ensures the stability of the system and advances the low pressure difference linear voltage stabilization performance.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
YUKAI VSL-BASED Vt-COMPENSATION FOR NAND MEMORY
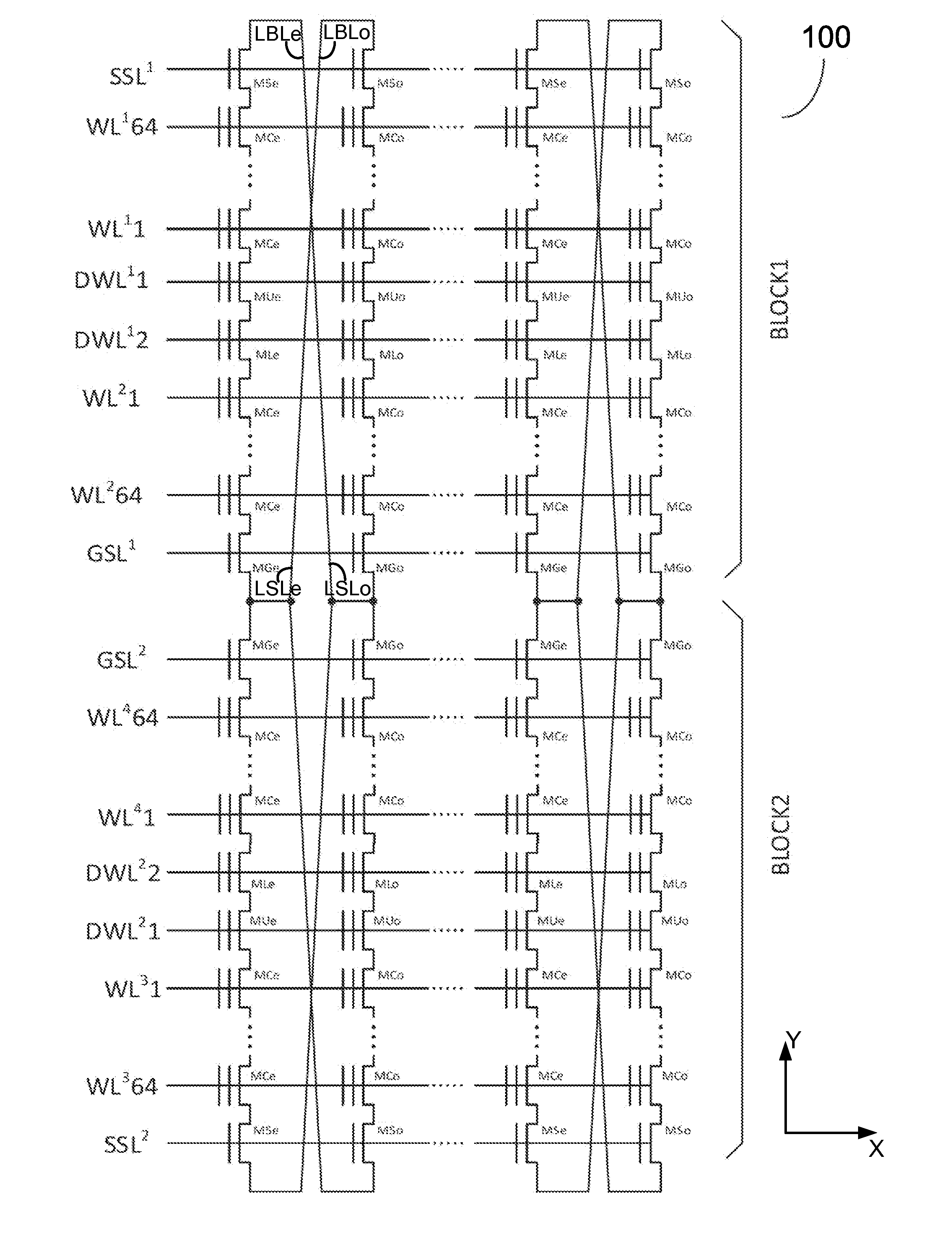
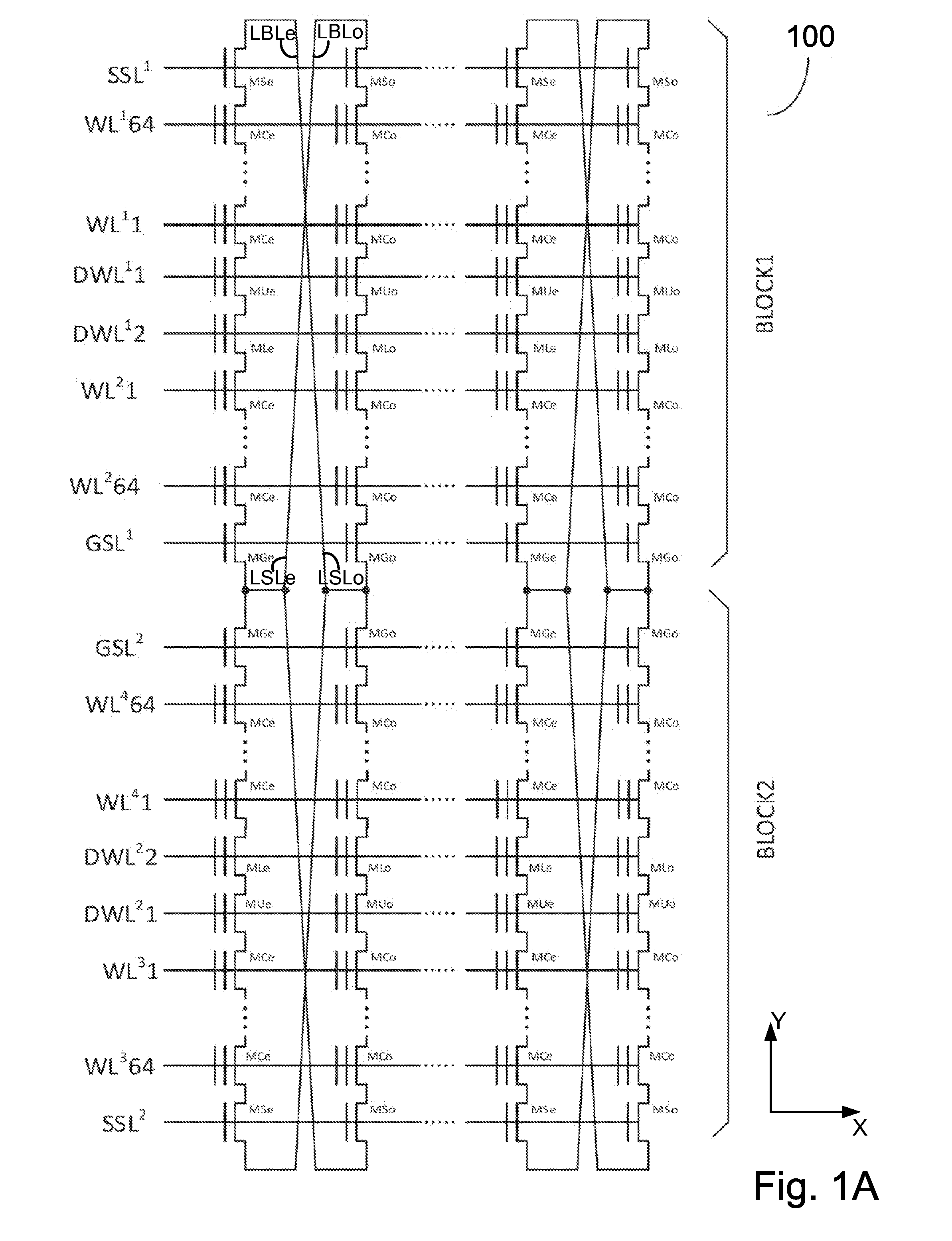
ActiveUS20160027504A1Less Yupin coupling effectLess capacitanceRead-only memoriesDigital storageVirtual cellBatch processing
A YUKAI NAND array comprising multiple strings associated with hierarchical global / local bit lines (GBL / LBL) and each string being associated with one LBL and having adjacent LBL as a dedicated local source line (LSL) without a common source line to connect all strings. Each of the LBLs is interleavingly associated with either an Odd or Even string selected via one pair of dummy cells inserted in each string and is used as one on-chip PCACHE register with full BL-shielding without wasting extra silicon area to allow batch-based multiple concurrent MLC All-BL, All-Vtn-Program and Alternative-WL program, Odd / Even read and verify operations with options of providing individual and common VSL-based Vt-compensation and VLBL compensations to mitigate high WL-WL and BL-BL coupling effects. Bias conditions in each string are provided to correctly sense highly-negative erase-verify voltage, multiple negative program-verify voltages and without VDS punch-through, breakdown and body-effect in both boundary and non-boundary WLs cells.
Owner:LEE PETER WUNG
System for automated problem detection, diagnosis, and resolution in a software driven system
InactiveUS7100085B2Simple interfaceEffortless and reliable and affordable supportFault responseDetecting faulty hardware by remote testInstabilityTheoretical computer science
In many systems, computer software is a common source of failure or instability. The proliferation of multiple interacting applications from several different software vendors leads to “emergent” problems that are difficult or impossible to predict or prevent. The problems are compounded by the use of networks, which introduce the added complexity of applications on multiple machines interacting in complex scenarios. As a result, many business and home users are hindered from using software-based systems to their fullest potential. More effective use of these systems can be aided by an application which can provide services for monitoring, diagnosing, and solving problems that occur in the operation of the machines at a customer facility. In the system described herein, a database contains entries with executable code that can make use of these services in order to monitor, diagnose, and solve specific problems. Each entry in the database addresses a specific problem. The executable code is designed to isolate and recognize the problem, and then implement a fix or workaround for that problem. The executable code is designed to completely automate the entire process of detection and resolution of the problem. Further, manual intervention may be employed to complete the diagnosis or solution.
Owner:HFN LLC
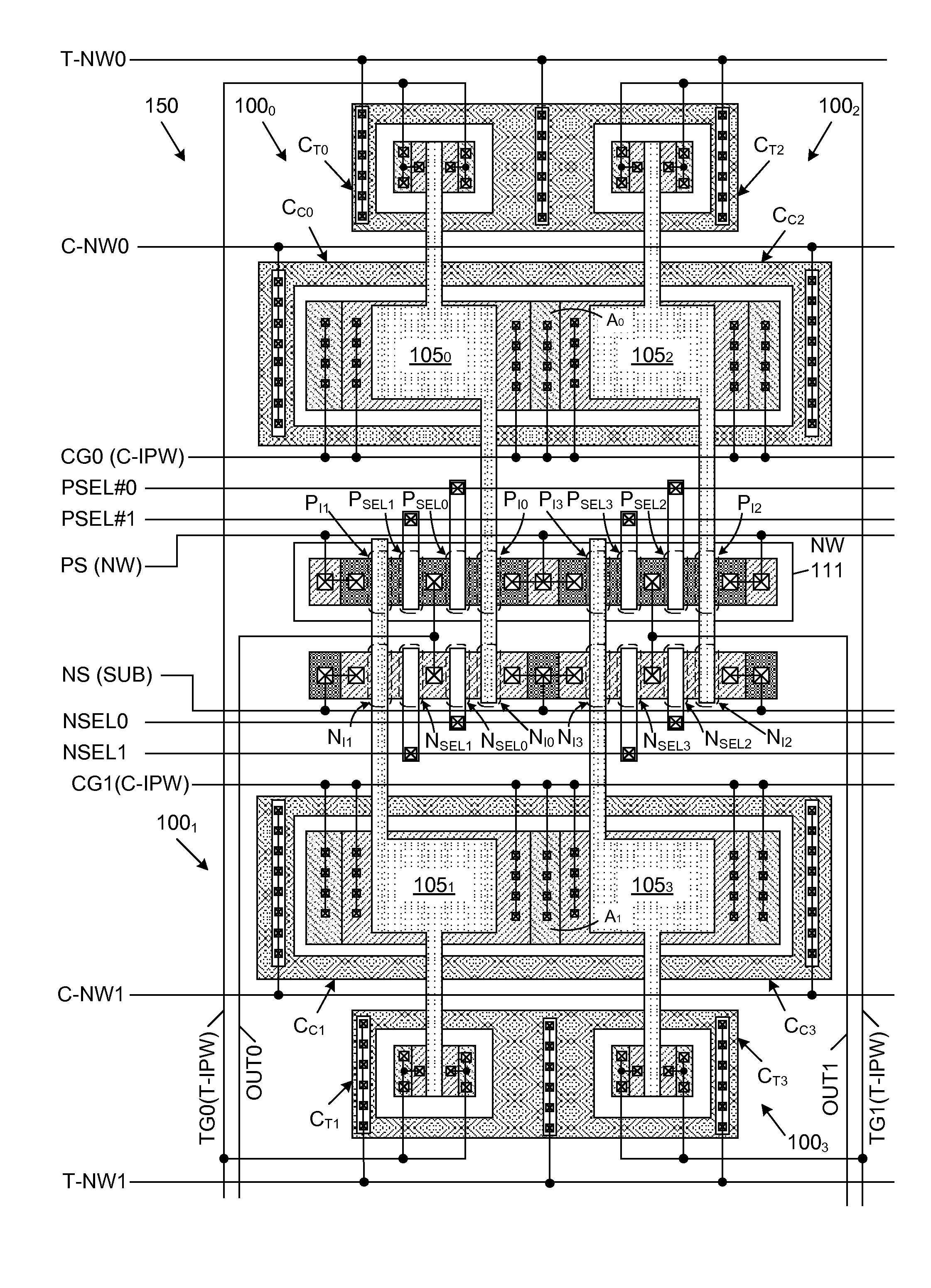
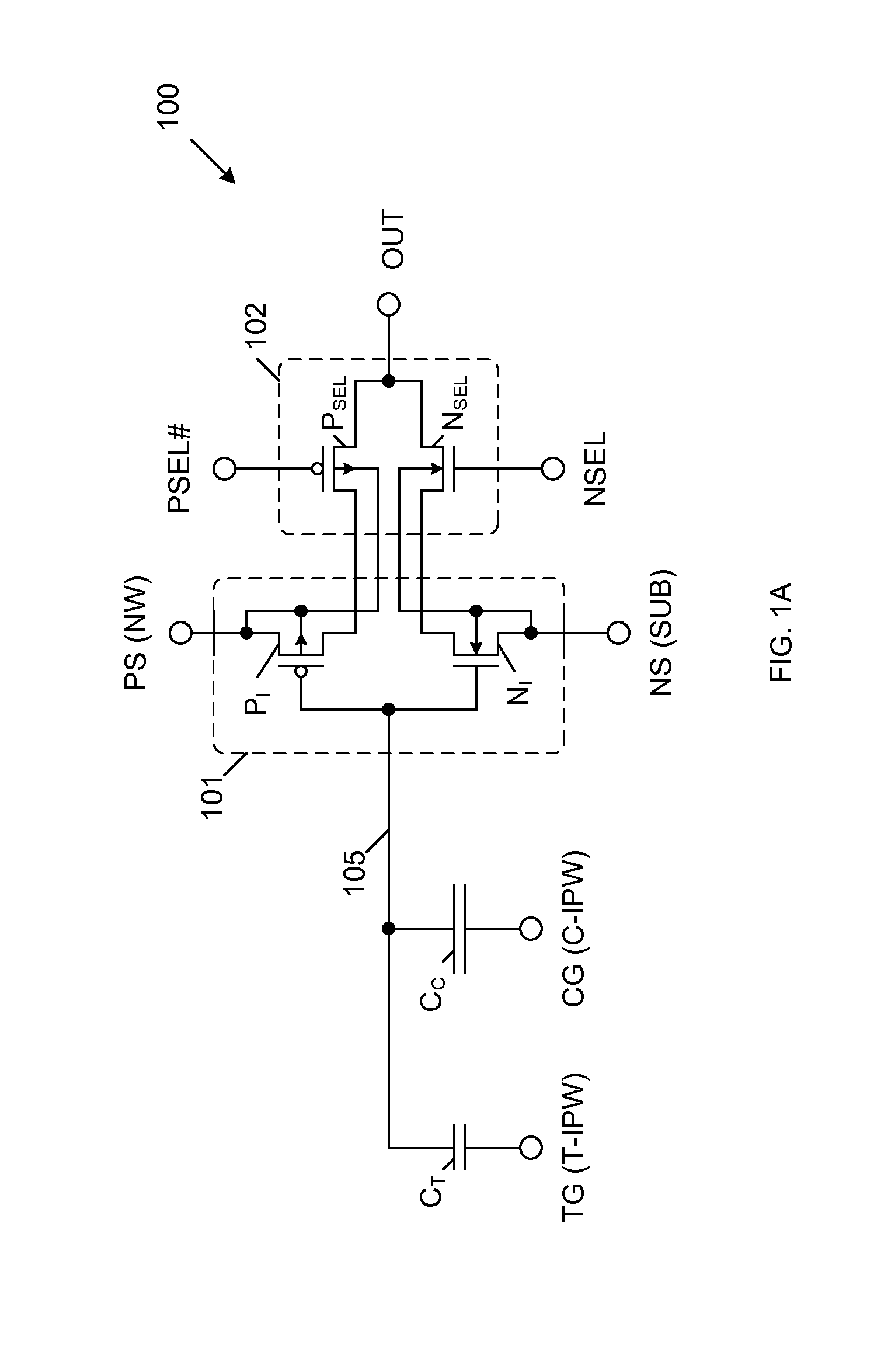
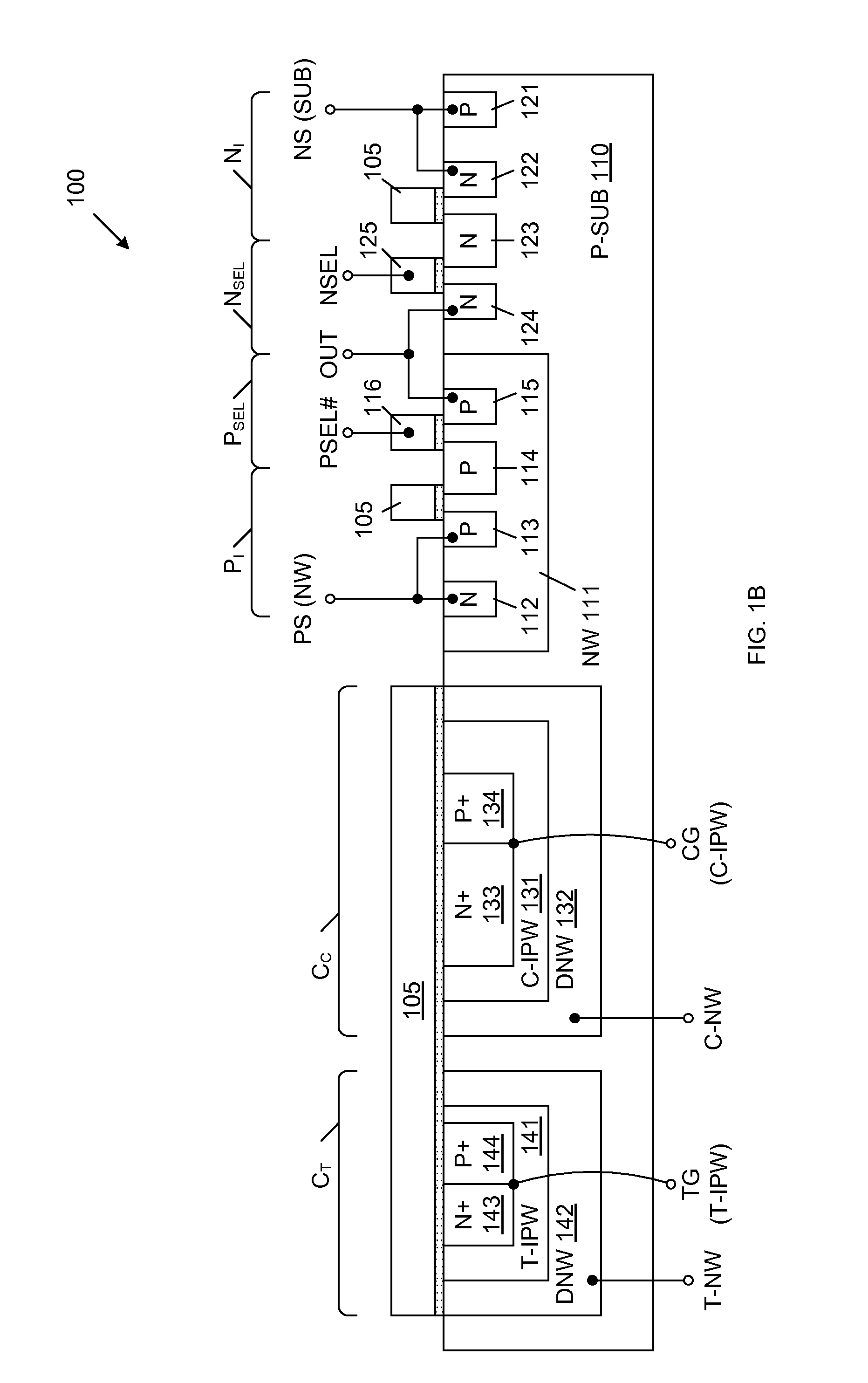
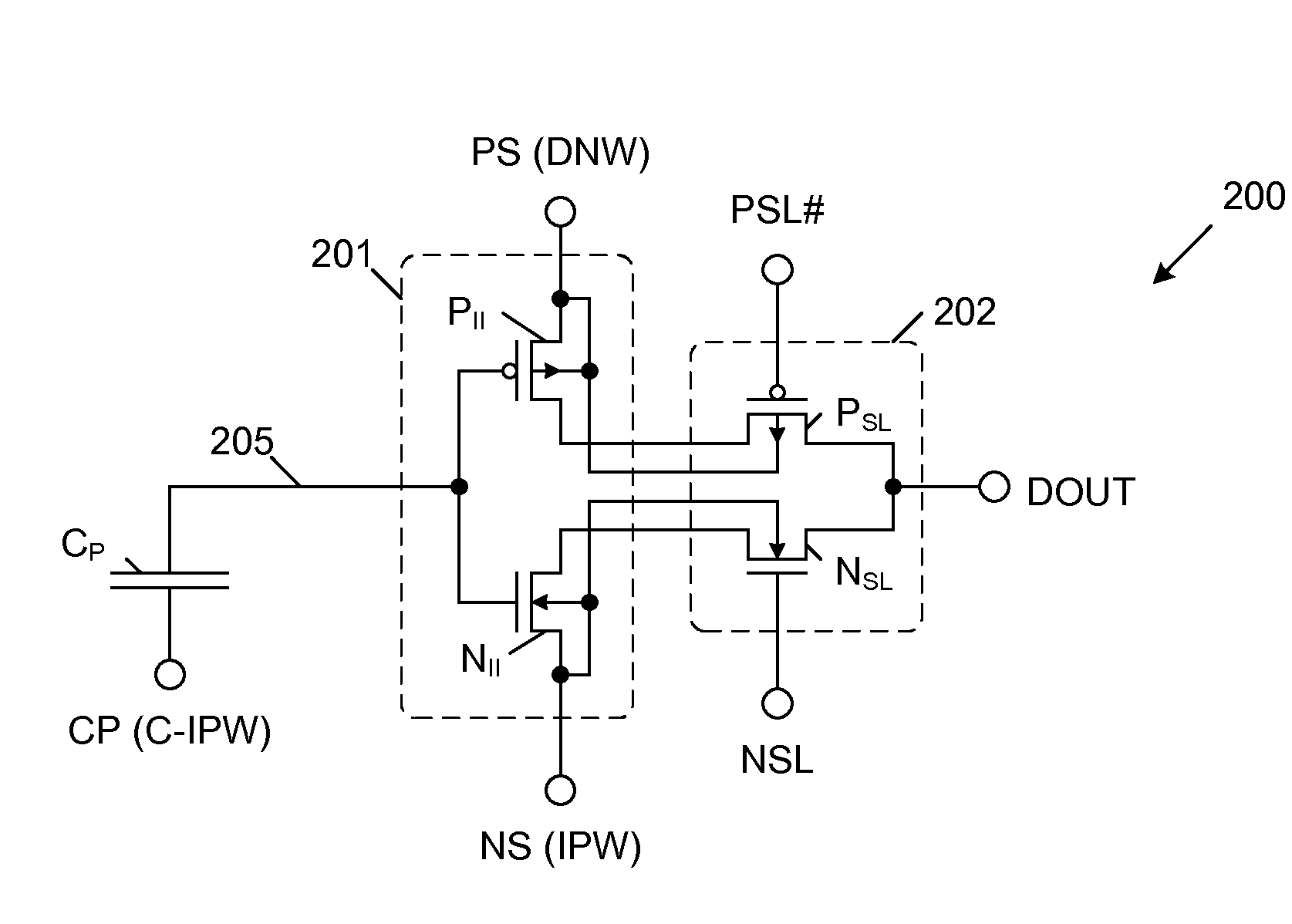
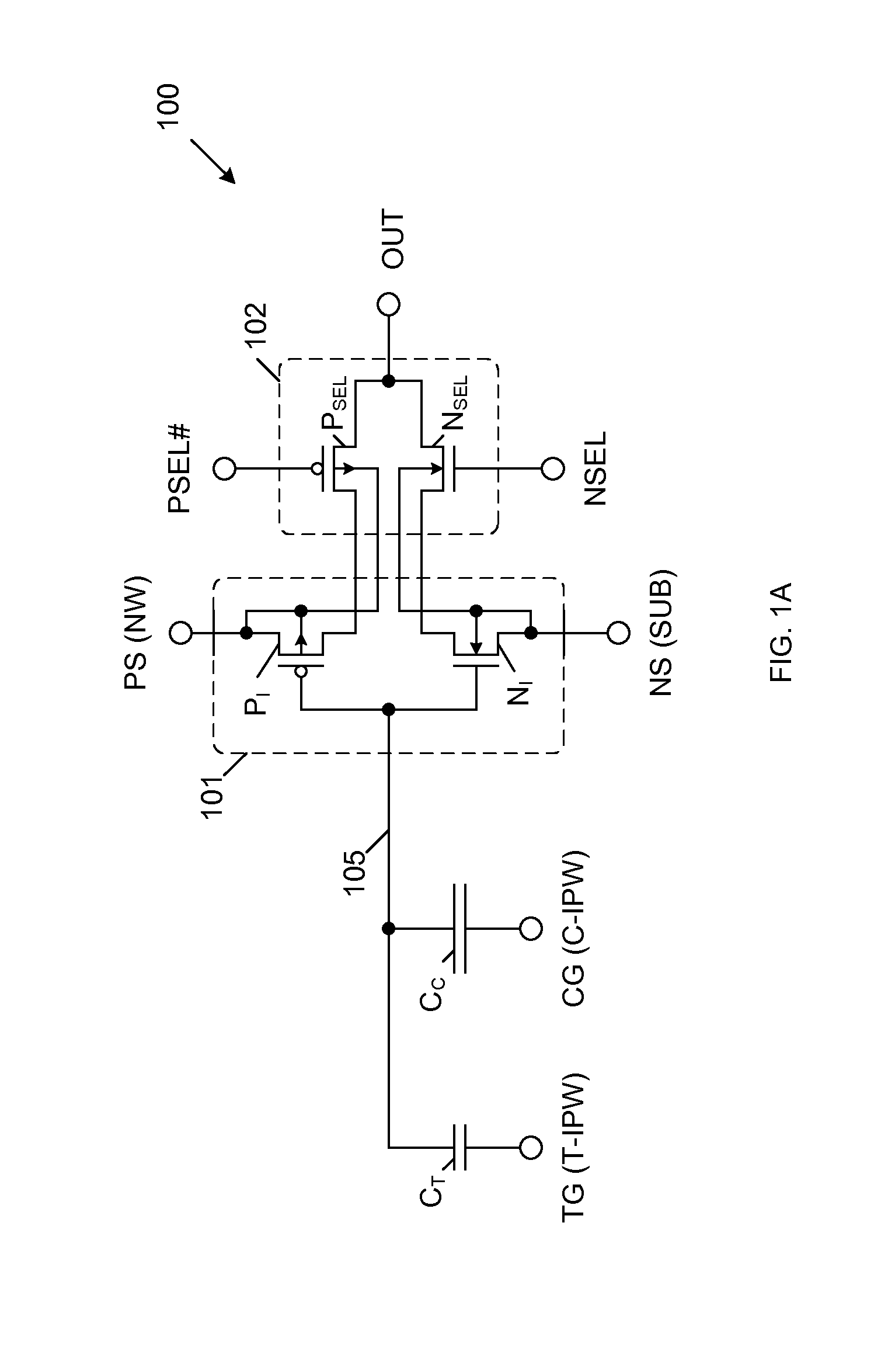
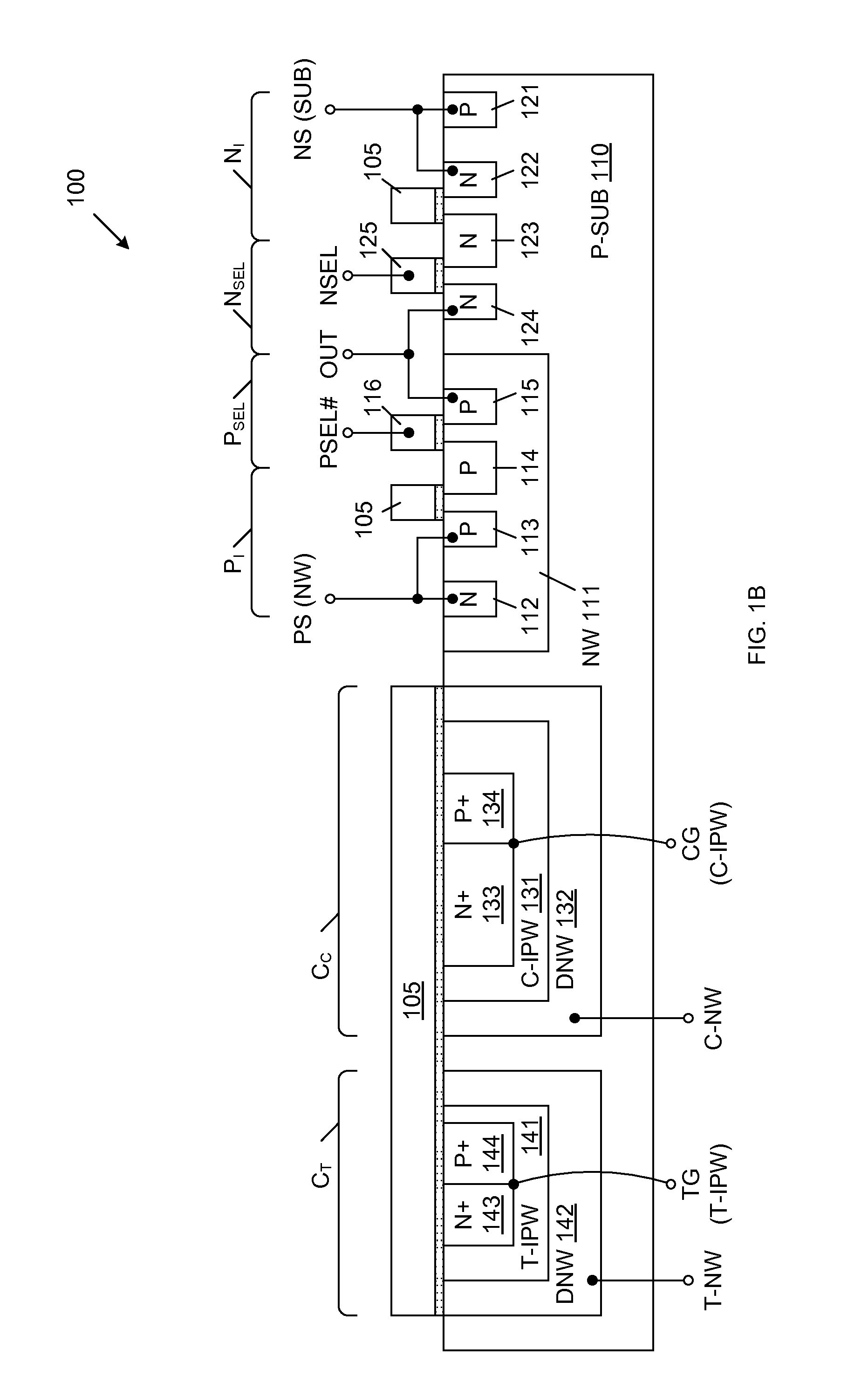
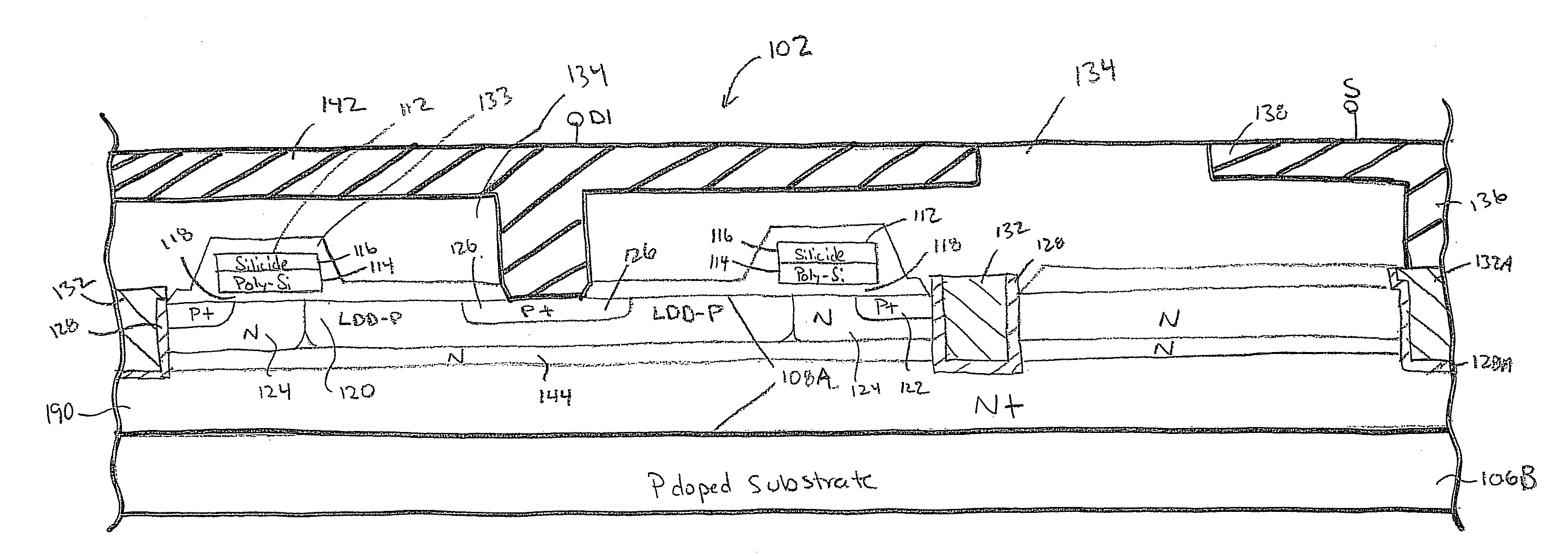
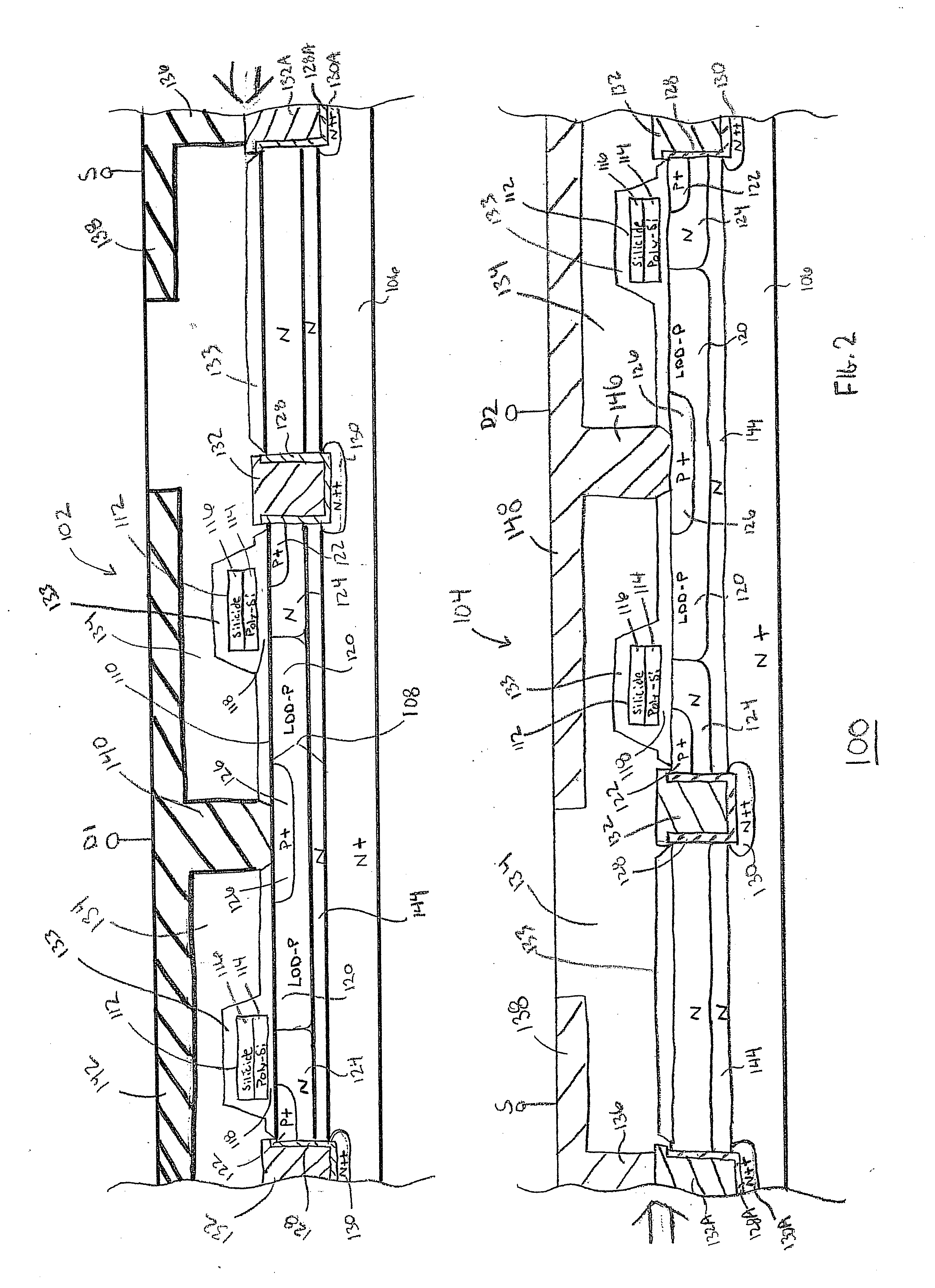
Mos transistor device in common source configuration
A semiconductor device includes a semiconductor substrate, a first p-channel laterally diffused metal oxide semiconductor (LDMOS) transistor formed over the semiconductor substrate and additional p-channel LDMOS transistors formed over the semiconductor substrate. First drain and gate electrodes are formed over the substrate and are coupled to the first LDMOS transistor. Additional drain and gate electrodes are formed over the substrate and are coupled to the second LDMOS transistor. A common source electrode for the first and second LDMOS transistors is also formed over the substrate.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR LEHIGH VALLEY
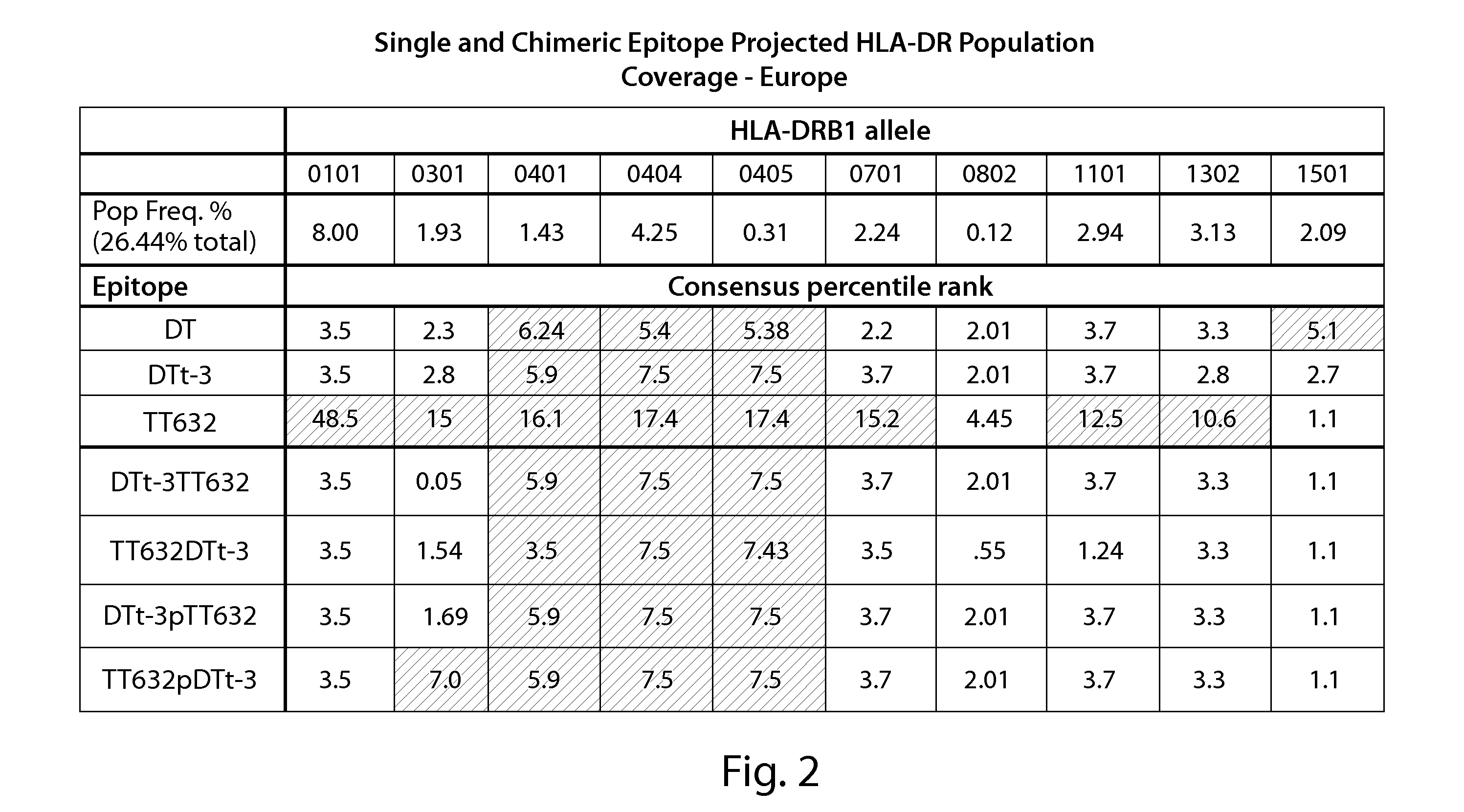
Targeted multi-epitope dosage forms for induction of an immune response to antigens
InactiveUS20120070493A1Induce and enhance and cytokine productionAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryAntigenBinding peptide
Provided herein are compositions and methods related to MHC II binding peptides. In some embodiments, the peptides are obtained or derived from a common source. In other embodiment, the peptides are obtained or derived from an infectious agent to which a subject has been repeatedly exposed.
Owner:SELECTA BIOSCI
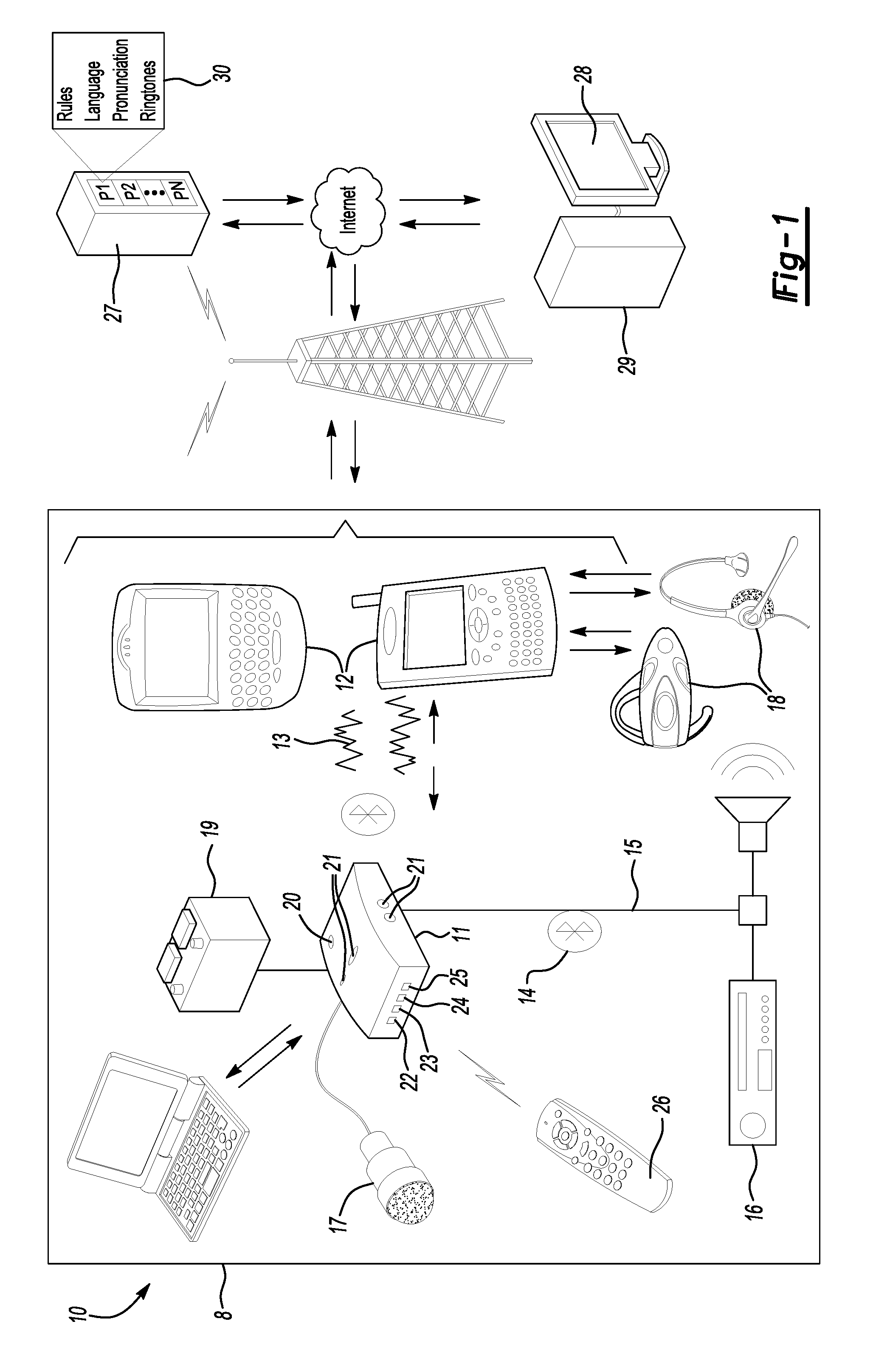
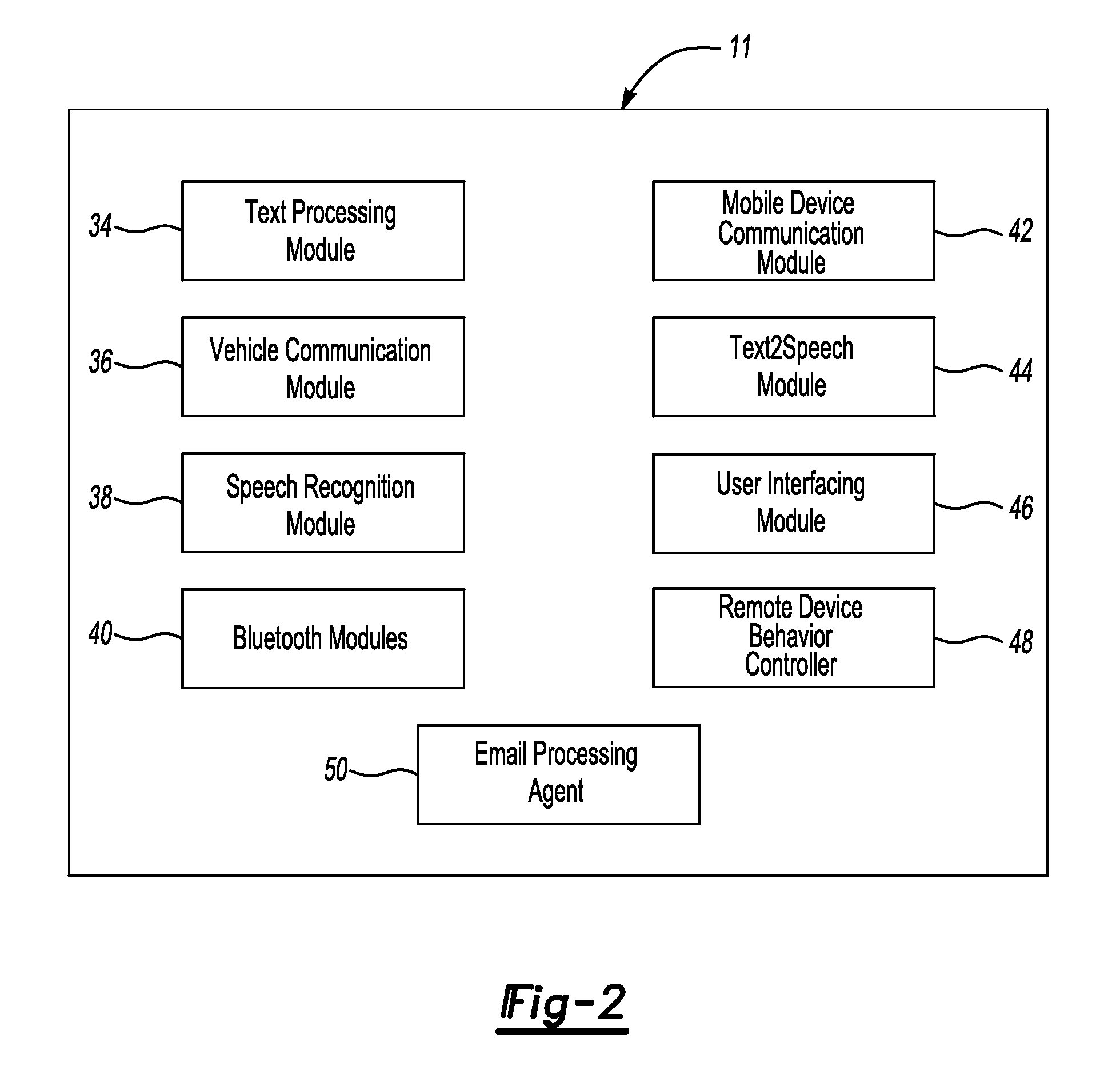
Vehicle communication system with news subscription service
ActiveUS20080140408A1Convenient and safe hands-free interfaceImprove driving experienceMultiple digital computer combinationsSubstation equipmentPersonalizationElectronic book
A vehicle communication system facilitates hands-free interaction with a mobile device in a vehicle or elsewhere. The invention also provides remote access to information such as existing news sources (i.e. existing RSS feeds) and supported websites. This also includes subscription to value-added services including: weather, custom alerts (i.e. stock price triggers), traffic conditions, personalized news, e-books (not limited to audio books, but any e-book), personalized audio feeds, and personalized image or video feeds for passengers. The system obtains, translates, and provides personalized news content in audible form within a vehicle without explicit user requests. An individual may set their preferences by selecting from a set of common sources of information, or by specifying custom search criteria. When new information is available and relevant to the individual's preferences, it is read out loud to the individual when appropriate. Appropriate instances can be specified by the individual using a combination of in-vehicle presence detection, time-of-day, and importance of the information relative to other personal events including email, phone calls, meetings and text messages.
Owner:VALUE8 CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com