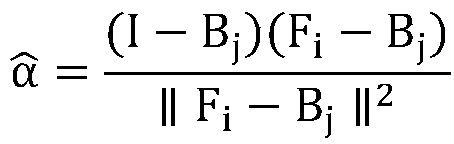Patents
Literature
37 results about "Channel knowledge" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
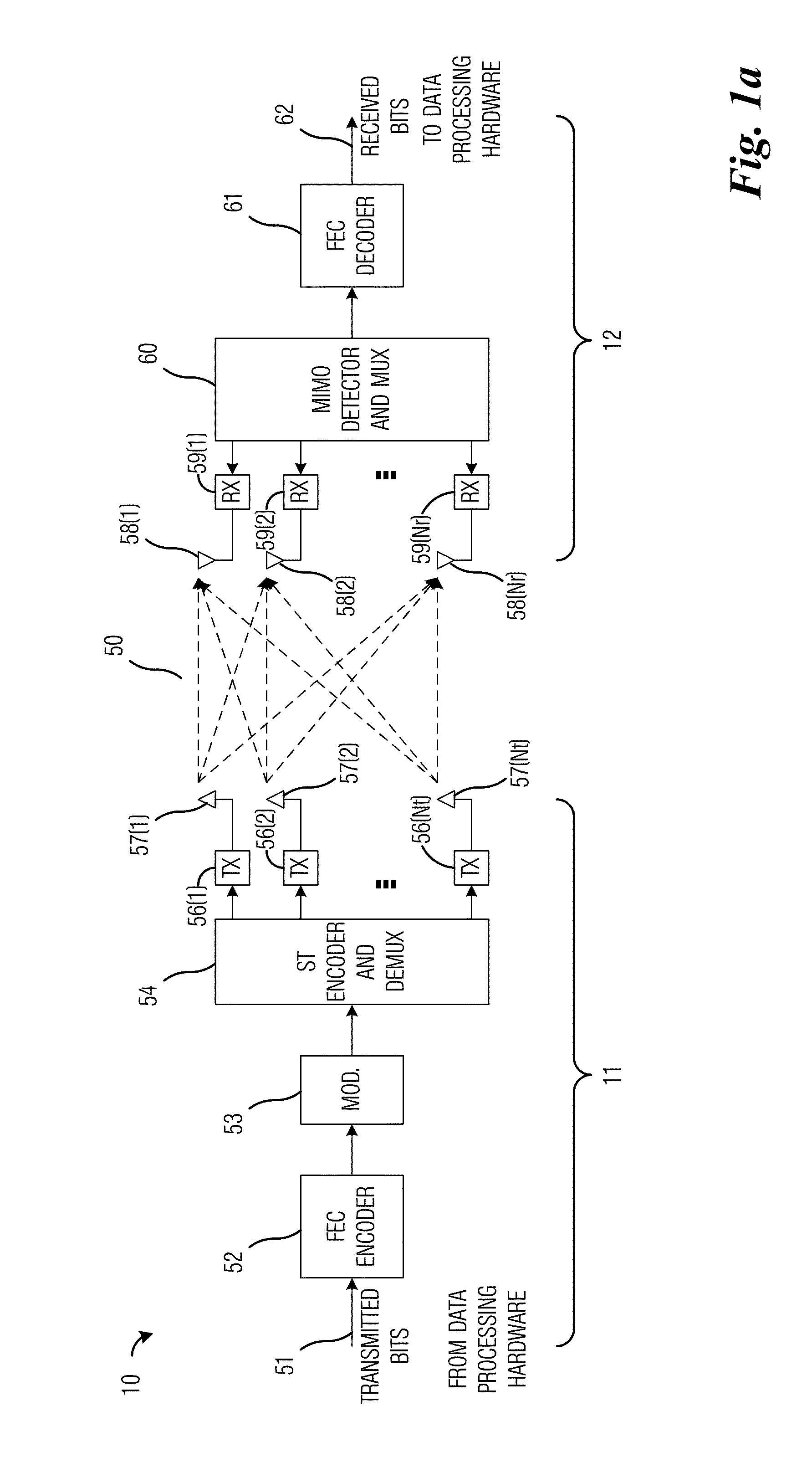
Mimo signal processing method involving a rank-adaptive matching of the transmission rate
InactiveUS20060193294A1Reduce complexityReliable data transmissionPower managementTransmission control/equalisingData streamTransmitted power
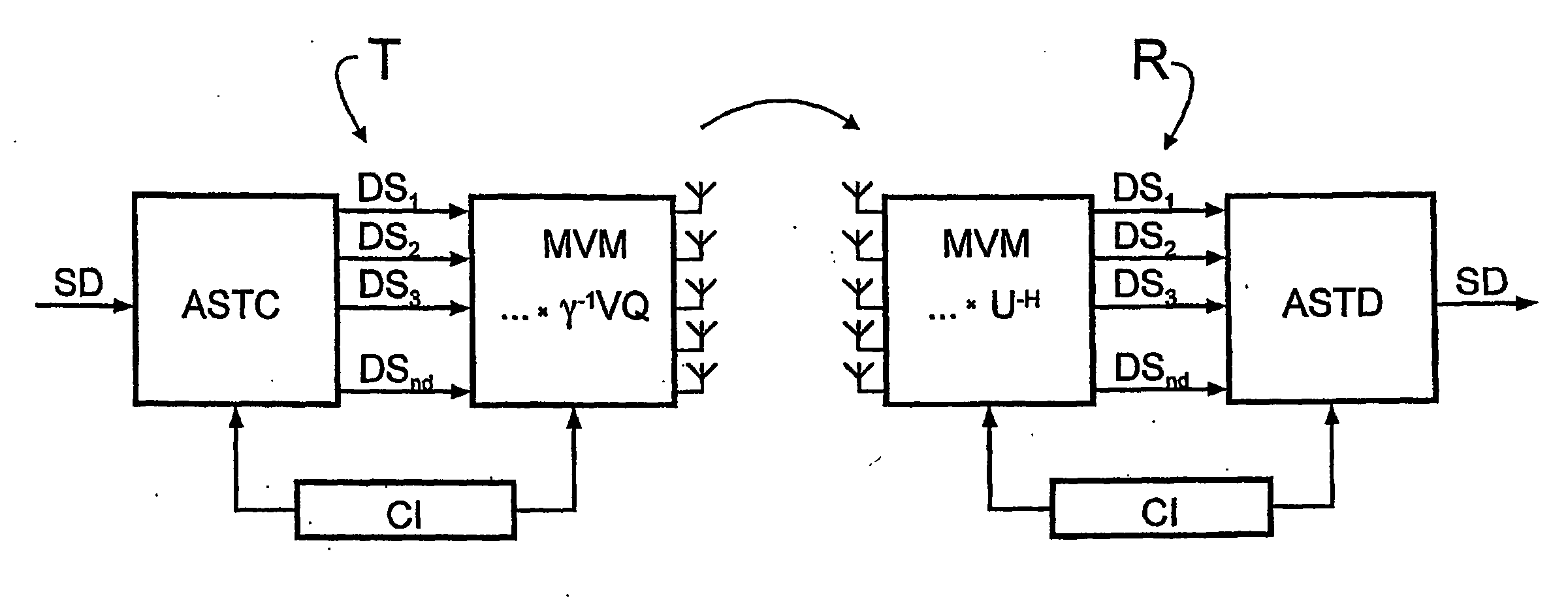
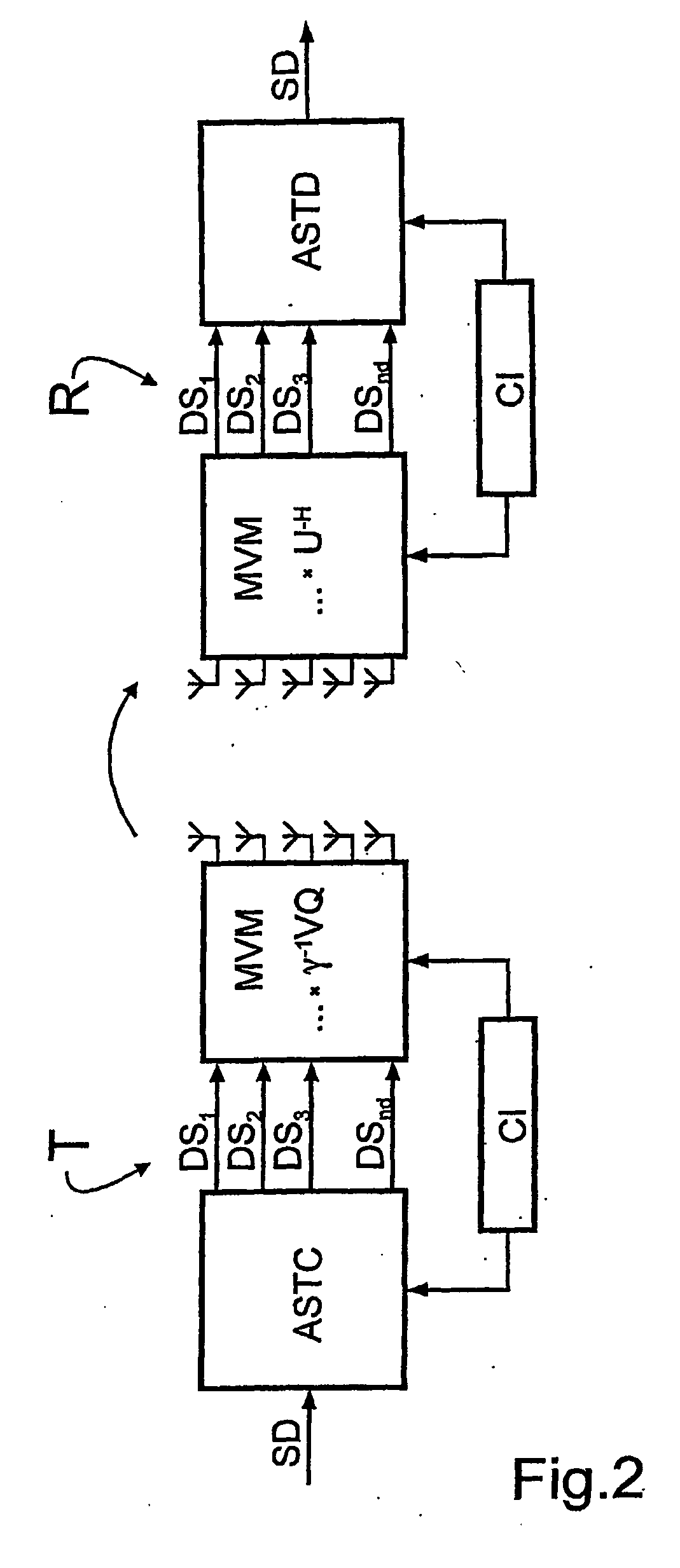
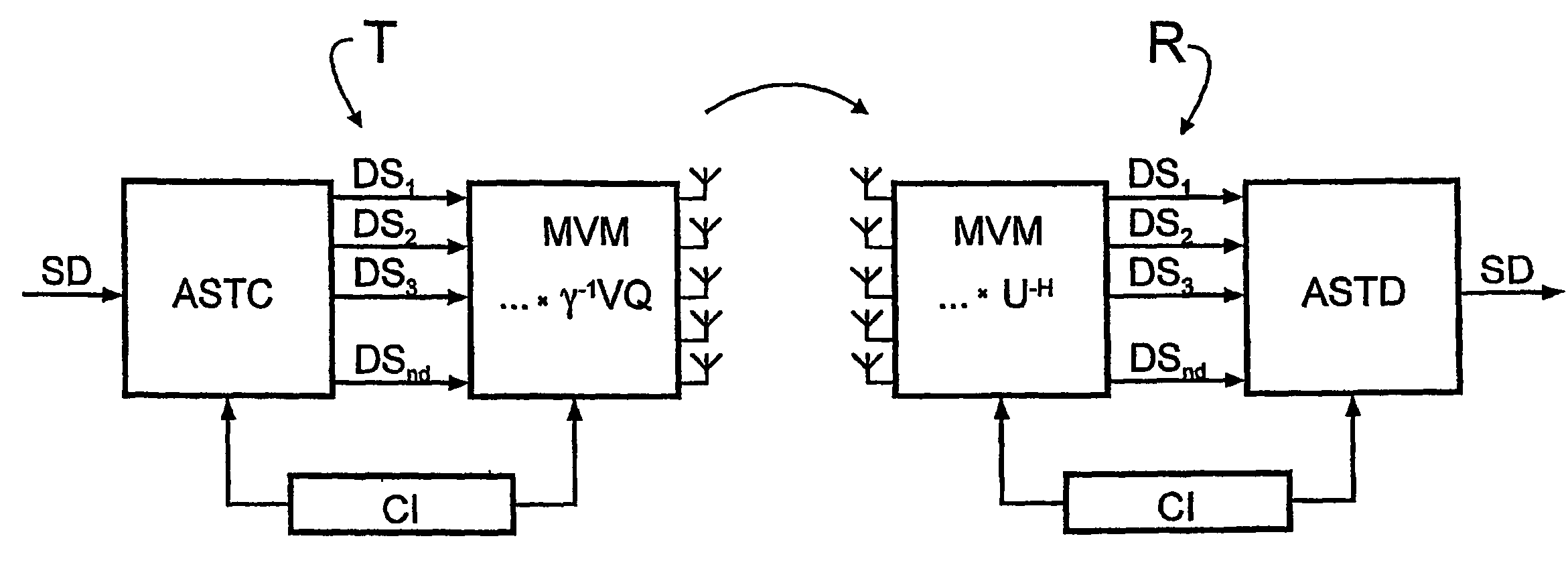
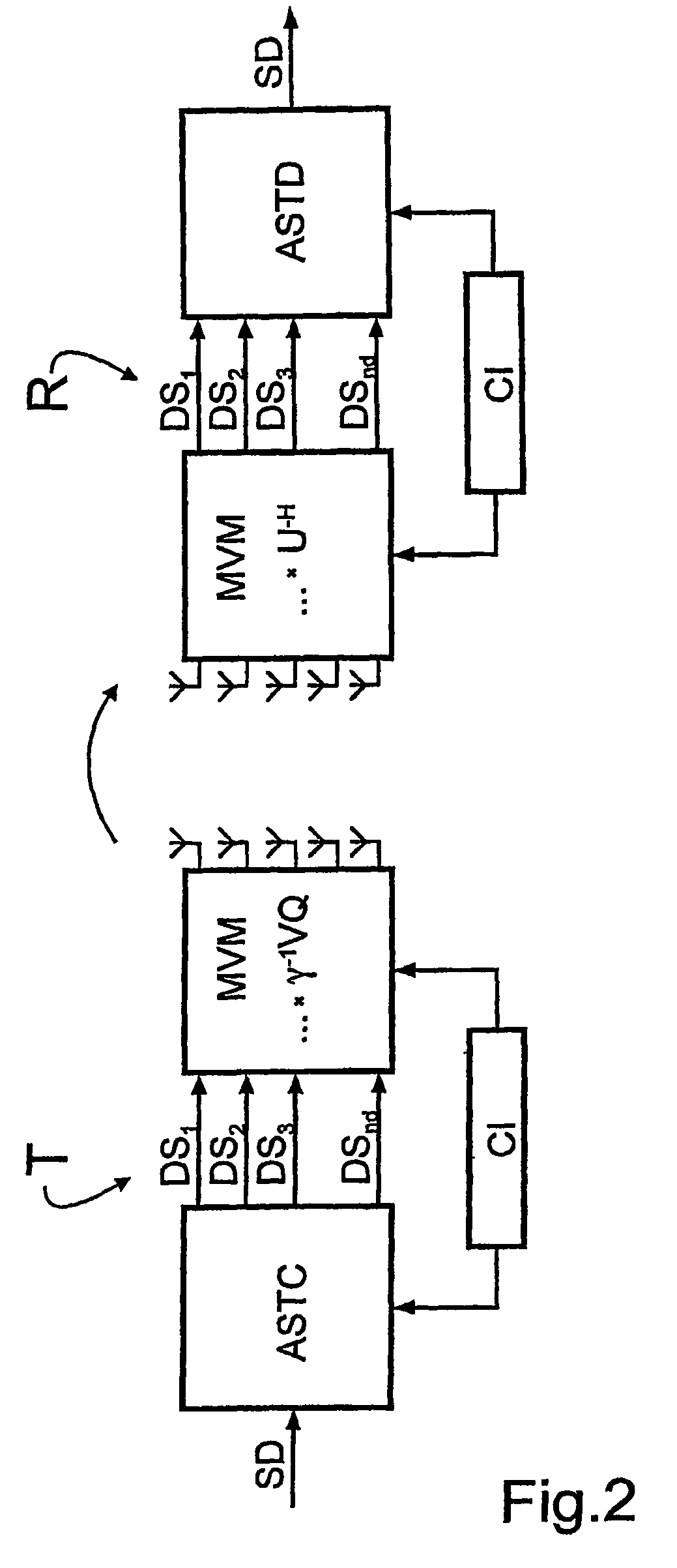
A bidirectional signal processing method uses parallel transmission of digital transmitted data streams in a multiple input-multiple output system. Related art methods generate high bit error rates mostly in singular transmission channels. For this reason, the rank-adaptive signal processing method provides that the number nd of active subchannels are varied according to the actual channel behavior in order to effect a robust data transmission even in singular radio channels based on a transmit-side and receive-side channel knowledge and a modification of the data vector by a linear matrix vector multiplication while introducing a factor gamma for limiting the maximum transmit power. The maximum transmit power is then only distributed to the currently activated subchannels so that no transmit power remains unused. Another optimization of the number of subchannels nd occurs when selecting the modulation and encoding methods. During the optimal rank-adaptation according to the water-filling principle, another power is allocated to each subchannel. Another modulation and encoding method is accordingly selected for each data stream. During the suboptimal rank-adaptation according to the channel inversion principle, all subchannels have the same power whereby enabling the data streams to be modulated and encoded in a common source
Owner:SIEMENS AG
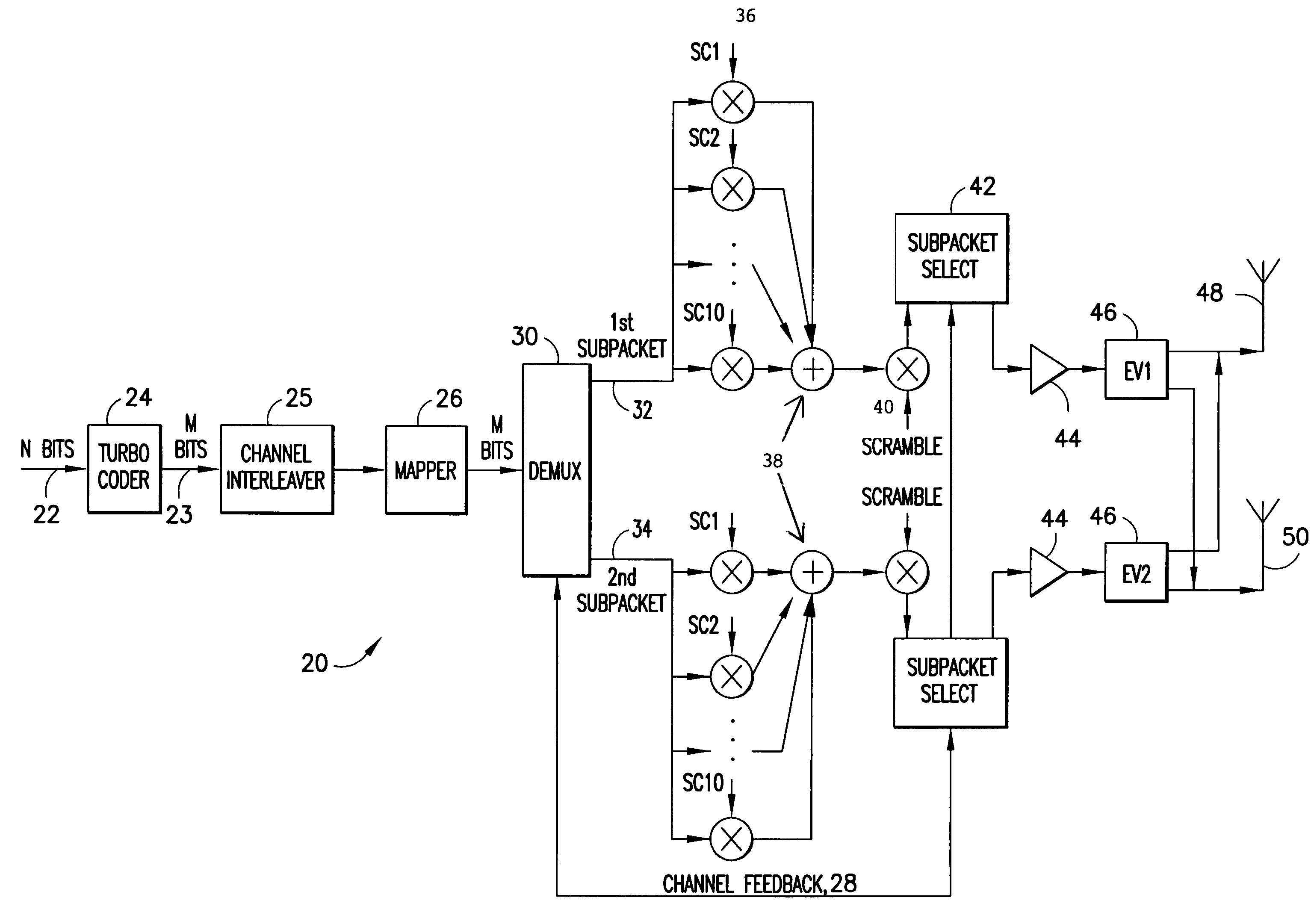
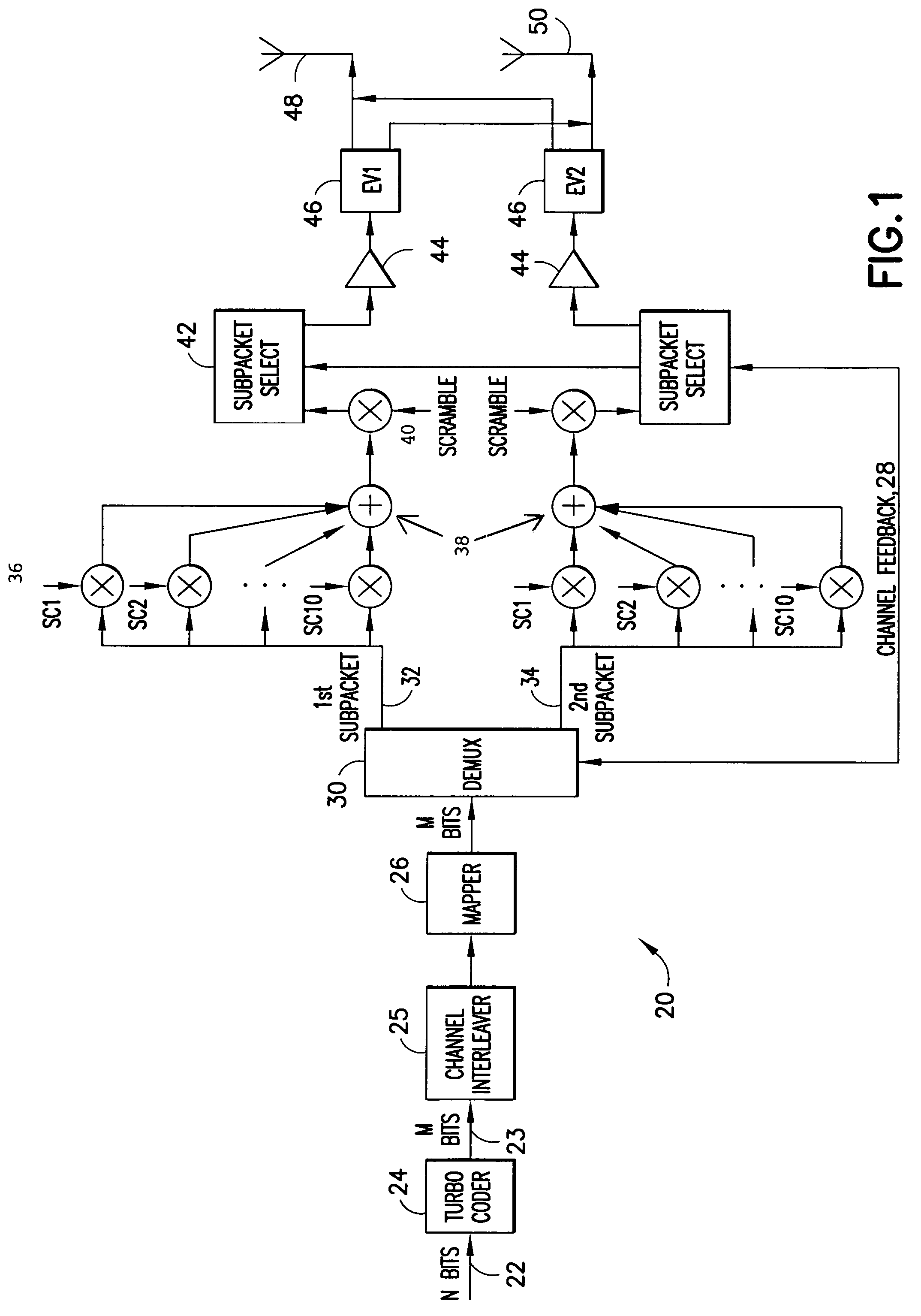
Flexible rate split method for MIMO transmission
InactiveUS20050111376A1Wide diversityReduce error rateSpatial transmit diversityFrequency-division multiplex detailsMimo transmissionSelection system
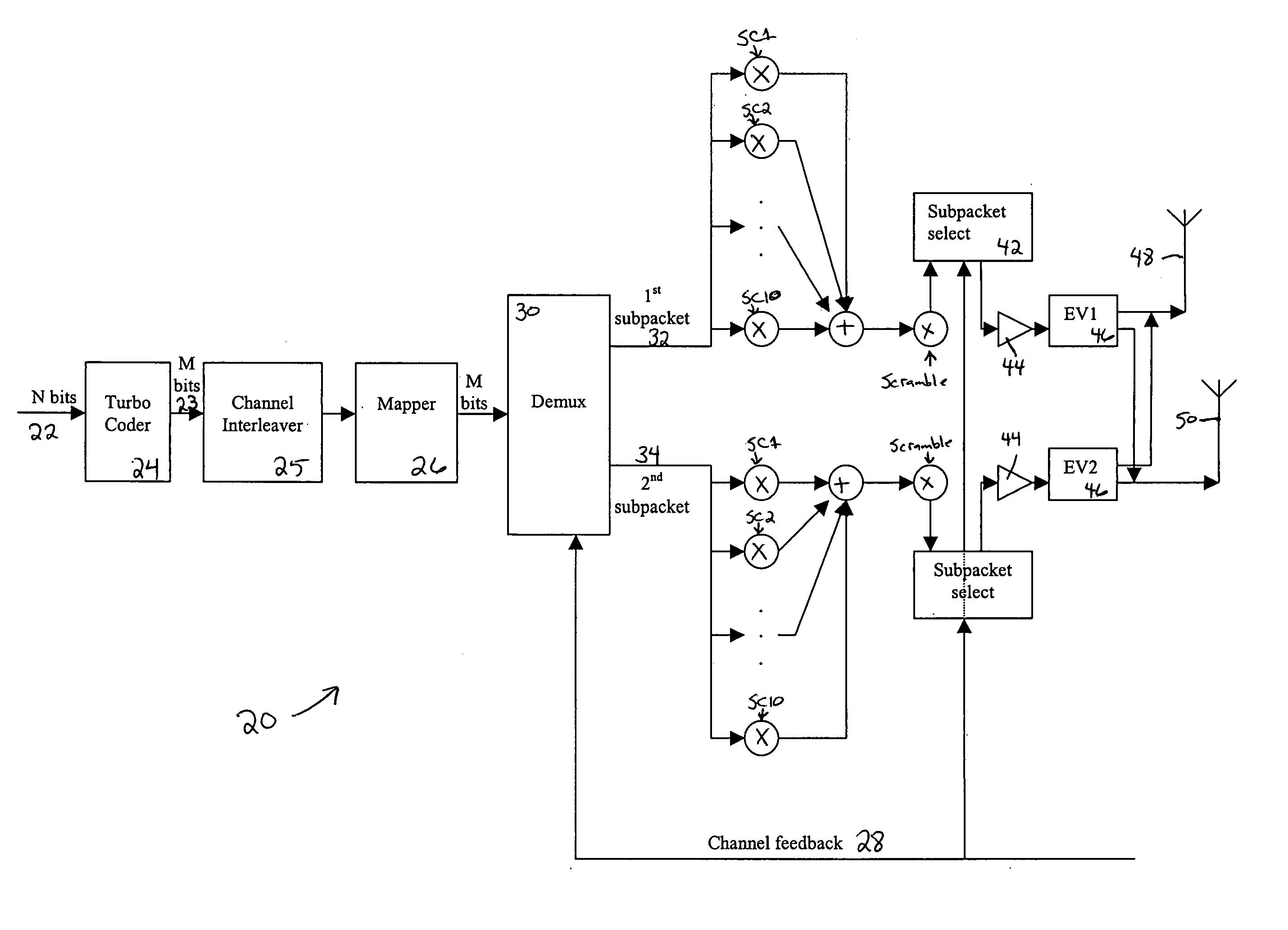
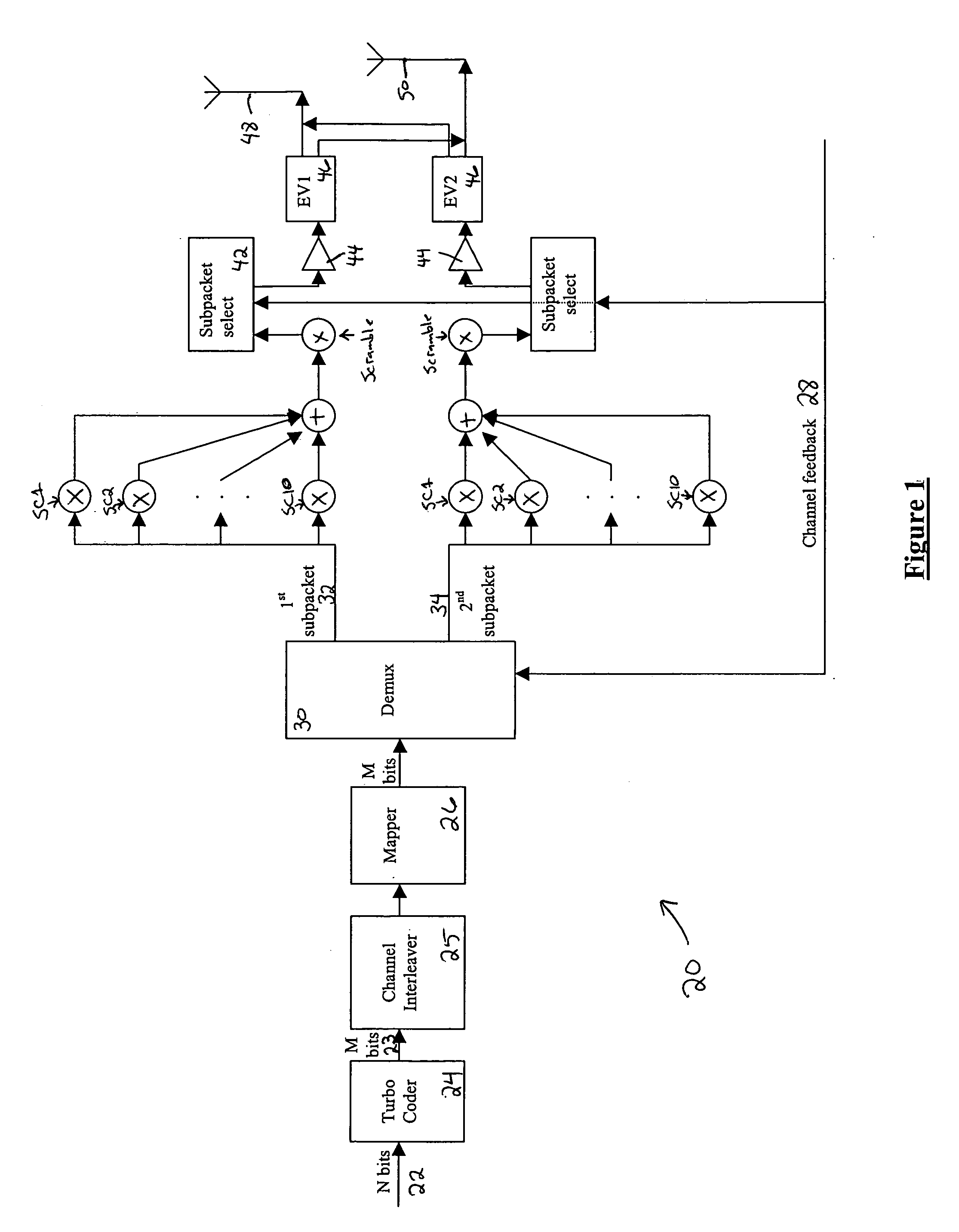
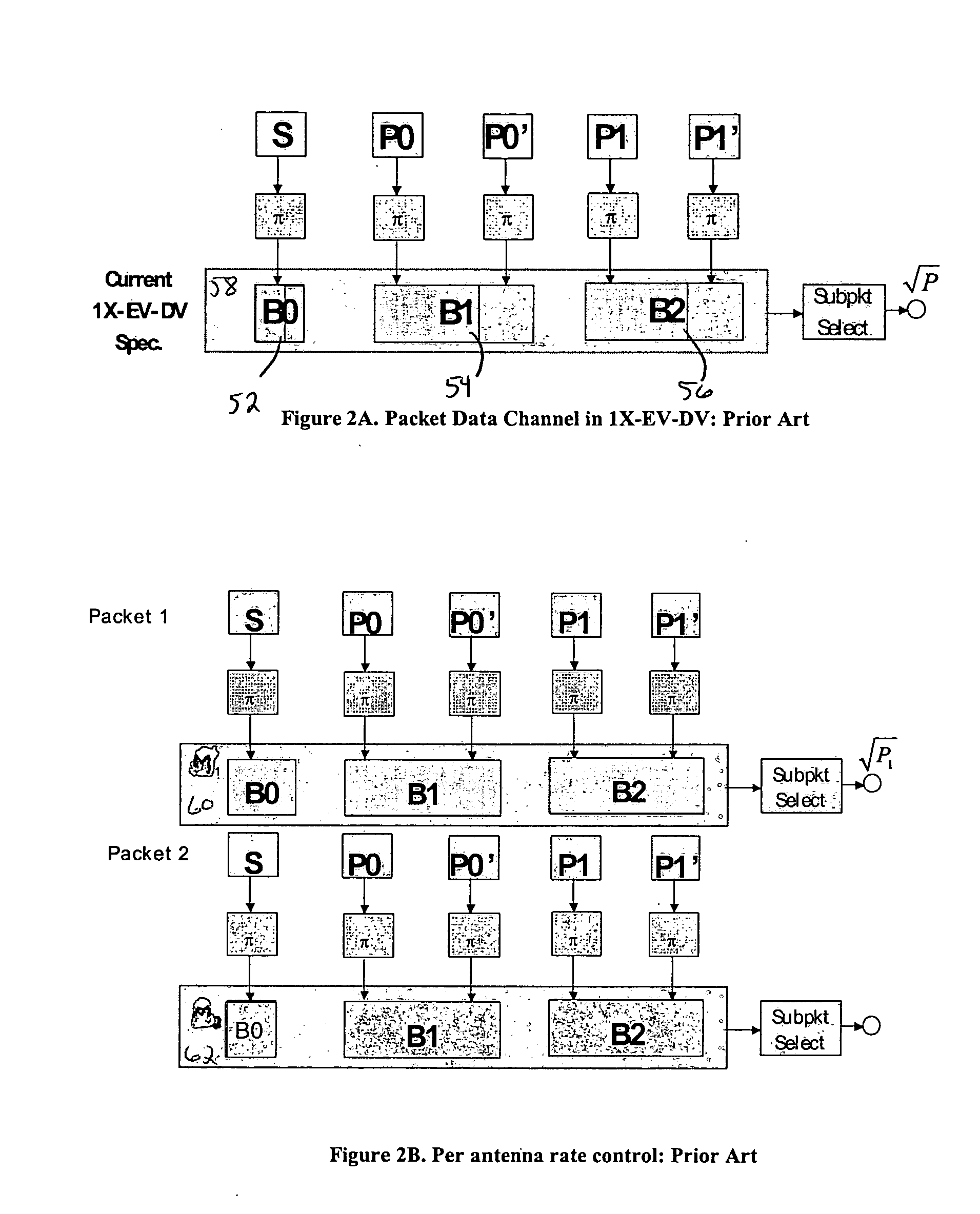
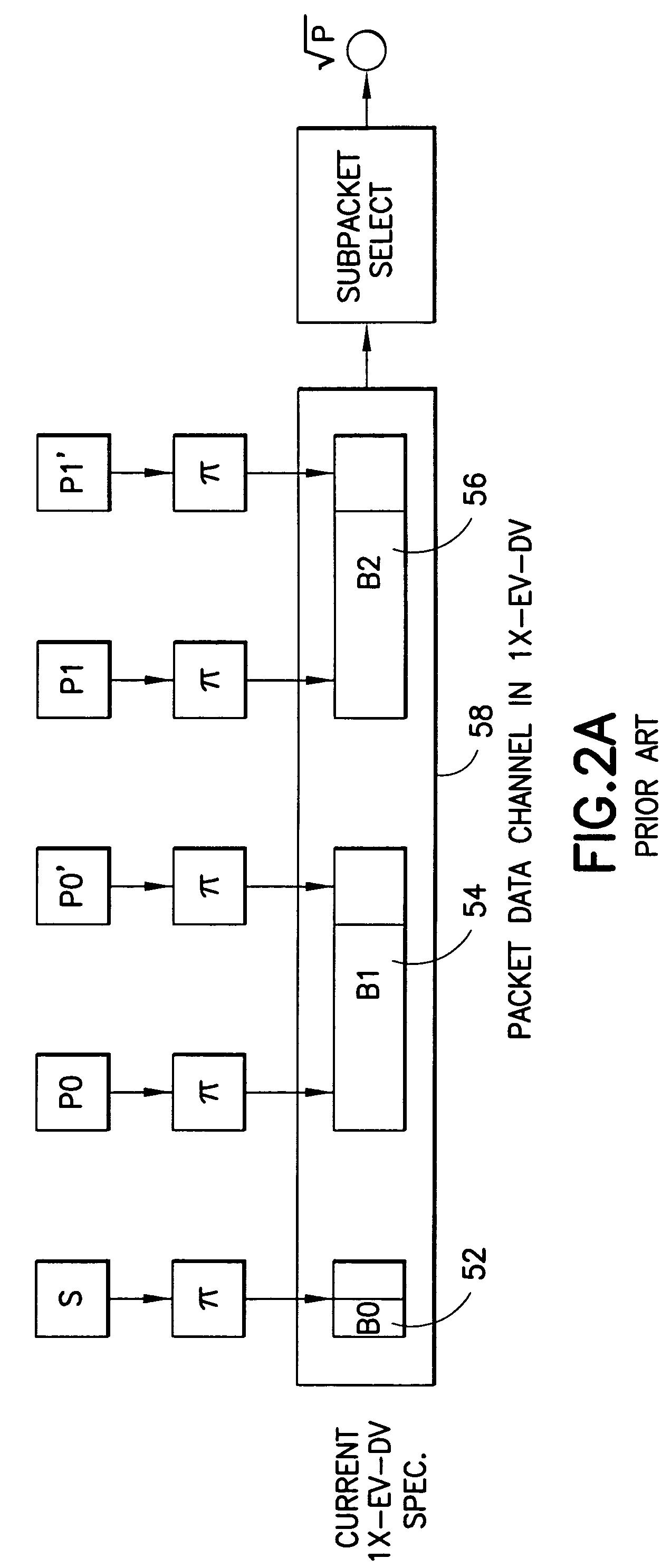
A method for transmitting a packet of N input bits includes encoding all of the N bits as a single entity, such as with an interleaver of length N within a turbo coder, outputting M encoded bits, channel interleaving the M bits, splitting the M encoded bits into a parallel first and second portion, and transmitting them over separate channels to achieve spatial diversity. The size of the first and second portion is determined based on a closed feedback loop that provides some knowledge of the channel, preferably a measure of channel capacity. The feedback loop may also provide channel knowledge to a subpacket selector associated with each transmit antenna, which determines an appropriate rate for that channel and selects subpackets to fill a transmission packet for that channel. The subpacket selectors choose a subpacket of systematic bits and fill the remaining transmission packet size with subpackets of parity bits. Eigenvectors may be employed to transmit each transmission packet over more than one channel with a power disparity between the channels. A transmitter according to the present invention is also described.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
MIMO signal processing method involving a rank-adaptive matching of the transmission rate
InactiveUS7450548B2Reduce complexityNo loss of transmit powerPower managementTransmission control/equalisingMulti inputData stream
A bidirectional signal processing method uses parallel transmission of digital transmitted data streams in a multiple input-multiple output system. Related art methods generate high bit error rates mostly in singular transmission channels. For this reason, the rank-adaptive signal processing method provides that the number nd of active subchannels are varied according to the actual channel behavior in order to effect a robust data transmission even in singular radio channels based on a transmit-side and receive-side channel knowledge and a modification of the data vector by a linear matrix vector multiplication while introducing a factor gamma for limiting the maximum transmit power. The maximum transmit power is then only distributed to the currently activated subchannels so that no transmit power remains unused. Another optimization of the number of subchannels nd occurs when selecting the modulation and encoding methods. During the optimal rank-adaptation according to the water-filling principle, another power is allocated to each subchannel. Another modulation and encoding method is accordingly selected for each data stream. During the suboptimal rank-adaptation according to the channel inversion principle, all subchannels have the same power whereby enabling the data streams to be modulated and encoded in a common source.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
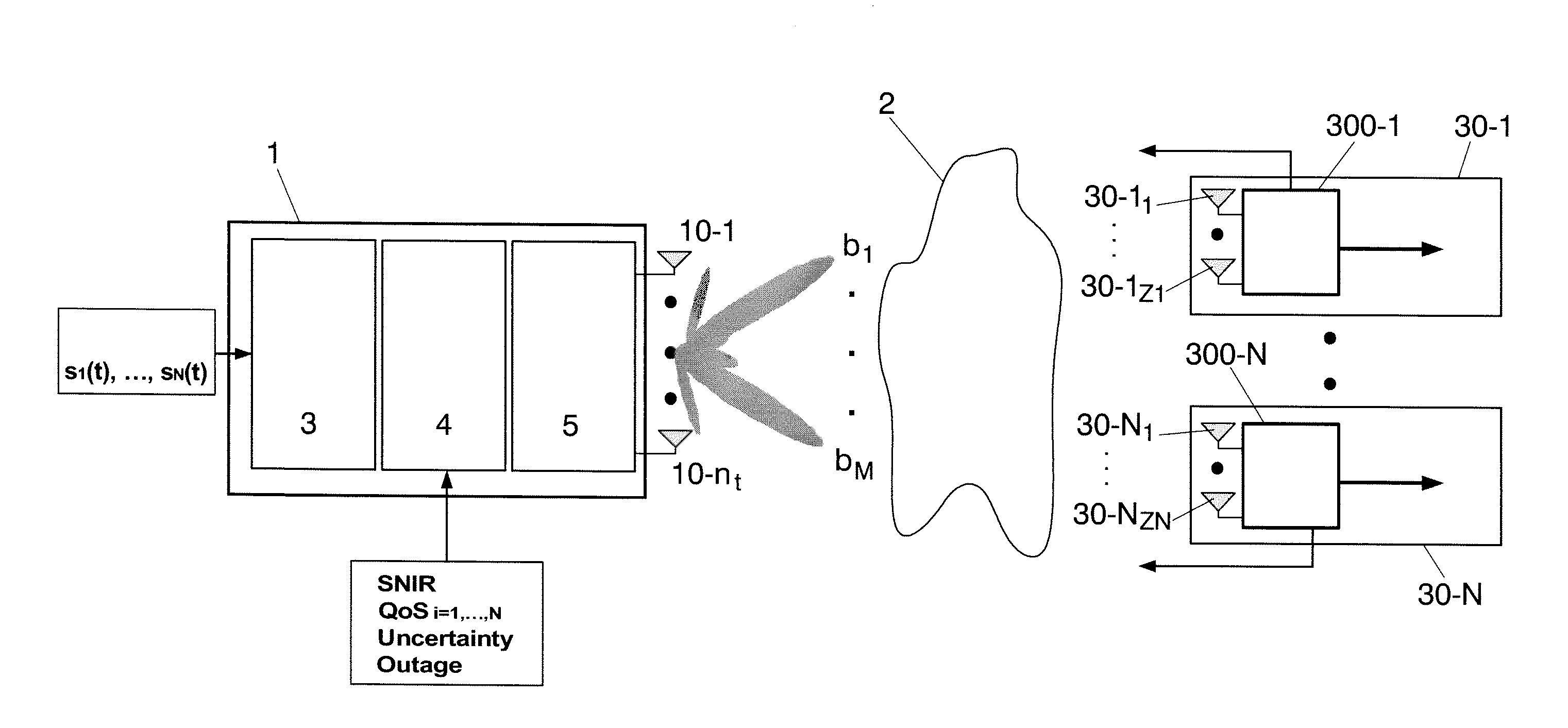
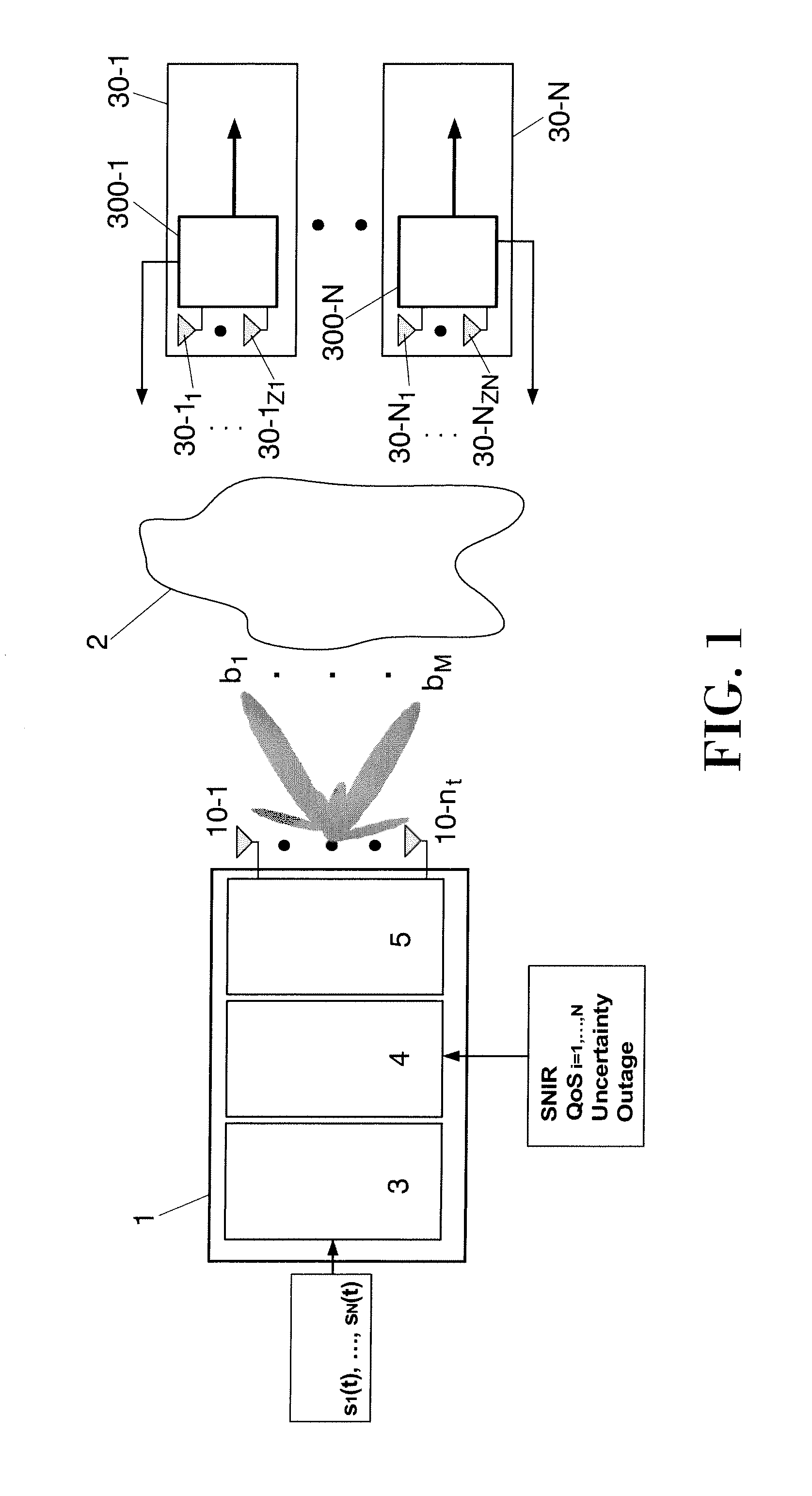
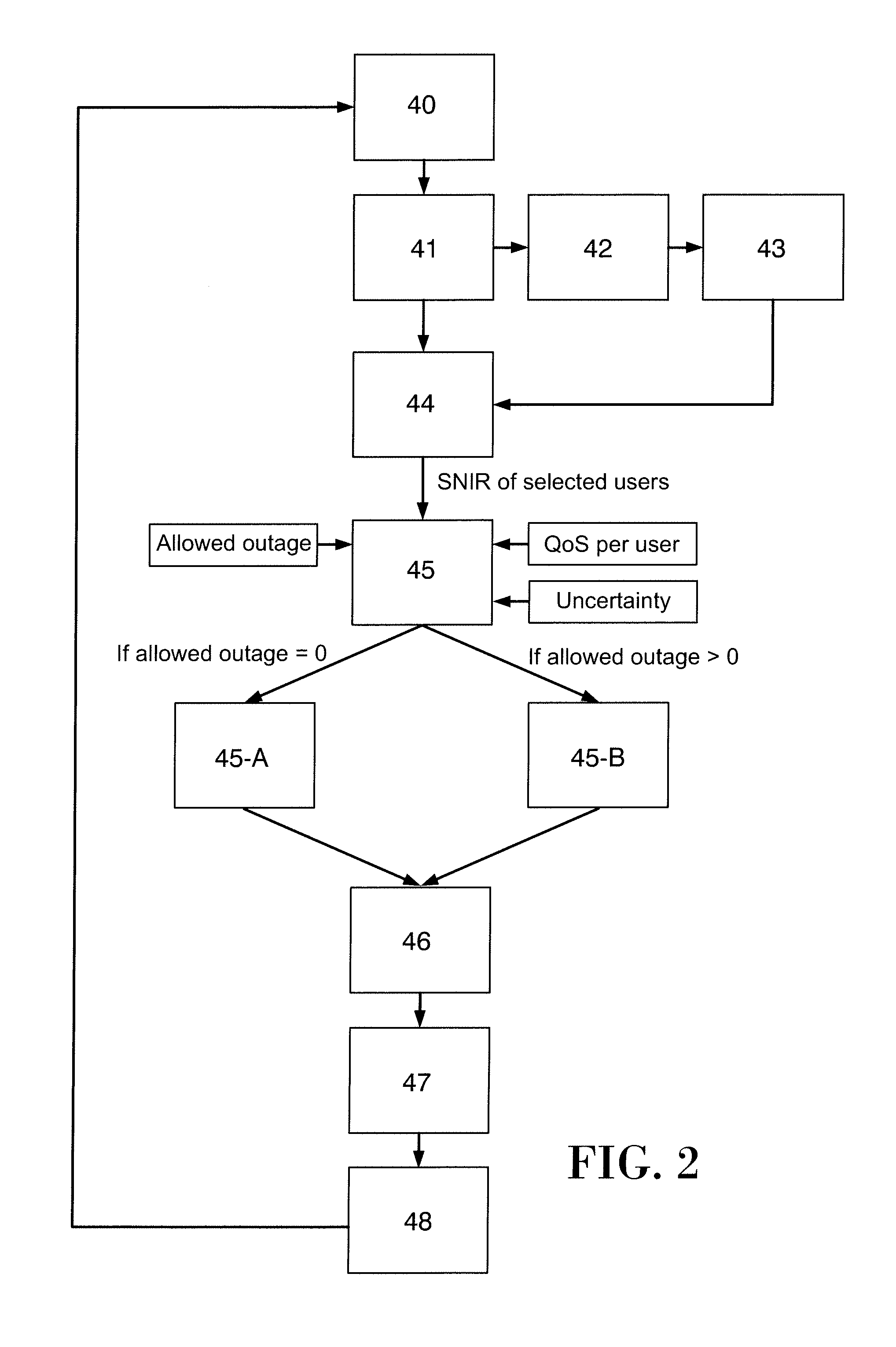
Power allocation method in multiantenna systems under partial channel knowledge
InactiveUS20100182967A1Energy efficient ICTPower managementChannel state informationInterference ratio
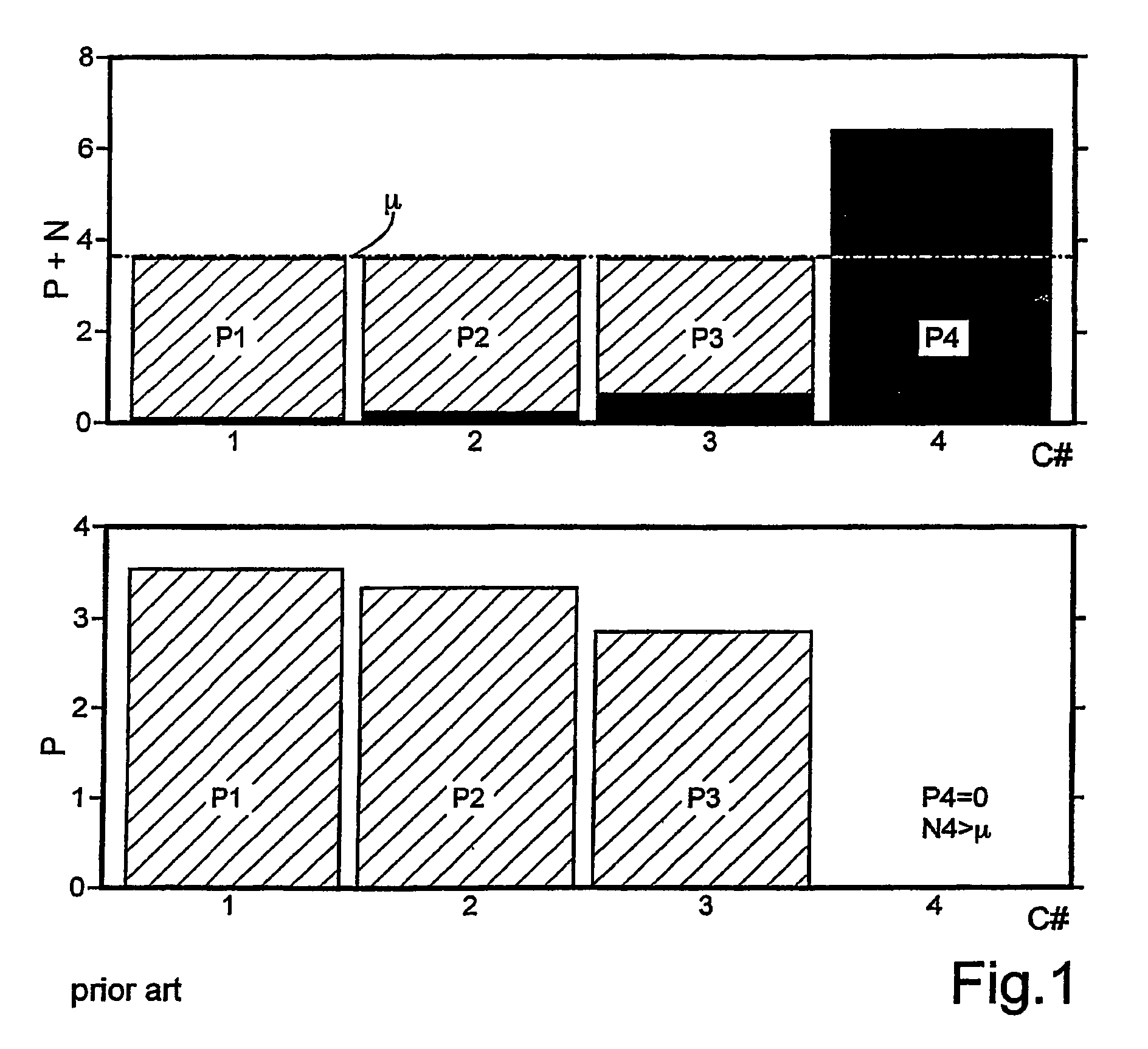
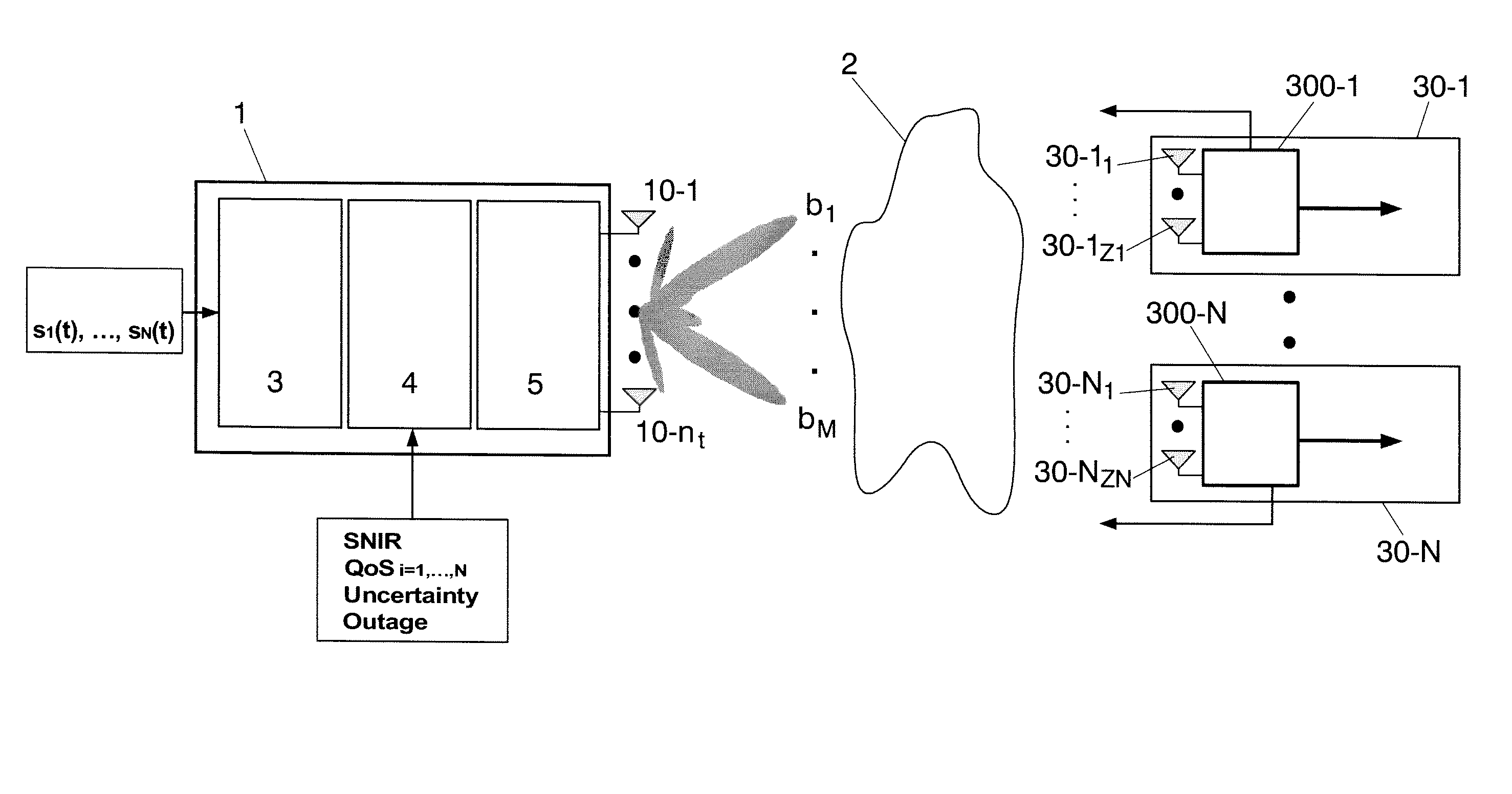
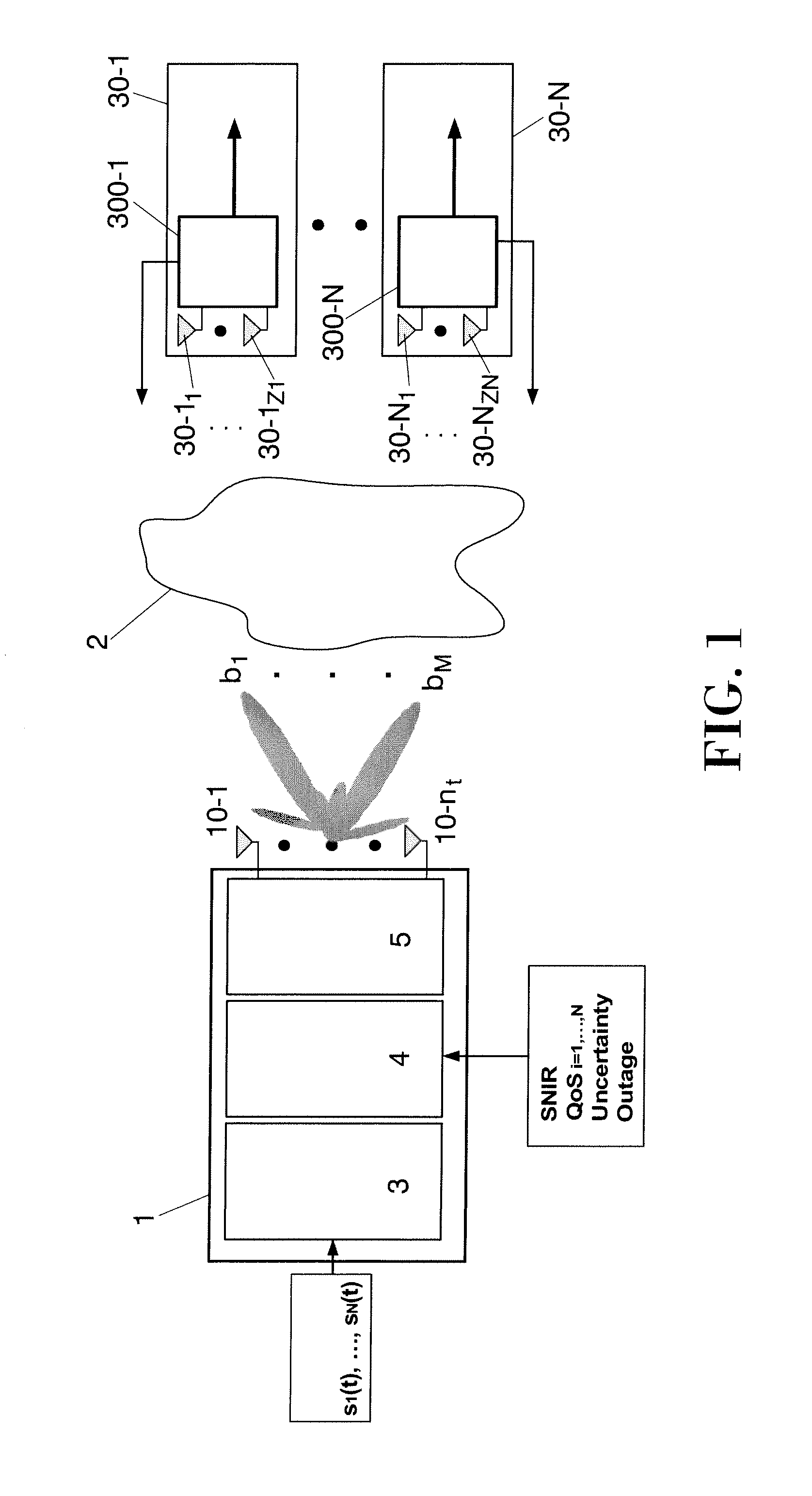
Method for allocating a minimum downlink power from a transmitter (1) having nt transmit antennas of a cellular multi-user multi-antenna communications system with N users attached to said transmitter (1). Each user comprises at least one antenna. The method comprising the steps of: generating at said transmitter (1) M random beams (b1 . . . bM); sending said M random beams through all the transmit antennas; calculating at each user a signal-to-noise-interference-ratio for each random beam sent by said transmitter (1); sending back to said transmitter (1) said calculated values of signal-to-noise-interference-ratio, said signal-to-noise-interference-ratio representing a partial channel state information; selecting at said transmitter (1) the M best users which correspond to the M best values of signal-to-noise-interference-ratio per beam.
Owner:FUNDACIO PRIVADA CENT TECNOLOGIC DE TELECOMUNICACIONS DE CATALUNYA
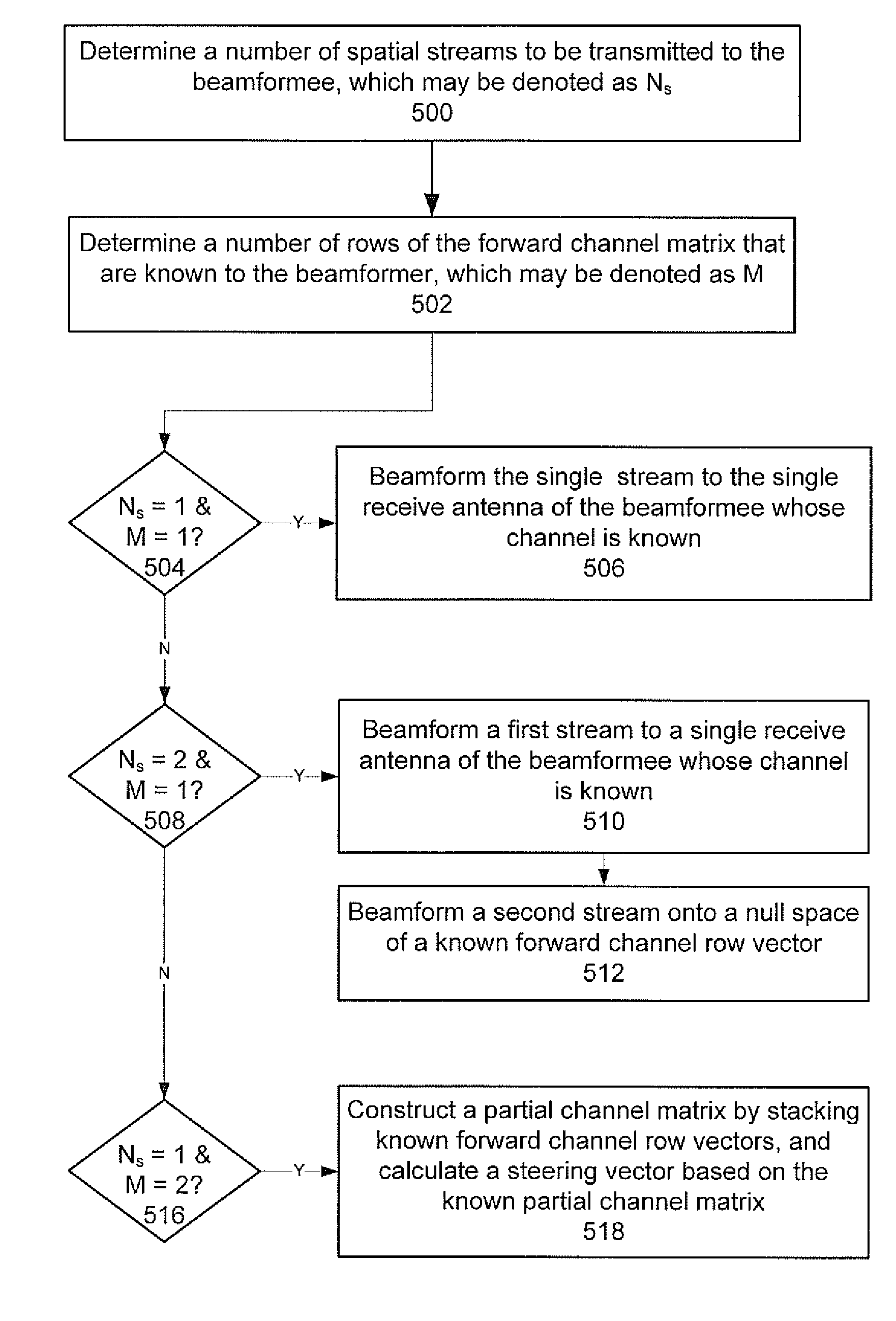
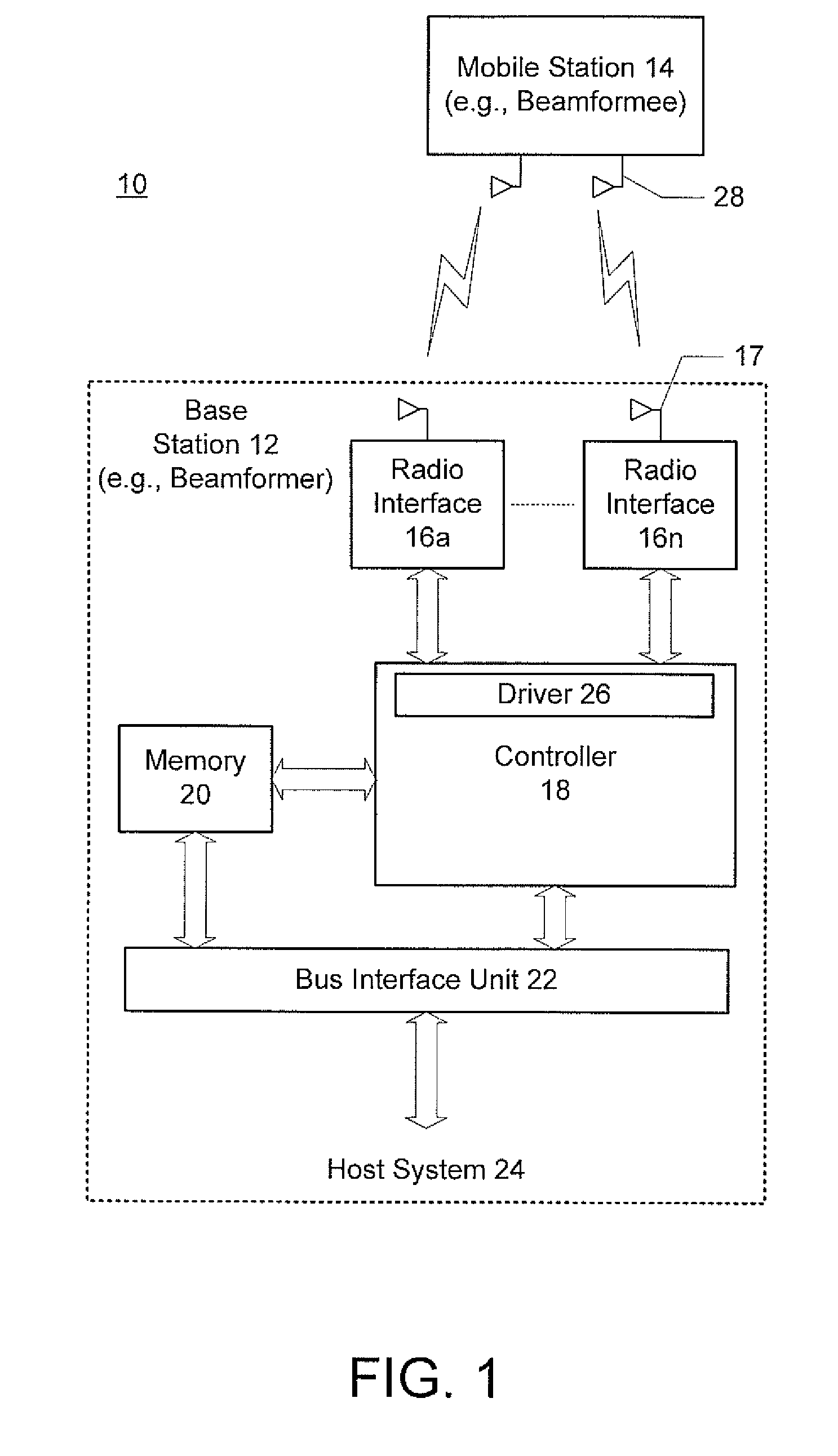
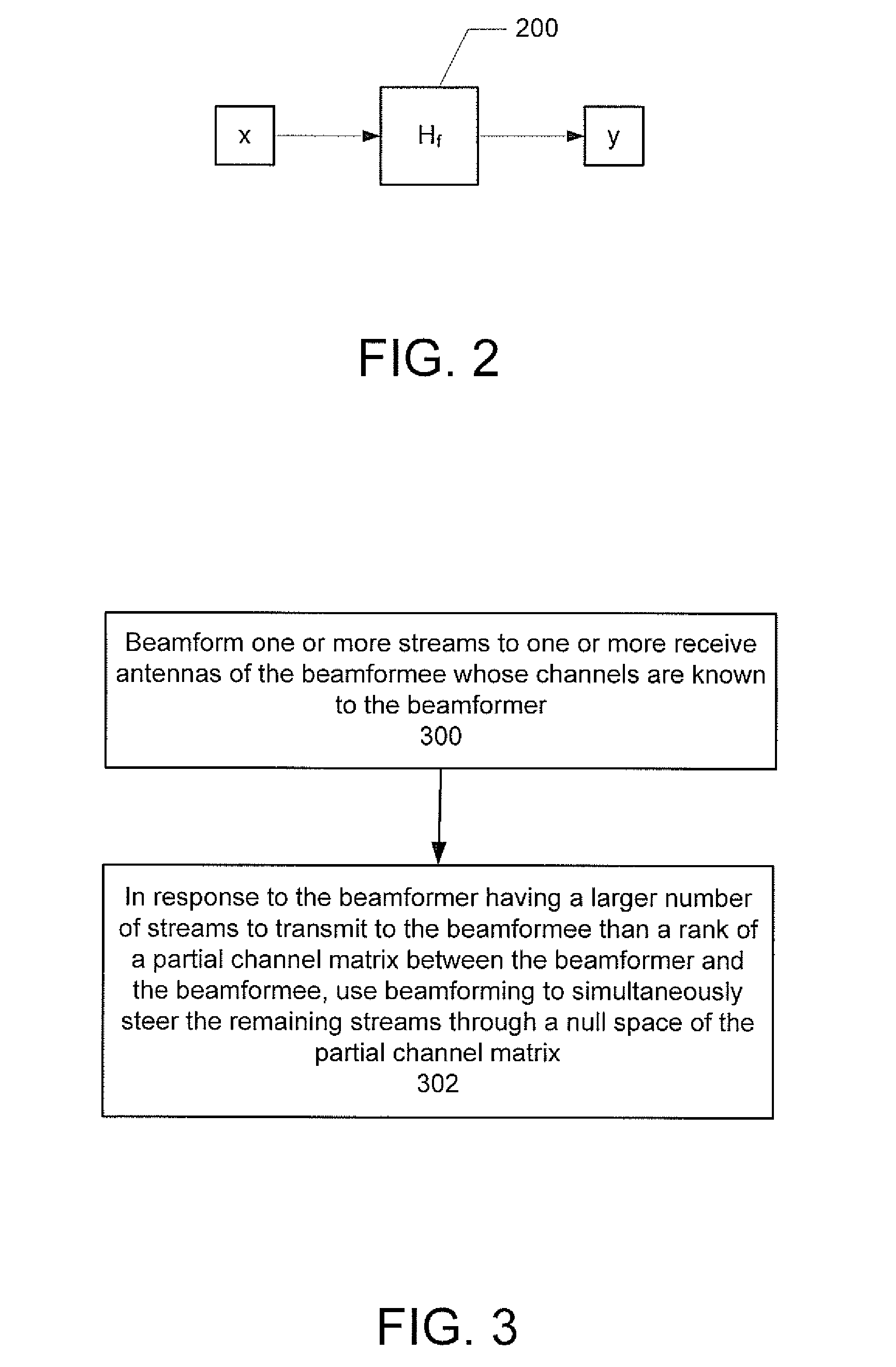
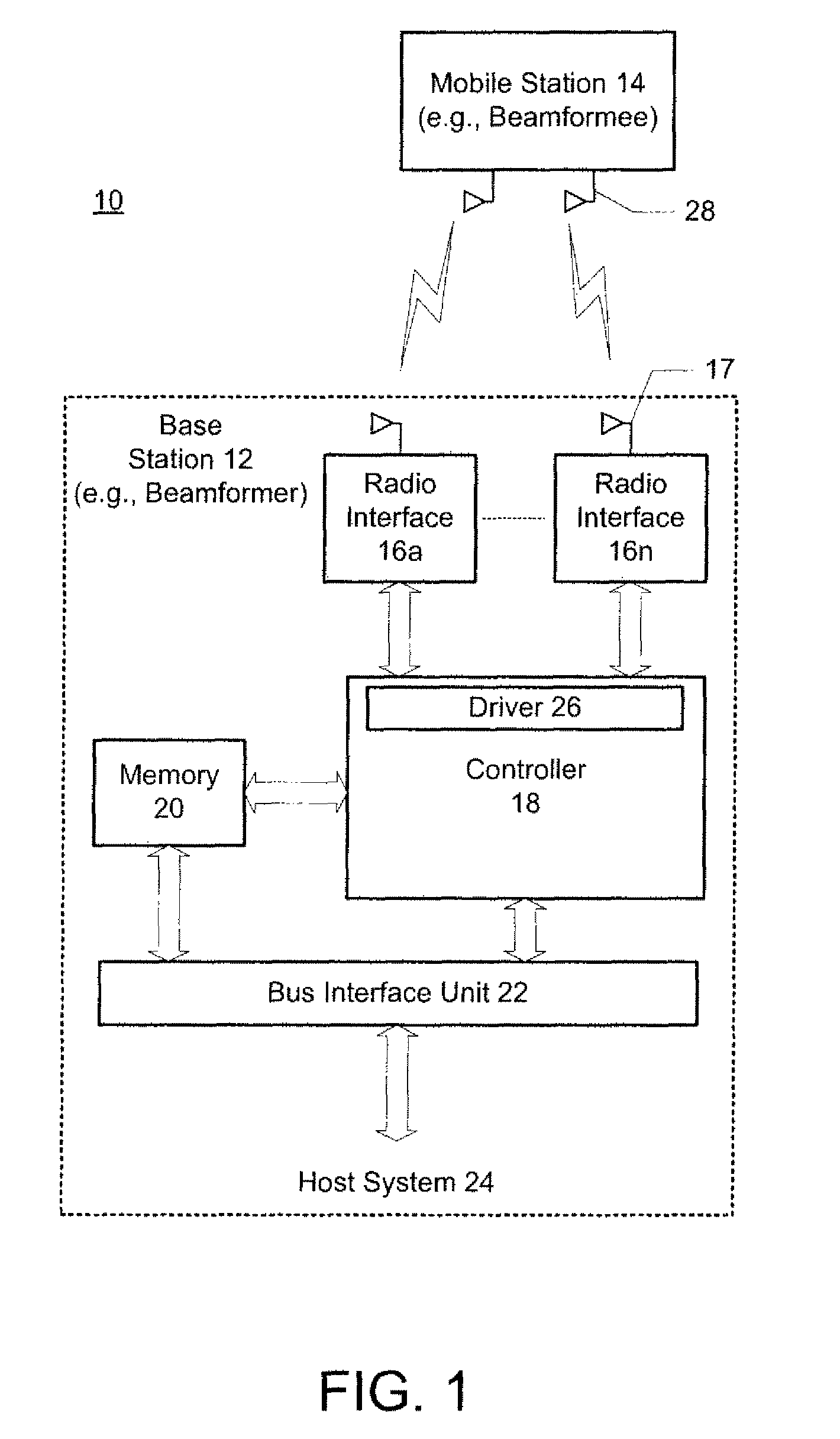
Beamforming with partial channel knowledge
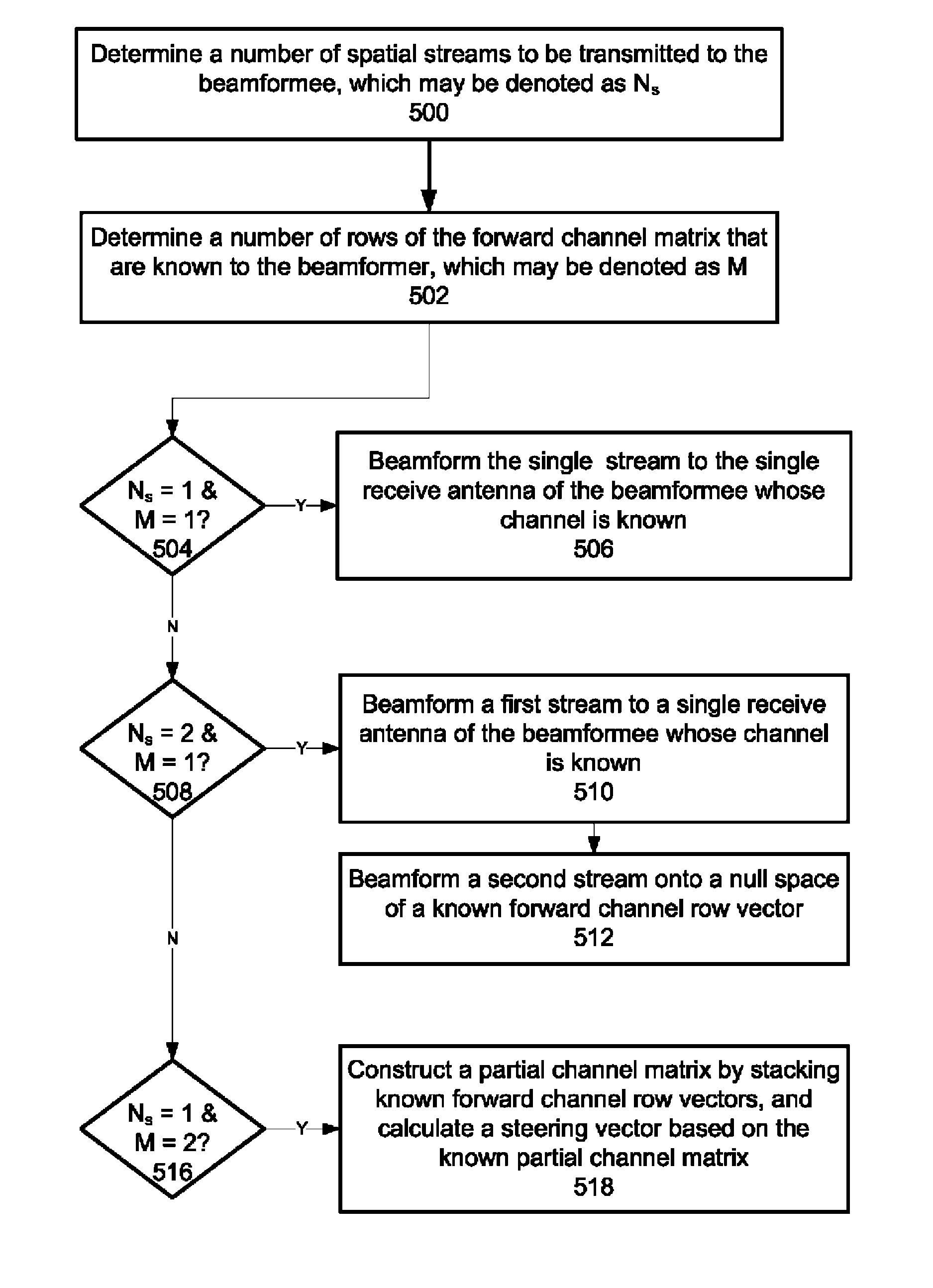
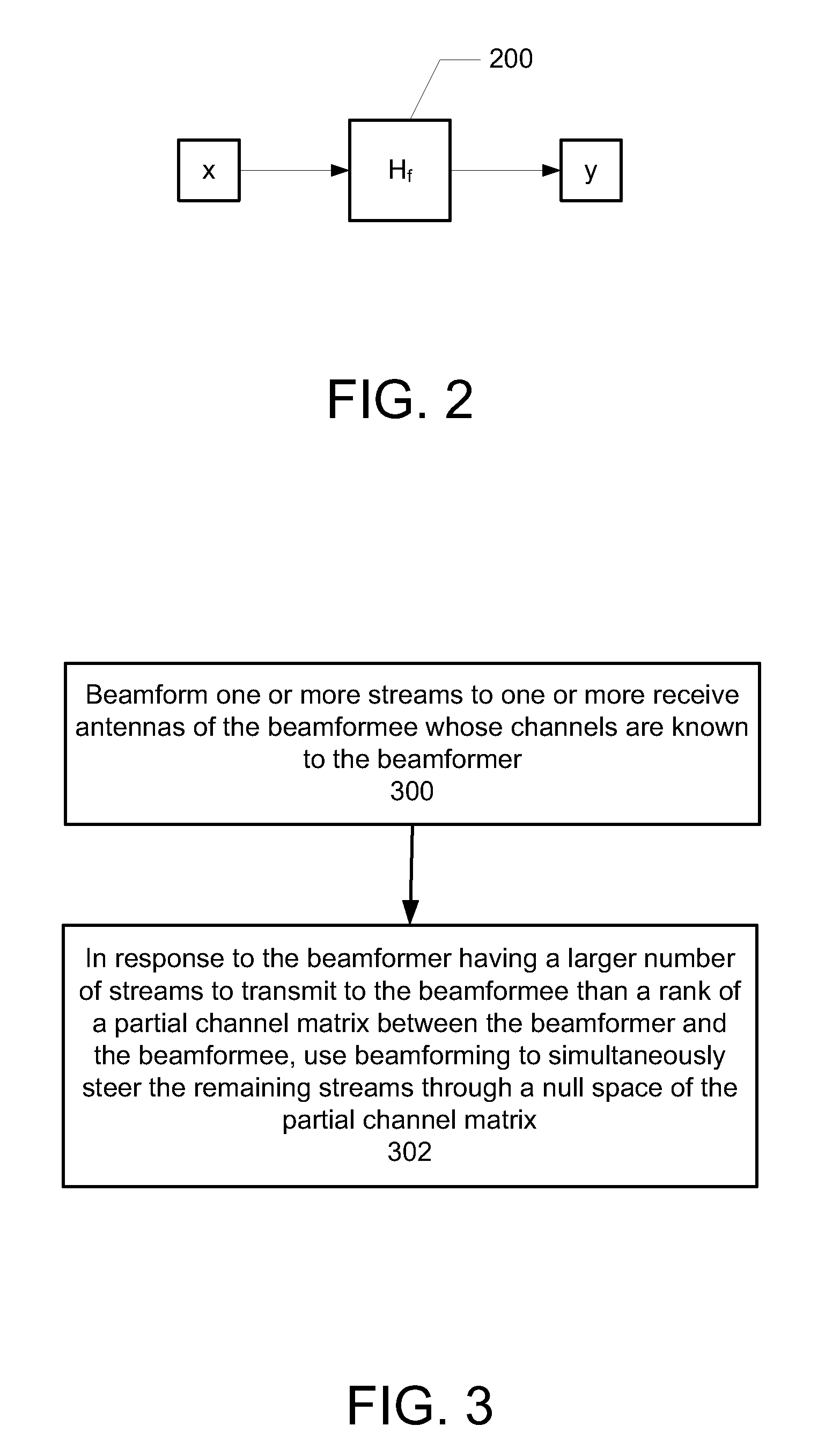
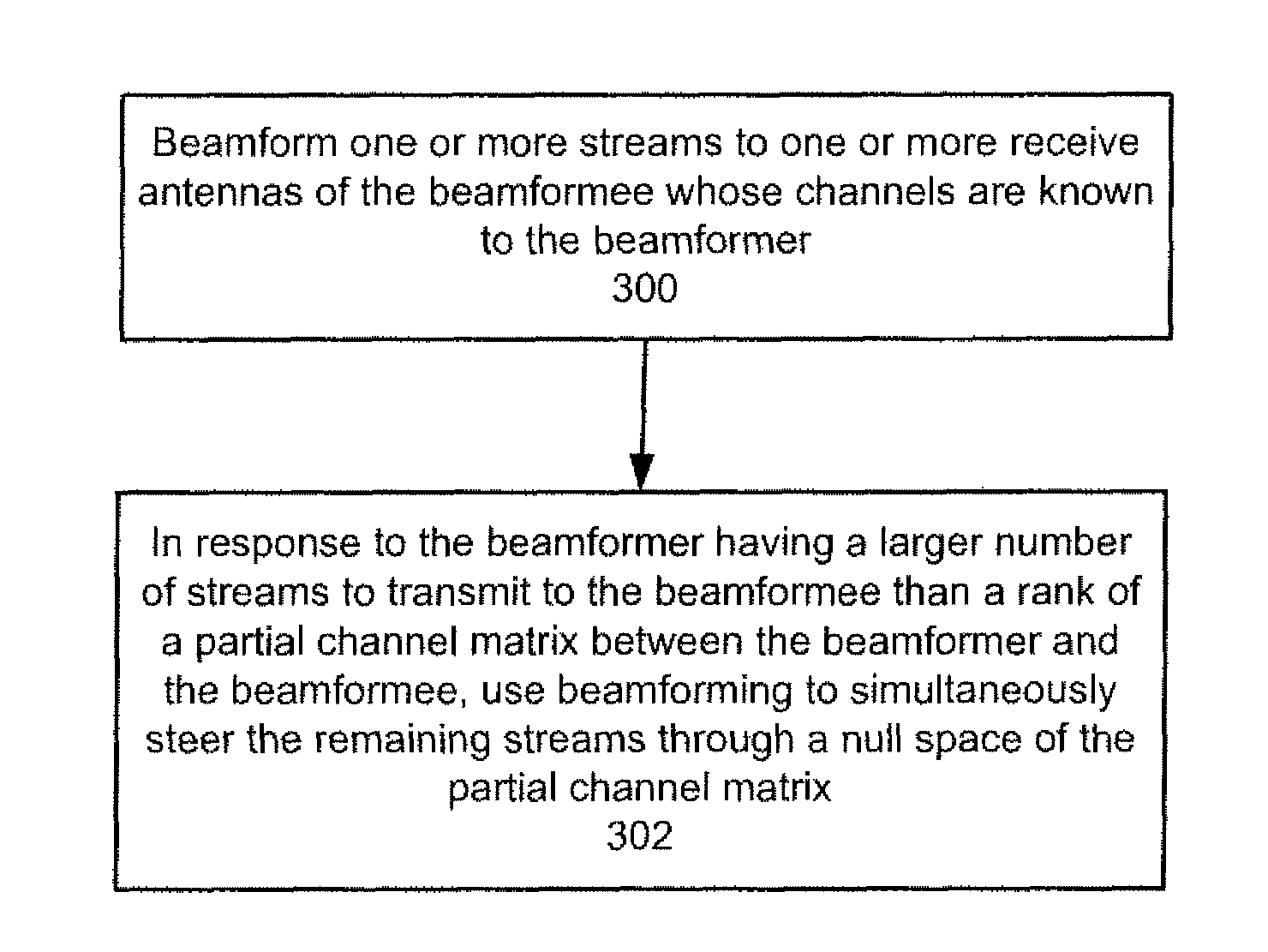
A method and system for beamforming with partial channel knowledge comprises beamforming one or more streams from a beamformer to one or more receive antennas of a beamformee whose channels are known to the beamformer. In response to the beamformer having a larger number of streams to transmit to the beamformee than a rank of a partial channel matrix between the beamformer and the beamformee, beamforming is used to steer remaining streams through a null space of the partial channel matrix.
Owner:NXP USA INC
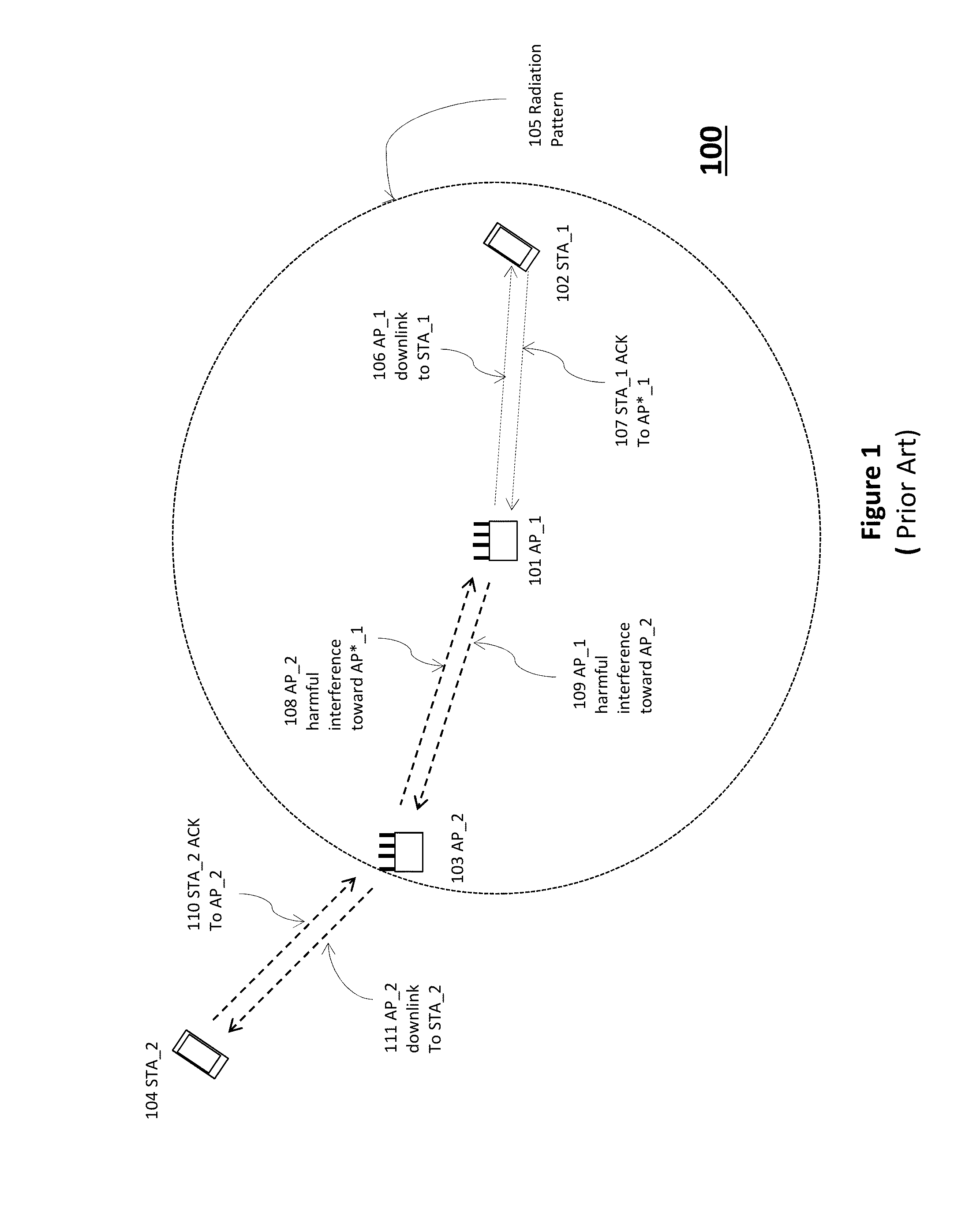
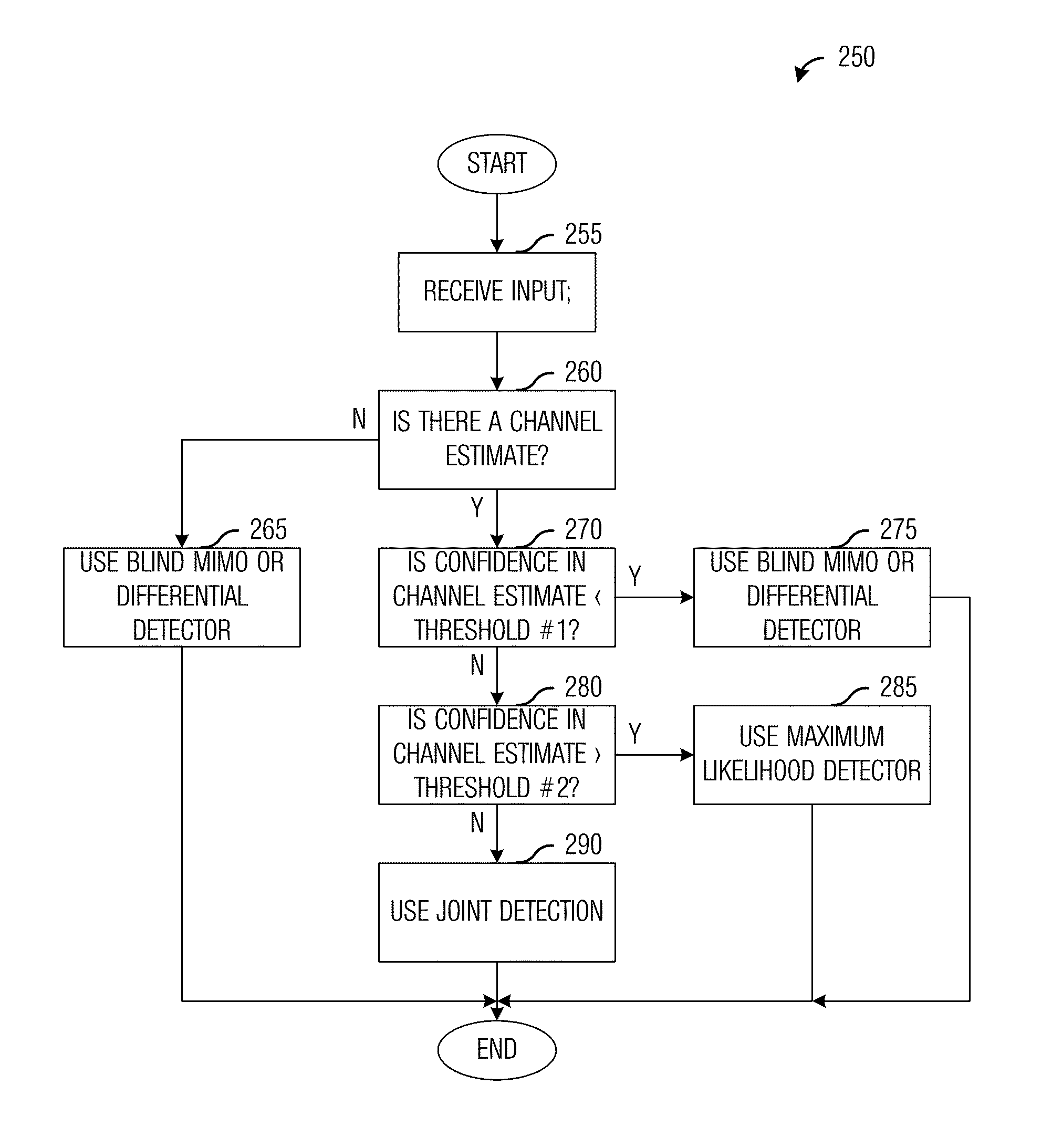
System and Method for Transmitter and Receiver Operation for Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output Communications Based on Prior Channel Knowledge
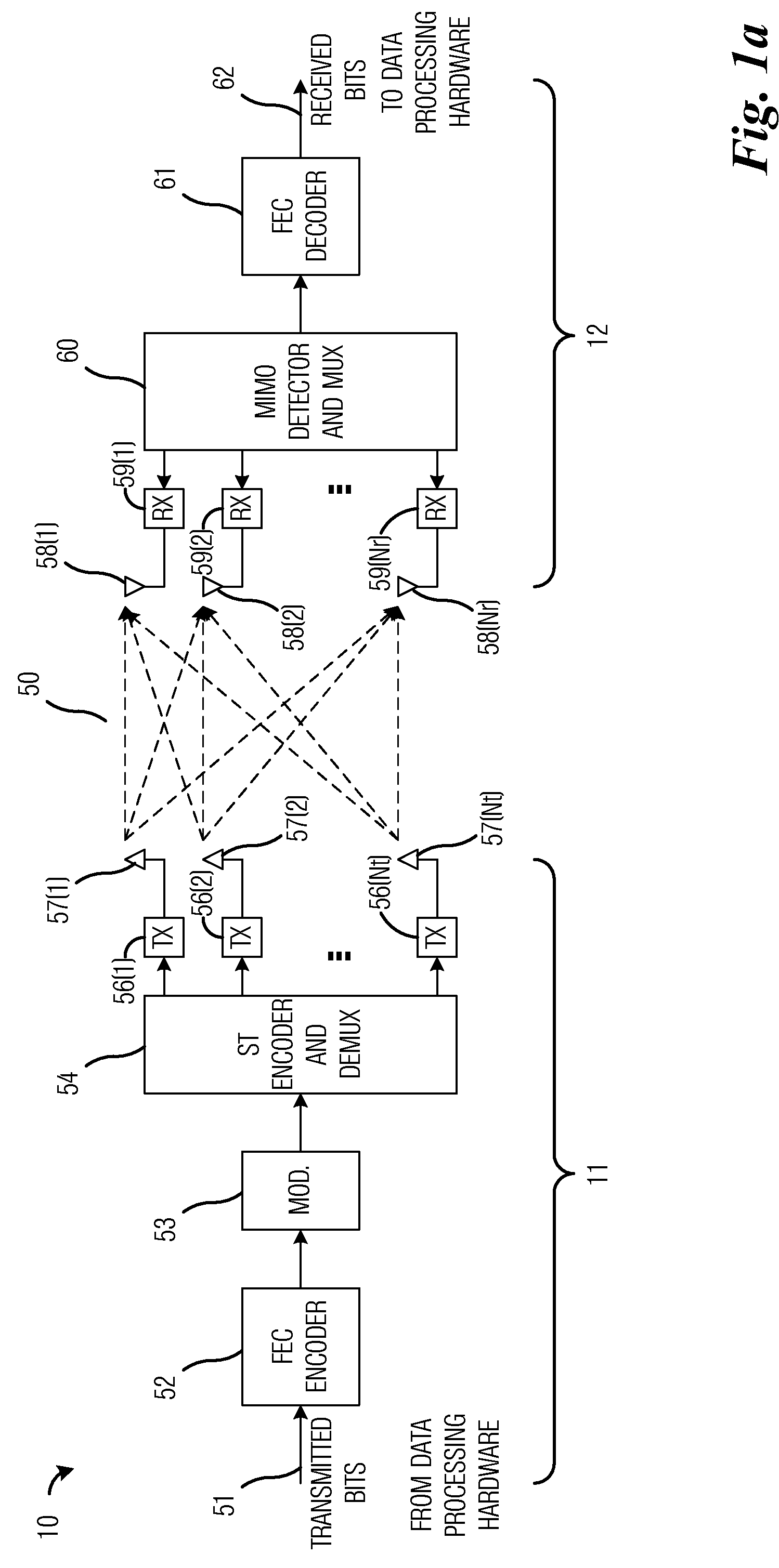
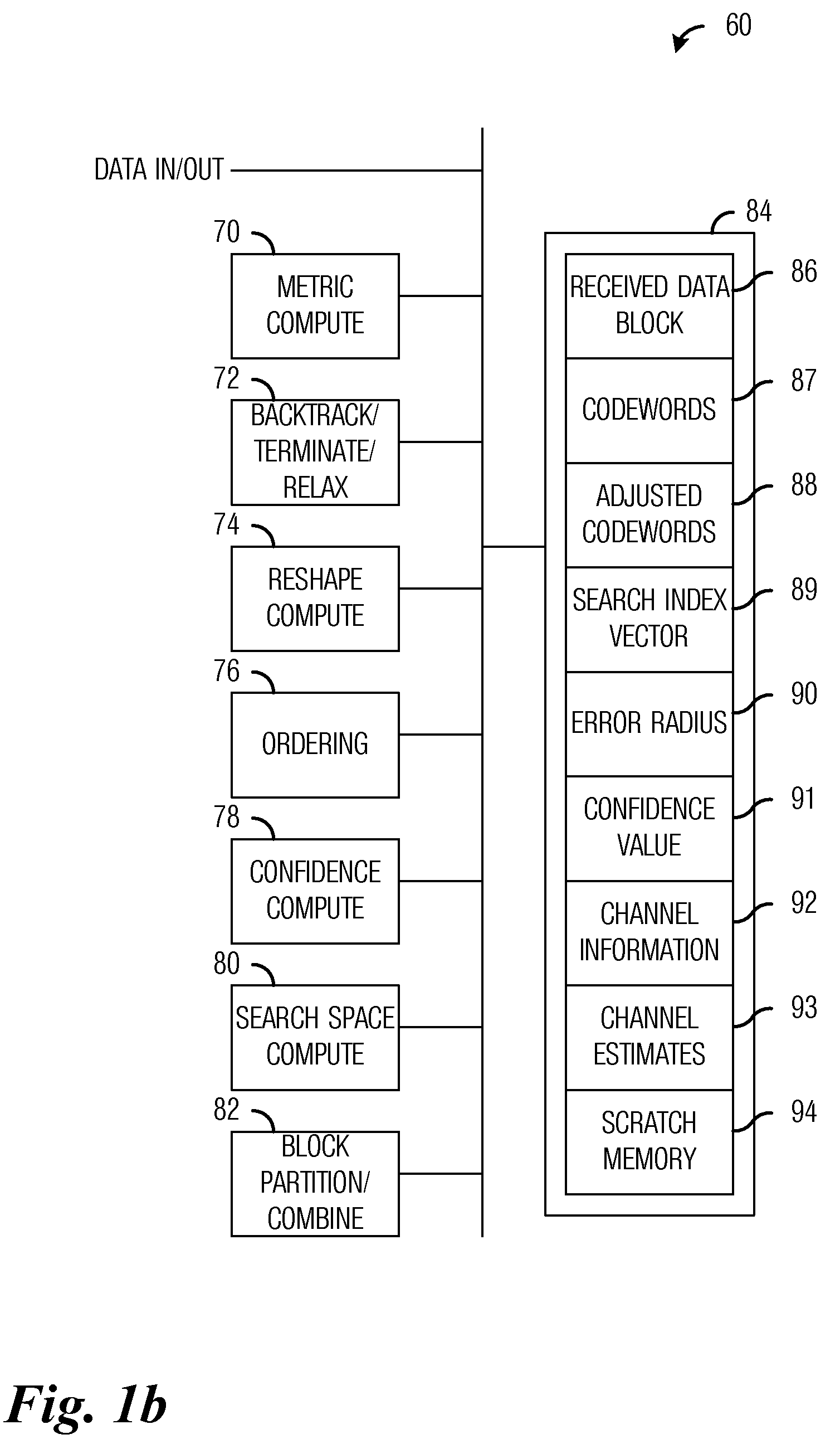
ActiveUS20110064167A1Reduce complexityImprove performanceError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsOperational systemMultiple input
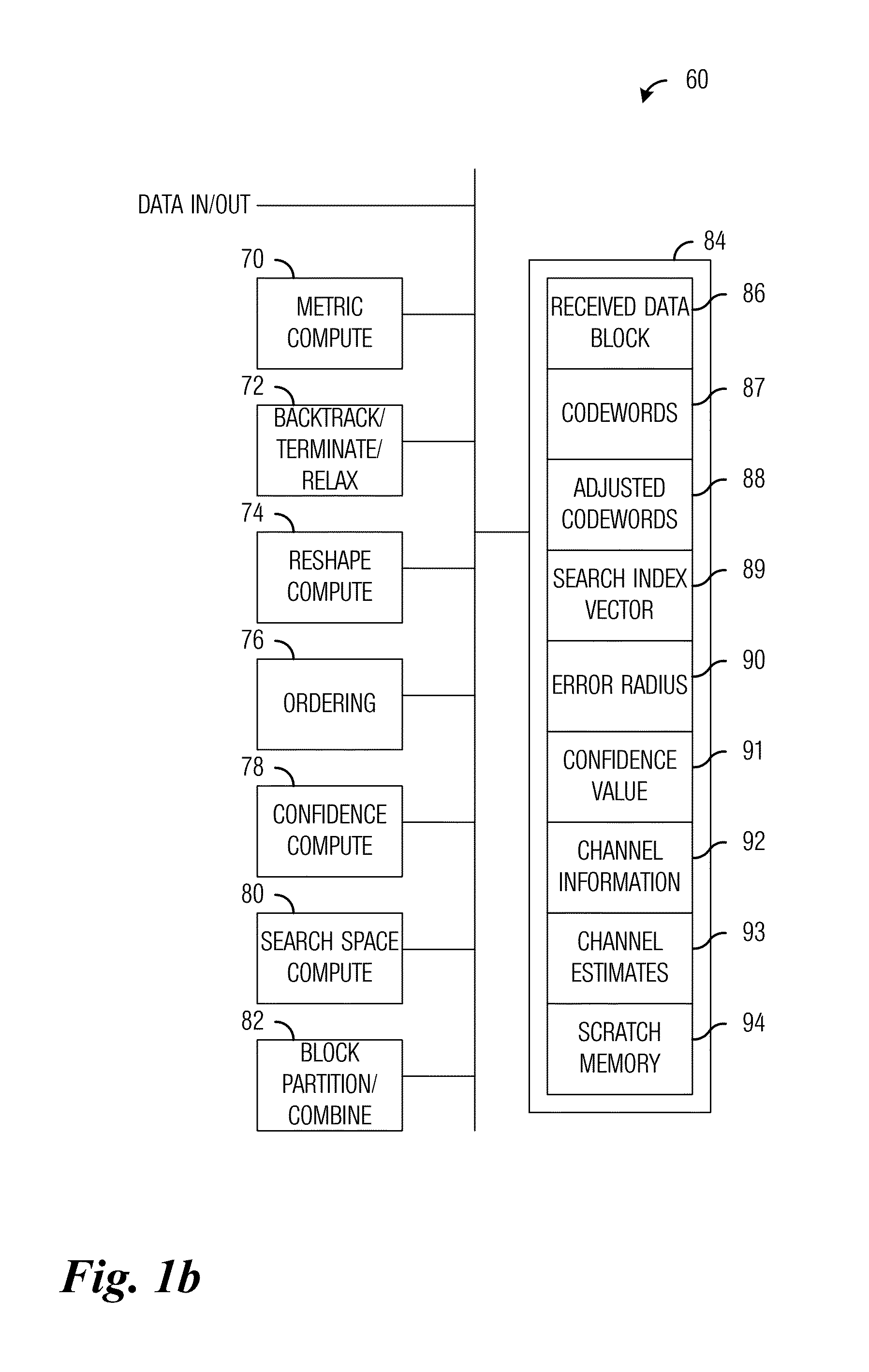
A system and method for transmitter and receiver operation for multiple-input, multiple-output (MIMO) communications based on prior channel knowledge are provided. A method for receiver operations includes receiving a data block, determining if there is confidence in information related to a channel, detecting data in the data block with a first detector in response to determining that there is confidence in the information, and detecting the data in the data block with a second detector in response to determining that there is no confidence in the information. The data block is received over the channel.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Flexible rate split method for MIMO transmission
InactiveUS7746800B2Wide diversityReduce error rateSpatial transmit diversityFrequency-division multiplex detailsMimo transmissionTurbo encoder
A method for transmitting a packet of N input bits includes encoding all of the N bits as a single entity, such as with an interleaver of length N within a turbo coder, outputting M encoded bits, channel interleaving the M bits, splitting the M encoded bits into a parallel first and second portion, and transmitting them over separate channels to achieve spatial diversity. The size of the first and second portion is determined based on a closed feedback loop that provides some knowledge of the channel, preferably a measure of channel capacity. The feedback loop may also provide channel knowledge to a subpacket selector associated with each transmit antenna, which determines an appropriate rate for that channel and selects subpackets to fill a transmission packet for that channel. The subpacket selectors choose a subpacket of systematic bits and fill the remaining transmission packet size with subpackets of parity bits. Eigenvectors may be employed to transmit each transmission packet over more than one channel with a power disparity between the channels. A transmitter according to the present invention is also described.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Interactive matting method, medium and computer device
InactiveCN109389611AImplement an interactive matting methodImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionChannel knowledge
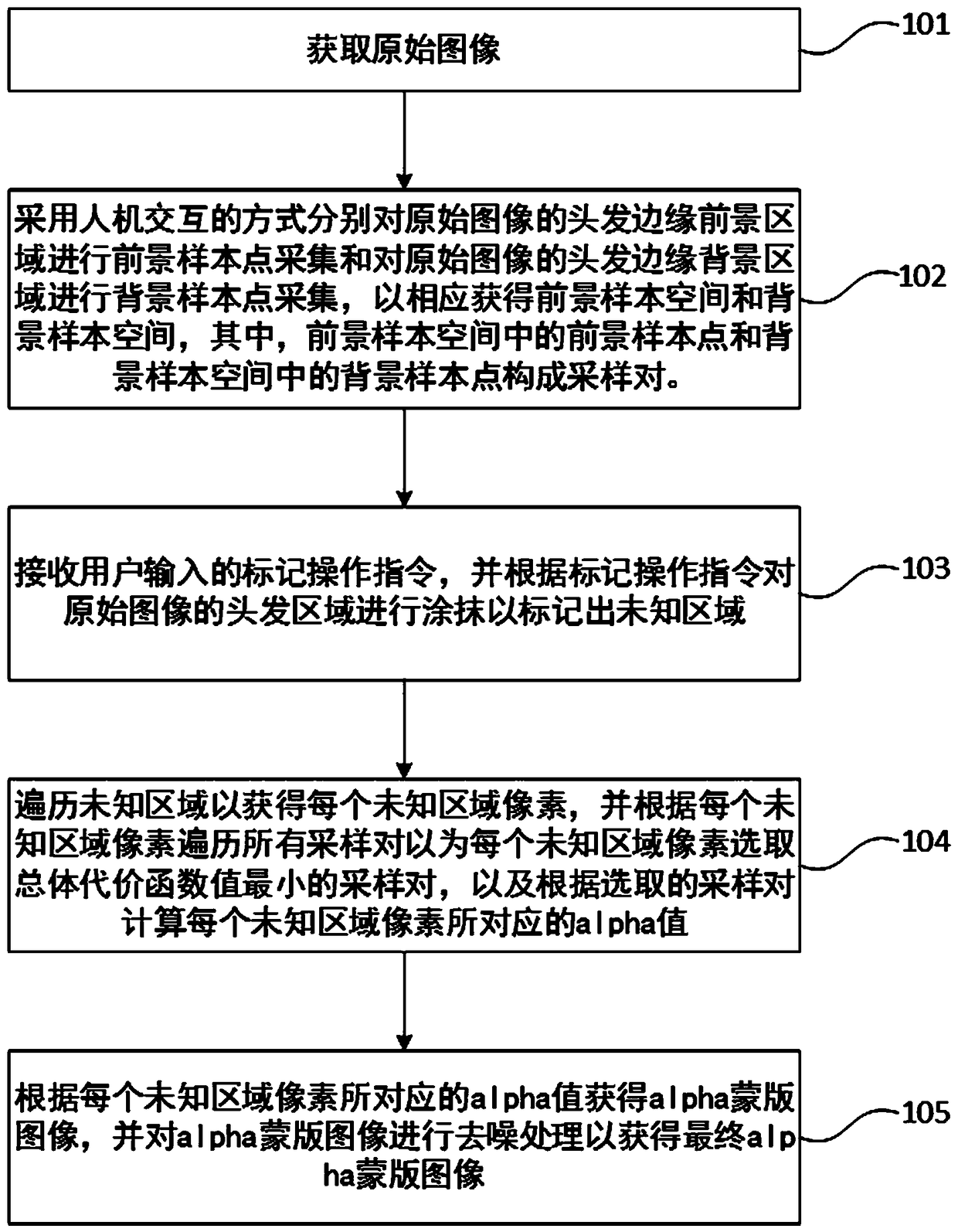
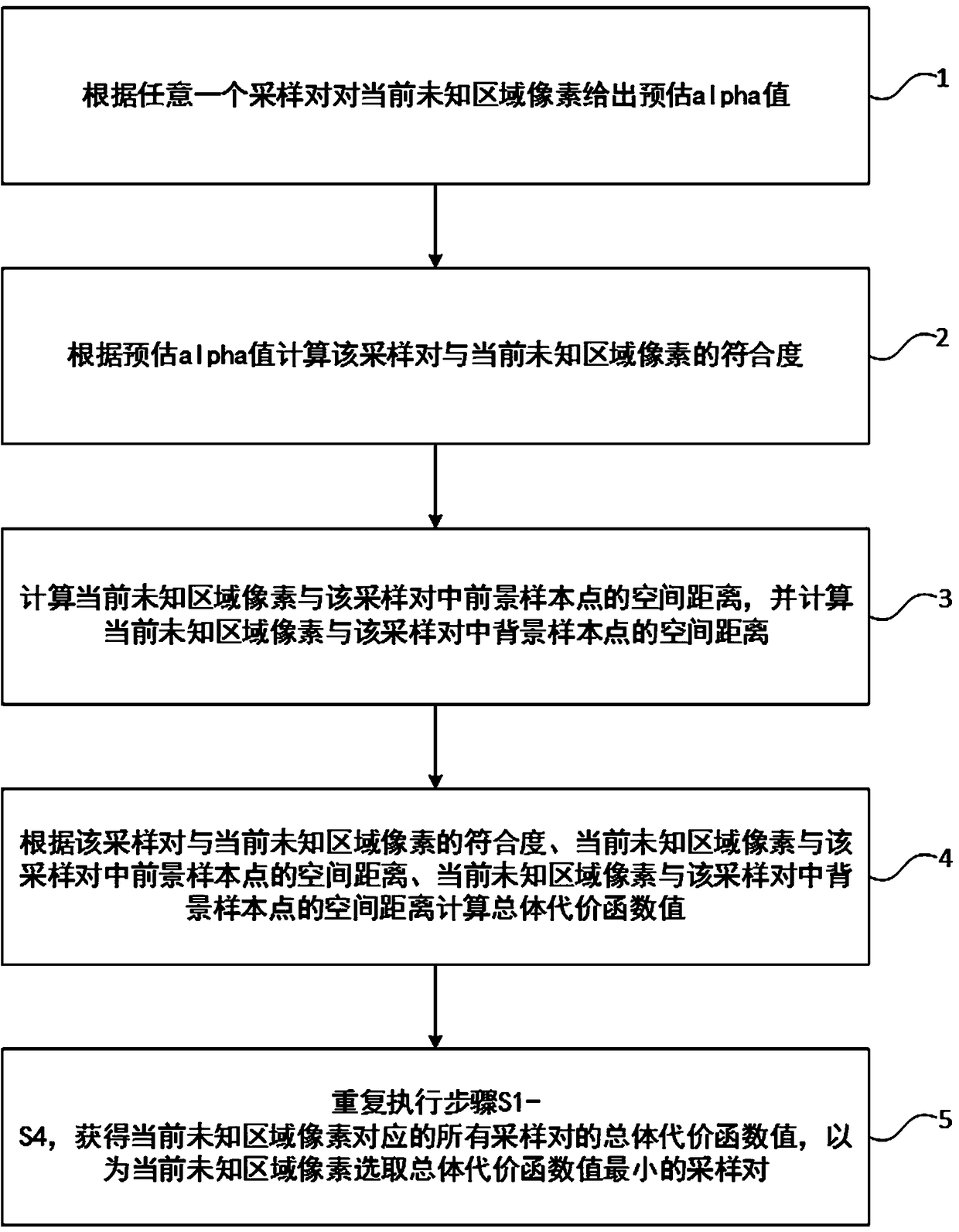
The invention discloses an interactive matting method, a medium and a computer device. The foreground sample space and background sample space are obtained by human-computer interaction. According toa marking operation instruction, smearing a hair region of the original image to mark an unknown region; Obtaining pixels of each unknown region, traversing all sample pairs according to each pixel ofthe unknown region to select a sample pair with the smallest total cost function value, and calculating an alpha value corresponding to each pixel of the unknown region according to the selected sample pair; The alpha mask image is obtained according to the alpha value corresponding to each pixel of the unknown region, and the alpha mask image is denoised to obtain the final alpha mask image; andthe alpha mask image is denoised to obtain the final alpha mask image. Thus, sample pairs and unknown regions can be determined through simple interaction, and the alpha value of pixels in the unknown regions can be calculated according to the sample pairs, so that users can complete accurate matting of hair edges without mastering rich PS technology and color channel knowledge.
Owner:GAODING XIAMEN TECH CO LTD
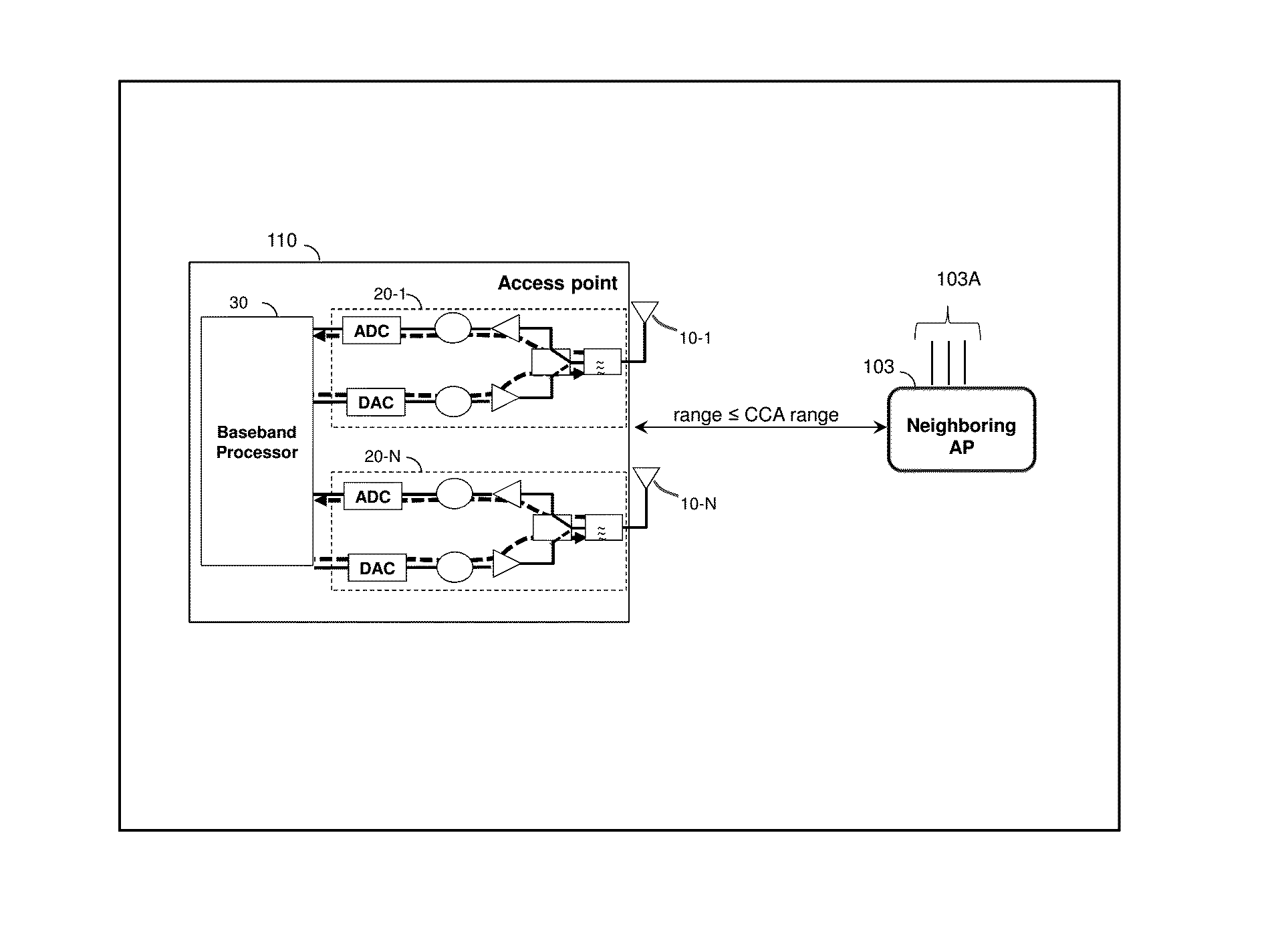
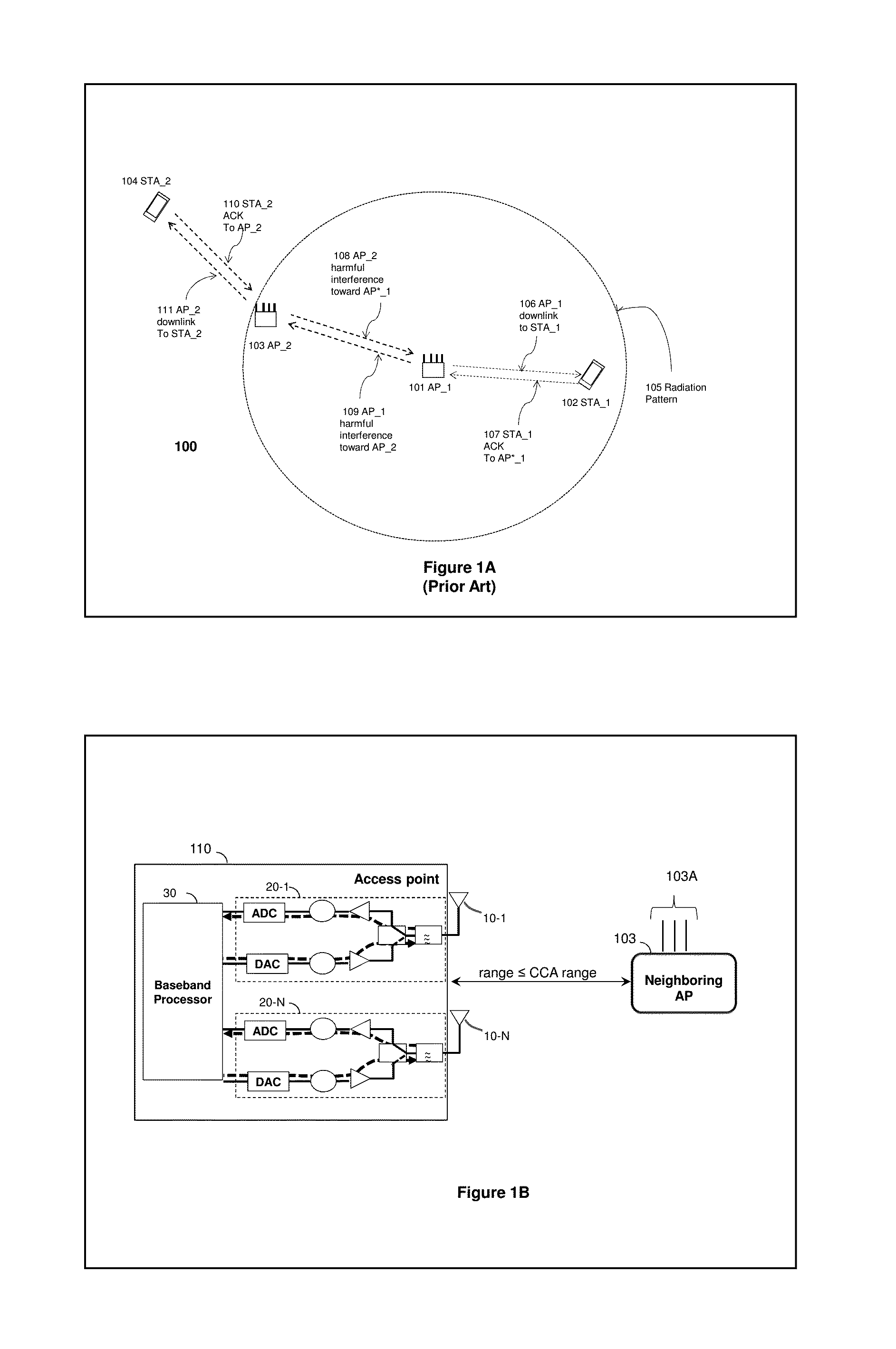
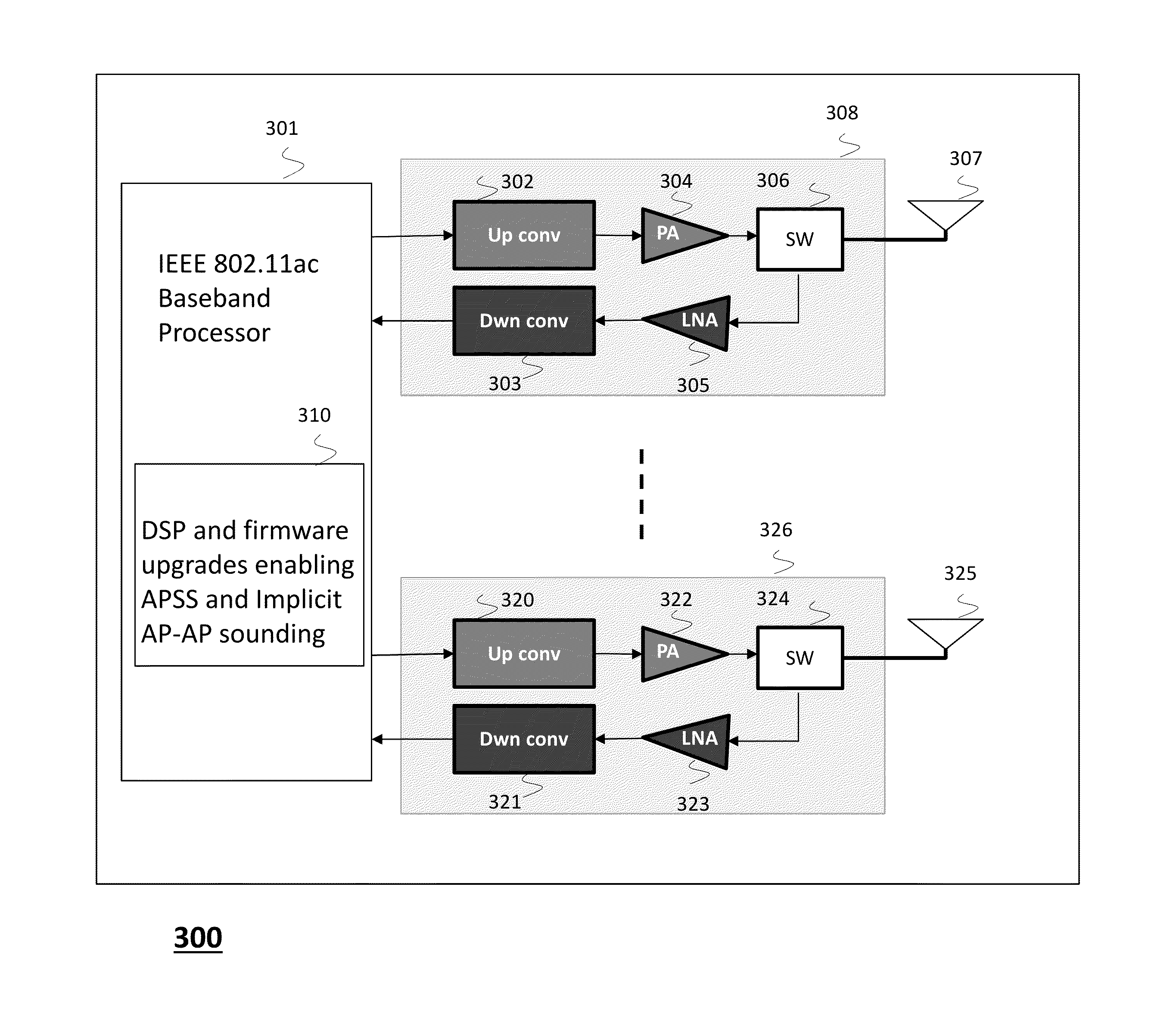
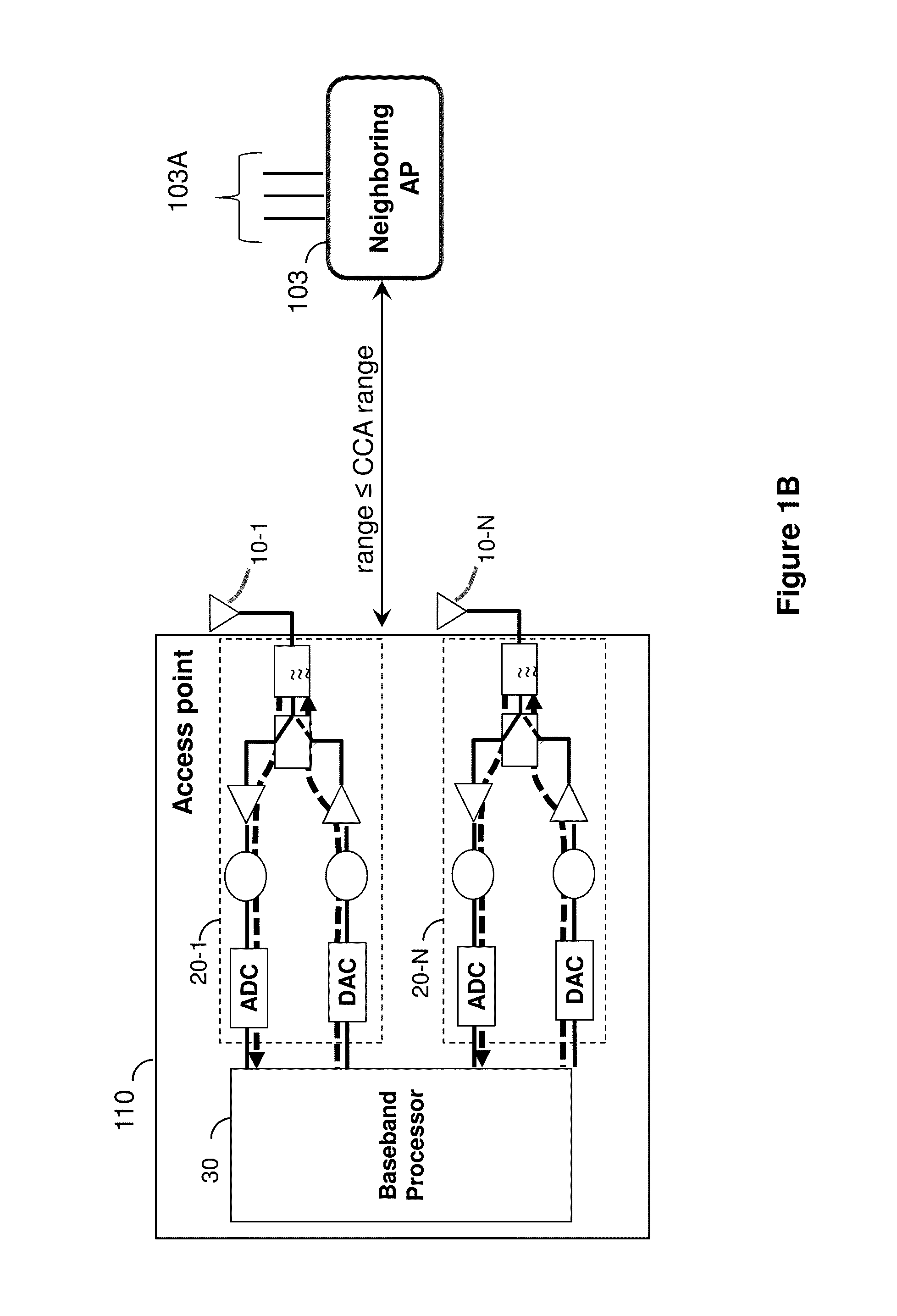
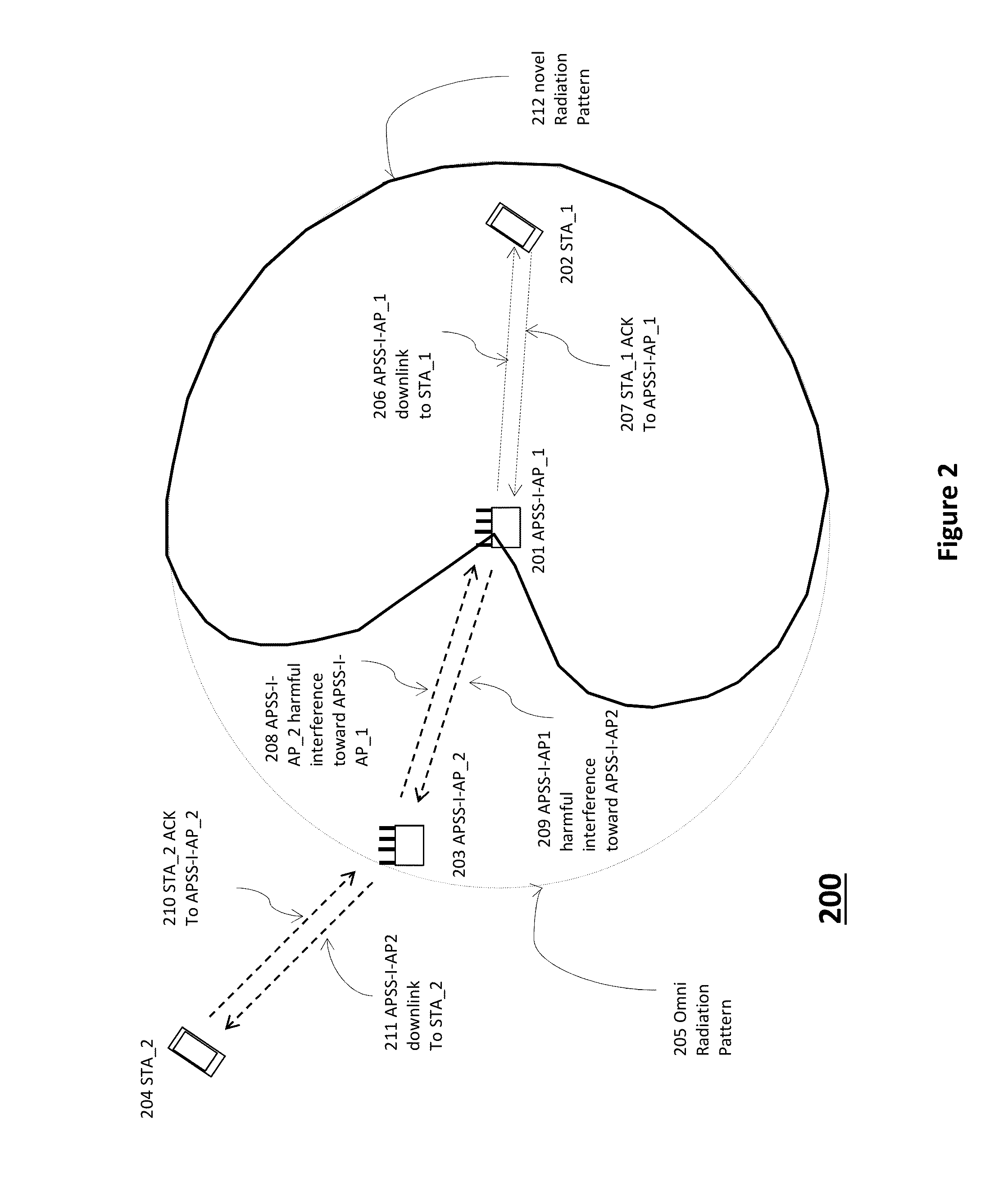
Method and system for explicit ap-to-ap sounding in an 802.11 network
InactiveUS20150341807A1Spatial transmit diversityCriteria allocationChannel state informationTelecommunications
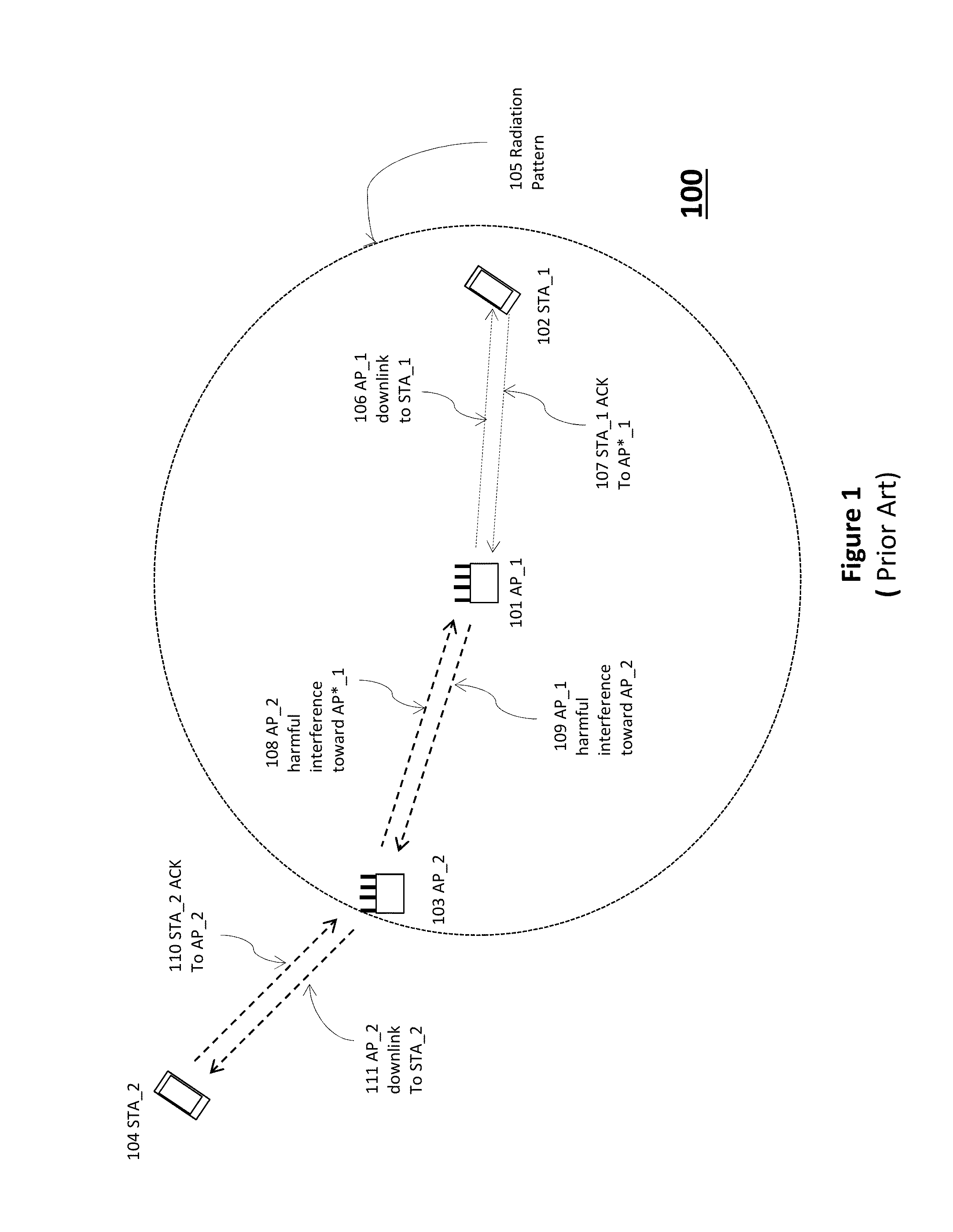
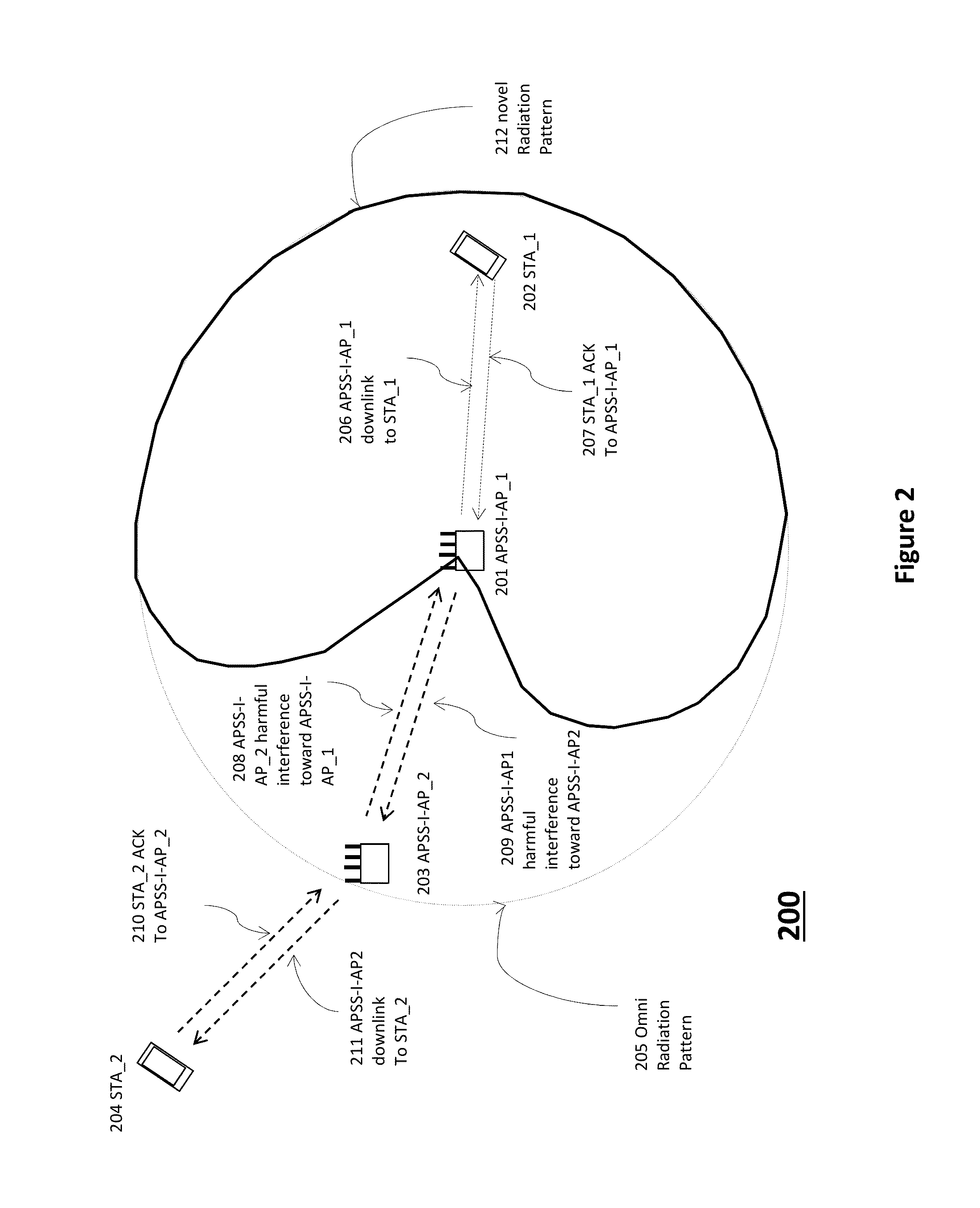
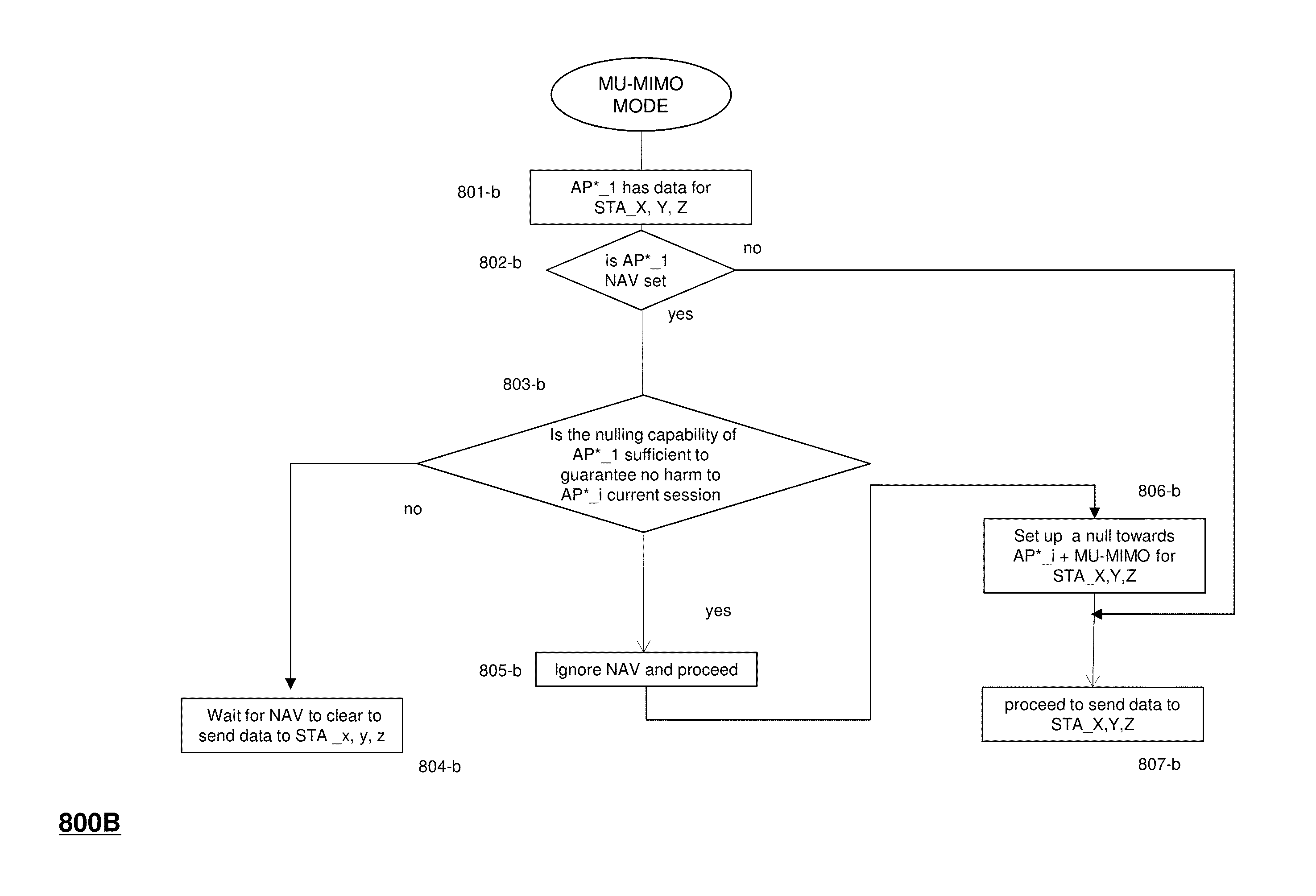
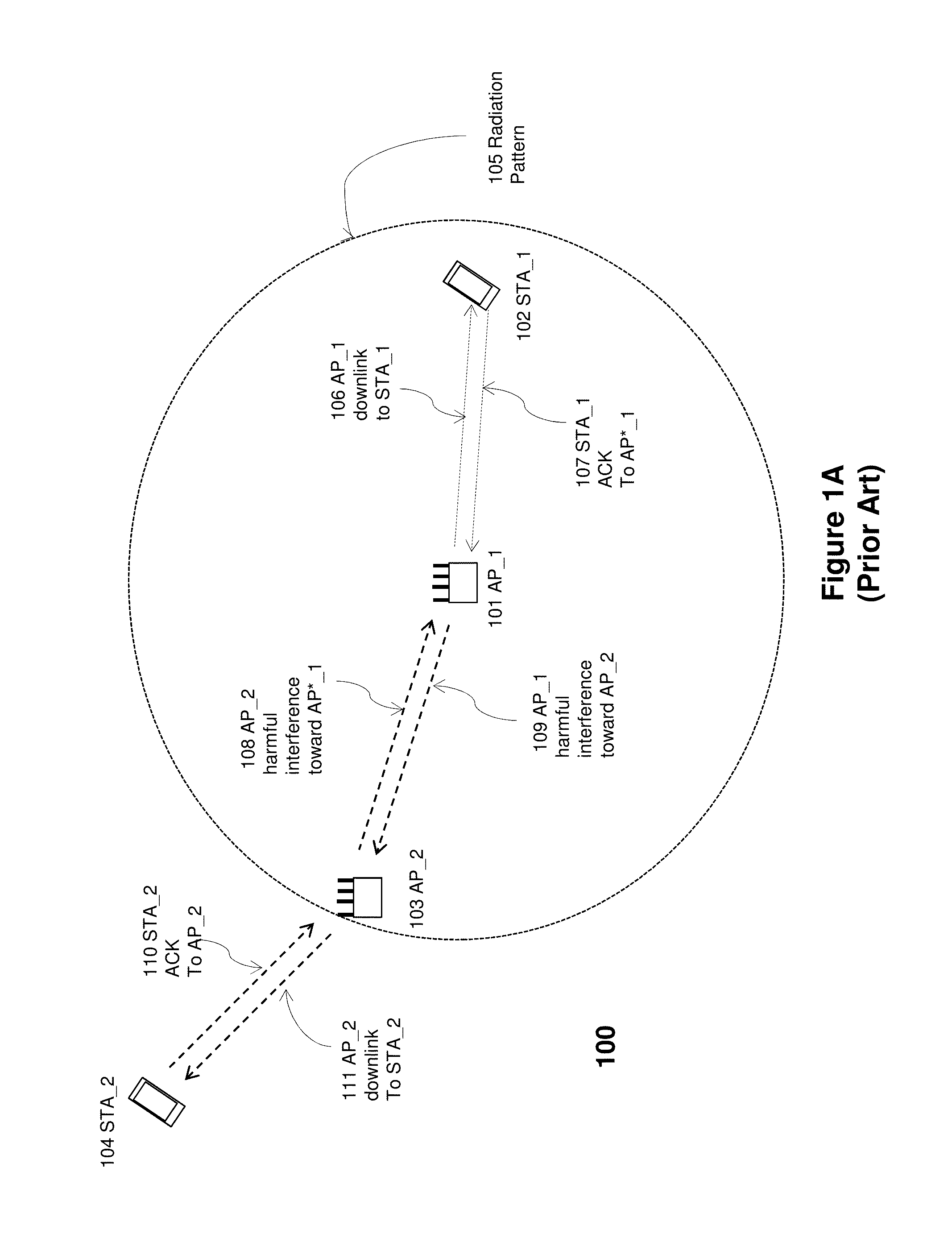
A method of one AP accessing a channel occupied by a neighboring AP within CCA range, by acquiring channel knowledge via performing cooperative sounding and setting a null towards the neighboring AP, under certain conditions verifications, is provided herein. The method may include: transmitting and receive signals via a plurality of radio circuitries connected to plurality of antennas; monitoring signals received by the radio circuitries and generating a list of neighboring co-channel access points that each has plurality of antennas and are further located within a clear channel assessment (CCA) range of the access point; and instructing the radio circuitries to transmit a sounding sequence to the list of neighboring access points, and receive Channel State Information (CSI).
Owner:MAGNOLIA BROADLAND INC
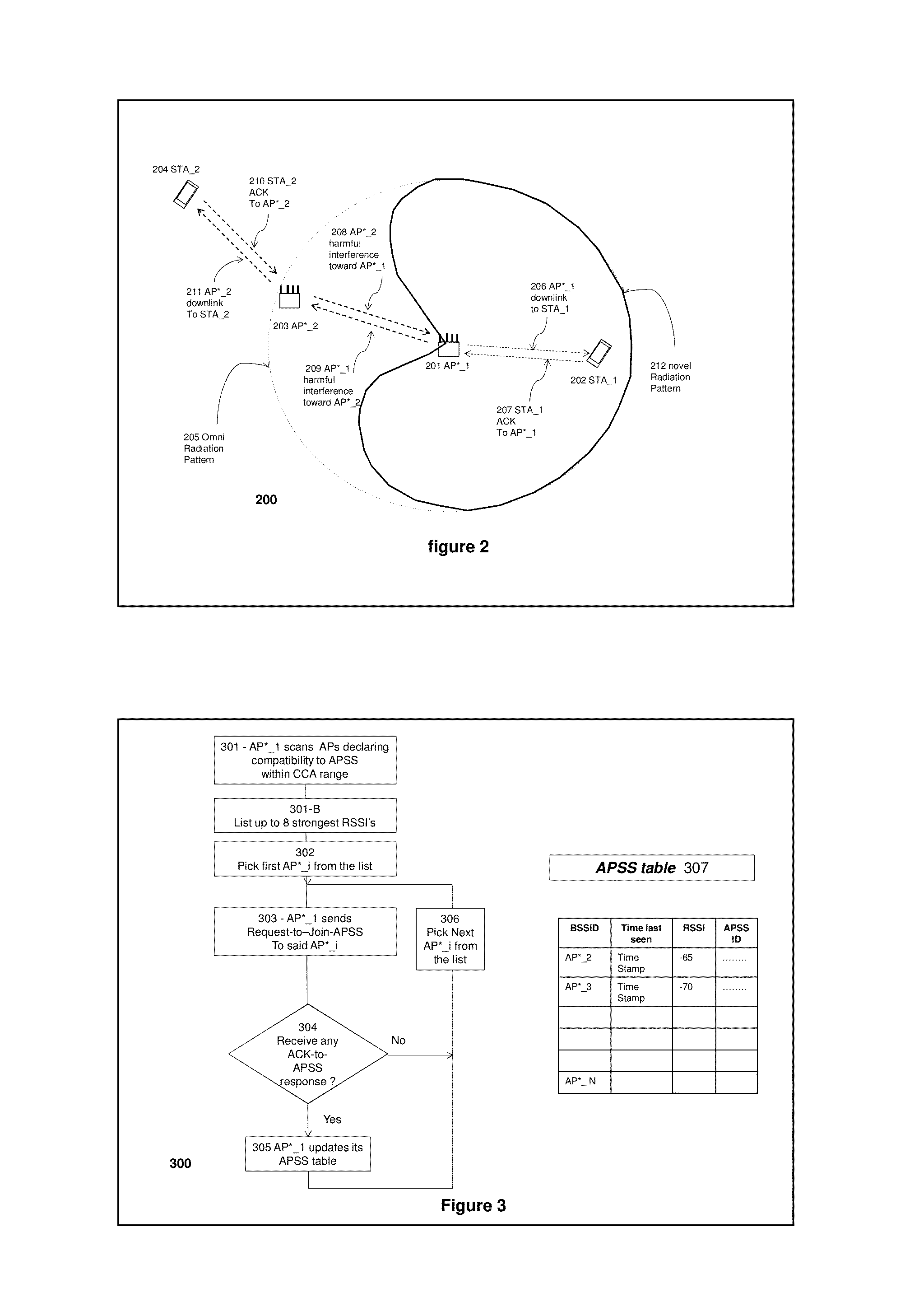
Method and system for supporting sparse explicit sounding by implicit data
ActiveUS20150270880A1Reduce distractionsSite diversitySpatial transmit diversityChannel assessmentComputer science
A method and apparatus for an access point (AP) accessing a channel occupied by a neighboring AP within clear channel assessment (CCA) range. The method is implemented by setting a transmit null towards the neighboring AP, while acquiring accurate channel knowledge with minimal bandwidth penalty to surrounding networks, via a combination of sparse explicit sounding, and a following implicit channel estimation of the neighboring APs for updating the explicit data achieved by the sparse explicit sounding. An AP implementing the method is also disclosed.
Owner:MAGNOLIA BROADLAND INC
Method and system for explicit AP-to-AP sounding in an 802.11 network
ActiveUS9100154B1Improve accuracySpatial transmit diversityError preventionChannel state informationTelecommunications
A method of one AP accessing a channel occupied by a neighboring AP within CCA range, by acquiring channel knowledge via performing cooperative sounding and setting a null towards the neighboring AP, under certain conditions verifications, is provided herein. The method may include: transmitting and receive signals via a plurality of radio circuitries connected to plurality of antennas; monitoring signals received by the radio circuitries and generating a list of neighboring co-channel access points that each has plurality of antennas and are further located within a clear channel assessment (CCA) range of the access point; and instructing the radio circuitries to transmit a sounding sequence to the list of neighboring access points, and receive Channel State Information (CSI).
Owner:MAGNOLIA BROADLAND INC
Cayley-encodation of unitary matrices for differential communication
InactiveUS7170954B2Maximize distanceModulated-carrier systemsRadio transmissionSkew-HermitianUnitary matrix
Differential unitary space-time (DUST) communication is a technique for communicating via one or more antennas by encoding the transmitted data differentially using unitary matrices at the transmitter, and decoding differentially without knowing the channel coefficients at the receiver. Since channel knowledge is not required at the receiver, DUST is ideal for use on wireless links where channel tracking is undesirable or infeasible. Disclosed are a class of Cayley codes for DUST communication that can produce sets of unitary matrices that work with any number of antennas, and has efficient encoding and decoding at any rate. The codes are named for their generation via the Cayley transform, which maps the highly nonlinear Stiefel manifold of unitary matrices to the linear space of skew-Hermitian matrices. The Cayley codes can be decoded using either successive nulling / cancelling or sphere decoding.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
Finding channel state information with reduced codebook in a multi-antenna wireless communication system
Multiple antennas employed at the transmitter (110) and receiver (120) can significantly increase a MIMO system (100) capacity, especially when channel knowledge is available at the transmitter (110). Channel state information may be provided to the transmitter (110) by the receiver (120) in a codebook based precoding feedback. In a proposed approach is proposed in which the receiver (120) conducts a search of precoder elements of a codebook to provide the transmitter (110) with rank information and precoder control index that enhances capacity. Unlike the conventional exhaustive search, the proposed approach reduces complexity by reducing the search space of precoder elements for consideration. Performance loss is minimized by reducing the search space of higher rank precoder elements. For some ranks, the complexity is reduced without any performance sacrifice by grouping the precoder elements of the rank into groups of equivalent capacities and including at most one precoder element from each group into the search space.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method for multiple antenna transmission
ActiveUS7499499B2Spatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsPhase correlationCommunications system
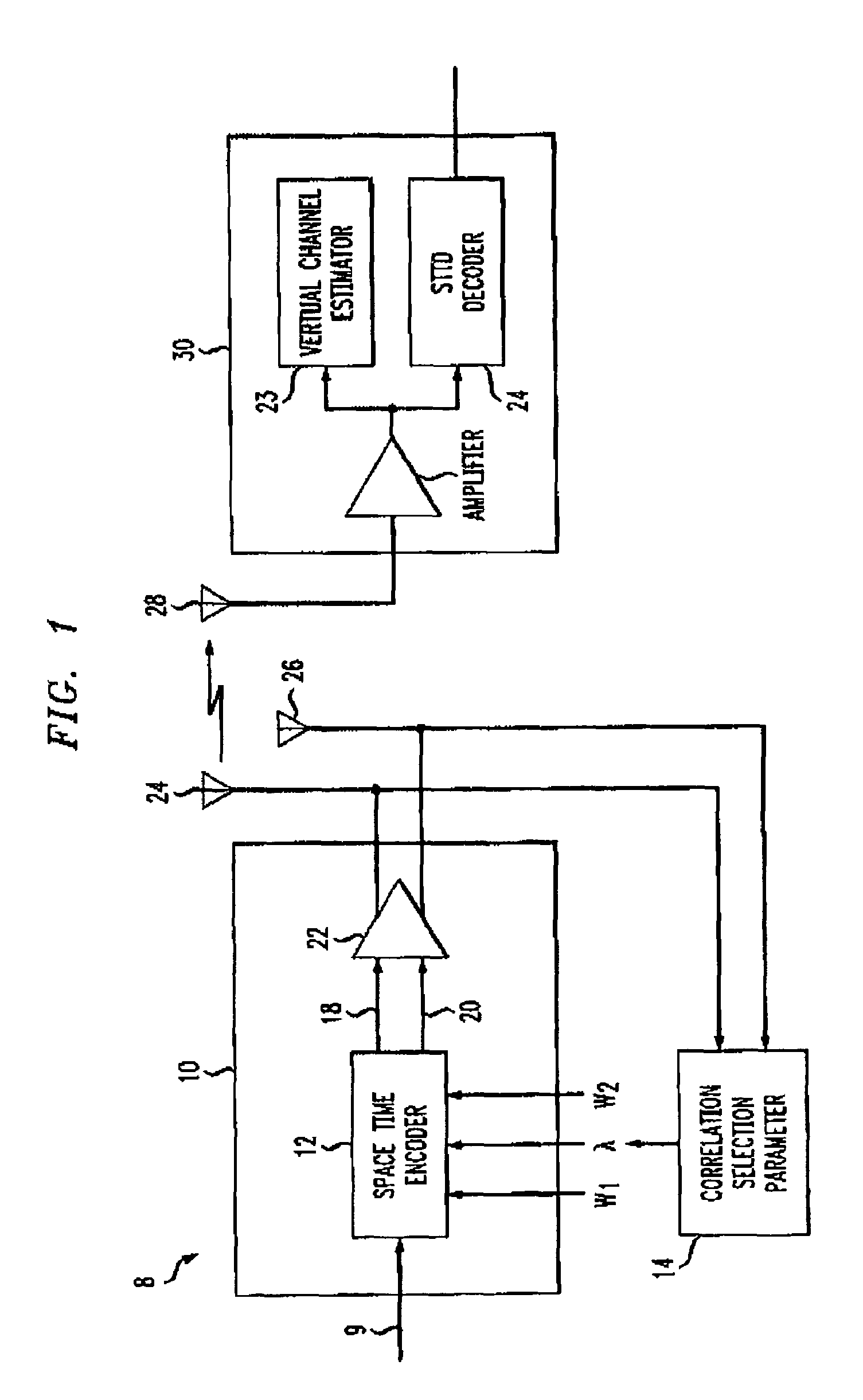
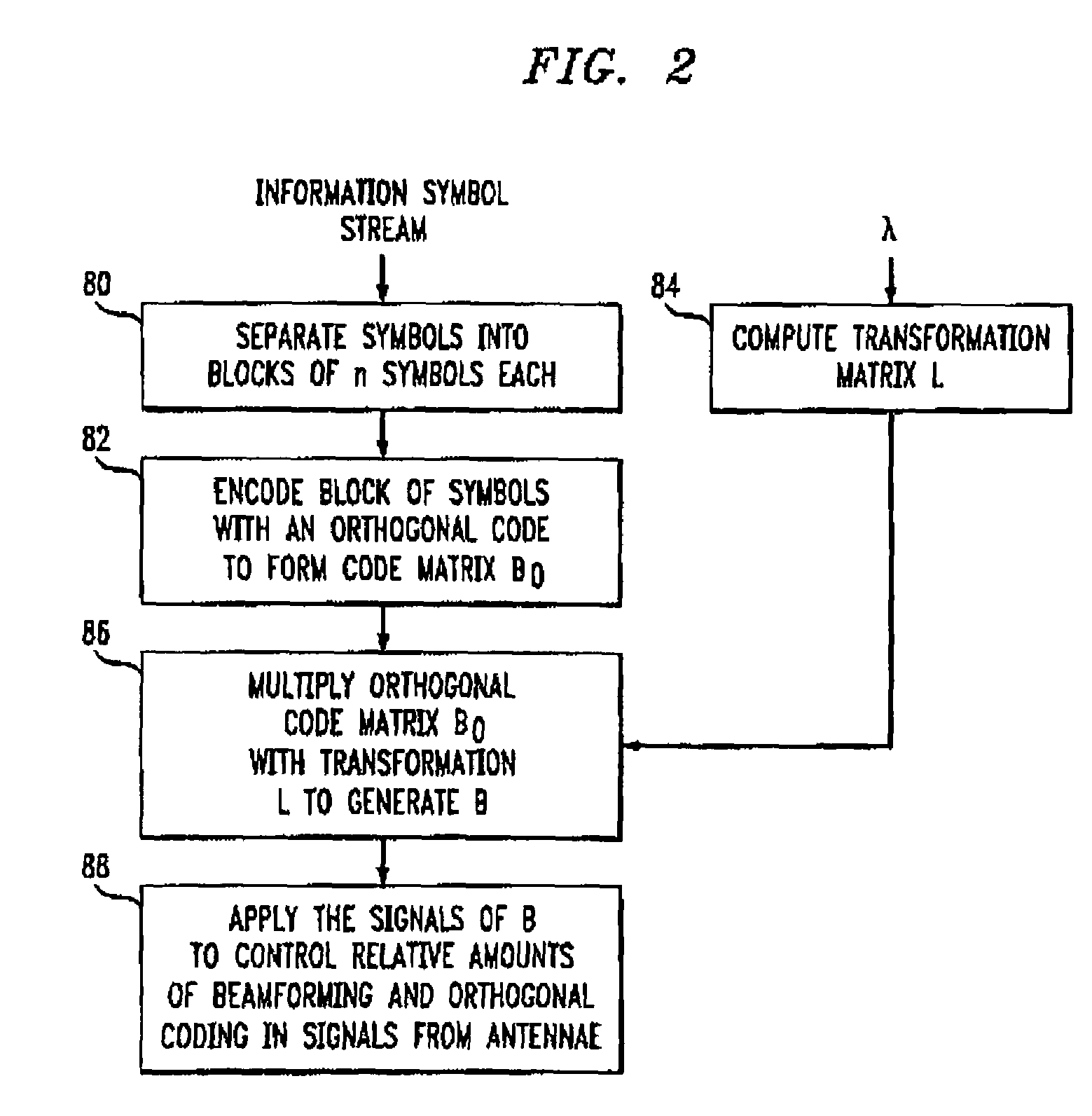
There is disclosed a duplex communication system having multiple antennae at the forward link transmitter. One method of transmitting a stream of information symbols from the antennae is by beamforming. With beamforming the transmitter typically operates in closed loop and uses channel information from the receiver to change beams in the forward link. Another approach employs orthogonal coding. Orthogonal coding can be simpler to implement because it can operate in an open loop system that is without channel knowledge at the transmitter. Each has its advantages and disadvantages. What is here disclosed is a method which is an alternative to using only beamforming or orthogonal coding. The signals transmitted from at least two antennae are by beamforming or orthogonal coding; or by beamforming in combination with orthogonal coding in a proportion that is determined by a reference value which is related to the differences between the signals from the antennae. The reference value can be related to the amplitude or phase of the signals and it can be either measured or estimated.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
Intelligent customer service multi-channel unified management system and method
InactiveCN109325778AImprove the convenience of operation and maintenanceImprove intelligenceCommerceKnowledge contentData management
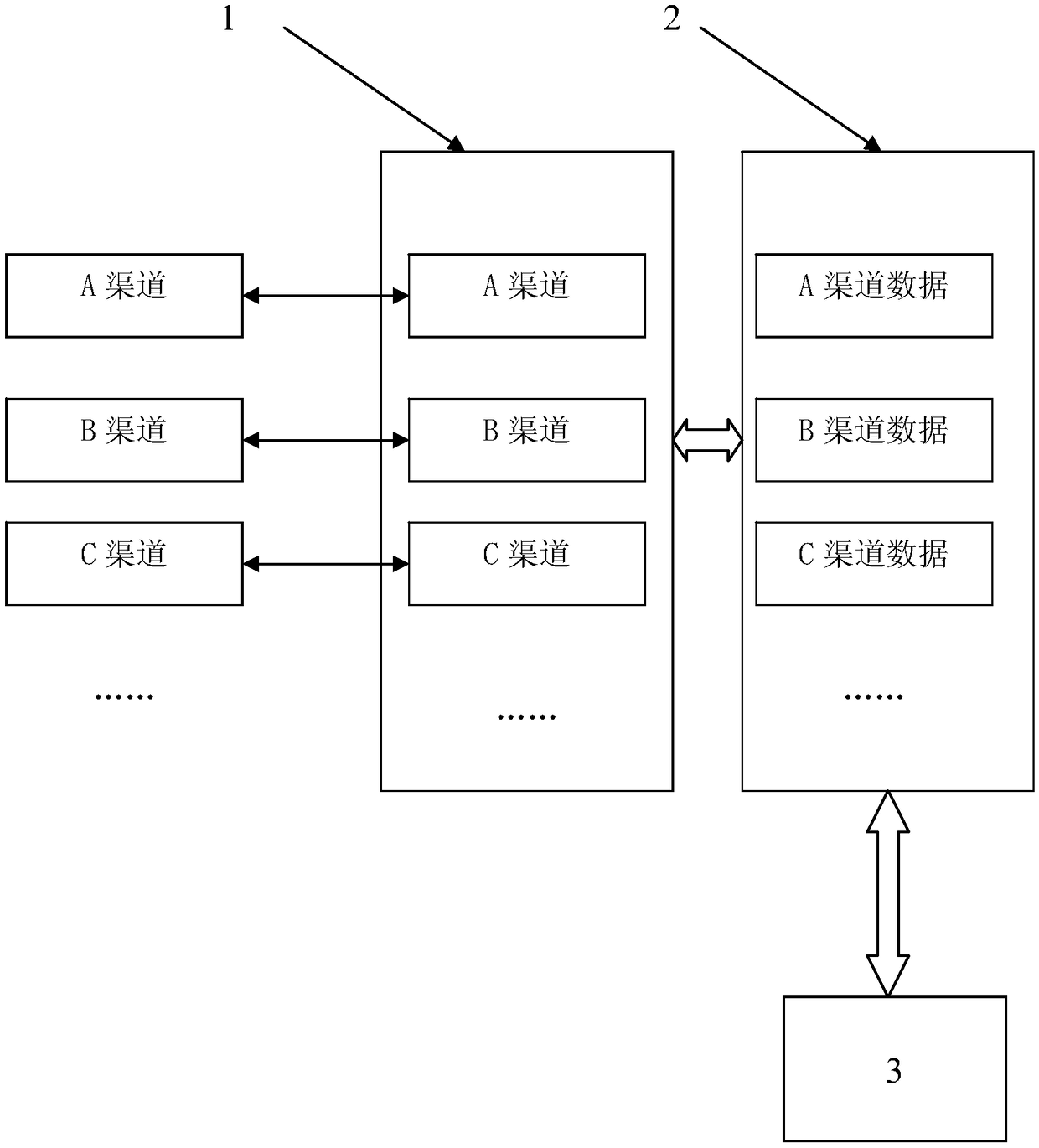
The invention relates to an intelligent customer service multi-channel unified management system and method. The purpose is to provide the intelligent customer service multi-channel unified managementsystem and method for realizing the data sharing. The intelligent customer service multi-channel unified management system includes: a channel communication identification module, a data storage module and a data management background. The channel communication identification module provides the functions of receiving external request communication and outputting result data, and the received request is transmitted to the data management background for acquiring corresponding data. The data management background stores and produces the unified response content; According to the different channels, the data storage module makes the reply content of the data management background into the channel reply data according to the characteristics of the channel, and forwards it to the channel communication identification module for distribution. The invention can maintain the knowledge content of different channels on the same platform, meanwhile, the data of different channels can be shared and used, and the separate maintenance of multiple output data is not required, thereby improving the operation and maintenance convenience.
Owner:国家电网有限公司客户服务中心
Beamforming with partial channel knowledge
An apparatus for use in transmit beamforming to a beamformee having NR receive antennas. The apparatus includes a controller configured to i) construct a partial channel matrix that describes a multiple input, multiple output (MIMO) channel between a beamformer and M receive antennas, wherein M is less than NR, and ii) generate L independent vectors using the partial channel matrix, wherein L is a rank of the partial channel matrix. When a number NS of one or more streams is greater than L, the controller is further configured to i) select the L independent vectors as steering vectors to steer L streams of the plurality of streams, and ii) select NS−L orthogonal vectors in a null space of the L independent vectors as steering vectors to steer a remainder of the streams in the plurality of streams.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Method and system for supporting sparse explicit sounding by implicit data
InactiveUS9172446B2Reduce distractionsSite diversitySpatial transmit diversityChannel assessmentComputer science
A method and apparatus for an access point (AP) accessing a channel occupied by a neighboring AP within clear channel assessment (CCA) range. The method is implemented by setting a transmit null towards the neighboring AP, while acquiring accurate channel knowledge with minimal bandwidth penalty to surrounding networks, via a combination of sparse explicit sounding, and a following implicit channel estimation of the neighboring APs for updating the explicit data achieved by the sparse explicit sounding. An AP implementing the method is also disclosed.
Owner:MAGNOLIA BROADLAND INC
System and method for transmitter and receiver operation for multiple-input, multiple-output communications based on prior channel knowledge
ActiveUS8699606B2Reduce complexityImprove performanceError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsData miningMultiple input
A system and method for transmitter and receiver operation for multiple-input, multiple-output (MIMO) communications based on prior channel knowledge are provided. A method for receiver operations includes receiving a data block, determining if there is confidence in information related to a channel, detecting data in the data block with a first detector in response to determining that there is confidence in the information, and detecting the data in the data block with a second detector in response to determining that there is no confidence in the information. The data block is received over the channel.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
System for acquiring channel knowledge and method thereof
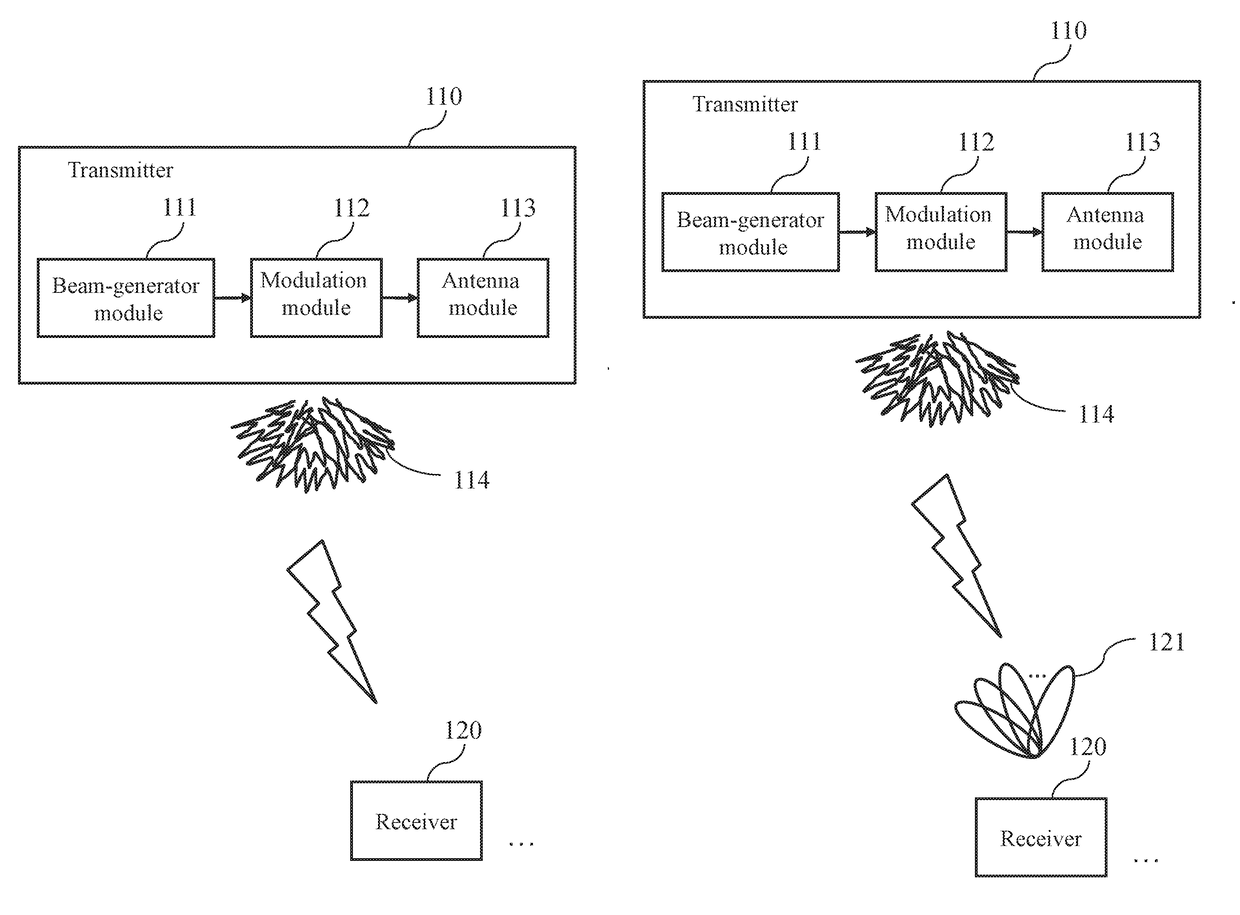
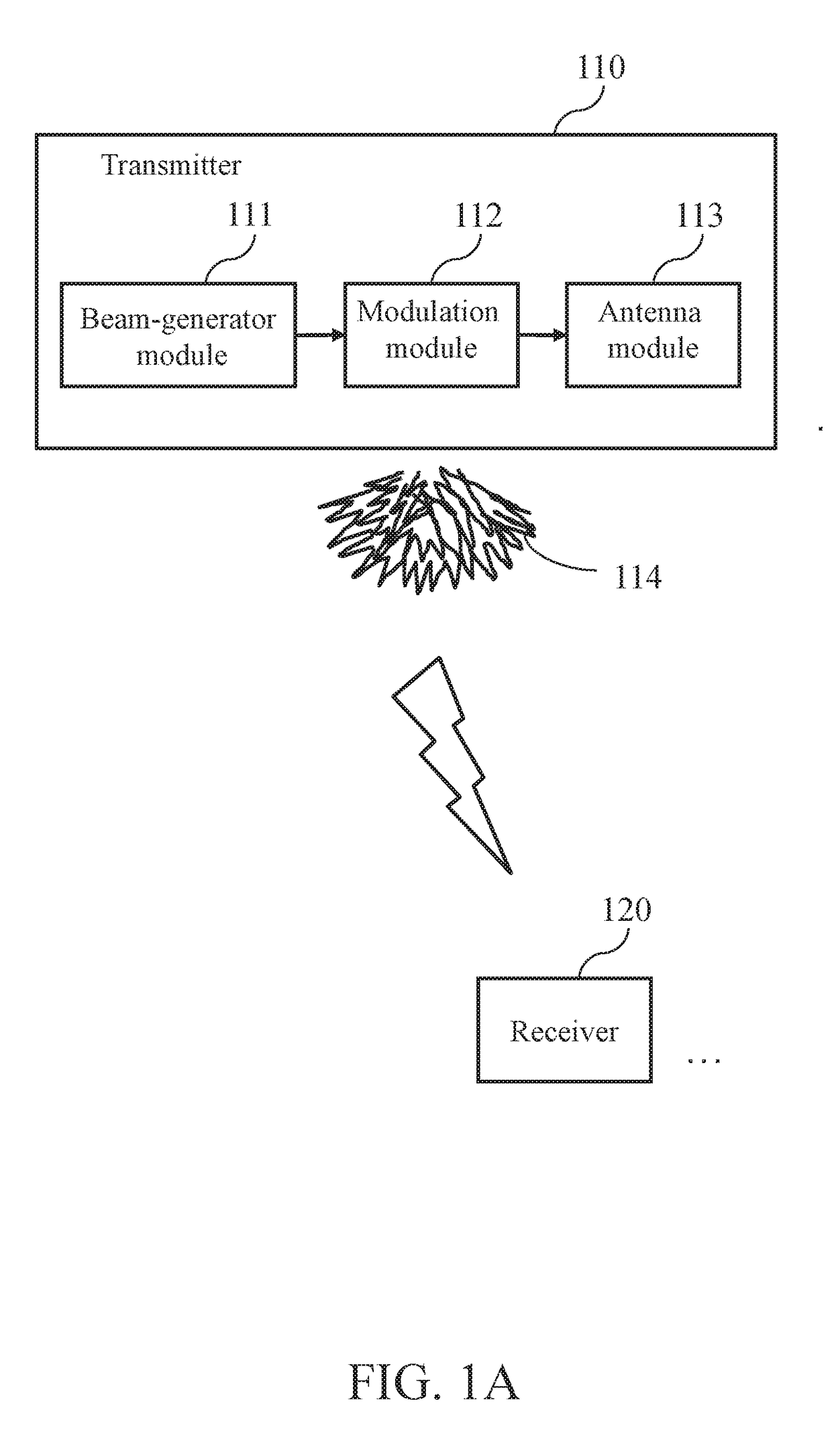
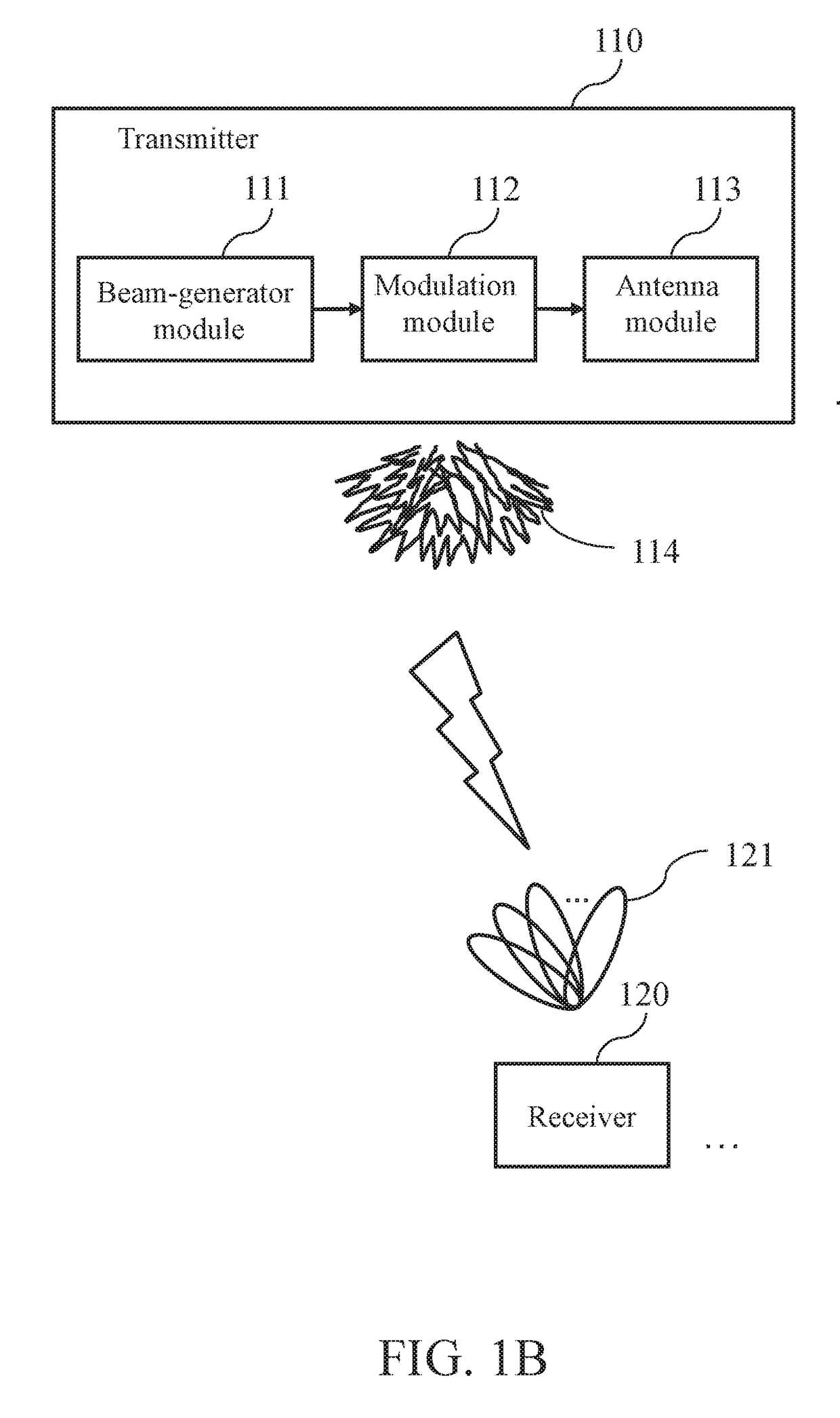
ActiveUS20170272132A1Reduce training overheadSpatial transmit diversityChannel estimationRelevant informationEngineering
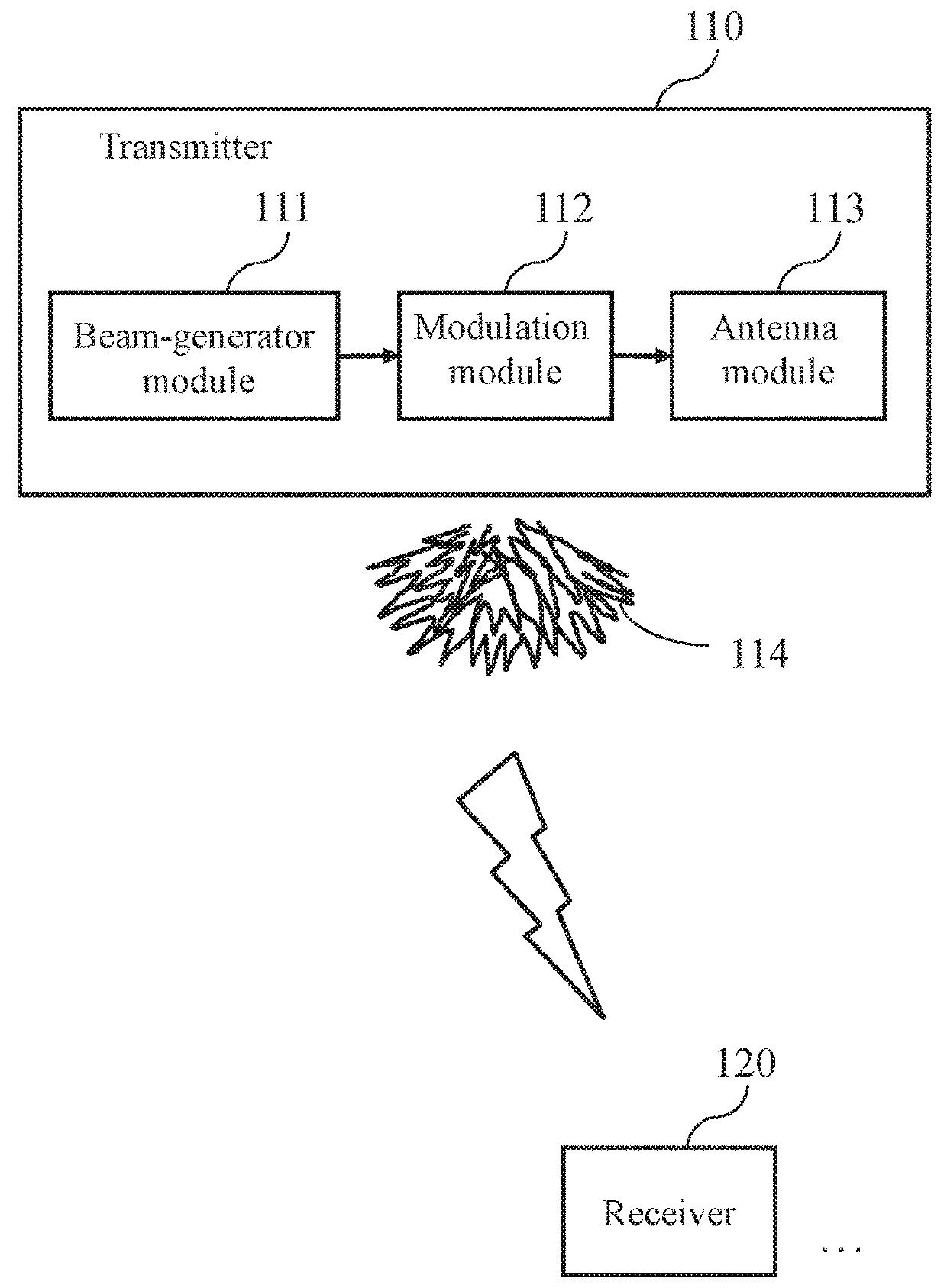
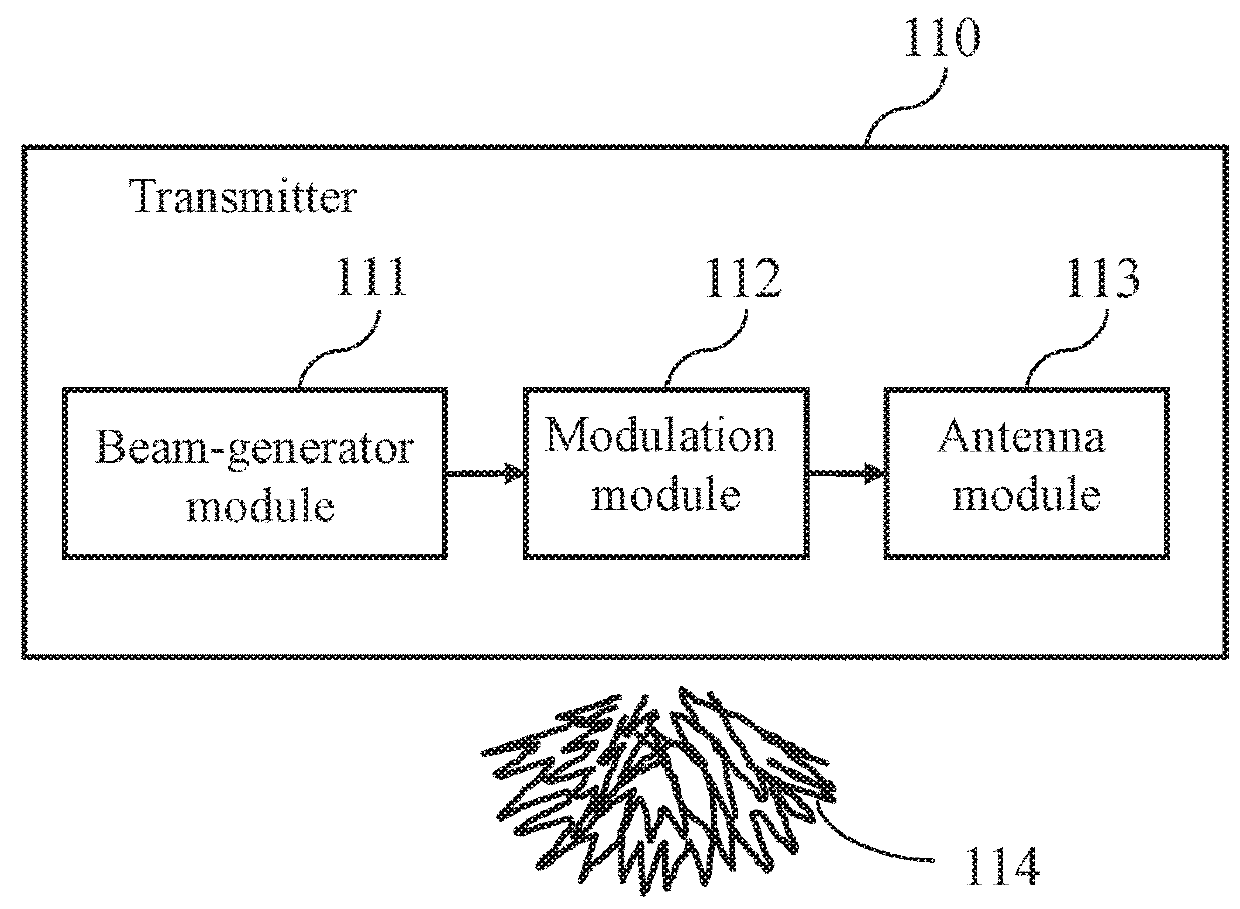
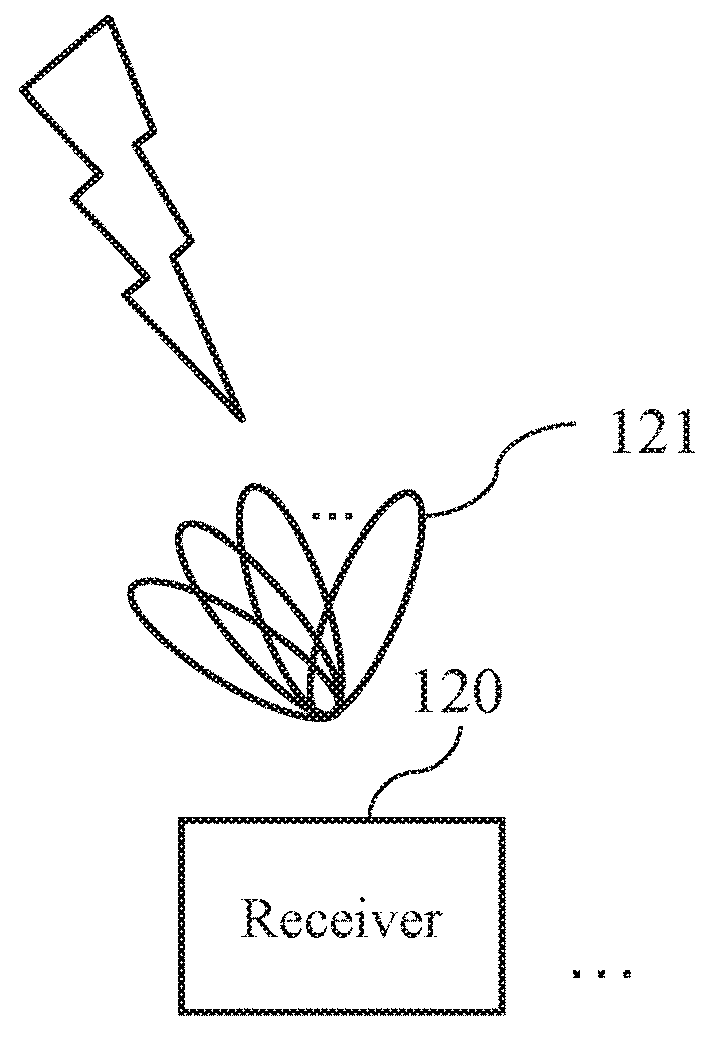
A system for acquiring channel knowledge and a method thereof are provided. At least one transmitter generates multiple directional beams in different directions, next modulates the directional beams in the different directions by means of at least one spreading sequence, so as to enlarge the beam range of each directional beam in the different directions and use the modulated directional beams as training-specific beams in the different directions, and sweeps the training-specific beams in the different directions by means of a plurality of antennas, so that at least one receiver measures at least one training-specific beam, and determines the channel knowledge according to the measurement result and beam-related information associated with the at least one training-specific beam, so as to achieve a technical effect of reducing training overhead.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC +1
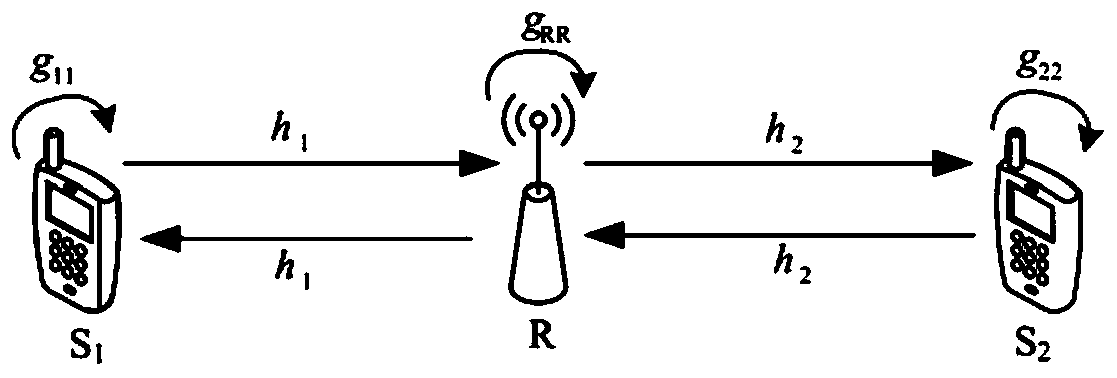
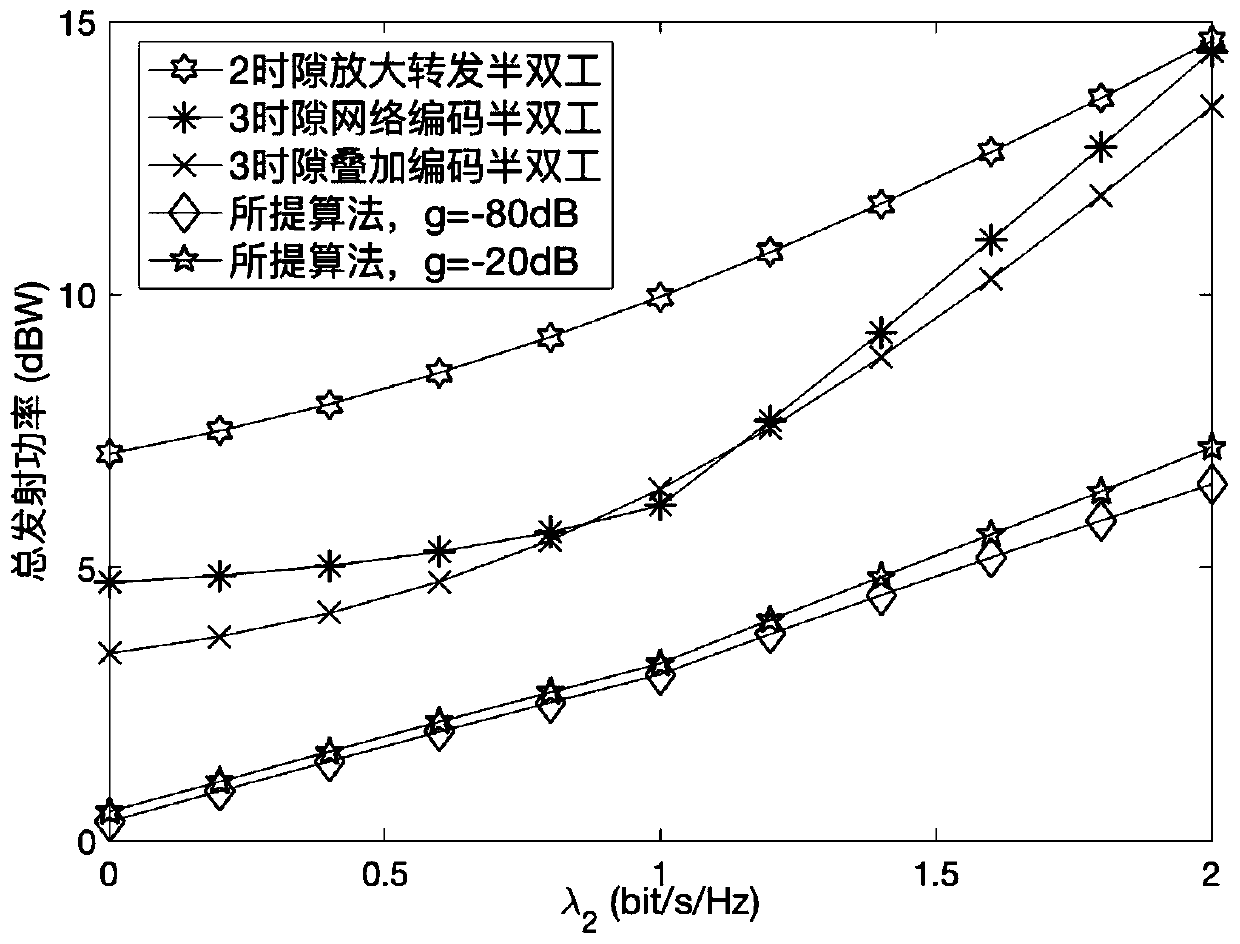
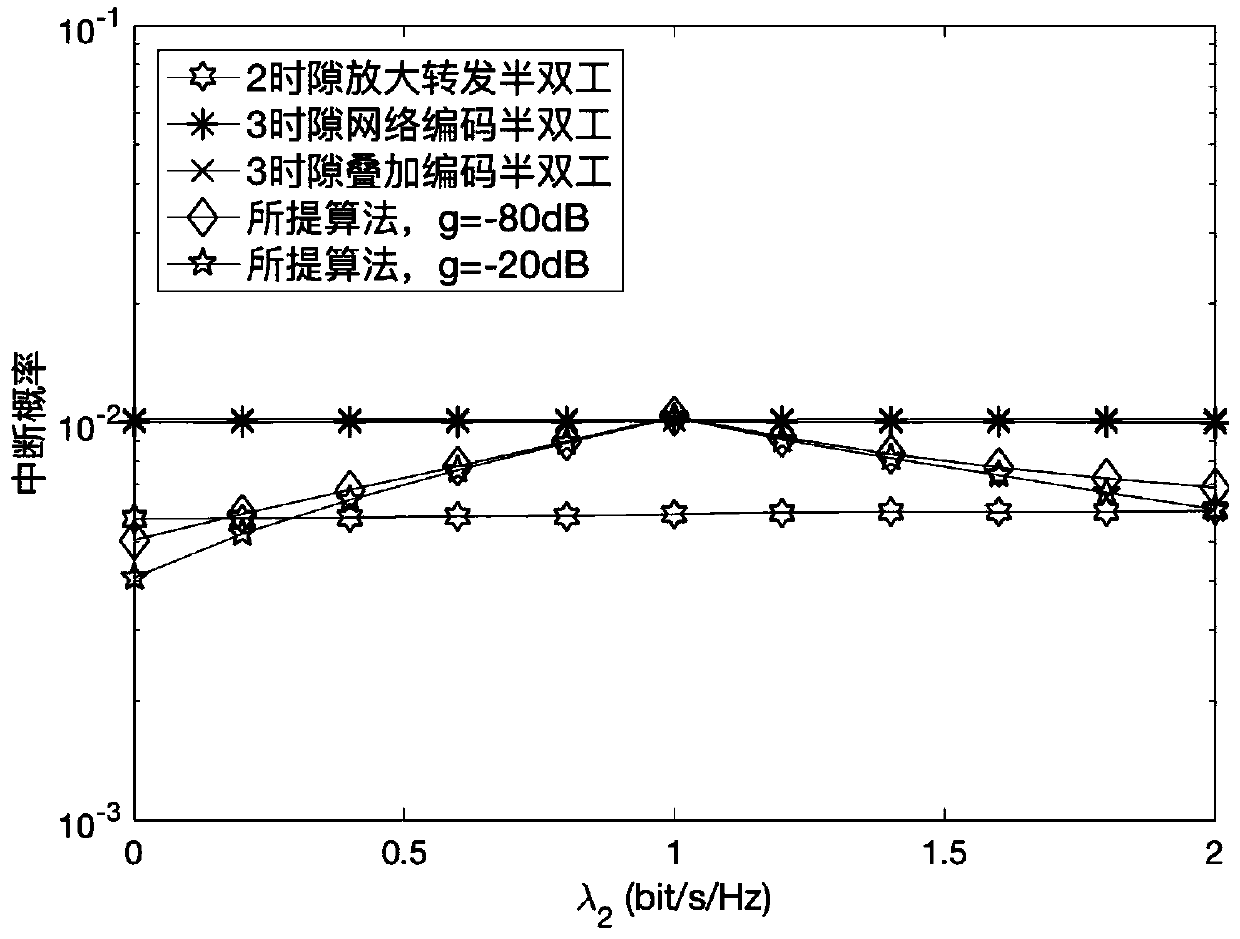
Method for controlling node transmitting power of full duplex bidirectional relay system
The invention discloses a method for controlling the node transmitting power of a full duplex bidirectional relay system, which is suitable for a decoding and forwarding full duplex bidirectional relay system adopting superposition coding. The method aims to minimize the node transmitting power sum by taking the QoS requirement of the system and the limitation of superposition coding power distribution factor values as constraint conditions. By utilizing channel knowledge and according to the requirement of a source node on a data rate, the transmitting power of transmitters of the source nodeand a relay node and a superimposed coded power distribution factor at the relay node are dynamically adjusted, and the sum of the transmitting power of the nodes is minimized under the condition ofmeeting the QoS requirement of a system.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
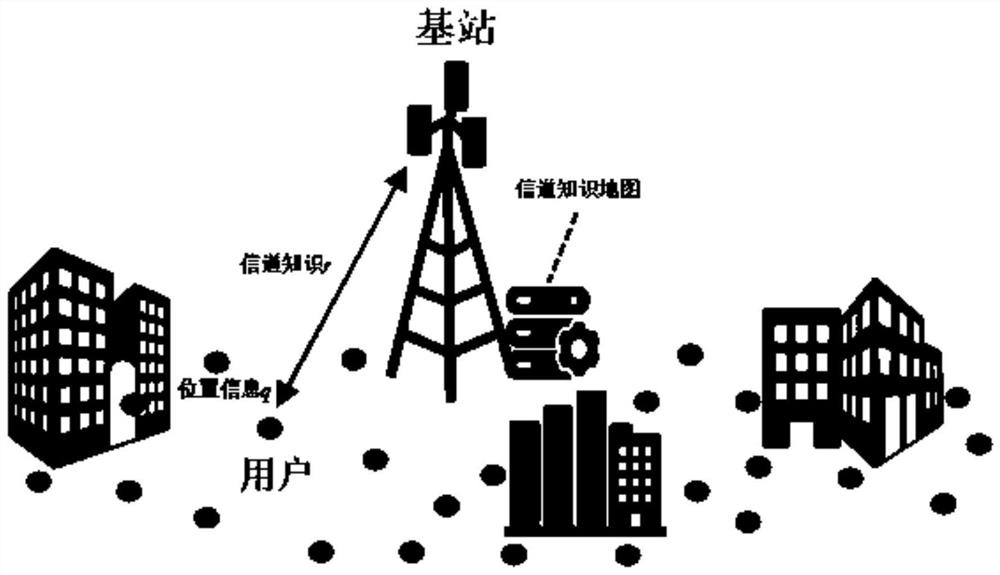
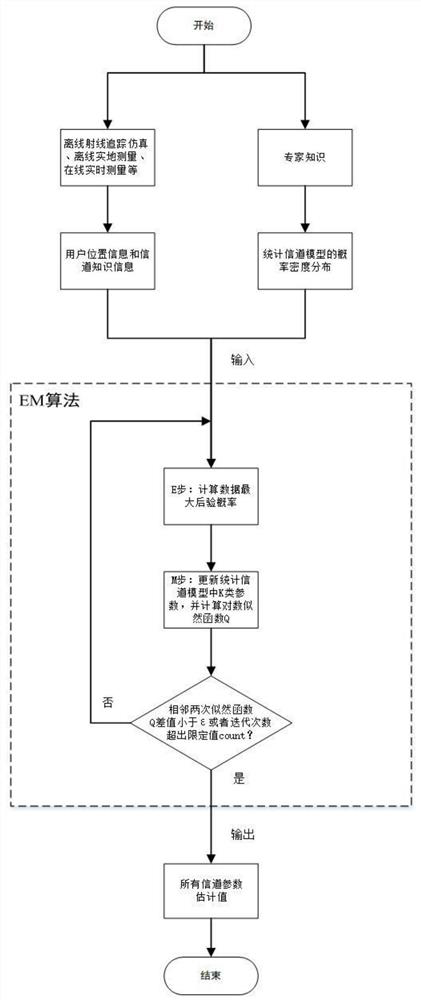
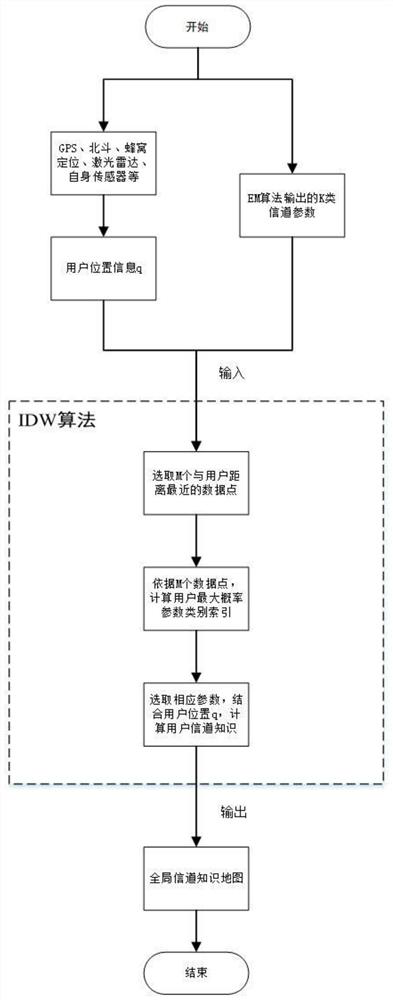
Channel knowledge map construction method based on expectation maximization algorithm
PendingCN113938935AReduce storage capacity requirementsAvoid Huge Data VolumesCharacter and pattern recognitionTransmission monitoringExpectation–maximization algorithmChannel state information
The invention discloses a channel knowledge map construction method based on an expectation maximization algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining channel knowledge data of a local communication environment through any mode of offline ray tracing simulation, offline field measurement or online real-time measurement; carrying out statistical modeling on related channel knowledge according to expert knowledge, estimating K-class parameters of a mixed statistical model by using an EM algorithm, and constructing a channel knowledge map reflecting a local signal propagation environment; and when a user needs to communicate, obtaining real-time position information through GPS, Beidou, cellular positioning, laser radar and self-sensor positioning modes, and obtaining channel knowledge of a target position by using the previously constructed channel knowledge map and a mode based on inverse distance weighting. Therefore, the method is used for environment perception adaptive communication. According to the invention, the problems of low accuracy, large data storage capacity demand and high training complexity of a channel prediction method based on a pure model or pure data are solved, so that the cost for acquiring real-time channel state information is reduced.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Recognition method and device for non-standard channel name
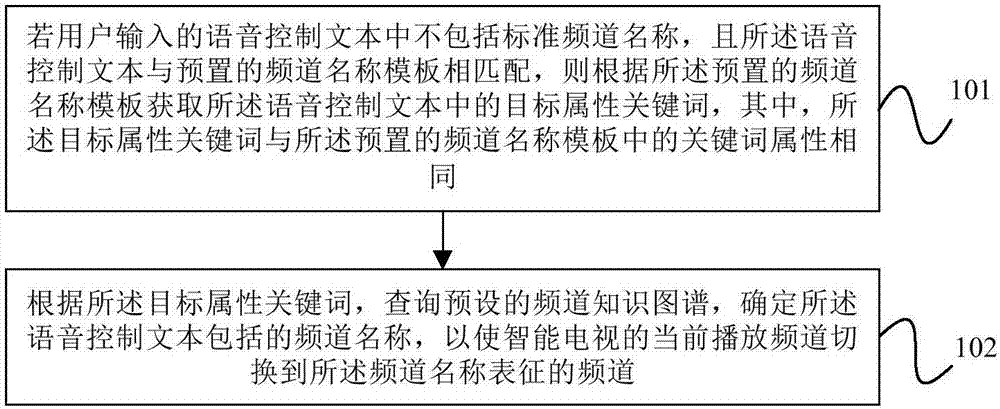
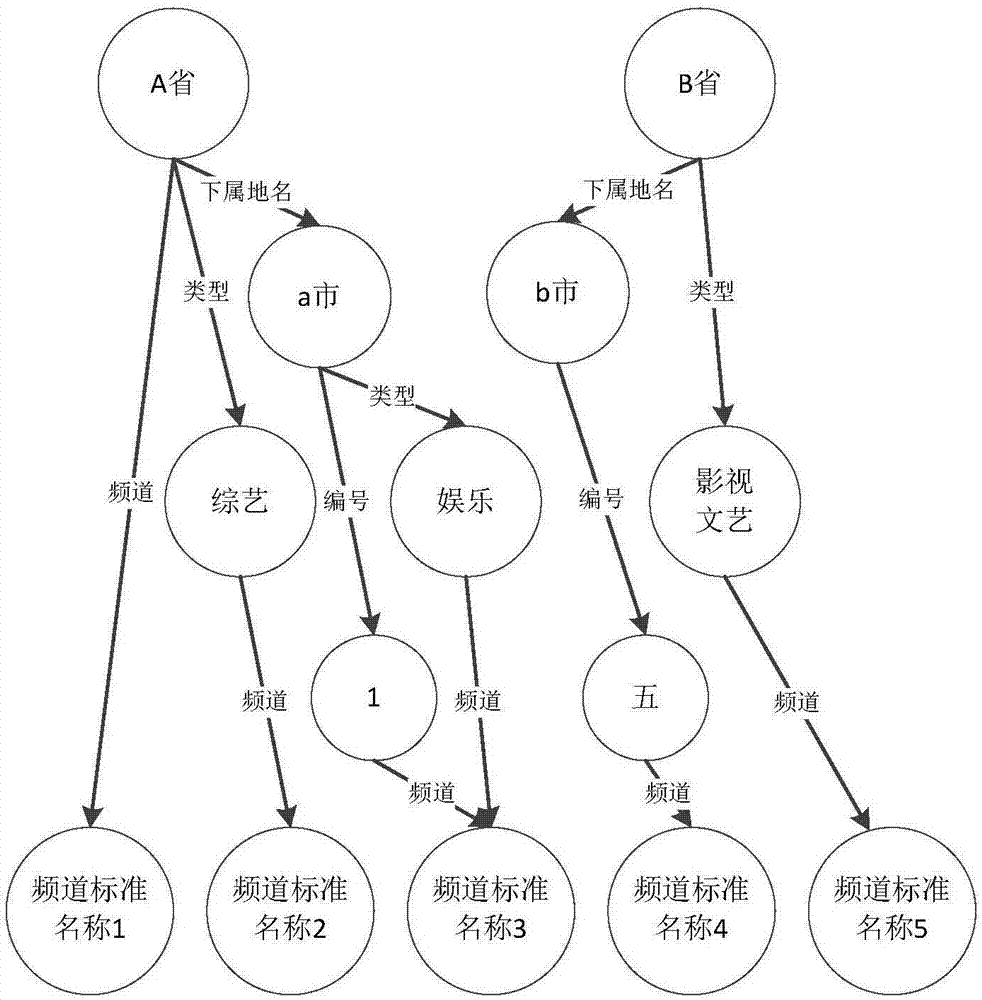
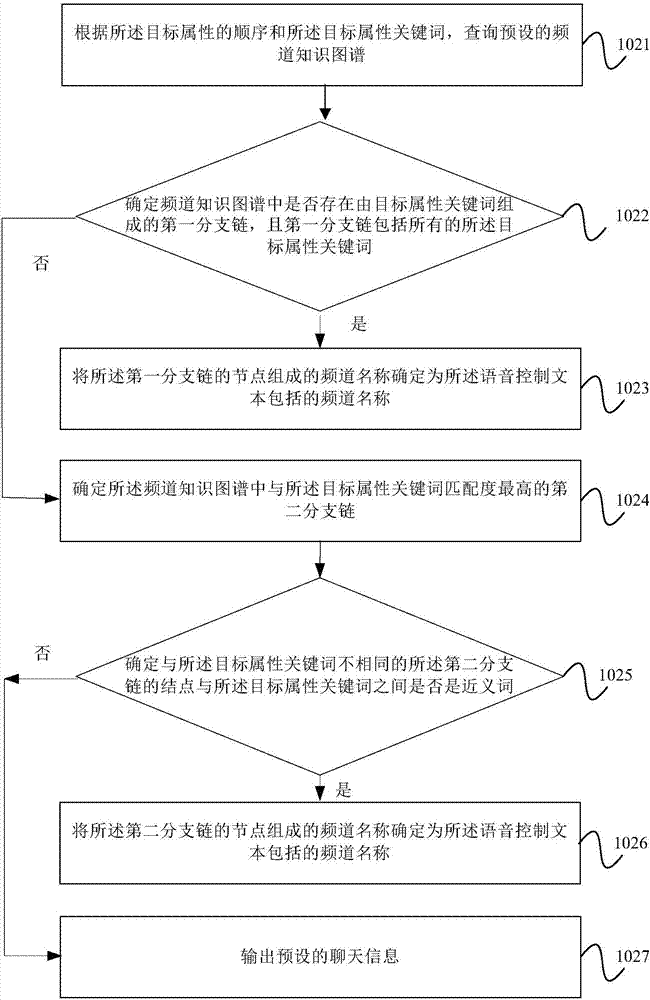
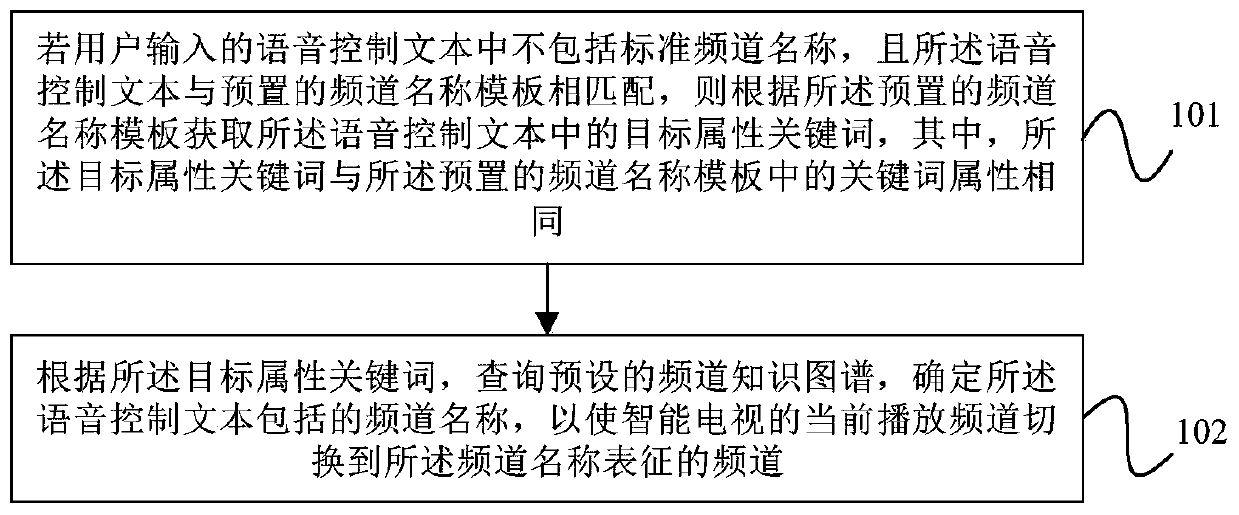
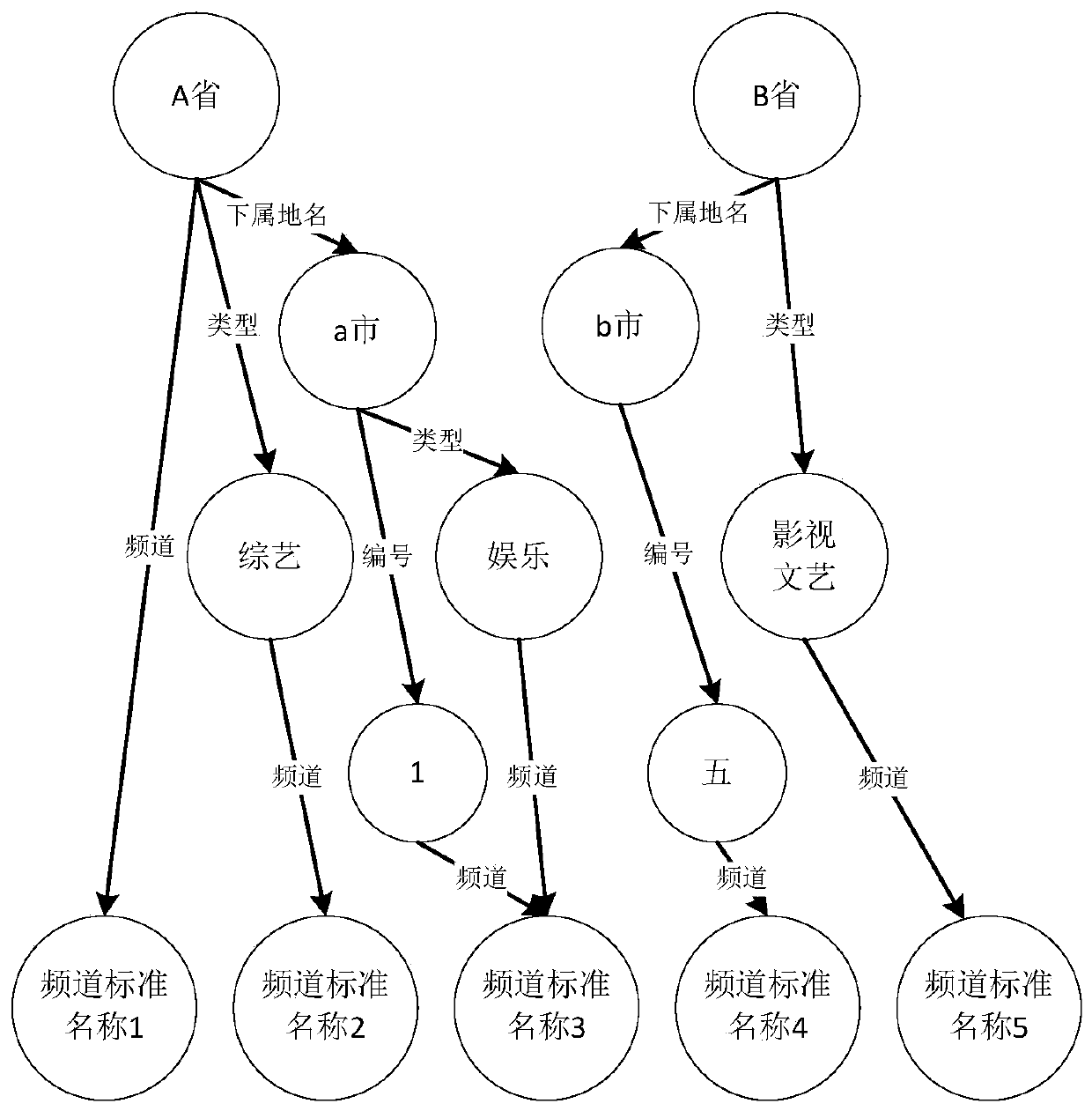
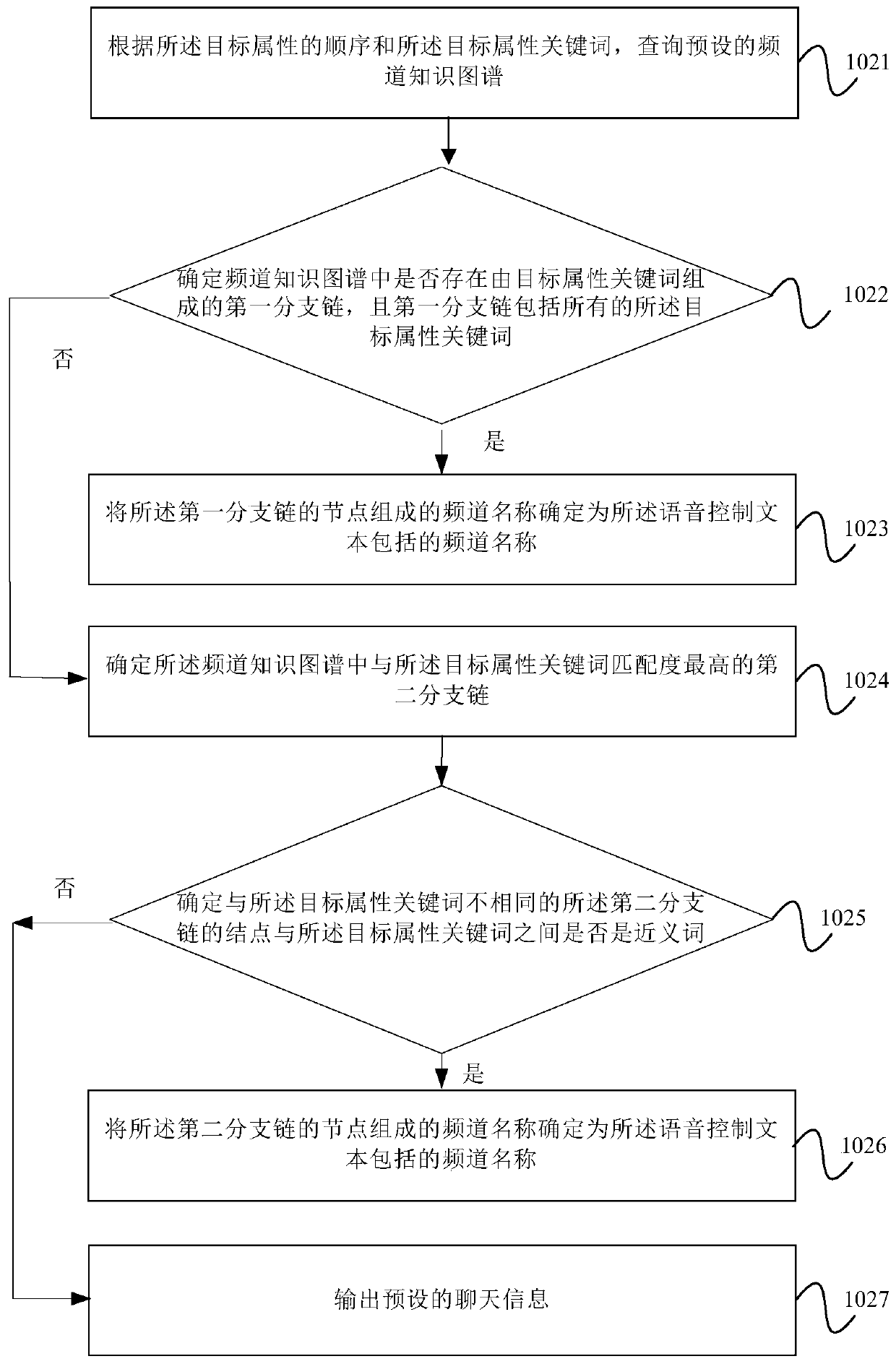
ActiveCN107027065AImprove experienceAccurate identificationSelective content distributionUser inputSpeech sound
The embodiment of the invention provides a recognition method and a recognition device for a non-standard channel name. The method comprises the steps of if a speech control text input by a user does not include a standard channel name and matched with a preset channel name template, acquiring a target attribute keyword included in the speech control text according to the preset channel name template, wherein the target attribute keyword and the keyword in the preset channel name templates are the same in attribute; and querying a preset channel knowledge graph according to the target attribute keyword to determine the channel name included by the speech control text, thus allowing a smart television to be switched to a channel indicated by the channel name from the current playing channel. According to the recognition method and the recognition device for the non-standard channel name provided by the embodiment of the invention, a recognition rate of the non-standard channel name during a speech interaction process can be improved, and user experience can be enhanced.
Owner:HISENSE
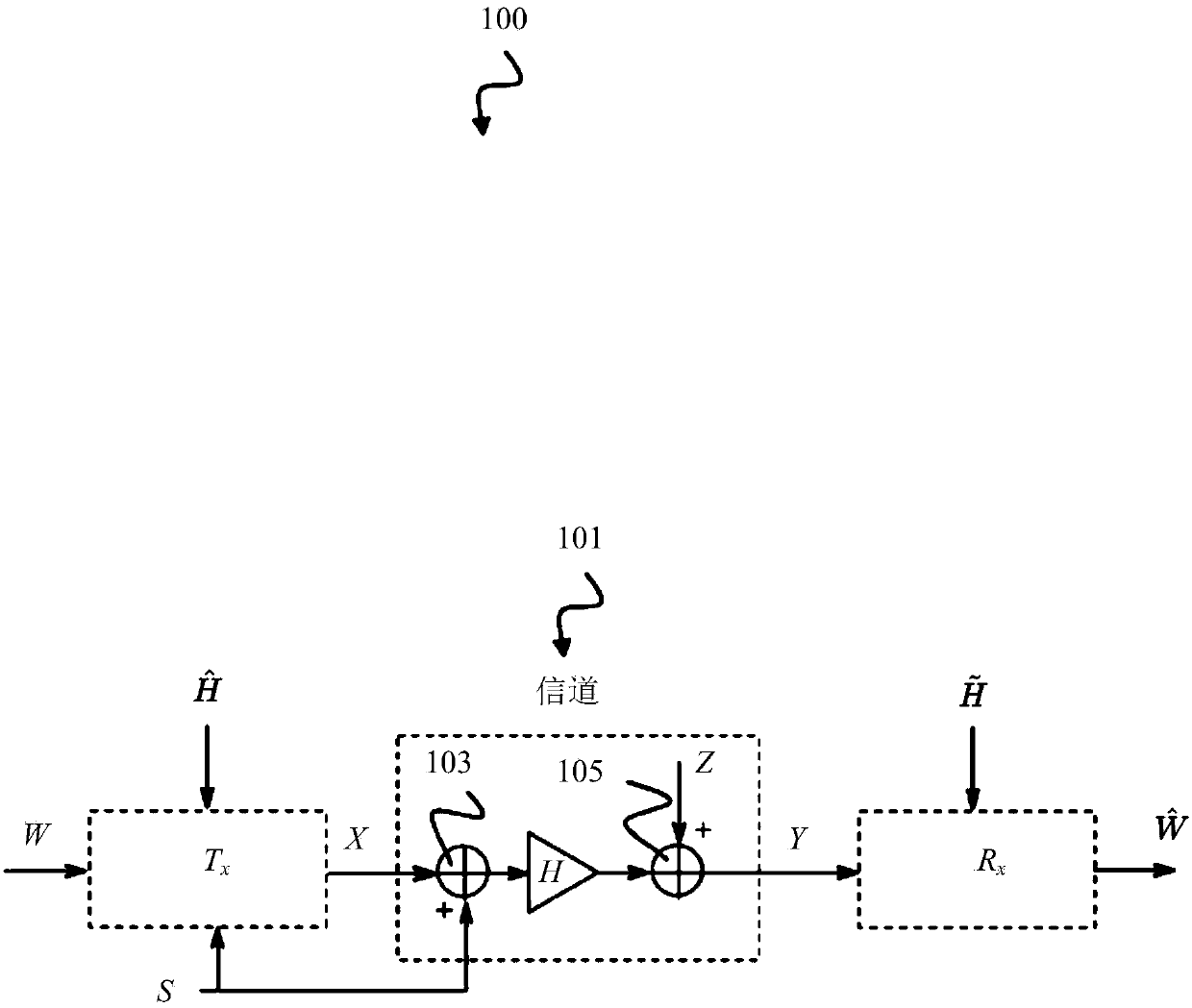
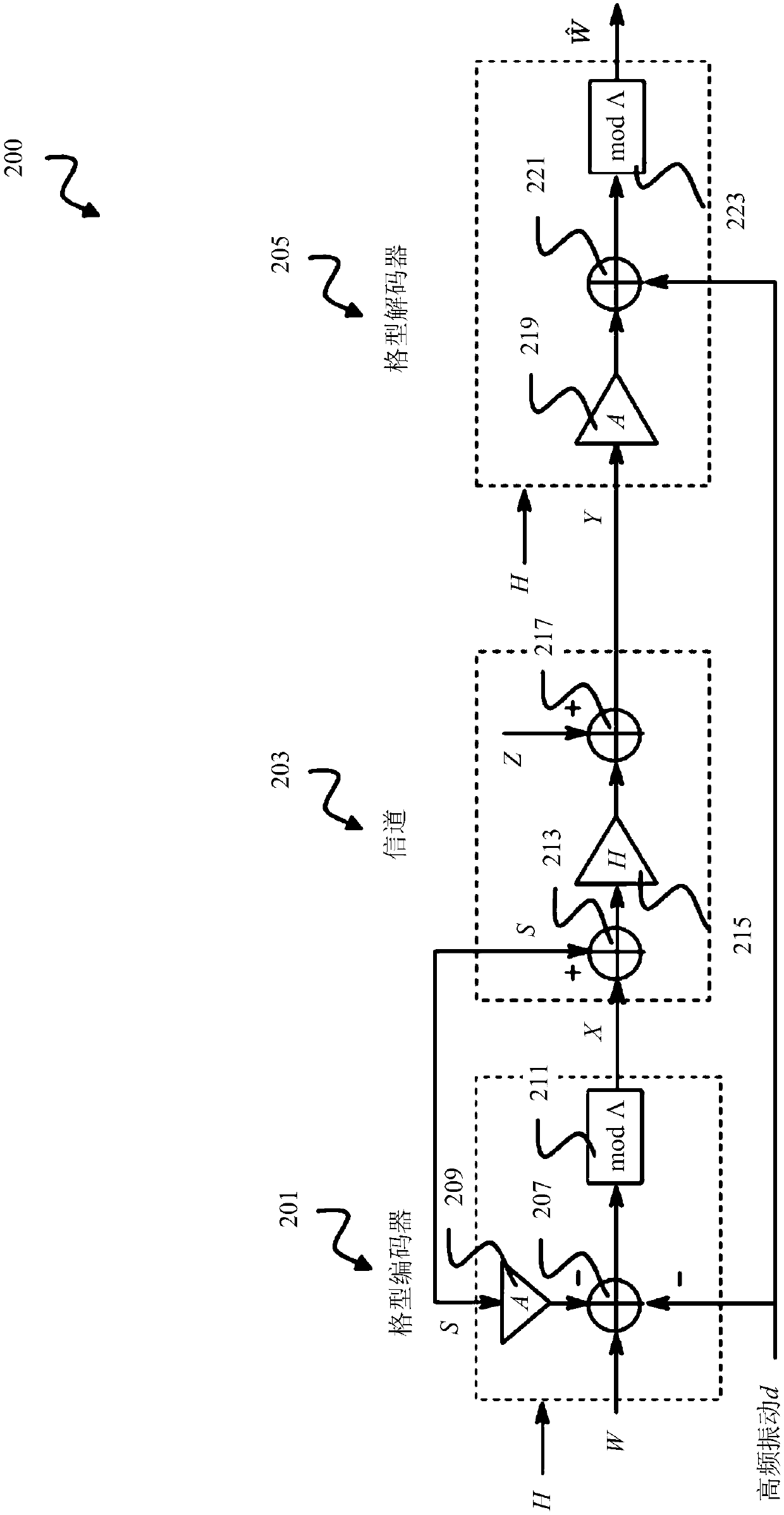
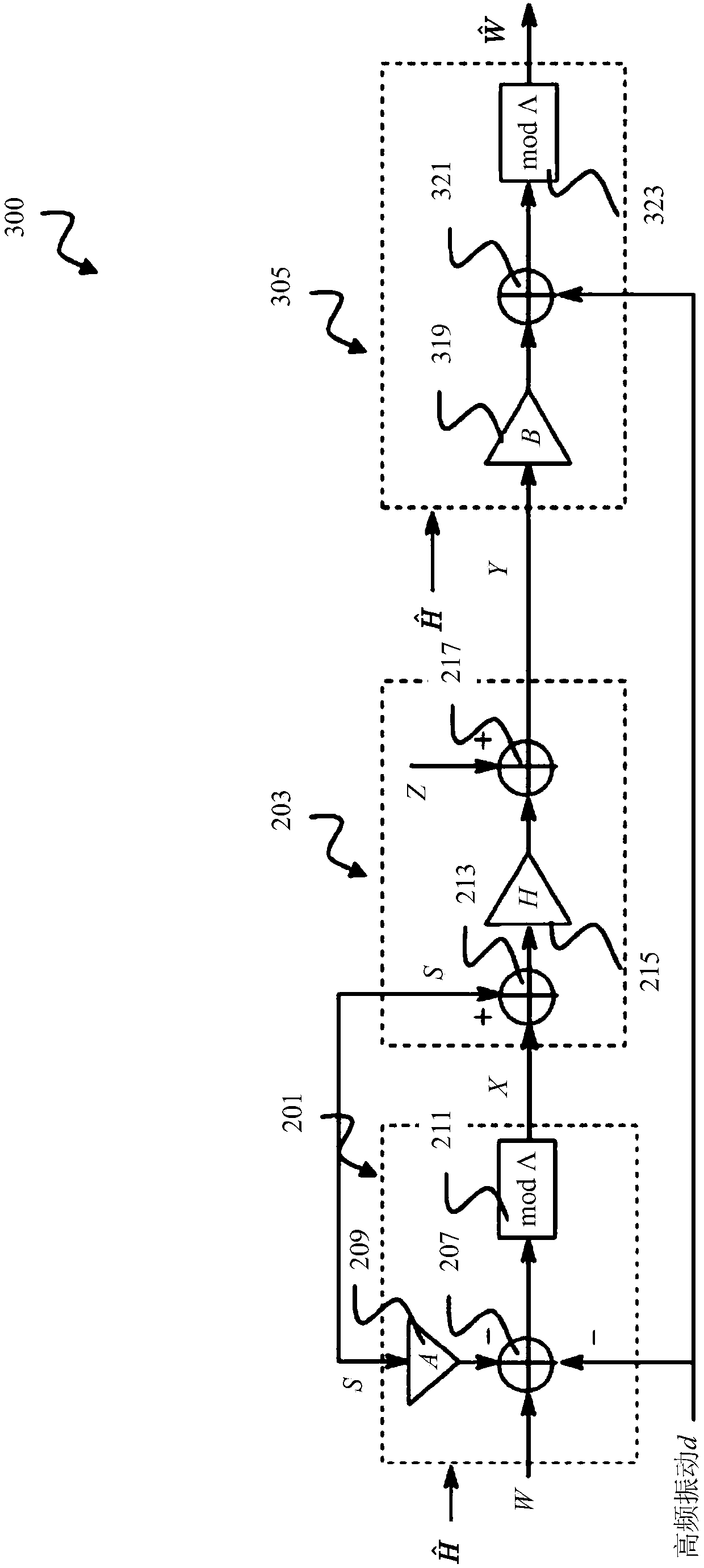
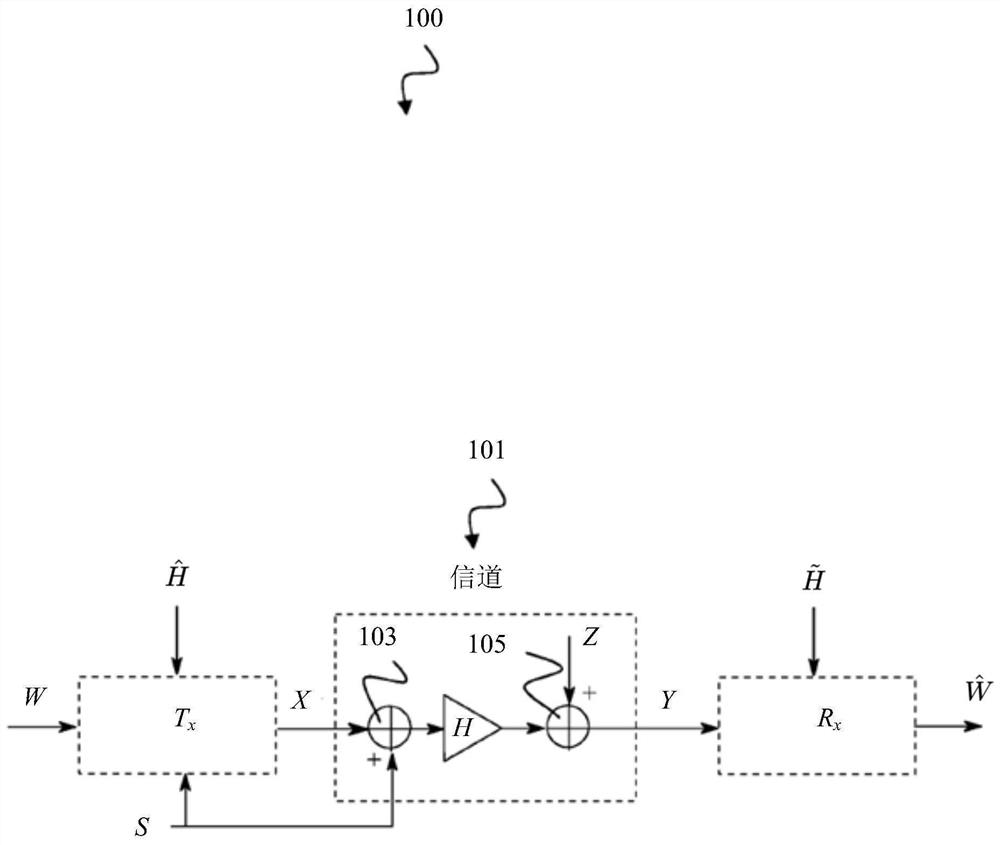
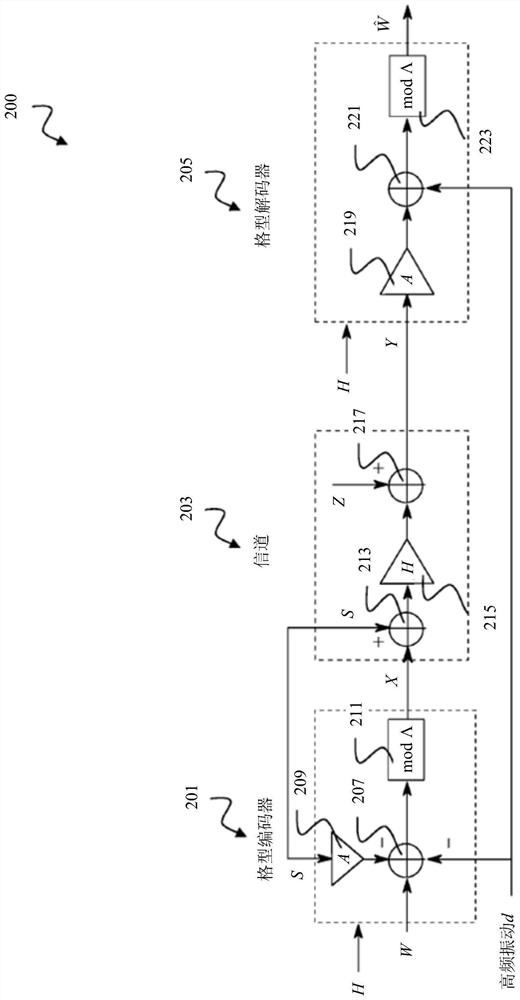
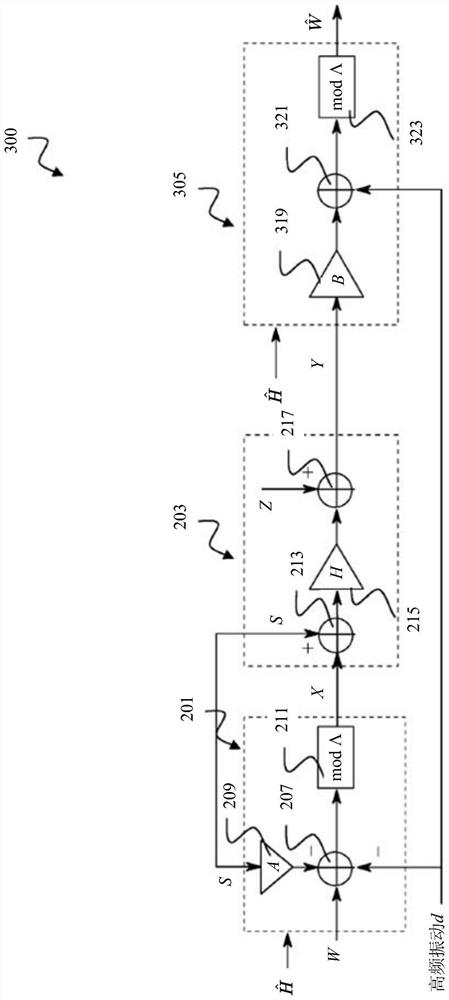
Receiver and precoding system using asymmetric imperfect channel knowledge
ActiveCN108476183ASpatial transmit diversityTransmitter/receiver shaping networksChannel state informationPrecoding
The disclosure relates to a receiver (400), including: a decoder (305) comprising an adjustable receive filter (319) for decoding a receive signal (Y) received over a communication channel; and a first channel state information (CSI) handler (401) configured to provide the decoder (305) with receive-side channel state information (H-~) indicating a receive-side estimate of a channel state (H) of the communication channel and to provide the decoder (305) with transmit-side channel state information (H-hat) indicating a transmit-side estimate of the channel state (H) of the communication channel, wherein the decoder (305) is configured to adjust the receive filter (319) based on the transmit-side channel state information (H-hat) if the transmit-side channel state information (H-hat) is a less good estimate of the channel state (H) of the communication channel than the receive-side channel state information (H-~). The disclosure further relates to a precoding system (500) including suchreceiver (400).
Owner:XFUSION DIGITAL TECH CO LTD
System for acquiring channel knowledge and method thereof
ActiveUS10009073B2Reduce training overheadSpatial transmit diversityChannel estimationRelevant informationEngineering
A system for acquiring channel knowledge and a method thereof are provided. At least one transmitter generates multiple directional beams in different directions, next modulates the directional beams in the different directions with at least one spreading sequence, so as to enlarge the beam range of each directional beam in the different directions and use the modulated directional beams as training-specific beams in the different directions, and sweeps the multiple training-specific beams in the different directions by using a plurality of antennas, so that at least one receiver measures at least one training-specific beam, and determines the channel knowledge according to the measurement result and beam-related information associated with the at least one training-specific beam, so as to achieve a technical effect of reducing training overhead.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC +1
Beamforming with partial channel knowledge
Owner:NXP USA INC
Power allocation method in multiantenna systems under partial channel knowledge
InactiveUS8208952B2Time-division multiplexRadio transmissionChannel state informationCommunications system
Method for allocating a minimum downlink power from a transmitter (1) having nt transmit antennas of a cellular multi-user multi-antenna communications system with N users attached to said transmitter (1). Each user comprises at least one antenna. The method comprising the steps of: generating at said transmitter (1) M random beams (b1 . . . bM); sending said M random beams through all the transmit antennas; calculating at each user a signal-to-noise-interference-ratio for each random beam sent by said transmitter (1); sending back to said transmitter (1) said calculated values of signal-to-noise-interference-ratio, said signal-to-noise-interference-ratio representing a partial channel state information; selecting at said transmitter (1) the M best users which correspond to the M best values of signal-to-noise-interference-ratio per beam.
Owner:FUNDACIO PRIVADA CENT TECNOLOGIC DE TELECOMUNICACIONS DE CATALUNYA
Method and device for identifying non-standard channel names
ActiveCN107027065BImprove experienceAccurate identificationSelective content distributionKnowledge graphSpeech sound
The embodiment of the invention provides a recognition method and a recognition device for a non-standard channel name. The method comprises the steps of if a speech control text input by a user does not include a standard channel name and matched with a preset channel name template, acquiring a target attribute keyword included in the speech control text according to the preset channel name template, wherein the target attribute keyword and the keyword in the preset channel name templates are the same in attribute; and querying a preset channel knowledge graph according to the target attribute keyword to determine the channel name included by the speech control text, thus allowing a smart television to be switched to a channel indicated by the channel name from the current playing channel. According to the recognition method and the recognition device for the non-standard channel name provided by the embodiment of the invention, a recognition rate of the non-standard channel name during a speech interaction process can be improved, and user experience can be enhanced.
Owner:HISENSE
Receivers and Precoding Systems Using Asymmetric Incomplete Channel Knowledge
The disclosure relates to a receiver (400), including: a decoder (305) comprising an adjustable receive filter (31 9) for decoding a receive signal (Y) received over a communication channel; and a first channel state information (CSI) handler (401) configured to provide the decoder (305) with receive-side channel state information (H̃) indicating a receive-side estimate of a channel state (H) of the communication channel and to provide the decoder (305) with transmit-side channel state information (Ĥ) indicating a transmit-side estimate of the channel state (Η) of the communication channel, wherein the decoder (305) is configured to adjust the receive filter (319) based on the transmit-side channel state information (Ĥ) if the transmit-side channel state information (Ĥ) is a less good estimate of the channel state (Η) of the communication channel than the receive-side channel state information (H̃). The disclosure further relates to a precoding system (500) including such receiver (400).
Owner:XFUSION DIGITAL TECH CO LTD
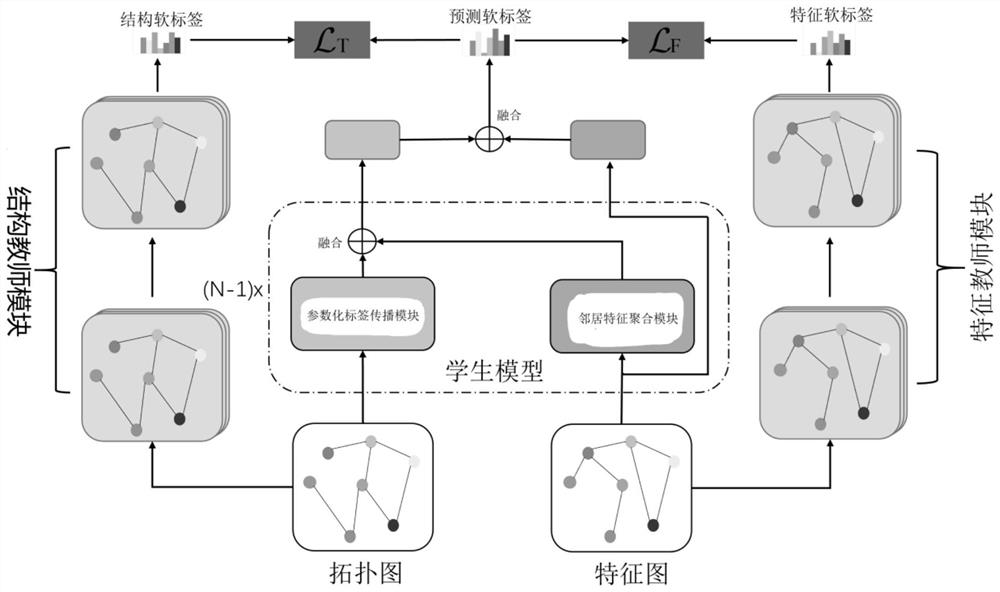
Node classification method based on dual-channel knowledge distillation
InactiveCN113869425AImprove the comprehensiveness of knowledgeImprove classification accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesClassification methodsEngineering
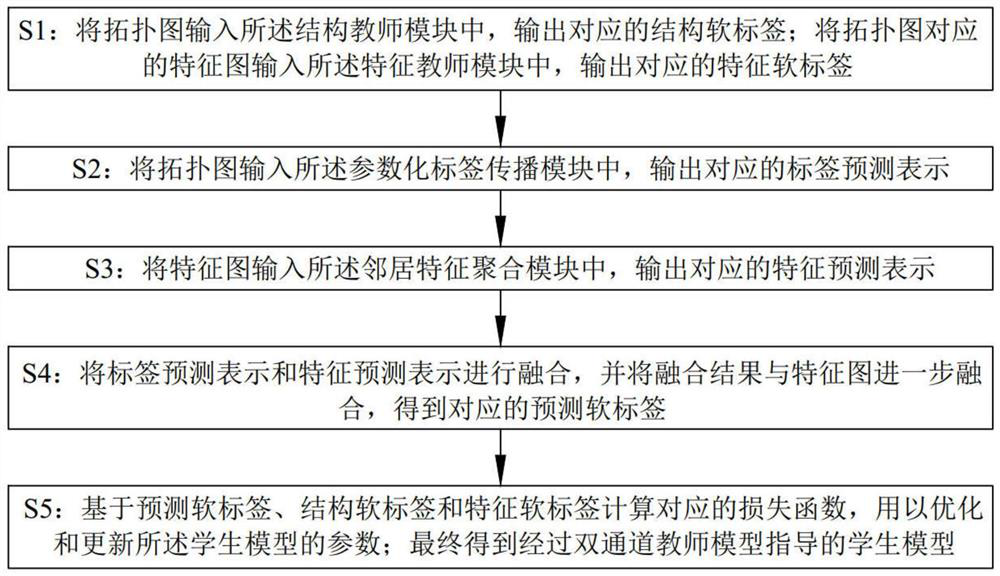
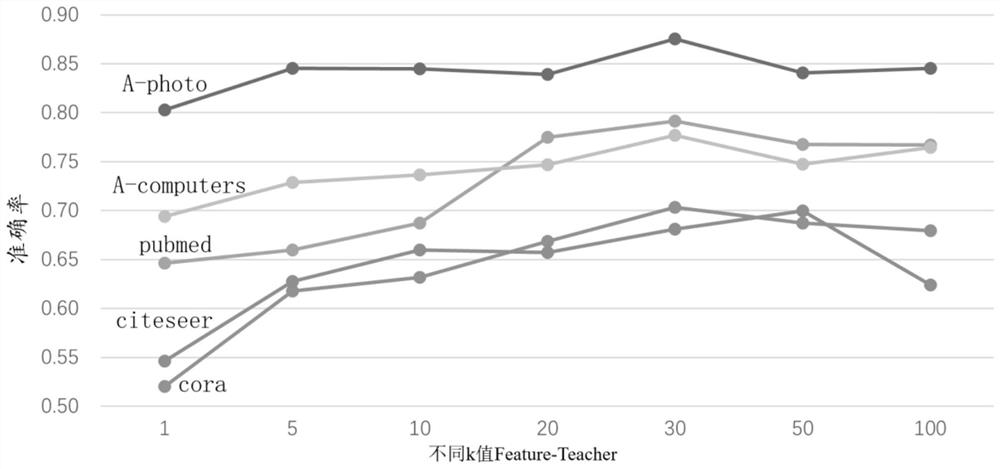
The invention relates to the technical field of semi-supervised node classification, in particular to a node classification method based on dual-channel knowledge distillation, and the method comprises the steps that a dual-channel teacher model and a corresponding student model are set; during training, the two-channel teacher model learns knowledge information of a spatial topological structure and knowledge information of node and neighbor node feature attributes, and instructs the student model to train based on knowledge levels corresponding to the two kinds of knowledge information, so that the student model keeps structure-based priori knowledge and feature-based priori knowledge; during testing, the trained student model is used for node classification. According to the node classification method based on dual-channel knowledge distillation, the knowledge comprehensiveness and classification accuracy of the student model can be improved, so that the classification effect of node classification is assisted to be improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
Self-adaptive communication method and system for links among micro-nano satellite groups
ActiveCN113141206AImprove transmission efficiencyRadio transmissionTransmission monitoringReliable transmissionNano satellite
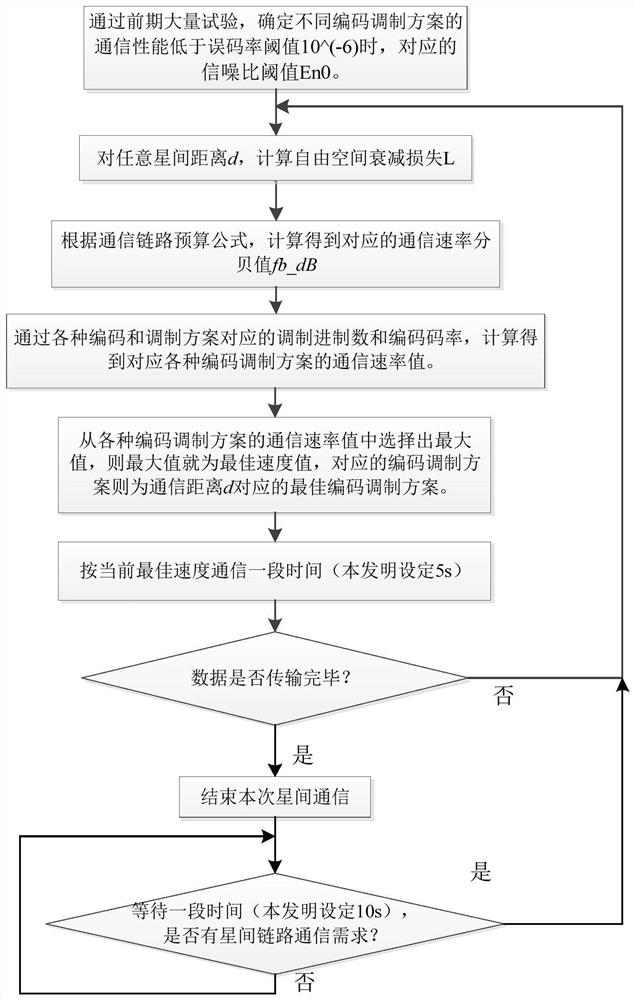
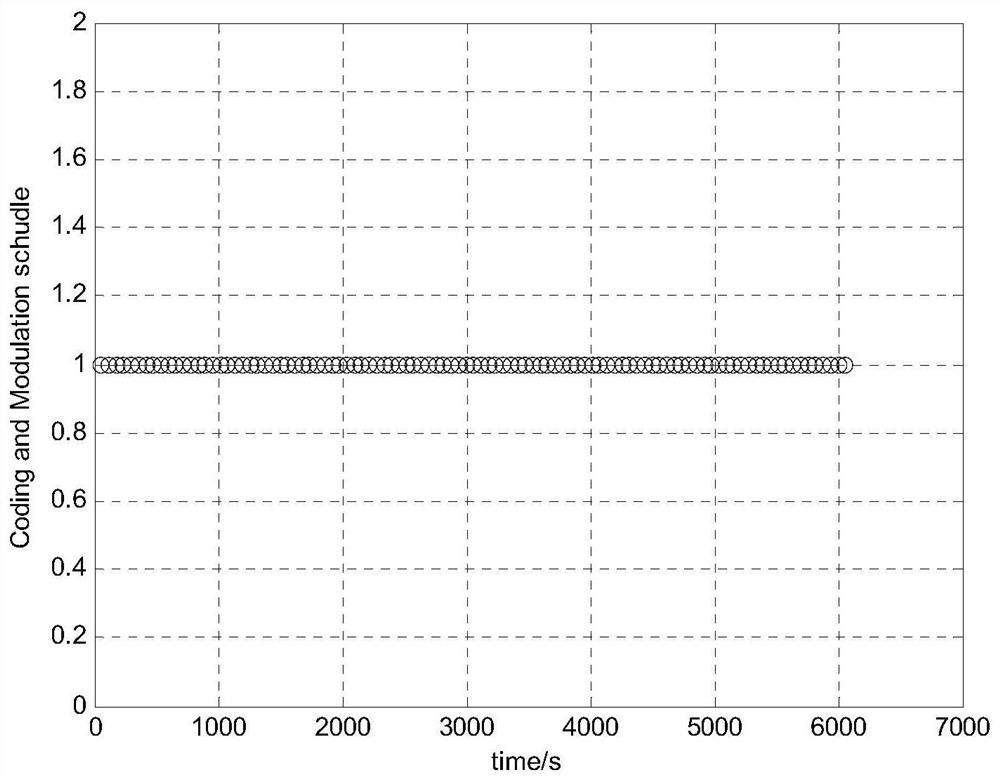
The invention discloses a self-adaptive communication method and system for links among micro-nano satellite groups, belongs to the technical field of communication among micro-nano satellite groups, and aims to solve the problem of low communication efficiency or data loss caused by the fact that the communication rate cannot be dynamically adjusted in the conventional inter-satellite link communication method. The method is technically characterized by comprising the following steps of: establishing an inter-satellite link communication channel knowledge base according to an inter-satellite link communication error rate threshold value requirement of a micro-nano satellite group; according to the real-time communication distance between the two micro-nano satellites, selecting the maximum communication rate value as the optimal communication rate value, and selecting the corresponding coding modulation scheme as the optimal coding modulation scheme; and carrying out coding and modulation processing on inter-satellite communication data according to the optimal coding modulation scheme, and carrying out inter-satellite link communication according to the optimal communication rate value. According to the method, high-efficiency and reliable transmission of telemetry data is realized, and the method is of great significance in improving self-adaptive signal processing of inter-satellite links of a micro-nano satellite group system.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH AT WEIHAI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com