Patents
Literature
6659 results about "Data loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Data loss is an error condition in information systems in which information is destroyed by failures or neglect in storage, transmission, or processing. Information systems implement backup and disaster recovery equipment and processes to prevent data loss or restore lost data.
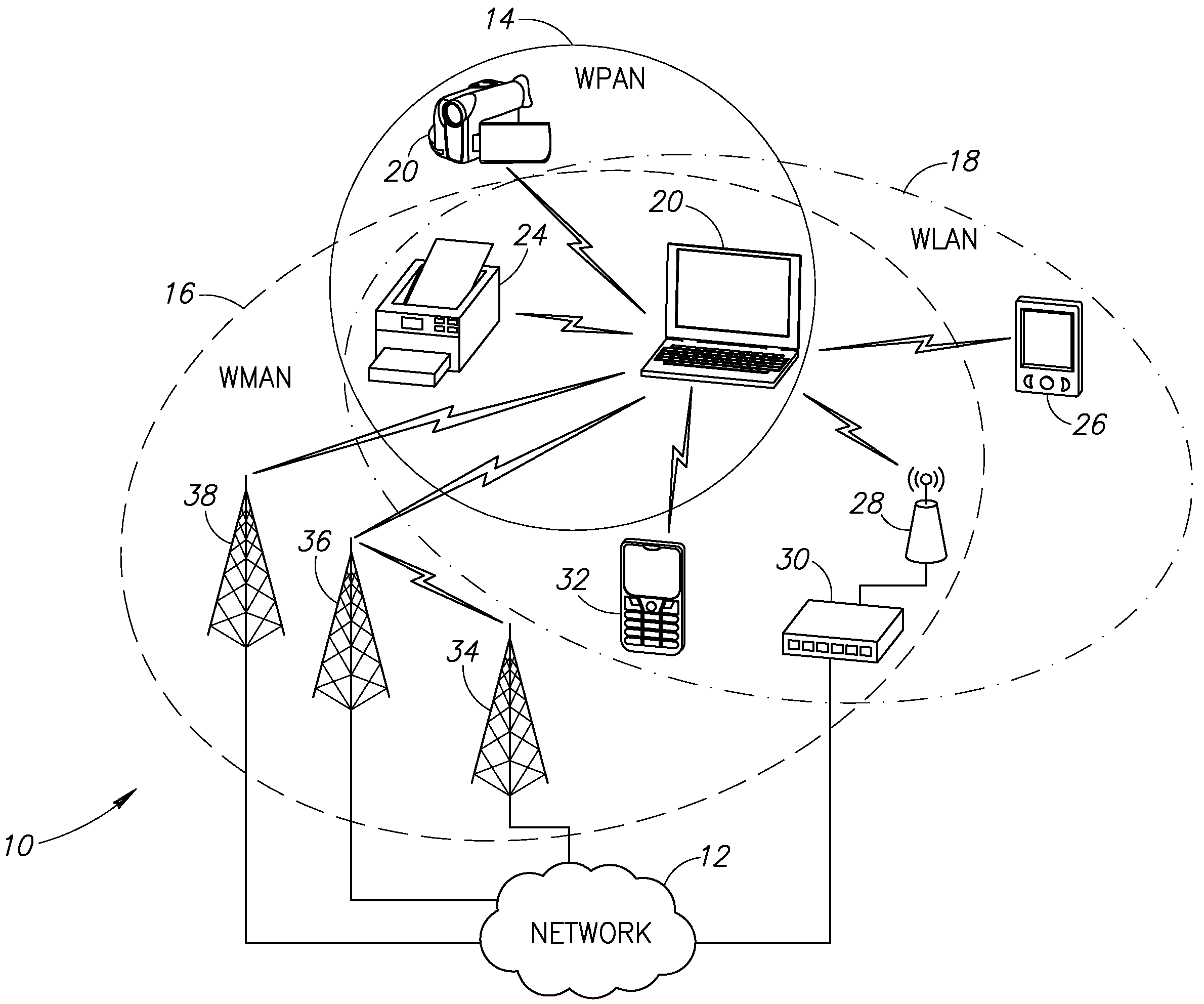
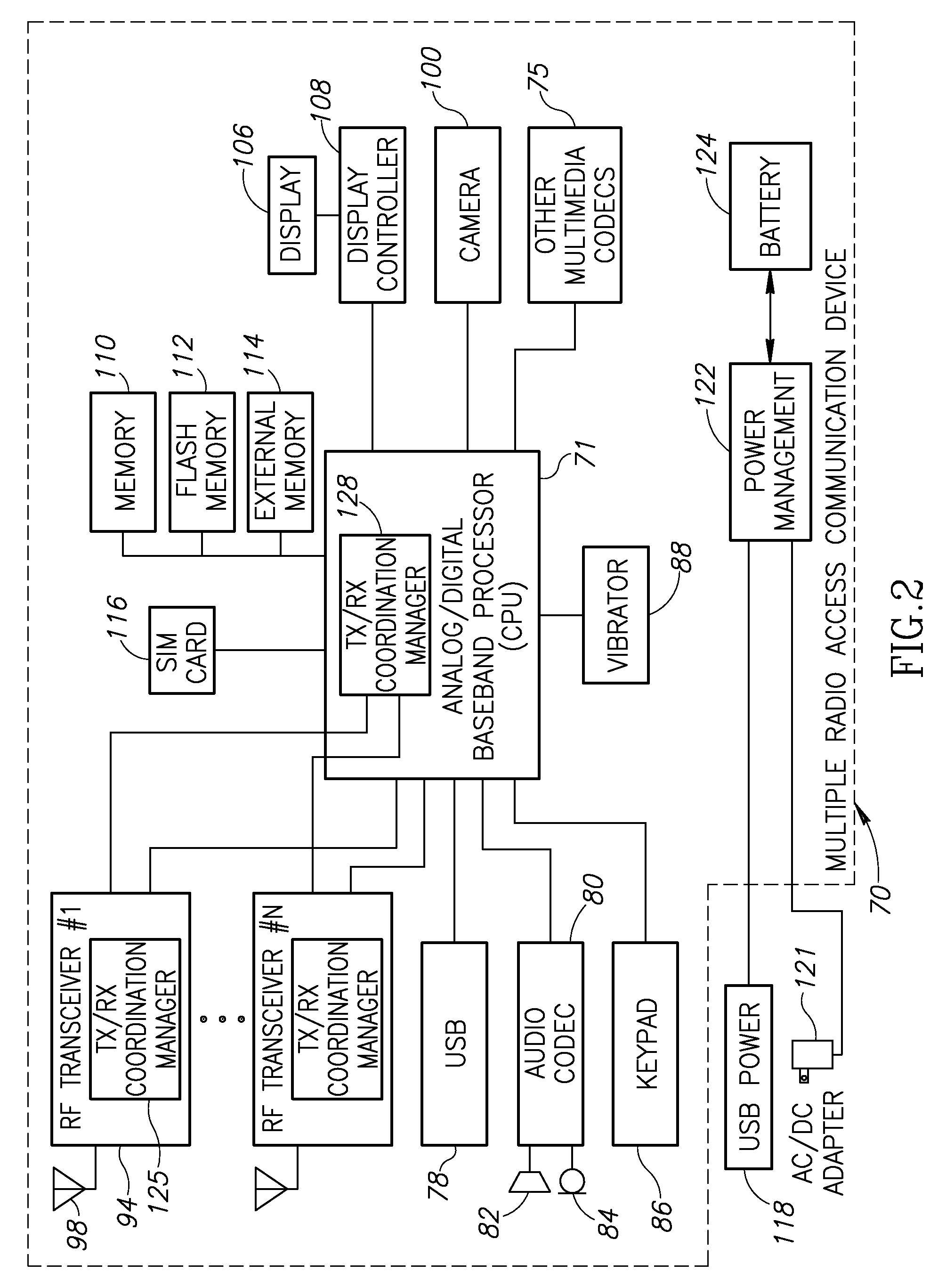
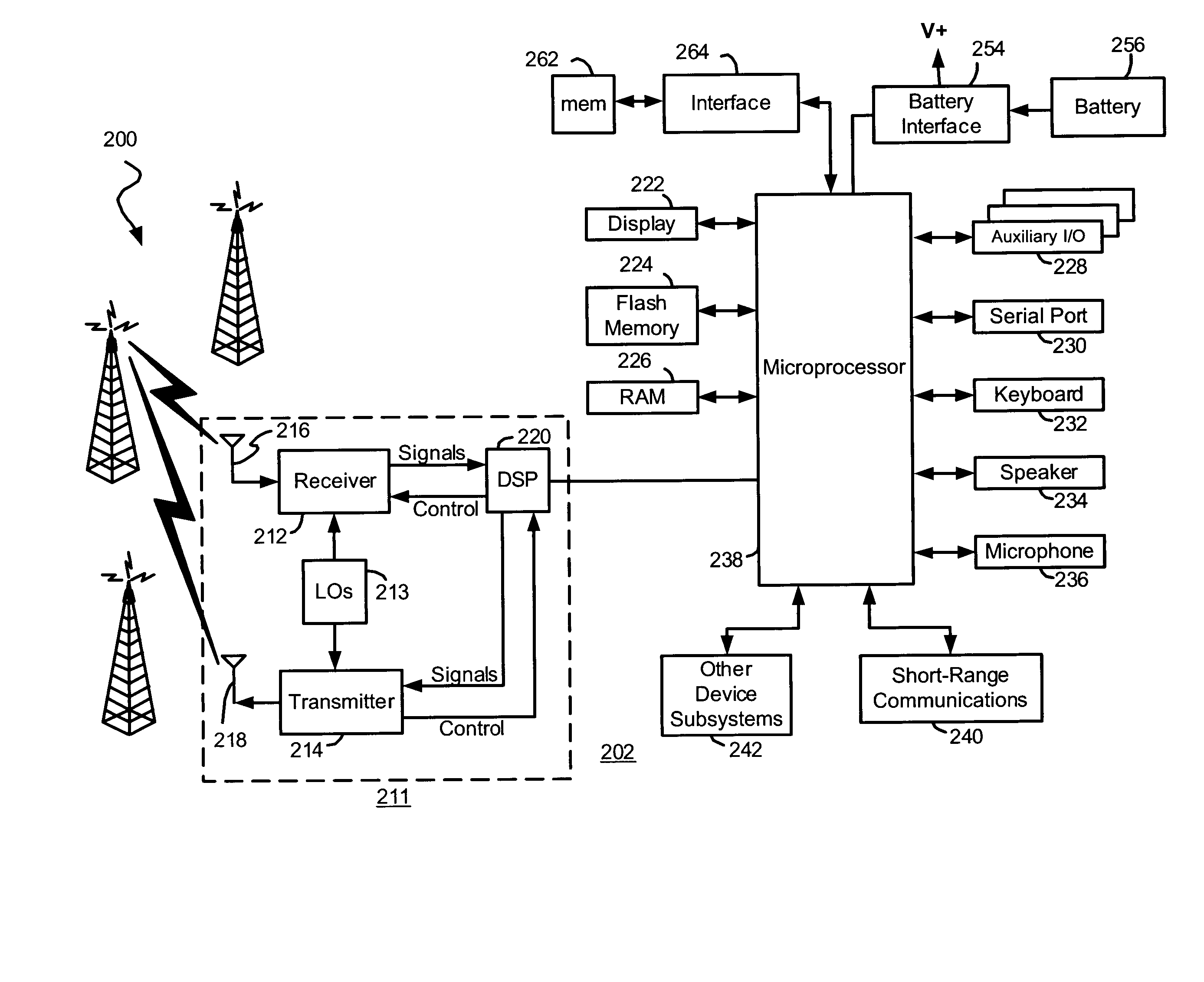
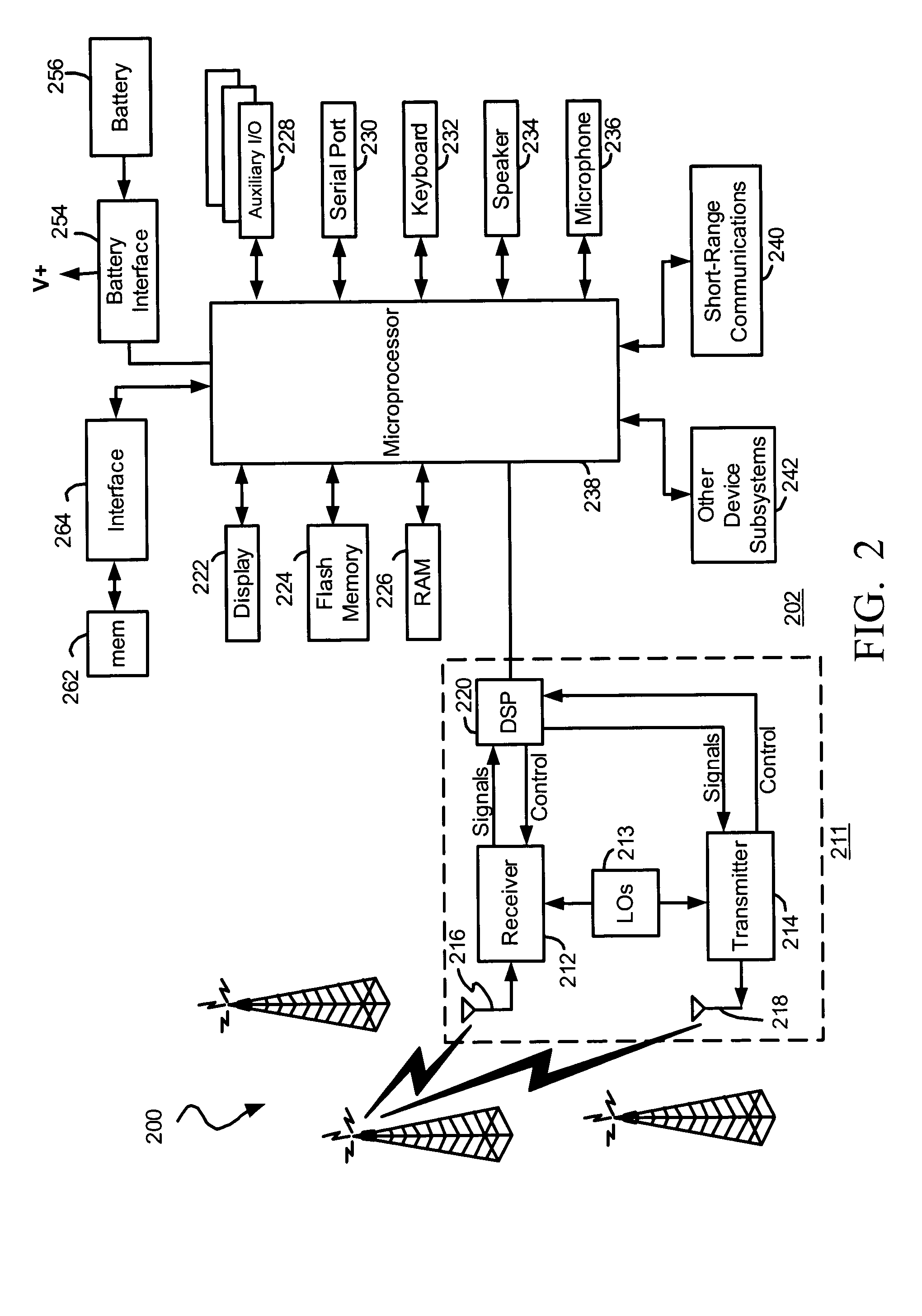
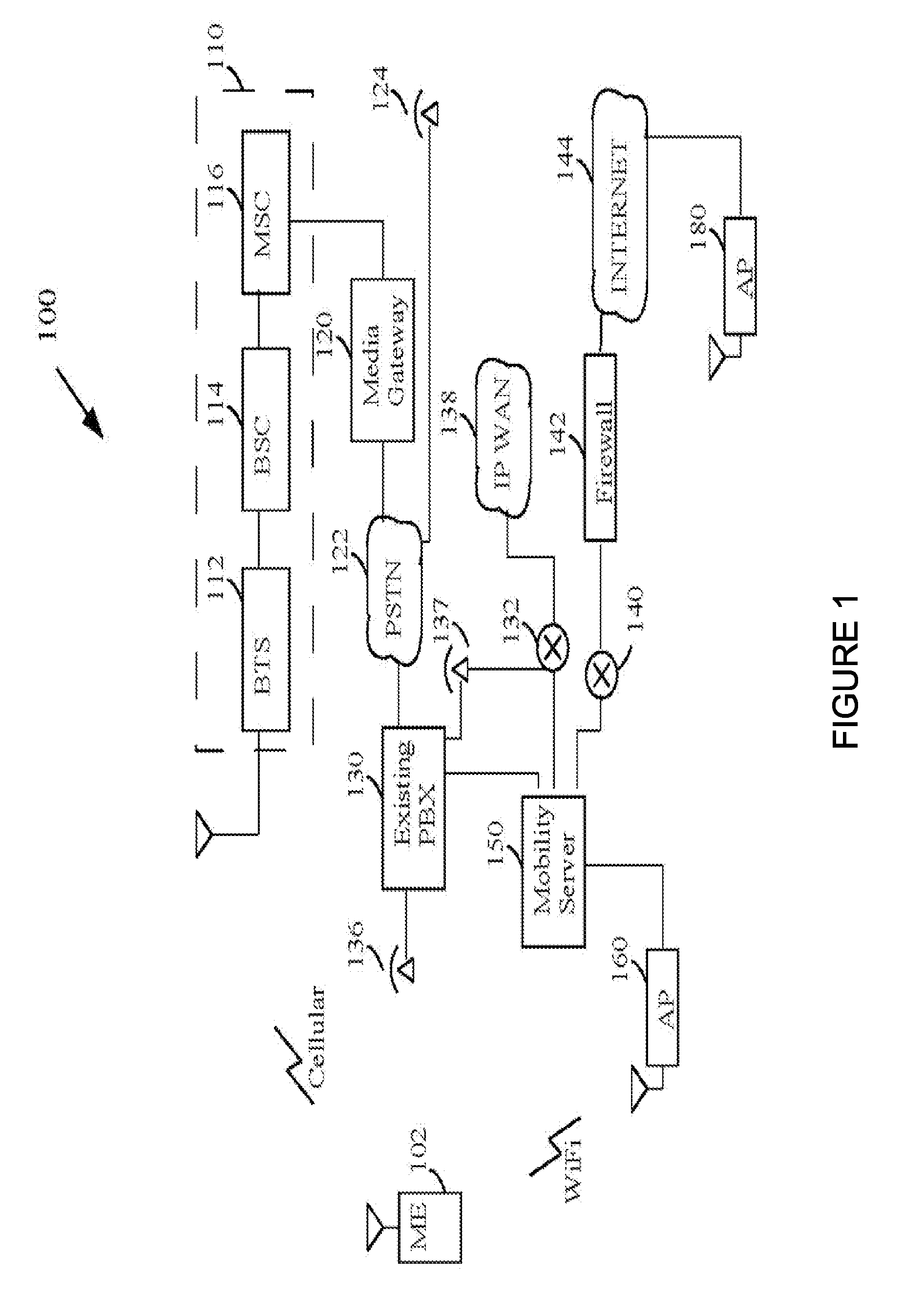
Apparatus for and method of coordinating transmission and reception opportunities in a communications device incorporating multiple radios
InactiveUS20090180451A1Avoid interferenceDelay transitionNetwork topologiesSubstation equipmentOperation modeMobile station
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of coordinating the allocation of transmission and reception availability and / or unavailability periods for use in a communications device incorporating collocated multiple radios. The mechanism provide both centralized and distributed coordination to enable the coordination (e.g., to achieve coexistence) of multiple radio access communication devices (RACDs) collocated in a single device such as a mobile station. A distributed activity coordinator modifies the activity pattern of multiple RACDs. The activity pattern comprises a set of radio access specific modes of operation, (e.g., IEEE 802.16 Normal, Sleep, Scan or Idle modes, 3GPP GSM / EDGE operation mode (PTM, IDLE, Connected, DTM modes), etc.) and a compatible set of wake-up events, such as reception and transmission availability periods. To prevent interference and possible loss of data, a radio access is prevented from transmitting or receiving data packets while another radio access is transmitting or receiving. In the event two or more RATs desire to be active at the same time, the mechanism negotiates an availability pattern between the MS and a corresponding BS to achieve coordination between the RATs.
Owner:COMSYS COMM & SIGNAL PROC
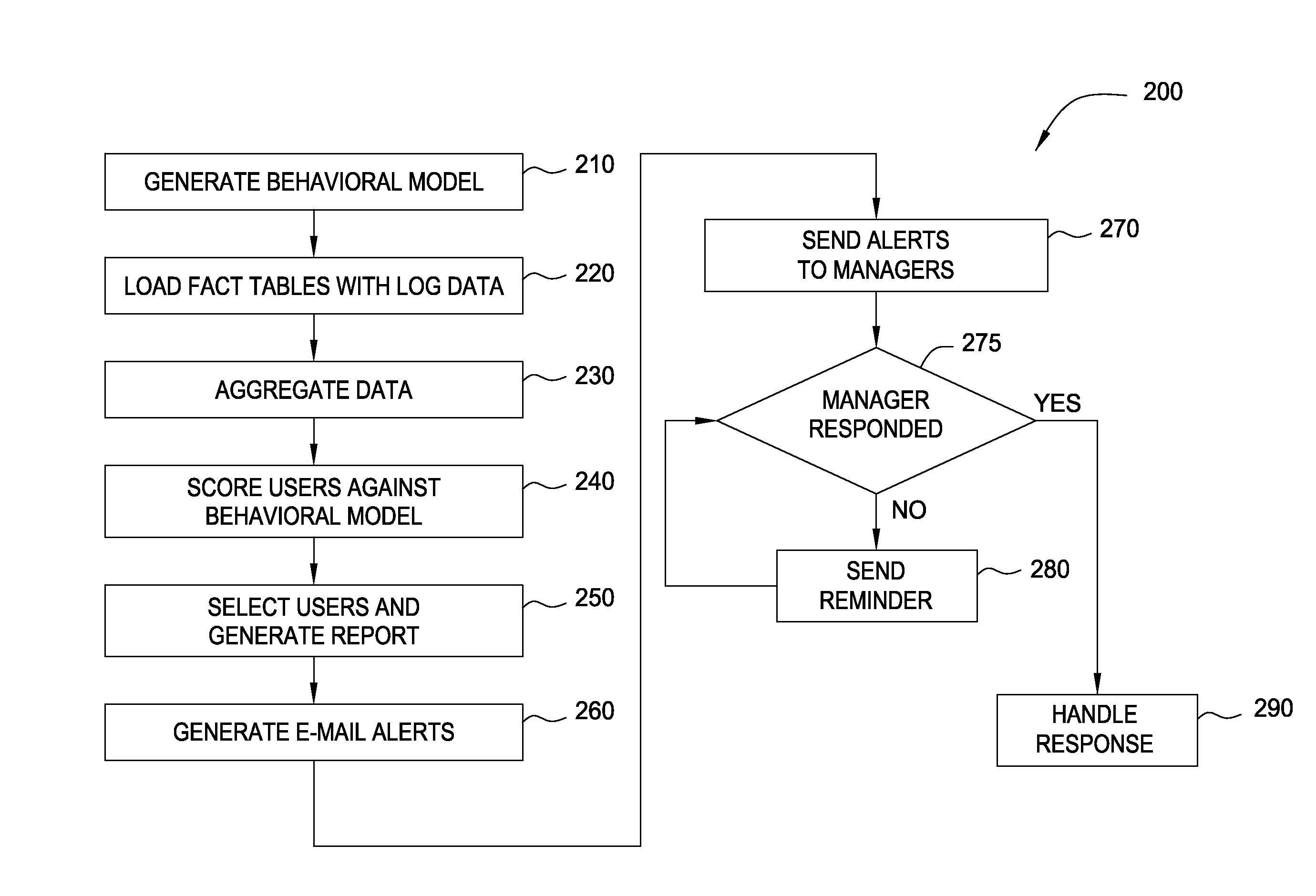
Deviation detection of usage patterns of computer resources
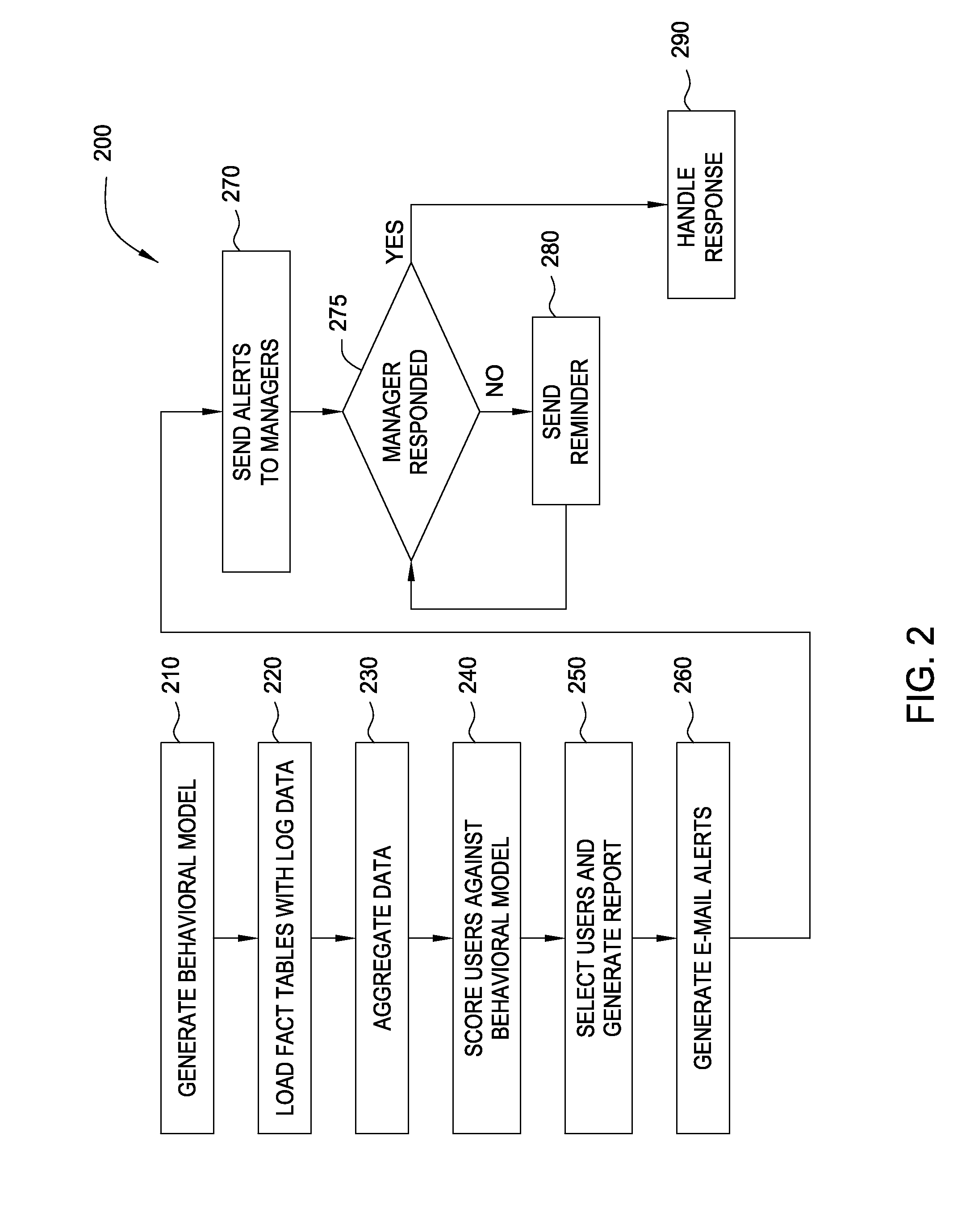
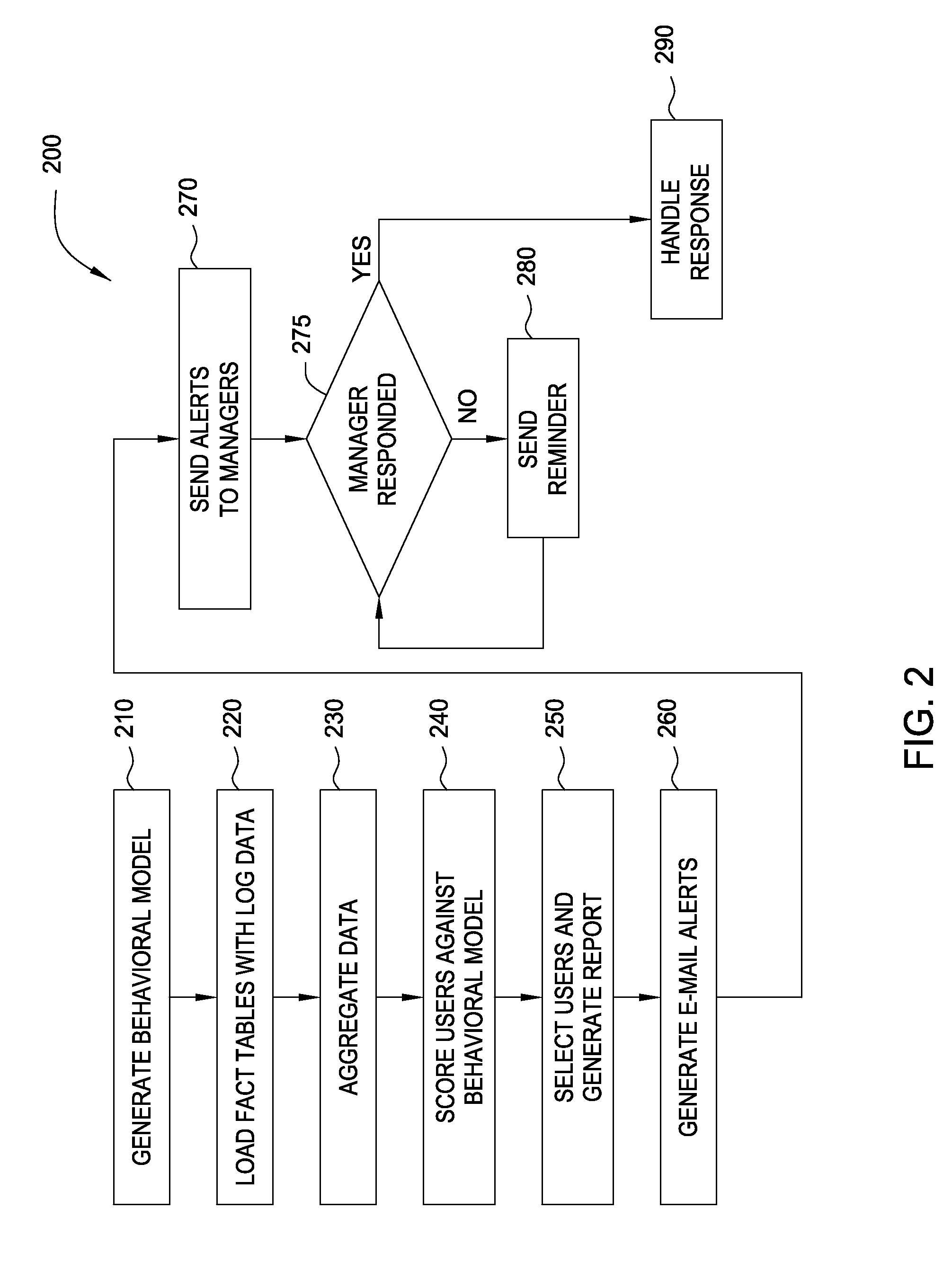
Embodiments of the invention provide a method for detecting changes in behavior of authorized users of computer resources and reporting the detected changes to the relevant individuals. The method includes evaluating actions performed by each user against user behavioral models and business rules. As a result of the analysis, a subset of users may be identified and reported as having unusual or suspicious behavior. In response, the management may provide feedback indicating that the user behavior is due to the normal expected business needs or that the behavior warrants further review. The management feedback is available for use by machine learning algorithms to improve the analysis of user actions over time. Consequently, investigation of user actions regarding computer resources is facilitated and data loss is prevented more efficiently relative to the prior art approaches with only minimal disruption to the ongoing business processes.
Owner:IBM CORP
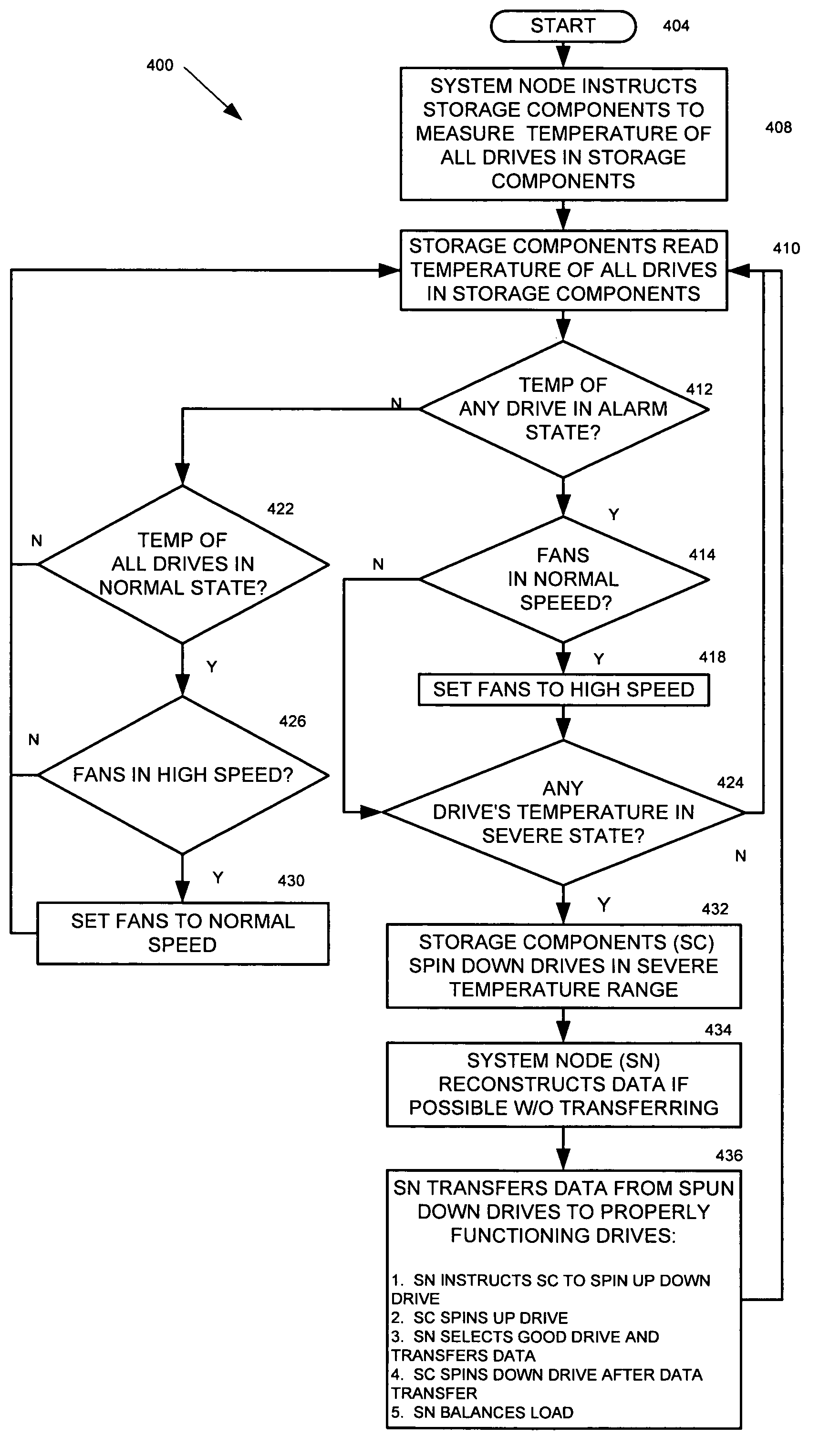
Preventing damage of storage devices and data loss in a data storage system
ActiveUS7146521B1Prolong lifeAvoid data lossThermometer detailsEnergy efficient ICTData CorruptionData loss
A data storage system and method capable of reducing the operating temperature of the data storage system, removing any overheating storage devices from operation, reconstructing data, and evacuating data from the overheating storage devices before the devices and the data are damaged or lost.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD
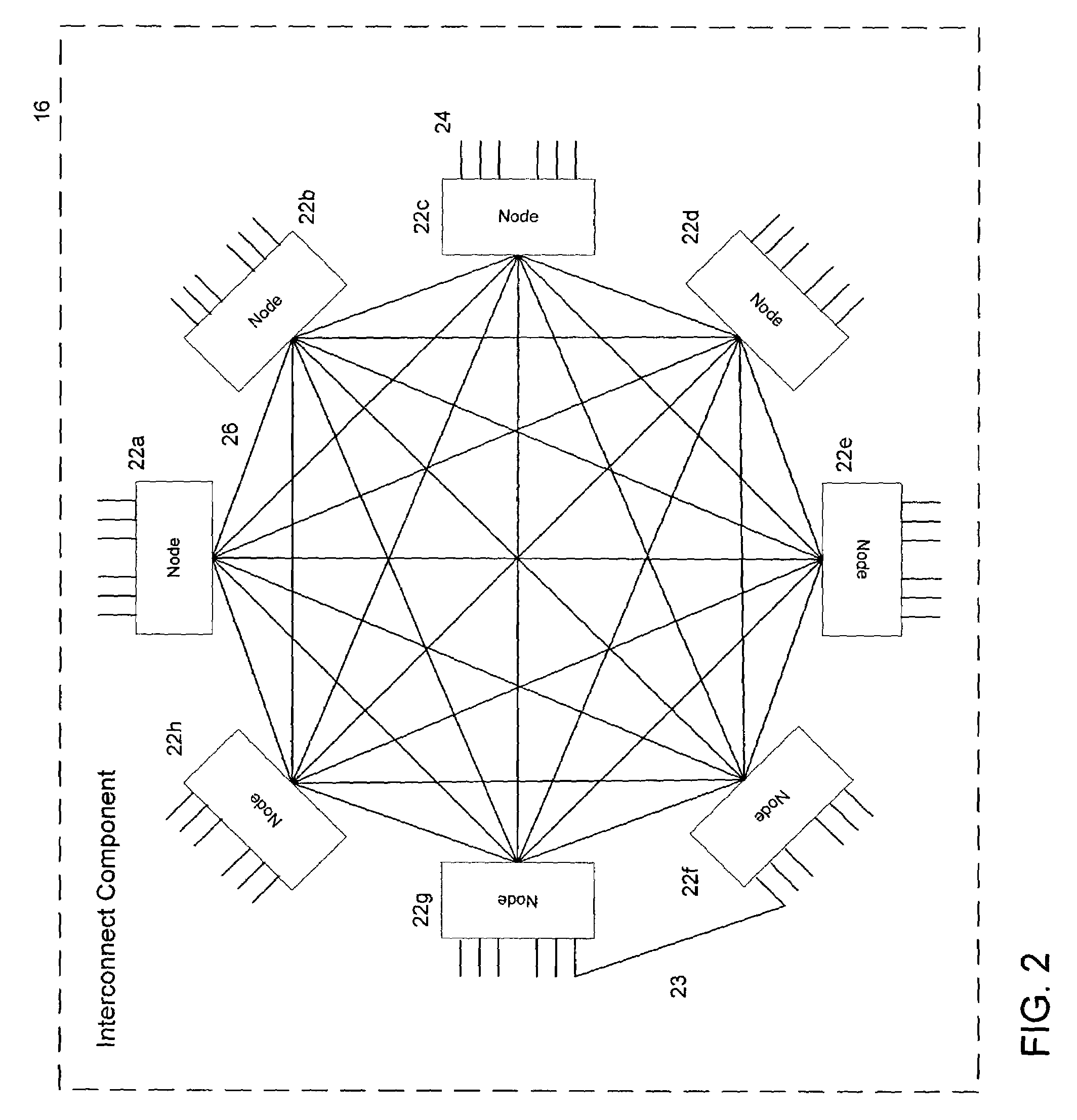
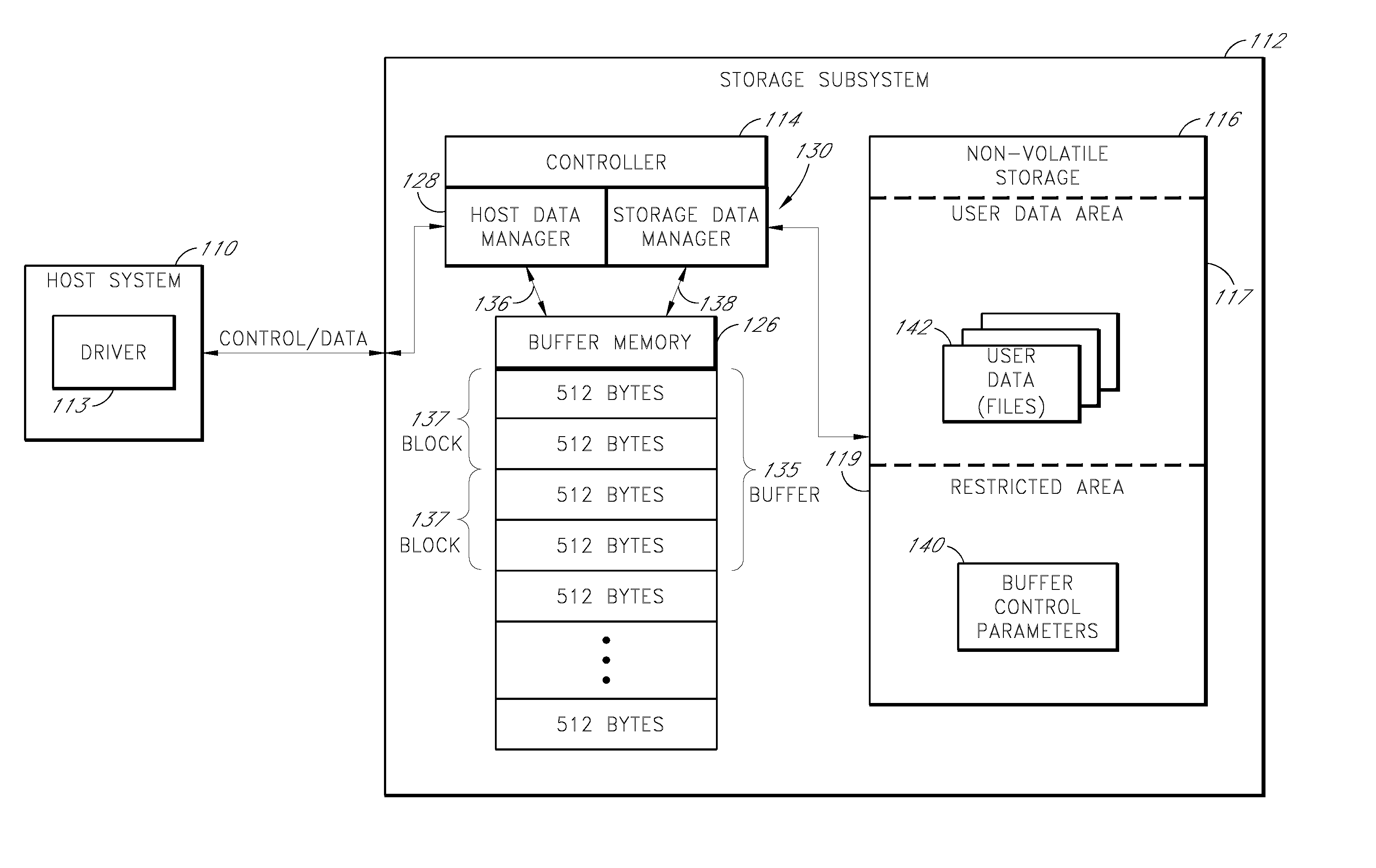
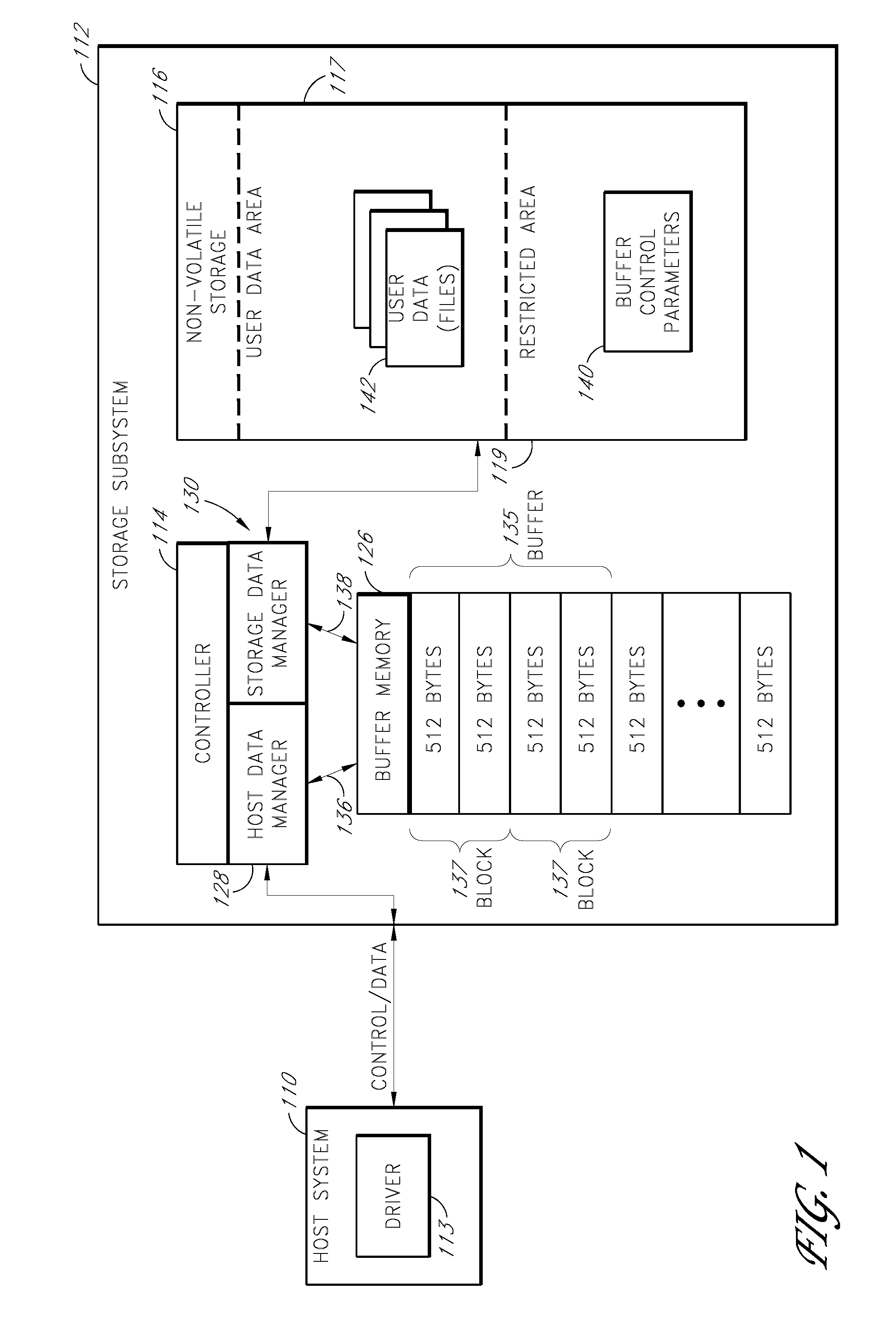
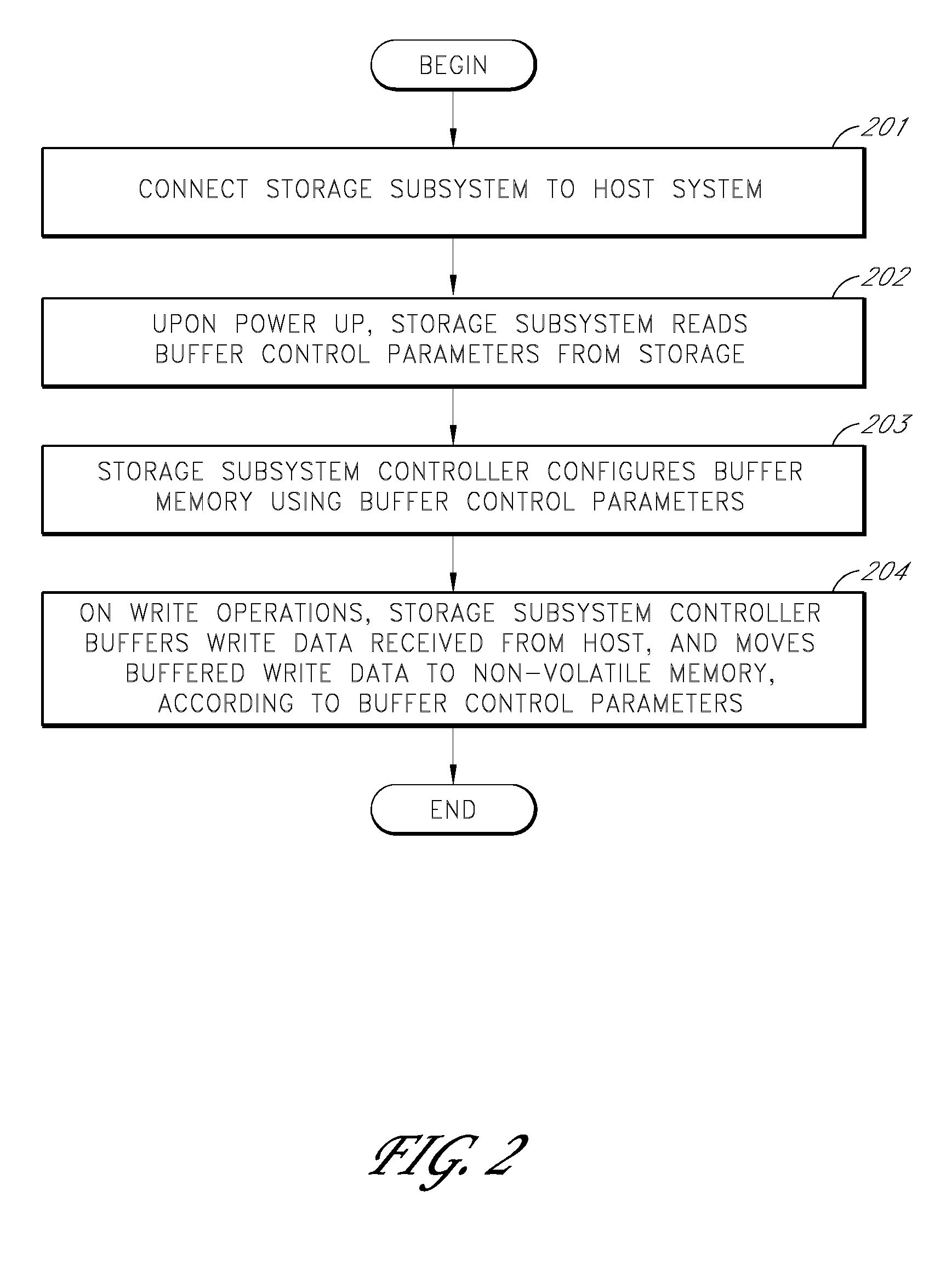
Storage subsystem with configurable buffer
ActiveUS7596643B2Reduce riskImprove performanceRecord information storageInput/output processes for data processingWrite bufferData loss
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
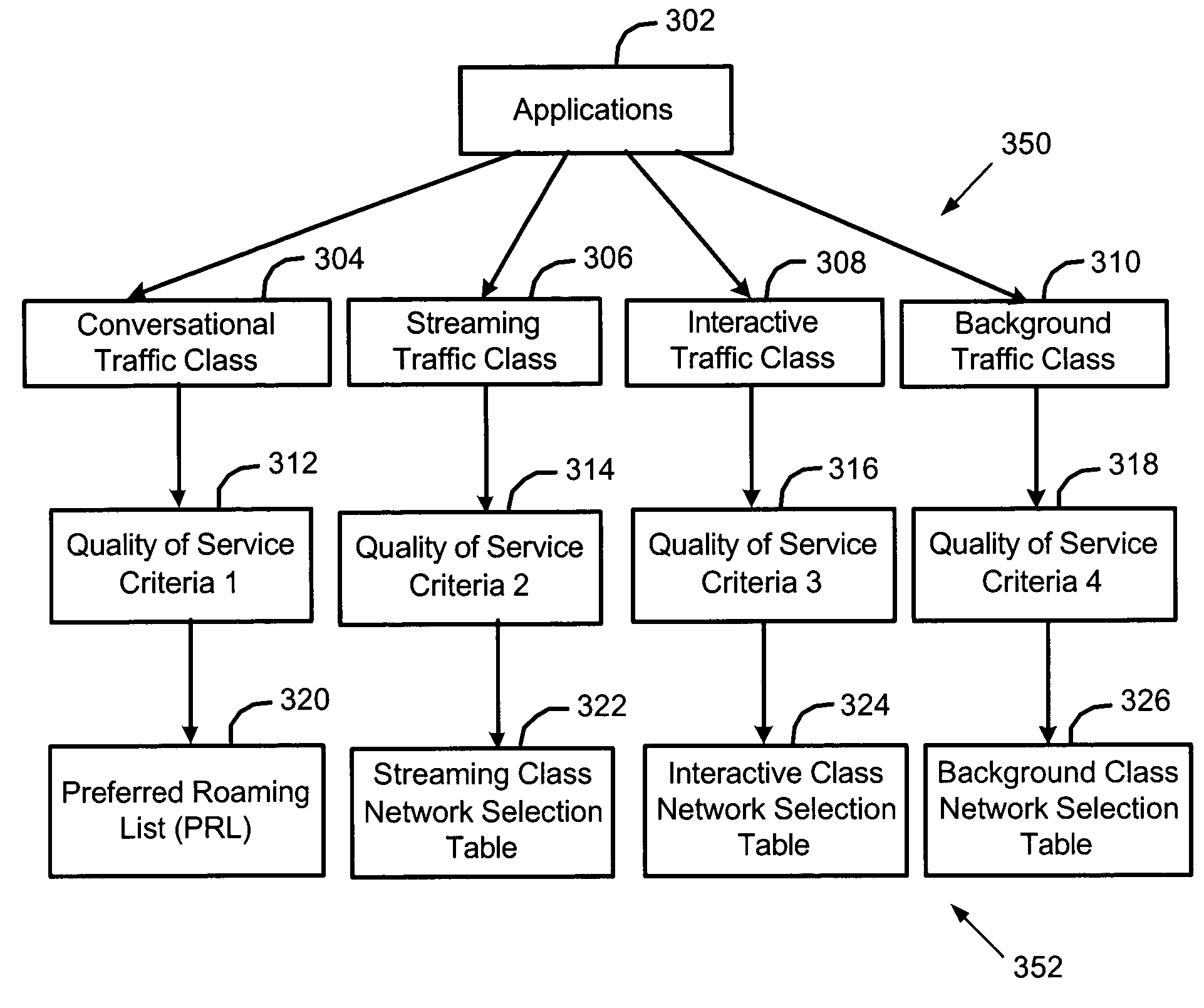
Methods and apparatus for selecting a wireless network based on quality of service (QoS) criteria associated with an application
ActiveUS20050059397A1Assess restrictionMultiple digital computer combinationsQuality of serviceVideo player
Methods and apparatus for selecting a wireless communication network based on quality of service criteria associated with an application are disclosed. In one illustrative example, one of several different software applications of a mobile communication device is executed. The software application may be, for example, an e-mail application, an Internet data application, a voice-over-IP application, a video player application, an audio player application, or a video game application. Each software application is associated with different quality of service (QoS) criteria for data communications through a wireless network. The quality of service criteria may include, for example, a bandwidth criterion, a delay criterion, a delay variation criterion, and a data loss criterion. A scanning operation is performed to identify a plurality of a wireless networks available in a coverage area of the mobile device. One of the identified wireless networks is selected for communication based on a match between its available quality of service and the quality of service criterion associated with the executed software application. Advantageously, the most suitable network may be chosen and utilized for each software application.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
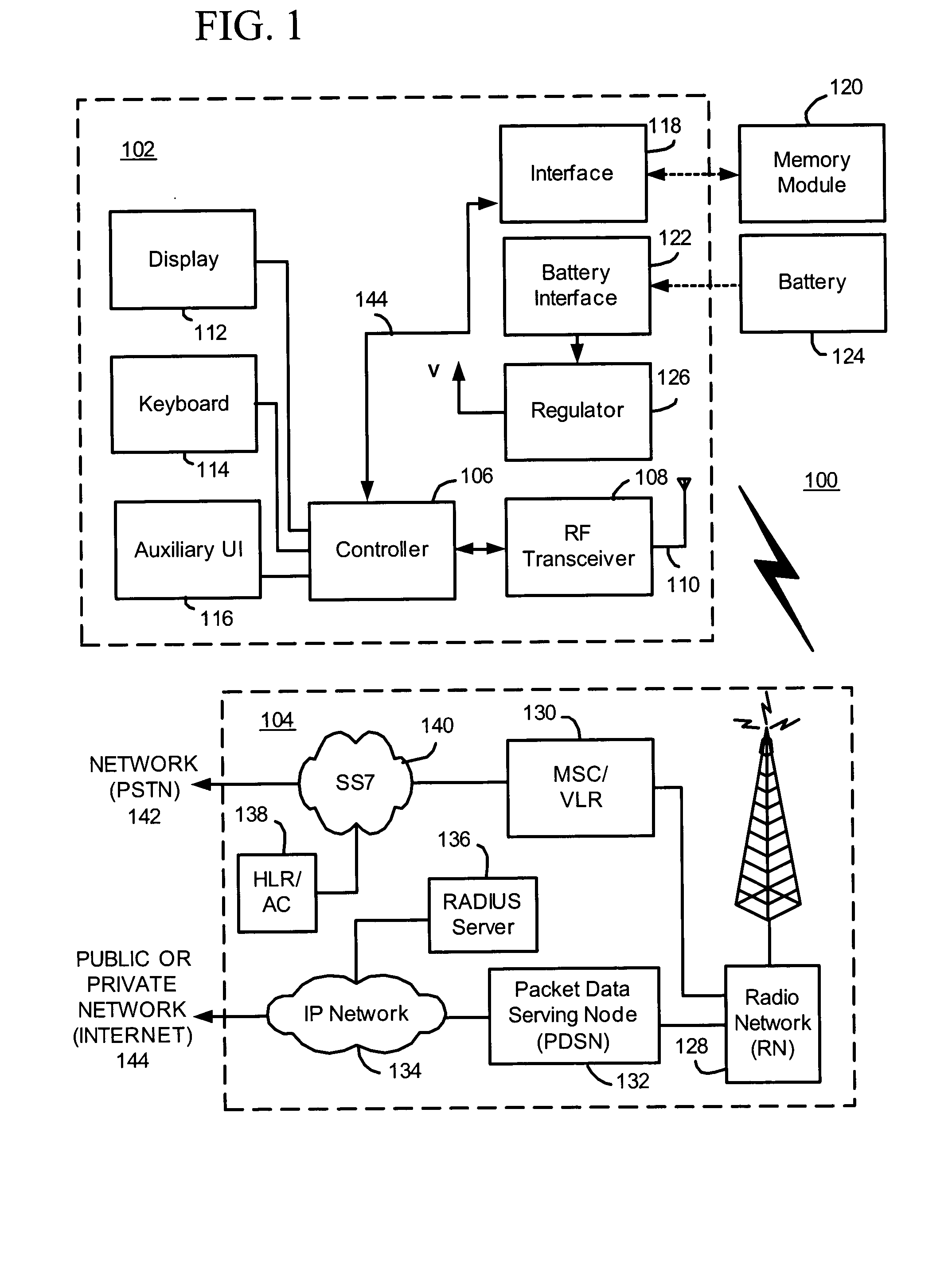
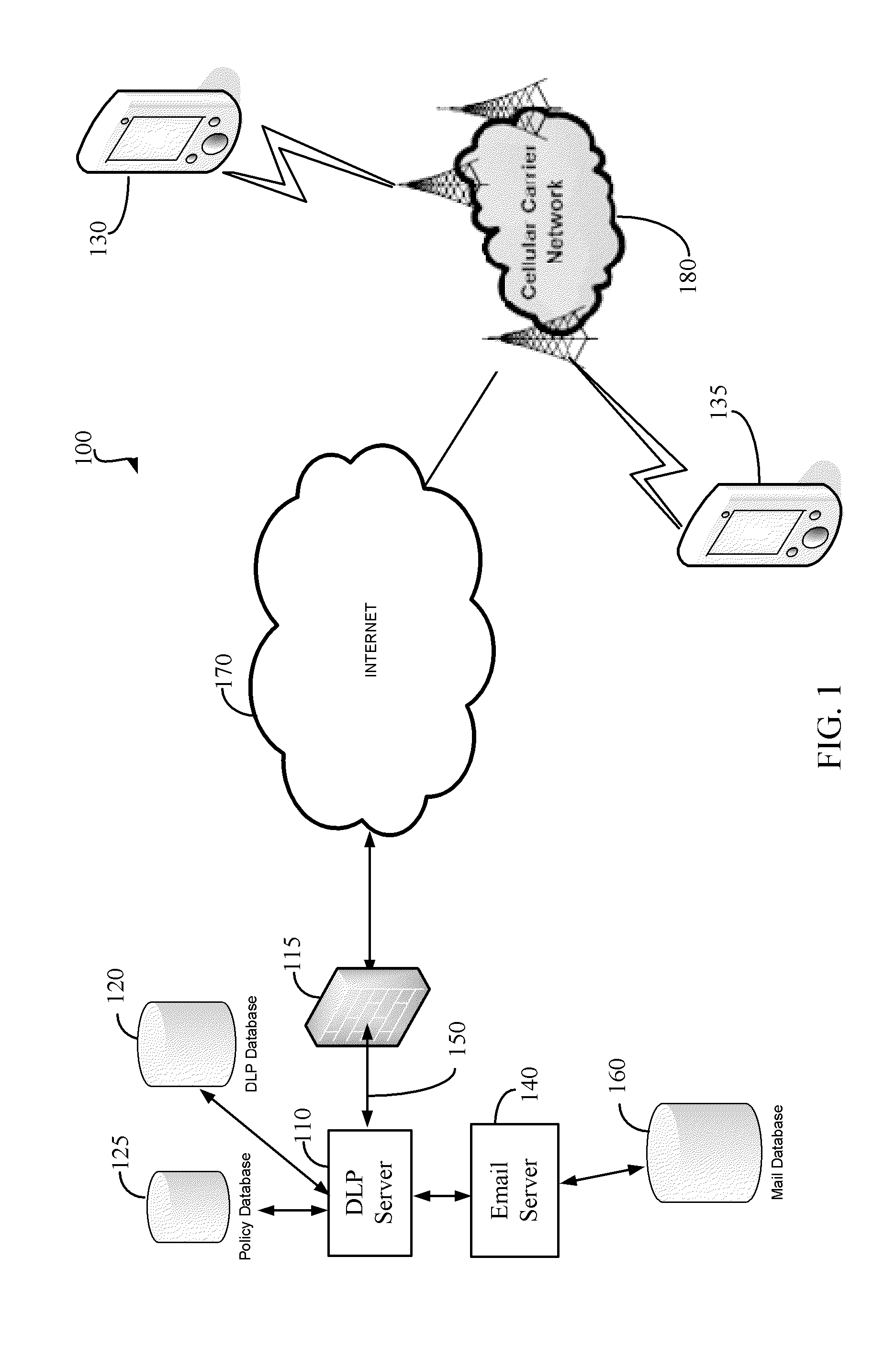
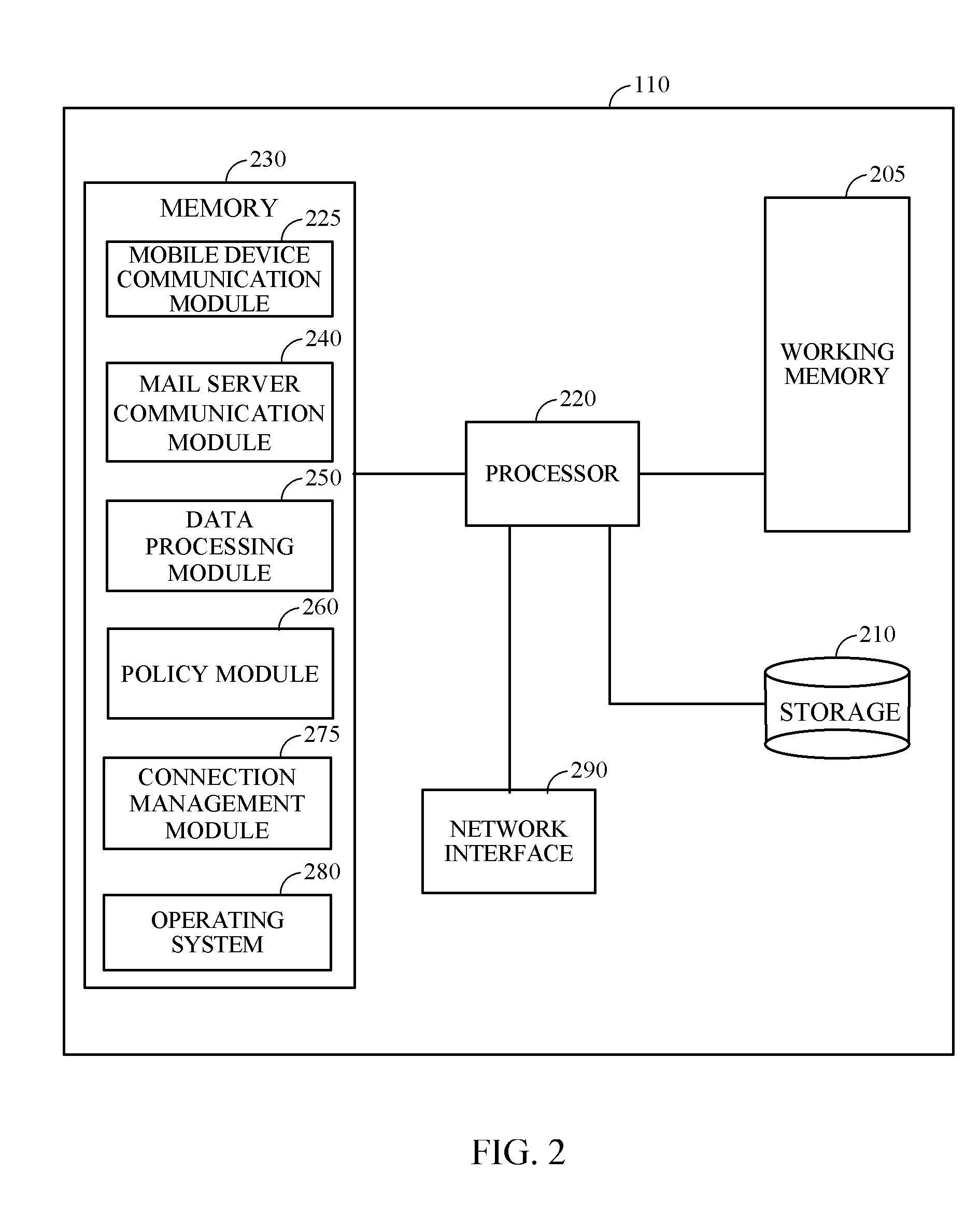
Method and apparatus for managing the transfer of sensitive information to mobile devices
ActiveUS9241259B2Avoid lostUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionData switching networksAnalysis dataMobile device
Methods and apparatus provide data loss protection for mobile devices. In one aspect, data is analyzed by a data loss protection server to determine if it is authorized by data loss protection policies to be transferred to a mobile device. The time necessary to analyze the data may exceed a mobile device timeout value. To prevent the mobile device from timing out, the DLP server may send one or more portions of a response to the mobile device at a time interval less than the mobile device timeout value. Some portions of the response may be sent before the analyzing of the data is completed.
Owner:FORCEPOINT LLC
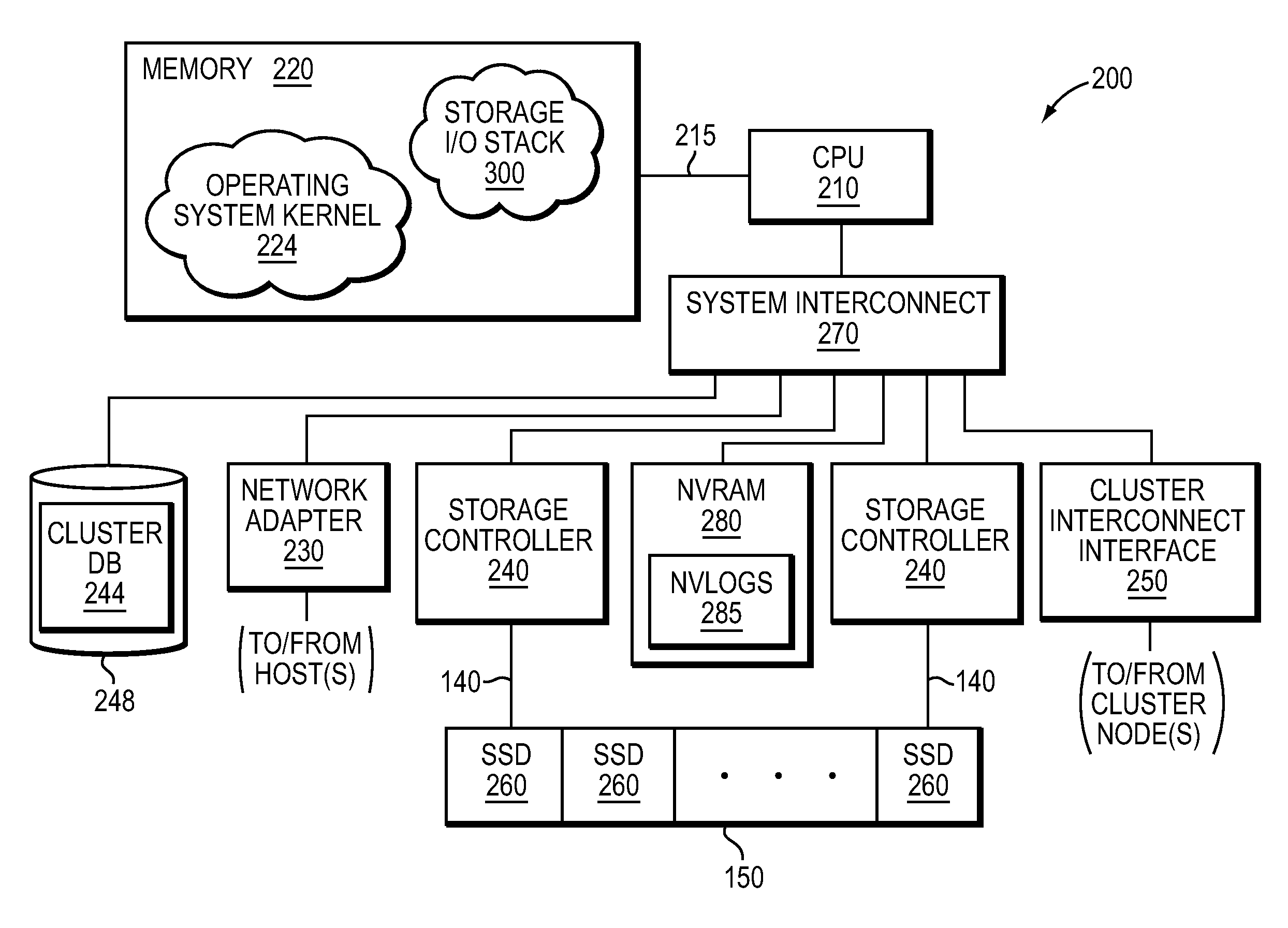
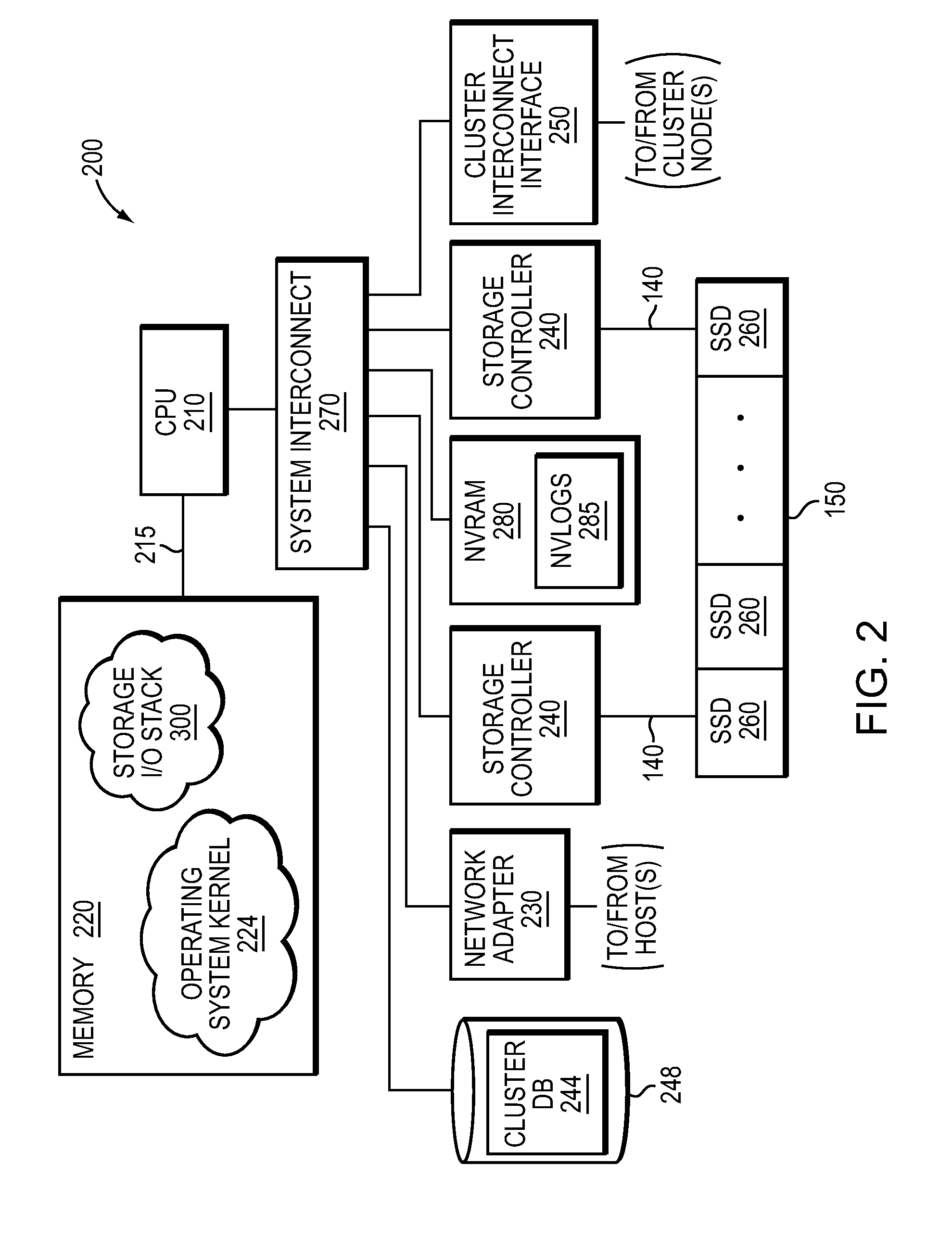
NVRAM caching and logging in a storage system
ActiveUS8898388B1Memory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersLatency (engineering)Solid-state drive
In one embodiment, non-volatile random access memory (NVRAM) caching and logging delivers low latency acknowledgements of input / output (I / O) requests, such as write requests, while avoiding loss of data. Write data may be stored in a portion of an NVRAM configured as, e.g., a persistent write-back cache, while parameters of the request may be stored in another portion of the NVRAM configured as one or more logs, e.g., NVLogs. The write data may be organized into separate variable length blocks or extents and “written back” out-of-order from the write back cache to storage devices, such as solid state drives (SSDs). The write data may be preserved in the write-back cache until each extent is safely and successfully stored on SSD (i.e., in the event of power loss), or operations associated with the write request are sufficiently logged on NVLog.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
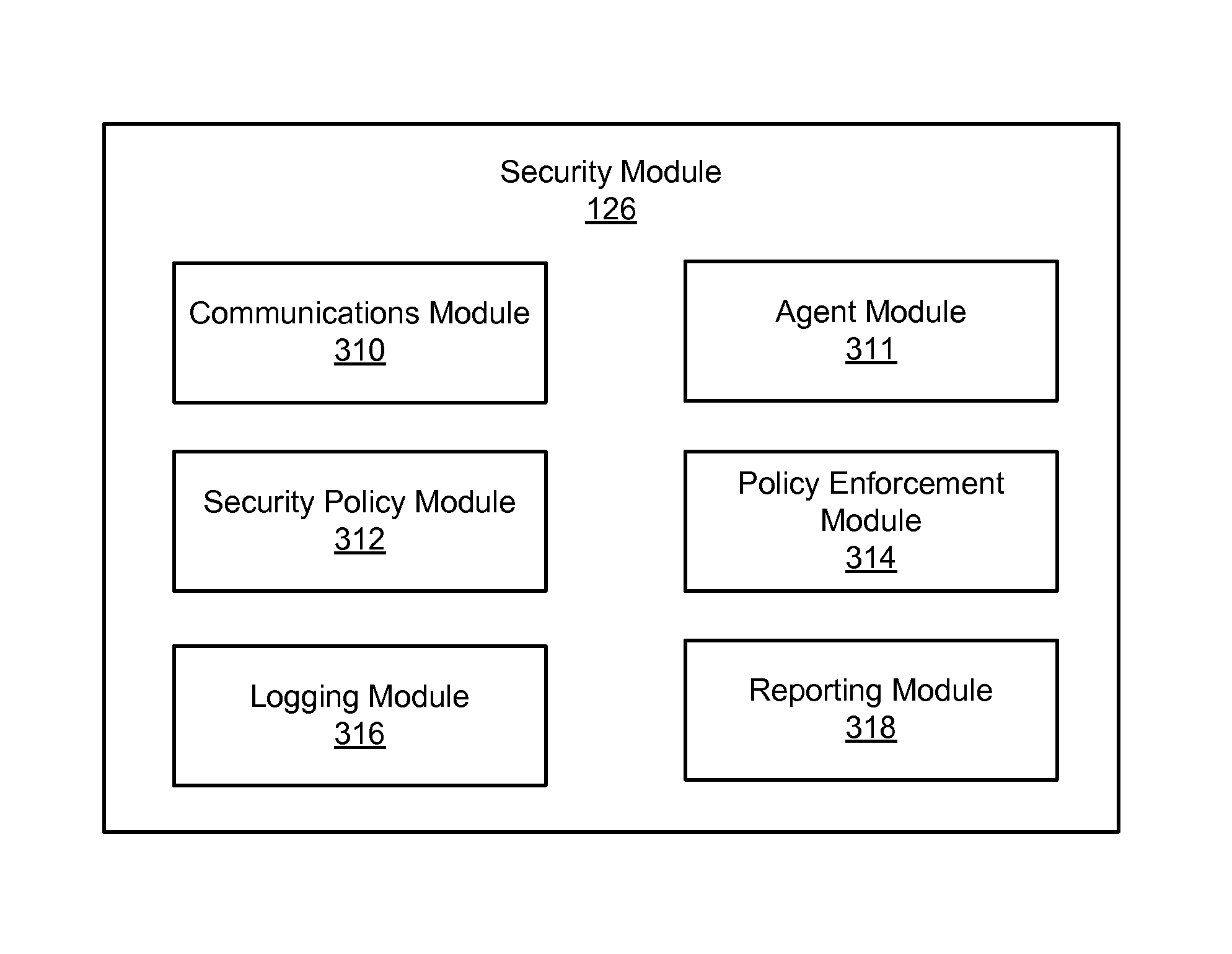
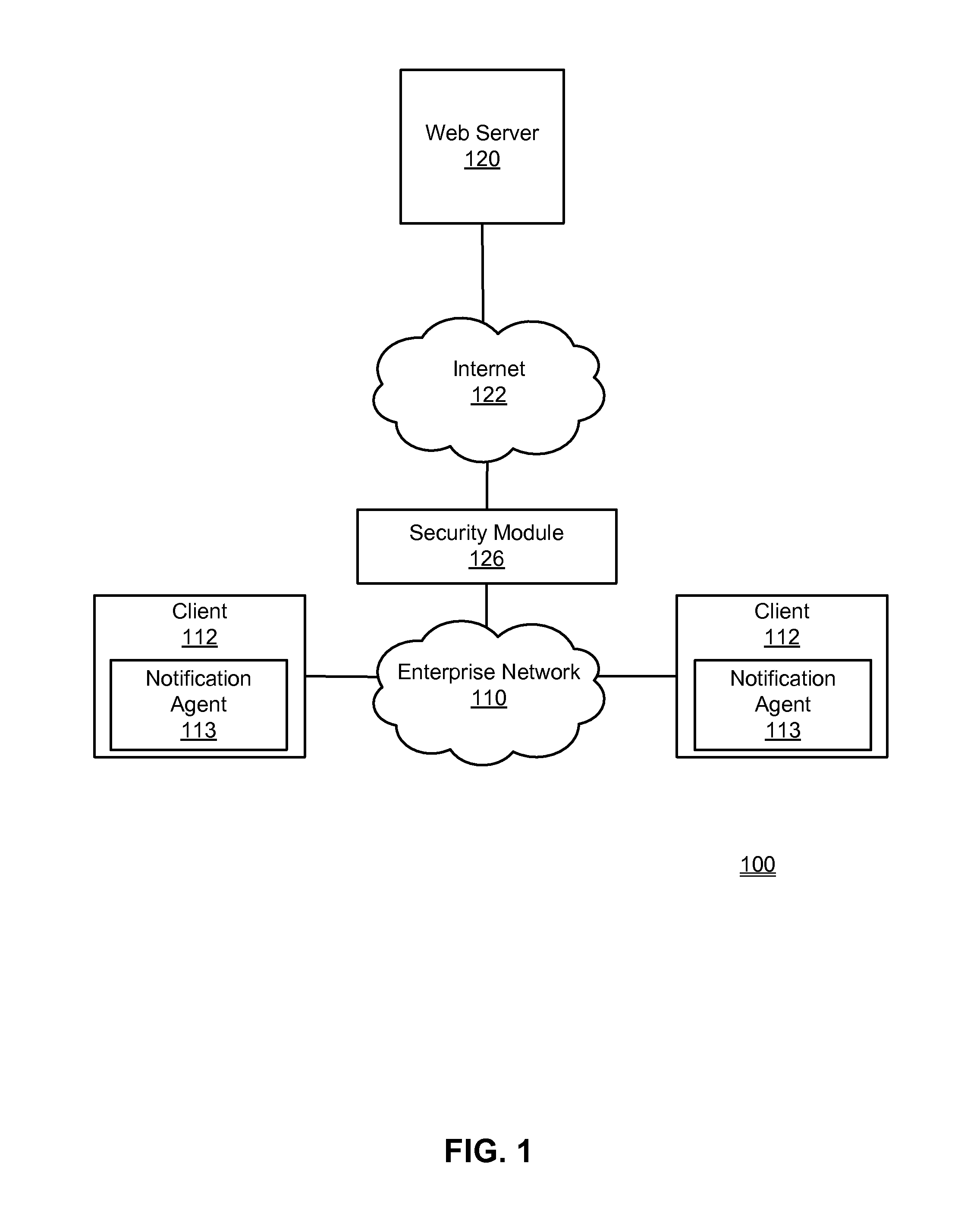
Sending out-of-band notifications
Out-of-band notifications are used to inform users of clients of security policy enforcement actions, such as enforcement of a data loss prevention (DLP) policy. Code for instantiating a notification agent at a client used by a user is inserted into network traffic inbound to the client. Outbound network traffic sent from the client to a server is monitored for compliance with one or more security policies. If it is determined that the network traffic violates a security policy, an enforcement action is taken. An out-of-band notification message describing the enforcement action is inserted into a response to the outbound network traffic and sent to the client. The notification agent at the client receives the notification message and presents the message to the user.
Owner:CA TECH INC
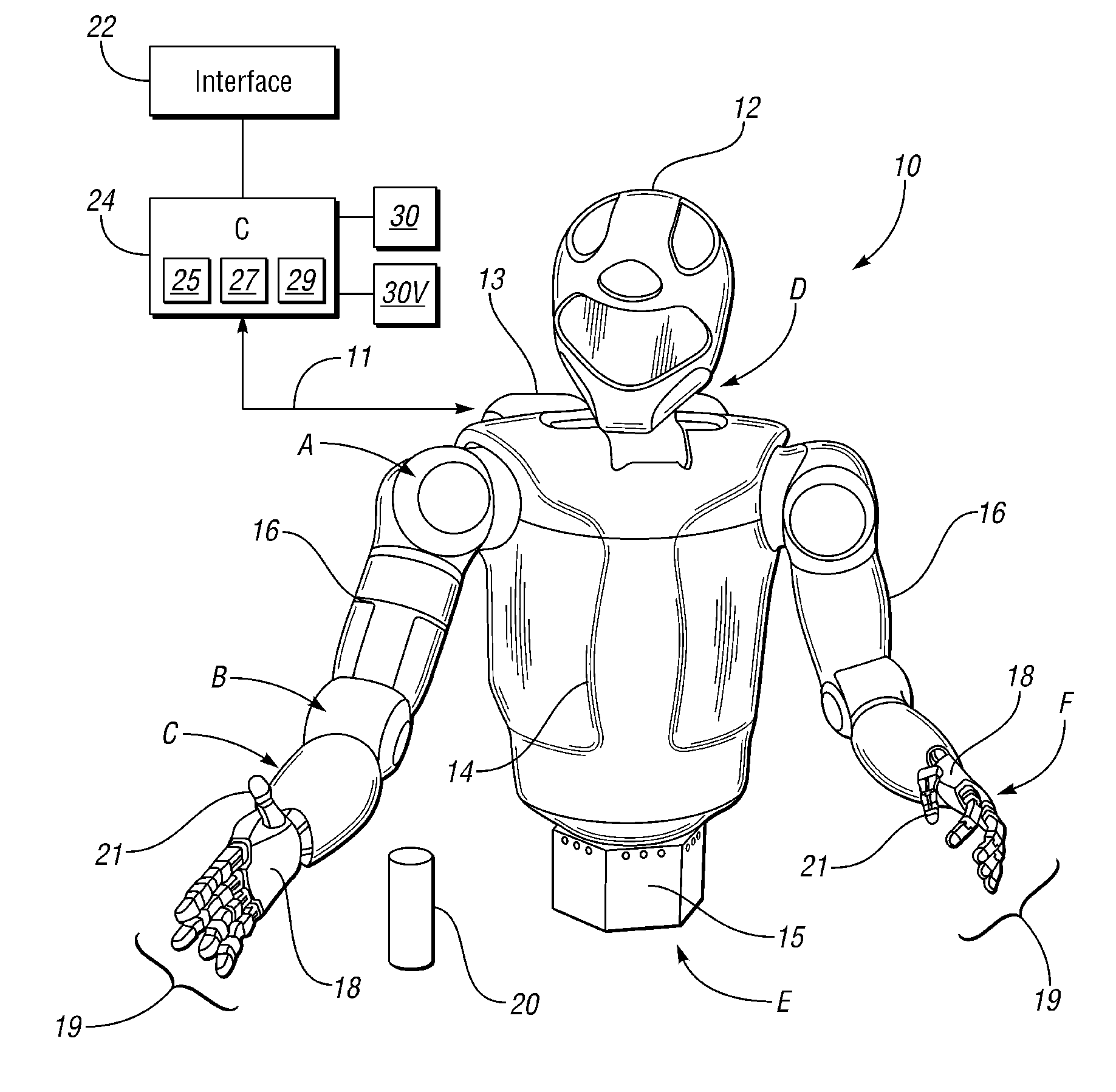
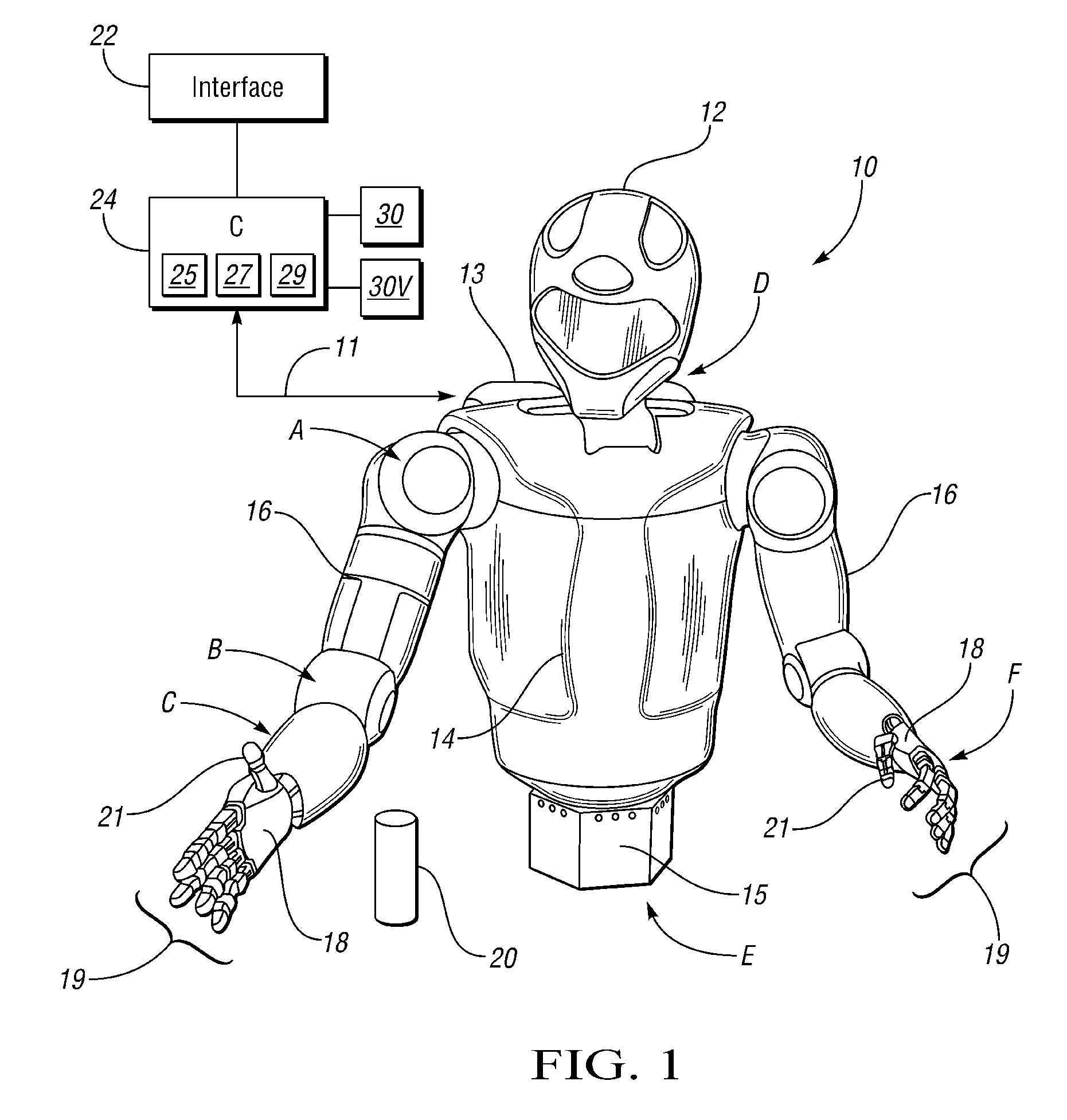
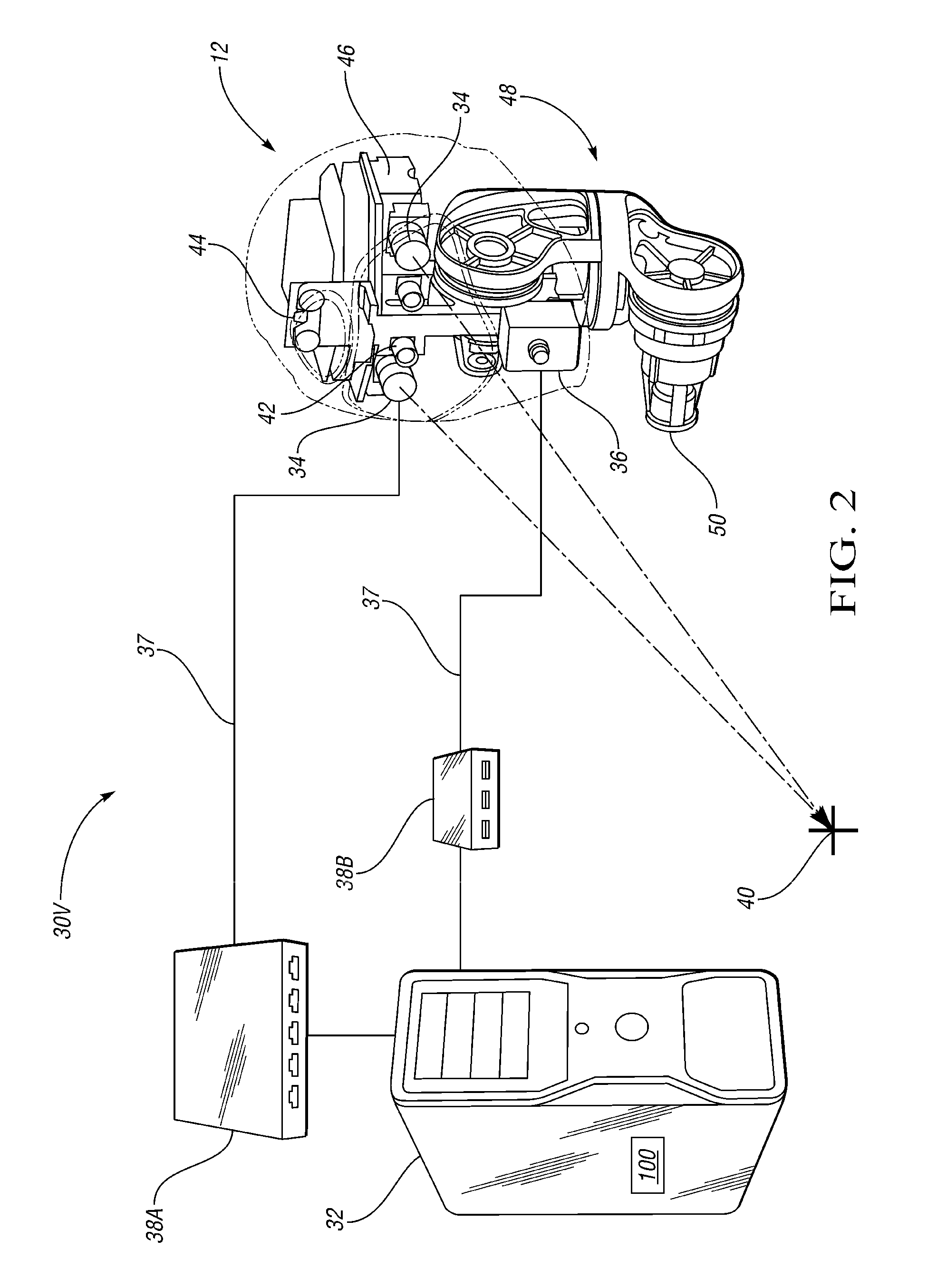
Visual perception system and method for a humanoid robot
ActiveUS20110071675A1Luminance is optimizedAvoid data lossImage enhancementTelevision system detailsRobotic systemsHumanoid robot nao
A robotic system includes a humanoid robot with robotic joints each moveable using an actuator(s), and a distributed controller for controlling the movement of each of the robotic joints. The controller includes a visual perception module (VPM) for visually identifying and tracking an object in the field of view of the robot under threshold lighting conditions. The VPM includes optical devices for collecting an image of the object, a positional extraction device, and a host machine having an algorithm for processing the image and positional information. The algorithm visually identifies and tracks the object, and automatically adapts an exposure time of the optical devices to prevent feature data loss of the image under the threshold lighting conditions. A method of identifying and tracking the object includes collecting the image, extracting positional information of the object, and automatically adapting the exposure time to thereby prevent feature data loss of the image.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
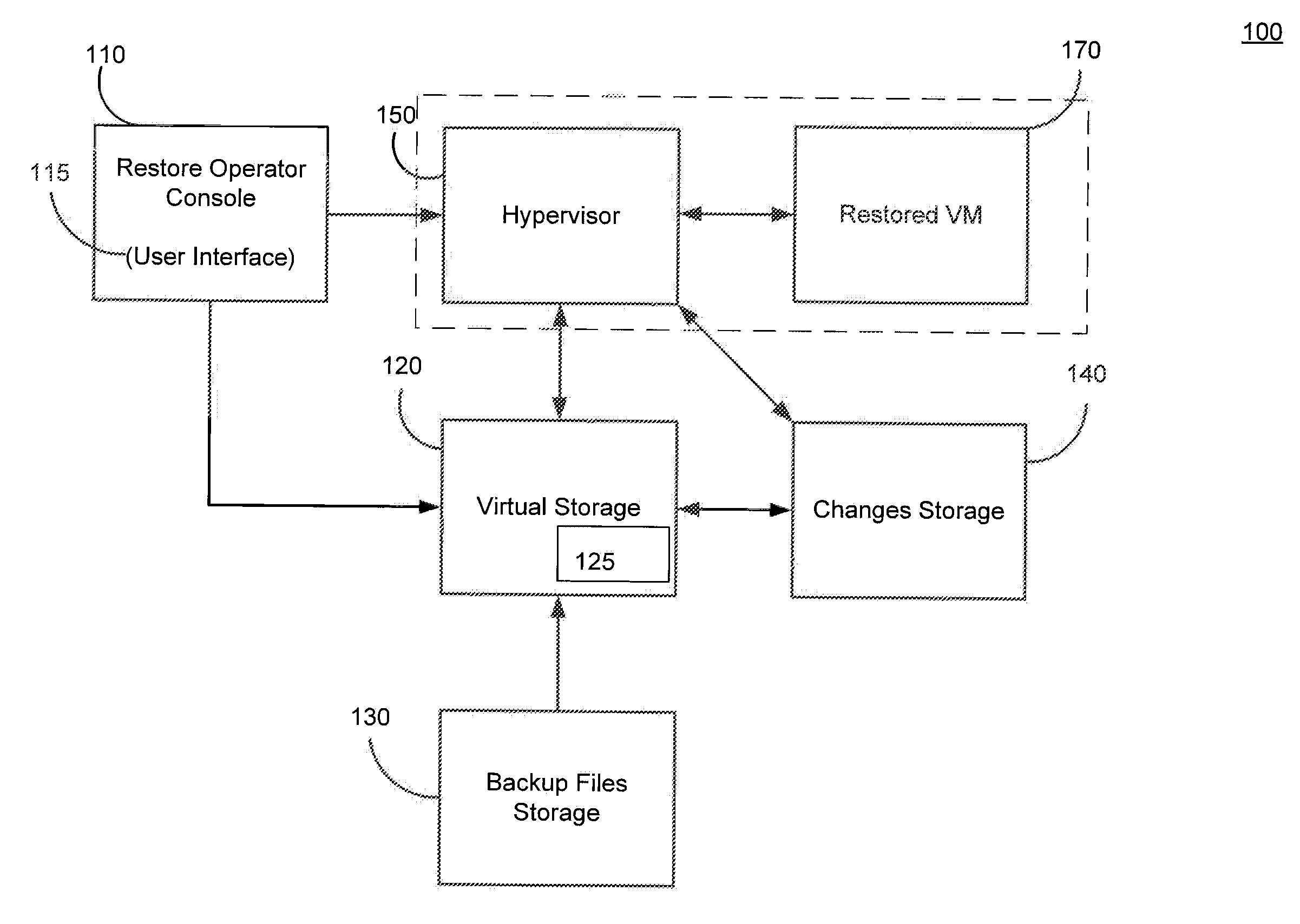
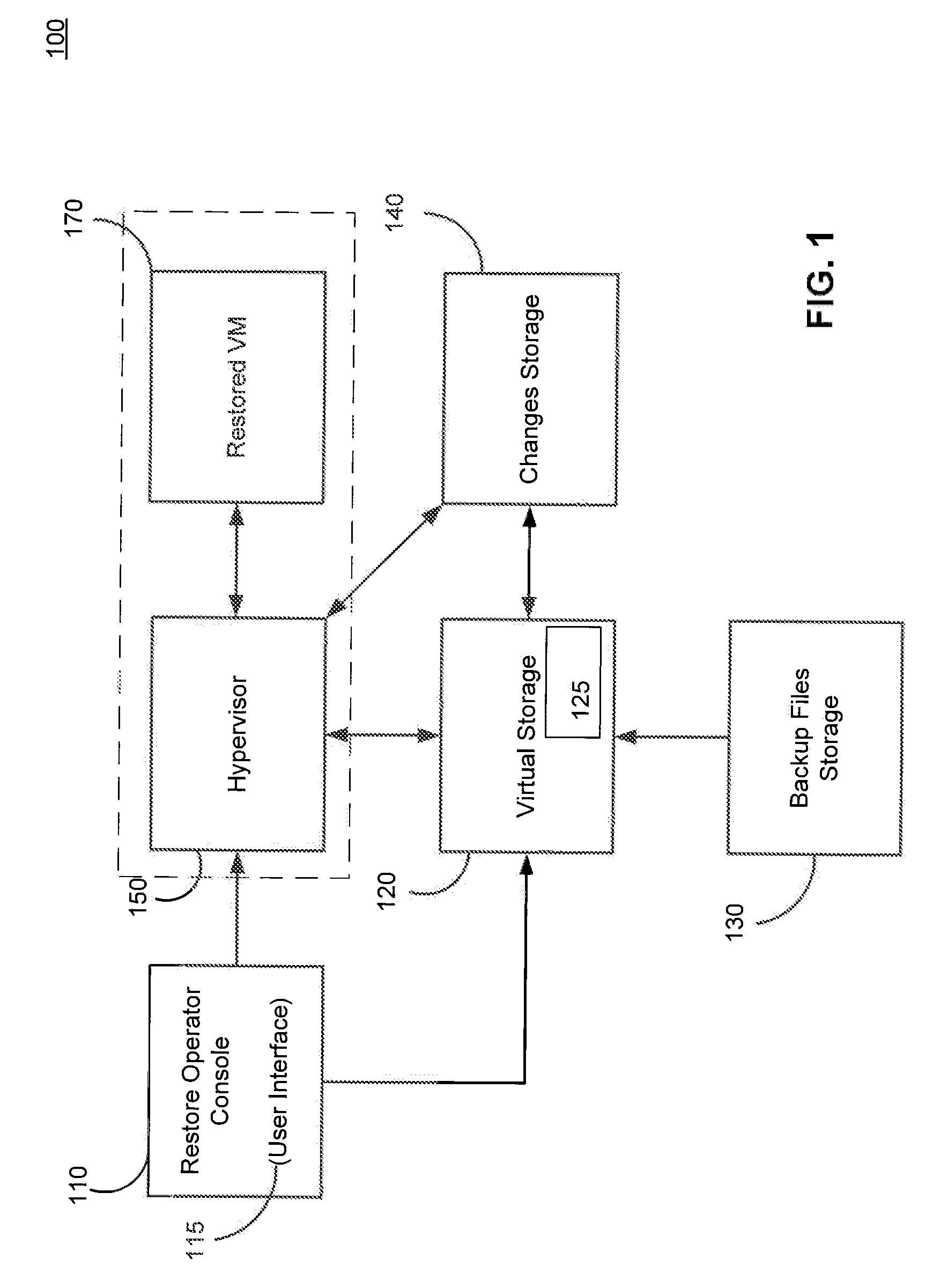
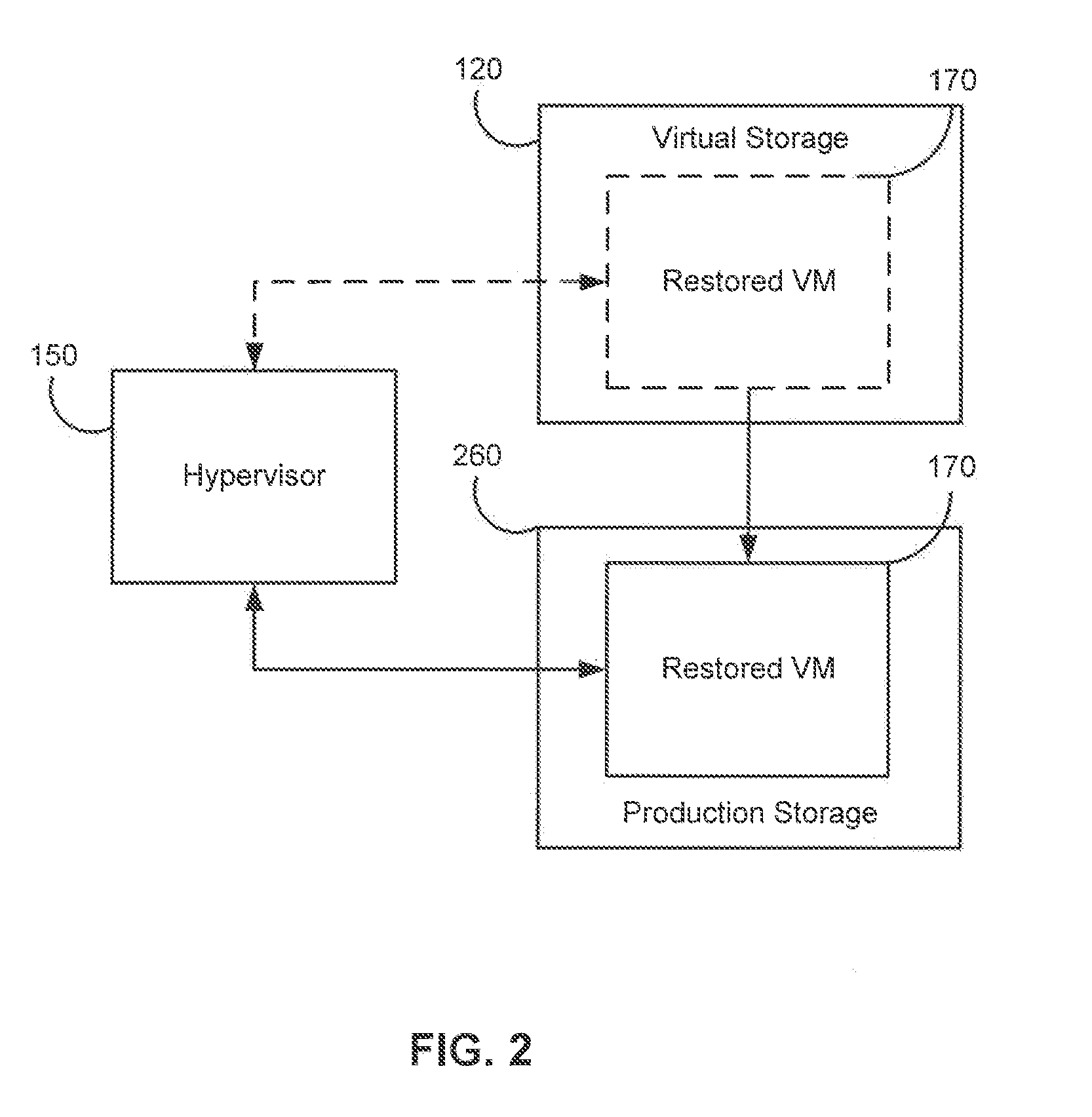
Systems, Methods, and Computer Program Products for Instant Recovery of Image Level Backups
ActiveUS20120017114A1Fault responseSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationOperational systemDowntime
Systems, methods, and computer program products are provided for instant recovery of a virtual machine (VM) from a compressed image level backup without fully extracting the image level backup file's contents to production storage. The method receives restore parameters and initializes a virtual storage. The method attaches the virtual storage to a hypervisor configured to launch a recovered VM. The method stores virtual disk data changes inflicted by a running operating system (OS), applications, and users in a changes storage. The method provides the ability to migrate the actual VM disk state (taking into account changed disk data blocks accumulated in changes storage) so as to prevent data loss resulting from the VM running during the recovery and accessing virtual storage, to production storage without downtime. In embodiments, the method displays receives restore parameters in an interactive interface and delivers the recovery results via an automated message, such as an email message.
Owner:VEEAM SOFTWARE GROUP GMBH
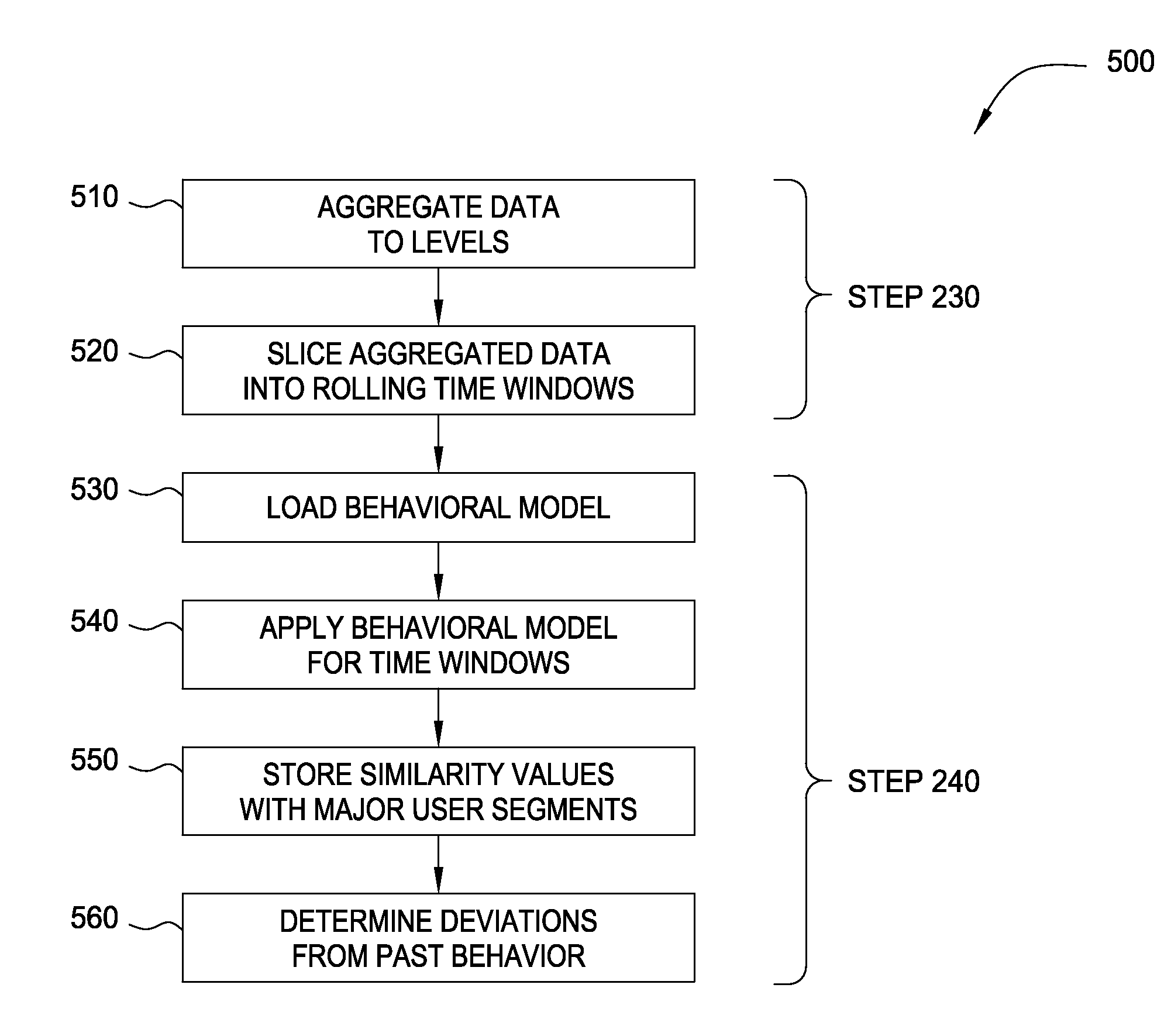
Modeling user access to computer resources
ActiveUS20090292743A1Memory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsComputer resourcesData loss
Embodiments of the invention provide a method for detecting changes in behavior of authorized users of computer resources and reporting the detected changes to the relevant individuals. The method includes evaluating actions performed by each user against user behavioral models and business rules. As a result of the analysis, a subset of users may be identified and reported as having unusual or suspicious behavior. In response, the management may provide feedback indicating that the user behavior is due to the normal expected business needs or that the behavior warrants further review. The management feedback is available for use by machine learning algorithms to improve the analysis of user actions over time. Consequently, investigation of user actions regarding computer resources is facilitated and data loss is prevented more efficiently relative to the prior art approaches with only minimal disruption to the ongoing business processes.
Owner:DAEDALUS BLUE LLC
Apparatus and methods providing redundant routing in a switched network device
InactiveUS6628649B1Improve fault toleranceHigh degreeMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationData transmissionData loss
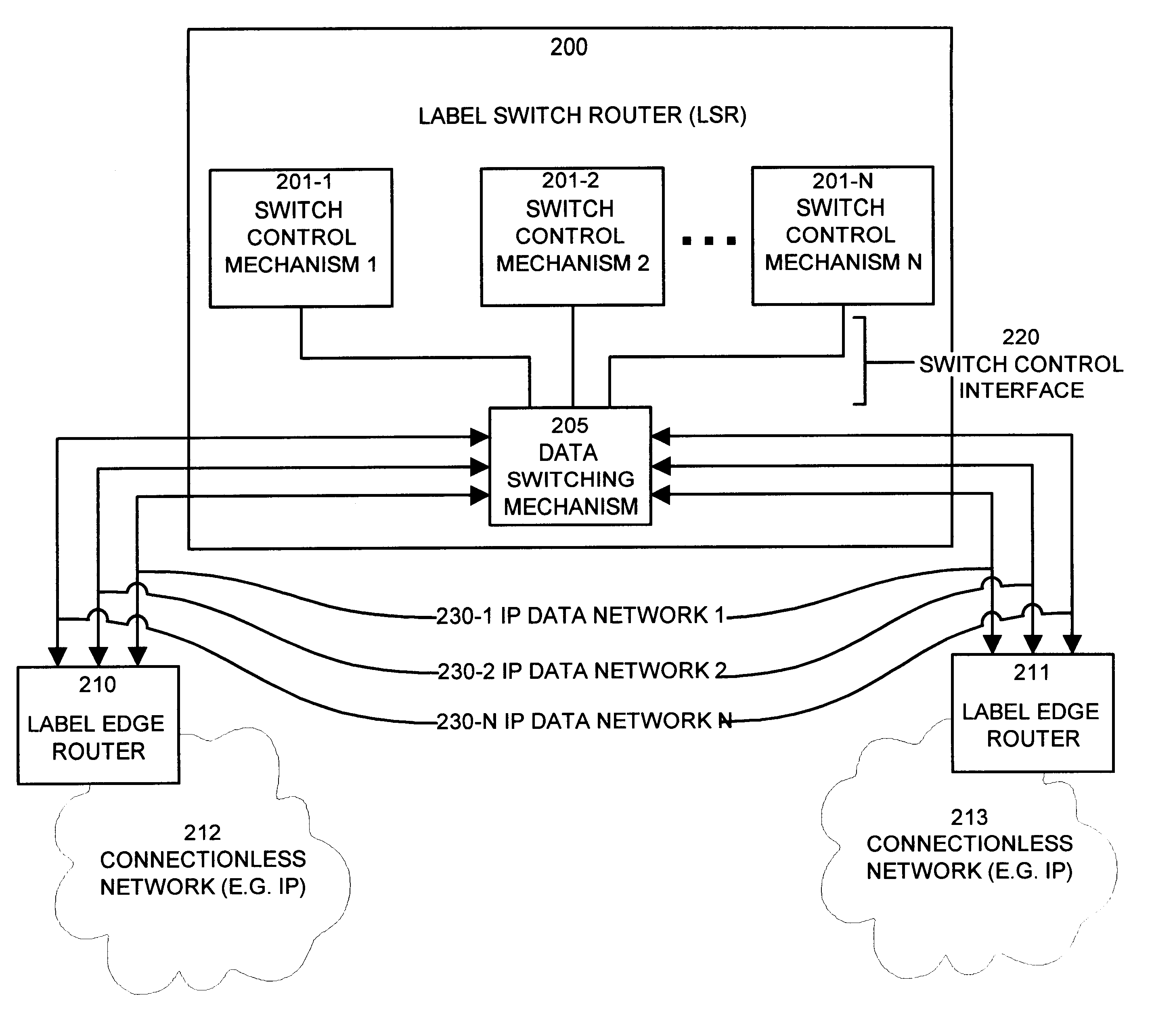
The invention provides unique architectures and techniques for routing redundancy in a data switch configured to use label switching. Multiple label switch controllers (LSCs) each operate concurrently but independently of each other to provide routes through a data switching mechanism. Preferred embodiments provide a plurality of LSCs offering MPLS capabilities coupled to a single switch, such as an ATM switch. The similarly configured LSCs each can concurrently support a route for data (e.g., labeled ATM cells) within the data switching mechanism in parallel, thereby providing the ability to support redundant and multiple parallel data networks. The configuration is called a label switch router (LSR). A fully-meshed embodiment allows selected routes to share bandwidth on ports, while a fully parallel embodiment provides separate ports for selected routes. Since each LSC provides parallel routes with the other LSCs in an LSR, a communications between an LSR and a label edge router (LER) can use multipath routing to concurrently distribute data equally across the parallel routes for each destination. Alternatively, unipath routing techniques can select one route for use for each destination from the available routes concurrently offered by each LSC. In the event of a failure of one of the LSCs, multipath routing implementations can exclude transmission of data onto the failed network, while continuing to use the other parallel networks supported by non-failed LSCs in a concurrent manner. Alternatively, if a failure occurs with unipath routing, a new route offered by another LSC can be selected for data transfers. In either case, the LSC that fails does not need to provide state or connection information to the LSCs that operate subsequently to the failure, since they are already configured in parallel to support the same route. Upon an LSC failure, switch resources such as bandwidth that were used by the failed LSC are made available to the remaining non-failed LSCs. The design allows failures are handled gracefully without diminished network capacity or data loss resulting in a highly reliable routing capability provided within connection-based or circuit-switched networks.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Apparatus for reducing data corruption in a non-volatile memory
InactiveUS20050024968A1Loss and corruption can be preventedEliminate requirementsReliability increasing modificationsRead-only memoriesTime segmentData Corruption
The loss of data and / or the corruption of data that may occur in flash memory when a reset signal is received during a memory write cycle is prevented by delaying reset signals sent to the flash memory for a time period sufficient for a write cycle to be completed. The loss of data and / or the corruption of data that may occur in flash memory when the power supply is interrupted during a write cycle is prevented by providing a DC-to-DC converter with one or more large capacitors in parallel with its input as the power supply to the flash memory. If the system power supply fails or is interrupted, the discharge of the capacitor(s) delays the voltage decay at the input of the DC-to-DC converter such that the output of the DC-to-DC converter remains within tolerance for a time sufficient for the flash memory to complete a write cycle.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
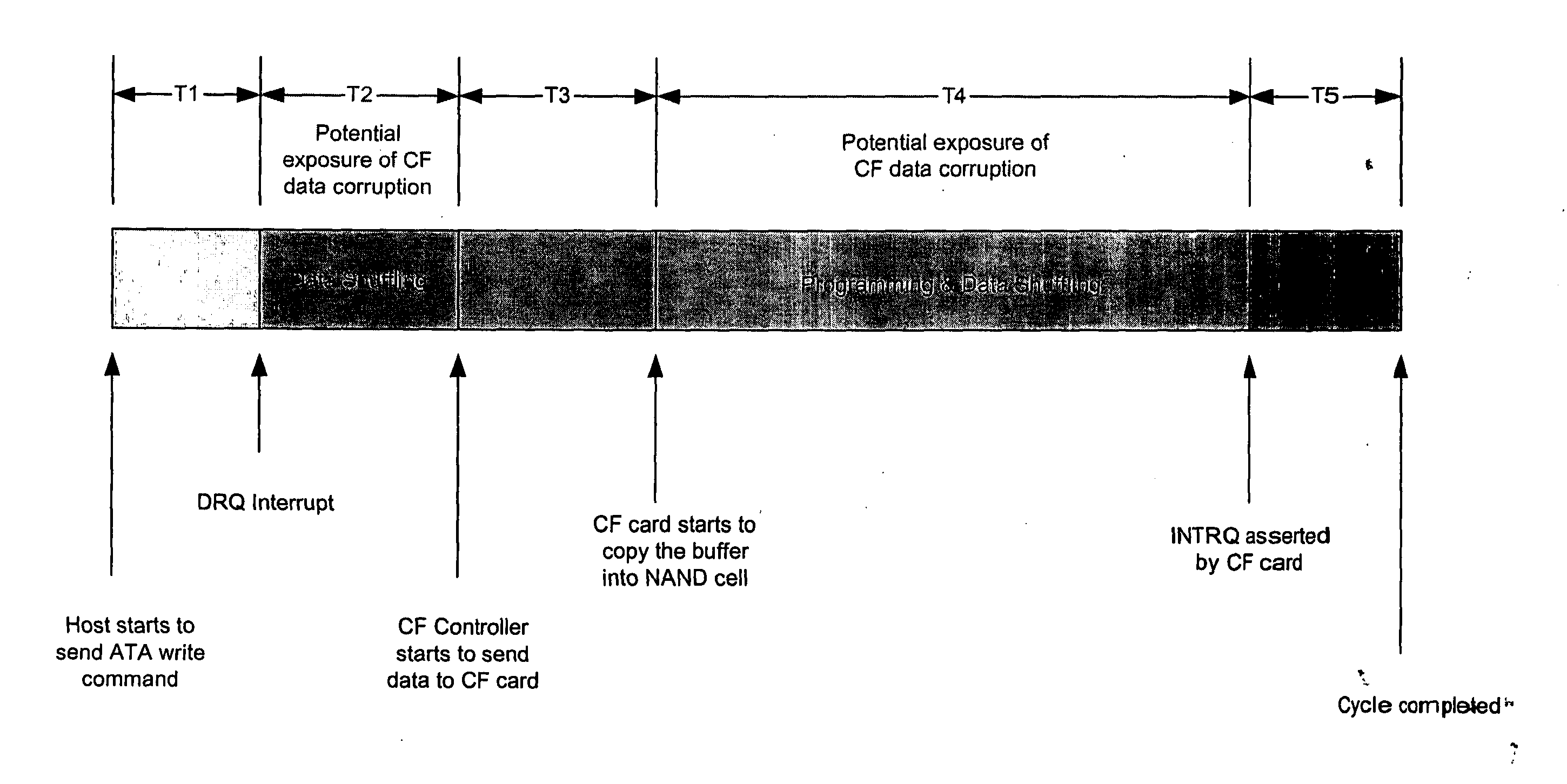
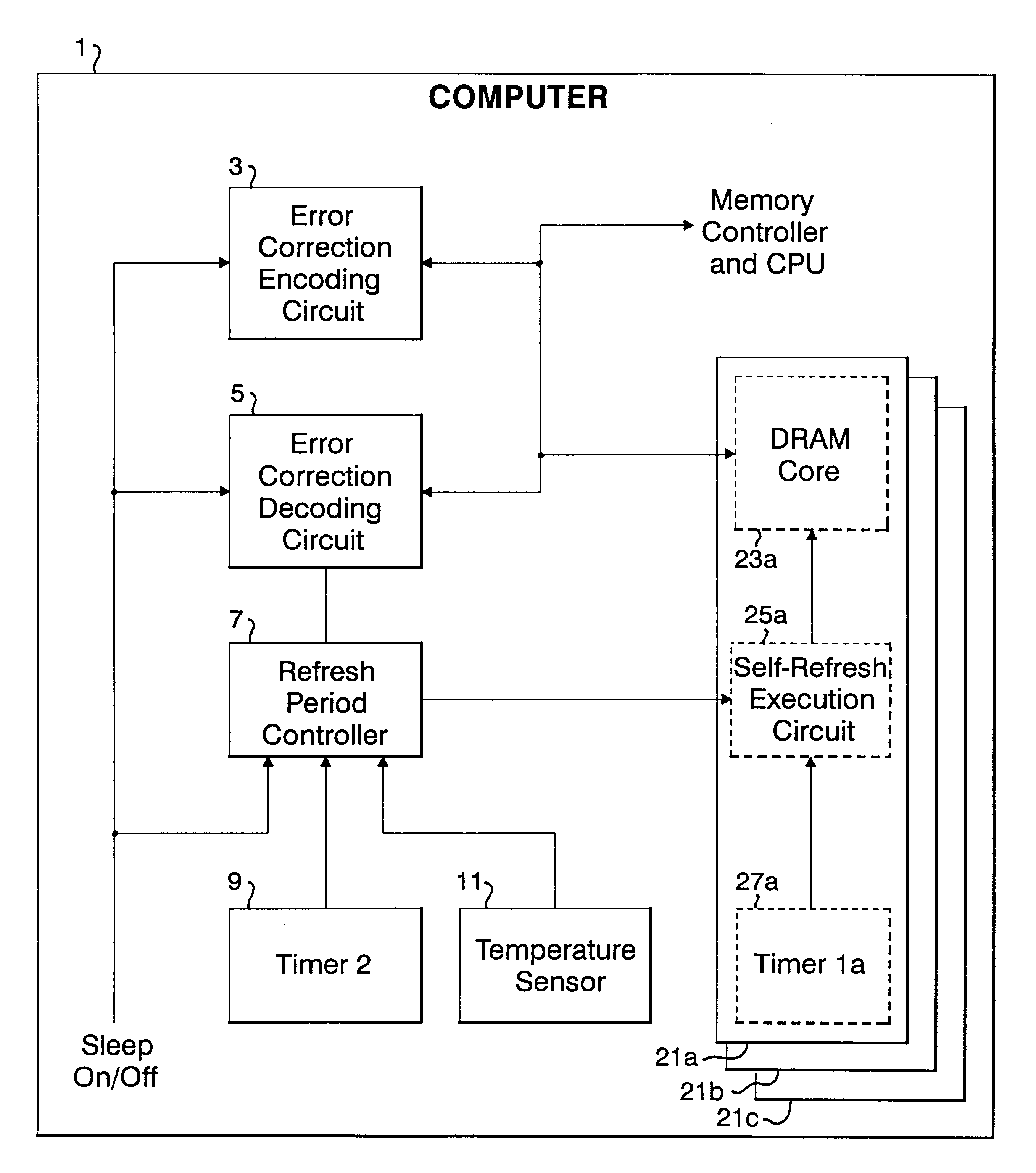
Refresh period control apparatus and method, and computer
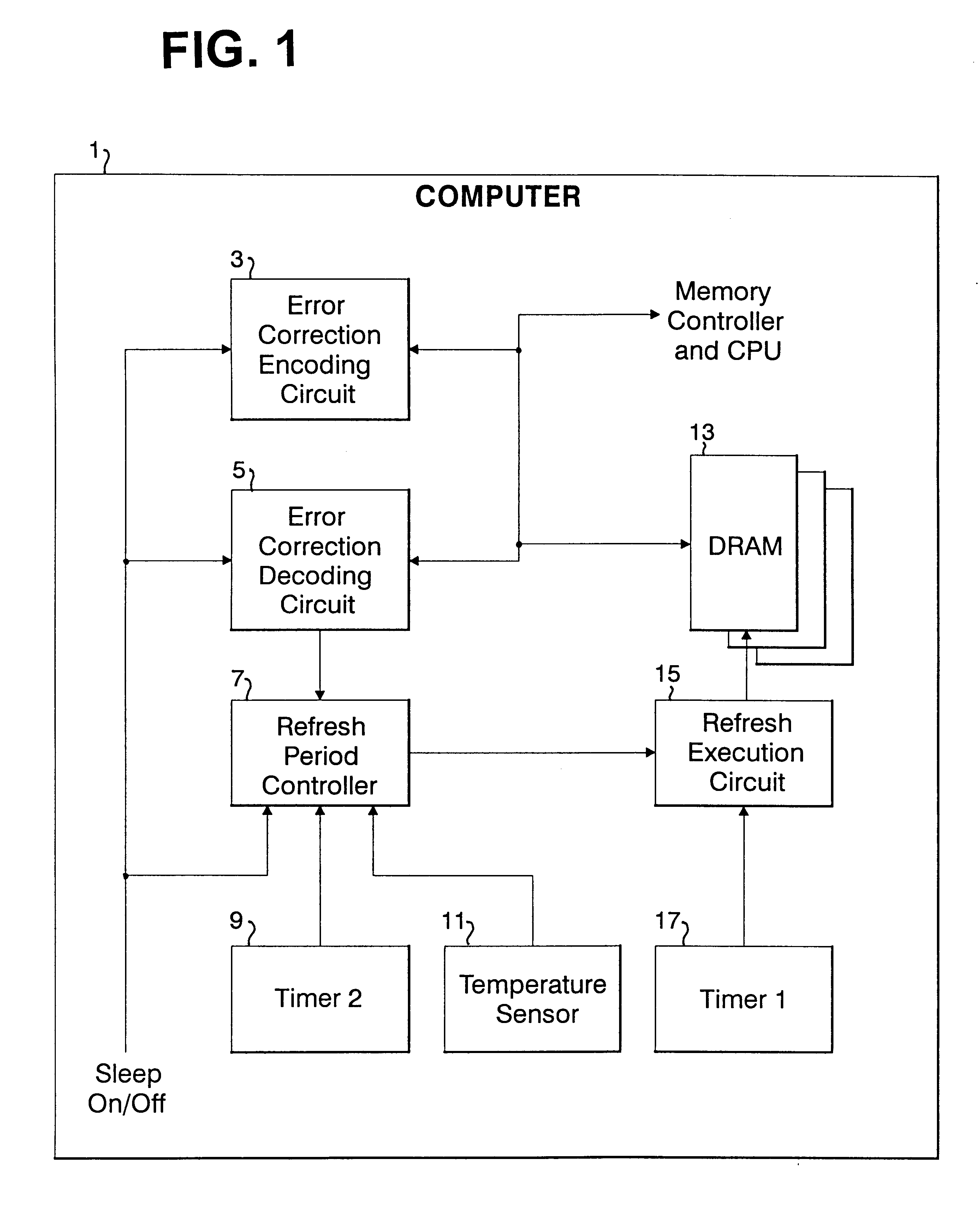
InactiveUS6199139B1Highly effective error correction functionLow costEnergy efficient ICTCode conversionComputer hardwareRefresh cycle
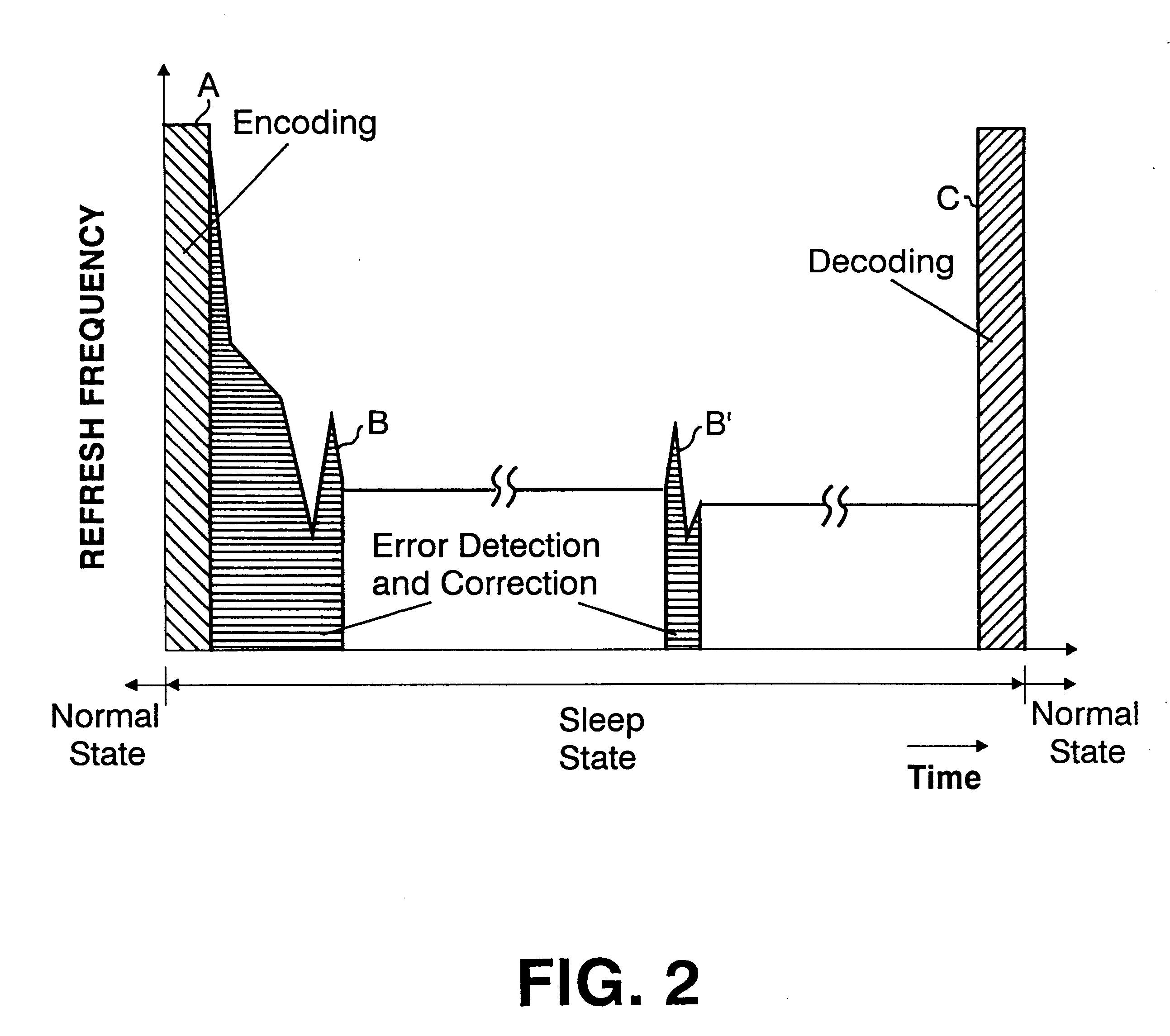
The present invention provides a memory system that optimizes, during a sleep mode, a refresh period for a memory device, such as DRAM, which stores meaningful data and for which a refresh operation is required to prevent the loss of data. More particularly, the present invention is directed to an apparatus for controlling, in a sleep mode, a refresh period for a memory device 13 that requires a refresh operation, comprises: an encoding circuit 3 for encoding data to obtain code that can be used to correct errors equal to or more than dual errors; a decoding circuit 5 for correcting errors and for decoding the corrected code; and a refresh period controller 7 for, following a transition to the sleep mode, changing a refresh period by using data, which is stored in the memory device 13 and encoded by the encoding circuit 3, until the refresh period becomes longest in a condition where there is no error that can not be corrected by the decoding circuit 5 and the number of correctable errors does not exceed a predetermined count, and where a refresh execution circuit 15 for performing the refresh operation for the memory device can deal with the changed refresh period, and for, following the first end of the change of the refresh period, setting the refresh execution circuit 15 so that the refresh of the memory device 13 is performed at the refresh period at the first end of the change of the refresh period.
Owner:IBM CORP
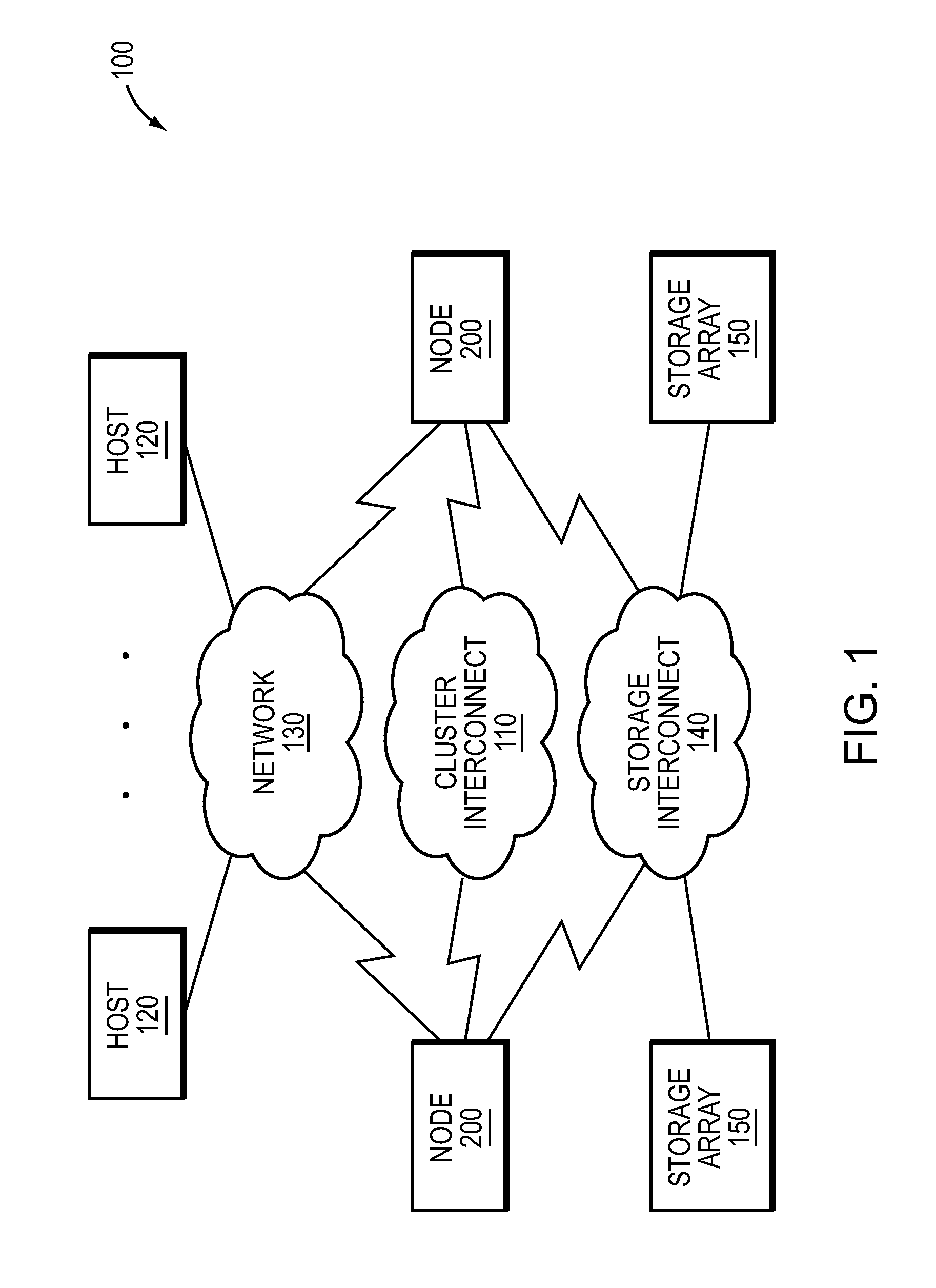
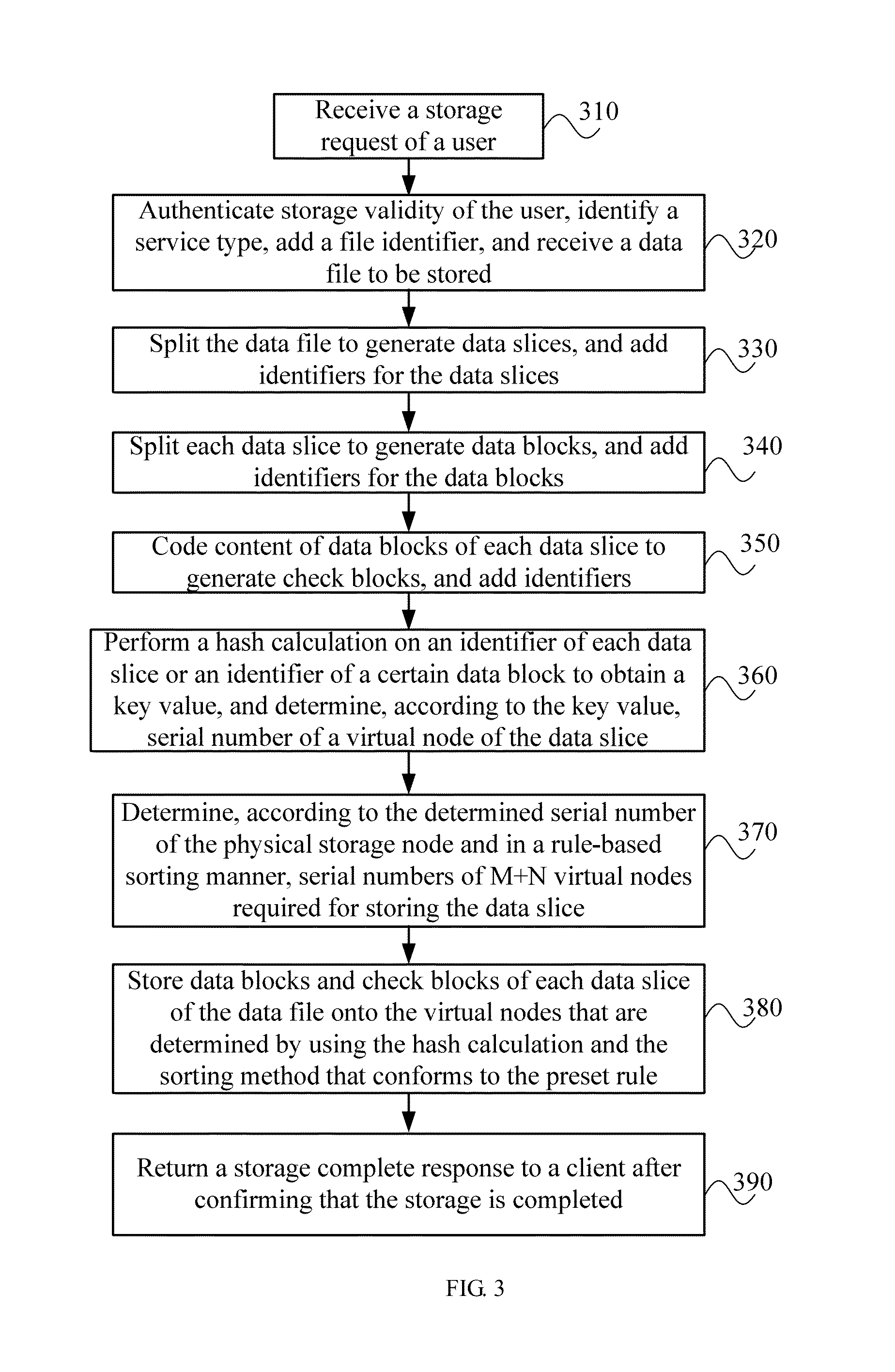
Distributed storage method, apparatus, and system for reducing a data loss that may result from a single-point failure
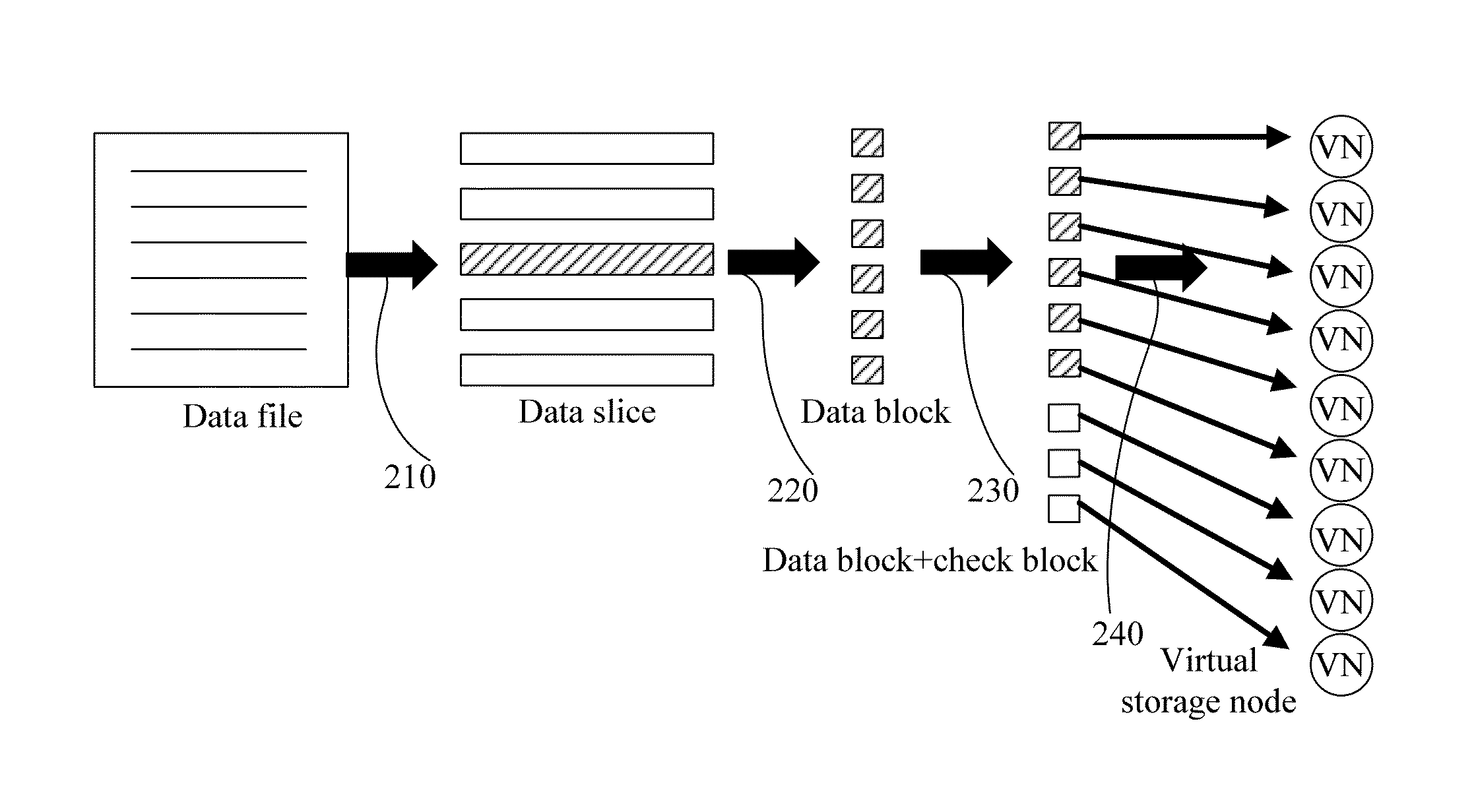
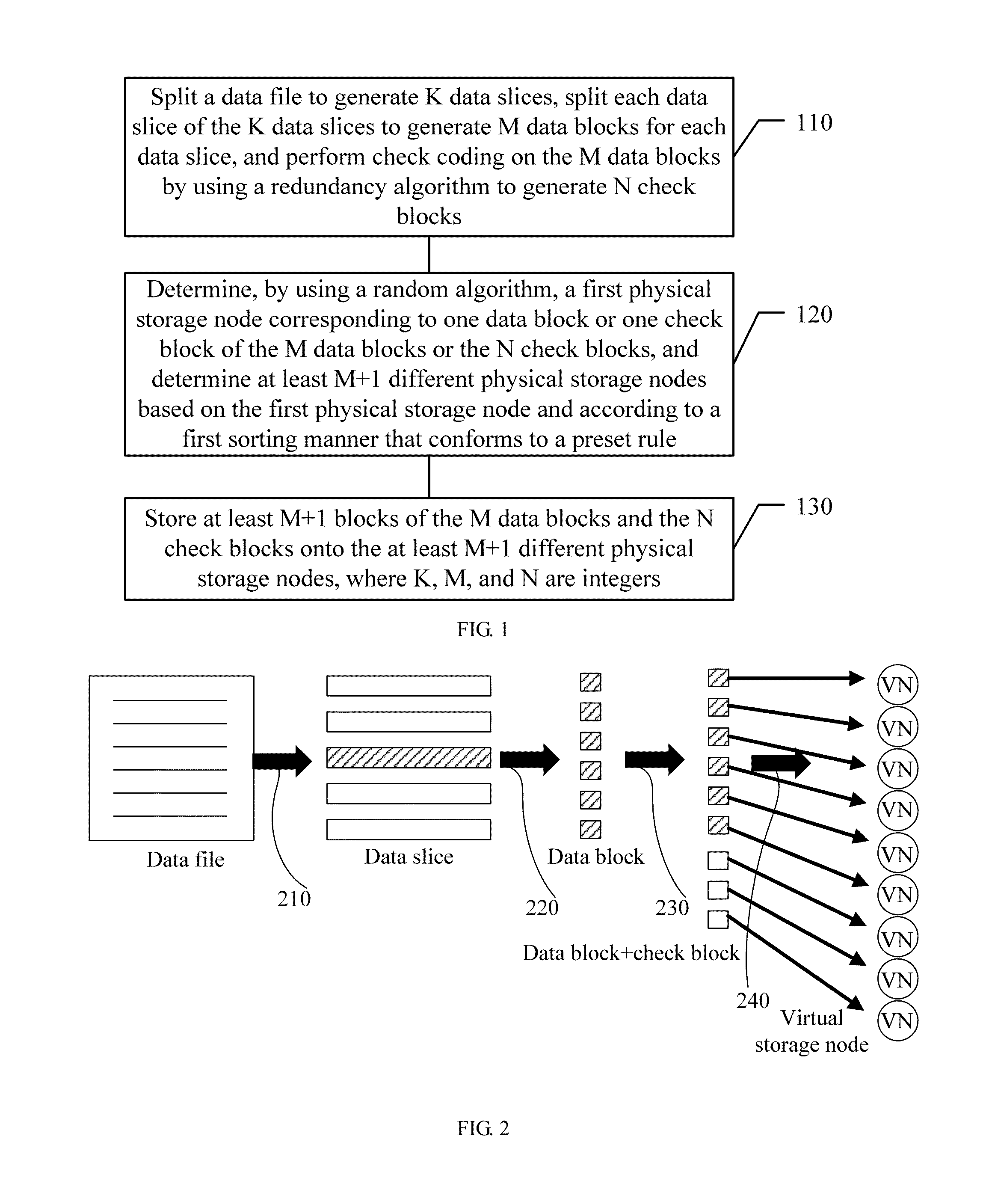
ActiveUS8862847B2Improve reliabilityInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData fileSingle point of failure
A distributed data storage method, apparatus, and system for reducing a data loss that may result from a single-point failure. The method includes: splitting a data file to generate K data slices, splitting each data slice of the K data slices to generate M data blocks for each data slice, and performing check coding on the M data blocks by using a redundancy algorithm to generate N check blocks; determining, by using a random algorithm, a first physical storage node corresponding to one block of the M data blocks and the N check blocks, and determining at least M+1 different physical storage nodes based on the determined first physical storage node and according to a first rule-based sorting manner; and storing at least M+1 blocks of the M data blocks and the N check blocks onto the at least M+1 different storage nodes, where K, M, and N are integers.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Protecting Information Using Policies and Encryption
ActiveUS20130097421A1Ensure confidentialityAvoid data lossDigital data protectionSecuring communicationDocumentation procedureConfidentiality
A technique and system protects documents at rest and in motion using declarative policies and encryption. Encryption in the system is provided transparently and can work in conjunction with policy enforcers installed at a system. A system can protect information or documents from: (i) insider theft; (ii) ensure confidentiality; and (iii) prevent data loss, while enabling collaboration both inside and outside of a company.
Owner:NEXTLABS
Systems and methods for providing conflict handling for peer-to-peer synchronization of units of information manageable by a hardware/software interface system
InactiveUS20050044187A1Efficient application developmentFacilitate data sharingDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsThree stageUsability
Various embodiments of the present invention are directed to conflict handling for conflicts that occur in a peer-to-peer synchronization system, where the ability to correctly and efficiently handle conflicts minimizes data loss while retaining good usability and reduces the need for user intervention during synchronization. Conflict handling in the synchronization service is divided into three stages: (1) conflict detection; (2) automatic conflict resolution and logging; and (3) conflict inspection and resolution. Certain embodiments are directed to a conflict handling schema comprising one or more of the follow conflict handling elements: (a) schematized representation of conflicts; (b) detection of conflicts; (c) logging of conflicts into a durable store; (d) automatic resolution of conflicts according to a flexible and configurable azqsxqxwdconflict resolution policy; (e) composable and extensible conflict handlers to filter and resolve conflicts; (f) automatic detection and removal of obsolete conflicts; and (g) programmatic conflict resolutions.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Methods and apparatus for selecting a wireless network based on quality of service (QoS) criteria associated with an application
ActiveUS7318111B2Assess restrictionMultiple digital computer combinationsQuality of serviceVideo player
Methods and apparatus for selecting a wireless communication network based on quality of service criteria associated with an application are disclosed. In one illustrative example, one of several different software applications of a mobile communication device is executed. The software application may be, for example, an e-mail application, an Internet data application, a voice-over-IP application, a video player application, an audio player application, or a video game application. Each software application is associated with different quality of service (QoS) criteria for data communications through a wireless network. The quality of service criteria may include, for example, a bandwidth criterion, a delay criterion, a delay variation criterion, and a data loss criterion. A scanning operation is performed to identify a plurality of a wireless networks available in a coverage area of the mobile device. One of the identified wireless networks is selected for communication based on a match between its available quality of service and the quality of service criterion associated with the executed software application. Advantageously, the most suitable network may be chosen and utilized for each software application.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
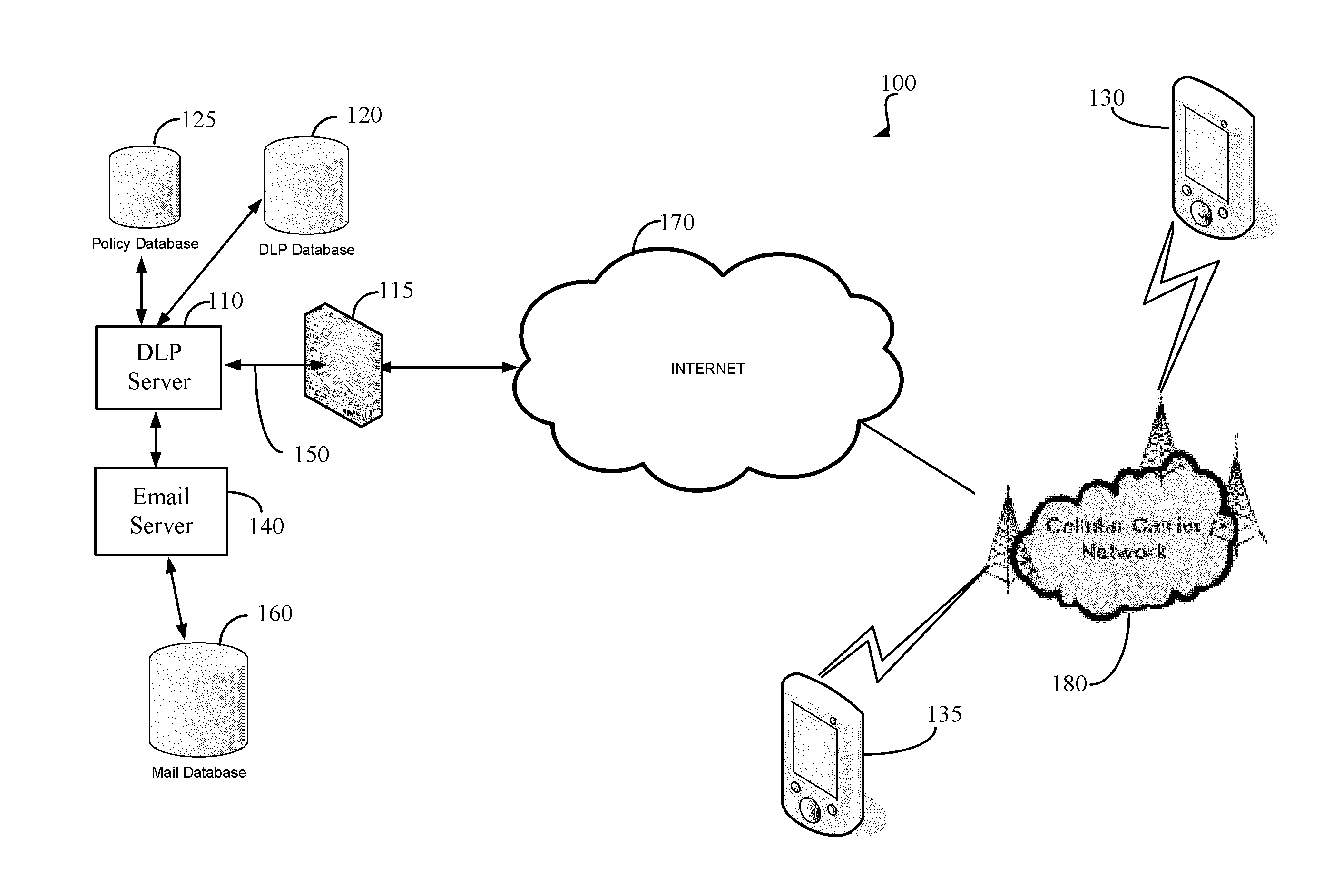
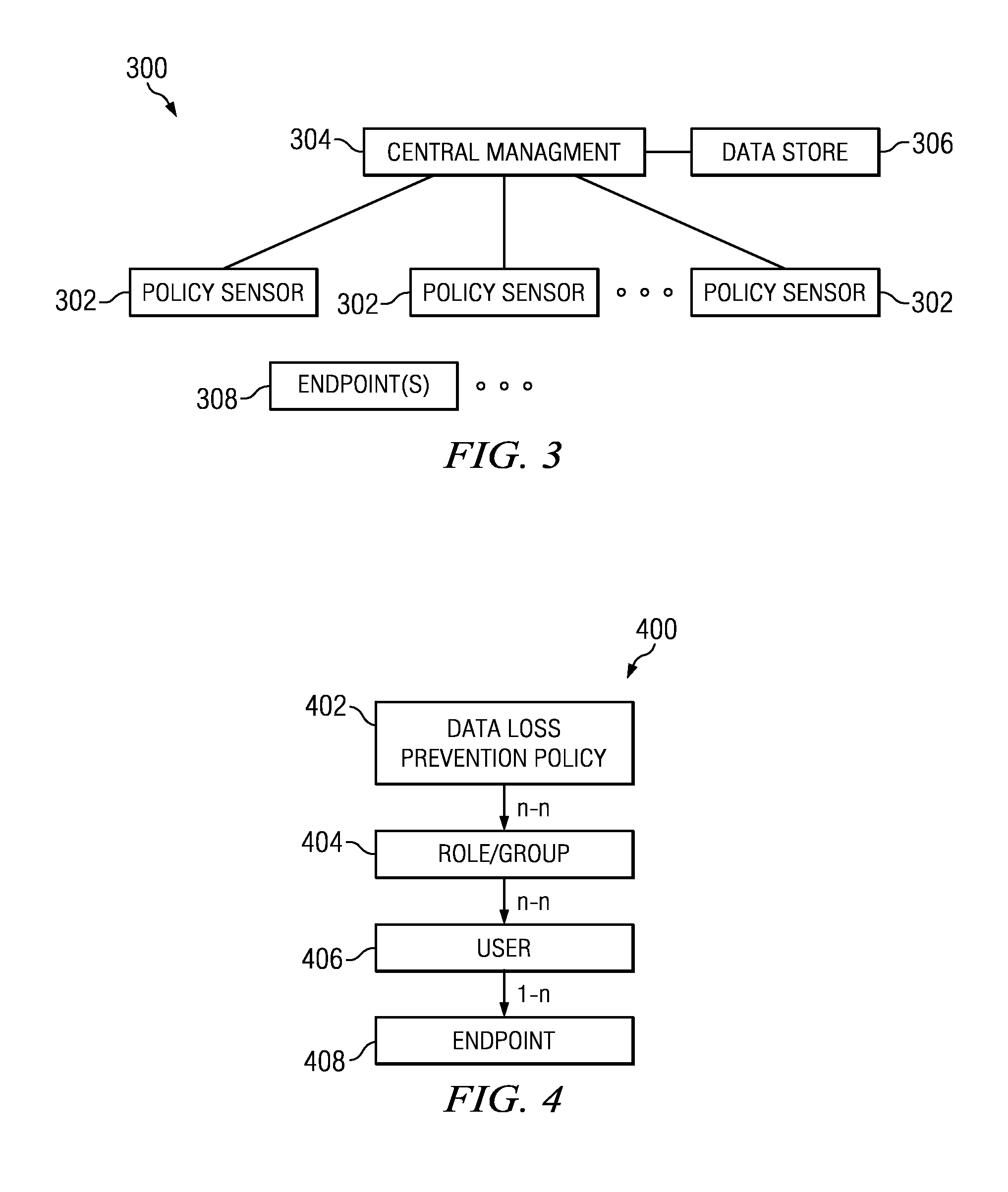
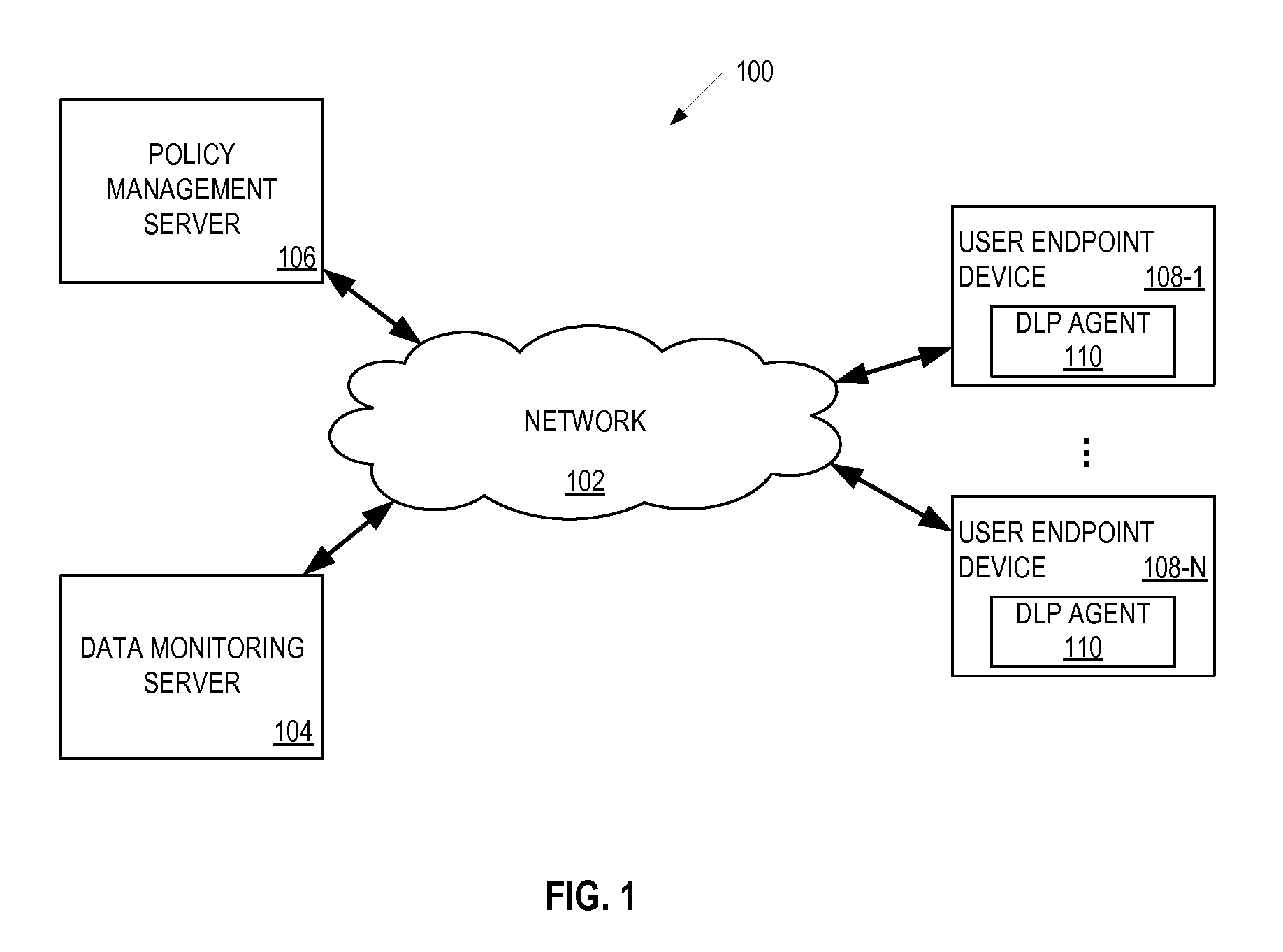
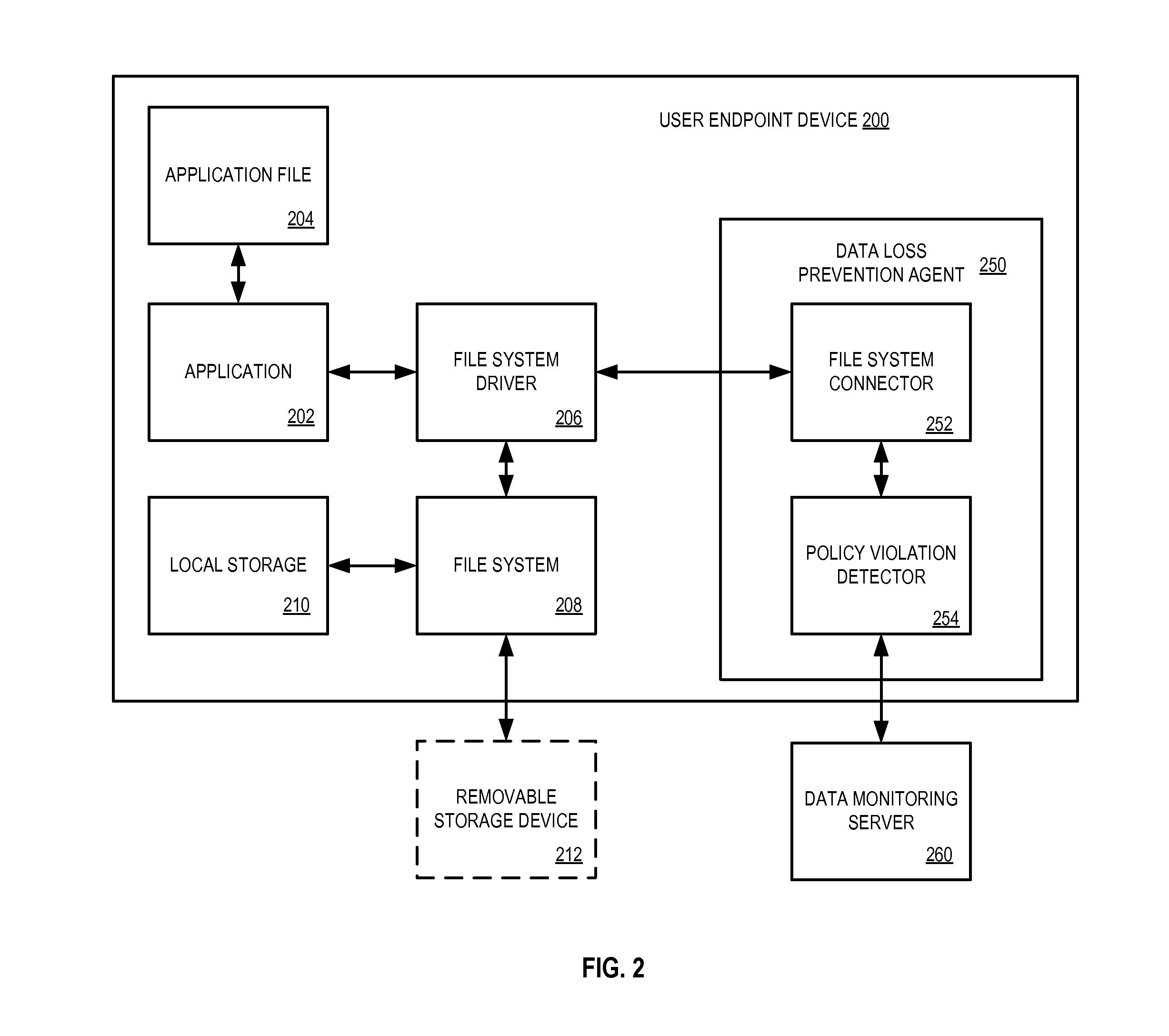
Method and apparatus for associating data loss protection (DLP) policies with endpoints
A method of policy management in a Data Loss Prevention (DLP) system uses a policy model that associates a user with one or more DLP endpoints. When an endpoint is added to the system, a set of policies for that endpoint are determined using an identity of the user that is associated with the endpoint and a list of roles or groups for that user. At policy distribution time, the method determines a set of endpoints to which the policy is to be distributed.
Owner:SAILPOINT TECH HLDG INC
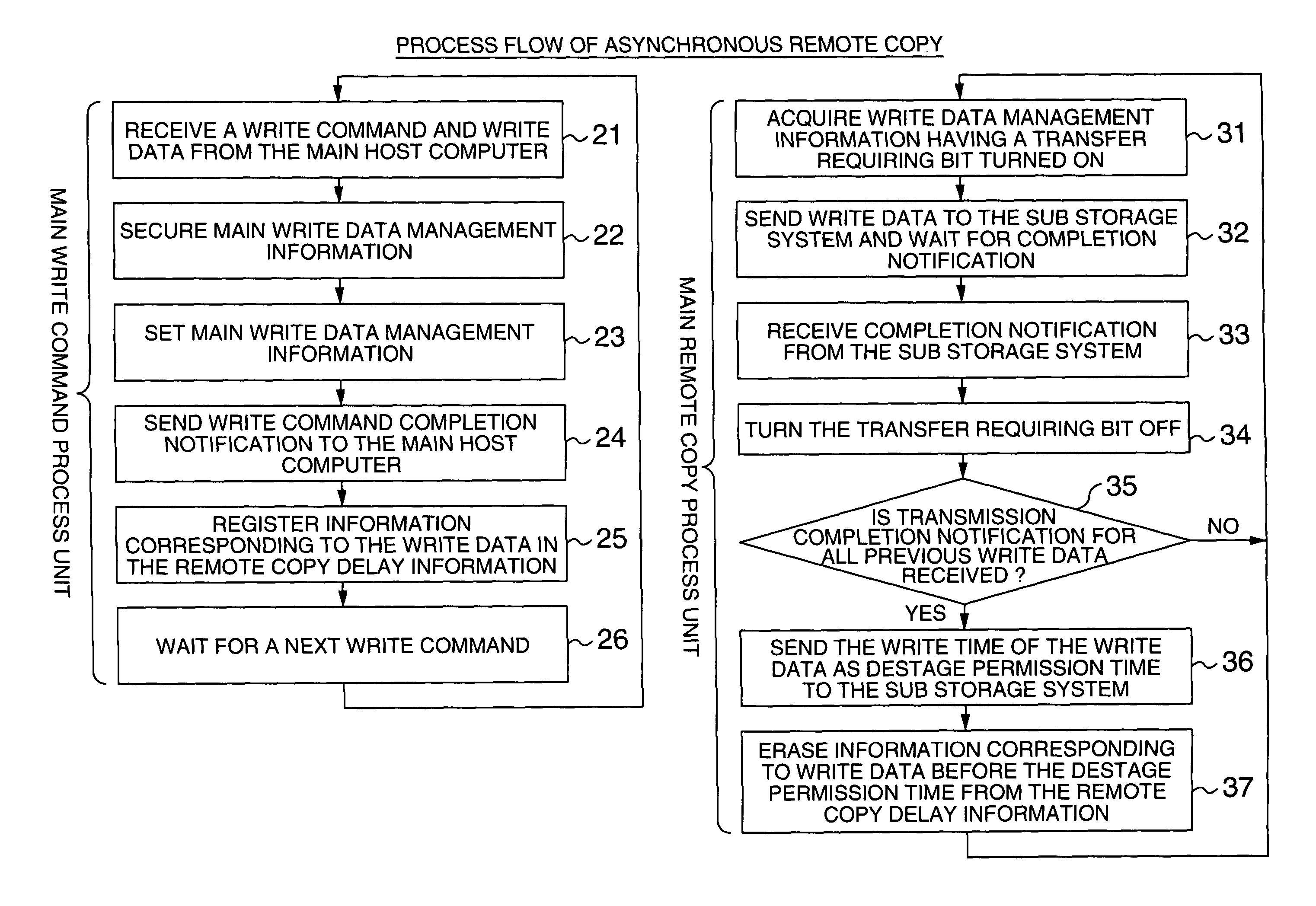
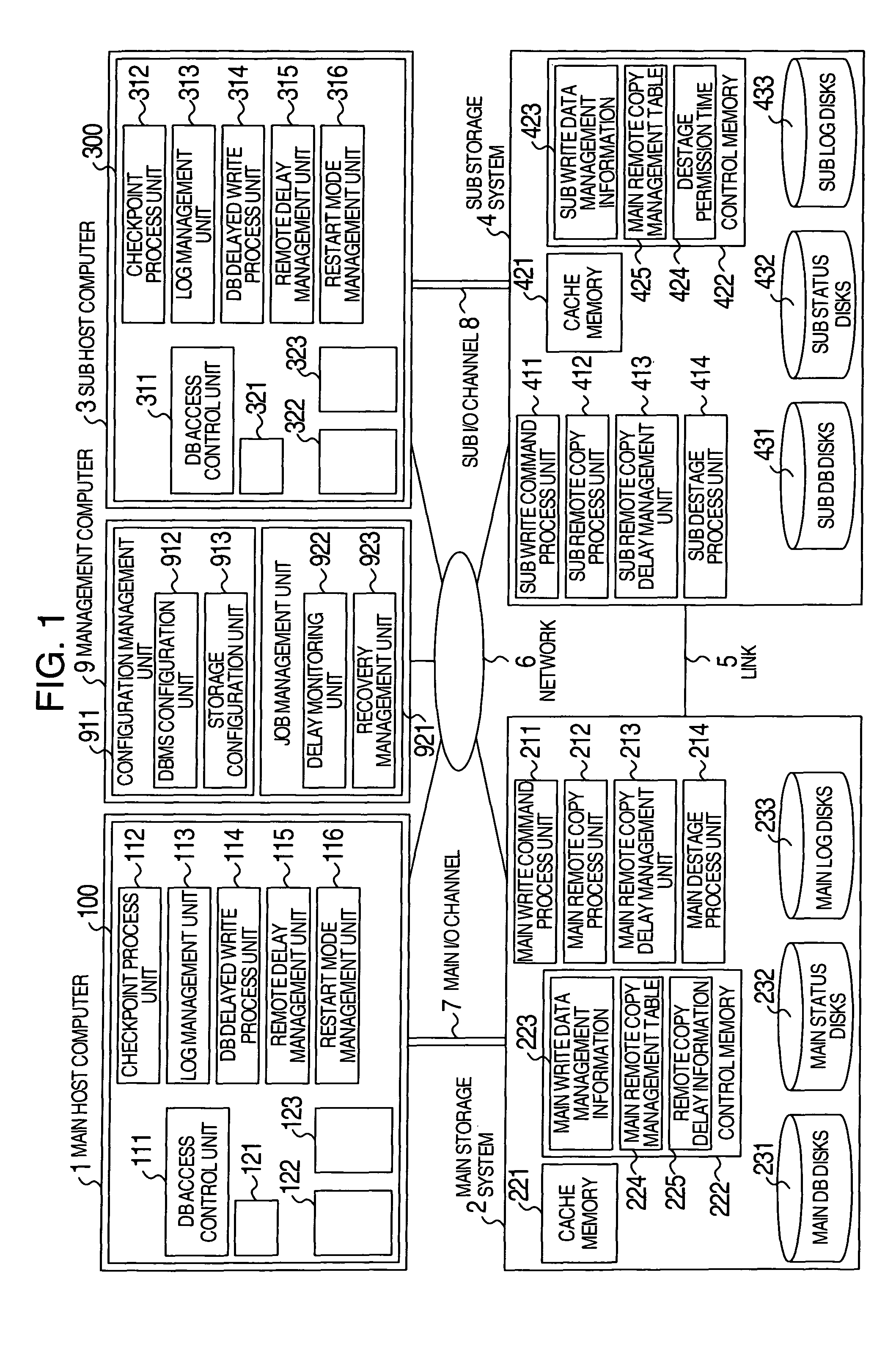
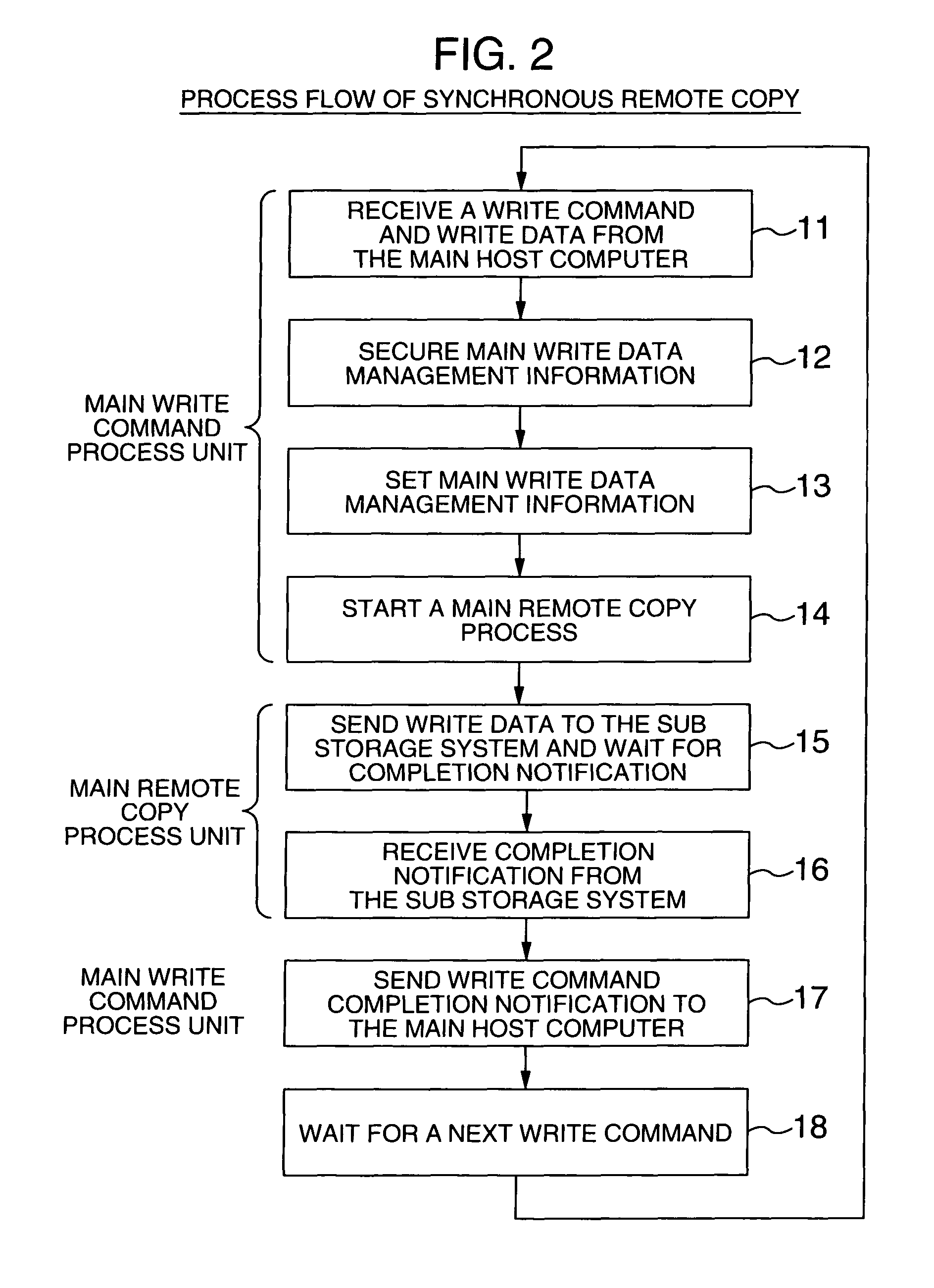
System executing log data transfer synchronously and database data transfer asynchronously
InactiveUS7890461B2Missing of transactionDeterioration in performance of an active database management system is preventedInput/output to record carriersDigital data processing detailsData lossData library
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Modeling user access to computer resources
Embodiments of the invention provide a method for detecting changes in behavior of authorized users of computer resources and reporting the detected changes to the relevant individuals. The method includes evaluating actions performed by each user against user behavioral models and business rules. As a result of the analysis, a subset of users may be identified and reported as having unusual or suspicious behavior. In response, the management may provide feedback indicating that the user behavior is due to the normal expected business needs or that the behavior warrants further review. The management feedback is available for use by machine learning algorithms to improve the analysis of user actions over time. Consequently, investigation of user actions regarding computer resources is facilitated and data loss is prevented more efficiently relative to the prior art approaches with only minimal disruption to the ongoing business processes.
Owner:DAEDALUS BLUE LLC
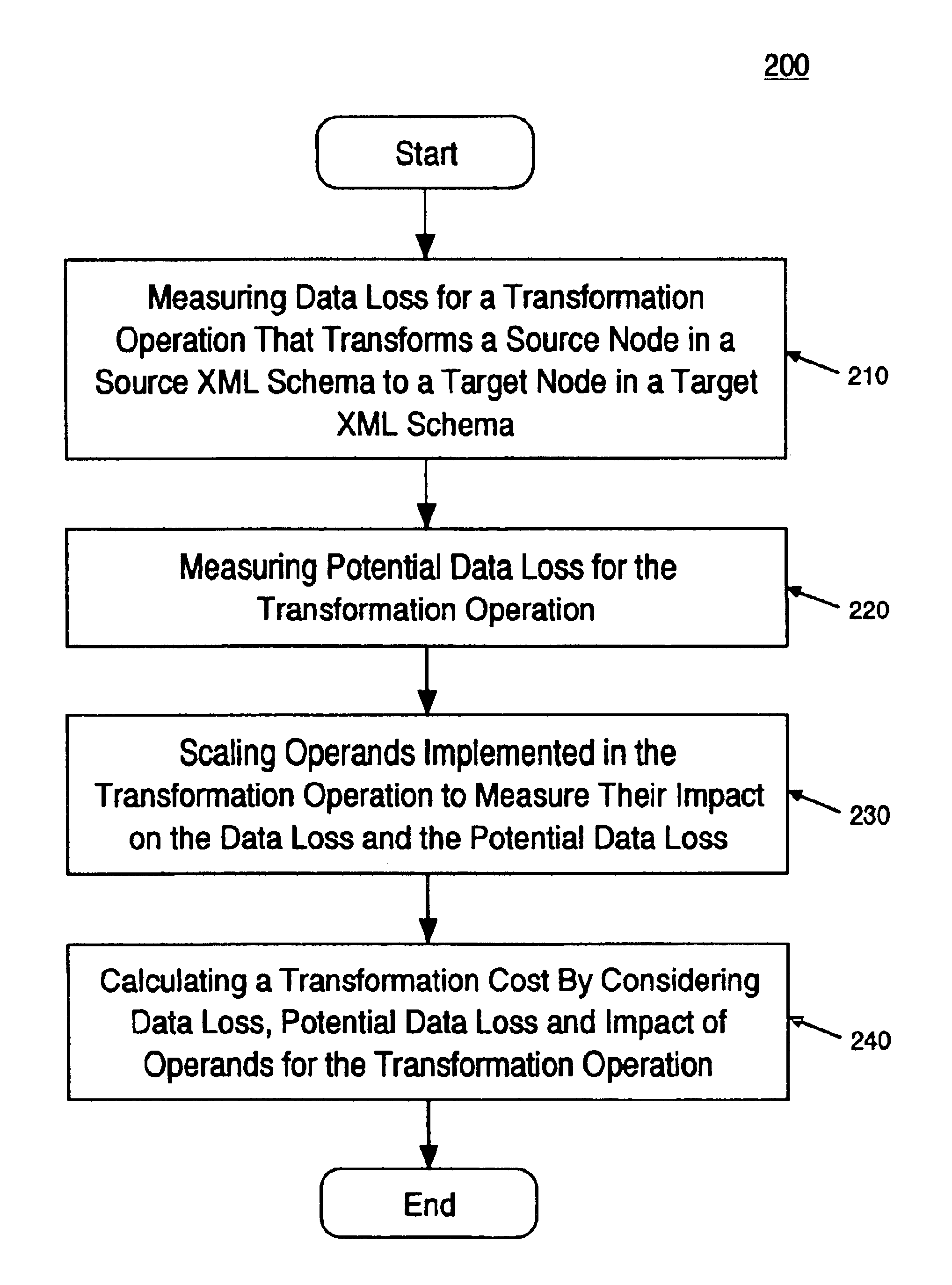
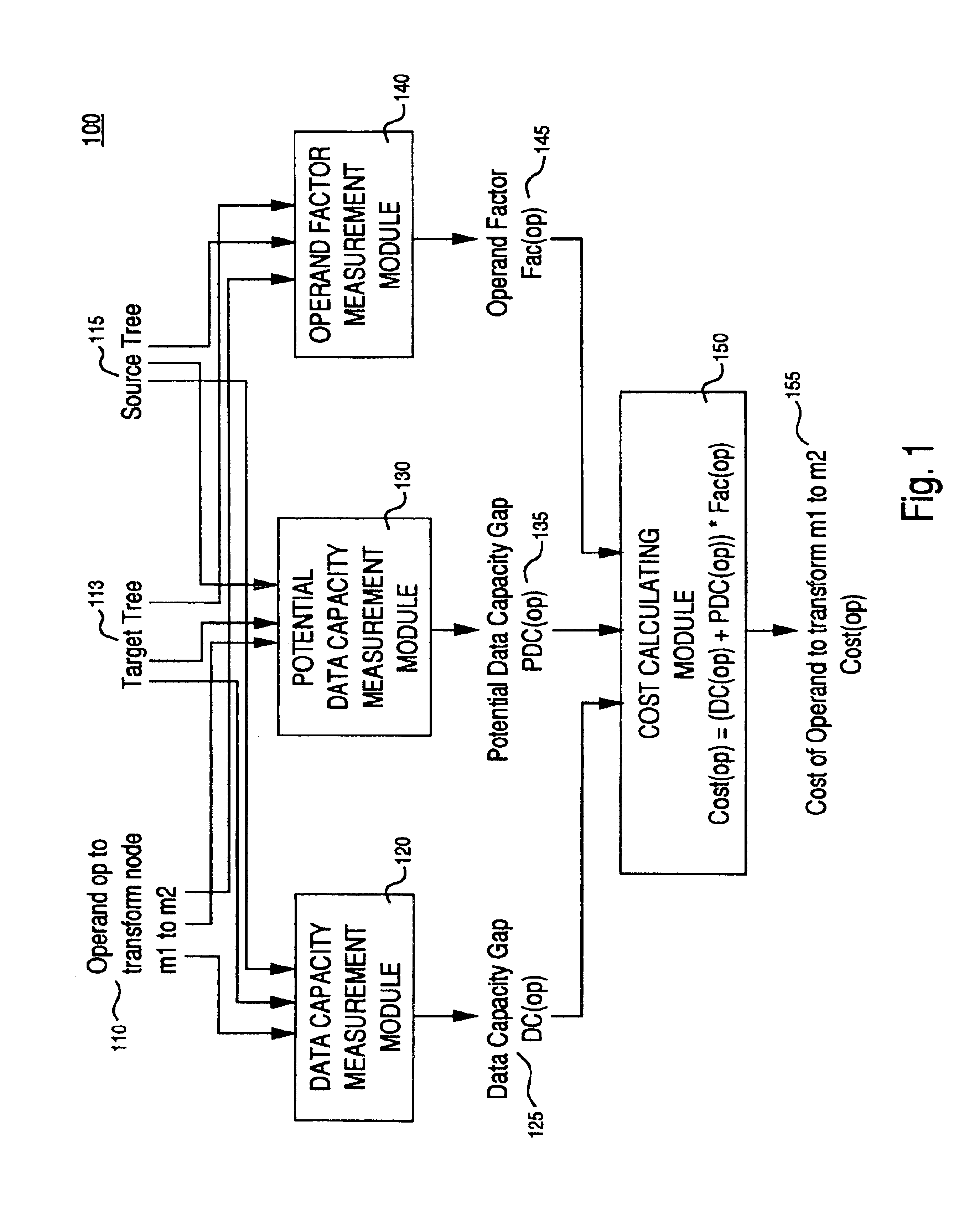
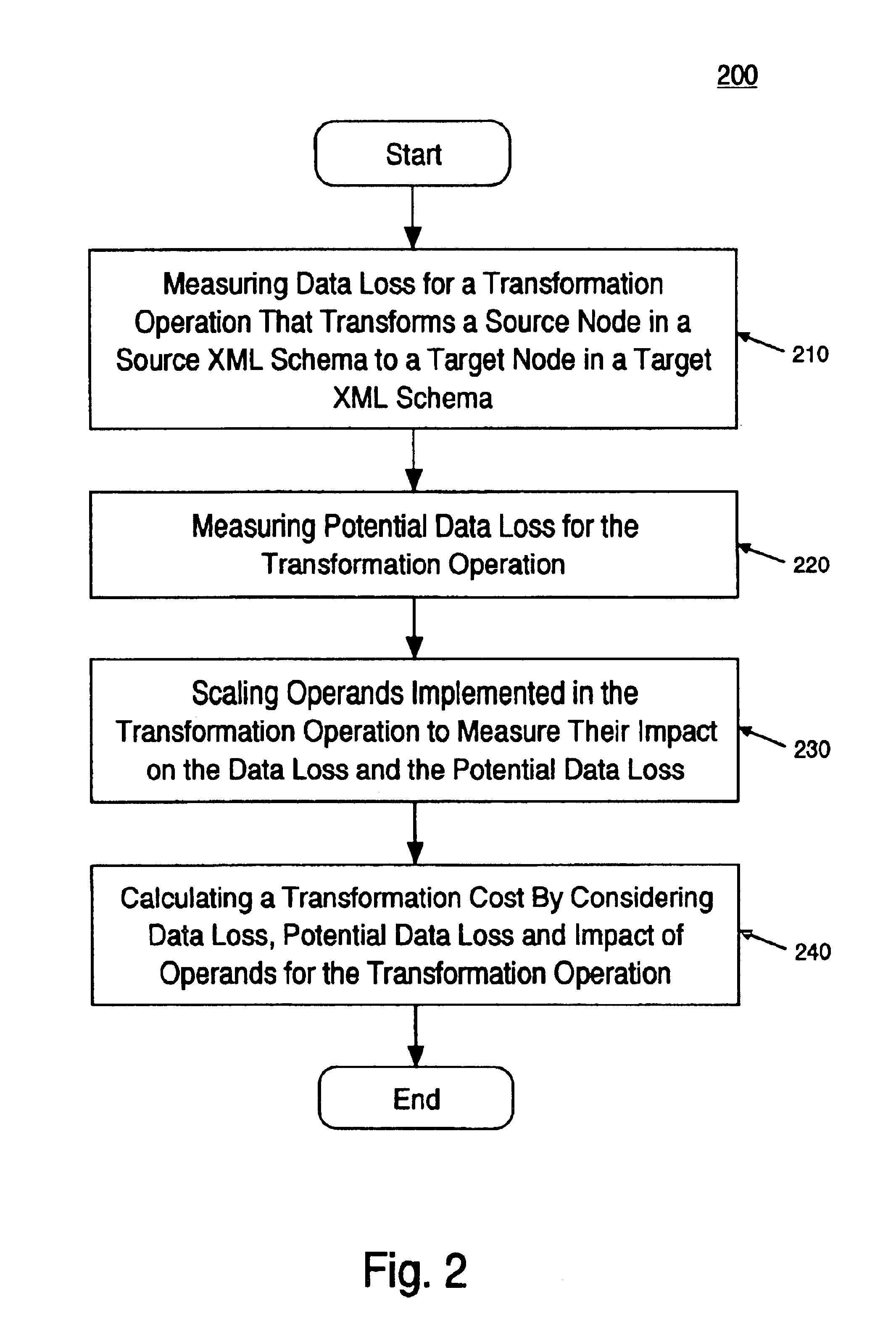
Method and system of valuing transformation between extensible markup language (XML) documents
InactiveUS6845380B2Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsOperandExtensible markup
A method and system of valuing transformation between XML documents. Specifically, one embodiment of the present invention discloses a method for calculating a transformation cost for a transformation operation that transforms a source node in a source XML document to a target node in a target XML document. A data loss and potential data loss is measured for the transformation operation. Also, the operands in the transformation operation are scaled to measure their impact on the data loss and potential data loss. A transformation cost is calculated by considering the data loss, potential data loss, and scaling.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
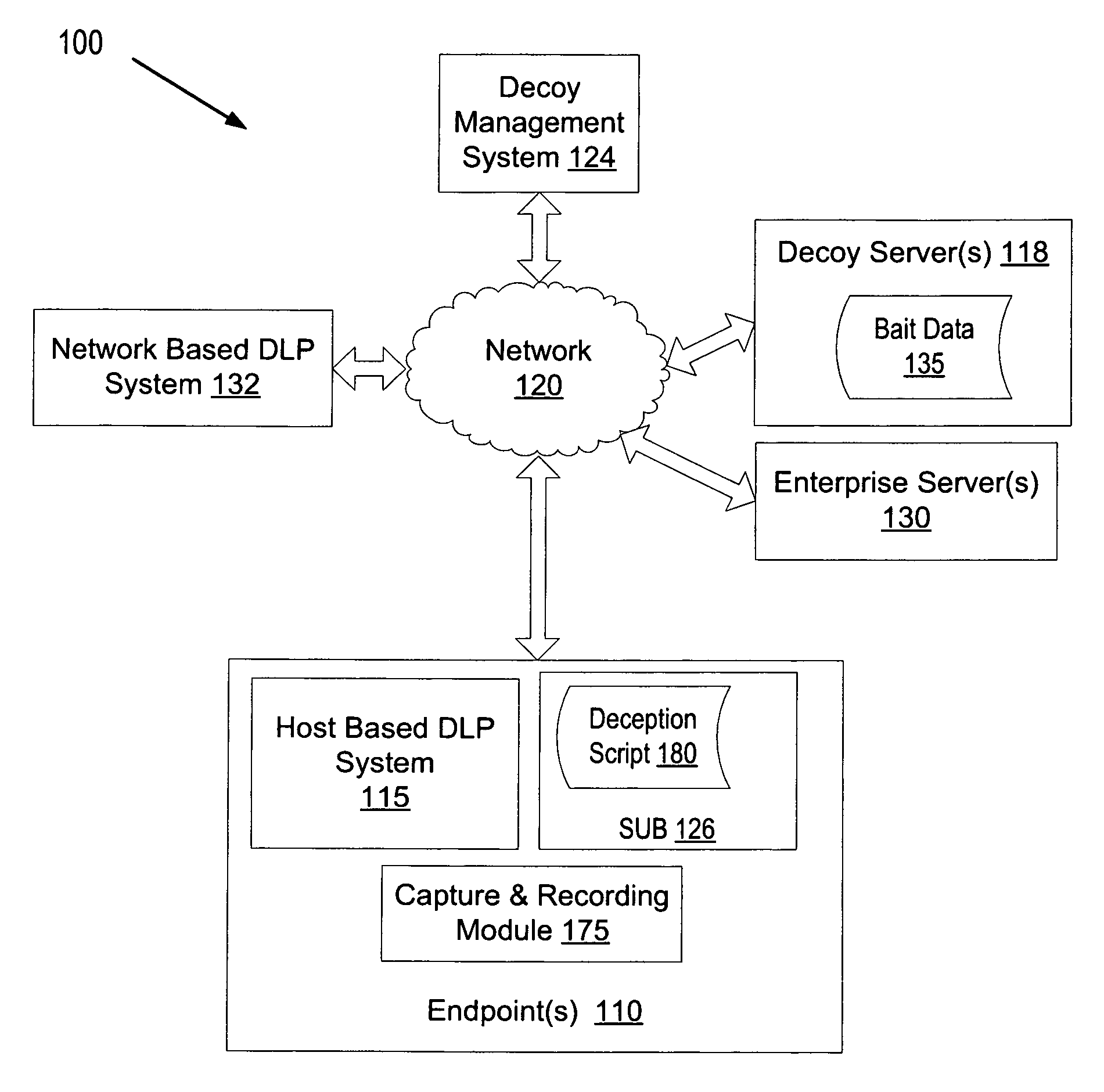
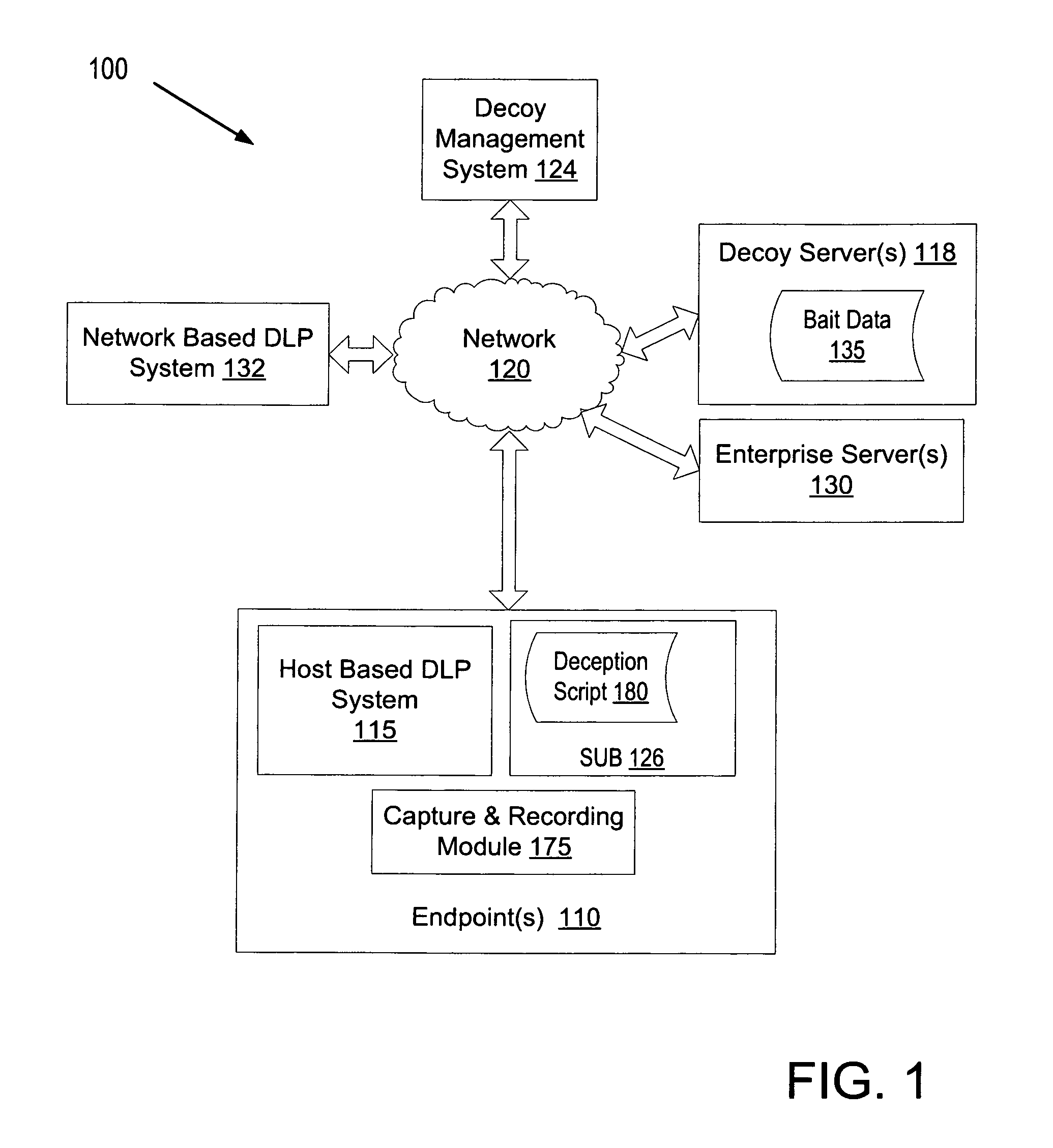
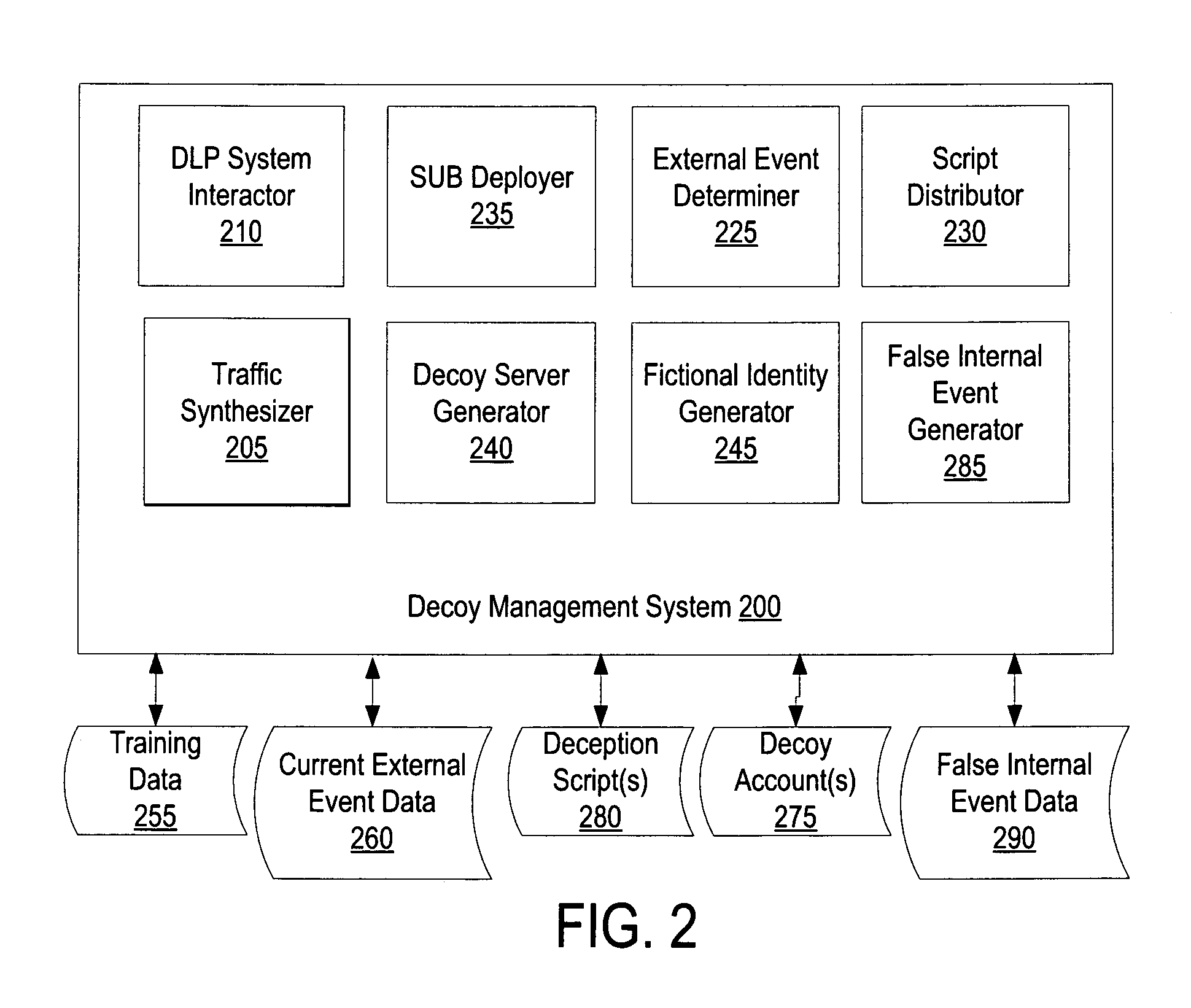
Using decoys by a data loss prevention system to protect against unscripted activity
A computing device executing a data loss prevention (DLP) system tracks bait data on at least one of the computing device or a network. The DLP system identifies a potential security threat in response to detecting unscripted activity associated with the bait data. The DLP system performs an action in response to identifying the potential security threat.
Owner:GEN DIGITAL INC +1
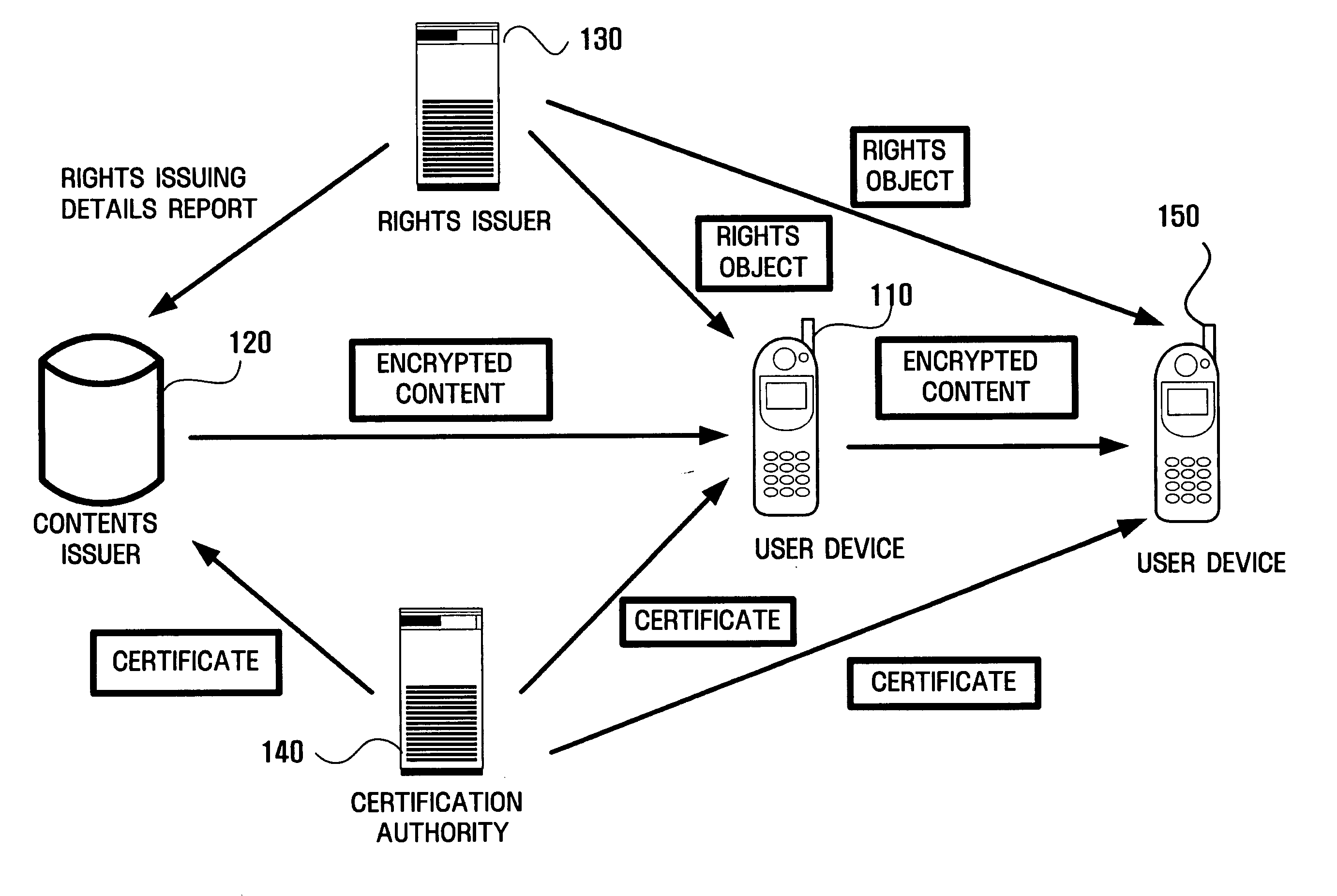
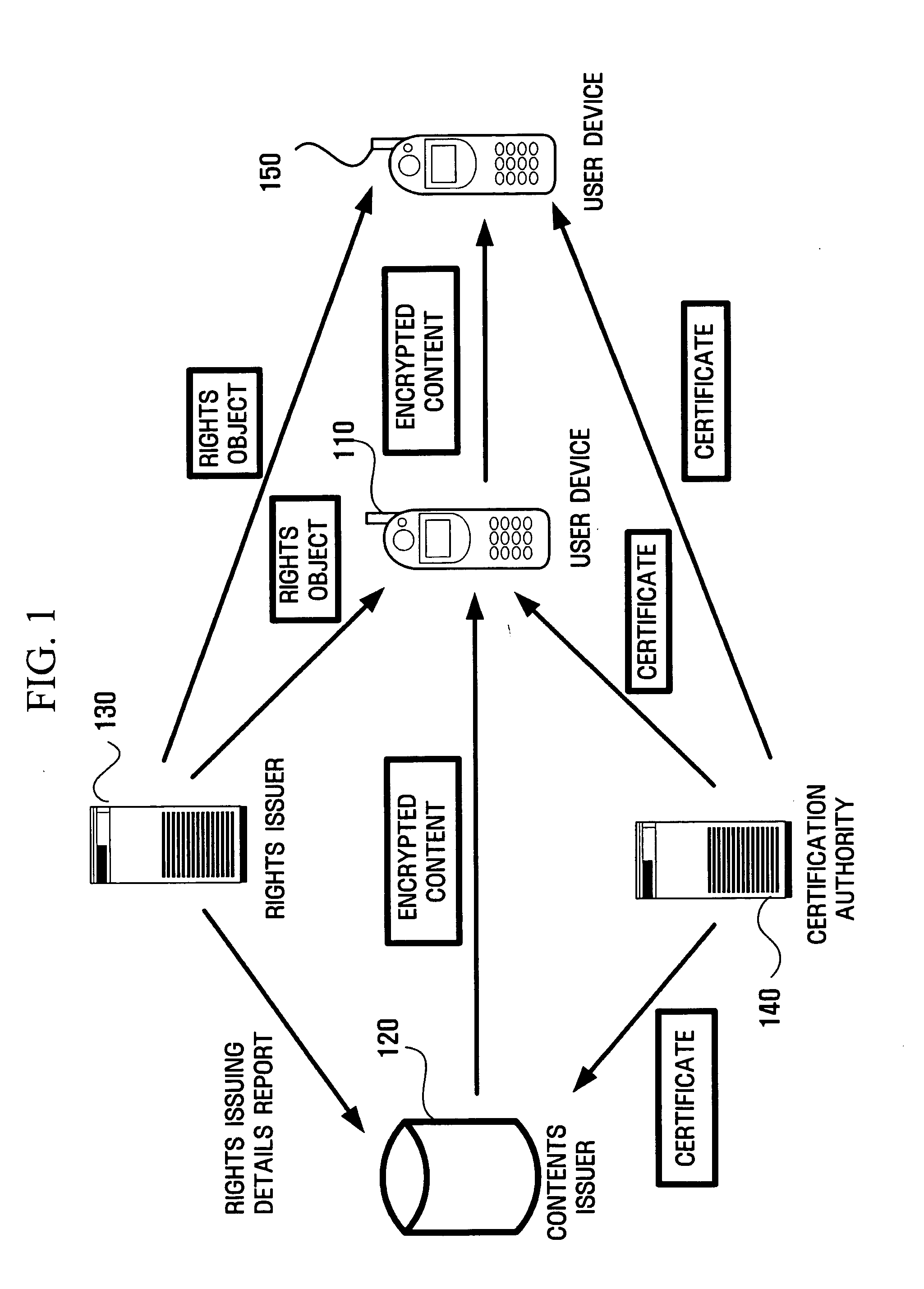
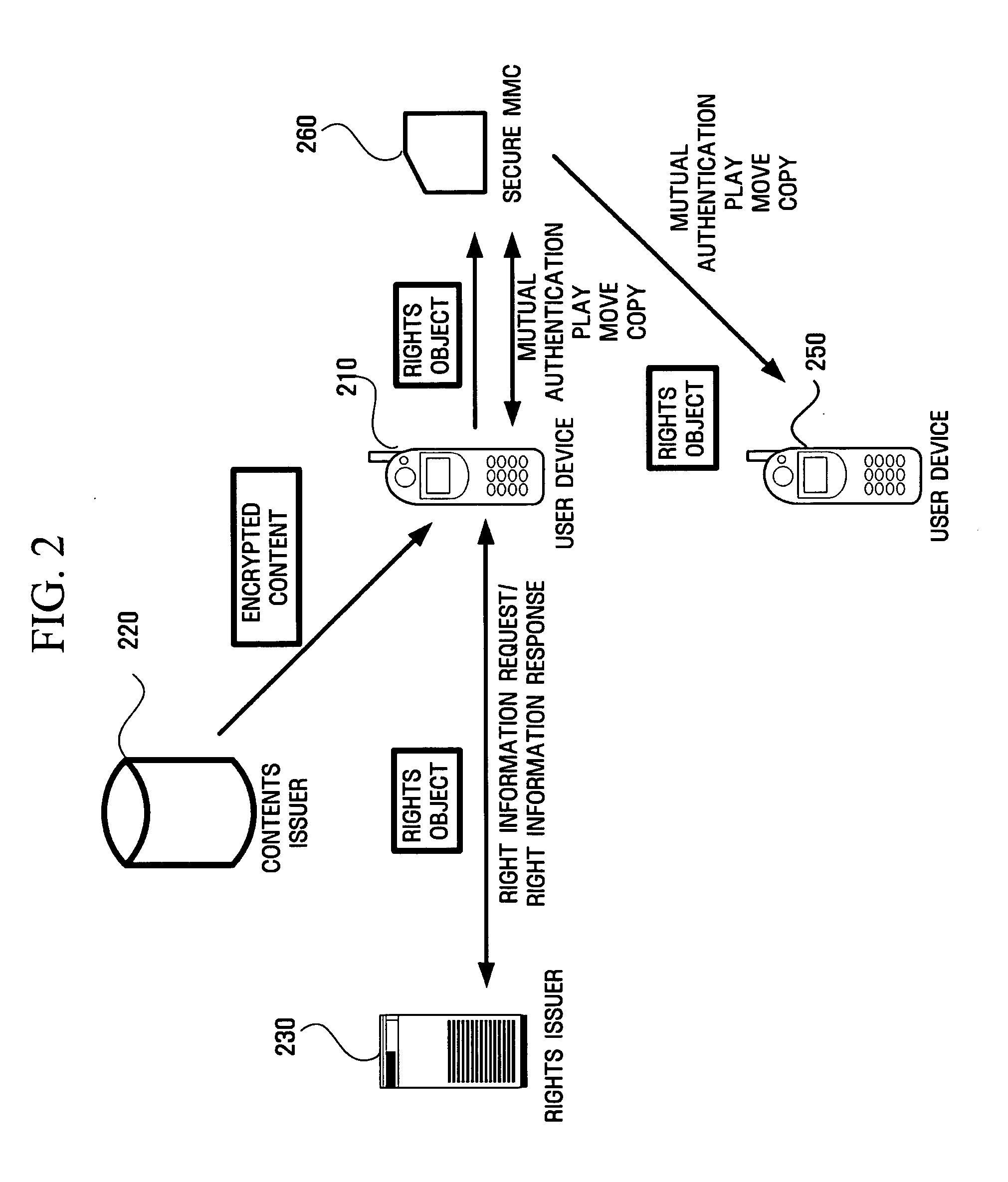
Apparatus and method for moving and copying rights objects between device and portable storage device
InactiveUS20050210249A1Efficient of digital contentEfficient managementKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsComputer hardwareDigital content
A method and apparatus for copying or moving a rights object having right information regarding digital contents between a device and a portable storage device to copy or move the digital contents there between are provided. According to the method and apparatus, the digital works can be prevented from being recklessly and randomly copied and moved, and therefore, copyright can be protected. In addition, data loss or unauthorized access can be prevented.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
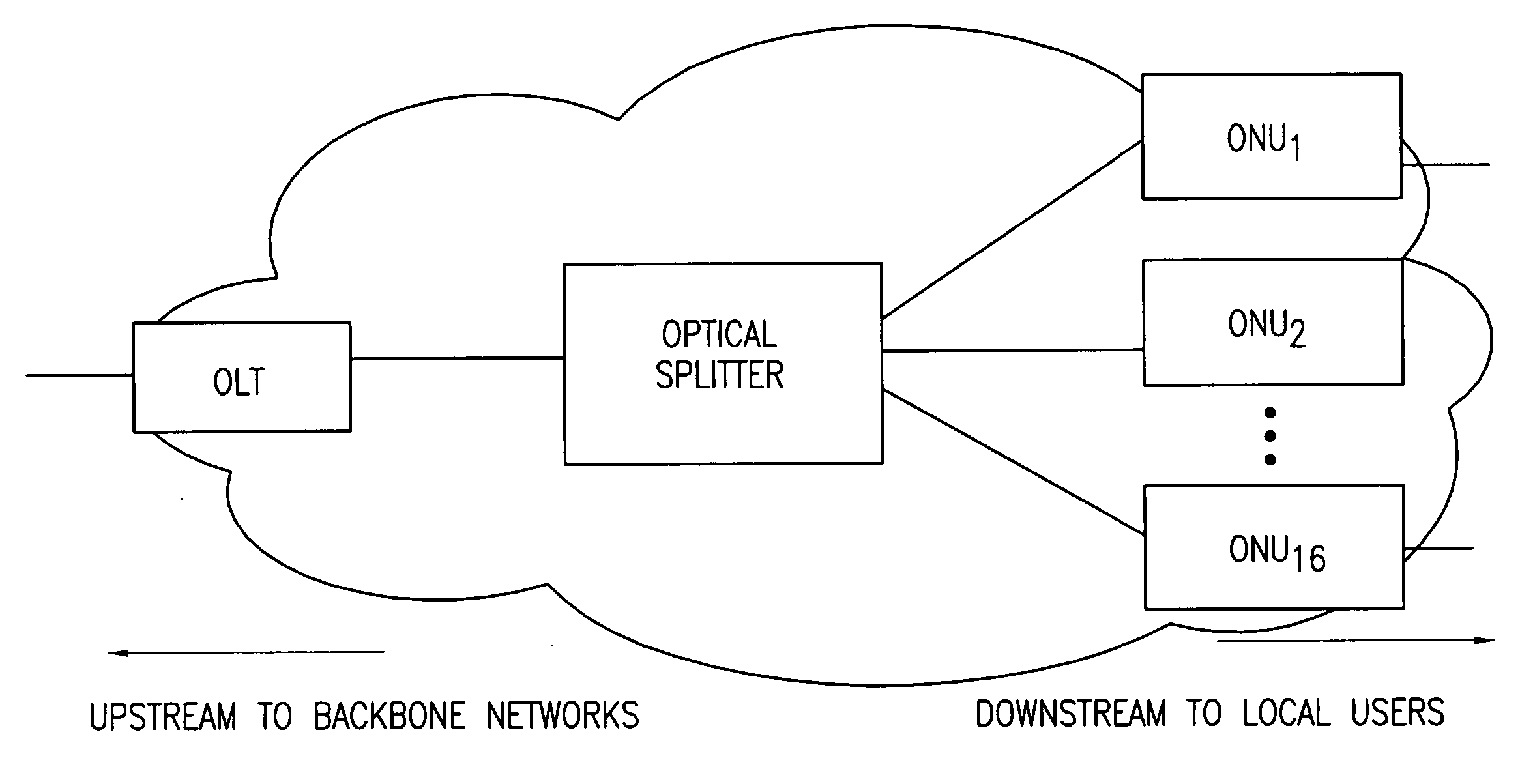
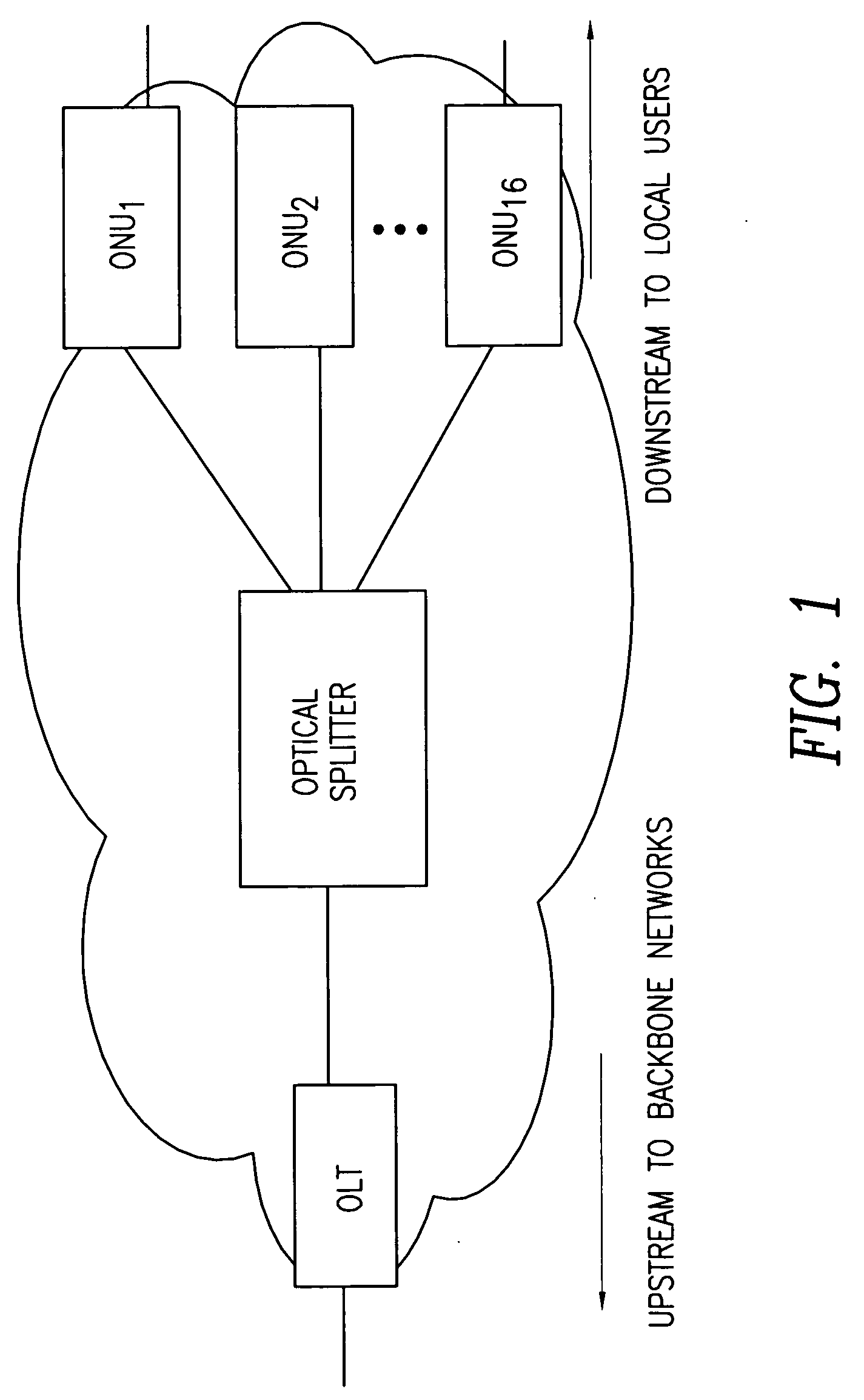
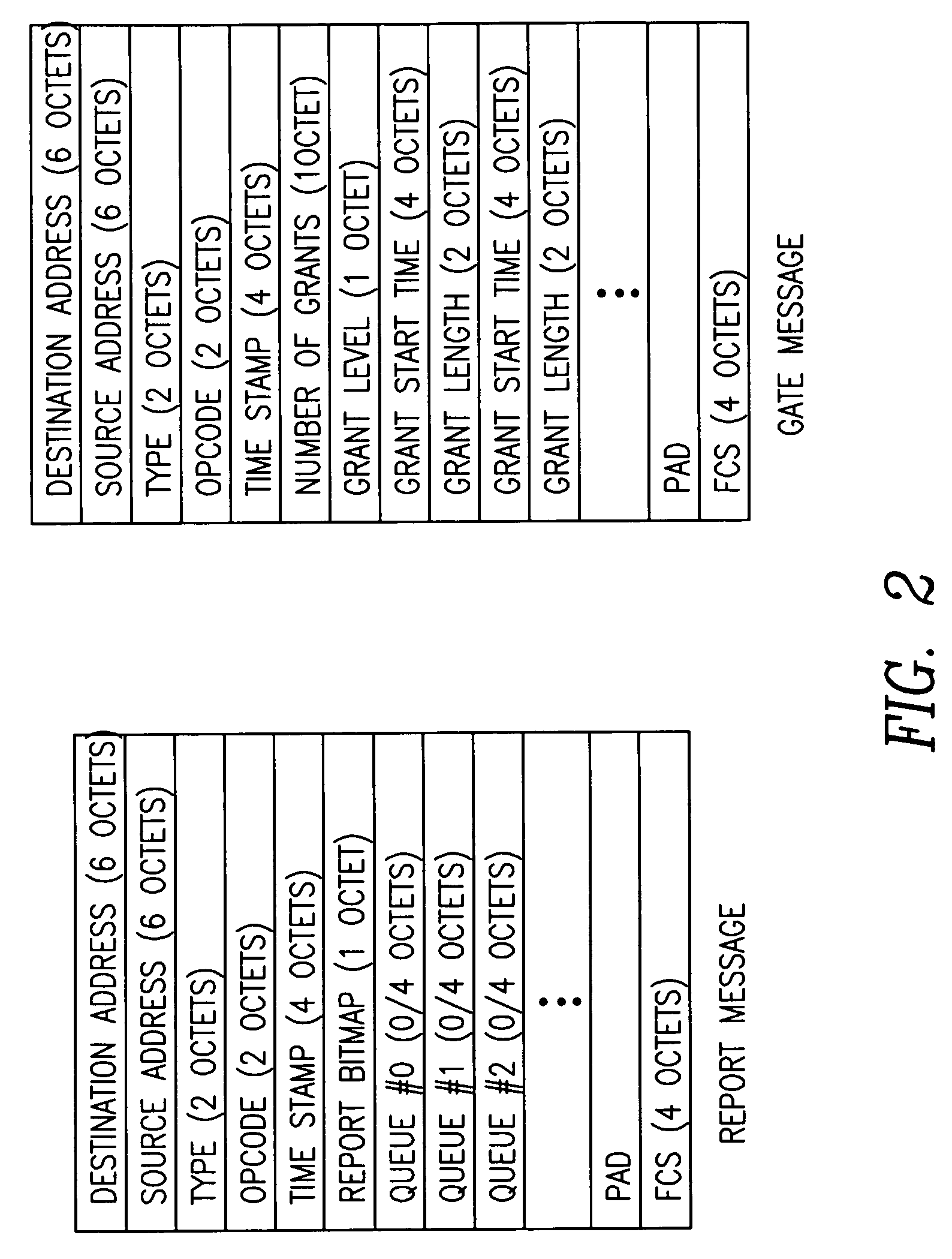
Dynamic bandwidth allocation and service differentiation for broadband passive optical networks
InactiveUS20060268704A1Effective bandwidthSpace complexityMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionService-level agreementTraffic prediction
A dynamic upstream bandwidth allocation scheme is disclosed, i.e., limited sharing with traffic prediction (LSTP), to improve the bandwidth efficiency of upstream transmission over PONs. LSTP adopts the PON MAC control messages, and dynamically allocates bandwidth according to the on-line traffic load. The ONU bandwidth requirement includes the already buffered data and a prediction of the incoming data, thus reducing the frame delay and alleviating the data loss. ONUs are served by the OLT in a fixed order in LSTP to facilitate the traffic prediction. Each optical network unit (ONU) classifies its local traffic into three classes with descending priorities: expedited forwarding (EF), assured forwarding (AF), and best effort (BE). Data with higher priority replace data with lower priority when the buffer is full. In order to alleviate uncontrolled delay and unfair drop of the lower priority data, the priority-based scheduling is employed to deliver the buffered data in a particular transmission timeslot. The bandwidth allocation incorporates the service level agreements (SLAs) and the on-line traffic dynamics. The basic limited sharing with traffic prediction (LSTP) scheme is extended to serve the classified network traffic.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
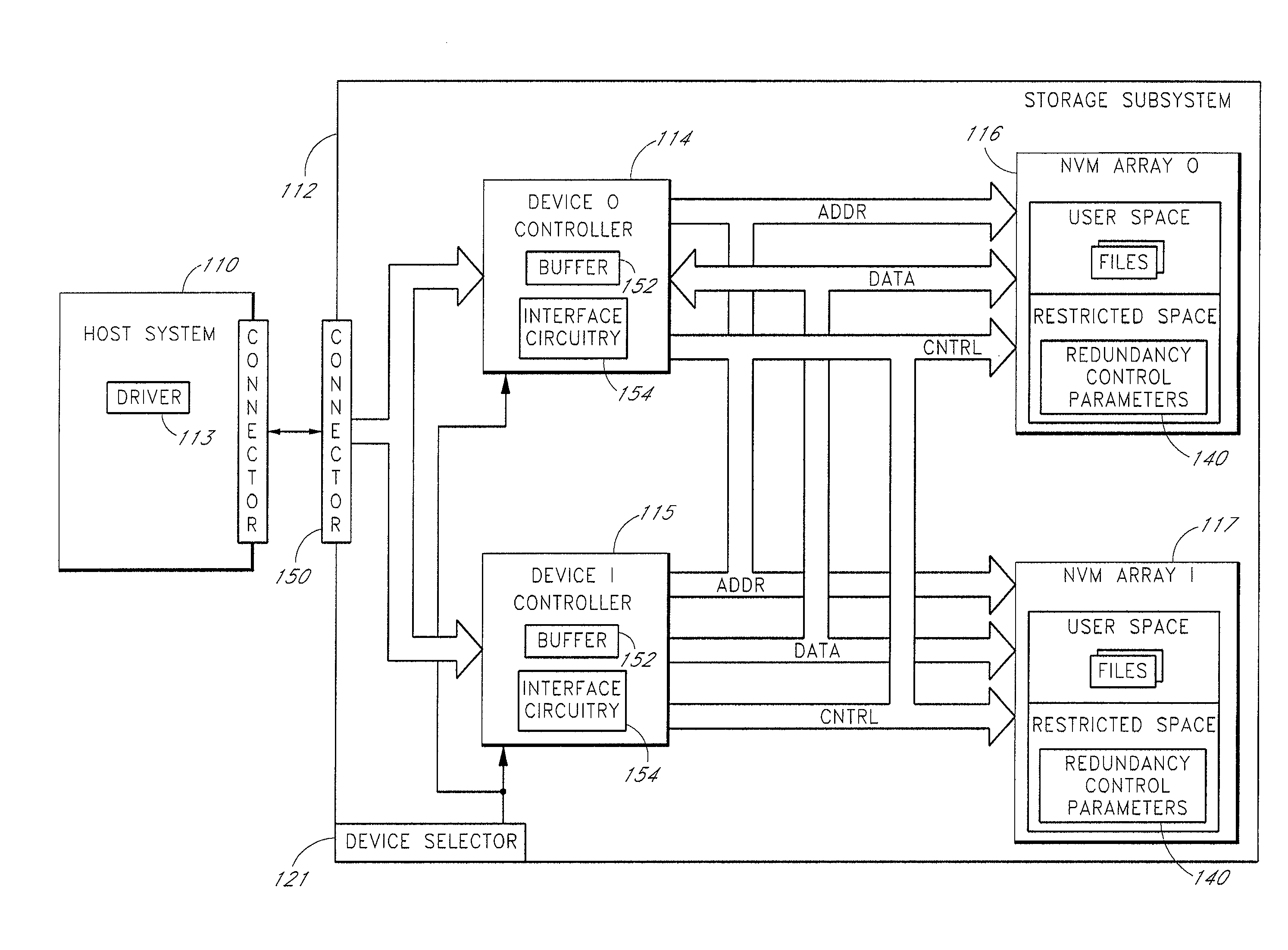
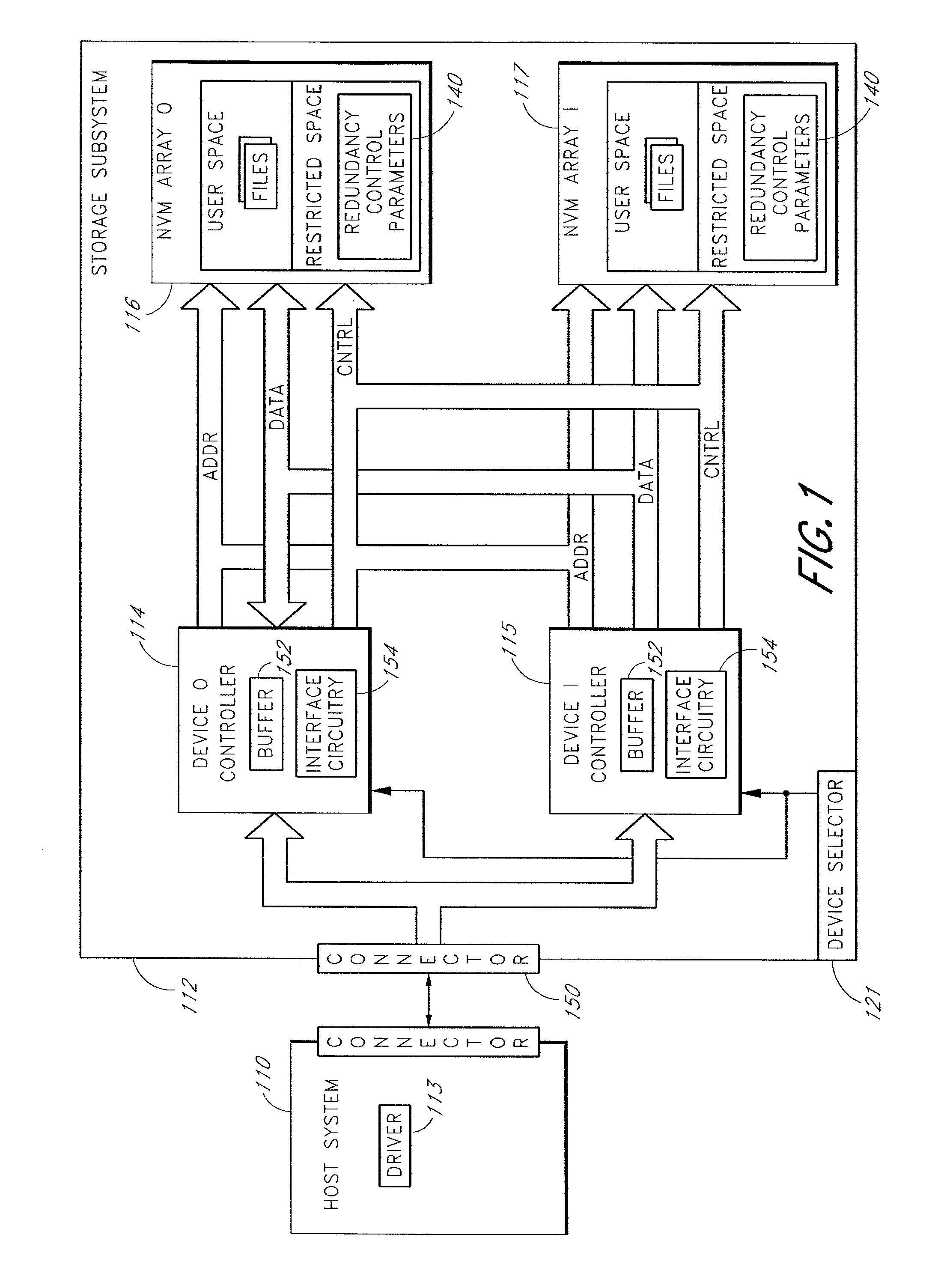
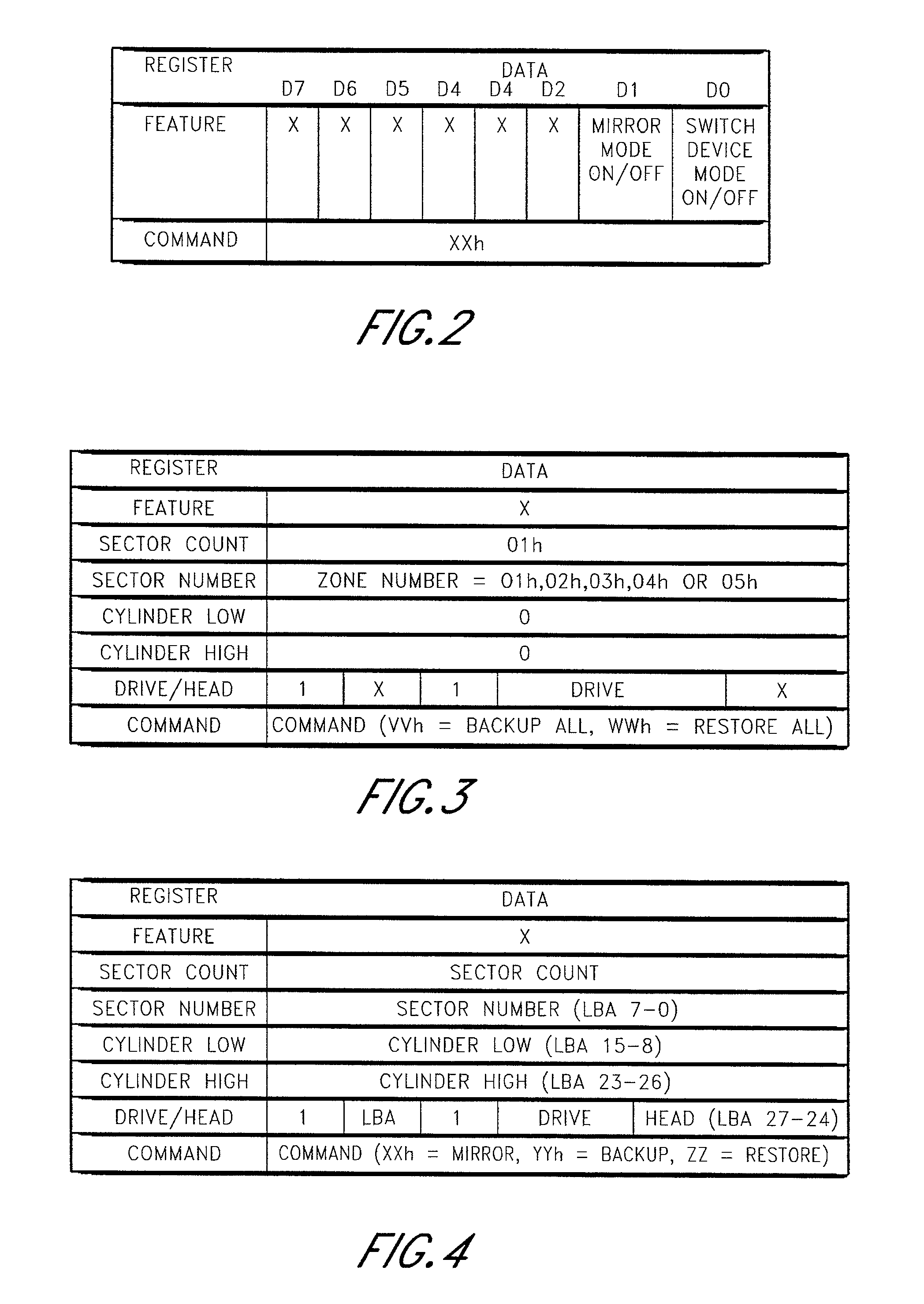
Storage subsystem with multiple non-volatile memory arrays to protect against data losses
A storage subsystem contains multiple non-volatile memory arrays that are accessible to a host system when the storage subsystem is connected thereto. The storage subsystem implements commands and / or modes for enabling the host system to create and use backup copies of files, such that the host system can recover when files become corrupted or otherwise lost. In one embodiment, the storage subsystem presents the non-volatile memory arrays to the host's operating system as distinct storage devices (e.g., ATA device 0 and 1), and implements special commands for copying data between these storage devices. The subsystem may alternatively present the memory arrays to the host operating system as a single storage device. The storage subsystem may have a standard form factor, such as a form factor commonly used for memory cards.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
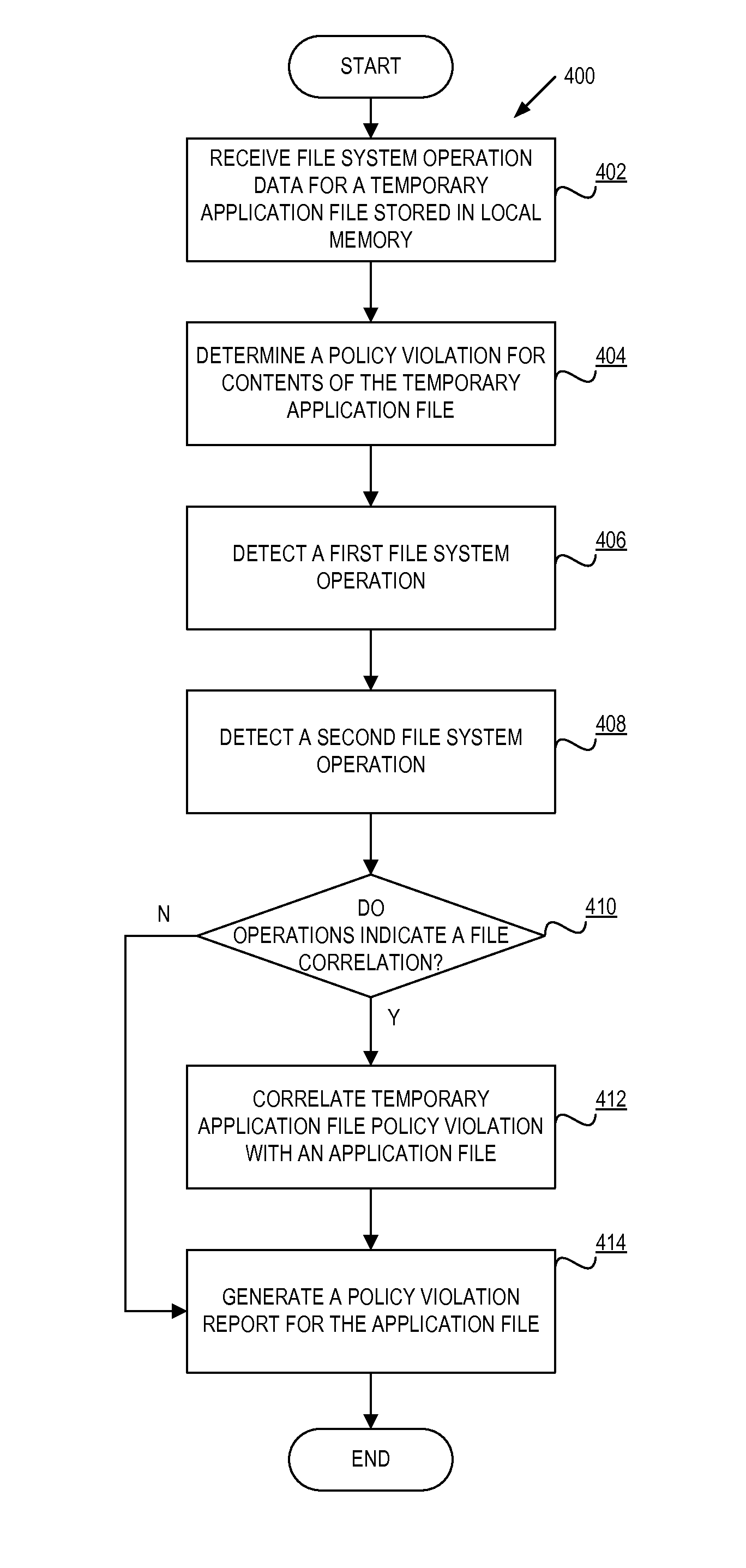
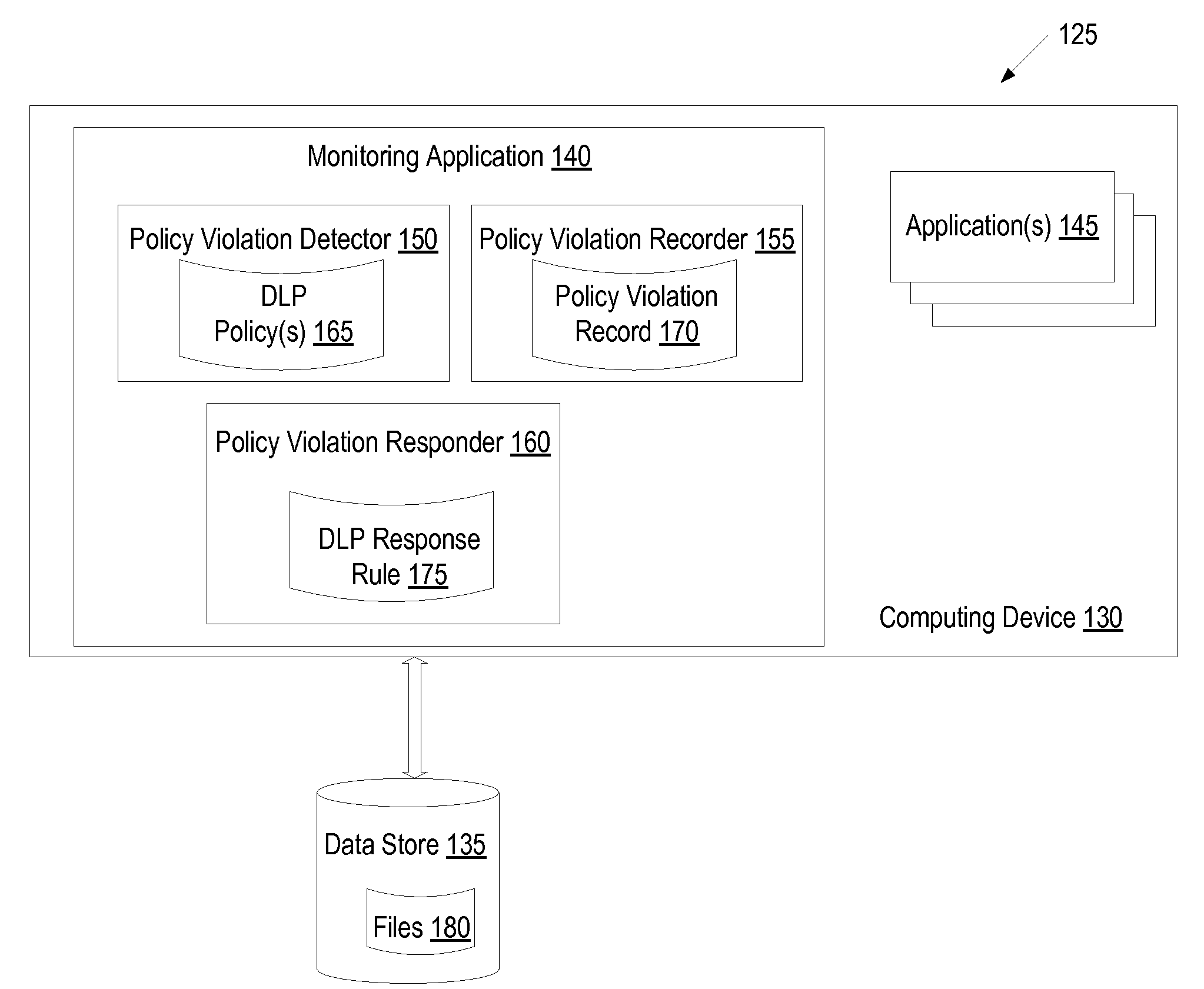
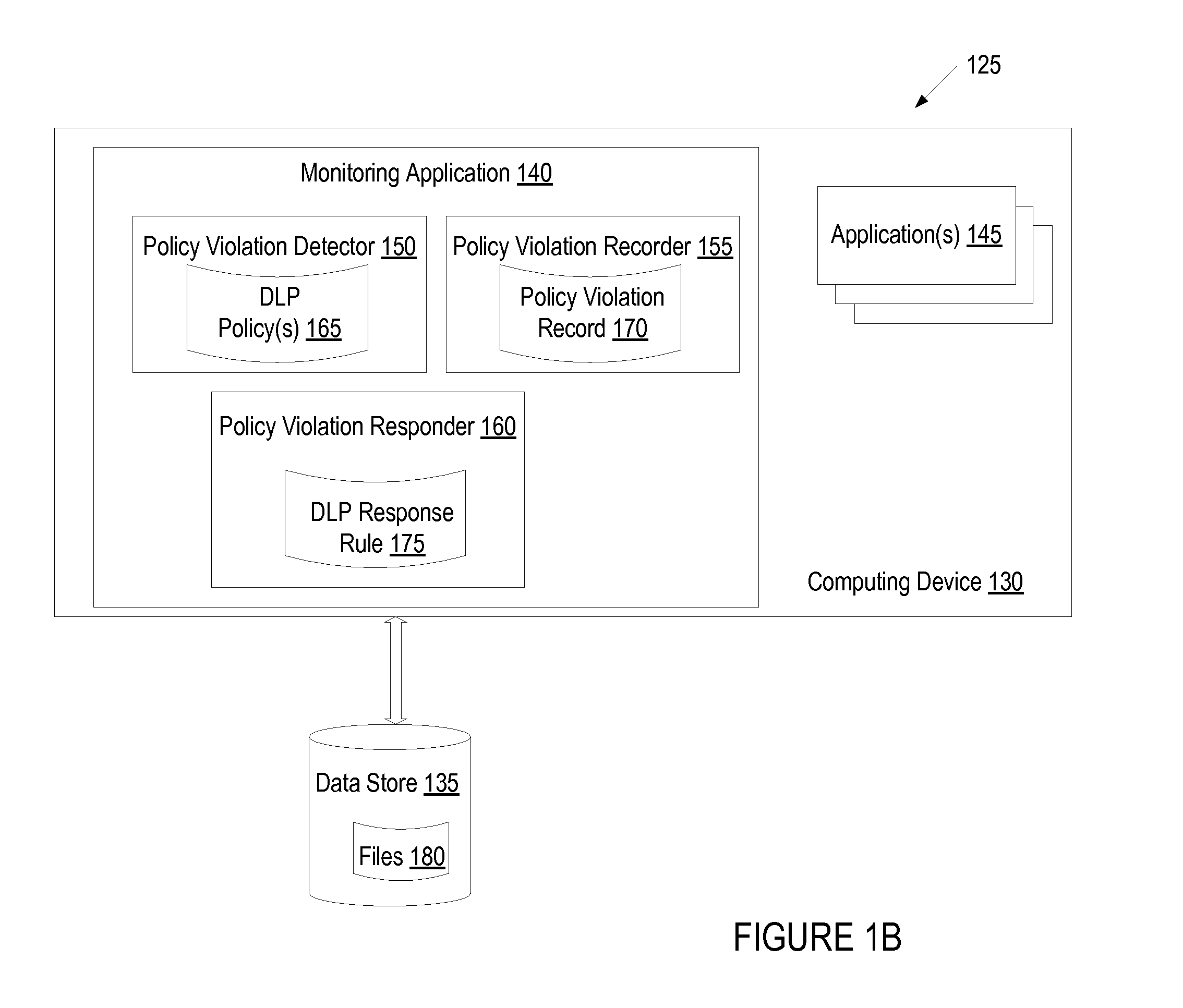
System and method for managing data loss due to policy violations in temporary files
InactiveUS7991747B1Memory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsClient agentApplication software
A method and apparatus for managing data loss due to policy violations in temporary files is described. In one embodiment, the method includes monitoring, by a client agent, information content on a client for violations of a policy. The method further includes determining, by the client agent, that a violation of the policy has occurred for content of a temporary file of an application. In one embodiment, the policy violation of the temporary file is correlated, by the client agent, with an original file of the application.
Owner:CA TECH INC
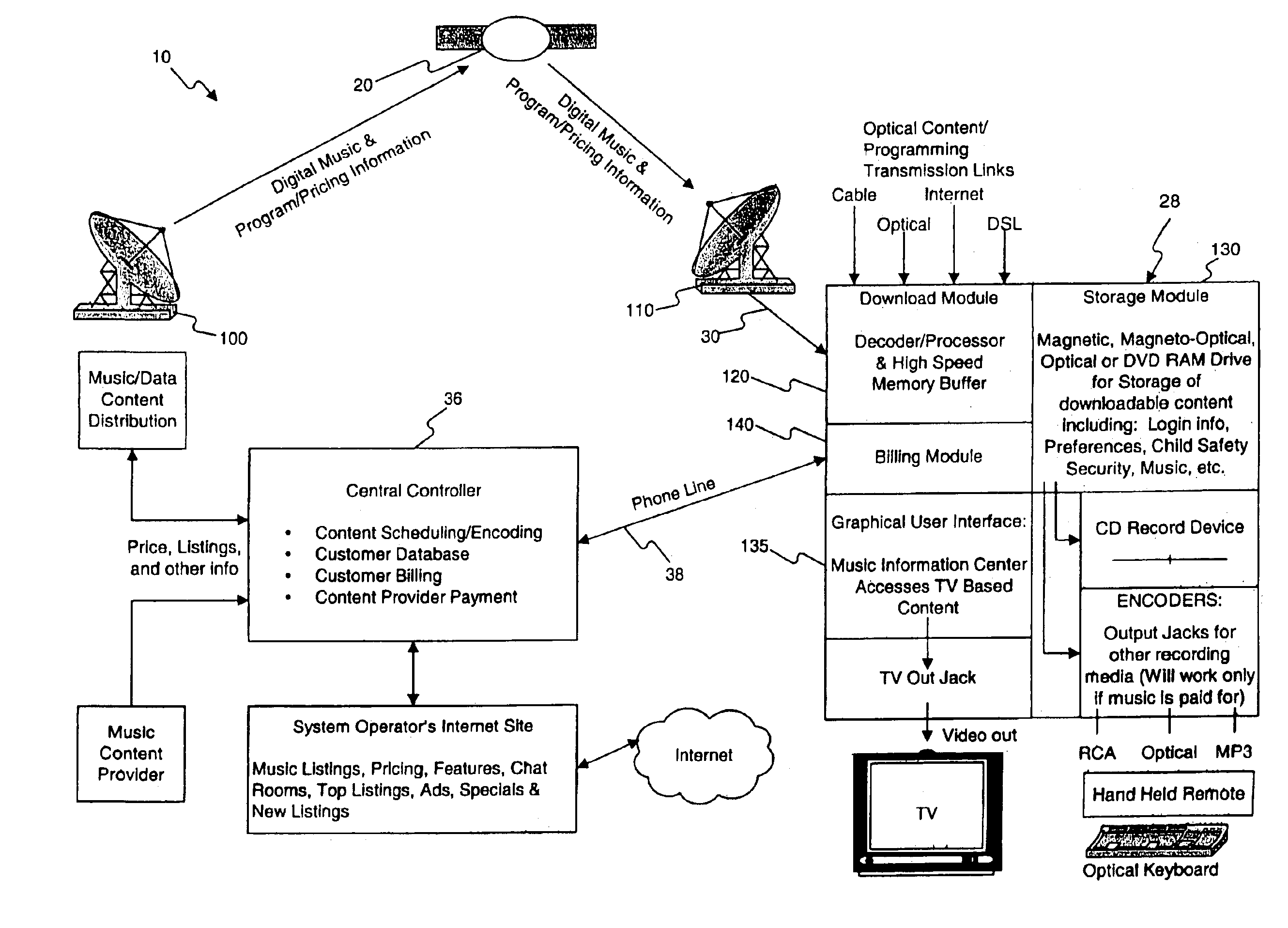
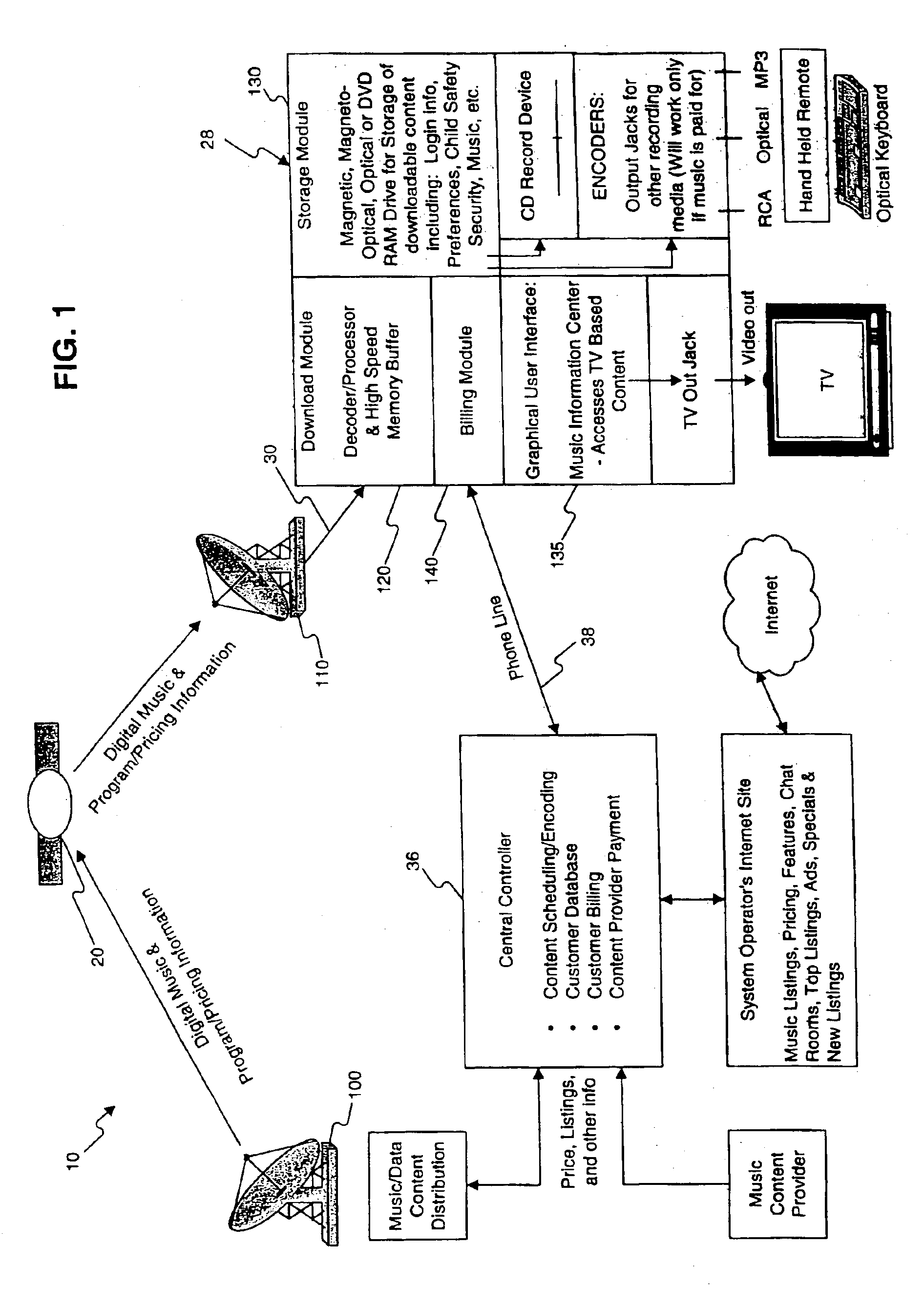
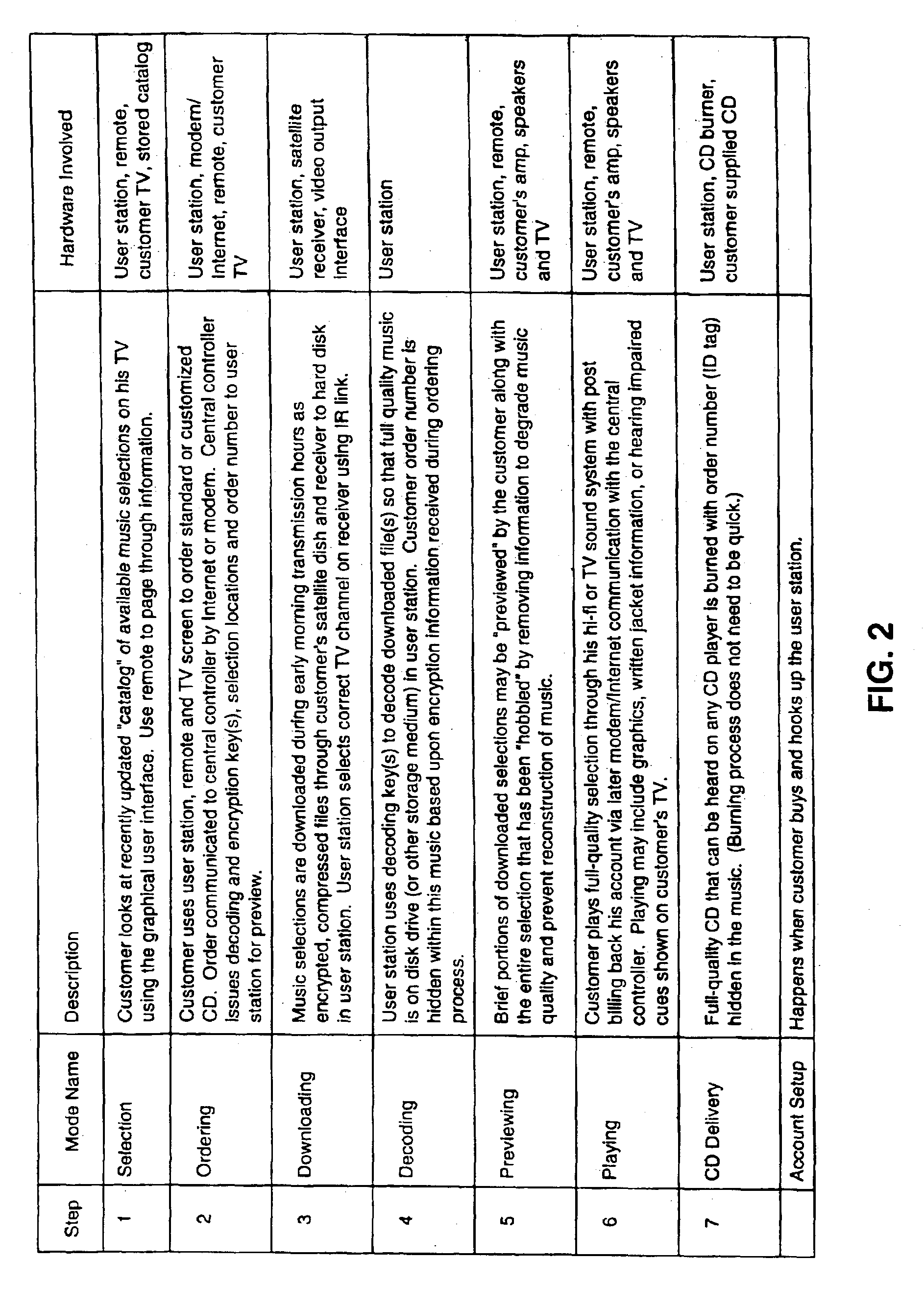
Music distribution systems
InactiveUS7209900B2Easy accessGood choiceCoin-freed apparatusBroadcast transmission systemsTelecommunicationsDistribution system
Owner:WORLD THEATRE INC
Adaptive data loss prevention policies
ActiveUS20100162347A1Risk minimizationComputer security arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsData lossSelf adaptive
A monitor detects a policy violation on a computing device, wherein the policy violation includes a user attempt to perform an operation to move data that includes sensitive information off the computing device. The monitor determines whether one or more previous policy violations have occurred on the computing device. The monitor performs an action to minimize a risk of data loss based on the one or more previous policy violations.
Owner:CA TECH INC
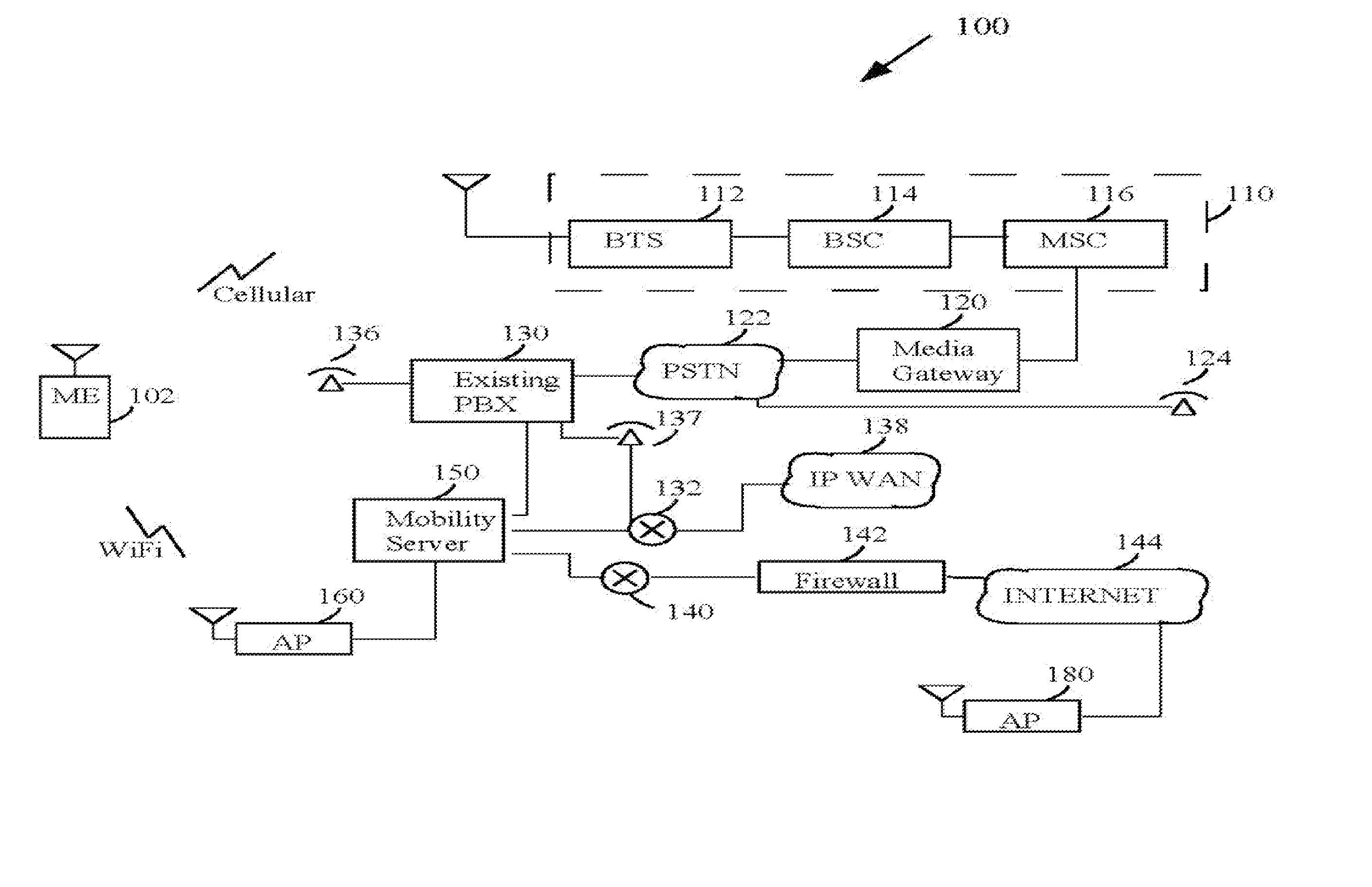
Reducing data loss during handoffs in wireless communication
InactiveUS20070091848A1Reduce data lossCommmunication supplementary servicesWireless network protocolsTelecommunicationsClient-side
A method for reducing data loss when a client device performs a handoff from a first radio station to a second radio station. The method includes detecting imminence of the handoff using one or more criteria. The method also includes buffering incoming data upon the imminence of the handoff to generate buffered incoming data, the incoming data being addressed to the client device. The method further includes transmitting the buffered incoming data to the client device through the second radio station if the handoff is completed and if the buffered incoming data is not discarded.
Owner:DIVITAS NETWORKS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com