Patents
Literature
571 results about "Unavailability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Unavailability is the probability that an item will not operate correctly at a given time and under specified conditions. It opposes availability. Numerical values associated with the calculation of availability are often awkward, consisting of a series of 9s before reaching any significant numerical information (e.g. 0.9999999654). For this reason, it is more convenient to use the complement measure of availability, namely, unavailability. Expressed mathematically, unavailability is 1 minus the availability. Therefore, a system with availability 0.9999999654 is more concisely described as having an unavailability of 3.46E-8.
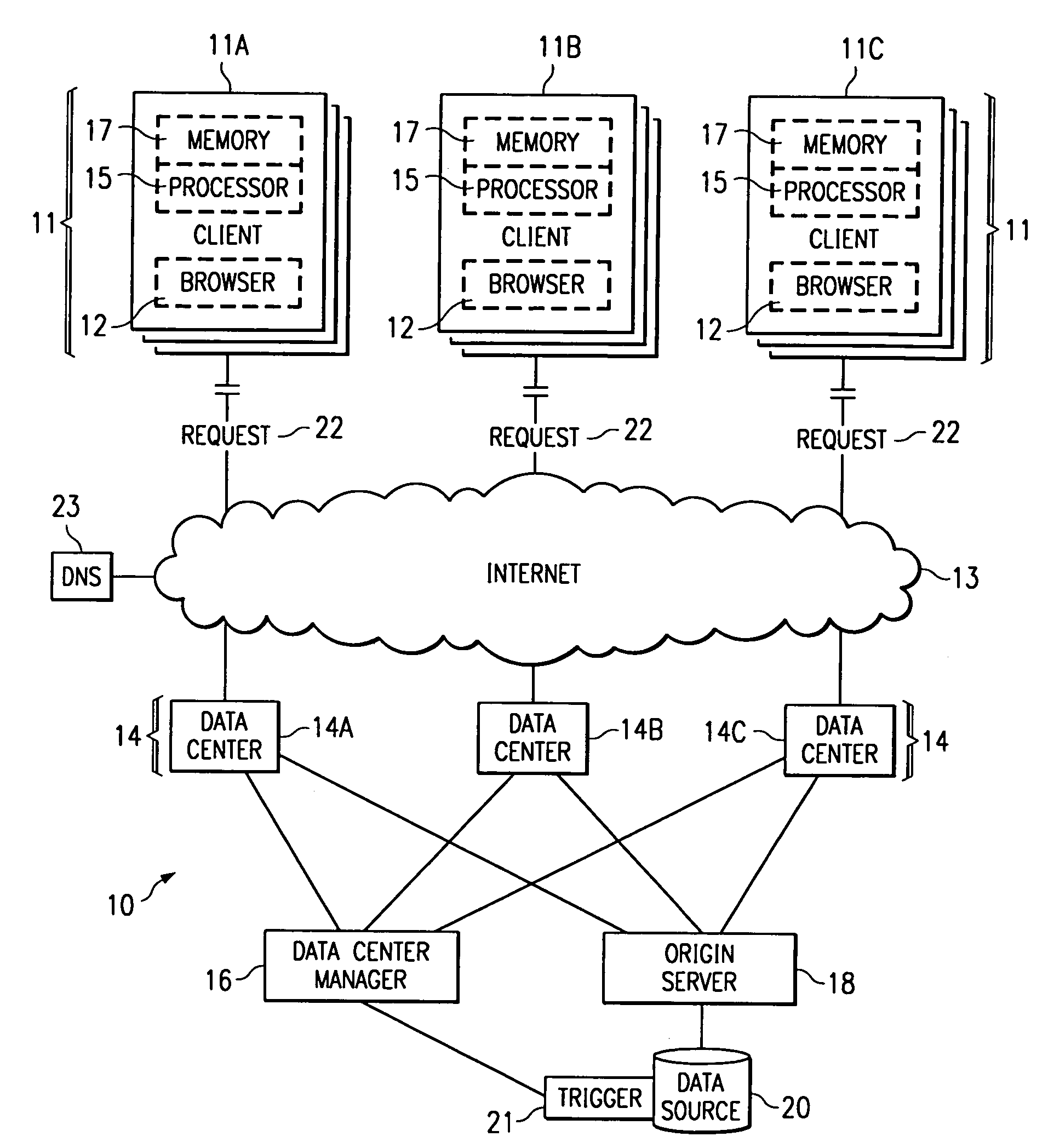
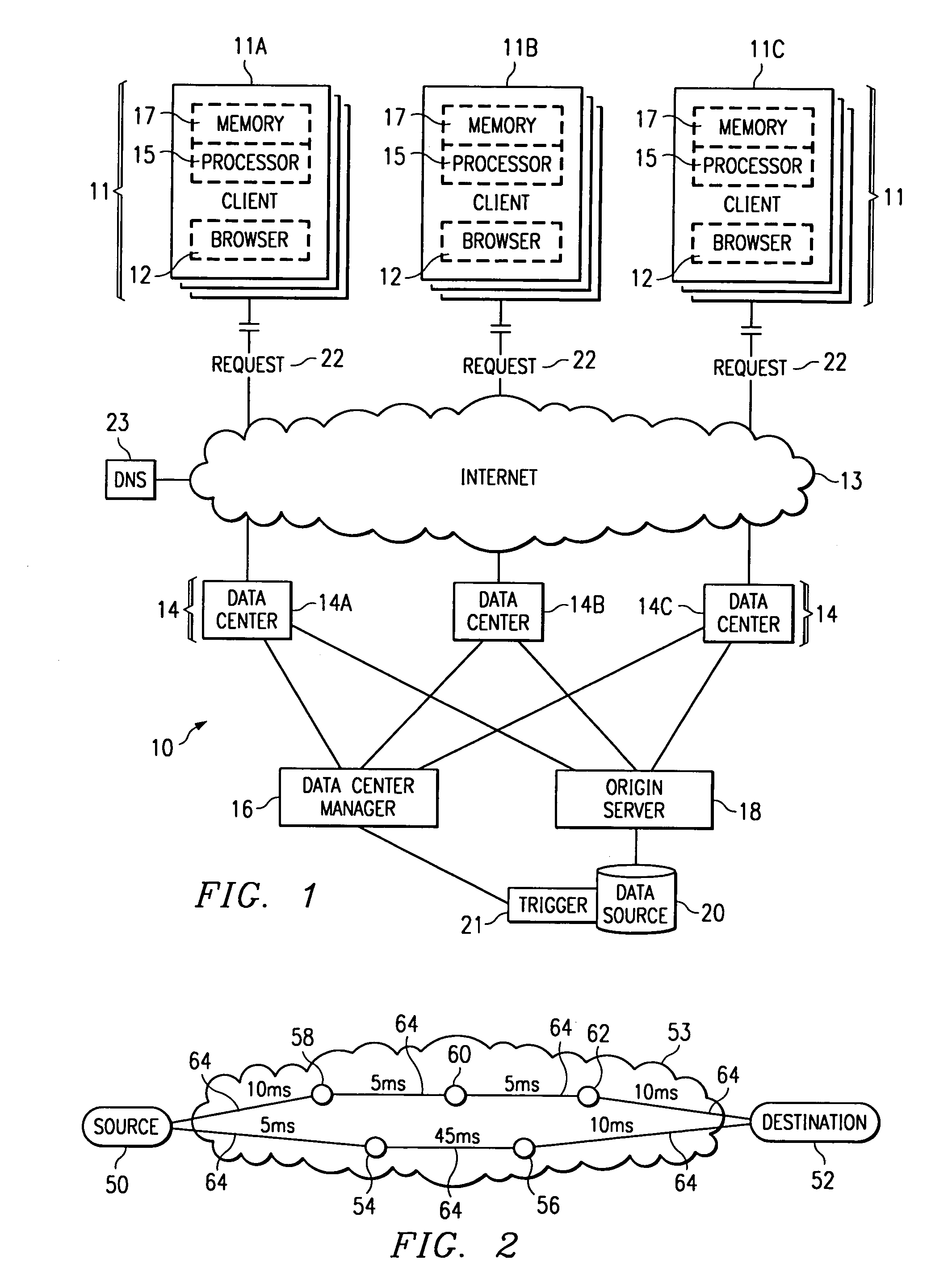
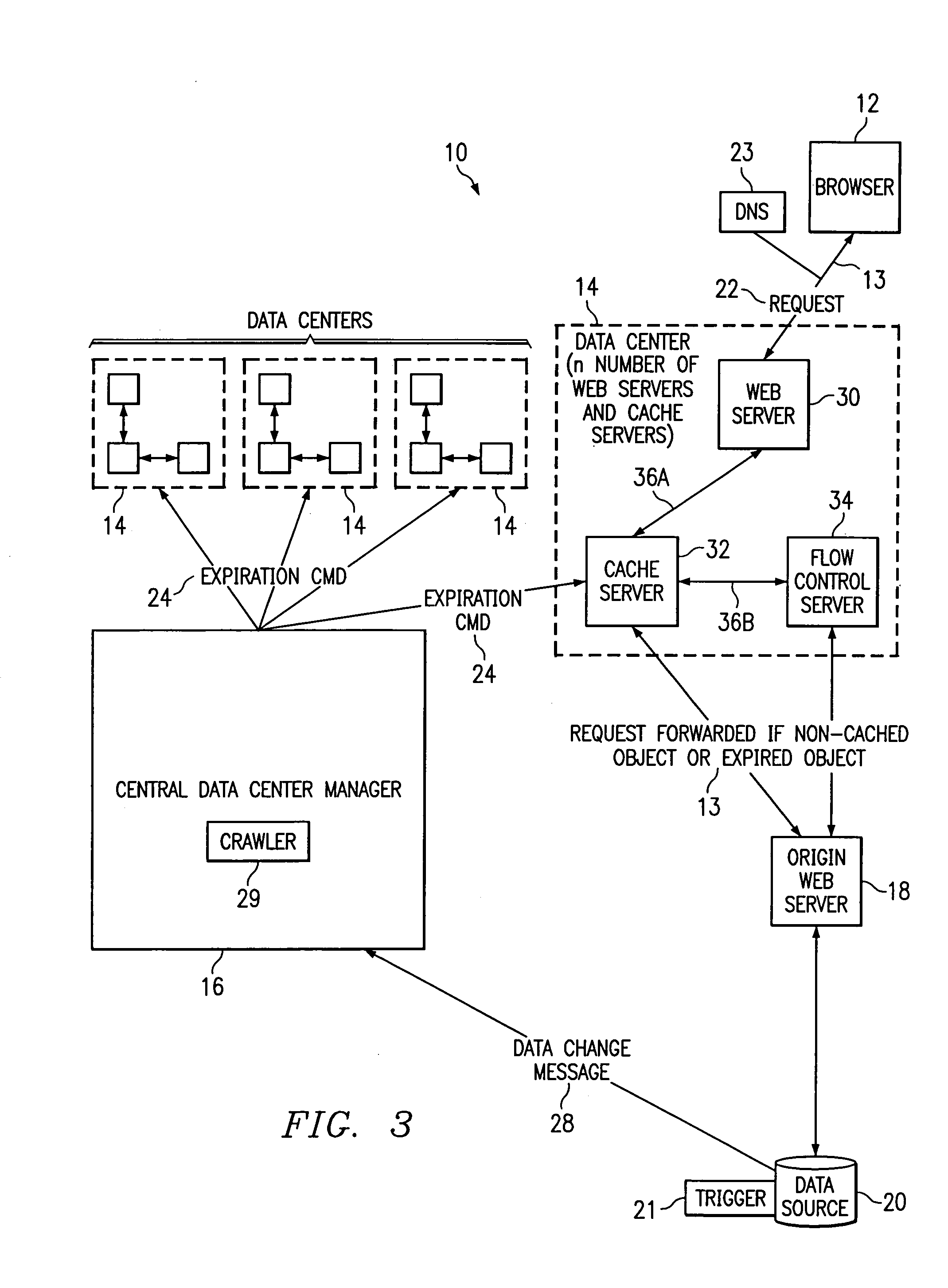
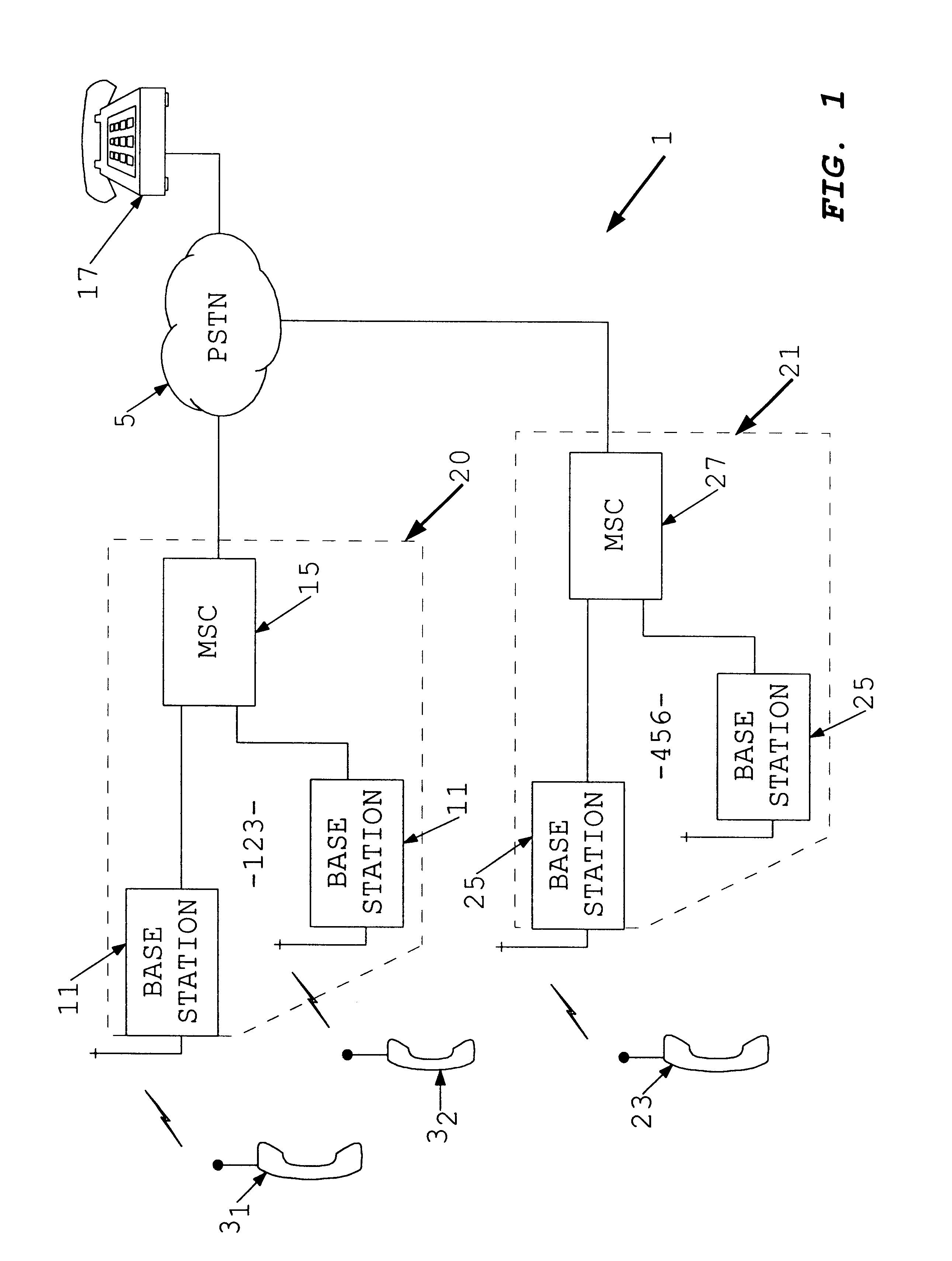
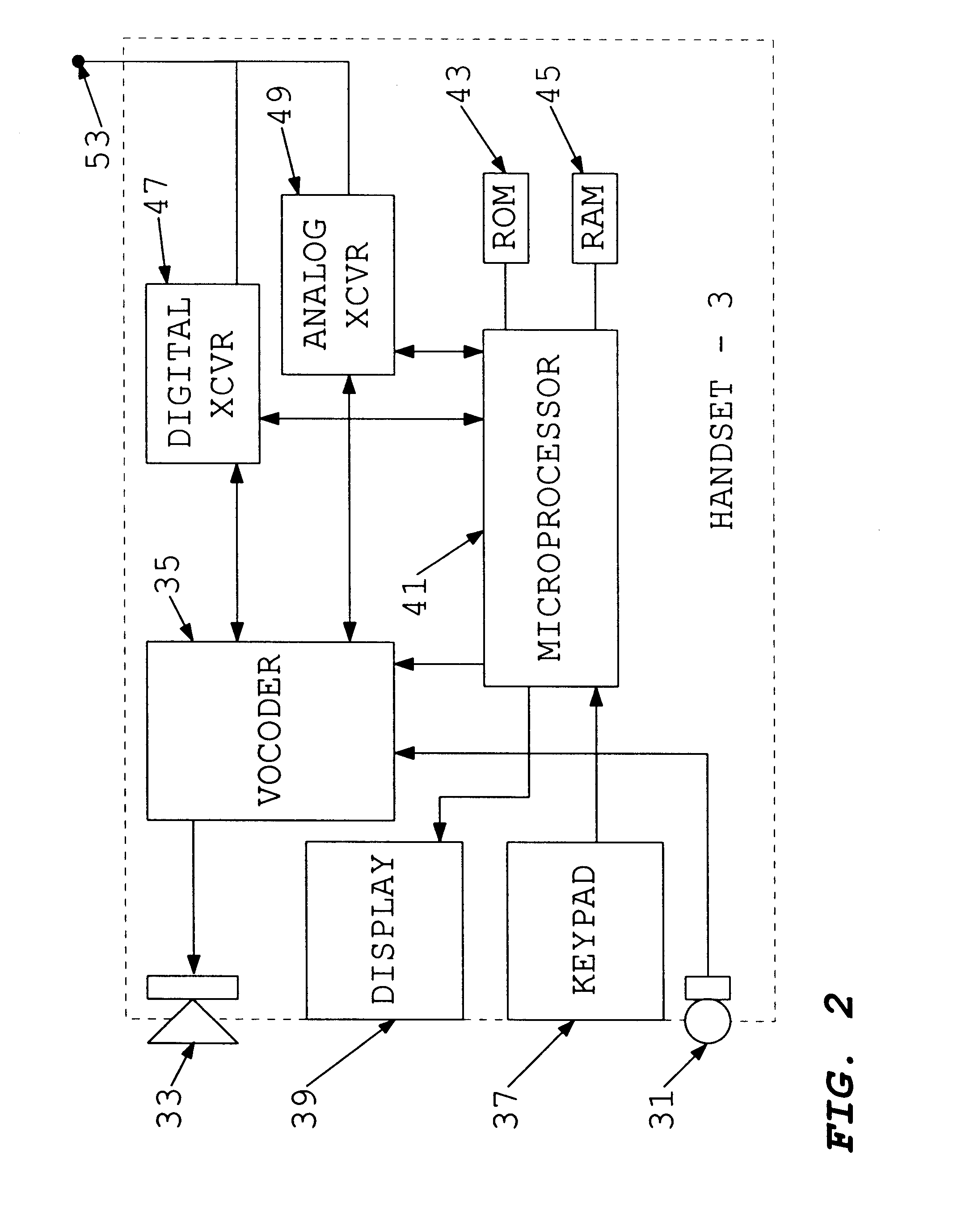
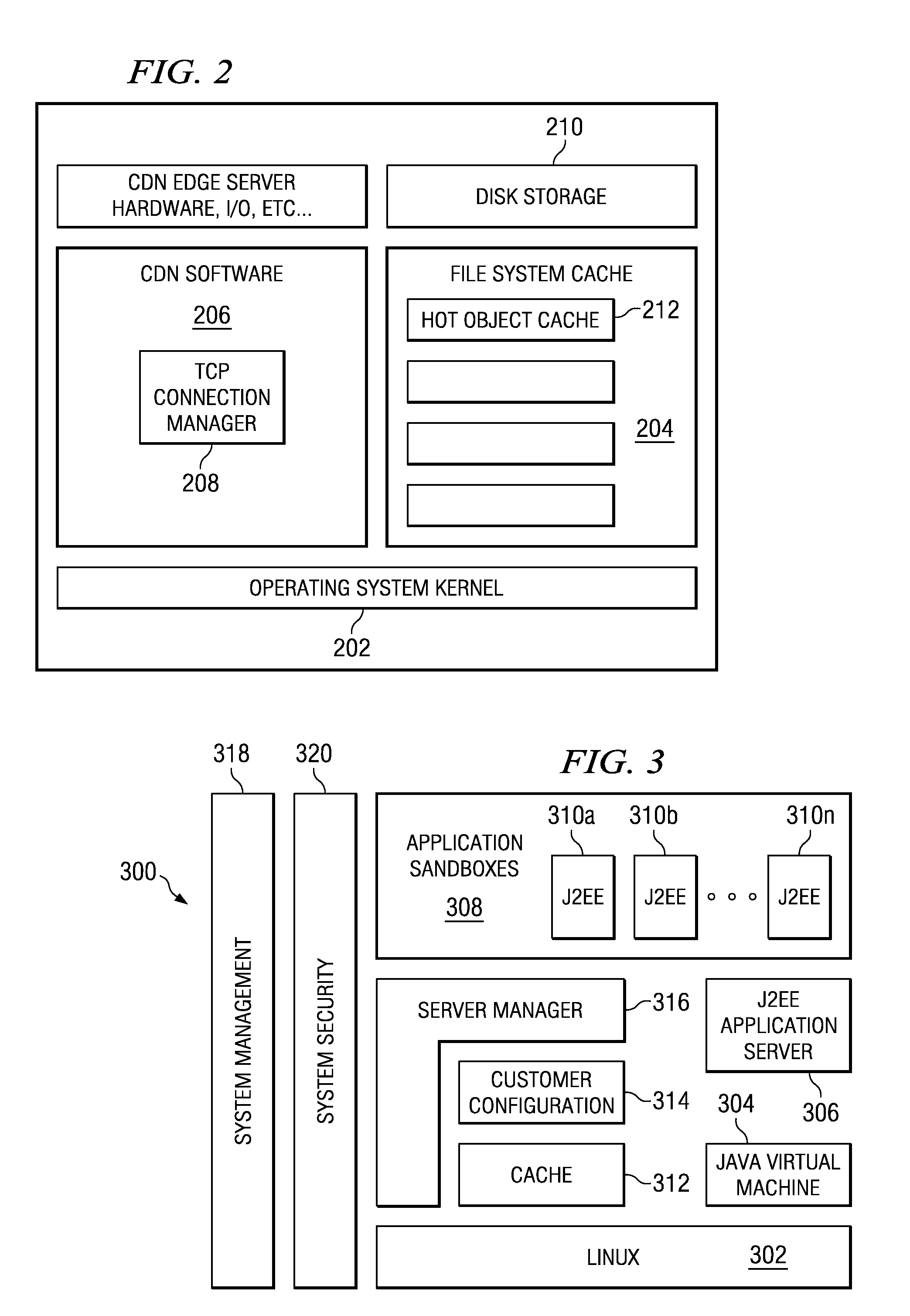
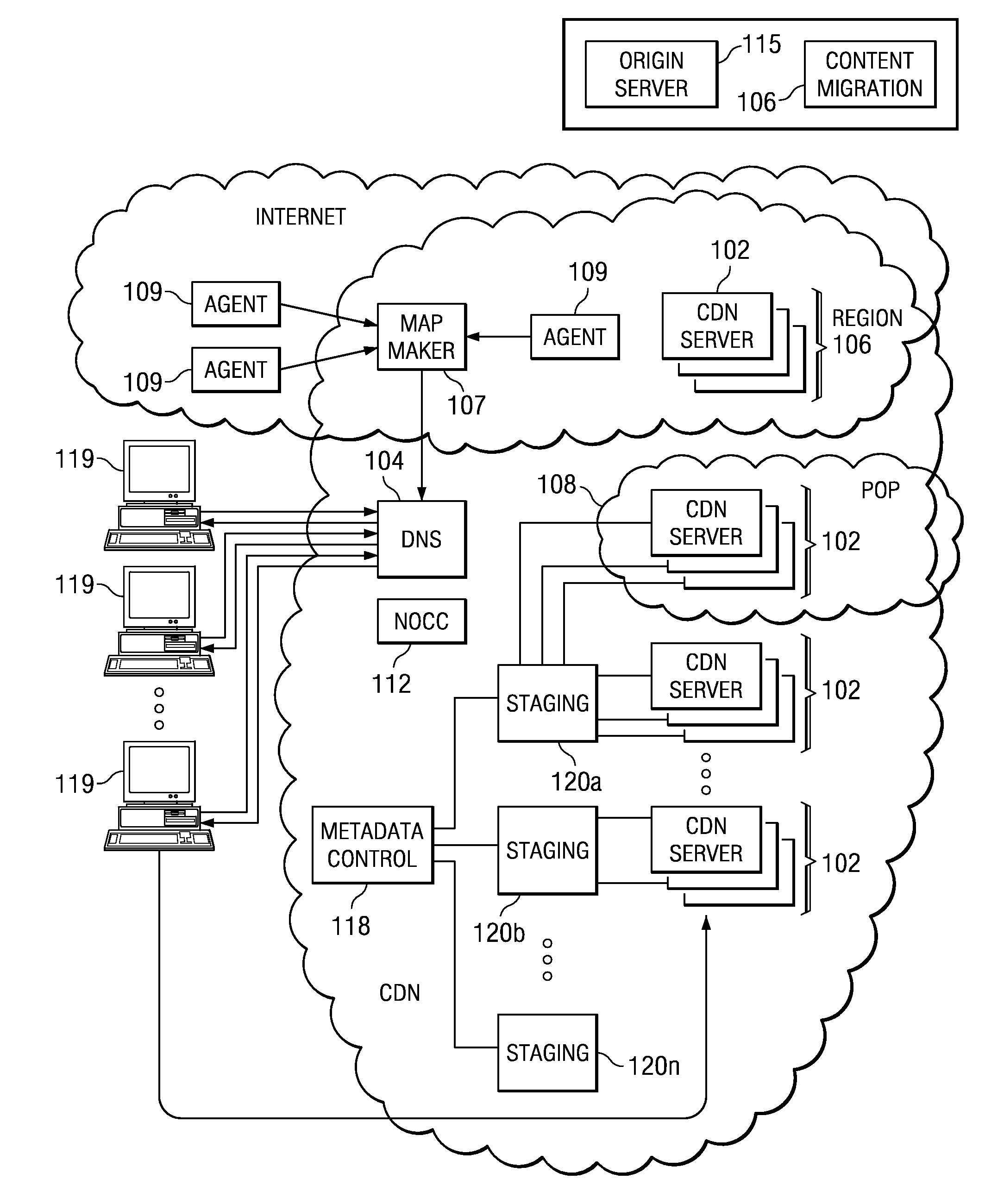
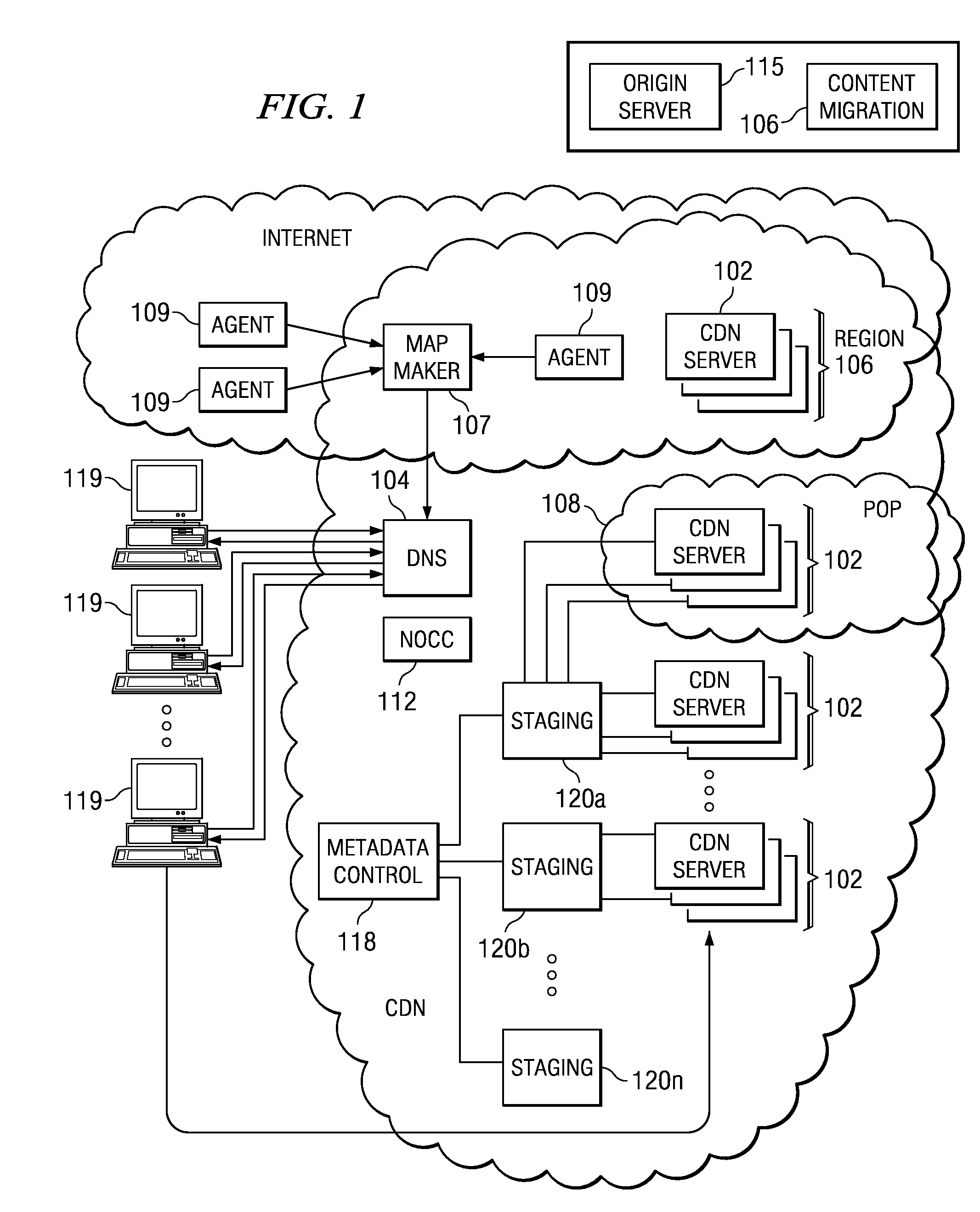
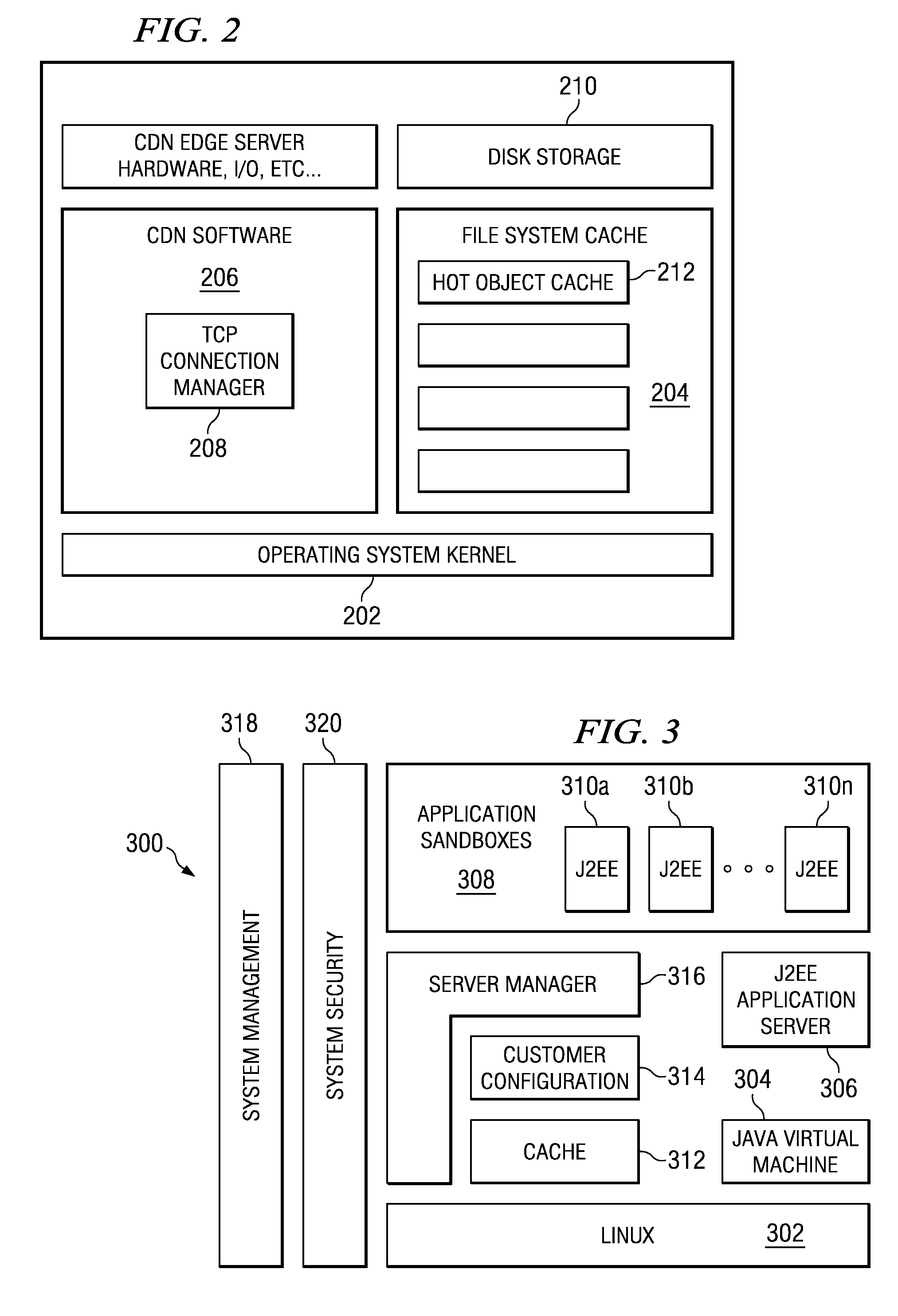
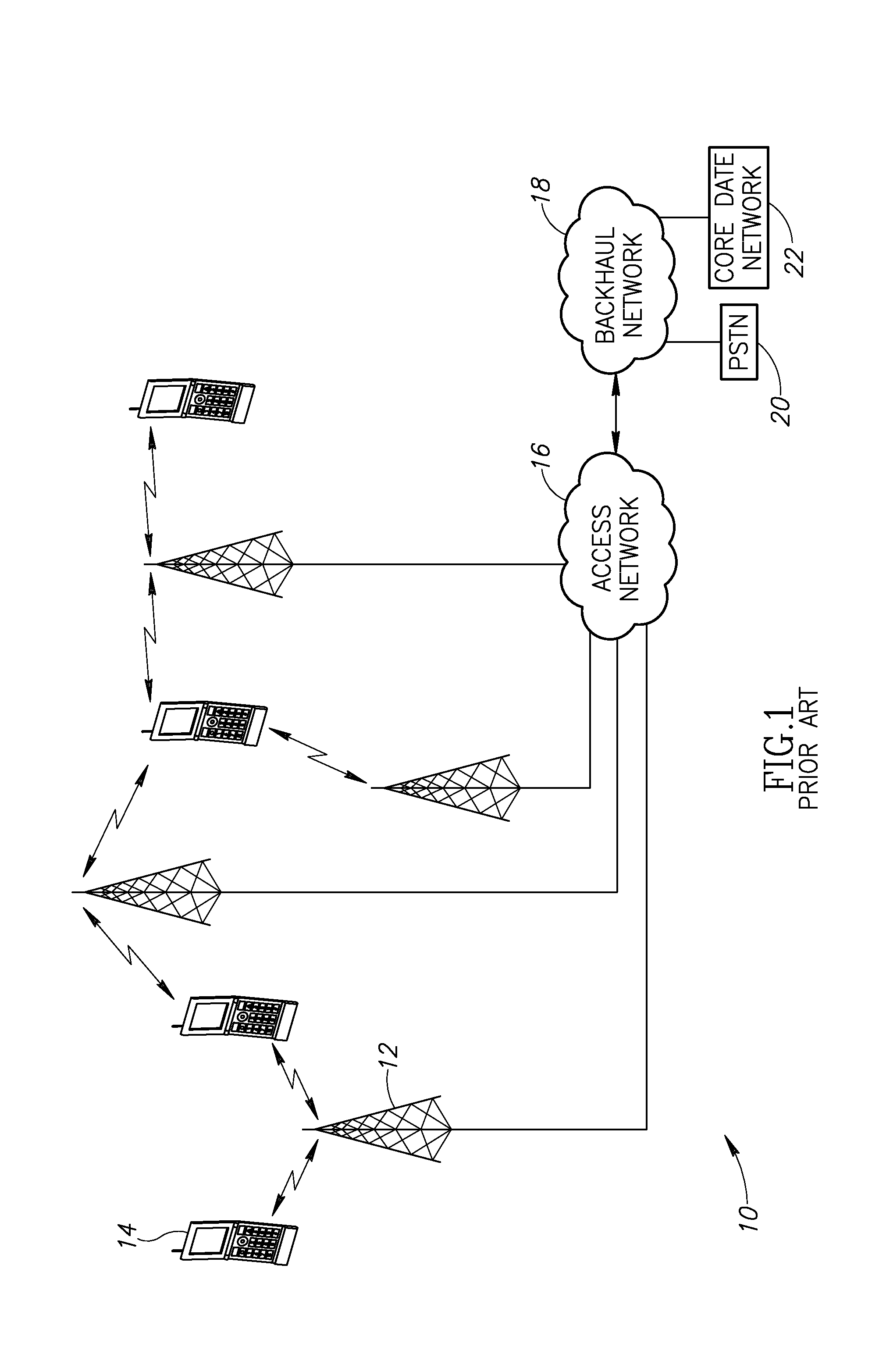
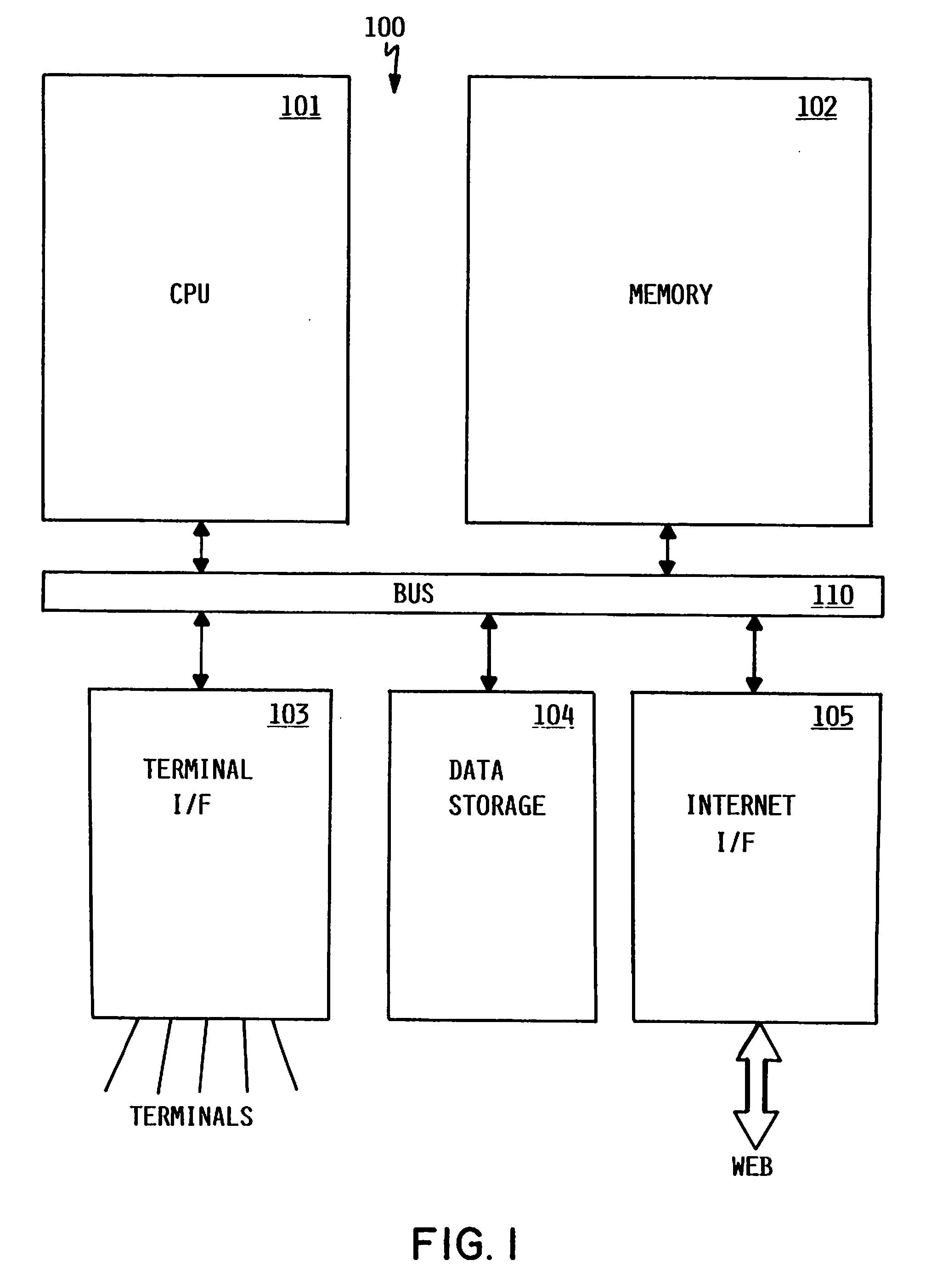
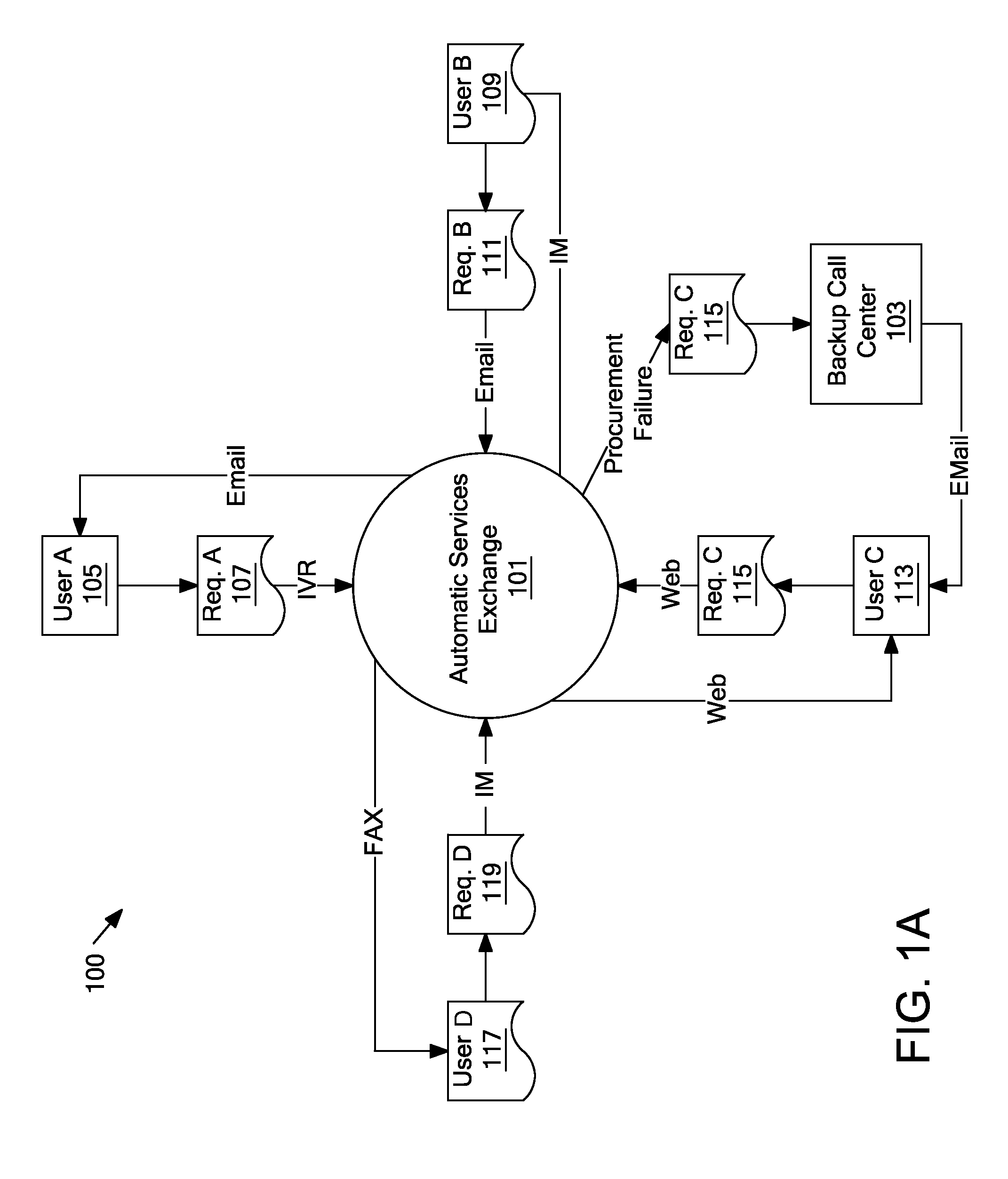
Method and apparatus for dynamic data flow control using prioritization of data requests
InactiveUS7454457B1Independent controlImprove efficiencyMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionData centerDynamic data
A data center (14) receives a request (22) for content from a browser (12) on a client (11). The data center determines whether the requested content is available at the data center. The content is available when the content is both present at the data center and current. The content may be expired and marked as non-available in response to an expiration command (24). When the requested content is available at the data center, the data center returns the requested content to the data center. When the requested content is locally unavailable at the data center, the requested content is retrieved from an origin server (18). The retrieval of the content from the origin server may be delayed based on the processing load at the origin server. When retrieval of the content is delayed, the request is prioritized and placed in a queue for handling by the origin server based on the priority of the request. Also, when retrieval of the content is delayed, a status page may be communicated to the browser to inform a user of the delay and provide alternate content (139) and status information related to the request determined as a function of the request or the current state of the origin server.
Owner:PARALLEL NETWORKS
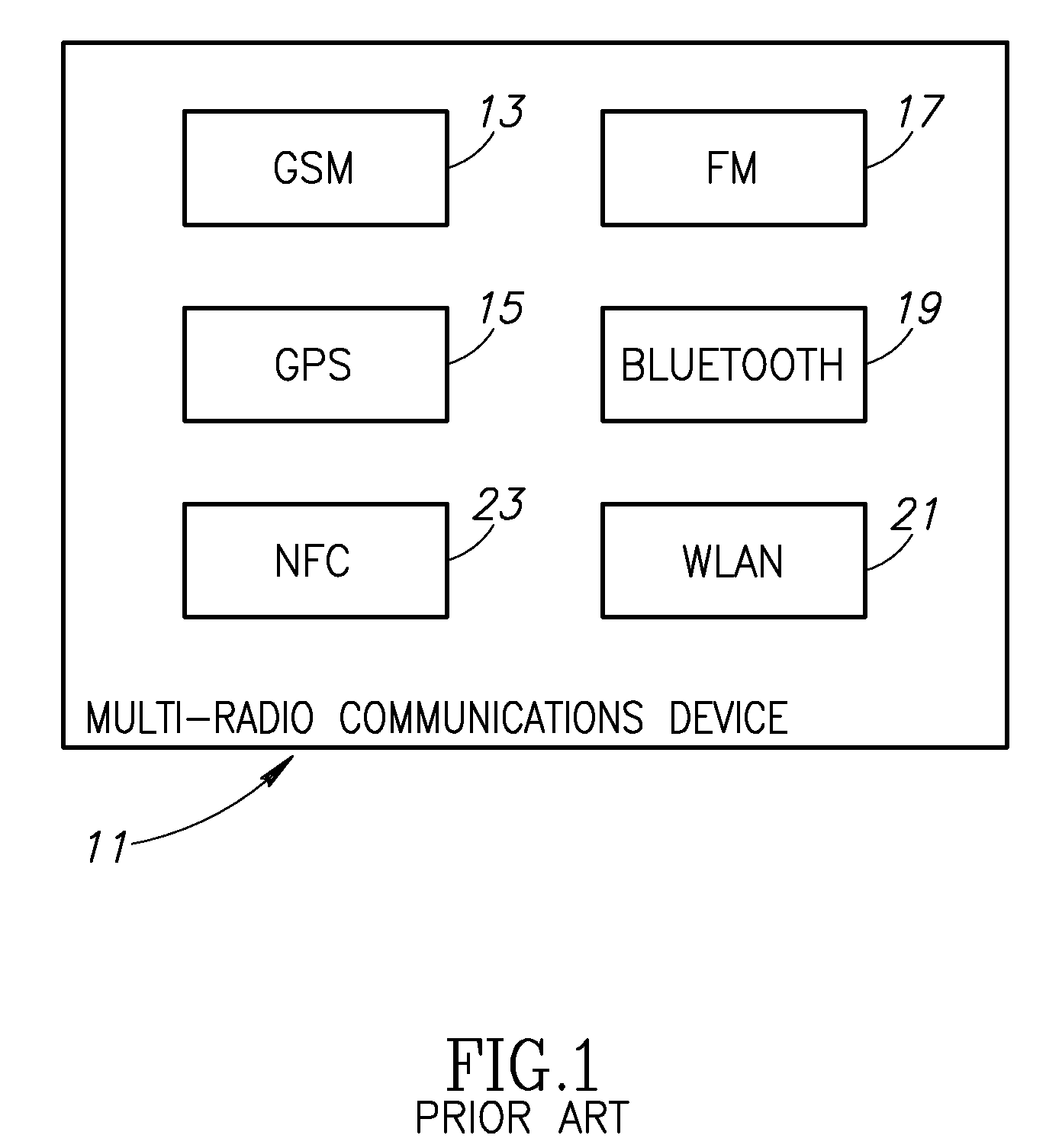
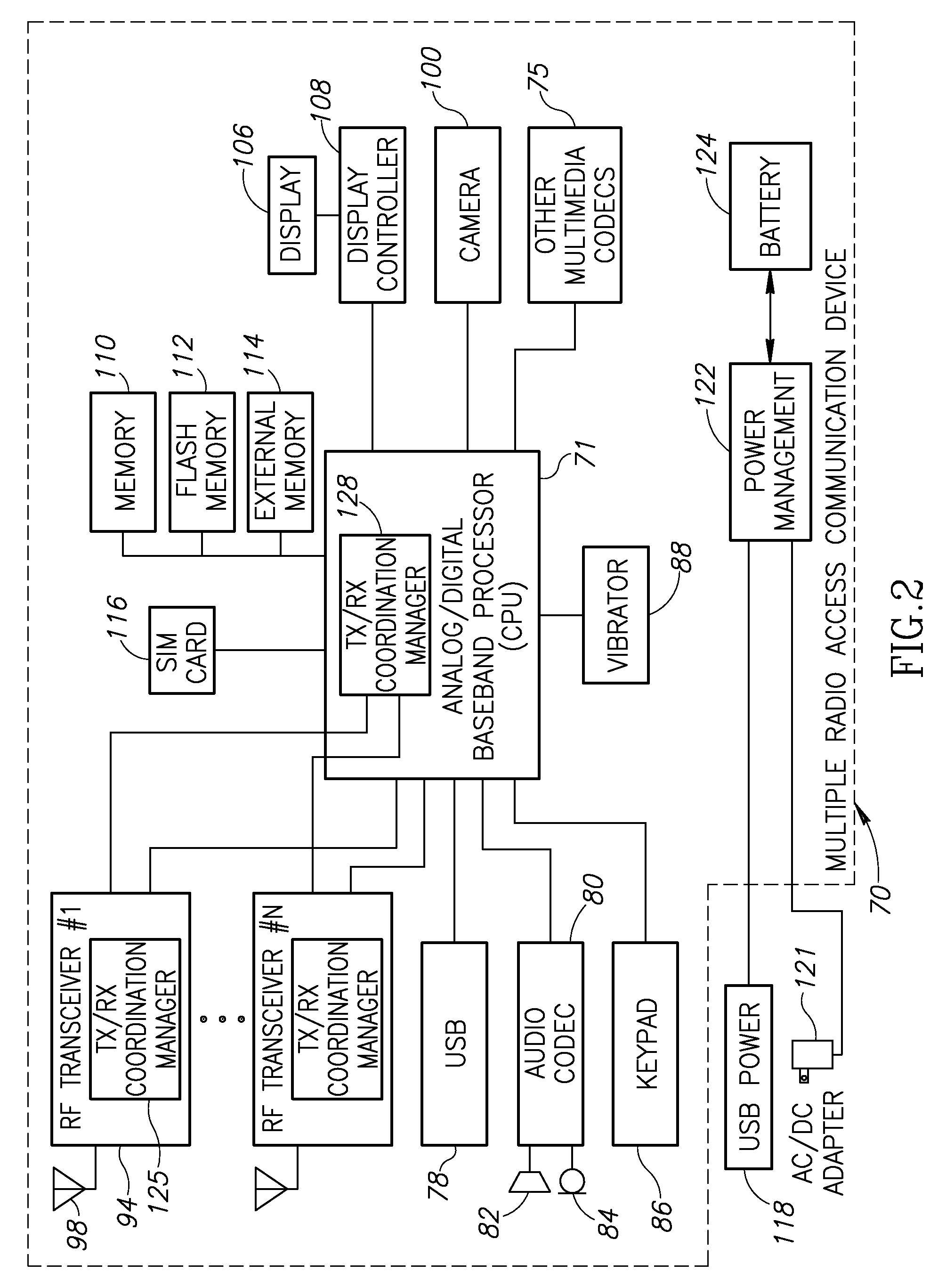
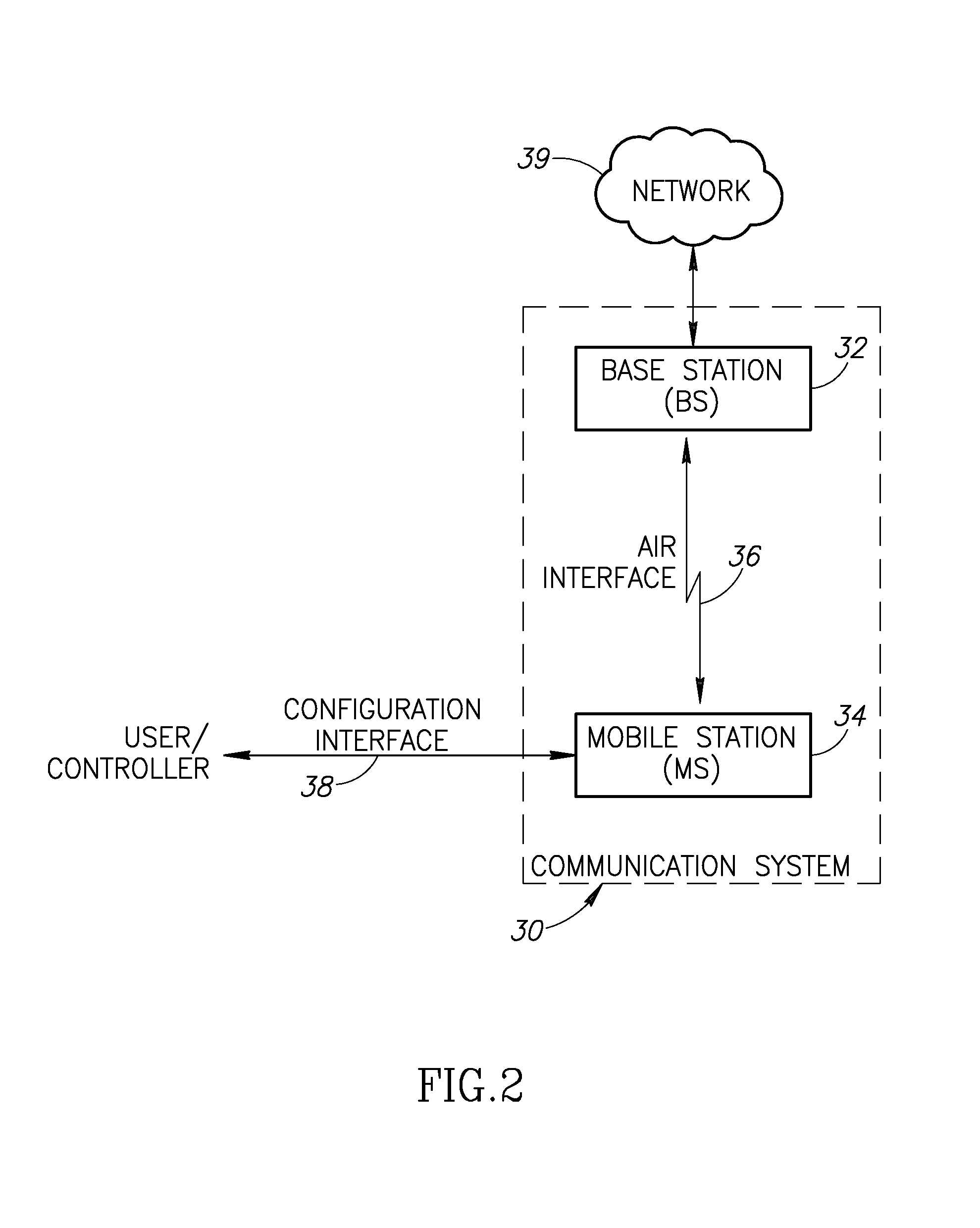
Apparatus for and method of coordinating transmission and reception opportunities in a communications device incorporating multiple radios
InactiveUS20090180451A1Avoid interferenceDelay transitionNetwork topologiesSubstation equipmentOperation modeMobile station
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of coordinating the allocation of transmission and reception availability and / or unavailability periods for use in a communications device incorporating collocated multiple radios. The mechanism provide both centralized and distributed coordination to enable the coordination (e.g., to achieve coexistence) of multiple radio access communication devices (RACDs) collocated in a single device such as a mobile station. A distributed activity coordinator modifies the activity pattern of multiple RACDs. The activity pattern comprises a set of radio access specific modes of operation, (e.g., IEEE 802.16 Normal, Sleep, Scan or Idle modes, 3GPP GSM / EDGE operation mode (PTM, IDLE, Connected, DTM modes), etc.) and a compatible set of wake-up events, such as reception and transmission availability periods. To prevent interference and possible loss of data, a radio access is prevented from transmitting or receiving data packets while another radio access is transmitting or receiving. In the event two or more RATs desire to be active at the same time, the mechanism negotiates an availability pattern between the MS and a corresponding BS to achieve coordination between the RATs.
Owner:COMSYS COMM & SIGNAL PROC
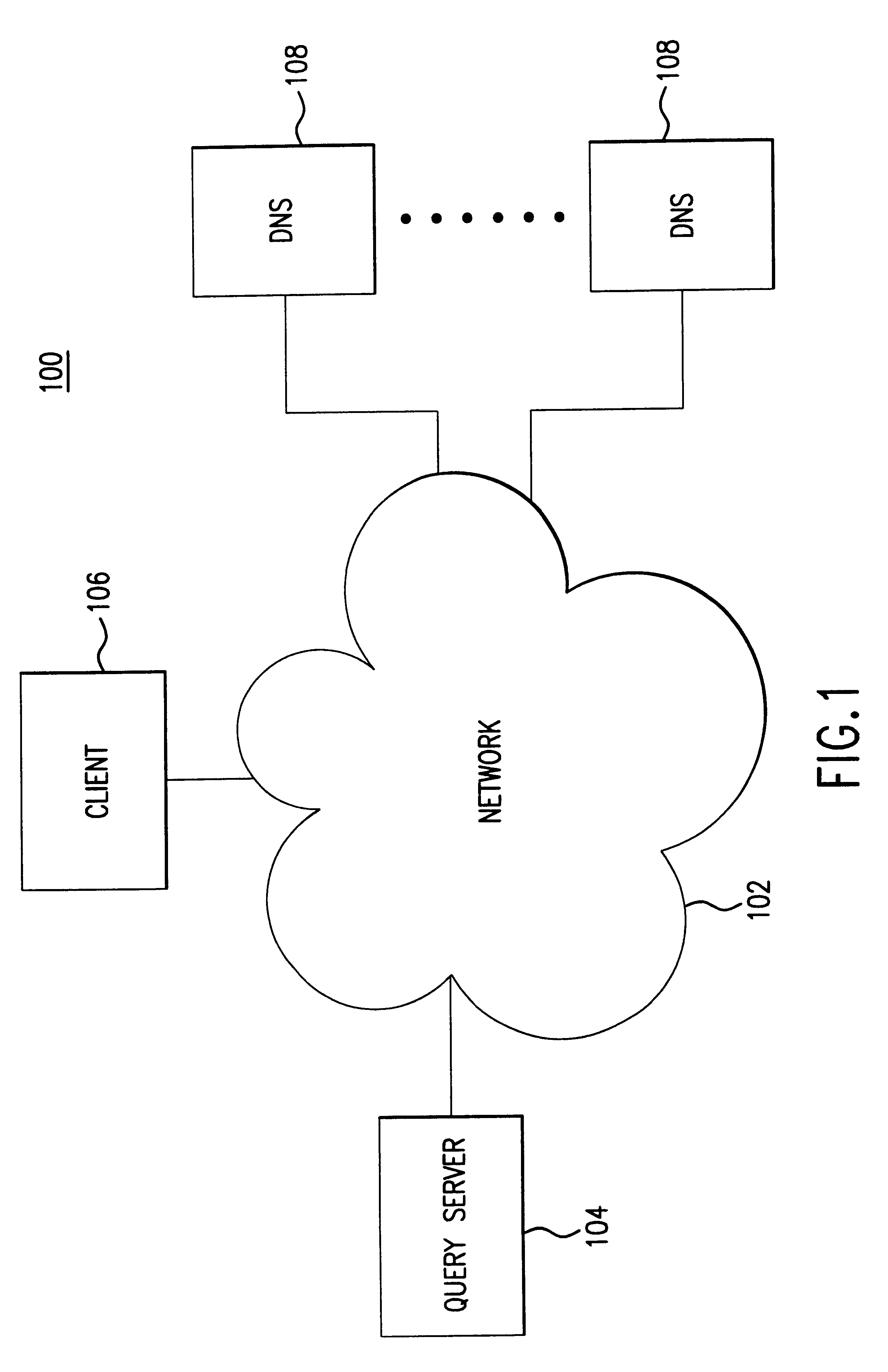
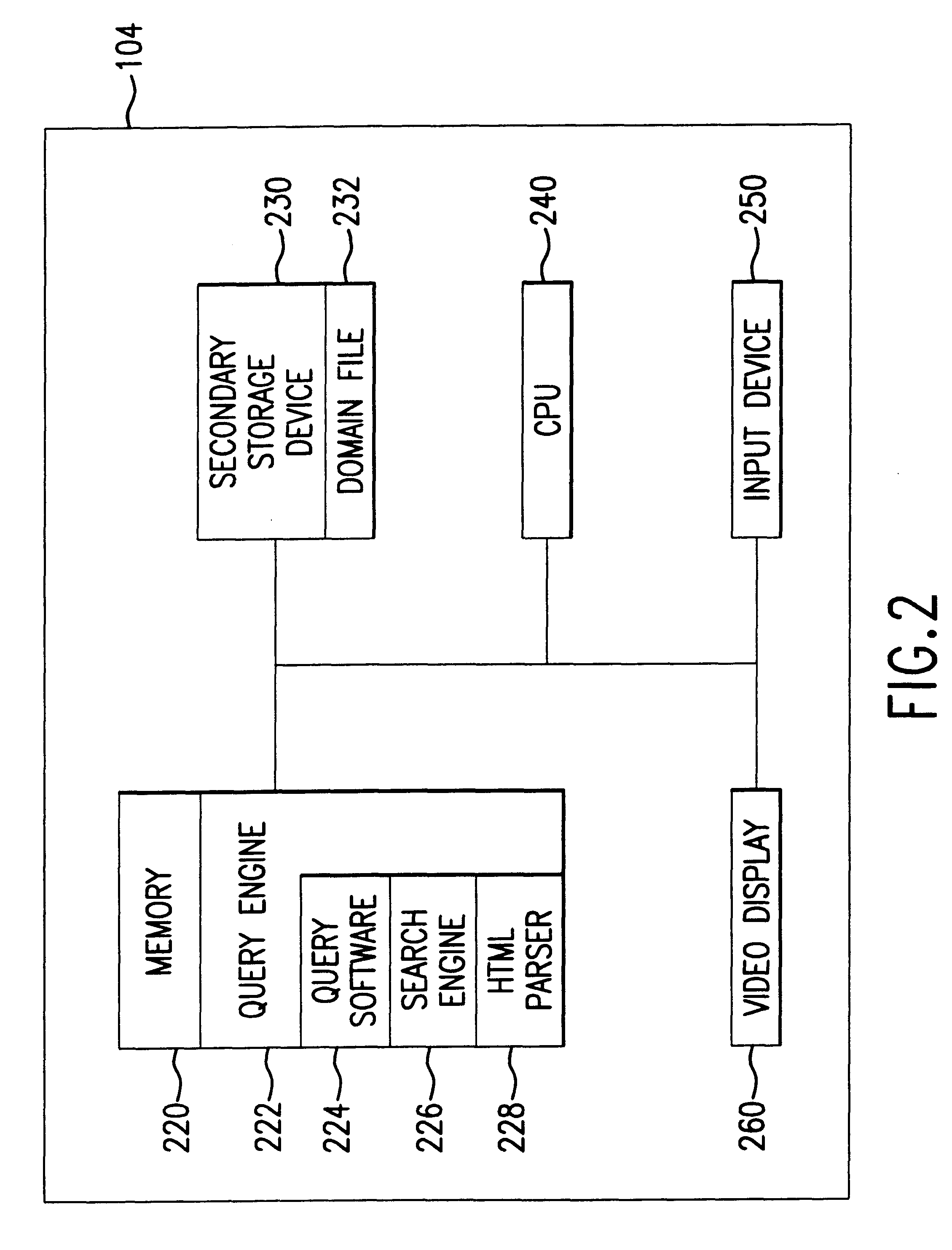
Method of determining unavailability of an internet domain name
Methods, systems, and articles of manufacture consistent with the present invention provide an improved query server that overcomes the shortcomings of existing domain name searching techniques by performing a multitude of searches simultaneously, transparent to the user. Specifically, the improved query server searches for existing domain name records in various domains and then displays the results in a formatted manner, thus eliminating the need for a user to perform individual searches.
Owner:VERISIGN REGISTRY SERVICES
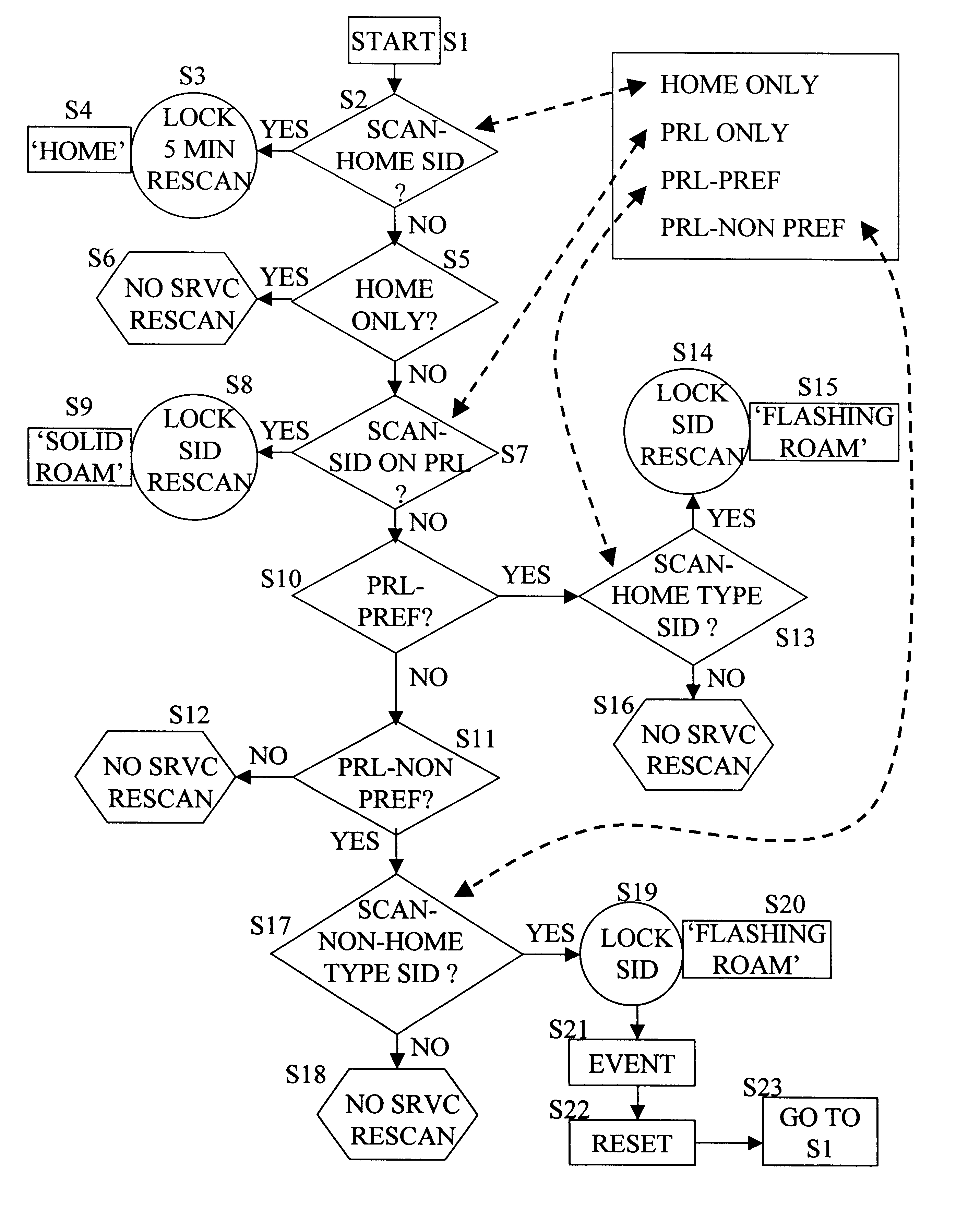
Preferred roaming list and system select feature
InactiveUS6625451B1Overcome problemsAssess restrictionSubstation equipmentPartial systemOperation mode
The System Select feature provides user selectable modes of operation in a mobile communication station, which allow certain fall-back options when a preferred system may not be available, but still steers the bulk of the system selection operations to preferred systems. In a first user selected mode, the mobile station scans for a broadcast system identifier or "SID" that matches an identifier of a preferred system stored in memory of the station. The second mode allows the user at least one option, which involves selection of a less than preferred system, but with this mode, the mobile station will still make a first attempt to register with a system having a SID matching one stored in memory of the station. A preferred implementation offers the user four system selection options. Options based on stored identifiers include an option to select only the home system, and an option to select from a preferred roaming list (PRL) if the home system is unavailable. In the other two options, if the scanning operations for the home system and systems on the PRL are ineffective, one option involves scanning a band corresponding to that used by the home system. In contrast, the other option involves scanning a band other than that used by the home system. The System Select programming, however, limits the operation in the last optional setting, for example to a set time period or until completion of one call. The preferred embodiment facilitates a substantially one-rate service, where the service provider charges the one rate for all calls through the home system, all systems on the PRL list and any system found during a scan of the home-system band.
Owner:BELL ATLANTIC MOBILE SYST
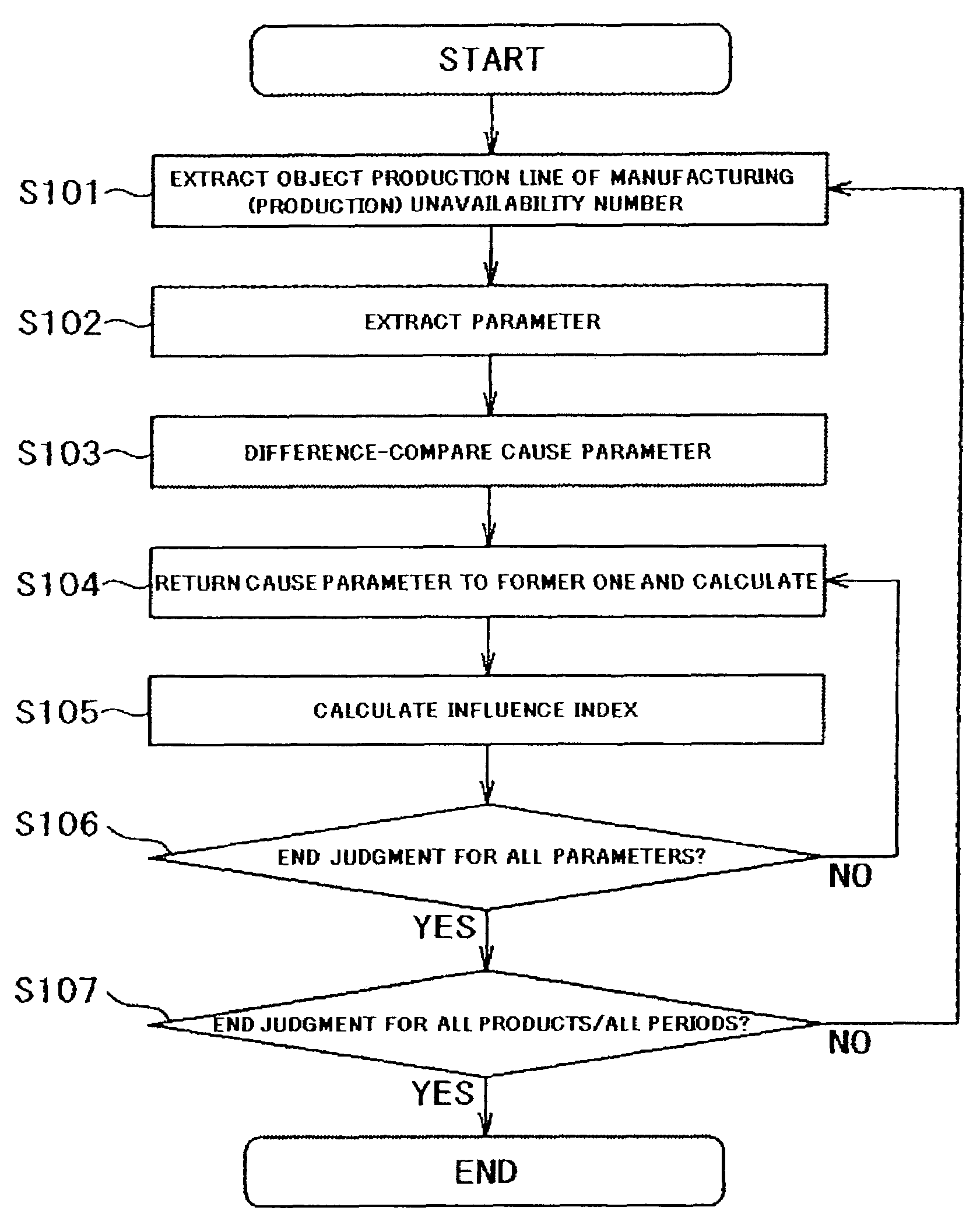
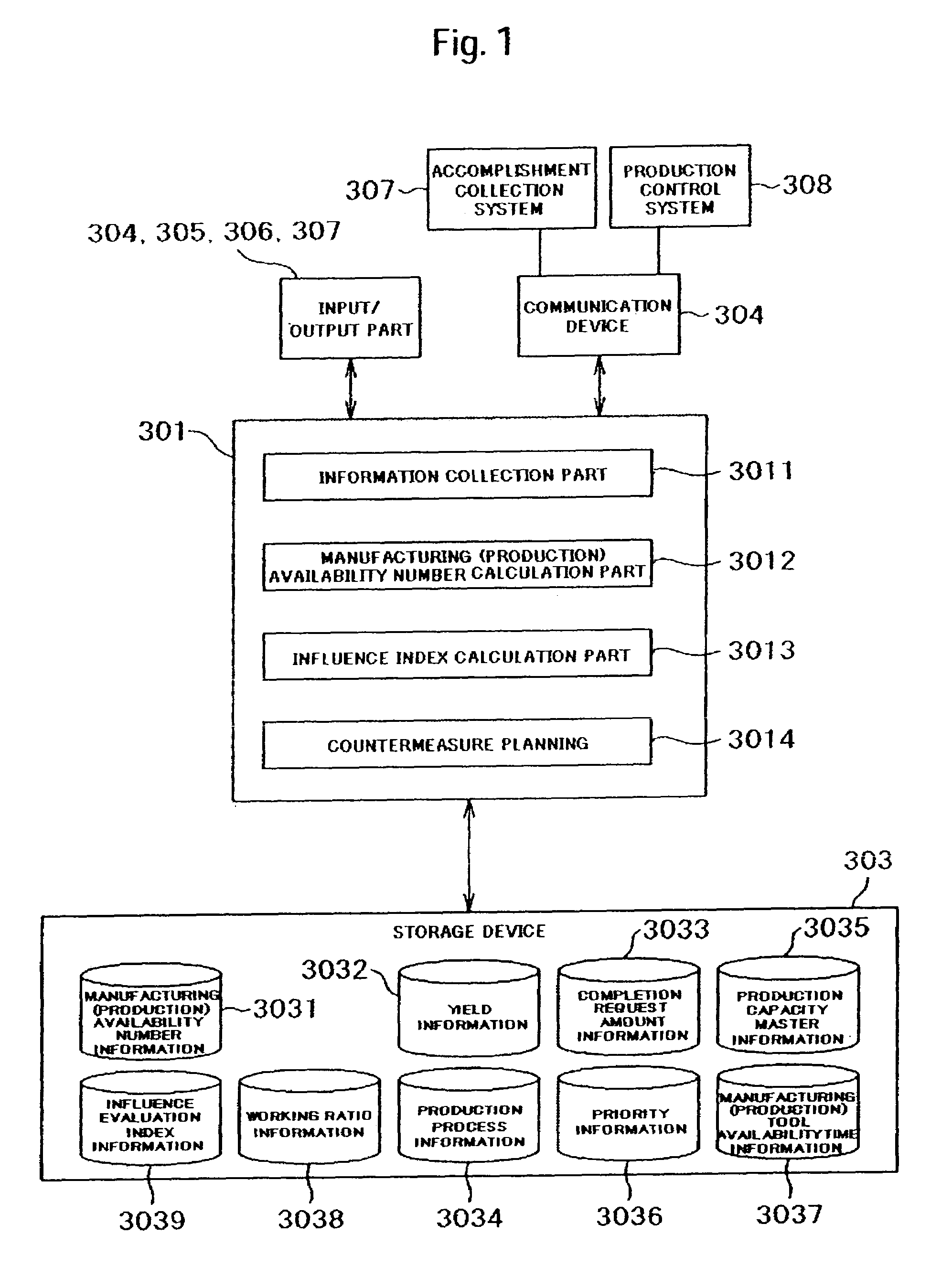
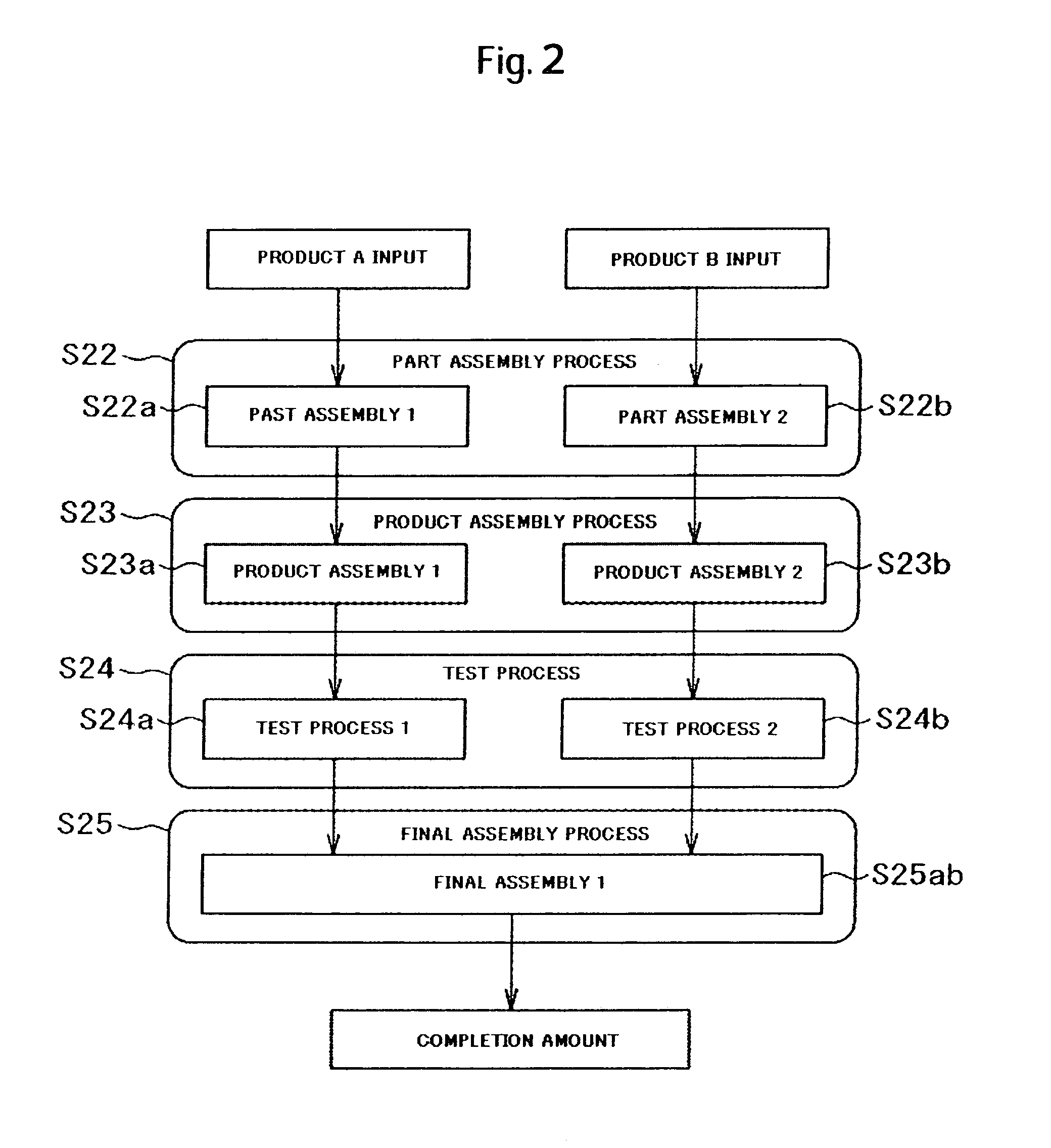
Production planning method and production planning system
InactiveUS7693593B2Change in yield of the production line is vigorousComplicated processingForecastingResourcesProduction lineUnavailability
Embodiments of the present invention provide a production planning method and system. Where a manufacturing apparatus is shared by a plurality of products in a production line, if a manufacturing (production) availability number is changed, a cause parameter is automatically investigated so that a production plan with high precision can be prepared in a short time. With respect to a production plan as the previous / current comparison objects, a production process used in the production plan in which a change occurs, is extracted. From the production process, a parameter item to be used in the production capacity evaluation is extracted for all products, a difference comparison is made between the value of the previous parameter and the value of the current parameter, so that the parameter item as the cause is specified. The combination of the cause parameter items is calculated, and a cause parameter list is prepared. Next, from the specified parameter list, the parameter item is sequentially changed, and the manufacturing (production) availability number is recalculated. An influence index given to the manufacturing (production) unavailability number by the cause parameter, is calculated.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
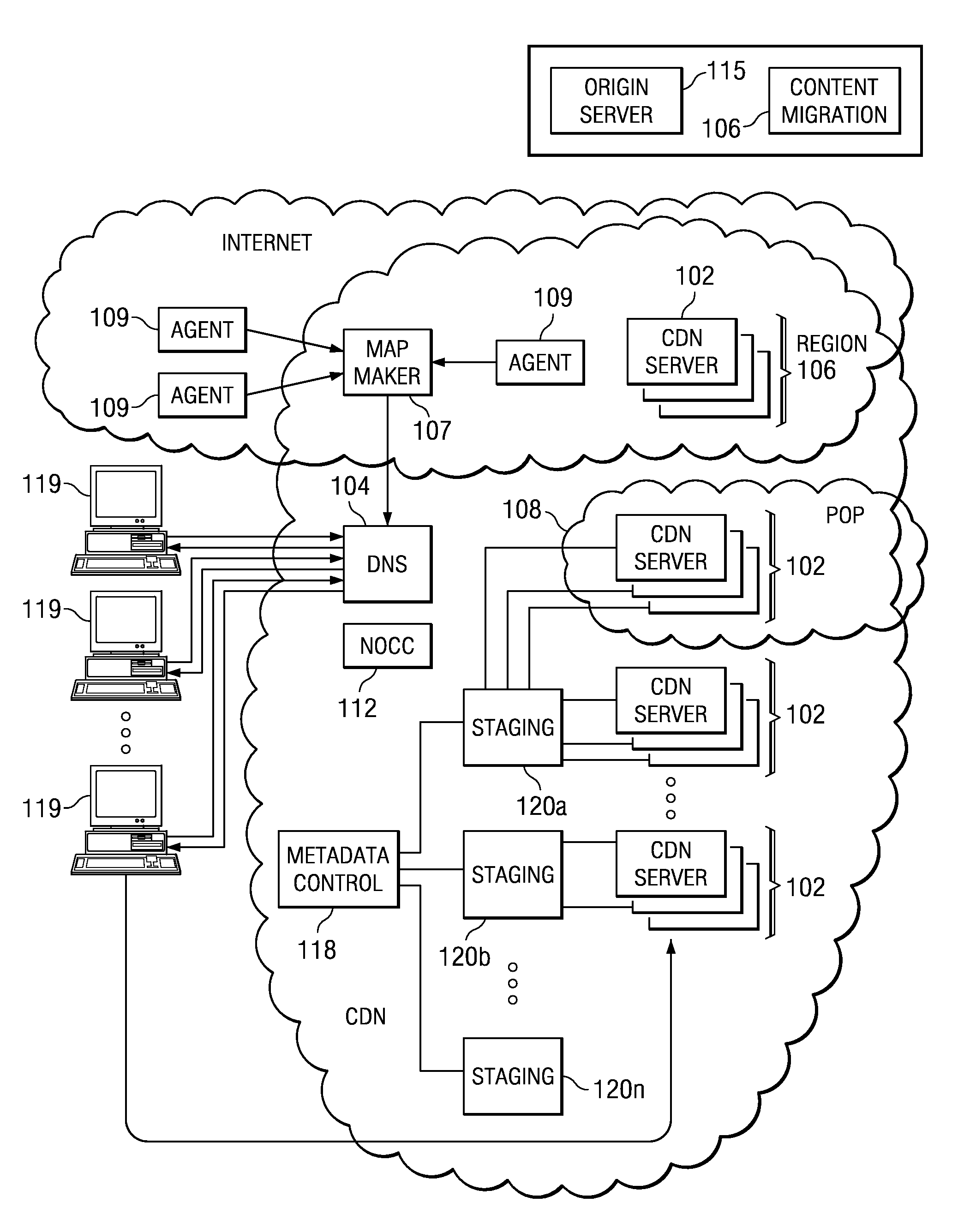
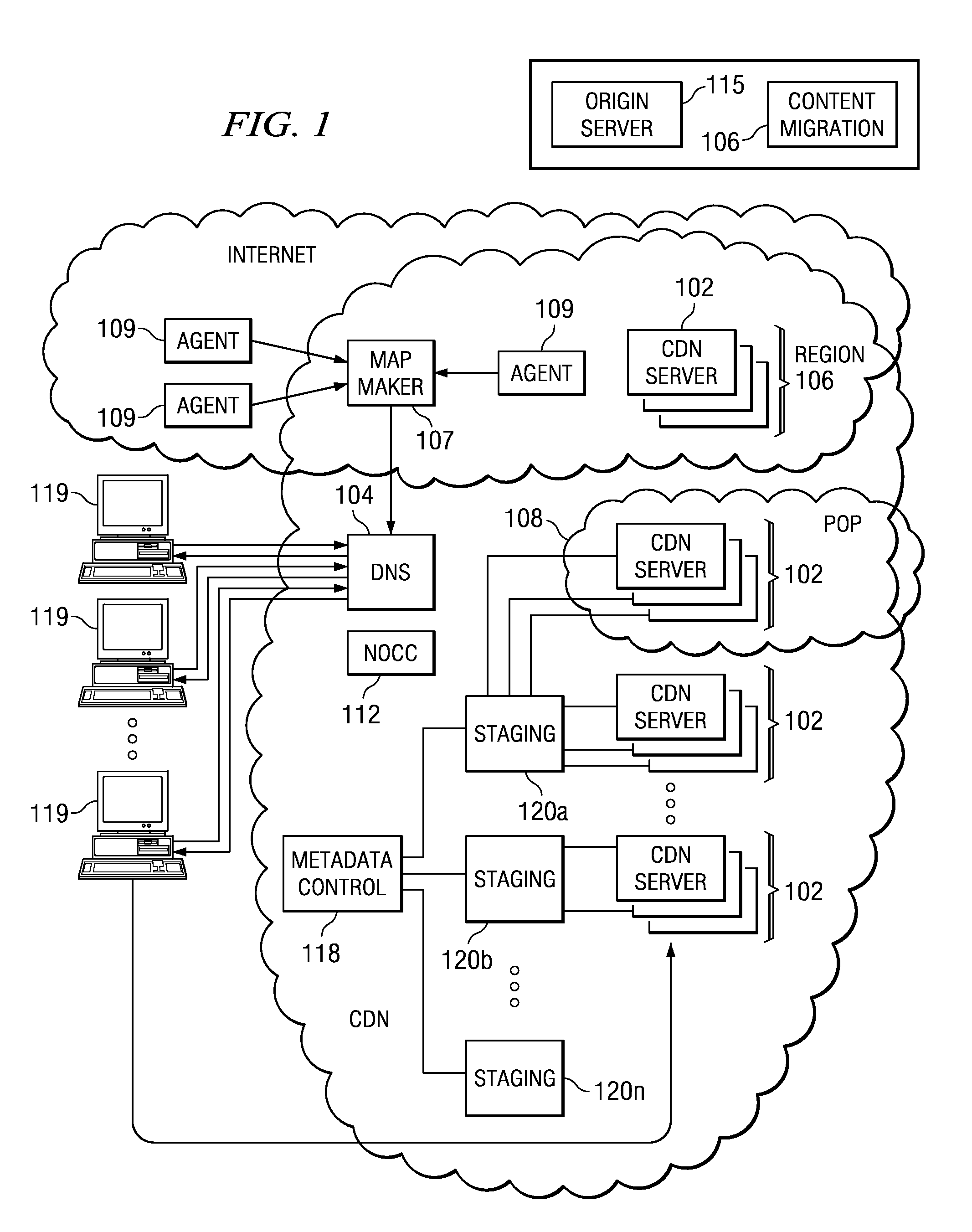
Managing web tier session state objects in a content delivery network (CDN)
ActiveUS7254634B1Error detection/correctionMultiple digital computer combinationsEdge serverApplication software
Business applications running on a content delivery network (CDN) having a distributed application framework can create, access and modify state for each client. Over time, a single client may desire to access a given application on different CDN edge servers within the same region and even across different regions. Each time, the application may need to access the latest “state” of the client even if the state was last modified by an application on a different server. A difficulty arises when a process or a machine that last modified the state dies or is temporarily or permanently unavailable. The present invention provides techniques for migrating session state data across CDN servers in a manner transparent to the user. A distributed application thus can access a latest “state” of a client even if the state was last modified by an application instance executing on a different CDN server, including a nearby (in-region) or a remote (out-of-region) server.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
Managing web tier session state objects in a content delivery network (CDN)
InactiveUS7765304B2Error detection/correctionMultiple digital computer combinationsEdge serverApplication software
Business applications running on a content delivery network (CDN) having a distributed application framework can create, access and modify state for each client. Over time, a single client may desire to access a given application on different CDN edge servers within the same region and even across different regions. Each time, the application may need to access the latest “state” of the client even if the state was last modified by an application on a different server. A difficulty arises when a process or a machine that last modified the state dies or is temporarily or permanently unavailable. The present invention provides techniques for migrating session state data across CDN servers in a manner transparent to the user. A distributed application thus can access a latest “state” of a client even if the state was last modified by an application instance executing on a different CDN server, including a nearby (in-region) or a remote (out-of-region) server.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
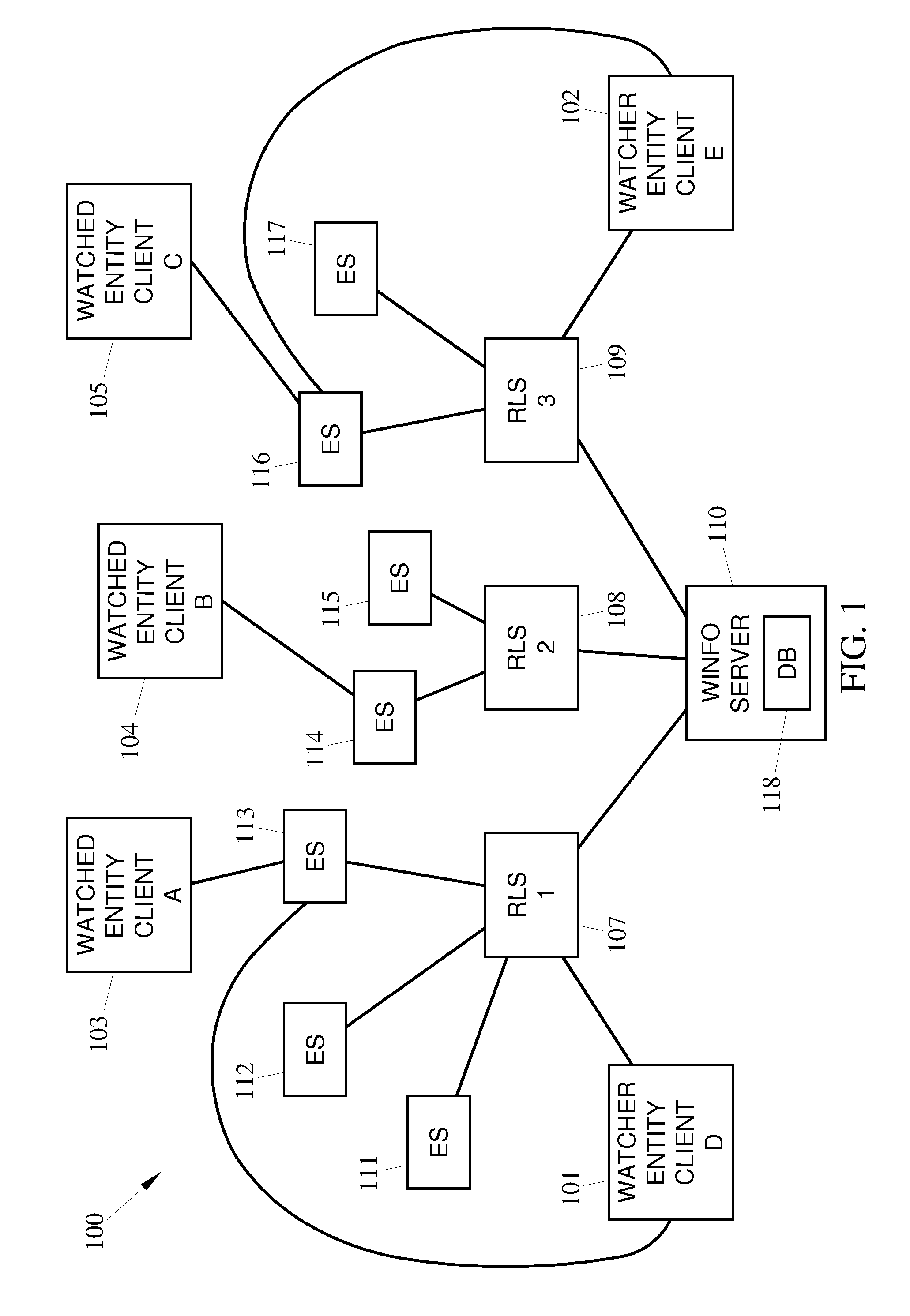
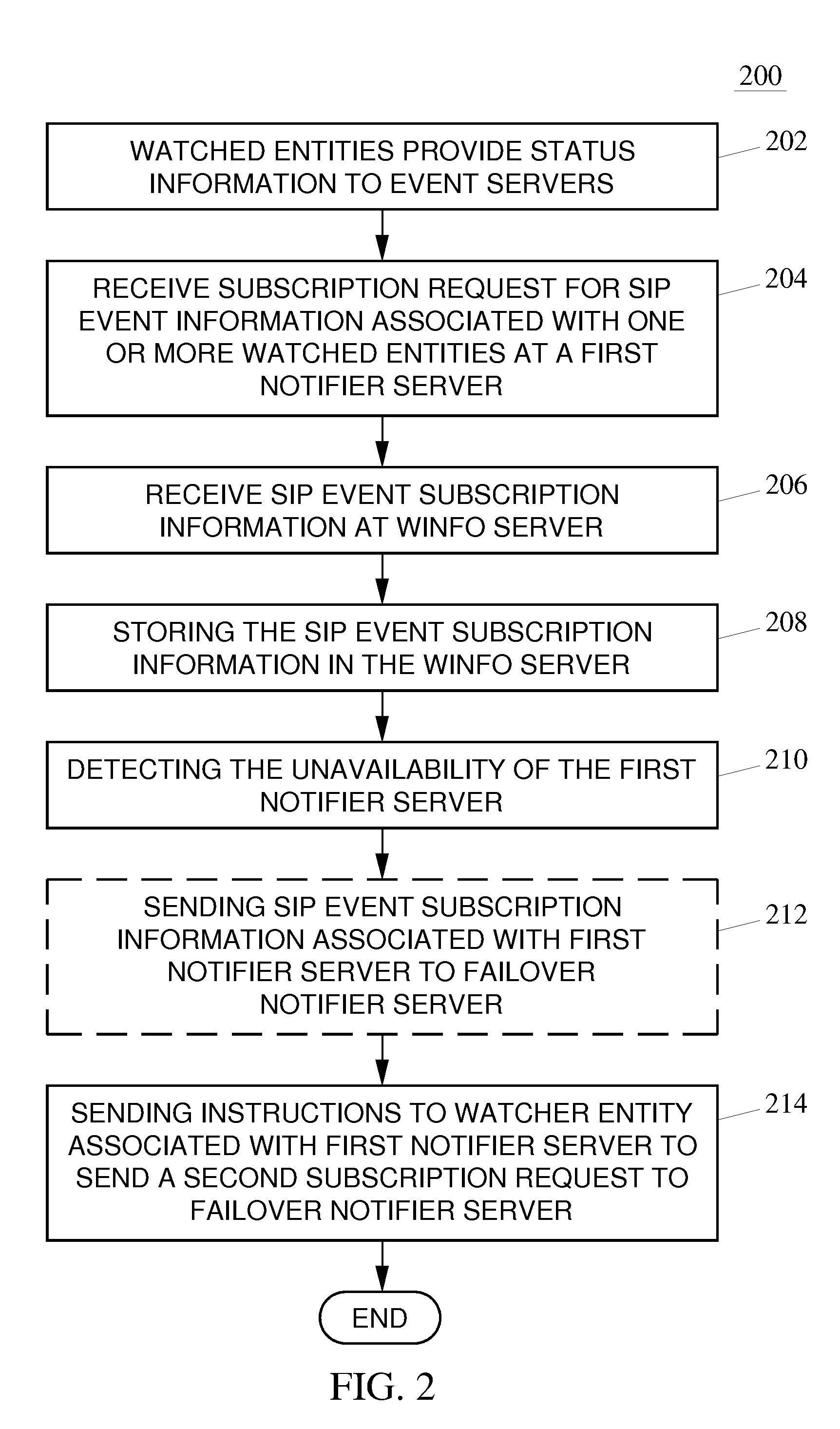
Methods, systems and computer readable media for providing a failover measure using watcher information (WINFO) architecture
Methods, systems, and computer readable media system for collecting and distributing session initiation protocol (SIP) event watcher entity subscription information in a communications network are disclosed. According to one aspect, the method includes receiving, at a first notifier server from a watcher entity client, a first subscription request for SIP event information associated with one or more watched entity clients. The method also includes receiving, at a watcher information (WINFO) entity, SIP event subscription information that includes an identifier indicating that the first notifier server serves the watcher entity client, storing the SIP event subscription information in the WINFO entity, detecting the unavailability of the first notifier server. The method further includes sending an instruction message, based on the identifier in the stored SIP event subscription information, to direct the watcher entity to generate a second subscription request associated for the SIP event information.
Owner:TEKELEC
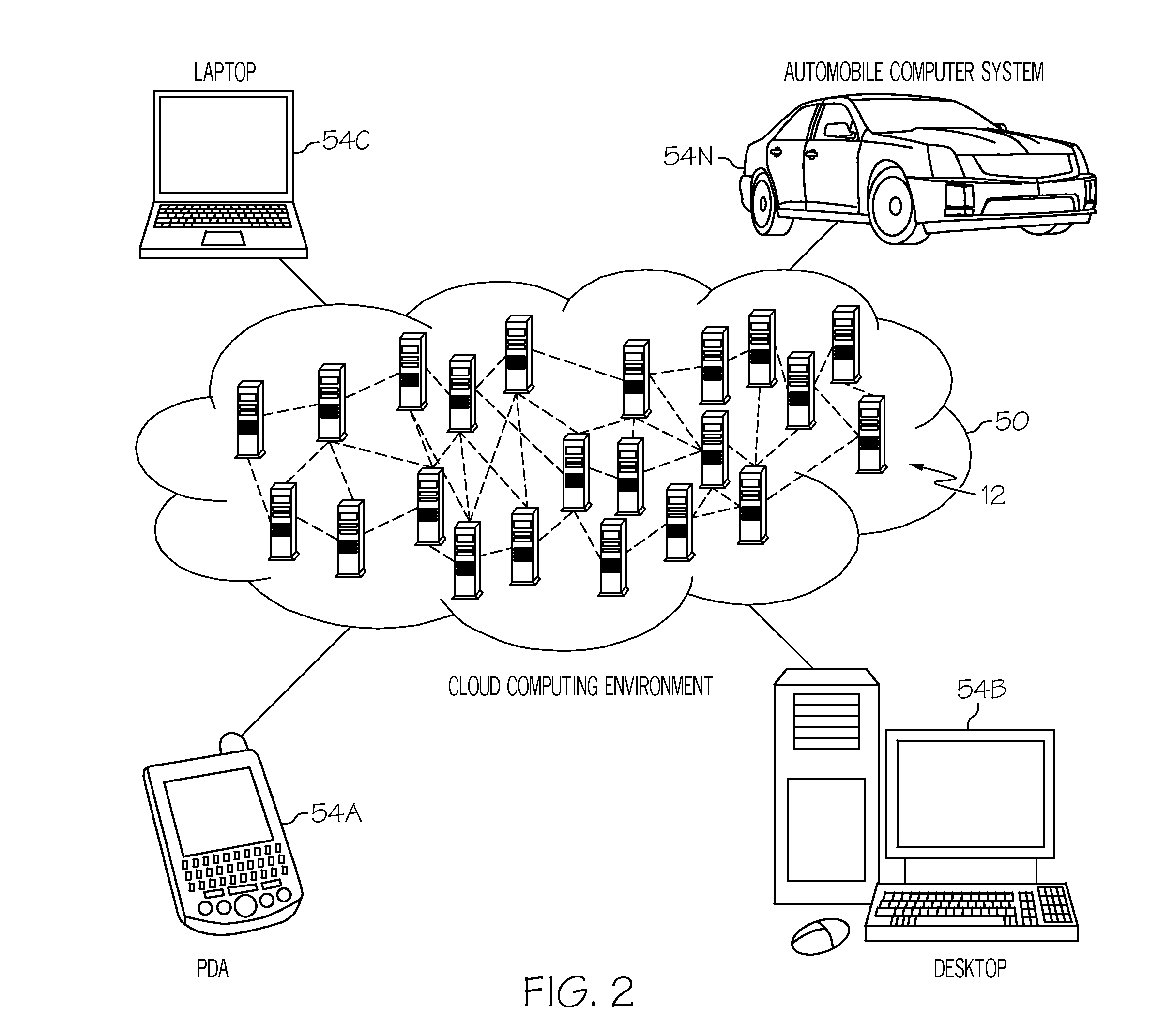
Resource exchange management within a cloud computing environment
ActiveUS20110145413A1Improve usabilityReduce unavailabilityFinanceGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsResource managementResource based
The present invention provides a solution for resource sharing (e.g., inter-Cloud) within a Cloud-computing environment. One objective of the present invention is to better utilize idle public or private Cloud infrastructures and improve the availability of Cloud services by allowing different Cloud service providers to virtually combine their services and infrastructures. In the event that there is not enough capacity for a single Cloud service provider to manage its workload, the workload may be shifted to additional infrastructures within the Cloud. The result of the workload shift may reduce the unavailability of Cloud services to the Cloud end-user by allowing another Cloud service provider to temporarily handle the workload. Based on the resource sharing activities, compensation (e.g., credits / tokens) can be exchanged between the participating Cloud providers to reflect their participation in the resource exchange.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
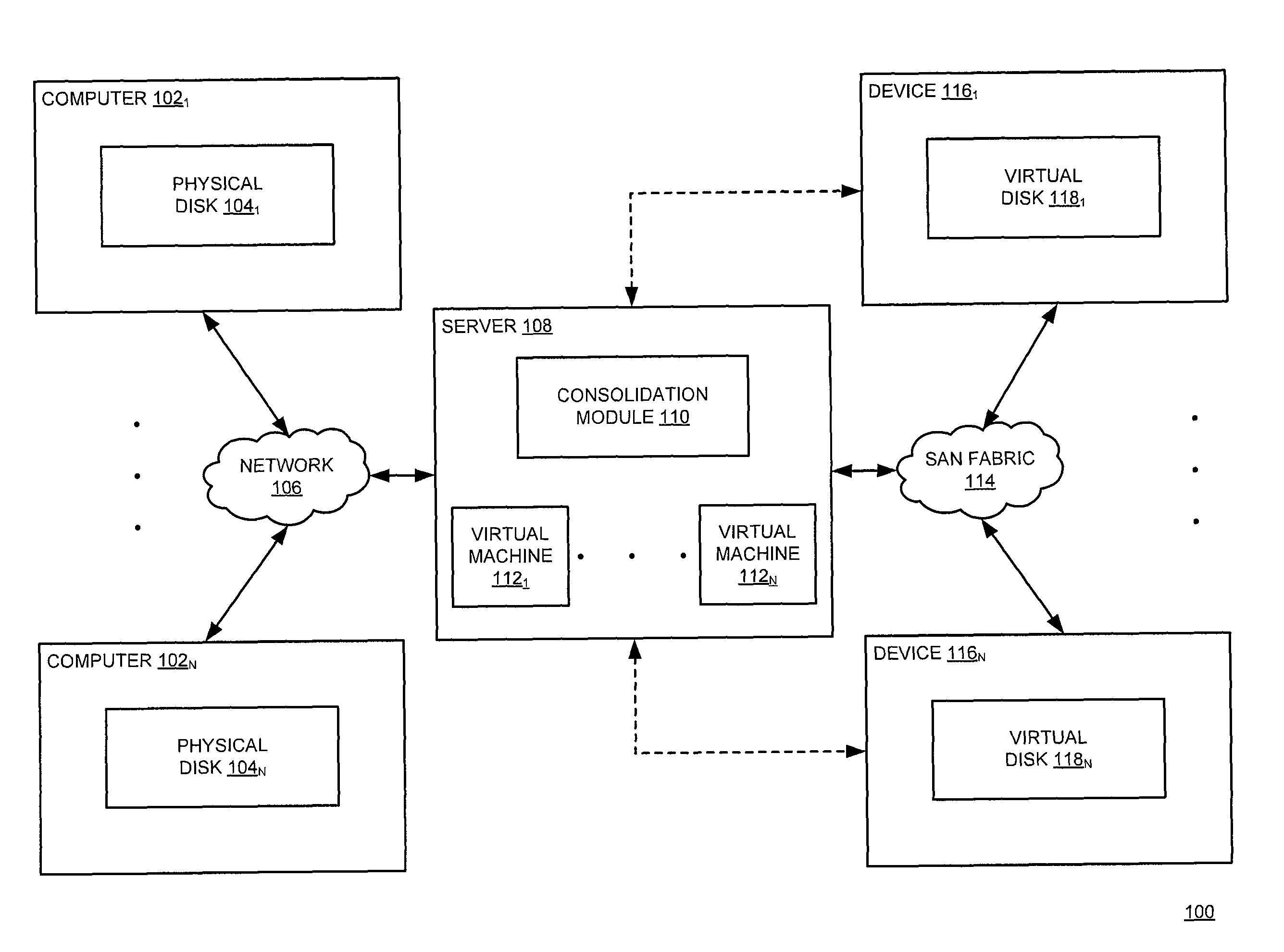
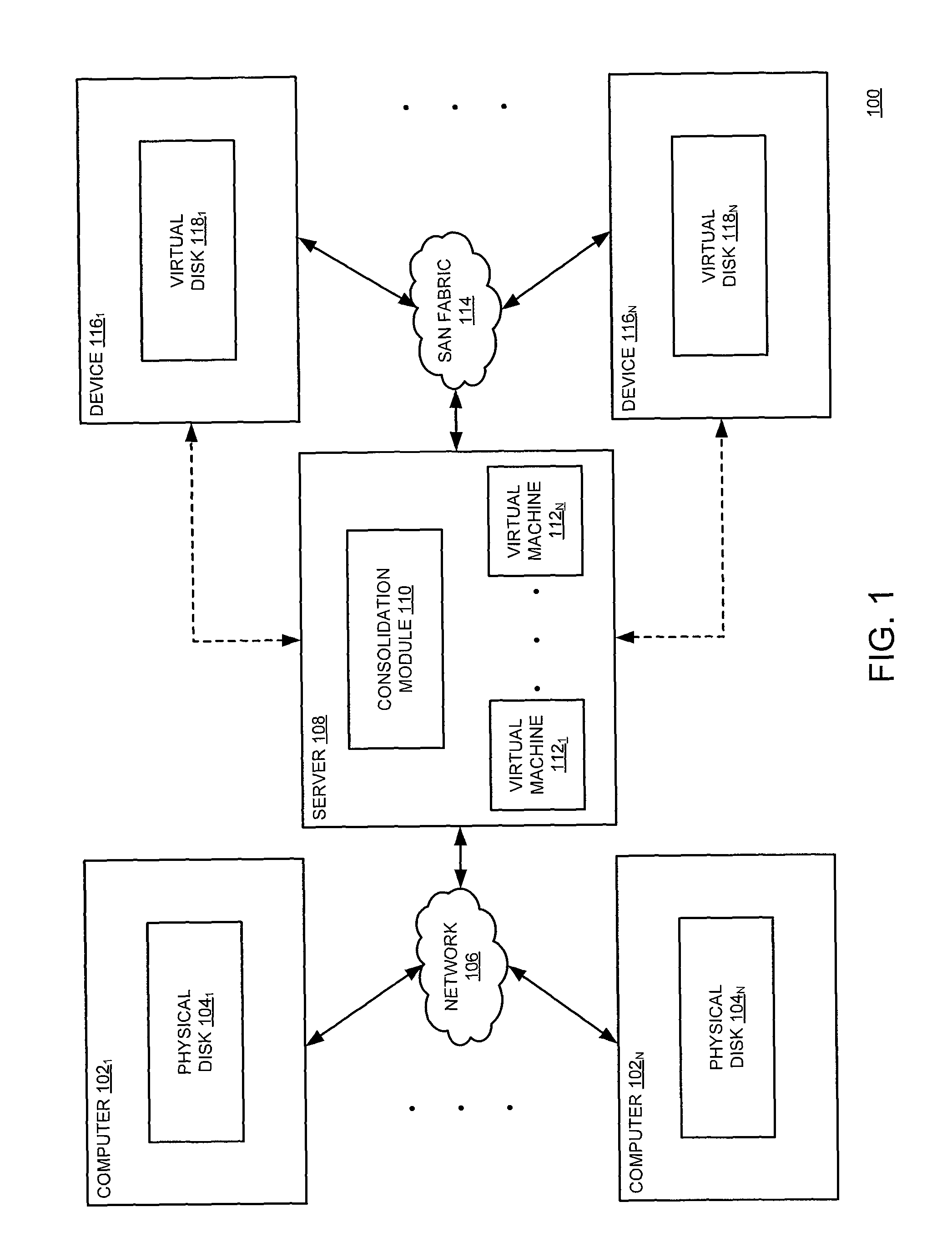
Method and apparatus for synchronizing a physical machine with a virtual machine while the virtual machine is operational
A method for synchronizing, using at least one processor, a physical machine with a virtual machine while the virtual machine is operational in memory is disclosed. In one embodiment, the method includes monitoring a physical machine that utilizes a physical disk for storing computer data, consolidating a virtual disk with modifications to the physical disk, wherein the modifications to the physical disk are replicated on the virtual disk in response to unavailability of the physical machine, operating a virtual machine that utilizes the virtual disk for storing the computer data and migrating the virtual machine, using the virtual disk, to a computer.
Owner:VERITAS TECH
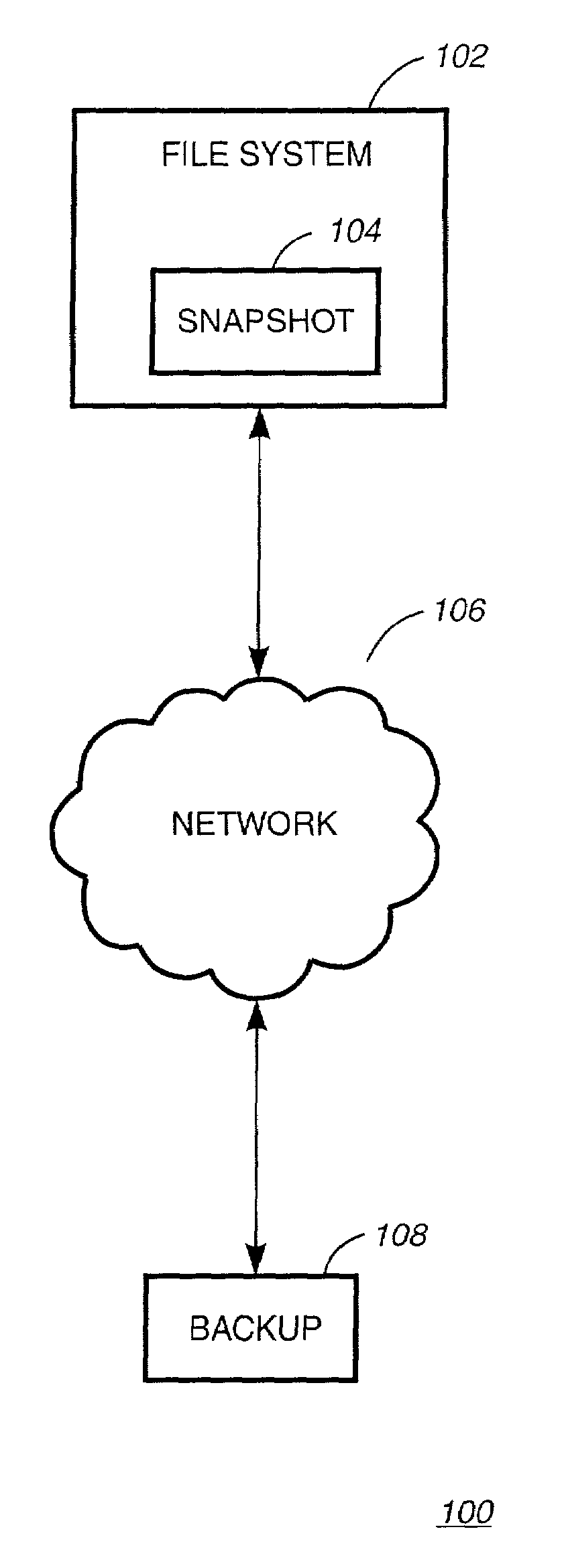
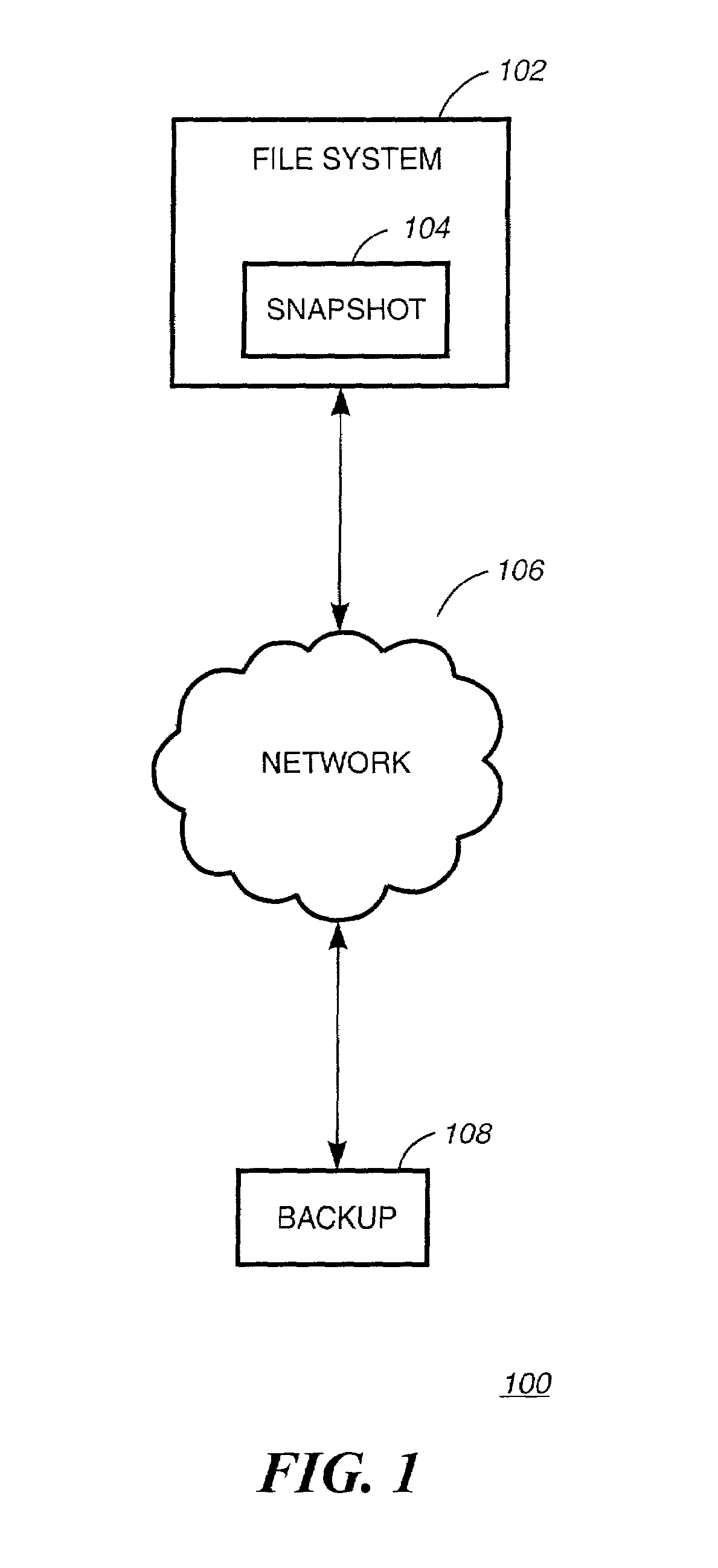
Generating data set of the first file system by determining a set of changes between data stored in first snapshot of the first file system, and data stored in second snapshot of the first file system
InactiveUS6959310B2Data processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsData setFile system
A system, method and computer readable medium for providing a standby file system with snapshot feature is disclosed. A first snapshot of a primary file system is generated. Next, a standby file system restores the first snapshot of the primary file system in the standby file system and a snapshot of the standby file system is taken. Then, a second snapshot of the primary file system is taken and a data set capturing the differences between the first snapshot of the primary file system and a previous data set of the primary file system is generated. Subsequently, the data set is applied to the standby file system. Upon unavailability of the primary file system, the standby file system is initialized as the new primary file system. Upon recovery of the old primary file system, the old primary file system is initialized as a new standby file system.
Owner:IBM CORP
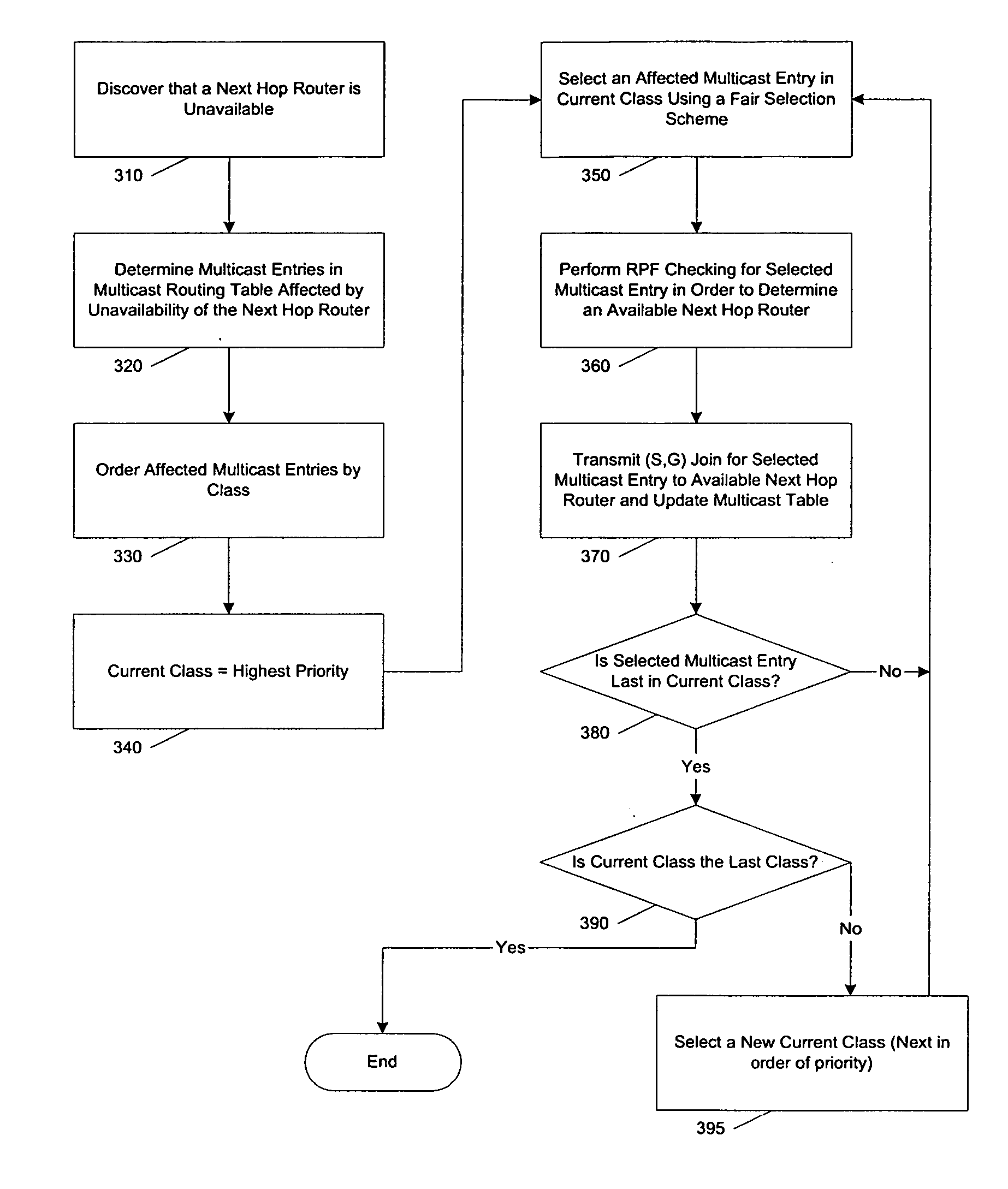
Multicast operations using prioritized state information
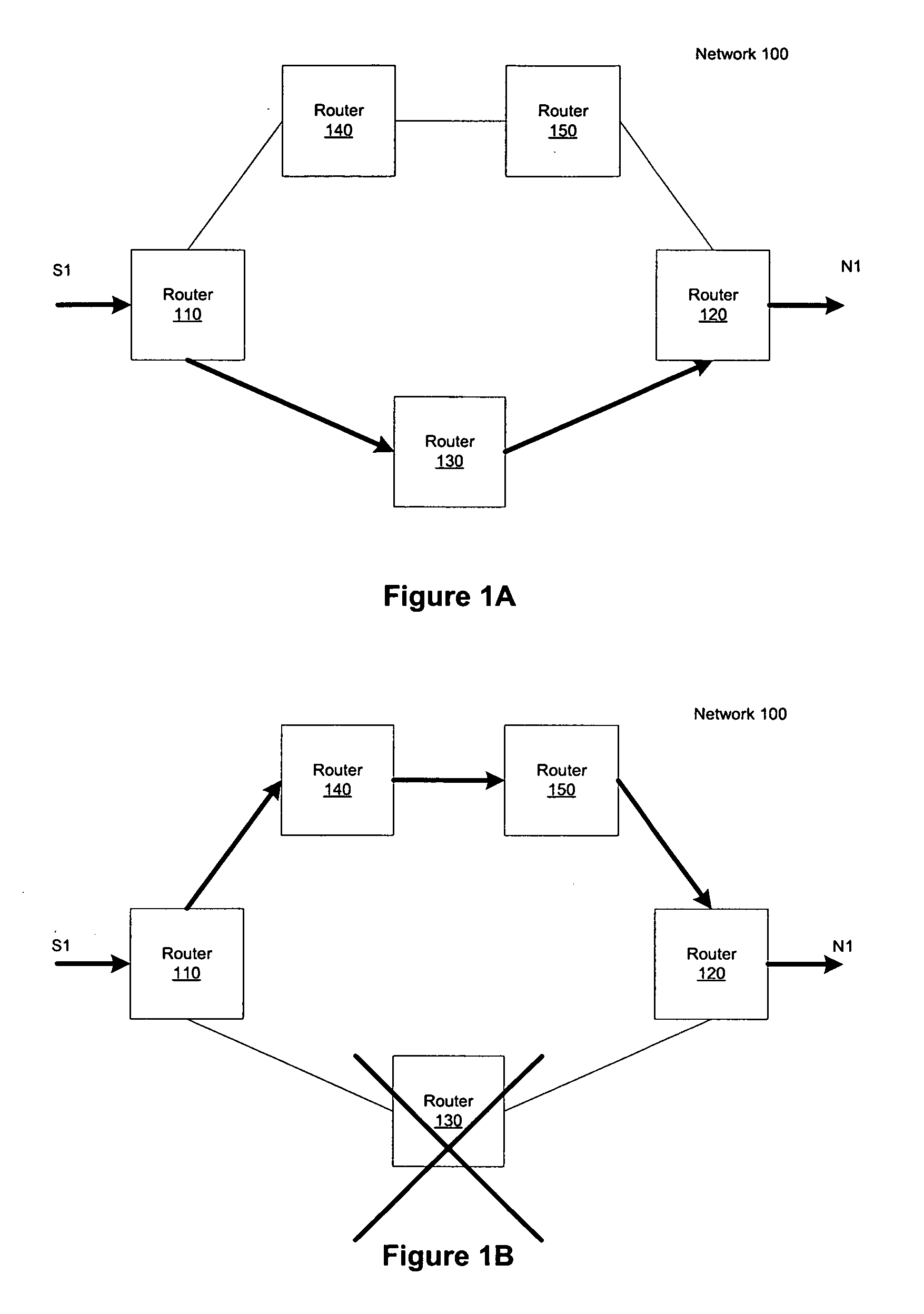
ActiveUS20070140107A1Special service provision for substationError preventionDistribution treeUnavailability
A classification mechanism to allow selected classes of multicast entries to be acted upon in a chosen order of priority during multicast distribution tree convergence is provided. Such prioritization allows for the designation of customers, networks or multicast groups to receive faster convergence of multicast distribution trees to modified multicast distribution trees in response to unavailability of an upstream router, and in performing other multicast-related tasks (e.g., PIM joins and prunes). One aspect of the present invention provides for multicast entries (also called multicast states) that are at a same priority level to be acted upon in a fair manner, thereby avoiding having certain multicast entries and their associated users from being acted upon consistently last.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
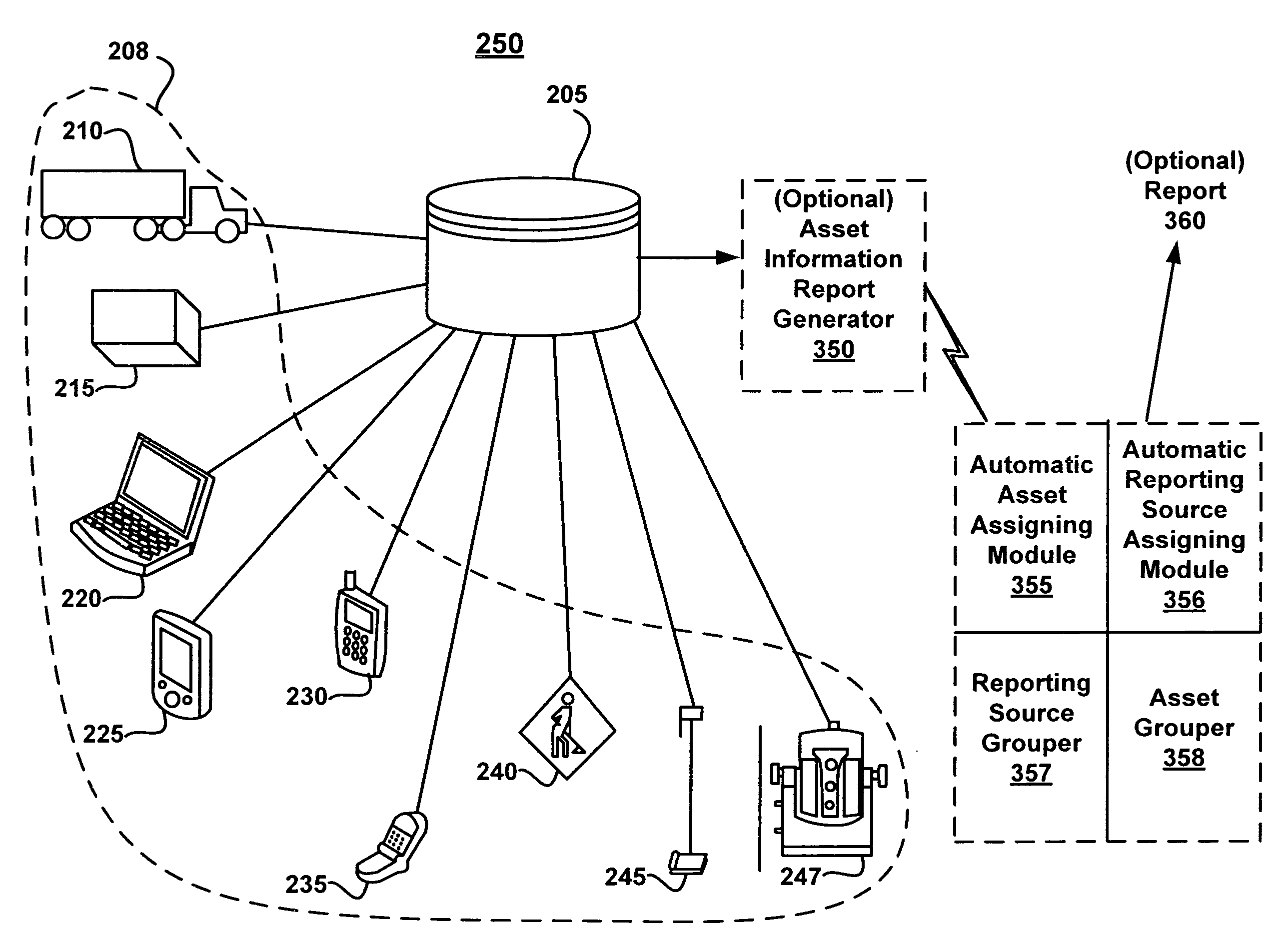
Utilizing historical data in an asset management environment
A method and system for utilizing historical data in an asset management environment are disclosed. According to one embodiment, a method generates an asset information report from a database, wherein the asset information report comprises at least a portion of real-time information about the asset when the real-time information about the asset is available. In addition, the asset information report is augmented by extrapolating at least a portion of historical asset information stored at the database when at least a portion of the real-time information is not available.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
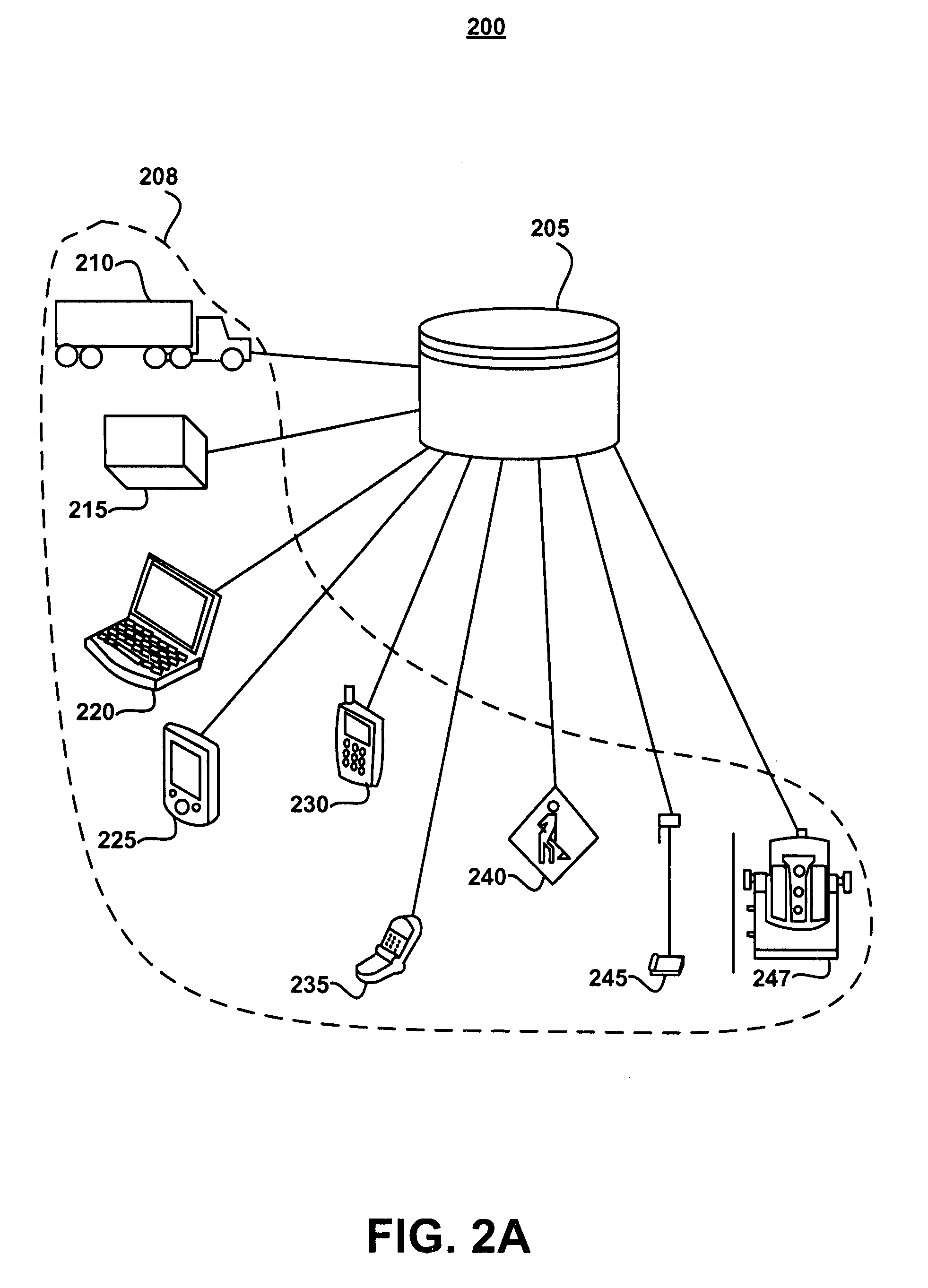
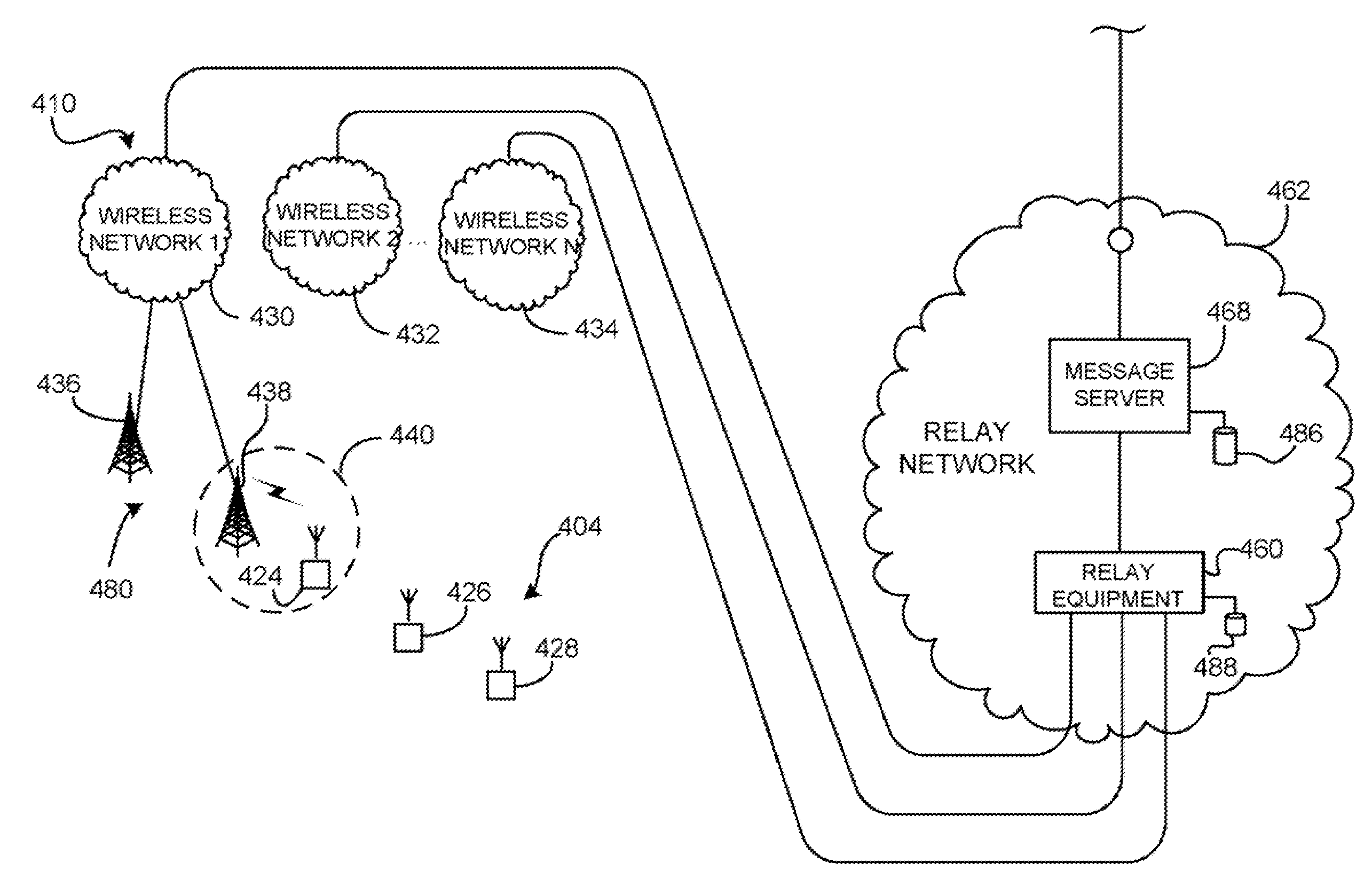
Pushback methods and apparatus for use in communicating messages to mobile communication devices
ActiveUS20070072617A1Multiple digital computer combinationsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsComputer hardwareMobile device
One illustrative method for use by a host server in pushing messages to a mobile communication device involves the steps of causing a message to be sent to a relay network for delivery to the mobile communication device through one of a plurality of wireless communication networks which are communicatively coupled to the relay network; receiving, from the relay network, a result message when the mobile communication device is unavailable to receive the message through the wireless communication network, the result message comprising a message identifier which uniquely corresponds to the message; maintaining storage of the message in memory accessible by the host server after the result message is received; receiving, from the relay network, a status message which indicates that the mobile communication device is available to receive the message when the mobile communication device is available to receive the message through the wireless communication device; and causing the message to be sent again to the relay network for delivery to the mobile communication device in response to receiving the status message. During the unavailability of the mobile device, the relay network refrains from maintaining storage of the message in memory of the relay network.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Method and system for remote computing session management
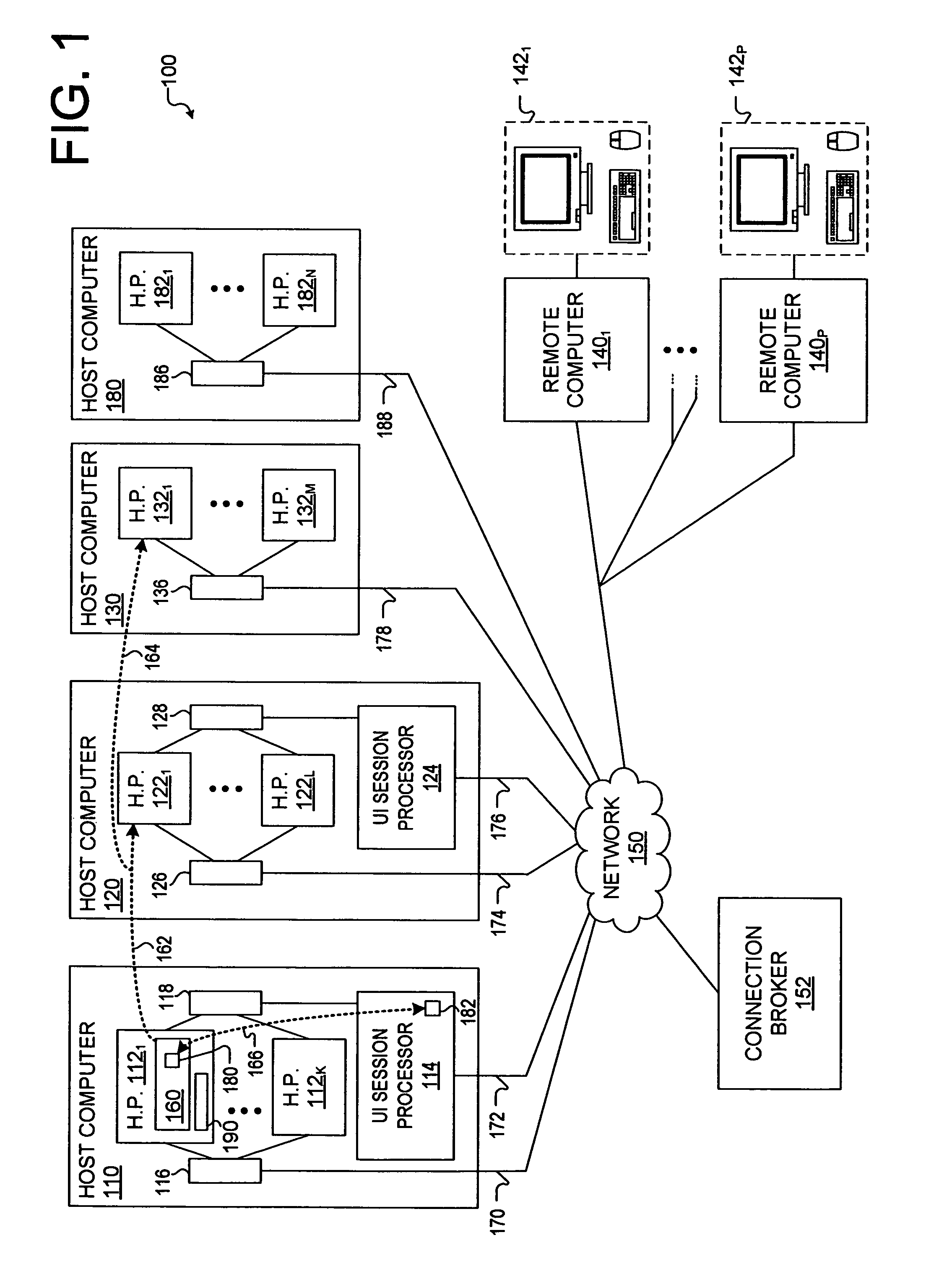
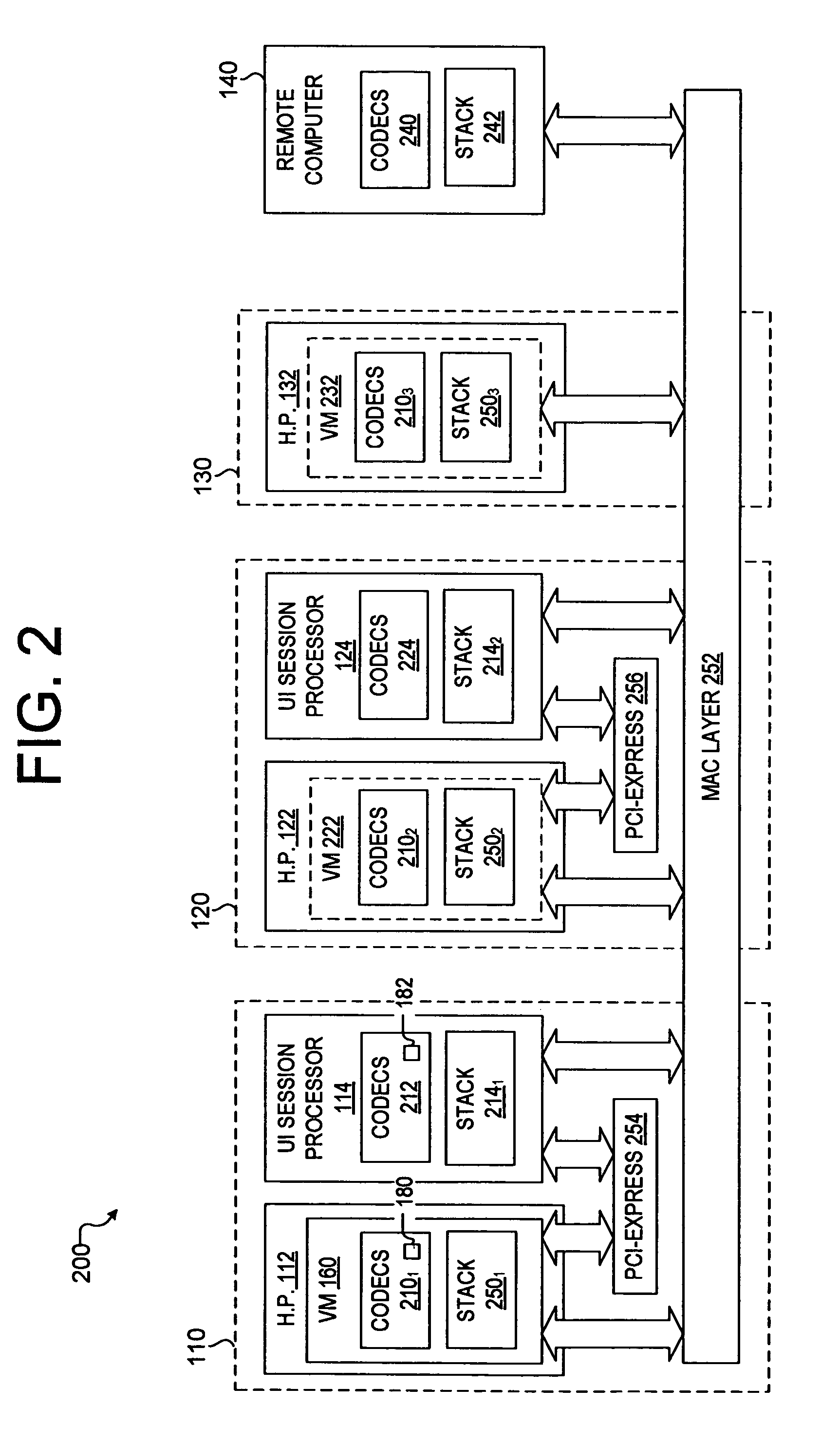
ActiveUS8224885B1Multiple digital computer combinationsExecution for user interfacesSession managementRemote computer
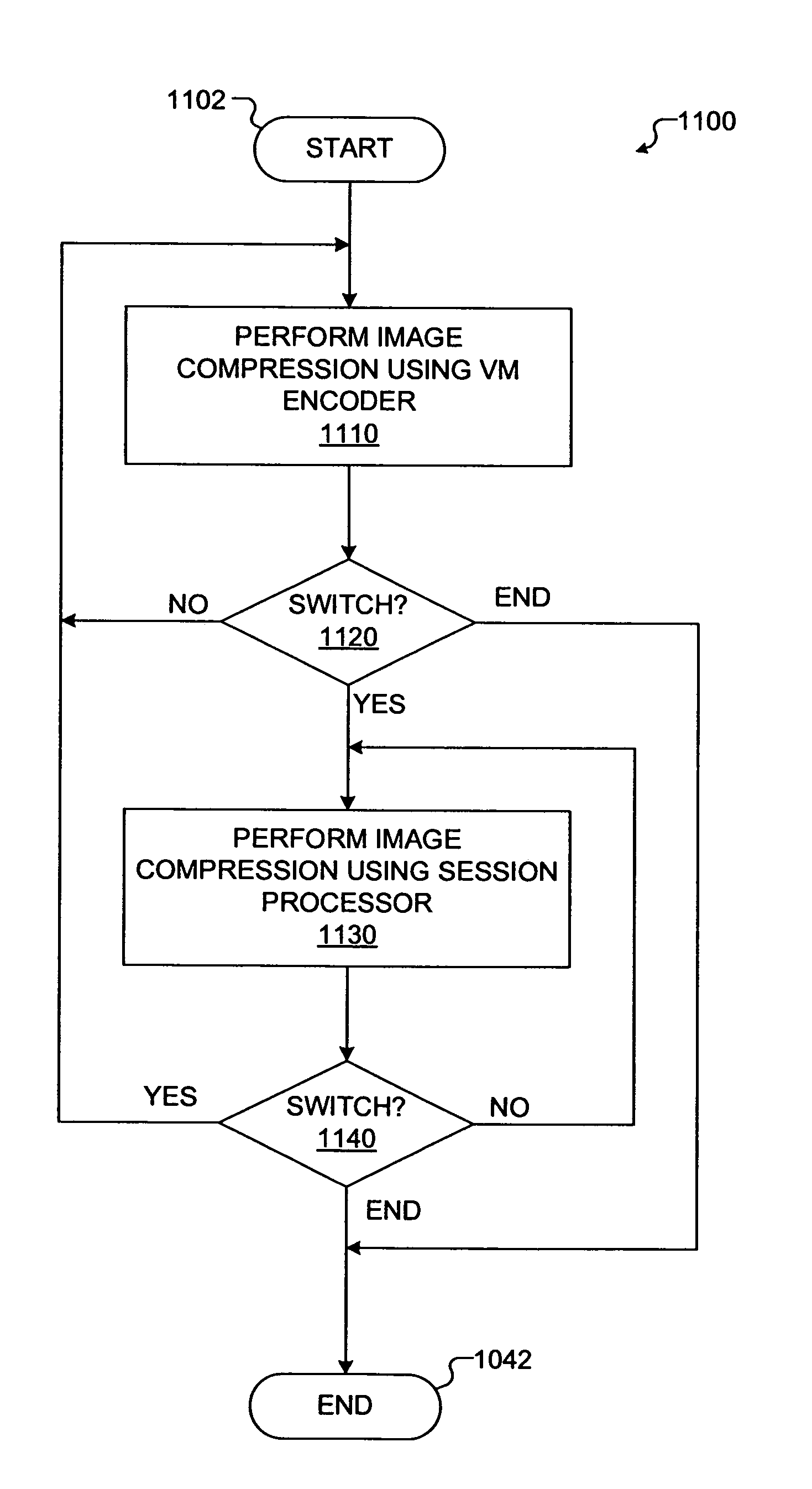
A method and system for communicating a display image. The method comprises (a) compressing, by a first application on a first processor, initial updates; (b) determining, by the first application, availability of a second processor comprising compression hardware not in the first processor; (c) determining, by a second application on the first processor, a requirement to compress, by the second processor, future image updates; (d) compressing, by the second processor a first future image update; (e) initiating, by the first application on the first or a third processor, compressing by the second processor of a second future image update; (f) determining, by the first application, an unavailability of the second processor; (g) compressing, by the first application subsequent future image updates, including the second future image update, to generate compressed updates; and (h) transmitting the compressed initial updates, the compressed first update, and the compressed updates to a remote computer.
Owner:TERADICI CORP
Apparatus for and method of managing paging interval access on a mobile station
InactiveUS20100317374A1Operation efficiency can be improvedSubstantial amount of power savingPower managementEnergy efficient ICTMobile stationUnavailability
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of managing paging availability of a mobile station in a wireless communications network. The paging availability mechanism of the present invention is able to achieve a substantial amount of power saving by modifying mobile station access to paging intervals. The mechanism dynamically controls access to the wireless network after unavailability periods when mobile stations enter into idle mode. Paging listening intervals for one or more mobile stations are scheduled and synchronized in accordance with the values of one or more parameters or metrics such as link quality. In one embodiment, this is achieved by the mobile station modifying the paging listening intervals access pattern received from the base station. Depending on the one or more parameters or metrics, one or more paging intervals may be skipped thus reducing the power consumption of the mobile station.
Owner:COMSYS COMM & SIGNAL PROC
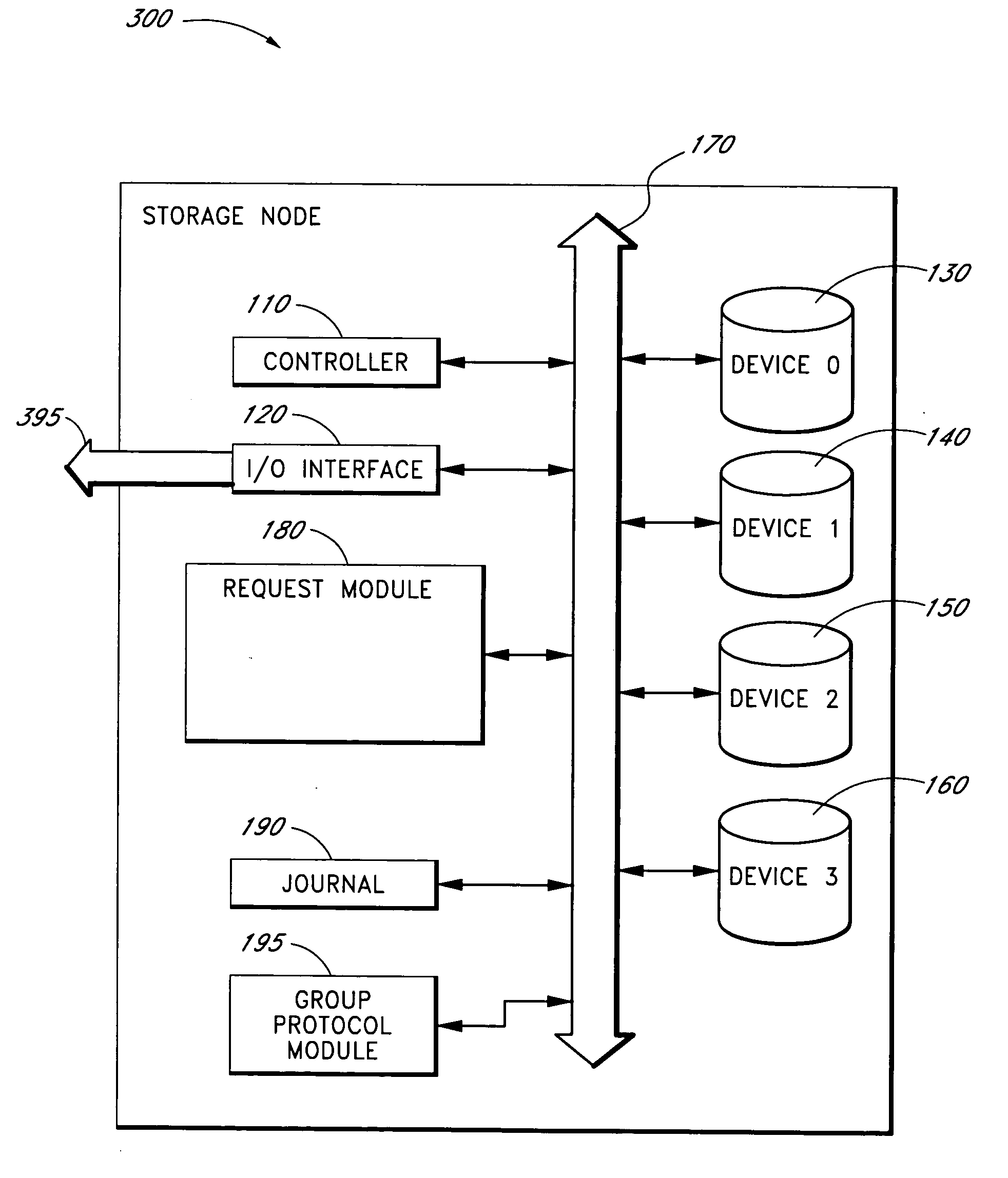
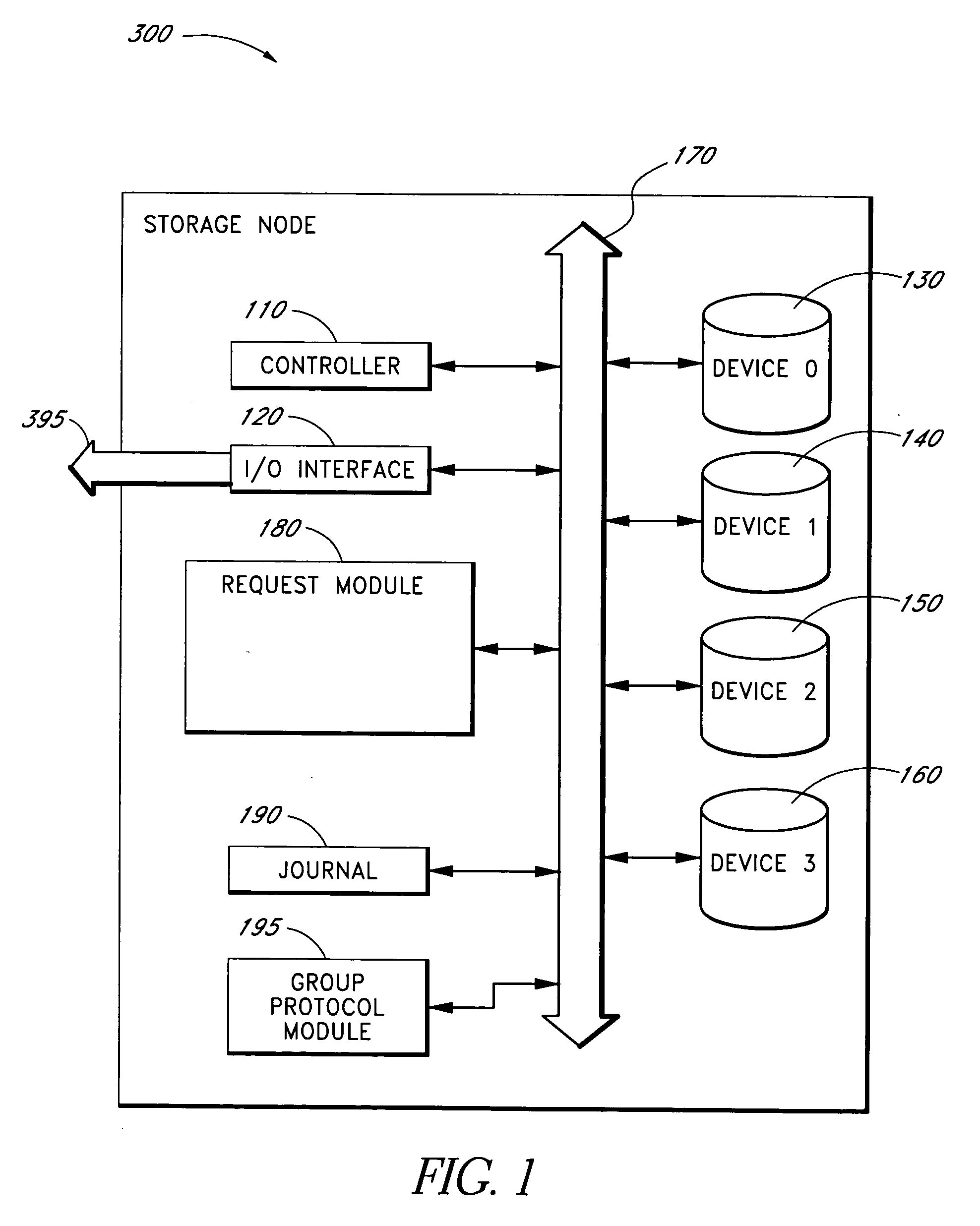
Systems and methods for managing unavailable storage devices
In some embodiments, storage devices, such as a storage drive or a storage node, in an array of storage devices may be reintroduced into the array of storage devices after a period of temporary unavailability without fully rebuilding the entire previously unavailable storage device.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Apparatus and method in a cached raid controller utilizing a solid state backup device for improving data availability time
ActiveUS20050283648A1Improve data availabilityShorten the timeEnergy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsRAIDControl store
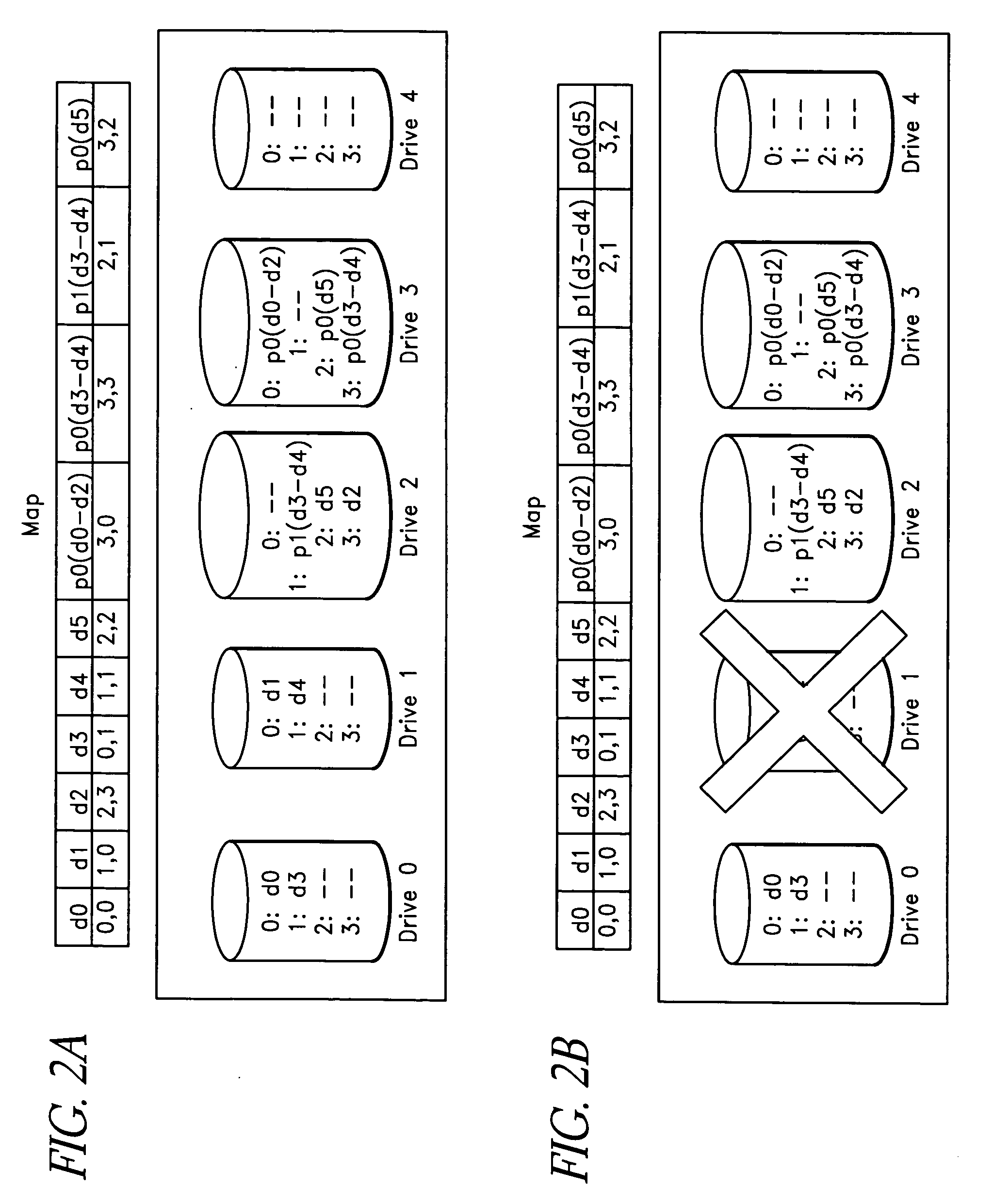
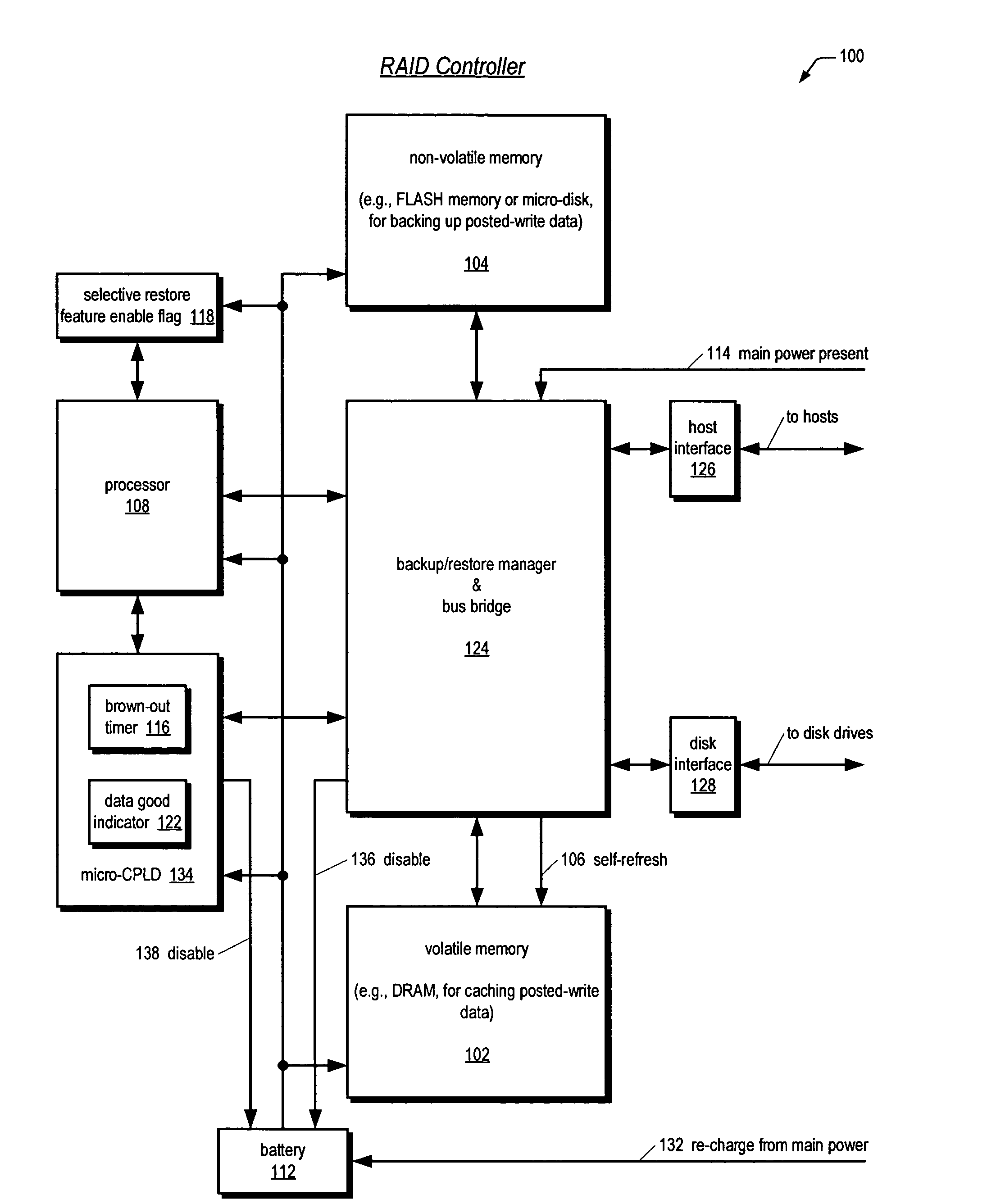
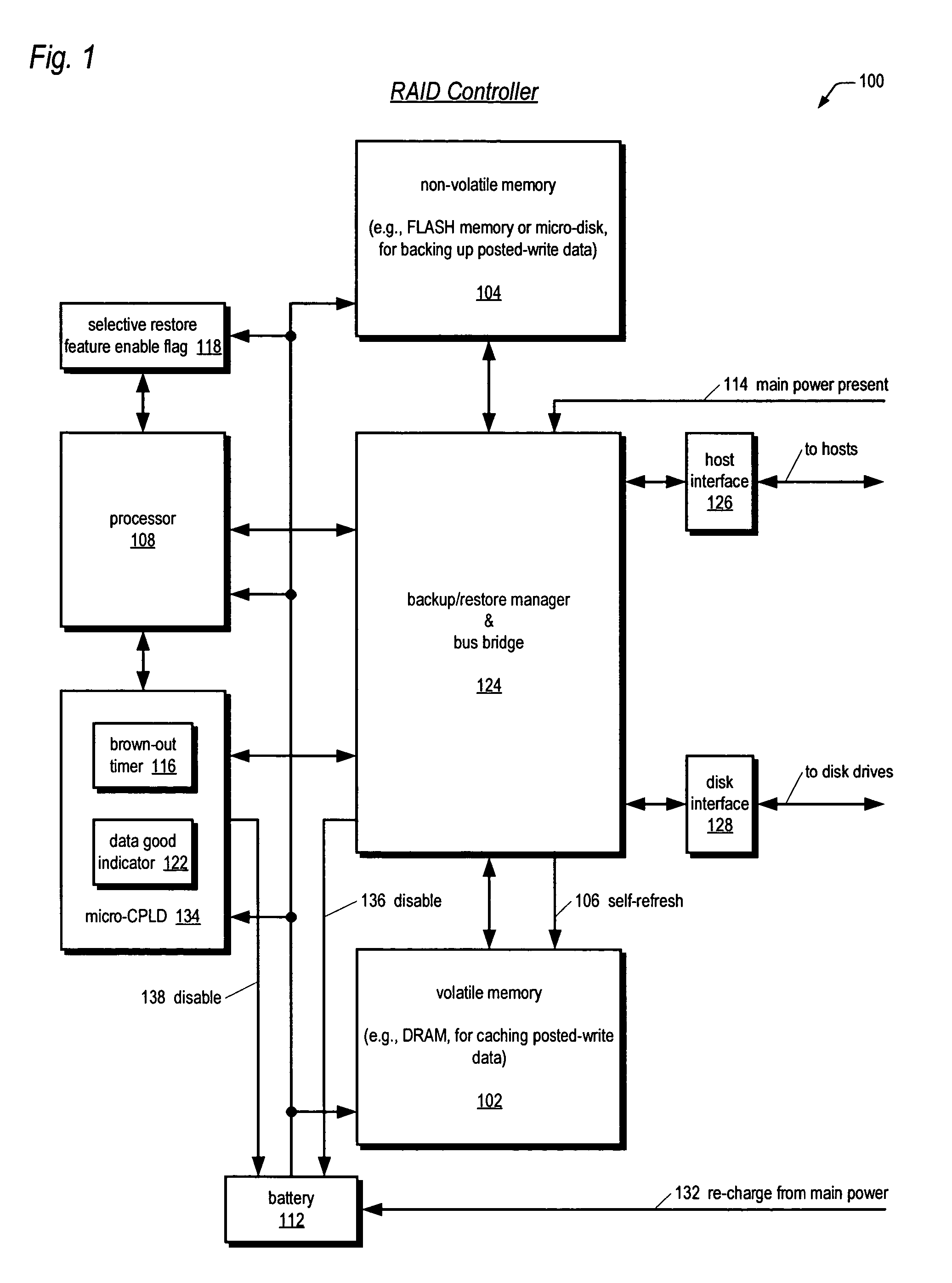
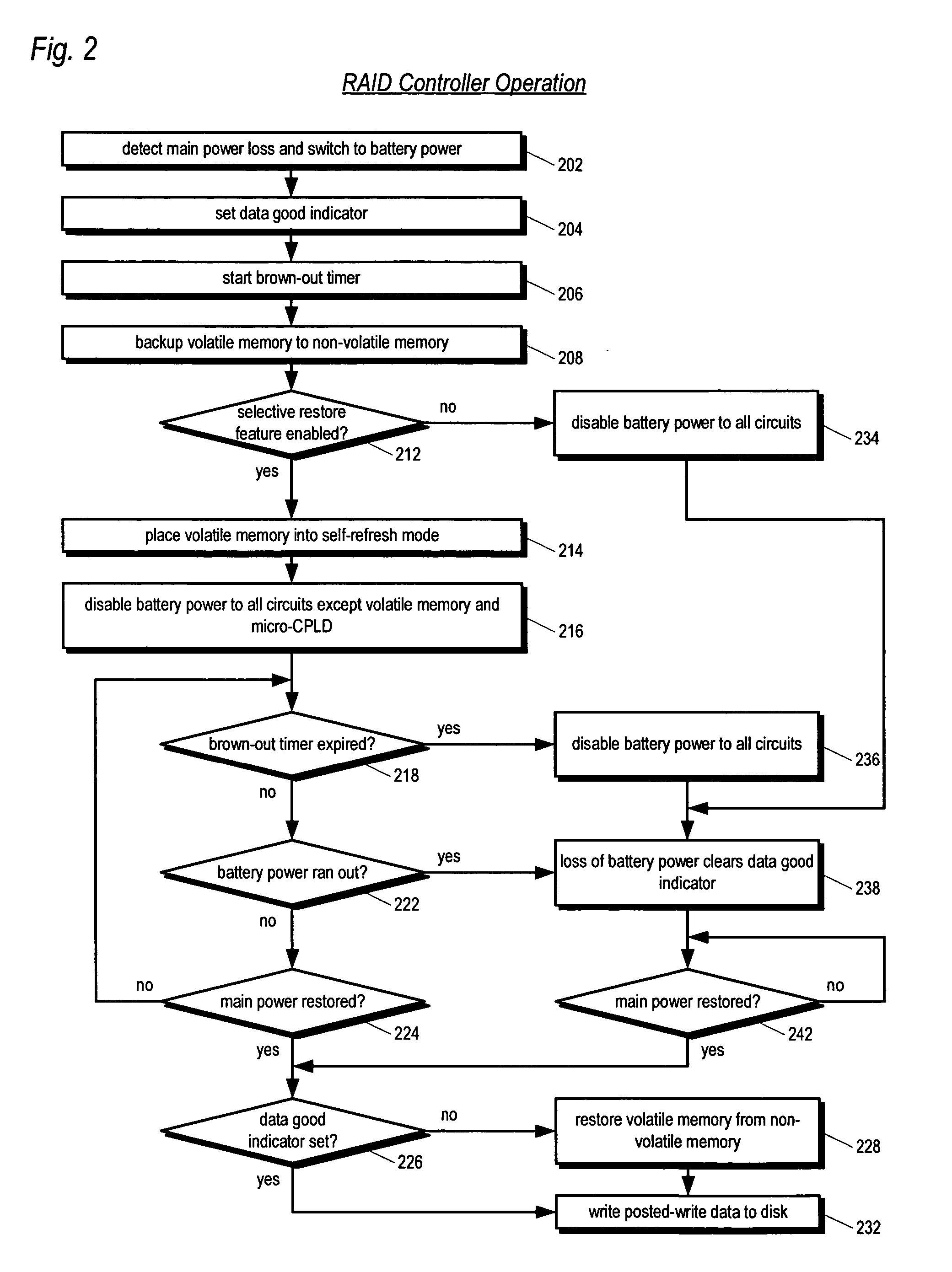
An apparatus for reducing data unavailability time after a loss of main power in a storage controller is described. The controller backs up its volatile memory containing posted-write data to a non-volatile memory upon detecting a loss of main power. The controller continues to provide battery power to the volatile memory to sustain the posted-write data. If the battery is able to supply power to the volatile memory until main power is restored, the controller foregoes restoring the posted-write data to the volatile memory from the non-volatile memory. By not incurring the restore time, which may be substantial if the volatile memory is large since read rates from volatile memories are typically slow, the data unavailability time is reduced. The selective restore feature is user-disableable and also includes a brown-out timer for allowing a user to specify how long to battery-power the volatile memory if the feature is enabled.
Owner:DOT HILL SYST
Instant text reply for mobile telephony devices
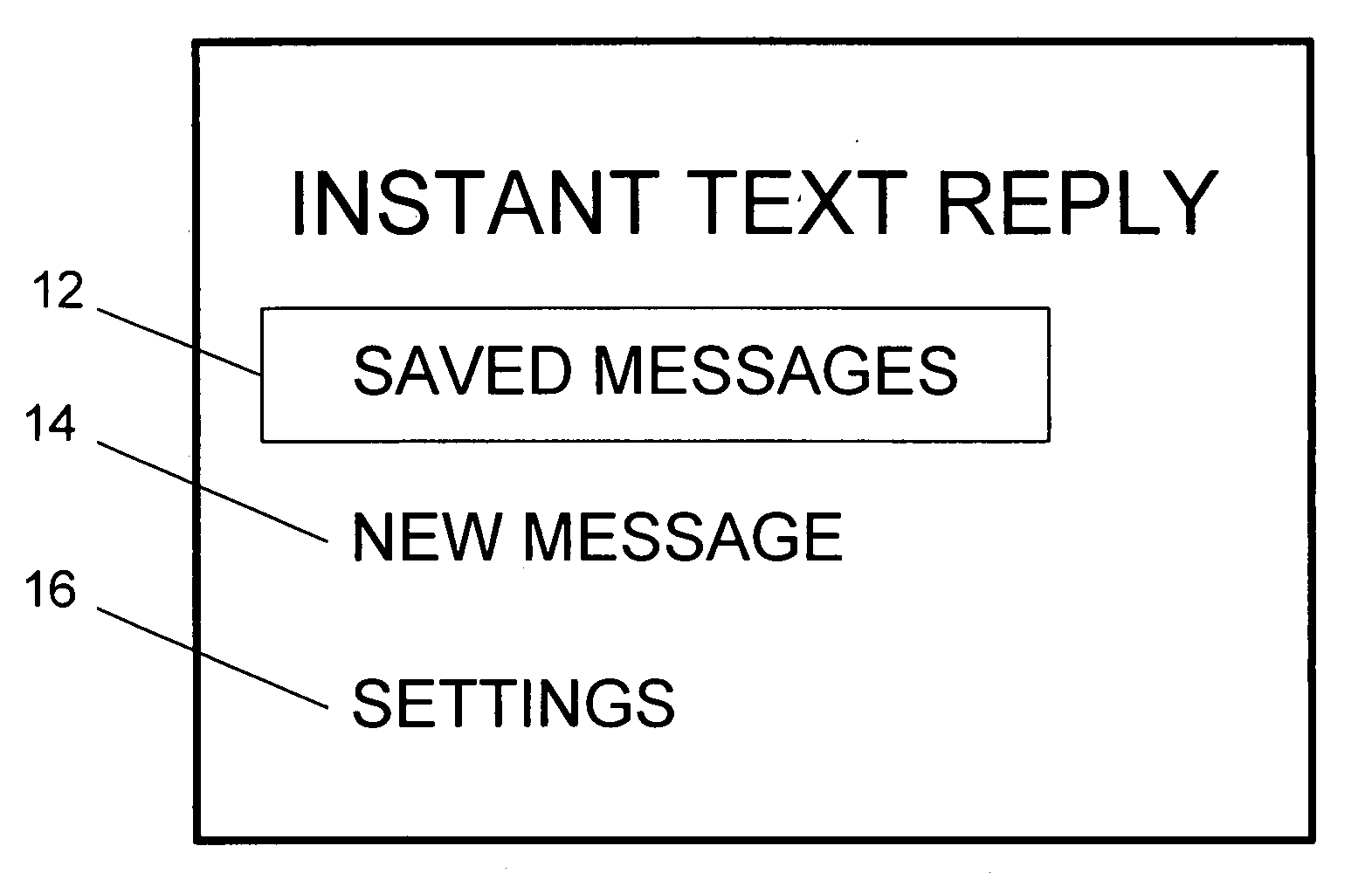
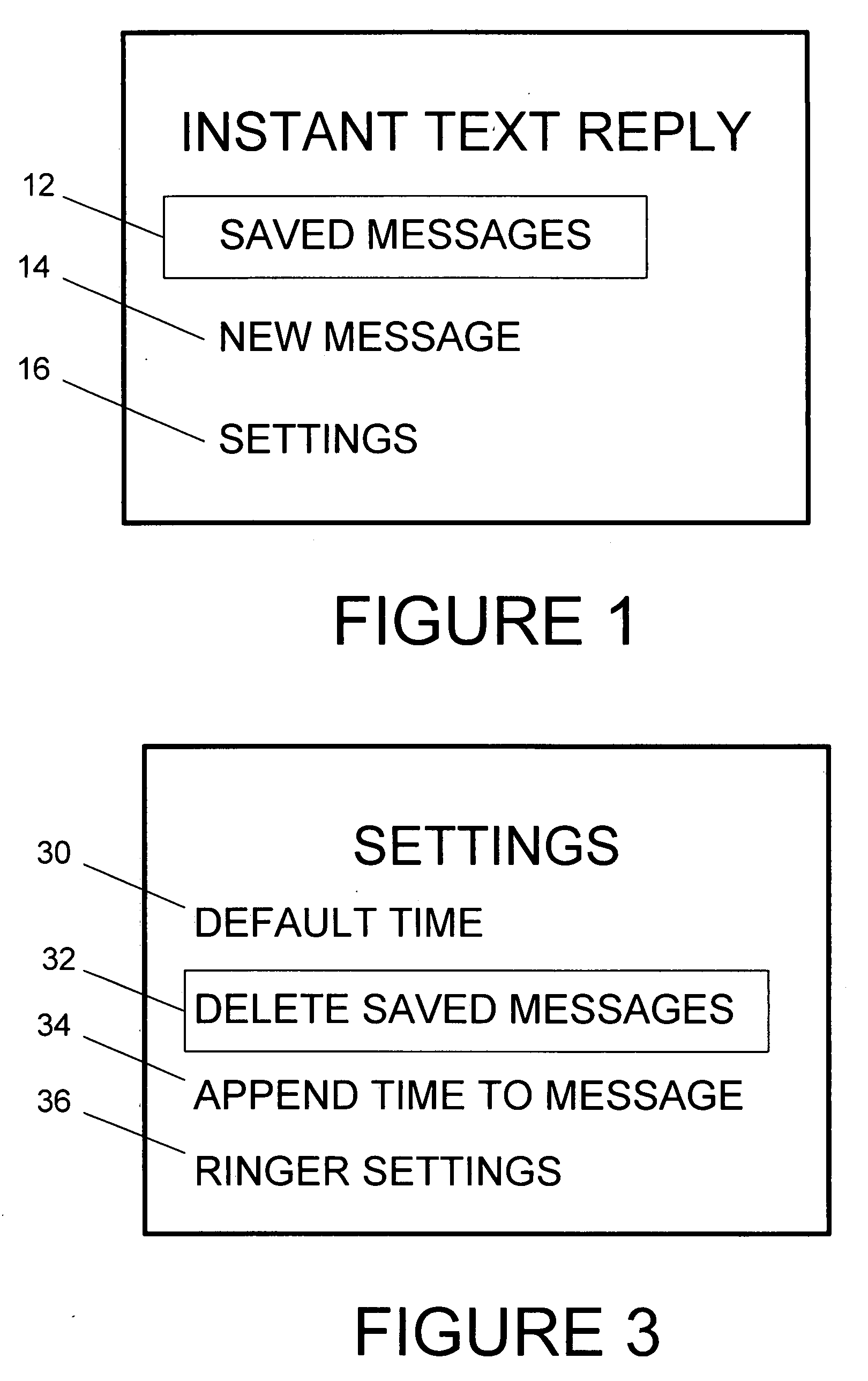
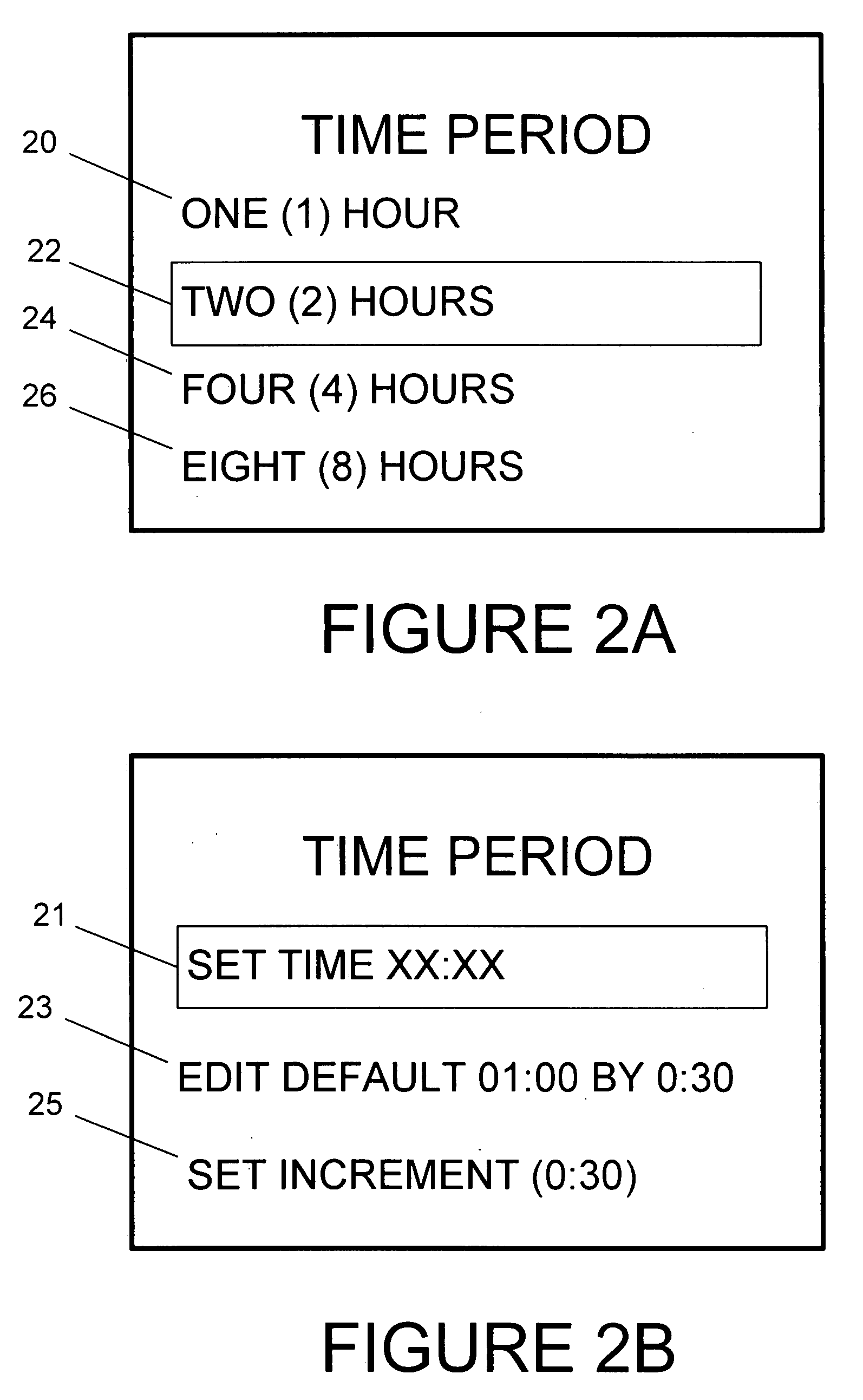
InactiveUS20070238474A1Many optionsAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingCommmunication supplementary servicesSpeech soundUser interface
A cellphone program or service is disclosed to allow a user to set up an instant text reply for both incoming voice calls and SMS messages from other cellphone users via an SMS message (hereinafter, Instant Text Reply) stating the reason for the user's unavailability. In use, a cellphone user can create, save, and select various outgoing SMS messages from their cellphone user interface. The cellphone user then selects the desired instant text reply message that will be automatically sent to other cellphone users attempting to contact them for a predetermined time period. At the end of the time period for operation of the Instant Text Reply, the operation of the cellphone is returned to its ordinary function. The invention can be implemented with a program on the cellphone or at the carrier level. When used in combination with a carrier program, the cellphone user can optionally turn off their cellphone.
Owner:BALLAS PAUL +1
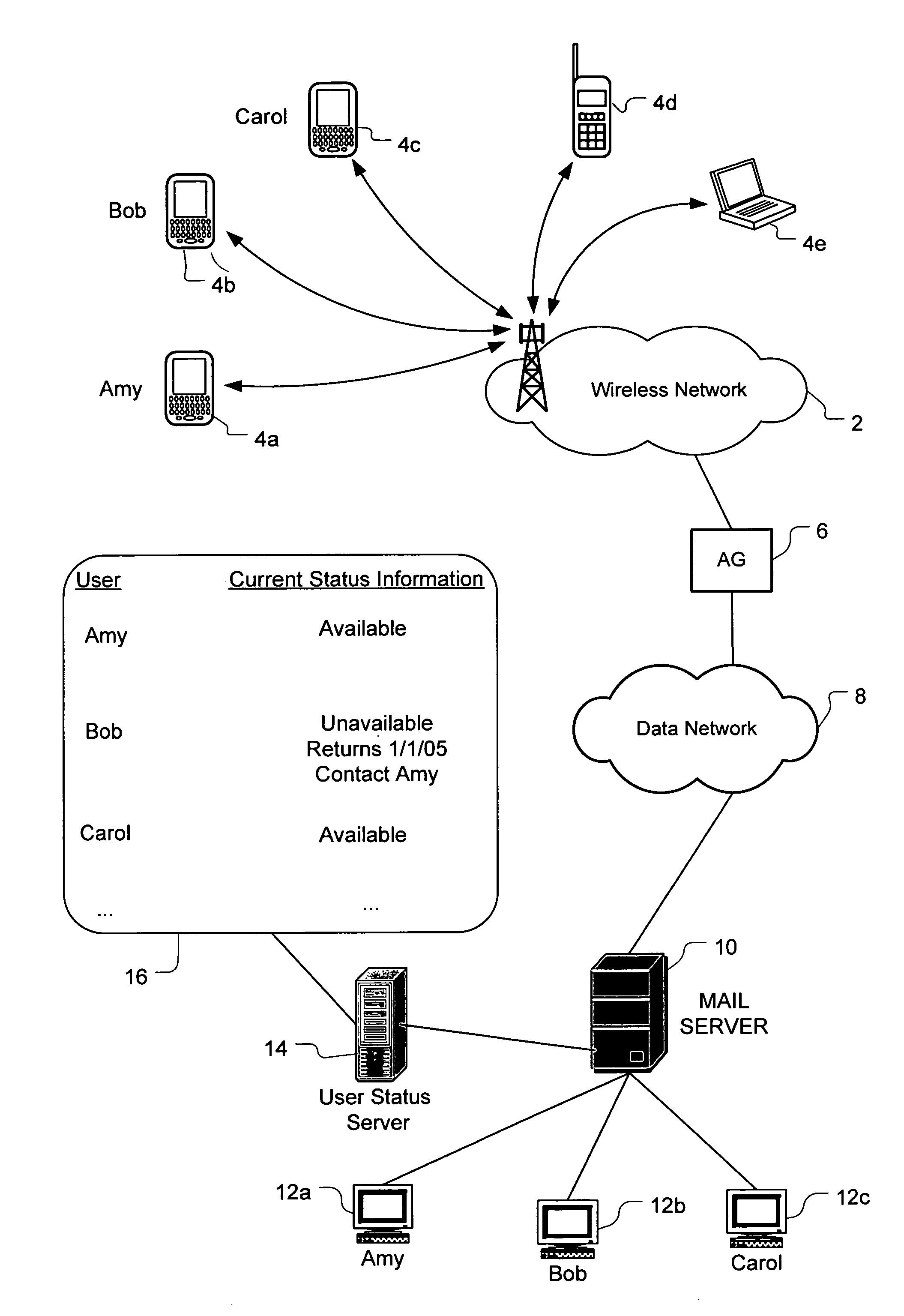
System and method of sharing auto-reply information
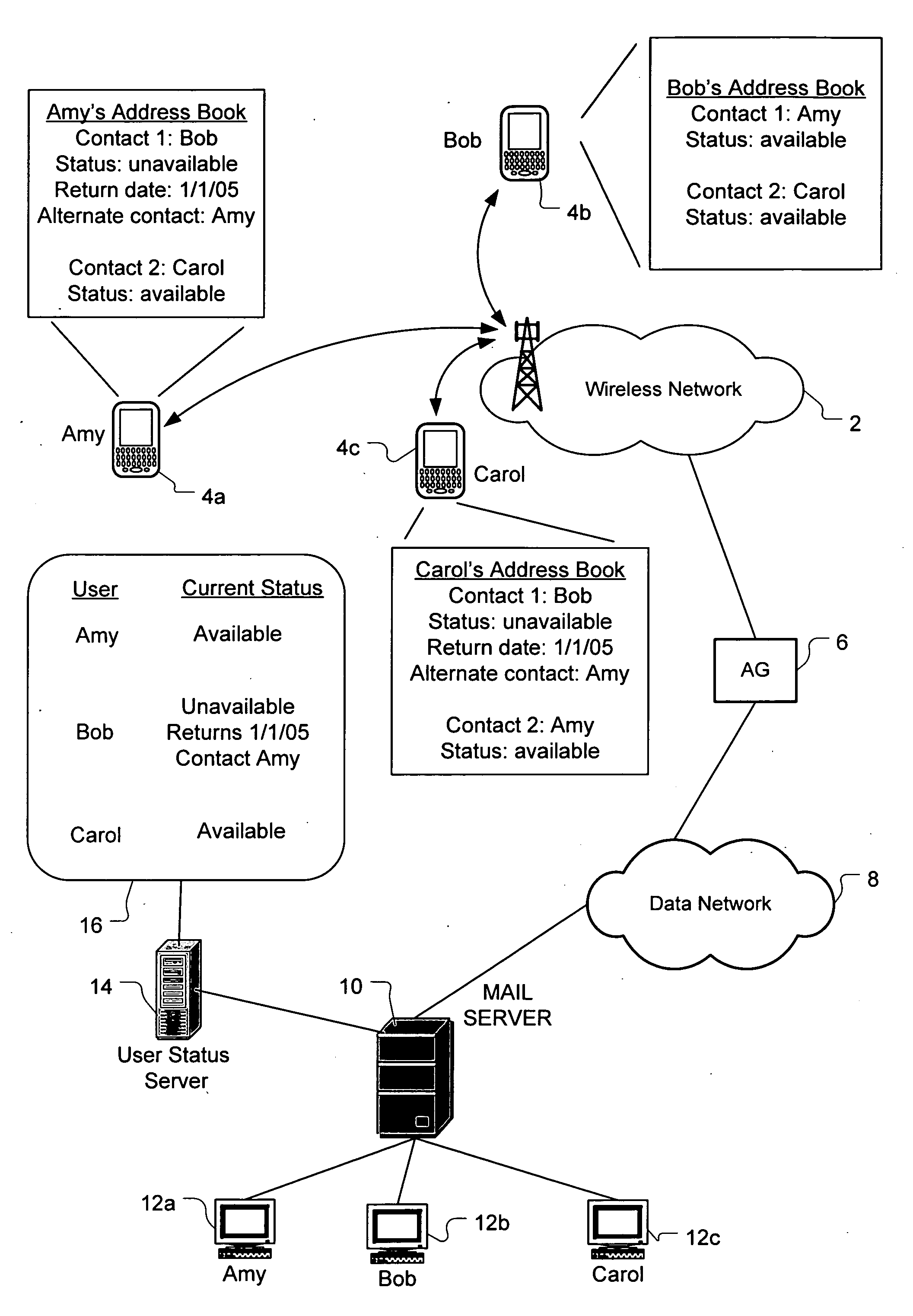
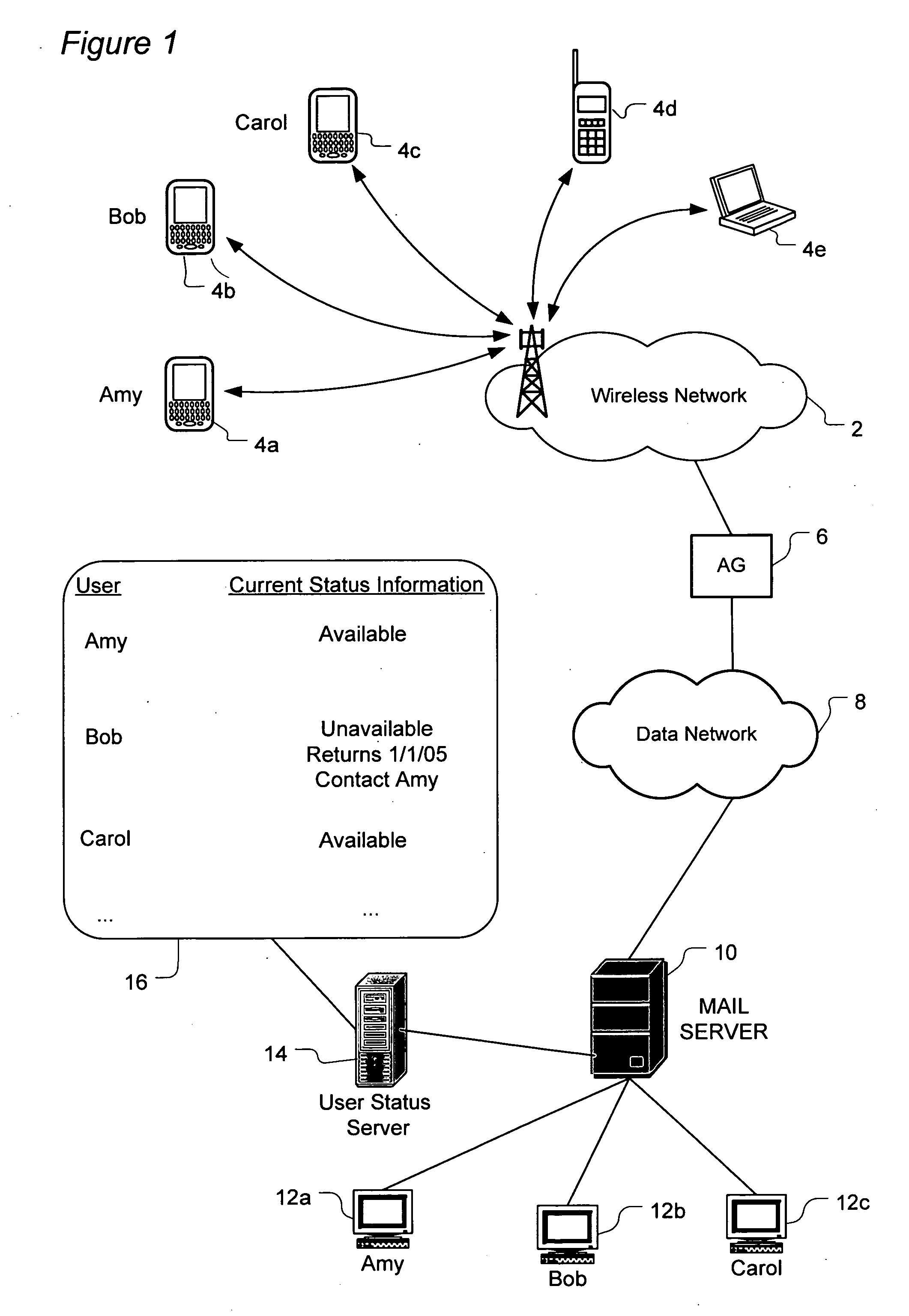
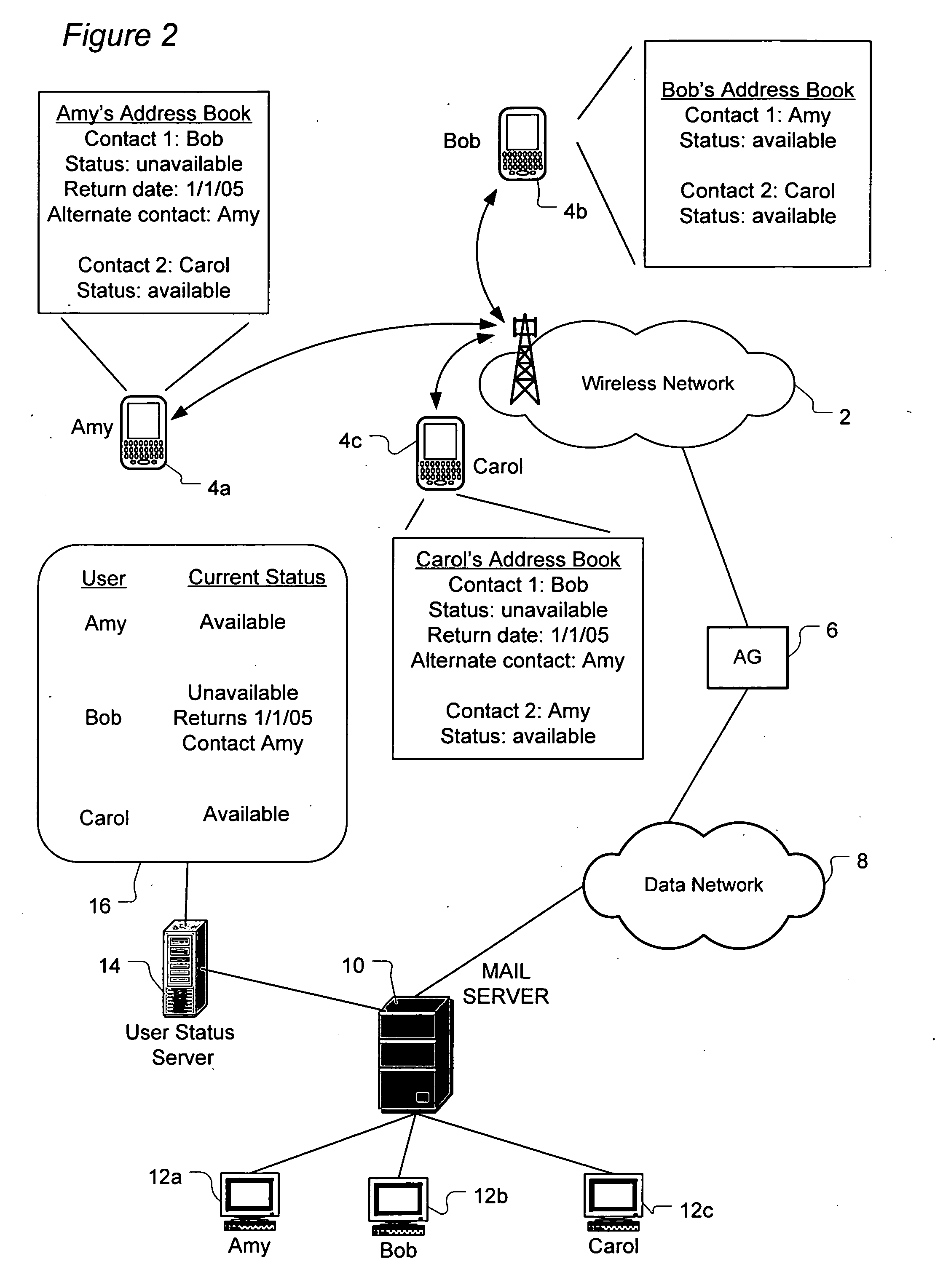
ActiveUS8296370B2Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksComputer hardwareAddress book
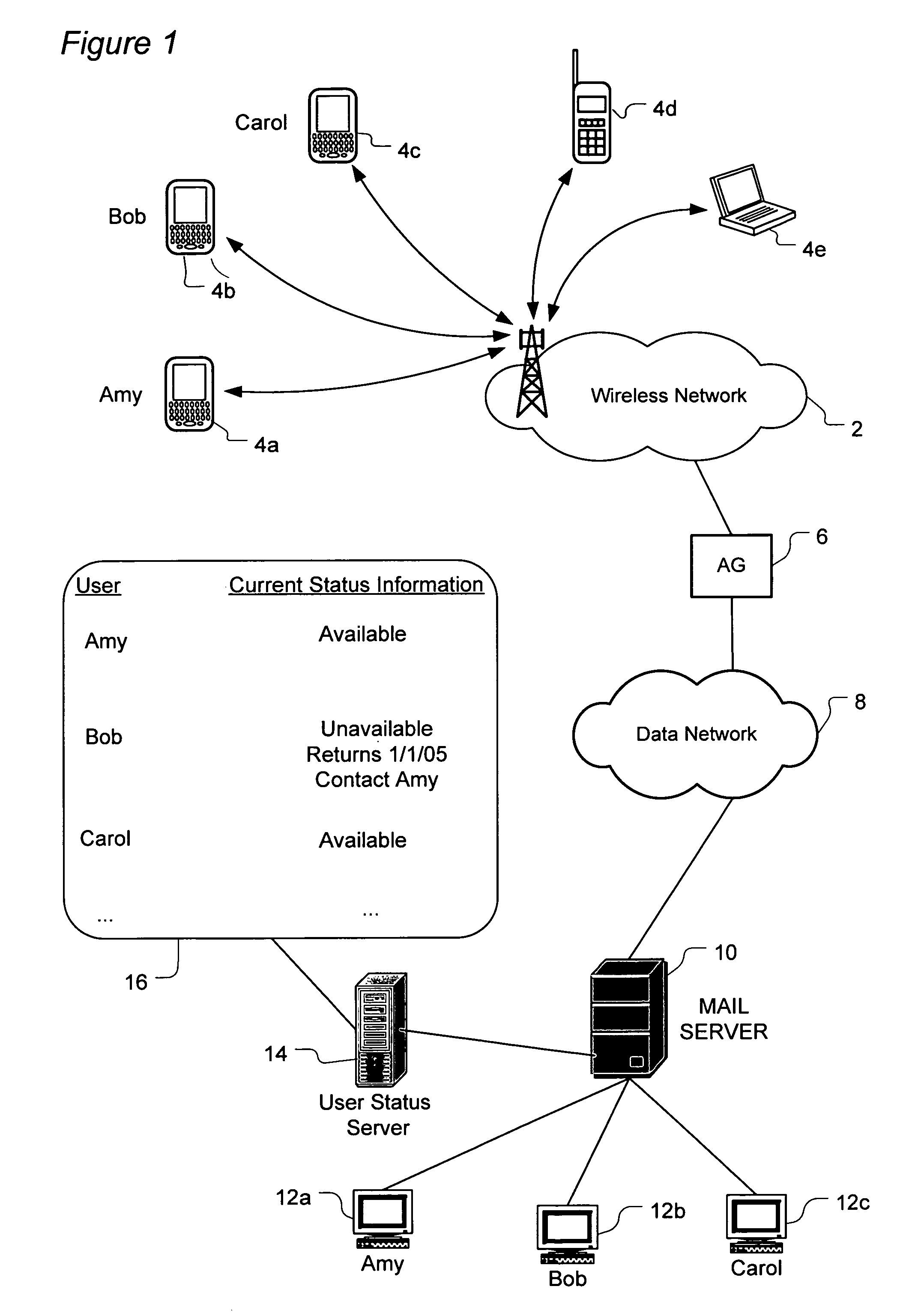
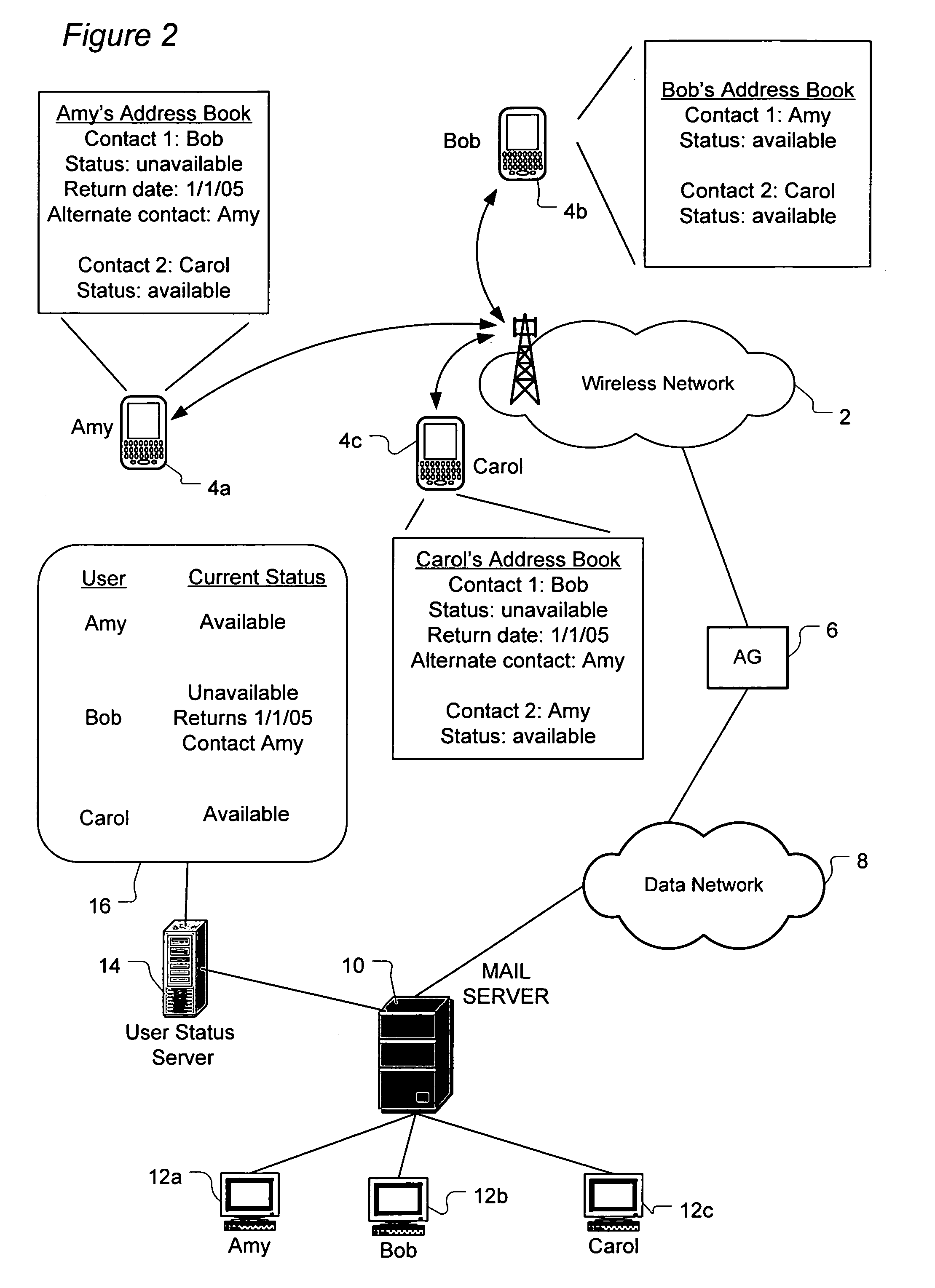
A system and method routes messages based on an intended recipient's availability to receive messages. Each network user's current status is determined by tracking when the user activates and deactivates an auto-reply feature. The user's current status, return date and alternate contact(s) are specified in the auto-reply and stored and updated on a user status server which periodically communicates to each user the current status information for each contact listed in that user's address book. When the current status information indicates that the intended recipient is unavailable, message routing options are presented to the sender. These options include sending the message to the user regardless of the intended recipient's current unavailability, not sending the message at all, routing the message to at least one specified alternate contact, sending the message to the intended recipient while sending a copy of the message to the alternate contact.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Method and apparatus for memory management in a multi-processor computer system
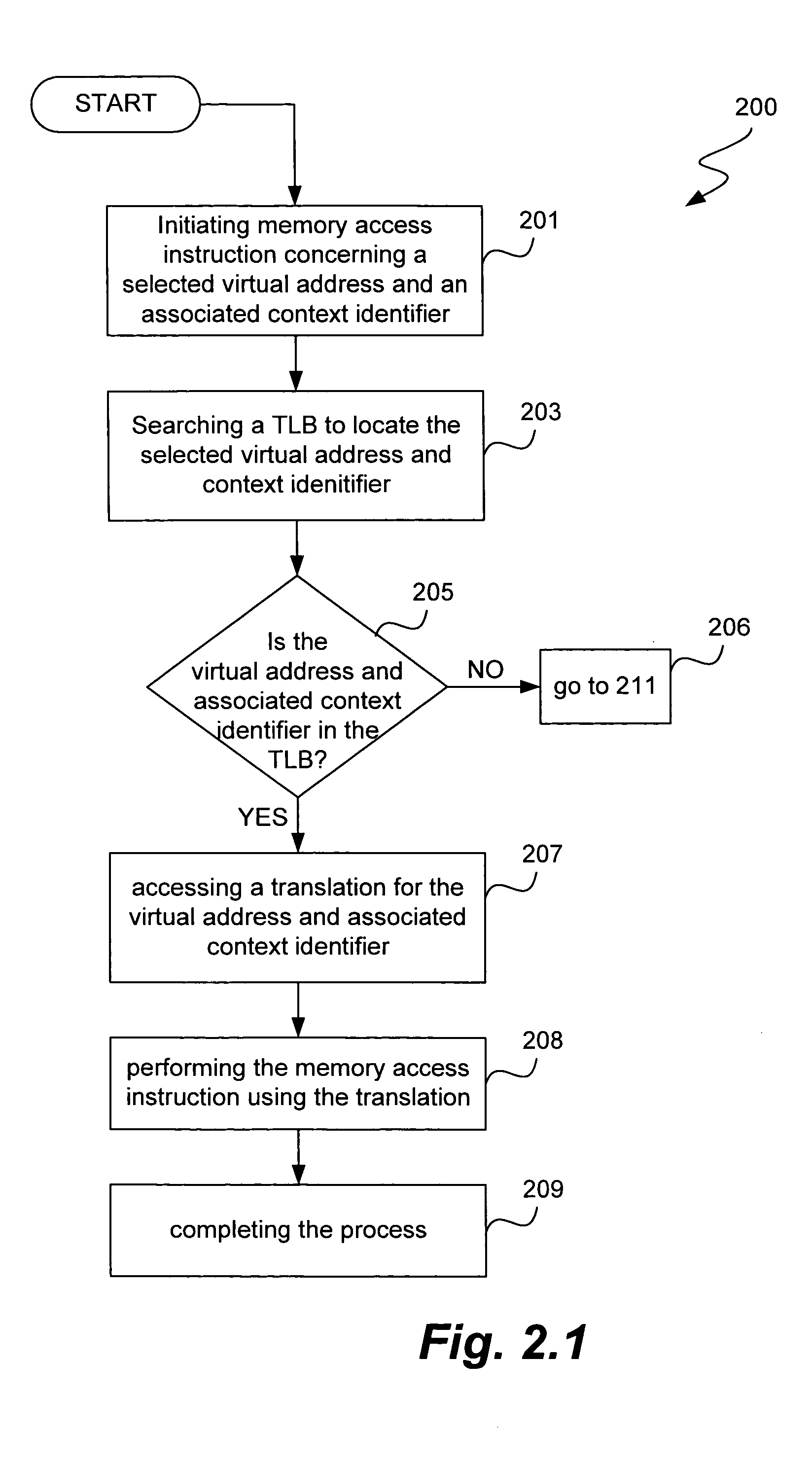
ActiveUS20050172099A1Avoid accessMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationManagement unitMulti processor
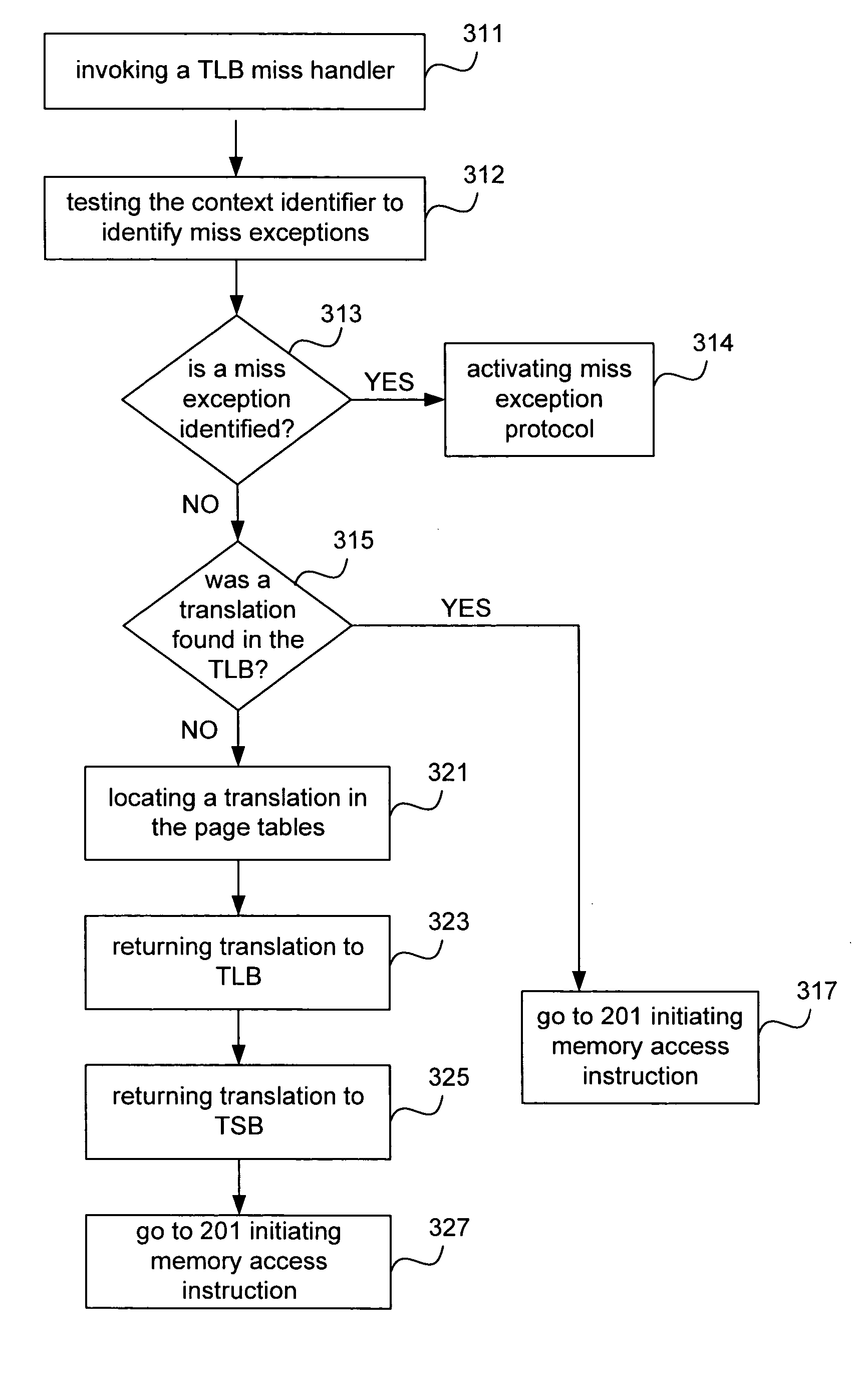
Improved techniques and systems for accommodating TLB shootdown events in multi-processor computer systems are disclosed. A memory management unit (MMU) having a TLB miss handler and miss exception handler is provided. The MMU receives instructions relative to a virtual address. A TLB is searched for the virtual address, if the virtual address is not found in the TLB, secondary memory assets are searched for a TTE that corresponds to the virtual address and its associated context identifier. The context identifier is tested to determine if the TTE is available. Where the TTE is available, the TLB and secondary memory assets are updated as necessary and the method initiates memory access instructions. Where the TTE is unavailable, the method either resolves the unavailability or waits until the unavailability is resolved and then initiates memory access instructions, thereby enabling the desired virtual address information to be accessed.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
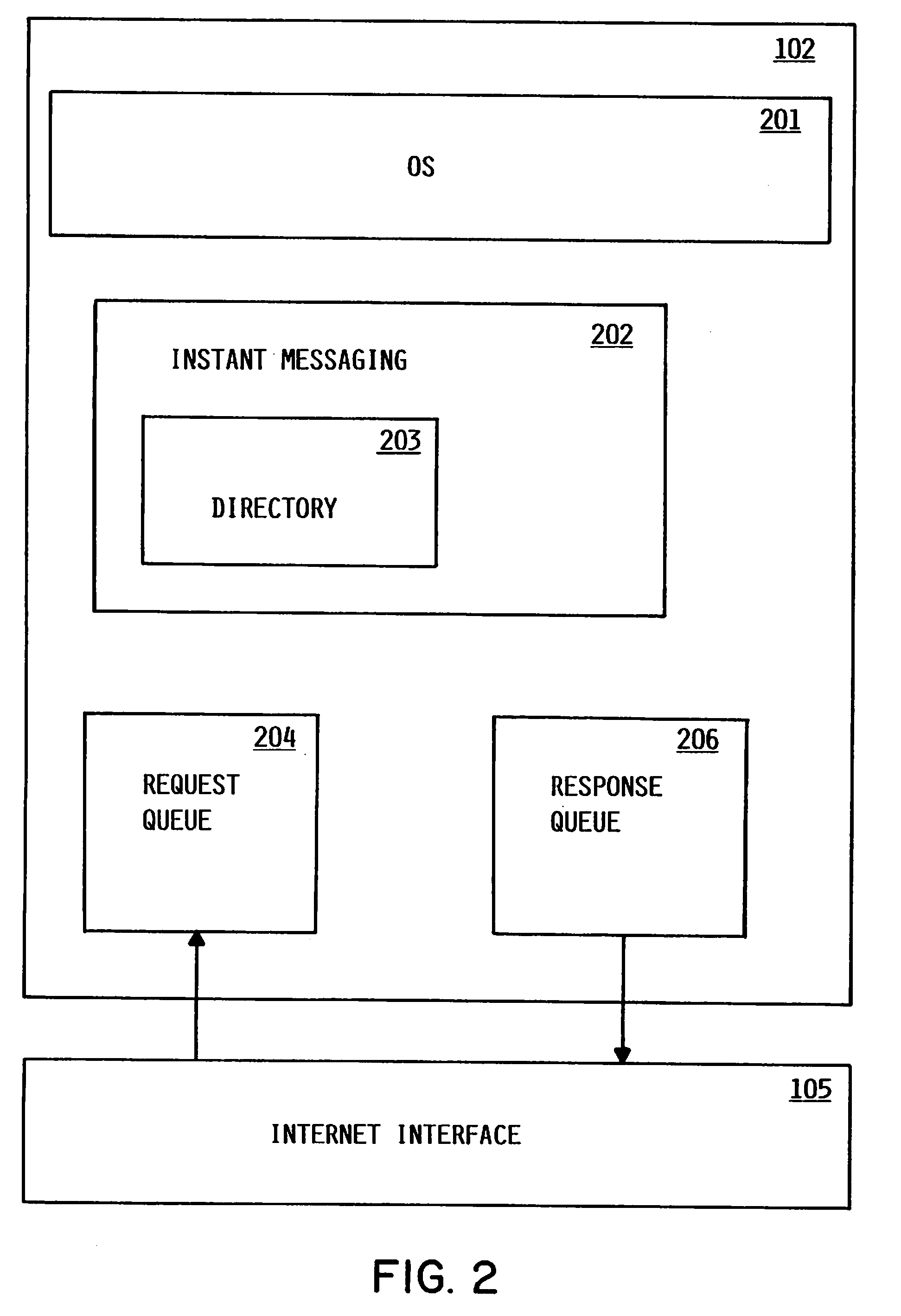
Method and apparatus for determining availability of a user of an instant messaging application
An instant messaging application intelligently infers a user's unavailability from one or more indicia which include the user's electronic calendar. Preferably, the instant messaging application may report not only that a user is unavailable, but also give a reason for inferring unavailability, in order to provide other users with additional potentially useful information. Preferably, the user may specify which indicia and which parameters may be used to infer his unavailability in an editable profile. When another user requests status, this value is returned by the server. An intelligent instant messaging application as described herein provides other users with more accurate and complete availability information.
Owner:HCL TECH LTD
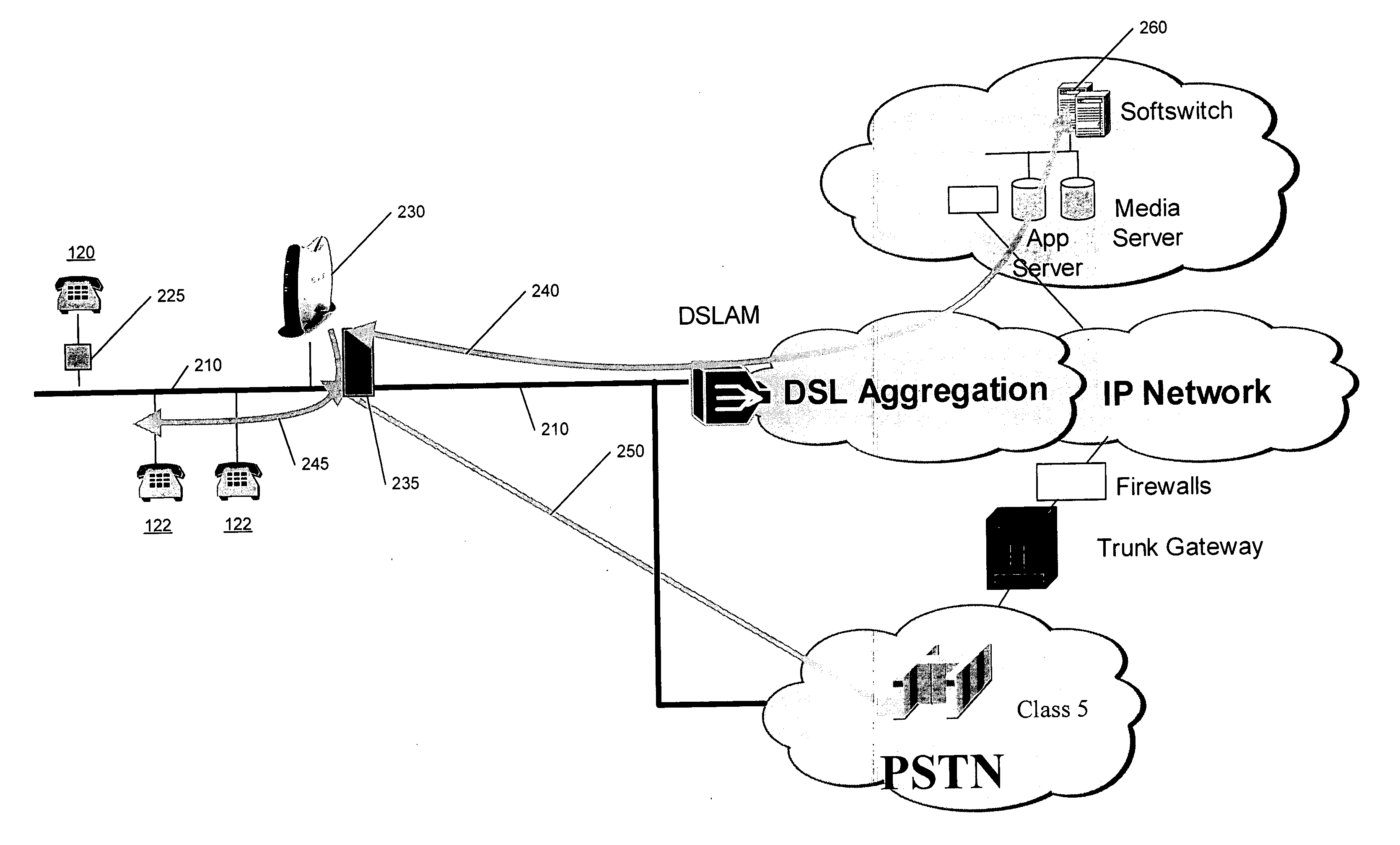
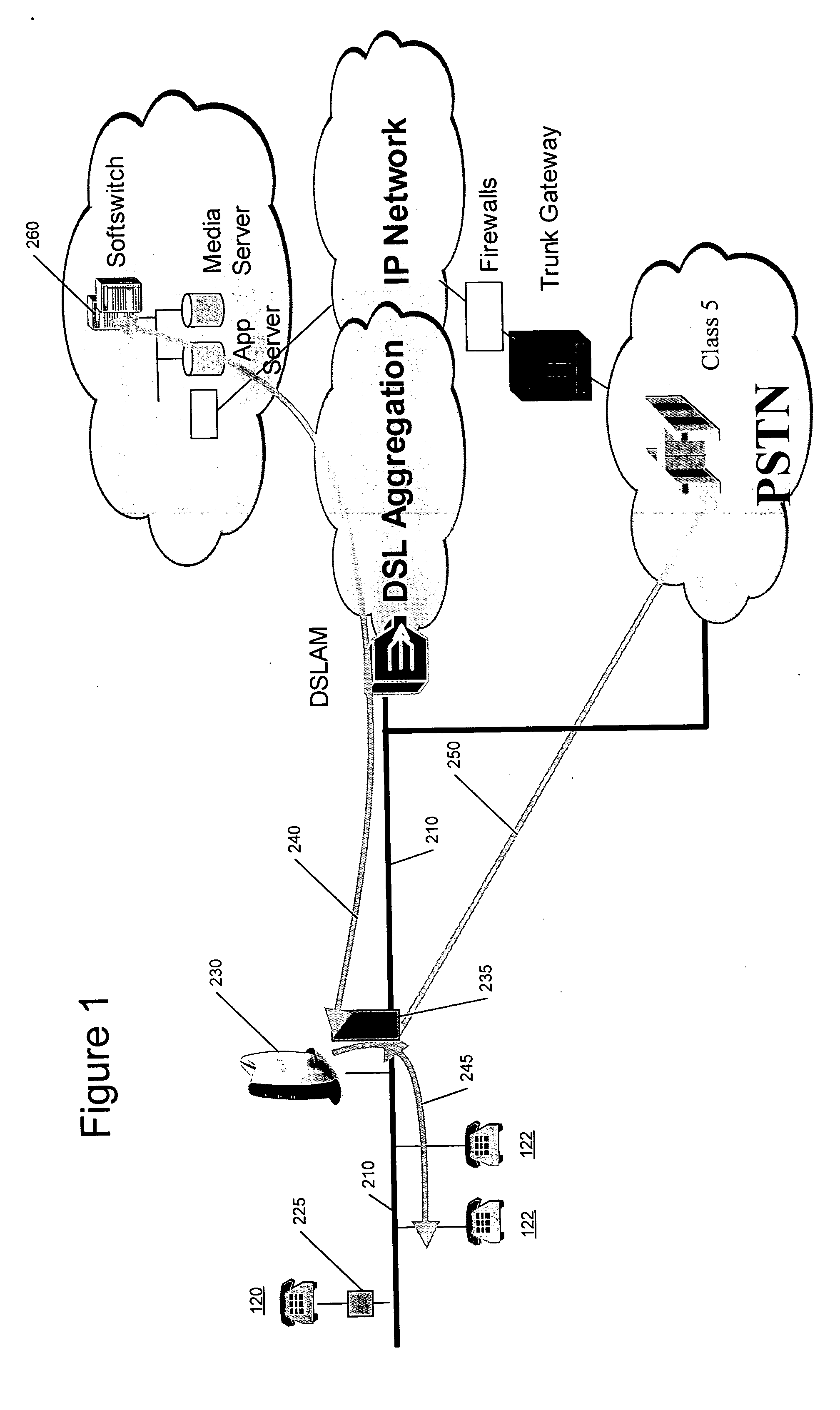
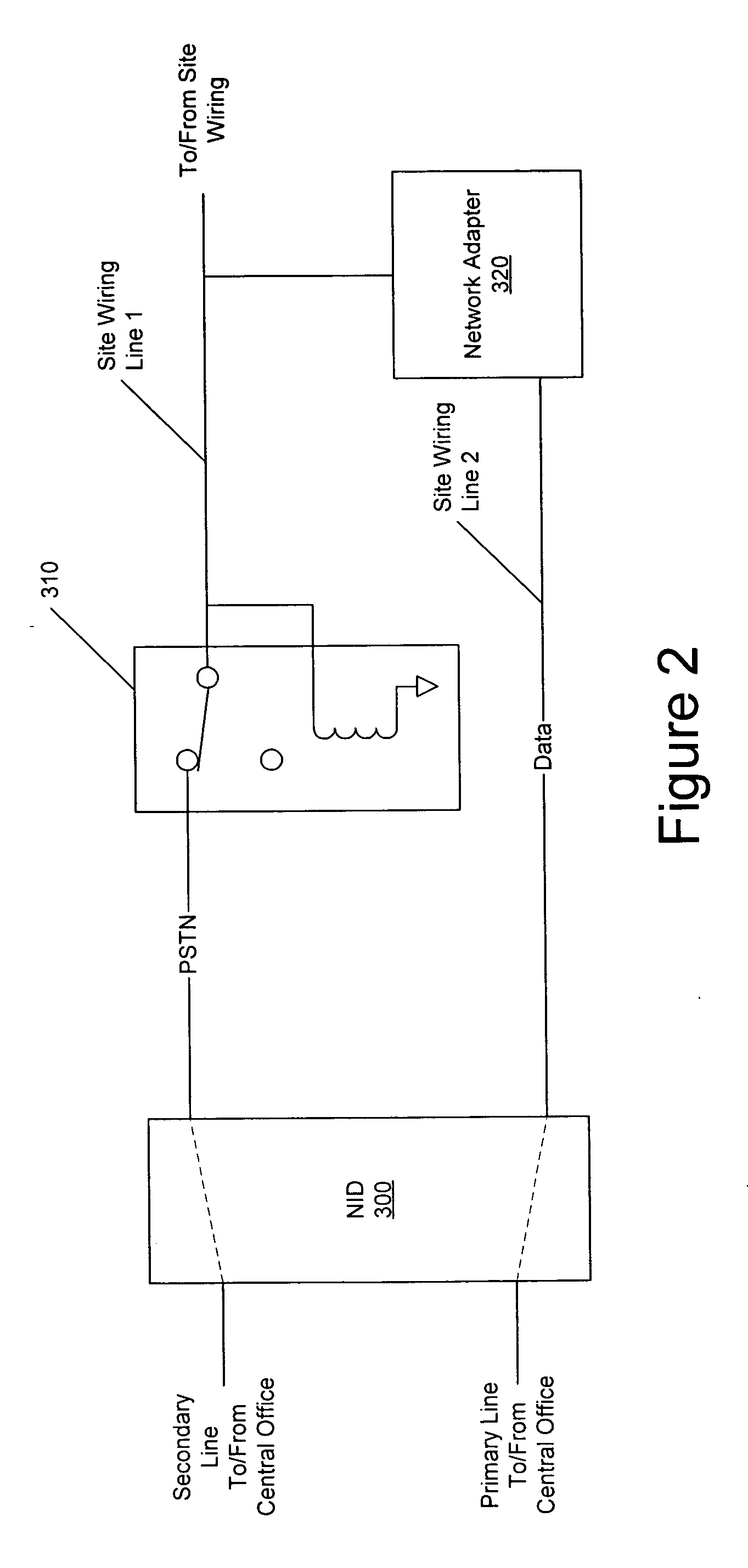
Systems and methods for automatic public switched telephone network backup of Voice over Internet Protocol services
InactiveUS20060039290A1Interconnection arrangementsError preventionUnavailabilityNetwork connectivity
A backup public switched telephone network (PSTN) line is provided to a broadband network connection by detecting unavailability of the broadband network connection and automatically connecting local site wiring to the PSTN line responsive to detecting unavailability of the broadband network connection and disconnecting local site wiring from the PSTN line if unavailability is not detected.
Owner:BELLSOUTH INTPROP COR
Method and Apparatus for Determining Availability of a User of an Instant Messaging Application
InactiveUS20080082620A1Multiple digital computer combinationsOffice automationMessage passingInstant messaging
An instant messaging application intelligently infers a user's unavailability from one or more indicia which include the user's electronic calendar. Preferably, the instant messaging application may report not only that a user is unavailable, but also give a reason for inferring unavailability, in order to provide other users with additional potentially useful information. Preferably, the user may specify which indicia and which parameters may be used to infer his unavailability in an editable profile. When another user requests status, this value is returned by the server. An intelligent instant messaging application as described herein provides other users with more accurate and complete availability information.
Owner:HCL TECH LTD
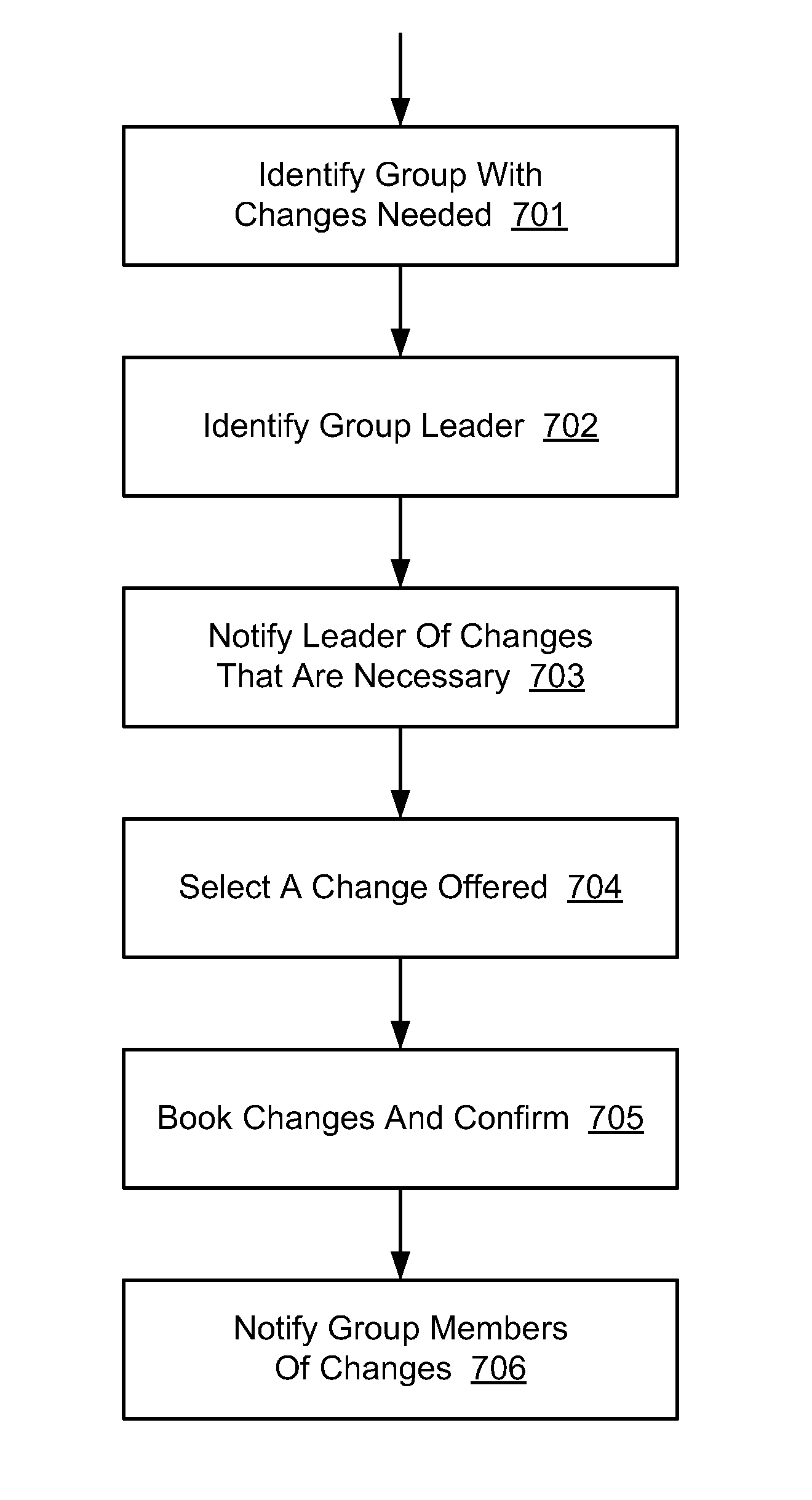
Method and system for delegation of travel arrangements by a temporary agent
A method and system for delegation of service procurement by a temporary agent. In one embodiment, in response to an event, a first entity is automatically identified to adjust travel or meeting plans pre-established for one or more group members. The identified first entity adjusts the pre-established travel or meeting plans for one or more members, and notifies one or more group members of the adjustment to the pre-established travel or meeting plans. In one embodiment, the identified first entity is at least one of the one or more group members, not one of the one or more group members, or a software agent. In one embodiment, in response to an unavailability of the first entity, a predetermined alternative first entity is identified to adjust the pre-established travel or meeting plans. In one embodiment, in response to receiving a decline from one or more group members, the one or more group members are presented with one or more second travel or meeting adjustments. In one embodiment, the adjusting of the pre-established travel or meeting plans is based at least in part on a profile of one or more group members.
Owner:TALARIS CORP +1
Reliability evaluation system, reliability evaluating method, and reliability evaluation program for information system
InactiveUS7730363B2Reduce the burden onImprove usabilityTesting/monitoring control systemsReliability/availability analysisEvaluation systemComputer science
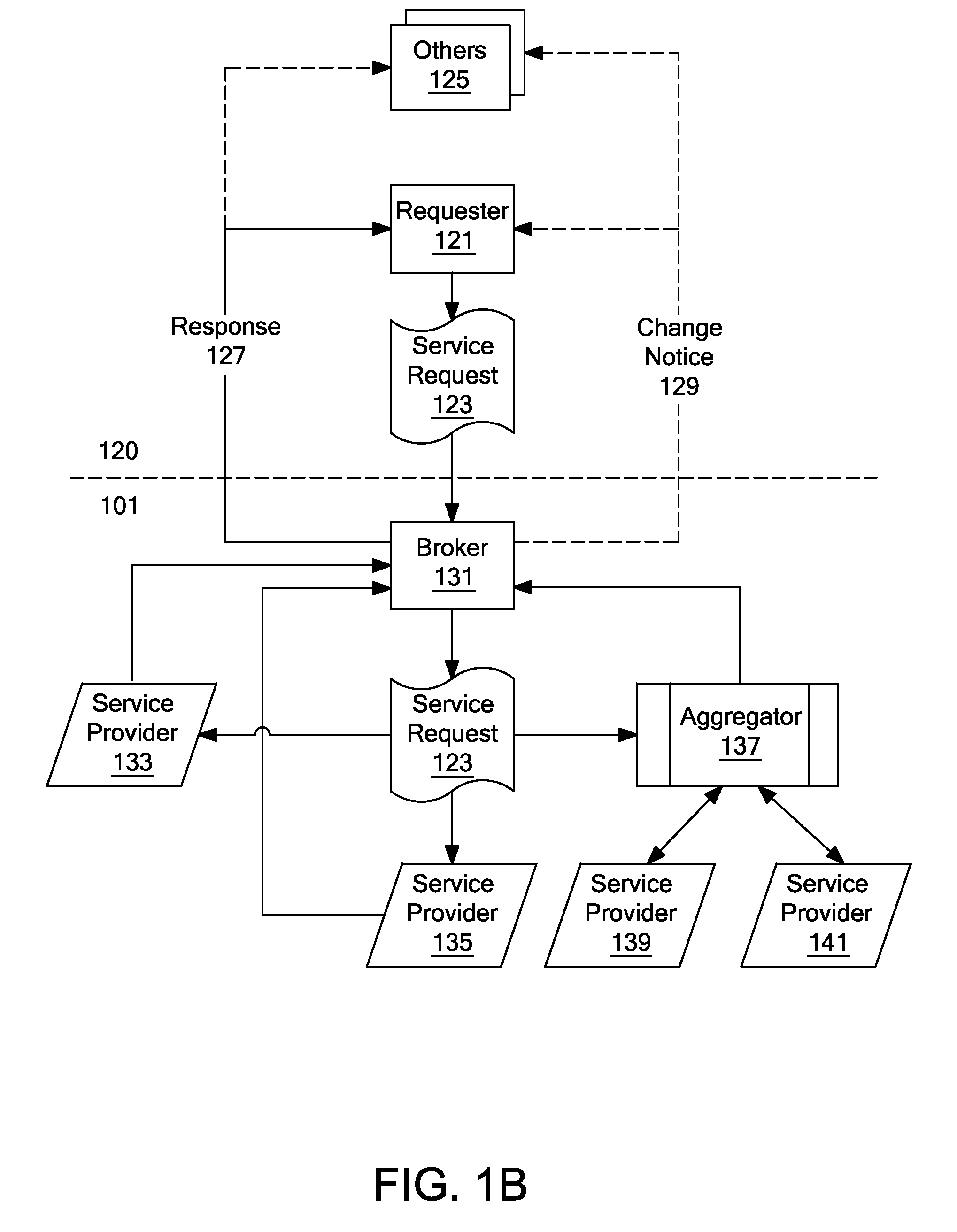
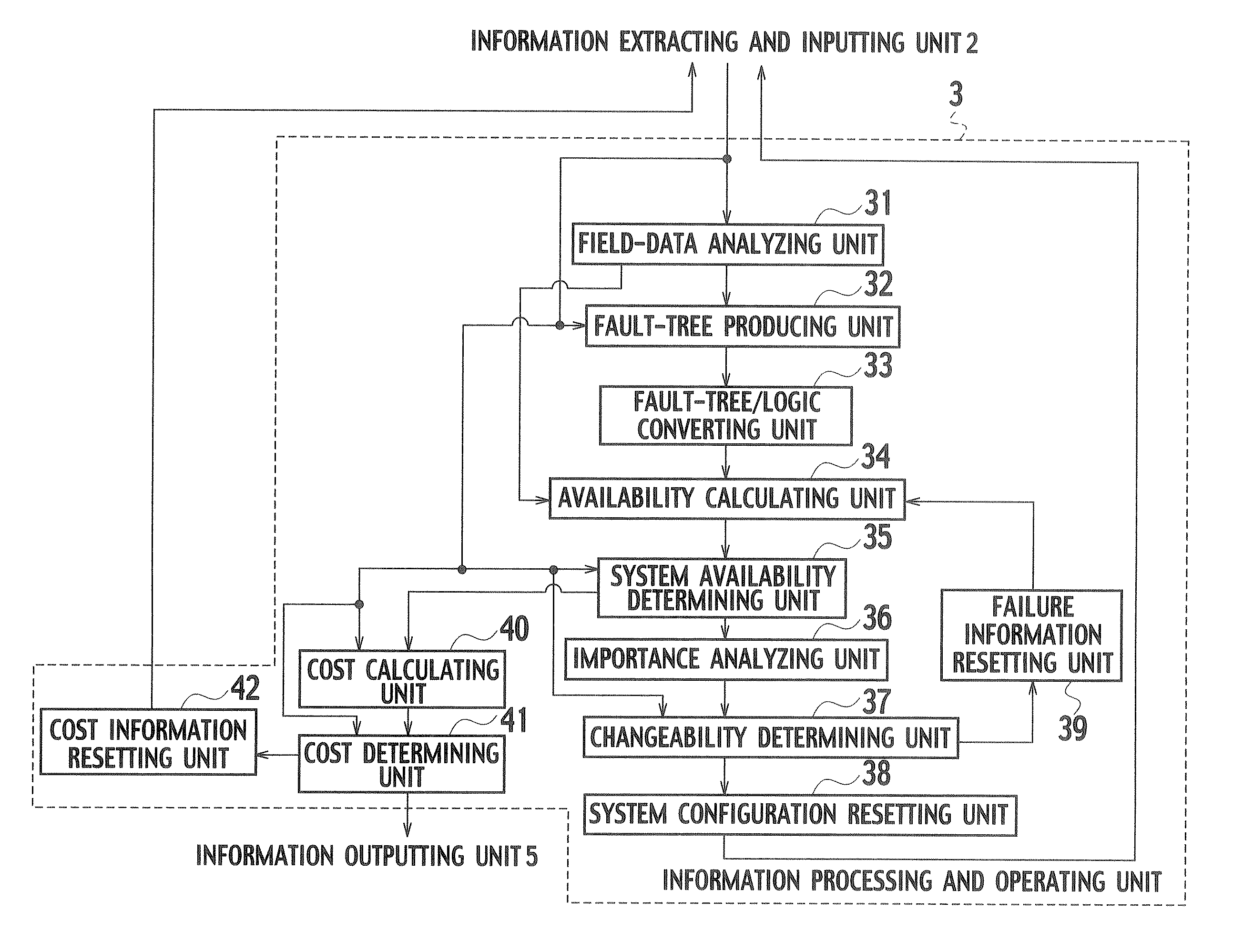
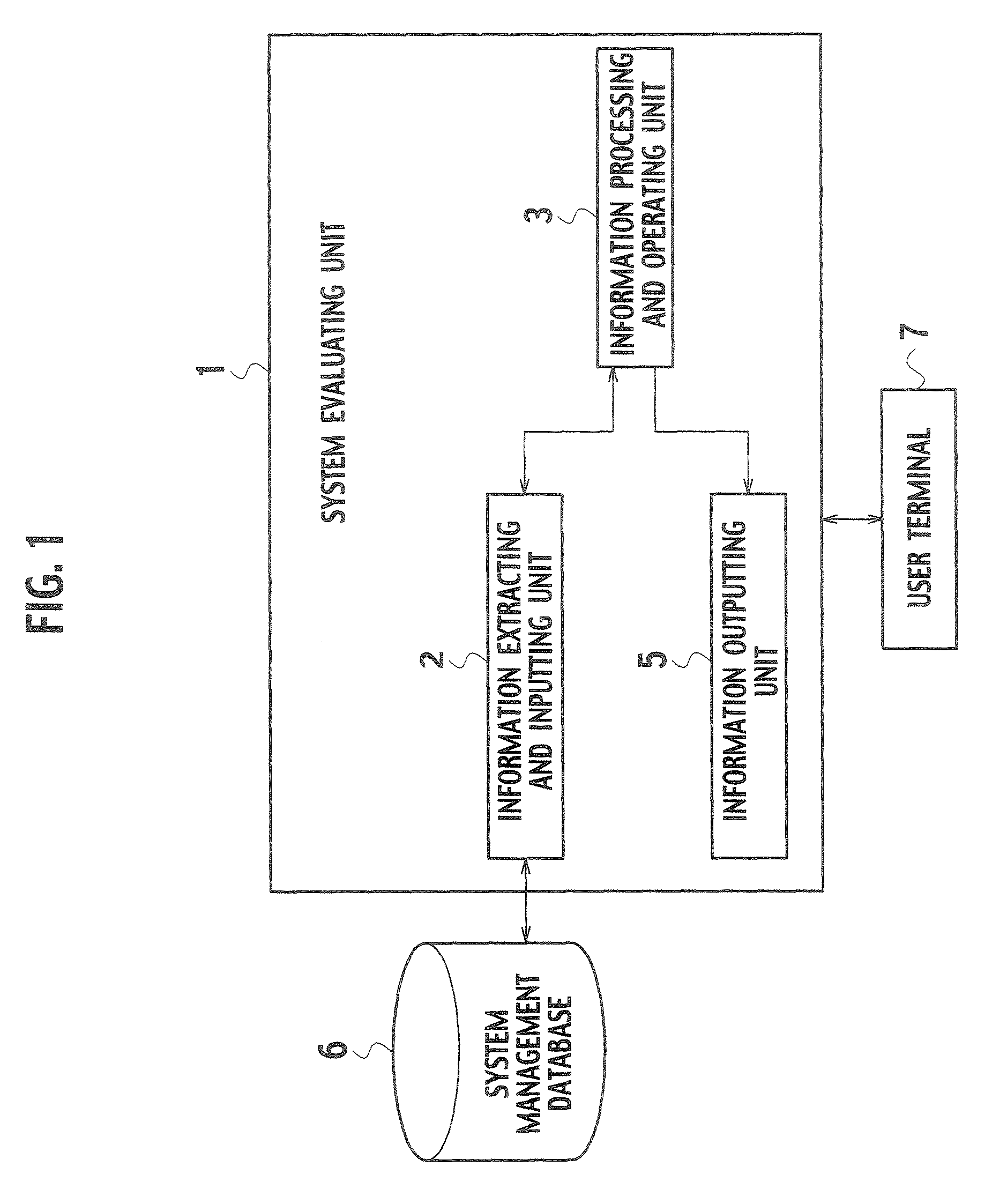
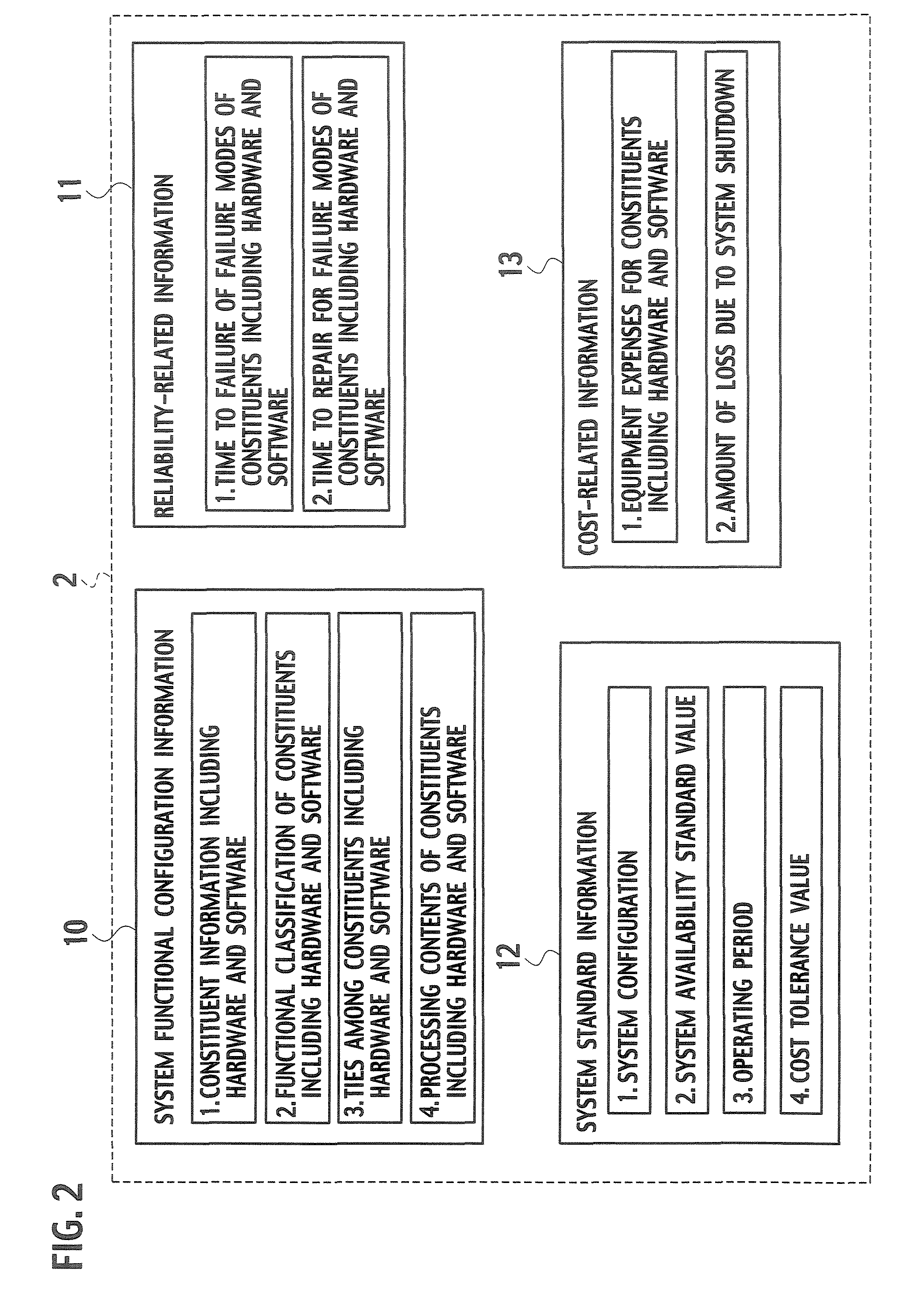
A system includes an input unit (2) to which failure information corresponding to failure modes of constituents indicating software and hardware, a system configuration information and a standard value of system availability are inputted, a producing unit (32) producing a fault tree based on the system configuration information, a calculating unit (34) calculating unavailability corresponding to the failure modes based on a result of analyzing the failure information, and calculating system availability based on the calculated unavailability and the fault tree, a determining unit (35) determining whether the system availability meets the standard value, an extracting unit (36) extracting a basic event related to an increase in the system availability when the system availability is determined to be below the standard value, and resetting units (38, 39) resetting new unavailability and the like based on whether it is possible to reduce the unavailability of the extracted basic event.
Owner:TOSHIBA SOLUTIONS
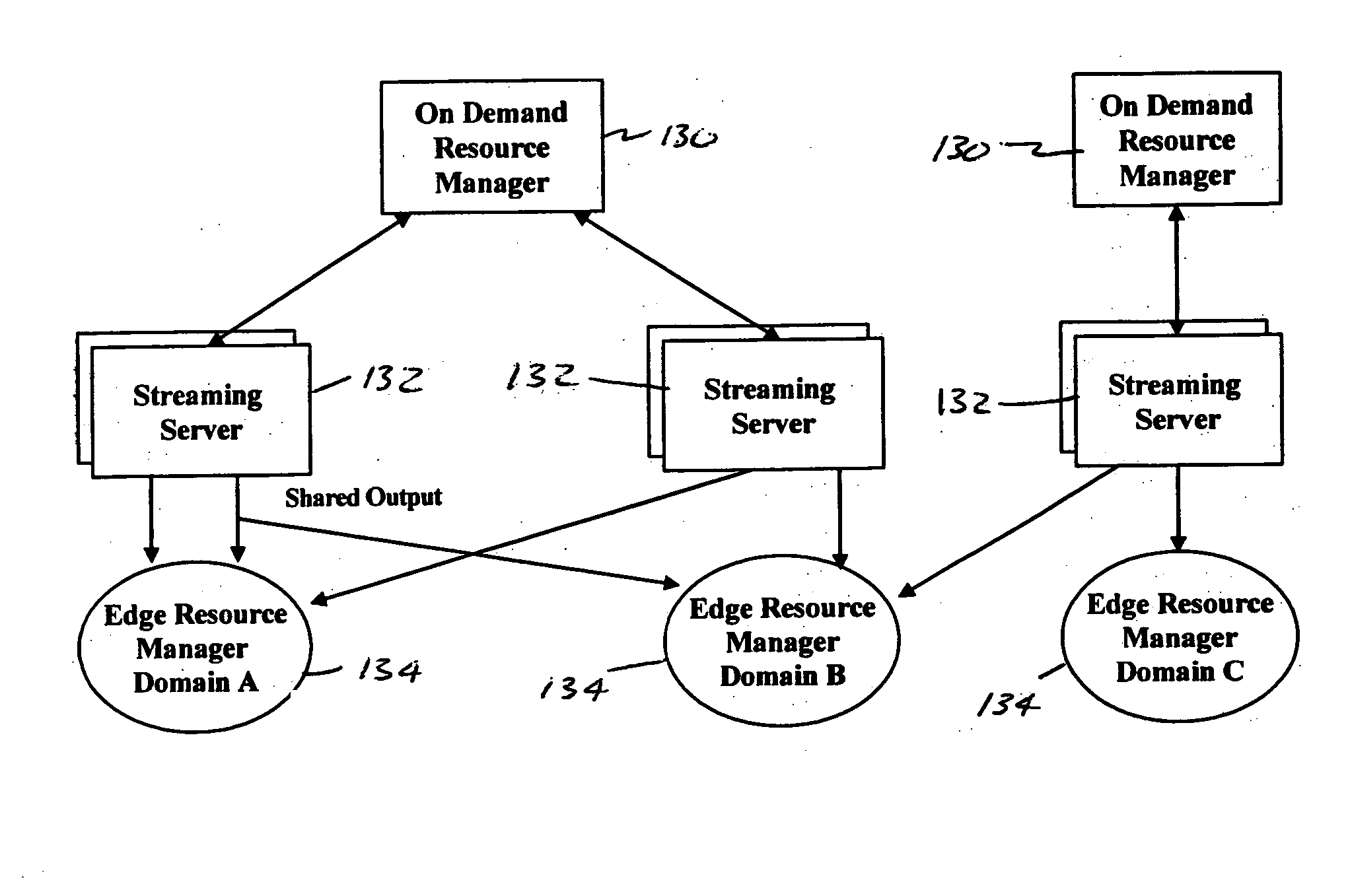
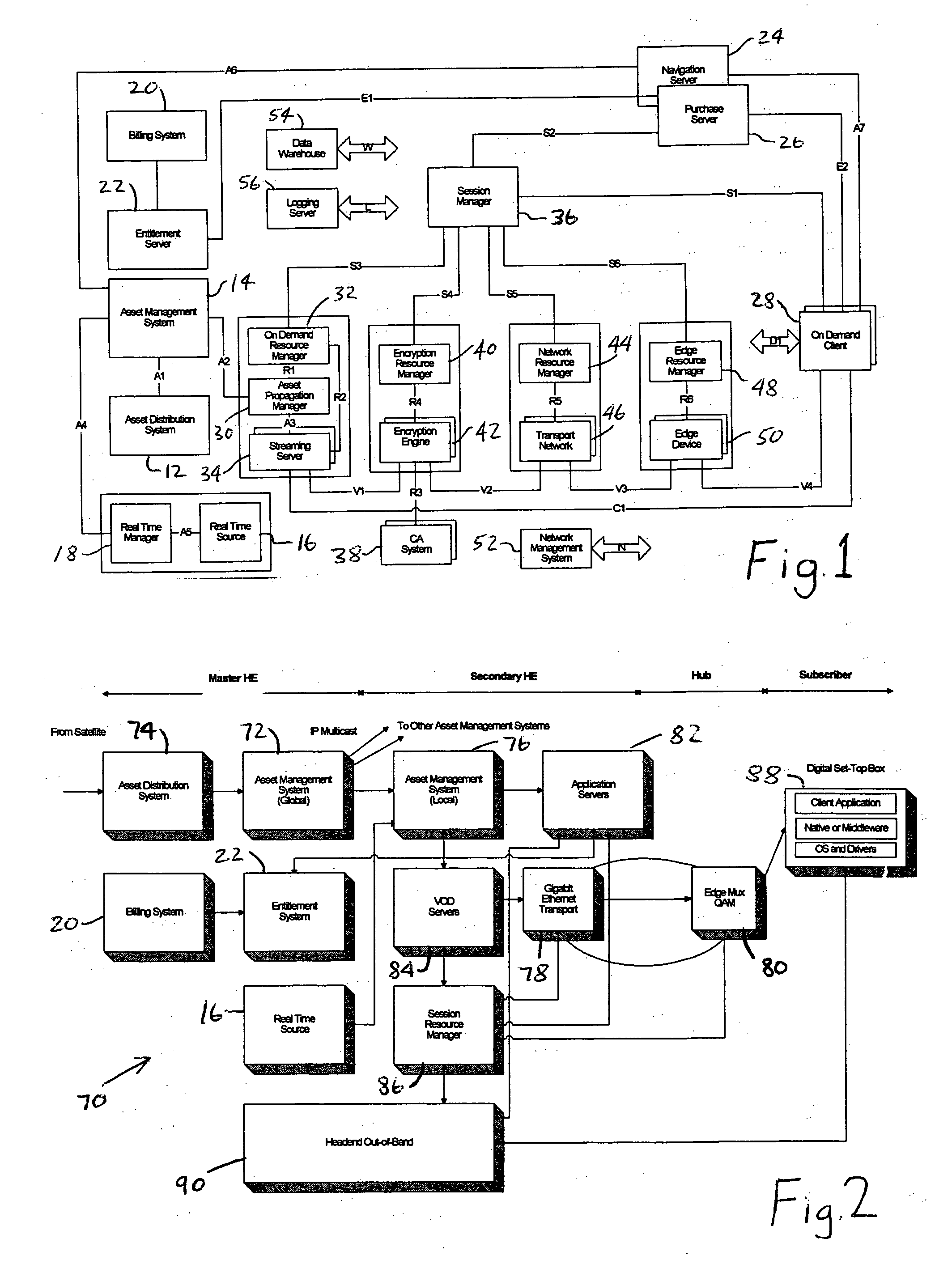
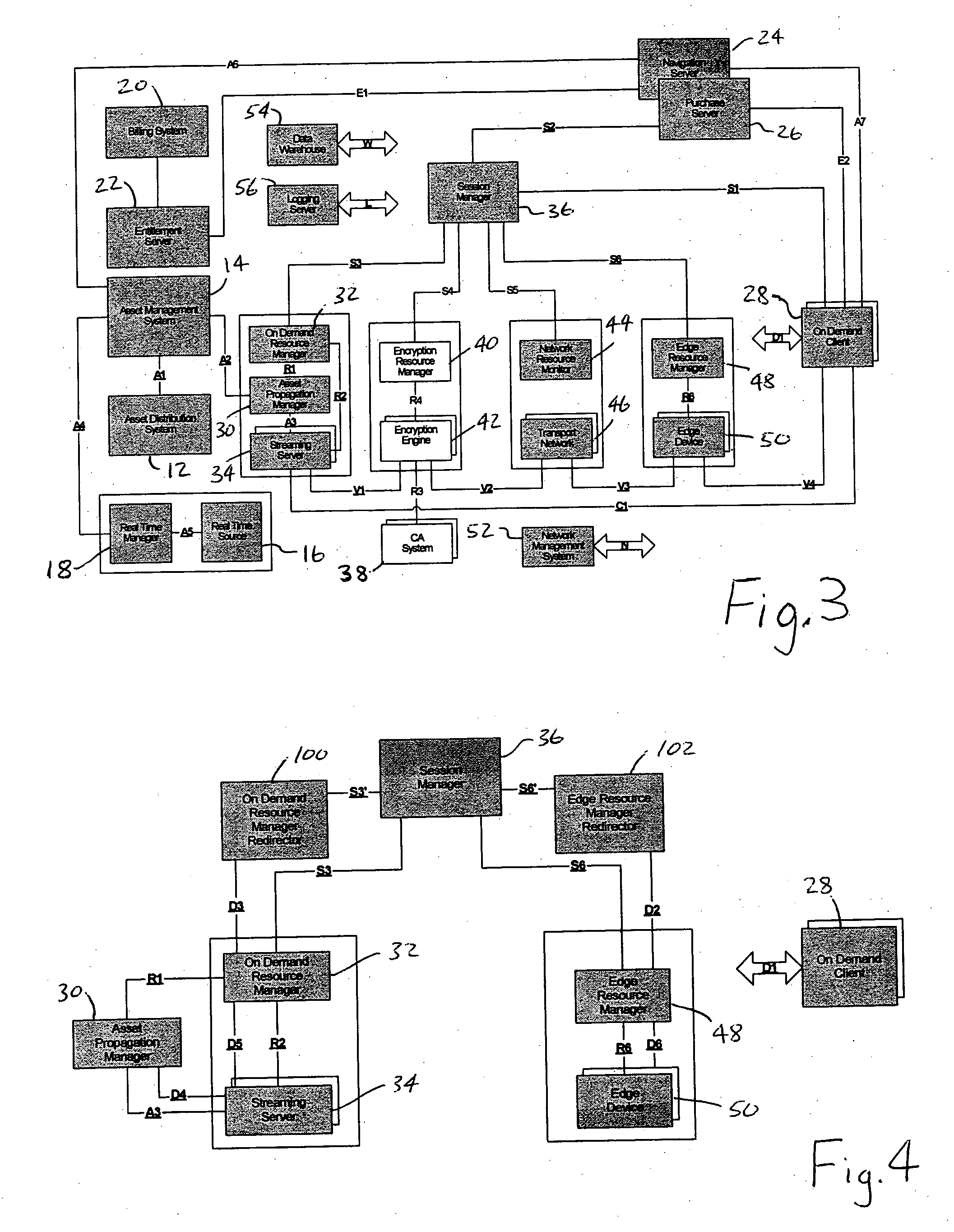
Signaling redirection for distributed session and resource management
A system for on demand session and resource management in an on demand platform for the delivery of on demand digital assets involve a session manager, a plurality of resource managers, and a resource manager redirector. These components cooperate to provide a distributed and scalable system for on demand session and resource management. Redirection of session and resource signaling messages among various session and resource managers by the resource manager redirector allows the unavailability of devices or resources to remain transparent to the session manager. The resource manager redirector redirects messages from the session manager as appropriate.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM LLC
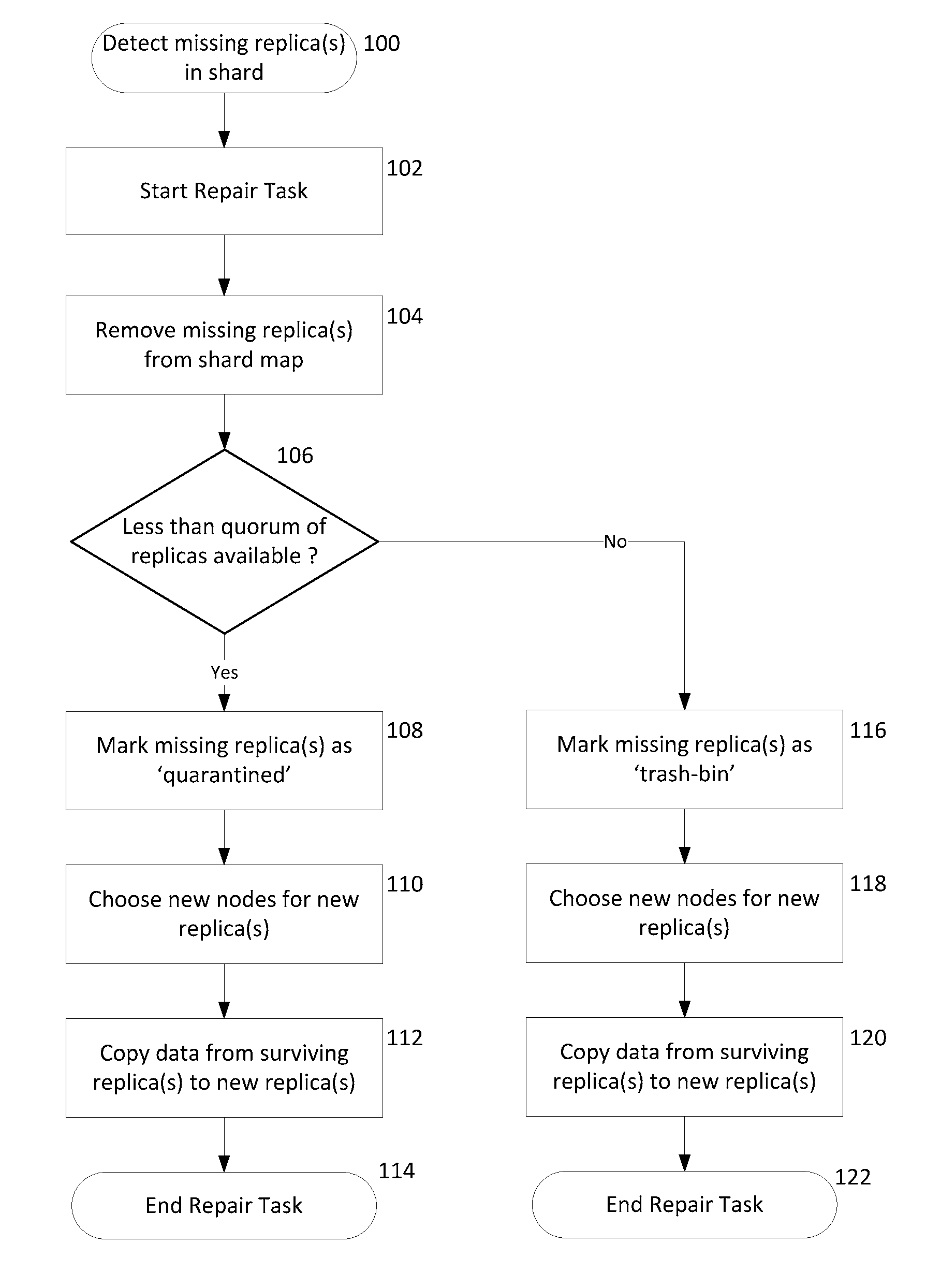
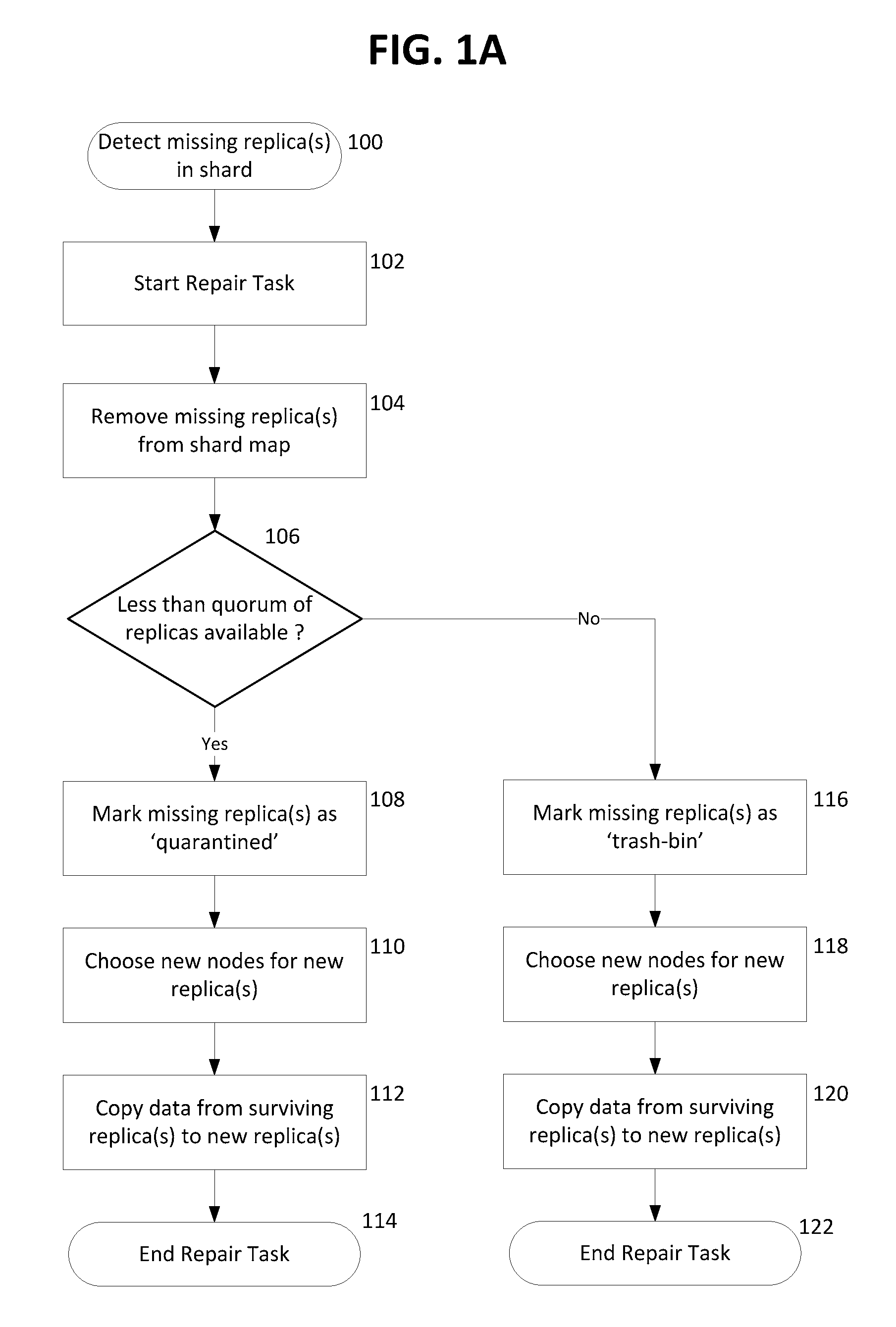
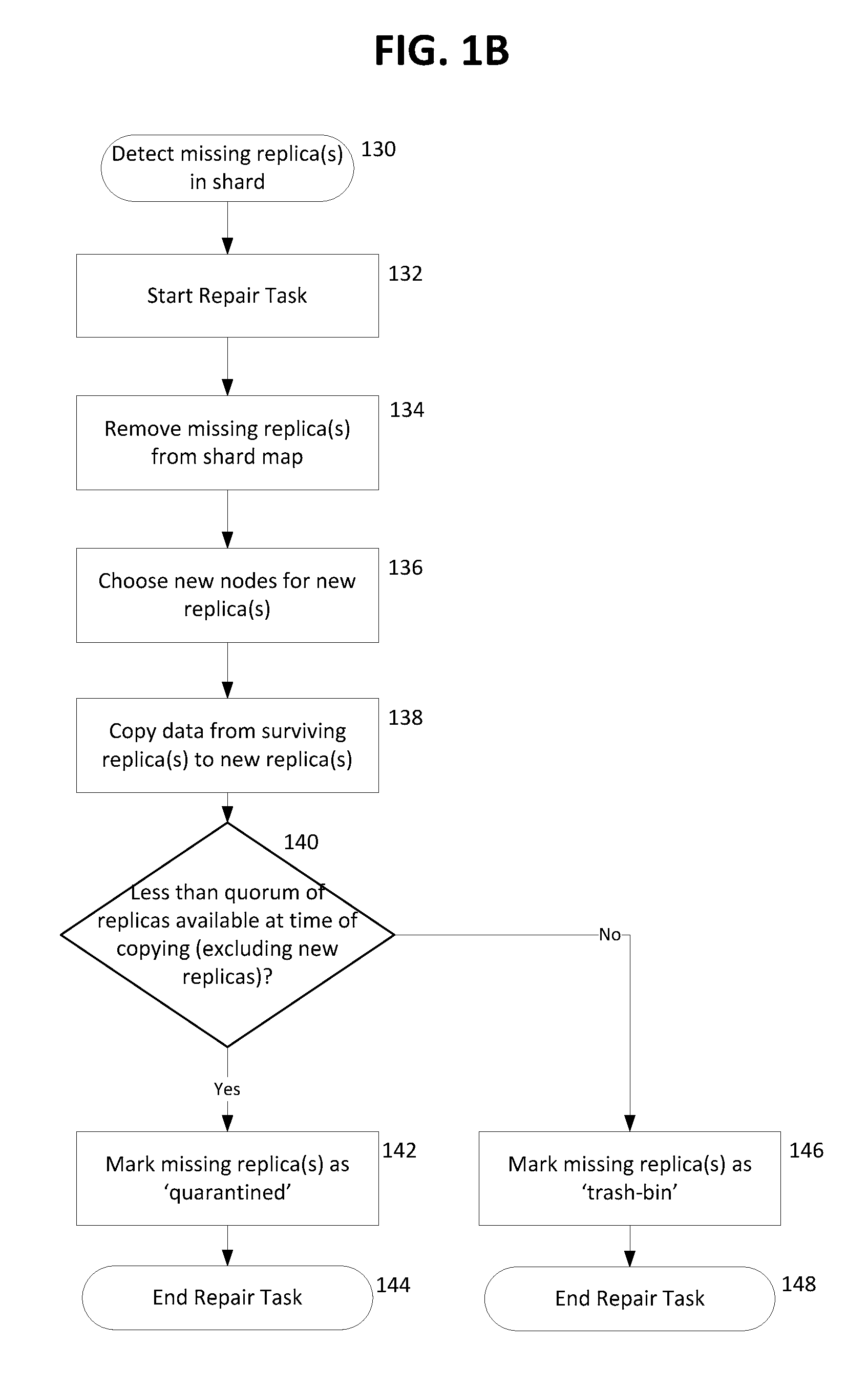
Quarantine and repair of replicas in a quorum-based data storage system
ActiveUS20150278324A1Digital data processing detailsDatabase distribution/replicationFault toleranceQuarantine
A data storage system with quorum-based commits sometimes experiences replica failure, due to unavailability of a replica-hosting node, for example. In embodiments described herein, such failed replicas can be quarantined rather than deleted, and subsequently such quarantines can be recovered. The teachings hereof provide data storage with improved fault-tolerance, resiliency, and data availability.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
System and method of sharing auto-reply information
ActiveUS20070192418A1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksComputer hardwareAddress book
A system and method routes messages based on an intended recipient's availability to receive messages. Each network user's current status is determined by tracking when the user activates and deactivates an auto-reply feature. The user's current status, return date and alternate contact(s) are specified in the auto-reply and stored and updated on a user status server which periodically communicates to each user the current status information for each contact listed in that user's address book. When the current status information indicates that the intended recipient is unavailable, message routing options are presented to the sender. These options include sending the message to the user regardless of the intended recipient's current unavailability, not sending the message at all, routing the message to at least one specified alternate contact, sending the message to the intended recipient while sending a copy of the message to the alternate contact.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
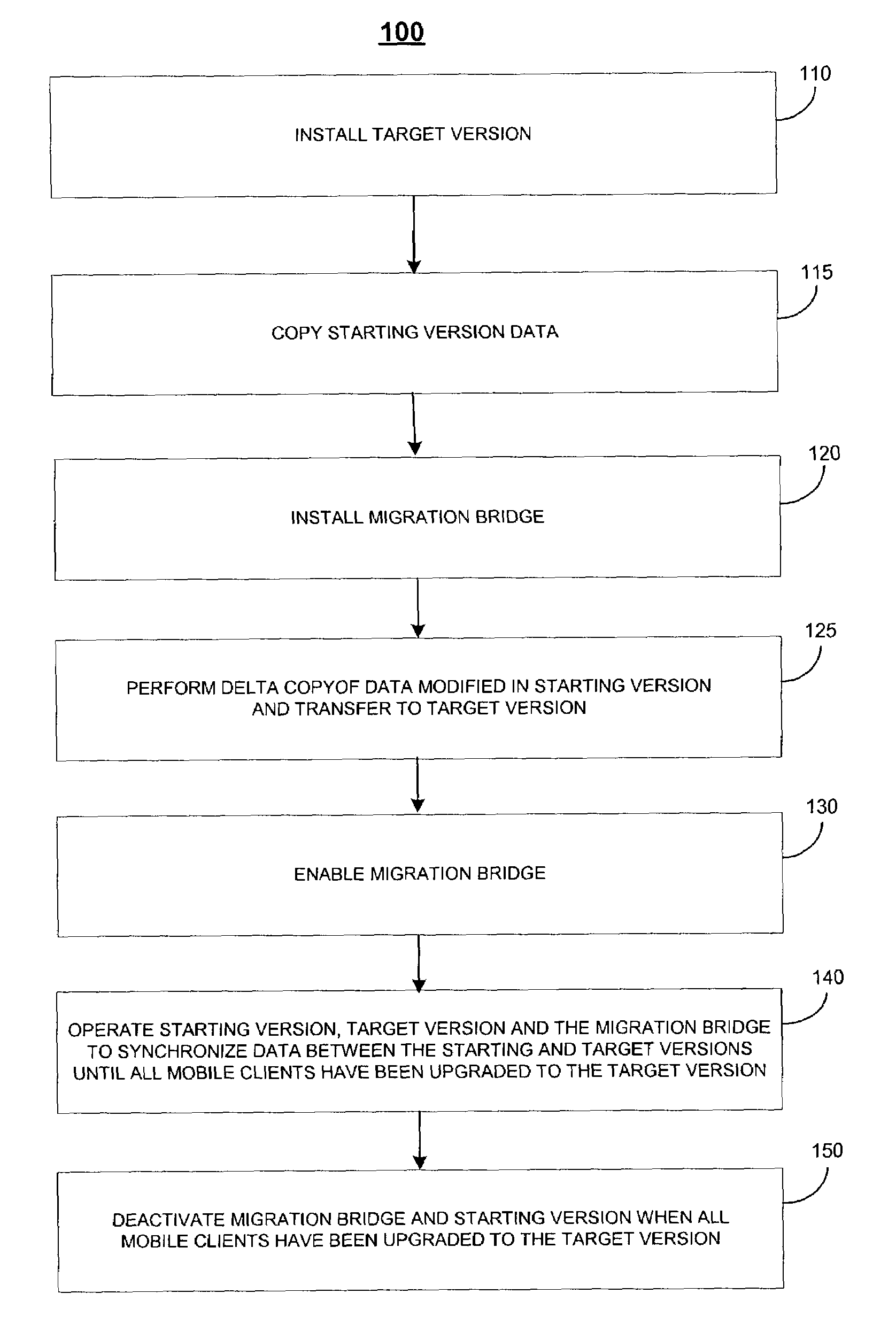
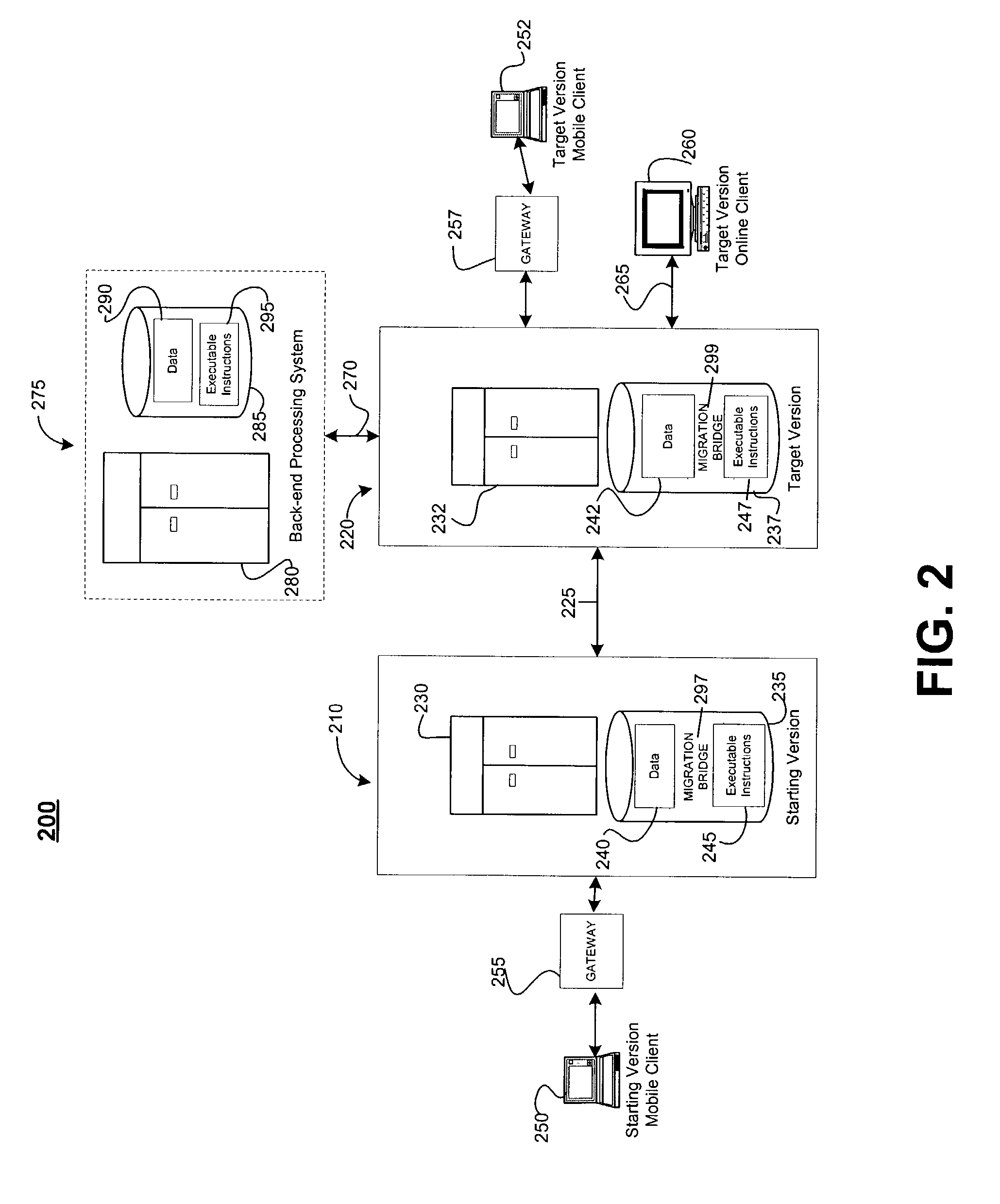
Phased upgrade of a computing environment
ActiveUS7263698B2Minimizing unavailabilitySoftware engineeringProgram loading/initiatingApplication serverDowntime
Techniques are provided to permit a gradual or phased migration of a computing environment including groups of mobile clients to a new version of an application program such that the unavailability or downtime of any mobile client is minimized. In one general aspect, the techniques permit a mobile client to connect with an application server of the corresponding version for synchronization whether the mobile client is operating on the starting-version or the new or target-version of the application program and migrates the data between the two versions of the application program. A migration bridge between the starting-version and the target-version of the application program synchronizes the data in the two versions of the application program.
Owner:SAP AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com