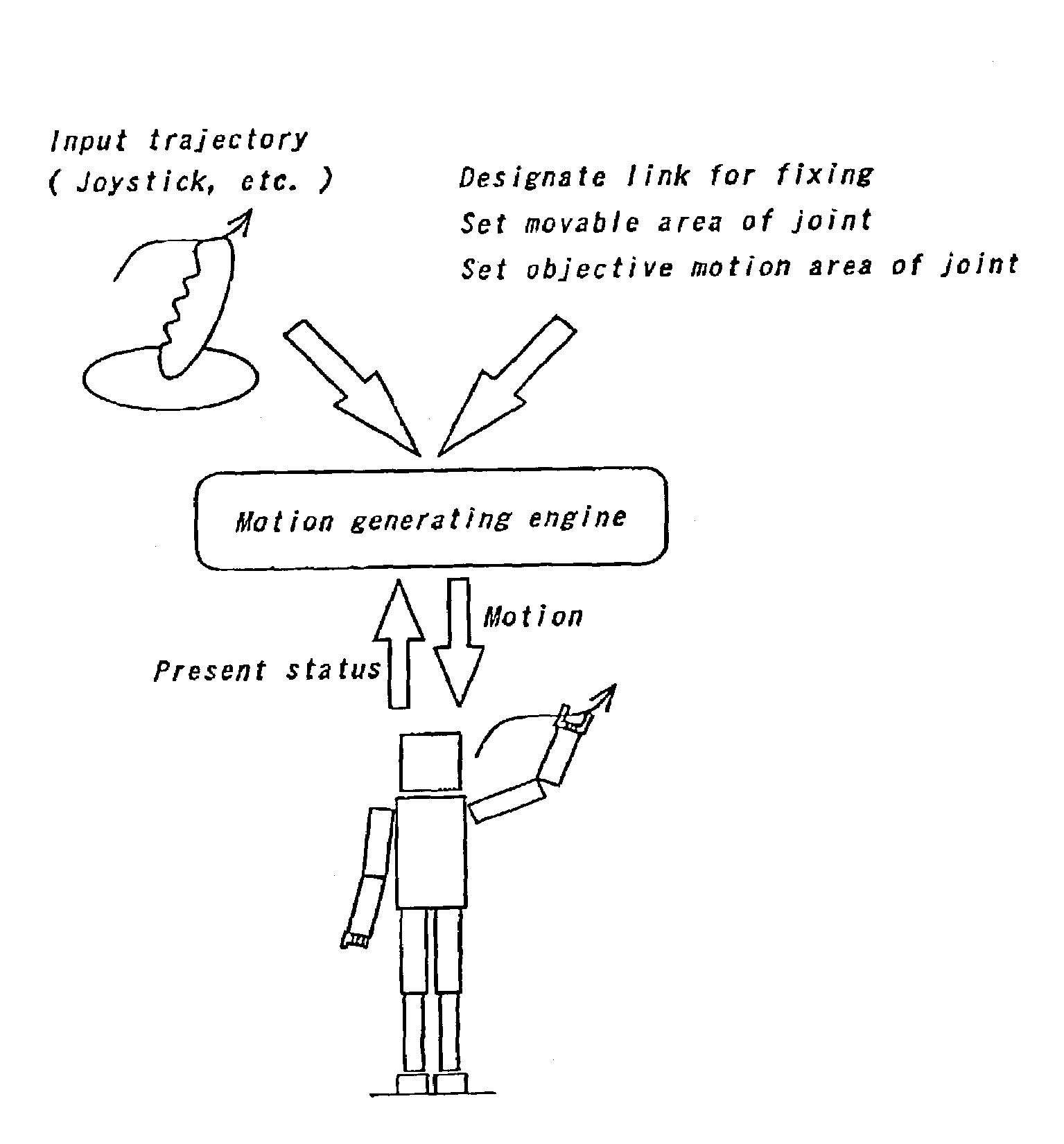
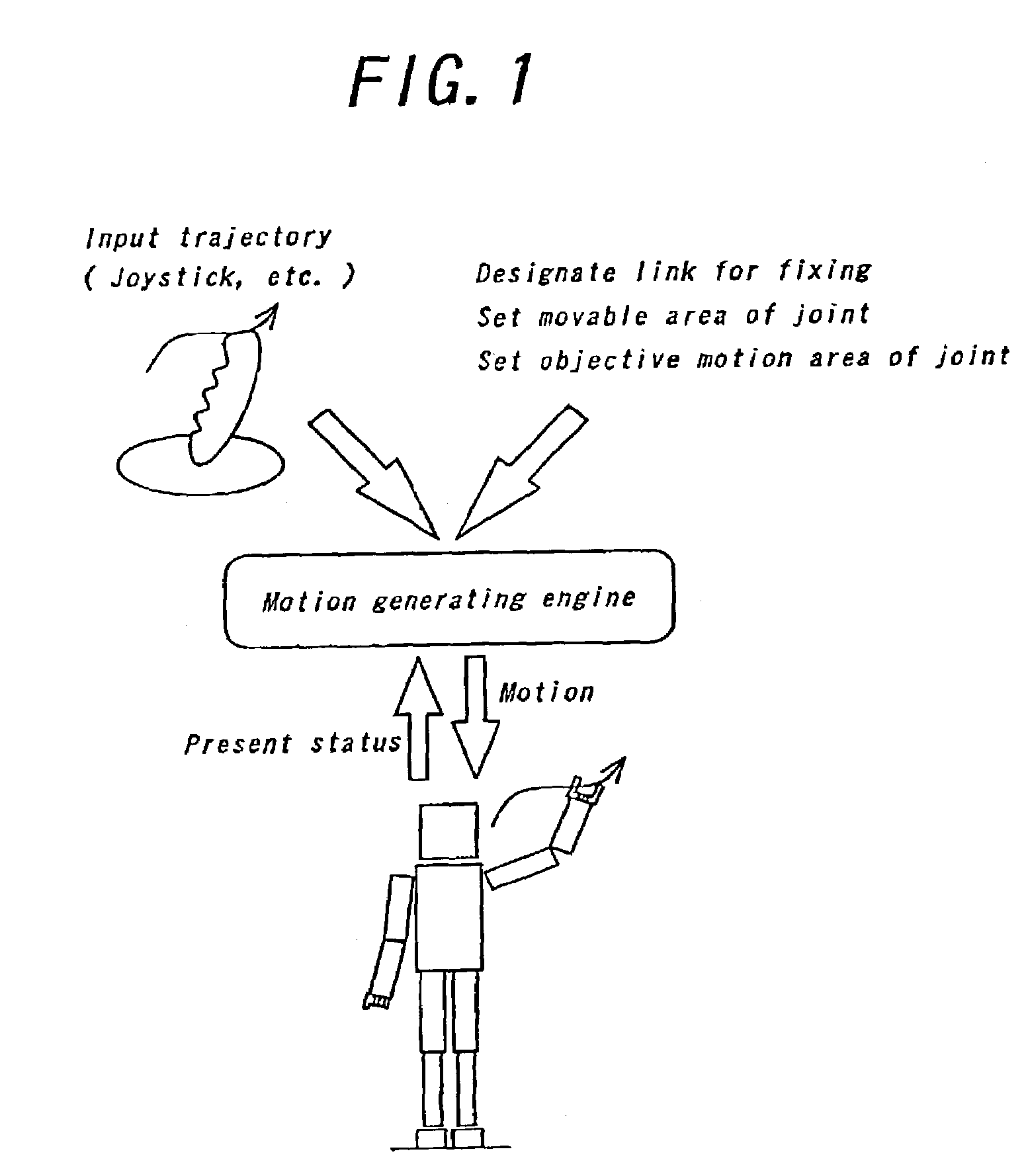
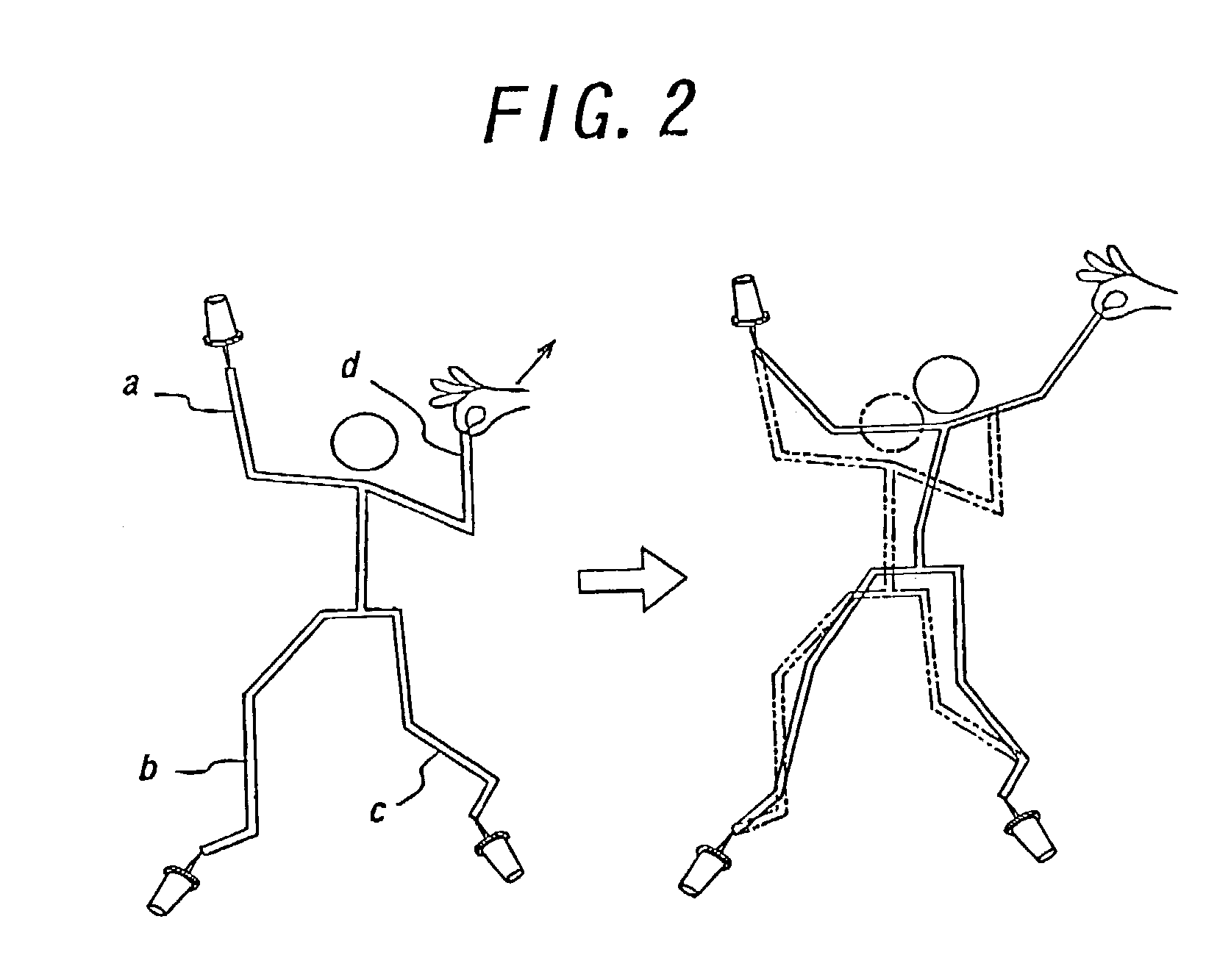
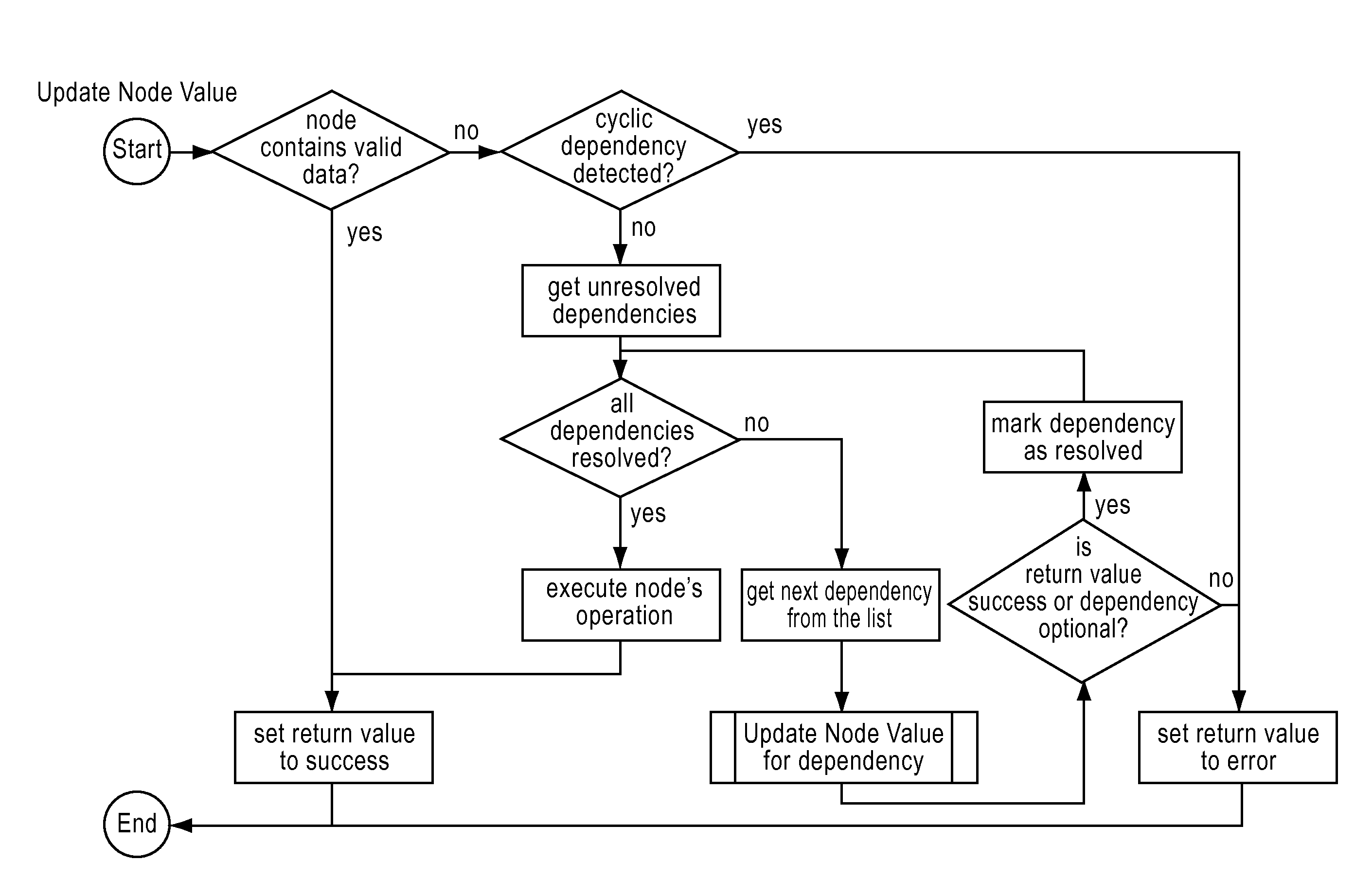
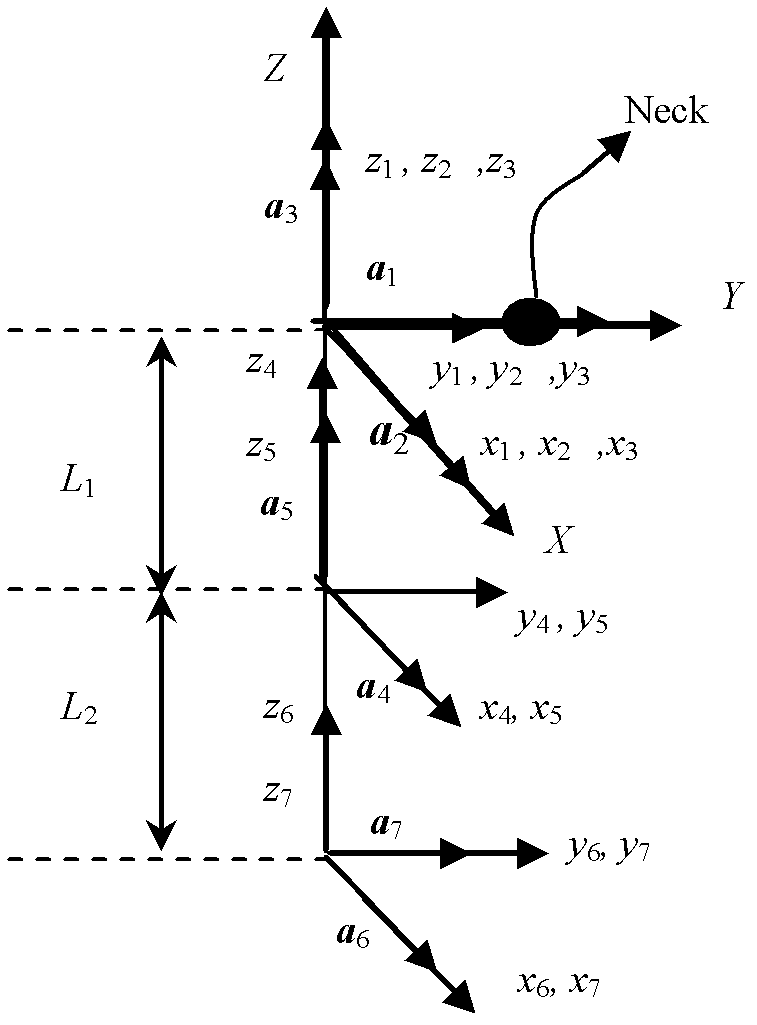
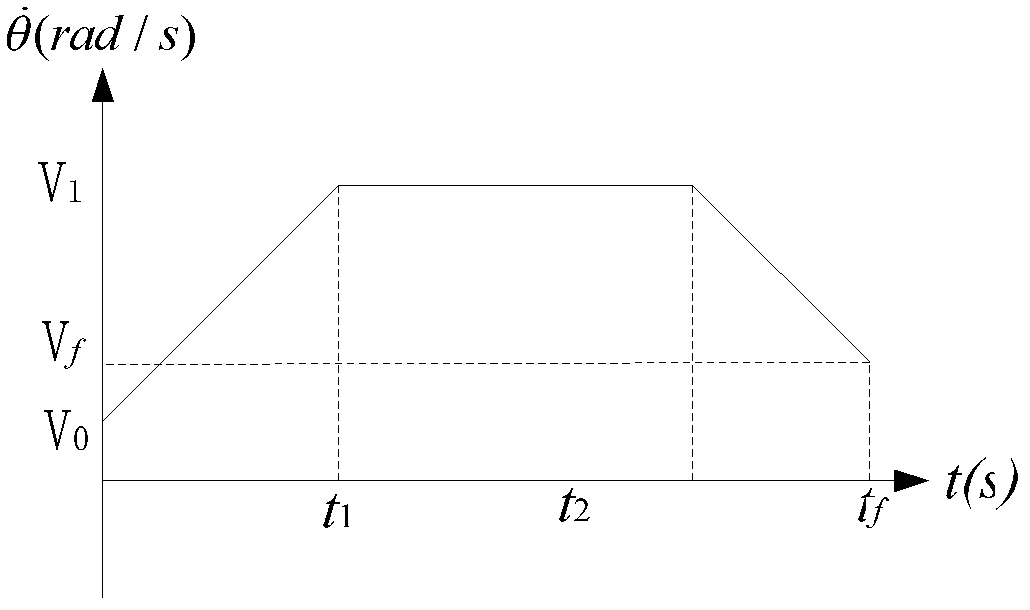
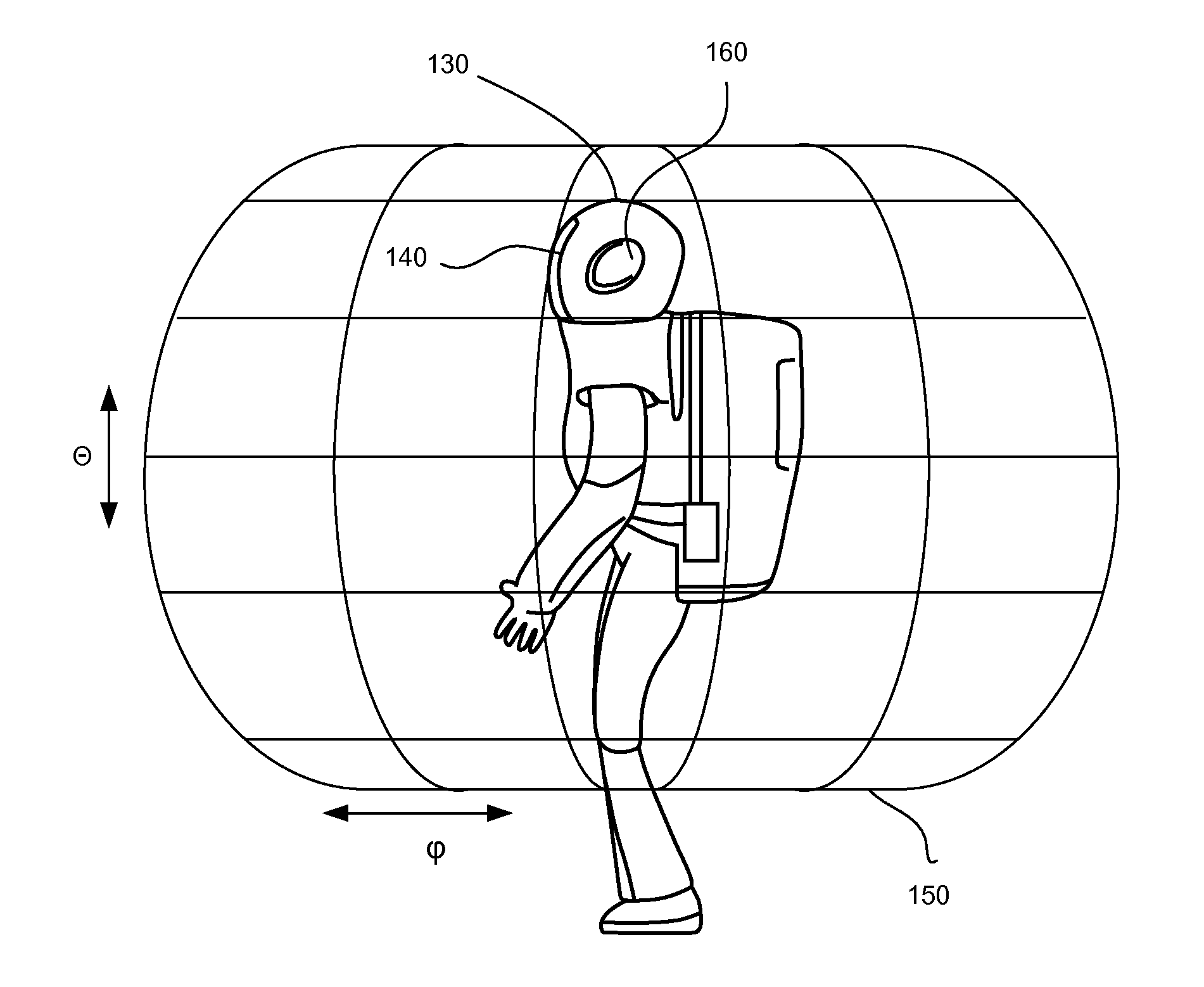
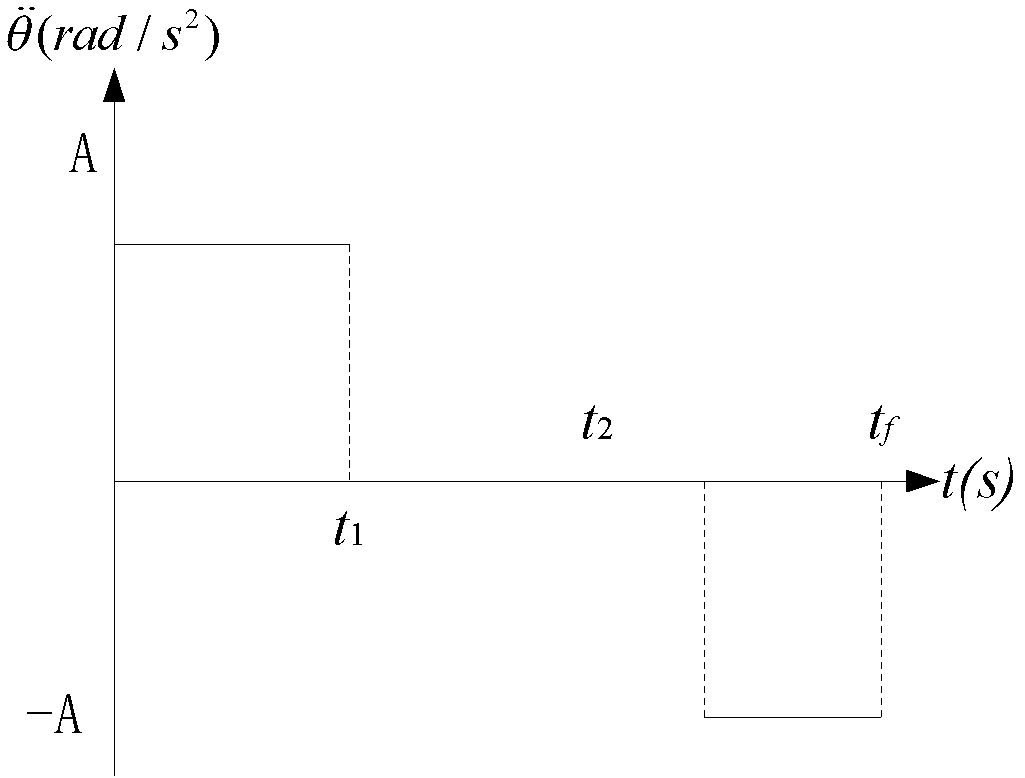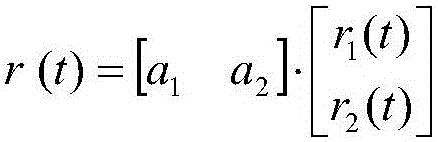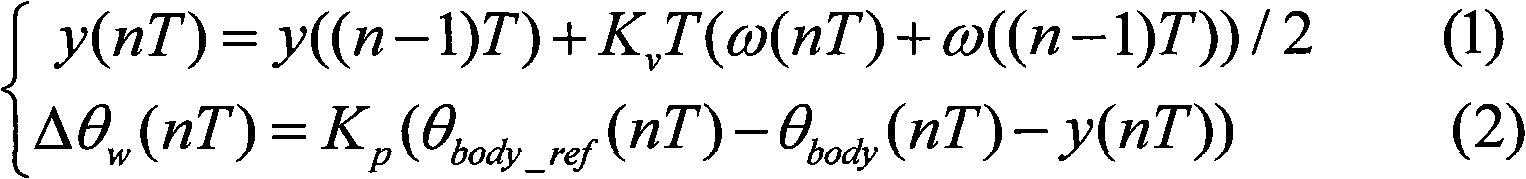Patents
Literature
677 results about "Humanoid robot" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
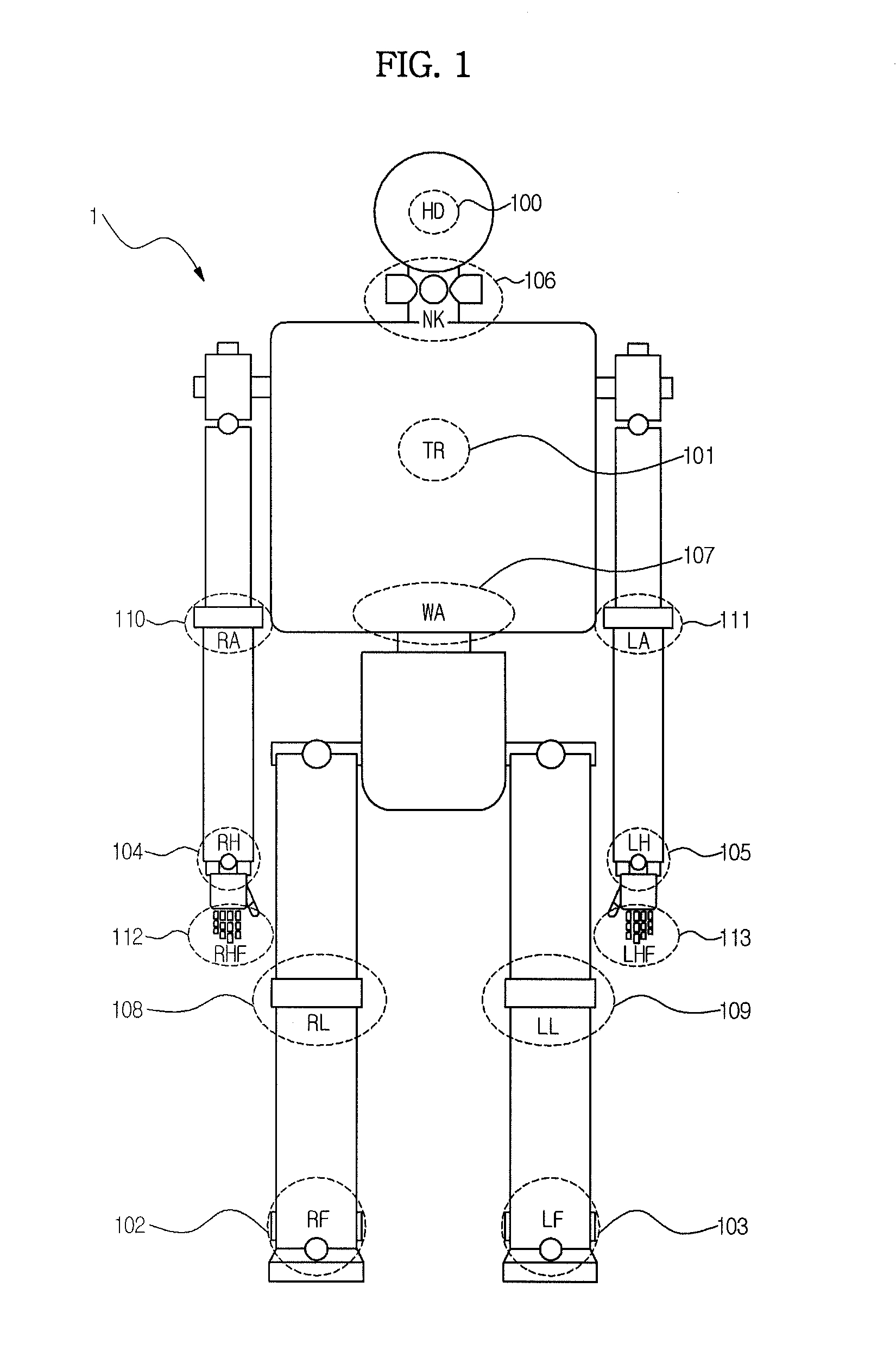
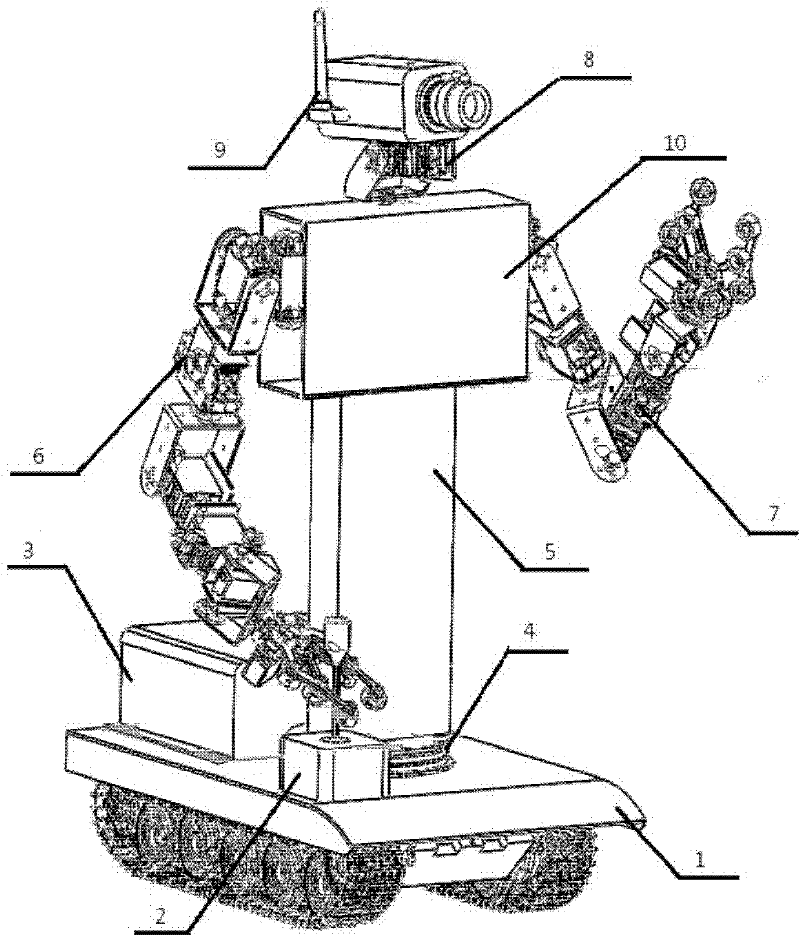
A humanoid robot is a robot with its body shape built to resemble the human body. The design may be for functional purposes, such as interacting with human tools and environments, for experimental purposes, such as the study of bipedal locomotion, or for other purposes. In general, humanoid robots have a torso, a head, two arms, and two legs, though some forms of humanoid robots may model only part of the body, for example, from the waist up. Some humanoid robots also have heads designed to replicate human facial features such as eyes and mouths. Androids are humanoid robots built to aesthetically resemble humans.
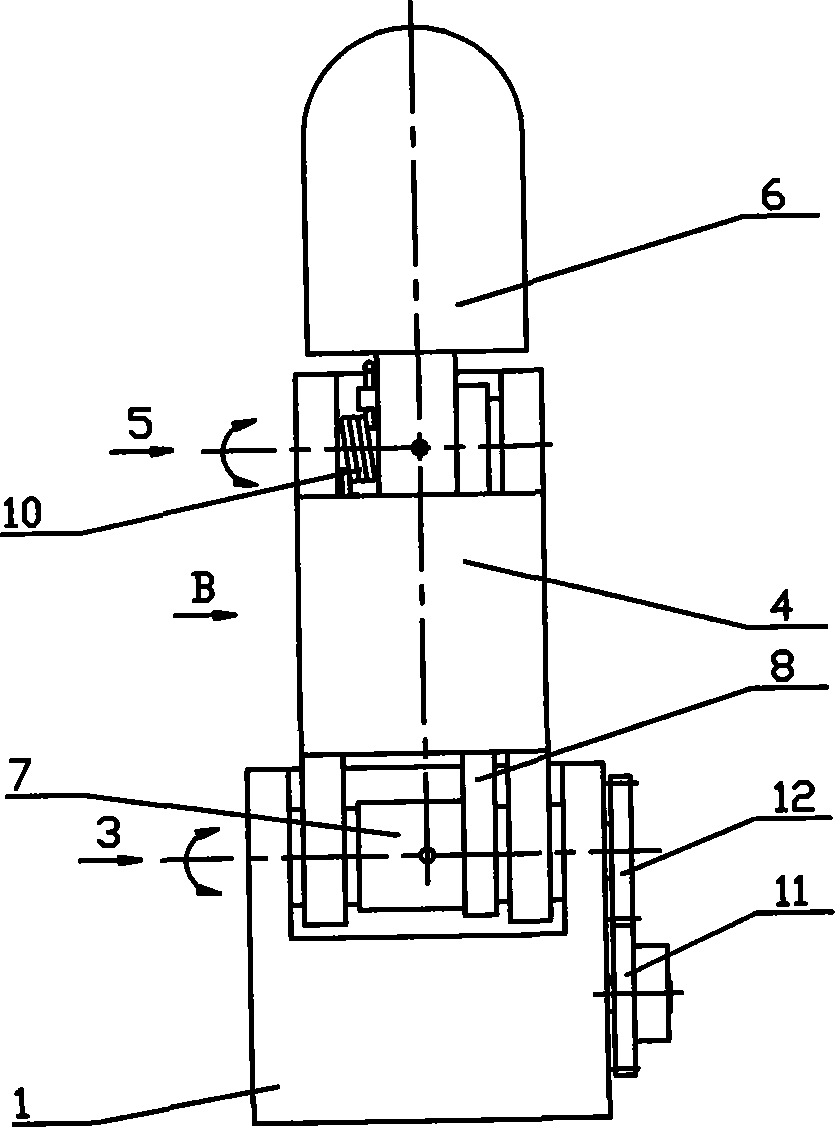
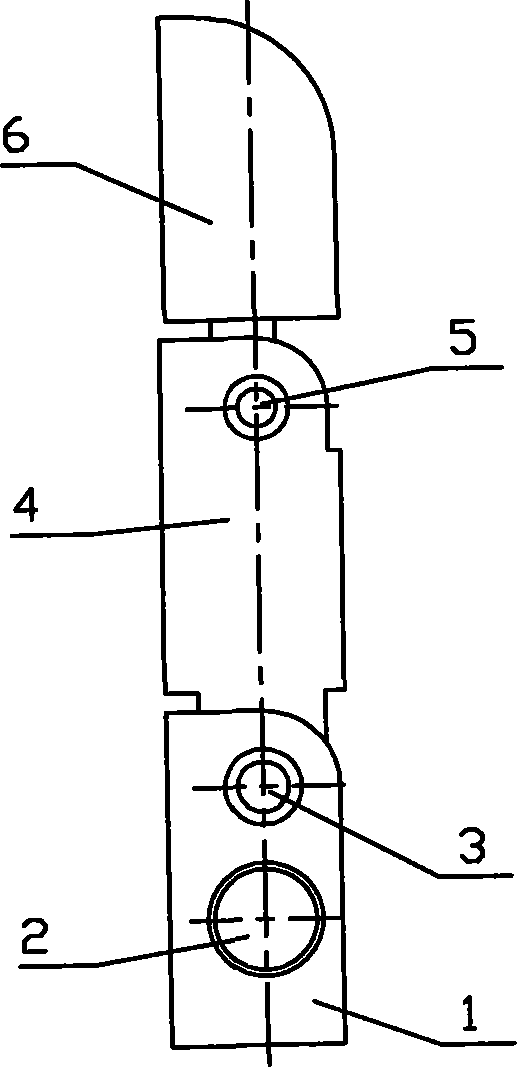
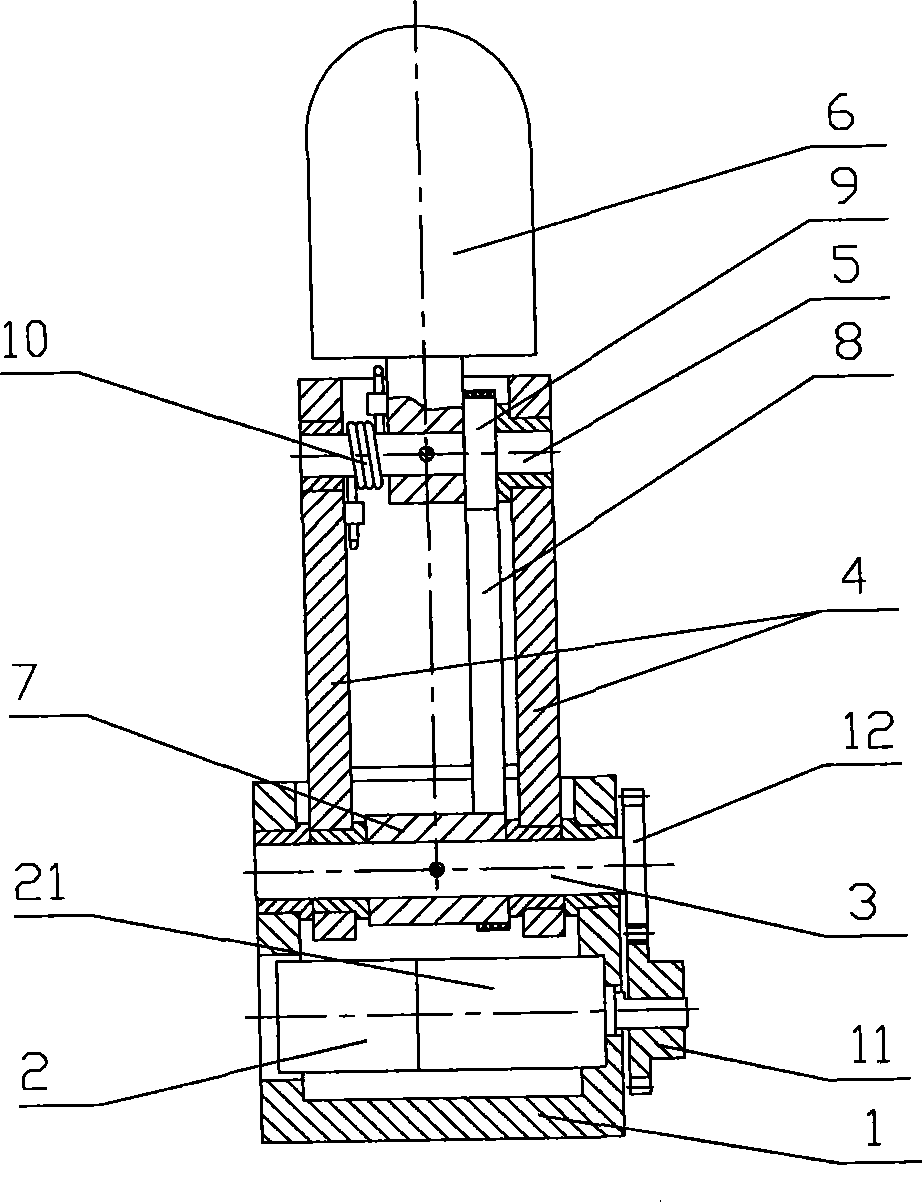
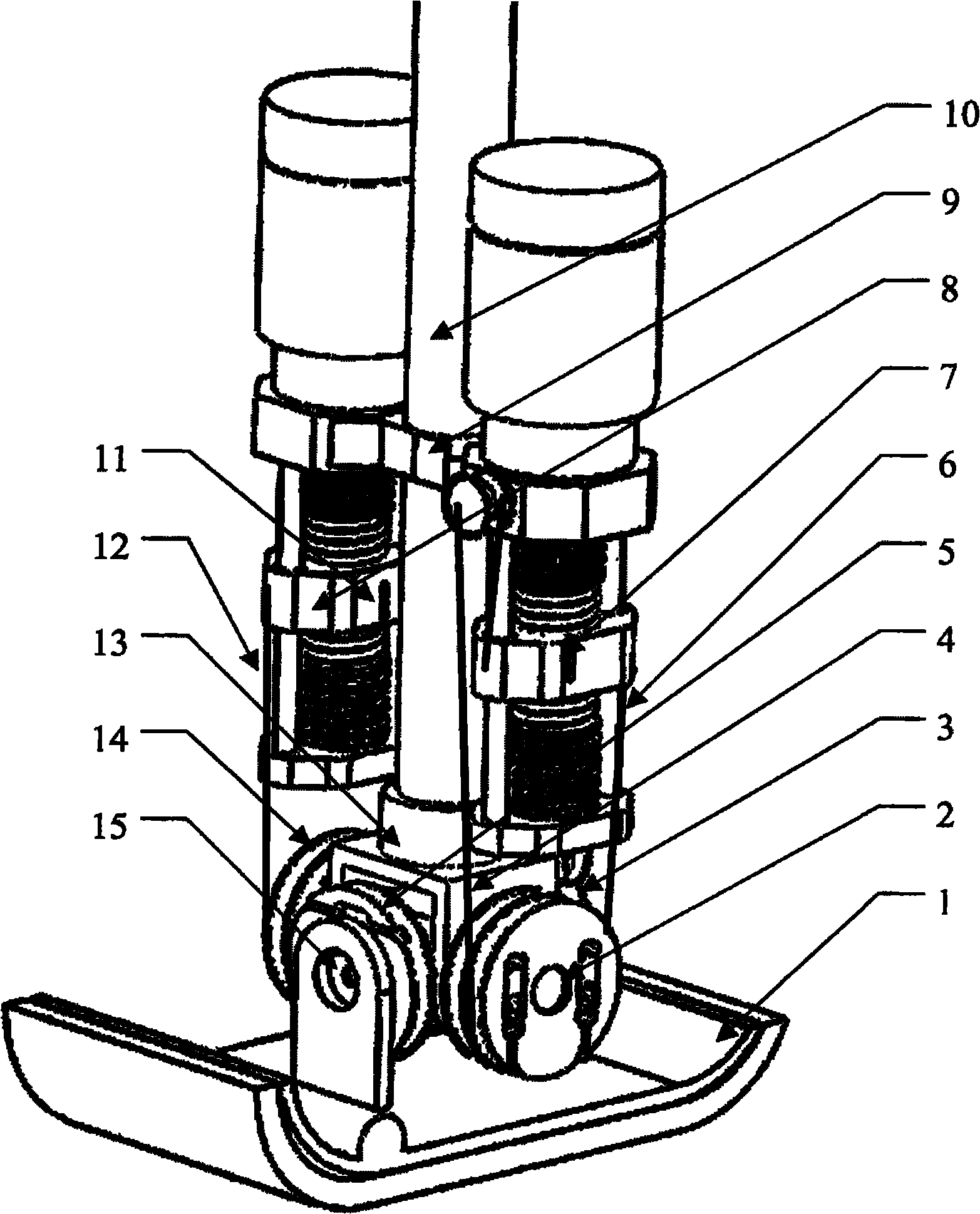
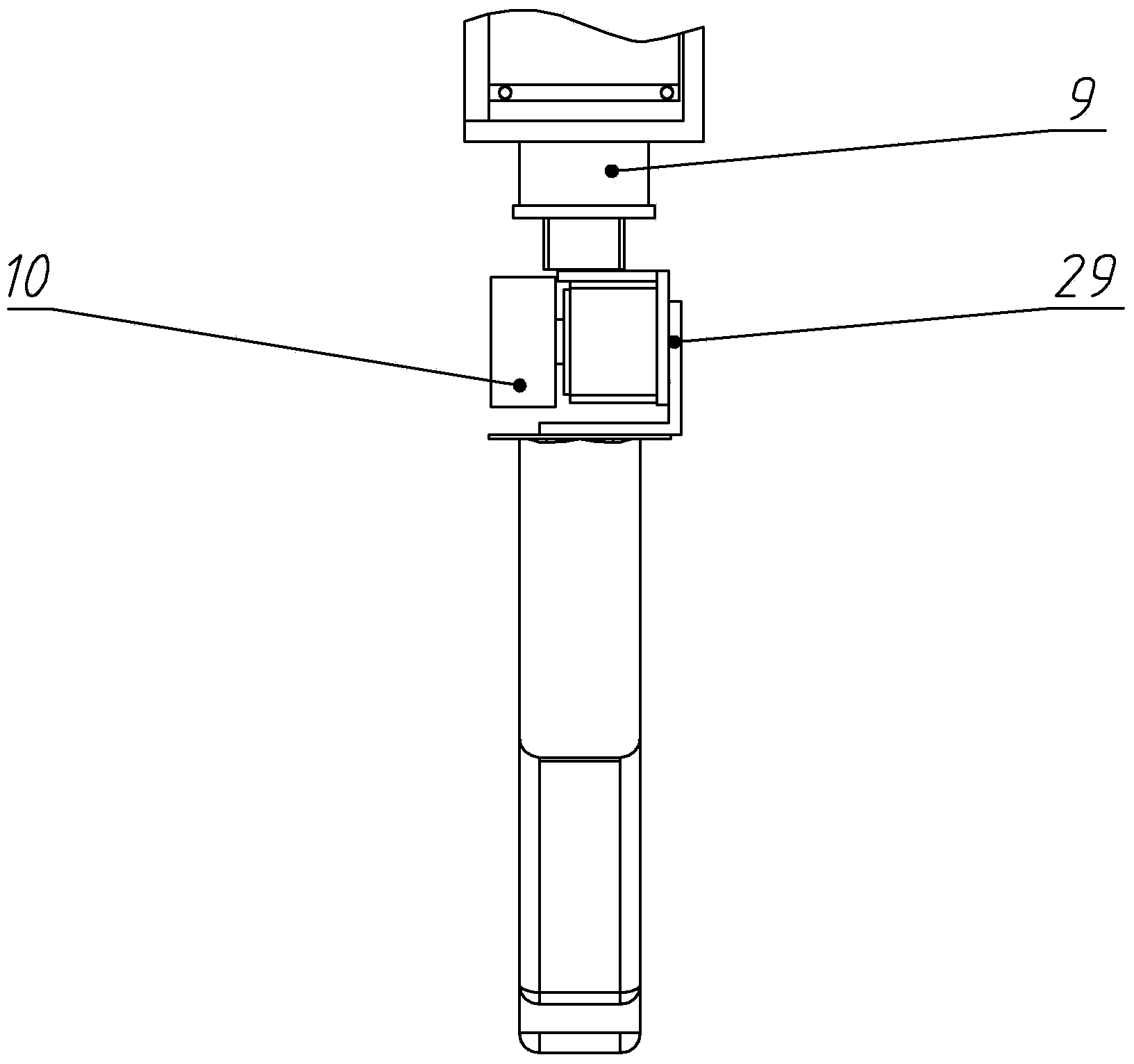
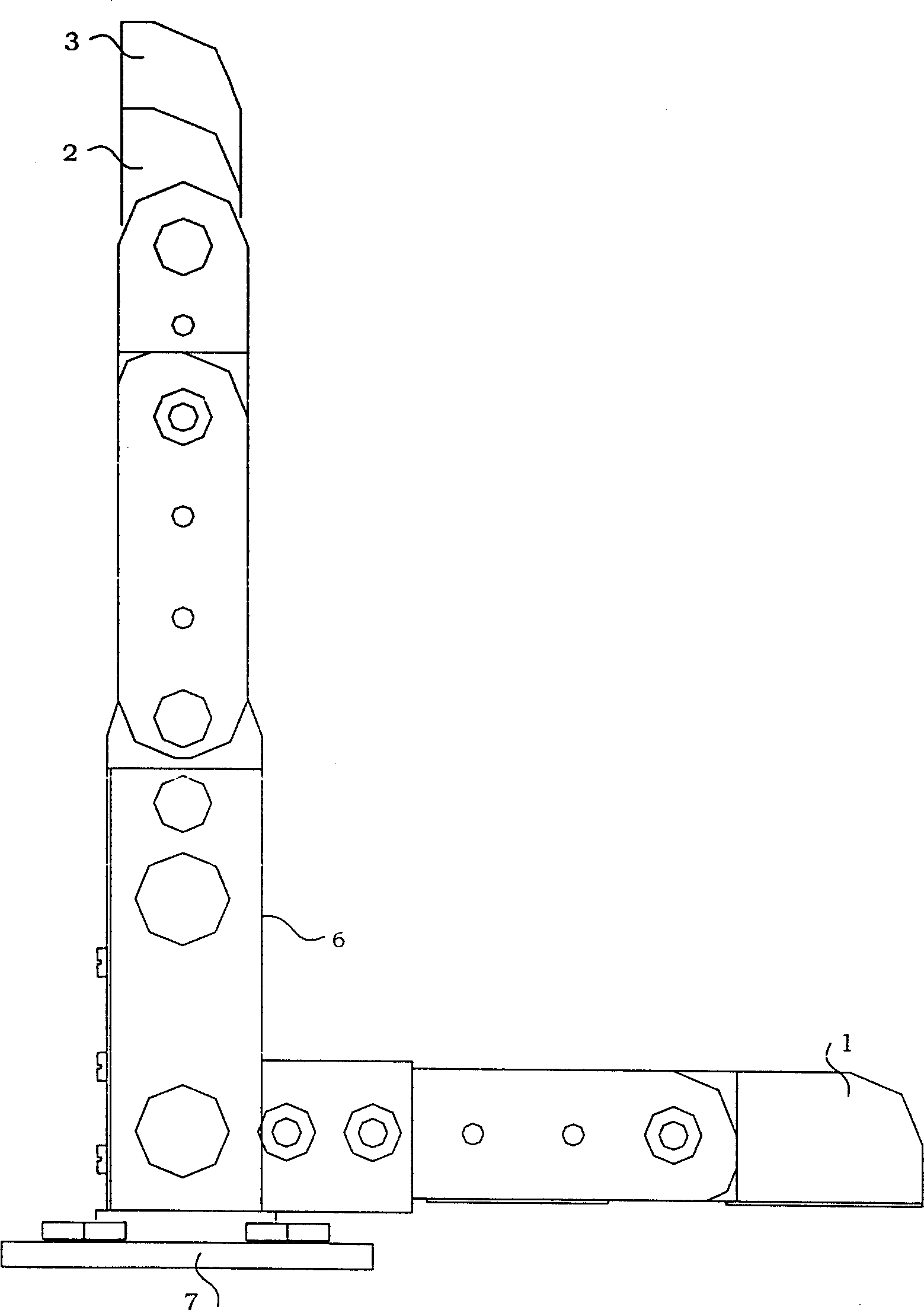
Belt wheel under-driven robot finger device
The invention provides a wheel driving robot finger device, belonging to a robot technical field which comprises a base, a motor, a reducer, a first gear, a second gear, a close joint shaft, a middle part finger, a far joint shaft and a terminal finger section as well as a driver, a transmission part, a driven wheel, a spring part. The middle part finger is sleeved on the close joint shaft. Two terminals of the spring part are respectively connected with the middle and the terminal finger sections. The device uses a pair of wheel mechanisms to sleeve a plurality of active middle part fingers with the decoupling effect of the spring part comprehensively to realize the special effect that the double joints drive the finger to bend so as to catch the objects. With simple structure, reliability, low cost, convenient installation and maintenance, small volume and light weight, the wheel driving robot finger device similar to human fingers is especially suitable for being used as a thumb of the hand of the humanoid robot or a part of other fingers that uses fewer drivers to drive more rotation joints to automatically adjust to catch the objects of different shapes and sizes.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
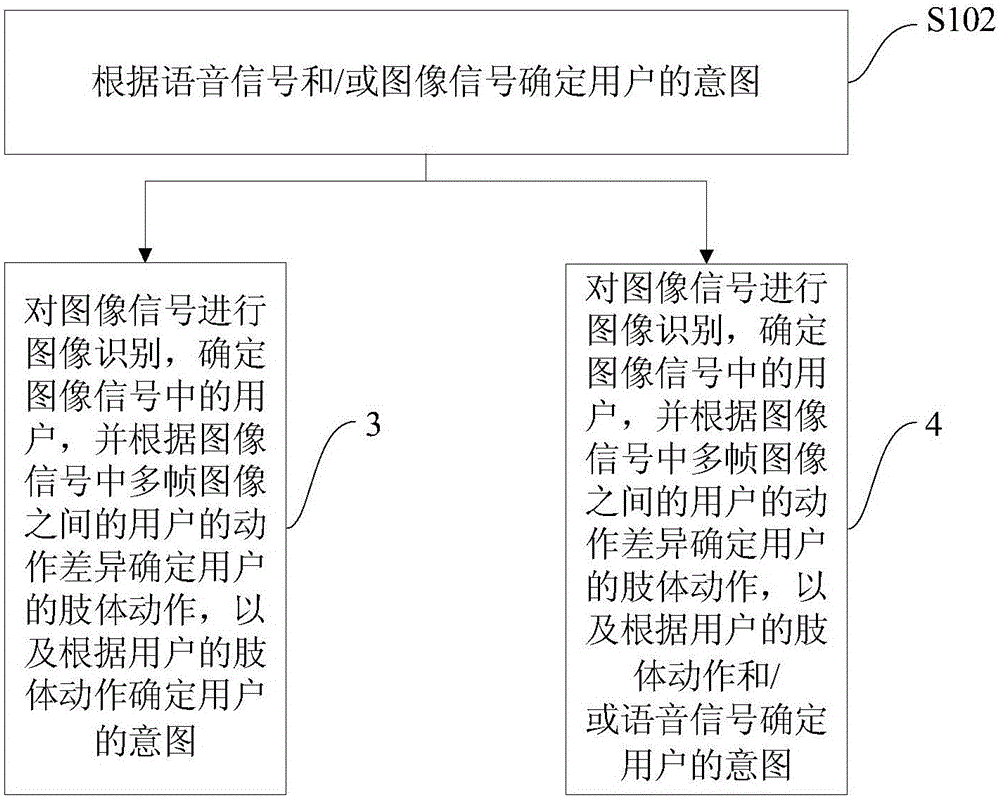
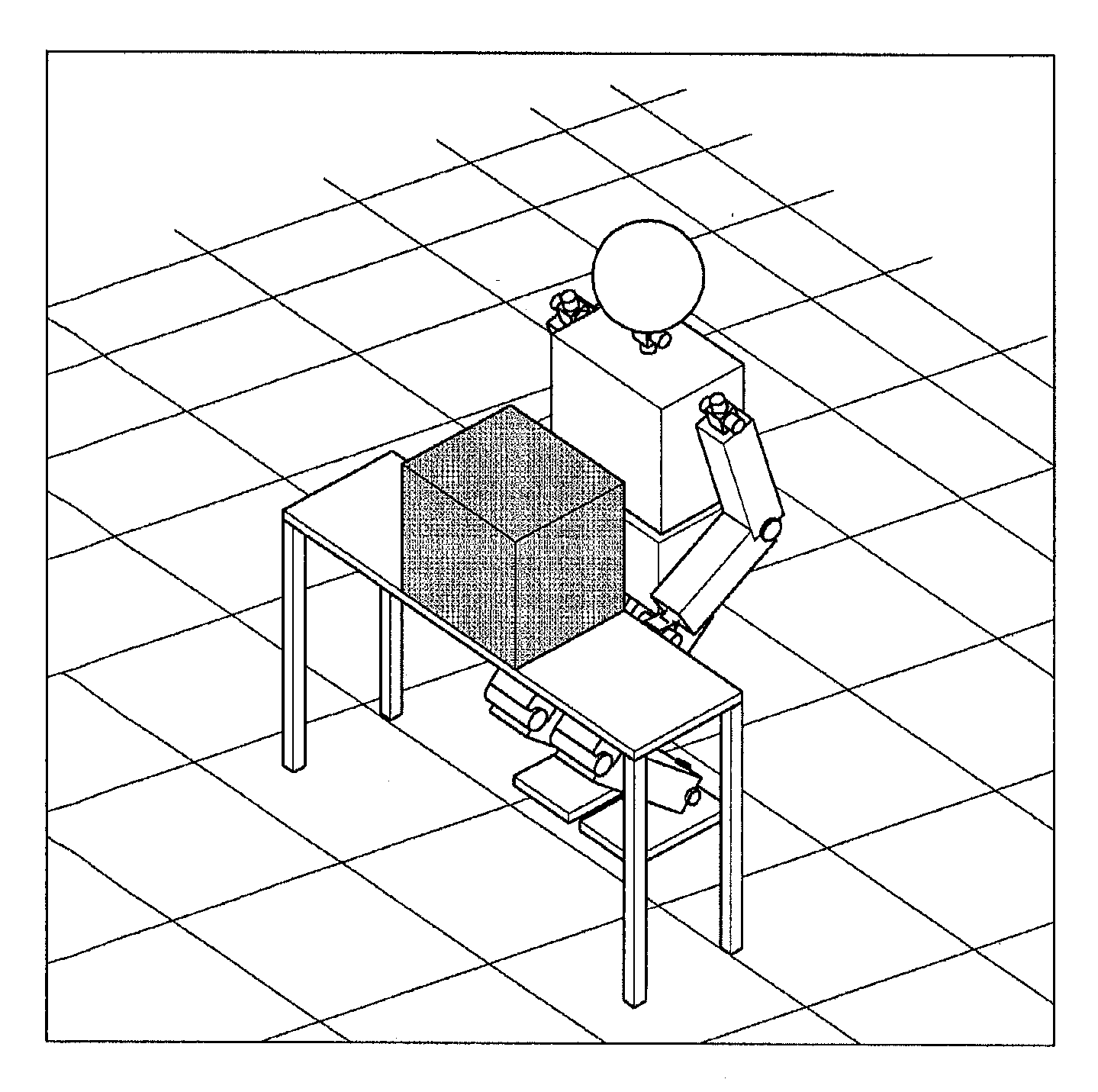
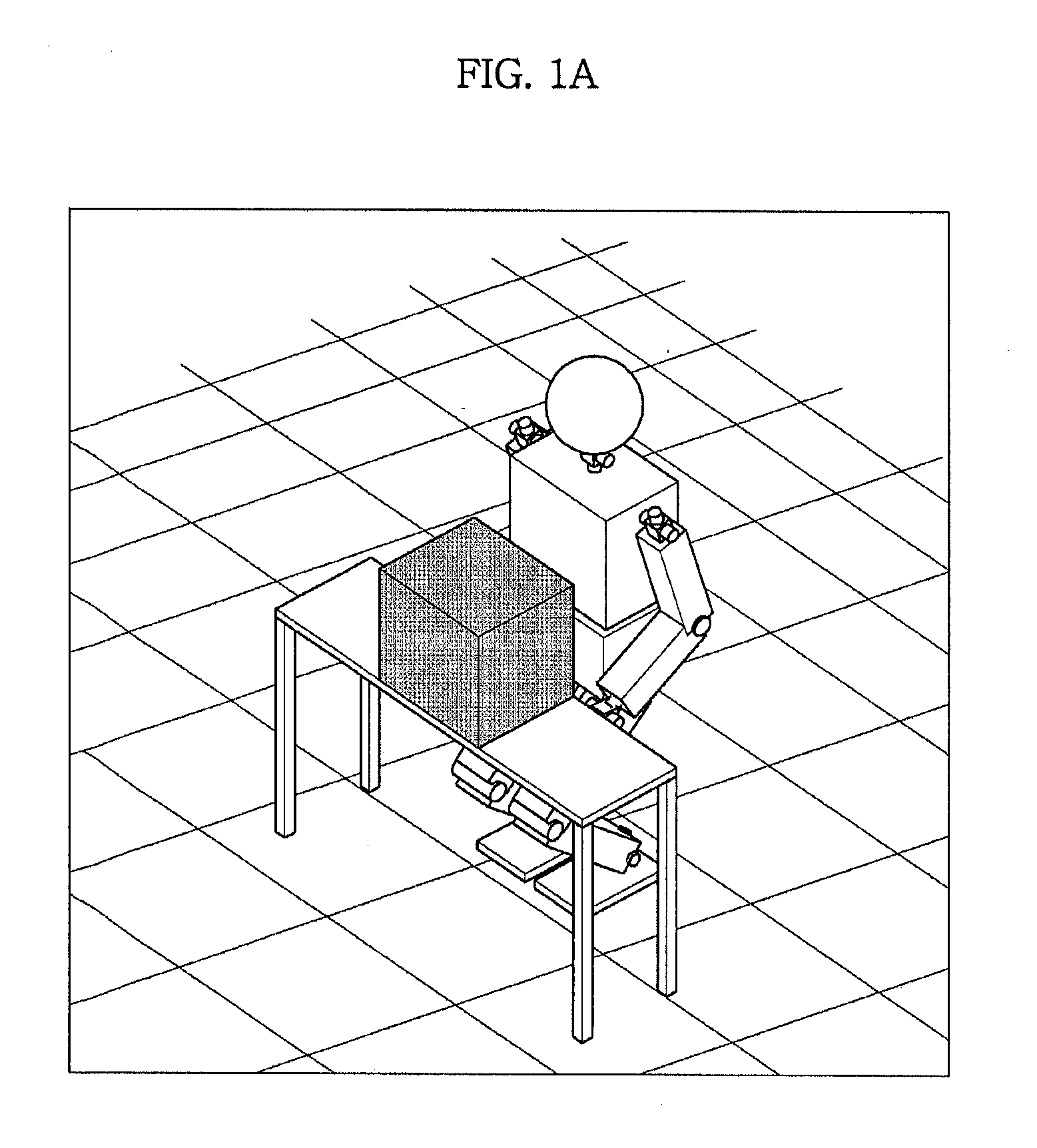
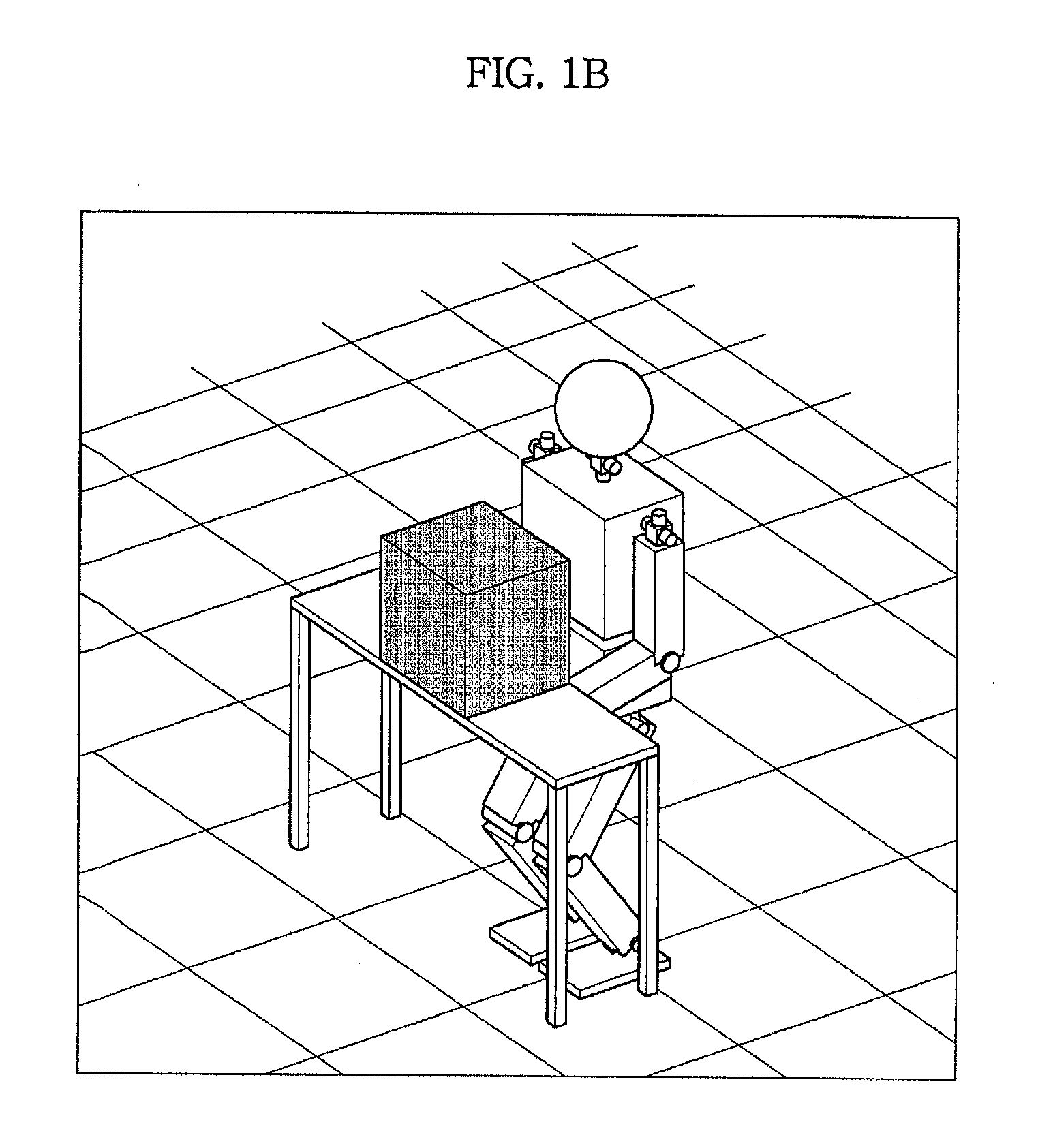
Humanoid robot control method based on artificial intelligence, system and the humanoid robot
InactiveCN105093986AEasy to operateFully embodies intelligenceProgramme control in sequence/logic controllersAlgorithmUser input
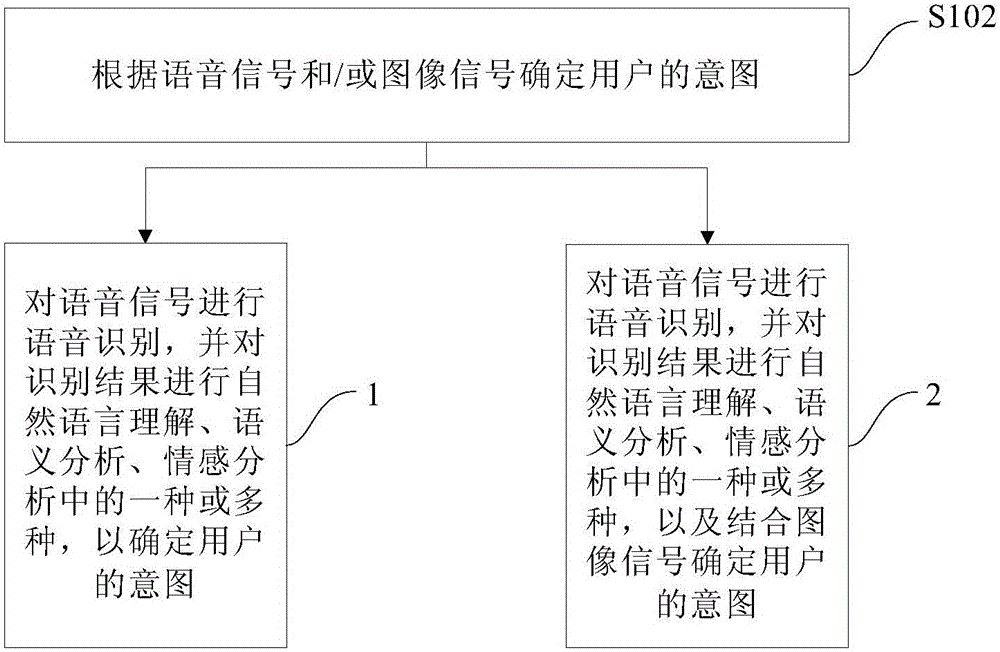
The invention provides a humanoid robot control method based on artificial intelligence, a system and the humanoid robot. The method comprises the following steps of receiving a voice signal input by a user and / or an image signal; according to the voice signal and / or the image signal, determining a user intention; processing the user intention and feeding back a processing result as a multi-modal output mode to the user, wherein the multi-modal output mode comprises one or more of a motion output mode of the humanoid robot, an image or video output mode and an audio output mode. By using the method, according to the collected voice signal and / or image signal of the user, after artificial intelligence analysis, the humanoid robot is autonomously controlled to interact with the user as several modes so that an artificial intelligence result can be visually and effectively displayed and an affine and effective effect is achieved in propaganda, demonstration and service fields.
Owner:BAIDU ONLINE NETWORK TECH (BEIJIBG) CO LTD
Apparatus and method for stabilizing humanoid robot
Disclosed is a humanoid robot apparatus, method and computer-readable medium thereof related to lifting and holding a heavy object having a weight unknown to the robot, by measuring an external force acting on the robot. Linear momentum and rotational momentum are compensated for stepwise according to the degree of stability of the robot which is determined based on the measured external force. Accordingly, the robot stably lifts and holds the object without losing its balance.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for generating a motion of a human type link system
InactiveUS7136722B2Easy to understandSimple interfaceProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlInverse dynamicsClassical mechanics
A human-type link system, such as a humanoid robot having a dynamically feasible motion of the link system that is generated when a reference joint acceleration that is only calculated from a kinematical constraint condition is determined not feasible by an evaluation of external force computed based on an inverse dynamics calculation, or is generated by calculating from a dynamic constraint condition and a kinematical constraint condition simultaneously, the dynamic constraint condition is formulated by using an actuation space inverse inertial matrix that represents the relation of force acting on the link system and the acceleration of the link system caused by the force.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Artificial vision system and method for knowledge-based selective visual analysis
InactiveUS20100223216A1Adapt processing resourceImprove representationDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionHumanoid robotVisual perception
Generally the background of the present invention is the field of artificial vision systems, i.e. systems having a visual sensing means (e.g. a video camera) and a following processing stage implemented using a computing unit. The processing stage outputs a representation of the visually analysed scene, which output can then be fed to control different actors, such as e.g. parts of a vehicle (automobile, plane, . . . ) or a robot, preferably an autonomous robot such as e.g. a humanoid robot.
Owner:HONDA RES INST EUROPE
Variable-rigidity flexible joint design of humanoid robot
The invention discloses a variable-rigidity flexible joint of a humanoid robot, which mainly comprises a variable flexible joint driver and a 2D differential drive joint mechanism, wherein, the variable flexible joint driver mainly comprises a micro-drive unit, a motor support and an elastic unit; and the 2D differential drive joint mainly comprises flexible cable input wheels, an output wheel and a flexible cable. The variable-rigidity flexible joint is characterized in that the variable-rigidity flexible joint driver introduces a special elastic element which can realize variable rigidity to adapt to the need of the joint rigidity in different walking stages and store / release energy and absorb shock; the variable flexible joint driver is connected with the 2-DOF differential drive joint mechanism through the flexible cable and has no redundant drive; and the variable-rigidity flexible joint adopts the 2-DOF differential mechanism and flexible cable transmission, thus having simple structure, small friction, no hysteresis error and reduced joint size of the robot compared with a gear design, and realizing drive torque redistribution according to the angle of energy consumption distribution of human.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Humanoid Robot that can Dynamically Walk with Limited Available Footholds in the Presence of Disturbances
ActiveUS20130184861A1Robust and simple balancingRobust and simple and walking mechanismSpecial data processing applicationsPosition/course control in two dimensionsHumanoid robot naoControl system
A control system for a bipedal humanoid robot that utilizes certain fundamental characteristics of bipedal motion to provide a robust and relatively simple balancing and walking mechanism. The system primarily utilizes the concept of “capturability,” which is defined as the ability of the robot to come to a stop without falling by taking N or fewer steps. This ability is considered crucial to legged locomotion and is a useful, yet not overly restrictive criterion for stability. In the preferred embodiment, the bipedal robot is maintained in a 1-step capturable state. This means that future step-locating and driving decisions are made so that the robot may always be brought to a balanced halt with the taking of one step. Other embodiments maintain the bipedal robot in an N-step capturable state, in which the robot may always brought to a balanced halt by taking N or fewer steps.
Owner:FLORIDA INST FOR HUMAN & MACHINE COGNITION
Humanoid robot and walking control method thereof
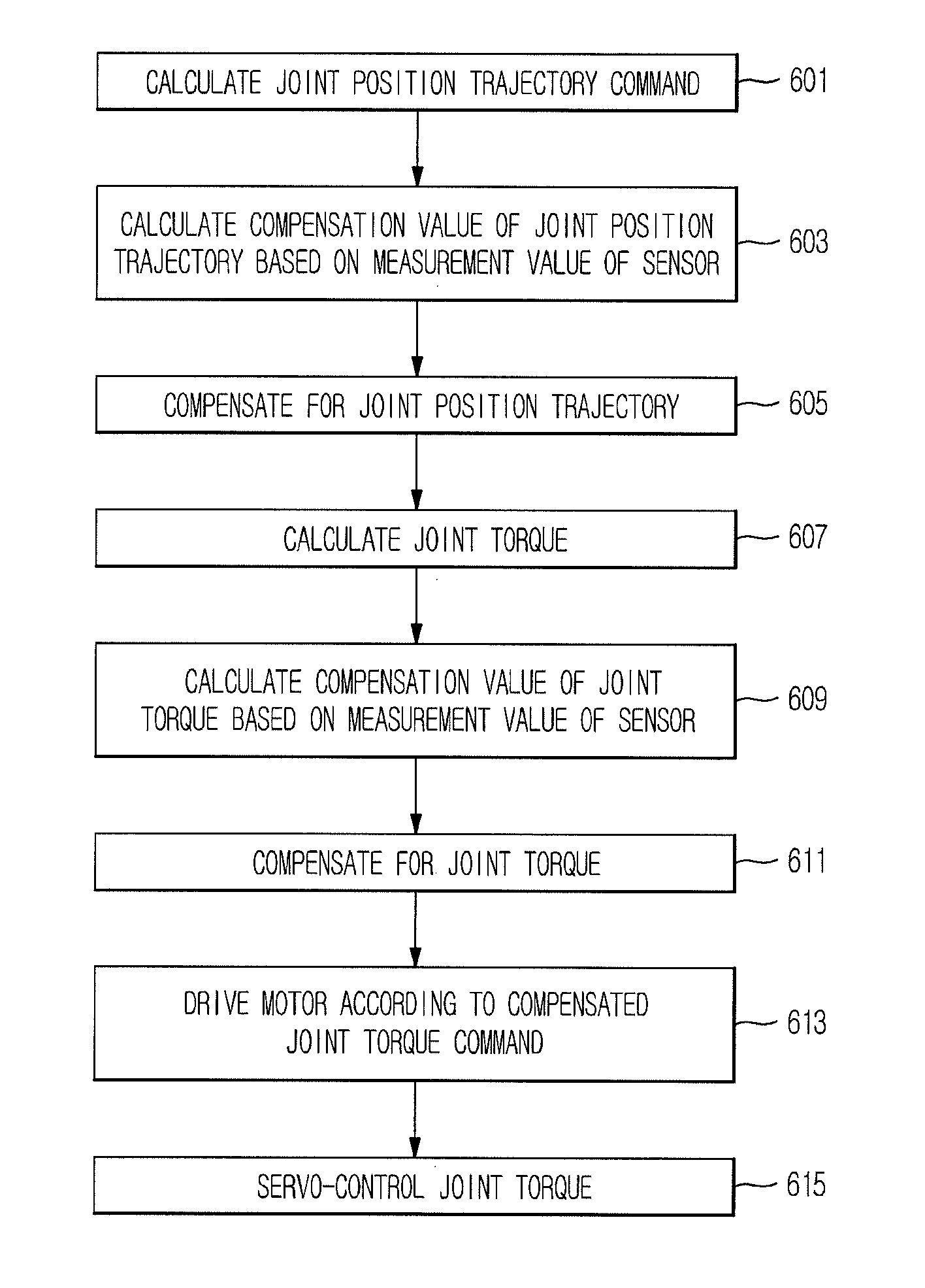
A humanoid robot that achieves stable walking based on servo control of a joint torque and a walking control method thereof. The humanoid robot calculates a joint position trajectory compensation value and a joint torque compensation value using a measurement value of a sensor, compensates for a joint position trajectory and a joint torque using the calculated compensation value, and drives a motor mounted to each joint according to the compensated joint torque.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Novel biped humanoid robot system based on pneumatic artificial muscles
ActiveCN104401419AMeet the needs of multidisciplinary scientific research teachingUnique shapeVehiclesSystems designKnee Joint
The invention provides a novel biped humanoid robot system based on pneumatic artificial muscles, belongs to the technical field of robots, and in particular relates to a biped robot having powerful athletic ability and flexible humanoid characteristics. The biped humanoid robot system comprises a mechanical body and an electrical control system; the biped humanoid robot system is characterized in that the mechanical body is mainly composed of seven parts, namely a waist, a hip joint, thighs, knee joints, shanks, feet and the like, and has 13 degrees of freedom in total; in the 13 degrees of freedom, 3 degrees of freedom of the waist are realized by virtue of the cooperation of four pneumatic muscles and the waist spine, and the single degree of freedom of each of the hip joint, the knee joints and the ankle joints is realized by use of one pneumatic muscle and one spring which are pulled to each other to produce opposed rotating force. According to the design of the novel biped humanoid robot system, a control platform is provided; the system relates to the fields of control science and intelligent control in addition to robotics, and is capable of meeting the requirements of scientific research and teaching of a plurality of disciplines.
Owner:廊坊市奥联科技有限公司
Six-degree-of-freedom humanoid robot arm
The invention discloses a six-degree-of-freedom humanoid robot arm, and relates to a robot arm. The invention aims to solve the problems that the existing robot arm is cumbersome in joint structure, heavy in self weight, low in load bearing ratio and complicated to control. A shoulder rotating joint, a shoulder joint, an upper arm, an elbow rotating joint, a elbow swing joint, a fore arm, a wrist rotating joint, a wrist swing and a hand are sequentially arranged from top to bottom, wherein an arm swing motor is connected with a worm by virtue of a conveyor belt, an arm rotating motor is connected with a shoulder swing support by virtue of a conveyor belt, an upper arm shell is arranged between a shoulder joint and an elbow joint, an elbow rotating drive motor and a speed reducer are sequentially arranged in the upper arm shell from top to bottom, an elbow swing joint motor is arranged in an elbow joint shell and is connected with an elbow joint conveyor belt, an elbow joint speed reducer is arranged in the elbow joint shell, a hand connecting support is arranged between the fore arm and the hand, a wrist joint swing motor is arranged on one side of the hand connecting support, and a wrist joint rotating motor is arranged at the upper end of the hand connecting support. The six-degree-of-freedom humanoid robot arm is applied to a humanoid robot.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
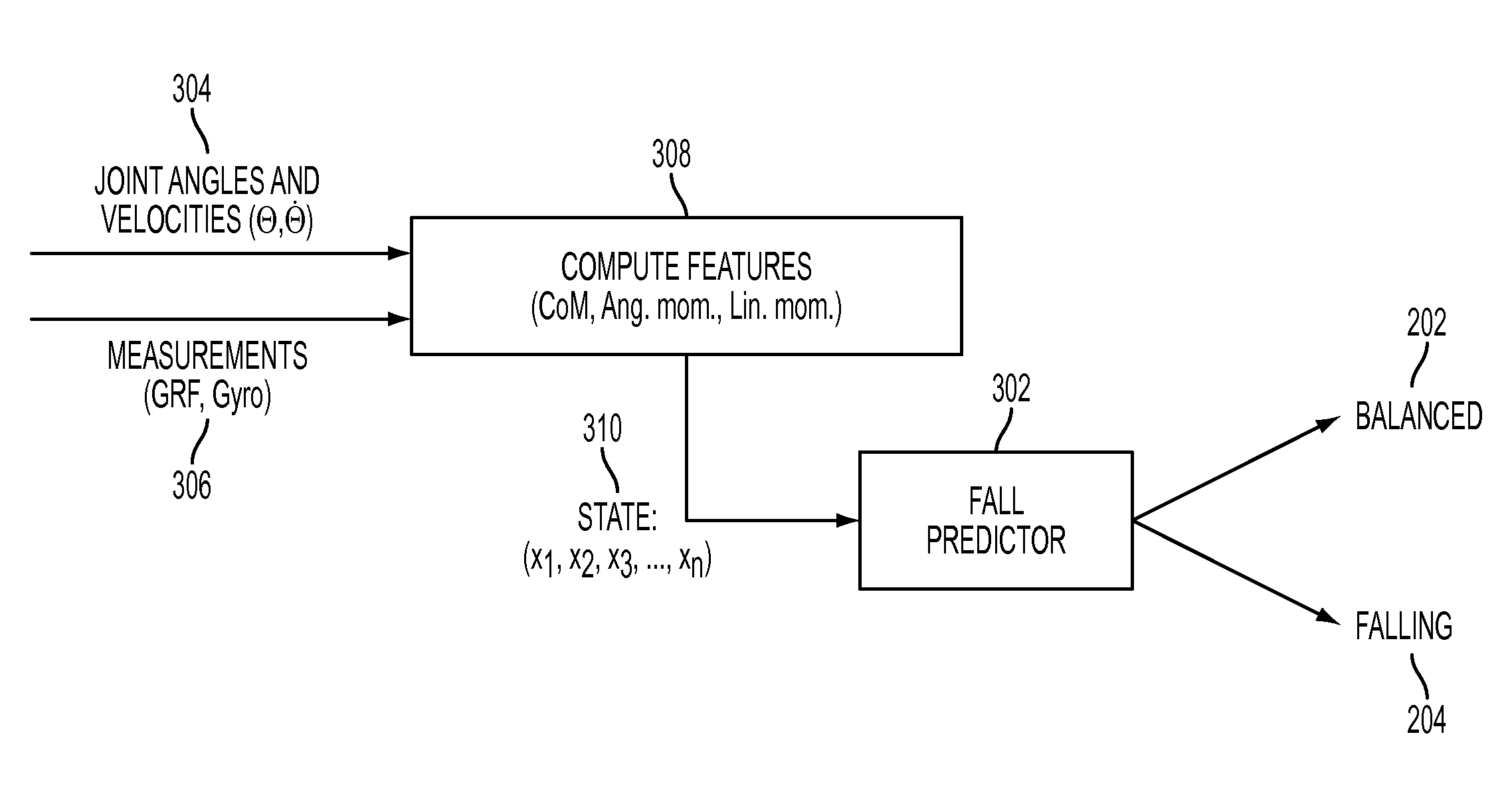
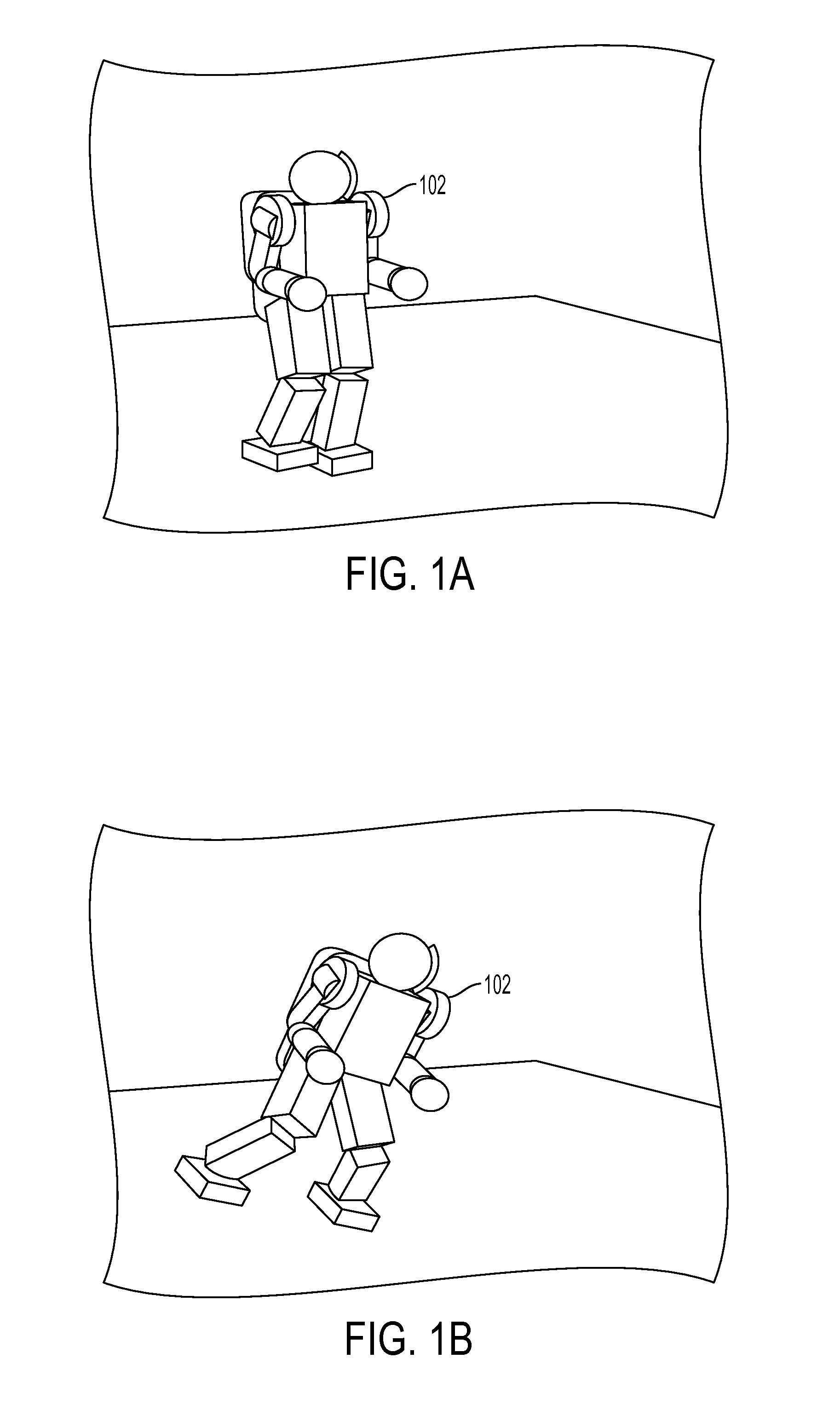
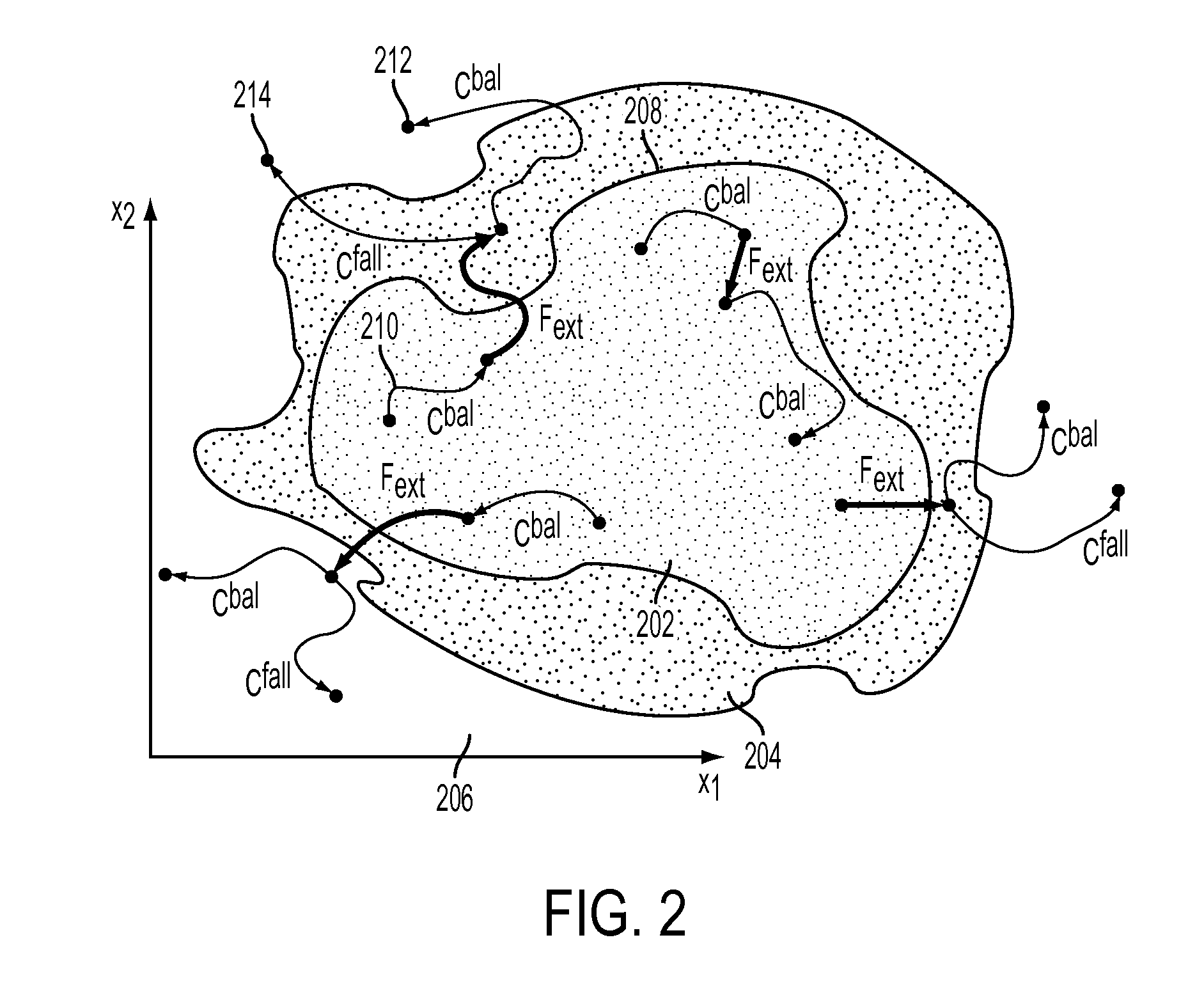
Machine Learning Approach for Predicting Humanoid Robot Fall
ActiveUS20100292838A1Reduce harmProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlAnalog robotSimulation
A system and method is disclosed for predicting a fall of a robot having at least two legs. A learned representation, such as a decision list, generated by a supervised learning algorithm is received. This learned representation may have been generated based on trajectories of a simulated robot when various forces are applied to the simulated robot. The learned representation takes as inputs a plurality of features of the robot and outputs a classification indicating whether the current state of the robot is balanced or falling. A plurality of features of the current state of the robot, such as the height of the center of mass of the robot, are determined based on current values of a joint angle or joint velocity of the robot. The current state of the robot is classified as being either balanced or falling by evaluating the learned representation with the plurality of features of the current state of the robot.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Motion trajectory planning method of mechanical arm of humanoid robot for preventing collision
ActiveCN102646148ARealize collision avoidanceIncrease success rateSpecial data processing applicationsTrajectory planningJoint spaces
The invention provides a motion trajectory planning method of mechanical arms of a humanoid robot for preventing collision. In the prior art, the collision problem is not solved fundamentally. The method adopts a joint space-based interpolation method to solve the collision problem between the mechanical arms and a table caused by motion trajectory generation of the mechanical arms, and mainly aims at operation of humanoid arms of the humanoid robot oriented to tabletops or objects similar to tabletops. The mechanical arm freedom degree includes three freedom degrees of the shoulder, two freedom degrees of the elbow and two freedom degrees of the wrist. The concrete implementation method comprises under the premise of ensuring completion of target operation at a fixed moment, properly bending the elbow at the collision occurring moment during the motion of the mechanical arms to prevent collision. With such scheme, the mechanical arms can move without collision while realizing high flexibility and large operation space.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
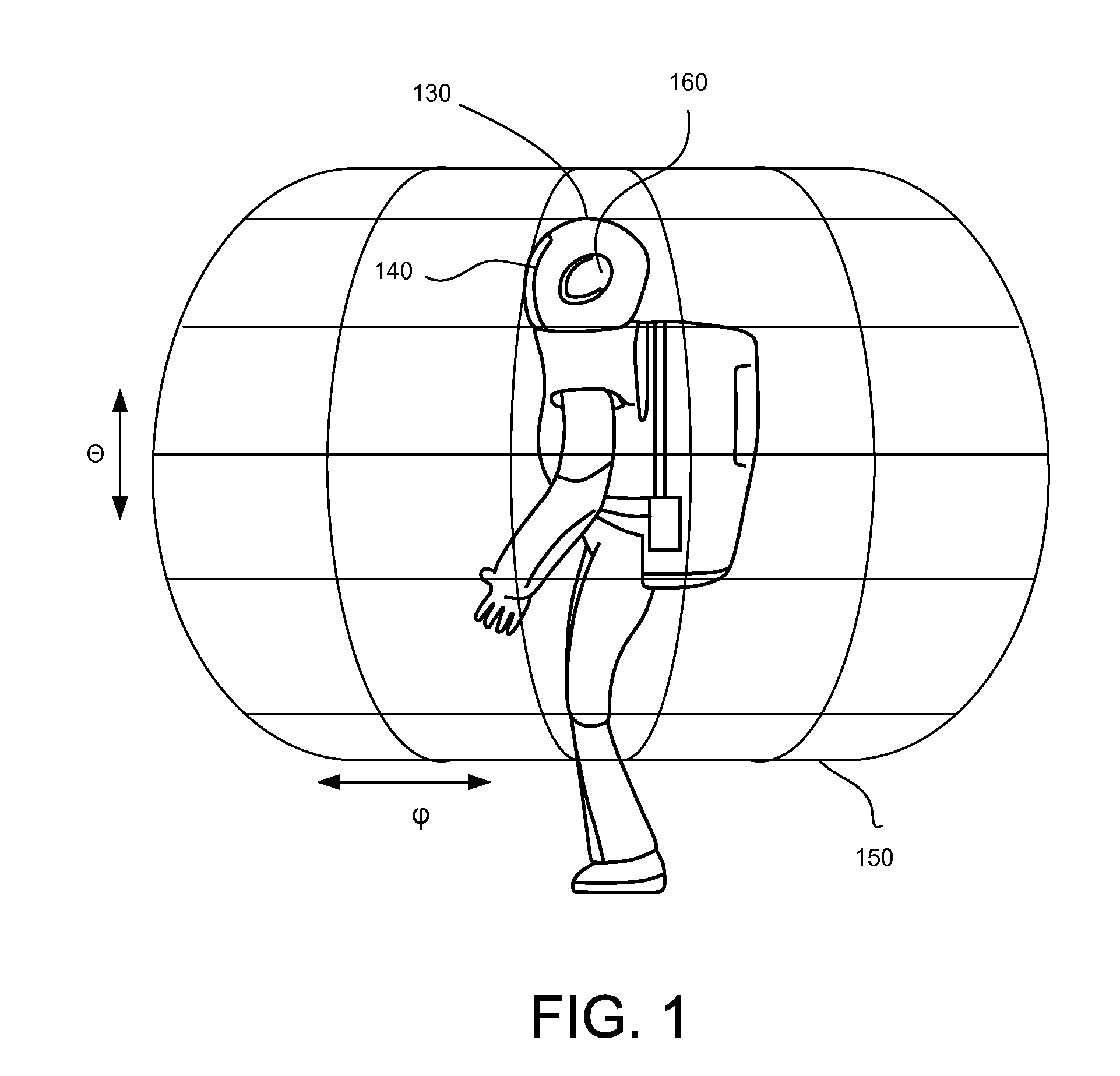
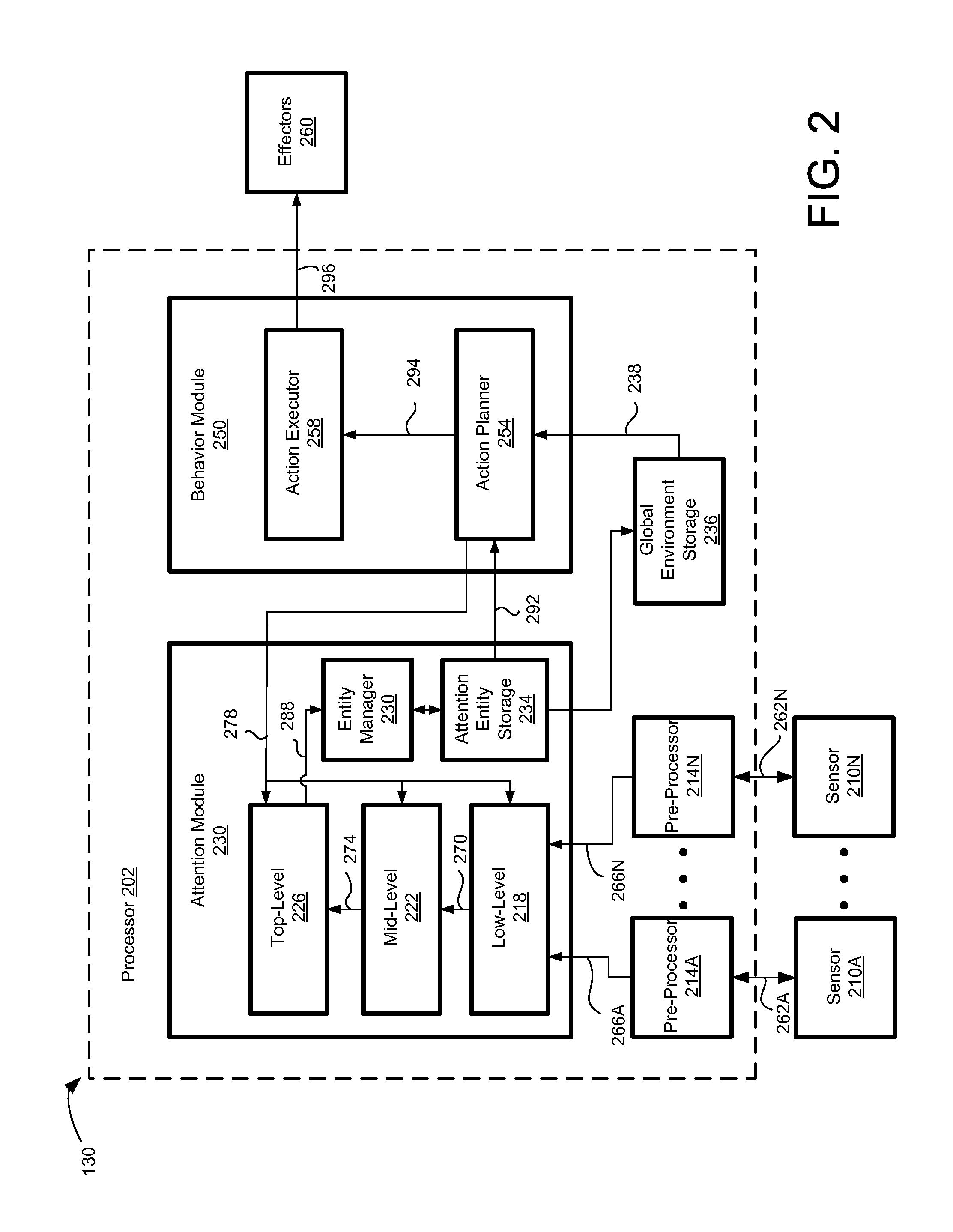
Panoramic Attention For Humanoid Robots
ActiveUS20110004341A1Reduce signalingProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlPanoramaComputer graphics (images)
A robot using less storage and computational resources to embody panoramic attention. The robot includes a panoramic attention module with multiple levels that are hierarchically structured to process different levels of information. The top-level of the panoramic attention module receives information about entities detected from the environment of the robot and maps the entities to a panoramic map maintained by the robot. By mapping and storing high-level entity information instead of low-level sensory information in the panoramic map, the amount of storage and computation resources for panoramic attention can be reduced significantly. Further, the mapping and storing of high-level entity information in the panoramic map also facilitates consistent and logical processing of different conceptual levels of information.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
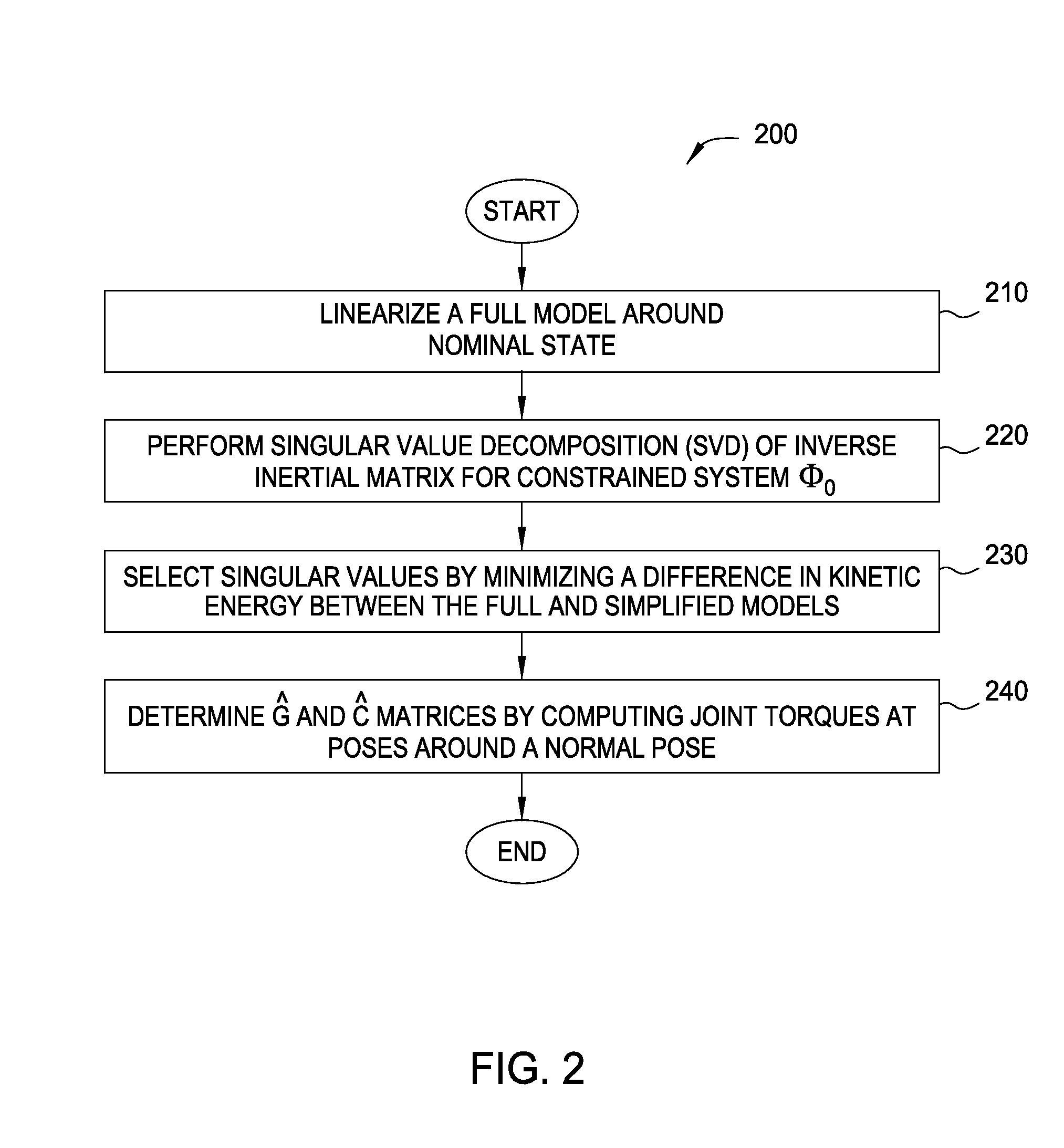
Systemic derivation of simplified dynamics for humanoid robots
The disclosure provides an approach for determining simplified models of humanoid robots. A simplification application linearizes a robot model around a nominal state and performs a singular value decomposition of an inertial term of the model, selecting singular values and corresponding singular vectors to be kept in an inertial term of a simplified model by matching a kinetic energy of the original model to a kinetic energy of the simplified model. Further, a gravitational forces term and a velocity-dependent forces term may be determined by computing active joint torques at sample poses around the nominal pose and solving for the gravitational forces term and the velocity-dependent forces term. A mapping from the simplified model to the original model may be determined using, e.g., numerical optimization.
Owner:DISNEY ETERPRISES
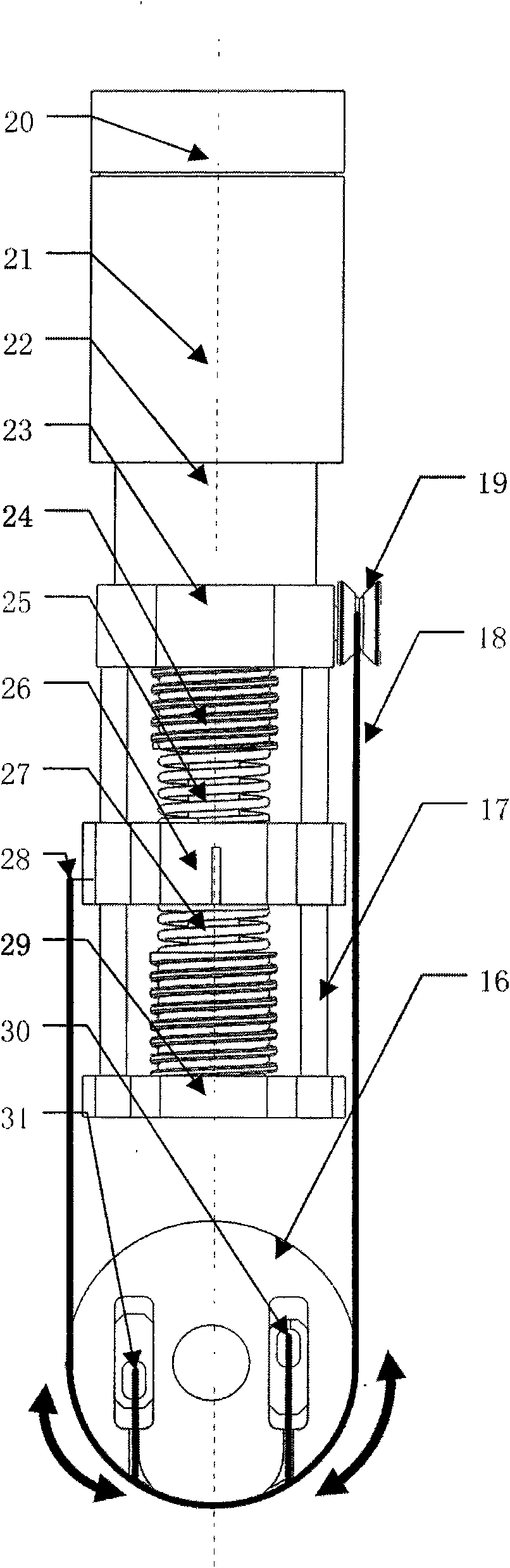
Bending self-locking pneumatic under-actuated robot finger device
InactiveCN103659825AAchieve bendingInhibit sheddingGripping headsLocking mechanismElectric machinery
The invention relates to a bending self-locking pneumatic under-actuated robot finger device, and belongs to the technical field of humanoid robot hands. The device comprises a first finger section, a second finger section, an under-actuated joint, a motor, a transmission mechanism, a locking mechanism and a first spring piece. The transmission mechanism comprises a tendon rope and a winding reel. The locking mechanism comprises a ratchet wheel oscillating bar, a pawl, a rotating shaft and a second spring piece. The device achieves a self-adaptive under-actuated effect by adopting a pneumatic mode; one-way bending is achieved by adopting a ratchet wheel and the pawl, and an object is prevented from getting loose when an counteraction face is withdrawn or vibration interference occurs; stable grasping force applied to the object by the second finger section is generated through the deformation of the spring pieces, and thus form sealing and force sealing grasping is achieved; the restraint to the ratchet wheel by the pawl is relieved through the motor, and thus the object is released; the device is simple in structure, small in size, low in weight, low in manufacturing and maintaining cost and similar to the fingers of the human hands.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
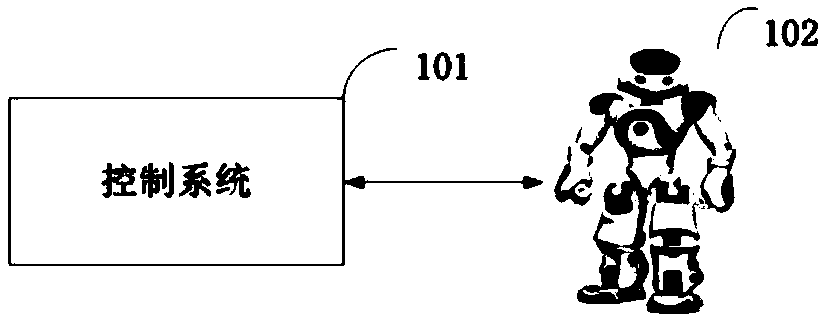
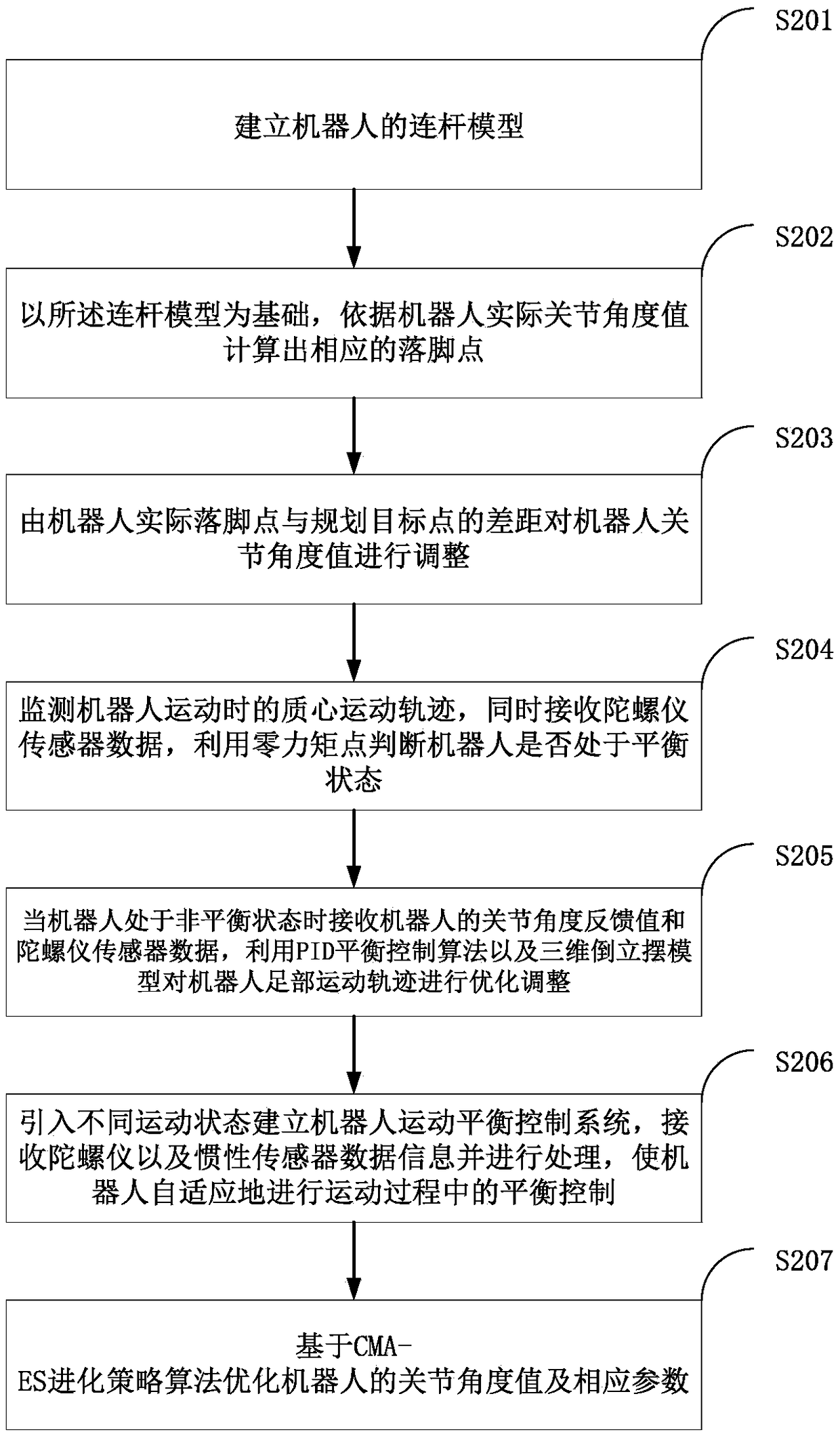
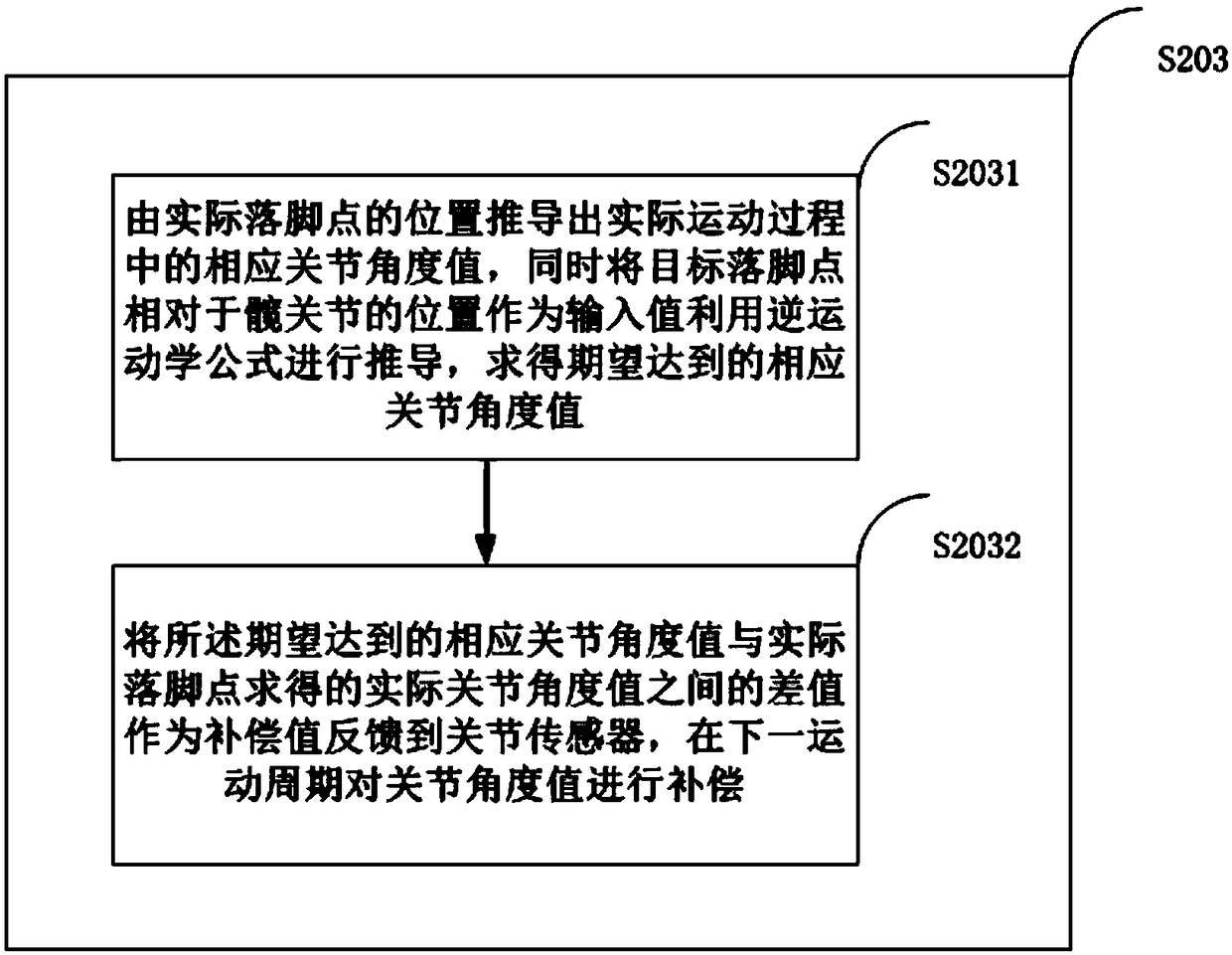
Method, device and system for self-adaption balance control of humanoid robot in complex terrain
The invention relates to the field of robot control, in particular to a method, device and system for self-adaption balance control of a humanoid robot in a complex terrain. The method comprises the following steps of establishing a connecting rod model of a robot; calculating a corresponding foothold; adjusting the joint angle value of the robot; monitoring the mass center curve of the robot, receiving gyroscope sensor data, and judging whether the robot is in a balanced state; receiving a joint angle feedback value and the gyroscope sensor data when the robot is in an unbalanced state, and optimizing and adjusting the foot movement curve of the robot; enabling the robot to be self-adaptively subjected to balance control in the movement process; optimizing the joint angle value and relevant parameters of the robot. The robot can be applied to movement balance control of biped and quadruped robots and the like, the application range is wide, the self-adaptive capacity of the robot to an application environment can be greatly enhanced, and the hardware loss can be effectively reduced in the actual application process.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Humanoid manipulator mechanism
InactiveCN1283429CImprove work flexibilityImprove adaptabilityGripping headsLittle fingerKinematic coupling
The invention discloses a mechanism of a humanoid robot hand, which is composed of a palm, five fingers and a mechanical interface. The five fingers are installed on the palm, and the root of the palm is provided with a mechanical interface. The connection between the mechanism and the robot arm. In the humanoid robotic hand mechanism of the present invention, the thumb and forefinger each have a degree of freedom and are respectively driven by a motor; the middle finger, ring finger and little finger share a degree of freedom and are driven by the same motor, and the transmission of the three fingers adopts the same modular design, The only difference lies in the length of the distal knuckles of the three fingers. The first two joints of the index, middle, ring, and little fingers are kinematically coupled individually. There is a motion decoupling device at the connection shaft between the proximal knuckles of each finger and the palm. When the proximal knuckles of the fingers are blocked from touching the object, the other knuckles can continue to move to complete the envelope grasping of the object.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
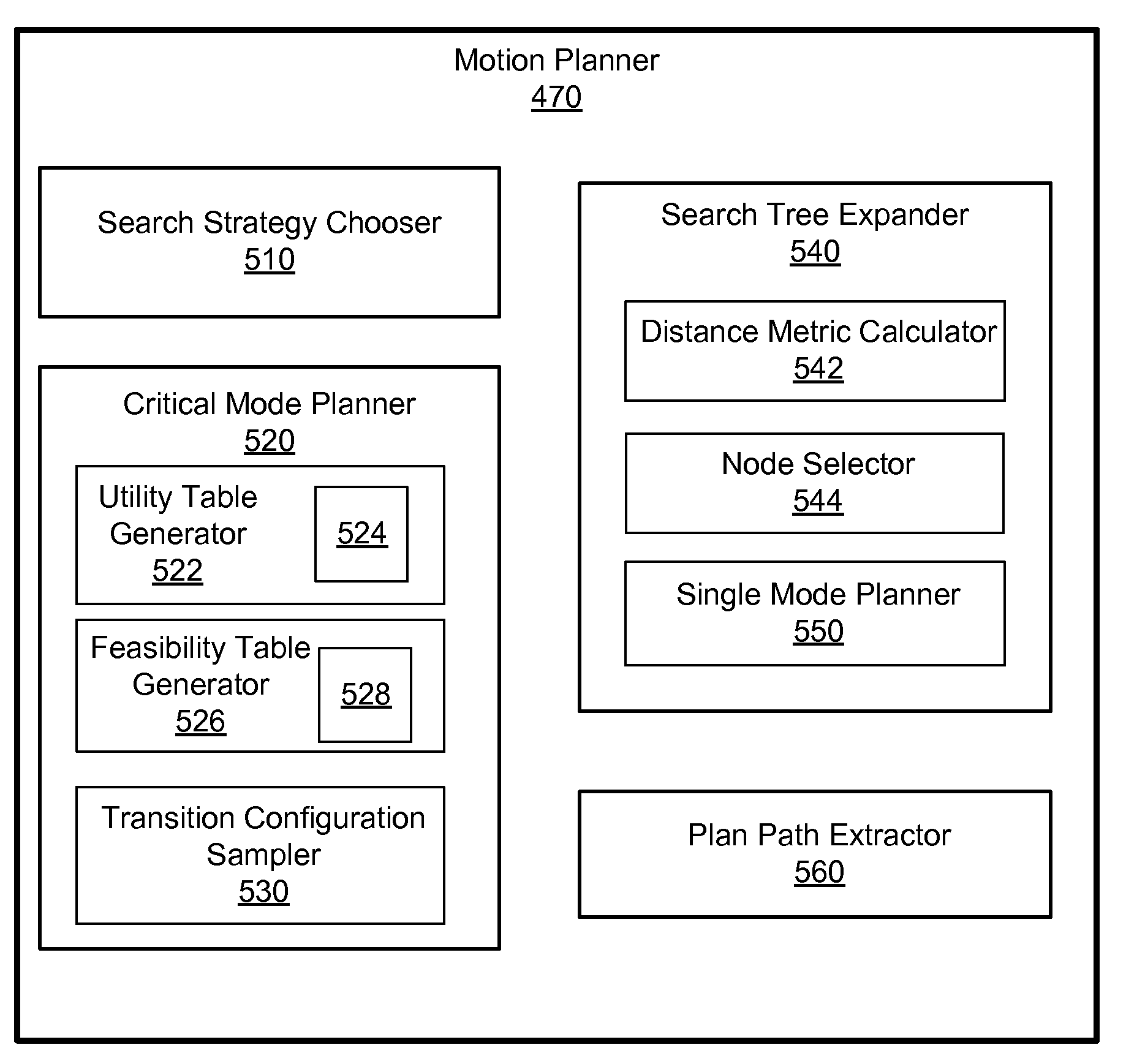
Multi-Modal Push Planner for Humanoid Robots
ActiveUS20080306628A1Programme-controlled manipulatorSpecial data processing applicationsHigh probabilityPlanning method
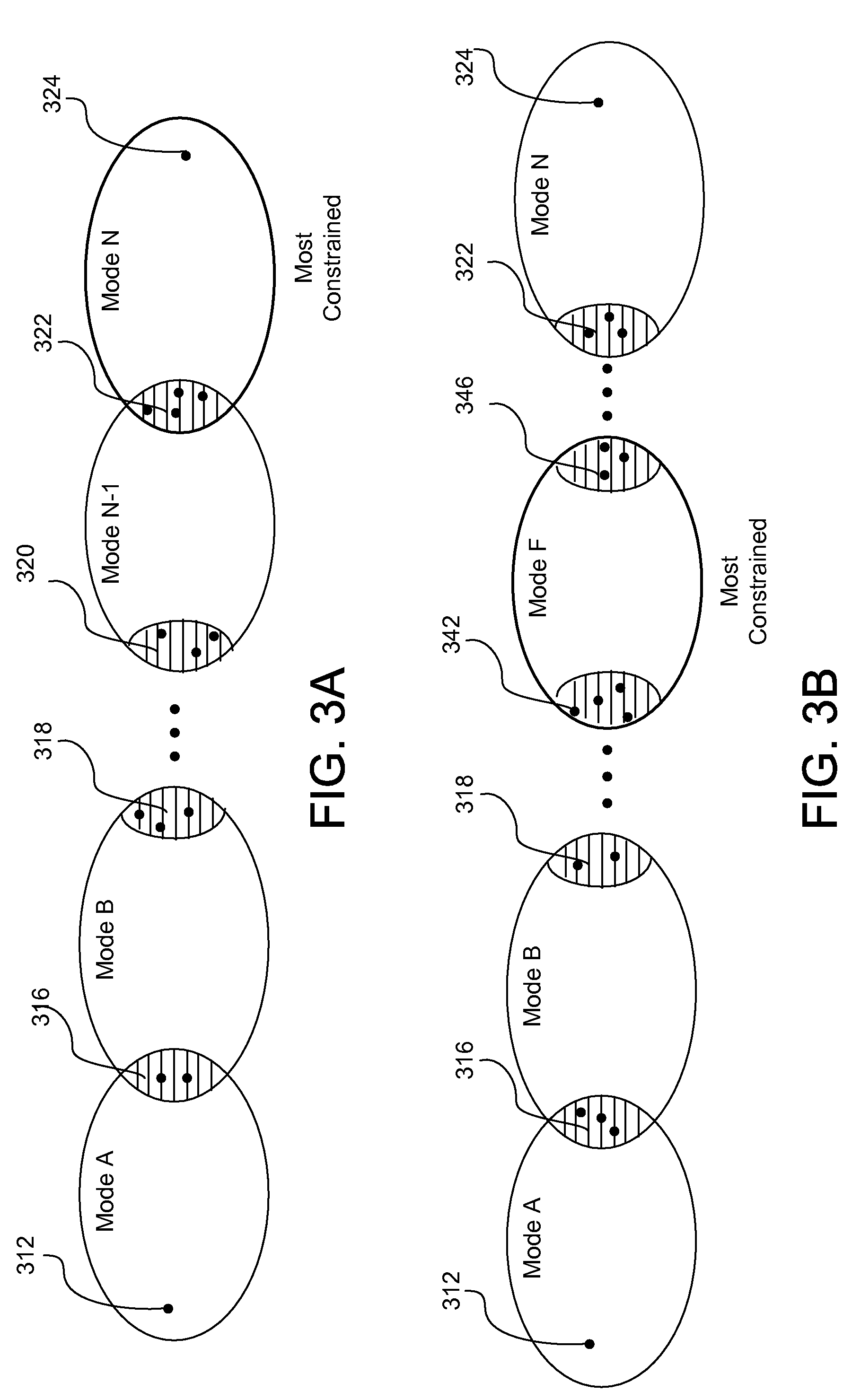
Multi-modal planning method and system that search a path for the most constrained mode first, and then expands the searches for path in a less constrained mode. By searching the path for the most constrained mode first, less resource are wasted on searching for paths that does not result in a feasible path in the most constrained mode. Multi-modal planning is performed by precomputing feasibility and utility of transition configurations of two adjacent modes. The feasibility is used to exclude non-feasible transition configurations in the most constrained mode from being sampled. The utility is used to bias sampling of the transition configuration so that transition configurations with higher utility are sampled with higher probability. Paths of configurations with higher utility and efficiency are obtained by biasing the sampling of the transition configurations.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Method for controlling the walk of humanoid robot
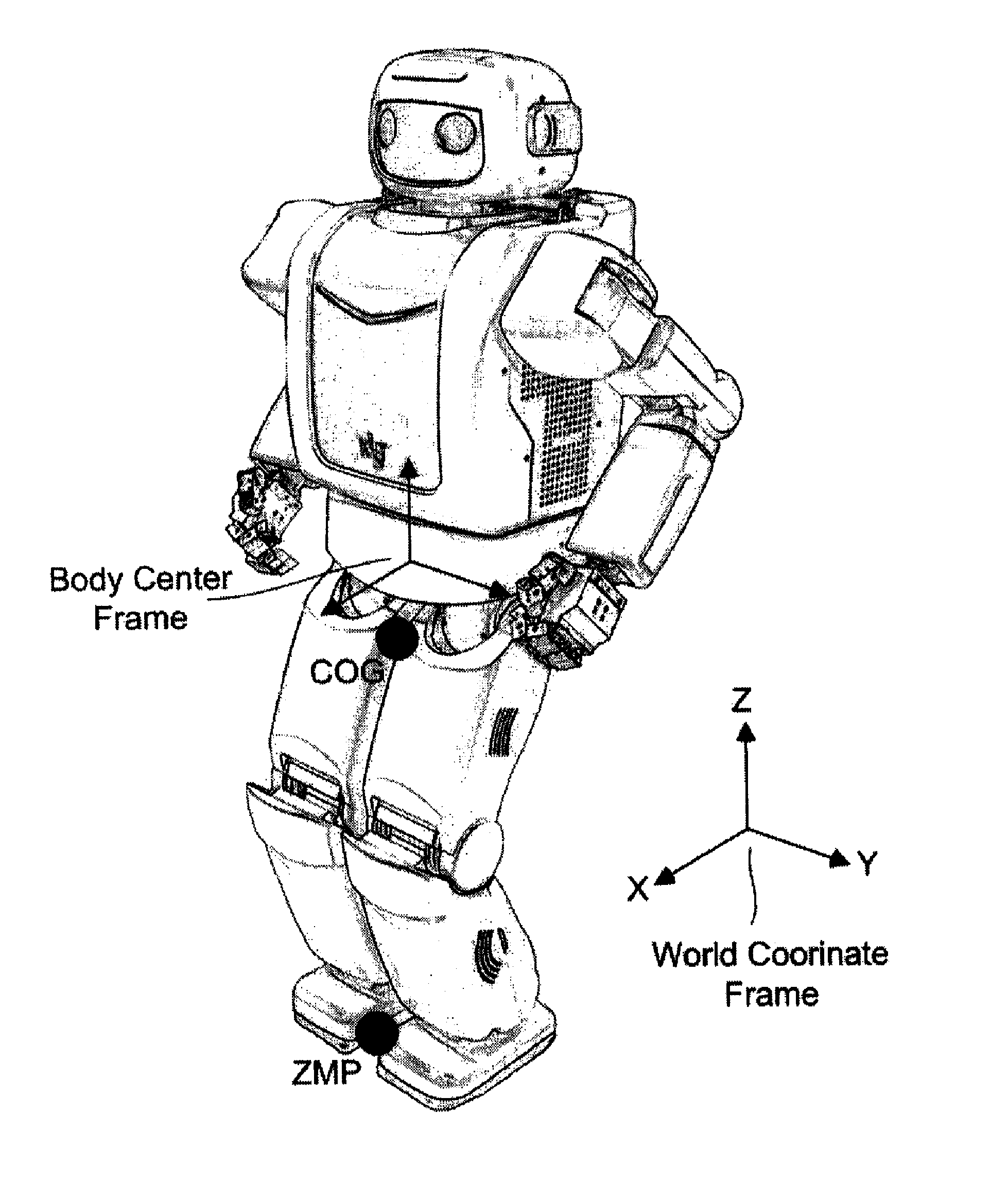
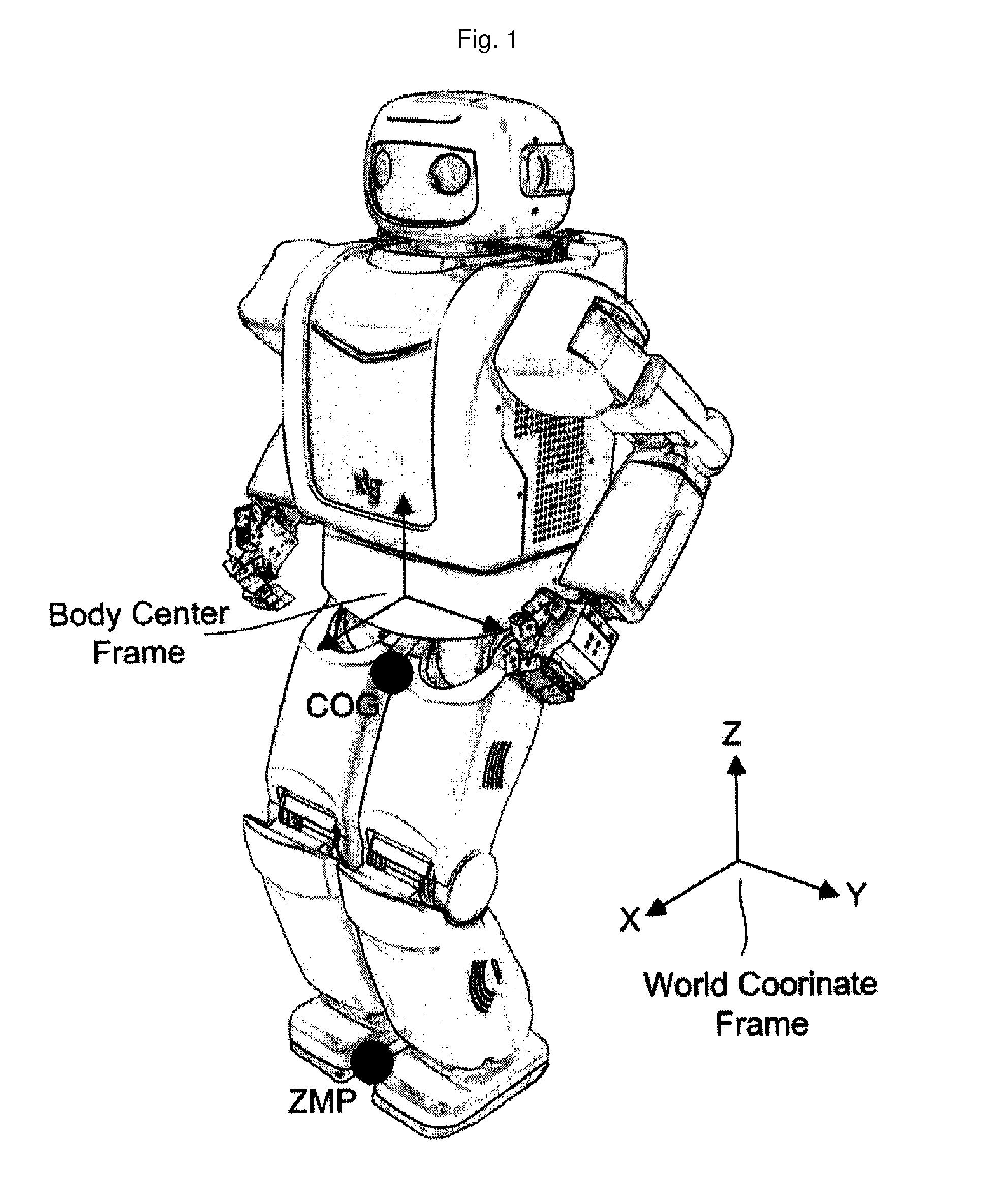
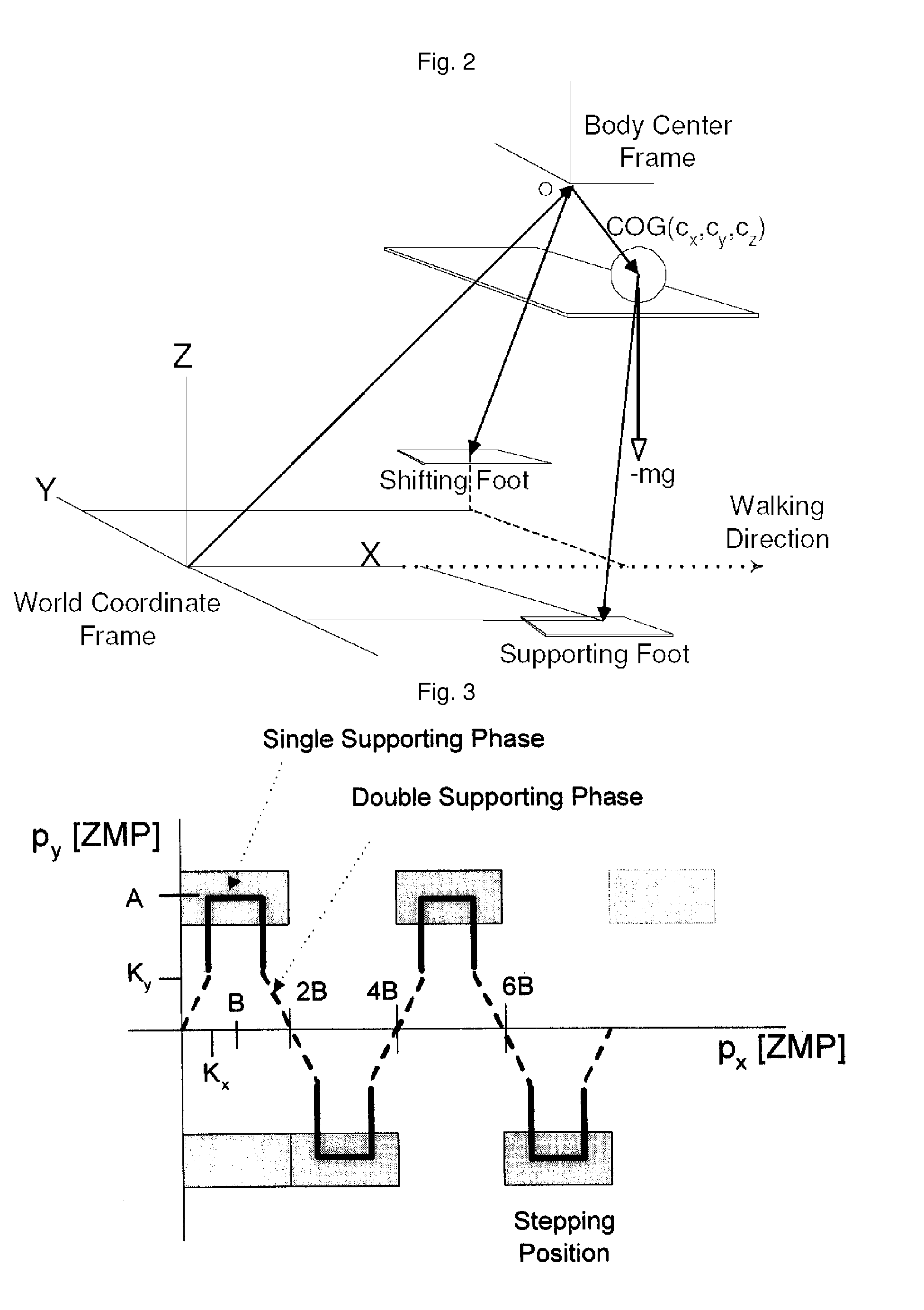
The invention relates to a method for controlling walking of humanoid bipedal walking robot. More specifically, the invention comprises steps of designing a zero momentum position (ZMP) of a robot for the ground surface (a); calculating trajectories of a center of gravity (COG) of the robot along with the trajectory of the ZMP (b); calculating an angular velocity of driving motors of two feet, which has the robot walk according to the trajectory of the ZMP (c); and controlling walking of the robot by driving the driving motors according to the angular velocity of the driving motors calculated above. The robot walking control method according to the invention has stability against disturbances.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Muscle strength model optimizing method for humanoid robot synergic movement
ActiveCN103761392AImprove accuracySpecial data processing applications3D modellingMuscle strengthBiomechanics
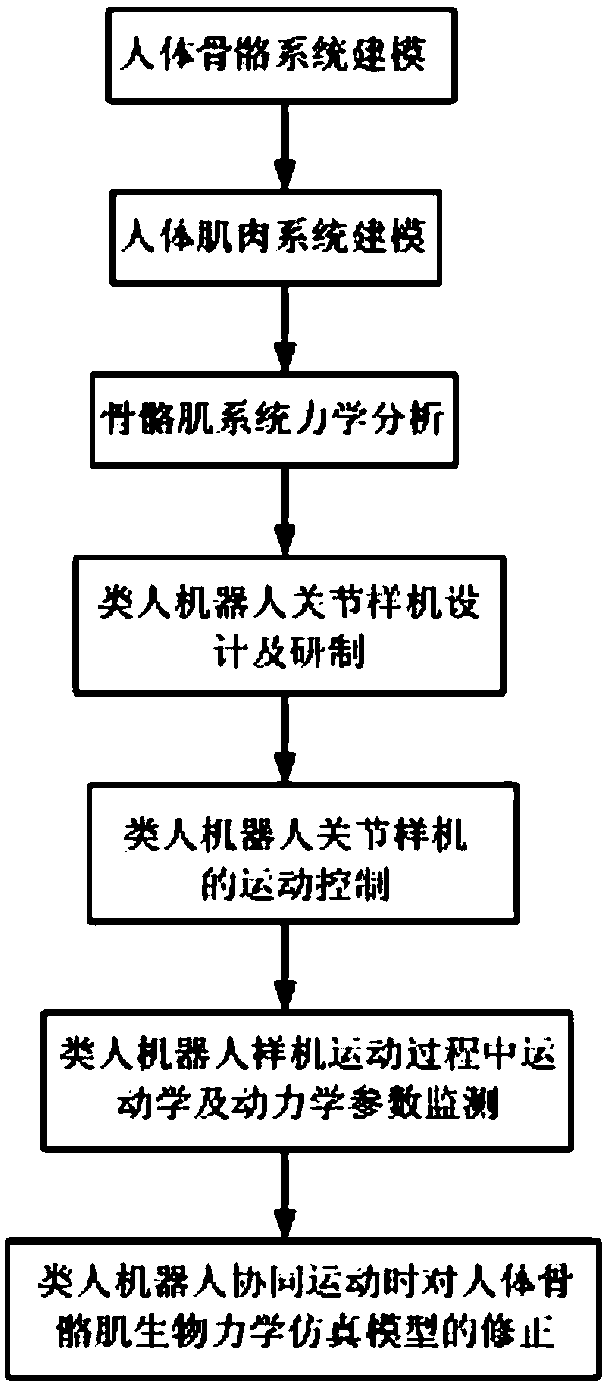
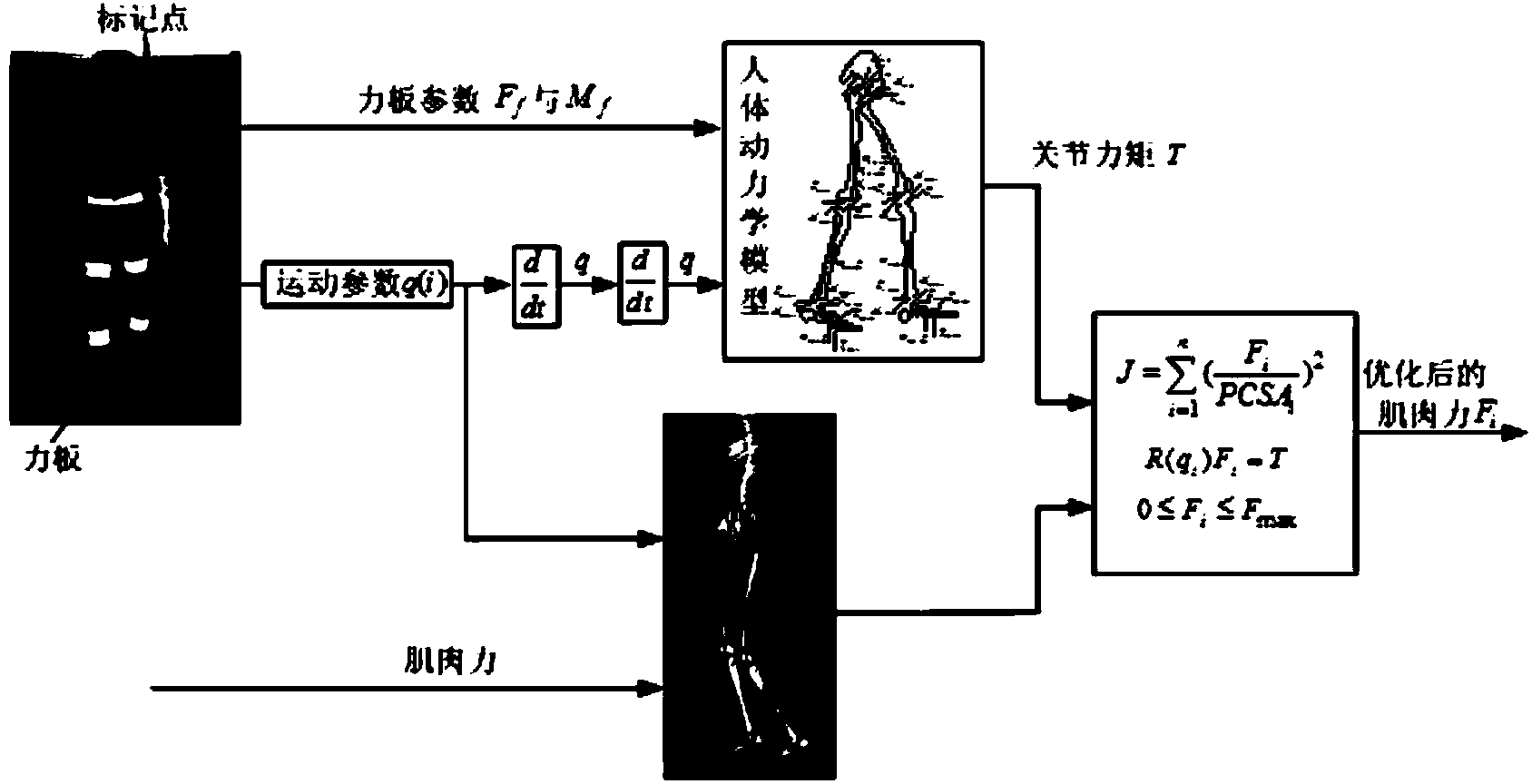
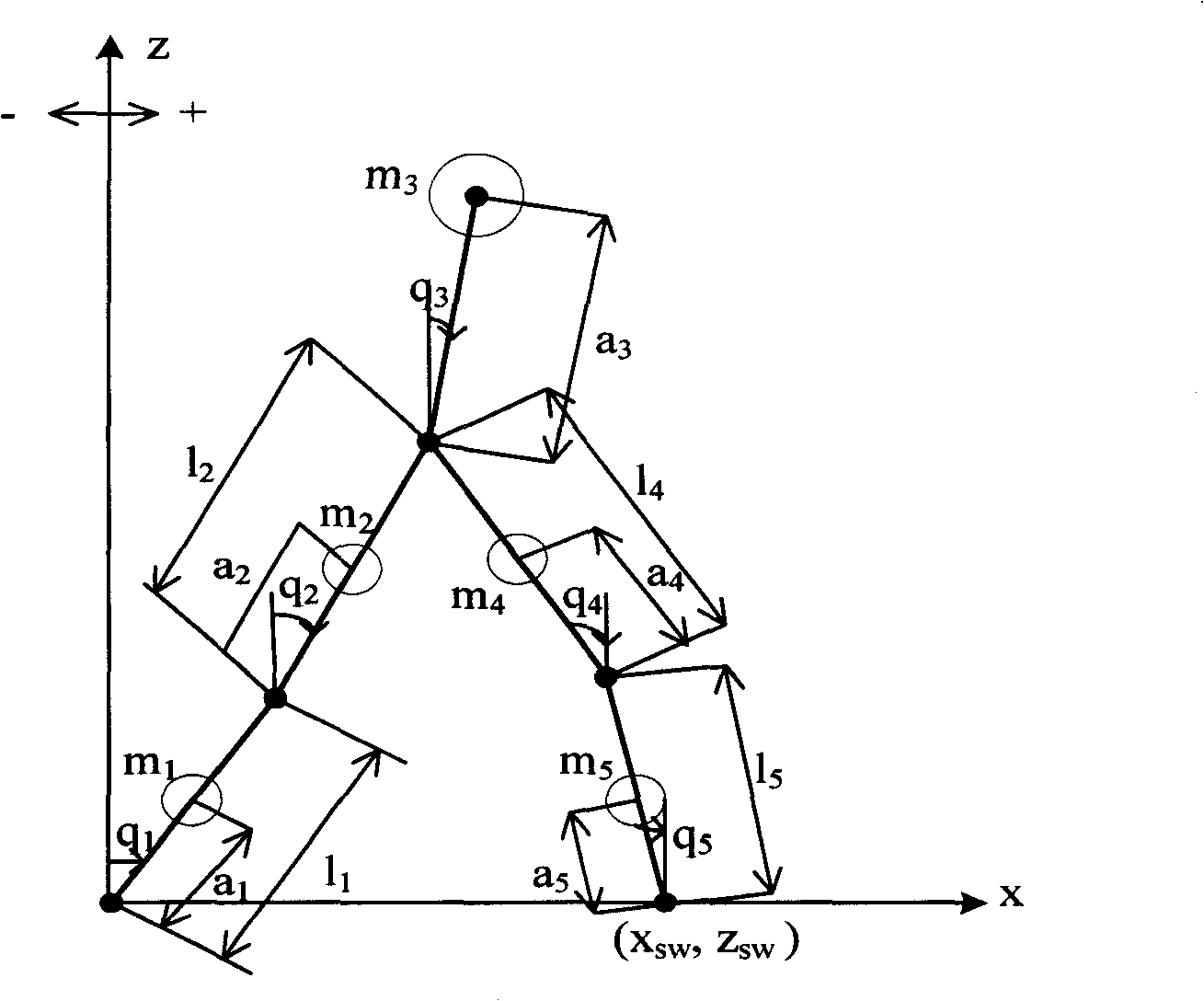
The invention provides a muscle strength model optimizing method for humanoid robot synergic movement. Programming and modeling are carried out on a human skeletal muscle simulation model, and a humanoid robot is designed and developed by reference to an experiment object; the humanoid robot is controlled to do the same movement by reference to the experiment object; movement detection data of the humanoid robot and output data of the human skeletal muscle simulation model are compared, design parameters of the humanoid robot and a muscle strength prediction formula in the simulation model are modified repeatedly until the design parameters and the formula are similar, and an optimized muscular strength prediction model is obtained. The muscle strength model optimizing method for the humanoid robot synergic movement can solve the problems that muscular strength during body movement can not be directly measured through experiments in biomechanics researches of a skeletal system and a muscular system, can only be calculated by means of a muscular strength model and is uncertain, and accuracy of the simulation model is improved.
Owner:NANJING INST OF TECH
Robot ambulation control method based on confirmation learning theory
InactiveCN101320251AReal learningShorten the timeAdaptive controlPosition/course control in two dimensionsDynamic modelsClosed loop
The invention relates to a robot walking control method based on the determined study theory. The method comprises the processes such as the establishment of robot walking model, the establishment of referenced gait model, the study on the neural network, the establishment of constant neural network, the completion of walking task by utilizing the constant RBF neural network, etc. The invention overcomes the disadvantages of learning ability in the current neural network study and the control method and realizes the accurate study of the unknown dynamic model of a robot closed-loop control system along the periodic gait track of the robot within a local area, and can study the effective knowledge of the system dynamics during the stable dynamic control process and apply the knowledge to the subsequent same or similar tasks successfully. The method not only can realize the rapid walking on the basis of energy saving, but also provides the powerful support for the development of the humanoid robots.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
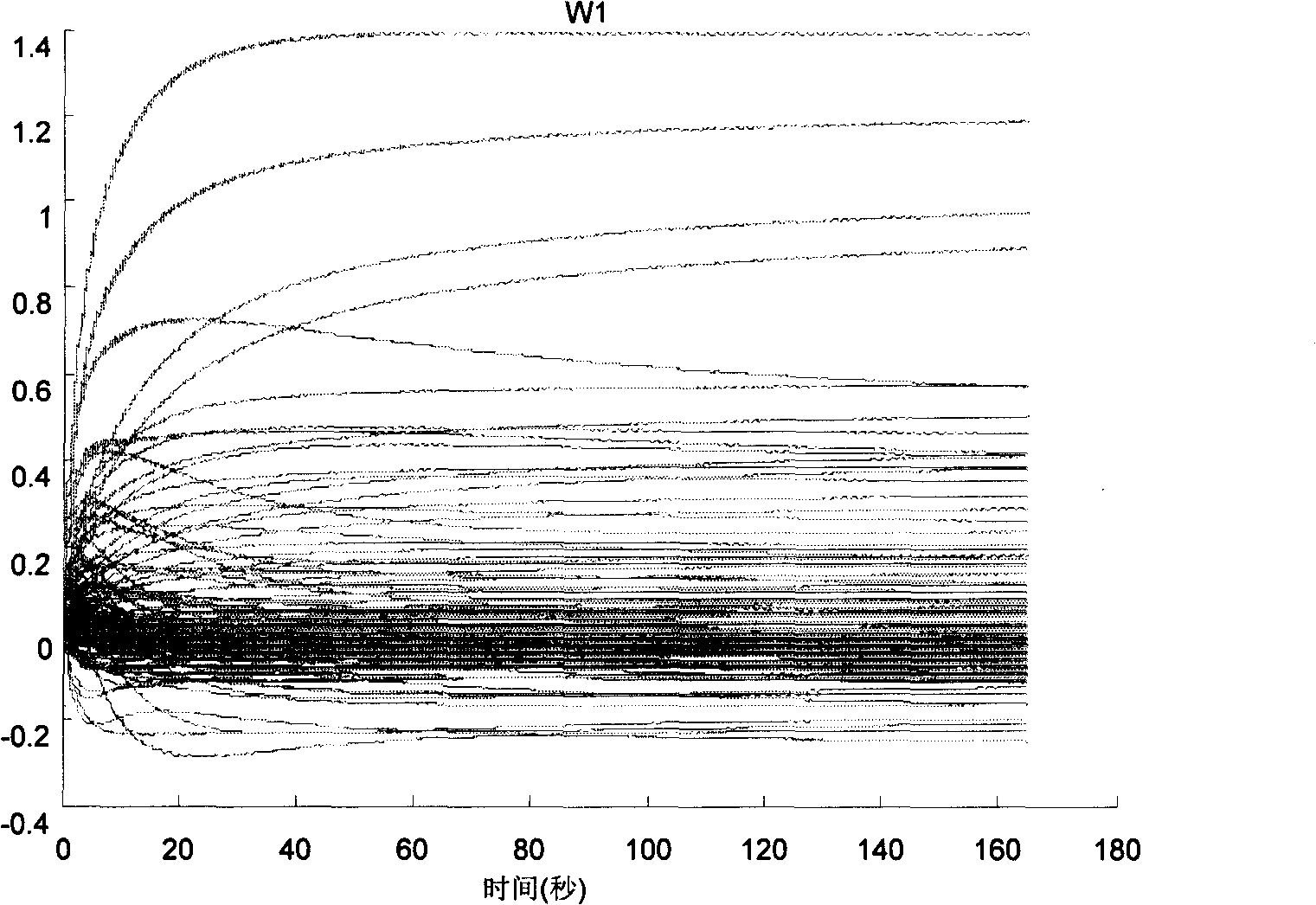
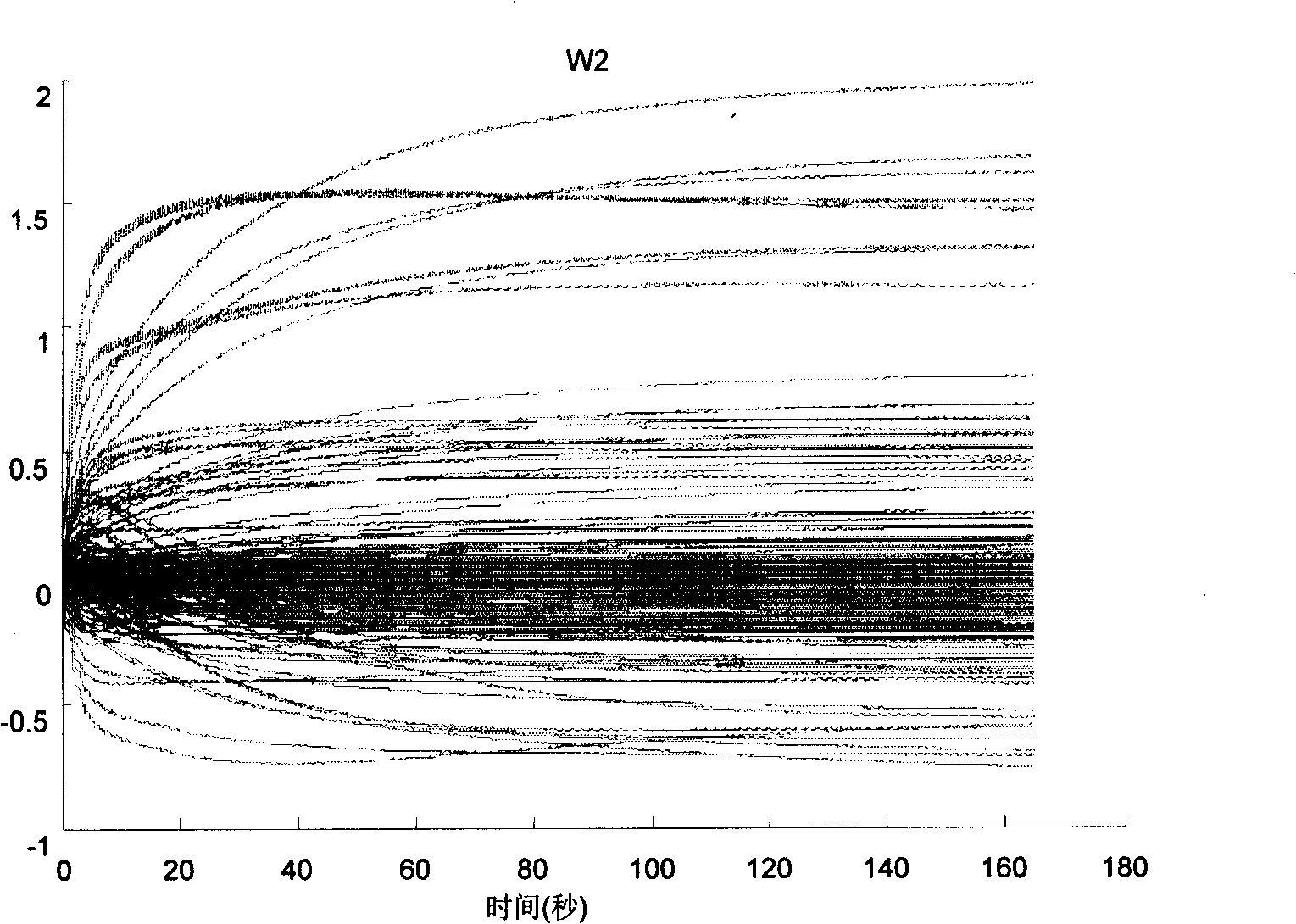
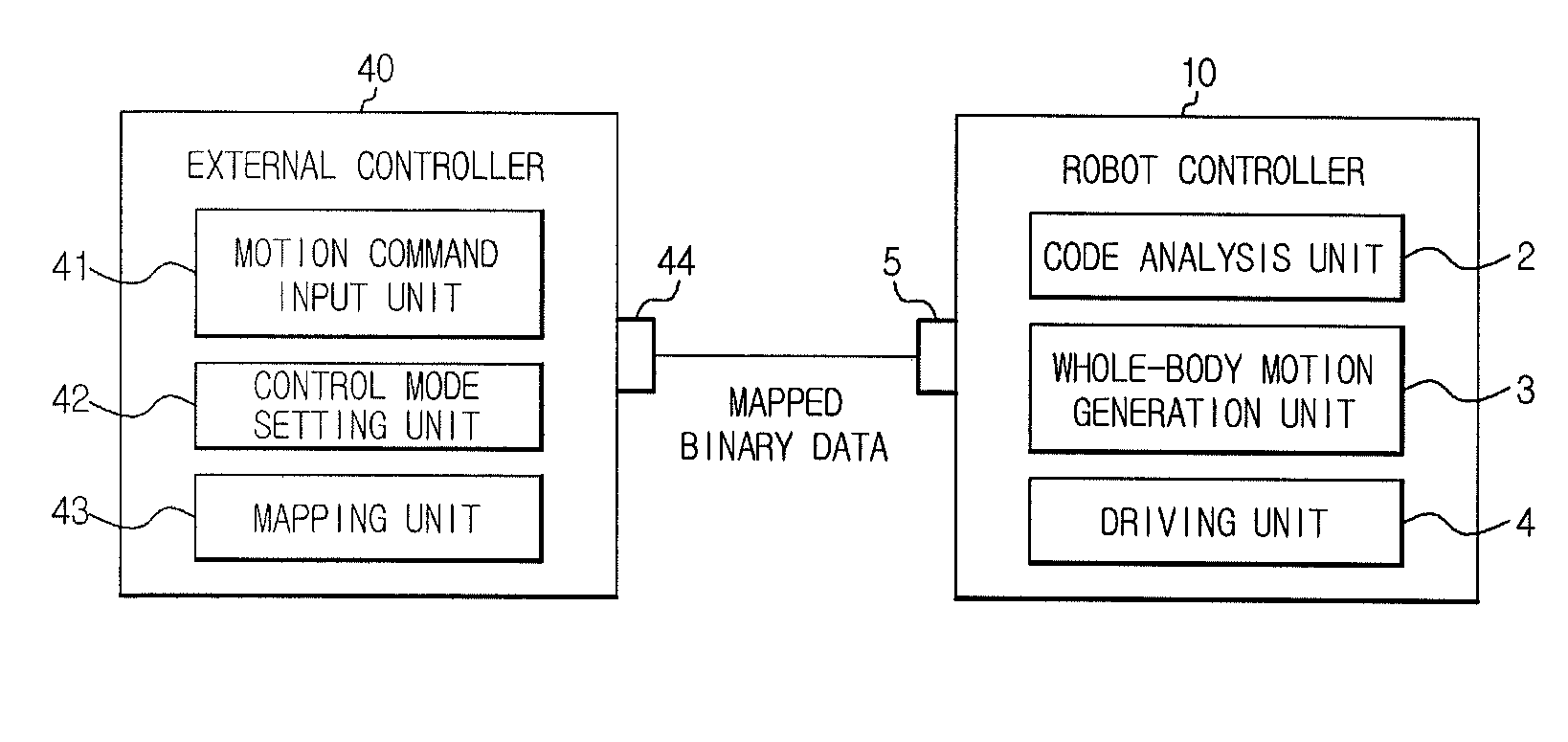
Apparatus, method and computer-readable medium controlling whole-body operation of humanoid robot
InactiveUS20110040405A1Easy to understandRapidly and appropriately copeProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorMedia controlsWhole body
Disclosed are an apparatus, a method and a computer-readable medium controlling whole-body operation of a humanoid robot. The humanoid robot recognizes a motion control code using binary data mapped according to a motion command represented by a language understood by a human to implement a whole-body operation. Since a control mode corresponding to a task space control and a control mode corresponding to a joint space control are used together to describe whole-body motion, the whole-body operation more similar to a human action may be easily implemented.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Humanoid robot gait control method based on model correlated reinforcement learning
ActiveCN106094813AImprove convergence rateImprove control effectPosition/course control in two dimensionsLearning controllerSimulation
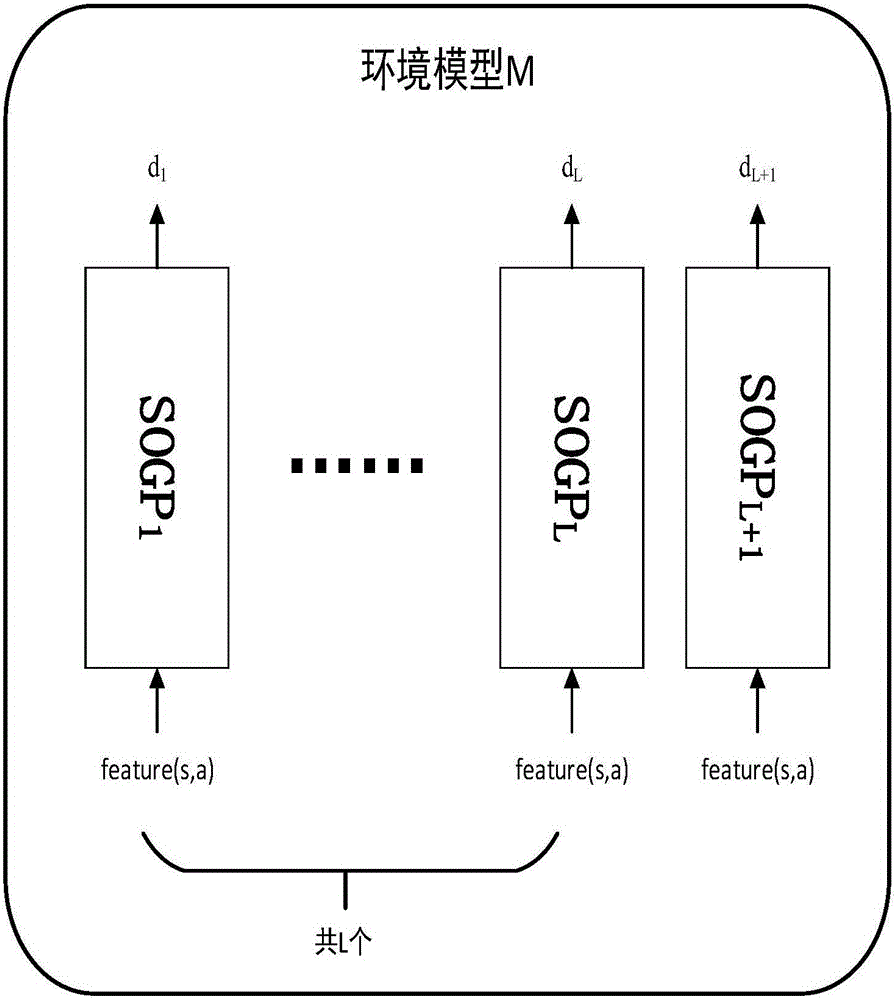
The invention discloses a humanoid robot gait control method based on model correlated reinforcement learning. The method comprises steps of 1) defining a reinforcement learning framework for a stable control task in forward and backward movements of a humanoid robot; 2) carrying out gait control of the humanoid robot with a model correlated reinforcement learning method based on the sparse online Gaussian process; and 3) improving a motion selection method of a reinforcement learning humanoid robot controller by a PID controller, and taking the improved operation as an optimizing initial point for the PID controller obtaining the motion selection operation of the reinforcement learning controller. The invention utilizes reinforcement learning to control gaits of the humanoid robot in movement, and thus the movement control of the humanoid robot can be automatically adjusted via interaction with the environment, a better control effect is achieved, and the humanoid robot is enabled to be stable in forward and backward directions.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
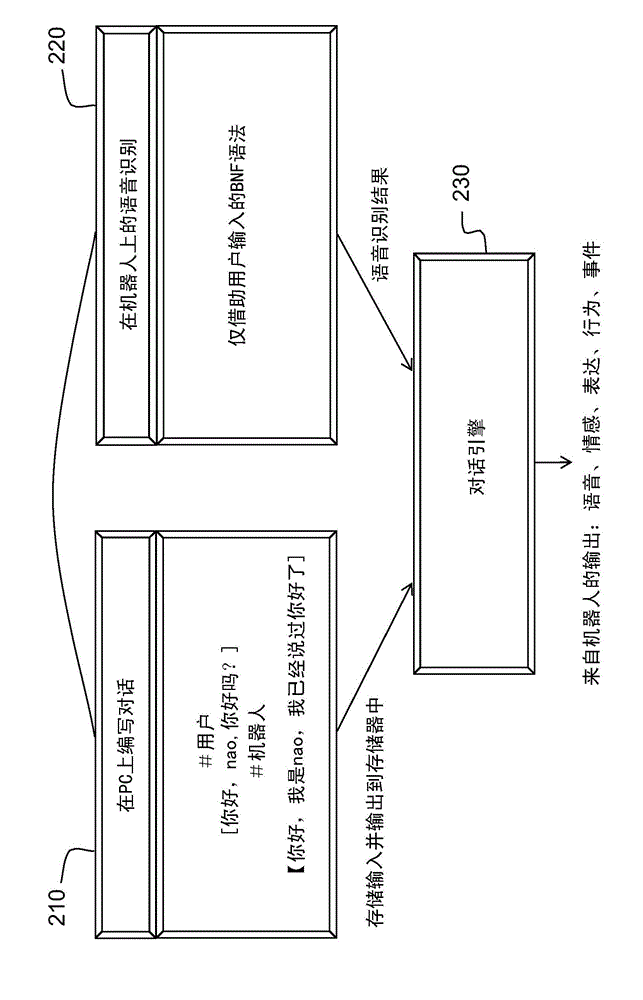
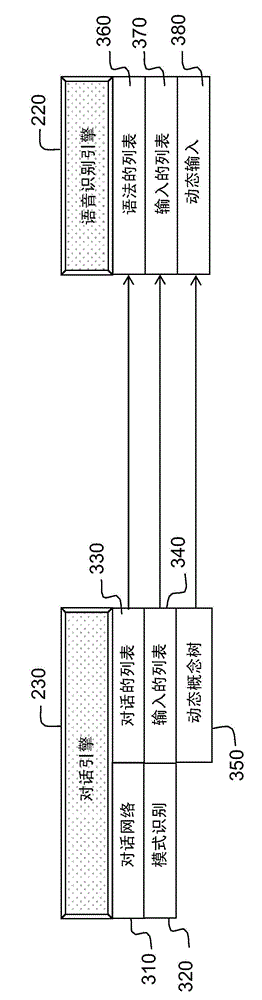
Robot capable of incorporating natural dialogues with a user into the behaviour of same, and methods of programming and using said robot
InactiveCN104350541AImprove ergonomicsSmooth creationProgramme-controlled manipulatorDigital data information retrievalSpeech identificationHuman–computer interaction
The invention concerns a humanoid robot, said robot being capable of holding a dialogue with at least one user, said dialogue using two speech recognition modes, one open and the other closed, the closed mode being defined by a concept characterising a sequence of dialogue. The dialogue can also be influenced by events that are neither speech nor a text. The robot of the invention is capable of executing behaviour and generating expressions and emotions. Relative to the robots of the prior art, the invention provides the advantage of considerably reducing the programming time and latency of execution of the sequences of dialogue, which provides a fluency and a nature close to human dialogues.
Owner:ALDEBARAN ROBOTICS SA
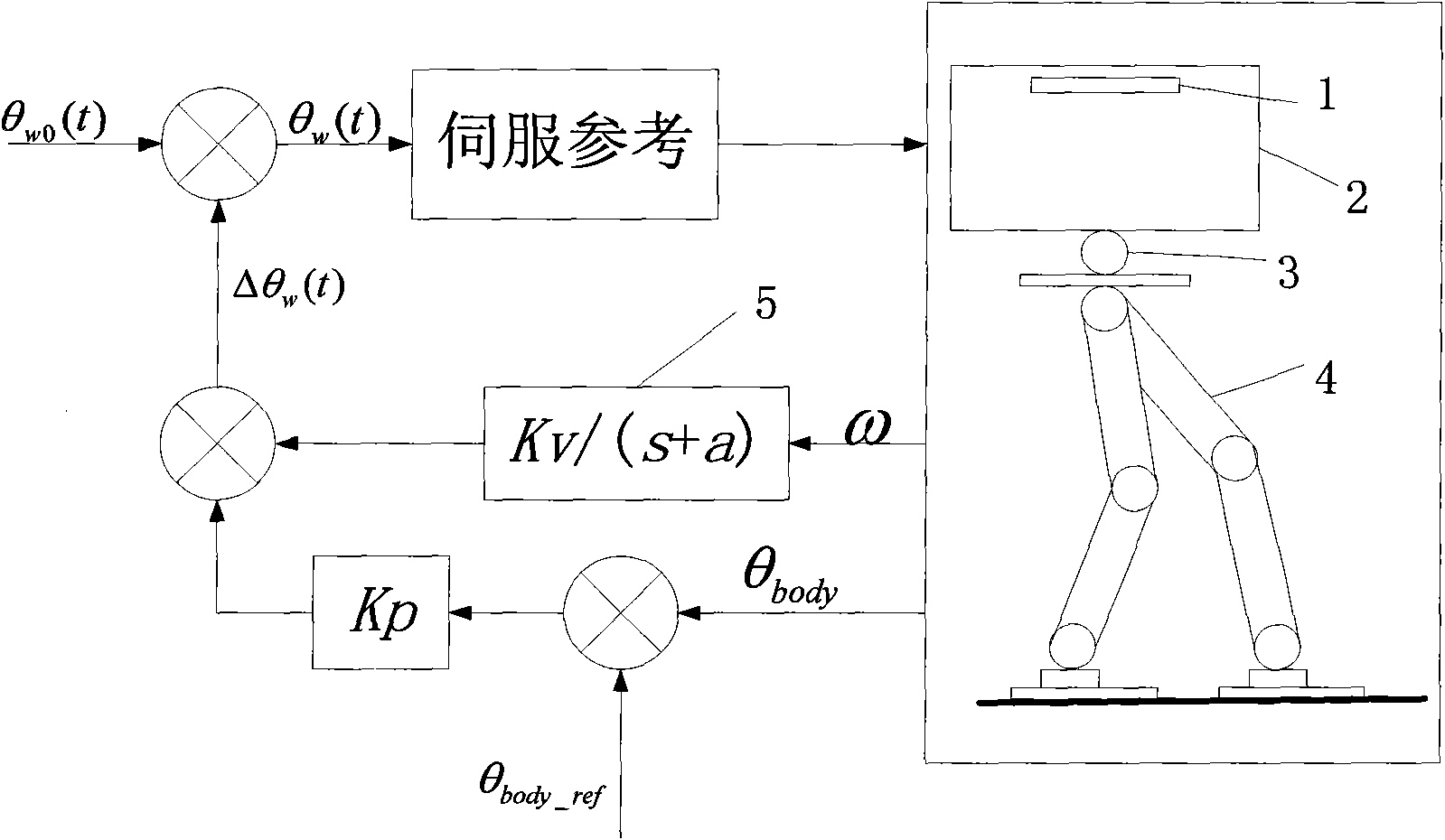
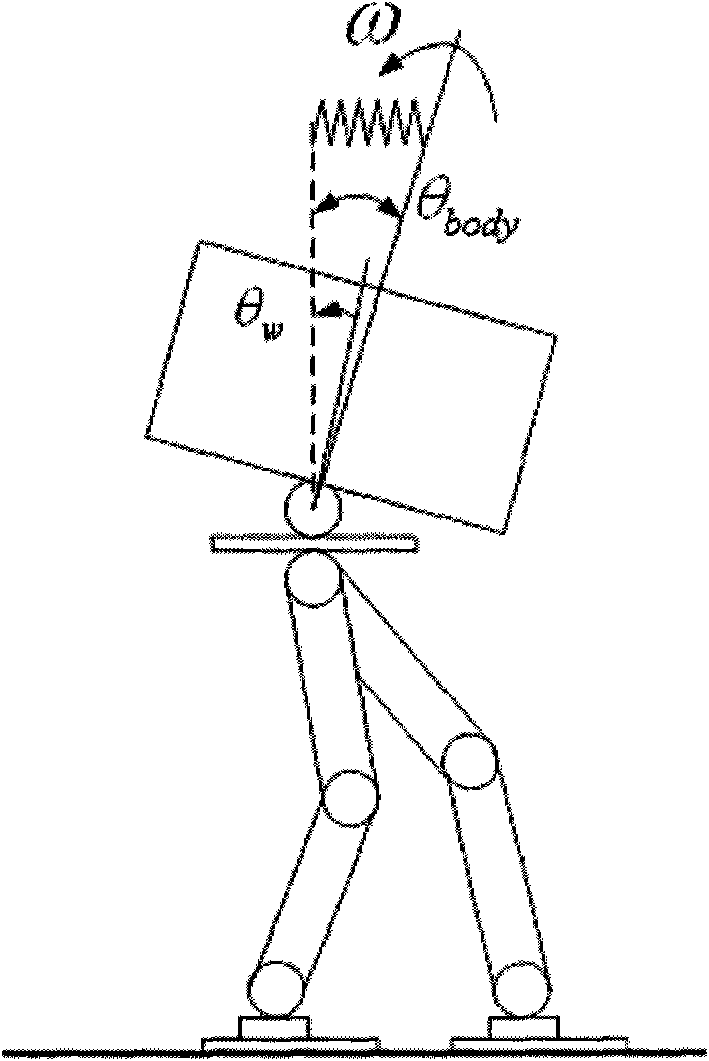
Control method for eliminating upper body posture shaking of double-foot humanoid robot
The invention provides a control method for eliminating the upper body posture shaking of a double-foot humanoid robot. The robot is provided with a waist part and a posture sensor. The method comprises the following steps of: generating a planned gait of the robot; measuring the inclination angle and the angular speed of the upper body of the robot through the posture sensor; calculating the correction of a joint of the waist part according to the inclination angle and the angular speed; and adjusting the joint according to the correction so as to eliminate the upper body posture shaking of the robot. In the method, only the waist joint is adjusted without affecting the landing time of the robot; and the method achieves effects in the entire walking process or operating process of the robot.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
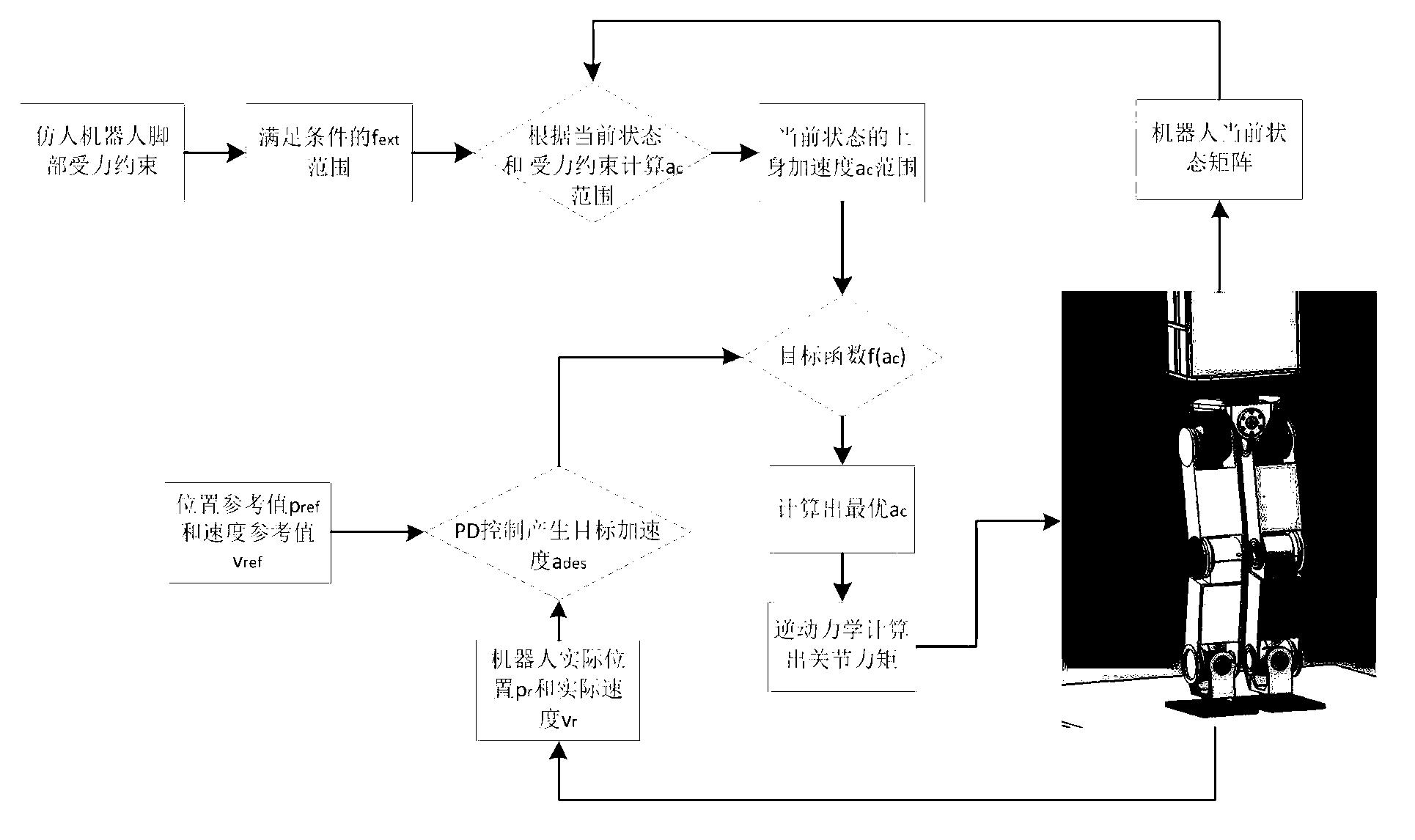
Humanoid robot inverse dynamics controller based on acceleration optimization
ActiveCN103019096AAvoid Unpredictable MovementStable controlAdaptive controlSimulationControl theory
The invention discloses a humanoid robot inverse dynamics controller based on acceleration optimization and belongs to the technical field of robots. The controller comprises the following steps of: according to the motion constraint of the humanoid robot, obtaining the relation between the upper body acceleration of the humanoid robot and the external force required by the soles; calculating the range of the upper body acceleration according to the constraint of the external force; and calculating out the optimal upper body acceleration by cost function and then calculating out the external force and the joint moment deserved by the robot. According to the method, the foot stress constraint of the robot is appointed, the actual stress of the robot meets the constraint condition by optimizing the upper body acceleration of the robot, and the robot is prevented from producing un-predictable motion due to external interference, thus the purpose of stably controlling the humanoid robot is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
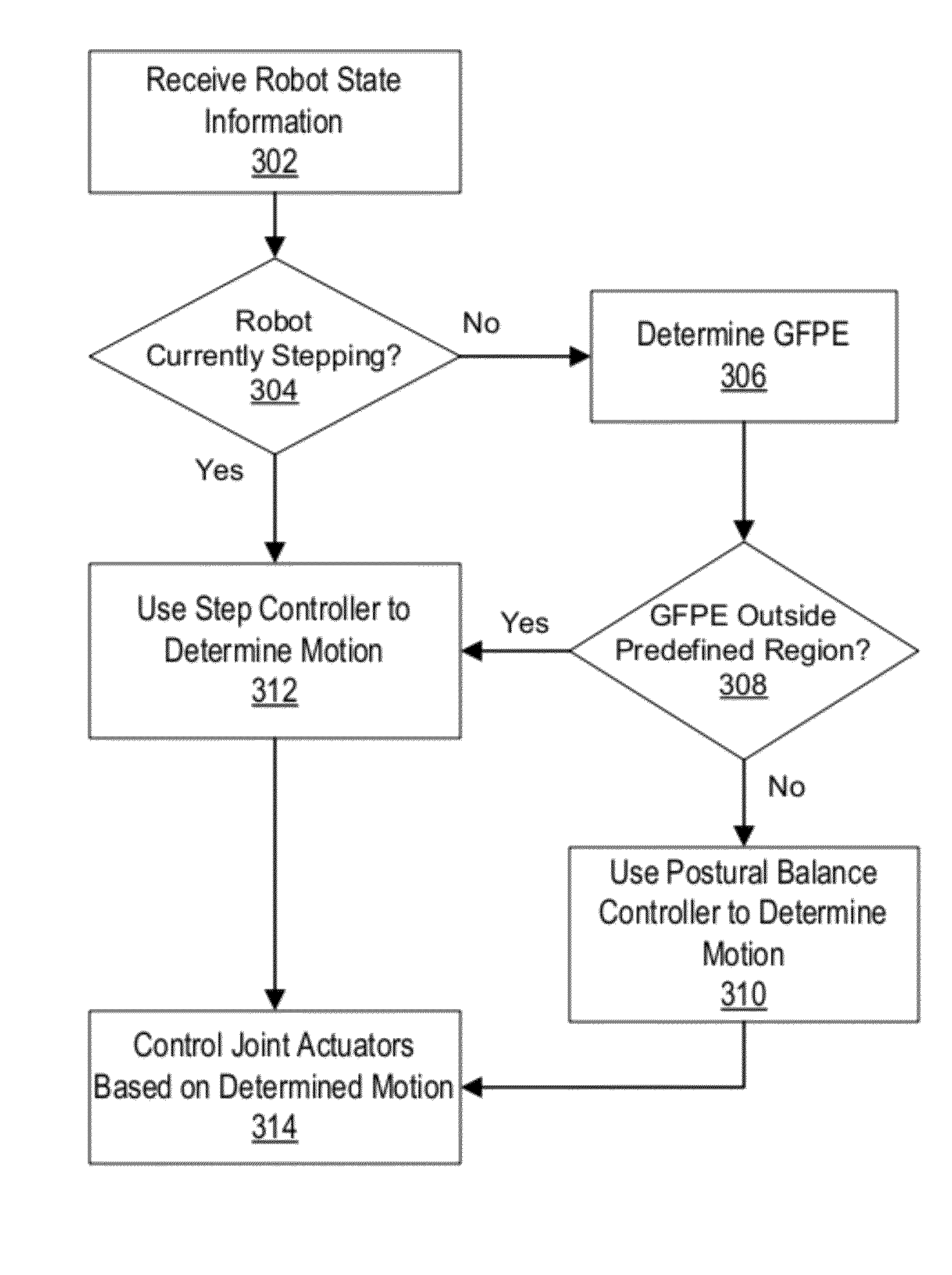
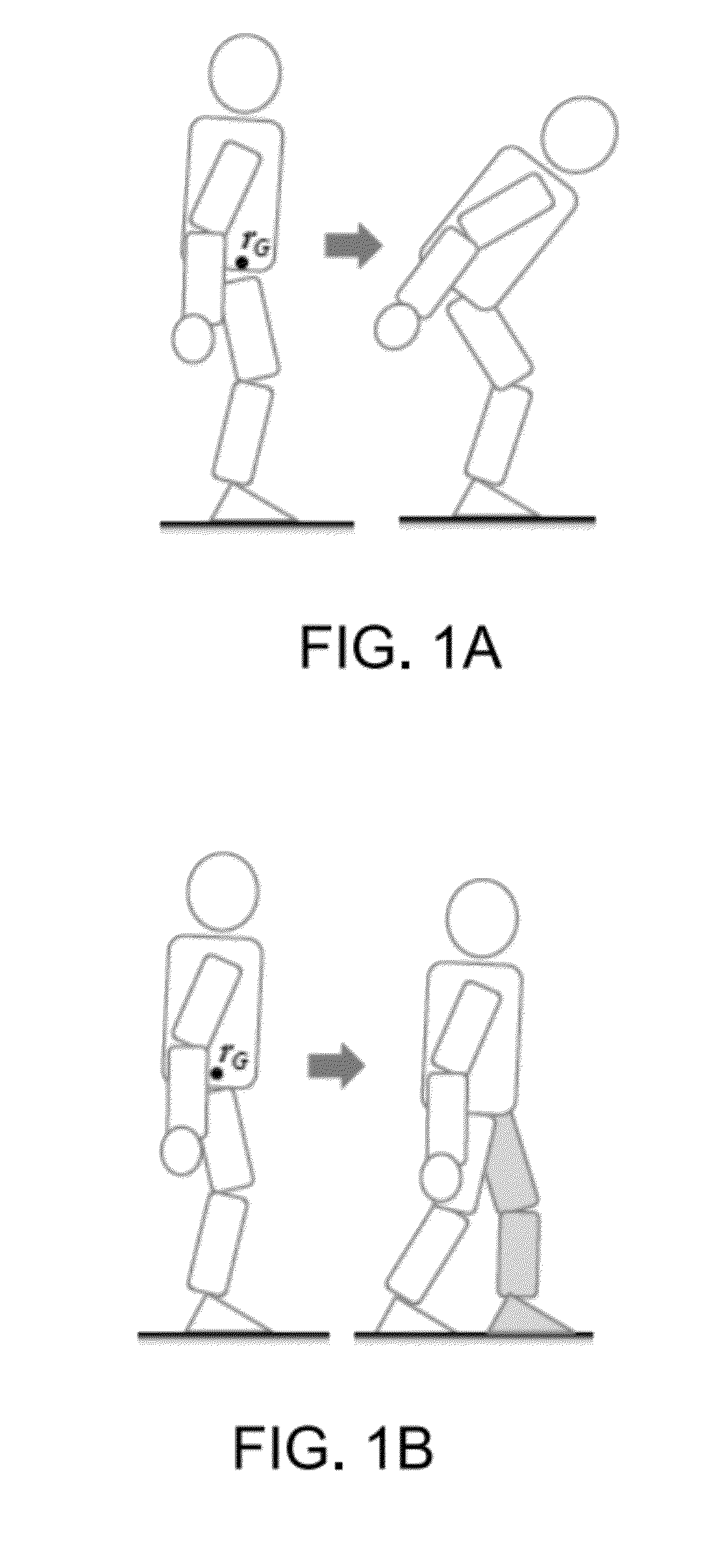
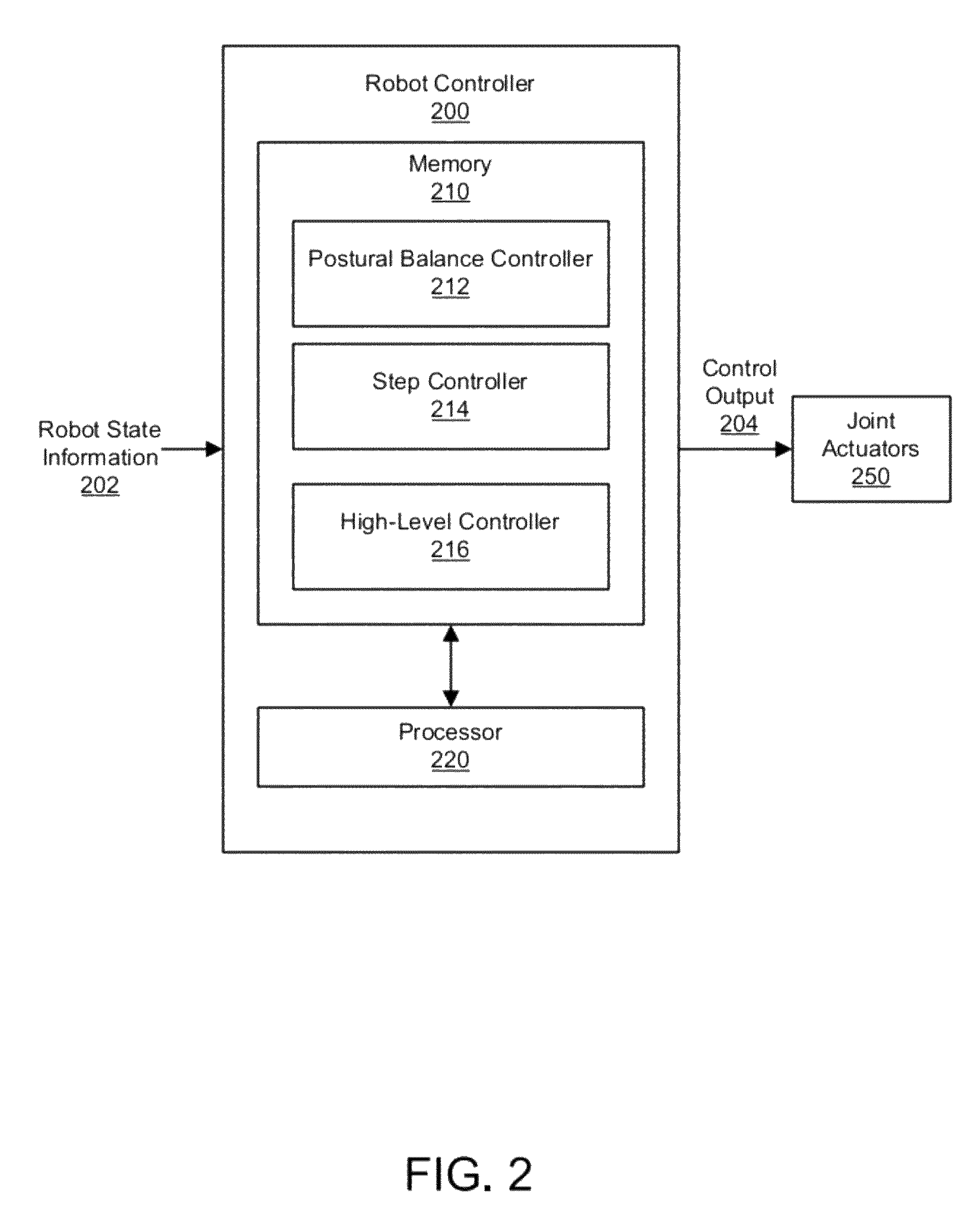
Humanoid robot push recovery on level and non-level ground
ActiveUS8849454B2Maintain balanceProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlEngineeringControl theory
A robot controller controls a robot to maintain balance in response to an external disturbance (e.g., a push) on level or non-level ground. The robot controller determines a predicted stepping location for the robot such that the robot will be able to maintain a balanced upright position if it steps to that location. As long as the stepping location predicted stepping location remains within a predefined region (e.g., within the area under the robot's feet), the robot will maintain balance in response to the push via postural changes without taking a step. If the predicted stepping location moves outside the predefined region, the robot will take a step to the predicted location in order to maintain its balance.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
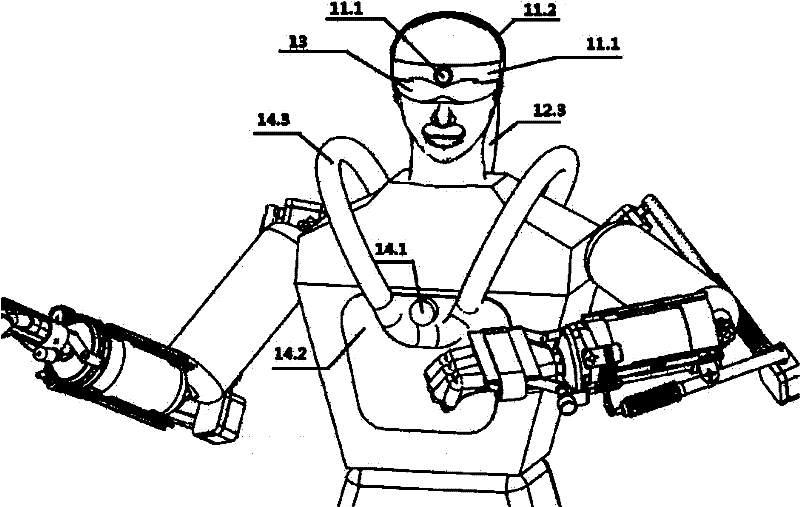
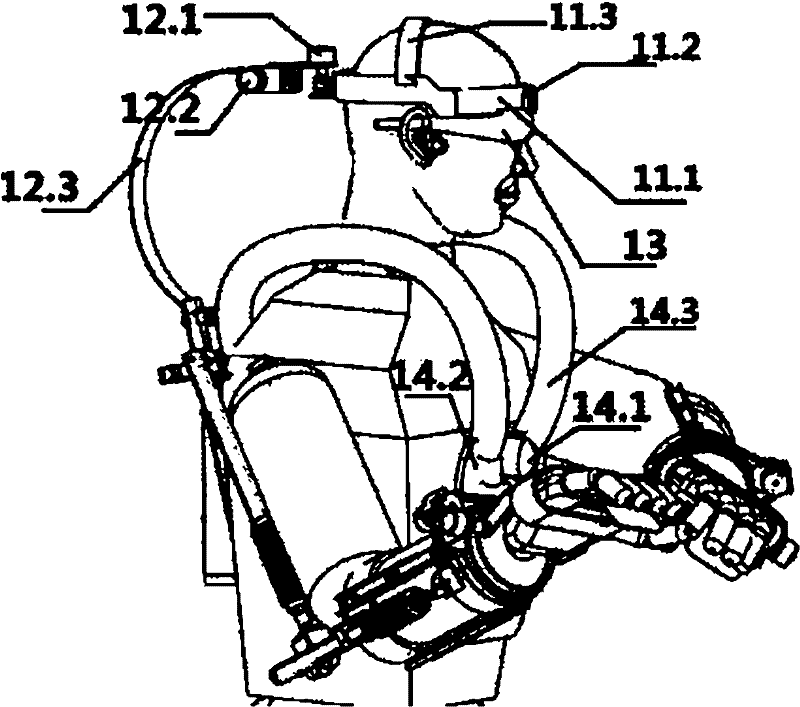
Remote control humanoid robot system based on exoskeleton human posture information acquisition technology
The invention relates to a remote control humanoid robot system based on an exoskeleton human posture information acquisition technology, and belongs to the technical field of robots. A humanoid robot lacks freedom of the lower body, and cannot simulate the action of the human lower limb. Exoskeleton type human posture information acquisition clothes lack a posture acquisition device of ten fingers. The exoskeleton type human posture information acquisition clothes of the system are worn on a user, and human action information is acquired through a sensor action acquisition module. The human action information is transmitted to a robot control module through a wireless communication module to control the humanoid robot to perform corresponding action operation. The system is suitable for the users of different figures to use, and the humanoid robot can reproduce human upper body actions of 16 degrees of freedom in real time.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
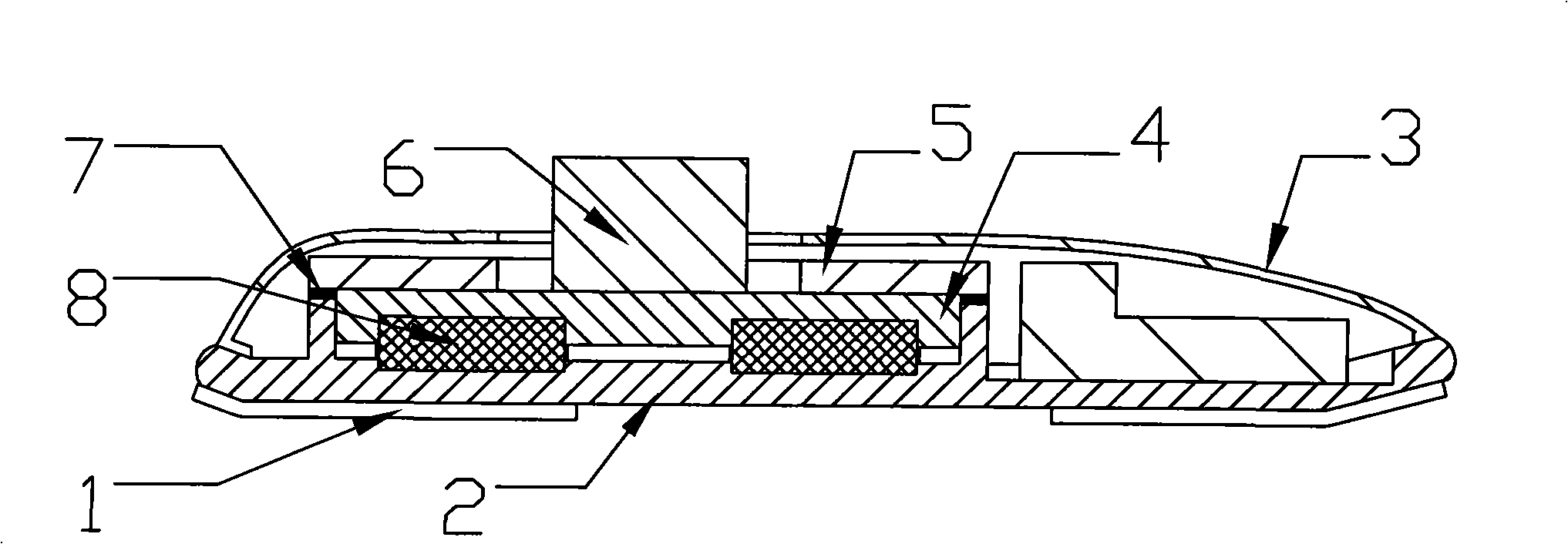
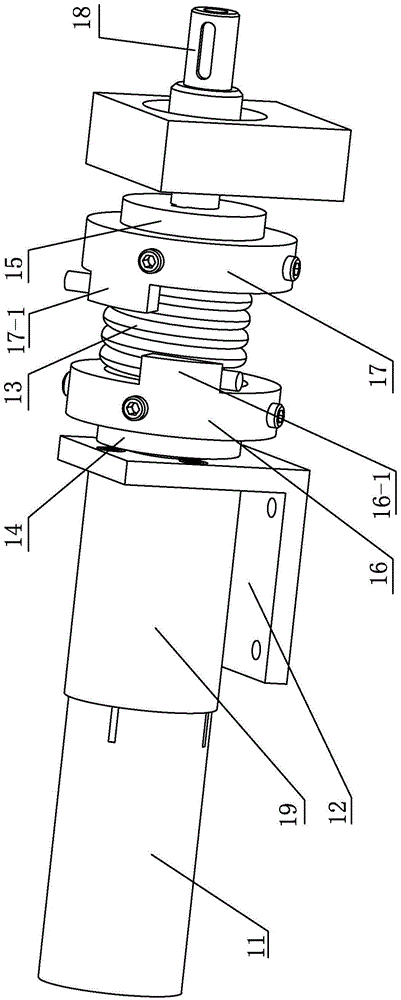
Humanoid robot foot section impact absorption mechanism
ActiveCN101402380AFlexible and continuously adjustableFlexible and easy to changeSelf-moving toy figuresVehiclesLeading edgeEngineering
The invention discloses a food shock absorbing mechanism for an anthropomorphic robot, which comprises soles, wherein damping columns are arranged on the soles; upper surfaces of the damping columns are provided with upper pressure plates; force transducers and upper cover plates are arranged on the upper pressure plates; the upper cover plates are connected with the soles through four upper cover plate mounting holes; four groups of adjusting washers are arranged between the upper cover plates and the soles; the force transducers are connected with legs of the robot; the number of the damping columns is four, and the four damping columns are connected with the soles through the four damping column mounting holes which are positioned on the soles; front ends of the soles are provided with front sole bevels, and rear ends of the soles are provided with rear sole bevels; and non-skid mats are arranged below the soles. The invention designs the more compact and more effective shock absorbing mechanism, realizes continuous flexible adjustment of the shock absorbing mechanism, and can make the anthropomorphic robot easier to meet different operation requirements.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
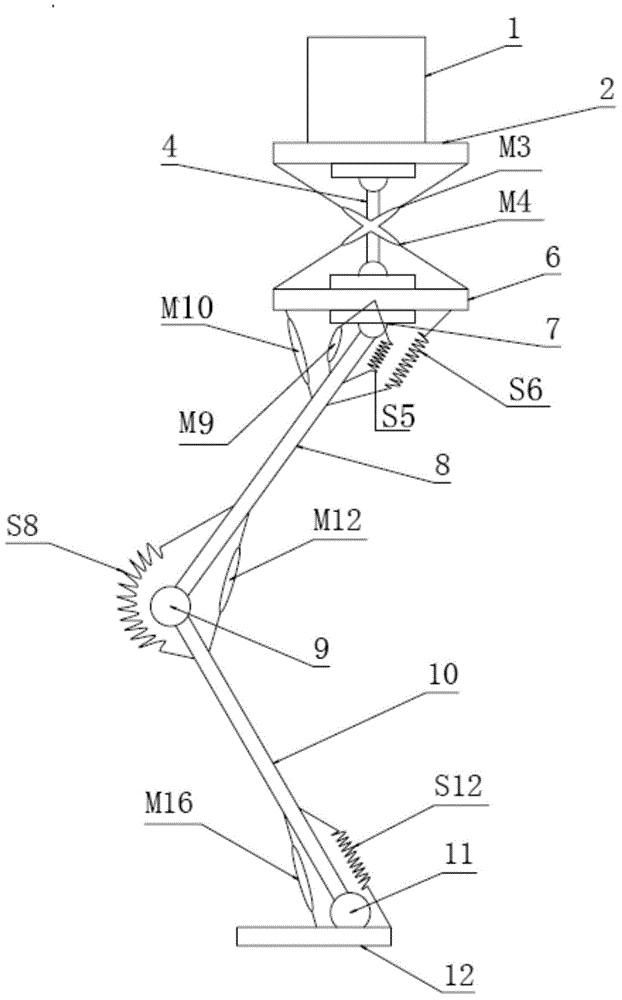
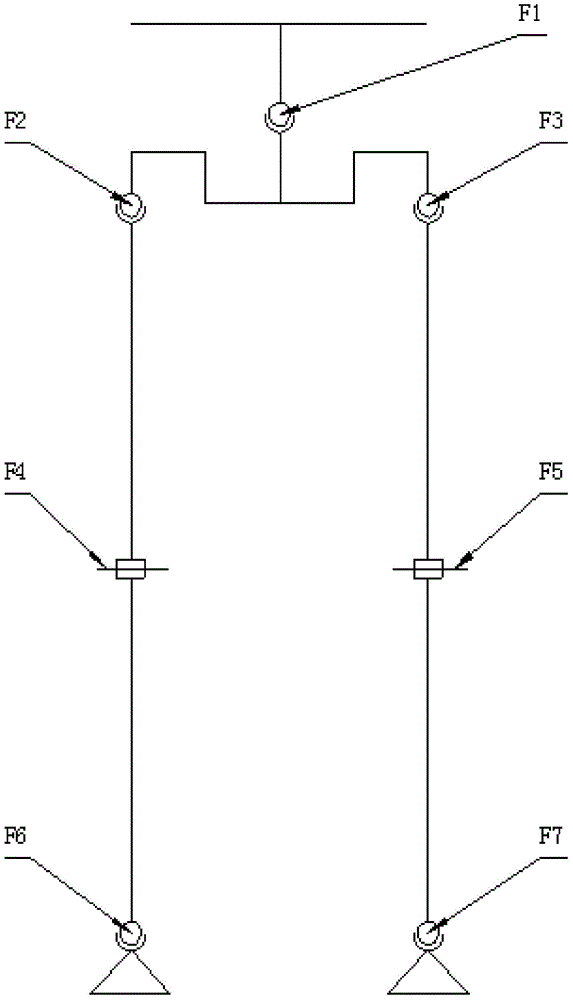
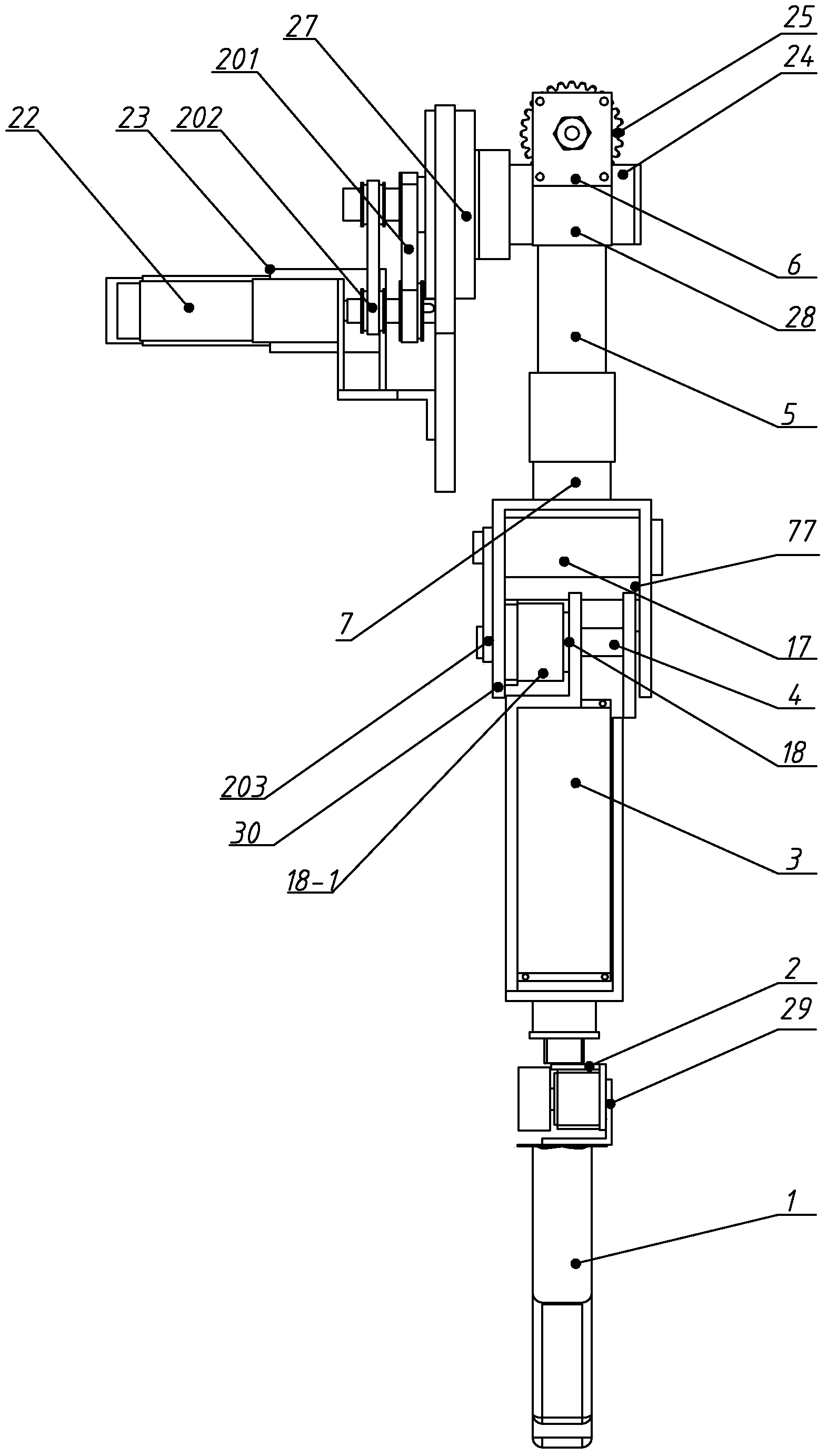
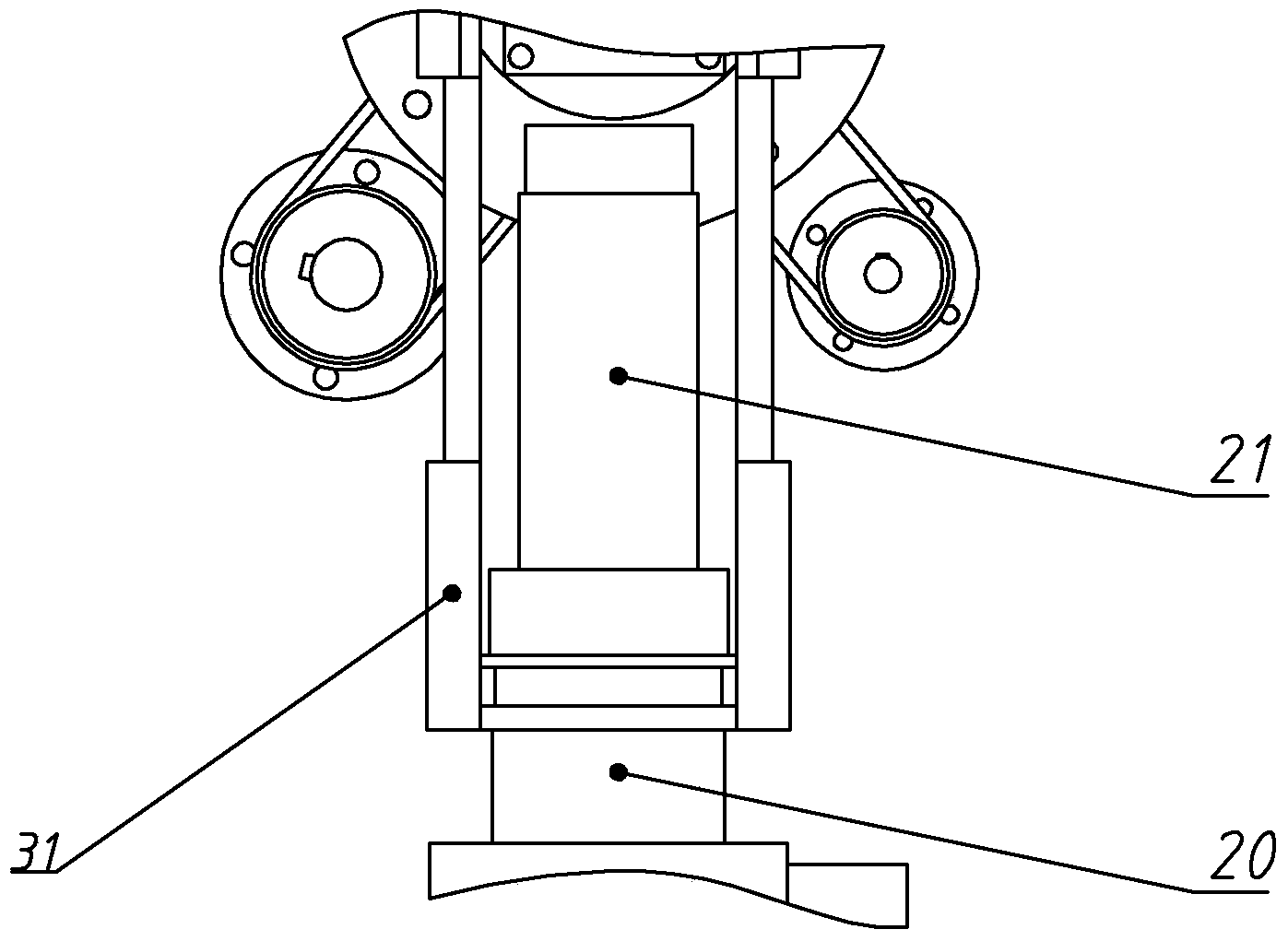
Pneumatic-electric combined driving flexible biped robot
The invention relates to a flexible biped robot, in particular to a pneumatic-electric combined driving flexible biped robot. The problems that linkage between joint flexibility and a dynamic response characteristic of existing flexible biped robots is poor, the walking efficiency of the robots is low and the dynamic stability of the robots is poor are solved. The pneumatic-electric combined driving flexible biped robot comprises a left leg, a right leg and a pelvis. The left leg and the right leg each comprise a thigh, a shank, a foot, a hip joint, a knee joint and an ankle joint. Each hip joint comprises a one-way series-connection elastic driver and a hip joint transmission mechanism. Each one-way series-connection elastic driver comprises a motor, a motor seat, a torsion spring, a first hub, a second hub, a first clamping ring, a second clamping ring and a hip joint driving shaft. Each hip joint transmission mechanism comprises a driving belt wheel, a driven belt wheel, a driving belt and a hip joint driven shaft. The driving belt wheels are mounted on the hip joint driving shafts correspondingly. Each knee joint comprises a knee joint driving mechanism and a knee joint transmission mechanism. The pneumatic-electric combined driving flexible biped robot belongs to the field of humanoid robots.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com