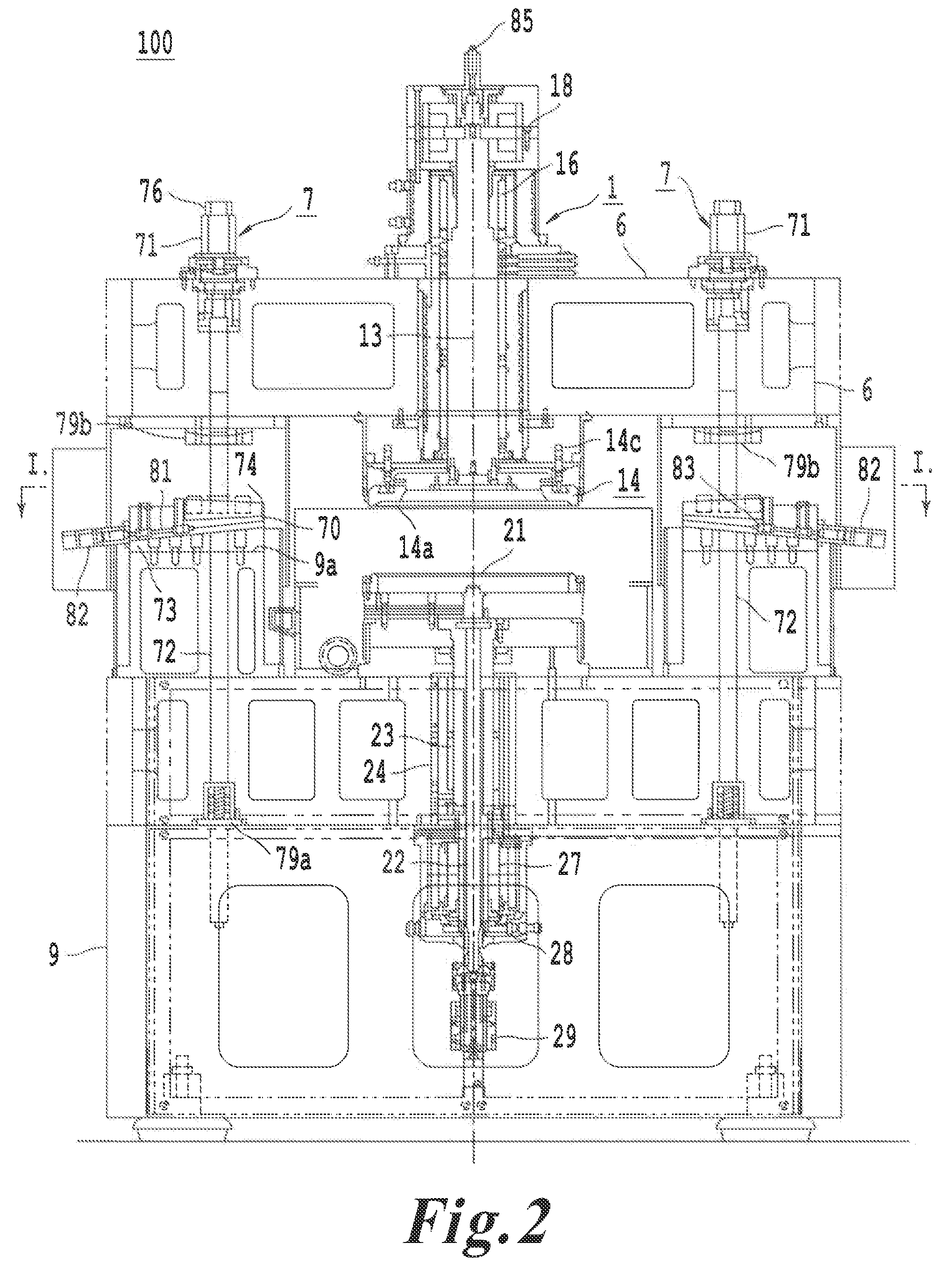Patents
Literature
134 results about "Kinematic coupling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
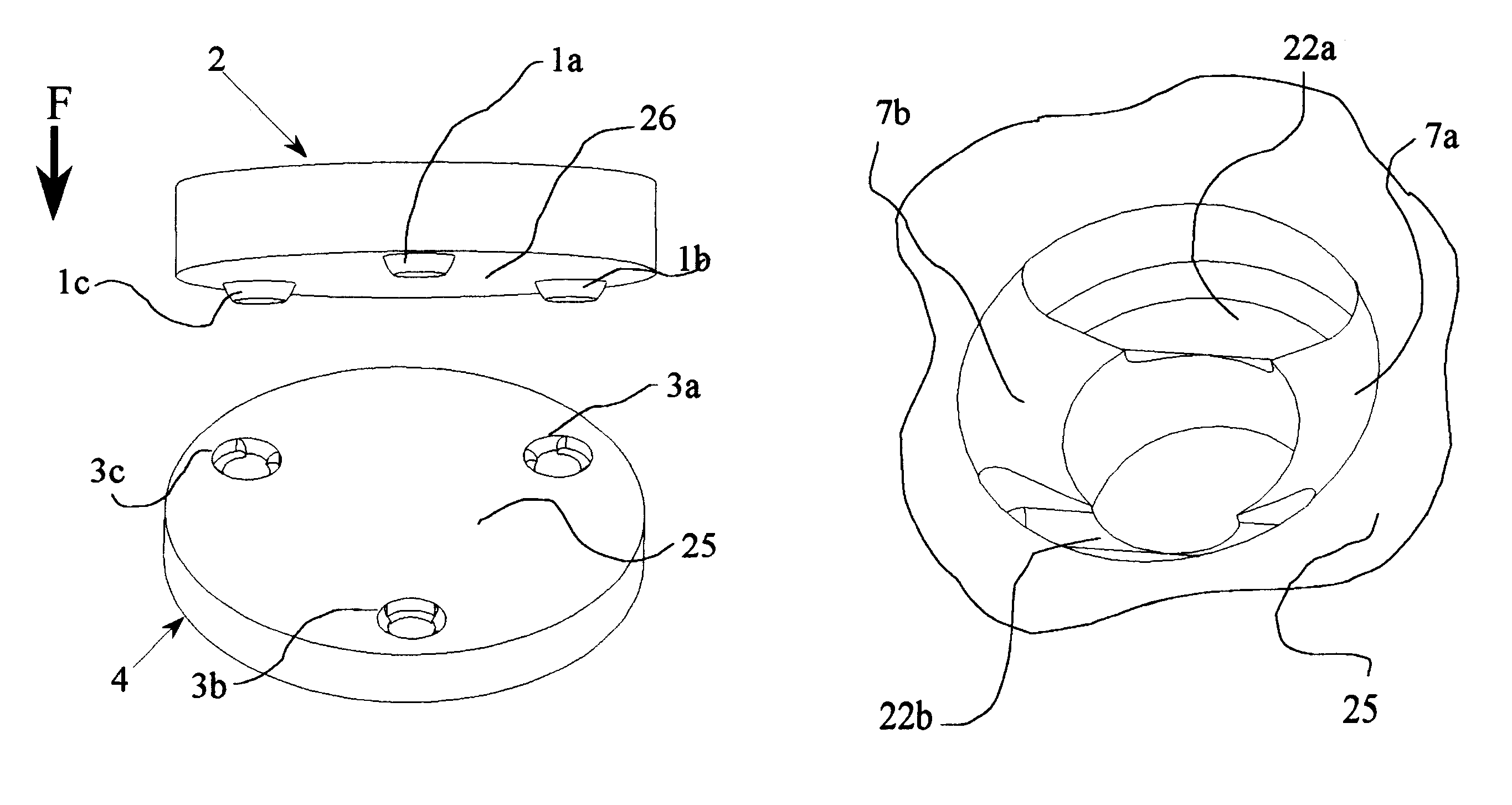
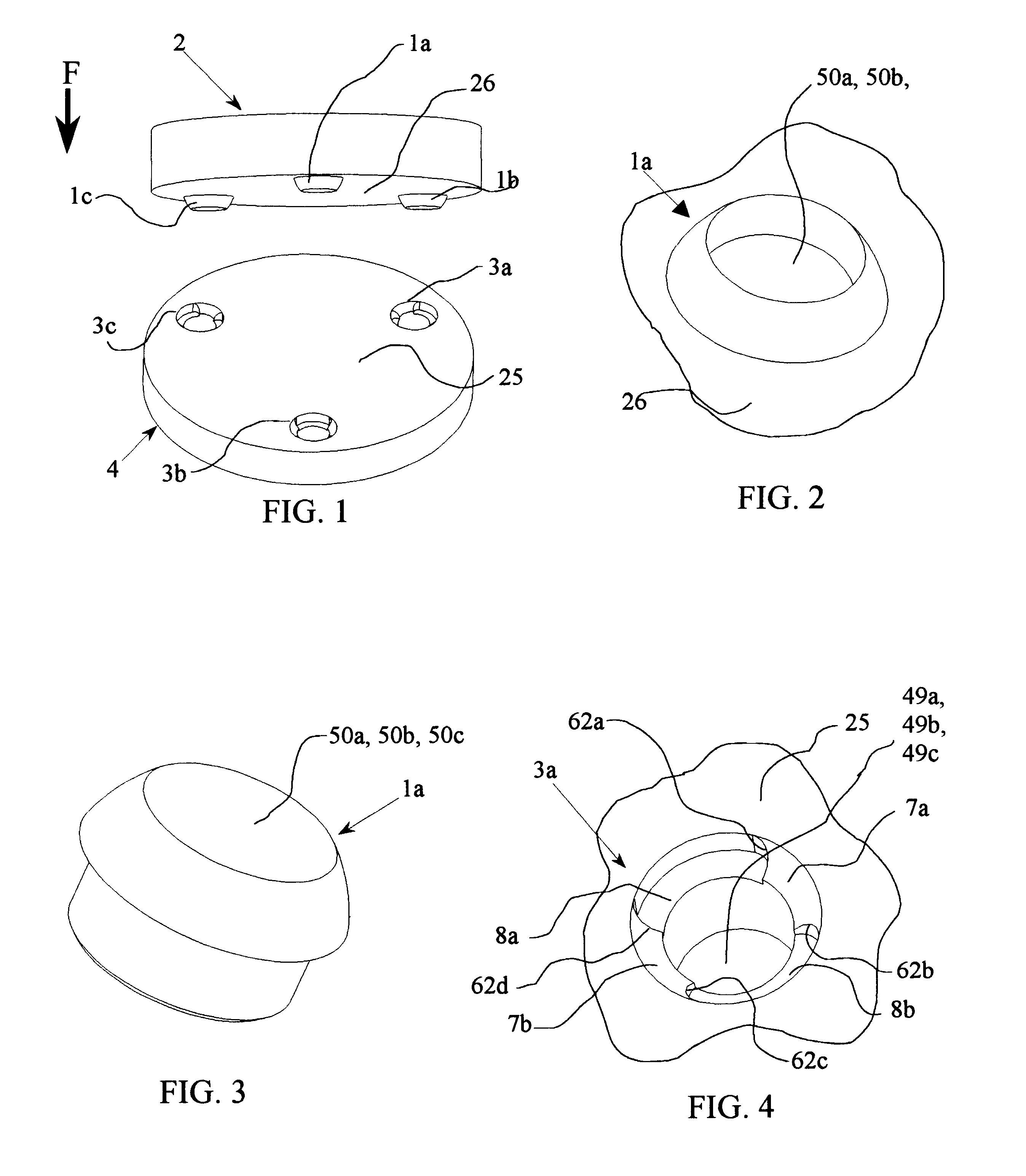
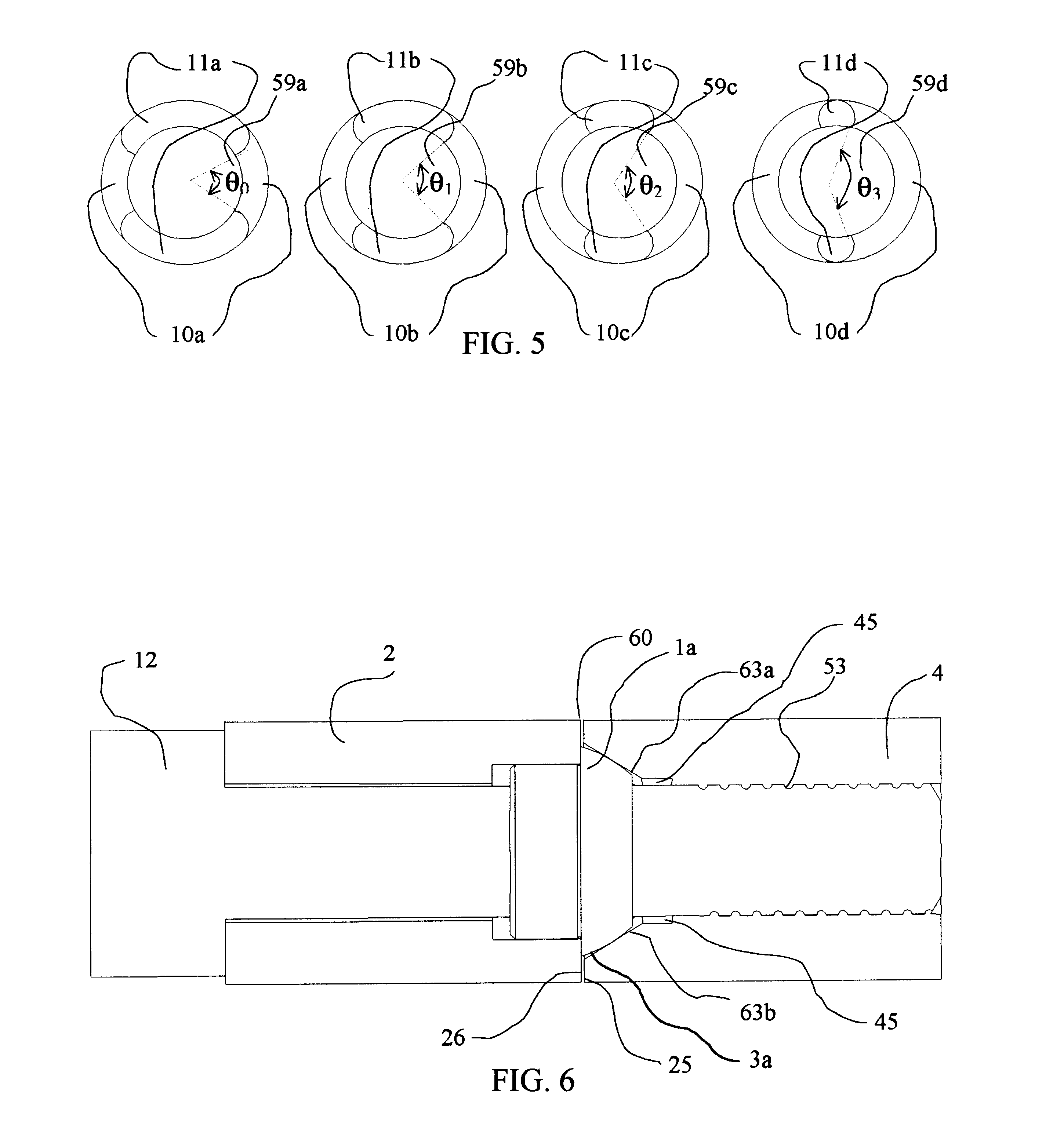
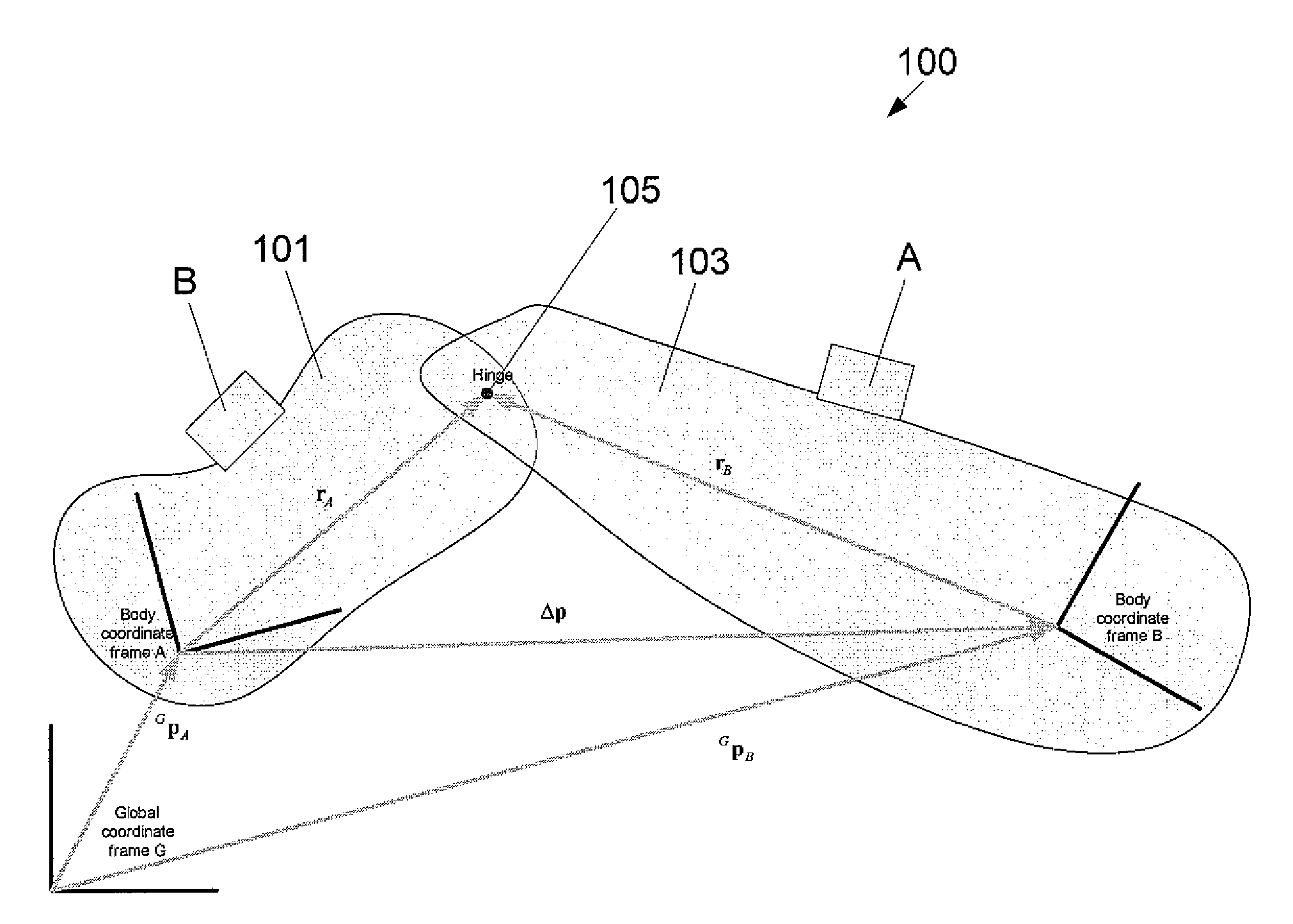
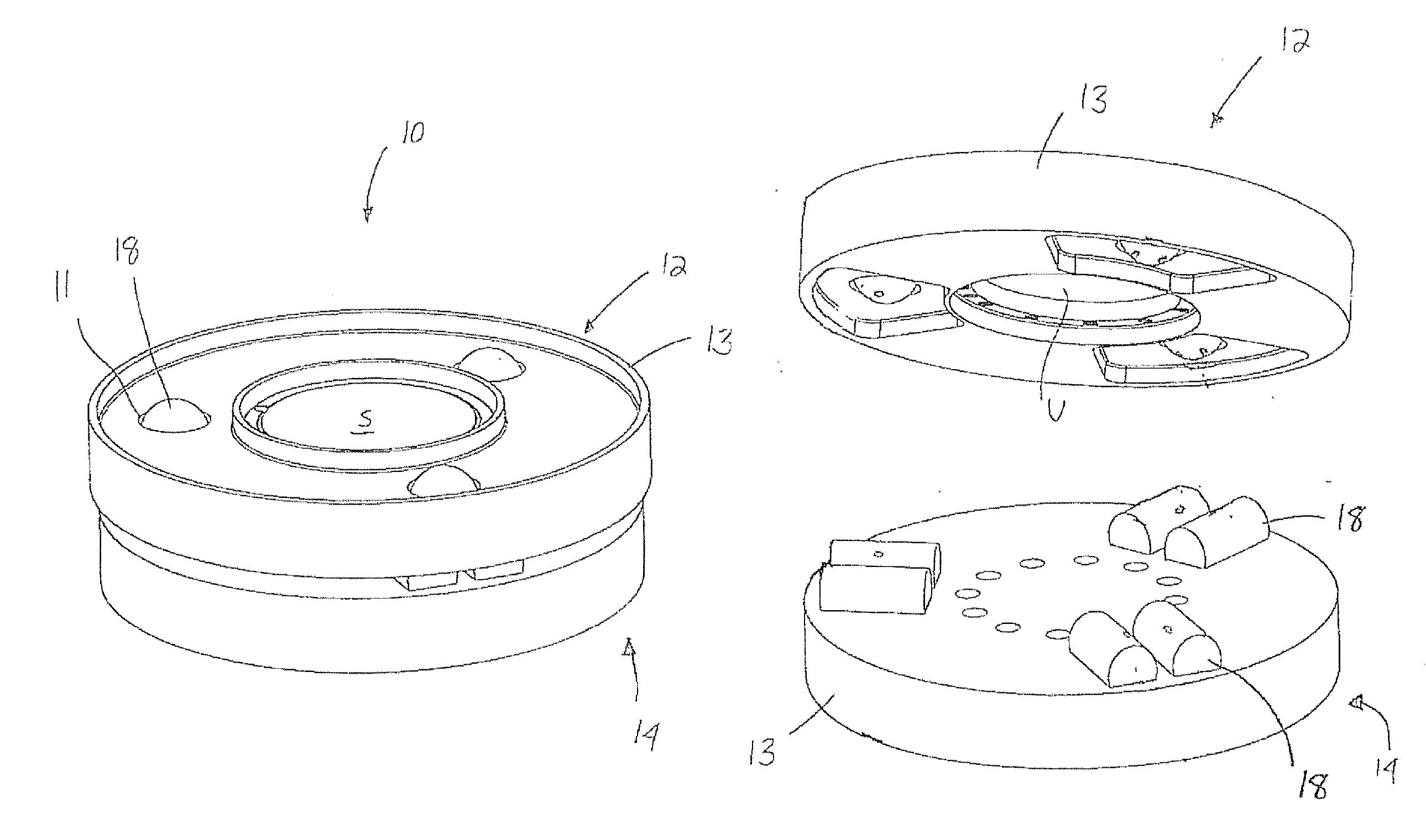
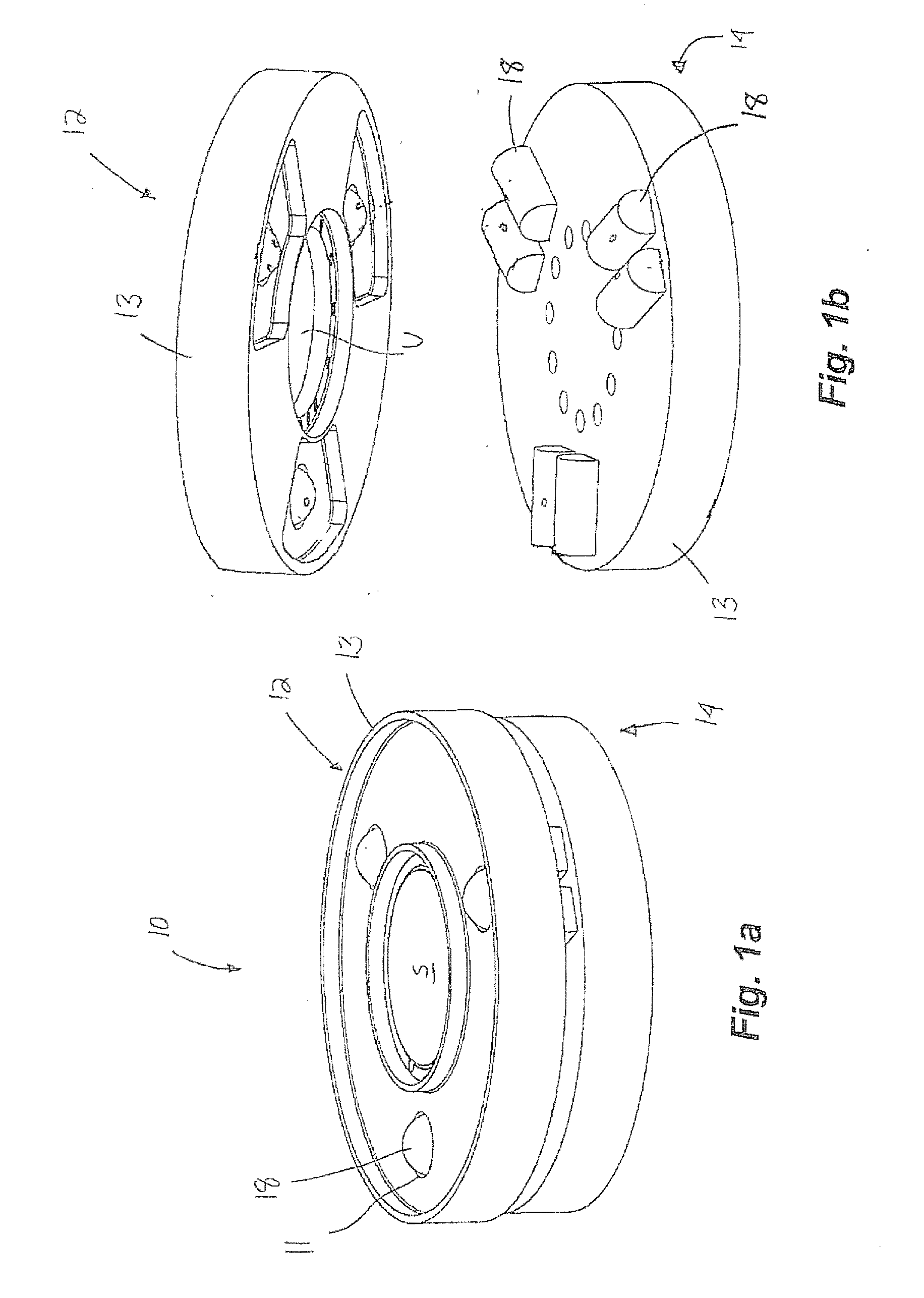
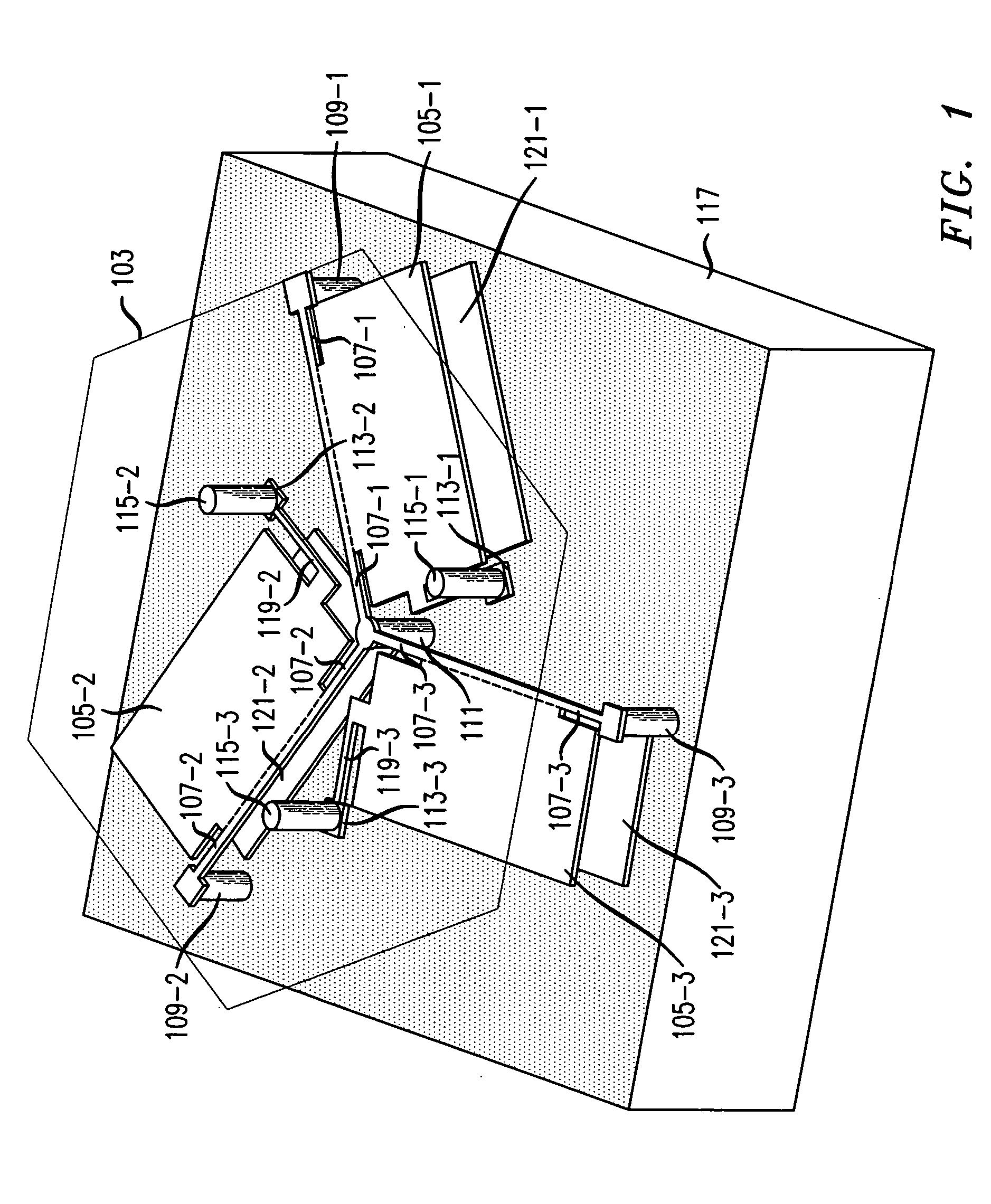
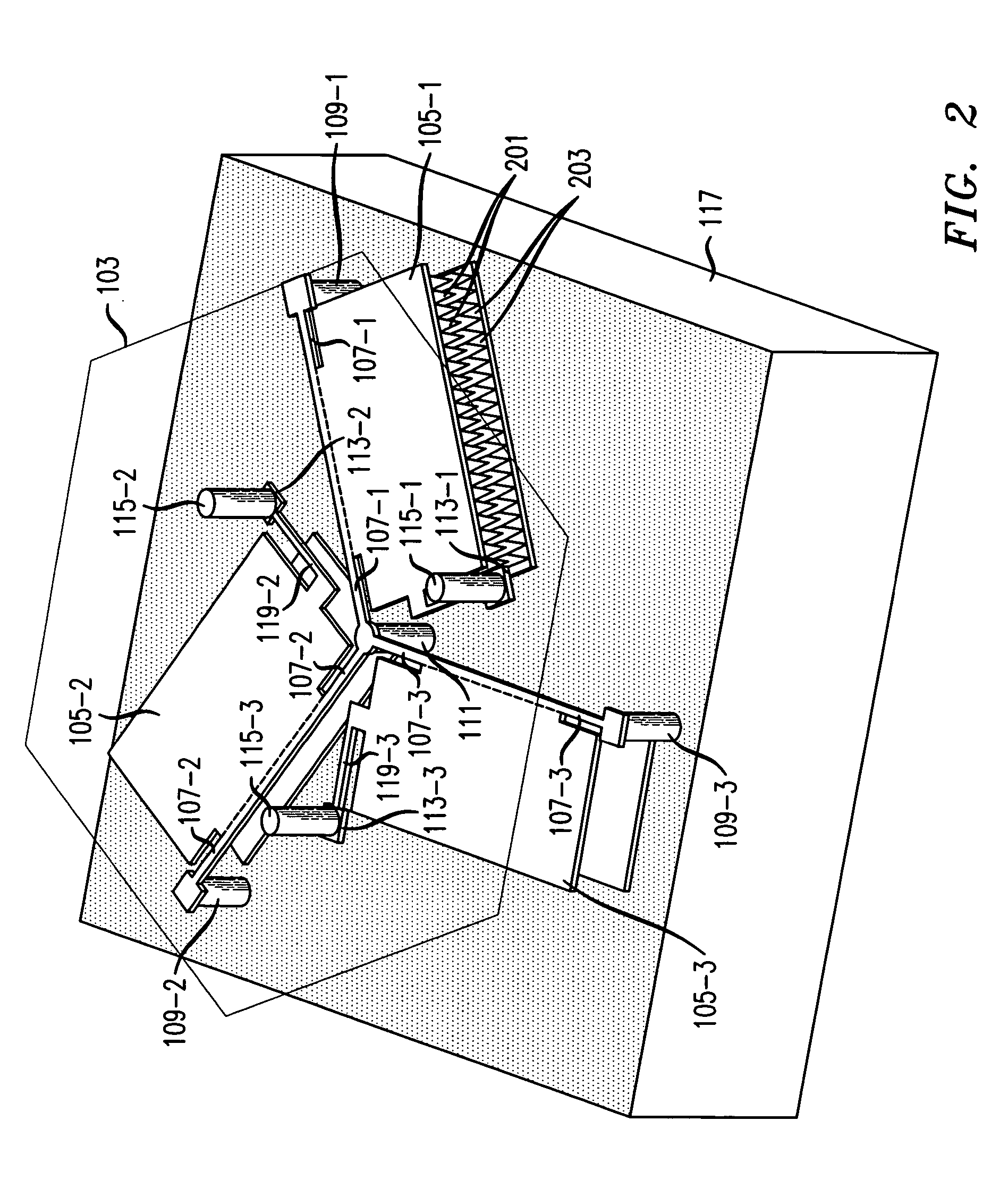
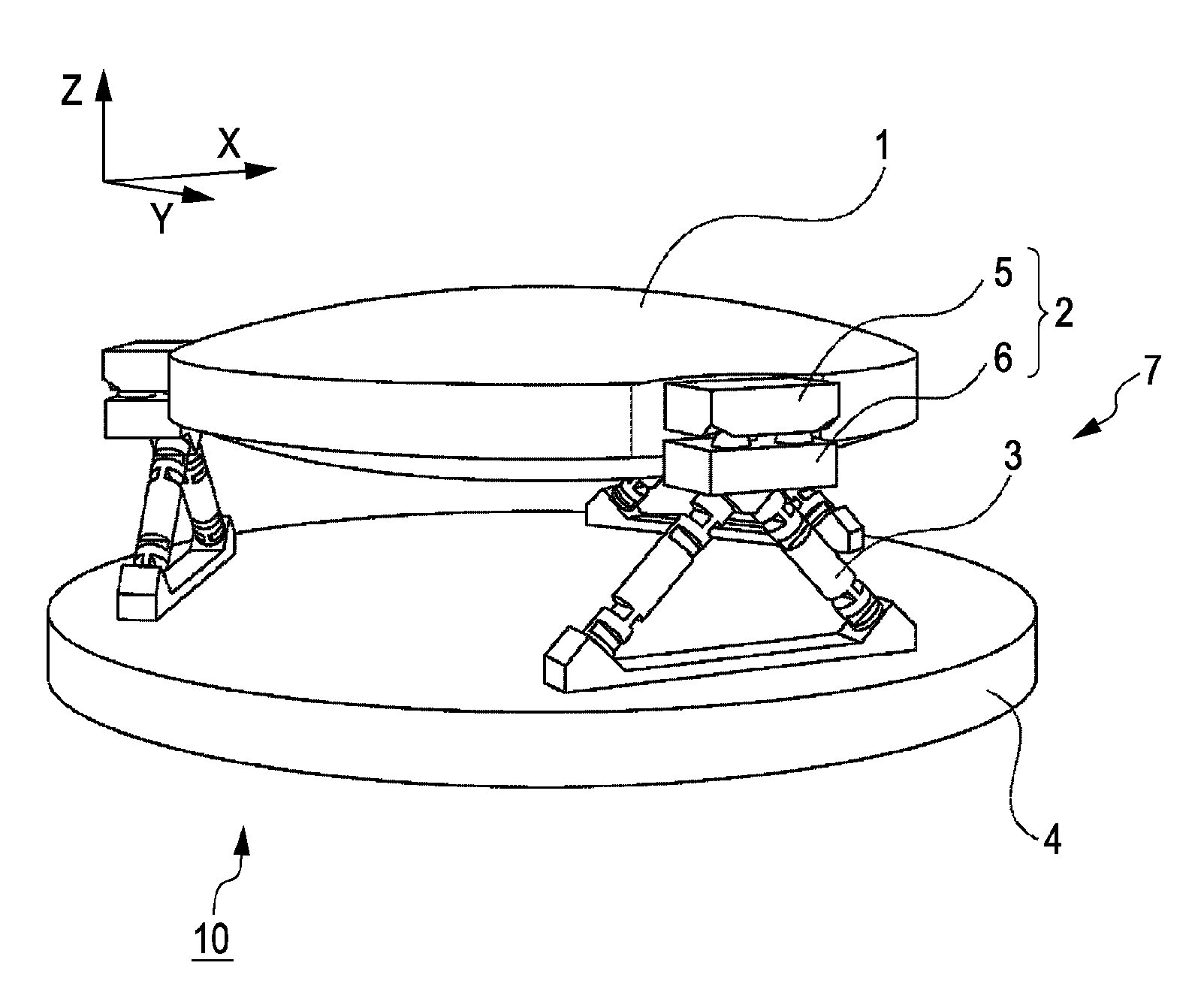
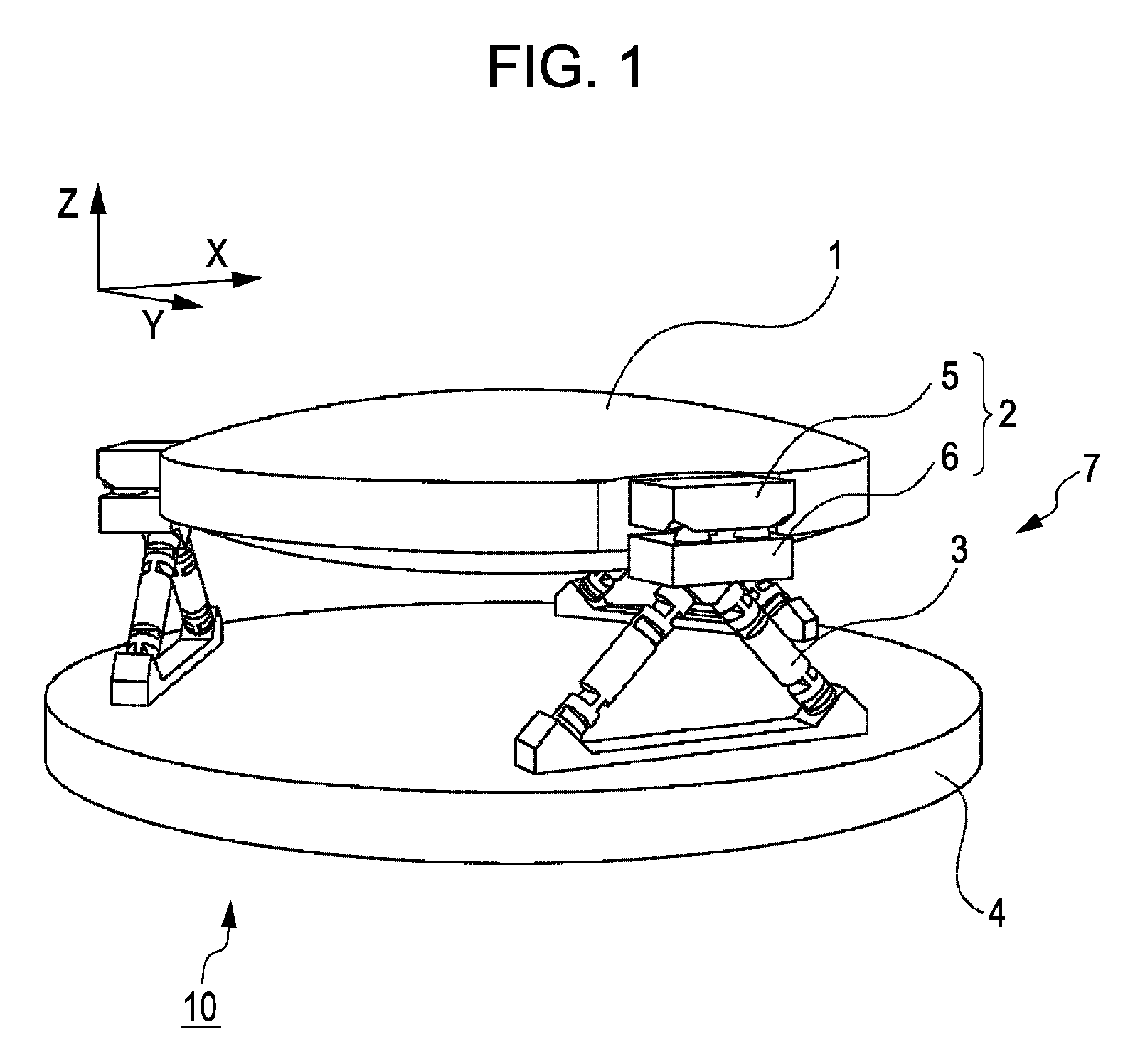
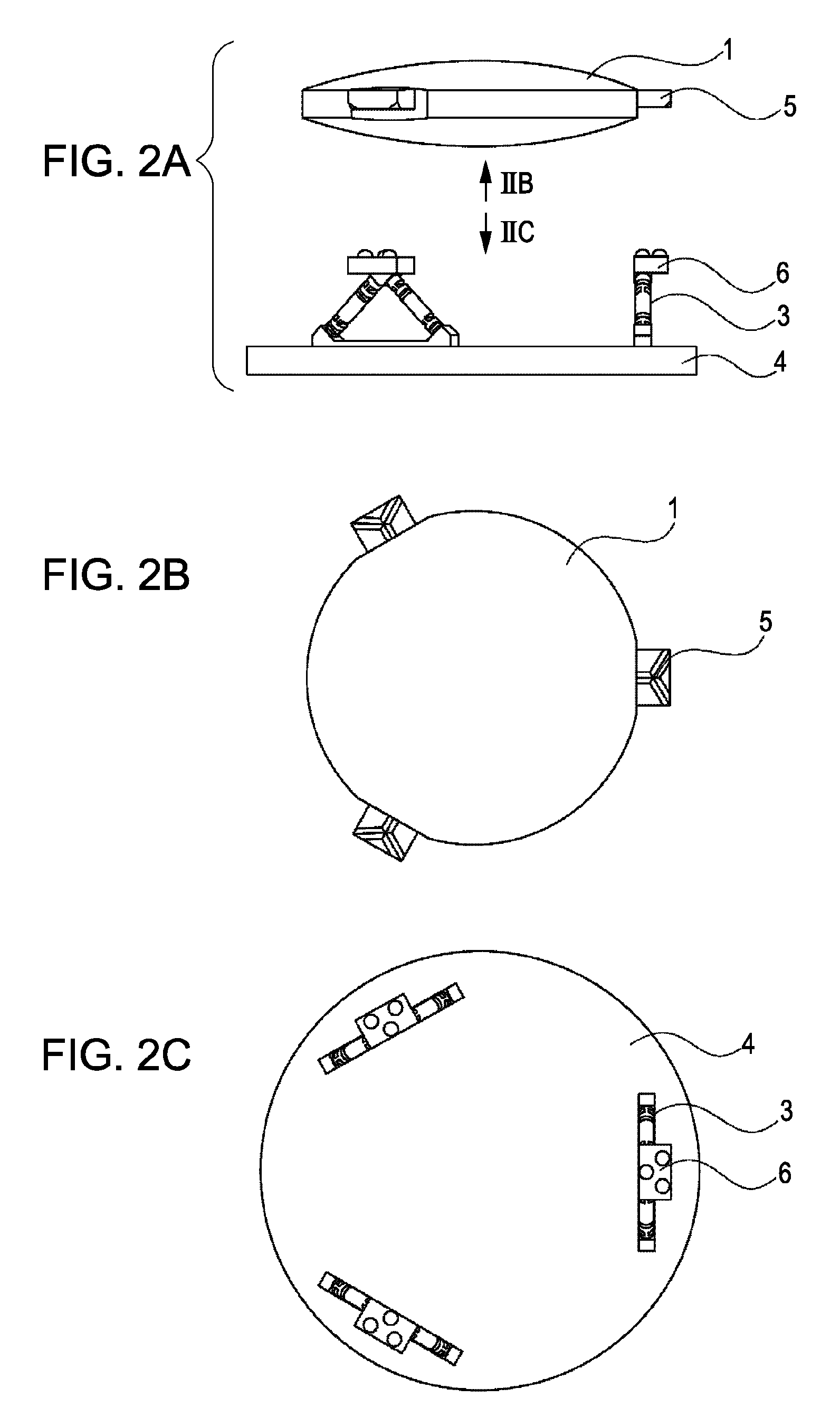
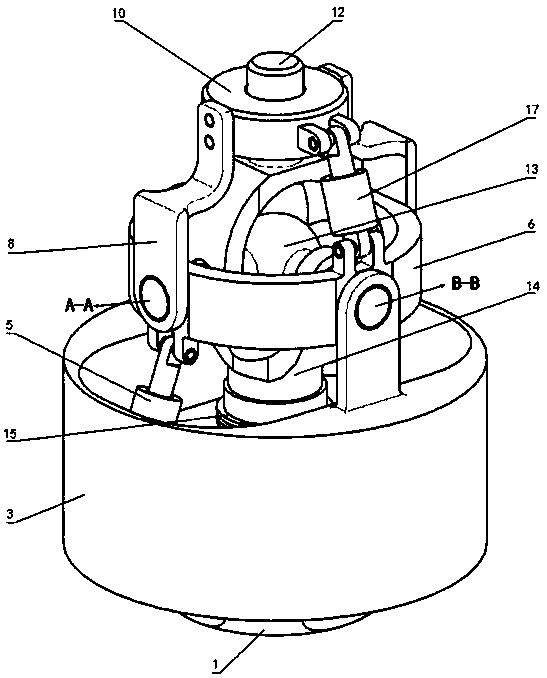
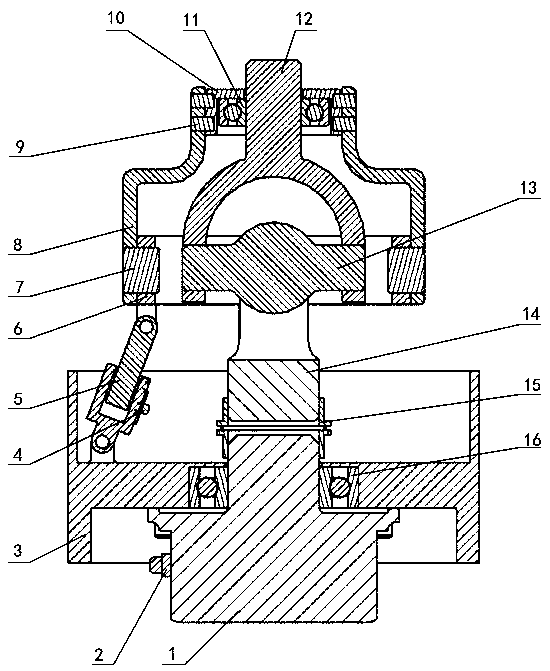
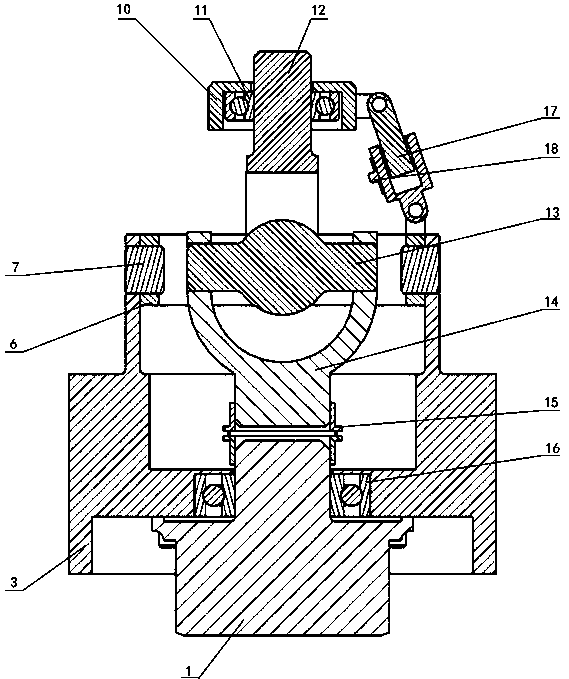
Kinematic coupling describes fixtures designed to exactly constrain the part in question, providing precision and certainty of location. A canonical example of a kinematic coupling consists of three radial v-grooves in one part that mate with three hemispheres in another part. Each hemisphere has two contact points for a total of six contact points, enough to constrain all six of the part's degrees of freedom. An alternative design, consists of three hemispheres on one part that fit respectively into a tetrahedral dent, a v-groove, and a flat.
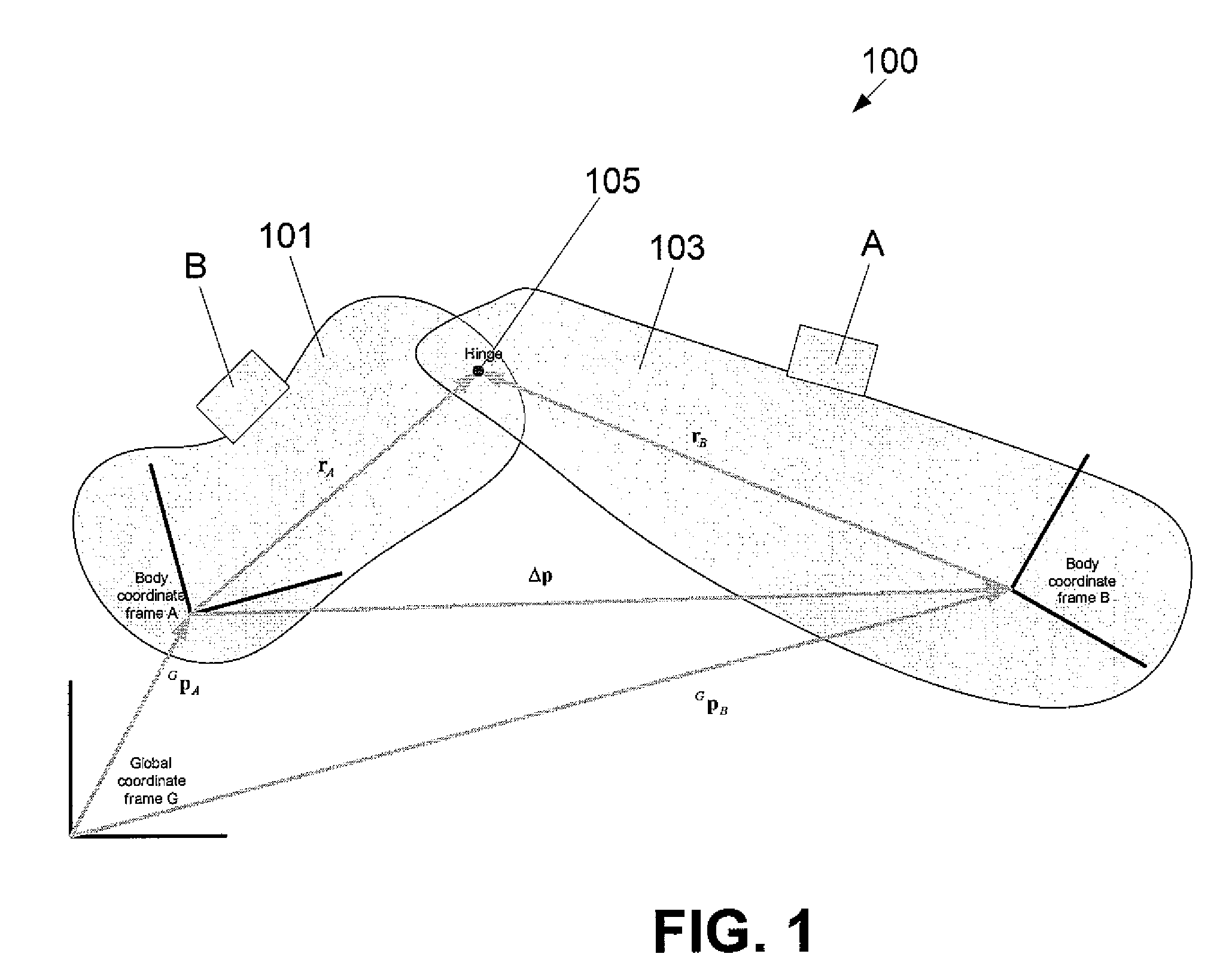
Inertially tracked objects
ActiveUS9226799B2Eliminate driftAvoid disadvantagesDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsKinematic couplingPostural orientation
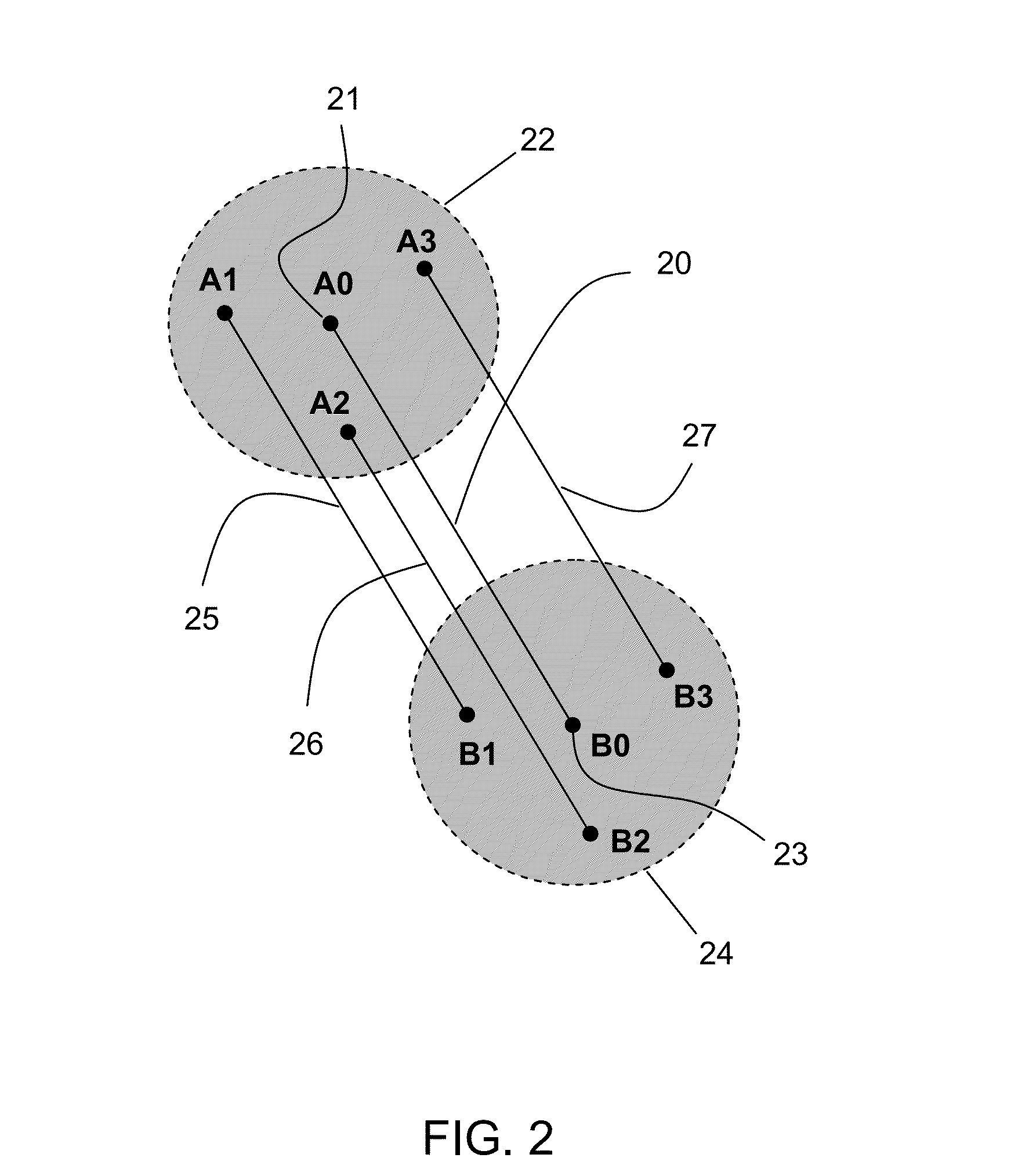
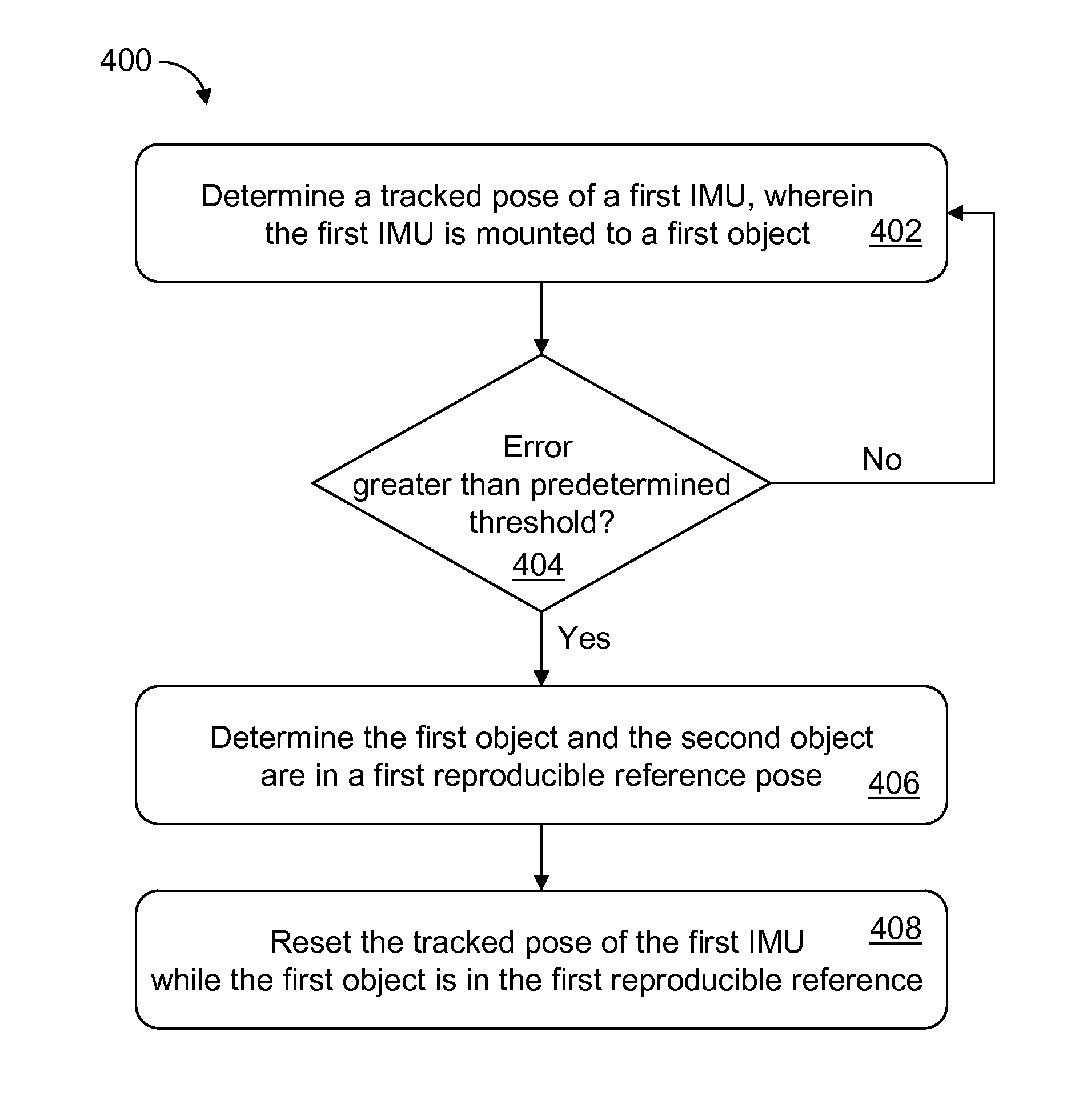
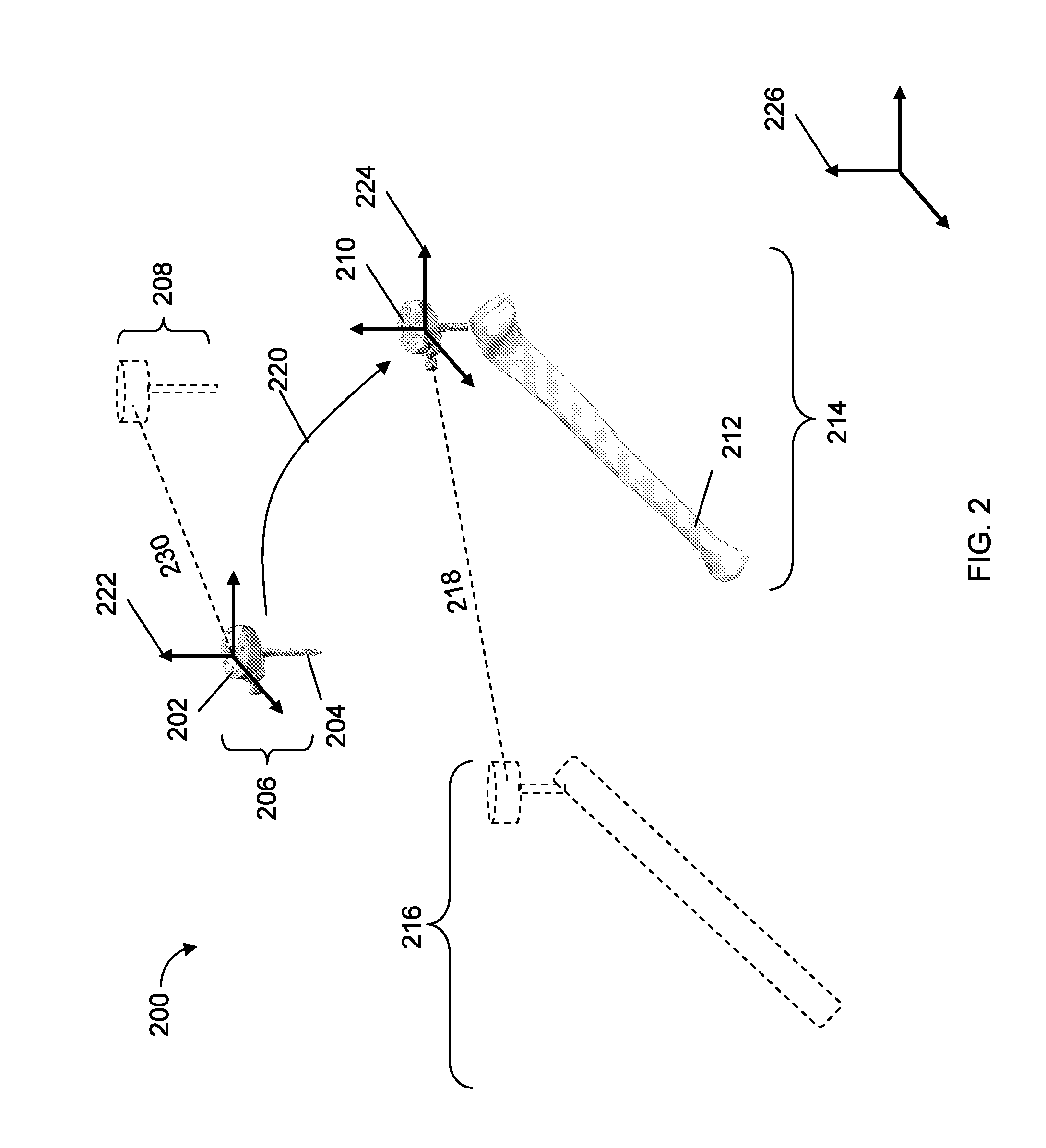
Described are computer-based methods and apparatuses, including computer program products, for inertially tracked objects with a kinematic coupling. A tracked pose of a first inertial measurement unit (IMU) is determined, wherein the first IMU is mounted to a first object. The tracked pose of the first IMU is reset while the first object is in a first reproducible reference pose with a second object.
Owner:MAKO SURGICAL CORP
Quasi-kinematic coupling and method for use in assembling and locating mechanical components and the like
InactiveUS6193430B1Low costLess repeatabilityControlling membersRopes and cables for vehicles/pulleyKinematic couplingMechanical components
A quasi-kinematic coupling for mating components (mechanical parts, surfaces, assemblies and the like) employing mating sets of surface of revolution, (conical) grooves and cooperative surface of revolution (spherical / conical) protrusions for establishing six lines (not just prior points) of contact at the kinematic interfaces, and with elastic compliance therebetween and preferably with relief features to define the effective orientation as a clamping force seats the protrusions in the grooves and seals the component mating surfaces into contact.
Owner:AESOP
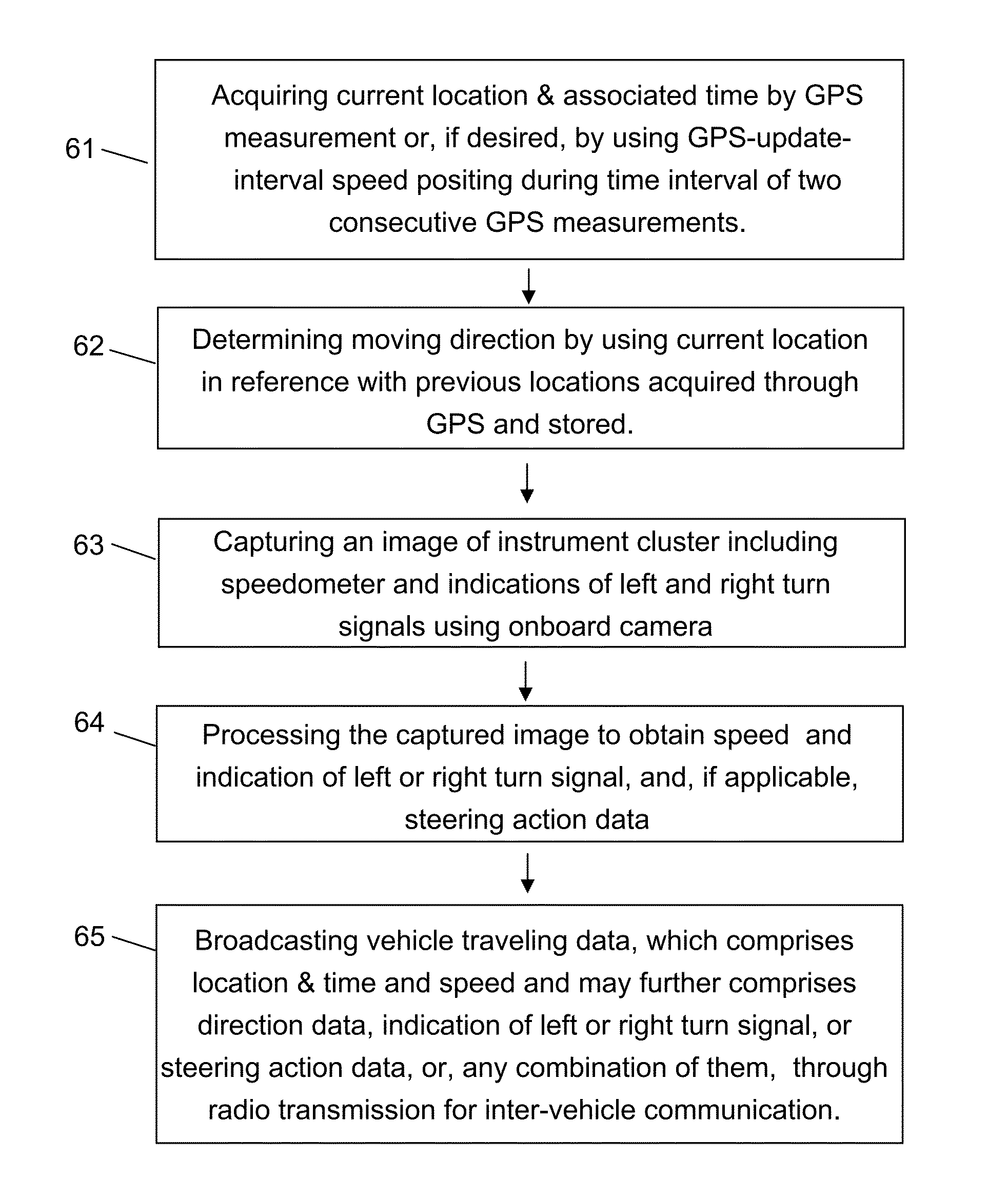
Methods for road safety enhancement using mobile communication device
InactiveUS20130082874A1Sufficiently accurateQuick responseRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDetection of traffic movementKinematic couplingSimulation
Methods for road safety enhancement use mobile communication device (MCD) onboard vehicle to share traveling data through inter-vehicle communication broadcasting, perform road hazard warning, enhance road navigation, and provide autonomous road assistance. The methods have a variety of vehicle status data, such as moving data, steering data, or indicator data, obtained through GPS or image capturing and recognition of instrument cluster of vehicle. The image capturing and recognition allows to get speed data from indication of speedometer, indication of left or right turn signal, steering action data corresponding to steering wheel rotation, and light-on indication of system status indicators. To facilitate that, the MCD may be placed in front of steering wheel, and, if applicable, also in coupling with movement of steering wheel. The MCD may perform relative positioning map-matching lane correlation and GPS-update-interval speed positioning to improve data quality regarding vehicle moving status.
Owner:ZHANG WEI
Inertially Tracked Objects
ActiveUS20110320153A1Eliminate driftAvoid disadvantagesDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsKinematic couplingInertial measurement unit
Described are computer-based methods and apparatuses, including computer program products, for inertially tracked objects with a kinematic coupling. A tracked pose of a first inertial measurement unit (IMU) is determined, wherein the first IMU is mounted to a first object. The tracked pose of the first IMU is reset while the first object is in a first reproducible reference pose with a second object.
Owner:MAKO SURGICAL CORP
Compound lift device
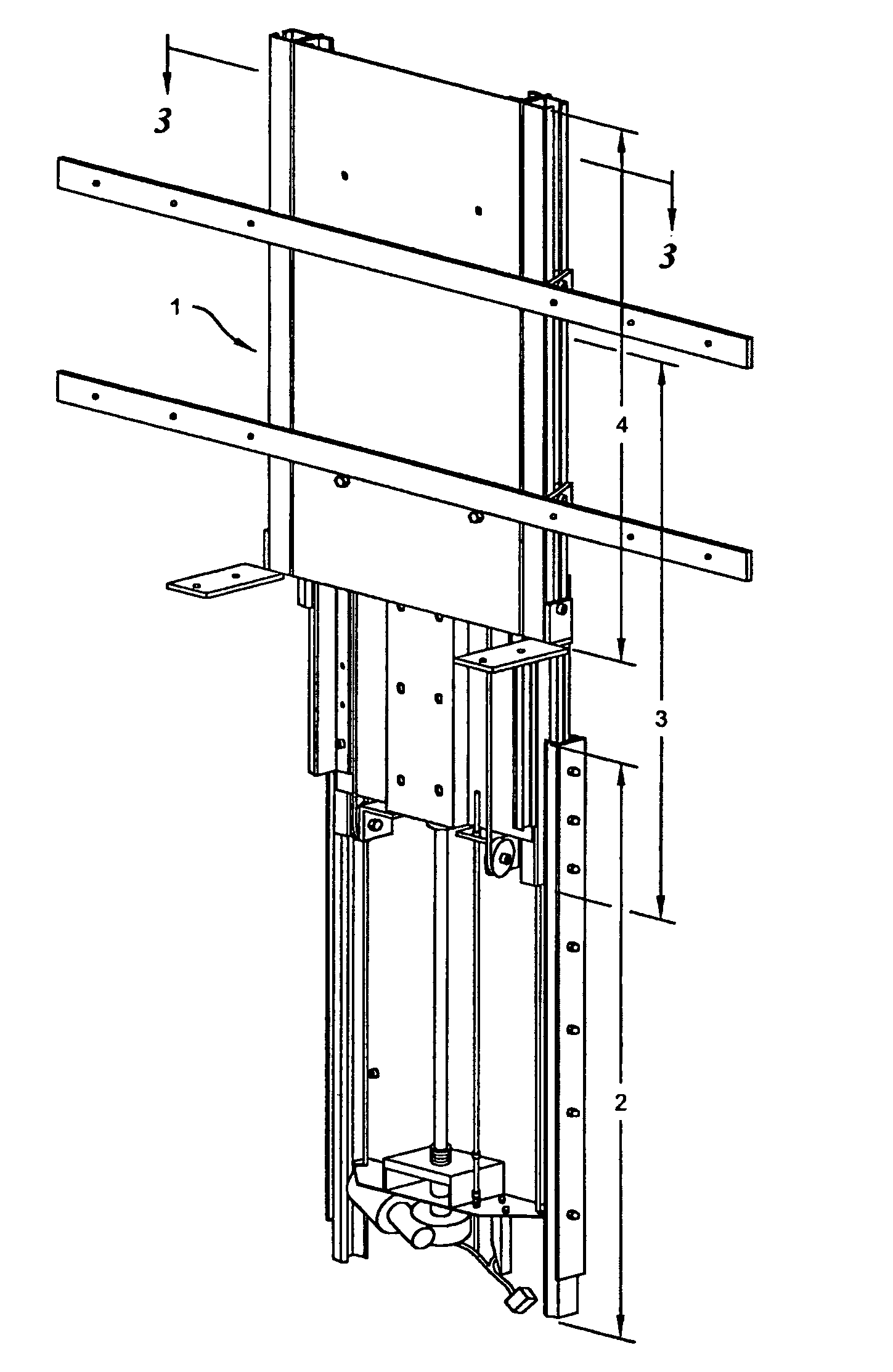
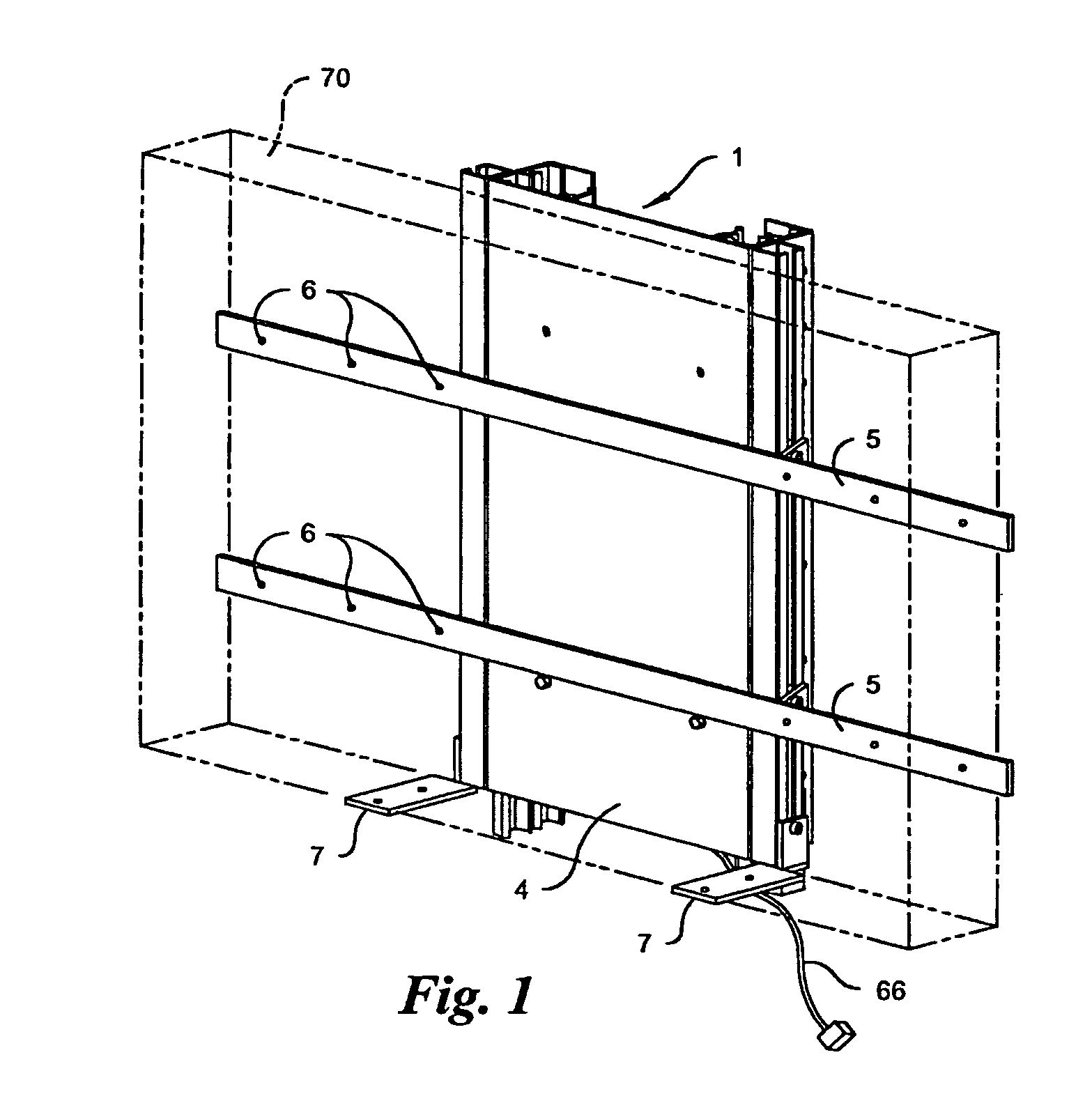
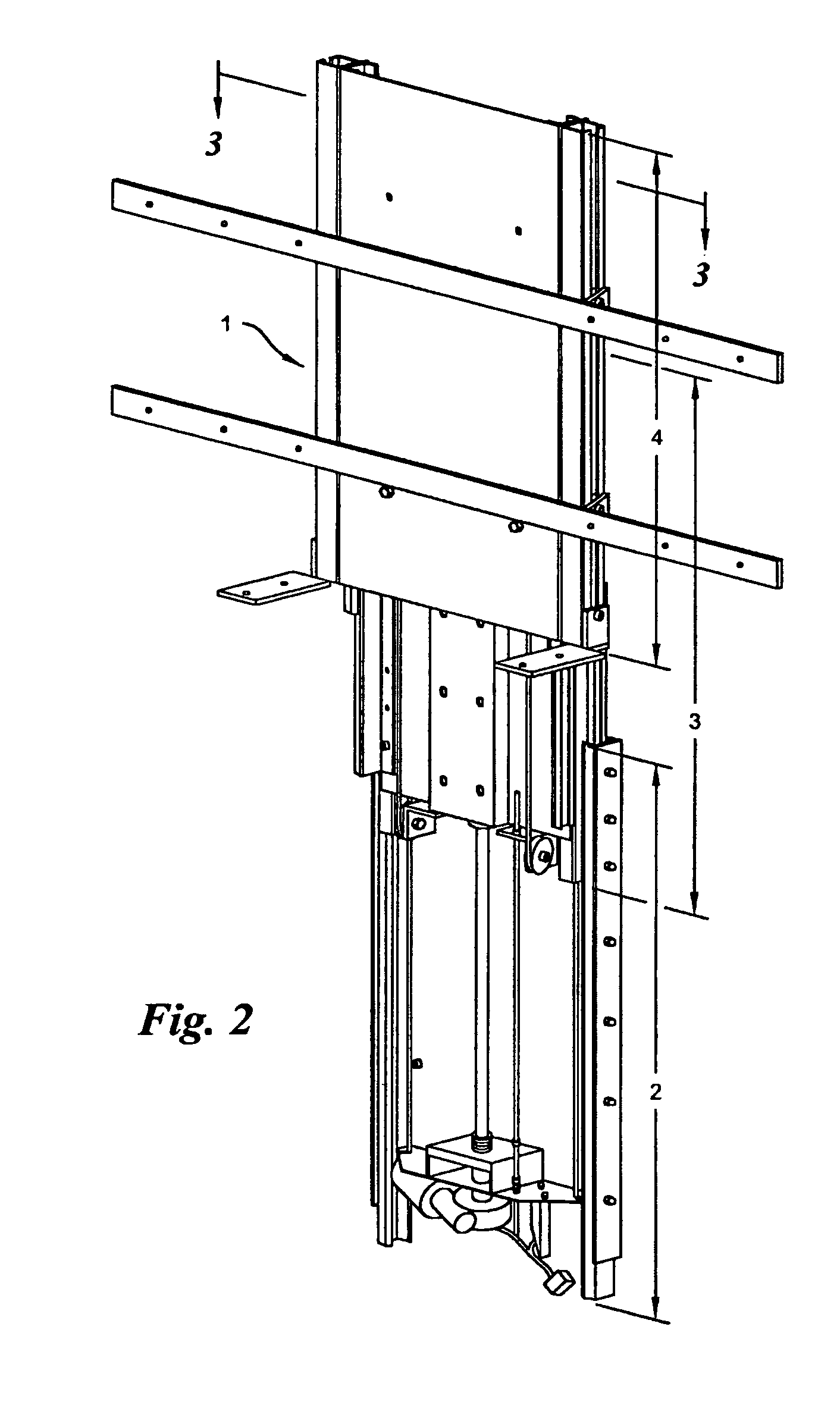
InactiveUS7044423B2Compact storageFacilitating the uninterrupted and nearly noiseless movement of a low-profile televisionTelevision system detailsFurniture partsKinematic couplingMotor drive
The present invention is a compound motorized lift device facilitating the uninterrupted and nearly noiseless movement of a low-profile television. The invention is comprised of a base unit, an intermediate unit, and a support unit slidably disposed in a telescoping fashion in the described order. A pair of linearly extensible slides are fastened between base and intermediate units and between intermediate and support units. The intermediate unit is extended and retracted with respect to the base unit in a linear fashion via a motor driven screw. The support unit is extended and retracted in a linear fashion via a cable-pulley arrangement that couples motion by the intermediate unit in a likewise direction to the support unit.
Owner:BOBER WIESLAW
Inertial Sensor Kinematic Coupling
InactiveUS20110028865A1DistanceAccurate estimateIndoor gamesPerson identificationKinematic couplingThigh musculature
A method is disclosed for measuring the motion of an object, composed of multiple segments connected by joints, via the estimation of the 3D orientation of the object segments relative to one another without dependence on a magnetic field as a reference for heading. The method includes first applying a plurality of inertial sensor units to the segments of the object, e.g., a user thigh, shank, foot, etc. Next an approximation of the distance between each inertial sensor unit and at least one adjacent joint is provided and the joint is subjected to an acceleration, e.g., as the user takes a step or two. The relative orientations of the segments are calculated and the orientations are used to form an estimation of the 3D orientation of the object segments relative to one another without using the local magnetic field as a reference for heading.
Owner:XSENS HLDG BV
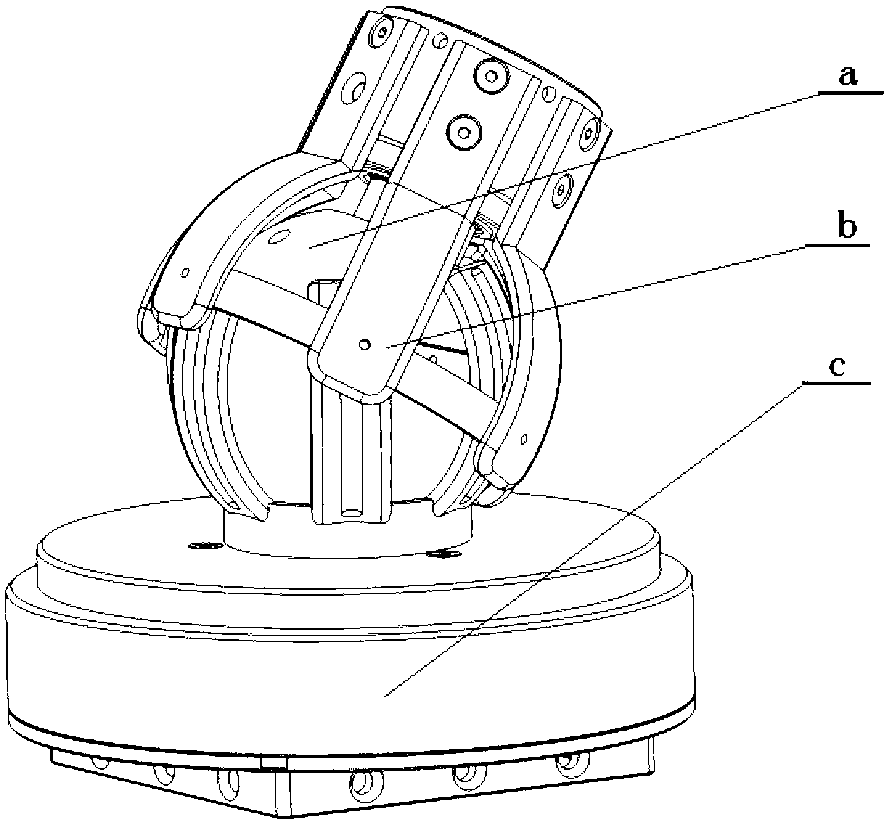
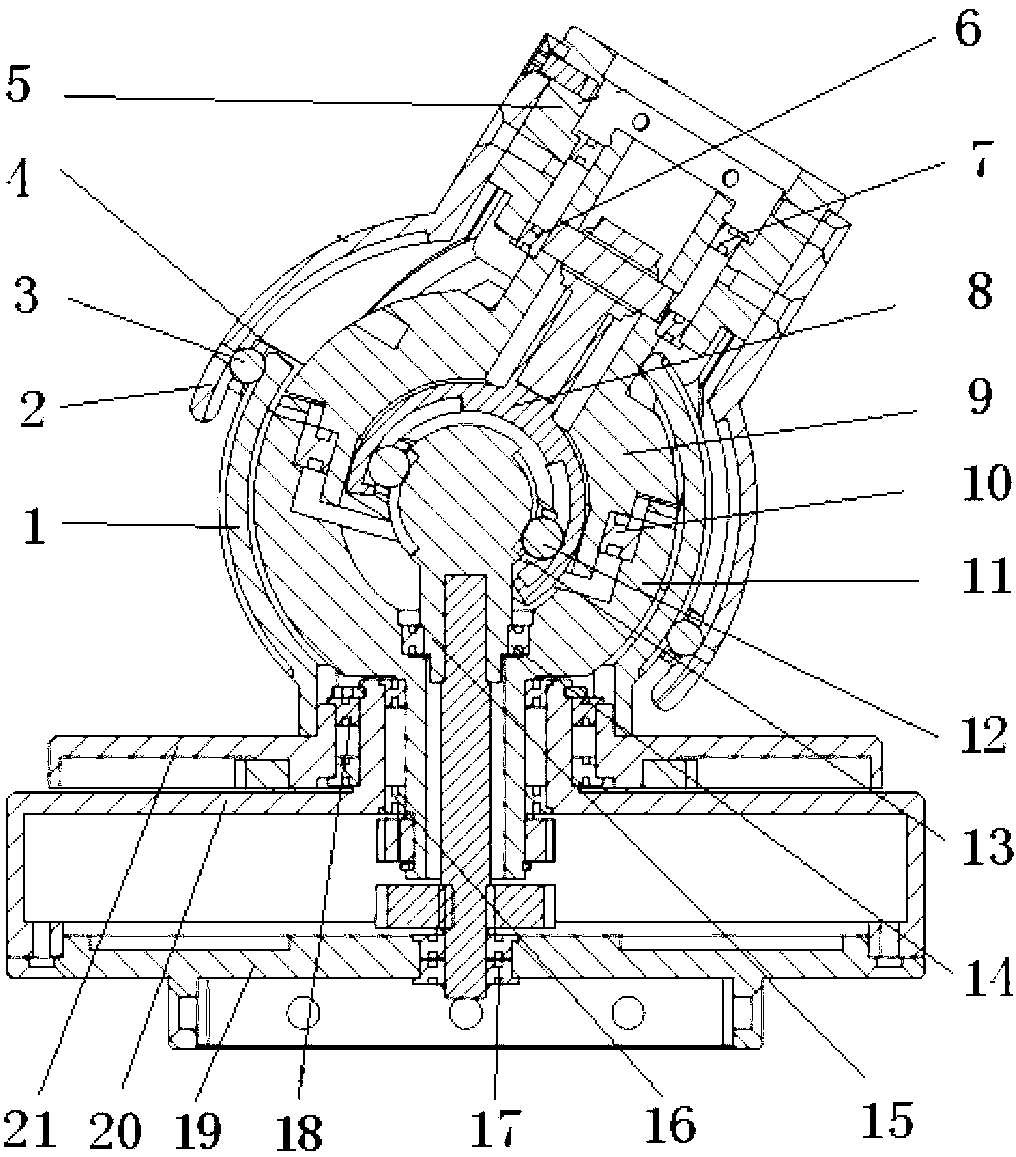
Three-freedom-degree constant speed decoupling space robot active spherical wrist and universal compliant control method
ActiveCN103341865AImprove stabilityIncreased range of angle adjustmentJointsKinematic couplingUniversal joint
The invention relates to a three-freedom-degree constant speed decoupling space robot active spherical wrist and a universal compliant control method. The offset mode that the included angles are formed among rotation plane normal and rotating shafts is adopted for both an upper hemisphere rotating body and a lower hemisphere rotating body. The intersection point of the two rotating shafts of the upper rotating body and the lower rotating body is the sphere center of hemispheres of the upper rotating body and the lower rotating body, the intersection point of the two rotating shafts coincides with the rotating center of an inner ball cage universal joint and the rotating center of an outer ball cage universal joint respectively, and then constant speed decoupling of three input movements is achieved; the output end of the outer ball cage universal joint is connected with a shaft neck of the upper rotating body through a bearing in a suspension mode, three absolute corner coded discs are connected with the upper rotating body, the lower rotating body, a motor conducting spinning motion, and the output end of a speed reducing system respectively, a six-dimensional ATI sensor is installed at the output tail end of the wrist, and a wrist universal compliant follow-up control mode is achieved by a rotating joint of an upper hemisphere, a rotating joint of a lower hemisphere and a joint conducting spinning motion through a system friction force compensation technology. The three-freedom-degree constant speed decoupling space robot active spherical wrist and the universal compliant control method are accurate in locating, stable in movement, and capable of avoiding oscillation phenomena of movement coupling and mechanical arms and effectively relieving mechanical interference in a spherical wrist full compliant mode.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Substrate flat grinding device
InactiveUS20090203299A1Superior flat thickness distributionImprove rigidityEdge grinding machinesPolishing machinesKinematic couplingEngineering
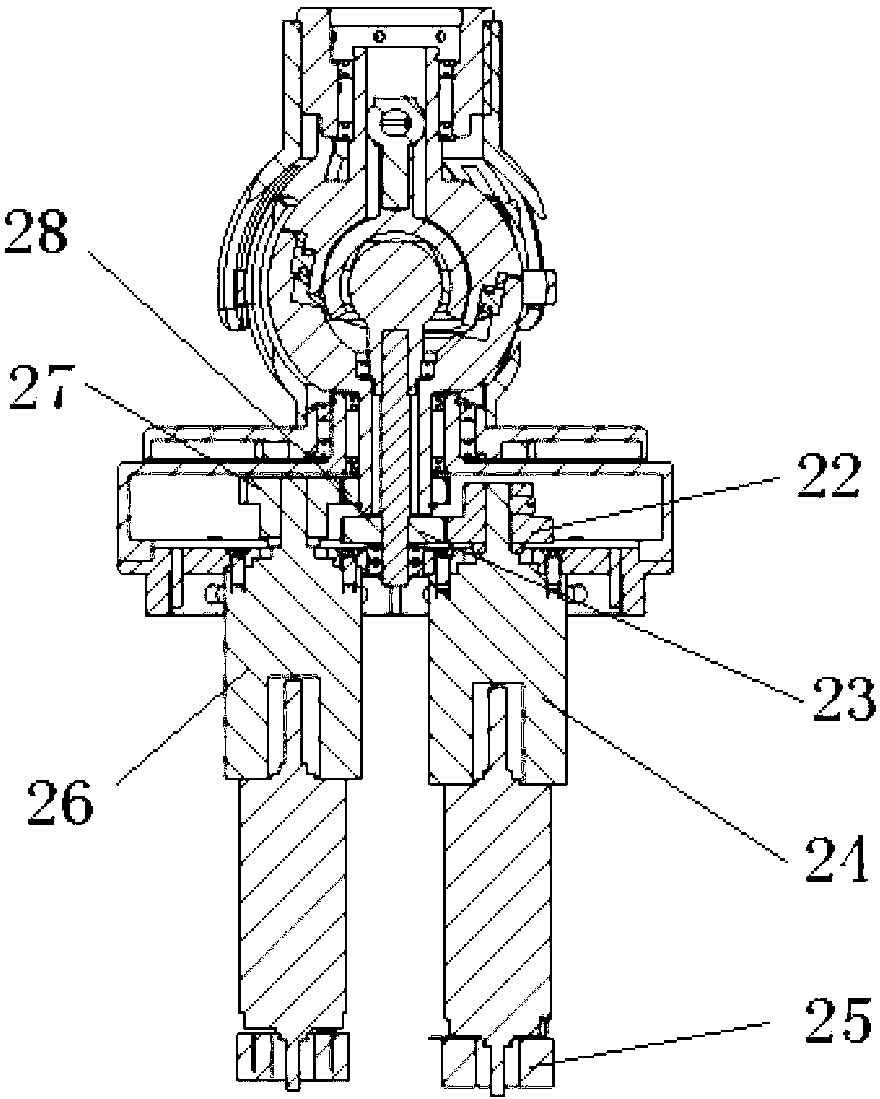
To provide a high-rigidity flat grinding device, a substrate flat grinding device has three fastening plate lifting-and-lowering mechanisms that have kinematic couplings and a cylinder rod that move the fastening plate upward or downward. Being a high-rigidity grinding device in which the load of the fastening plate 6 also is a load on the grindstone 14 that does the grinding, there is little deflection in the thickness distribution of the substrates that are obtained, even if they are semiconductor substrates having a large substrate diameter of 450 mm.
Owner:OKAMOTO MACHINE TOOL WORKS LTD
Demountable optical connector for optoelectronic devices
InactiveUS20160161686A1Precise alignmentReduce dependenceCoupling light guidesMetal working apparatusKinematic couplingEngineering
A reconnectable connection between an optical bench supporting an optical fiber and a photonic integrated circuit (PIC), which a foundation and a connector that is configured and structured to be removably attachable for reconnection to the foundation in alignment therewith. The foundation can be aligned to electro-optical elements in the PIC. The foundation may be permanently attached with respect to the opto-electronic device. The optical bench can be removably attached to the foundation. Alignment between the foundation and the connector is achieved by kinematic coupling, quasi-kinematic coupling, or elastic-averaging coupling.
Owner:SENKO ADVANCED COMPONENTS
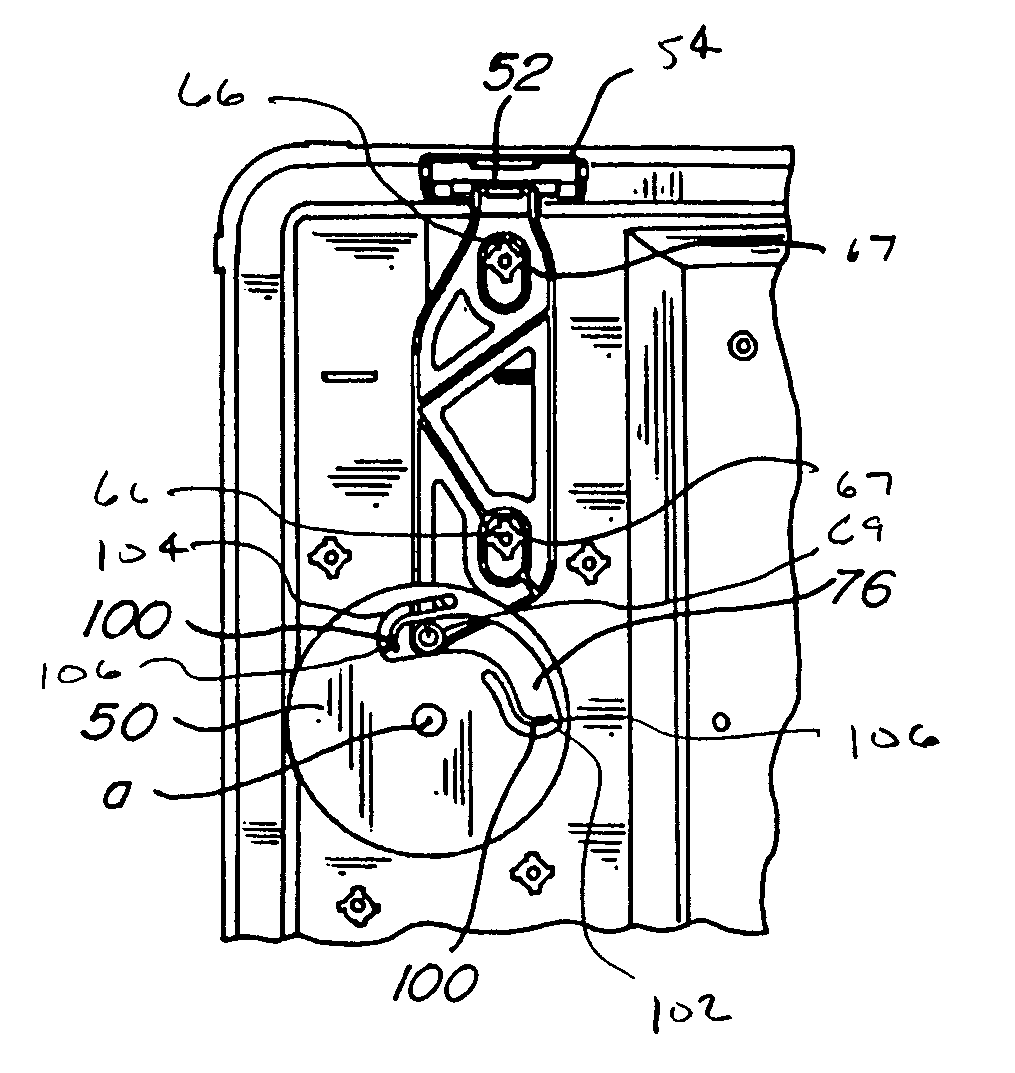
Wafer container and door with vibration dampening latching mechanism
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Humanoid manipulator mechanism
InactiveCN1283429CImprove work flexibilityImprove adaptabilityGripping headsLittle fingerKinematic coupling
The invention discloses a mechanism of a humanoid robot hand, which is composed of a palm, five fingers and a mechanical interface. The five fingers are installed on the palm, and the root of the palm is provided with a mechanical interface. The connection between the mechanism and the robot arm. In the humanoid robotic hand mechanism of the present invention, the thumb and forefinger each have a degree of freedom and are respectively driven by a motor; the middle finger, ring finger and little finger share a degree of freedom and are driven by the same motor, and the transmission of the three fingers adopts the same modular design, The only difference lies in the length of the distal knuckles of the three fingers. The first two joints of the index, middle, ring, and little fingers are kinematically coupled individually. There is a motion decoupling device at the connection shaft between the proximal knuckles of each finger and the palm. When the proximal knuckles of the fingers are blocked from touching the object, the other knuckles can continue to move to complete the envelope grasping of the object.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
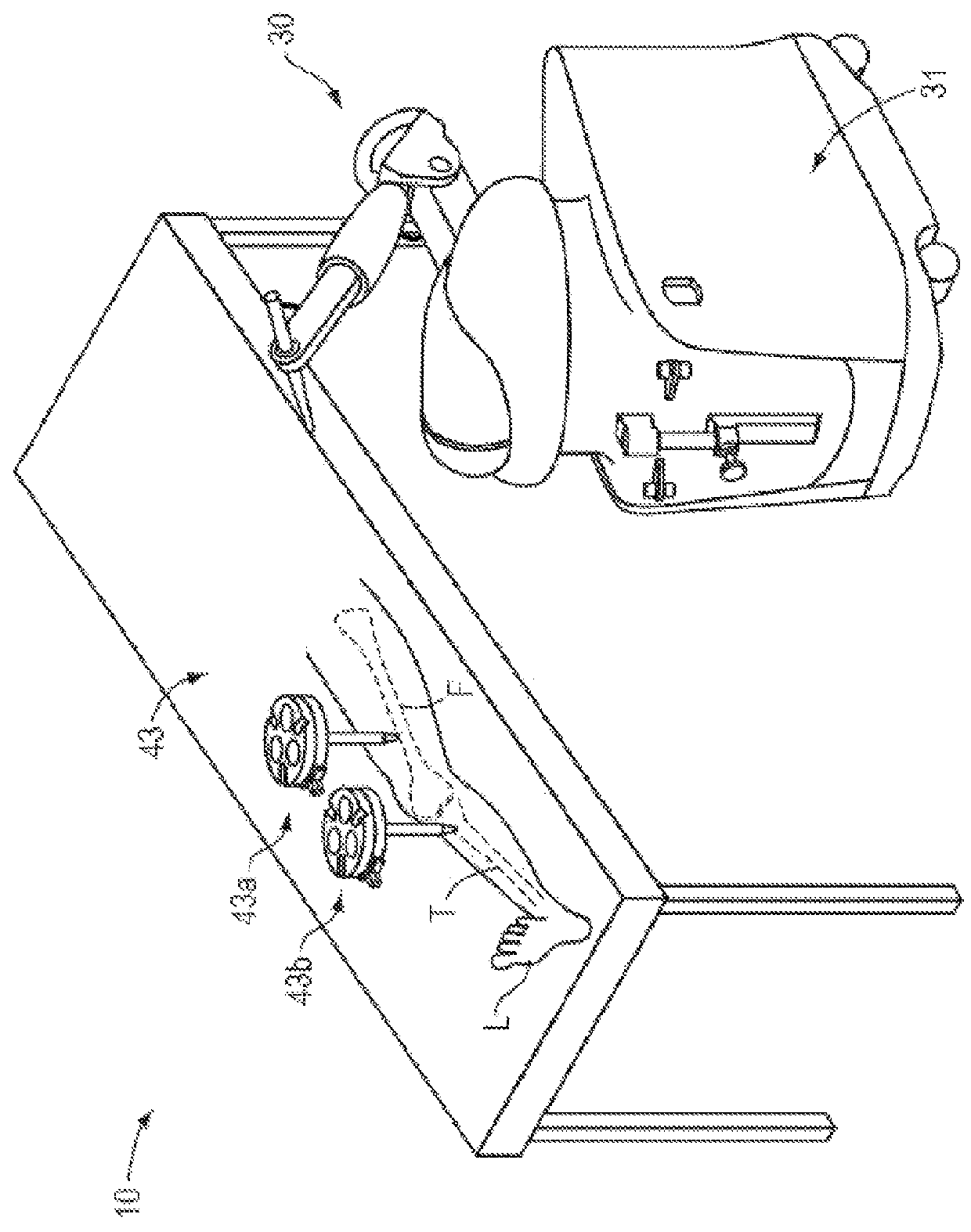
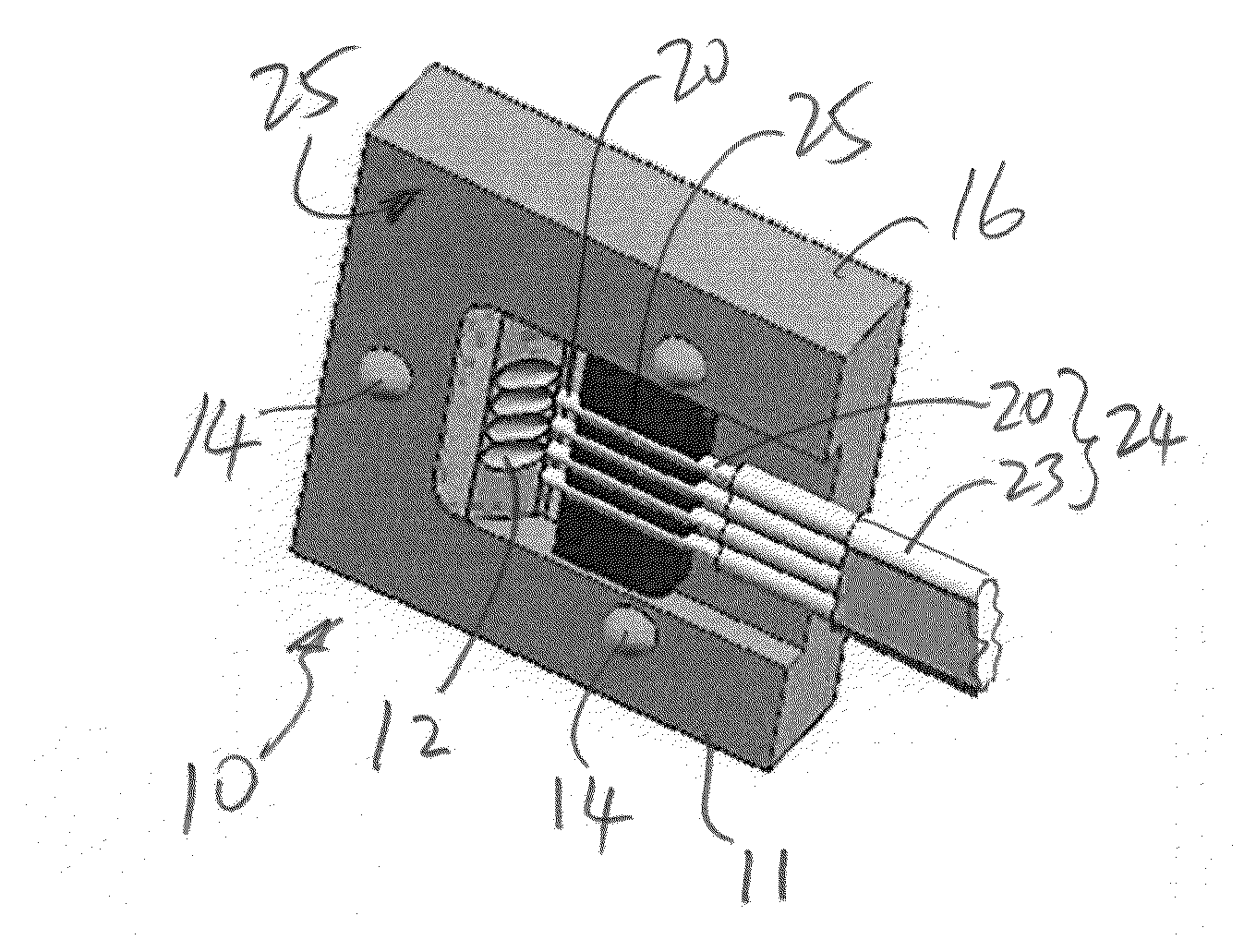
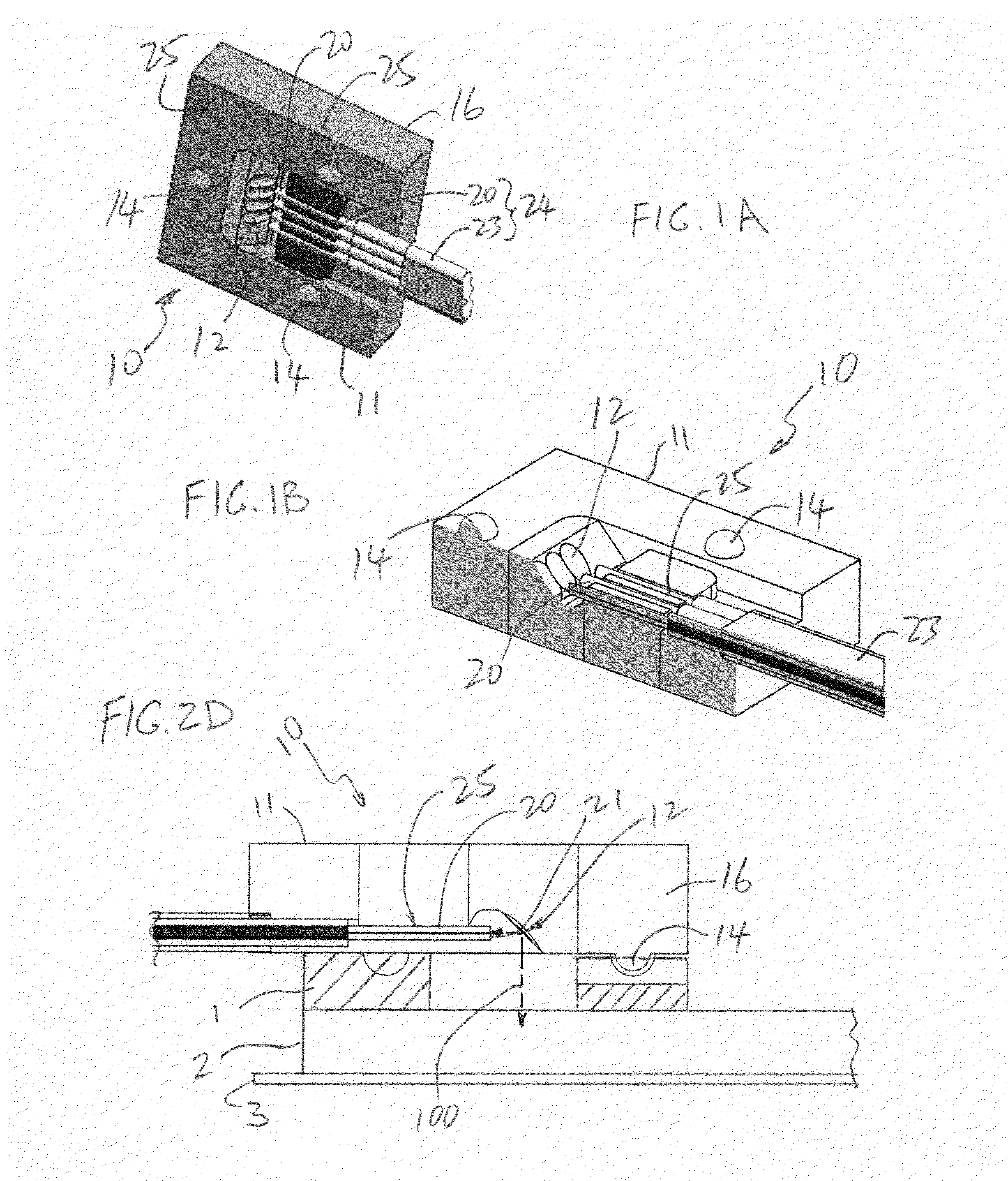
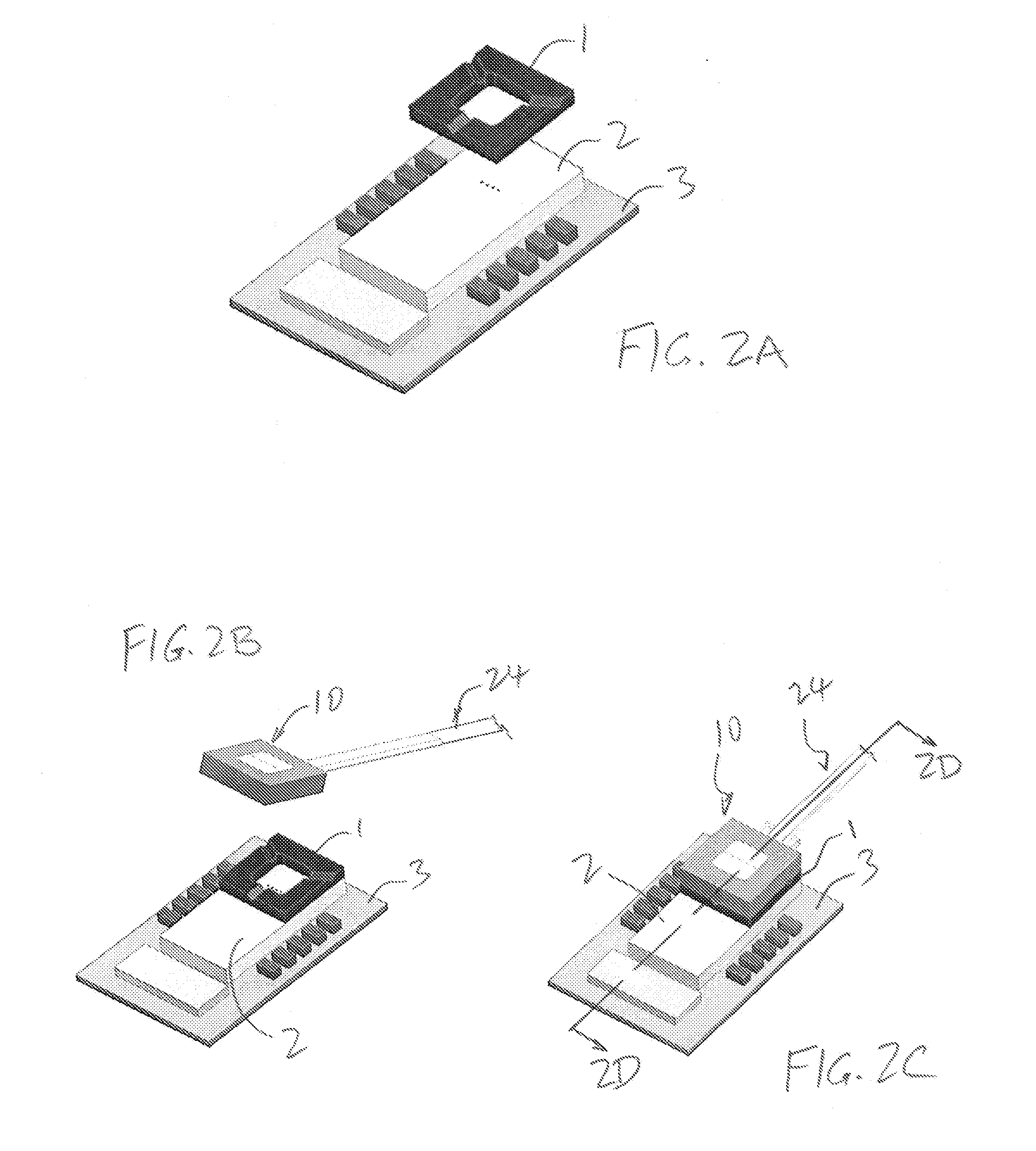
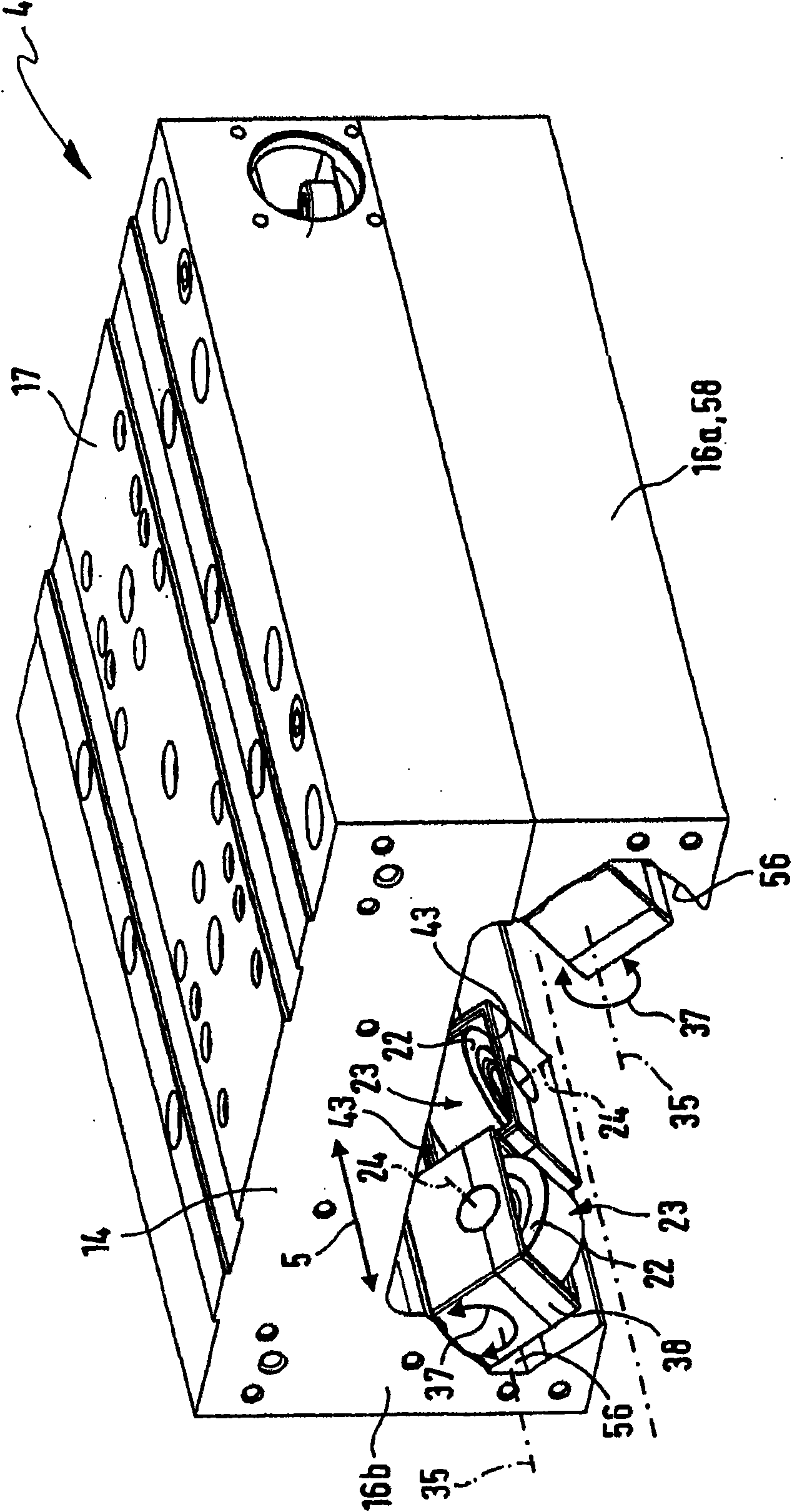
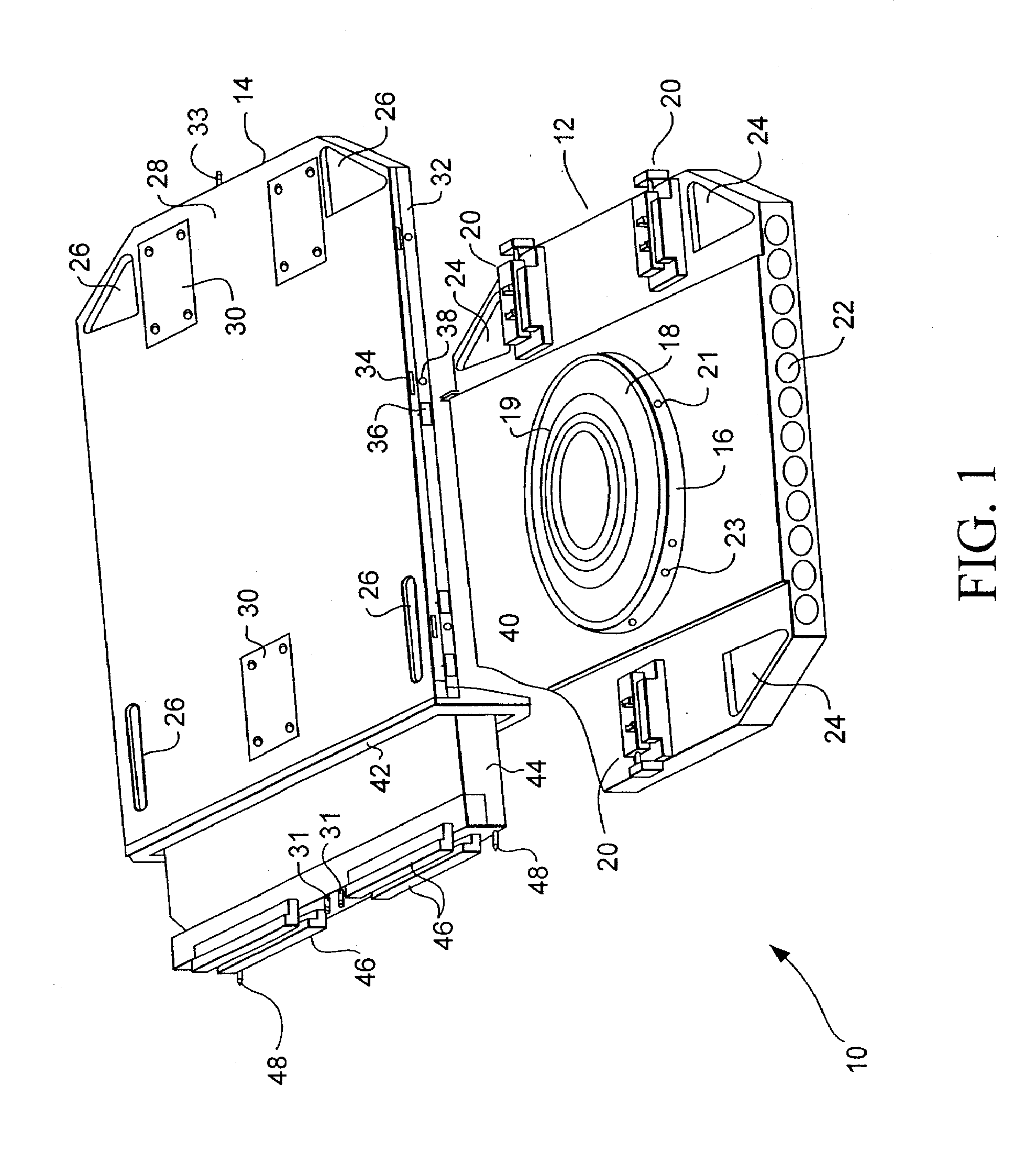
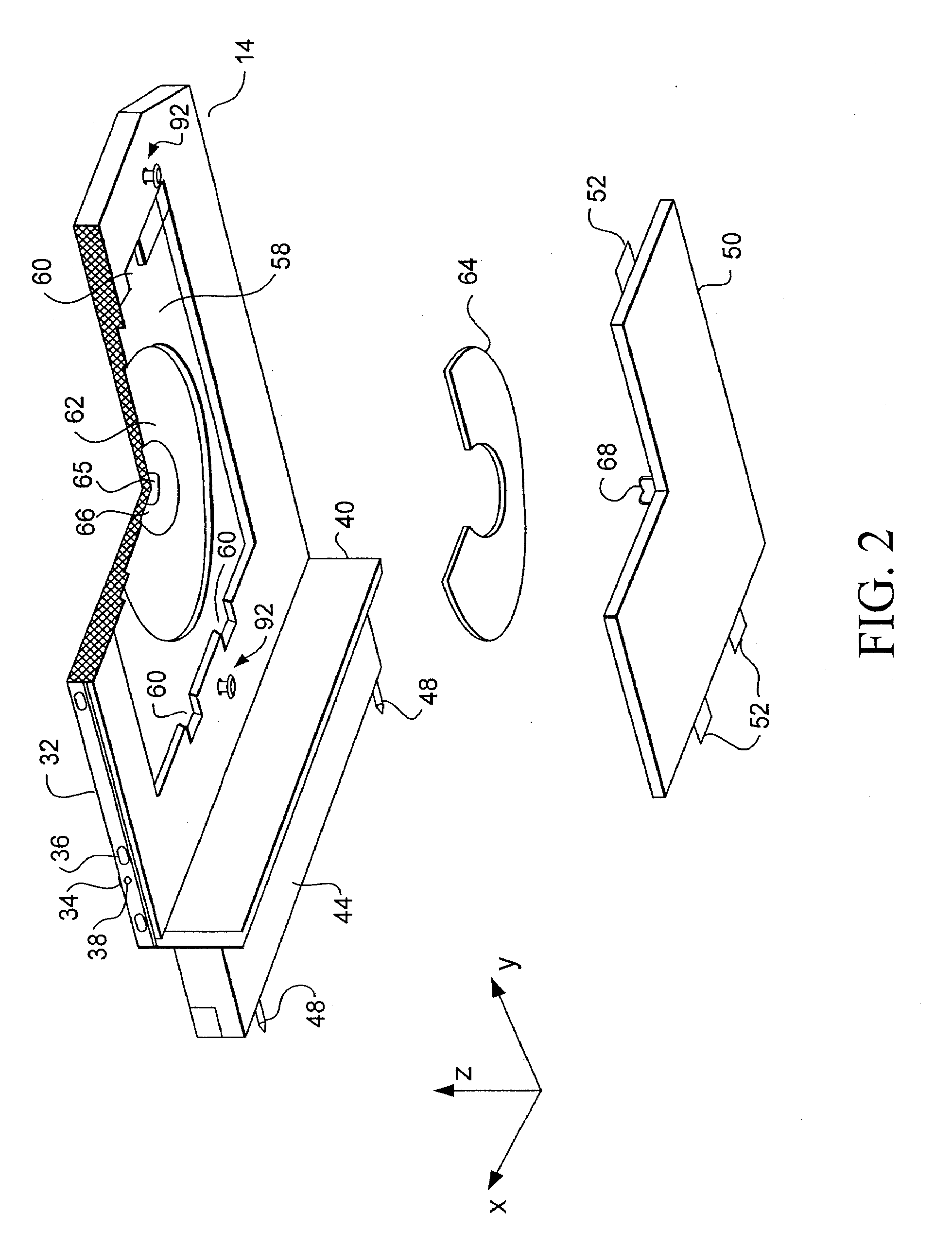
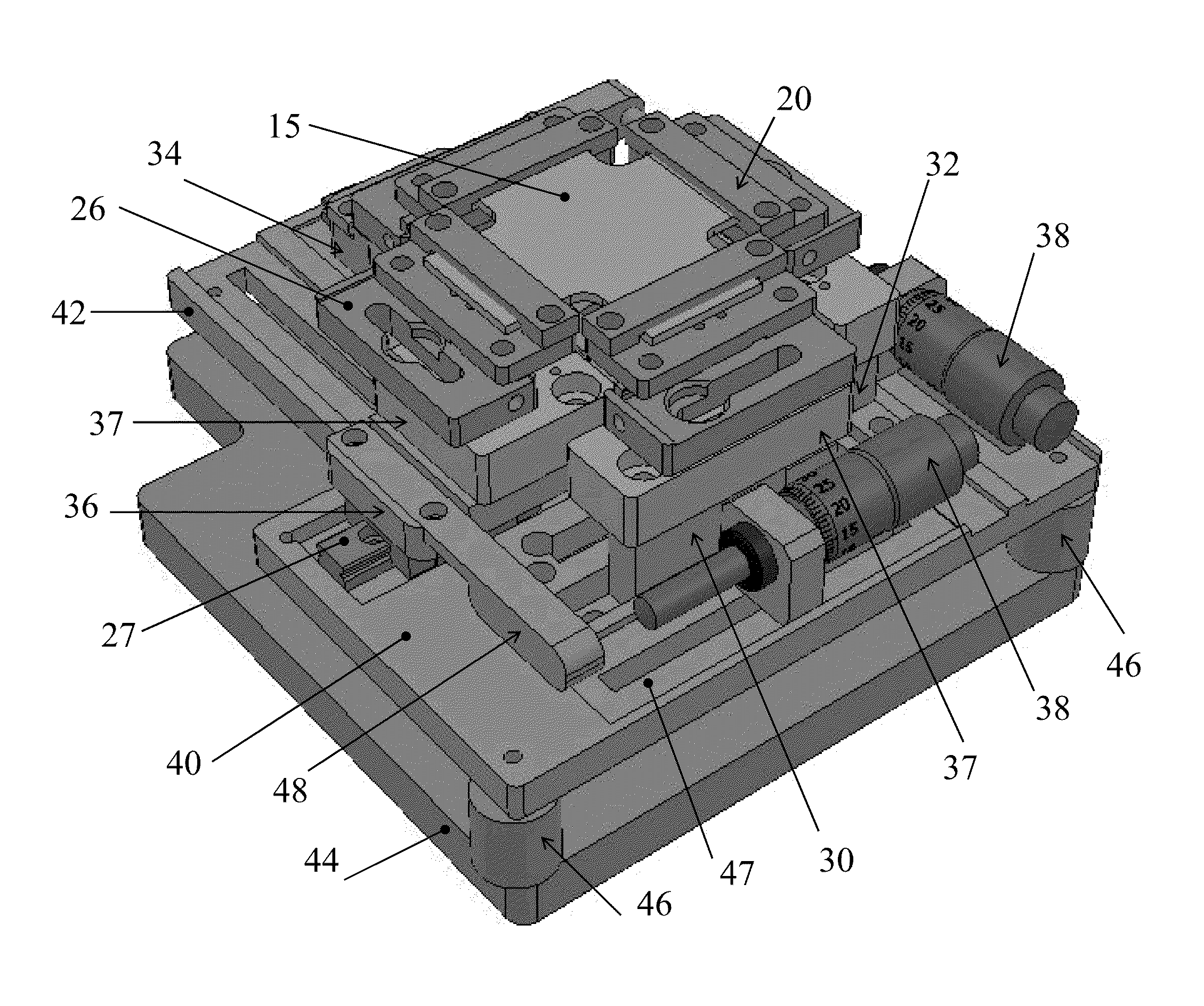
Apparatus for forming a kinematic coupling and related methods
In one aspect, an apparatus for use in forming a kinematic coupling having at least one component including a plate adapted for carrying a plurality of bearing elements comprises a template including a plurality of supports adapted for engaging and assisting in aligning the plurality of bearing elements relative to the plate of the component. The template may be used in forming either a top or base of the kinematic coupling. The top may further be adapted to be inverted relative to the base, which may also include bearing elements for receiving bearing elements associated with the top. Related methods are also disclosed.
Owner:AMT NANO
Apparatus and methods for forming kinematic coupling components
In one aspect, an apparatus for use in forming a kinematic, or quasi-kinematic, coupling having at least one component including a plate adapted for carrying a plurality of bearing elements comprises a template including a plurality of supports adapted for engaging and assisting in aligning the plurality of bearing elements relative to the plate of the component. The template may be used in forming either a top or base of the coupling. The top may further be adapted to be inverted relative to the base, which may also include bearing elements for receiving bearing elements associated with the top. A further embodiment relates to using a first template adapted to form a first component to create a second template adapted to form a second component. Another embodiment relates to creating a base adapted for engaging a top on two opposing sides. Related methods are also disclosed.
Owner:AMT NANO
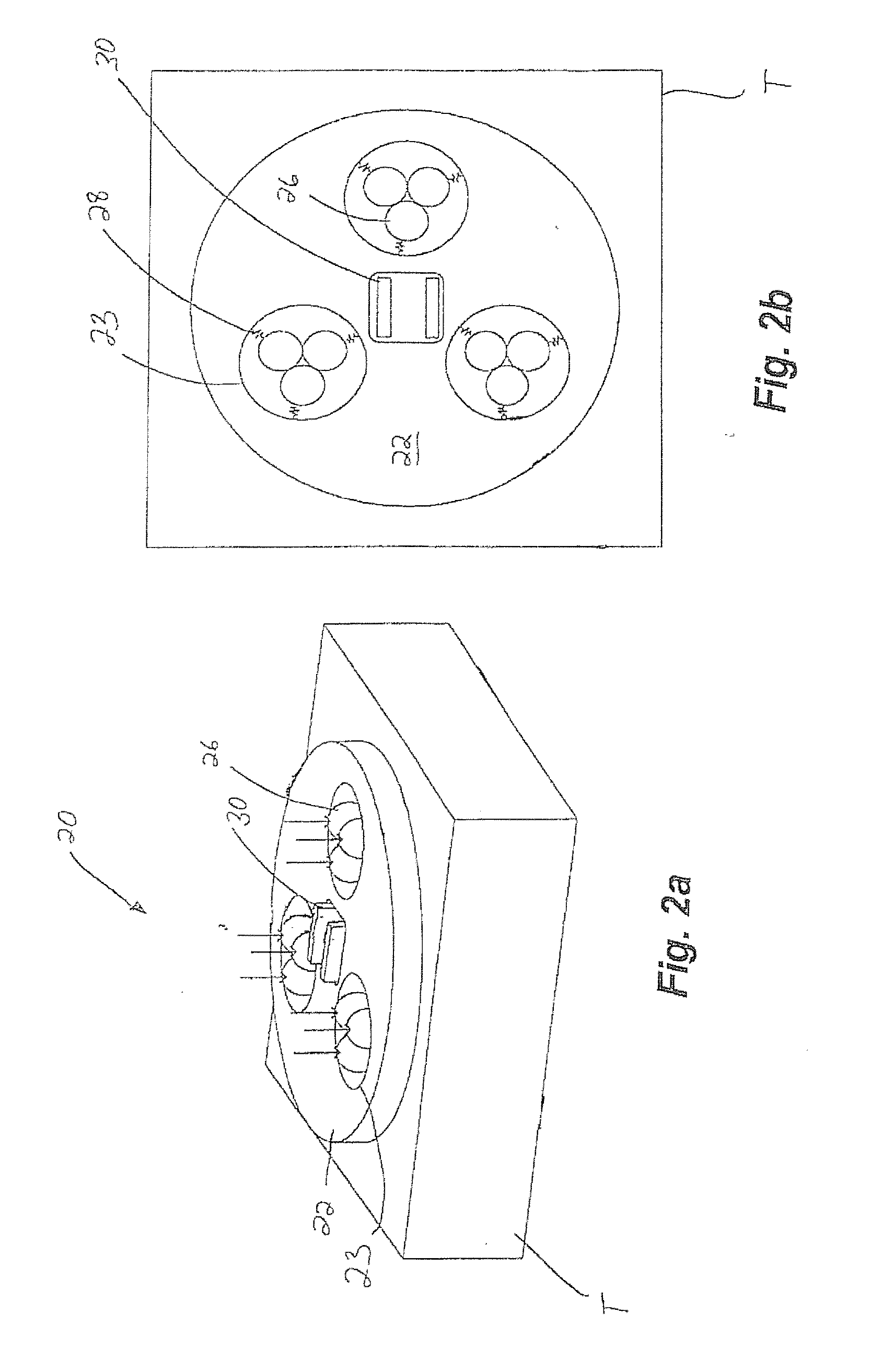
Tip-tilt-piston actuator
ActiveUS20050219675A1Avoid slow motionHigh frequency responseMirrorsElectrostatic generators/motorsKinematic couplingEngineering
A freely rotatable micromechanical plate is achieved by employing at least three rotatable plates that are each suspended from a substrate via respective springs, and are coupled via other respective springs to at least three moveable plate attachment points, so that rotation of the rotatable plates about an axis transfers motion to the moveable plate attachment points. Respective posts couple the movement of each respective moveable plate attachment point to a moveable plate. In operation, the rotatable plates may be individually rotated, and the resulting motion of each rotatable plate is passed to its respective moveable plate attachment point. The combined motion of the moveable plate attachment points is passed to the moveable plate via the posts. Using proper control, the plate may be made to tip, tilt and piston. Advantageously, the piston motion may achieve a high vertical movement frequency response.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
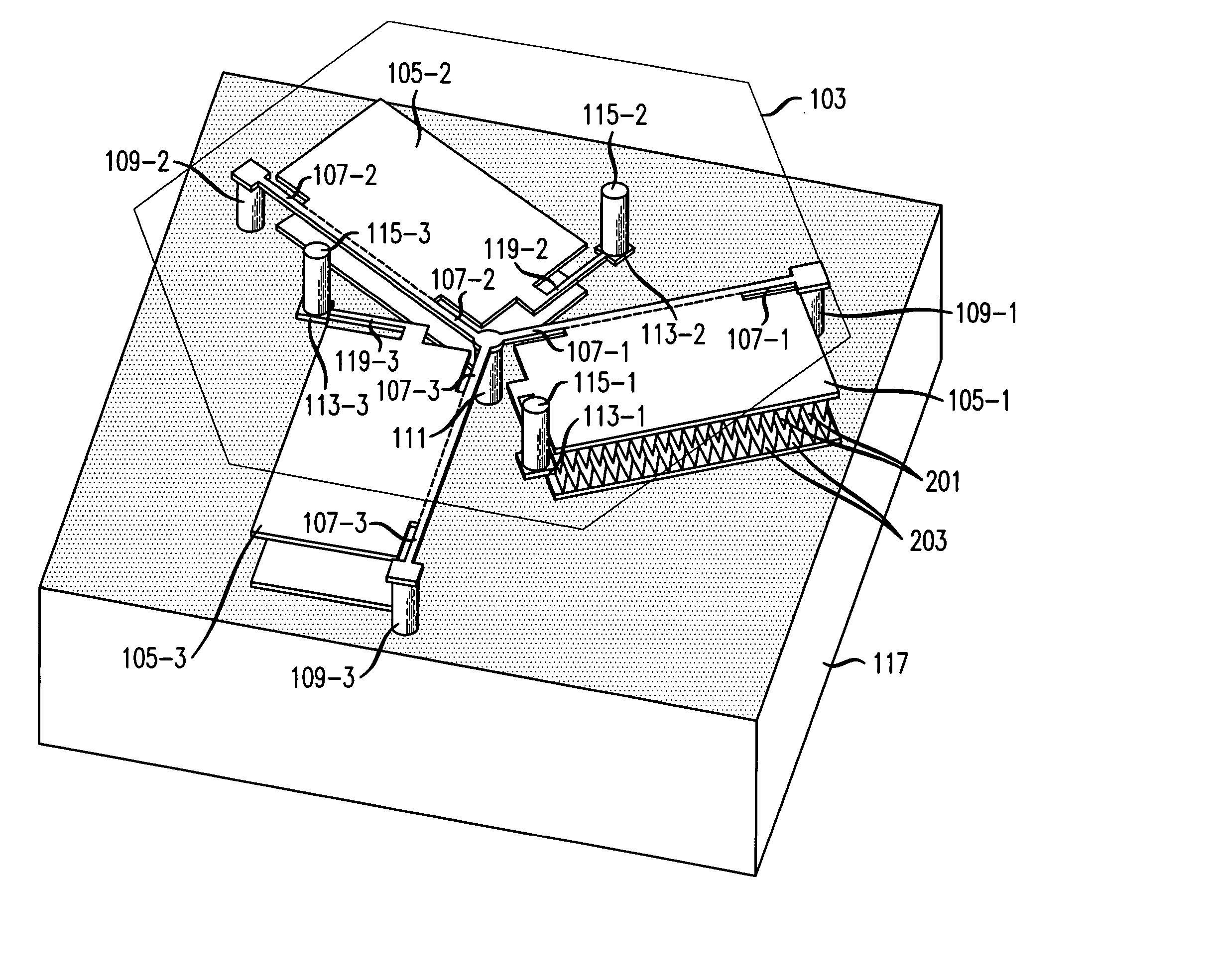
Double-end force measurement device and double-end measurement method
InactiveCN104198154ARealize aerodynamic dynamic measurementSuitable for special tests of pneumatic/kinematic coupling force measurementAerodynamic testingKinematic couplingMeasurement device
The invention discloses a double-end force measurement device and a double-end measurement method and belongs to the technical field of aerodynamic force measurement of aerospace force test. The device and the method are used for measuring high-precision and high-accuracy six-component aerodynamic force of segmented test models during force test of wind tunnel aerodynamic / kinematic coupling research. The double-end force measurement device of a internal hollow structure is machined from a whole piece of high-elasticity steel and comprises a front-segment model connecting end, a front-segment balance, a fixing end, a rear-segment balance and a rear-segment model connecting end, and a *-beam and an I-beam different in specific size are respectively adopted as elastic sensitive elements of the front-segment balance and the rear-segment balance. The measurement method includes measuring aerodynamic resultant force and moment of force of the test model through the front-segment balance and the rear-segment balance. The problem about simultaneous six-component force measurement of the segmented models in special test is solved, and the device and the method can be widely applied to wind tunnel force test in model middle support modes such as hanger support, bracing wire support and web support modes.
Owner:INST OF HIGH SPEED AERODYNAMICS OF CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
Brake booster
ActiveCN103802814AHigh axial position detection accuracyReduce intensityBraking action transmissionBrake action initiationsKinematic couplingMaster cylinder
The invention provides a brake booster in a vehicle brake system. The brake booster comprises a brake force transmission element, a boosting force transmission element, a first rotation sensor and a second rotation sensor, wherein the brake force transmission element is constructed to be capable of moving in the axial direction so that the pedal brake force can be transmitted to a brake main cylinder of a vehicle, the boosting force transmission element is constructed to be capable of moving in the axial direction so that the brake boosting force can be transmitted to the brake main cylinder, the first rotation sensor realizes the kinematic coupling with the brake force transmission element through a moving conversion mechanism used for converting the translational movement into the rotation movement, and is used for detecting the axial position of the brake force transmission element, the second rotating sensor realizes the kinematic coupling with the boosting force transmission element, and is used for detecting the axial position of the boosting force transmission element, and the brake force generation is controlled on the basis of the detection results of the first and second rotation sensors. The brake booster has the advantages that the movement of the brake force transmission element and the boosting force transmission element can be precisely detected, so the action of the brake booster can be precisely controlled.
Owner:BOSCH AUTOMOTIVE PROD SUZHOU
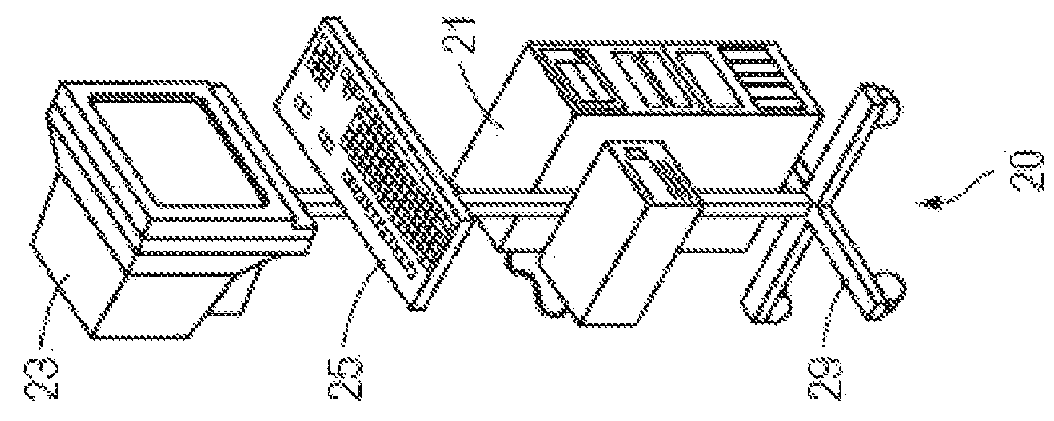
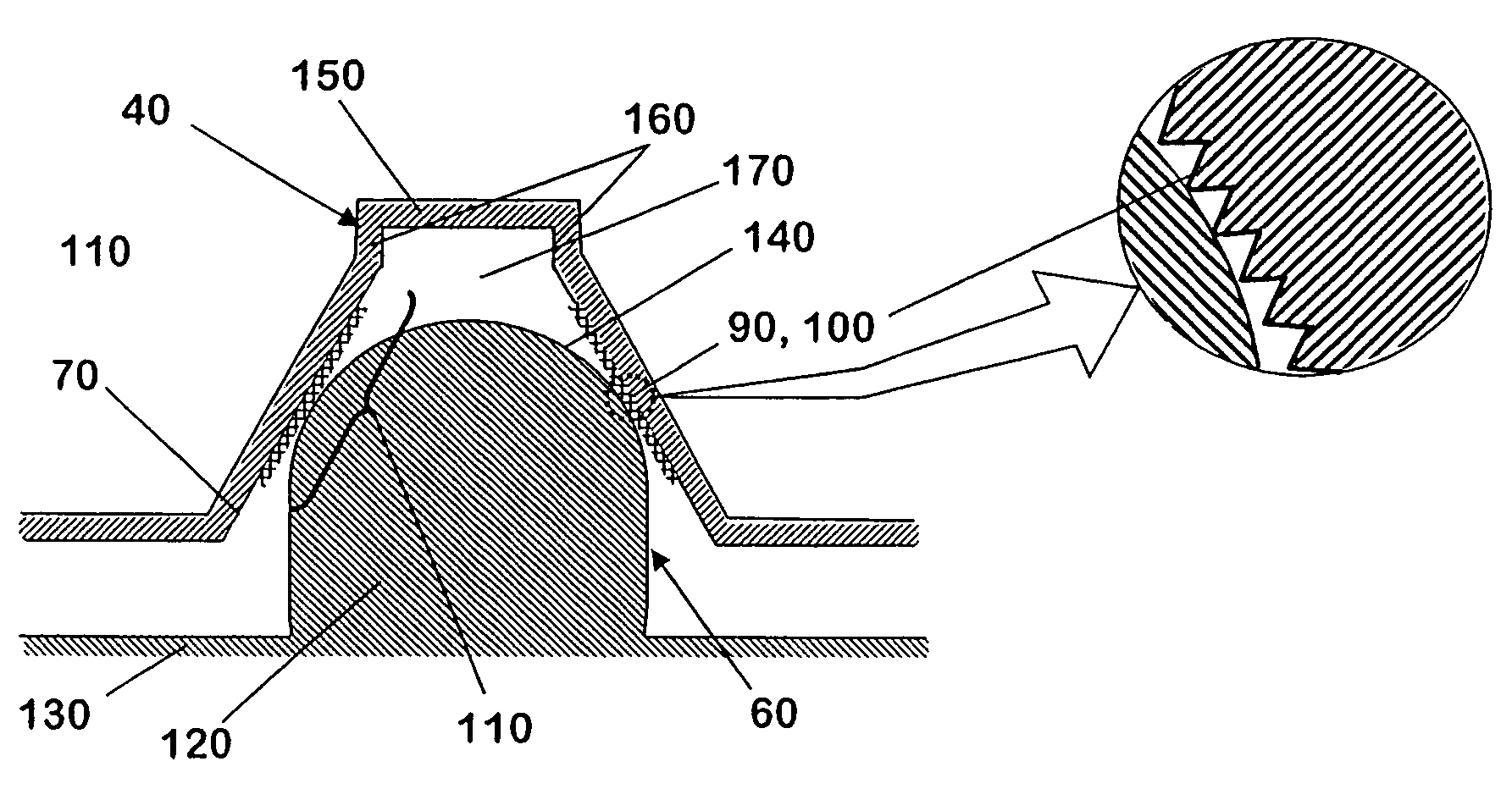
Kinematic coupling with textured contact surfaces
ActiveUS7422107B2Reduce areaReduce frictionLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingKinematic couplingBlow molding
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Wafer carrier
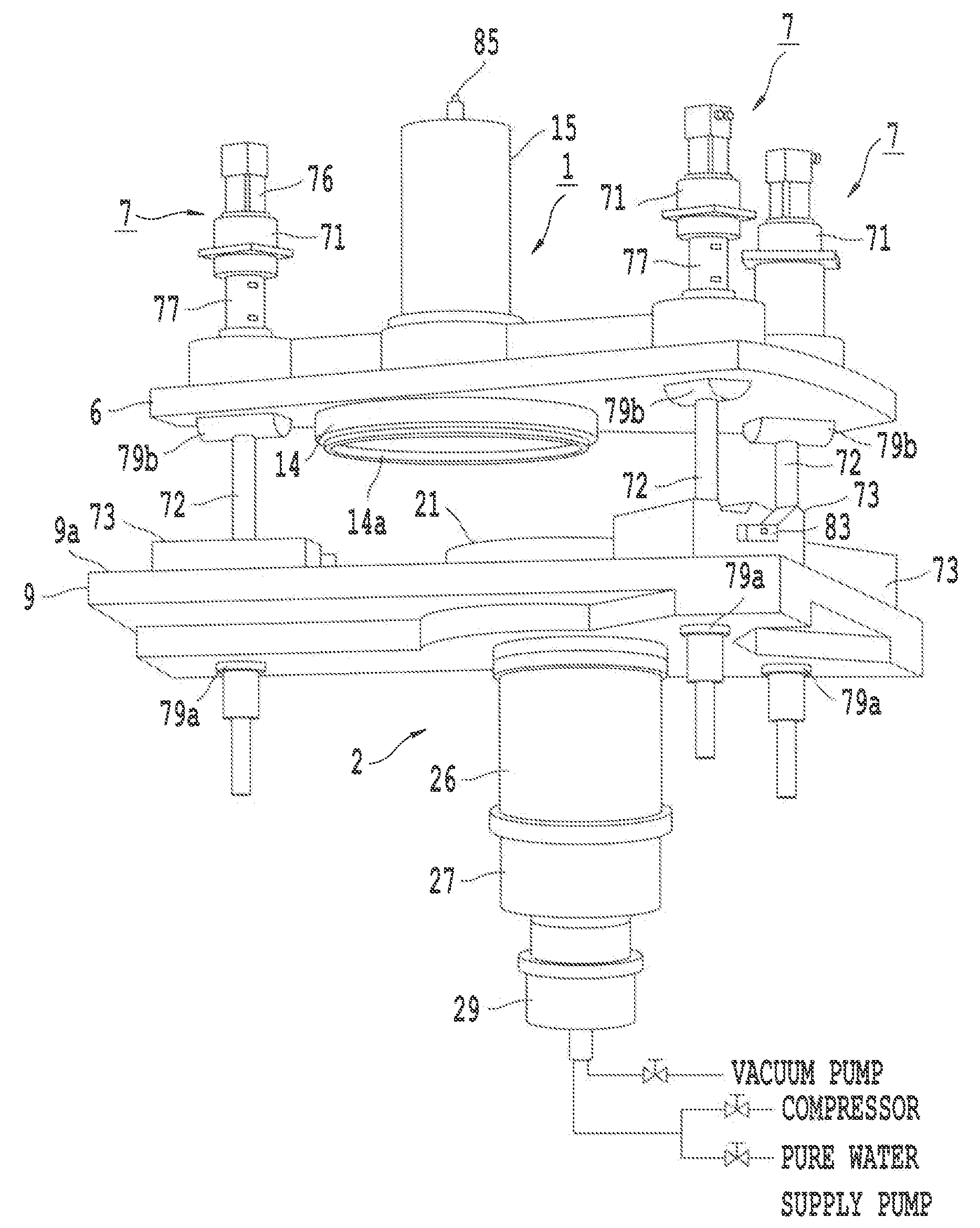
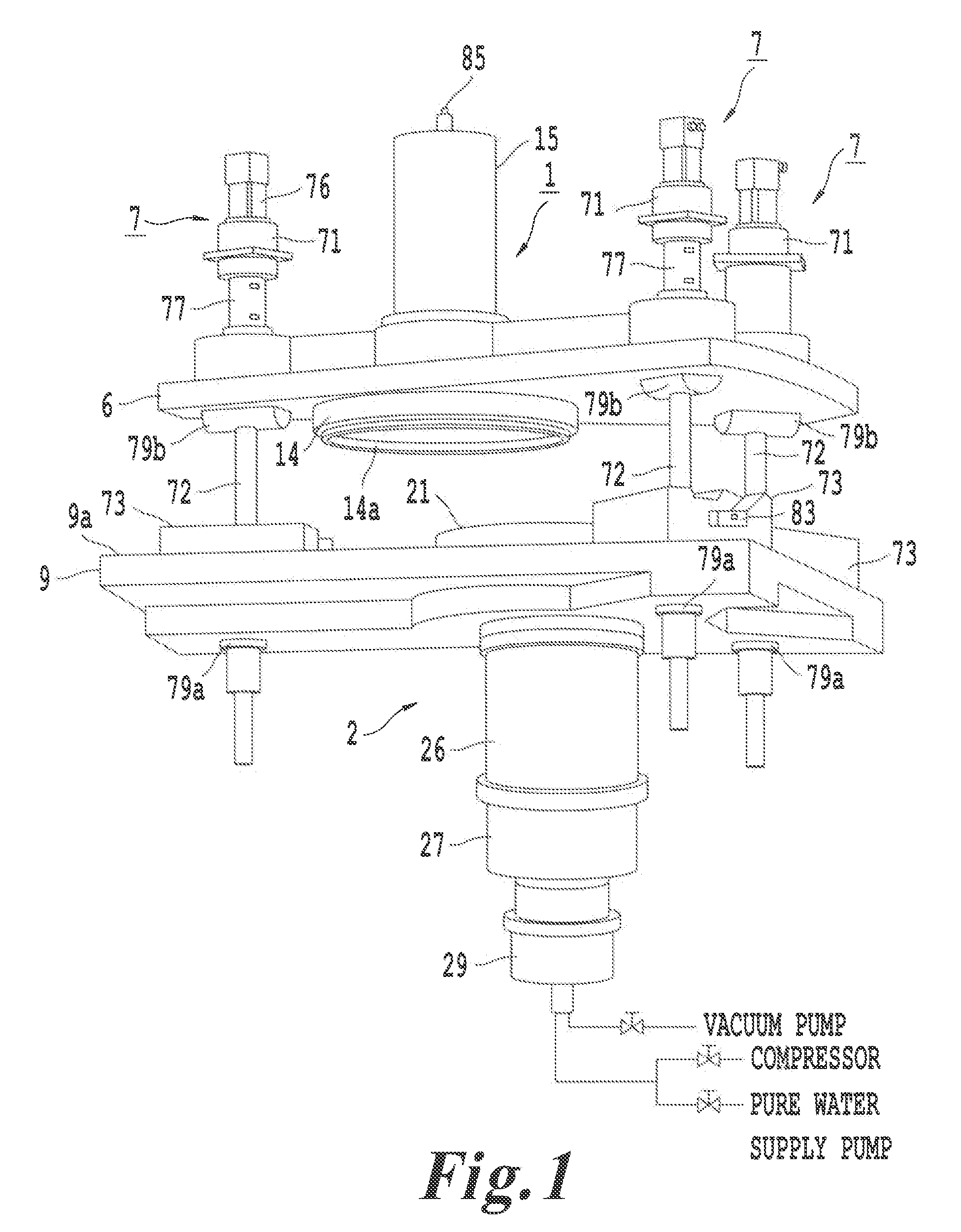
ActiveUS20150041353A1Readily and robustly and precisely attachFirmly connectedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOther accessoriesKinematic couplingDetent
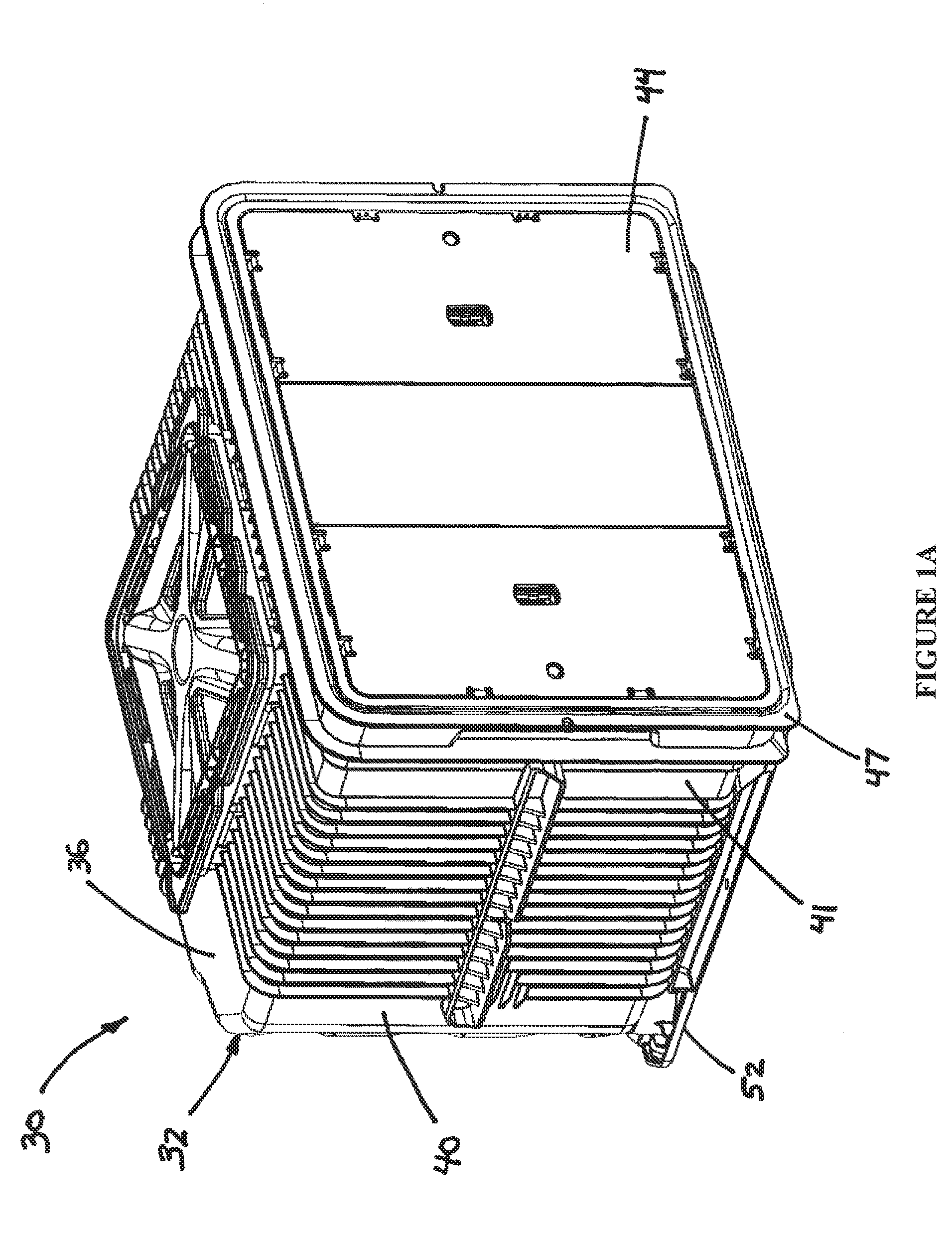
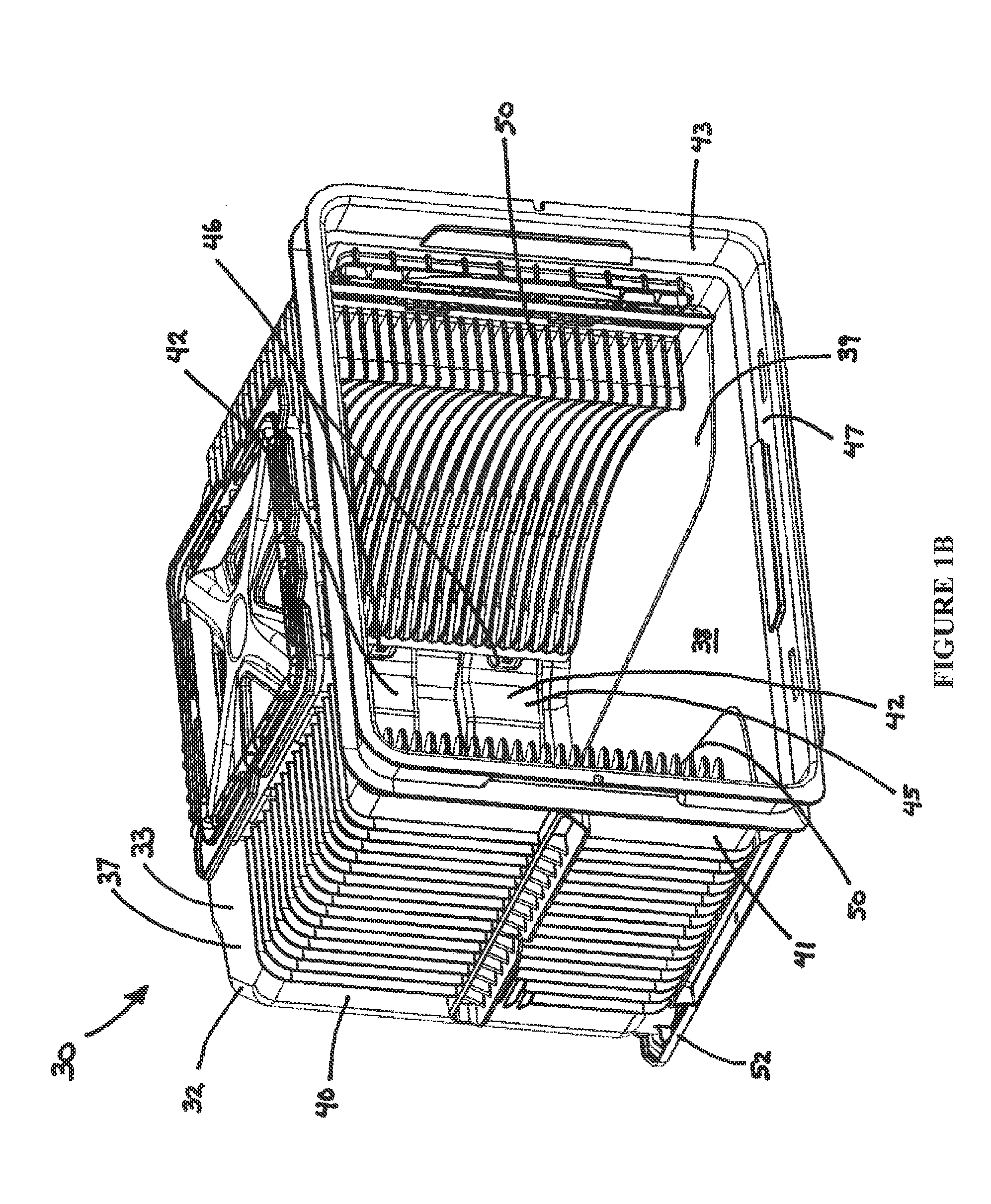
A front opening wafer container suitable for large wafers such as 450 mm utilizes componentry with separate fasteners to lock the componentry together in an expedient manner providing robust connections and cost efficiencies. A container portion has an open front and receives on a bottom surface a base plate secured by twist lock connectors that also provide recesses for purge grommets. Kinematic coupling components readily and robustly lock onto the base plate. Interior wafer support components latch onto brackets on the side walls utilizing a separate locking insert with holding tabs and locking detents. A wafer retainer provides support and counters enhanced wafer sag associated with 450 mm wafers when the door is installed and seated.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Cooperative control method for target capturing by space dual-arm robot
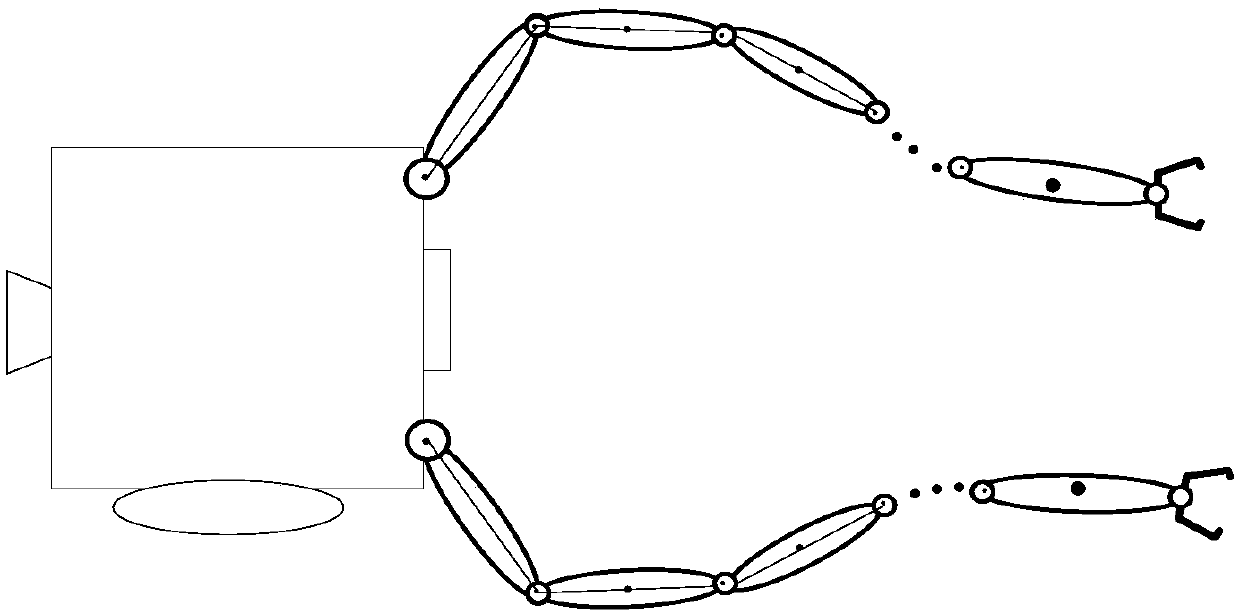
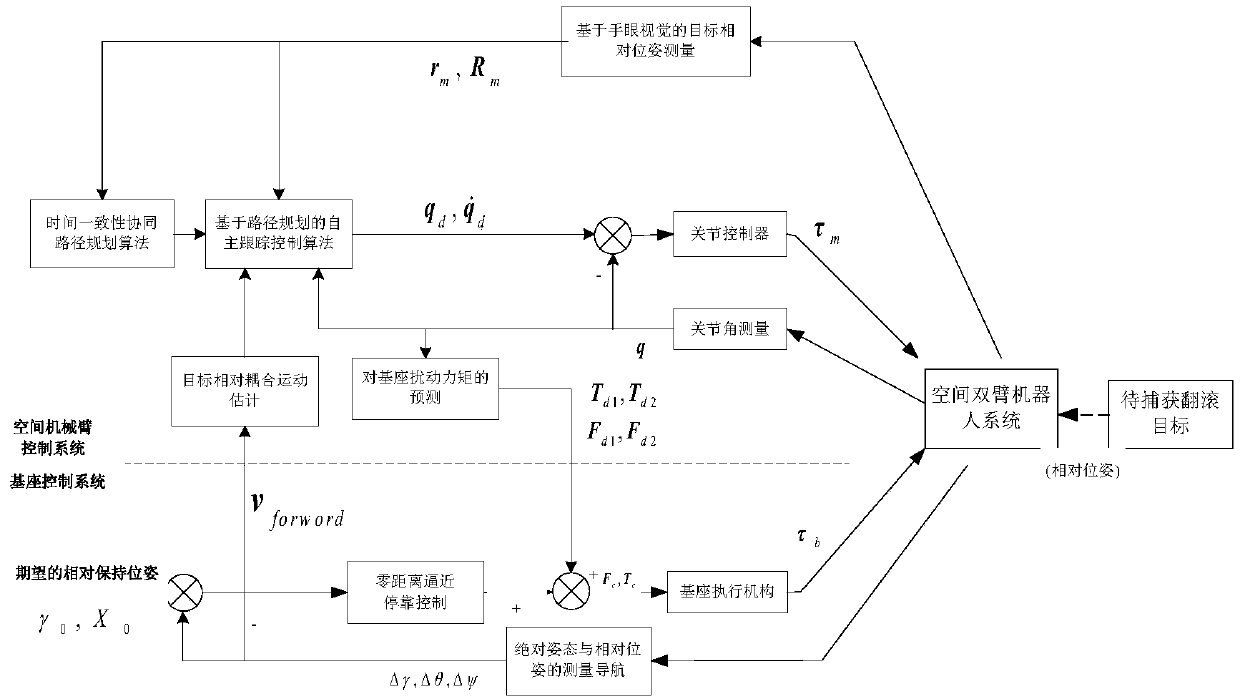
ActiveCN109606753AHigh capture accuracyProgramme-controlled manipulatorToolsKinematic couplingTarget capture
The invention discloses a cooperative control method for target capturing by a space dual-arm robot. The method comprises: establishing a space dual-arm robot base and an independent dynamic model ofthe robot; according to a zero-distance stop control method of a space robot base, controlling relative positions and line-of-sight pointing of two aircrafts; enabling two robotic arms to reach a target at the same time based on visual-servo-based collaborative planning and control method; and according to a dynamic and kinematic coupling compensation method of the space robot, estimating couplingof relative movement of the base and the target based on relative navigation information, compensating the movement of the robotic arms, and estimating the counter-acting force on the platform by using the states of the robotic arms to realize feedforward compensation pedestal control. According to the invention, a cooperative control method for catching the rolling target is provided to solve the capturing problem of the space dual-arm robot; and the time consistency of target catching by two arms is ensured. On the basis of mutual compensation of the base and the two robotic arms, the high-precision catching is realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE SYST ENG INST
Two-phase synchronous electric motor with permanent magnets for mechanical priming washing pumps of dishwashers and similar washing machines
ActiveUS20090001824A1Association with control/drive circuitsTableware washing/rinsing machine detailsKinematic couplingPermanent magnet rotor
The present invention relates to a two-phase synchronous electric motor (1), comprising a permanent-magnet rotor (2), rotating around a respective rotation axis (X), and a core lamination-pack (10) stator (4), wherein a first (6) and second (7) pairs of pole pieces (8) define a housing / rotation seat (5) for said rotor (2) and wherein each pole piece (8) comprises a core (9), having an end associated to the core lamination pack (10) and a free end portion (11), facing the rotor (2) housing / rotation seat (5), a coil (12) on a respective support (13) wedged on said core (9). Advantageously, at least the free end portion (11) of the core (9) of each pole piece (8) comprises a core lamination pack (15) extending in respective parallel planes to the rotation axis (X) of the permanent-magnet rotor (2). Advantageously, the core laminations (15) have a variable length to form a surface of said free end portion (11) of the core (9) of each pole piece (8) being concave in the axial direction and partially wrapping the rotor (2).The particular structure of the stator (4) can be advantageously matched to the double-joint kinematic coupling between the rotor (2) and the load (31) and to the phase displacement capacitor C expedient between the windings associated to one of the pole piece pairs.
Owner:ASKOLL HLDG SRL
Double-end calibration device and calibration method
ActiveCN104198113ARealize mock loadingSimple structureForce/torque/work measurement apparatus calibration/testingKinematic couplingMeasurement device
The invention relates to a double-end calibration device and a calibration method and belongs to the technical field of aerodynamic force measurement of aerospace force test. The double-end calibration device with the middle fixed and two ends free is used for calibration during force test of wind tunnel aerodynamic / kinematic coupling research. The double-end calibration device mainly comprises two sets of L-shaped sliders and loading heads which are used cooperatively, one end of the front L-shaped slider is connected with the front loading head while the other end of the same is connected with the front end of a double-end force measurement device, and the rear L-shaped slider is connected with the rear loading head while the other end of the same is connected with the rear end of the double-end force measurement device; the loading heads are four-point type frame loading heads, do not interference with each other in space and are used for applying longitudinal load; the L-shaped sliders are connecting pieces between the force measurement device and the loading heads, do not interference with each other in space, are provided with a pair of longitudinally-symmetrical resistance loading points, and are used for applying axial load. The problem about calibration of the double-end force measurement device in special test is solved, six components can be calibrated at most, and the device and the method are simple and feasible special force measurement device calibration schemes indeed.
Owner:INST OF HIGH SPEED AERODYNAMICS OF CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
Tip-tilt-piston actuator
ActiveUS7068409B2Avoid slow motionHigh frequency responseMirrorsElectrostatic generators/motorsKinematic couplingEngineering
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
Flexible linking device for an aircraft propulsion system
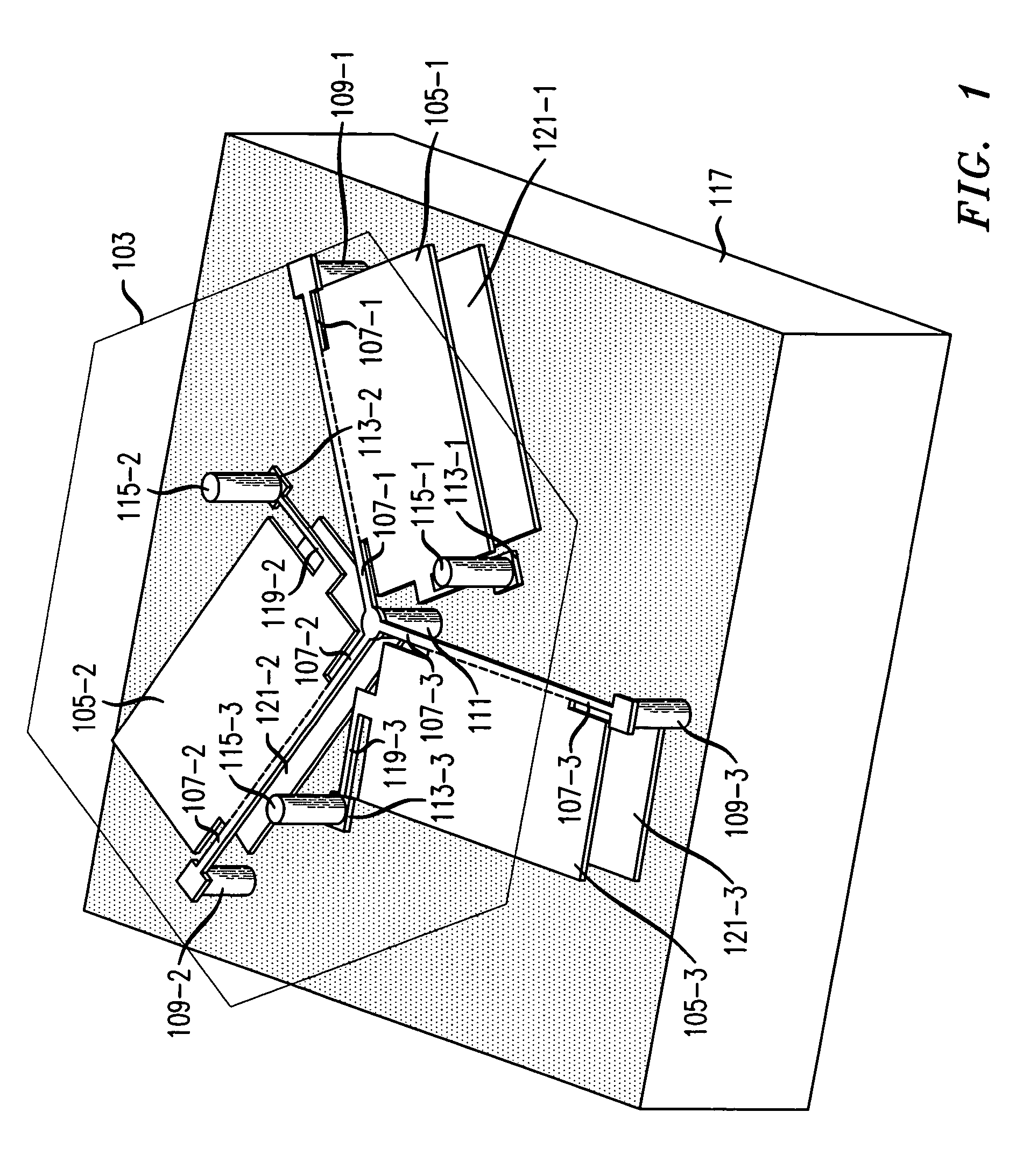
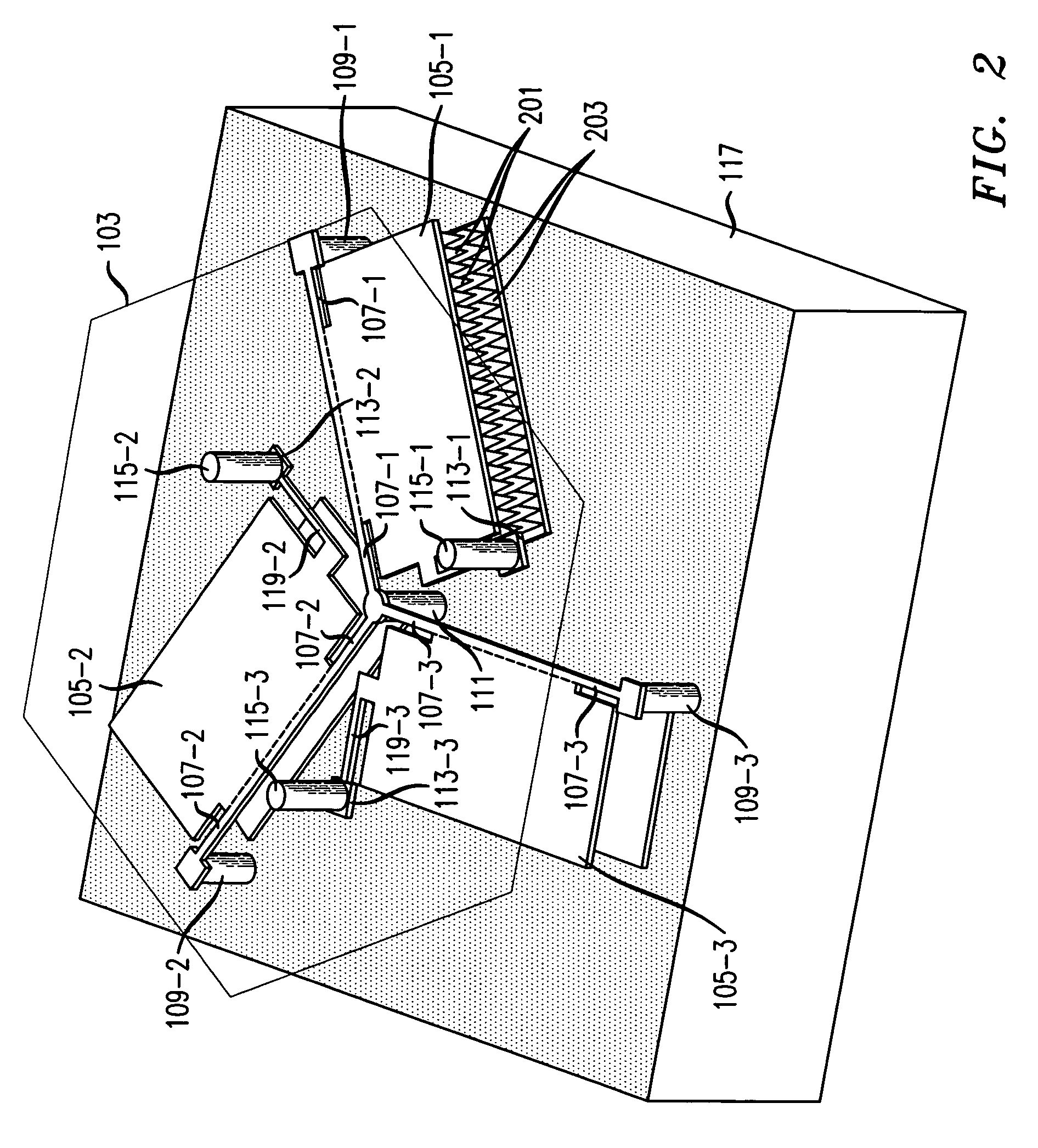
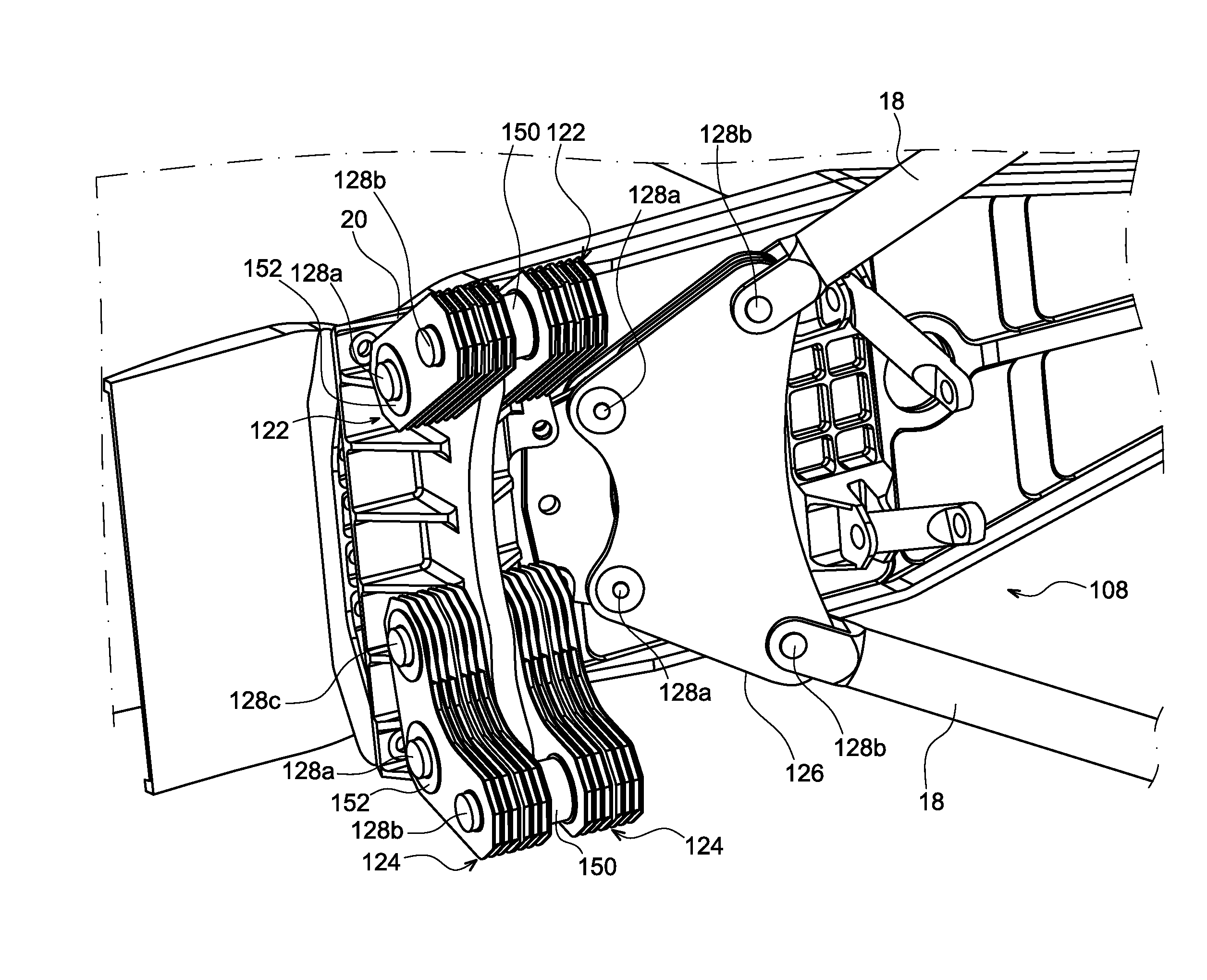
ActiveUS20140183298A1Certain flexibilityReduce transmissionPower plant constructionRubber-like material springsSpacecraft propulsionElastomer
A linking device including two hinge pins and having flexibility allowing vibrations between these two shafts to be filtered. The device includes a stack of plates connected to one another by layers of elastomer material. Plates of a first type are coupled to one of the shafts in relation to the movements parallel to the plates, while the plates of a second type are coupled to the other shaft in relation to the movements parallel to the plates, so as to allow relative movement of the shafts parallel to the plates. This linking device may be used in particular as a connecting rod, spreader beam or three-point shackle used in connecting a turbine engine to a pylon in a propulsion system of an aircraft such as an airplane.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
Aircraft empennage regulation mechanism with pitching and yawing completely decoupled
ActiveCN105151280AAchieve mechanical decouplingReduce weightWithout power ampliicationWeight reductionKinematic couplingTailplane
The invention discloses an aircraft empennage regulation mechanism with pitching and yawing completely decoupled. The aircraft empennage regulation mechanism comprises an empennage fixing part, an empennage pitching part and an empennage yawing part, wherein the empennage fixing part, the empennage pitching part and the empennage yawing part are sequentially arranged on the aircraft tail from front to back, the empennage fixing part and the empennage pitching part are hinged, and the empennage pitching part and the empennage yawing part are hinged. The aircraft empennage regulation mechanism further comprises a pitching steering engine and a yawing steering engine, wherein the pitching steering engine and the yawing steering engine are arranged on an aircraft body. The pitching steering engine rotates to drive a connecting rod to move to drive the empennage pitching part to swing around the axis of a pitching rotation shaft. The yawing steering engine rotates to pull two traction ropes to move to drive the empennage yawing part to swing around the axis of a yawing rotation shaft. According to the invention, the structure style of arranging a drive steering engine on the aircraft tail traditionally is abandoned, and the weight of the aircraft tail is effectively lowered. In addition, compared with a traditional kinematic coupling empennage regulation mechanism, the aircraft empennage regulation mechanism can regulate empennages through mechanical decoupling, and the reliability, the stability and the regulation accuracy of a system are greatly improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Linear unit
InactiveCN101629600AUniform force transmissionReduce wearLinear bearingsFluid-pressure actuatorsKinematic couplingBearing surface
The linear unit (1) has a base element, at which a carriage (4) is mounted in a linear movable manner in axial direction of a main axis (3). The base element has multiple longitudinal guide paths (12,12a,12b) extended to the main axis. A supporting roller (22) is fixed with a carriage body (14) of a carriage. The supporting roller is movement-coupled with circumferential-sided circular-cylindrical bearing surface (23) such that supporting roller is unrolled during the linear movement of the carriage on the assigned guide paths.
Owner:FESTO AG & CO KG
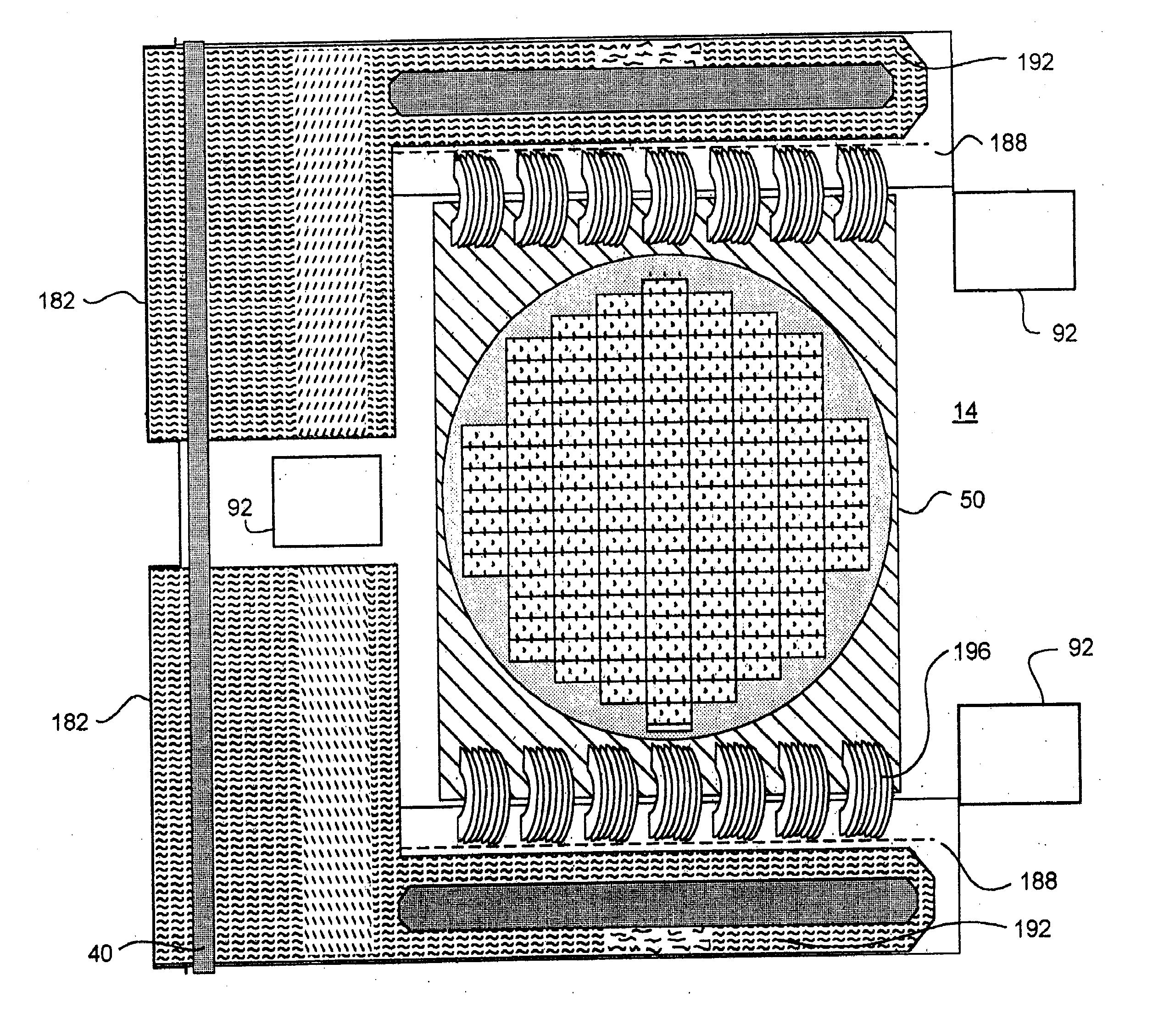
Wafer Burn-In and Test Employing Detachable Cartridge
InactiveUS20060132154A1Clamping forcePrevent exitElectronic circuit testingElectrical measurement instrument detailsKinematic couplingProbe card
A cartridge (10) includes a chuck plate (12) for receiving a wafer (74) and a probe plate (14) for establishing electrical contact with the wafer. In use, a mechanical connecting device (90) locks the chuck plate and the probe plate fixed relative to one another to maintain alignment of the wafer and the probe plate. Preferably, electrical contact with the wafer is established using a probe card (50) that is movably mounted to the probe plate by means of a plurality of leaf springs (52.) The mechanical connecting device is preferably a kinematic coupling including a male connector (94) and first and second opposed jaws (122, 124.) Each of the jaws is pivotable from a retracted position in which the male connector can be inserted between the jaws and an engaging position in which the jaws prevent withdrawal of the male connector from between the jaws. The male connector is movable between an extended and a retracted position, and is biased towards the retracted position. This provides a positive clamping force that pulls the chuck and probe plates together when the mechanical connecting device is engaged. To load a wafer into the cartridge, the wafer is placed on the chuck plate, the probe plate is aligned with the wafer, and the chuck plate and the probe plate are locked together. The cartridge can then be removed from the alignment device and placed in a burn-in or test chamber that does not itself require means for aligning the wafer or for providing a probe actuation force.
Owner:AEHR TEST SYST
Holding apparatus for holding optical element above a base, exposure apparatus including the holding apparatus, and device manufacturing method using the exposure apparatus
InactiveUS7878665B2Reduces change in surface shapeProjectorsPhotomechanical apparatusKinematic couplingEngineering
Owner:CANON KK
Movement decoupling hydraulic driving three-degree-of-freedom spherical wrist
The invention belongs to the technical field of robots, and particularly relates to a movement decoupling hydraulic driving three-degree-of-freedom spherical wrist. The problems that the flexibility,the posture adjustment capacity and the precision positioning capacity of an end effector are conducted due to the fact that a wrist is complex in structure, incompact, small in power intensity, low in integration level and high in self weight, a transmission chain is long, and movement coupling exists are solved. The movement decoupling hydraulic driving three-degree-of-freedom spherical wrist comprises a rotation hydraulic motor, an angle sensor, a machine frame, a displacement sensor, a pitching hydraulic oil cylinder, a pitching ring, a side-sway end cover, a bearing, a transmission shaft,a transmission shaft coupler and a side-sway hydraulic oil cylinder. The pitching axis, the side-sway axis and the rotation axis of the movement decoupling hydraulic driving three-degree-of-freedom spherical wrist cross at one point, uncoupling of three active input movements including pitching, side-sway and rotation can be achieved, thus, the posture of the wrist is easy and convenient to control, the control precision is high, the posture capacity is high, and the mechanical arm vibrating phenomenon caused by movement coupling generated during joint matching adjustment is avoided.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Biaxial tensile stage for fabricating and tuning wrinkles
ActiveUS20150202821A1Small sizeQuickly and accurately registerConfectioneryVacuum evaporation coatingKinematic couplingWrinkle skin
Wrinkling of thin films is a strain-driven process that enables scalable and low-cost fabrication of periodic micro and nano scale patterns. However, real-world application is limited by the inability of current tools to provide the means for applying large, accurate, and non-equal biaxial strains via a device that can fit within the vacuum chambers that are required for thin film deposition / growth during wrinkling. The present biaxial tensile stage is a compact system that enables one to apply large and accurate non-equal biaxial strains to elastomeric films. It consists of (i) fixtures to clamp and hold films onto the stage, (ii) linear bearings for motion guidance, (iii) integrated actuators for real-time stretch control, (iv) base with kinematic coupling for registration to a metrology system, and (v) the structural frame.
Owner:SAHA SOURABH KUMAR
Flexible linking device for an aircraft propulsion system
ActiveUS9180975B2Certain flexibilityReduce transmissionPower plant constructionRubber-like material springsSpacecraft propulsionElastomer
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com