Patents
Literature
32results about How to "Achieve mechanical decoupling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
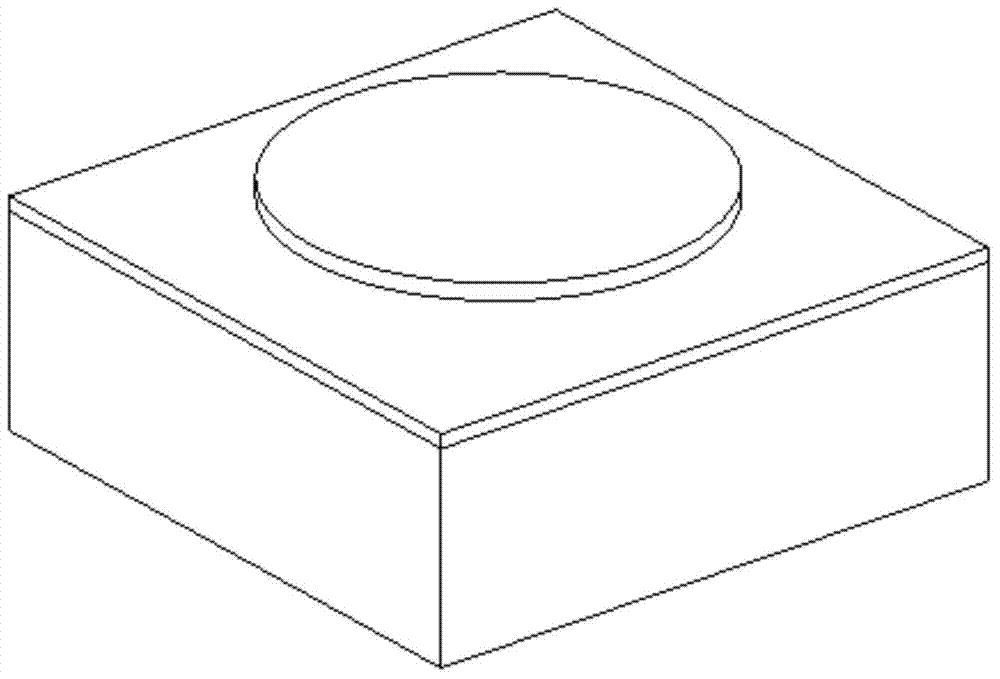
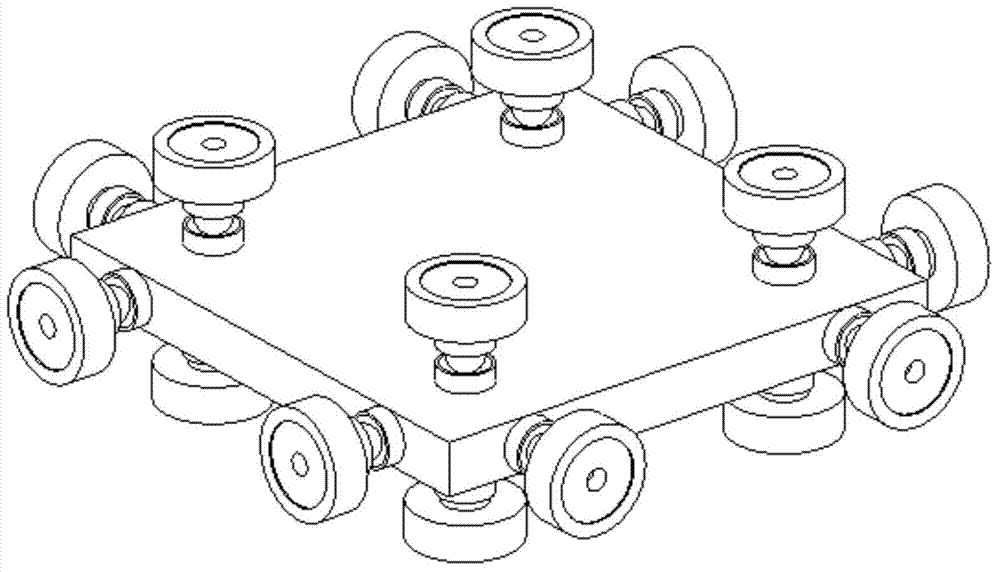
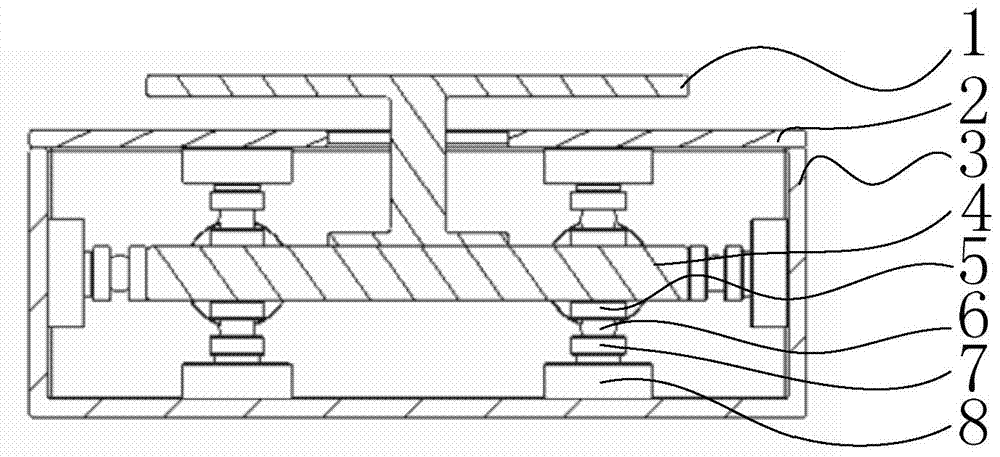
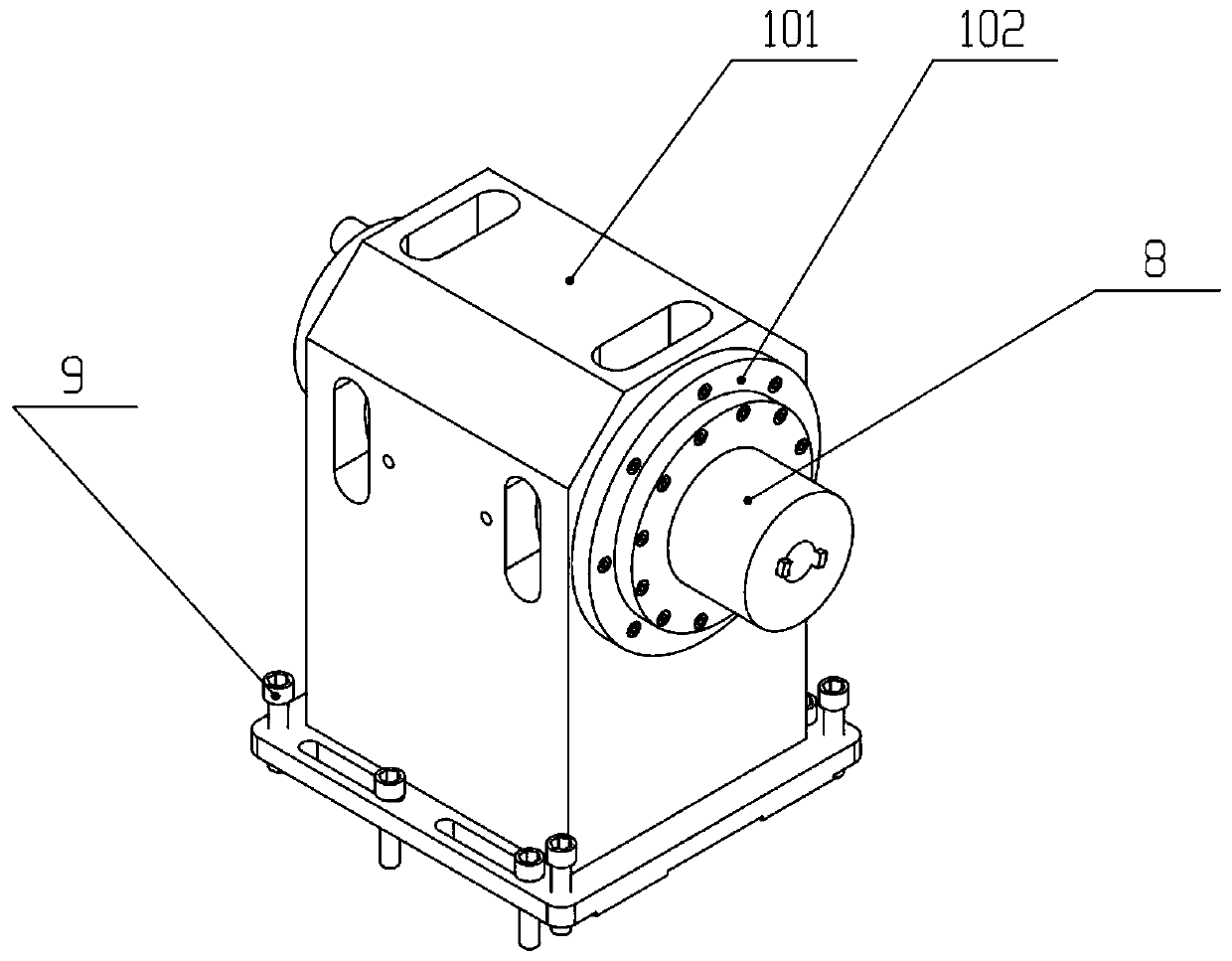
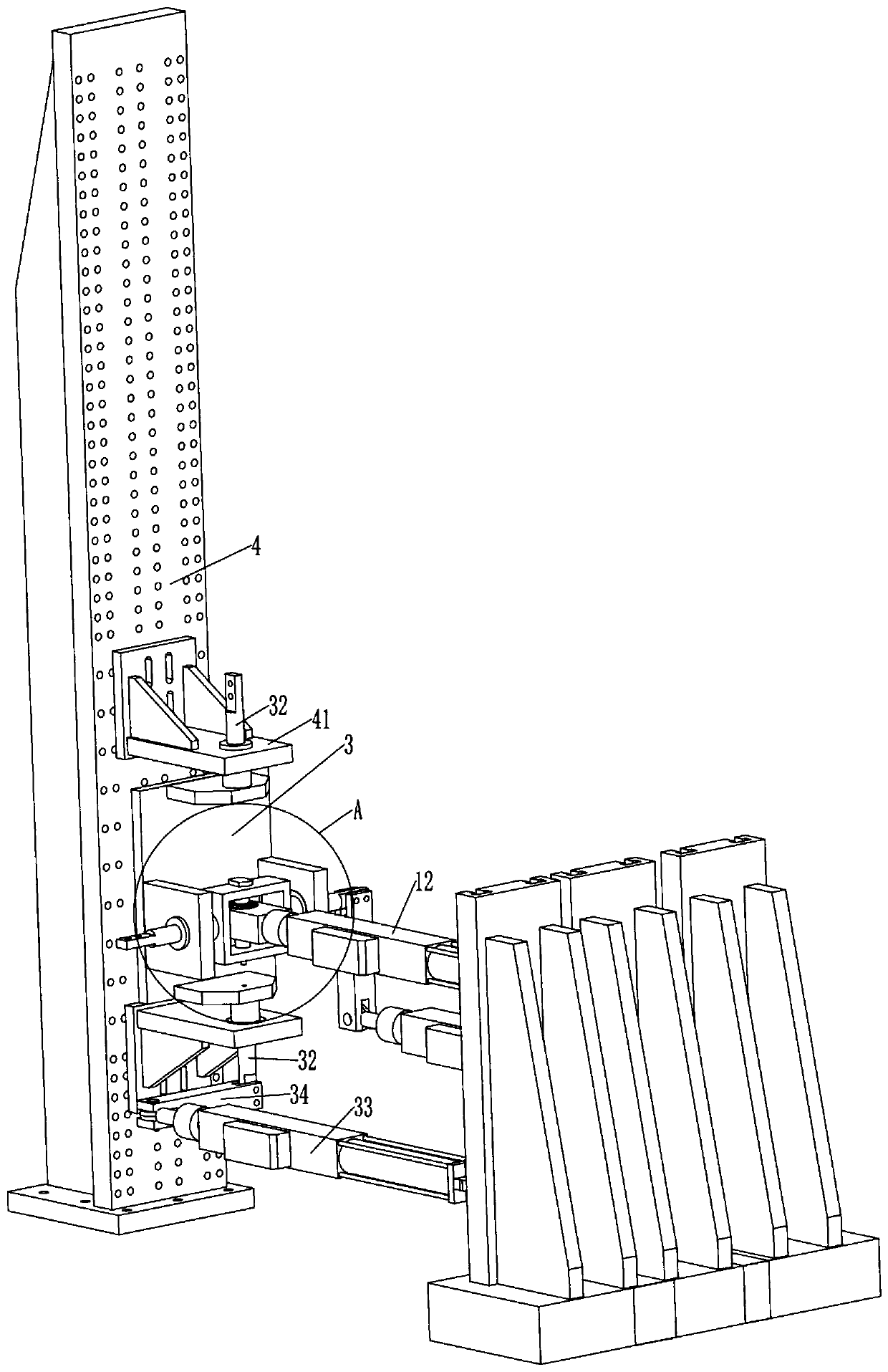
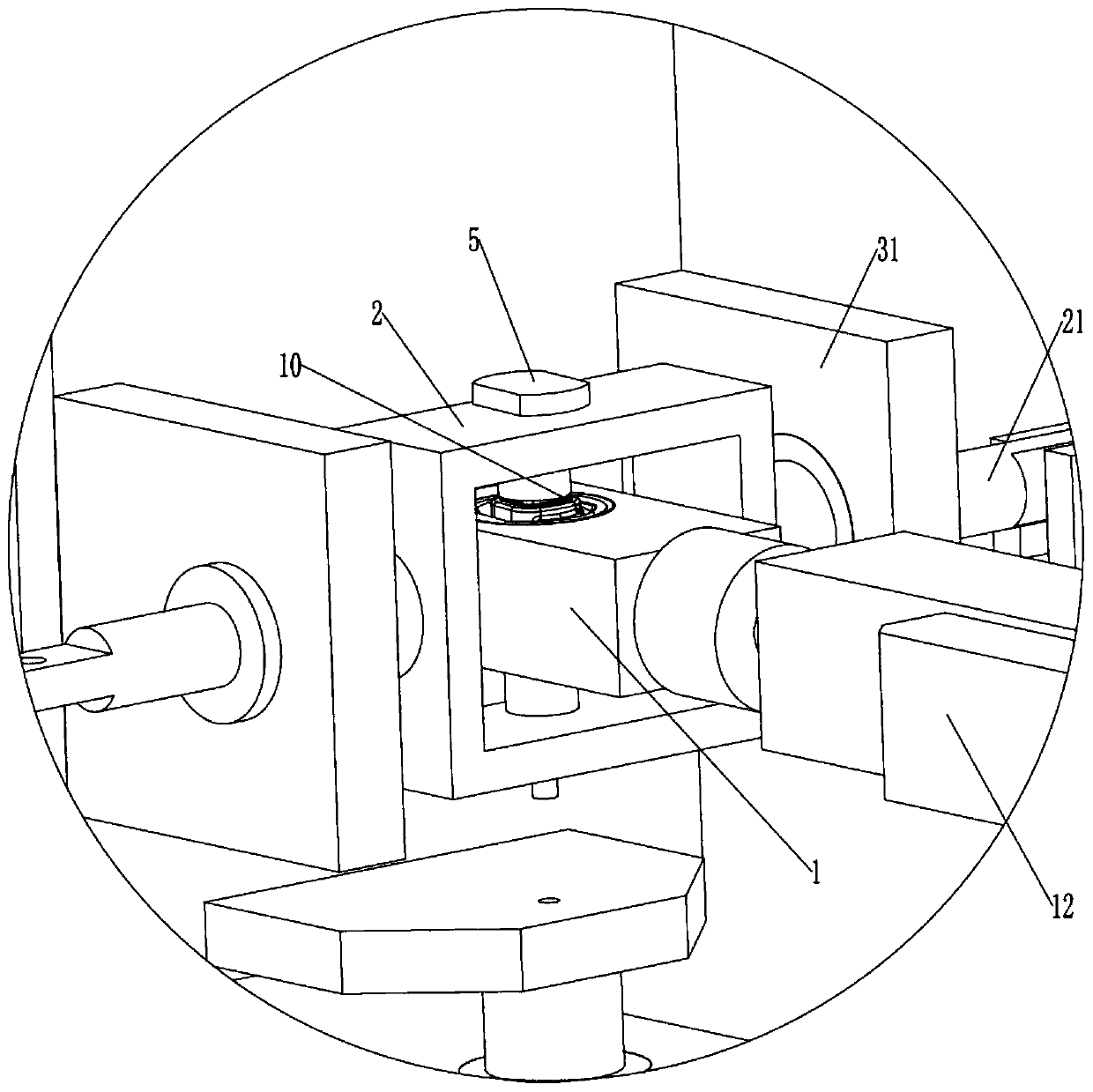
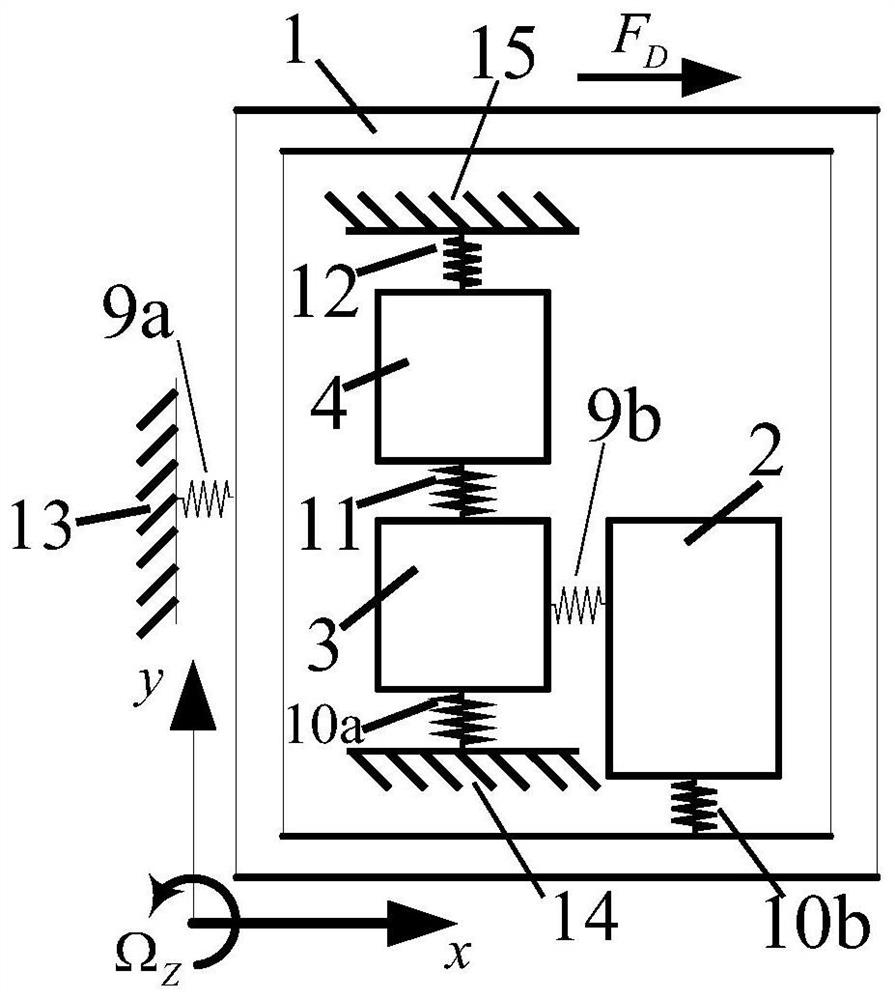
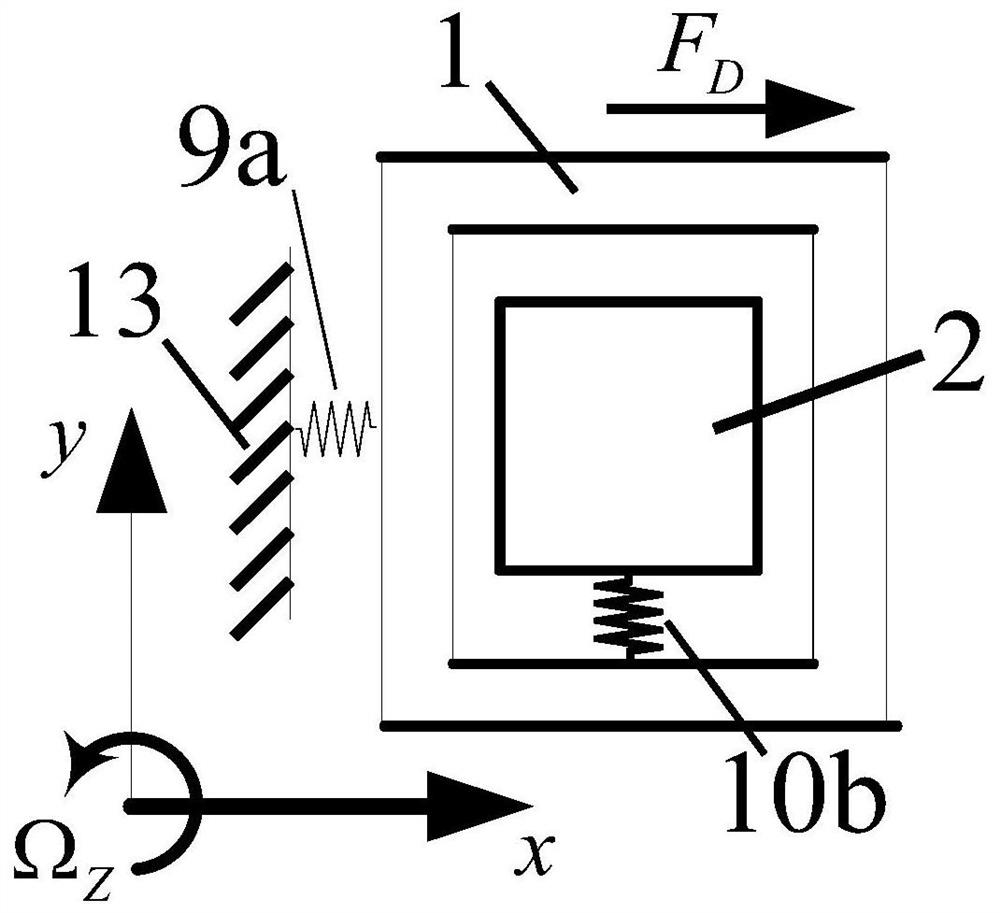
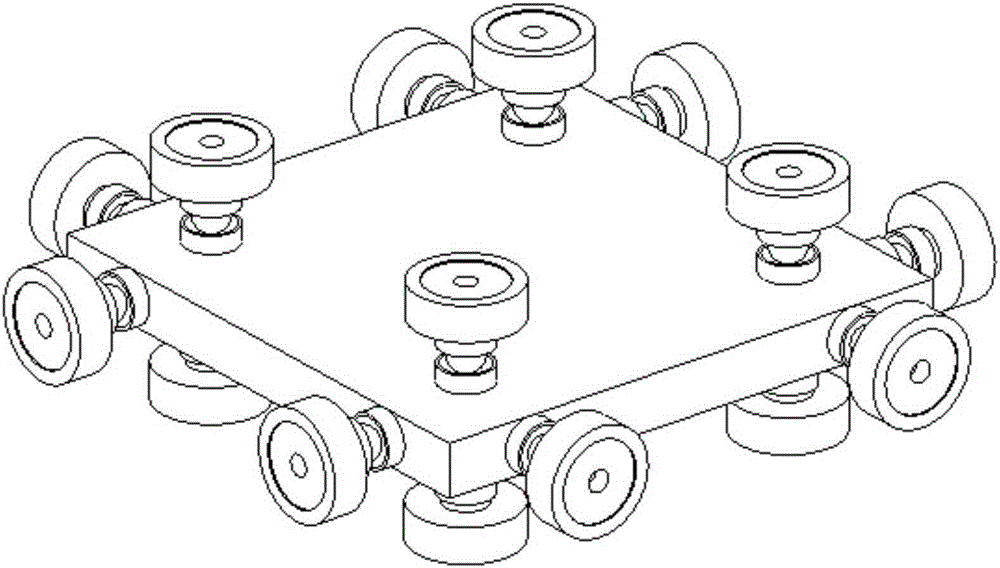
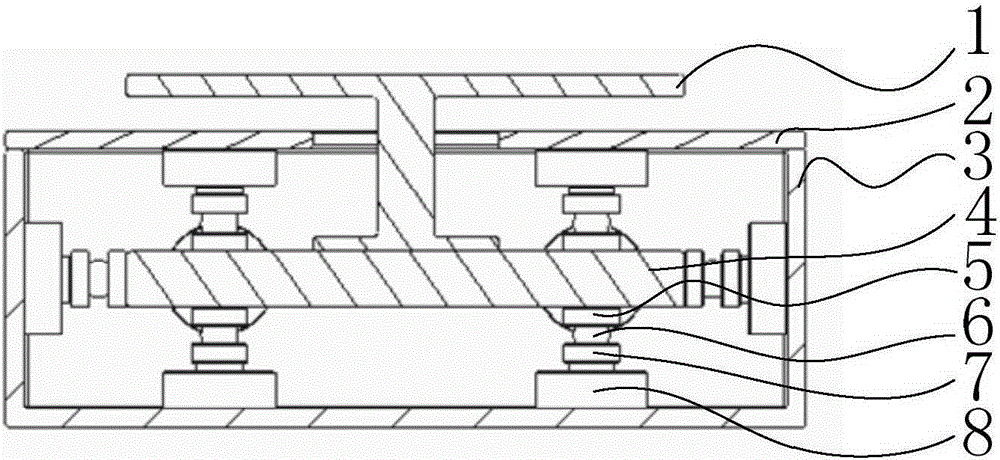
Mechanical decoupling heavy load parallel six-dimension force measuring platform
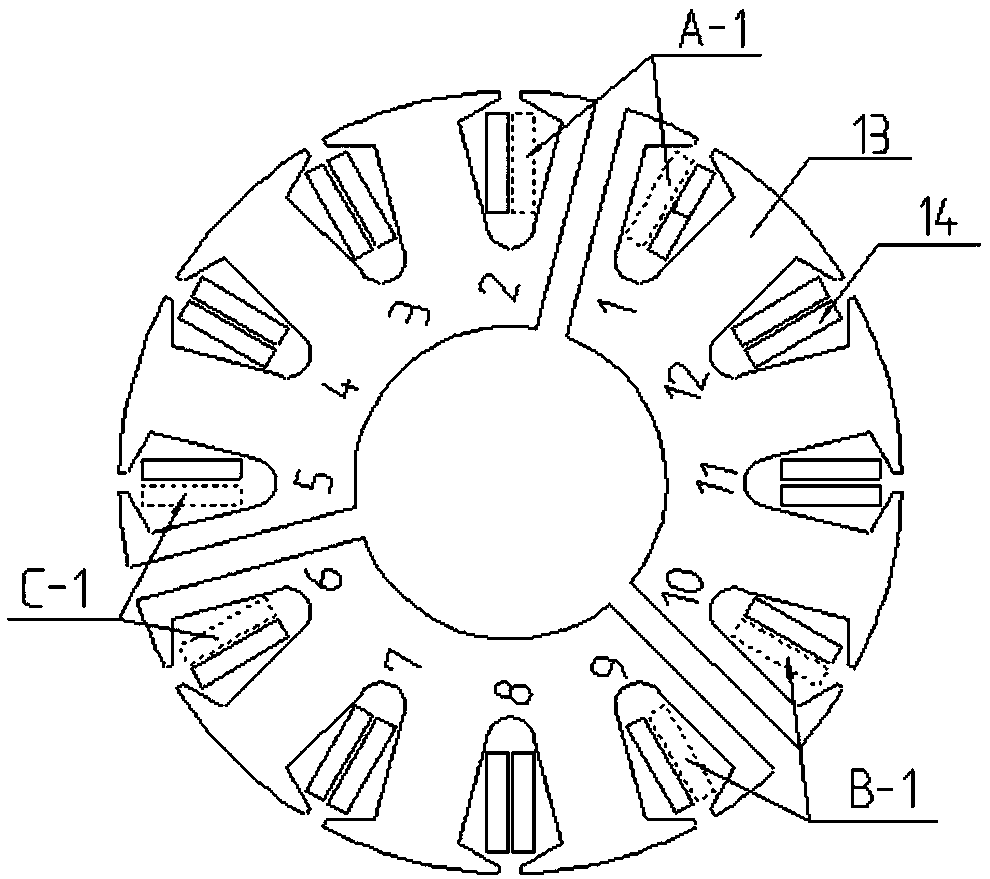
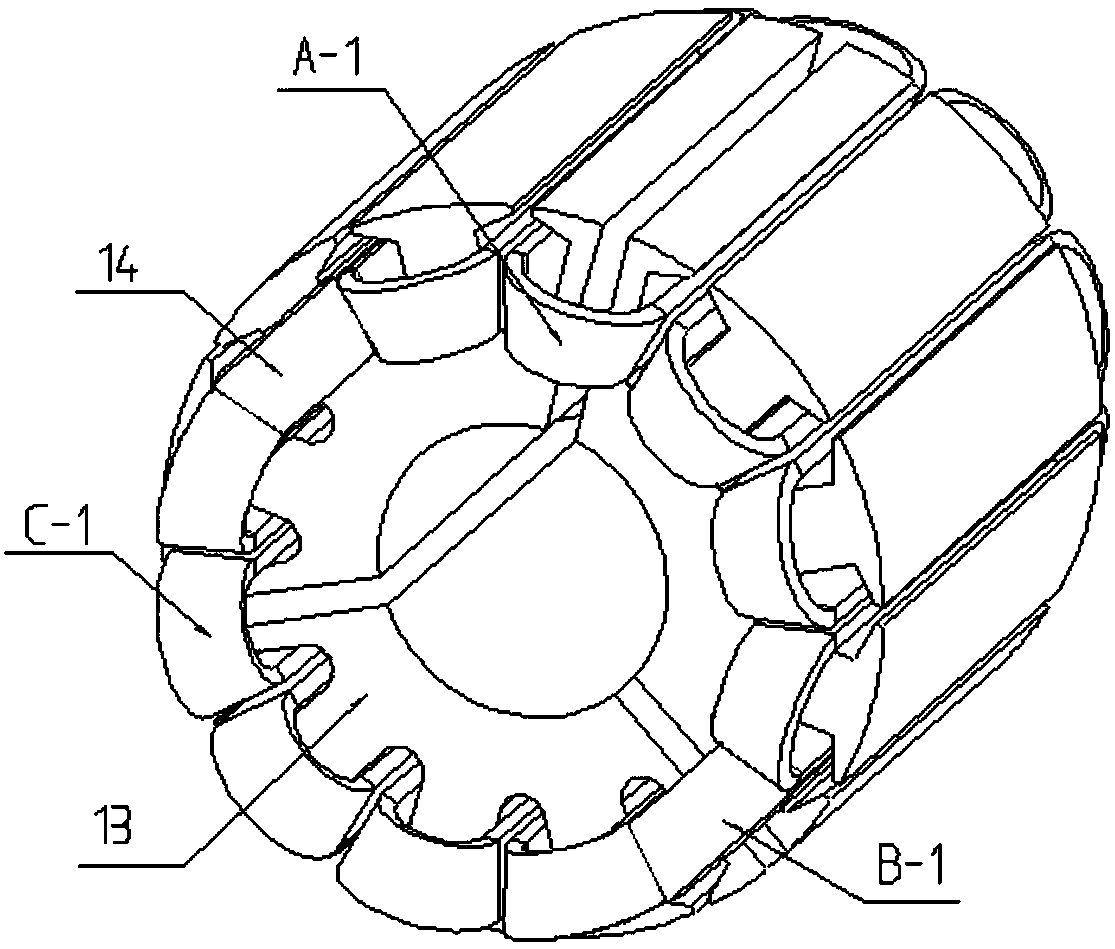
InactiveCN103616116AReduced measurement accuracyAchieve mechanical decouplingMeasurement of force componentsCouplingSteel ball
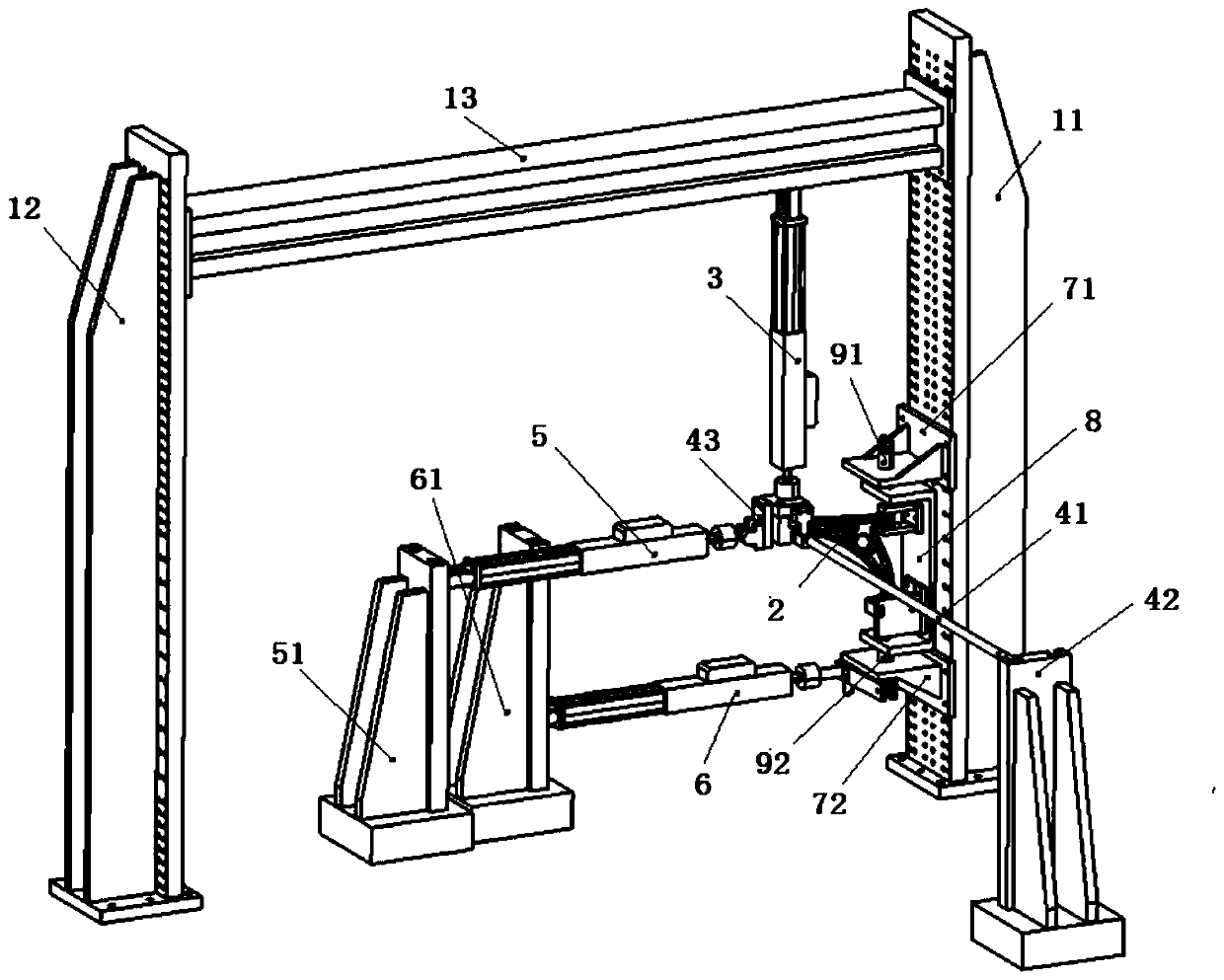
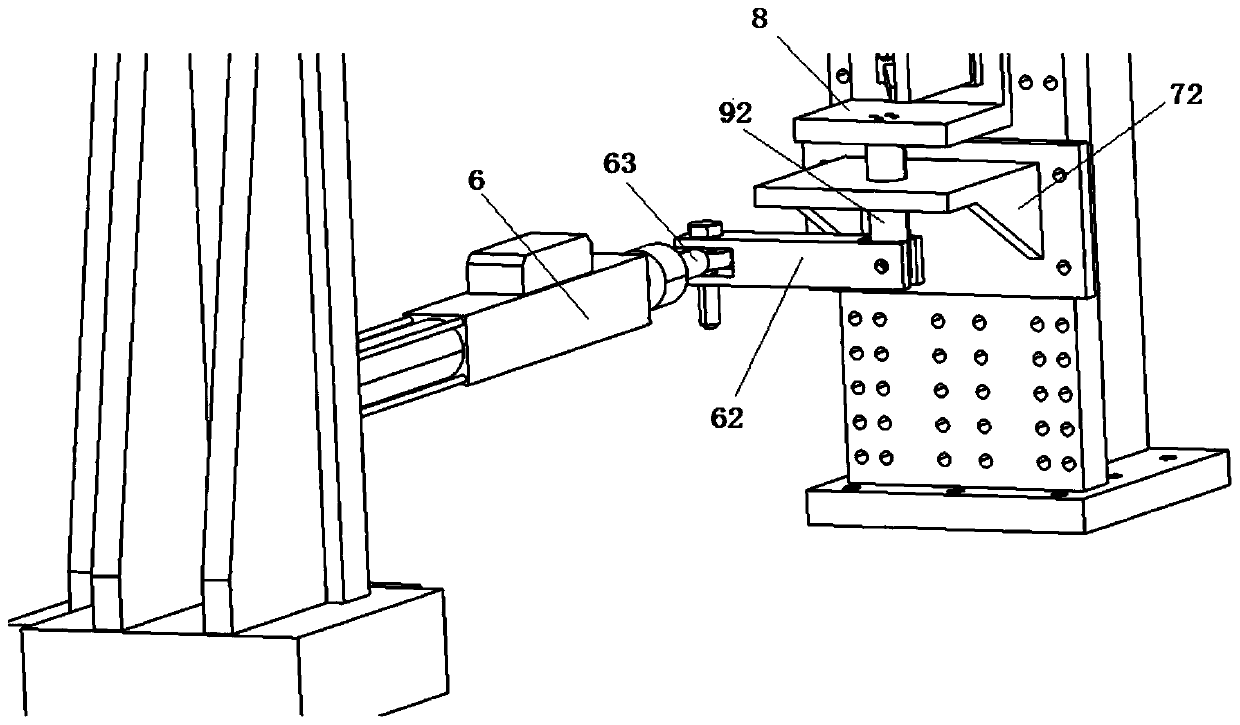
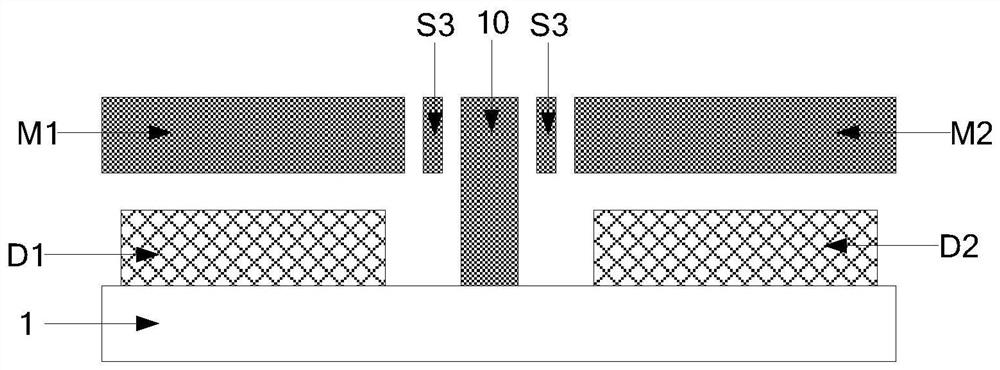
A mechanical decoupling heavy load parallel six-dimension force measuring platform comprises a loading plate, a force measuring plate, an upper cover plate, a bottom frame and more than 12 decoupling force measuring supporting chains. The upper end of the bottom frame is covered with the upper cover plate, a box body is formed, a lower plate of the loading plate is fixed at the plane center of the force measuring plate, an upper plate of the loading plate extends out of an opening in the upper cover plate, the force measuring plate, the upper cover plate and the bottom frame are connected through the decoupling force measuring supporting chains which are distributed on the six faces of the force measuring plate and are fixed on the upper face, the lower face and the four side faces of the force measuring plate respectively, one end of a pressing head A in each decoupling force measuring supporting chain is fixed on the force measuring plate, one end of a pulling pressing force sensor is fixed on the bottom frame and the upper cover plate respectively, the other end of the pulling pressing force sensor and one end of a pressing head B are fixed, the other end of the pressing head A and the other end of the pressing head B are both concave faces, and a steel ball is embedded between the two concave faces. The mechanical decoupling heavy load parallel six-dimension force measuring platform is simple in structure, mechanical decoupling is achieved through the steel ball, dimension-between coupling is small, measuring accuracy is high, and the mechanical decoupling heavy load parallel six-dimension force measuring platform is very suitable for heavy load large-tonnage measuring.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
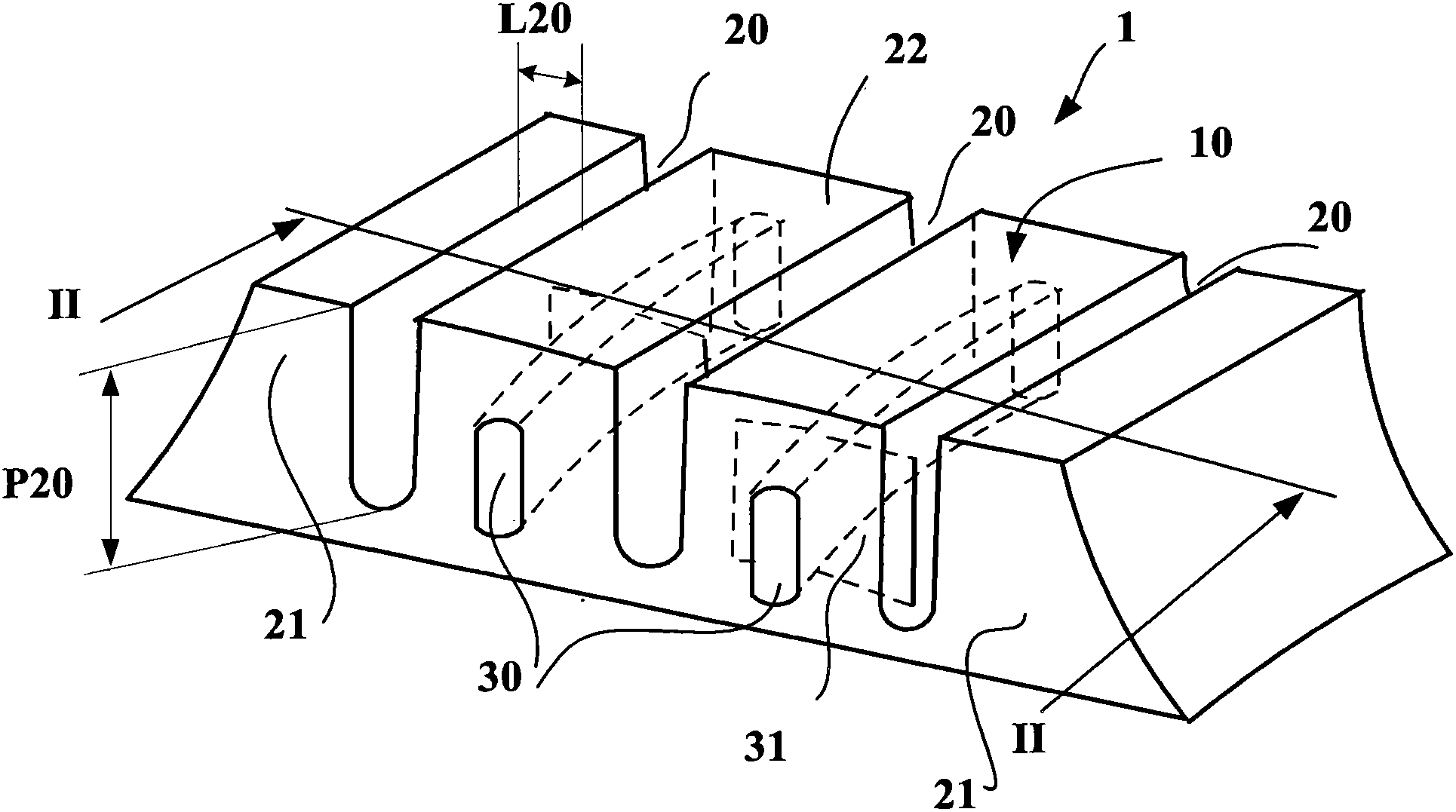
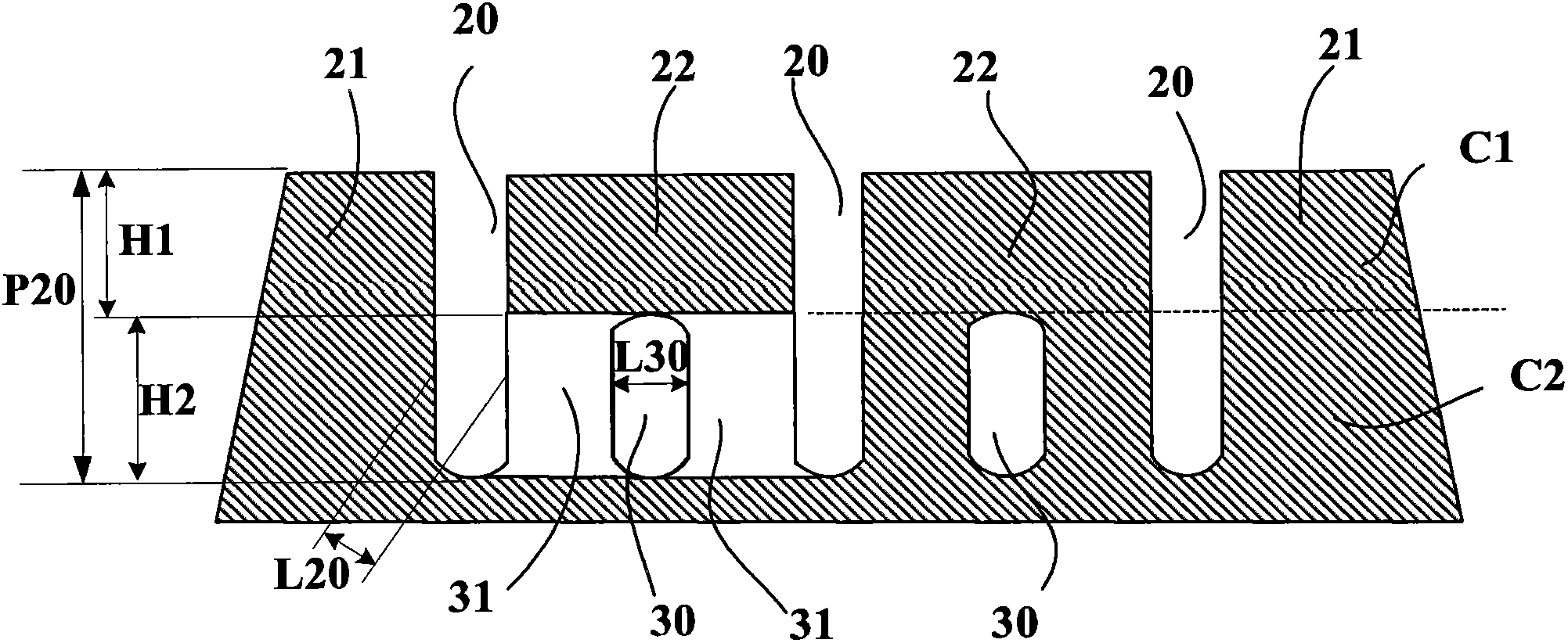
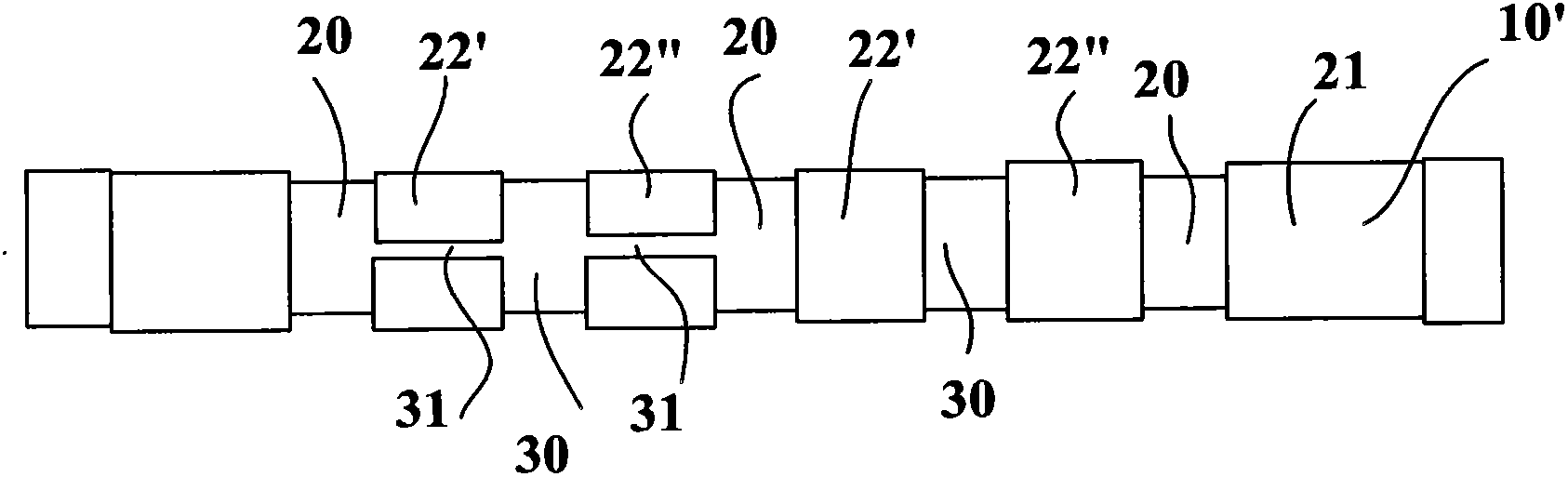
Tread with an improved drainage space
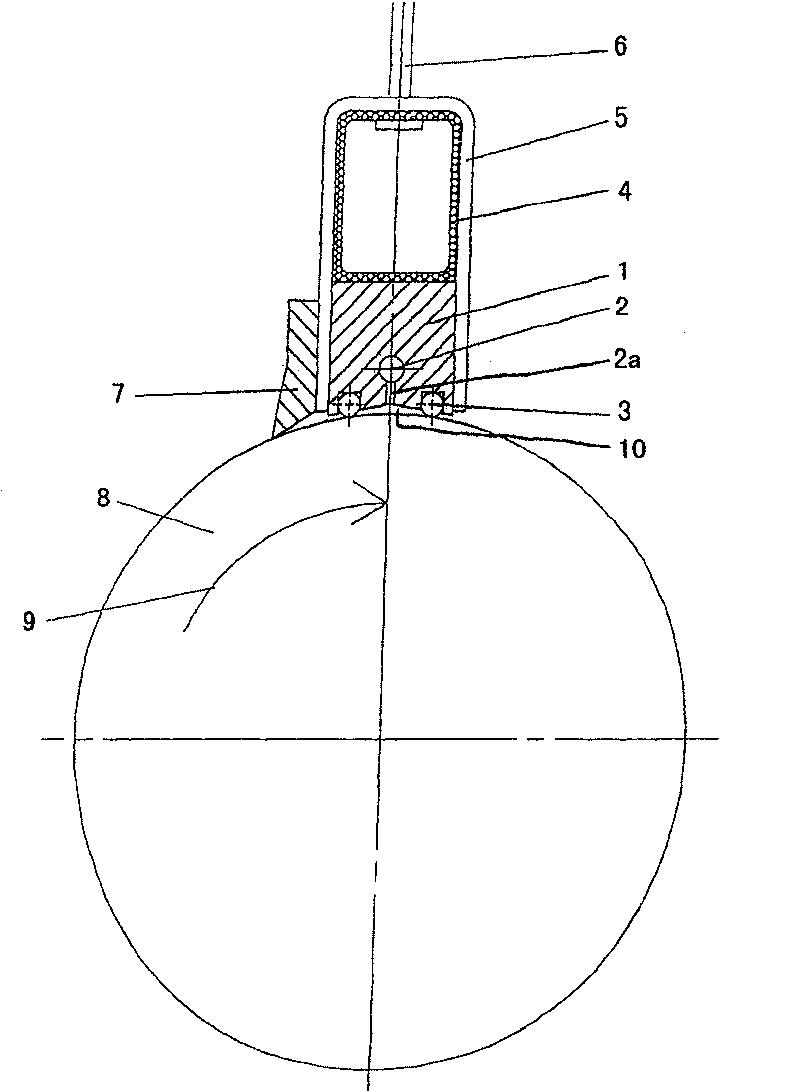
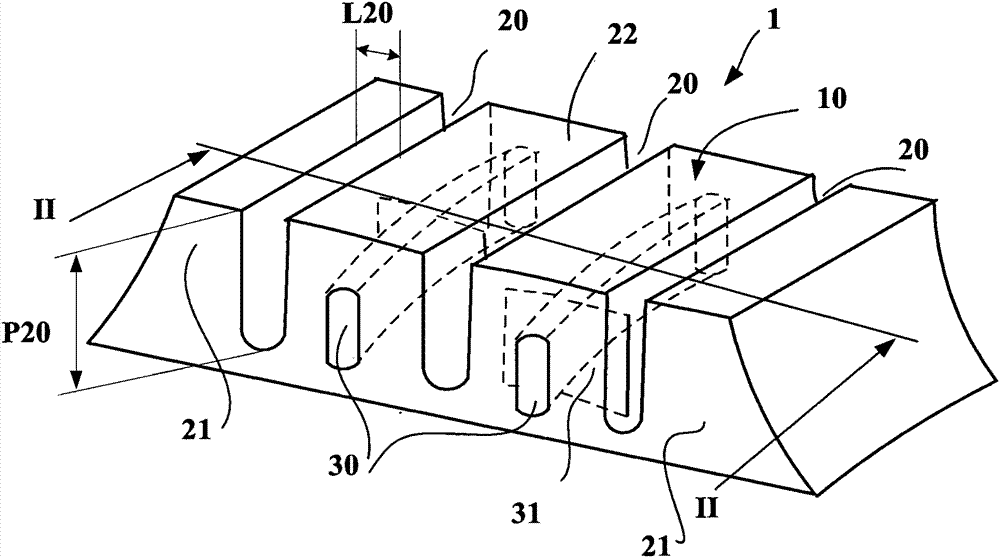
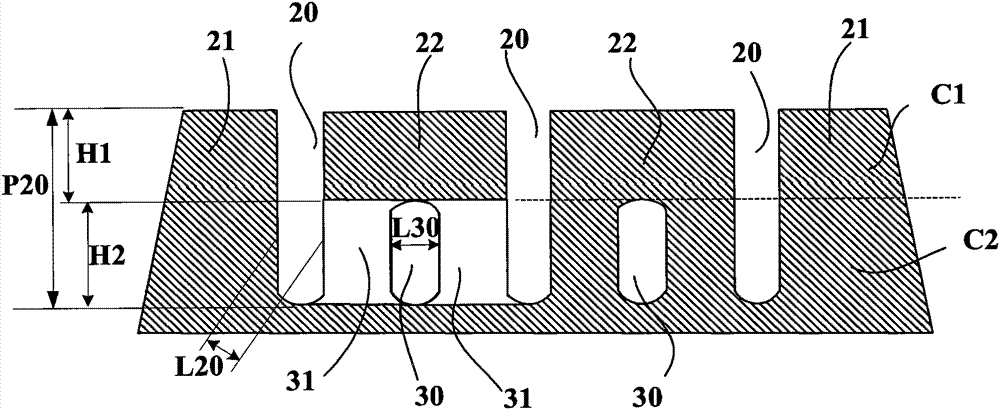
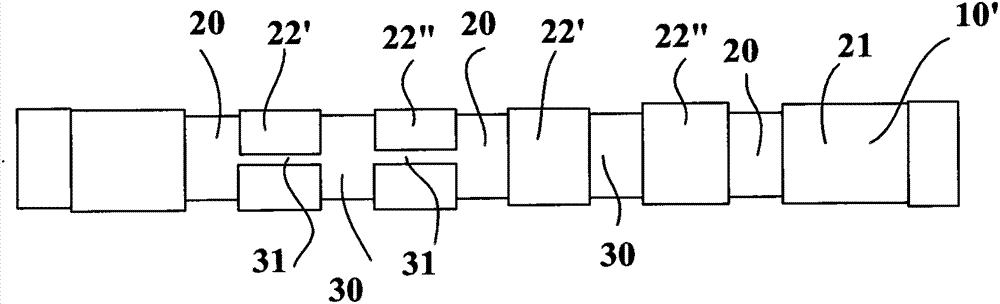
The invention relates to a tread (1) for a tyre having a wheel tread (10), at least two wearing courses (C1, C2, C3) overlapping in the body of the tread, a first wearing course (C1) made up of a plurality of raised elements (21, 22) each including a contact area, including at least circumferential grooves (20, 20'), and contacting the road when the tread is new, and at least one other wearing course (C2, C3) contacting the road once the first course (C1) is completely worn out, said courses comprising at least one channel (30) extending in the circumferential direction, and leading into the wheel tread whenever said wearing course is reached, each of the other wearing courses (C2, C3) comprising a plurality of transverse cuts (31) distributed in the circumferential direction and extending from a channel (30); of the course in question in a direction other than the circumferential direction to completely or partially lead into at least one other circumferential groove (20, 20'), regardless of the wear of said other wearing course.
Owner:OCIETE DE TECH MICHELIN
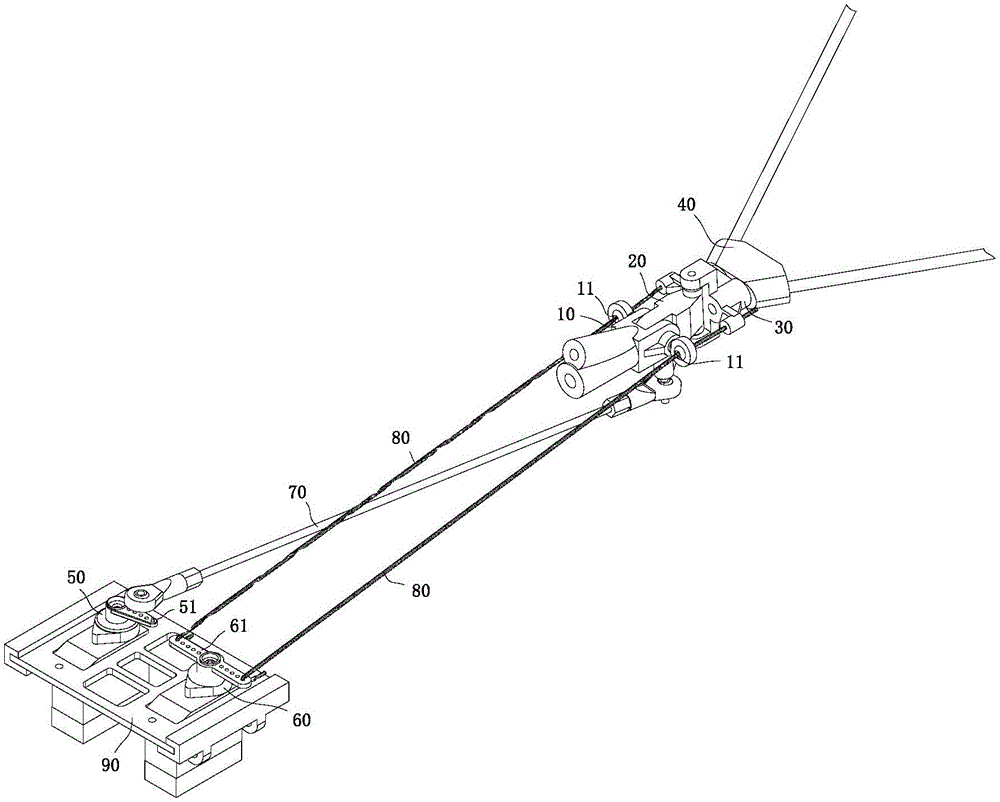
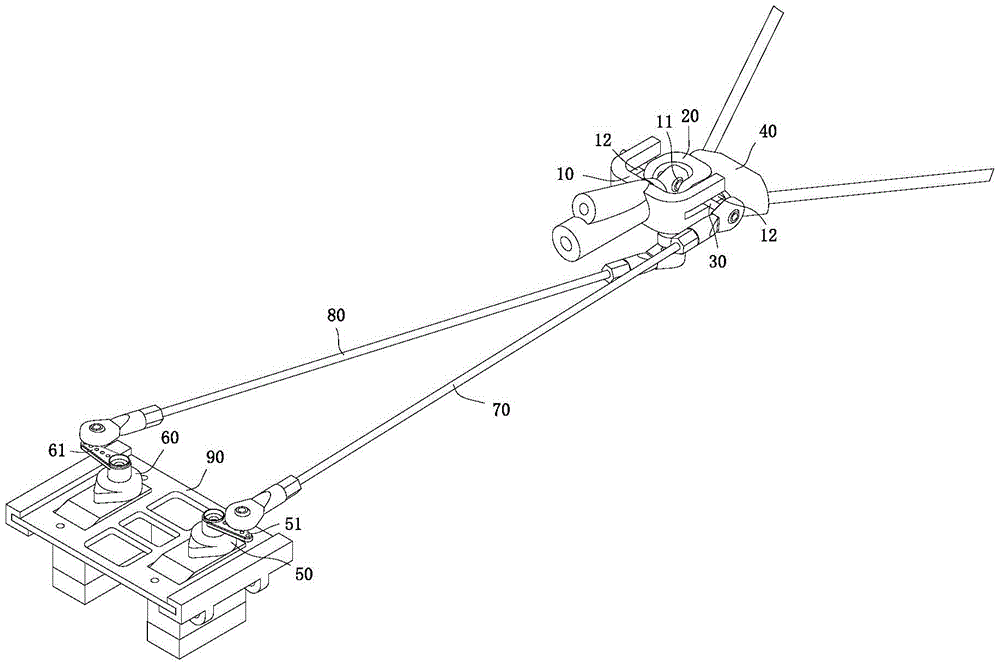
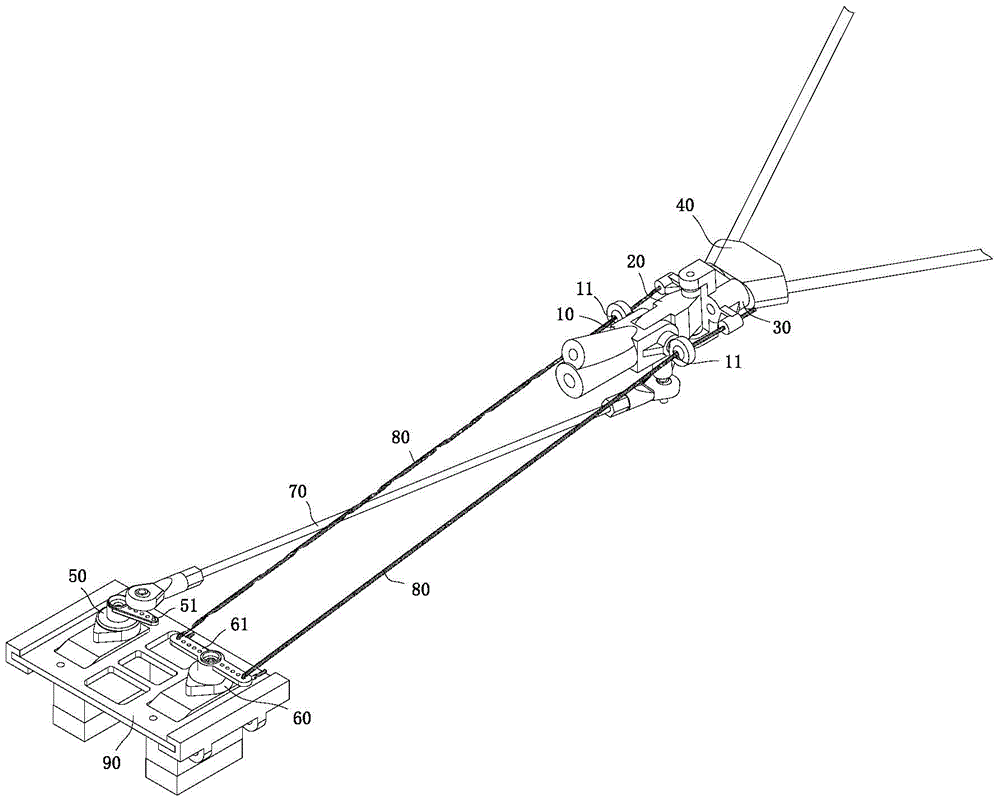
Aircraft empennage regulation mechanism with pitching and yawing completely decoupled
ActiveCN105151280AAchieve mechanical decouplingReduce weightWithout power ampliicationWeight reductionKinematic couplingTailplane
The invention discloses an aircraft empennage regulation mechanism with pitching and yawing completely decoupled. The aircraft empennage regulation mechanism comprises an empennage fixing part, an empennage pitching part and an empennage yawing part, wherein the empennage fixing part, the empennage pitching part and the empennage yawing part are sequentially arranged on the aircraft tail from front to back, the empennage fixing part and the empennage pitching part are hinged, and the empennage pitching part and the empennage yawing part are hinged. The aircraft empennage regulation mechanism further comprises a pitching steering engine and a yawing steering engine, wherein the pitching steering engine and the yawing steering engine are arranged on an aircraft body. The pitching steering engine rotates to drive a connecting rod to move to drive the empennage pitching part to swing around the axis of a pitching rotation shaft. The yawing steering engine rotates to pull two traction ropes to move to drive the empennage yawing part to swing around the axis of a yawing rotation shaft. According to the invention, the structure style of arranging a drive steering engine on the aircraft tail traditionally is abandoned, and the weight of the aircraft tail is effectively lowered. In addition, compared with a traditional kinematic coupling empennage regulation mechanism, the aircraft empennage regulation mechanism can regulate empennages through mechanical decoupling, and the reliability, the stability and the regulation accuracy of a system are greatly improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Hydraulic braking force adjusting device for electric-driven vehicle
ActiveCN105015528AAchieve mechanical decouplingEnsure safetyBraking action transmissionElectricityWheel cylinder
The invention relates to a hydraulic braking force adjusting device for an electric-driven vehicle. The hydraulic braking force adjusting device comprises an oil storage chamber, a pressure adjusting device, a brake master cylinder, a left front wheel cylinder, a right rear wheel cylinder, a left rear wheel cylinder, a right front wheel cylinder, a vacuum booster and a brake pedal, wherein the oil storage chamber comprises a first oil port, a second oil port, a third oil port and a fourth oil port; the first oil port and the second oil port are connected with the pressure adjusting device, respectively; the third oil port and the fourth oil port are connected with a first brake fluid inlet and a second brake fluid inlet of the brake master cylinder, respectively; a first brake fluid outlet and a second brake fluid outlet of the brake master cylinder are connected with the pressure adjusting device, respectively; the pressure adjusting device is connected with the left front wheel cylinder, the right rear wheel cylinder, the left rear wheel cylinder and the right front wheel cylinder, respectively; and the brake master cylinder is also connected with the brake pedal through the vacuum booster. The hydraulic braking force adjusting device for the electric-driven vehicle, provided by the invention, has the advantages of simplicity in making, convenience in mounting and low cost.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Telescopic steering wheel and control method thereof
PendingCN110001752AAchieve mechanical decouplingIncrease control flexibilitySteering controlsElectric energy managementControl engineeringSteering wheel
The invention discloses a telescopic steering wheel. The telescopic steering wheel comprises a road feeling motor, a steering shaft, a steering shaft sleeve, a shell body, an adjusting motor and a supporting limiting block, wherein the steering shaft is composed of three coaxially and fixedly connected assembly units, the first assembly unit and the second assembly unit are correspondingly locatedat the two ends of the third assembly unit, and even annular gear racks are arranged on the surface of the third assembly unit; the steering shaft sleeve is a hollow cuboid with central through holeson the upper side and the lower side, through hole slideways are arranged on the both sides of the steering shaft sleeve, and the steering shaft is located in the steering shaft sleeve; the shell body is of a groove profile structure with an inner concave center, and a supporting plate extends out of the central position of the edge of the concave groove of one side of the shell body; the adjusting motor is fixedly connected to the upper part of the supporting plate of the shell body, an output shaft is arranged on one side of the adjusting motor, and a gear shaft is fixedly connected to thehead of the output shaft; and the two sides of the supporting limiting block are fixedly connected with the two sides of the inner concave groove of the shell body, and the middle of the supporting limiting block passes through the two side slideways of the steering shaft sleeve. The invention further provides a control method of the telescopic steering wheel, and the scalability of the steering wheel can be controlled according to the manual driving state or the unmanned driving state.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Electric main shaft reliability loading testbed for load comprehensive decoupling
PendingCN110542550AIncrease loading frequencyTwo-way loading implementationMachine part testingElectricityCoupling
The invention belongs to the technical field of the test of mechanical test equipment, and relates to an electric main shaft reliability loading testbed for load comprehensive decoupling. The testbedcomprises an electric main shaft clamping module, a radial force amplitude loading module, a radial force mean loading module, a cutting torque loading module, an axial force loading module and a loading unit module; the electric main shaft clamping module, the radial force amplitude loading module, the radial force mean loading module and the cutting torque loading module are fixed on horizontaliron; one end of a simulated handle in the loading unit module is connected with a bellows coupling in the cutting torque loading module, and the other end is matched with a main shaft conical surfacethrough a simulated real handle conical surface; the axial force loading module are connected with two sides of a front end of a dynamometer base in the cutting torque loading module through bracketsat two ends. The loaded state under a main shaft real working status is simulated by adopting the collaborative loading of an electrodynamics vibration generator and an electric cylinder, the load comprehensive decoupling is realized by adopting the flexible loading structure, and the loading accuracy is improved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
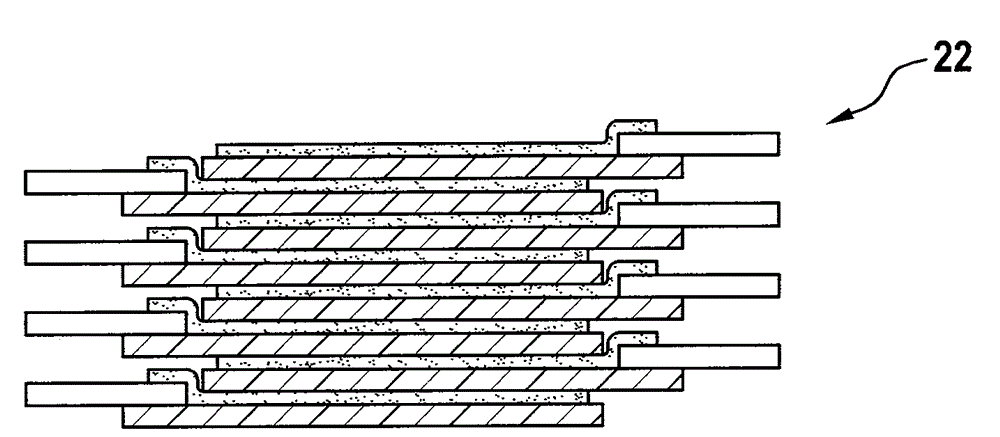
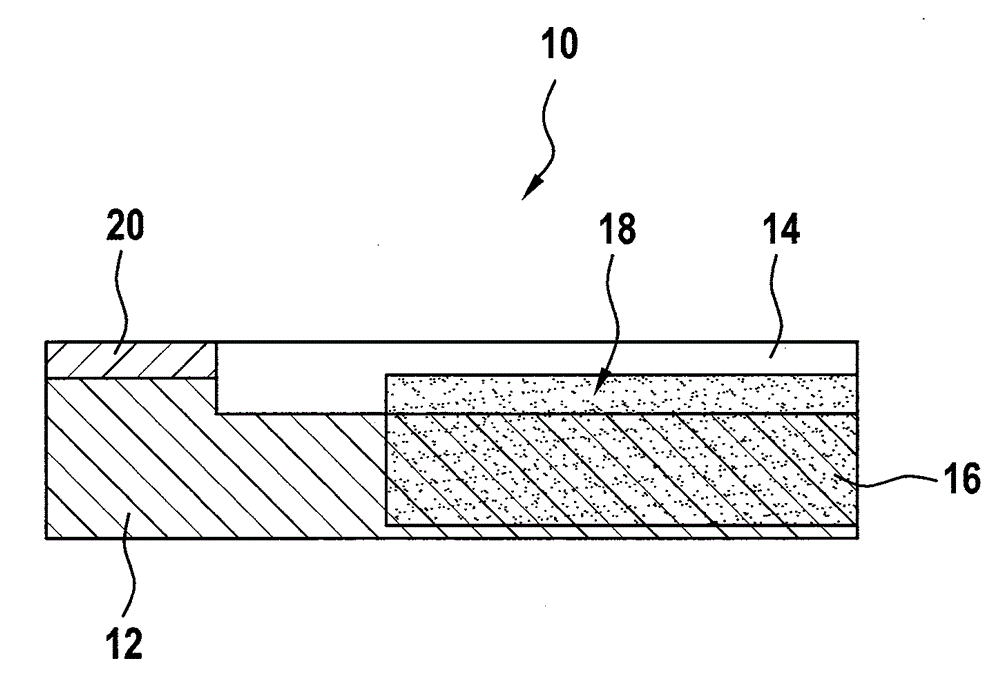
Mixed film applied to energy converter
ActiveCN104157783AImprove efficiencyImprove sexual functionPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyEngineeringEnergy converter
The invention relates to a mixed film applied to an energy converter (22) and preferably applied to a wave energy converter. The mixed film is an electroactivity polymer film. The mixed film is provided with a carrier film (20), a base film (12), a contact film (14) and an electrode coating layer (16). After the mixed film is used in the energy converter (22), good efficiency and functionality in the energy converter (22) can be realized.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Three-degree-of-freedom two-body satellite vibration isolation ground test system
ActiveCN106500750AAchieve mechanical decouplingHigh precisionStructural/machines measurementPilot systemThree degrees of freedom
A three-degree-of-freedom two-body satellite vibration isolation ground test system is provided. A load platform simulator and a service platform simulator are located in the middle of an air floating platform. A visual measurement system is arranged on the upper part of the load platform simulator and the service platform simulator. A plane mirror 1 is fixed on the air floating platform on a side of the load platform simulator side. A plane mirror 2 is fixed on the air floating platform on a side of the service platform simulator. A ground console is arranged on a side of the air floating platform. A vibration isolation device is installed at a position between the two simulators. The test system uses the non-contact vibration isolation device to divide a traditional satellite into two parts which are a load module and a service module, thereby realizing the mechanical decoupling of the two modules, and cutting off the transmission of the vibration. The test system can provide a working environment with ultra-high precision and stability for a sensor carried by the load module, avoids the interference of the vibration of the satellite components and has a high application value to the future ultra-high precision sensor.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Workpiece clamping device with oscillating drive and vacuum supporting functions and relevant vacuum clamp
InactiveCN107081440AFast processingSimple and precise machiningChucksPositioning apparatusEngineeringMechanical engineering
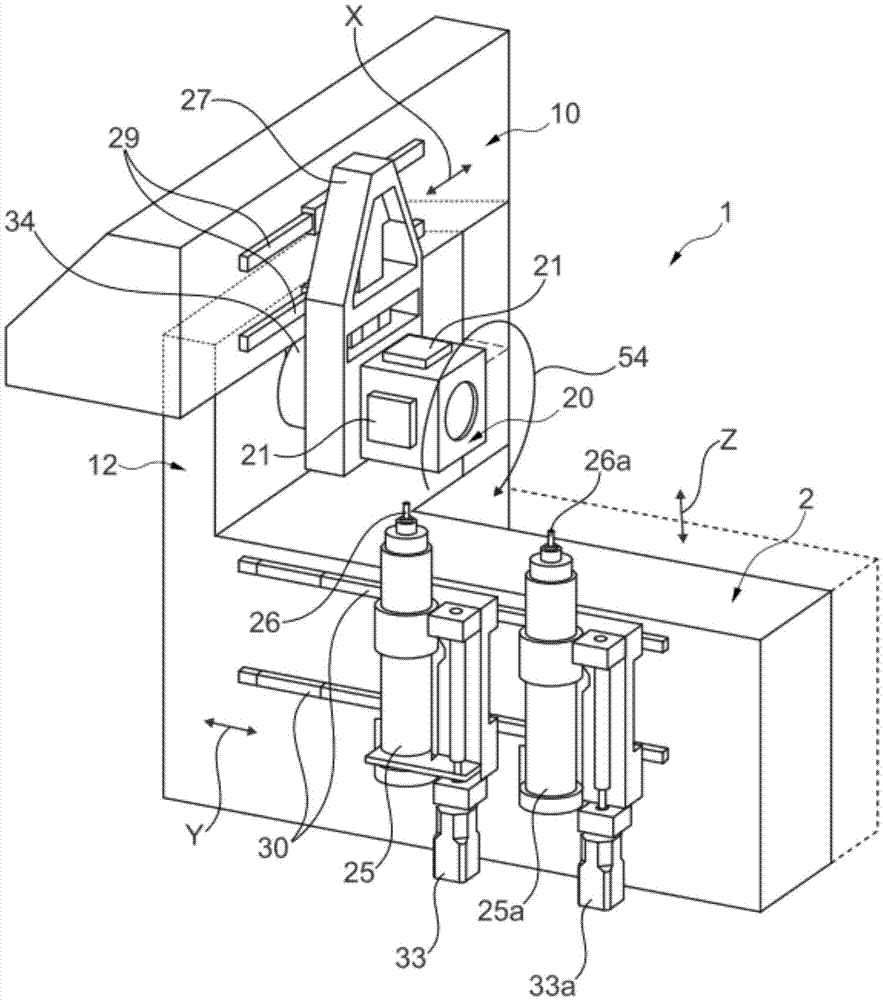
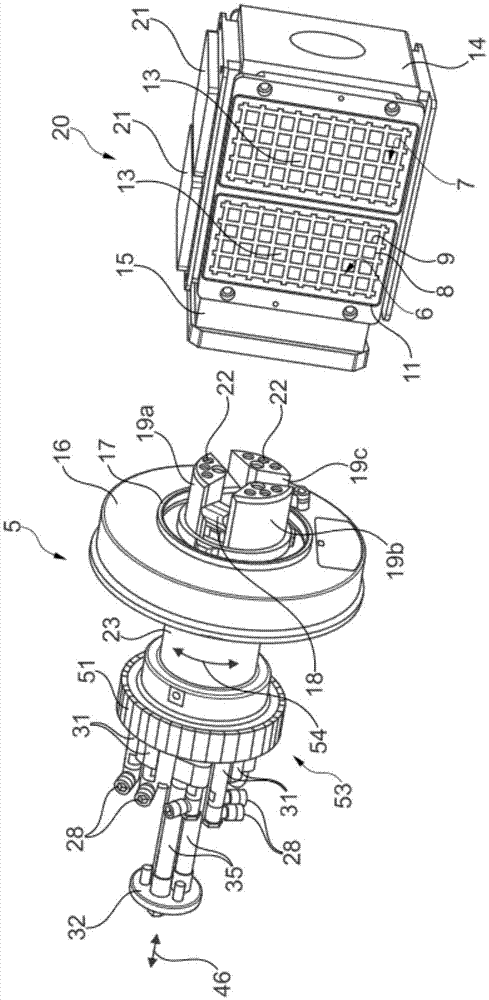
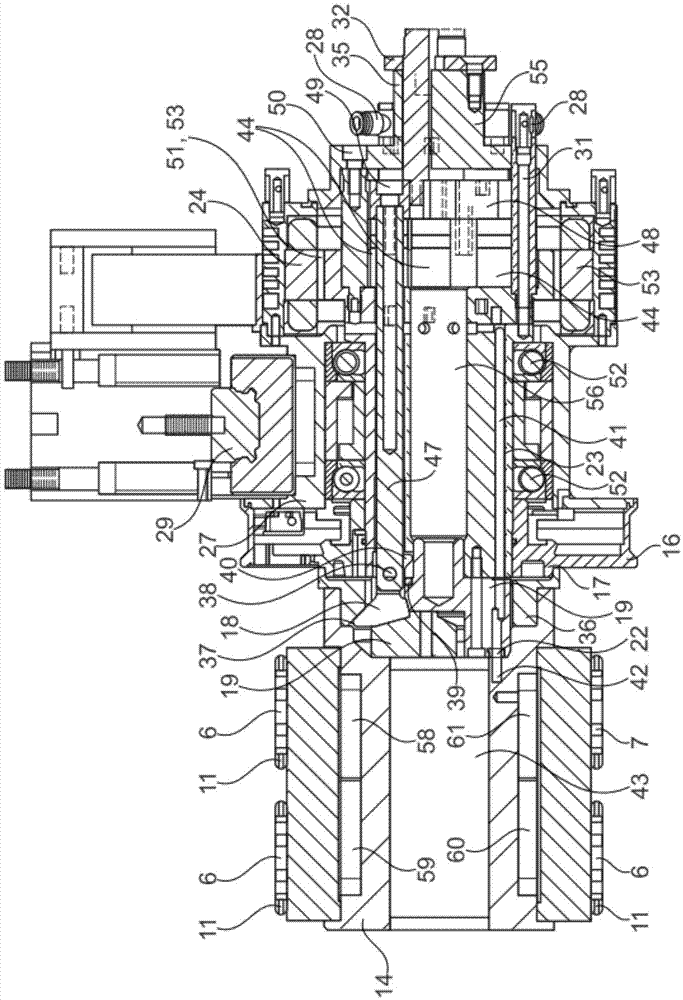
The invention provides a workpiece clamping device (20) with an oscillating drive function, and the workpiece clamping device (20) is used for machining a workpiece (21) in a workpiece machining device (1). The workpiece clamping device (20) is provided with a plurality of vacuum clamping plates (6 and 7) distributed on different planes on the circumference, and the vacuum clamping plates (6 and 7) are connected with a vacuum clamp (5) in an airtight mode.
Owner:英格博格马夸特
Three-dimensional rotation mechanism for force sense feedback and rotation attitude measurement
ActiveCN107239095AAchieve mechanical decouplingRotational attitude measurement is convenientControlling membersMagneto rheological damperMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a three-dimensional rotation mechanism for force sense feedback and rotation attitude measurement. The three-dimensional rotation mechanism for force sense feedback and rotation attitude measurement is characterized by comprising a rotating shaft A, a rotating shaft C and a rotating shaft B, wherein the rotating shaft A, the rotating shaft C and the rotating shaft B are located in three-dimensional axial directions of X, Y and Z respectively. The rotating shaft A and the rotating shaft B are connected through a connecting part II. The rotating shaft B and the rotating shaft C are connected through a connecting part I. The rotating shaft A, the rotating shaft B and the rotating shaft C are respectively provided with a magneto-rheological damper in the axial direction. An inertia measurement unit is installed on each magneto-rheological damper. According to the technical scheme of the invention, a mechanical structure, a force sense mechanism and a measuring mechanism are combined. Therefore, the force sense output is achieved and the controlling purpose is achieved through the rotation attitude measurement.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Attachment device for electrical energy source for providing traction for vehicle, preferably for electric vehicle
PendingCN113246707AAchieve mechanical decouplingFixed, safe and reliableElectric propulsion mountingUnderstructuresEngineeringStructural engineering
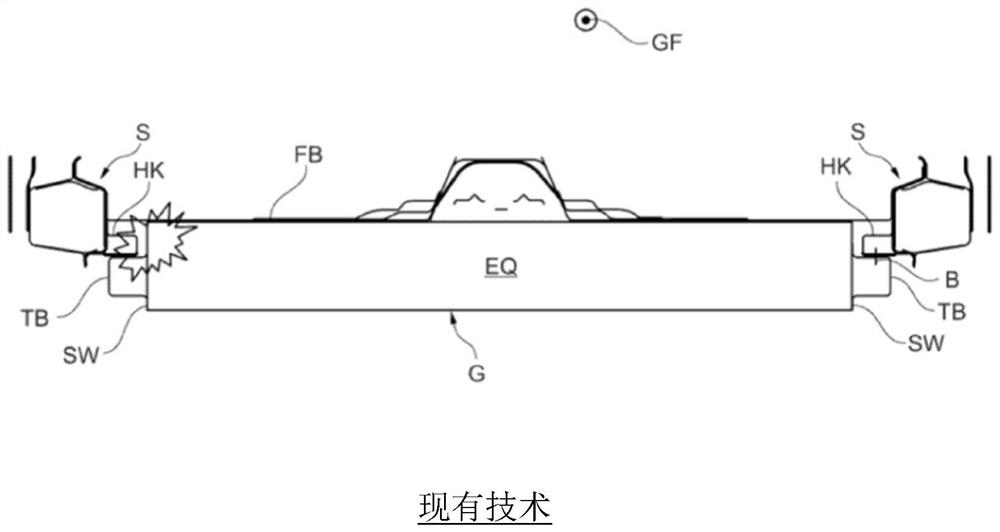
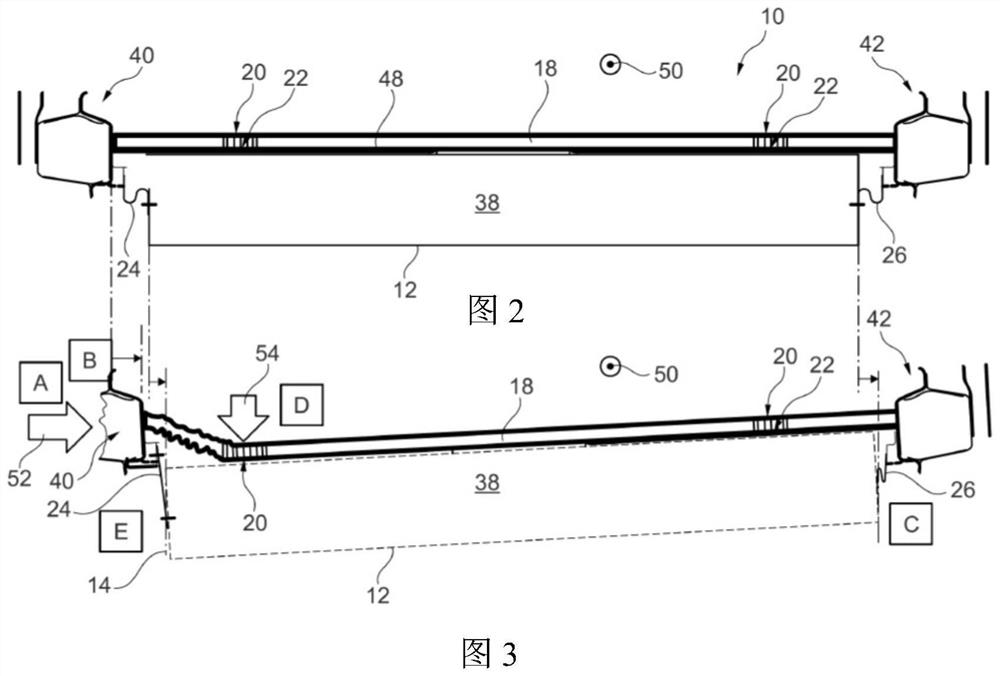
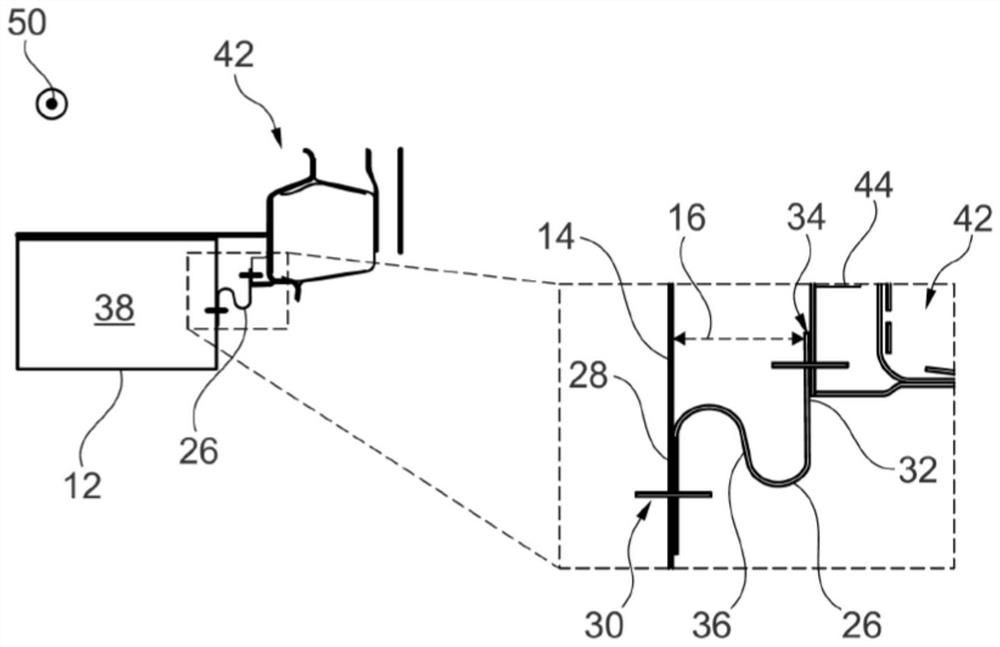
The invention relates to an attachment device (10) for an electrical energy source (38) for providing traction for a vehicle, preferably for an electric vehicle which can be arranged below a vehicle floor (48) between thresholds (40, 42) of the vehicle. The attachment device (10) has a housing (12) for accommodating and securing an electrical energy source (38) and a plurality of attachment elements (24, 26) for attaching the housing (12) to a body of a vehicle, in particular an electric vehicle. According to the invention, a plurality of attachment elements (24, 26) have a housing side end (28) attached to the housing (12) and a sill side end (32) attached to one of the sills (40, 42). In this case, the attachment element (24, 26), in the mounted state, has an at least partially curved contour with at least one inflection point (36) between the housing side end (28) and the sill side end (32) in at least one virtual plane arranged perpendicularly to the straight direction (50) of the vehicle.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Rubber bushing test system
ActiveCN110243579AReduce the impactAchieve mechanical decouplingMachine part testingEngineeringTorsional load
The invention relates to the technical field of automobile part tests, and discloses a rubber bushing test system which comprises a loading seat, a warping seat and a torsion seat. The loading seat is provided with a containing hole for pressing the rubber bushing, and the loading seat is configured to apply radial load to the rubber bushing; the warping seat comprises a connecting rod, and is used for penetrating through an inner hole of the rubber bushing to fix the rubber bushing on the warping seat; and the warping seat is rotatably connected to the torsion seat, the torsion seat is capable of rotating about an axis of the connecting rod, and the torsion seat is configured to apply a torsional load to the rubber bushing. The rubber bushing test system realizes mechanical decoupling, and can simultaneously apply three dynamic loads of radial, torsion and warping to the rubber bushing, the installation and connection modes of the rubber bushing are consistent with that of a real vehicle, and the rubber bushing test system can truly simulate the actual working condition of the rubber bushing, and accurately tests the rubber bushing.
Owner:CHINA FIRST AUTOMOBILE
Driving unit and multi-mode driving vehicle for mining low distributed support carrier
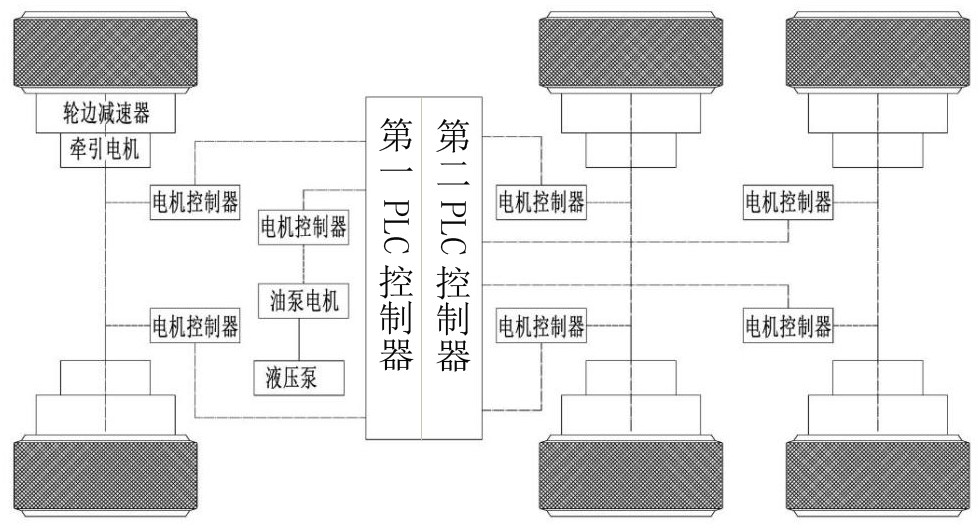
InactiveCN112549937AReduce the overall heightPrecise adjustment of power outputElectric propulsion mountingControl devicesDrive wheelReduction drive
The invention belongs to the technical field of underground coal mine transportation equipment, and relates to a driving unit and a multi-mode driving vehicle for a mining low distributed support carrier. The driving vehicle comprises a traction motor, a hub reduction gear and wheels, the hub reduction gear comprises a first-stage reduction mechanism, a second-stage reduction mechanism, a wet brake, a front bearing frame and a rear U-shaped frame, the front bearing frame and the rear U-shaped frame are connected to each other, the driving units are arranged at the two sides of the front bearing frame, and the driving units, a first electric control box and a second electric control box are arranged on the two sides of the rear U-shaped frame respectively. According to the driving system ofthe driving vehicle, six sets of traction motor and hub reduction gear distributed modes are adopted, multiple driving modes such as full six-wheel driving, two-wheel front driving and four-wheel rear driving are achieved through multi-motor coordination control, power output of the driving wheels is accurately adjusted according to actual working conditions, and the purposes of energy conservation and efficiency improvement are achieved. The invention provides an effective solution to the problem of difficult configuration of the carrying vehicle for the underground low-space operation of the coal mine.
Owner:TAIYUAN INST OF CHINA COAL TECH & ENG GROUP +1
Cart console and minimally invasive surgery robot
PendingCN114587607AReduce volumeLow integrationSurgical robotsMinimal invasive surgeryPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The invention discloses a cart control console and a minimally invasive surgery robotic.The cart control console comprises a push-pull module, a torsion module and a control module used for controlling the push-pull module and the torsion module, and the torsion module comprises a torsion sensing assembly connected with the control module. By the adoption of the cart control console, when a user pushes the control module, overall micro-motion of the torsion sensing assembly is achieved through the connection mode between the micro-motion seat and the first shell, and therefore the influence of push-pull force on the torque sensor is eliminated; and the generated torque signal and torsion are transmitted to the first shell and the second shell through the sliding rod, so that the influence of the torsion on the tension and compression sensor is eliminated, namely, the mechanical decoupling of the tension and compression sensor and the torque sensor is realized, and the movement of the slave hand can be relatively easily controlled.
Owner:杭州唯精医疗机器人有限公司
Driving device and vehicle
PendingCN114435126AReduce power lossAchieve mechanical decouplingControl devicesGear wheelElectric machinery
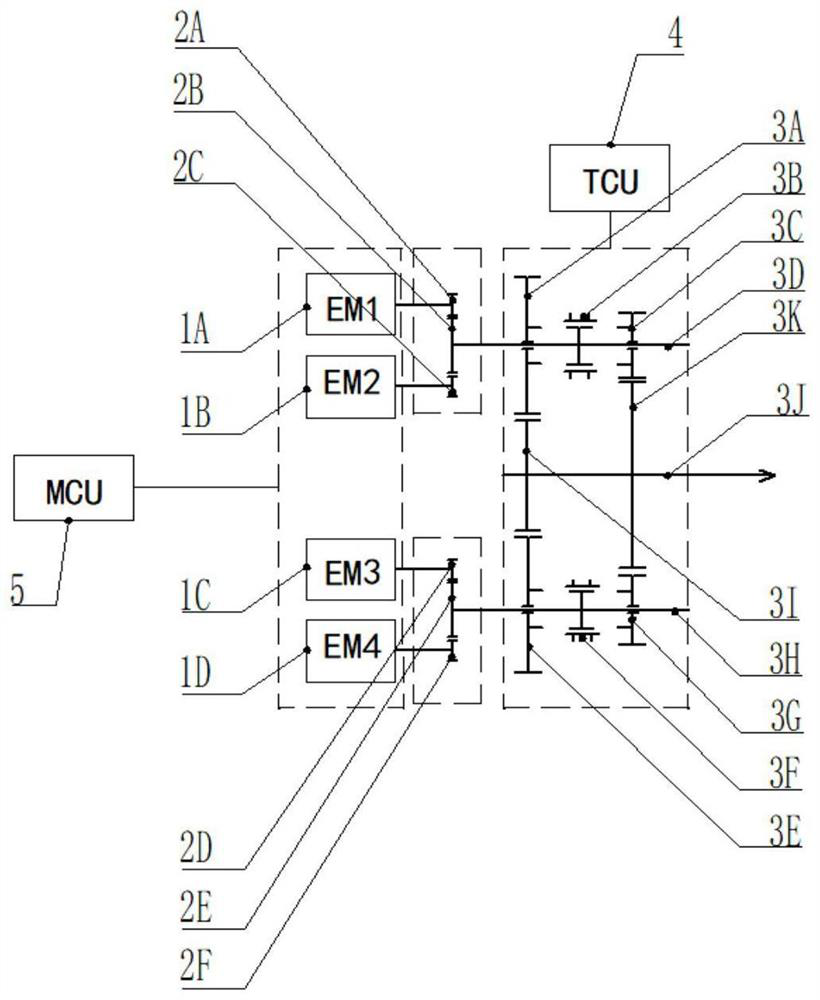
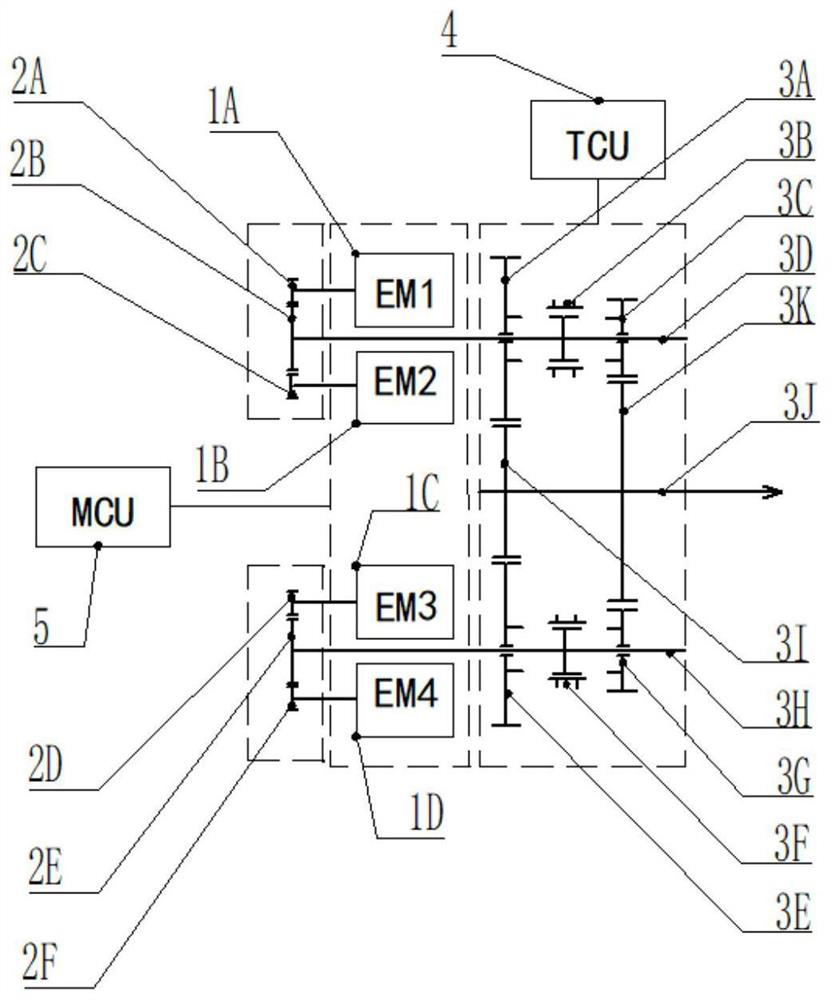
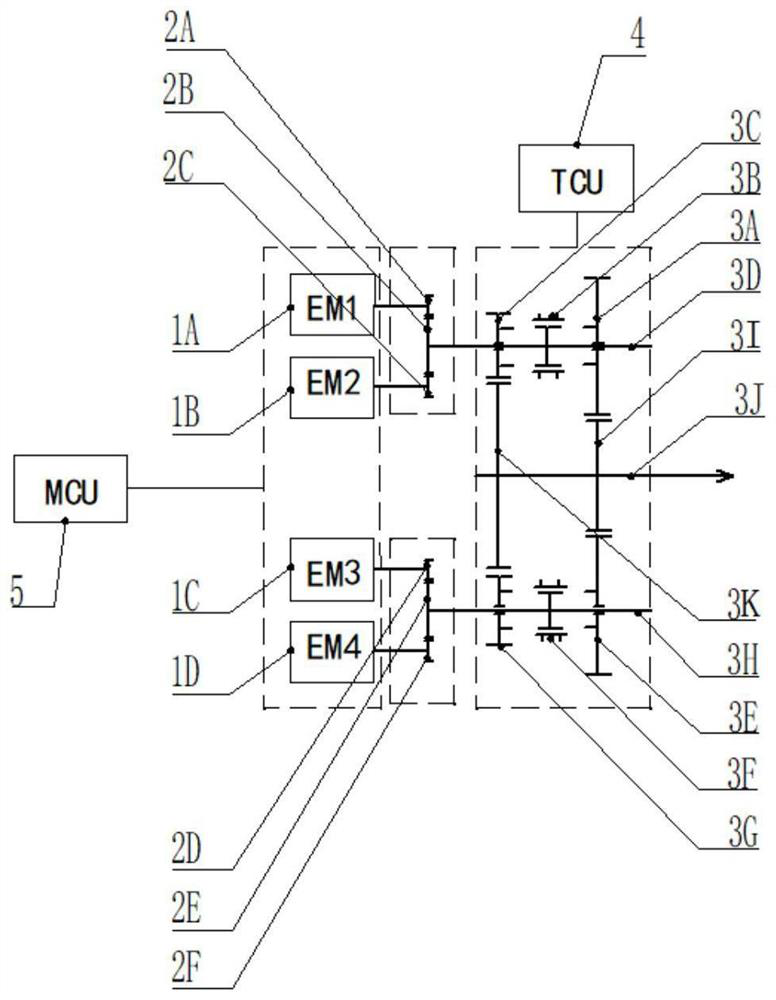
The invention provides a driving device and a vehicle, the device comprises a driving part, a transmission assembly, a driving controller and a variable speed controller, the driving part comprises N sets of driving assemblies, the transmission assembly comprises a power output shaft and N sets of variable speed assemblies, and the power output end of each set of driving assembly is used for inputting driving force to the corresponding variable speed assembly; a synchronizer and M input gears are arranged on the speed change input shaft of each set of speed change assembly, M output gears are arranged on the power output shaft, and the input gears are meshed with the output gears so that when the output gears are used for bearing driving force, output power of the corresponding gears can be output through the power output shafts. The synchronizer is used for adjusting the output gear currently used for bearing the driving force; the driving controller is used for controlling the working state of each group of driving components, and the variable speed controller is used for controlling the synchronizer to perform gear shifting operation. According to the driving device, mechanical decoupling between the motors is achieved, the transmission efficiency is high, power interruption is avoided during gear shifting, and control is relatively simple.
Owner:浙江远程智芯科技有限公司 +3
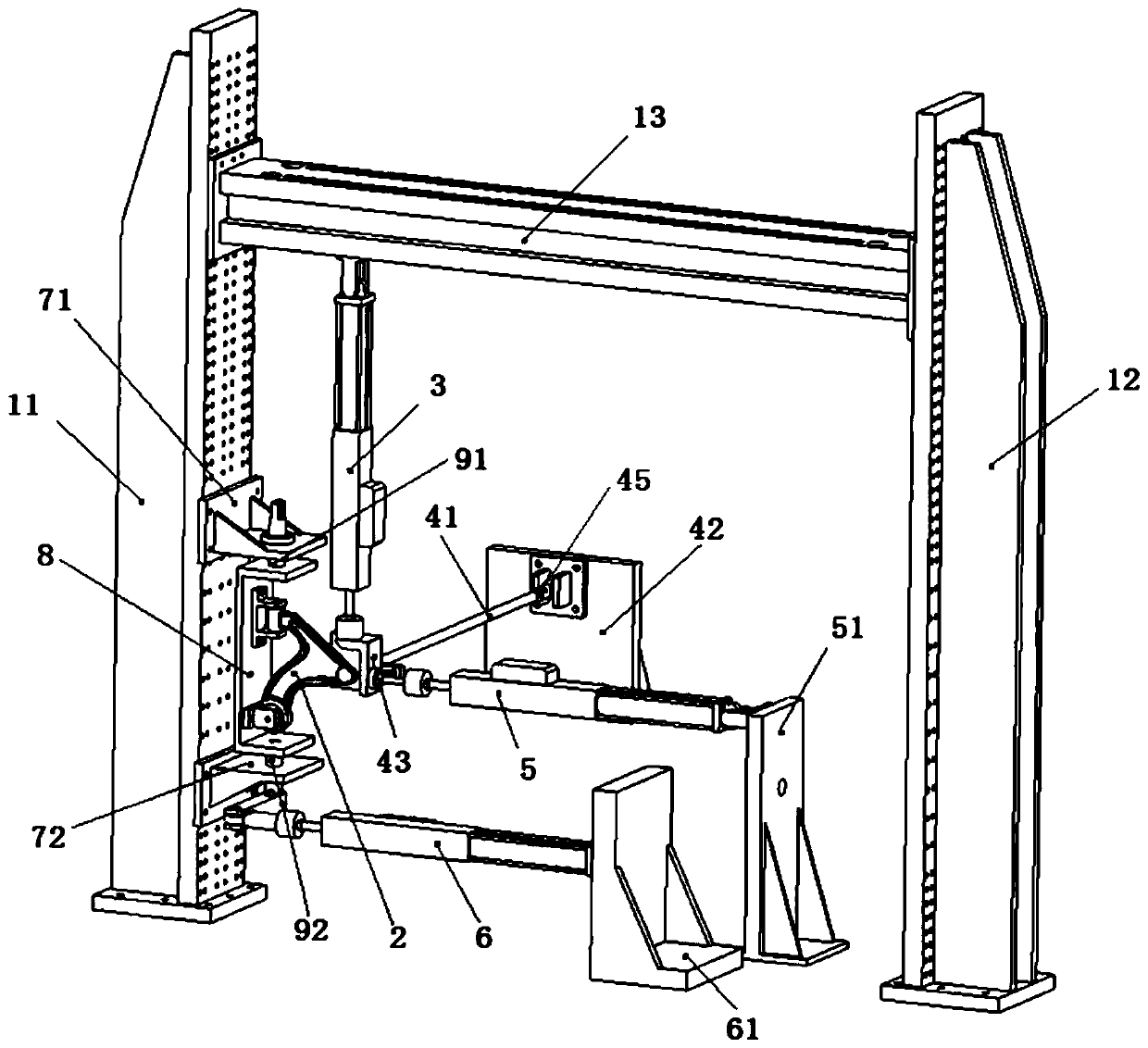
Control arm assembly bench test system for Mcpherson suspension of passenger vehicle
InactiveCN110006666AVerify DurabilityShorten the development cycleVehicle testingPilot systemVertical jumping
The invention relates to a control arm assembly bench test system for Mcpherson suspension of a passenger vehicle. The control arm ball stud end of the system is connected with a loading seat, the loading seat and a guiding rod are connected through a hinge, the axis of the guiding rod is perpendicular to the plane where the center point of a ball stud and the axis of a lining, the vertical displacement of the control arm ball stud is limited, a torsional seat which is coaxial with the rotating axis of the control arm assembly lining end is loaded through a linear actuator, vertical jumping ofthe control arm assembly ball stud end of the real vehicle is converted into torsion of the lining end, and meanwhile influences of the vertical load on the lateral load and the longitudinal load arereduced; and in lateral and longitudinal loading mechanisms, a lateral loading linear actuator and a loading seat are connected through a ball hinge, a longitudinal loading linear actuator and the loading seat are in rigid connection, and mutual influences of the transverse load and the longitudinal load are reduced. Mechanical uncoupling is achieved, the load spectrum iteration accuracy can be improved, and the bench test accuracy is improved.
Owner:CHINA FIRST AUTOMOBILE
A hydraulic braking force adjustment device for an electric drive vehicle
ActiveCN105015528BAchieve mechanical decouplingEnsure safetyBraking action transmissionElectricityWheel cylinder
The invention relates to a hydraulic braking force adjusting device for an electric-driven vehicle. The hydraulic braking force adjusting device comprises an oil storage chamber, a pressure adjusting device, a brake master cylinder, a left front wheel cylinder, a right rear wheel cylinder, a left rear wheel cylinder, a right front wheel cylinder, a vacuum booster and a brake pedal, wherein the oil storage chamber comprises a first oil port, a second oil port, a third oil port and a fourth oil port; the first oil port and the second oil port are connected with the pressure adjusting device, respectively; the third oil port and the fourth oil port are connected with a first brake fluid inlet and a second brake fluid inlet of the brake master cylinder, respectively; a first brake fluid outlet and a second brake fluid outlet of the brake master cylinder are connected with the pressure adjusting device, respectively; the pressure adjusting device is connected with the left front wheel cylinder, the right rear wheel cylinder, the left rear wheel cylinder and the right front wheel cylinder, respectively; and the brake master cylinder is also connected with the brake pedal through the vacuum booster. The hydraulic braking force adjusting device for the electric-driven vehicle, provided by the invention, has the advantages of simplicity in making, convenience in mounting and low cost.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
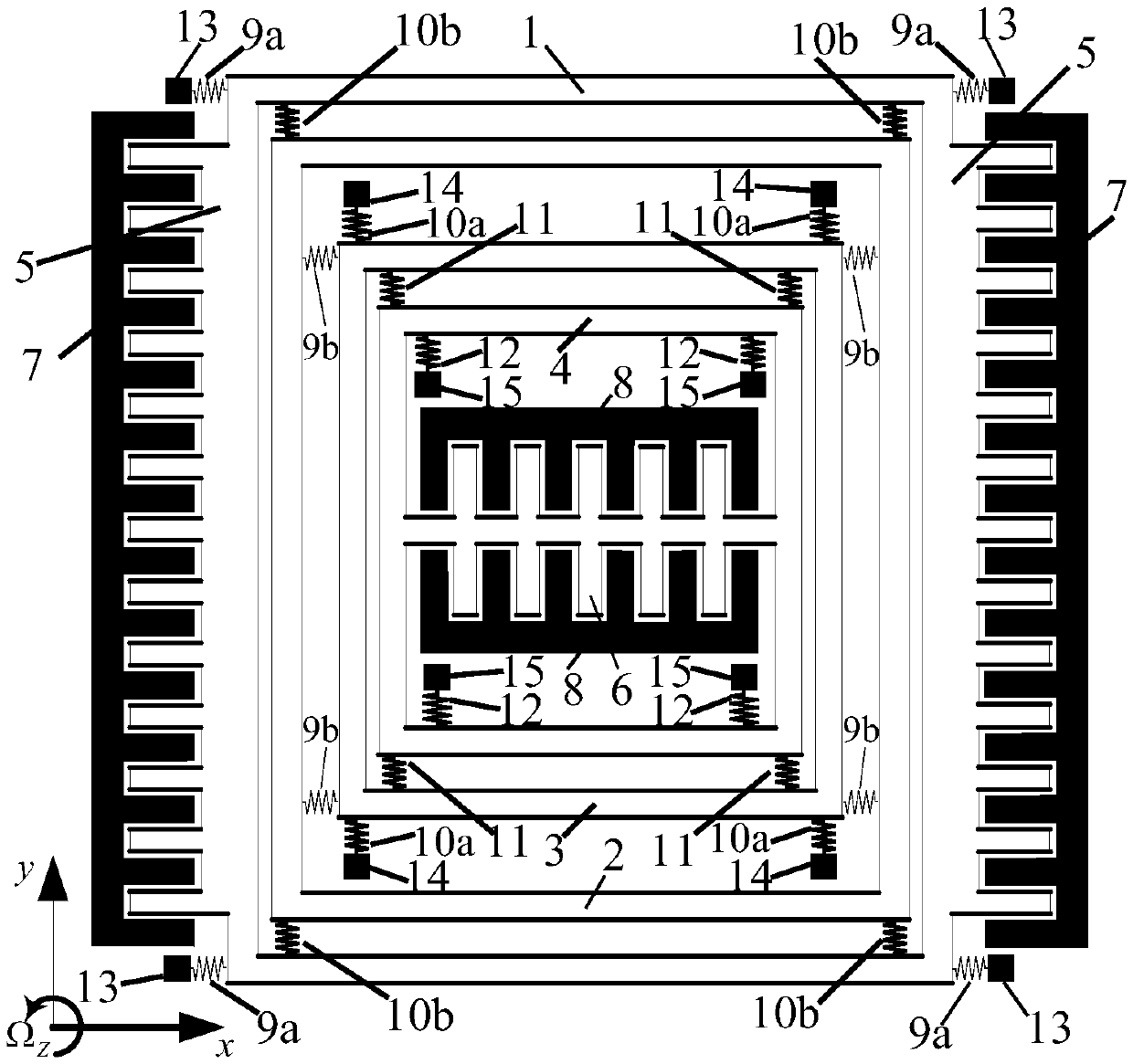
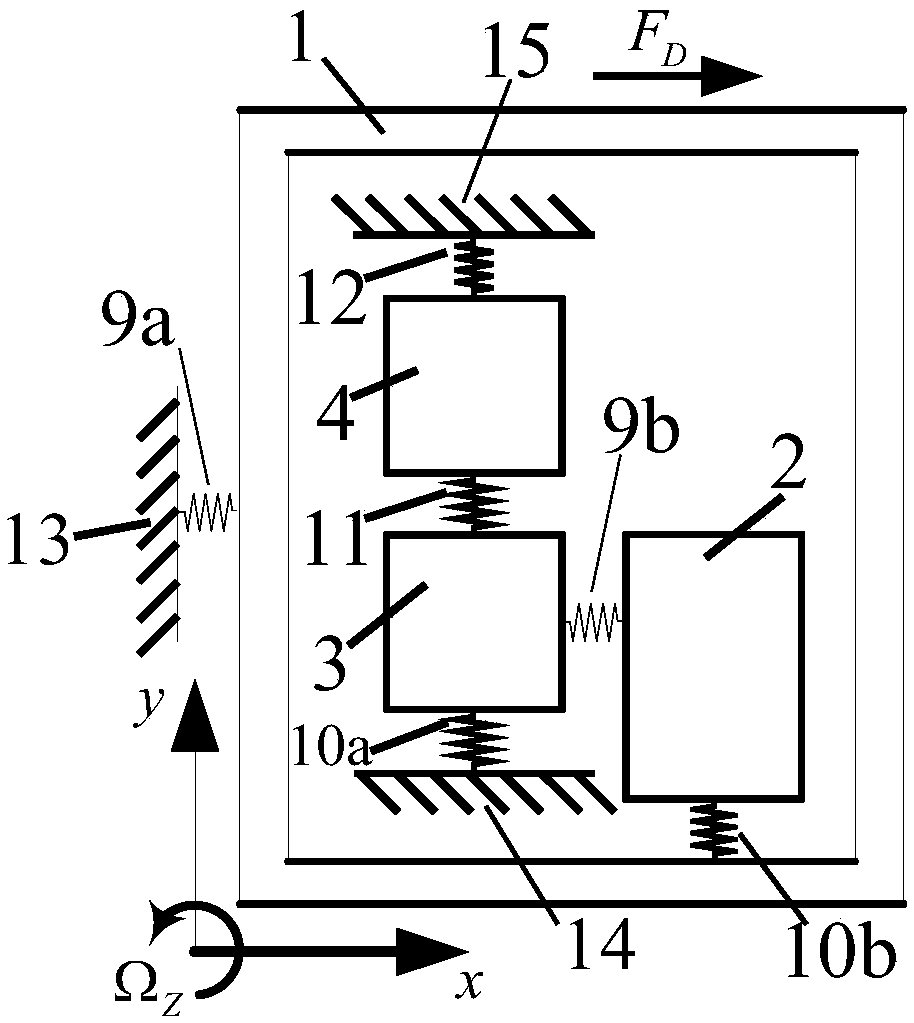
A fully decoupled three-degree-of-freedom micromechanical gyroscope
ActiveCN109668550BHigh sensitivityAchieve mechanical decouplingSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopes/turn-sensitive devicesGyroscopeInterference resistance
The invention discloses a fully decoupled three-degree-of-freedom micro-mechanical gyroscope, which improves the mechanical decoupling performance of the micro-mechanical gyroscope. The micromechanical gyroscope structure of the present invention includes a single-degree-of-freedom driving mode and a complete two-degree-of-freedom sensitive mode, and is respectively connected to the driving frame and the detection frame through the decoupling mass block, and simultaneously realizes the mechanical solution of the driving mode and the sensitive mode coupling and energy conversion. The complete two-degree-of-freedom structure can increase the stable bandwidth of sensitive modes and improve the stability and anti-interference ability of the gyro system. The invention has the advantages of mechanical decoupling, good stability and anti-interference, and works under normal pressure, which is beneficial to actual processing and application.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
An empennage adjustment mechanism with conditional decoupling of pitch and yaw for aircraft
ActiveCN105151281BSimple structureReduce weightWithout power ampliicationWith power amplificationKinematic couplingFlight vehicle
The invention discloses a pitching and yawing conditional decoupling empennage regulating mechanism for an aircraft. The regulating mechanism comprises an empennage fixed part and an empennage movable part arranged at the tail part of the aircraft, as well as a yawing steering engine and a pitching steering engine arranged on the aircraft body, wherein the empennage fixed part is provided with an oscillating bearing; a rotating shaft is connected in the oscillating bearing in a sleeved manner; the rotating shaft is fixedly connected with the empennage movable part; the yawing steering engine and the rotating shaft are in rigid transmission connection through a yawing connecting rod; the pitching steering engine and the empennage movable part are in rigid transmission connection through a pitching connecting rod; the pitching steering engine and the yawing steering engine are arranged in the fuselage of the aircraft body; the structural form that a driving steering engine is arranged at the tail part of the aircraft traditionally is abandoned, so that the tail part weight of the aircraft is effectively reduced. Compared with the traditional movement decoupling empennage regulating mechanism, the pitching and yawing conditional decoupling empennage regulating mechanism, disclosed by the invention, can realize mechanical decoupling of an empennage mechanism under certain path instead of decoupling through software resolving and greatly improves the reliability, stability and regulation precision of a system.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
A rubber bushing test system
ActiveCN110243579BAchieve mechanical decouplingEasy to installMachine part testingClassical mechanicsEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of auto parts testing, and discloses a rubber bushing test system, which includes a loading seat, a warping seat and a twisting seat; the loading seat is provided with accommodating holes for press-fitting rubber bushings, and the loading seat is covered by It is configured to be able to apply a radial load to the rubber bushing; the warping seat includes a connecting rod, which is used to pass through the inner hole of the rubber bushing to fix the rubber bushing on the warping seat, and the warping seat can be wound vertically The direction of the axis of the connecting rod rotates, and the warping seat is configured to apply a warping load to the rubber bushing; the warping seat is rotatably connected to the torsion seat, and the torsion seat can rotate around the axis of the connecting rod, and the torsion seat is configured to apply a warping load to the rubber bushing. The sleeve applies a torsional load. The rubber bushing test system achieves mechanical decoupling, and can apply three dynamic loads of radial, torsional and warping to the rubber bushing at the same time. The installation and connection method of the rubber bushing is consistent with that of the real vehicle, which can truly simulate the rubber bushing. The actual working condition of the sleeve is used to accurately test the rubber bushing.
Owner:CHINA FIRST AUTOMOBILE
Full decoupling three-freedom micromechanical gyroscope
ActiveCN109668550AHigh sensitivityAchieve mechanical decouplingSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopes/turn-sensitive devicesGyroscopeEngineering
The invention discloses a full decoupling three-freedom micromechanical gyroscope. The mechanical decoupling performance of the micromechanical gyroscope is improved. The micromechanical gyroscope structurally comprises a freedom driving model and a complete two-freedom sensitive model which are respectively connected with a driving framework and a detection framework through a decoupling mass block; meanwhile, the mechanical decoupling and energy conversion of the driving model and the sensitive model are realized at the same time. The complete two-freedom structure can increase the stable bandwidth of the sensitive model; the stability and the anti-interference capability of the gyroscope system are improved. The full decoupling three-freedom micromechanical gyroscope has the advantagesof mechanical decoupling, high stability and anti-interference, works at the normal pressure and is favorable for practical processing and application.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Micro-inertial navigation gyroscope with multi-detection vibration units
InactiveCN108731659AEliminate bandwidthEliminate the defect that the output amplitudes restrict each otherNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopeDegrees of freedom
The invention discloses a micro-inertial navigation gyroscope with multi-detection vibration units. A 1-DOF (degree of freedom) vibration unit and a 2-DOF vibration unit are introduced into the gyroscope simultaneously to serve as a composite sensitive vibration unit, frequency in a bandwidth range is divided by difference and complementarity of amplitude-frequency response characteristics of the1-DOF vibration unit and the 2-DOF vibration unit in different frequency ranges, and output curve of the whole sensitive vibration unit is enabled to have better amplitude-frequency response characteristics. With adoption of the combined detection by selecting different vibration units in different frequency ranges, the defect of mutual restriction between bandwidth and output amplitude of a sensitive vibration unit in traditional microgyroscope design is overcome, and the multiple vibration units provide signals continuously, so that information redundancy and backup are provided for a data processing part of the gyroscope.
Owner:SOUTHWEST CHINA RES INST OF ELECTRONICS EQUIP
Moistening device for a roll or a cylinder of an offset press
InactiveCN1891456BIncreasing the thicknessReduce thicknessCylinder pressesLiquid surface applicatorsActuatorOffset printing
A moistening device for a roll or a cylinder of an offset press is disclosed. The moistening device includes a chamber-type doctor which is attached for moistening to the roll or to the cylinder. At least one actuator is arranged on the chamber-type doctor, with which actuator the pressing force of the chamber-type doctor on the roll or the cylinder can be varied along the length of the roll or the cylinder.
Owner:MANROLANAD AG
Tread with improved drainage space
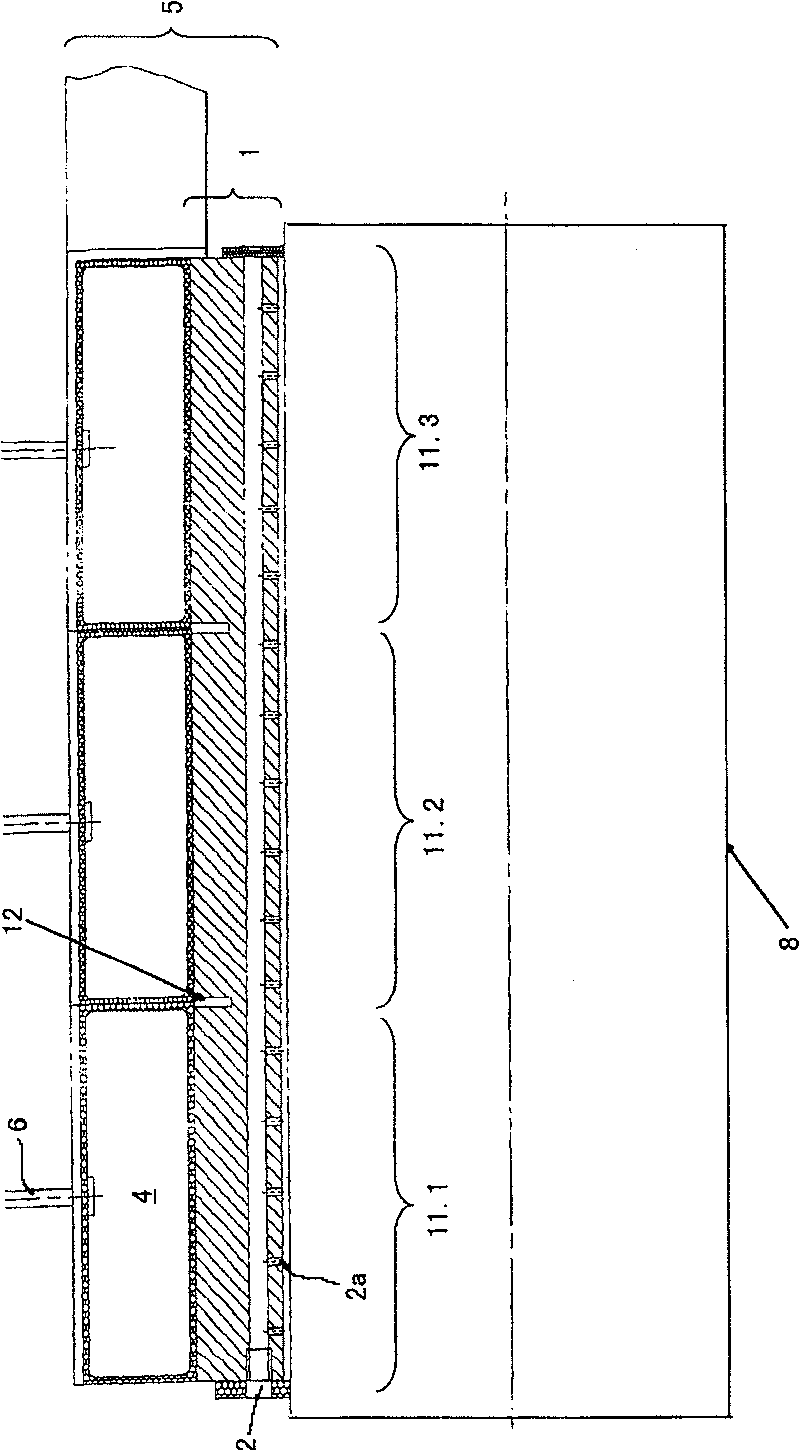
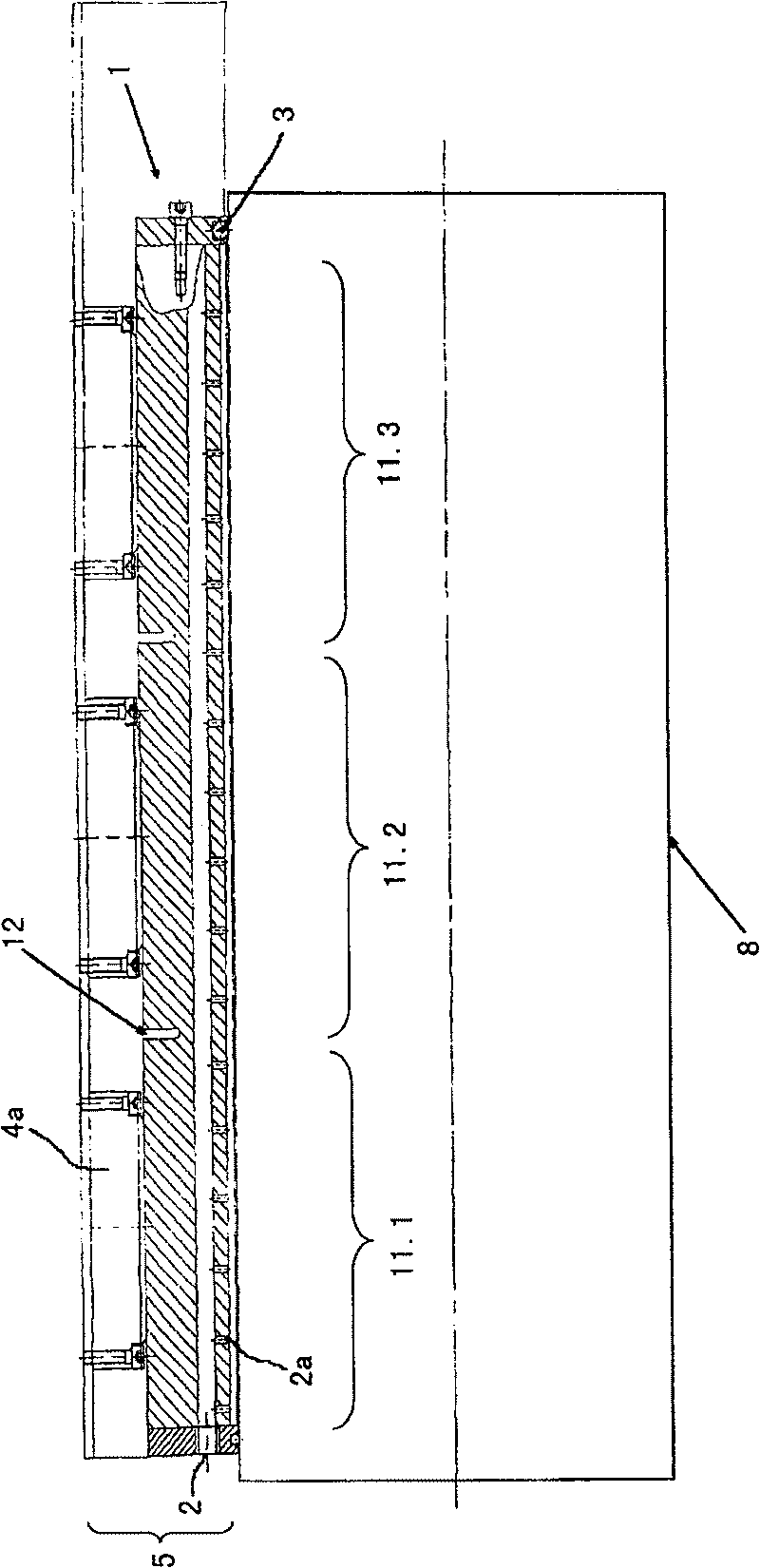
ActiveCN102256812BReduce depthLimit compressibilityTyre tread bands/patternsTransverse incisionEngineering
Tyre tread band (1) having a tread surface (10) to come into contact with the road surface, this tread band comprising at least two wearing layers (C1, C2, C3) which are superposed in the thickness of the tread, this tread band (1) having a first wearing layer (C1) formed by a plurality of raised elements (21, 22) each comprising a contact surface, this first layer comprising at least grooves (20, 20′) of circumferential overall orientation, this first layer being intended to be in contact with the road surface when the tread is new, and at least one other wearing layer (C2, C3) coming into contact with the road surface after the first layer (C1) has entirely worn away, each other wearing layer comprising at least one channel (30) extending in the circumferential overall direction, each channel (30) opening onto the tread surface as soon as the said wearing layer is reached after the wearing layer that proceeds it has completely worn away, this tread band being such that each wearing layer (C2, C3), distinct from the first wearing layer (C1), comprises a plurality of transverse incisions (31) distributed in the circumferential direction, each transverse incision extending from a channel (30) of the layer in question in a direction which is not circumferential so as to open fully or partially into at least one other circumferentially oriented channel or groove, and do so irrespective of the level of wear of the said other wearing layer.
Owner:OCIETE DE TECH MICHELIN
A fully decoupled tail adjustment mechanism for aircraft pitch and yaw
ActiveCN105151280BAchieve mechanical decouplingReduce weightWithout power ampliicationWeight reductionKinematic couplingTailplane
The invention discloses an aircraft empennage regulation mechanism with pitching and yawing completely decoupled. The aircraft empennage regulation mechanism comprises an empennage fixing part, an empennage pitching part and an empennage yawing part, wherein the empennage fixing part, the empennage pitching part and the empennage yawing part are sequentially arranged on the aircraft tail from front to back, the empennage fixing part and the empennage pitching part are hinged, and the empennage pitching part and the empennage yawing part are hinged. The aircraft empennage regulation mechanism further comprises a pitching steering engine and a yawing steering engine, wherein the pitching steering engine and the yawing steering engine are arranged on an aircraft body. The pitching steering engine rotates to drive a connecting rod to move to drive the empennage pitching part to swing around the axis of a pitching rotation shaft. The yawing steering engine rotates to pull two traction ropes to move to drive the empennage yawing part to swing around the axis of a yawing rotation shaft. According to the invention, the structure style of arranging a drive steering engine on the aircraft tail traditionally is abandoned, and the weight of the aircraft tail is effectively lowered. In addition, compared with a traditional kinematic coupling empennage regulation mechanism, the aircraft empennage regulation mechanism can regulate empennages through mechanical decoupling, and the reliability, the stability and the regulation accuracy of a system are greatly improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
A micro-electromechanical two-axis gyroscope
ActiveCN107167123BReduce output errorImprove output accuracySpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopes/turn-sensitive devicesMicrocomputerGyroscope
The invention provides a micro-electromechanical two-axis gyroscope, the driving structure includes a driving mass and a driving electrode, and the driving mass and the driving electrode constitute a driving capacitor; the driving capacitor is used to drive the driving mass to reciprocate in a specific direction Vibration; each detection structure includes a detection mass and a detection electrode, and the detection mass and the detection electrode constitute a detection capacitance; the detection capacitance is used to detect the Coriolis force generated on the drive mass to drive the detection mass around the first axis or the second axis Capacitance change due to motion. Since the direction of reciprocating vibration of the driving mass is different from the direction of motion of the detection mass, that is, the direction of movement around the first axis and the second axis, therefore, in the case of no angular velocity input, that is, no Coriolis force, the driving mass does not It will drive the movement of the detection mass, so that the mechanical decoupling of the driving structure and the detection structure in the driving mode can be realized, thereby reducing the output quadrature error of the gyroscope and improving the output accuracy of the gyroscope.
Owner:SENODIA TECH (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
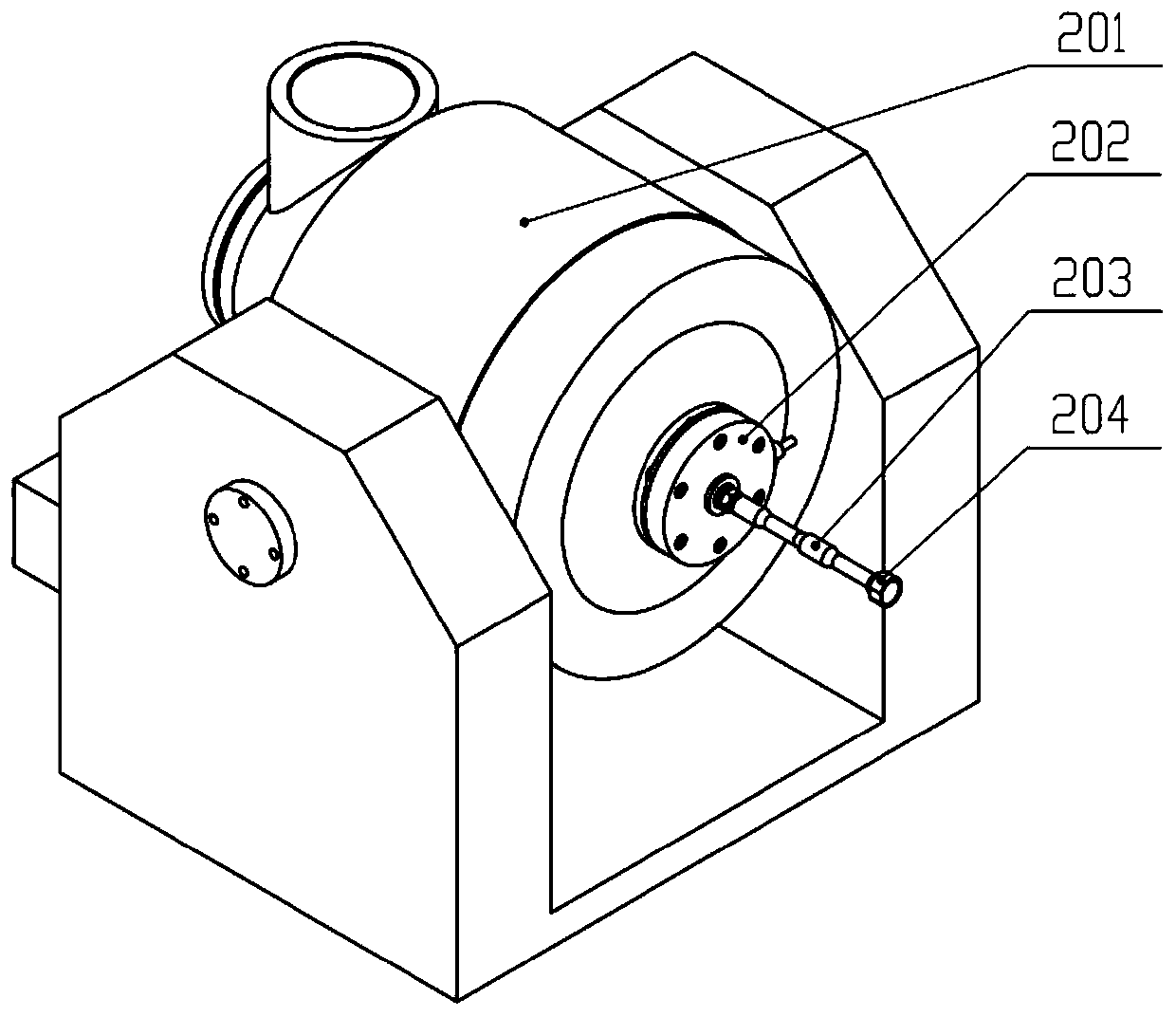
Planar Parallel 3D Force Sensor
ActiveCN104568269BSimple structureLow costMachine bearings testingApparatus for force/torque/work measurementIsosceles trapezoidFriction torque
A plane parallel connection three-dimensional force sensor mainly comprises a fixed ring, a force measuring ring, six force measuring branches and a cover plate, wherein three groups of symmetric triangular notch grooves are uniformly distributed in the outer annular surface of the fixed ring; an included angle formed by the bottom extension surfaces of two notch grooves is 120 degrees; stepped through holes are formed in the bottoms of each group of triangular notch grooves, the center lines of the stepped through holes are perpendicular to the bottoms of the triangular notch grooves, an opening in the other end of each stepped through hole is formed in the triangular notch groove in the inner annular surface of the fixed ring, three groups of isosceles-trapezoid-like notch grooves corresponding to the outer annular surface are formed in the inner annular surface, the annular force measuring ring is arranged in the inner annular surface of the fixed ring, three trapezoid bosses corresponding to the three groups of triangular notch grooves in the inner annular surface of the fixed ring are arranged on the outer annular surface, and a cylindrical slotted hole is formed in each of two lateral surfaces of each trapezoid boss; the force measuring branches are arranged in the stepped through holes of the fixed ring and the corresponding cylindrical slotted holes of the force measuring ring, and two force measuring branches of each group are symmetrically arranged; the cover plate is arranged on the end face of the fixed ring. The plane parallel connection three-dimensional force sensor is simple in structure, convenient to assemble and debug, small in multi-dimensional coupling and high in measuring accuracy, and can synchronously measure the radial force and friction torque of a bearing on line.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Coil grouping method for stator module combined motor
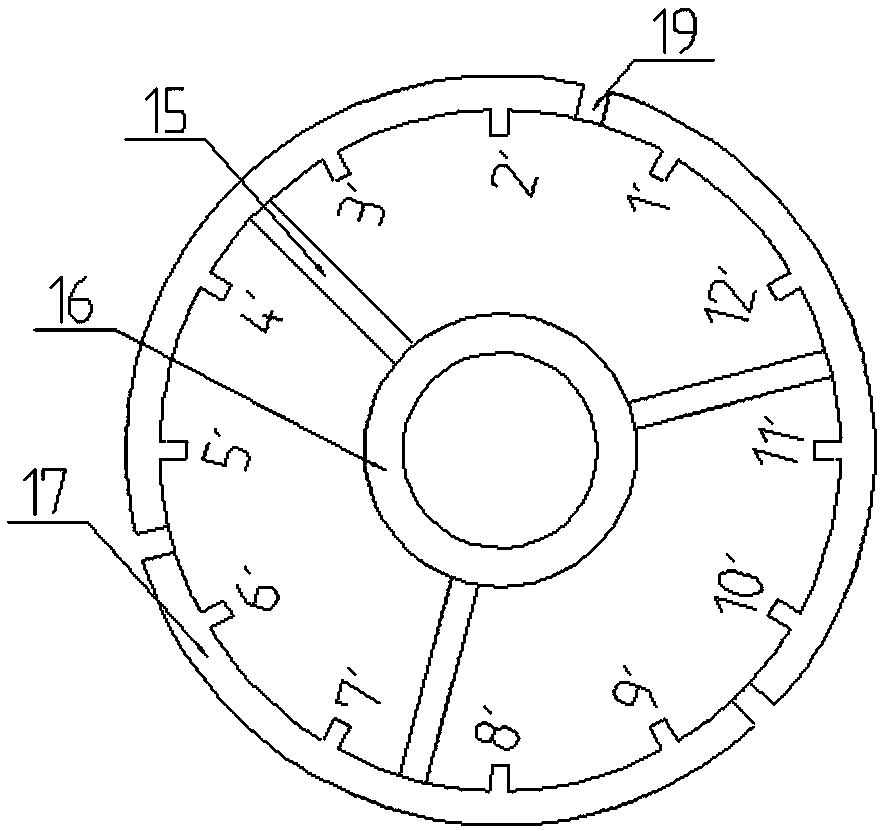
InactiveCN109599967AEasy to combineAchieve mechanical decouplingMagnetic circuit stationary partsEmbedding prefabricated windingsGroup methodMiddle line
The invention belongs to the technical field of motors, and relates to a coil grouping method for a stator module combined motor. Stator slots are uniformly formed in the periphery of a stator core, acoil is embedded into the stator slots according to the law of spanning one stator tooth, the number of the stator slots of the motor is Q1, equal partitioning is performed according to the rule thatthe number of module slots of a single stator sub-block is Q0=Q1 / s, Q0 must also satisfy Q0=12*(n / 6+k), wherein n=1, 2, 4 or 5, k=natural numbers 0, 1, 2 or 3..., the number of stator sub-blocks is s, s is 3 or integral multiples of 3, the coils that are embedded across the teeth are removed at the stator sub-blocks, and partitioning is performed at the center line of the tooth part after the coil is removed. The scheme of the invention brings convenience to the stator module combination, and solves the problem of cutting dispersion by innovatively using a fixed cylinder.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Mechanical decoupling heavy load parallel six-dimensional force measuring platform
InactiveCN103616116BReduced measurement accuracyAchieve mechanical decouplingMeasurement of force componentsCouplingSteel ball
A mechanical decoupling heavy load parallel six-dimension force measuring platform comprises a loading plate, a force measuring plate, an upper cover plate, a bottom frame and more than 12 decoupling force measuring supporting chains. The upper end of the bottom frame is covered with the upper cover plate, a box body is formed, a lower plate of the loading plate is fixed at the plane center of the force measuring plate, an upper plate of the loading plate extends out of an opening in the upper cover plate, the force measuring plate, the upper cover plate and the bottom frame are connected through the decoupling force measuring supporting chains which are distributed on the six faces of the force measuring plate and are fixed on the upper face, the lower face and the four side faces of the force measuring plate respectively, one end of a pressing head A in each decoupling force measuring supporting chain is fixed on the force measuring plate, one end of a pulling pressing force sensor is fixed on the bottom frame and the upper cover plate respectively, the other end of the pulling pressing force sensor and one end of a pressing head B are fixed, the other end of the pressing head A and the other end of the pressing head B are both concave faces, and a steel ball is embedded between the two concave faces. The mechanical decoupling heavy load parallel six-dimension force measuring platform is simple in structure, mechanical decoupling is achieved through the steel ball, dimension-between coupling is small, measuring accuracy is high, and the mechanical decoupling heavy load parallel six-dimension force measuring platform is very suitable for heavy load large-tonnage measuring.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
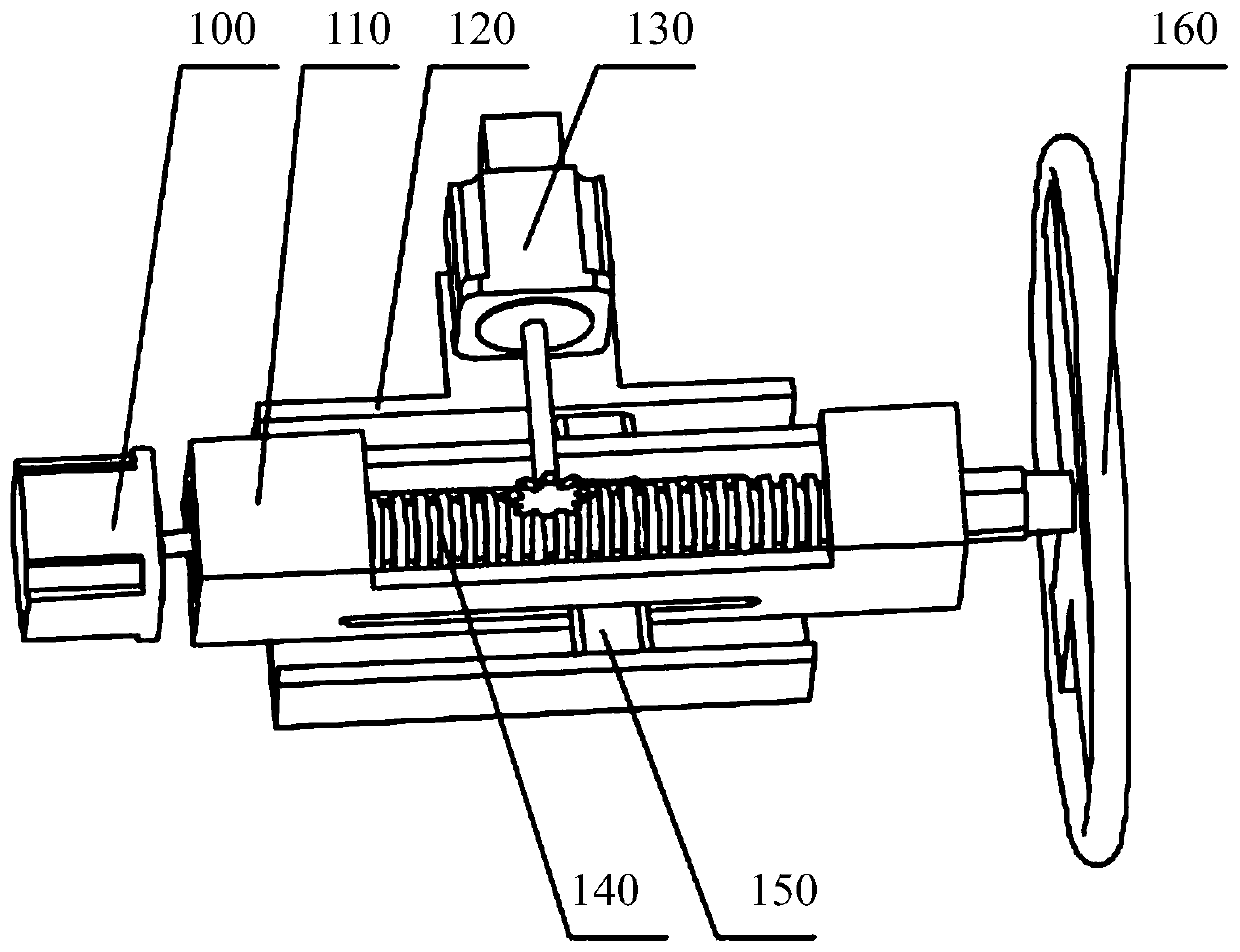
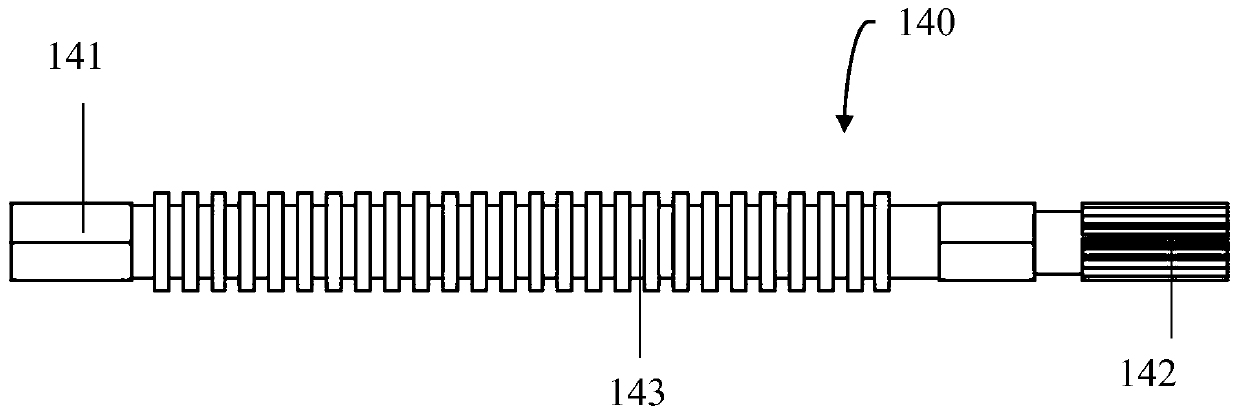
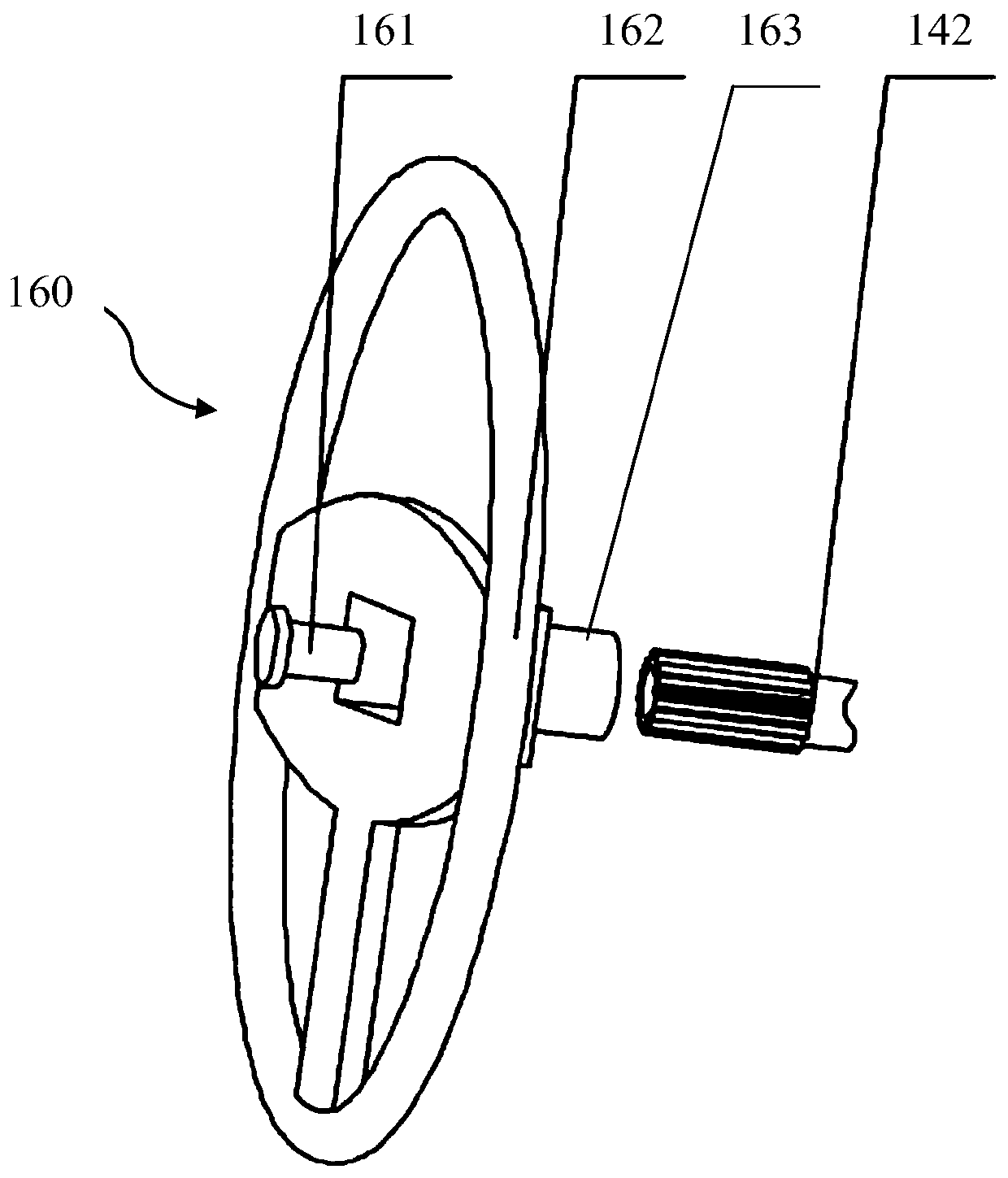
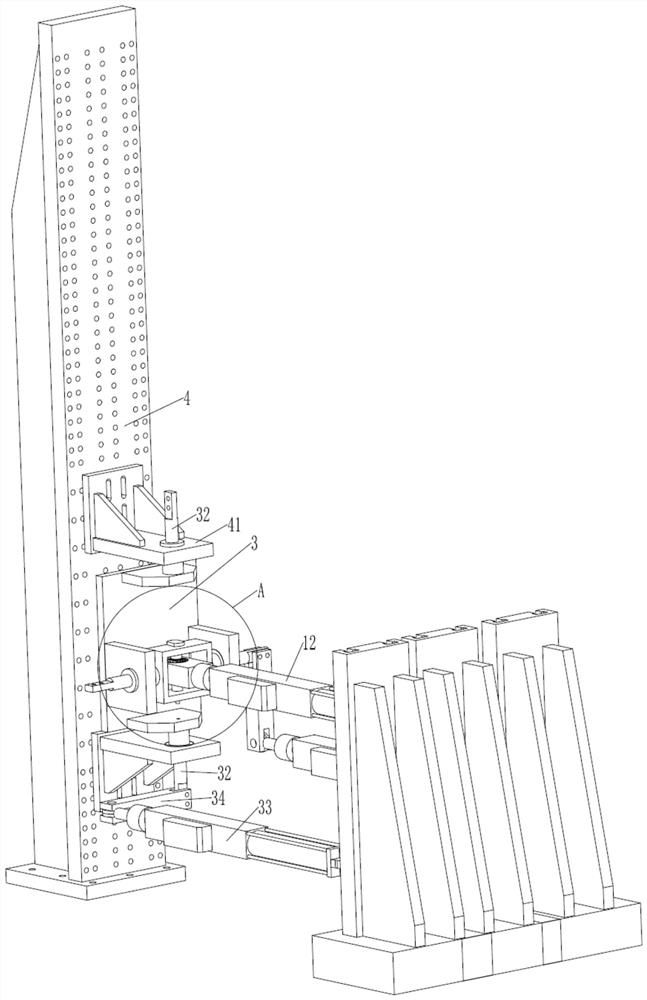
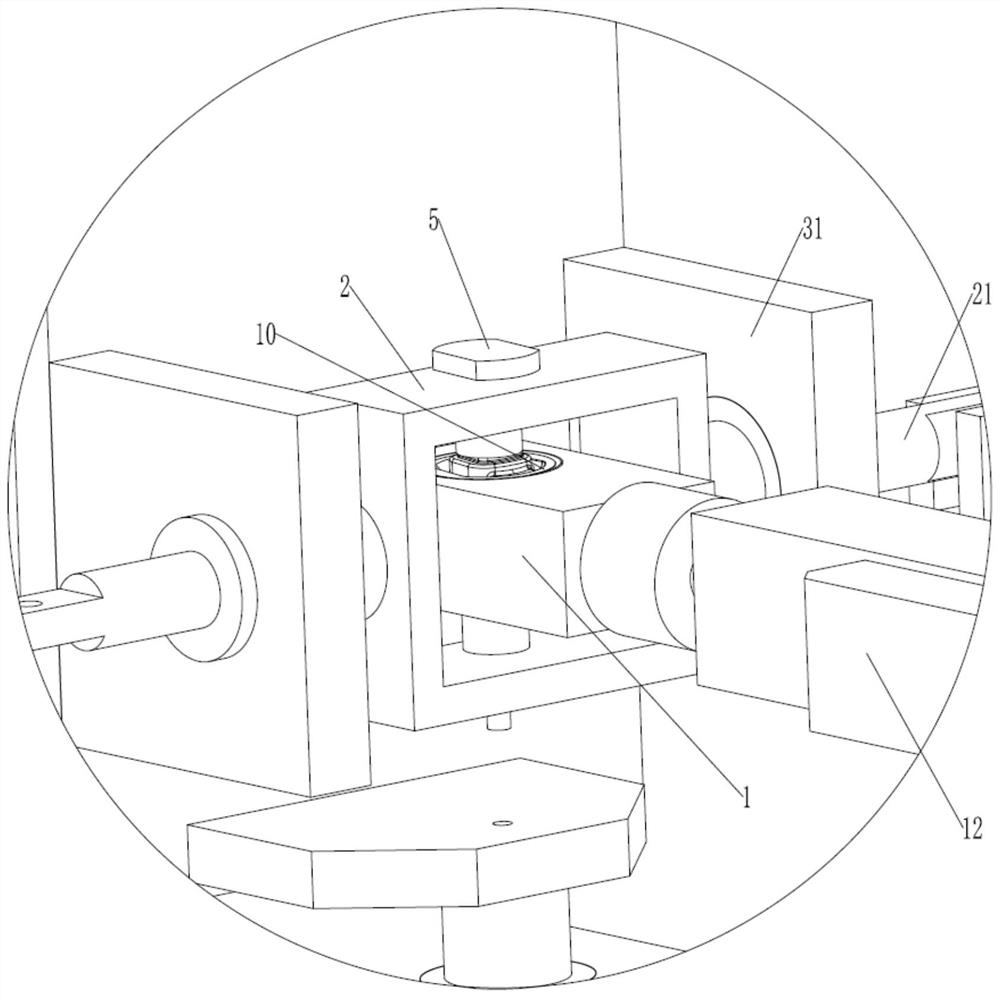
A Tractor Driving Robot Based on Force/Position Hybrid Control
ActiveCN105068595BRealize autonomous drivingAchieve mechanical decouplingMechanical control devicesDriver/operatorSteering wheel
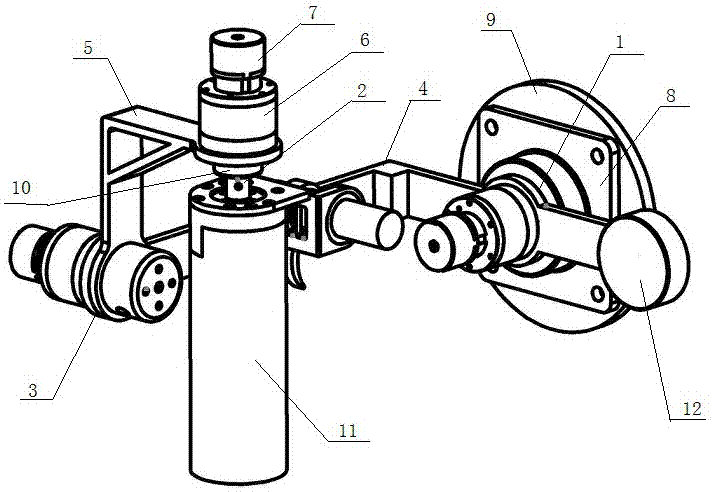
The invention discloses a force / position hybrid control-based tractor driving robot and belongs to the tractor automatic driving device technical field. The robot comprises a base, an accelerator mechanical leg, a brake mechanical leg, a clutch mechanical leg, a gear shifting mechanical hand and a steering mechanical hand. The tractor driving robot of the invention can be nondestructively installed on tractors of various kinds of models. According to the force / position hybrid control-based tractor driving robot, a force / position hybrid control method is adopted to control the gear shift levers, accelerator pedals, clutch pedals, brake pedals and steering wheels of the tractors. The force / position hybrid control-based tractor driving robot can replace a driver to complete driving operation on the tractors.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com