Patents
Literature
1654 results about "Brake fluid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
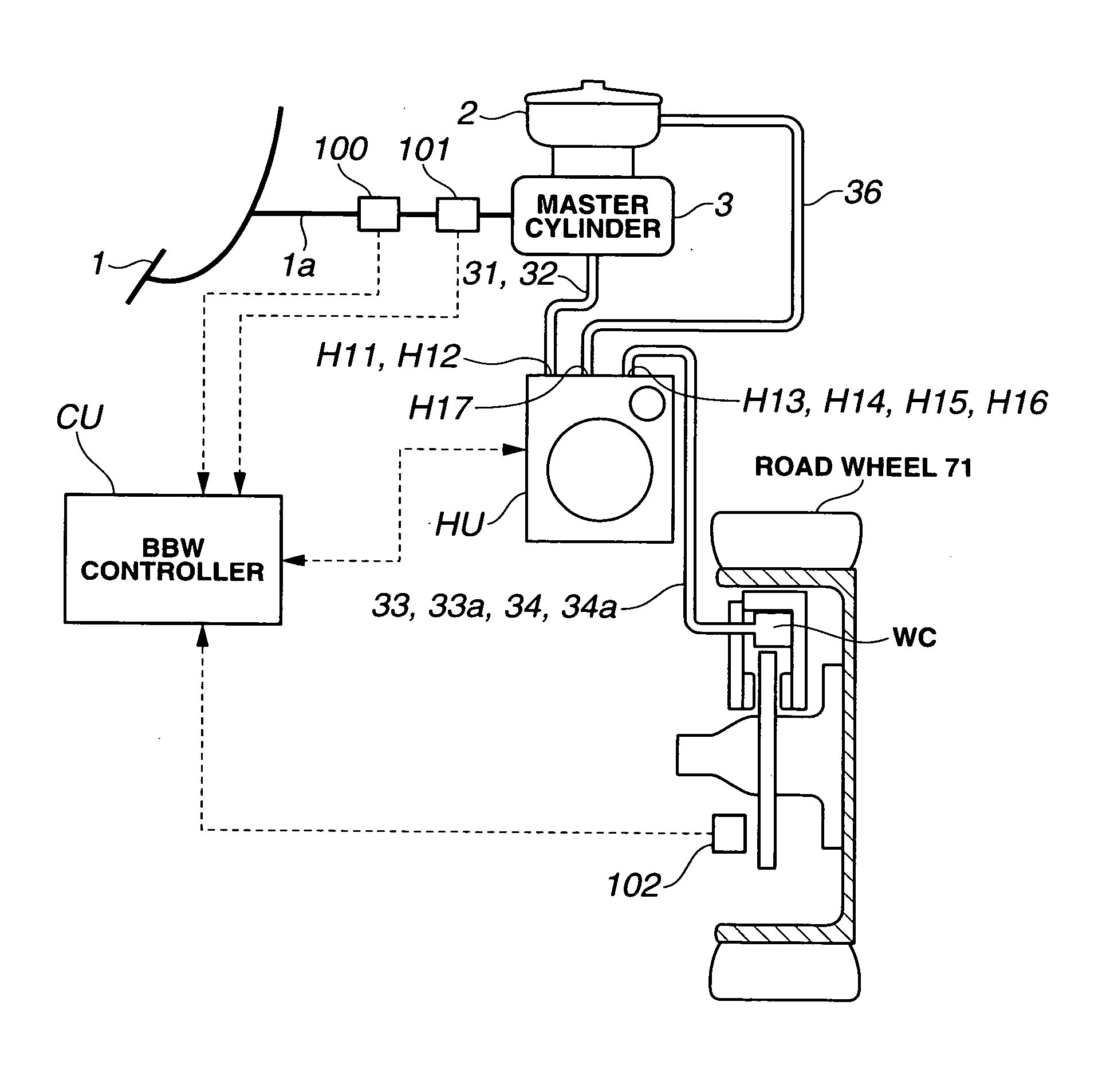
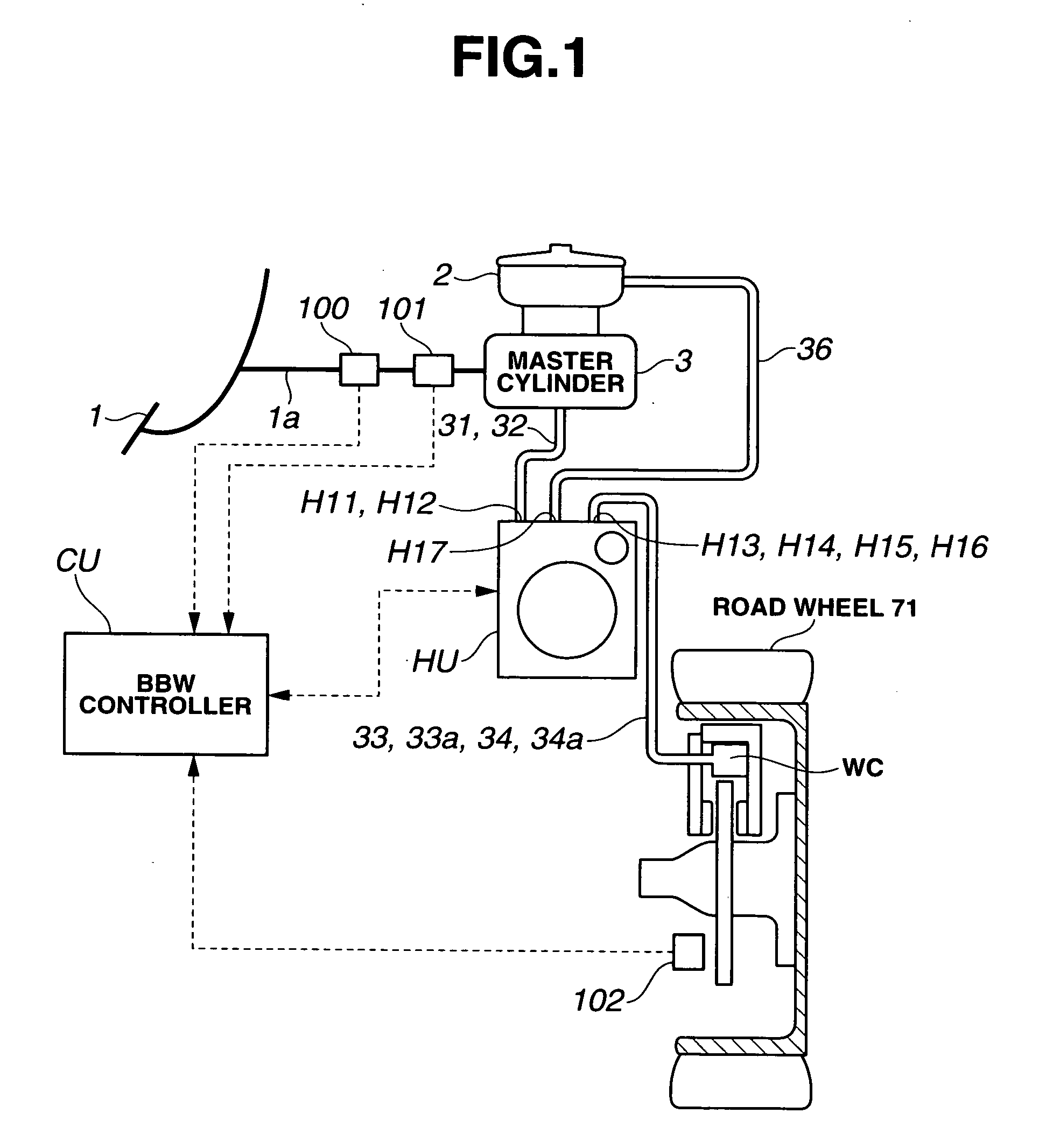
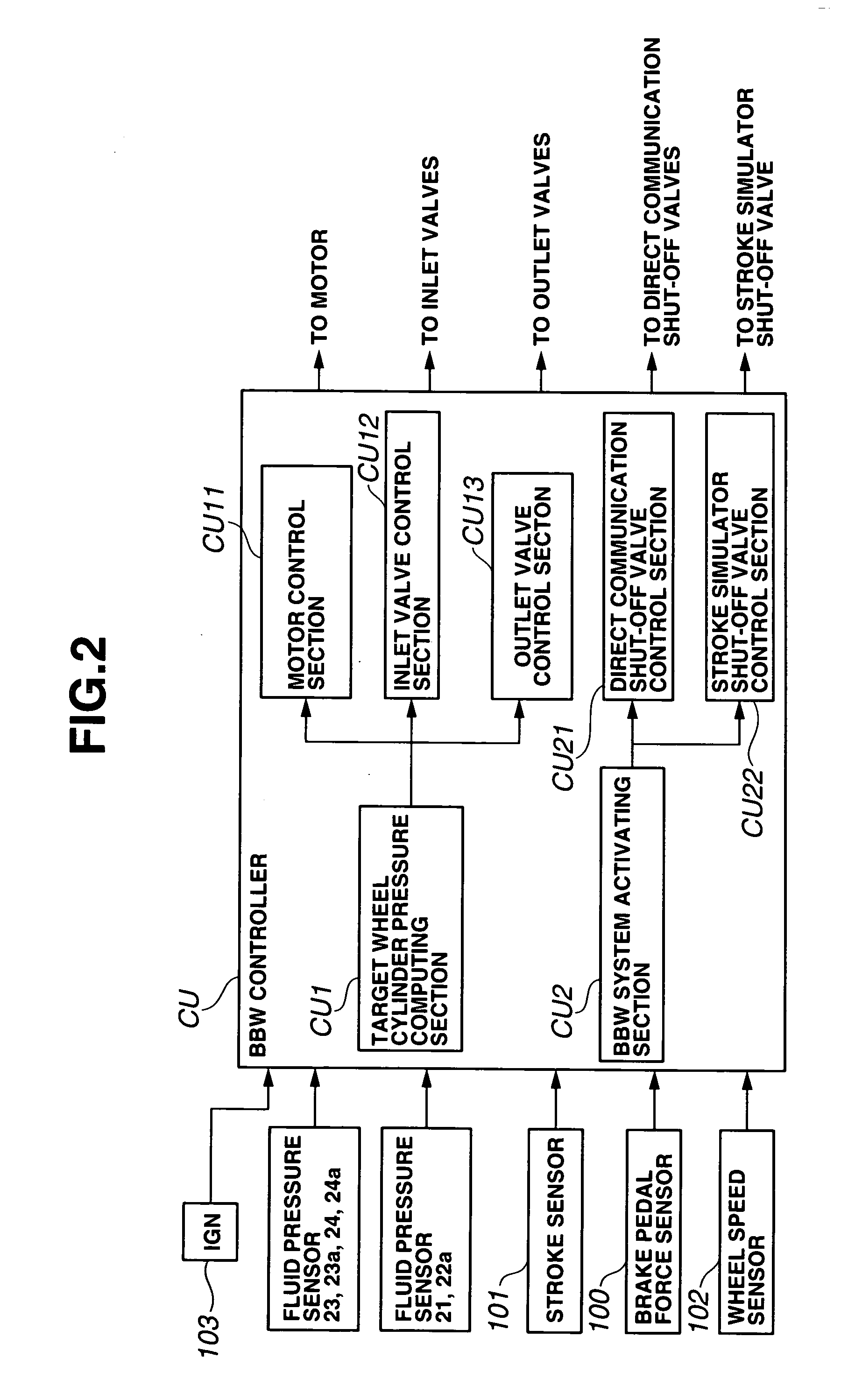
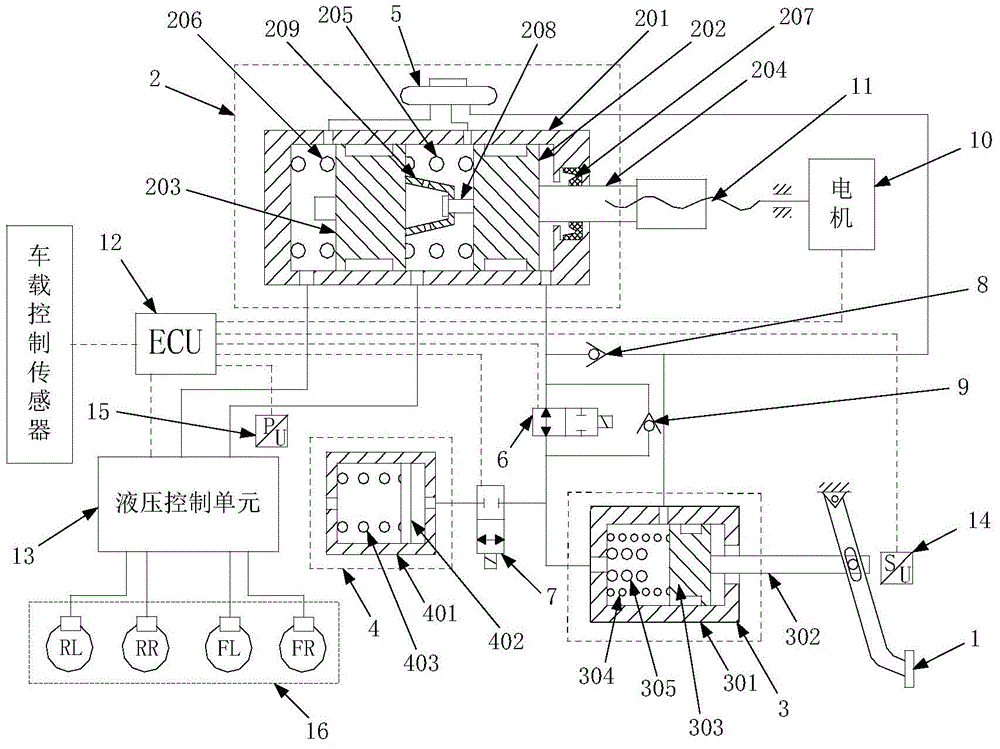
Brake fluid is a type of hydraulic fluid used in hydraulic brake and hydraulic clutch applications in automobiles, motorcycles, light trucks, and some bicycles. It is used to transfer force into pressure, and to amplify braking force. It works because liquids are not appreciably compressible.
Double-motor driving type electronic hydraulic brake system capable of actively simulating pedal feeling
InactiveCN104760586AMeet braking requirementsImprove securityBraking action transmissionEnergy recoveryElectric control
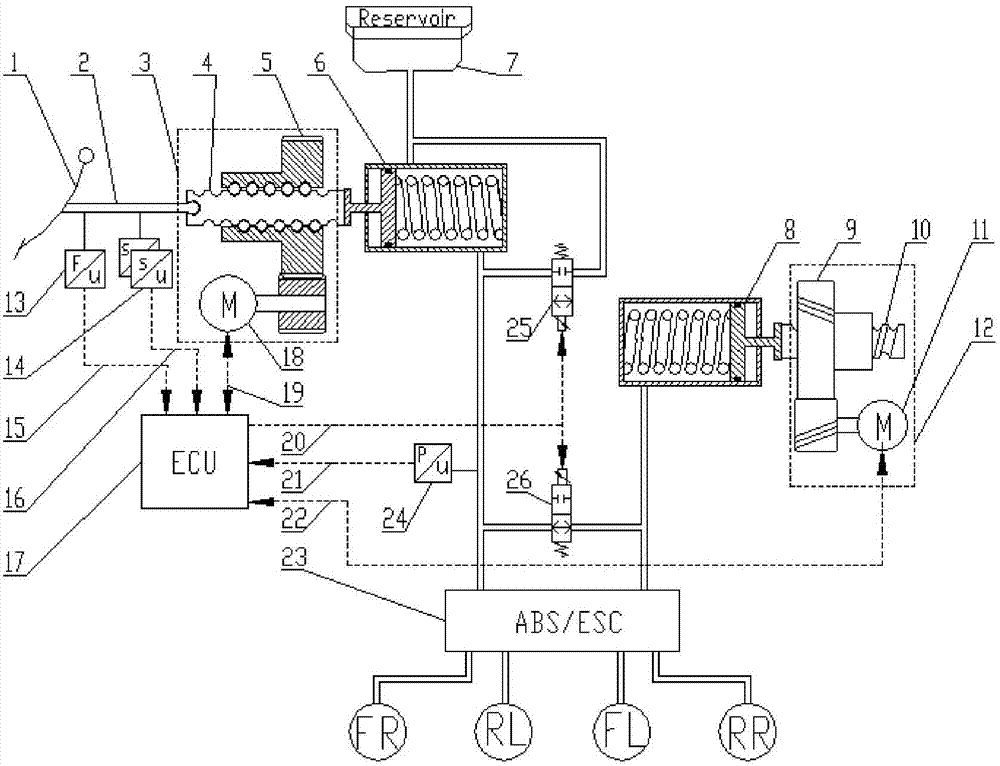
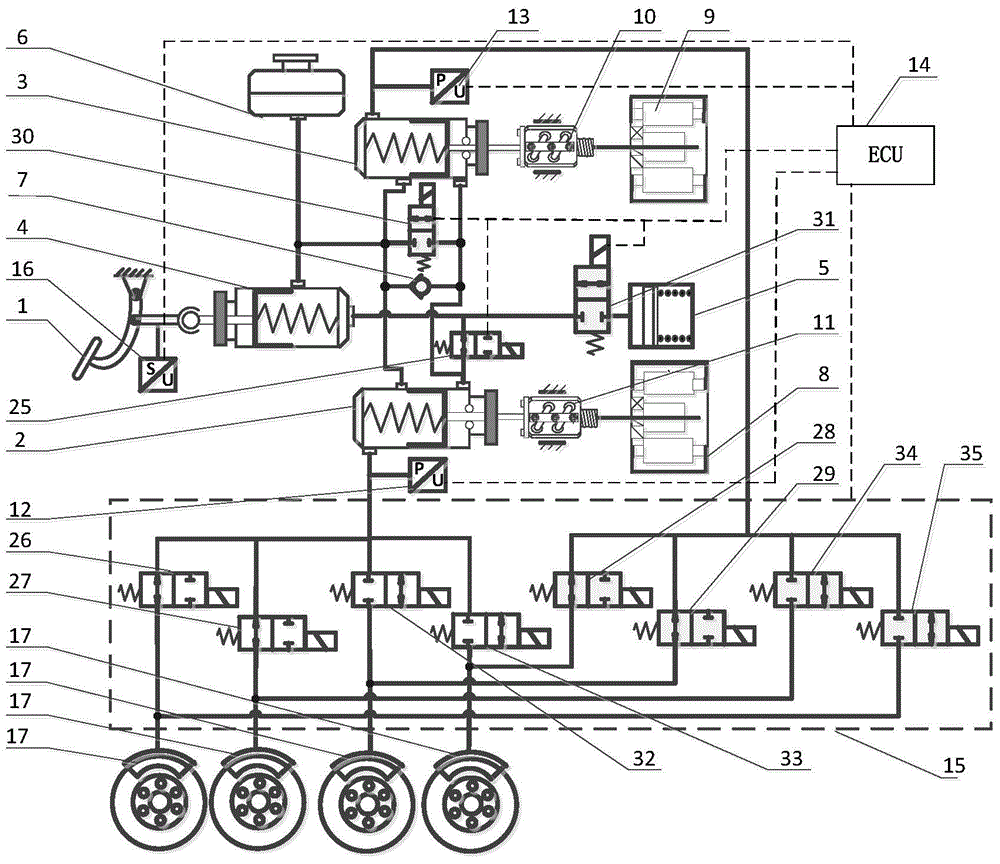
A double-motor driving type electronic hydraulic brake system capable of actively simulating pedal feeling comprises a brake pedal, a fluid storage tank used for storing brake fluid, a pedal displacement sensor, a pedal force sensor, a hydraulic force sensor, an electronic control unit, an electromagnetic valve, an electronic stability control module, a brake master cylinder and a secondary master cylinder. An electric control linear movement module comprises a rotating motor and a speed reduction and moment increasing mechanism which converts the rotating movement of the motor into linear movement to achieve the active control over system hydraulic brake force and pedal force. The pedal force of a driver can be fully used for reducing pressure. While the active control over the pedal force is achieved, a pedal force simulator of a complex structure is omitted, the feeling of a brake pedal is guaranteed, and the accurate automobile brake condition is fed back to the driver. The active control over the hydraulic force is achieved, and the brake requirement for automatic driving vehicles is met; maximum braking energy recovery is achieved, control is precise, and the response speed is high; double-loop braking is achieved, failure protection is considered thoroughly, and the safety is good.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Motor-driven electronic hydraulic braking system
ActiveCN103754210AQuick responsePrecise control of hydraulic braking forceBraking action transmissionSystems designLinear control
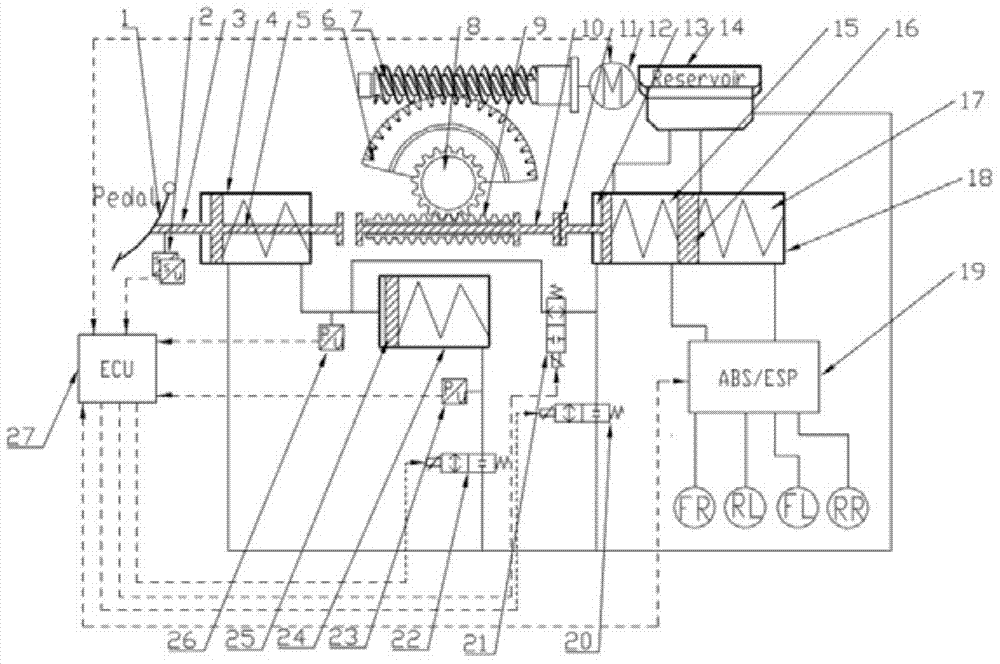
A motor-driven electronic hydraulic braking system comprises a brake pedal, a pedal displacement sensor, a secondary master cylinder, a pedal simulator pressure sensor, a pedal simulator, pedal simulator solenoid valves, a push rod, an electrically-controlled linear movement module, a brake master cylinder and an ABS / ESP (anti-skid brake system / electronic stability program) module. The electrically-controlled linear movement module drives the push rod to move by means of driving a movement regulating mechanism through a motor, the motor is controlled through a displacement signal, and linear control on braking pressure is realized. The brake master cylinder passes the ABS / ESP module to be hydraulically coupled with vehicle wheel brakes. The ABS / ESP module can passively regulate pressure transmitted from the master cylinder to the wheel brakes, and can actively regulate the pressure of the brake of each wheel. The motor-driven electronic hydraulic braking system has the advantages of rapid response, accurate control on brake fluid pressure, capabilities of well simulating brake pedal feeling of a driver and maximally recovering braking energy, and the like; meanwhile, the system is designed with a dual failure protection mode, thereby having high safety and reliability.
Owner:上海同驭汽车科技有限公司
Slip Control Boost Braking System
A braking system is provided for applying pressurized hydraulic brake fluid to a plurality of vehicle brakes. The system includes a source of pressurized brake fluid, a first brake fluid circuit, and a boost valve for controlling a flow of brake fluid from the source to the first circuit. A first brake actuator is actuated by brake fluid from the first circuit and a second brake actuator operated by an application of brake fluid from the first circuit. The system further includes a second brake fluid circuit and a third brake fluid circuit. A third brake actuator is actuated by brake fluid from the second circuit. A fourth brake actuator actuated by brake fluid from the third circuit. A master cylinder includes a primary piston, a first secondary piston, and second secondary piston. The first and second secondary pistons are capable of being each independently operably displaced by an application of pressurized fluid from the first circuit to pressurize brake fluid in, respectively, the second circuit to operate the third brake actuator and the third circuit to operate the fourth brake circuit.
Owner:KELSEY HAYES CO
Brake device
InactiveUS20110285199A1Sufficient forceImprove responseBraking action transmissionGas pressure propulsion mountingEngineeringControl valves
A brake device includes: a mechanical pressure regulating part having a high-pressure port, a low-pressure port, a pilot pressure input port, and an output port which outputs fluid pressure corresponding to the pressure supplied to the pilot pressure input port by fluid pressures supplied to both of the high- and low-pressure ports, to a chamber for a master piston; a high-pressure source connected to the high-pressure port and the pilot pressure input port; a low-pressure source connected to the low-pressure port and the pilot pressure input port; and an electrically-operated pilot pressure generating part which includes control valves for controlling flows of the brake fluid between the high-pressure source and the pilot pressure input port, and between the low-pressure source and the pilot pressure input port, respectively, and which outputs desired fluid pressure to the pilot pressure input port by controlling flow of the brake fluid with control valves.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
Brake system
InactiveUS20080079309A1Prevents hydraulic pressure changePrevent leakageApplication and release valvesEngineeringWheel cylinder
When an electrical fluid pressure generator fails and a wheel cylinder is operated by brake fluid pressure generated by a master cylinder, if a first fluid pressure system leading to a rear fluid chamber of the electrical fluid pressure generator fails and is opened to the atmosphere, braking is performed by brake fluid pressure of a second fluid pressure system transmitted from the master cylinder through a front fluid chamber of the electrical fluid pressure generator to a wheel cylinder. At this time, a front supply port, which communicates through a front second cup seal facing rearward with the rear fluid chamber opened to the atmosphere due to the failure, does not communicate with the master cylinder but with a reservoir. Therefore, it is possible to prevent leakage of the brake fluid pressure generated by the master cylinder through the front supply port, the front second cup seal and the rear fluid chamber, thereby ensuring braking by the second fluid pressure system leading to the front fluid chamber of the electrical fluid pressure generator.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Apparatus for and method of controlling brakes
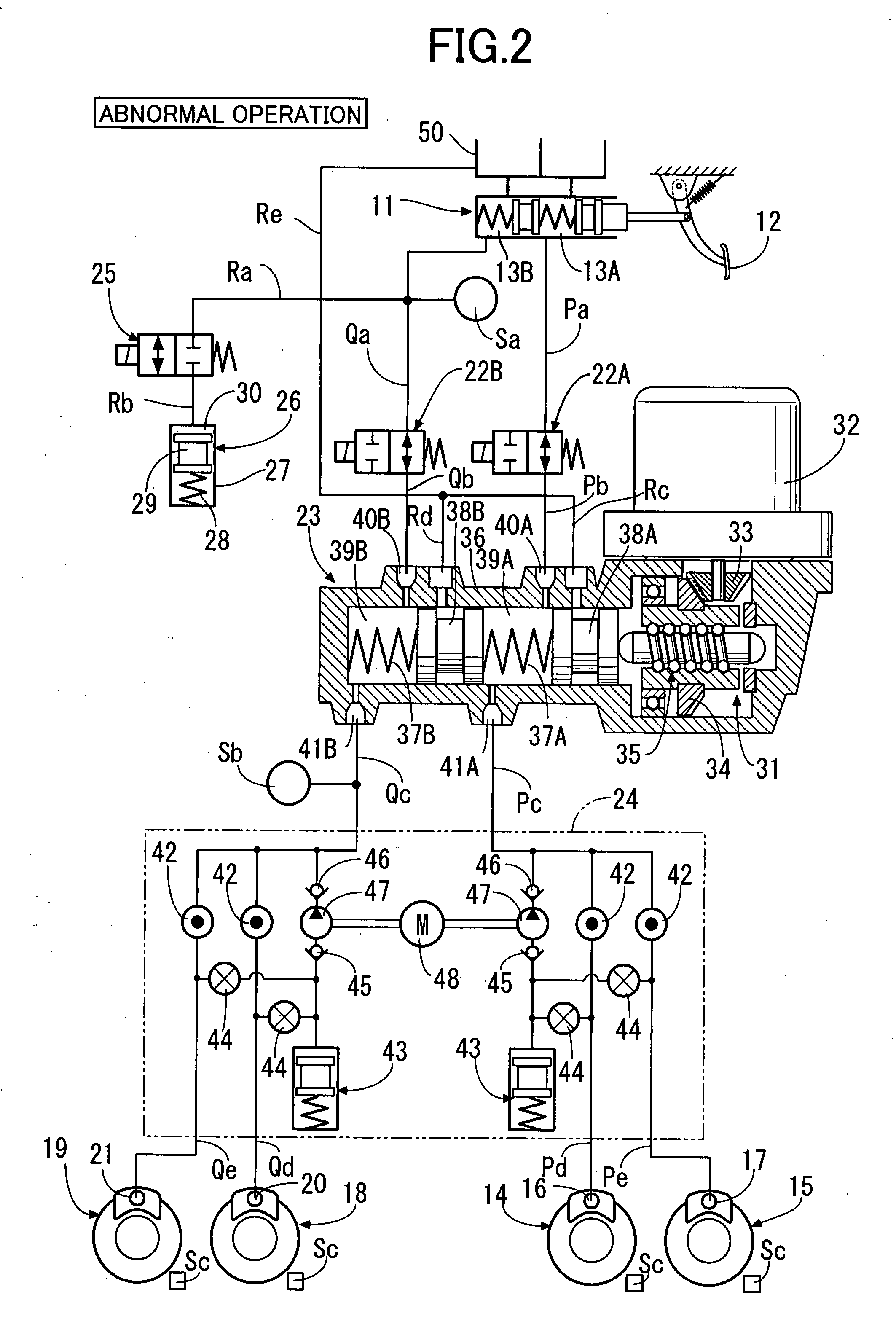
InactiveUS20090072615A1Improve controllabilityDigital data processing detailsAutomatic initiationsEngineeringWheel cylinder
An apparatus for controlling brakes, includes a first brake circuit for supplying brake fluid, pressure-increased by a booster, to a wheel-brake cylinder, a first control valve disposed in the first brake circuit for establishing and blocking fluid communication between a master cylinder and the wheel-brake cylinder, a second brake circuit arranged in parallel with the first brake circuit for supplying brake fluid, pressure-increased by a fluid-pressure source, to the wheel-brake cylinder, and a second control valve disposed in the second brake circuit for establishing and blocking fluid communication between the fluid-pressure source and the wheel-brake cylinder. Also provided is a control unit, which is configured to selectively control the first and second control valves when building-up wheel-cylinder pressure, and further configured to build-up the wheel-cylinder pressure by operating the fluid-pressure source when at least the second control valve is controlled to a valve-open position.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Brake control apparatus
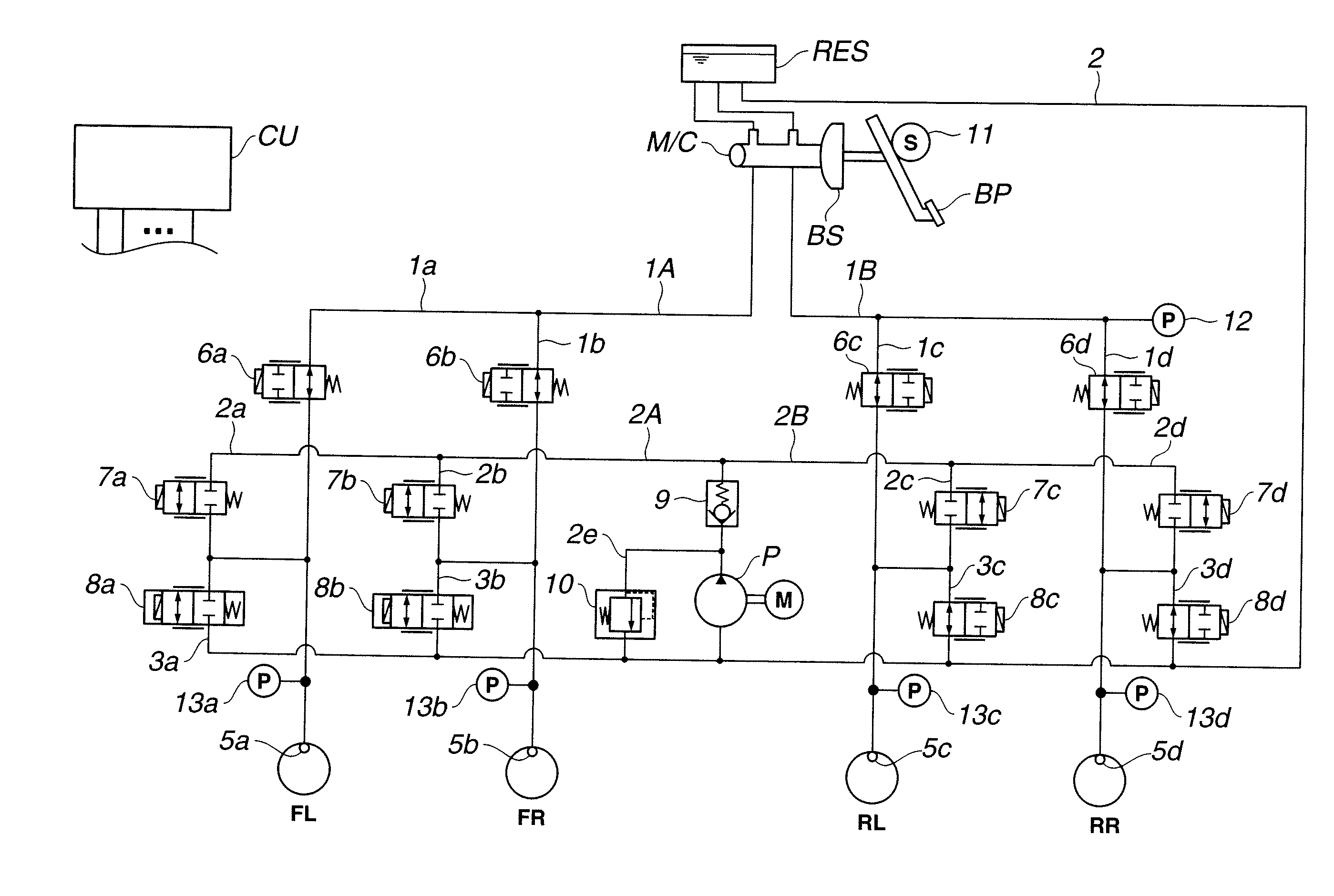
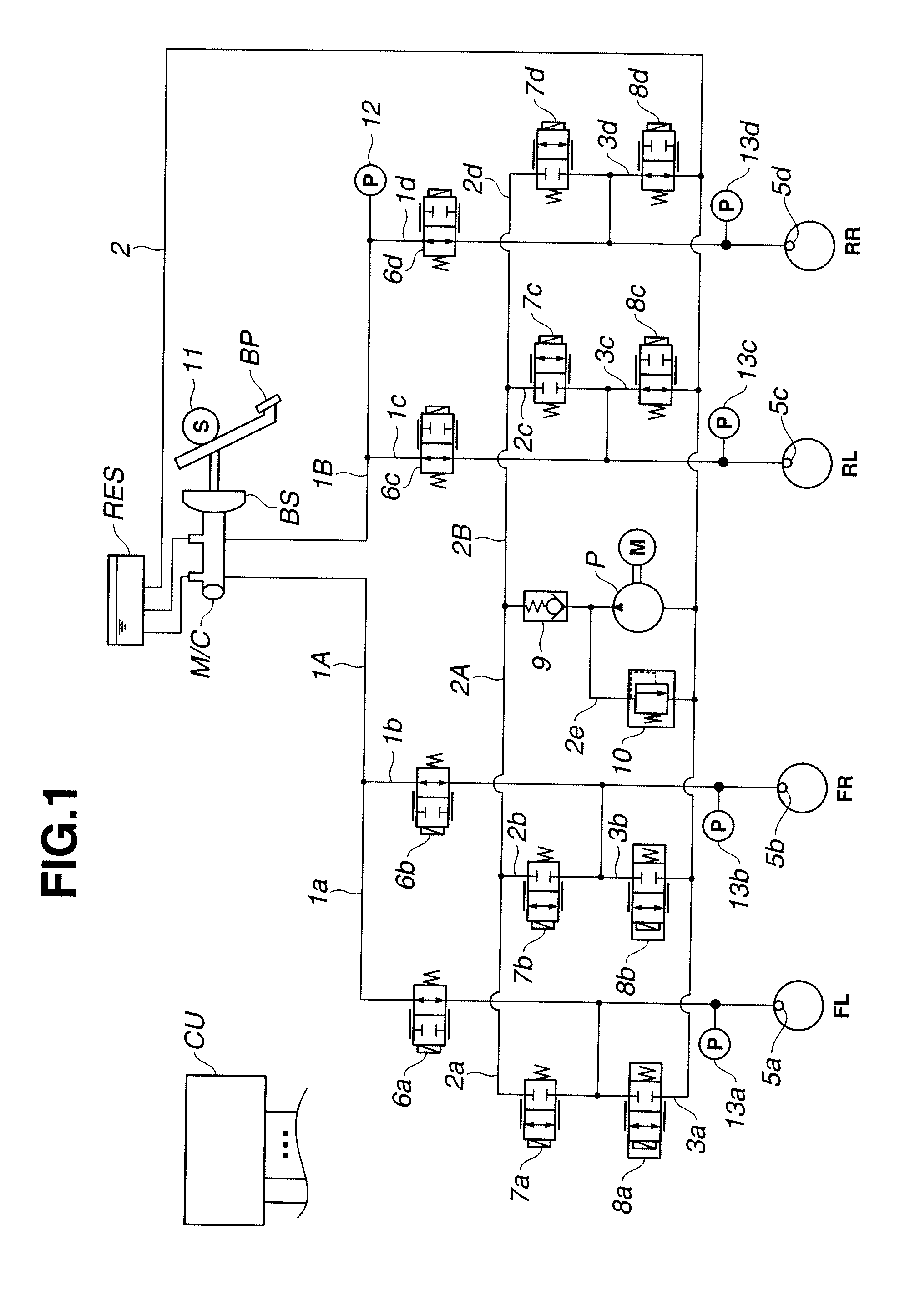
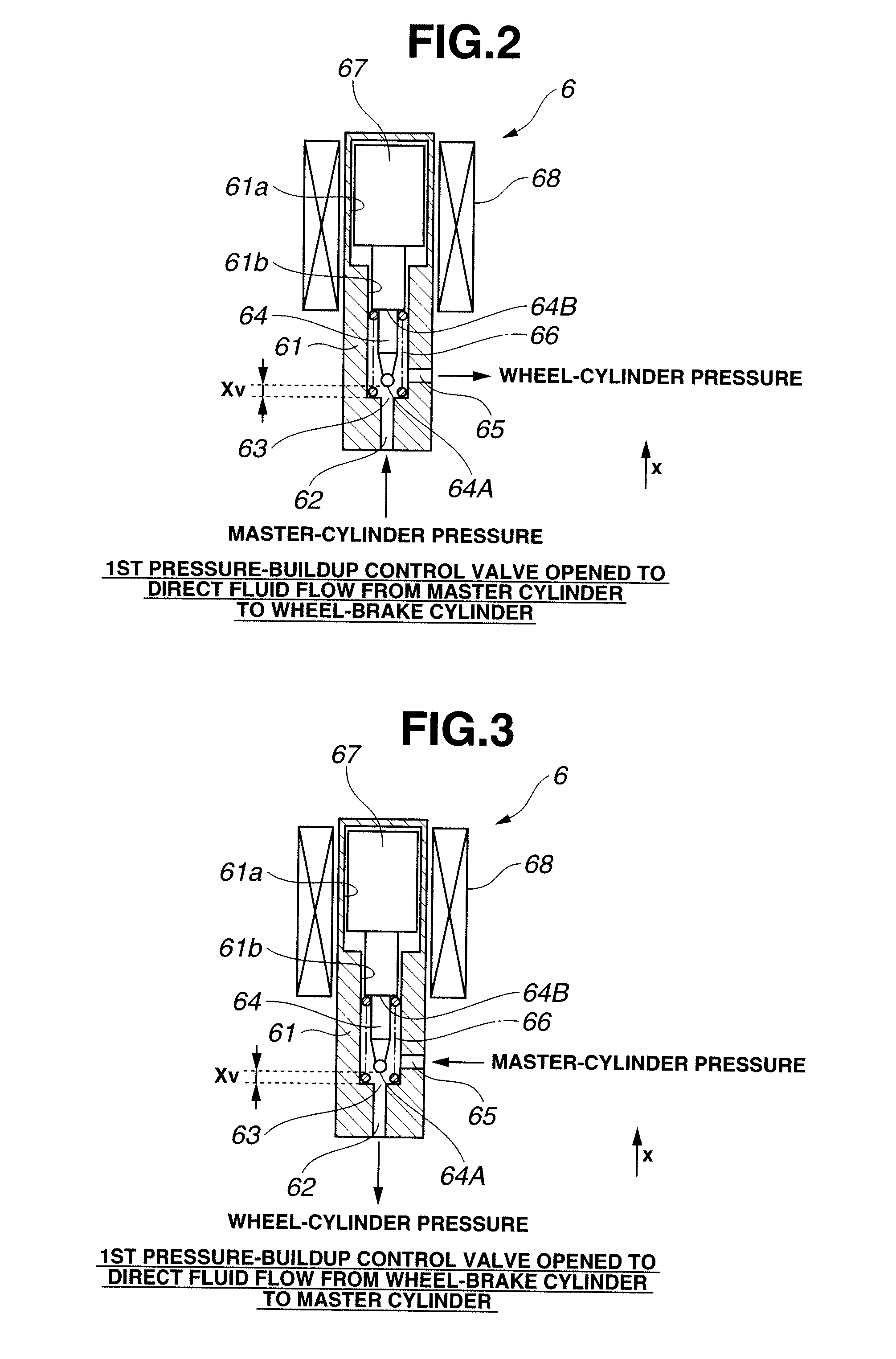
ActiveUS20070018498A1Increase flexibilityEfficiency and flexibilityFluid braking transmissionApplication and release valvesLine tubingEngineering
A brake control apparatus includes a brake unit. The brake unit includes: a first port set hydraulically connected to a master cylinder via a first fluid line set; a second port set hydraulically connected to a wheel cylinder set via a second fluid line set; a first fluid passage hydraulically connecting the first port set to the second port set; a first switching valve arranged to vary a state of fluid communication through the first fluid passage; a fluid pressure source arranged to produce a fluid pressure supplied to the second port set; a fluid accommodating section adapted to accommodate a variable amount of brake fluid; a branch fluid passage hydraulically connecting the first port set to the fluid accommodating section; and a second switching valve arranged to vary a state of fluid communication through the branch fluid passage.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Electro-hydraulic composite braking system with electric braking assistant force and brake-by-wire function
ActiveCN103552557AWith electric brake assistFunctionalBraking action transmissionElectric machineElectro hydraulic
The invention discloses an electro-hydraulic composite braking system with an electric braking assistant force and a brake-by-wire function. The electro-hydraulic composite braking system provided by the invention has various working modes In the case of an electric braking assistant force mode, a brake fluid is input into a master cylinder from a man-power cylinder by a brake pedal, and meanwhile, an electronic control unit controls the output torque of a motor to apply an assistant force, so as to output brake pressure to a wheel cylinder. In the case of a regenerative braking mode, the electronic control unit controls the on / off of an electromagnetic valve, the brake fluid is input into the simulation cavity of a pedal travel simulator from the man-power cylinder by the brake pedal so as to generate pressure and provide a brake pedal feeling; if automobile deceleration requirement can not be met by the regenerative braking, the electronic control unit controls the output torque of the motor so as to allow the master cylinder to output brake pressure into the wheel cylinder to assist friction brake. In case of an active braking mode, the electronic control unit controls the output torque of the motor so as to allow the master cylinder to output brake pressure to the wheel cylinder. The electro-hydraulic composite braking system provided by the invention has the advantages of integration of advantages of wire control and non-wire control working modes, small pressure fluctuation, and high pressure regulation precision.
Owner:南京经纬达汽车科技有限公司
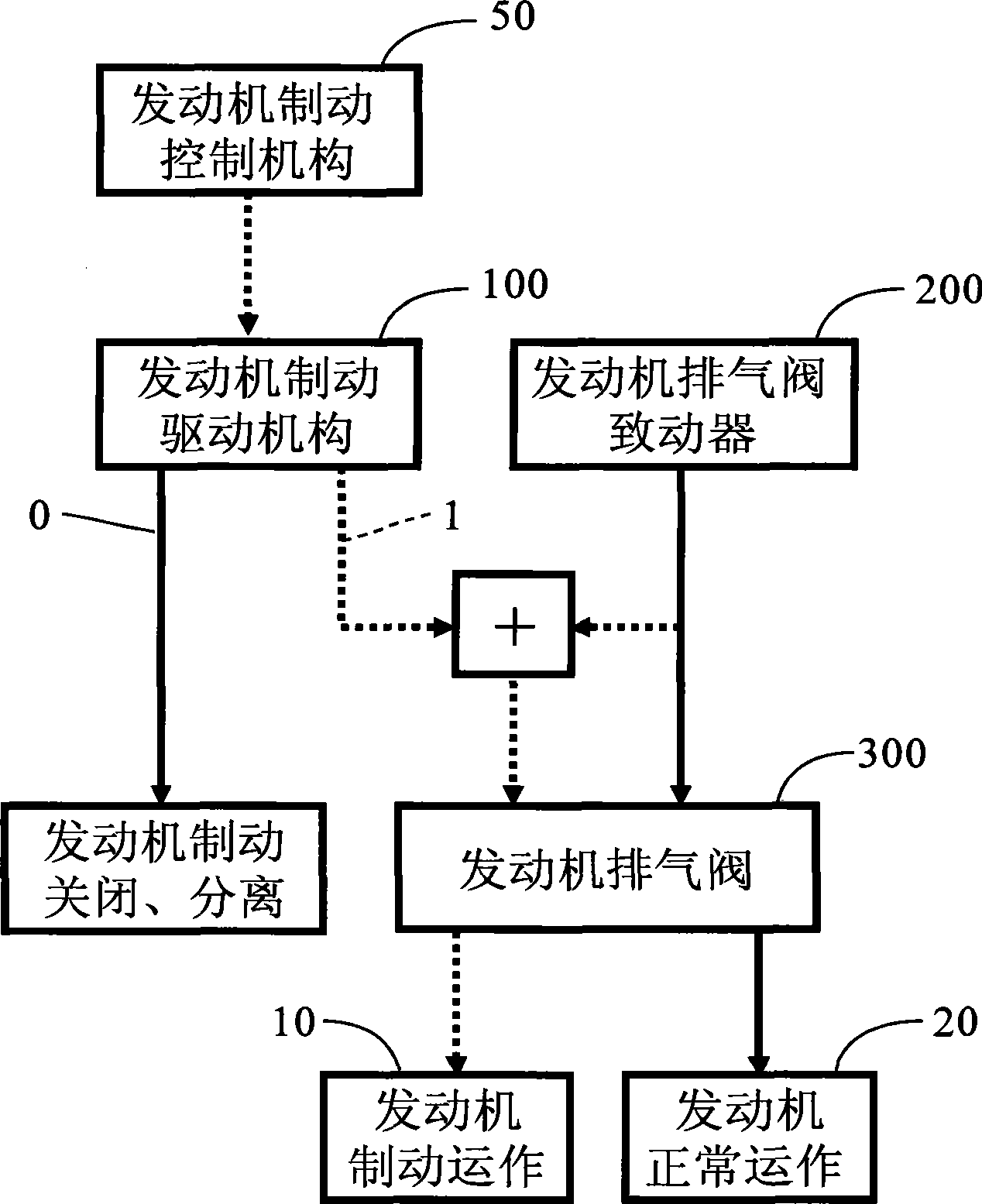
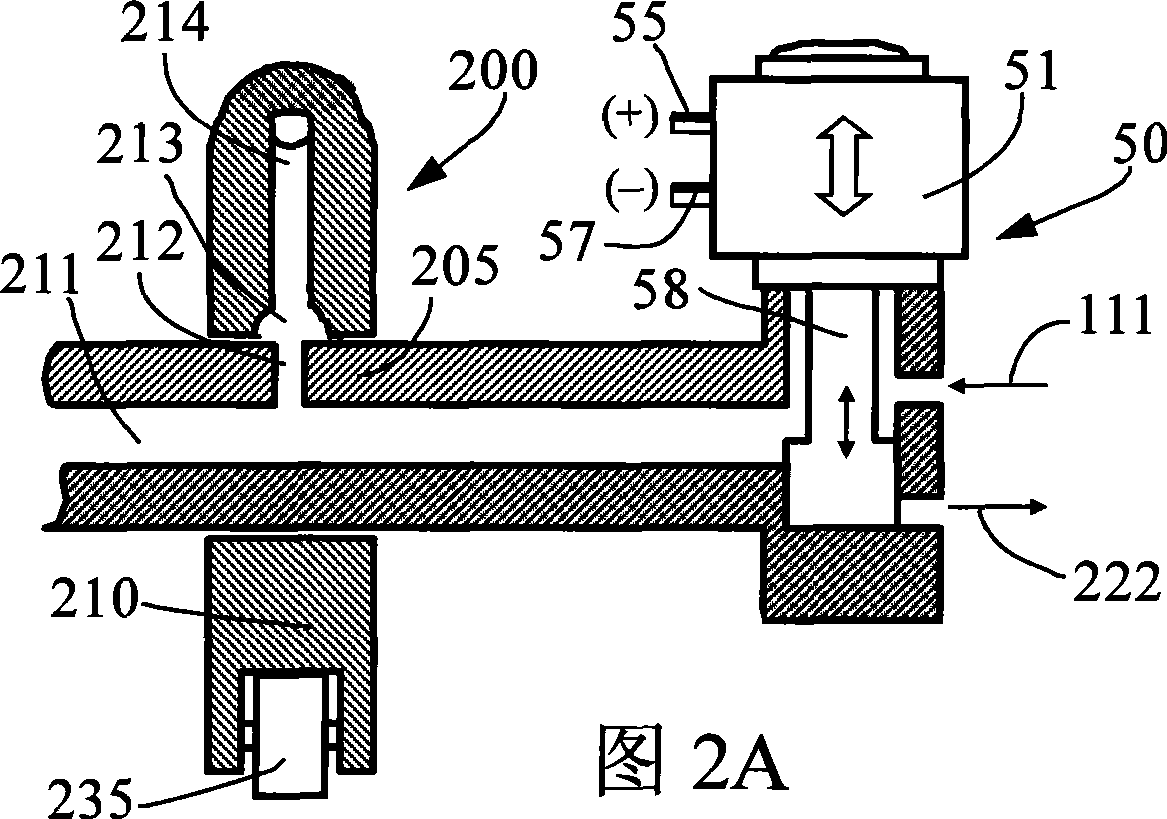
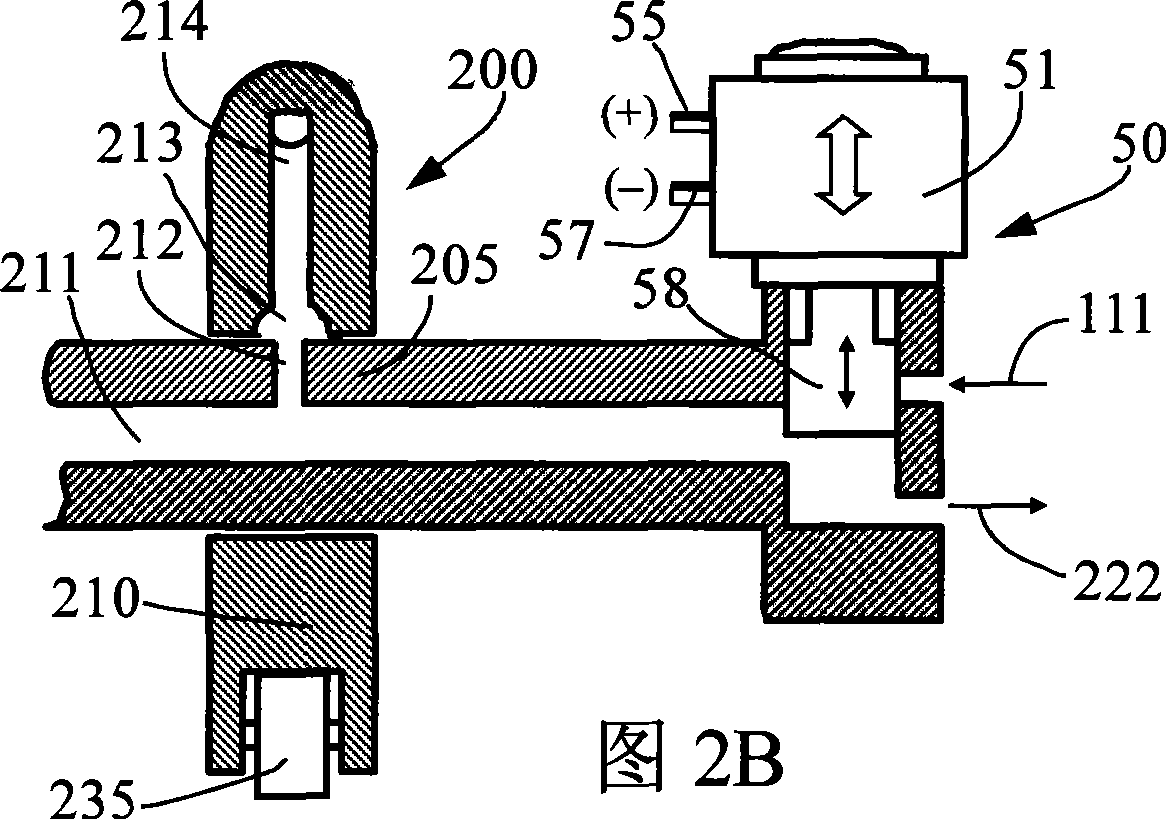
Engine braking apparatus and method using single valve and bridge of valve
ActiveCN101392667AReduce braking loadReduce or even eliminate unsymmetrical loadsValve drivesMachines/enginesExhaust valveValve actuator
The invention discloses an engine braking device (engine retarder) and an engine braking method for using a single valve and a valve bridge. A driving mechanism of the device comprises a braking hydraulic system integrated in an exhaust valve system as well as a braking bearing system and a brake valve actuator which are integrated in an exhaust valve actuator of an engine. The braking hydraulic system comprises a braking piston arranged in the valve bridge. The device also comprises a control mechanism used to control the piston to move between the non-operating position and the operating position. At the non-operating position, the braking piston retracts for braking the normal separation of the driving mechanism and the engine; at the operating position, the braking piston extends out for braking the driving mechanism to open one of two exhaust valves to produce the braking operation of the engine. The braking device uses a simple and reliable reset mechanism, reduces or even eliminates asymmetrical load produced by the braking of the single valve, does not increase the height and the weight of the engine, reduces elements and the complexity, reduces manufacturing cost, and improves the reliability of a system.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSOON AUTOPARTS CO LTD
Maximum road friction force estimating device and brake torque control device
InactiveUS20050012386A1Accurate estimateBraking action transmissionApplication and release valvesBrake torqueRoad surface
A brake torque control device obtains inertia torque Tine based upon an equation of motion (Tine=Tw−Ft·Rt) about the rotation of a tire based upon a wheel torque Tw according to a brake torque exerted on the tire, road friction force Ft and a radius Rt of the tire. When the inertia torque Tine exceeds a predetermined reference value, road friction force Ft at this time is set as estimated maximum road friction force Fmax. The instructed brake torque is calculated under the condition that the value that is obtained by adding the predetermined value corresponding to the inertia torque Tine to the torque Fmax·Rt based upon this estimated maximum road friction force Fmax is set as an upper limit value of the instructed brake torque. This allows to clearly set, as one value, the target value of the instructed brake torque upon an ABS control, thereby being capable of more accurately executing the pressure-increasing control and pressure-reducing control of the brake fluid pressure.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
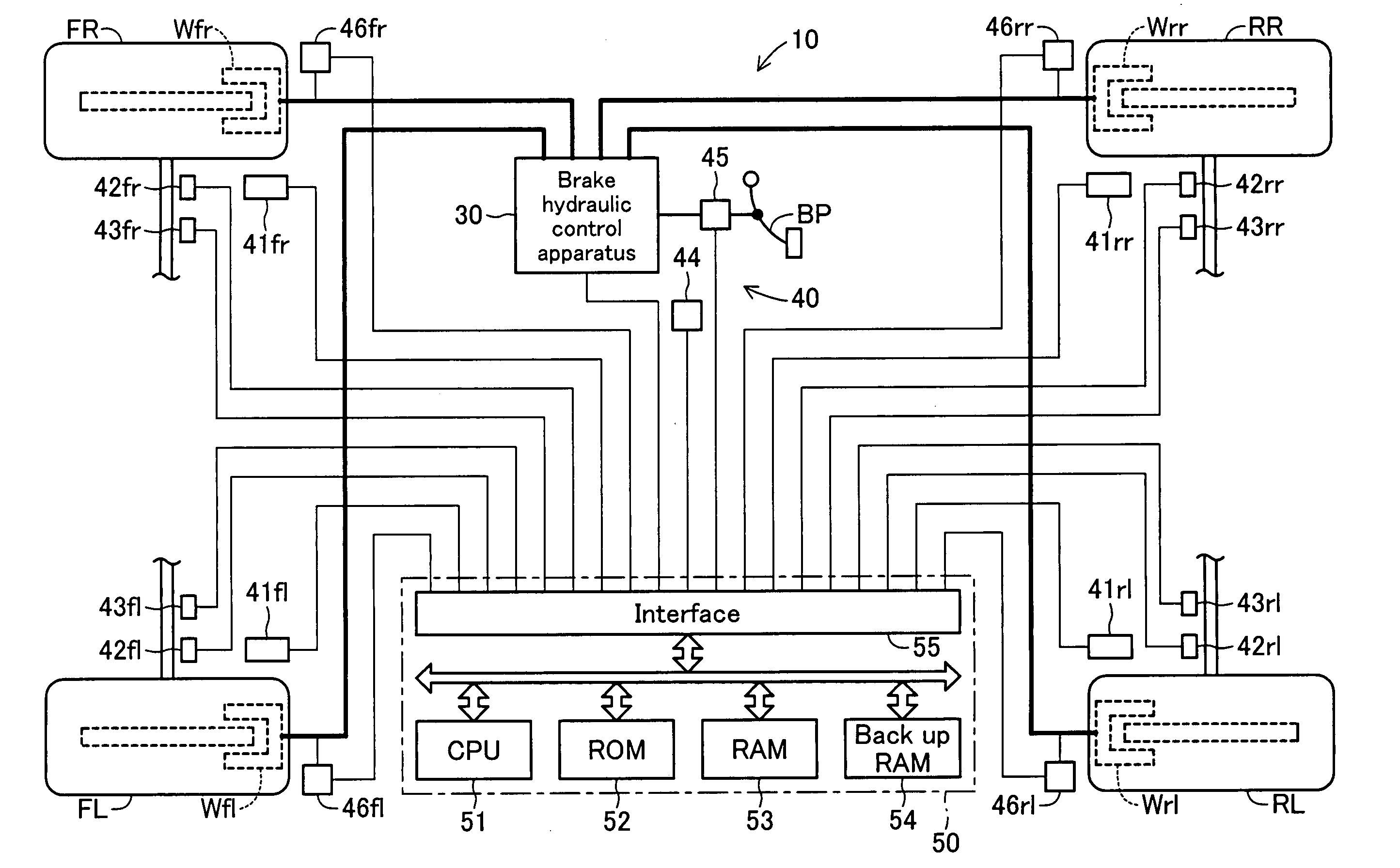
Brake Controller
ActiveUS20110073419A1Feel goodPrevents elevationBraking action transmissionFoot actuated initiationsMaster cylinderEngineering
In a brake controller, a slope climbing vehicle stop detecting means determines when the vehicle is stopped while climbing a slope, and a pedal release detecting means determines that the pedal is released. An assist control unit interpolates a decrement in brake fluid pressure in the master cylinder due to an input piston movement caused by a release of a brake pedal. An assist piston is controlled by an electric motor to restore and maintain the fluid pressure within the master cylinder.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Brake caliper including heat pipes
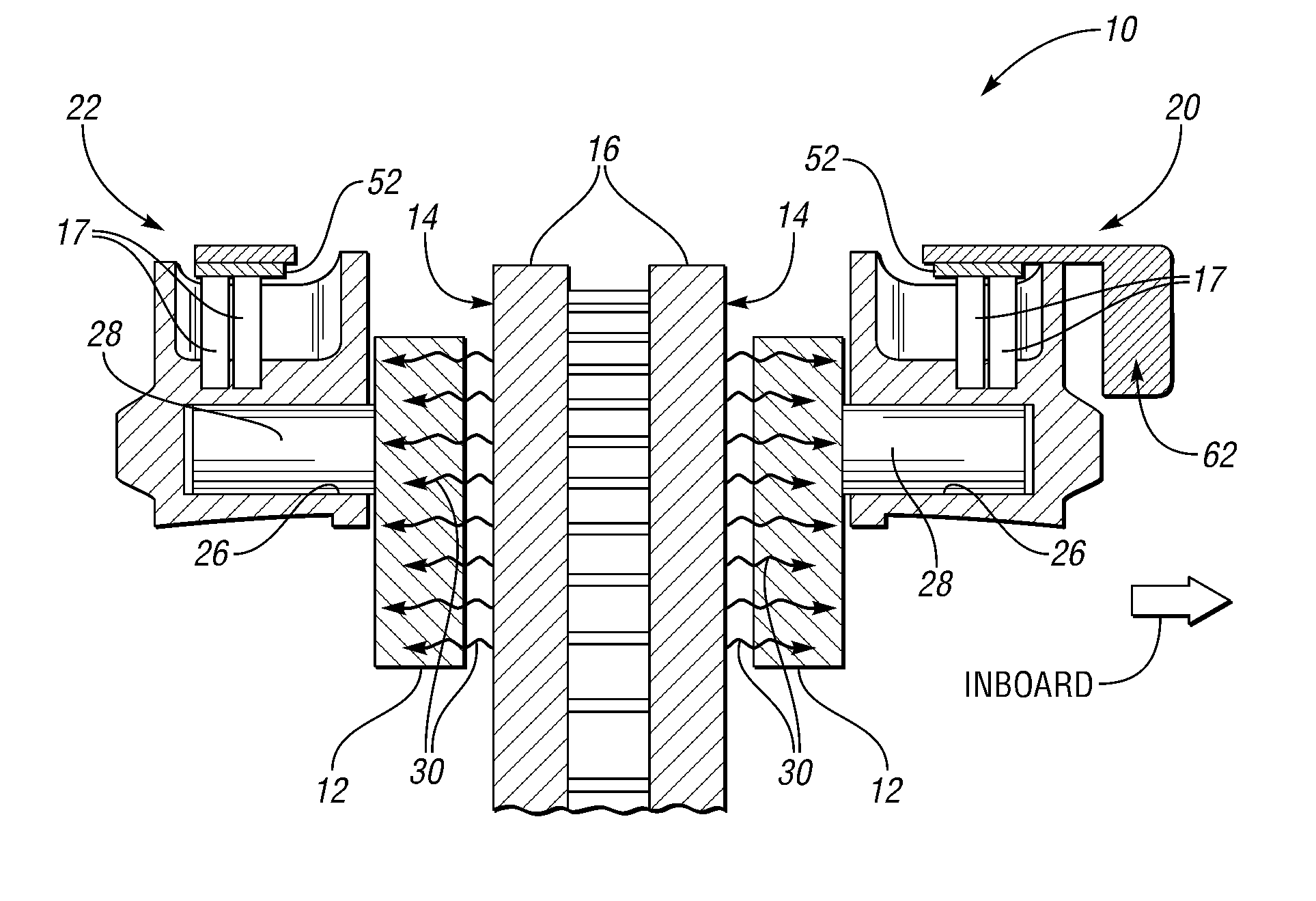
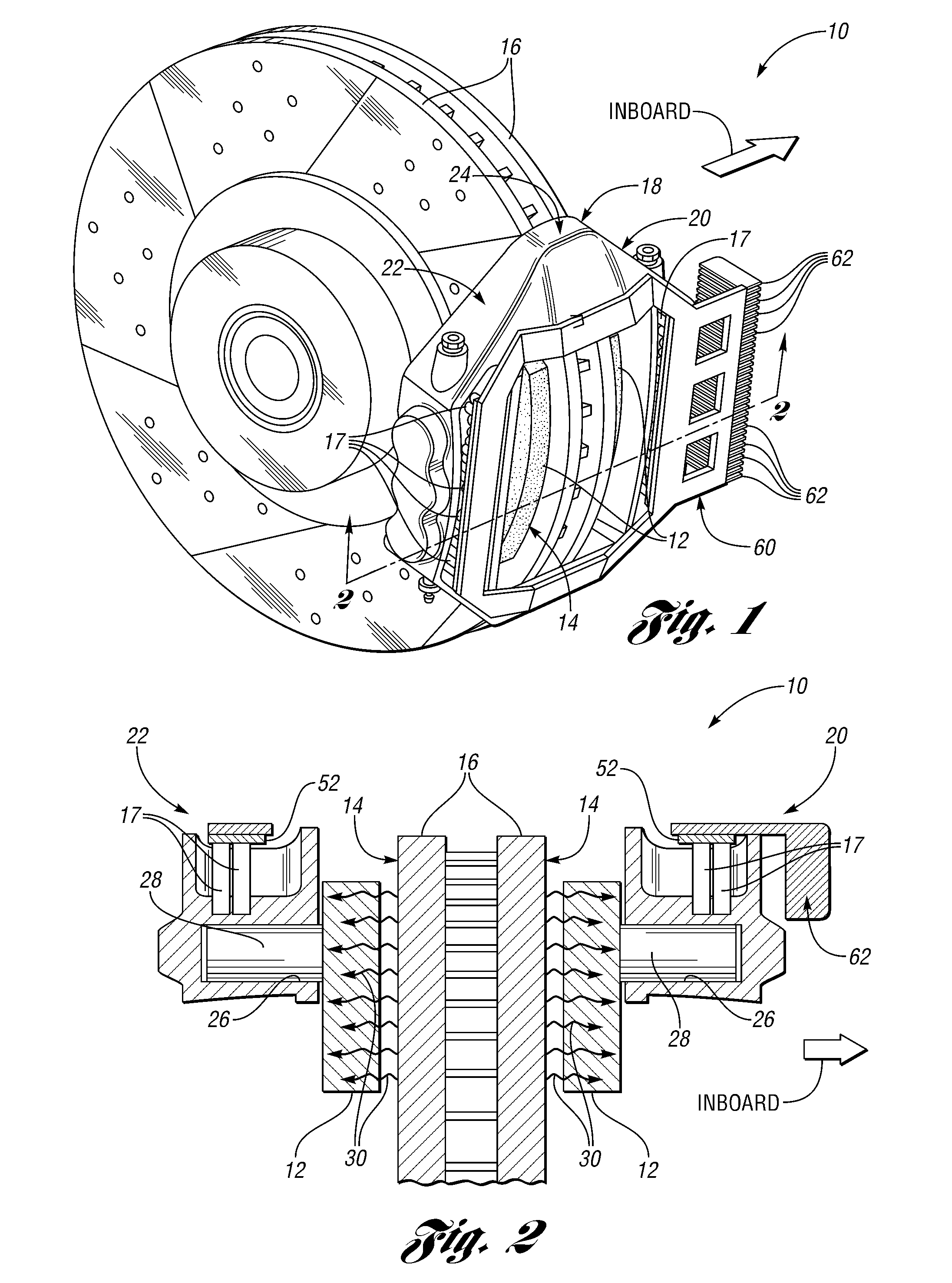
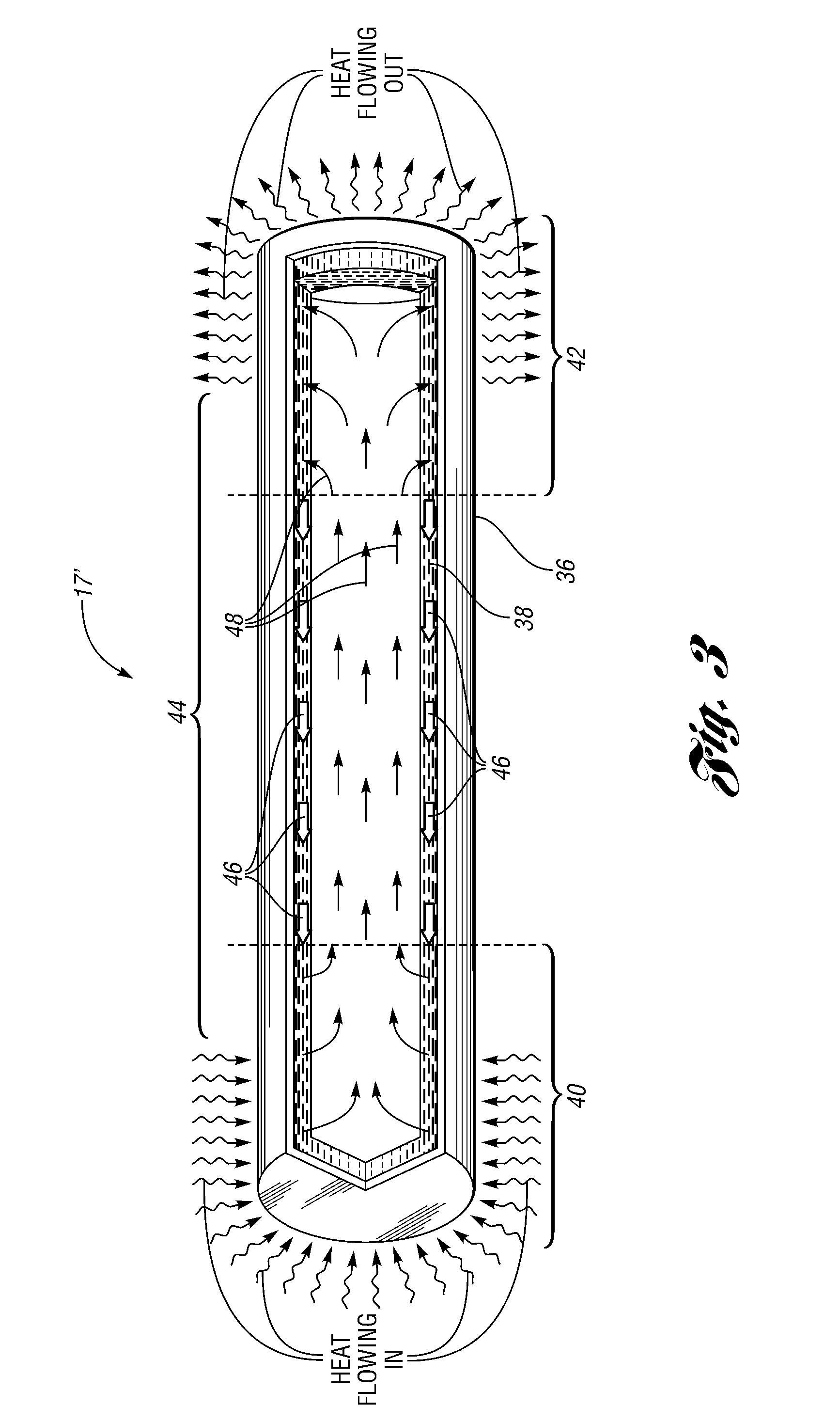
A brake caliper including a caliper body and heat pipes at least partially embedded within the caliper body. The caliper body includes spaced inboard and outboard portions. In addition, at least one of the portions includes piston bores. The caliper body further includes a connector between the inboard and outboard portions whose spacing permits brake pads and a periphery of a brake rotor to be received between the inboard and outboard portions. Also, the brake caliper includes pistons disposed in the piston bores to press the brake pads against the periphery of the brake rotor when brake fluid moves the pistons and the brake pads toward the brake rotor. As the brake pads heat the brake caliper, the heat pipes transfer heat away from the piston bores thereby cooling the brake caliper and brake fluid in, around, or near the piston bores.
Owner:FINKEL BRIAN G
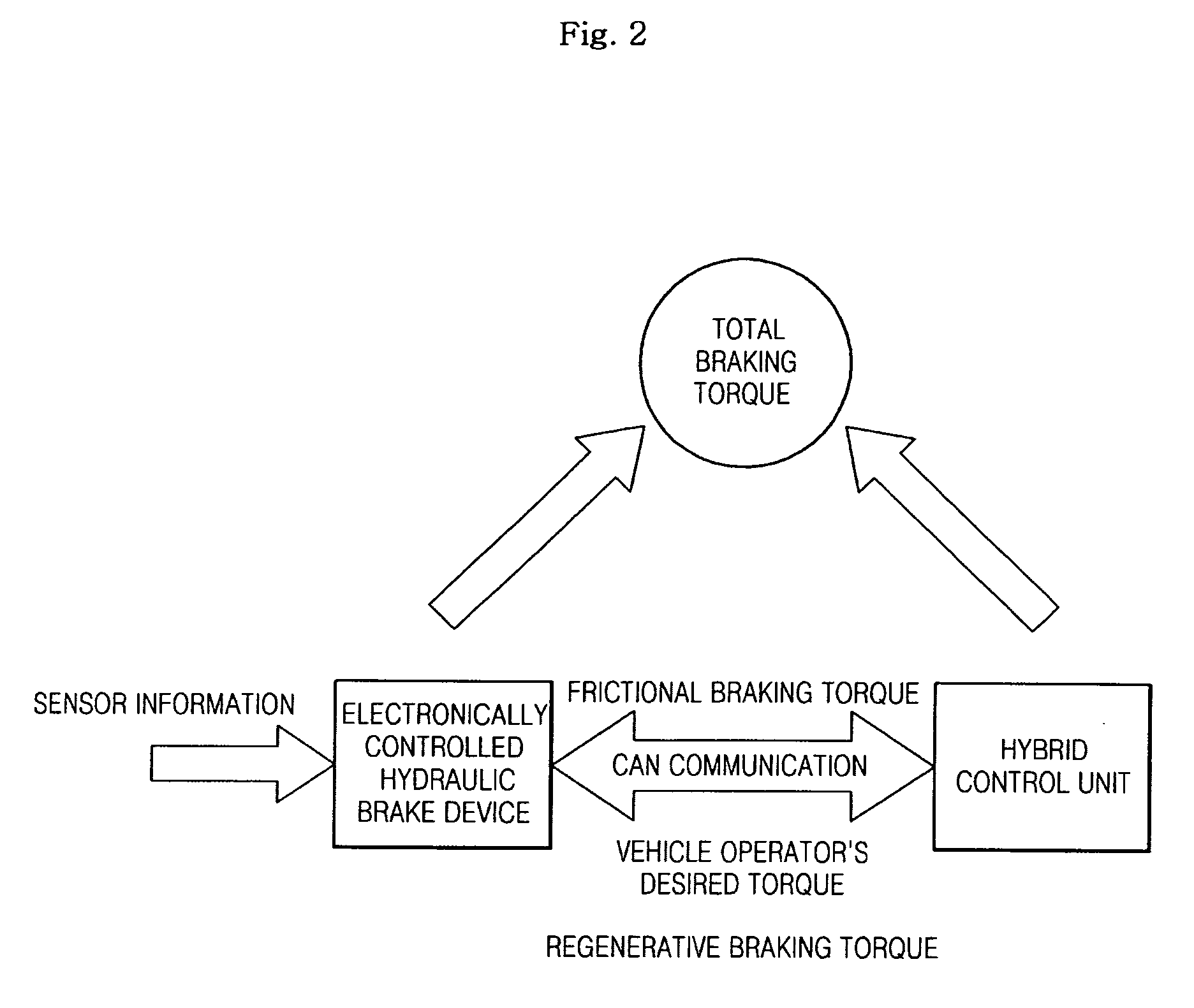
Brake control system for an electrically driven vehicle
ActiveUS20120139330A1Comfortable brake feelSafe recoveryBraking element arrangementsAnalogue computers for trafficRegenerative brakeControl system
During regenerative coordinate braking control, a target brake force is defined by eliminating influences of brake system component tolerances to achieve a comfortable brake feel and secure regenerative energy. A brake control system includes a master cylinder, wheel cylinders, a VDC brake fluid pressure unit and a motor controller. In response to a brake pedal operation by a driver, a brake pedal stroke position is detected at which a pressure in a master cylinder actually begins to be generated. A target deceleration characteristic is adjusted from a theoretical characteristic so that the target deceleration equals a maximum value of an add-on brake force (i.e., the regenerative brake gap) at the detected brake pedal stroke position.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
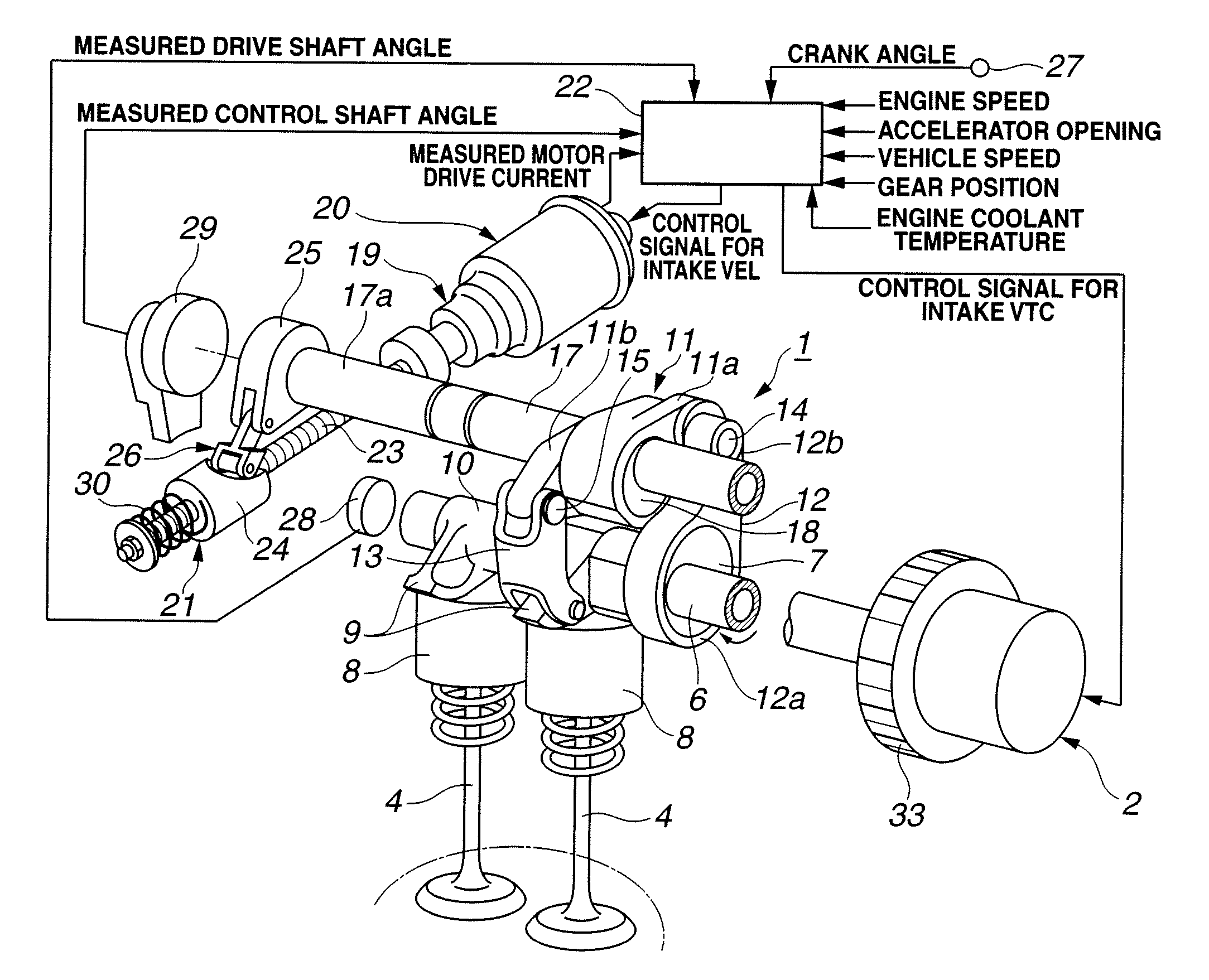
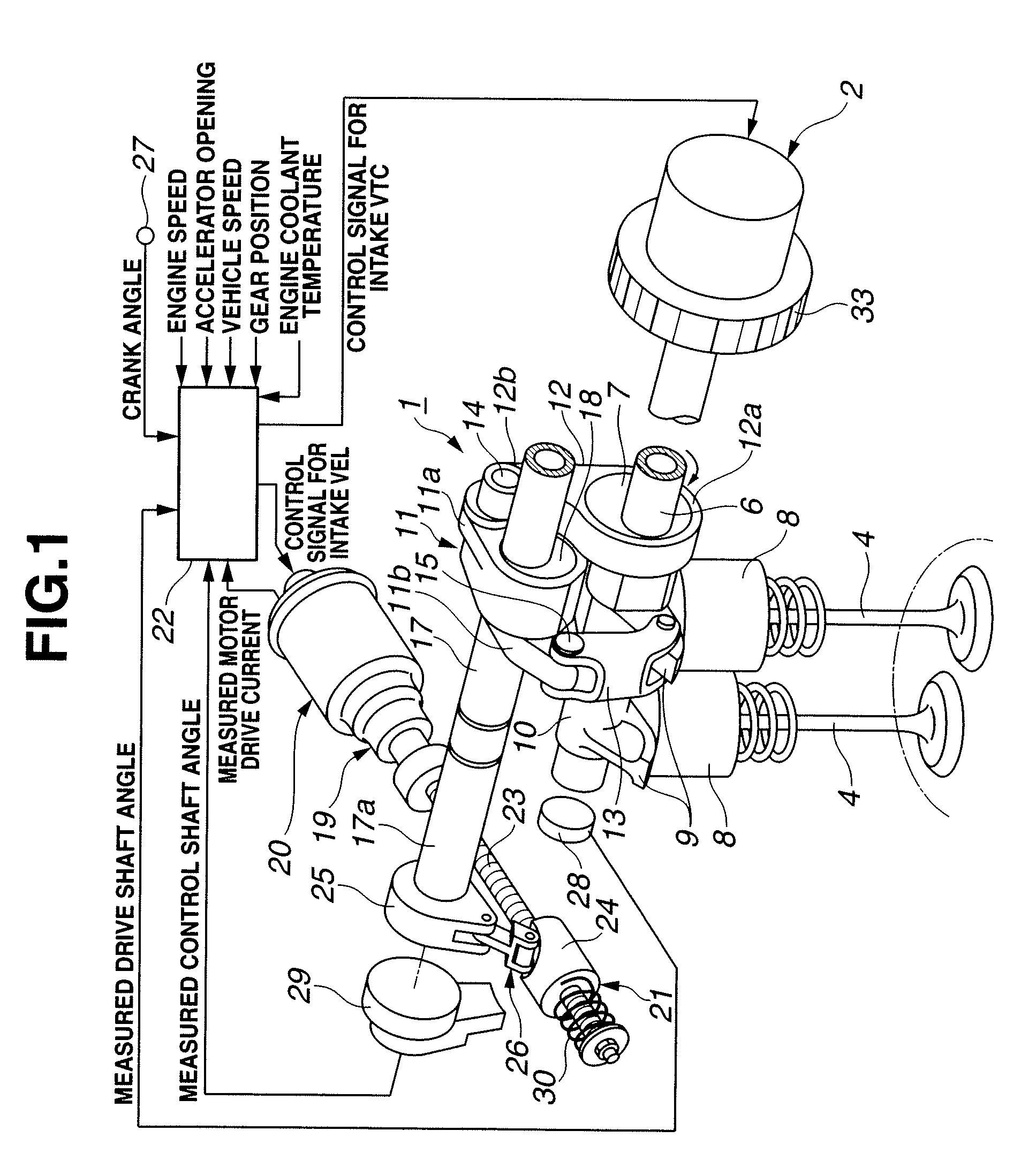
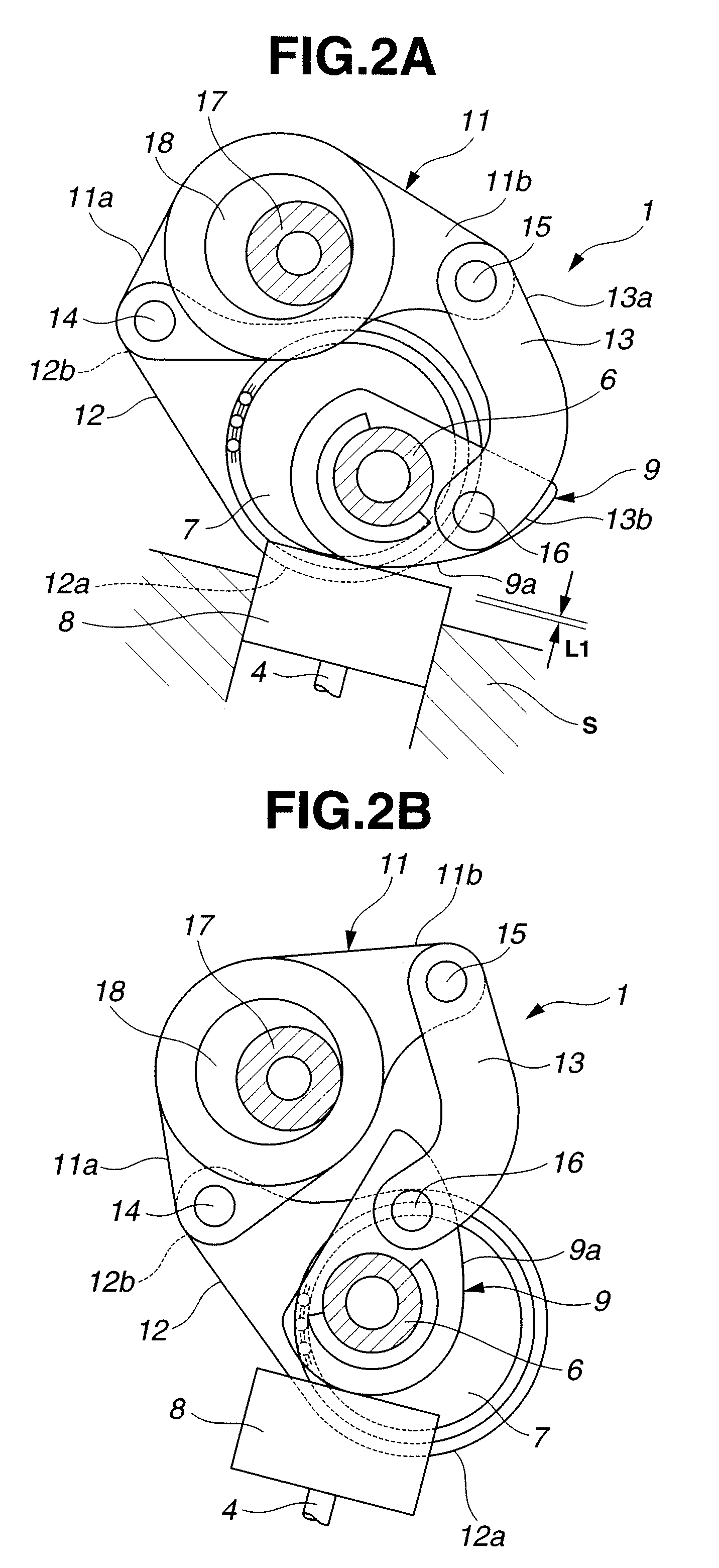
Variable valve actuating apparatus for internal combustion engine
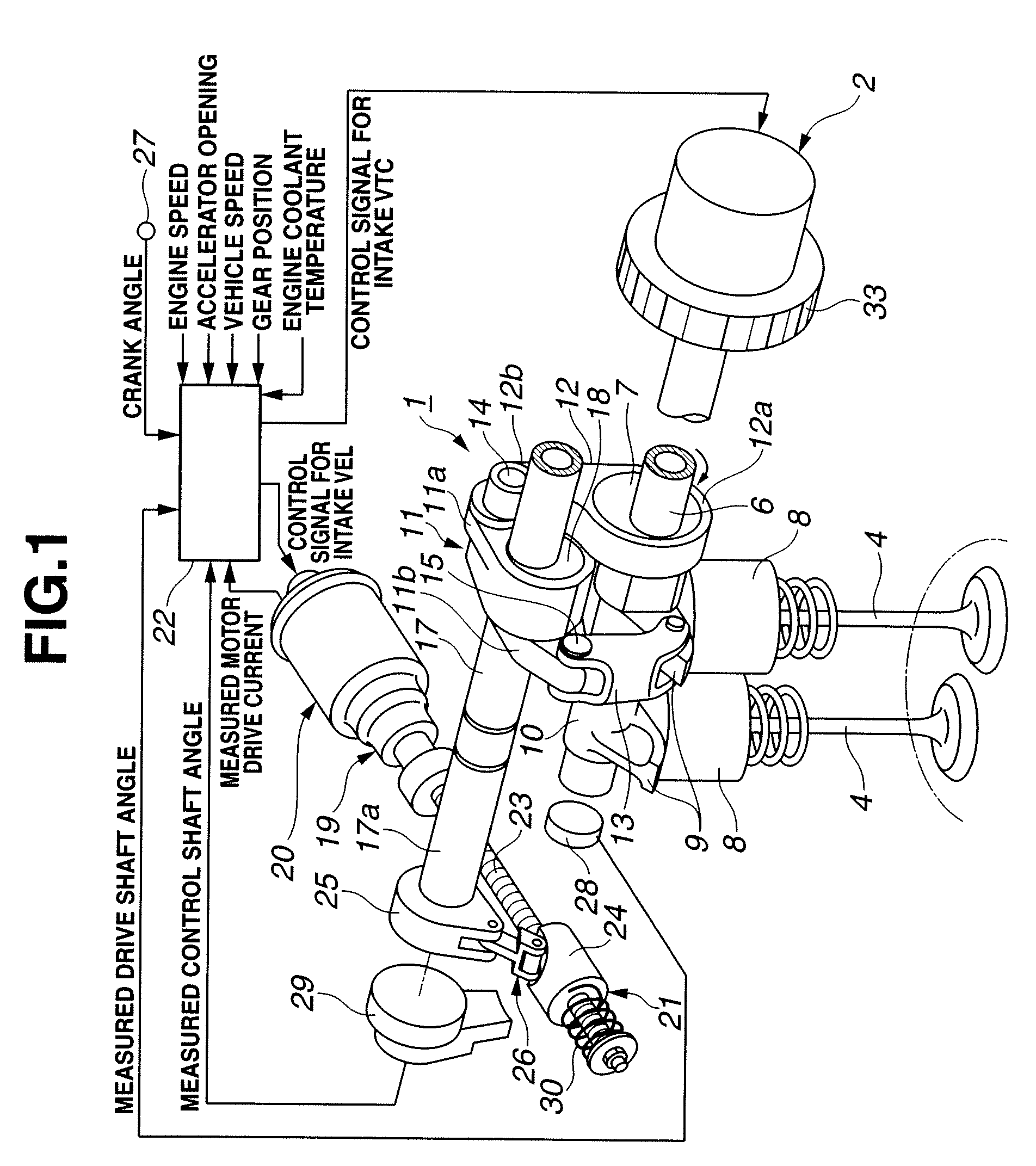
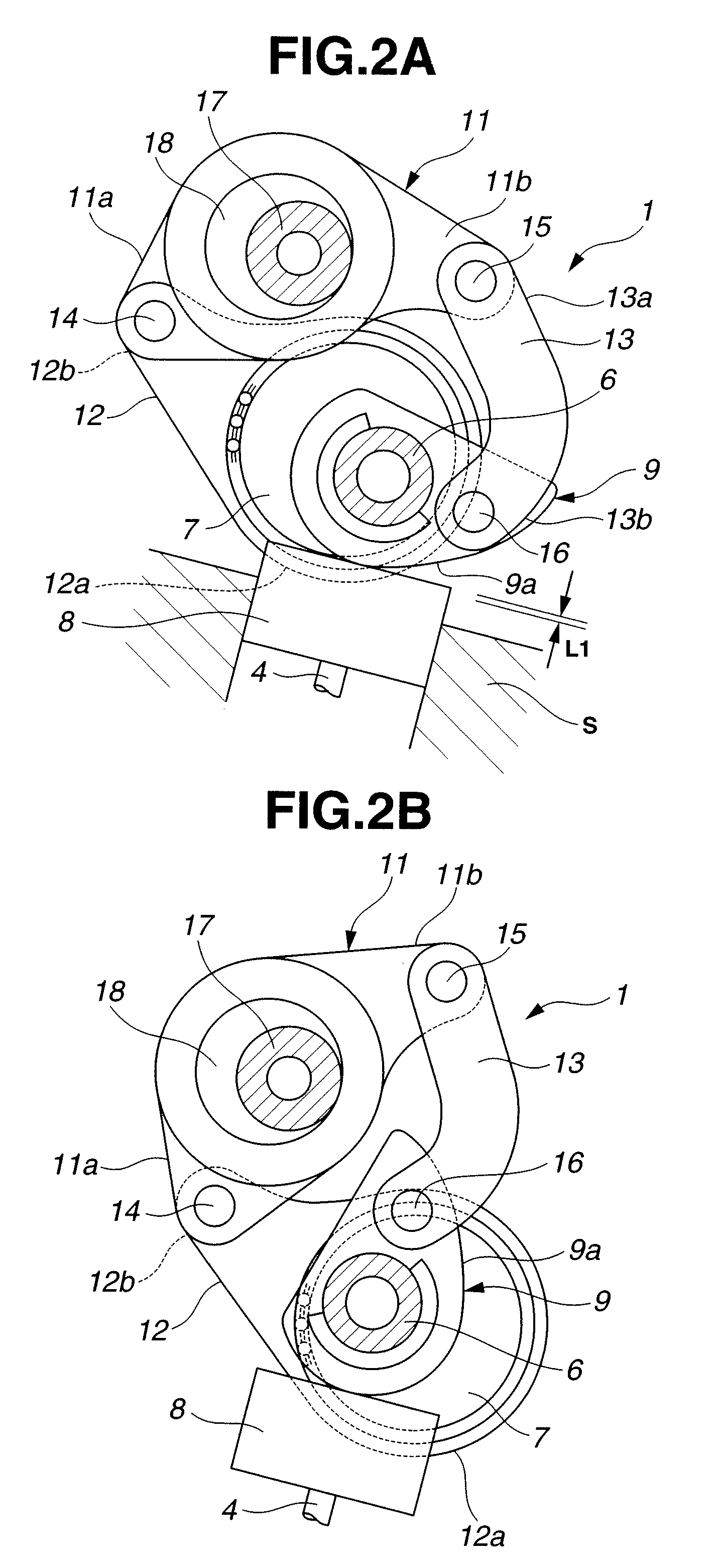
InactiveUS7793625B2Avoid timeYielding couplingInternal combustion piston enginesDrive shaftExternal combustion engine
Owner:HITACHI LTD
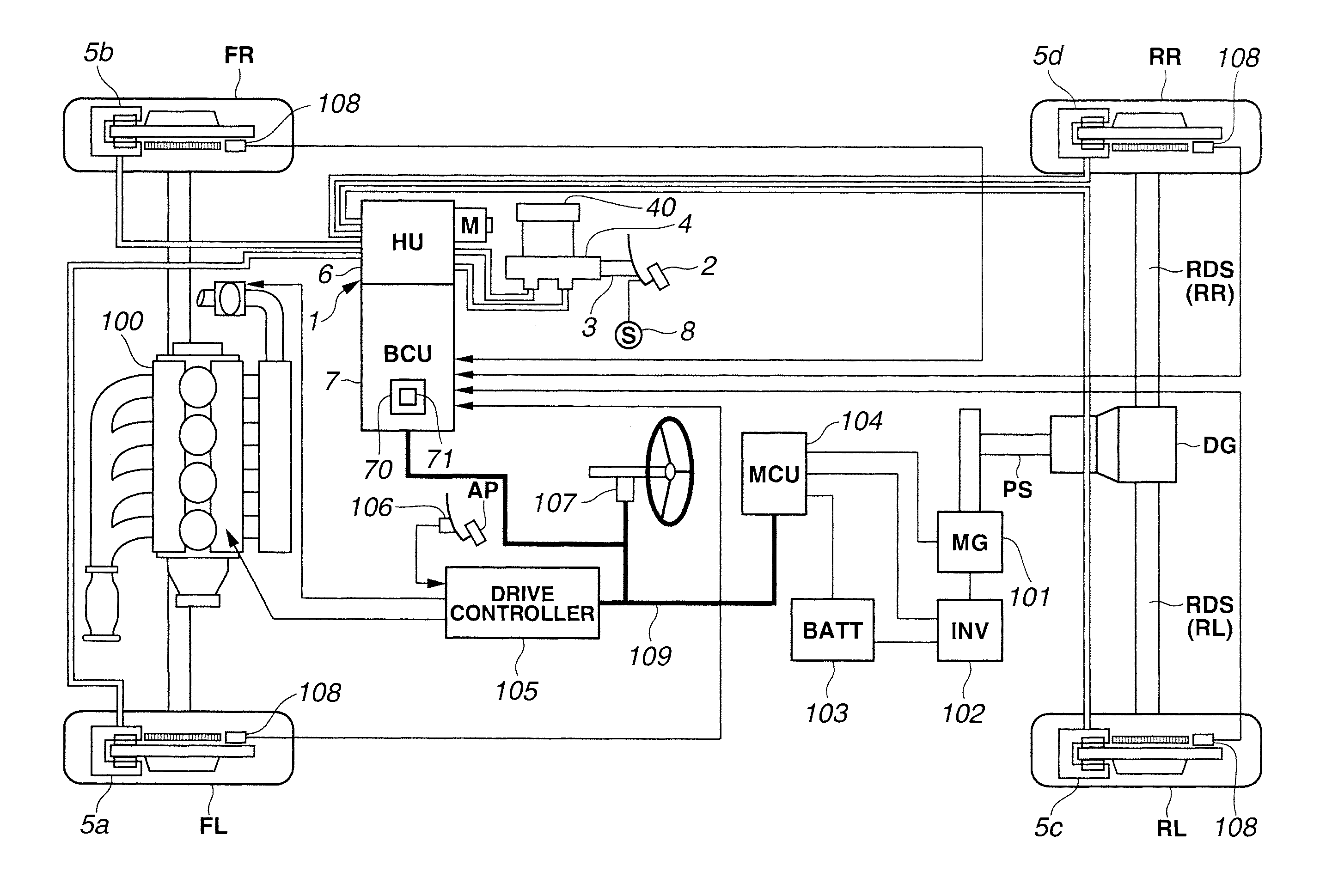
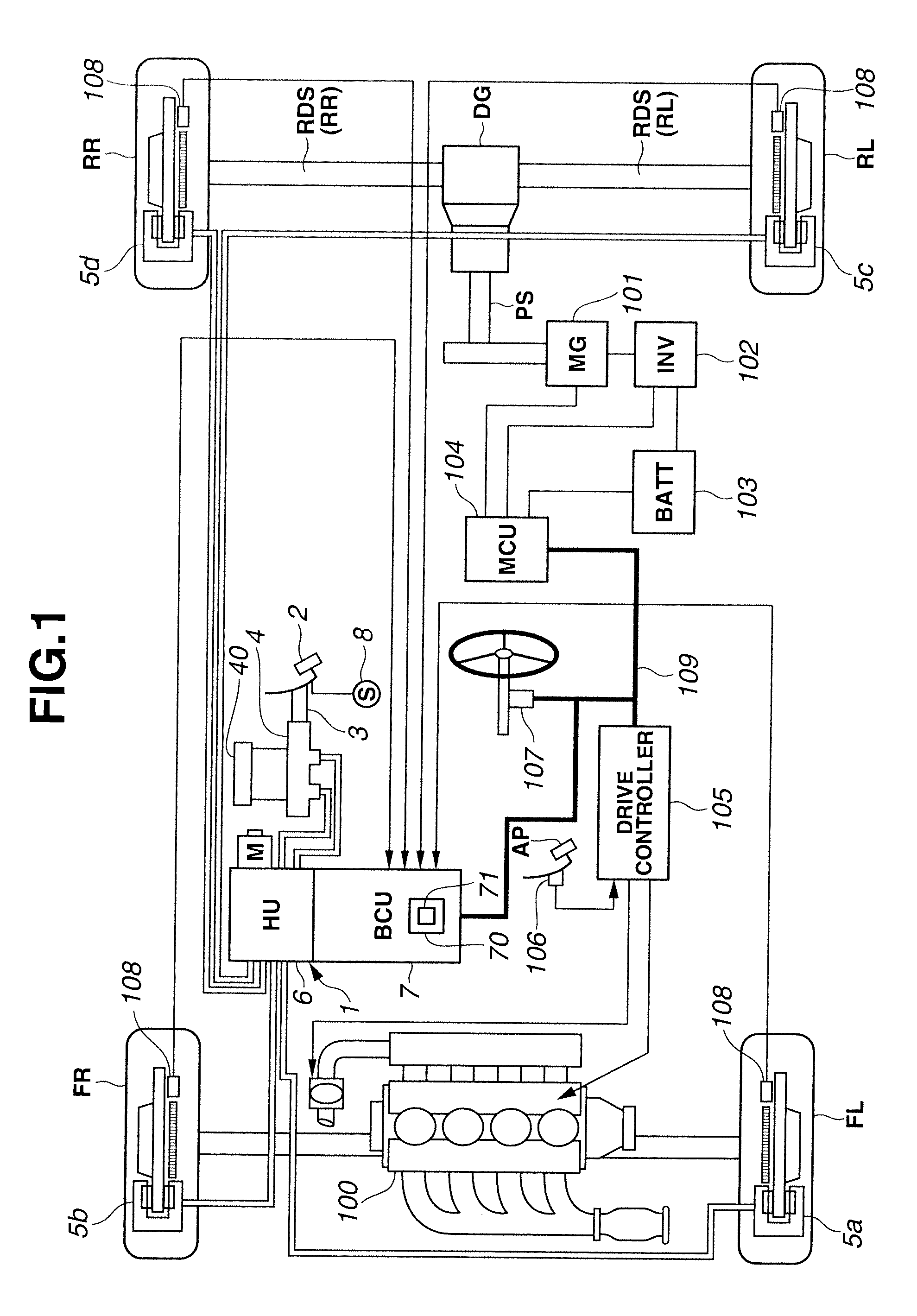
Brake control apparatus
InactiveUS20130062932A1Easy to operateBraking element arrangementsVehicular energy storageWheel cylinderBrake fluid
A brake control apparatus for a vehicle provided with a regenerative braking device, the brake control apparatus includes: a first brake circuit connecting a master cylinder configured to generate a brake hydraulic pressure by a brake operation of a driver, and a wheel cylinder to which the brake hydraulic pressure is applied; a booster configured to increase a pressure of a brake fluid within the master cylinder, and to transmit the pressurized brake fluid to the wheel cylinder through a second brake circuit connected with the first brake circuit; a third brake circuit bifurcated from the first brake circuit, and connected with the booster; a reservoir provided on the third brake circuit; and a recirculating device configured to recirculate the brake fluid stored in the reservoir, to the first brake circuit's side.
Owner:HITACHI AUTOMOTIVE SYST LTD
Rotary pump for braking apparatus
InactiveUS6905321B2Increase in drive torquePrevent and inhibit increase in drive torqueOscillating piston enginesSealing arrangement for pumpsRotary pumpEngineering
In a rotary pump for a braking apparatus, a discharge trench is formed on an axial direction end surface of a second side plate that forms a mechanical seal. As a result, rotors are pressed back toward a side of a first side plate by a discharge pressure of brake fluid channeled to the discharge trench. Accordingly, a force pressing the rotors toward the second side plate is reduced and frictional resistance is reduced.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD +1
Dual-motor BBW (brake-by-wire) system with multiple working modes and voltage regulation modes
ActiveCN103552556AFeel adjustableWith active braking functionBraking action transmissionFoot actuated initiationsAxial thrustWheel cylinder
The invention discloses a dual-motor BBW system with multiple working modes and voltage regulation modes. A brake fluid in a manual cylinder flows into two main cylinders by means of a brake pedal, and brake pressure is generated; and meanwhile, output power torque of two motors is controlled, and axial thrust is overlaid to pistons of the two main cylinders through a transmission device, so that electric power brake is realized. Through control of output torque of the two motors, pressure of the two main cylinders is transmitted to wheel cylinders, brake by wire is realized, and a pedal travel simulator is used for providing force for the brake pedal. Under the condition that the brake pedal is not stepped, the output torque of the two motors is controlled, so that the two cylinders generate pressure which is transmitted to the wheel cylinders through a hydraulic control unit, and accordingly, the active brake is realized. The invention further discloses a structure of a hydraulic control system, and the structure has multiple voltage regulation modes. The dual-motor BBW system has the advantages as follows: the system has multiple braking modes and voltage regulation modes, the most appropriate braking mode and voltage regulation mode can be selected according to dynamic properties of the motors during implementation and application, the reliability is high, and the failure protection capacity is high.
Owner:南京经纬达汽车科技有限公司
Variable valve actuating apparatus for internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20090007862A1Avoid timeYielding couplingInternal combustion piston enginesDrive shaftExternal combustion engine
A variable valve actuating apparatus for an internal combustion engine includes an intake valve operating angle varying mechanism, and an intake valve timing varying mechanism. The intake valve timing varying mechanism includes a housing rotating in synchronization with a crankshaft, and a vane member coupled to a drive shaft for intake valve operation, and movably mounted in the housing. The vane member includes a vane defining first and second fluid pressure chambers on first and second opposite sides of the vane. A hydraulic circuit is arranged to rotate the vane member relative to the housing by supply and return of a brake fluid to and from the first and second fluid pressure chambers so as to change the intake valve maximum lift phase. Coil springs are arranged to bias the vane member relative to the housing in a direction to retard the intake valve maximum lift phase.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Brake system
A brake system including: a master cylinder that generates brake fluid pressure in response to a braking action of a driver, a wheel cylinder that brakes a wheel when actuated by brake fluid pressure, and an electric fluid pressure generator which also generates brake fluid pressure, is connected to the master cylinder through a first fluid passage, and is connected to the wheel cylinder through a second fluid passage. The electric fluid pressure generator being actuated to generate brake fluid pressure by an electric signal corresponding to the braking action of the driver. The system also includes an opening-closing valve that allows and prevents a communication through the first fluid passage and a controller that controls operation of the electric fluid pressure generator and operation of the opening-closing valve. When ending a braking action of the wheel cylinder, the controller closes the opening-closing valve and makes the electric fluid pressure generator output negative fluid pressure to the second fluid passage
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Brake structure for wheel rotating device
InactiveUS20080053719A1Small sizeIncrease the diameterMechanically actuated brakesElectric propulsion mountingEngineeringBrake fluid
A brake structure for a wheel rotating device is disclosed, which comprises a motor provided in a wheel and is driven for rotating the wheel, and a braking mechanism for actuating brake to brake the wheel. The motor includes: a motor housing; a stator positioned in and fixed to the motor housing; and a rotor positioned in the motor housing and facing to the stator. The braking mechanism includes: a brake rotor to rotate with the wheel; frictional members to be in contact with the brake rotor for generation of braking force; a pressing force generating unit for generating pressing force of the frictional members so that the frictional members are urged to and pressed against the brake rotor by supplying brake fluid through a brake fluid passage to transmit fluid pressure; and a housing for the pressing force generating unit. The brake fluid passage is formed inside a wall of the motor housing, and is connected to a brake fluid supply port provided in the housing for the pressing force generating unit.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Pump assembly for a slip-controlled hydraulic brake system for a vehicle
InactiveUS6389955B1Avoid damagePrevent rotationEngine sealsPositive displacement pump componentsEngineeringBrake fluid
A pump assembly having a piston pump, which is driven by an eccentric element. To prevent leakage brake fluid from reaching an eccentric element chamber, a groove surrounds the pump piston in the pump housing and a seal and a porous metal sintered ring is inserted into the groove. A drain which extends obliquely downwardly from the groove drains leakage fluid from the sintered ring.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Waterborne Coatings With Improved Early Water Blushing And Chemical Resistance
ActiveUS20090163619A1Excellent early water blushingExcellent early whitening resistancePlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsWood layered productsGasolineEngineering
This invention relates to waterborne coatings with enhanced early water blushing resistance, chemical resistance, and adhesion to substrates. These waterborne coatings can be paints, varnishes, and water sealers that offer excellent early water blushing as well as. excellent resistance to common household chemicals, such as gasoline, motor oil, brake fluid, transmission fluid, household cleaners, window cleaning fluids, antifreeze, and the like.
Owner:LUBRIZOL ADVANCED MATERIALS INC
Vehicular brake system component
ActiveUS20050061379A1Peel strengthHigh peel strengthAccumulator installationsPipe elementsBrake fluidBraking system
Owner:NHK SPRING CO LTD +2
Brake structure for wheel rotating device
InactiveUS7938211B2Small sizeIncrease the diameterMechanically actuated brakesElectric propulsion mountingEngineeringBrake fluid
A brake structure for a wheel rotating device is disclosed, which comprises a motor provided in a wheel and is driven for rotating the wheel, and a braking mechanism for actuating brake to brake the wheel. The motor includes: a motor housing; a stator positioned in and fixed to the motor housing; and a rotor positioned in the motor housing and facing to the stator. The braking mechanism includes: a brake rotor to rotate with the wheel; frictional members to be in contact with the brake rotor for generation of braking force; a pressing force generating unit for generating pressing force of the frictional members so that the frictional members are urged to and pressed against the brake rotor by supplying brake fluid through a brake fluid passage to transmit fluid pressure; and a housing for the pressing force generating unit. The brake fluid passage is formed inside a wall of the motor housing, and is connected to a brake fluid supply port provided in the housing for the pressing force generating unit.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Motor driven electro-hydraulic brake (EHB) system with main cylinder improved
ActiveCN106891878AMake full use of regenerative braking forceGood pedal feelBraking action transmissionLiquid storage tankEngineering
The invention discloses a motor driven electro-hydraulic brake (EHB) system with a main cylinder improved. The motor driven EHB system comprises a brake control unit, a mechanical pedal feeling simulator, the modified brake main cylinder, a motor power brake device, an ECU, a liquid storage tank, an electromagnetic valve and a sensor. A working front cavity of the brake main cylinder is connected with a pedal push rod. During braking, front cavity oil liquid is pushed into the liquid storage tank through the normally-closed electromagnetic valve. A second working cavity of the brake main cylinder is connected with the motor power brake device. Meanwhile, a first working cavity and the second working cavity pass through an ABS / ESC module to be in hydraulic coupling with wheel cylinders. A motor is controlled to rotate to drive a ball screw mechanism so as to push a piston to move, and precise adjustment to the wheel cylinder pressure of all wheels can be achieved. By adoption of the motor driven EHB system, complete decoupling of a brake pedal and the hydraulic brake system is achieved, and a regenerative brake system can fully utilize the motor for braking to maximally recover brake energy; and regenerative braking force and hydraulic braking force are cooperatively controlled, and the requirements of various different working conditions are met.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Vehicle gradient estimating device and vehicle traveling control device
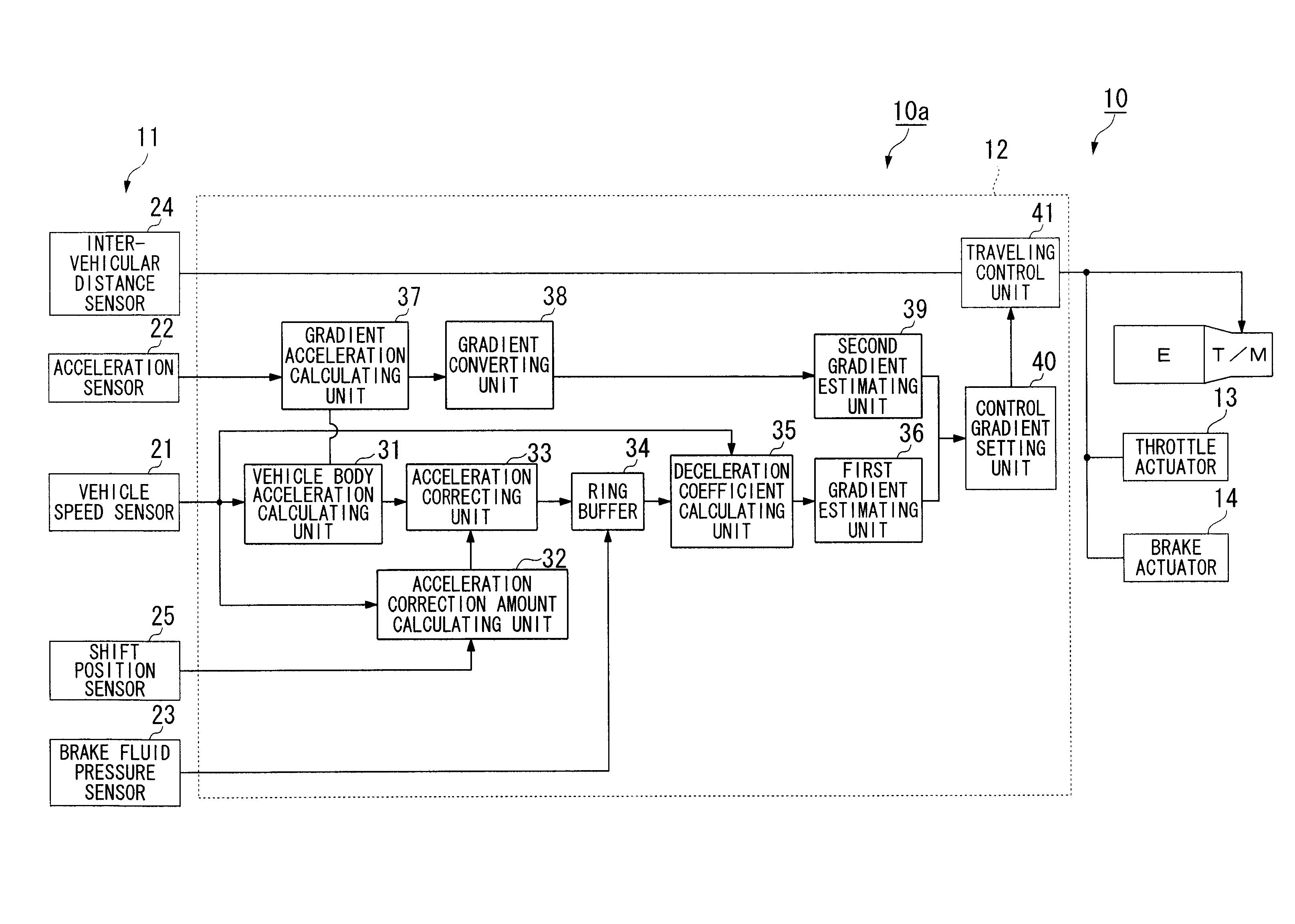
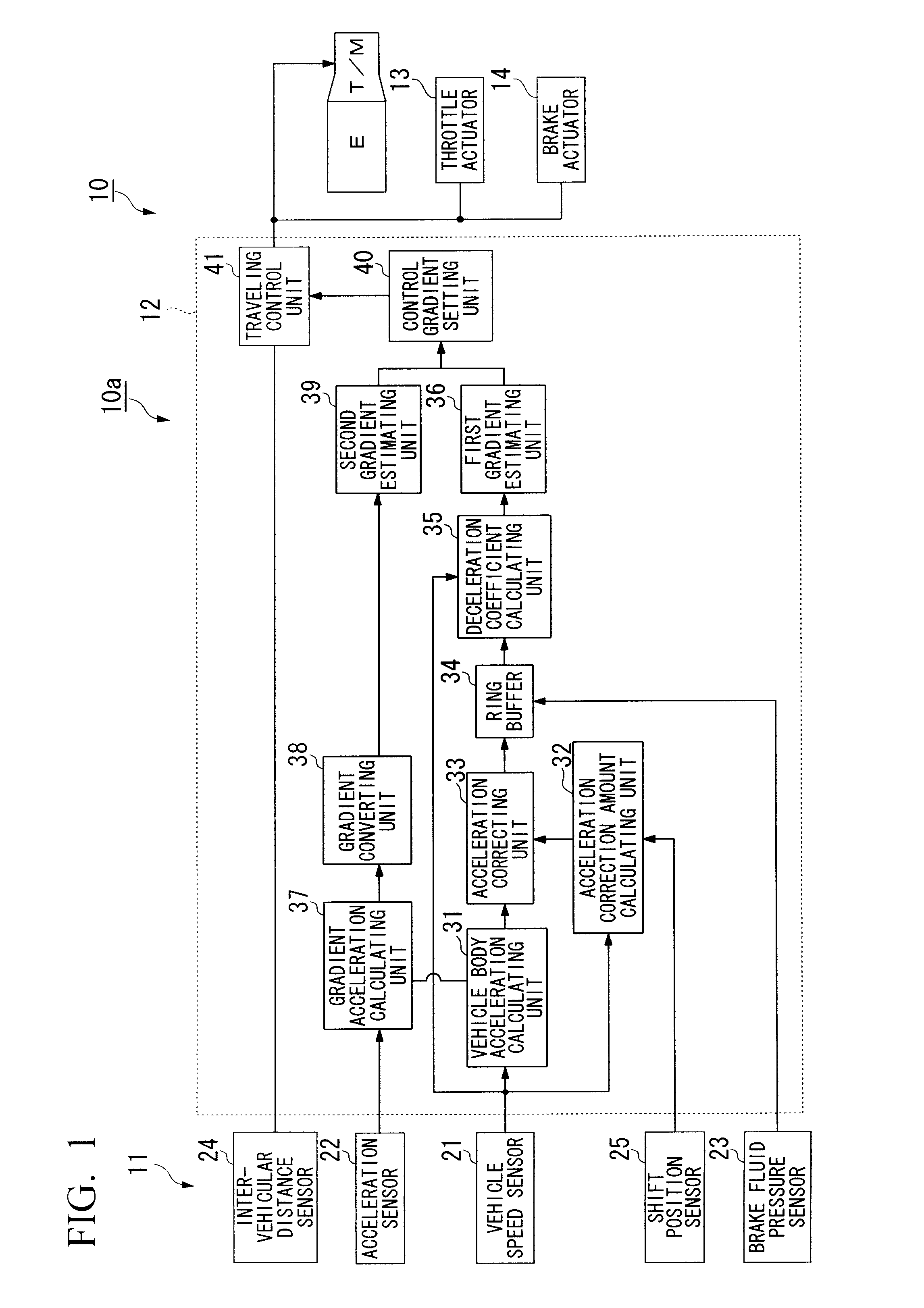
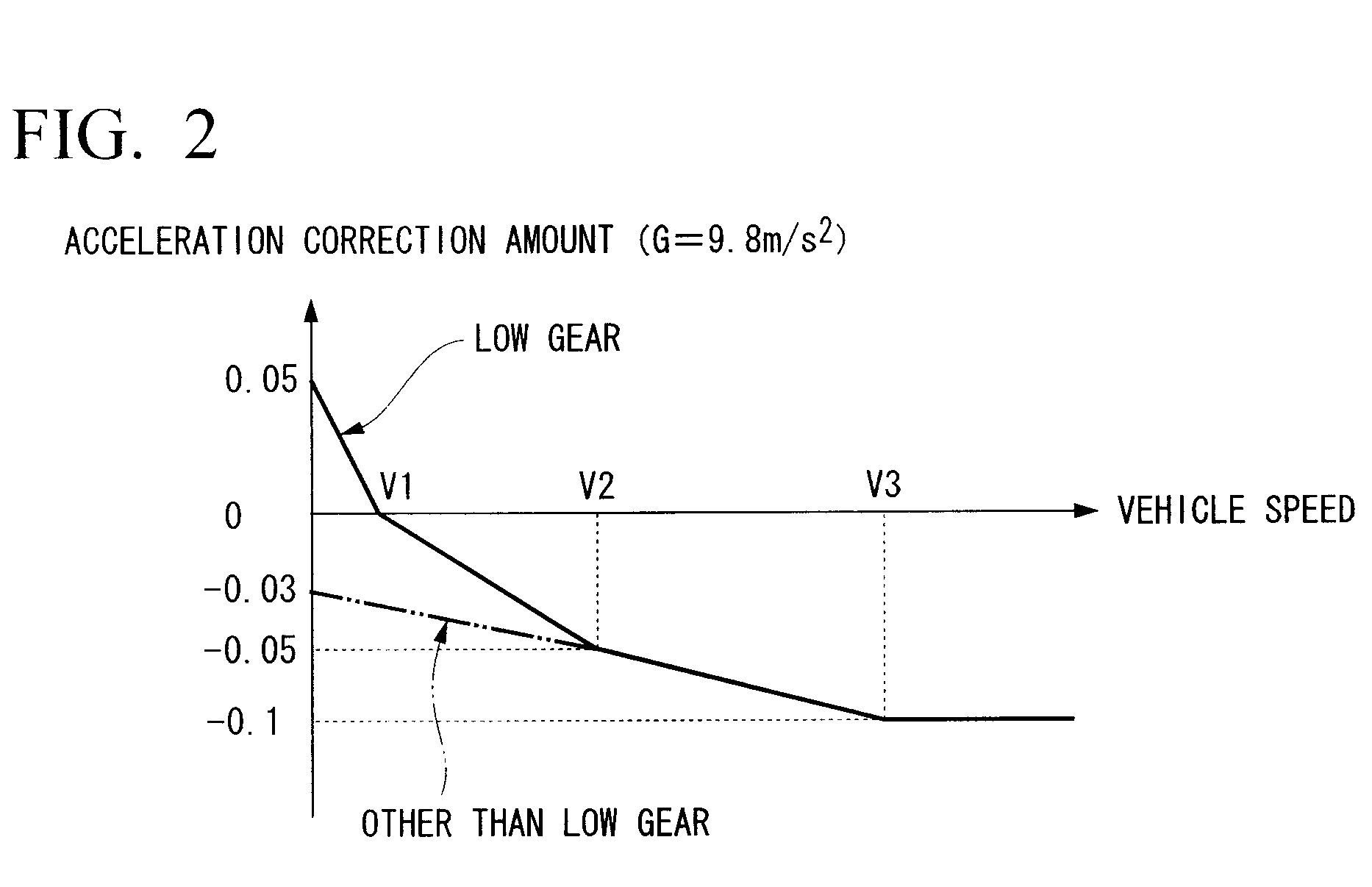
InactiveUS20100268416A1Good estimateAccurate estimateVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesBrake fluidAcceleration Unit
A vehicle gradient estimating device includes: a vehicle speed sensor which detects a traveling speed of a subject vehicle; an acceleration calculating unit which calculates an acceleration of the subject vehicle on the basis of the traveling speed; an engine load deceleration calculating unit which calculates a deceleration due to an engine load of the subject vehicle; an acceleration correcting unit which corrects the acceleration by using the deceleration; a brake fluid pressure detecting unit which detects a brake fluid pressure of the subject vehicle; and a first gradient estimating unit which estimates a gradient of a road being traveled of the subject vehicle, wherein the first gradient estimating unit estimates the gradient on the basis of a ratio between the brake fluid pressure and the acceleration corrected by the acceleration correcting unit.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Composite Commercial Walk-In Van Body
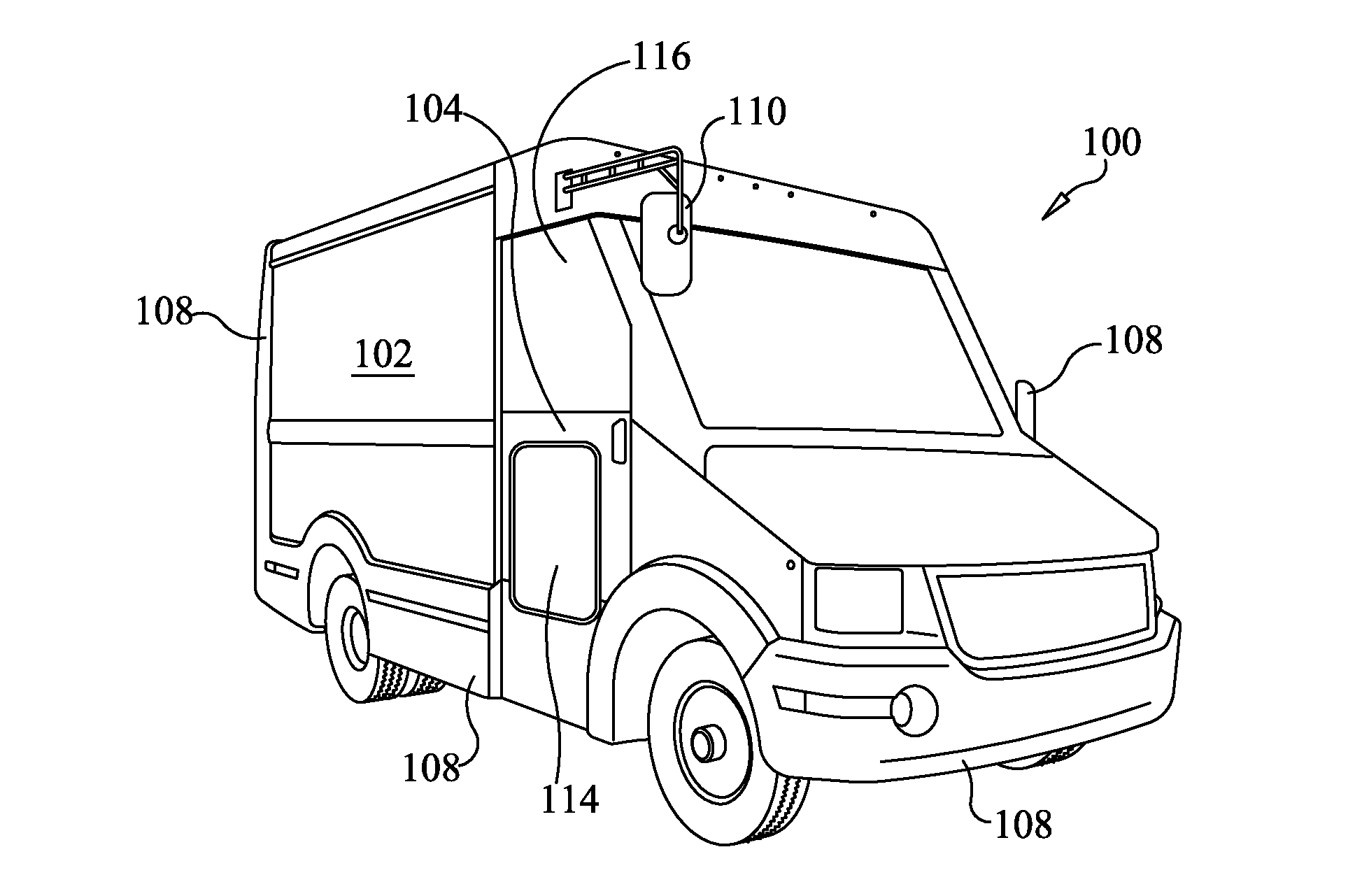
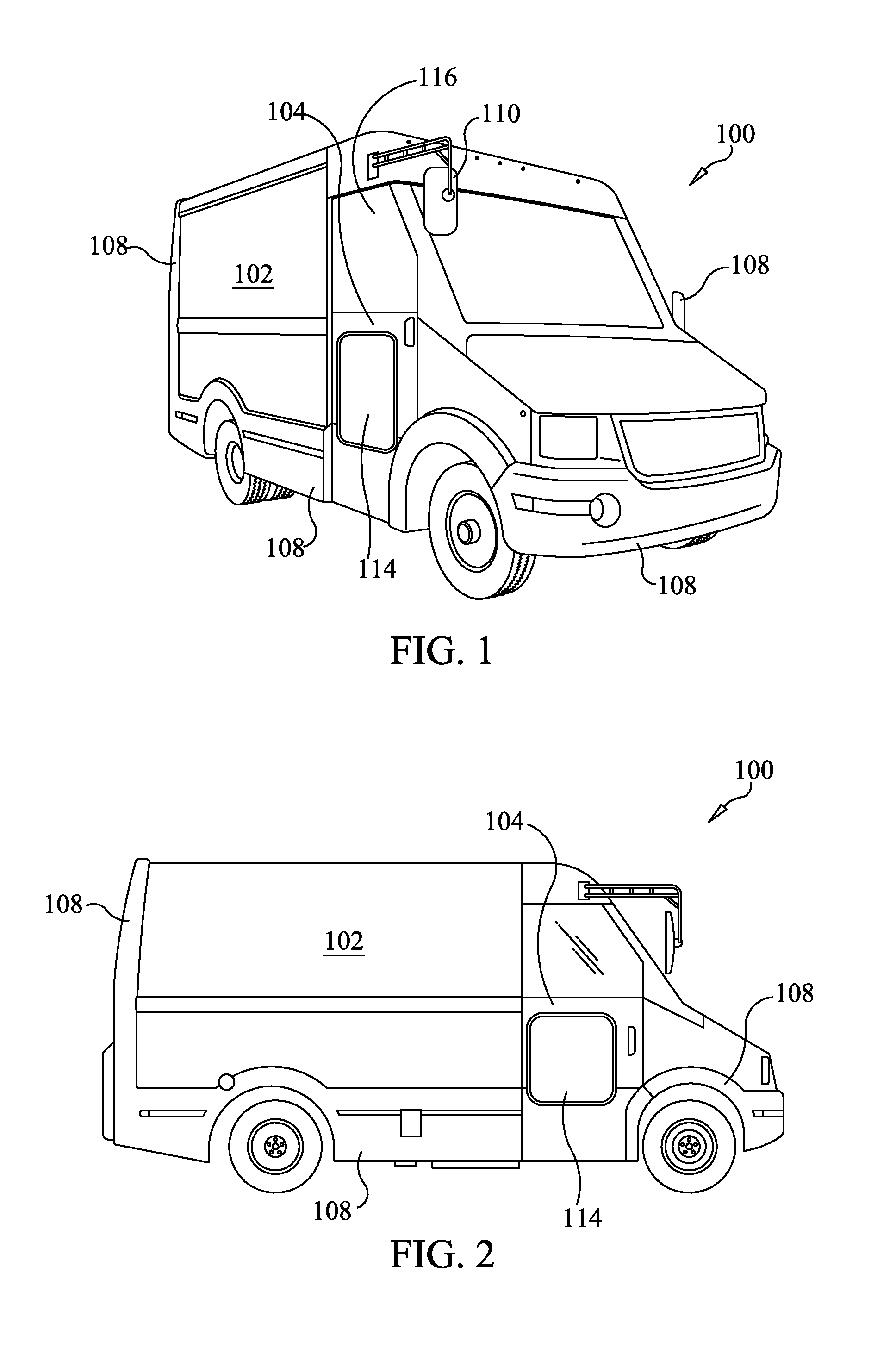
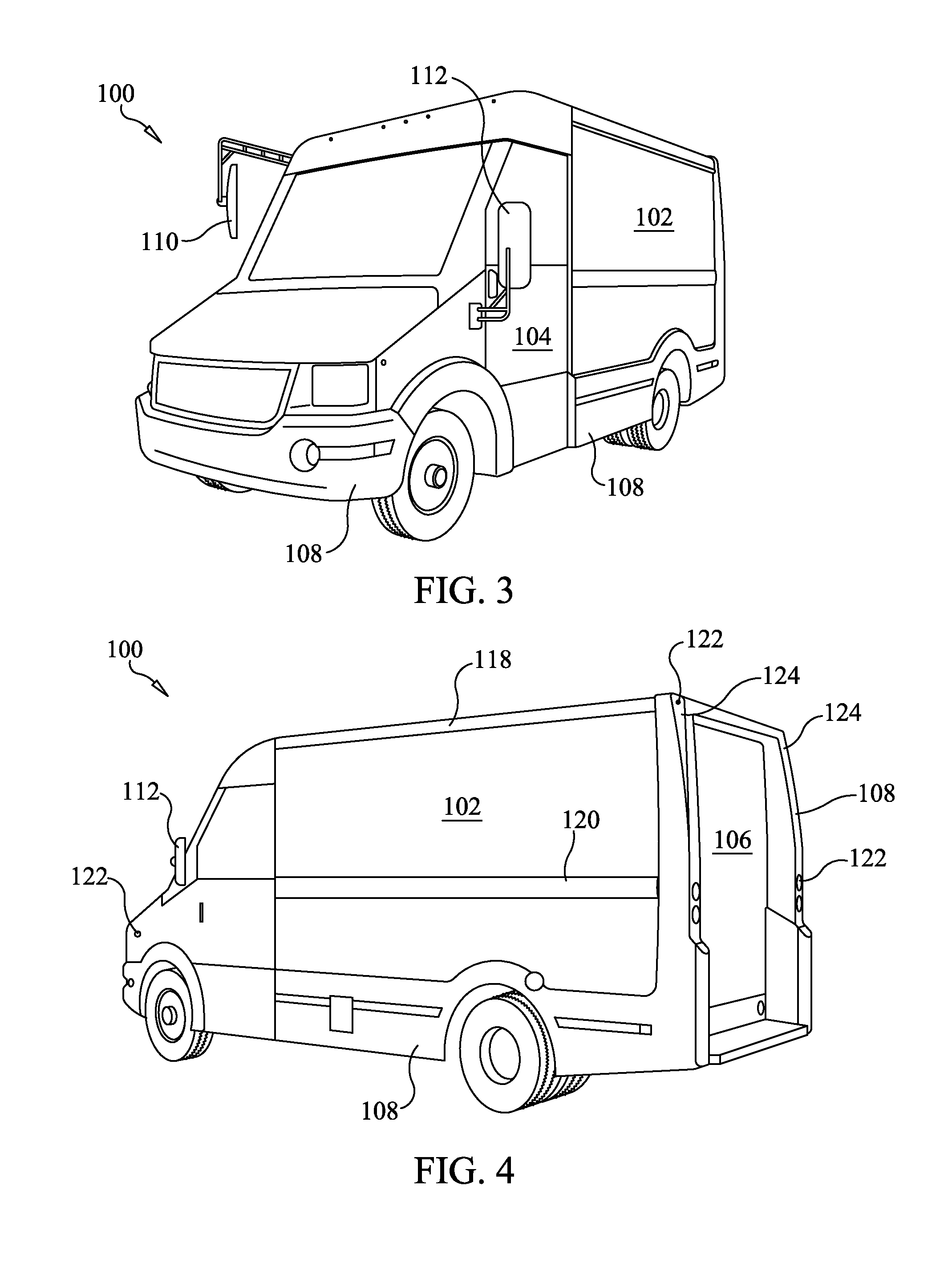
InactiveUS20140054916A1Reduce operating costsReduce consumptionMetal-working apparatusSmall article transportationEngineeringOperability
A composite commercial walk-in van body is constructed via lightweight, composite structures. A composite floor structure having integral logistic tracks are joined to composite sidewalls that include integral rub rails that also integrally formed logistic tracks on an interior thereof. Pigment molded lower body panels that extend beyond the sidewalls are fully replaceable to enhance durability and maintenance of the walk-in van body. A one-piece molded roof eliminates leaks. Any necessary rivets are captured so as to prevent any wet-to-dry surface penetration. An easily accessible washer fluid and brake fluid reservoir aid in the maintenance and operability of the walk-in van body. Such elements contribute to substantial weight reduction, and increase in durability, functionality, and fuel economy of walk-in vans utilizing such a composite body.
Owner:SPARTAN MOTORS
Oscillation damper for damping fluid oscillation in a hydraulic anti-slip control braking system in motor vehicles
InactiveUS6017099ASufficient compression volumeReduce rigidityServomotorsPipe elementsElastomerEngineering
PCT No. PCT / DE96 / 00917 Sec. 371 Date Feb. 23, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Feb. 23, 1998 PCT Filed May 25, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 02971 PCT Pub. Date Jan. 30, 1997The vibration damper has a sleevelike shaped part comprising an elastomer as a diaphragm. The shaped part is received tightly on the opening end of a bore of a housing and surrounds an extension of a support body disposed in the bore. Provided on a side face of the extension is a groove, which communicates with a chamber in the extension. The shaped part, which on its outside is exposed to the brake fluid, with the inside of its jacket wall defines a hollow chamber, formed toward the extension of the support body and having atmospheric pressure. The vibration damper can be used in a slip-controlled hydraulic brake systems of motor vehicles.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
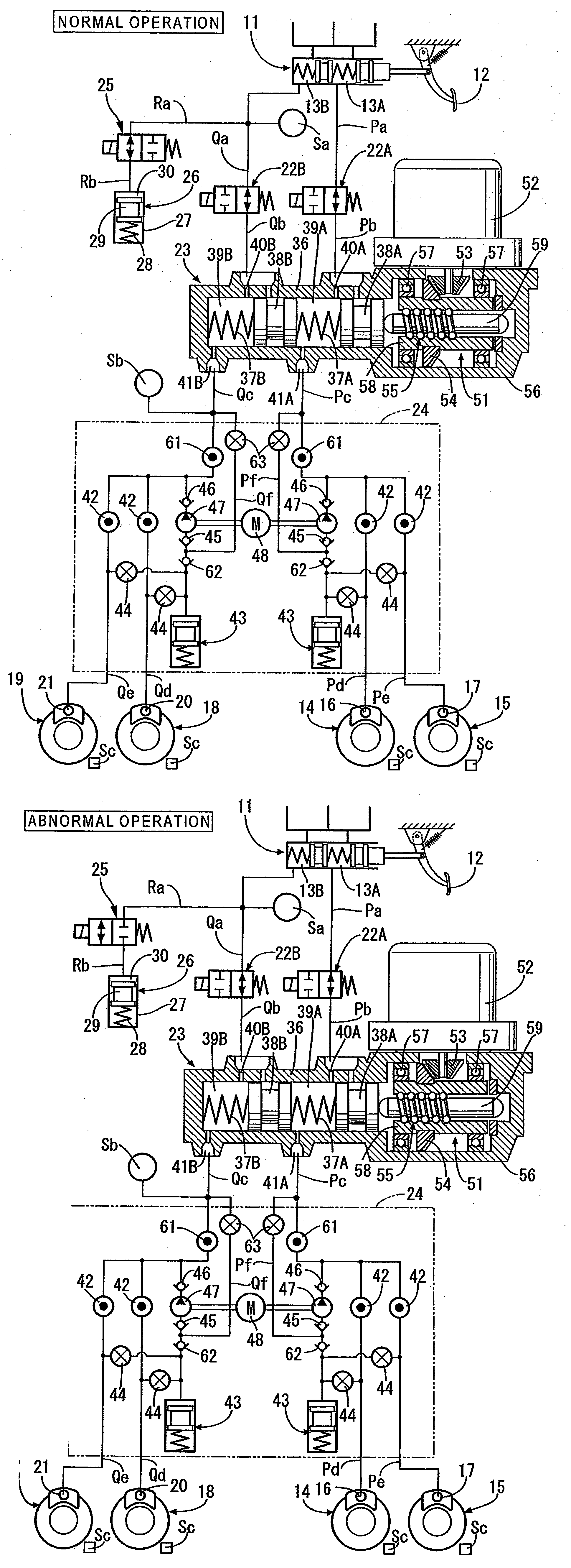
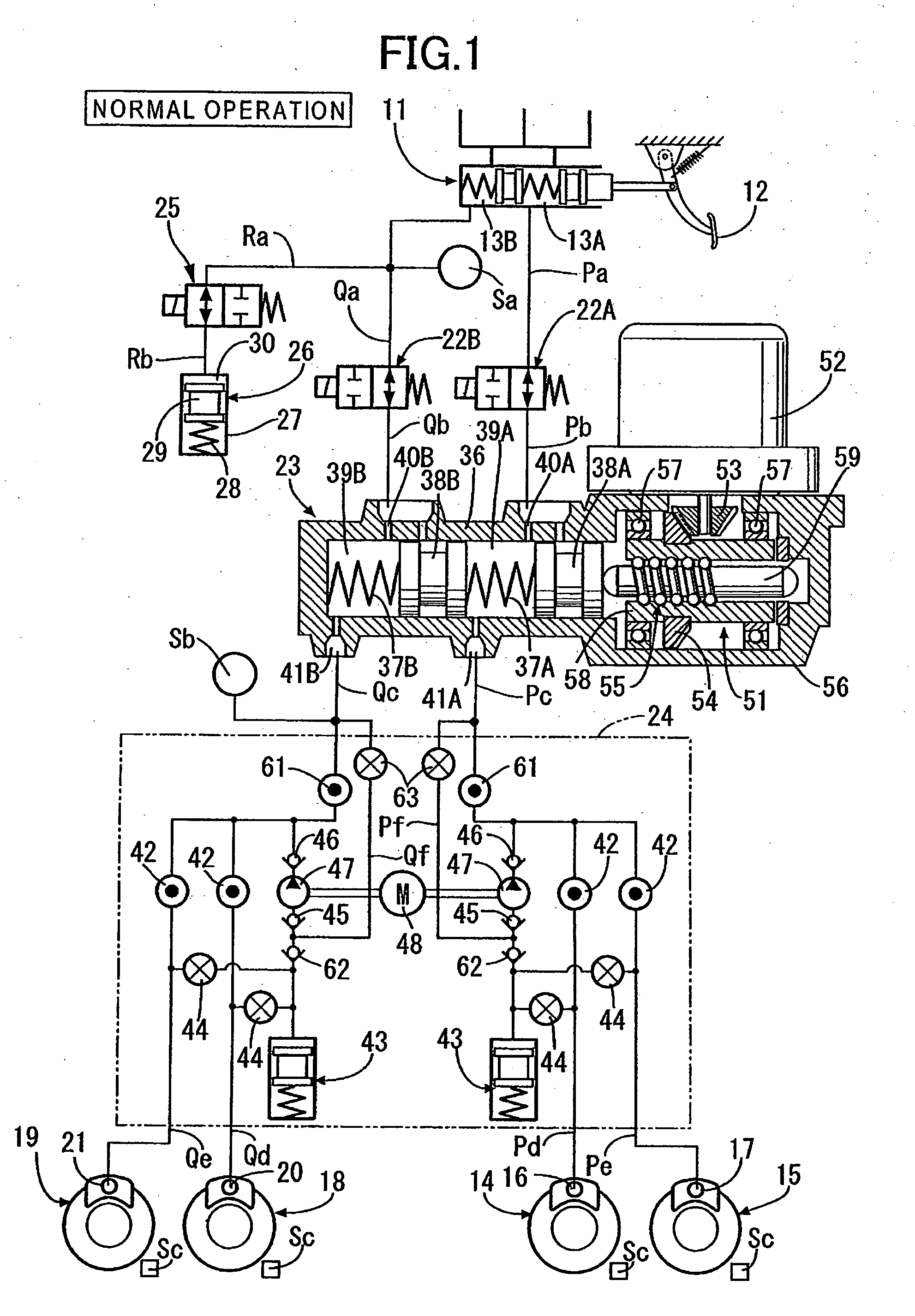
Brake control device
ActiveUS20120200148A1Easy loadingOvercomes drawbackBrake control systemsPump/compressor arrangementsLow voltageHydraulic circuit
A brake control device for a brake system. The control device can perform both an interlocking brake control and an antilock brake control. The brake system includes a front-wheel hydraulic circuit, a front-wheel-side braking part; a rear-wheel hydraulic circuit, a rear-wheel-side braking part; and an electrically-operated pump which pressurizes the brake fluid. The brake control device includes a usual voltage mode where the interlocking brake control or the anti-lock brake control is performed when the supply voltage is a first voltage or more, and a low voltage mode where at least one of the interlocking brake control and the anti-lock brake control is performed in a limited manner when the supplied voltage is a second, lower voltage. An operation mode is changed from the usual voltage mode to the low voltage mode when it is determined that the supply voltage becomes lower than the first voltage.
Owner:BOSCH CORP +1
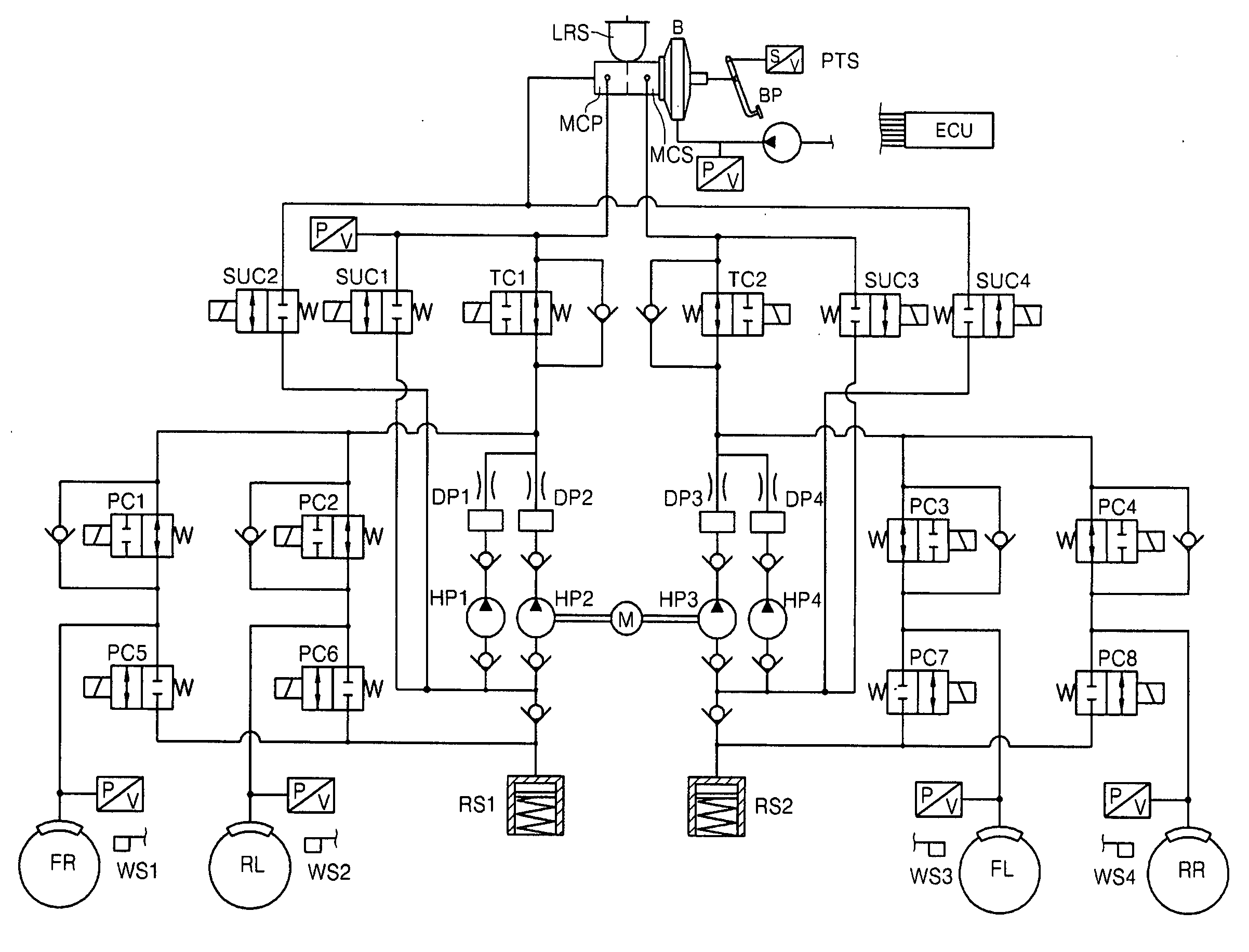
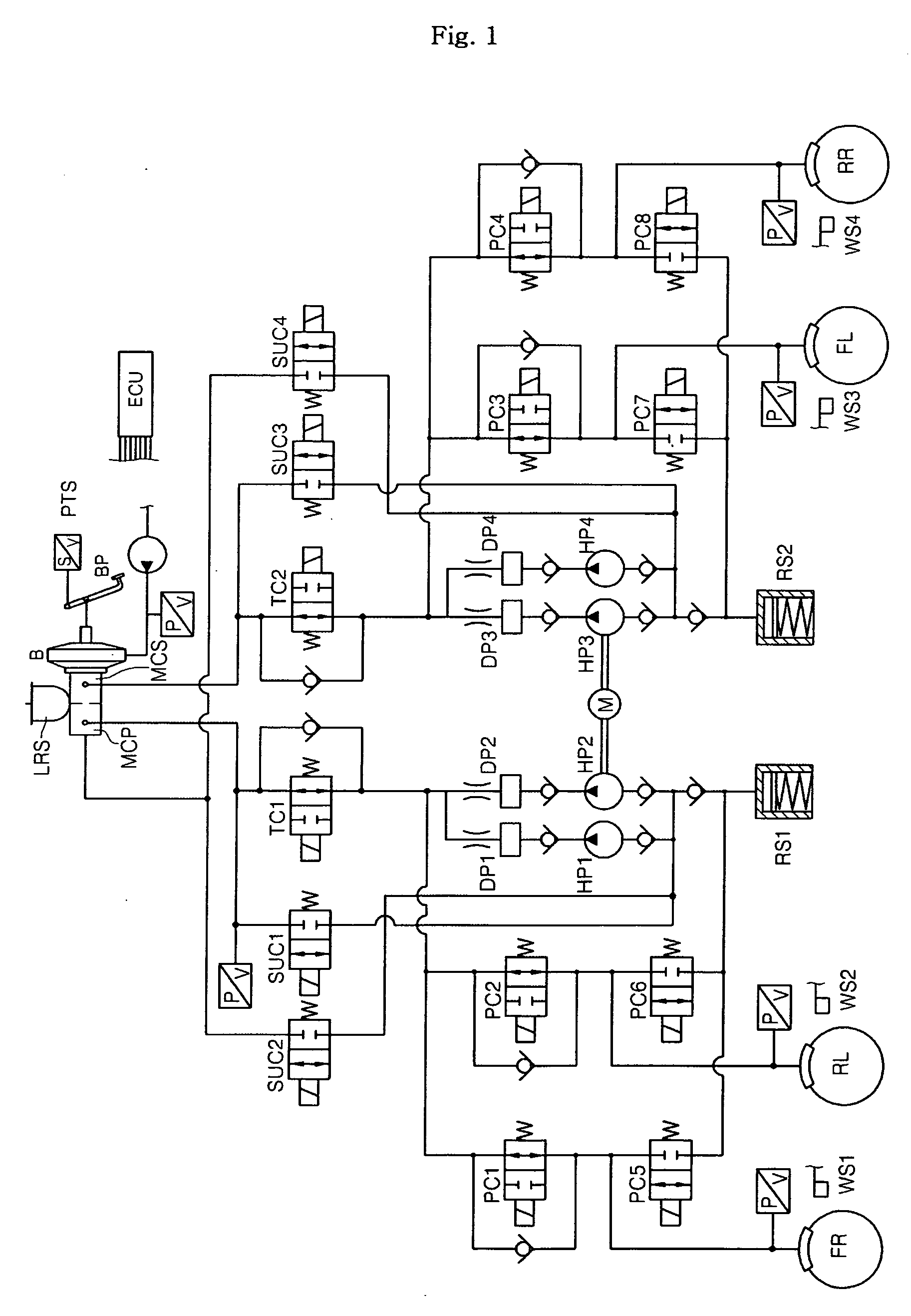
Regenerative braking method for vehicle having electric motor
ActiveUS20070126382A1Feel the sameAvoid problemsDc motor stoppersAsynchronous induction motorsDrive wheelRegenerative brake
A regenerative braking method for a vehicle having an electric motor. During an initial stage of a regenerative braking operation related to the vehicle having the electric motor, a flow rate of brake liquid as much as the amount of regenerative braking is delivered into a reservoir through opened exit valves of non-driving wheels, so as to generate a hydraulic braking force needed after subtracting the amount of regenerative braking from the amount of braking desired by a vehicle operator. When the amount of regenerative braking increases, exit valves of driving wheels are controlled to fulfill the total amount of braking desired by the vehicle operator. Also, when the amount of regenerative braking decreases, wheel pressures have to be increased to fulfill the vehicle operator's desire to brake. In the regenerative braking method for generating a residual amount of braking needed after subtracting the amount of regenerative braking, which corresponds to an amount generated by the electric motor, from the amount of braking desired by the vehicle operator, during the regenerative braking operation, based on a pressure difference between a pressure in the master cylinder and wheel pressures, entrance valves of the driving wheels are controlled to realize an operator's pedal feeling, and the exit valves of the driving wheels are controlled to allow the wheel pressures to follow a target pressure.
Owner:HL KLEMOVE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com