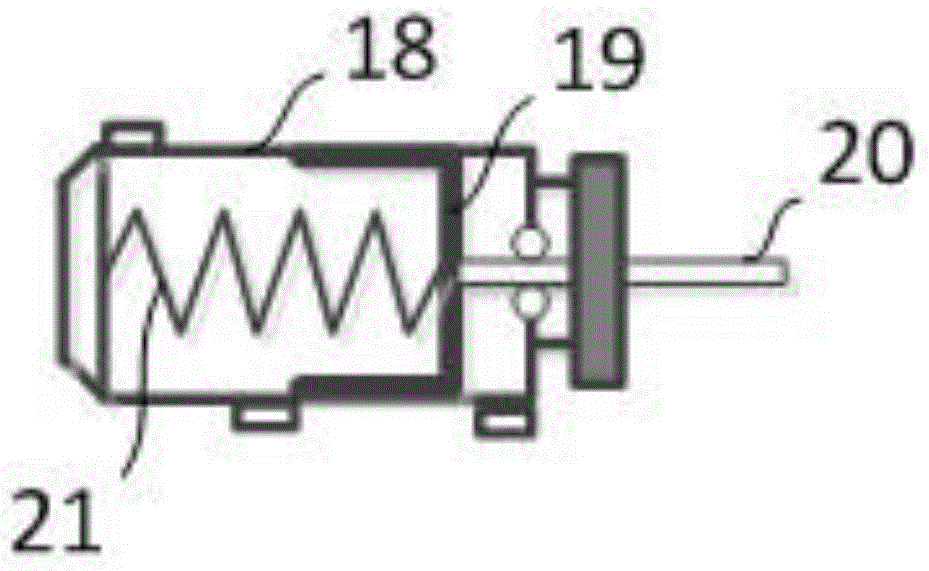
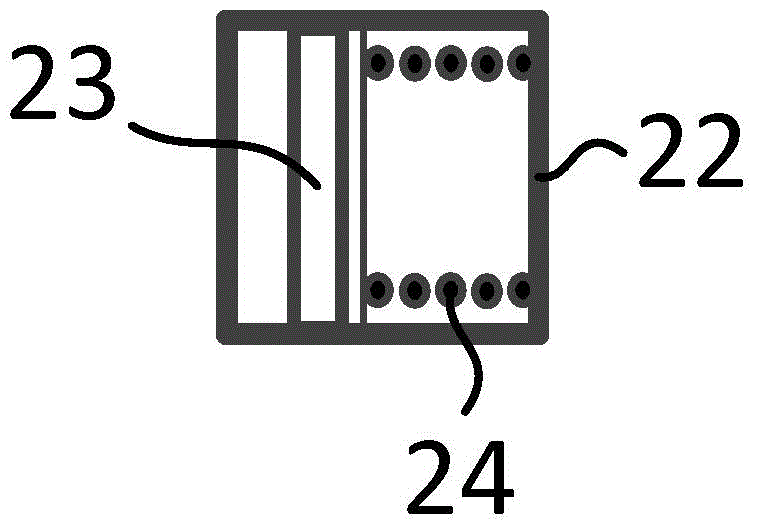
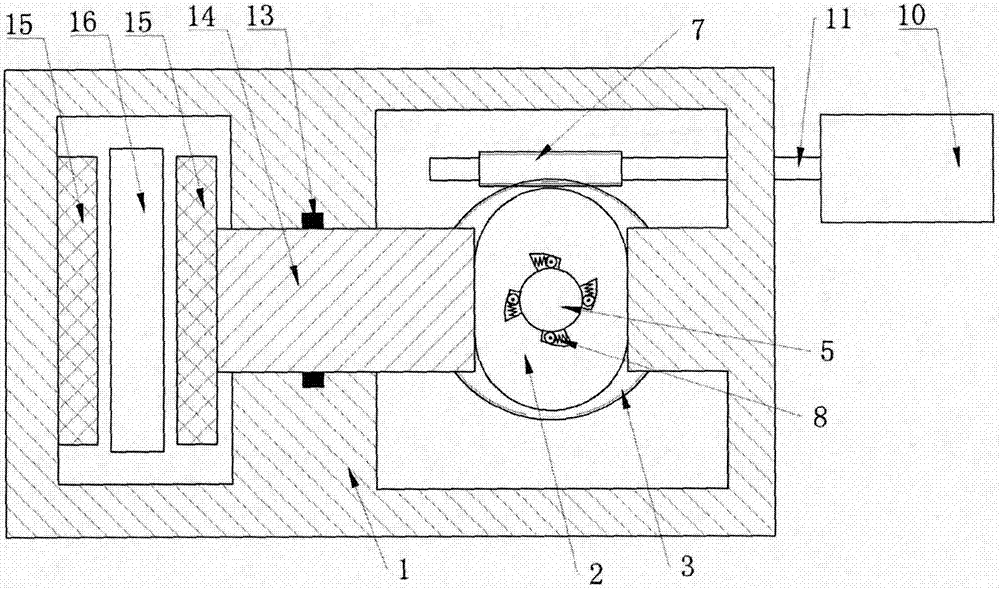
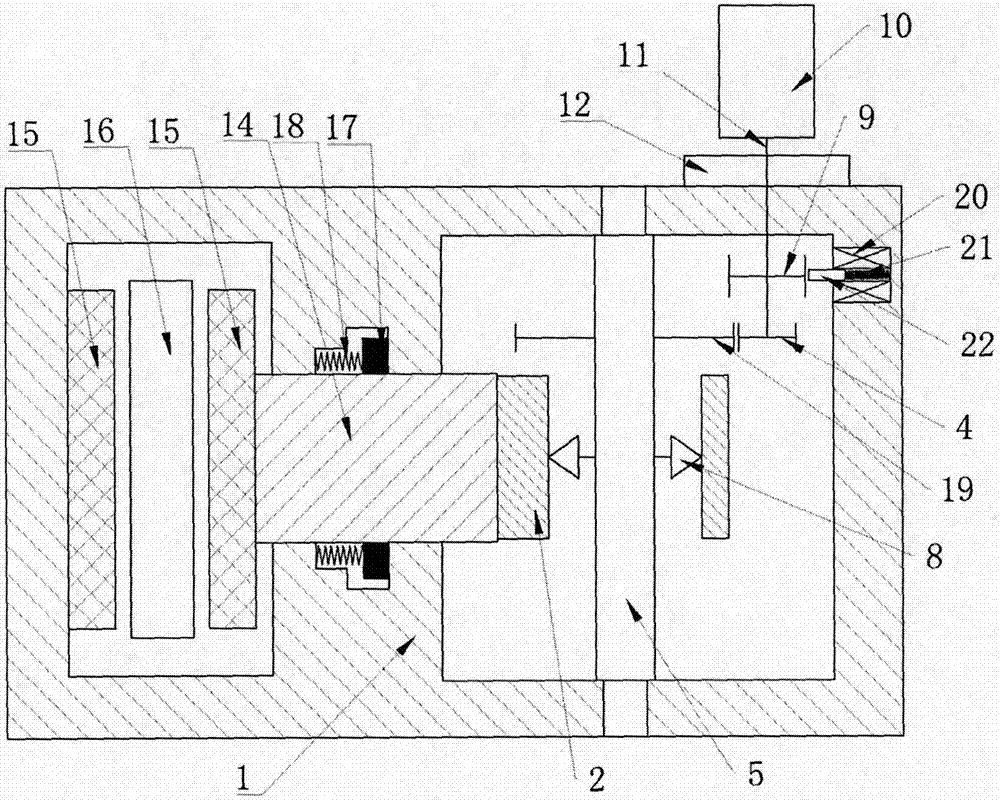
Patents
Literature
602 results about "Brake-by-wire" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
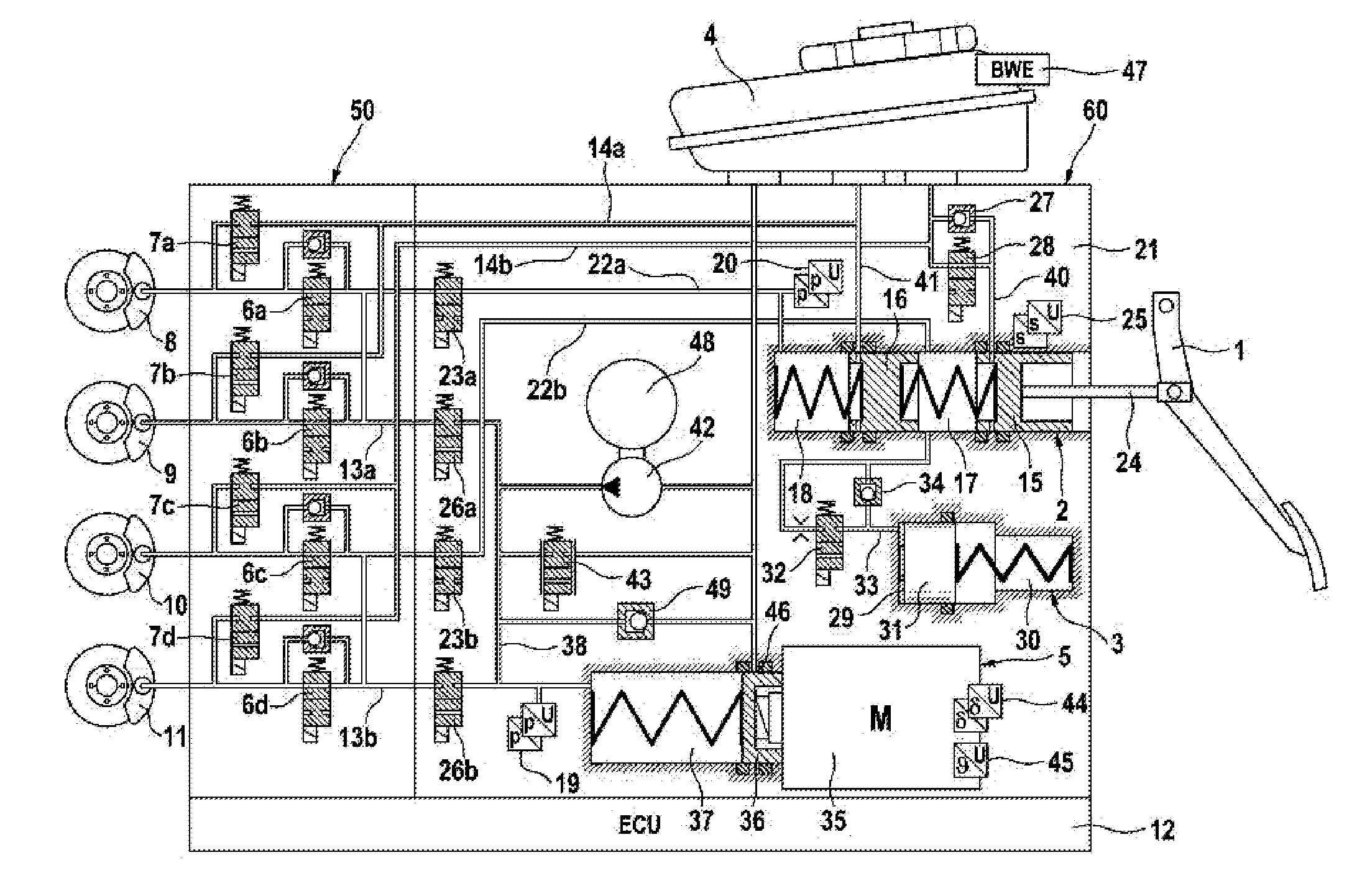
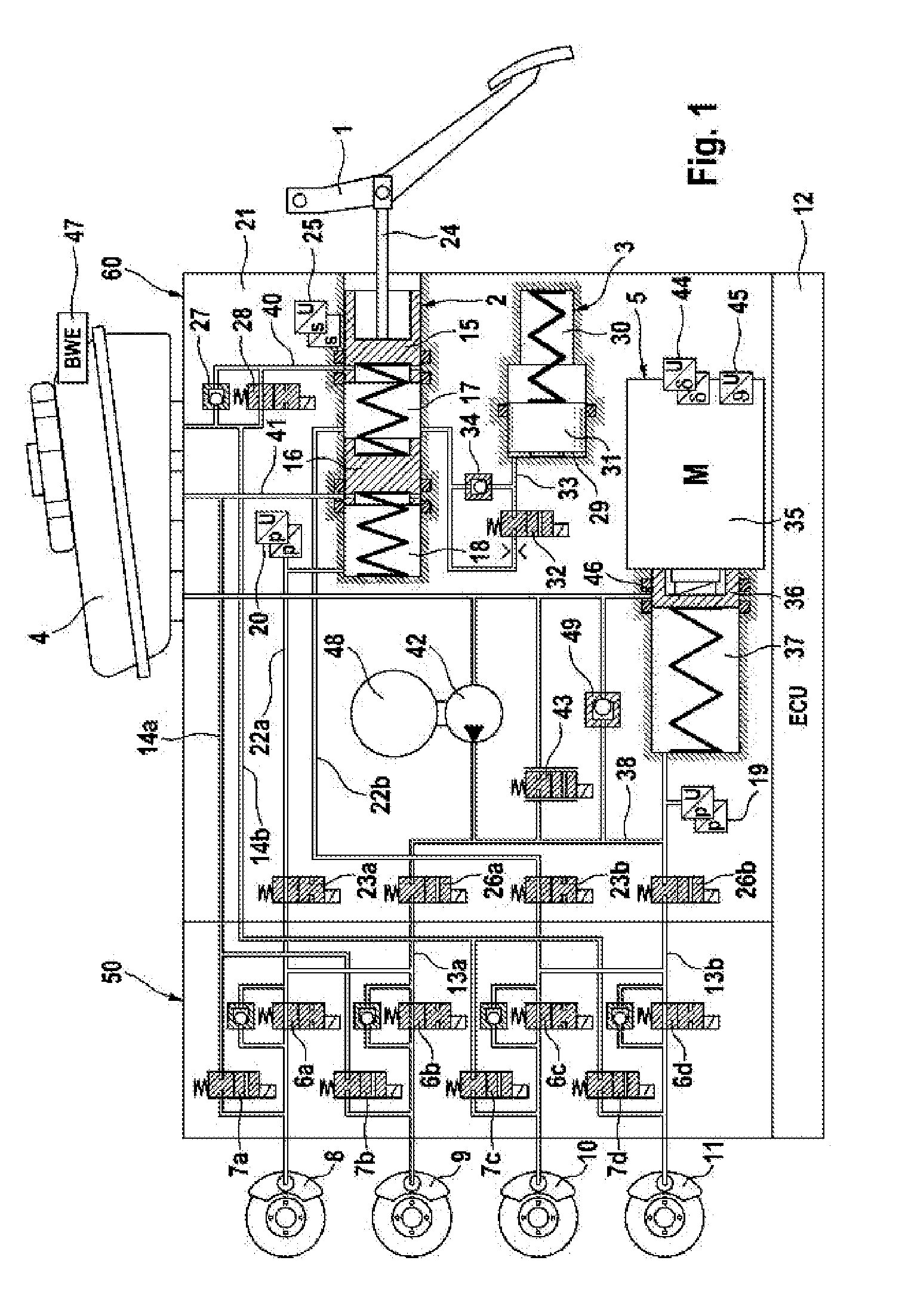
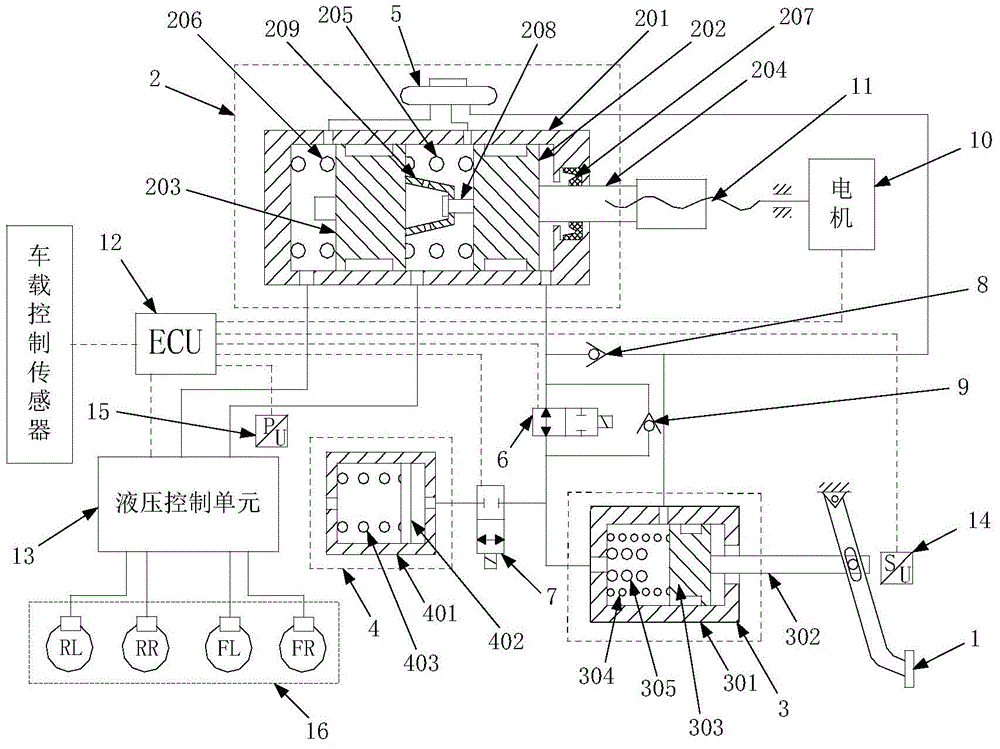
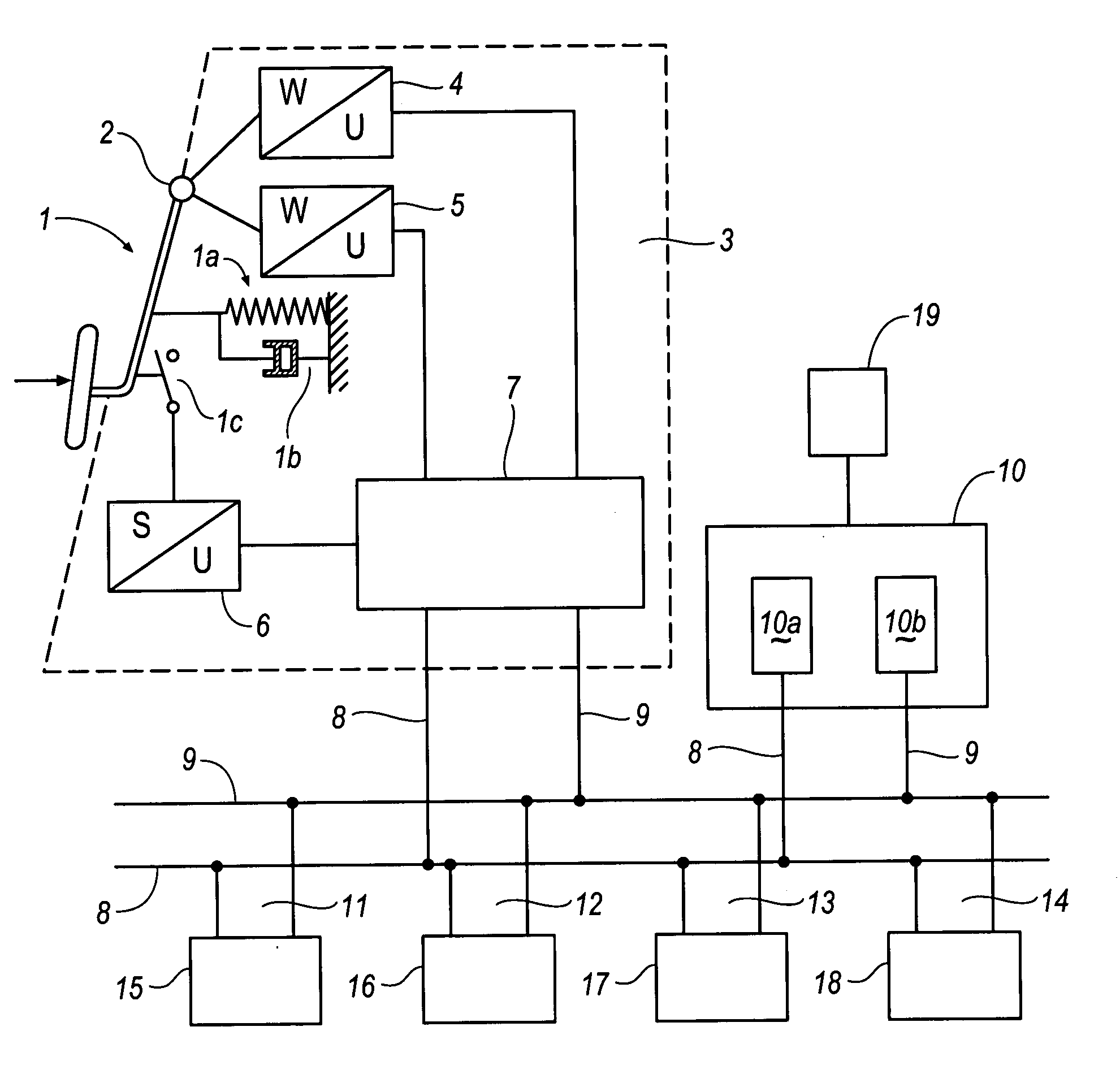
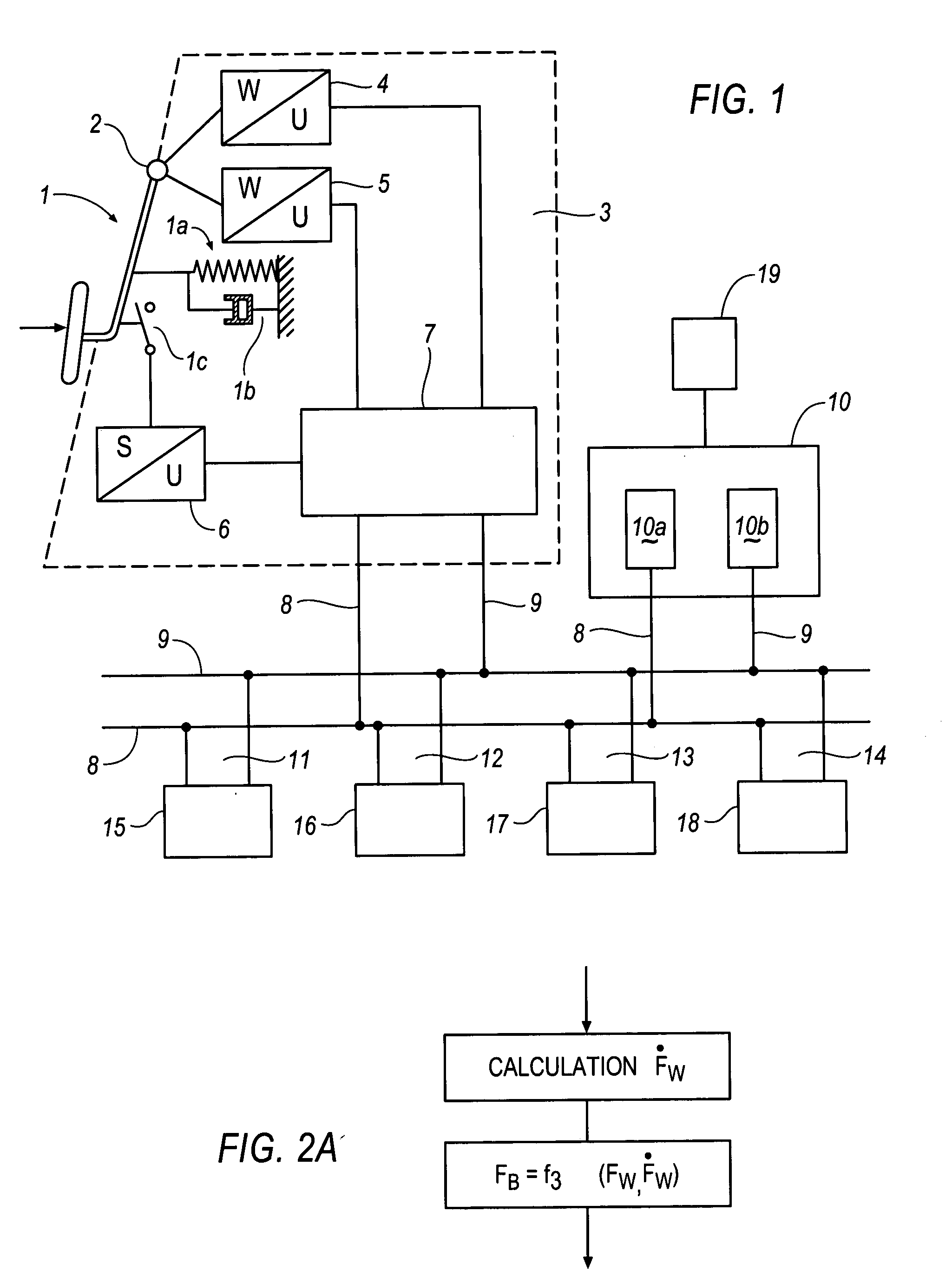
In the automotive industry, brake-by-wire technology is the ability to control brakes through electrical means. It can be designed to supplement ordinary service brakes or it can be a standalone brake system.
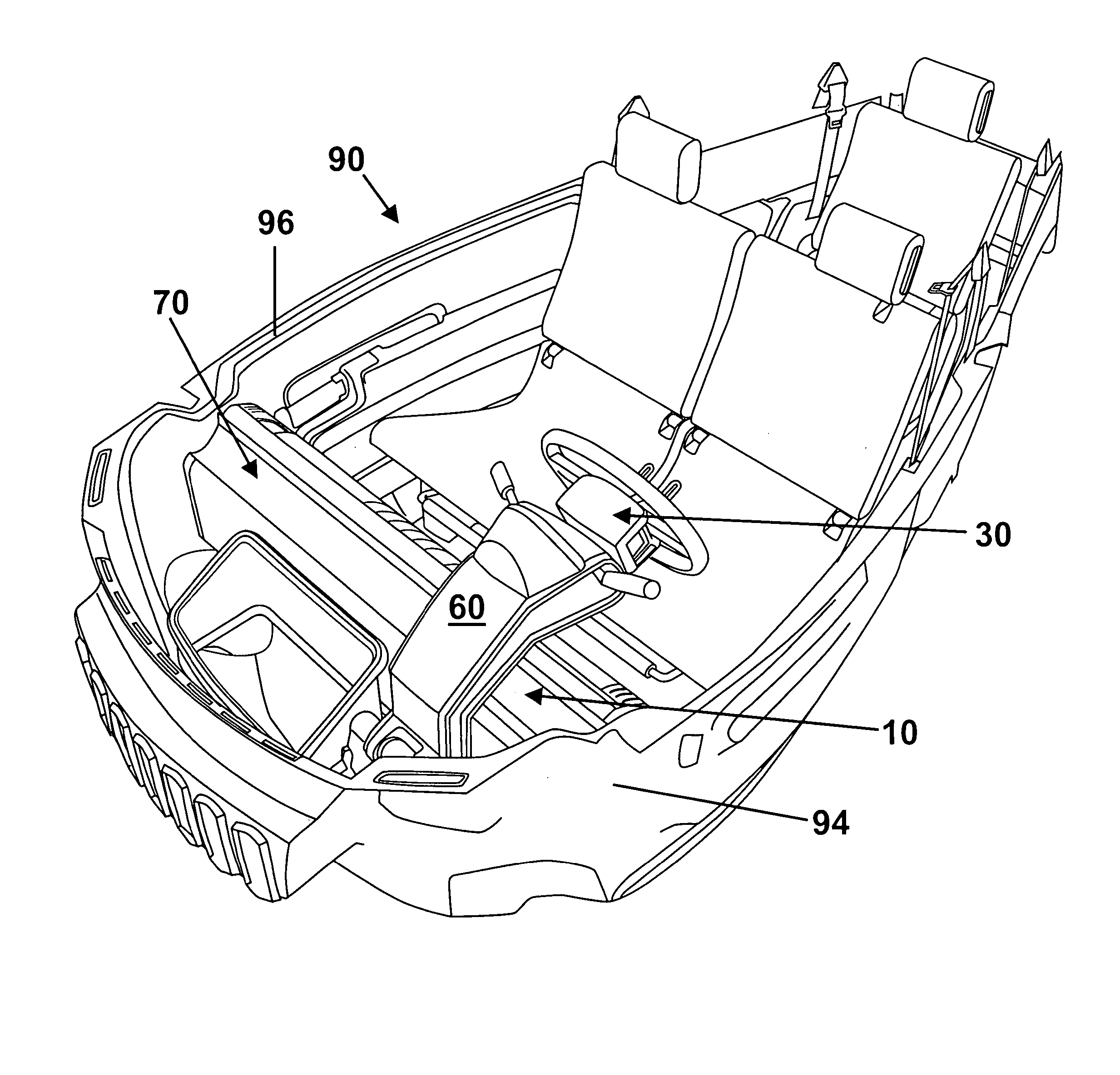
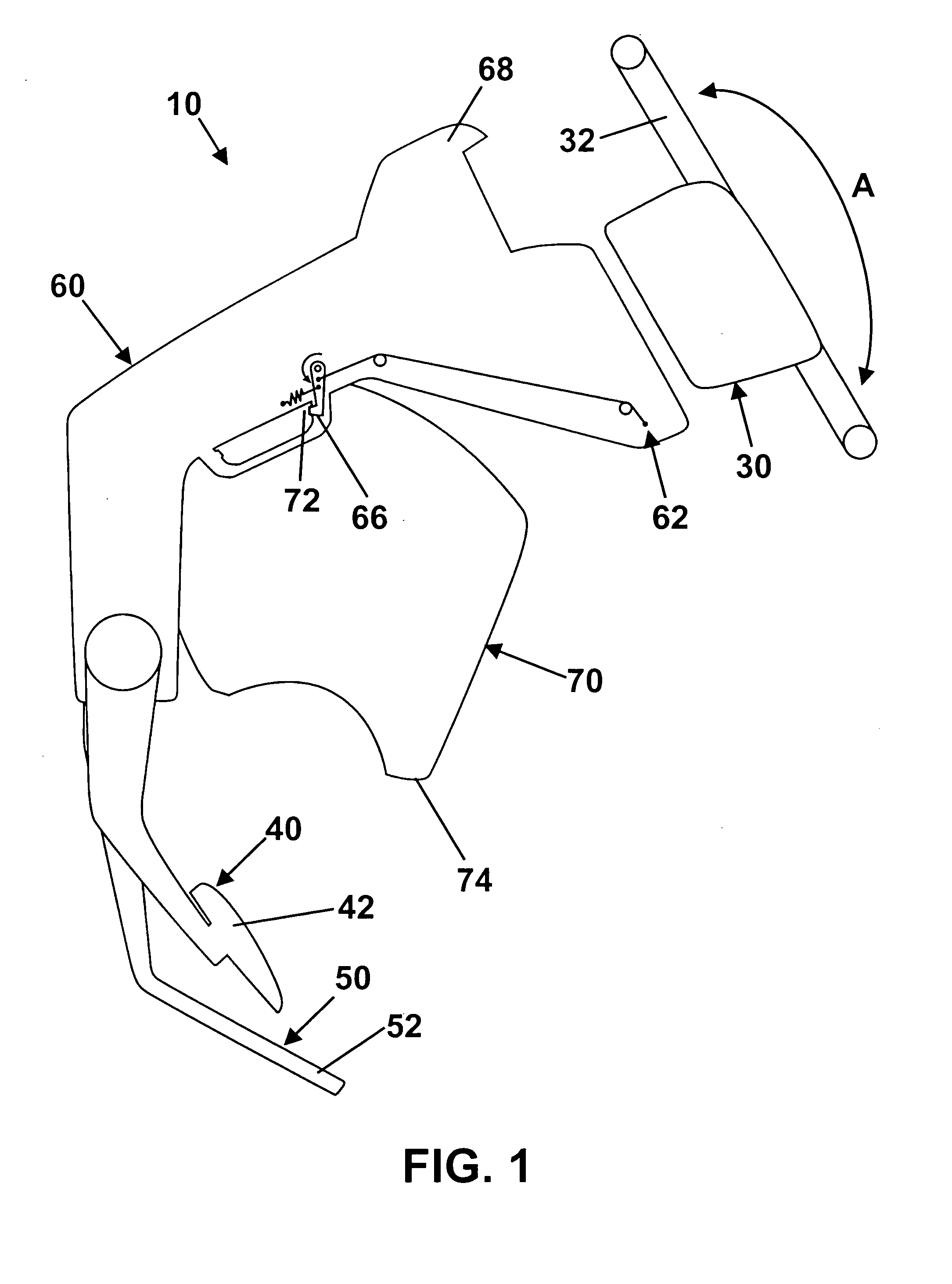
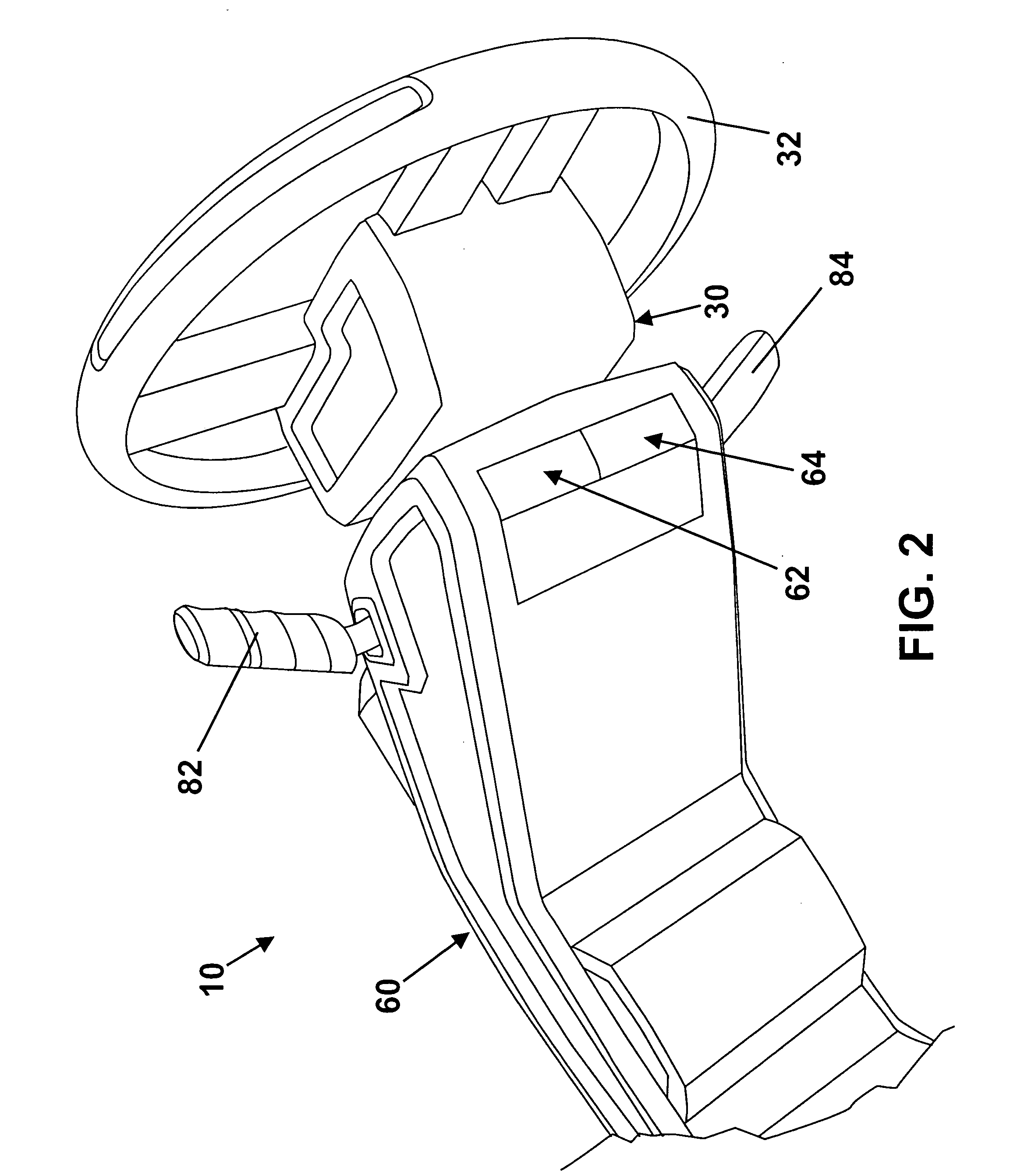
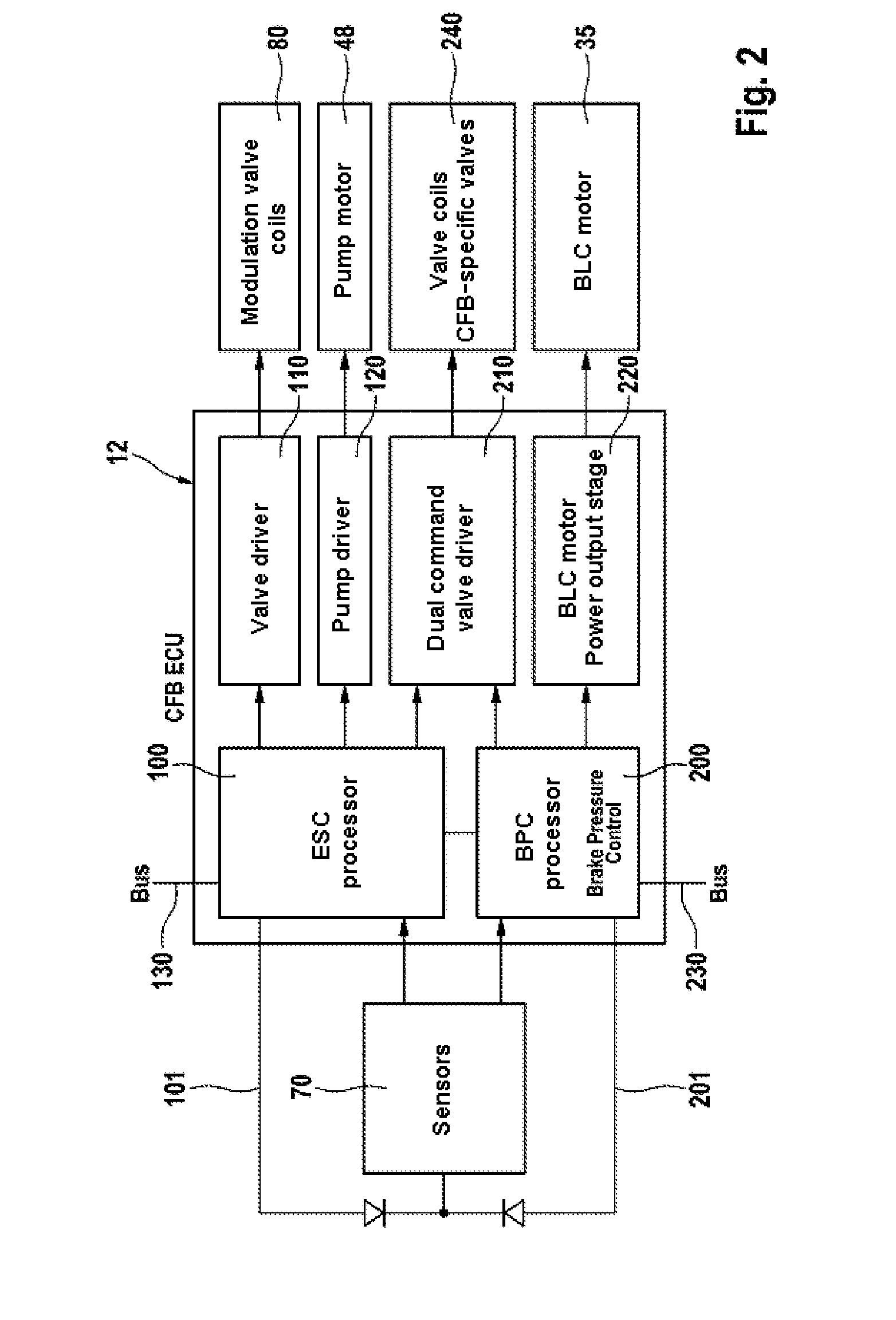
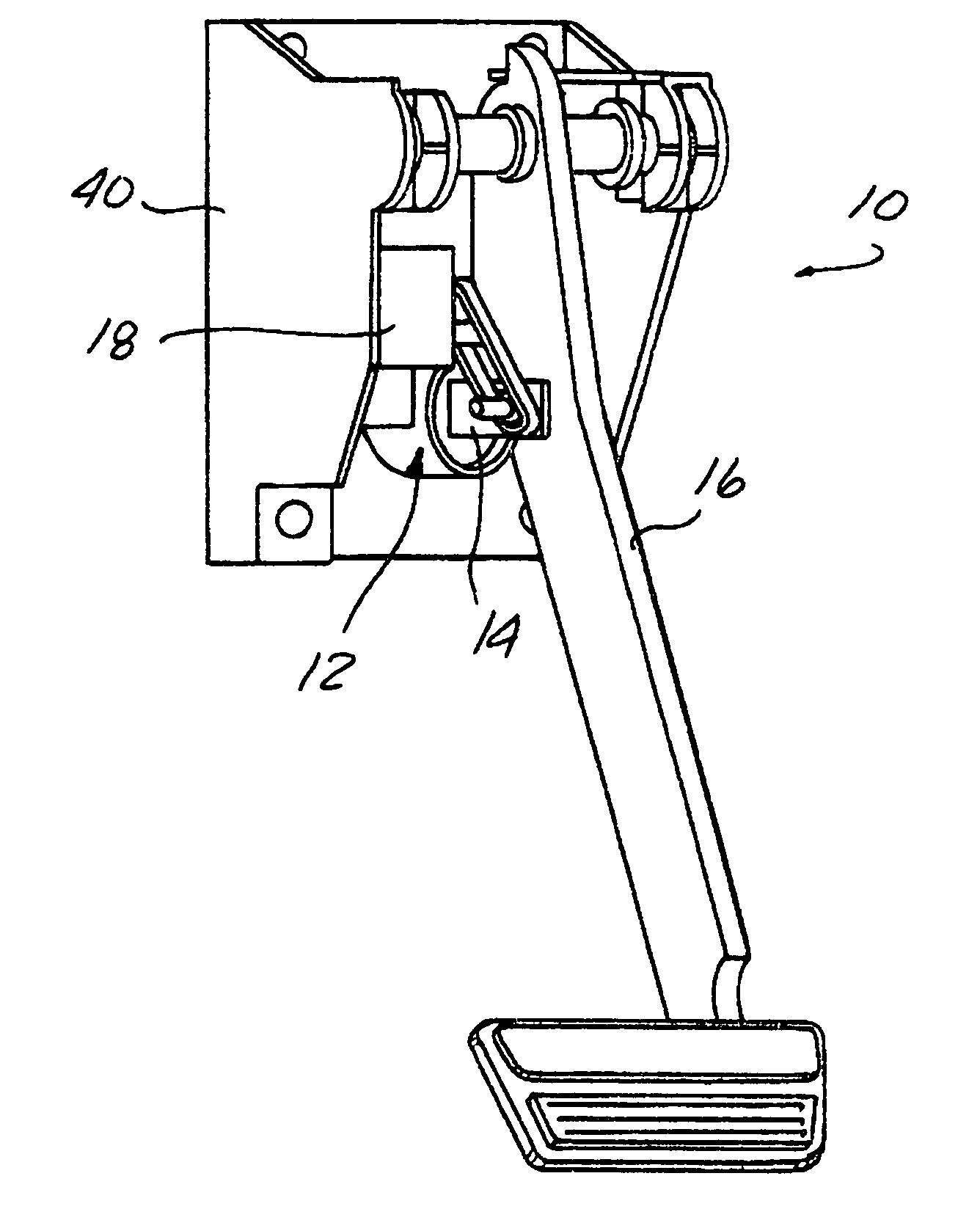
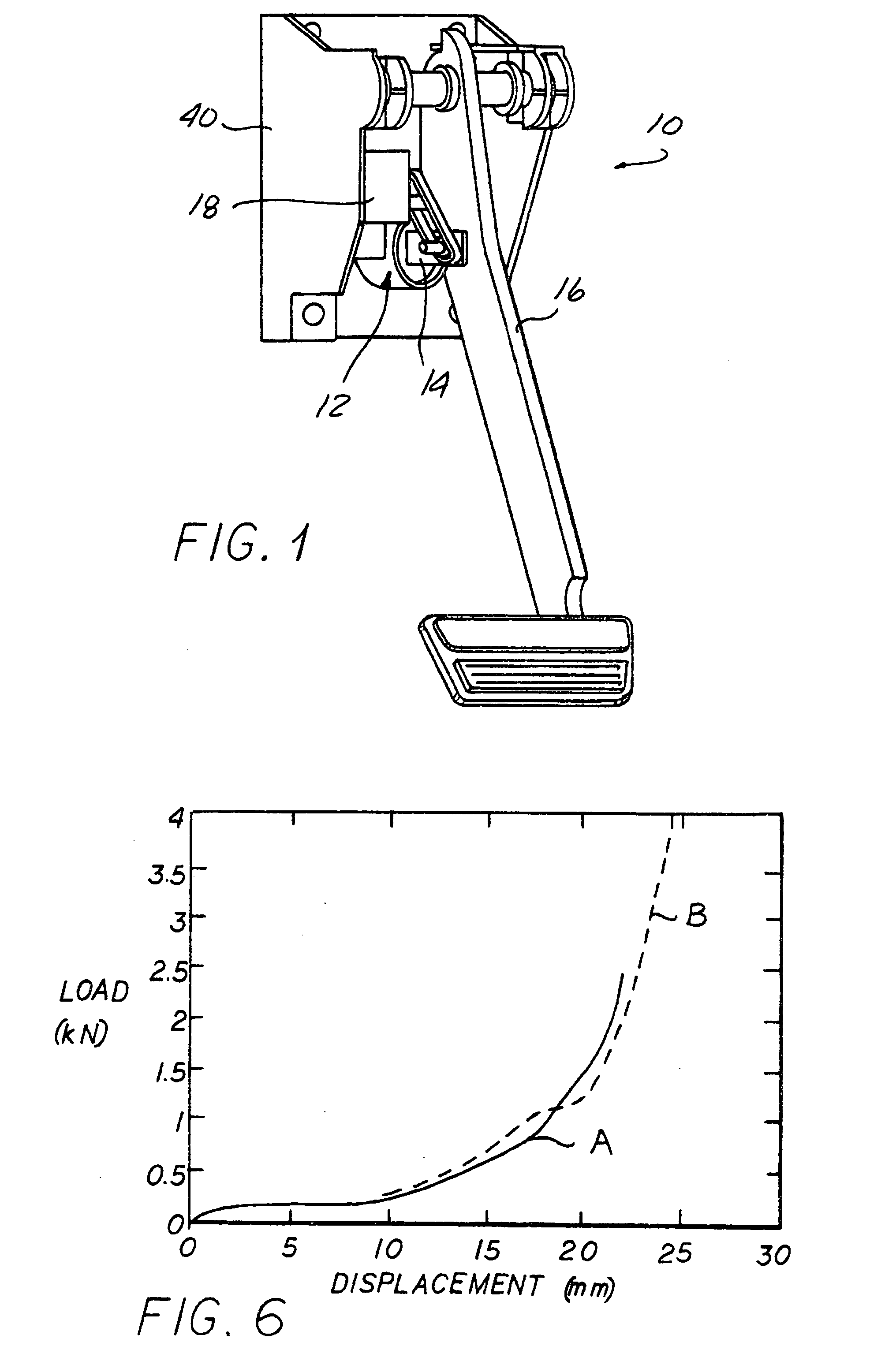
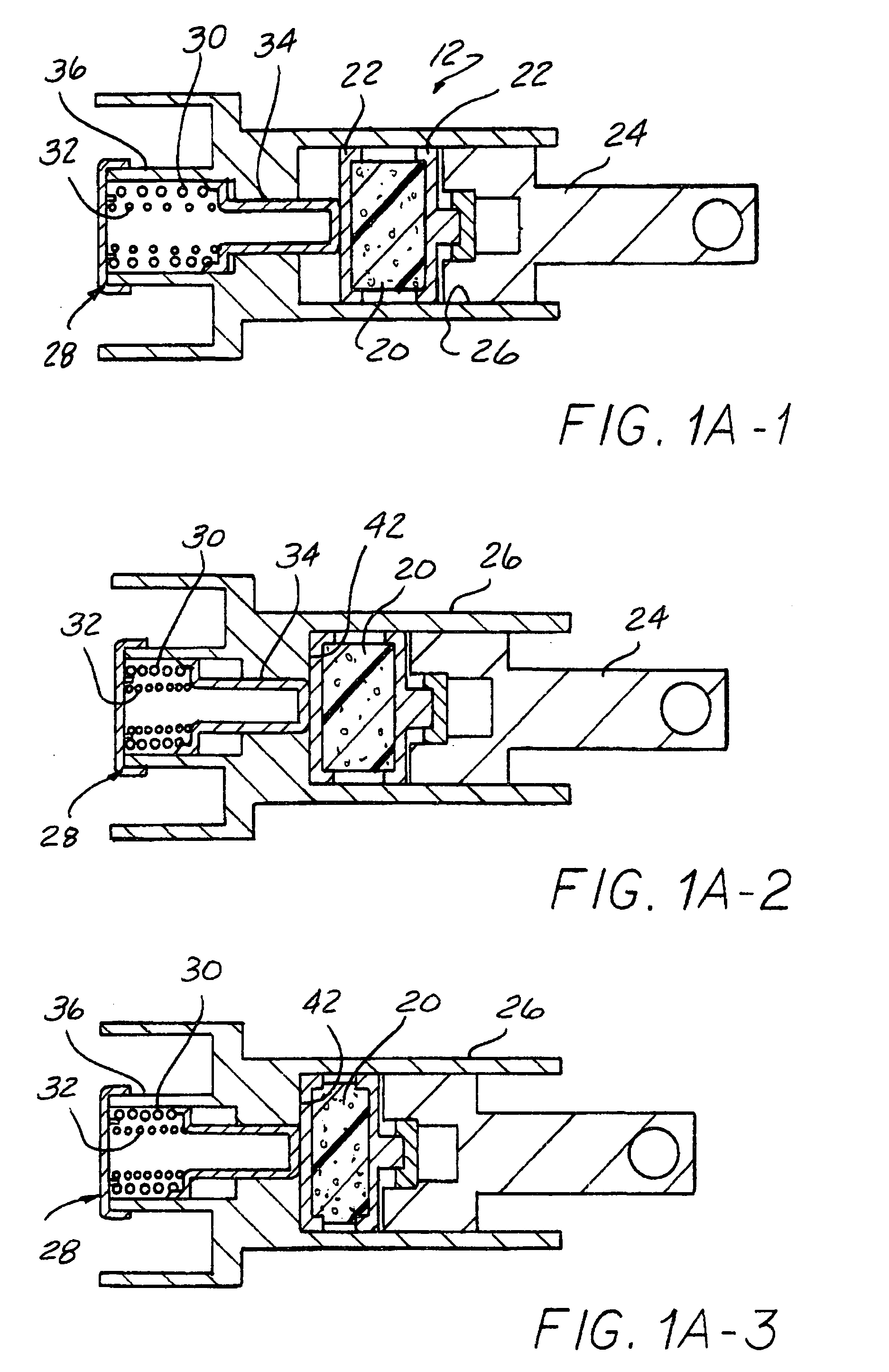
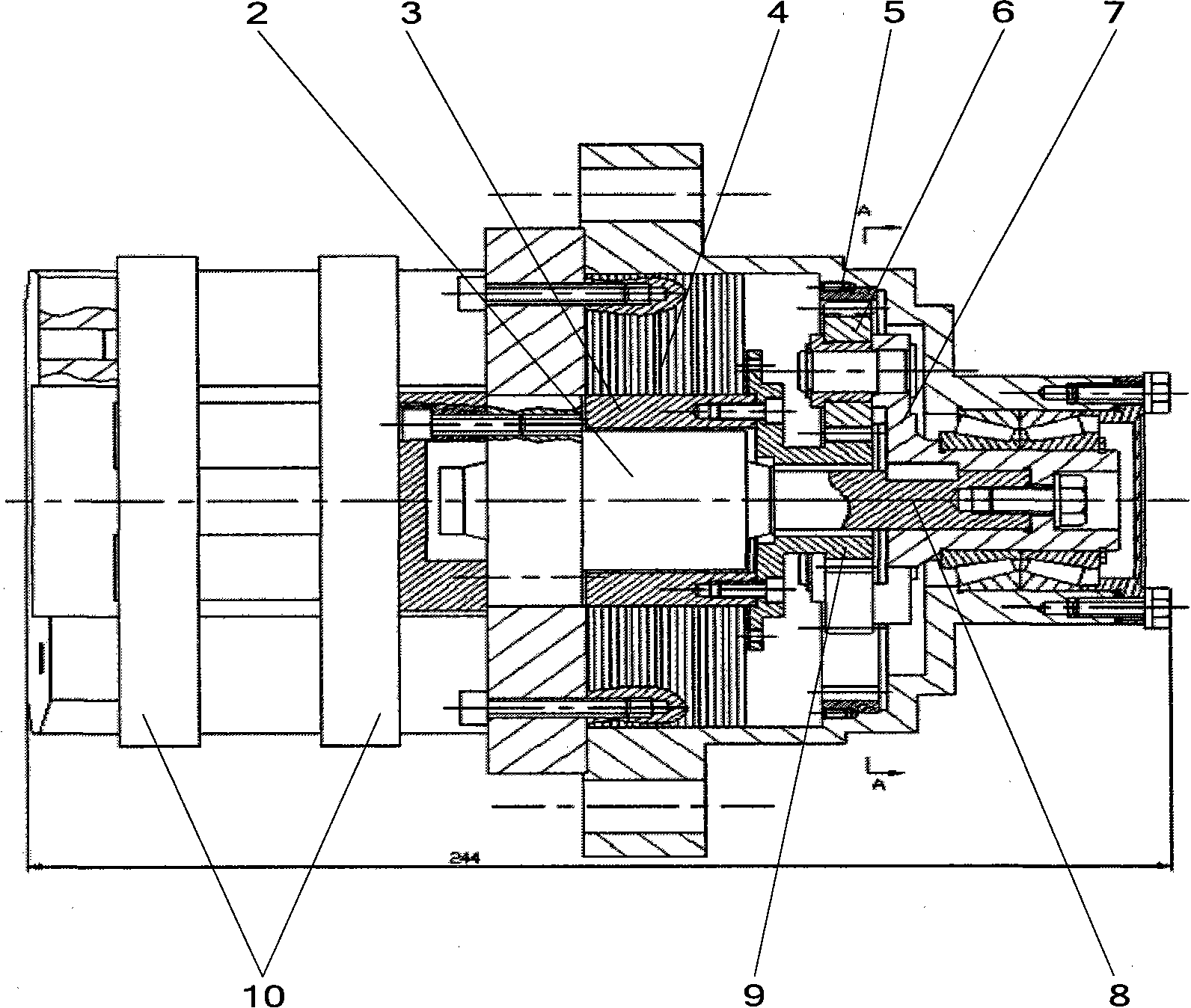
Brake by-wire actuator
InactiveUS20060163941A1High brake pressureReduce tractionBraking action transmissionFoot actuated initiationsMobile vehicleDistributor
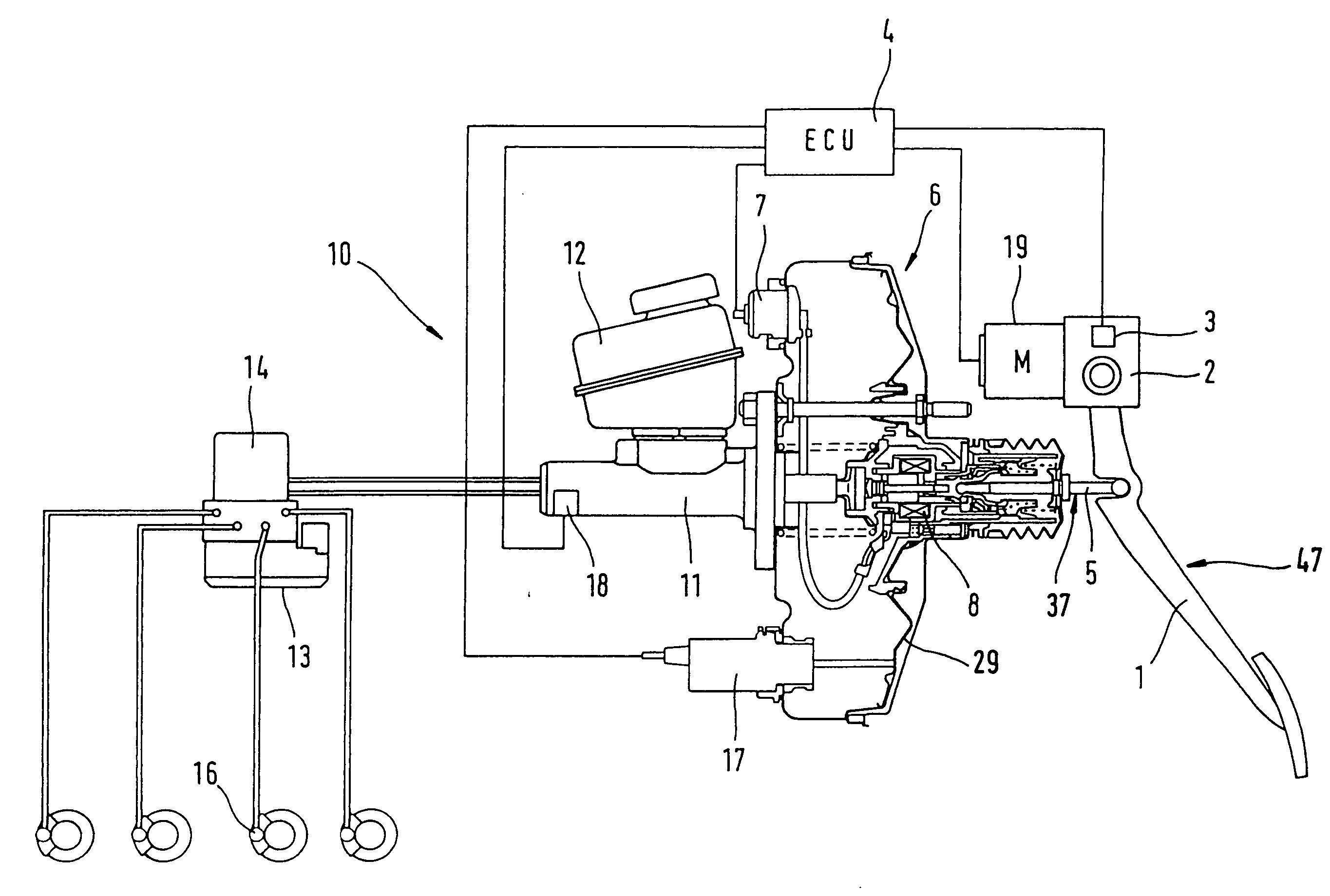
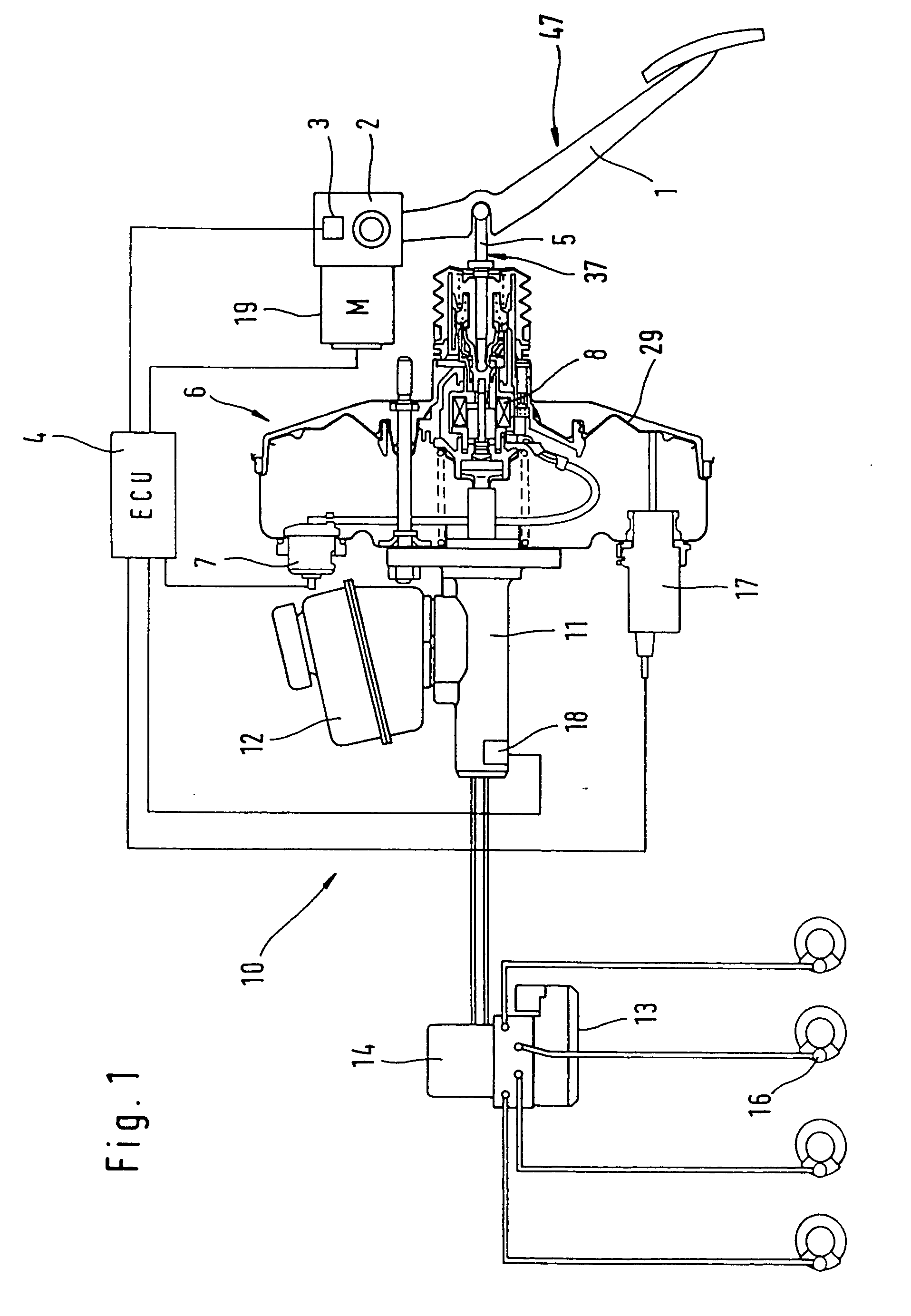
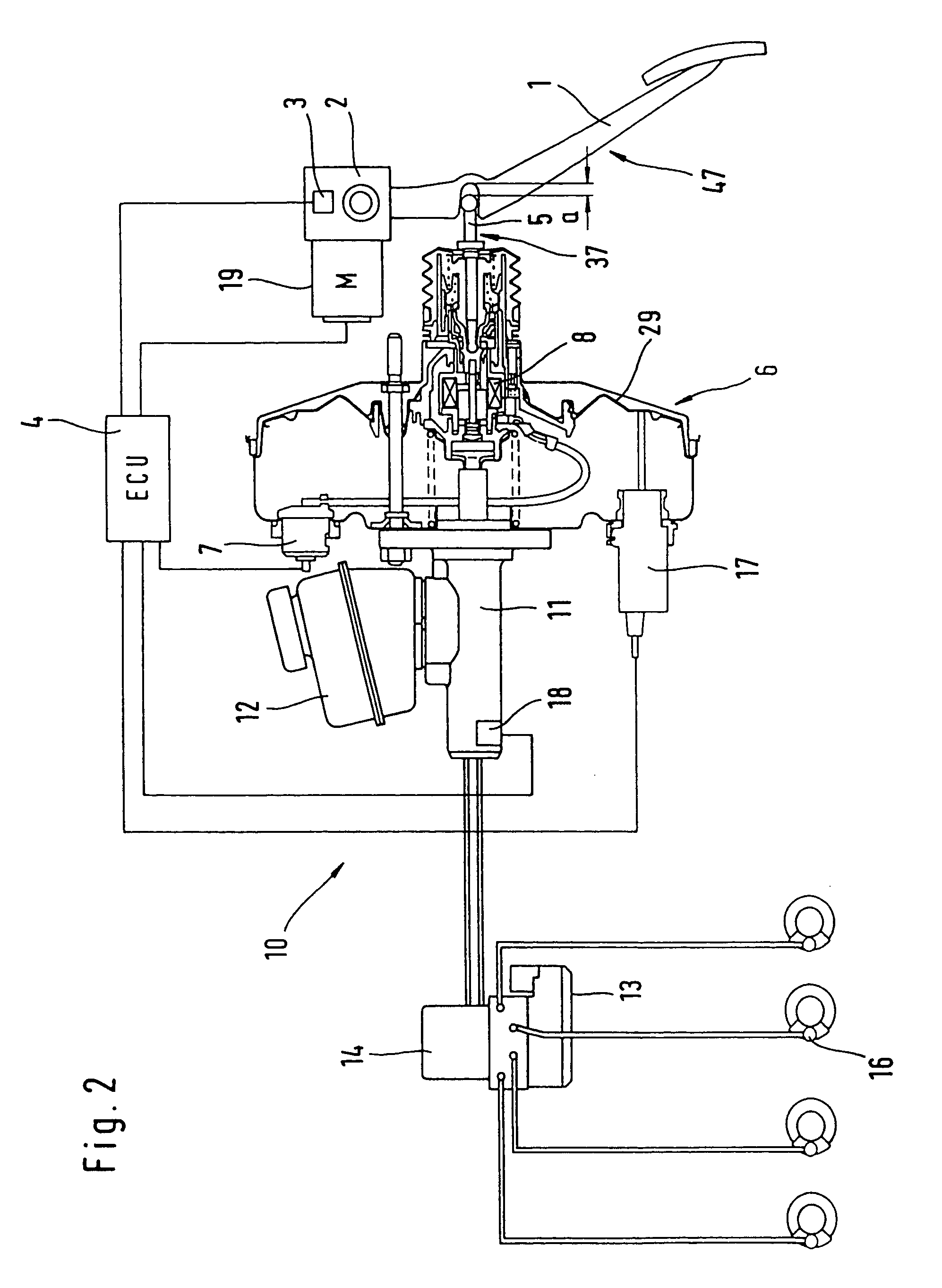
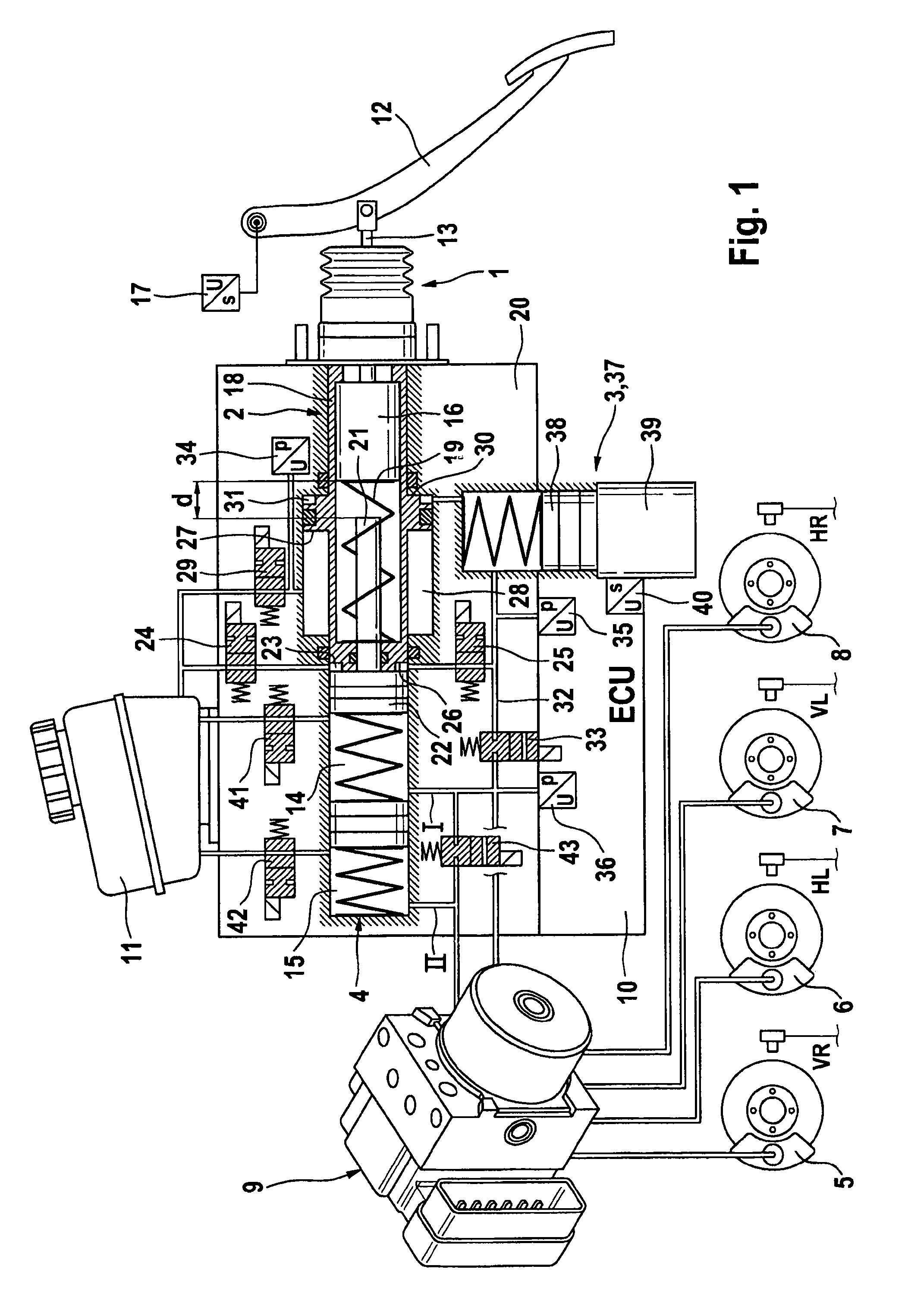
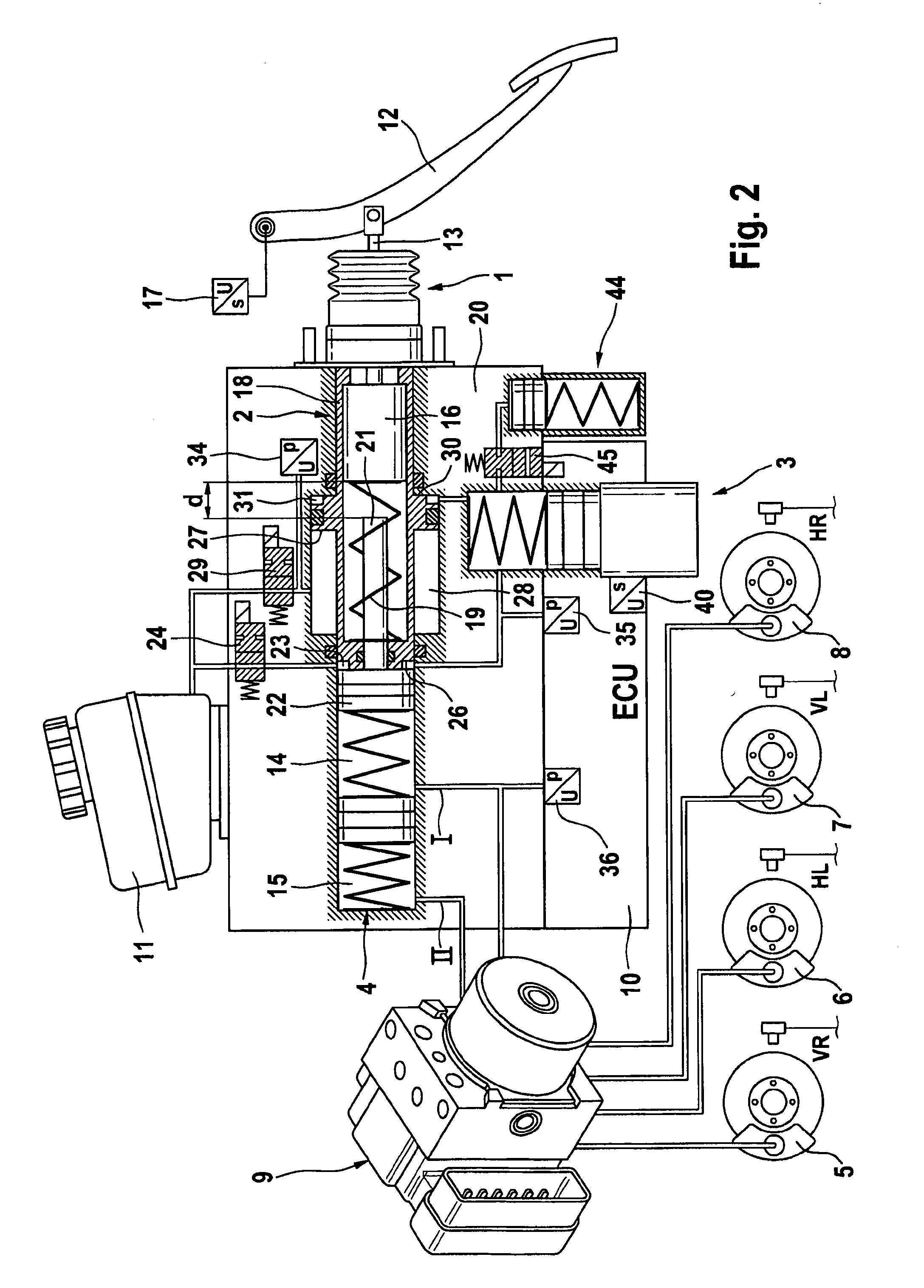
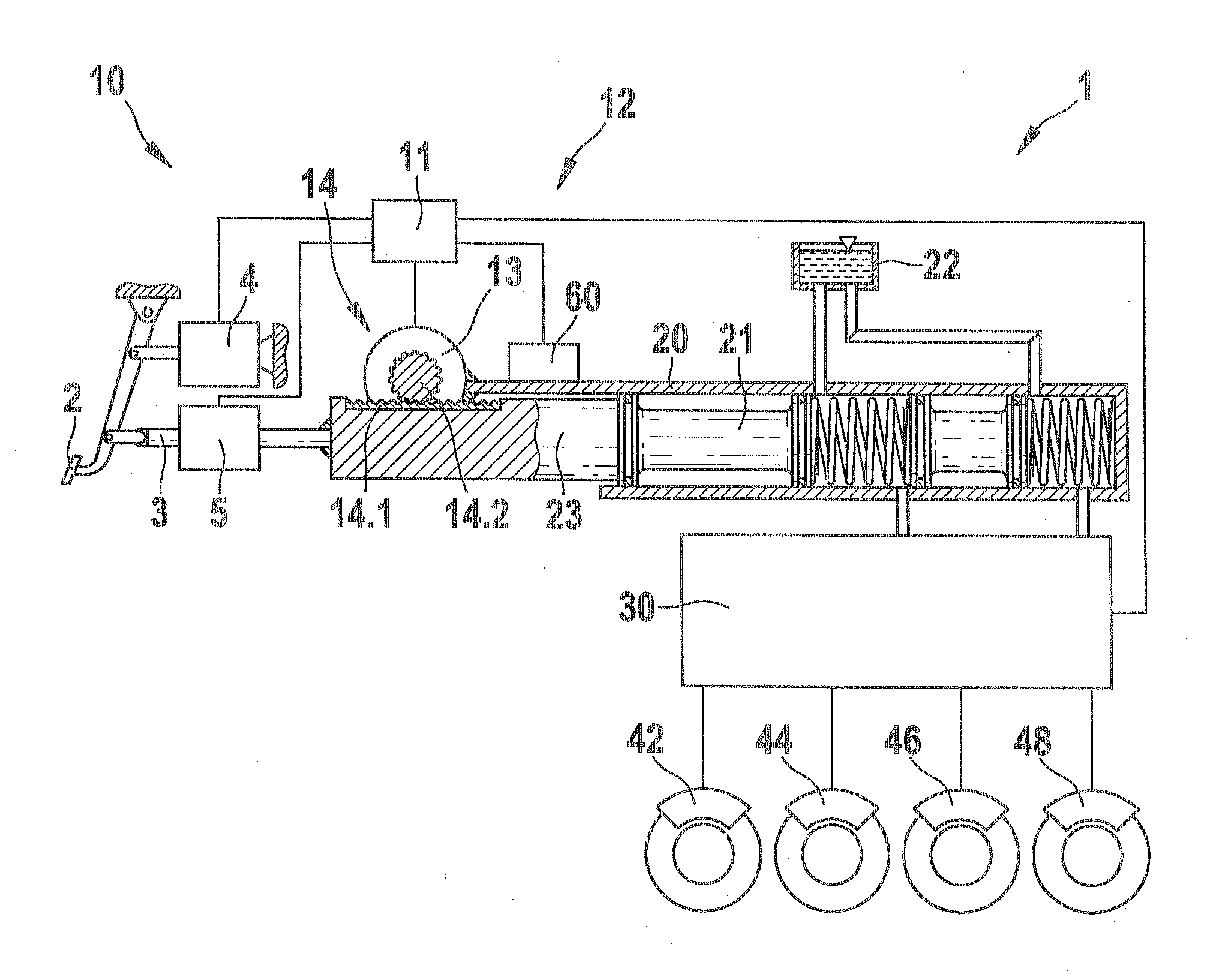
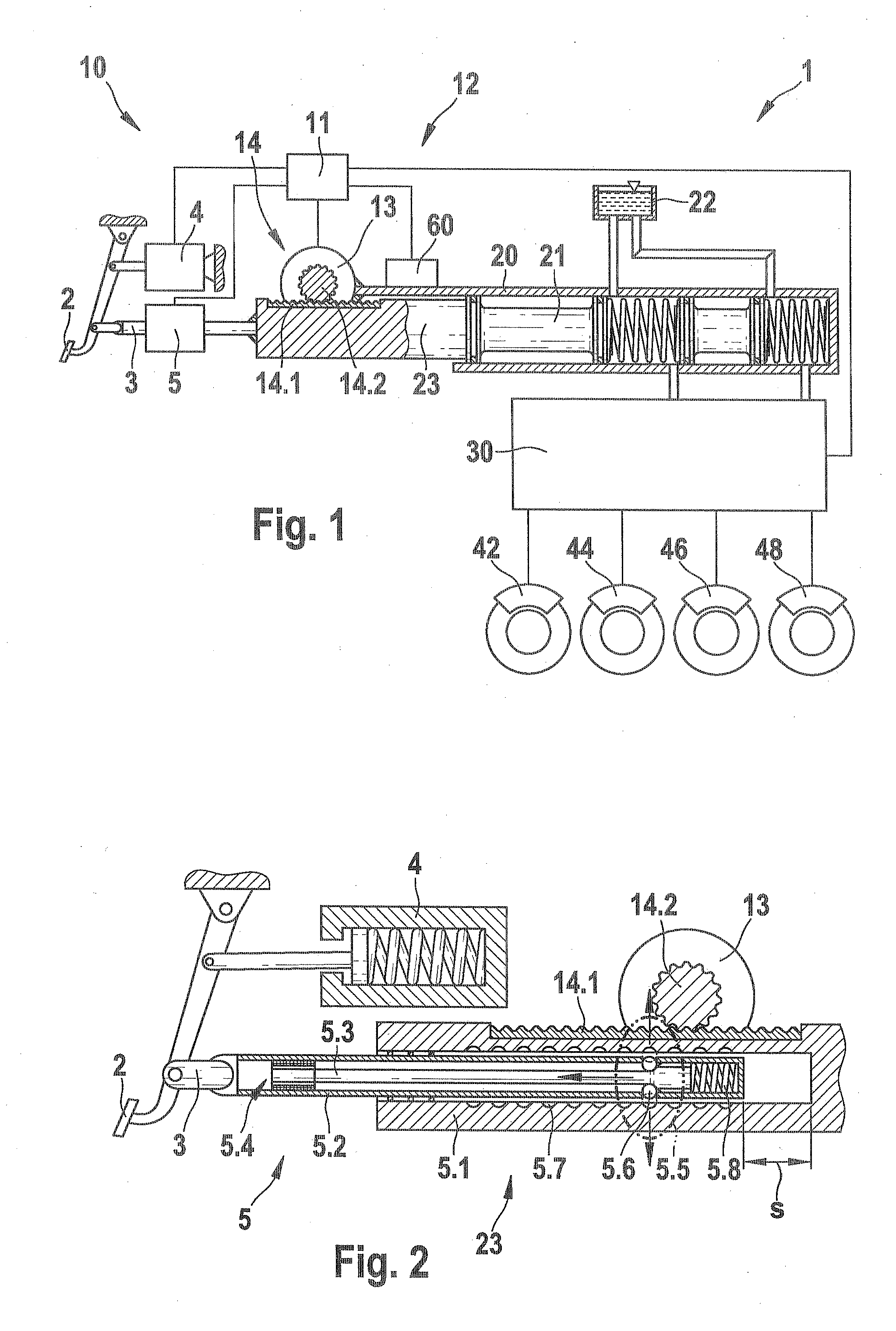
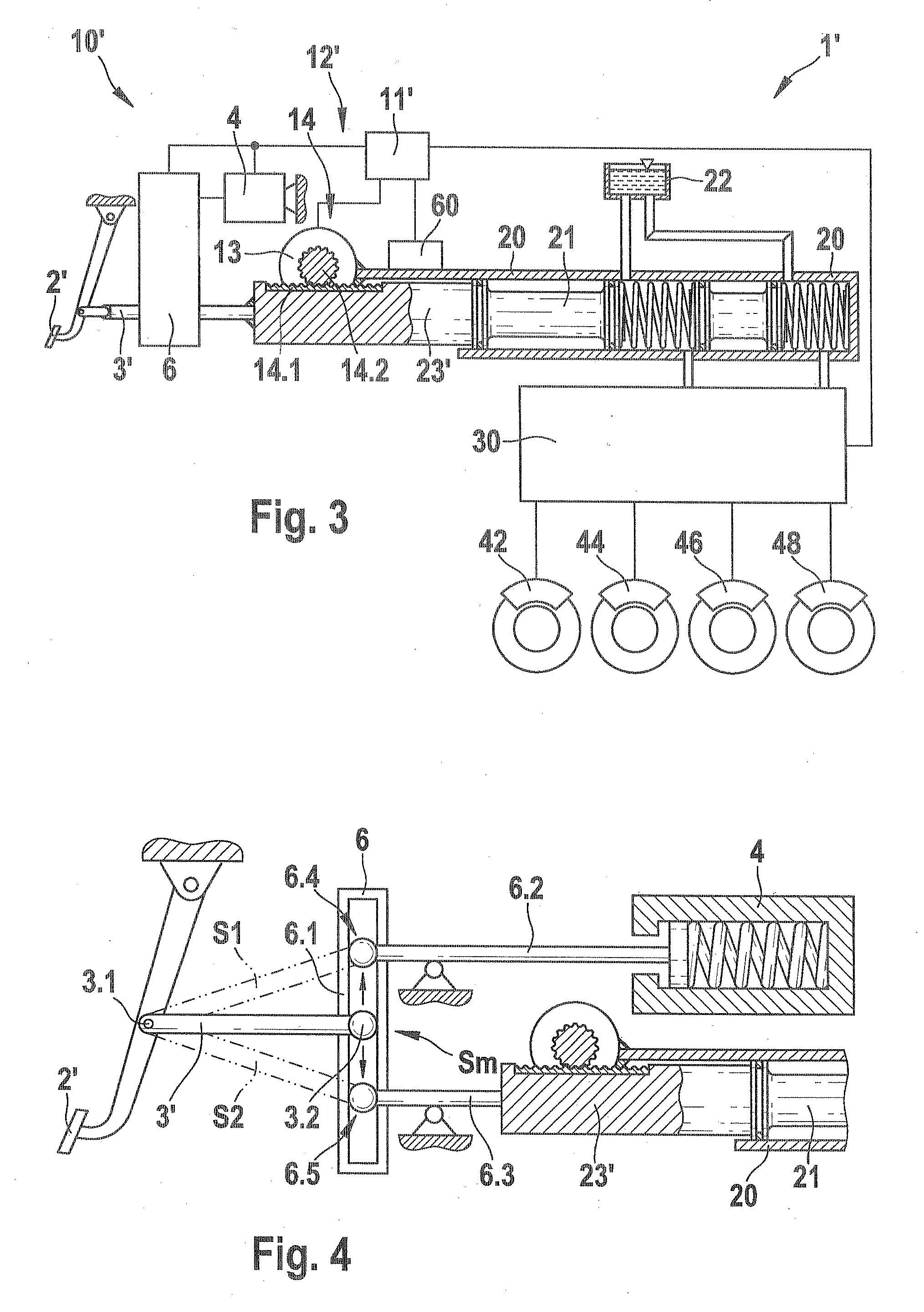
The present invention relates to a brake-by-wire actuator for actuating the brake system of a motor vehicle, comprising a simulator which can be acted upon by a brake pedal, with a signal of an actuation sensor being sent to an electronic control unit which controls a pressure source in response to the signal of the actuation sensor, and wherein an output of the pressure source is connected to a distributor device for the brake force and actuates individual wheel brakes of the vehicle, also comprising means for enabling actuation of the brakes by muscular power within a fallback mode. In order to provide an improved fallback mode in a brake-by-wire actuator, according to the invention, a lost travel is provided between a first actuation component such as a brake pedal in particular or a component articulated at the brake pedal and an actuation component that is connected downstream in the flux of force, in particular an input member, in order to uncouple the first actuation component mechanically from the reactions of force of the motor vehicle brake system in the by-wire mode.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Brake system for motor vehicles
ActiveUS20110115282A1Braking action transmissionAutomatic initiationsMechanical engineeringBraking system
A brake system includes a main brake cylinder and a pedal decoupling unit provided with a holding piston, the first ring surface thereof together with a first primary brake cylinder piston defining a first hydraulic chamber that is hydraulically pressurized with an electrically controllable pressure supply device. In order to improve the pedal characteristics of the brake system, in particular in a brake-by-wire brake system, the holding piston is embodied as a differential piston, the second ring surface thereof defining a second, blockable hydraulic chamber, and a piston effect in the second chamber corresponds to a force that acts counter to the direction of actuation on the holding piston.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Method for operating a vehicle brake system
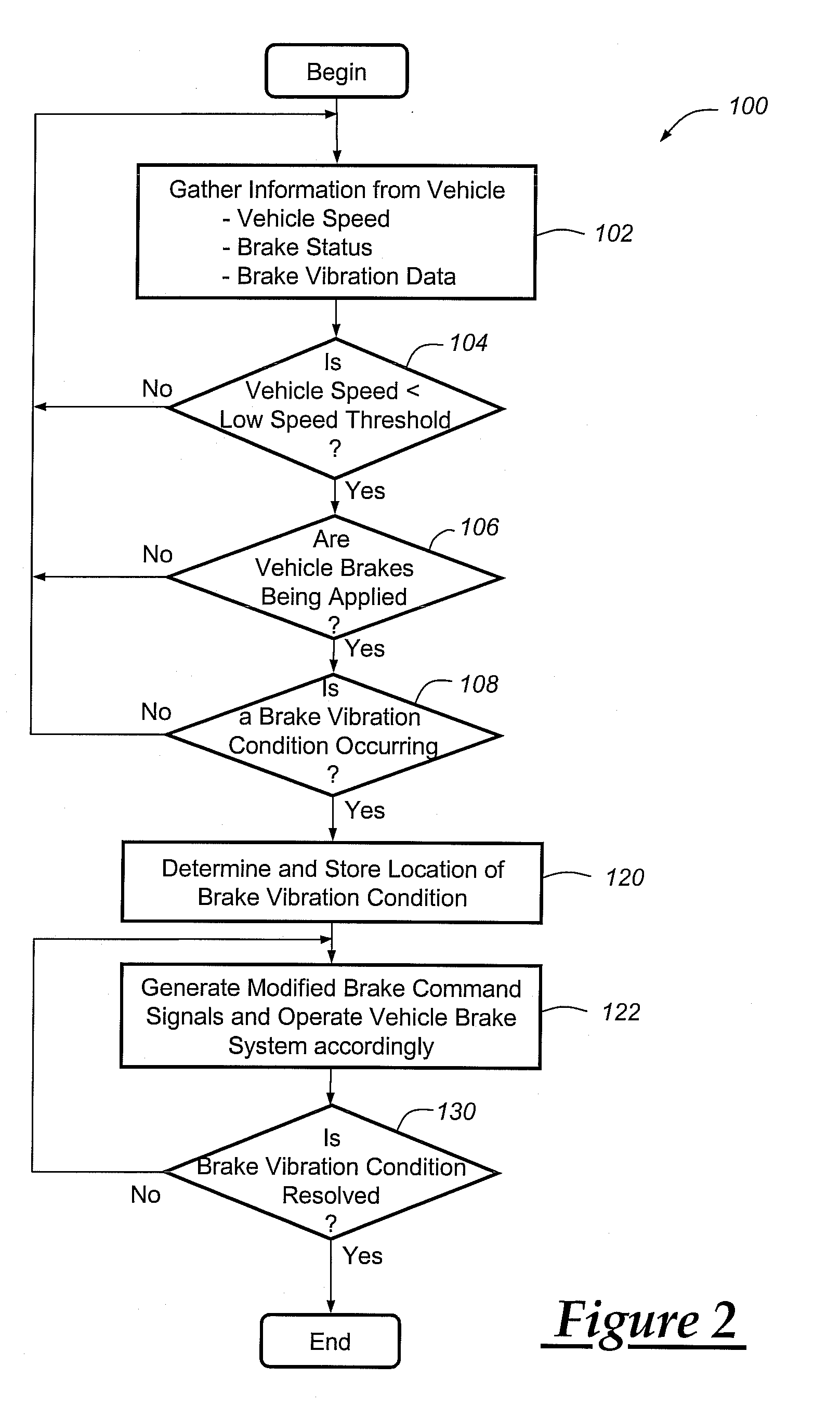
InactiveUS20100250081A1Reducing brake groan noiseReduce noiseVehicle testingNoise/vibration controlBrake torqueVehicle brake
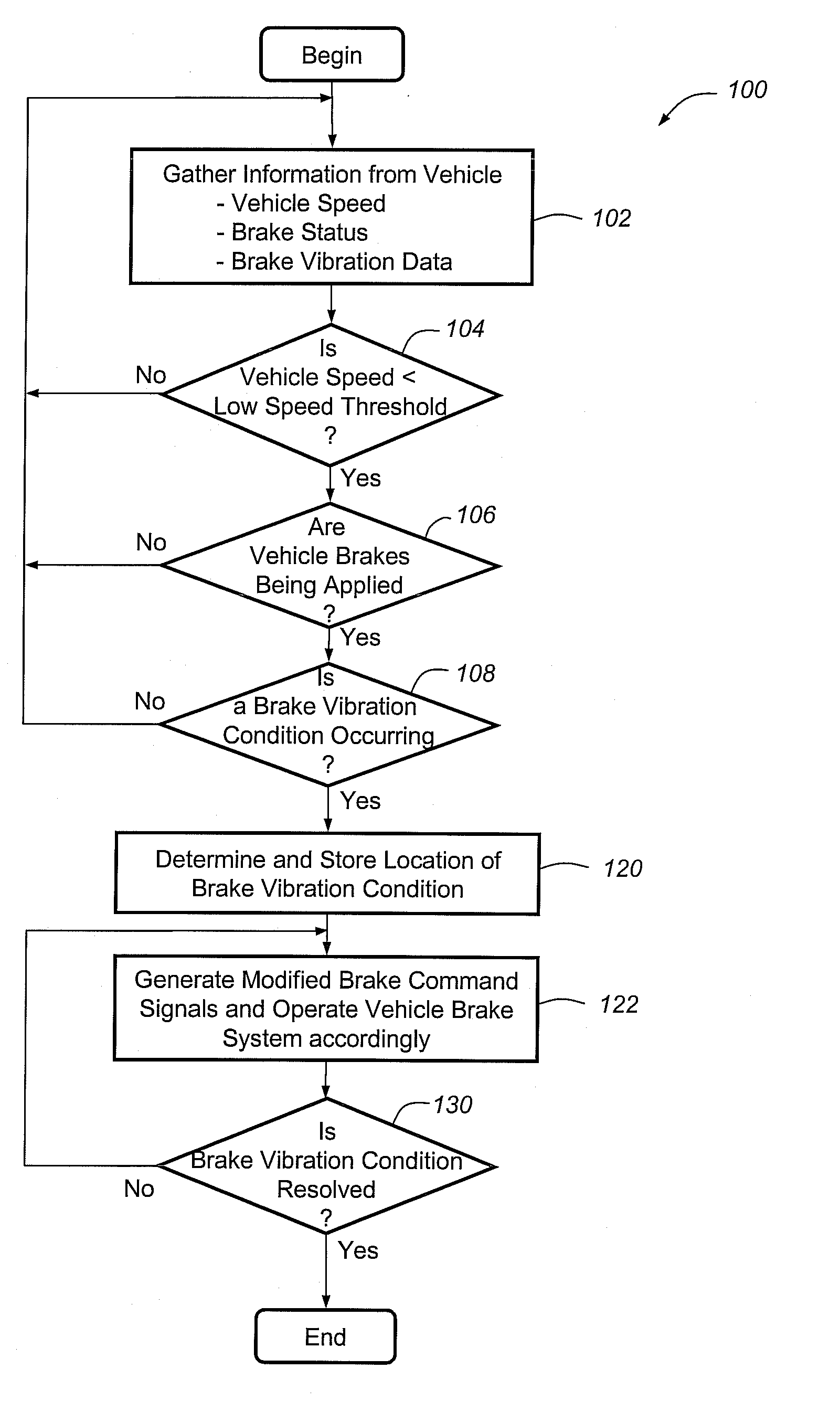
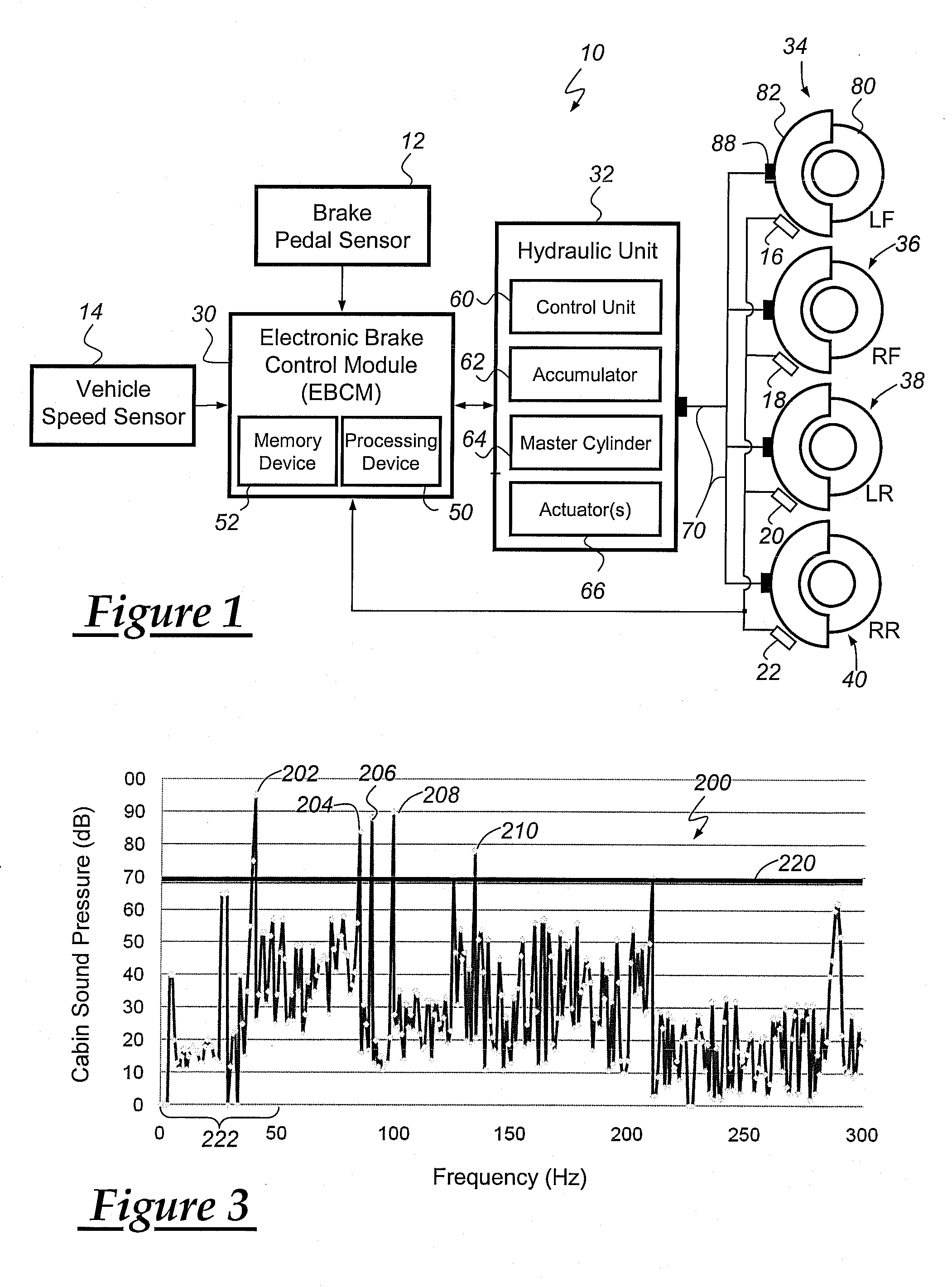
A method for reducing or mitigating the effects of vibration in a vehicle brake system, particularly those that can lead to brake groan or other unwanted noise. According to an exemplary embodiment, when the vehicle brake system detects certain vibratory conditions, it makes slight braking adjustments (e.g., adjustments to fluid pressure, brake force, brake torque, etc.) that are aimed to address the brake groan. The vehicle brake system can then determine the effectiveness of the braking adjustments and, if need be, make additional braking adjustments. The method is particularly well suited for use with brake-by-wire systems, but can be used with a number of different vehicle braking systems.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Brake System for Motor Vehicles. and Method for Operating the Brake System
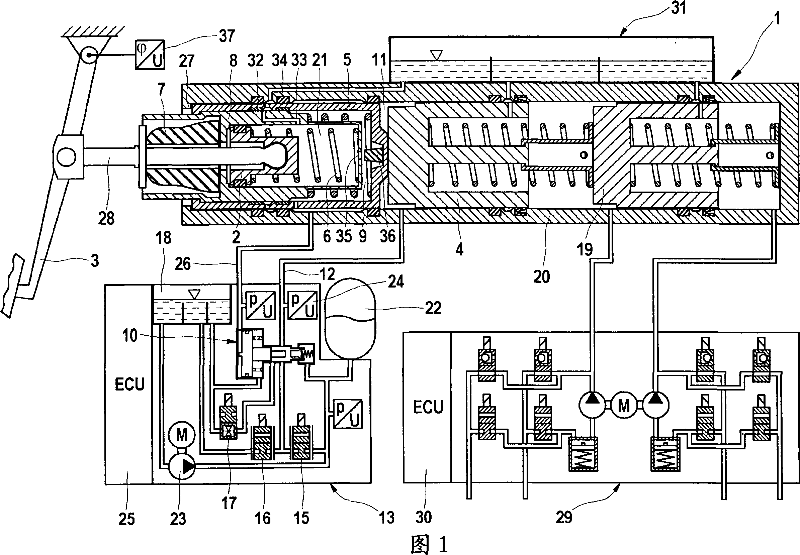
A motor vehicle brake system actuated in brake-by-wire and fallback operating modes, having a brake master cylinder, brake circuits, a pressure medium storage vessel, a brake pedal, a separating valve for separating the brake circuit into a first section connected to the separating valve the master cylinder, and a second section connected to the separating valve and the wheel brakes. A first pressure provision device has a piston actuated by an actuator, a simulation device connected by a simulator release valve to the master cylinder for a pleasant brake pedal feel in the brake-by-wire operating mode. A first electronic control and regulating unit actuates the first pressure provision device, the separating valves and the simulator release valve. A second pressure provision device has a suction connector and a pressure connector per brake circuit being connected to the inlet of the separating valve.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Re-positionable vehicle control-by-wire assembly, method, and system
ActiveUS20050283288A1Digital data processing detailsInstrument arrangements/adaptationsControl theoryVehicle control
A vehicle control assembly and a method and system for controlling a vehicle. The assembly includes a controller. A steer-by-wire component, a brake-by-wire component, and an accelerator-by-wire component are each operably attached to the controller. A track is operably attached to the vehicle. The controller is laterally re-positionable with respect to the track. The method includes the steps of providing a controller, and steering, braking, and accelerating the vehicle by-wire with the controller. The method further includes the step of re-positioning the controller between a first vehicle side to a second vehicle side. The system includes controller means, and means for steering, braking, and accelerating the vehicle by-wire with the controller means. The system further includes means for reversibly positioning the controller means from a first vehicle side to a second vehicle side.
Owner:FCA US
Motor vehicle braking system
InactiveCN101263033AImprove operational reliabilityGuaranteed uptimeBraking action transmissionMobile vehicleEngineering
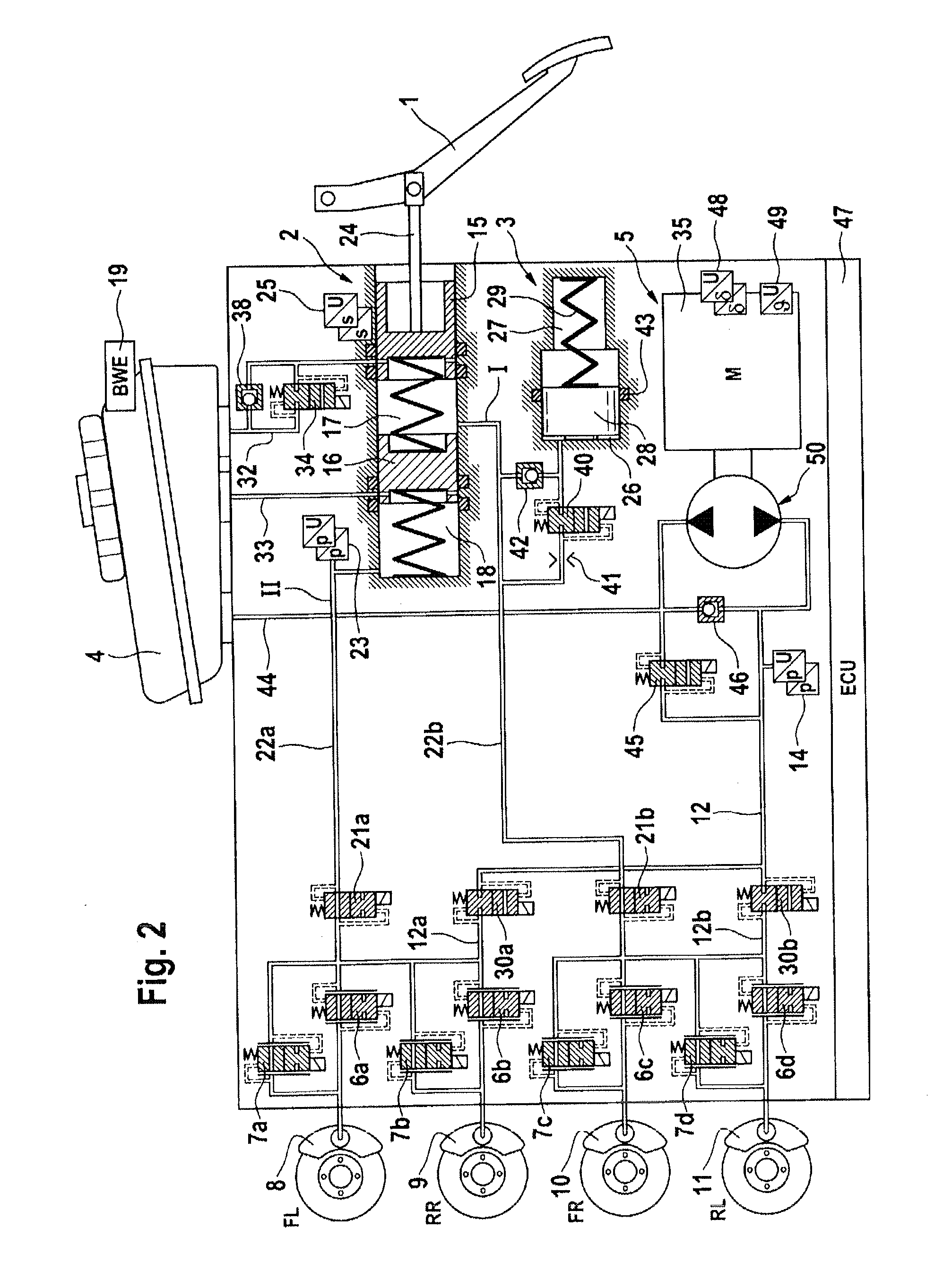
The invention relates to a 'Brake-by-wire' braking system comprising a main cylinder (3) and wheel braking circuits (I, II) associated thereto and two brake booster pressure fluid circuits which are completely separated from said wheel braking circuits wheel braking circuits. In order to use a pressure control valve (34) associated with the first brake booster pressure fluid circuit for controlling a pressure in an intermediate space (21) not only by pressing on a pedal but also electrically, means (39, 40) for electrically controlling the intermediate space (21) pressure are provided with the pressure control valve (34).
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Brake System for Motor Vehicles and Method for Operating the Brake System
InactiveUS20140225425A1Braking action transmissionBrake action initiationsElectricityMaster cylinder
A brake system includes a brake pedal for actuating a master cylinder having two pistons and corresponding pressure chambers, where the system can be operated in a brake-by-wire mode and also a fallback mode. The system also includes a first electrically controllable pressure source and a second electrically controllable pressure source. The first and second electrically controllable pressure sources each have corresponding output flows that are connected together. The second electrically controllable pressure source can therefore provide output volume flow in the event the first electrically controllable pressure source fails.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
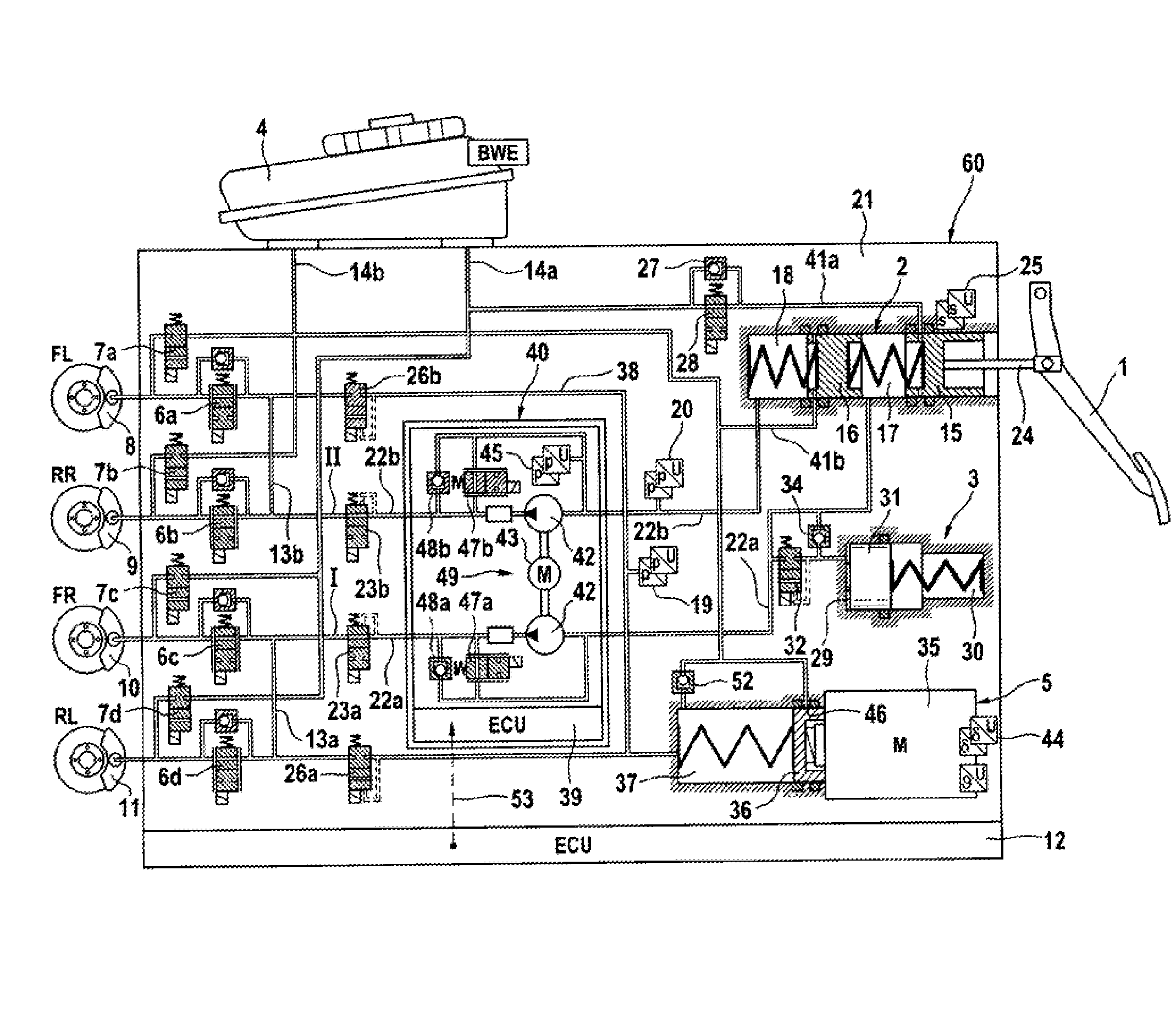
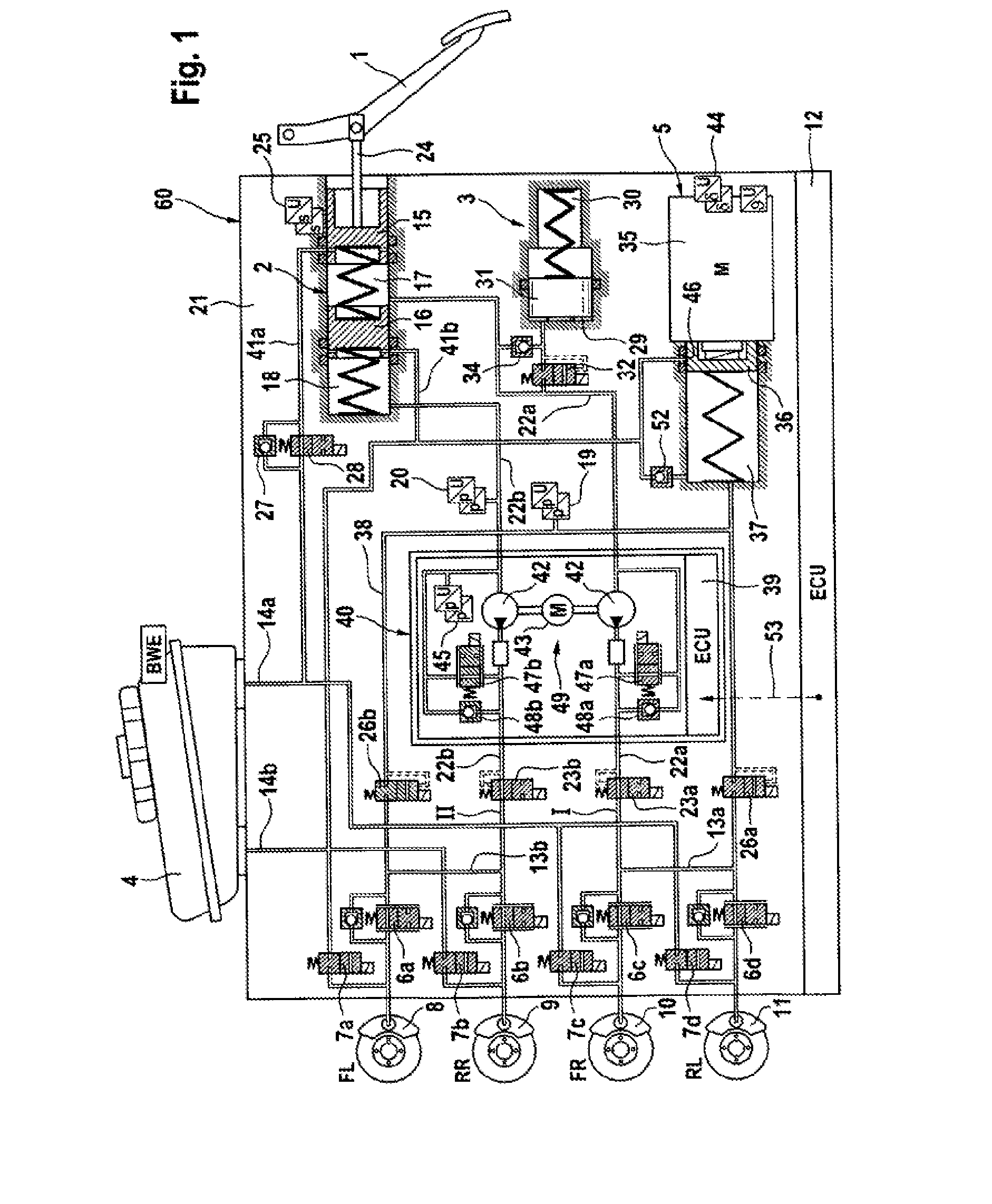
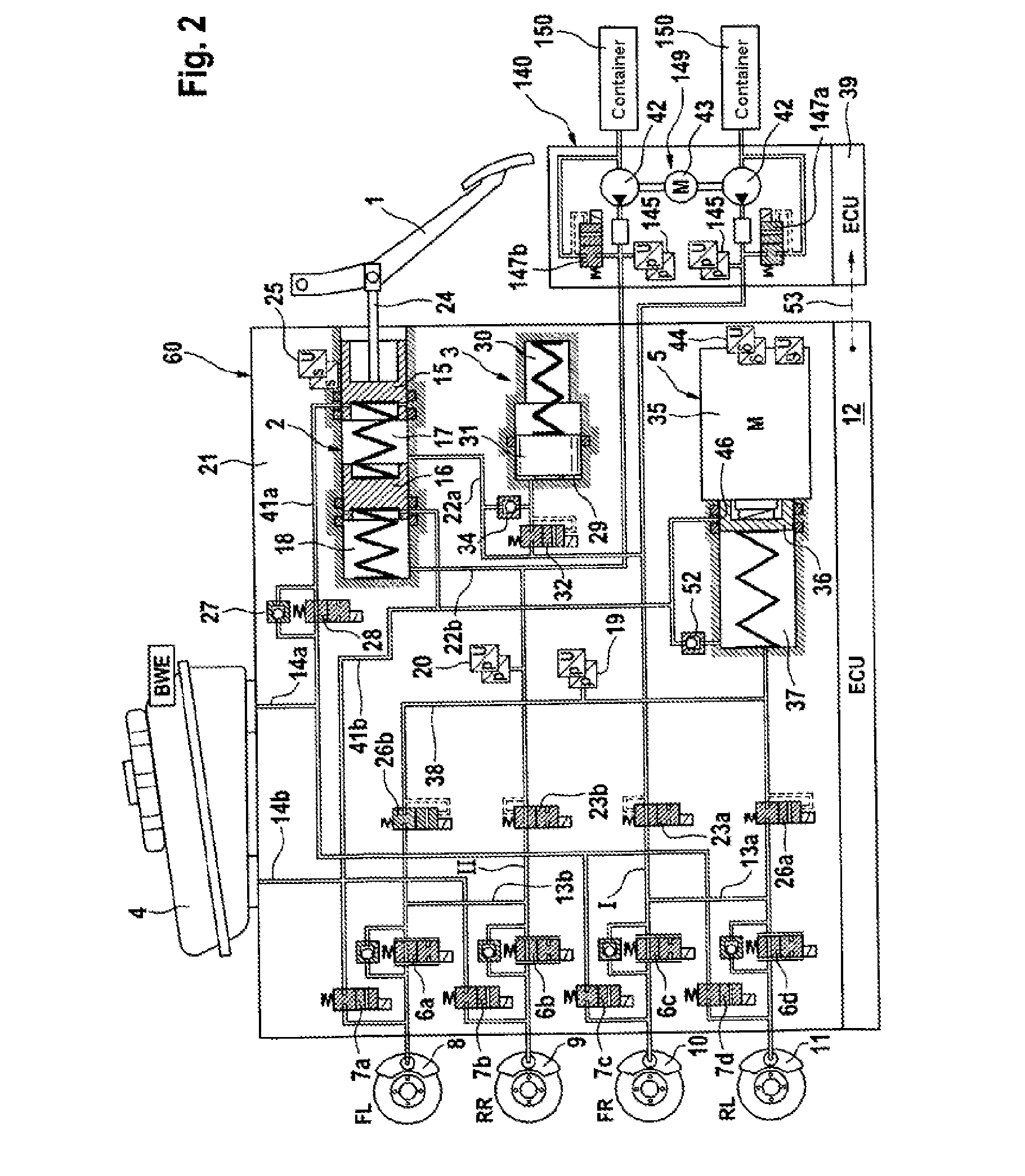
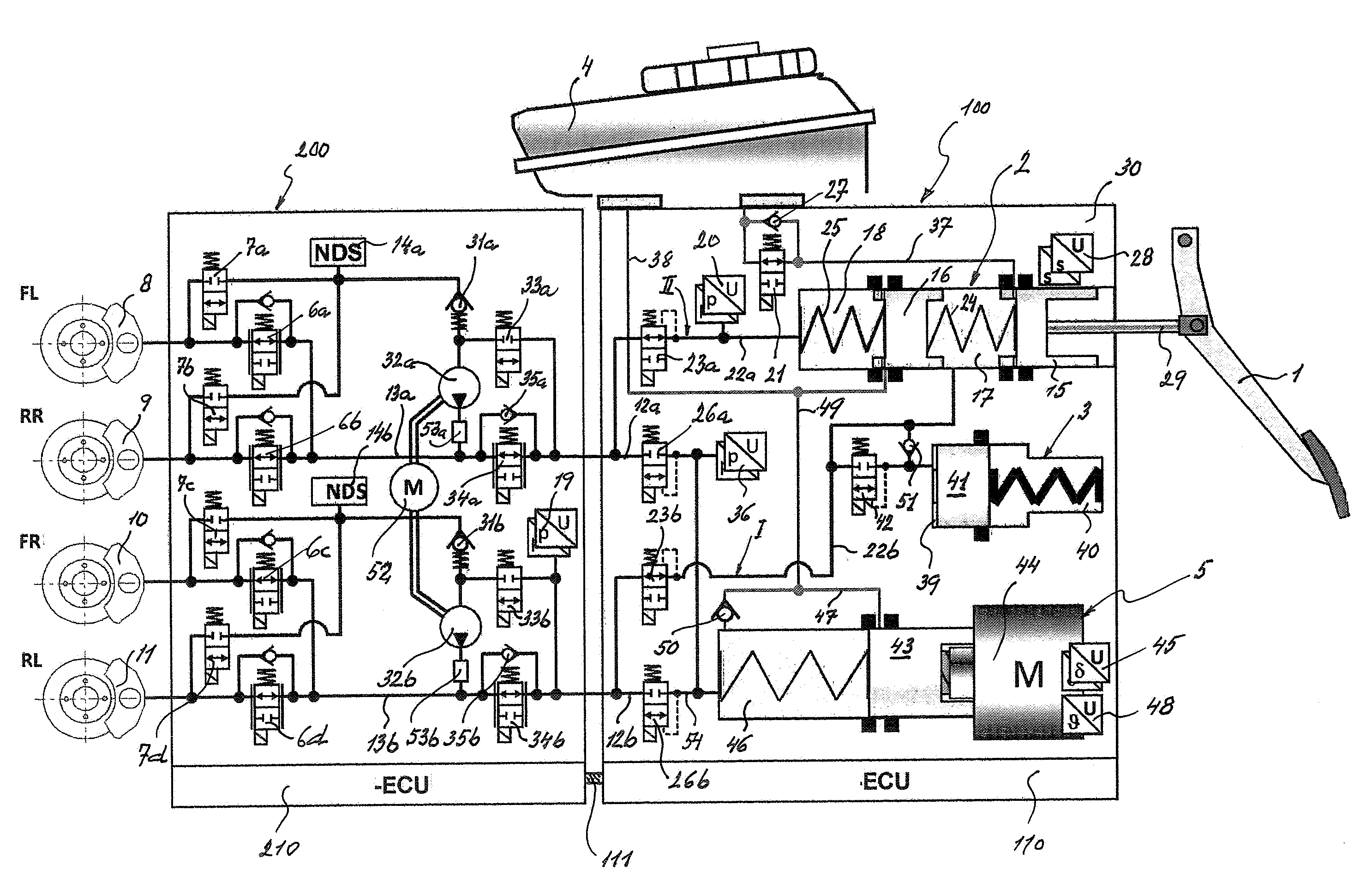
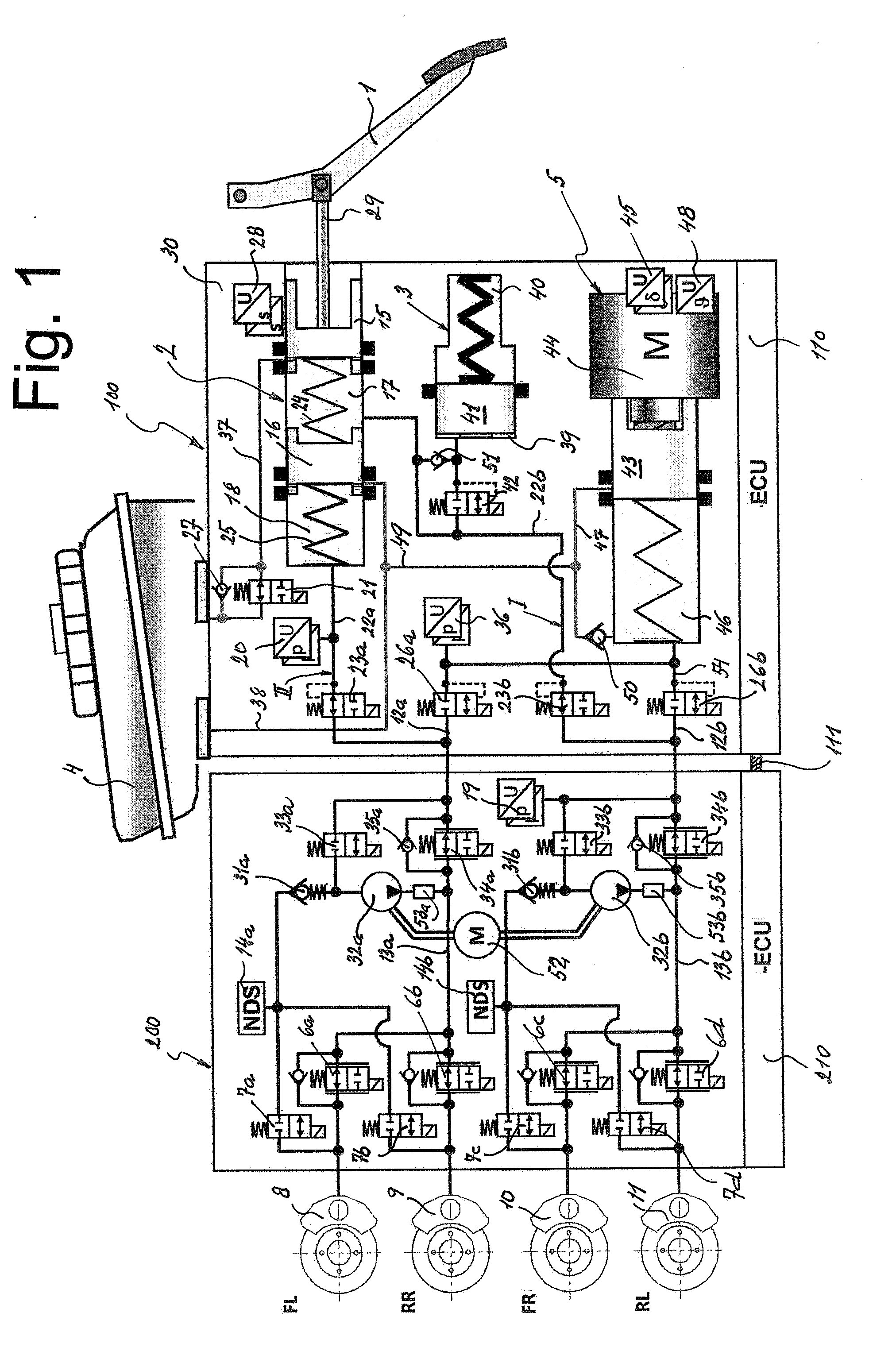
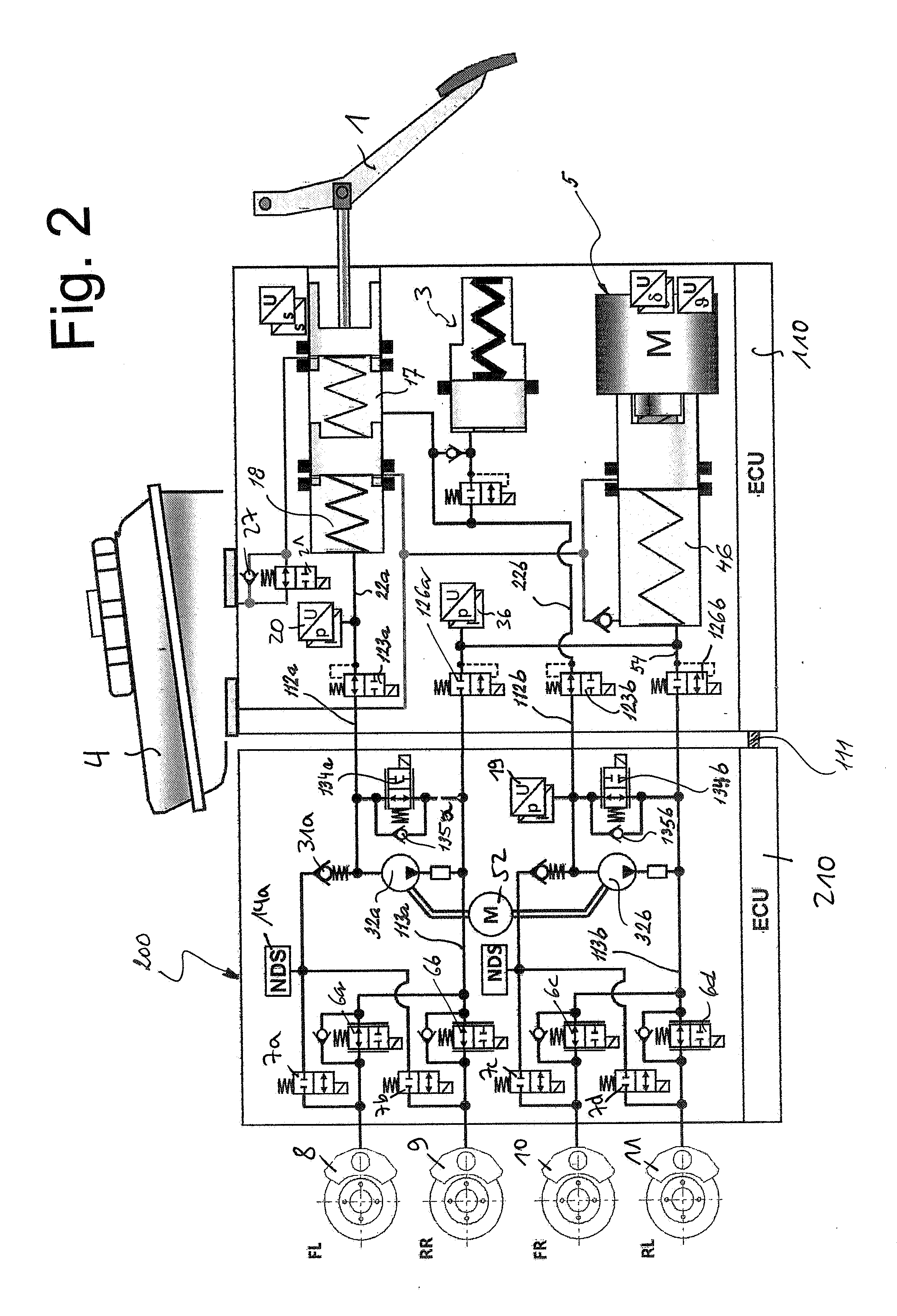
Brake System for Motor Vehicles
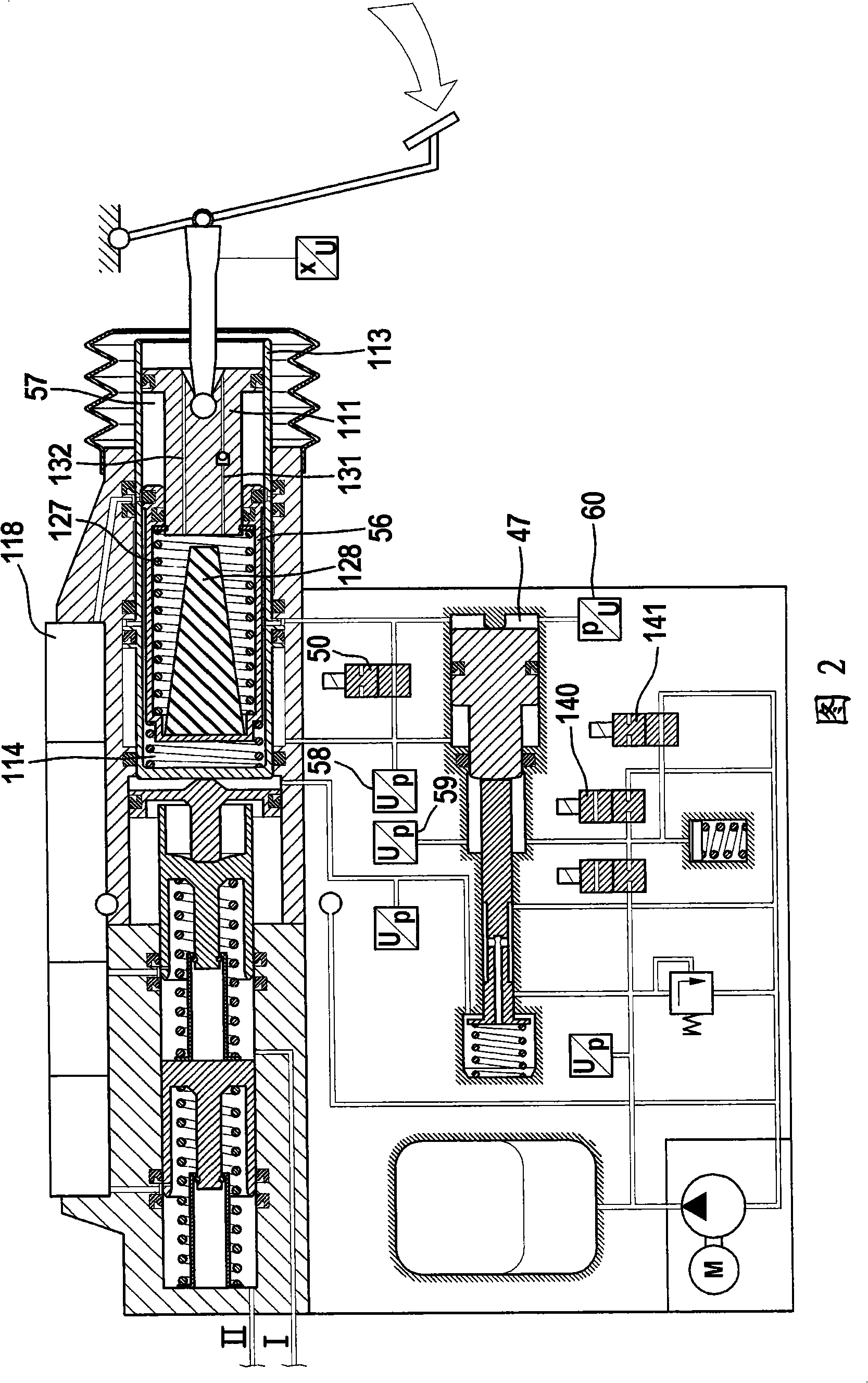
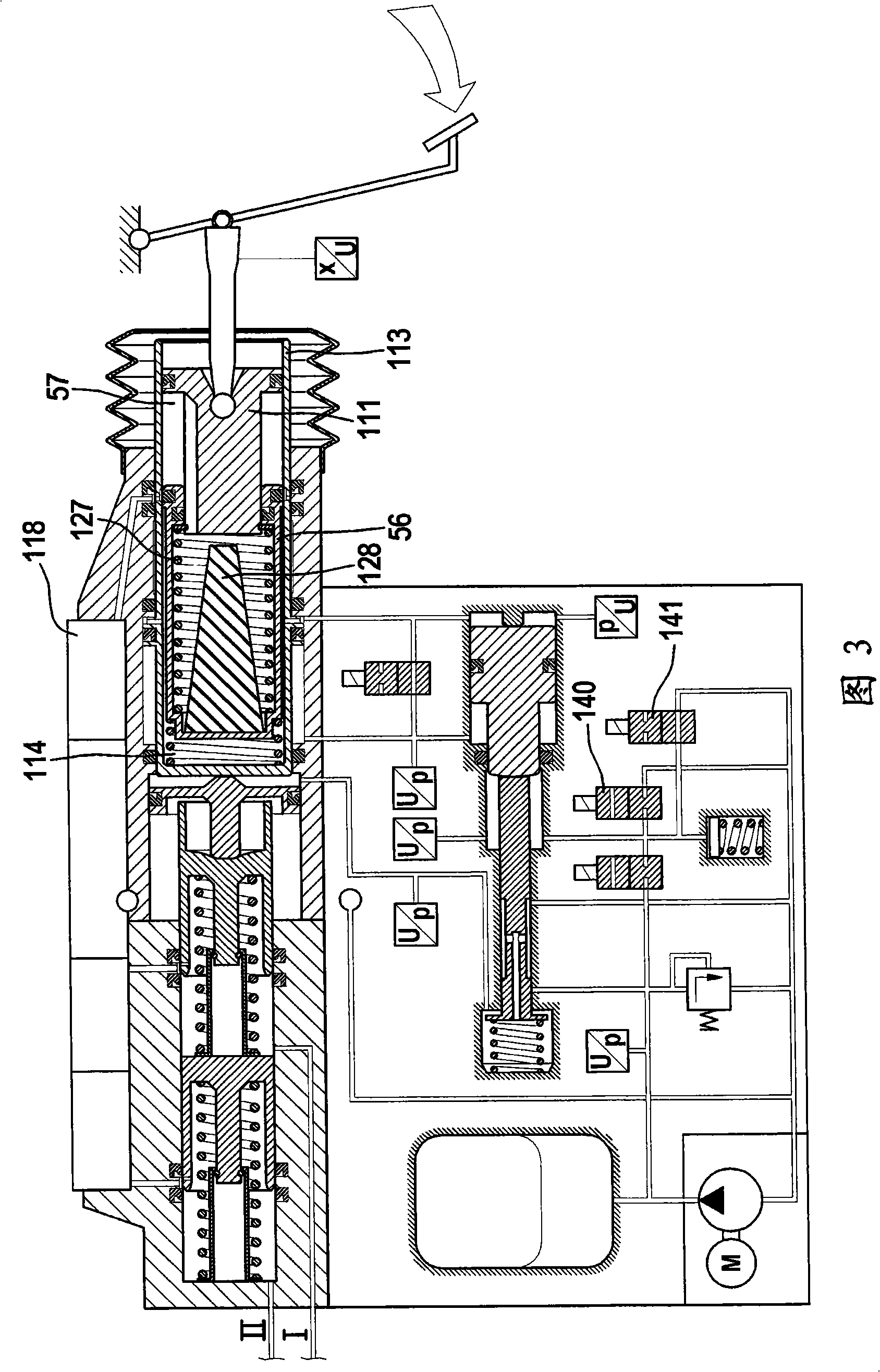
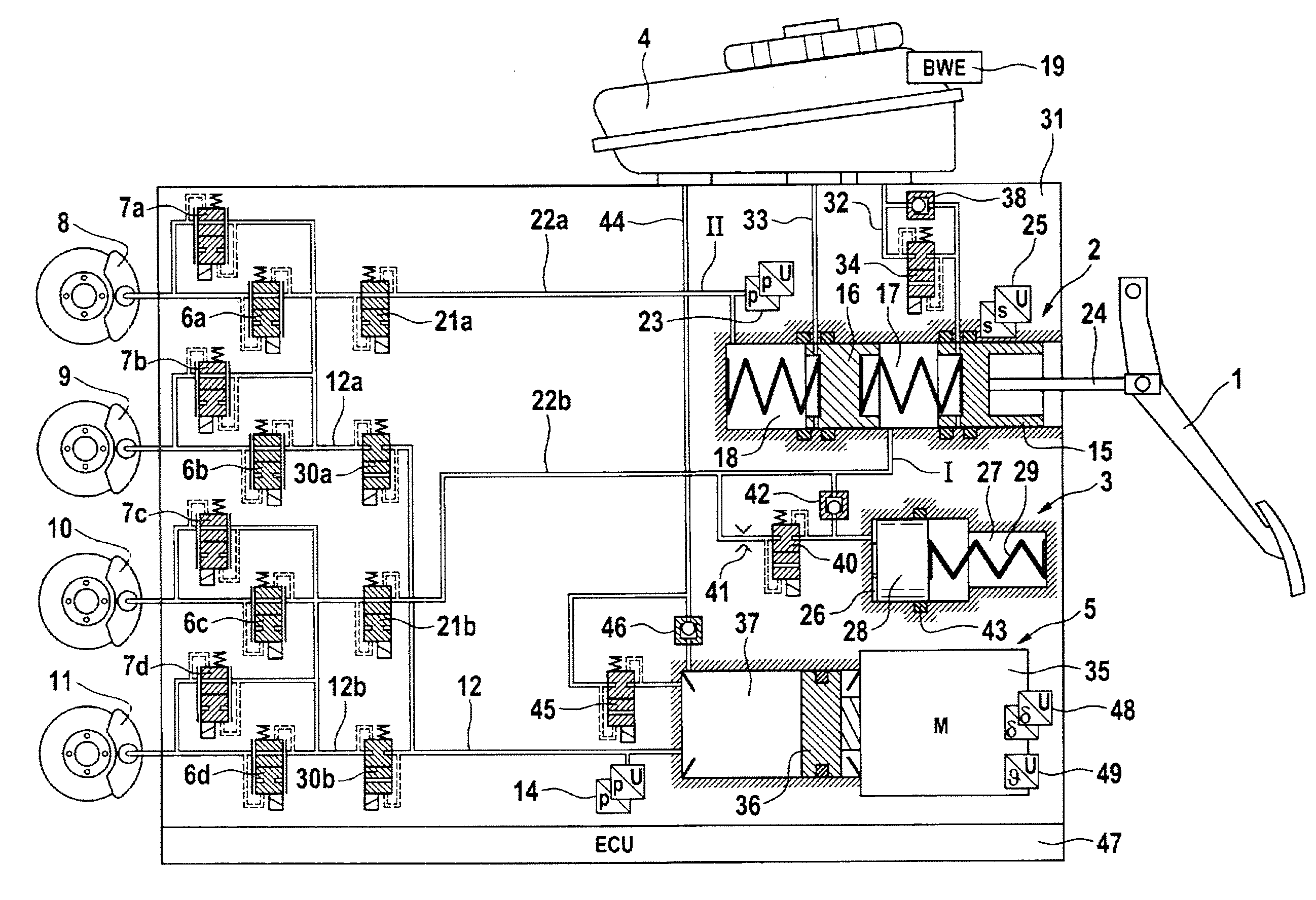
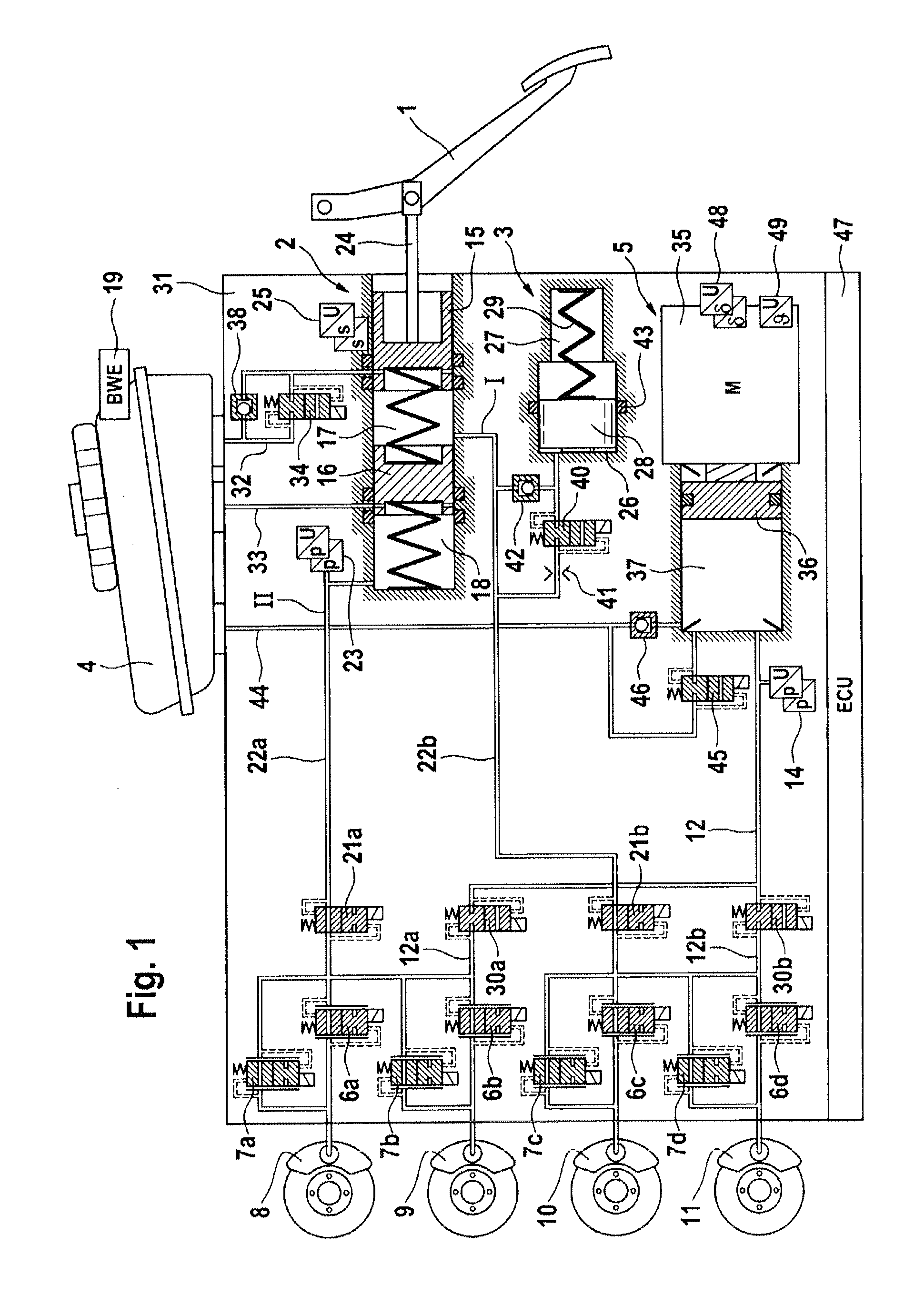
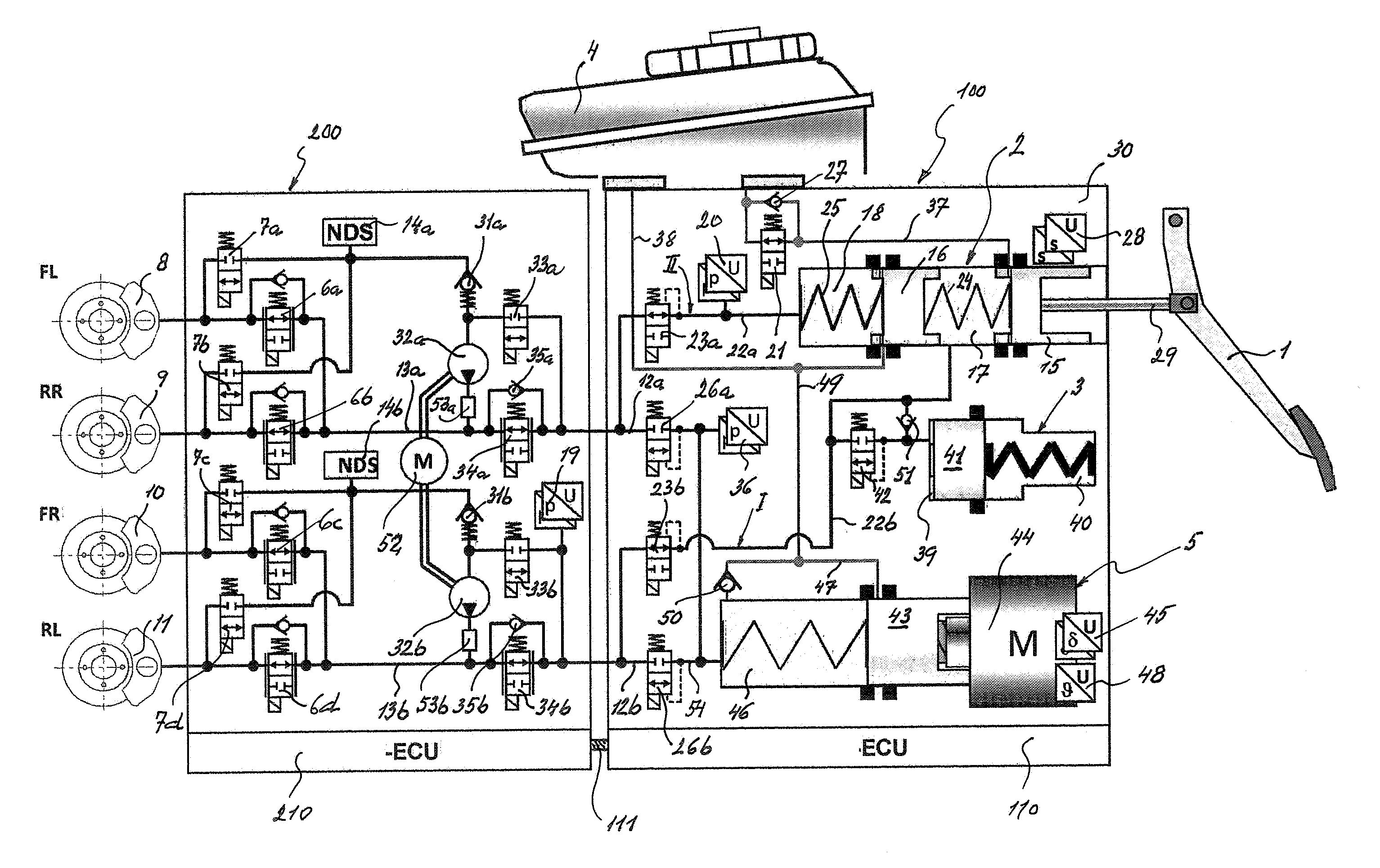
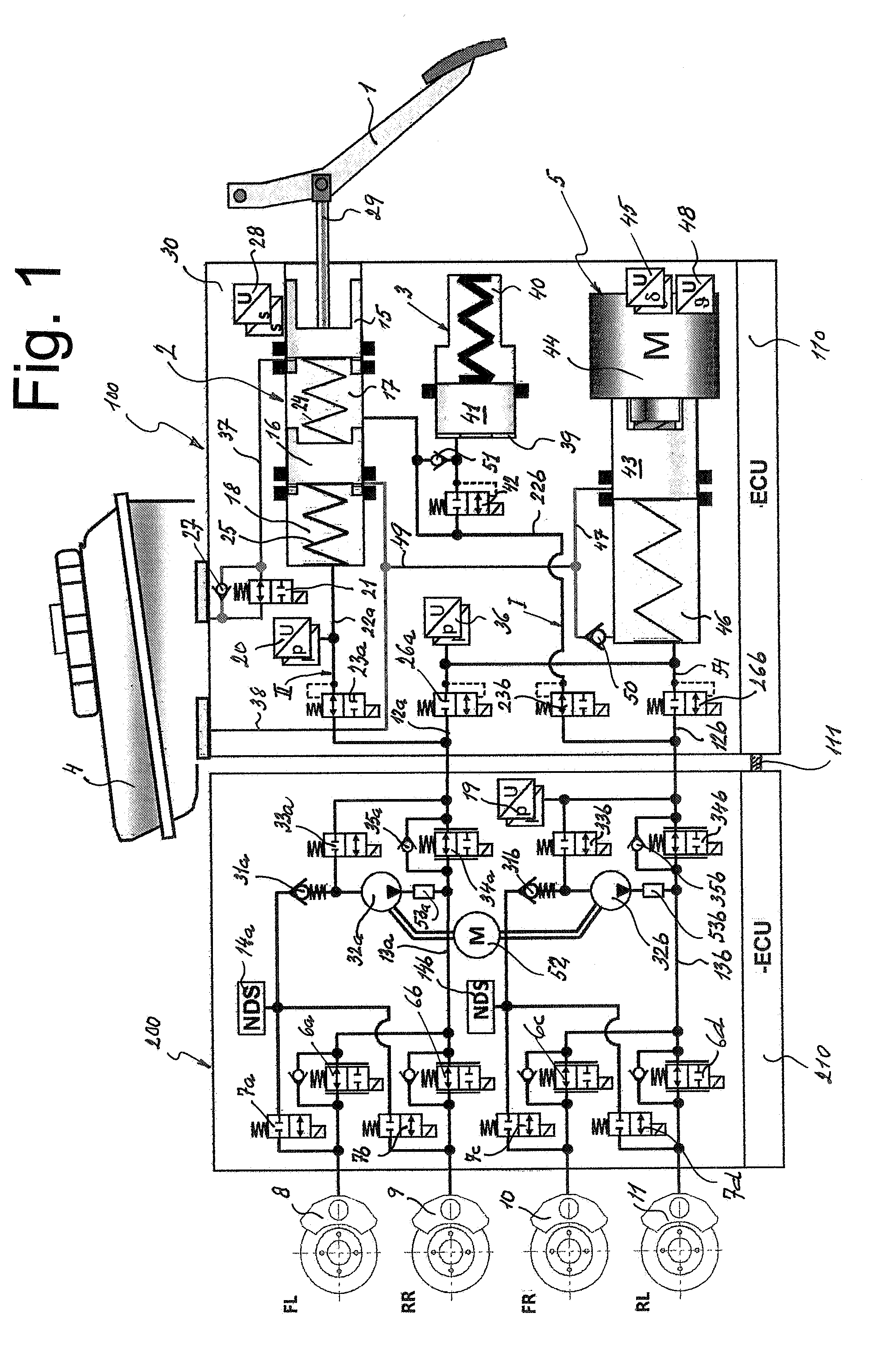
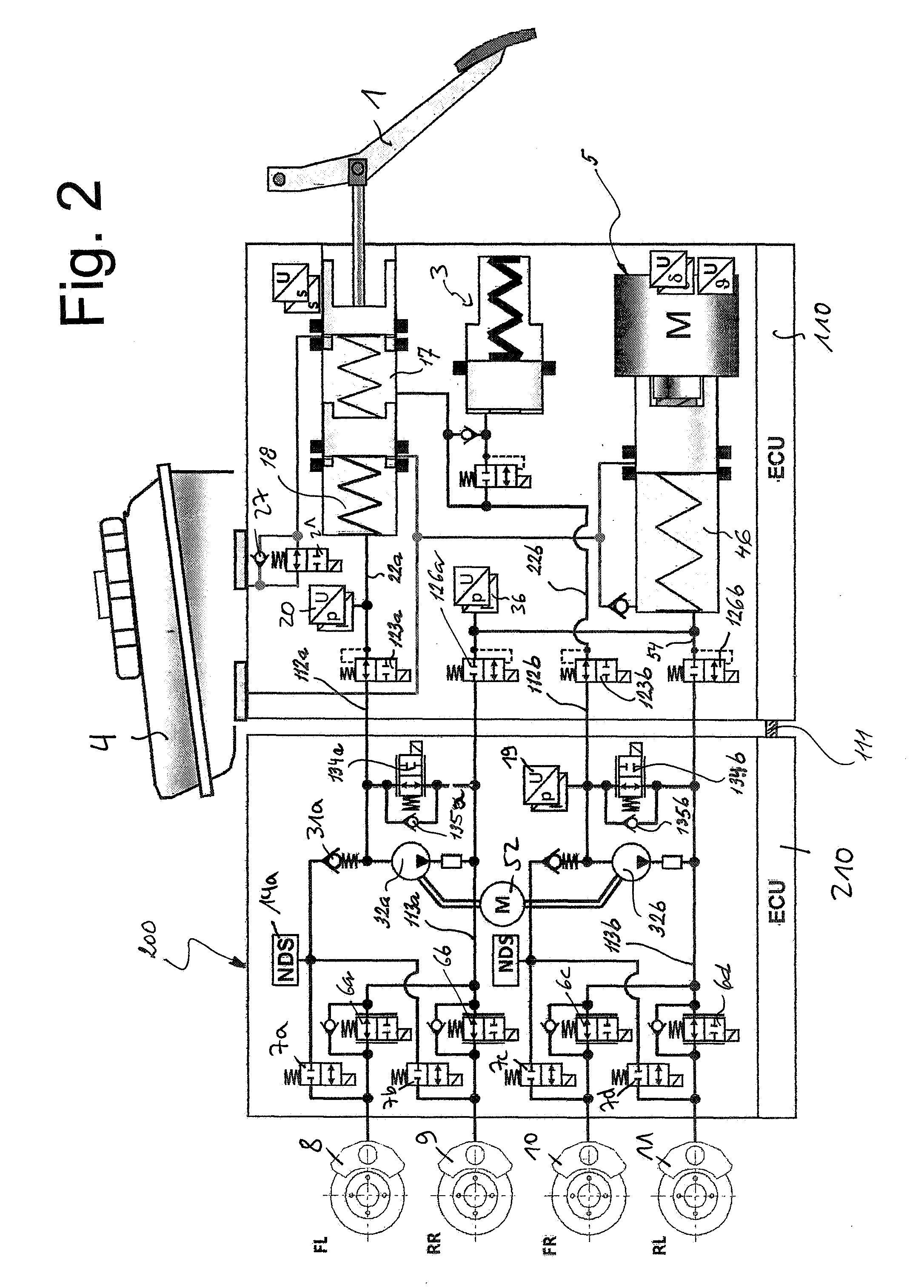
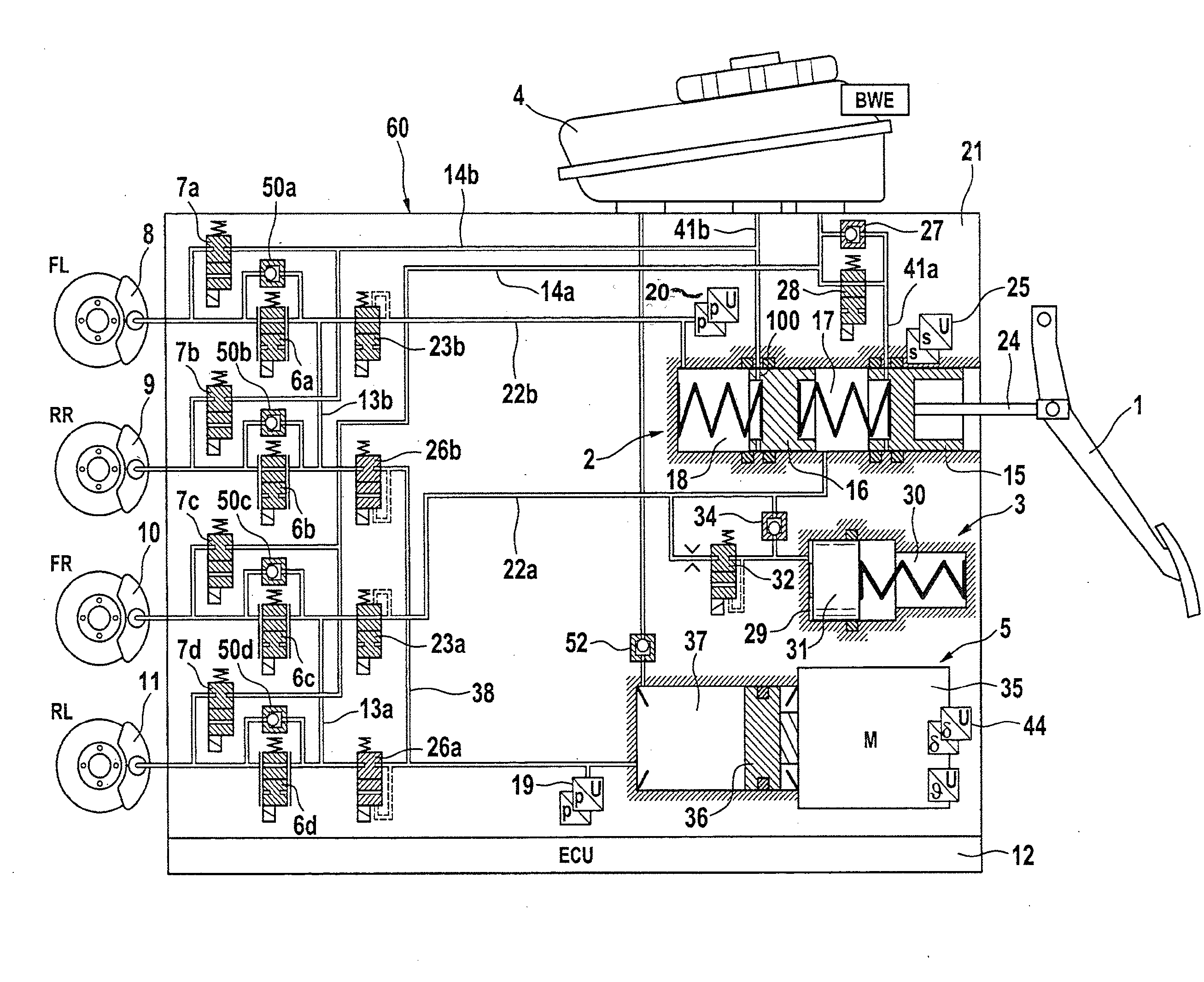
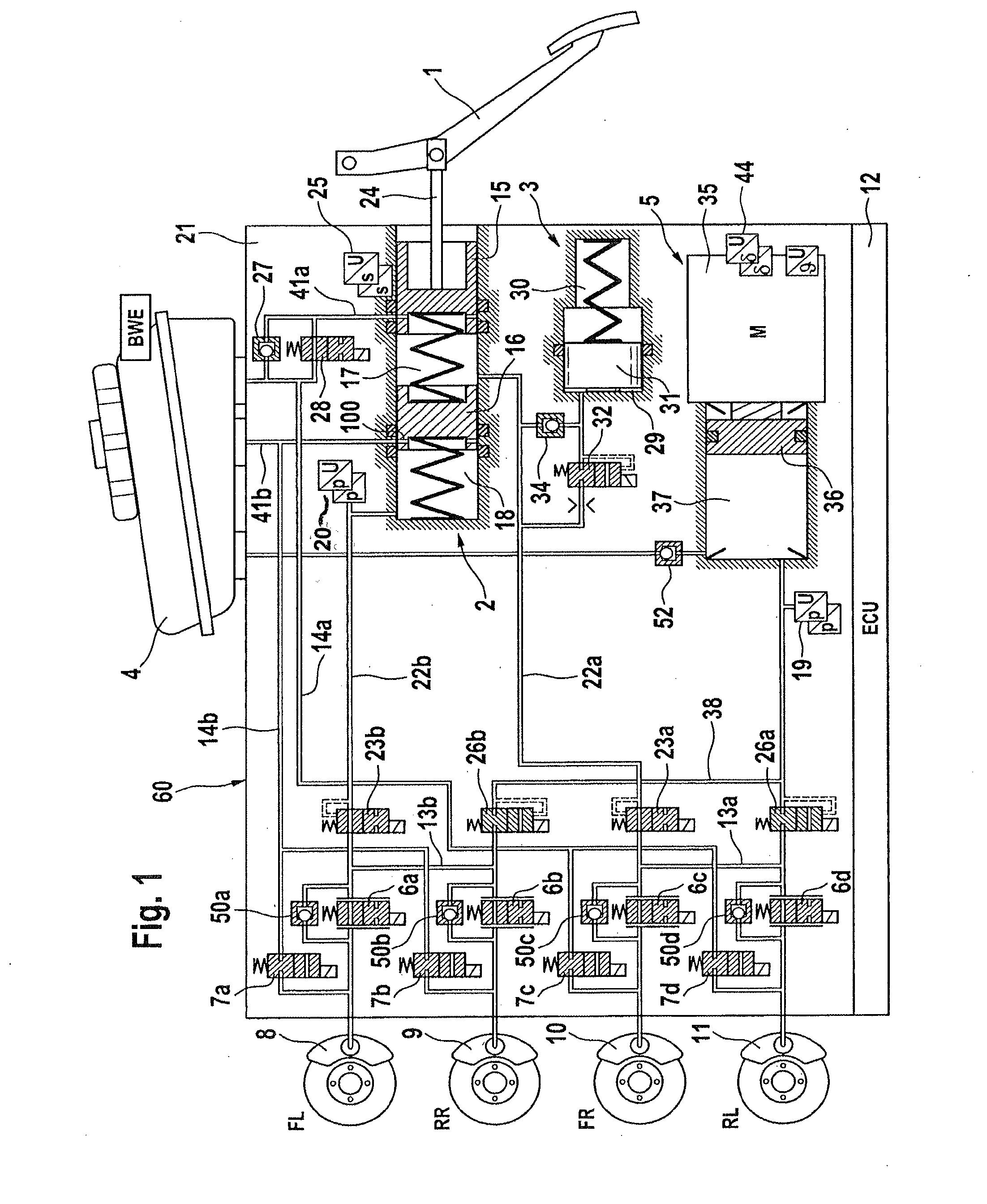
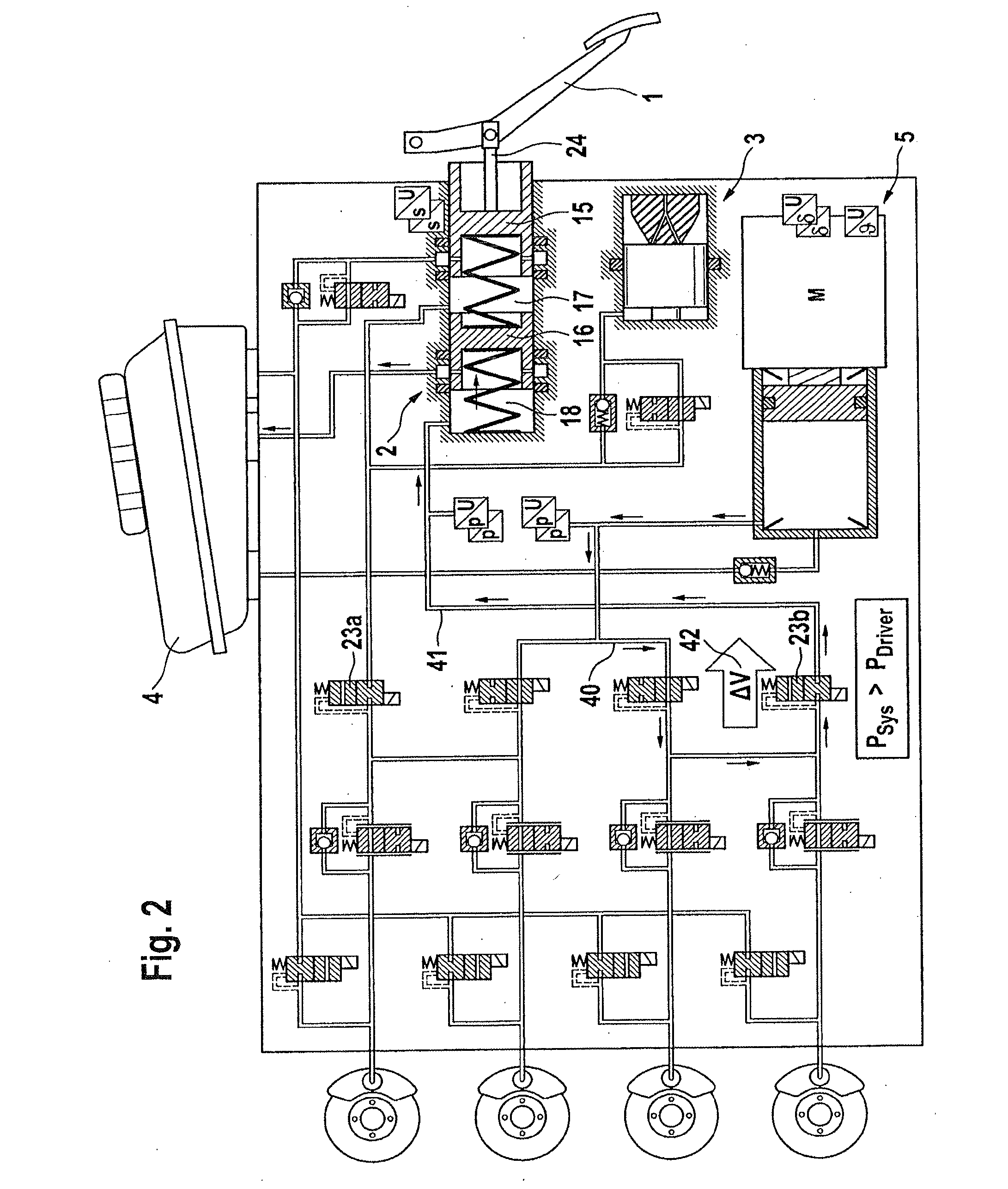
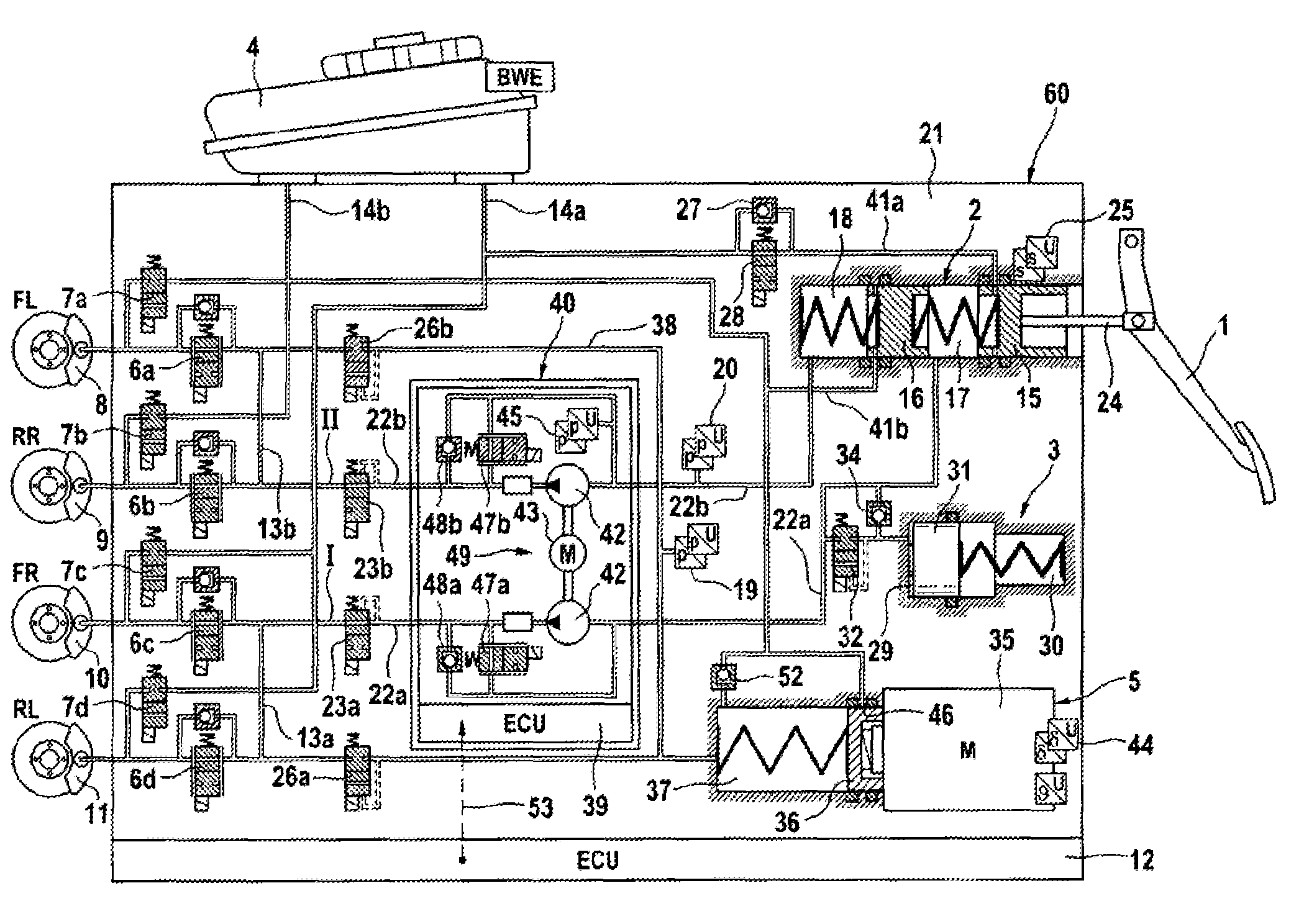
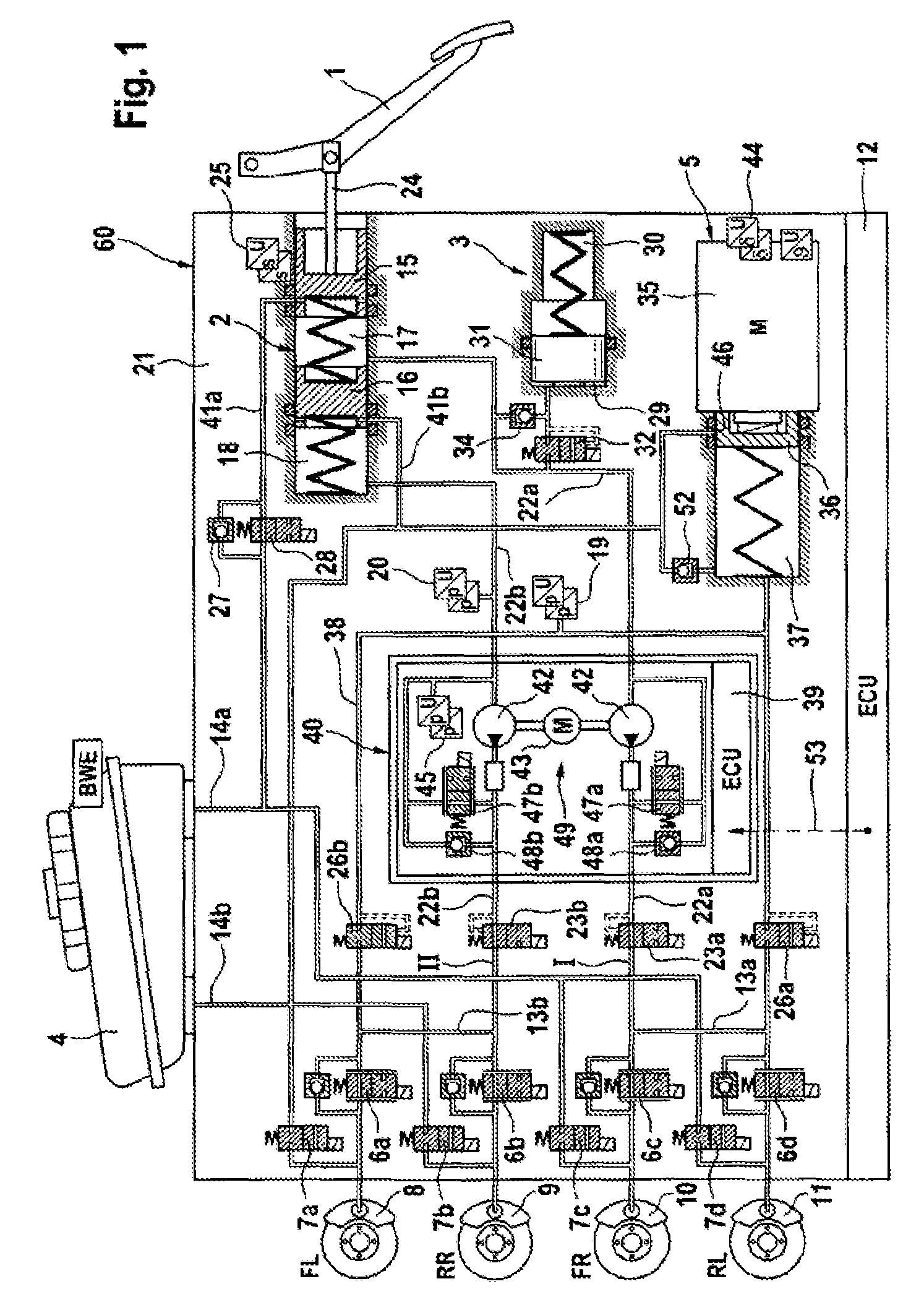
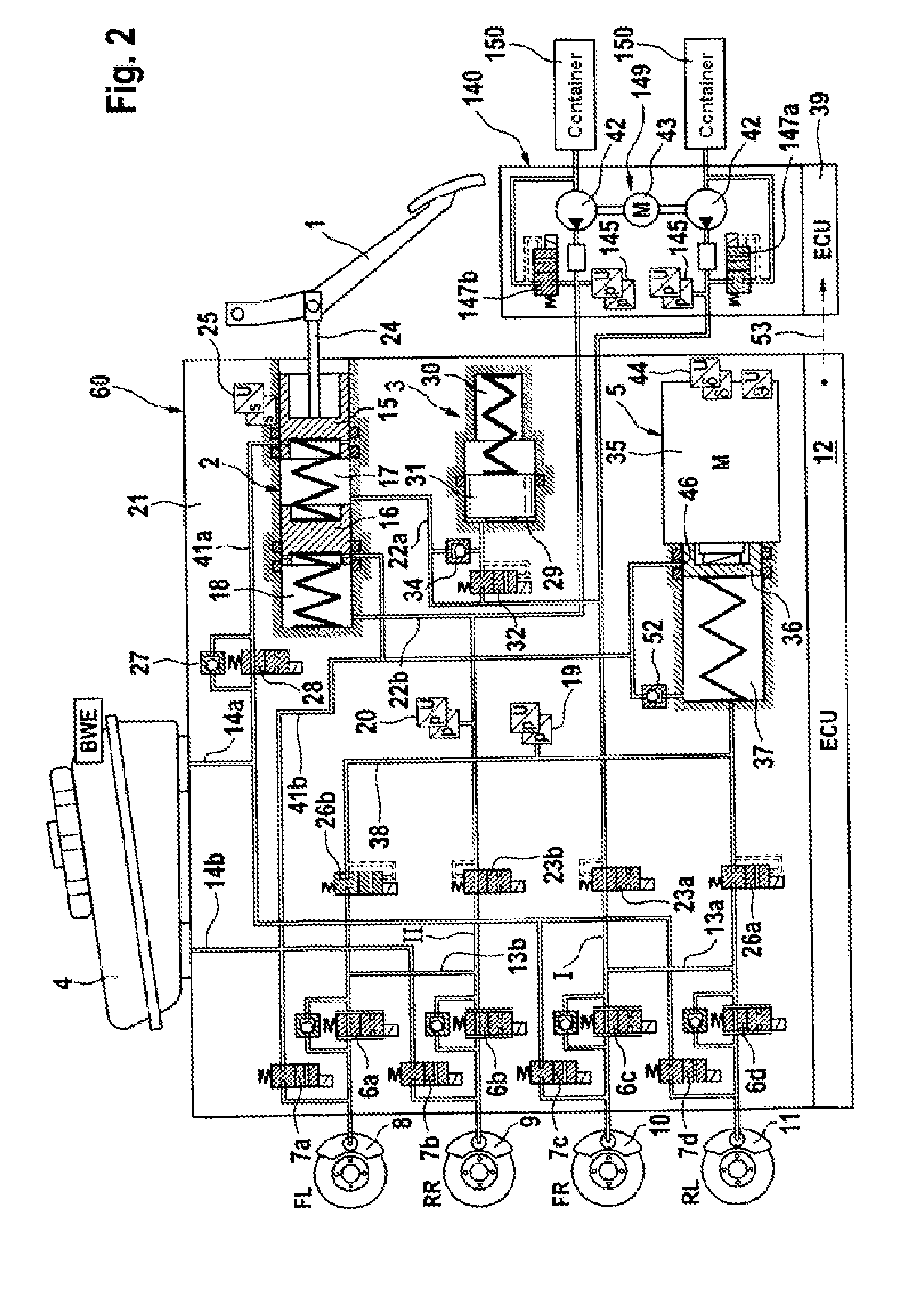
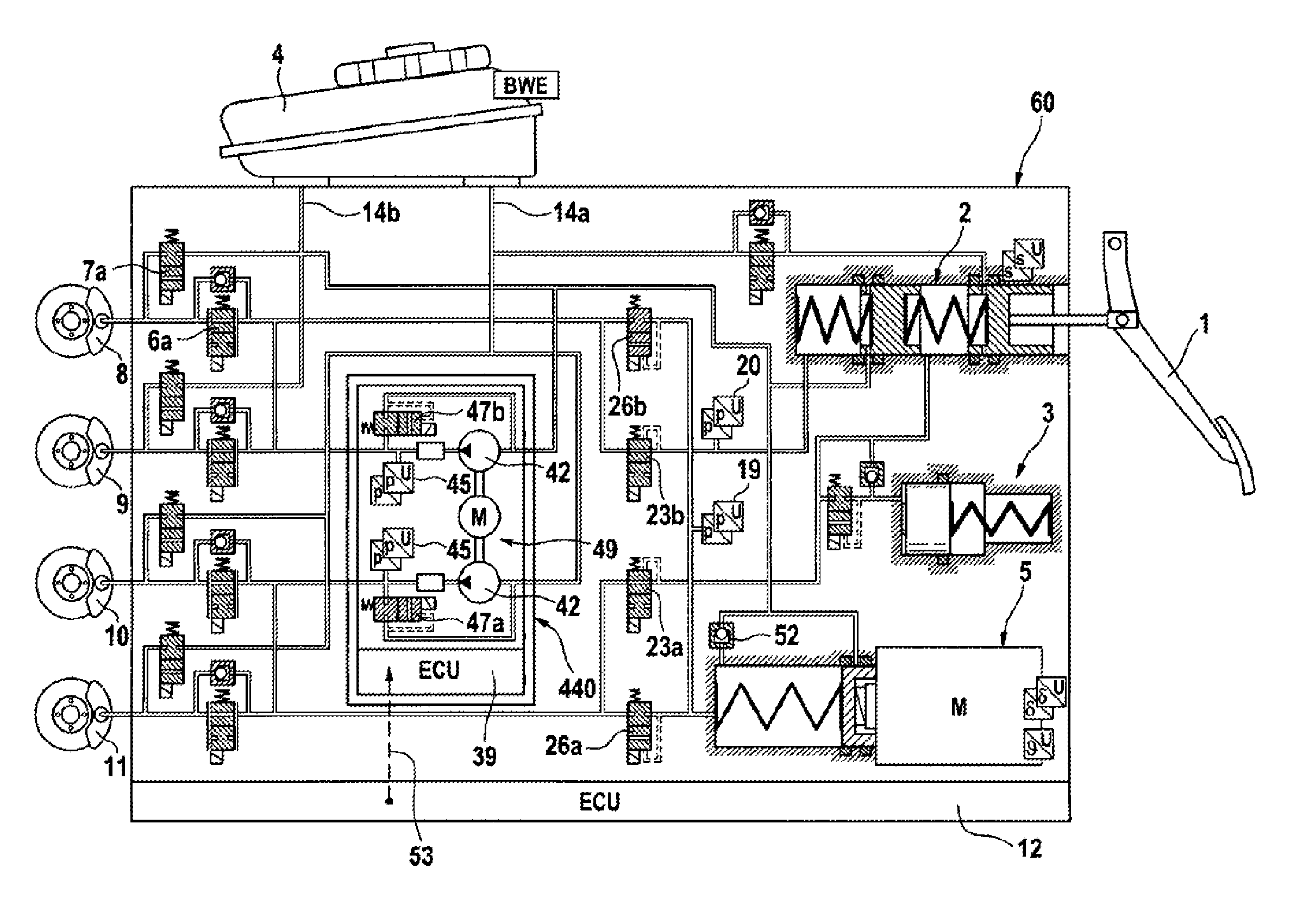
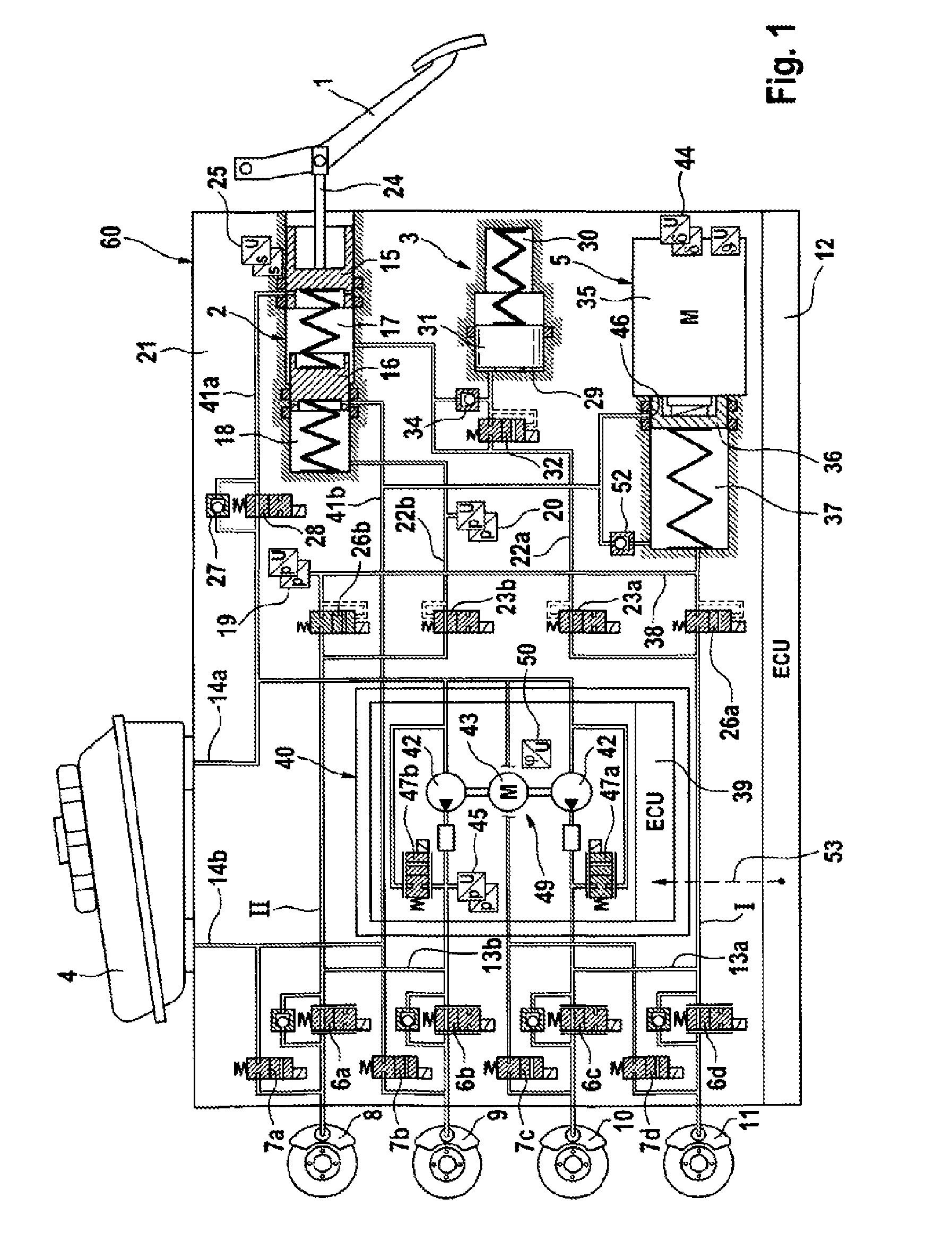
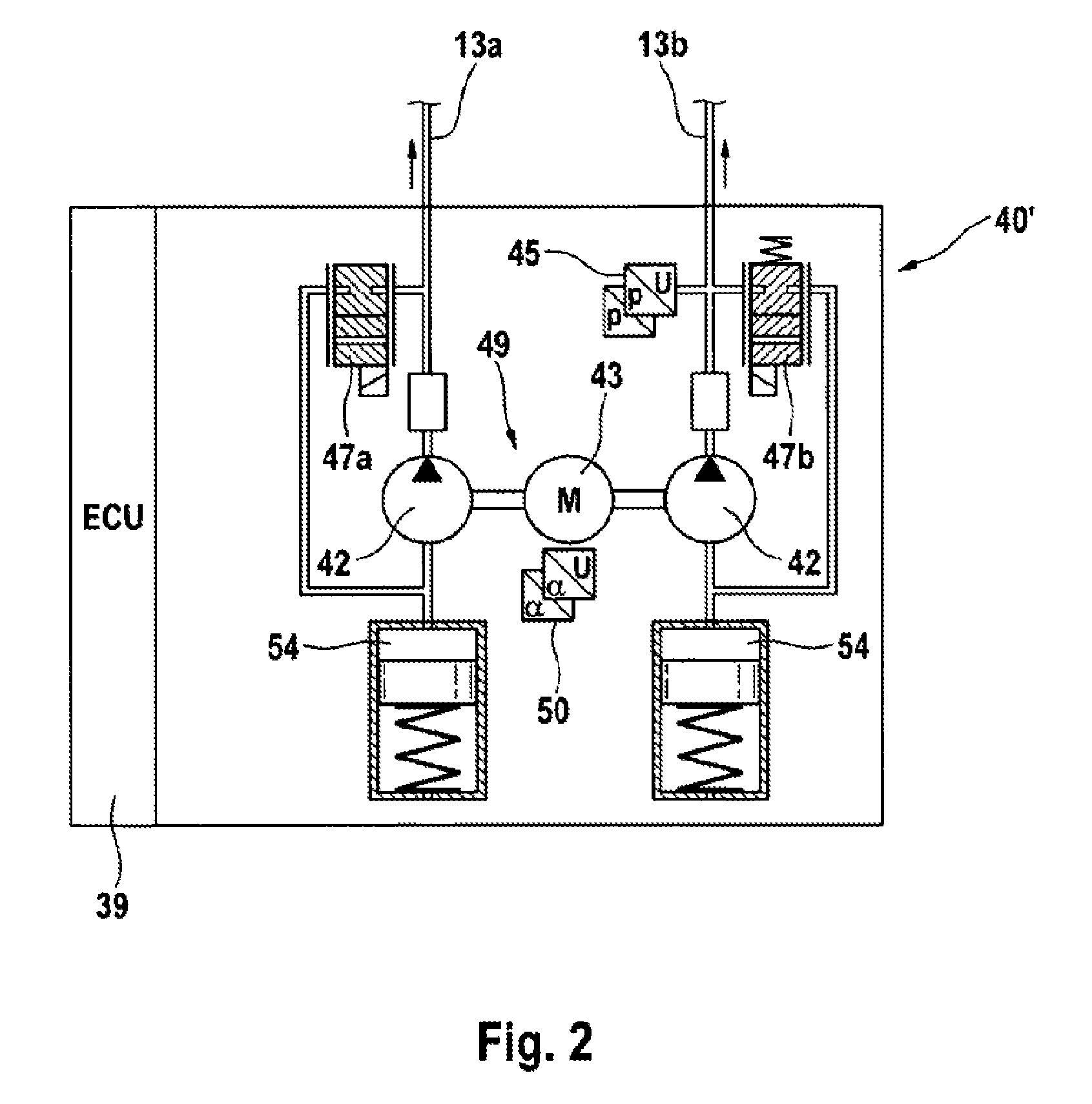
A motor vehicle brake system operable in a brake-by-wire and fallback modes. The system includes a brake pedal (1), a master cylinder (2), a reservoir (4), a travel simulator (3), an electrically controllable pressure source (5), isolation valves (23a, 23b) pumps (32a, 32b) and a low-pressure accumulator (14a, 14b), an inlet valve (6a-6d) and an outlet valve (7a-7d) for each wheel brake (8, 9, 10, 11), valves (34a, 34b; 134a, 134b) connected to the pumps (32a, 32b), and a control and regulation unit (110, 210). A valve arrangement (23a, 23b) establishes for each brake circuit (I, II) a connection from the pressure chamber (17, 18) of the master cylinder (2) to the modulator admission pressure line (13a, 13b; 113a, 113b) and disconnects the connection when unenergized, the valve arrangement (23a, 23b) preventing the pressure source (5) from being subjected to pressure from the pressure chambers (17, 18).
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Pedal feel emulator mechanism for brake by wire pedal
InactiveUS20050082909A1Optimization mechanismIncrease rate increaseControlling membersBraking action transmissionHysteresisGas spring
A brake pedal emulator mechanism includes a foamed plastic elastomeric piece compressed by a brake pedal which piece has a variable spring rate and produces hysteresis when compressed to emulate the brake pedal feel of a conventional hydraulic brake system. The foamed plastic may comprise microcellular urethane or a foamed silicone elastomer. Various combinations of the foamed plastic piece with mechanical springs, solid elastomeric pieces, or gas springs can be used to create a particular reaction force characteristic, as well as various shapes of the foamed plastic elastomeric piece itself.
Owner:DURA GLOBAL TECH
Automobile brake controlled by wire
ActiveCN102853000ASave installation spaceIt has the function of deceleration and torque increaseAxially engaging brakesBrake actuating mechanismsAuto regulationLinear motion
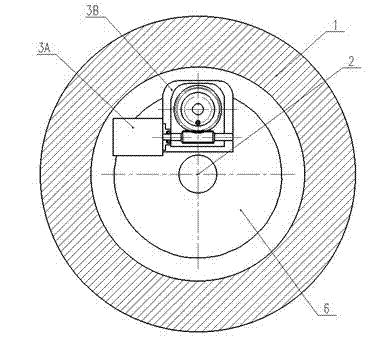
The invention discloses an automobile brake controlled by a wire, which comprises a brake disc, wherein a friction plate is arranged on each of the two sides of the brake disc; the friction plates are fixedly connected with a piston which can axially move along a brake caliper body and is connected with a trapezoid nut; the trapezoid nut can axially move along an inner hole of the piston and is in fit connection with a trapezoid threaded end of a screw rod; a driving nut is movably arranged on a ball screw section of the screw rod and is fixedly connected with a worm gear; the worm gear is engaged with a worm which is fixedly connected with an output end of a driving motor of the brake to covert the rotation motion of the driving motor of the brake into linear motion; and the driving motor of the brake is perpendicular to a brake caliper of the brake. The automobile brake controlled by the wire has automatic regulation and parking braking functions, can improve reinforcement effect, is high in braking performance, simple in structure, convenient to mount, easy to maintain and less in energy consumption, and can ensure the constancy of brake response speed of a vehicle so as to further ensure the braking performance.
Owner:RES INST OF ZHEJIANG UNIV TAIZHOU
Method for operating a brake system and a brake system
ActiveUS20150035353A1Quality is easy to controlFoot actuated initiationsFluid braking transmissionMobile vehicleDriver/operator
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Electro-hydraulic composite braking system with electric braking assistant force and brake-by-wire function
ActiveCN103552557AWith electric brake assistFunctionalBraking action transmissionElectric machineElectro hydraulic
The invention discloses an electro-hydraulic composite braking system with an electric braking assistant force and a brake-by-wire function. The electro-hydraulic composite braking system provided by the invention has various working modes In the case of an electric braking assistant force mode, a brake fluid is input into a master cylinder from a man-power cylinder by a brake pedal, and meanwhile, an electronic control unit controls the output torque of a motor to apply an assistant force, so as to output brake pressure to a wheel cylinder. In the case of a regenerative braking mode, the electronic control unit controls the on / off of an electromagnetic valve, the brake fluid is input into the simulation cavity of a pedal travel simulator from the man-power cylinder by the brake pedal so as to generate pressure and provide a brake pedal feeling; if automobile deceleration requirement can not be met by the regenerative braking, the electronic control unit controls the output torque of the motor so as to allow the master cylinder to output brake pressure into the wheel cylinder to assist friction brake. In case of an active braking mode, the electronic control unit controls the output torque of the motor so as to allow the master cylinder to output brake pressure to the wheel cylinder. The electro-hydraulic composite braking system provided by the invention has the advantages of integration of advantages of wire control and non-wire control working modes, small pressure fluctuation, and high pressure regulation precision.
Owner:南京经纬达汽车科技有限公司
Brake system for motor vehicles
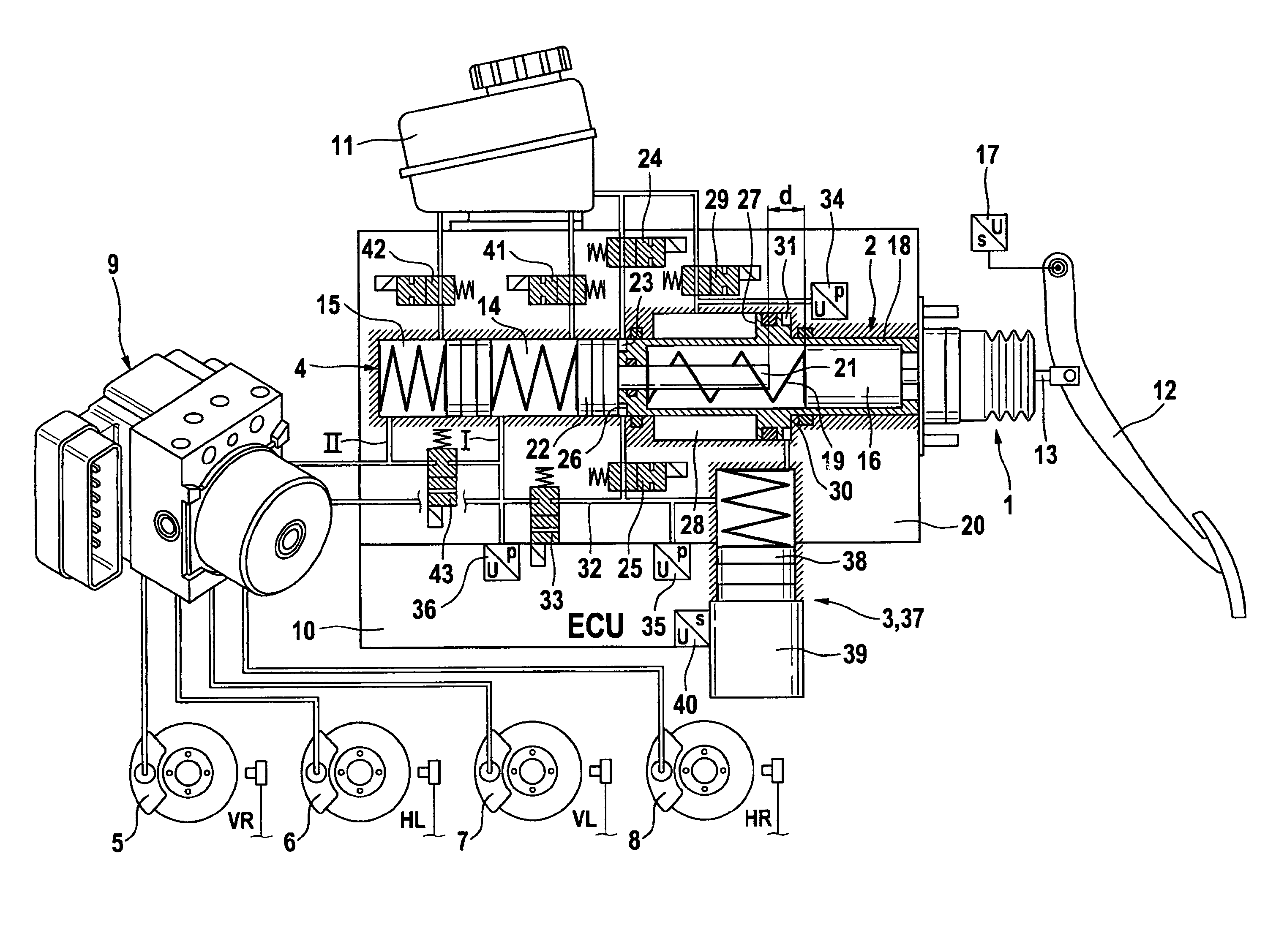
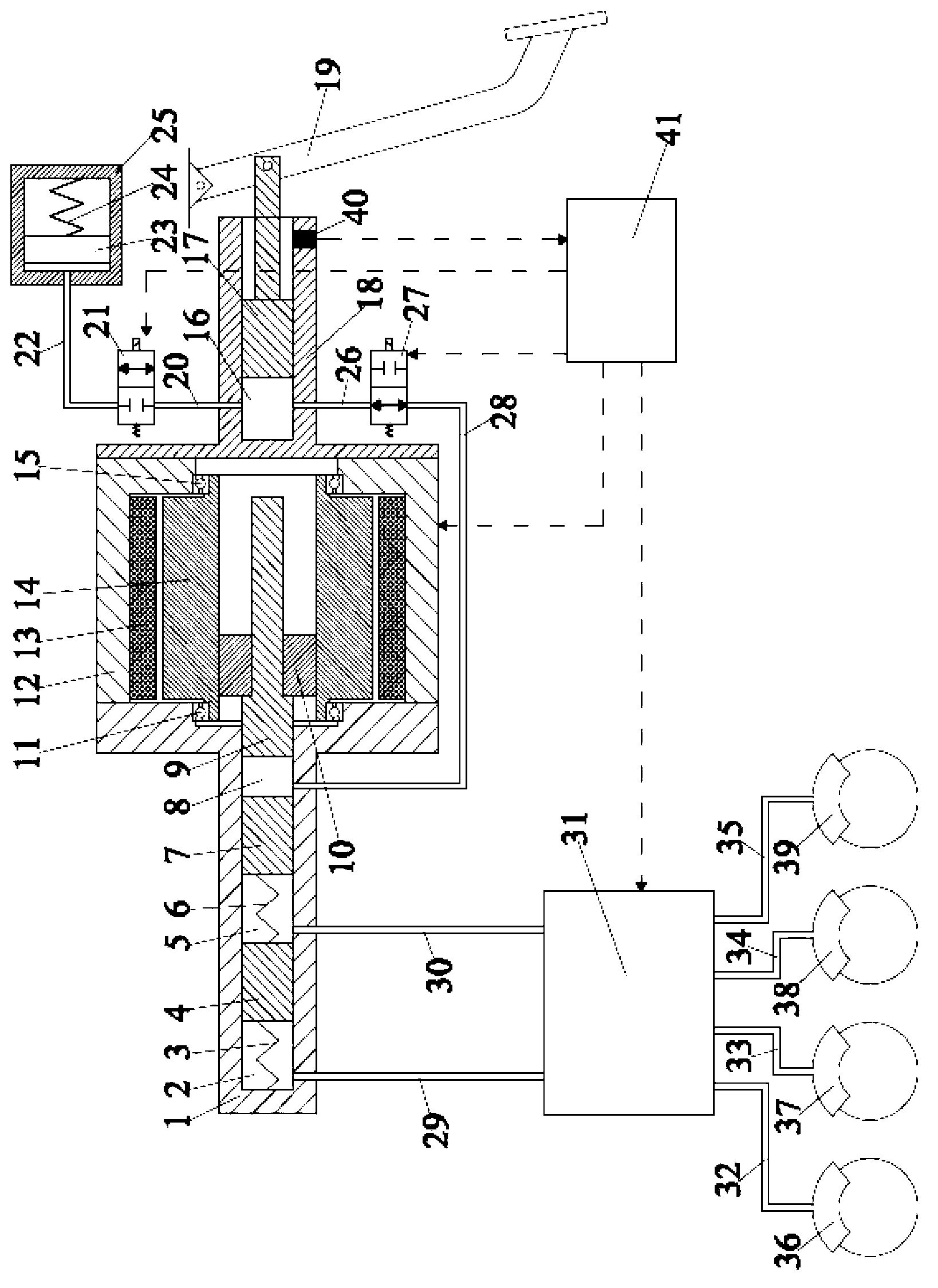
The invention relates to a brake system with a pedal travel simulator that, during the braking mode brake-by-wire , conveys a comfortable pedal feel to the vehicle driver. In order to boost the actuation force even in the event of a breakdown of the control electronics or loss of electric power supply, the invention provides that a fourth piston (8) is mounted between the first (2) and the third piston (5), and this fourth piston, while interacting with the third piston (5), delimits a hydraulic chamber (9) having a hydraulic connection to a pressure medium reservoir (31), said connection being able to be blocked by an actuation of the brake pedal, and pressure can be built up in the chamber by the actuation forces. The invention also provides that a valve assembly (10) can be controlled by the hydraulic pressure built-up inside the chamber (9), and the pressure built-up in the intermediate space (11) can be changed by this valve assembly.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Brake system for motor vehicles
A motor vehicle brake system operable in a brake-by-wire and fallback modes. The system includes a brake pedal (1), a master cylinder (2), a reservoir (4), a travel simulator (3), an electrically controllable pressure source (5), isolation valves (23a, 23b) pumps (32a, 32b) and a low-pressure accumulator (14a, 14b), an inlet valve (6a-6d) and an outlet valve (7a-7d) for each wheel brake (8, 9, 10, 11), valves (34a, 34b; 134a, 134b) connected to the pumps (32a, 32b), and a control and regulation unit (110, 210). A valve arrangement (23a, 23b) establishes for each brake circuit (I, II) a connection from the pressure chamber (17, 18) of the master cylinder (2) to the modulator admission pressure line (13a, 13b; 113a, 113b) and disconnects the connection when unenergized, the valve arrangement (23a, 23b) preventing the pressure source (5) from being subjected to pressure from the pressure chambers (17, 18).
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Vehicle brake system
InactiveCN101274623AExtended pedal travelAvoid consumptionBraking action transmissionIn vehicleMaster cylinder
A vehicle brake system, capable of realizing a brake-by-wire construction which can be installed in vehicles in the same manner as conventional brake systems, is provided with a booster device, a master cylinder, wheel brakes, and a hydraulic pressure control device interposed between the master cylinder and the wheel brakes. The system is further provided with a stroke sensor for detecting the moving stroke of a brake pedal, a simulator for applying to the brake pedal a pseudo reaction force corresponding to the moving stroke of the brake pedal, a play or idling component arranged between the booster device and the hydraulic pressure control device for absorbing the moving stroke of the brake pedal by a predetermined amount, and an electronic control device for controlling the hydraulic pressure control device based on an input from the stroke sensor.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
Brake-by-wire and steer-by-wire hardware-in-the-loop test bench for vehicle
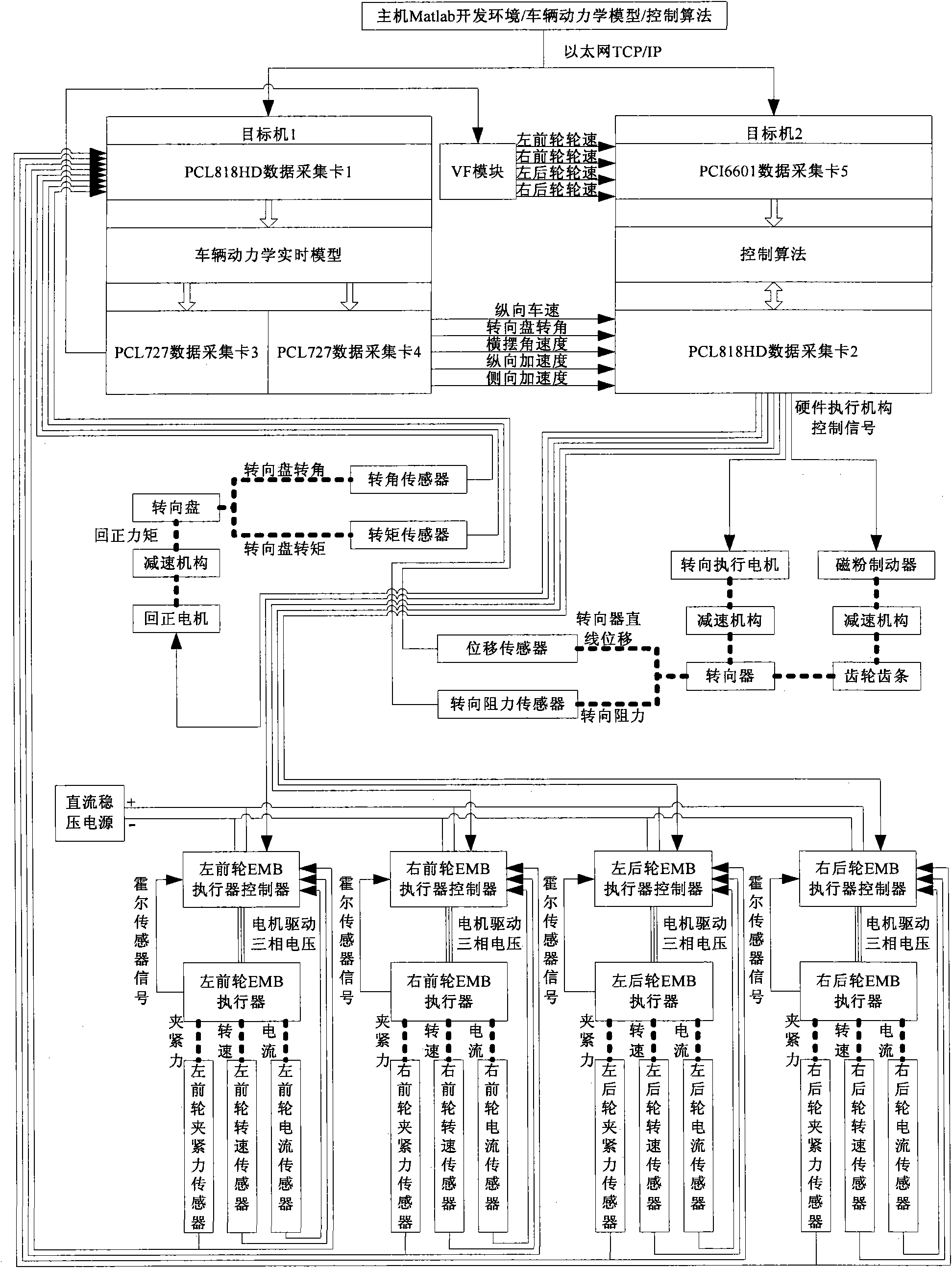
InactiveCN101561353AThe simulation prediction results are accurate and reliableReduce development difficultyVehicle steering/rolling behaviourData acquisitionCurrent sensor
The invention discloses a brake-by-wire and steer-by-wire hardware-in-the-loop test bench for a vehicle. The test bench integrates a brake-by-wire system and a steer-by-wire system into a whole, and is divided into a software part, a real-time platform, a signal processing part and a hardware part, wherein the real-time platform consists of a host and target machines 1 and 2; the host and the target machines 1 and 2 are connected by a wireless network communication system; the signal processing part consists of first and second data acquisition cards with the model of PCL-818HD, third and fourth data acquisition cards with the model of PCL-727, a fifth data acquisition card with the model of PCI-6601 and a V / F conversion module; and the hardware part comprises a rotary angle sensor (12), a torque transducer (13), an opposite rotary motor (16), a steering resistance sensor (21), a steering actuating motor (18), an EMB actuator controller, and EMB actuator, a clamping force sensor, a revolution transmitter and a current sensor.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Brake-by-wire system of automobile
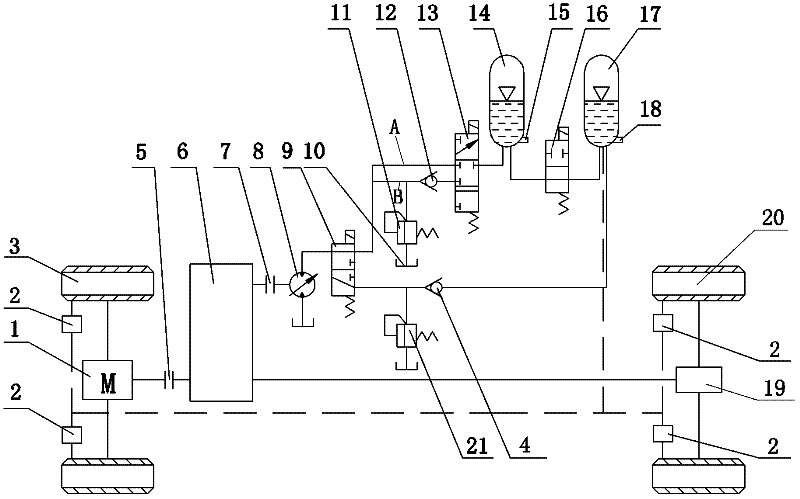
ActiveCN103010199AEliminate bad effectsOptimize layoutBraking action transmissionHydraulic control unitElectric machinery
The invention relates to a brake-by-wire system of an automobile and belongs to the technical field of automobile brake systems. In the brake system, a vacuum booster of the traditional vacuum booster hydraulic brake system is replaced with a motor, and a piston in a brake main cylinder is pushed to move to generate brake hydraulic pressure, so that dependence on vacuum degree of an engine is canceled; through the adoption of a pedal simulator, influences on feelings of a brake pedal during coordinated control of feedback and brake are eliminated; a hydraulic control unit of the traditional brake system is kept to implement hydraulic adjustment; and as a standby hydraulic brake system is integrated, braking with certain strength can be implemented by a driver under a situation that the power supply of the system is ineffective. Compared with the traditional distributed brake-by-wire scheme, the brake-by-wire system provided by the invention has the advantages as follows: the structure is changed when compared with the structure of the traditional vacuum booster hydraulic brake system, the system can be mounted on the automobile more conveniently, and more existing technologies in the traditional brake system can be succeeded in the control aspect.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for providing haptic information to the driver of a motor vehicle
ActiveUS20150061854A1Simple electronic meansFoot actuated initiationsElectric propulsion mountingDriver/operatorFunctional Relationship
The invention relates to a method for providing haptic information to the driver of a motor vehicle, equipped with a brake-by-wire brake system, about the operating state of the brake system, in which method the brake pedal characteristic is generated by a pedal travel simulator, in the form of a functional relationship between the brake pedal opposing force and the brake pedal travel, and is modified as a function of an operating state. In order to provide the driver with the haptic information channel via which electronically controlled information can be communicated to the driver during braking, without the impression of a defect arising, the invention proposes that a basic brake pedal characteristic is generated by a passive simulator spring which assigns pedal travel, on which pedal return travel transporting the haptic information is superimposed, to a given pedal force in an unchanging, constant relationship.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Redundant architecture for brake-by-wire system
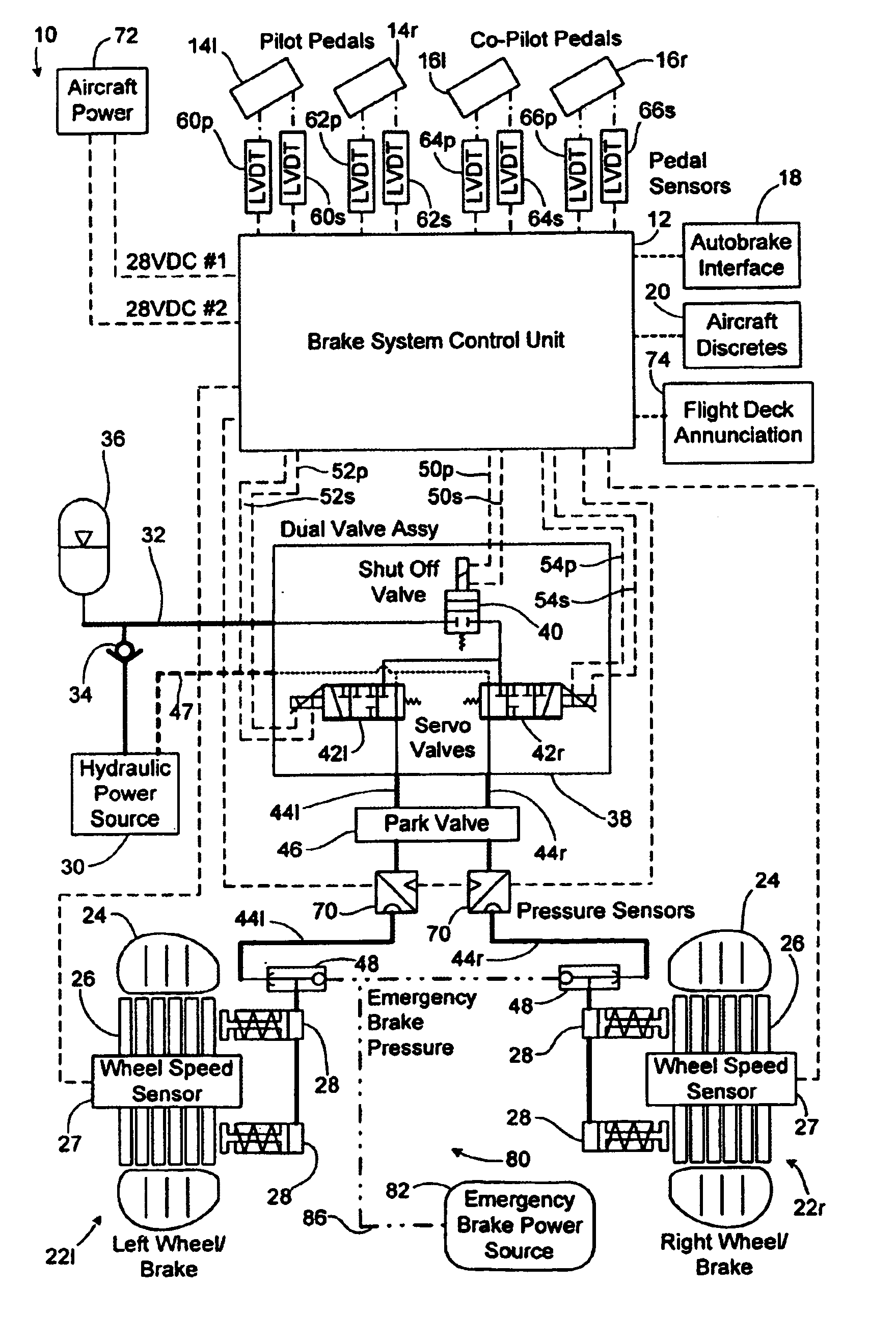
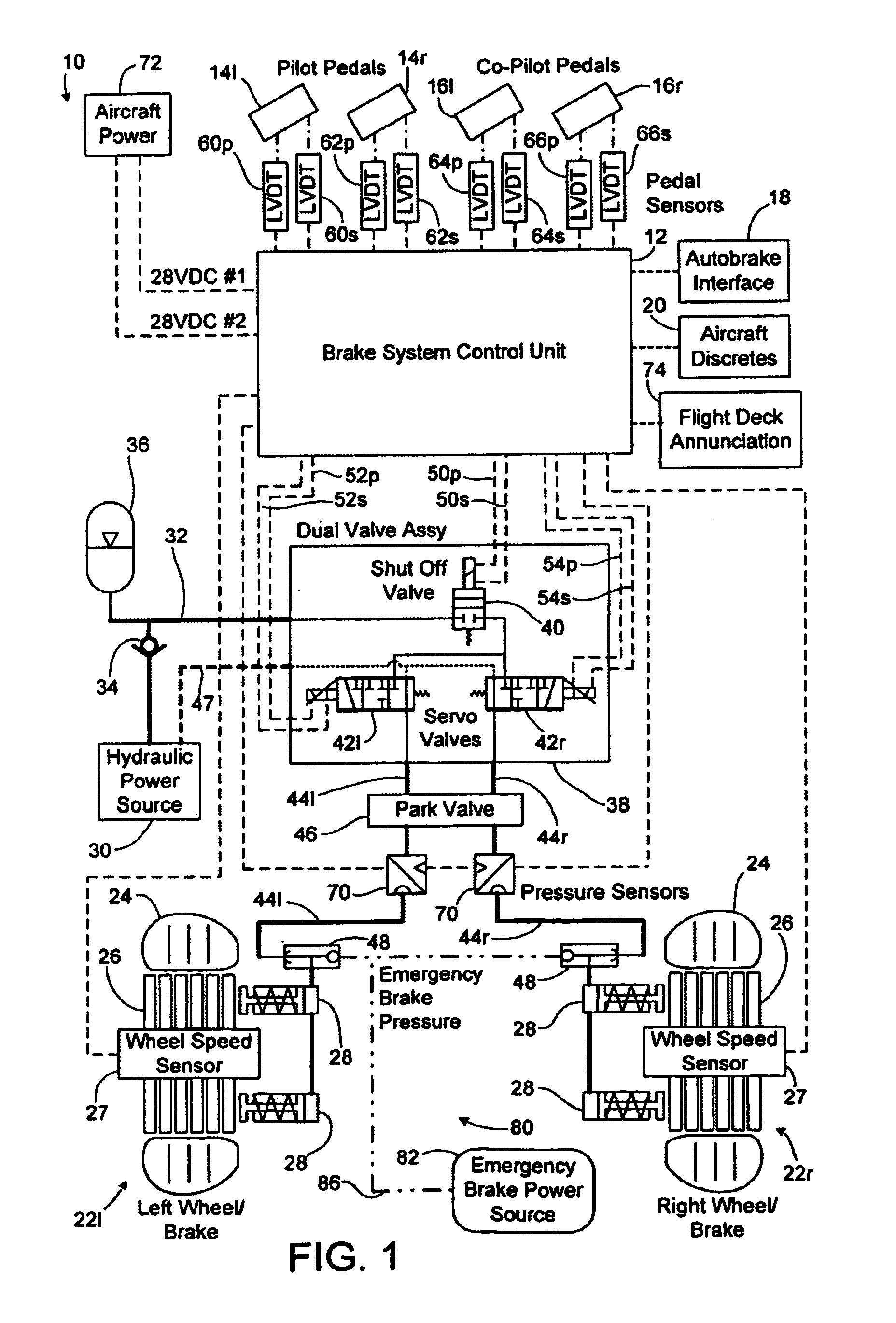
ActiveUS7128376B2Relieve stressAutomatic braking sequenceBraking action transmissionEngineeringControl theory
A redundant architecture for a brake-by-wire system is provided. The system includes a pressure source; at least one brake actuator for exerting a braking force on a wheel as a result of pressure provided by the pressure source; at least one servo valve for controlling an amount of pressure provided from the pressure source to the at least one brake actuator in response to a servo valve command signal; a shutoff valve in line with the at least one servo valve for preventing pressure from the pressure source from being provided to the at least one brake actuator in response to a shutoff valve command signal; a processor which executes code in order to carry out brake control operations, the processor outputting the servo command signal and the shutoff valve command signal in response to system inputs provided to the processor; a shutoff valve enable device for performing brake control operations redundant at least in part with the processor and based on the system inputs, and selectively enabling shutoff valve command signals from the processor to be provided to the shutoff valve based on the redundant brake control operations.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Brake system for motor vehicles and method for operating the brake system
A motor vehicle brake system actuated in brake-by-wire and fallback operating modes, having a brake master cylinder, brake circuits, a pressure medium storage vessel, a brake pedal, a separating valve for separating the brake circuit into a first section connected to the separating valve the master cylinder, and a second section connected to the separating valve and the wheel brakes. A first pressure provision device has a piston actuated by an actuator, a simulation device connected by a simulator release valve to the master cylinder for a pleasant brake pedal feel in the brake-by-wire operating mode. A first electronic control and regulating unit actuates the first pressure provision device, the separating valves and the simulator release valve. A second pressure provision device has a suction connector and a pressure connector per brake circuit being connected to the inlet of the separating valve.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Brake system for motor vehicles and method for operating a brake system
InactiveUS9145119B2Reduce travel requirementsBraking action transmissionBrake action initiationsMobile vehicleElectricity
A brake system includes a hydraulic actuating unit, which can be actuated by way of a brake pedal, a travel simulator interacting with the hydraulic actuating unit, a pressure medium reservoir under atmospheric pressure assigned to the hydraulic actuating unit, a first electrically controllable pressure supply device, a second electrically controllable pressure supply device, an electronic control unit and an electronically controllable pressure modulation device for setting wheel-specific brake pressures. The brake system preferably operates in a “brake-by-wire” mode but can also operate in a fallback mode. The second electrically controllable pressure supply device can provide boost volume during braking in a fallback mode.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Energy regeneration device of drive-by-wire braking system and control method of braking system
ActiveCN102442286AImprove starting performanceImprove acceleration performanceAuxillary drivesBraking element arrangementsElectric machineElectromagnetic clutch
An energy regeneration device of a drive-by-wire braking system comprises a gearbox, an oil tank, an electromagnetic clutch, a hydraulic oil pump / motor, an electromagnetic distributing valve, a first electromagnetic reversing valve, a high-pressure energy accumulator, a second electromagnetic reversing valve and a low-pressure energy accumulator. A hydraulic brake is additionally arranged on a brake disc of each wheel, and an increasing gear mechanism is additionally mounted on an output shaft of the gearbox. By the aid of a method for accumulating and releasing braking energy, accumulated energy of the high-pressure energy accumulator can be released when an automobile starts and accelerates, a starting performance and an acceleration performance of the automobile are improved, accumulated energy in the low-pressure energy accumulator can also be directly applied to the wheels during braking and used with a braking motor of the drive-by-wire braking system to realize braking of the automobile, and braking energy recycle efficiency is improved. When the drive-by-wire braking system fails and cannot work normally, the device can be used as an emergency braking system, and the accumulated energy in the energy accumulators is used for realizing parking braking of the automobile. The energy regeneration device is particularly suitable for pure electric automobiles.
Owner:江苏久通汽车零部件有限公司
Brake by-wire control system
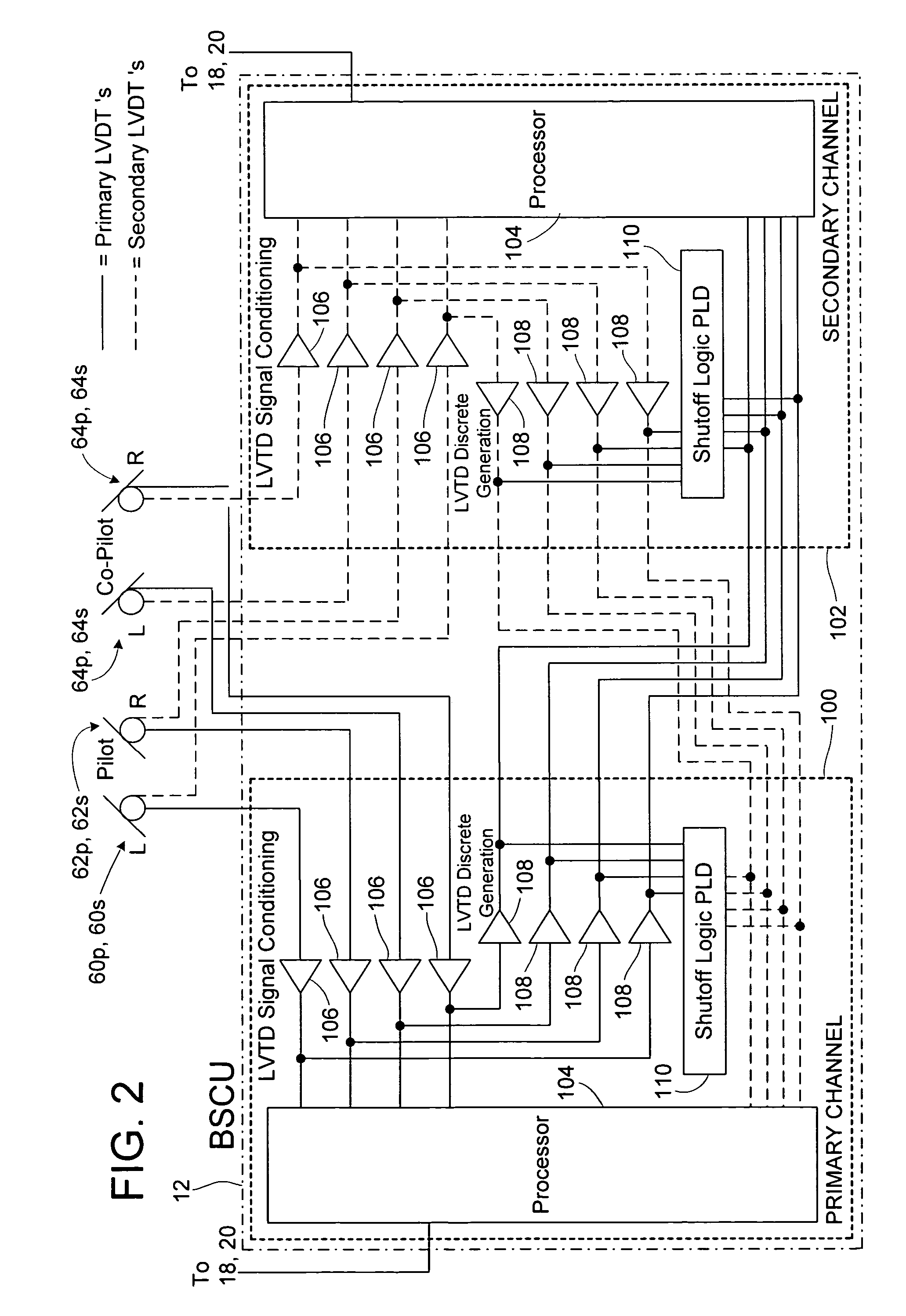
InactiveUS20050225165A1Reduce system complexityIncrease redundancyBraking action transmissionBrake control systemsController architectureControl system
A brake control system for brake by wire applications having a dual fail-silent pair controller architecture. The system utilizes two supervisory controllers and a shared monitoring controller to achieve the dual fail-silent pair configuration. The brake control system also features a mechanism whereby the monitoring controller ensures the fail-silent operation of the brake control units in the event of certain undesired events occurring within the system by assuming control of the affected brake control units. The control system further assures that no single event, including an event related to the monitoring controller, causes loss of more than half the braking functionality. The control system also features additional redundancy with regard to the brake command signals by sharing a separate unprocessed brake command signal with each of the supervisory controllers and the monitoring controller.
Owner:GENERAL MOTORS COMPANY
Brake system for a vehicle
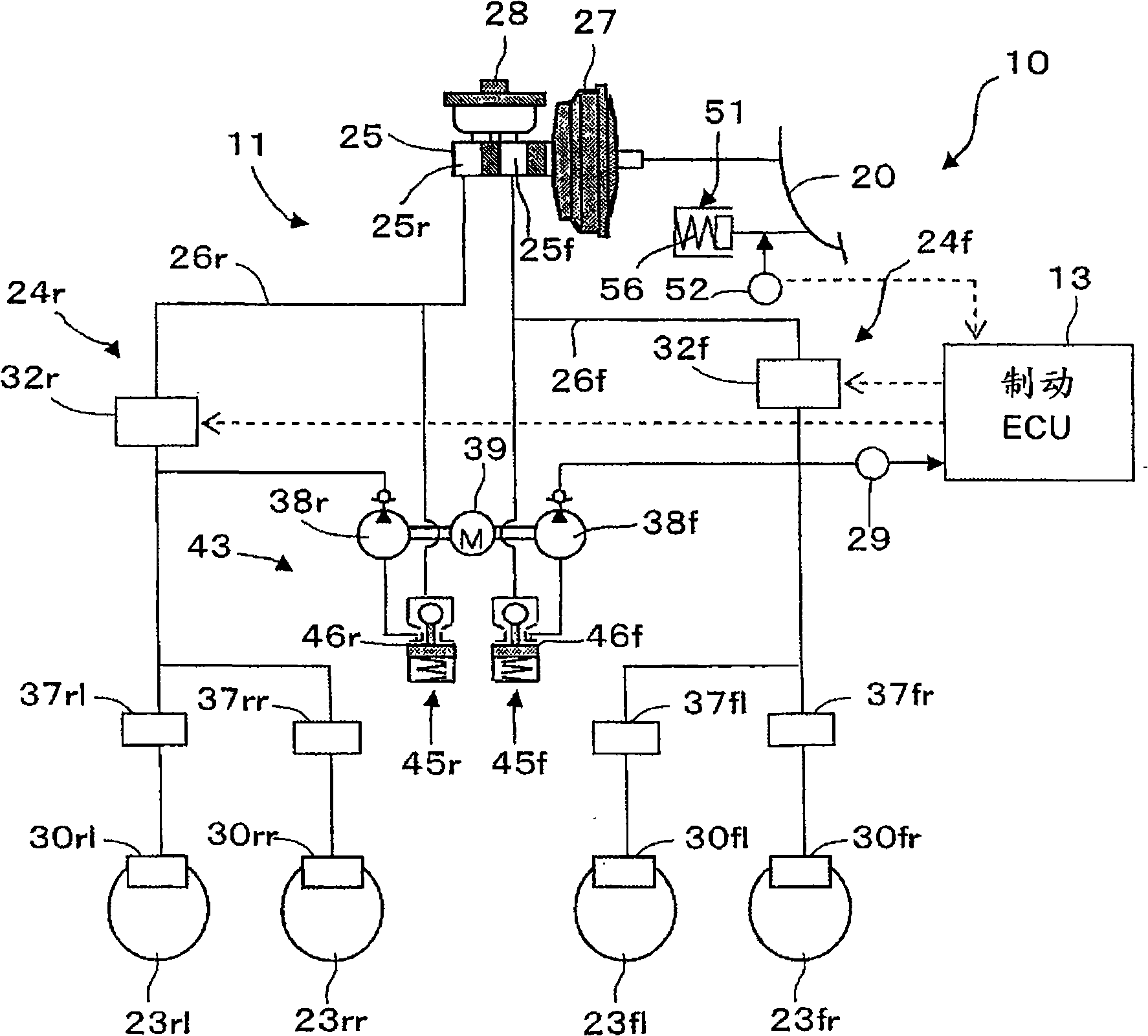
InactiveUS20100114444A1Achieve feedbackFully activeAnalogue computers for trafficComputations using stochastic pulse trainsAudio power amplifierPiston
The invention relates to a braking system (1) comprising an actuator unit (10), said actuator unit comprising a brake pedal (2), a pedal simulator (4), and a brake servo (12), and a main brake cylinder (20) by way of which at least one wheel brake (42, 44, 46, 48) may be actuated, said wheel brake having a braking pressure that may be predetermined, wherein the brake pedal (2) or the brake servo (12) acts on the main brake cylinder (20) to increase or decrease a braking force. According to the invention, during a first operating mode, preferably a brake-by-wire operating mode, the braking force amplifier (12), controlled by an analysis and control unit (11), generates an outside force that acts on a piston (21) of the main brake cylinder (20), wherein the actuator unit (10) comprises a first transmission device (5) that, controlled by the analysis and control unit (11), mechanically decouples the brake pedal (2) from the piston (21) of the main brake cylinder (20) as a function of predetermined criteria during the first operating mode, or couples the brake pedal (2) to the piston (21) of the main brake cylinder (20) such that the pedal force generated at the brake pedal (2) additionally acts at least partially on the piston (21) of the main brake cylinder (20).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Dual-motor BBW (brake-by-wire) system with multiple working modes and voltage regulation modes
ActiveCN103552556AFeel adjustableWith active braking functionBraking action transmissionFoot actuated initiationsAxial thrustWheel cylinder
The invention discloses a dual-motor BBW system with multiple working modes and voltage regulation modes. A brake fluid in a manual cylinder flows into two main cylinders by means of a brake pedal, and brake pressure is generated; and meanwhile, output power torque of two motors is controlled, and axial thrust is overlaid to pistons of the two main cylinders through a transmission device, so that electric power brake is realized. Through control of output torque of the two motors, pressure of the two main cylinders is transmitted to wheel cylinders, brake by wire is realized, and a pedal travel simulator is used for providing force for the brake pedal. Under the condition that the brake pedal is not stepped, the output torque of the two motors is controlled, so that the two cylinders generate pressure which is transmitted to the wheel cylinders through a hydraulic control unit, and accordingly, the active brake is realized. The invention further discloses a structure of a hydraulic control system, and the structure has multiple voltage regulation modes. The dual-motor BBW system has the advantages as follows: the system has multiple braking modes and voltage regulation modes, the most appropriate braking mode and voltage regulation mode can be selected according to dynamic properties of the motors during implementation and application, the reliability is high, and the failure protection capacity is high.
Owner:南京经纬达汽车科技有限公司
Electronic and mechanical drive-by-wire brake
ActiveCN107477109ASimple structureWork reliablyAxially engaging brakesBrake actuating mechanismsMotor driveControl system
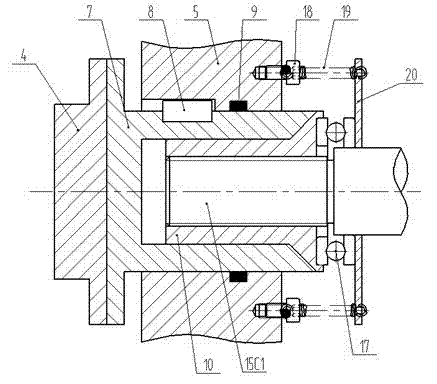
The invention relates to an electronic and mechanical drive-by-wire brake. The electronic and mechanical drive-by-wire brake comprises a motor, a transmission mechanism, a one-way clutch, a cam, a piston, a friction limiting device and the like. The motor drives the one-way clutch to rotate through the transmission mechanism, the one-way clutch is united to drive the cam to move, the piston and a brake caliper body are driven to move in the opposite direction, friction plates are compressed with the same force from the two sides of a brake disc, and an efficient braking effect is achieved. The electronic and mechanical drive-by-wire brake is simple in structure, reliable in work and high in braking efficiency, and can automatically adjust the brake clearance, compensate the influence caused by friction plate wear, simplify the design of a control system and be used for service braking and parking braking.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
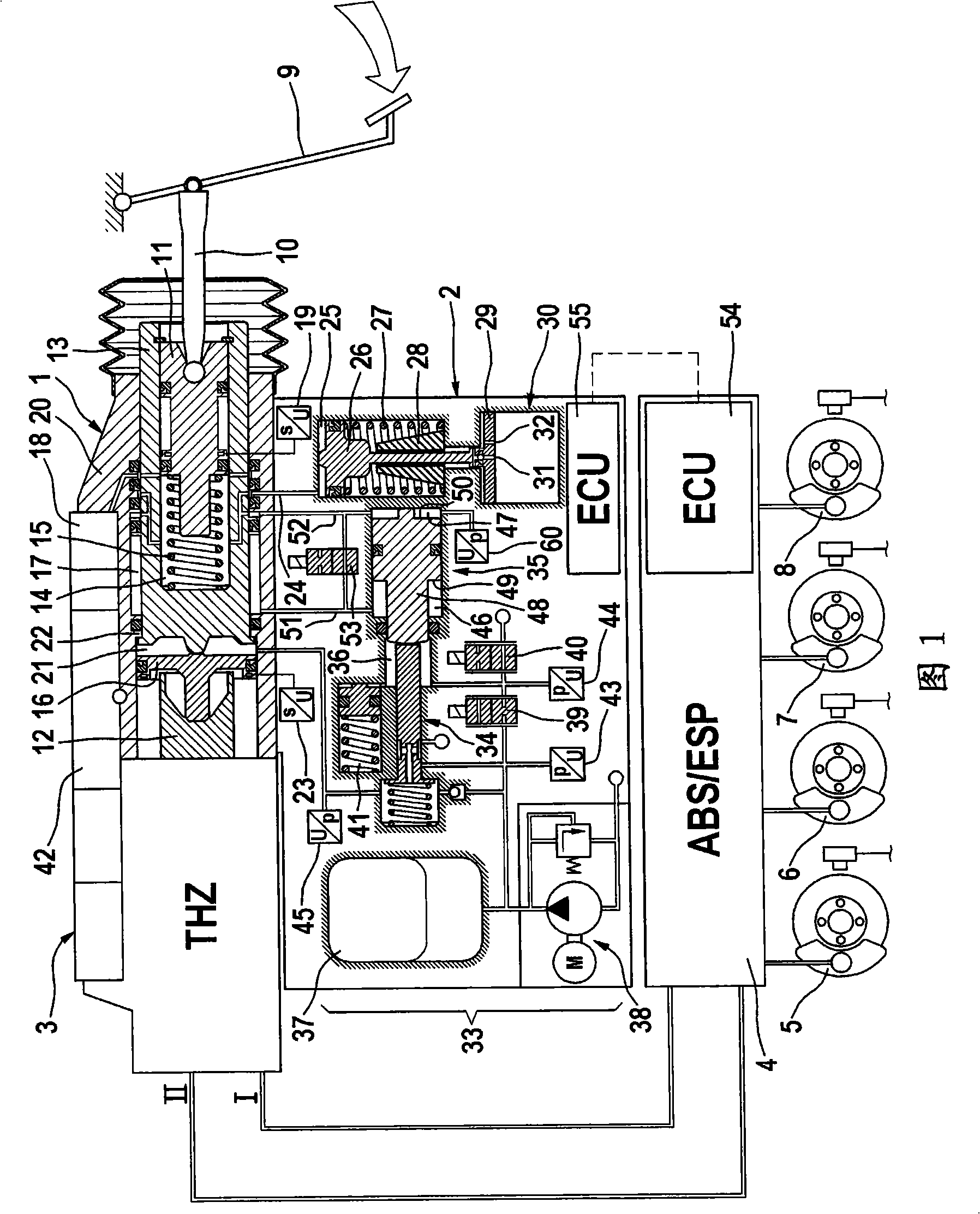
Method and device for controlling or regulating the brake system of a motor vehicle according to the "brake by wire" principle
InactiveUS20050173980A1Improve availabilityImprove reliabilityDigital data processing detailsFoot actuated initiationsMobile vehicleMeasurement device
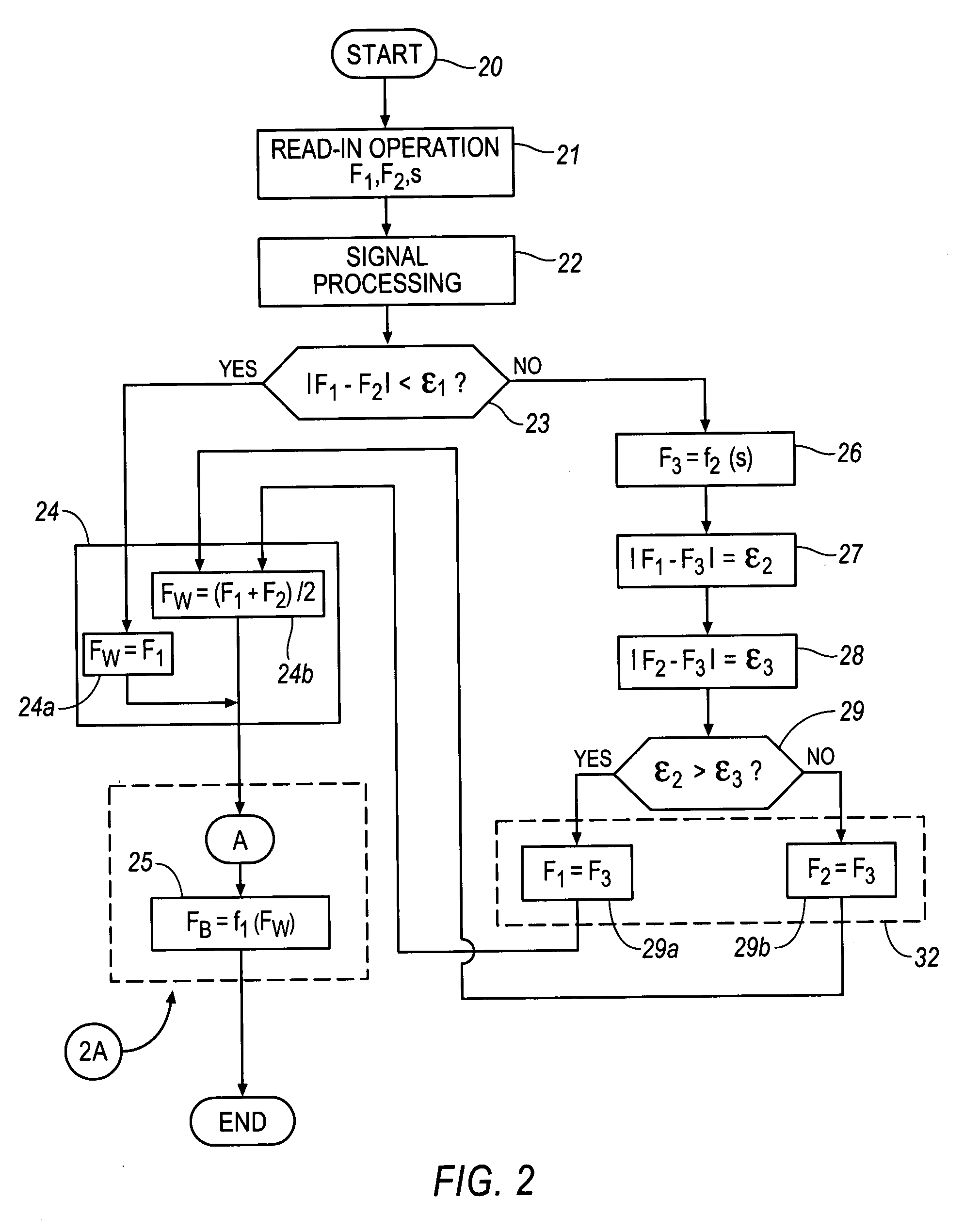
The most important aspect of brake systems in motor vehicles functioning according to the brake-by-wire principle is that the driver's braking requirements are detected quickly and reliably. Fulfilling this requirement primarily depends on the pedal sensor system associated with the brake pedal and its measuring devices for determining the characteristic values of the brake pedal actuation. The present invention provides for at least two measuring devices for determining the braking requirement, with such measuring devices sensing the same characteristic value of the brake pedal actuation, e.g. the brake-pedal actuation force, brake-pedal travel or brake-pedal angle. These braking requirement signals are compared to a signal from a third measuring device in order to monitor the braking requirement measuring devices.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
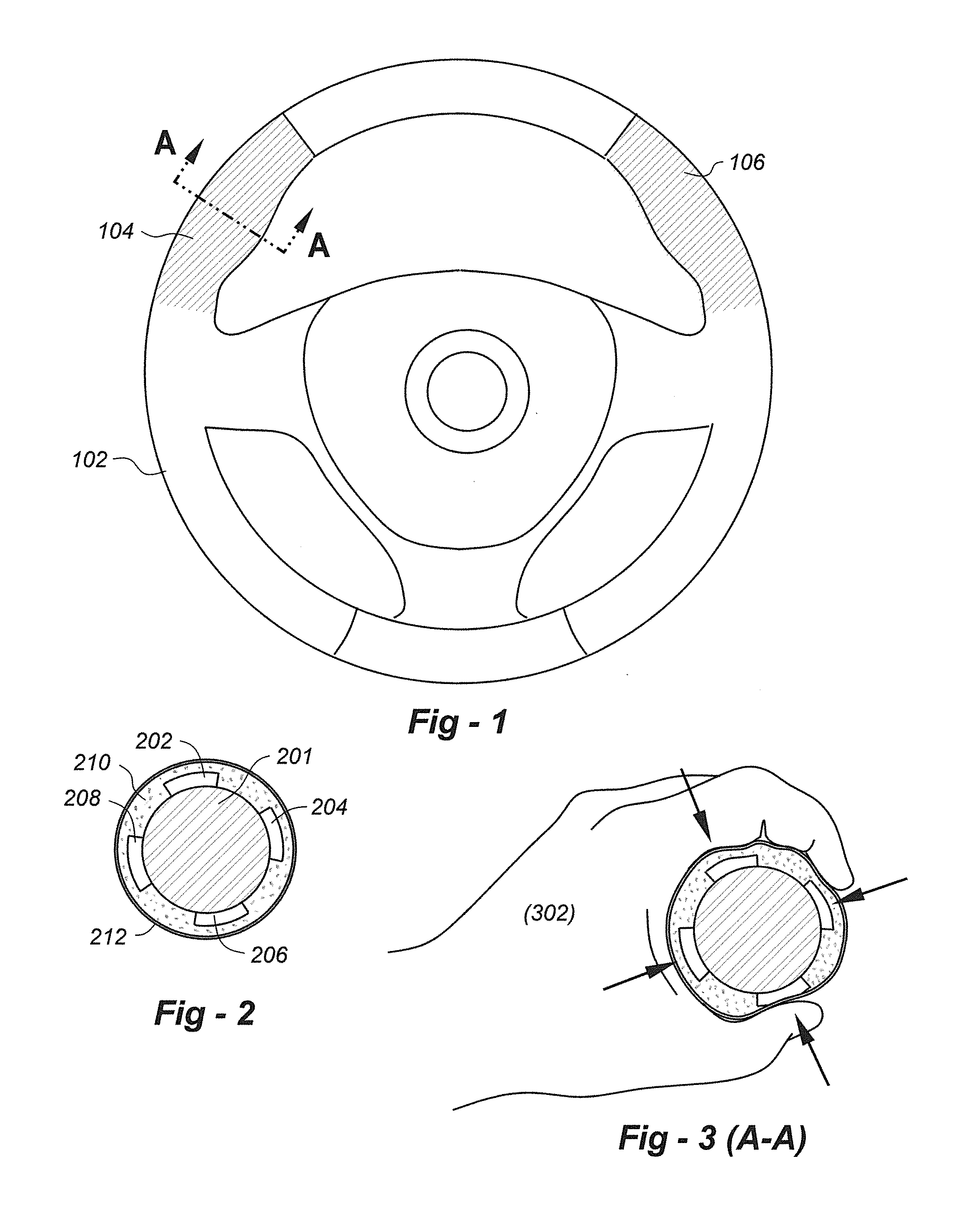
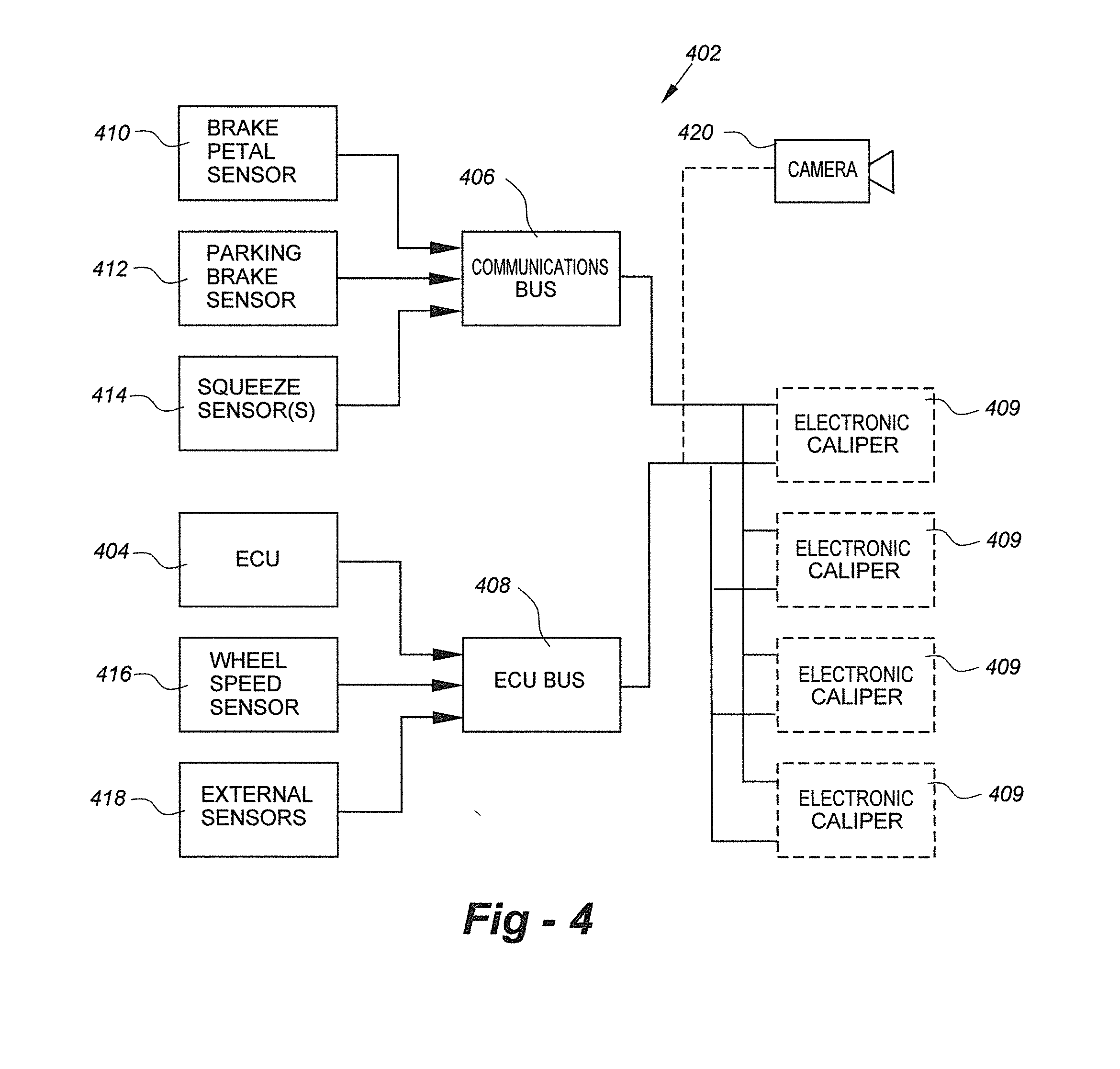
Steering wheel squeeze-activated vehicle braking system
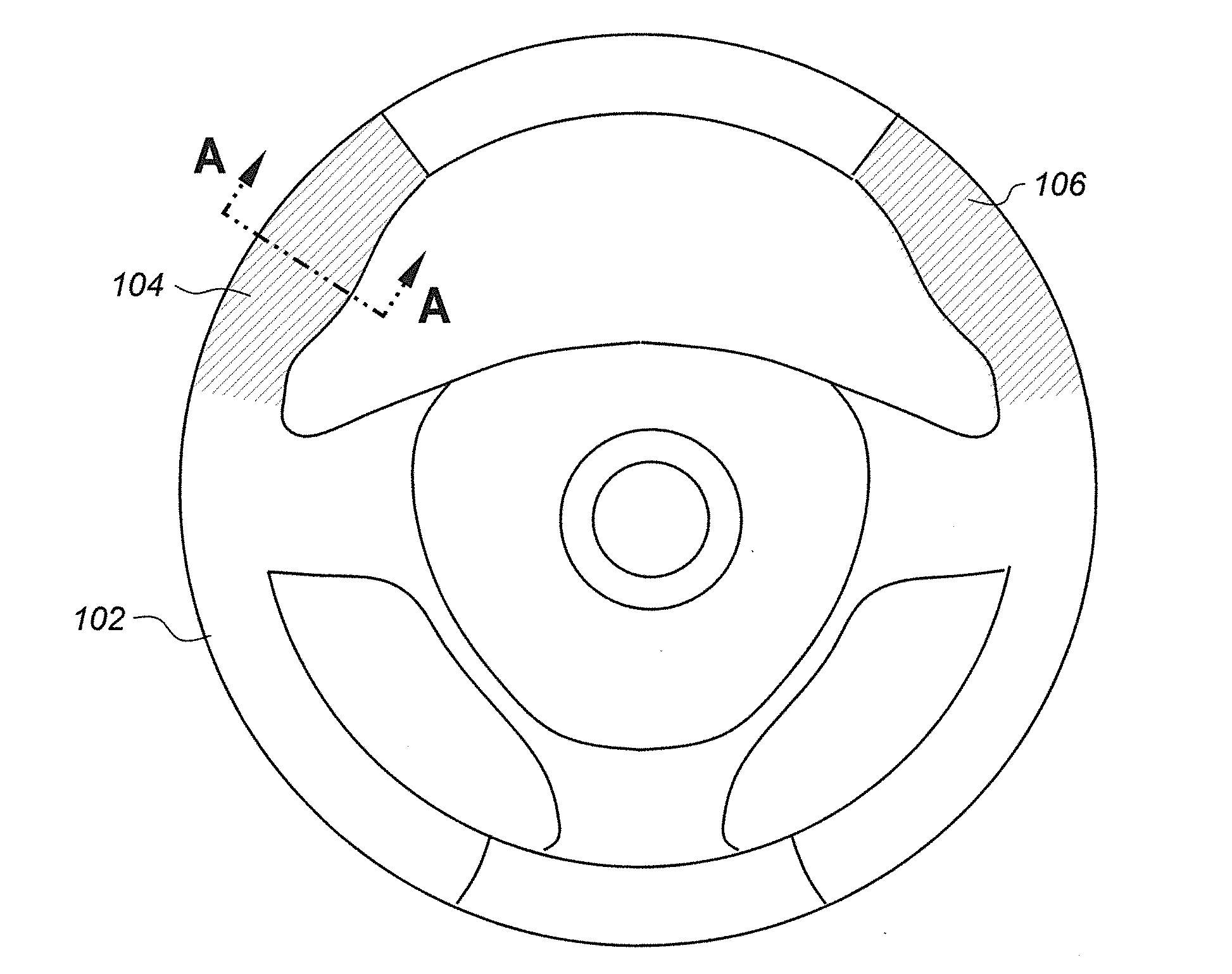
ActiveUS20140224600A1Stop his or her vehicle more quicklyFaster vehicle stopBraking action transmissionElectrodynamic brake systemsLow speedDriver/operator
A brake-by-wire vehicle braking system is augmented with “squeeze” sensors placed in the steering wheel of the vehicle enabling a vehicle operator to stop the vehicle more quickly in an emergency situation by eliminating the significant times that it takes to move a driver's foot from the accelerator to the brake pedal and then depress the brake pedal. An important objective is to achieve a faster vehicle stop by allowing the driver to optionally eliminate foot movement from the accelerator pedal to the brake pedal and also the depression of the brake pedal. This invention also potentially allows a driver to squeeze a steering wheel to slow a vehicle, perhaps to comply with a lower speed limit, or accomplish the fastest possible “hard-stop” in an emergency situation.
Owner:REDEVEX
Brake system for motor vehicles
InactiveCN102099231ABraking action transmissionBrake action initiationsMotor vehicle partMaster cylinder
The invention relates to a brake system comprising a main brake cylinder (4) and a pedal decoupling unit (2) provided with a holding piston (18), the first ring surface thereof (26) together with a first primary brake cylinder piston (22) defining a first hydraulic chamber (23) that is hydraulically pressurised with an electrically controllable pressure supply device (3). In order to improve the pedal characteristics of the brake system, in particular in a brake-by-wire brake system, the holding piston (18) is embodied as a differential piston, the second ring surface (27) thereof defining a second, blockable hydraulic chamber (28), and a piston that effects in the second chamber (28) corresponds to a force that acts counter to the direction of actuation on the holding piston.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Brake system
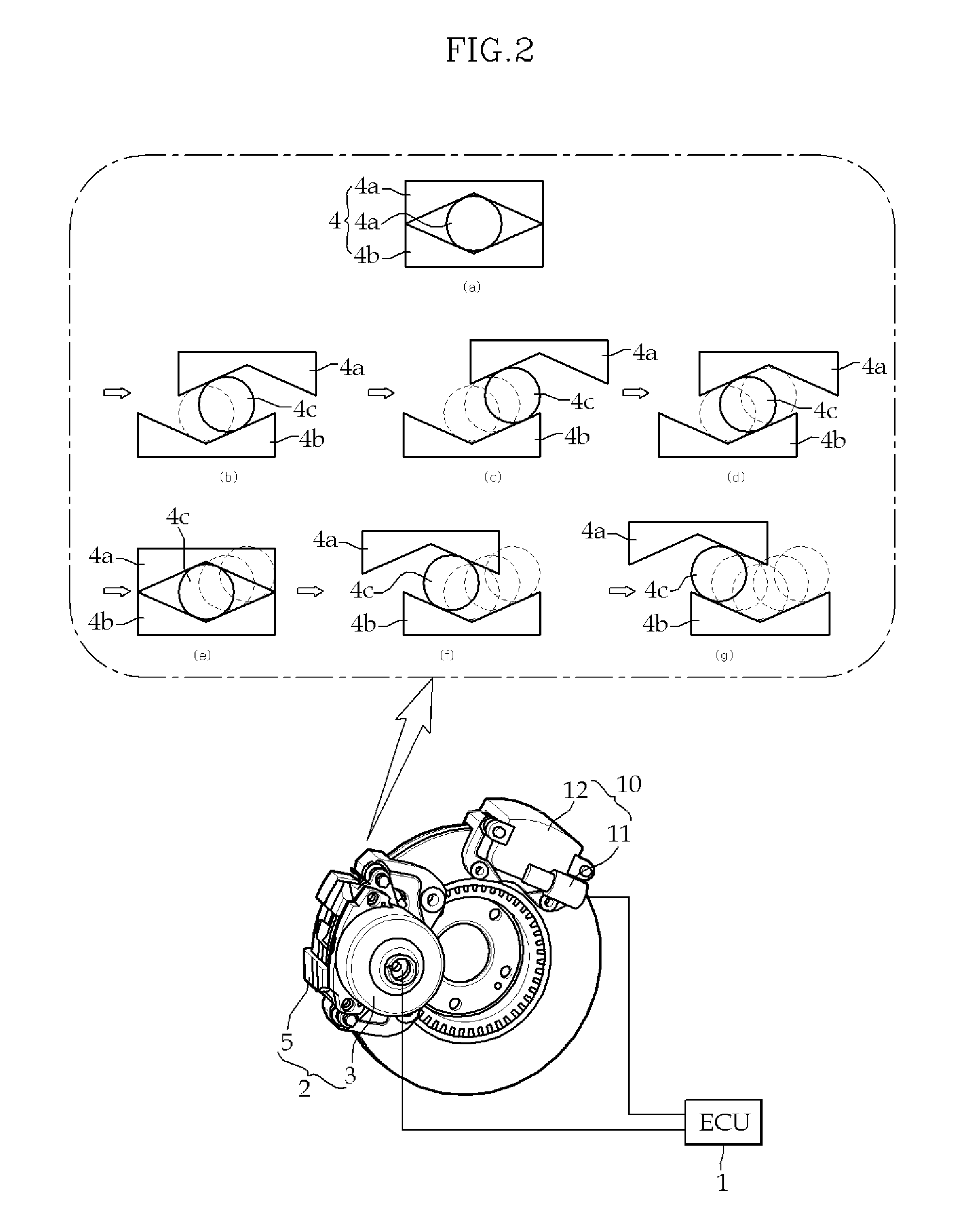
ActiveUS20100147633A1Minimize priceMinimize weightMechanically actuated brakesBrake control systemsFailure rateHydraulic brake
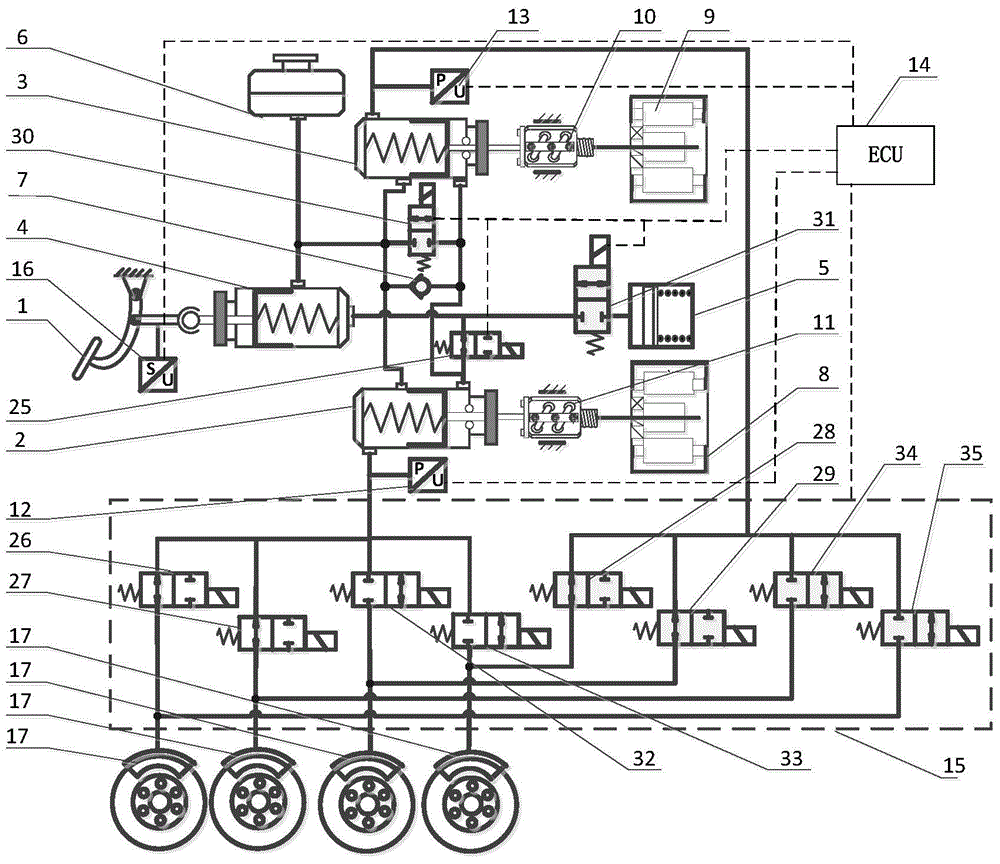
A brake system of the present invention is a dual braking system, which includes an ECU that controls parts for braking when a brake pedal is operated, a main brake that is controlled by ECU by locking a wheel disc for braking in normal braking, and a sub-brake that is mounted on the wheel disc and achieves sub-braking function to achieve emergency braking for safety by locking the wheel disc by control of ECU that has detects failure of main brake. Therefore, it is possible to improve safety by achieving emergency braking while achieving F-S (Fail-Safe), when the motor of main brake fails. Further, it is possible to also achieve stable FR (Failure Rate) in an EWB or an EMB that is practically applied to a vehicle, as in a hydraulic brake system, and to expedite common use of brake systems where a BBW (Brake By Wire) technology, such as EMB and EWB, is applied.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOBIS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com