Patents
Literature
85results about "Automatic braking sequence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
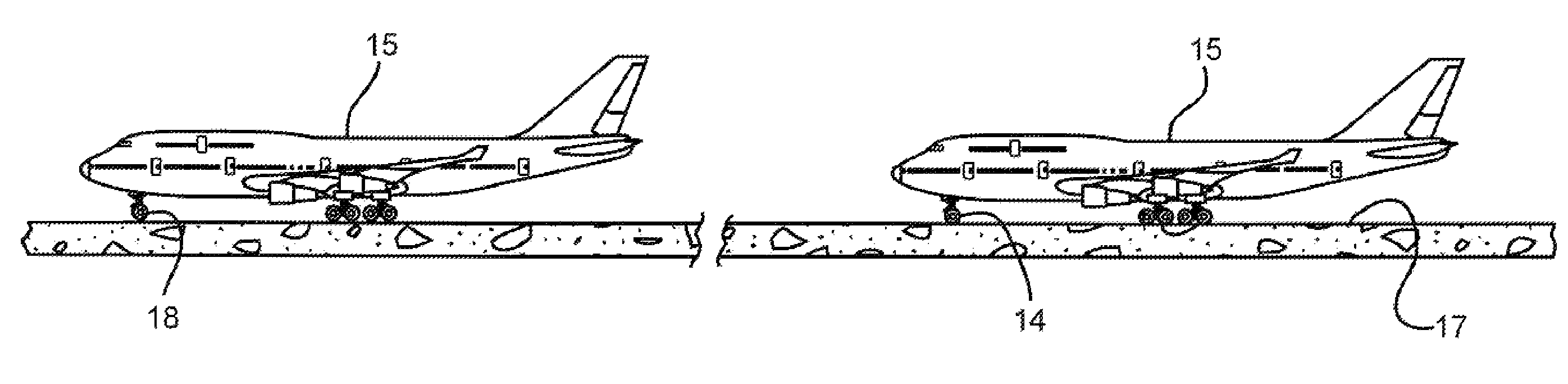
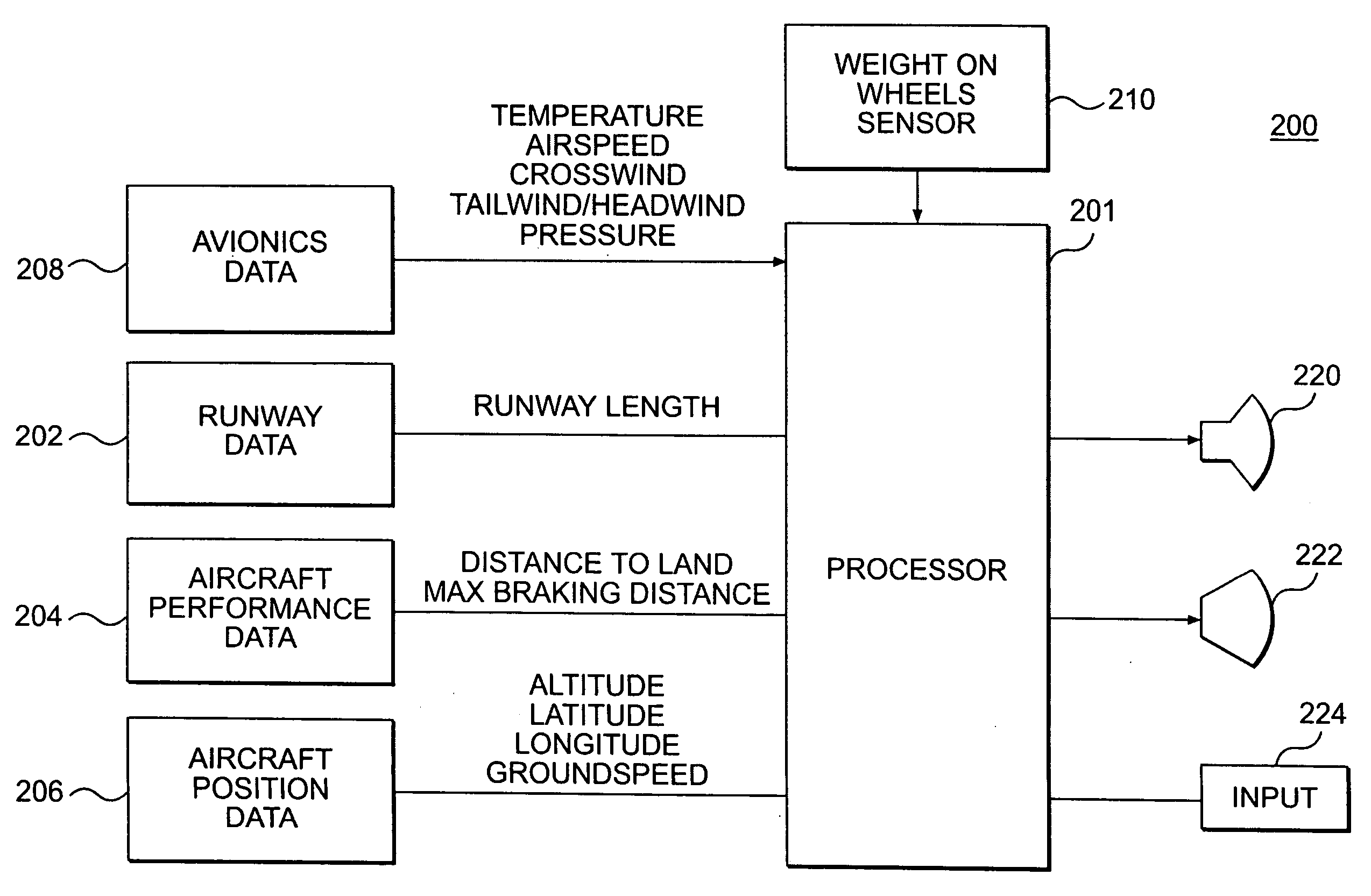
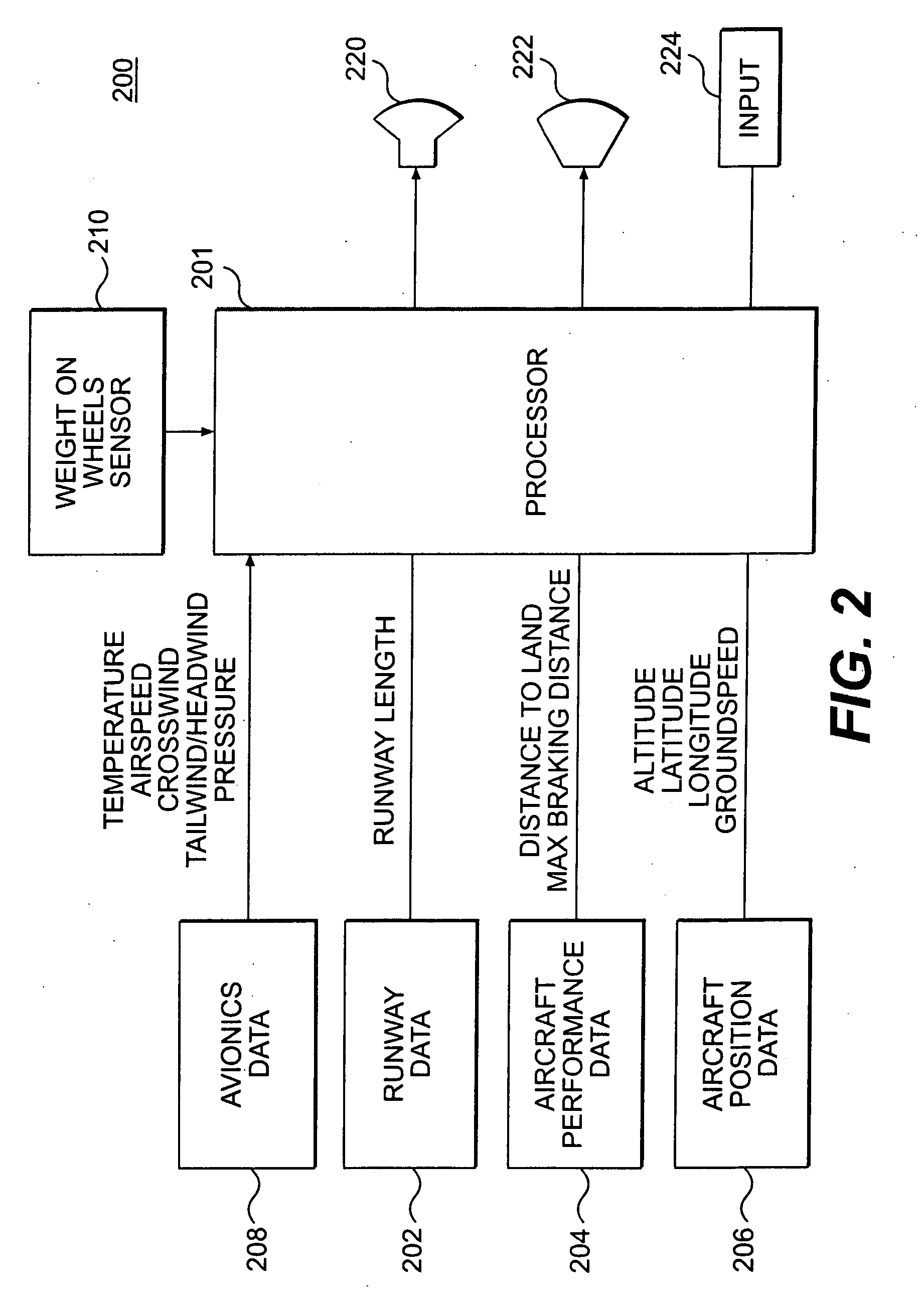
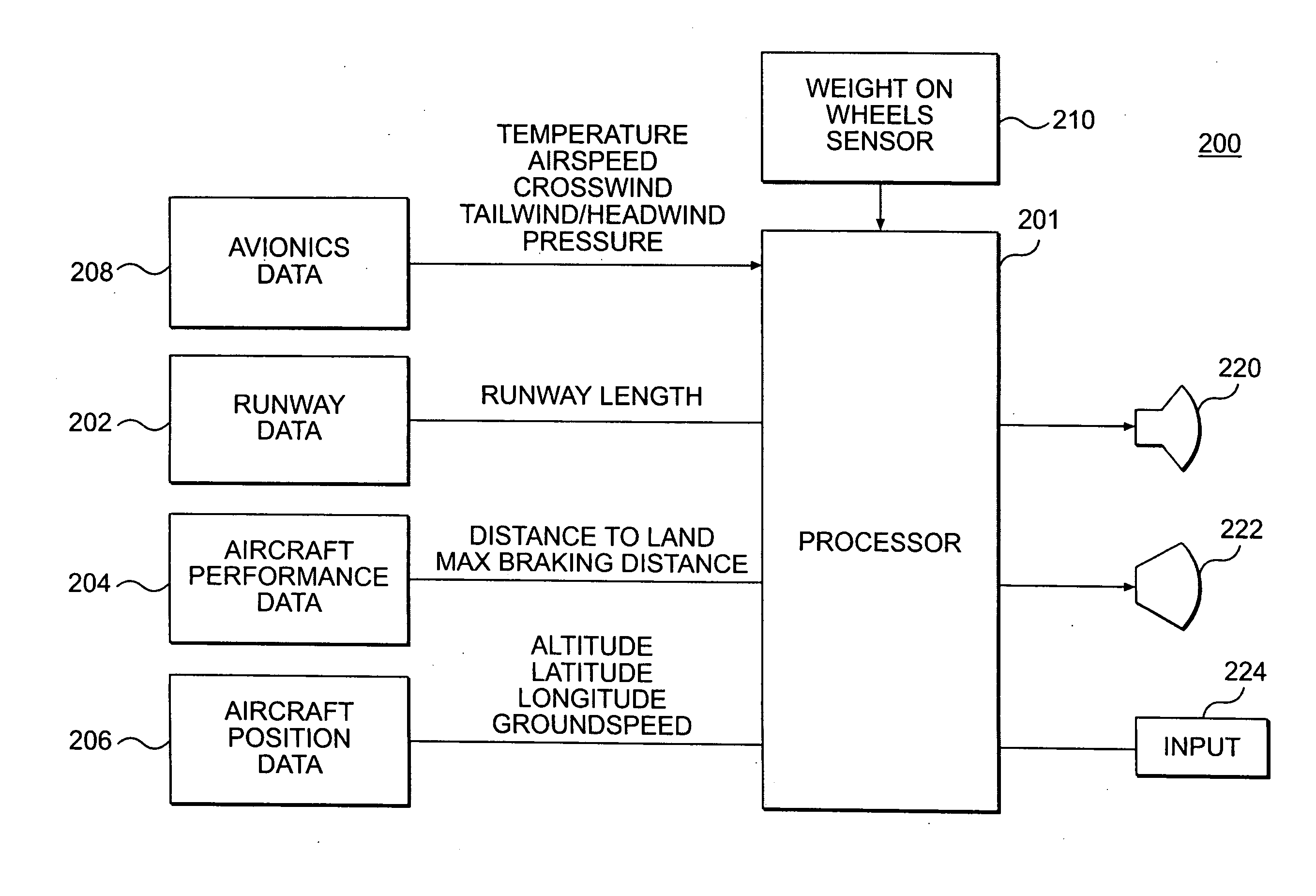
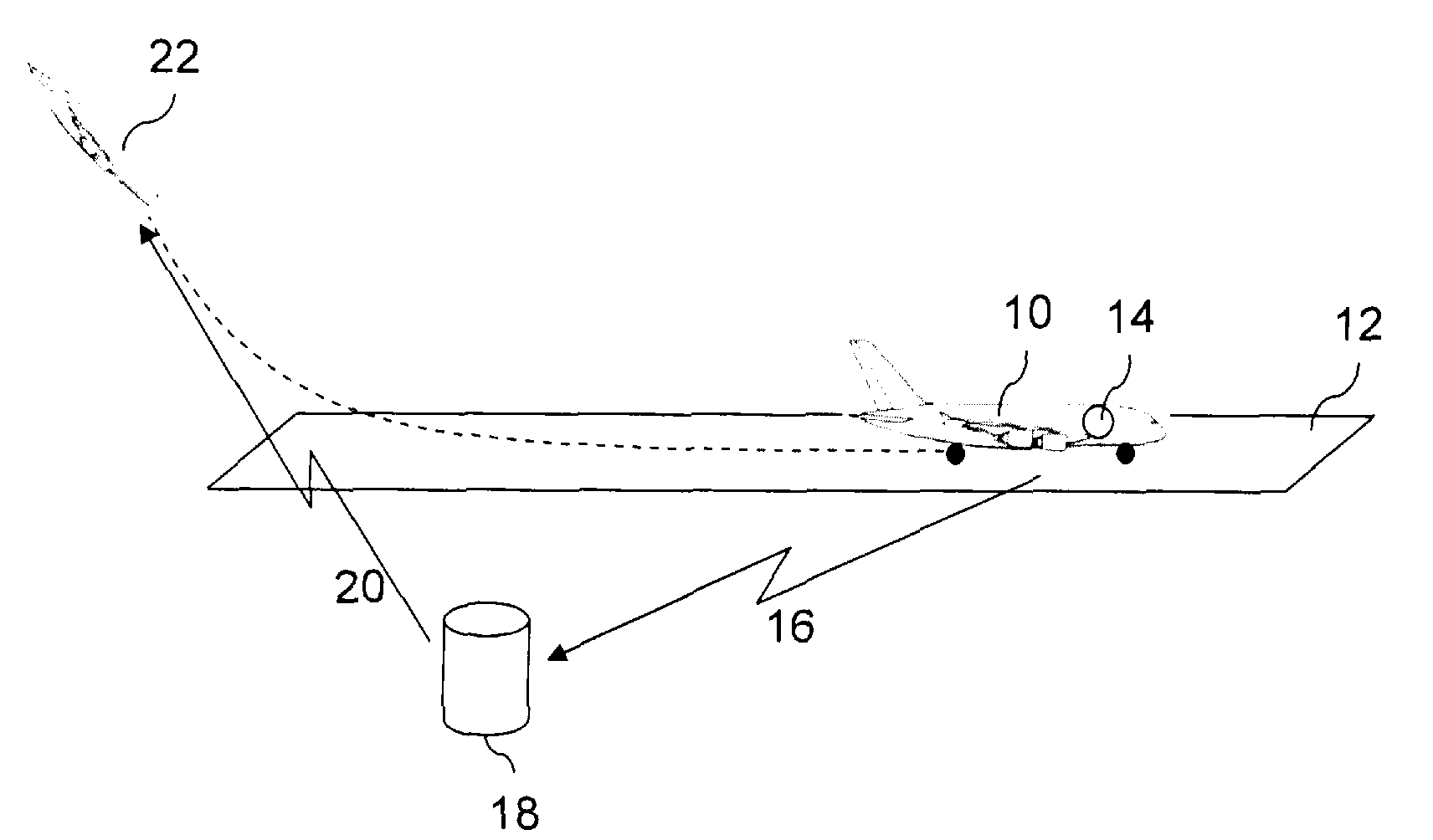
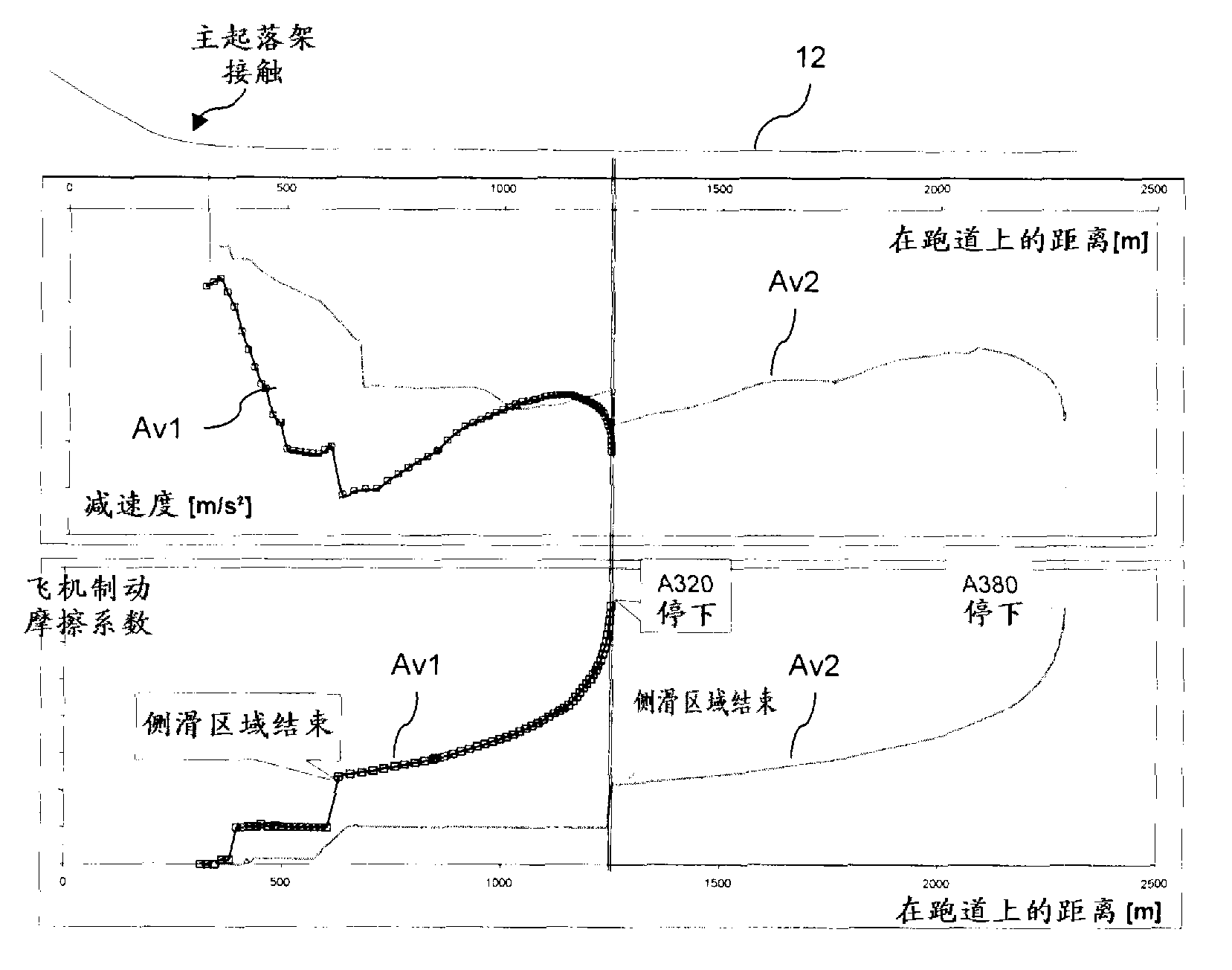
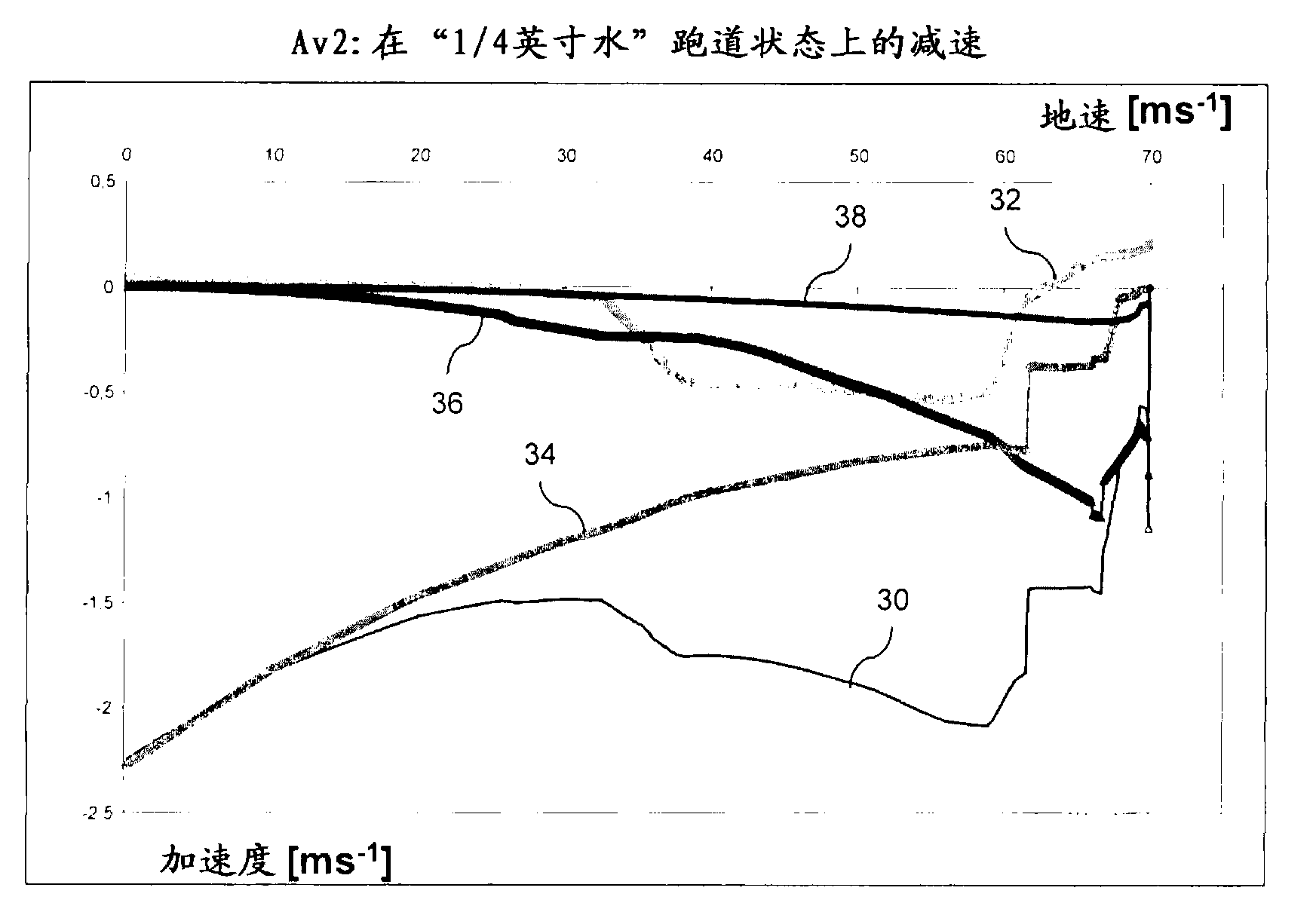
Determination of runway landing conditions
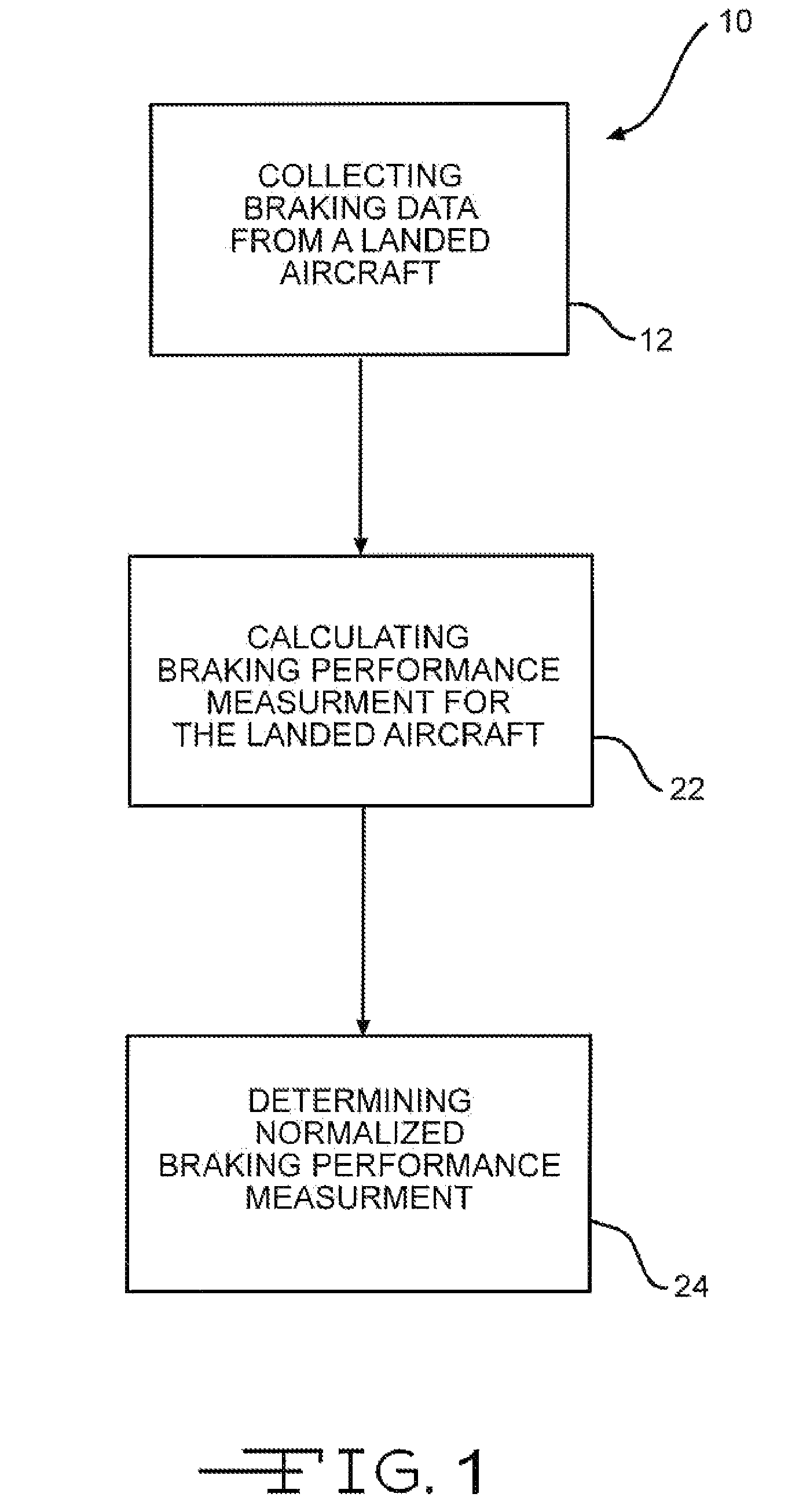
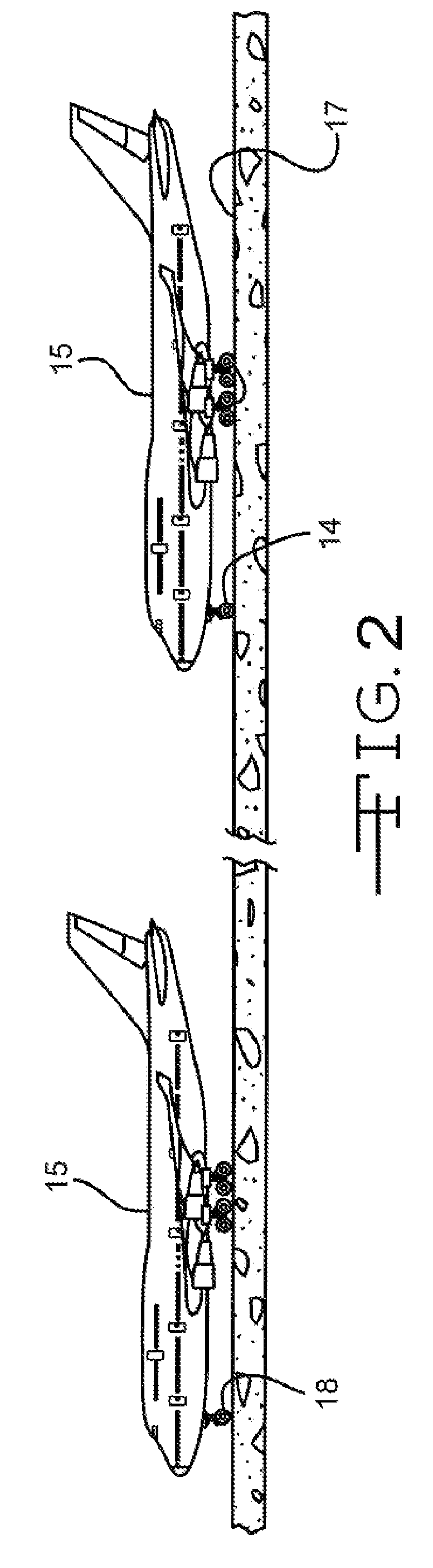
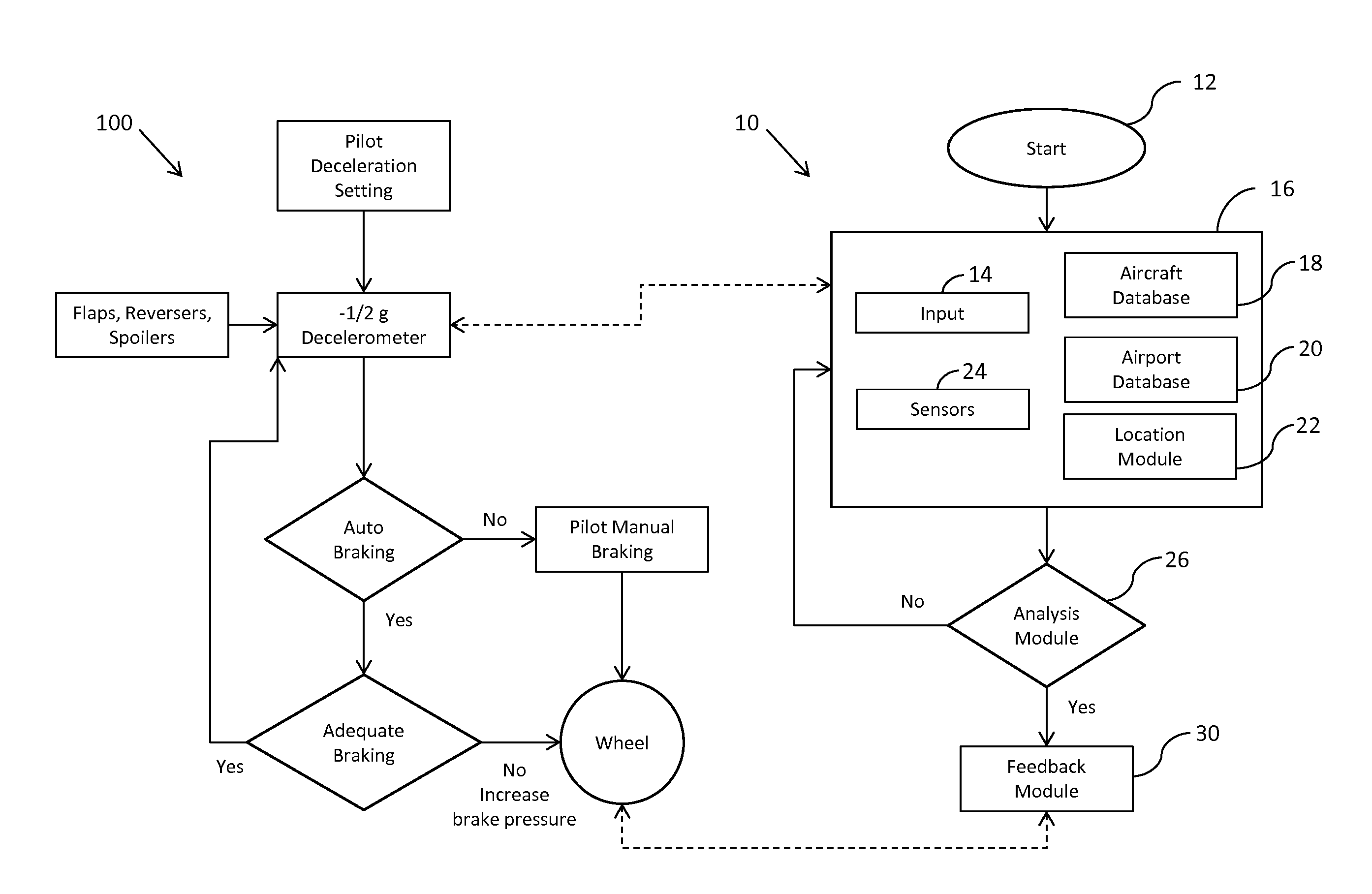
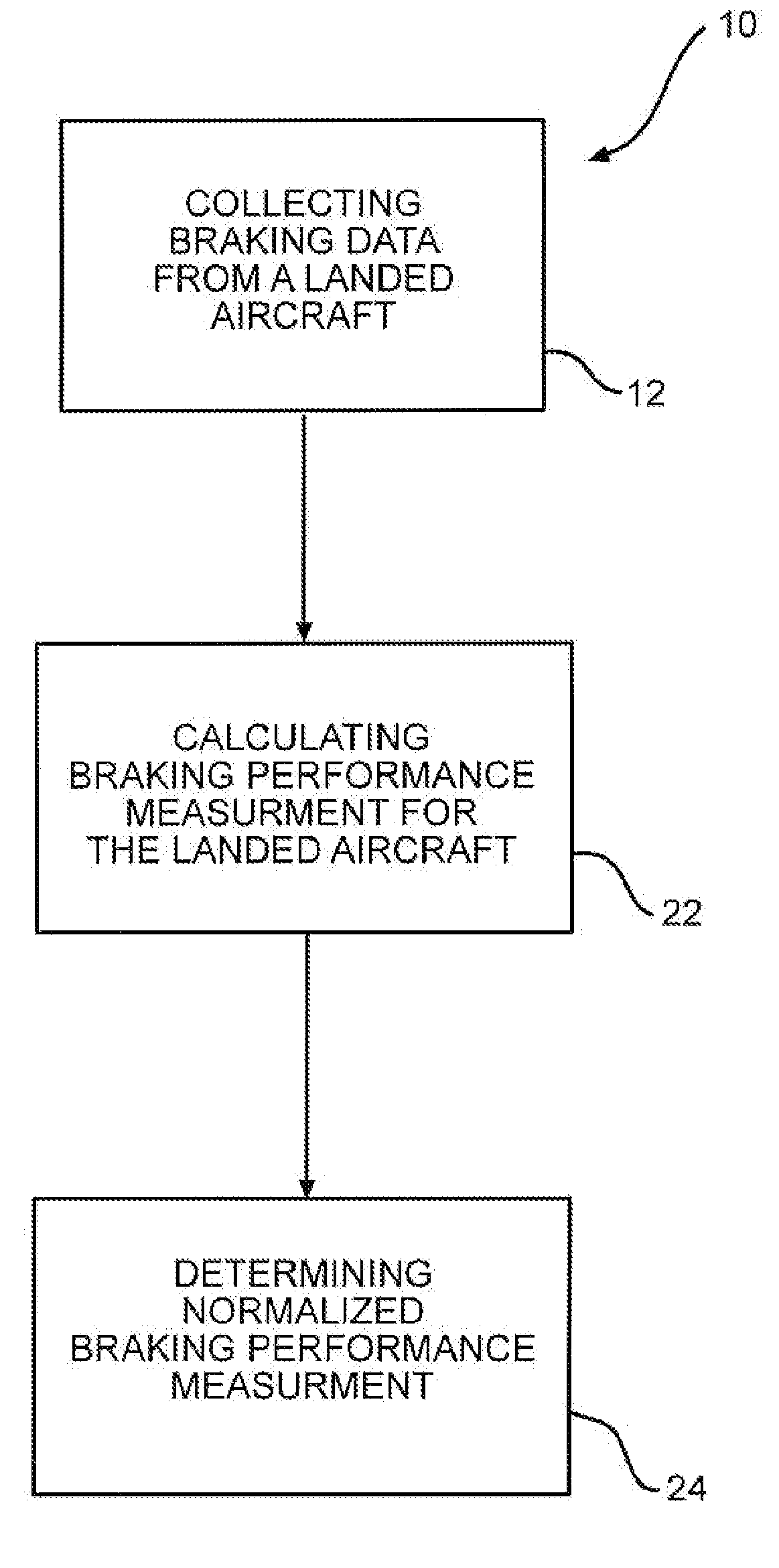
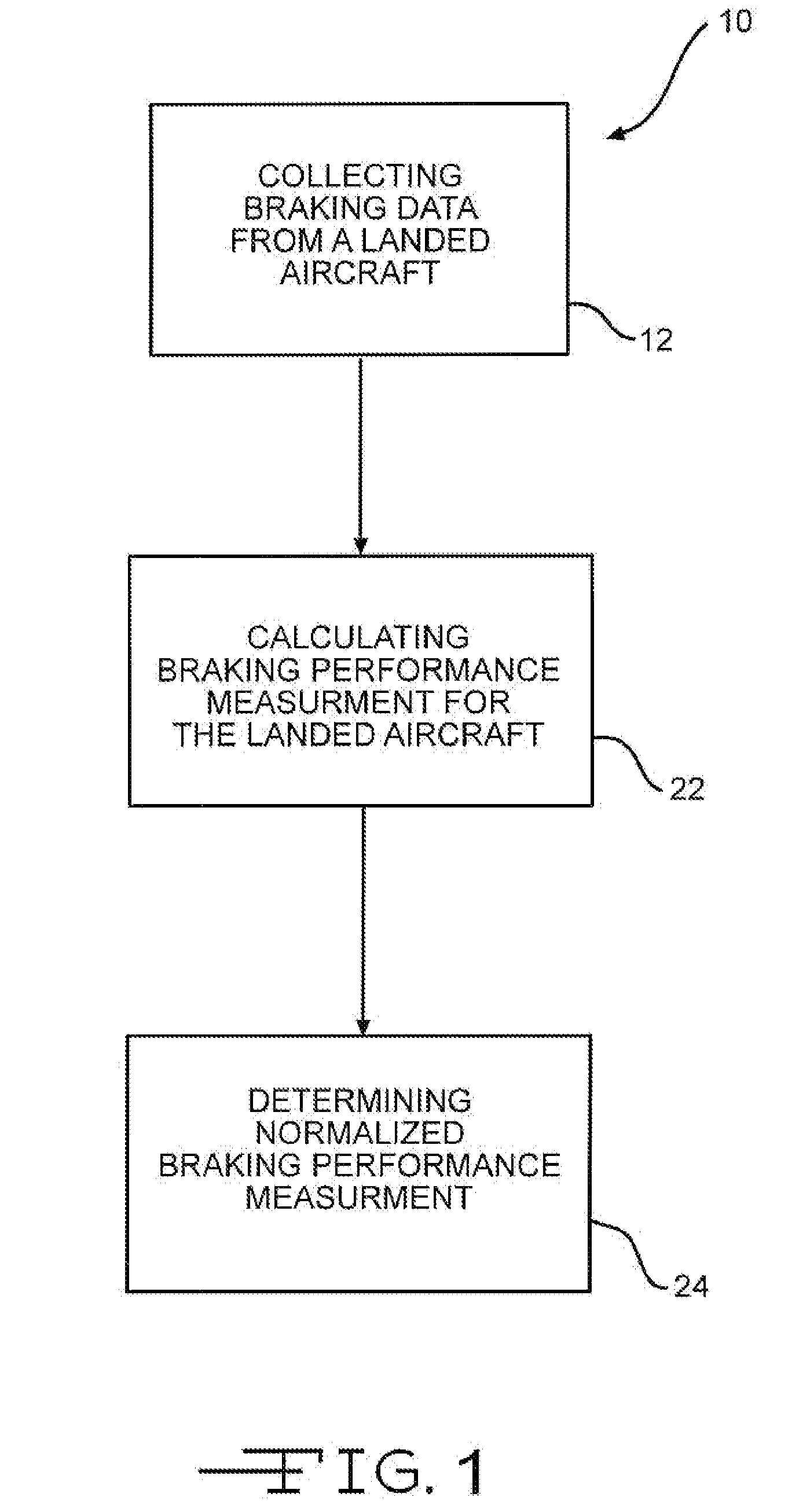
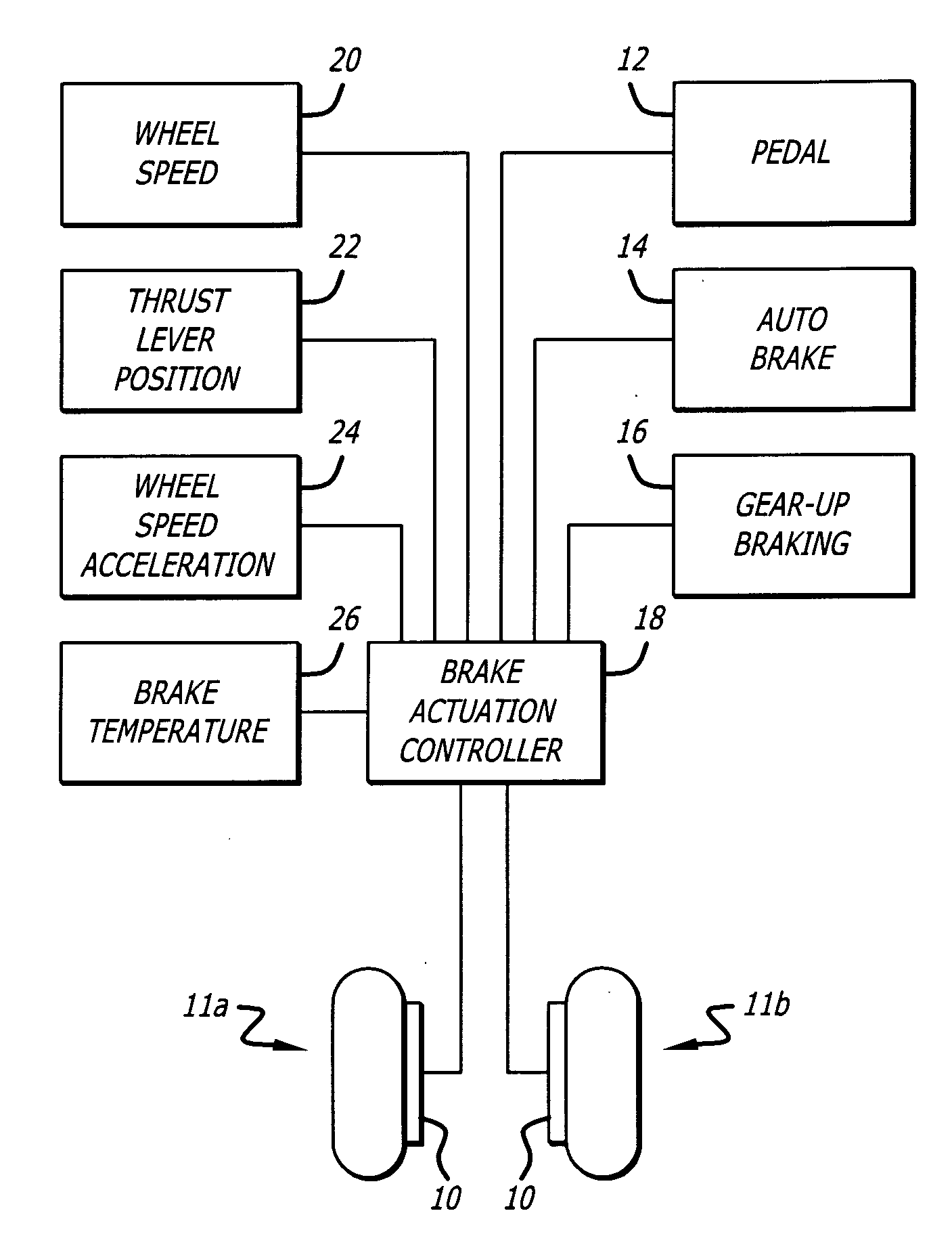
The invention discloses differing embodiments of methods, aircraft, and apparatus for determining the landing conditions of a runway. In one embodiment, braking data may be collected from an aircraft which has landed on the runway; a braking performance measurement of the aircraft may be calculated based on the braking data; and a normalized braking performance measurement may be determined based on the braking performance measurement. The invention may be utilized to predict the expected braking performance of various types of aircraft on the runway. The invention may provide landing performance information to a broad host of users, and / or may be used as a basis for the development of a new aviation standard for the reporting of runway braking action.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
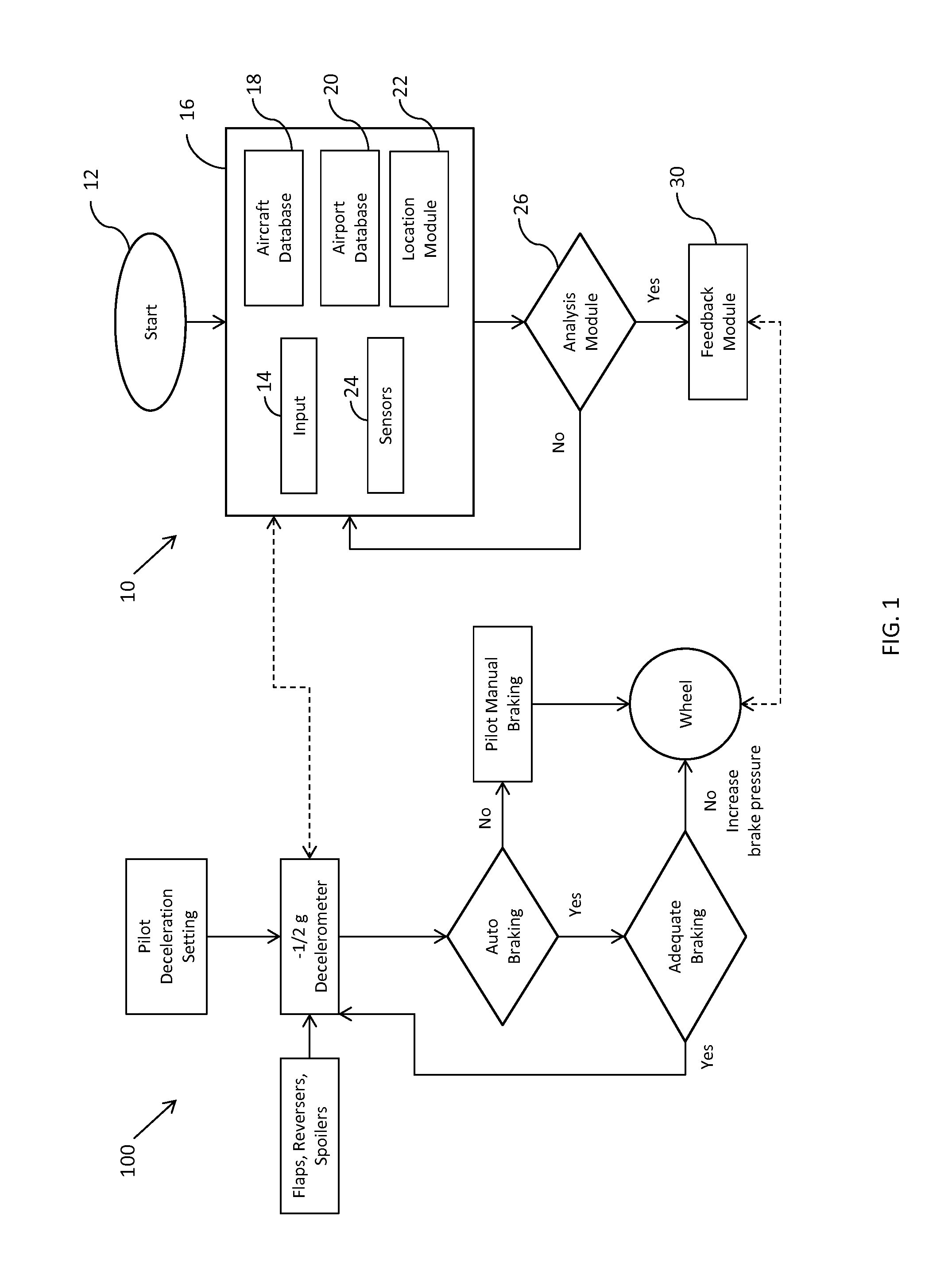
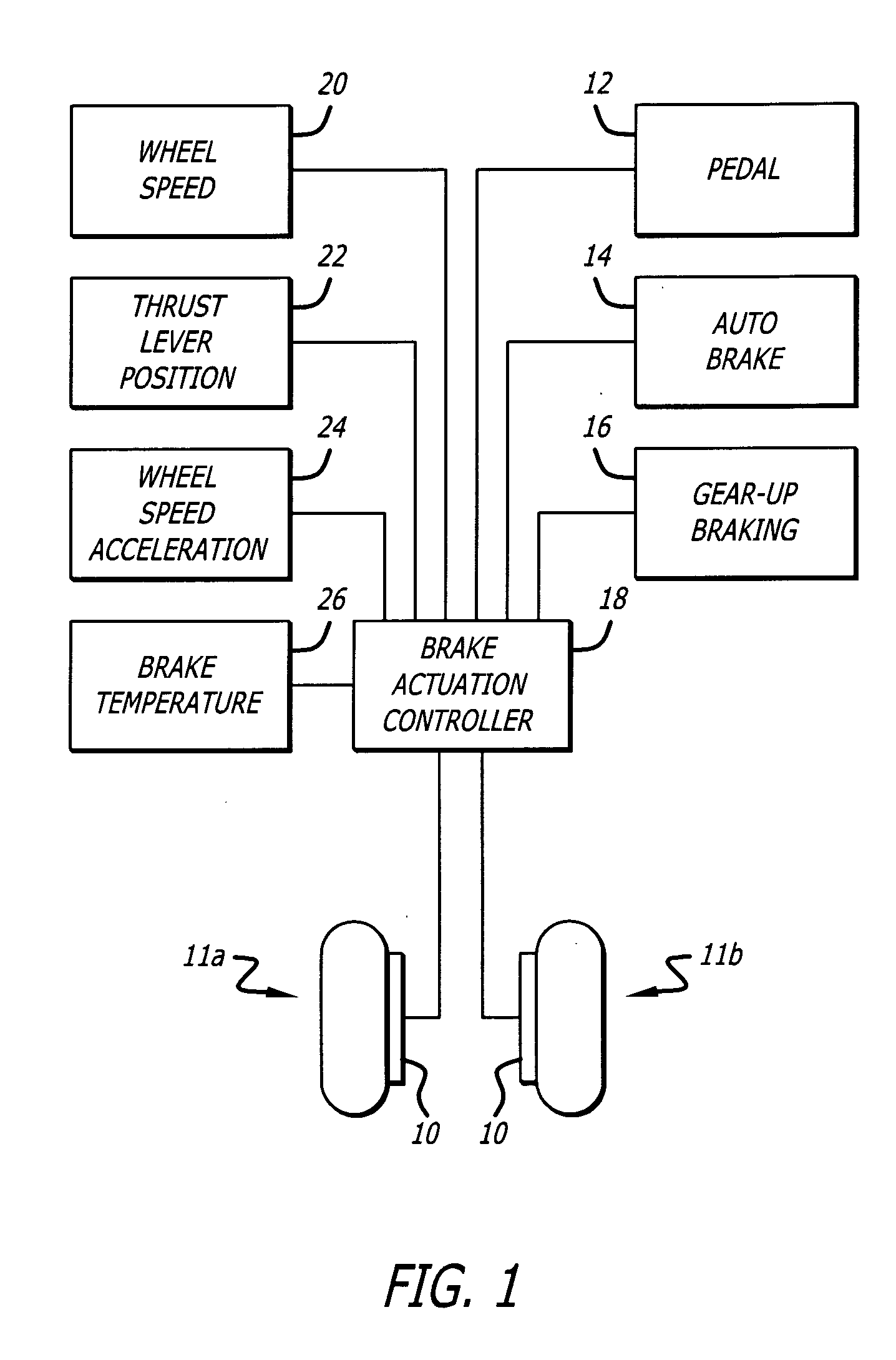
Aircraft braking early warning system
ActiveUS20140257603A1Well formedAnalogue computers for vehiclesAutomatic braking sequenceEarly warning systemFlight vehicle
A method provides alert information, regarding an aircraft wheel braking system, to an operator of an aircraft during an aircraft landing. An input of a target deceleration rate for the landing aircraft is received prior to the aircraft having landed on a ground surface. At least one sensor electronically collects information relevant to a real-time deceleration rate of the aircraft after the aircraft has landed on the ground surface, and the real-time deceleration rate of the aircraft is calculated. The target deceleration rate is compared to the calculated deceleration rate to determine an effectiveness of the aircraft wheel braking system. A visual, audible, or tactile alert is optionally provided to the operator of the aircraft, and data from this system could also be used as an input for various other aircraft safety systems. A system for performing the method is also provided.
Owner:3RD MILLENNIUM SOLUTIONS
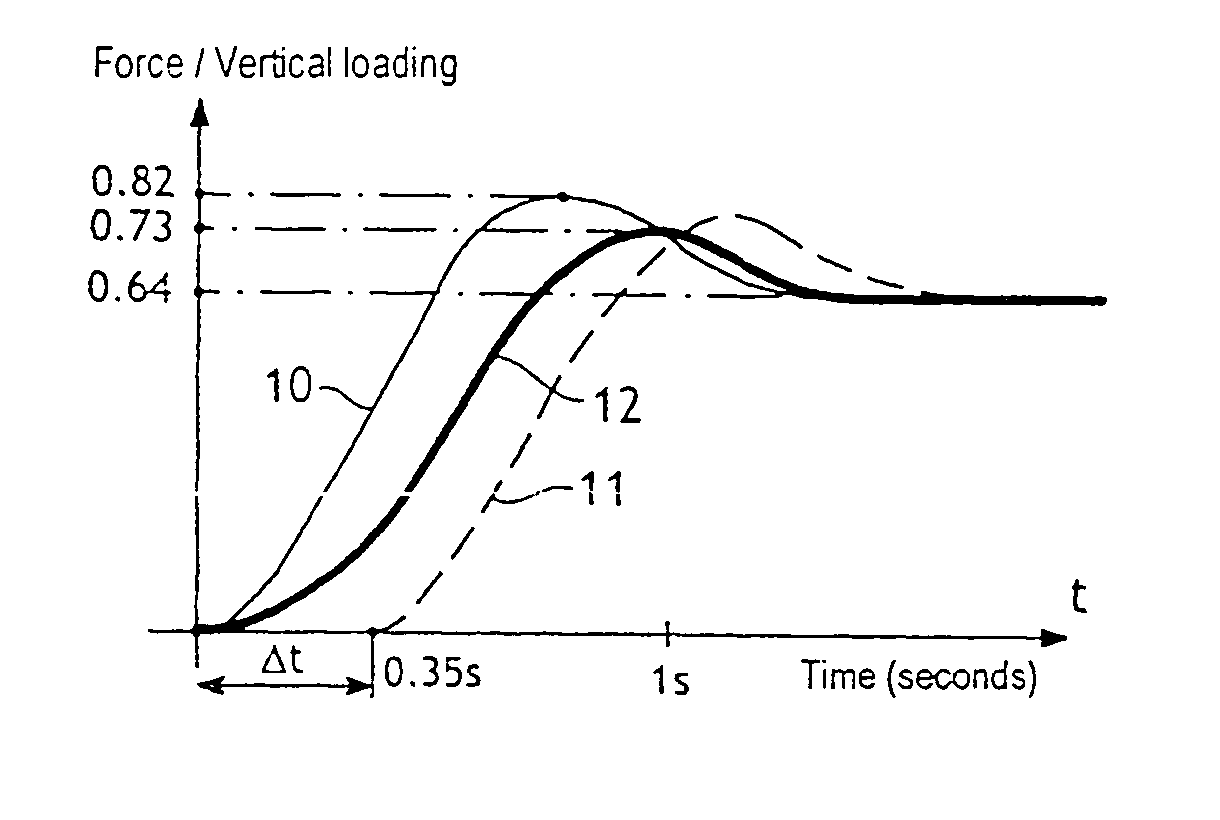
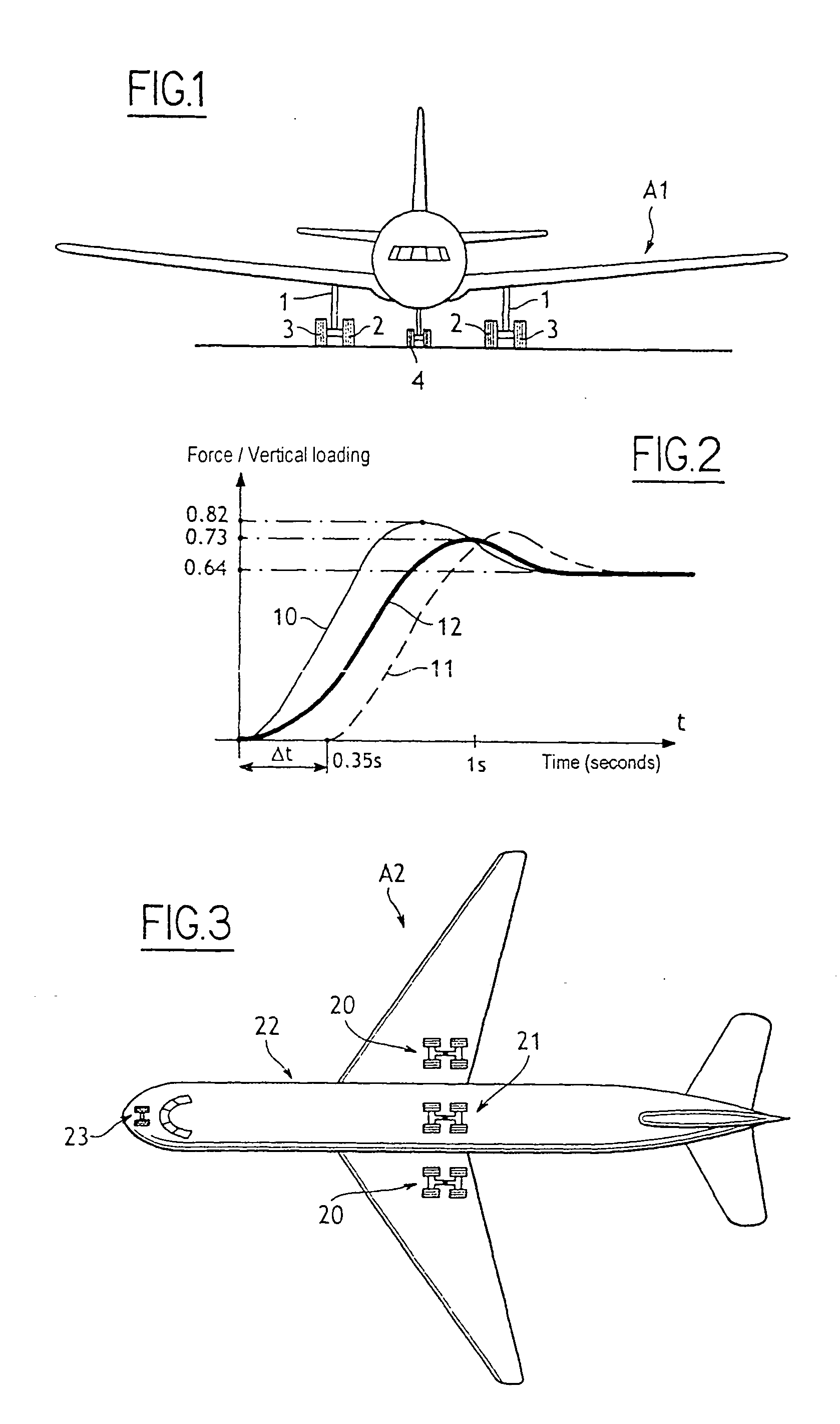
Method of braking an airplane having a plurality of braked wheels
InactiveUS20050231030A1Reduce maximum braking forceAvoid disadvantagesAutomatic braking sequenceBraking systemsJet aeroplaneControl manner
The invention relates to a method of braking an airplane having a plurality of wheels capable of being braked in controlled manner, the method comprising the step of applying braking to a first group of wheels of the airplane, and then after a time offset, applying braking to a second group of wheels of the airplane.
Owner:MESSIER BUGATTI INC
Method of actuating an airplane brake fitted with at least one electromechanical actuator
InactiveUS20050104446A1Fast response timeShorten the timeAutomatic braking sequenceBraking action transmissionJet aeroplaneControl manner
The invention provides a method of actuating an airplane brake fitted with at least one electromechanical actuator including a pusher that can be displaced in controlled manner in register with a stack of disks to apply a force on the stack of disks in response to a braking reference signal, the method comprising the steps of: when the braking reference signal crosses a contact threshold, controlling the actuator so that the pusher approaches the stack of disks, until the pusher reaches a contact position with the stack of disks; storing said contact position; and then immediately afterwards, controlling the actuator so that the pusher applies a force on the stack of disks in response to the braking reference signal.
Owner:MESSIER BUGATTI INC
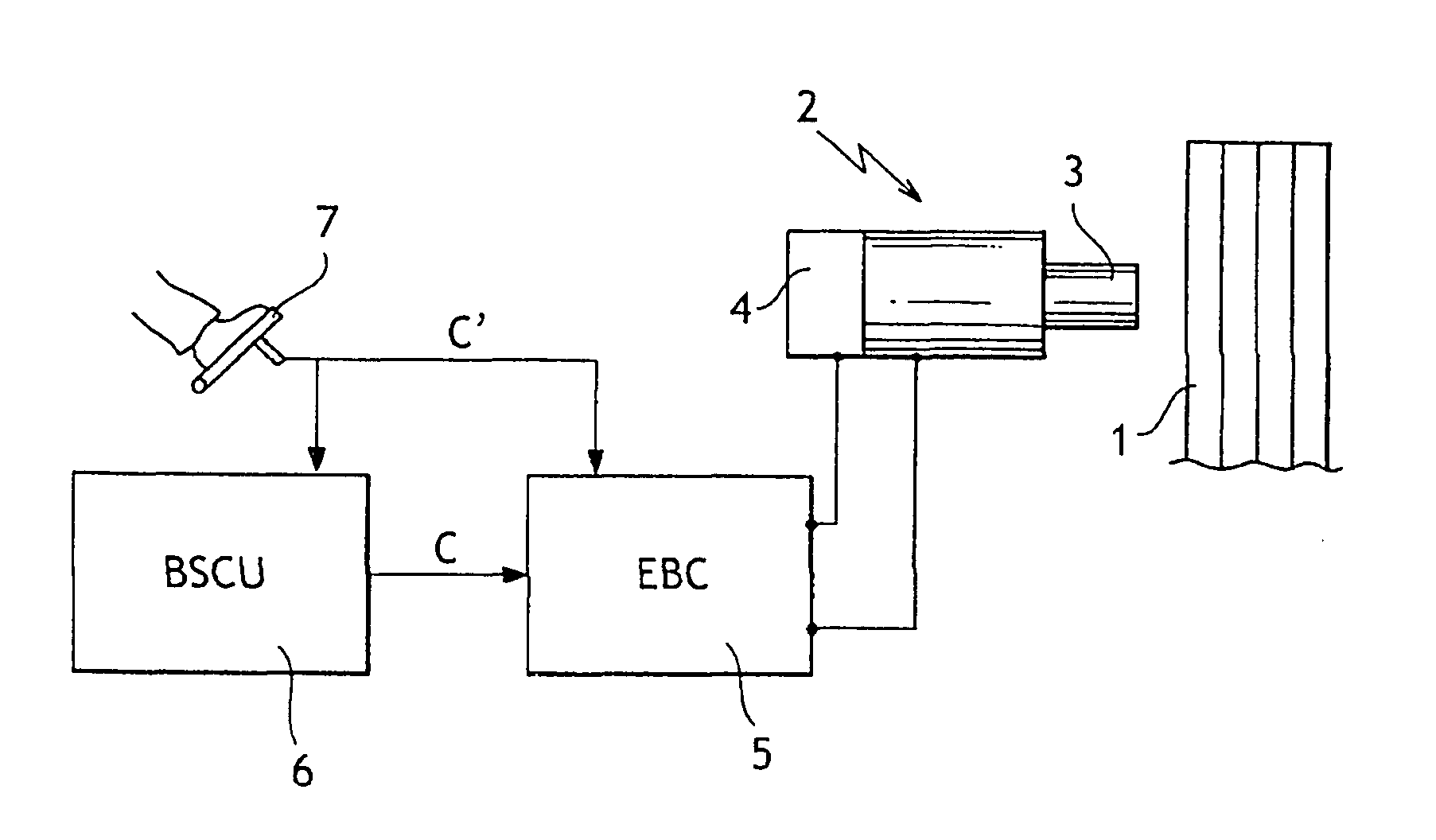
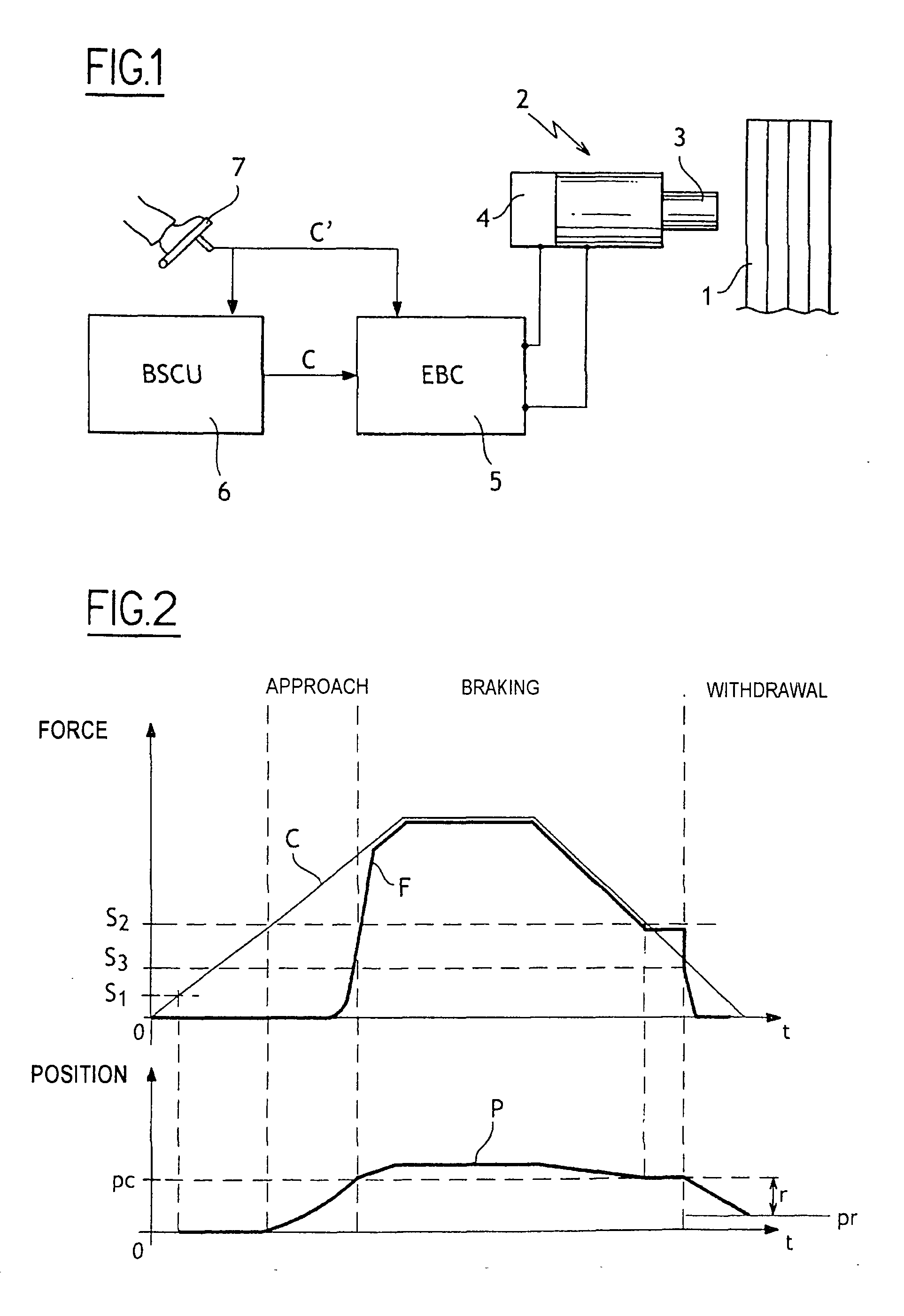
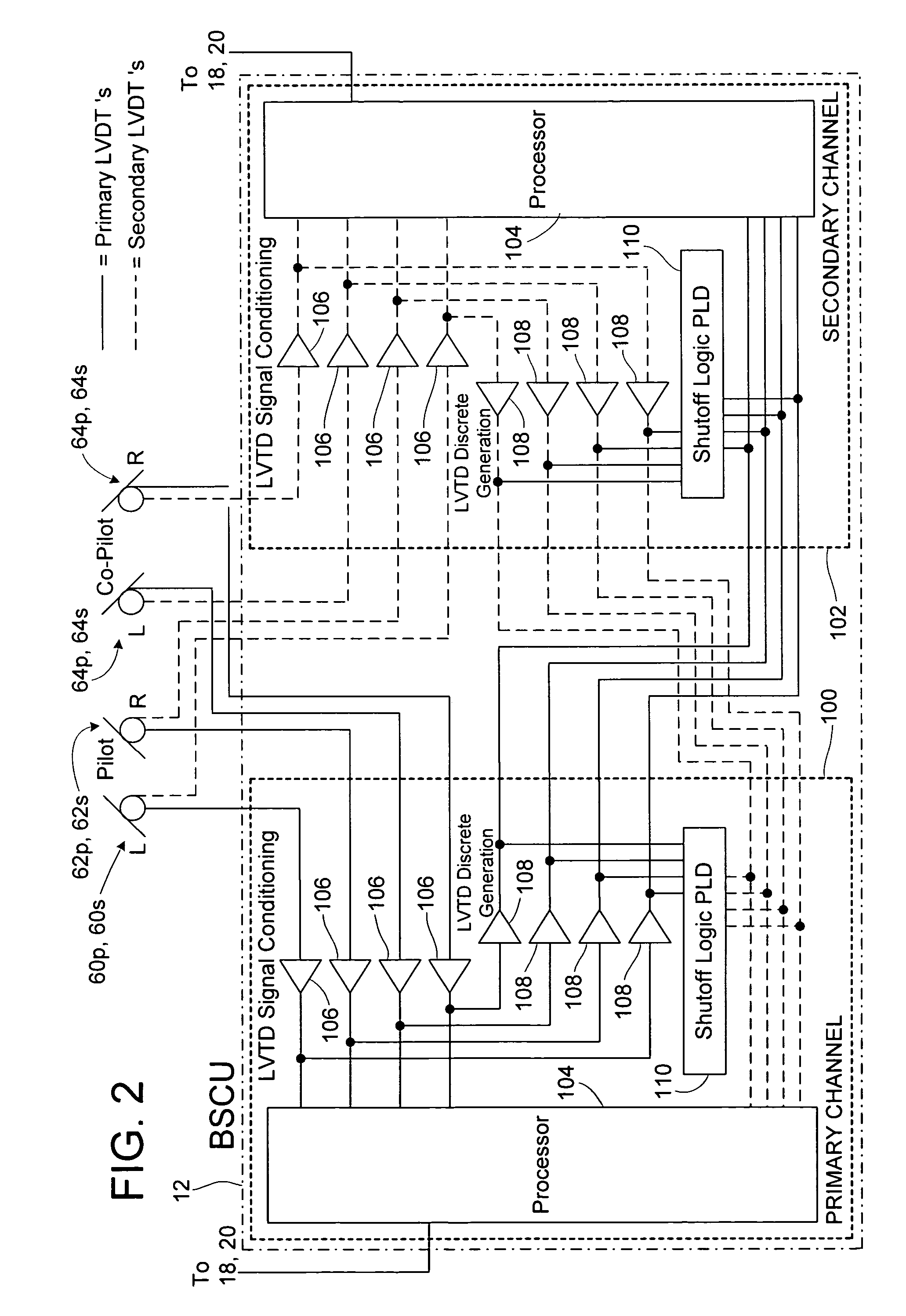
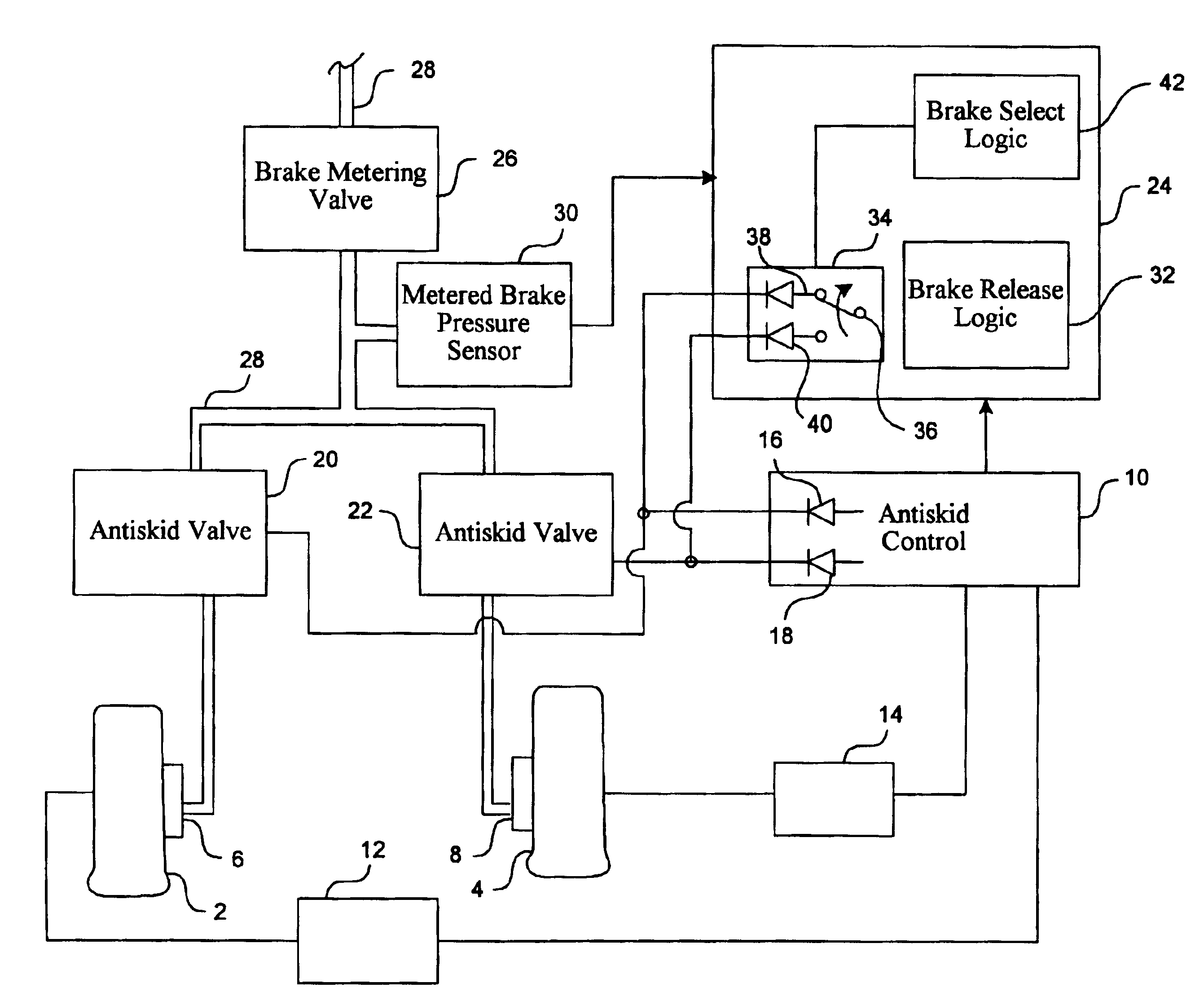
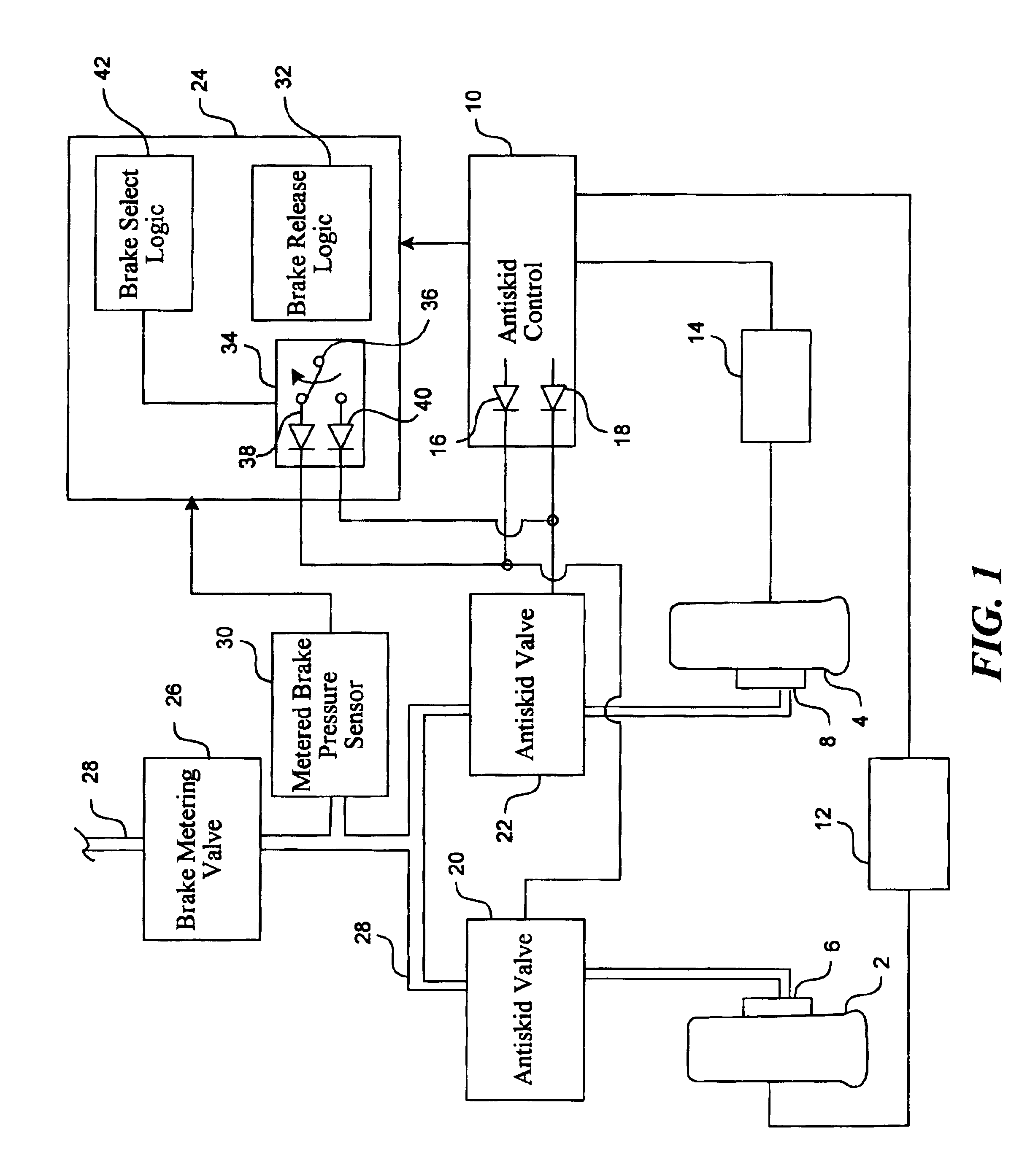
Redundant architecture for brake-by-wire system
ActiveUS7128376B2Relieve stressAutomatic braking sequenceBraking action transmissionEngineeringControl theory
A redundant architecture for a brake-by-wire system is provided. The system includes a pressure source; at least one brake actuator for exerting a braking force on a wheel as a result of pressure provided by the pressure source; at least one servo valve for controlling an amount of pressure provided from the pressure source to the at least one brake actuator in response to a servo valve command signal; a shutoff valve in line with the at least one servo valve for preventing pressure from the pressure source from being provided to the at least one brake actuator in response to a shutoff valve command signal; a processor which executes code in order to carry out brake control operations, the processor outputting the servo command signal and the shutoff valve command signal in response to system inputs provided to the processor; a shutoff valve enable device for performing brake control operations redundant at least in part with the processor and based on the system inputs, and selectively enabling shutoff valve command signals from the processor to be provided to the shutoff valve based on the redundant brake control operations.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
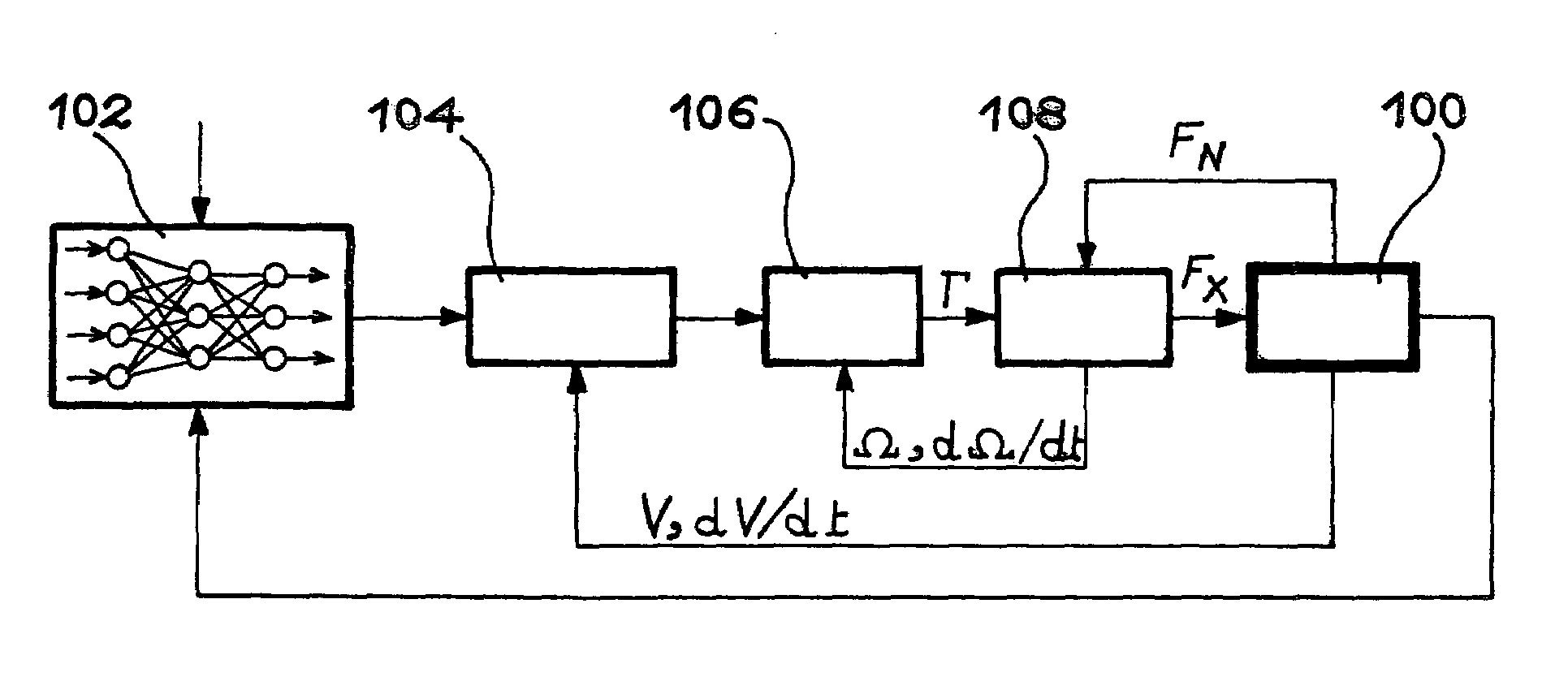
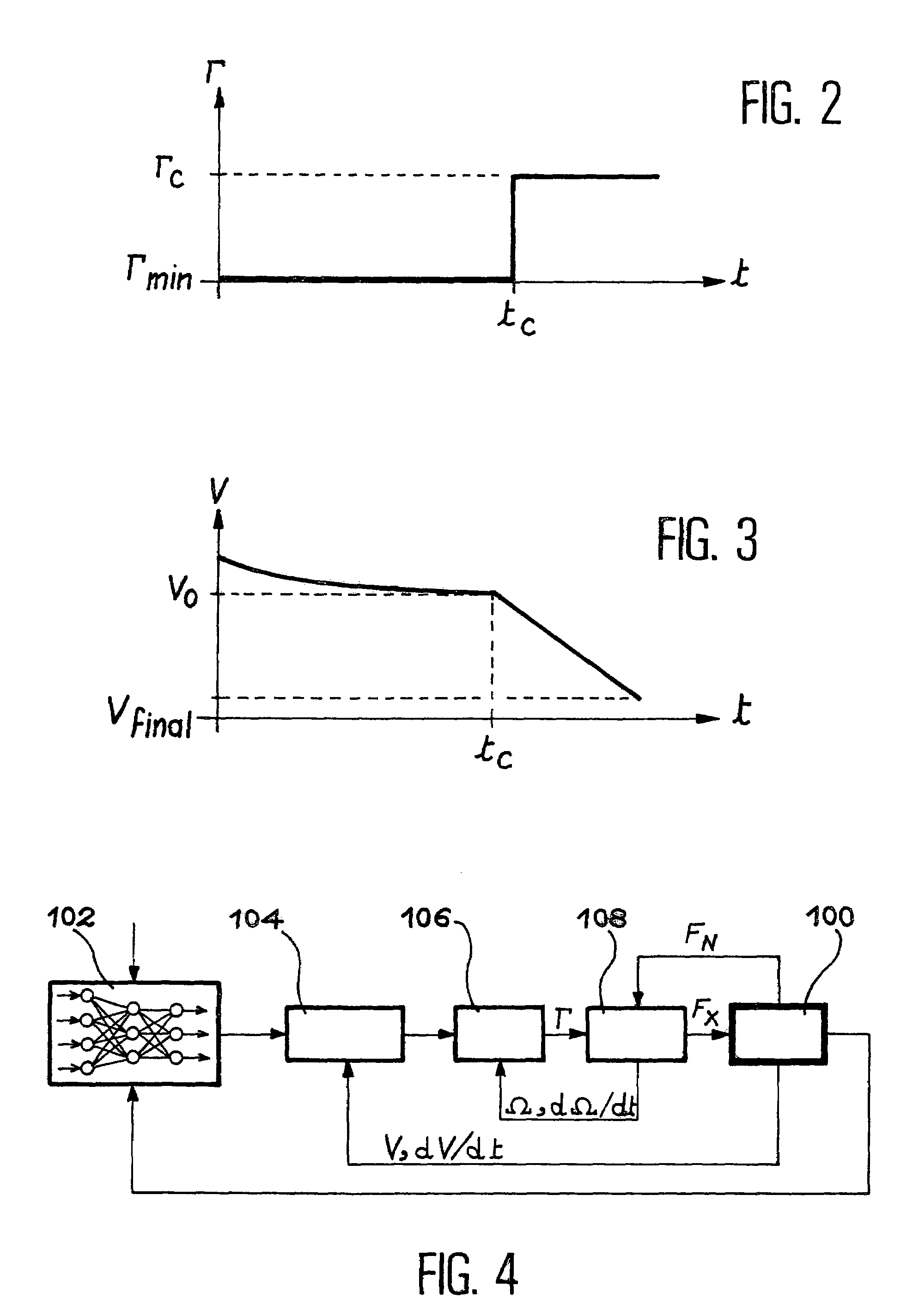
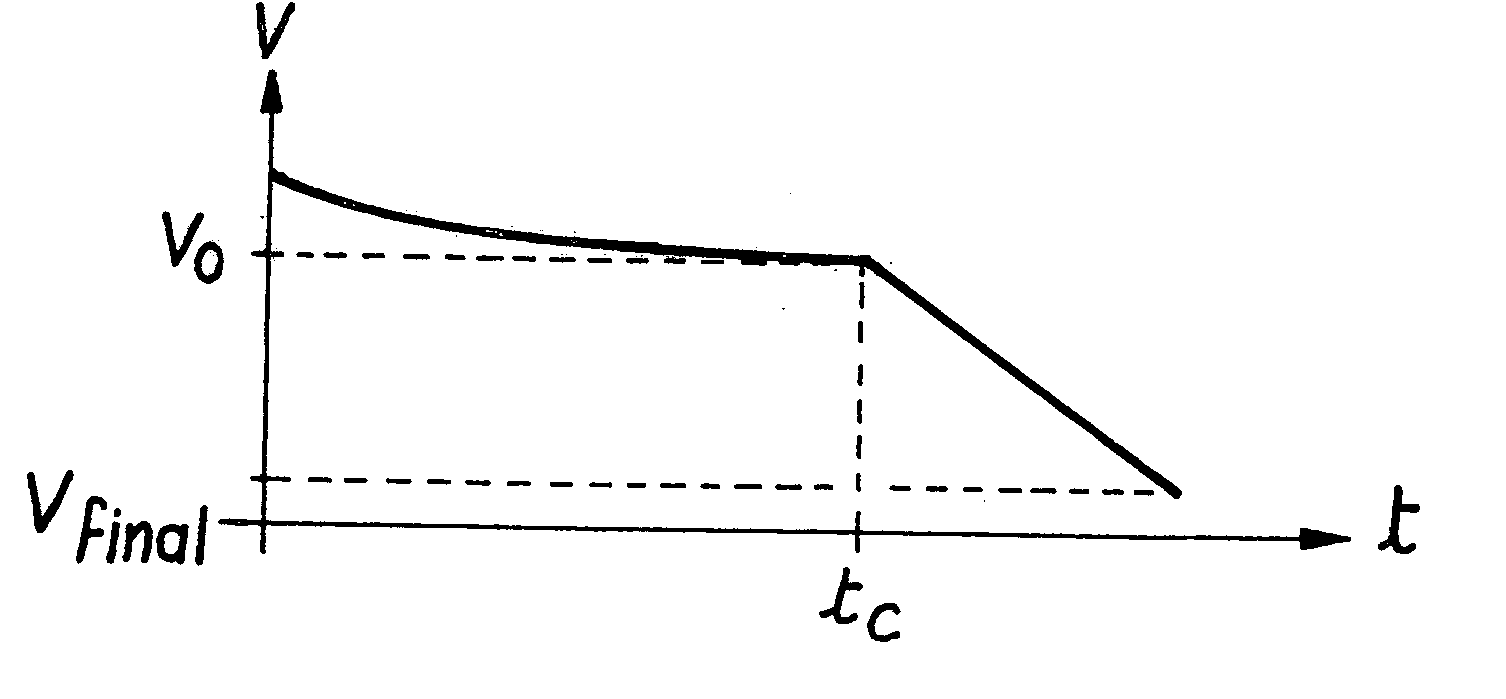
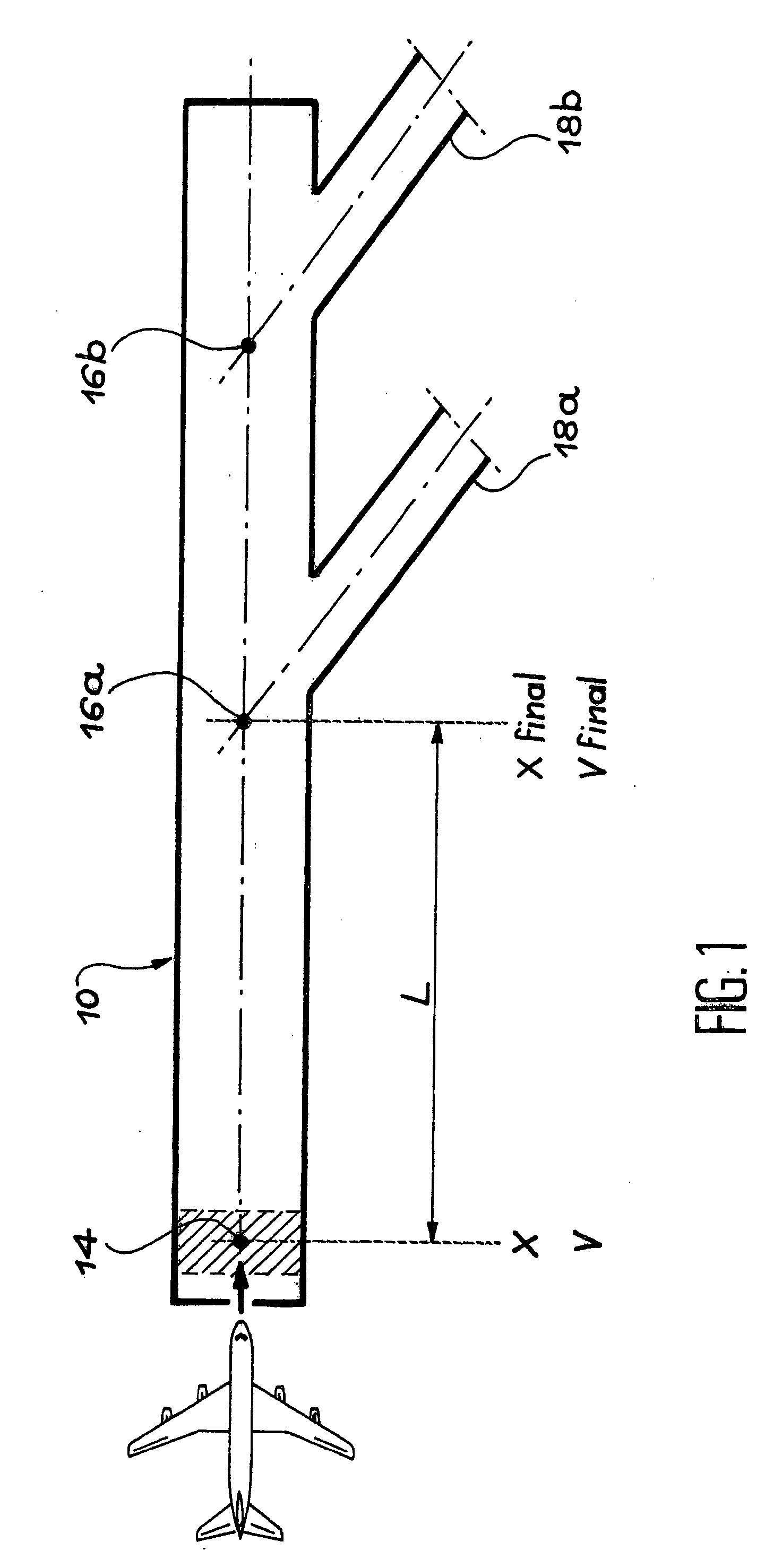
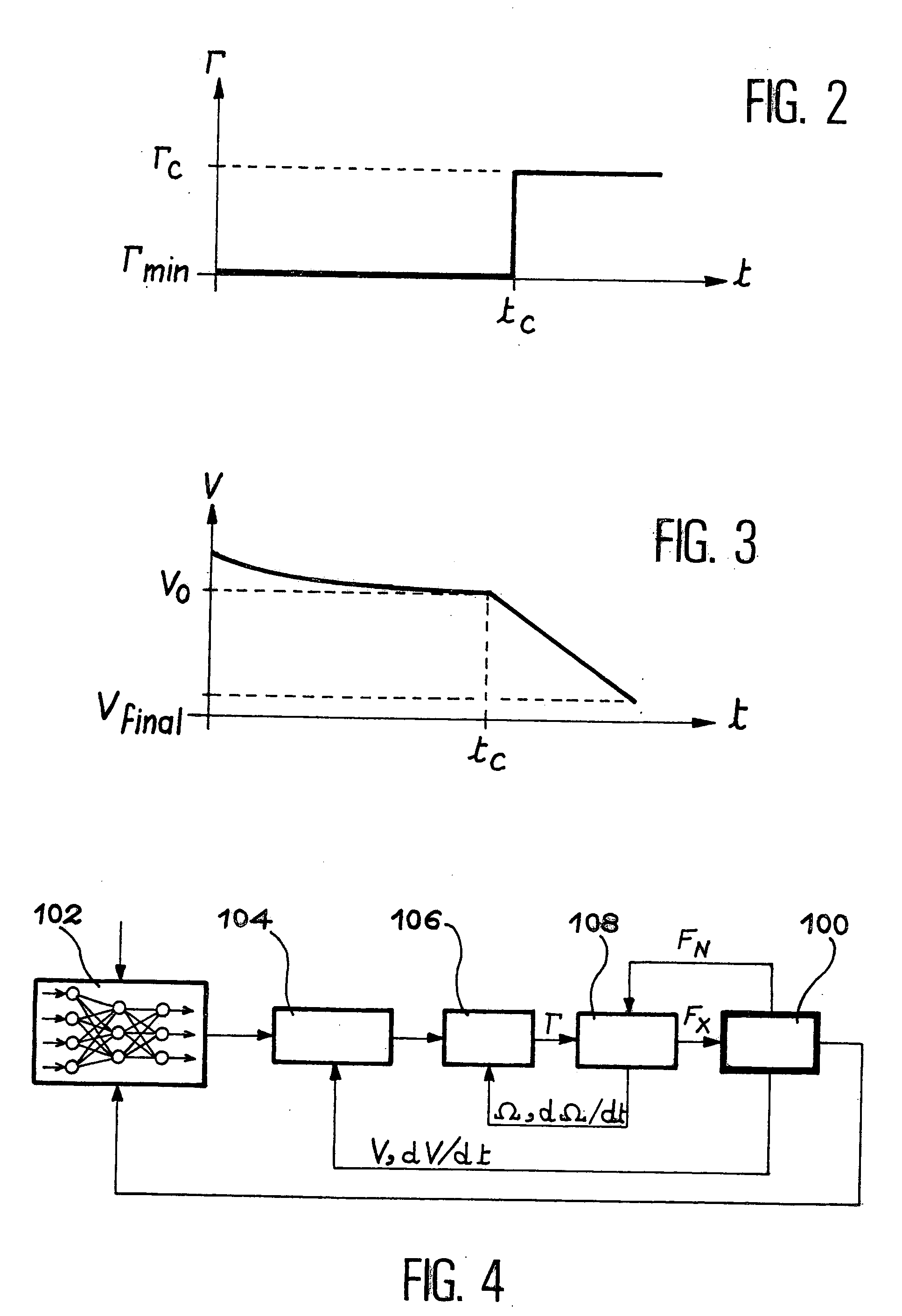
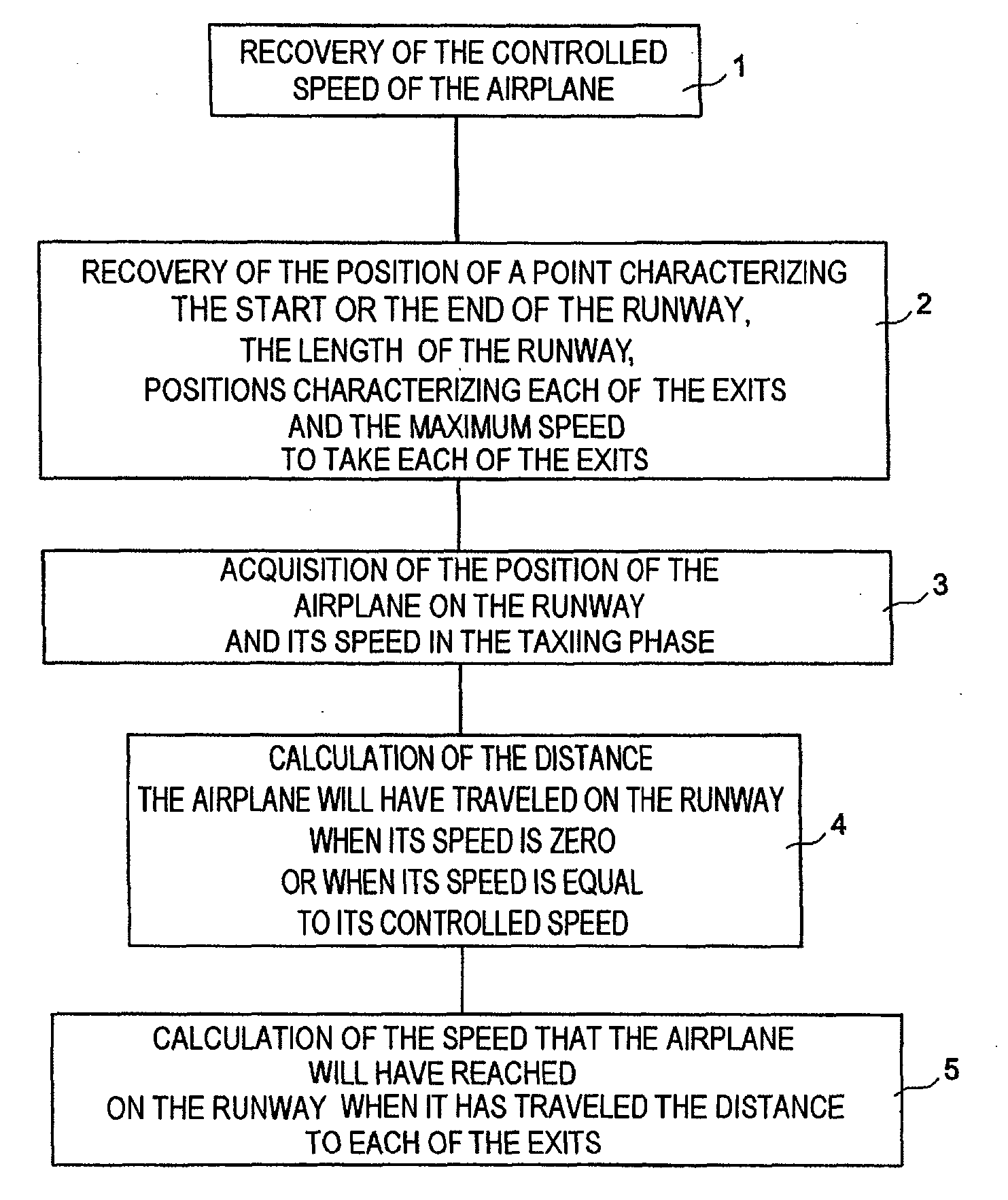
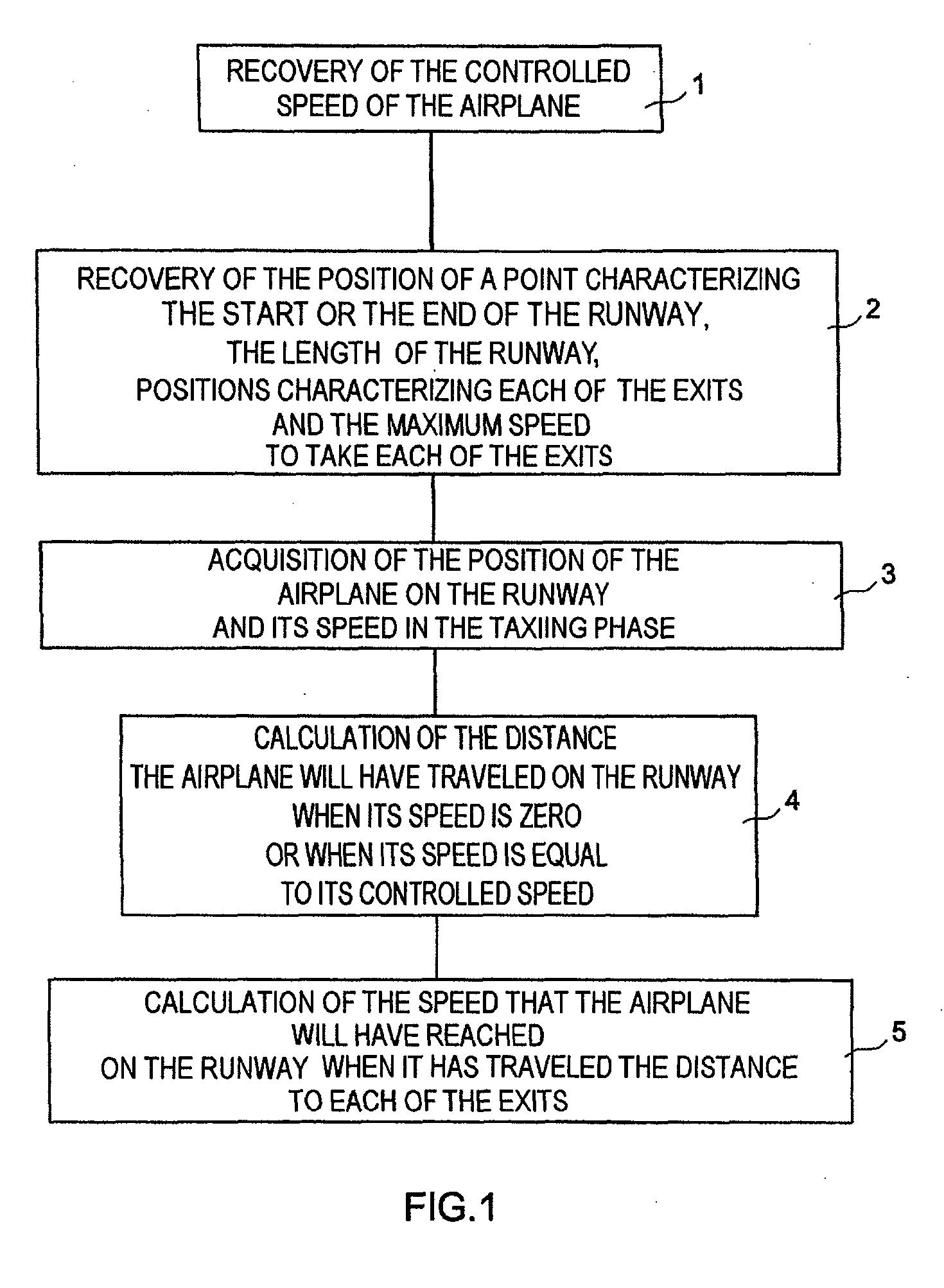
Method and device for automatic control of an aircraft deceleration in running phase
InactiveUS6991304B2Increase speedShorten the timeAutomatic braking sequenceAlighting gearAutomatic controlSet point
The invention relates to a system to control the deceleration of an aircraft during the taxiing phase on a landing strip, the system has a detector of the current position of the aircraft on the strip, and of the current speed of the aircraft on the strip, a calculator receiving position and speed values from the detector, to define, as a function of the desired final speed of the aircraft at the so-called final position on the strip, a deceleration set-point modification time, after the current time, and a new deceleration set-point to apply from the modification time, to reach the final position at the desired speed.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
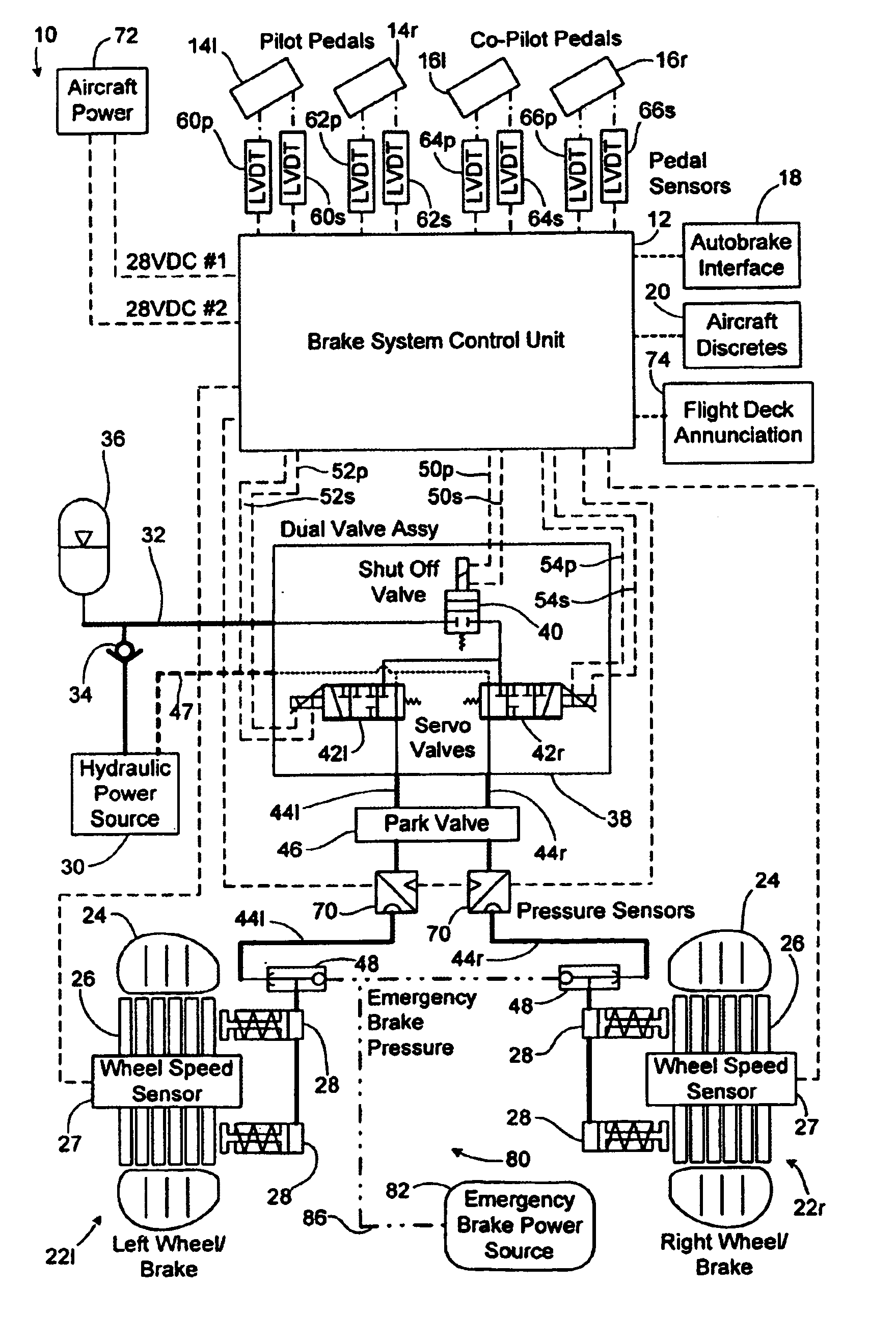
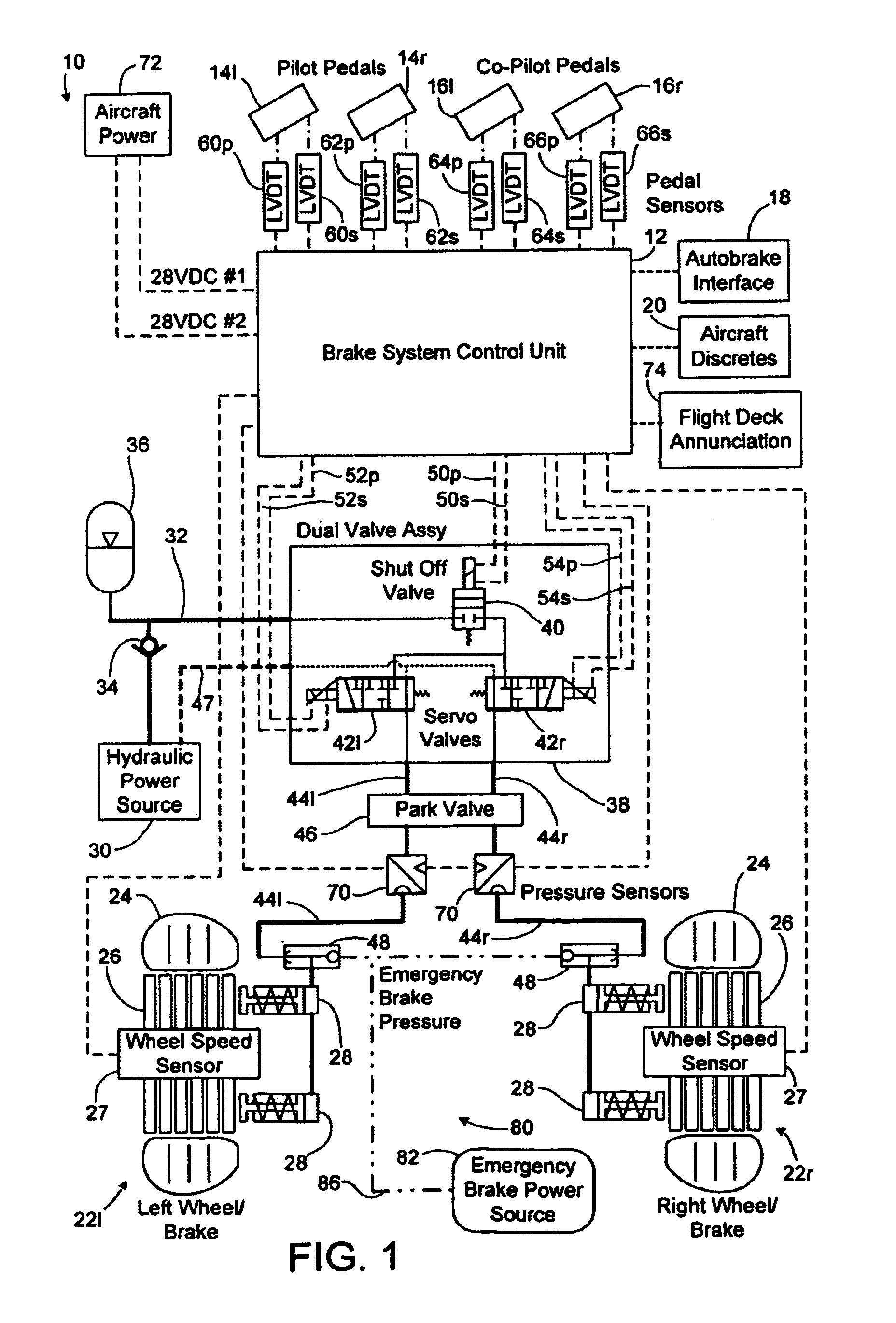
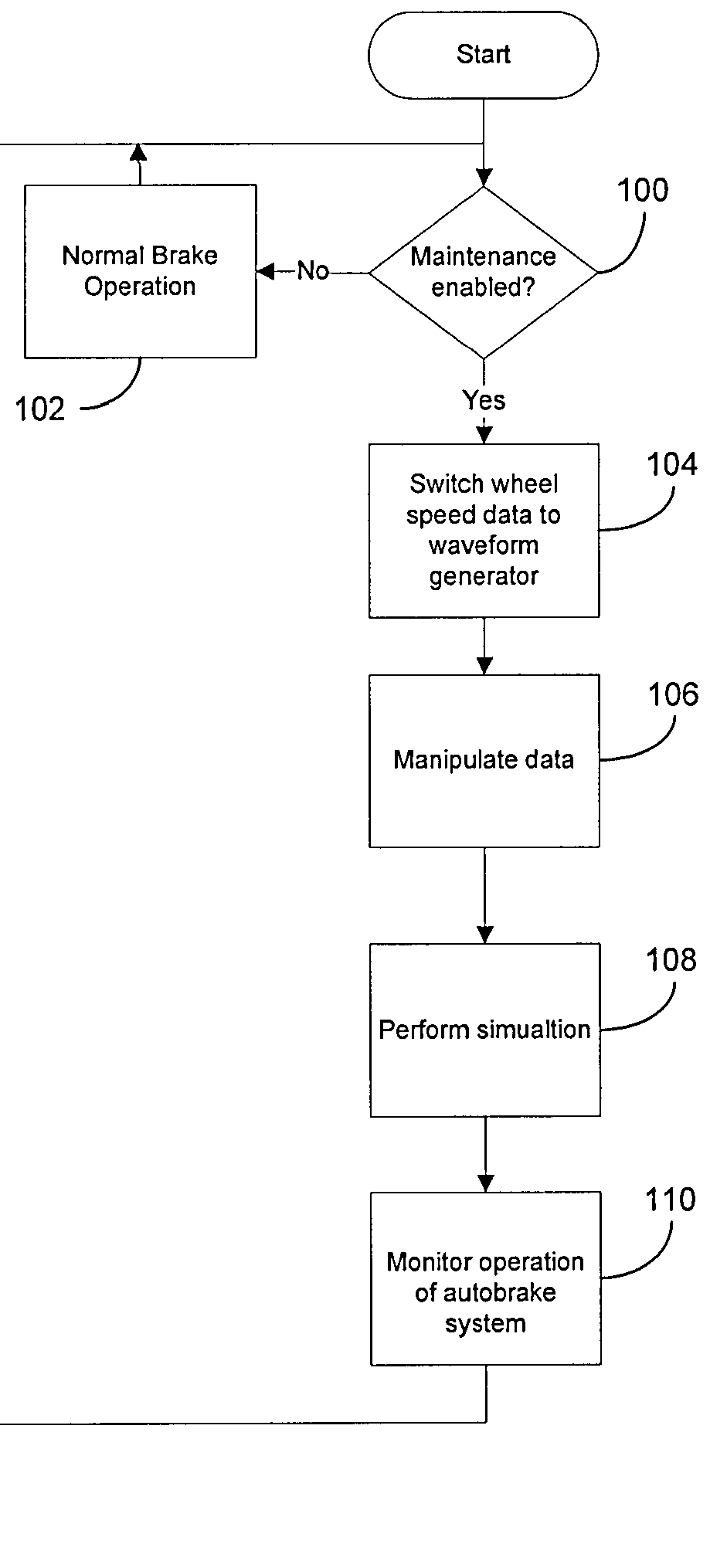
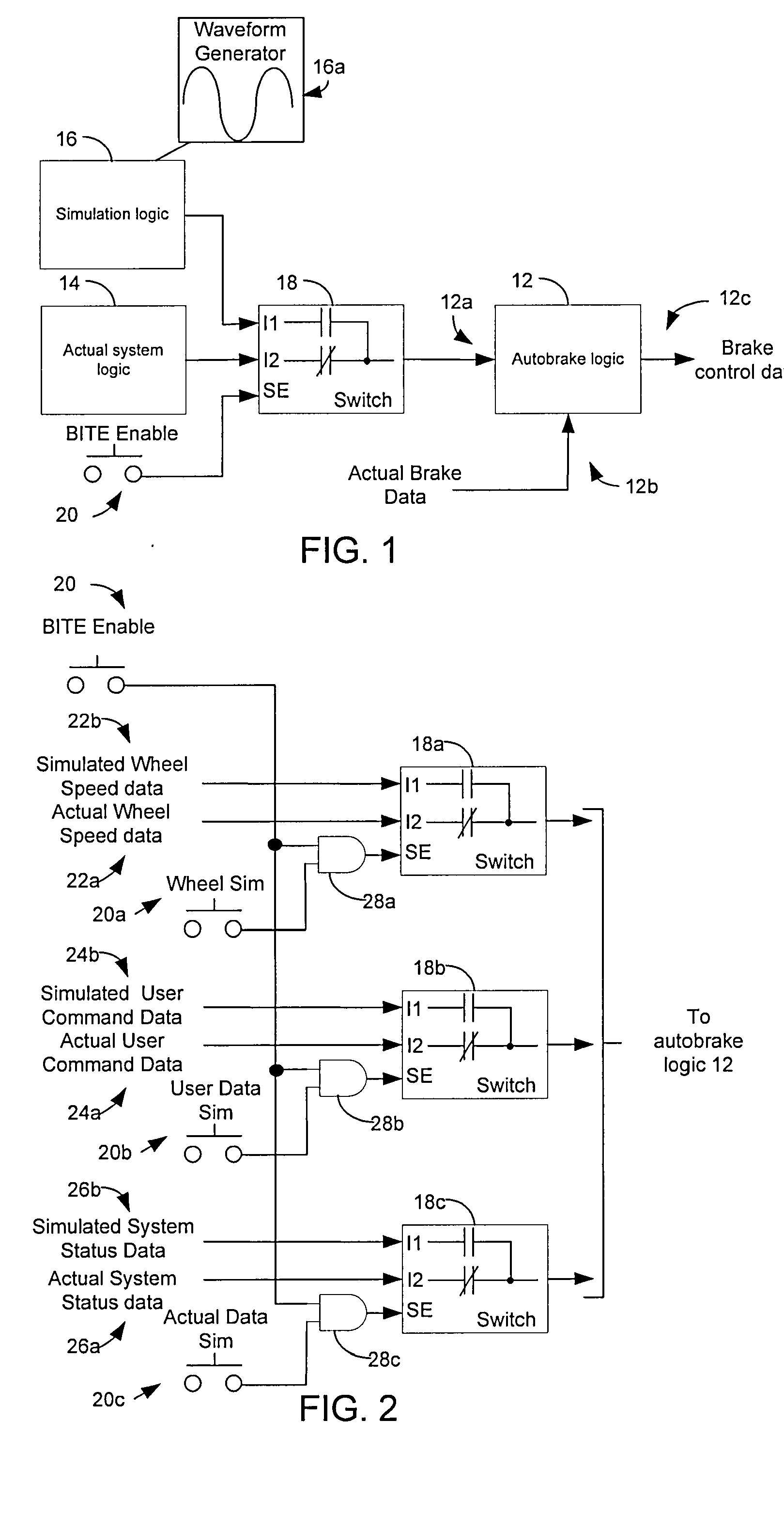
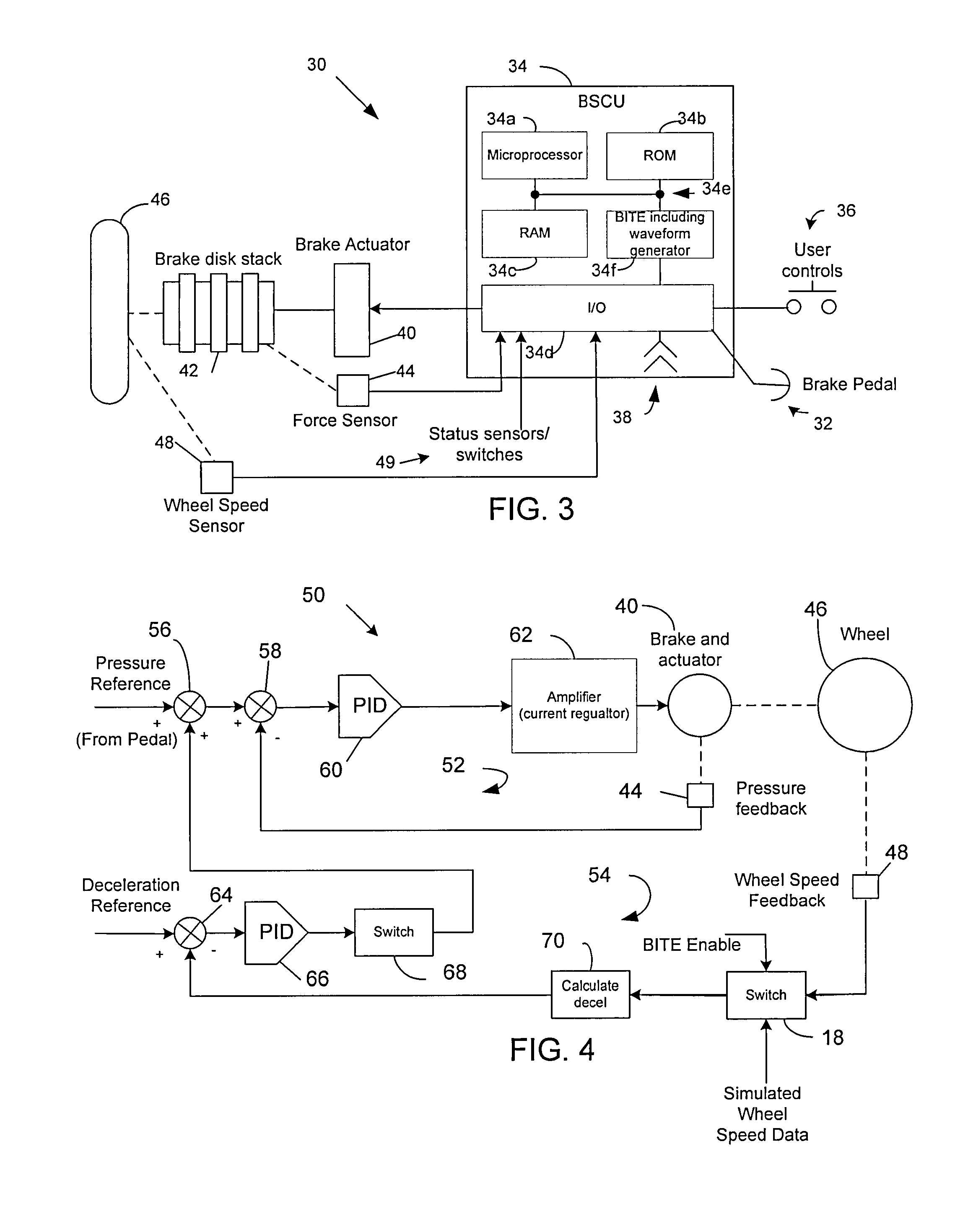
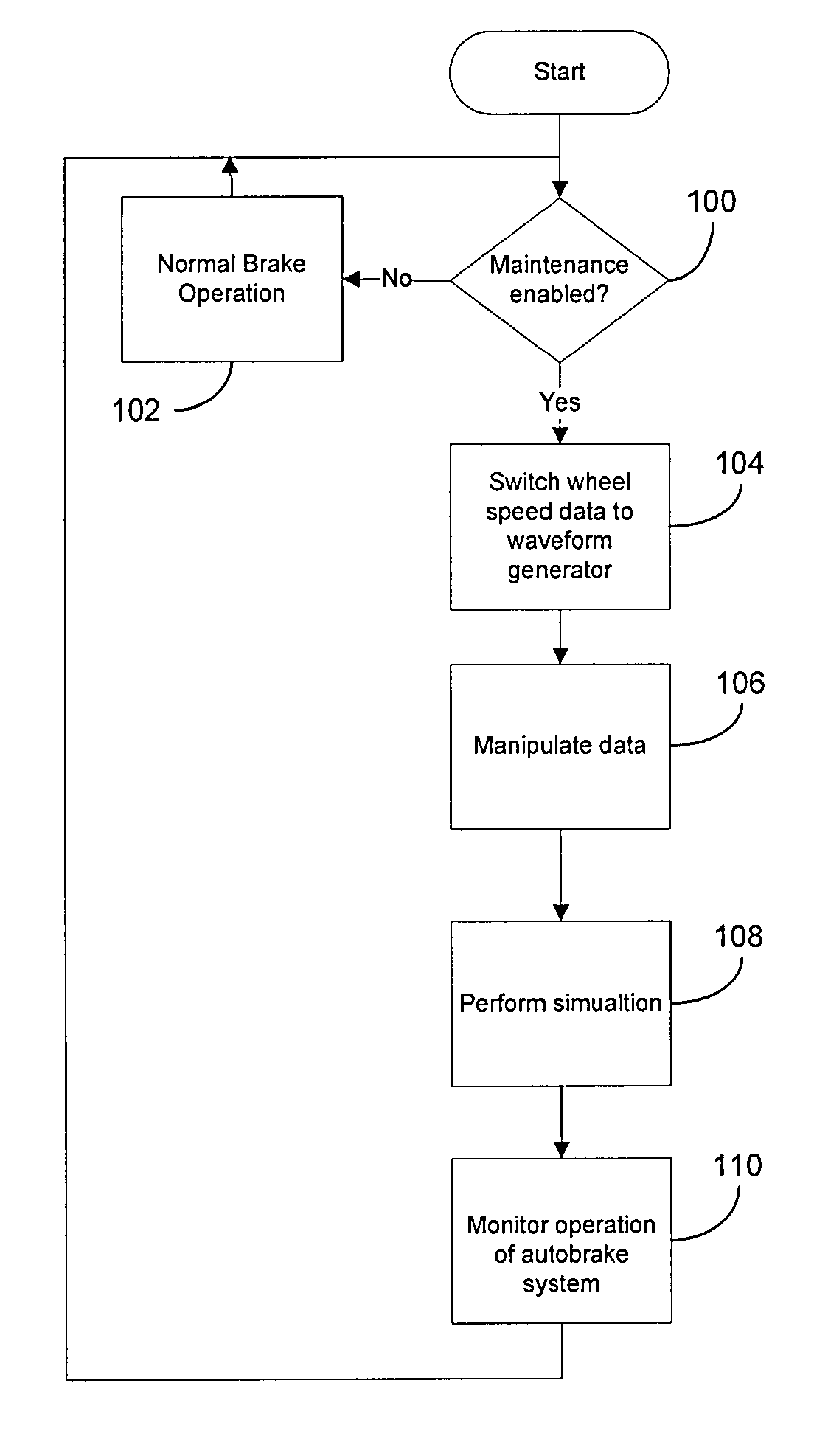
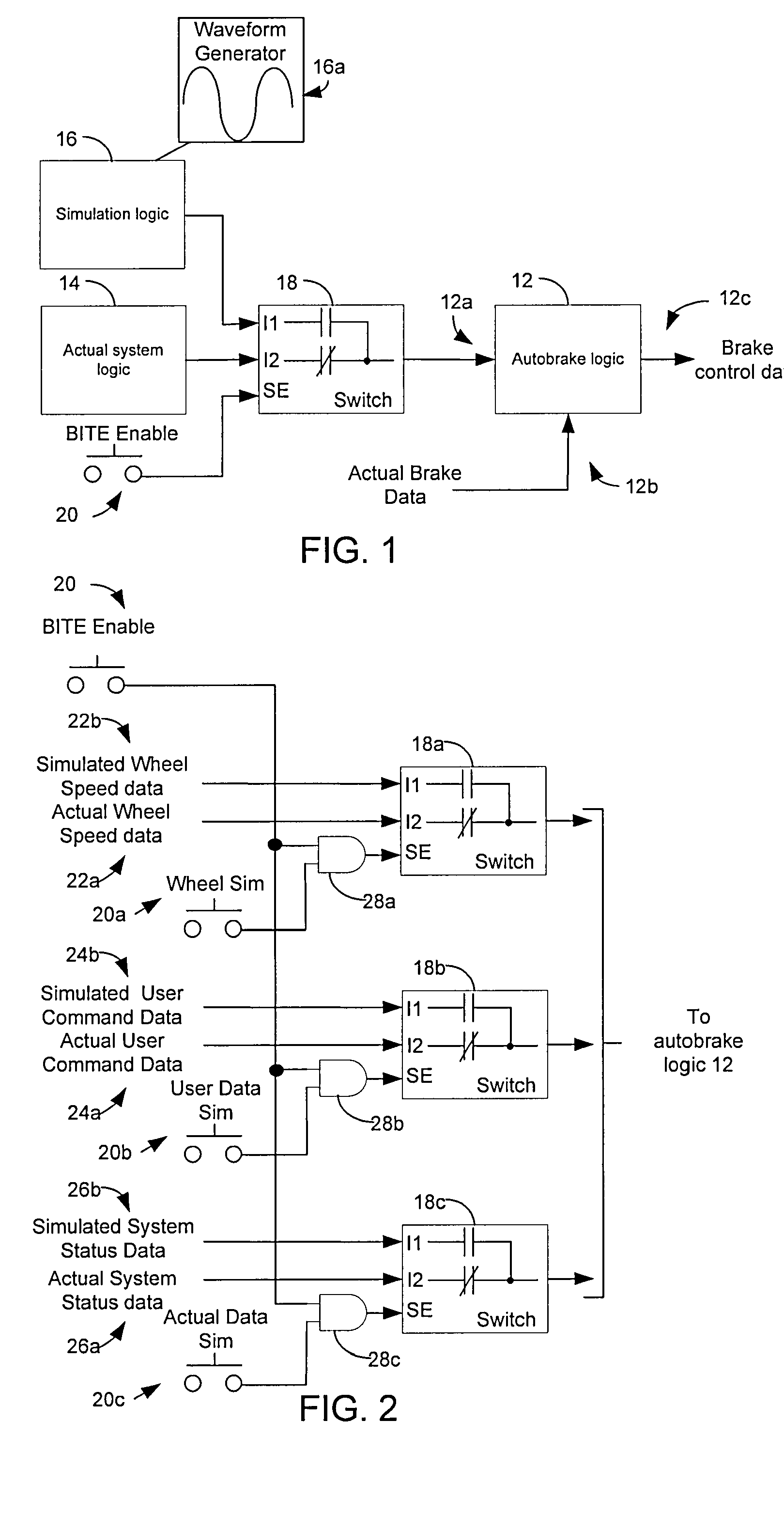
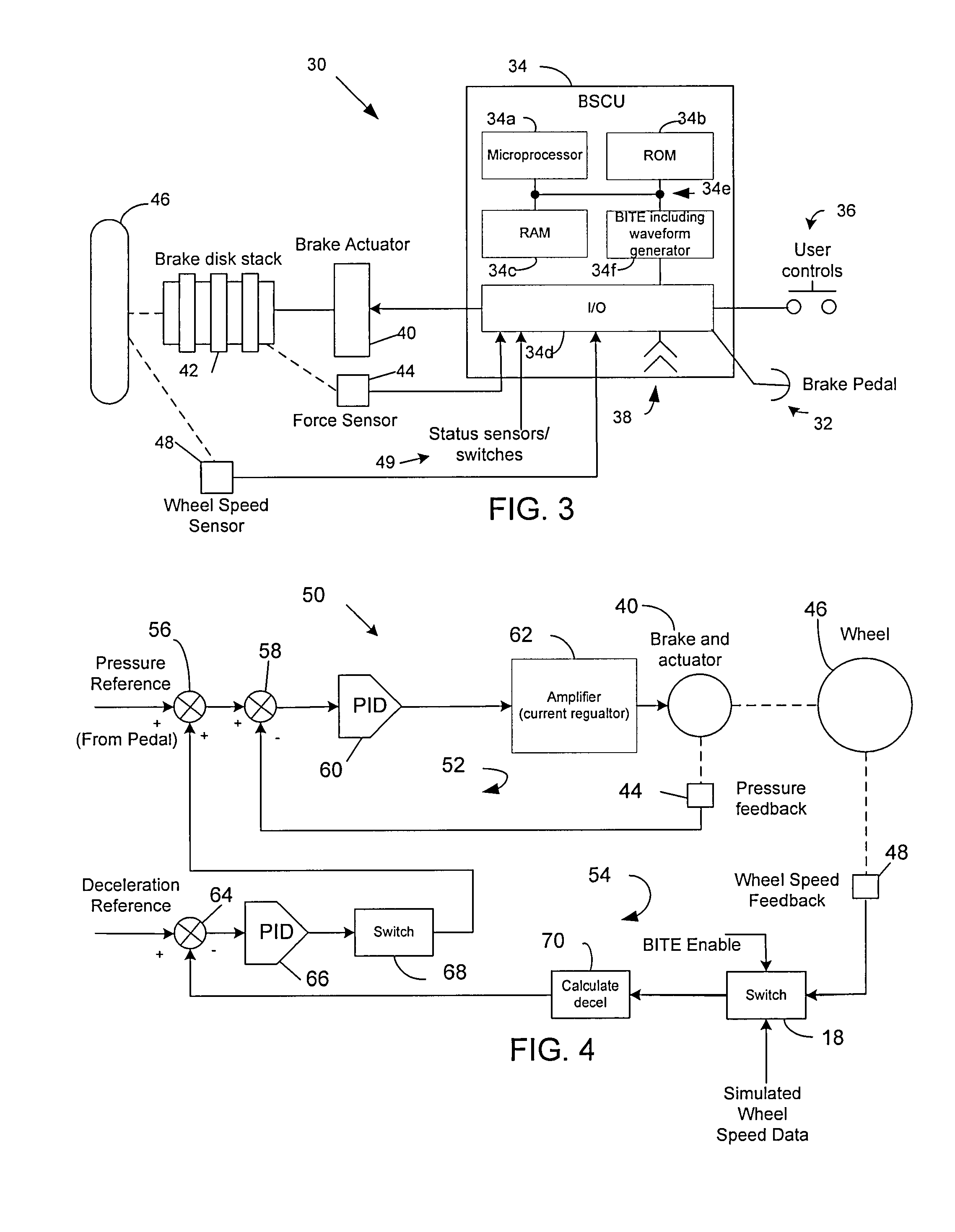
Autobrake and decel control built-in test equipment
ActiveUS20100286880A1View accuratelyVehicle testingAutomatic braking sequenceOperational systemSignal generator
A system, apparatus and method provide a means for testing operation of a vehicle brake system. More particularly, a brake controller for controlling operation of the brake system includes a signal generator that can generate data indicative of wheel speed. Based on a user command, the controller uses either actual wheel speed data or simulated wheel speed data as inputs for controlling brake operation. The controller also includes logic for exercising various braking functions so as to enable maintenance personal to determine operational systems of the brake system.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
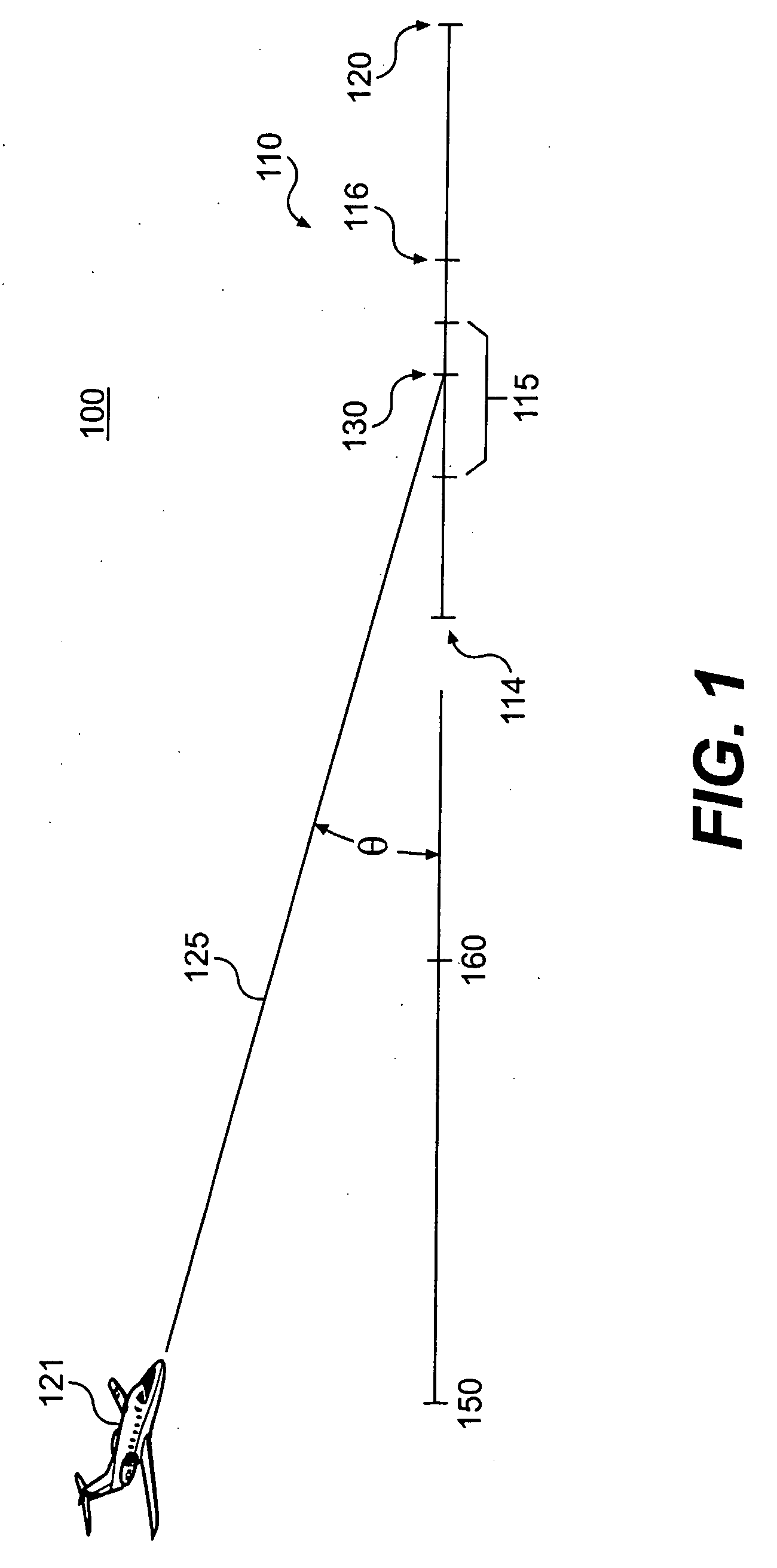
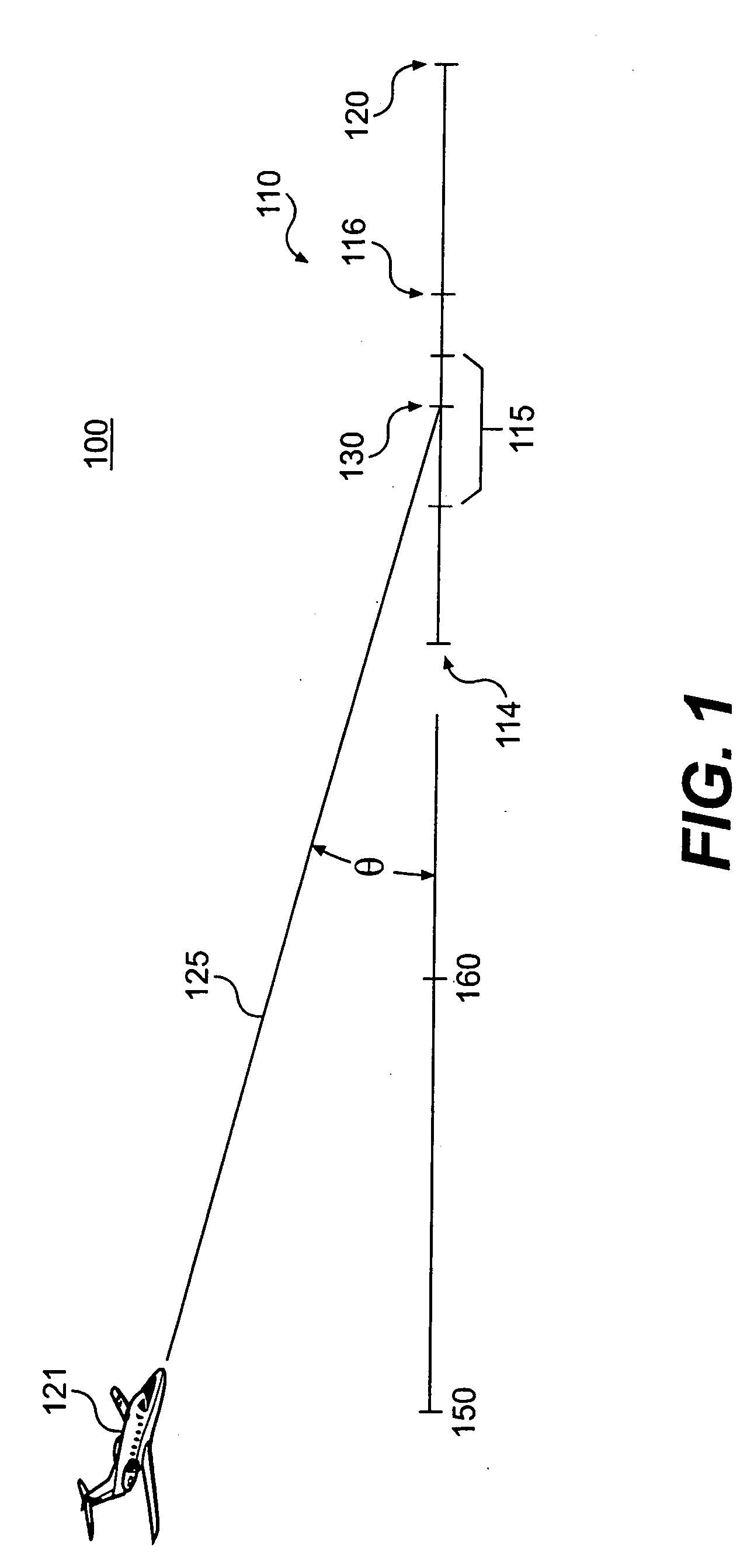
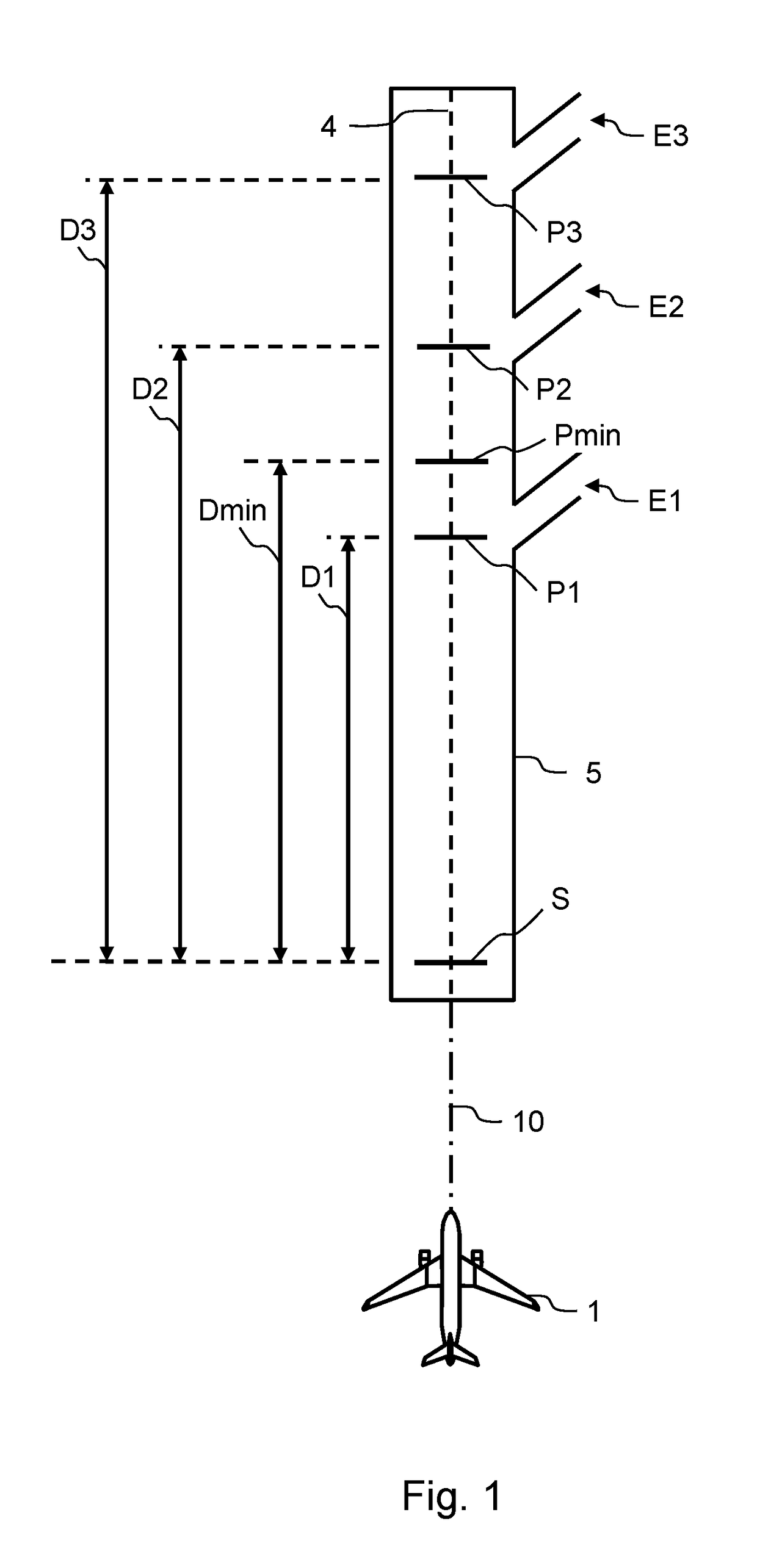
Method and apparatus for predicting runway overrun
A critical point on a runway indicates a point at which an aircraft may experience a runway overrun if landing beyond the critical point. A path projection is extended from the aircraft at a descent slope angle to determine whether the aircraft will land beyond the critical point at the current descent slope. Timely alerts may be provided by accounting for the time required to announce a distance value, and the distance traveled during the announcement.
Owner:RYAN INT
Method and apparatus for predicting runway overrun
A critical point on a runway indicates a point at which an aircraft may experience a runway overrun if landing beyond the critical point. A path projection is extended from the aircraft at a descent slope angle to determine whether the aircraft will land beyond the critical point at the current descent slope. Timely alerts may be provided by accounting for the time required to announce a distance value, and the distance traveled during the announcement.
Owner:AVIDYNE CORPORATION
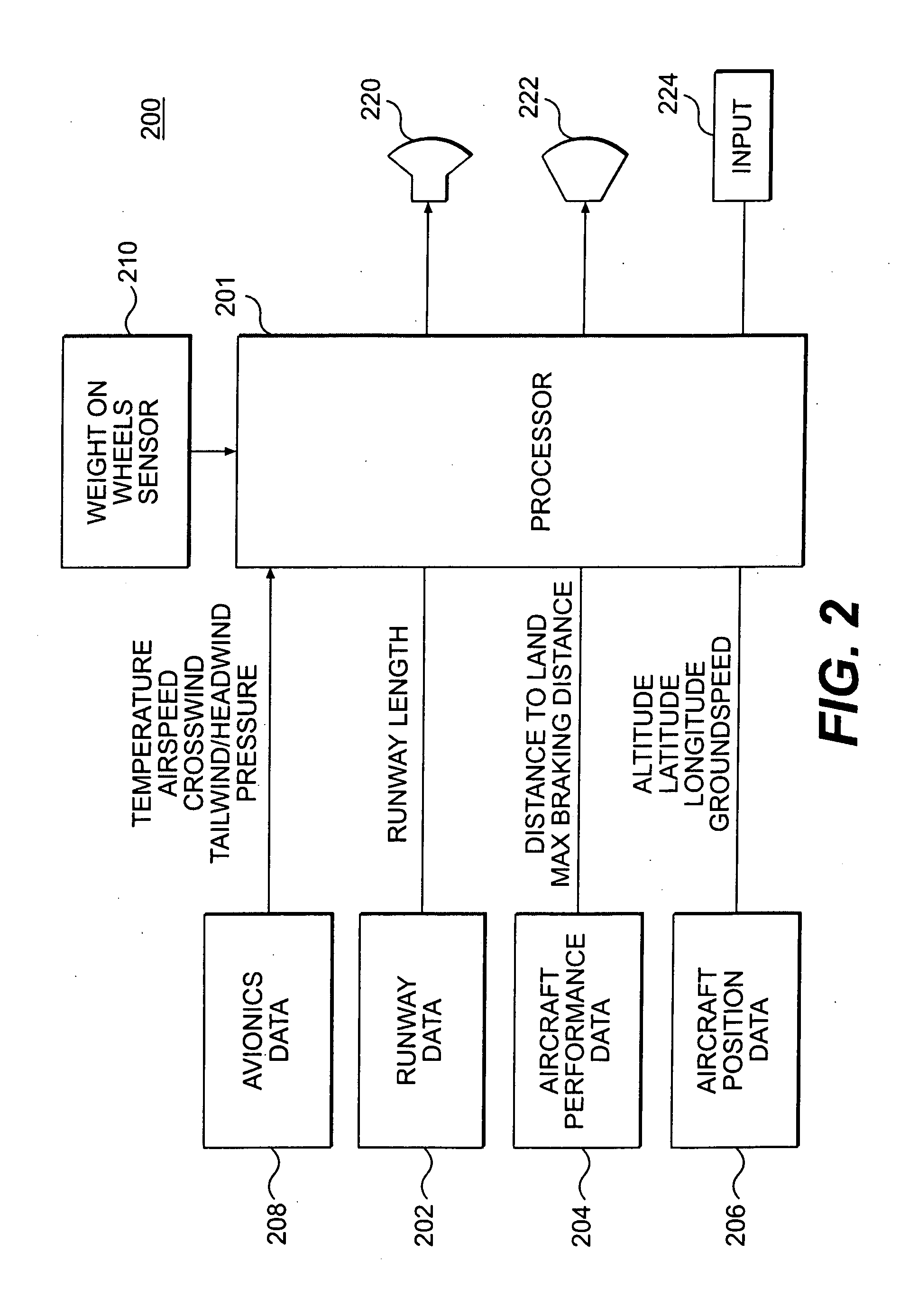
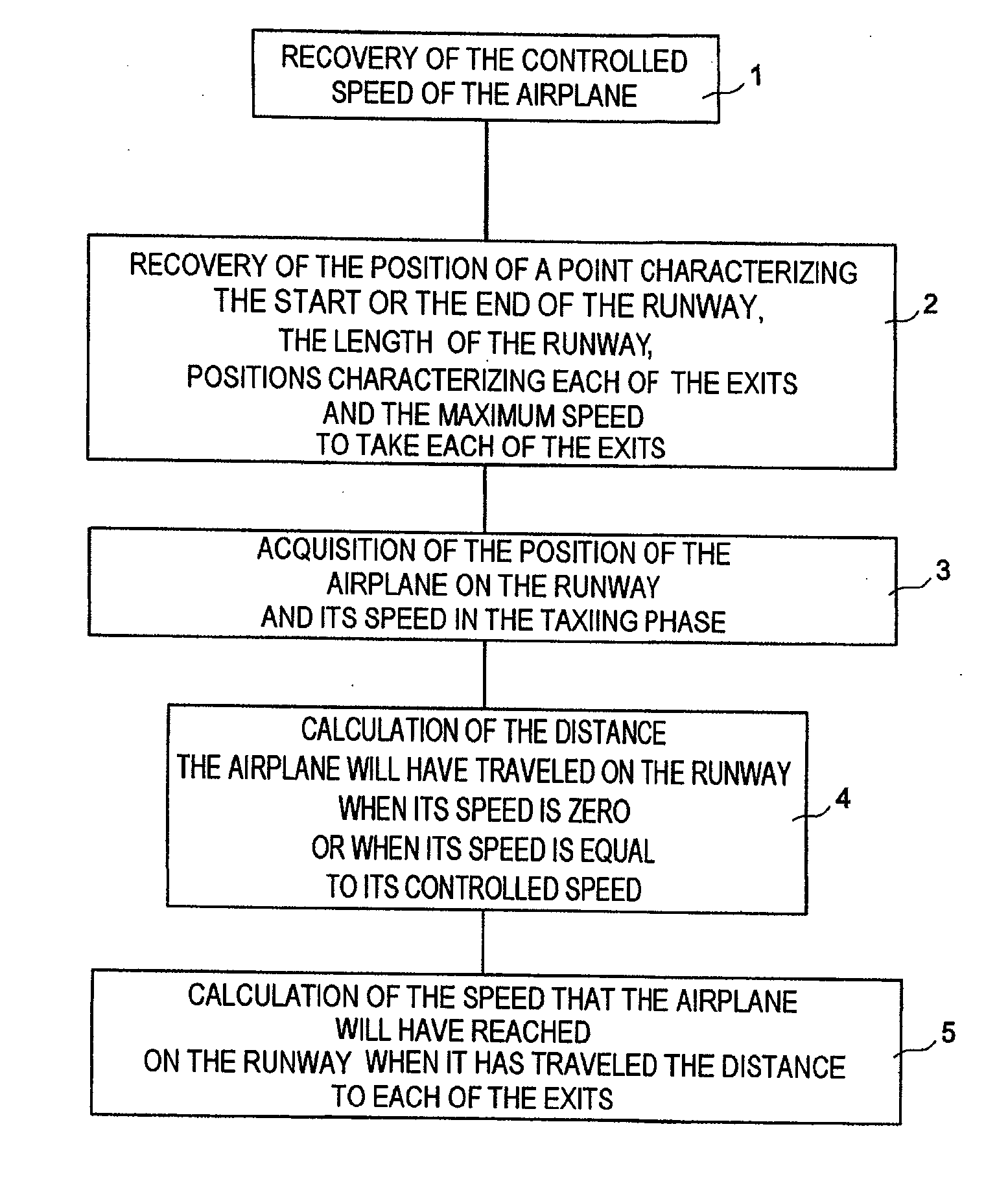
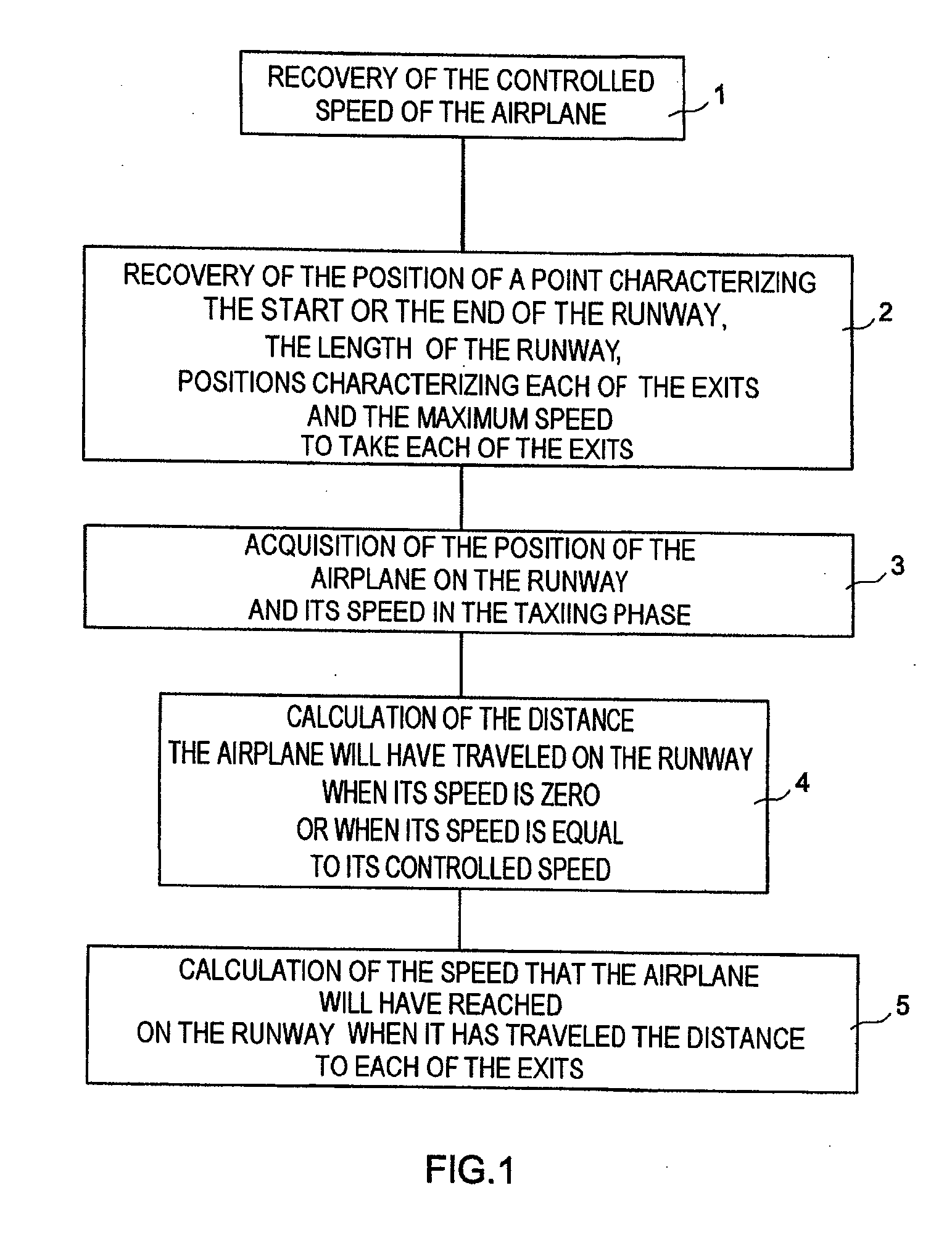
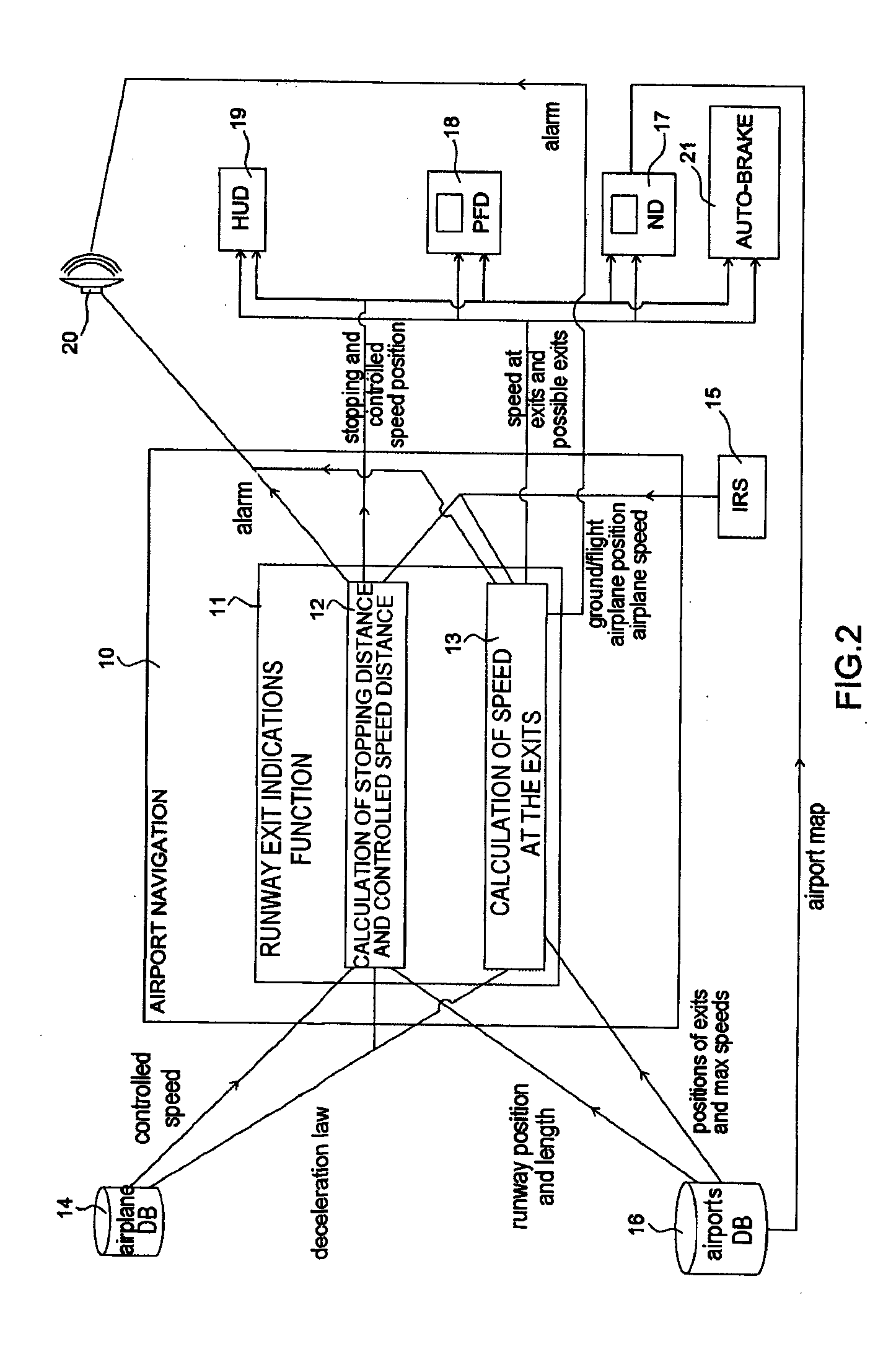
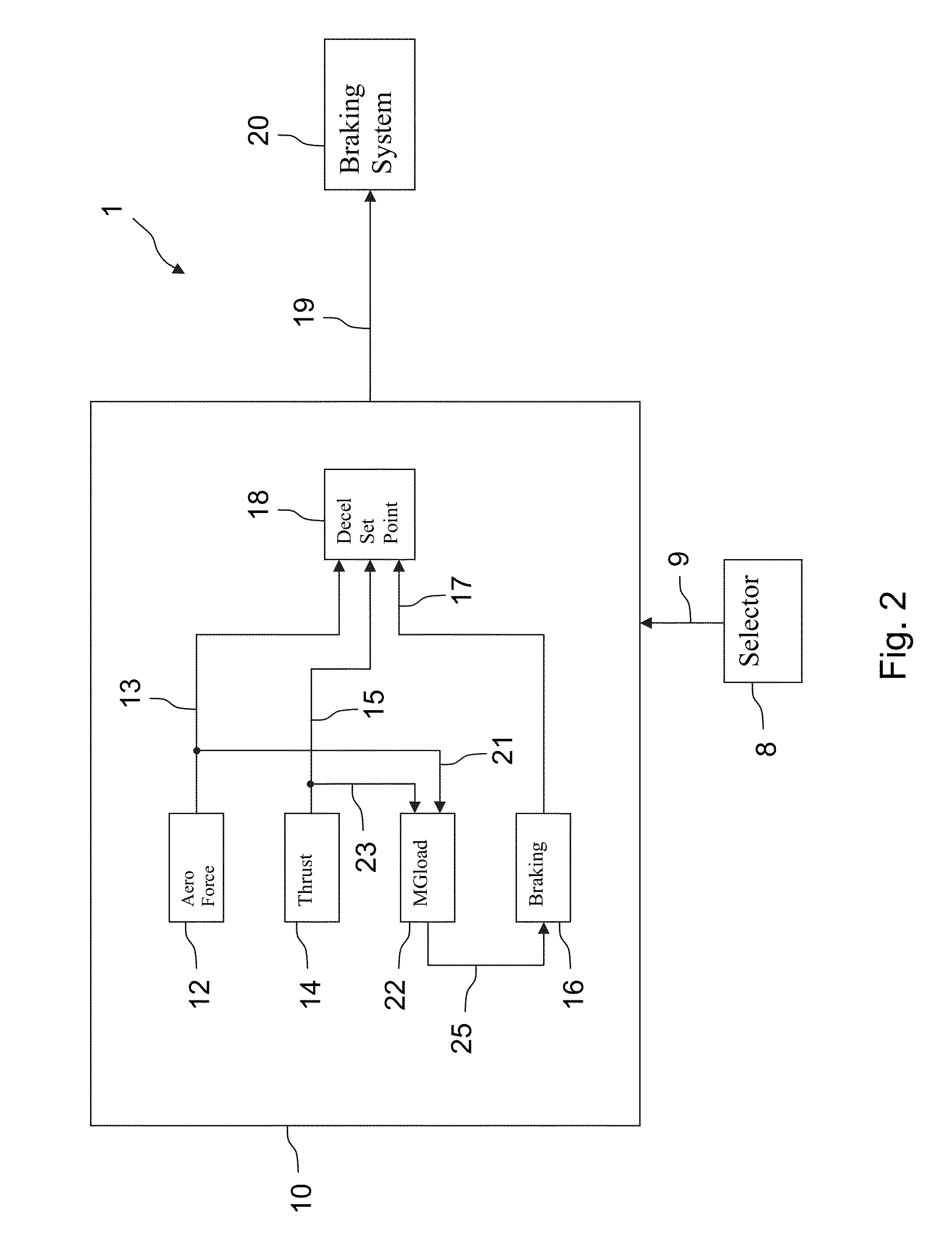
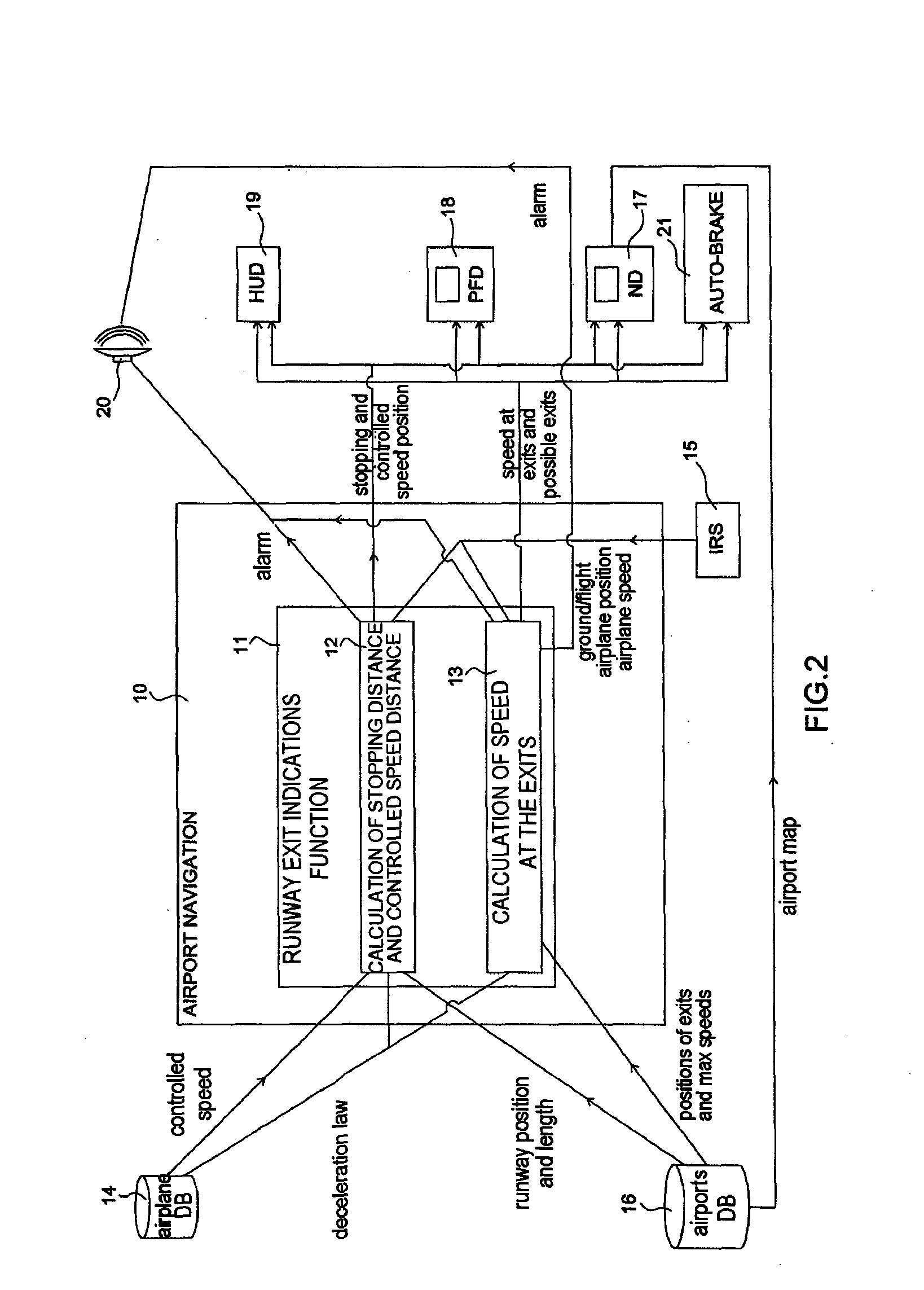
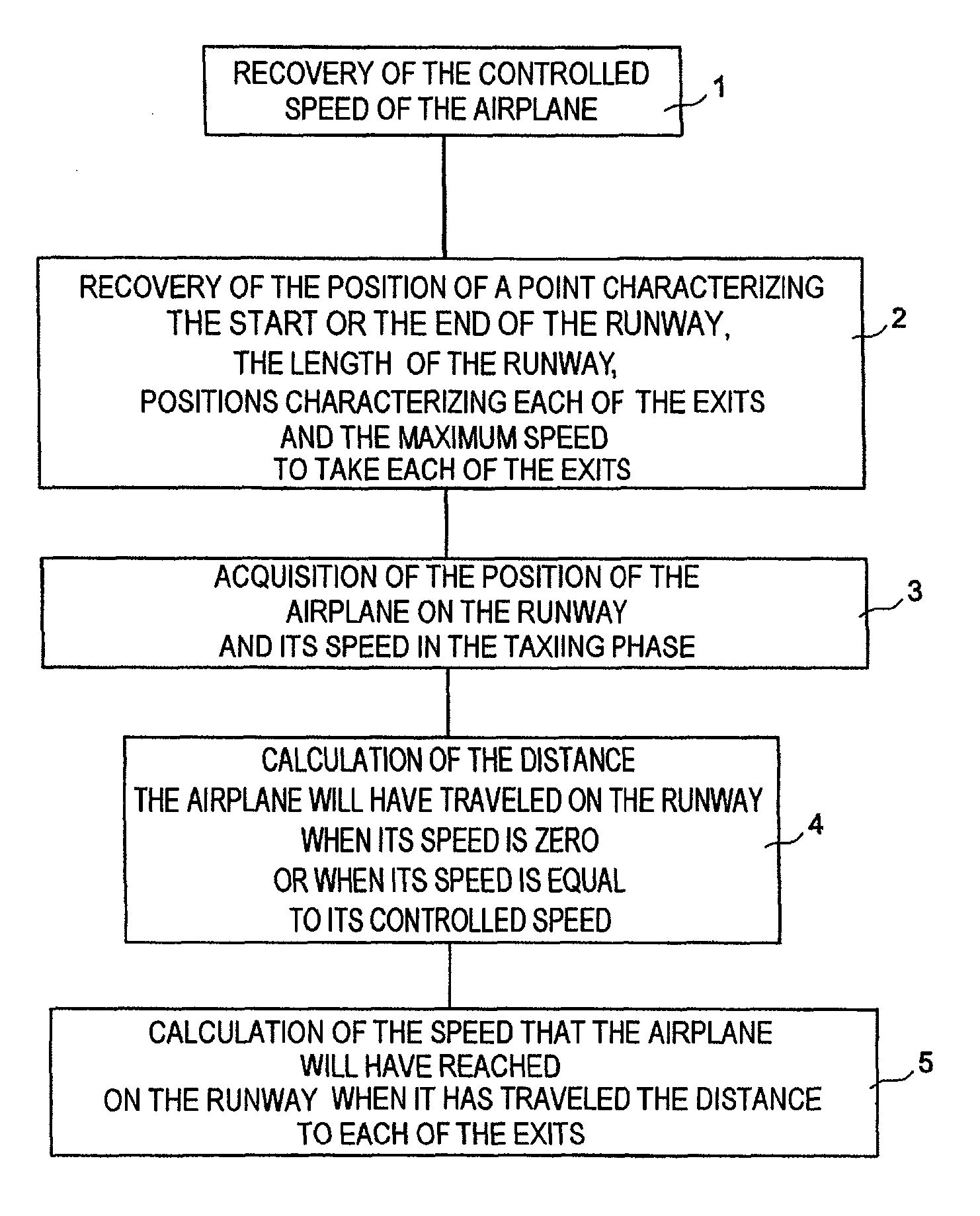
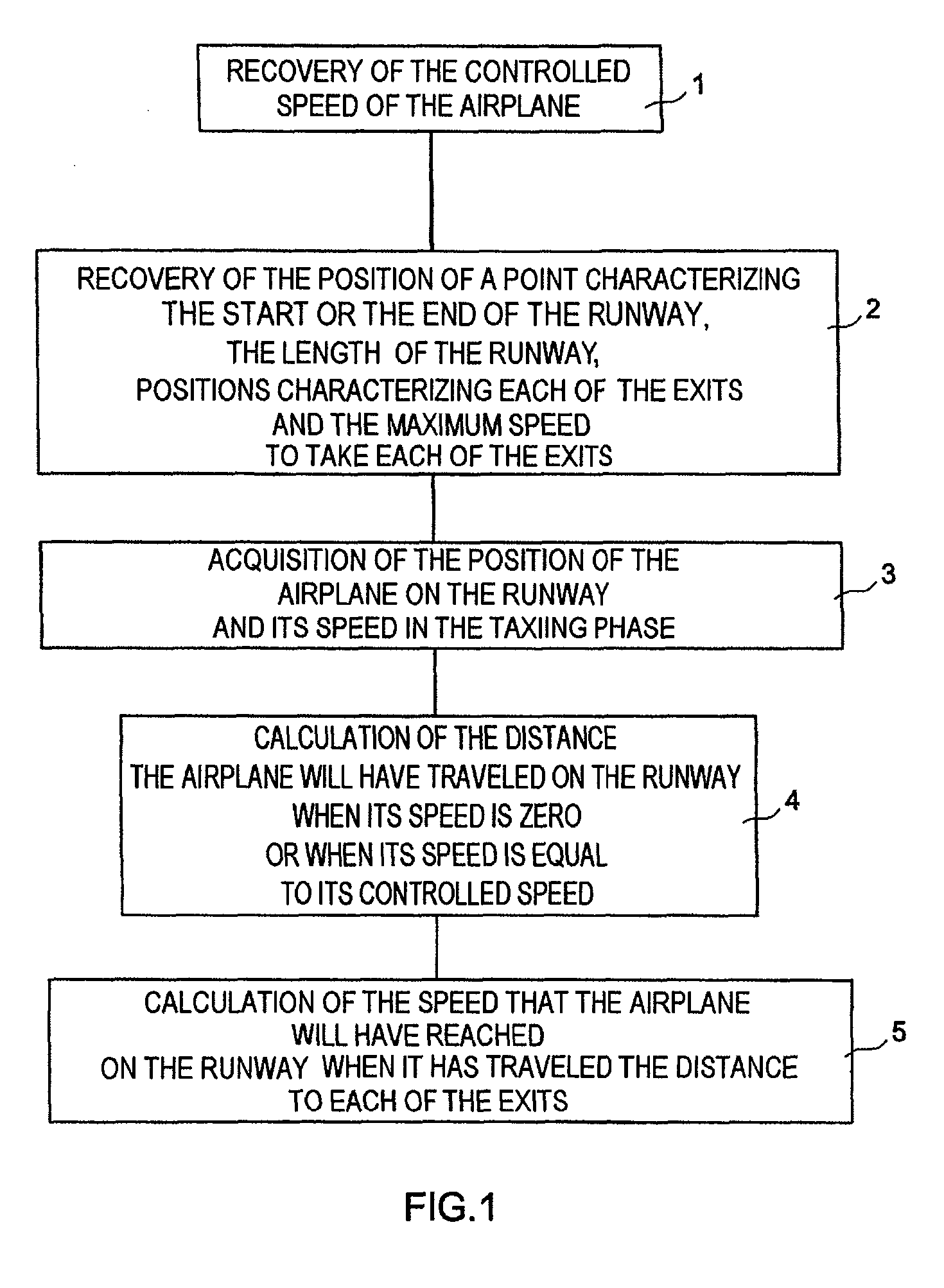
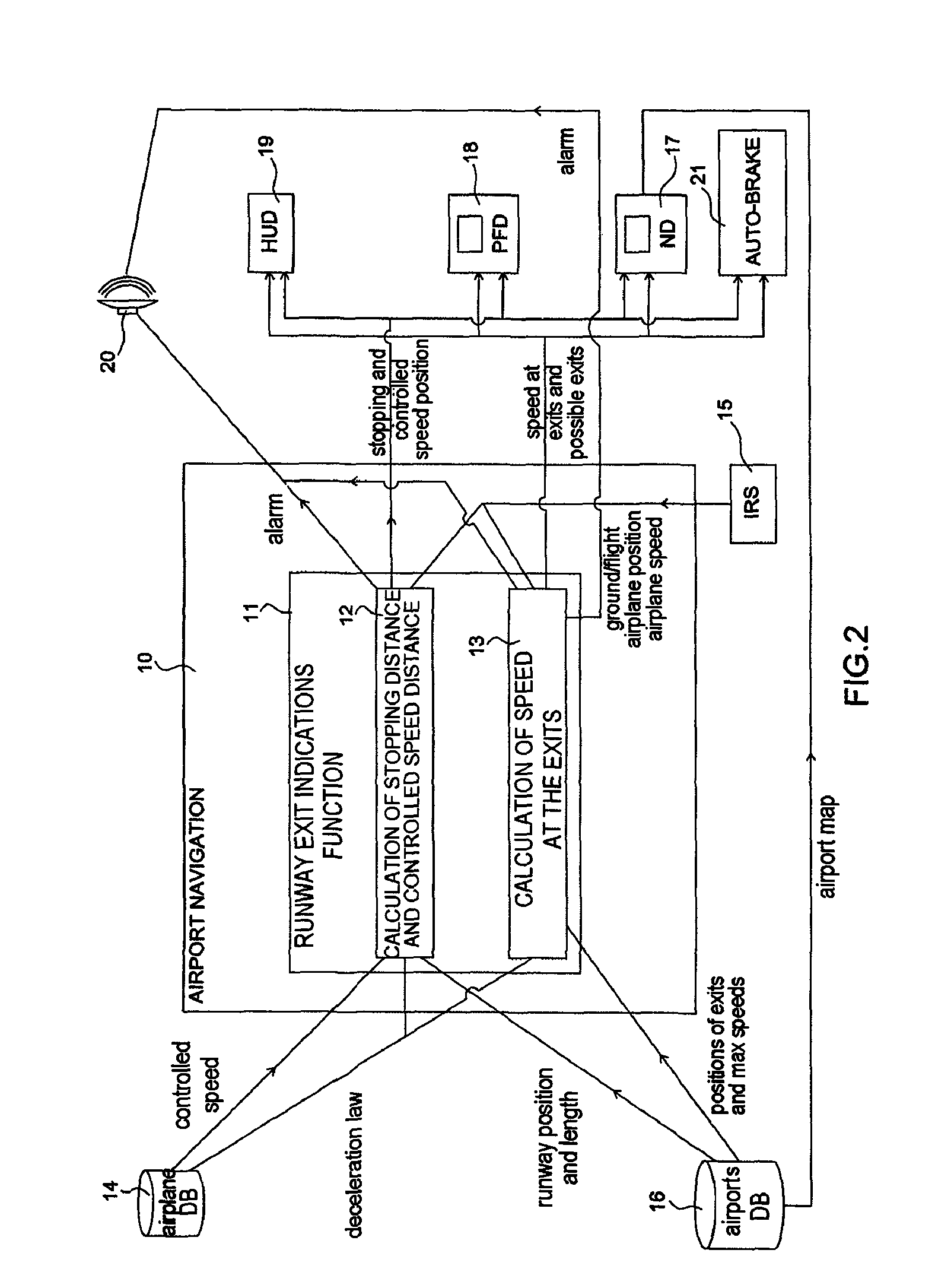
System and method to assist in the braking of an aircraft on a landing runway
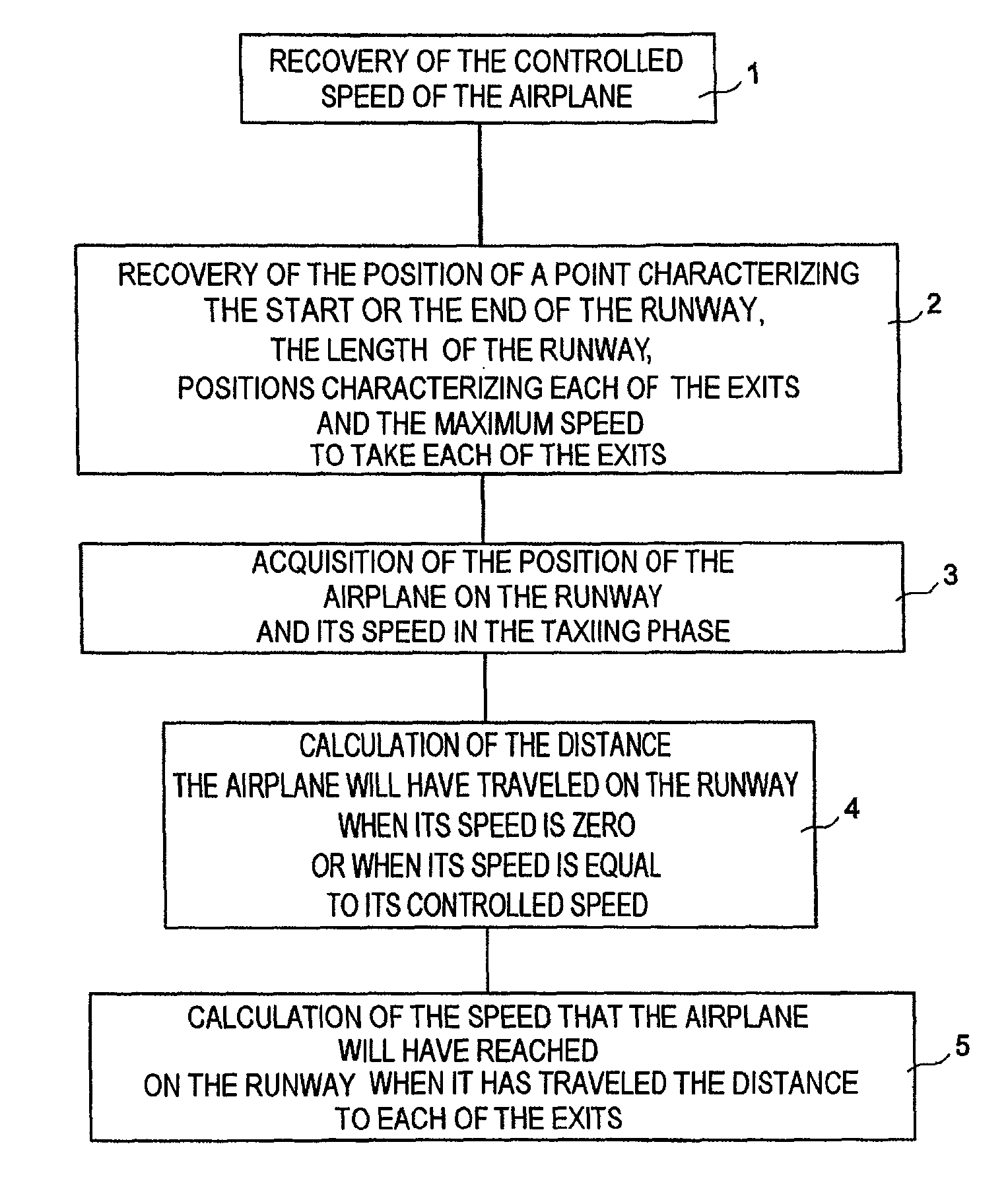
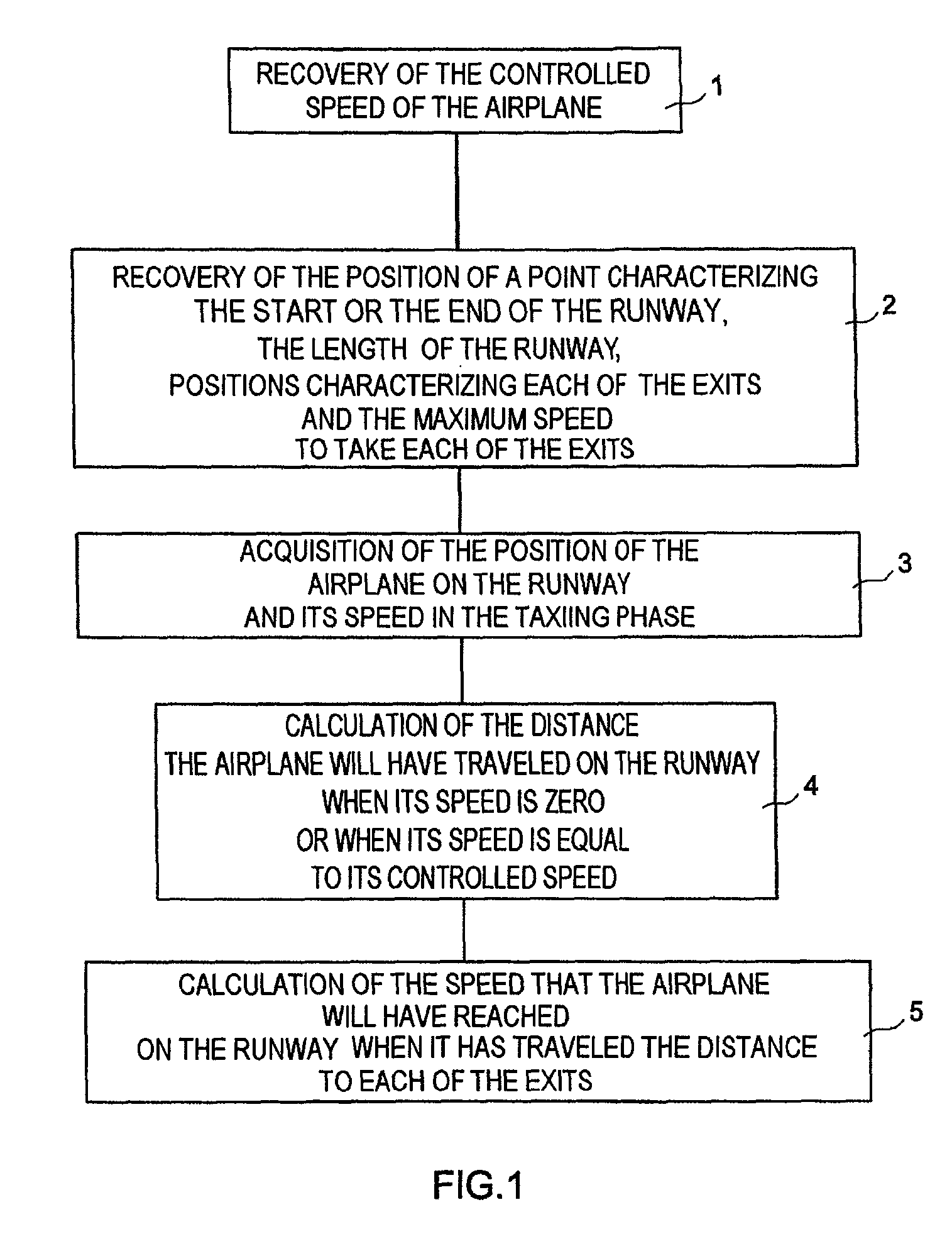
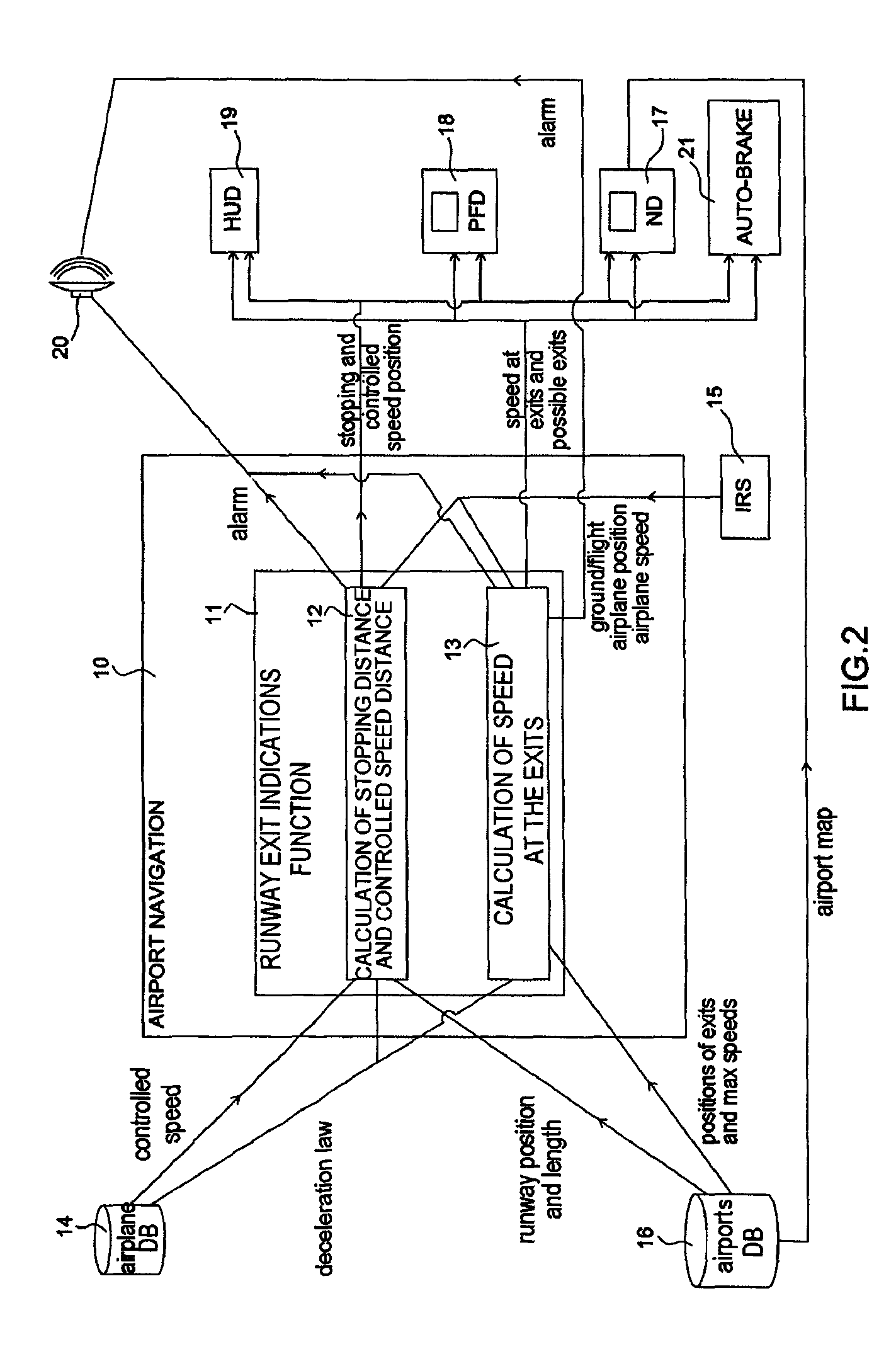
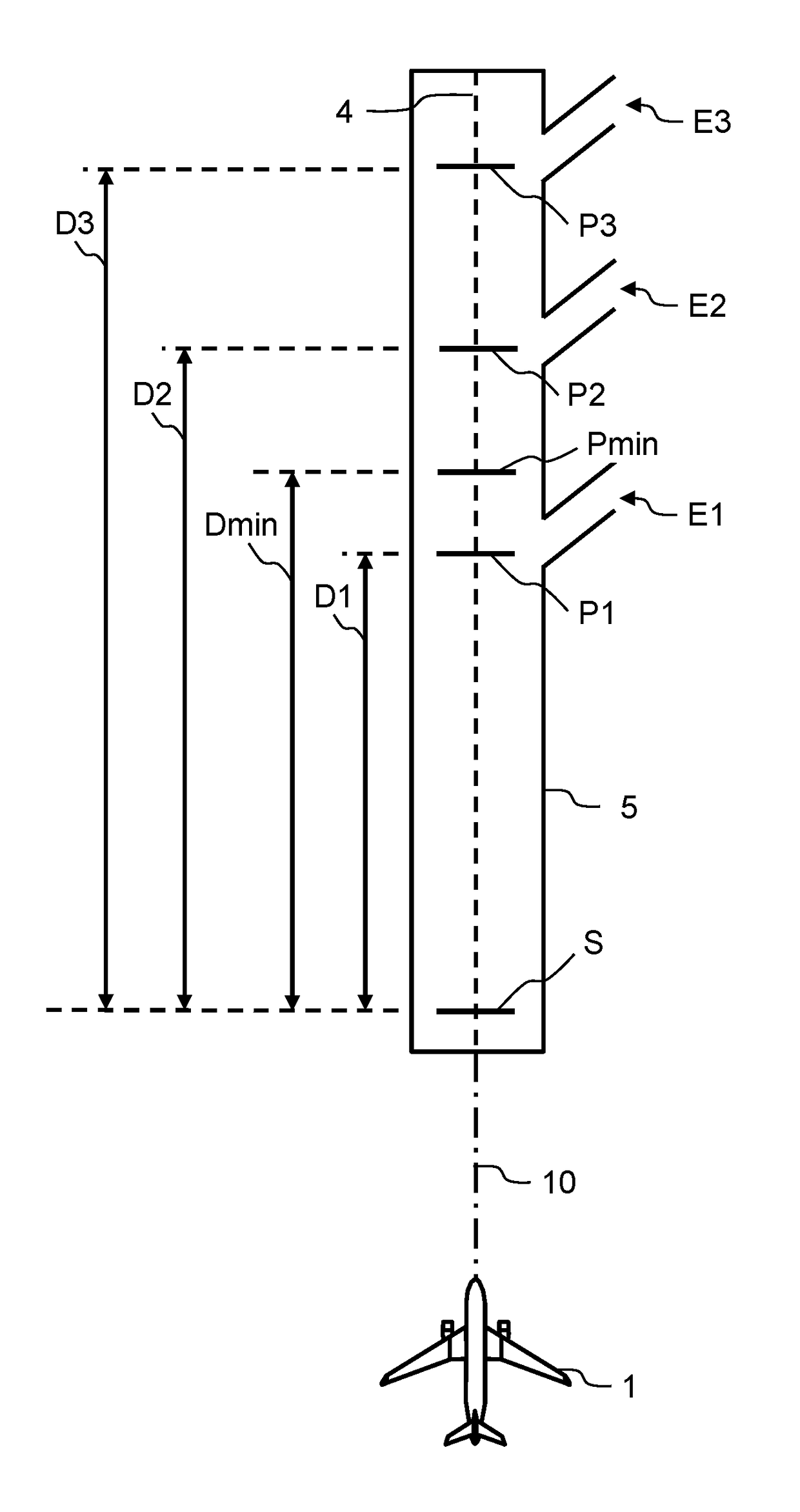
A system includes a means of acquiring the position of the aircraft on the runway and its speed in the taxiing phase, a means of storing data concerning the runway and a predefined deceleration law, a function for calculating the distance that the aircraft will have traveled on the runway when it has reached a certain speed and / or the speed that it will have reached when it has traveled a certain distance: the calculated distance makes it possible to adapt the braking by comparison with the distance remaining to reach the end of the runway; the calculated distance makes it possible to adapt the braking by comparison with the distance remaining to reach the end of the runway; the calculated speed makes it possible to adapt the braking by comparison with the maximum speed to take the exit.
Owner:THALES SA
The determination of runway landing conditions
The invention discloses differing embodiments of methods, aircraft, and apparatus for determining the landing conditions of a runway. In one embodiment, braking data may be collected from an aircraft which has landed on the runway; a braking performance measurement of the aircraft may be calculated based on the braking data; and a normalized braking performance measurement may be determined based on the braking performance measurement. The invention may be utilized to predict the expected braking performance of various types of aircraft on the runway. The invention may provide landing performance information to a broad host of users, and / or may be used as a basis for the development of a new aviation standard for the reporting of runway braking action.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
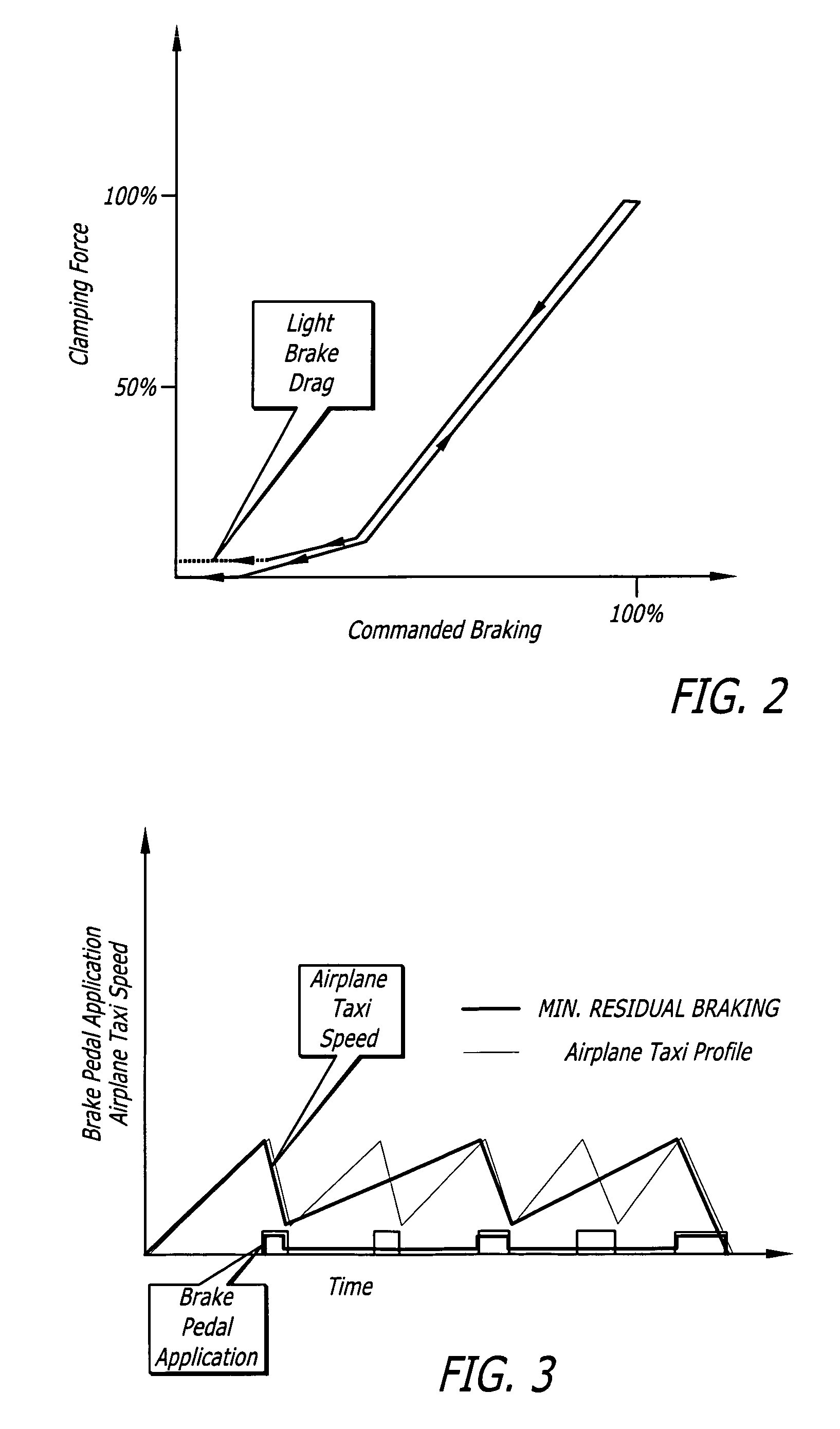
Method to reduce carbon brake wear through residual brake force
ActiveUS20060186736A1Reduced brake wearAvoid excessive frictionAutomatic braking sequenceBraking action transmissionAirplaneBrake force
The method for reducing aircraft carbon brake wear involves monitoring the commanded initiation of braking, and setting a residual brake clamping force to a predetermined minimum residual brake clamping force, which is maintained following the commanded initiation of braking to prevent release of braking during taxiing of the aircraft. The minimum residual brake clamping force is applied despite a commanded release of braking until at least one predetermined control logic condition occurs.
Owner:HYDRO AIRE AEROSPACE CORP
Method and device for automatic control of an aircraft deceleration in running phase
InactiveUS20040026992A1Automatic braking sequenceAlighting gearAutomatic controlAutomatic train control
The invention relates to a system to control the deceleration of an aircraft during the taxiing phase on a landing strip, the system comprising: acquisition means (100) of the current position of the aircraft on the strip, acquisition means (100) of the current speed of the aircraft on the strip, calculation means (102), receiving position and speed values from the acquisition means, to define, as a function of the desired final speed of the aircraft at the so-called final position on the strip, a deceleration set-point modification time, after the current time, and a new deceleration set-point to apply from the modification time, to reach the final position at the desired speed.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
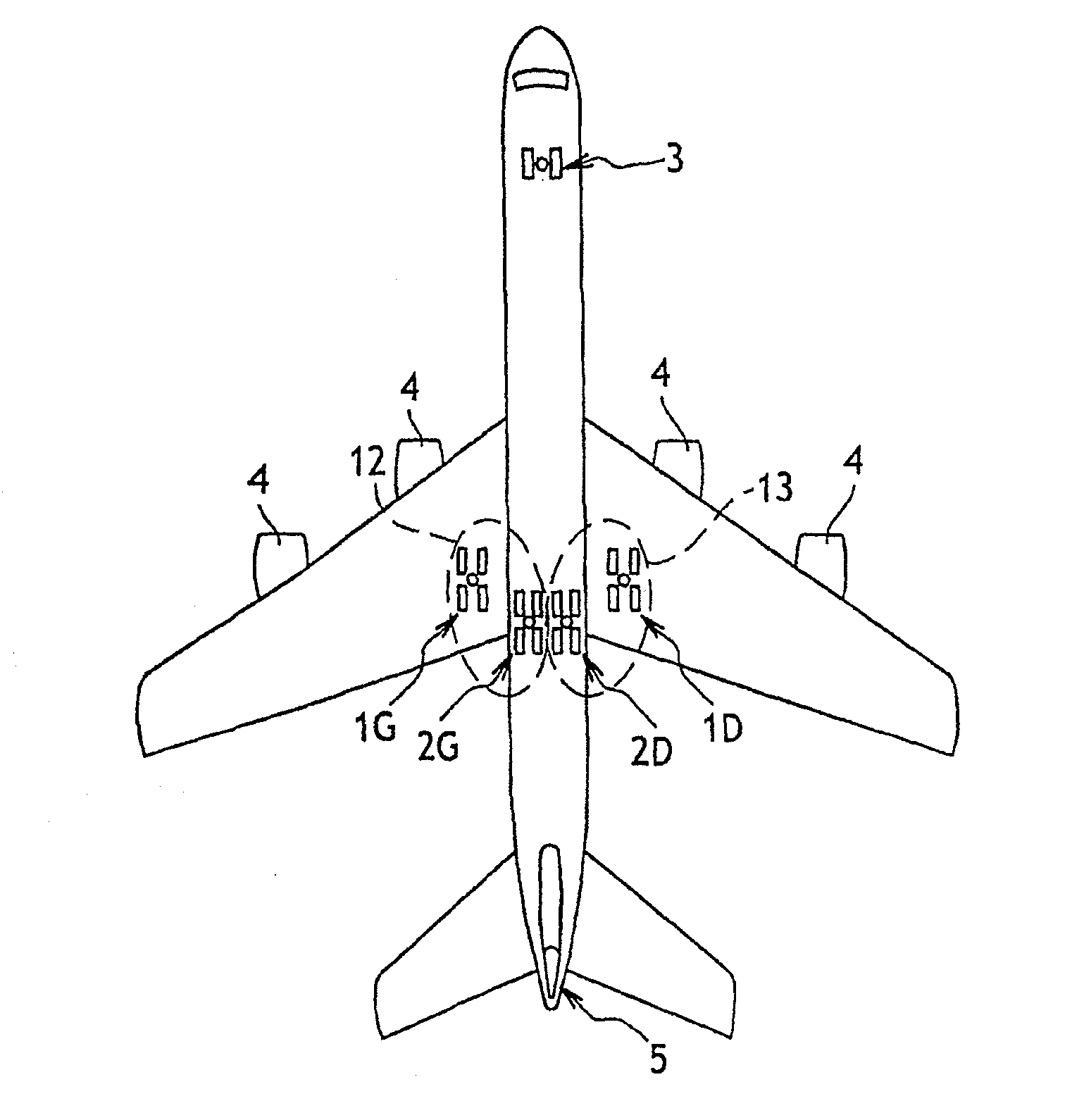
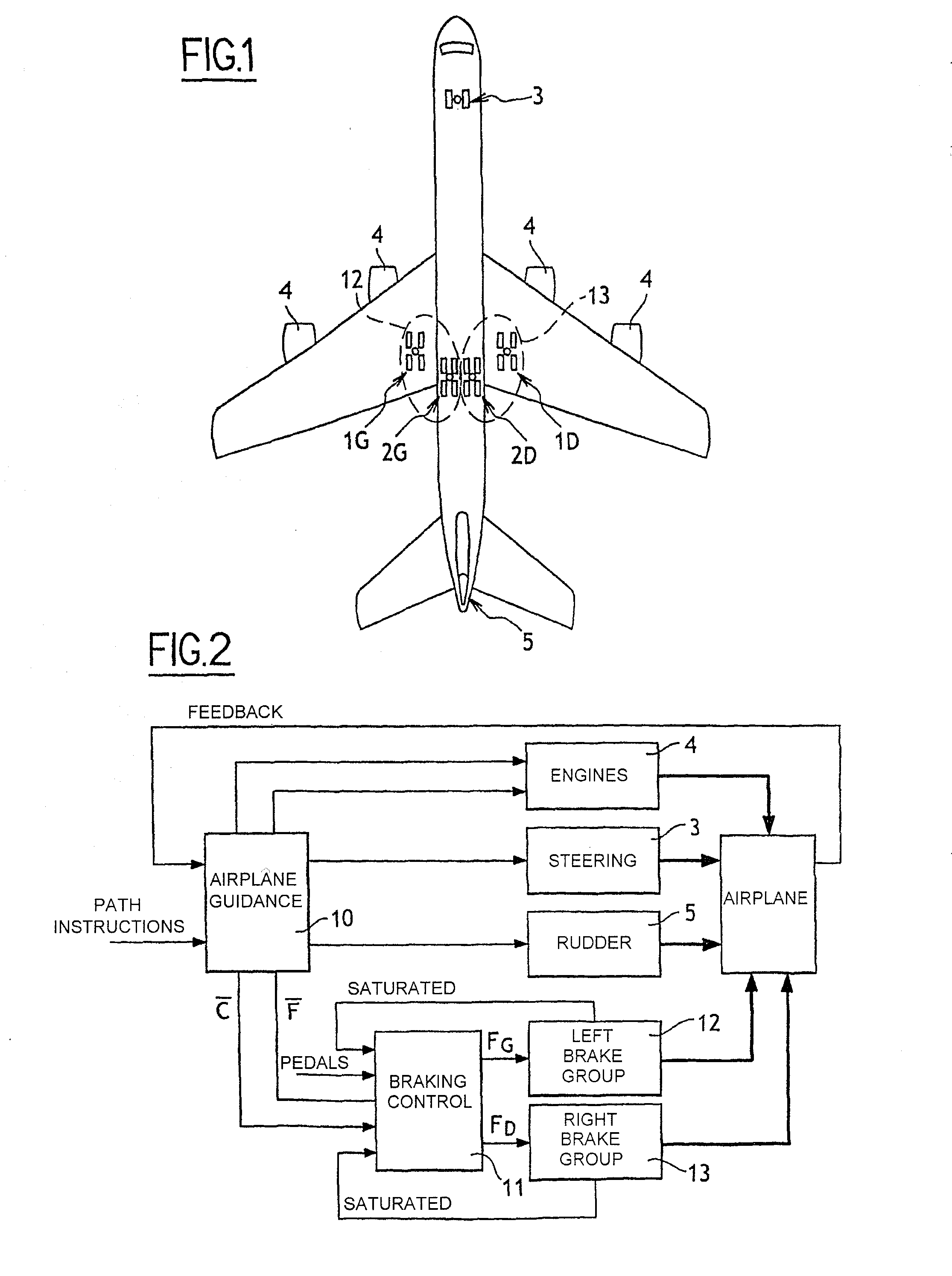
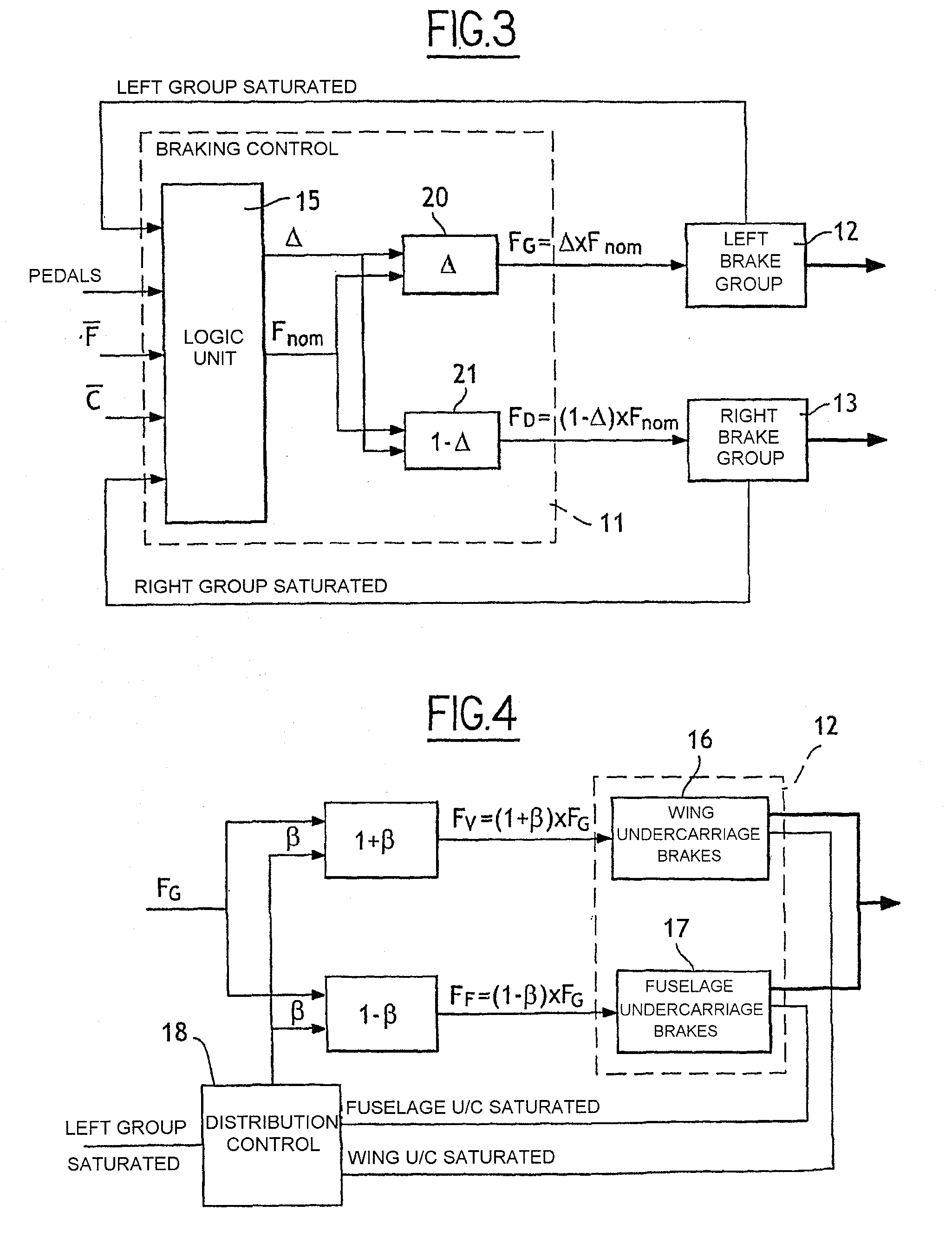
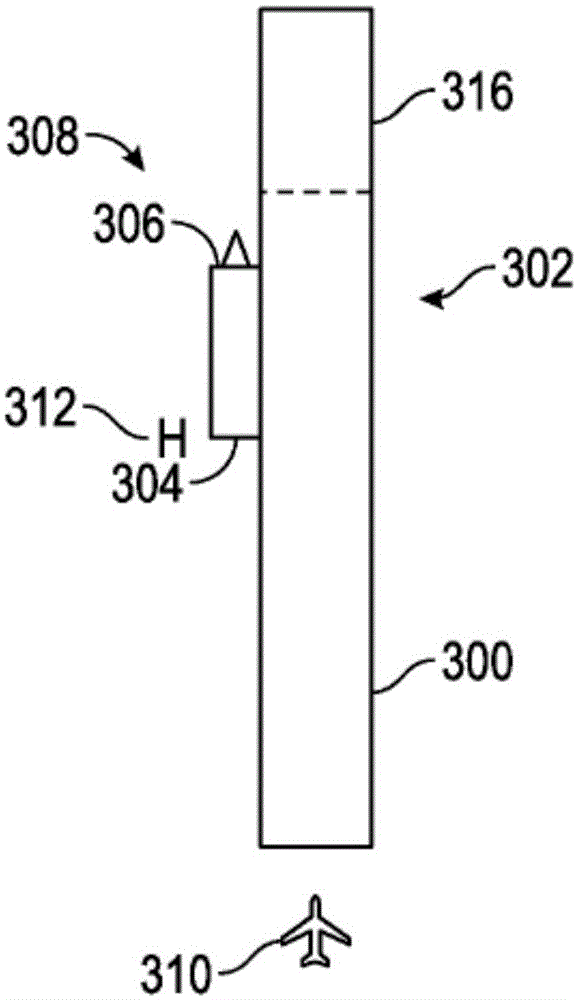
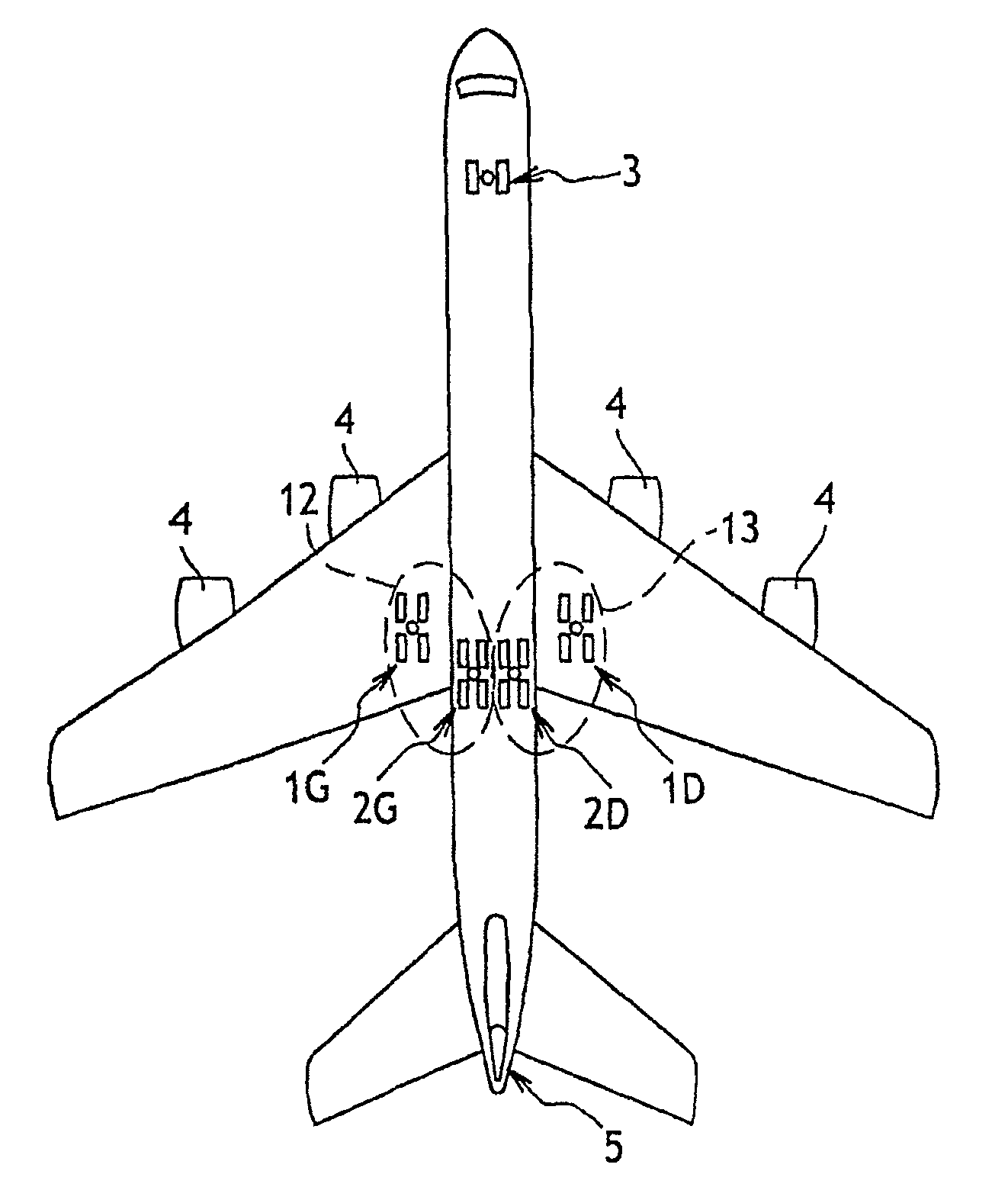
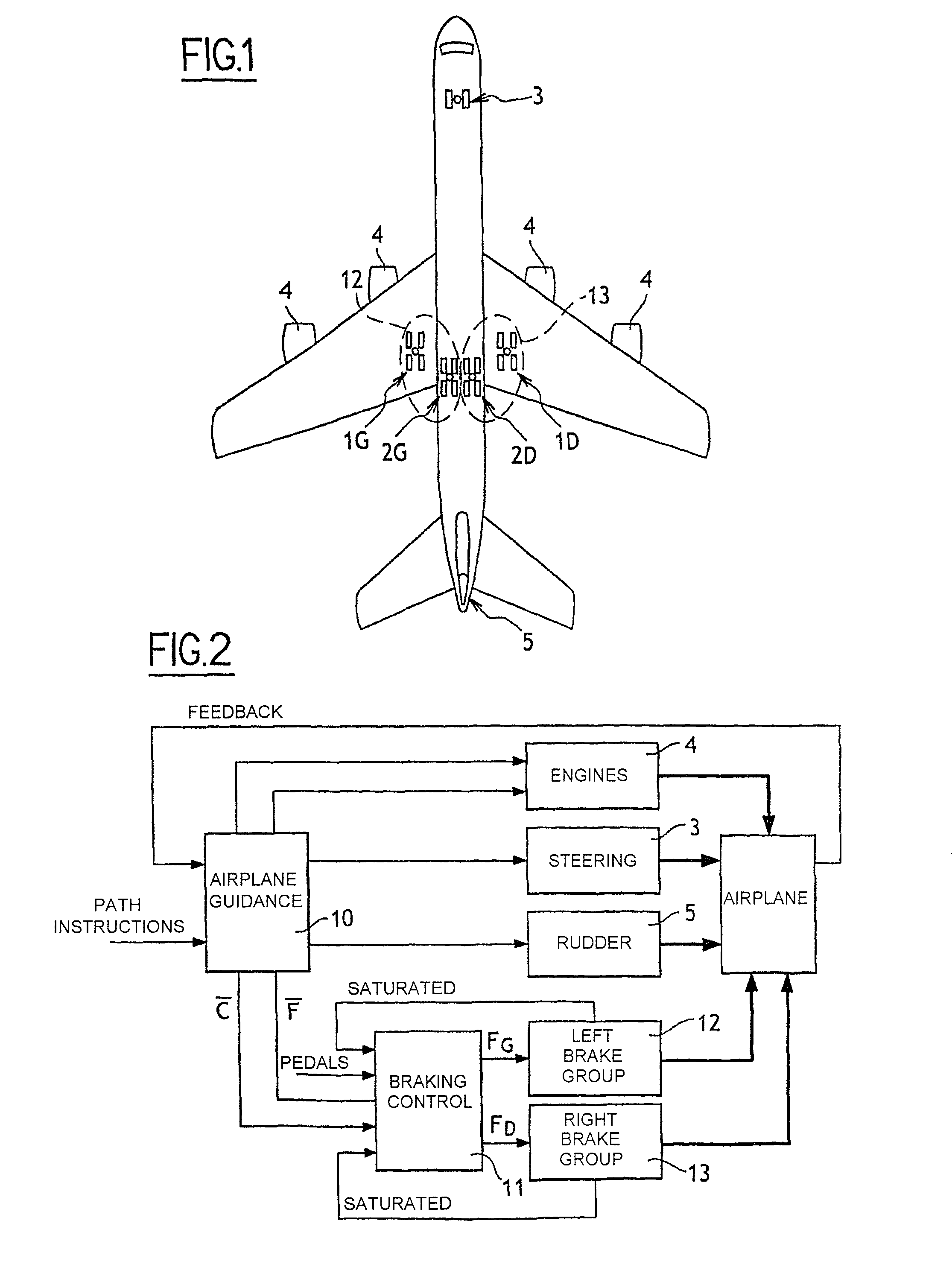
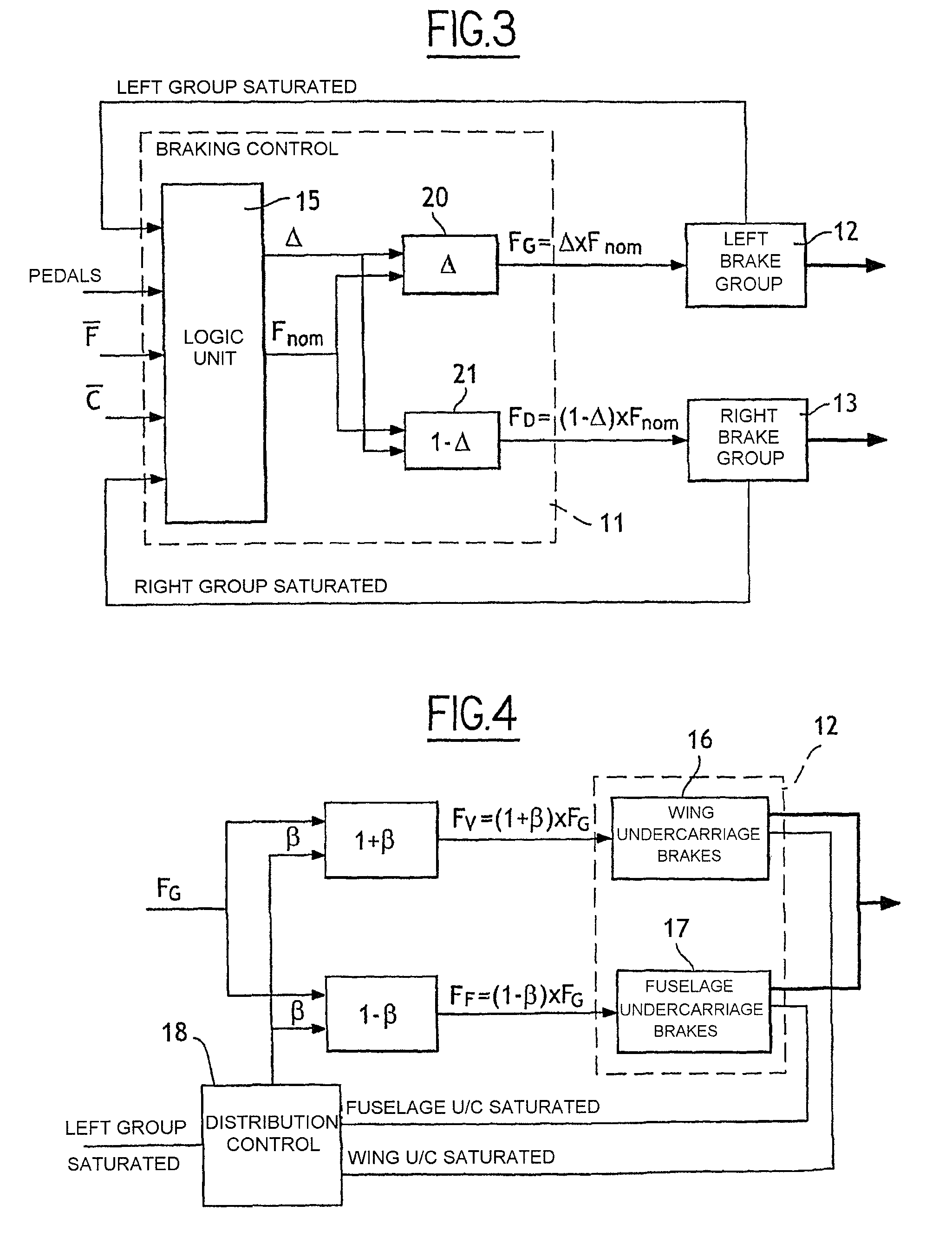
Method of Distributing Braking Within at Least One Group of Brakes of an Aircraft
ActiveUS20080201025A1Energy levelAnalogue computers for vehiclesAutomatic braking sequenceEngineeringOperant conditioning
The invention provides a method of managing the braking of an aircraft having a plurality of brakes comprising friction elements, the method comprising the following steps for at least one group (12, 13) of brakes:estimating an energy level (ΔE) to be dissipated by the brakes of the group; andestimating individual braking setpoints (Fi) for each of the brakes of the group so that the individual braking setpoints make it possible, at least under normal operating conditions of the brakes, to implement braking that dissipates said energy level, the individual braking setpoints also being determined so as to satisfy at least one other given operating objective.
Owner:SAFRAN LANDING SYSTEMS
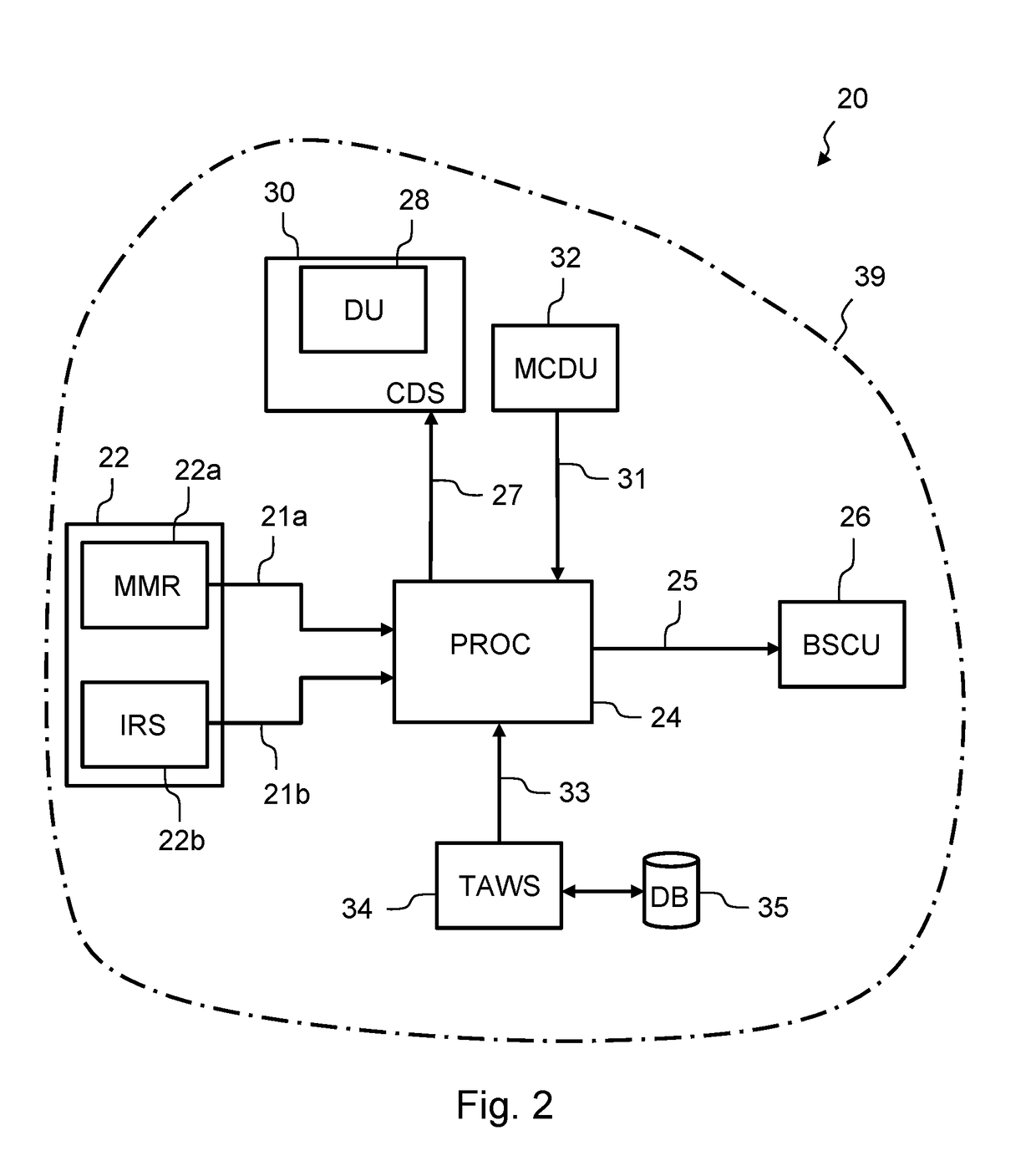
Device and method for determining runway condition, relevant drive assistance system and relevant aircraft
ActiveCN102910284AReliable estimateAccurate estimateAutomatic braking sequenceVehicle position/course/altitude controlAdhesion coefficientAuxiliary system
The invention relates to a device and a method for determining a runway condition (12), an aircraft equipped with such a device and an aircraft drive assistance system equipped with such a device. The method comprises a step of collecting (A1) measurement data related to at least a physical quantity of an aircraft (10) during a phase when the aircraft is taxiing on a runway; a step of obtaining (A2) a set of estimated adhesion coefficient values mu of the runway by using the collected measurement data, wherein the estimated adhesion coefficient values of the runway correspond to a set of corresponding moments of movement of the aircraft taxing on the runway; a step of obtaining (A3) a slip ratio value s for at least a wheel of the aircraft at each skiing moment by using the acquired data to obtain (A4) [mu, s] pairs, and a step of determining the condition of the runway by comparing (A5.2) a profile of the [mu, s] pairs of values with a predetermined profile.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
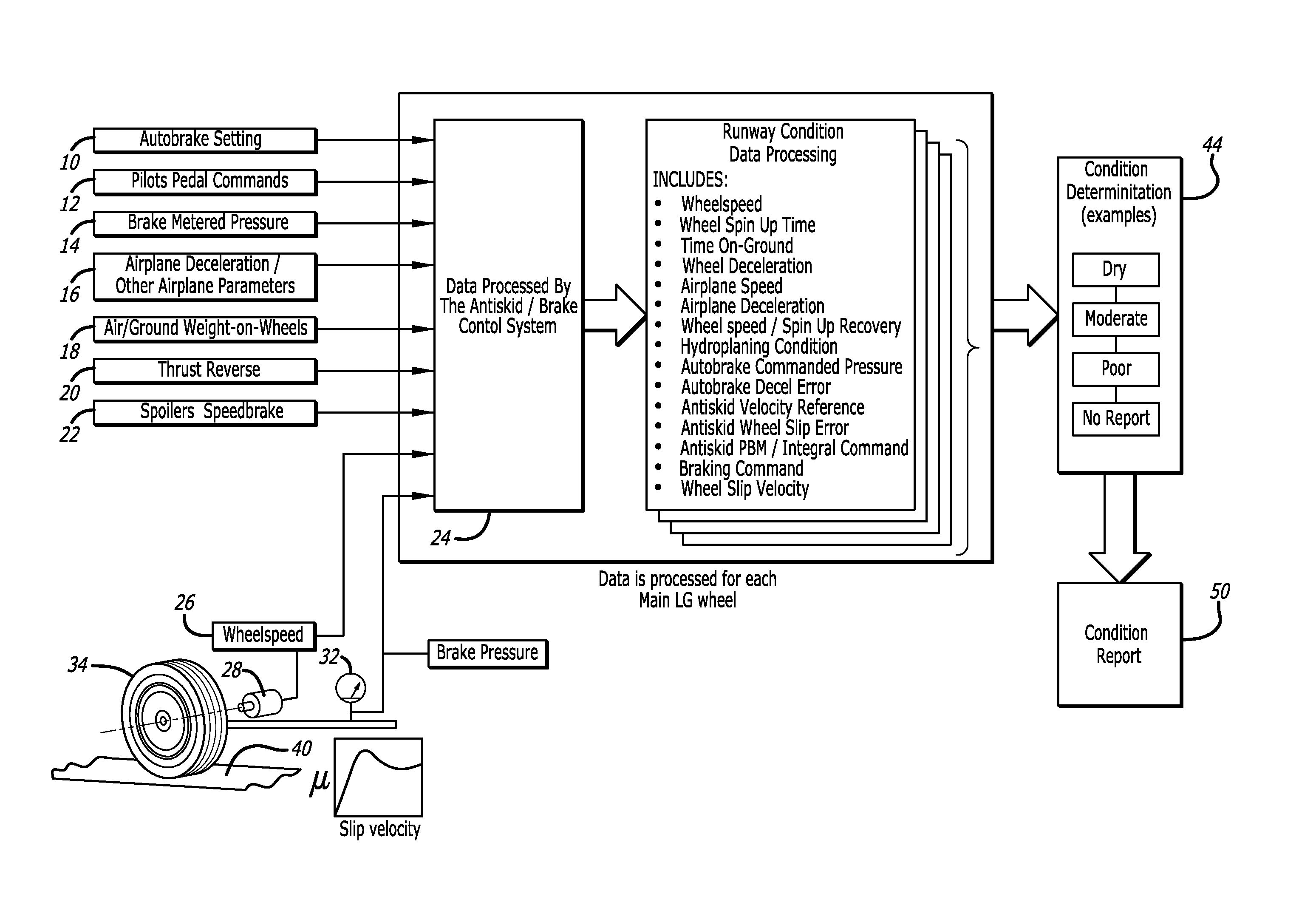
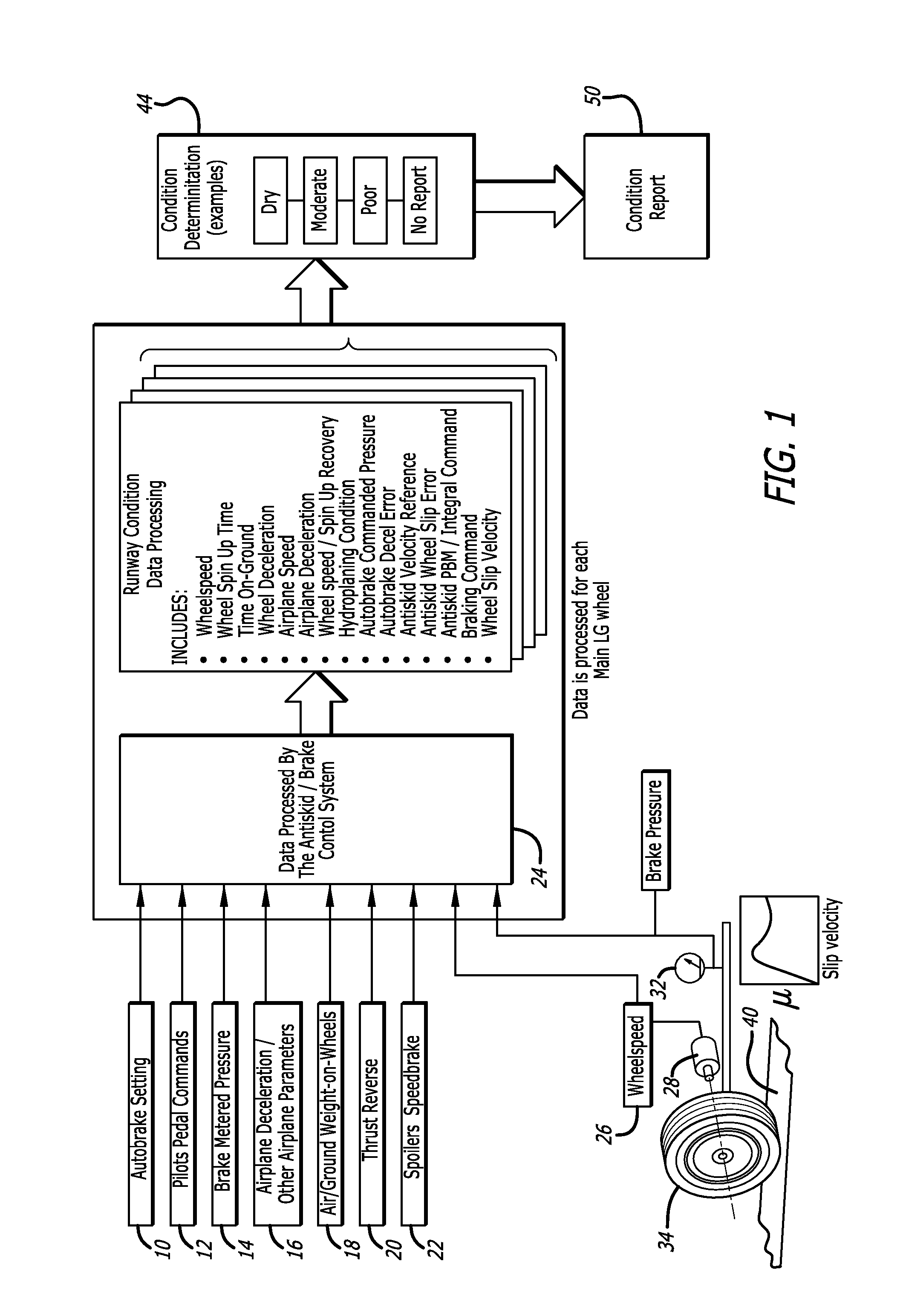
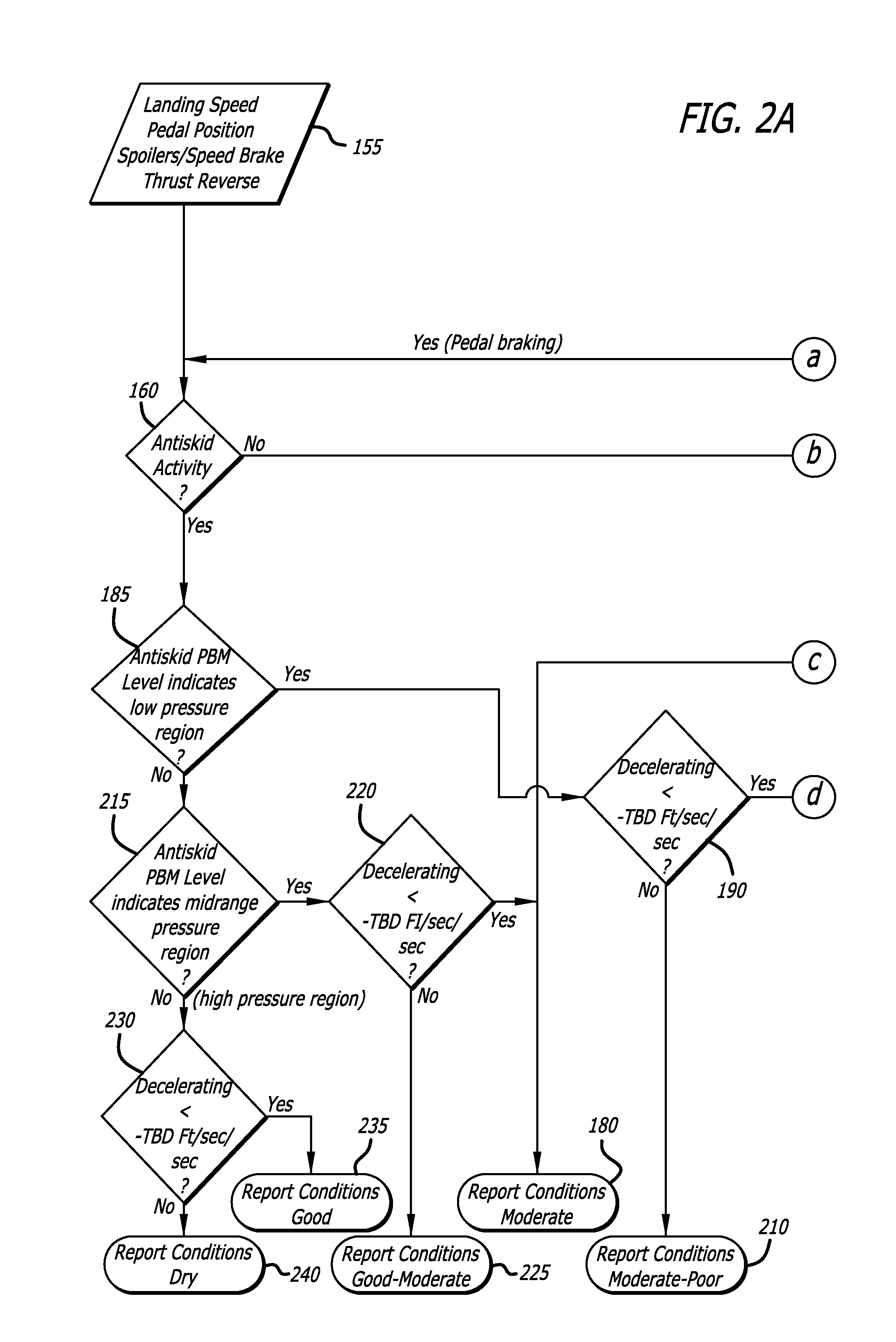
Method of reporting runway condition using brake control system
ActiveUS20150254990A1Safer landing environmentAnalogue computers for vehiclesAutomatic braking sequenceControl systemAircraft landing
A system and method for objectively evaluating an airport runway condition, where conditions pertaining to aircraft landing factors are compiled and used to determine a runway braking condition. One set of conditions pertains to aircraft landing factors, including brake metered pressure, wheel speed, and aircraft deceleration, and a second set of factors relate to pilot controlled parameters. A condition report is generated and made available to pilots of subsequently landing aircrafts prior to landing.
Owner:HYDRO AIRE AEROSPACE CORP
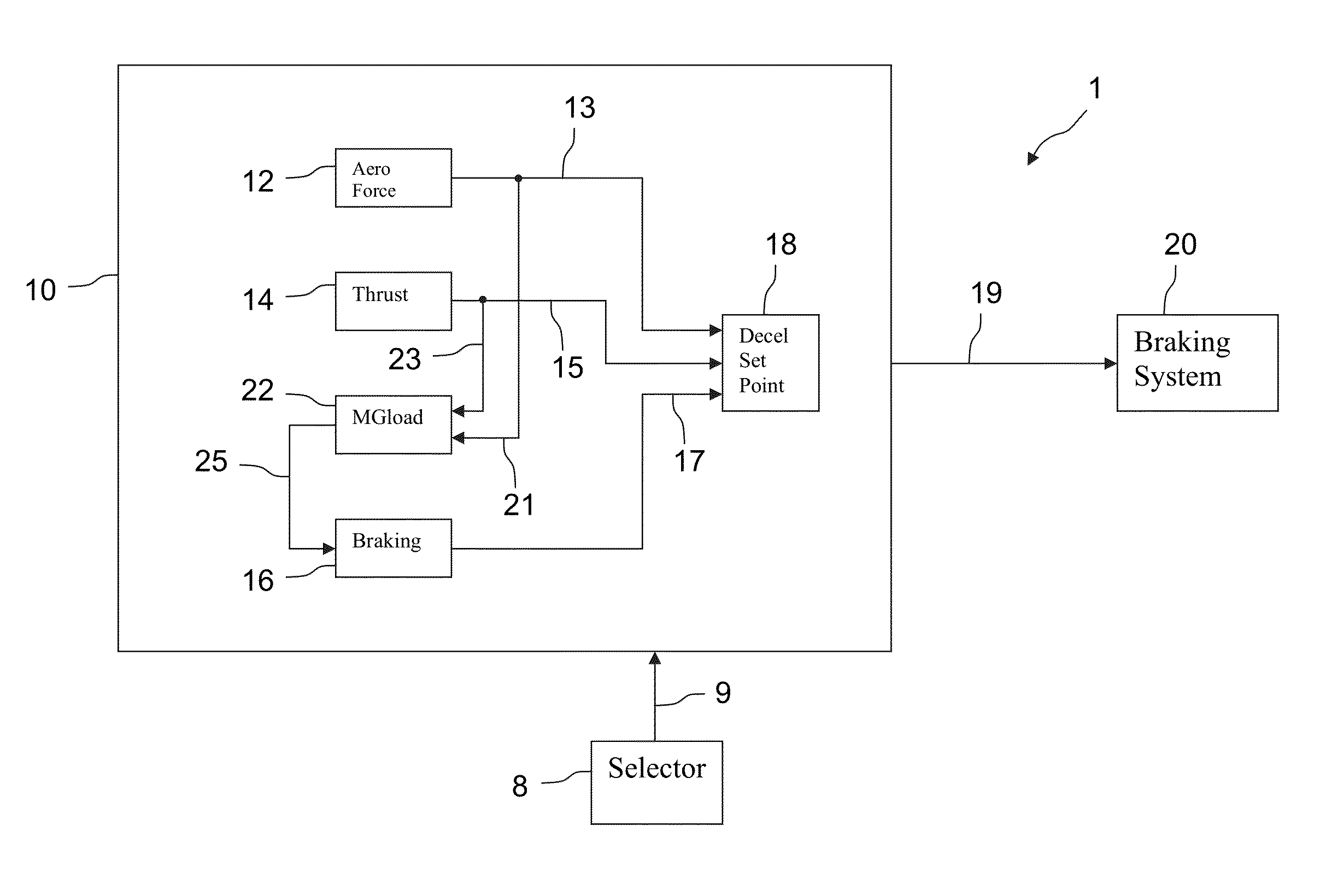
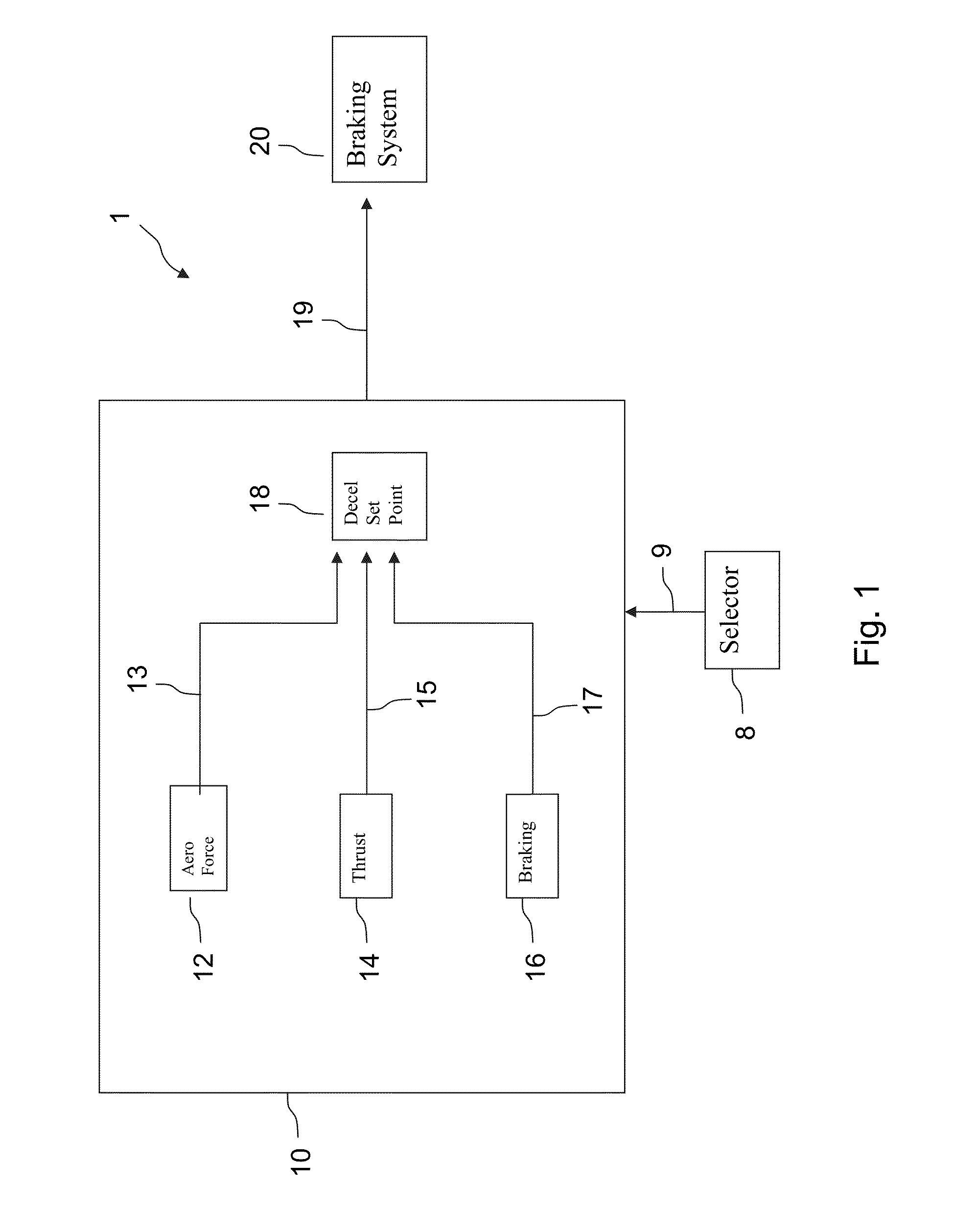
Method and system for controlling aircraft braking on a runway
ActiveUS20130261920A1Low costShorten the timeAutomatic braking sequenceAnalogue computers for trafficJet aeroplaneAirplane
A method to control braking of an aircraft on a landing runway including: selecting a dummy runway state corresponding to a level of adhesion of wheels of the aircraft to a runway which is lower, over an entire speed range of the aircraft while braking on a runway, than an adhesion level of the wheels of the aircraft to the landing runway; calculating a set point of a deceleration value for the aircraft on the landing runway based on the landing runway for the selected dummy runway state, wherein the calculated set point corresponds to maximum braking value of the aircraft, and controlling the braking of the aircraft using the set point.
Owner:AIRBUS SAS +1
System and method to assist in the braking of an aircraft on a landing runway
A system includes a means of acquiring the position of the aircraft on the runway and its speed in the taxiing phase, a means of storing data concerning the runway and a predefined deceleration law, a function for calculating the distance that the aircraft will have traveled on the runway when it has reached a certain speed and / or the speed that it will have reached when it has traveled a certain distance: the calculated distance makes it possible to adapt the braking by comparison with the distance remaining to reach the end of the runway; the calculated distance makes it possible to adapt the braking by comparison with the distance remaining to reach the end of the runway; the calculated speed makes it possible to adapt the braking by comparison with the maximum speed to take the exit.
Owner:THALES SA
Autobrake and decel control built-in test equipment
ActiveUS8712626B2View accuratelyVehicle testingAutomatic braking sequenceOperational systemEngineering
A system, apparatus and method provide a means for testing operation of a vehicle brake system. More particularly, a brake controller for controlling operation of the brake system includes a signal generator that can generate data indicative of wheel speed. Based on a user command, the controller uses either actual wheel speed data or simulated wheel speed data as inputs for controlling brake operation. The controller also includes logic for exercising various braking functions so as to enable maintenance personal to determine operational systems of the brake system.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
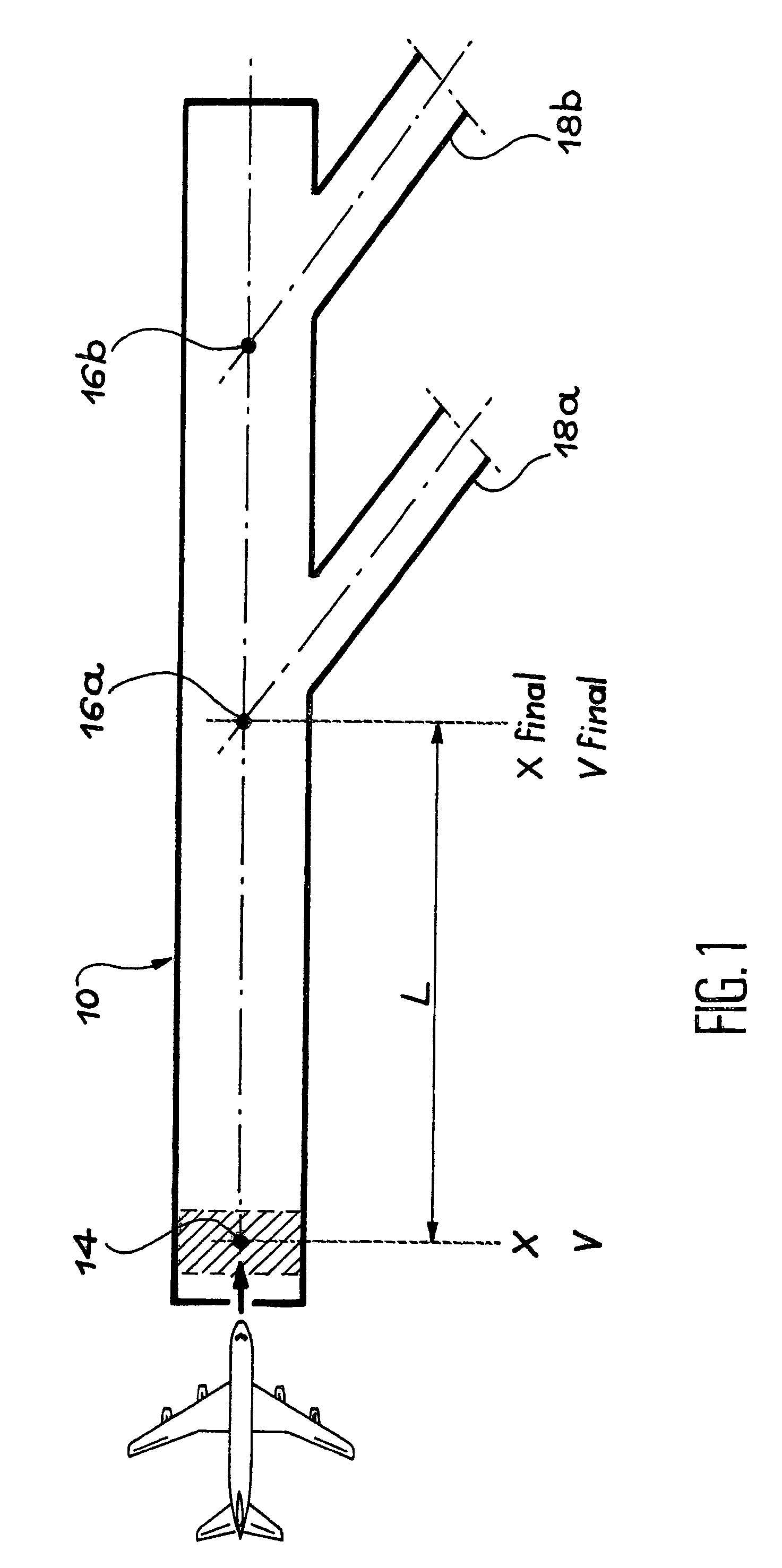
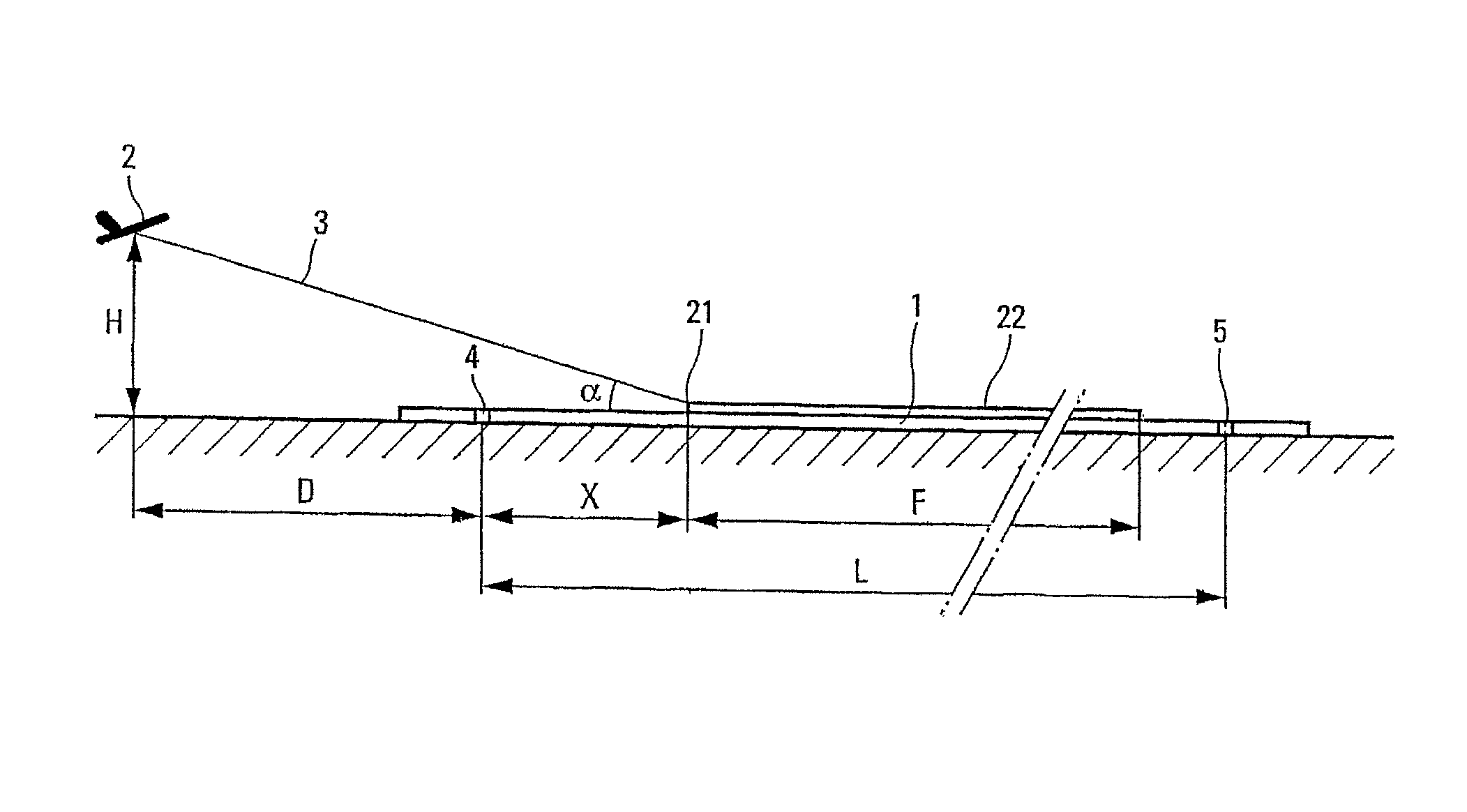
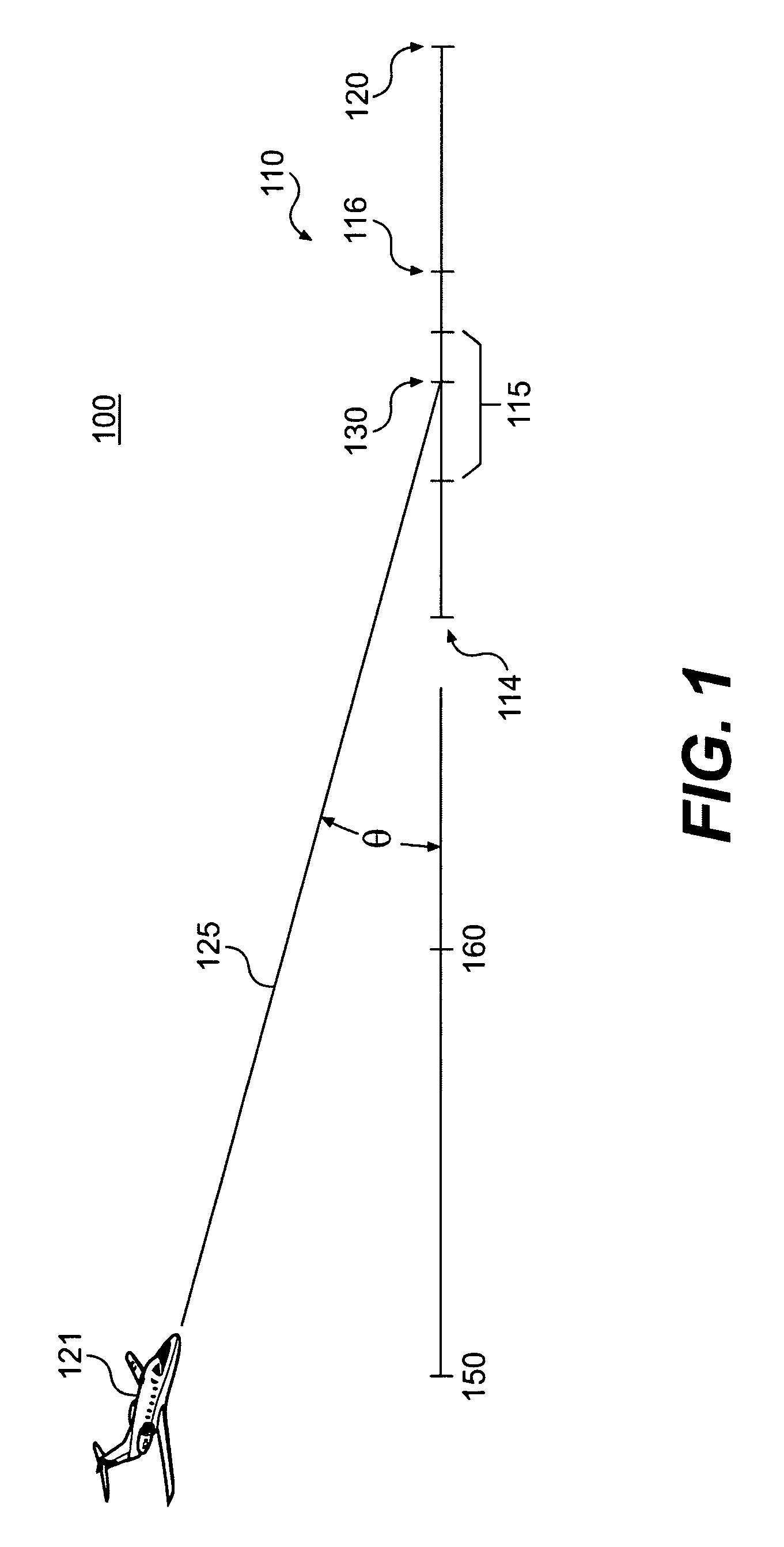
Method and system for predicting the possibility of complete stoppage of an aircraft on a landing runway
ActiveUS8428795B2Improve flight safetyAvoid accidentsAnalogue computers for vehiclesAutomatic braking sequenceFlight vehicleAirplane
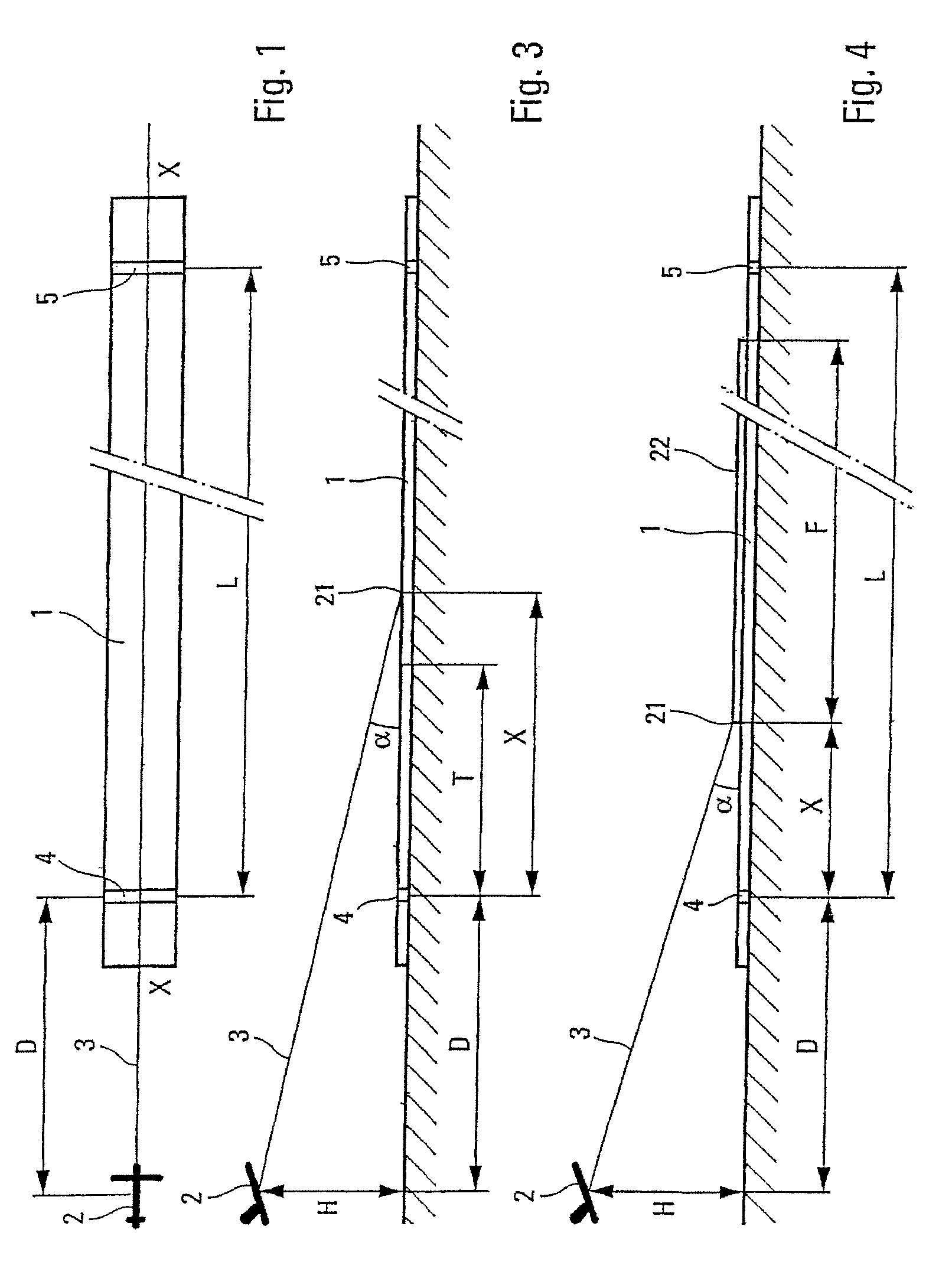
Method and system for predicting the possibility of complete stoppage of an aircraft on a landing runway. According to the invention: a) the altitude (H) of the aircraft (2) is measured and the horizontal distance (D) separating said aircraft (2) from the proximal end threshold (4) of the landing runway (1) is calculated; b) an estimated finishing position (21) of said aircraft on said landing runway (1) is calculated on the basis of the altitude (H) and of the horizontal distance (D) determined in a), as well as on the basis of the angle of approach (α); and c) said estimated finishing position (21) calculated in b) is utilized to determine said possibility.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
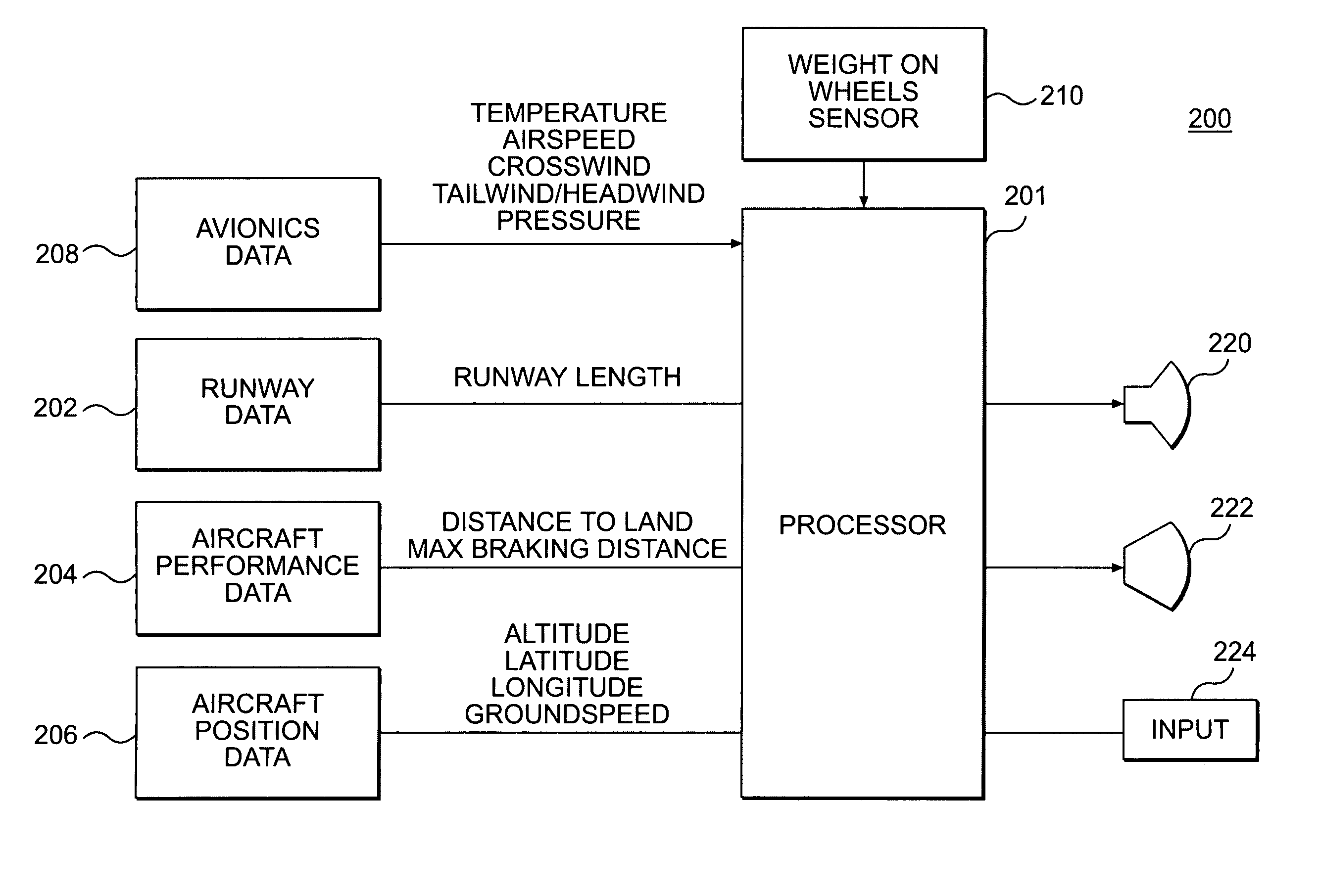
Runway overrun monitor
Disclosed is a runway alerting method and system for a landing an aircraft. The method includes determining stopping positions for the aircraft along the runway using aircraft energy state, deceleration and braking information and displaying the stopping positions on a display. A system is provided that includes a first apparatus that is configured to determine an aircraft speed relative to the ground, a second apparatus that is configured to determine the aircraft's position, and a third apparatus that can provide information about the runway of intended landing. A flight system coupled to the first and second apparatus is configured to determine a minimum and corporate stopping position for the aircraft using the aircraft speed and the position relative to the runway. The minimum and corporation stopping positions are presented to the aircraft pilot on a display to as assist the pilot in safely landing the aircraft.
Owner:GULFSTREAM AEROSPACE CORP
Method of distributing braking within at least one group of brakes of an aircraft
ActiveUS8311685B2Energy levelAnalogue computers for vehiclesAutomatic braking sequenceOperant conditioningAirplane
The invention provides a method of managing the braking of an aircraft having a plurality of brakes comprising friction elements, the method comprising the following steps for at least one group of brakes:estimating an energy level (□E) to be dissipated by the brakes of the group; andestimating individual braking setpoints (Fi) for each of the brakes of the group so that the individual braking setpoints make it possible, at least under normal operating conditions of the brakes, to implement braking that dissipates said energy level, the individual braking setpoints also being determined so as to satisfy at least one other given operating objective.
Owner:SAFRAN LANDING SYSTEMS
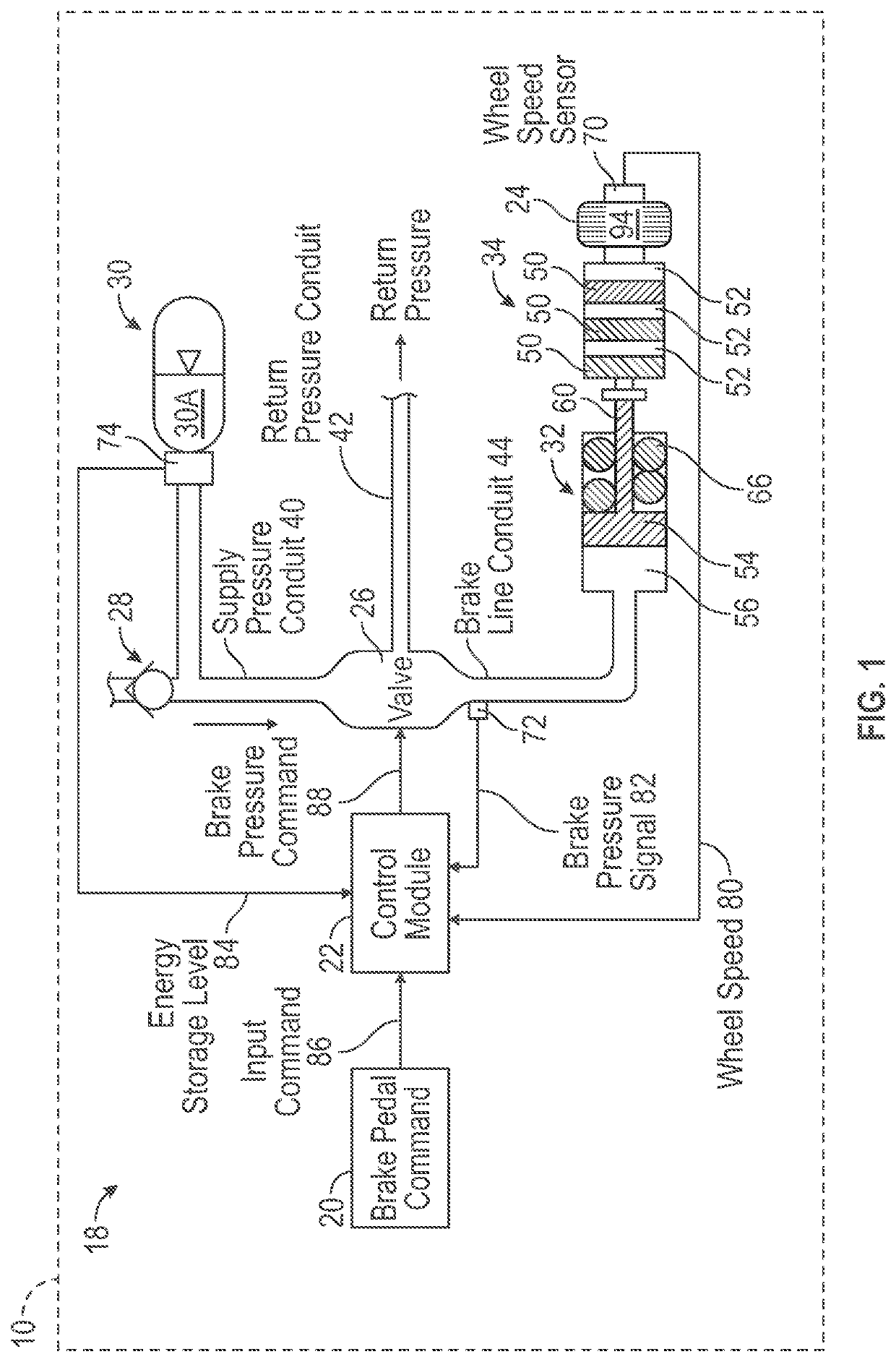
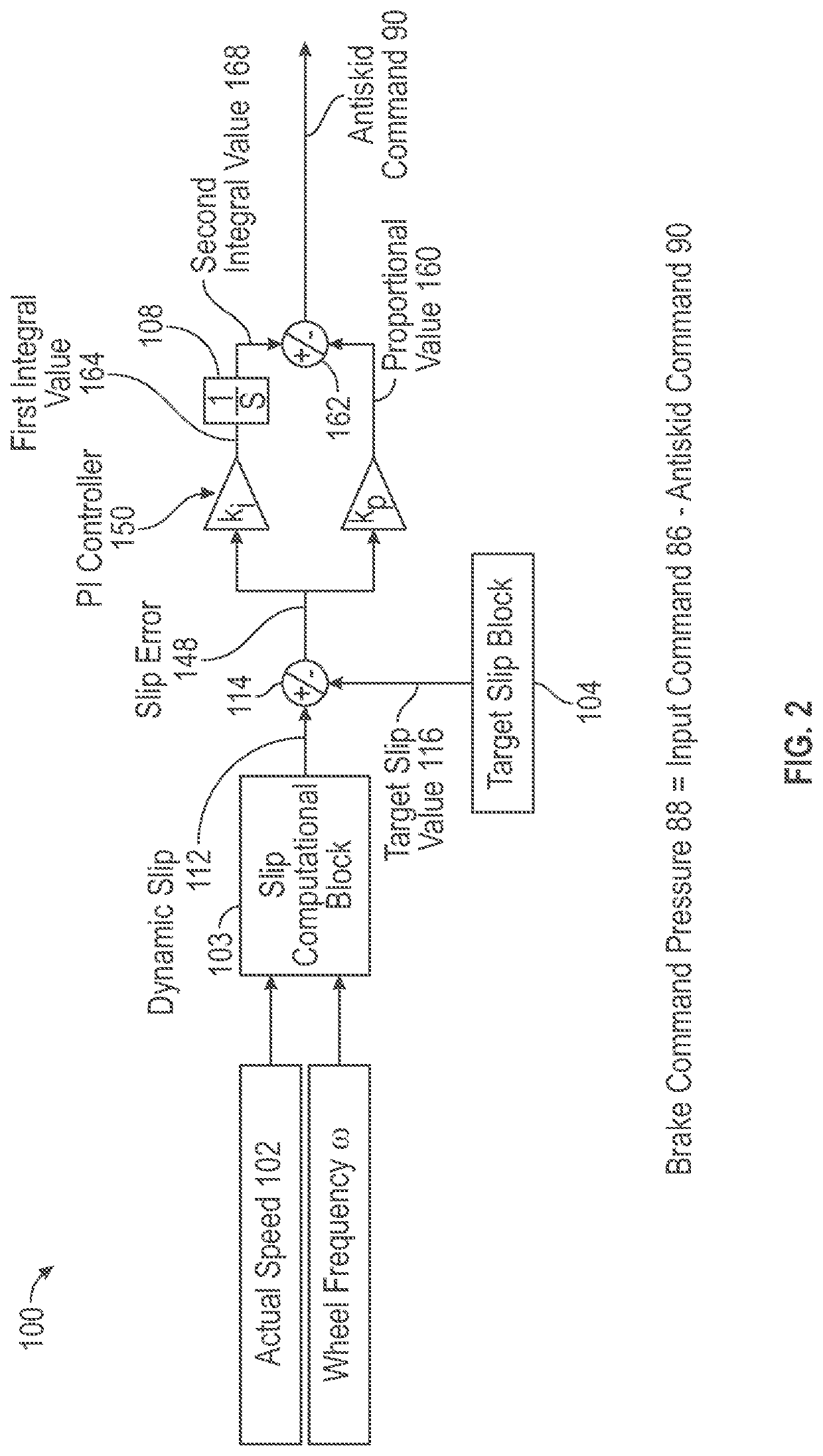
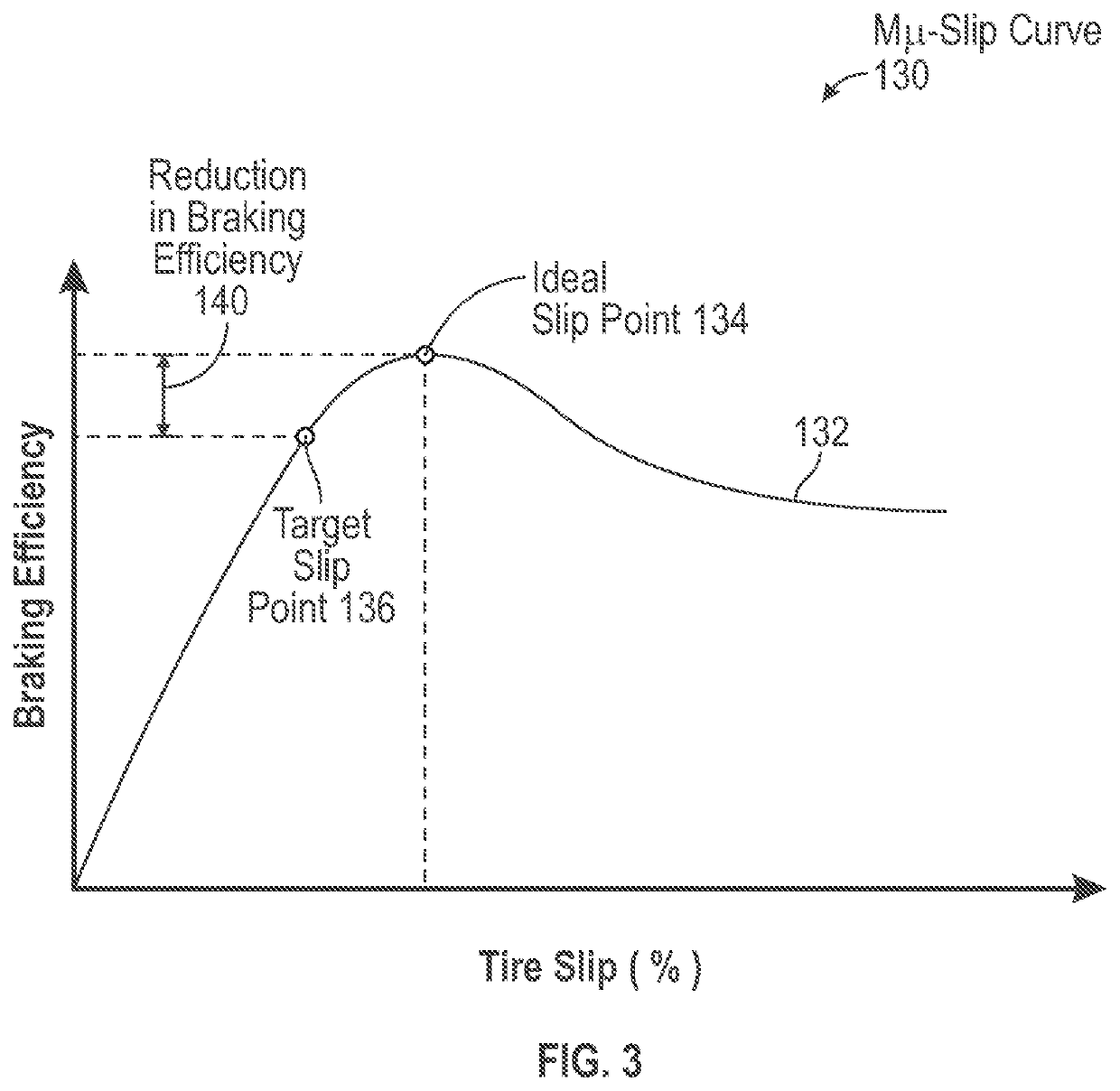
Brake system providing limited antiskid control during a backup mode of operation
ActiveUS20200407049A1Reducing braking efficiencySave energyAutomatic braking sequenceBrake regulatorsControl engineeringControl theory
A brake system for a vehicle is disclosed and includes an energy storage device configured to store and discharge energy, a plurality of wheels, one or more processors operatively coupled to the energy storage device, and a memory coupled to the one or more processors. The memory stores data comprising a database and program code that, when executed by the one or more processors, causes the brake system to determine the brake system is operating in a backup mode of operation. In response to determining the brake system is operating in the backup mode of operation, the brake system calculates a dynamic slip of the plurality of wheels. The brake system is caused to determine a slip error by comparing the dynamic slip with a target slip value of the plurality of wheels. The brake system is also caused to calculate an antiskid command based on the slip error.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Carbon brake wear for aircraft
InactiveUS6938857B2Promotes even distributionAvoid overall overheatingAutomatic braking sequenceBraking drumsFlight vehicleAirplane
Owner:THE BOEING CO
System and method to assist in the braking of an aircraft on a landing runway
InactiveUS8515601B2Analogue computers for vehiclesAutomatic braking sequenceLaws of thermodynamicsAirplane
A system includes a means of acquiring the position of the aircraft on the runway and its speed in the taxiing phase, a means of storing data concerning the runway and a predefined deceleration law, a function for calculating the distance that the aircraft will have traveled on the runway when it has reached a certain speed and / or the speed that it will have reached when it has traveled a certain distance: the calculated distance makes it possible to adapt the braking by comparison with the distance remaining to reach the end of the runway; the calculated distance makes it possible to adapt the braking by comparison with the distance remaining to reach the end of the runway; the calculated speed makes it possible to adapt the braking by comparison with the maximum speed to take the exit.
Owner:THALES SA
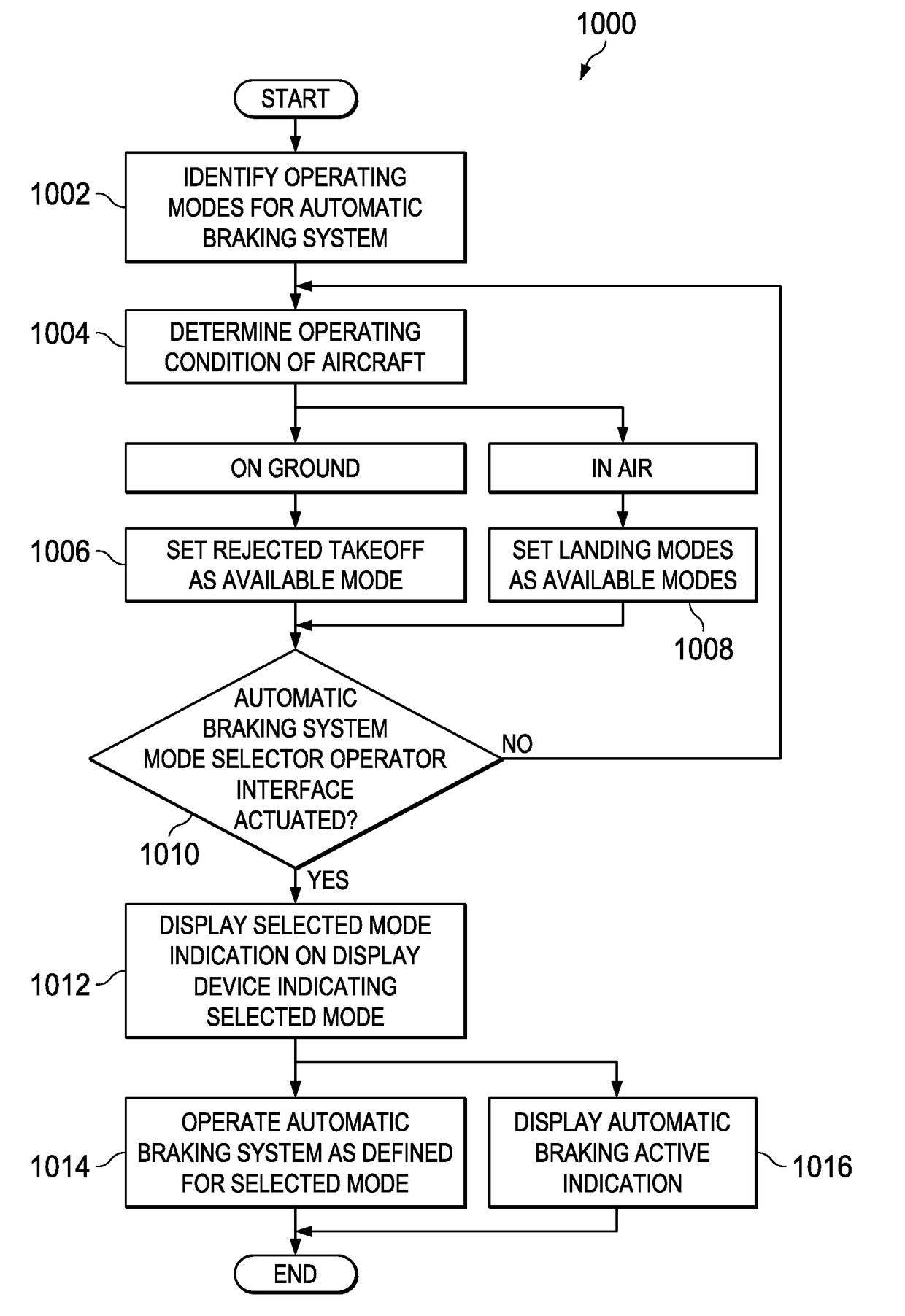
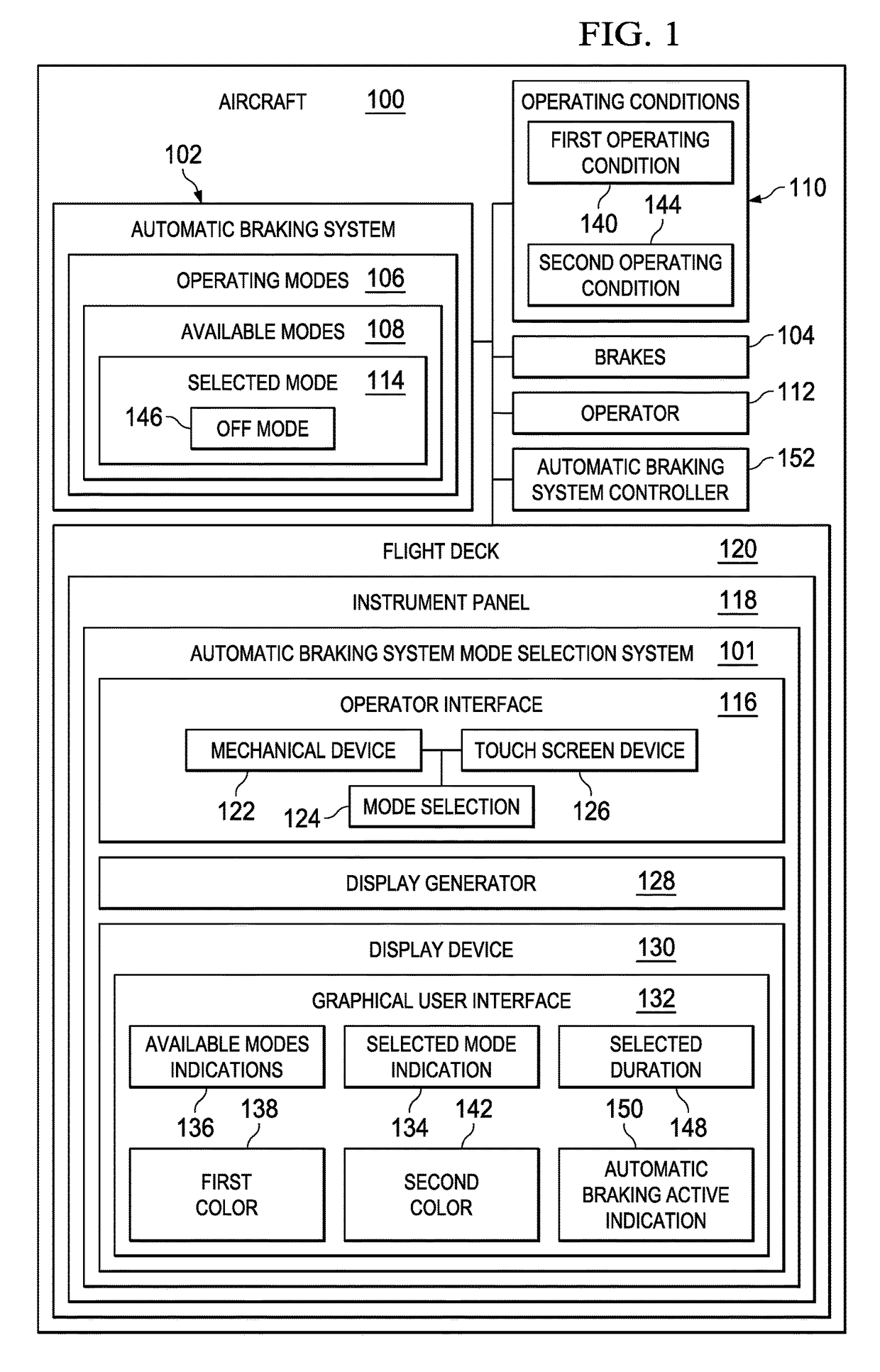
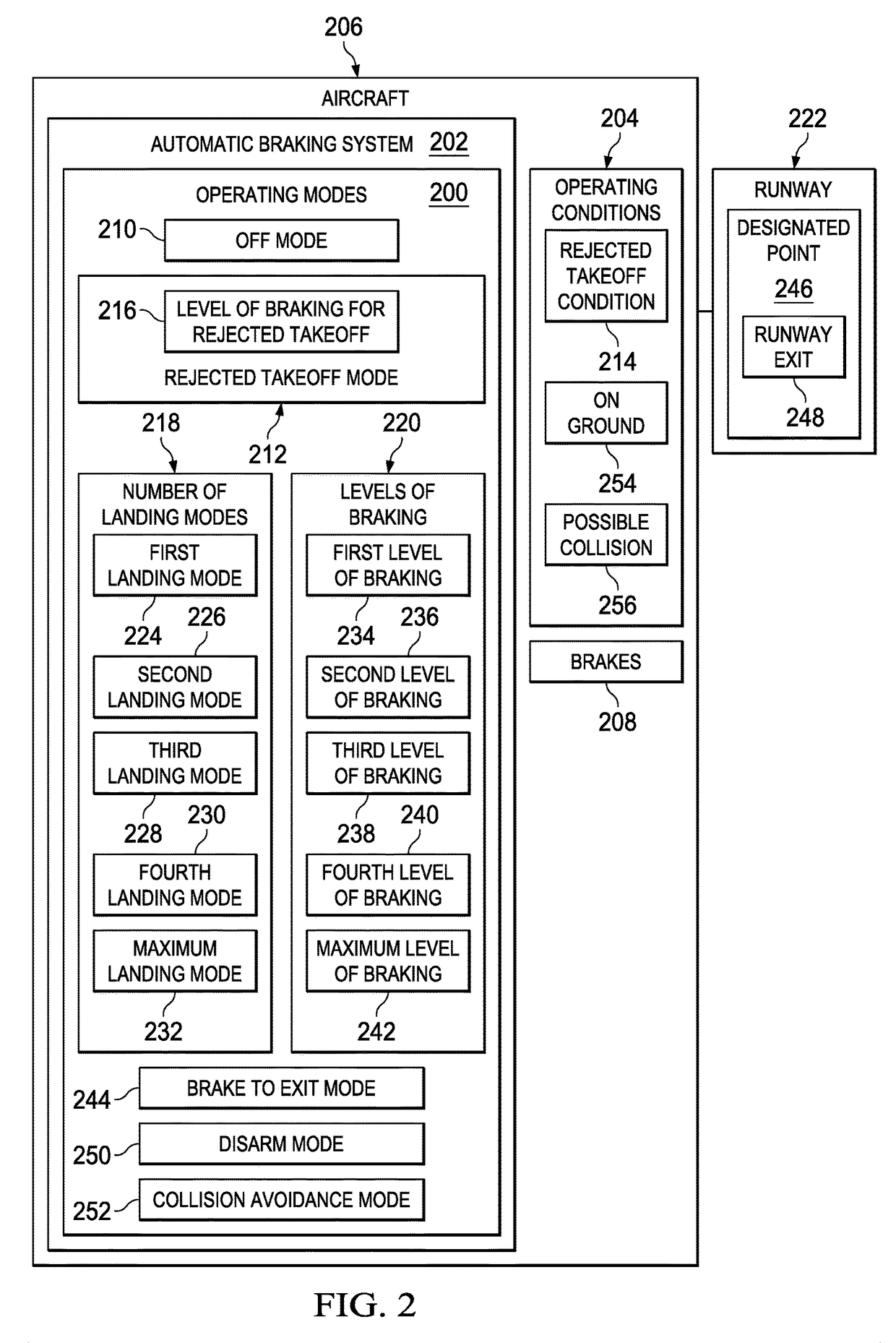
Display-based flight deck autobrake selection
A system and method for braking an aircraft. A processor unit identifies an operating condition of the aircraft. The processor unit displays available modes indications on a display device on the aircraft. The available modes indications indicate modes of operating an automatic braking system on the aircraft that are available for selection by an operator based on the operating condition of the aircraft. The processor unit receives a mode selection from an operator interface. The mode selection indicates a selected mode of operating the automatic braking system that is selected by the operator from the available modes. The processor unit displays on the display device a selected mode indication indicating the selected mode.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
System and method to assist in the braking of an aircraft on a landing runway
A system includes a means of acquiring the position of the aircraft on the runway and its speed in the taxiing phase, a means of storing data concerning the runway and a predefined deceleration law, a function for calculating the distance that the aircraft will have traveled on the runway when it has reached a certain speed and / or the speed that it will have reached when it has traveled a certain distance: the calculated distance makes it possible to adapt the braking by comparison with the distance remaining to reach the end of the runway; the calculated distance makes it possible to adapt the braking by comparison with the distance remaining to reach the end of the runway; the calculated speed makes it possible to adapt the braking by comparison with the maximum speed to take the exit.
Owner:THALES SA
Method and system for assisting the braking of an aircraft
ActiveUS20170129623A1Reduce use costMinimal braking distanceAutomatic braking sequenceAircraft landing aidsMan machineAircraft landing
A method for assisting the braking of an aircraft on a runway comprises the steps implemented automatically, including: before the landing of the aircraft on the runway, receiving the input, by a crew member of the aircraft, of a target braking distance by a man-machine interface associated with a processing unit, the target braking distance corresponding to a distance between a threshold of the runway and a selected exit of the runway; engaging an automatic optimized braking mode of the aircraft making it possible for the aircraft to attain the target speed when it reaches the selected runway exit; and—controlling a braking system of the aircraft, while the aircraft is running on the runway, according to this automatic optimized braking mode.
Owner:AIRBUS SAS
Method and apparatus for predicting runway overrun
A critical point on a runway indicates a point at which an aircraft may experience a runway overrun if landing beyond the critical point. A path projection is extended from the aircraft at a descent slope angle to determine whether the aircraft will land beyond the critical point at the current descent slope. Timely alerts may be provided by accounting for the time required to announce a distance value, and the distance traveled during the announcement.
Owner:AVIDYNE CORPORATION
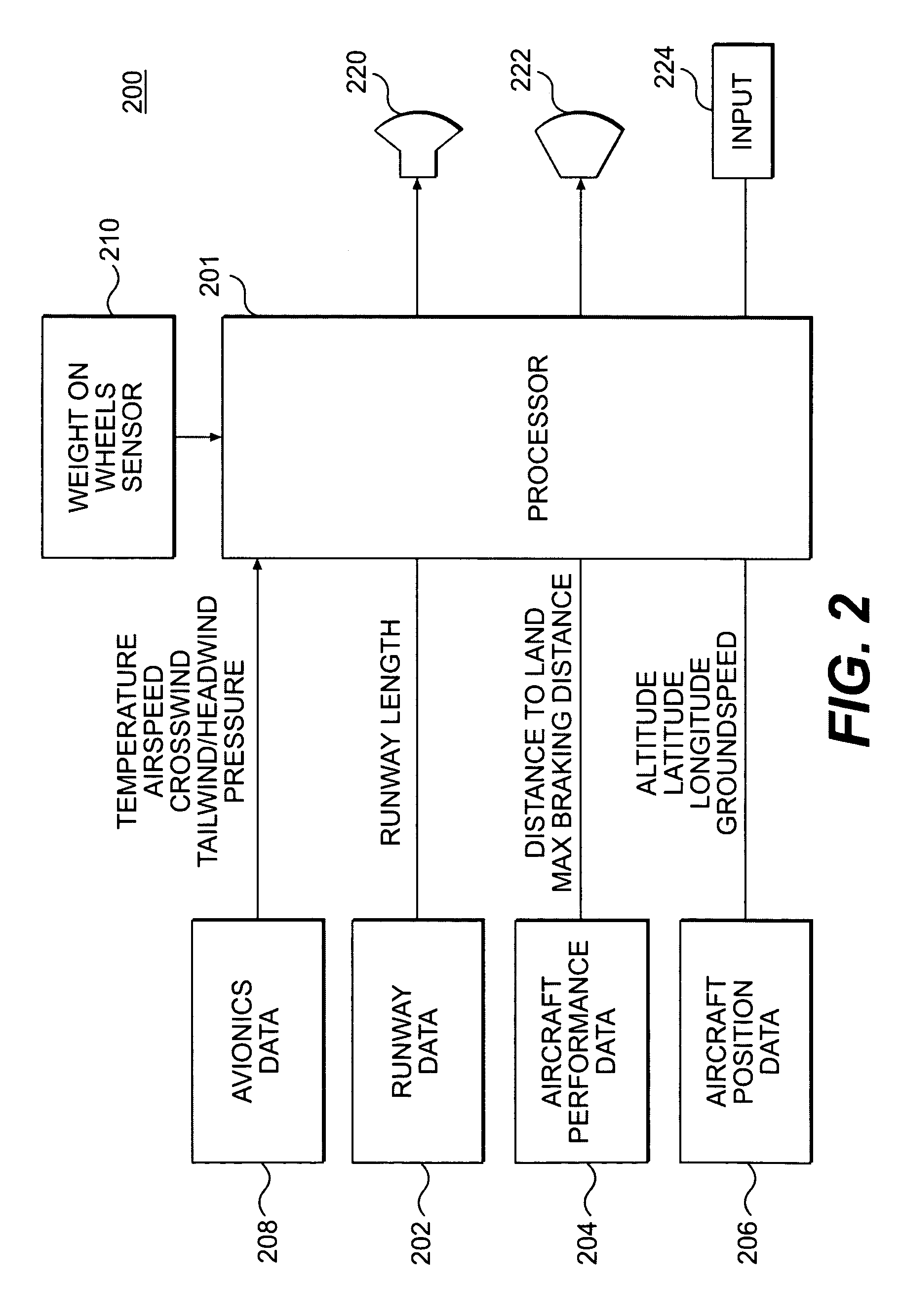
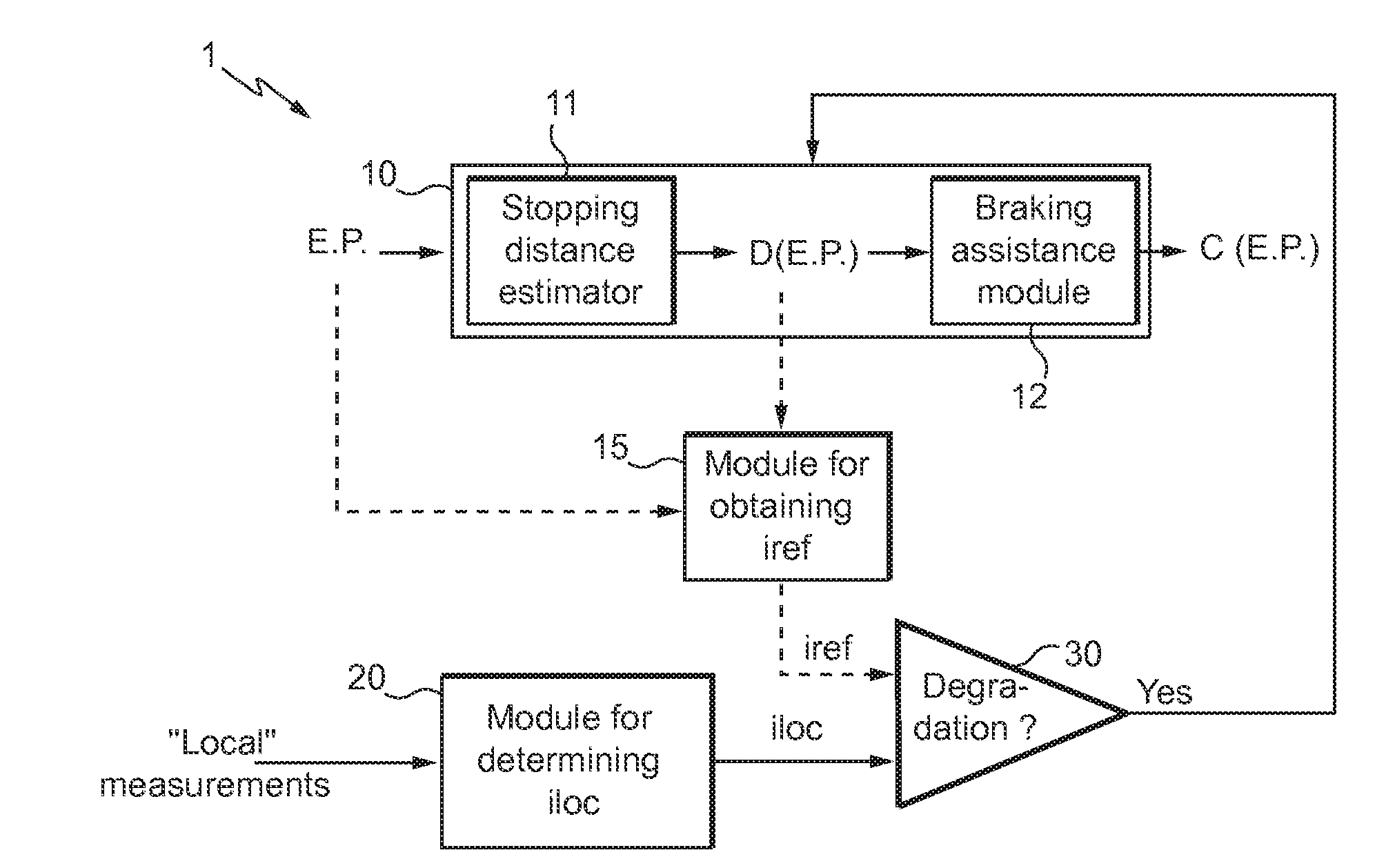
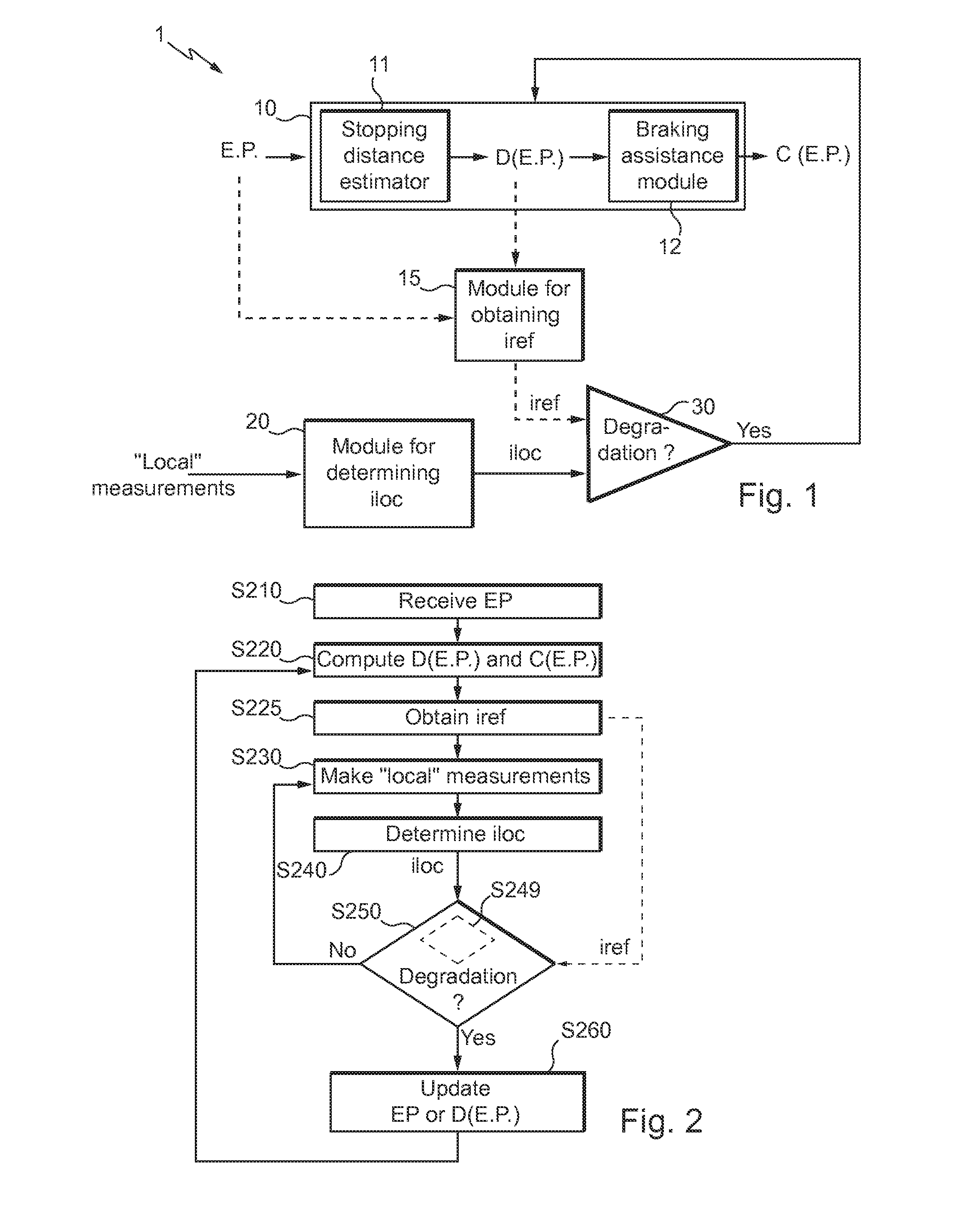
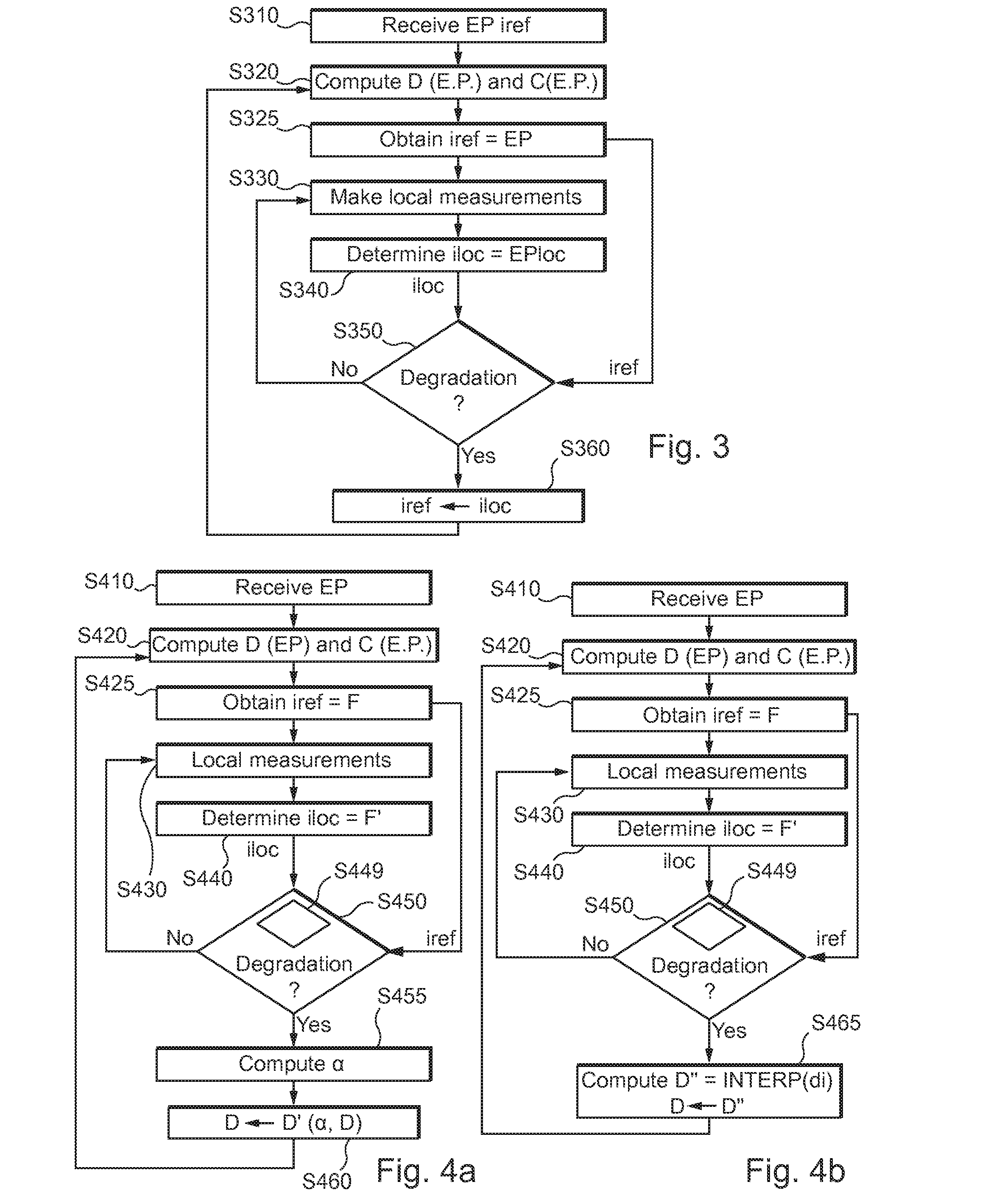
Method and system for assisting the piloting of an aircraft in landing phase
ActiveUS20140371958A1Improve securityAnalogue computers for vehiclesAutomatic braking sequenceAuxiliary systemAirplane
A method and system for determining local information which is dependent on a local runway state when the aircraft is in movement on the runway in order to update, in real-time, or practically in real-time, data used by a braking assistance system, according to whether the local runway state associated with the determined local information indicates a runway deterioration relative to a reference runway state used initially.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS) +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com