Patents
Literature
3234results about "Application and release valves" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
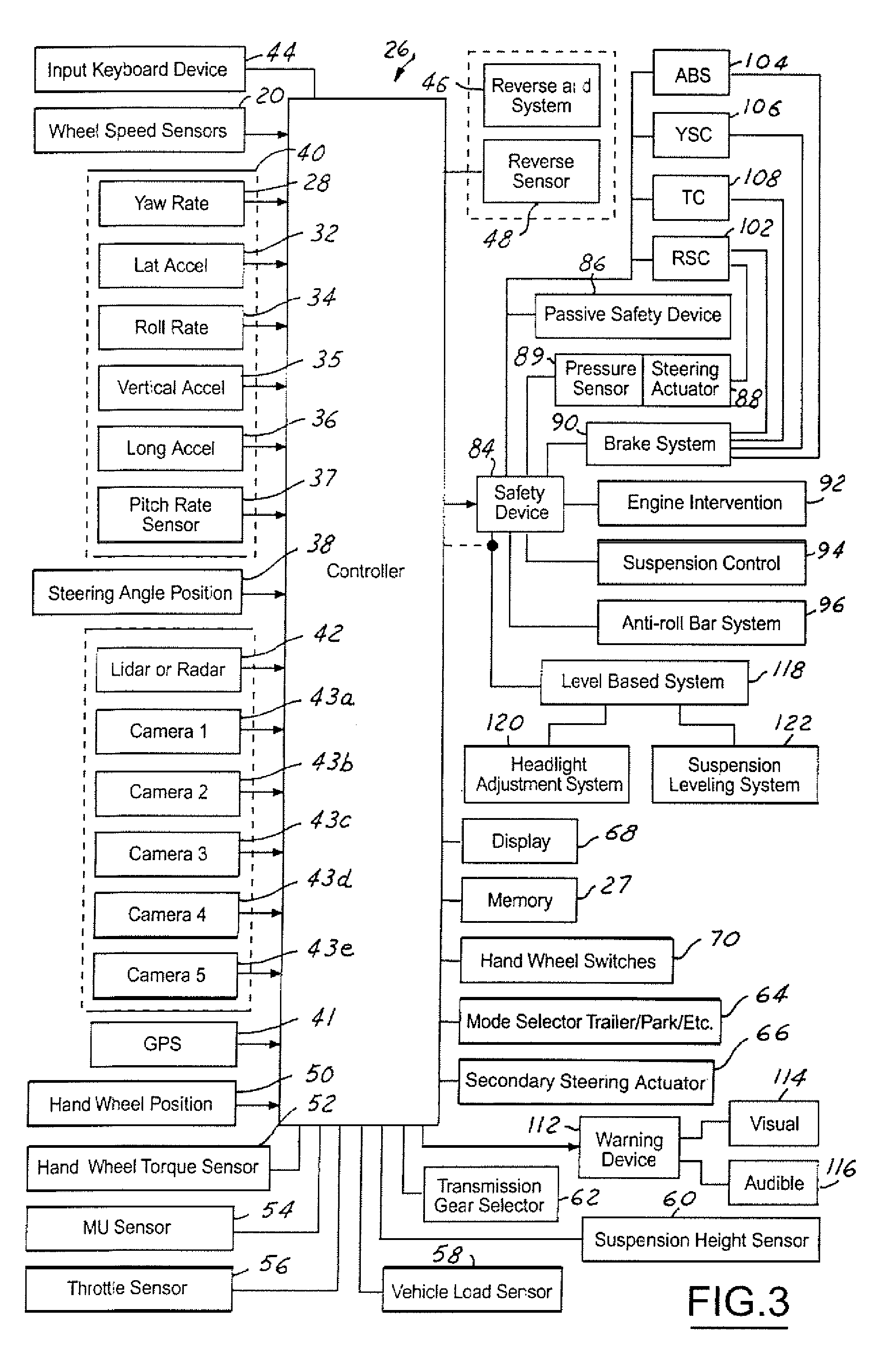
Collision avoidance with active steering and braking
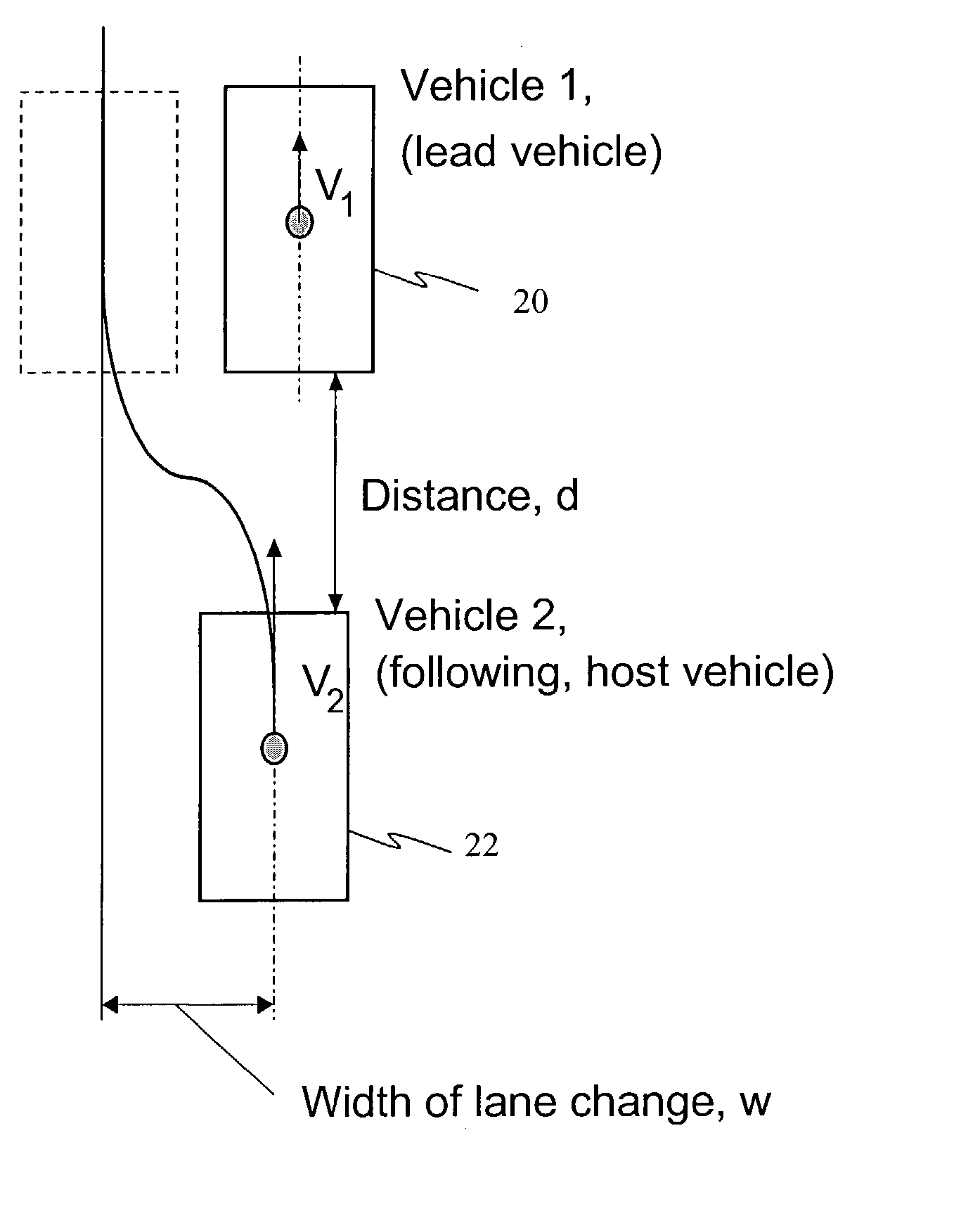
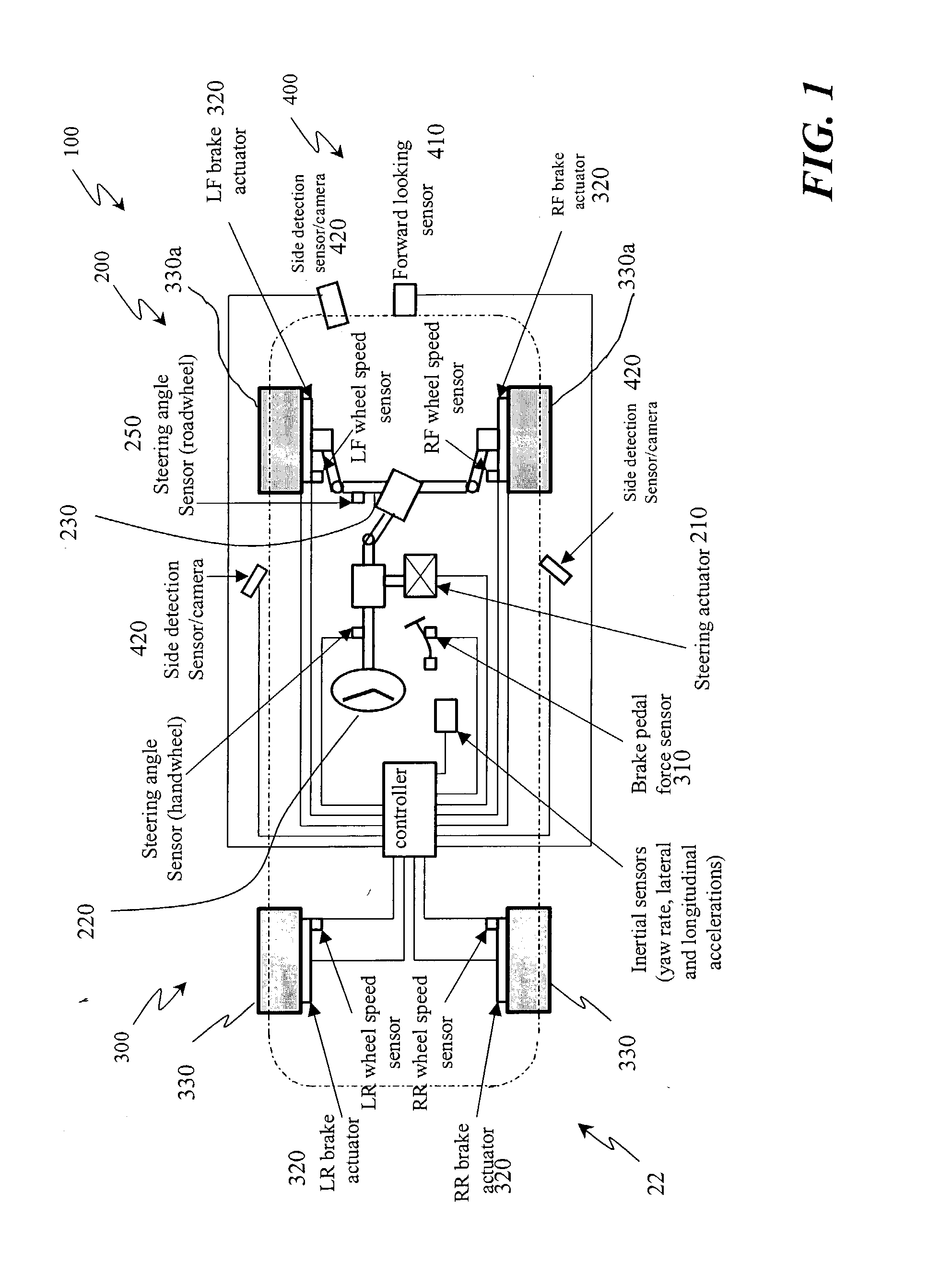
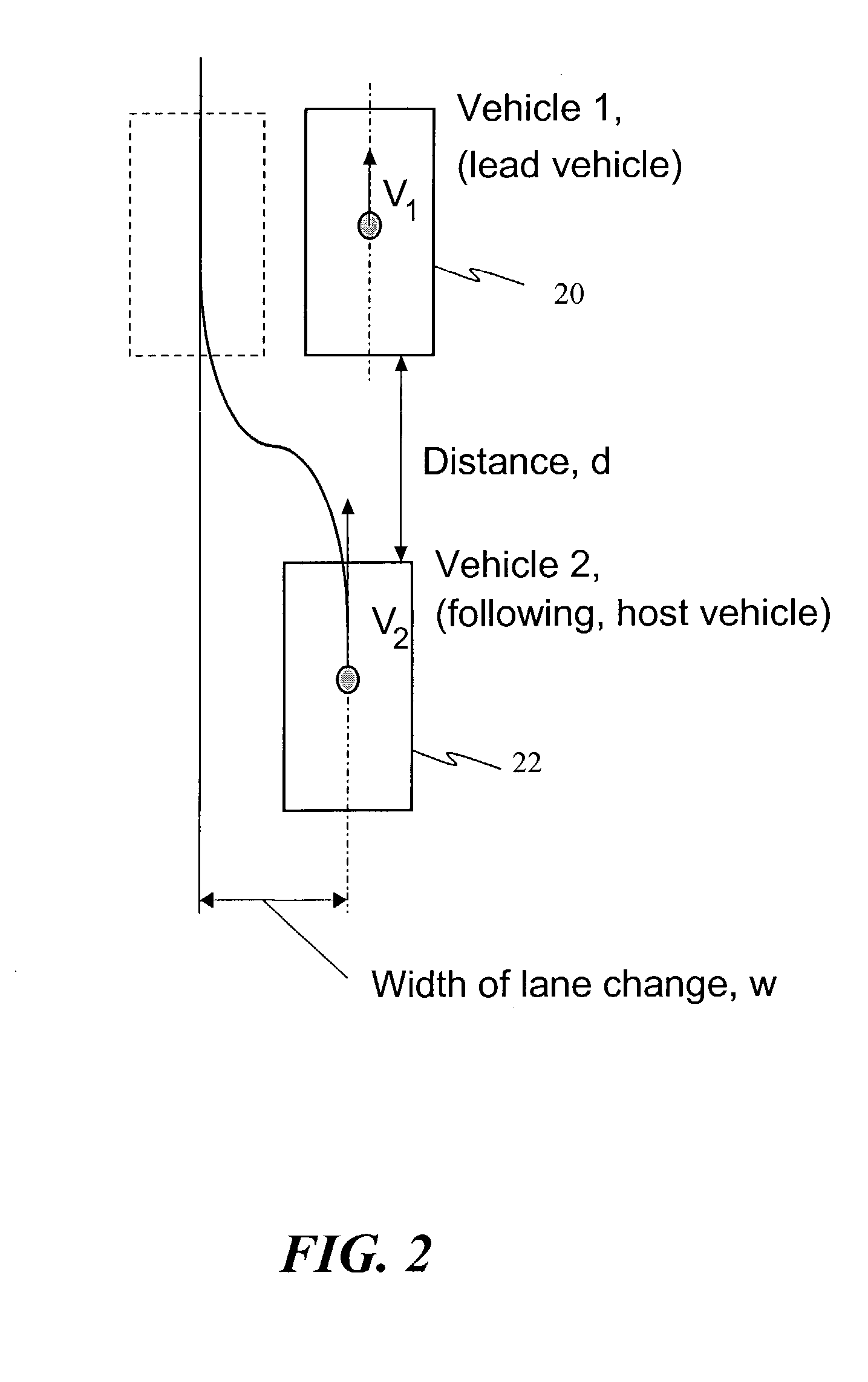
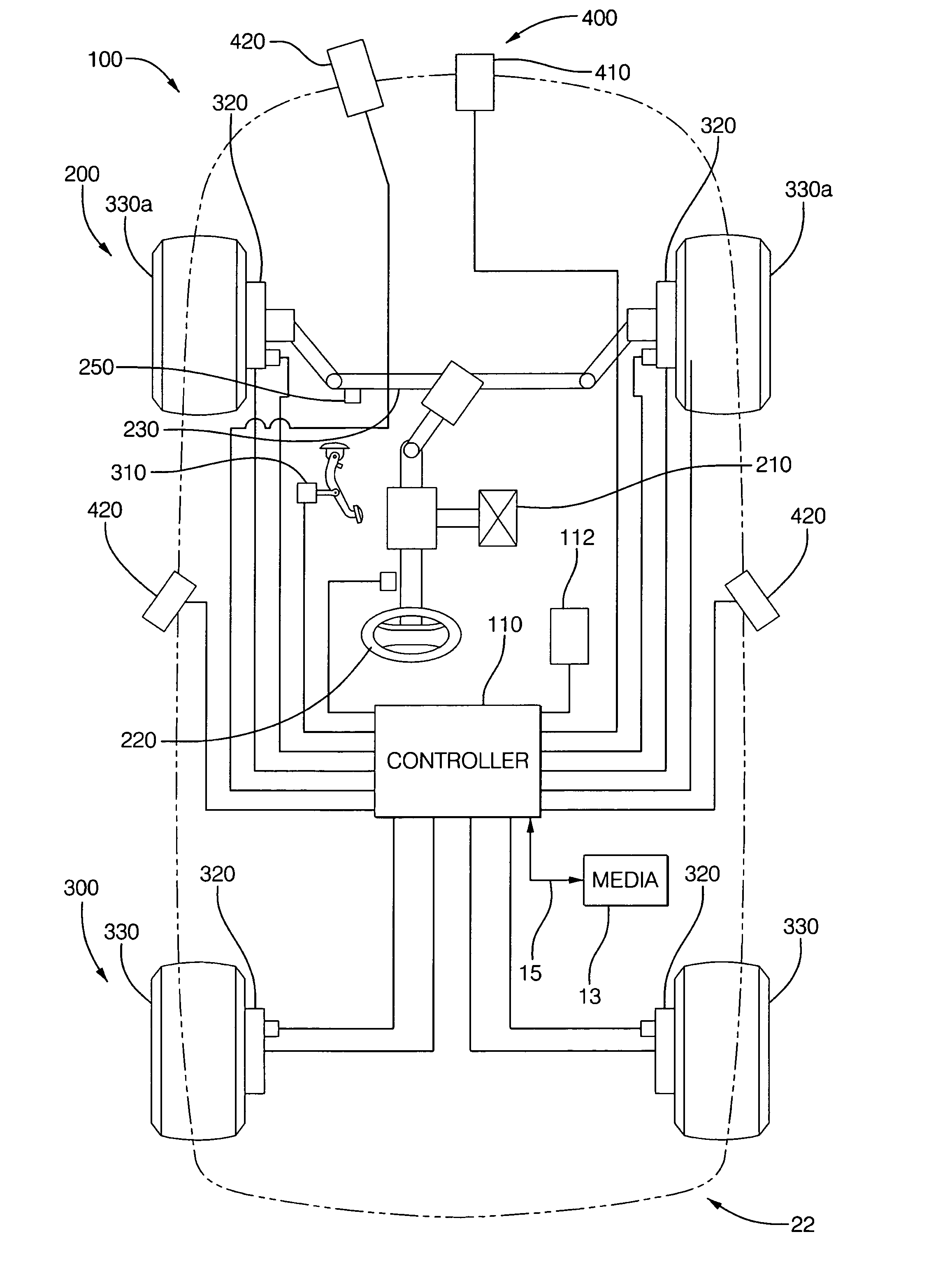
A method for collision avoidance using automated braking and steering comprising: determining an actual distance to an obstacle in a path of a vehicle; determining a relative velocity between the obstacle and the vehicle; determining a first distance sufficient to avoid collision by braking only; determining a second distance sufficient to avoid collision by combined braking and steering around the obstacle. The method also includes: applying braking if at least one of, the first distance exceeds the actual distance and the first distance is within a selected threshold of the actual distance. If the actual distance exceeds the second distance and a lane change is permitted, steering control to affect a lane change is applied.
Owner:BWI +1
Collision avoidance with active steering and braking
A method for collision avoidance using automated braking and steering comprising: determining an actual distance to an obstacle in a path of a vehicle; determining a relative velocity between the obstacle and the vehicle; determining a first distance sufficient to avoid collision by braking only; determining a second distance sufficient to avoid collision by combined braking and steering around the obstacle. The method also includes: applying braking if at least one of, the first distance exceeds the actual distance and the first distance is within a selected threshold of the actual distance. If the actual distance exceeds the second distance and a lane change is permitted, steering control to affect a lane change is applied.
Owner:BWI CO LTD SA +1
Method of controlling an automotive vehicle having a trailer
ActiveUS7690737B2Turning radius of the combination of the vehicle and trailer may be reducedLow costAutomatic initiationsFluid braking transmissionMobile vehicleMotorized vehicle
A system and method of controlling an automotive vehicle and trailer includes determining the presence of a trailer and applying brake-steer to the vehicle in response to the trailer to reduce the turning radius of the vehicle and the trailer.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
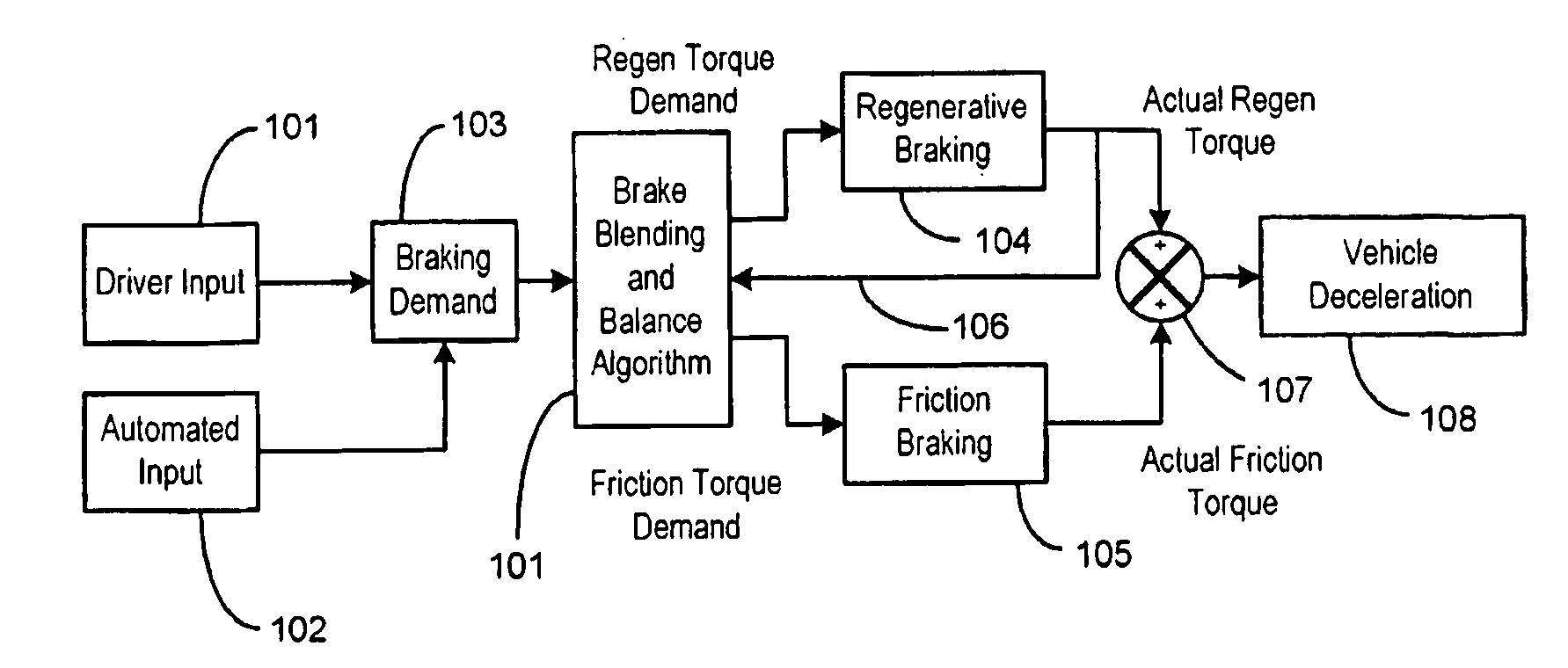
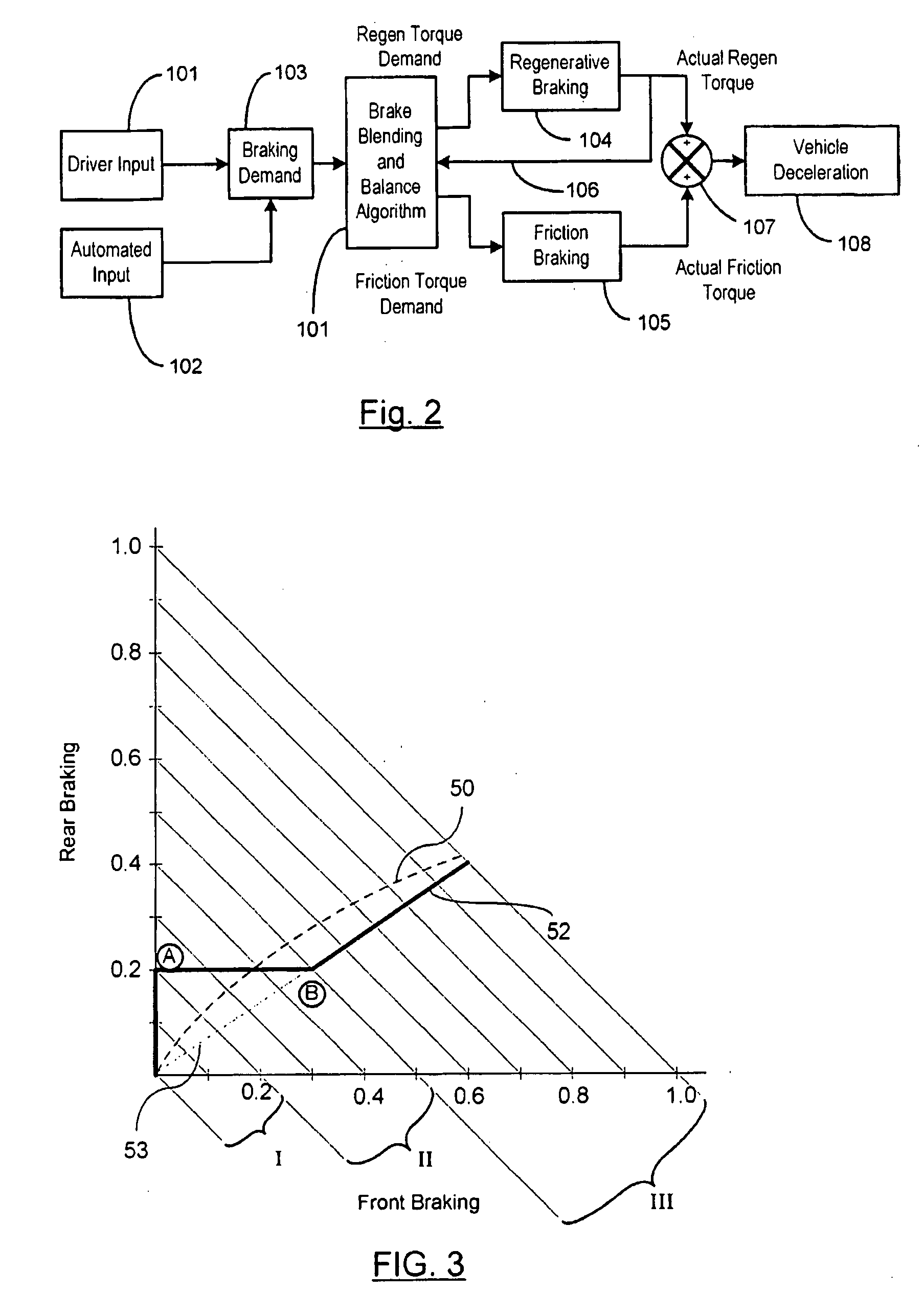
Vehicle System Having Regenerative Brake Control
ActiveUS20080100129A1Analogue computers for trafficBraking action transmissionRegenerative brakeKinetic energy
A method is provided for controlling the braking of a vehicle that has a first set of friction brakes for applying a first apply brake force to a first set of wheels and a second set of friction brakes for applying a second brake apply force to a second set of wheels. A powertrain assembly is coupled to the second set of wheels. The powertrain assembly includes a regenerative braking unit capable of recapturing kinetic energy from the second set of wheels. The vehicle is braked in a first phase of control using regenerative braking to brake the second set of wheels to achieve up to a first value of braking. The vehicle is braked in a second phase of control using the regenerative braking to maintain braking of the second set of wheels at the first value of braking force while selectively applying the first friction brakes to the first set of wheels up to a second value of braking.
Owner:KELSEY HAYES CO
Fluid-pressure brake system for a vehicle
InactiveUS20050029859A1Guaranteed functionObvious advantagesBraking action transmissionAnti-theft devicesElectricityActuator
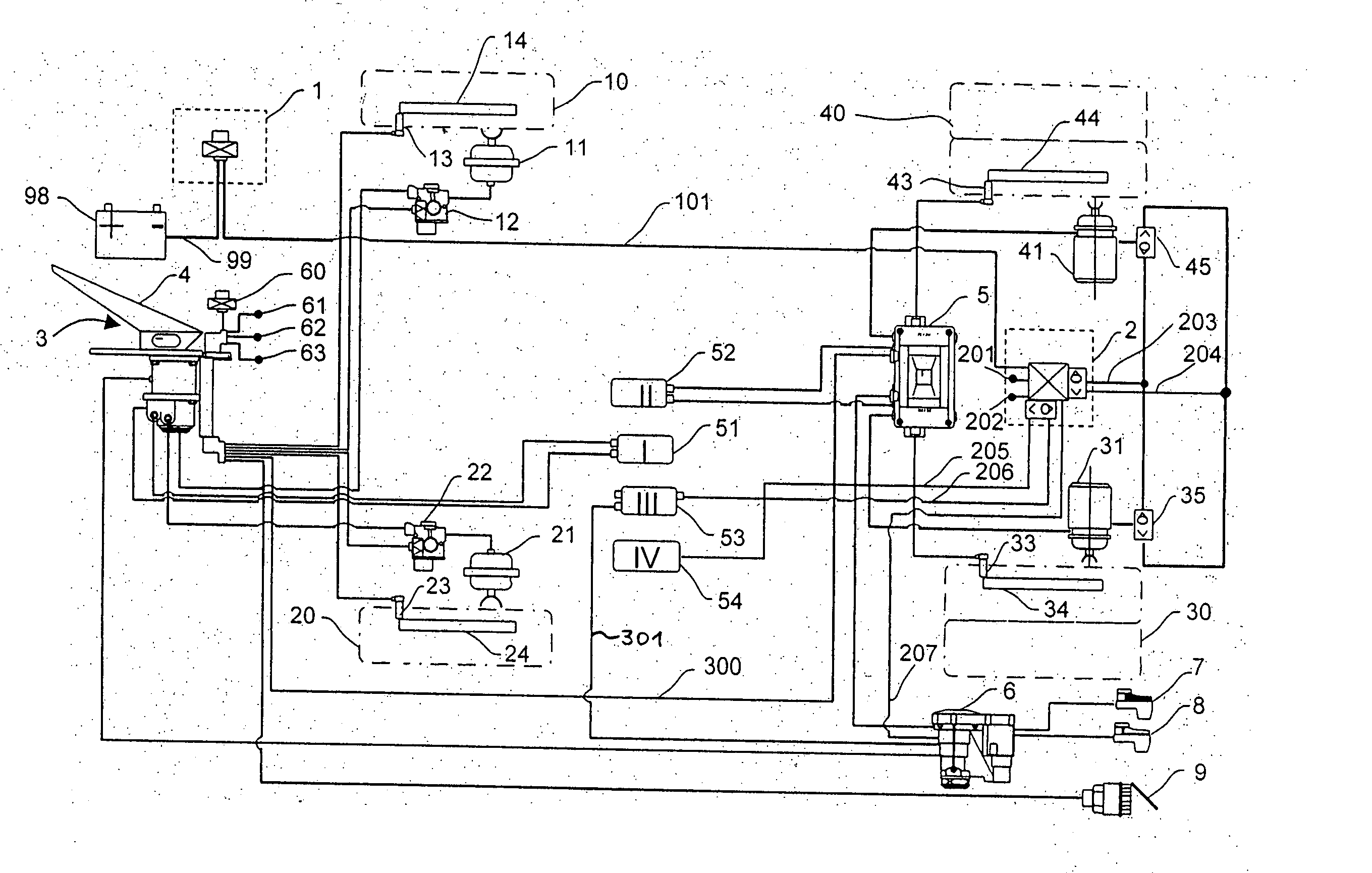
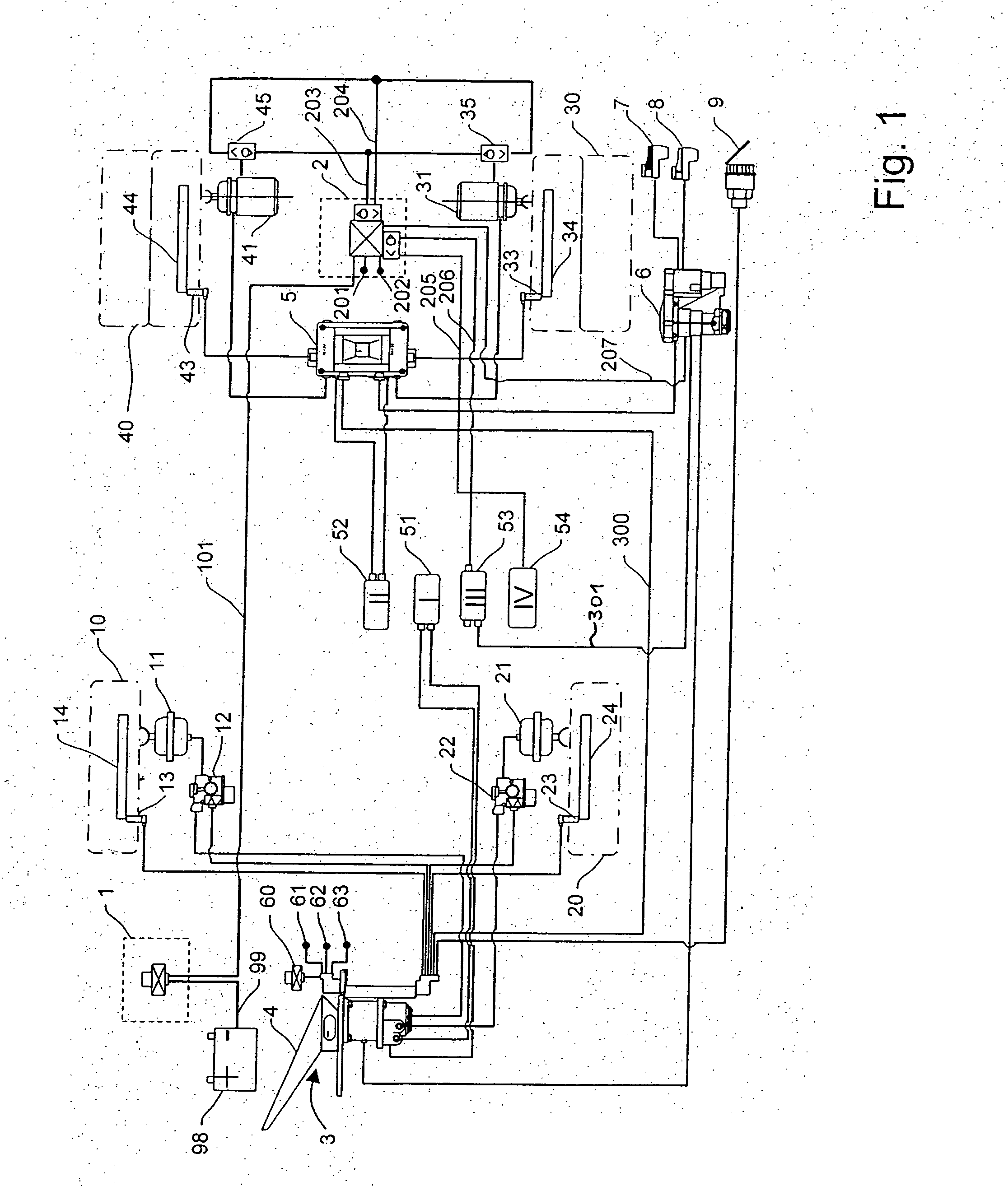
A fluid-pressure brake system for a vehicle having a parking brake function in which, in response to actuation of an electrical parking brake signal transmitter, and without actuation of a brake pedal, at least one wheel brake of the brake system is actuated via an actuator to which the fluid is admitted. A parking brake module is provided in which there is integrated an electronic control unit as well as valve devices that are electrically actuatable by the electronic control unit. The electronic control unit actuates the parking brake function upon receiving from the parking brake signal transmitter an electrical actuating signal demanding actuation of the parking brake function and, as part of the parking brake function, the electronic control unit controls the admission of fluid to the actuator by means of the electrically actuatable valve devices.
Owner:WABCO GMBH
Brake by-wire actuator
InactiveUS20060163941A1High brake pressureReduce tractionBraking action transmissionFoot actuated initiationsMobile vehicleDistributor
The present invention relates to a brake-by-wire actuator for actuating the brake system of a motor vehicle, comprising a simulator which can be acted upon by a brake pedal, with a signal of an actuation sensor being sent to an electronic control unit which controls a pressure source in response to the signal of the actuation sensor, and wherein an output of the pressure source is connected to a distributor device for the brake force and actuates individual wheel brakes of the vehicle, also comprising means for enabling actuation of the brakes by muscular power within a fallback mode. In order to provide an improved fallback mode in a brake-by-wire actuator, according to the invention, a lost travel is provided between a first actuation component such as a brake pedal in particular or a component articulated at the brake pedal and an actuation component that is connected downstream in the flux of force, in particular an input member, in order to uncouple the first actuation component mechanically from the reactions of force of the motor vehicle brake system in the by-wire mode.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Method of controlling an automotive vehicle having a trailer
ActiveUS20050206224A1Low costTurning radius of the combination of the vehicle and trailer may be reducedAutomatic initiationsFluid braking transmissionMotorized vehicleTurning radius
A system and method of controlling an automotive vehicle and trailer includes determining the presence of a trailer and applying brake-steer to the vehicle in response to the trailer to reduce the turning radius of the vehicle and the trailer.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
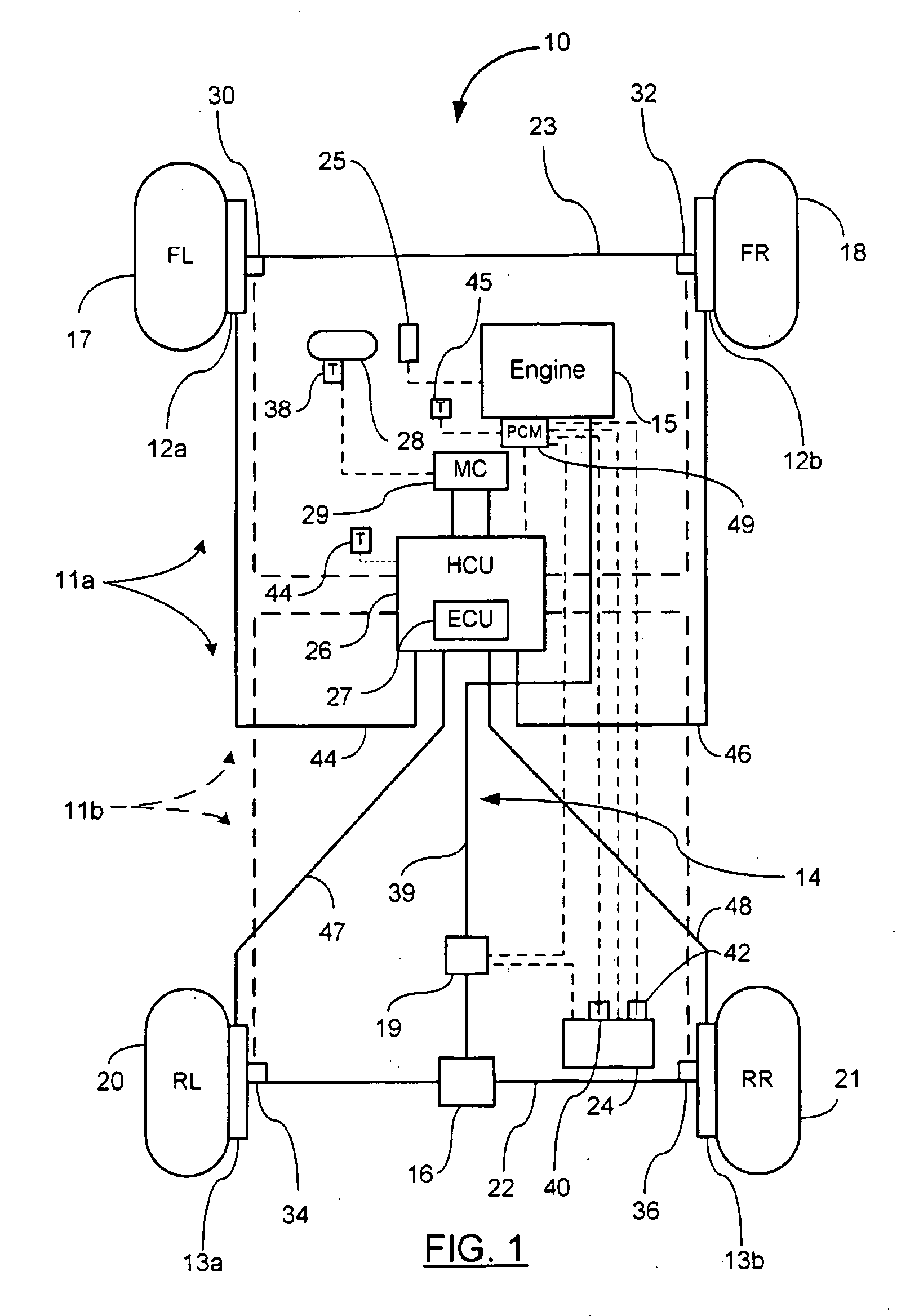
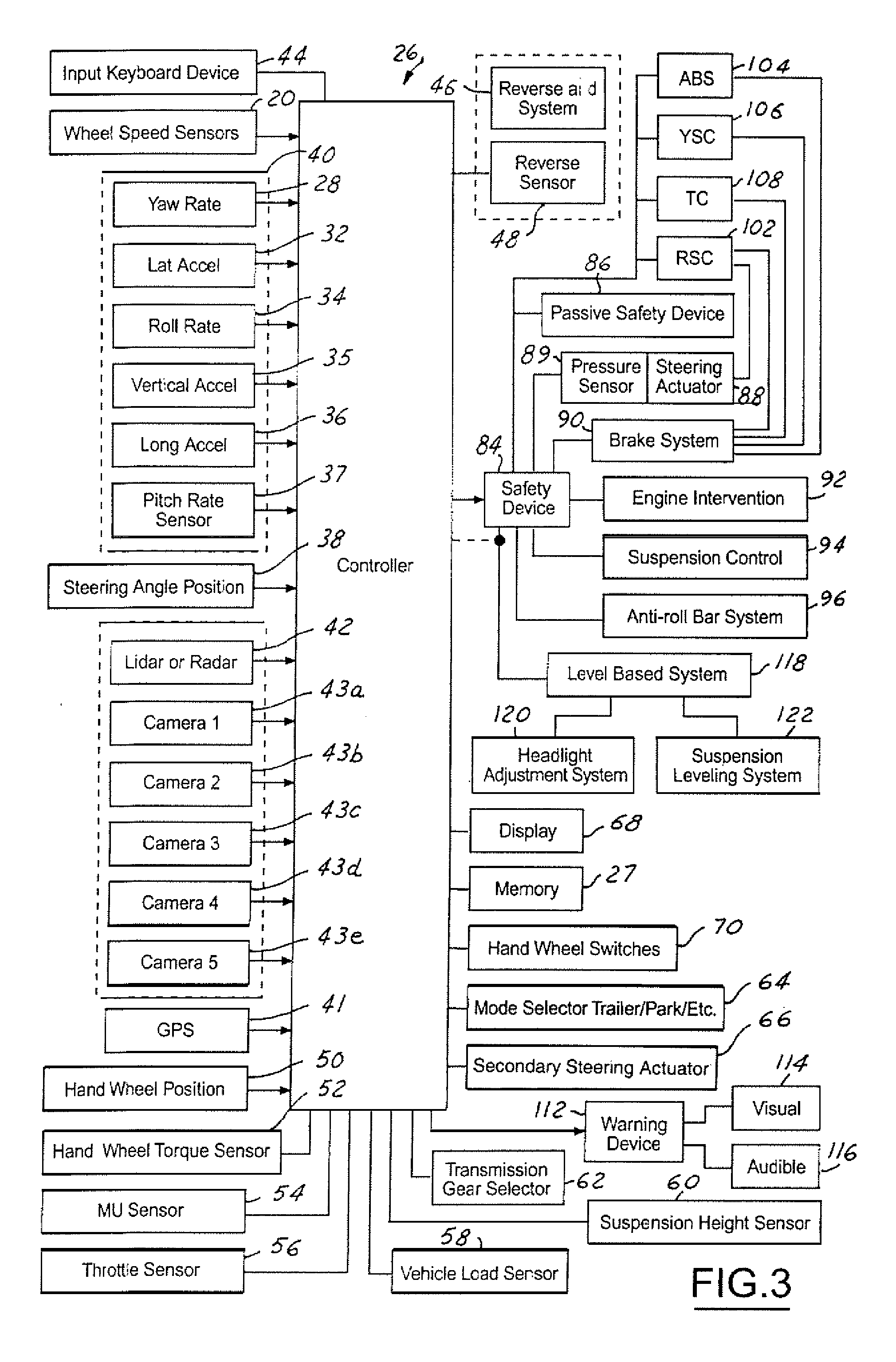
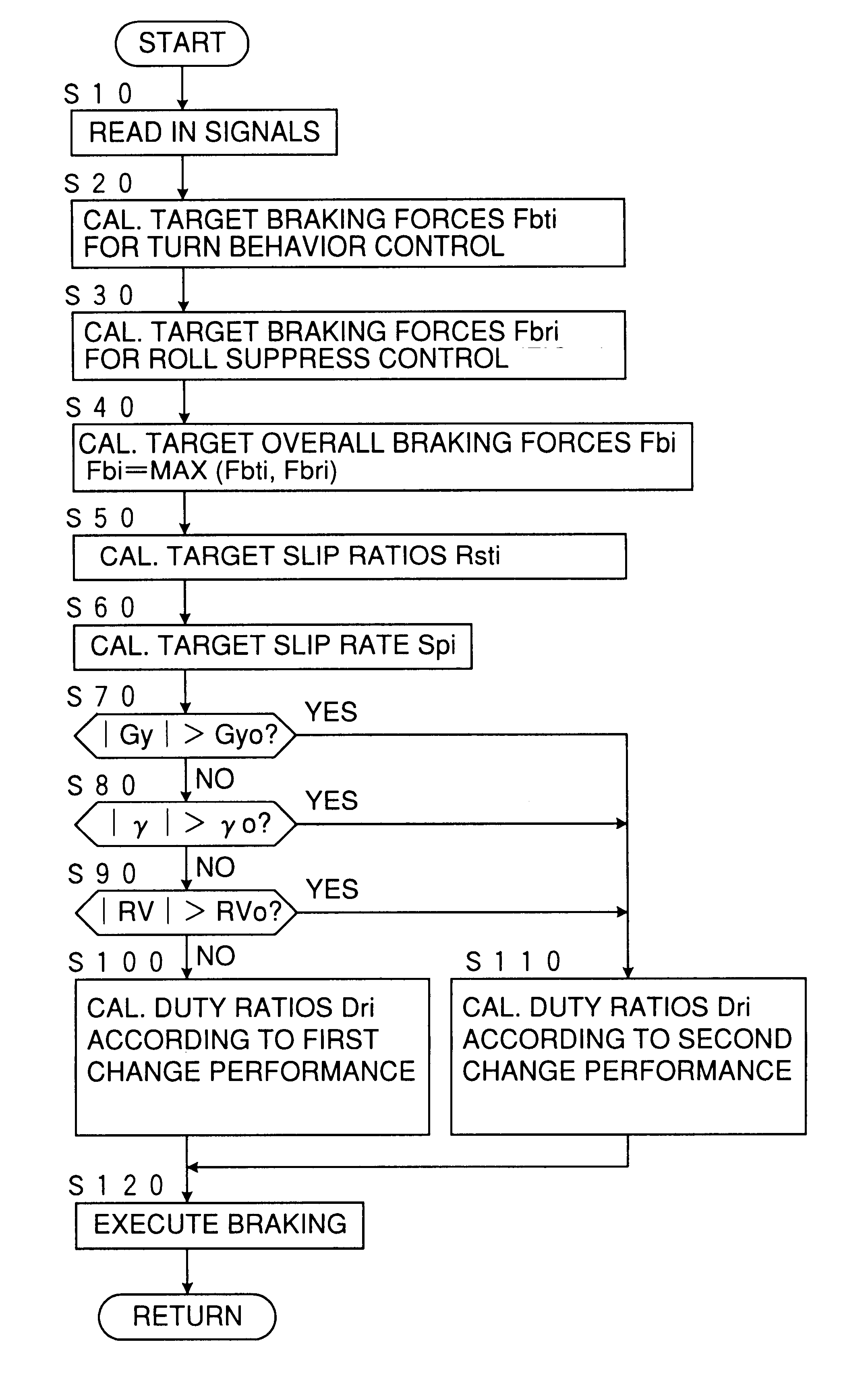
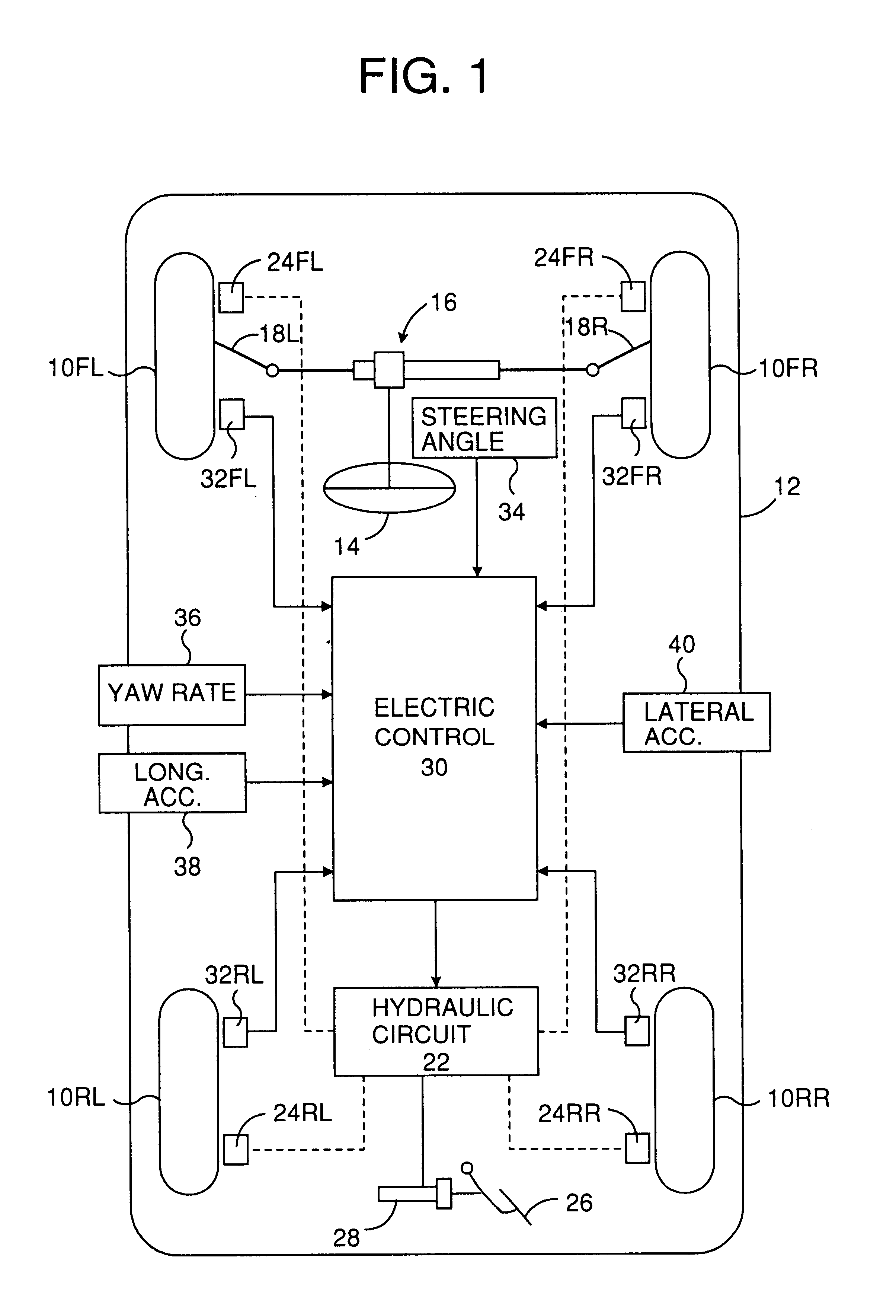
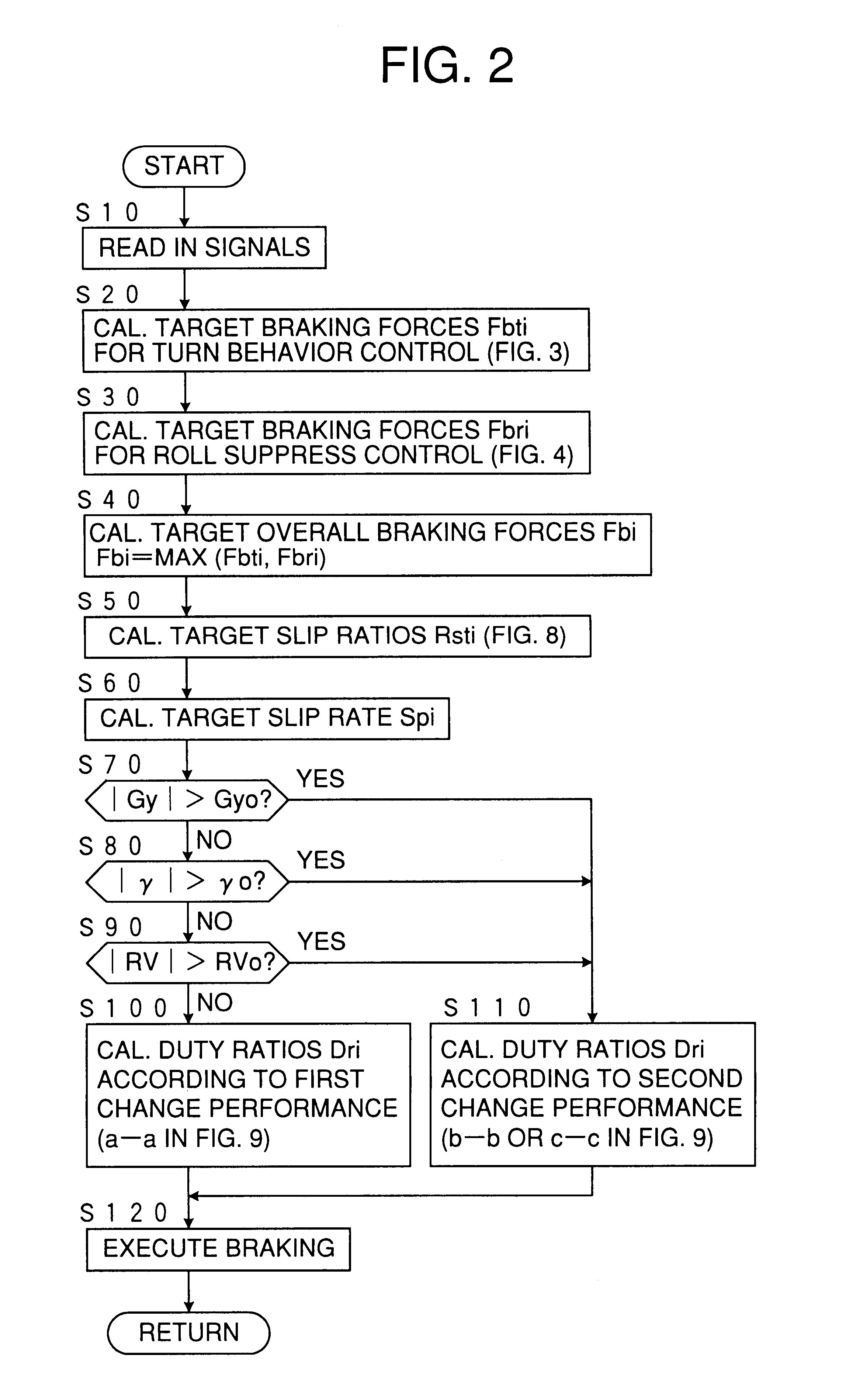
Device for controlling spin/driftout of vehicle compatibly with roll control
InactiveUS6278930B1Suppress a vehicle from excessively rollingHand manipulated computer devicesAnalogue computers for trafficInstabilityEngineering
A moving behavior control device for a vehicle calculates first target braking forces to be applied to the respective wheels for stabilizing the vehicle against a turn instability, second target braking forces to be applied to the respective wheels for stabilizing the vehicle against a roll instability, and target overall braking forces to be applied to the respective wheels by integrating the first and second target braking forces, and applies braking forces to the respective wheels according to the target overall braking forces, wherein the applied braking forces are decreased according to a first rate schedule by which the applied braking forces are decreased at a first rate according to an excess of the applied braking forces relative to the target overall braking forces when the vehicle is running at no probability of rolling beyond a predetermined threshold roll, and according to a second rate schedule by which the braking forces are lowered at a second rate smaller than the first rate according to the excess when the vehicle is running at such a probability.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
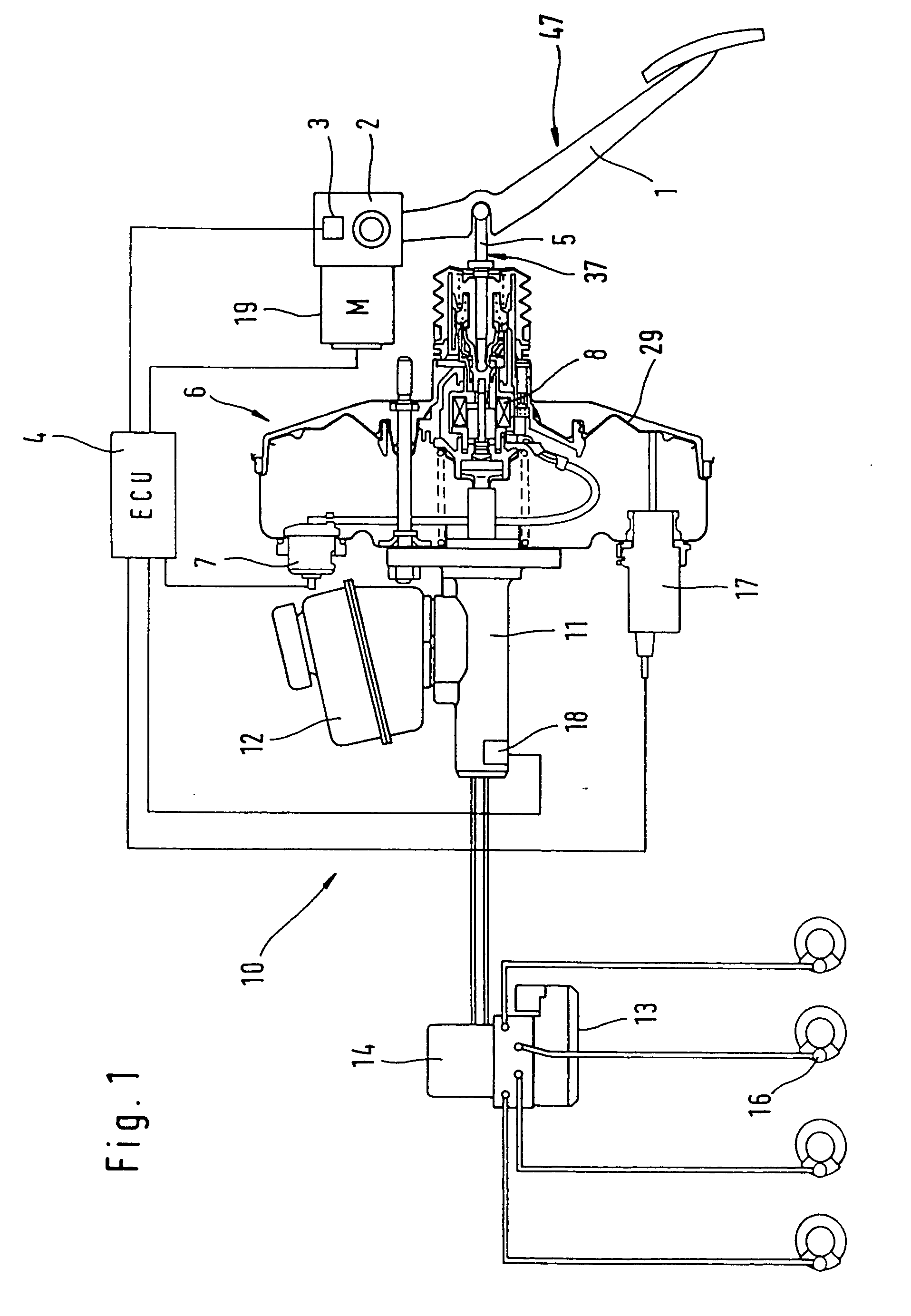
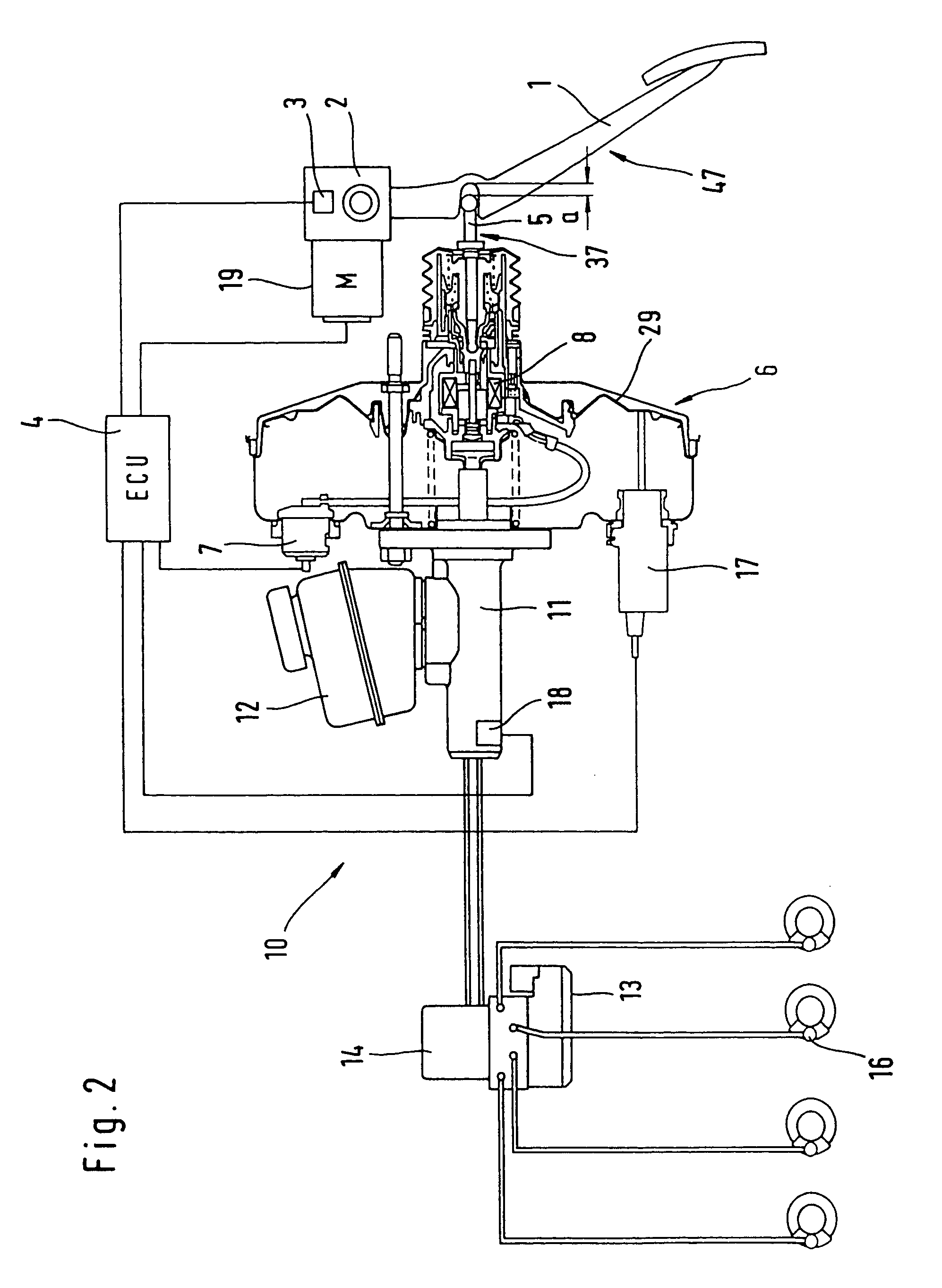
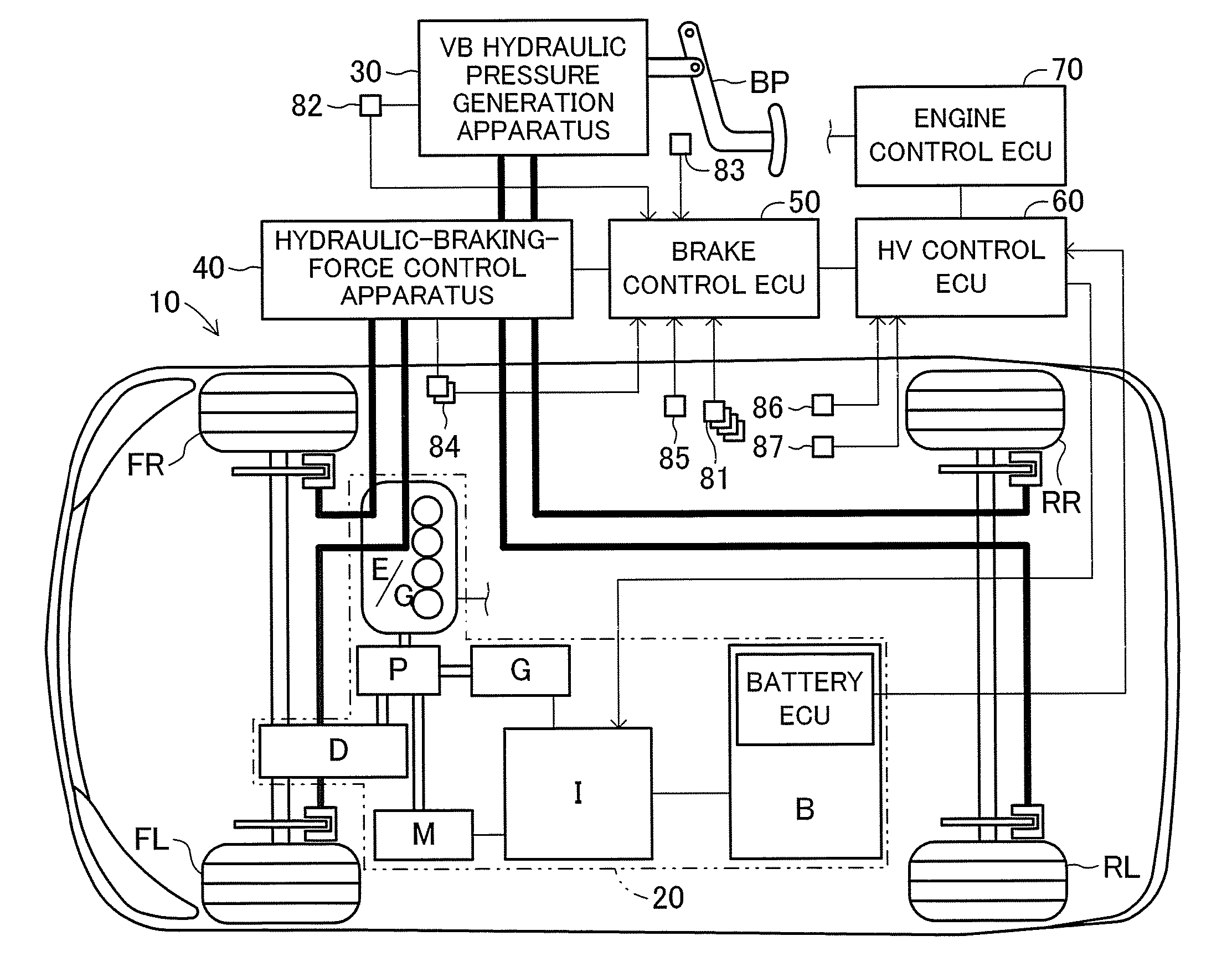
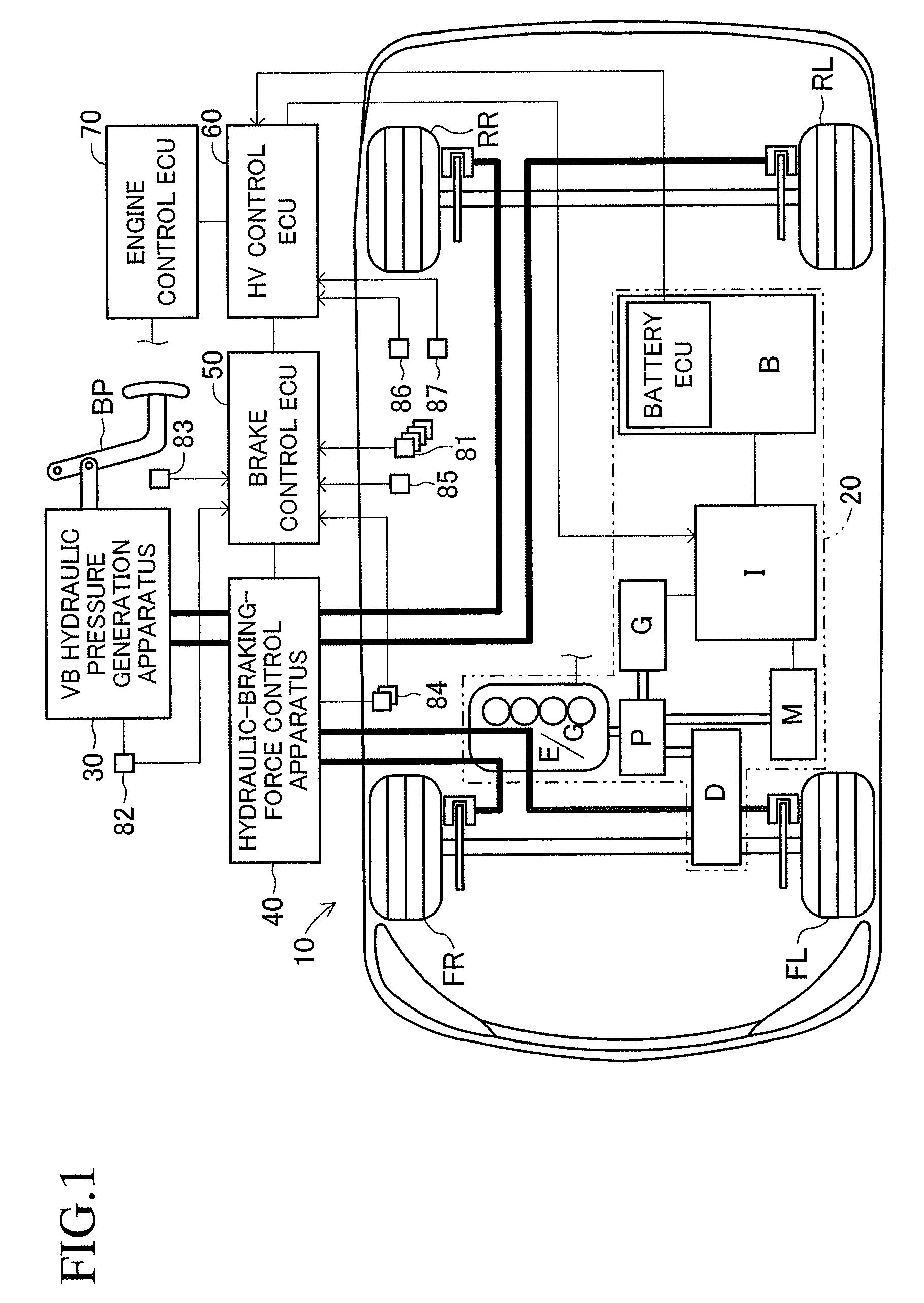
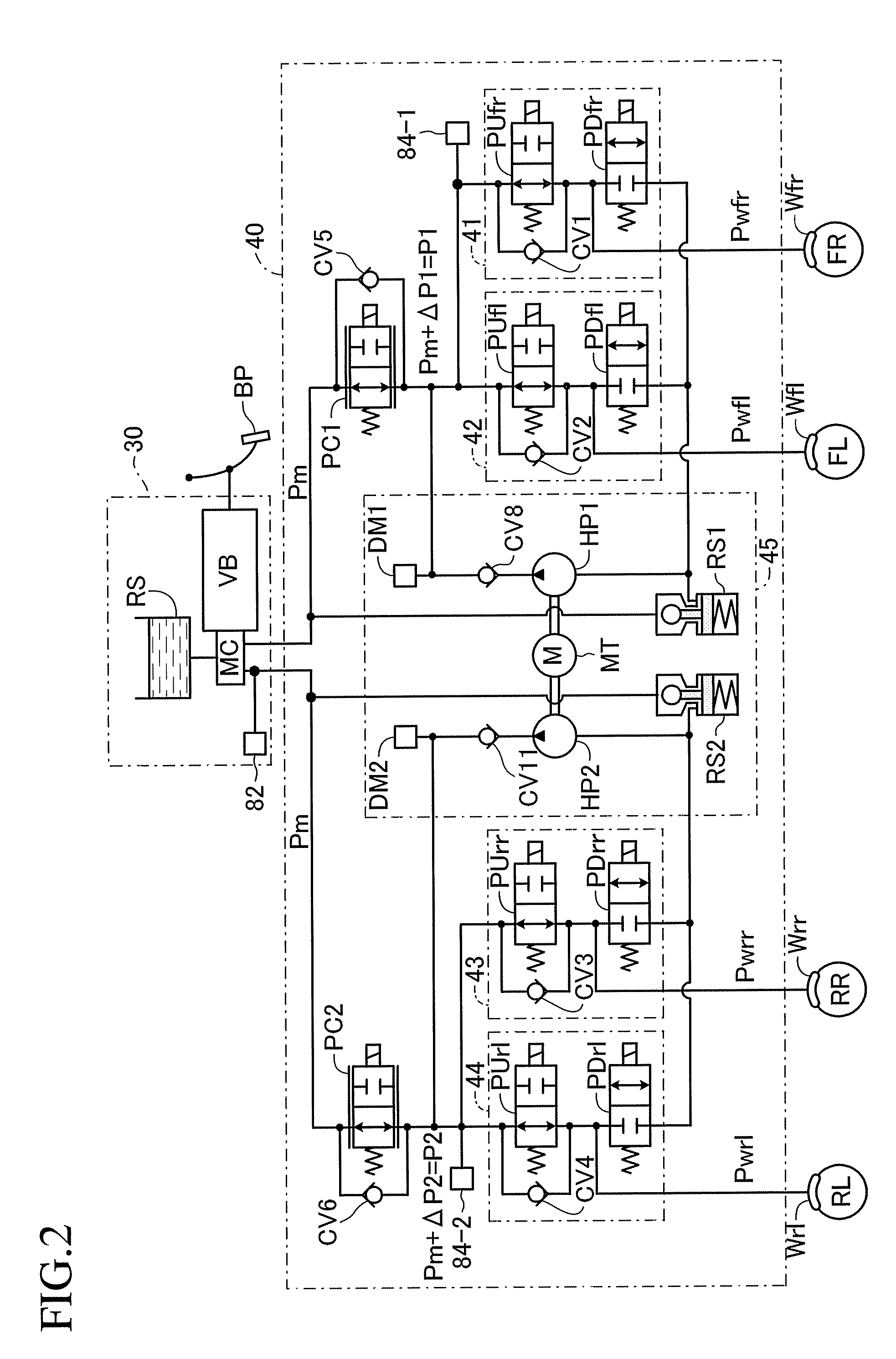
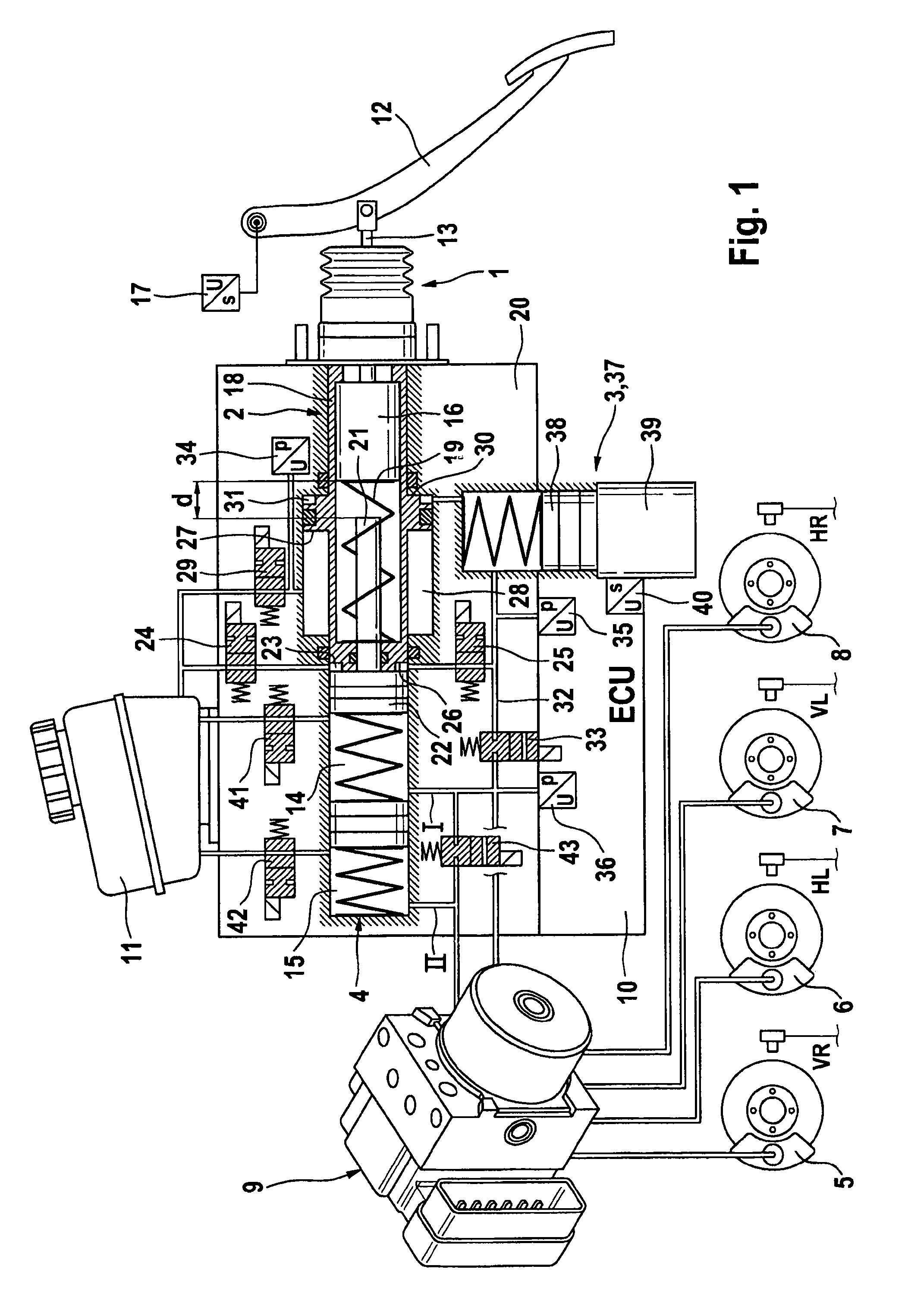
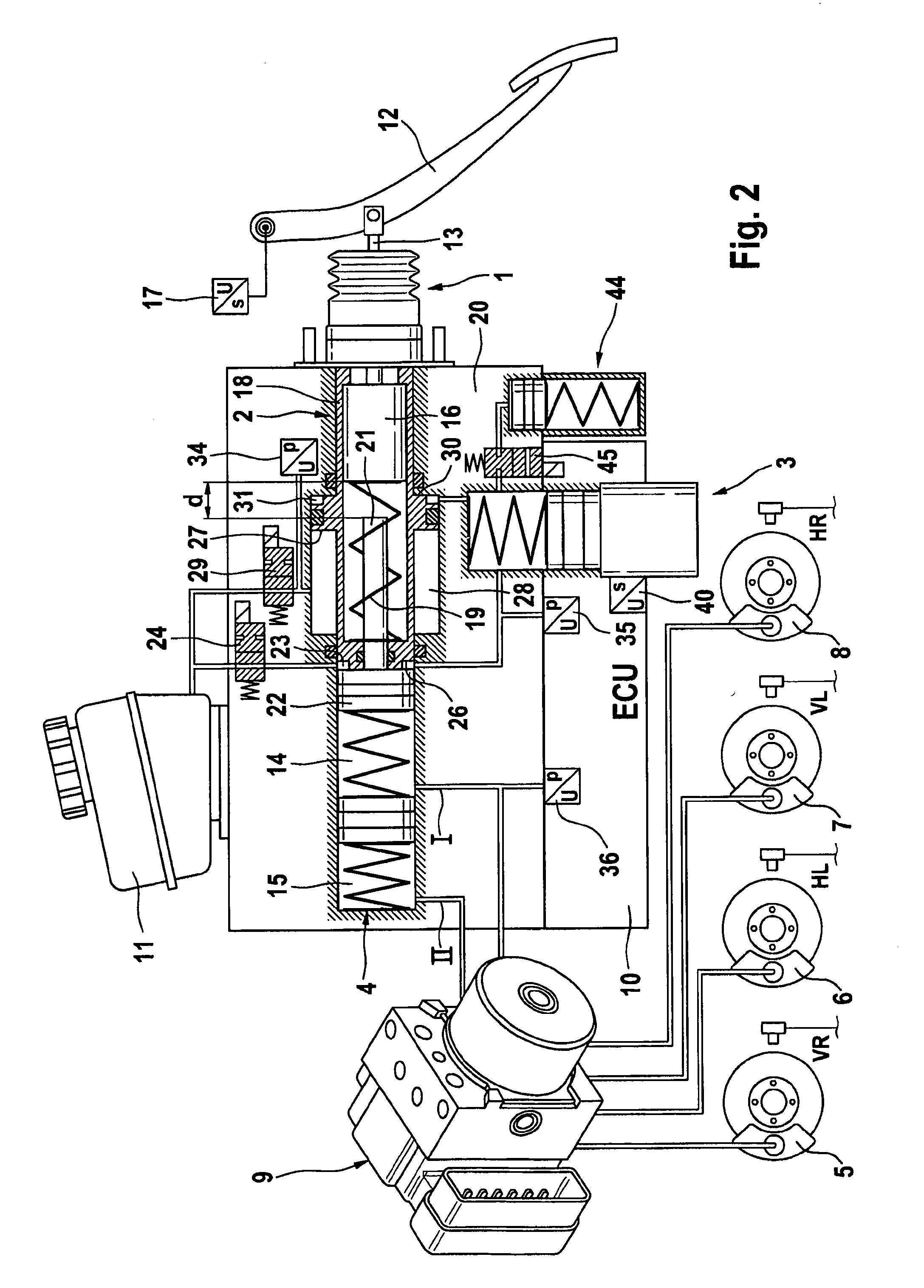
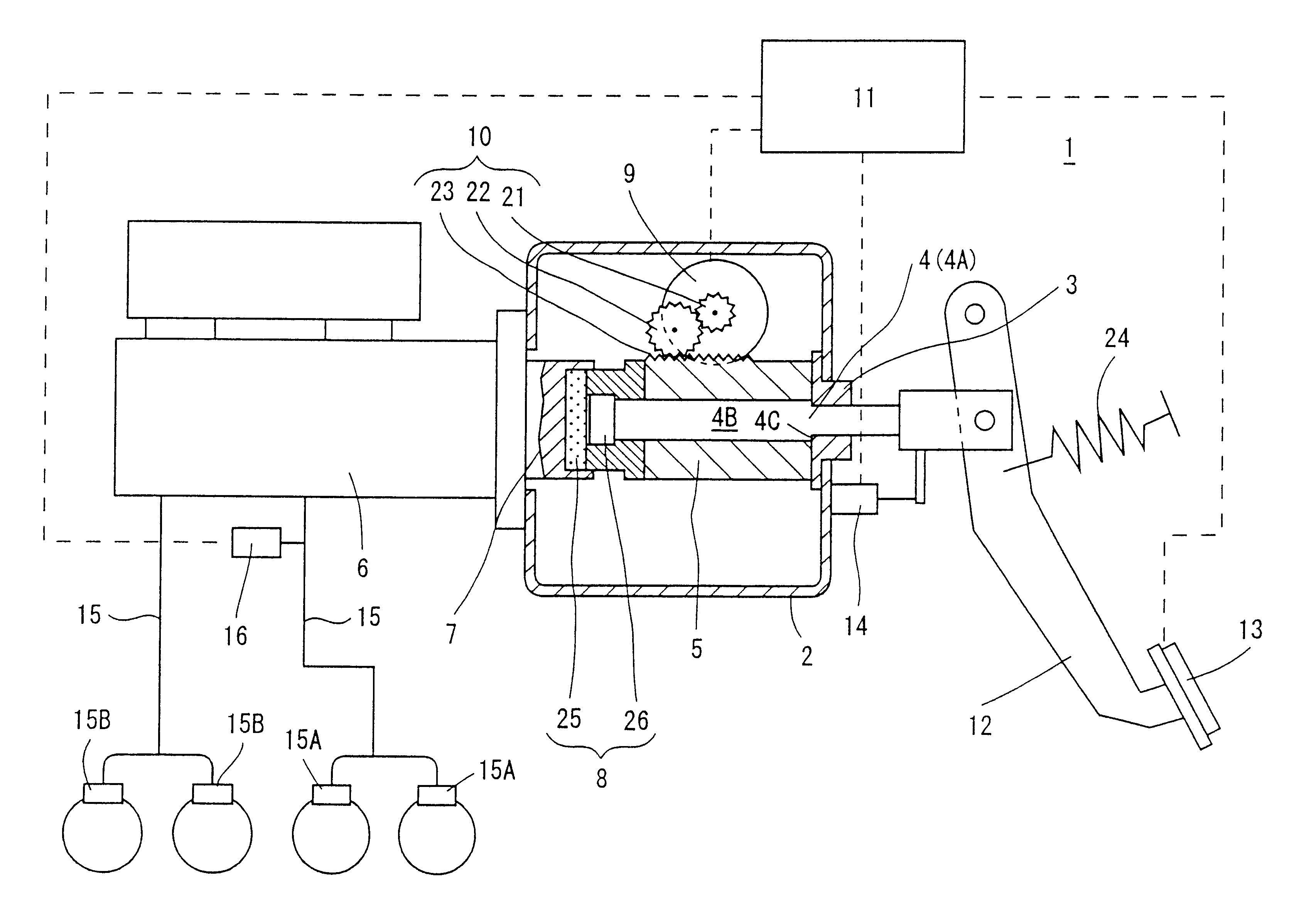
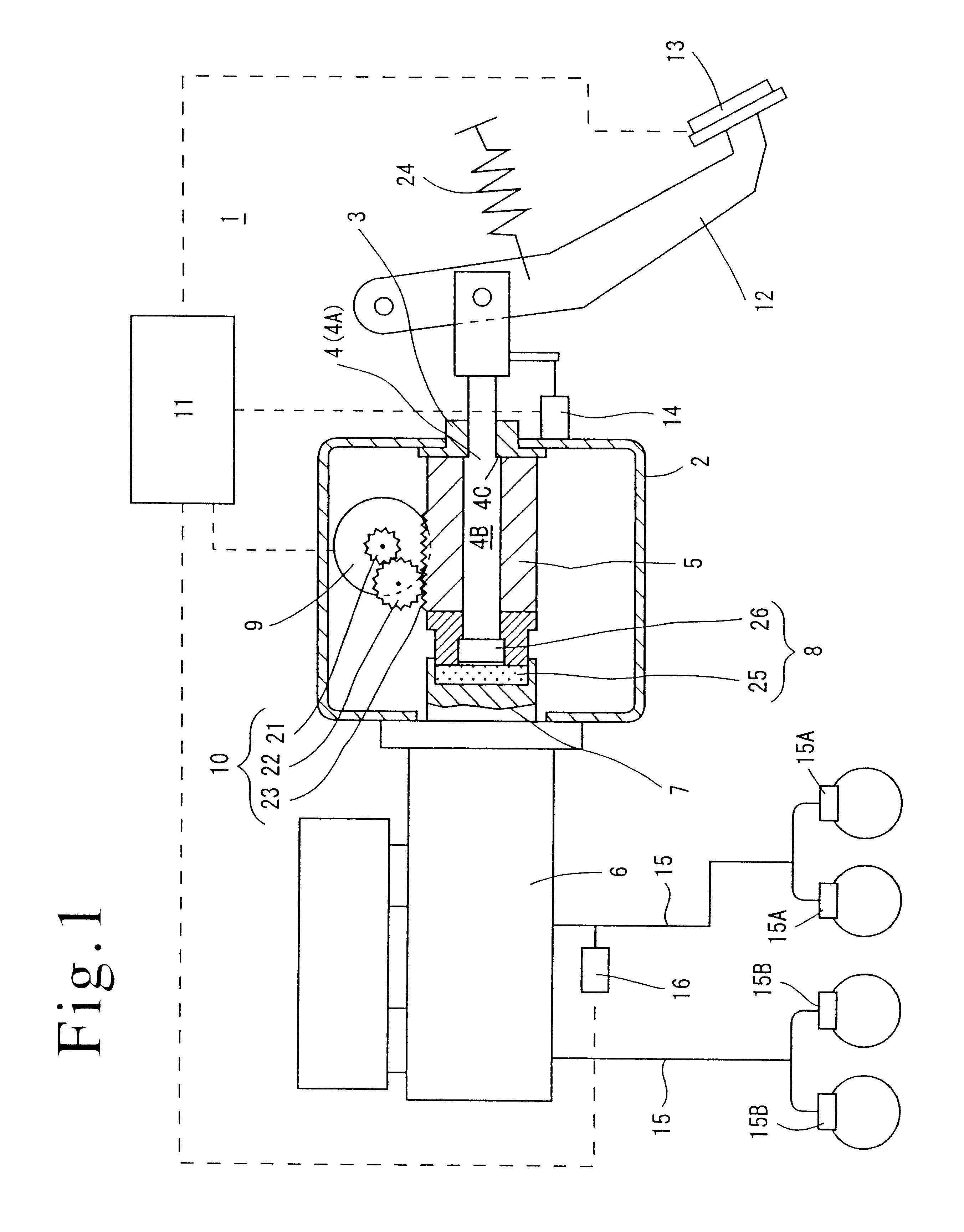
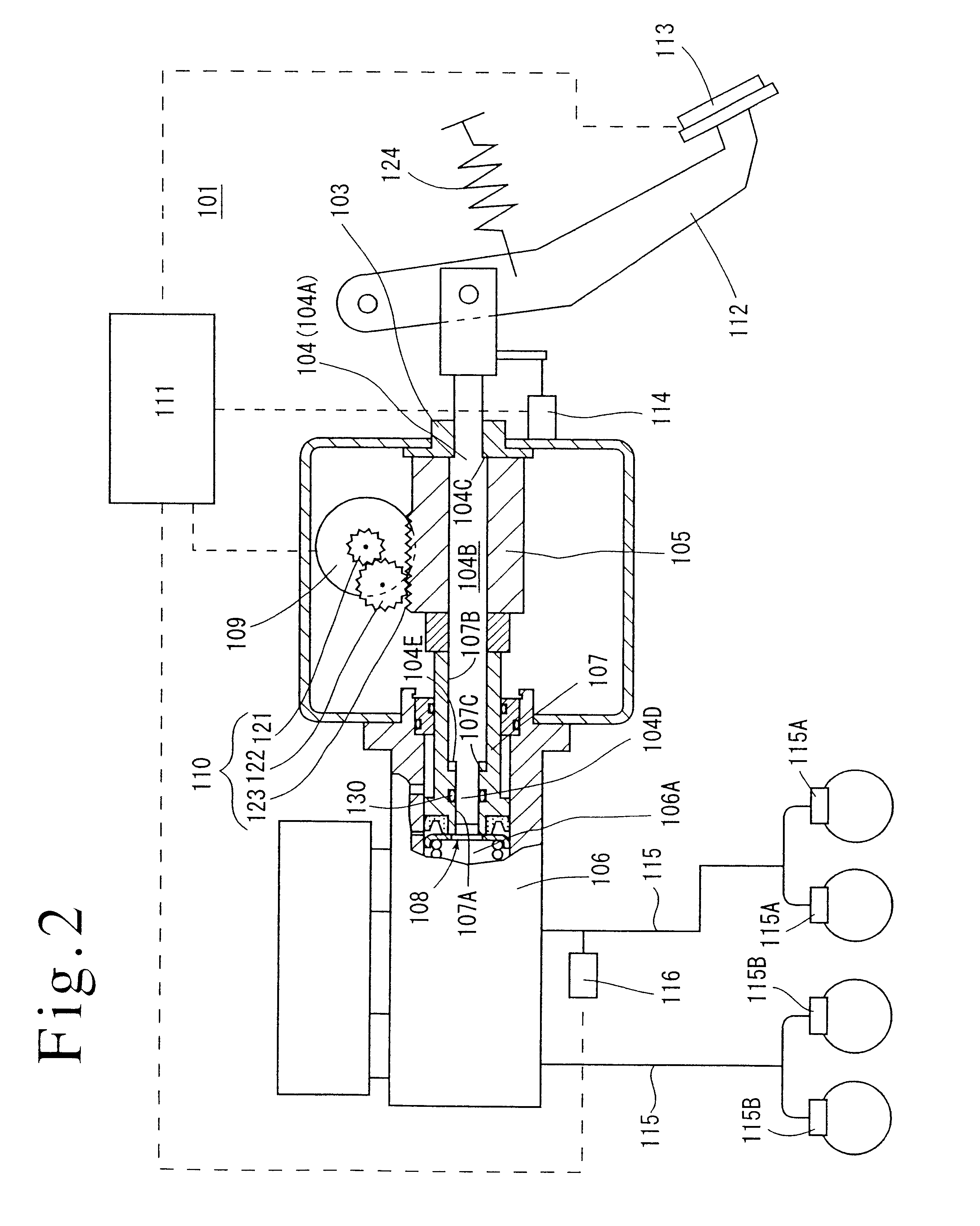
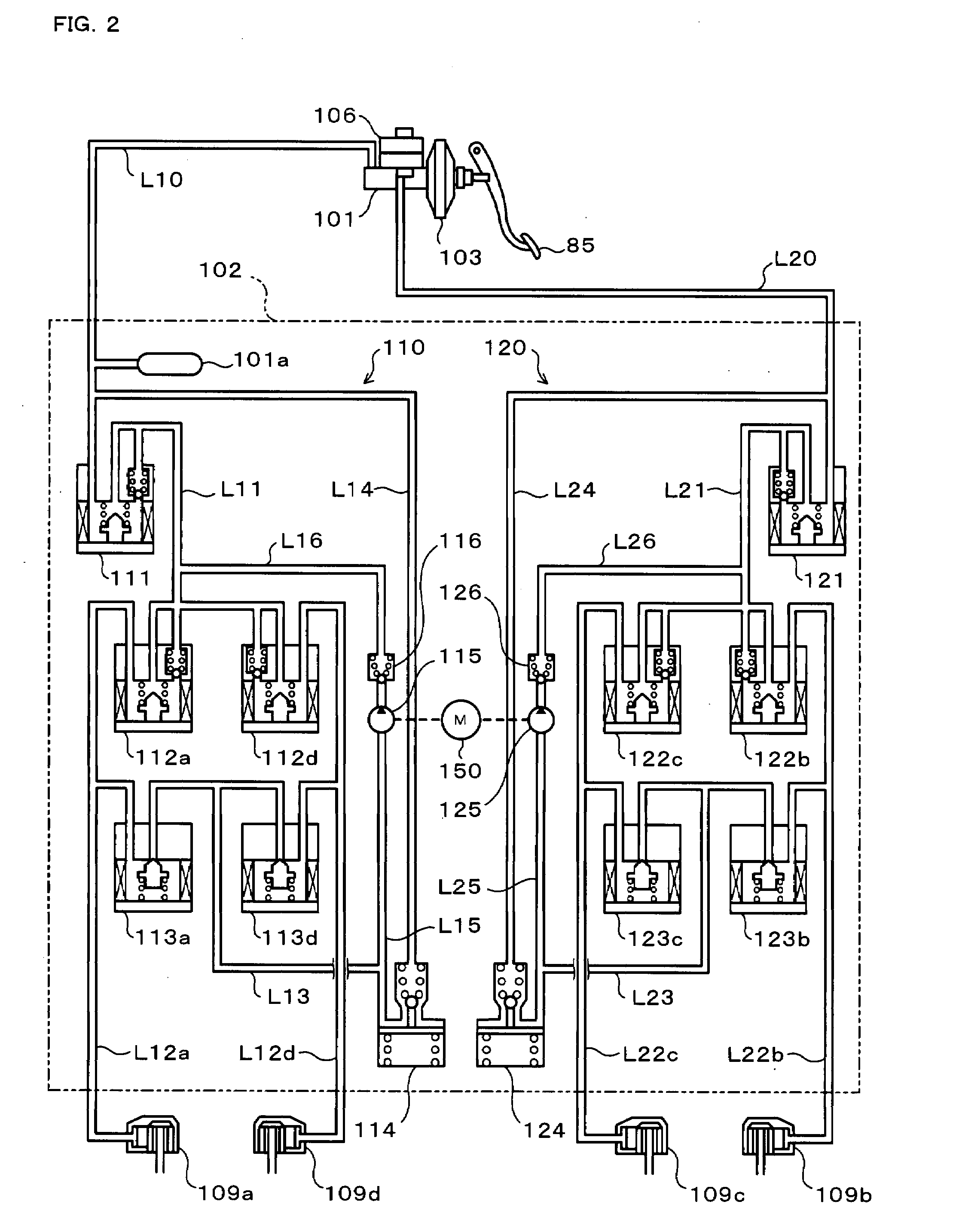
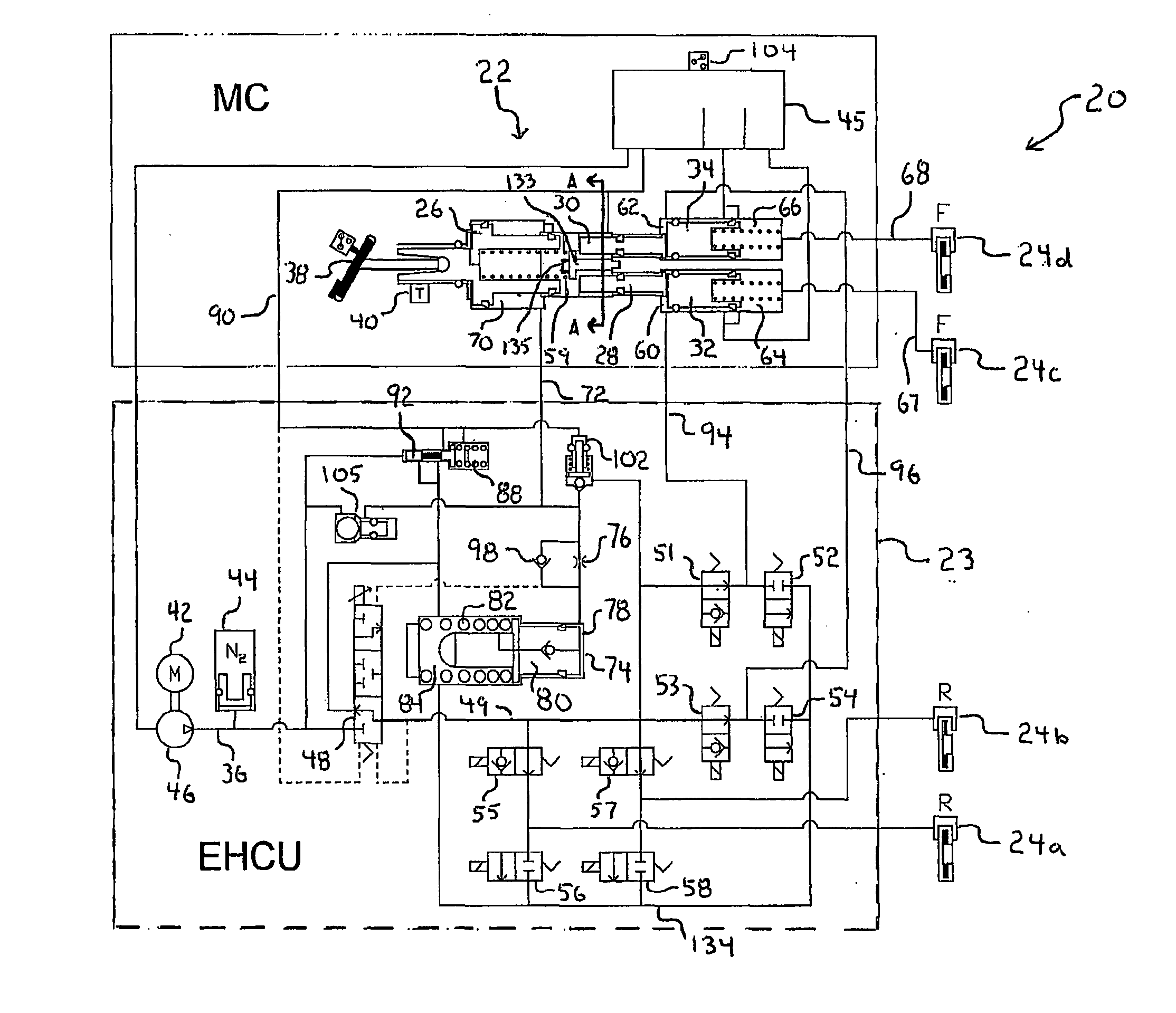
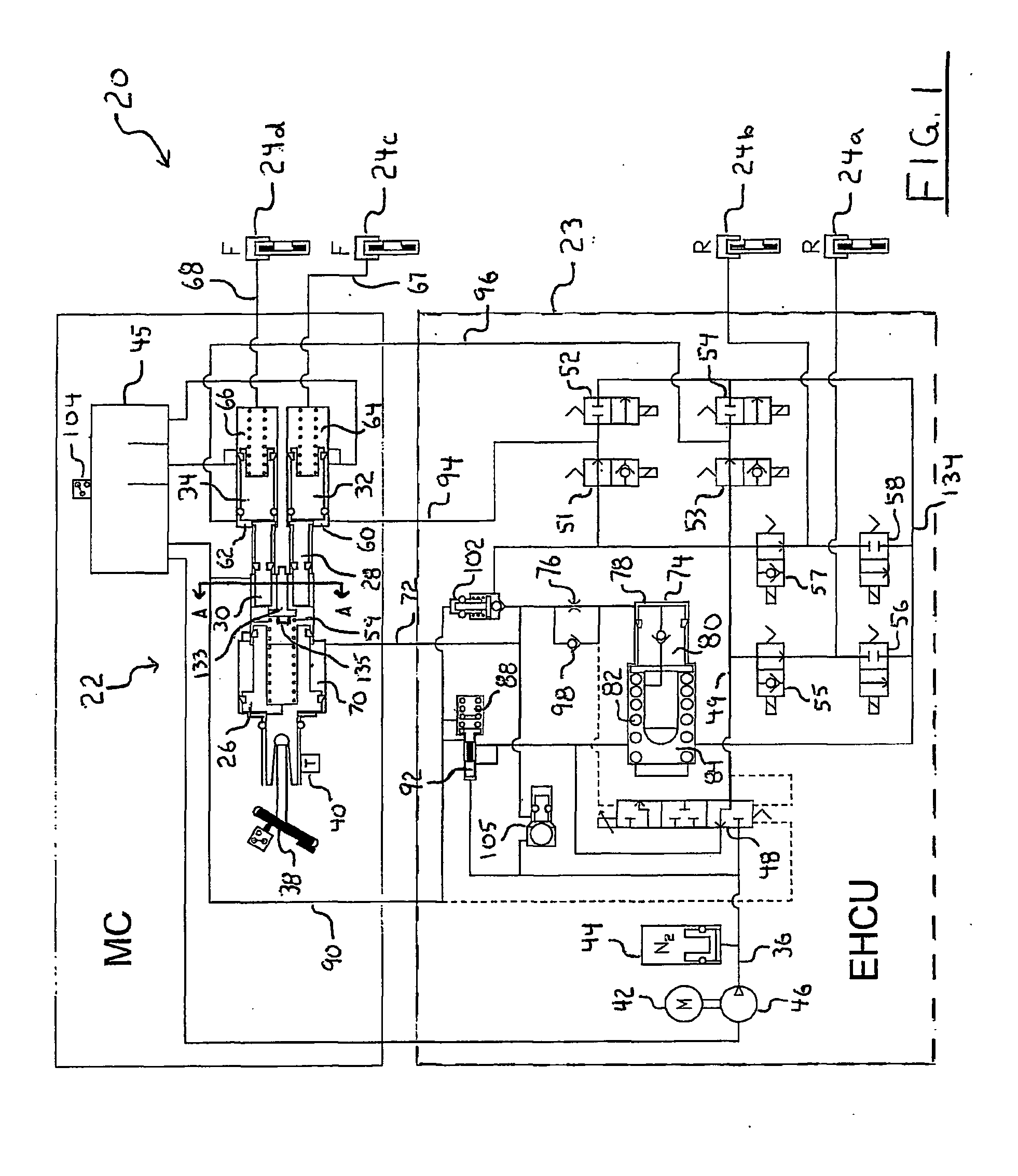
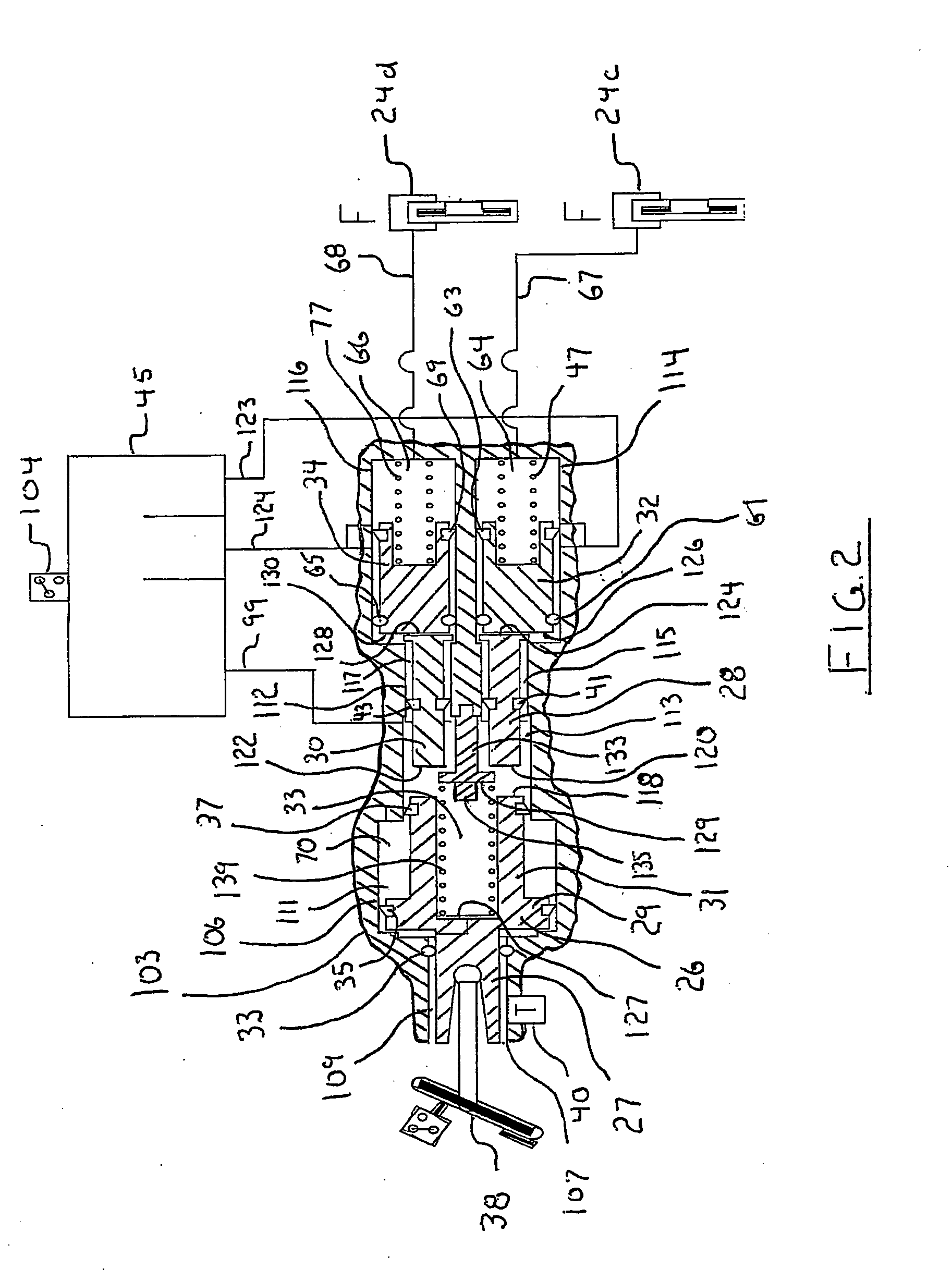
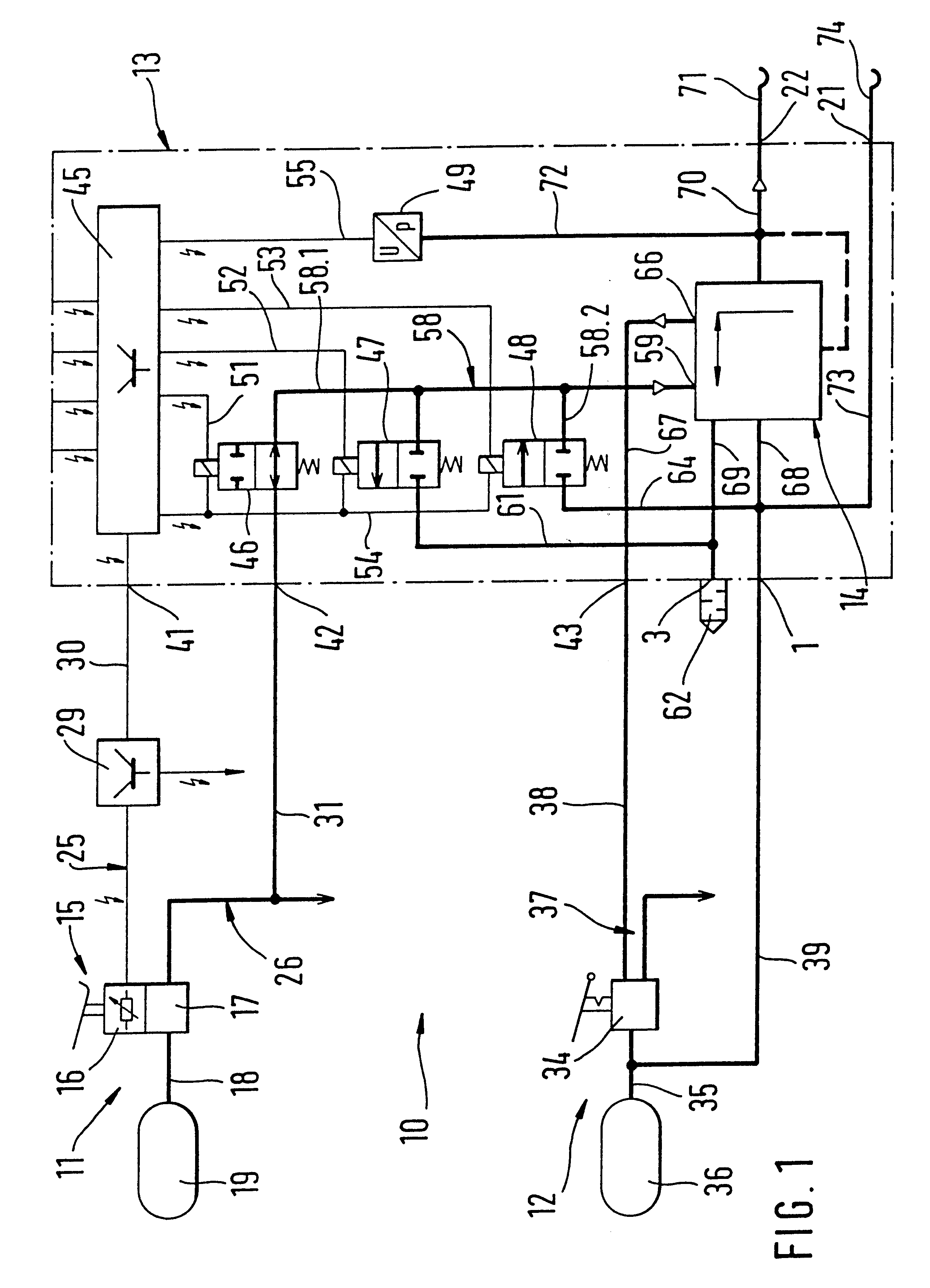
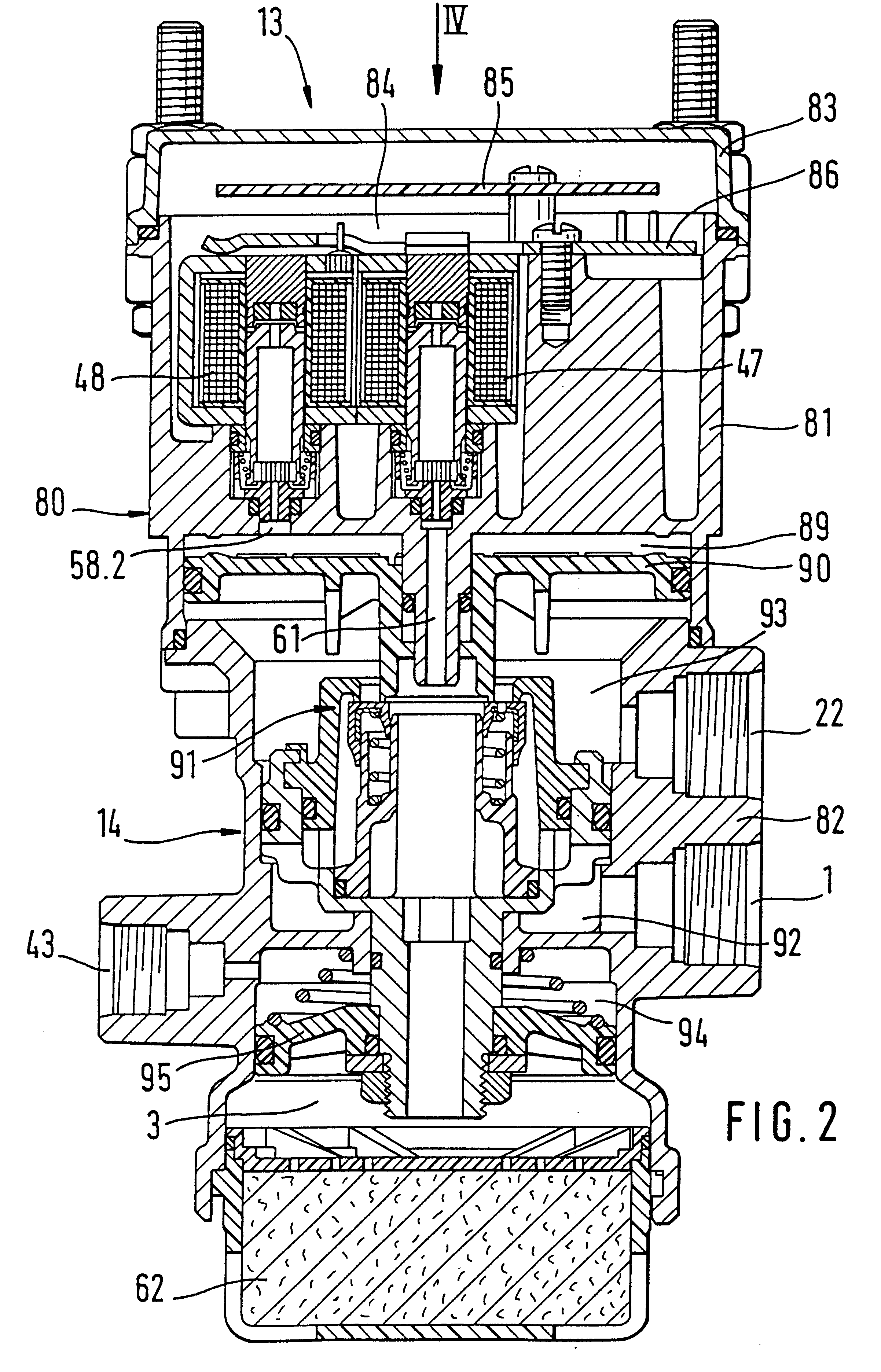
Brake control apparatus and method
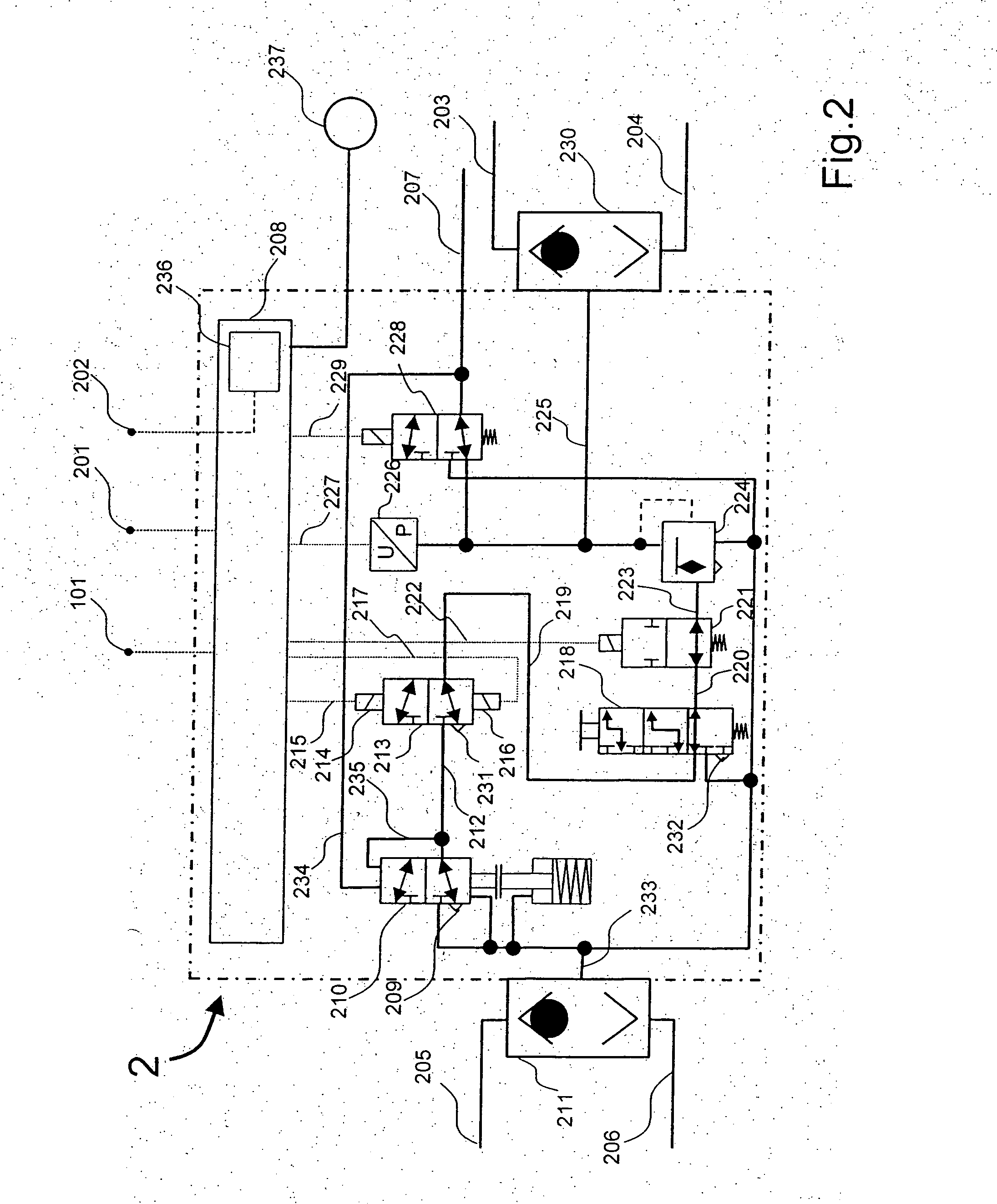
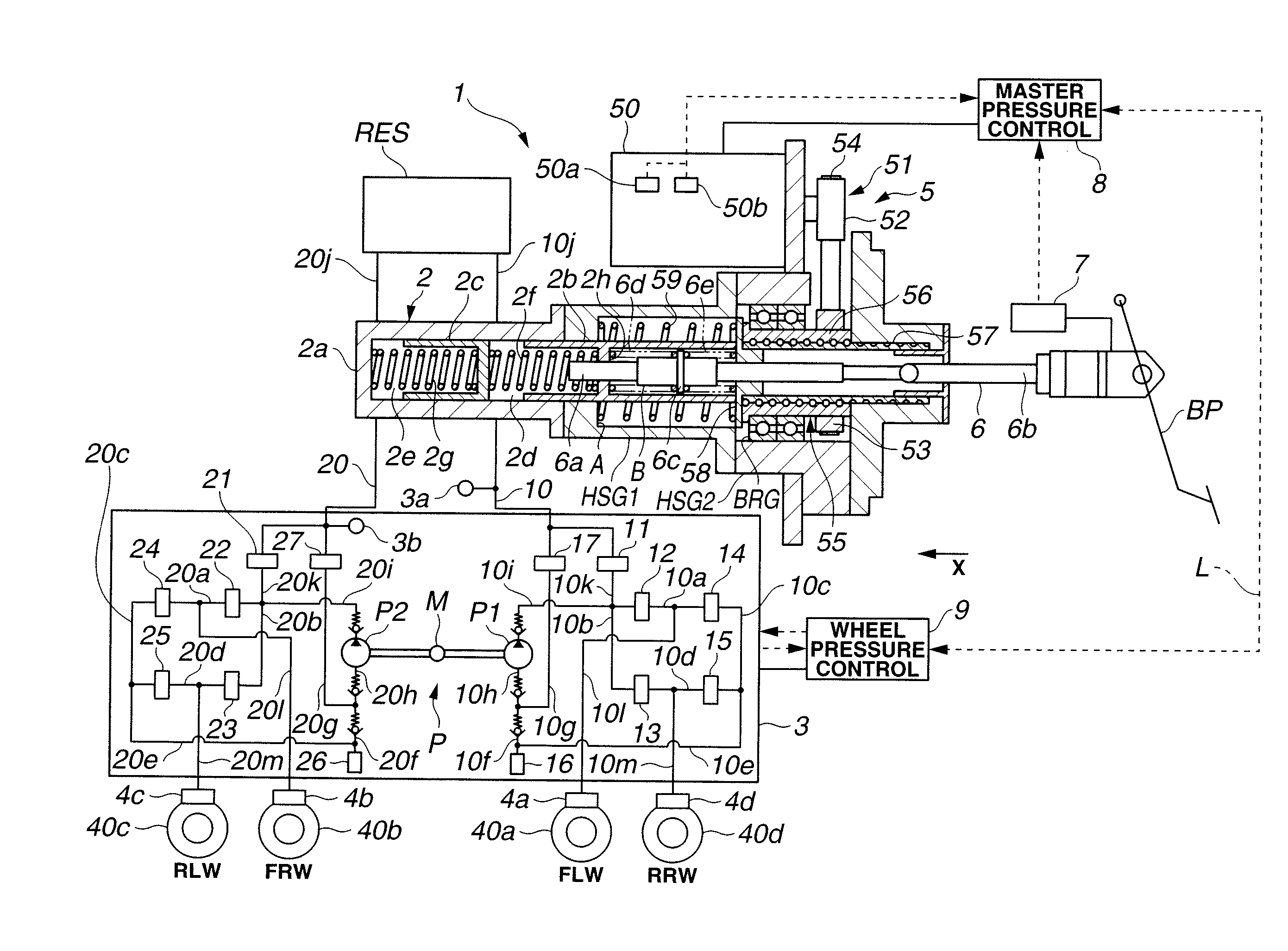
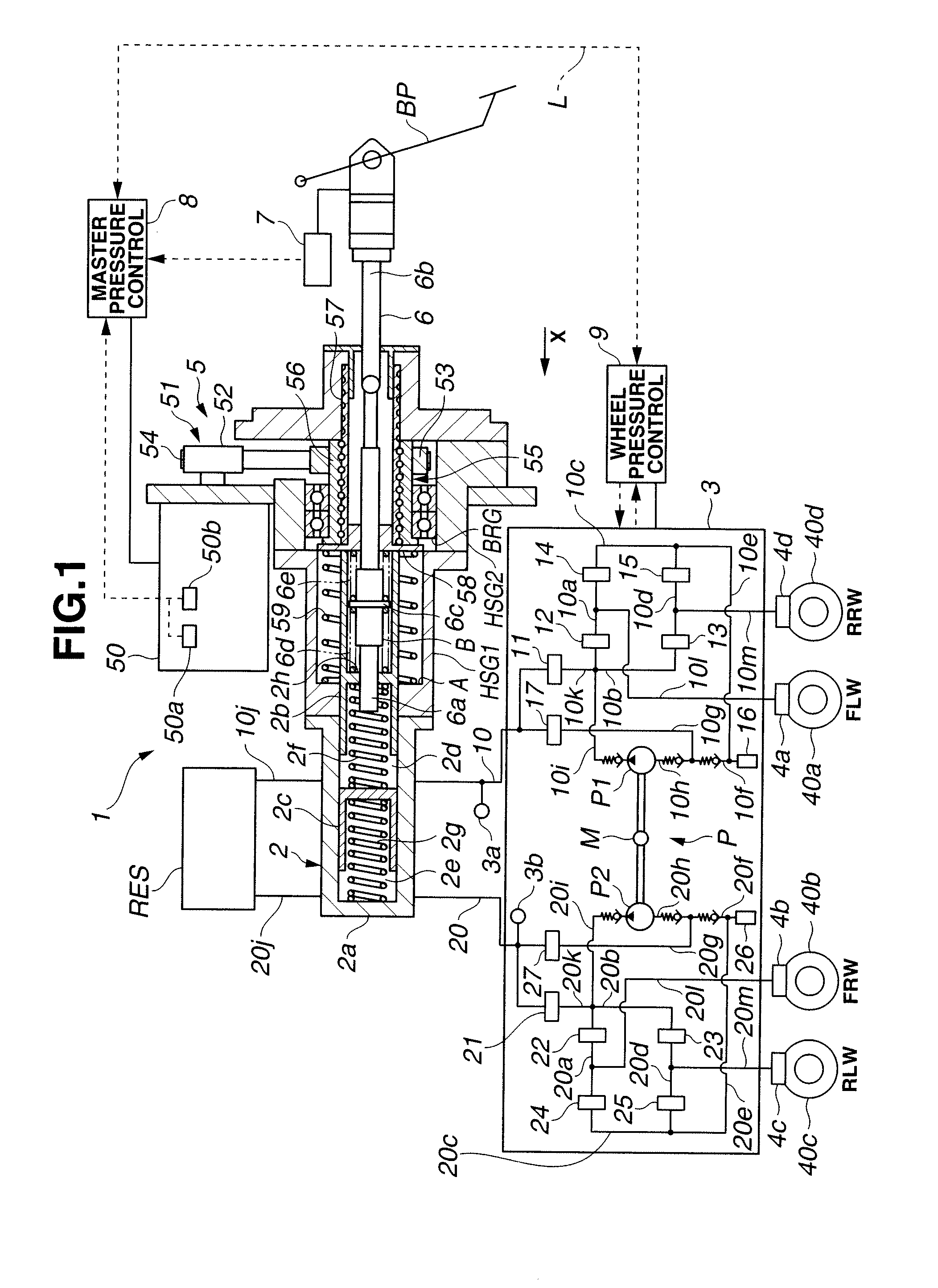
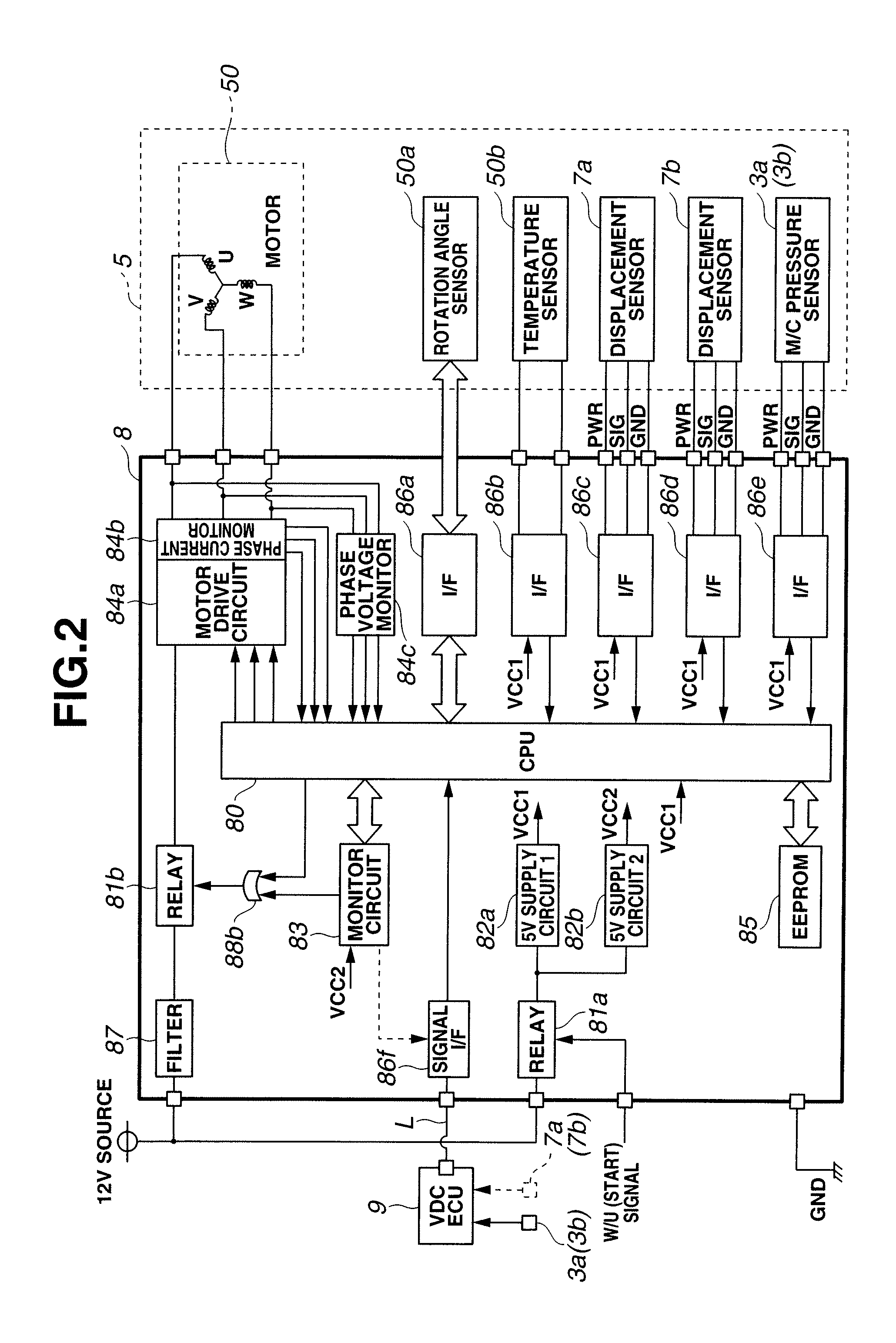
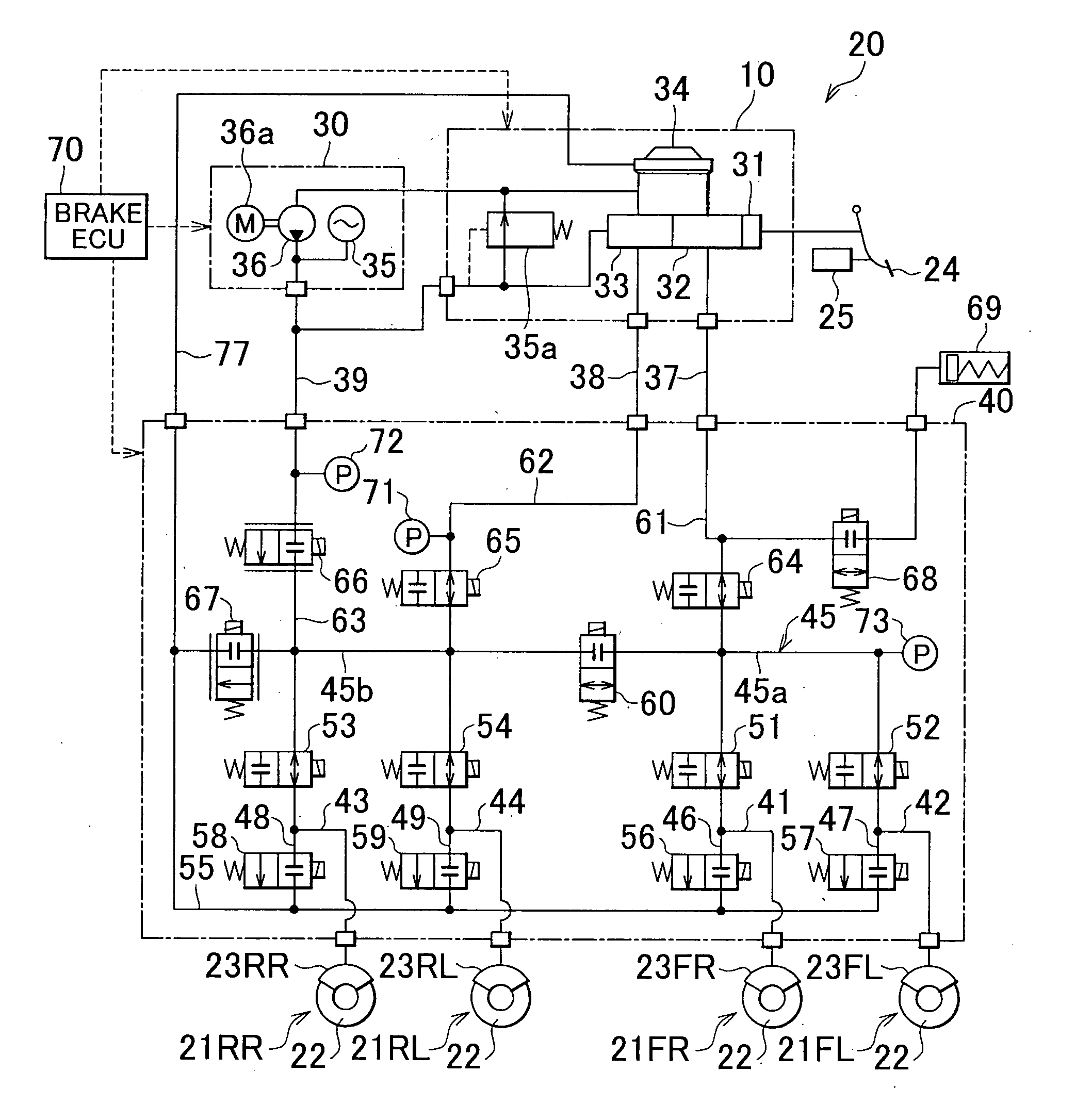
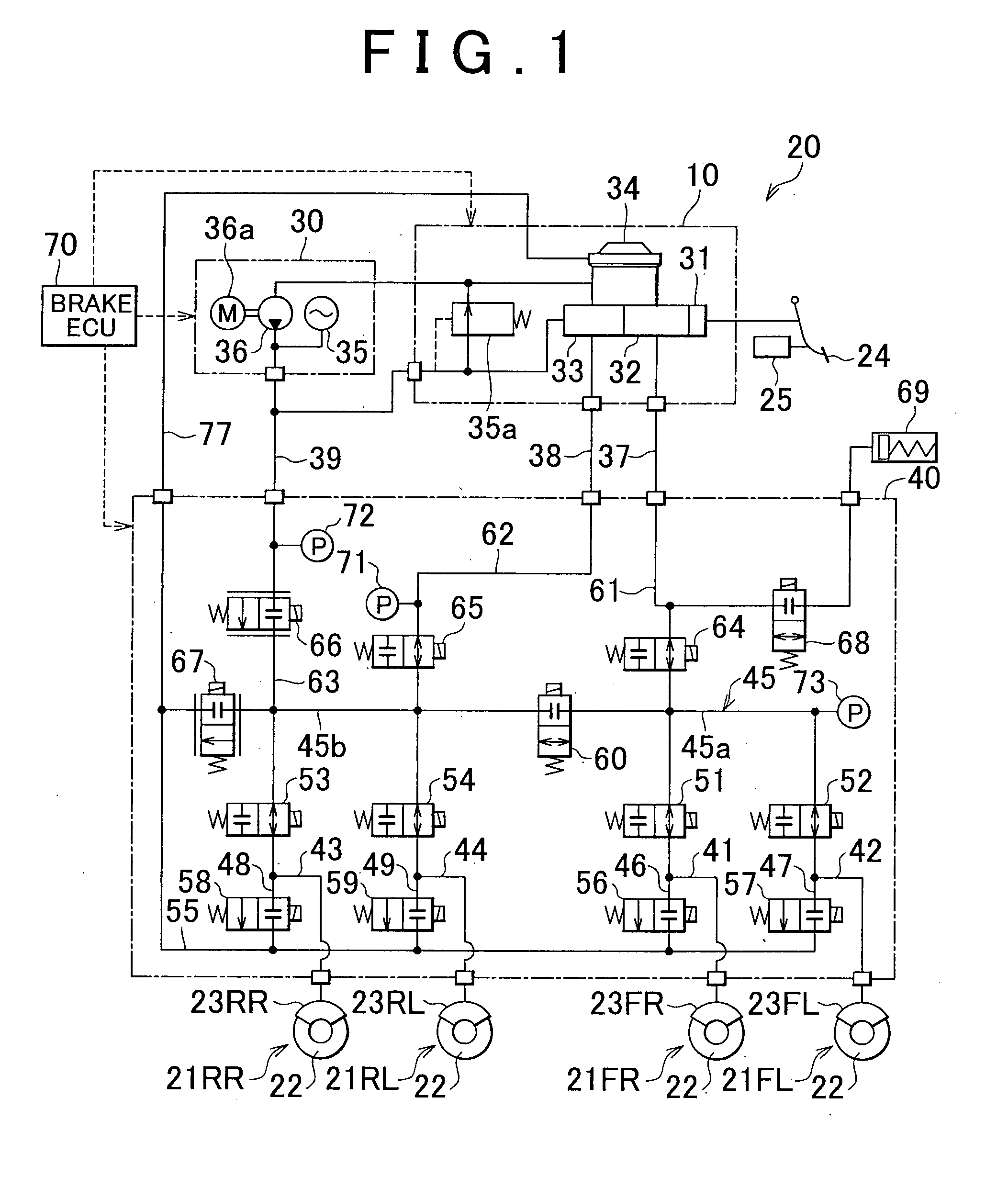
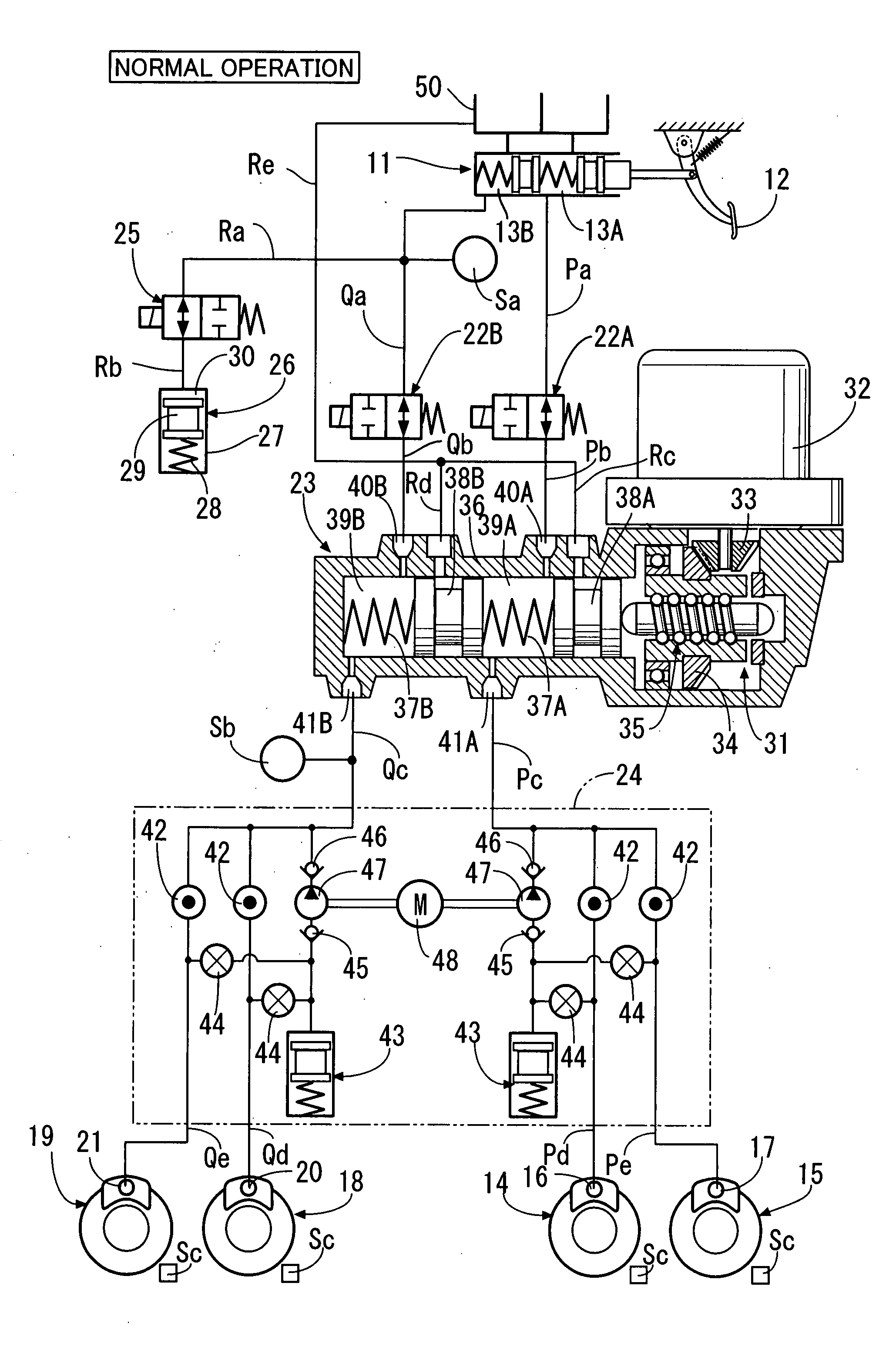
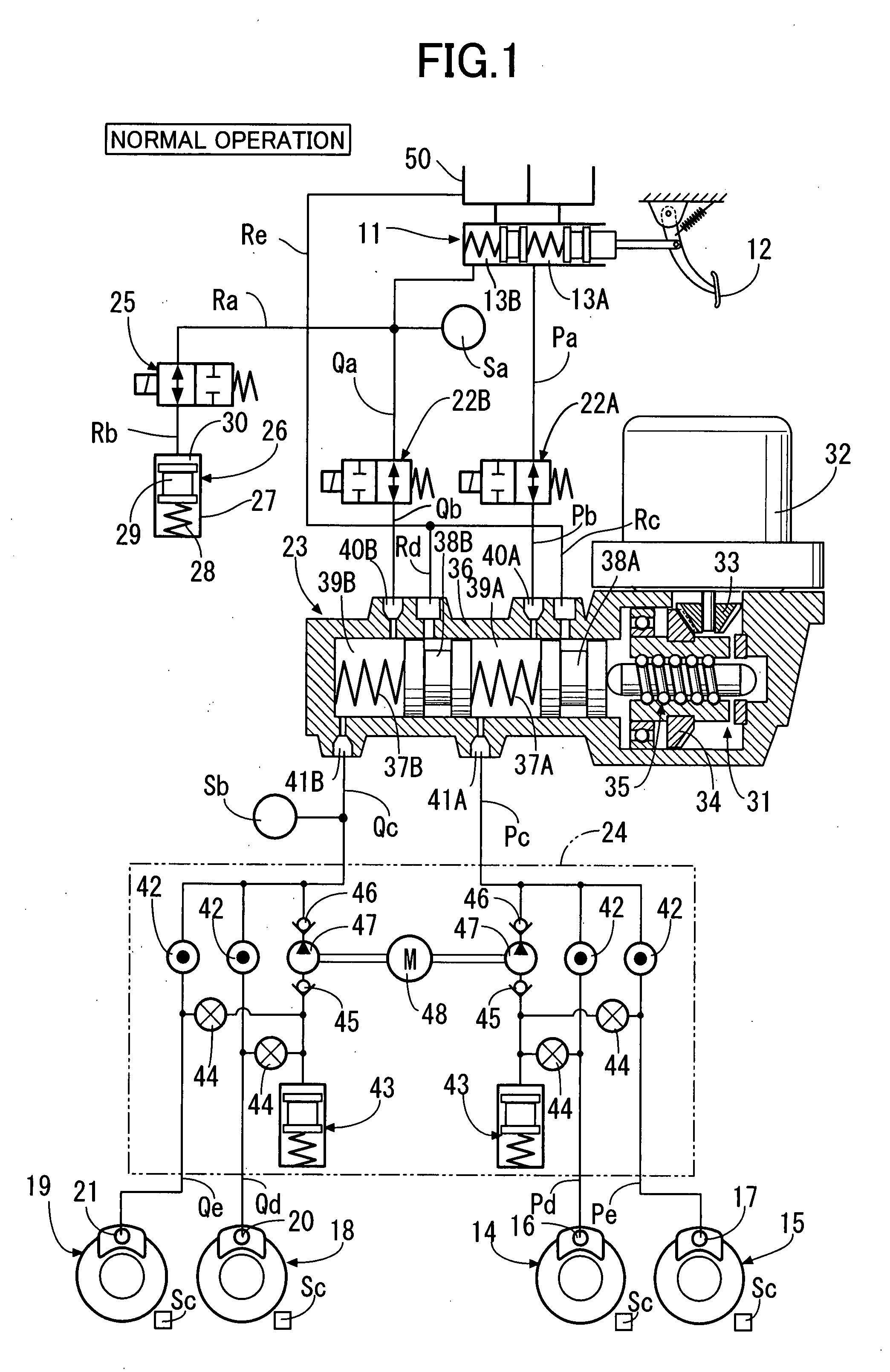
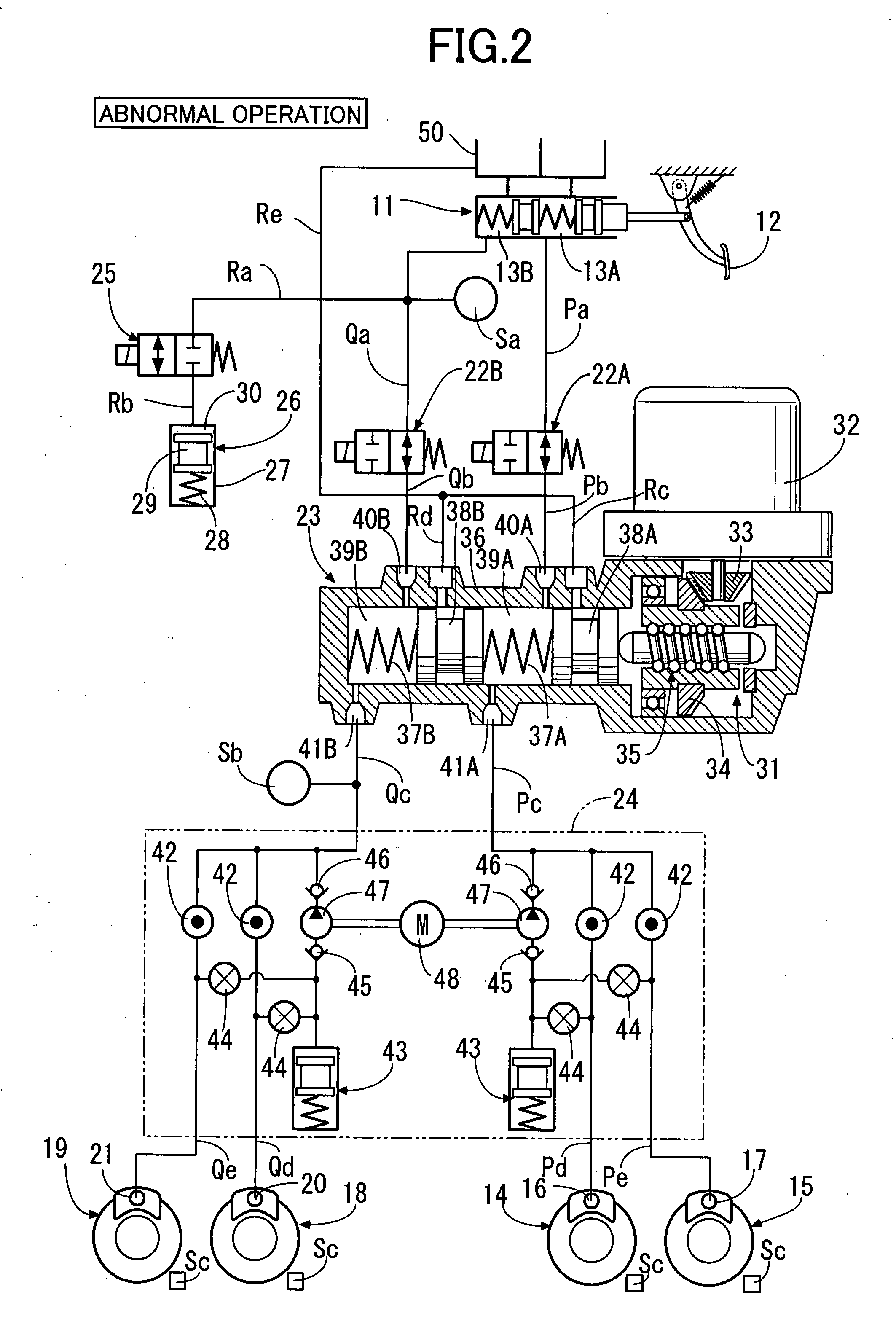
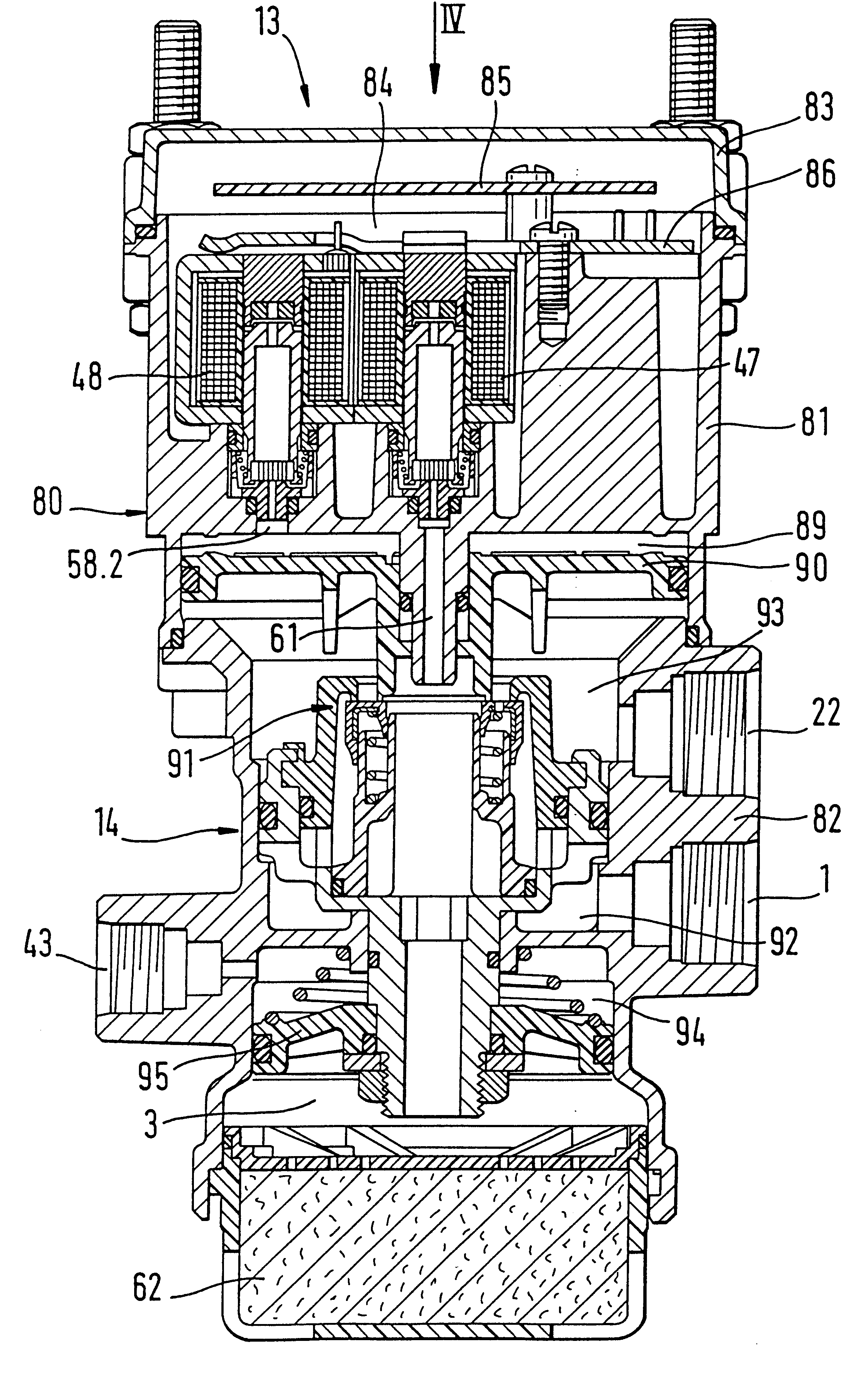
ActiveUS20090045672A1Improve securityApplication and release valvesBrake action initiationsControl systemWheel cylinder
A brake control system includes a master cylinder to produce a master cylinder pressure, a brake booster to assist the master cylinder, a first control unit to control the booster, a hydraulic modulator to supply a wheel cylinder pressure to a wheel cylinder, and a second control unit to control the hydraulic modulator. The hydraulic modulator includes a pressure source, such as a pump, to increase the wheel cylinder pressure. The first and second control units are connected together by a communication line. The brake control system may further include a boost condition transmitting section to transmit, through the communicating line, a condition of a boost system formed by the brake booster and the first control unit.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
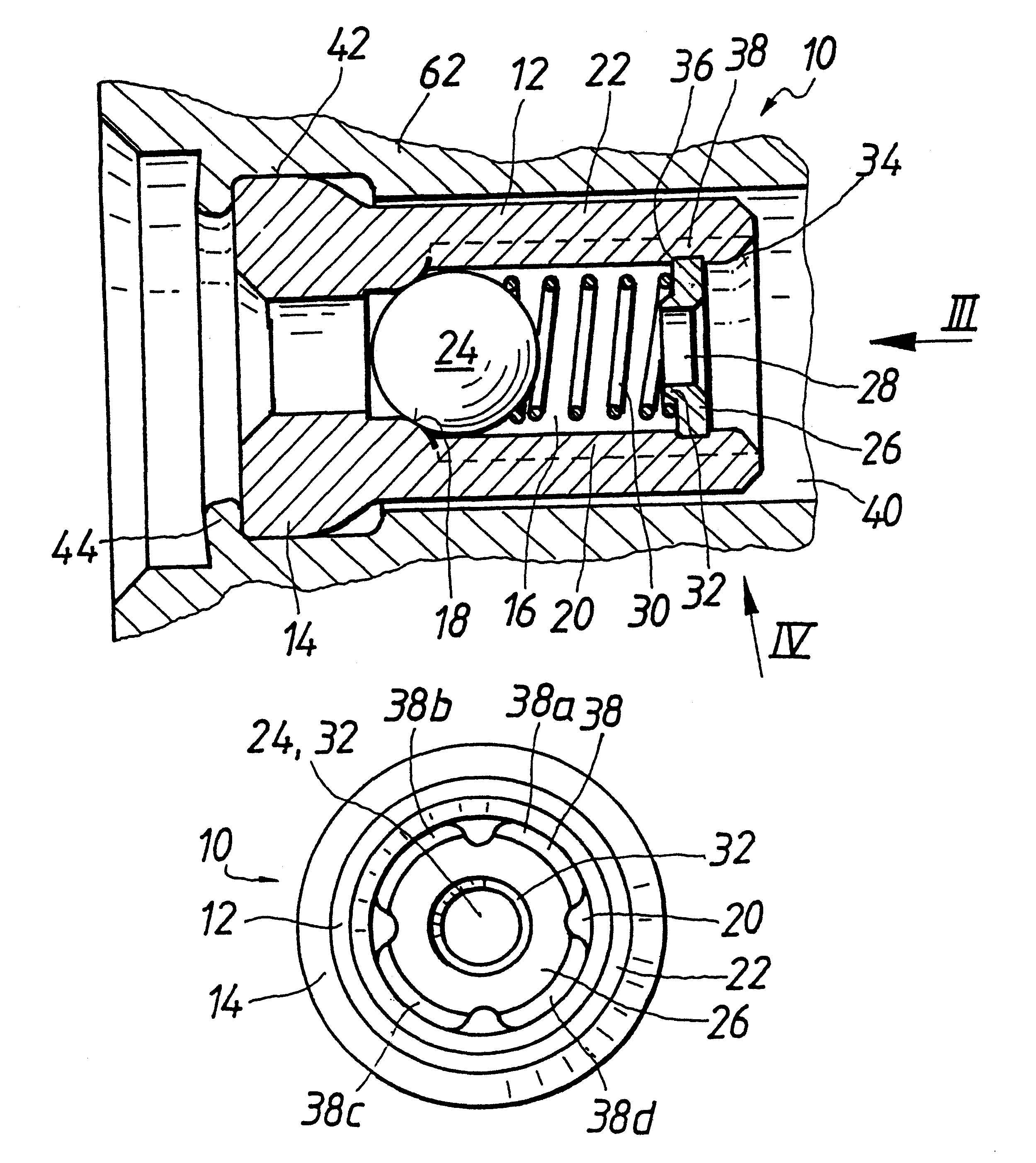
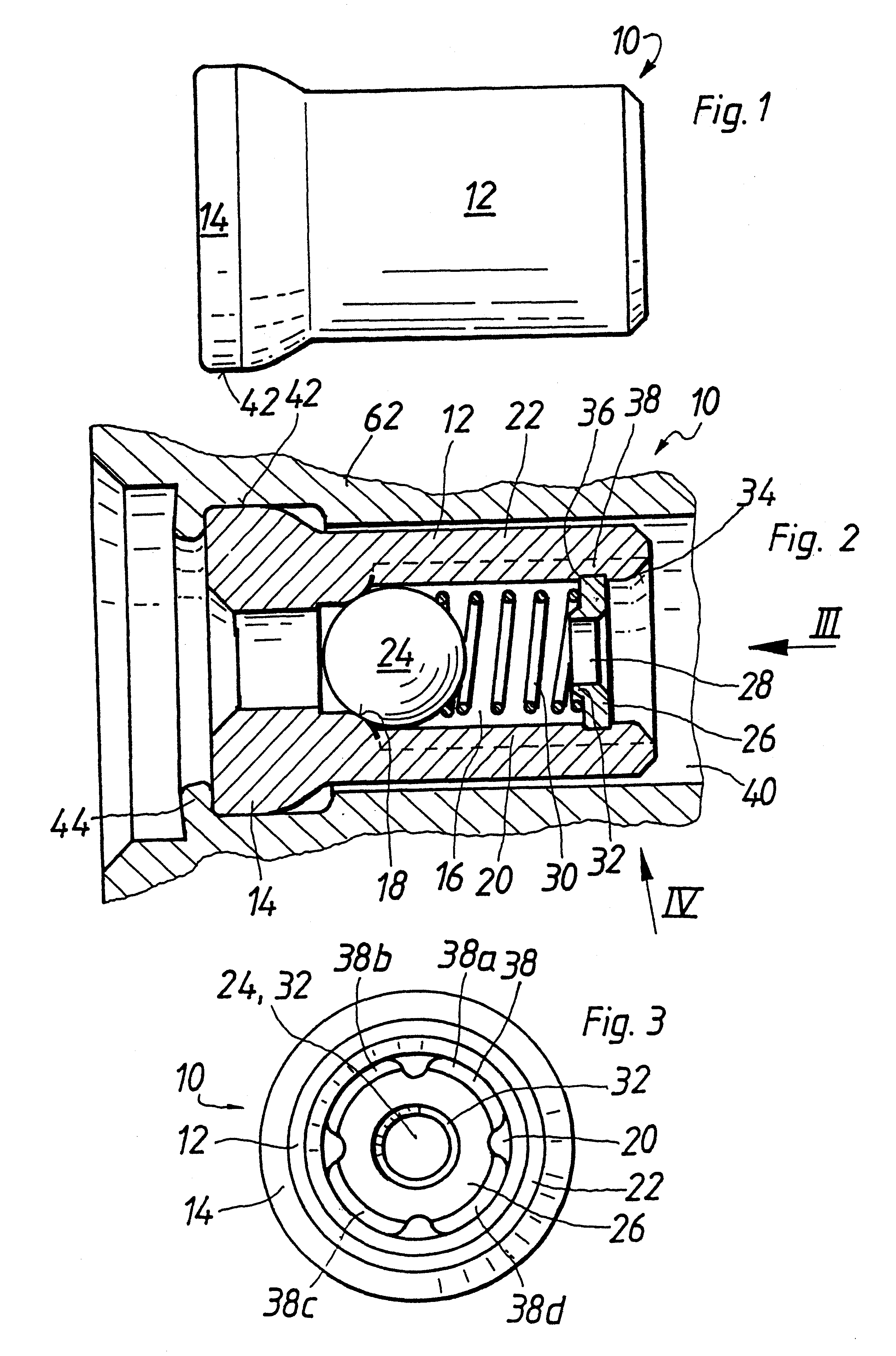
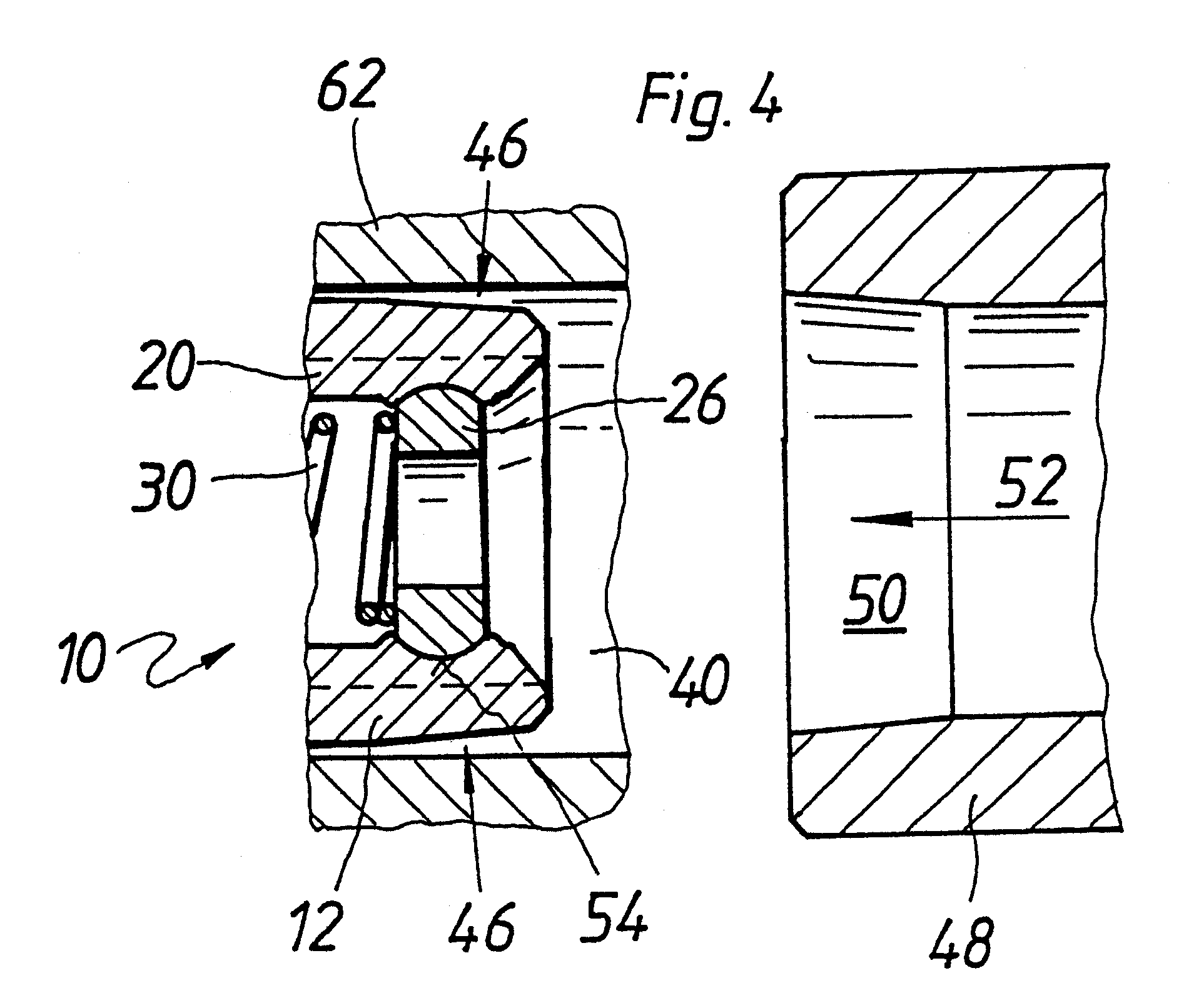
Check valve for a piston pump in a fluid circulation system
The invention relates to a check valve with a tubular valve housing in which a valve ball is received. To make a large flow cross section available and to prevent closure by the valve ball when the check valve is fully open, a perforated disk is press-fitted between longitudinally extending guide ribs of the valve housing and a circumferential wall of the valve housing there is an interstice as an outflow opening, which is not closed even the valve ball contacts the perforated disk. The valve housing is made by stamping, in which the guide ribs and a valve seat are made in one operation and are thereby aligned exactly with one another. In this way, a small radial play of the valve ball can be realized.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Brake control unit
Towed vehicles can be extremely heavy. Accordingly, it is too much of a burden to the braking system of a towing vehicle to not have brakes on the towed vehicle. Controlling the brakes of the towed vehicle must be accurately applied otherwise undesirable conditions can be created. There is a need for a method for controlling braking of a towed vehicle. This method comprises receiving a first signal via a communication bus of a towing vehicle, the first signal relating to at least one operating condition of at least one the towing vehicle and a towed vehicle, sending a second signal to brakes of the towed vehicle, the second signal based on said first signal.
Owner:HORIZON GLOBAL AMERICAS INC
Electric brake position and force sensing and control
InactiveUS20050269872A1Braking action transmissionElectrodynamic brake systemsControl signalEngineering
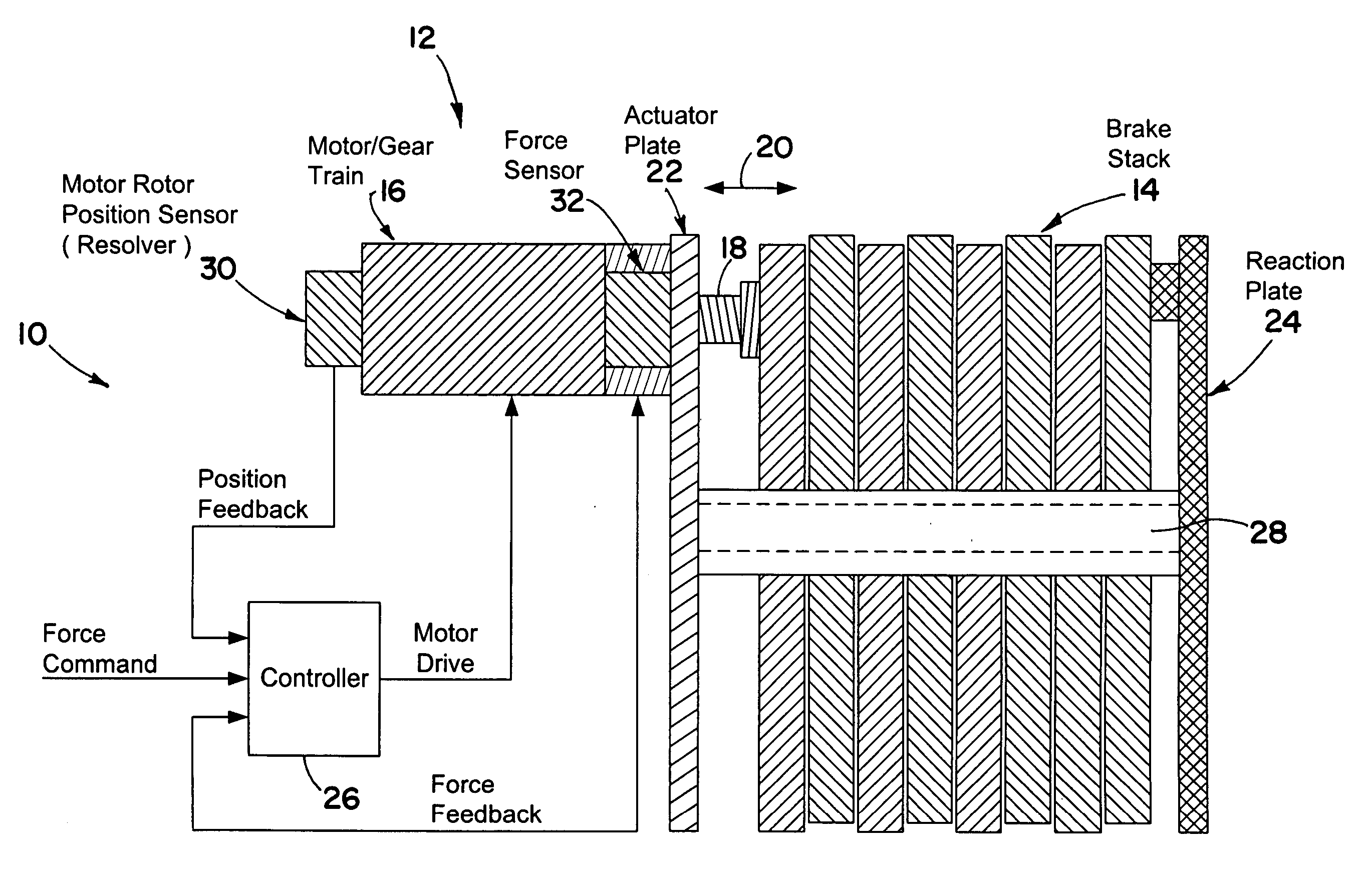
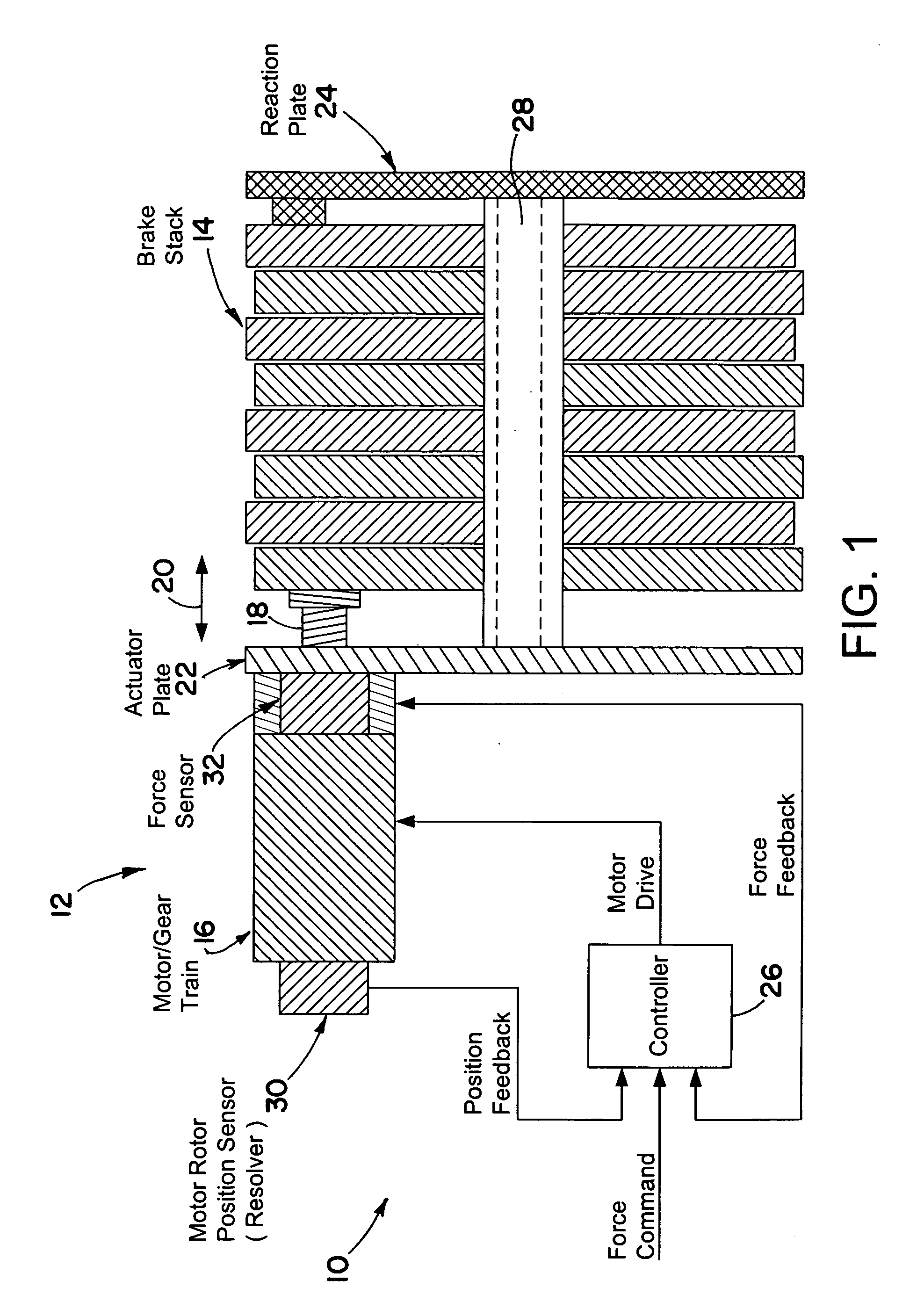
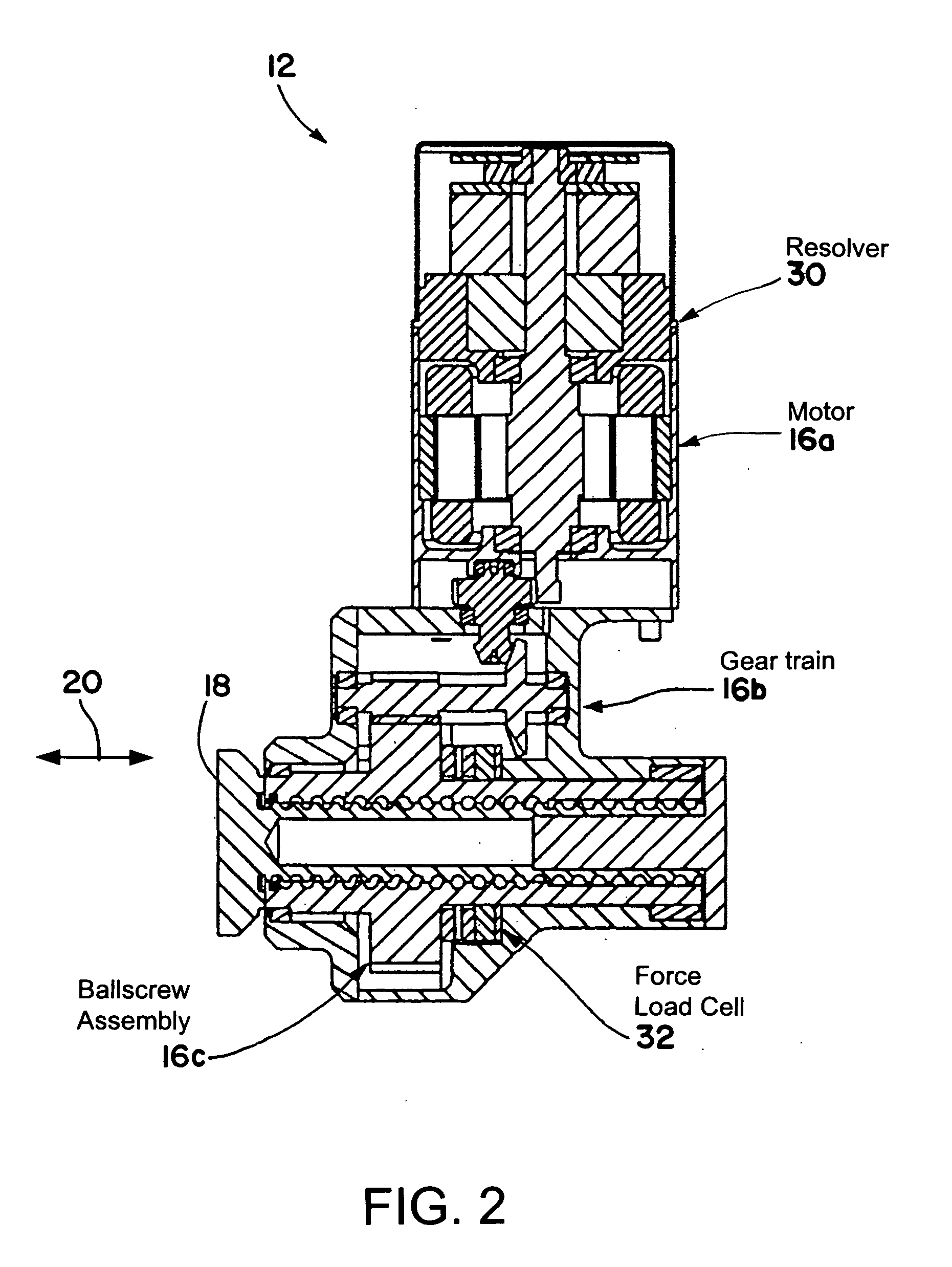
A brake system including an electromechanical brake actuator having an actuator ram for exerting a brake force on a brake stack of a wheel to be braked in response to a control signal. In addition, the brake system includes a force sensor for sensing the brake force exerted on the brake stack by the actuator ram and outputting a force feedback signal based thereon; and a position sensor for sensing a position of the actuator ram and outputting a position feedback signal based thereon. Moreover, the brake system includes a controller for providing the control signal to the electromechanical brake actuator based on the force feedback signal and the position feedback signal.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Brake control apparatus for vehicle
InactiveUS20060220453A1Improve energy efficiencyBraking element arrangementsBraking action transmissionRegenerative brakeDifferential pressure
A brake apparatus for a vehicle controls braking force acting on front wheels by hydraulic braking force (front-wheel-side vacuum-booster hydraulic pressure fraction+linear-valve differential pressure fraction), which is frictional braking force, and regenerative braking force, and controls braking force acting on rear wheels by hydraulic braking force (rear-wheel-side vacuum-booster hydraulic pressure fraction) only, to thereby perform regeneration-coordinative brake control. During performance of ABS control, the apparatus sets the limit regenerative braking force to a force under which locking of the front wheels does not occur in a case in which the force acts on the front wheels, which are wheels undergoing regenerative braking, and adjusts the regenerative braking force such that the regenerative braking force does not exceed the limit regenerative braking force.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
Brake system for motor vehicles
ActiveUS20110115282A1Braking action transmissionAutomatic initiationsMechanical engineeringBraking system
A brake system includes a main brake cylinder and a pedal decoupling unit provided with a holding piston, the first ring surface thereof together with a first primary brake cylinder piston defining a first hydraulic chamber that is hydraulically pressurized with an electrically controllable pressure supply device. In order to improve the pedal characteristics of the brake system, in particular in a brake-by-wire brake system, the holding piston is embodied as a differential piston, the second ring surface thereof defining a second, blockable hydraulic chamber, and a piston effect in the second chamber corresponds to a force that acts counter to the direction of actuation on the holding piston.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Hydraulic circuit having a rotary type pump and brake apparatus for a vehicle provided with the same
InactiveUS6142581APrevent leakagePrevent liquid leakageBraking action transmissionAutomatic initiationsRotary pumpDrive shaft
A hydraulic circuit has a rotary type pump comprising a rotor rotating with a driving shaft and a casing which holds the rotor and the driving shaft. The casing further comprises an inlet port through which fluid is introduced to spaces formed by the rotor, an outlet port through which fluid is discharged from the spaces, and a hydraulic path for leading fluid from clearance around said driving shaft to the outside of the casing. A reservoir is provided to store fluid coming through the hydraulic path. A return conduit is disposed between the reservoir and an upstream side conduit connected to the inlet port in order that fluid stored in the reservoir is returned to the upstream side conduit. In the return conduit, a check valve is disposed to prevent the reverse flow of fluid from the upstream side conduit to the reservoir.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Motorcycle with antilock brake system
ActiveUS20050134114A1Improve braking performanceImprove engine performanceElectric propulsion mountingGas pressure propulsion mountingMaster cylinderEngineering
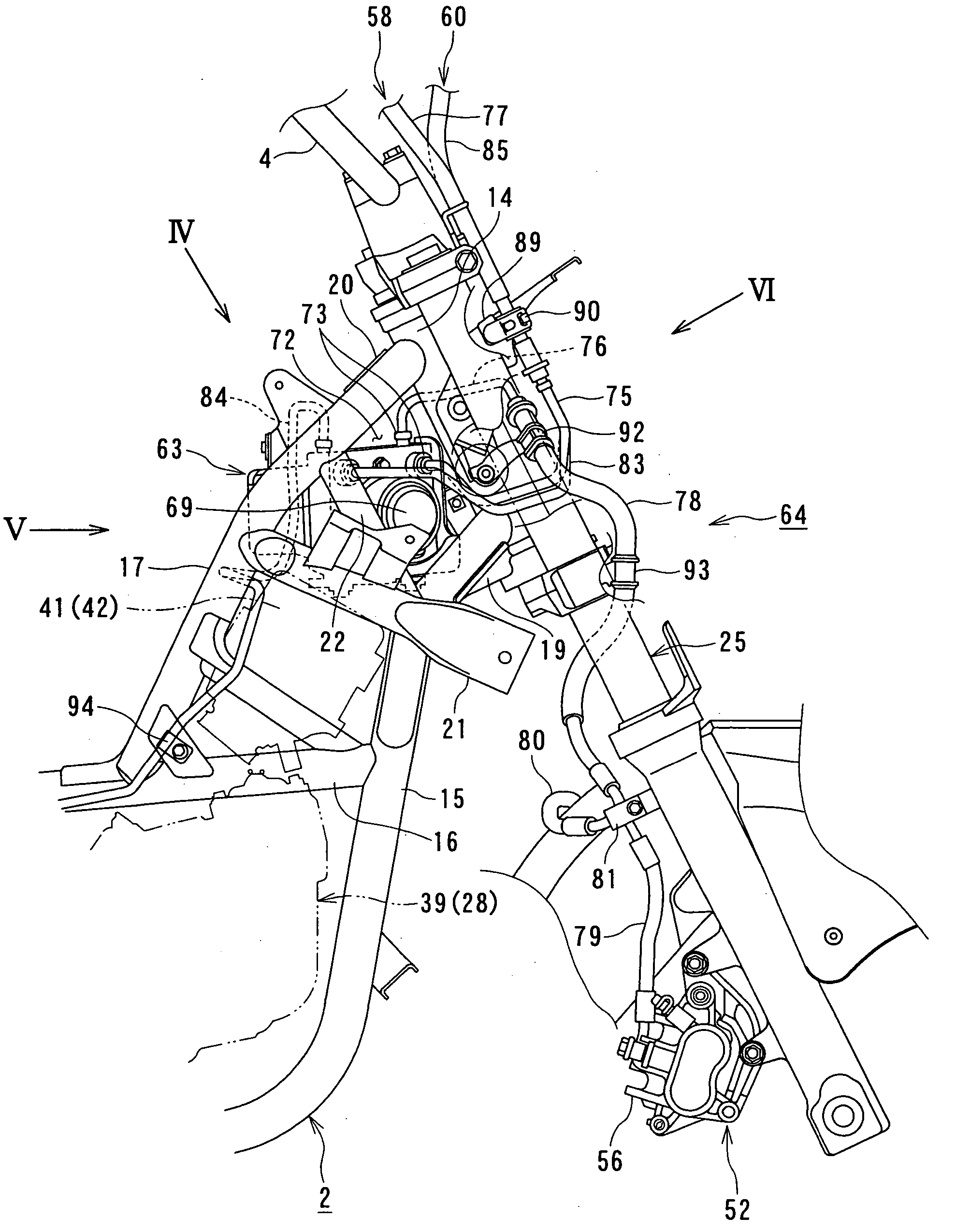
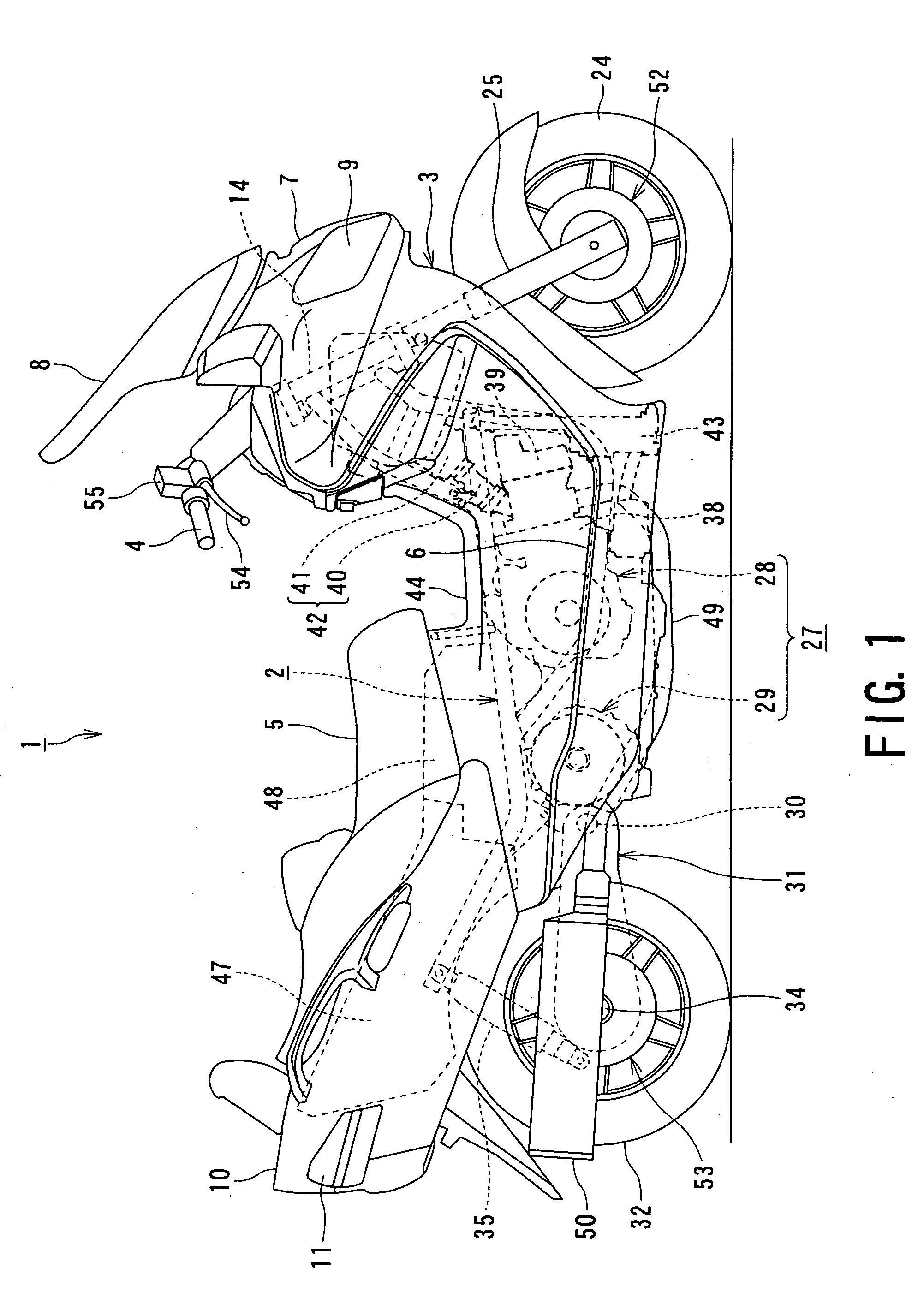
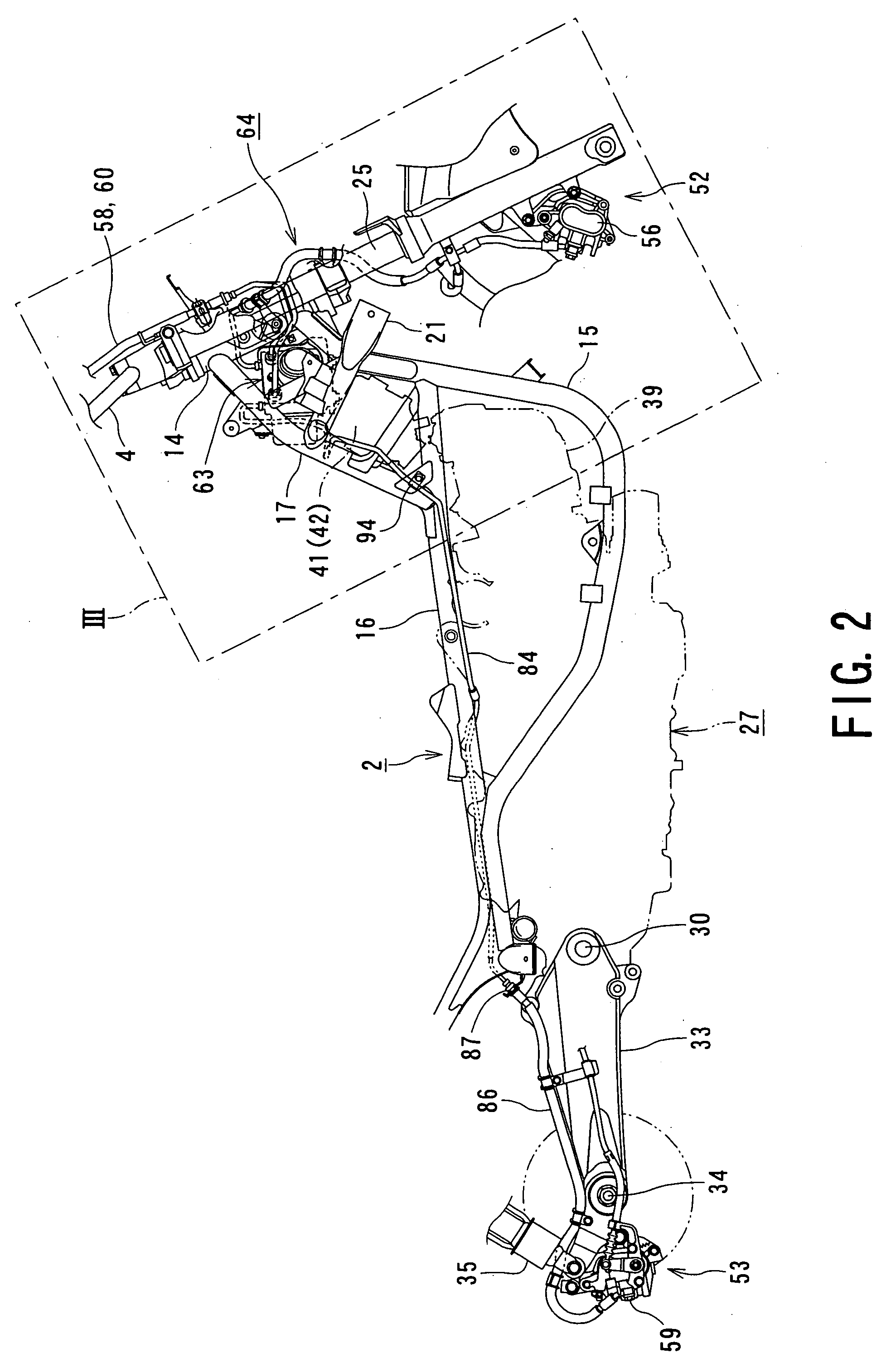
In a motorcycle provided with an antilock brake system, a front fork supporting a front wheel of a motorcycle is supported to be rotatable by a head pipe which is located at the front end portion of a body frame of a motorcycle, a handle-bar is secured to an upper end portion of the head pipe, master cylinders attached to the handle-bar are connected to hydraulic wheel brakes, respectively, via brake pipes. An antilock brake system includes an ABS-unit for antilock control disposed in an intermediate portion of the brake pipes. The ABS-unit is disposed immediately behind the head pipe and between a pair of body frame components disposed on both lateral sides of the motorcycle body and extending, from the head pipe, obliquely downward and backward, while extending outward in directions opposite to each other in the width direction of the motorcycle body.
Owner:SUZUKI MOTOR CORP
Electrically driven brake booster
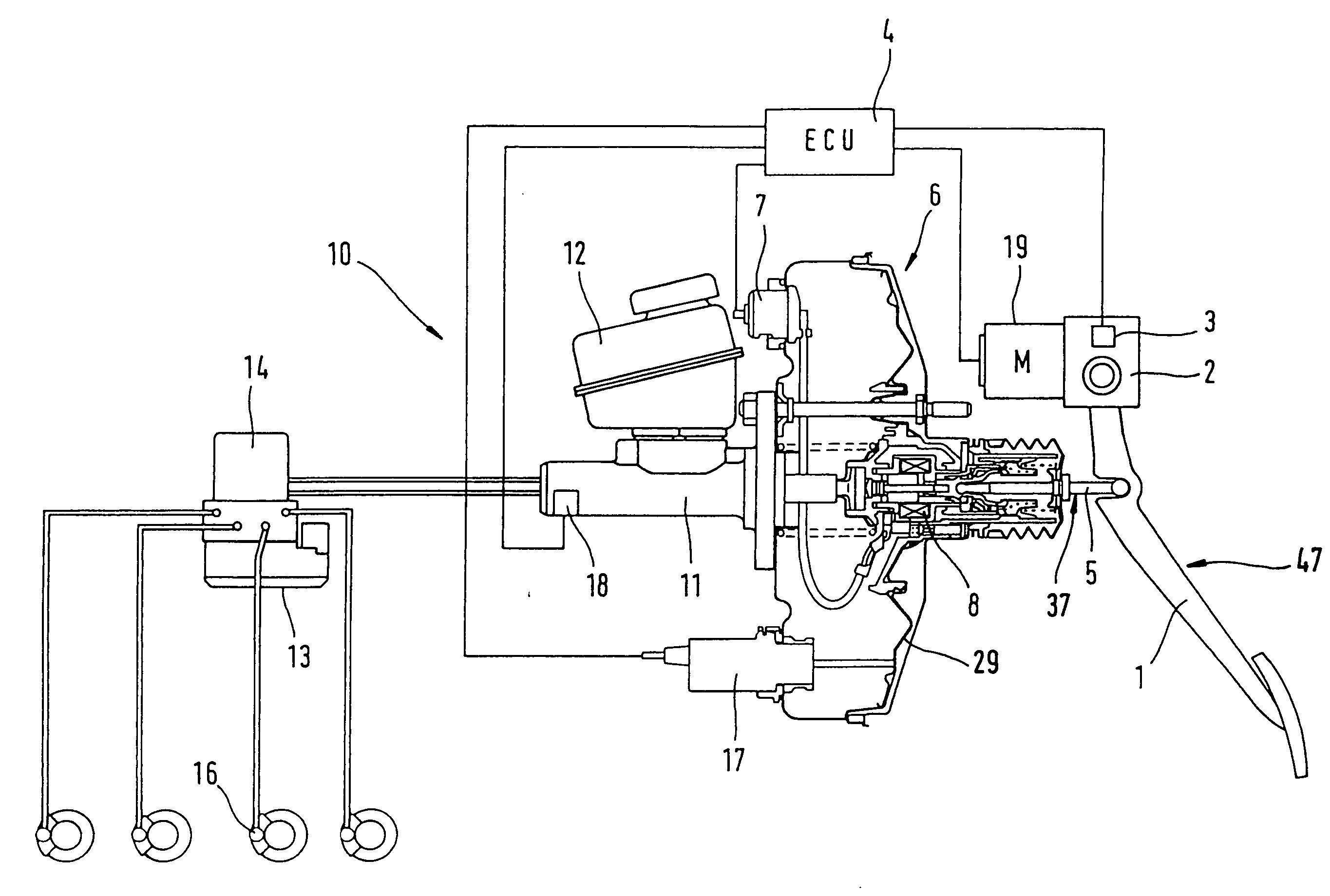
InactiveUS6634724B2Reduce weightEasy constructionServomotor componentsRotary clutchesLinear motionMaster cylinder
An electrically driven brake booster (1) includes an input member (4) disposed in operative association with a brake pedal (12), an output member (5) disposed in operative association with the master cylinder (6), and drive transmitting device (10) for translating a rotating motion of a motor (9) into a linear motion to be transmitted to the output member (5). The drive transmitting device (10) comprises a rack (23) formed on the output member (5), and pinions (21, 22) disposed in operative association with the motor (9) and in meshing engagement with the rack (23). Also, reaction transmitting device (8) which transmits a brake reaction to the input member (4) and the output member (5) at a given proportion is provided. In comparison to conventional drive transmitting device, the drive transmitting device (10) of the present invention has a simple construction, a reduced weight and a better transmission efficiency. The provision of reaction transmitting device allows a correct brake control to be achieved on the basis of a brake reaction.
Owner:DIESEL KIKI CO LTD
Actuator apparatus and method for improved deflection characteristics
InactiveUS20040160118A1Minimal actuation forceElectrostatic/electro-adhesion relaysApplication and release valvesActuatorControl theory
A micromachined actuator including a body or platform mounted to a suspension system anchored to a substrate. In one embodiment, the suspension system is comprised of a set of one or more spring flexures connecting the actuator body to the substrate with strain relief provided via connecting torsional elements. In another embodiment, the suspension system includes a first set of one or more spring flexures each with one end anchored to a largely rigid intermediate frame and the other end attached to the body. A second set of one or more flexures is attached between the intermediate frame and the substrate. A third actuator embodiment maximizes force electrode area to minimize voltage required for electrostatic actuation. A fourth embodiment provides electrical interconnect to an actuator or an actuator array using polysilicon with silicon nitride isolation. Actuators may be fabricated by combining the key features of all four embodiments or actuators may be fabricated using any combination of two or three of the embodiments.
Owner:KNOLLENBERG CLIFFORD F +1
Wheel braking system
A wheel braking system comprises a motor driven gear pump, a relief line connecting the pump discharge to the pump intake, a wheel brake unit connected to the pump discharge, and a flow restriction in the relief line. A control unit controls the motor for the pump in response to an output signal of a brake pedal sensor. The brake pedal sensor generates the output signal indicative of the brake pedal stamping force. The control unit determines a desired motor speed for the sensed brake pedal stamping force and operates the motor.
Owner:UNISIA JECS CORP
Brake system and method
ActiveUS20090195058A1Solve insufficient braking forceBraking action transmissionAutomatic initiationsActuatorParking brake
An electromechanical parking brake system for a heavy vehicle braked by air-actuated service brakes includes an EPB-ECU and a first electromechanical parking brake actuator controlled by the EPB-ECU. The electromechanical parking brake system further includes a redundant sub-system for applying a second parking brake in an event of a failure in the EPB-ECU or the first electromechanical parking brake actuator.
Owner:MERITOR HEAVY VEHICLE BRAKING SYST (UK) LTD
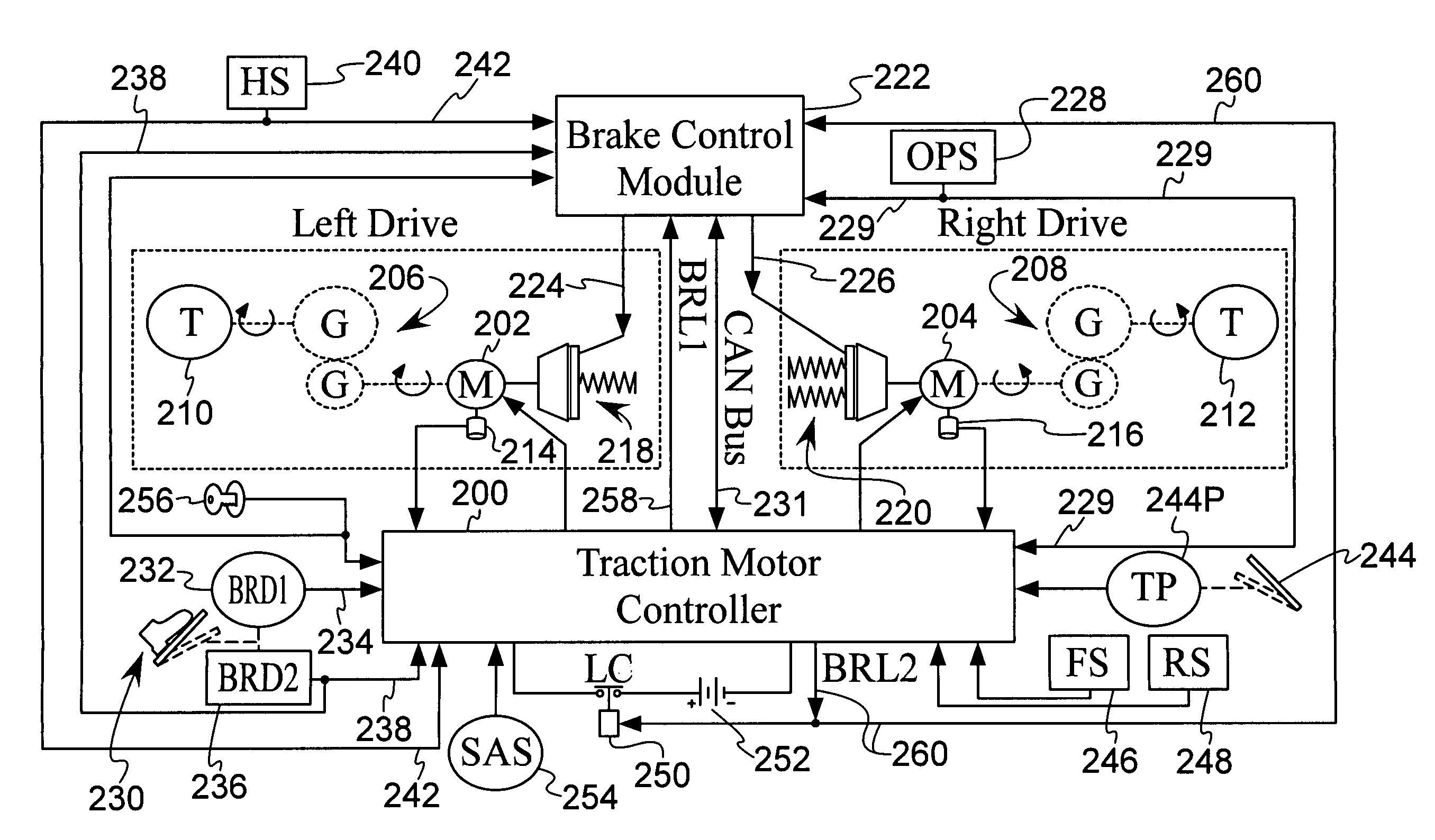
Braking system for a lift truck
Owner:CROWN EQUIP CORP
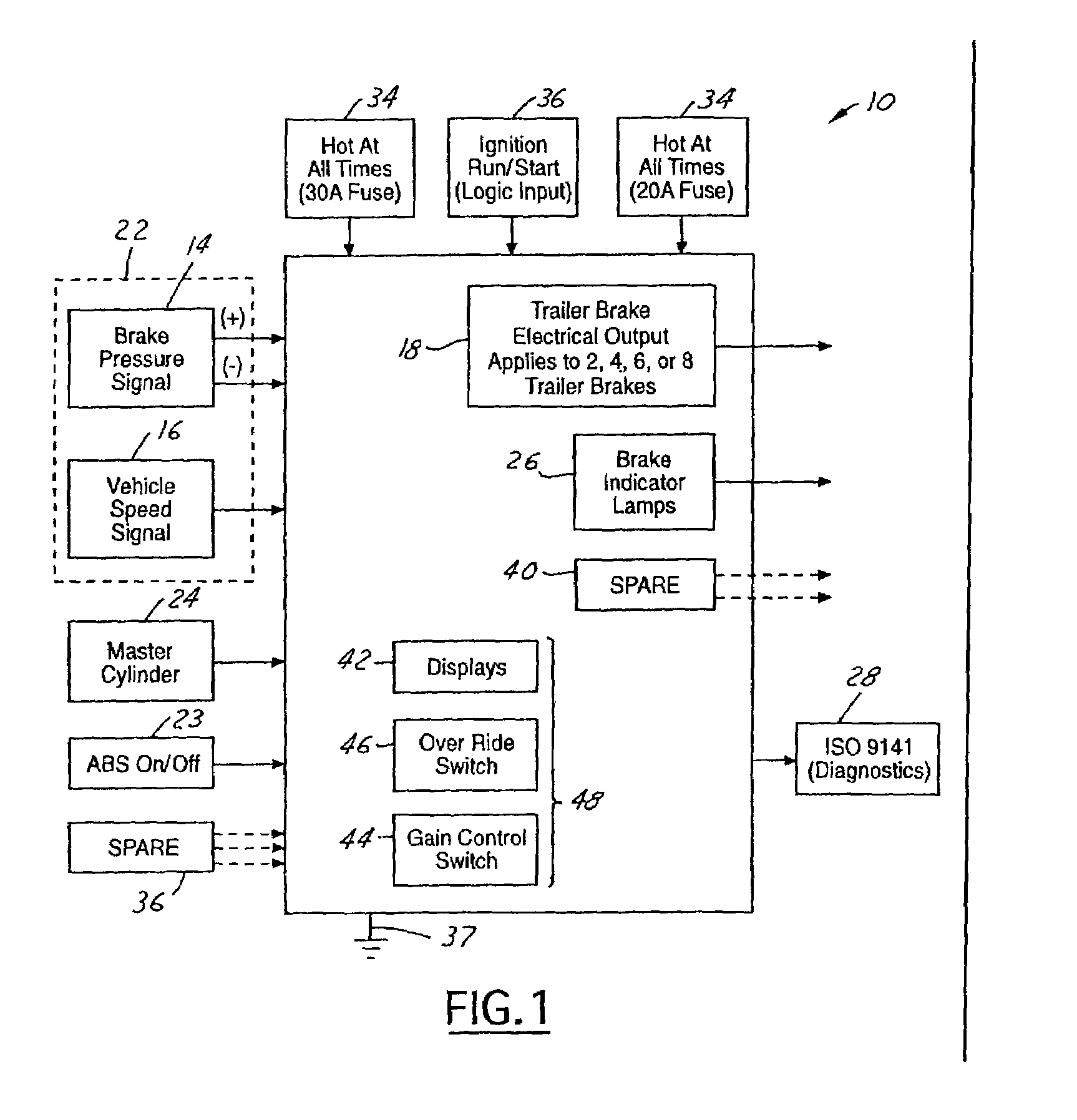
Integrated passenger vehicle trailer brake controller
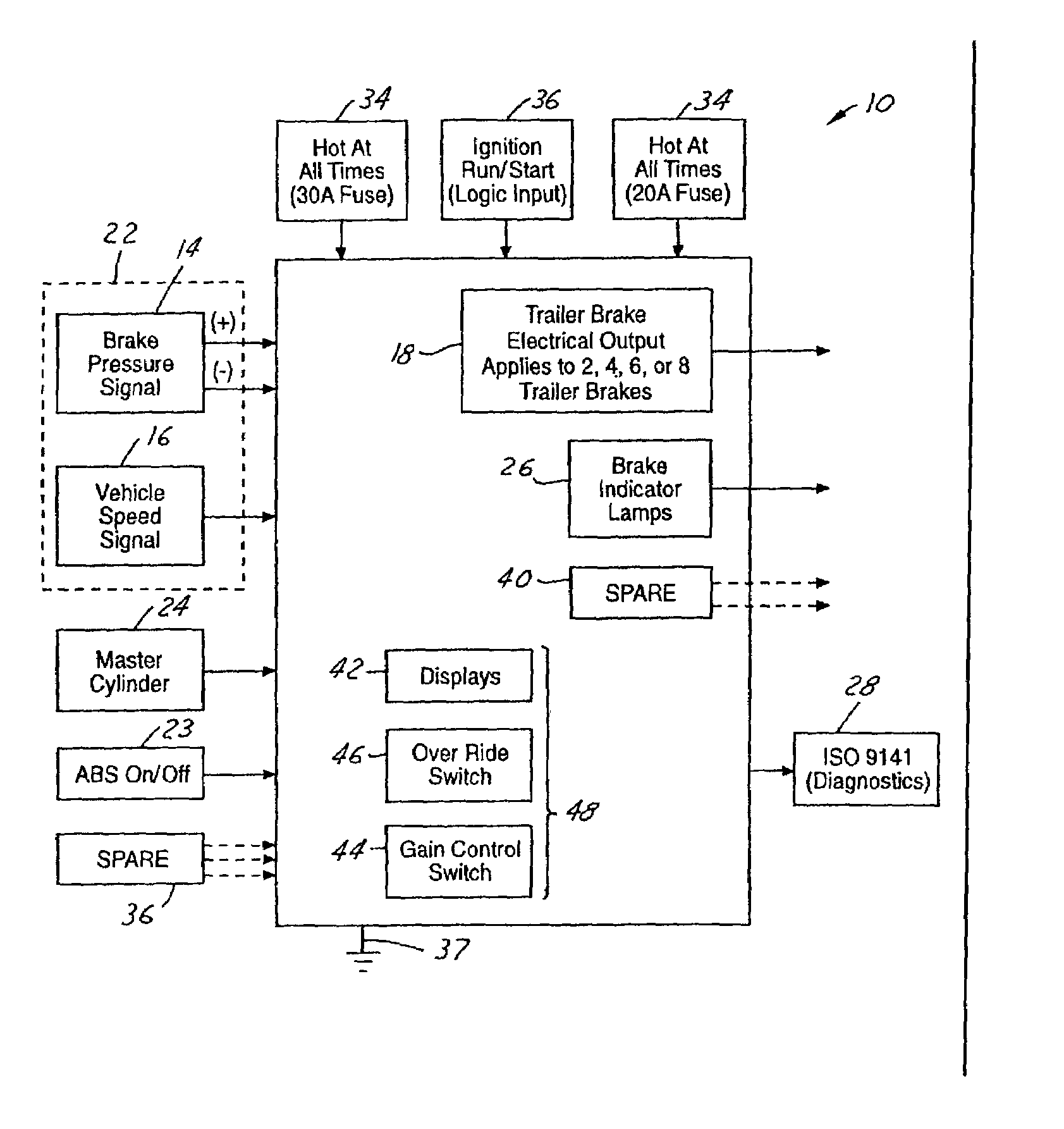
InactiveUS6966613B2Improve cooperationBraking action transmissionAutomatic initiationsTrailer brake controllerVehicle brake
A trailer brake controller 10 for use in a passenger vehicle 12 is provided, including a control element 11 positioned within the passenger vehicle 12, a vehicle speed input 16 and a vehicle brake pressure input 14 providing speed and brake pressure data to the control element 11, and a trailer brake output 18 sending a signal to the trailer in response to the vehicle speed input 16 and the vehicle brake pressure input 14.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
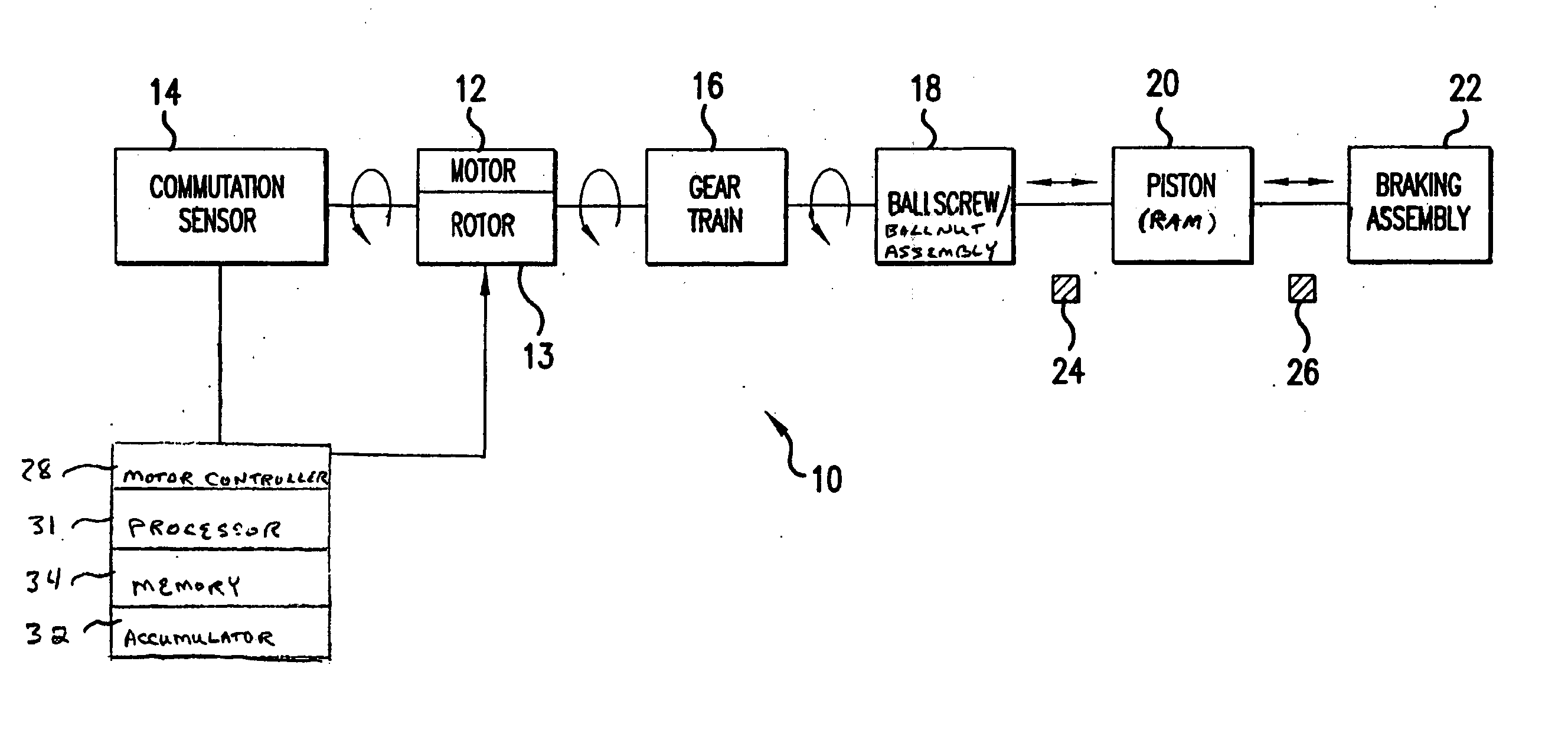
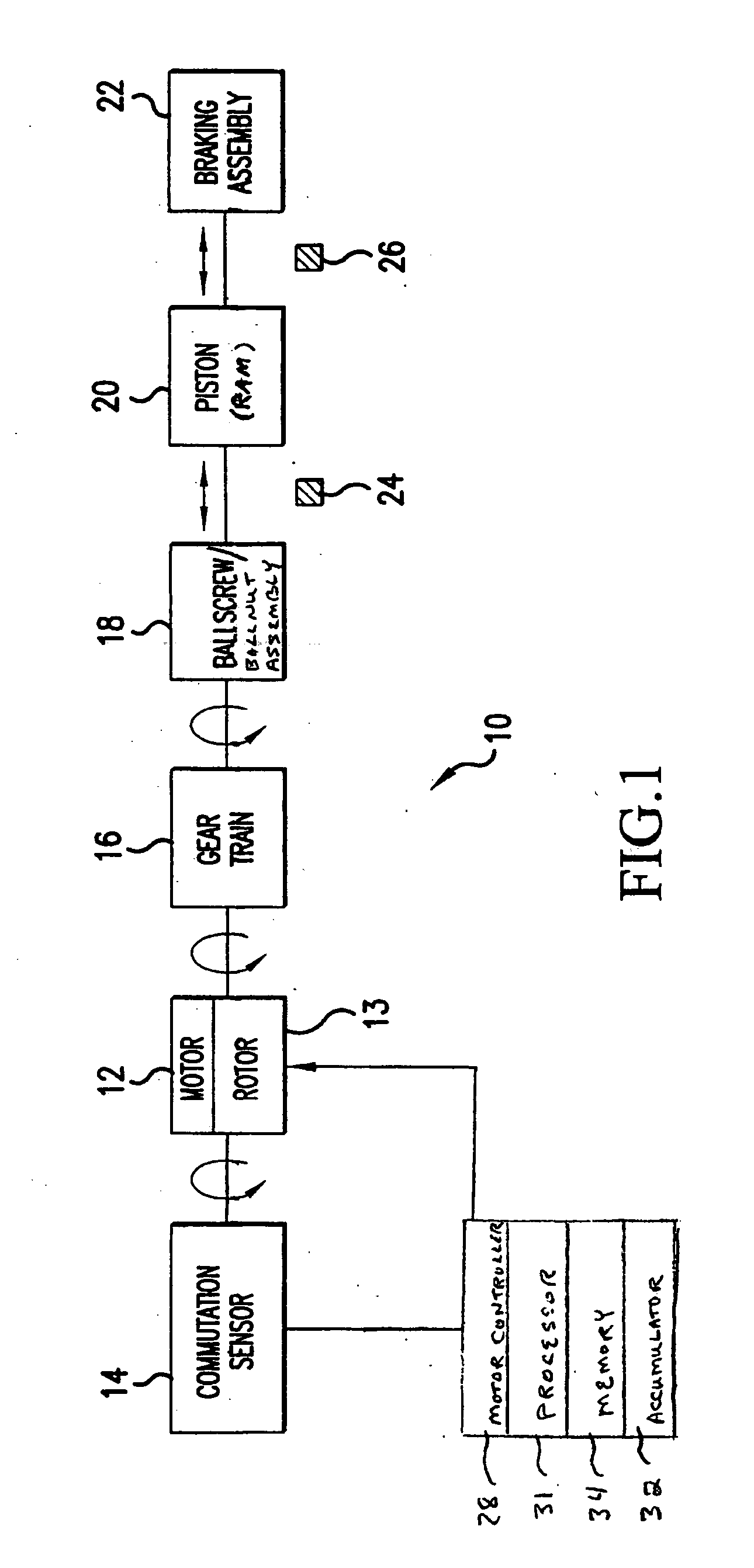
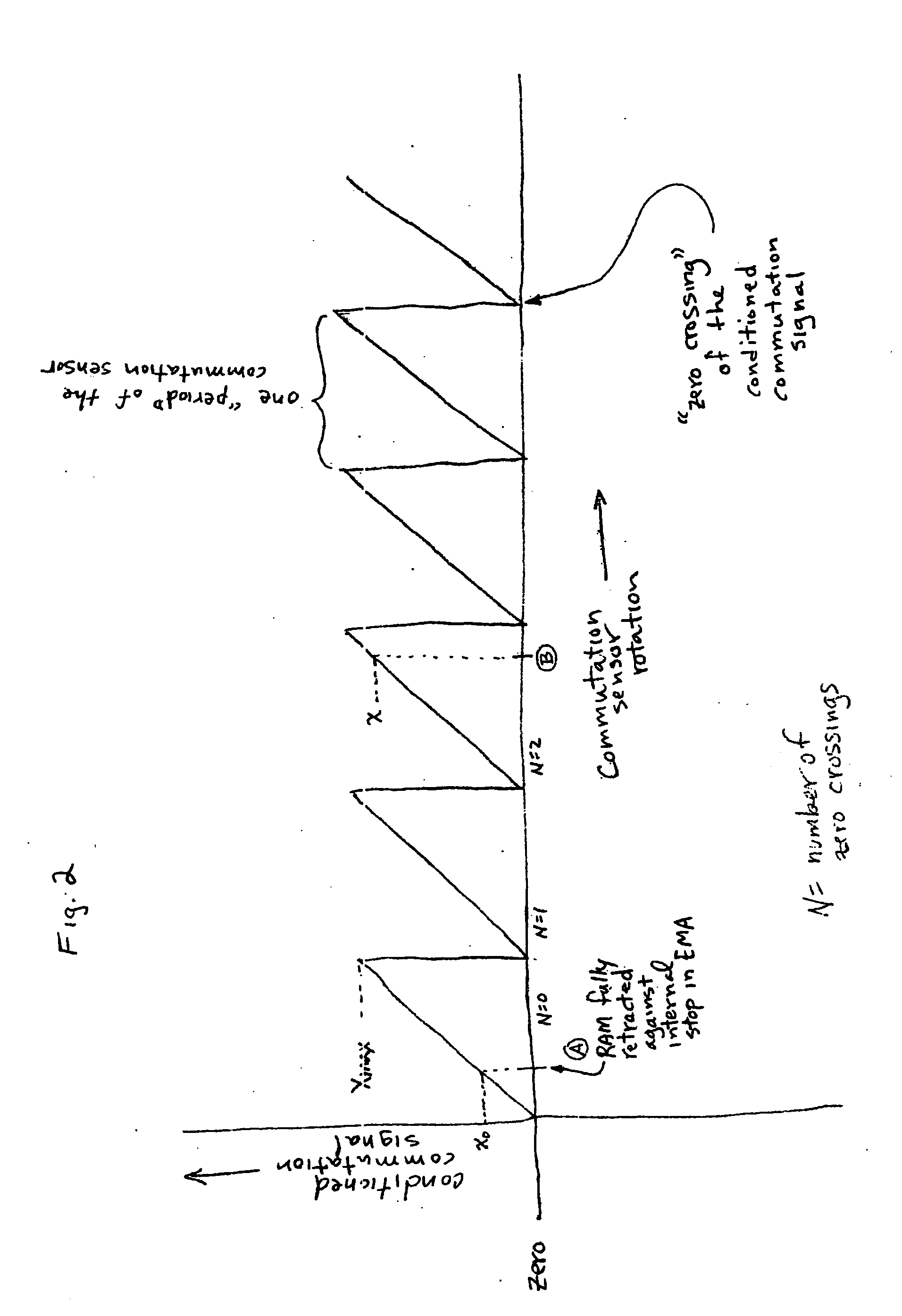
Electro-mechanical actuator braking apparatus and method using motor commutation sensor output to derive piston displacement
A braking system is disclosed that includes a brake (22), a ram (20) shiftable in a linear direction relative to the brake (22) for actuating the brake (22), and a stop (24) for limiting movement of the ram (20). The system further includes a motor (12) for moving the ram (20) which motor (12) includes a stator and a rotor (13) and a commutation sensor (14) producing an output. A motor controller (28) receives a commutation signal based on the output and controls the motor (12) based on the commutation signal. A processor (31) also uses the commutation signal to generate a position signal indicative of the position of the ram (20) relative to the stop (24). Methods of using this system are also disclosed.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
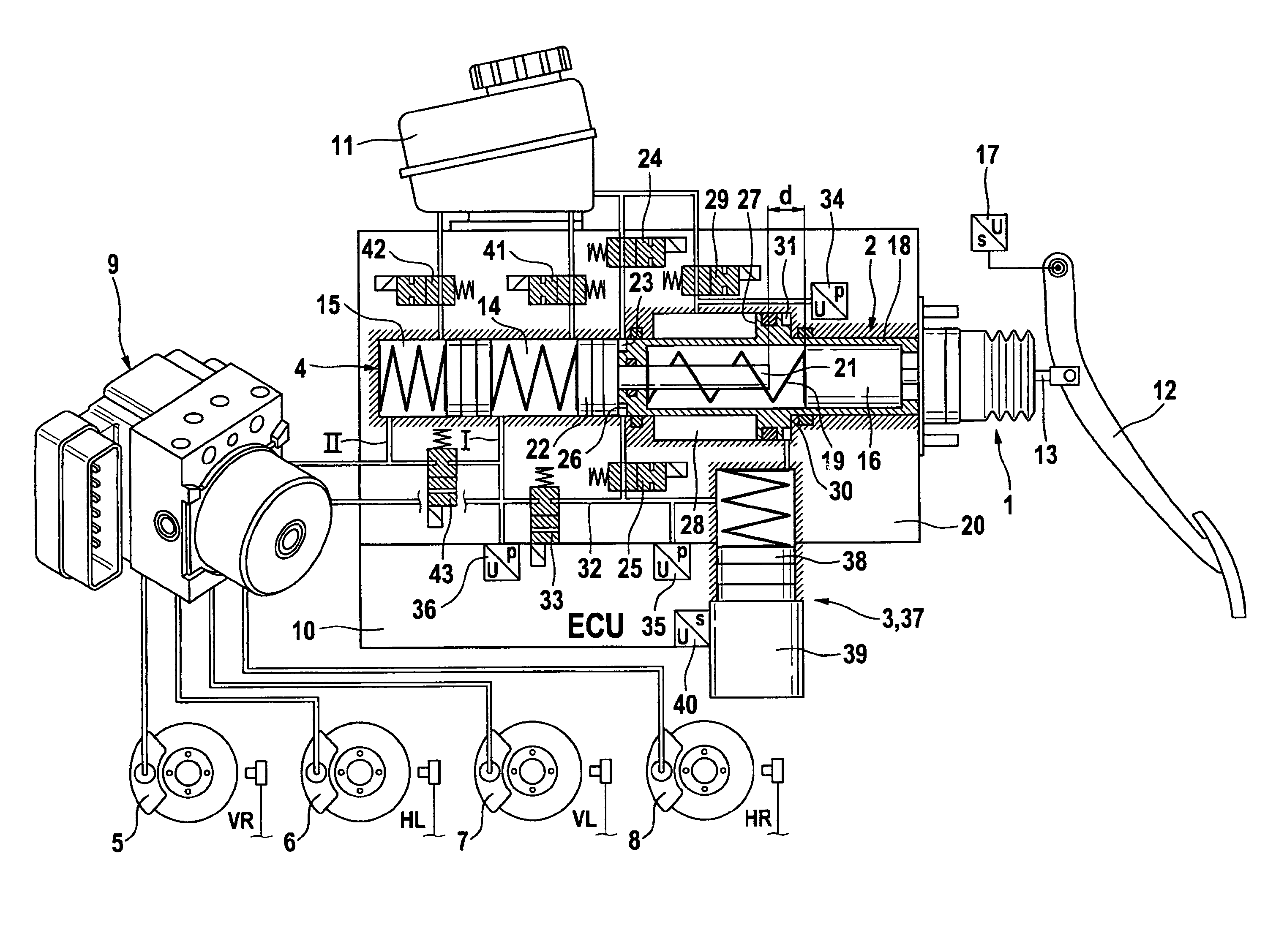
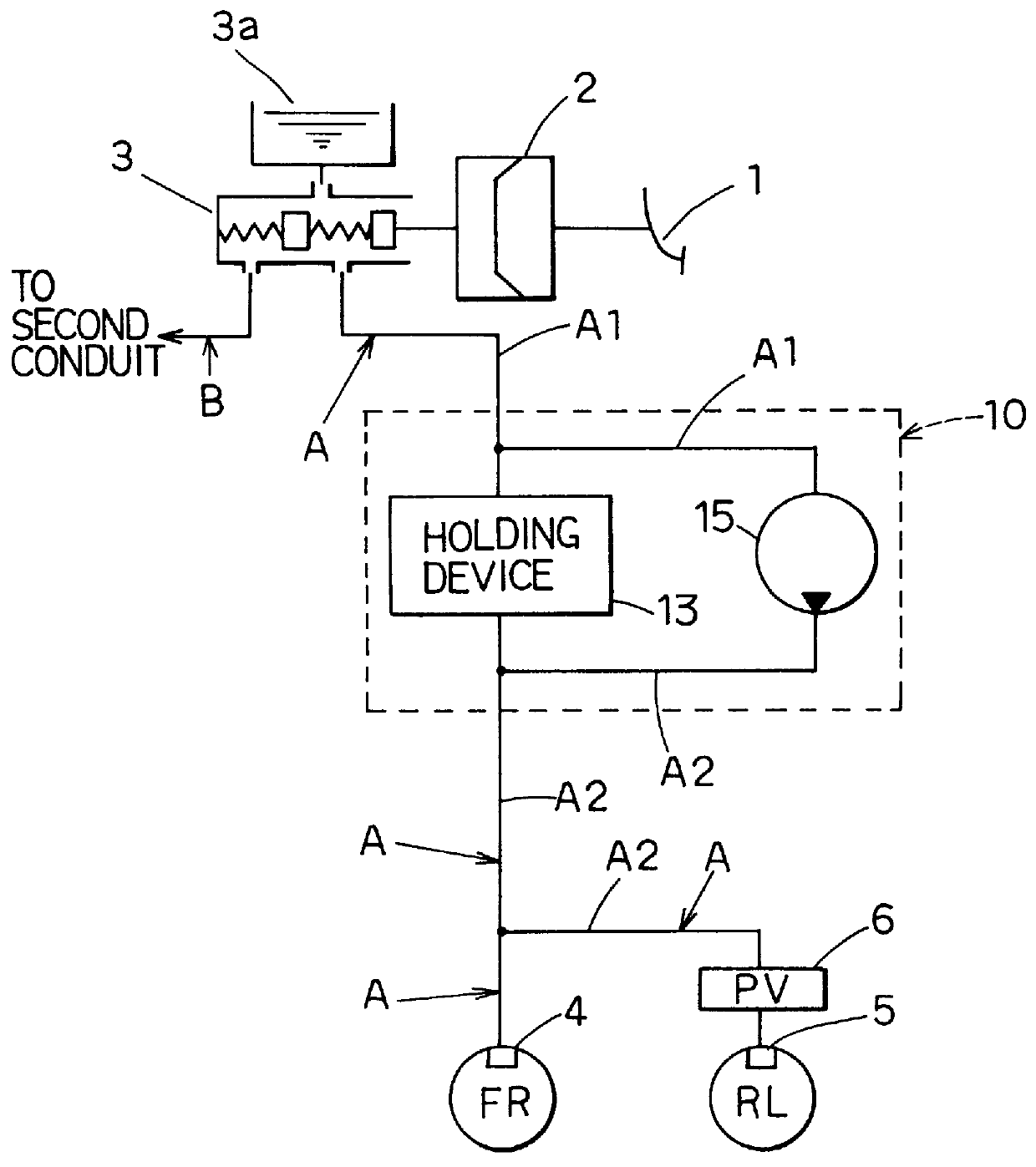
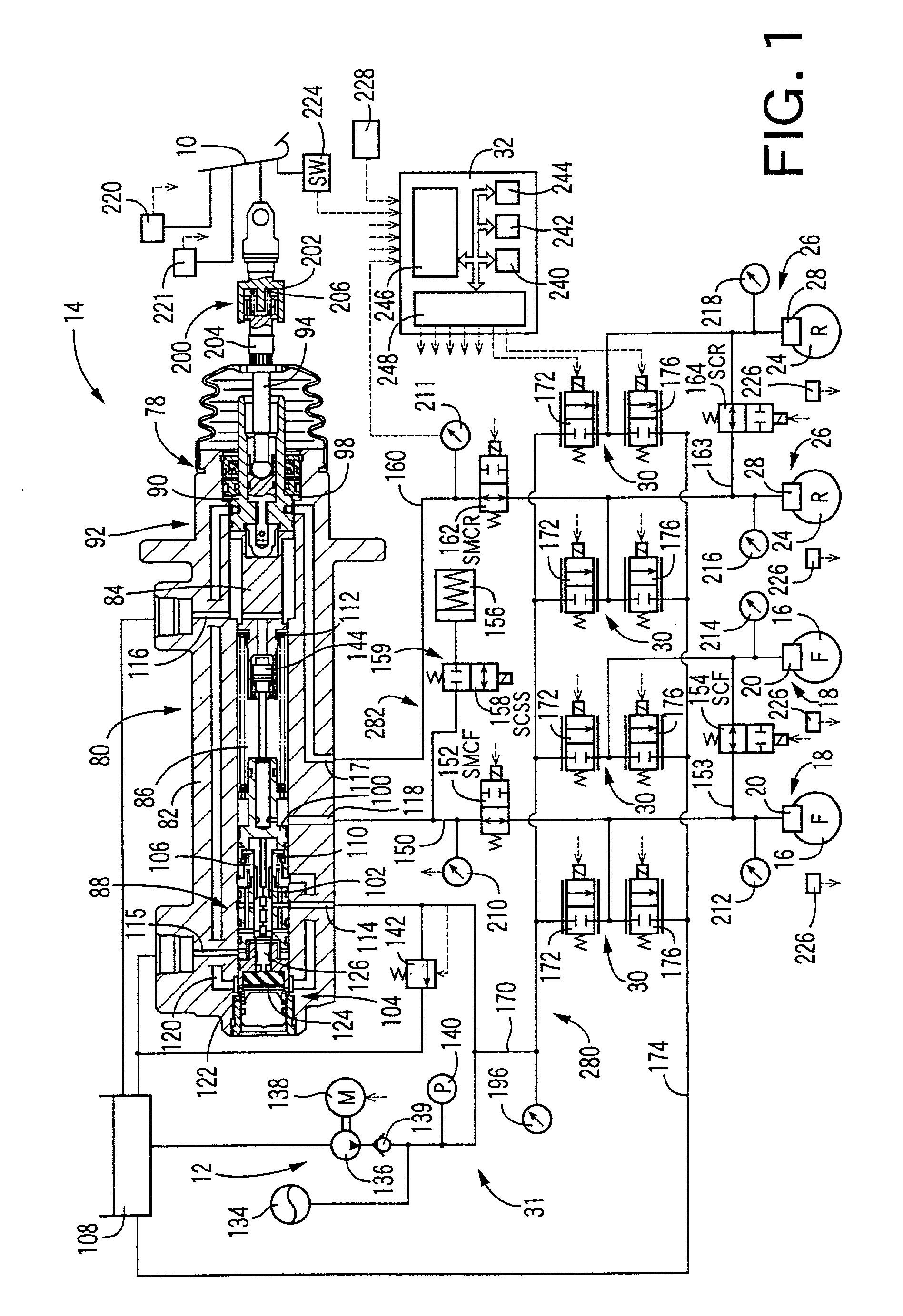
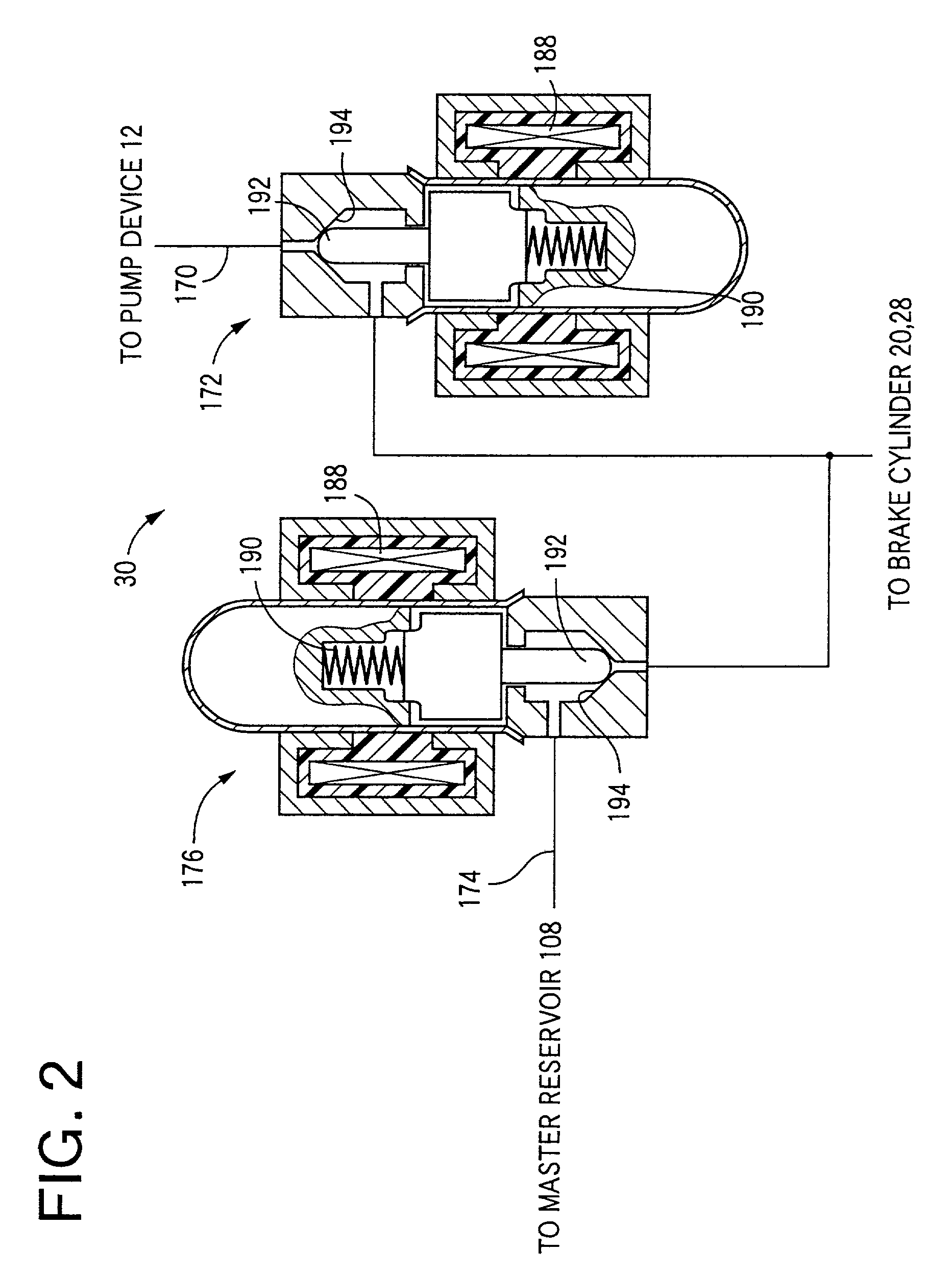
Braking pressure control apparatus capable of switching between two brake operating states using power-operated and manually operated pressure sources, respectively
InactiveUS20010006306A1Efficient workBraking action transmissionBrake control systemsPressure controlled ventilationBraking system
A braking pressure control apparatus including a first pressure source including a power-operated pressurizing device, a second pressure source operable by a manually operable brake operating member to pressurize a fluid to a pressure higher than a level corresponding to the operating force of the brake operating member, a switching device for selectively placing the braking system in a first state in which a brake cylinder is operated with the fluid pressurized by the first pressure source and a second state in which the brake cylinder is operated with the fluid pressurized by the second pressure source, and a change restricting device operable upon a switching between the first and second states, to restrict a change of the operating state of the brake operating member and a change of the brake cylinder pressure, which change take place due to the switching, or a switching control device for controlling the switching device on the basis of the running condition of a vehicle whose wheel is braked by the braking pressure.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Brake control apparatus and control method for the brake control apparatus
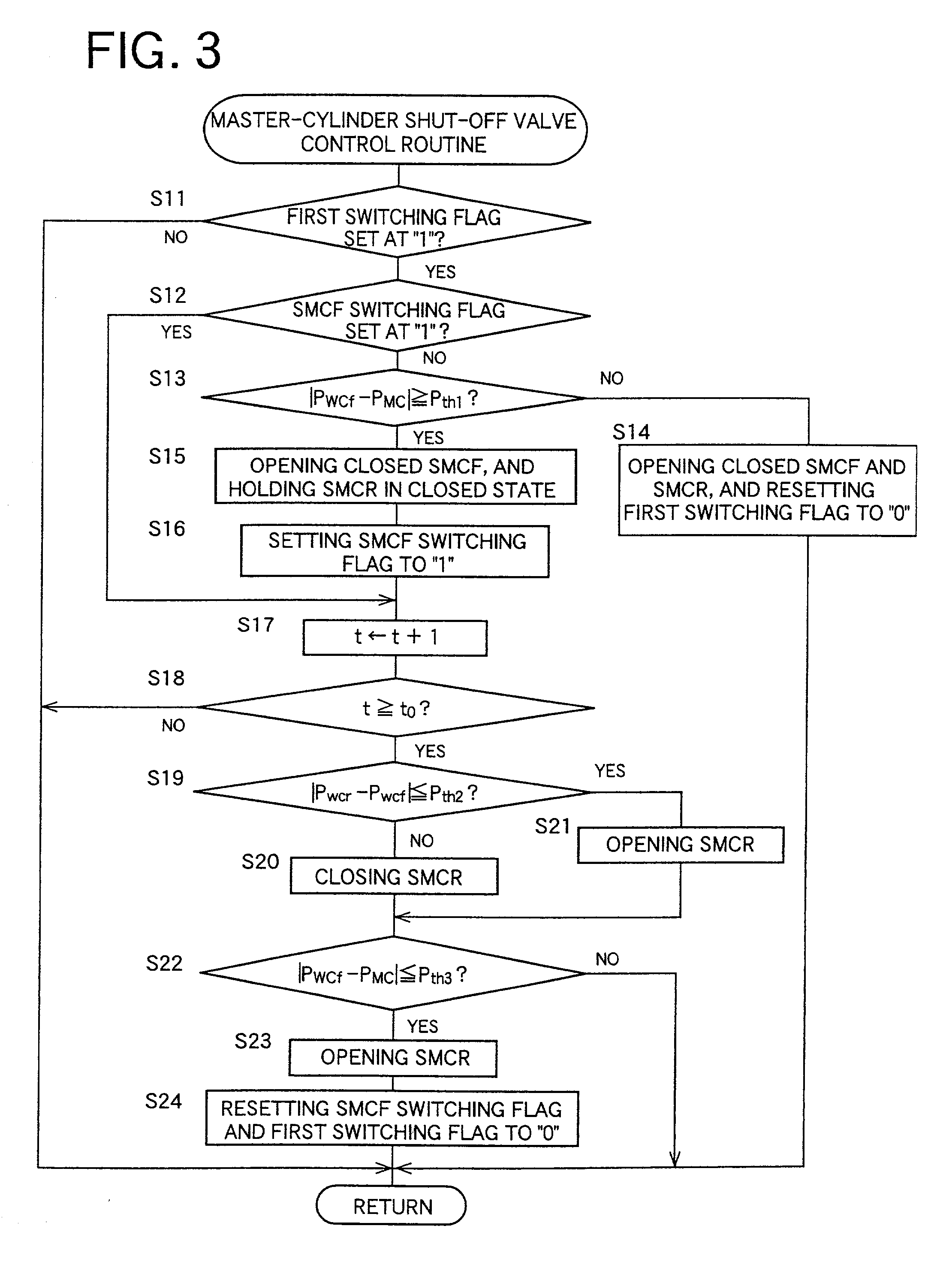
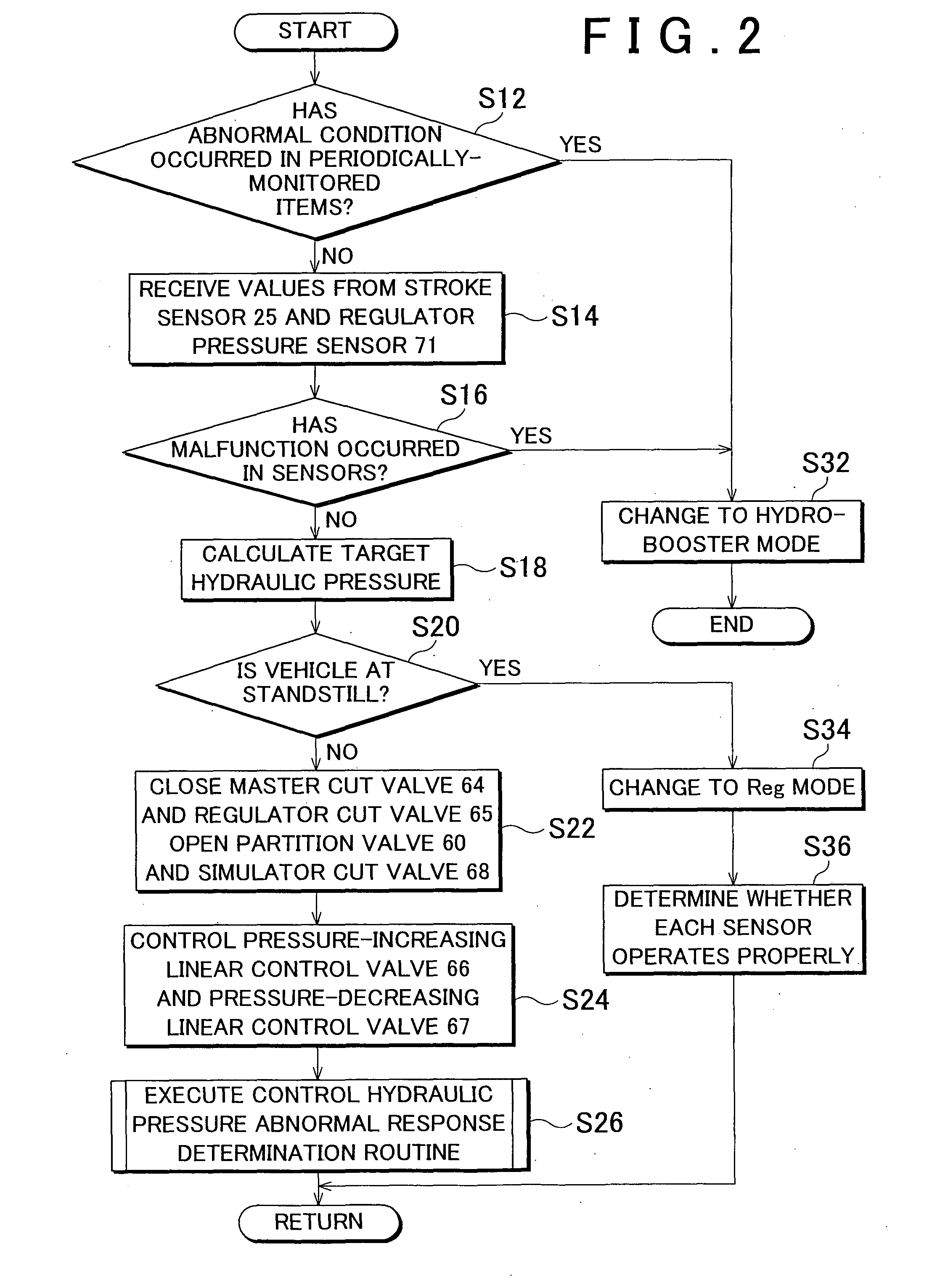
ActiveUS20100211282A1Suppress occurrence of a malfunction in the pressure sensorAnalogue computers for trafficBraking action transmissionPressure decreaseHydraulic circuit
In a brake control apparatus that controls braking forces which are applied to wheels based on the pressure of the hydraulic fluid, when the pressure detected by a control pressure sensor (73) is equal to or higher than a predetermined value while a partition valve (60) is closed, a master cut valve (64) is closed to suppress an increase in the pressure in a first passage (45) in a first hydraulic circuit (37), to which the control pressure sensor (73) is connected. Alternatively, the control pressure sensor (73) is protected against overpressure by opening the outlet valve (56,57) or the pressure-decreasing valve (67).
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Antilock brake systems employing a sliding mode observer based estimation of differential wheel torque
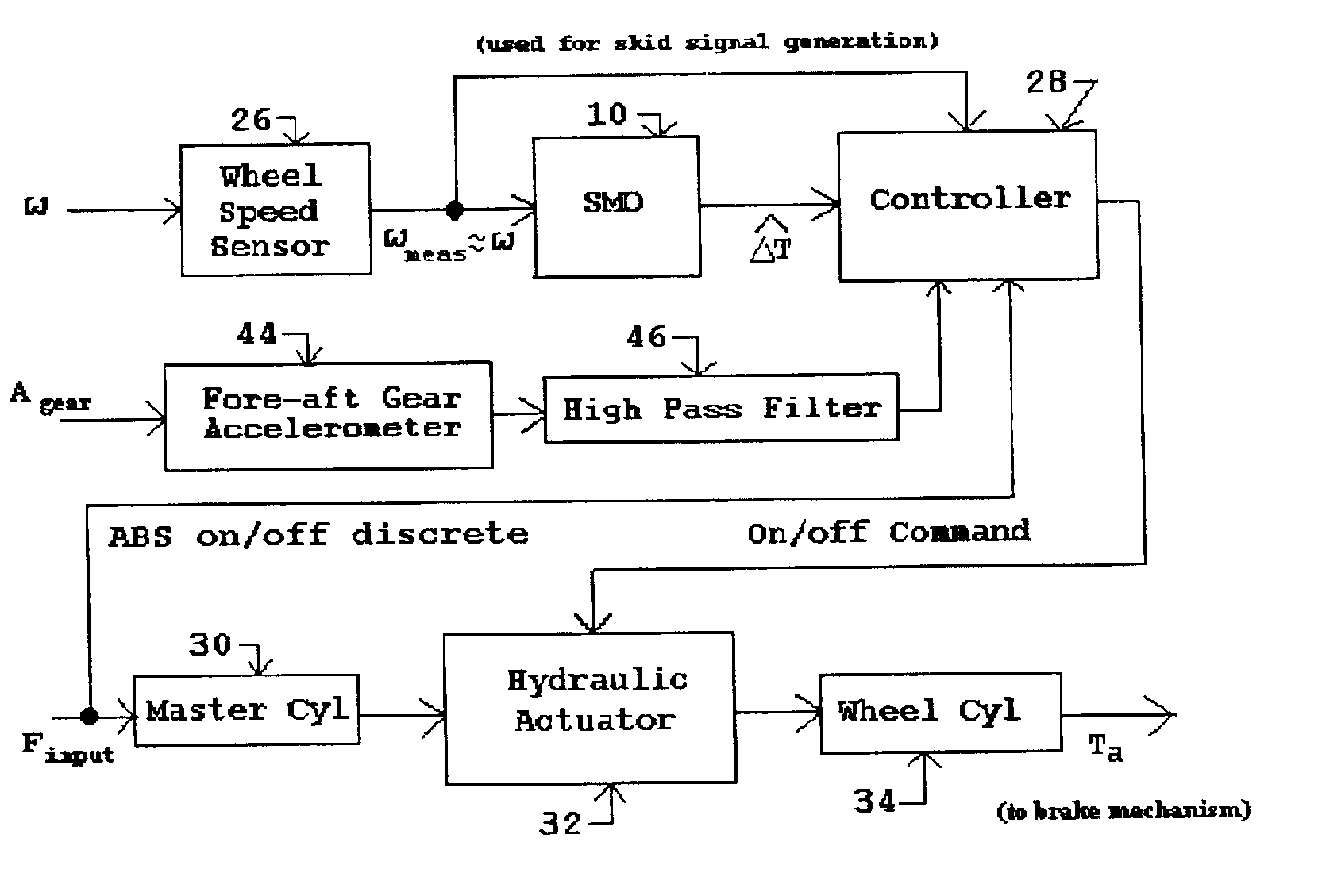
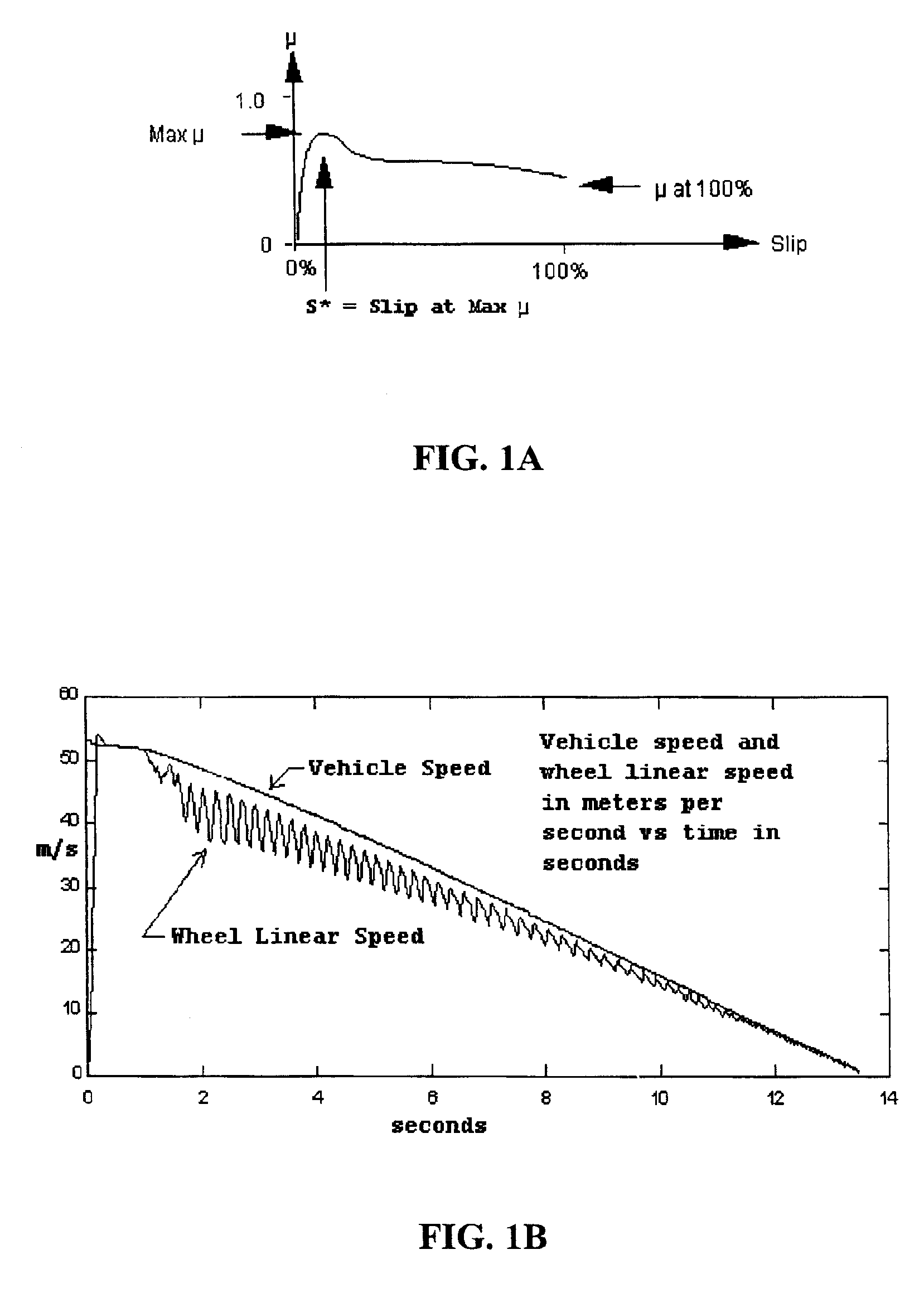
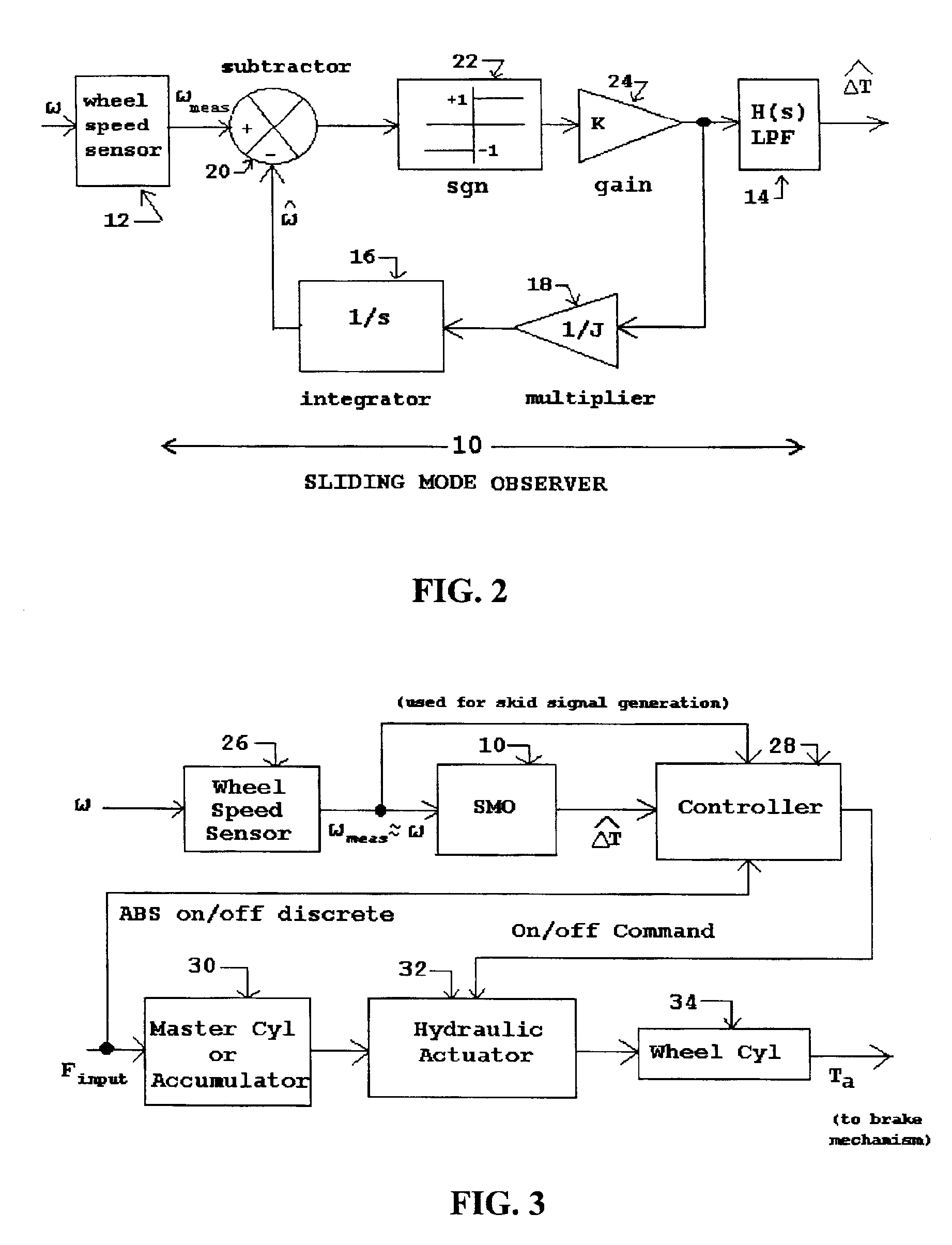
InactiveUS6890041B1Easy to implementOptimize wheel slip during brakingBraking action transmissionBrake regulatorsAccelerometerControl signal
Improved methods and systems for controlling hydraulically or electrically actuated anti-lock brake systems (ABS) on air and land vehicles requiring only measurement of wheel angular speed although brake torque measurements can also be employed if available. A sliding mode observer (SMO) based estimate of net or different wheel torque (road / tire torque minus applied brake torque) derived from the measured wheel speed is compared to a threshold differential wheel torque derived as a function of a “skid signal” also based on wheel speed only to generate a braking control signal. The braking control signal can be employed to rapidly and fully applying and releasing the brakes in a binary on-off manner and, as an additional option, possibly modulating the maximum available brake hydraulic pressure or electrical current when the brakes are in the “on” state in a continuous manner. In the case of the basic on-off component of braking, the brakes are released when the estimate of differential wheel torque is less than the threshold differential wheel torque (i.e. for relatively high values of brake torque), and the brakes are applied fully when the estimate of differential wheel torque is greater than or equal to the threshold differential wheel torque. For aircraft landing gear applications, a fore-aft accelerometer mounted on the landing gear can be used to suppress nonlinear gear displacement oscillations commonly called gear walk in the direction of wheel roll.
Owner:SMO GRP
Vehicle and control method of vehicle
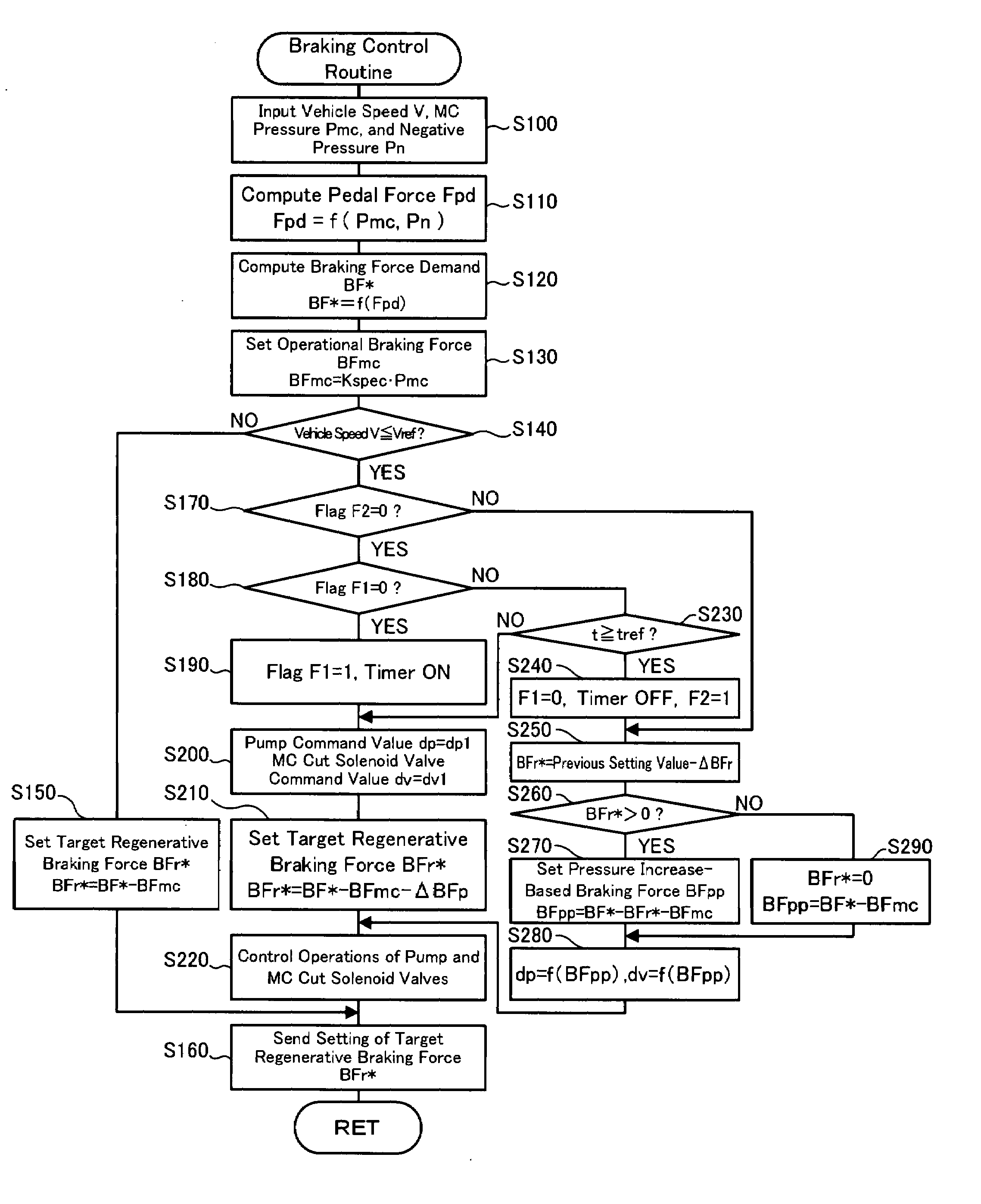
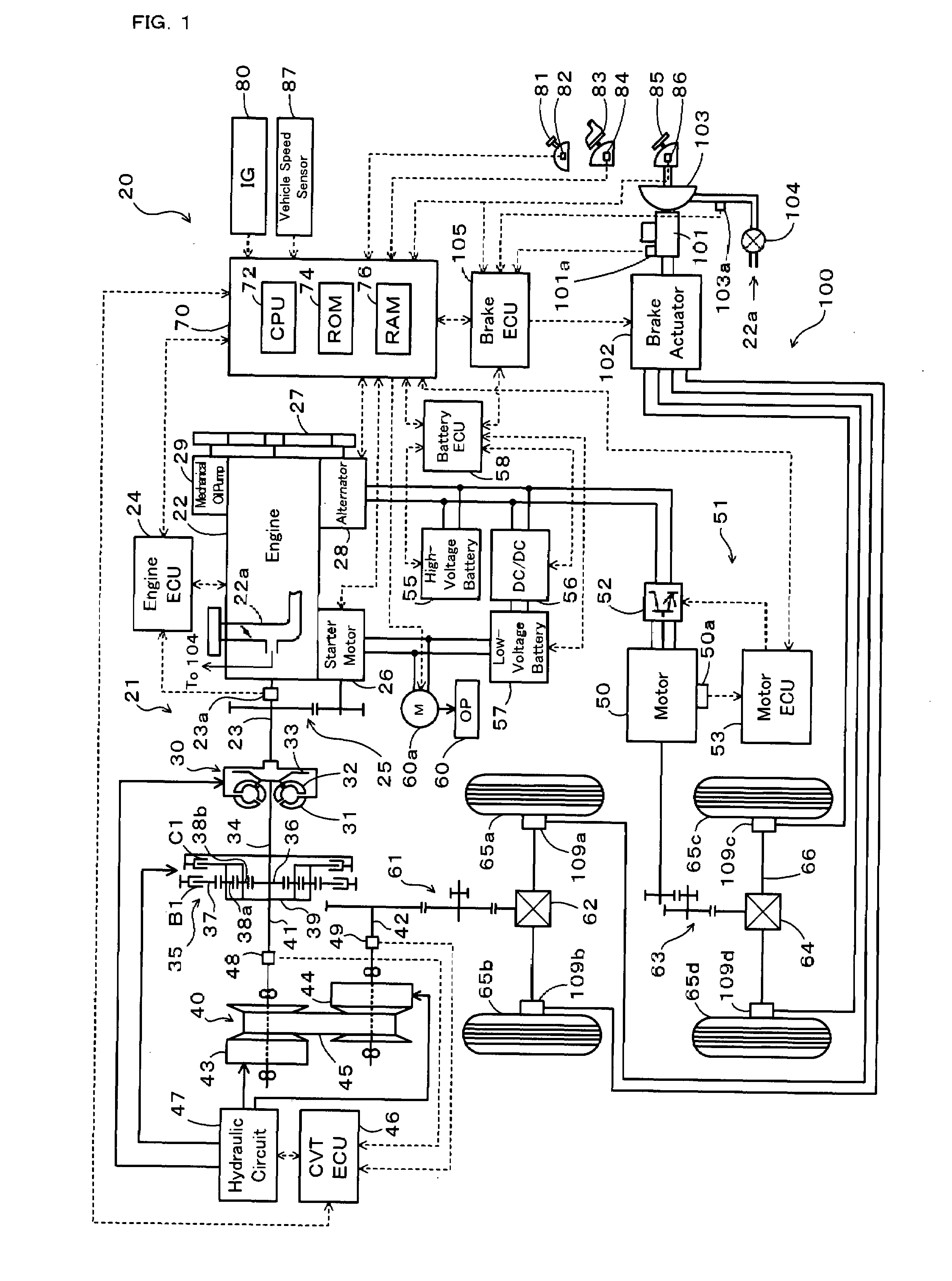
ActiveUS20070241611A1Ensure correct executionGuaranteed outputBraking element arrangementsPlural diverse prime-mover propulsion mountingRegenerative brakeDriver/operator
When vehicle speed V decreases to or below a preset reference vehicle speed Vref during output of regenerative braking force from a motor in response to the driver's depression of a brake pedal, the vehicle of the invention performs a replacement pre-operation (steps S190 to S220 and S160) and a replacement operation (steps S240 to S280 and S160) and controls the motor and an electronically controlled hydraulic braking system to satisfy a braking force demand BF*. The replacement pre-operation actuates and controls pumps included in a brake actuator of the electronically controlled hydraulic braking system to exert their proper pressurization performance. The replacement operation decreases the regenerative braking force output from the motor and enhances a pressure increase by the pumps to replace the regenerative braking force with a pressure increase-based braking force BFpp.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Slip Control Boost Braking System
A braking system is provided for applying pressurized hydraulic brake fluid to a plurality of vehicle brakes. The system includes a source of pressurized brake fluid, a first brake fluid circuit, and a boost valve for controlling a flow of brake fluid from the source to the first circuit. A first brake actuator is actuated by brake fluid from the first circuit and a second brake actuator operated by an application of brake fluid from the first circuit. The system further includes a second brake fluid circuit and a third brake fluid circuit. A third brake actuator is actuated by brake fluid from the second circuit. A fourth brake actuator actuated by brake fluid from the third circuit. A master cylinder includes a primary piston, a first secondary piston, and second secondary piston. The first and second secondary pistons are capable of being each independently operably displaced by an application of pressurized fluid from the first circuit to pressurize brake fluid in, respectively, the second circuit to operate the third brake actuator and the third circuit to operate the fourth brake circuit.
Owner:KELSEY HAYES CO
Brake system
InactiveUS20080079309A1Prevents hydraulic pressure changePrevent leakageApplication and release valvesEngineeringWheel cylinder
When an electrical fluid pressure generator fails and a wheel cylinder is operated by brake fluid pressure generated by a master cylinder, if a first fluid pressure system leading to a rear fluid chamber of the electrical fluid pressure generator fails and is opened to the atmosphere, braking is performed by brake fluid pressure of a second fluid pressure system transmitted from the master cylinder through a front fluid chamber of the electrical fluid pressure generator to a wheel cylinder. At this time, a front supply port, which communicates through a front second cup seal facing rearward with the rear fluid chamber opened to the atmosphere due to the failure, does not communicate with the master cylinder but with a reservoir. Therefore, it is possible to prevent leakage of the brake fluid pressure generated by the master cylinder through the front supply port, the front second cup seal and the rear fluid chamber, thereby ensuring braking by the second fluid pressure system leading to the front fluid chamber of the electrical fluid pressure generator.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Trailer control valve for a compressed air brake system for motor vehicles
InactiveUS6206481B1Low structural costSimple designBraking action transmissionApplication and release valvesMobile vehicleElectrical control
A trailer control valve having control pistons for actuating a double seat valve, which can control the communication between a compressed air reservoir, a compressed air consumer, and a pressure relief location. In order to structurally simplify the trailer control valve, a control piston is provided that is jointly associated with an electrical control circuit and a pneumatic control circuit of a service brake system. Furthermore, a valve is provided that is connected to the pneumatic control circuit of the service brake system, which closes the pneumatic control circuit of the service brake off from to the trailer control valve when the electrical control circuit is functional, and in the event of a failure of the electrical control circuit, unblocks the pneumatic control circuit of the service brake system.
Owner:KNORR-BREMSE SYST FUER NUTZFAHRZEUGE GMBH
Popular searches
Anti-collision systems Speed/accelaration control Wheel adhesion Complex mathematical operations Radio wave reradiation/reflection Non vehicle mounted steering controls External condition input parameters Vehicle position/course/altitude control Driver input parameters Analogue processes for specific applications
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com