Patents
Literature
19735 results about "Friction force" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The friction force is the force exerted by a surface as an object moves across it or makes an effort to move across it. There are at least two types of friction force - sliding and static friction. Though it is not always the case, the friction force often opposes the motion of an object.
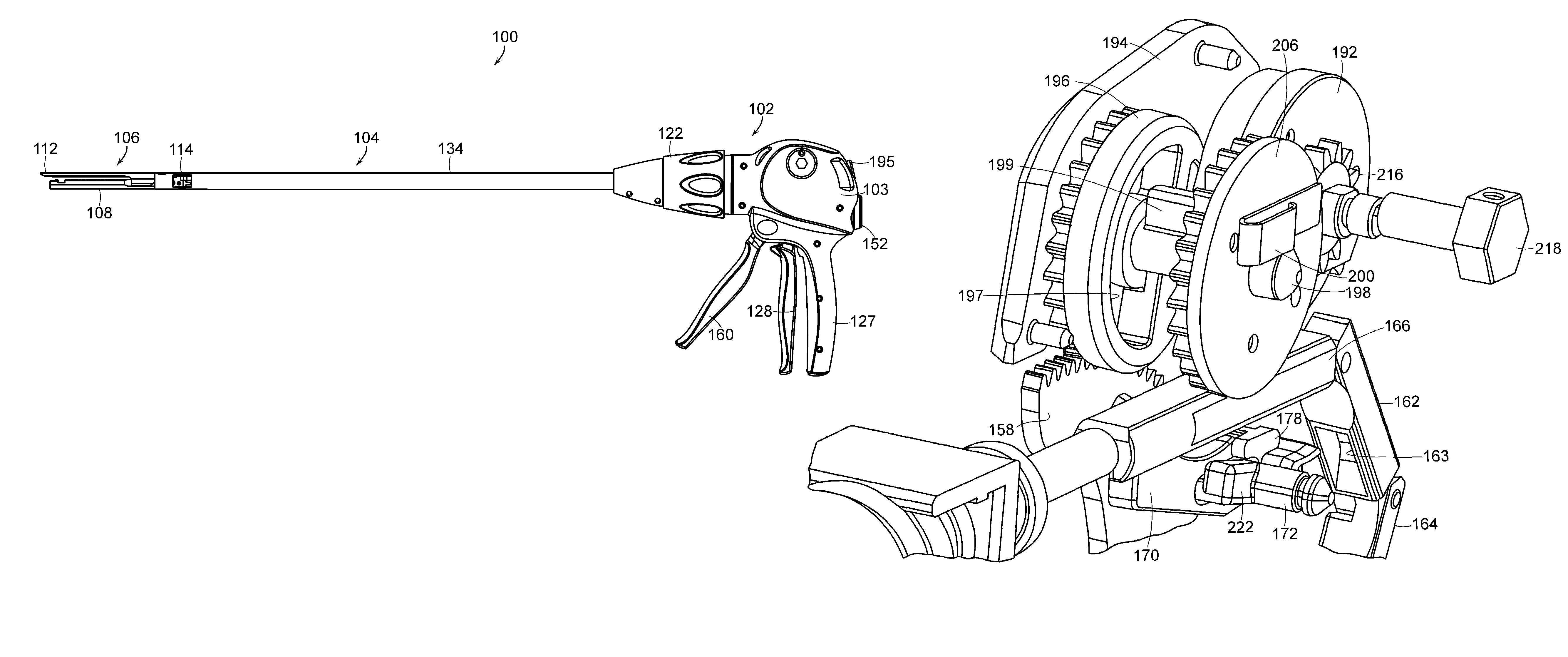
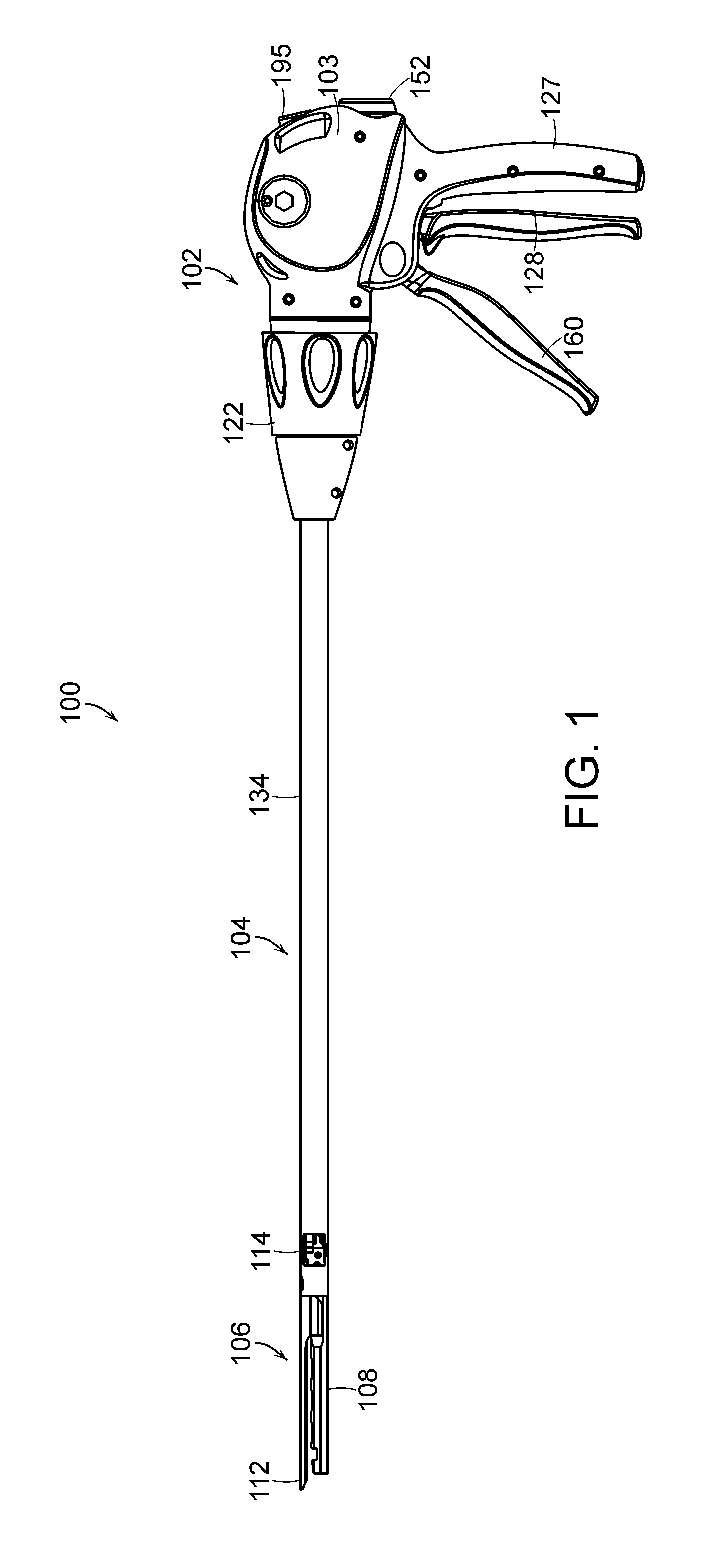
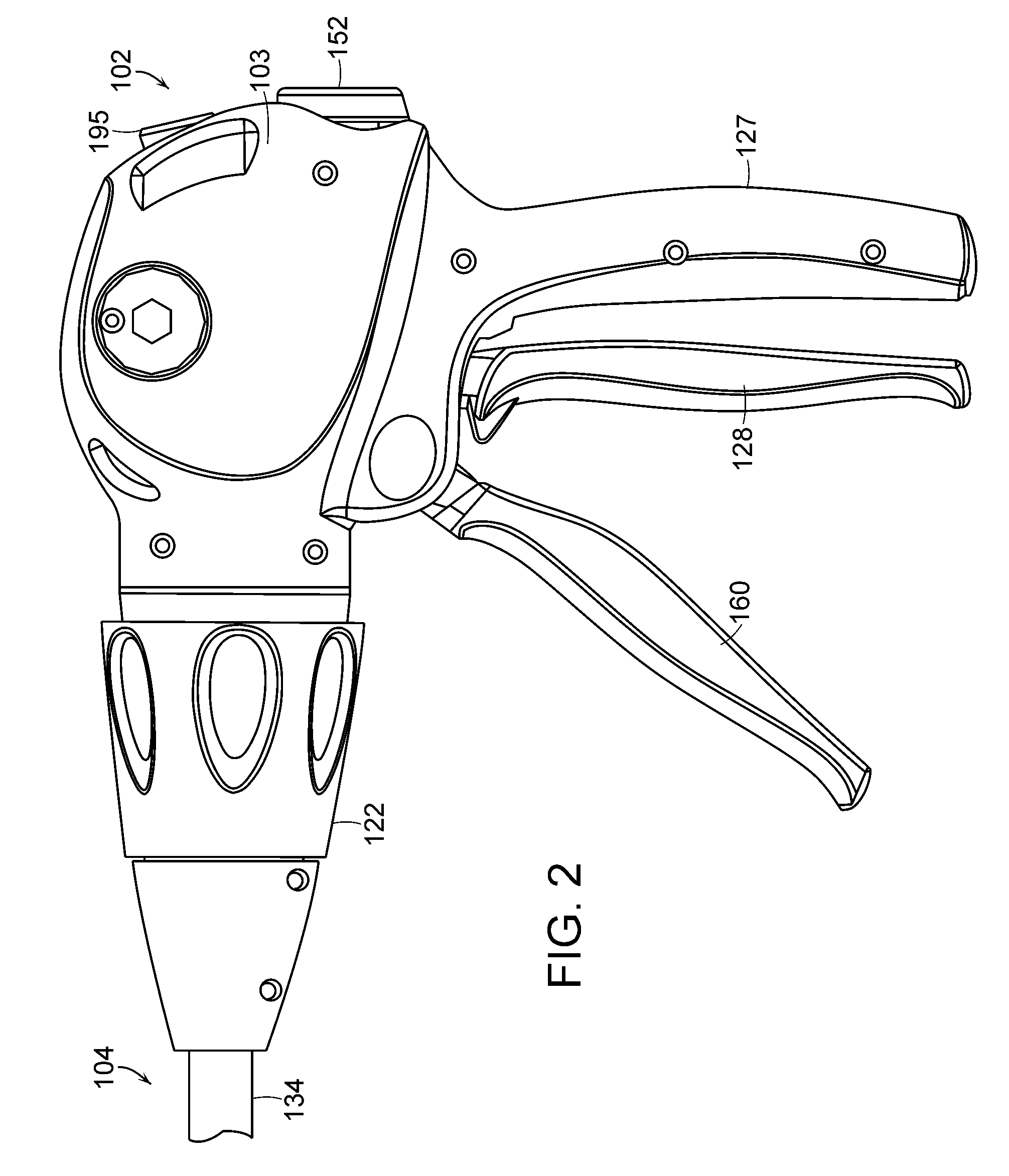
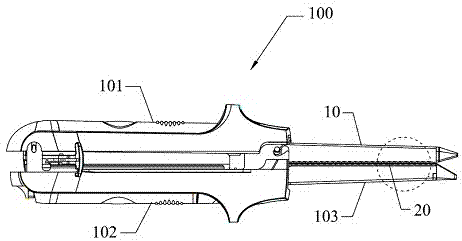
Surgical stapling instrument with an anti-back up mechanism
A surgical instrument including a firing drive configured to advance a cutting member and / or staple driver within an end effector, and a brake configured to prevent, or at least partially inhibit, the relative movement of the cutting member and / or staple driver. The surgical instrument can further include a firing member operably engaged with the cutting member, for example, a band connected to the firing member, and a reel, where the band can be configured to be wound around the reel. In various embodiments, the brake can be selectively engageable with the reel and / or band to prevent, or limit, the movement of the band. The brake can include a brake surface where relative movement between the band and the brake surface can generate a friction force therebetween which can hold the firing member in position until a sufficient force is applied to the firing member to overcome the friction force.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Linear suturing and cutting device
Owner:TOUCHSTONE INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL SCIENCE CO LTD
Linear Suture Cutting Device
The invention discloses a linear suturing and cutting device. The linear suturing and cutting device comprises an upper forceps holder and a lower forceps holder which can be closed and opened mutually. The upper forceps holder comprises a nail anvil, the lower forceps holder comprises a nail cartridge rack, the nail cartridge rack is detachably provided with a nail cartridge, and the inside of the nail cartridge is sequentially provided with a nail cartridge hole which penetrates the surface of the nail cartridge and a nail pushing sheet which is arranged inside the nail cartridge and can slide relative to the nail cartridge hole; the inside of the nail cartridge is also slidingly provided with a trigger sheet, the trigger sheet is provided with a wedge-shaped nail pushing unit which can drive the nail pushing sheet to slide inside the nail cartridge hole, and the nail cartridge hole is inclined to the far end of the nail cartridge. Therefore, when the nail pushing sheet inside the nail cartridge sheet is pushed, the stress direction of the nail pushing sheet is identical to the extension direction of the nail cartridge hole, relatively high friction force between the nail pushing sheet and the inner wall of the nail cartridge hole can be avoided, so that the nail pushing sheet can be pushed more smoothly, and further the surgical difficulty can be reduced.
Owner:TOUCHSTONE INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL SCIENCE CO LTD
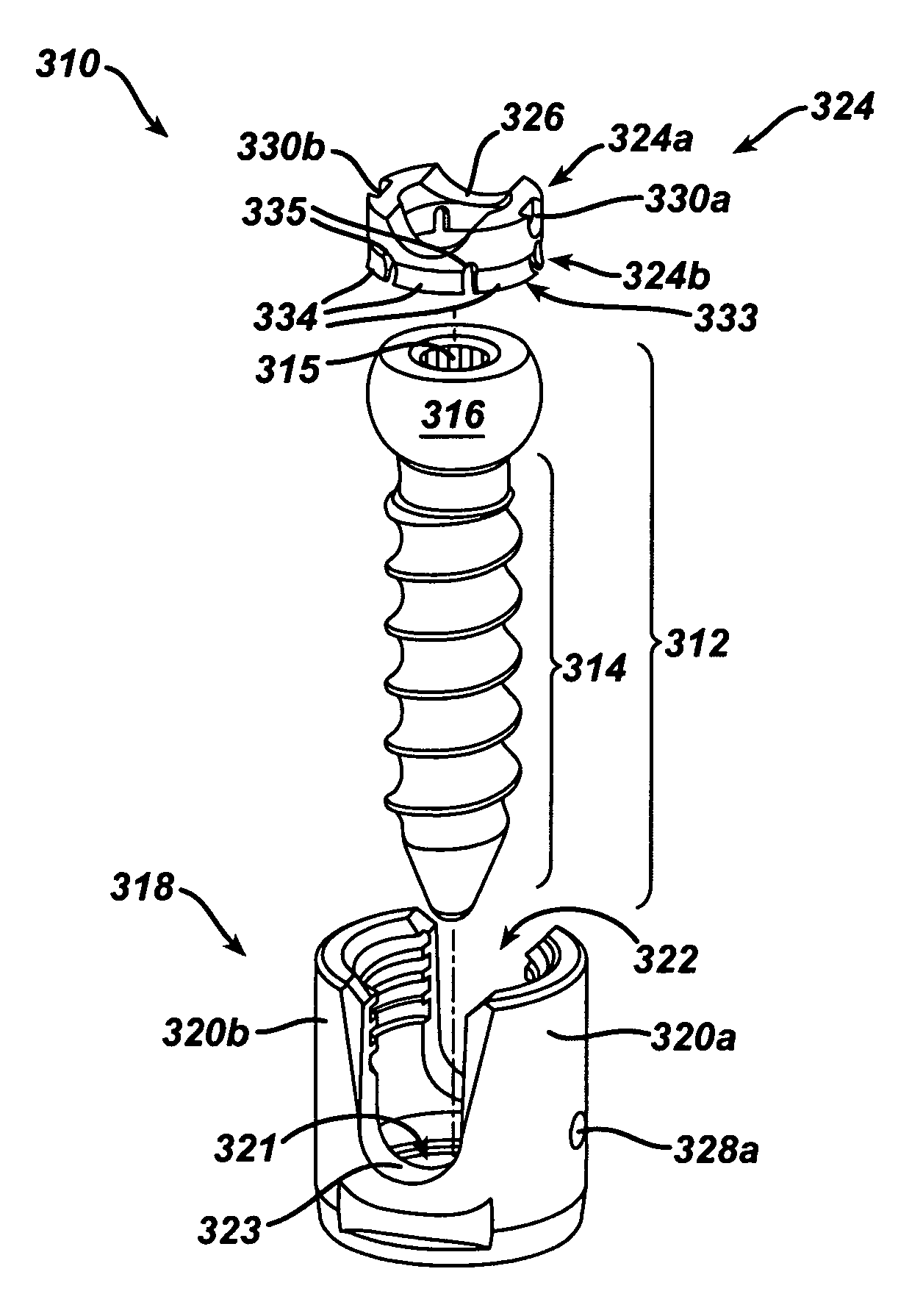
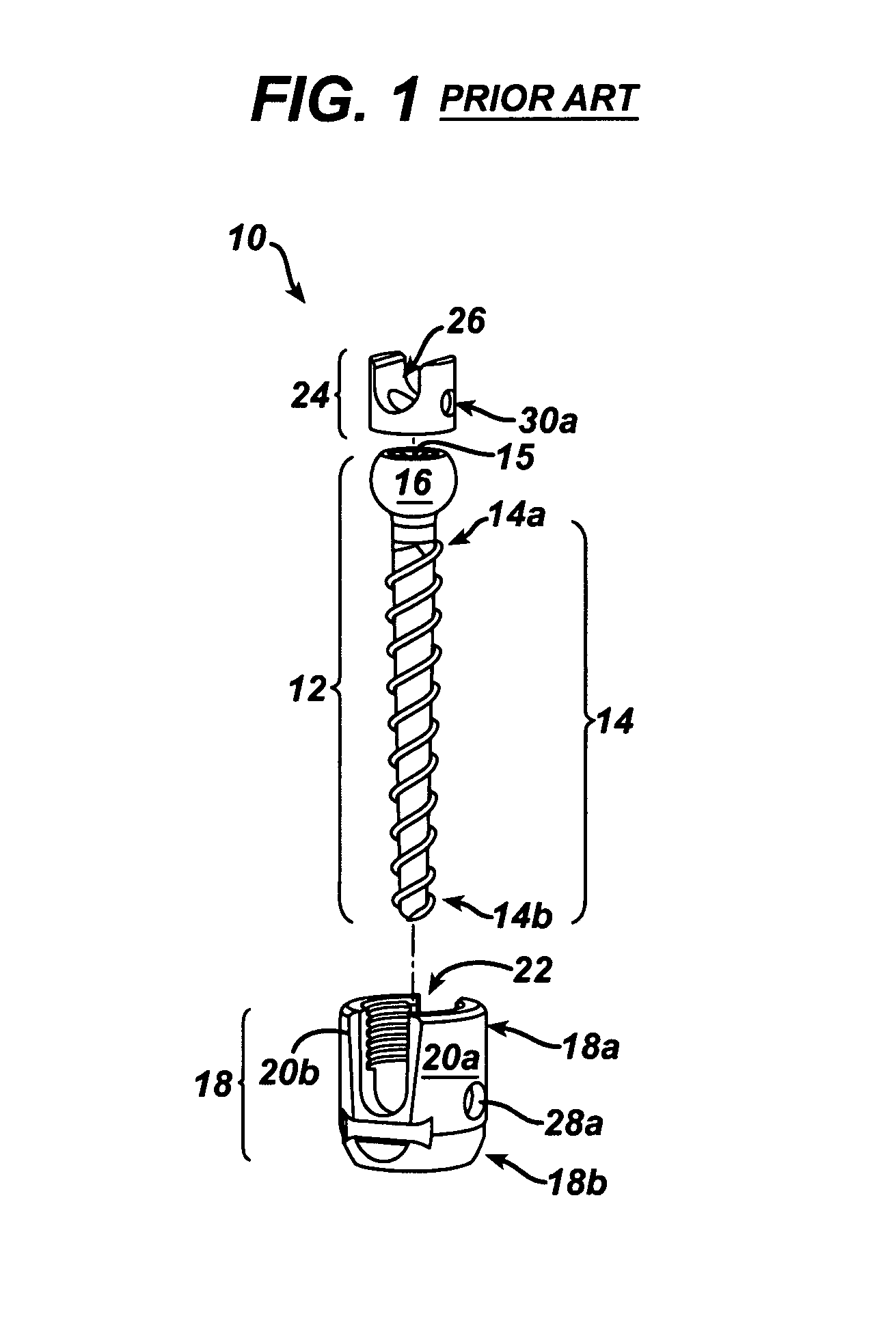
Polyaxial bone screw
ActiveUS7087057B2Efficient retentionSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisAngular orientationFriction force
The present invention generally provides a polyaxial fixation device having a shank with a spherical head formed on a proximal end thereof, and a receiver member having an axial passage formed therein that is adapted to polyaxially seat the spherical head of the shank. The polyaxial bone screw further includes an engagement member that is adapted to provide sufficient friction between the spherical head and the receiver member to enable the shank to be maintained in a desired angular orientation before locking the spherical head within the receiver member.
Owner:HAND INNOVATIONS +1
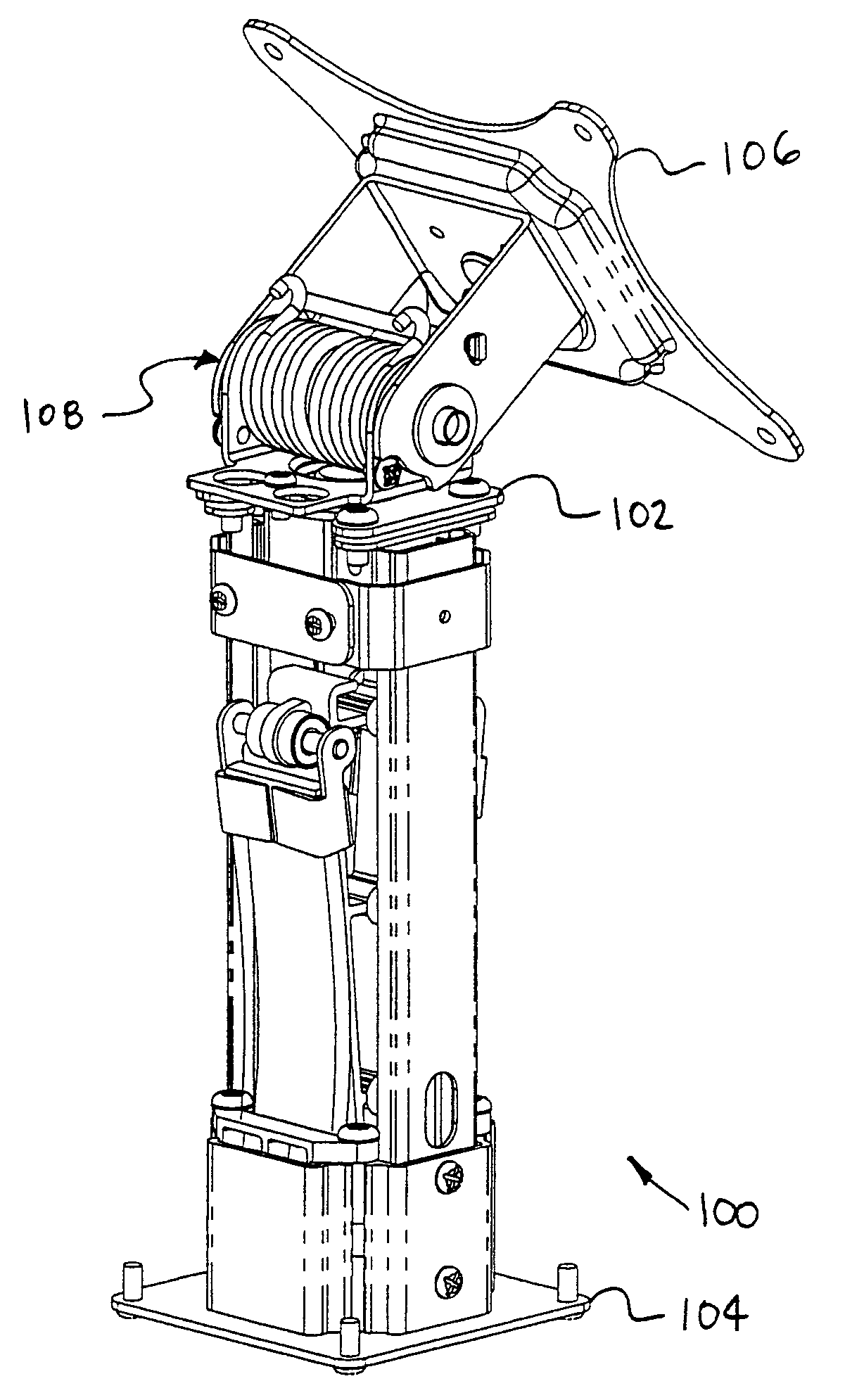
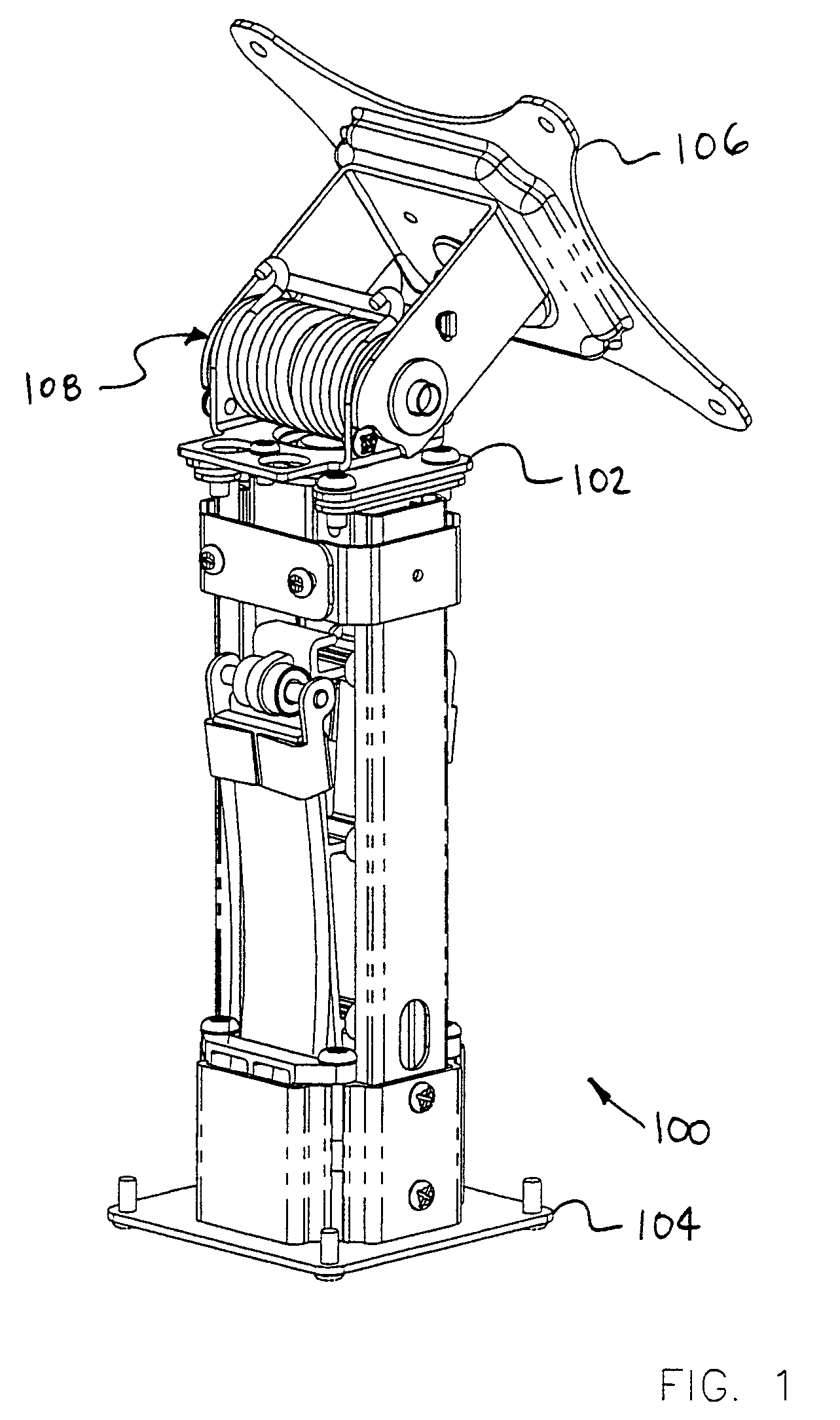
Stand
InactiveUS6997422B2Improve stabilitySmooth movementStands/trestlesKitchen equipmentRelative motionEngineering
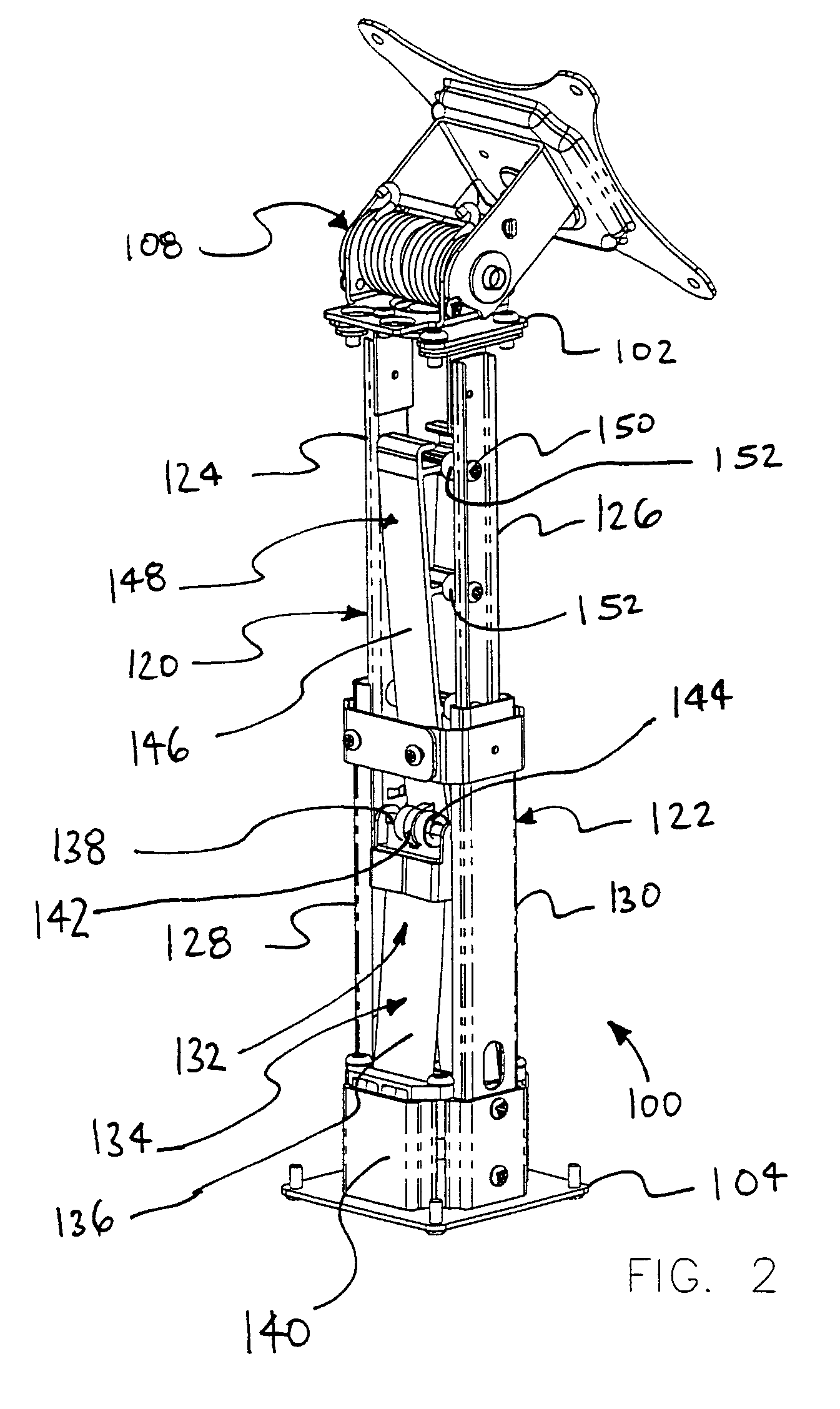
Methods and apparatus for providing an adjustable balancing force are provided. This mechanism can be used as a lifting force, a counter balancing mechanism or as a horizontal or other force mechanism. A stand in accordance with an exemplary embodiment of the present invention comprises a first component that is slidingly coupled to a second component. A spring mechanism provides a balancing force between the first component and the second component. In some advantageous embodiments of the present invention, the magnitude of the balancing force is substantially equal to a first load. In some advantageous embodiments, a friction force is provided for resisting relative movement between the first component and the second component.
Owner:ERGOTRON
System and method for electronically controlling resistance of an exercise machine
ActiveUS20060003872A1Increases pedal resistanceDecreases pedal resistanceMovement coordination devicesMuscle exercising devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceControl system
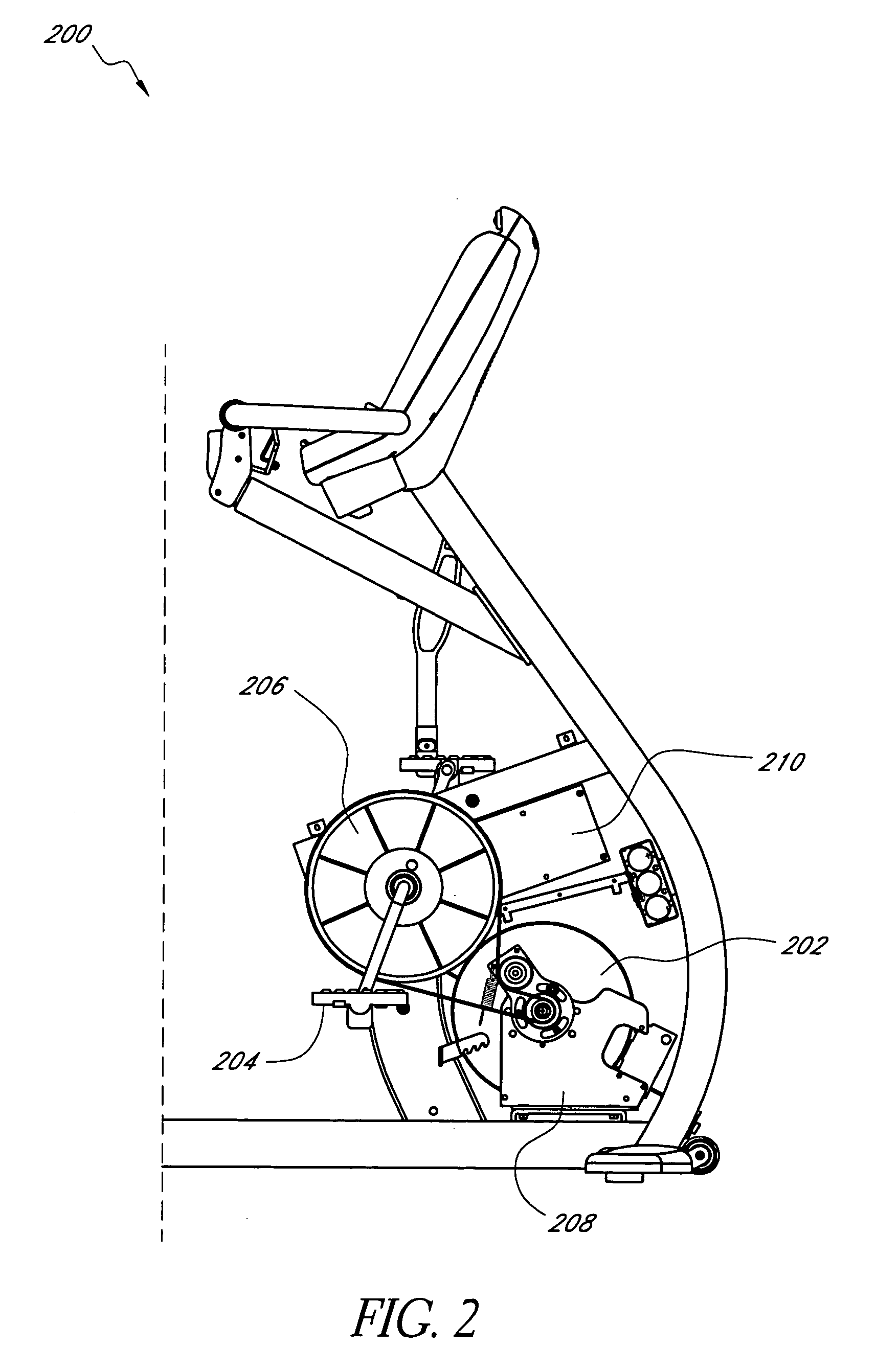
A stationary exercise machine includes a system for electronically controlling a pedal resistance so as to simulate the riding of a road-going bicycle. The exercise machine includes a control system that monitors pedal velocity and that controls the resistive load generated by an electronically-controlled resistance mechanism. In one example, an electromagnetic device may vary a resistive load placed on a flywheel, which, in turn, varies the pedal resistance experienced by a user. When the user increases the pedal velocity, the resistance mechanism increases the resistive load. When the user decreases the pedal velocity, the resistance mechanism decreases the resistive load. In another example, the resistance mechanism varies the resistive load based on a gear selection by the user. The control system may also take into account other factors, such as the grade of the simulated ride, simulated wind resistance, or other frictional forces when calculating the resistive load.
Owner:CORE HEALTH & FITNESS
Safe correlator system for automatic car wash
InactiveUS20080028974A1Reduce wearExtended service lifeCleaning apparatus with conveyorsTramway railsAxial displacementEngineering
A correlator system for automatic car wash has roller assemblies for supporting the front left and right wheels of a vehicle entering a car wash line. A set of guide rails or bars cooperate with the roller assemblies to adjust axial displacement and angular misalignment between the vehicle's front end and a conveyor track transporting the vehicle through the car wash facility. The rollers in the roller assembly rotate freely with minimal friction, axially displacing the front end of the vehicle and adjusting the angular misalignment of the front wheels. The low friction, easy-to-rotate rollers are provided with a plurality of braking elements that generate friction against the rollers, retarding their rotation when a worker steps thereon. The friction generated by the braking elements is insufficient to prevent roller rotation during alignment of the front end with the conveyor track. Injuries to car wash personnel caused by loss of balance when stepping on the rollers are virtually eliminated, and an accurate alignment of the vehicle's front end with the car wash conveyor track is reliably achieved.
Owner:BIANCO ARCHANGEL J
Overrunning coupling assembly
InactiveUS6186299B1Reduce wearLower requirementFriction clutchesInterengaging clutchesForward slidingCoupling
An overrunning coupling assembly includes a notch plate and an annular coupling pocket plate positioned in face-to-face relationship with respect to each other along a common axis. The pocket plate has strut pockets disposed at angularly spaced positions about the common axis. The notch plate has notch recesses at angularly spaced positions about the common axis and positioned in juxtaposed relationship with respect to the strut pockets. Torque-transmitting struts are positioned in each of the strut pockets. Each strut has first and second ears at one edge thereof for enabling pivotal motion of the struts about an ear axis intersecting the ears. The opposite edge of each strut is movable between disengaged and engaged positions with respect to one of the notch recesses whereby one-way torque transfer may occur between the plates. A lubricant flows between the notch plate and pocket plate. A spring is positioned in each strut pocket and biases the respective strut toward the notch plate. Each spring engages the respective strut intermediate the ear axis and the opposite edge. Each strut pocket provides sufficient clearance forward of the respective opposite edge of the strut to allow forward sliding movement of the respective strut during overrunning to cause the engagement of the respective spring and strut to occur nearer the ear axis, thereby reducing the length of a moment arm about which the spring acts upon the strut which enables frictional forces of the flowing lubricant to hold the strut in its disengaged position to prevent the strut from slapping against the notch recesses as the notch plate and pocket plate are respectively counterrotated.
Owner:MEANS IND INC
Surgical stapling instrument with an anti-back up mechanism
A surgical instrument including a firing drive configured to advance a cutting member and / or staple driver within an end effector, and a brake configured to prevent, or at least partially inhibit, the relative movement of the cutting member and / or staple driver. The surgical instrument can further include a firing member operably engaged with the cutting member, for example, a band connected to the firing member, and a reel, where the band can be configured to be wound around the reel. In various embodiments, the brake can be selectively engageable with the reel and / or band to prevent, or limit, the movement of the band. The brake can include a brake surface where relative movement between the band and the brake surface can generate a friction force therebetween which can hold the firing member in position until a sufficient force is applied to the firing member to overcome the friction force.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Integrated feature for friction less movement of force sensitive touch screen
ActiveUS8144453B2Reduce dependenceIncrease volumeSubstation/switching arrangement detailsDigital data processing detailsSensitive touchDifferential pressure
A suspension system for a differential-pressure touch sensitive panel suspended over force sensors, for use in either fixed or mobile devices such as point of sales terminals, kiosks, laptops, monitors, PDAs, cell phones, UMPCs and more. In one embodiment, each side of the lens is encircled and supported by a looped string, monofilament or flexible wire, which is then looped around the back cover or base plate, forming a figure-8. The figure 8-loops bring the lens into a fixed state in the xy-plane without the addition of any friction causing physical contact. Other alternative implementations include continuous suspensions, bender suspensions and 3-dimensional force suspensions. Moreover, the present invention proposes the use of a flexible padding under the force sensors to allow the sensors to be slightly preloaded, which reduces the dependency on extremely tight mechanical tolerances.
Owner:APPLE INC
Viscometer
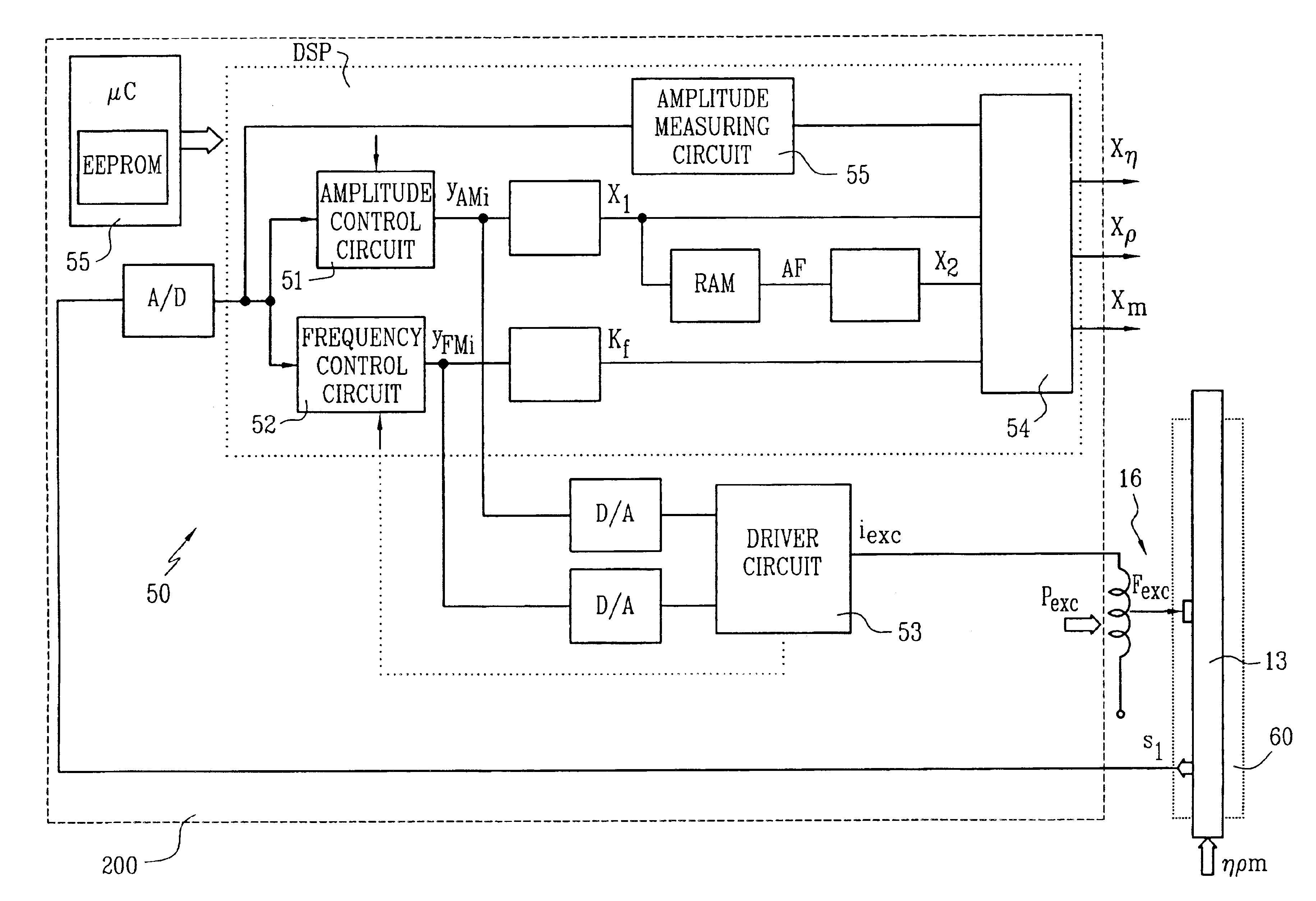
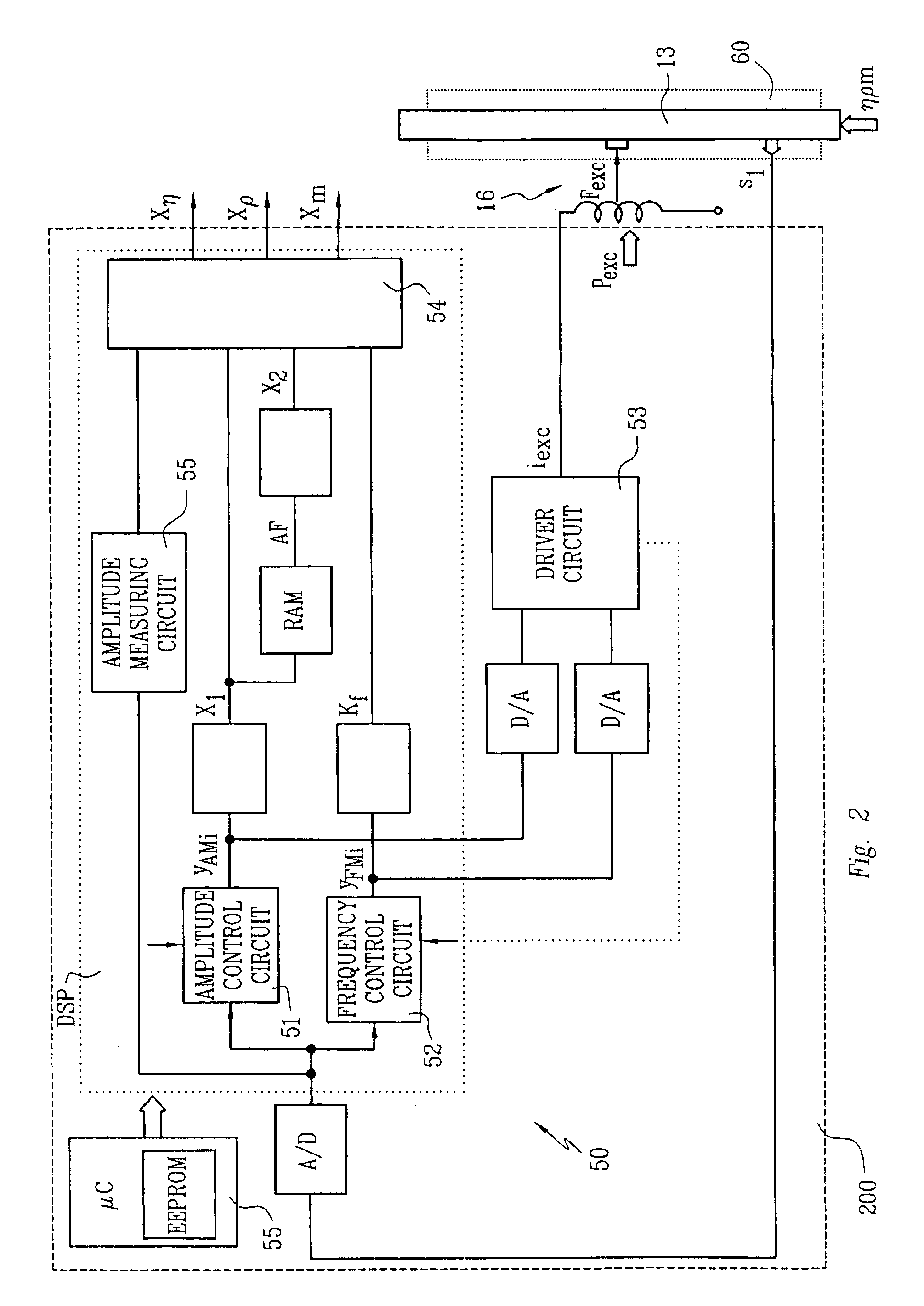
The viscometer provides a viscosity value (Xη) which represents the viscosity of a fluid flowing in a pipe connected thereto. It comprises a vibratory transducer with at least one flow tube for conducting the fluid, which communicates with the pipe. Driven by an excitation assembly, the flow tube is vibrated so that friction forces are produced in the fluid. The viscometer further includes meter electronics which feed an excitation current (iexc) into the excitation assembly. By means of the meter electronics, a first internal intermediate value (X1) is formed, which corresponds with the excitation current (iexc) and thus represents the friction forces acting in the fluid. According to the invention, a second internal intermediate value (X2), representing inhomogeneities in the fluid, is generated in the meter electronics, which then determine the viscosity value (Xη) using the two intermediate values (X1, X2). The first internal intermediate value (X1) is preferably normalized by means of an amplitude control signal (yAM) for the excitation current (iexc), the amplitude control signal corresponding with the vibrations of the flow tube. As a result, the viscosity value (Xη) provided by the viscometer is highly accurate and robust, particularly independently of the position of installation of the flow tube.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
Linear actuator
ActiveUS20050155444A1Guarantee efficiencyGuaranteed normal transmissionToothed gearingsGearing controlEngineeringParking brake
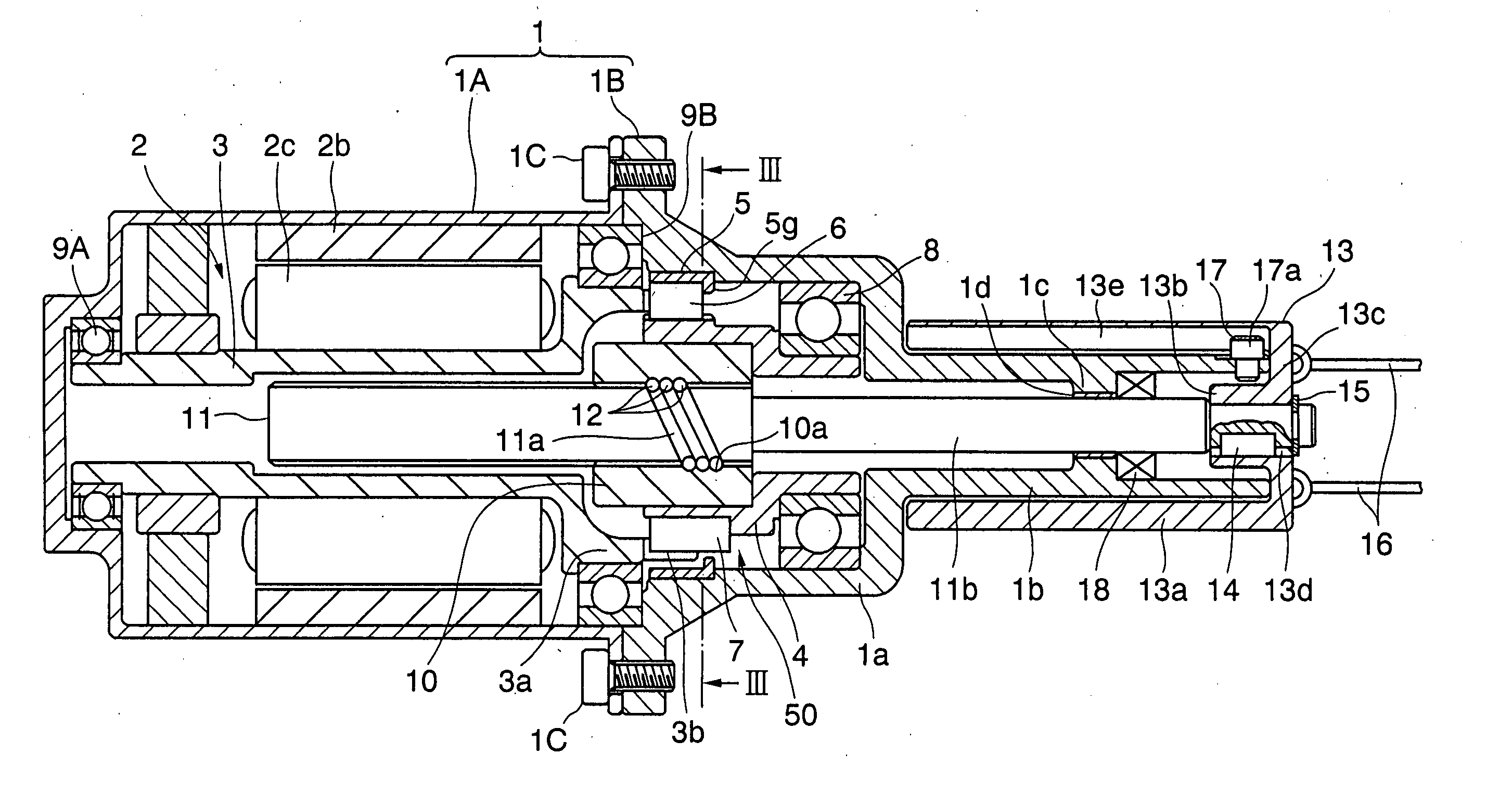
A rotary shaft (3) and a rotation driven member (4) are so connected as to be capable of transmitting motive power when the rotary shaft (3) rotates relatively to the rotation driven member (4). A roller (6) gets displaced to a first position where a frictional force with an outer race (5) and the rotation driven member (4) decreases, thereby permitting transmission of a rotational force from the rotary shaft (3) to the rotation driven member (4). When the rotation driven member (4) rotates relatively to the rotary shaft (3), the roller (6) gets displaced to a second position where the frictional force with the outer race (5) and the rotation driven member (4) increases, thereby rotationally fixing the rotation driven member (4) with respect to the outer race (5). The power transmission from a brake apparatus (e.g., a parking brake apparatus) to an electric motor (2) can be hindered while permitting the power transmission to the brake apparatus from the electric motor (2) by using neither a worm exhibiting a relatively low transmission efficiency nor a worm wheel. In a state where the brake apparatus exhibits its braking force, the roller (6) receives the force from the brake apparatus and is thereby biased toward the second position, whereby a construction of a power transmission mechanism (50) can be simplified and costs can be reduced to such an extent.
Owner:NSK LTD
Multiple-clutch device
InactiveUS6523657B1Large massLarge heat capacityRoad transportFluid actuated clutchesMobile vehicleDrivetrain
The invention is directed to a multiple-clutch device, such as a double-clutch device, for arranging in a drivetrain of a motor vehicle between a drive unit and a transmission, wherein the clutch device has a first clutch arrangement associated with a first transmission input shaft of the transmission and a second clutch arrangement associated with a second transmission input shaft of the transmission for transmitting torque between the drive unit and the transmission. According to one aspect of the invention, it is suggested that plates in a plate stack of a clutch arrangement constructed as a plate clutch arrangement which have at least one friction facing can be brought into frictional engagement with plates having no friction facing, wherein at least one of the plates not having a friction facing is thicker in axial direction than friction facing carrying elements of adjacent plates having at least one friction facing. Alternatively or in addition, it is suggested that at least one plate which has at least one friction facing of sintered material and at least one plate which has at least one friction facing made of another friction facing material are provided in the plate stack, wherein the other friction facing material has a progressive frictional coefficient curve (dlambd / dDELTAN) in relation to a slip speed (DELTAN).
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG +1
Magnetically actuated motion control device
InactiveUS6378671B1Damping frictionSpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionMovement controlFriction force
A magnetically actuated motion control device includes a housing defining a cavity and including a slot therethrough. A movable member is located within the cavity and is movable relative to the housing. A magnetic field generator located on either the housing or the movable member causes the housing to press against the movable member to develop a friction force.
Owner:LORD CORP
Friction reducing devices
InactiveUS7087806B2Enhance moisture and vapor transferIncrease flexibilityFinger bandagesAdhesive dressingsSkin breakdownSkin contact
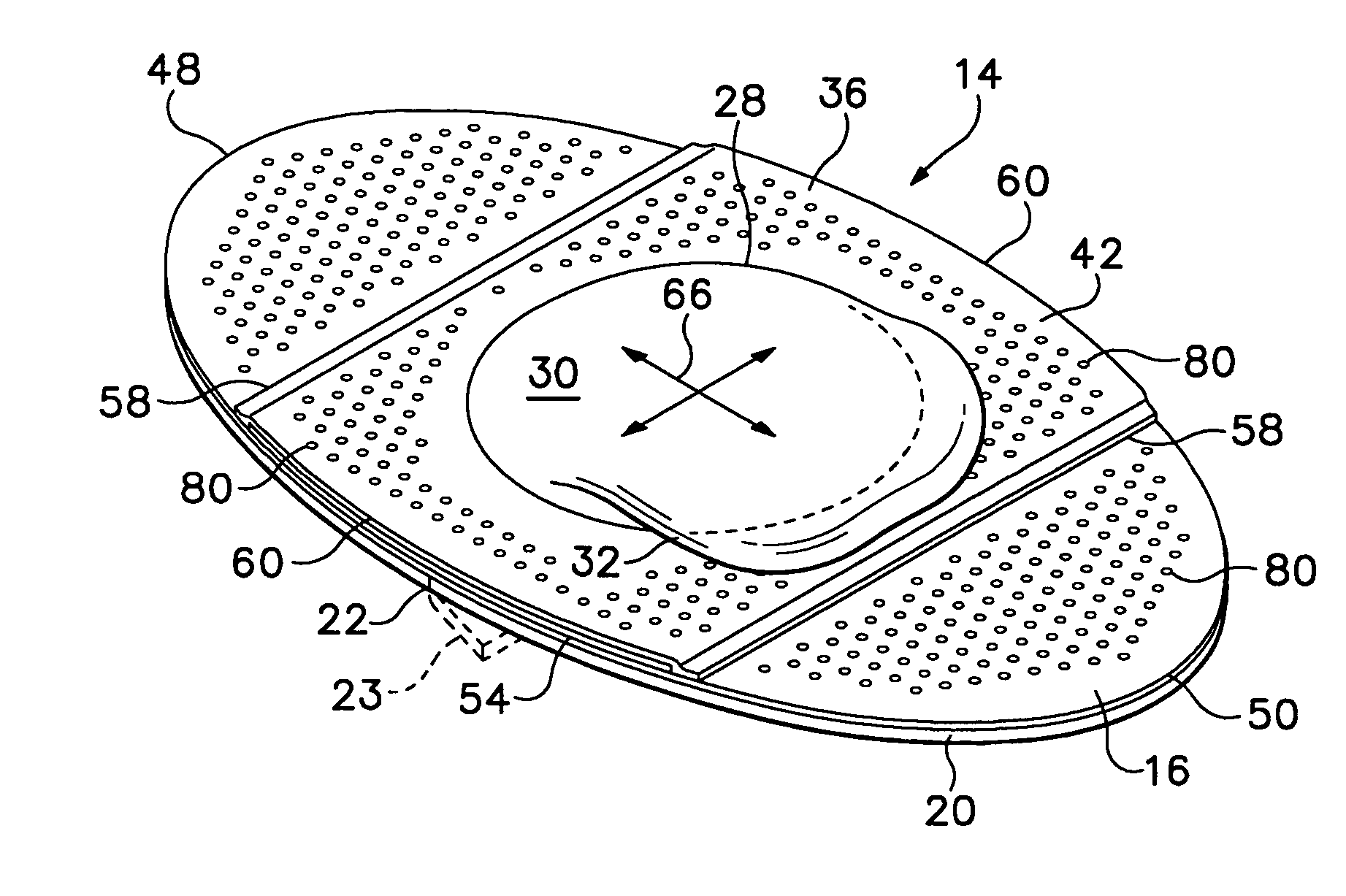
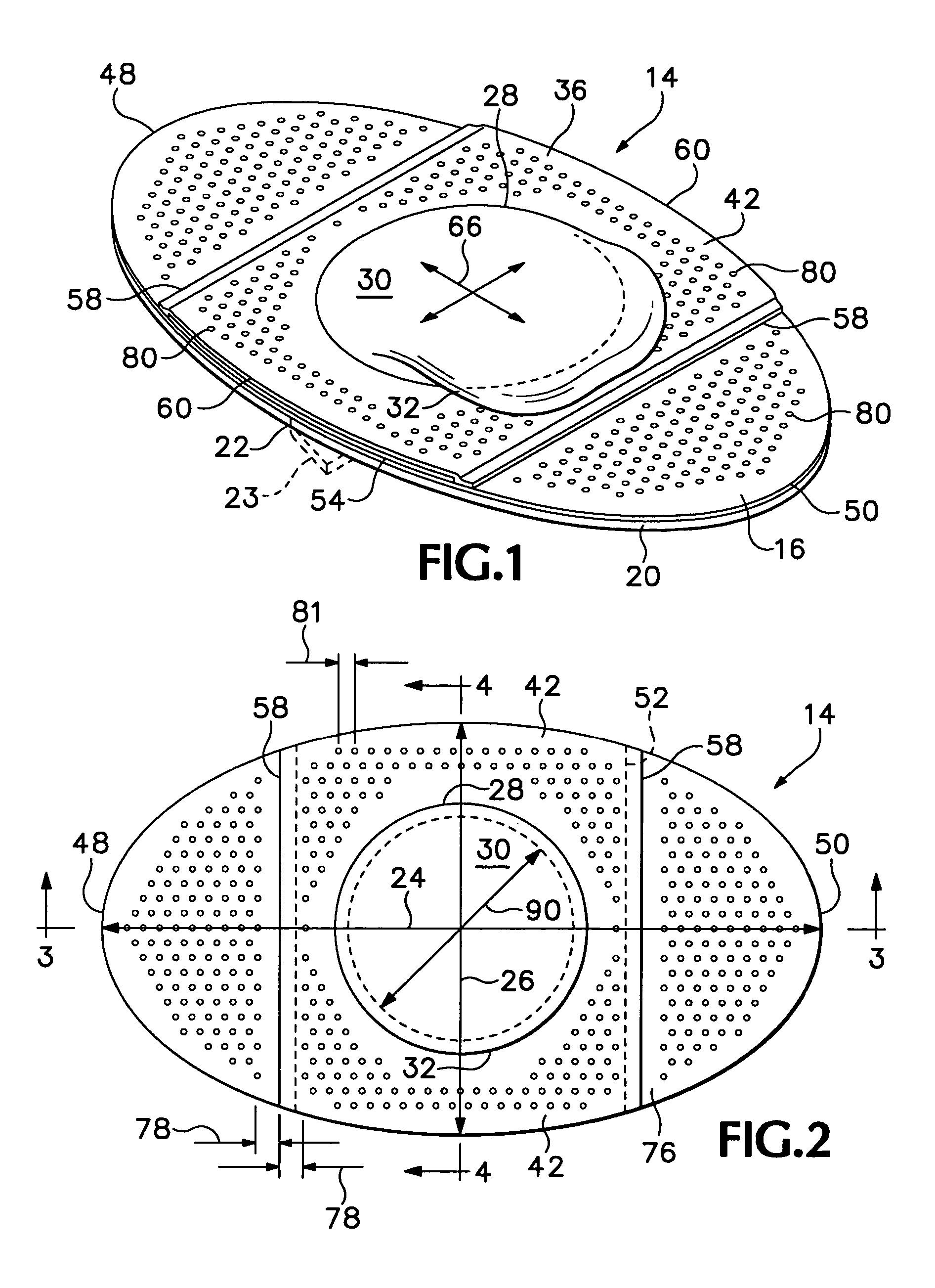
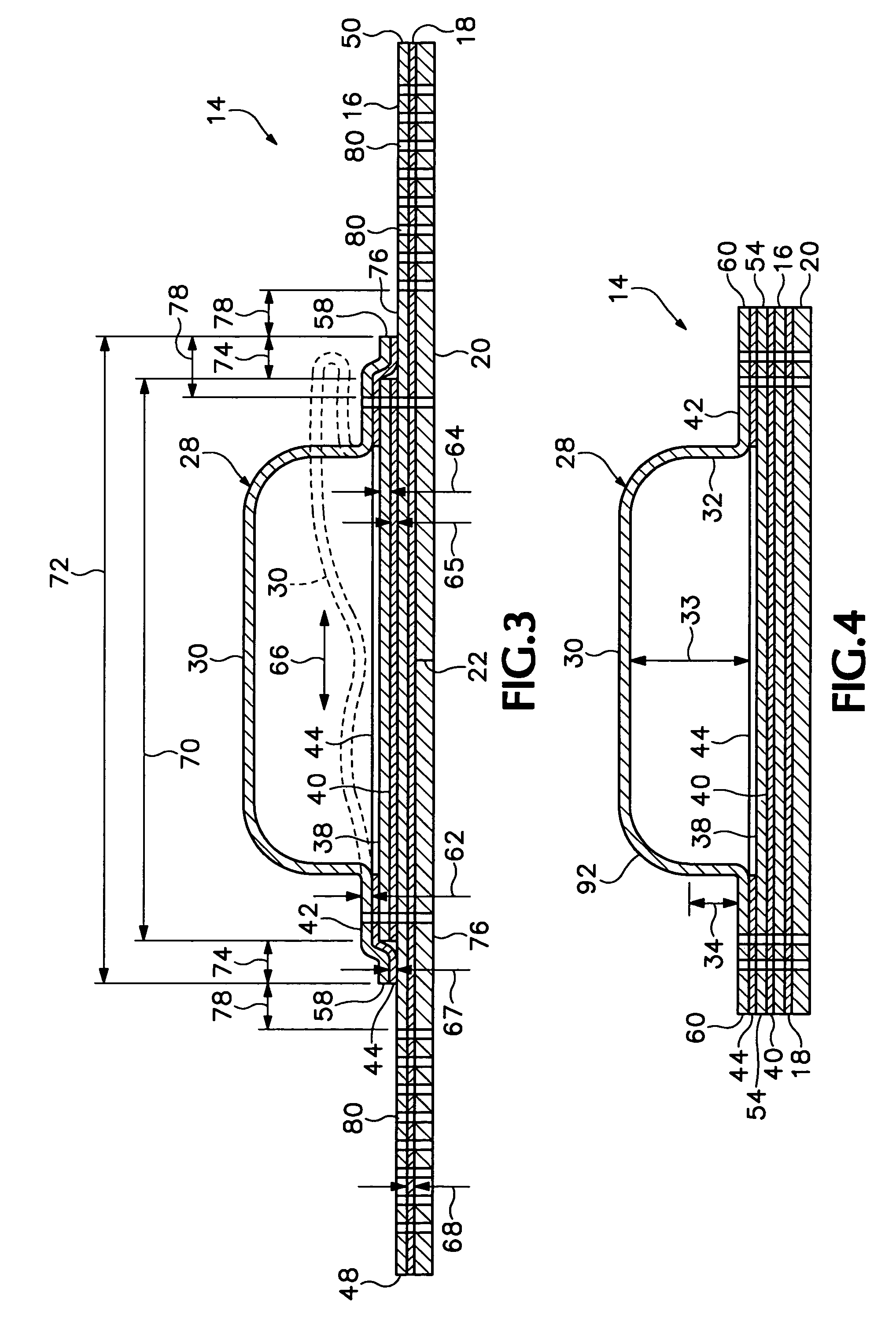
A self-adhesive bandage for prevention and treatment of skin breakdown by relief of friction and shear forces. The bandage includes a pair of thin film membranes, one of which is a portion of a dome and is free to move a limited distance with respect to the other. The dome is located on a skin contact layer that can be adhered to one's skin. A method of making such a bandage includes forming a dome in a flexible film and adhesively attaching a skirt surrounding the dome to a skin contact layer. Similar friction reducing devices may be incorporated in shoes, other clothing, or sports equipment.
Owner:ADVANCED WOUND SYST
Pneumatic automobile tire with integrated sensors and traction control system
InactiveUS6339956B1Complicates of longitudinal forceReduce brake pressureForce measurement using piezo-electric devicesTyre beadsTire beadTraction control system
A pneumatic vehicle tire includes a carcass, a bead with a bead core arranged in the bead, and a first sensor located within the bead. The first sensor delivers signals which are correlated to frictional forces transmitted by the pneumatic vehicle tire during operation. This sensor has a first end and a second end, wherein the first end includes a heel attached to the bead core and the second end extends radially outward from the bead core within the tire. A plurality of such sensors can be included in each tire, some for measuring longitudinal forces in a circumferential direction of the tire and others for measuring lateral forces in an axial direction of the tire.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AG
Self boosting packing element
ActiveUS7392841B2Increase frictionIncrease forceFluid removalSealing/packingSingle elementLocking mechanism
A packer assembly features one or more elements that preferably swell when in contact with well fluids and have a feature in them that responds to an applied load in a given direction by retaining such a boost force with a locking mechanism. A single element can have two such mechanisms that respond to applied forces from opposed directions. Friction force for adhering the element to the mandrel is enhanced with surface treatments between them that still allow the locking mechanisms to operate.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Circular cutter with a friction-provided plate
InactiveUS6874397B2Clamp tightlyPrevent rotationMetal sawing devicesGuide fencesScrew threadFriction force
Owner:P & F BROTHER INDAL
Automatic Speed Reducing Ratio-Switching Apparatus
ActiveUS20070191177A1Smooth transmissionToothed gearingsDifferential gearingsGear wheelStatic friction
An automatic speed reducing ratio-switching apparatus comprising an input side carrier, an output side carrier, and an intermediate carrier includes first and second planetary gear mechanisms juxtaposed in the axial direction of an input shaft, first and second inner clutch members which are rotatable in one direction while locking rotation in the other direction of the input shaft, and have mutually different locking directions, first and second outer clutch members which are rotatable in one direction while locking rotation in the other direction of the input side or output side ring gear, and have mutually different locking directions, and a viscous resistance member functioning under a static frictional force to integrally rotate the input side or output side sun gear, the input side or output side planet gears, and the input side or output side ring gears respectively in an identical direction.
Owner:SMC CORP
Fluid control valve
InactiveUS6920899B2Operating means/releasing devices for valvesMultiple way valvesInterior spaceJoystick
A fluid control valve for controlling the delivery of water includes a control lever that is movable in two directions by rotation of the lever about two independent axes. The fluid control valve includes a valve body assembly with flow passageways and a housing assembly attached to the valve body assembly to define an interior space. A flow control mechanism positioned in the interior space is constructed to enable movement of the lever about a first axis for translating rotational movement into sliding motion of an upper disk against a lower disk to adjust the water temperature. Rotation of the lever in a second direction translates rotational movement into sliding motion of the upper disk in a second direction to control the water flow rate. A drag spring positioned as part of the control mechanism changes the frictional force or feel between the two directions of lever movement.
Owner:MASCO CORP
Thermal container
InactiveUS20020130131A1Easy to manufactureLight weightLighting and heating apparatusVessel wallsThermal energyElectrical conductor
A thermal insulation container for storing materials at predetermined temperatures over extended periods including thermal energy storage units and means for substantially eliminating thermal conductors and providing improved insulation properties by mechanically absorbing temperature induced frictional forces. Highly efficient vacuum thermal insulators embedded within components of the container contribute significantly to its superior temperature maintaining characteristics.
Owner:ZUCKER HANS +2
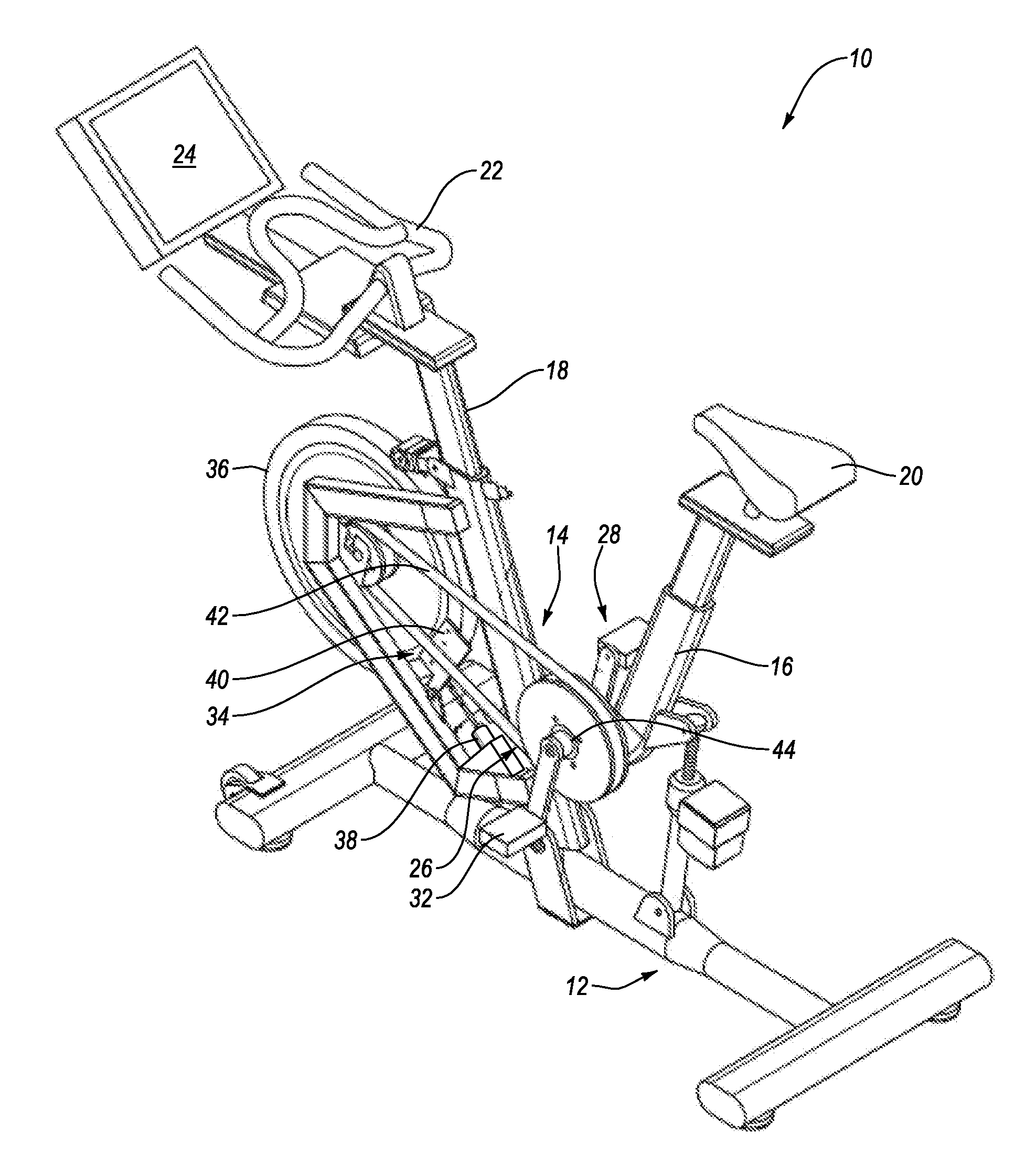
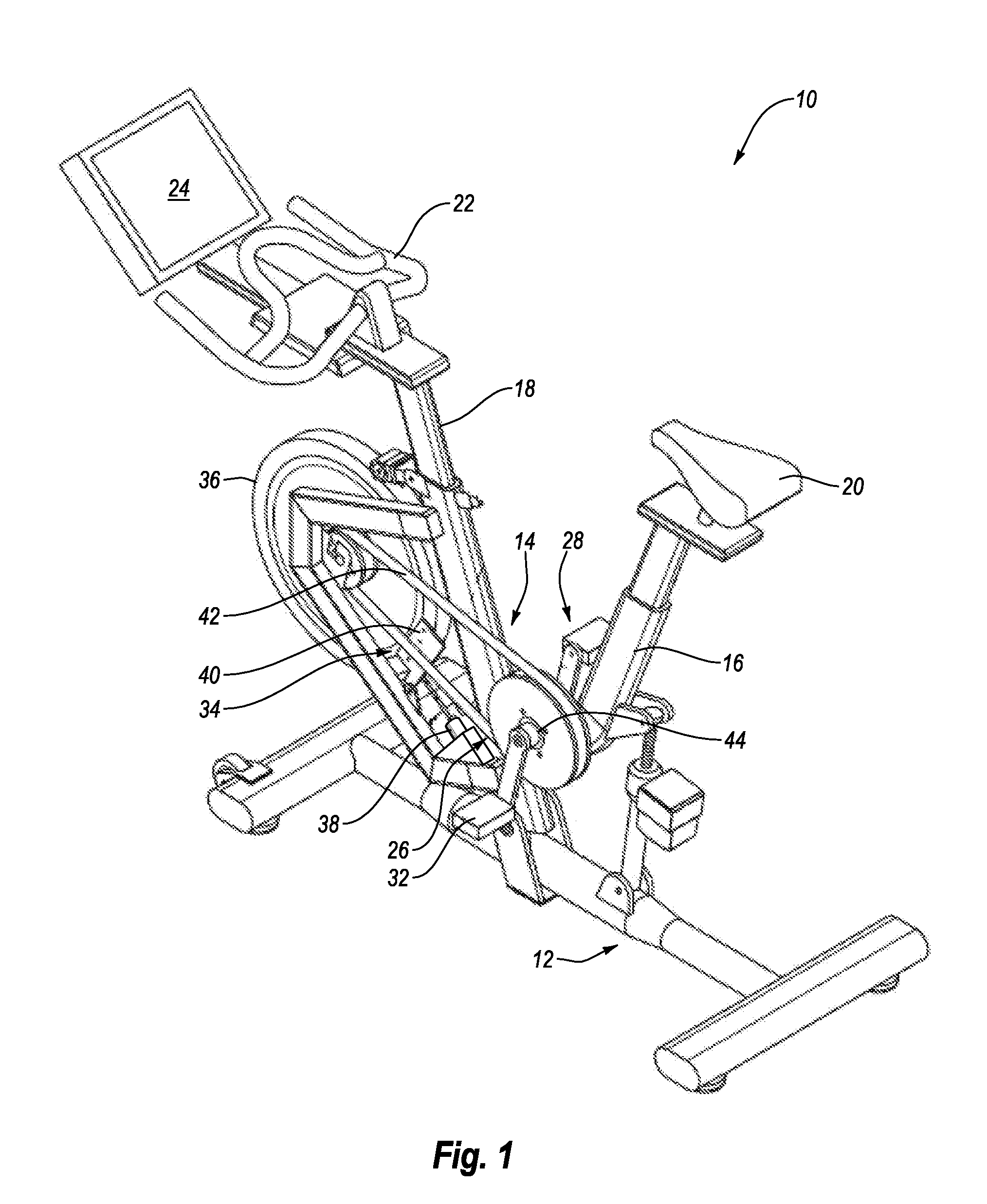
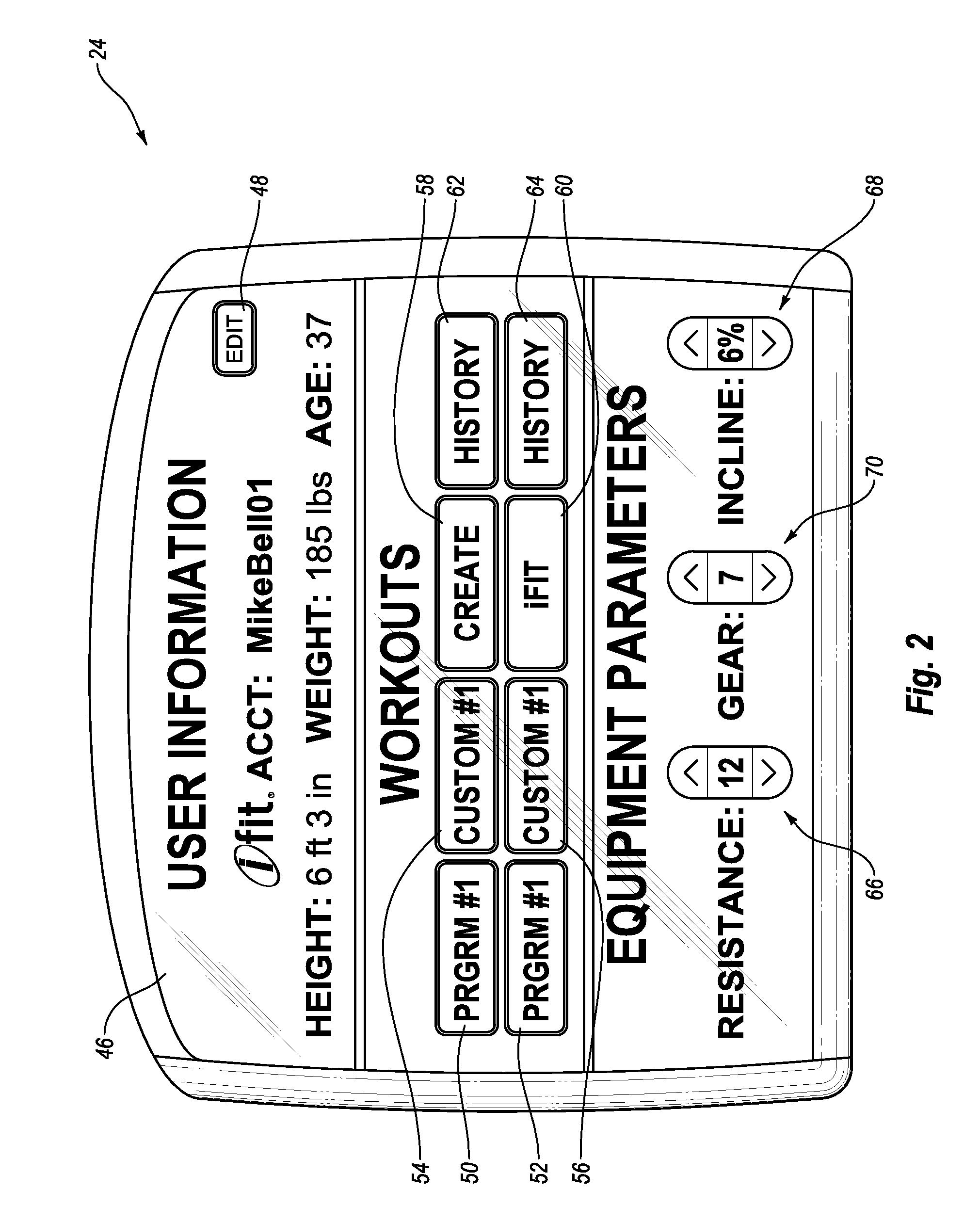
System and Method for Simulating Environmental Conditions on an Exercise Bicycle
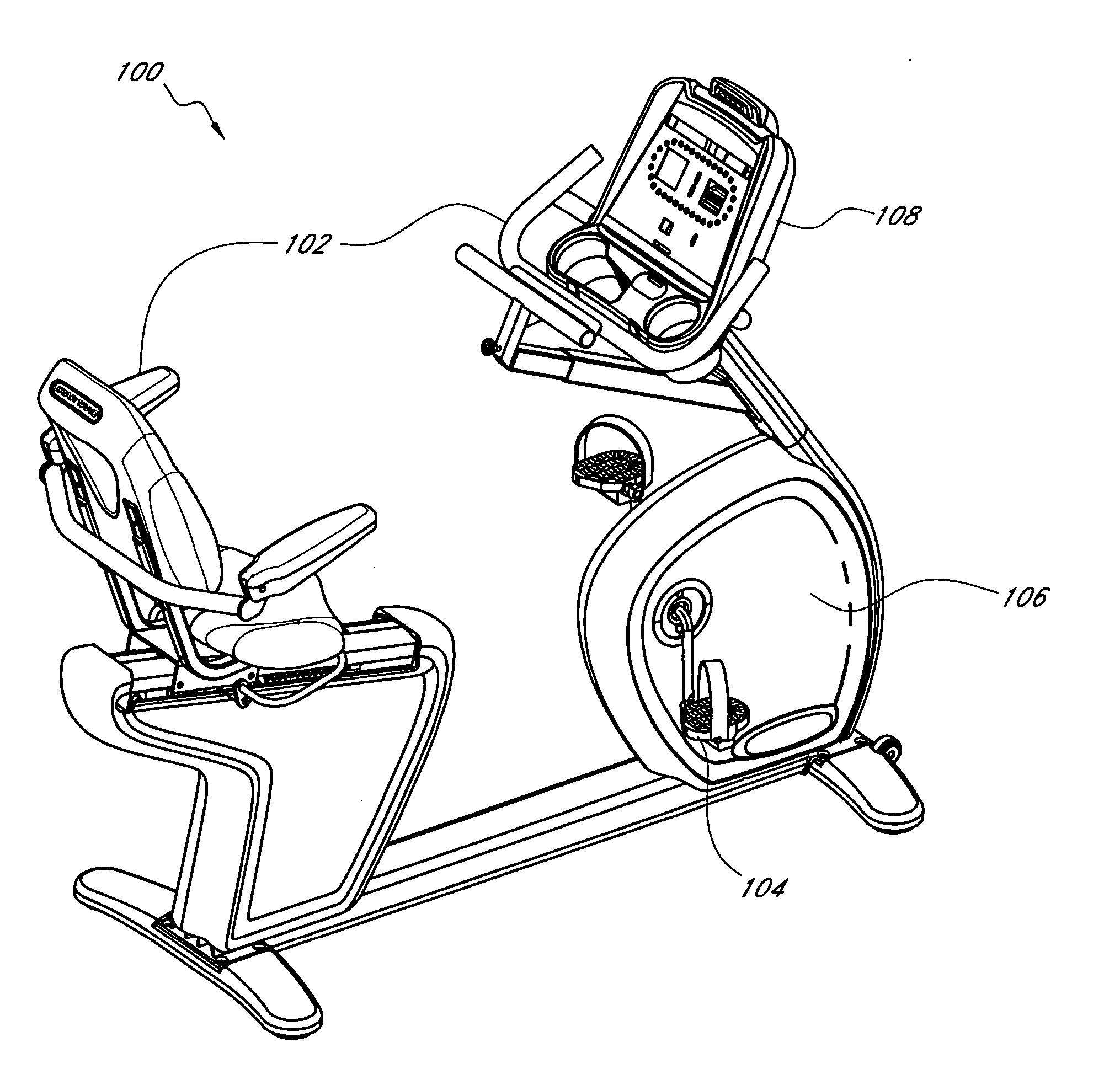
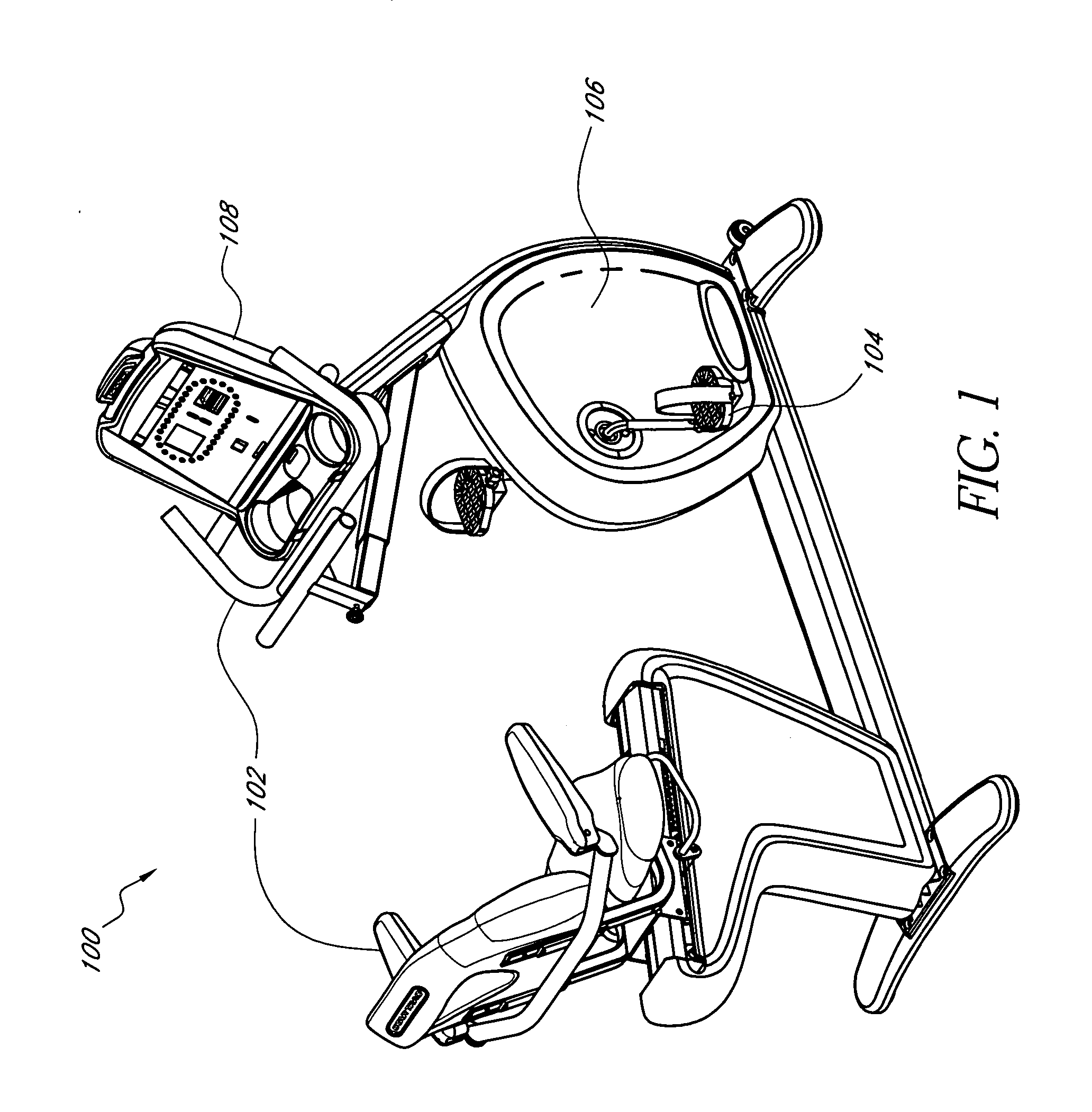
A stationary exercise cycle includes a simulation system for simulating real-world terrain based on environmental and other real-world conditions. Using topographical or other data, an actual location can be simulated. The exercise cycle may include a resistance mechanism that is adjusted based on changes in simulated slope, and by amounts simulating actual frictional and gravitational forces. The simulated speed of the rider, as well as speed and direction of a simulated wind, are used to determine a simulated air speed. Based on the simulated air speed, the simulation system determines the simulated air resistance hindering the rider, and changes reflective of the simulated air resistance are made by the resistance mechanism. The stationary exercise cycle takes into account actual or approximate physical information of the user in determining the real-world conditions that are simulated, including the height, weight, shape, and / or rising position of the rider.
Owner:IFIT INC
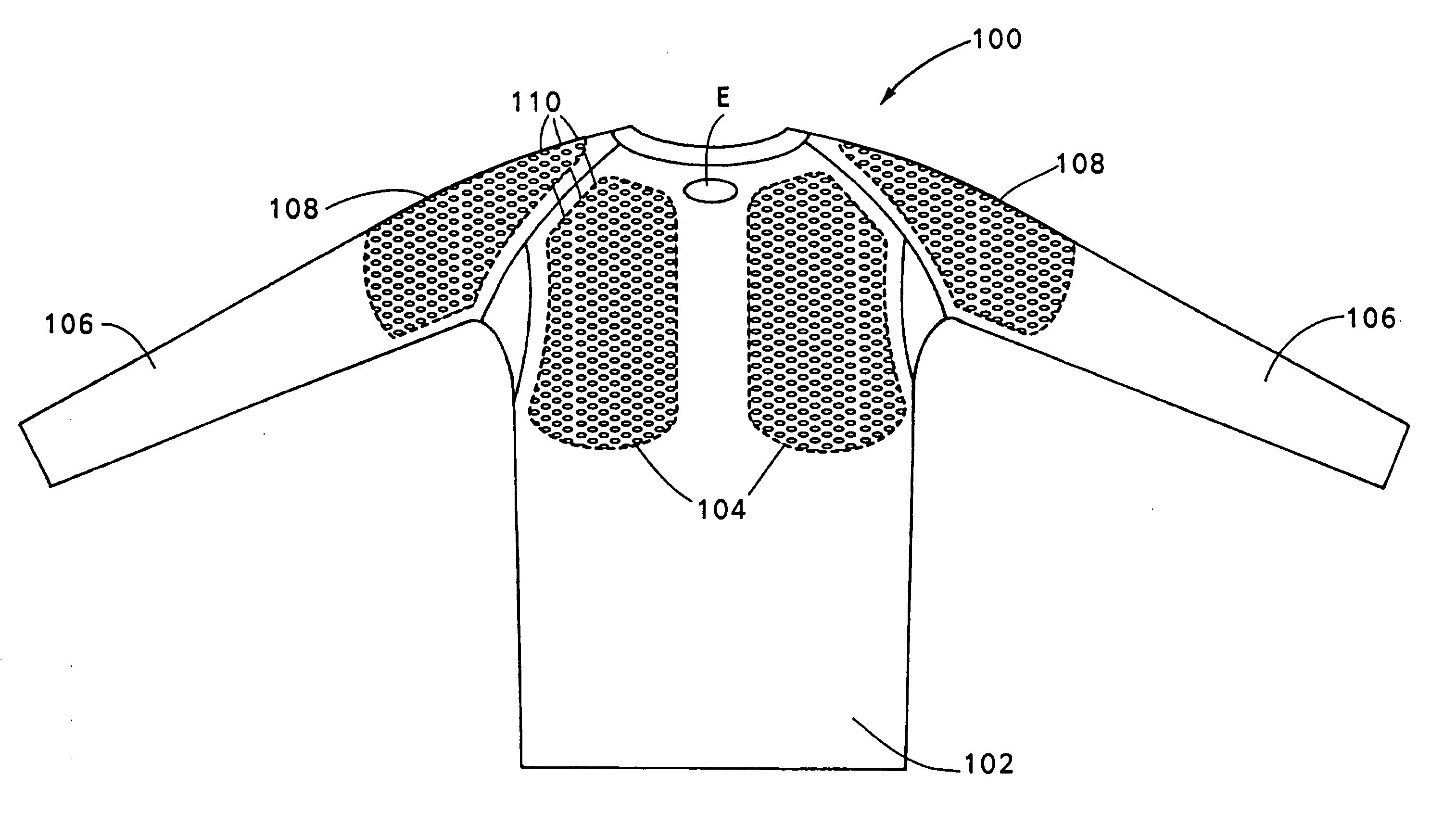
Garment having improved contact areas
Owner:UNDER ARMOUR
Microactuated dimple for head suspensions
InactiveUS7256968B1Move preciselyTrack finding/aligningRecord information storageDynamic storageEngineering
A head suspension for supporting a head slider over a disk in a dynamic storage device and providing precise movement of the head slider relative to tracks on the disk. The head suspension includes a load beam, a flexure having a slider mounting region, and a dimple interface transmitting a load beam force to the slider mounting region. The head suspension further includes a microactuator mounted to the load beam. Movement of the microactuator is transmitted through the dimple interface by action of frictional forces at the dimple interface so as to cause movement of the slider mounting region transverse to tracks on the disk. A method of precisely moving a head slider supported by a head suspension includes providing and driving a microactuator configured to transmit movement of the microactuator to a slider mounting region through a dimple interface by action of frictional forces at the dimple interface.
Owner:HUTCHINSON TECH
Rotary damper
InactiveUS6336252B1Enhanced level of machining precisionImprove the forceBuilding braking devicesWing fastenersFriction forceBase line
A rotary damper is adapted to exert braking force to an upswung door, a toilet lid or the like when the door is closed and dampen the impact produced by the closing door by a damping force far greater than the one obtained by a conventional rotary damper using viscous shearing resistance. The rotary damper can also make the door open by a force far smaller than a conventional rotary damper. A movable shaft is rotatably housed in a casing and has a cylindrical shaft section including an arcuate non-resilient section extending from a peripheral edge thereof to an axial base line close to the other free peripheral edge thereof and an eccentric resilient section extending from the axial base line to the other free peripheral edge thereof with its eccentricity increasing as a function of the distance from the base line relative to the radius of curvature of the inner peripheral surface so as resiliently abut the inner peripheral surface. The frictional force between the eccentric rest section and the inner peripheral surface increases when the movable shaft is driven to rotate to close the door to which it is fitted but falls remarkably when the movable shaft is driven to rotate in the opposite sense to open the door.
Owner:SUGATSUNE IND CO LTD
Operation feeling imparting type trackball device
InactiveUS20120038495A1Improve the quality of operationEasily realizing compact sizeElectronic switchingInput/output processes for data processingActuatorFriction force
A trackball device includes a friction plate rockably supported having opening in which a top portion of the sphere is exposed, as a brake unit applying braking force (friction force) to the sphere, and an actuator capable of driving the friction plate to a lower side. When the friction plate is driven by the actuator, the circumference portion of the opening of the friction plate is pressed to be in contact with the sphere from an upper side. A supporting member rotatably holding the sphere includes a plurality of supporting small spheres contacts the sphere at a point and a base member in which the supporting small spheres is arranged to be dispersed in the circumferential direction. The base member rockably supports the friction plate.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
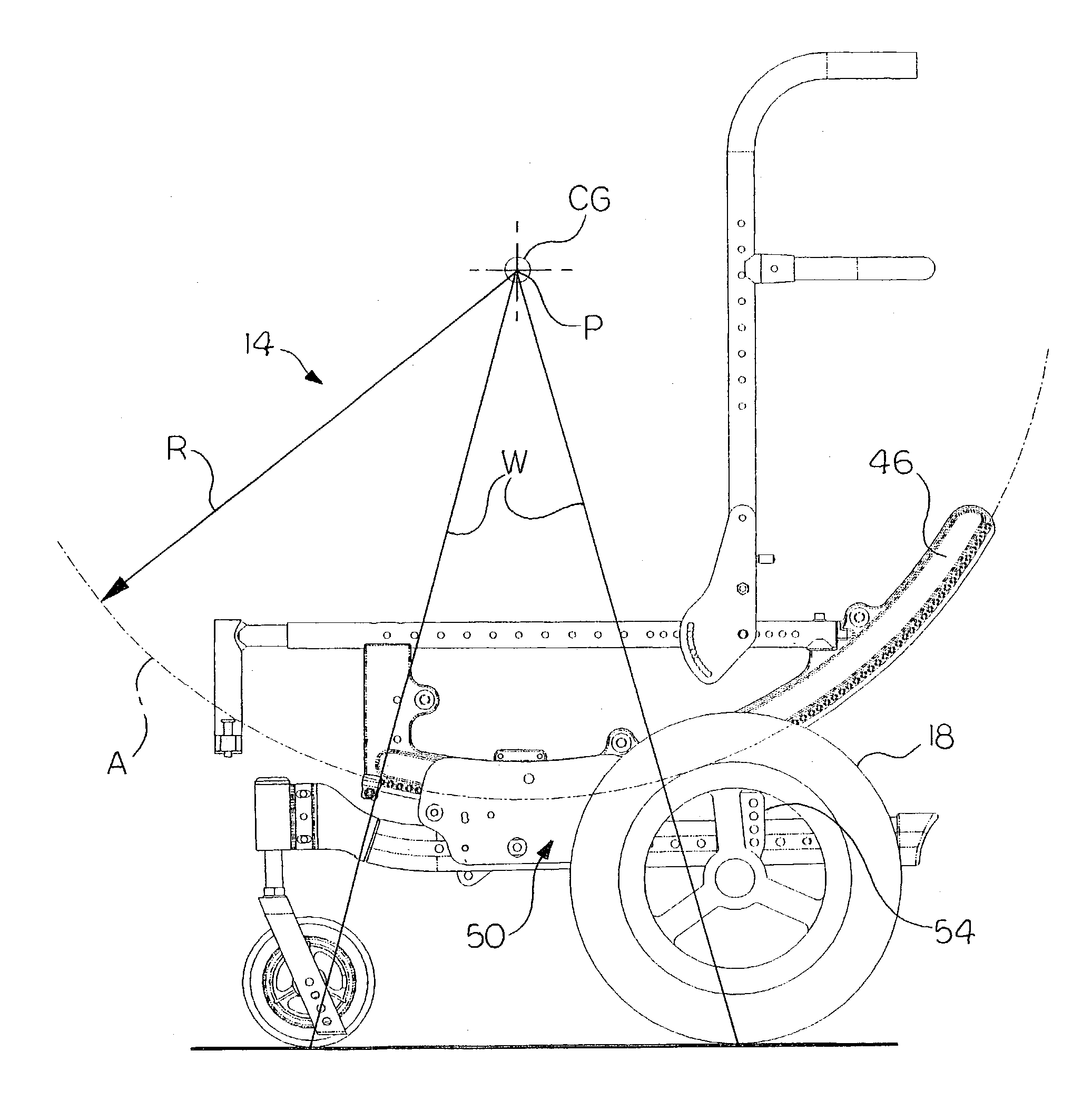
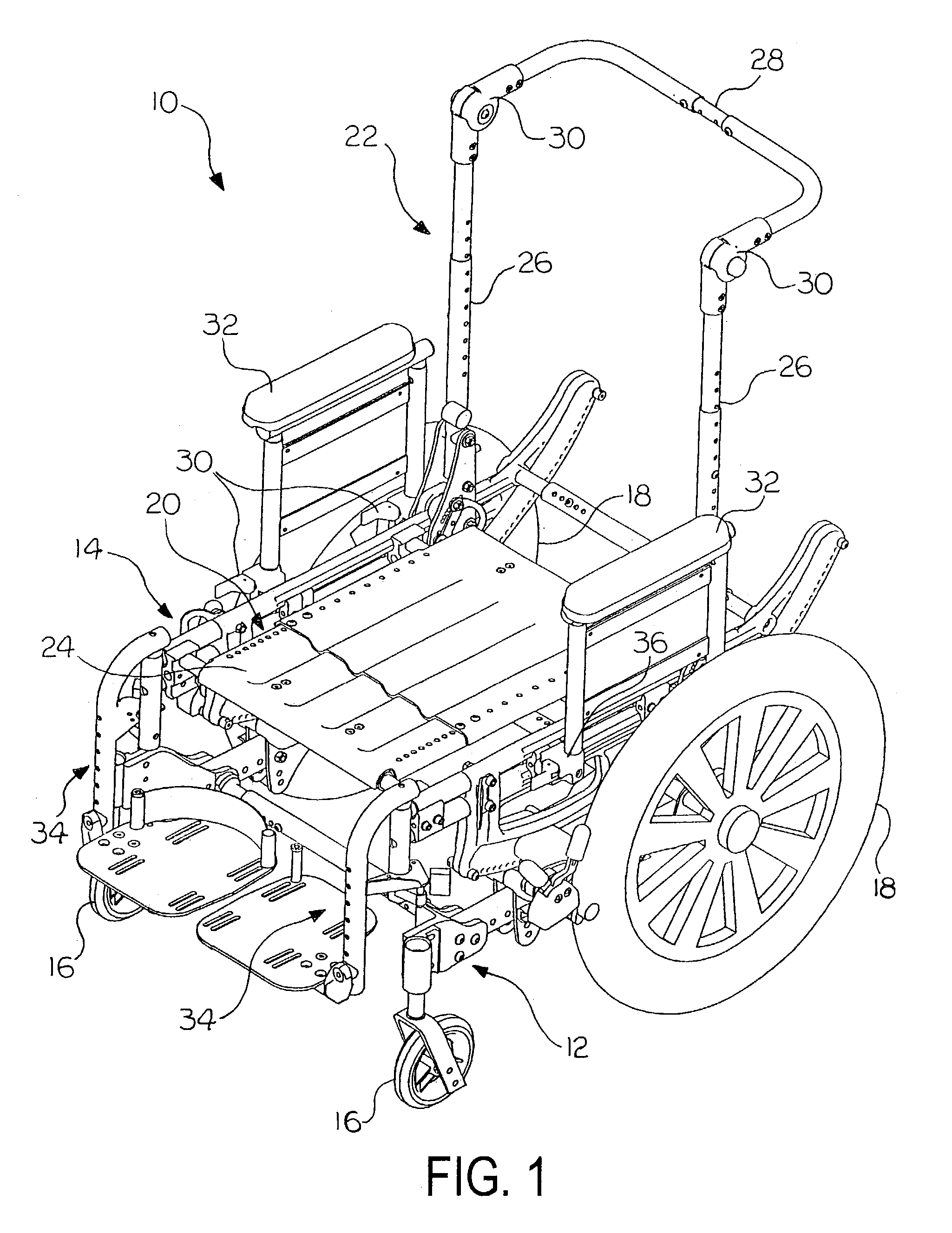
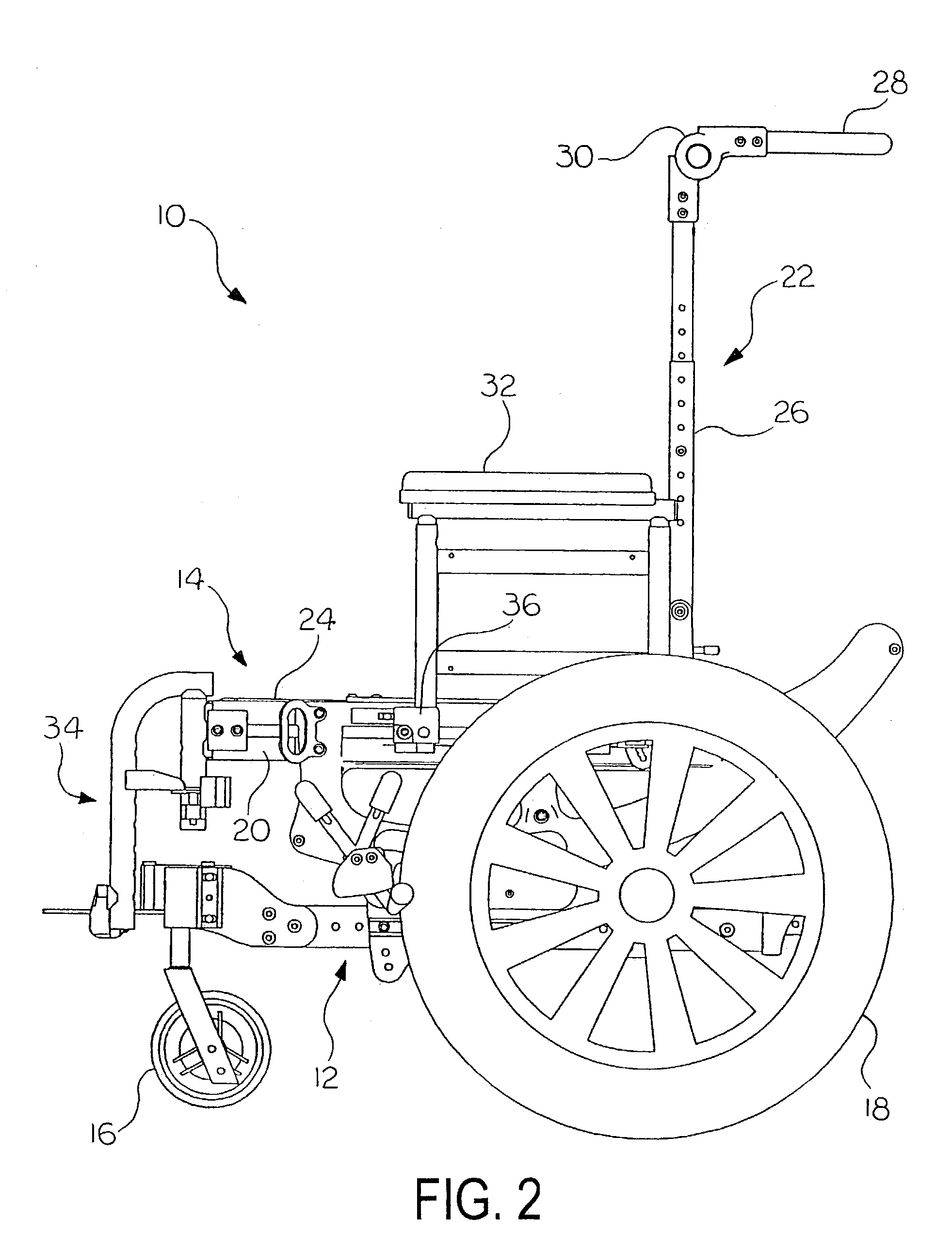
Center-of-gravity tilt-in-space wheelchair
A center-of-gravity tilt-in-space wheelchair includes a base, a seat for supporting an occupant, and tracks supporting the seat for selective seat movement relative to the base. Wheels are adapted to support the base relative to a supporting surface. The tracks serve as rolling or sliding surfaces that allow the seat to rotate with respect to the base. Each track has a constant-radius arc with a focal point that is adapted to be coincident with the center of gravity of the wheelchair occupant. A low-friction supports the base relative to the seat. The low-friction support may include low friction elements that mate with the tracks to support for the tracks. The support can be adjustable to permit the overall tilt angle range of the tracks to be adjusted. The wheelchair seat can be adjusted to maintain the focal point of the constant-radius arc of the tracks coincident with the center of gravity of the wheelchair occupant. The front and rear wheels can be adjusted fore and aft relative to the focal point. A coupling includes plates having upper ends operatively attached to one another with seat canes therebetween and lower ends releasably attached relative to the side tubes. The lower ends can be movable in a longitudinal direction relative to the side tubes while remaining operatively connected to the side tubes. A base frame can include side frames having an offset at a front end and a caster housing supported by the offset. The offset is directed up to minimize the height of the side frames and down to maximize the height.
Owner:SUNRISE MEDICAL (US) LLC
Rail car door opener
A servo that is attachabley secured to the rail car frame at each door lock that is connected to the latch via a draw bar with sufficient modulus to withstand the repeated force required to move the latch thus opening the door. The servo provides a pulling action with the motive force being pneumatic pressure but not limited to pneumatic whereas hydraulic or electric energy can be supplied to the servo providing the motive force to pull the draw bar attached to the latch, that when said servo provides a pulling force sufficient to over come the friction ot the latch to the striker plate the latch moves in a upward direction thus releasing the door to open. A second element of the servo is to provide a pushing action via the draw bar to the door latch to drive it all the way into the closed position.
Owner:MARCHIORI DAVID +1
Portable handheld exercise apparatus which can be attached to a multiplicity of body parts
InactiveUS7087001B1Full rangeHigh variationTaming and training devicesFrictional force resistorsBall bearingHand held
The present invention is directed to a portable personal training and exercise device with a cable and pulley mechanism which also is a mobile personal training and exercise device having an ergonomic plastic external housing that with the use of straps fits in the hand as well as against different parts of the body. The present invention has a cable and pulley mechanism inside a housing which has a pulley rotatably mounted on a shaft that spins in only one direction. The pulley spins in both directions so that it is spring biased for rewinding a cord onto the pulley. Next to the pulley is a brake wheel or brake bushing that is attached to the shaft. The brake wheel or brake bushing and a pulley spinning on a single shaft inserts into a sealed ball bearing on both ends. A spring is connected to the bottom of the pulley. In the center of the pulley is a combination ball bearing / one-way clutch that turns the shaft only in one direction. The shaft is attached to the brake wheel or brake bushing. Secured around the outer edge of the brake wheel is a brake band. Secured around the outer edge of the brake bushing is a brake clamp. The brake band or brake bushing can be tightened for variable resistance through a tension adjustment assembly including a tension bolt. There is also a multi-directional guide unit mounted on the housing for allowing the pulley cords to be pulled in multiple directions with variable amounts of friction. The cord, which is wrapped around the pulley, emerges through a multi-directional bearing that rotates 360 degrees, thus allowing full range of three dimensional motion. Therefore, a user may pull the cords of the pulley for exercising various muscles of the user and adjust the resistance force of the cord at an appropriate level from the user. Different attachments can be connected to the snap at the end of the cord or cable such as a grip handle, wrist strap, waistband, ankle strap and foot strap.
Owner:IHLI STEPHEN P
Sliding Pendulum Seismic Isolation System
ActiveUS20060174555A1Increase effective frictionReduce earthquake forceStands/trestlesKitchen equipmentCost effectivenessSeismic gap
An inventive method is presented for a sliding pendulum seismic isolation system that reduces seismic forces on the supported structure and reduces the costs of the isolation bearings, seismic gaps, and supported structural frame. The inventive method is to configure the isolation system to achieve increased effective friction with increased displacement amplitudes, and to employ specific bearing configurations that suit the different types and magnitudes of loads present at particular structure support locations. Three bearing configurations are presented which are comprised of multiple sliders that slide along different concave spherical surfaces, each constituting an independent sliding pendulum mechanism having a specified pendulum length and friction. Two bearing configurations are presented which are comprised of multiple sliders that slide along different concave or convex cylindrical surfaces, one configured to carry both compression and tension loads, and one configured to be cost-effective for carrying light compression loads and accommodating large displacements.
Owner:EARTHQUAKE PROTECTION SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com