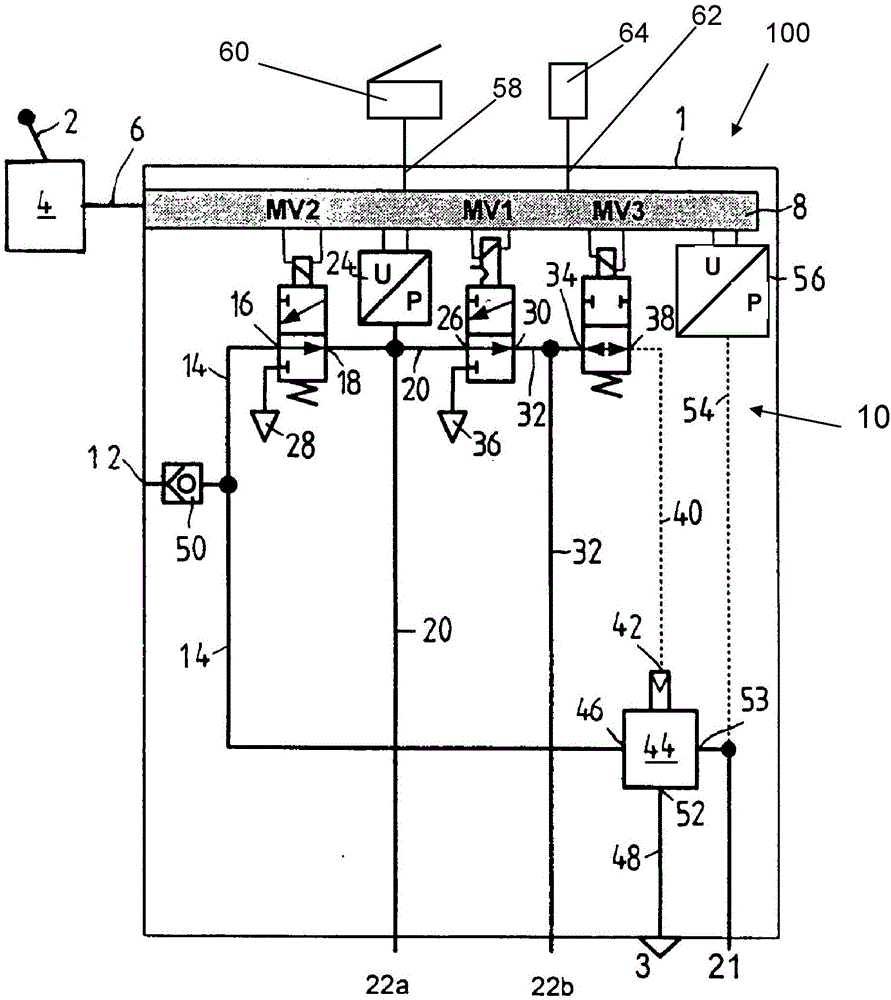
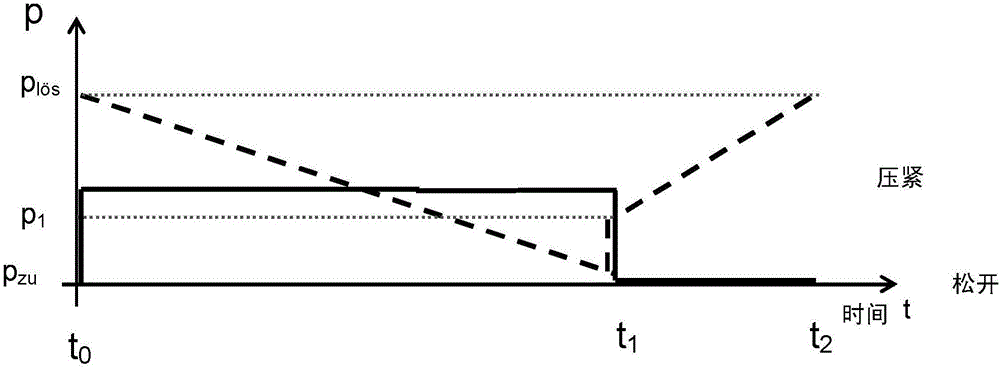
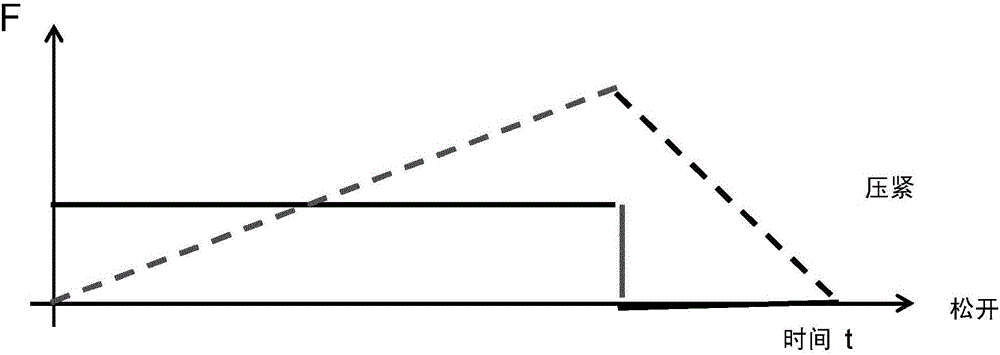
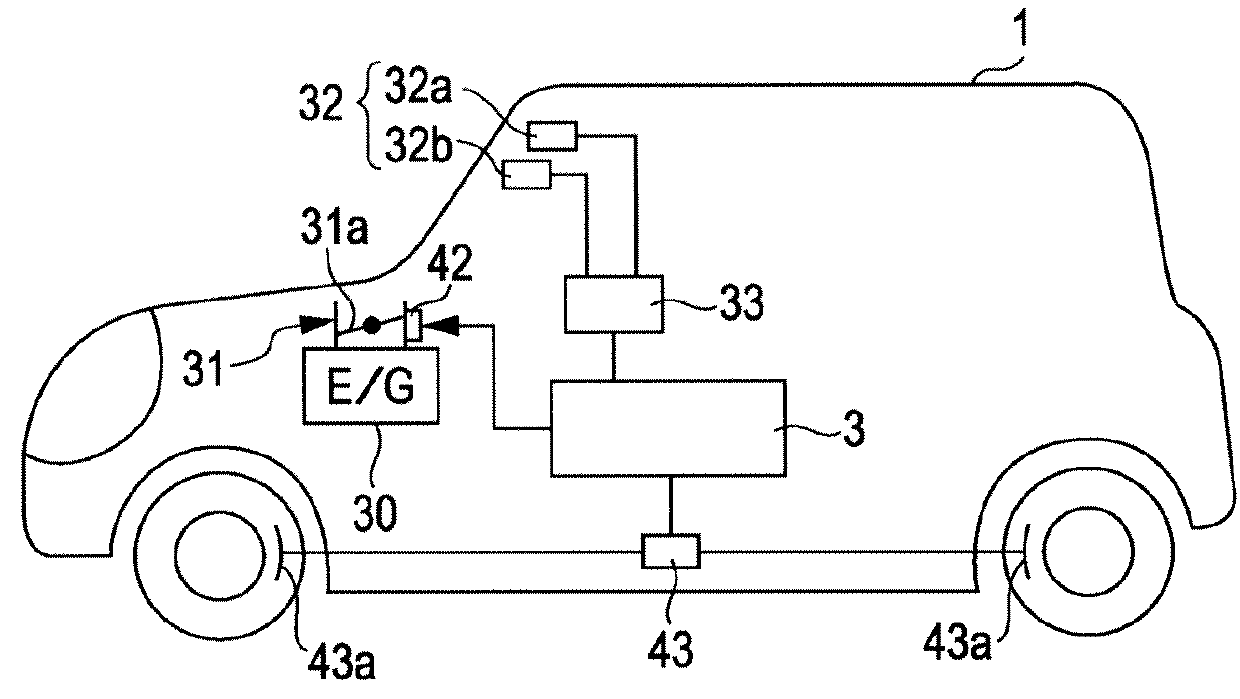
Patents
Literature
106results about How to "Reduce brake pressure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
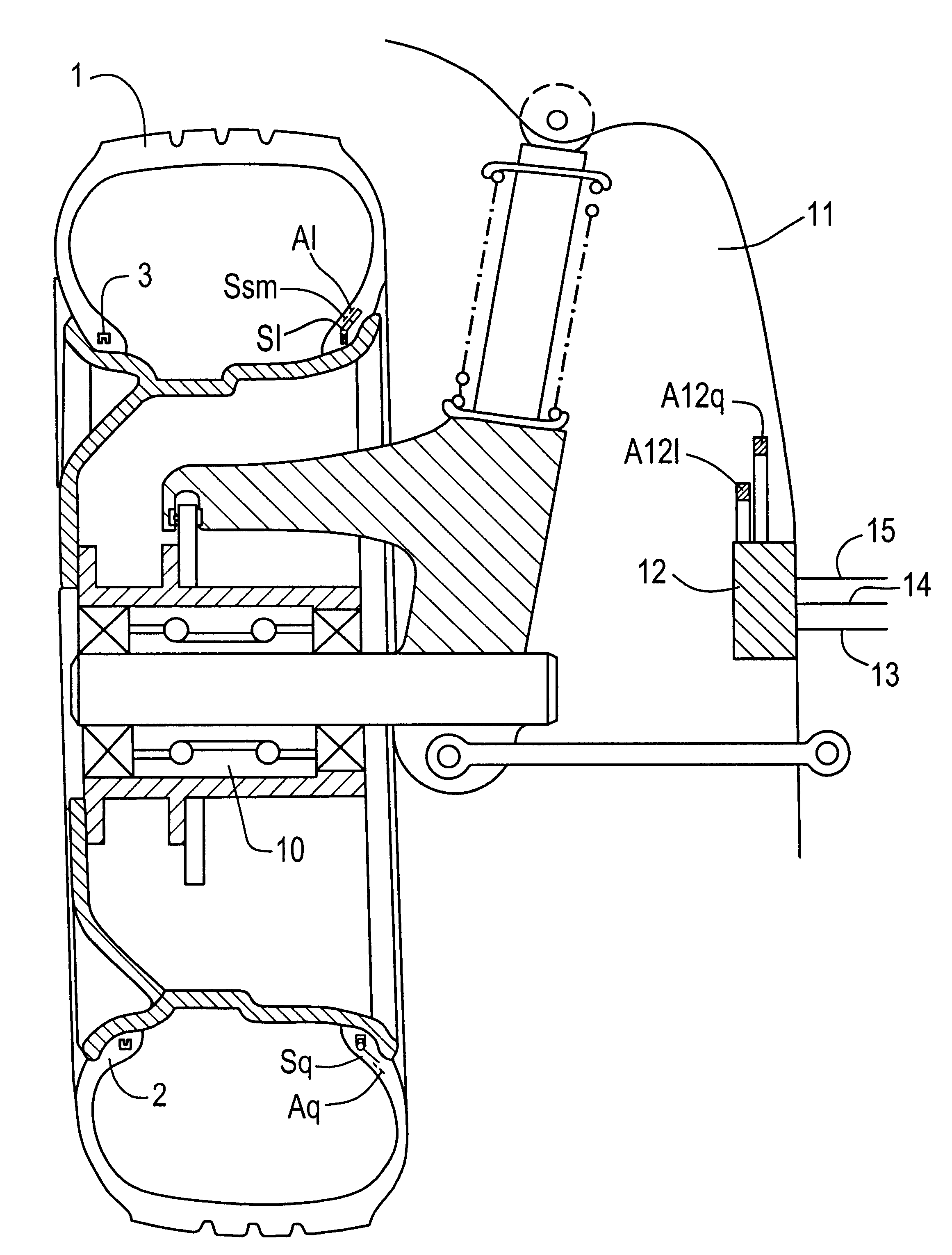
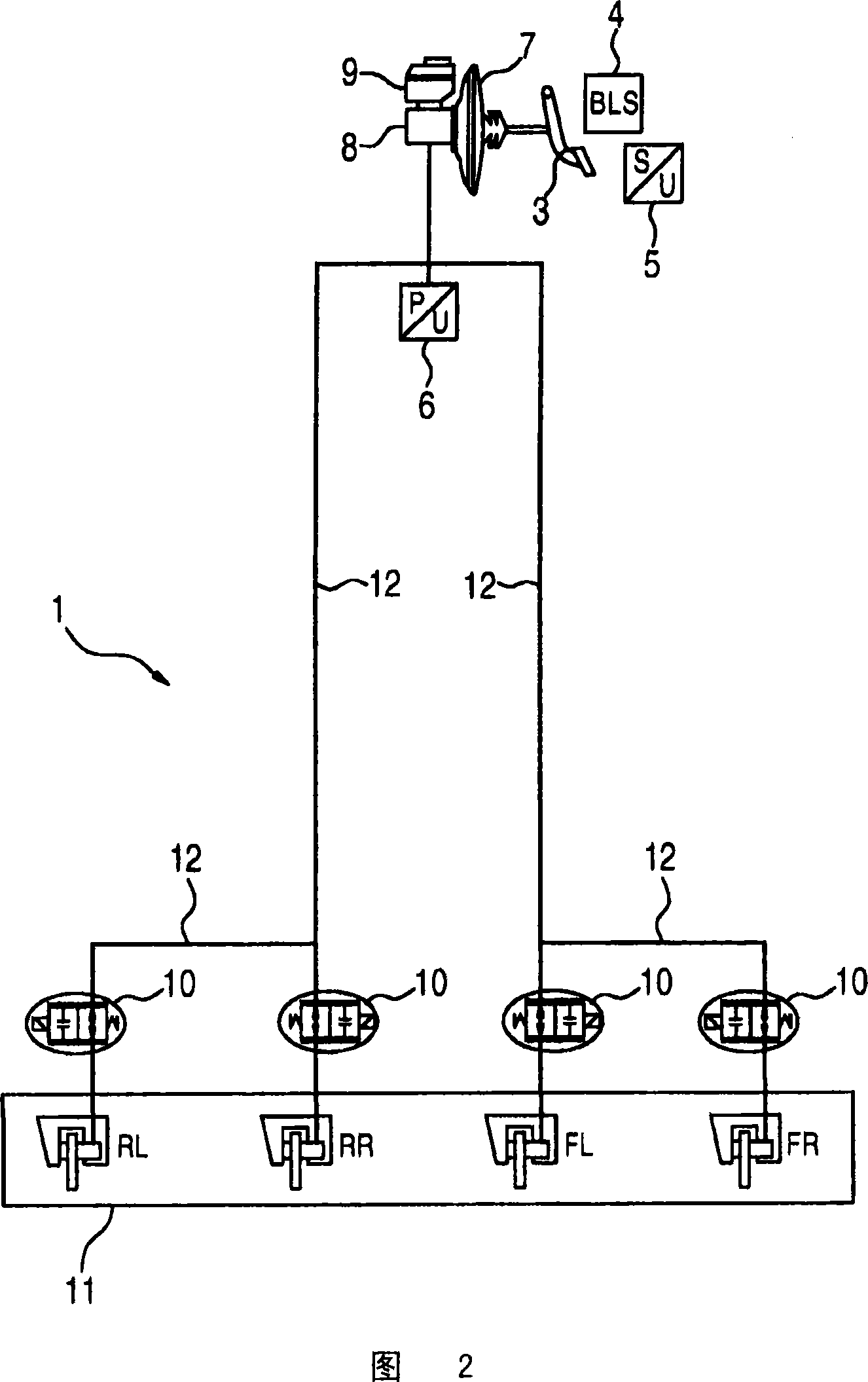
Pneumatic automobile tire with integrated sensors and traction control system
InactiveUS6339956B1Complicates of longitudinal forceReduce brake pressureForce measurement using piezo-electric devicesTyre beadsTire beadTraction control system
A pneumatic vehicle tire includes a carcass, a bead with a bead core arranged in the bead, and a first sensor located within the bead. The first sensor delivers signals which are correlated to frictional forces transmitted by the pneumatic vehicle tire during operation. This sensor has a first end and a second end, wherein the first end includes a heel attached to the bead core and the second end extends radially outward from the bead core within the tire. A plurality of such sensors can be included in each tire, some for measuring longitudinal forces in a circumferential direction of the tire and others for measuring lateral forces in an axial direction of the tire.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AG
Soft-stop braking control
InactiveUS20070182243A1Eliminating a hard stop (wrap-upReduce brake pressureBraking action transmissionAutomatic initiationsActuatorVehicle brake
A method is provided for applying a soft-stop control to the vehicle brake actuators of a vehicle during a vehicle stop operation. A brake apply operation is detected. A determination is made whether the vehicle speed is below a first threshold stopping speed. Braking pressure to the vehicle actuators is reduced as a function of vehicle speed, vehicle deceleration, and brake apply pressure if the vehicle speed is below the first threshold stopping speed.
Owner:KELSEY HAYES CO
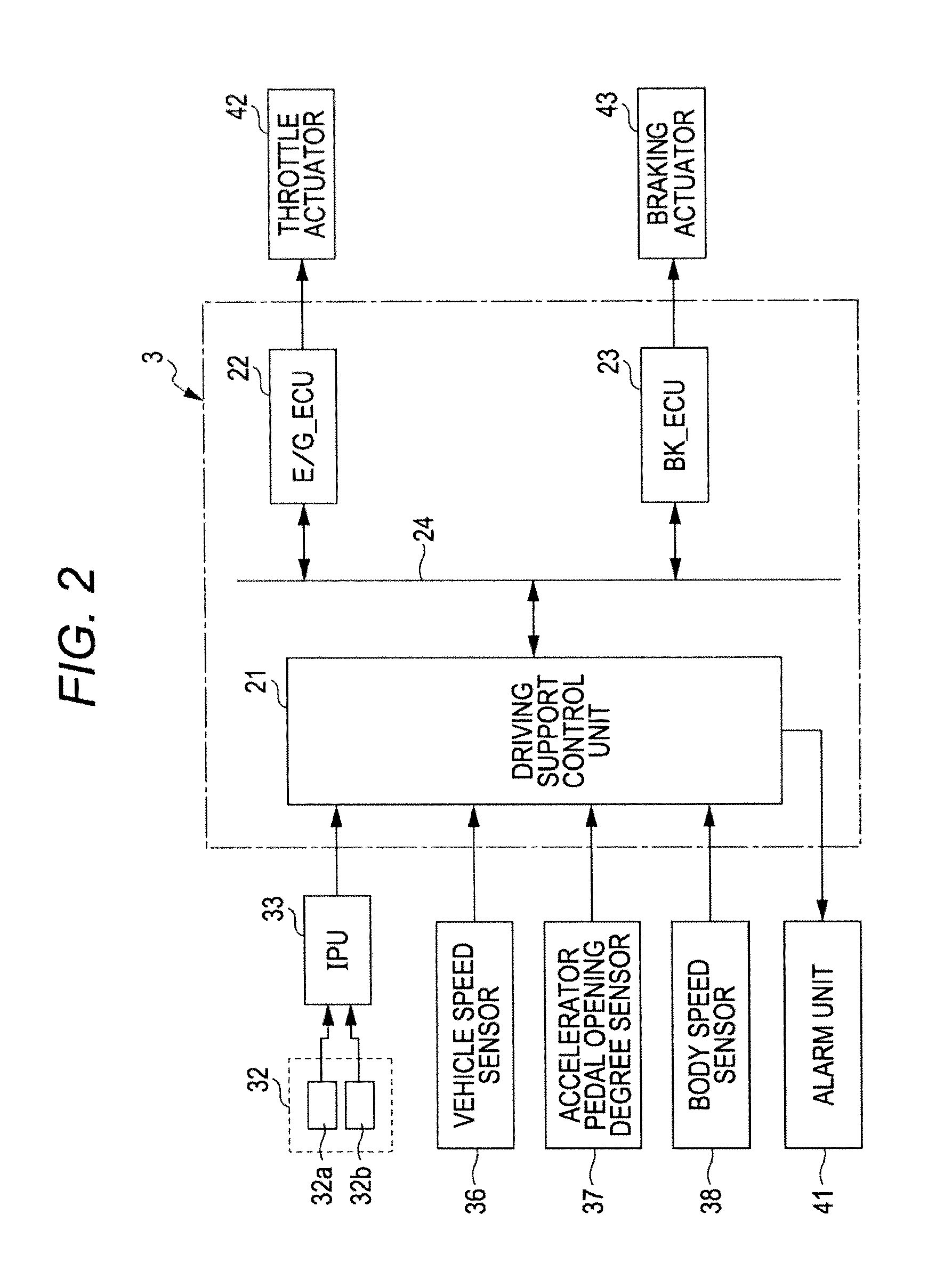
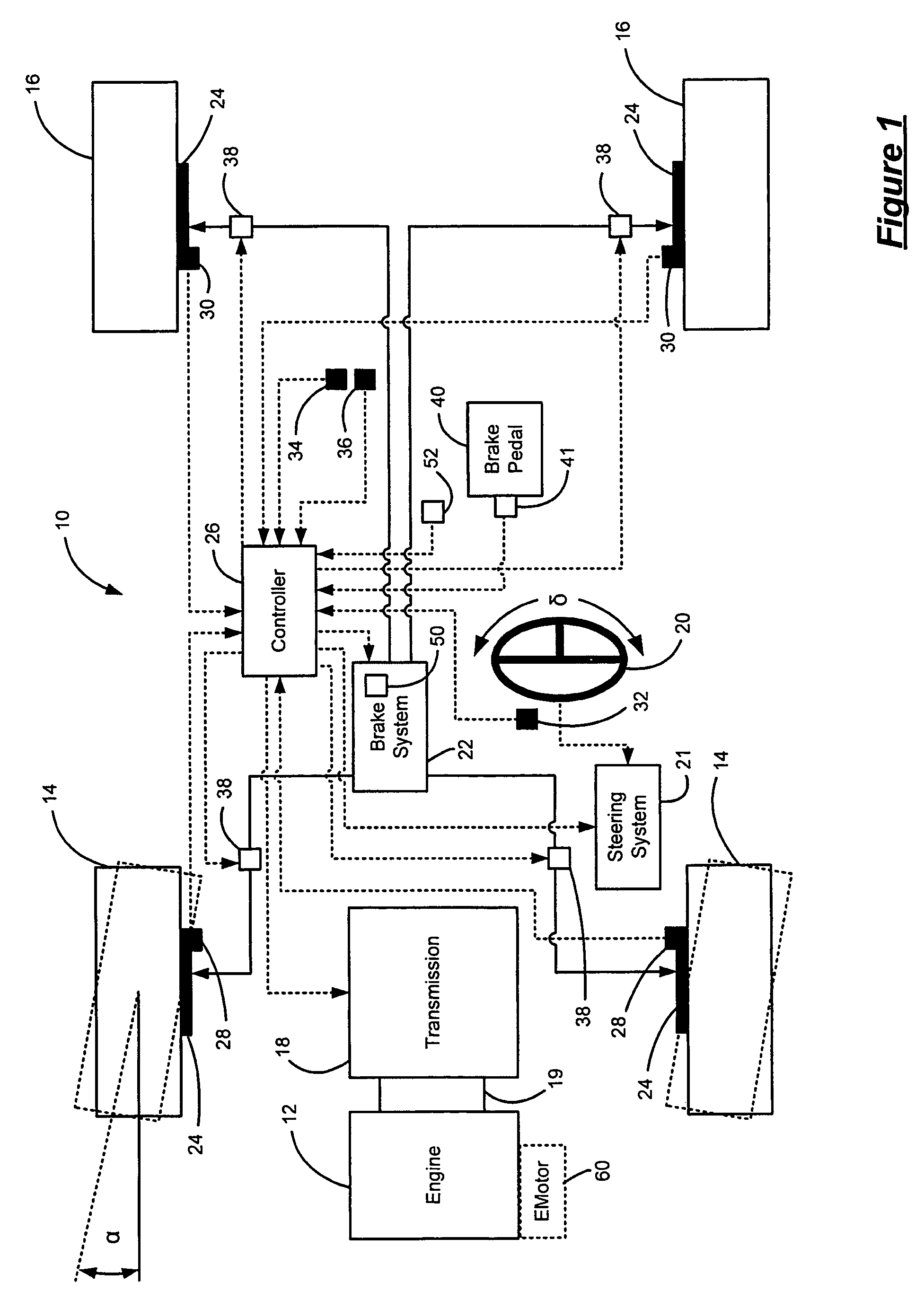
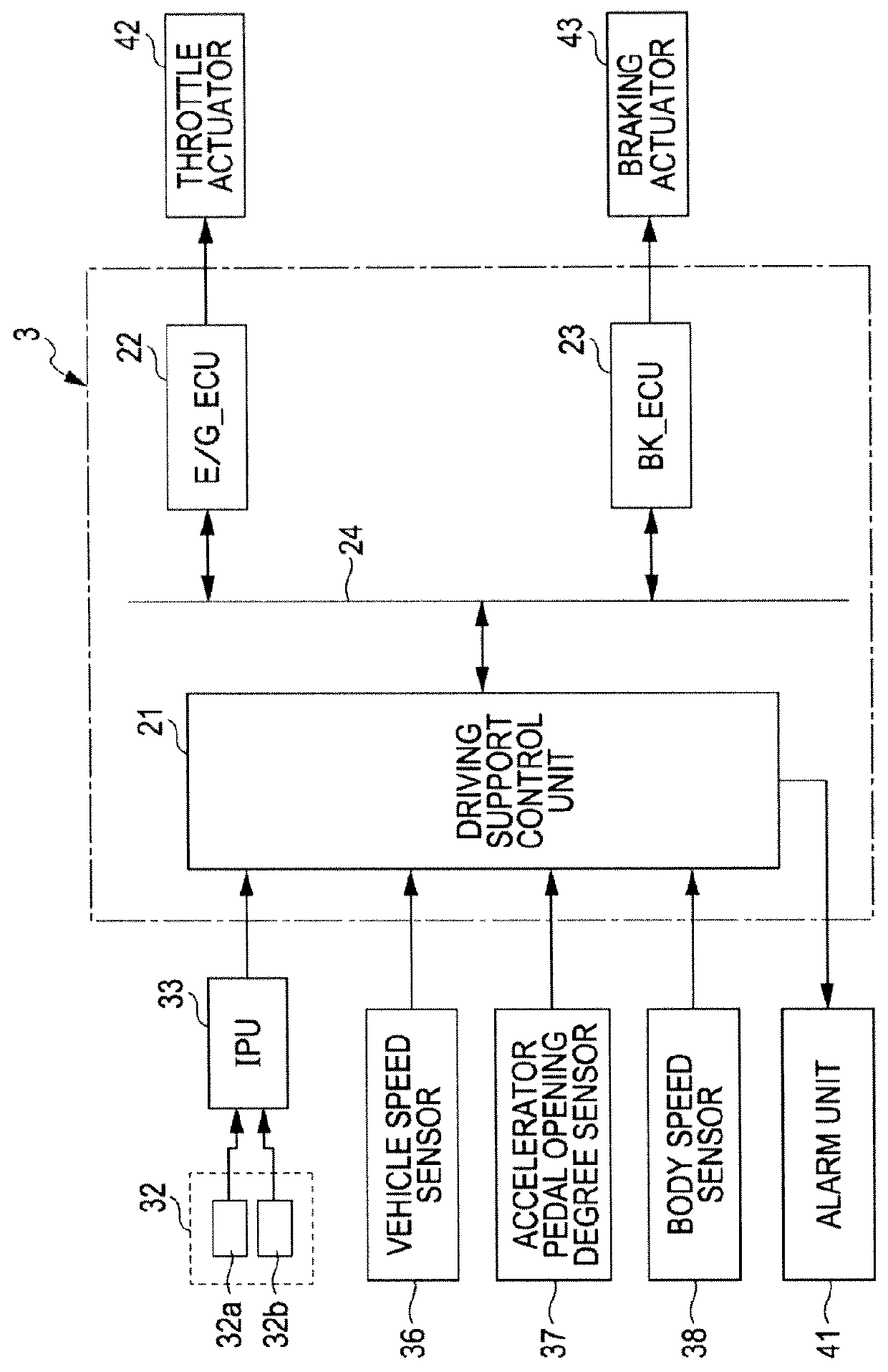
Vehicle driving support apparatus
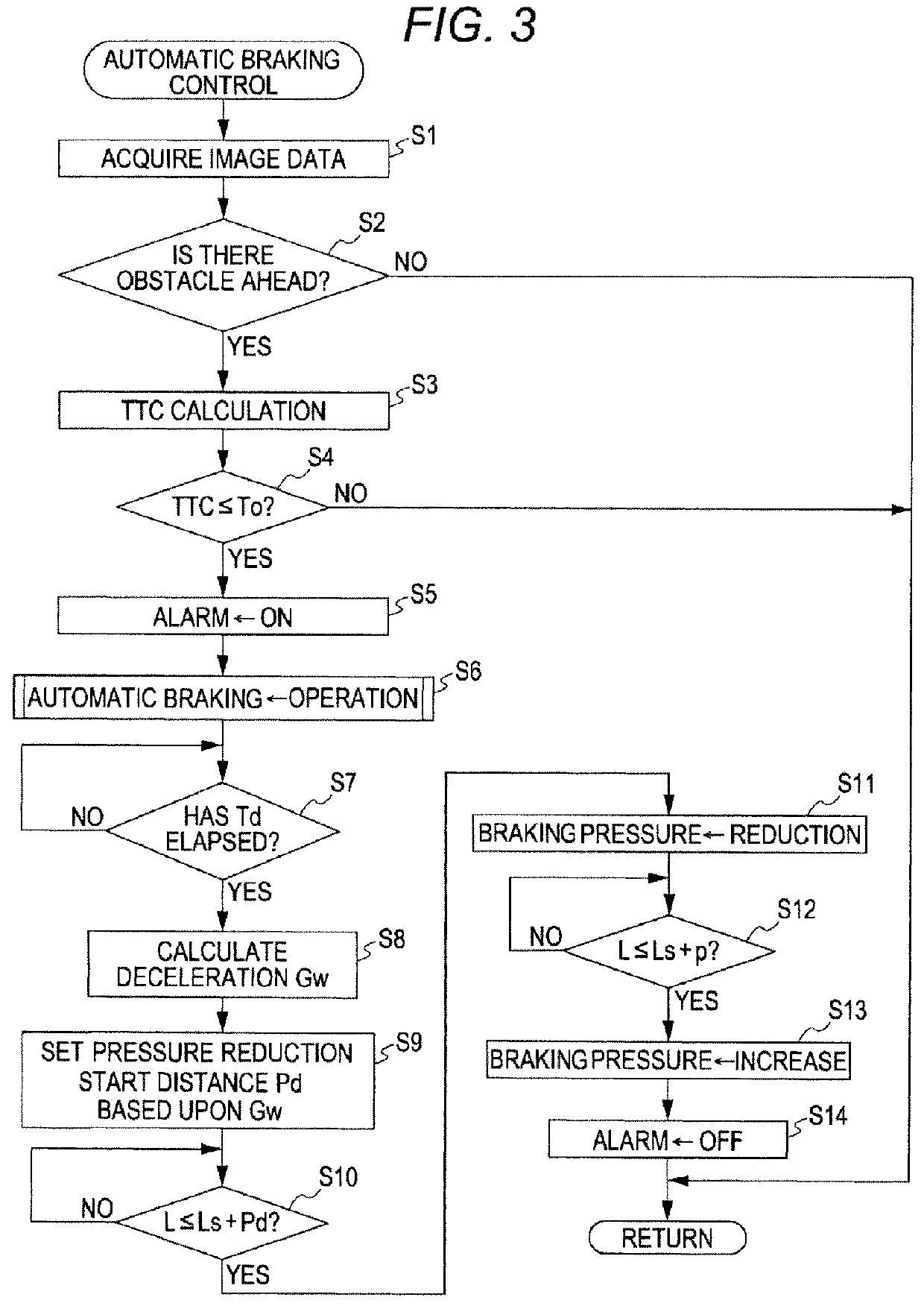
ActiveUS20120239266A1Reduce vibrationLess discomfortAnalogue computers for trafficAutomatic initiationsAutomatic brakingVehicle driving
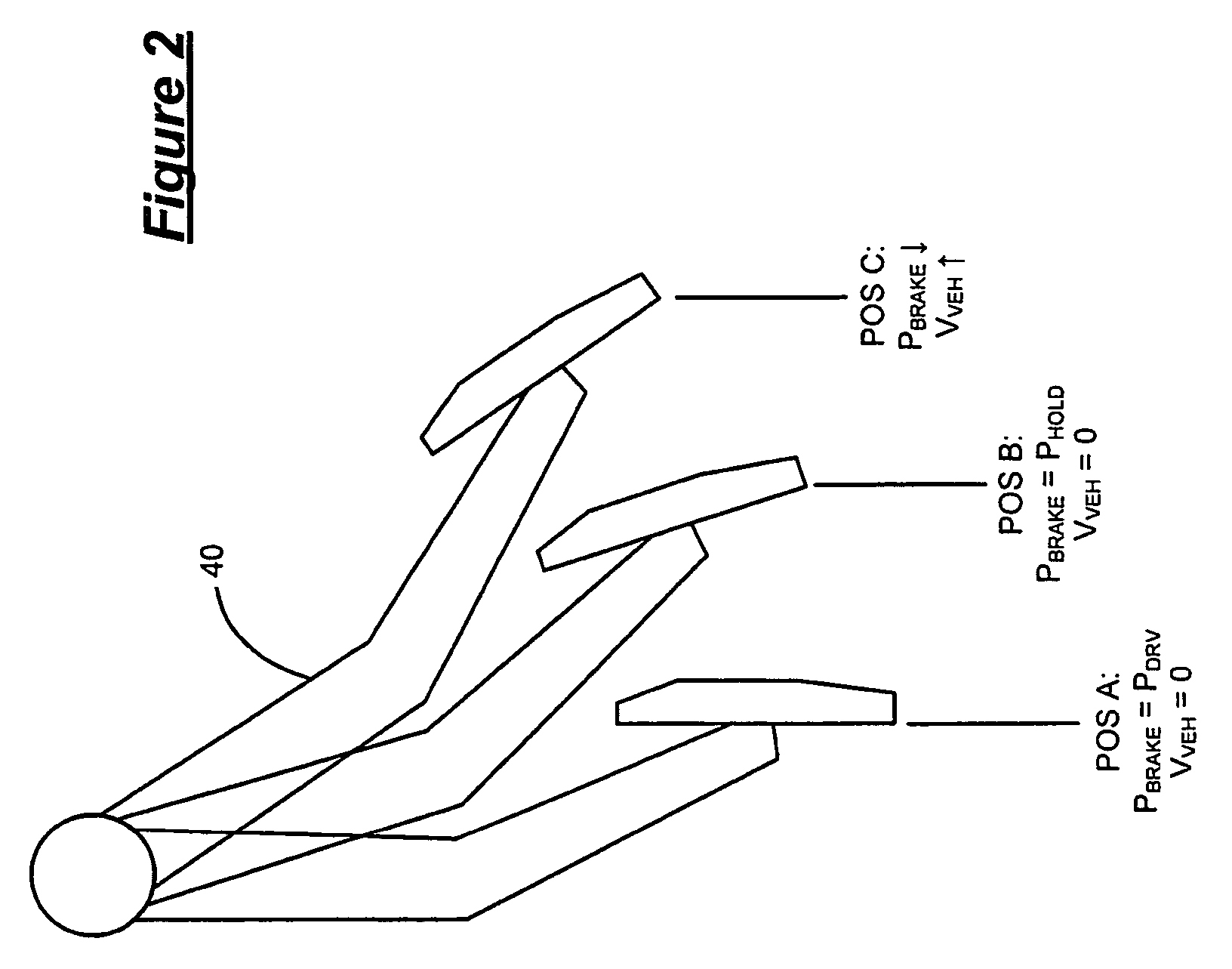
A pressure reduction start distance is obtained (S9) based upon a deceleration after an operation of an automatic brake. When an obstacle-to-vehicle distance between a vehicle and an obstacle ahead becomes a distance obtained by adding the pressure reduction start distance to a target stopping distance to the obstacle ahead, the reduction of the brake pressure is started (S11) to suppress a pitching vibration generated before and after the vehicle stops. When the obstacle-to-vehicle distance becomes a stopping brake start distance that is just before the target stopping distance, the brake pressure is increased (S13) so as to allow the vehicle to stop.
Owner:SUBARU CORP
Soft-stop braking control
InactiveUS7475953B2Eliminating a hard stop (wrap-upReduce brake pressureBraking action transmissionAutomatic initiationsActuatorVehicle brake
A method is provided for applying a soft-stop control to the vehicle brake actuators of a vehicle during a vehicle stop operation. A brake apply operation is detected. A determination is made whether the vehicle speed is below a first threshold stopping speed. Braking pressure to the vehicle actuators is reduced as a function of vehicle speed, vehicle deceleration, and brake apply pressure if the vehicle speed is below the first threshold stopping speed.
Owner:KELSEY HAYES CO
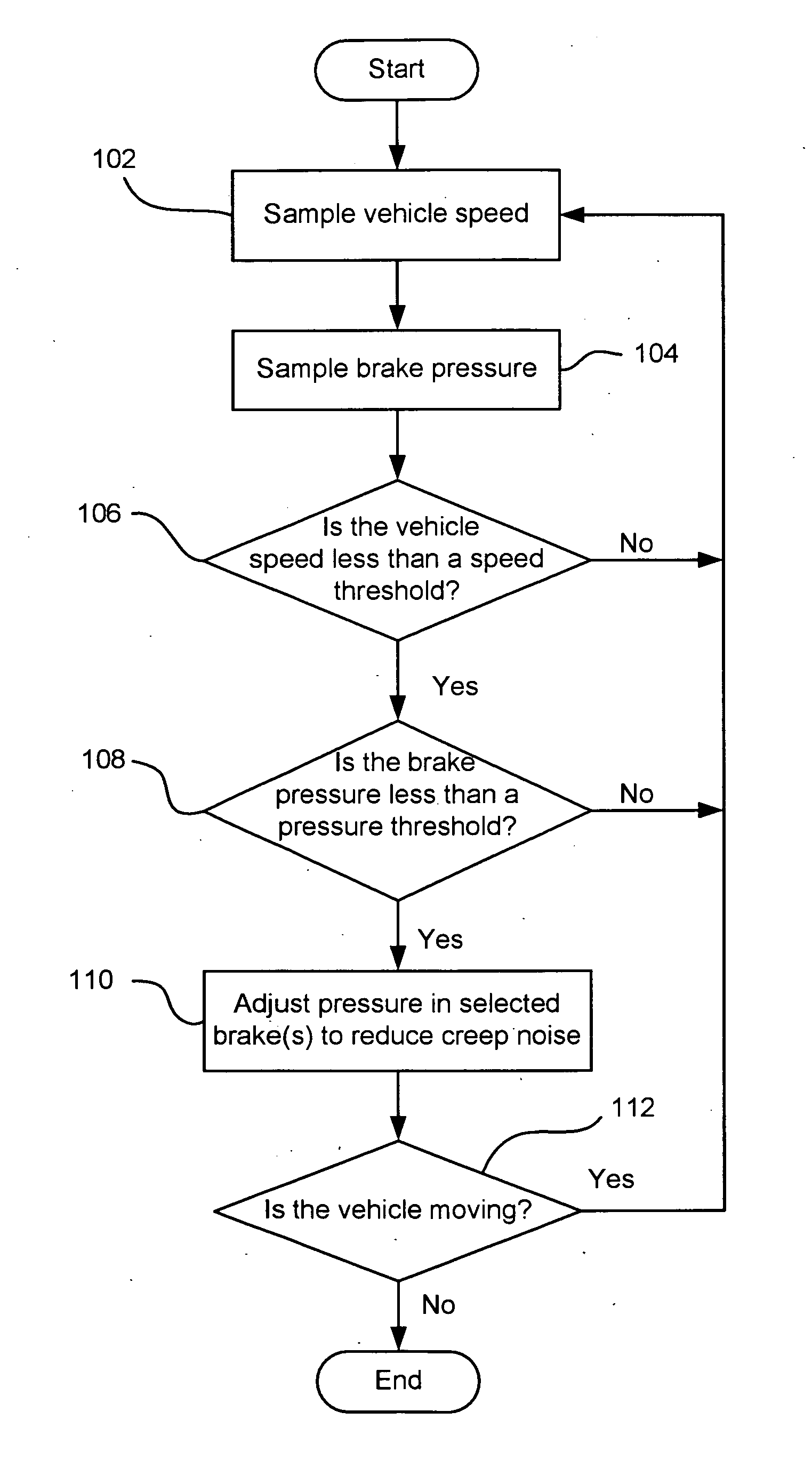
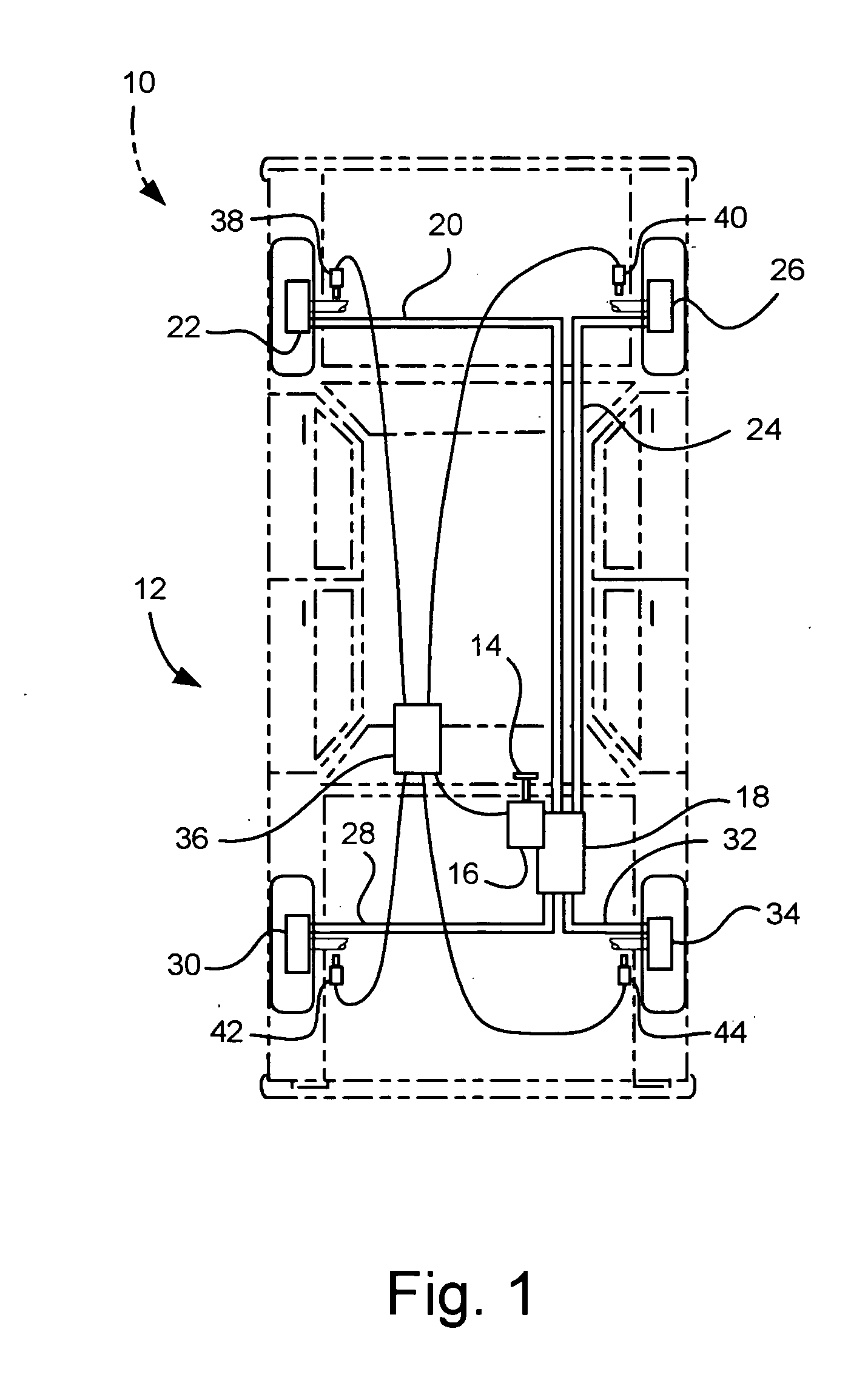
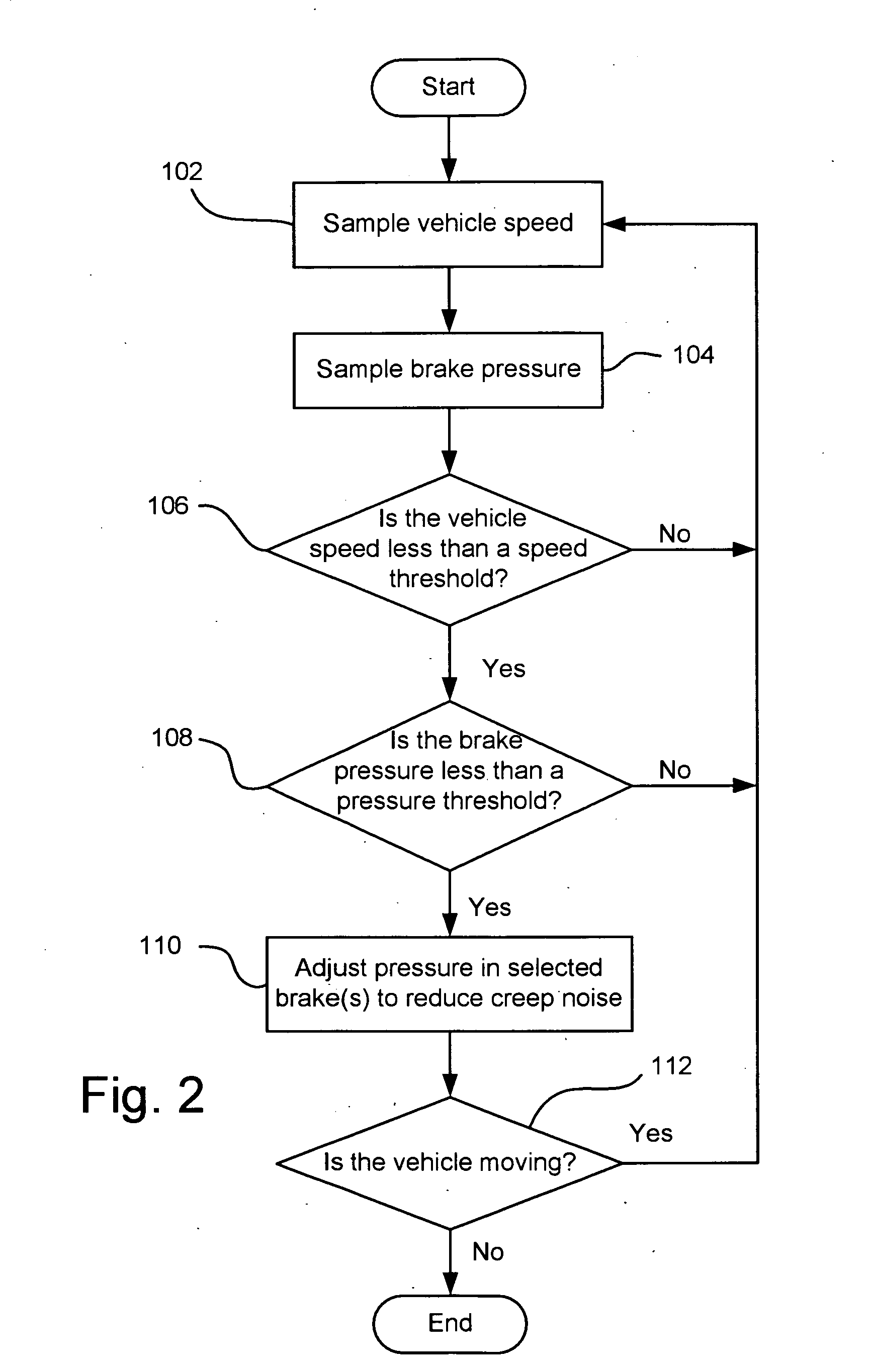
Method and system for reducing vehicle brake creep noise
InactiveUS20070216224A1Reducing creep groan noiseReduce noiseNoise/vibration controlBraking systemsPressure thresholdVehicle brake
The invention concerns a method and system for reducing vehicle brake creep noise by adjusting the pressure in selected wheel brake assemblies when the vehicle speed is less than a speed threshold and the brake pressure is less than a pressure threshold.
Owner:KELSEY HAYES CO
Recovery of energy in a hybrid vehicle comprising a hydraulic or pneumatic braking system
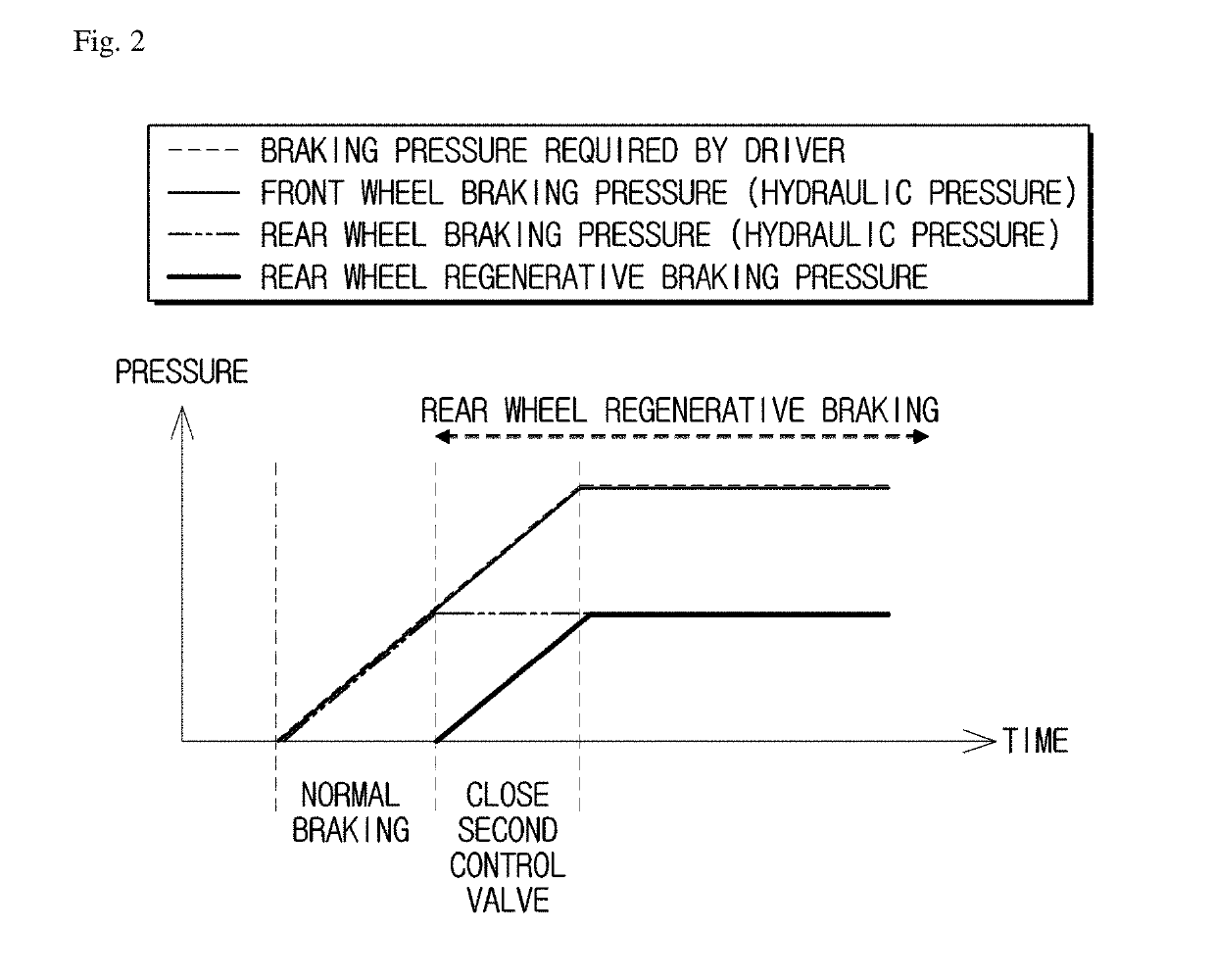
InactiveCN101242981AReduce brake pressureBraking element arrangementsBraking action transmissionElectricityDriver/operator
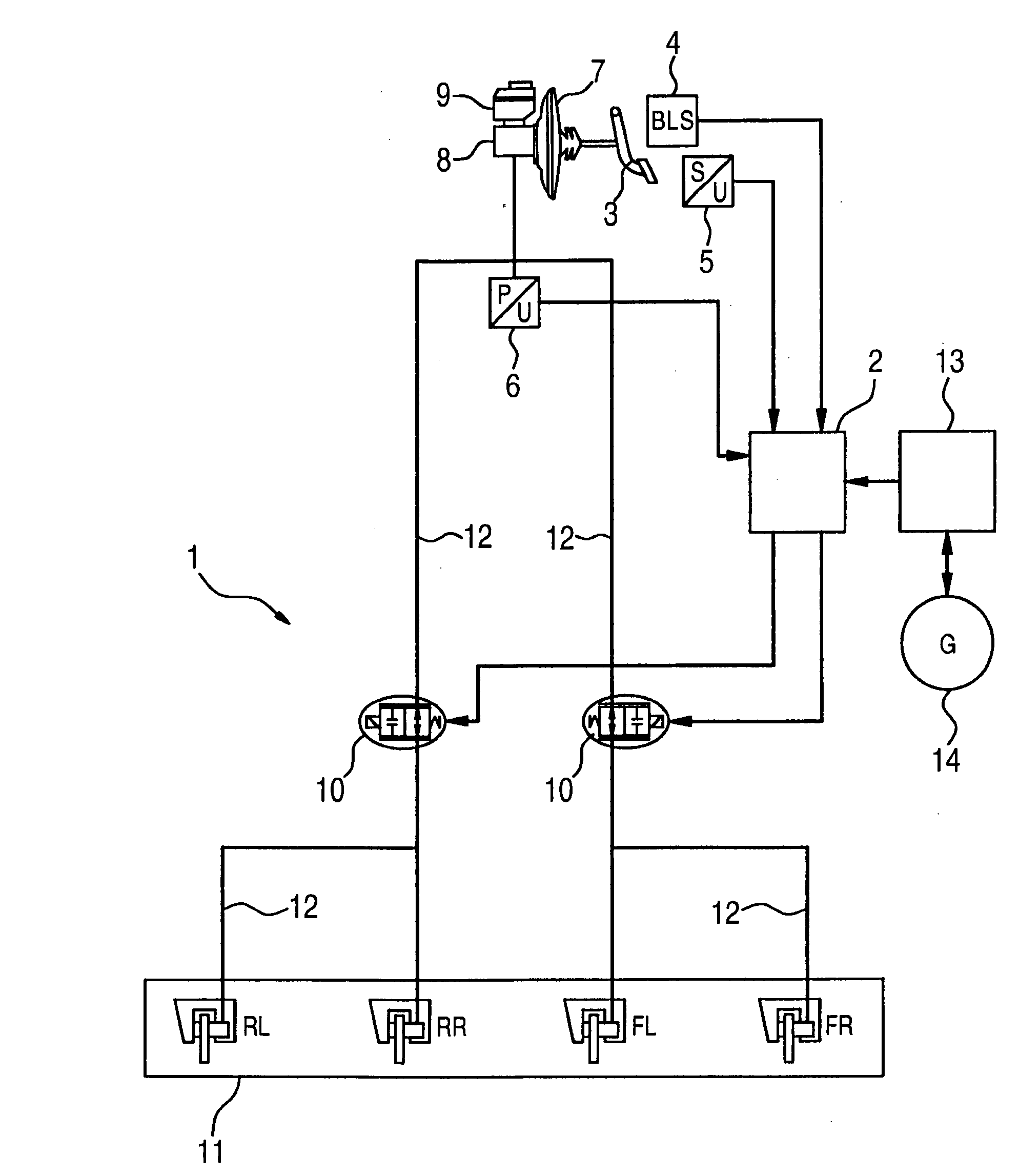
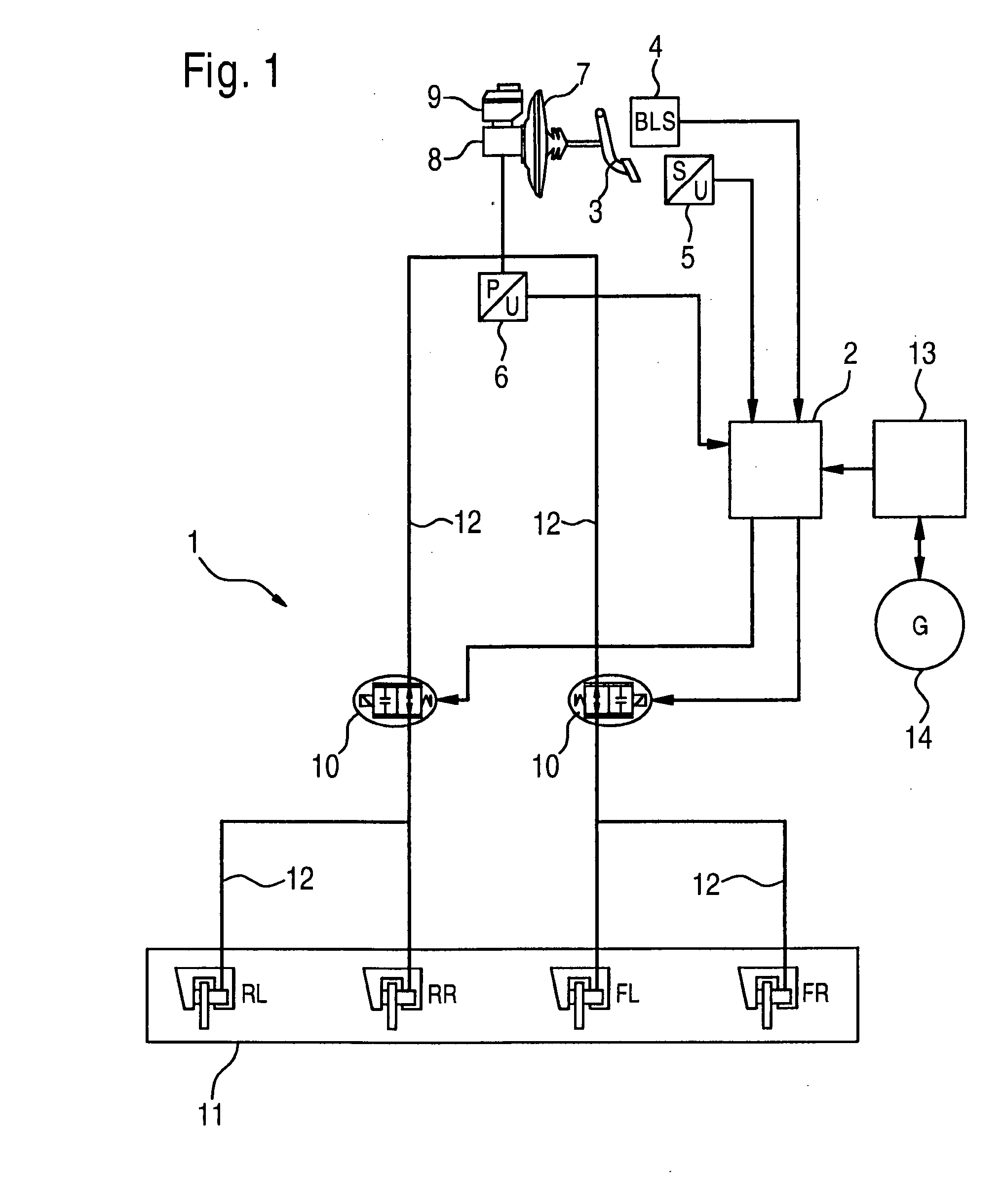
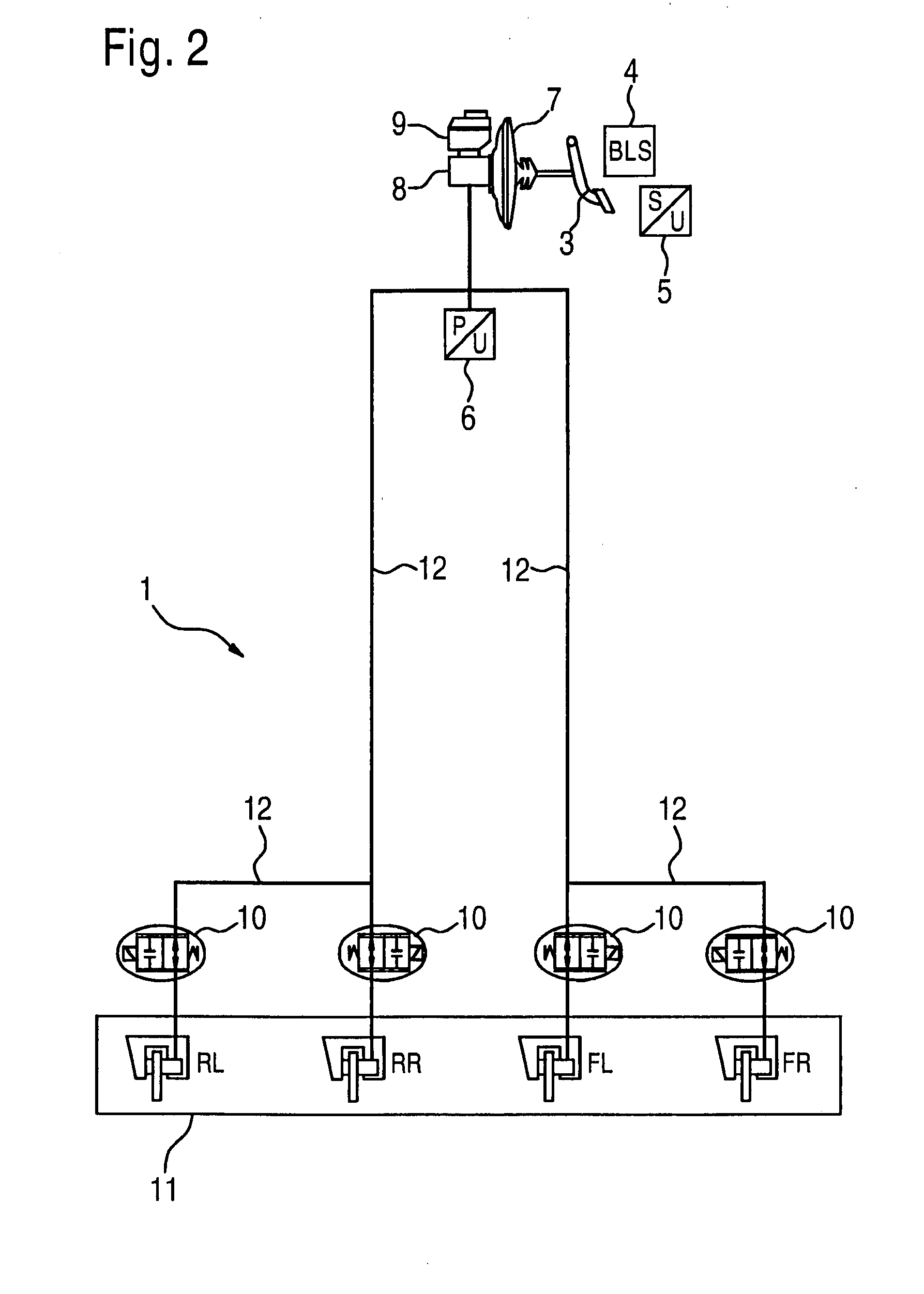
The invention relates to a method for recovering energy during a braking operation of a hybrid vehicle comprising an internal combustion engine and an electric drive (14), in addition to a hydraulic or pneumatic braking system (1). The use of the electric drive (14) can be optimised, if the braking system (1) comprises at least one pressure regulating valve (10), which is used to reduce the braking pressure exerted by the driver, in conjunction with the deceleration rate of the electric drive (14).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
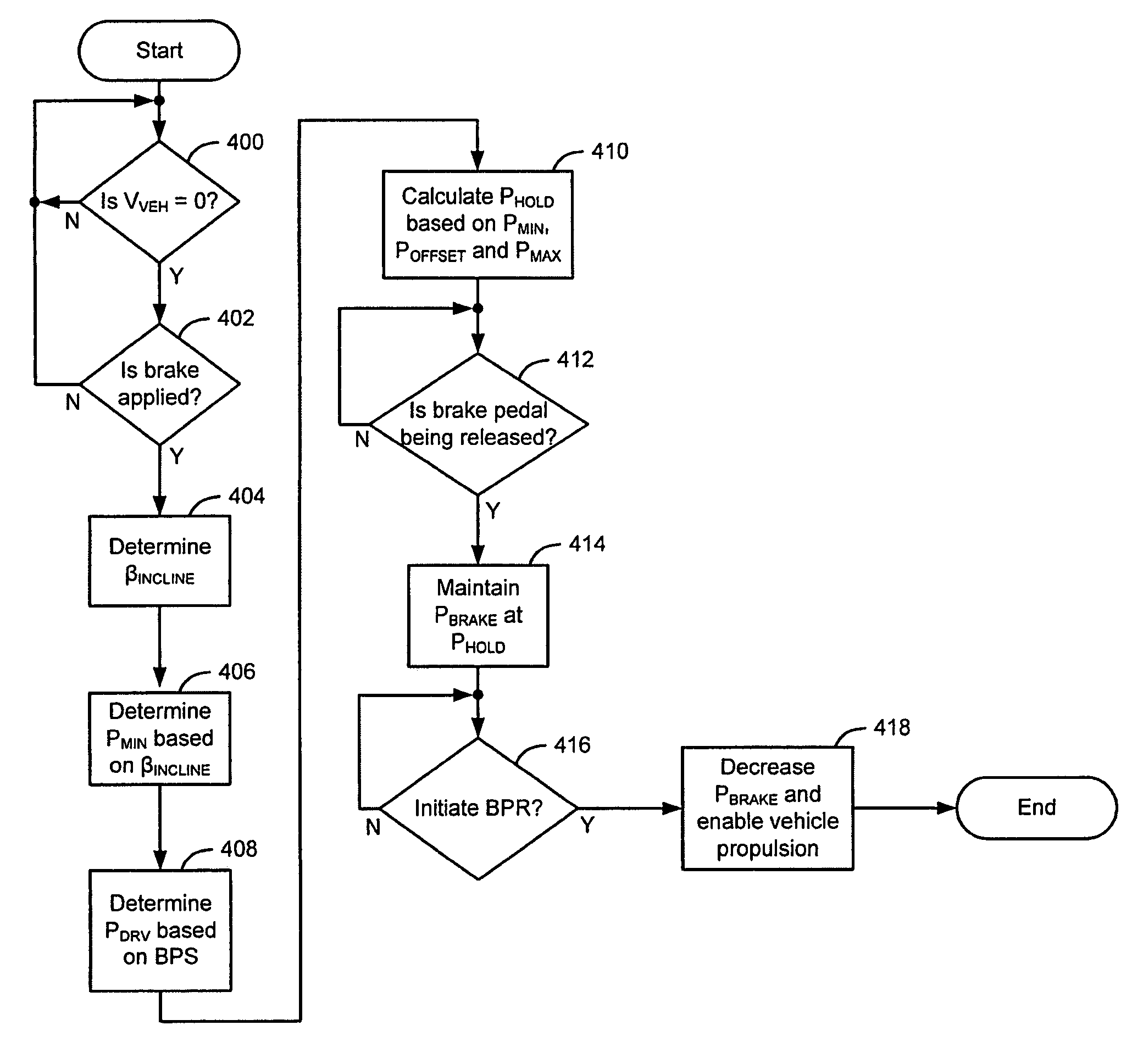
Rollback reduction in hybrid or conventional powertrain vehicle via vehicle stability enhancement system (VSES)
InactiveUS7600827B2Reduce brake pressurePrevent rollbackSpeed controllerBraking action transmissionDriver/operatorControl system
An anti-rollback control system for a vehicle having a brake system includes a brake pedal that is operable to induce a brake pressure in the brake system and a control module that holds the brake pressure equal to a hold pressure that is based on an incline angle to inhibit rollback of the vehicle when pressure is relieved from the brake pedal. The control module initiates forward propulsion of the vehicle based on a driver input and reduces the brake pressure from the hold pressure concurrent to initiating the forward propulsion.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Recovery of energy in a hybrid vehicle having a hydraulic or pneumatic braking system
InactiveUS20090299591A1Reduce brake pressureSimple and cost-effective adjustmentBraking element arrangementsAnalogue computers for trafficElectricityDriver/operator
In a method for recovering energy in a braking process of a hybrid vehicle which has an internal combustion engine and an electric drive, as well as a hydraulic or pneumatic braking system, the exploitation of the electric drive is able to be optimized if the braking system includes at least one pressure reduction valve, using which the braking pressure exerted by the driver is able to be reduced as a function of the deceleration proportion of the electric machine.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Automobile reinforcing brake auxiliary wheel system
InactiveCN101456410AReduce brake pressureGood directional controlBraking element arrangementsDriver/operatorDriving safety
The invention relates to a system for reinforcing the braking of an auxiliary wheel of an automobile. A vehicle bridge of the bottom of the automobile is provided with a set or a plurality of sets of tires capable of moving up and down. When the automobile has emergency brake, a driver steps on a foot brake and simultaneously presses a startup switch of the system; an auxiliary tire set is instantly ejected out and is contacted with the ground, thereby having braking force on the automobile; therefore, besides the tire of the automobile in normal driving has braking force, the braking force of the auxiliary tire on the automobile is increased so as to increase resultant force of automobile braking, thereby shortening the inertia forward distance after the automobile is braked; with the system, the braking force of a front wheel can be set to be small, that is, the front wheel can also have little rotation when being braked; the automobile has good direction control effect when being braked; and with two advantages, the automobile improves driving safety.
Owner:卢如年
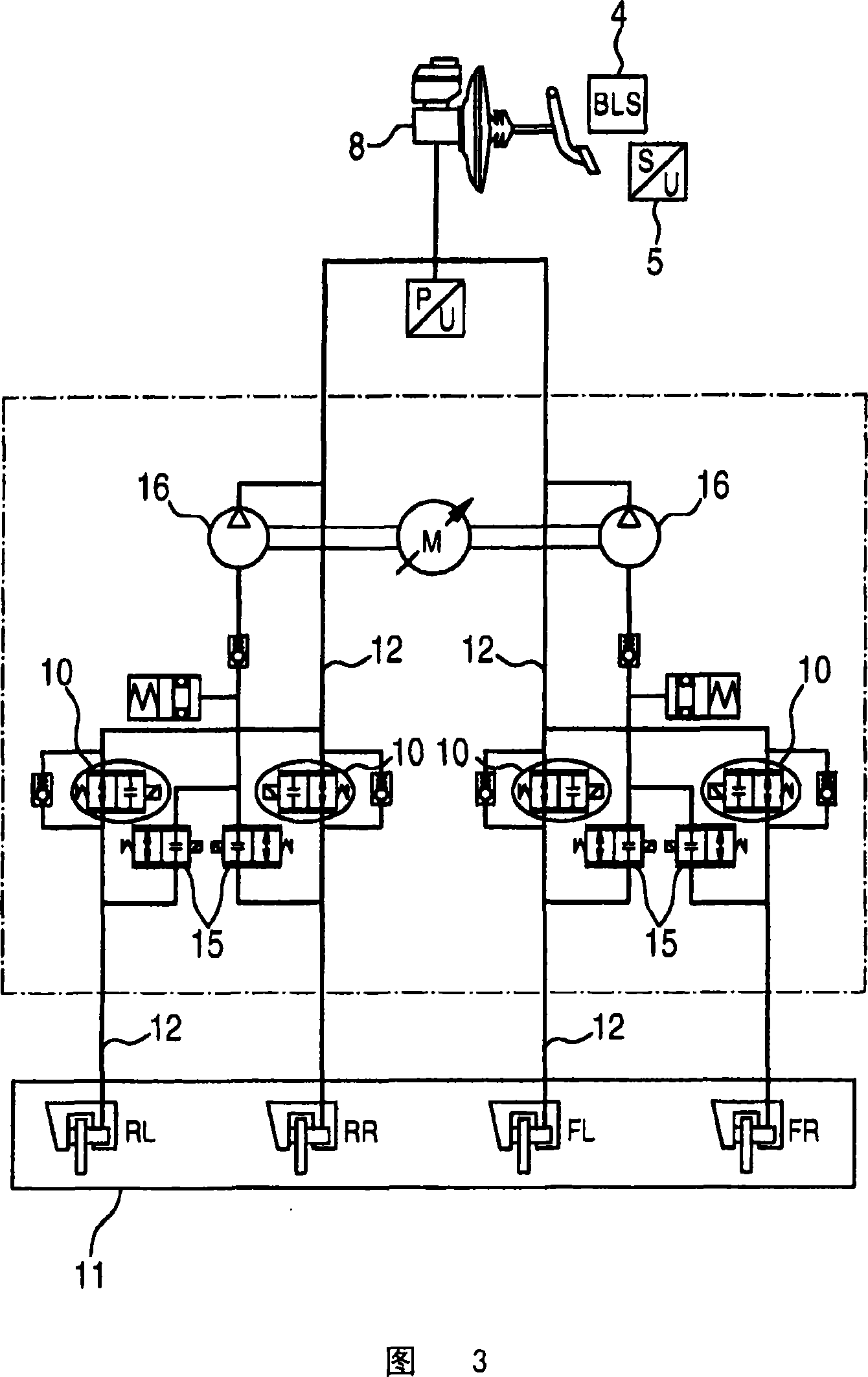
Brake system with electromotively driven piston/cylinder system
ActiveUS8371661B2Reduce brake pressureReduce assemblyBraking action transmissionRotary clutchesGuide tubePiston
The invention relates to a brake system which comprises an actuating device (26), especially a brake pedal (30), and a control / regulation device (22). Said control / regulation device (22) controls an electromotive drive device (8) in response to the movement and / or position (38) of the actuating device (30). The drive device (8) adjusts a piston (1) of a piston / cylinder system via a non-hydraulic transmission device (6), thereby adjusting a pressure in the working compartment (4′) of the cylinder (4). Said working compartment (4′) is connected to a wheel brake (15, 17) via a pressure conduit (13). In case of drive device (8) failure, the actuating device (26) adjusts the piston (1) or the drive device (8).
Owner:IPGATE
Device that uses gravity to move weights across a shaft assembly for rotation and torque and a braking apparatus to regulate rotation speed
InactiveUS20170191468A1Easy to produceEasy to assembleBraking membersMachines/enginesPistonGravitation
A rotation generation device is provided that includes: at least one pair of Cylindrical Containers having Chambers therein at each end to receive and discharge a fluid, the Cylindrical Containers interconnected via a tubular member and mounted essentially perpendicular to a Shaft; Threaded Caps with dual nozzles that screw on to each Chamber at the end of the Cylindrical Containers; two or more Pistons, each Piston interconnected to another Piston via a hollow tube, each Piston resides in a sliding relationship in a respective Cylindrical Container and wherein the hollow tube resides in the tubular member, the hollow tube having a length for a first of the two or more pistons to cause one of the Cylindrical Containers to receive fluid as the first piston slides within the respective Cylindrical Container, while a second of the two or more pistons causes another of the Cylindrical Containers to discharge fluid therein; a weight, residing and capable of moving laterally within the hollow tube; Pipes interconnecting adjacent Cylindrical Containers via the Cap nozzles; bellows within each Chamber of the Cylindrical Containers, wherein each bellow attaches on one end to a Piston and at an opposite end to the Chamber of the Cylindrical Container.
Owner:SEQUEIRA ANTHONY E
Safe escaper for high building
InactiveCN103041518ASafe and stable escapeEgo Control Escape VelocityBuilding rescueEngineeringGravitational potential
The invention discloses a safe escaper for a high building. The problem that a prior escaping device is not safe is solved. The escaper comprises an escaper housing and an escaping rope, wherein a rotary shaft is arranged in the escaper housing, the escaping rope winds the rotary shaft, the rotary shaft is provided with a braking device which can brake the rotation of the rotary shaft at any time, a slow-lifting device which can slow down the releasing speed of the escaping rope is arranged on the rotary shaft, and the escaper housing or the rotary shaft is provided with a fixing structure which is used for fixing a safety belt. The escaper housing is fixed to an escaping person, the slow-lifting device can remove the gravitational potential energy, the braking pressure of the braking device is reduced, the escaper can operate safely and reliably and the escaping person can escape safely.
Owner:陈喆
Anti-lock hydraulic braking system, in particular for motorized two-wheel vehicles
InactiveUS20080246334A1Simpler and less-expensiveDisruptive effectBraking action transmissionBraking systemBrake pressure
An anti-lock hydraulic braking system has a wheel brake circuit with a main brake cylinder, wheel brake cylinder and switching valve, and an auxiliary pressure circuit, connected in parallel between the switching valve and wheel brake cylinder on the wheel brake circuit. With ABS control, the switching valve can be switched from a basic position, where it hydraulically connects the main brake cylinder and wheel brake cylinder, to a switched position where it prevents a build-up of braking pressure on the wheel brake cylinder via the main brake cylinder, while the braking pressure on the wheel brake cylinder can be modulated by the auxiliary pressure circuit.
Owner:FTE AUTOMOTIVE GMBH & CO KG
Electric braking system and operation method thereof
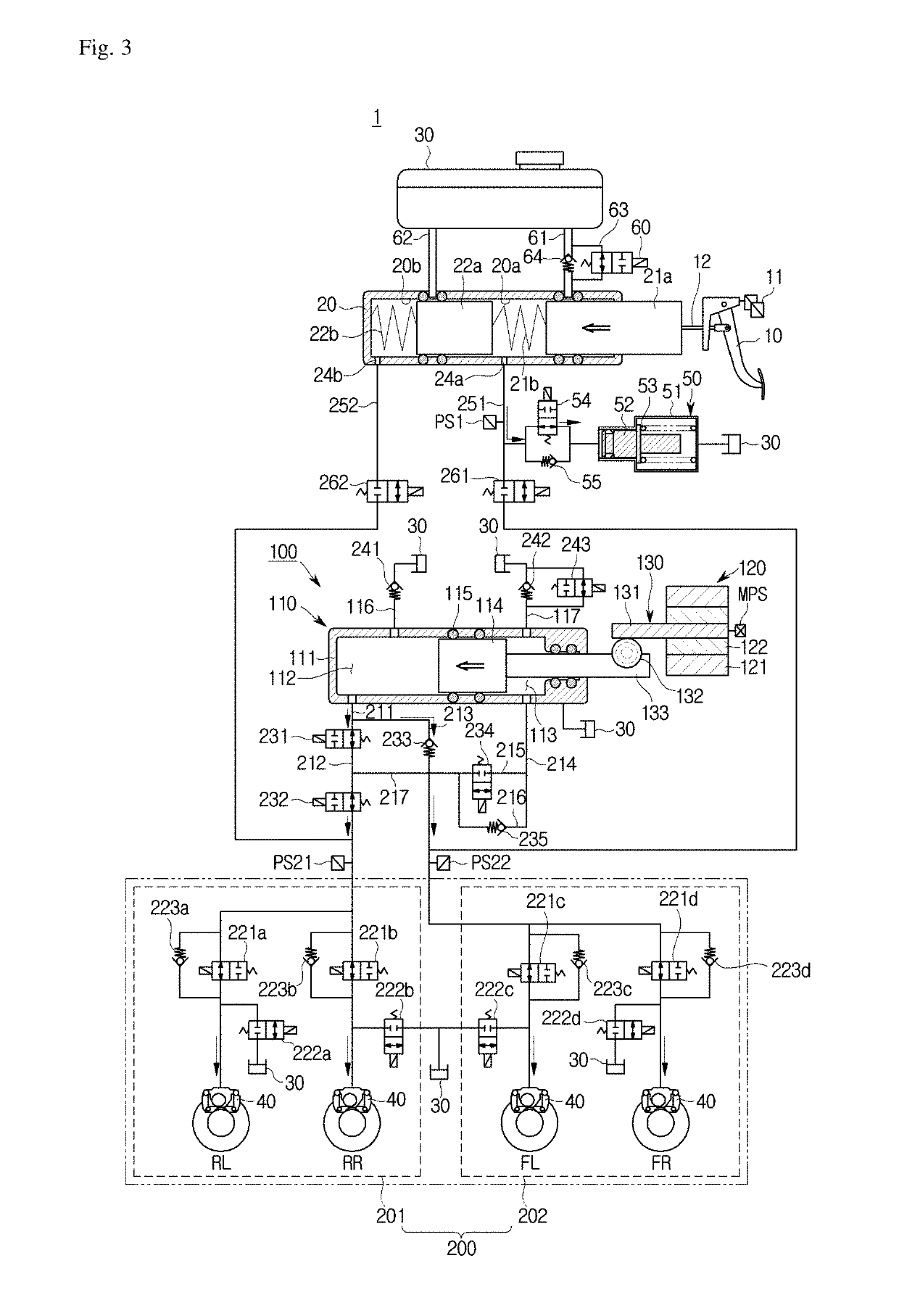
ActiveUS20190100185A1Effectively performing brakingFacilitating driving stability of vehicleBraking action transmissionFoot actuated initiationsRegenerative brakeWheel cylinder
Disclosed is an electronic braking system and operation method thereof. The electronic braking system and operation method thereof includes a hydraulic pressure supplier configured to create hydraulic pressure by moving a hydraulic piston based on an electric signal output to correspond to displacement of a brake pedal, and a hydraulic controller configured to control hydraulic pressure of a pressure medium applied to each wheel cylinder, and performs normal operation mode, abnormal operation mode, regenerative braking mode, and check mode by controlling a plurality of valves equipped in the hydraulic controller.
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
Control device for a hybrid vehicle
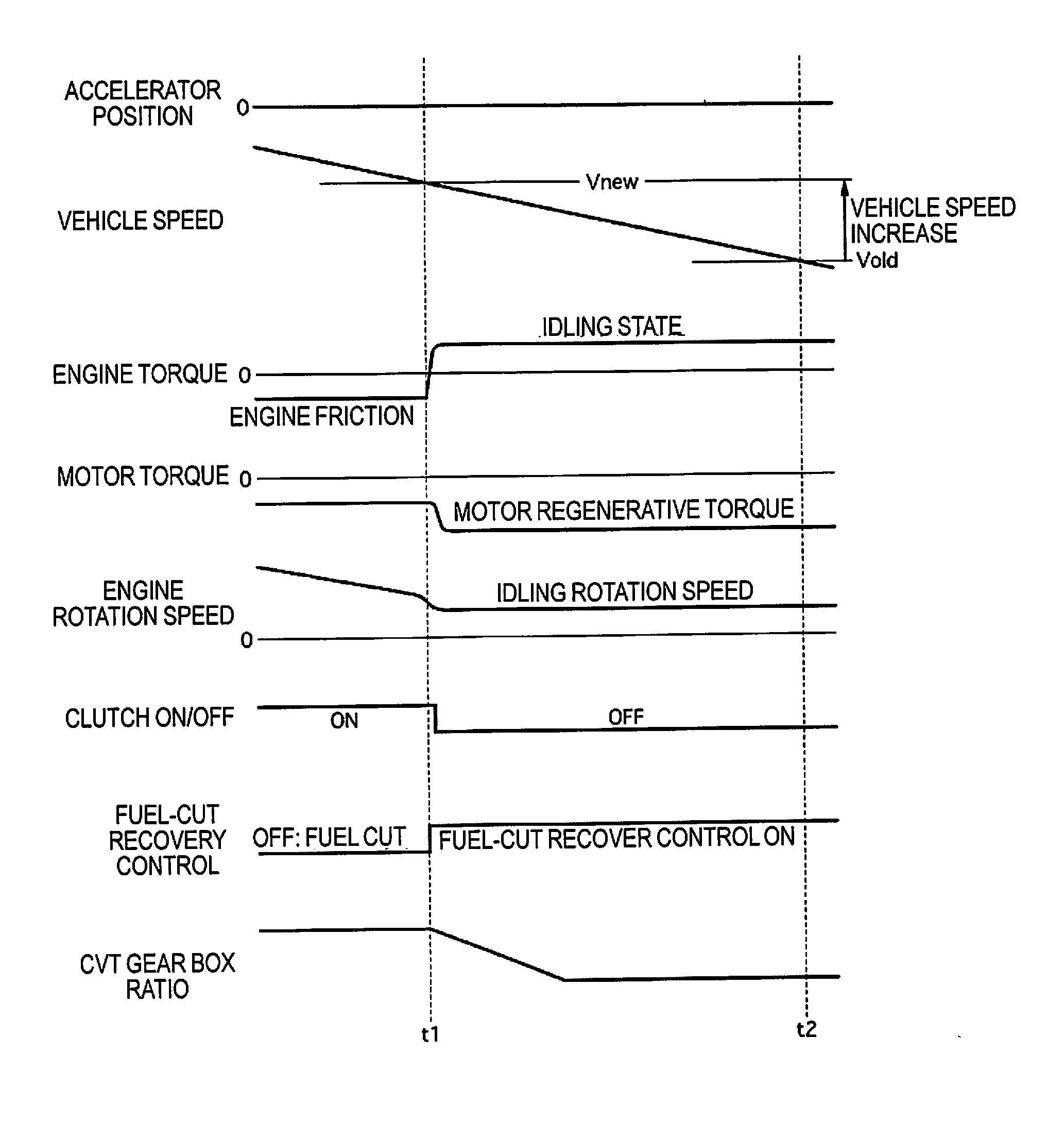
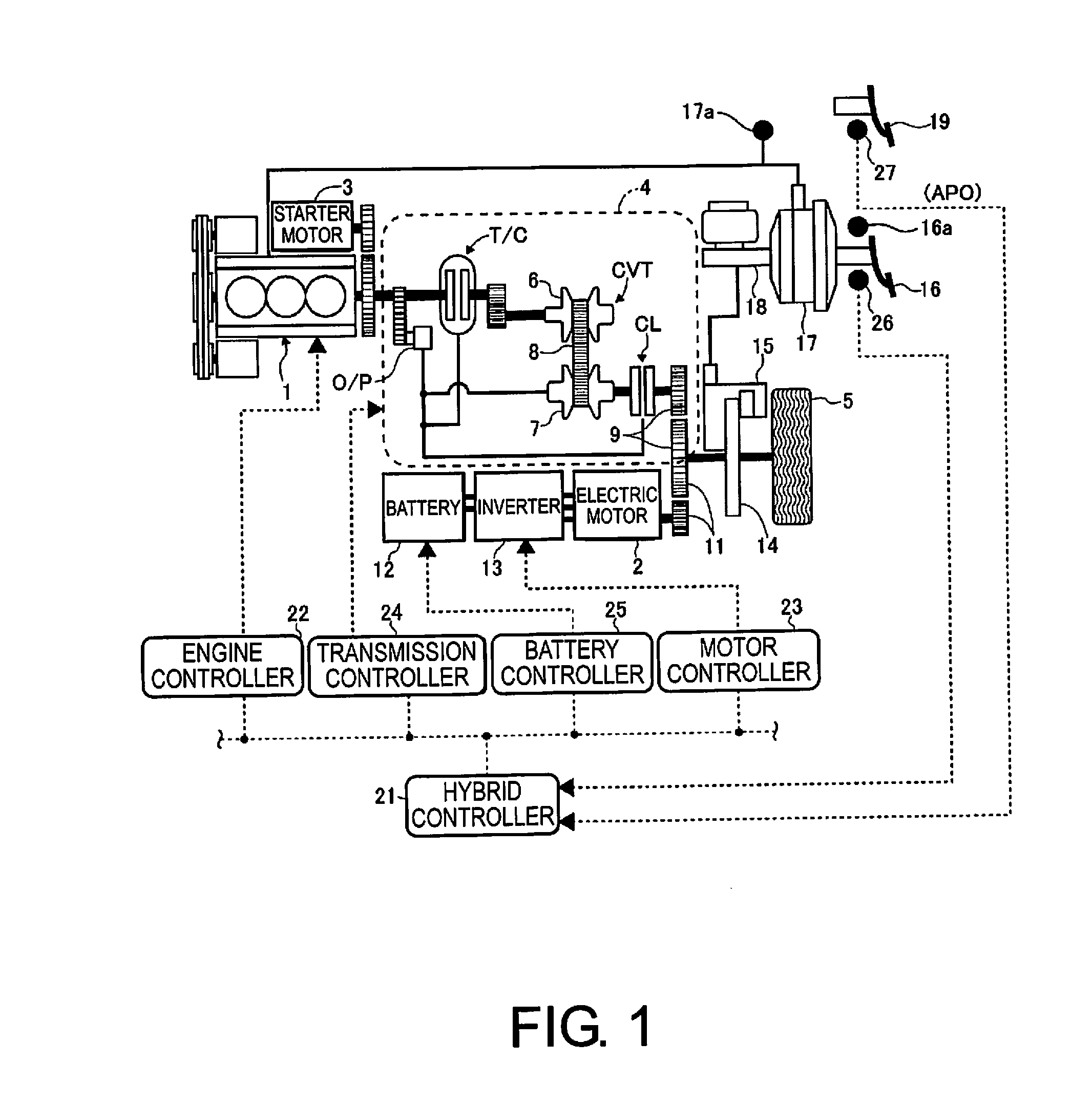
InactiveUS20160229391A1Recover regenerative energyEffective recoveryElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesHybrid vehicleAutomotive engineering
A control device in a hybrid vehicle includes a controller capable of switching, between an operating state and a non-operating state, a fuel-cut recovery control in which engine rotation speed is kept at or above a predetermined rotation speed by starting supply of fuel upon the engine rotation speed falling to the predetermined rotation speed from a state in which the engine rotation speed is higher than the predetermined rotation speed and the supply of fuel is stopped.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
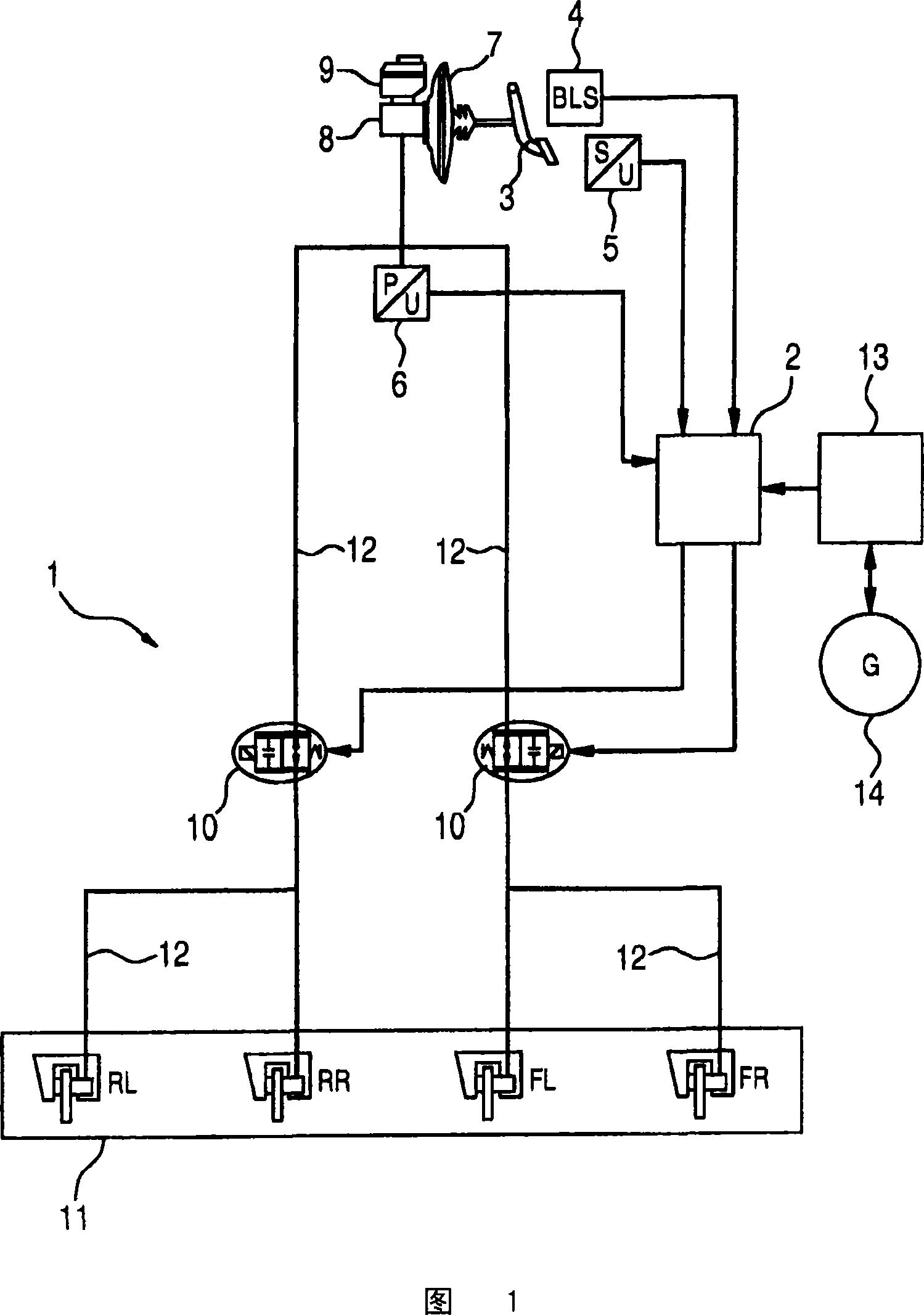
Control device for a hydraulic braking system of a vehicle, hydraulic braking system for a vehicle, and method for operating a hydraulic braking system of a vehicle
InactiveUS20160059706A1Avoids disadvantageReduce average brake pressureBraking action transmissionElectrodynamic brake systemsBrake pressureAutomotive engineering
A control device is provided for a hydraulic braking system of a vehicle, including an actuating device which is designed for outputting, at least temporarily, at least one first control signal and at least one second control signal in at least a first operating mode, taking into account at least one sensor signal. A known hydraulic braking system may be controlled with the aid of the control signals, output by the actuating device, in such a way that during an activation of a brake actuating element, at least one blending valve of a first brake circuit which is connected to the master brake cylinder via a first changeover valve is controlled into an at least partially open state in such a way that brake fluid is displaceable into at least one storage chamber, and at least one first brake pressure which is present in at least one first wheel brake cylinder of the first brake circuit is limitable, and a pressure relief valve of a second brake circuit, which is connected to the master brake cylinder via a second changeover valve, is controlled into an at least partially open state in such a way that brake fluid is displaceable into a brake fluid reservoir, and at least the first brake pressure is additionally reducible. Moreover, a hydraulic braking system is provided which includes the control device, and a method is provided for operating a hydraulic braking system.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Electropneumatic spring brake device of a motor vehicle with an abrupt pressure increase when releasing the brake
ActiveCN106414194AIncreased flow cross sectionAdjust the flow cross sectionFluid braking transmissionApplication and release valvesElectricityElectronic controller
The invention relates to an electropneumatic spring brake device (1) of a motor vehicle, including means for generating electric brake actuation signals that represents at least the "brake application" state and the "brake release" state; an electronic controller (8) which receives the brake actuation signals; an electropneumatic valve device (10) which is controlled by the electronic controller (8) dependent on the actuation signals; and at least one pneumatically actuated spring brake cylinder. The electropneumatic valve device (10) aerates the at least one spring brake cylinder by connecting to a compressed air supply (12) or de-aerates the spring brake cylinder by connecting to a pressure sink (3). A maximally aerated state, which can be brought about by the electronic controller (8), of the electropneumatic valve device (10) is produced in that the electropneumatic valve device (10) releases a maximum flow cross-section between the compressed air supply (12) and the at least one spring brake cylinder. According to the invention, the electronic controller (8) is designed to keep the electropneumatic valve device (10) in the maximally aerated state when switching from the "brake application" state to the "brake release" state while the vehicle is traveling until the pressure in the at least one spring brake cylinder is abruptly increased from a starting pressure value lying below a first gradient to a relatively higher first pressure value which still lies below a brake release pressure that fully releases the spring brake cylinder, and after the first pressure value has been reached, the electropneumatic valve device is switched to a state in which the pressure in the at least one spring brake pressure cylinder is increased from the first pressure value lying below a second gradient that is smaller than the first gradient to a second pressure value that is higher than the first pressure value in order to assume a partial release position or a full release position.
Owner:KNORR-BREMSE SYST FUER NUTZFAHRZEUGE GMBH
Vehicle driving support apparatus
ActiveUS9248811B2Less discomfortReduce vibrationAnalogue computers for trafficAutomatic initiationsAutomatic brakingVehicle driving
A pressure reduction start distance is obtained (S9) based upon a deceleration after an operation of an automatic brake. When an obstacle-to-vehicle distance between a vehicle and an obstacle ahead becomes a distance obtained by adding the pressure reduction start distance to a target stopping distance to the obstacle ahead, the reduction of the brake pressure is started (S11) to suppress a pitching vibration generated before and after the vehicle stops. When the obstacle-to-vehicle distance becomes a stopping brake start distance that is just before the target stopping distance, the brake pressure is increased (S13) so as to allow the vehicle to stop.
Owner:SUBARU CORP
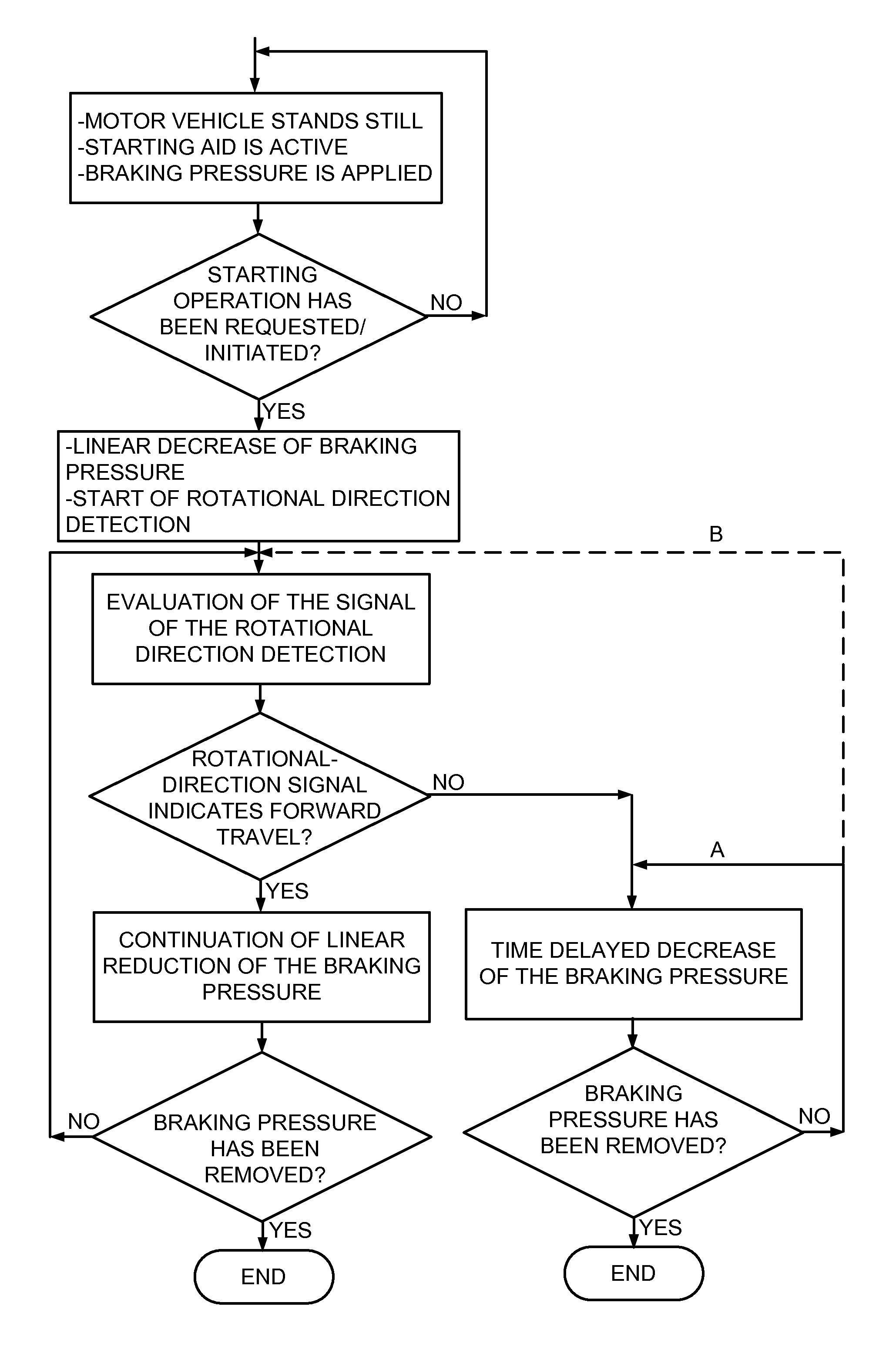
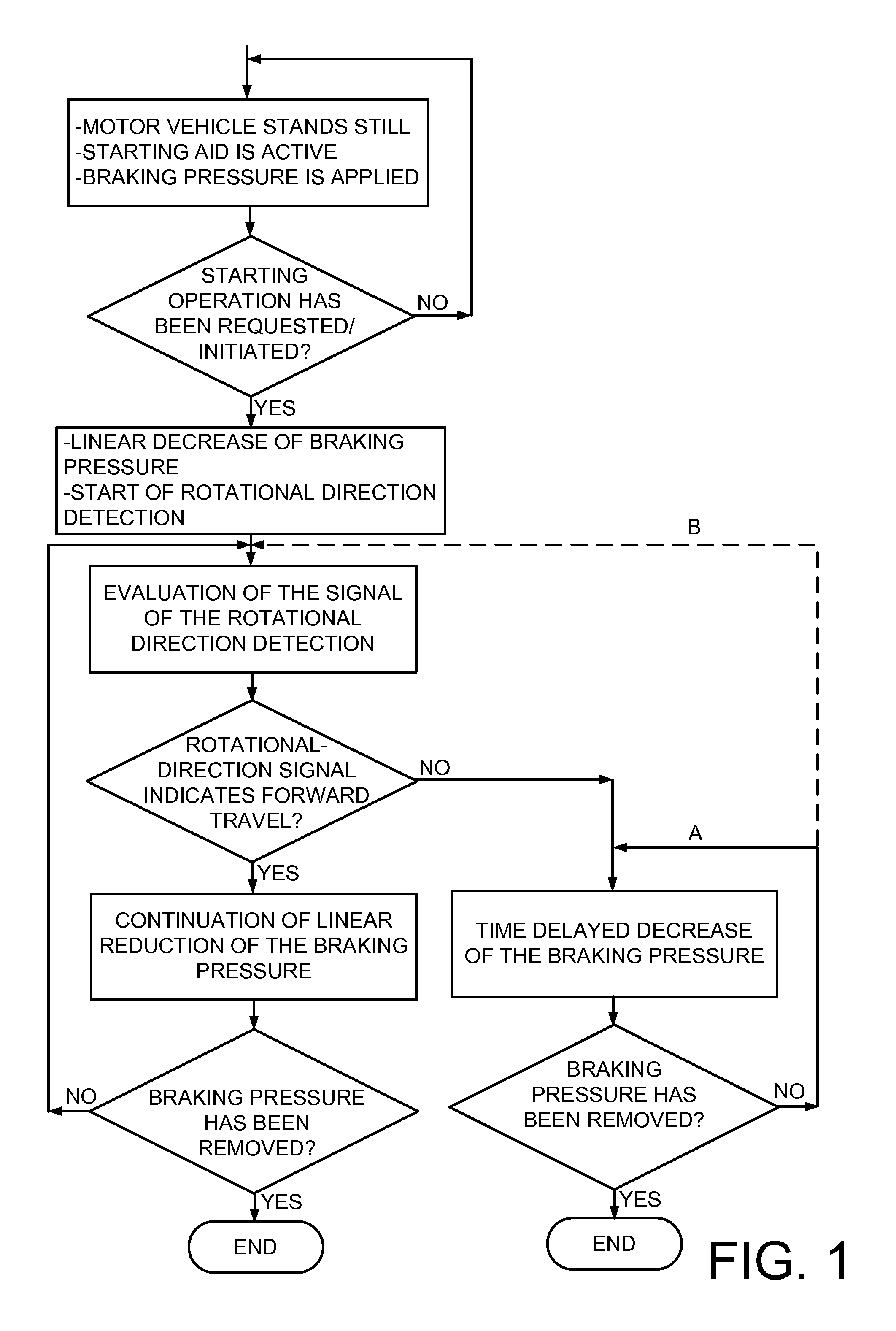
Method for controlling a starting aid of a motor vehicle
ActiveUS20130144499A1Reduce brake pressureEasy to operateAnalogue computers for trafficBraking action transmissionMobile vehicleDrive wheel
The invention concerns a method for controlling a starting aid of a motor vehicle, in particular of a bus. The release of the starting aid takes place as follows: reduction of the braking pressure in accordance with a predetermined first gradient; simultaneous detection of the rotational direction of an output shaft of a transmission of the motor vehicle or of another component which rotates as a function of the rotational speed of the drive wheels; upon detection of a rotational-direction signal, which indicates forward travel of the motor vehicle, continuation of the reduction in the braking pressure in accordance with the predetermined first gradient and upon detection of another signal, continuation of the reduction of the braking pressure by way of a second gradient which is reduced in comparison with the first gradient or an increase in the braking pressure.
Owner:VOITH PATENT GMBH
Incremented brake pipe pressure reduction
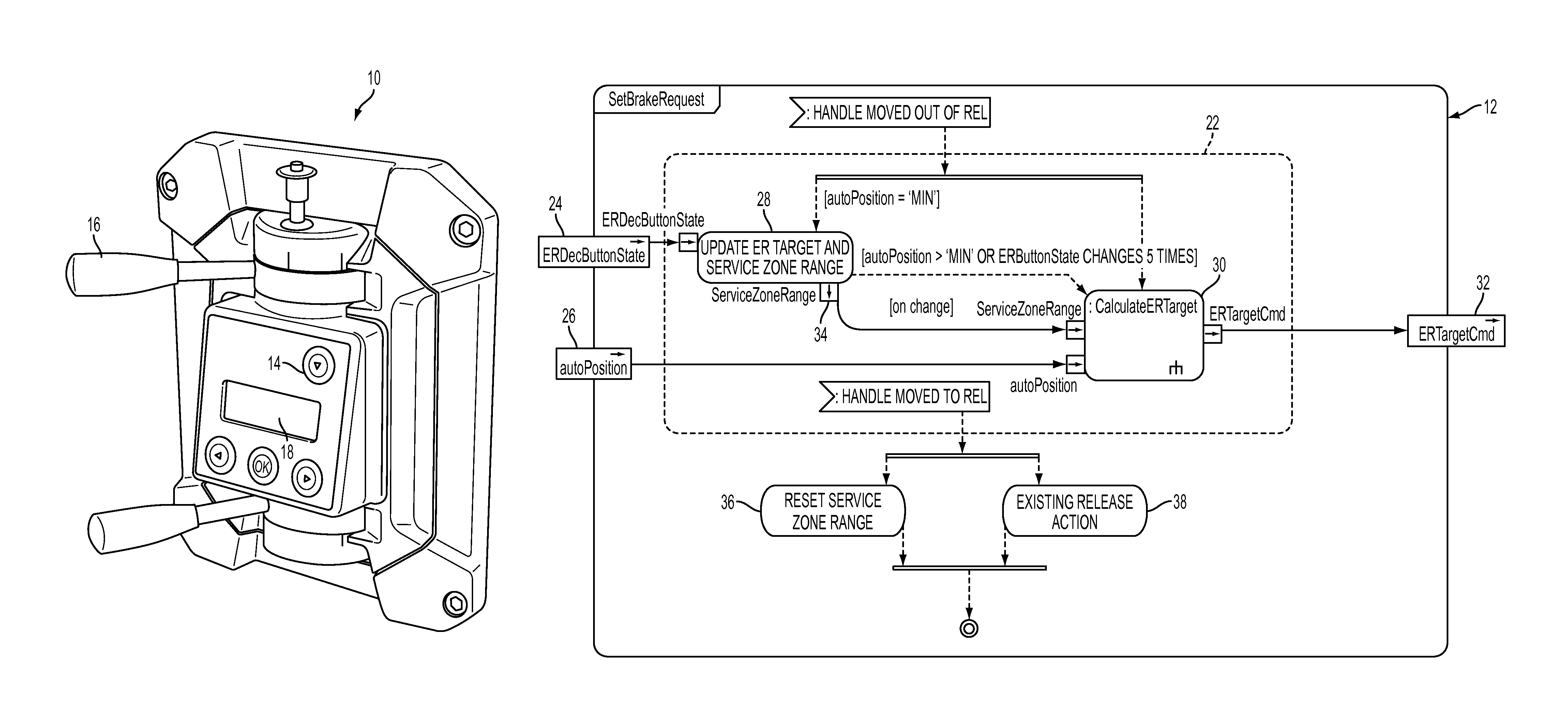
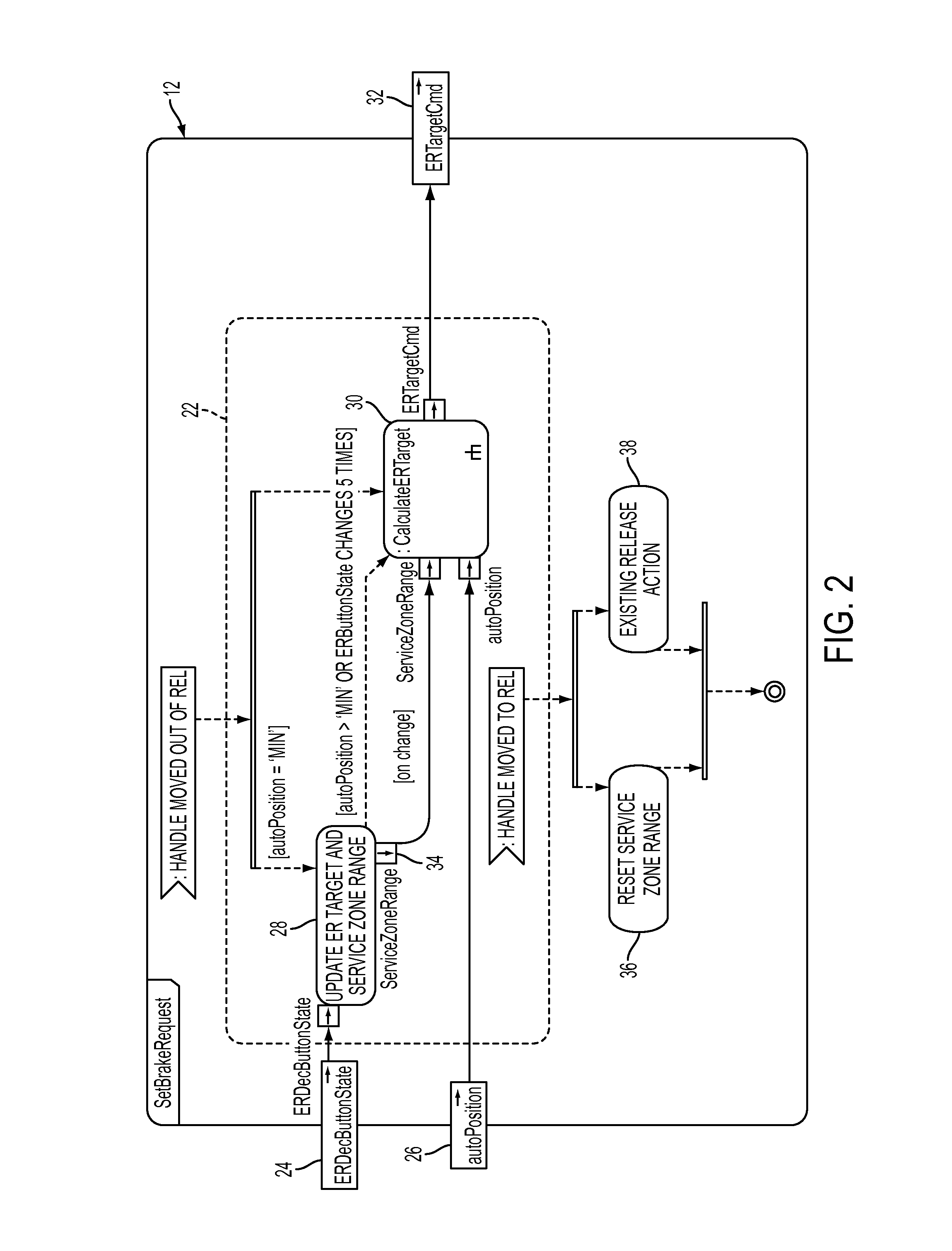
ActiveUS9238473B2Choose accuratelyReduce brake pressureControlling membersBraking action transmissionHuman–machine interfacePressure reduction
A system and method for incrementally accomplishing brake pipe reductions using an operator button, touch sensitive screen or other human machine interface. The system is preferably made available to the user when the brake handle is positioned in the ‘minimum’ brake application position and allows an operator to create a more precise target reduction value without having to manually move the brake handle to the location that the operator believes may result in the desired reduction. Using small, predetermined increments, the system allows for more precise control over brake pressure without an operator having to estimate what handle movement will accomplish the desired brake pressure.
Owner:NEW YORK AIR BRAKE CORP
Method for assisting drivers in the event of aquaplaning on road surface
ActiveCN107848509AReduce brake pressurePrevent lockVehicle sub-unit featuresBraking systemsVehicle dynamicsDriver/operator
Disclosed are a method and an device for assisting drivers in the event of aquaplaning on a road surface on which a vehicle travels; at least one variable relating to vehicle dynamics is used to verify whether an aquaplaning event is occurring, and if if an aquaplaning event is acknowledged, an intervention is performed on a rear wheel brake (42, 46) in order to change directions, the brake pressure being adjusted in accordance with a steering maneuver desired by the driver.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE TECH GMBH
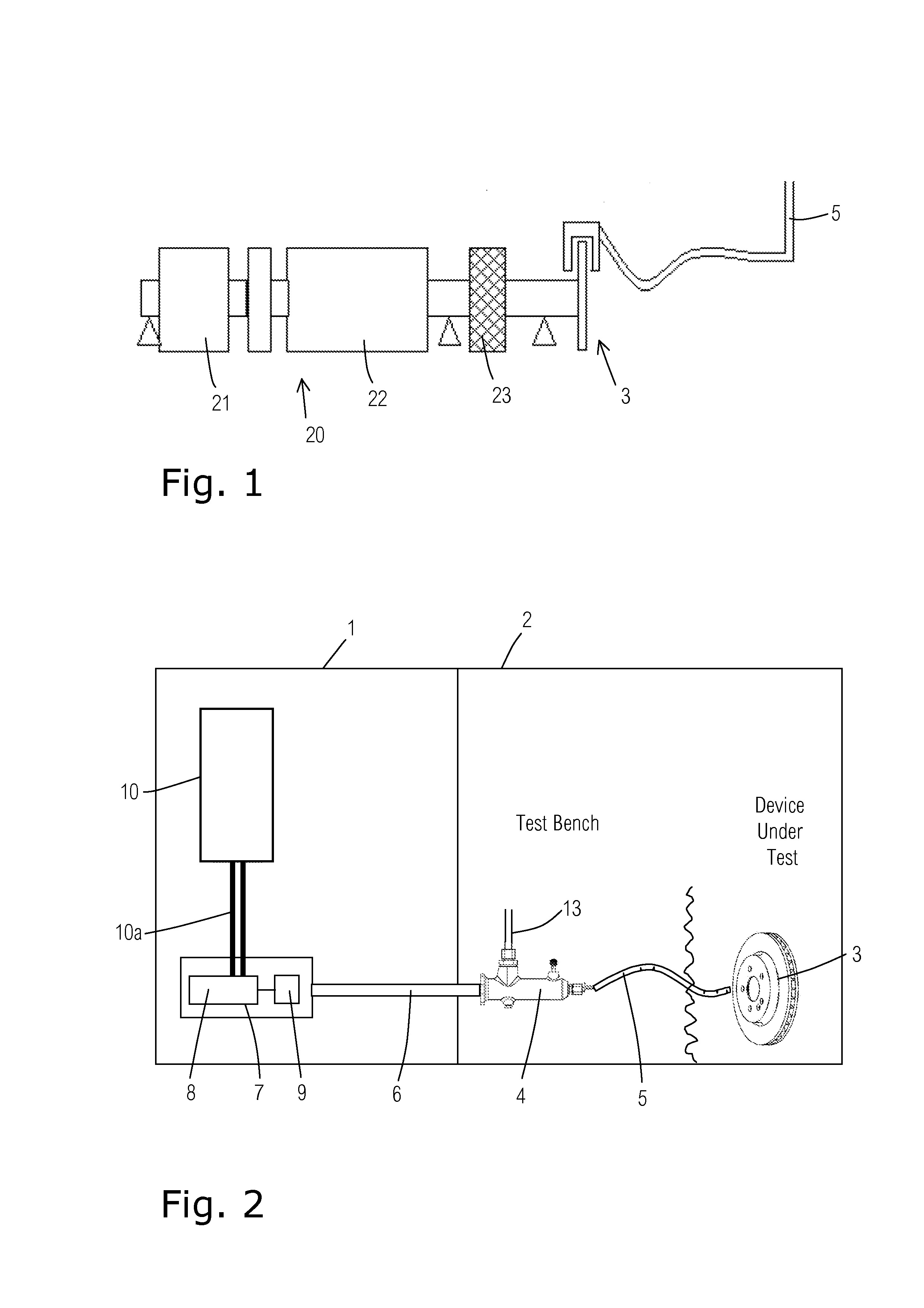
Brake Test Bench Having an Electrical Brake Actuator and Method for Same
ActiveUS20130174647A1High repeatabilitySufficient rateBrake control systemsGearingDriver/operatorRoller screw
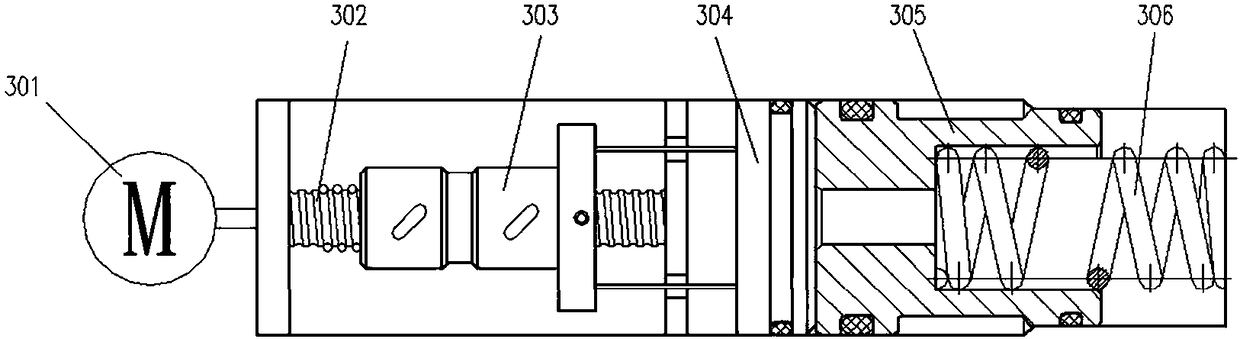
A test bench for testing a brake comprises a pressure generating assembly for providing a brake fluid with an increased hydraulic pressure, a test bench control, and an electromechanical brake actuator. The pressure generating assembly is actuated mechanically and the brake fluid is supplied to the brake to actuate the brake. The electromechanical brake actuator, which simulates a vehicle driver's braking foot, is provided for mechanical actuation of the pressure generating assembly. The brake actuator comprises an electric motor activated by the test bench control and a planetary roller screw drive driven by the electric motor. The planetary roller screw drive is mechanically coupled to the pressure generating assembly to mechanically actuate the pressure generating assembly.
Owner:HORIBA EURO
Brake system having a blending capability
InactiveCN106573600AAvoid excessive brakingPressure compensation ensuresBraking element arrangementsBrake control systemsHydraulic fluidHydraulic brake
Owner:AUDI AG
Brake control system for a utility vehicle having a trailer
A brake control device for a utility vehicle having a trailer, including: a pneumatic brake control circuit having a vehicle pressure path to output a brake pressure to a vehicle brake which brakes the utility vehicle, based on a target input of a driver of the utility vehicle, and having a trailer pressure path for outputting the brake pressure to a trailer brake, which brakes the trailer, on the basis of the target input; and a pneumatic start assist circuit to output a further brake pressure to a trailer brake of the trailer based on a speed of the utility vehicle, in which the pneumatic start assist circuit is pneumatically connected to the trailer pressure path of the pneumatic brake control circuit.
Owner:KNORR-BREMSE SYST FUER NUTZFAHRZEUGE GMBH
Pressure transmission device for a vehicle, power-assisted braking system and method
ActiveUS20140015309A1Solve the large power consumptionReduce brake pressureBraking action transmissionRotary clutchesPressure transmissionSystem pressure
A pressure transmission device for a power-assisted braking system of a vehicle; at its inlet, the pressure transmission device being connectible in a hydraulically operative manner to a master brake cylinder of the power-assisted braking system, and at its outlet, the pressure transmission device being connectible in a hydraulically operative manner to a wheel brake cylinder of the power-assisted braking system; the pressure transmission device including an accumulator and a linkage, which transmits a pressure difference between the inlet and the outlet to the accumulator and stores it in this.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Hydraulic brake system
InactiveCN102026857AReduce brake pressureHigh trigger forceBraking systemsControl theoryMechanical engineering
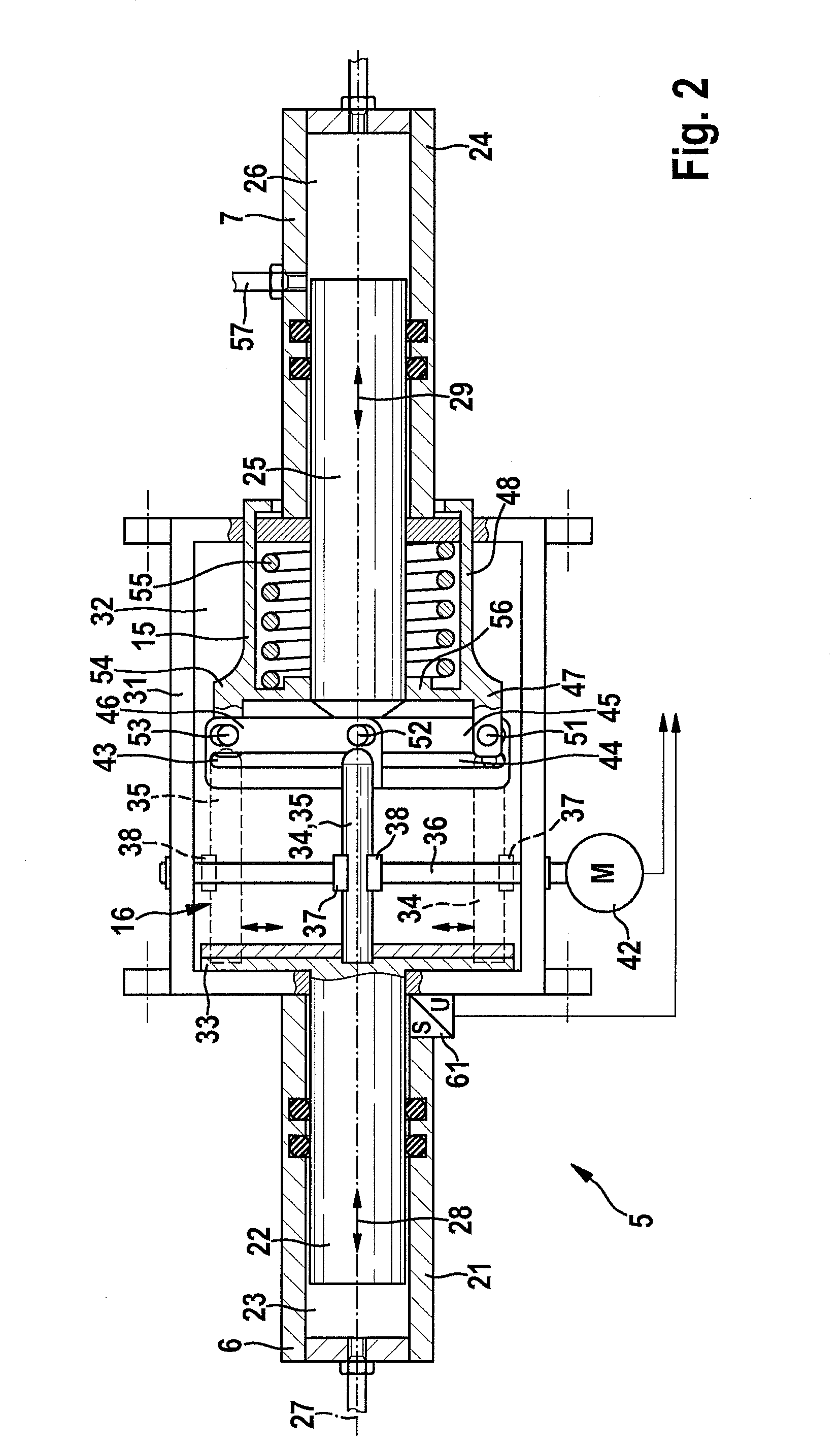
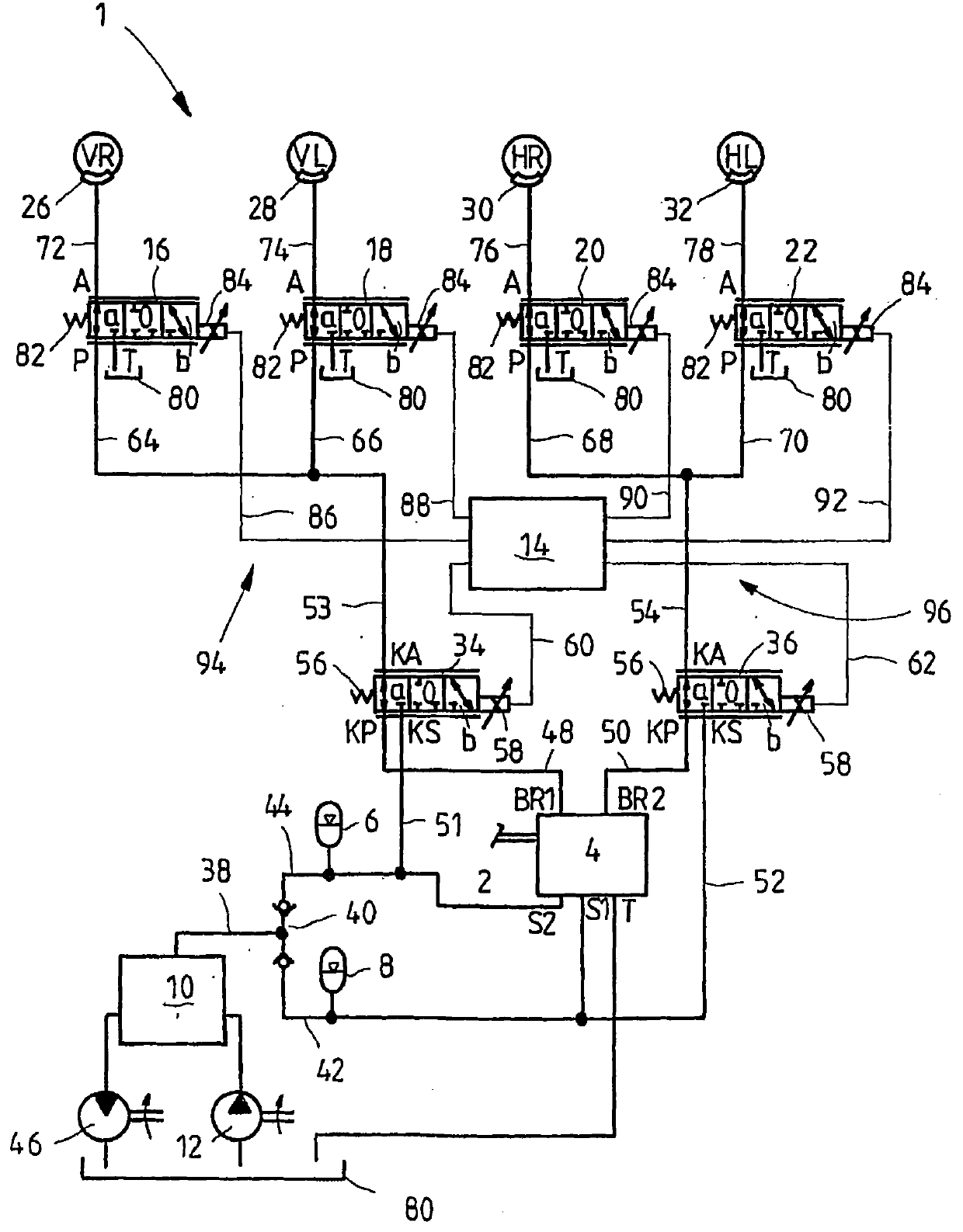
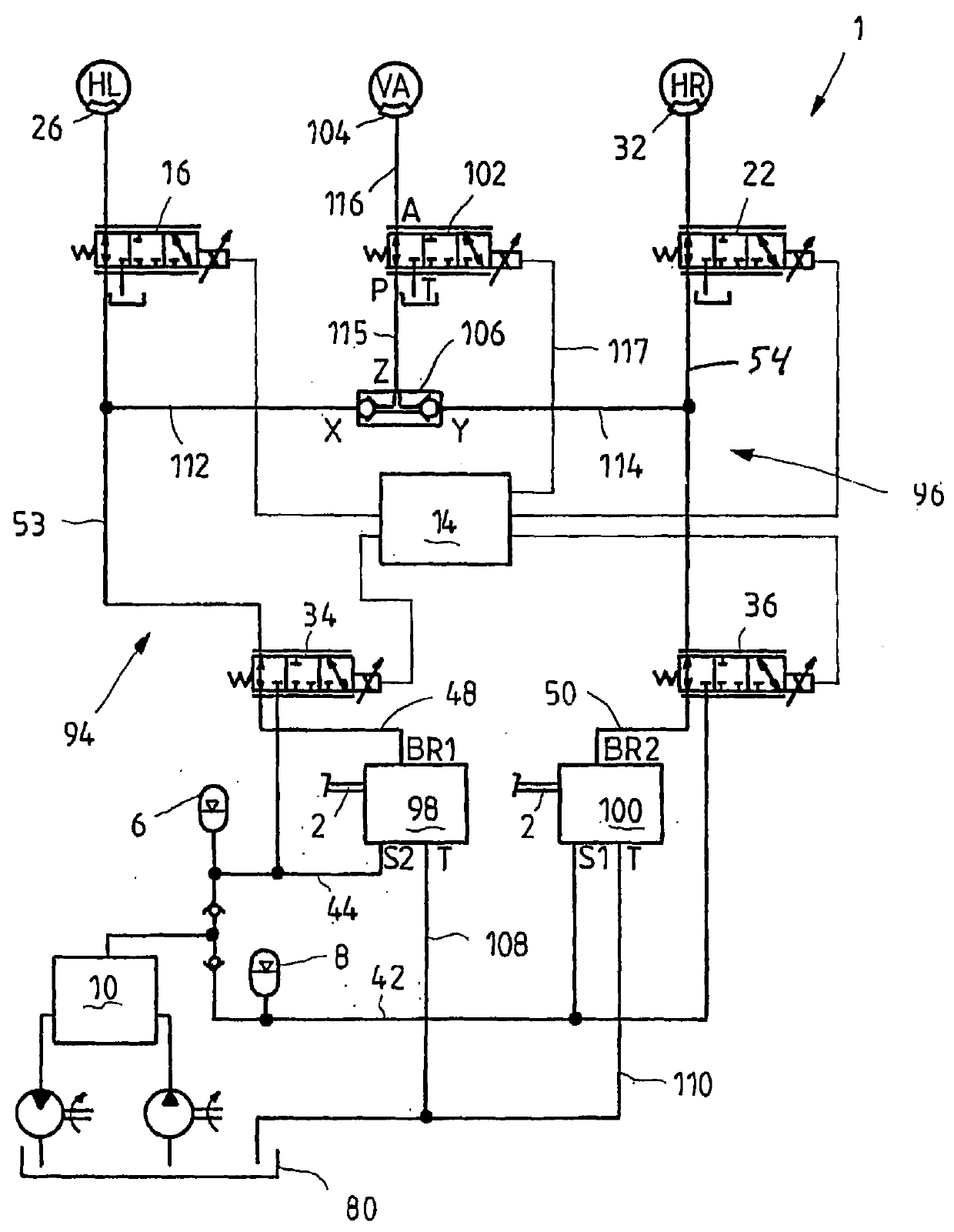
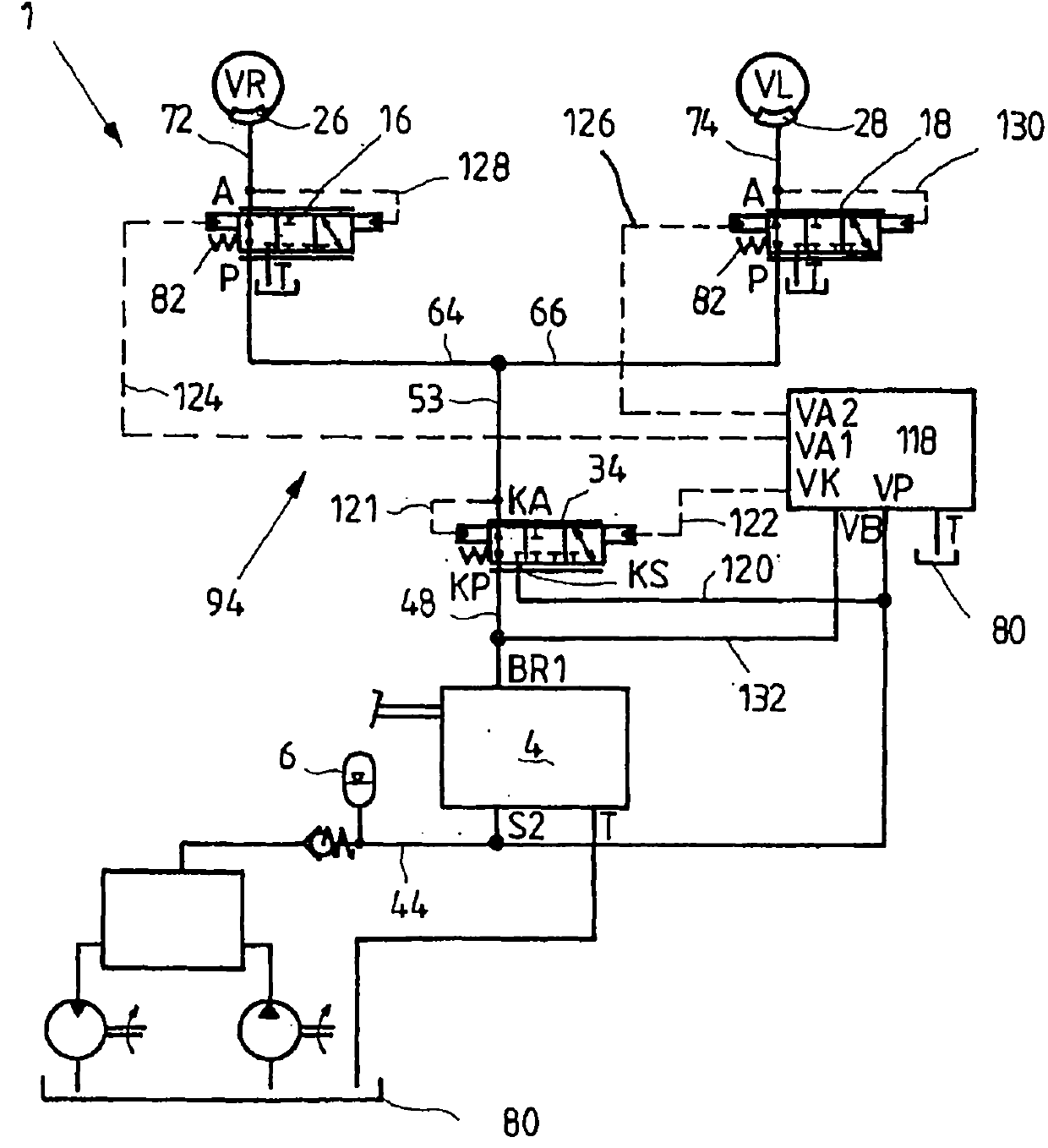
The invention relates to a hydraulic brake system (1), comprising at least one brake valve (4, 98, 100), which can be manually actuated and by way of which a pressurized medium connection between at least one brake line (53, 54) connected by way of a pressurized medium connection to a wheel brake cylinder (26, 28, 30, 32) and a hydraulic accumulator (6, 8) can be opened. To this end, a wheel valve (16, 18, 20, 22, 102, 176, 178, 180, 182) is disposed between the wheel brake cylinder (26, 28, 30, 32) and the brake valve (4, 98, 100) in the pressurized medium flow path, wherein said wheel valve can be controlled by way of a circuit valve (34, 36, 184, 186, 210, 212) or a control element actuating the brake valve (4, 98, 100), regardless of the manual actuation of the brake valve (4, 98, 100). A plurality of brake circuits (94, 96) can be provided in the brake system, each being associated with a circuit valve 34, 36, 184, 186, 210, 212). The wheel and brake valves are furthermore either electrically controlled or pilot-controlled by hydraulics.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Control system and method for vehicle pedal sense feedback based on decoupling brake system
ActiveCN108454600AImprove braking effectIncrease mileageBraking action transmissionFoot actuated initiationsControl systemMaster cylinder
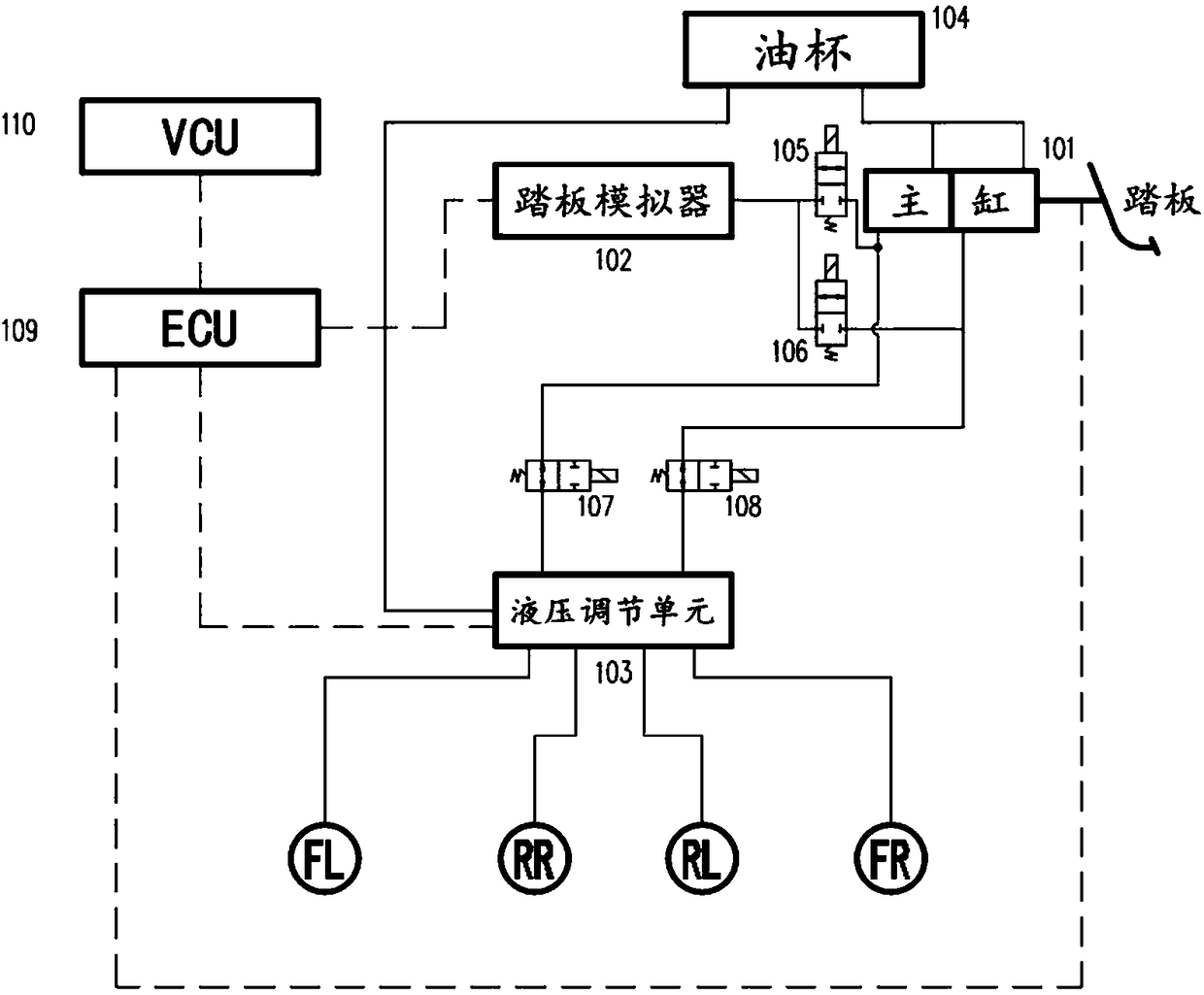
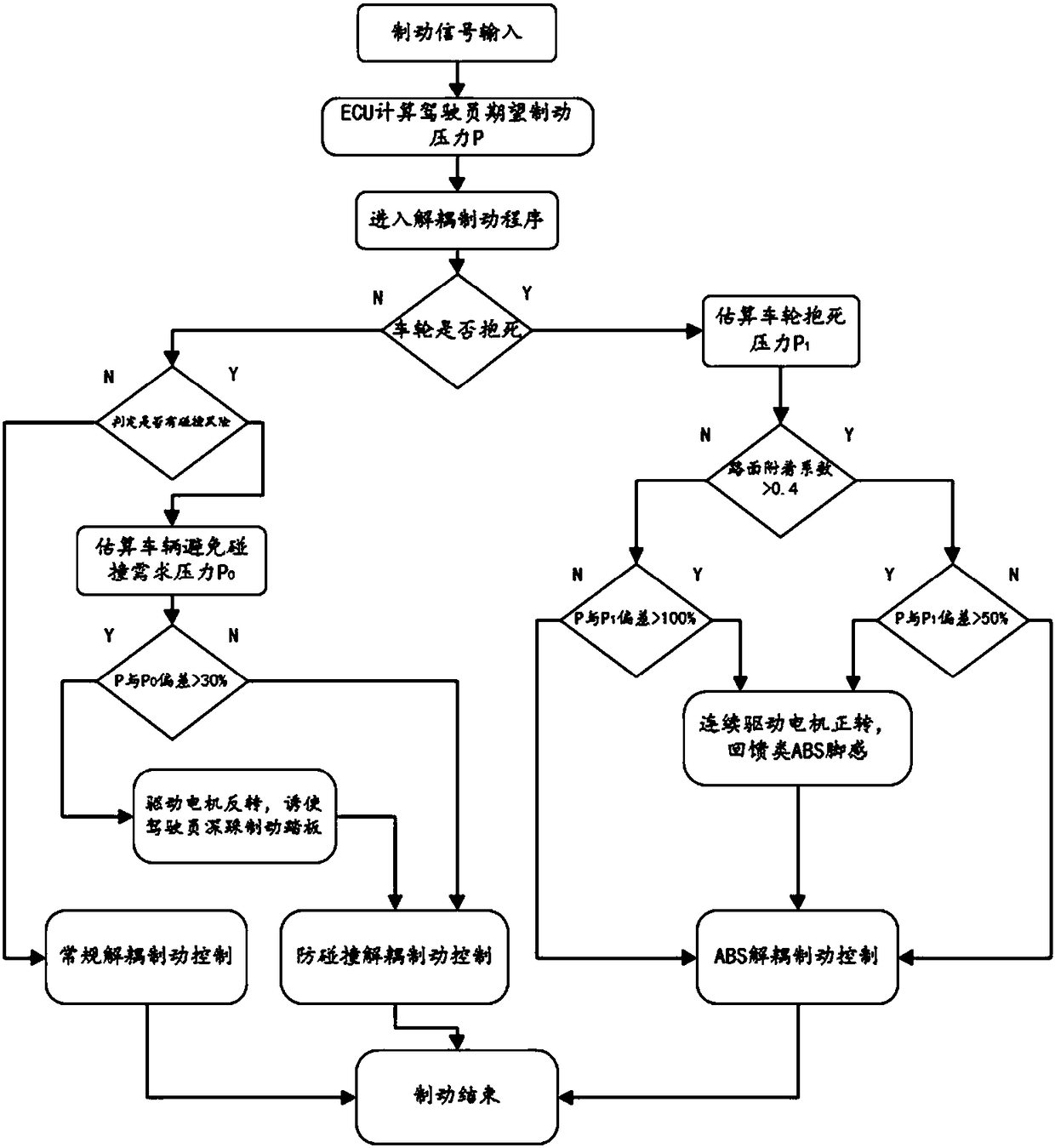
The invention discloses a control system and method for vehicle pedal sense feedback based on a decoupling brake system. A brake pedal is connected with a brake master cylinder, the brake master cylinder is connected with an oil cup, a pedal simulator and a hydraulic adjustment unit, the hydraulic adjustment unit is connected with the oil cup, the hydraulic adjustment unit is connected to a brakewheel cylinder, the brake pedal is provided with a pedal displacement sensor, a brake control unit is connected with the pedal displacement sensor, a vehicle control unit, the hydraulic adjustment unit and the pedal simulator, and the brake control unit controls the pedal simulator to make a pedal sense feedback action, and controls the hydraulic adjustment unit to work in a conventional decoupling brake mode, an anti-collision decoupling brake mode or an ABS decoupling brake mode. The system performs pedal sense feedback under certain working conditions through interaction of driver foot stepping brake pedal and the pedal simulator, and maximizes recovery of braking energy; when there is a risk of collision, bumping deep pedal stepping feeling is fed back, potential danger is reminded, and the brake pressure is adjusted to avoid the risk of the collision.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ASIA PACIFIC MECHANICAL & ELECTRONICS
Vehicle and front and rear wheel braking force distribution system thereof
ActiveCN108891395ALittle change in loadMeet braking force requirementsBraking action transmissionLoad sensingDistribution system
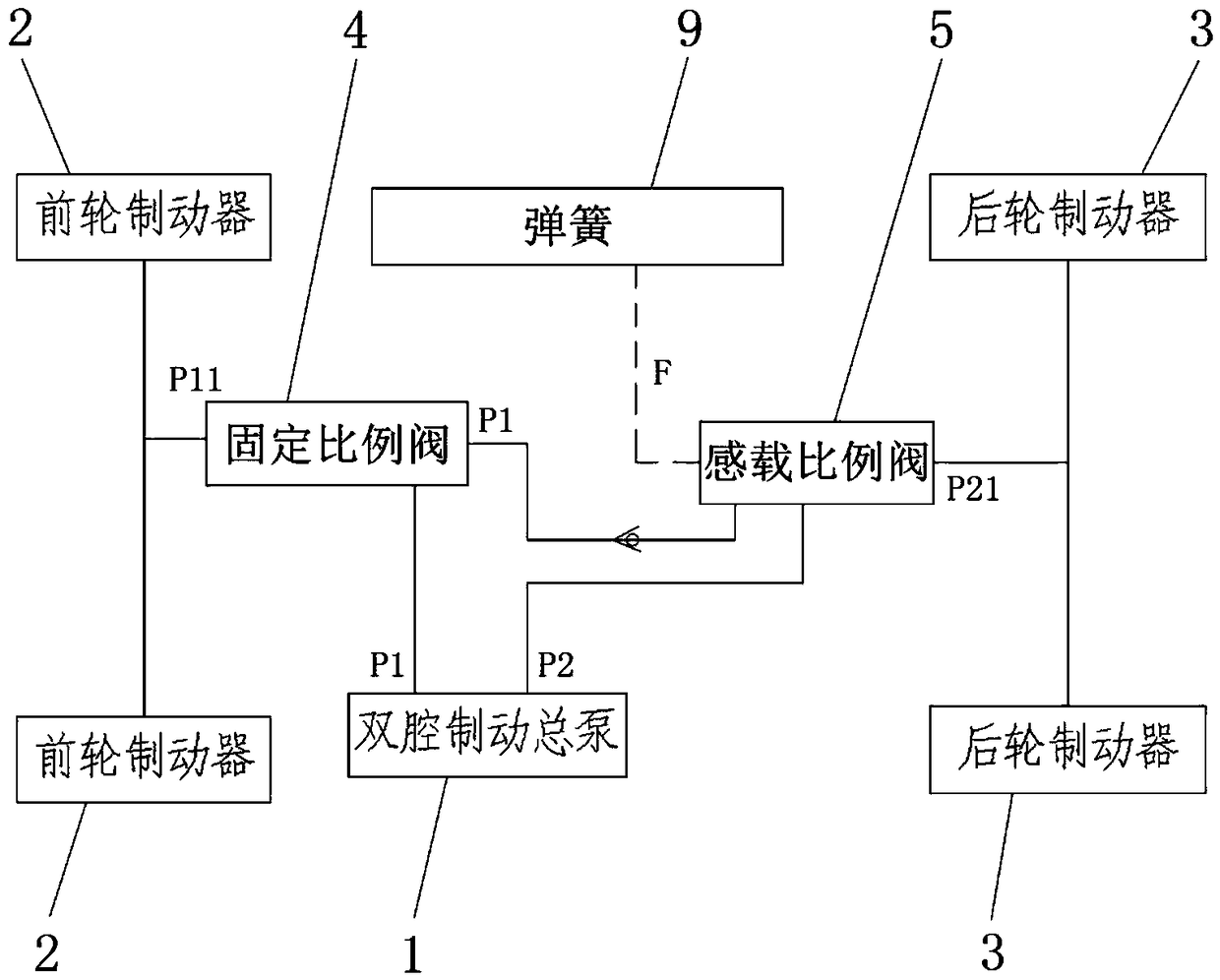
The invention discloses a front and rear wheel braking force distribution system of a vehicle. The system comprises a double-cavity brake master pump, a front wheel brake, a rear wheel brake, a fixedproportion valve and a load sensing proportion valve, the double-cavity brake master pump is used for providing brake pressure, the front wheel brake and the rear wheel brake are communicated with twoindependent oil outlets on the double-cavity brake master pump, the fixed proportion valve is communicated between the front wheel brake and one oil outlet of the double-cavity brake master pump, theload sensing proportion valve is communicated between the rear wheel brake and the other oil outlet of the double-cavity brake master pump and used for controlling the output pressure of the double-cavity brake master pump for the rear wheel brake according to the corresponding relationship between preset rear axle load variation and ideal rear axle braking force. According to the system, the braking force of a rear axle can be reasonably distributed according to load variation of a front axle and the rear axle, so that the rear axle has suitable braking force, insufficient or excessive braking of the rear axle is avoided, and braking stability and braking reliability of the vehicle are improved. The invention further discloses a vehicle which has the advantages.
Owner:HANGCHA GRP
Control valve, electronically controllable brake system and method for controlling the electronically controllable brake system
ActiveCN110901620AEasy to buildRealize pneumatic controlOperating means/releasing devices for valvesBrake control systemsControl valvesControl theory
The invention relates to a control valve, an electronically controllable brake system and a method for controlling the electronically controllable brake system. The control valve for applying a spring-loaded brake pressure to spring-loaded parts of a rear-axle wheel brake is pneumatically activated as a function of a parking-brake braking demand and a service-brake braking demand. A first controlchamber is connected via a first control piston to a control arrangement in the control valve. During an adjustment of the first control chamber via the service-brake control pressure, the spring-loaded brake pressure at the working output is a function of the service-brake control pressure or of the parking-brake control pressure. The first control piston is connected to a third control chamber,wherein the pressure in the first control chamber acts on the first control piston in one direction, and the pressure in the third control chamber acts on the first control piston in the opposite direction. The first control chamber is selectively connectable to the third control chamber via a switchable bypass valve.
Owner:WABCO EURO BVBA SPRL
Brake assisted vehicle engine restart on a road grade
ActiveUS20160280227A1Maintain brake friction torque capabilitySuppress powertrain torque disturbancesExternal condition input parametersDriver input parametersGear wheelBrake pressure
A method for restarting an engine of a vehicle stopped on a grade, comprising the steps of engaging a gear of a transmission through which the engine and wheels of the vehicle are drivably connected mutually, using brake pressure to engage wheel brakes and produce a road gradient wheel torque that holds the vehicle stationary on the grade, initiating an engine restart, operating the engine to produce wheel torque equal to or greater than the road gradient wheel torque, and releasing the brake pressure.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com