Patents
Literature
2224results about "Braking members" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
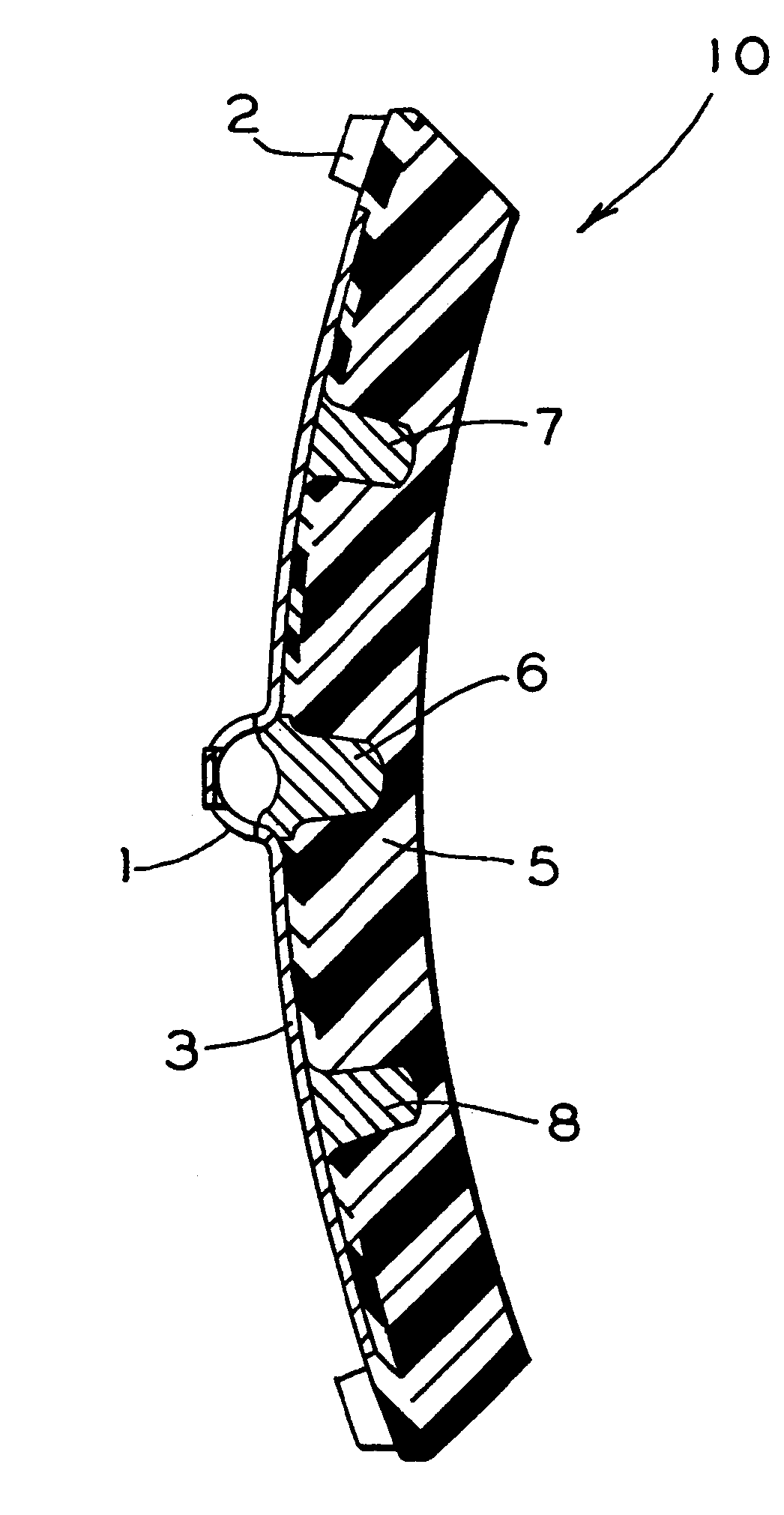
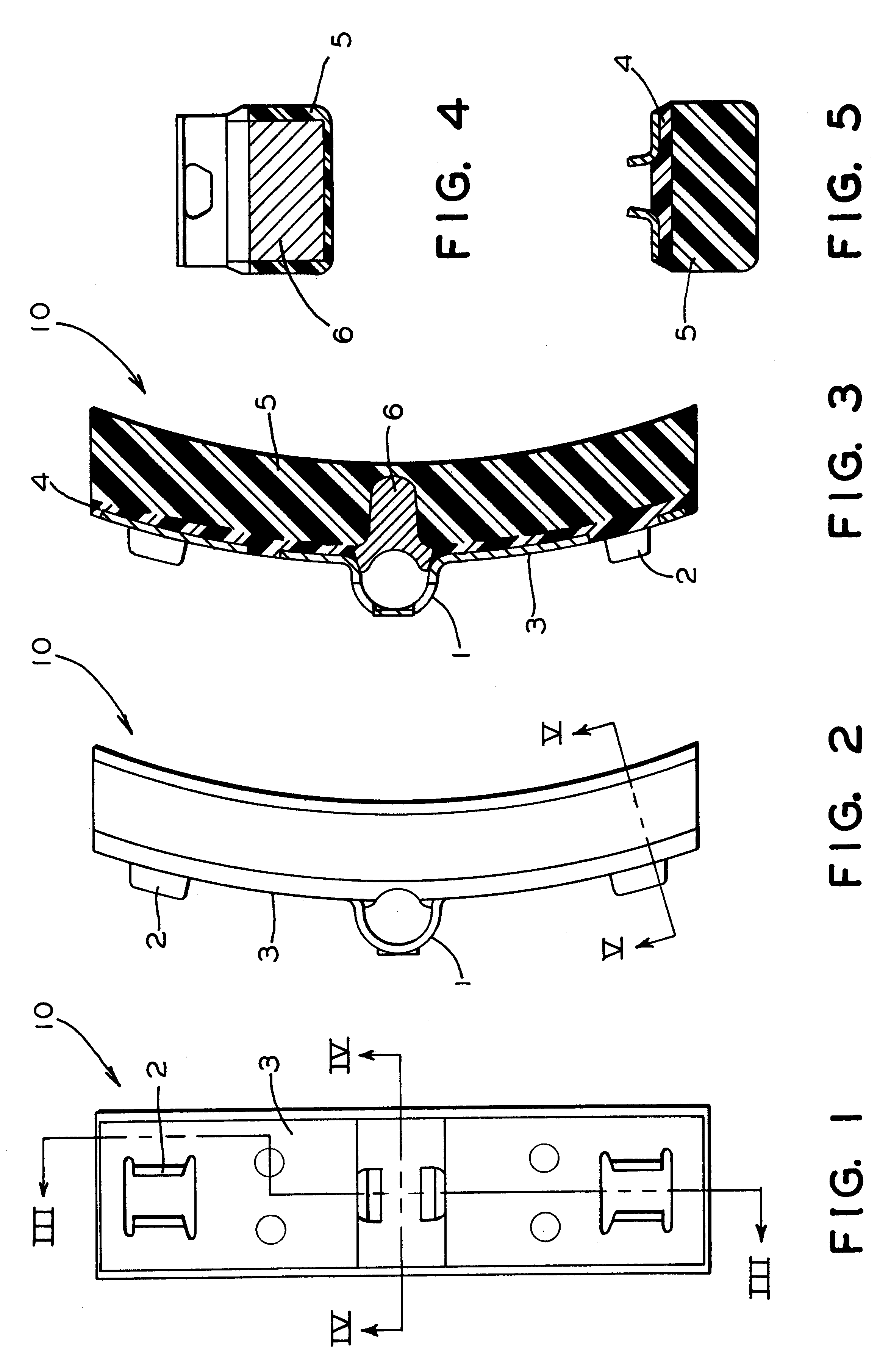
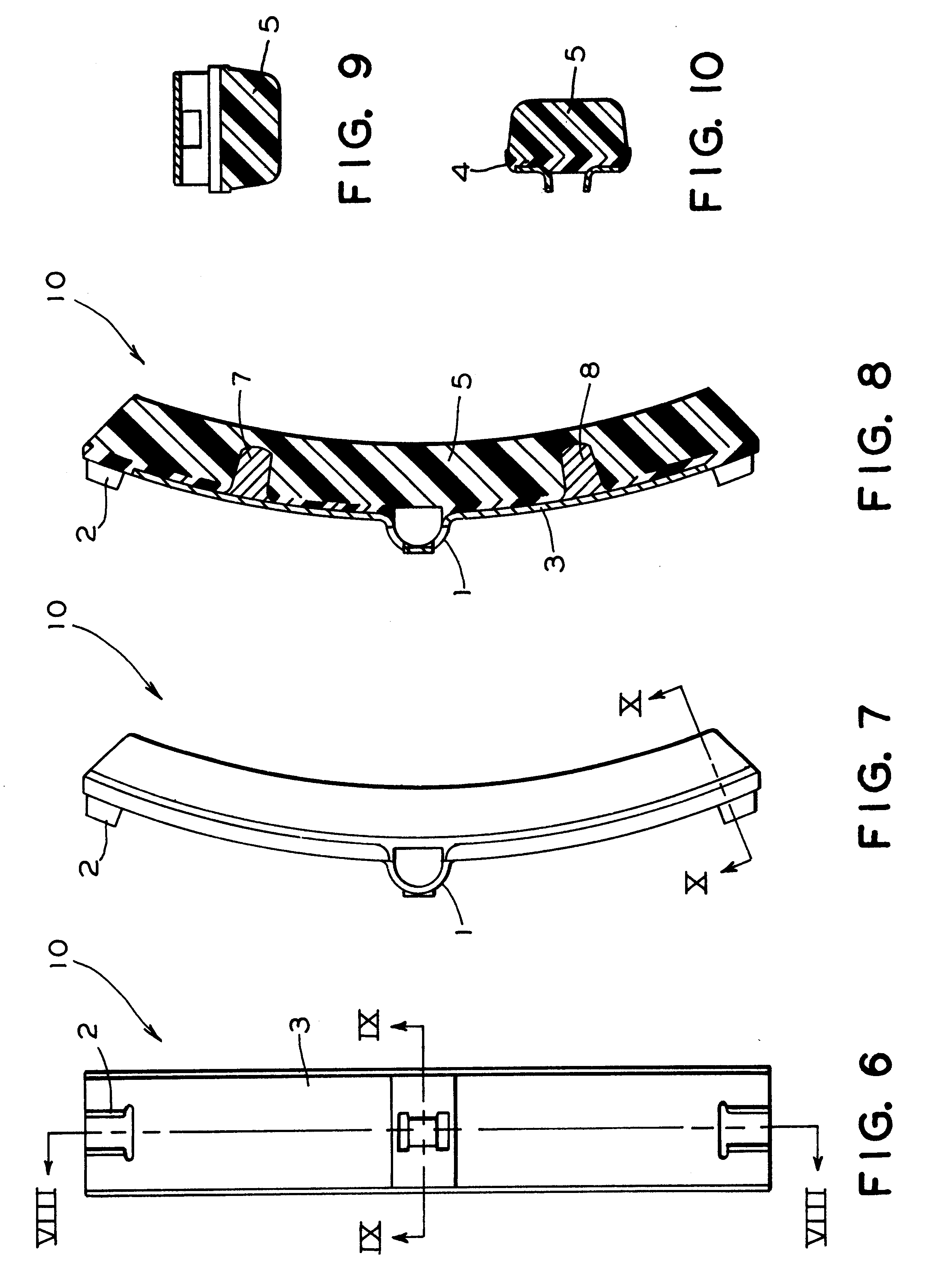
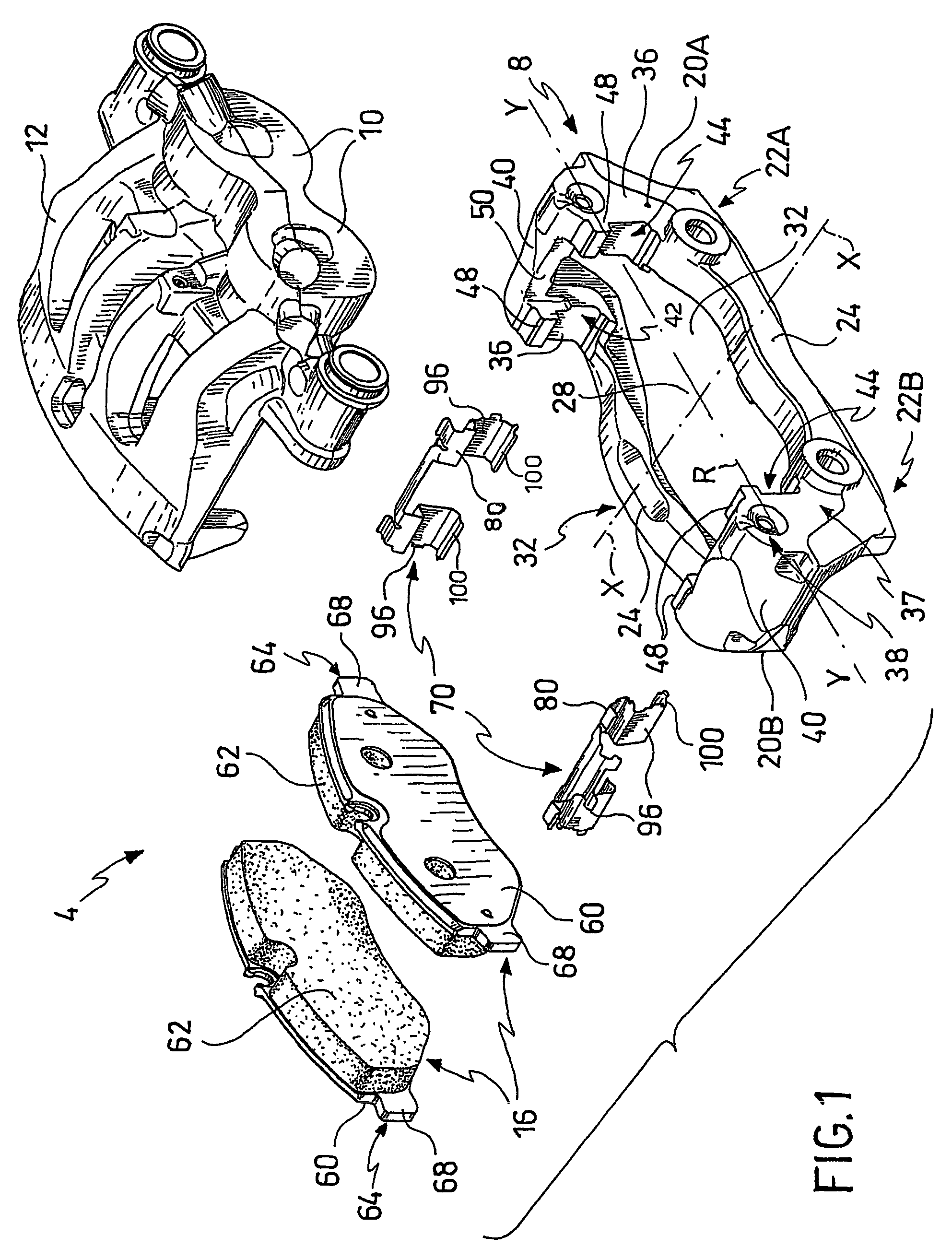
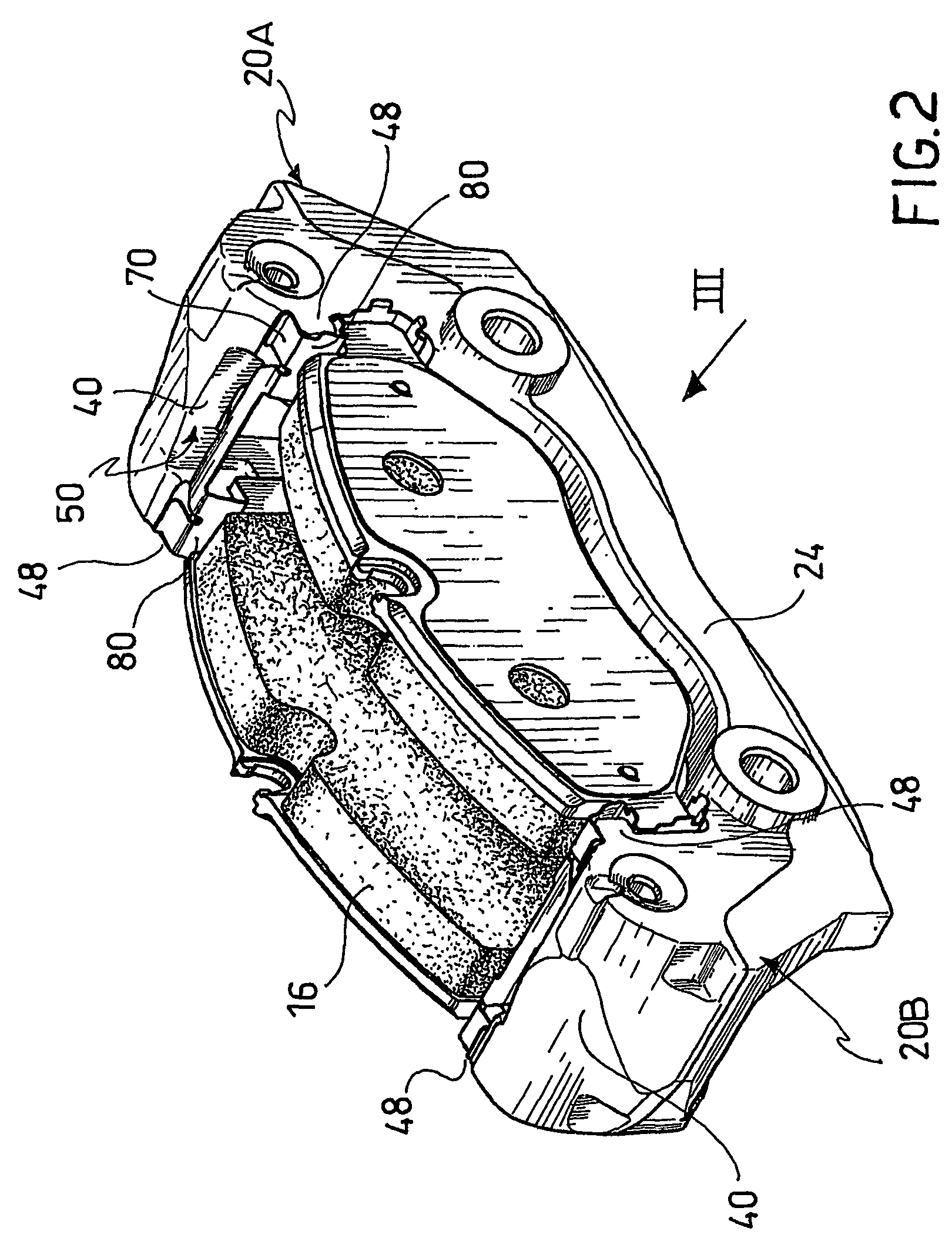
Multiple layer friction material brake pad
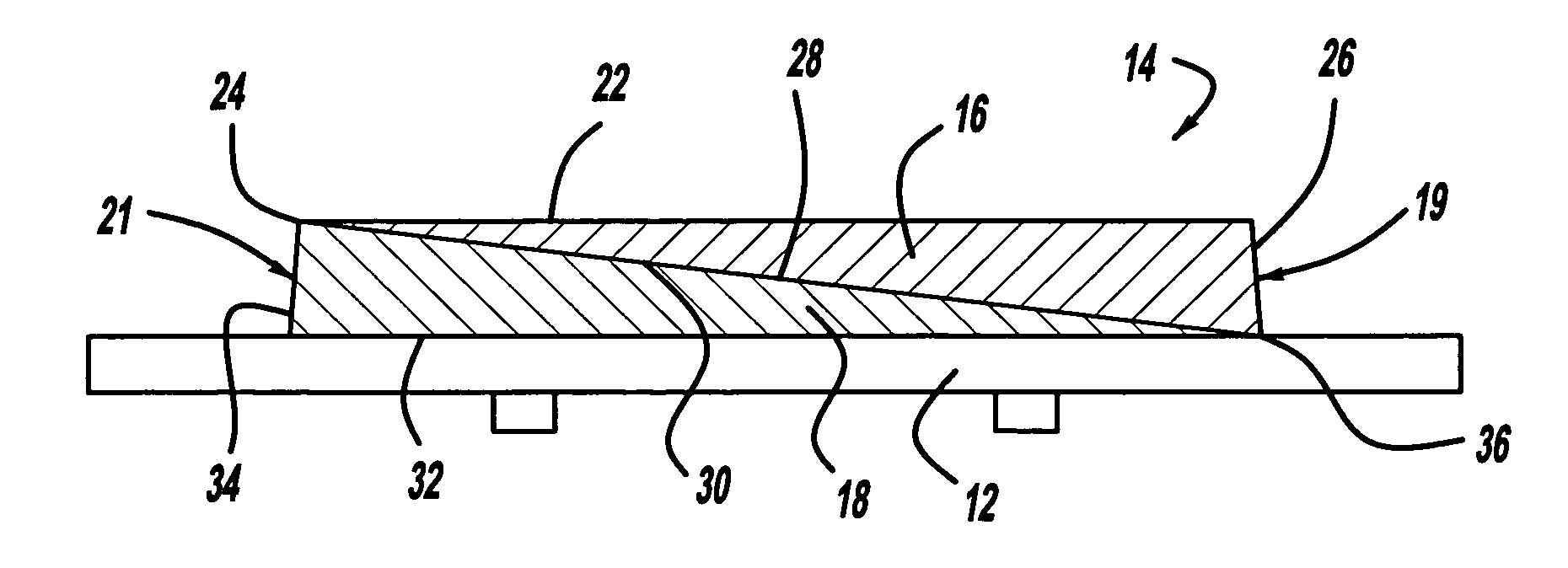
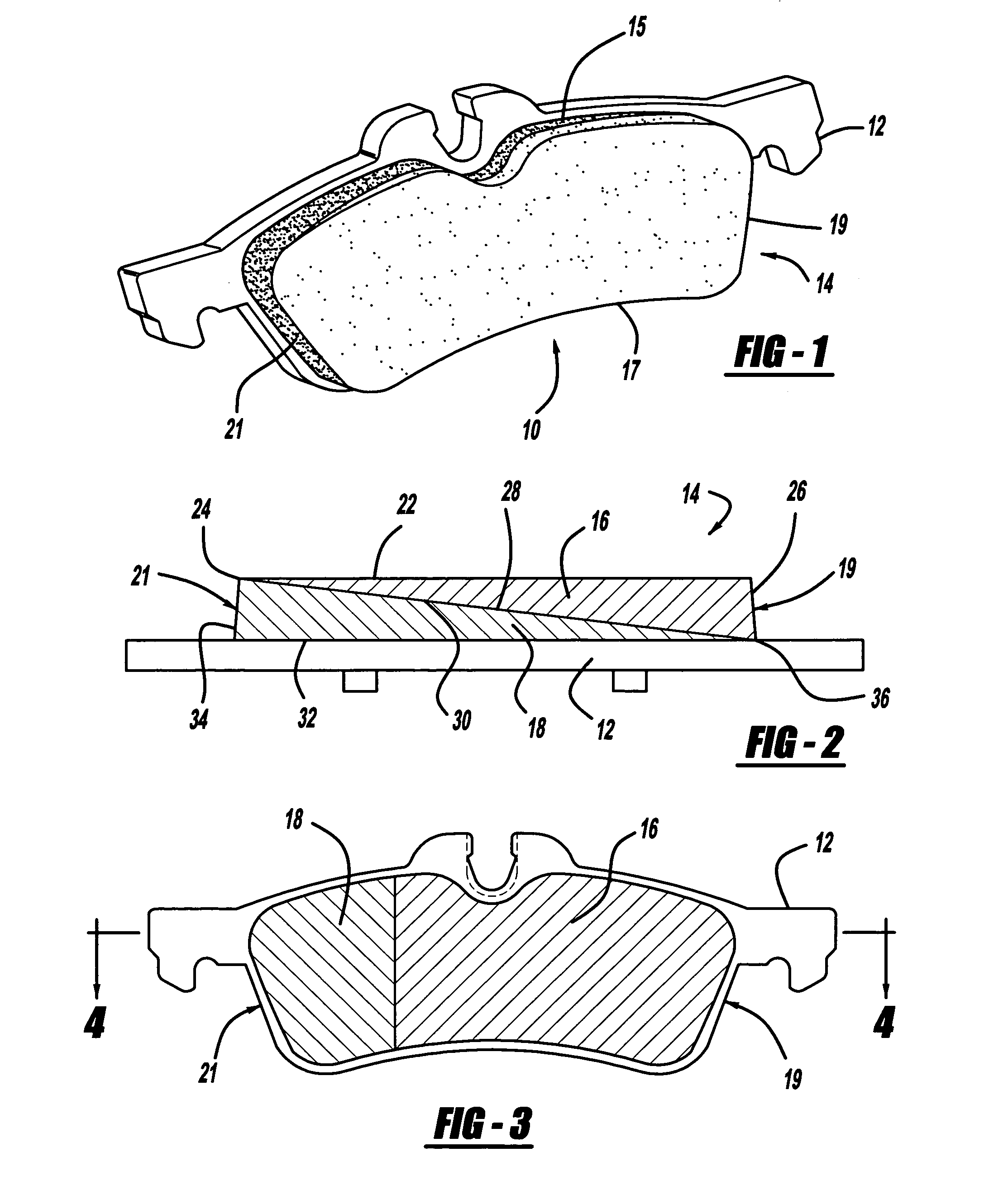
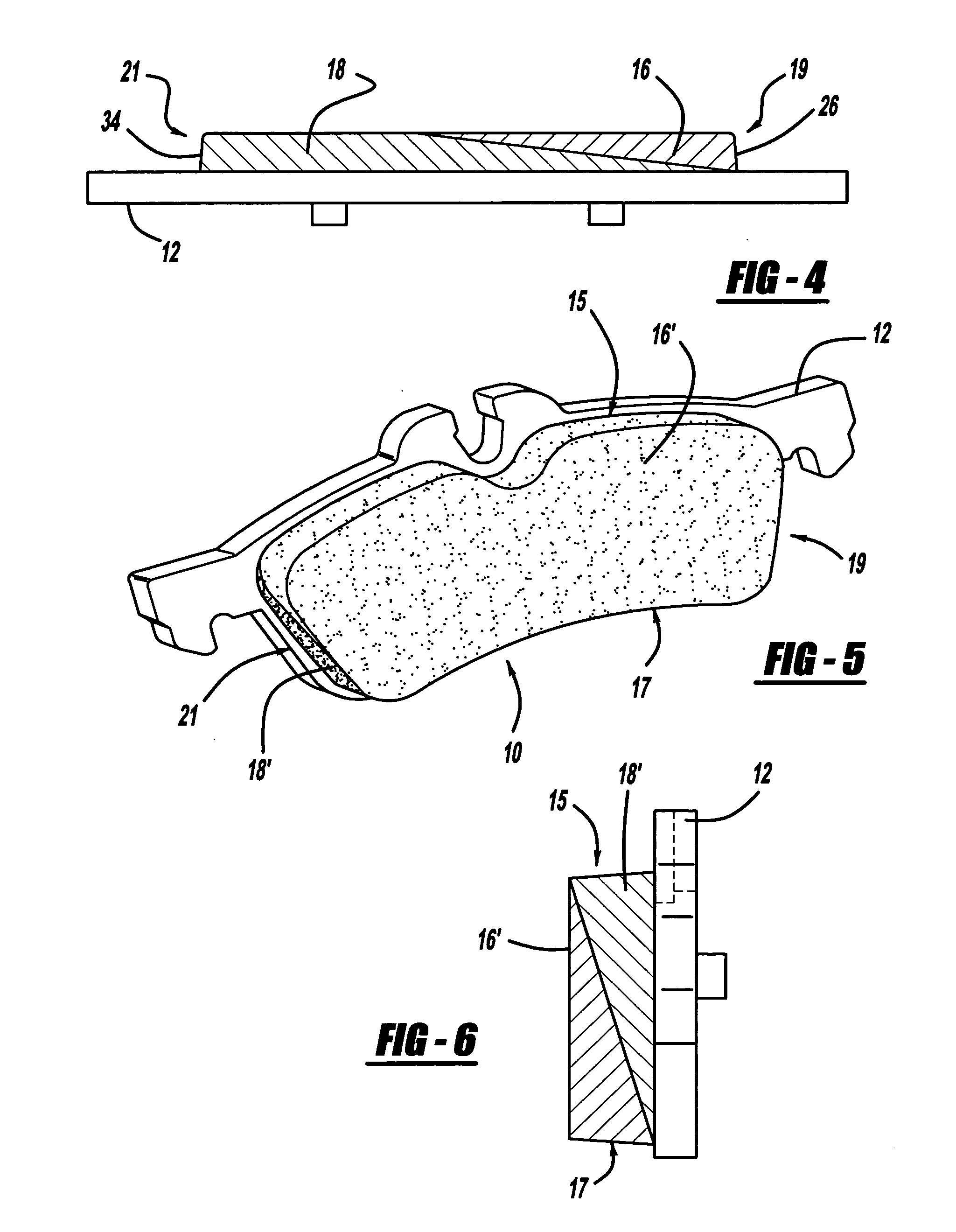
A brake pad has a backing plate and a friction pad. The friction pad is provided with a plurality of layers. Each layer is formed from a desired material such that at least two layers are formed from different materials. A first layer of said plurality of layers is adapted to contact a brake rotor. A second layer is covered by the first layer. At least one of said first and second layers has a tapered thickness from one edge of the friction pad to the other edge. As the first layer wears, the second layer gradually transitions into contact with the brake rotor.
Owner:AKEBONO CORP (NORTH AMERICA)
Motor-driven wheel drive device
InactiveCN1922047AEfficient deliveryFree rotationBraking element arrangementsBearing assemblyMotor driveGear wheel
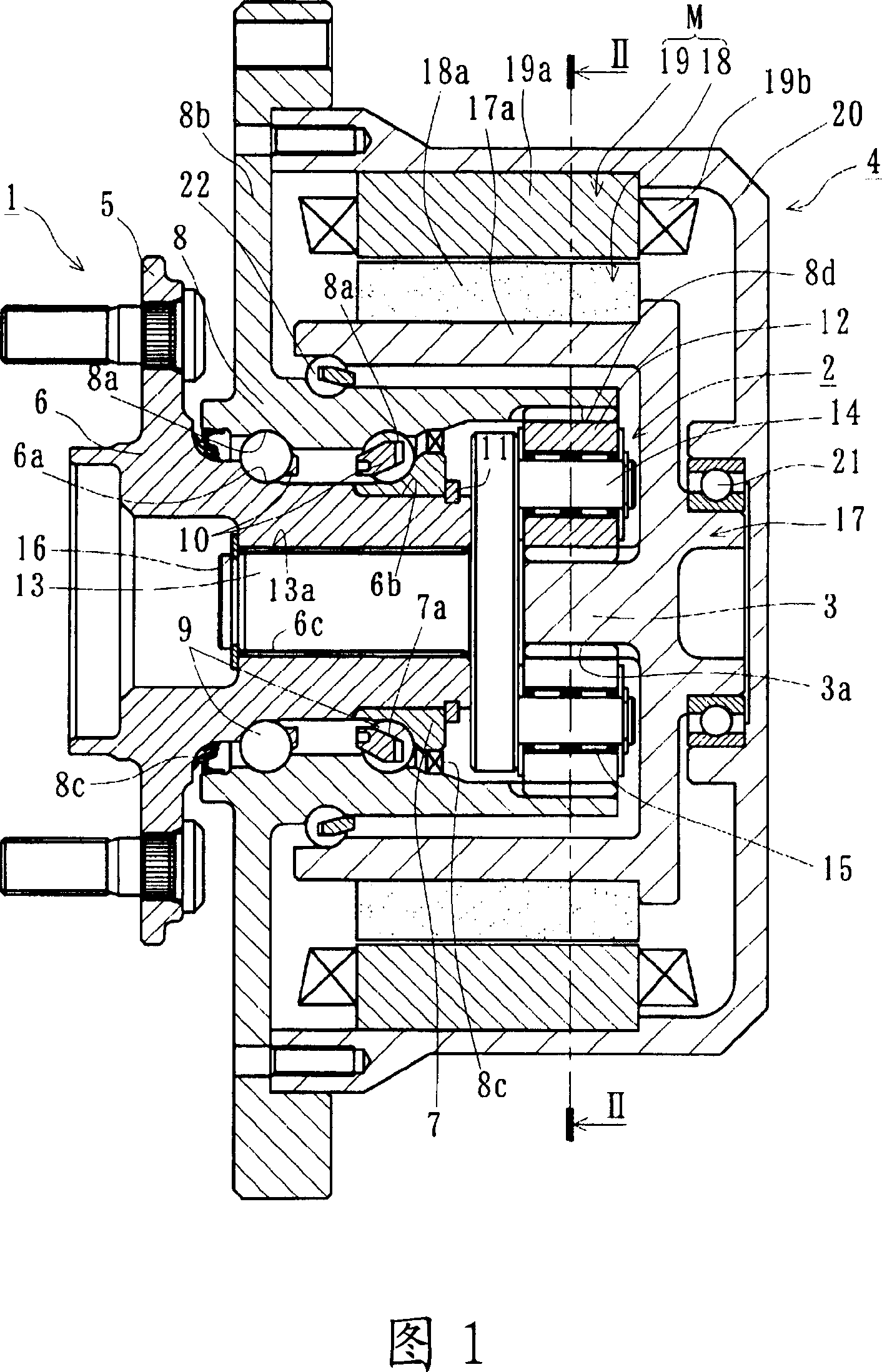
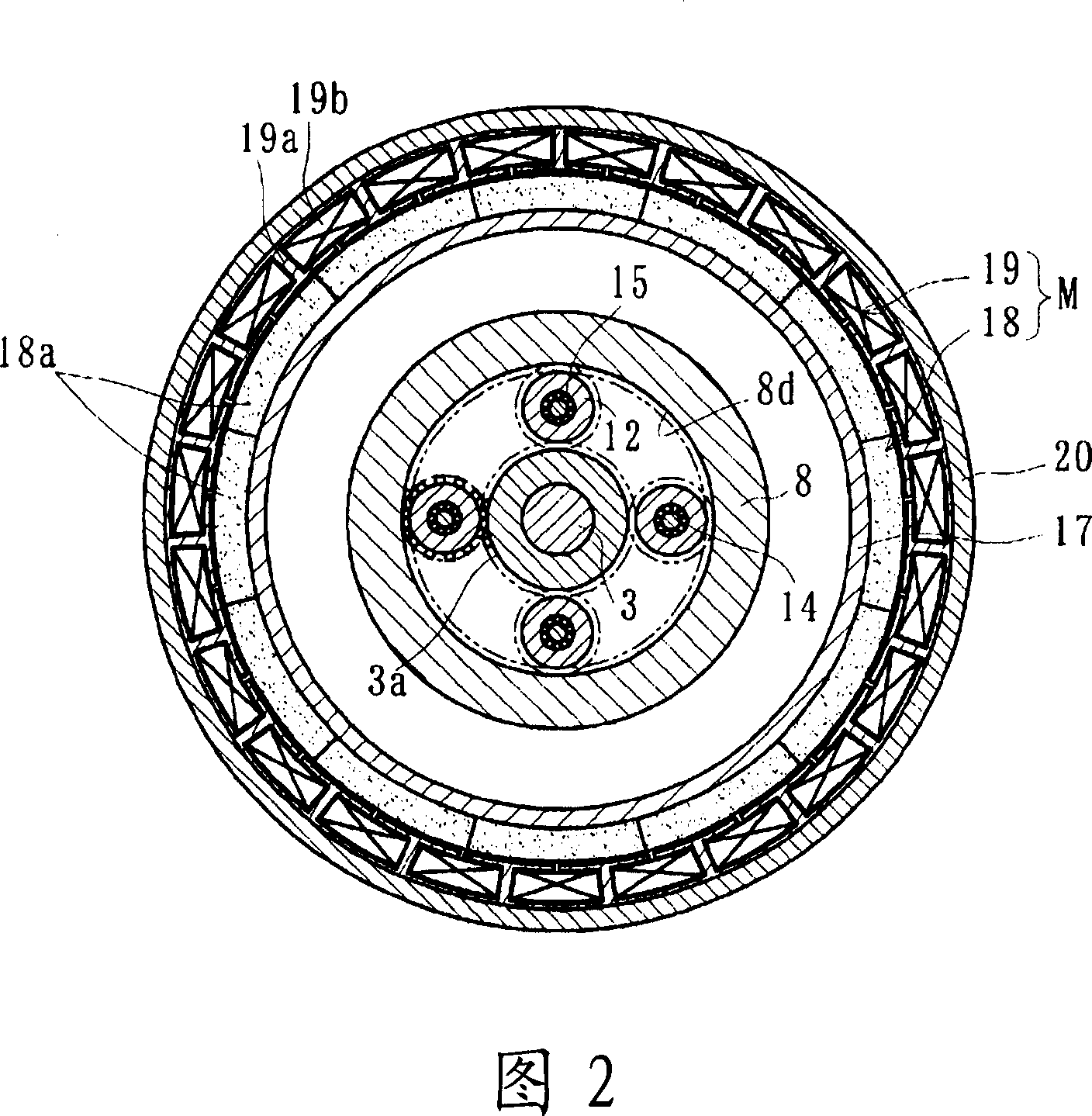
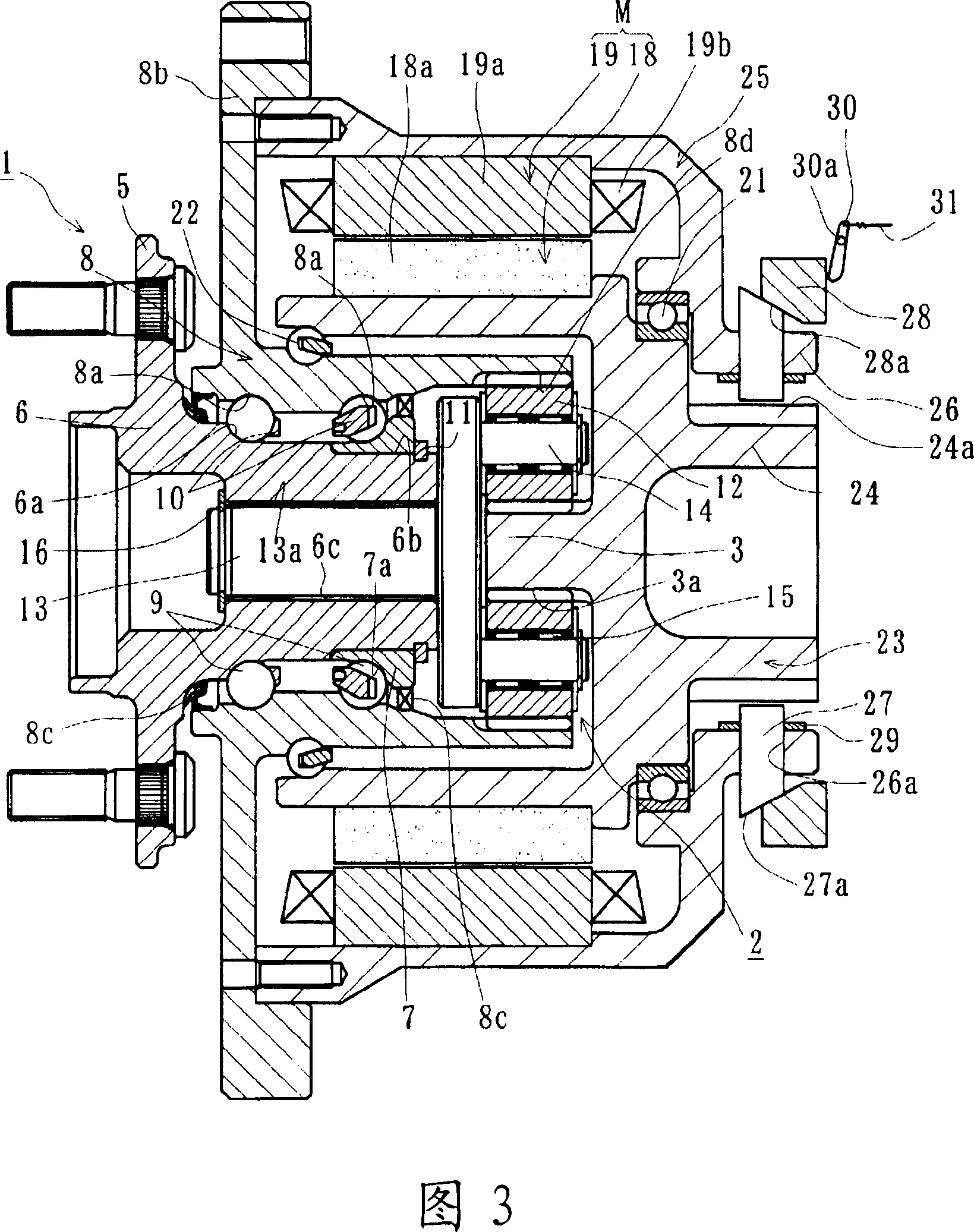
The invention provides a motor-driven wheel drive device in which the durability of a wheel bearing is increased, the weight and size thereof are reduced, and the disassembly and reassembly thereof is taken into account. [MEANS FOR SOLVING PROBLEMS] This motor-driven wheel drive device comprises a drive part (4) having an electric motor (M) driving a planetary speed reduction gear (2) installed in the wheel bearing (1) and a rotating member (17). The wheel bearing (1) further comprises a hub wheel (6) on which an inside rolling surface (6a) is formed, an inner ring (7) press-fitted to the hub wheel, an outer member (8) in which double rows of outside rolling surfaces (8a) are formed, and rolling elements (9). The planetary speed reduction gear (2) further comprises a sun gear (3) formed in a rotating member (17), a plurality of planetary gears (12) disposed between the outer member (8) and the sun gear (3), and carrier pins (14) pivotally supporting these planetary gears on a connection shaft (13). The drive part (4) further comprises the electric motor (M) releasably disposed on the outer member (8) and the rotating member (17). The connection shaft (13) is connected to the hub wheel (6) through a serration, and the rotation of the electric motor (M) is transmitted to the hub wheel (6) through the rotating member (17) and the planetary speed reduction gear (2).
Owner:NTN CORP
Brake drum and method for producing the same
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Brake systems, caliper assemblies and pads incorporating differential abutments
InactiveUS20120043168A1Transmission of forceImprove NVH performanceMechanically actuated brakesBraking membersPush pullEngineering
The present invention is directed to a unique solution for caliper assemblies, brake pads utilized in such caliper assemblies, support structures utilized in caliper assemblies and disc brake systems containing such caliper assemblies which utilize push pull or pull push abutment designs.
Owner:AKEBONO CORP (NORTH AMERICA)
Brake shoe with insert bonded to backing plate
InactiveUS6241058B1Reduce defectsLightweight productionBraking membersFriction liningBrake shoeTread
A composition brake shoe for use on a railway vehicle for reconditioning a wheel tread surface during a normal braking application on such railway vehicle is provided. The composition brake shoe includes a backing plate having a stirrup and a brake surface having a predetermined configuration and a predetermined surface area. It further includes a first friction type composition material extending over the surface area of such brake surface of such composition brake shoe. The composition brake shoe further contains a second friction type material, formed as at least one discrete insert, having a predetermined shape and molded into such first friction type composition material. Such second friction type material initially being completely embedded within such first friction type composition material. One surface of such at least one discrete insert being incrementally exposed as such first friction type composition material is eroded away due to frictional engagement with such wheel tread surface during normal braking operations, such second friction type material exhibiting greater abrasive properties than such first friction type composition material. Such at least one discrete insert of such second friction type material is bonded to such backing plate.
Owner:RFPC HLDG CORP
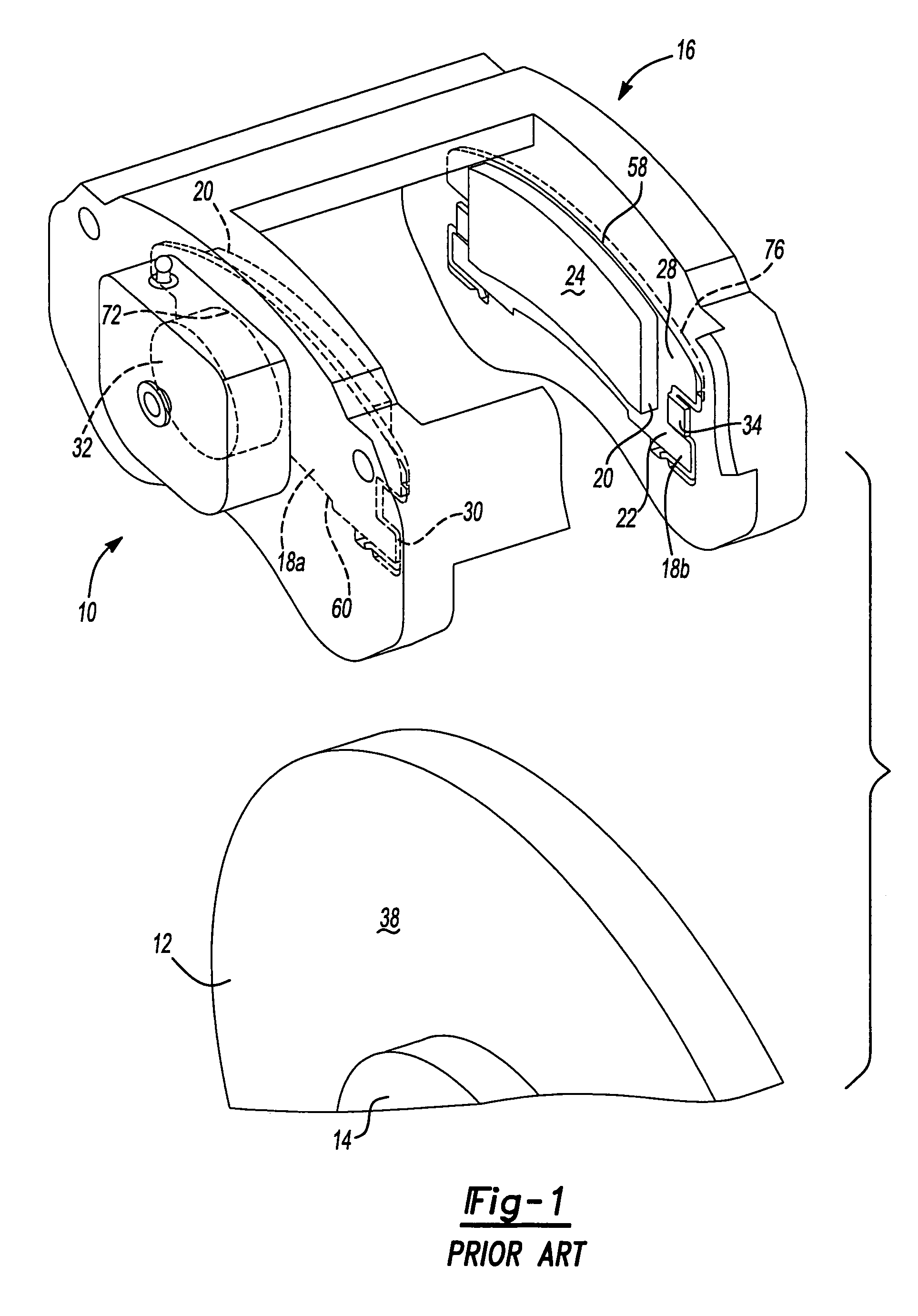
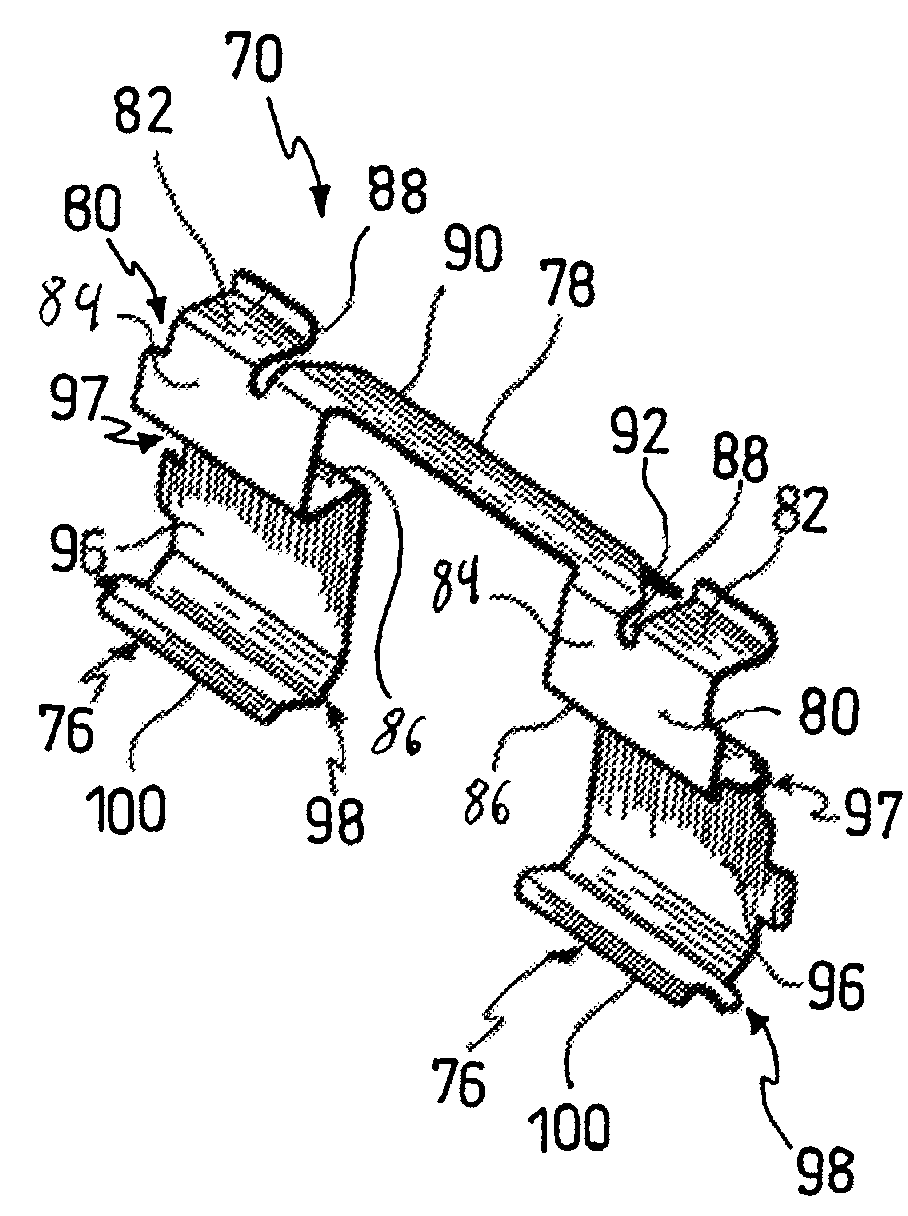
Pad retaining clips
A brake caliper mounting clip is disposed between a brake caliper having a brake pad channel and a brake pad having an edge member. The edge member moves in the brake pad channel between a rotor gap and a caliper housing. The clip further comprises a pad holding portion slidingly engaged with the edge member and having a plurality of pad retaining members. The pad retaining members are connected to the pad holding portion and disposed between the edge member and the rotor gap. The plurality of the pad retaining members is further configured to prevent the brake pad from falling into the rotor gap. Additionally the edge member of the brake pad and the plurality of pad retaining members are configured to prevent improper installation of the brake pads in the caliper.
Owner:AKEBONO BRAKE
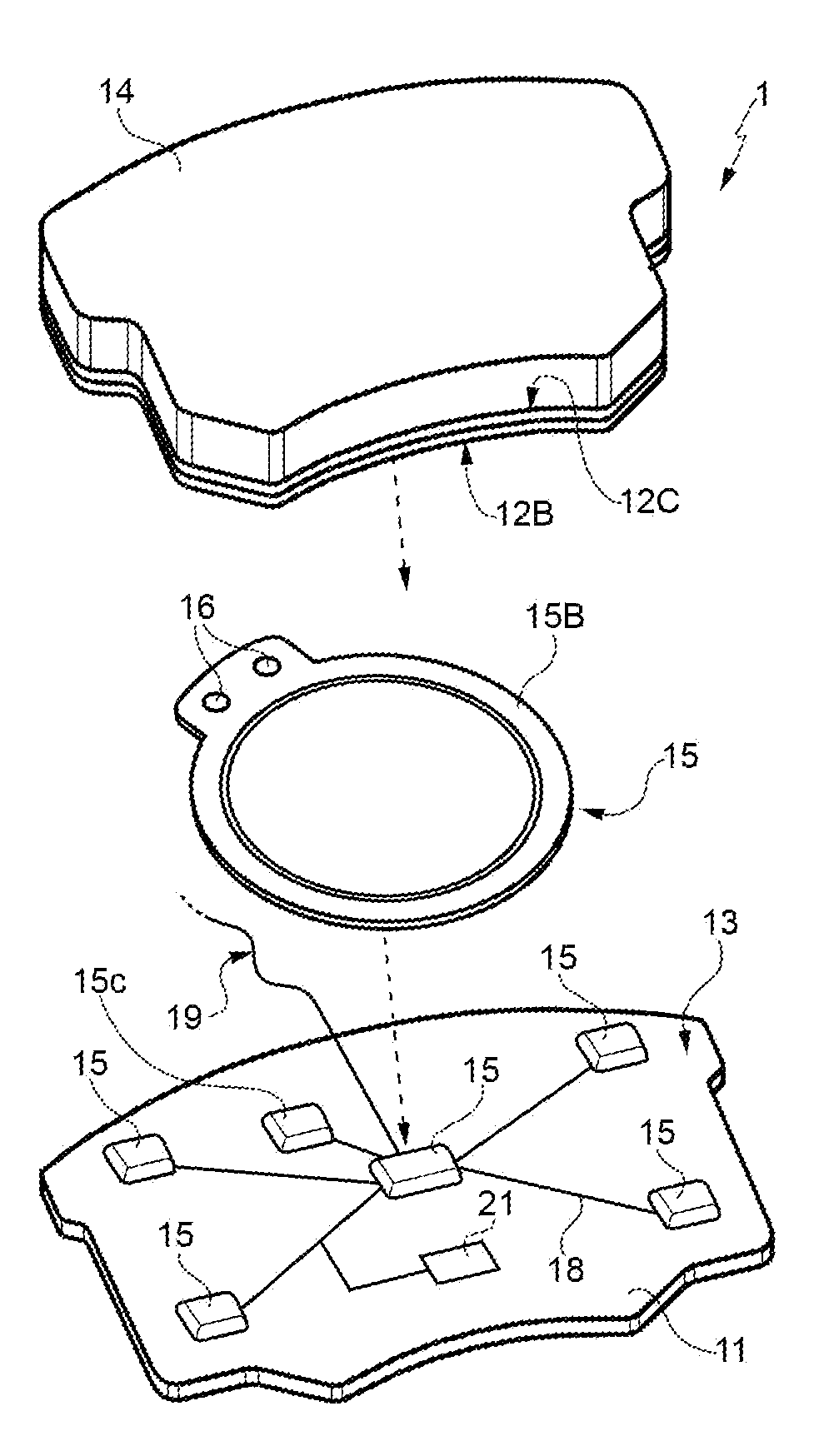
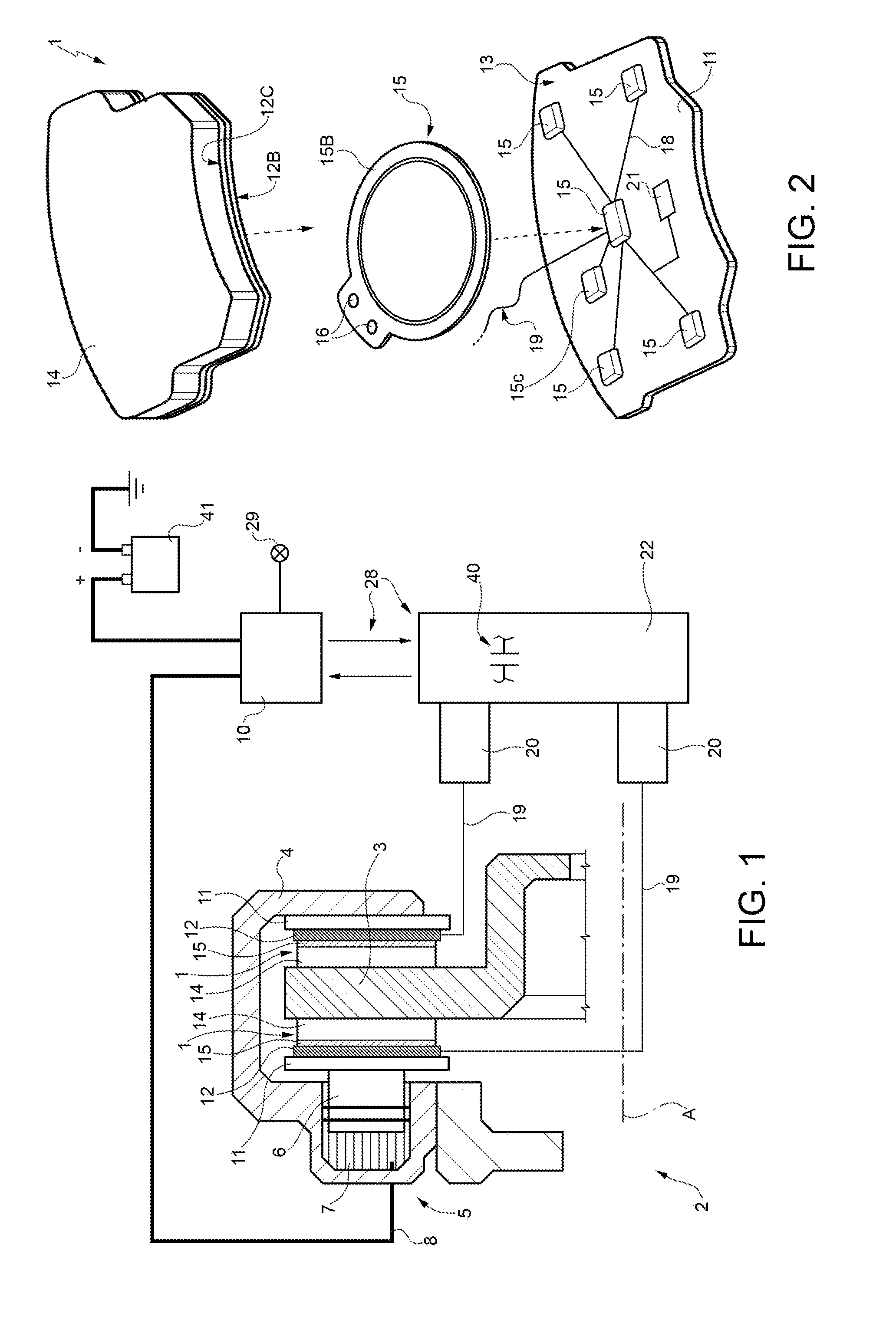
Method for manufacturing a braking element with integrated sensor, in particular a brake pad, brake pad with integrated sensor, vehicle braking system and associated method
ActiveUS20140311833A1Significant energy savingAvoid spendingPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyNoise/vibration controlElectricityPotential difference
A method in which at least one piezoceramic sensor, which converts every mechanical force to which it is subjected into an electrical signal and having a Curie temperature higher than 200° C., is solidarized directly onto the surface of a metal support element of a vehicle braking element, which during use faces a vehicle element to be braked. While in contact with such a surface, an electrical circuit is implemented that picks up and eventually processes the electrical signal, the electrical circuit being connected with a connector integrated with the metal support element. An electrically insulating layer sandwiches the at least one piezoceramic sensor and the electrical circuit, and a block of friction material with an underlying damping layer is formed upon the electrically insulating layer. After forming the block of friction material, the piezoceramic sensor is polarized by applying a predetermined potential difference thereto by means of the connector.
Owner:ITT ITAL SRL
Copper-free ceramic friction material with little falling ash and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101823856AAvoid secondary pollutionMeet the requirements of environmental protectionBraking membersFriction liningAdhesiveAramid
The invention discloses a copper-free ceramic friction material with little falling ash and a preparation method thereof. The copper-free ceramic friction material with little falling ash is prepared by mixing, shaping and thermally processing the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 5 to 14 percent of adhesive, 20 to 45 percent of reinforcing material, 10 to 40 percent of ceramic material, 10 to 18 percent of lubricant and the balance of filler, wherein nitrile rubber modified phenolic resin and nitrile rubber powder are used as the adhesive; the reinforcing material is one or a mixture of more of aramid fiber, carbon fiber, steel fiber, foam iron powder and aluminum oxide fiber; the ceramic material is one or a combination of more of molybdenum disulfide, magnesium oxide andferrous disulphide; the lubricant is the mixture of graphite and mica; and the filler is the mixture of composite filler, barite, friction powder and aluminum powder. The material has high friction performance, low brake noise and high heat fading resistance, and particularly shows high performance in aspects of wear resistance, long life and great reduction in the falling ash of a wheel hub; therefore, the material can meet both the requirement of a modern automobile braking system on operating conditions and the requirement on economy and environment friendliness when an automobile is used.
Owner:HUNAN BOYUN AUTOMOBILE BRAKE MATERIALS +1
Disk brake devices
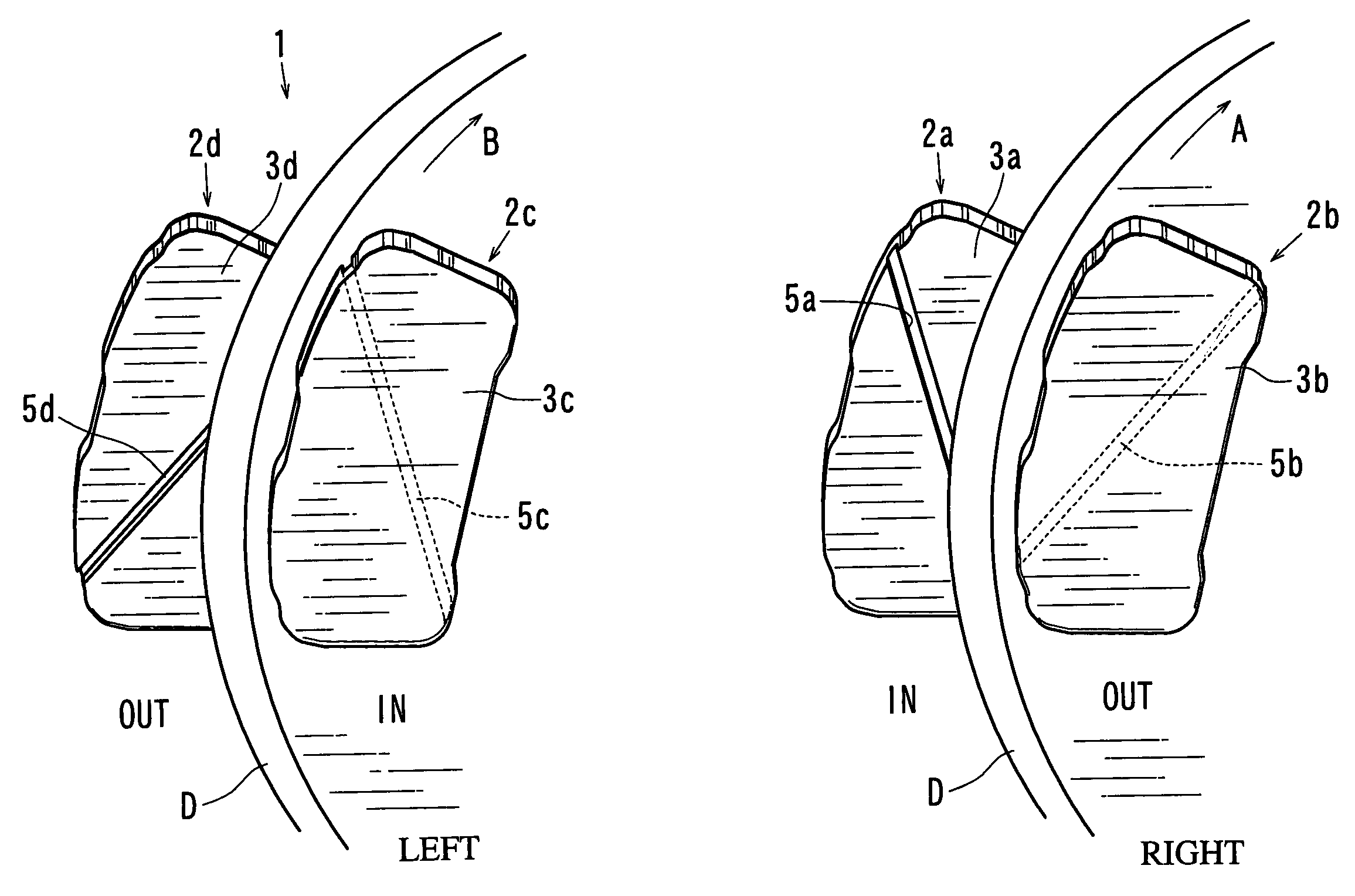
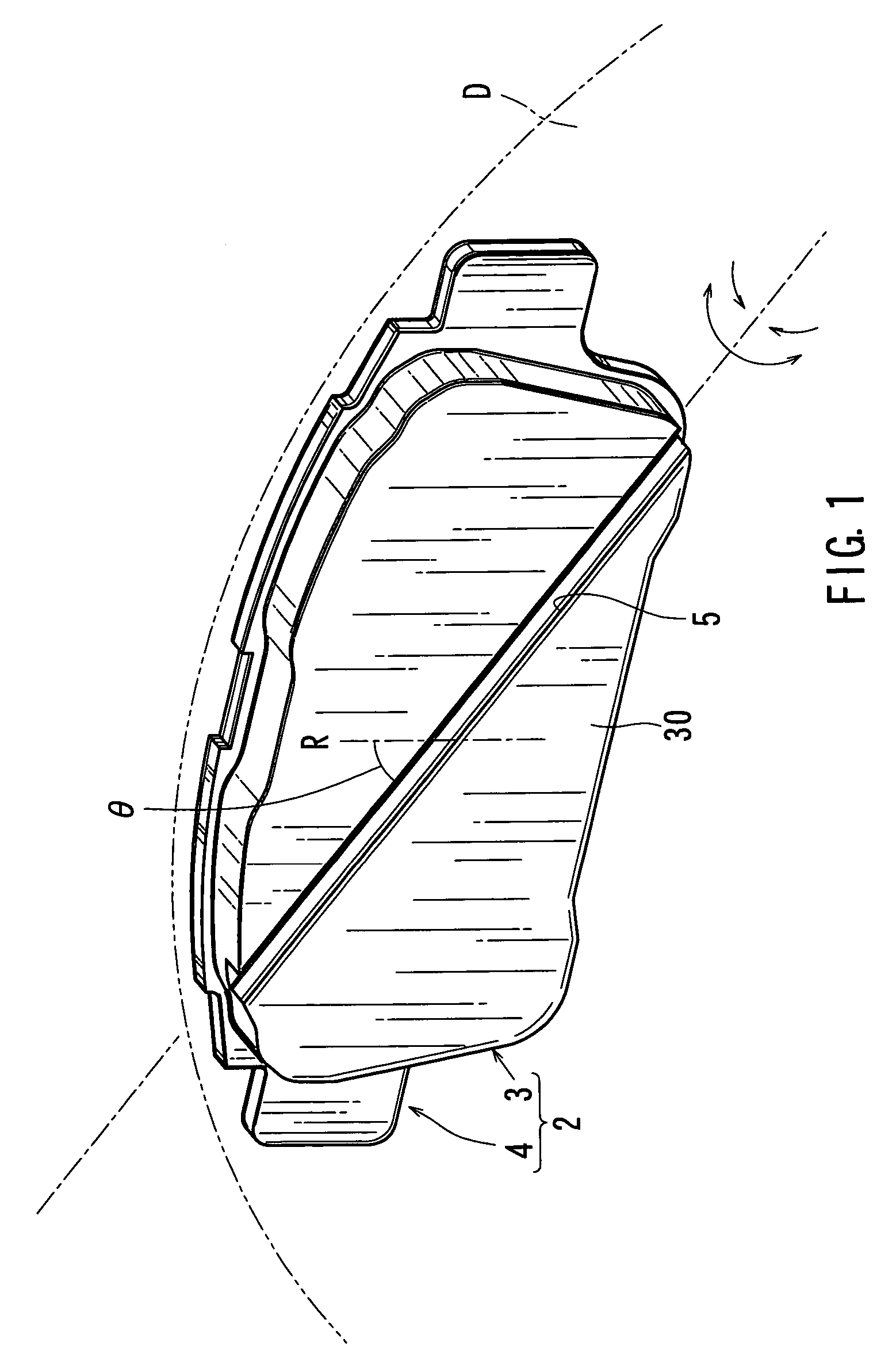
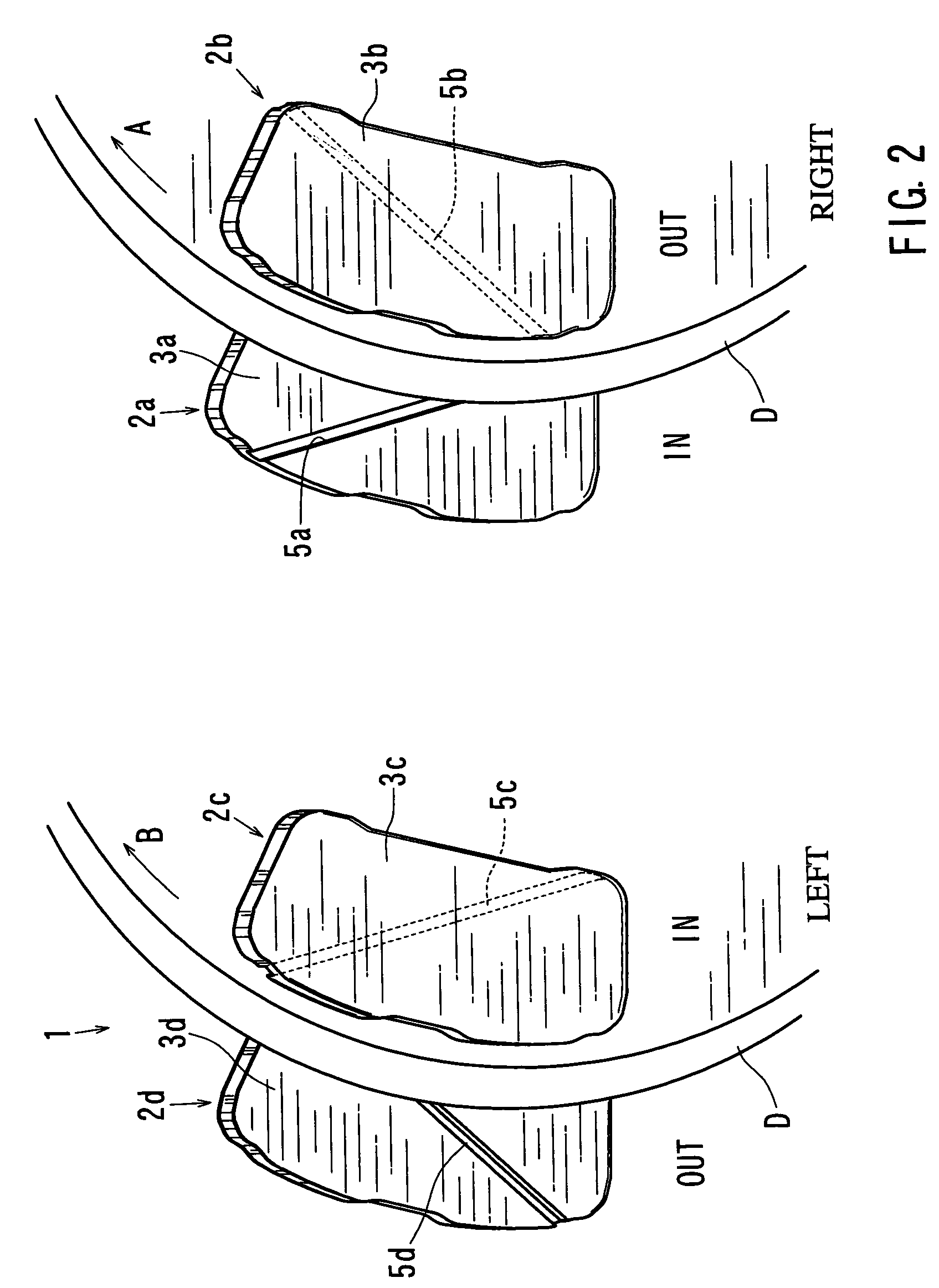
ActiveUS7111709B2Effectively reduce the squealing soundsImprove distortionNoise/vibration controlBraking membersEngineeringMechanical engineering
A disk brake device includes a pair of brake disks and right and left pairs of pads. Each pad includes a twisting compliant section that extends along a line inclined by an angle relative to a radial direction of the corresponding brake disk. The twisting compliant section facilitates the twisting of the pad about the compliant section. The twisting compliant sections of the right inner pad and the left inner pad are inclined in opposite directions relative to the twisting compliant sections of the right outer pad and the right inner pad. The twisting compliant sections of the right inner pad and the left inner pad are inclined in substantially the same direction with one another.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
Road vehicle brake disc made of carborundum foamed ceramics/aluminum alloy composite materials and production method of road vehicle brake disc
ActiveCN104235237AReduce weightImprove feeding capacityBraking membersSlack adjustersNanoceramicAlloy composite
The invention discloses a road vehicle brake disc made of carborundum foamed ceramics / aluminum alloy composite materials and a production method of the road vehicle brake disc. The body of the reinforced-aluminum-alloy brake disc with a carborundum foamed ceramics framework is made of reinforced aluminum alloy materials such as aluminum alloy or nano ceramics particles or carbon nano-tubes. The carborundum foamed ceramics framework is integrally casted on two symmetrical friction surfaces of the brake disc, and heat dissipation grooves or air holes can be casted or do not need to be casted on the friction surfaces. A plurality of heat dissipation ribs are casted in the peripheral direction of non-friction surfaces. Mounting holes are formed in the disc body. The production method includes the steps of production of the carborundum foamed ceramics framework, preprocessing of the framework, design and production of a casting mold of the brake disc, lower-pressure casting of the brake disc, heat treatment of the brake disc, precision processing of the brake disc and storage of a finished product. The brake disc is simple in production technology, light in weight, high and stable in friction factor, high in heat conductivity, long in service life and applicable to existing road vehicles.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG DONGDA HUITONG NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Adjustable stiffness leaf spring actuators
The present invention is a spring based actuator with a leaf spring having a length, width and thickness and a coil spring positioned over the leaf spring. The coil spring further comprises: a first end; a second end; and at least one force generator acting on either the first end of the coil spring and the second end of the coil spring to deflect the coil spring and the leaf spring.
Owner:HOLLANDER KEVIN +1
High friction composite brake shoe for railway freight car and manufacture method thereof
ActiveCN101391611AHigh compressive strengthHigh impact strengthBraking membersBrake arrangement with braking memberFiberEngineering
The invention discloses a high friction composite brake shoe for a railway wagon and a manufacturing method thereof. The composite brake shoe comprises: a steel back and a brake shoe body which is fixed on the steel back, wherein, the brake shoe body is prepared by materials which are synthesized by various components with the following weight ratio: 8 to13 parts of nitrile butadiene rubber, 2 to10 parts of styrene butasiene rubber, 5 to10 parts of cresol modified A-stage phenolic resin, 15 to 30 parts of steel fiber, 10 to 15 parts of magnesium oxide, 5 to 10 parts of calcined petroleum coke, 2 to 5 parts of silicon carbide, 10 to25 parts of mineral fiber, 5 to 10 parts of calcium hydride, 10 to 20 parts of barium sulfate, 5 to 10 parts of graphite, 1 to 5 parts of molybdenum disulfide, 1 to 5 parts of carbon black, 1 to 3 parts of sulfur and 1 to 3 parts of enhancer. The brake shoe can be used in the railway heavy-duty high-speed wagon and has stable friction performance and better wear resistance; the brake shoe can effectively inhibit the phenomena of metal inlay, cracks, dropping blocks and the like and reduce the damages on wheels; and the brake shoe is characterized by better impact resistance performance and good weatherability.
Owner:BEIJING RAILWAY STAR FORTUNE HIGH TECH
Copper-based powder metallurgy high speed brake lining
InactiveCN101493127AComply with work performance requirementsEffect of small friction propertiesBraking membersFriction liningBoron nitrideSilicon dioxide
The invention provides a copper based powder metallurgy high speed brake lining, which comprises a steel backing, a brake block, a framework, a spring washer and a swollen tail block. In the course of braking, the brake lining has smaller abrasion loss and can effectively prevent the edge dropping, angle dropping and camber wear of the brake block. The brake block uses copper based powder metallurgy friction material; copper powder, iron powder, tin powder, chromium powder, titanium powder, nickel powder, bismuth meal, graphite, boron nitride, aluminum oxide, silicon dioxide, zirconite and the like are well blended according to the proportion, stamped and sintered on the framework after cold pressing. The copper based powder metallurgy high speed brake lining has the characteristics of high mechanical strength, good thermal conduction, good thermal stability, strong heat-resistant fade performance, long service life, small abrasion on a retarding disc and stable friction performance and the like, and can effectively control very high way trains with 200-300km / h per hour.
Owner:贵州新安航空机械有限责任公司
Floating-type brake disk
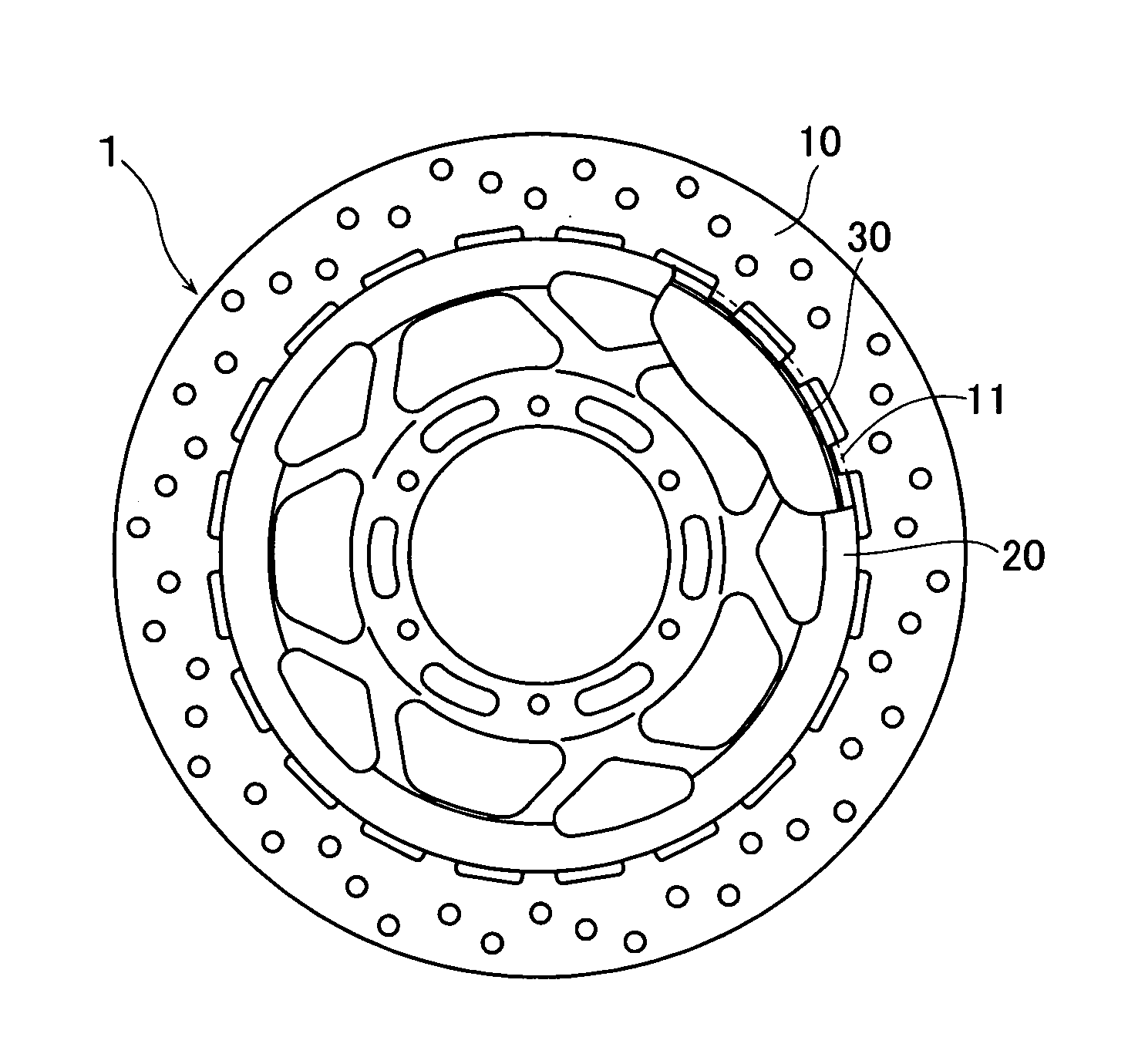
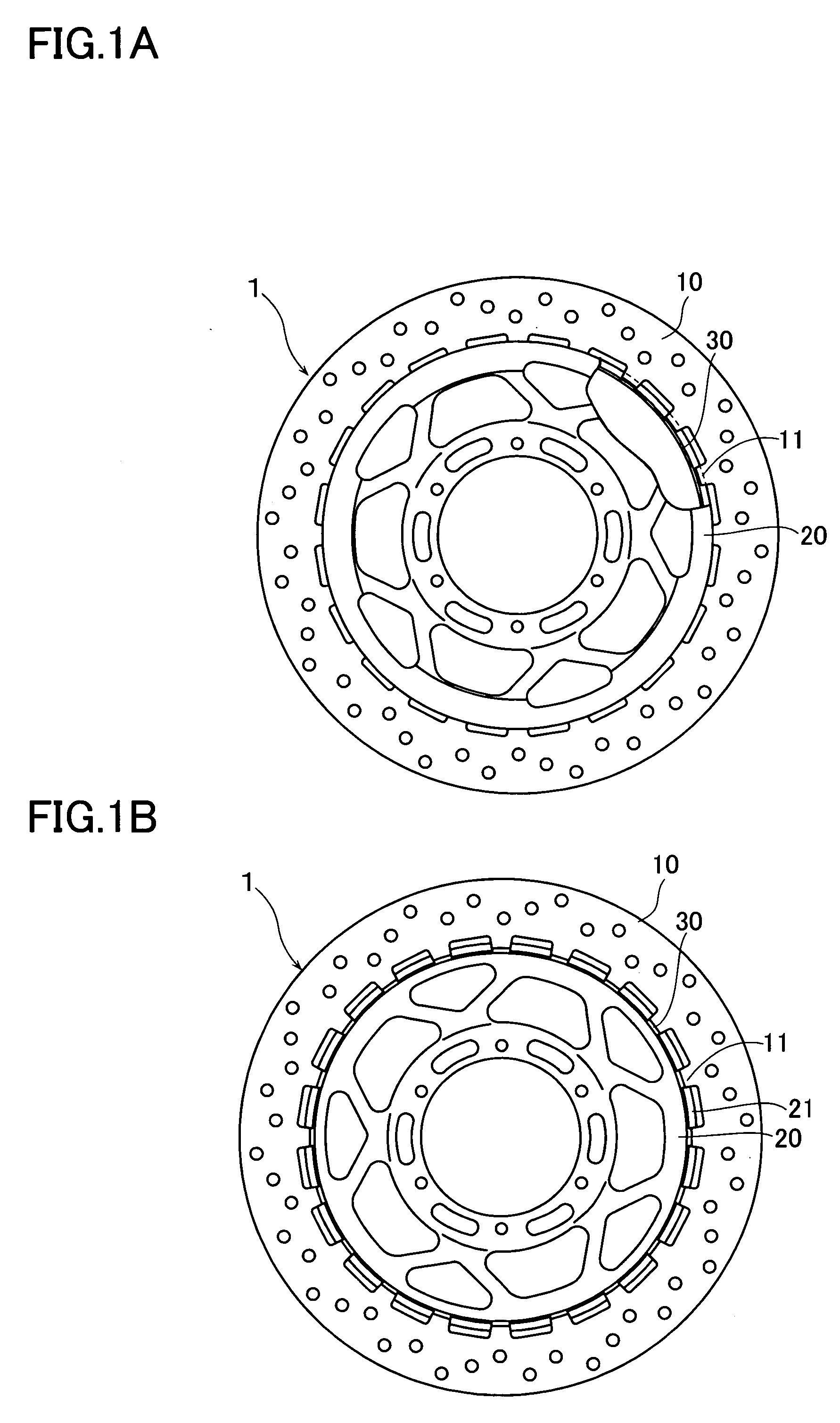
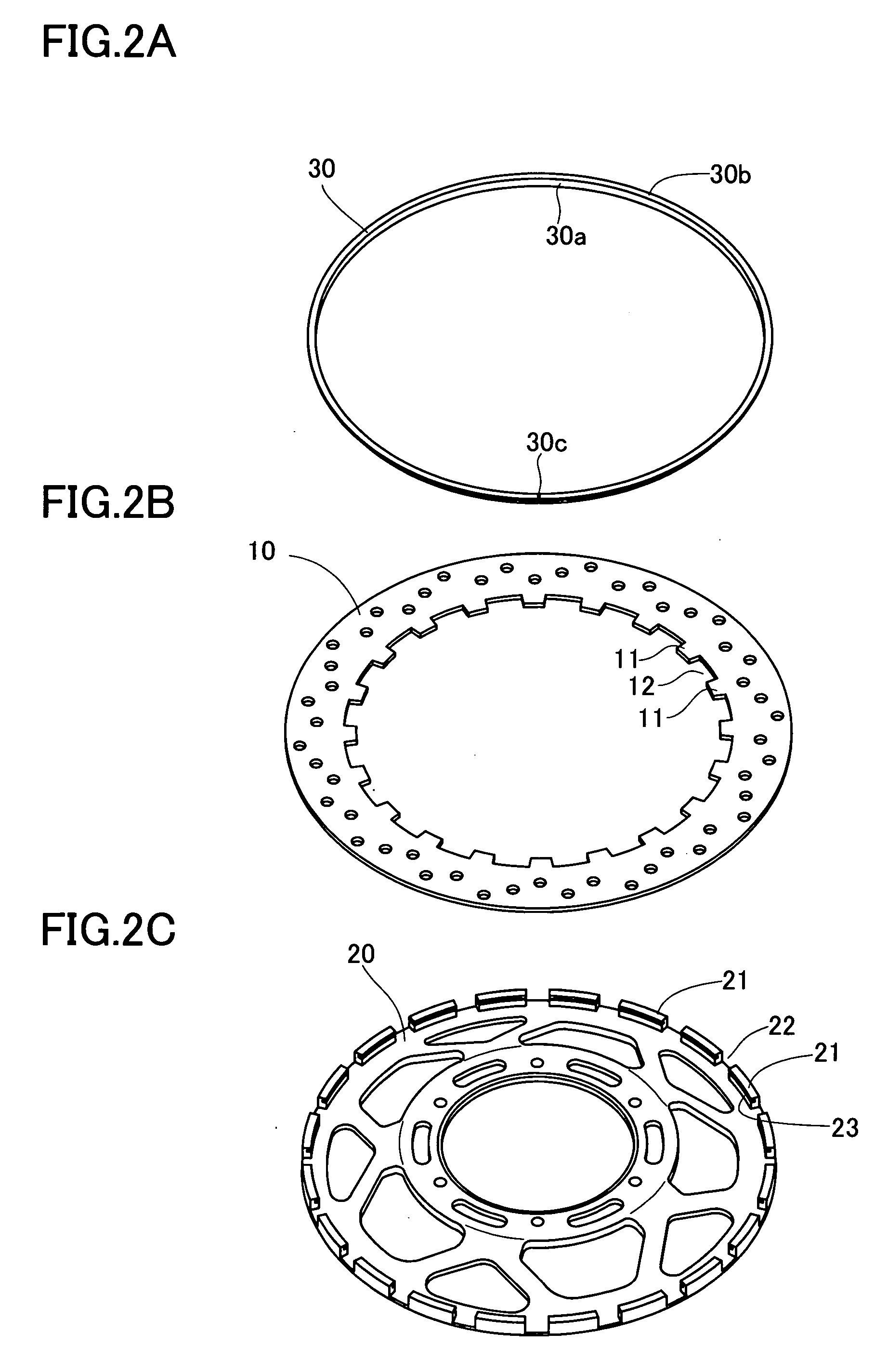
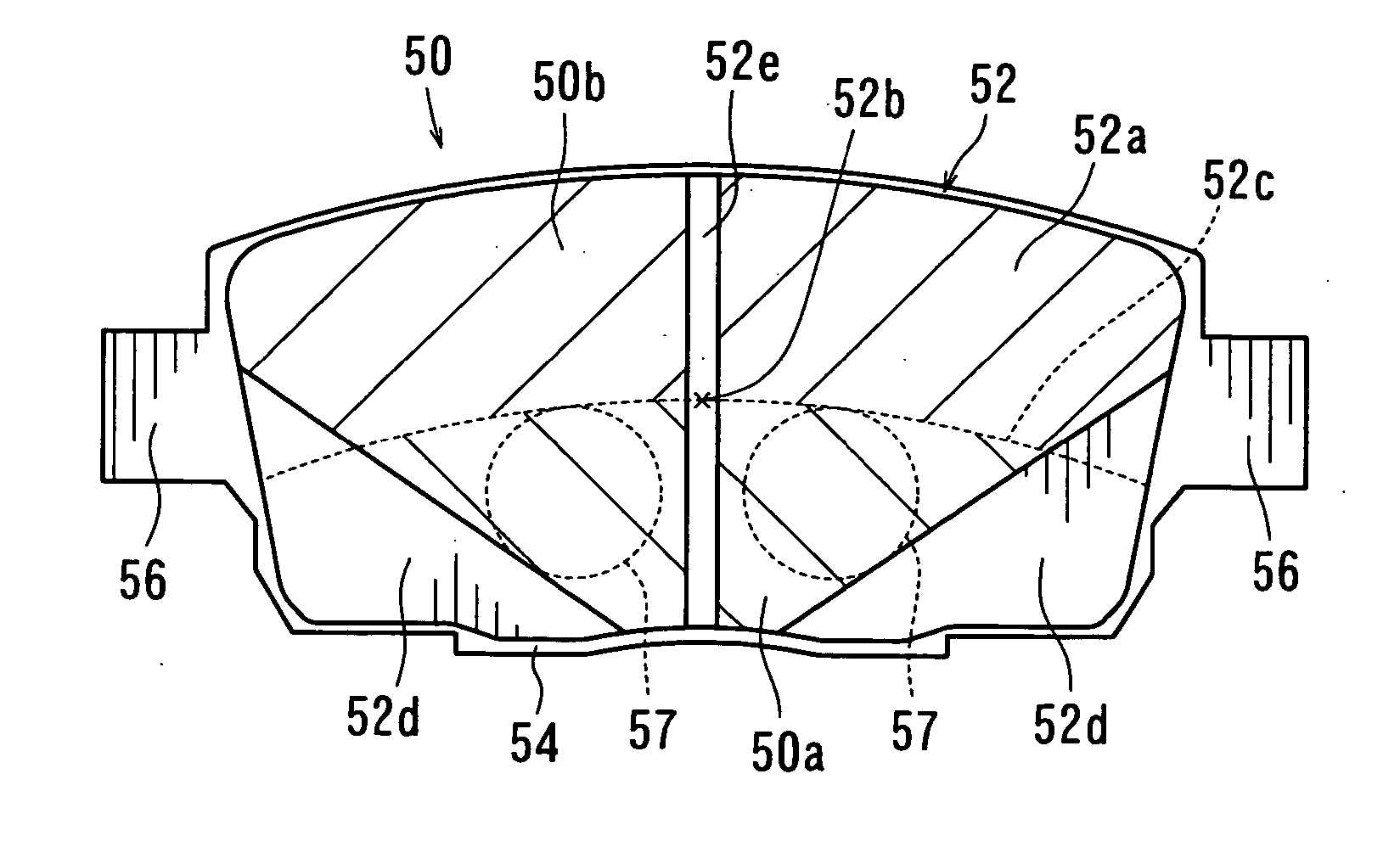
InactiveUS20050145452A1Reduce in quantityAvoid crackingBraking discsBraking membersMechanical engineeringEngineering
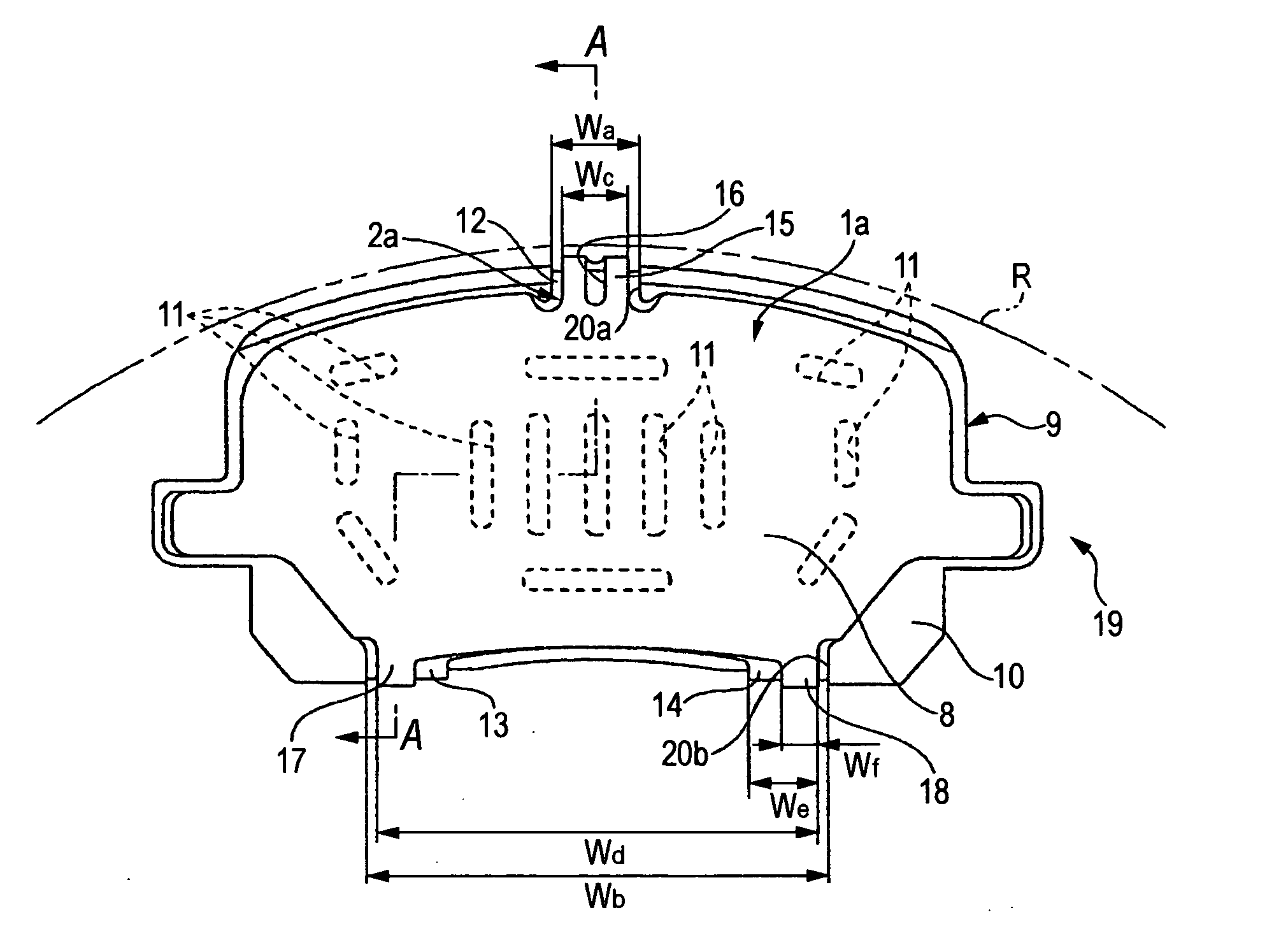
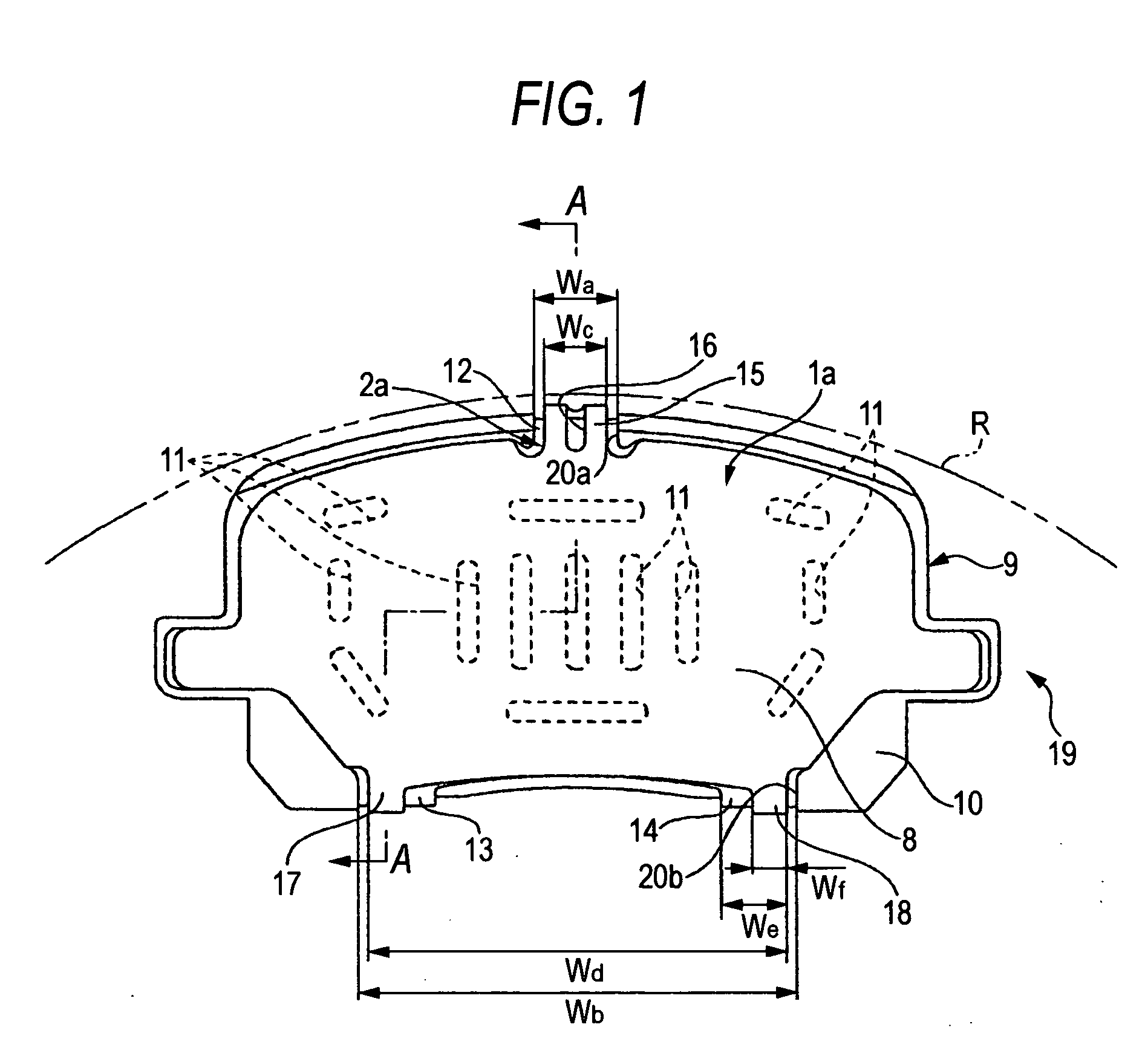
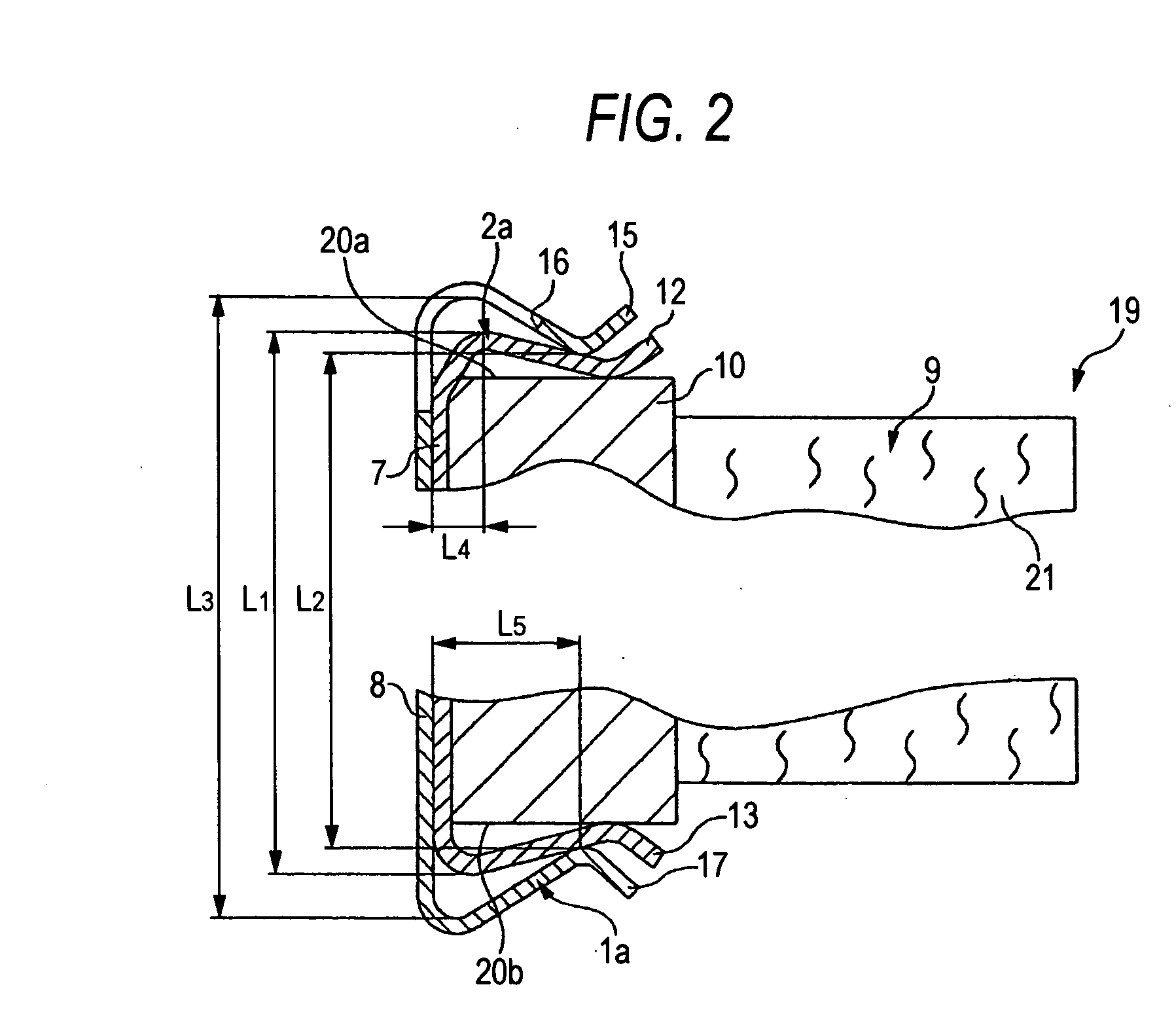
The invention provides a floating type brake disc which can absorb a shock applied to a hub from a rotor at a time of running on a punishing road, can improve a heat lowering performance and can widely reduce a number of parts. A brake disc (1) is constituted by a hub (20), a rotor (10) and a ring spring (30). A lot of protrusion portions (11) in a radial direction are provided along a peripheral direction in an inner peripheral edge portion of the rotor (10), the same number of projection portions (21) in an axial direction are provided along the peripheral direction in an outer peripheral edge portion of the hub (20), and the protrusion portions (11) are protruded to an inner side in the radial direction through a gap (22) between the projection portions (21). The ring spring (30) is constituted by an open ring having an approximately L-shaped cross section. A line (30b) in a radial direction of the ring spring is fitted and mounted to a groove (23) in an inner peripheral surface of the projection portion (21) of the hub protruding from the rotor, and an inner peripheral surface of a protrusion portion (12) in the rotor is pressed to an outer side in the radial direction by a line (30a) in the axial direction of the ring spring.
Owner:YUTAKA GIKEN CO LTD
Disc brake for vehicle
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
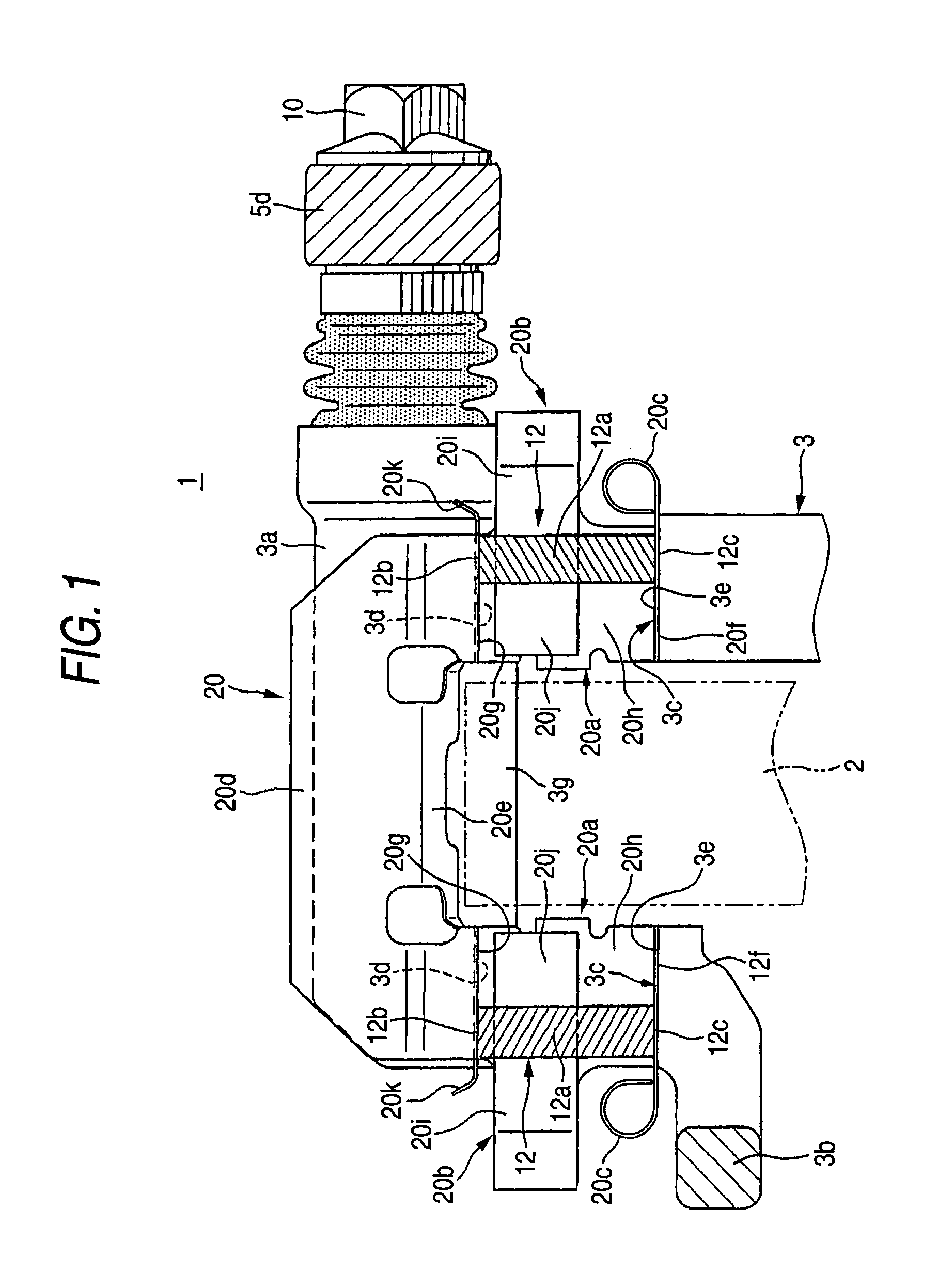
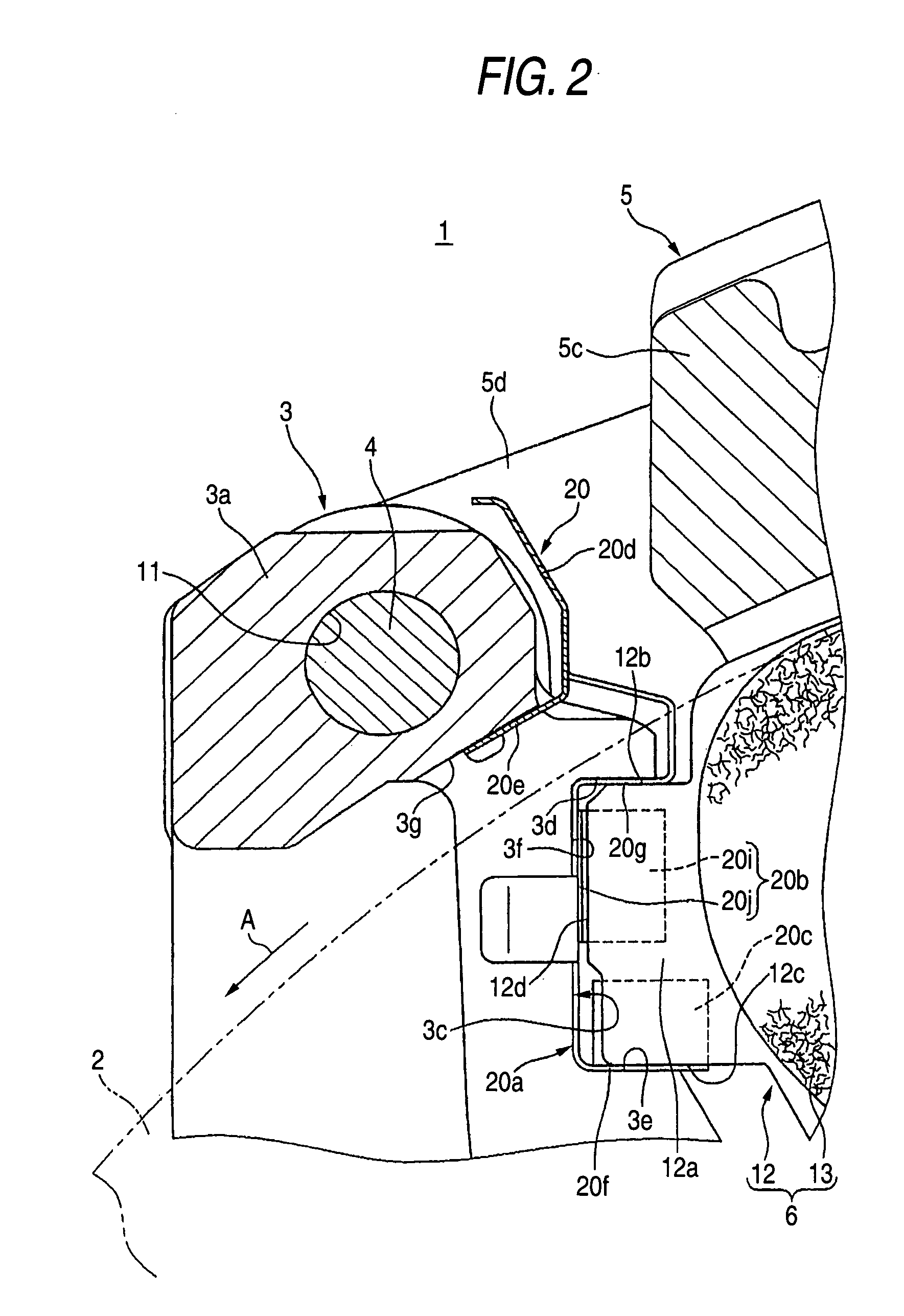
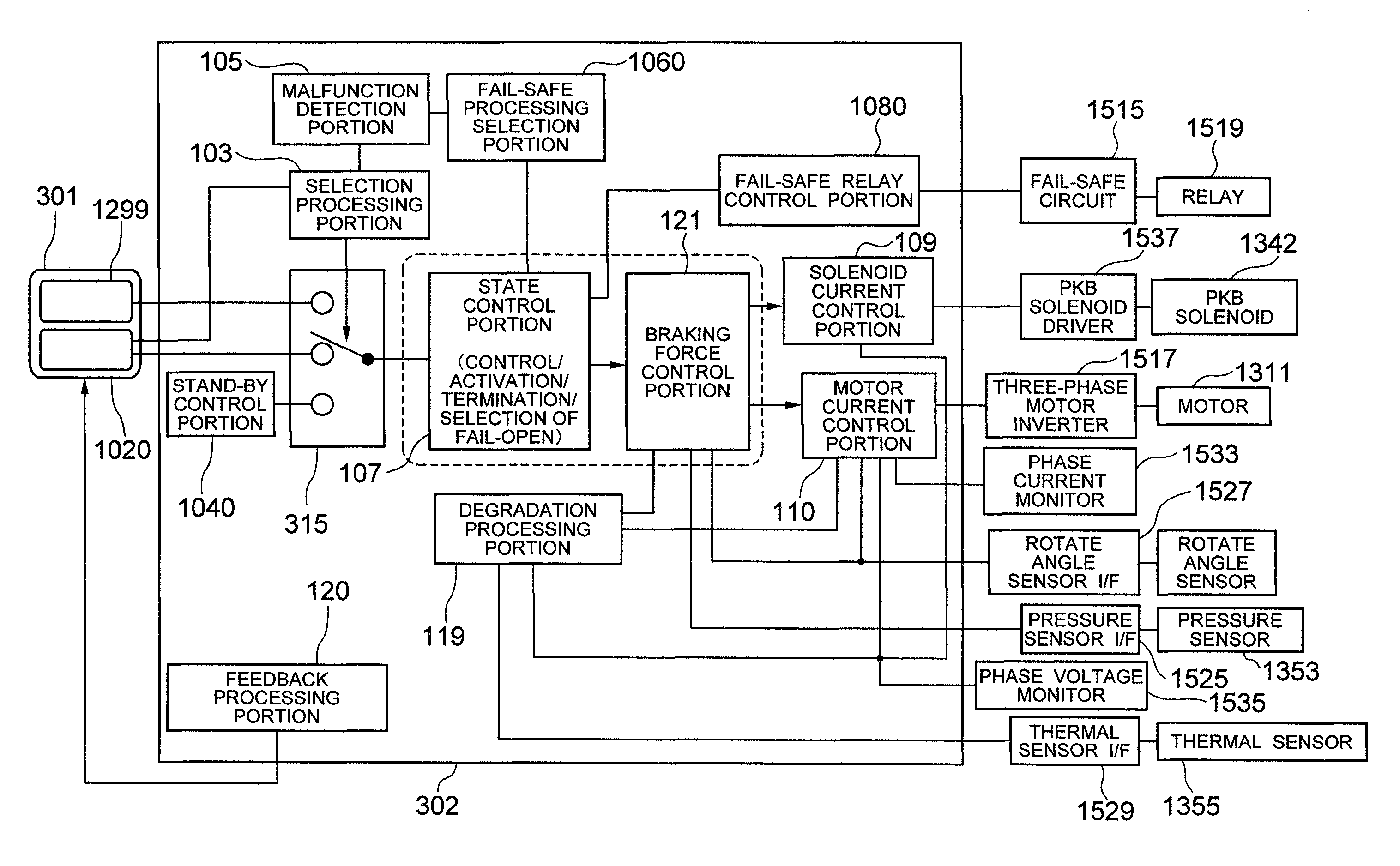
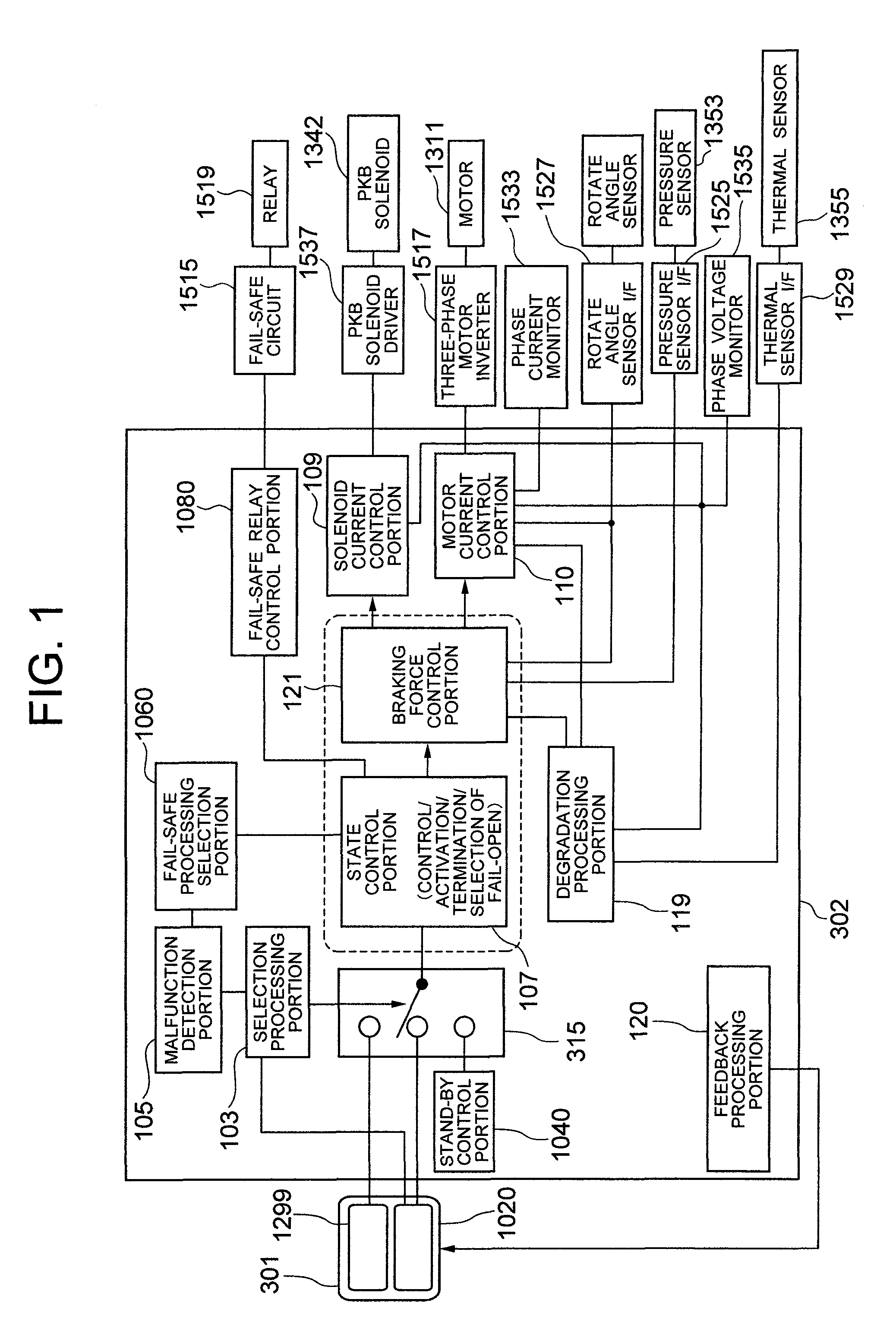
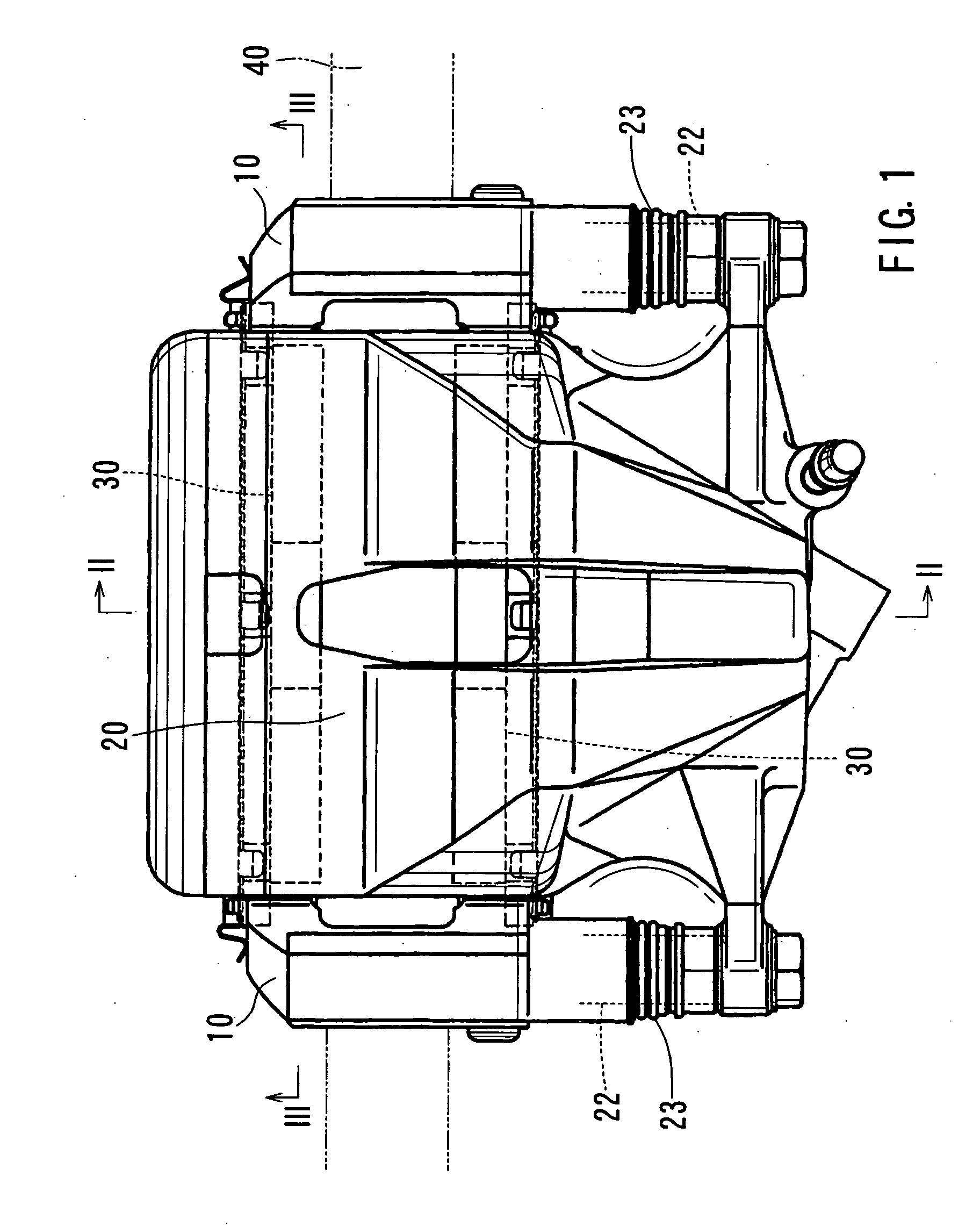
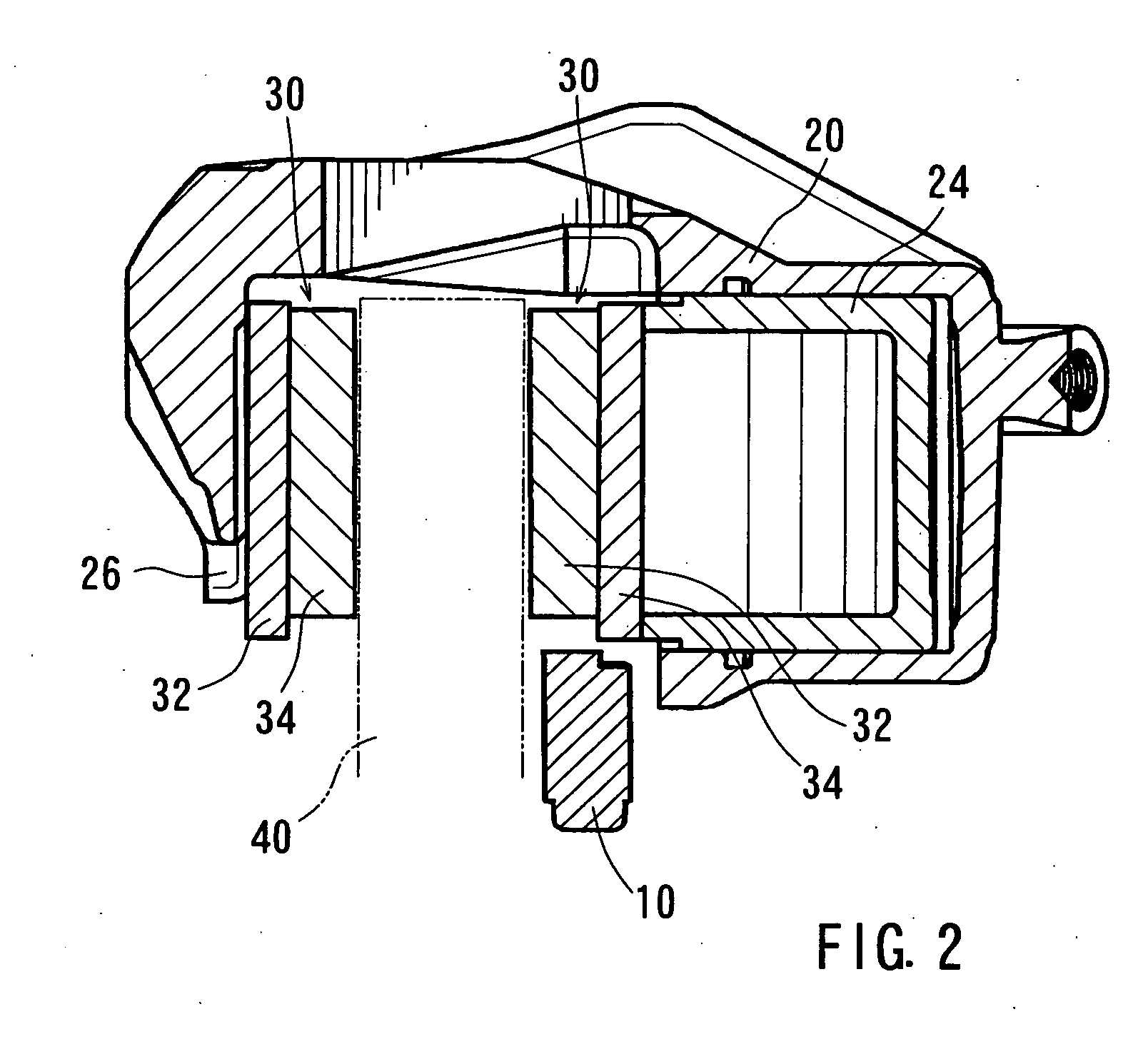
Electro Mechanical Brake
InactiveUS20080091326A1Increase the number ofHigh control precisionAxially engaging brakesAnalogue computers for trafficElectrical resistance and conductanceVoltage drop
When a caliper and an ECU are separately configured in an electro mechanical brake, the number of harness is increased, and therefore, the wiring layout of the harness becomes difficult, and when bending and twisting are applied to the harness, a problem of a breaking of the wiring and the like arises. Further, a voltage drop is caused by the electric resistance of the harness, and moreover, there is a risk of infiltration of noises. The ECU and the caliper are integrated, thereby making the distance between various sensors and control devices short. Further, the frame body of the ECU incorporates an inverter module driving a motor and its control device, thereby simplifying a wiring connection to the motor.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Brake assembly and coating
InactiveUS20060272909A1Reduce the possibilityMaintaining torqueMolten spray coatingAxially engaging brakesWear resistantCorrosion
A brake assembly is provided that includes a wear-resistant surface, or a surface prone to corrosion, wherein the surface is coated with a coating that optimizes wear-resistance, corrosion-resistance, adhesiveness, and friction factors of the coating. The coating includes a sacrificial corrosion constituent and a second constituent that is relatively harder than the sacrificial corrosion constituent wherein typical metals often employed as sacrificial anodes for example are contemplated. These include aluminum, zinc, and alloys thereof. The second constituent is potentially formed from a carbide, nitride, oxide, transitional metals and alloys thereof, and mixtures thereof.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC +1
Brake assembly with tuned mass damper
InactiveUS7032723B2Effective dampingEasily damagedNoise/vibration controlBraking membersSnubberTuned mass damper
A tuned mass damper for sound-dampening brake squeal noise is located within a hole formed in a brake component such as a backplate supporting a brake pad. The location of the hole and the weight and geometry of the tuned mass damper are tailored to provide effective damping for the particular frequencies that are to be eliminated in the brake system. Locating the tuned mass damper inside of a hole in the component has packaging and manufacturing advantages, and results in a tuned mass damper that is less susceptible to damage when in use. The hole may be blind, the bottom of the hole being thin enough to serve as a spring member to which a vibration damping mass is attached. In one embodiment, the tuned mass damper is a module adapted for insertion into the hole in the brake backplate. Contact between the module and inner surfaces of the hole transfers mechanical vibration of the backplate to the tuned mass damper.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
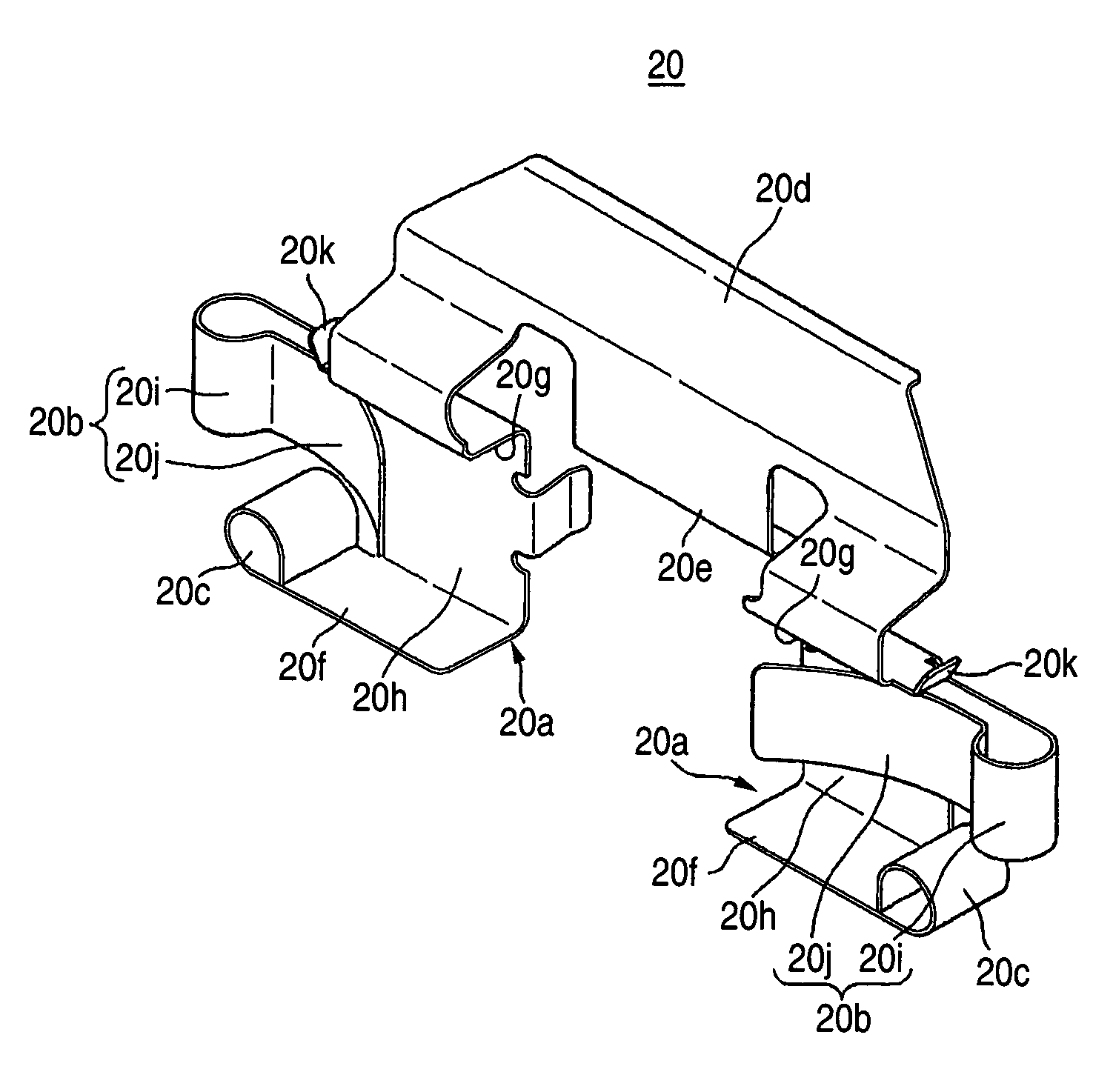
Clip for use in a disc brake assembly and disc brake assembly including such a clip
ActiveUS20130192938A1Reduce contact areaBraking element arrangementsNoise/vibration controlEngineeringMechanical engineering
This invention relates to a brake clip for use with a disc brake assembly. The brake clip includes a U-shaped section having a base leg with opposing first and second legs extending from the base leg. An abutment leg extends from at least one of the first and second legs of the U-shaped section. An extension leg extends from the abutment leg. The abutment leg is in contact with an anchor bracket of the disc brake assembly and the extension leg is in contact with a brake pad of the disc brake assembly when the brake clip is disposed therebetween.
Owner:KELSEY HAYES CO
Disk Brake
InactiveUS20090236187A1Good componentReduce thermal stressAxially engaging brakesBraking membersCalipersBrake lining
A disk brake having a brake caliper, which engages axially in a U shape around a rotatable brake disk is provided. The disk brake includes a caliper bridge, two caliper limbs and at least one actuating device. At least one brake lining is mounted in an axially movable fashion in the brake caliper. The caliper bridge has, in the peripheral direction, at least three substantially axially extending supports, wherein two of the supports are embodied as a main support and one support is embodied as a central support. These supports connect the two caliper limbs and in the process form two windows and axially project beyond the brake disk. The central support projects both beyond the brake disk and beyond the brake lining in the axial direction.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Metal matrix composites, and methods for making the same
A holder comprising an insert for reinforcing a metal matrix composite article and methods of making the same. In another aspect, the present invention provides metal matrix composite articles reinforced with an insert(s) and methods of making the same. Useful metal matrix composite articles comprising the inserts include brake calipers.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Disk brake pad
InactiveUS7275625B2Promote long pad-lifeInhibits uneven pad-wearBraking membersFriction liningCircular discClassical mechanics
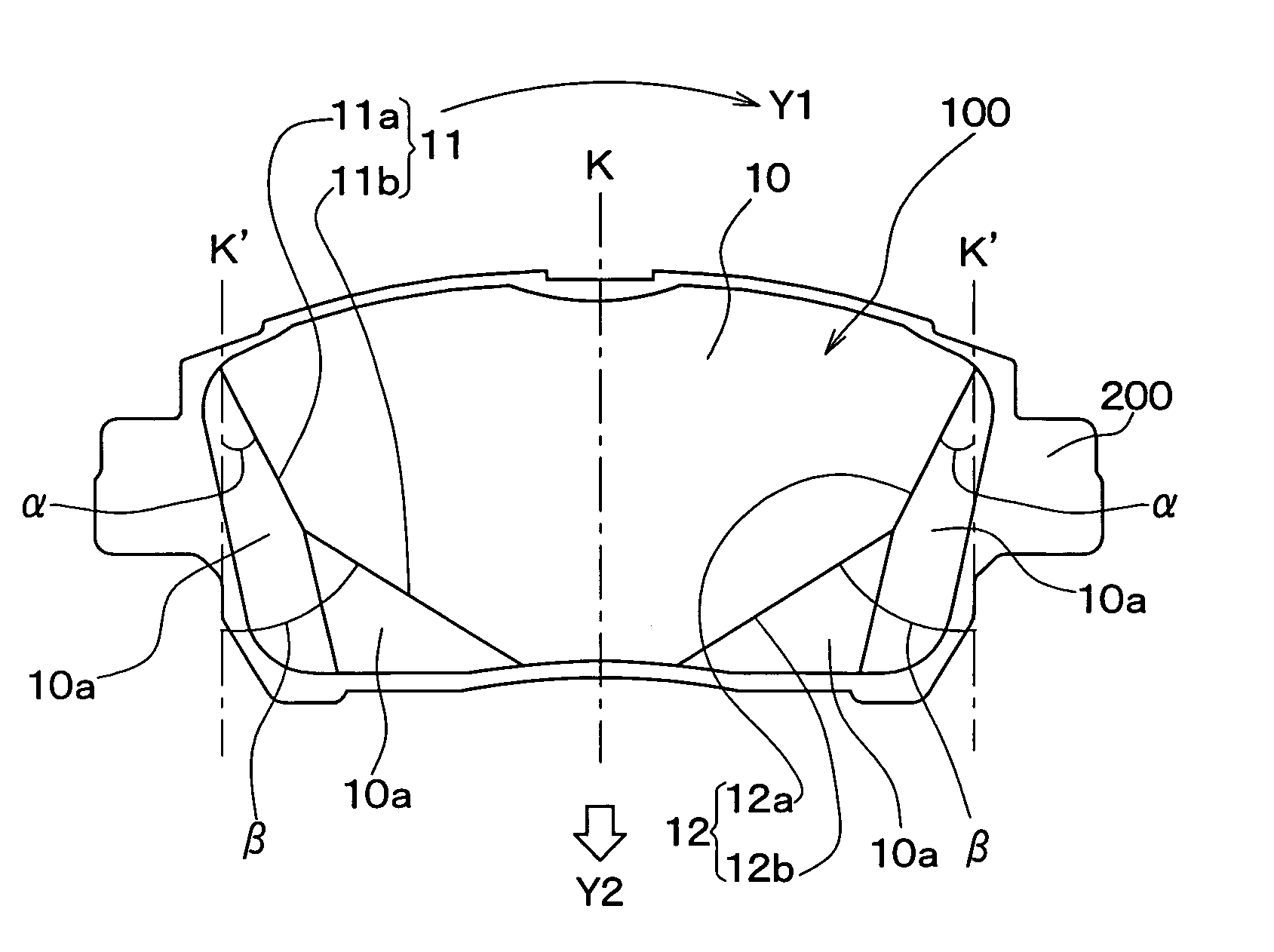
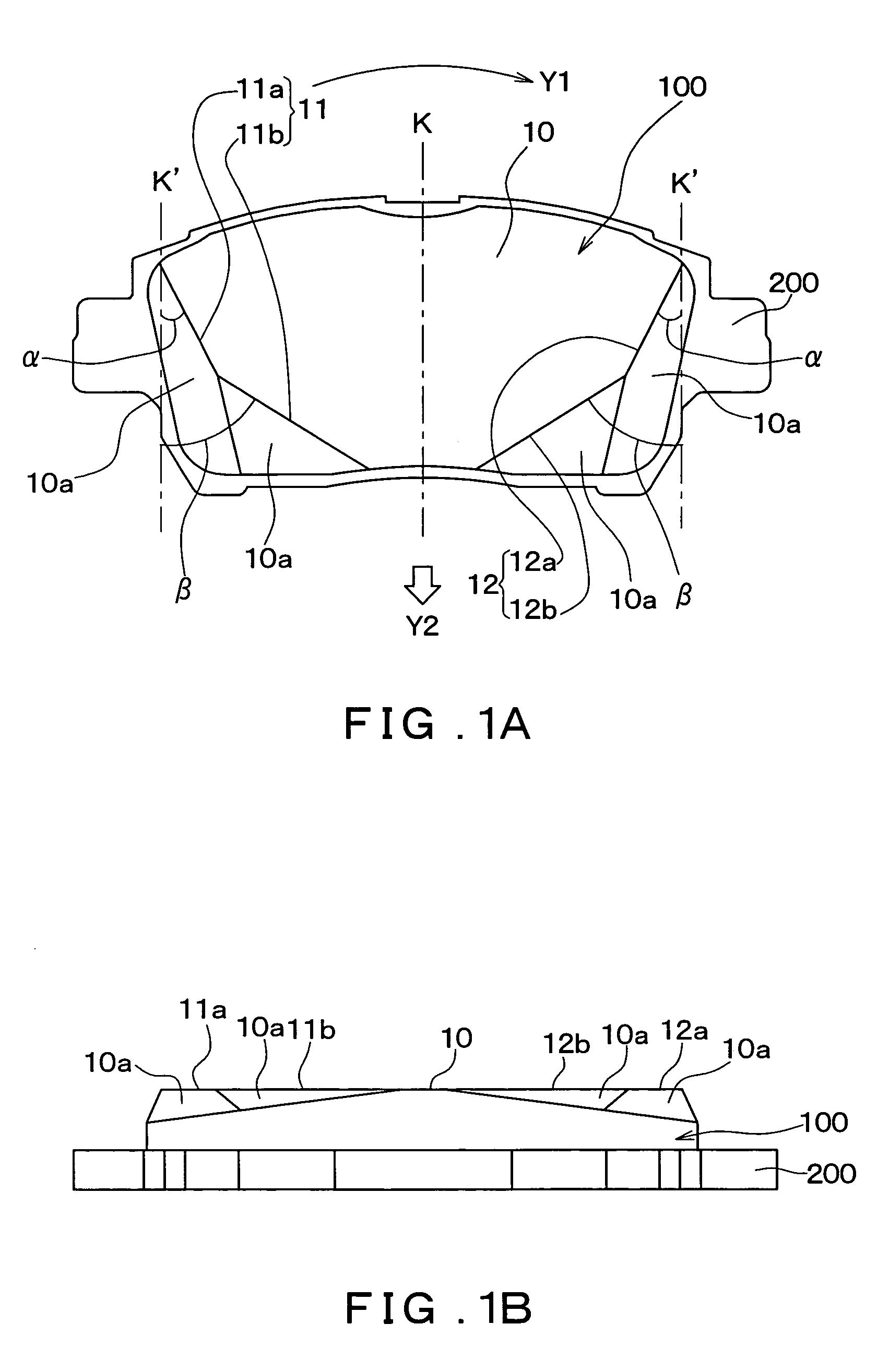
A disk brake pad controls rotation of a disk rotor by pushing a friction surface against the disk rotor while it is rotating. The disk brake pad is formed with respective chamfered portions at respective end portions of the disk brake pad at the incoming and outgoing disk-rotor-rotation sides thereof. An edge of an end portion of the friction surface of the disk brake pad at the incoming disk-rotor-rotation side, and an edge of an end portion at the outgoing disk-rotor-rotation side are formed in a stepped bending shape such that a length of the friction surface in a circumferential direction of the disk rotor becomes shorter in a center of rotation direction of the disk rotor.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
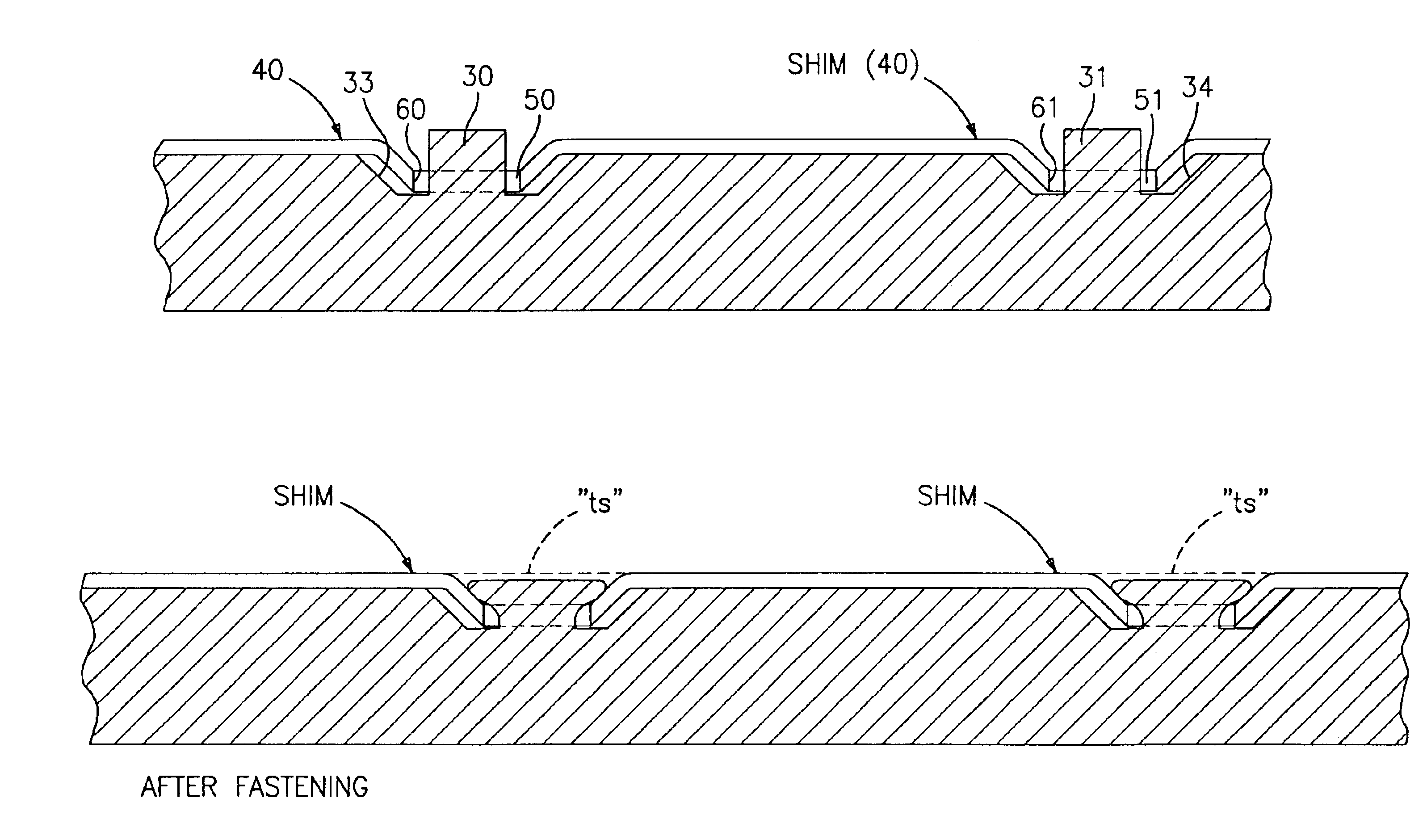
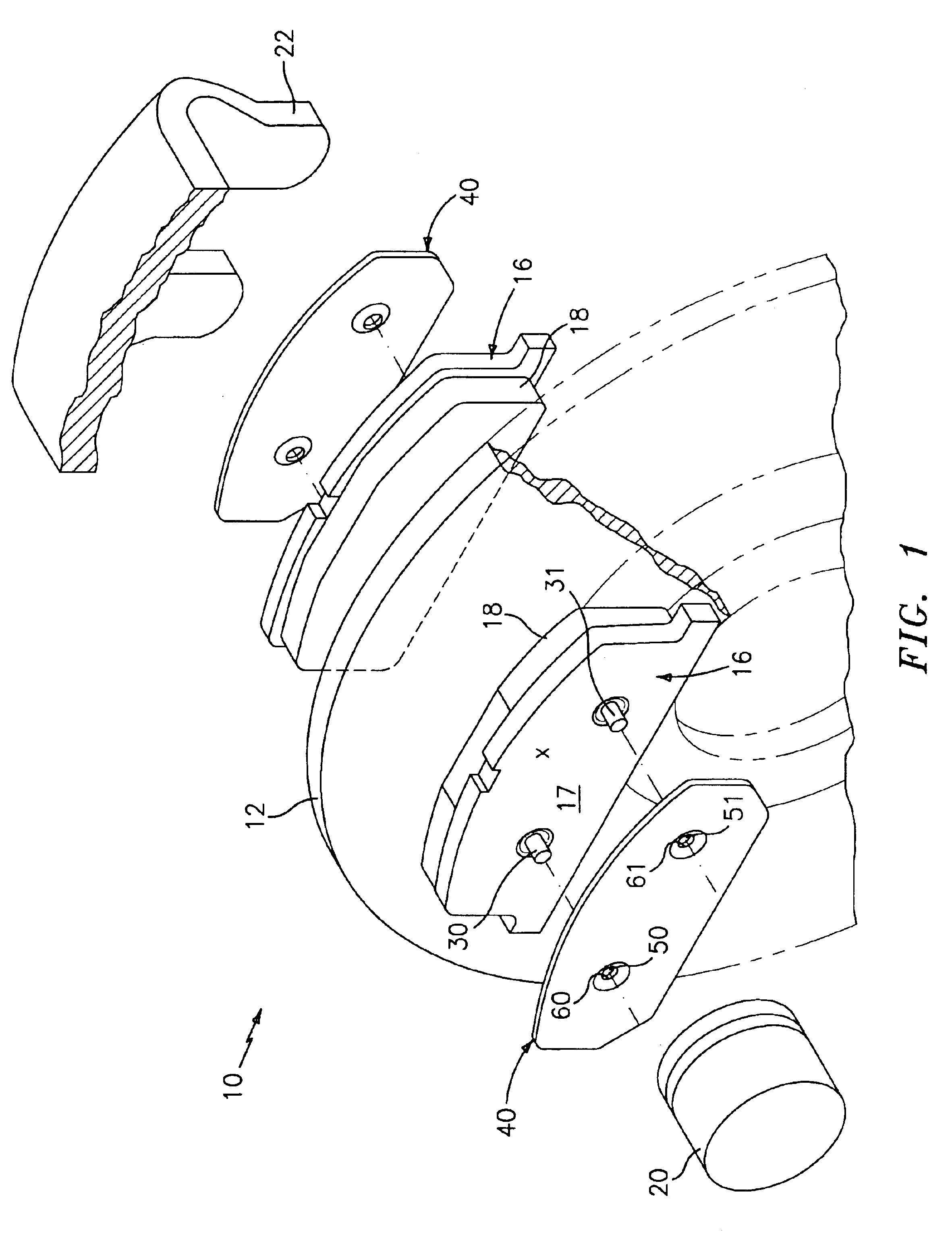
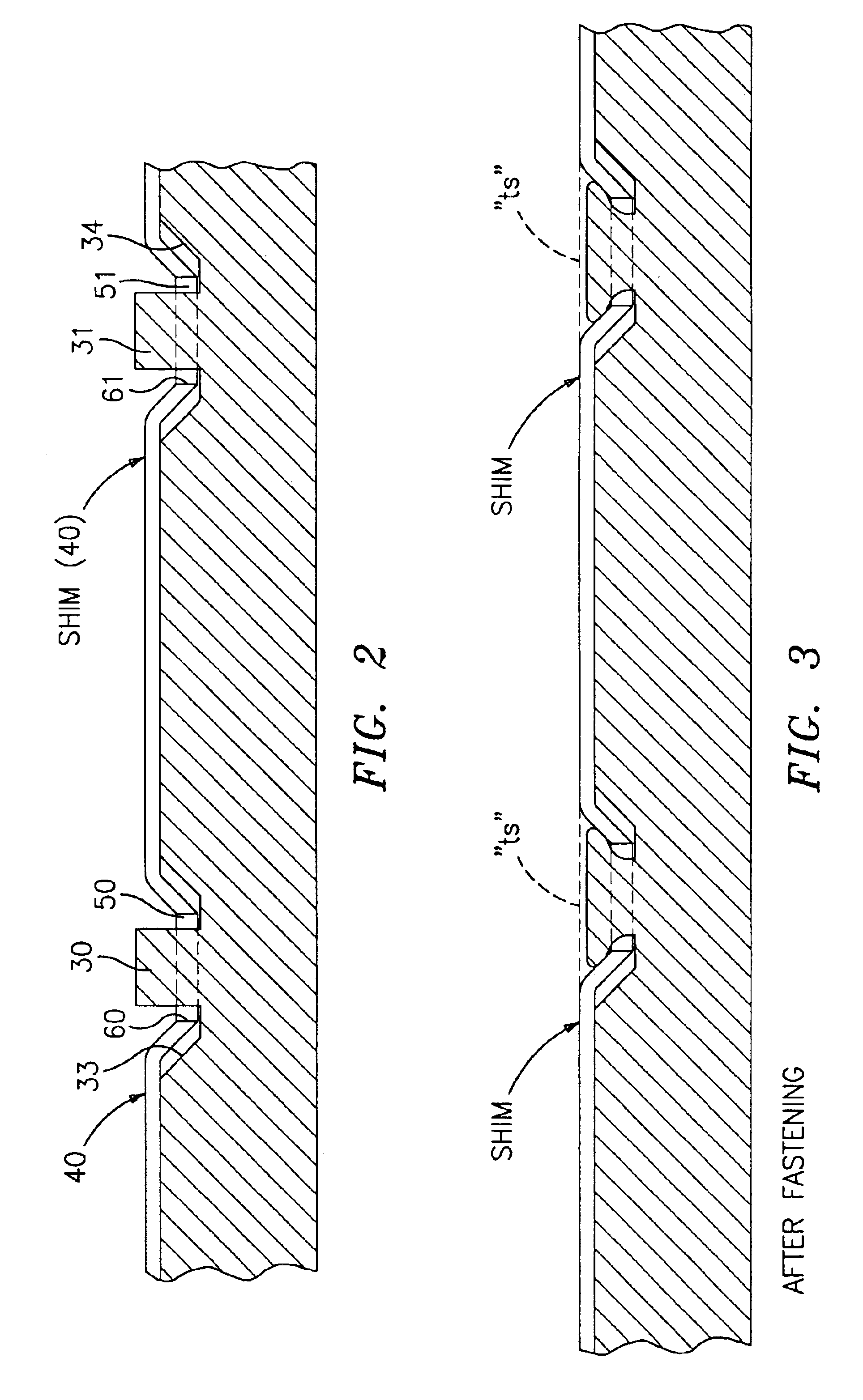
Method of securing a shim to a backing plate and subassembly formed thereby
InactiveUS6913120B2Reduce the possibilityBraking membersSlack adjustersClassical mechanicsEngineering
A method of securing a shim against a first side surface of a backing plate for use in a brake assembly. The first side surface of the backing plate has a first extending pin and at least a second extending pin spaced apart from the first extending pin and the shim has apertures that align with the extending pins. The shim is coupled against the first side surface of the backing plate and the apertures are aligned with their corresponding pins such that the pins extend through the apertures. Each pin is sufficiently deformed to directly contact and lock down at least a portion of the edge of each respective apertures to secure the shim against the first side surface of the backing plate such that the respective pins do not extend above the top surface of the shim after deformation.
Owner:ANSTRO MFG INC
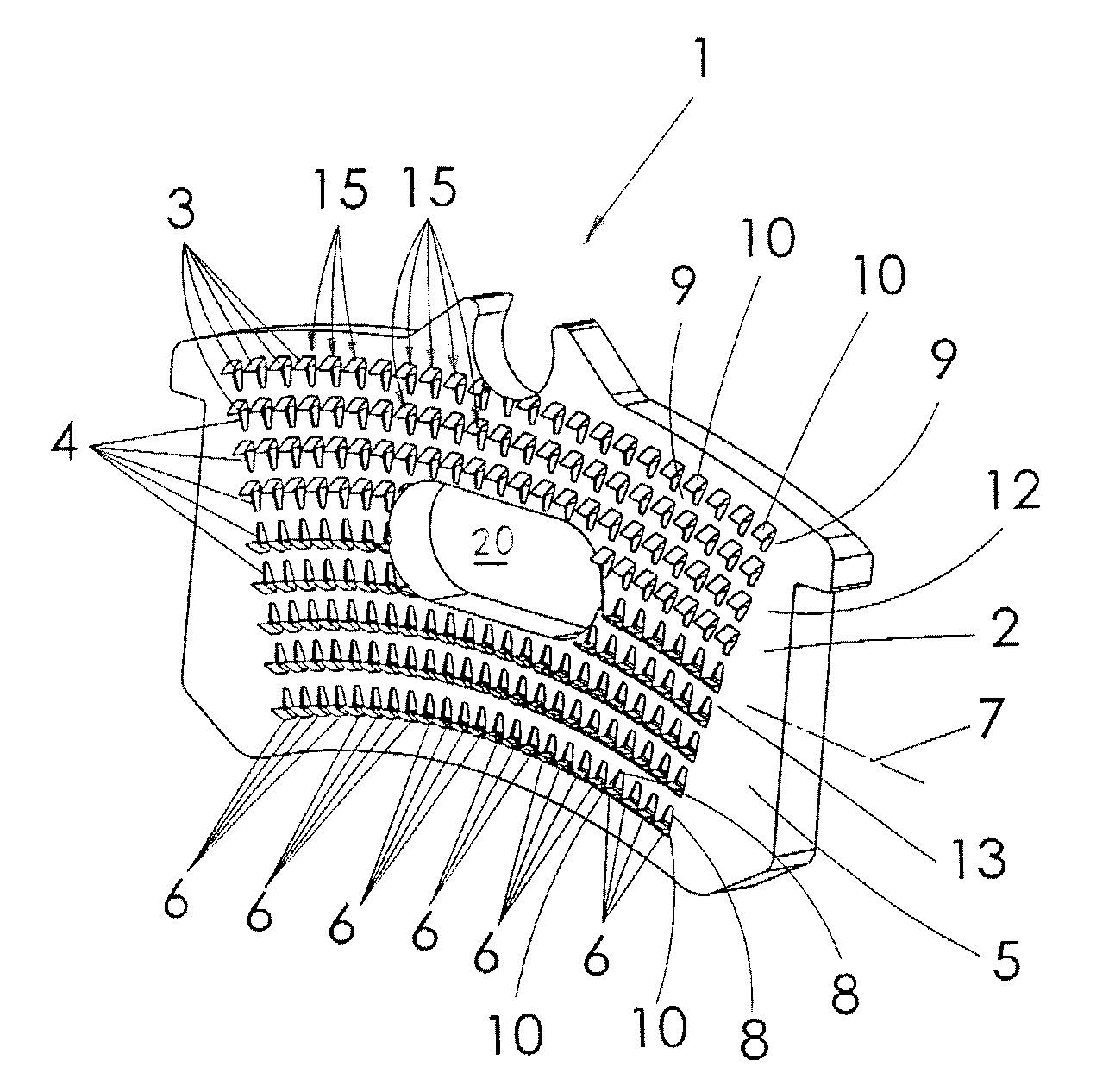
Brake plate
InactiveUS7686142B2Improve stressLarge braking forceMetal-working apparatusBraking membersEngineeringBrake lining
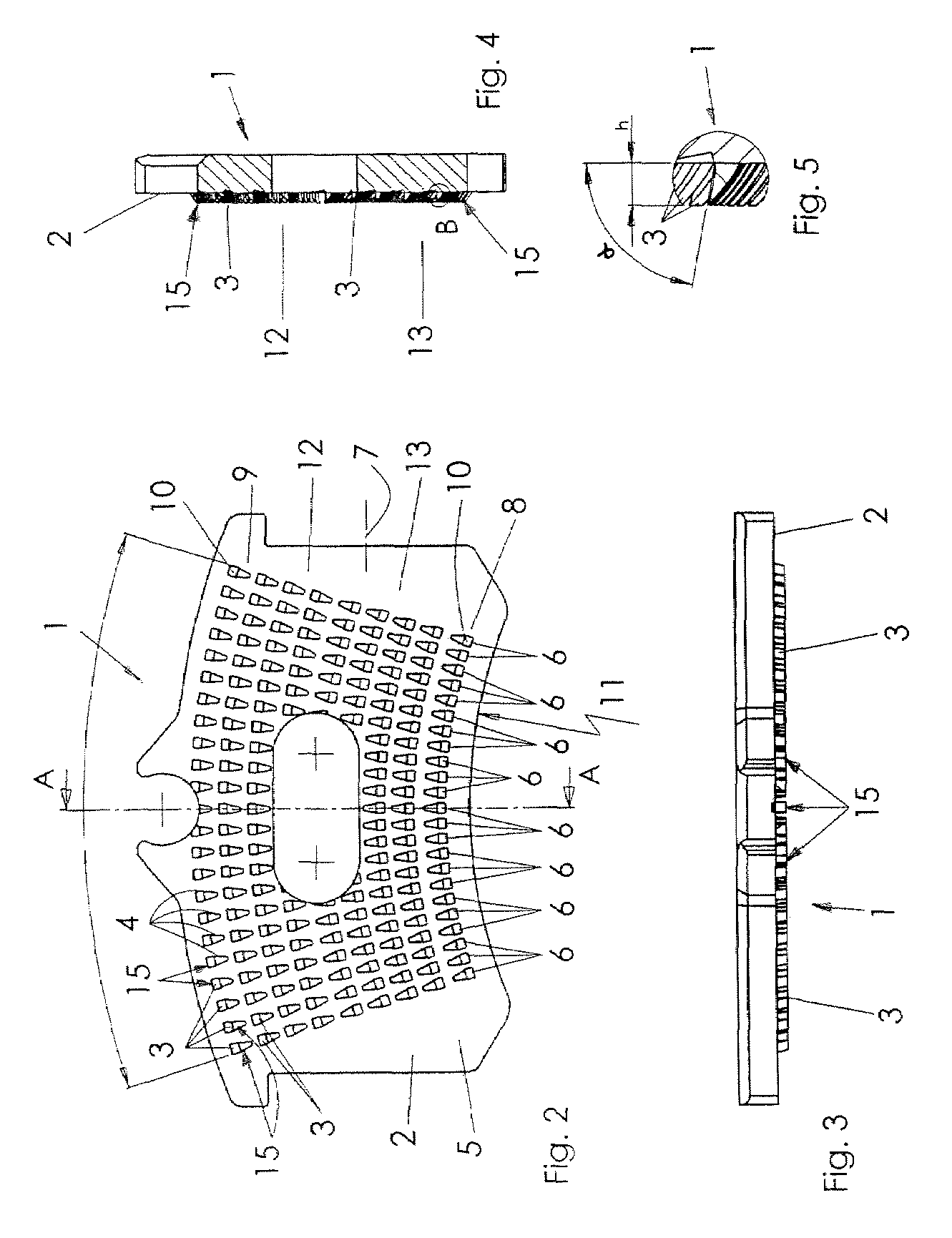
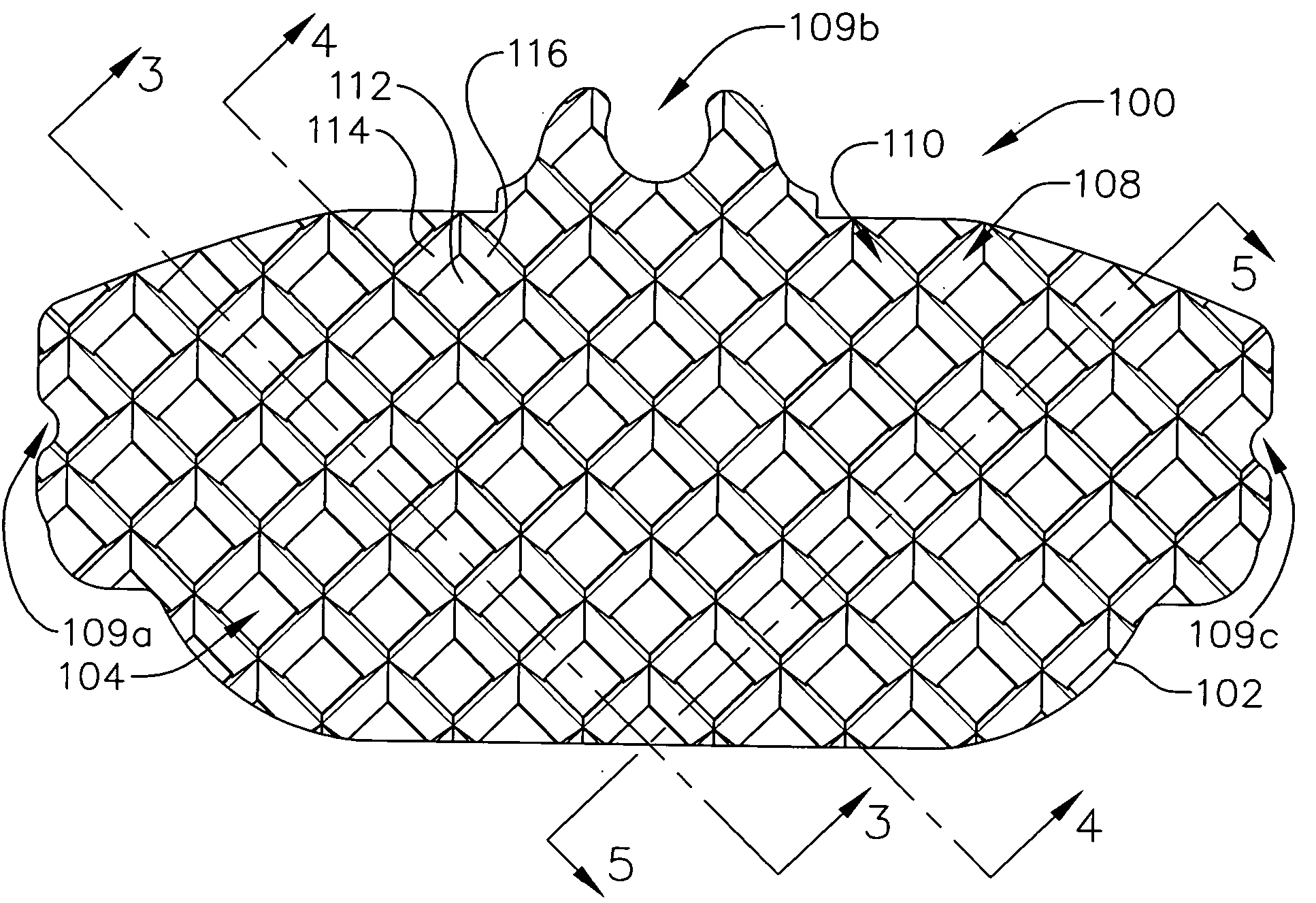
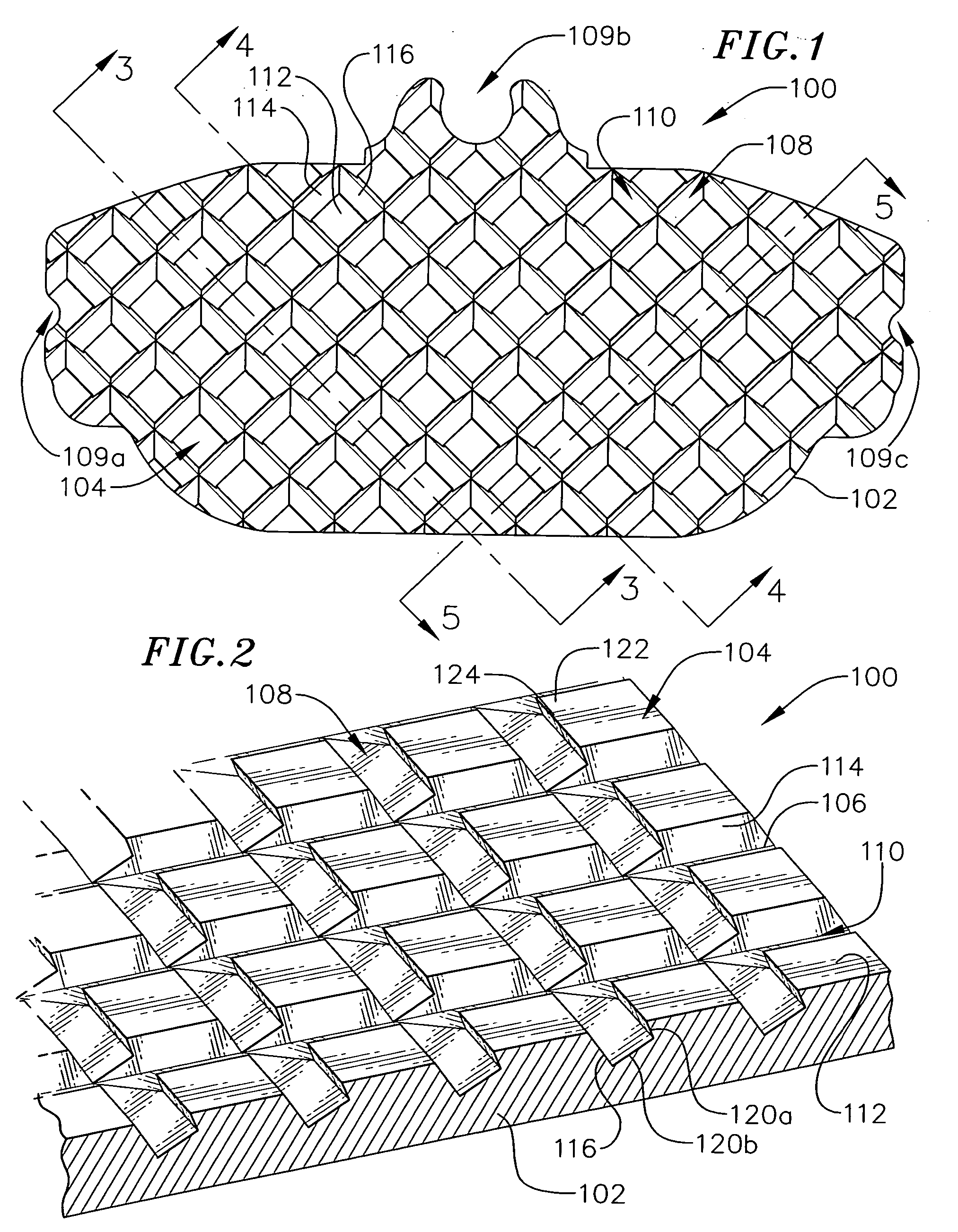
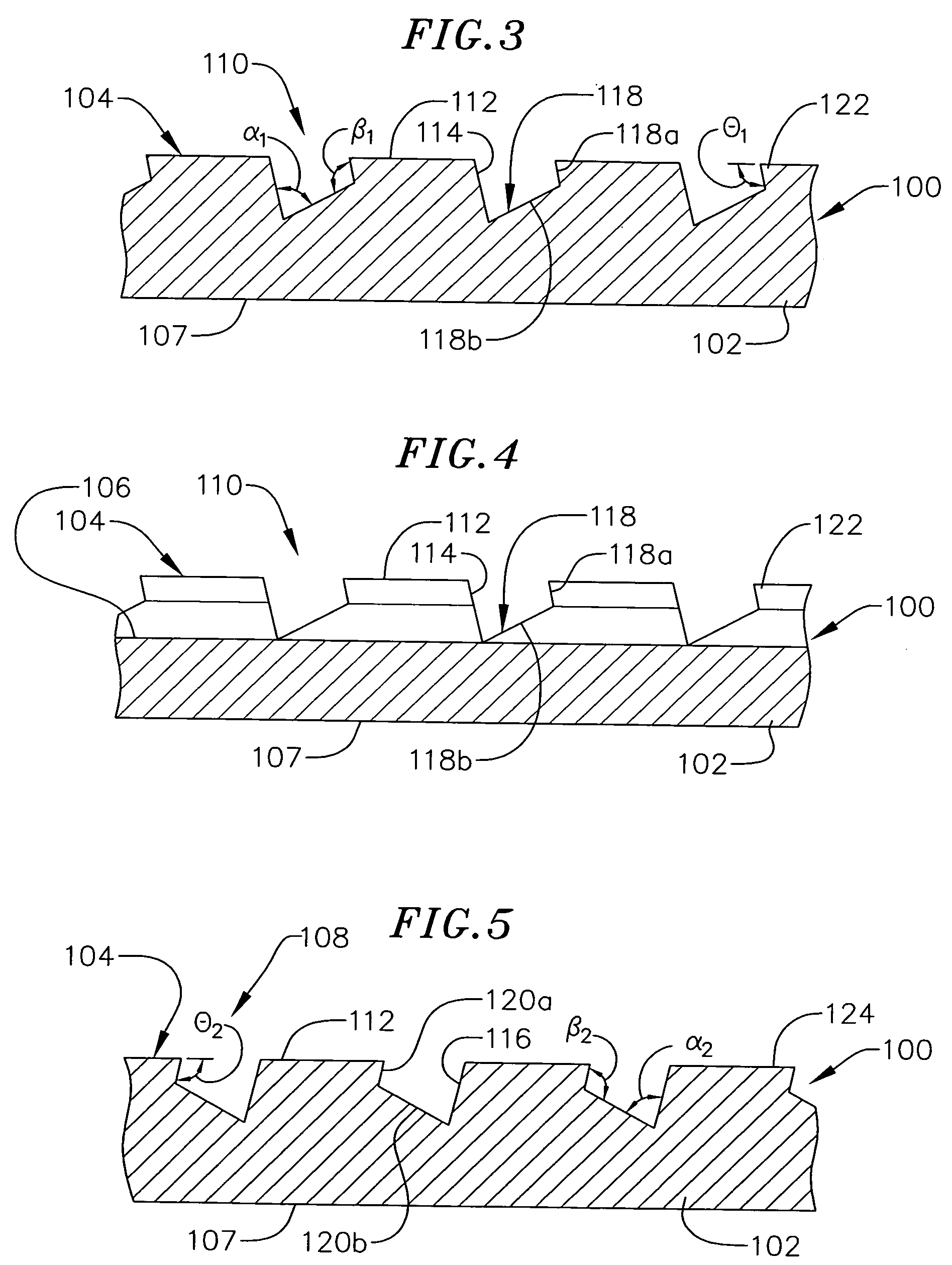
The invention relates to a brake lining carrier plate 1 to hold a friction lining, especially for installation into a vehicle brake system, with holding structures 15, 16 for the friction lining arranged in rows 6 on the lining side 2, whereby each holding structure 15, 16 has a protrusion 3 and a depression 4, whereby the protrusion 3 is made when the depression 4 is formed in the surface 5 through the displacement of material. Said protrusion 3 engages with the friction lining. The holding structures 15, 16 in the rows 6 are arranged in such a way that there is a protrusion 10 at the beginning 8 and at the end 9 of each row 6. In one embodiment, the rows 6 run essentially crosswise to the longitudinal axis 7 of the brake lining carrier plate 1.
Owner:AML LANXIDE EURO
Disk brake pad
InactiveUS20070039789A1Heat conductivityPrevent thermal deformationBraking membersProject areaThermal deformation
A disk brake pad has a friction member that slidably contacts to a rotating disk to generate braking force, and a backing plate that supports a back of the friction member. The friction member has a contact surface that slidably contacts to the disk. The backing plate has a heat transfer member located within a projected area, which reduces or restrains thermal deformation of a disk.
Owner:SANO TATSUYA
Pad assembly for disc brake
ActiveUS20060157307A1Smooth slidingSmooth movementBraking membersSlack adjustersEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:AKEBONO BRAKE IND CO LTD
High friction brake shoe assembly
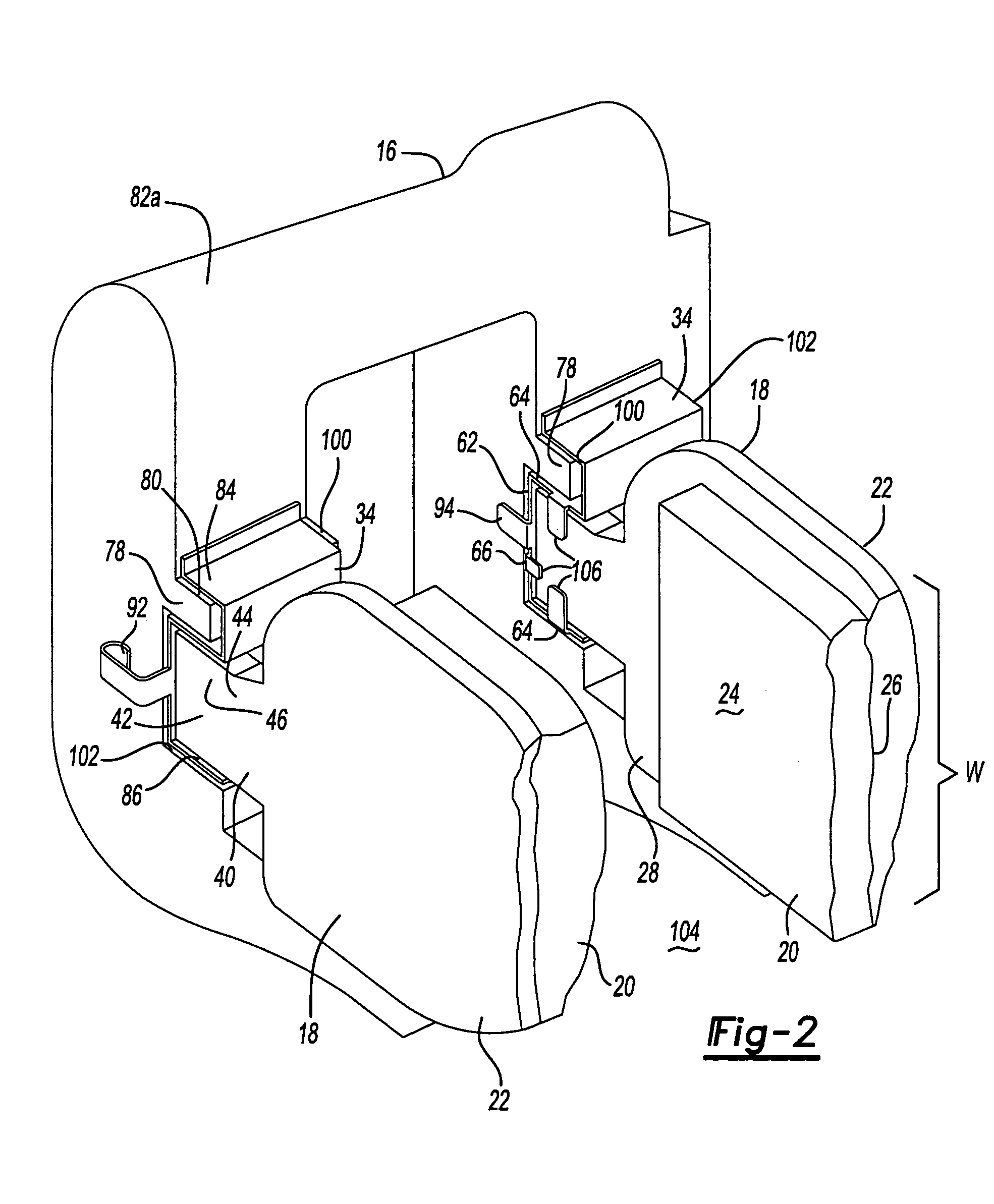
InactiveUS7320386B2Improve braking efficiencyGood friction propertiesBraking membersFriction liningEngineeringBrake shoe
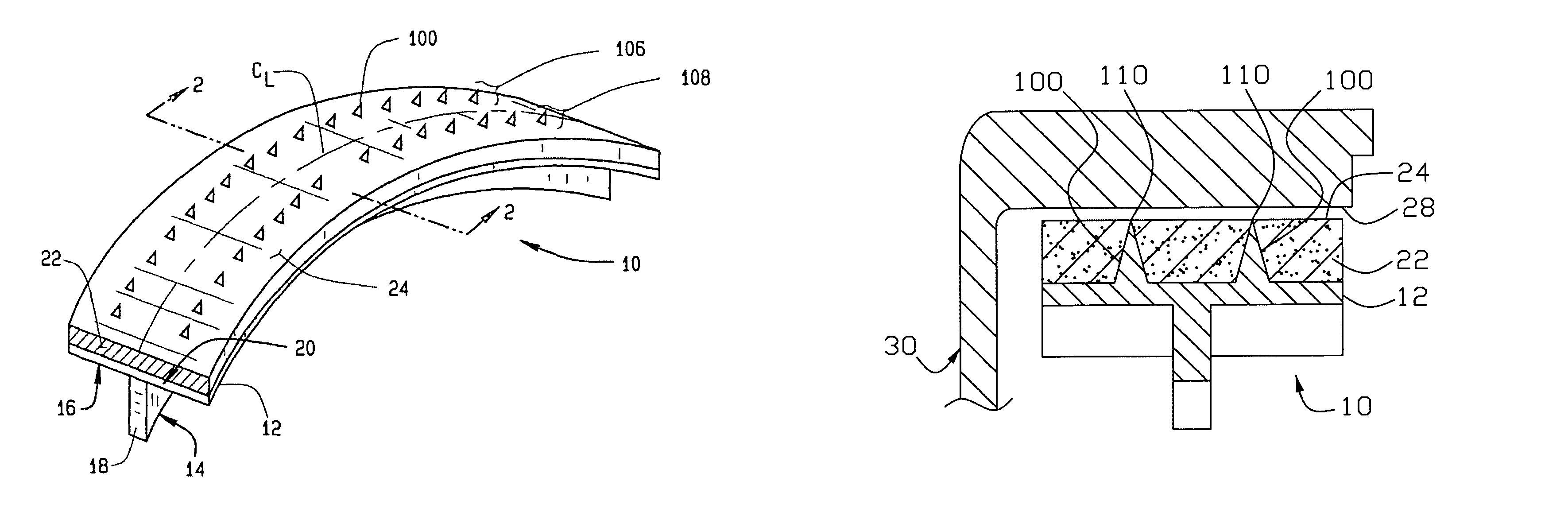
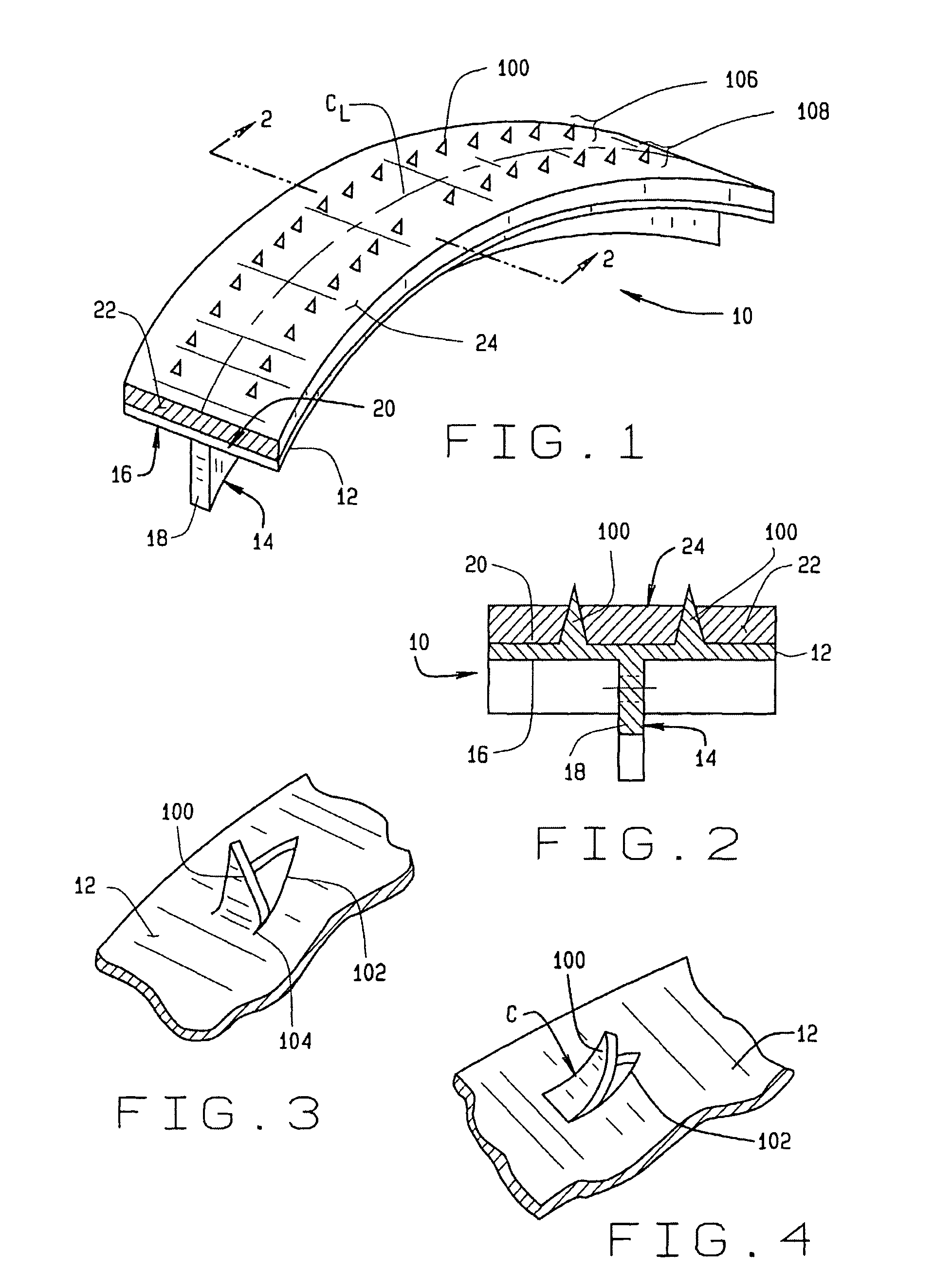
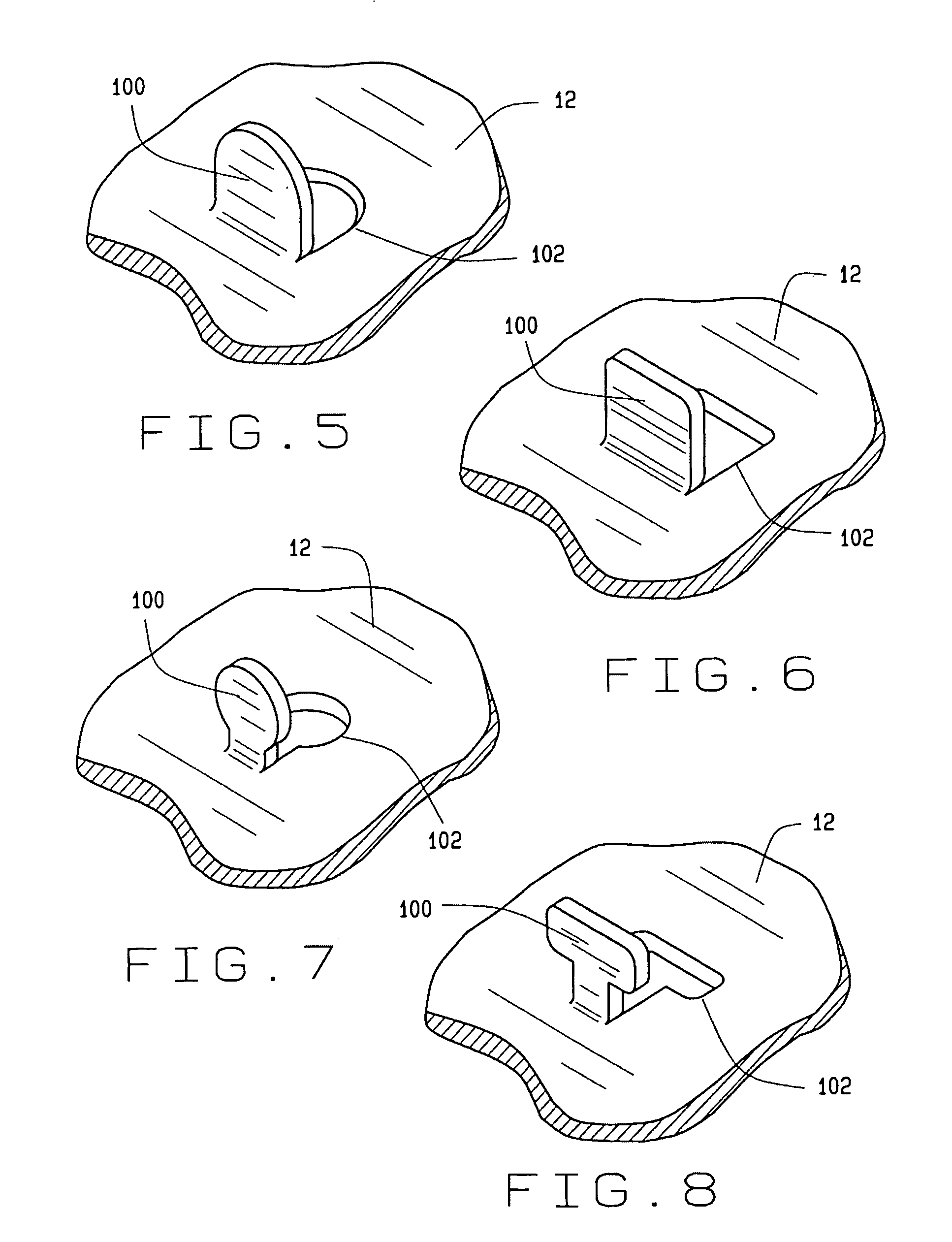
A vehicle brake shoe assembly (10) having a rigid backing plate (12) incorporating a plurality of extensions (100) which project through the brake friction material matrix (22) to the outer friction surface (24) of the brake shoe assembly (10). Each extension (100) is configured to cooperate with the brake friction material matrix (22) to engage a surface of an opposing friction element (28) simultaneously with the friction material (22), increasing the static and dynamic friction performance of the assembly (10) during initial use beyond that achieved from the application of either the brake friction material (22) or the projections (100) alone.
Owner:FEDERAL MOGUL WORLD WIDE
Defined brake pad abutment
InactiveUS7784591B2Assists in diagnosing NVH concerns during braking operationsBraking membersSlack adjustersEngineeringAbutment
A brake pad assembly includes a brake pad including a base portion, a first ear portion, and an opposed second ear portion. The first ear portion and the second ear portion extend outwardly from the base section. The first ear portion includes a first upper section, a first central section, and a first lower section. The second ear portion includes a second upper section, a second central section, and a second lower section. A first clip receives the first ear portion and a second clip receives the second ear portion. The first ear portion includes a first defined contact location and a second defined contact location in relation to the first clip. The second ear portion includes a third defined contact location in relation to the second clip.
Owner:KELSEY HAYES CO
Brake pad backing plate and method of making the same
InactiveUS20050161297A1Low costIncreased binding surface areaBraking membersFriction liningEngineeringBrake pad
Owner:HAYEK DR SALIM
Spring member for disc-brake calipers and disc-brake caliper
A spring member for disc-brake calipers is interposed between a lateral edge of at least one pad and reaction surfaces of the caliper so as to act resiliently on the pad. The spring member comprises a ‘U’-shaped portion suitable for forming a connection with a protuberance of the reaction surfaces, a first resilient portion suitable for acting on the pad in a tangential direction, and a second resilient portion suitable for acting on the pad in a radial direction. The first and second resilient portions constitute a single body projecting from a first connection end of the first resilient portion that is connected to the ‘U’-shaped portion, so that, when the at least one pad is in a mounted configuration, it is acted on resiliently by the spring member both in a radial direction and in a tangential direction.
Owner:FRENI BREMBO SPA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com