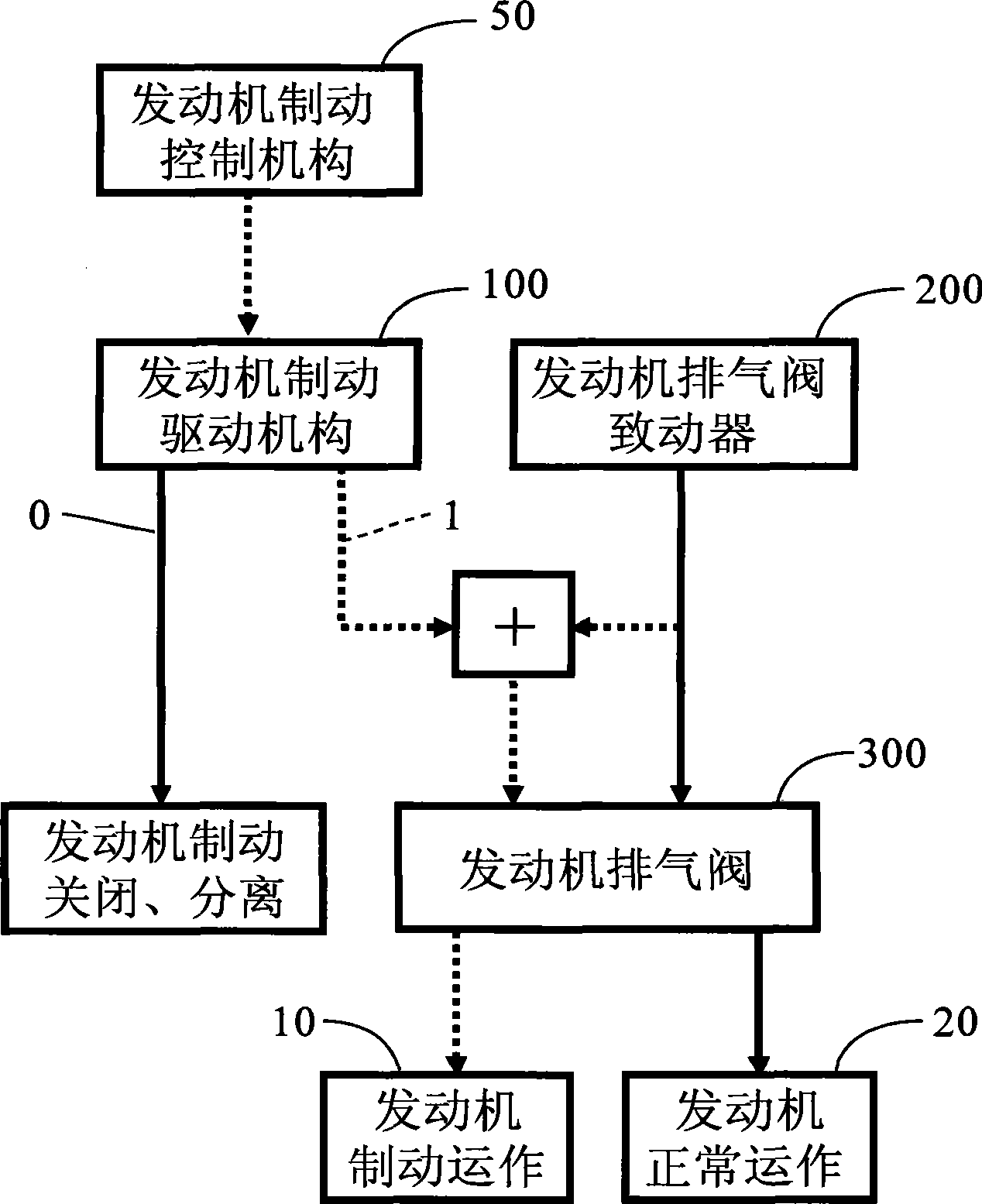
Engine braking apparatus and method using single valve and bridge of valve
A technology for engine braking and engine application in the direction of valve drive devices, valve devices, engine components, etc., which can solve problems such as failure to work normally, reduced braking performance, asymmetrical loads, etc., to eliminate asymmetrical loads and reduce braking load, effect of reducing complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0079] Figures 3A and 3B are schematic views of the first embodiment of the engine braking device of the present invention in its "OFF" and "ON" positions. The figure includes three main parts: the drive mechanism 100 for engine braking, the exhaust valve actuator 200 and the exhaust valve 300 . The exhaust valve actuator 200 includes a cam 230 , a rocker arm 210 , and an exhaust lash adjustment system. The cam 230 has a large raised portion 220 on the inner base circle 225 (relative to the smaller raised portion used for braking later) for normal operation of the engine. The rocker arm 210 is swingably mounted on the rocker shaft 205, with a cam follower 235 at one end, and a valve gap adjusting screw 110, a valve gap adjusting piston 112 and an elephant foot pad 114 at the other end of the exhaust valve gap adjusting system. . The valve gap adjusting screw 110 is fixed on the rocker arm 210 by the lock nut 105 . A spring 198 can be installed on the valve gap adjusting scr...
Embodiment 2
[0086] Figure 4 is a schematic view of a second embodiment of the engine braking device of the present invention in its "on" position. In this embodiment, a brake valve actuator and a brake reset mechanism 150 are added on the basis of the first embodiment. The brake valve actuator is integrated in the exhaust valve actuator 200 of the engine. In addition to the brake valve gap adjustment system, it also contains at least one small cam lobe for braking (this embodiment contains two small cam lobe portions 232 and 233). The small cam lobe portions 232 and 233 and the large cam lobe portion 220 of the engine are integrated on the existing engine cam 230 . In order to get over the small cam lobe portions 232 and 233 during normal engine operation, the large cam lobe portion 220 must be enlarged. The brake reset mechanism 150 is used to modify the valve lift curve generated by the increased large cam lobe 220 . Brake reset mechanism 150 is integrated with drive mechanism 100 . ...
Embodiment 3
[0091] Figure 5 is a schematic view of a third embodiment of the engine braking device of the present invention in its "on" position. This embodiment has a different brake reset mechanism 150 from the second embodiment. The brake reset piston 165 of the brake reset mechanism 150 is slidably disposed within the valve bridge 400 directly below the elephant foot pad 114 . The drain hole 197 on the brake piston 160 is replaced by a drain channel 167 in the valve bridge 400 . The spring 198 of the detent biases the exhaust valve actuator 200 with the reset piston 165 against the valve bridge 400 .
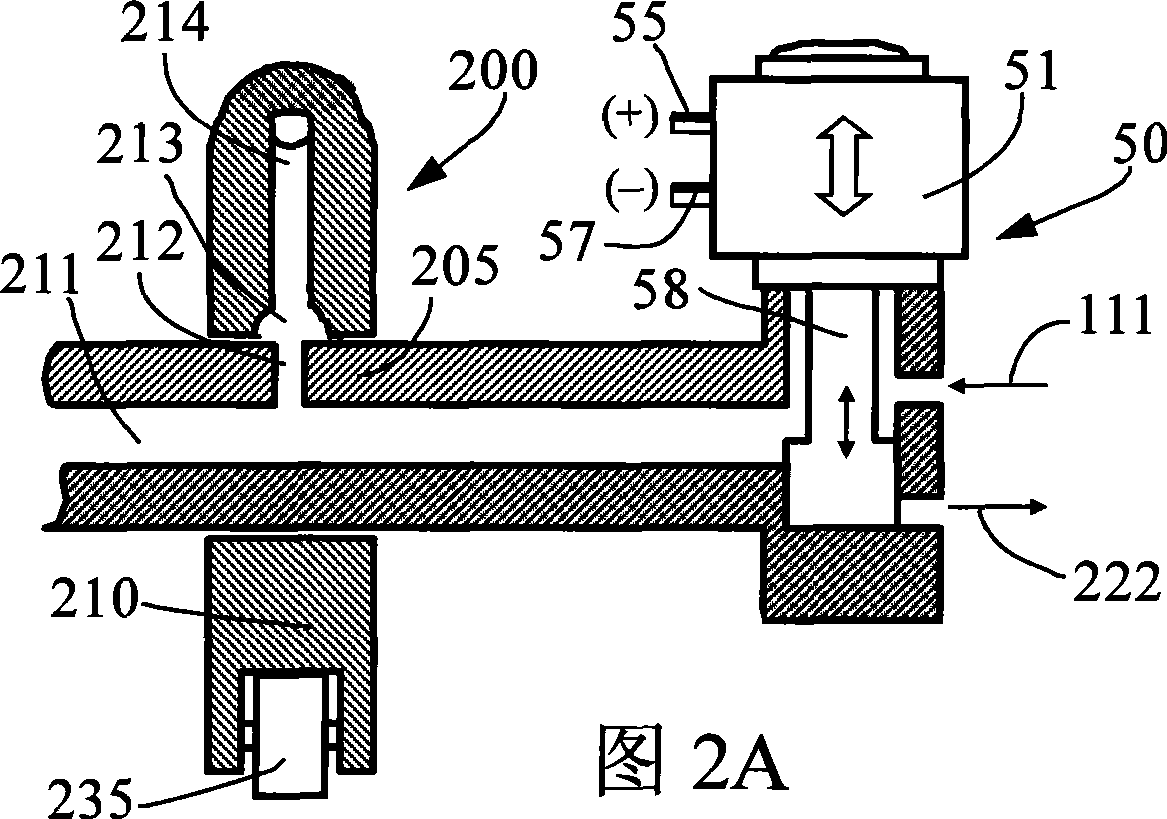
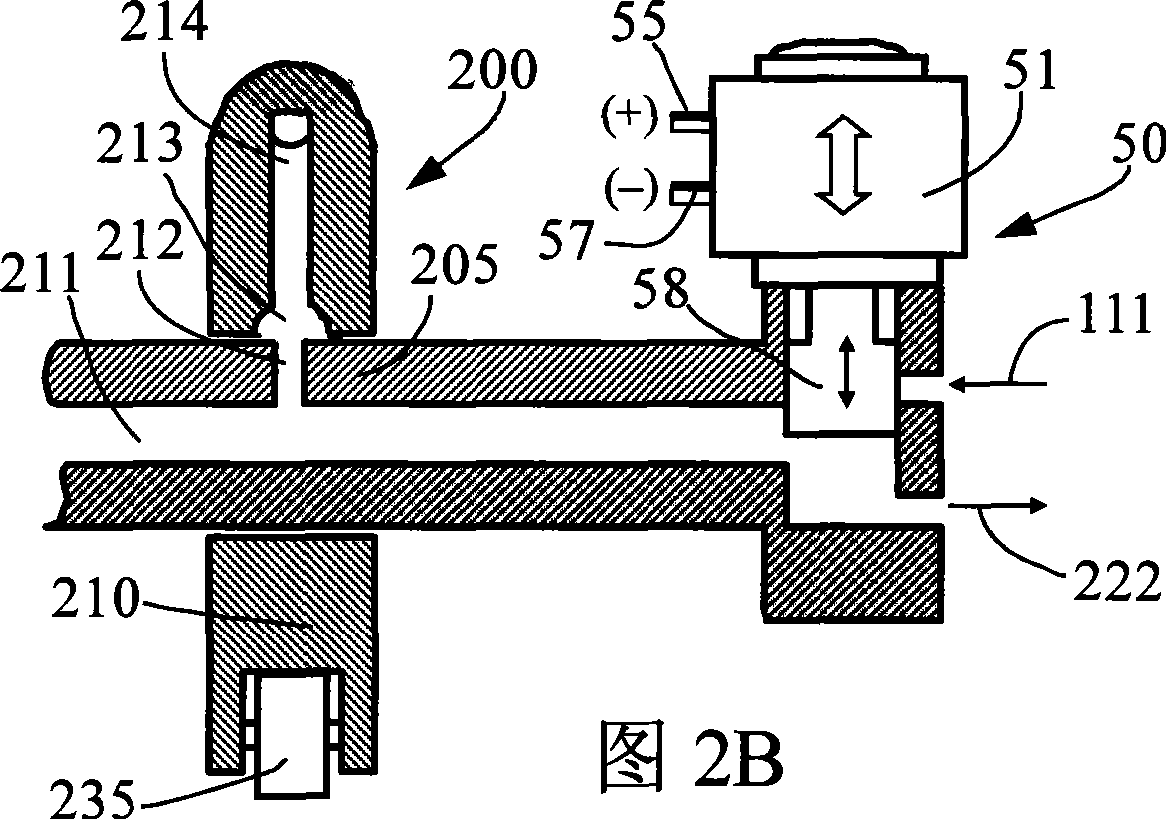
[0092] When engine braking is required, the engine braking control mechanism 50 is turned on (FIG. 2A). The fluid passes through the brake fluid network, including the fluid channels 113 and 115 in the slack adjustment screw 110, the fluid channel 197e in the reset piston 165, and the channel 412 in the valve bridge 400, and pushes open the one-way shut-off valve 170, from the valve ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com