Patents
Literature
1165 results about "Valve timing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
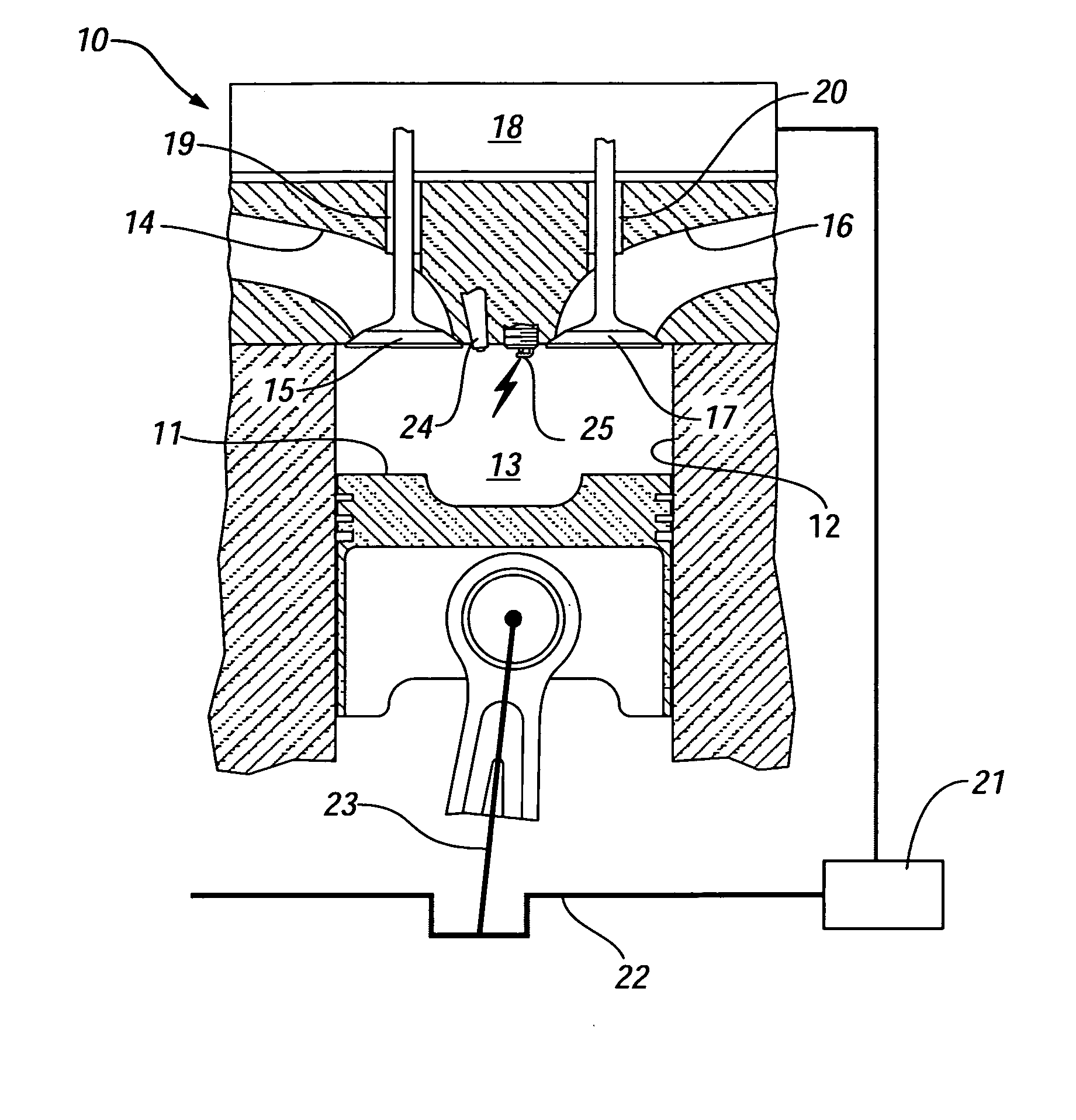
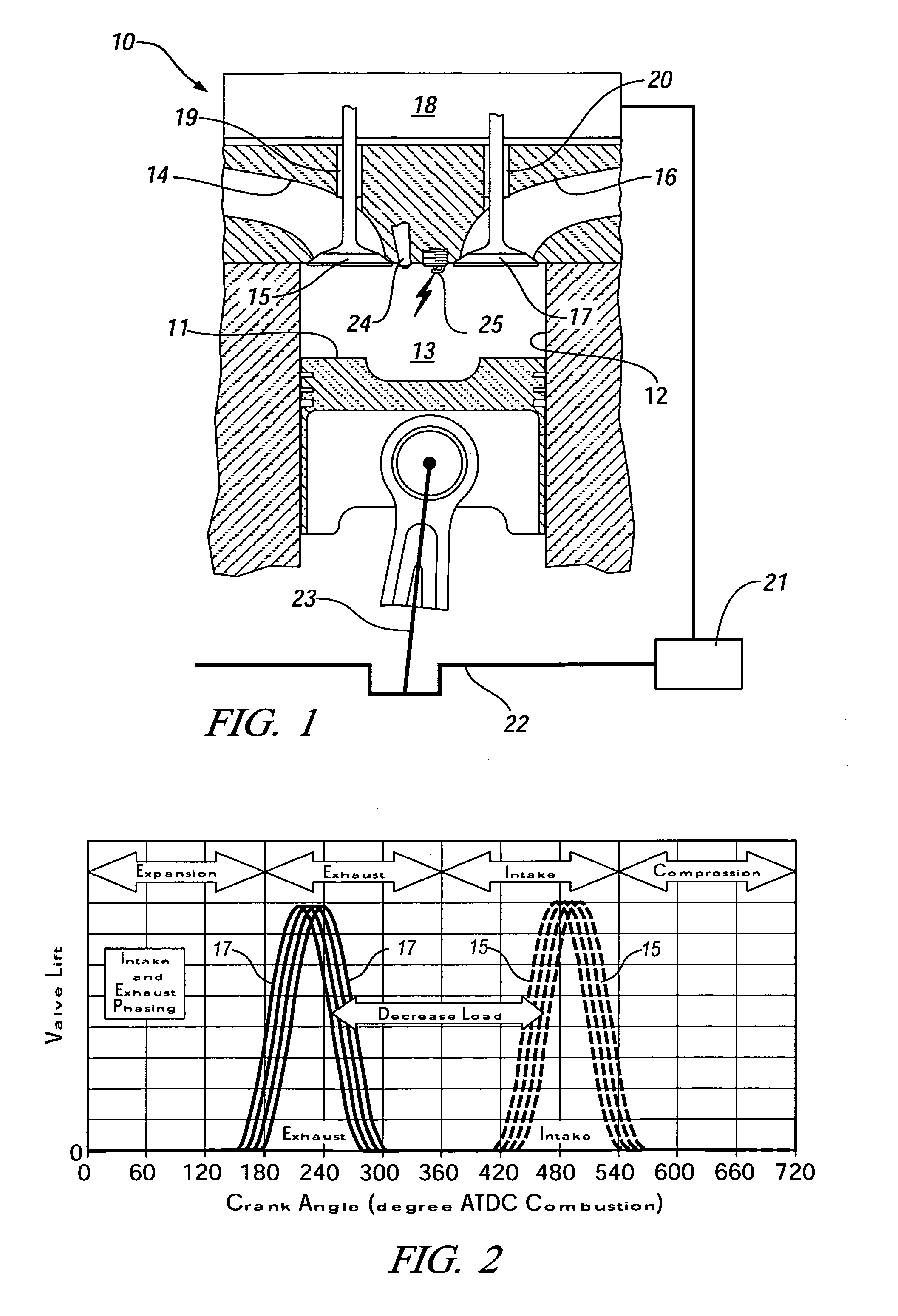
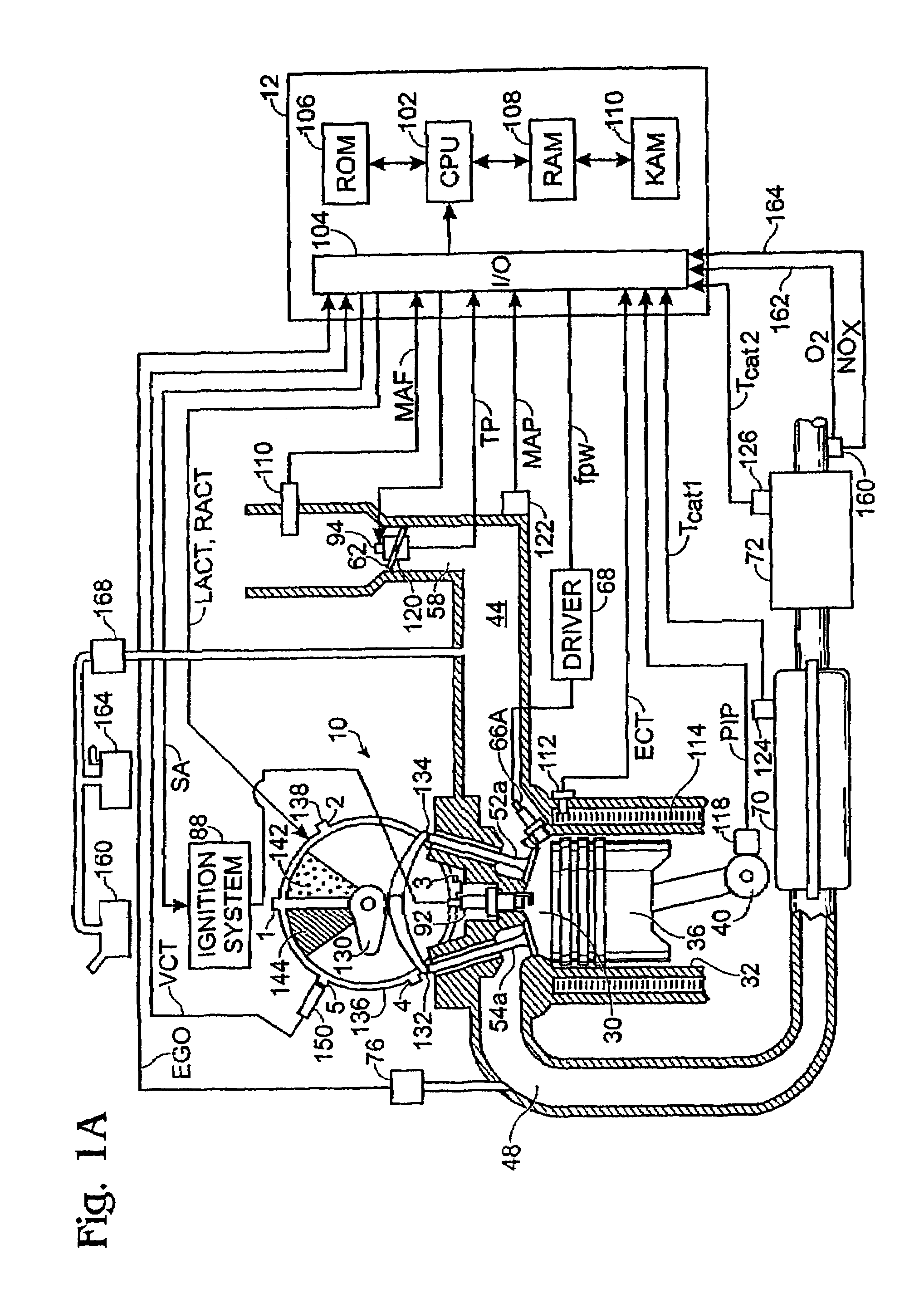
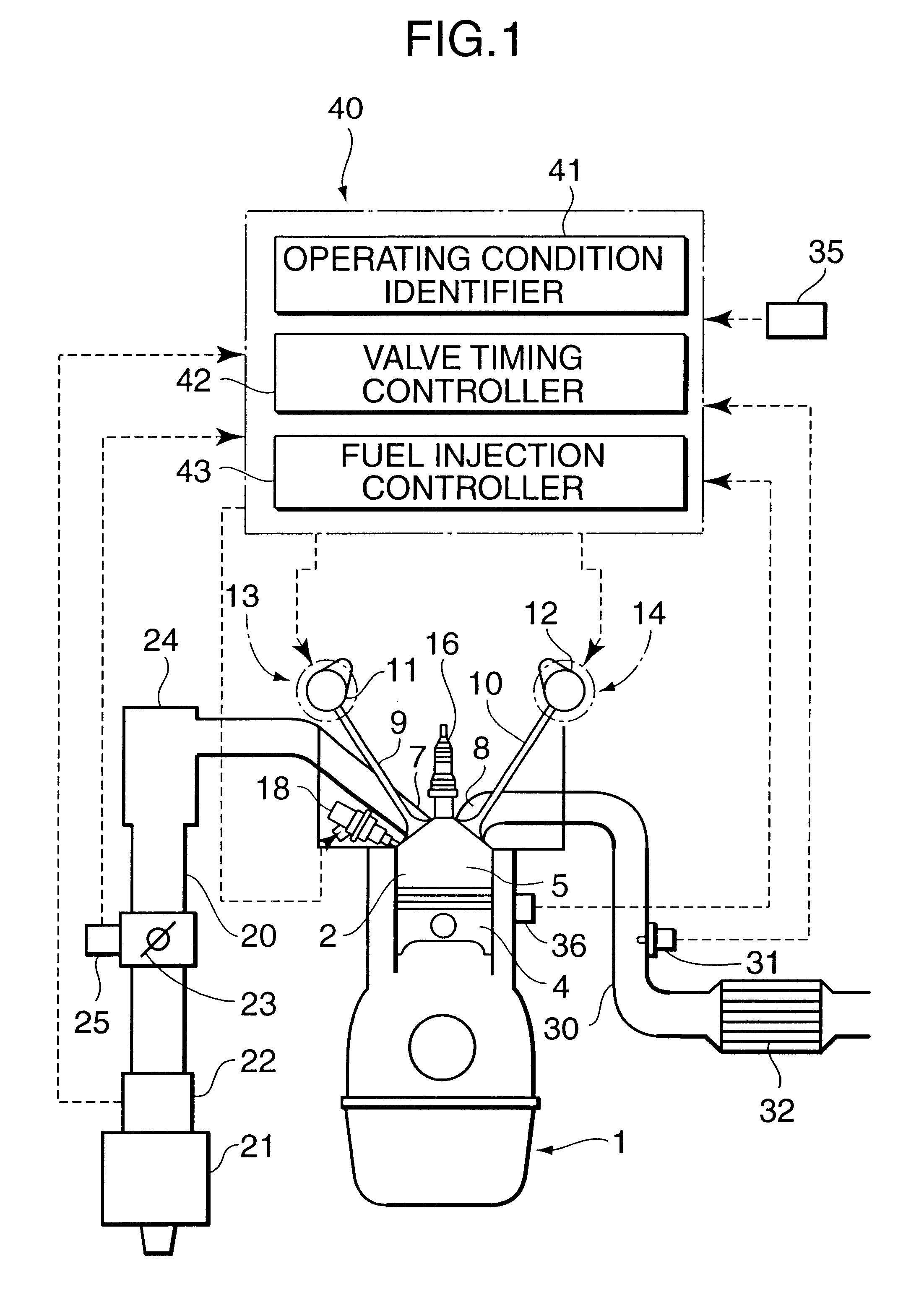
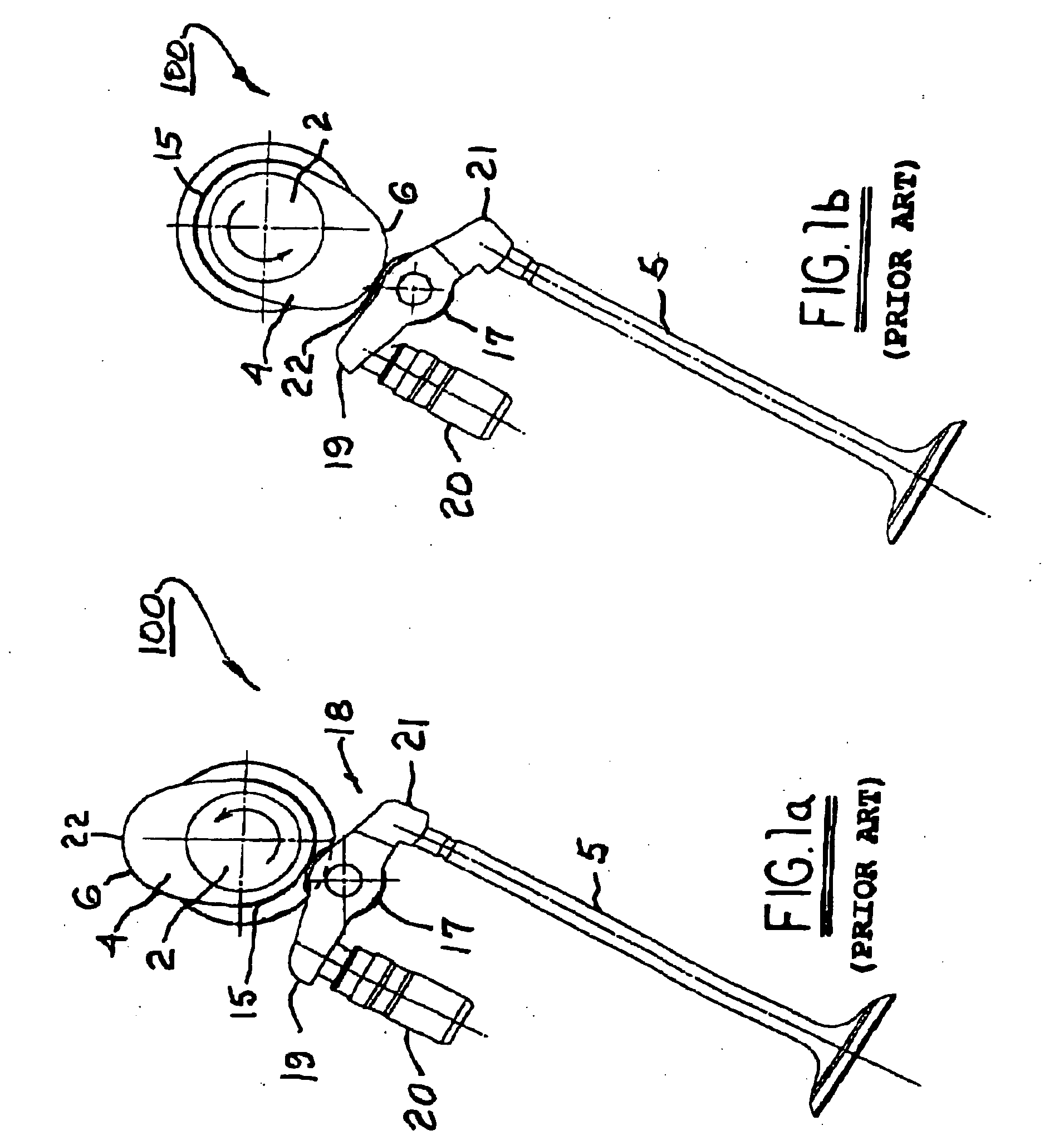
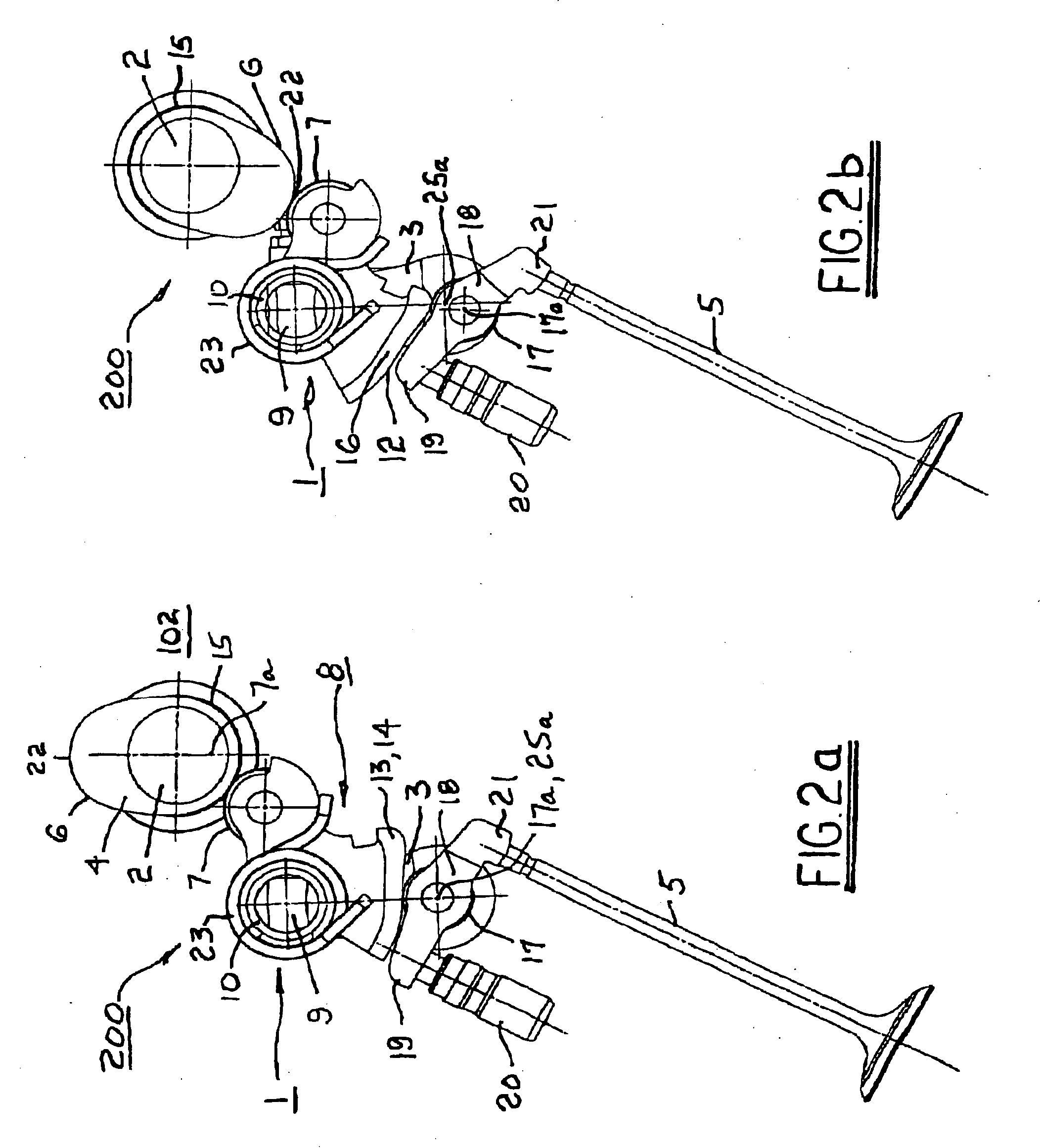
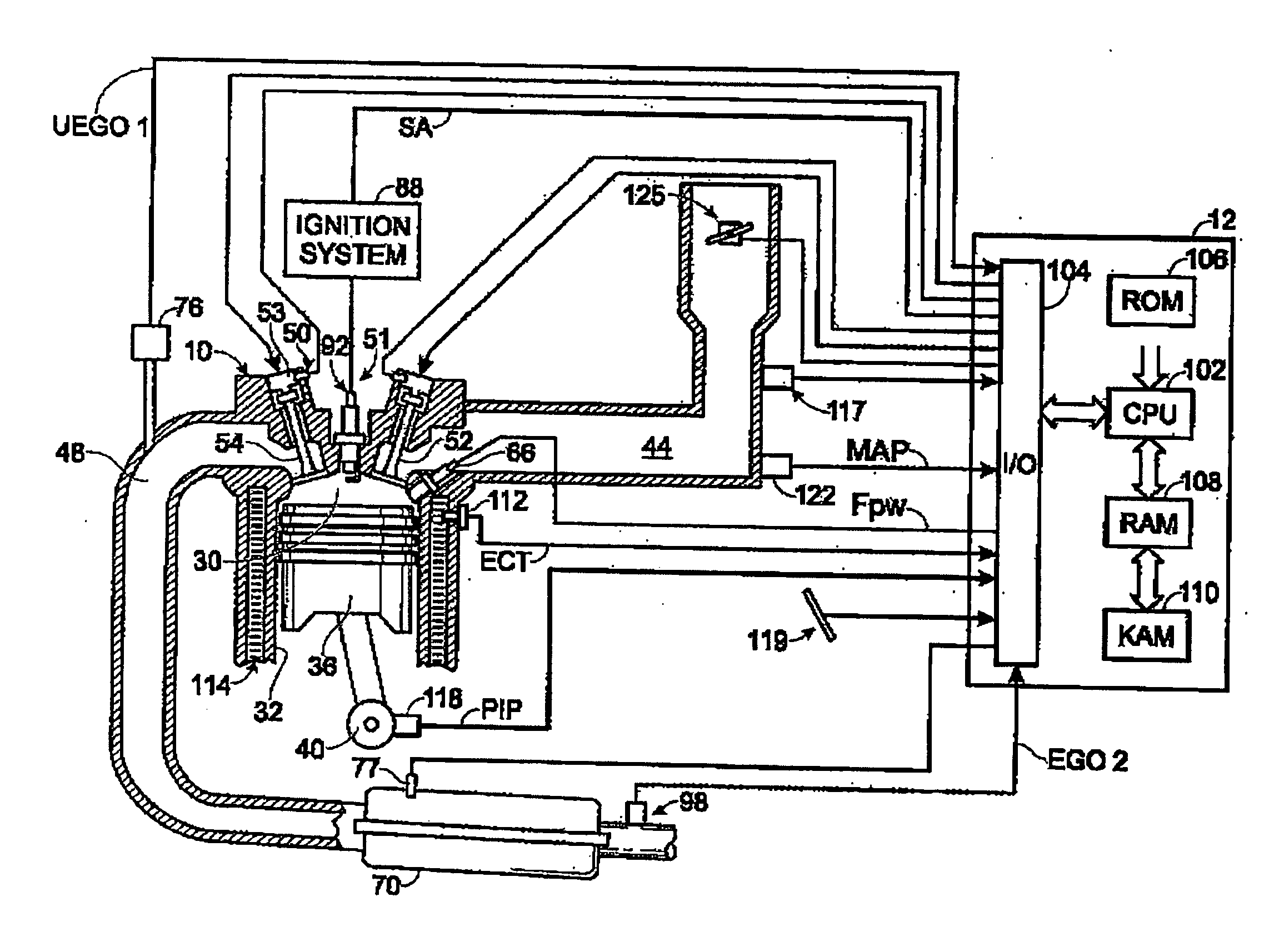
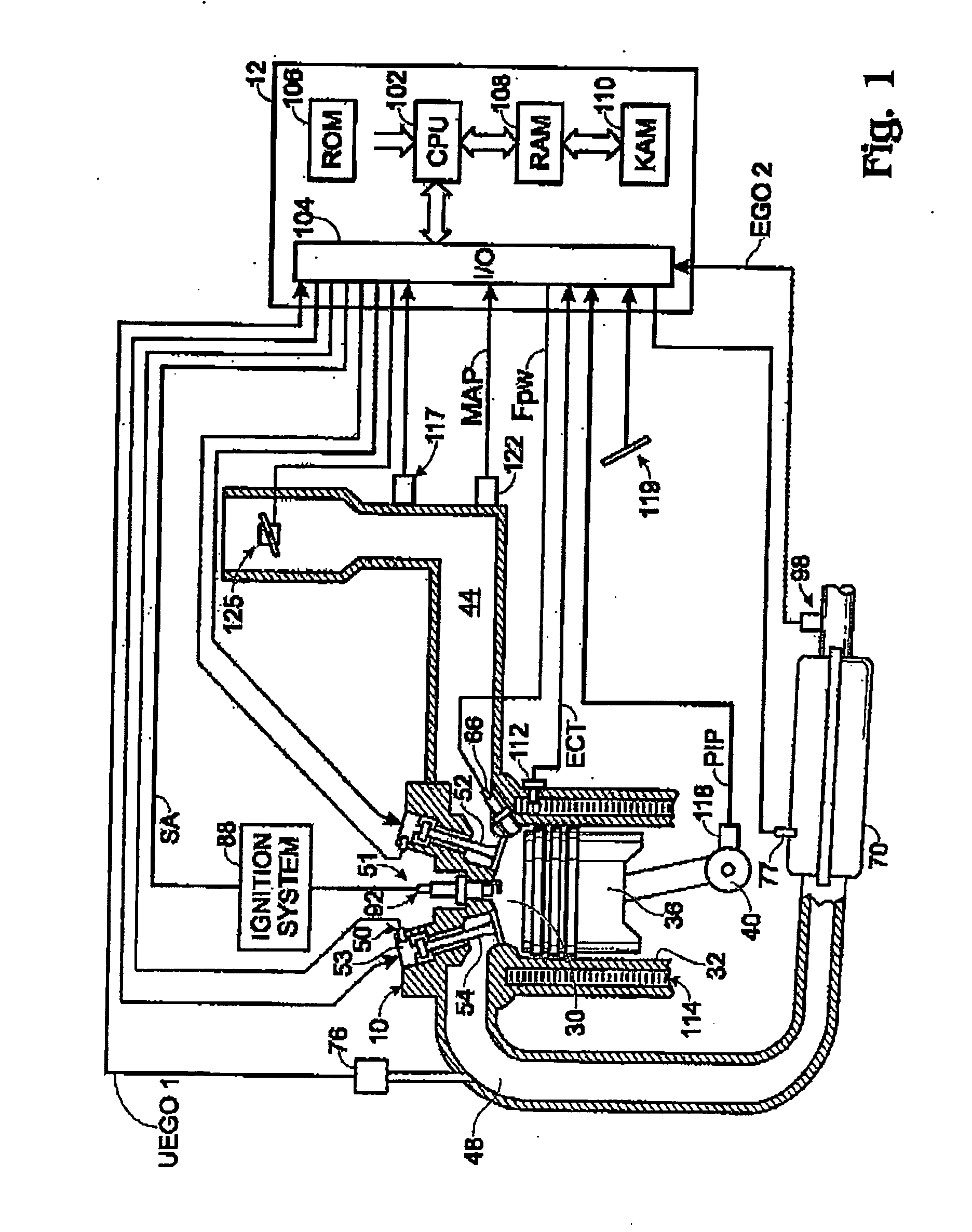
In a piston engine, the valve timing is the precise timing of the opening and closing of the valves. In an internal combustion engine those are usually poppet valves and in a steam engine they are usually slide valves or piston valves.
Method for transition between controlled auto-ignition and spark ignition modes in direct fuel injection engines
InactiveUS20060196466A1Eliminate misfiringEliminate partial burnValve arrangementsElectrical controlHomogeneous charge compression ignitionExhaust valve
A method is provided for control of transition between combustion modes of a direct-injection engine operable in a homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) mode at lower loads and a spark ignition flame propagation (SI) mode at higher loads. The engine includes a variable valve actuation system including two-step high and low lift valve actuation and separate cam phasing for both intake and exhaust valves. The method includes operating the engine at steady state, with fuel-air-exhaust gas mixtures at predetermined conditions, for each speed and load, and controlling the engine during mode changes between the HCCI mode and the SI mode by switching the exhaust and intake valves between low lift for HCCI operation and high lift for SI operation. High load may be an SI throttled mode with an intermediate unthrottled mode (SI / NTLC} in which transition between HCCI and SI / NTLC modes requires switching only the exhaust valve lift and transition between SI / NTLC and SI throttled modes requires switching only the intake valve lift, with predetermined phase adjustments in the valve timing phasing.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Engine system and method of control
InactiveUS7213566B1Reduce sensitivityHigh high economyElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesControl valvesValve timing
A method of operating an engine having a hotter and colder airstreams separately controlled to a cylinder is provided. The method controls valve timing during a transition in operating modes to provide improved operation.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
System for controlling valve timing of an engine with cylinder deactivation
InactiveUS7249583B2Sufficient NOx reduction and fuel economy benefitsEasy to operateValve arrangementsElectrical controlSystems designEngineering
Various systems and methods are disclosed for carrying out combustion in a fuel-cut operation in some or all of the engine cylinders of a vehicle. Further, various subsystems are considered, such as fuel vapor purging, air-fuel ratio control, engine torque control, catalyst design, and exhaust system design.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
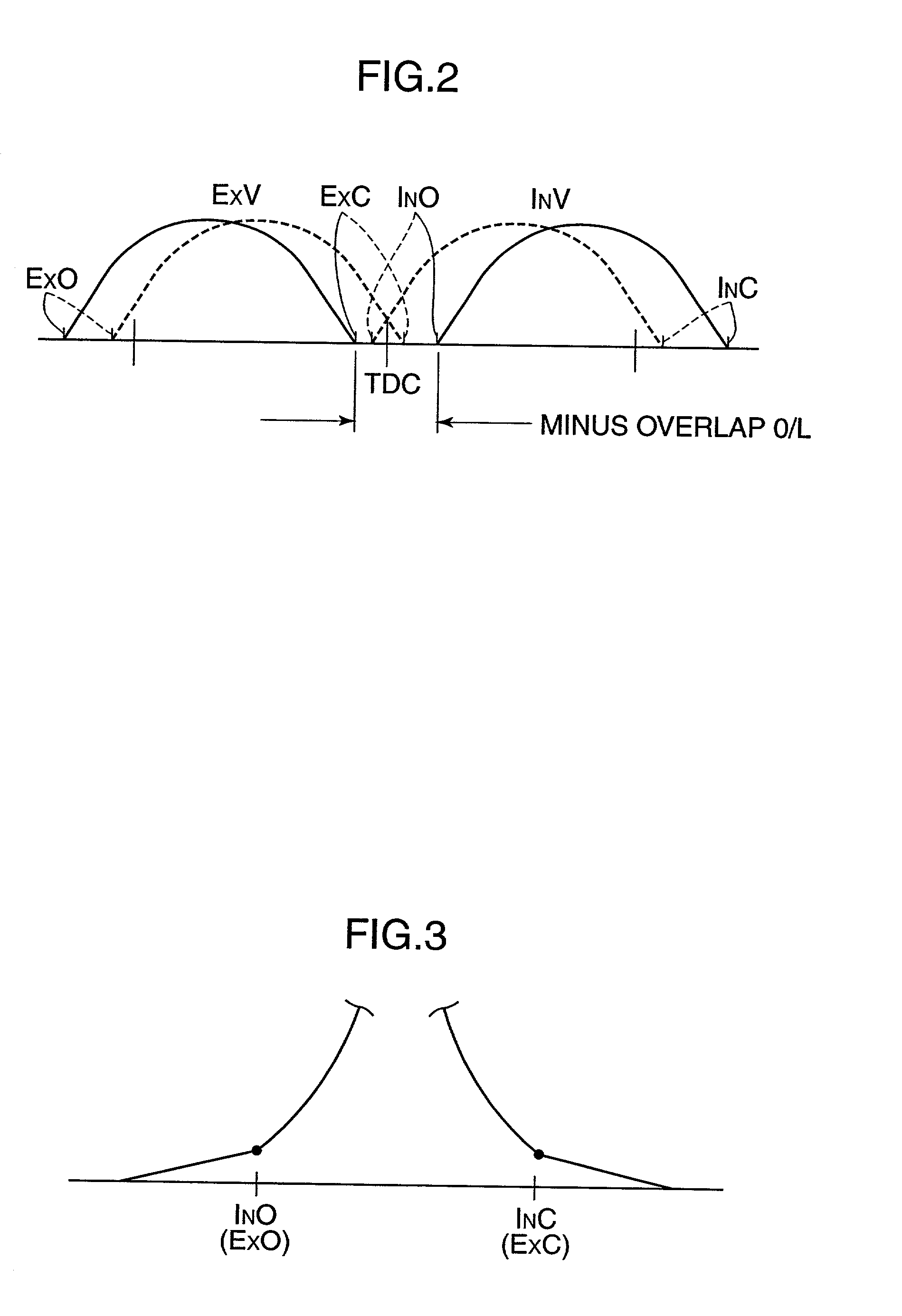
Automotive four-cycle engine
InactiveUS6626164B2Sufficient effectAvoid increase in combustion temperature and exhaust gas temperatureValve arrangementsElectrical controlExhaust valveTop dead center
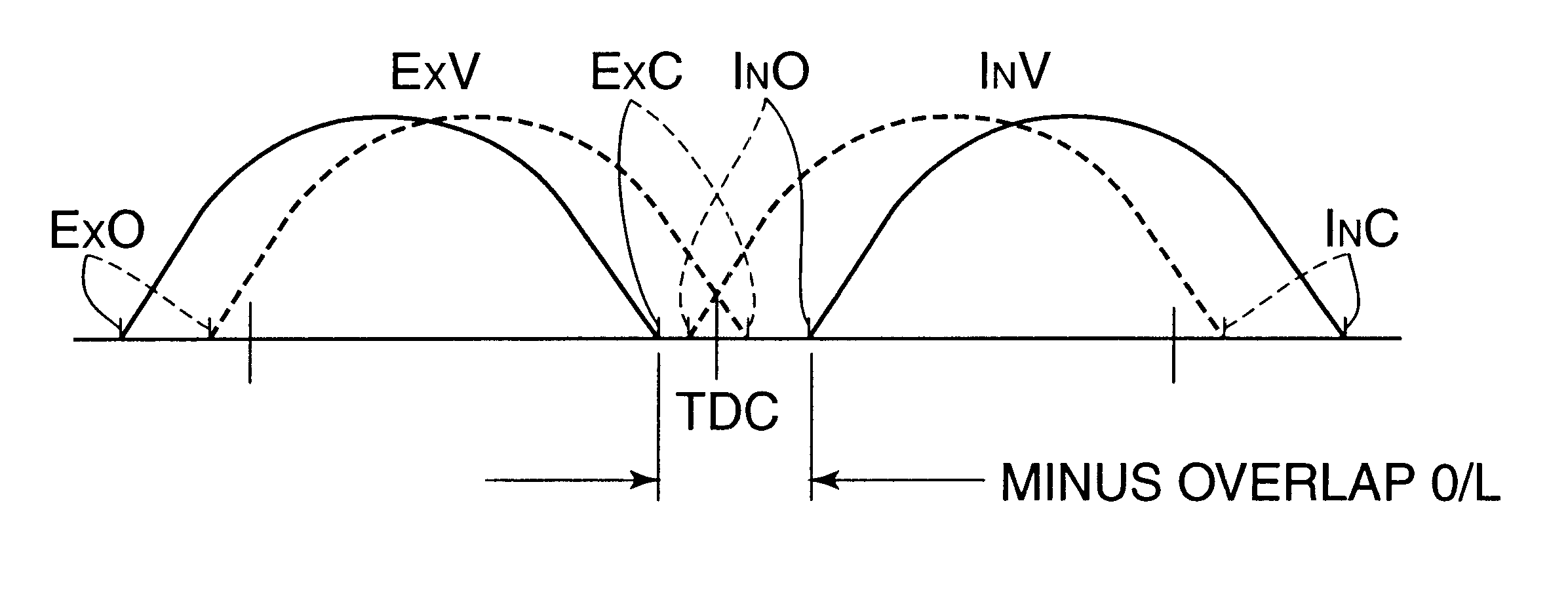
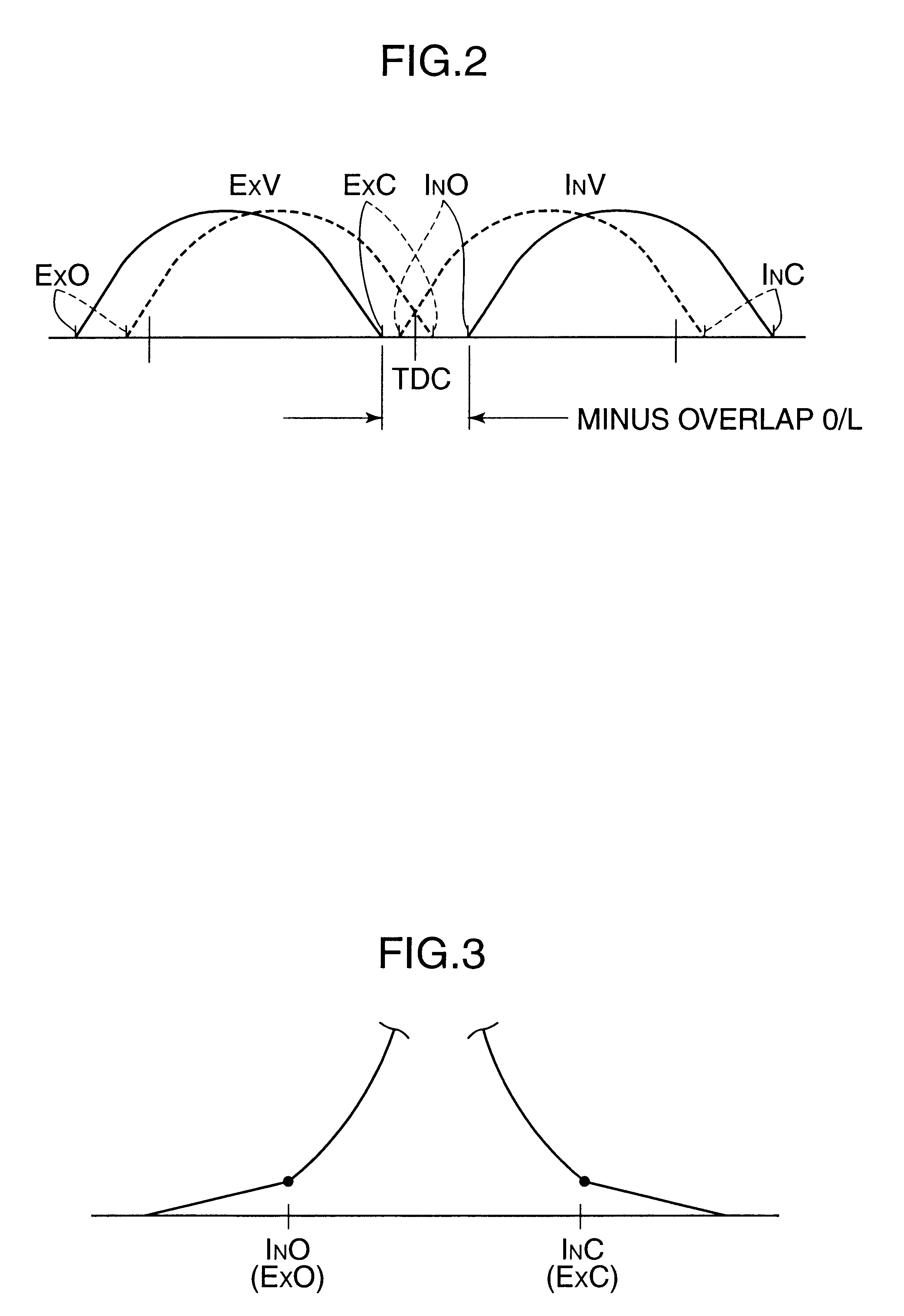
A four-cycle engine is provided with valve timing adjusters for adjusting opening and closing timing an and an exhaust valve. In medium- to high-speed ranges in medium- to high-load regions of the engine, a closing point (ExC) of the exhaust valve defined as a point of transfer from an acceleration portion to a constant speed portion on its valve lift characteristics curve is set to a point a specific period before an intake top dead center, and an opening point (InO) of the intake valve defined as a point of transfer from a constant speed portion to an acceleration portion on its valve lift characteristics curve is set to a point after the intake top dead center. In addition, the period from the closing point (ExC) of the exhaust valve to the opening point (InO) of the intake valve is made longer in the medium-speed range than in the high-speed range in the medium- to high-load regions of the engine.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
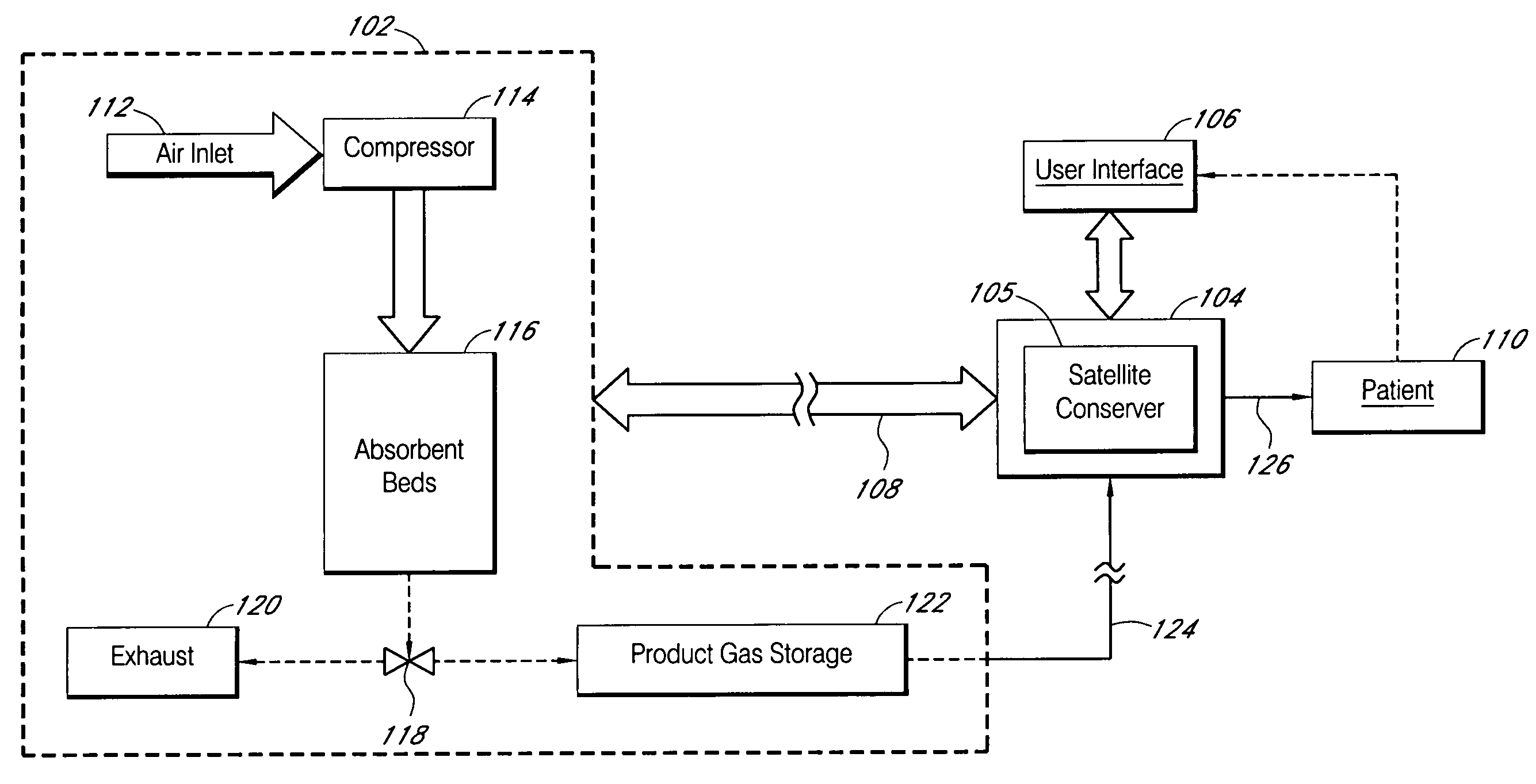
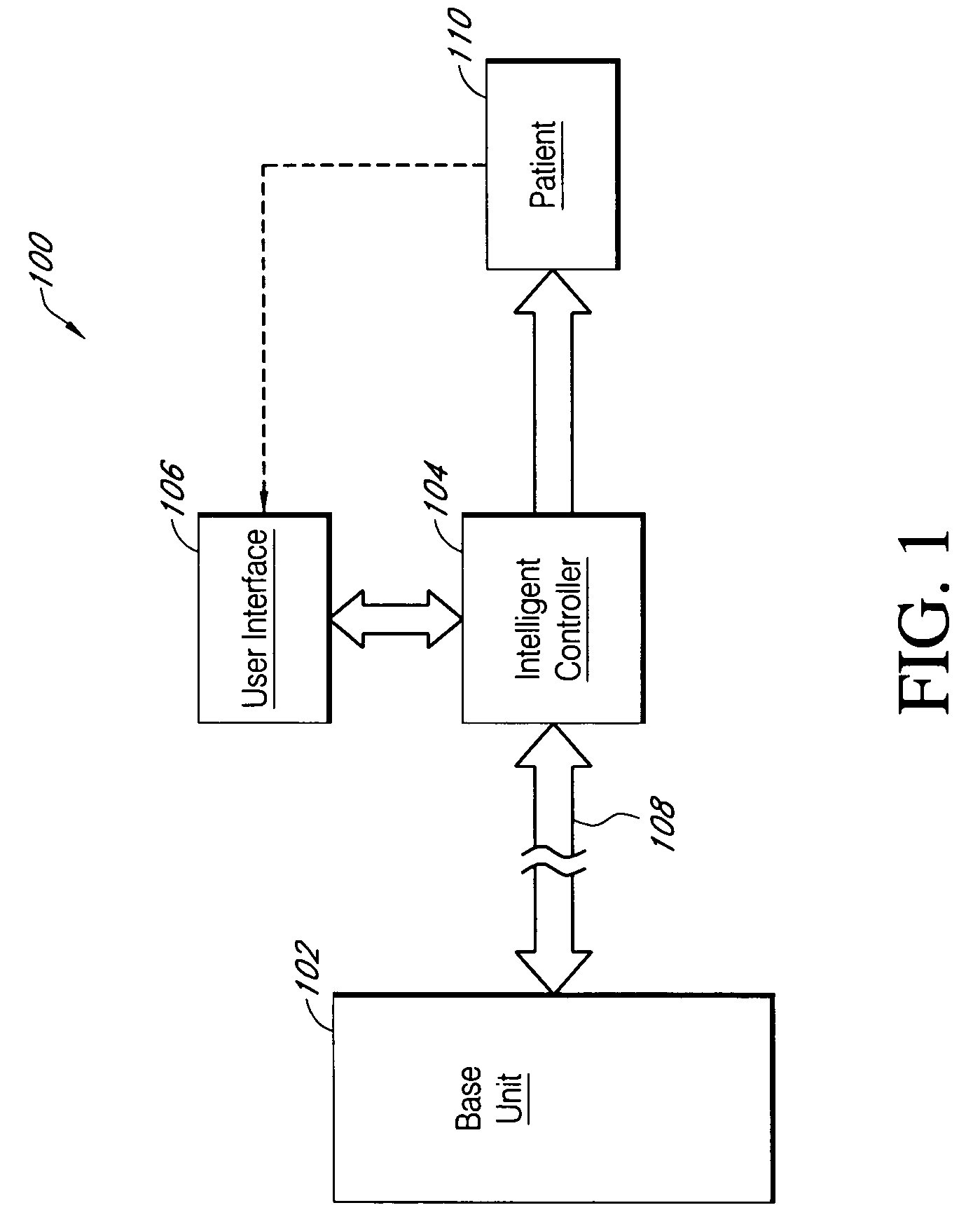
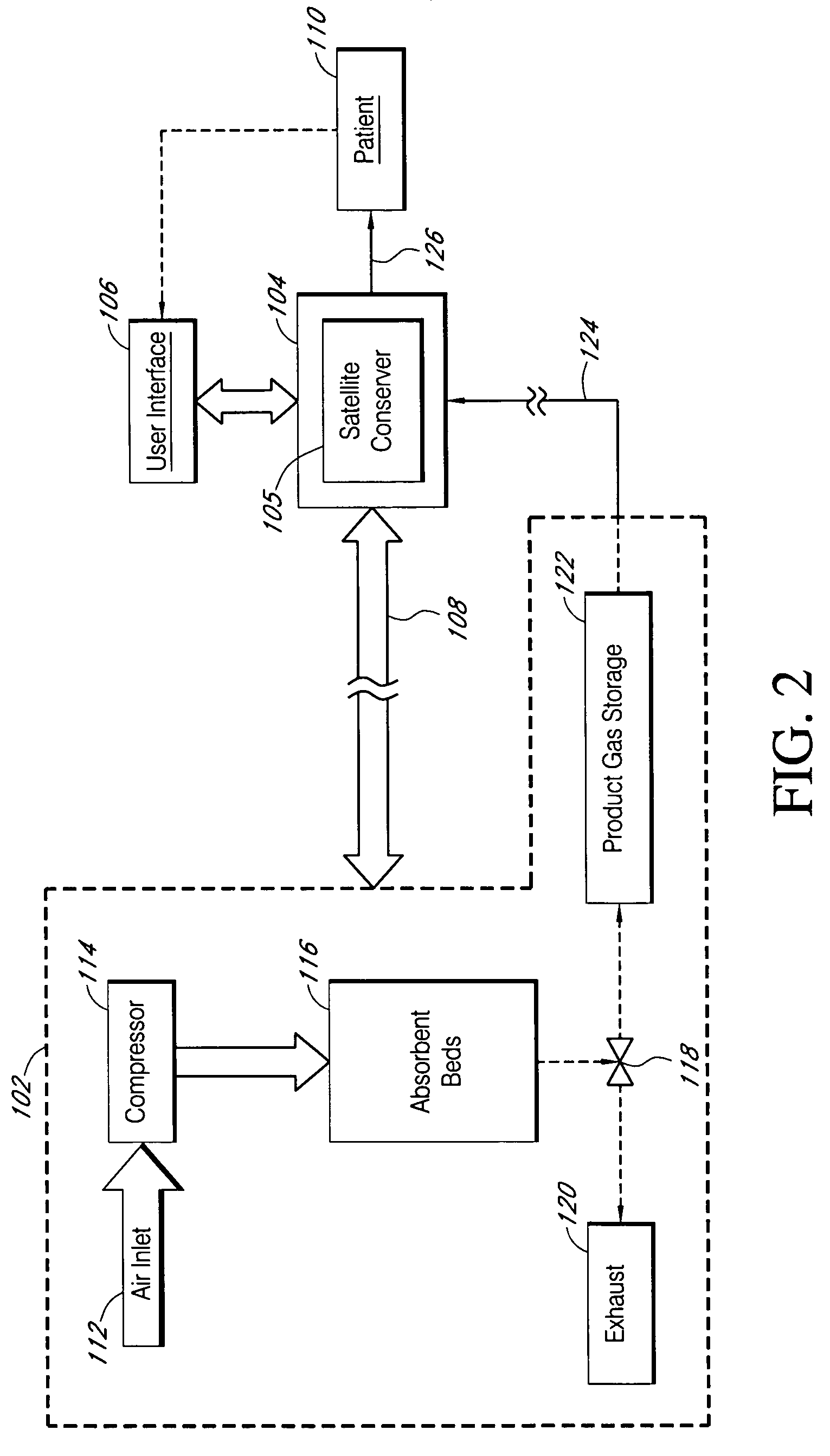
Portable intelligent controller for therapeutic gas systems
InactiveUS20060124128A1Communication is limitedRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesProduction rateEngineering
A apparatus for delivering oxygen to a patient is provided. The apparatus includes a gas source such as an oxygen concentrator and a portable intelligent controller that is movable relative to the gas source and operable over a distance from the gas source. The portable intelligent controller is compact, lightweight and configured to remotely monitor and control one or more functions of the gas source. The functions include compressor speed, product gas production rate, valve timing, power supply and the like. The portable intelligent controller also has a user interface which allows the user to remotely adjust one or more settings of the gas source. In some implementations, the portable intelligent controller also includes a satellite conserver, which delivers oxygen in metered amounts in response to sensed breaths of the patient.
Owner:INOGEN INC
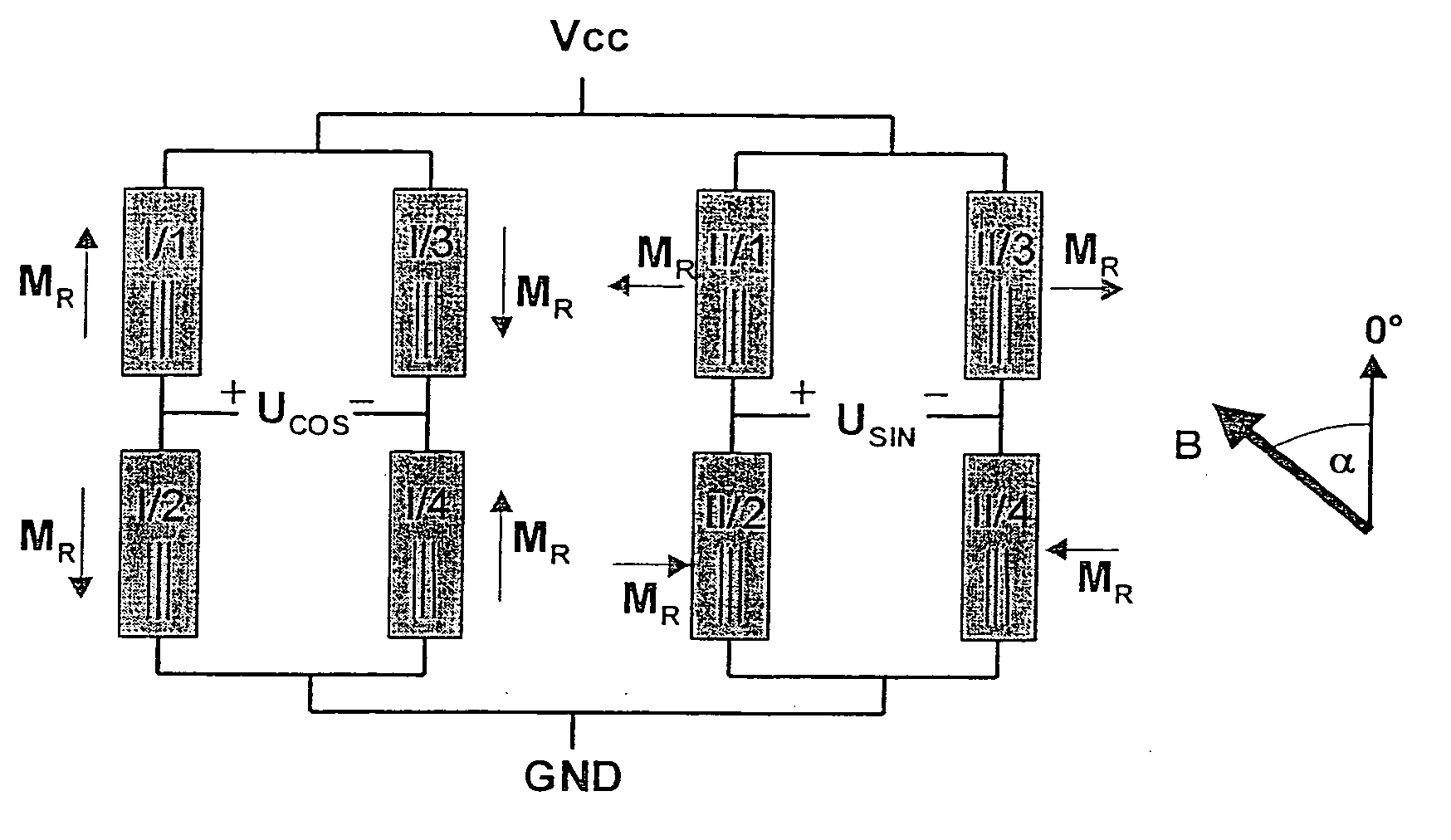
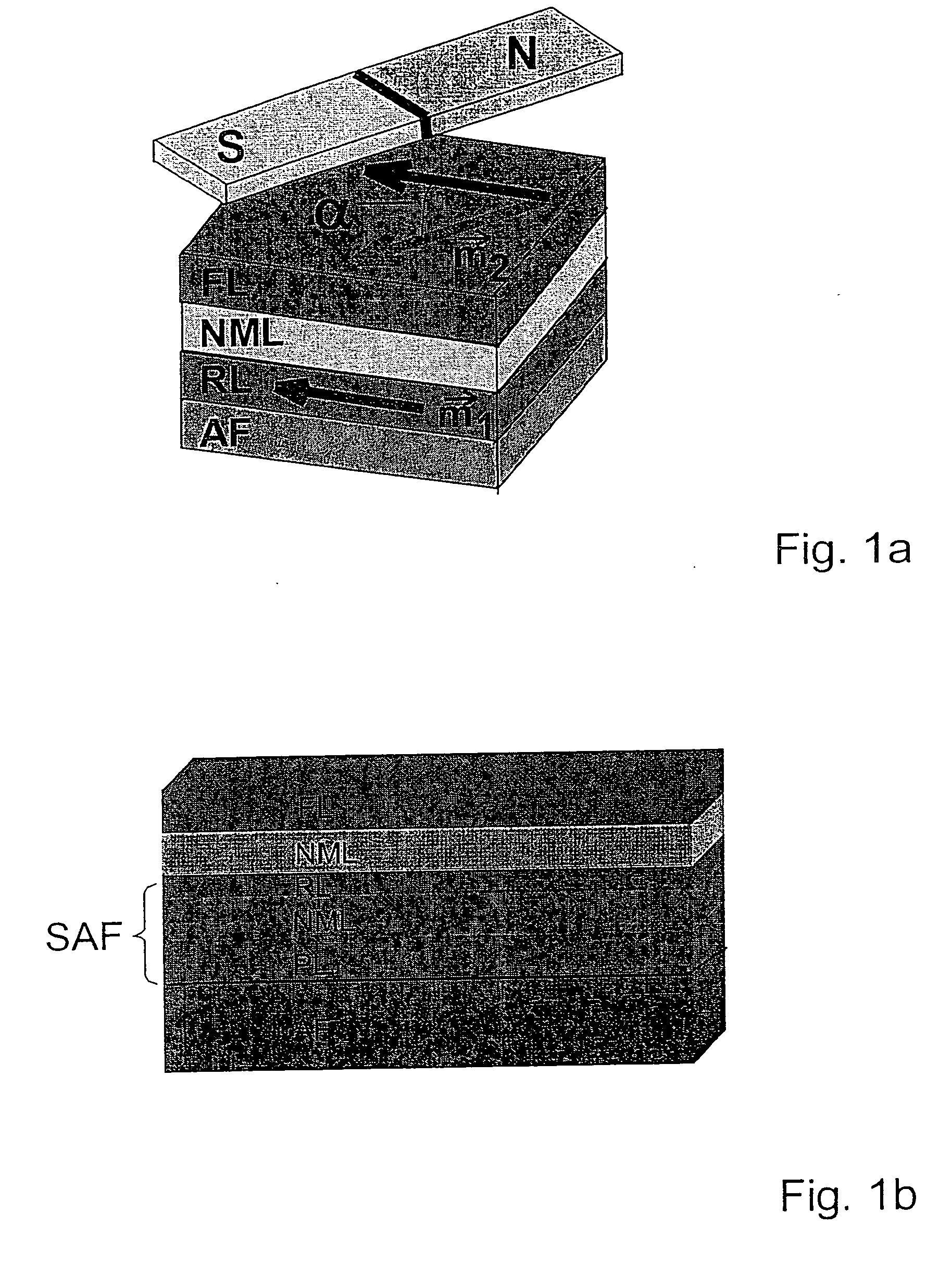
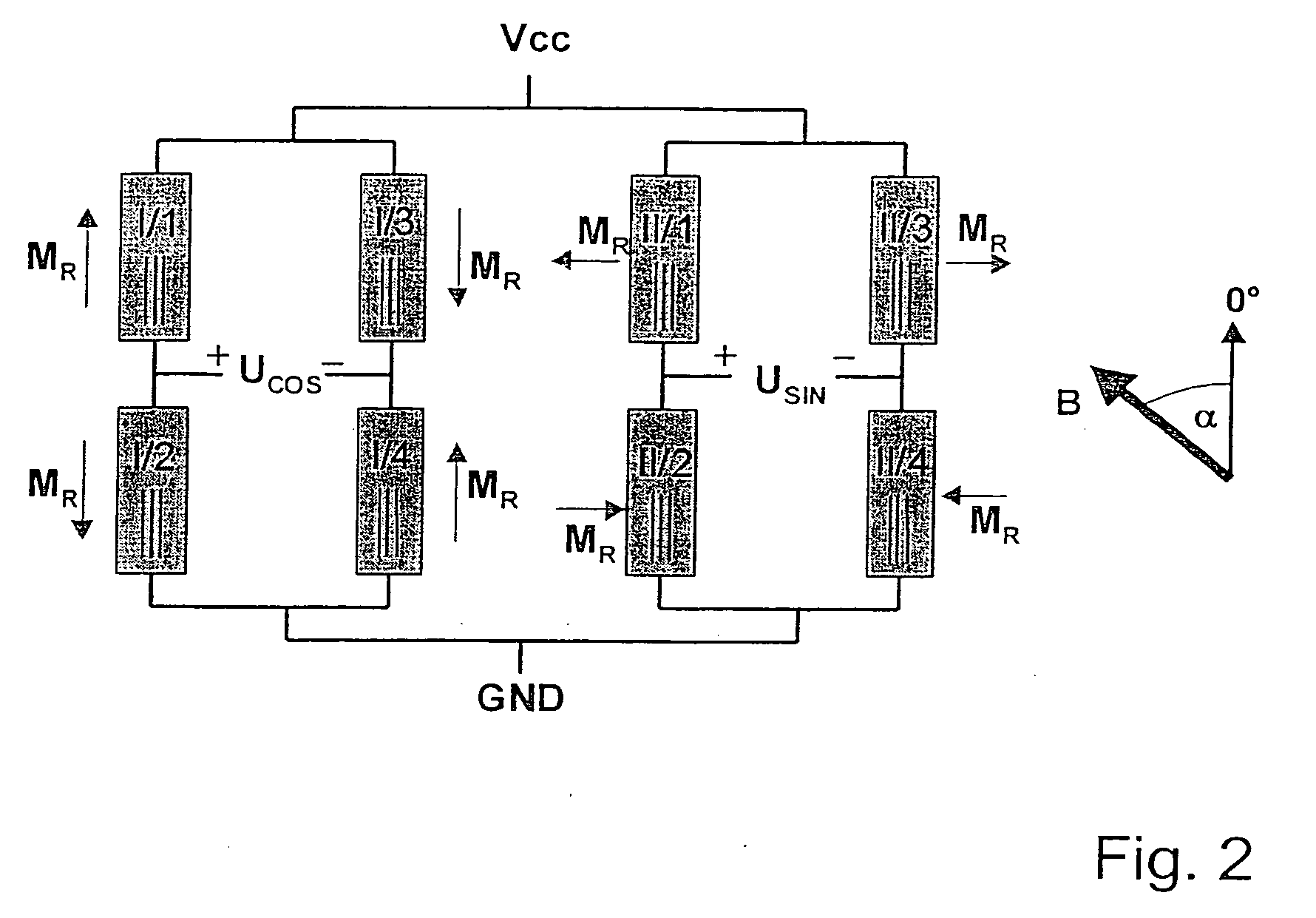
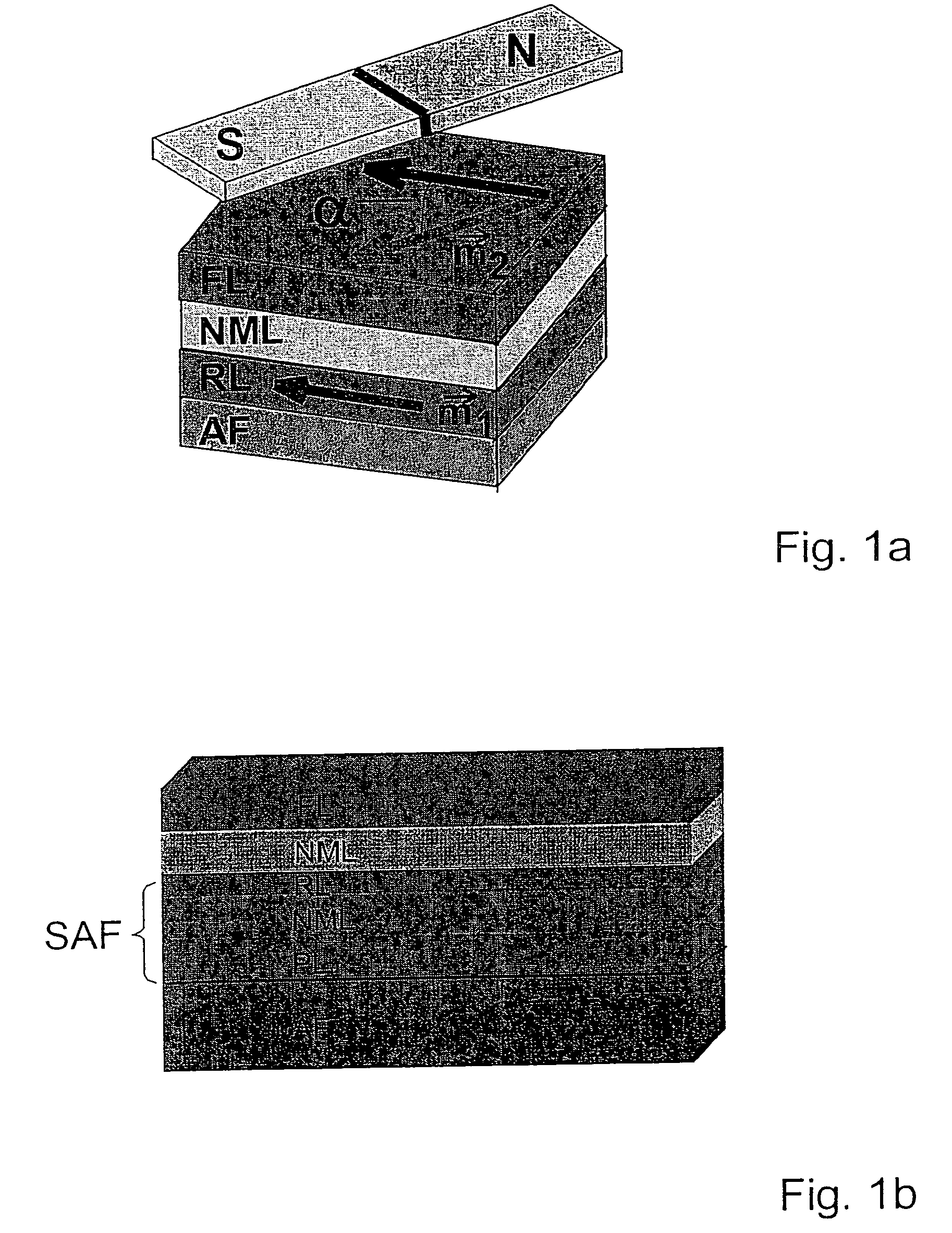
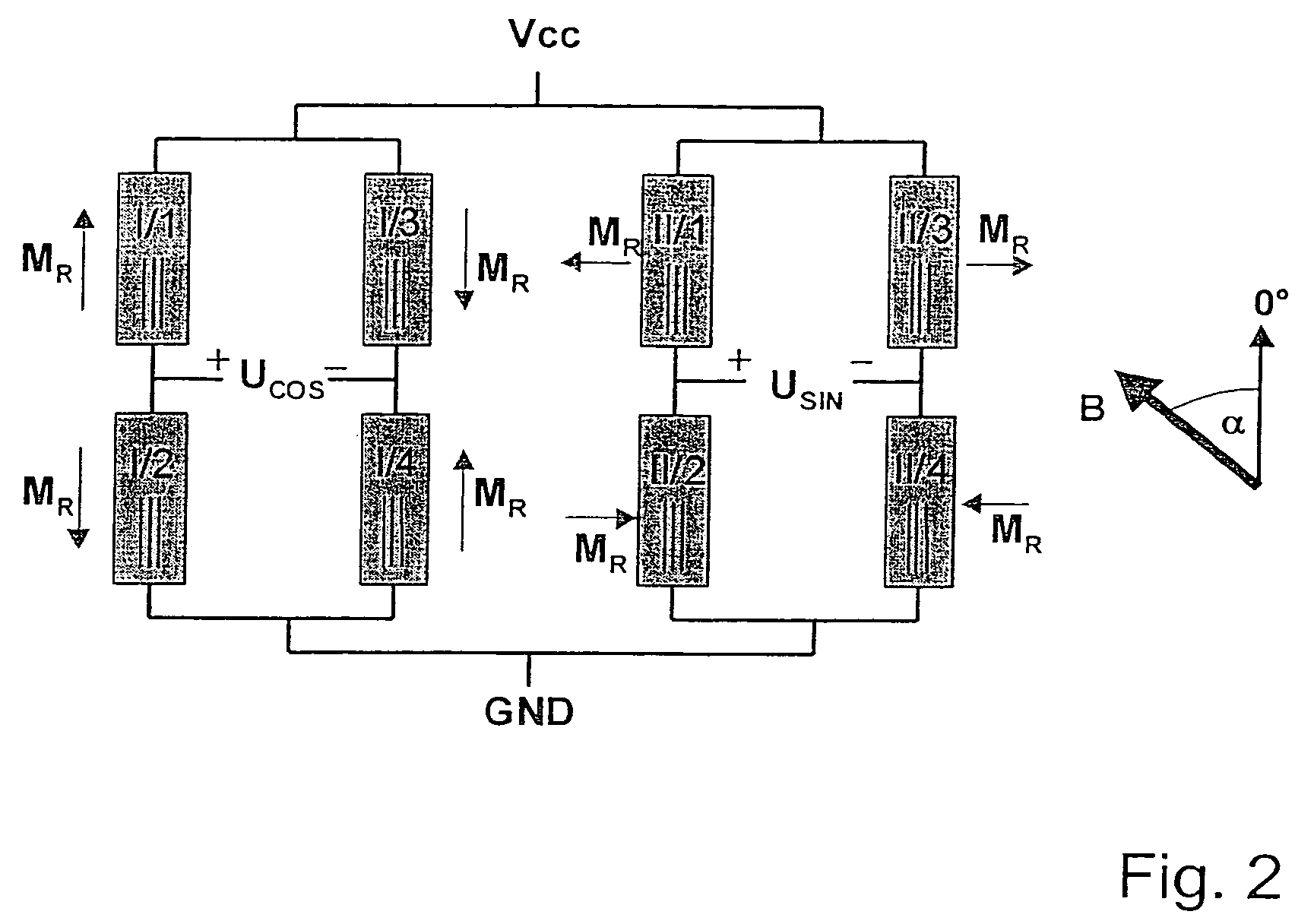
Gmr sensor element and its use
InactiveUS20060103381A1Improve long-term stabilityImprove signal stabilityValve arrangementsNanomagnetismSteering angleFull bridge
A GMR sensor element is proposed, having a rotationally symmetrical positioning of especially eight GMR resistor elements which are connected to each other to form two Wheatstone's full bridges. This GMR sensor element is especially suitable for use in an angle sensor for the detection of the absolute position of the camshaft or the crankshaft in a motor vehicle, particularly in the case of a camshaft-free engine having electrical or electrohydraulic valve timing, of a motor position of an electrically commutated motor, or of detection of a windshield wiper position, or in the steering angle sensor system in motor vehicles.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
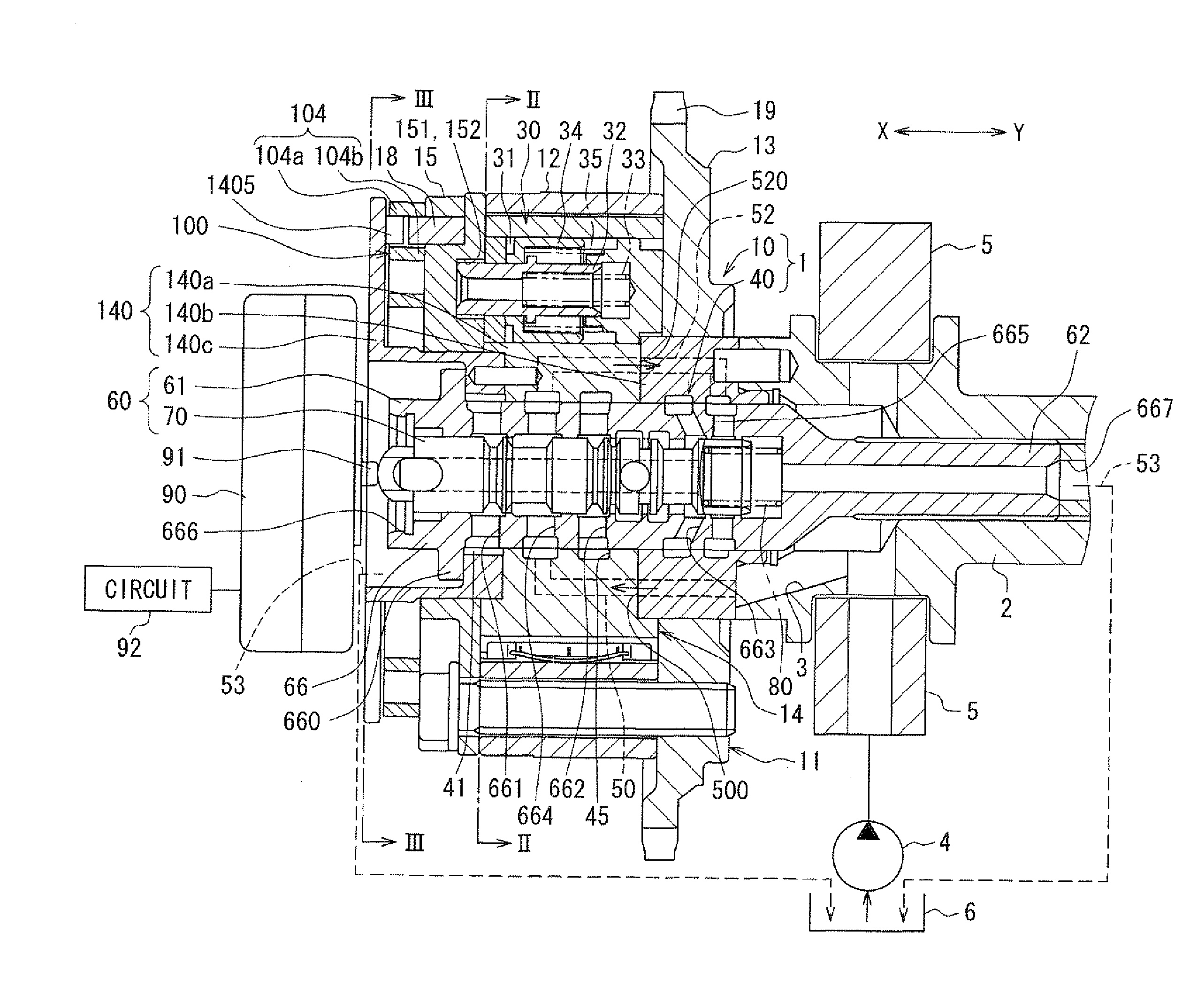
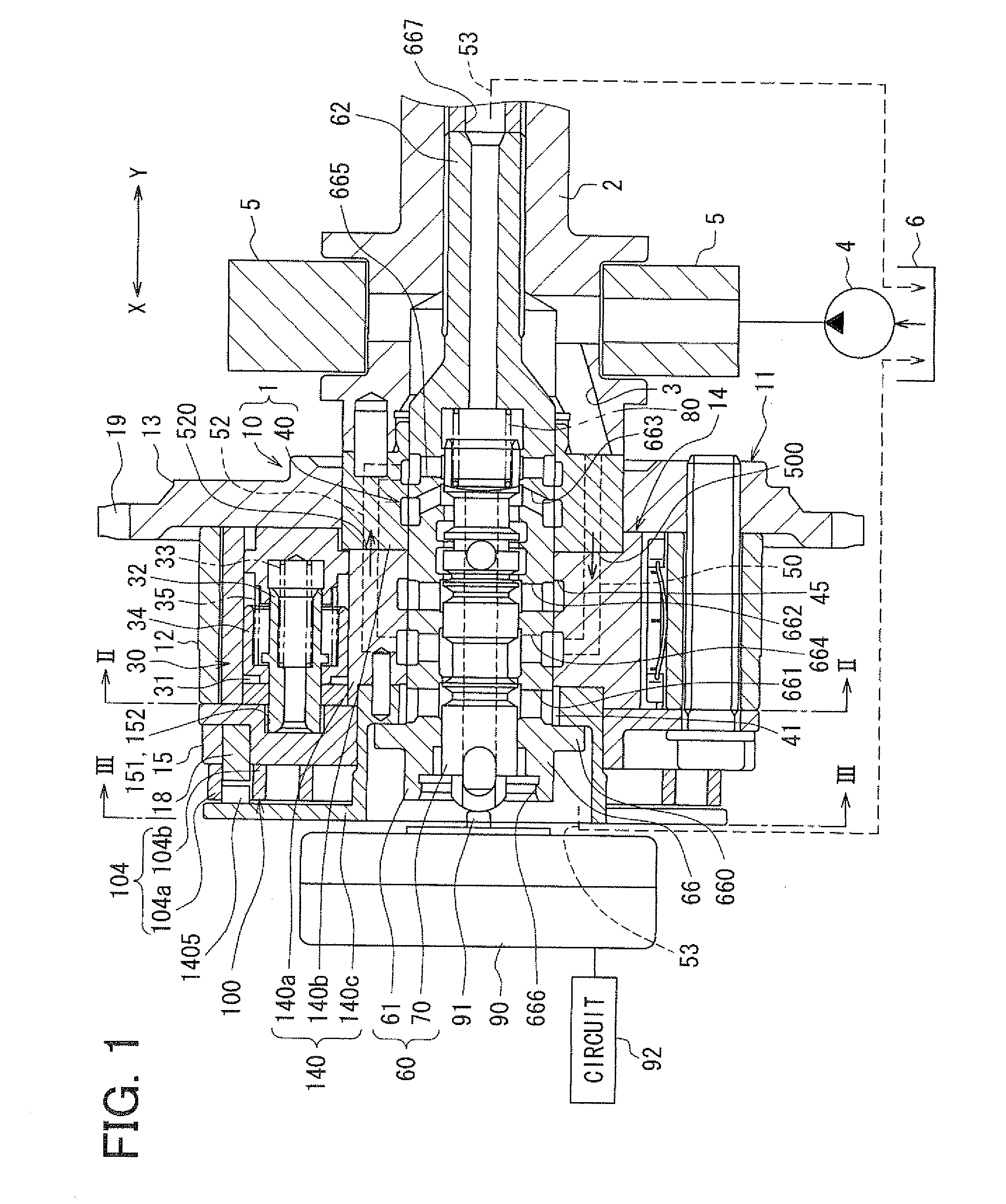
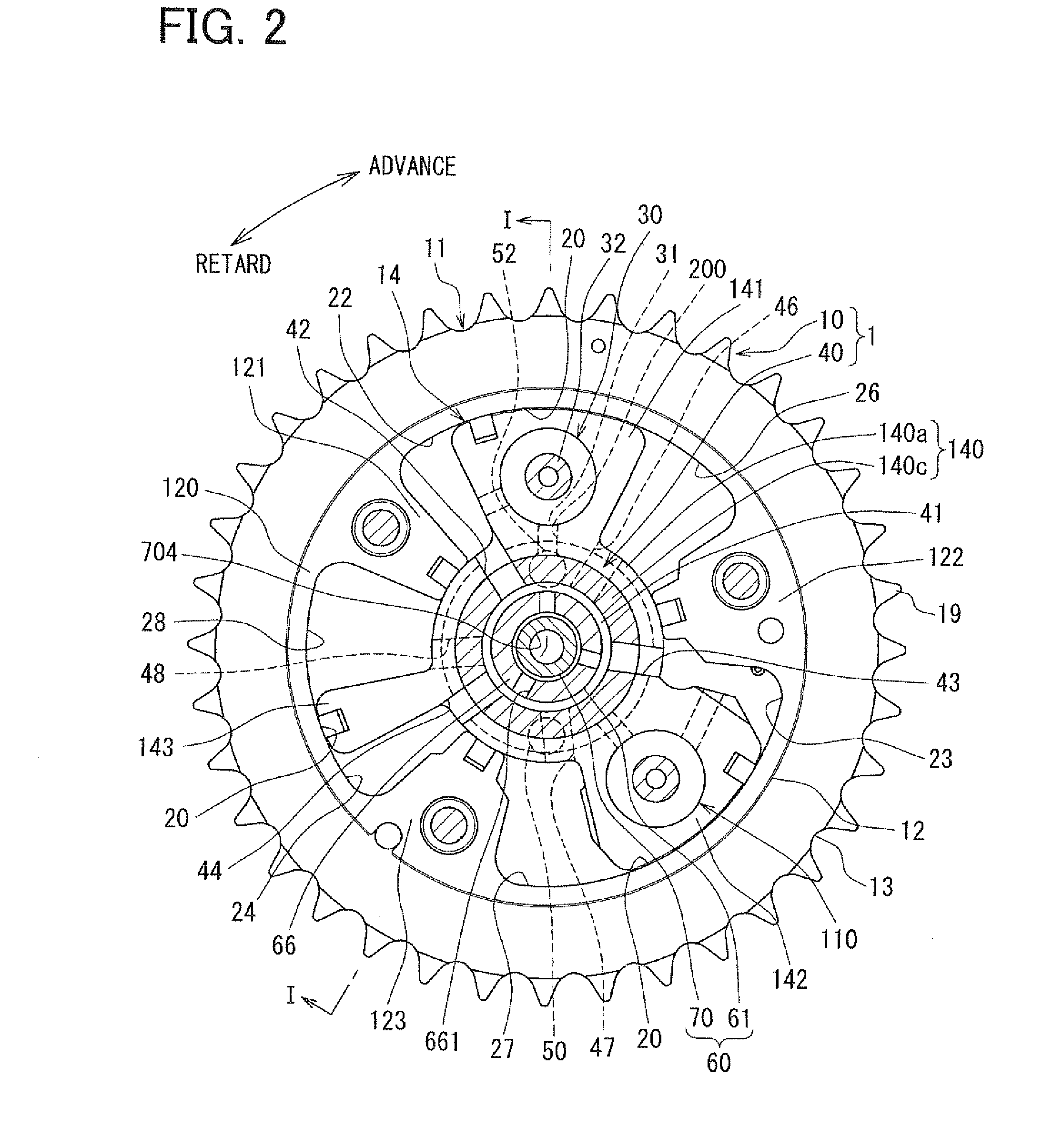
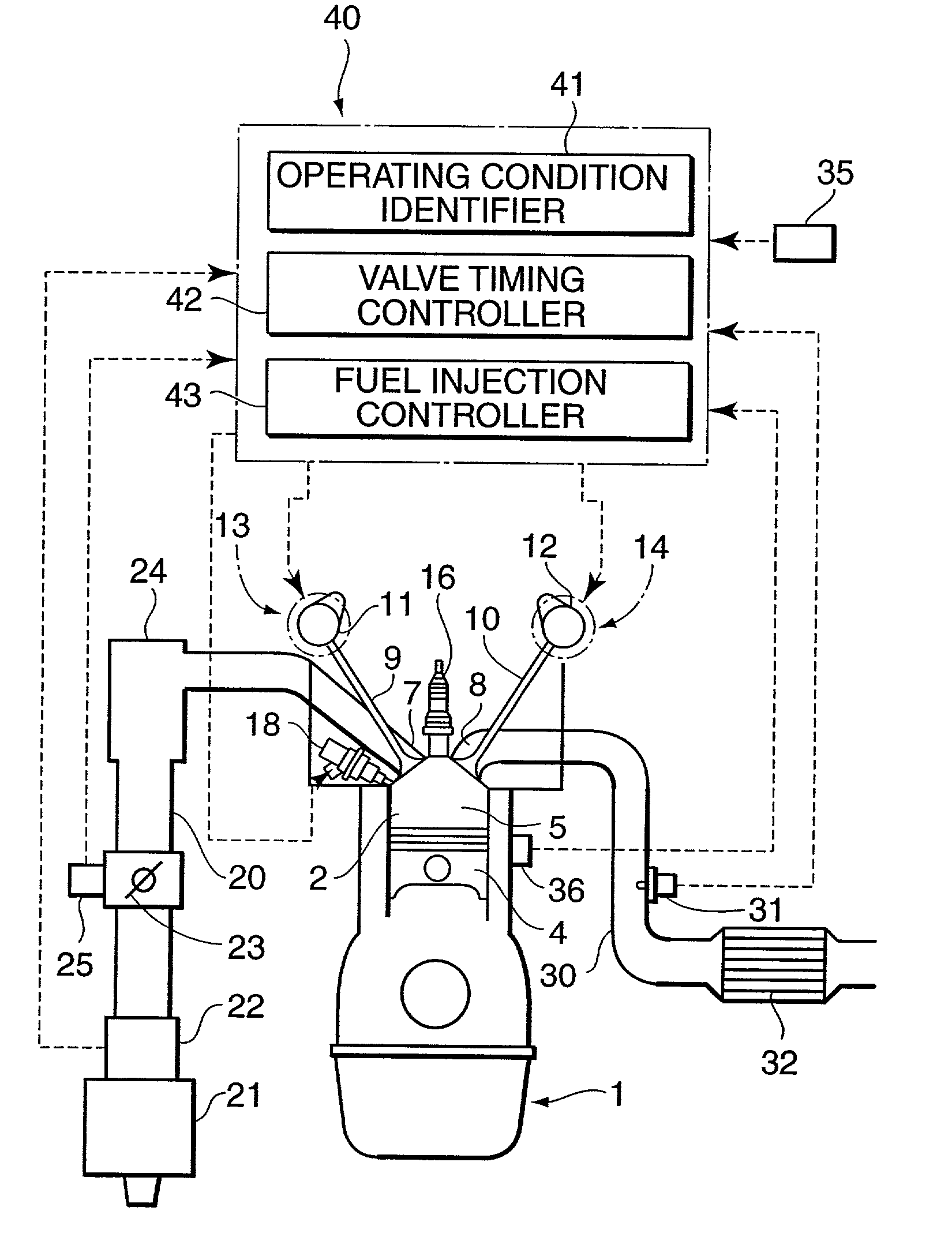
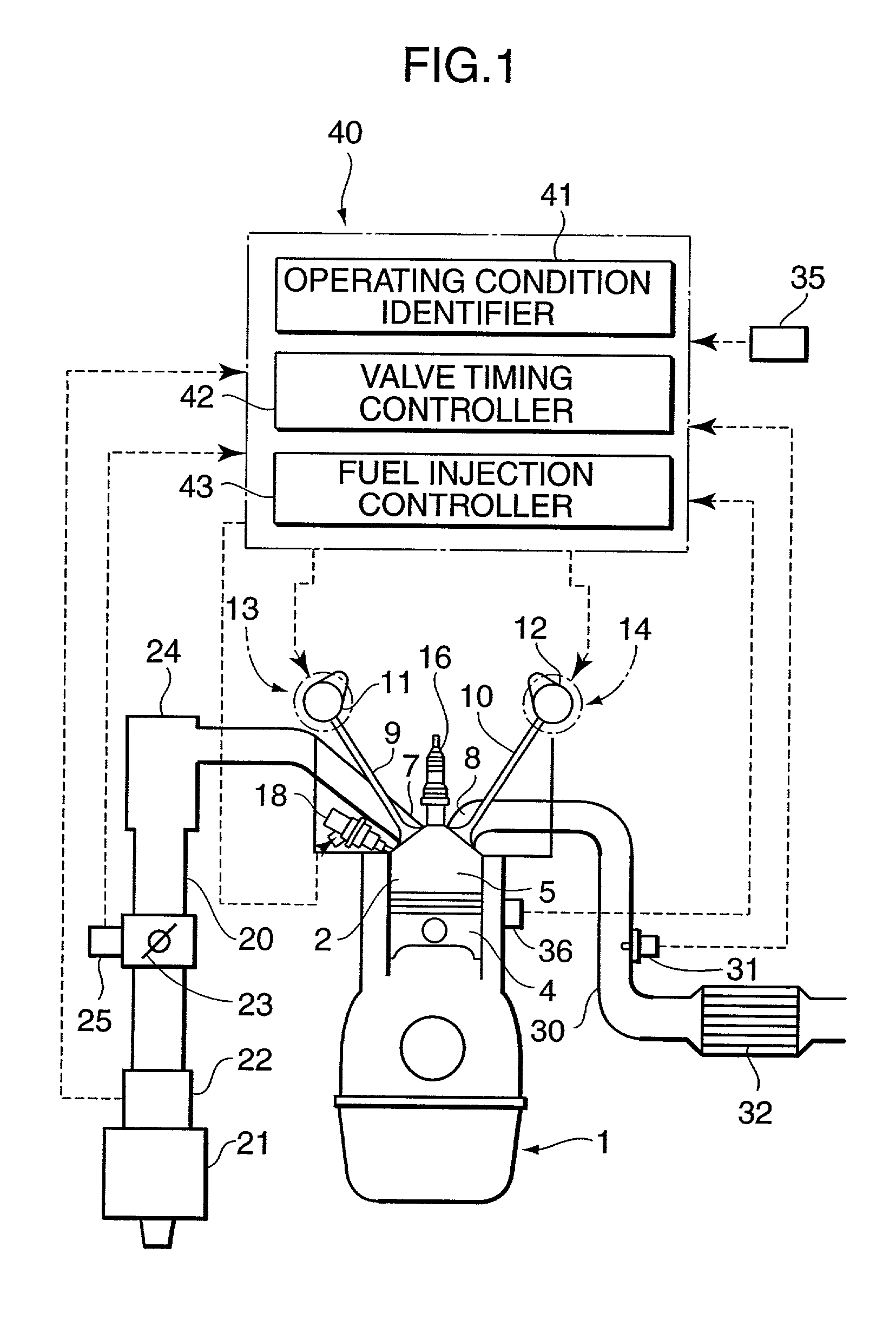
Valve timing control device
InactiveUS20020078913A1Avoid it happening againEasy to operateValve arrangementsMachines/enginesEngineeringResidual pressure
A valve timing control device includes a purge path communicating between a hydraulic chamber allowing the entry of hydraulic pressure on starting an engine and a backward pressurized section in an accommodation hole. When the hydraulic chamber allowing the entry of hydraulic pressure on starting the engine is the retardation side hydraulic chamber, a hydraulic pressure derived from an oil pump is supplied to the retardation side hydraulic chamber on starting the engine. On the way, air-mixed oil is discharged to outside of the device by way of a purge path, a backward pressurized section in the accommodation hole and the discharge hole. When the air is discharged, a residual pressure is produced in the backward pressurized section due to oil supplied thereto. The residual pressure results in the increase of an unlocking hydraulic pressure to prevent a locking member from being unlocked. When the application of a retardation side hydraulic pressure is switched to that of an advance side hydraulic pressure, the pressure presses a front end of a locking member against only a biasing force of a biasing means to unlock a locking relation. The valve timing control device allows the use of any kinds of locking pins, and prevents the occurrence of beat noise (abnormal noise) when air-mixed oil unlocks a locking relation on starting the engine.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Valve timing control apparatus
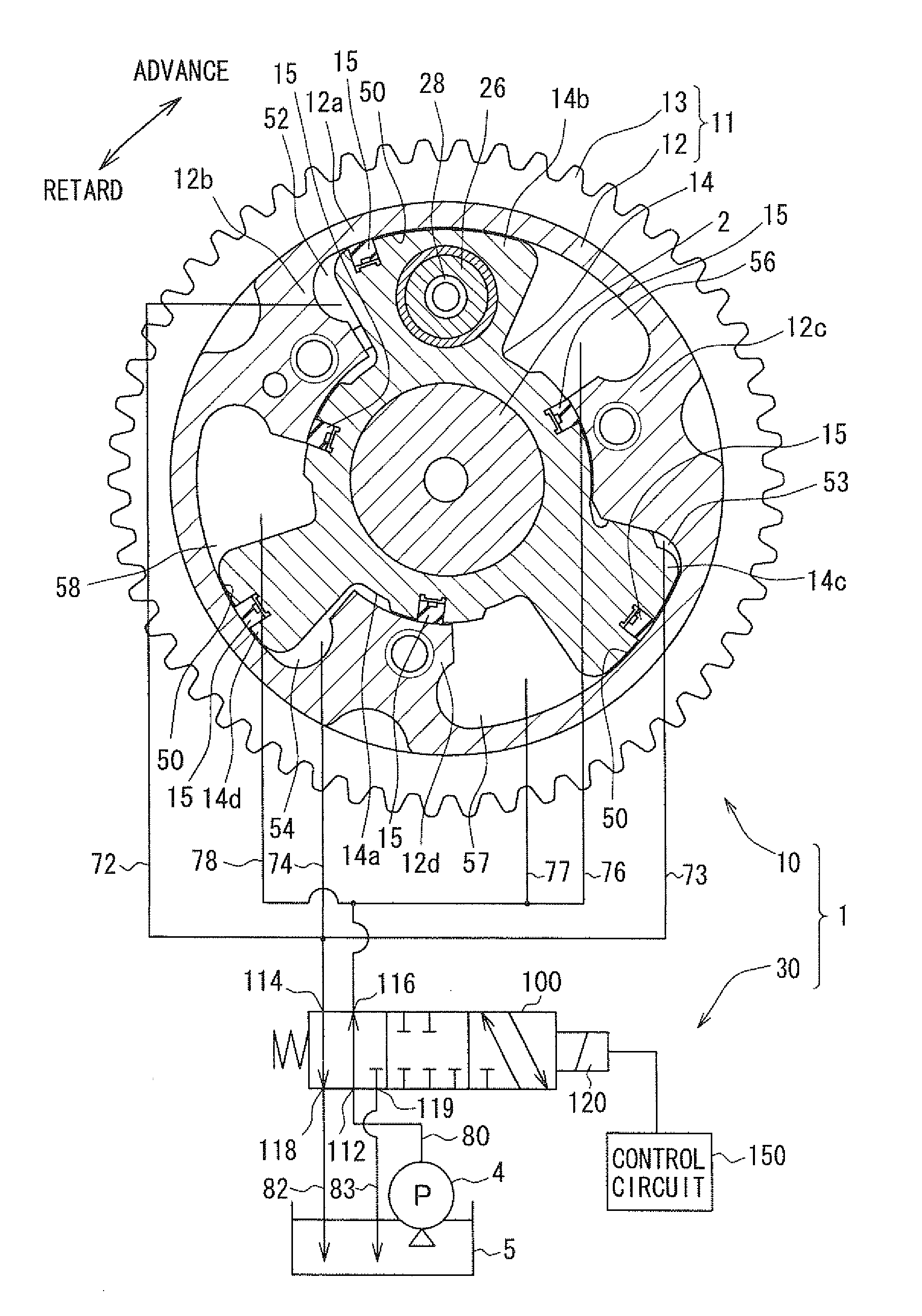
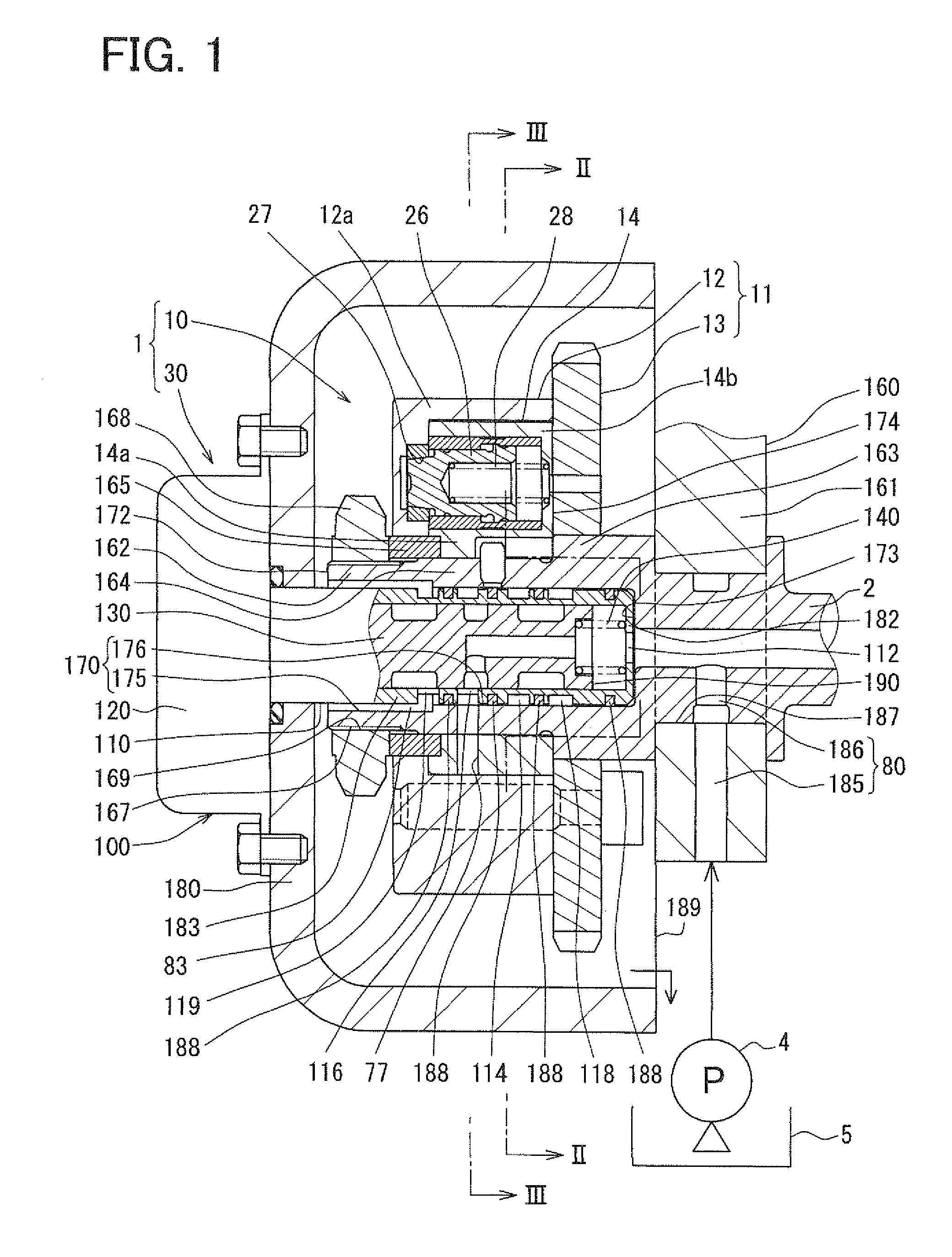
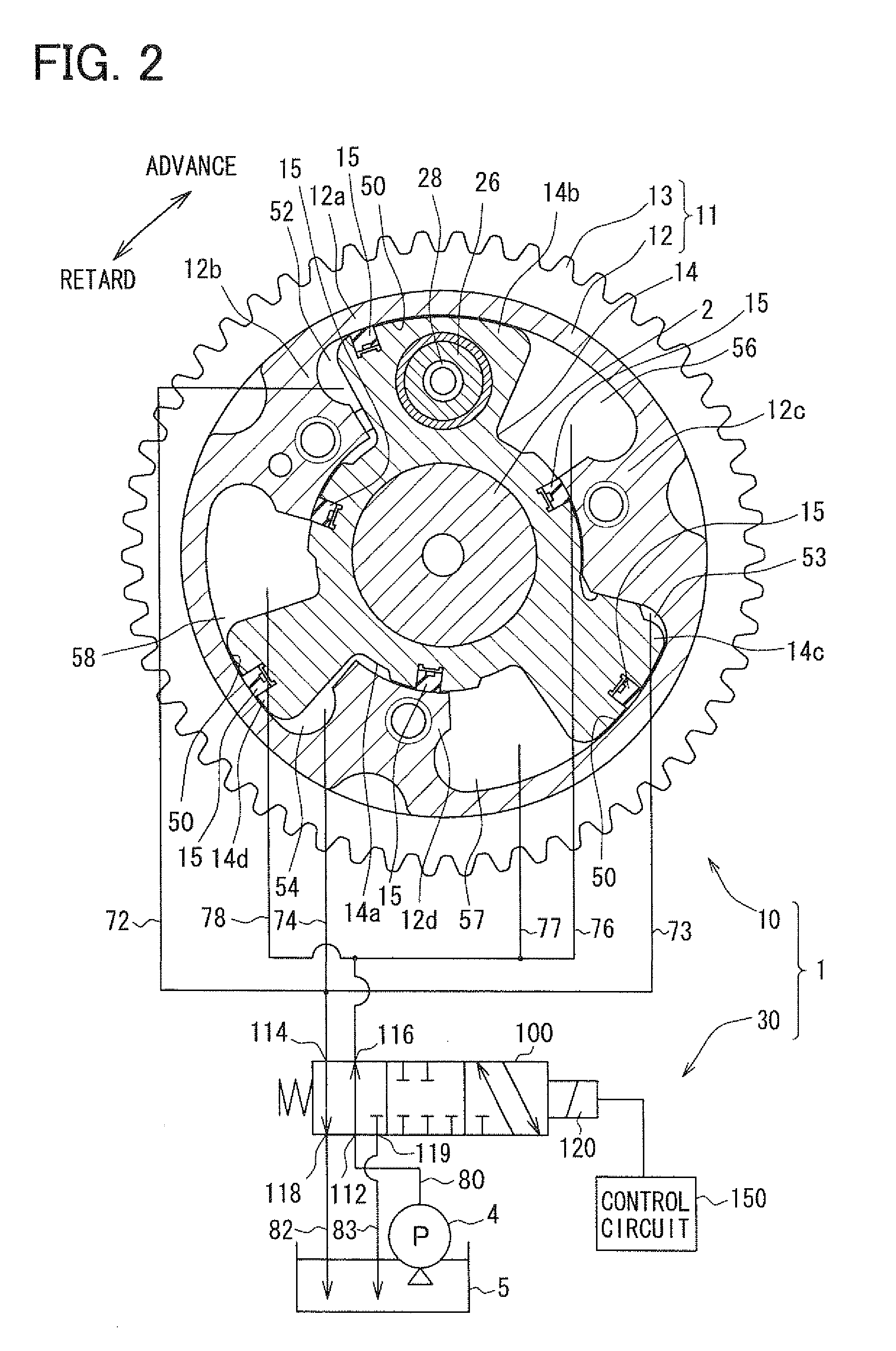
A valve timing control apparatus for controlling valve timing includes a first rotor, a second rotor, and a controller. The second rotor and the first rotor defines therebetween an advance chamber and a retard chamber. The controller includes a supply passage, at least one drain passage, a spool valve, at least one connection passage, and at least one check valve. The at least one connection passage connects the supply passage to the at least one drain passage when a spool of the spool valve is moved to one of the advance and retard positions. The at least one check valve is respectively provided in the at least one connection passage. The check valve allows working fluid to flow in a direction from the at least one drain passage toward the supply passage and limits working fluid from flowing in an opposite direction.
Owner:DENSO CORP
System for controlling valve timing of an engine with cylinder deactivation
ActiveUS20050268880A1Sufficient NOx reduction and fuel economy benefitsEasy to operateValve arrangementsElectrical controlSystems designControl valves
Various systems and methods are disclosed for carrying out combustion in a fuel-cut operation in some or all of the engine cylinders of a vehicle. Further, various subsystems are considered, such as fuel vapor purging, air-fuel ratio control, engine torque control, catalyst design, and exhaust system design.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
GMR sensor element and its use
InactiveUS7312609B2Reduce sensitivityUndesired AMR signal contributionValve arrangementsNanomagnetismMobile vehicleSteering angle
A GMR sensor element is proposed, having a rotationally symmetrical positioning of especially eight GMR resistor elements which are connected to each other to form two Wheatstone's full bridges. This GMR sensor element is especially suitable for use in an angle sensor for the detection of the absolute position of the camshaft or the crankshaft in a motor vehicle, particularly in the case of a camshaft-free engine having electrical or electrohydraulic valve timing, of a motor position of an electrically commutated motor, or of detection of a windshield wiper position, or in the steering angle sensor system in motor vehicles.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
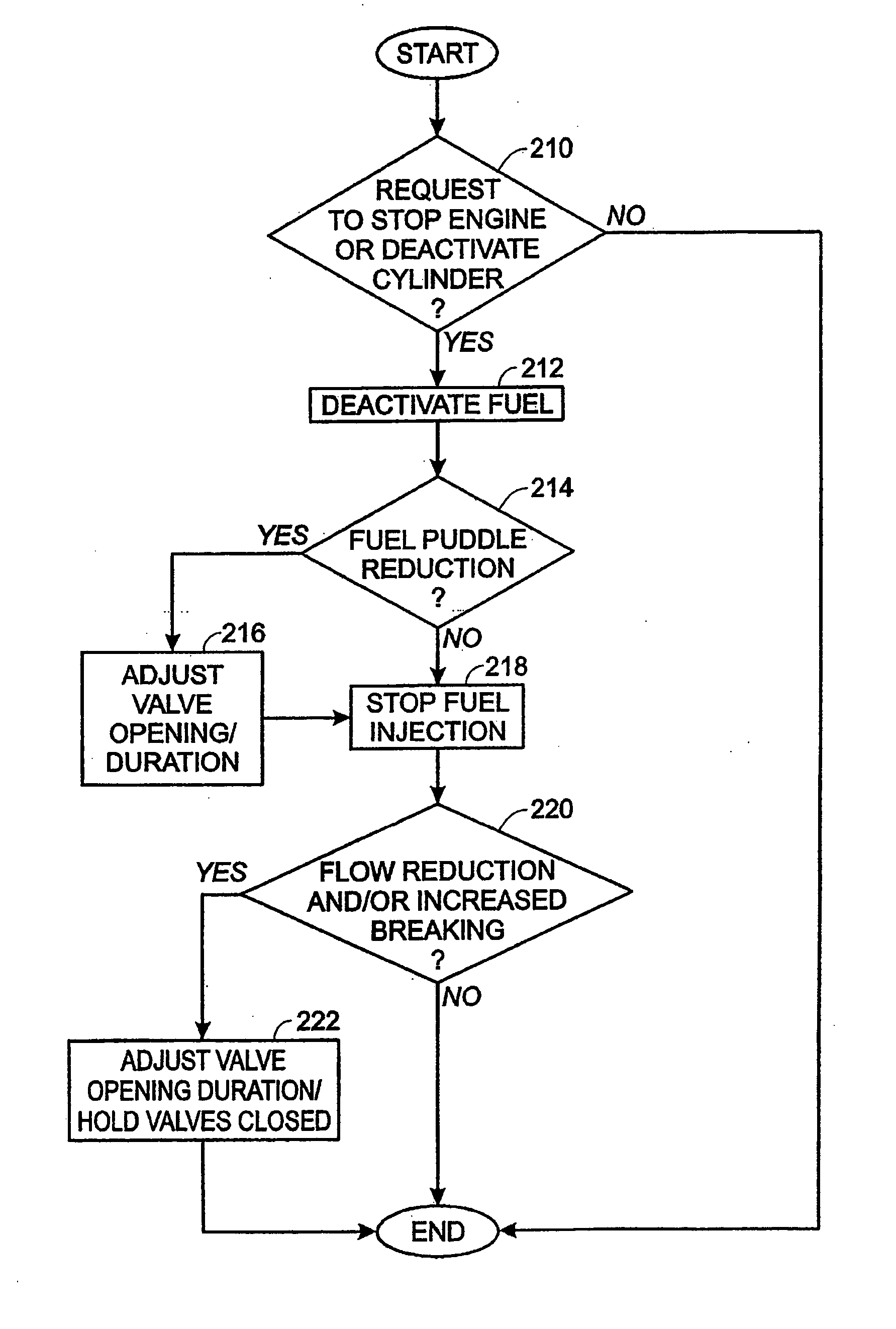
Engine shut-down for engine having adjustable valve timing
ActiveUS20050205049A1Reduce stopping engine stopping timeLess gasAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlBrake torqueExhaust valve
A method for operating at least an intake and exhaust valve in a cylinder with a piston of an engine in a vehicle, comprising during conditions of an engine shut-down, maintaining at least one of the intake and exhaust valves in a closed position, and during conditions where said at least one valve is in said closed position operating with the other of the intake and exhaust valve open, then closing the other of the intake and exhaust valve, and then opening the other of the intake and exhaust valve to generate braking torque to slow the engine.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method for transition between controlled auto-ignition and spark ignition modes in direct fuel injection engines
InactiveUS7370616B2Eliminate misfiring and partial burnsValve arrangementsElectrical controlHomogeneous charge compression ignitionExhaust valve
A method is provided for control of transition between combustion modes of a direct-injection engine operable in a homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) mode at lower loads and a spark ignition flame propagation (SI) mode at higher loads. The engine includes a variable valve actuation system including two-step high and low lift valve actuation and separate cam phasing for both intake and exhaust valves. The method includes operating the engine at steady state, with fuel-air-exhaust gas mixtures at predetermined conditions, for each speed and load, and controlling the engine during mode changes between the HCCI mode and the SI mode by switching the exhaust and intake valves between low lift for HCCI operation and high lift for SI operation. High load may be an SI throttled mode with an intermediate unthrottled mode (SI / NTLC} in which transition between HCCI and SI / NTLC modes requires switching only the exhaust valve lift and transition between SI / NTLC and SI throttled modes requires switching only the intake valve lift, with predetermined phase adjustments in the valve timing phasing.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
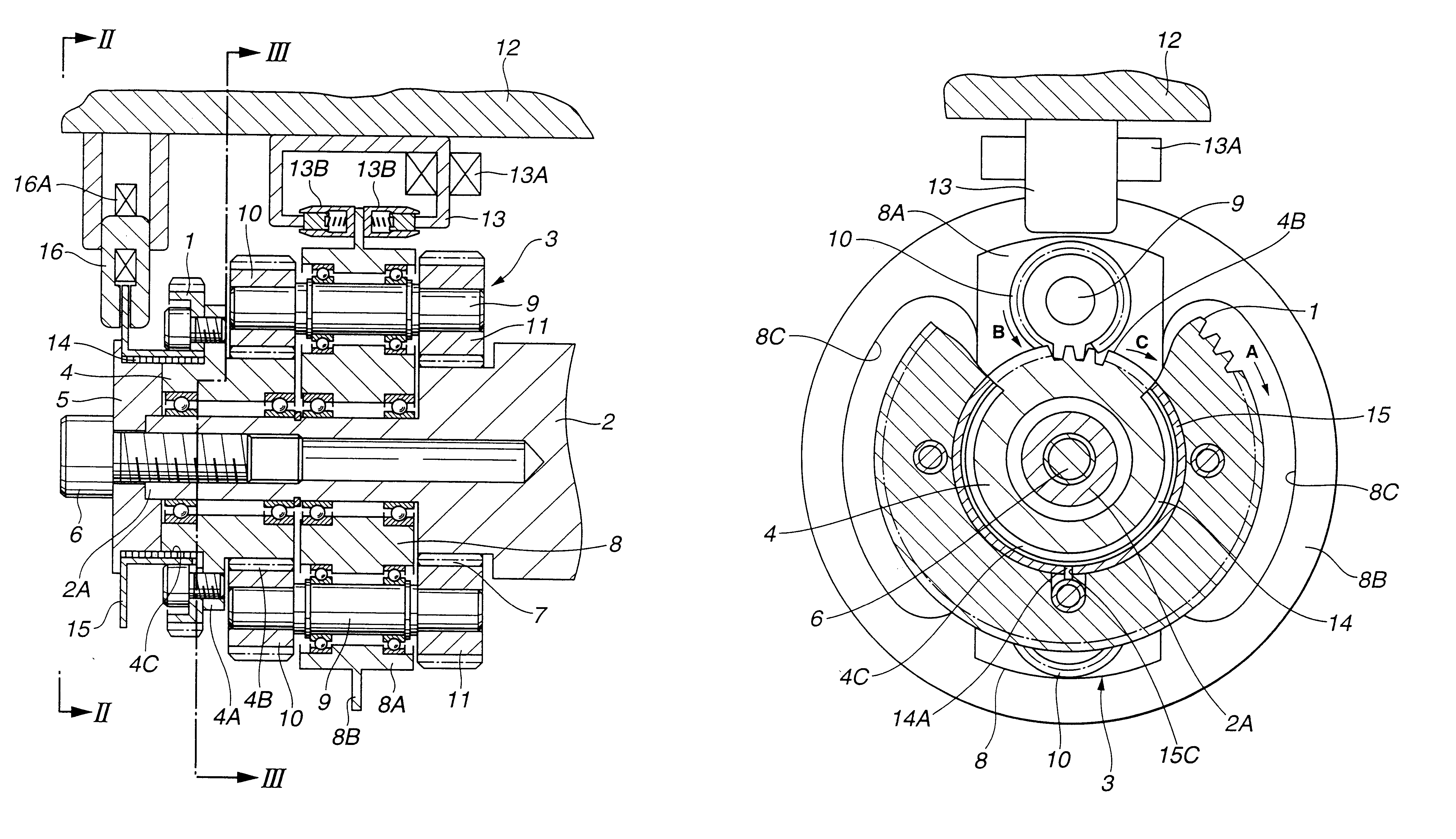
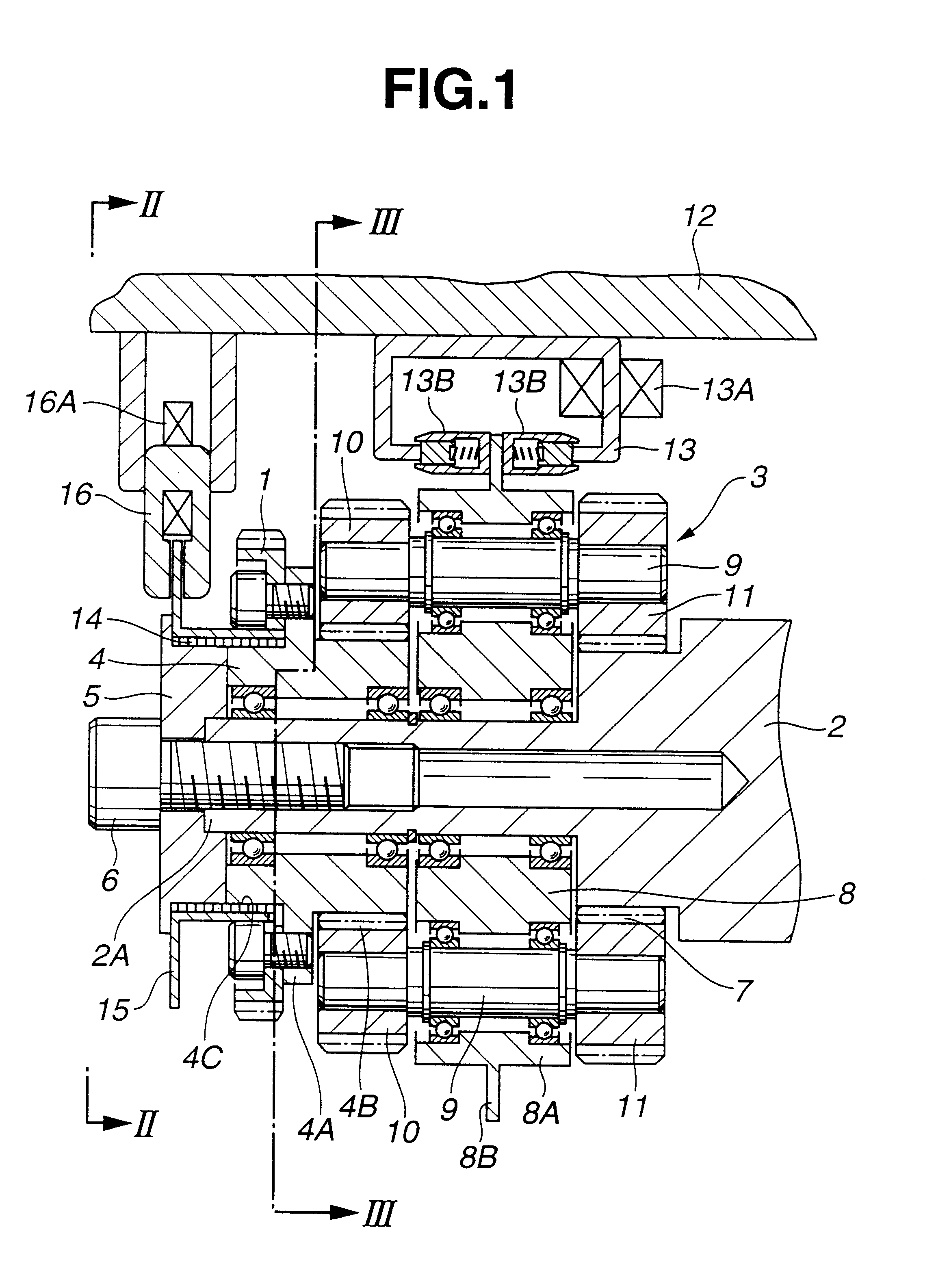
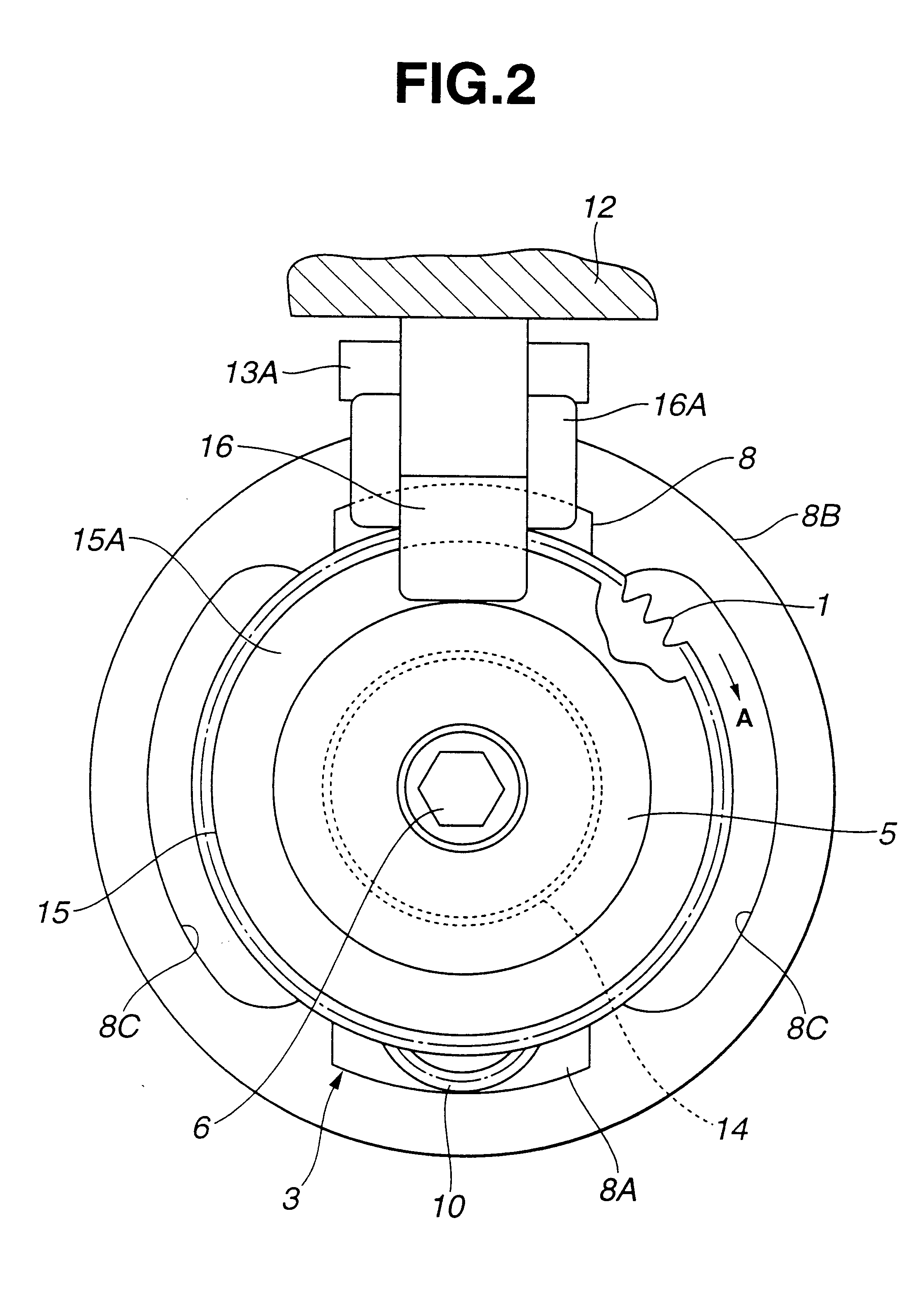
Valve timing adjusting apparatus
A valve timing adjusting apparatus for an internal combustion engine having a bearing includes a camshaft, a housing, a vane rotor, a control valve, and a fastening member. The fastening member is mounted on an axial end portion of the camshaft on a side of the vane rotor opposite from the bearing. The vane rotor is coaxially fastened to the camshaft between the fastening member and a step portion, which is provided to the camshaft on a side of the bearing. A sleeve of the control valve is coaxially received in an axial hole of the camshaft, which opens at an end surface of the end portion of the camshaft. Each of the advance output port and the retard output port is communicated with a corresponding one of the advance chamber and the retard chamber through the camshaft.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Control of autoignition timing in a hcci engine
ActiveUS20040134449A1Reduces and minimizesCompensation effectElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberExhaust valve
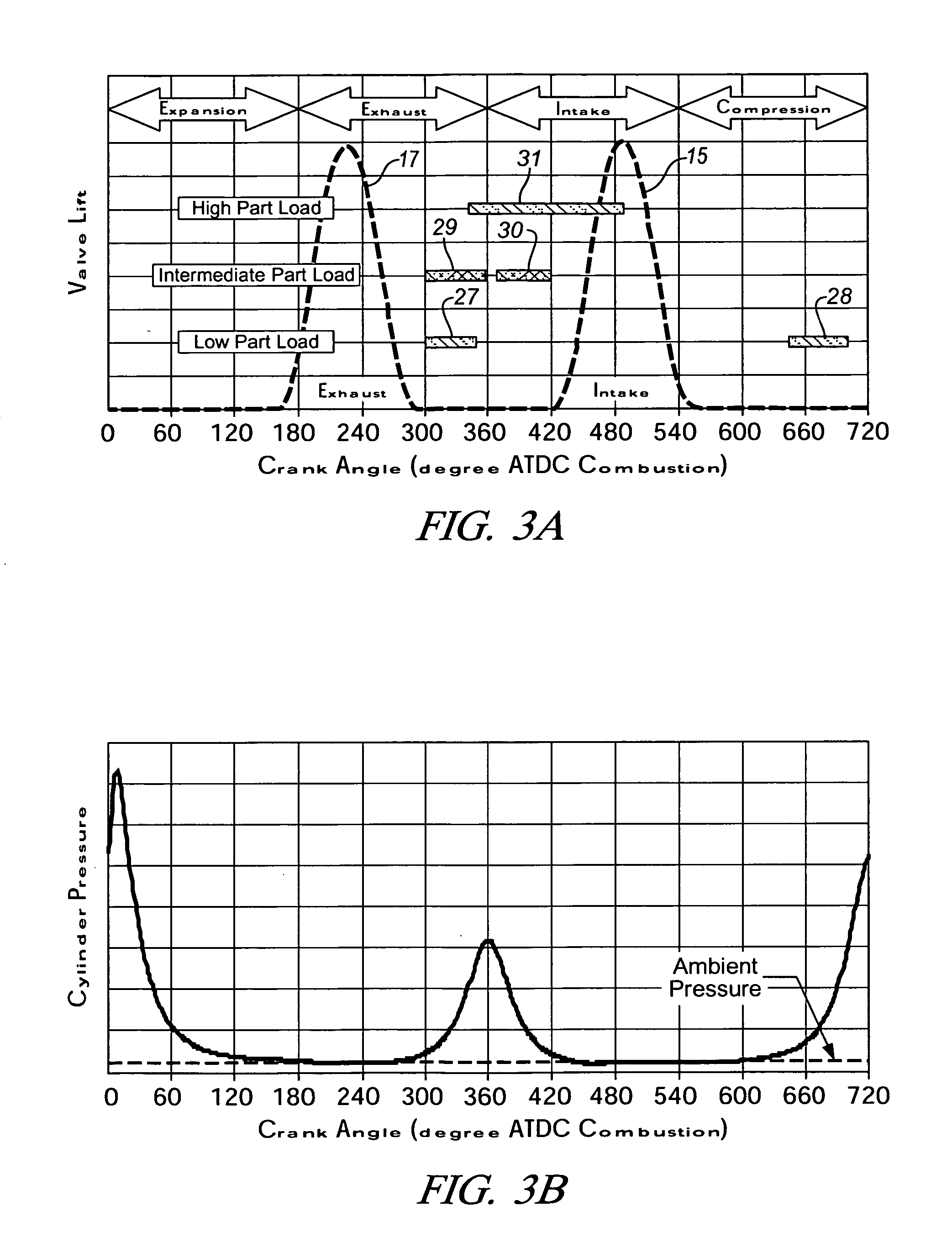
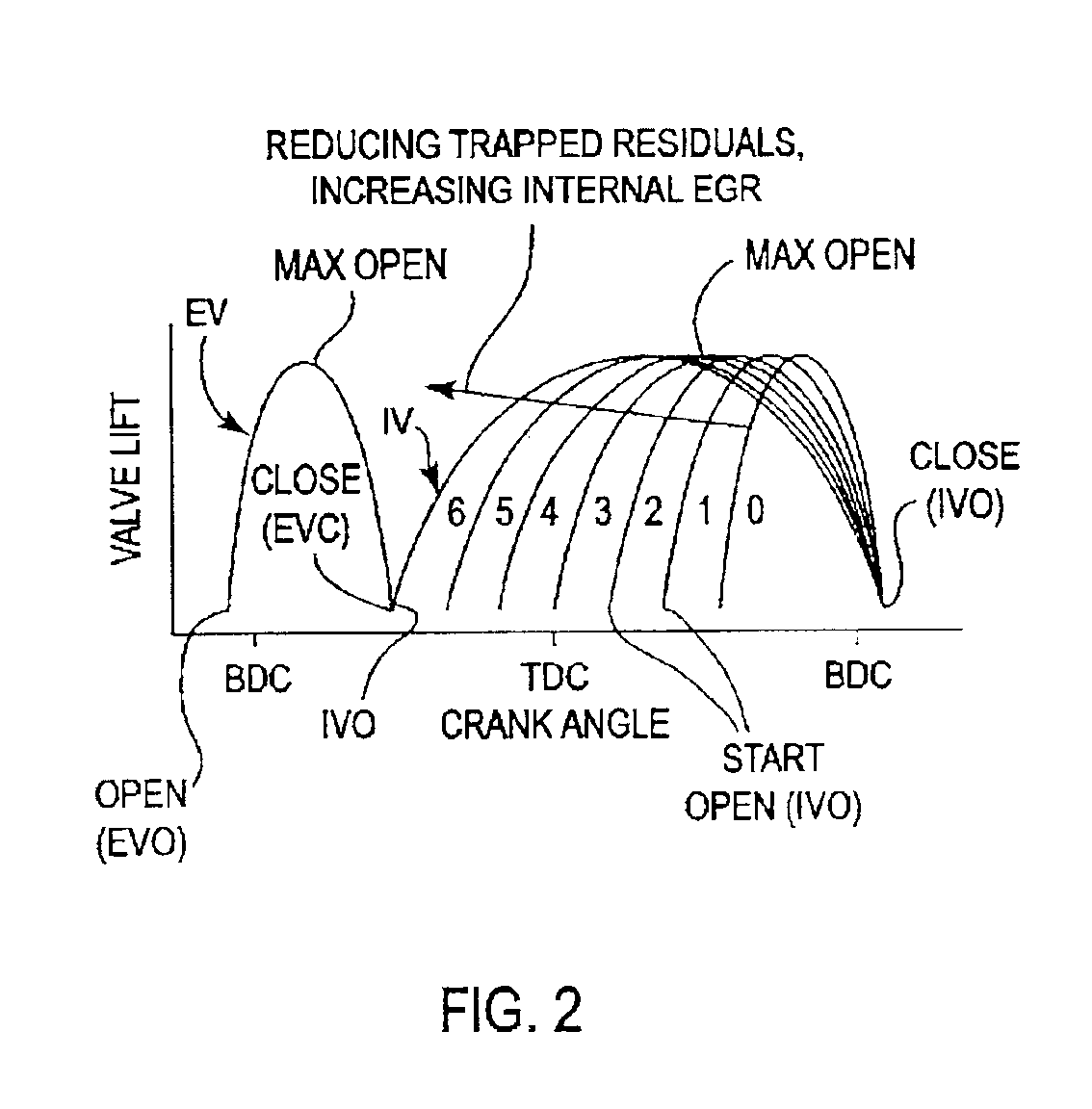
Method and system embody a valve timing strategy to control the autoignition timing of a four stroke internal combustion engine (10) operated in an HCCI mode at different engine operating conditions such as different engine speed and torque. A particular valve timing strategy varies lift timing of the intake valve (20) relative to the exhaust valve (28), or vice versa, and relative to top dead center in response to a change in engine torque, for example, to vary amount of trapped residual burned gas in the combustion chamber (12) flowing to an intake or exhaust port (16,18) and back to the combustion chamber during which the residual gas is cooled. Control of the flow of residual gas between the combustion chamber and intake or exhaust port and thus its temperature by the valve timing strategy, in turn, is used to control the temperature of the fresh air / residual gas / fuel mixture in the combustion chamber (12) and thus autoignition timing in response to a change in engine torque.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Engine Dynamic Load Leveling
ActiveUS20080135021A1Challenge and limitationLower efficiency benefitElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesHomogeneous charge compression ignitionControl theory
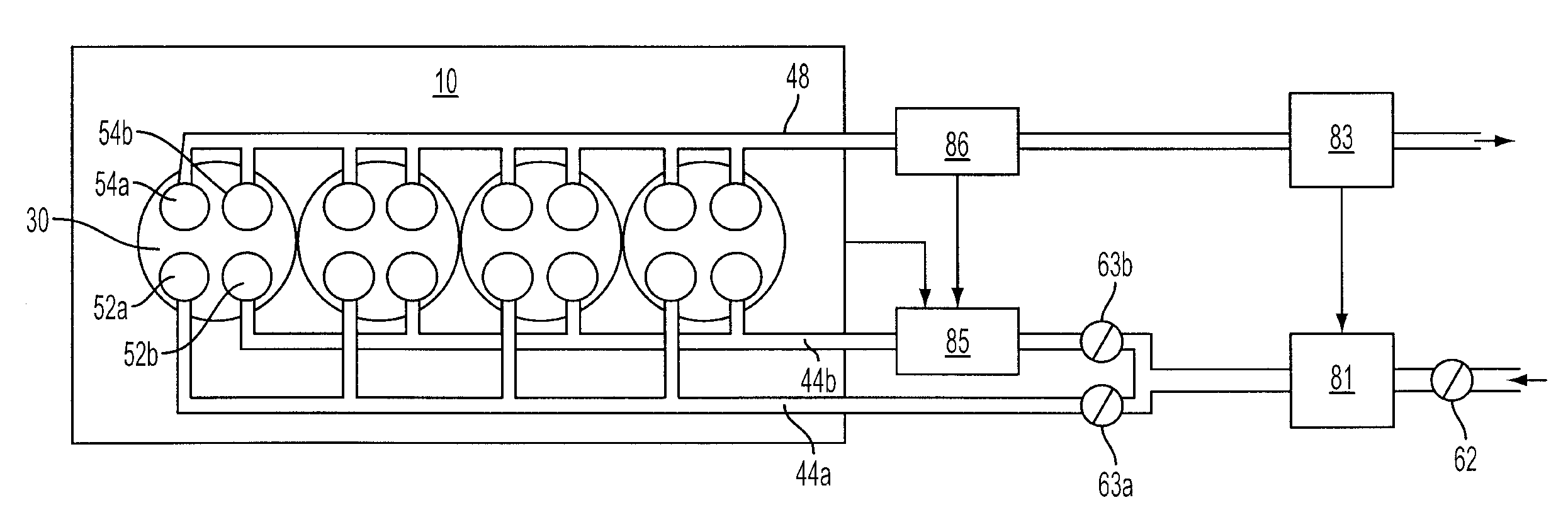
A method for controlling an internal combustion engine having a plurality of cylinders using electronic valve actuation, including operating a first portion of the cylinders in a homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) mode, operating a second portion of the cylinders in a non-HCCI mode, and adjusting the valve timing of the second portion of cylinders to dynamically load level the engine in response to a transient torque demand. A system for controlling a multiple cylinder internal combustion engine, including a first group of cylinders to operate in an HCCI mode, a second group of cylinders to operate in a non-HCCI mode, and an engine controller operably coupled to the first and second groups of cylinders, said controller to adjust the valve timing of the second group of cylinders to dynamically load level the engine in response to a transient torque demand.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Controller of cylinder injection type internal combustion engine
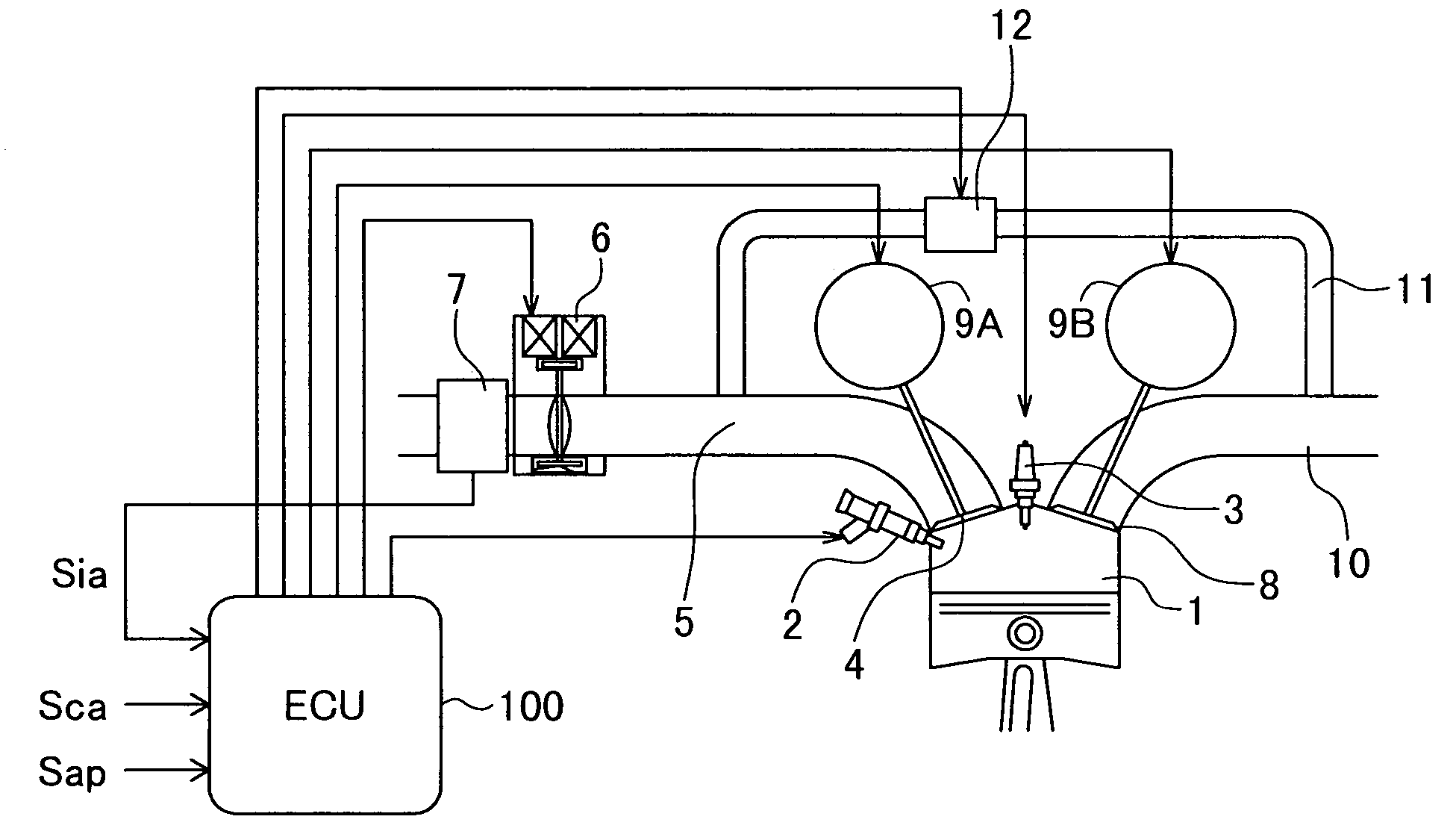
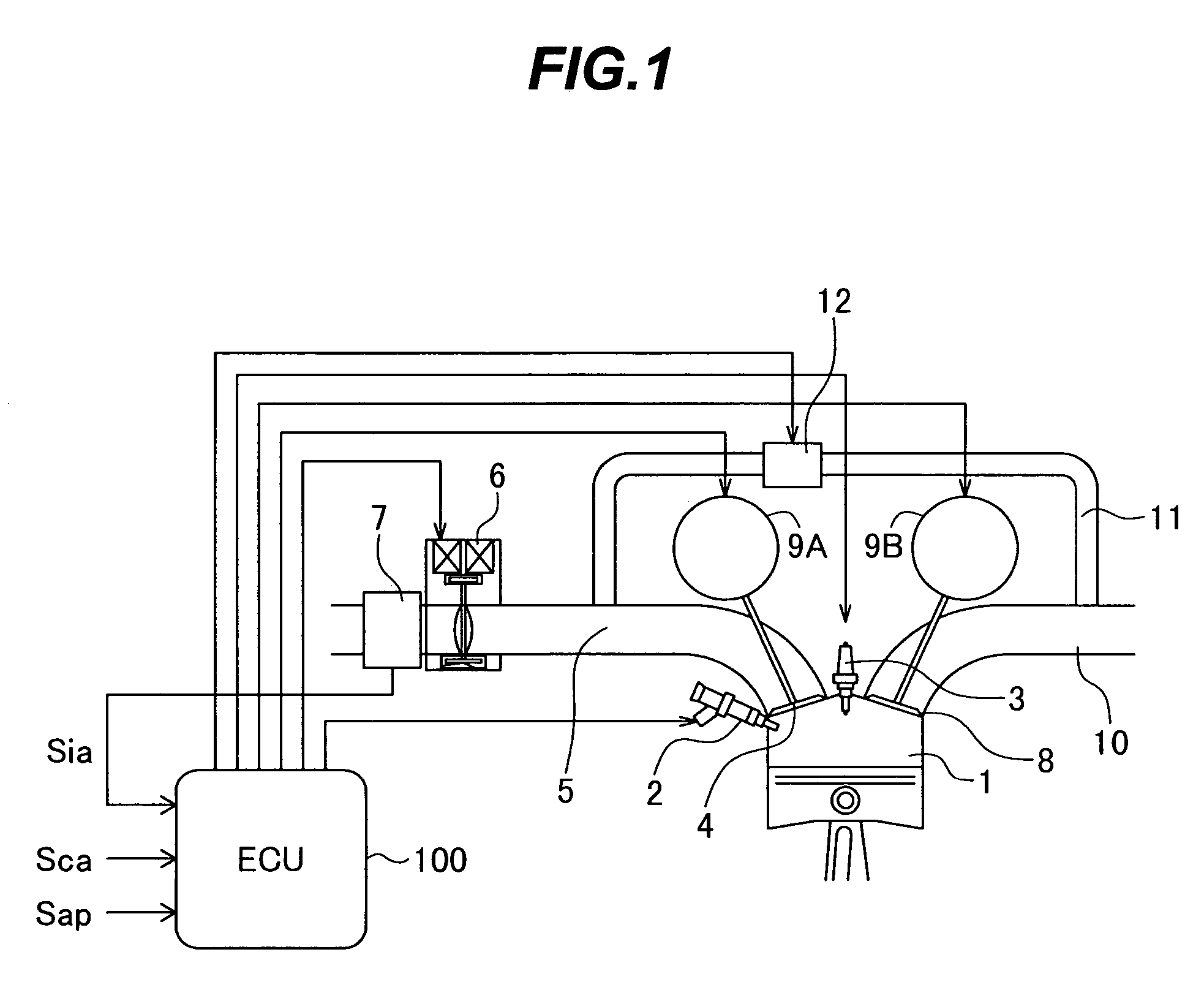
InactiveUS7000380B2Reduce the amount requiredValve arrangementsElectrical controlExhaust valveCombustion chamber
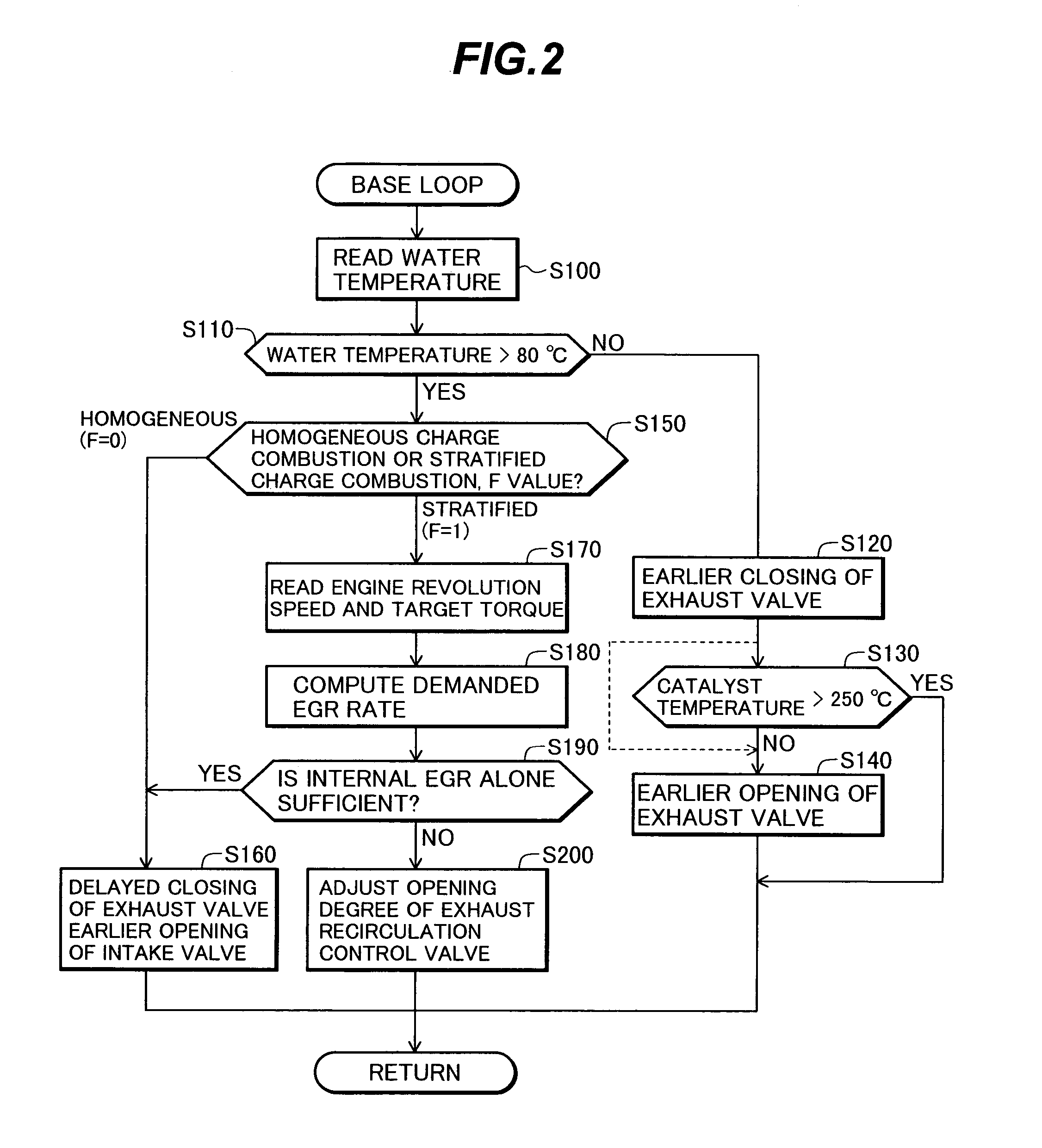
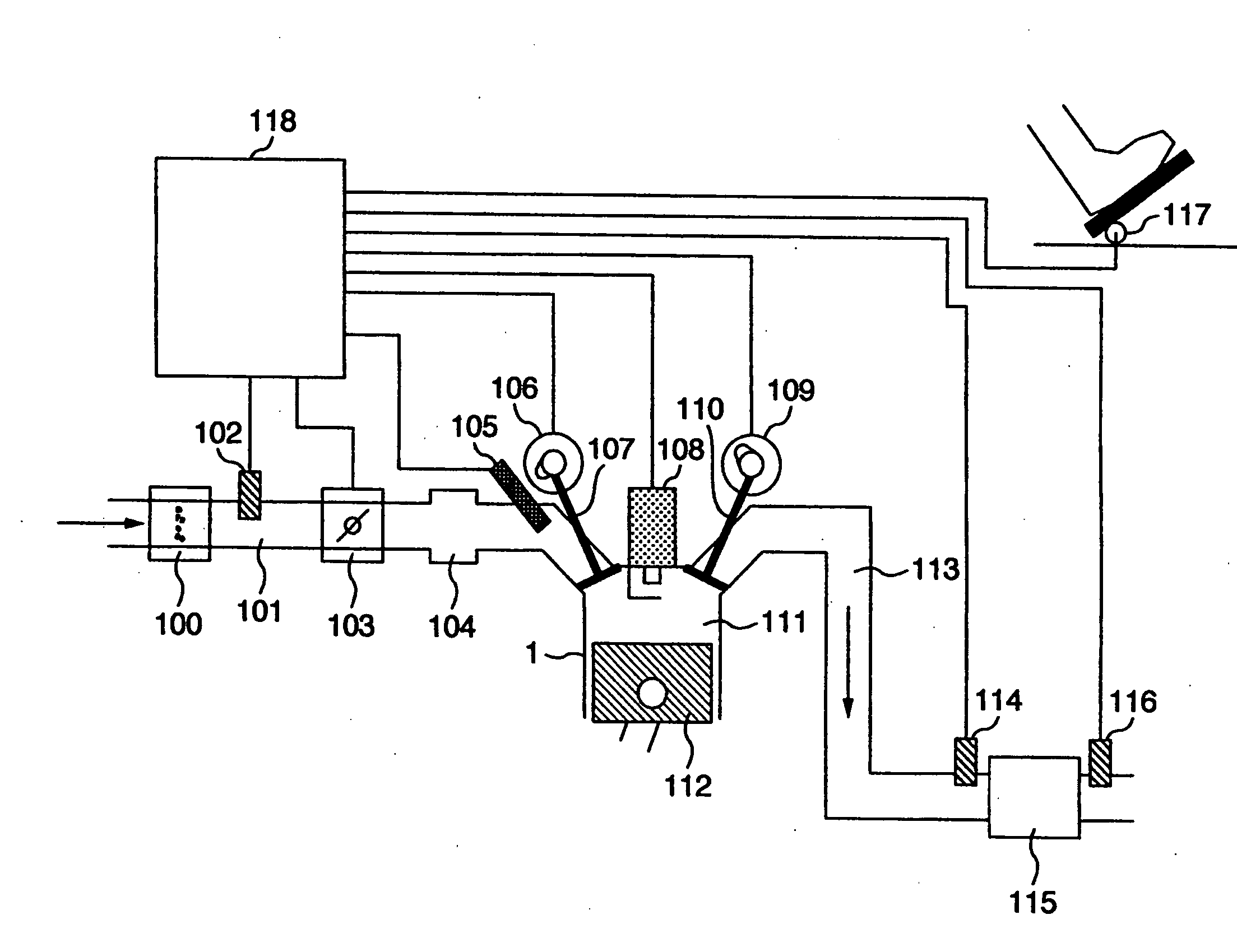
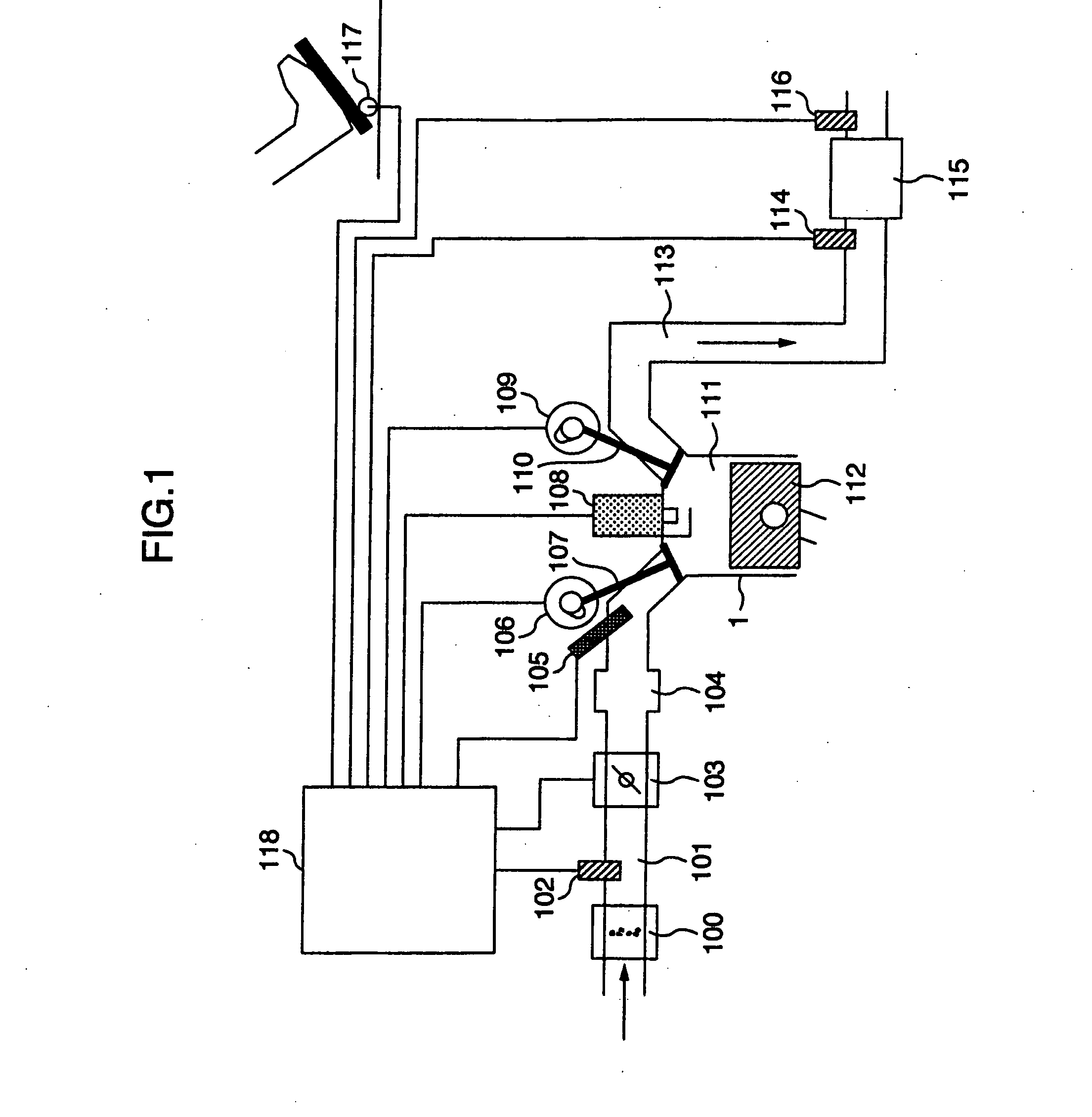
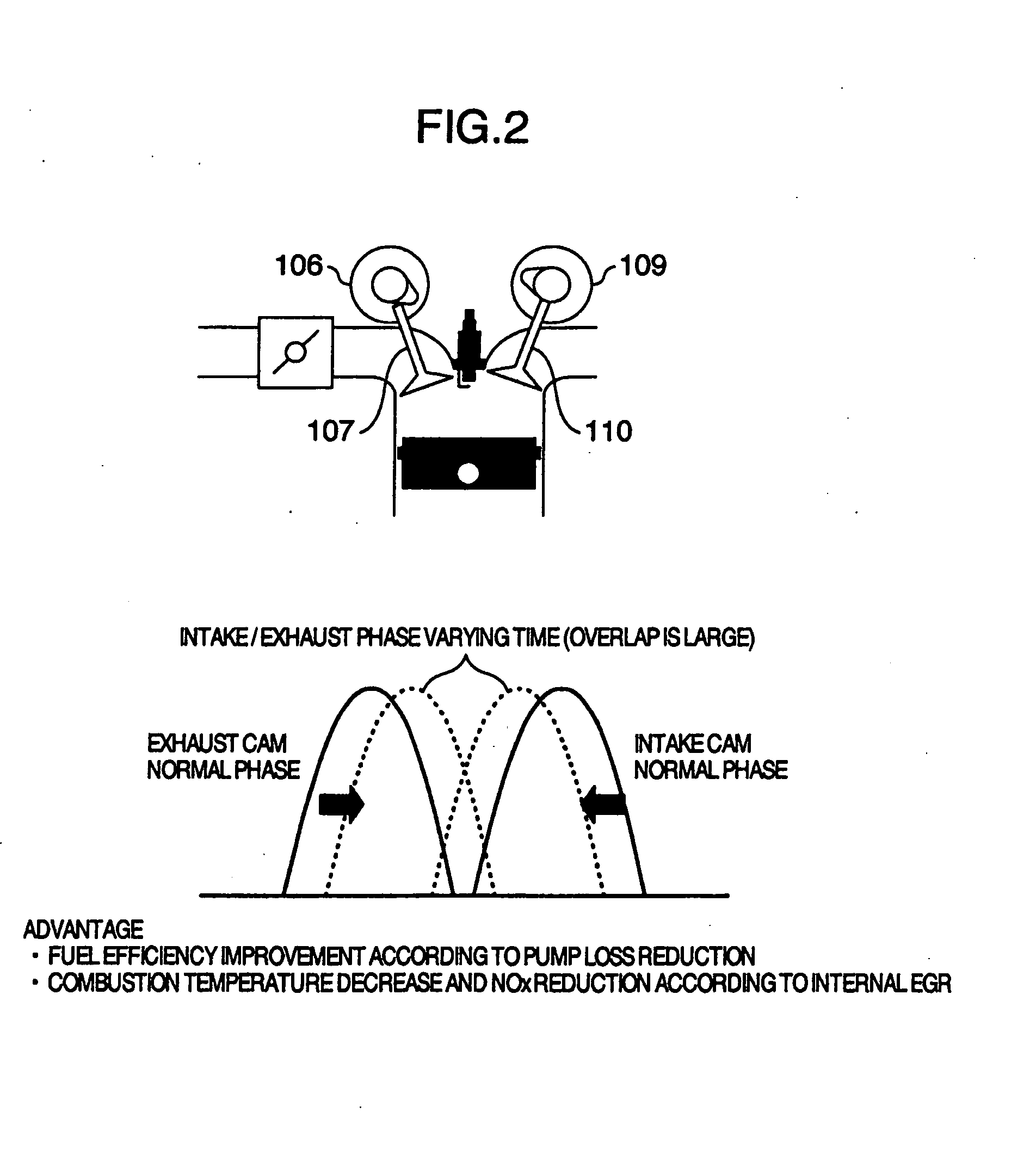
The present invention is intended to provide a control system for an direct injection internal combustion engine capable of effectively reducing the amounts of both HC and NOx exhausted from a combustion chamber during a period from the start of the engine operation to the stop of the engine operation. It comprises an external EGR passage (11) for returning a part of exhaust gas from an exhaust pipe (10) to an intake pipe (5), an external EGR control valve (12) for controlling an amount of exhaust gas returned to the external EGR passage (11), and a valve timing varying mechanism (9A, 9B) for varying timing of opening and closing at least one of an intake valve and an exhaust valve. An ECU 100 controls the valve timing varying mechanism (9A, 9B) to always return internal EGR gas in an operation region where exhaust gas recirculation is required, and controls the external EGR control valve (12) to return exhaust gas in a combination of internal EGR and external EGR when an internal EGR rate provided by the valve timing varying mechanism (9A, 9B) is not sufficient to satisfy an EGR rate demanded depending on an operation state.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Valve timing control apparatus
A vane rotor includes a vane to partition an advance chamber from a retard chamber. A valve element communicates a lock port with an exhaust port to drain a fluid from the lock port when moving in a first region including an end of a movable range in the first direction. The regulating member moves in the vane rotor in a thrust direction into a recess dented from an inner surface of the housing by being biased from a resilient member to lock the rotation phase in a regulation phase in the first region when a fluid is drained from the lock chamber. The valve element is configured to communicate an operation port with a supply port to supply a fluid into the advance chamber when being in a throttle region in the first region such that a flow of a fluid supplied to the advance chamber is throttled to be less than a flow of a fluid when the valve element is in the end of the movable range in the first direction.
Owner:DENSO CORP
System for controlling valve timing of an engine with cylinder deactivation
InactiveUS20050193988A1Improve system performanceEfficient use of fuelValve arrangementsElectrical controlSystems designControl valves
Various systems and methods are disclosed for carrying out combustion in a fuel-cut operation in some or all of the engine cylinders of a vehicle. Further, various subsystems are considered, such as fuel vapor purging, air-fuel ratio control, engine torque control, catalyst design, and exhaust system design.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Control of autoignition timing in a HCCI engine
InactiveUS7093568B2Reduces and minimizesCompensation effectElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberExhaust valve
Method and system embody a valve timing strategy to control the autoignition timing of a four stroke internal combustion engine (10) operated in an HCCI mode at different engine operating conditions such as different engine speed and torque. A particular valve timing strategy varies lift timing of the intake valve (20) relative to the exhaust valve (28), or vice versa, and relative to top dead center in response to a change in engine torque, for example, to vary amount of trapped residual burned gas in the combustion chamber (12) flowing to an intake or exhaust port (16,18) and back to the combustion chamber during which the residual gas is cooled. Control of the flow of residual gas between the combustion chamber and intake or exhaust port and thus its temperature by the valve timing strategy, in turn, is used to control the temperature of the fresh air / residual gas / fuel mixture in the combustion chamber (12) and thus autoignition timing in response to a change in engine torque.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
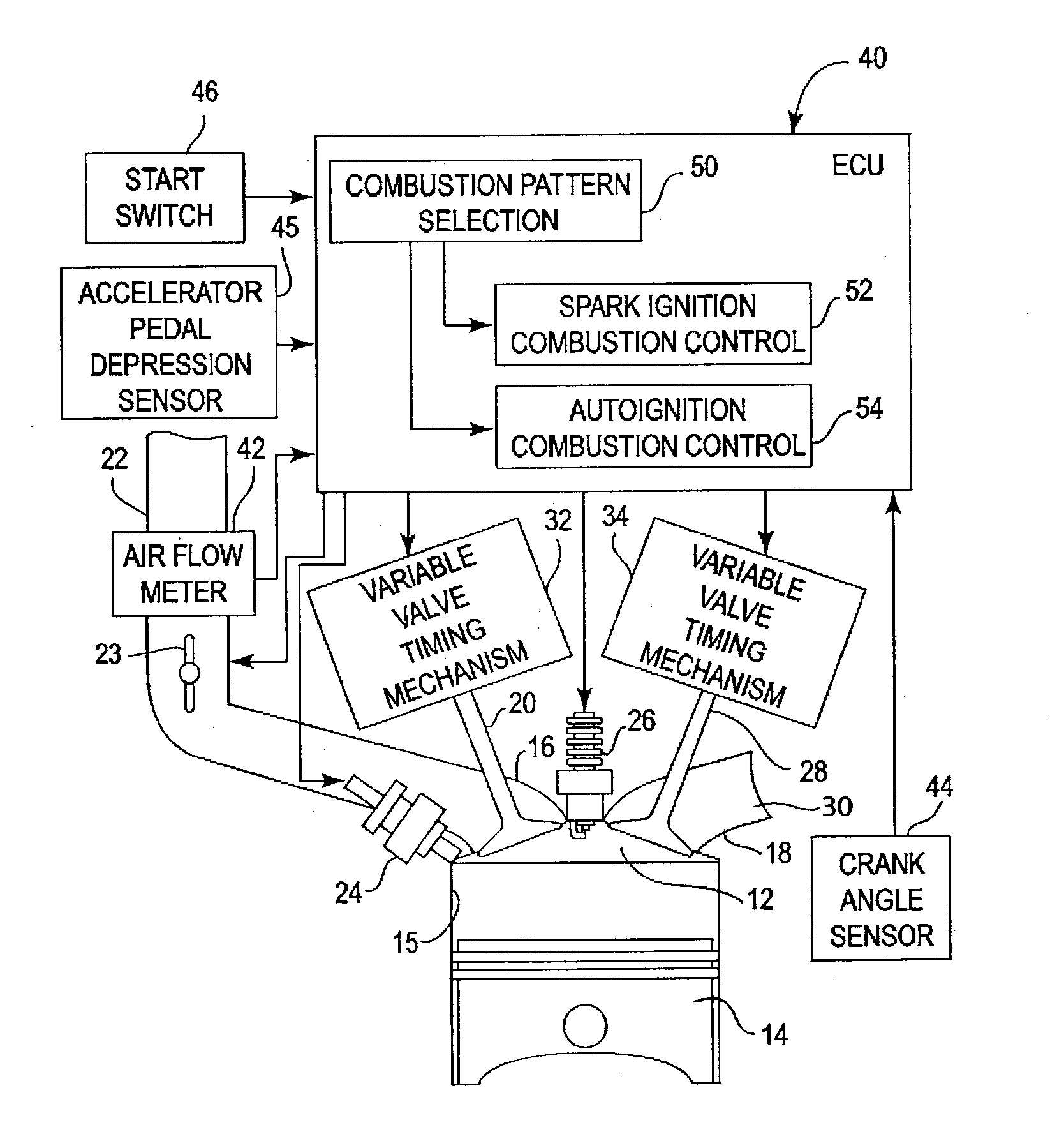
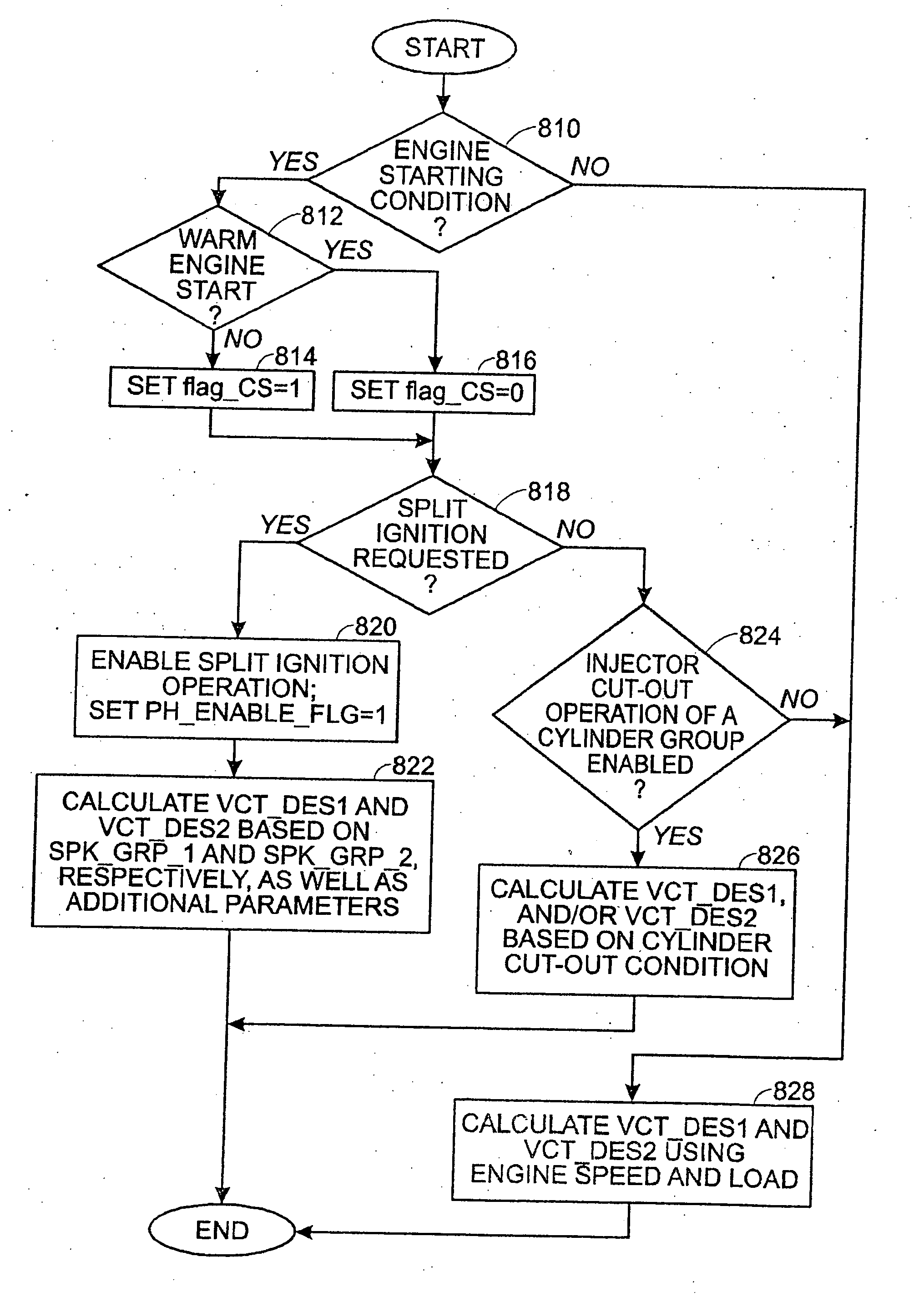
Control Method and Control Device for Engine
InactiveUS20090017987A1High-precise engine torque controlHigh precision controlElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesIgnition delayIgnition timing
In a control method and control device for an engine, in order to prevent torque control precision from deteriorating while performing an ignition retard control in a variable valve engine, when a torque down control is carried out by using the ignition retard, combustion duration is calculated in consideration of valve timing or an engine rpm for each driving state, and a characteristic of a reference ignition timing efficiency curve is corrected on the basis of a difference between the combustion duration and a combustion duration reference value which is set in advance.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Valve timing control device of internal combustion engine
InactiveUS6502537B2Small sizeAngle changes smoothlyValve arrangementsMachines/enginesEngineeringInternal combustion engine
A relative rotation angle control mechanism of a valve timing control device comprises a radial guide provided by one of drive and driven rotation members which are rotatable about a given axis. A movable control member is guided by the radial guide in a manner to move in a radial direction with respect to the given axis. A link links the movable control member to a given portion of the other of the drive and driven members. The given portion is positioned away from the given axis in a radial direction. An intermediate rotation member is rotatable about the given axis relative to both the drive and driven rotation members. A spiral guide is provided by the intermediate rotation member to guide the movement of the movable control member, so that rotation of the intermediate rotation member relative to the radial guide induces a radial movement of the movable control member. A sliding resistance reducing structure is further arranged between the movable control member and the intermediate rotation member to reduce a sliding resistance produced when the movable control member is moved.
Owner:UNISIA JECS CORP
System for variable valvetrain actuation
InactiveUS20070125329A1Simple taskReduce in quantityValve drivesMachines/enginesCylinder headGasoline
An electromechanical VVA system for controlling the poppet valves in the cylinder head of an internal combustion engine. The system varies valve lift, duration, and phasing in a dependent manner for one or more banks of engine valves. A rocker subassembly for each valve or valve pair is pivotably disposed on a control shaft between the camshaft and the roller finger follower. The control shaft may be displaced about a pivot axis outside the control shaft to change the angular relationship of the rocker subassembly to the camshaft, thus changing the valve opening, closing, and lift. A plurality of control shafts for controlling all valvetrains in an engine bank defines a control shaft assembly. The angular positions of the individual control shafts may be tuned to optimize the valve timing of each cylinder. The system is applicable to the intake and exhaust camshafts of diesel and gasoline engines.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
Engine control unit to valve control unit interface
InactiveUS20070118269A1Quick and accurate controlImprove operationAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlTelecommunications linkEngineering
A method for controlling engine torque during disruption of a primary communication link between an engine control unit and a valve control unit in an engine is provided. The method includes determining disruption of the primary communication link between the engine control unit and the valve control unit, operating a preset valve timing schedule upon determination of disruption of the communication link between the engine control unit and the valve control unit; and sending a status message from the valve control unit to the engine control unit regarding the operational status of the valve control unit.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
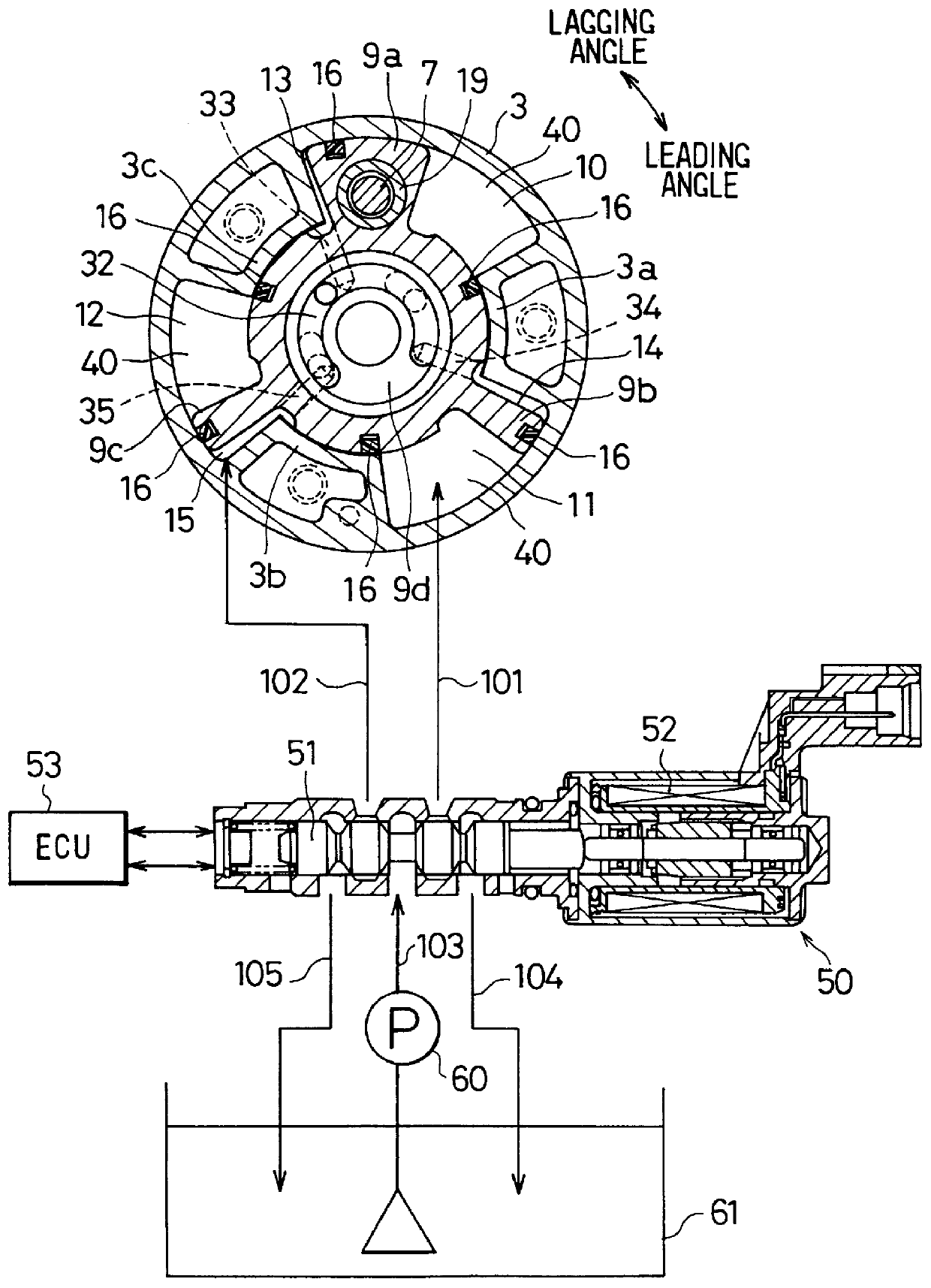
Valve timing control system for internal combustion engine
A valve timing control system includes; a rotor rotated by a crankshaft of the internal combustion engine; a camshaft rotated according to the rotation of the rotor to open and close an intake valve and an exhaust valve of the internal combustion engine; and a rotational phase controller for variably controlling a rotational phase of the camshaft relative to the rotor. The rotational phase controller is disposed between the rotor and the camshaft. The rotational phase controller includes; a clutch selectably put in one of a holding state for forbidding a relative rotation between the rotor and the camshaft in at least one of rotational directions and a releasing state for allowing the relative rotation; and a generator for generating a holding toque directing to the rotational direction forbidden by the clutch and applying the holding torque to the clutch when the clutch is put in the holding state.
Owner:UNISIA JECS CORP
Internal combustion engine shut-down for engine having adjustable valves
ActiveUS20050279323A1Reduce oxygen flowingImprove catalyst operationElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesBrake torqueInternal combustion engine
A method for operating an engine in a vehicle, the engine having at least a cylinder, is described. The method comprises decreasing rotational speed of the engine; and when said engine speed falls in a specified region, adjusting a valve timing of the cylinder to generate one of expansion or compression braking torque to stop rotation of said engine in a desired range.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Valve timing adjusting apparatus for internal combustion engines
InactiveUS6024061AEasy to manufactureHigh precisionCamsYielding couplingCombustionExternal combustion engine
A valve timing adjusting apparatus that selectively controls a restraint mechanism for restraining relative rotation between a housing member and a vane member to increase the operational life thereof. When a vane rotor is held at a most lagging angular position, an end holding mode is executed to pull out a stopper piston from a stopper hole by fluid pressures of both a leading angle side and a lagging angle side. As a result, when the vane rotor rotates from the most lagging angular position to the leading angle side, torsional forces on the stopper piston and the stopper hole can be minimized as the vane member direction of rotation changes. Since a fluid pressure has already been applied to each of leading angle fluid pressure chambers in the end holding mode, the vane rotor can be rotated from the most lagging angular position to the leading angle side quickly by increasing fluid pressure applied to each of the leading angle fluid pressure chambers without the need to switch a fluid path. In addition, since the fluid pressure applied to each of the leading angle fluid pressure chambers in the end holding mode is smaller than fluid pressure for rotating the vane rotor to the leading angle side, generation of impact sound due to collisions of vanes can be avoided.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Pneumatic valve return spring
InactiveUS6745738B1Simple installation and constructionImprove economyMachines/enginesLift valveEngineeringPneumatic valve
A valve spring device using pressurized gas for use in biasing a reciprocating valve which moves between a seated position and open position. The device features a static housing having a static chamber what is translateably engaged with dynamic housing. Chambers inside both housings are sealably engaged such that the dynamic housing translates away from the static housing when pressurized gas is communicated to the engaged sealed chambers thereby biasing the dynamic housing away from the static housing and moving the attached valve. Timing of oscillation of the translation and resulting valve timing is controlled by a controller activating a control valve between a pressurizing state and a venting state. The timing may be adjusted to accommodate the engine timing through varying the controller's activation of the control valve and optionally varying the pressure of the gas using a regulator.
Owner:BOSSCHER RICHARD J
Increased engine braking with adjustable intake valve timing
ActiveUS6951198B1Increase pressureImprove engine fuel economyElectrical controlOutput powerExhaust valveInlet valve
A system and method for operating at least an intake and exhaust valve in a cylinder with a piston of an engine in a vehicle are described. In one aspect, the method comprises maintaining at least the exhaust valve in a closed position during a period of net engine torque less than zero. Further, during said period of net engine torque less than zero, operating with at least the intake valve open, then closing the intake valve, and then opening the intake valve.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Automotive four-cycle engine
InactiveUS20020166536A1Improve engine performanceRaise the combustion temperatureValve arrangementsElectrical controlExhaust valveTop dead center
A four-cycle engine is provided with valve timing adjusters for adjusting opening and closing timing an and an exhaust valve. In medium- to high-speed ranges in medium- to high-load regions of the engine, a closing point (ExC) of the exhaust valve defined as a point of transfer from an acceleration portion to a constant speed portion on its valve lift characteristics curve is set to a point a specific period before an intake top dead center, and an opening point (InO) of the intake valve defined as a point of transfer from a constant speed portion to an acceleration portion on its valve lift characteristics curve is set to a point after the intake top dead center. In addition, the period from the closing point (ExC) of the exhaust valve to the opening point (InO) of the intake valve is made longer in the medium-speed range than in the high-speed range in the medium- to high-load regions of the engine.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
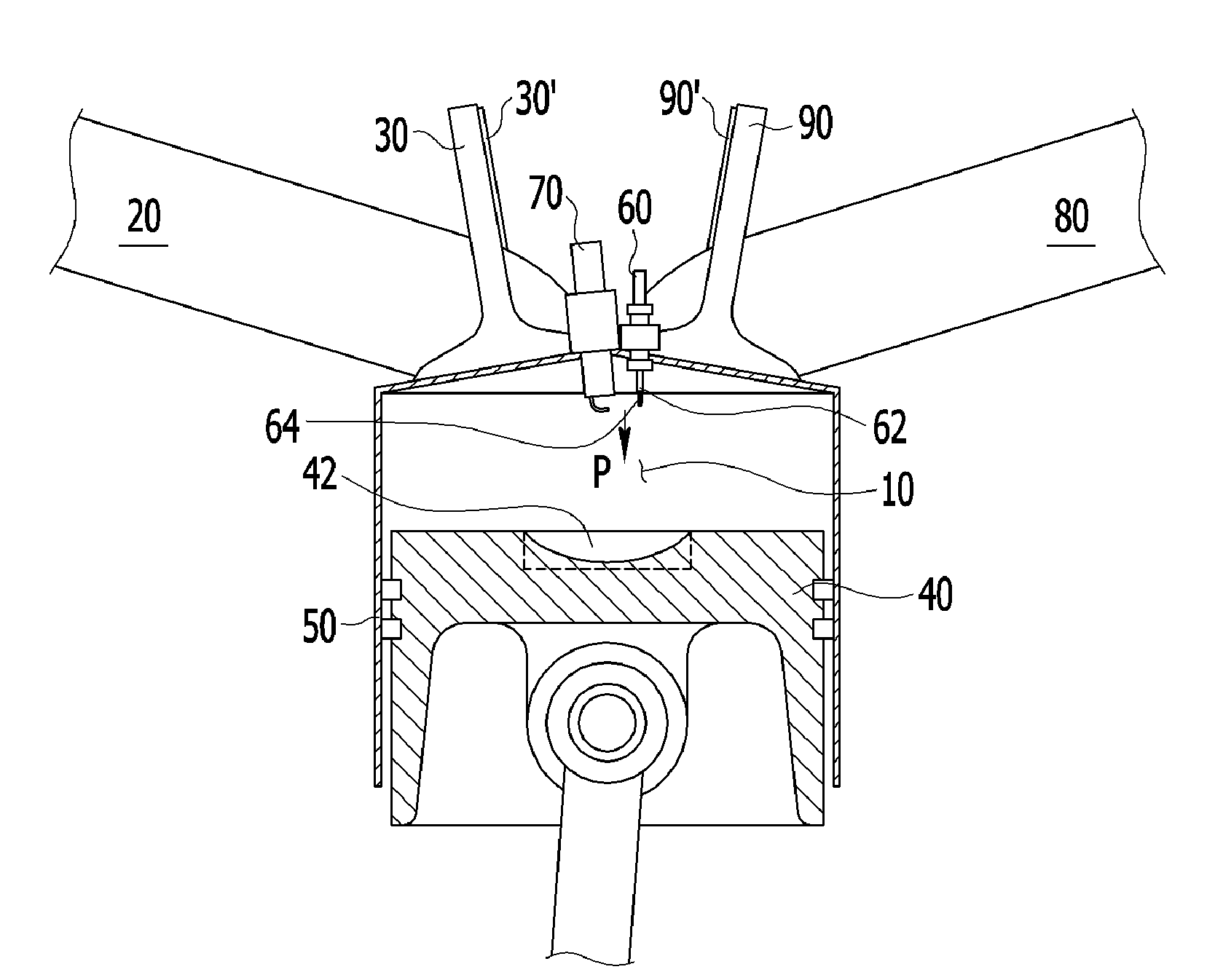
Compression ignition gasoline engine
ActiveUS20110108001A1Suppress excessive self-ignitionRapid increase of combustion noiseValve arrangementsElectrical controlCombustion chamberExhaust valve
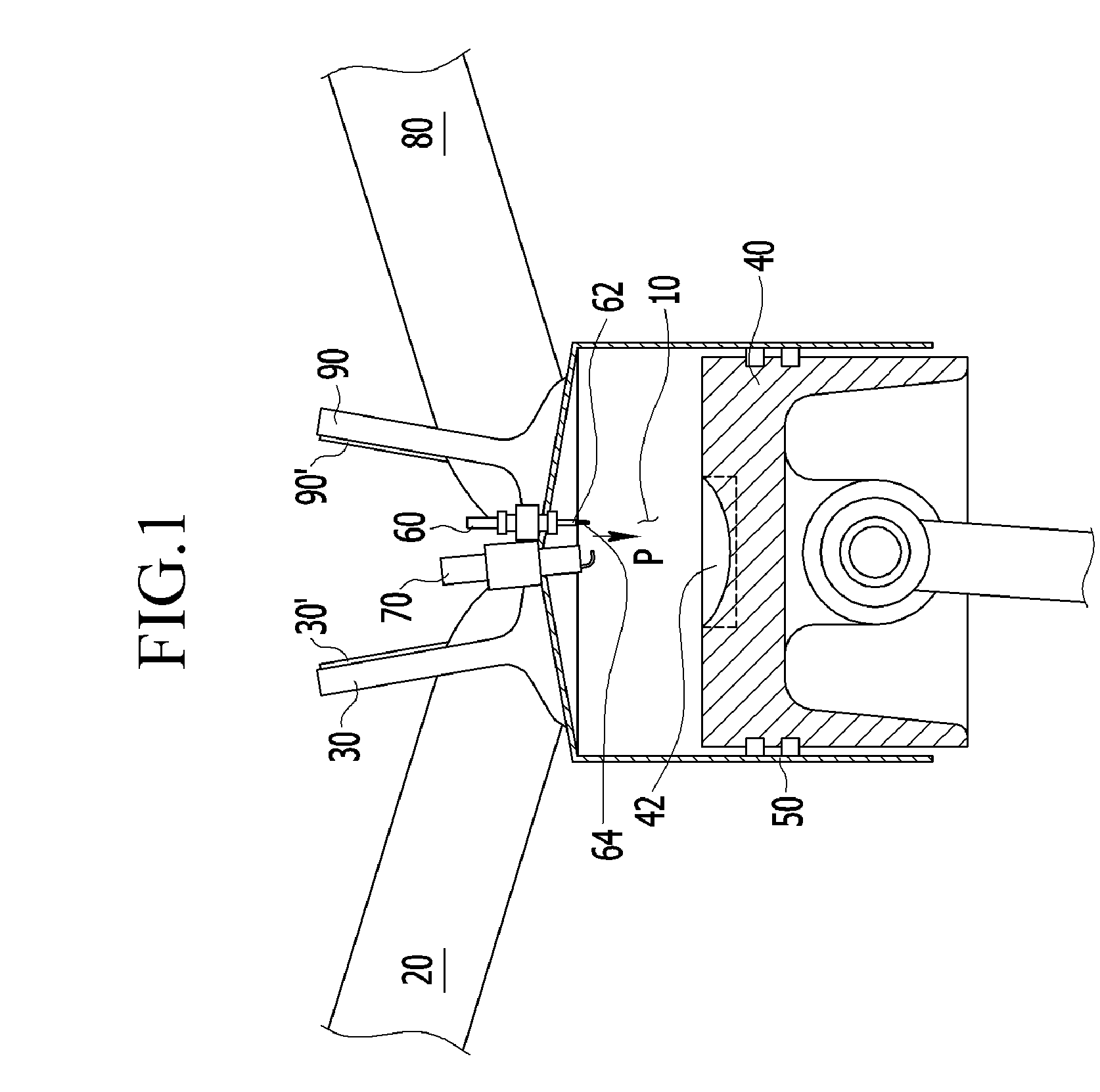
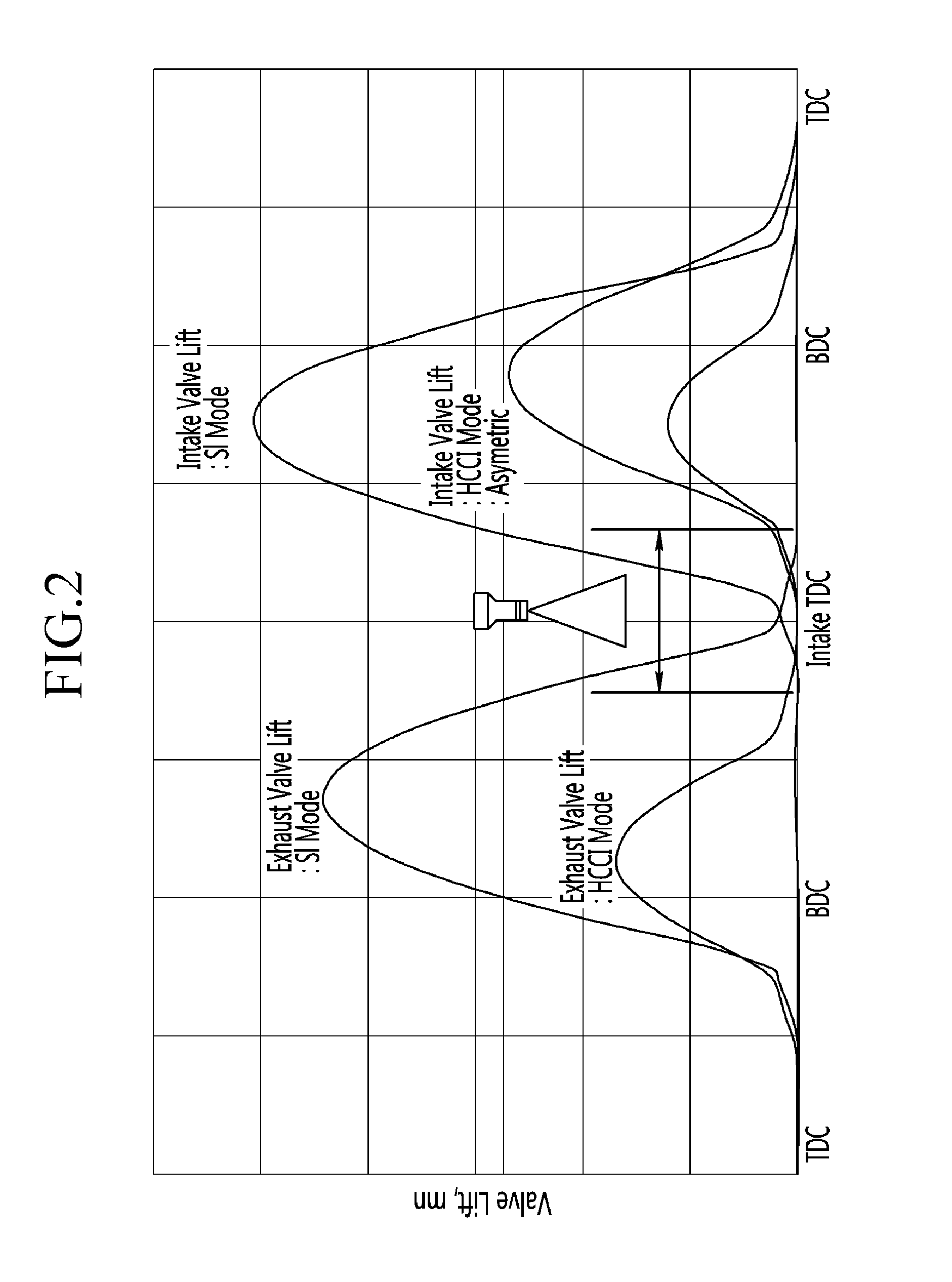
A compression ignition gasoline engine uses low-cetane number fuel, such as gasoline. The engine includes a combustion control device having an injector directly injecting fuel into a combustion chamber, intake and exhaust valves, and a variable valve device changing a valve timing, in which the compression ignition gasoline engine includes: at least two intake valves and two exhaust valves; a spark plug positioned at the center portion of the combustion chamber; and an injector positioned adjacent to the spark plug toward the center portion of the combustion chamber, in which the exhaust valve is a symmetric valve lift in which the lift and the opening section of the tow exhaust valves are the same in low lift, and the intake valve is an asymmetric valve lift in which the lift and the opening of the two intake valves are different in the low lift.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com