Patents
Literature
516 results about "Residual pressure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Residual Pressure. Residual Pressure is a term used in AS 2419.1 and refers to the pressure remaining in a pipe during flow conditions. It is often referred to during water supply adequacy testing for fire fighting flow.
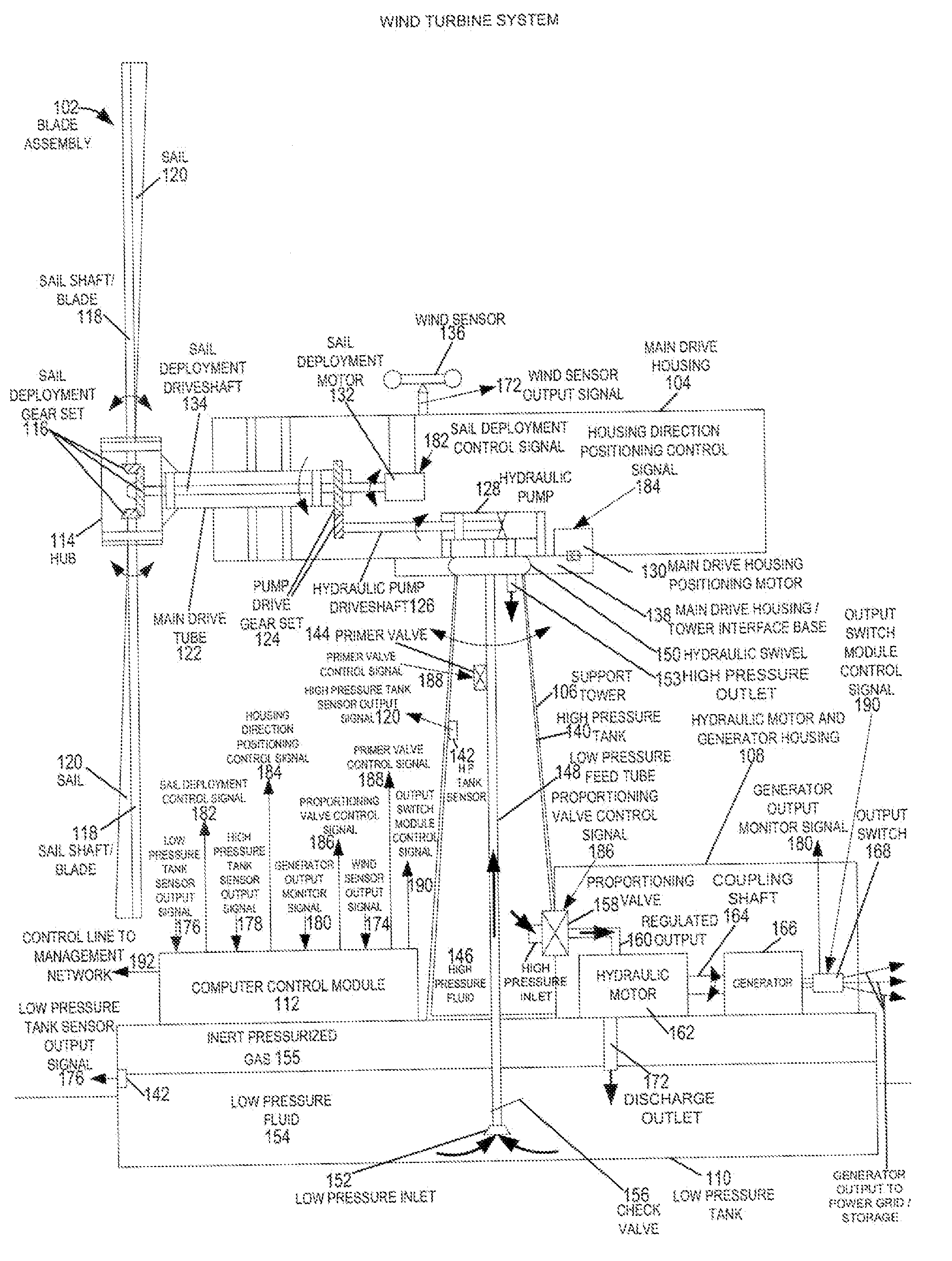
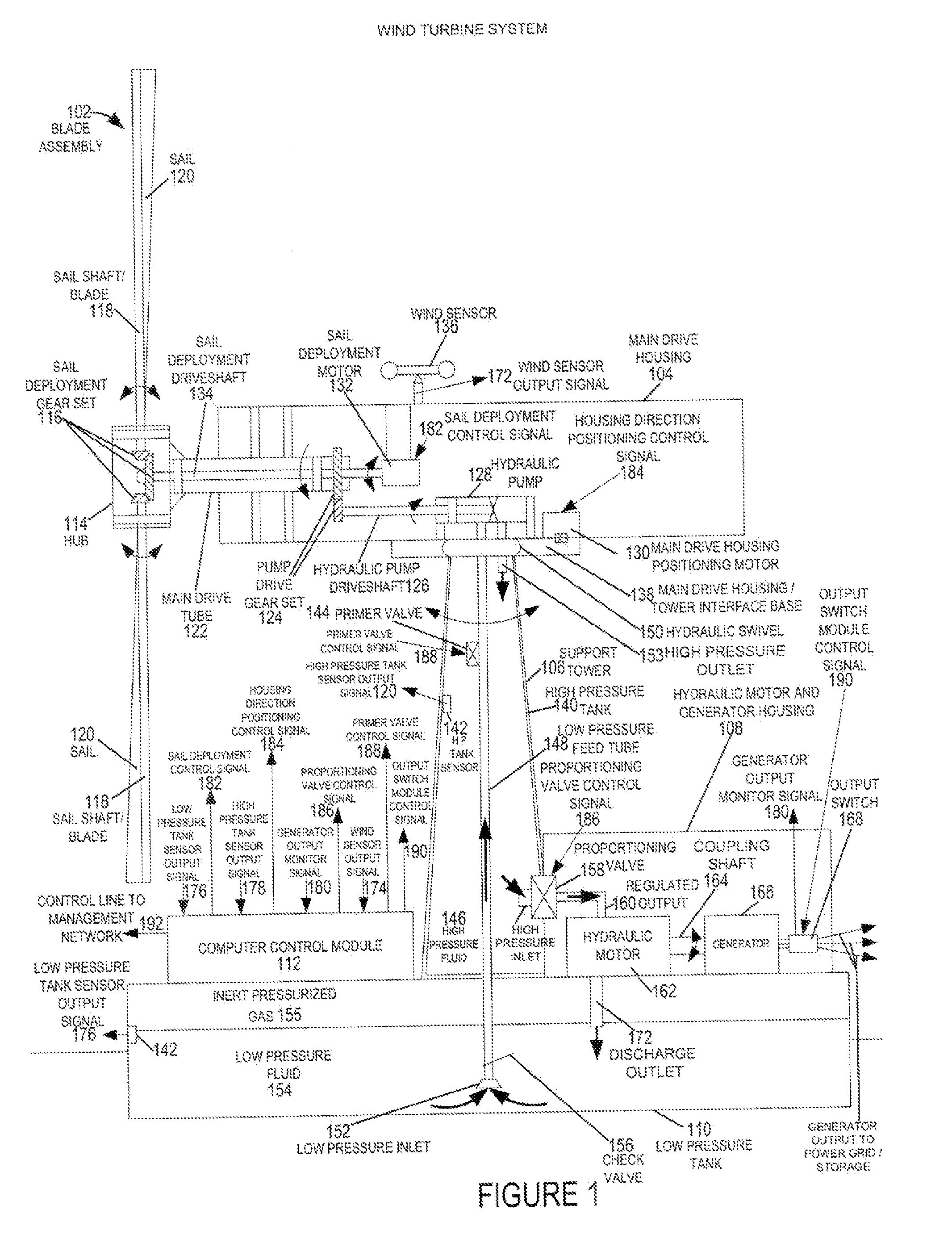
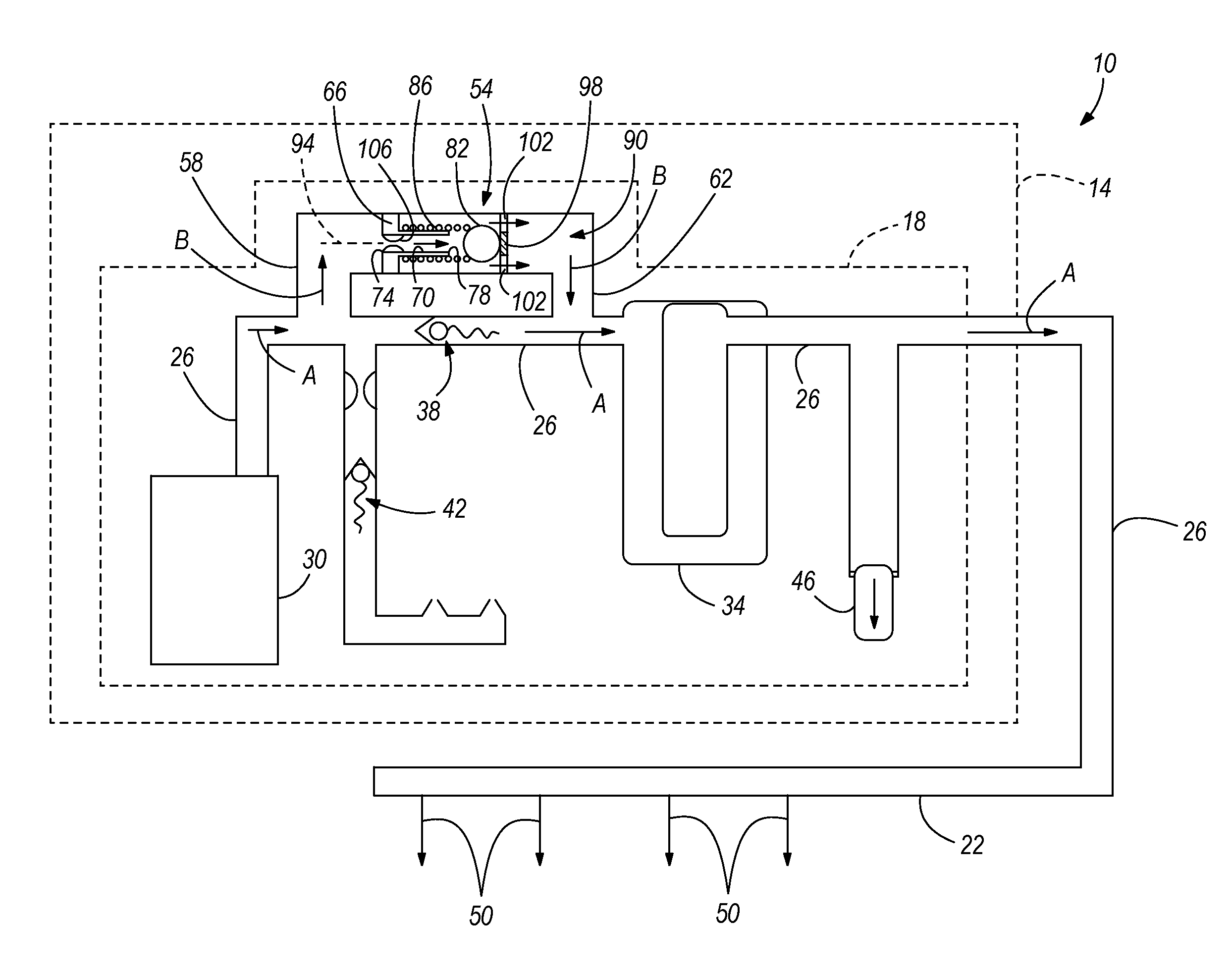
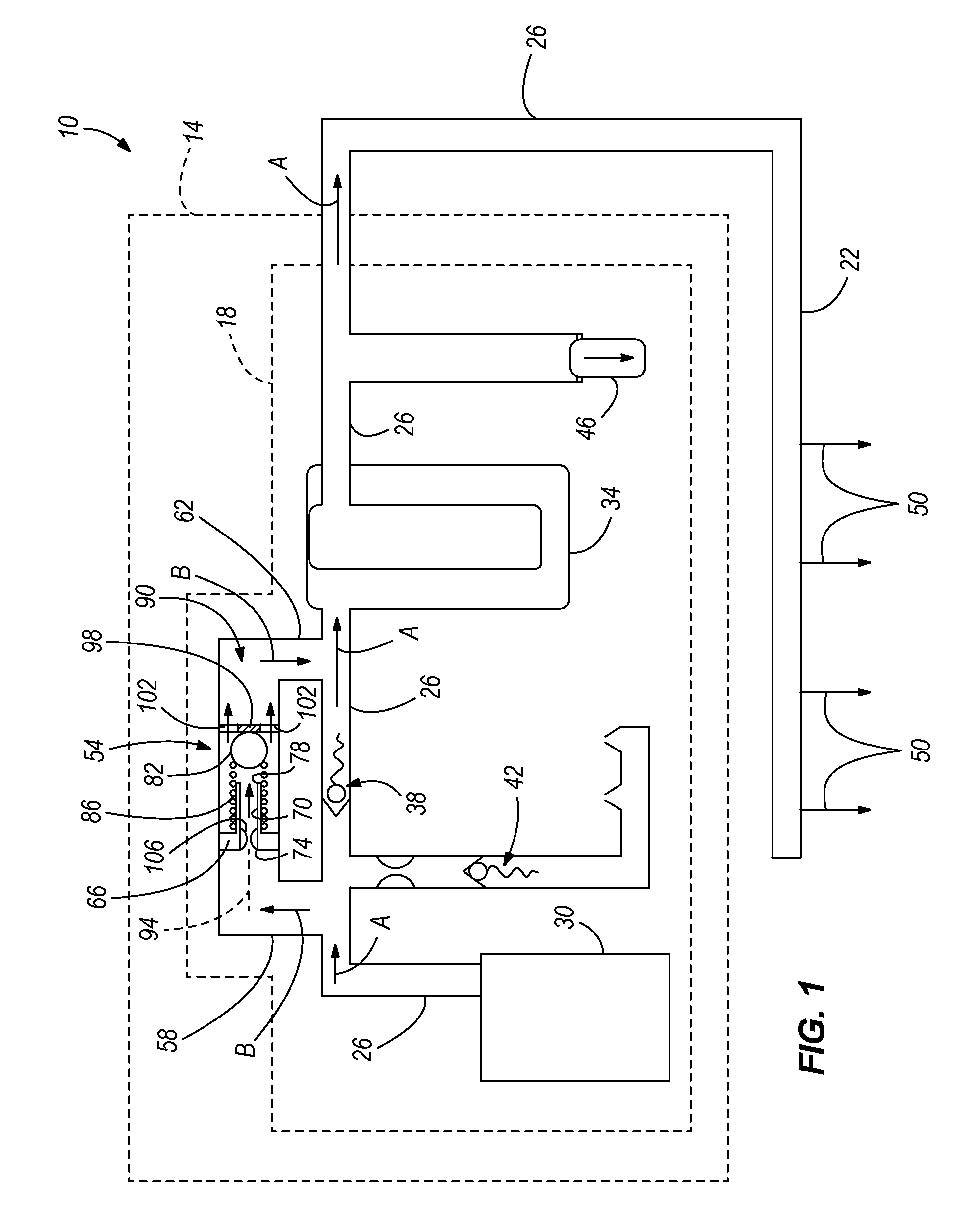
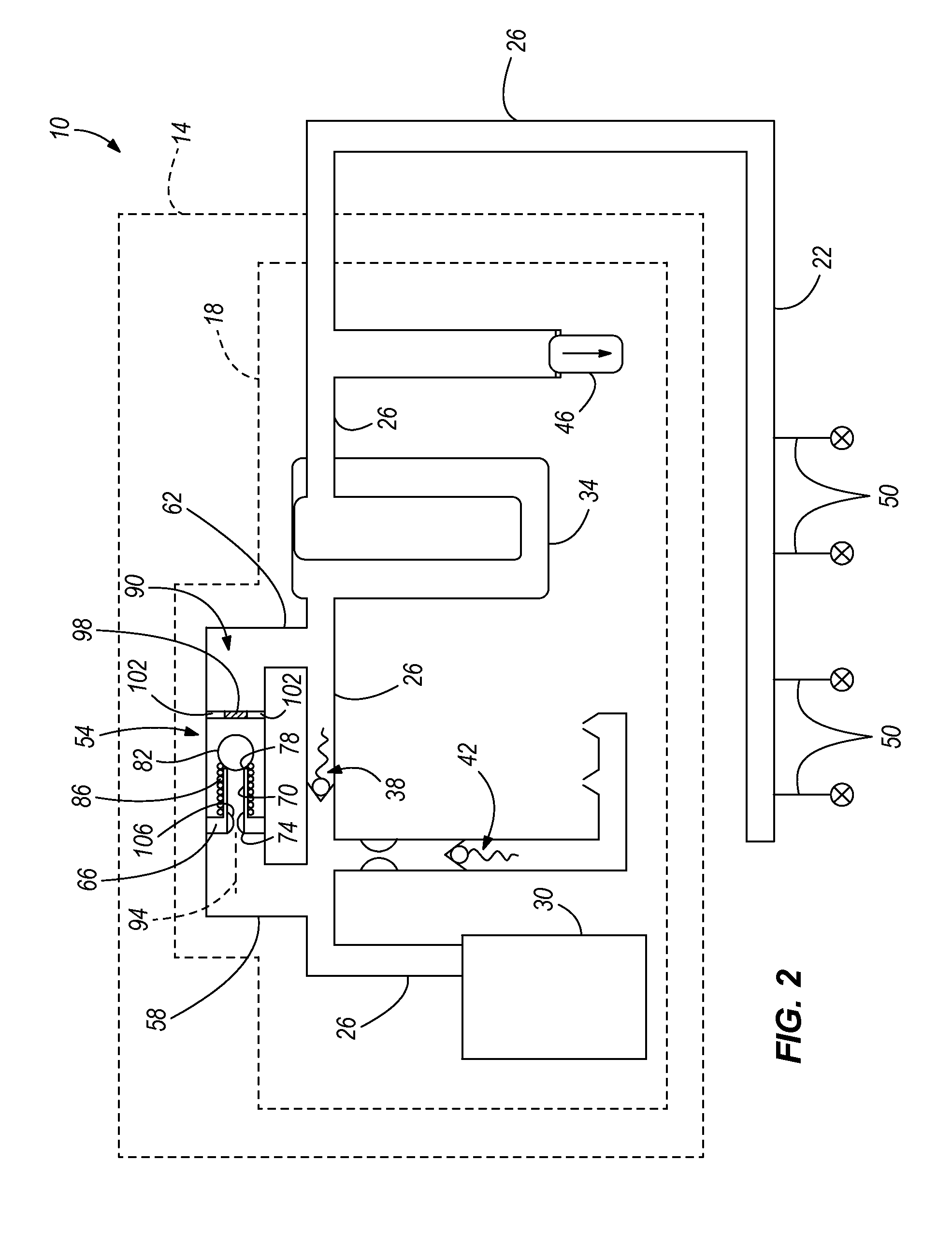
Methods and apparatus for advanced wind turbine design
ActiveUS20070024058A1Eliminate needReduced pressure levelWind motor controlEngine fuctionsHigh energyHydraulic pump
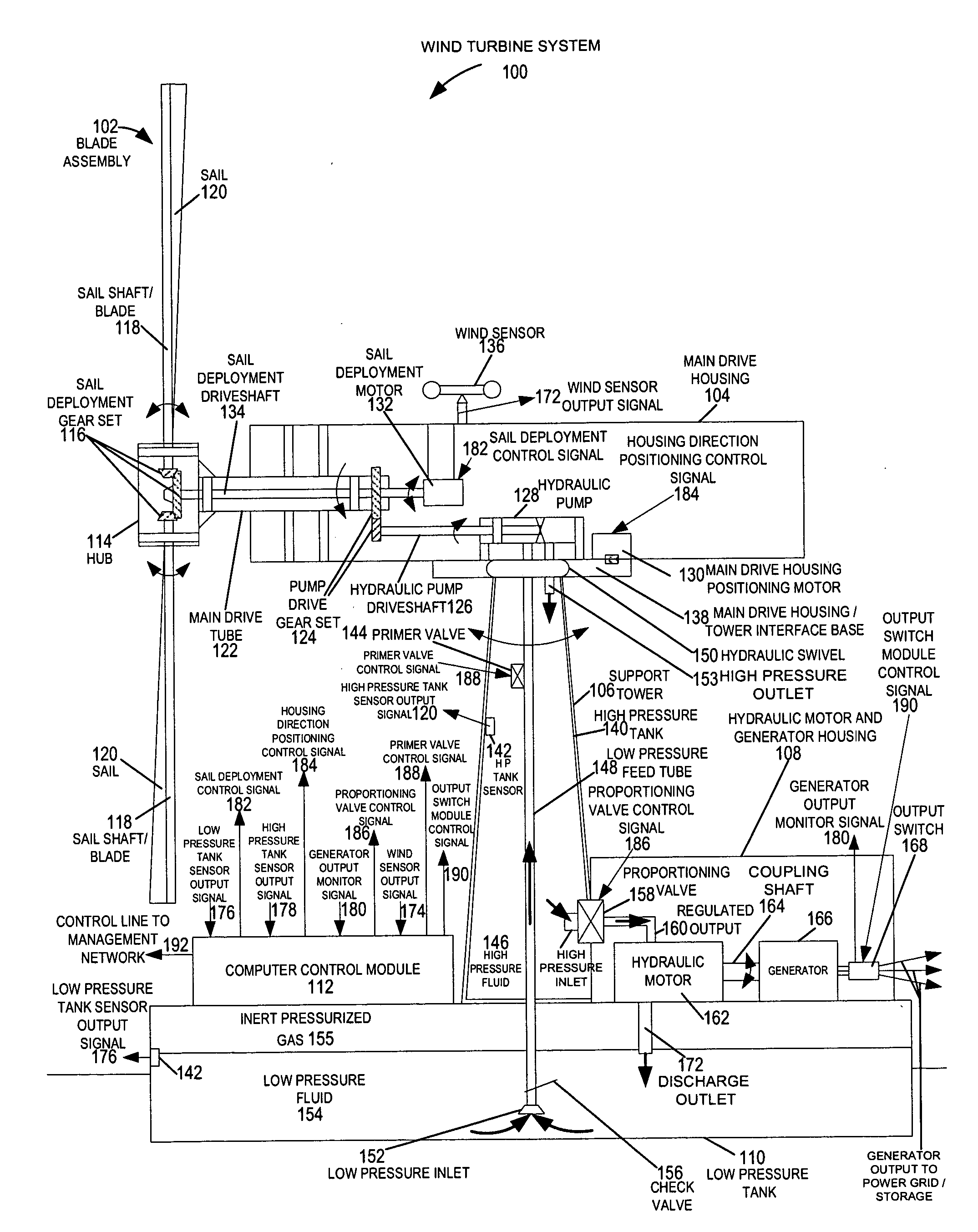
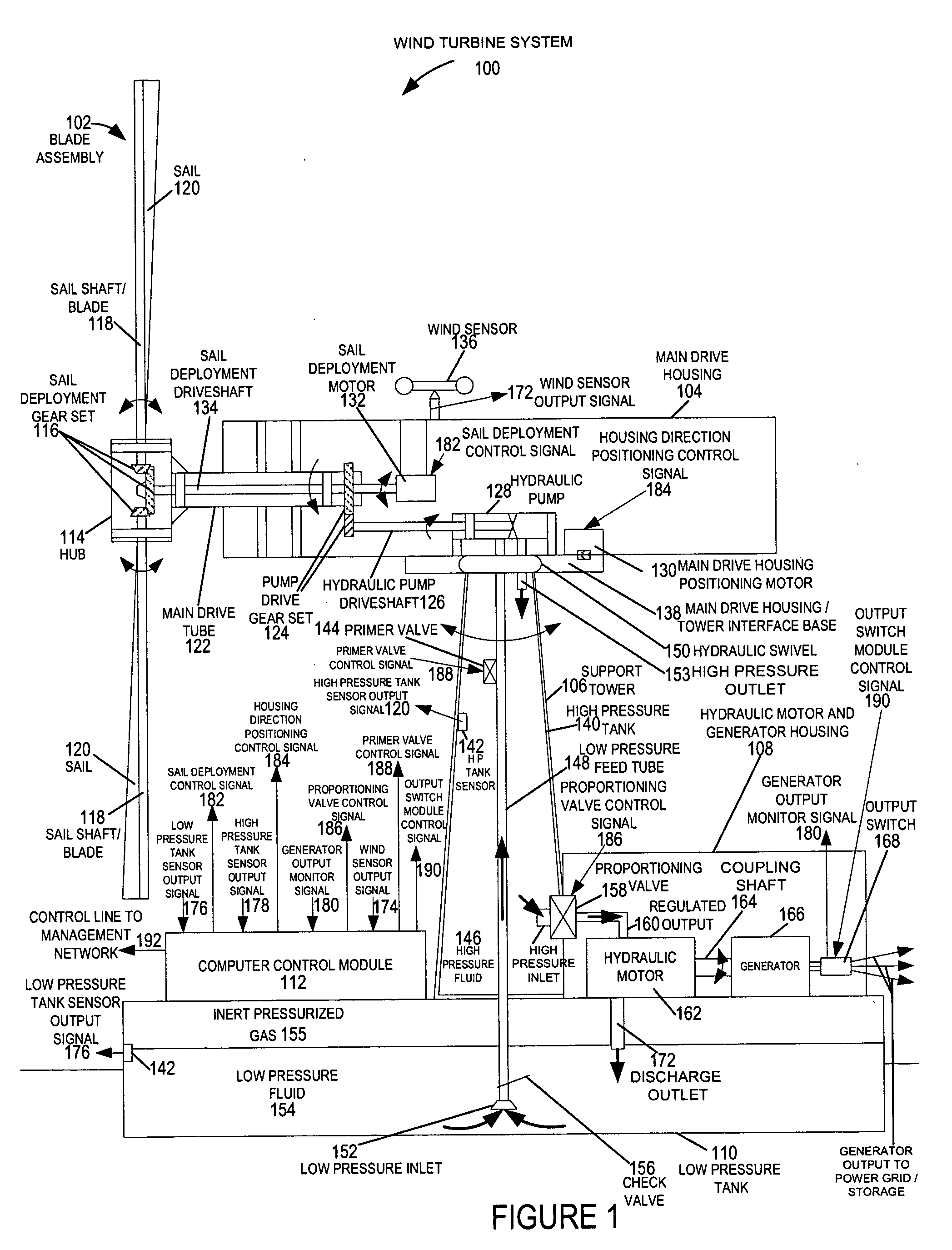
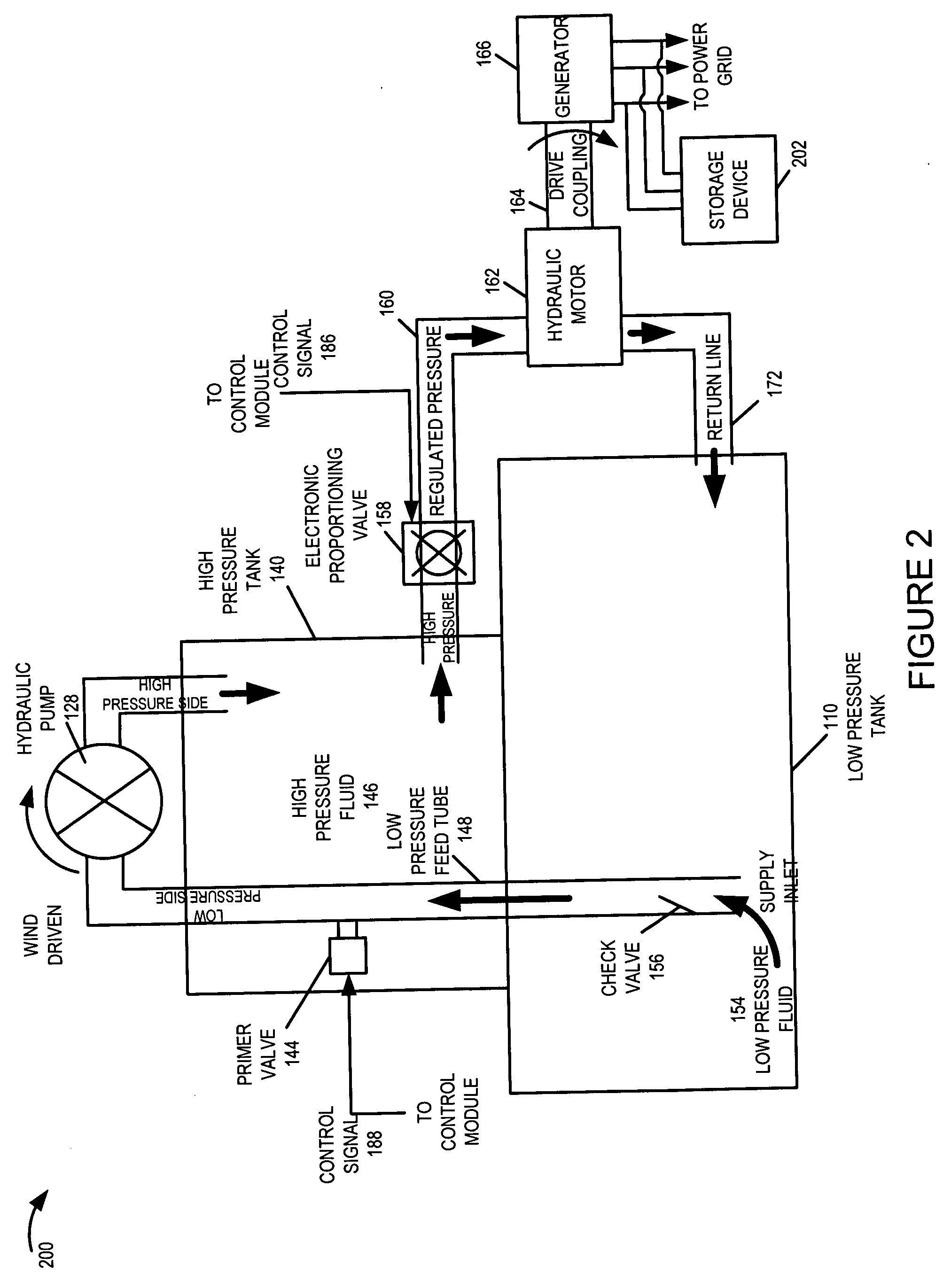
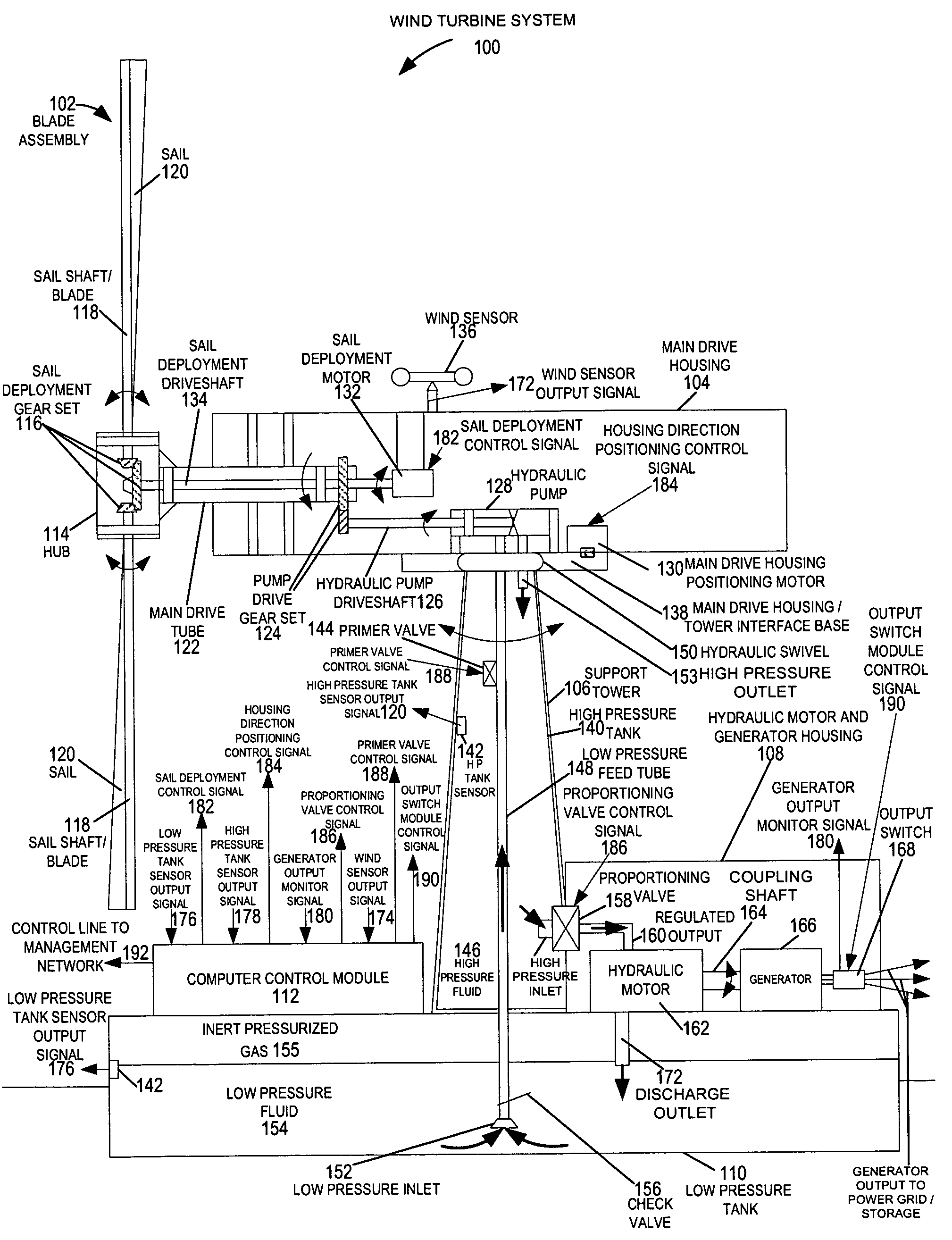
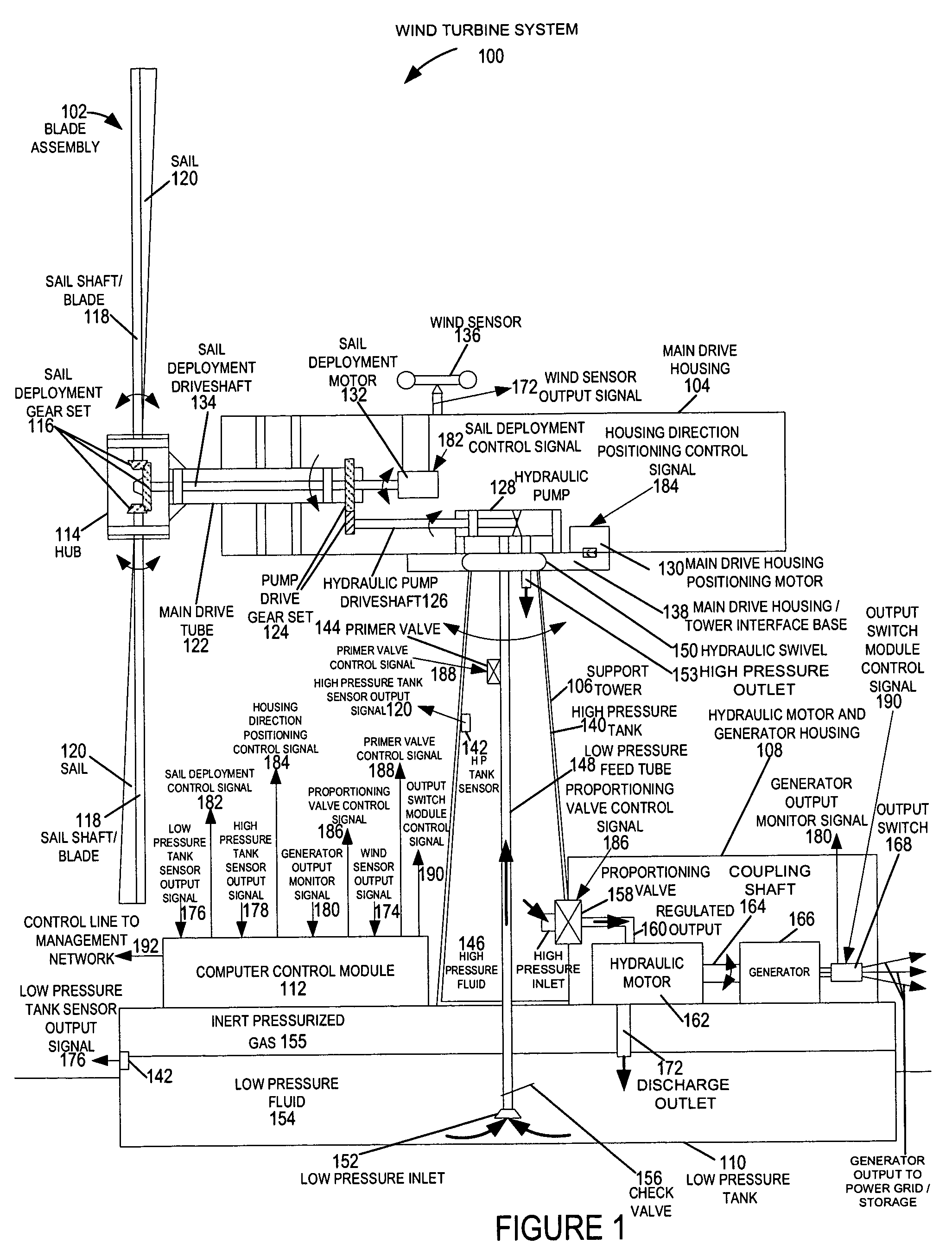
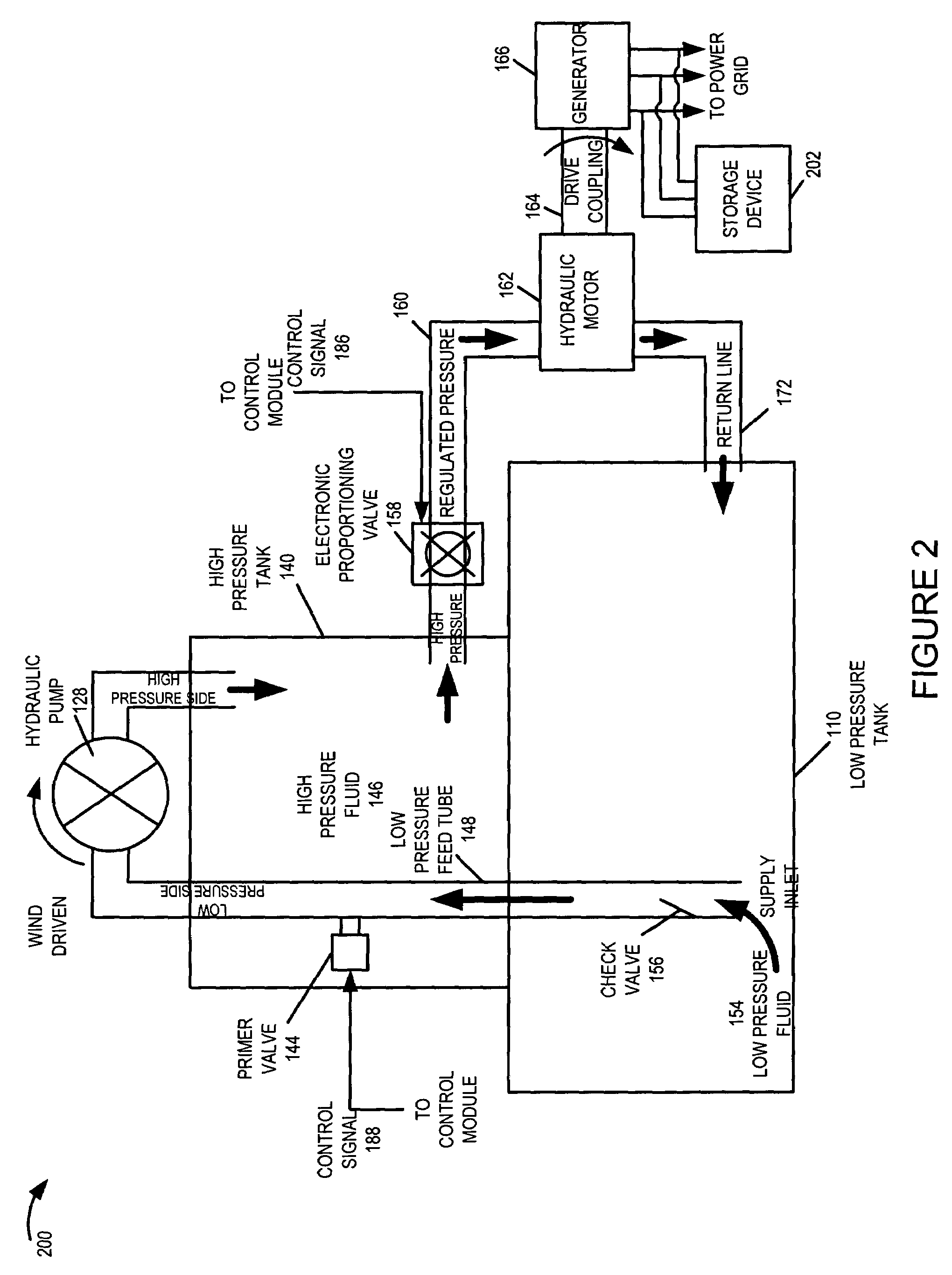
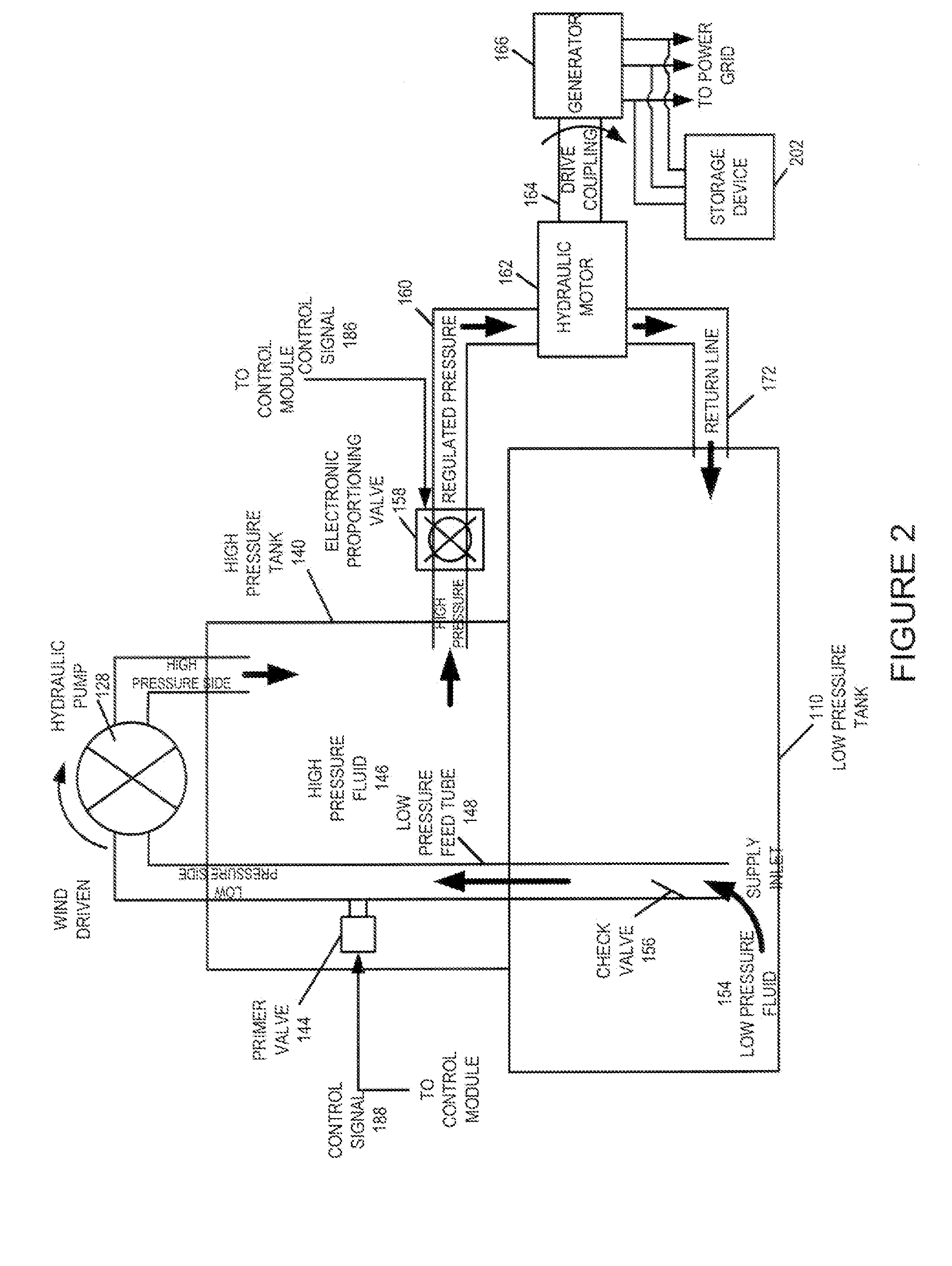
A wind turbine system includes a variable blade assembly including adjustable sails and wing shaped masts expanding the wind velocity capture envelope. The blade assembly turns a hydraulic pump, which pressurizes fluid and stores the pressurized fluid in a chamber in the support tower. Pressurized fluid is directed via an electronically controllable proportioning valve to a hydraulic motor which is coupled to an electric generator. A computer control module operates the proportioning valve regulating pressure to the hydraulic motor, maintaining generator rotational speed, and providing consistent output frequency to the power grid. Stored energy in the high pressure tank is used to continue generator operation after the winds cease, allowing early warning notification to the power management system of impending power loss. Residual pressure maintained in the high pressure tank allows restart operations via hydraulic pressure rather than power grid energy drain. On site high energy capacitors store additional energy.
Owner:MCCLINTIC FRANK
Methods and apparatus for advanced wind turbine design
ActiveUS7183664B2Eliminate needReduce pressureWind motor controlEngine fuctionsHigh energyHydraulic pump
A wind turbine system includes a variable blade assembly including adjustable sails and wing shaped masts expanding the wind velocity capture envelope. The blade assembly turns a hydraulic pump, which pressurizes fluid and stores the pressurized fluid in a chamber in the support tower. Pressurized fluid is directed via an electronically controllable proportioning valve to a hydraulic motor which is coupled to an electric generator. A computer control module operates the proportioning valve regulating pressure to the hydraulic motor, maintaining generator rotational speed, and providing consistent output frequency to the power grid. Stored energy in the high pressure tank is used to continue generator operation after the winds cease, allowing early warning notification to the power management system of impending power loss. Residual pressure maintained in the high pressure tank allows restart operations via hydraulic pressure rather than power grid energy drain. On site high energy capacitors store additional energy.
Owner:MCCLINTIC FRANK
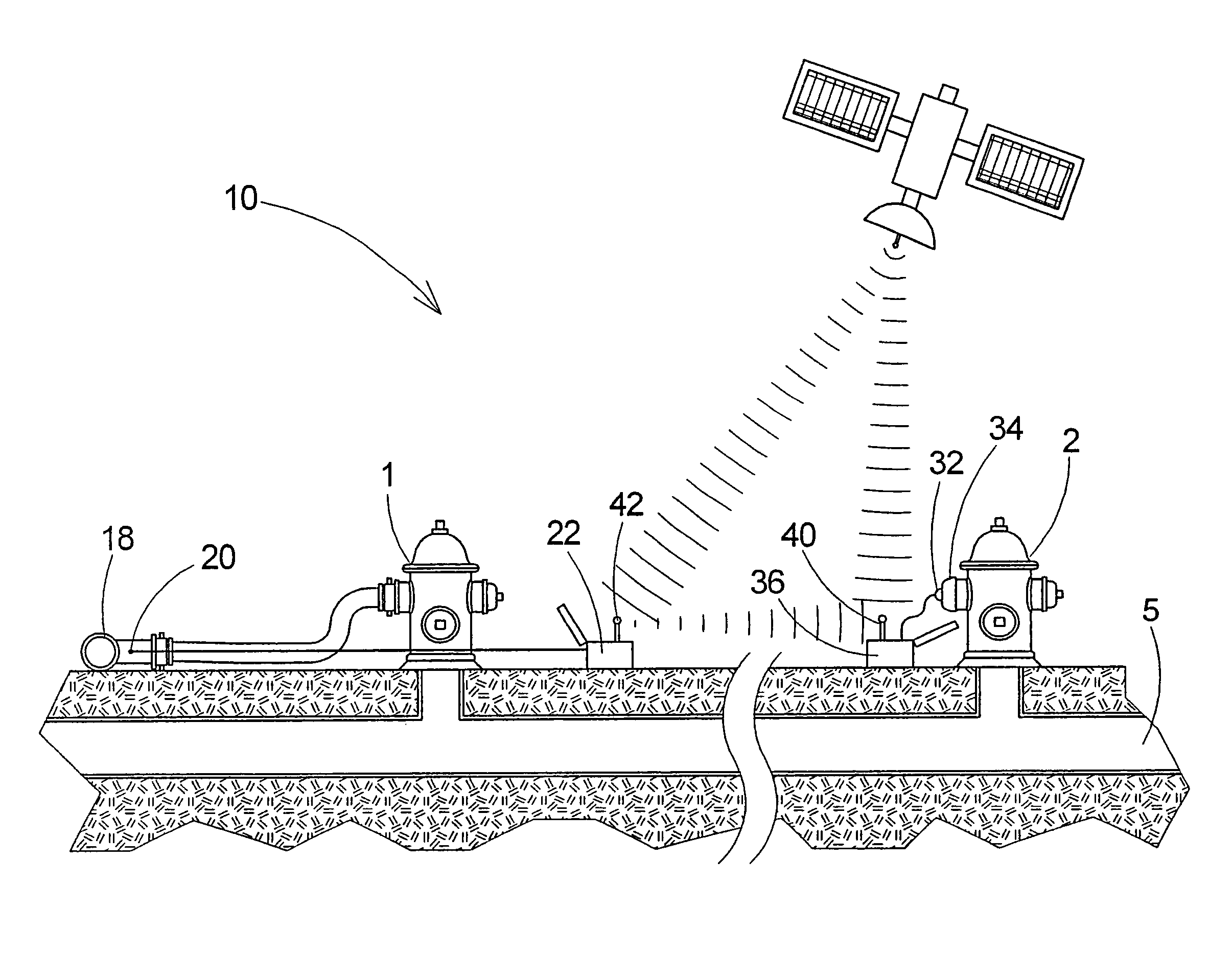
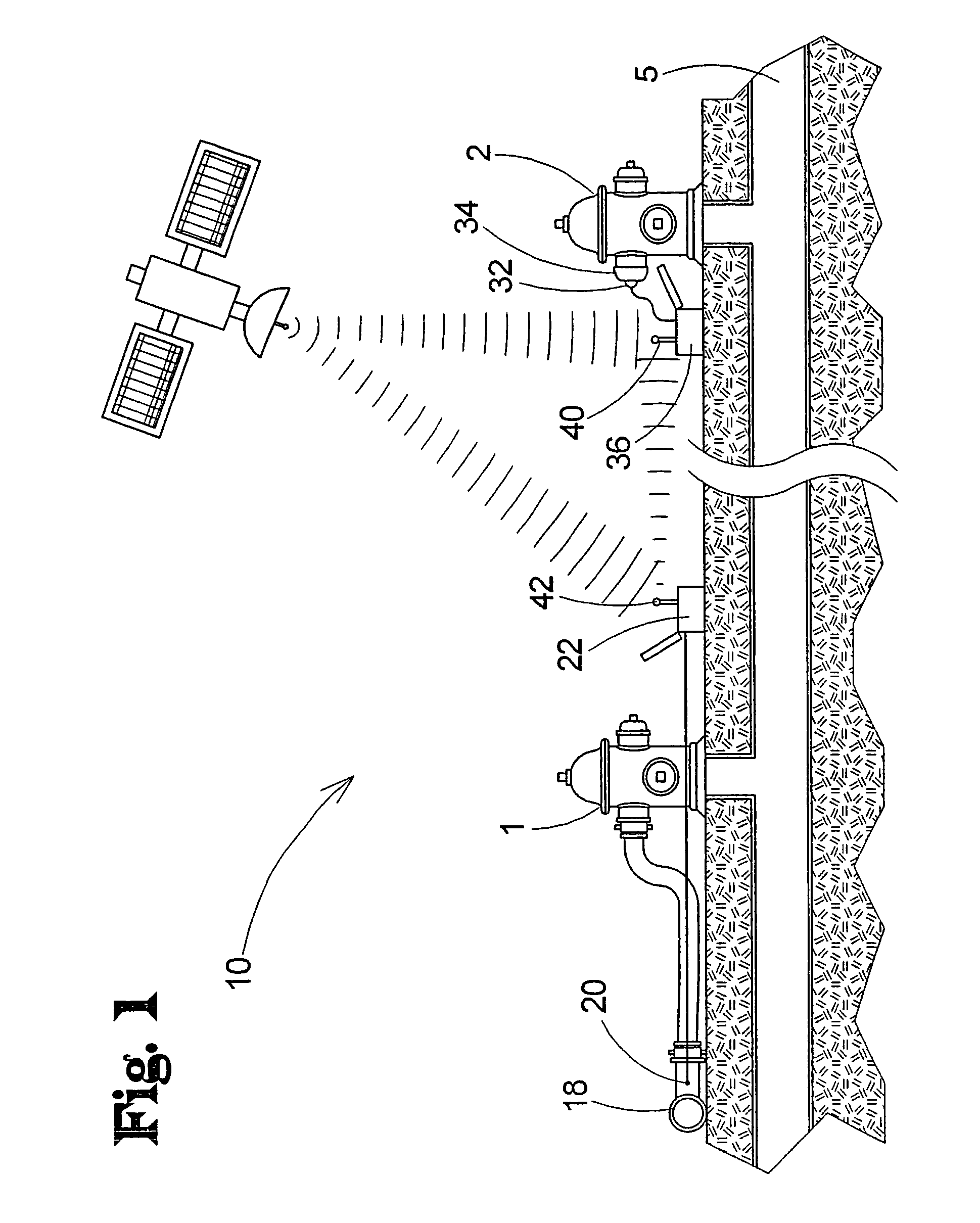
Flow testing system for fluid networks
ActiveUS20080281534A1Way accurateEasy to useVehicle testingAerodynamic testingEngineeringData transmission
An apparatus, system, method and kit for testing fluid flow and pressure is provided. The apparatus, system, method and kit include or include the use of a flow unit which is configured to measure flow rate and / or flow velocity when interfaced with a flow valve or hydrant and a pressure unit configured to measure at least residual pressure when interfaced with a test valve or hydrant. At least one of the units is configured to wirelessly send data transmissions to the other unit which is configured to receive such transmissions.
Owner:HURCO TECH
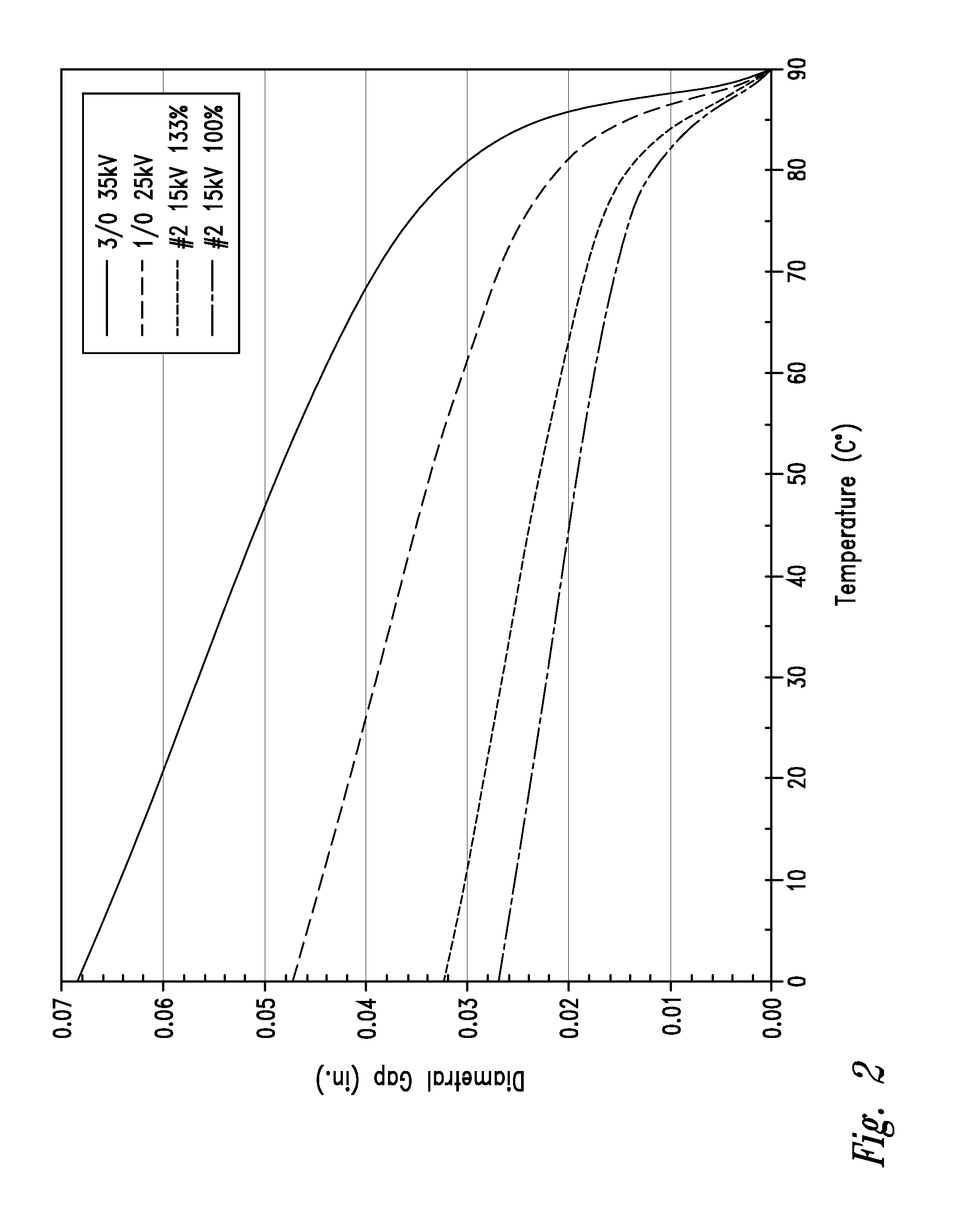
Method for treating electrical cable at sustained elevated pressure
ActiveUS20100095521A1Effective treatmentExcellent dielectric propertiesClimate change adaptationPower cables with screens/conductive layersElectrical conductorPolymer insulation
A method for enhancing the dielectric properties of an electrical cable segment having a central stranded conductor encased in a polymeric insulation jacket and an interstitial void volume in the region of the conductor, including filling the interstitial void volume with a dielectric property-enhancing fluid at a pressure below the elastic limit of the polymeric insulation jacket, and confining the fluid within the interstitial void volume at a residual pressure greater than about 50 psig, with the pressure being imposed along the entire length of the segment but below the elastic limit of the polymeric insulation jacket. Preferably, the residual pressure is sufficient to expand the interstitial void volume along the entire length of the cable segment by at least 5%.
Owner:NOVINIUM LLC
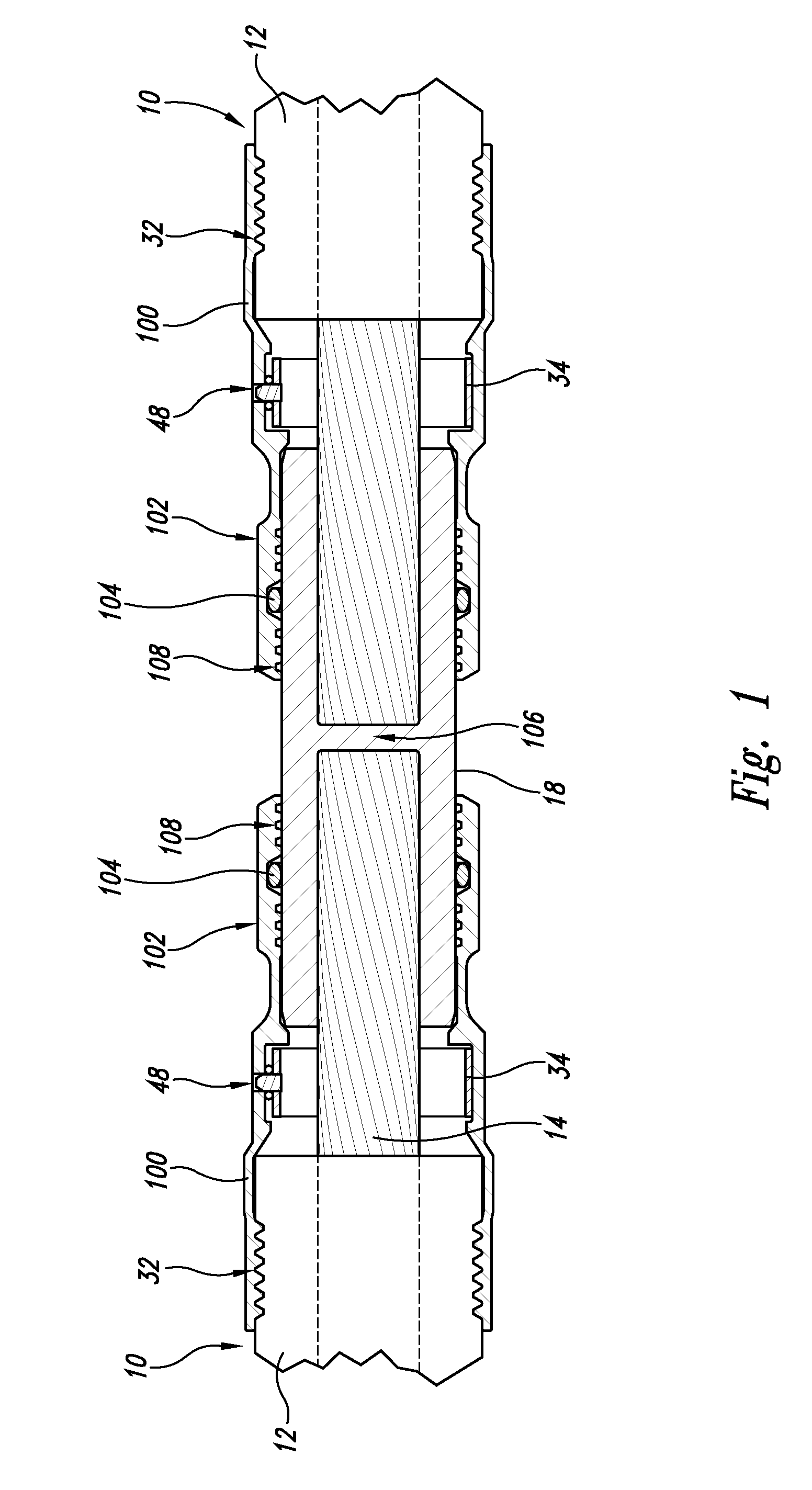
High-pressure power cable connector
ActiveUS20050191910A1Eliminate resistanceMaintaining fluid pressureCoupling device detailsTwo-part coupling devicesElectric forcePower cable
A high-pressure connector for an electrical power cable segment having a central stranded conductor encased in a polymeric insulation jacket with an interstitial void volume in the region of the conductor. The connector confines a fluid within the interstitial void volume at a residual pressure above atmospheric, but below the elastic limit of the insulation jacket. A housing interior chamber receives the conductor in fluid communication with the interstitial void volume. Some embodiments have the chamber sized to receive and overlap a portion of the insulation jacket with a housing end portion swaged thereto. A seal seals the insulation jacket with respect to the housing and a retaining member secures the cable segment to the housing to prevent pushback of the insulation jacket at the residual pressure.
Owner:NOVINIUM LLC
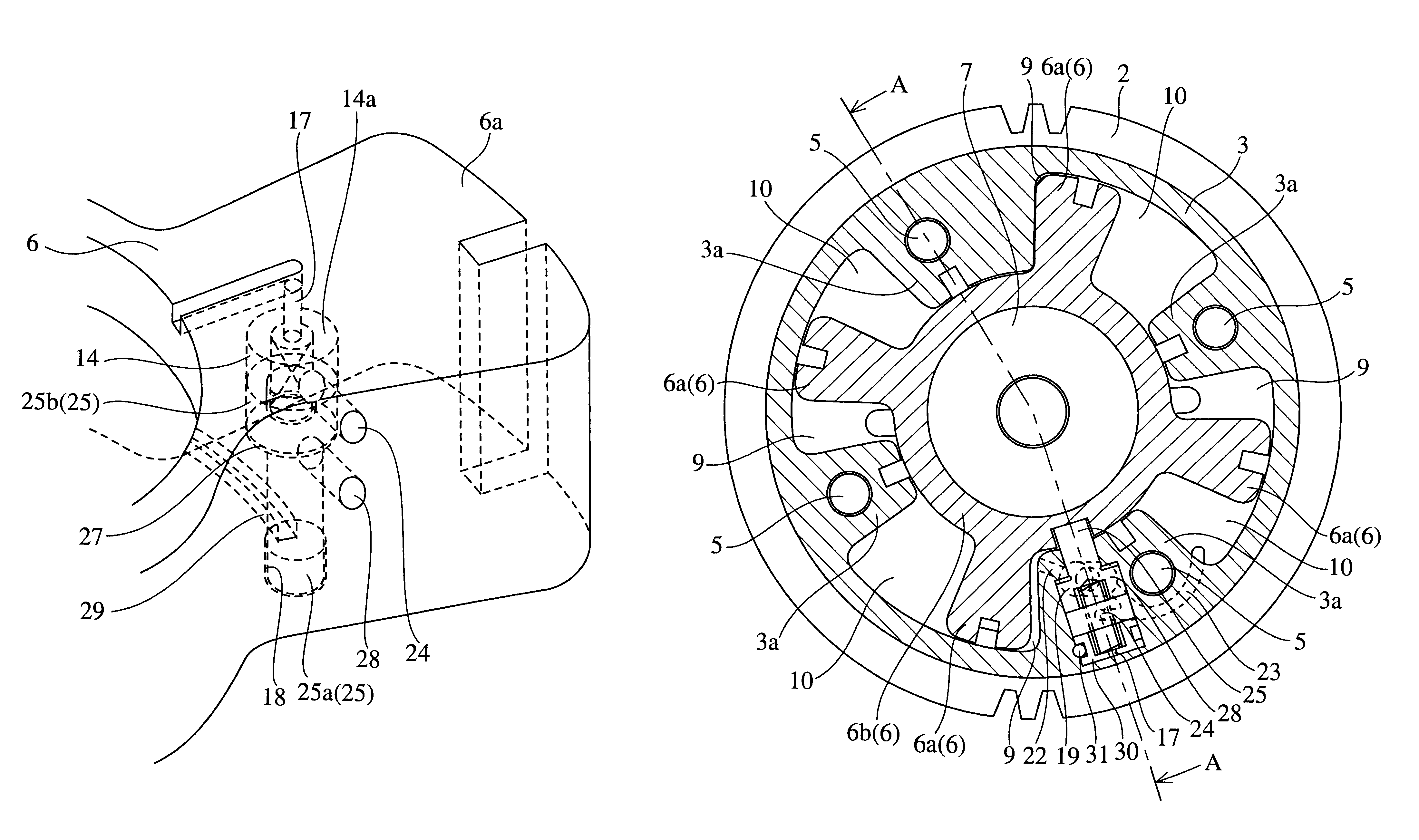
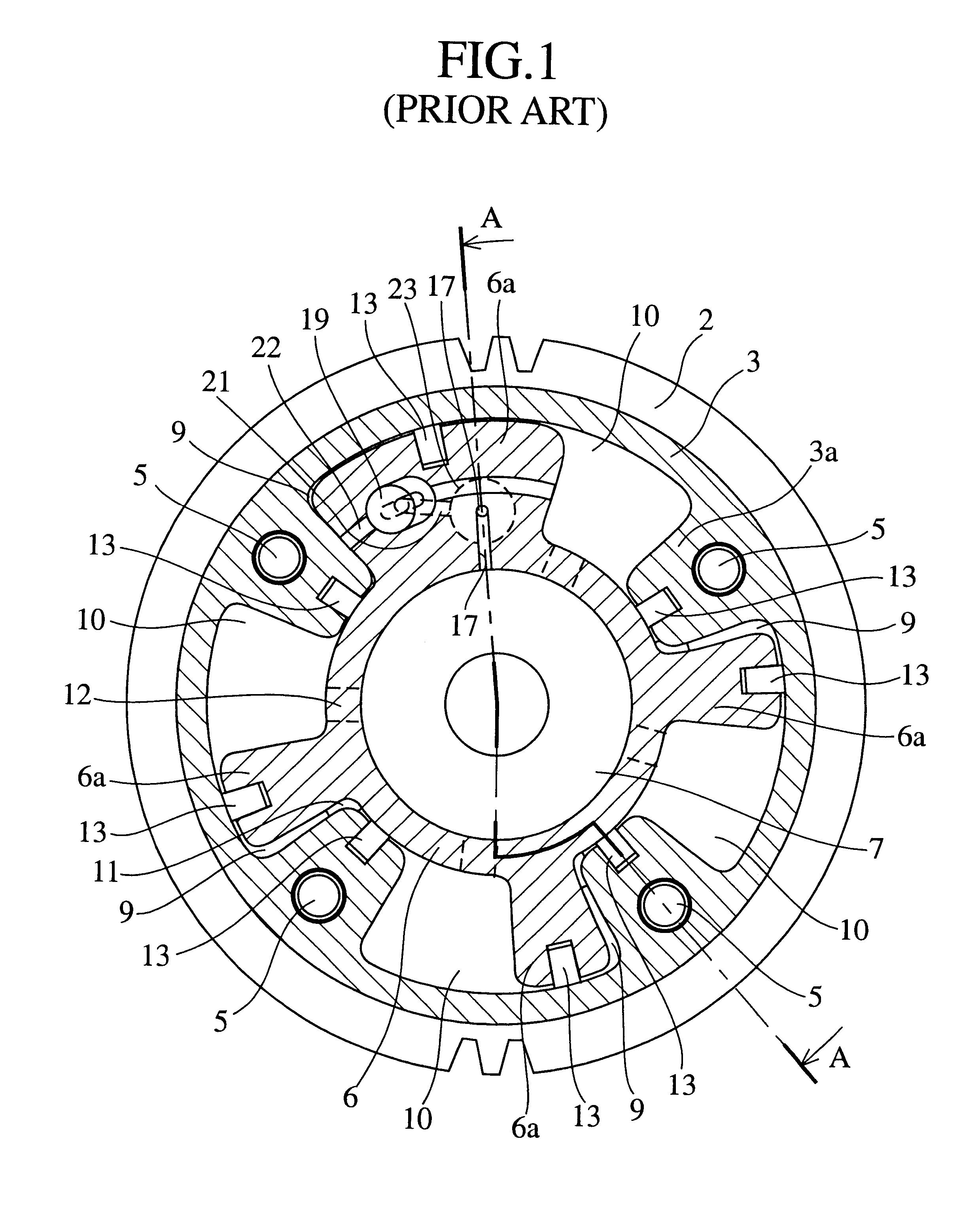
Valve timing control device
InactiveUS20020078913A1Avoid it happening againEasy to operateValve arrangementsMachines/enginesEngineeringResidual pressure
A valve timing control device includes a purge path communicating between a hydraulic chamber allowing the entry of hydraulic pressure on starting an engine and a backward pressurized section in an accommodation hole. When the hydraulic chamber allowing the entry of hydraulic pressure on starting the engine is the retardation side hydraulic chamber, a hydraulic pressure derived from an oil pump is supplied to the retardation side hydraulic chamber on starting the engine. On the way, air-mixed oil is discharged to outside of the device by way of a purge path, a backward pressurized section in the accommodation hole and the discharge hole. When the air is discharged, a residual pressure is produced in the backward pressurized section due to oil supplied thereto. The residual pressure results in the increase of an unlocking hydraulic pressure to prevent a locking member from being unlocked. When the application of a retardation side hydraulic pressure is switched to that of an advance side hydraulic pressure, the pressure presses a front end of a locking member against only a biasing force of a biasing means to unlock a locking relation. The valve timing control device allows the use of any kinds of locking pins, and prevents the occurrence of beat noise (abnormal noise) when air-mixed oil unlocks a locking relation on starting the engine.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
High-pressure power cable connector
ActiveUS7195504B2Eliminate resistanceAvoid resistanceCoupling device detailsTwo-part coupling devicesPower cableElectrical conductor
A high-pressure connector for an electrical power cable segment having a central stranded conductor encased in a polymeric insulation jacket with an interstitial void volume in the region of the conductor. The connector confines a fluid within the interstitial void volume at a residual pressure above atmospheric, but below the elastic limit of the insulation jacket. A housing interior chamber receives the conductor in fluid communication with the interstitial void volume. Some embodiments have the chamber sized to receive and overlap a portion of the insulation jacket with a housing end portion swaged thereto. A seal seals the insulation jacket with respect to the housing and a retaining member secures the cable segment to the housing to prevent pushback of the insulation jacket at the residual pressure.
Owner:NOVINIUM LLC
Method for treating electrical cable at sustained elevated pressure
ActiveUS20050189130A1Effective treatmentExcellent dielectric propertiesClimate change adaptationPower cables with screens/conductive layersElectrical conductorPolymer insulation
A method for enhancing the dielectric properties of an electrical cable segment having a central stranded conductor encased in a polymeric insulation jacket and an interstitial void volume in the region of the conductor, including filling the interstitial void volume with a dielectric property-enhancing fluid at a pressure below the elastic limit of the polymeric insulation jacket, and confining the fluid within the interstitial void volume at a residual pressure greater than about 50 psig, with the pressure being imposed along the entire length of the segment but below the elastic limit of the polymeric insulation jacket. Preferably, the residual pressure is sufficient to expand the interstitial void volume along the entire length of the cable segment by at least 5%.
Owner:NOVINIUM LLC
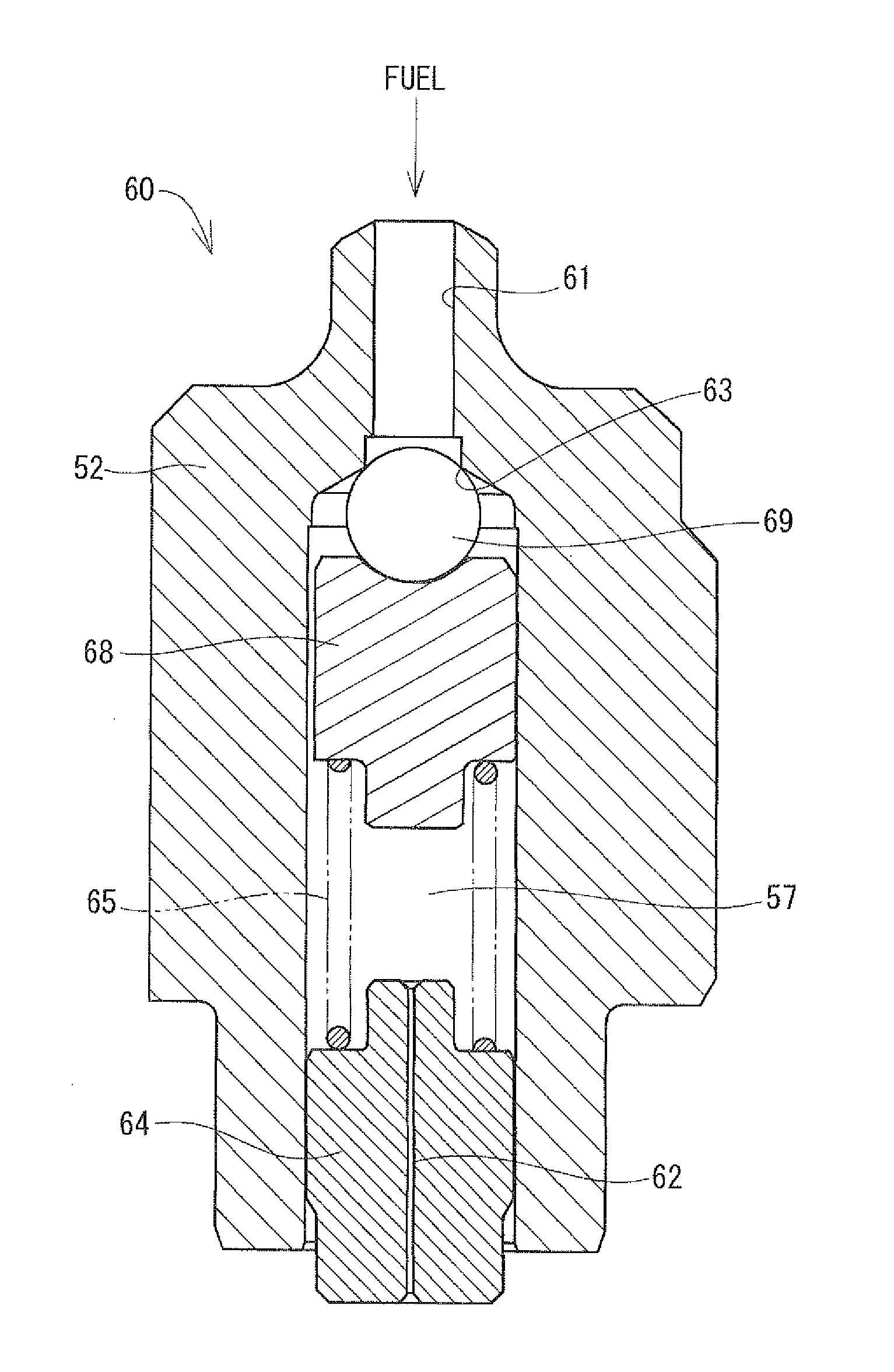
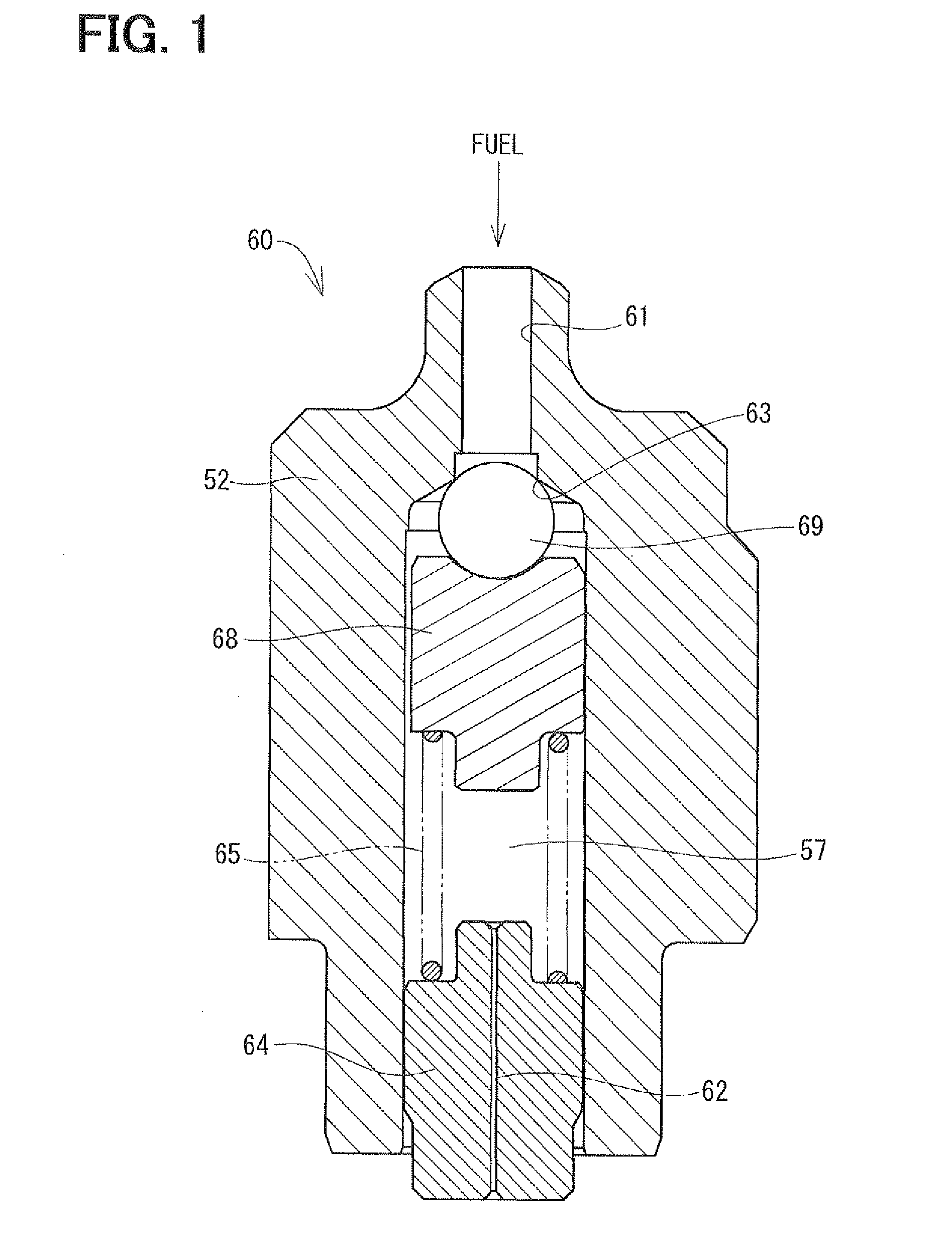
Fuel line check valve
ActiveUS7444990B1Reduce fuel leakageReduce evaporative emissionsCheck valvesLow pressure fuel injectionWorking pressureFuel line
A check valve includes a body defining a passageway through which fuel flows in a first fuel-flow direction during pump operation. The check valve also includes a seat, a seal member, and a biasing member biasing the seal member toward the seat. The seal member is movable between a first seated position in which the seal member is engaged with the seat and the pressure in the fuel rail is substantially equal to the operating pressure, and a second seated position in which the seal member is engaged with the seat and a residual pressure in the fuel rail is substantially less than the operating pressure. The seal member and the seat define a leak path between the fuel pump and the fuel rail permitting fuel to flow in a second fuel-flow direction opposite the first fuel-flow direction when the seal member is in the second seated position.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH CORP +1
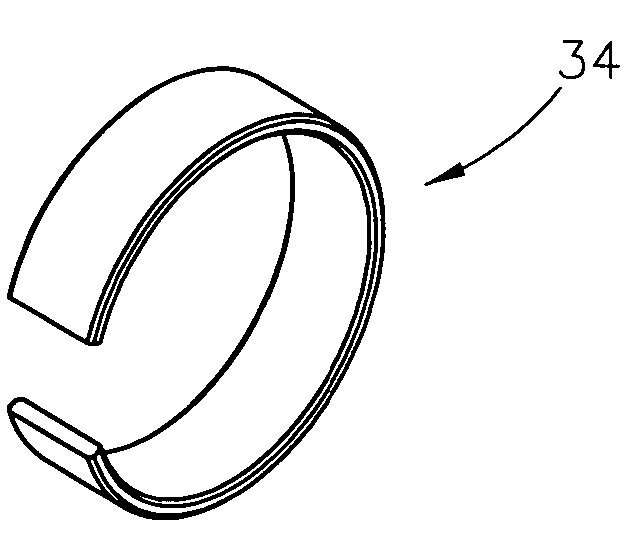
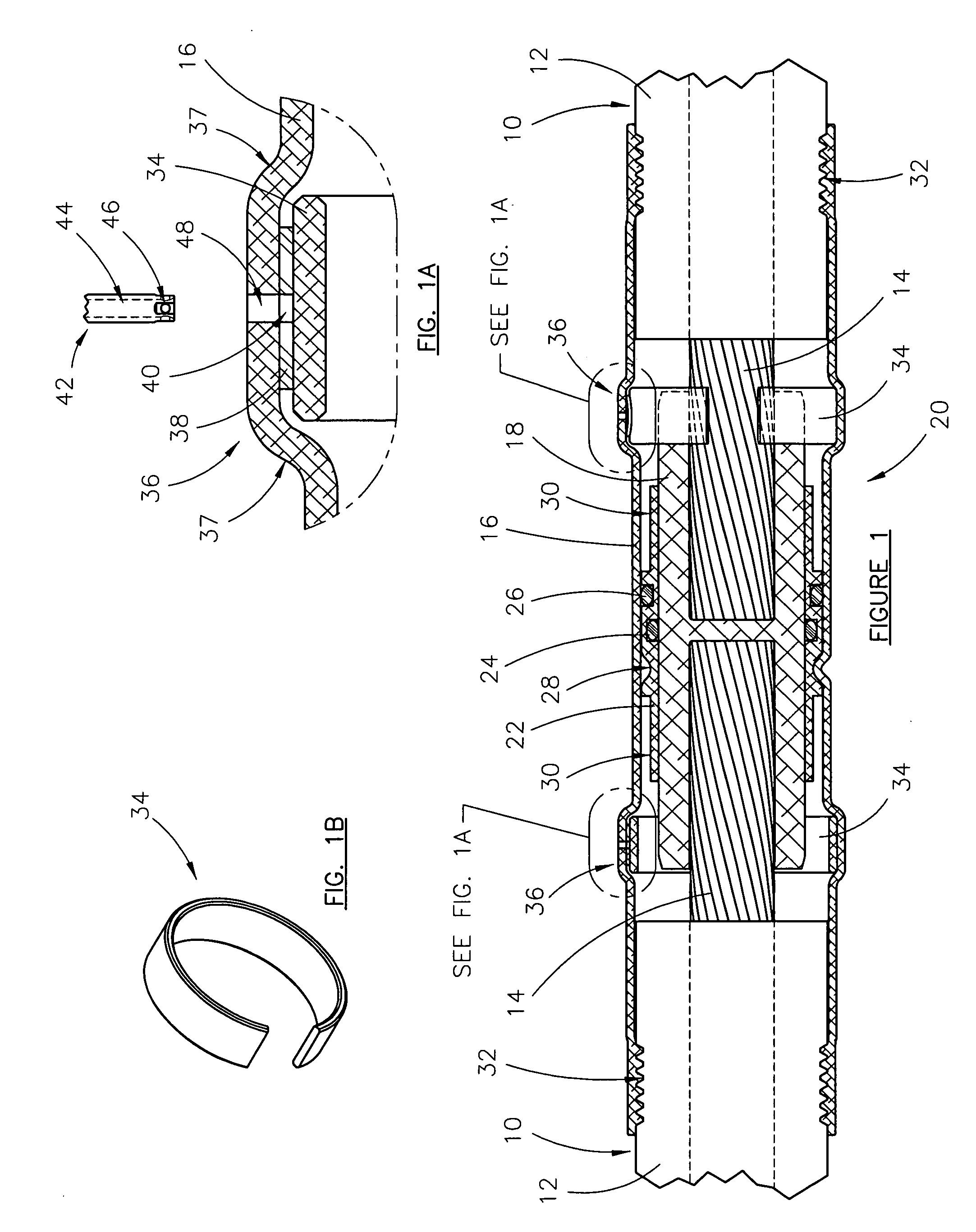
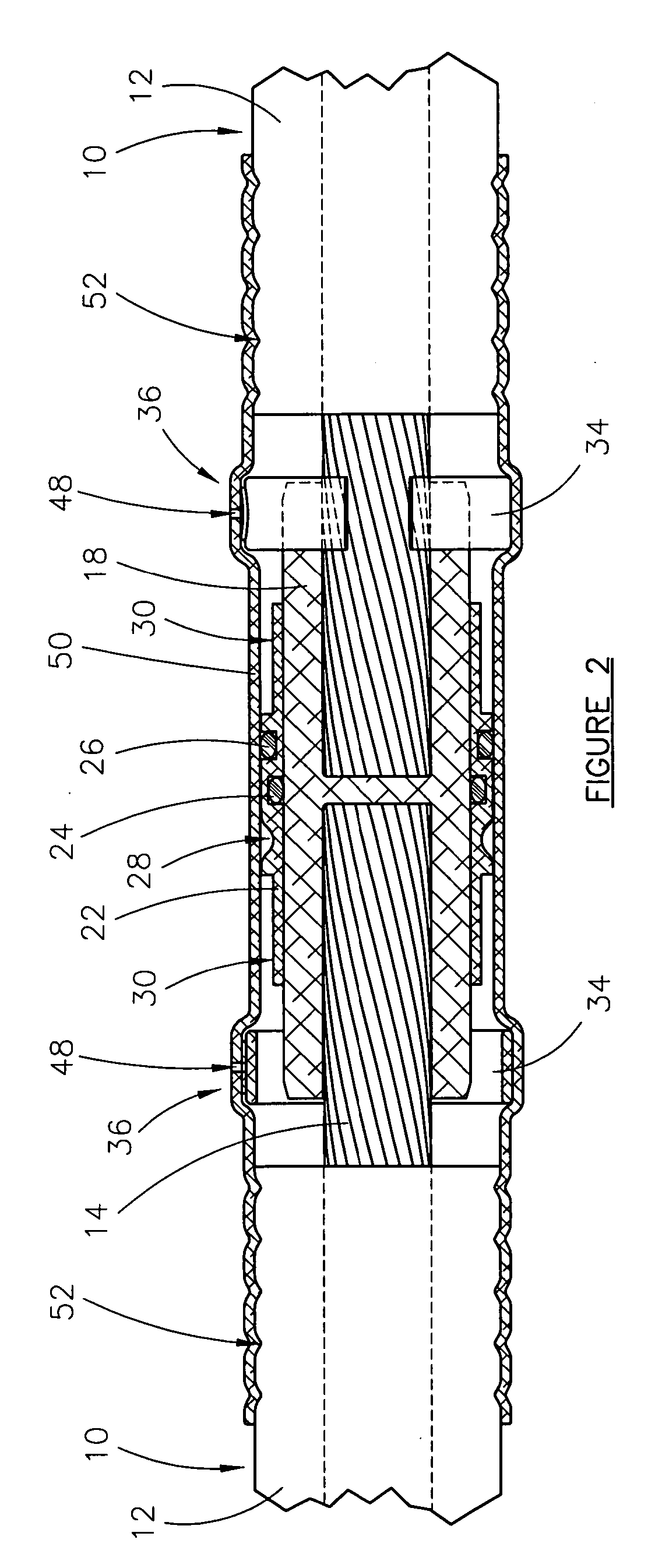
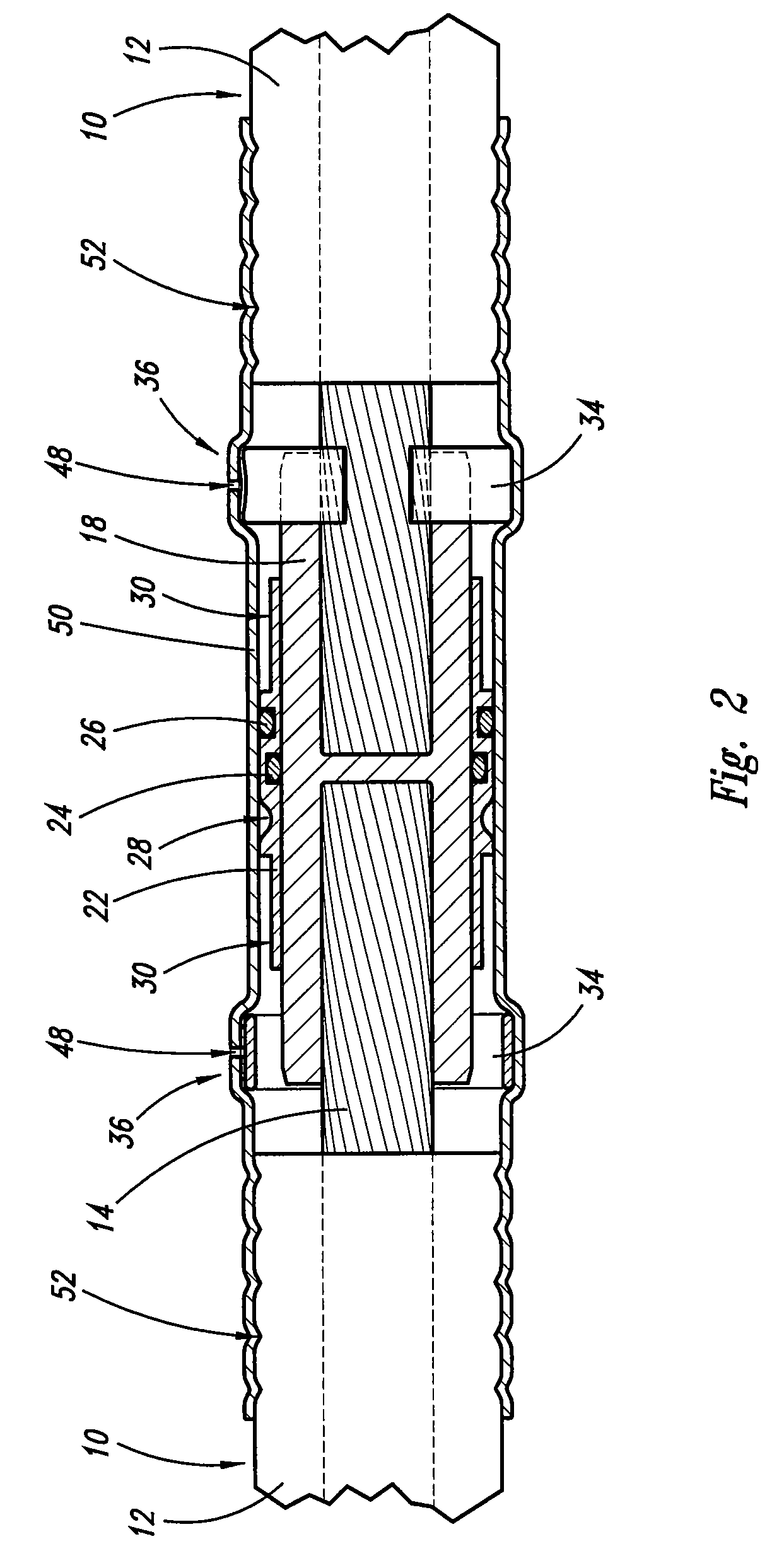
Swagable high-pressure cable connectors having improved sealing means
A high-pressure connector for an electrical power cable section having a central stranded conductor encased in a polymeric insulation jacket and having an interstitial void volume in the region of the stranded conductor, the high-pressure connector being suited for confining a fluid within the interstitial void volume at a residual pressure above atmospheric, but below the elastic limit of the polymeric insulation jacket, the high-pressure connector comprising a housing having a wall defining an interior chamber configured to be in fluid communication with the interstitial void volume and an end portion sized to receive the insulation jacket within the interior chamber and to overlap at least a portion of the insulation jacket at an end thereof with the cable section extending from the housing end portion and at least a portion of the stranded conductor positioned within the interior chamber. The housing wall of the housing end portion has an engagement portion comprised of a swagable material to secure the housing wall to the insulation jacket in fluid-tight sealed engagement therewith upon inward swaging of the engagement portion of the housing wall of the housing end portion to the insulation jacket to confine the fluid at the residual pressure within the interior chamber and the interstitial void volume. The housing includes at least one axially-projecting engagement member located within the interior chamber at the engagement portion of the housing wall of the housing end portion.
Owner:NOVINIUM LLC
Methods and apparatus for advanced wind turbine design
ActiveUS20070138798A1Eliminate needReduce pressureWind motor controlEngine fuctionsHigh energyHydraulic pump
A wind turbine system includes a variable blade assembly including adjustable sails and wing shaped masts expanding the wind velocity capture envelope. The blade assembly turns a hydraulic pump, which pressurizes fluid and stores the pressurized fluid in a chamber in the support tower. Pressurized fluid is directed via an electronically controllable proportioning valve to a hydraulic motor which is coupled to an electric generator. A computer control module operates the proportioning valve regulating pressure to the hydraulic motor, maintaining generator rotational speed, and providing consistent output frequency to the power grid. Stored energy in the high pressure tank is used to continue generator operation after the winds cease, allowing early warning notification to the power management system of impending power loss. Residual pressure maintained in the high pressure tank allows restart operations via hydraulic pressure rather than power grid energy drain. On site high energy capacitors store additional energy.
Owner:MCCLINTIC FRANK
Ionisation vacuum gauge
InactiveUS20050030044A1Improve performanceImprove directionalityVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGalvanometerVacuum pump
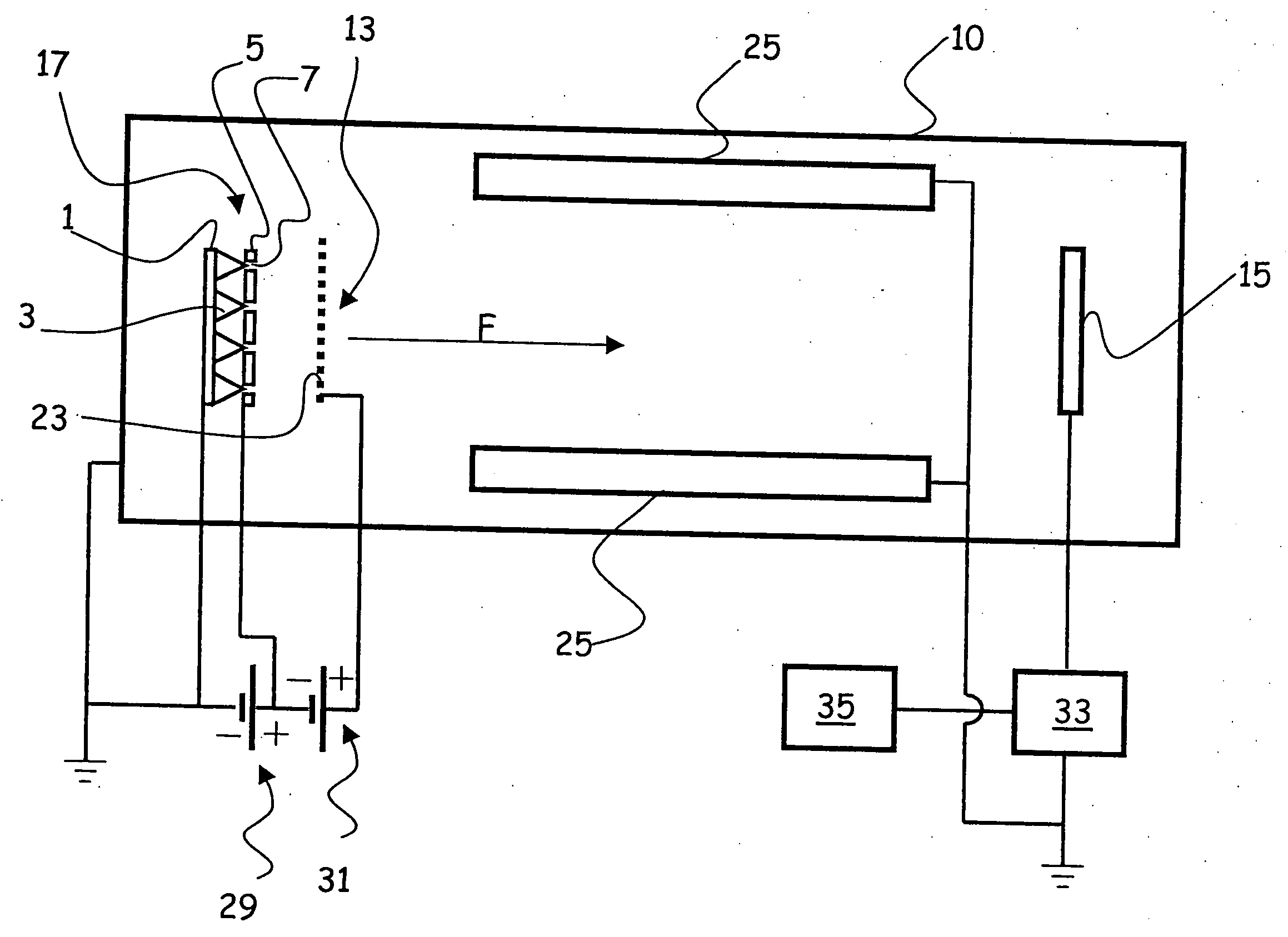
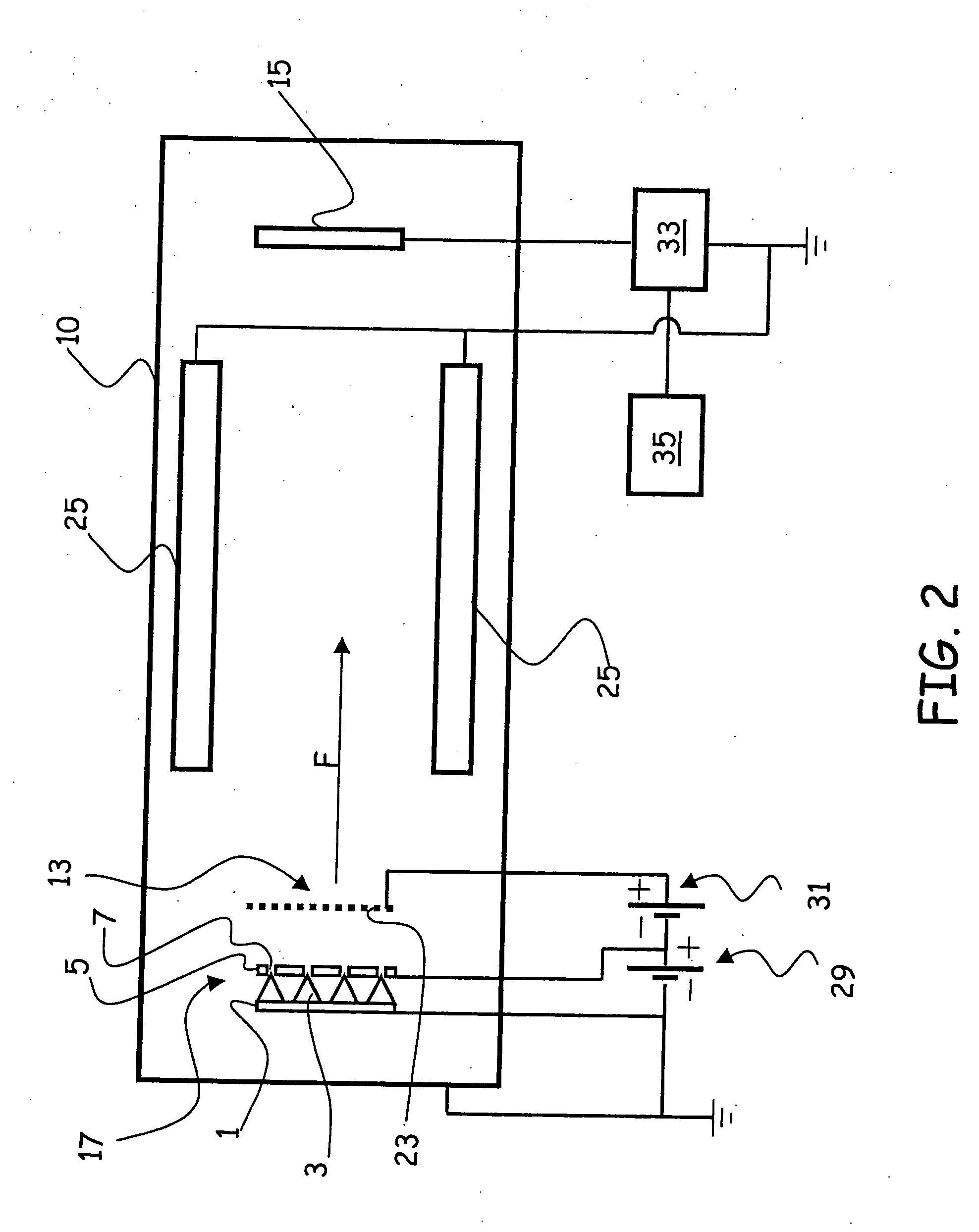
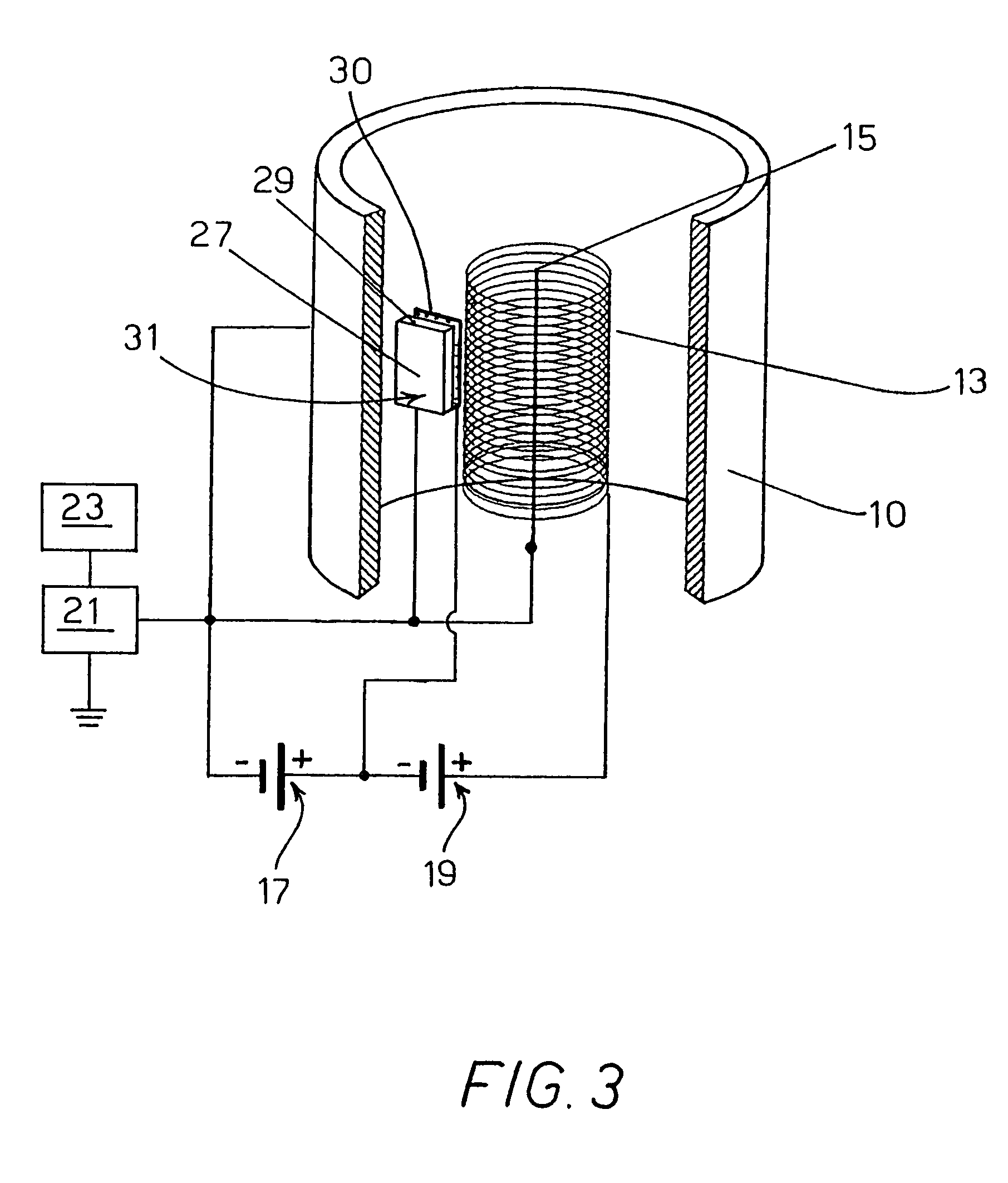
The present invention relates to an ionisation vacuum gauge for measuring the residual pressure of a gaseous material remaining in a container (10), more particularly after operation of a vacuum pump. The gauge comprises an electron-emitting cathode (17), a grid (13) for accelerating the electrons emitted by the cathode and a plate (15) collecting the ions and / or the ionised positive molecules of the gas, wherein said plate is placed outside said grid. Measuring the plate current by a galvanometer allows determining the value of the residual pressure inside the container.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Valve timing control device
InactiveUS6460496B2Avoid it happening againValve arrangementsMachines/enginesEngineeringResidual pressure
A valve timing control device includes a purge path communicating between a hydraulic chamber allowing the entry of hydraulic pressure on starting an engine and a backward pressurized section in an accommodation hole. When the hydraulic chamber allowing the entry of hydraulic pressure on starting the engine is the retardation side hydraulic chamber, a hydraulic pressure derived from an oil pump is supplied to the retardation side hydraulic chamber on starting the engine. On the way, air-mixed oil is discharged to outside of the device by way of a purge path, a backward pressurized section in the accommodation hole and the discharge hole. When the air is discharged, a residual pressure is produced in the backward pressurized section due to oil supplied thereto. The residual pressure results in the increase of an unlocking hydraulic pressure to prevent a locking member from being unlocked. When the application of a retardation side hydraulic pressure is switched to that of an advance side hydraulic pressure, the pressure presses a front end of a locking member against only a biasing force of a biasing means to unlock a locking relation. The valve timing control device allows the use of any kinds of locking pins, and prevents the occurrence of beat noise (abnormal noise) when air-mixed oil unlocks a locking relation on starting the engine.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
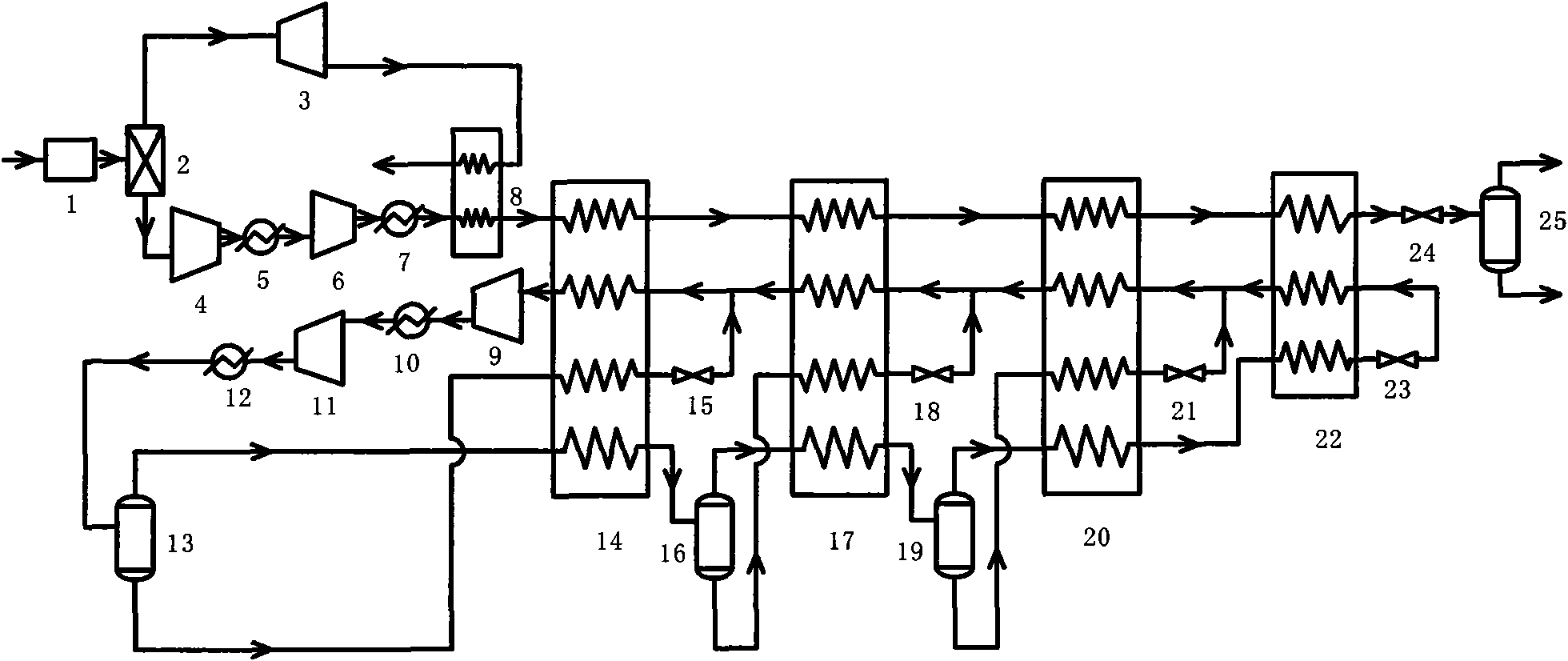
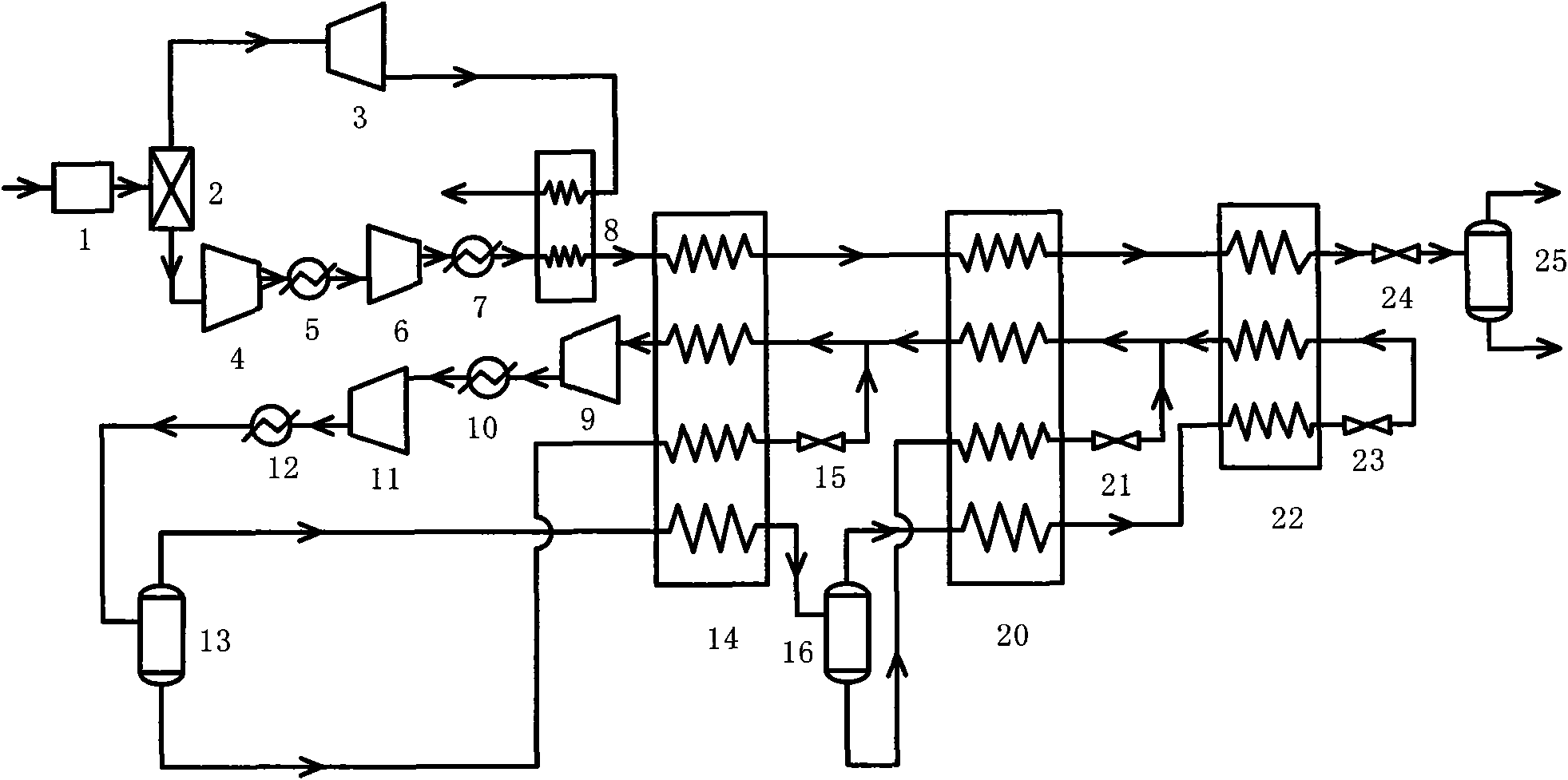
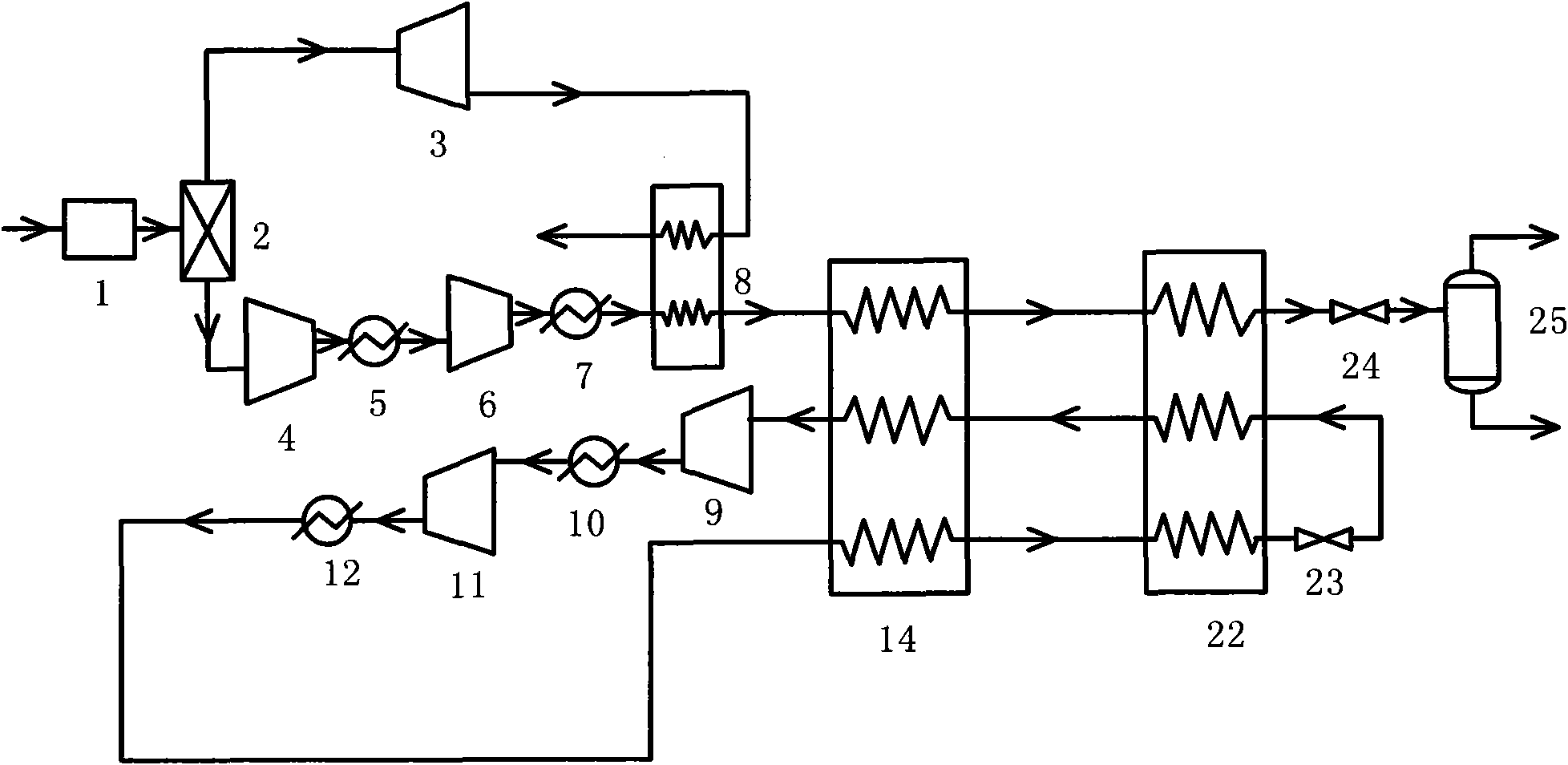
Mixed refrigerant re-circulated liquefaction process for precooling coalbed methane (CBM) by residual pressure of pressure swing adsorption (PSA)
InactiveCN101625190AReduce liquefaction power consumptionReduce power consumptionSolidificationLiquefactionChemical industryCryogenic technology
A mixed refrigerant re-circulated liquefaction process for precooling coalbed methane (CBM) by residual pressure of pressure swing adsorption (PSA) belongs to the technical field of chemical industry and low temperature. The invention provides an integrated process of adsorption and liquefaction of CBM with high nitrogen content. The process comprises the following steps: before liquefaction, firstly desorbing most nitrogen in the CBM by the PSA process, adopting the residual pressure of adsorption in the above nitrogen to precool the CBM after expanding the residual pressure and liquefying the CBM by the mixed refrigerant re-circulated liquefaction process which is widely applied in the natural gas liquefaction industry. The precooling process of the nitrogen with residual pressure saves the mixed refrigerant flow used for providing cooling capacity, thus reducing the overall power consumption of the system. With the increase of the nitrogen content of the CBM and the residual pressure of adsorption in the nitrogen, the temperature of the precooled CBM gradually decreases, the number of cooling stages of mixed refrigerant cycle can be correspondingly lessened and more power consumption is saved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
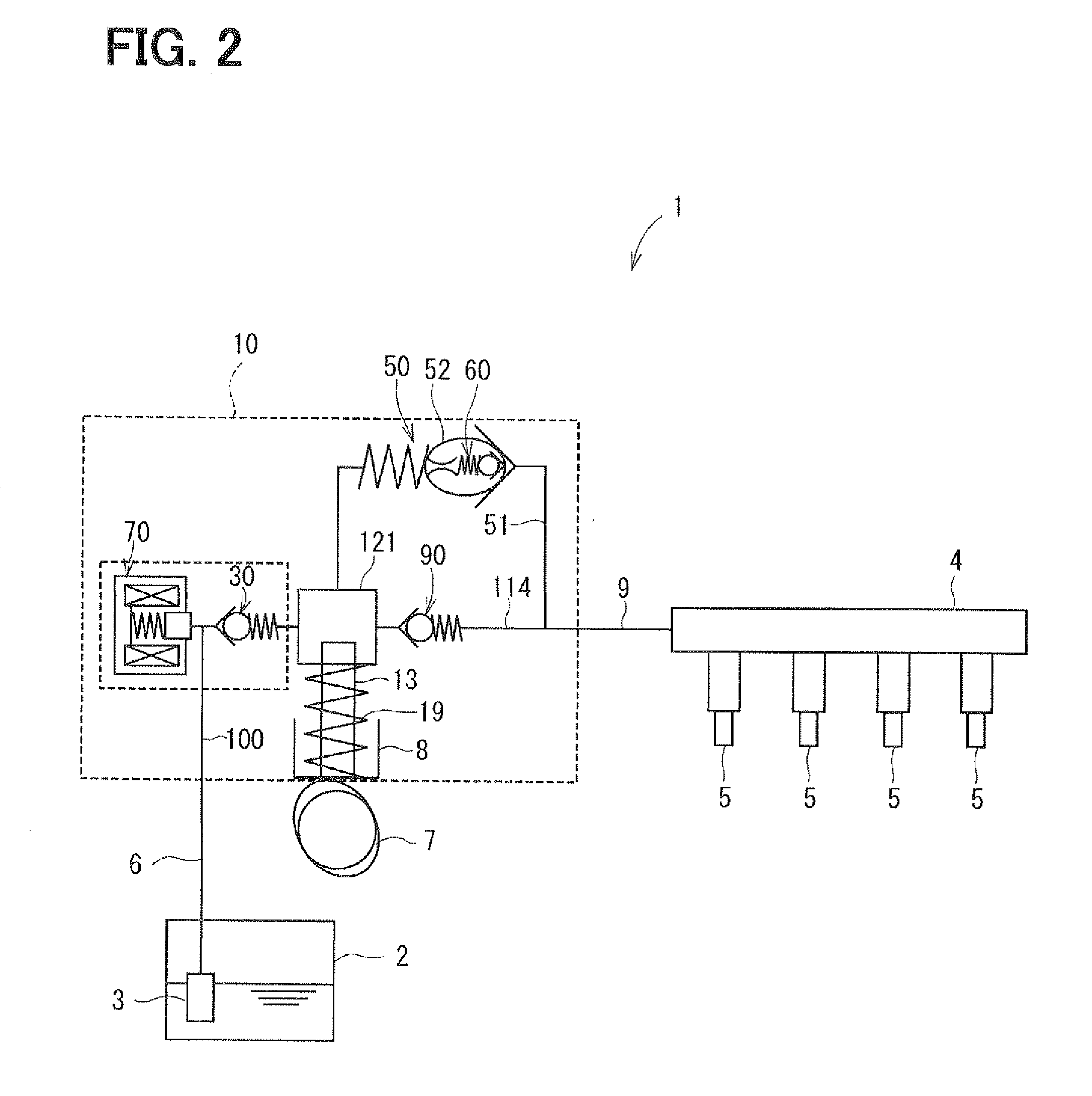
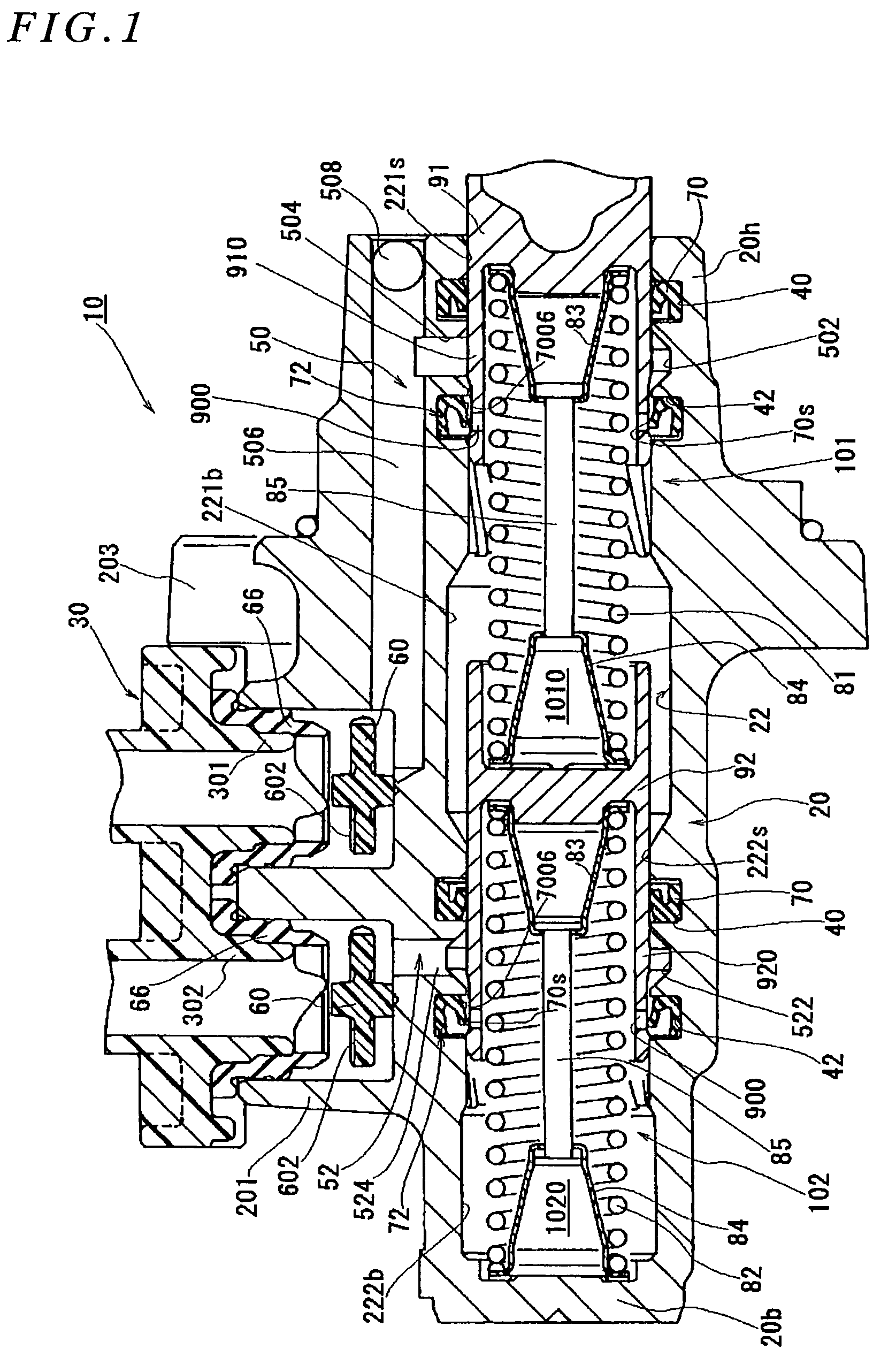
Constant-residual-pressure valve
A constant-residual-pressure valve is disposed in a communication passage connecting a high-pressure fuel passage through which pressurized fuel flows with a low-pressure fuel passage through which the fuel flows toward a high-pressure pump. The constant-residual-pressure valve includes a valve body, a spring, and a spring stopper. The valve body can sit on a valve seat formed in an inner passage. The spring biases the valve body toward the valve seat. The spring stopper has a downstream-orifice of which flow passage area is smaller than that of a passage upstream of the valve seat. Thereby, cavitation between the valve body and the valve seat is less generated.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
Plunger type master cylinder
InactiveUS7181911B2Improved seal durabilityInvalid stroke can be reducedPiston ringsRotary clutchesWorking fluidMaster cylinder
Owner:BOSCH CORP
Fuel pressure relief valve
ActiveUS7441545B1Reduce fuel leakage and evaporative emissionRelieve system pressureCheck valvesLow pressure fuel injectionEngineeringResidual pressure
A fuel pressure relief valve includes a body defining a passageway having an inlet end in communication with a fuel pump and an outlet end in communication with a fuel rail. The valve also includes a seal member moveable between a first position in which the seal member is seated against the outlet end, and a second position in which the seal member is unseated from the outlet end. The valve further includes a biasing member biasing the seal member toward the second position. The seal member moves from the second position to the first position immediately after fuel pump shutoff to maintain pressure in the fuel rail. The seal member moves from the first position to the second position when fuel in the fuel rail drops to a residual pressure substantially less than the operating pressure to provide a leak path between the fuel pump and the fuel rail.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH CORP +1
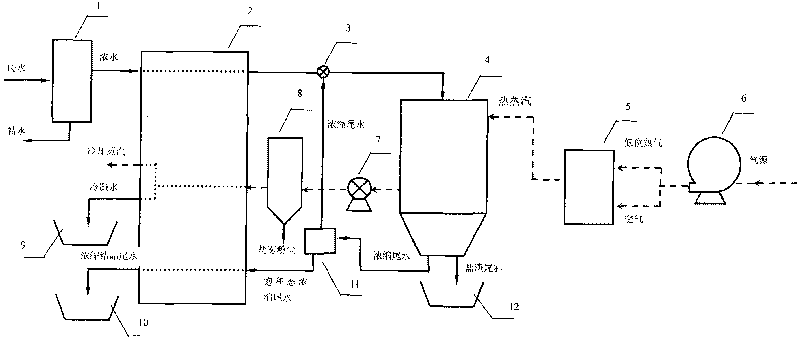
Method for spraying and desalting through residual pressure of reverse osmosis concentrated water
InactiveCN101712521ASave powerSimple structureGeneral water supply conservationWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisWater vaporReverse osmosis
The invention establishes a method for treating waste concentrated saltwater of reverse osmosis systems. The method mainly comprises the following steps that: the residual pressure of concentrated water produced by the self of a reverse osmosis system during water production is utilized to form high-salt spray so as to save power needed by conventional atomization; tiny water droplets quickly evaporate in floating air so as to separate water, salt and other impurities; meanwhile, organic matter contained by the water is oxidized to be carbon dioxide; vapor is input into a condensing chamber to turn into pure water, while salt and high-power tail water fall to the bottom of a separation chamber; the tail water and initial inflow water are mixed and circulated and then continue to be atomized and concentrated to a saturation state; the contained salt is subjected to heat-exchange condensation and then crystallization and precipitation; and water purification and salinity removal of reverse osmosis concentrated water are finally realized. The desalting and pollutant-reducing method for reverse osmosis concentrated water is suitable for the separation of the waste concentrated saltwater produced by every type of reverse osmosis systems.
Owner:TIANJIN ACADEMY OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Valve controlled residual pressure recovering equipment for impervious desalination system
InactiveCN1343528ASimple structureImprove use reliabilityGeneral water supply conservationWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisHydraulic cylinderEnergy recovery
A valve-controlled residual pressure recovering equipment for impervious seawater desalinating system is composed of hydraulic cylinder, free piston in the cylinder, and high-and low-pressure three-way electromagnetic valves at both ends of the said cylinder. The position and operating time of the cores of the said electromagnetic valves are controlled by computer program. The inlet of high-pressure concentrated saline and the outlet of pressurized seawater are opened or closed simultaneously. The inlet of raw seawater and the outlet of concentrated saline are opened or closed at same time. Its advantages are simple structure, high reliability,and high efficiency of recovering residual pressure (up to 70-90%).
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Liquid feed valve unit and liquid ejection device
A liquid feed valve unit is configured to switch between a releasing mode for forcibly opening a valve and a blocking mode for closing the valve, and the valve can therefore be opened and closed in a short time as needed. Since the releasing mode is implemented by pushing the peripheral part and the pressure-receiving part of the flexible member, the flexible member can be prevented from flexing toward the outside of the liquid accommodating chamber even in the case that the pressure-receiving part is pushed. In this case, since a residual pressure can be prevented from forming in the liquid accommodating chamber, there is no need to suspend operation, and it is possible to immediately proceed to the next operation. A fast-operating liquid feed valve unit can thereby be obtained.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method for flow control and autonomous valve or flow control device
Owner:DEN NORSKE STATS OLJESELSKAP AS
Steelmaking residual heat step recycling method
ActiveCN102851420ASolve effective useEnable fair useBlast furnace detailsIncreasing energy efficiencySteelmakingDitch
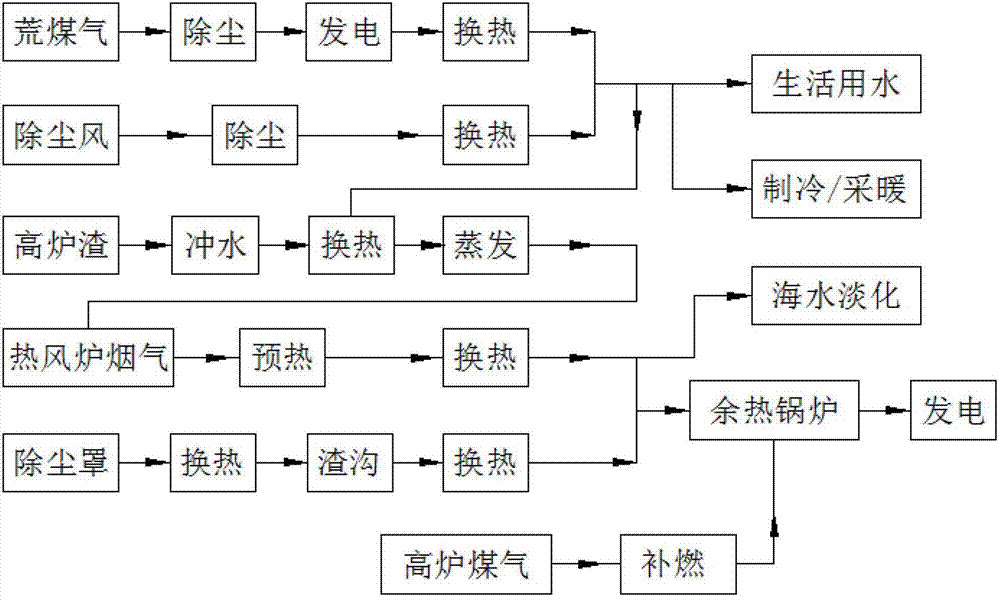
The invention discloses a steelmaking residual heat step recycling method. The invention belongs to the technical field of steel industry iron-making residual heat and residual energy utilization. The method is adopted under a condition for further utilizing iron-making low-grade residual heat, and comprises step recycling and high-efficiency utilizations of blast furnace gas residual heat, dust removal air residual heat, water slag residual heat, hot air furnace low-temperature flue gas waste heat, and dust cover and slag ditch residual heat. According to the technical scheme, blast furnace gas residual heat and dust removal air residual heat obtained after furnace top residual pressure power generation are connected in parallel, and are supplied for domestic water, cooling, or heating. Recycled water slag residual heat and flue gas residual heat obtained after hot air furnace gas heat exchanger are connected in parallel, and are used for supplying a heat source for low-temperature seawater desalination. Recycled dust cover residual heat and slag ditch surface radiation heat are connected in parallel, and are supplied for blast furnace gas supplementary firing residual heat boiler power generation. After powder generation, high-temperature seawater desalination is realized by a steam method. Cooling water and domestic water are treated and are adopted as inlet water replenishment. Through step recycling and graded utilization of the low-grade residual heat and residual energy, steel system comprehensive energy consumption can be reduced to a maximal extent, and energy resource reasonable utilization and comprehensive optimized utilization can be realized.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
Piezoelectric type jet nozzle device for micro-droplet generation
ActiveCN103434272AAttenuation of residual pressure wavesGuaranteed uptimePrintingElectricityUltrasound attenuation
The invention discloses a piezoelectric type jet nozzle device for micro-droplet generation. The piezoelectric type jet nozzle device comprises a jet body, a jet nozzle, a piezoelectric diaphragm, a pressure sensor and a pressure wave attenuation mechanism. The jet body is provided with a jet cavity, the jet nozzle is arranged at one end of the jet body, the piezoelectric diaphragm is arranged on the jet body and used for providing jet power, the pressure sensor is used for detecting change of fluid pressure in the jet cavity and outputting collected pressure signals, and the pressure wave attenuation mechanism is used for transmitting attenuation pressure waves used for attenuating residual pressure waves in the jet cavity according to the received pressure signals. According to the piezoelectric type jet nozzle device, the pressure sensor and the pressure wave attenuation mechanism work in cooperation with each other, change conditions of pressure waves in the jet cavity are detected in real time through the pressure sensor, the residual pressure waves in the jet cavity are quickly attenuated through the pressure wave attenuation mechanism under the premise of guaranteeing normal jet operation, therefore, jet waiting time is shortened, and jet frequency is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Hydraulic brake device
InactiveUS20060158026A1Eliminate the effects ofStop operationRotary clutchesFluid braking transmissionEngineeringResidual pressure
A normally closed secondary solenoid opening / closing valve 36 is provided along a secondary branched fluid pipe 35 establishing a communication between an accumulator 11 and a reservoir 8 through a fluid pressure input side to a fluid pressure output side of a regulator valve 3, and in the event that a fluid pressure supplied to the regulator valve 3 decreases down to or lower than a predetermined range due to something abnormal occurring in the accumulator 11, the state of the secondary solenoid opening / closing valve 36 is changed over from a closed state to an opened state, whereby a residual pressure in the accumulator 11 and a residual pressure in the output fluid pressure chamber 15 can be released through the reservoir 8 which is in communication therewith through an output fluid pipe 31 and the secondary branched fluid pipe 35 along which the secondary opening / closing valve 36 is provided.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Preparation process of alkanolamide
InactiveCN101774936ASimple processReduce energy consumptionOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationOrganic chemistryResidual pressure
The invention relates to a preparation process of alkanolamide, which comprises the following steps: the mol ratio of fatty acid ester and alkanolamine is 1: 1.1 to 2, the fatty acid ester and the alkanolamine are added into a reaction kettle according to the mol ratio, then alkaline catalyst is added into the reaction kettle, the addition quantity of the alkaline catalyst is 2 to 5 permillage ofthe total weight of the fatty acid ester and the alkanolamine, the temperature inside the reaction kettle is 50 to 100 DEG C, the reaction kettle is vacuum pumped to the residual pressure of 50 to 80mmHg, and after the reaction of 2 to 4 hours, an alkanolamide rough product is generated, a neutralizing agent is added, and after the pressure is released, excess alkanolamine is steamed, so the alkanolamide is obtained. The preparation process has the advantages of simple process, low energy consumption and high purity of the product.
Owner:CHINA RES INST OF DAILY CHEM IND
Ionization vacuum gauge
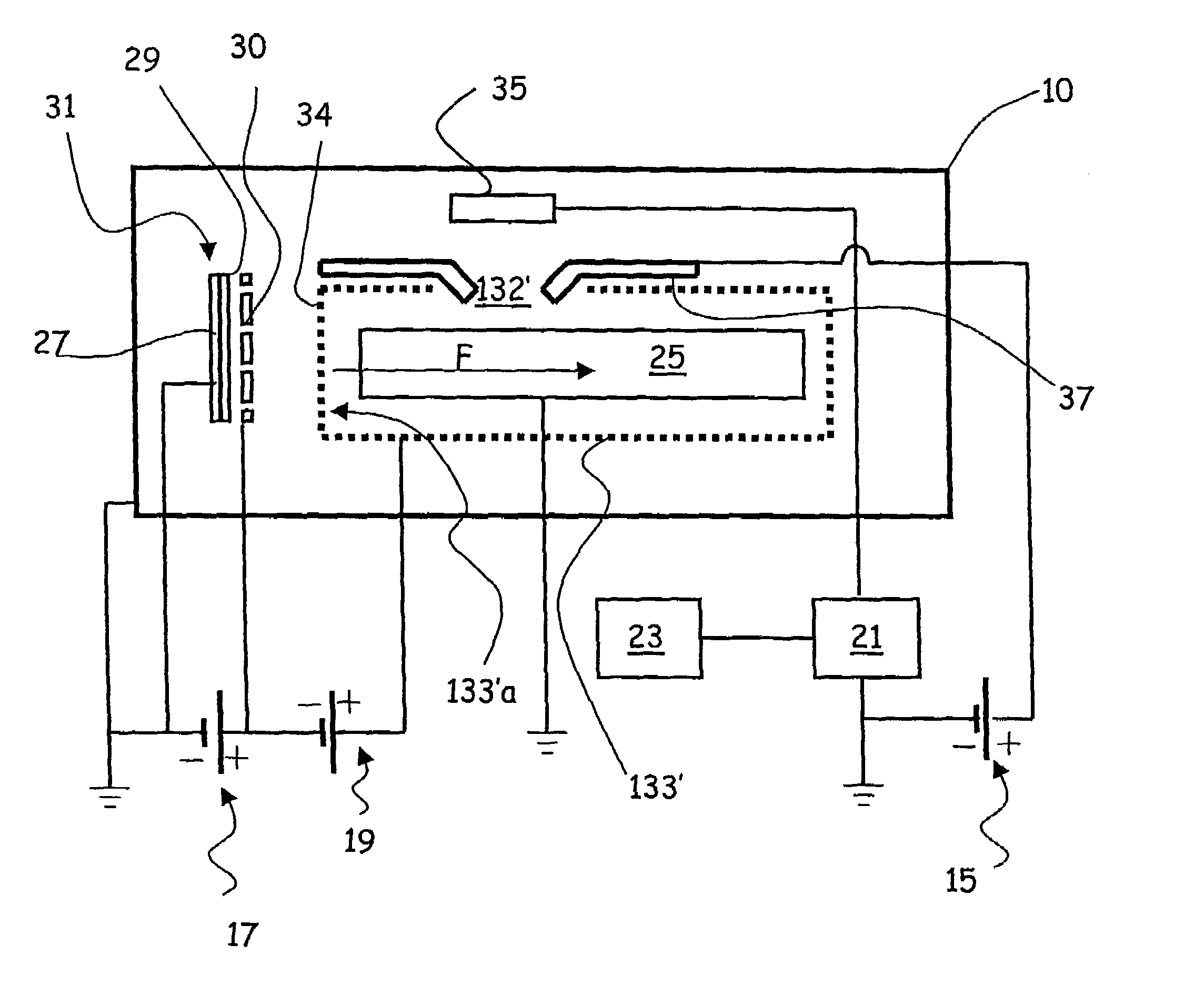
An ionisation vacuum gauge for measuring the residual pressure of a gaseous material remaining in a container (10), more particularly after operation of a vacuum pump comprises an electron-emitting cathode (31) made by exploiting the nanotube technology, a grid (13; 33; 133; 133′) for accelerating the electrons emitted by the cathode, and a plate (15; 35) collecting the ions and / or the ionised positive molecules of the gas. Measuring the plate current by a galvanometer allows for determining the value of the residual pressure inside the container.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
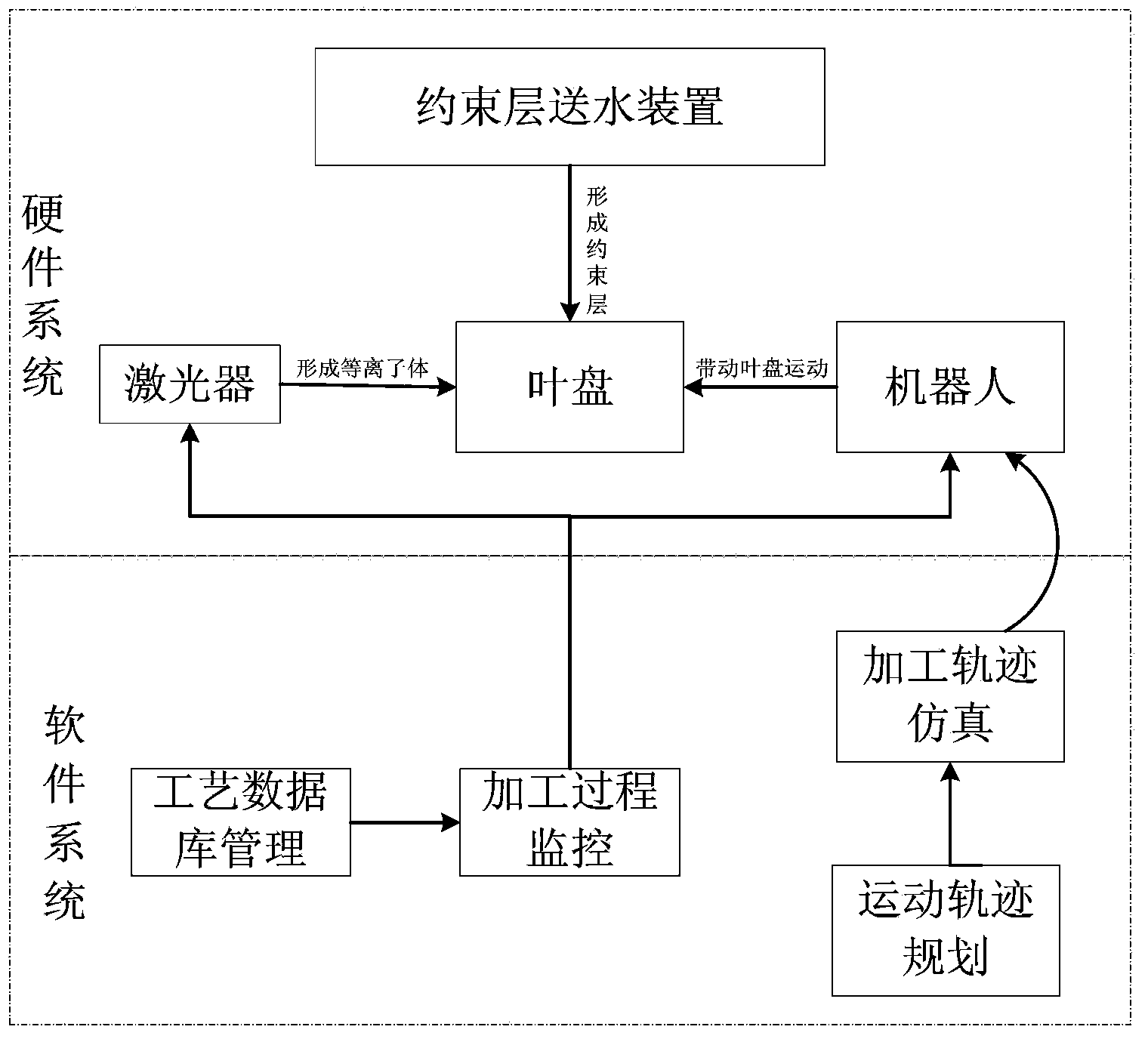
Laser shock peening method of blisk
The invention discloses a laser shock peening method of a blisk. The method is below: first installing the blisk on a flange at the terminal of a trajectory robot through a fixture; then setting an optical system to a third optical path (9) working state, a first optical path (15) working state, a fourth optical path (10) working state, a second optical path (14) working state, the fourth optical path (10) working state and the second optical path (14) working state in order; and respectively conducting laser shock peening on a blade back trailing edge region (3), a blade basin leading edge region (6), a blade basin trailing edge region (4), a blade back leading edge region (1), a blade basin tip region (5) and a blade back tip region (2) of a blisk blade. The laser shock peening method provided by the invention is simple, and after laser shock peening, the blisk has residual pressure stress reaching above 300 MPa, high frequency vibration fatigue life increased by about 6-30 times, and little deformation of the workpiece.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Flow testing system for fluid networks
ActiveUS7983869B1Way accurateVehicle testingAerodynamic testingMeasurement testPressure transmission
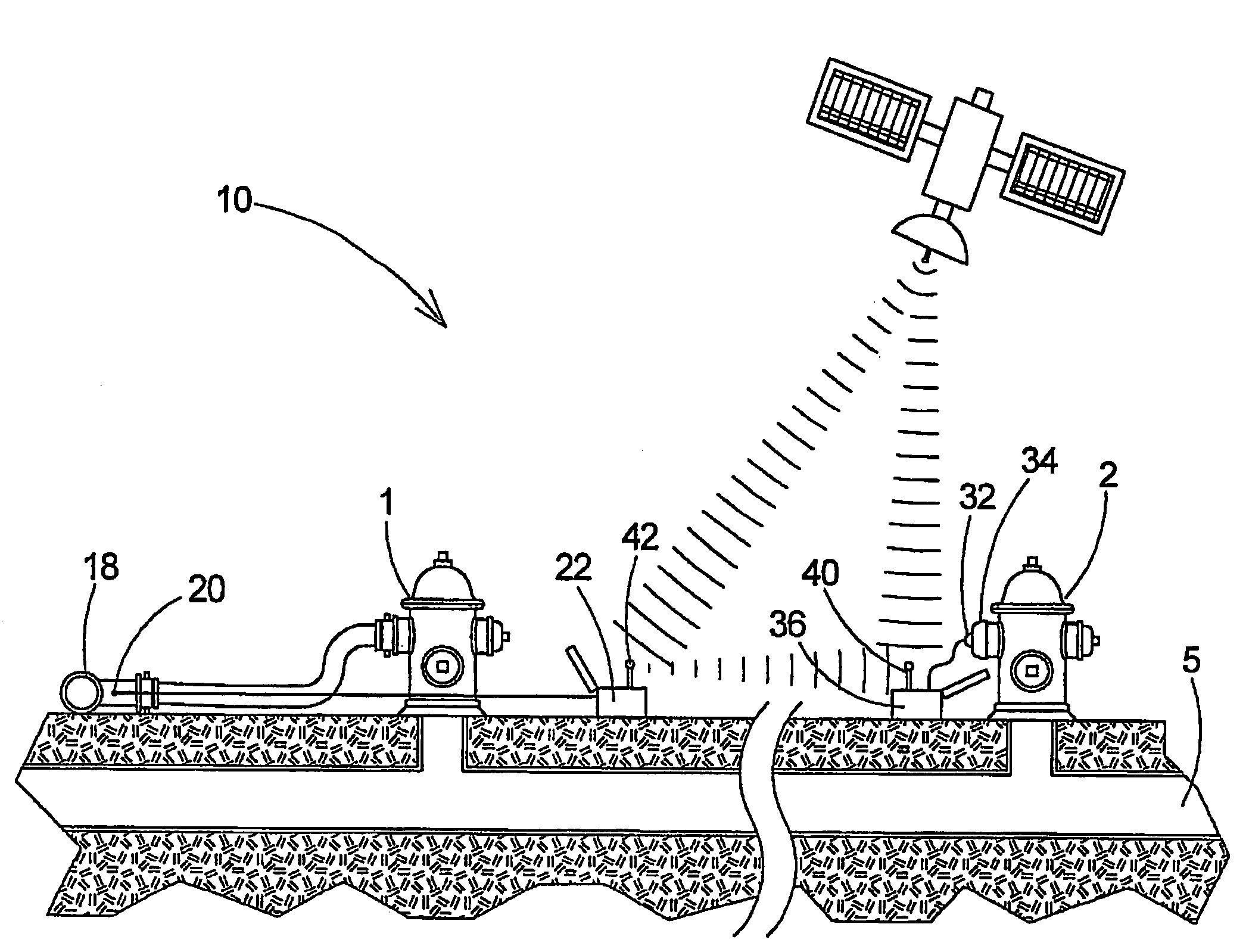
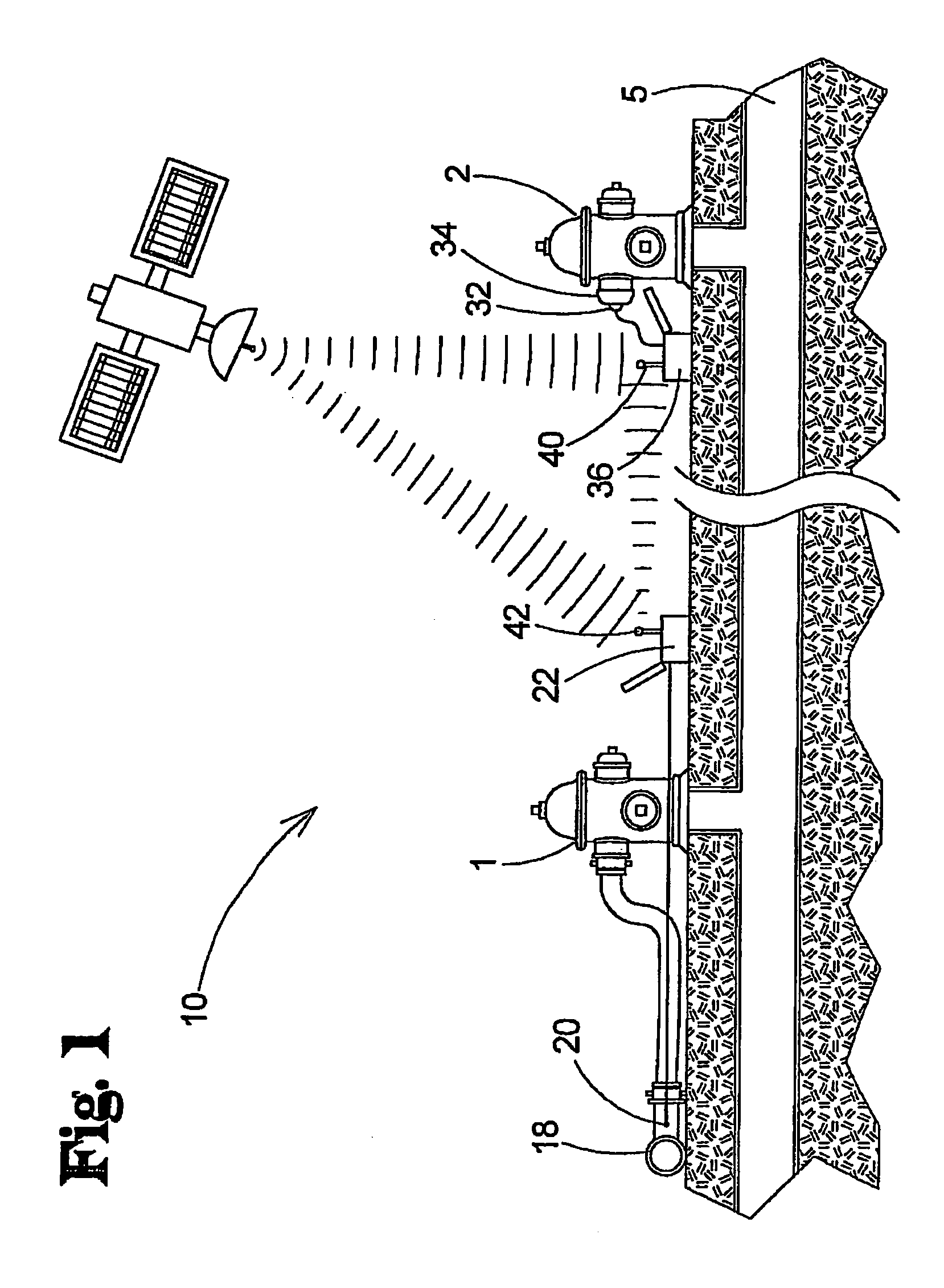
A flow testing system comprises a flow unit for interfacing with a flow hydrant, a pressure unit for interfacing with a test hydrant, a transmitter in a first one of the units to transmit data to a second one of the units, a receiver in the second unit to receive data from the transmitter, and a data storage medium in the second unit to record data. A method includes providing flow and pressure units, interfacing the pressure unit to a test hydrant and the flow unit to a flow hydrant, measuring static pressure by the pressure unit, initiating water flow through the flow hydrant, measuring pitot pressure in the flow, measuring residual pressure in the test hydrant, transmitting the residual pressure measurement from the pressure to the flow unit, and recording the pitot and residual pressure measurements.
Owner:HURCO TECH
Means for removing unwanted ions from an ion transport system and mass spectrometer
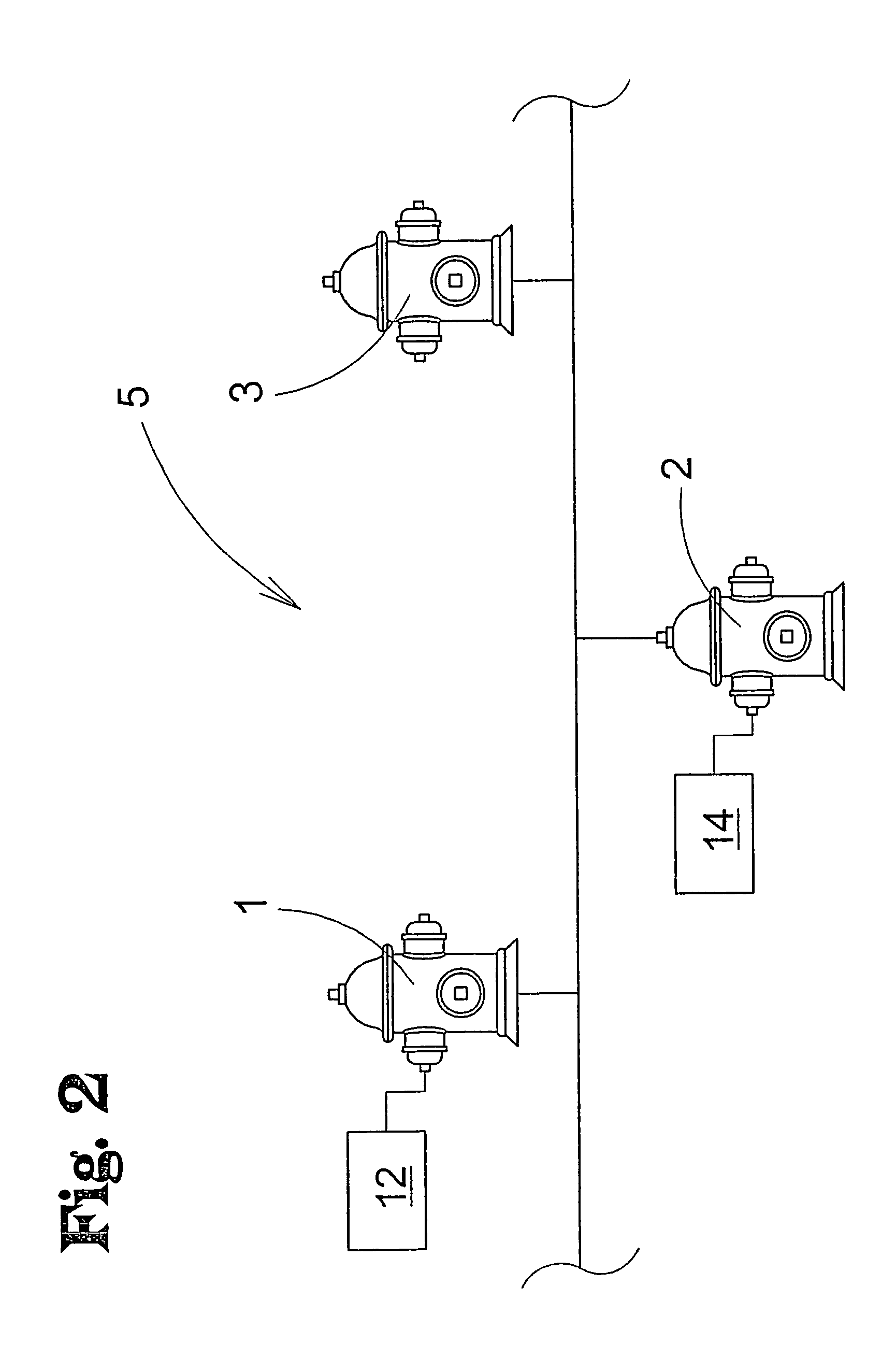
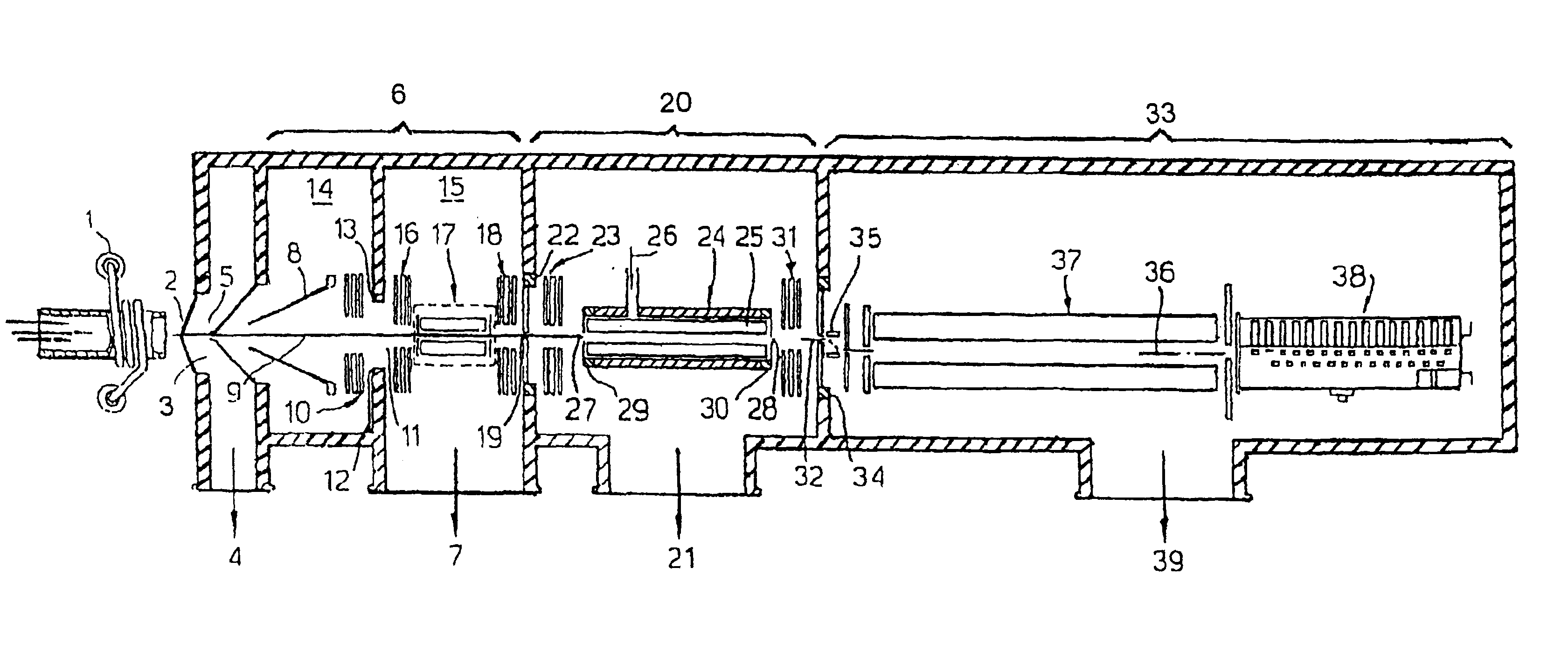
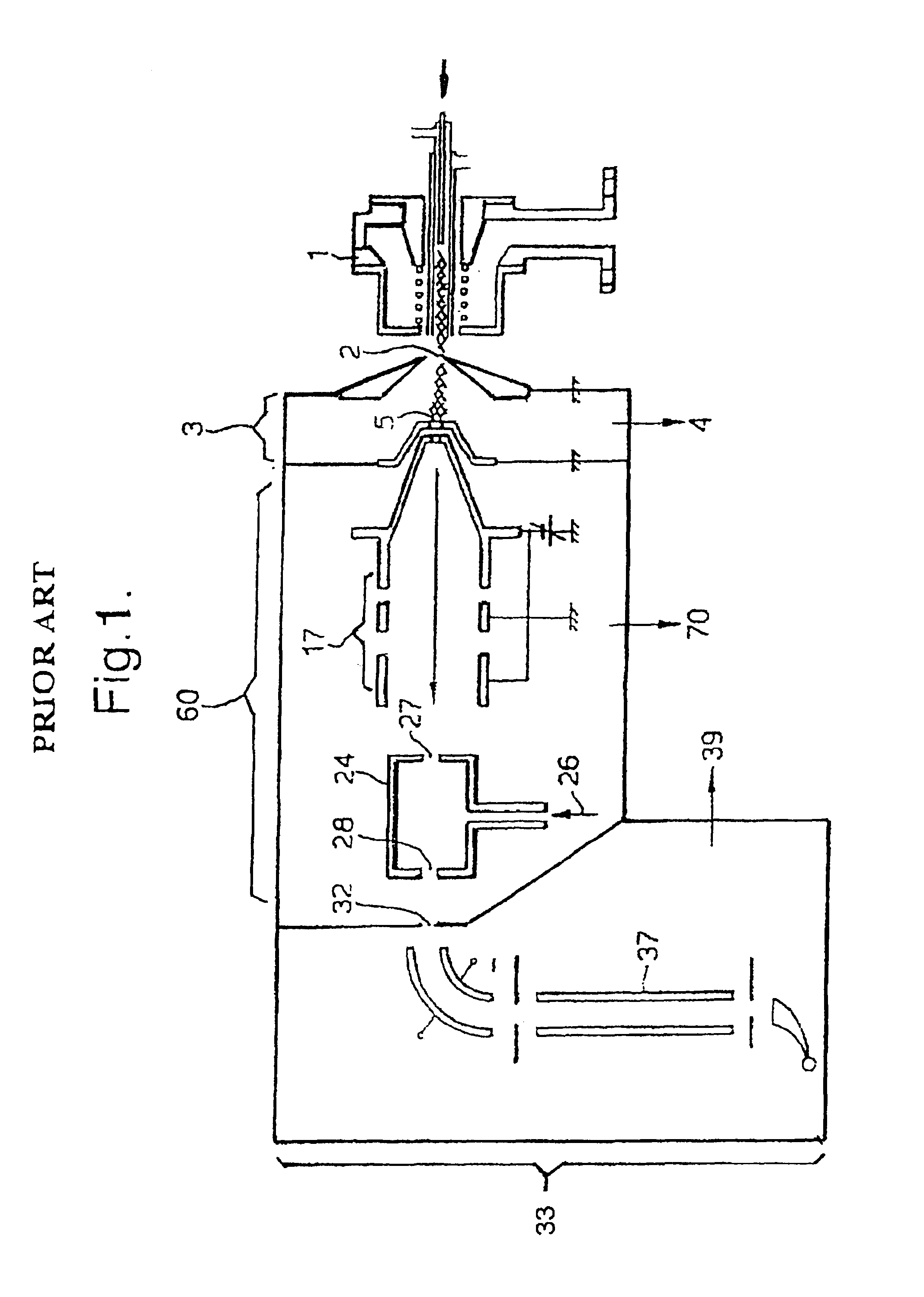
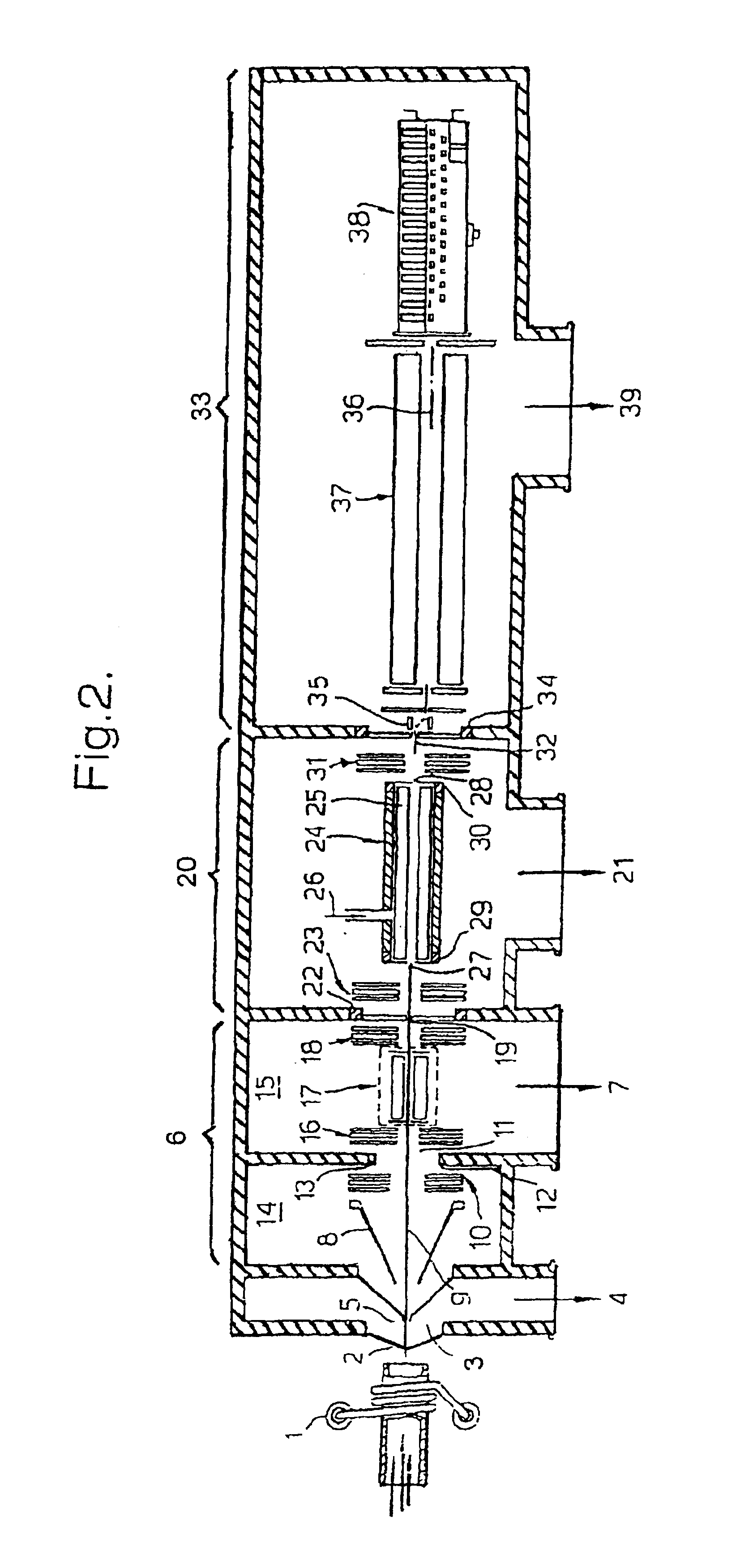
InactiveUS7202470B1Reduce gas loadSufficient transmissionStability-of-path spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionTransport systemIon beam
The present invention relates to inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICPMS) in which a collision cell is employed to selectively remove unwanted artefact ions from an ion beam by causing them to interact with a reagent gas. The present invention provides a first evacuated chamber (6) at high vacuum located between an expansion chamber (3) and a second evacuated chamber (20) containing the collision cell (24). The first evacuated chamber (6) includes a first ion optical device (17). The collision cell (24) contains a second ion optical device (25). The provision of the first evacuated chamber (5) reduces the gas load on the collision cell (24), by minimising the residual pressure within the collision cell (24) that is attributable to the gas load from the plasma source (1). This serves to minimise the formation, or re-formation, of unwanted artefact ions in the collision cell (24).
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI BREMEN +1
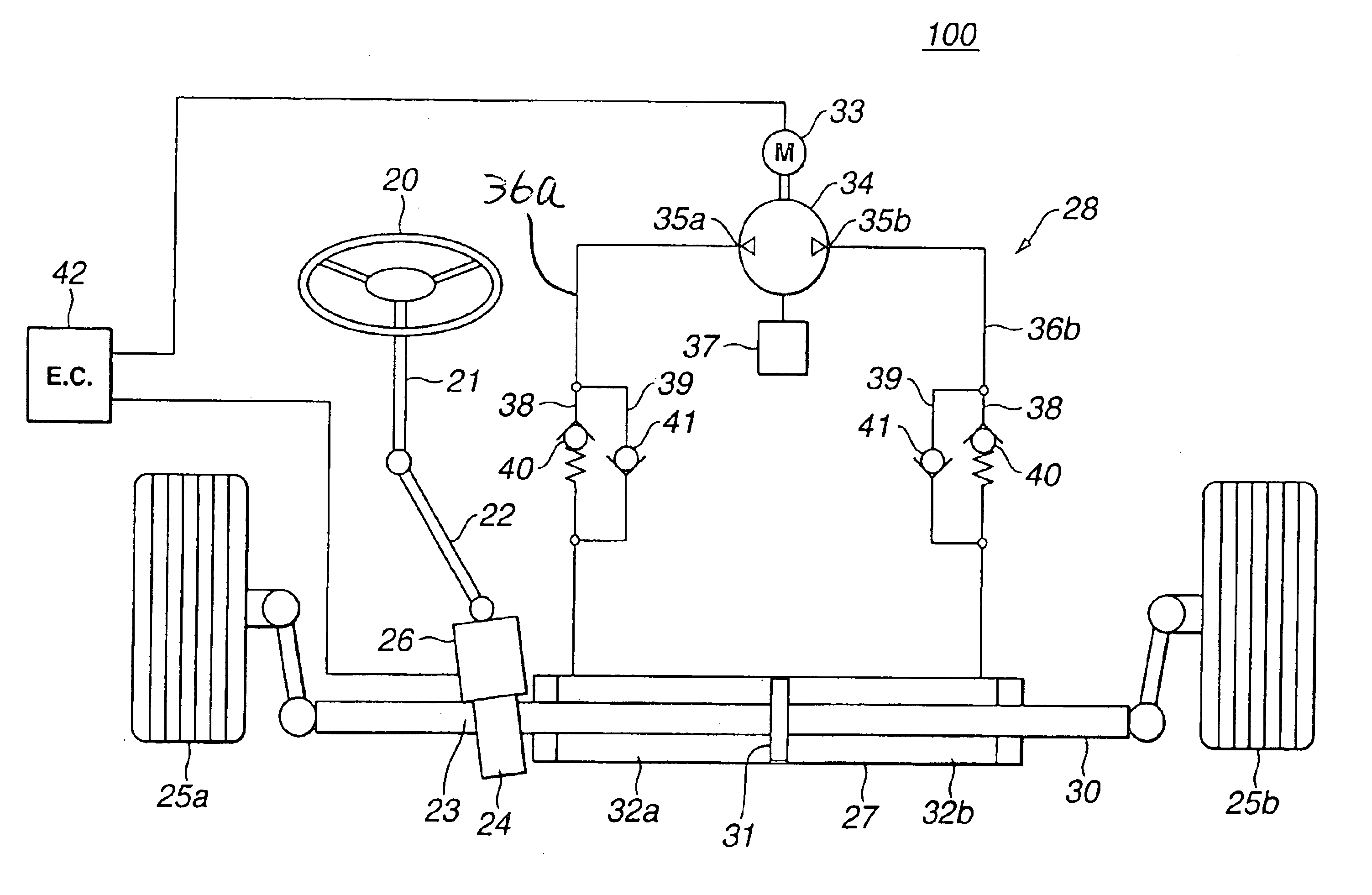
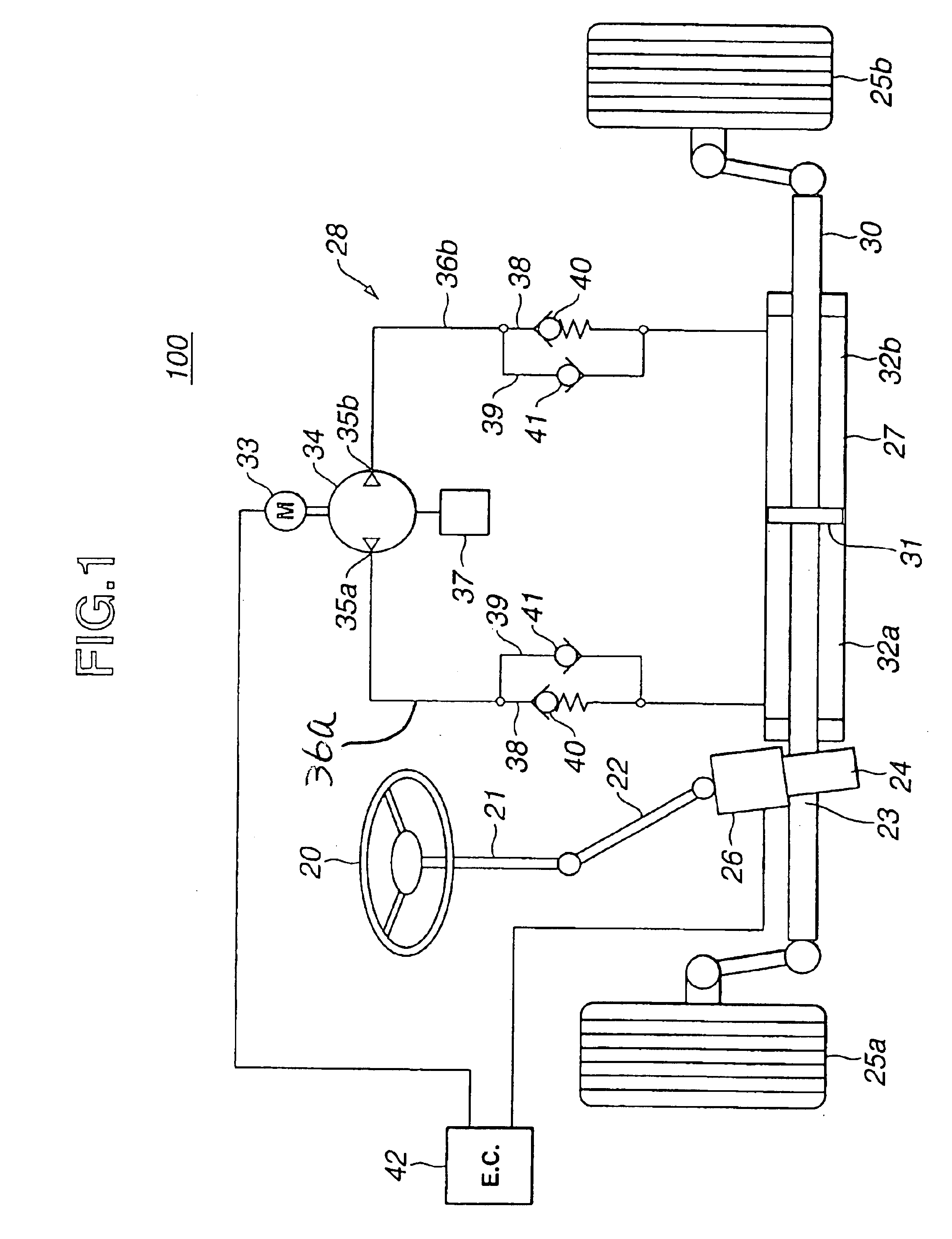
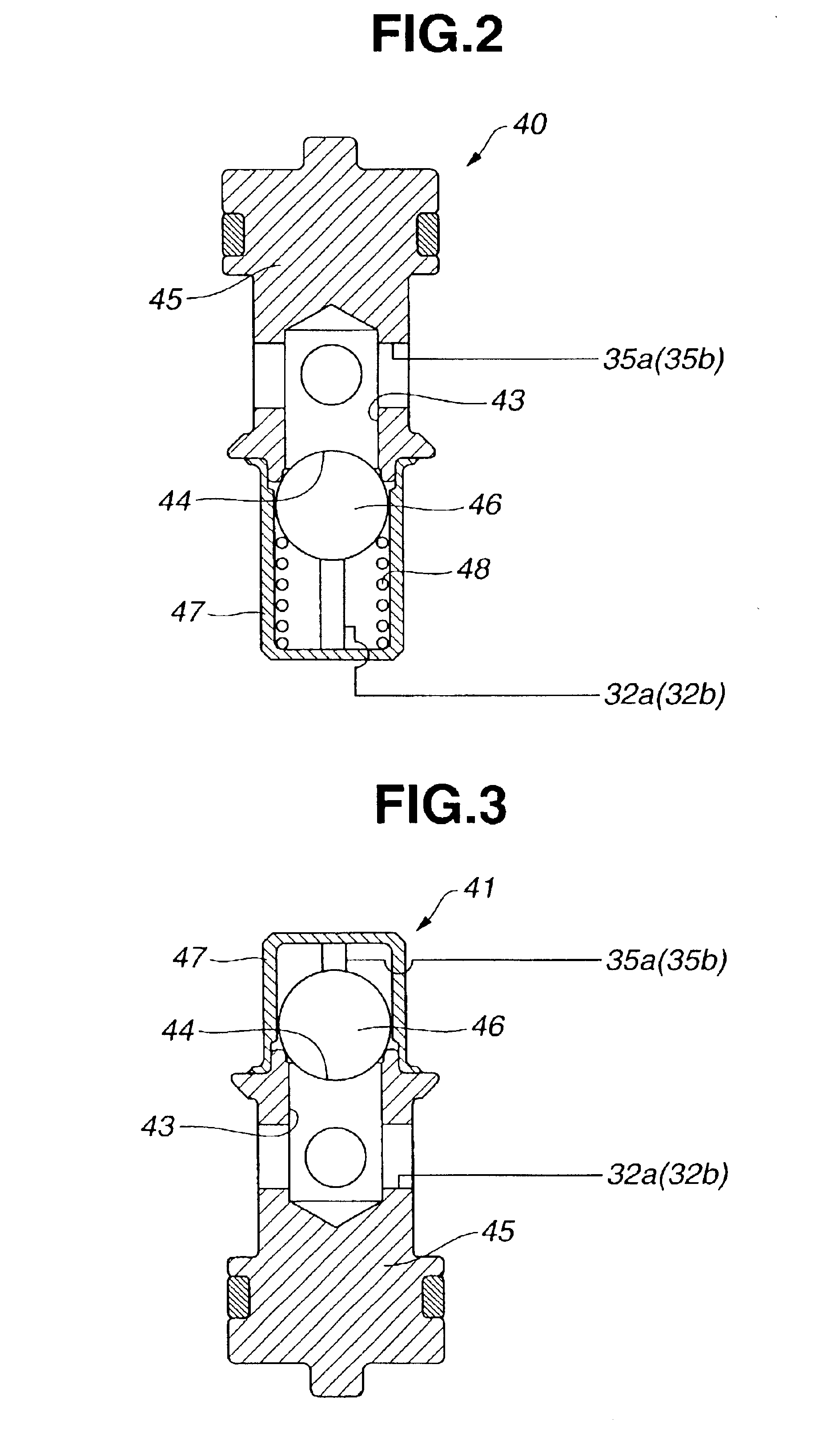
Power steering device
InactiveUS6880668B2Comfortable steering feelingSuppresses orFluid steeringDriver/operatorSteering wheel
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com