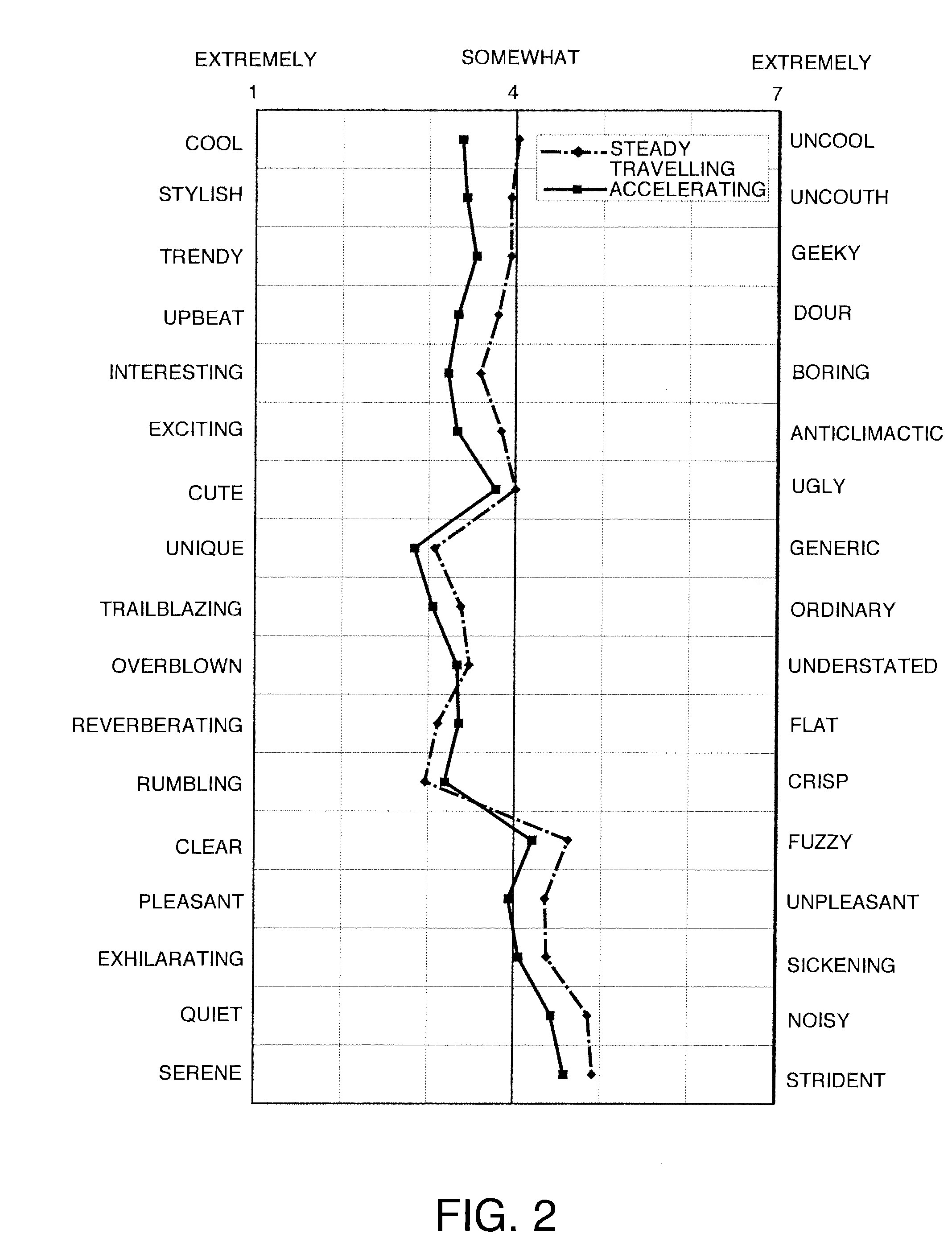
Patents
Literature
62 results about "Beat noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
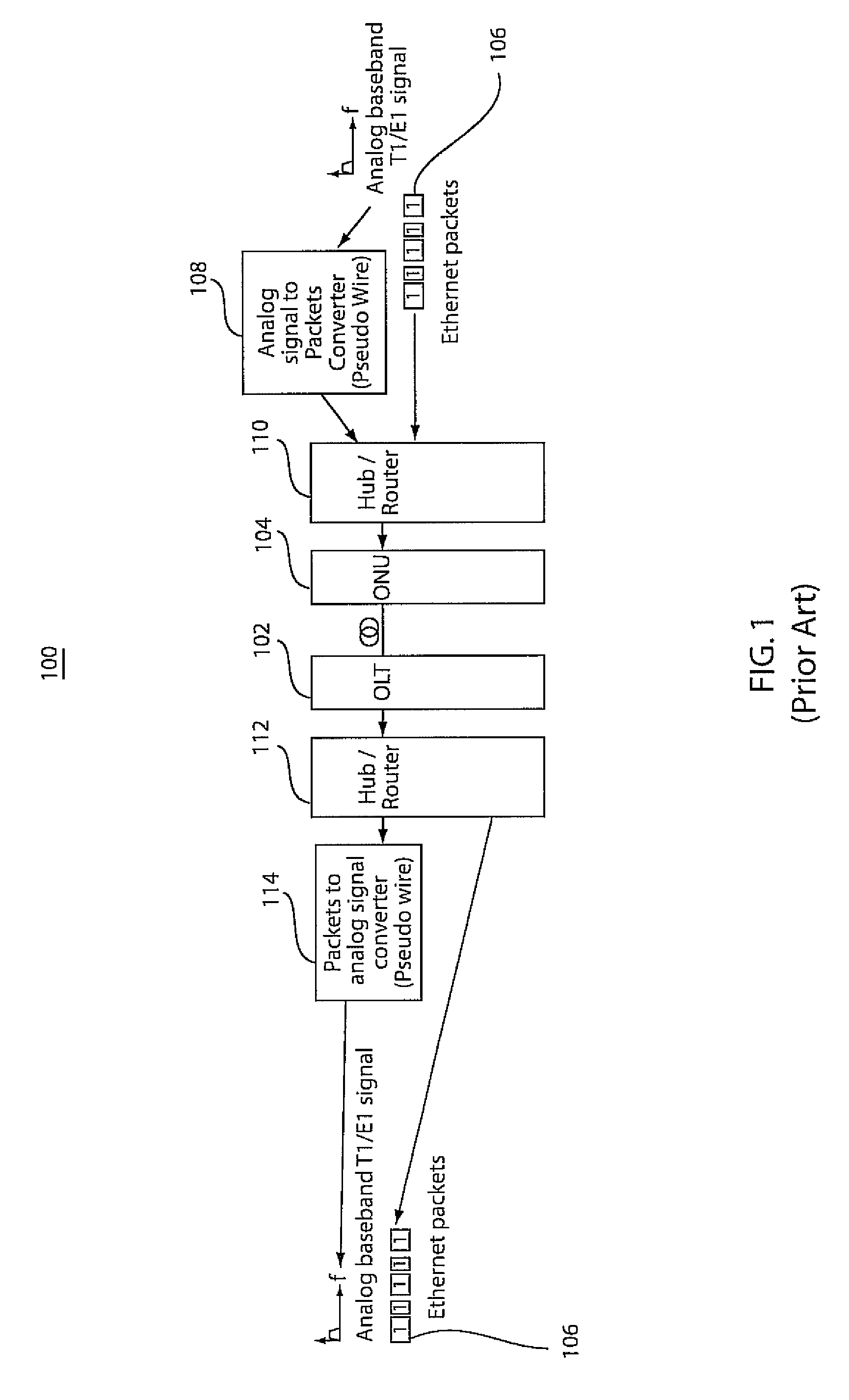
Single wavelength source-free ofdma-pon communication systems and methods
ActiveUS20100215368A1Low costReduce complexityOptical multiplexBaseband systemsSignal onCarrier signal
Owner:NEC CORP
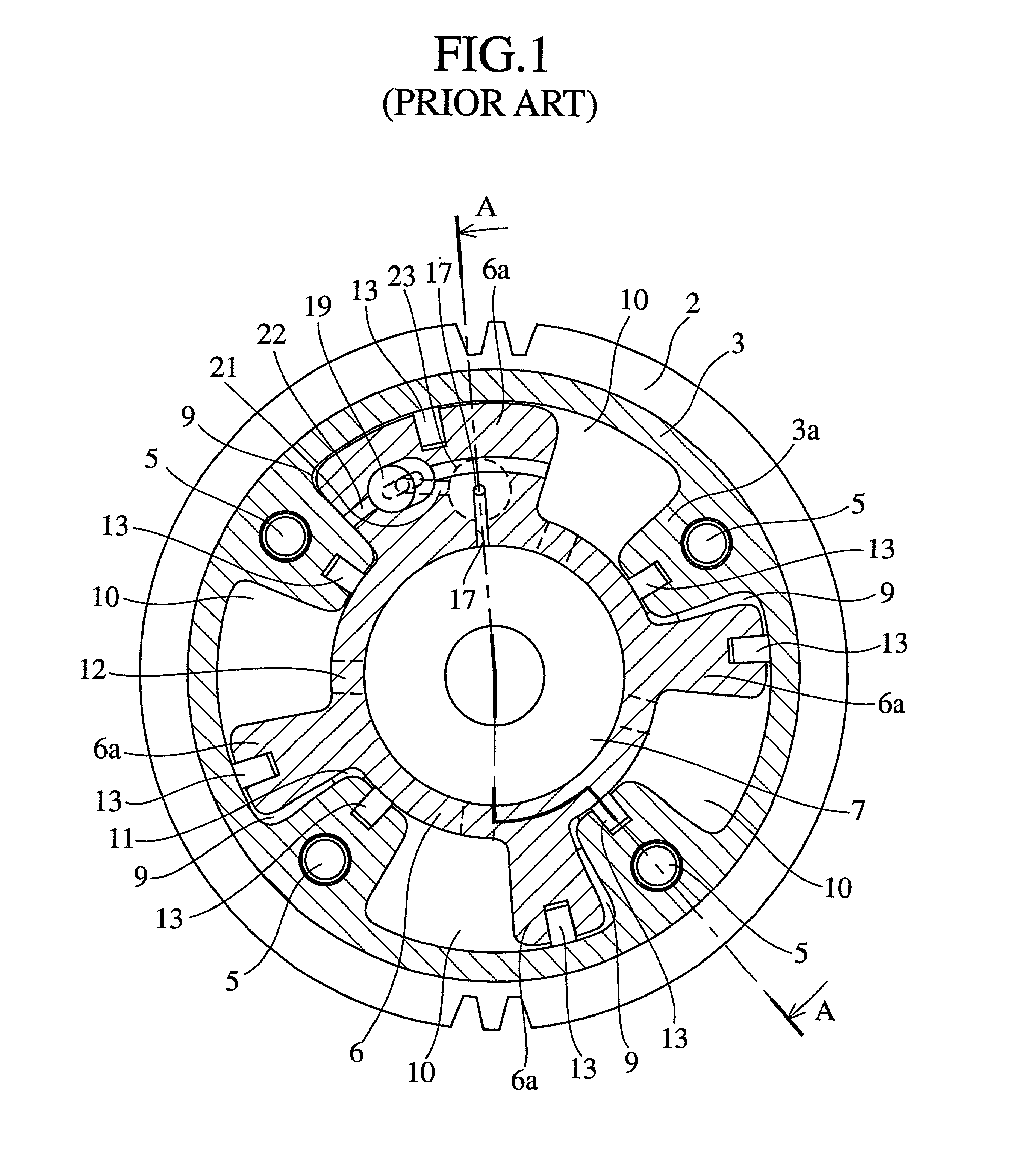
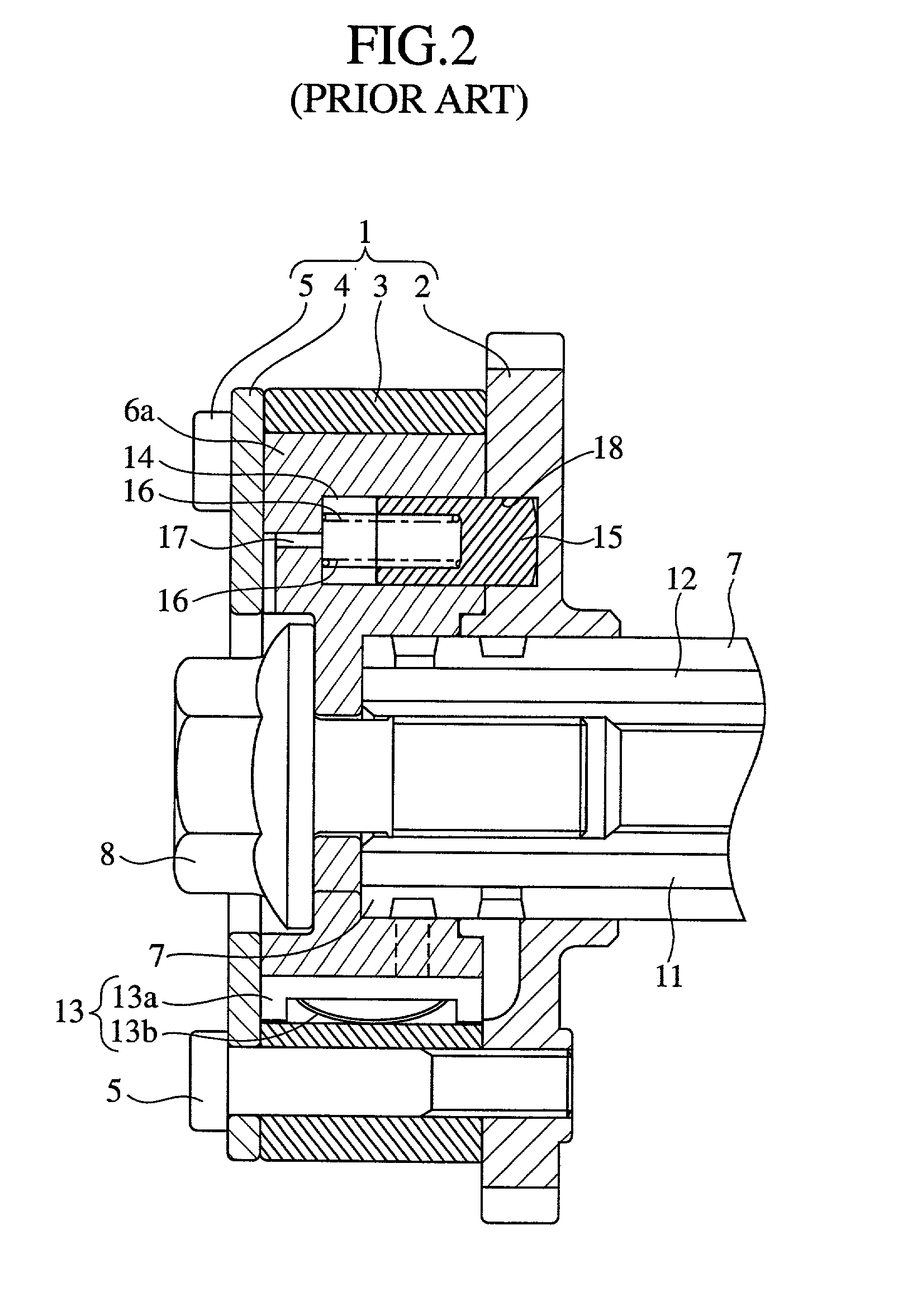
Valve timing control device
InactiveUS20020078913A1Avoid it happening againEasy to operateValve arrangementsMachines/enginesEngineeringResidual pressure
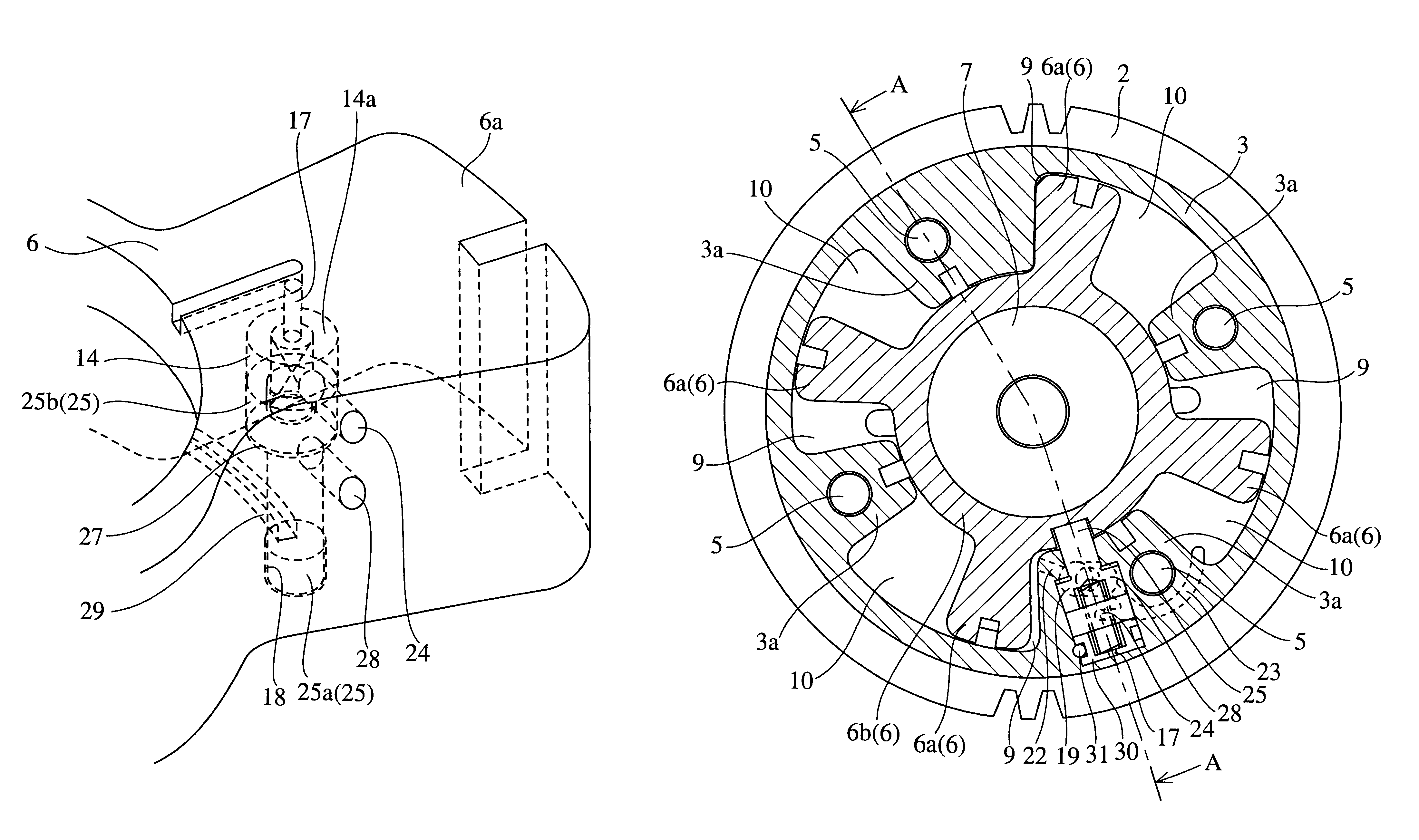
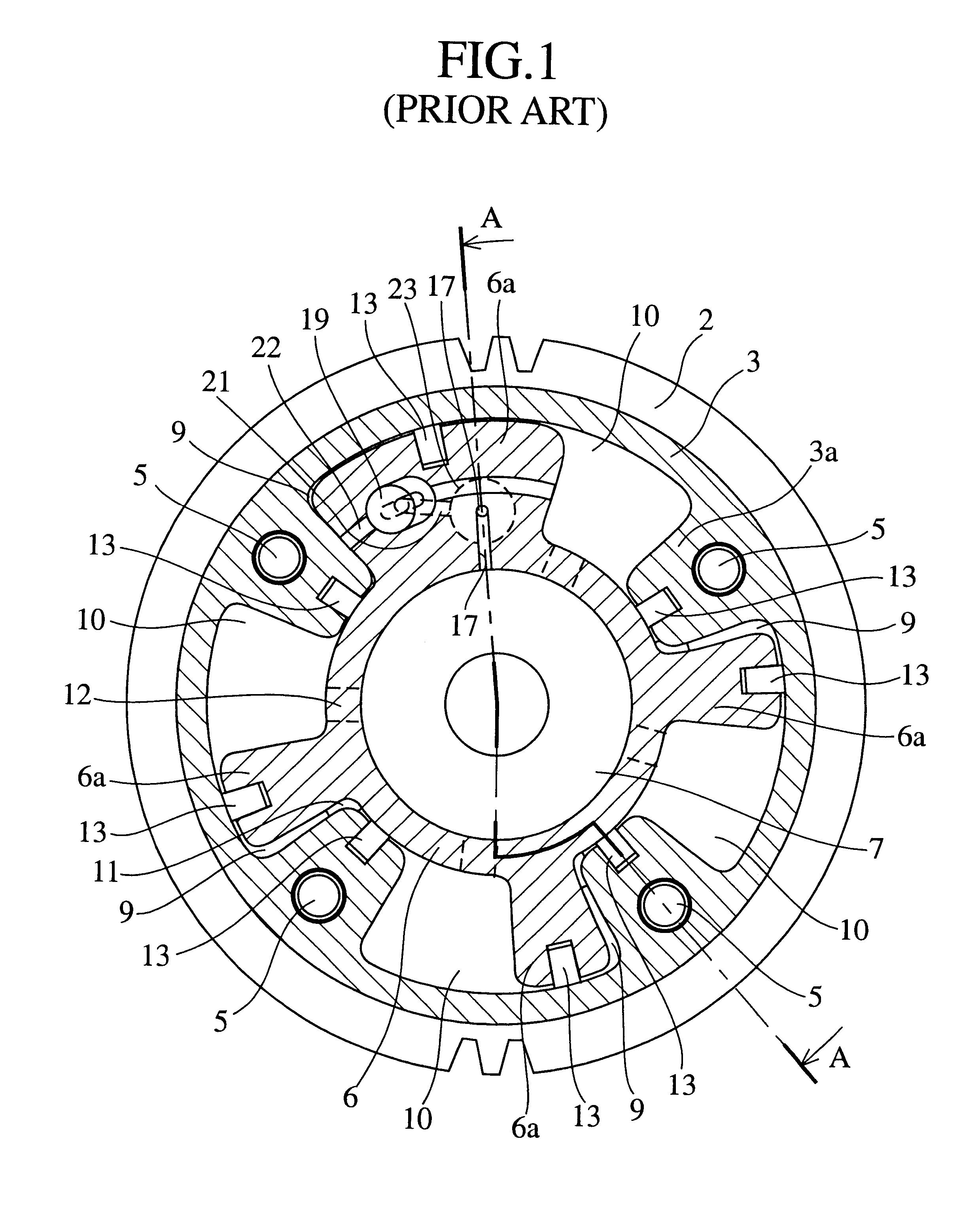
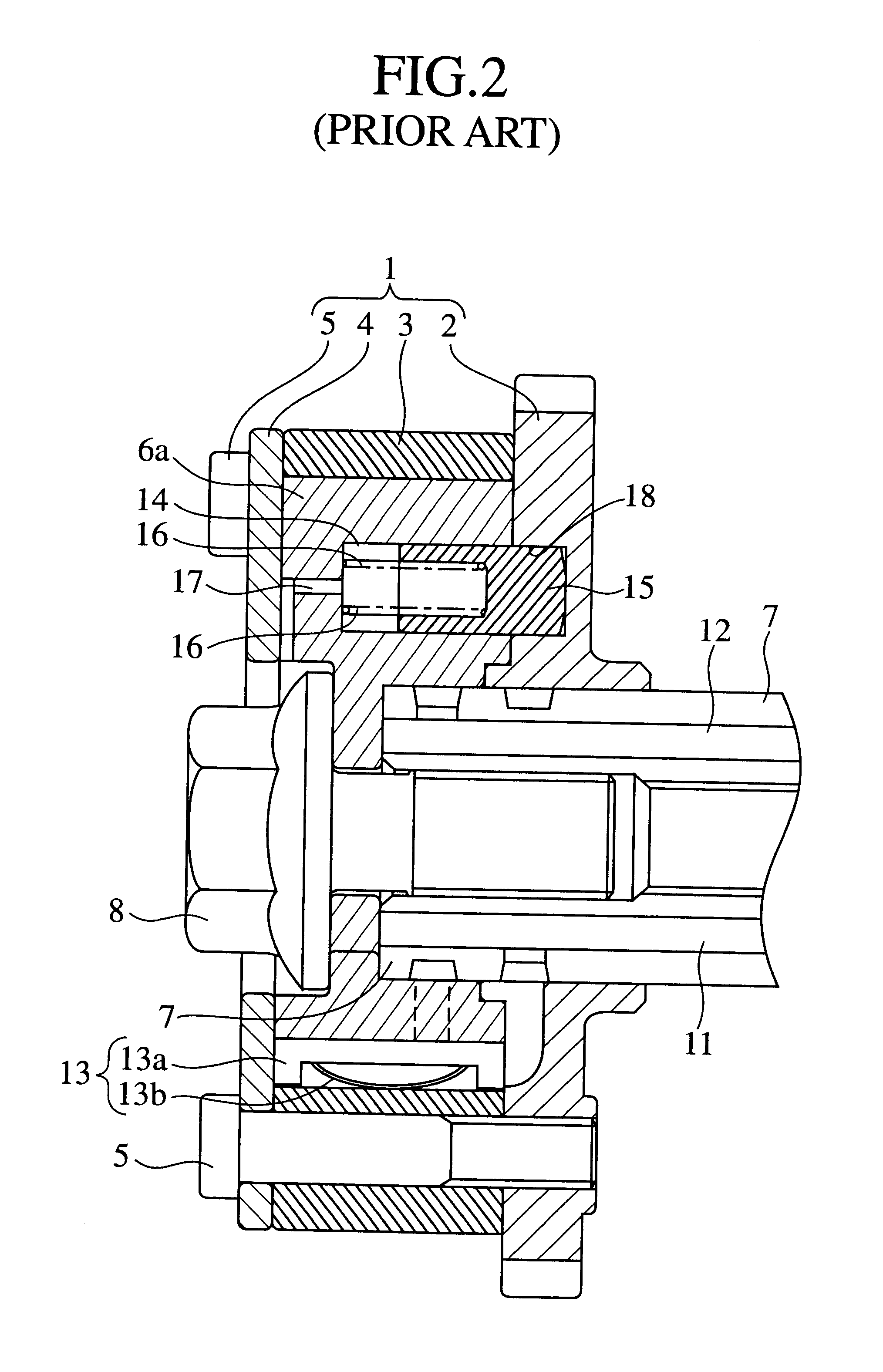
A valve timing control device includes a purge path communicating between a hydraulic chamber allowing the entry of hydraulic pressure on starting an engine and a backward pressurized section in an accommodation hole. When the hydraulic chamber allowing the entry of hydraulic pressure on starting the engine is the retardation side hydraulic chamber, a hydraulic pressure derived from an oil pump is supplied to the retardation side hydraulic chamber on starting the engine. On the way, air-mixed oil is discharged to outside of the device by way of a purge path, a backward pressurized section in the accommodation hole and the discharge hole. When the air is discharged, a residual pressure is produced in the backward pressurized section due to oil supplied thereto. The residual pressure results in the increase of an unlocking hydraulic pressure to prevent a locking member from being unlocked. When the application of a retardation side hydraulic pressure is switched to that of an advance side hydraulic pressure, the pressure presses a front end of a locking member against only a biasing force of a biasing means to unlock a locking relation. The valve timing control device allows the use of any kinds of locking pins, and prevents the occurrence of beat noise (abnormal noise) when air-mixed oil unlocks a locking relation on starting the engine.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Oven
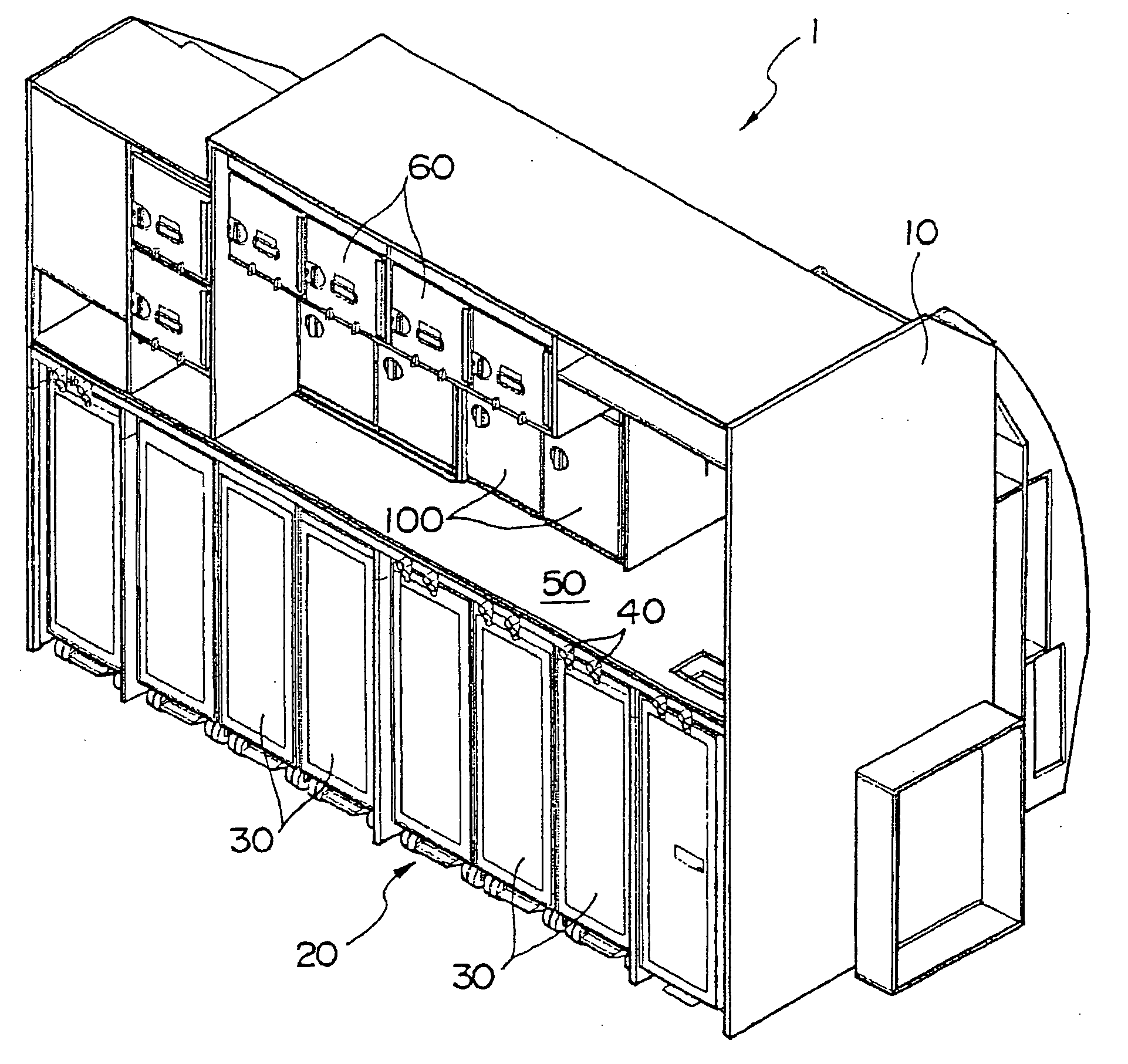
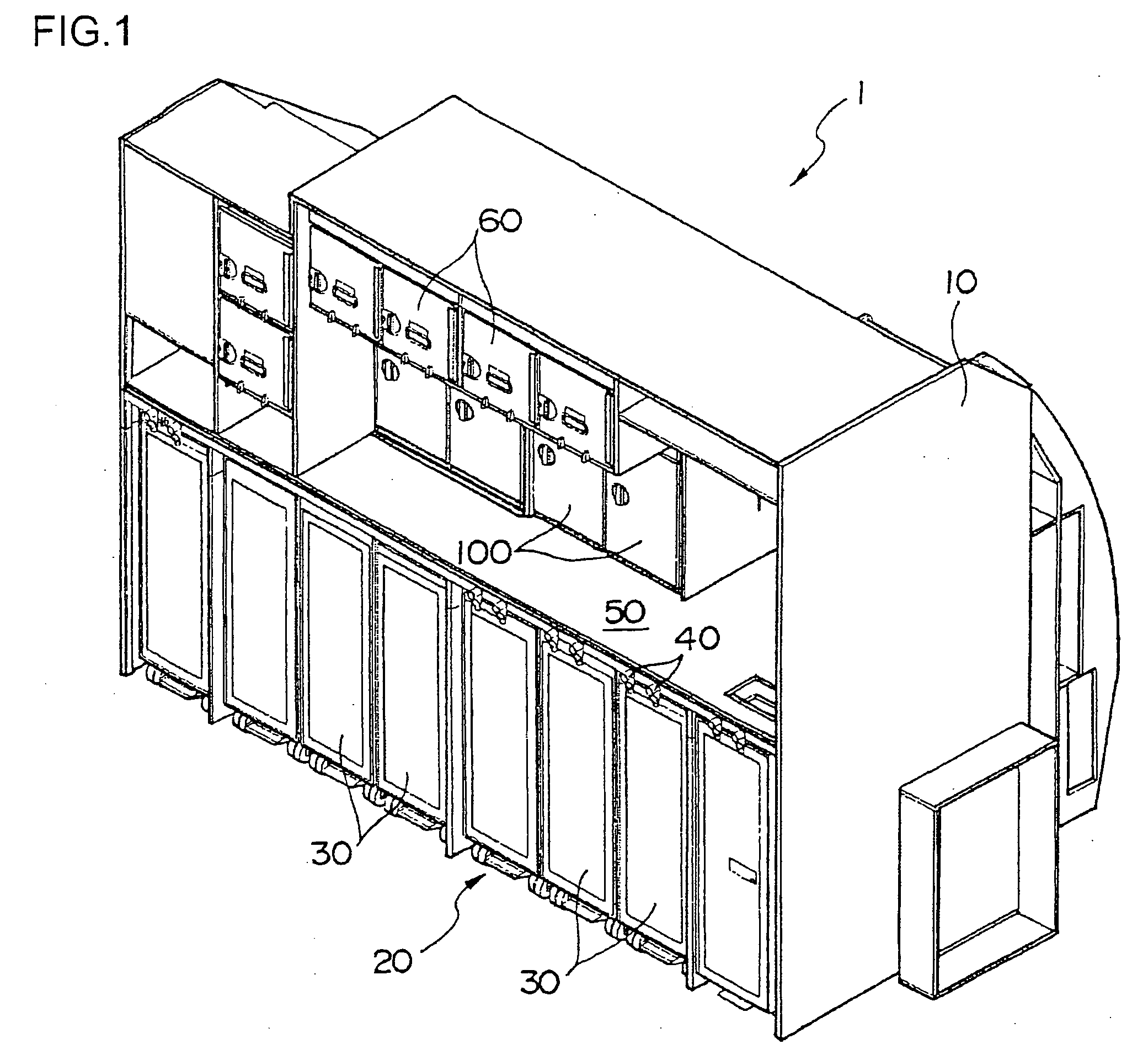
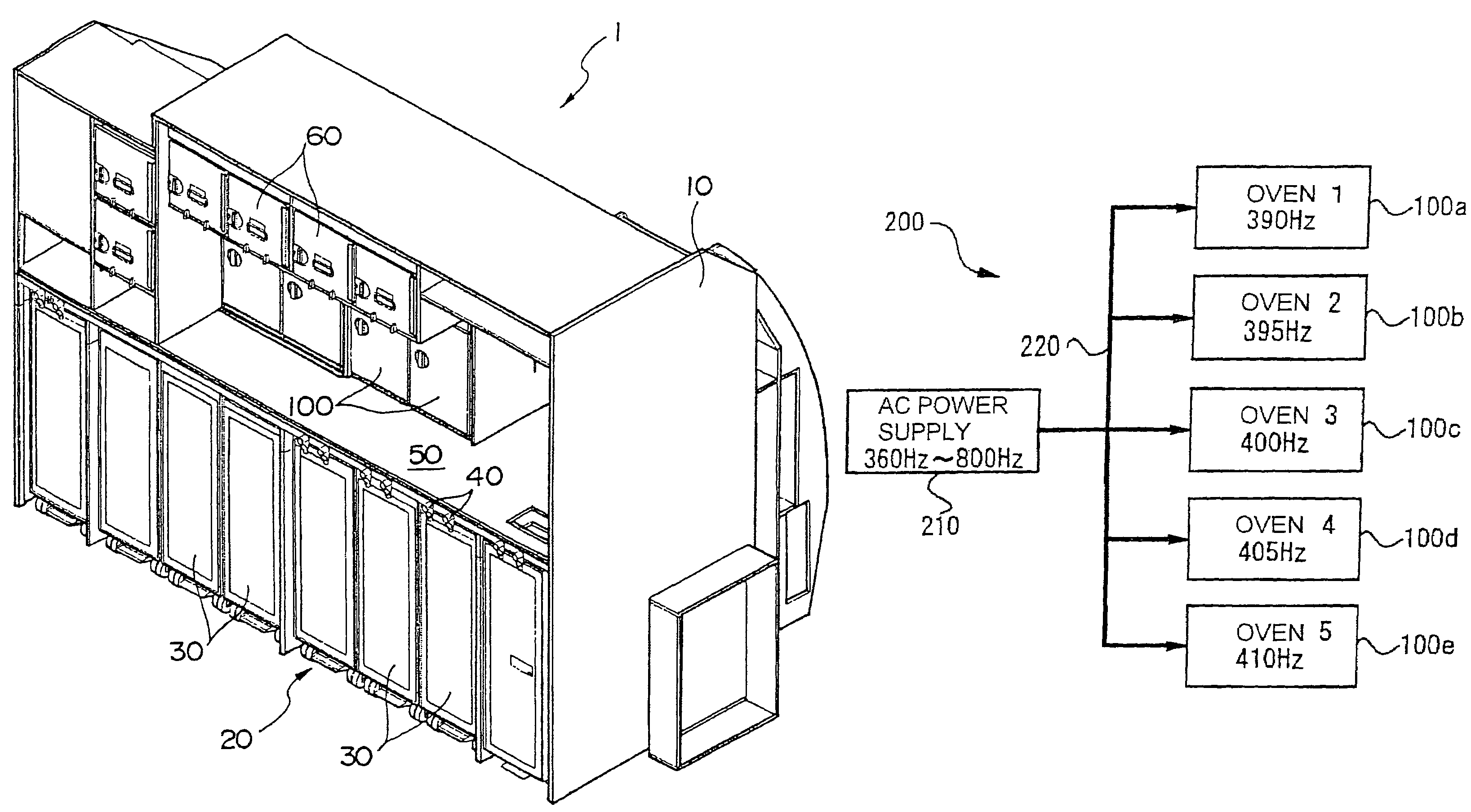
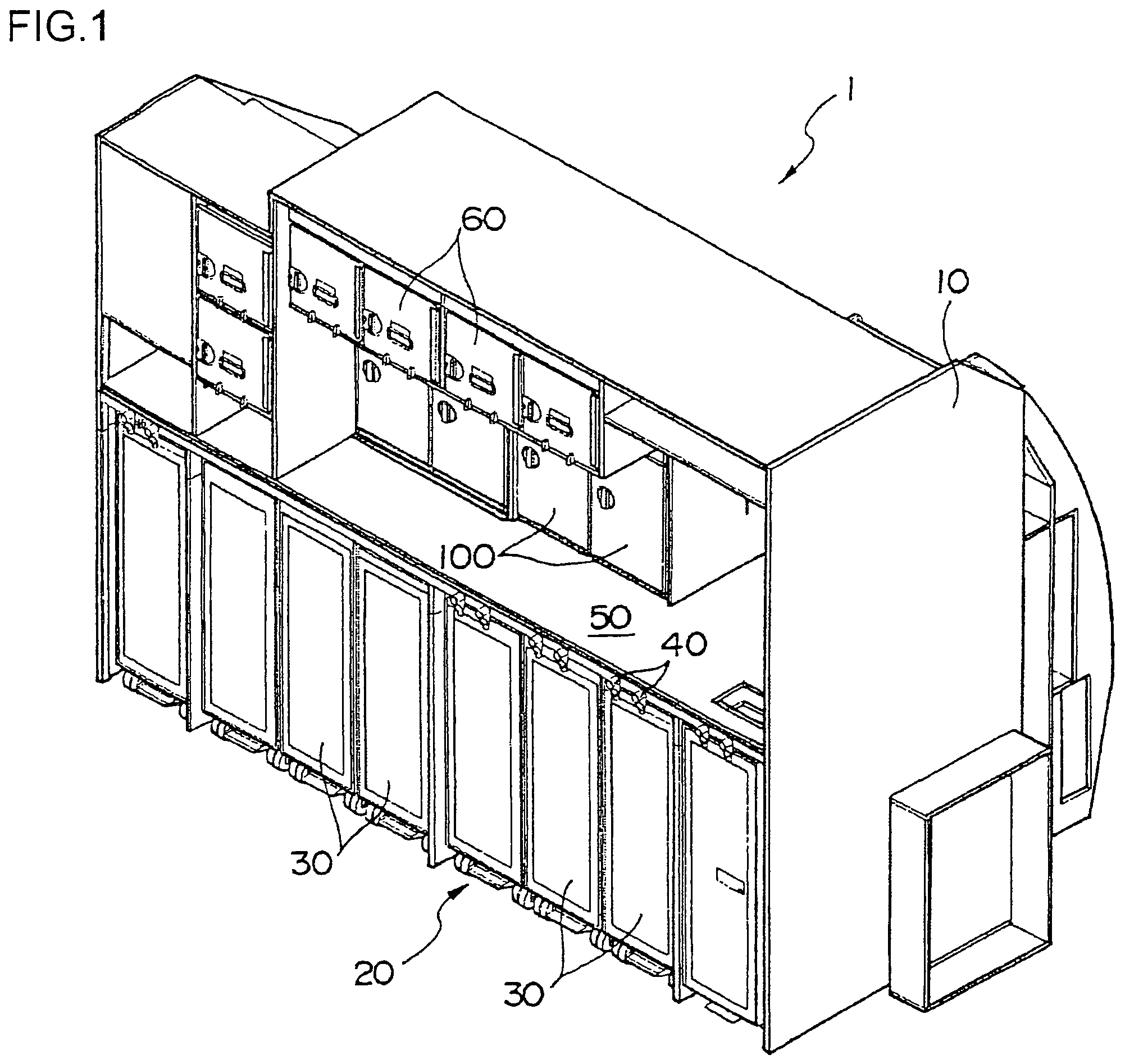
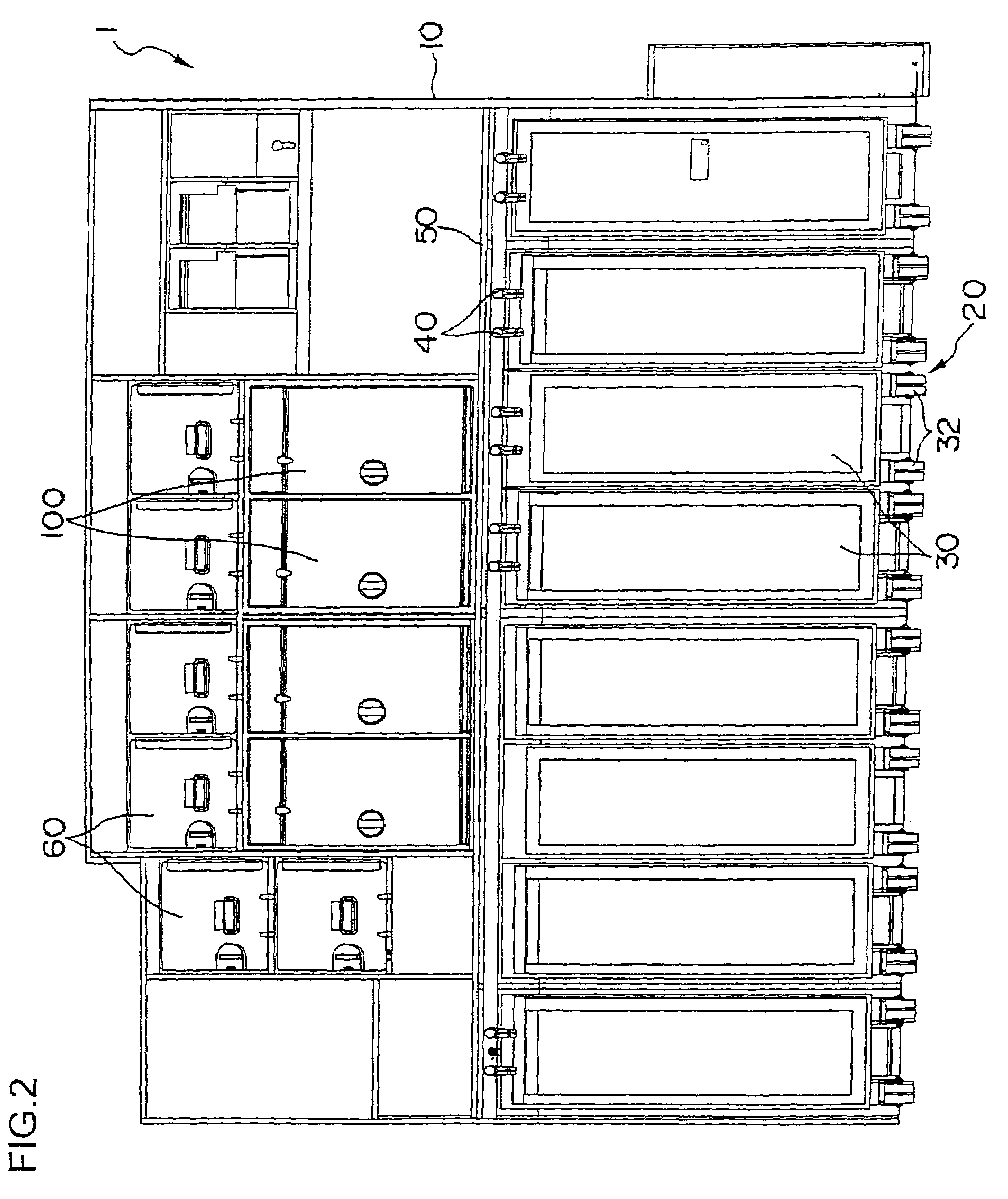
InactiveUS20060060181A1Prevents generation of beating noiseShow cabinetsDomestic stoves or rangesHoneycombEngineering
The invention aims at reducing the beating noise generated from motors of equipments placed in a galley unit of an aircraft. A galley unit 1 of an aircraft includes a cabinet 10 formed of honeycomb panels and the like. The cabinet 10 has a counter 50 for cooking, and a compartment 20 formed under the counter 50 for storing service carts 30. A plurality of ovens 100 for heating warm dishes are provided above the counter 50. Each oven 100 has a fan motor for making the inner heat even. If all the fan motors of the ovens are driven at the same rotation frequency, a beating noise will be generated from the motor and amplified through the compartment 20. Therefore, the rotation frequencies of the fan motors are slightly varied.
Owner:JAMCO
Valve timing control device
InactiveUS6460496B2Avoid it happening againValve arrangementsMachines/enginesEngineeringResidual pressure
A valve timing control device includes a purge path communicating between a hydraulic chamber allowing the entry of hydraulic pressure on starting an engine and a backward pressurized section in an accommodation hole. When the hydraulic chamber allowing the entry of hydraulic pressure on starting the engine is the retardation side hydraulic chamber, a hydraulic pressure derived from an oil pump is supplied to the retardation side hydraulic chamber on starting the engine. On the way, air-mixed oil is discharged to outside of the device by way of a purge path, a backward pressurized section in the accommodation hole and the discharge hole. When the air is discharged, a residual pressure is produced in the backward pressurized section due to oil supplied thereto. The residual pressure results in the increase of an unlocking hydraulic pressure to prevent a locking member from being unlocked. When the application of a retardation side hydraulic pressure is switched to that of an advance side hydraulic pressure, the pressure presses a front end of a locking member against only a biasing force of a biasing means to unlock a locking relation. The valve timing control device allows the use of any kinds of locking pins, and prevents the occurrence of beat noise (abnormal noise) when air-mixed oil unlocks a locking relation on starting the engine.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
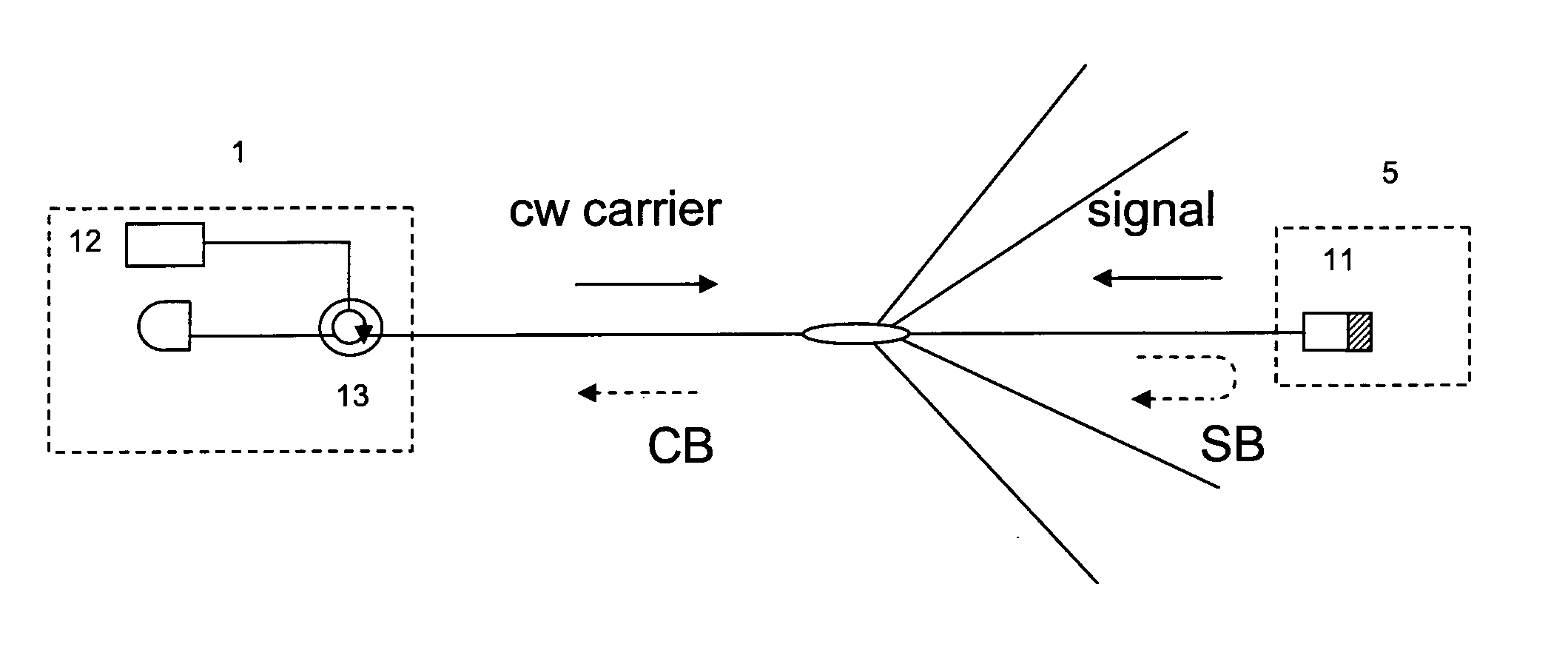
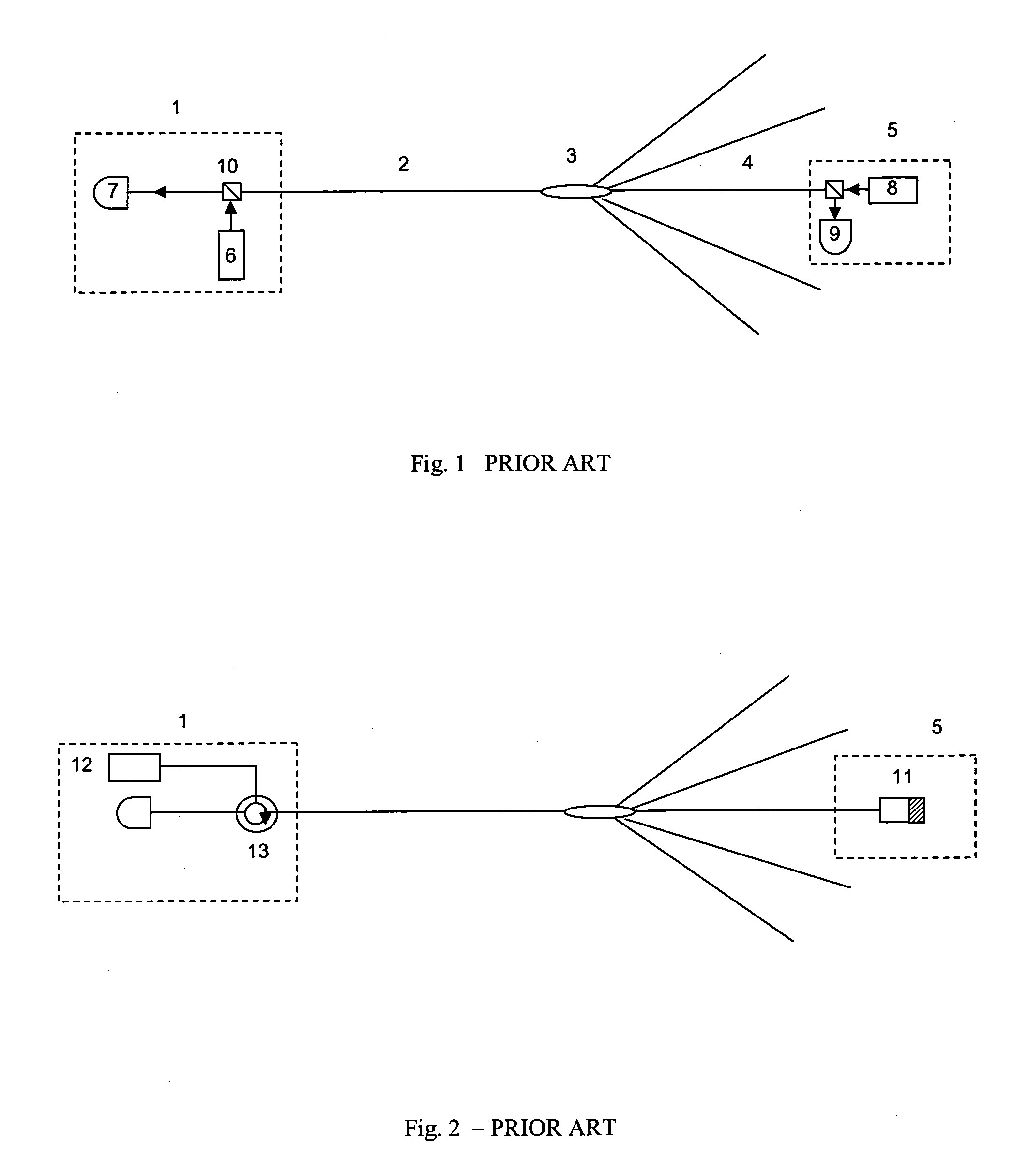
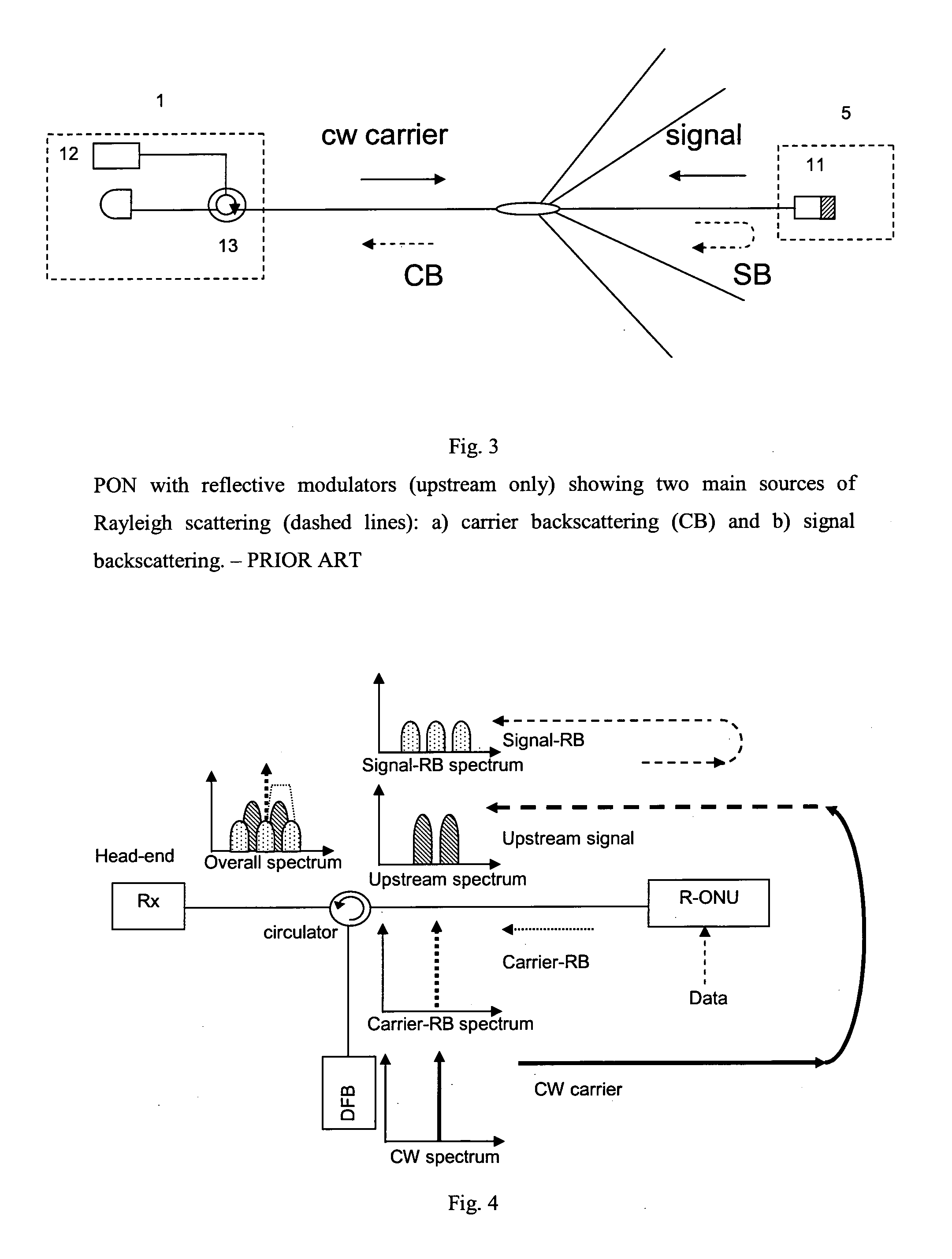
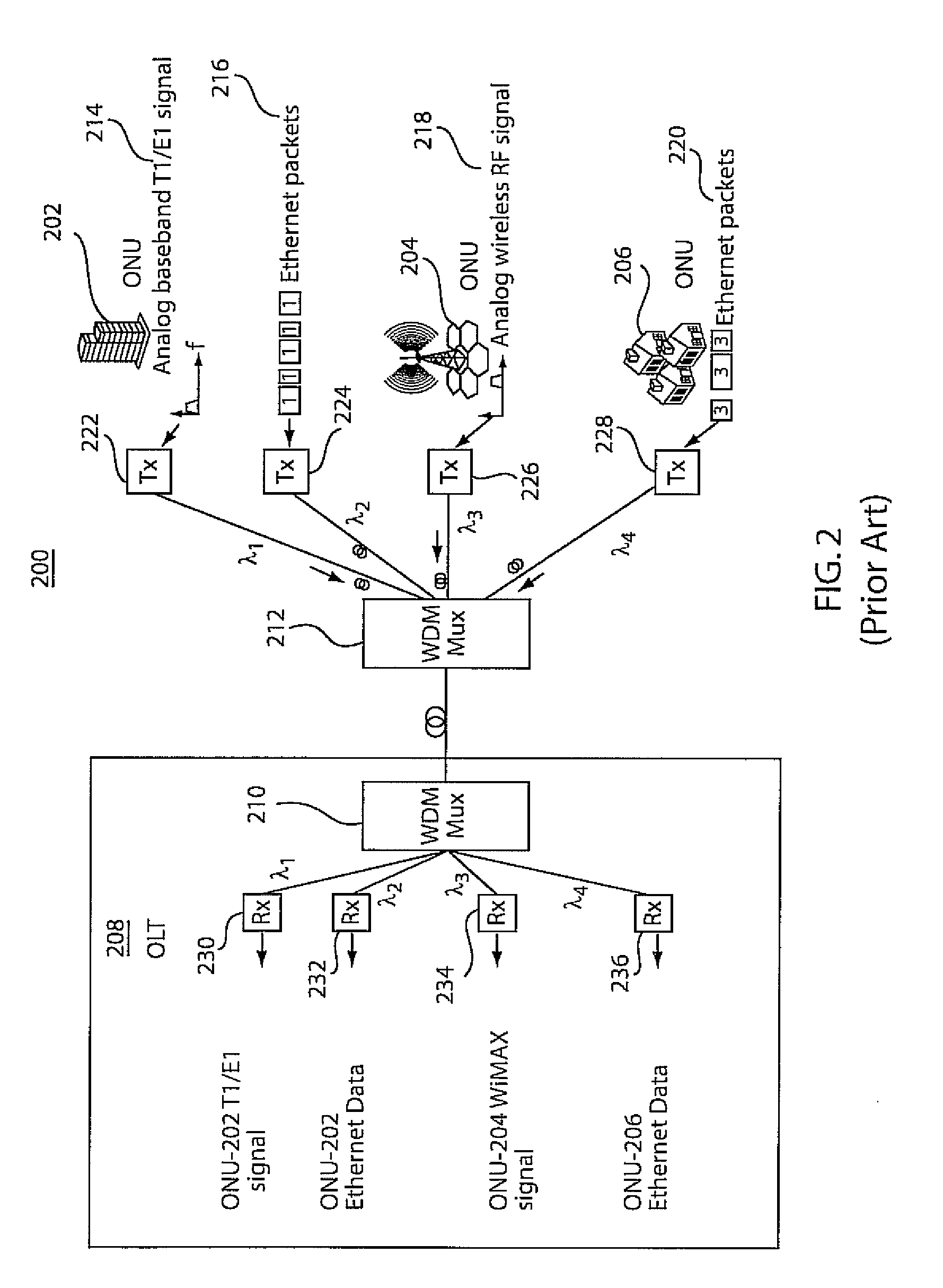
Optical communication system
InactiveUS20100111543A1Avoid noiseReduce disturbing noiseElectromagnetic transmittersMultiple station single light sourceData streamCarrier signal
An optical transmitter is of the reflective modulation type and has a means of generating reflection, a mixer for mixing a data stream and a sub-carrier, and an optical modulator for modulating an optical carrier with the output from the mixer in order to avoid optical beat-interference noise arising from, for example, Rayleigh backscattering. The modulator is in one embodiment of the interferometric type such as a Mach-Zehnder Modulator (MZM) operated to suppress the optical carrier at the transmitter output in order to reduce optical beat interference noise. The modulator preferably implements CSS-AMPSK modulation, which suppresses optical beat noise and achieves strong dispersion tolerance, enabling, for example, 10 Gb / s data transmission over 100 km distance without dispersion compensation. The transmitter may have a duobinary encoder, which encodes the data prior to mixing with the sub-carrier.
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE CORK NAT UNIV OF IRELAND CORK
Reduction of interferometer noise in an optical network
InactiveUS6134037AReduce noiseLaser detailsDistortion/dispersion eliminationComputer scienceCenter frequency
PCT No. PCT / GB94 / 01149 Sec. 371 Date Jan. 22, 1996 Sec. 102(e) Date Jan. 22, 1996 PCT Filed May 27, 1994 PCT Pub. No. WO94 / 28648 PCT Pub. Date Dec. 8, 1994In an optical network through which data is transmitted as a stream of bits during successive bit periods by an optical source with a given optical center frequency, to a receiver for detecting a frequency baseband, interferometric noise power, in particular incoherent beat noise power, is minimized by causing a variation in the center frequency of the source such as to cause a redistribution of the incoherent beat noise power from the baseband to higher frequencies, thereby reducing the noise in the baseband.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
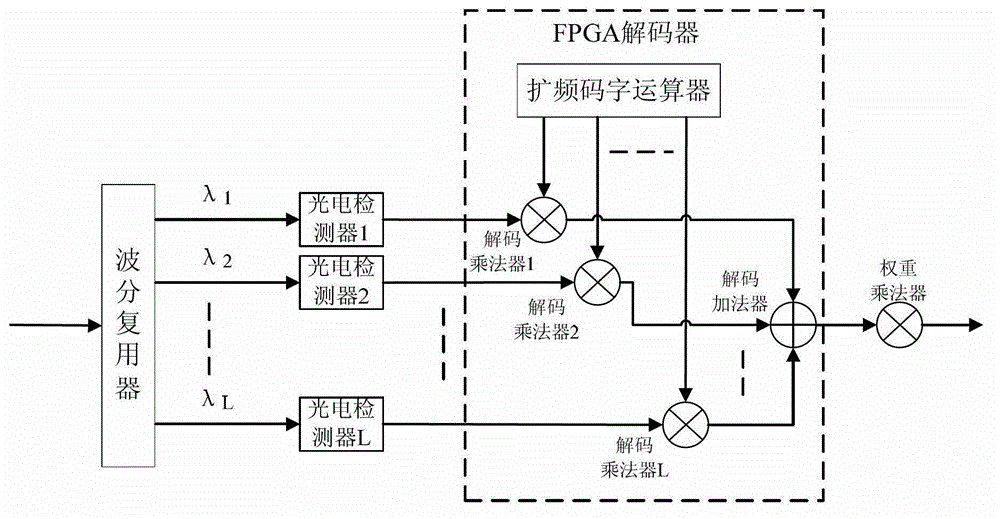
Optical code demultiplexing/multiplexing sending and receiving method and device based on electric domain encoding/decoding
InactiveCN102882631AAsynchronous random accessEliminate beat noiseWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic receiversTransmission performanceDigital signal
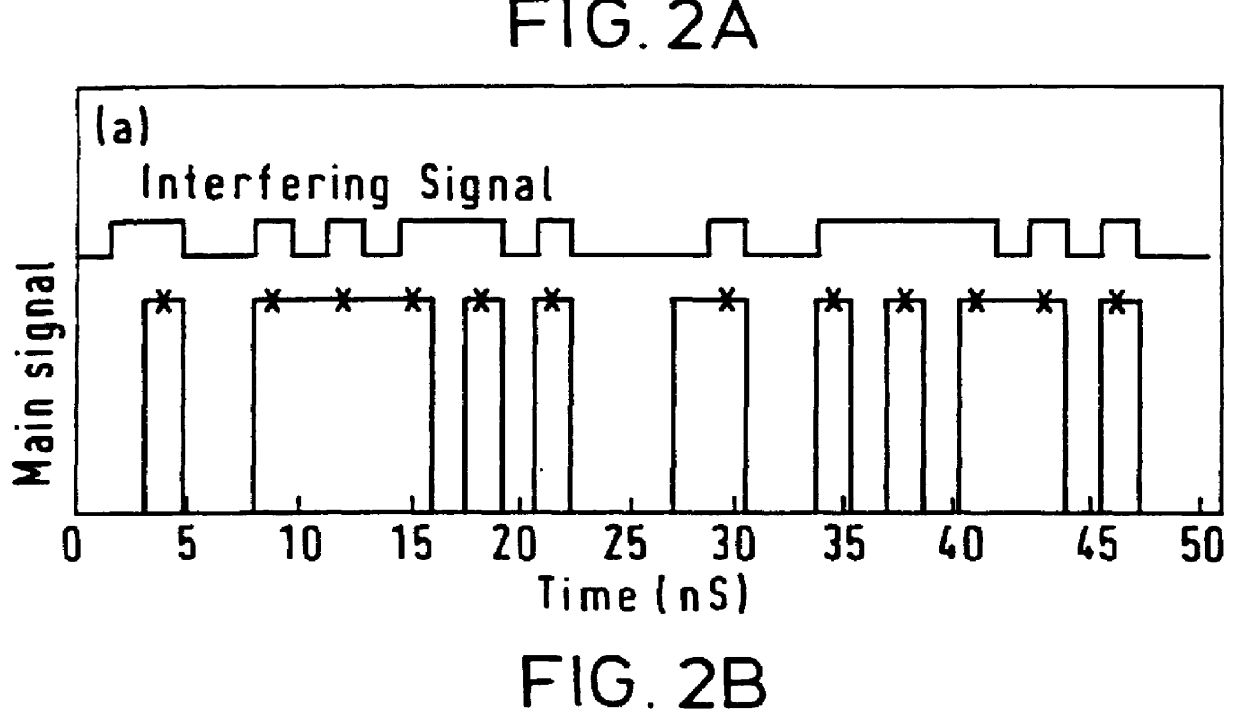
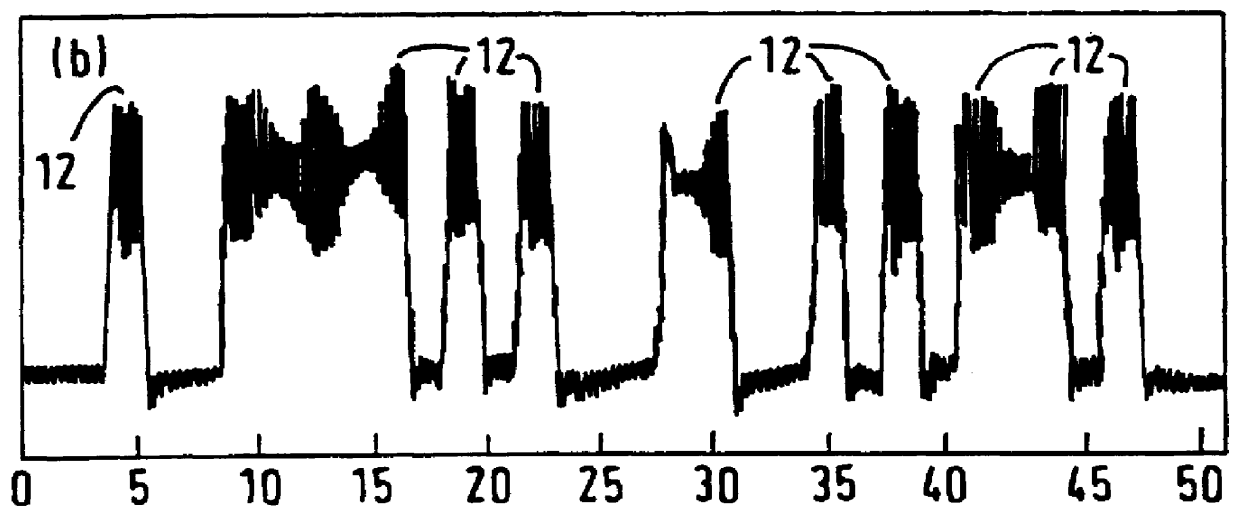
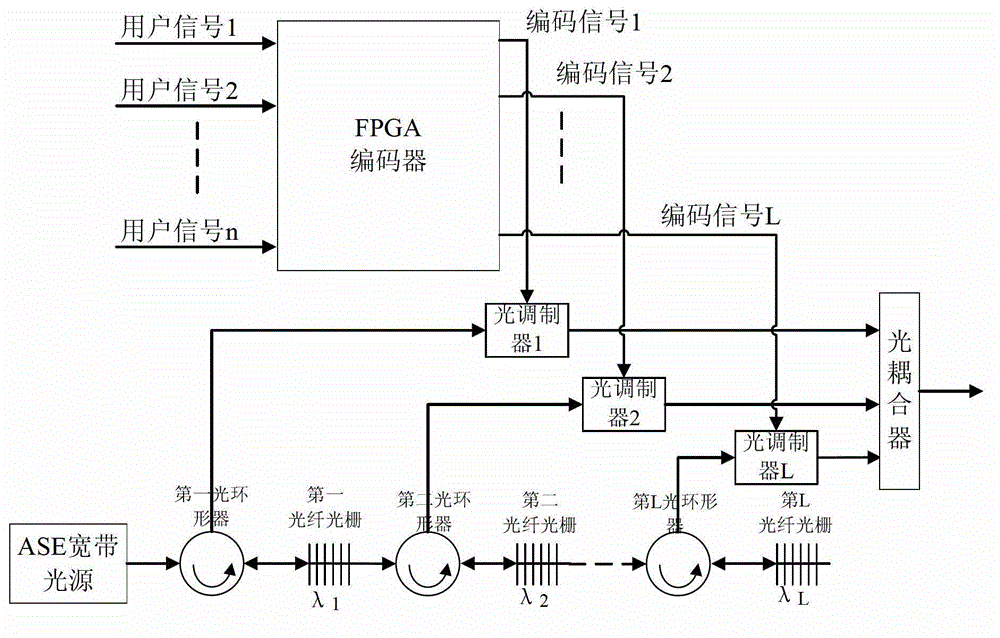
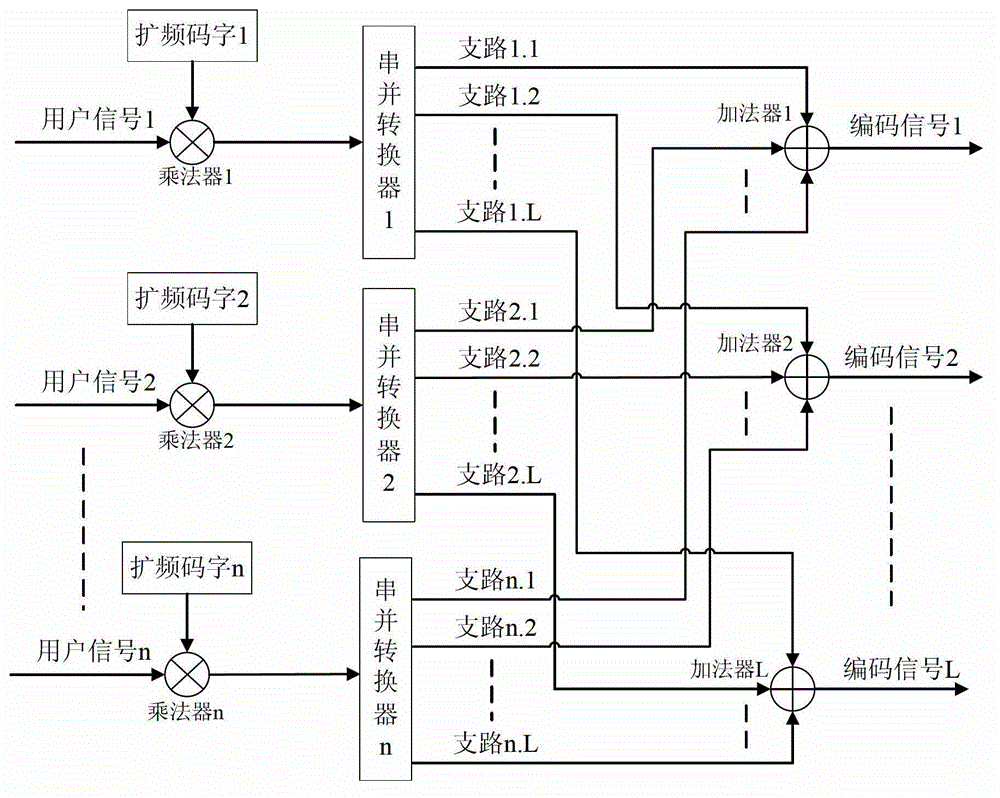
The invention discloses an optical code demultiplexing / multiplexing sending and receiving method and device based on electric domain encoding / decoding. Different spread spectrum codons are used for digital signals of different users, spread spectrum encoding is carried out by an electric domain encoder, electric encoding signals of all the users are multiplexed, and all the encoding signals are modulated on one group of optical signals with different wave lengths for transmission. Wavelength demultiplexing and photoelectric conversion are first carried out on received optical signals by a wave demultiplexer / multiplexer at a receiving end, and data signals of target users can be recovered as long as corresponding decoder structures are used for the electric signals with different wavelengths. Compared with a traditional incoherent optical code demultiplexing / multiplexing system, the method has the advantages that influence brought by beating noise and multiple access interference can be better eliminated, and better system transmission performance is obtained.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
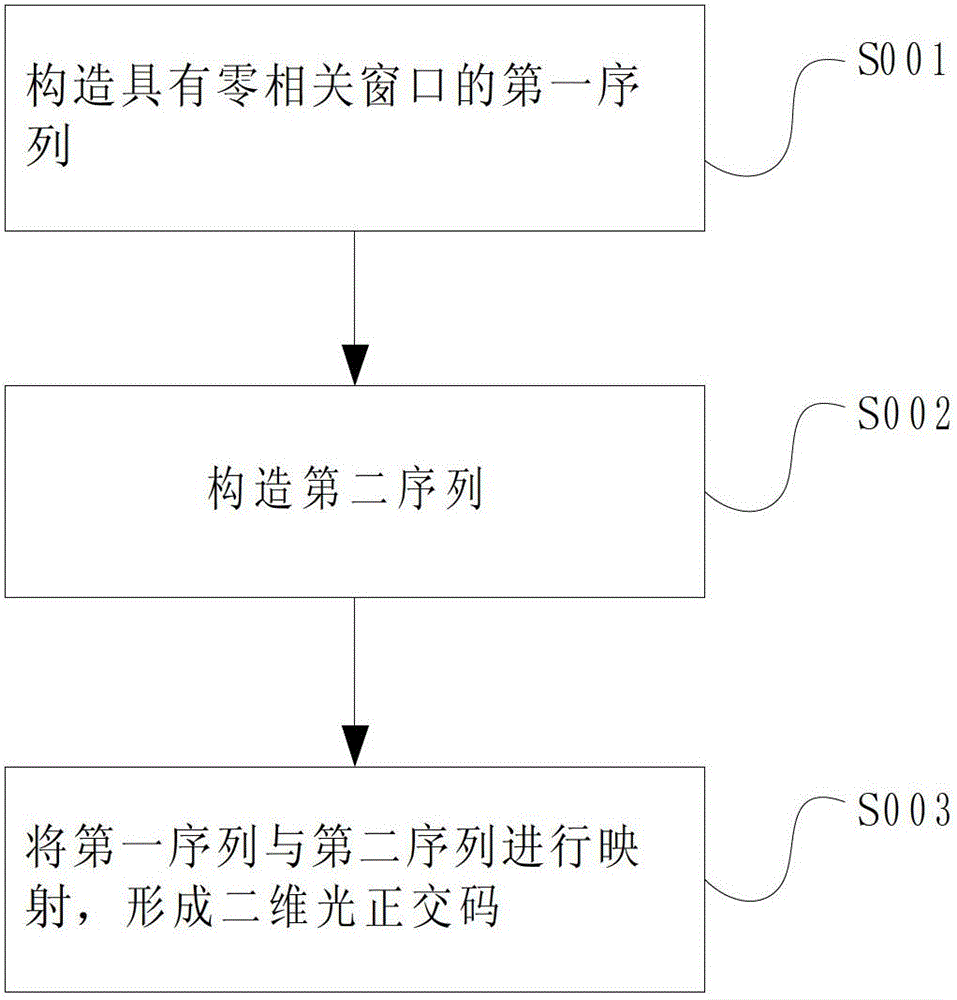
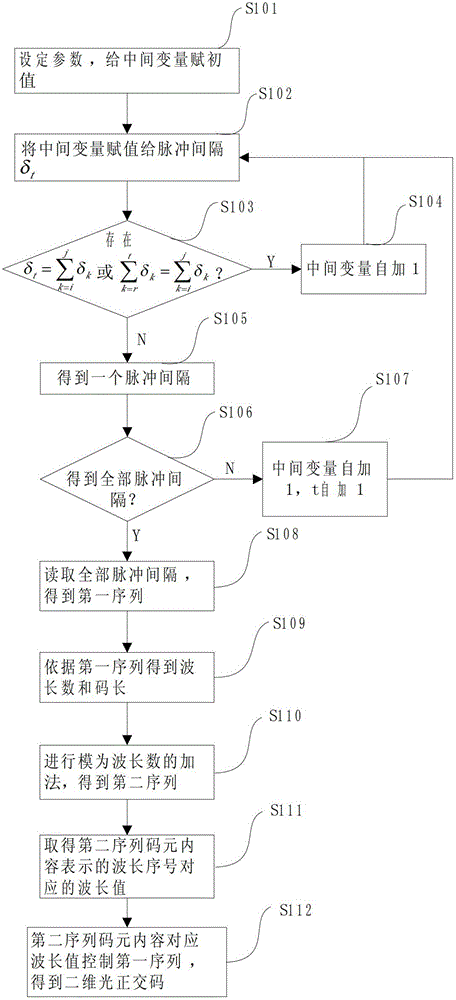
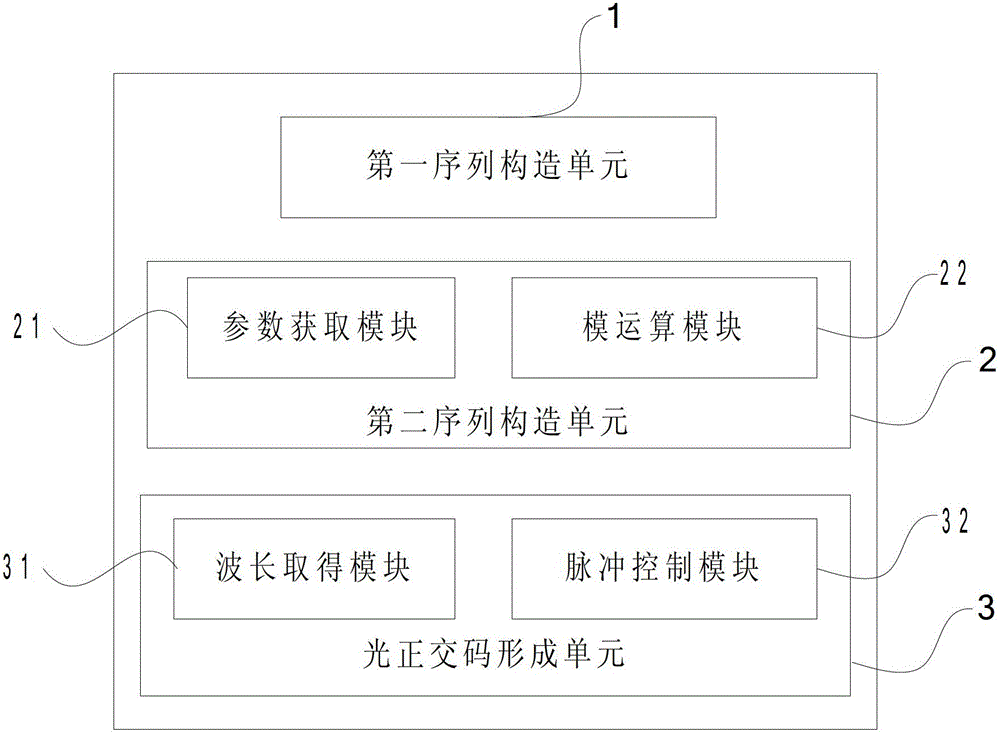
Method and device for forming two-dimensional optical orthogonal code with zero correlation window
ActiveCN102752067AEliminate distractionsCancel noiseMultiplex code generationOptical multiplexAccess networkCode division multiple access
The invention relates to a method for forming a two-dimensional optical orthogonal code with a zero correlation window, and the method comprises following steps of constructing a first sequence with the zero correlation window; constructing a second sequence; and mapping the first sequence and the second sequence to form the two-dimensional optical orthogonal code with the zero correlation window. The invention also relates to a device for realizing the method. The method and the device for forming the two-dimensional optical orthogonal code with the zero correlation window have following beneficial effects that the two-dimensional orthogonal code is completely orthogonal, i.e. the autocorrelation limit of the code is zero, cross-correlation limit of the code is also zero, and thus the multi-address interference and beat noise can be completely eliminated, the near-far effect of a two-dimensional optical code division multiple access (OCDMA) system also can be eliminated; therefore, the two-dimensional OCDMA system with large capacity can be realized, and the two-dimensional OCDMA system can be applied to an optical access network, an optical local area network, an optical code mark switching network, an optical fiber sensor network and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Oven
InactiveUS7565903B2Prevents generation of beating noiseDomestic stoves or rangesElectrical heating fuelHoneycombEngineering
The invention aims at reducing the beating noise generated from motors of equipments placed in a galley unit of an aircraft. A galley unit 1 of an aircraft includes a cabinet 10 formed of honeycomb panels and the like. The cabinet 10 has a counter 50 for cooking, and a compartment 20 formed under the counter 50 for storing service carts 30. A plurality of ovens 100 for heating warm dishes are provided above the counter 50. Each oven 100 has a fan motor for making the inner heat even. If all the fan motors of the ovens are driven at the same rotation frequency, a beating noise will be generated from the motor and amplified through the compartment 20. Therefore, the rotation frequencies of the fan motors are slightly varied.
Owner:JAMCO
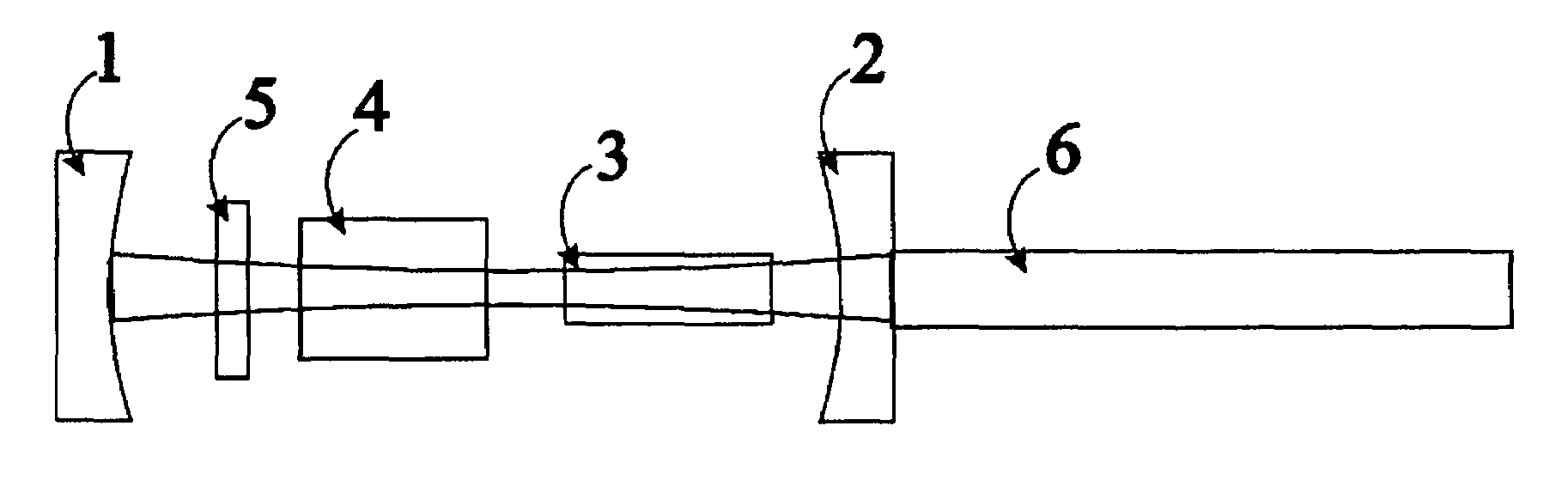
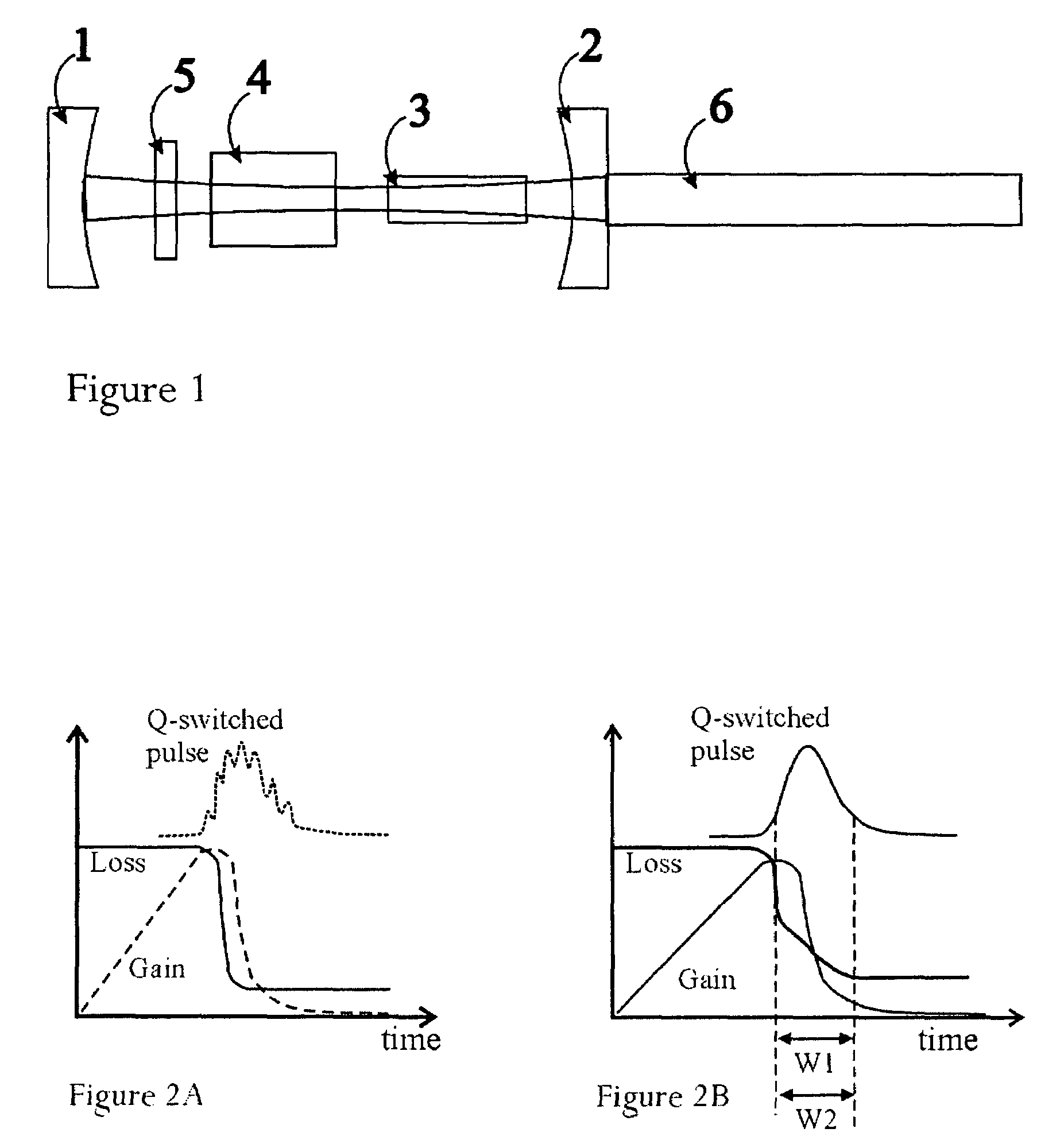
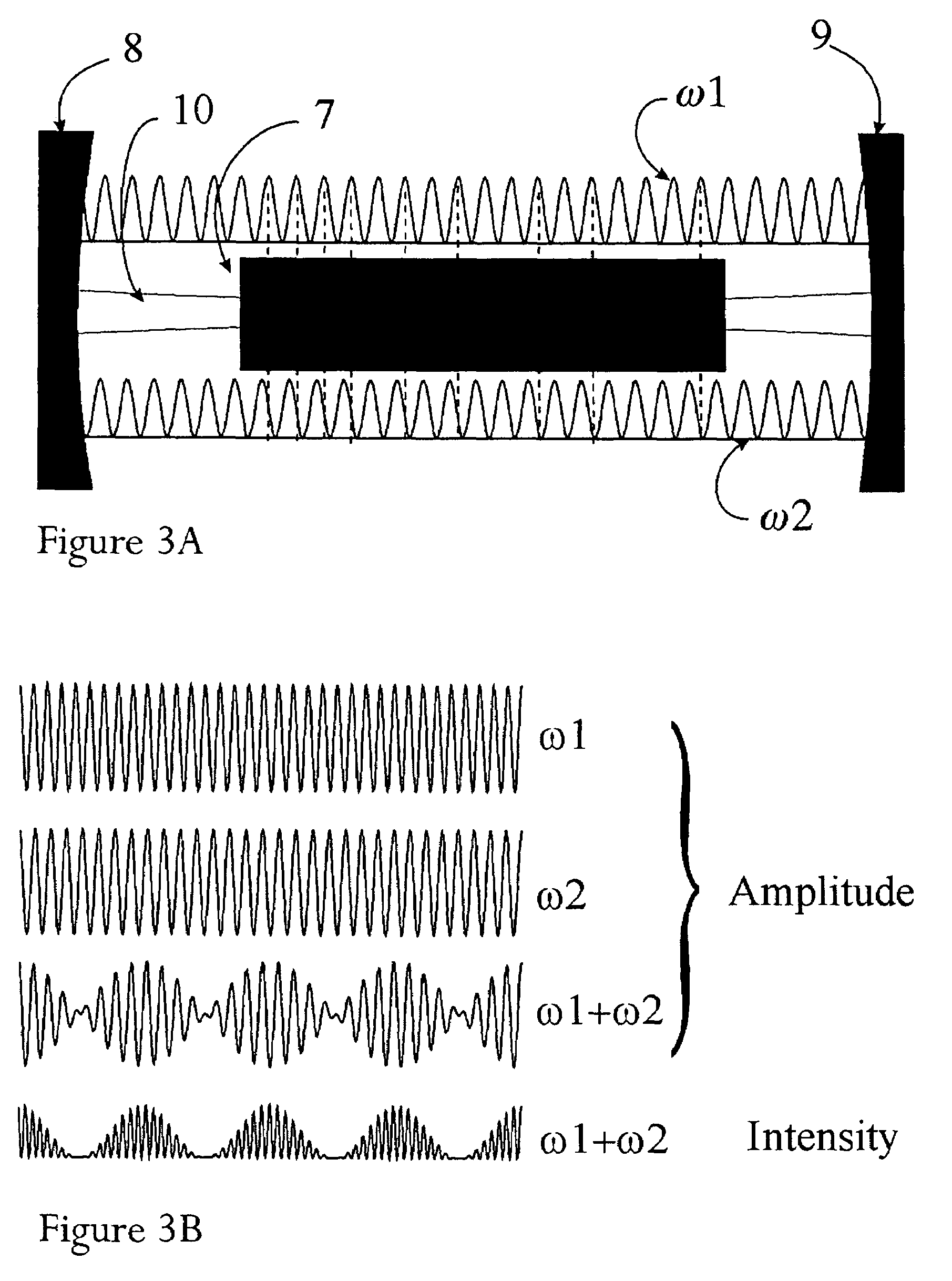
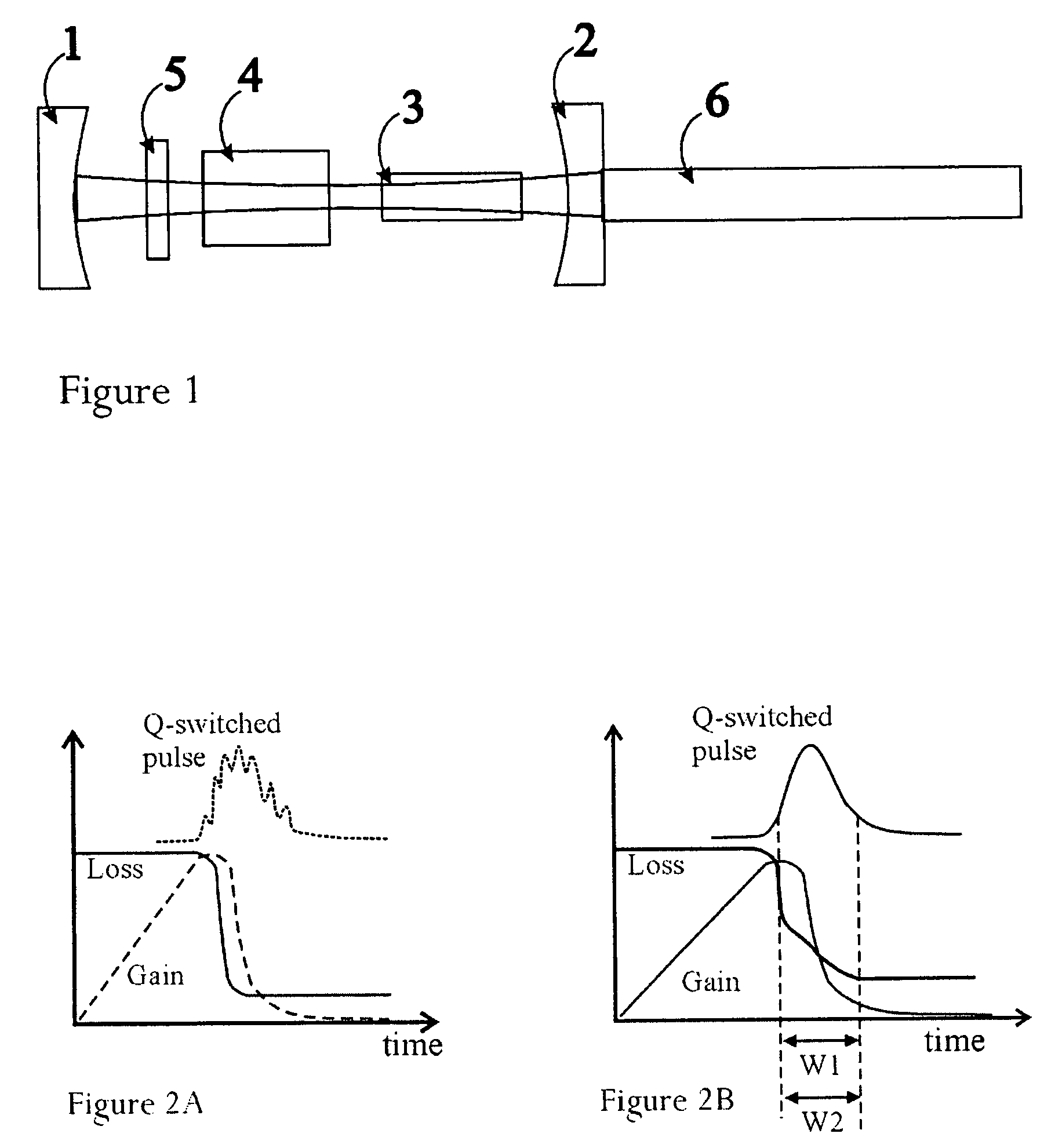
Suppression of mode-beating noise in a Q-switched pulsed laser using novel Q-switch device and applications
Owner:GENDRON DENIS J
Suppression of mode-beating noise in a Q-switched pulsed laser using novel Q-switch device and applications
A novel Q-switch device enables significant quality and value improvement for a Q-switched laser system by achieving a significant reduction of mode-beating noise during the pulsed output. The origin of mode-beating noise in a Q-switched laser is a result of high gain availability and amplification of competing standing-waves in formation, whose optical frequency is a product of natural selection via spatial hole burning in the gain medium. The novel Q-switch device employs an active, electro-optics or acousto-optics, Q-switch in combination with a saturable absorber device, to provide an optimized soft opening of the optical path and a controlled timing of a Q-switched laser. This novel combination offers larger modulation loss than otherwise possible with the active modulator alone, and it allows for higher gain build-up and energy extraction efficiency. Specifically, it will enable a low-voltage modulator (<100 V) for high gain (small-signal gain >10) and Q-switched operation at high repetition rate (>10 kHz). The combination is devised to slow down the signal build-up and to sweep the fundamental longitudinal mode frequency at least within the free spectral range of the resonator, such that it varies adiabatically during the Q-switched pulse formation. A laser geometry amenable to high gain and high power is proposed for use in conjunction with the proposed novel Q-switch device. The invention will enable the deployment of cost-effective Q-switched lasers operating in both single-longitudinal and single-transverse (TEM00) mode.
Owner:GENDRON DENIS J
System for flexible multiple broadcast service delivery over a WDM passive optical network based on RF block-conversion of RF service bands within wavelength bands
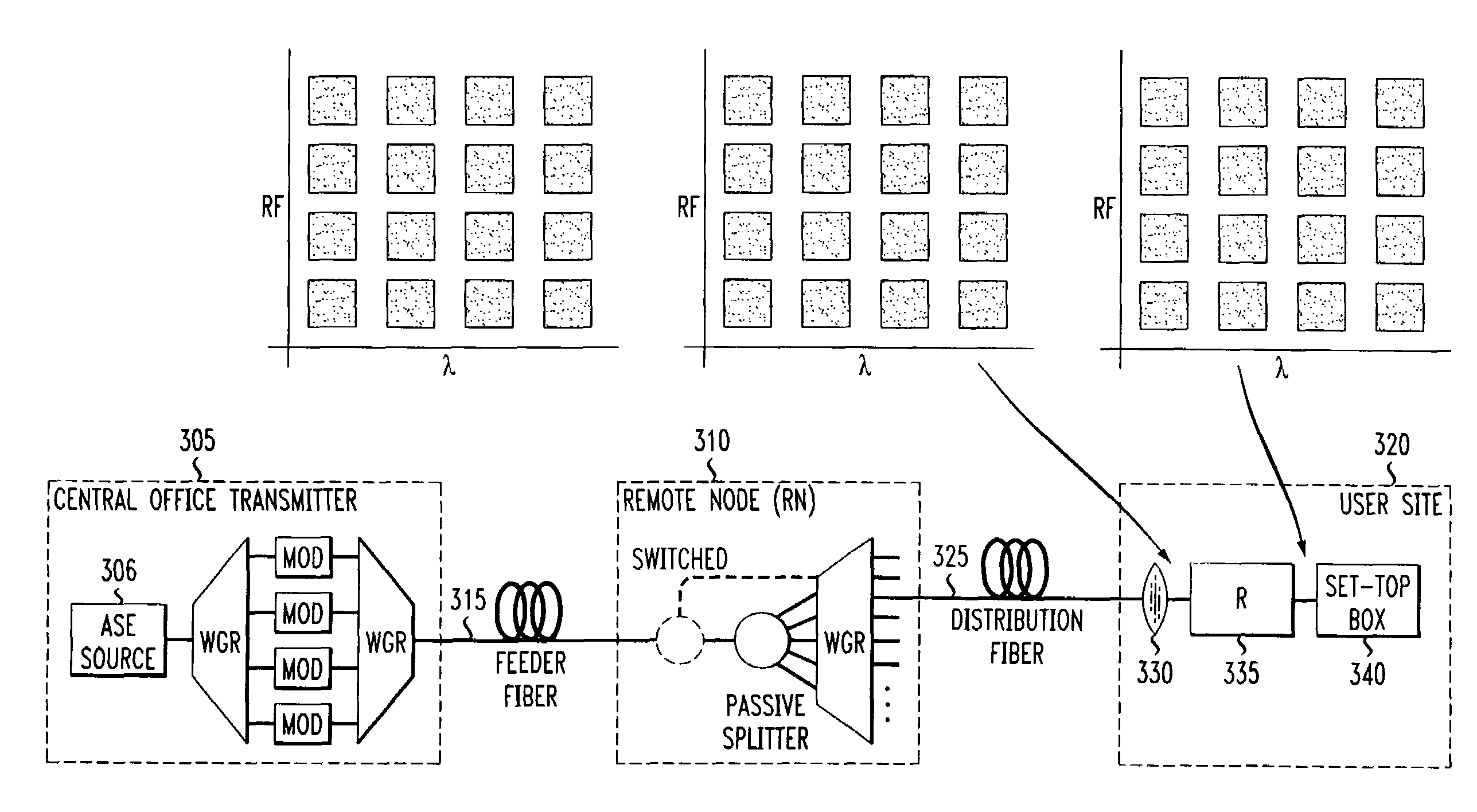
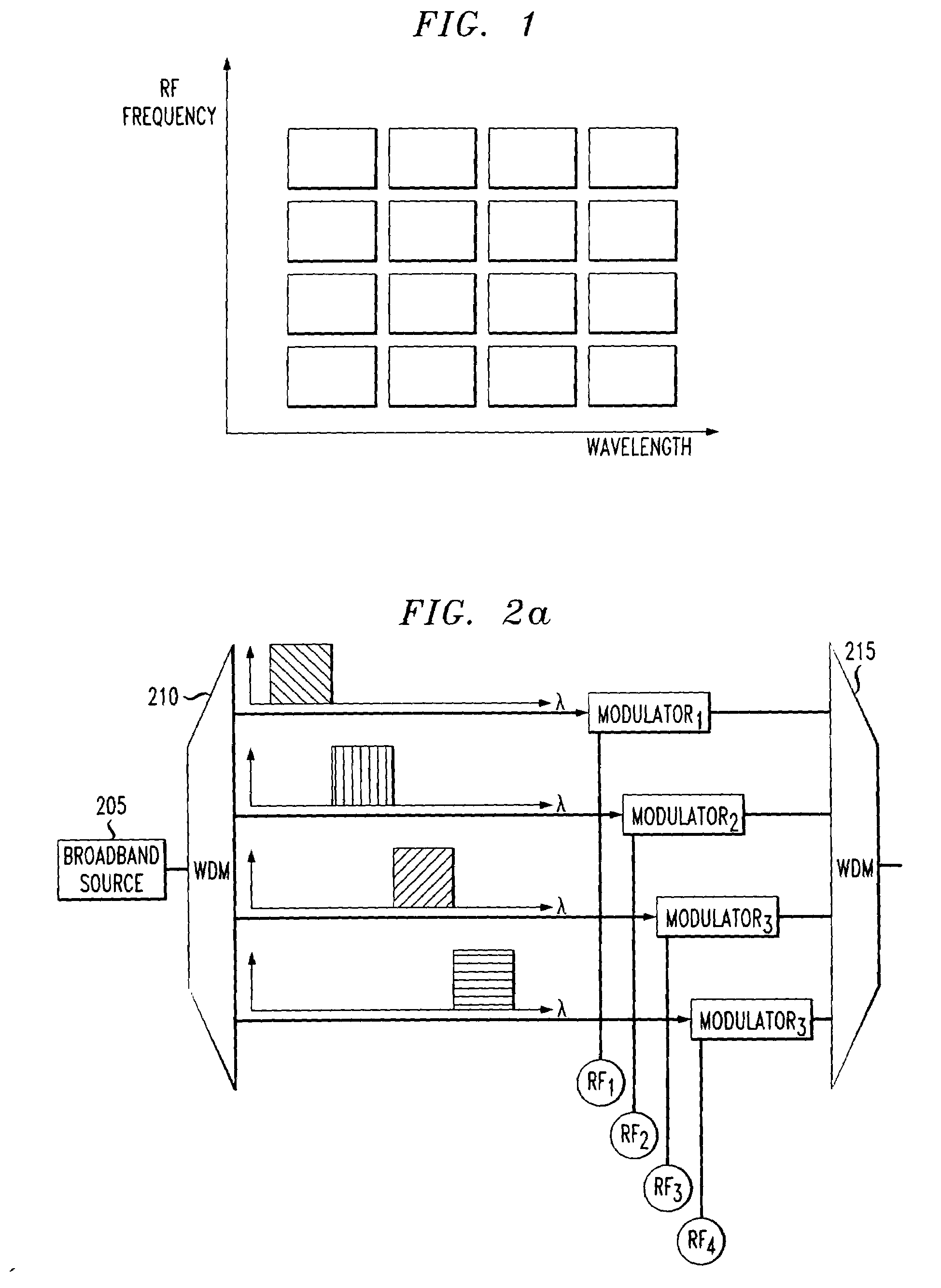
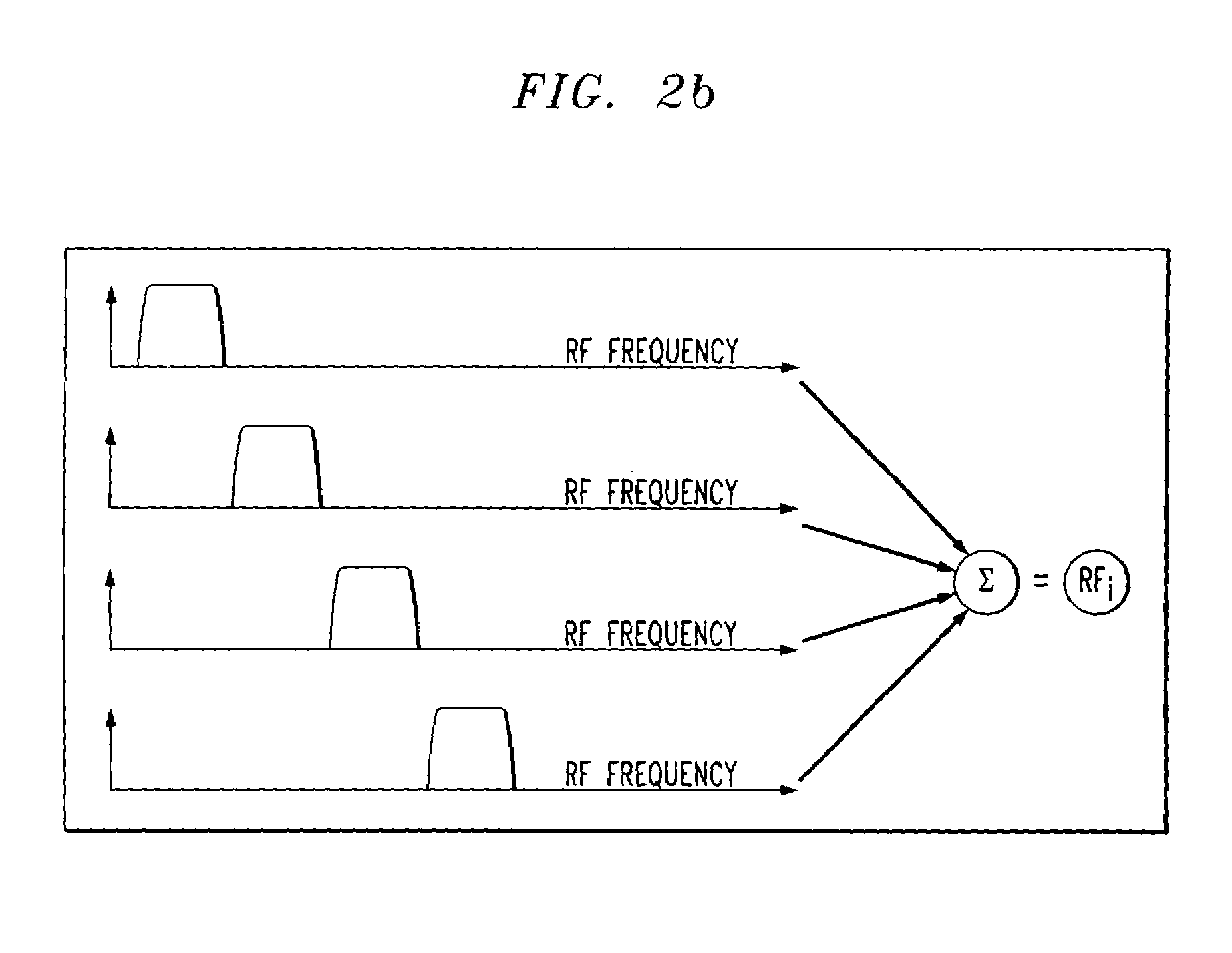
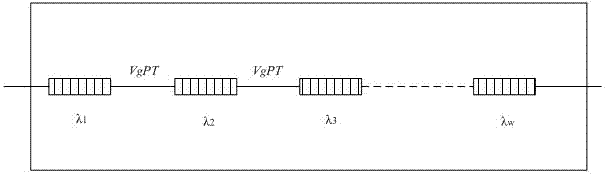
InactiveUS7085495B2Increases capacity (and flexibility)Capacity of knownTime-division optical multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberEngineering
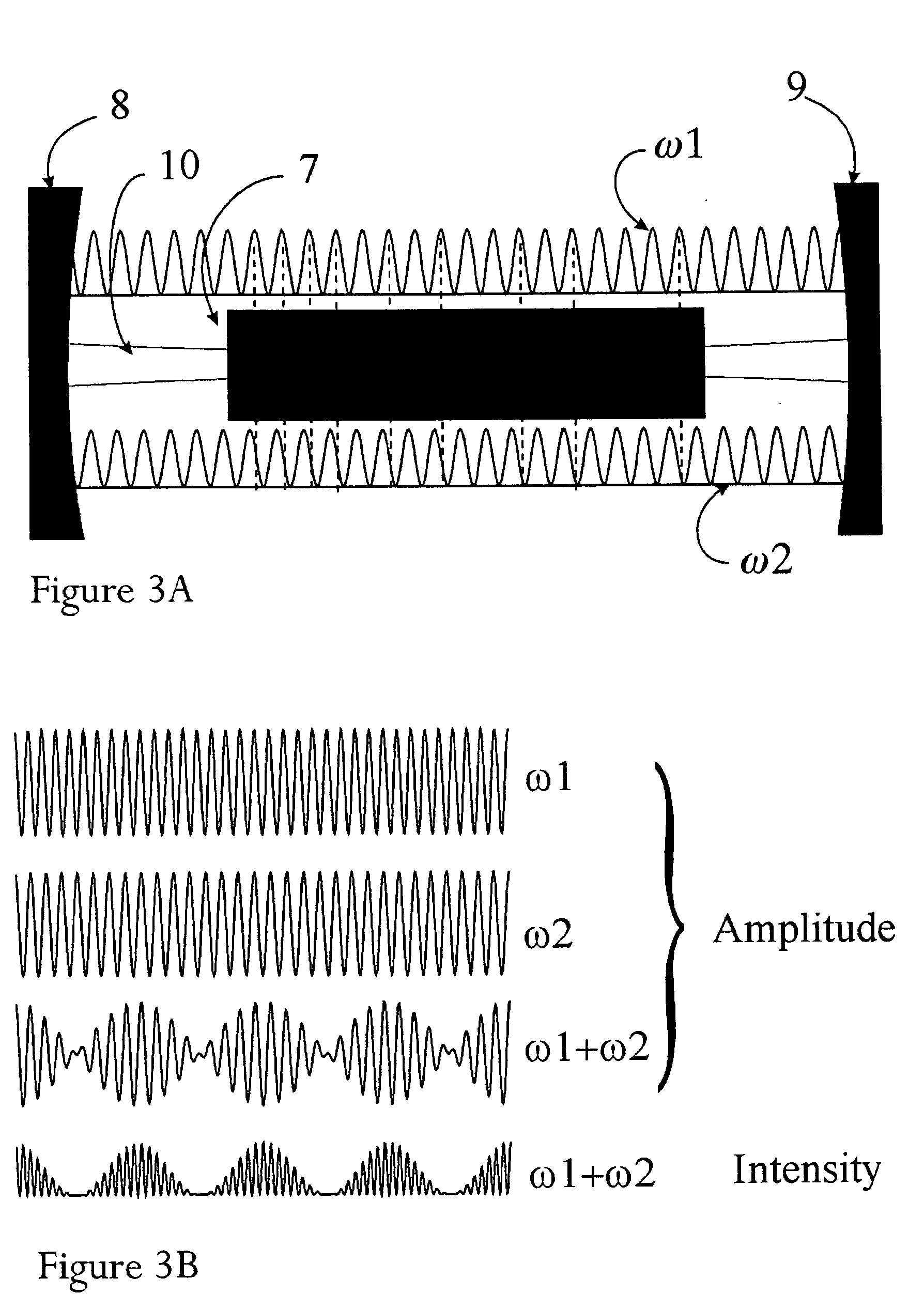
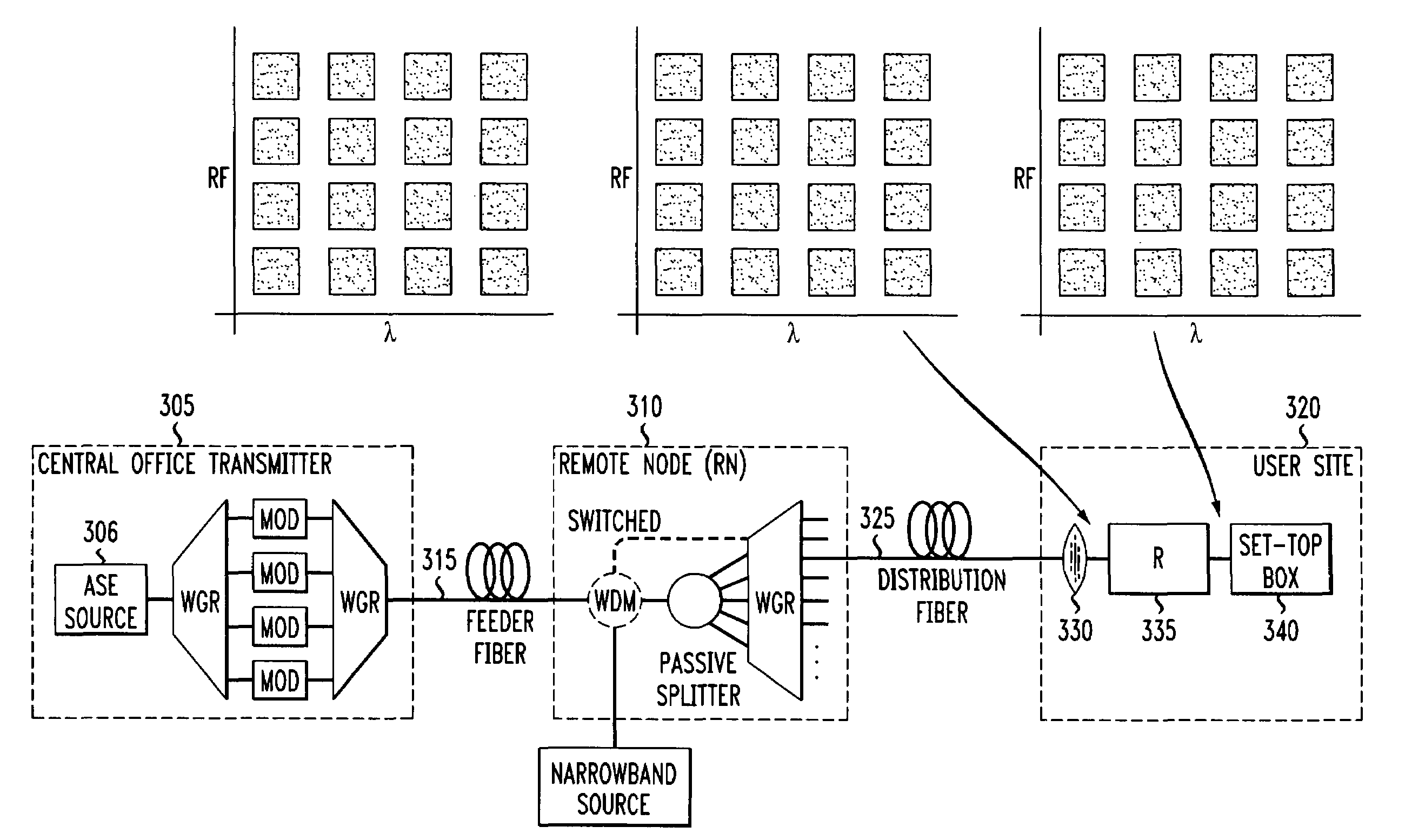
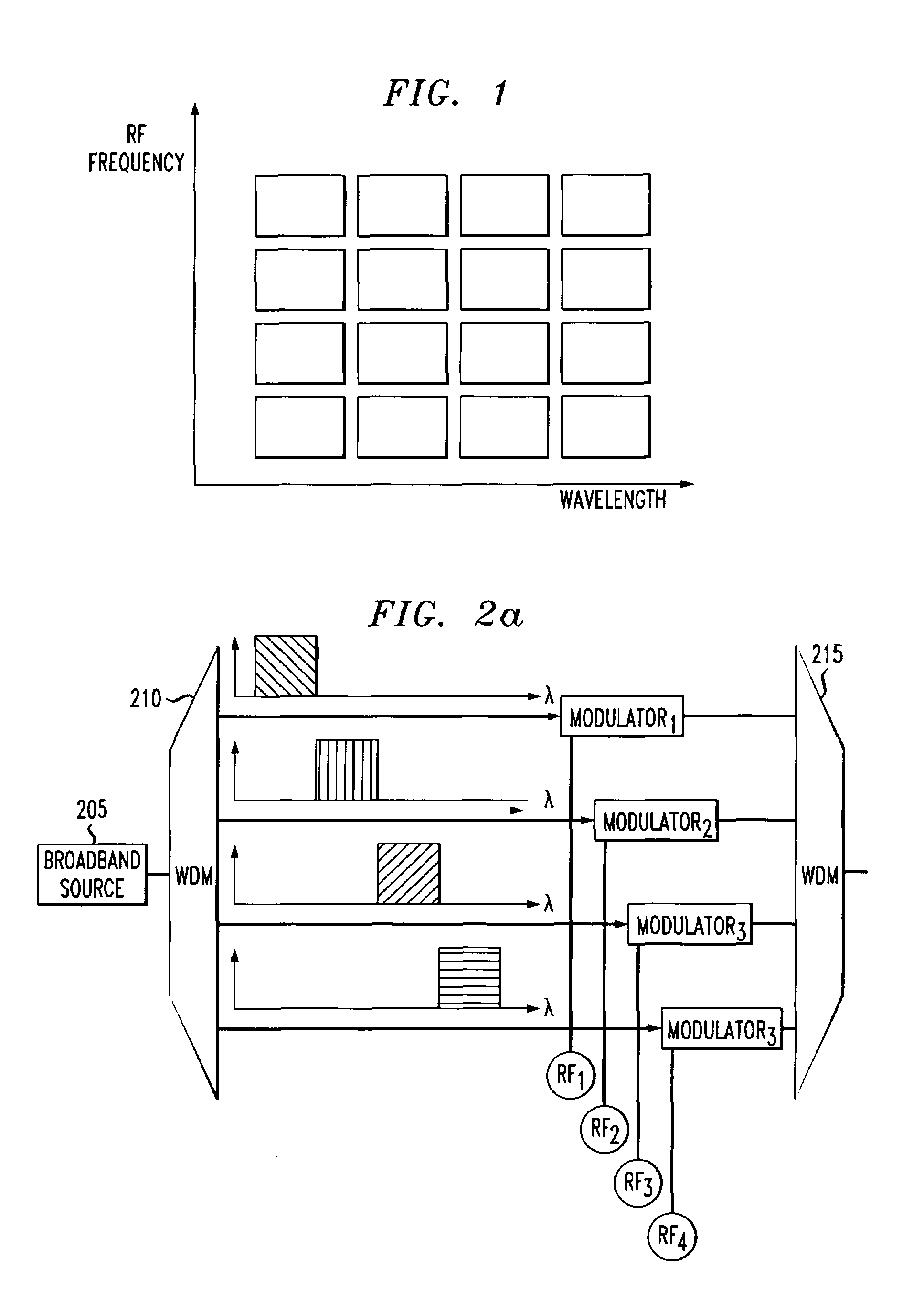
A system and method for simultaneous delivery of a plurality of independent blocks of 500 MHz digital broadcast television services, stacking a plurality of RF blocks on a plurality of spectrally sliced WDM optical bands. The method for delivering a plurality of video blocks to a user terminal serviced by a remote node comprises the steps of receiving, by a first WDM, a broadband signal from a broadband signal source, separating, by the first WDM, the broadband signal into a plurality of optical bands, modulating each of the plurality of optical bands with a composite signal representing data in a plurality of independent RF blocks to form a plurality of modulated signals, forwarding the plurality of modulated signals to a second WDM to form a combined broadcast signal, transmitting the combined broadcast signal over feeder fiber to a remote node, selecting a RF block for distribution over a distribution fiber to a conventional satellite set-up box at a user's site and forwarding the selected RF block to the user's site. A novel method and system for reducing spontaneous beat noise is also disclosed.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Method of flexible multiple broadcast service delivery over a WDM passive optical network based on RF Block-conversion of RF service bands within wavelength bands
InactiveUS7286761B2Increases capacity (and flexibility)Capacity of knownWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmissionFiberEngineering
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
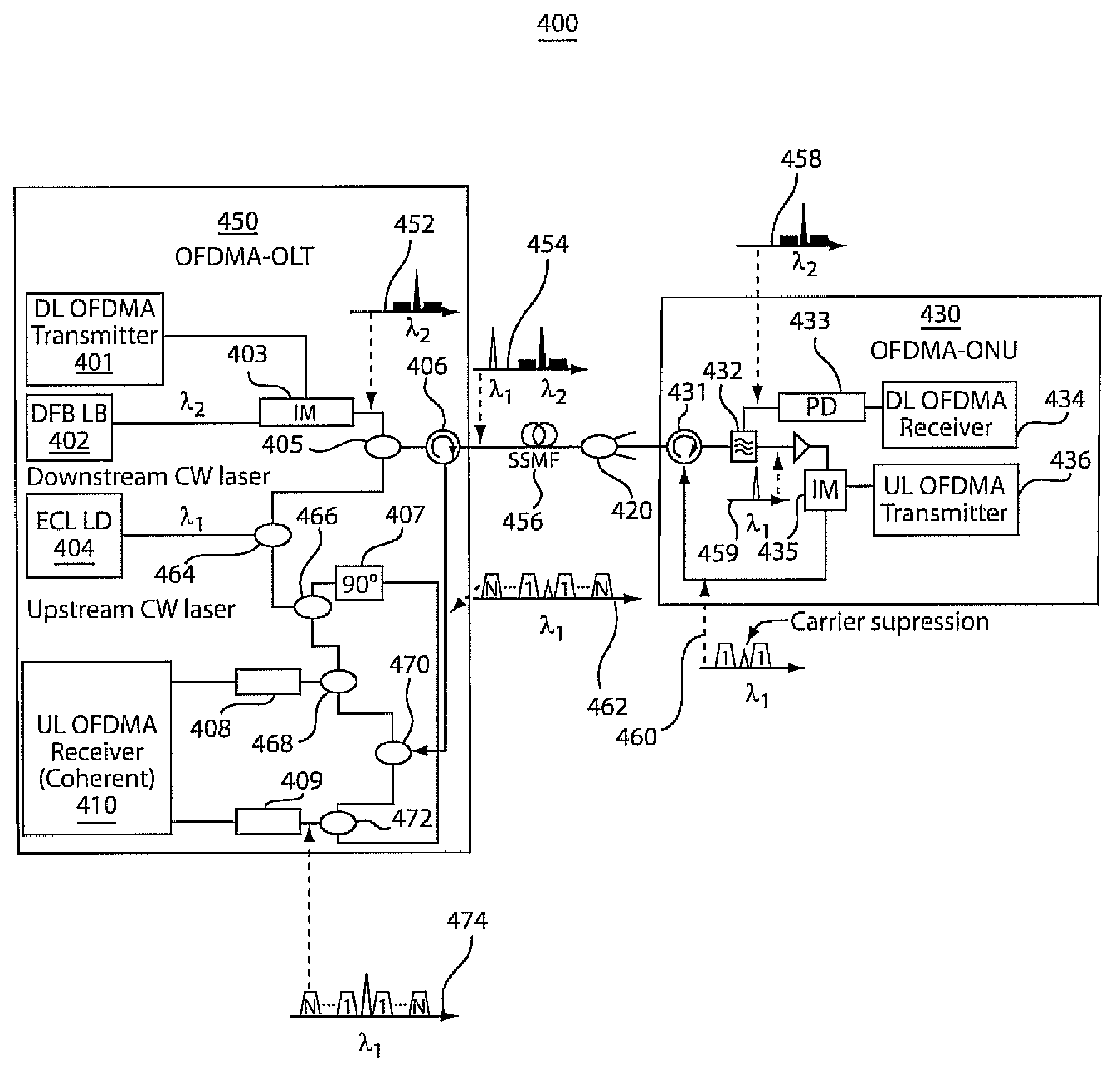
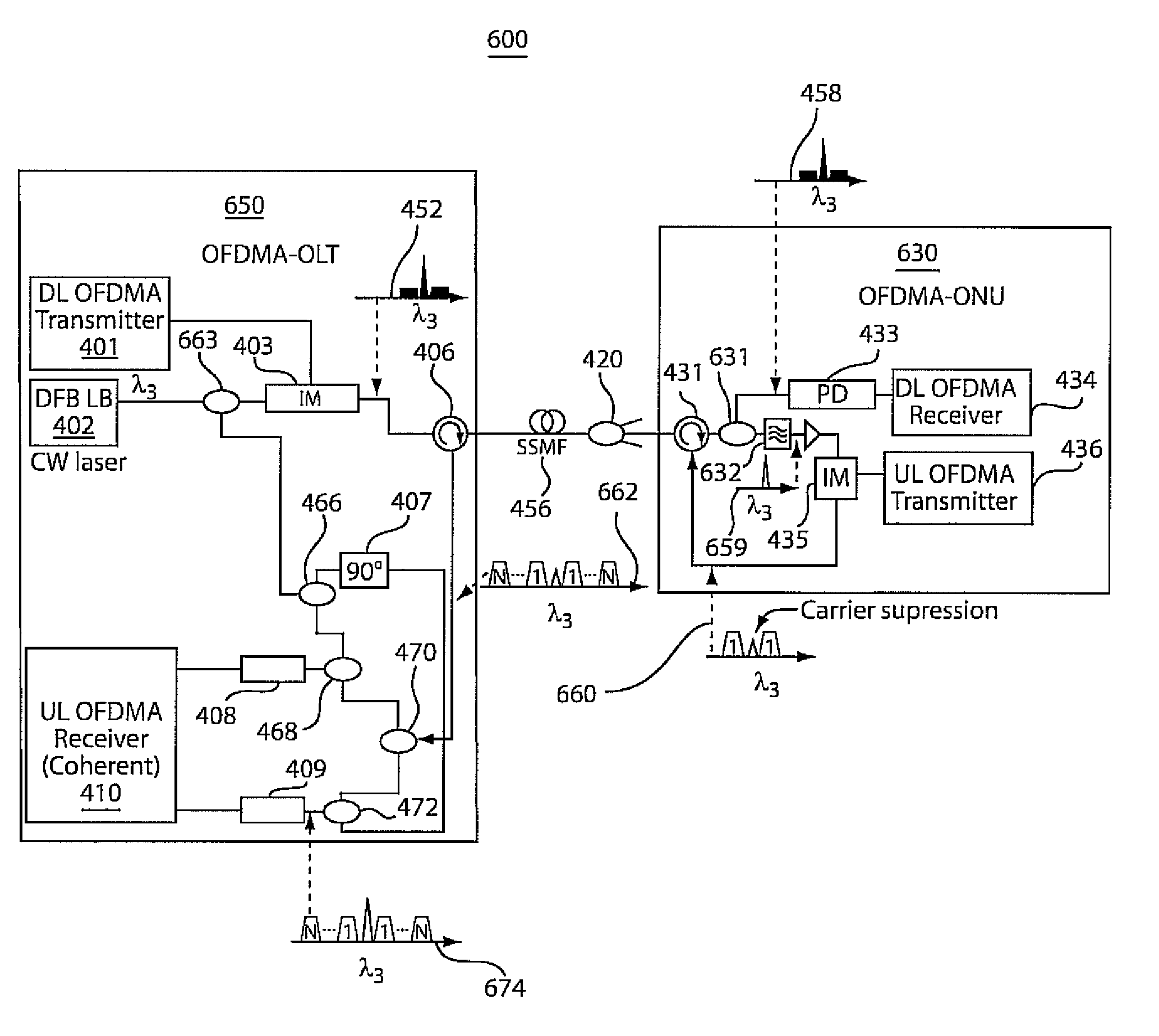
Single wavelength source-free OFDMA-PON communication systems and methods
ActiveUS8233797B2Reduce complexityLow costOptical multiplexElectromagnetic transmissionSignal onCarrier signal
Methods and systems for processing communication signals in an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA)-Passive Optical Network (PON) are disclosed. An optical carrier at a wavelength generated at an optical line terminal (OLT) may be reused by optical network units (ONUs) in the network for upstream transmission of data signals to the OLT. In addition, each ONU may perform carrier suppression to avoid broadband beating noise resulting from the simultaneous transmission of upstream data signals on the same wavelength. Further, the optical source at the OLT used to generate the optical carrier may be reused as a local oscillator for coherent detection of received upstream signals to minimize any frequency offsets.
Owner:NEC CORP
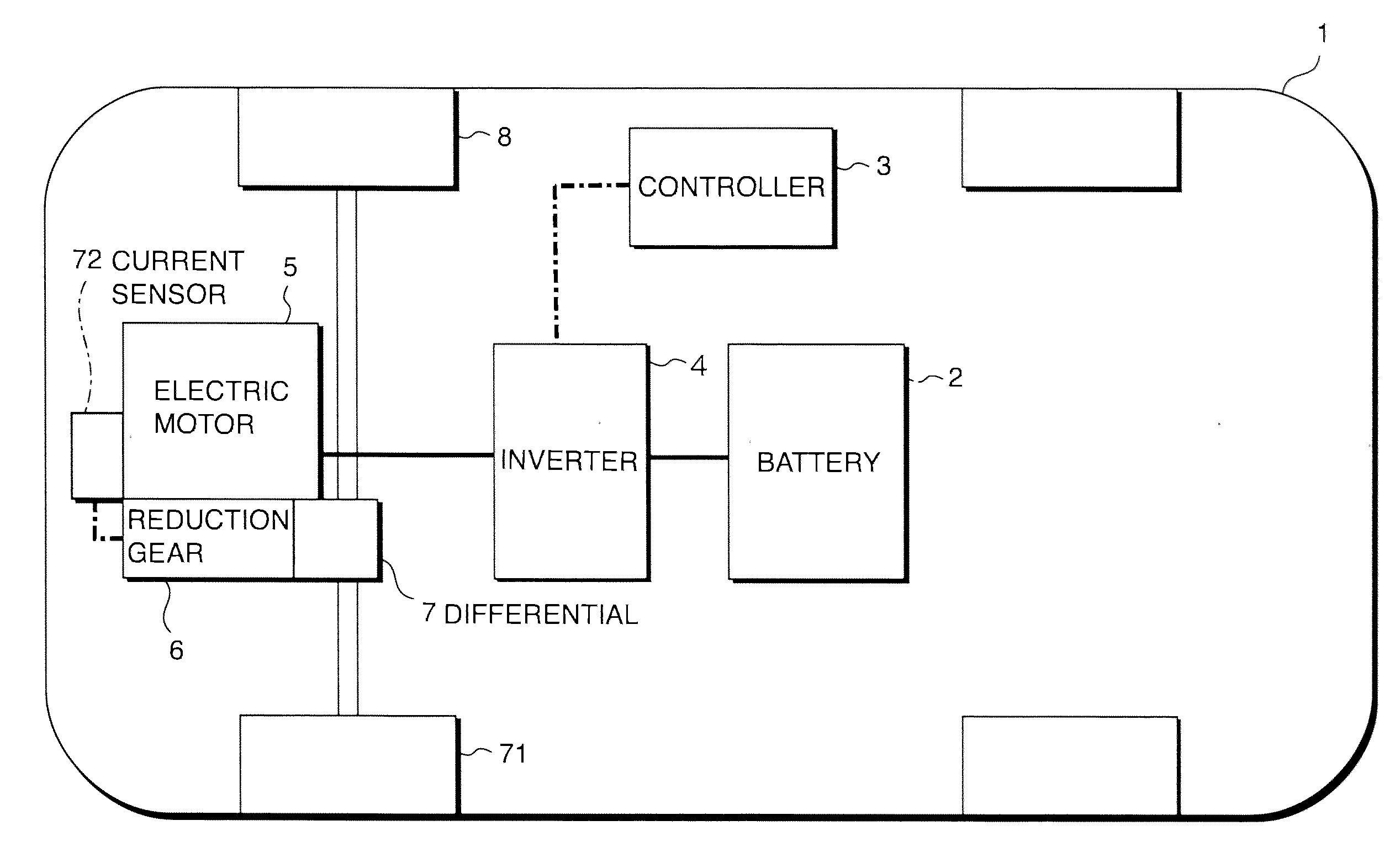
Operating noise control device and operating noise control method for vehicle
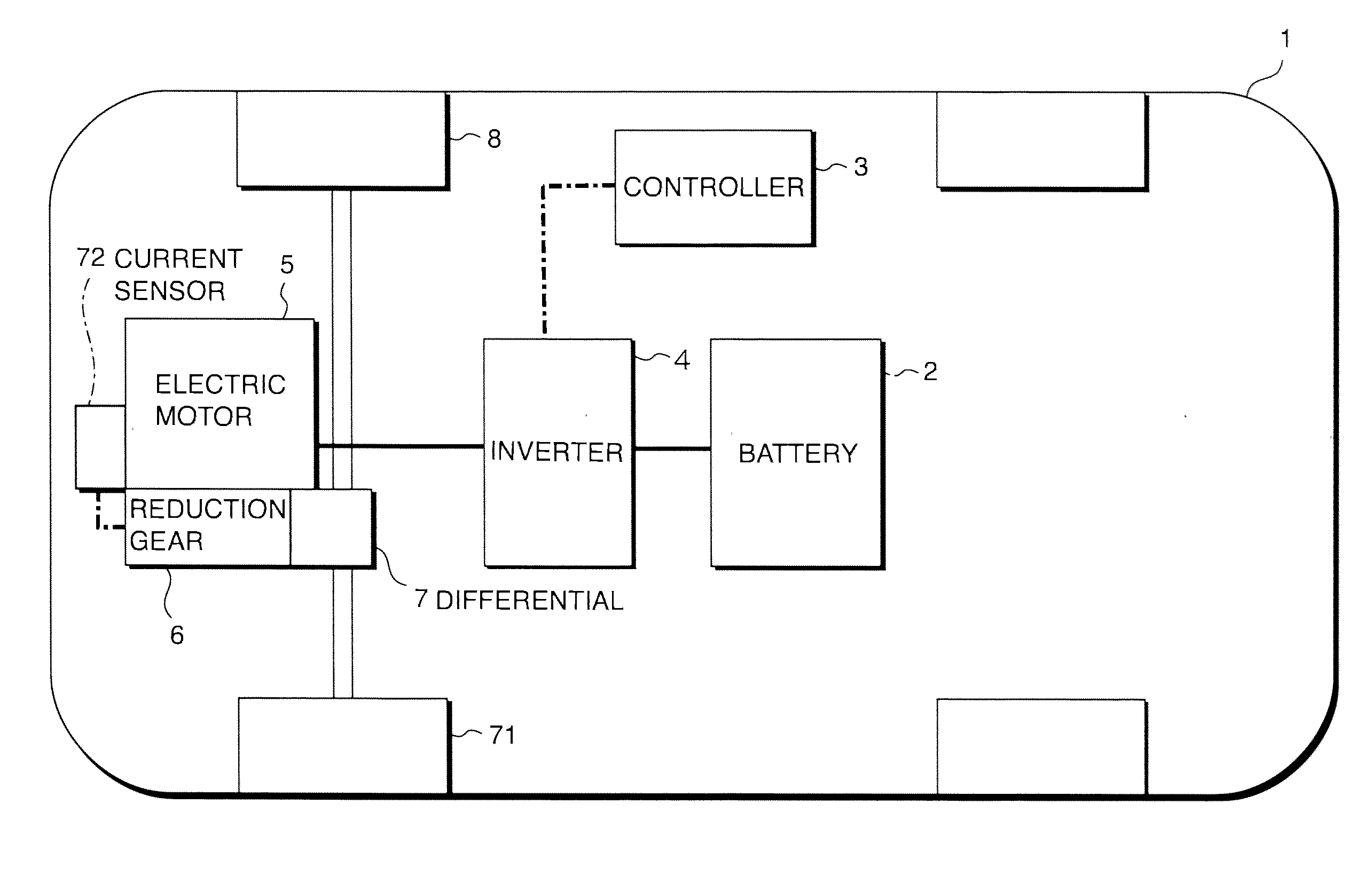
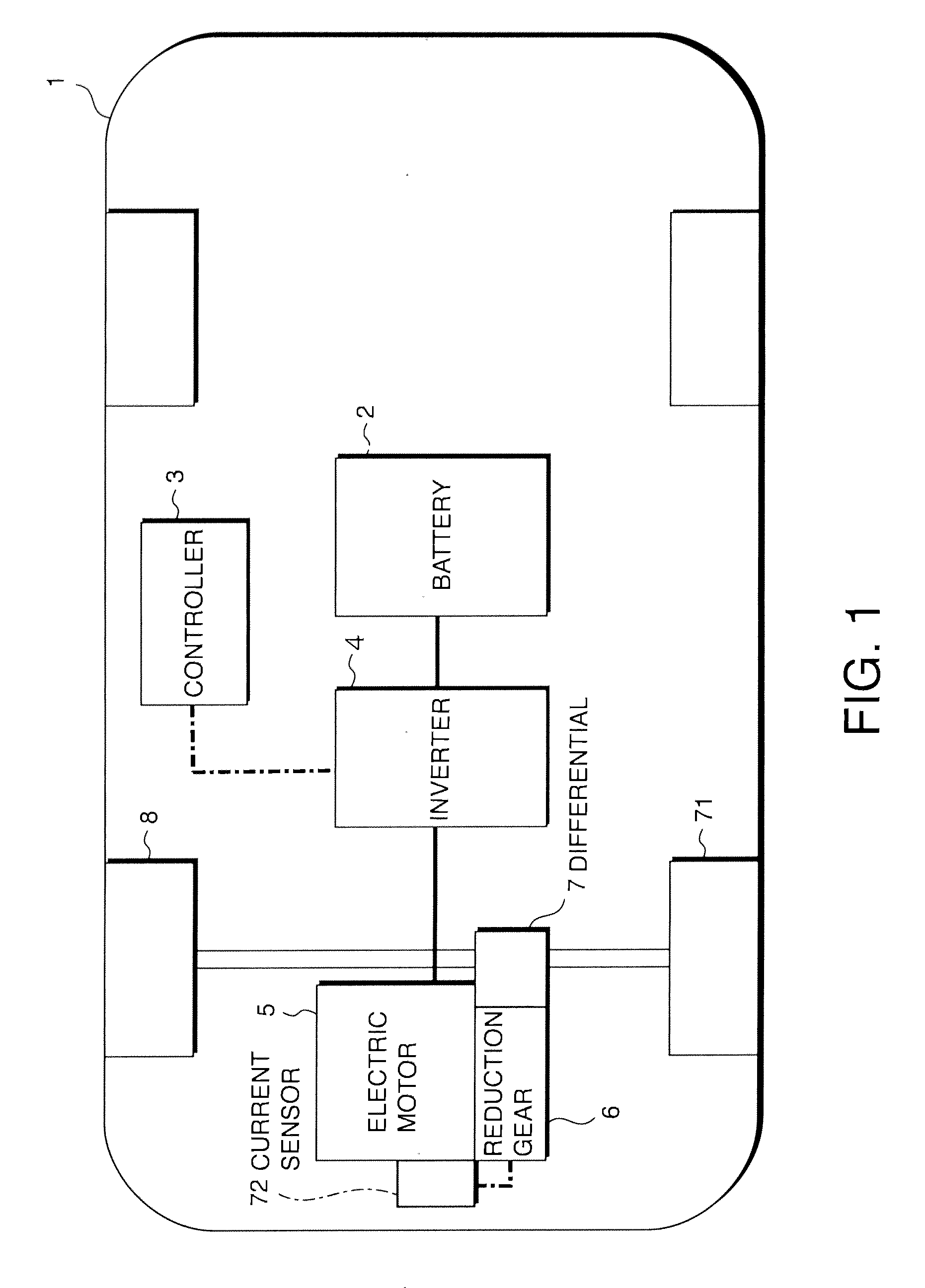
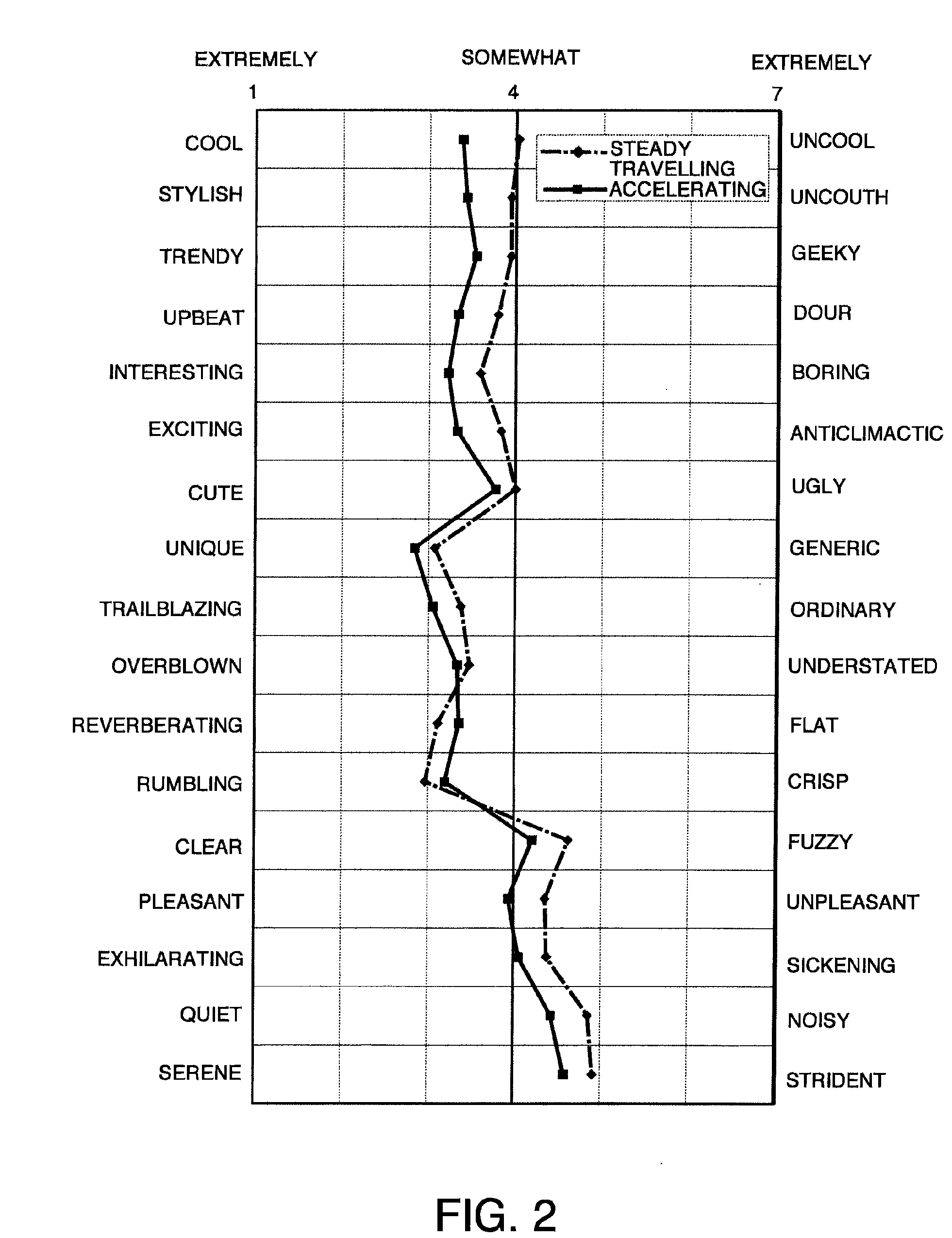
ActiveUS20110153133A1Increased operating noiseAC motor controlElectric motor controlElectricityDriving current
A vehicle (1, 17) includes an electric drive motor (5, 19), an inverter (4) that provides a drive current to the electric motor (5, 19) and a controller (13) that controls the inverter (4). The controller (13) functions as a beat noise generation system that creates beat noise by generating a second operating noise containing a component an order of which is very close to a value representing an order of an operating noise generated in proportion to a rotation speed of the electric motor (5, 19) so as to create desirable traveling noise corresponding to an accelerating state while the vehicle accelerates.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD +1
Frequency hopping period optical coding and decoding method and optical coder decoder
ActiveCN102378072ALarge codeword capacityIncrease user capacityMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionMulti user interferenceTime domain
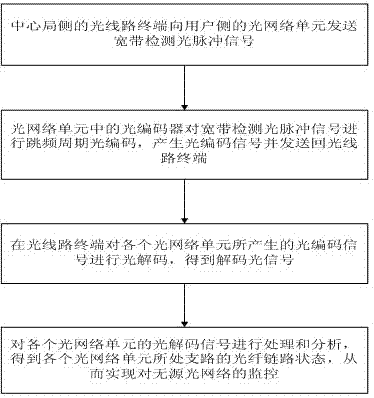
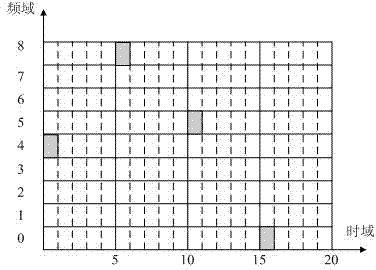
The invention discloses a frequency hopping period optical coding and decoding method, which is used for monitoring optical fiber links of a passive optic network. According to the frequency hopping period optical coding and decoding method, the coding and decoding are simultaneously performed in time domains and frequency domains; and optical code words are periodically coded and decoded in the time domains and are coded and decoded in a frequency hopping way in the frequency domains. The invention also discloses an optical coder decoder for realizing the coding and decoding method and a method for monitoring the optical fiber links of the passive optic network. The optical coder decoder consists of a plurality of optical fiber Bragg optical gratings which are connected in series through optical fiber delay lines; the optical fiber delay lines among the optical gratings have the same length, and the length depends on the period values of the frequency hopping period optical code words and the width of the time domains of detection optical pulse; and the center reflection wavelength of each optical grating depends on frequency hopping sequences on the frequency domains. In the method for monitoring the optical fiber links, the frequency hopping period optical coding and decoding method is adopted. According to the methods, code word capability of the optical code words can be improved, related distance of the optical code words can be reduced, the multi-user interference and beating noise can be effectively restrained, and the system monitoring performance can be improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
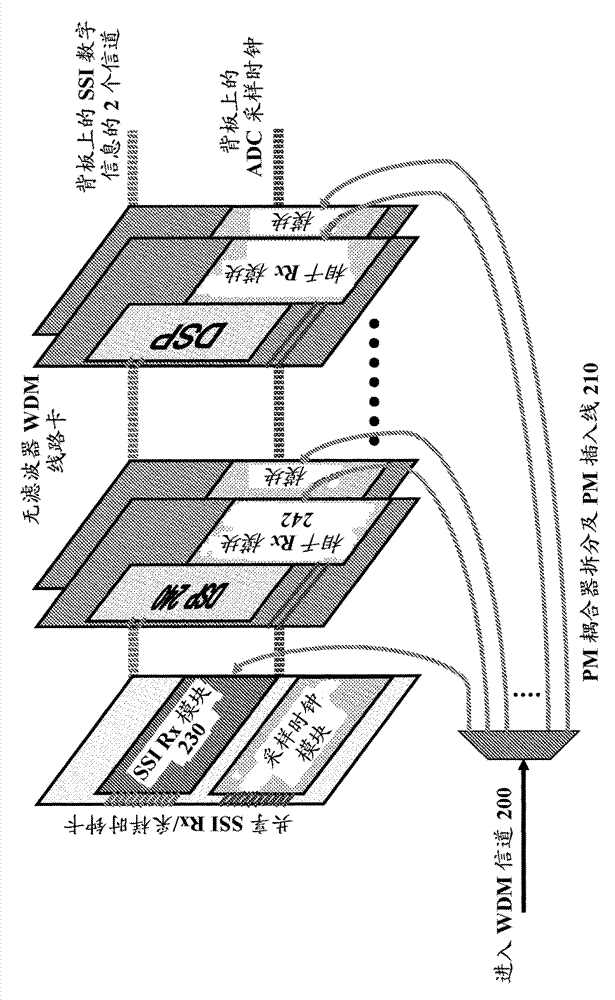
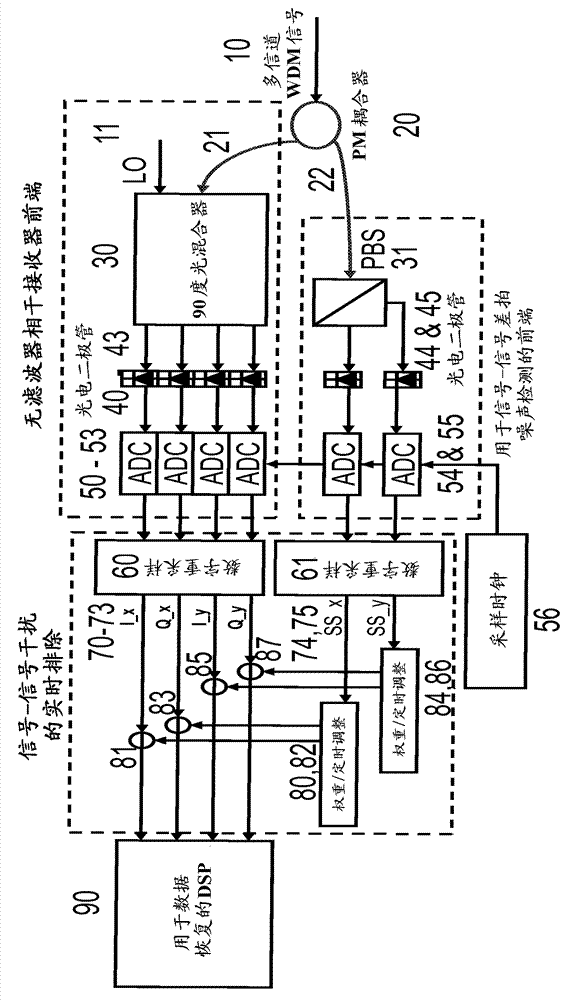
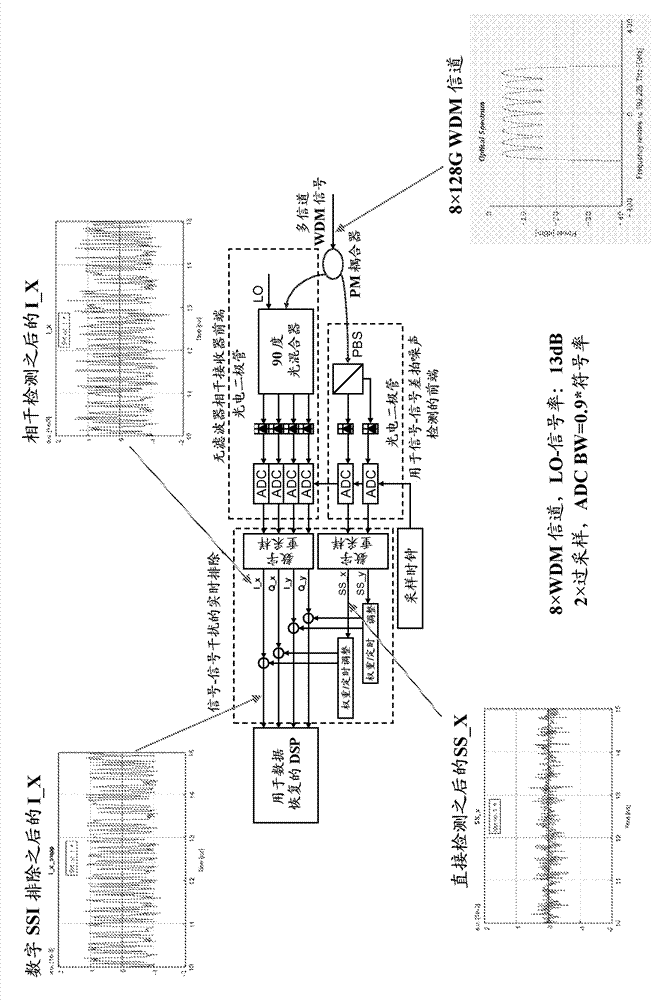
Digital signal-to-signal beat noise for filter-less coherent receiving system
ActiveCN103370891ALow costReduce performance degradationPolarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsParticle physicsReceiver front end
Systems and methods are disclosed for a filter-less coherent receiving system with a filter-less coherent receiver frontend; a signal-signal beat-noise detector coupled to the filter-less coherent receiver frontend; and a real-time processor coupled to the filter-less coherent receiver frontend and the signal-signal beat-noise detector to reject signal-signal interference.
Owner:NEC CORP
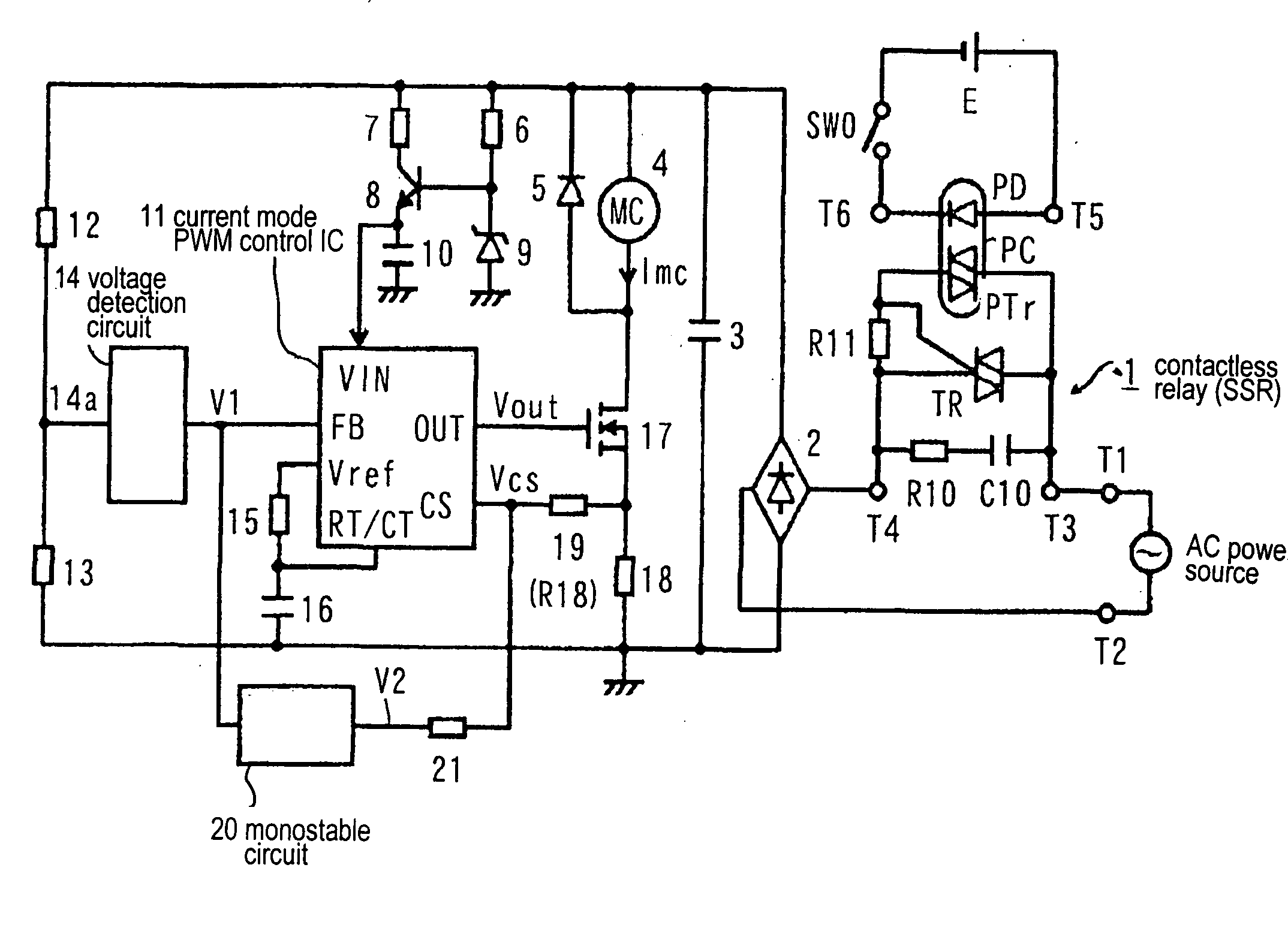
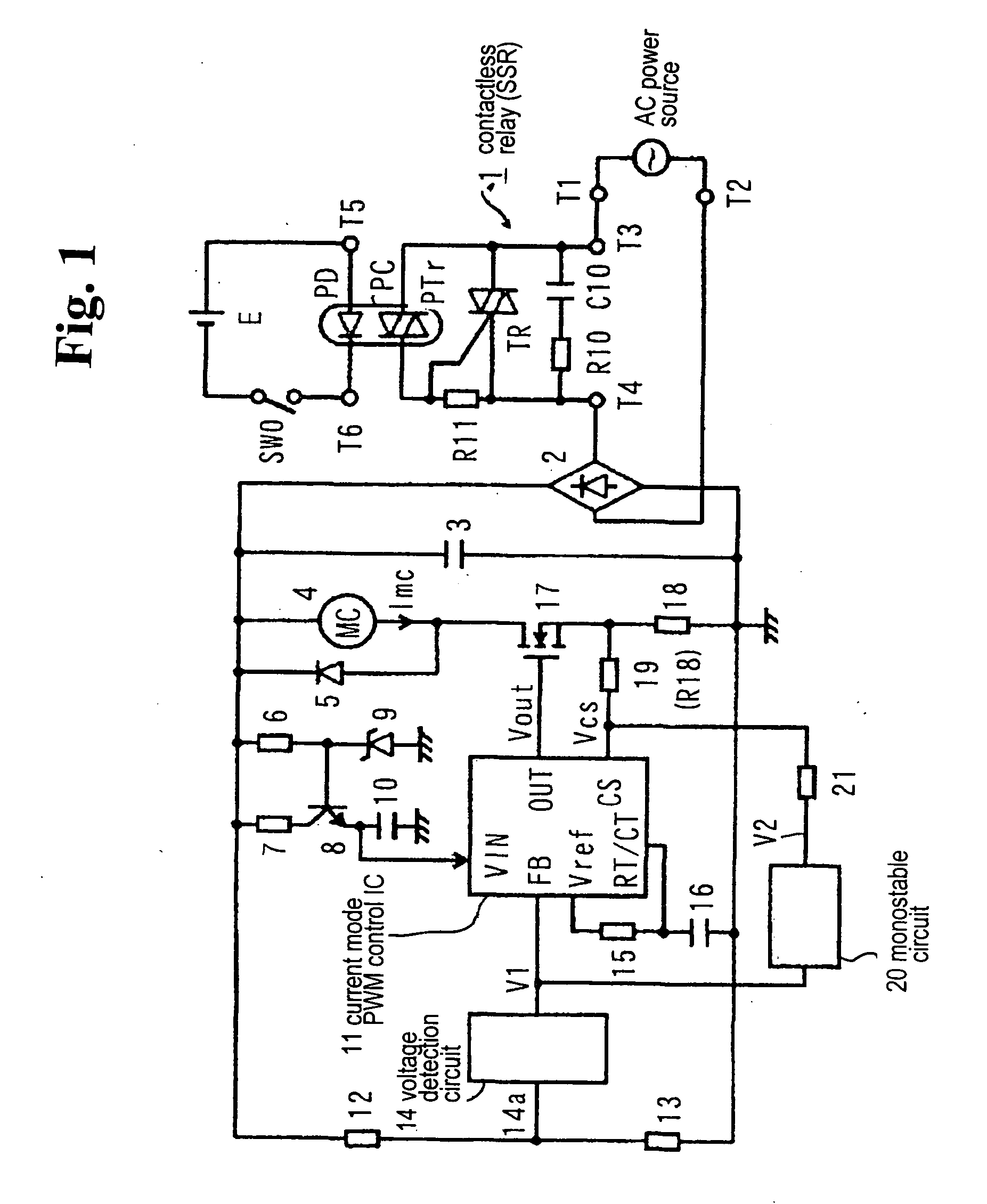
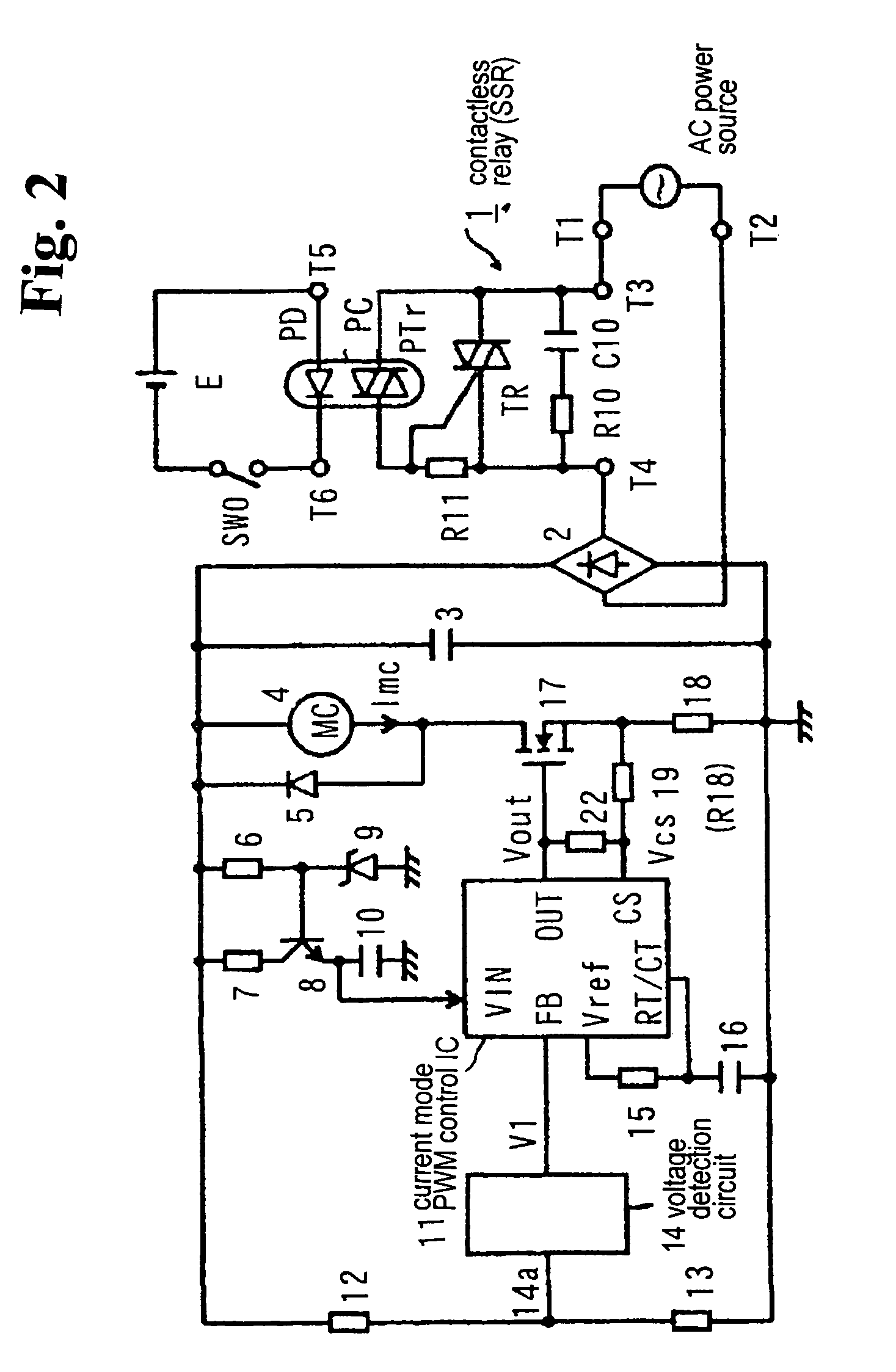
Electromagnetic apparatus drive apparatus
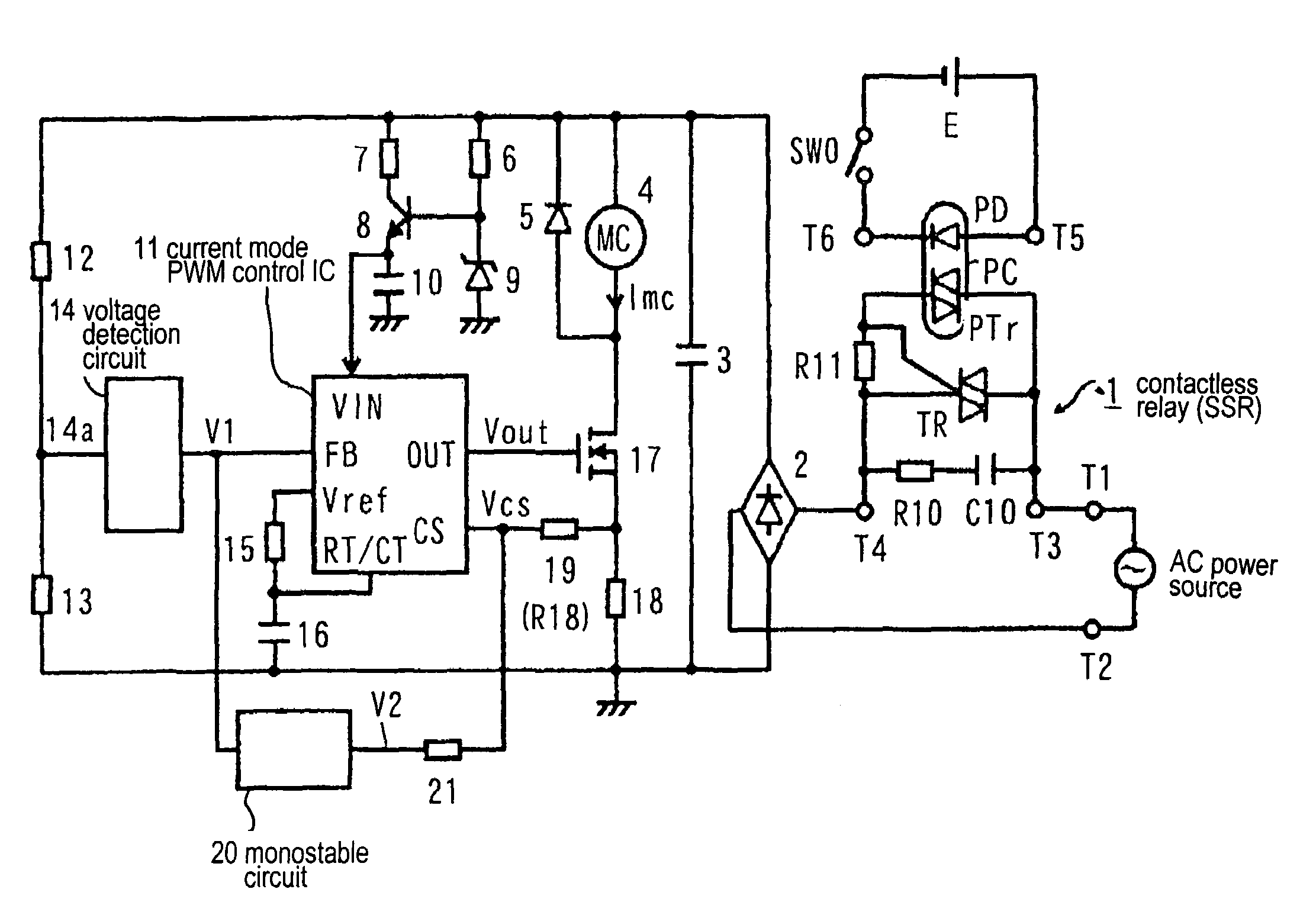
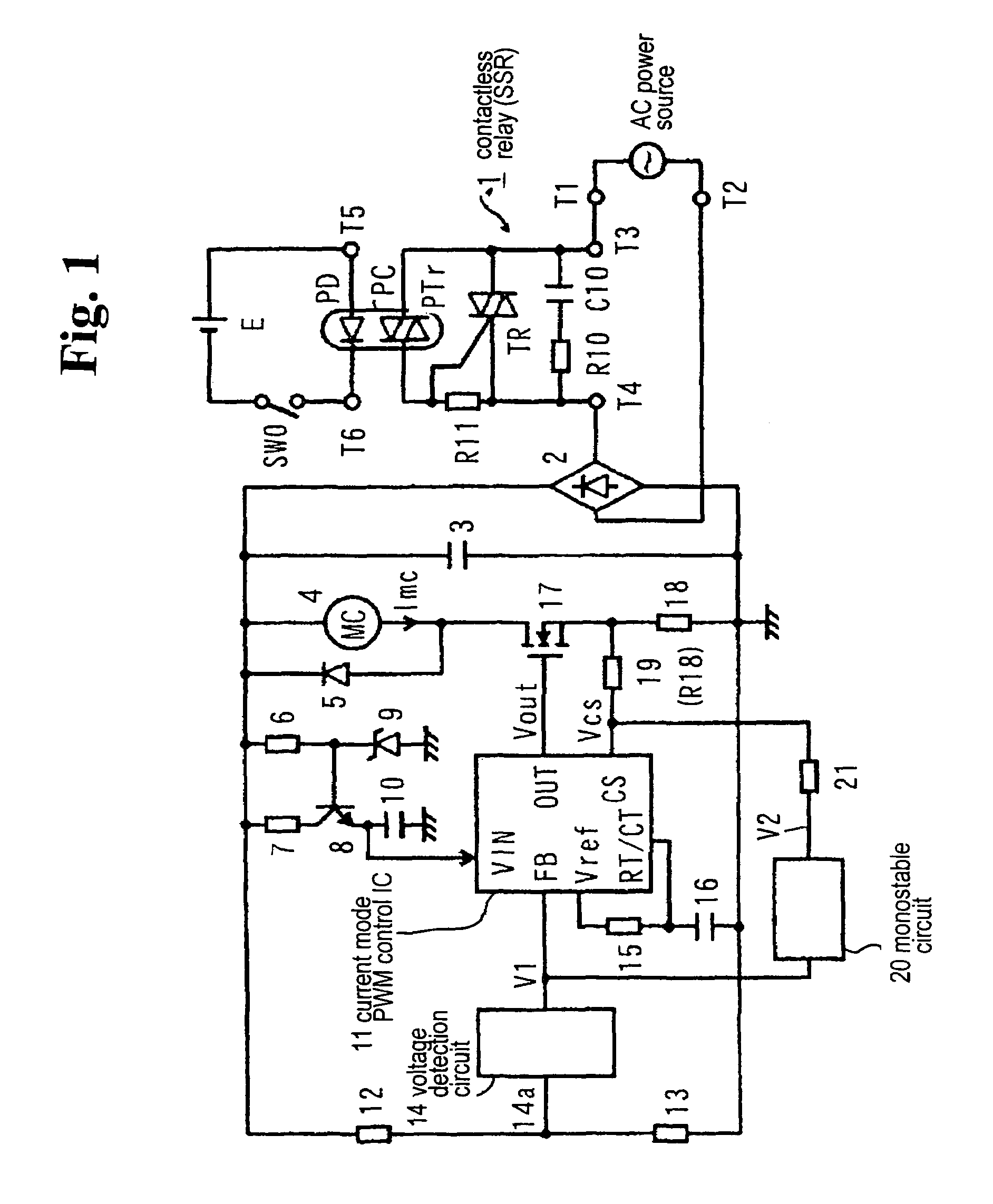
InactiveUS20050047052A1Increase currentReliable releaseAc-dc conversion without reversalRelaysSwitching cycleAC power
Conventionally, a non-conductive period is provided in a region in the vicinity of zero of an AC power voltage via a voltage detection circuit 14 to turn off reliably. The FET 17 maintains the ON state within several switching cycles after the non-conductive interval to rapidly restore the magnetizing coil current, so that the magnetizing coil current rapidly increases. An object is to suppress beat noise in the electromagnetic device. Within a prescribed interval following the non-conductive interval, a partial voltage at a resistor 19 of an output V2 of a mono-stable circuit 20 is added as a bias voltage to a detection voltage of a magnetizing coil current at a resistor 18, and is detected by the IC 11. The IC 11 drives a FET 17 with a constant switching period after the non-conductive interval, thereby preventing the increase in the magnetizing coil current and resolving the problem.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC FA COMPONENTS & SYST CO LTD
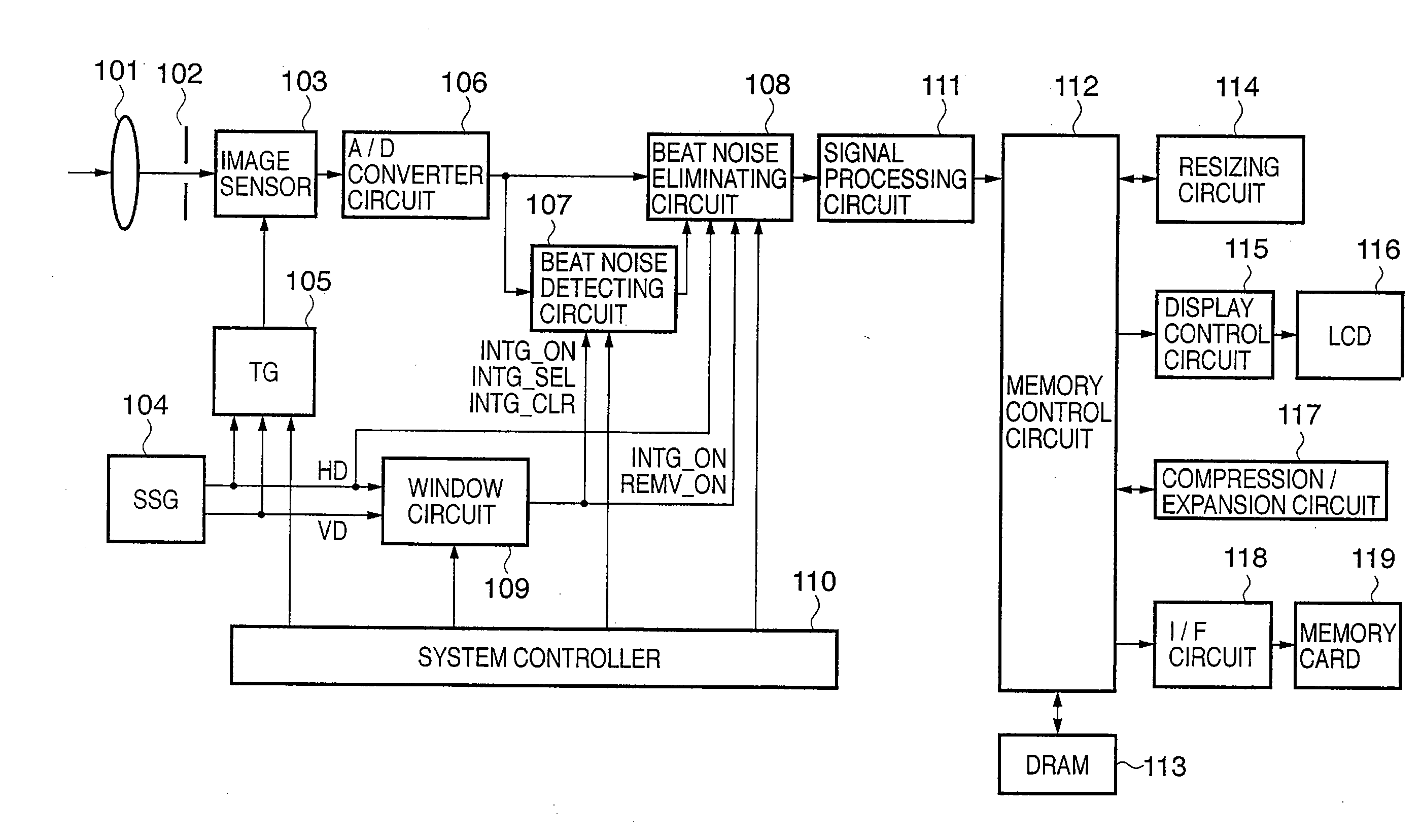
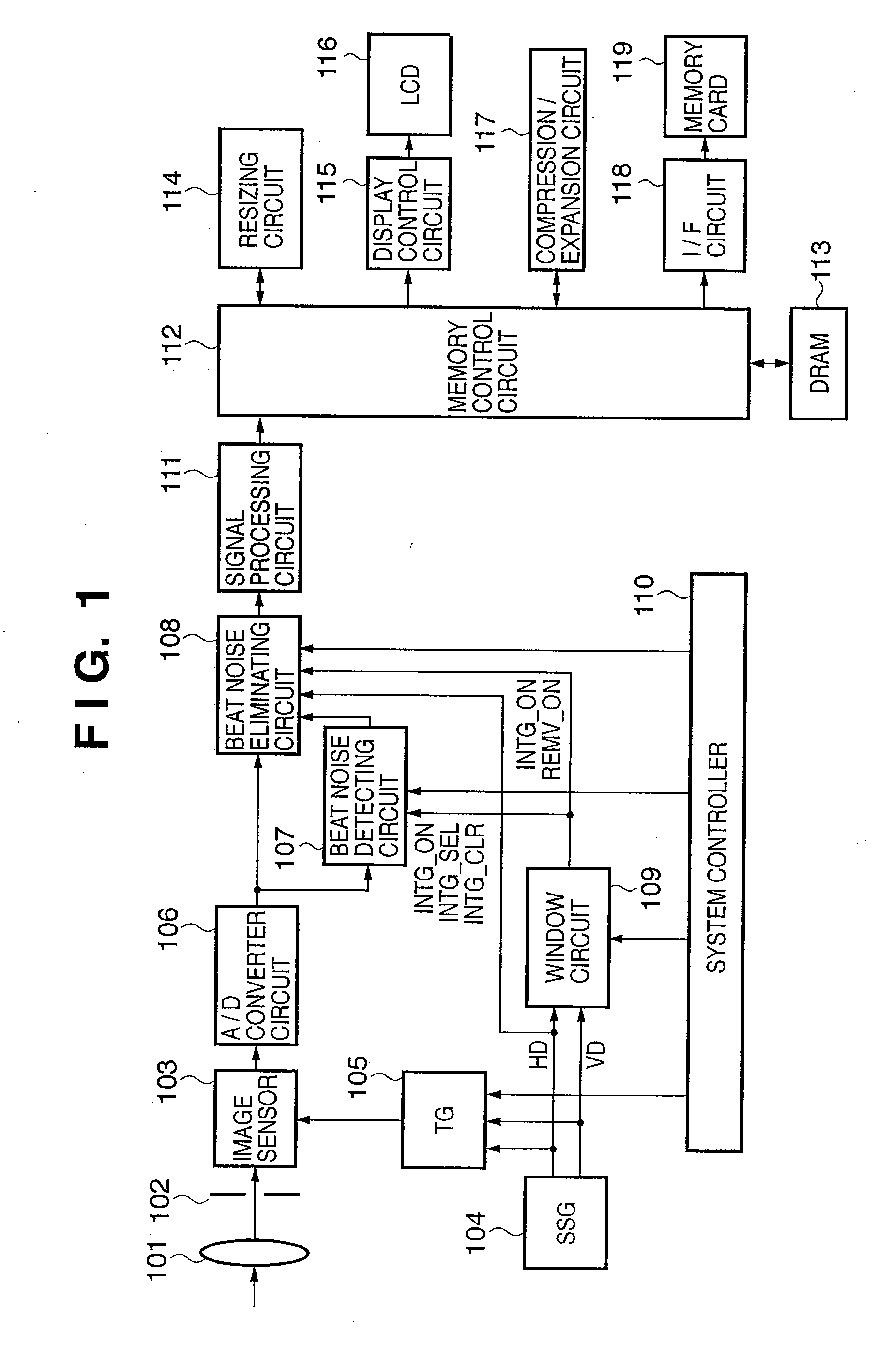
Image processing apparatus and method of controlling image processing apparatus
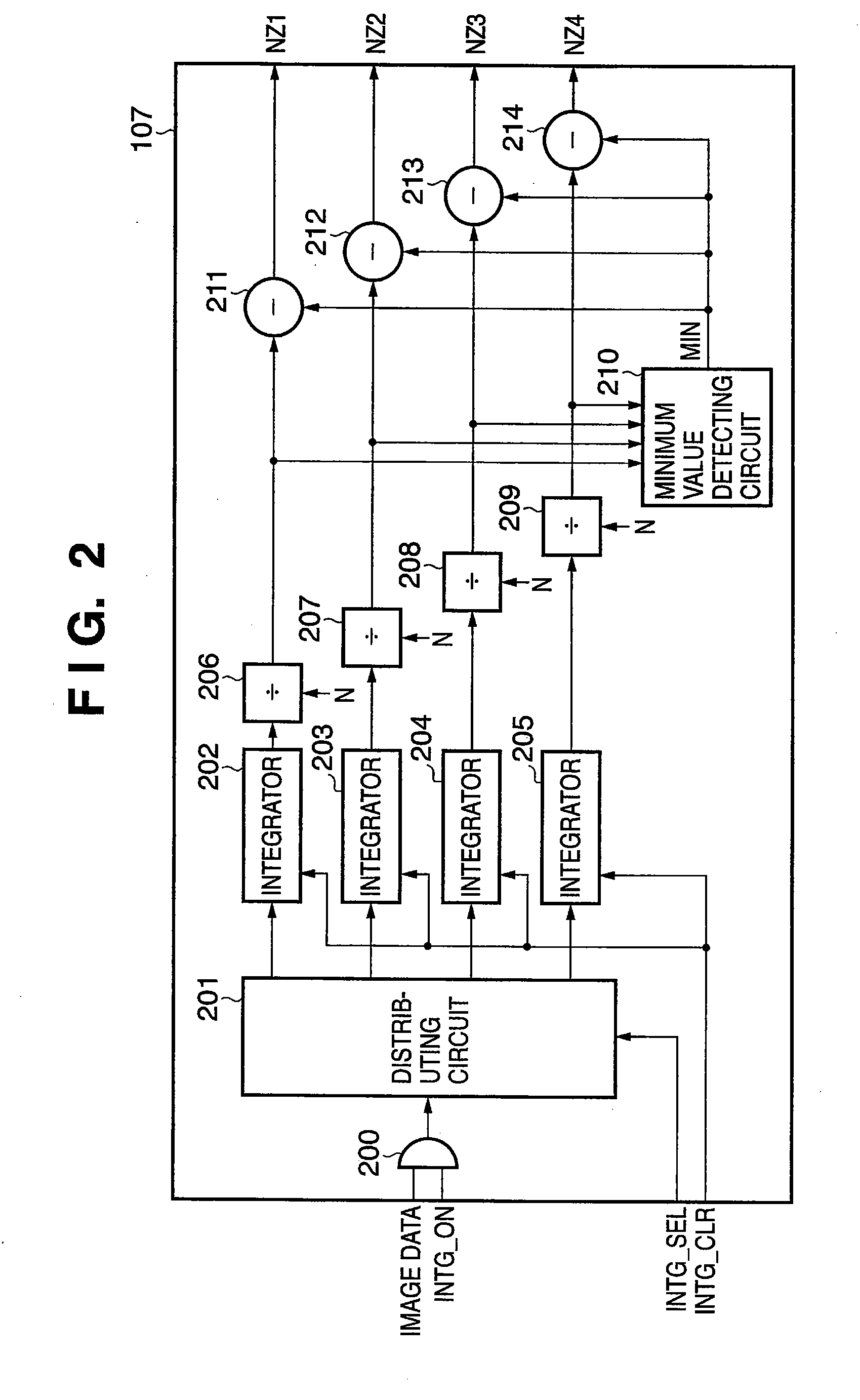
InactiveUS20080013858A1Accurate extractionEliminate beat noise components from the image signalImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionImaging processing
A noise elimination method capable of handling even beat noise occurring in an oblique direction is proposed. In an image processing apparatus that is provided with a correcting unit that subtracts cyclic data of beat noise from effective pixel data included in inputted digital image data, the correcting unit comprises: a distributing unit that sequentially and cyclically distributes optical black area pixel data included in the digital image data; an integrating unit to which the optical black area pixel data distributed by the distributing unit is sequentially inputted; a first calculating unit that divides the integration result of the integrating unit by the number of integrations; a minimum value detecting unit that detects a minimum value of the output of the first calculating unit; and a second calculating unit that calculates the minimum value and the division result to obtain the cyclic data of the beat noise.
Owner:CANON KK
Metal zipper
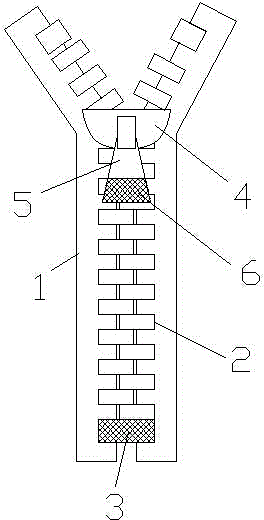
InactiveCN104382299ANot easy to hit noiseReduce scrolling up and downSlide fastenersEngineeringMagnet
The invention discloses a metal zipper. The metal zipper comprises two symmetrically arranged fixed cloth strips, zipper teeth, terminal-end limiting codes, a zipper head and a pull tab, wherein the zipper teeth respectively and correspondingly arranged on the two fixed cloth strips; the zipper head is connected between the fixed cloth strips on the two sides by virtue of the zipper teeth; the pull tab is connected to the zipper head; the terminal-end limiting codes are arranged on the bottom of the fixed cloth strips; the zipper teeth are made of steel, and the zipper head is made of steel; a magnet is fixedly arranged on the bottom of the pull tab; a magnetic adhesive tape is attached on the surface of each terminal-end limiting code. Through the way above and according to the metal zipper, the pull tab is absorbed on the zipper teeth under the action of the magnet after the zipper is closed, so that the pull tab is not easy to swing to result in beating noise; the zipper head is absorbed at the terminal-end limiting codes under the action of the magnetic adhesive tapes after the zipper is separated, so that upward and downward sliding is reduced, and the metal zipper is good in quietness.
Owner:JIANGSU HONGDA ZIPPER MFR
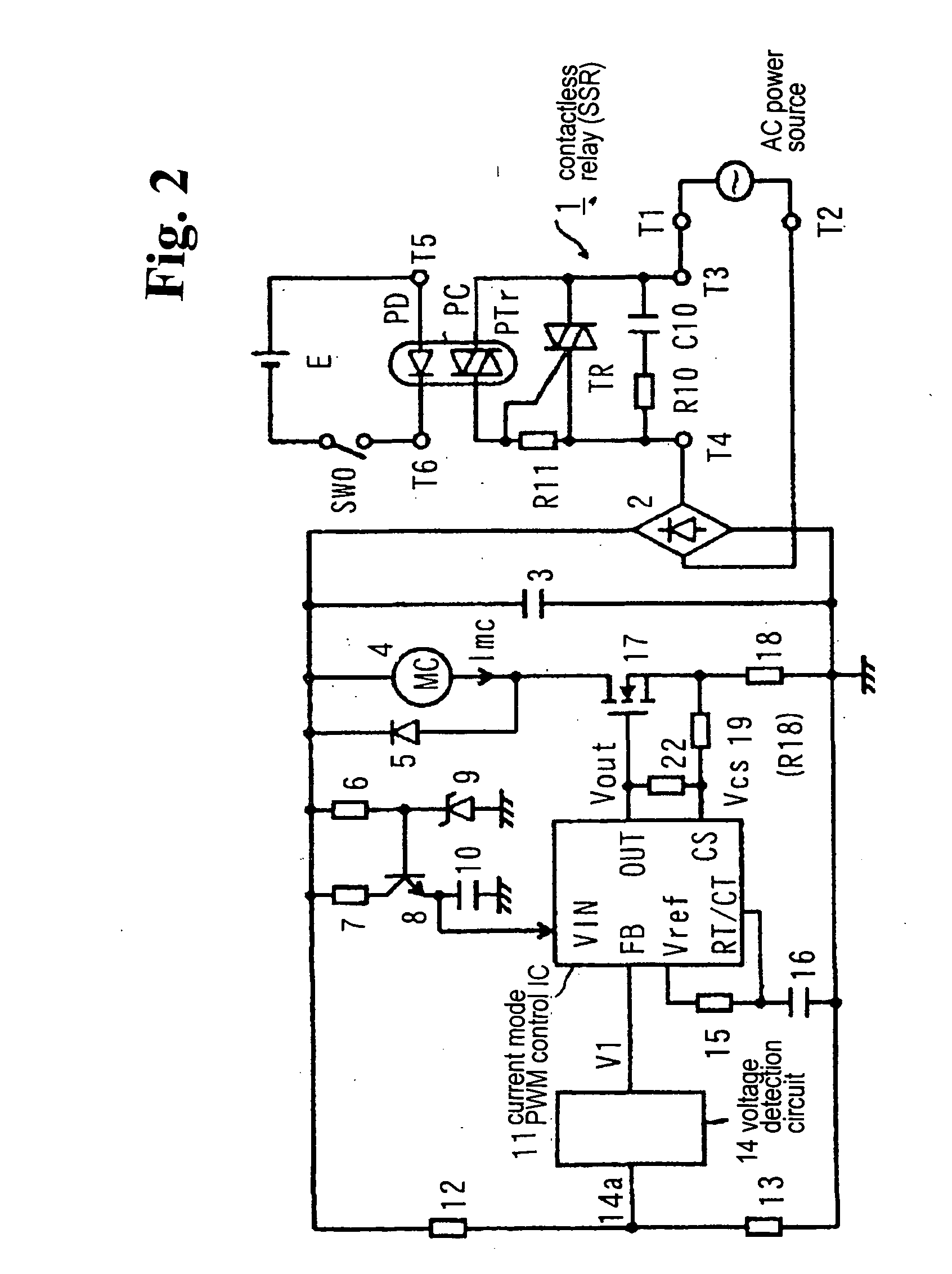
Electromagnetic apparatus drive apparatus
InactiveUS7042692B2Reliable releaseReduce power consumptionAc-dc conversion without reversalRelaysSwitching cycleEngineering
Conventionally, a non-conductive period is provided in a region in the vicinity of zero of an AC power voltage via a voltage detection circuit 14 to turn off reliably. The FET 17 maintains the ON state within several switching cycles after the non-conductive interval to rapidly restore the magnetizing coil current, so that the magnetizing coil current rapidly increases. An object is to suppress beat noise in the electromagnetic device. Within a prescribed interval following the non-conductive interval, a partial voltage at a resistor 19 of an output V2 of a mono-stable circuit 20 is added as a bias voltage to a detection voltage of a magnetizing coil current at a resistor 18, and is detected by the IC 11. The IC 11 drives a FET 17 with a constant switching period after the non-conductive interval, thereby preventing the increase in the magnetizing coil current and resolving the problem.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC FA COMPONENTS & SYST CO LTD
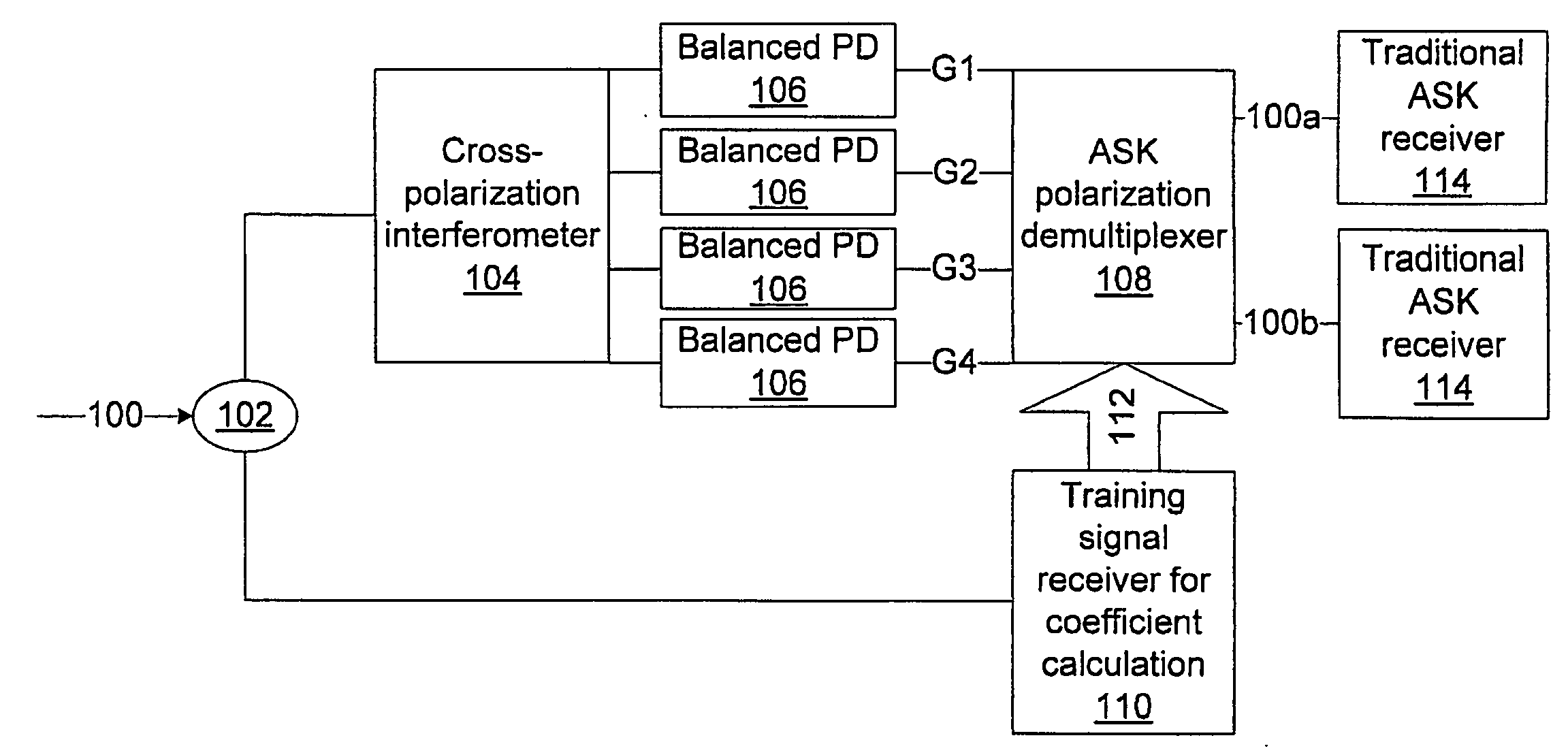
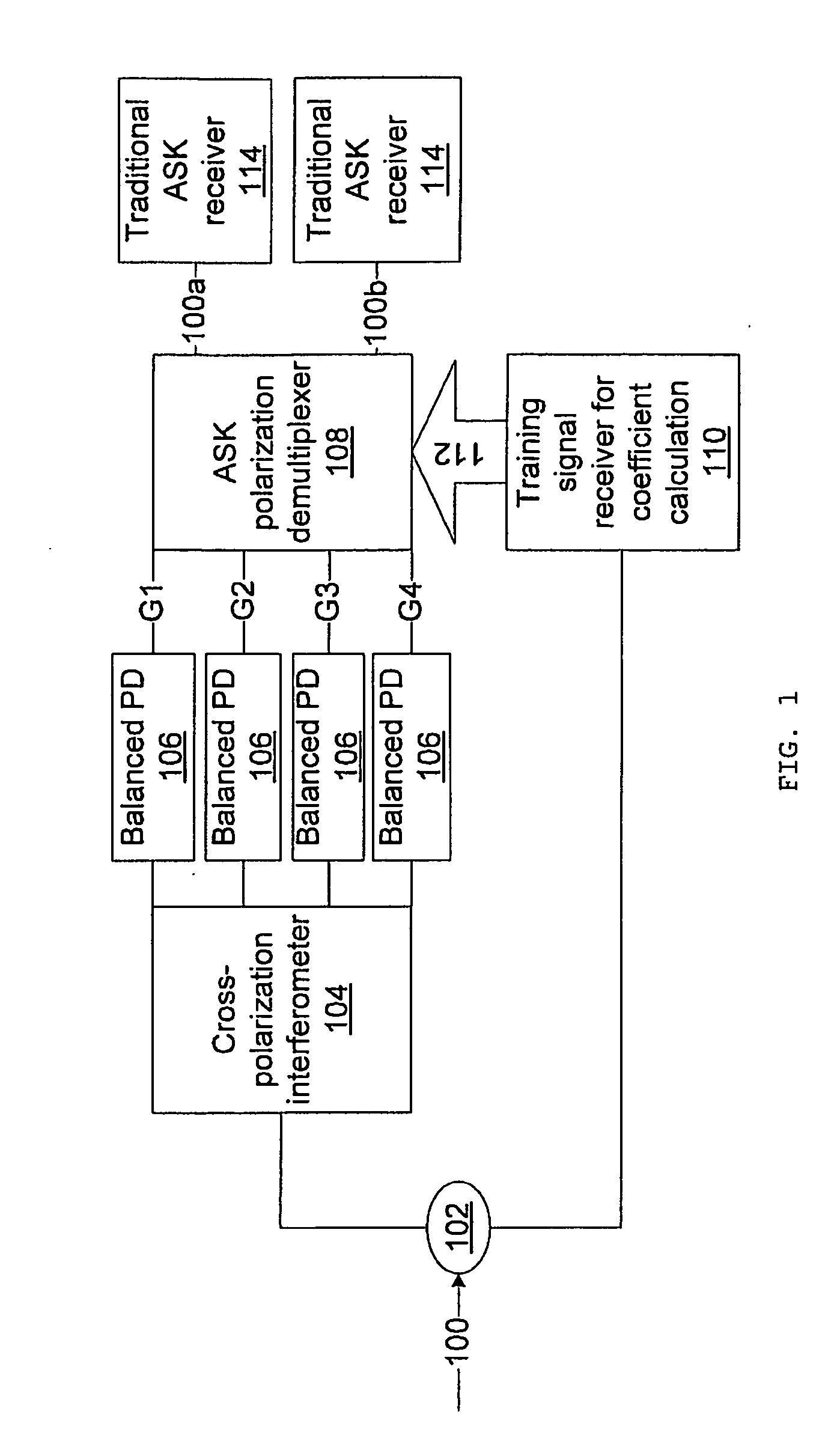
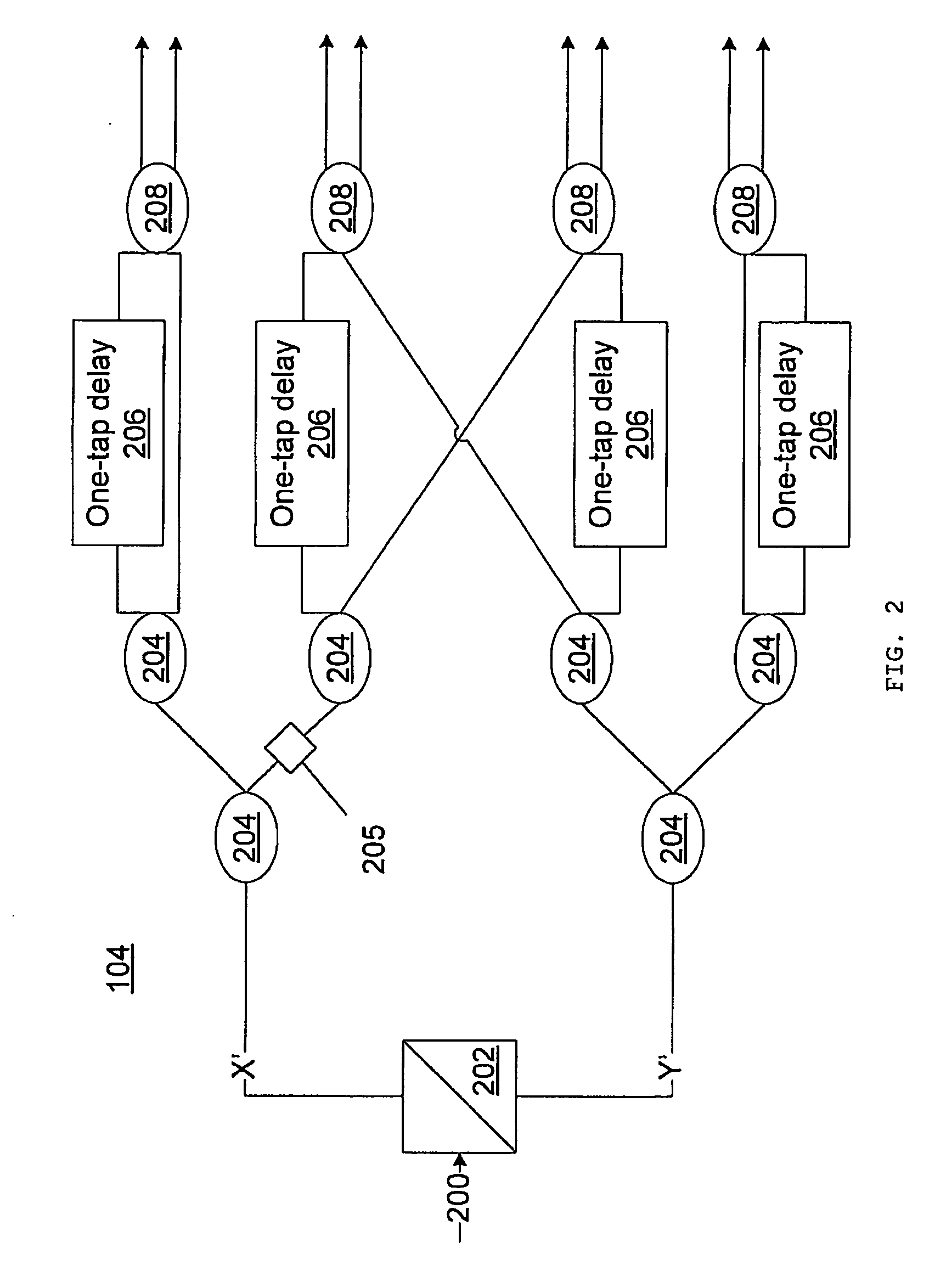
Direct detection receiver using cross-polarization interferometer for polmux-ask system
ActiveUS20090310966A1Polarisation multiplex systemsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsPhotodetectorCross polarization
A differential delay detection system and method includes an optical splitter to split an incoming optical signal between a first path and a second path. The first path includes a cross-polarization interferometer configured to separately generate polarization independent outputs using split paths and to generate cross-polarization interference outputs, balanced photodetectors to aid in removing cross-polarization beating noise, and a polarization demultiplexer configured to combine the polarization independent outputs and the cross-polarization interference outputs from the cross-polarization interferometer with updated coefficients received from the second path to remove the cross-polarization mixed signals. The second path includes a training signal receiver configured to compute the updated coefficients and output the updated coefficients to the polarization demultiplexer.
Owner:NEC CORP
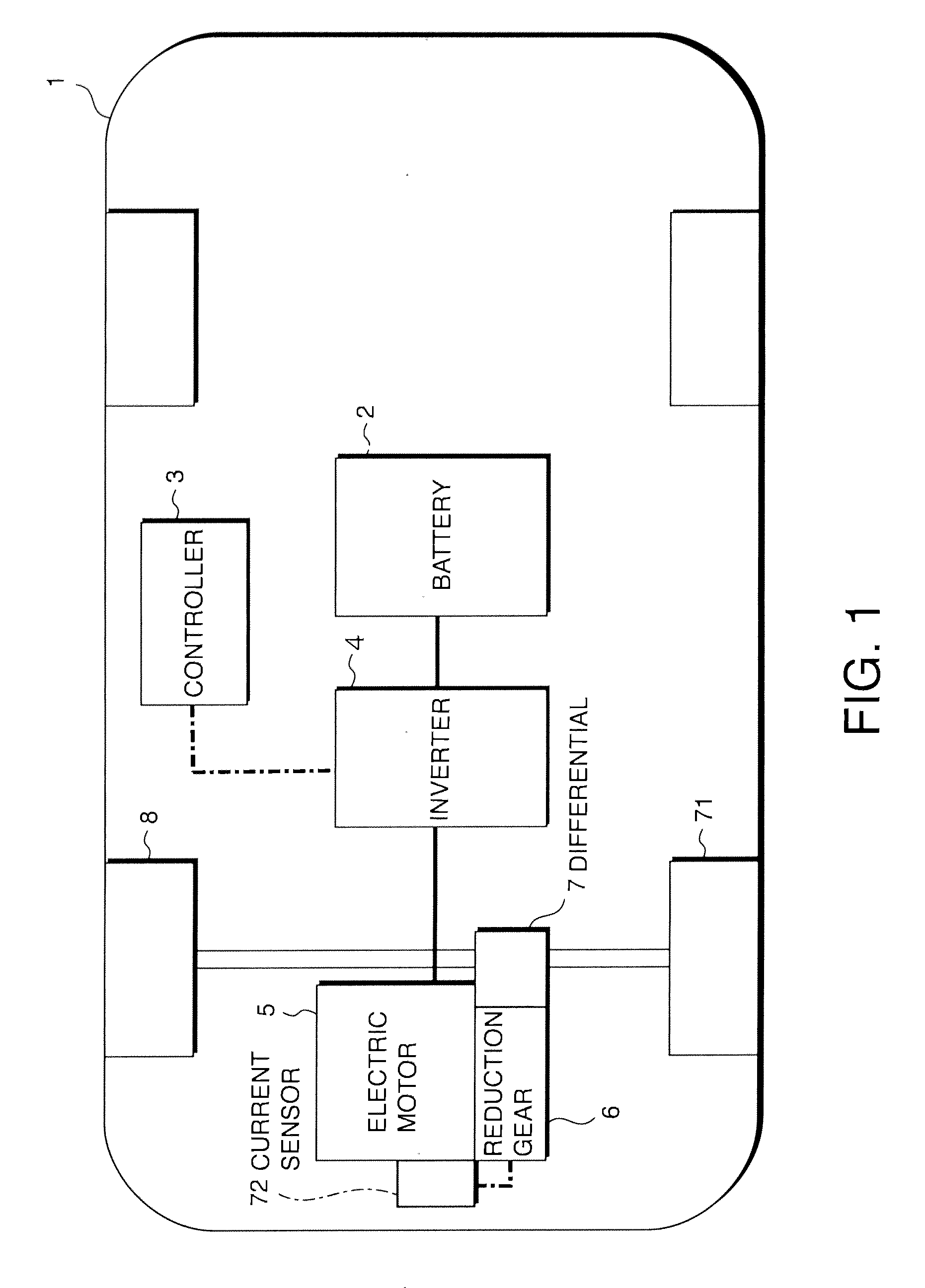
Operating noise control device and operating noise control method for vehicle
A vehicle (1, 17) includes an electric drive motor (5, 19), an inverter (4) that provides a drive current to the electric motor (5, 19) and a controller (13) that controls the inverter (4). The controller (13) functions as a beat noise generation system that creates beat noise by generating a second operating noise containing a component an order of which is very close to a value representing an order of an operating noise generated in proportion to a rotation speed of the electric motor (5, 19) so as to create desirable traveling noise corresponding to an accelerating state while the vehicle accelerates.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD +1
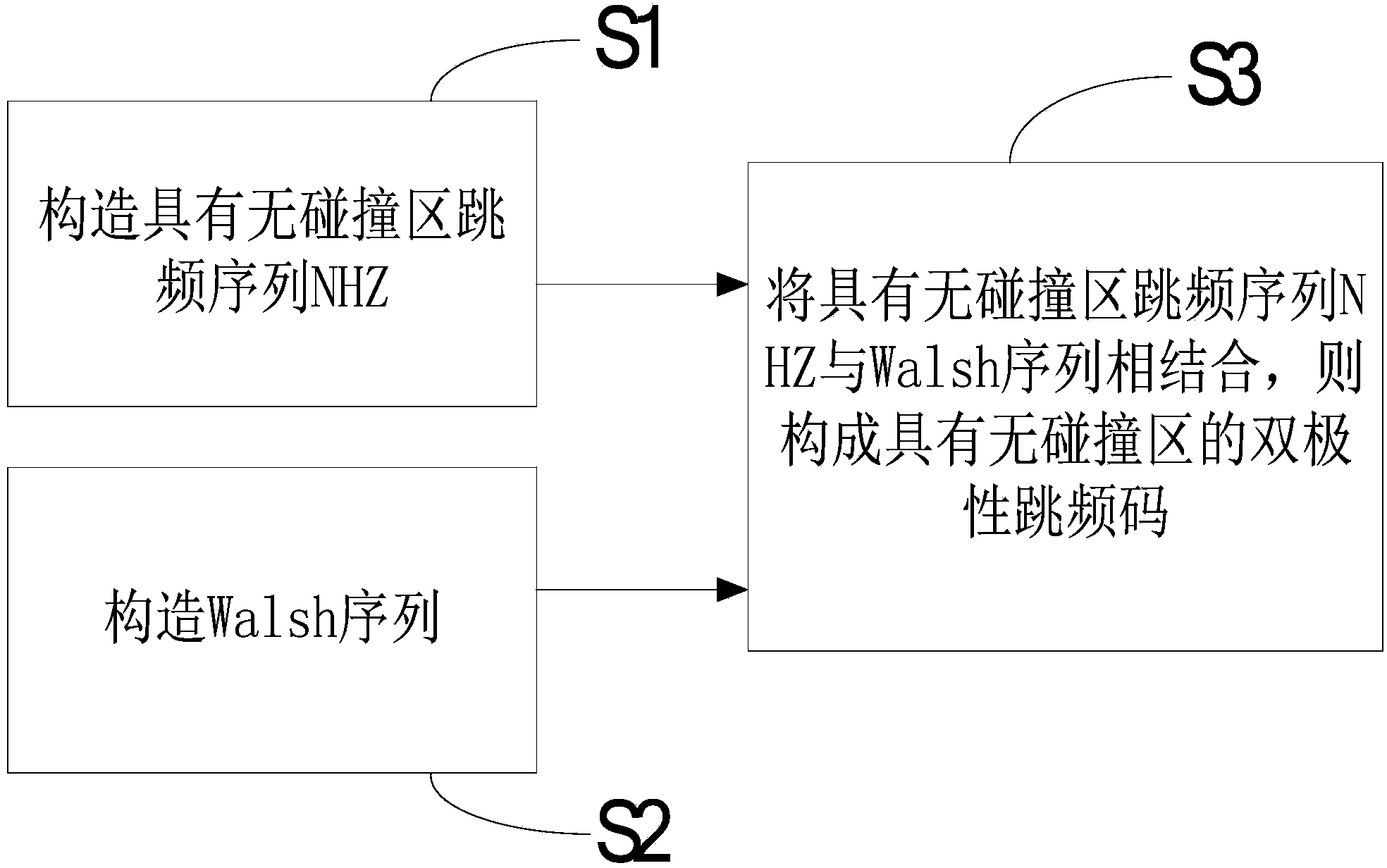
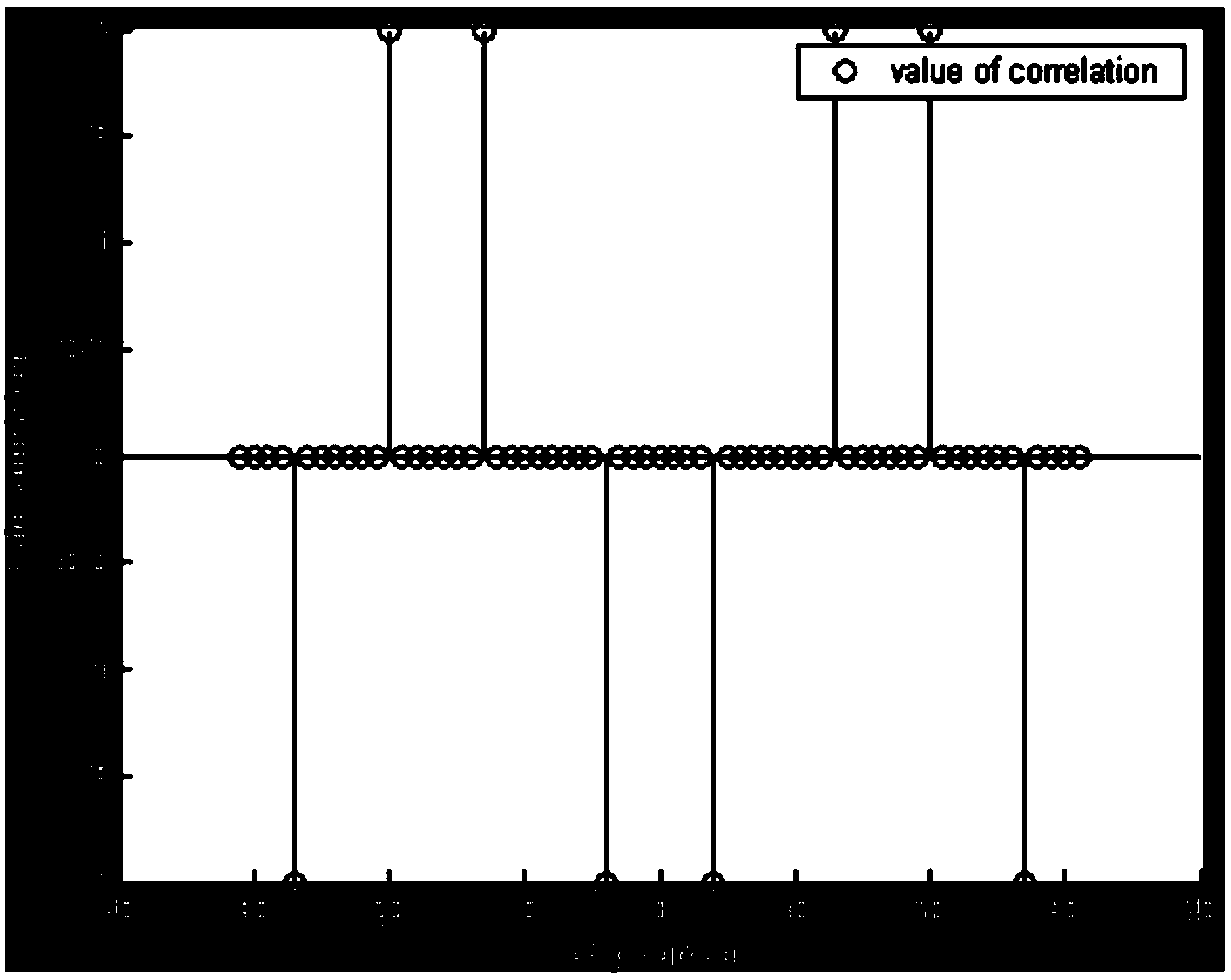
Method and system for constructing no-hit-zone bipolar frequency hopping code
The invention provides a method and system for constructing a no-hit-zone bipolar frequency hopping code. The method for constructing the no-hit-zone bipolar frequency hopping code includes the steps that first, a no-hit-zone frequency hopping sequence NHZ is constructed; second, a Walsh sequence is constructed; third, the no-hit-zone frequency hopping sequence NHZ and the Walsh sequence are combined to form the no-hit-zone bipolar frequency hopping code. The method and system for constructing the no-hit-zone bipolar frequency hopping code have the advantages that according to the constructed no-hit-zone bipolar frequency hopping code, all codons are totally orthogonal as long as the delay between users is within a zero correlation zone, so that multi-site interference and beat noise of a two-dimensional coherent OCDMA system will be completely eliminated, and the near-far effect of the two-dimensional coherent OCDMA system can also be eliminated. Therefore, by means of the no-hit-zone bipolar frequency hopping code constructed through the method and system, a high-capacity two-dimensional coherent OCDMA system can be achieved, and the no-hit-zone bipolar frequency hopping code can be applied to an optical access network, an optical local area network, an optical code label switching network, an optical fiber sensor network and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
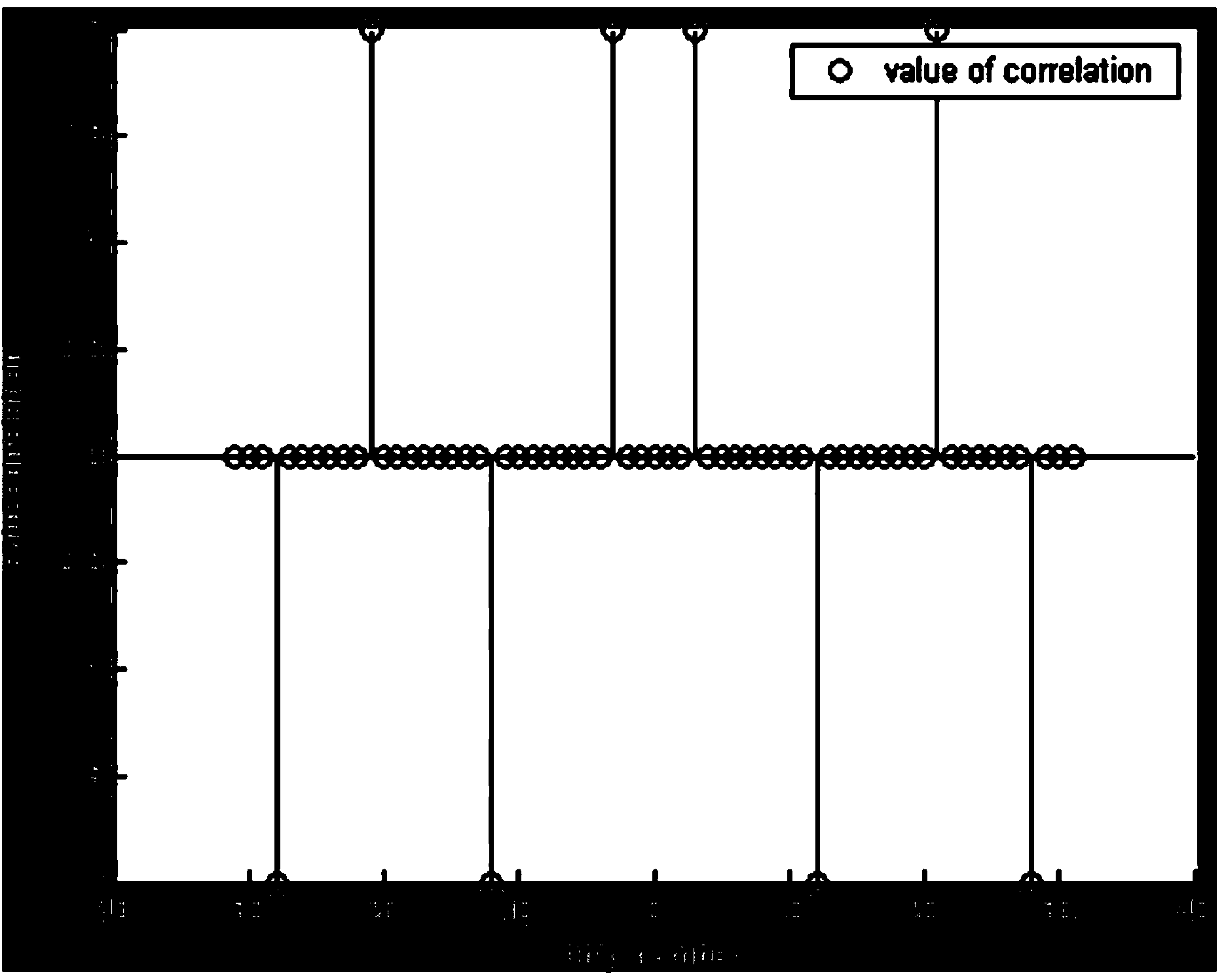
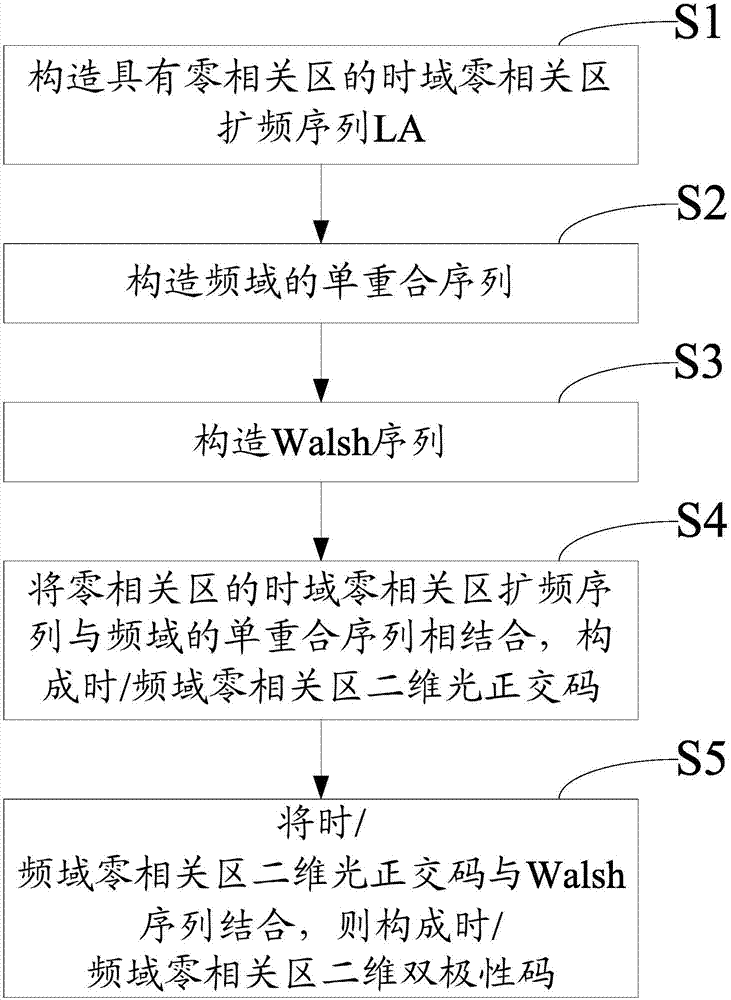
Constructing method and system for two-dimensional bipolar code of zero-correlation region in time/frequency domain
ActiveCN106877968AEliminate distractionsCancel noiseOptical code multiplexMultiplex code generationMulti siteWalsh sequences
The invention provides a constructing method and system for the two-dimensional bipolar code of a zero-correlation region in time / frequency domain. The constructing method comprises the steps that A a time domain zero-correlation region spread-spectrum sequence LA with the zero-correlation region is constructed; B a single coincidence sequence in frequency domain is constructed; C a Walsh sequence is constructed; D the time domain zero-correlation region spread-spectrum sequence of the zero-correlation region is combined with the single coincidence sequence in frequency domain are combined to form a time / frequency domain zero-correlation region two-dimensional optical orthogonal code; and E the time / frequency domain zero-correlation region two-dimensional optical orthogonal code is combined with the Walsh sequence to form the two-dimensional bipolar code of the zero-correlation region in time / frequency domain. The method and the system have the advantages that multi-site interference and beat noise of a two-dimensional coherent OCDMA system are completely eliminated; the near-far effect of the two-dimensional coherent OCDMA system can be eliminated; the large-capacity two-dimensional coherent OCDMA system can be realized; and the method and the system can be applied to an optical access network, an optical local area network, an optical code tag switching network, a fiber optic sensor network and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Pressure opening and closing valve
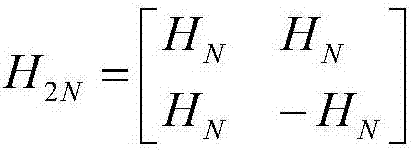
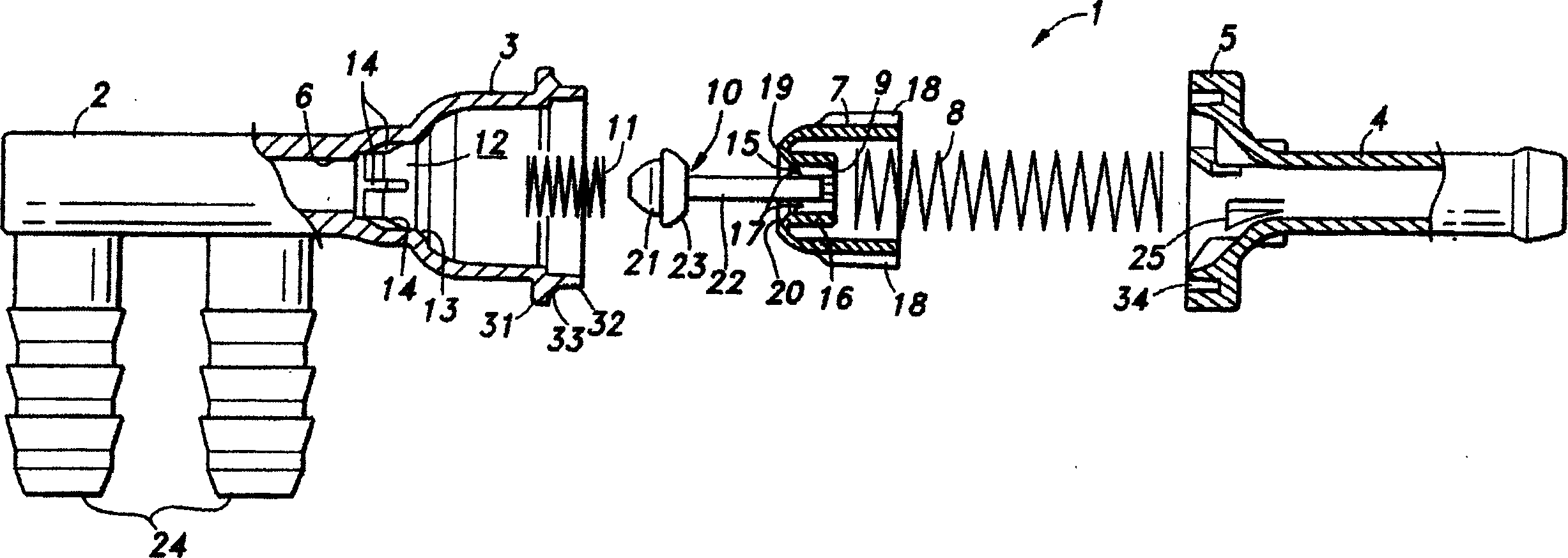
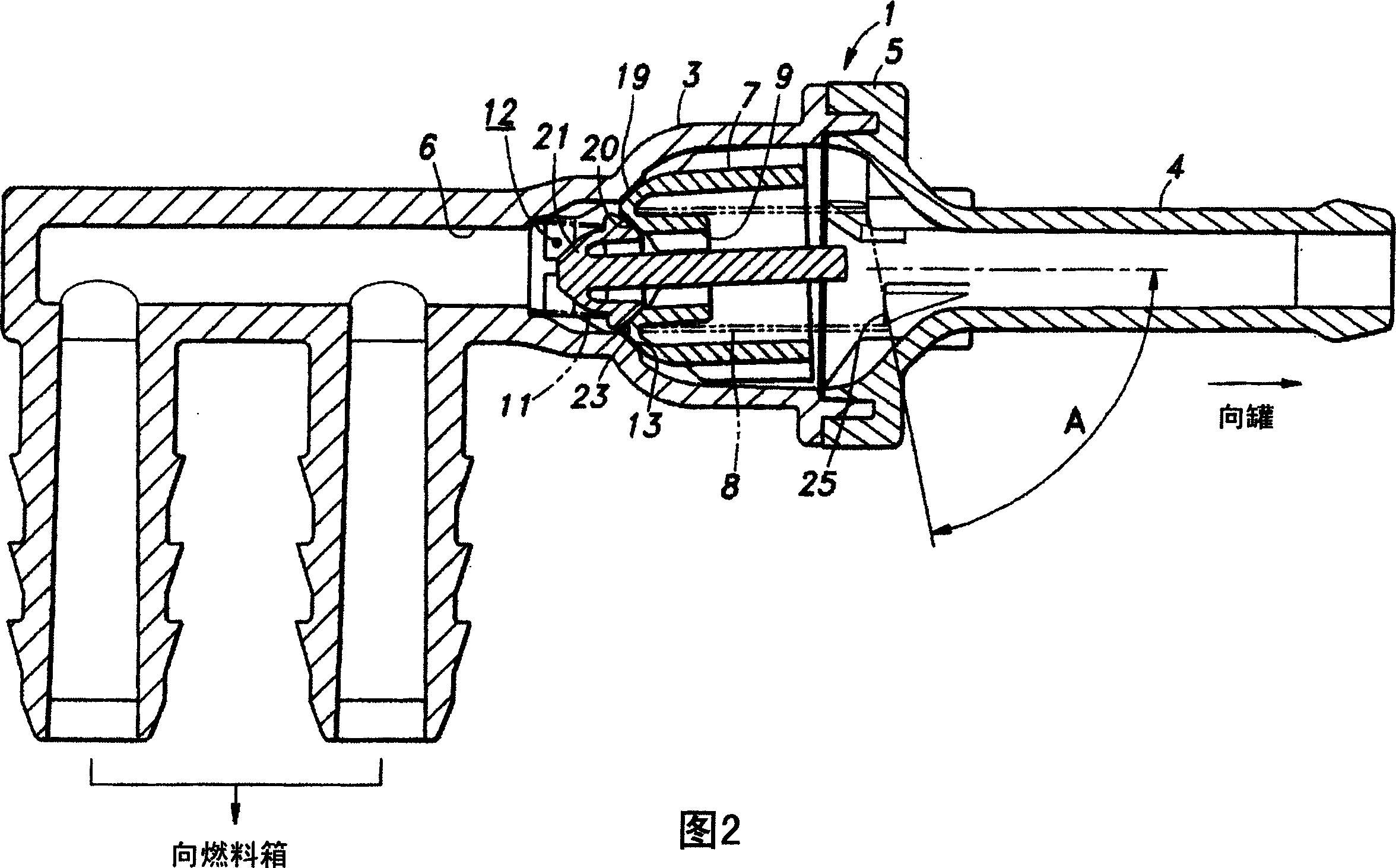
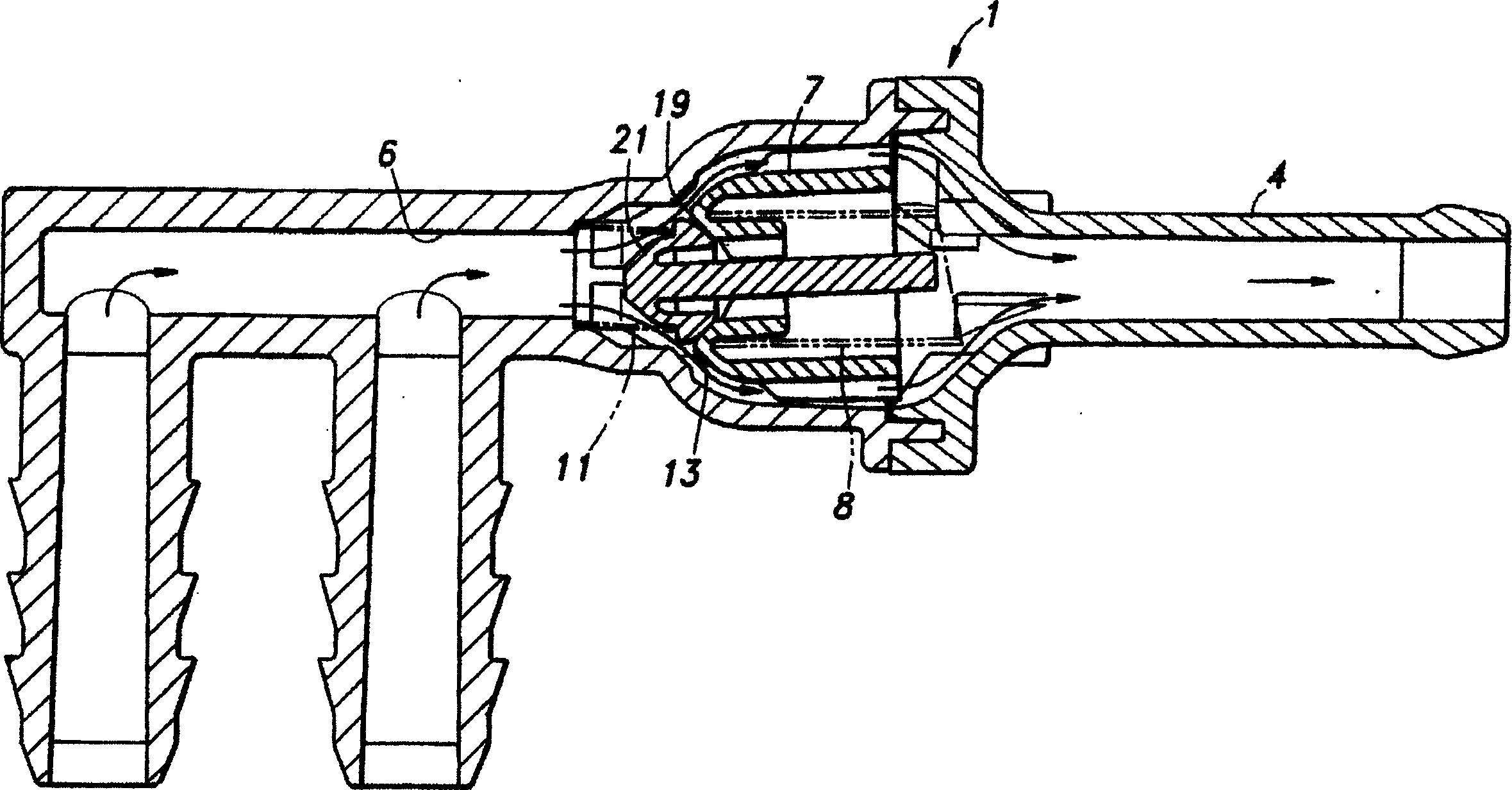
InactiveCN1590820ANo beatingIntentional contactNon-fuel substance addition to fuelEqualizing valvesPositive pressureDifferential pressure
To provide a pressure opening and shutting valve capable of controlling occurrence of beating noises without blocking smoothness of operation. The opening and shutting valve (1) comprises a housing (a housing body 3 and a housing cap 5) having first port (a fluid passage 6) and a second port (hose connecting nozzle 4), and a valve body (positive pressure valve body 7), which is housed in the housing, normally blocking the first port by urging with a spring (a coil spring 8 with a large diameter) and opening when differential pressure between the first port and the second port exceeds a designated value. An axis of urging force for closing a valve by means of the valve body is set to be non-parallel to an axis of a valve seat (a positive pressure valve seat 13) that brings into contact with the valve body.
Owner:NIFCO INC +1
Imbalanced-Mach-Zehnder-based demodulation device for multiplexing optical fiber interferometer
InactiveCN102183866BSuppression of motion errorsHigh precision measurementCoupling light guidesLight demodulationSensor arrayLine width
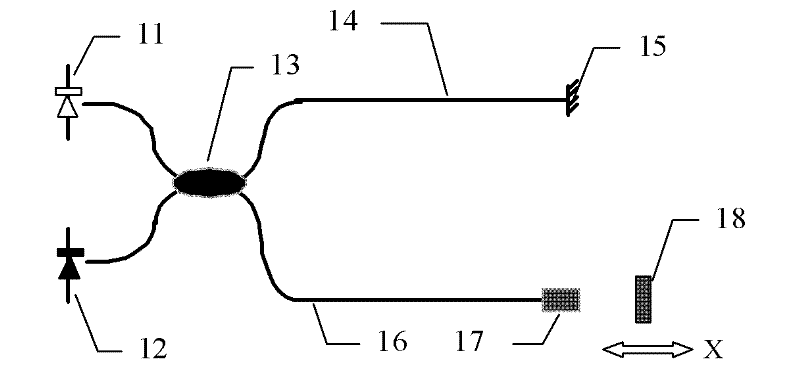
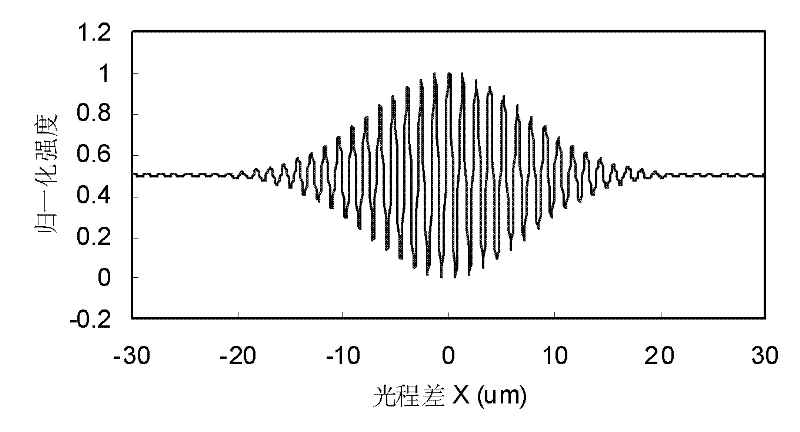
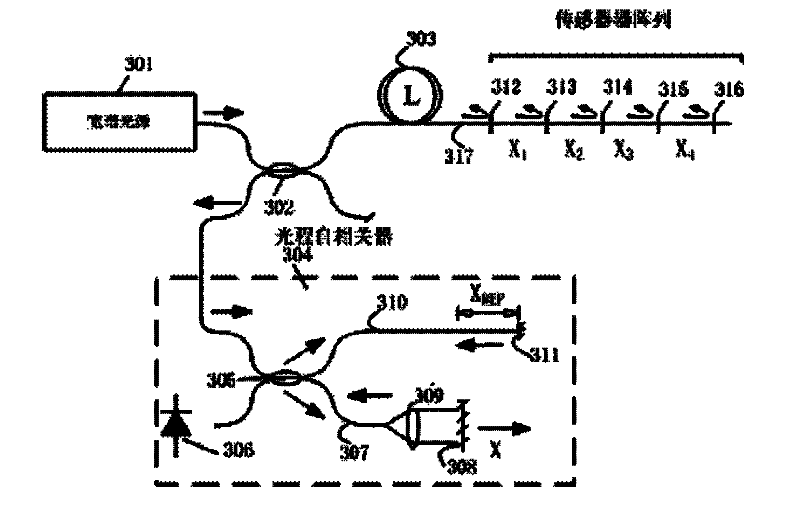
The invention provides an imbalanced-Mach-Zehnder-based demodulation device for a multiplexing optical fiber interferometer. The device consists of a broadband light source, an optical circulator, an optical divider, a sensor array switching and transmitting optical fiber, an optical fiber sensor array, an imbalanced-Mach-Zehnder optical autocorrelator and an interference signal detecting unit inconnection, wherein the imbalanced-Mach-Zehnder interferometer forms an optical path correlator, narrow linewidth laser complexed in the correlator evaluates scanning amplitude and uniformity of the optical path, the optical path scanning error is compensated, and the measuring accuracy of the sensor is improved; the interference beating noise of the interferometer can be reduced, and multiplexing number of interferometers is improved; the optical autocorrelator demodulates signals of a multiplexing optical fiber sensor; and the unique optical path matching condition suppresses interference noise of secondary optical path matching. The device can be applied in the fields of real-time monitoring and measuring of multi-point stress or temperature and other physical quantities, monitoring oflarge-scale intelligent structures and the like.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method and system for adopting colourless and nonluminous optical network units in optical access network
ActiveCN104363532AImprove transmission distanceIncrease transfer rateMultiplex system selection arrangementsFibre transmissionAccess networkRayleigh scattering
The invention provides a method and system for adopting colourless and nonluminous optical network units in an optical access network. The method comprises the steps that a binary downlink original signal and an uplink seed signal orthorhombic with the downlink original signal are overlapped together on an optical line terminal and modulated to a light carrier, then the modulated downlink combined optical signal is transmitted to the optical network units, and the optical network units do not comprise a light source; the optical network units receive the downlink combined optical signal, the signal is processed, and the downlink original signal is obtained; a binary uplink original signal is modulated to the downlink combined optical signal through the optical network units, and the modulated uplink modulation signal is transmitted to the optical line terminal; the optical line terminal receives the uplink modulation signal from the optical network units, and then the uplink original signal is restored. The same wavelength light source is adopted in the downlink signal and the uplink signal. The downlink signal does not need to be wiped, and when the uplink signal is received, frequency beating noise caused by rayleigh scattering can be eliminated.
Owner:WUHAN POST & TELECOMM RES INST CO LTD
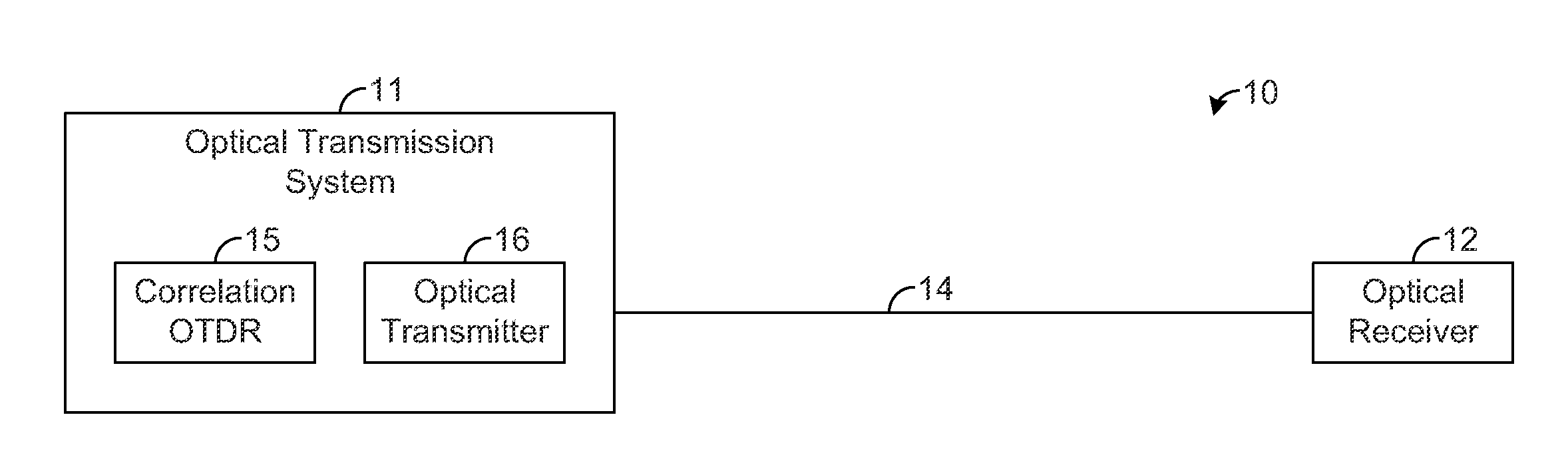
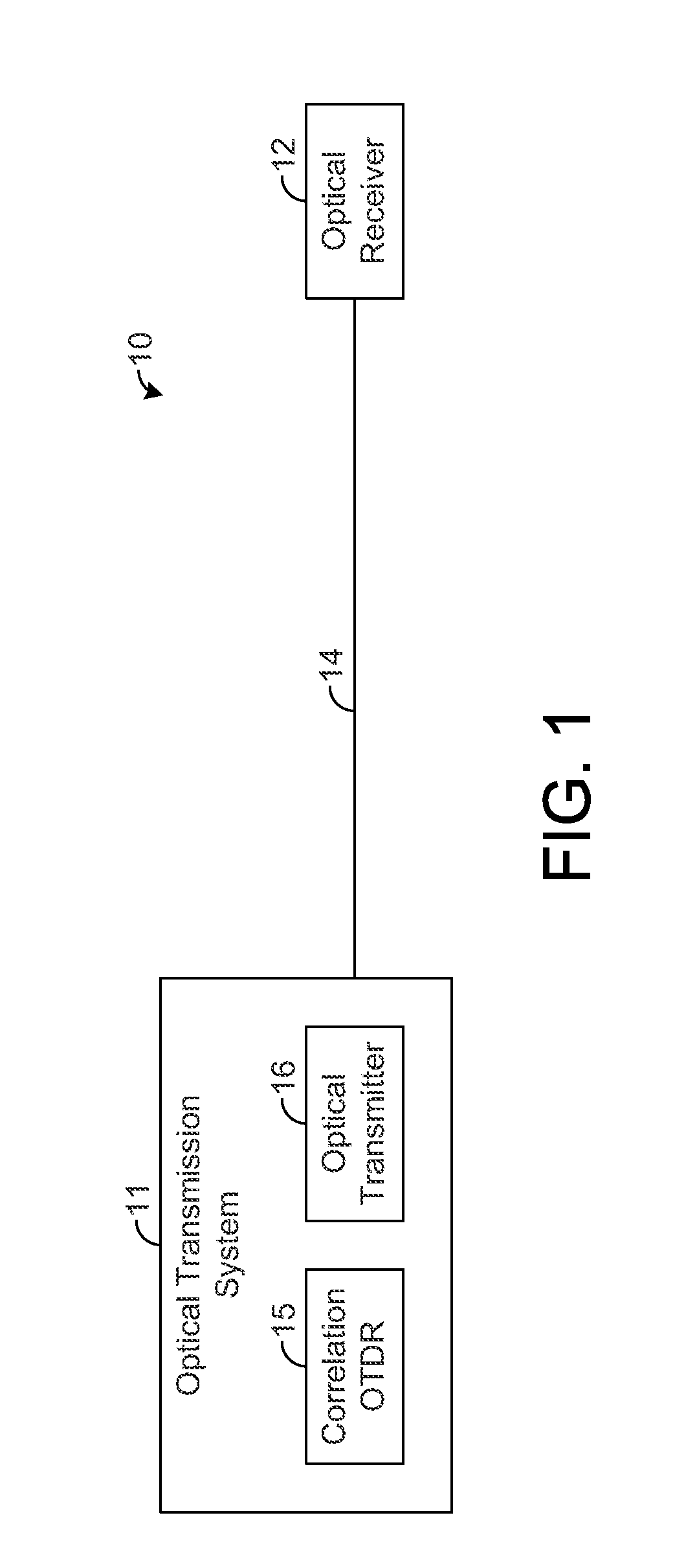
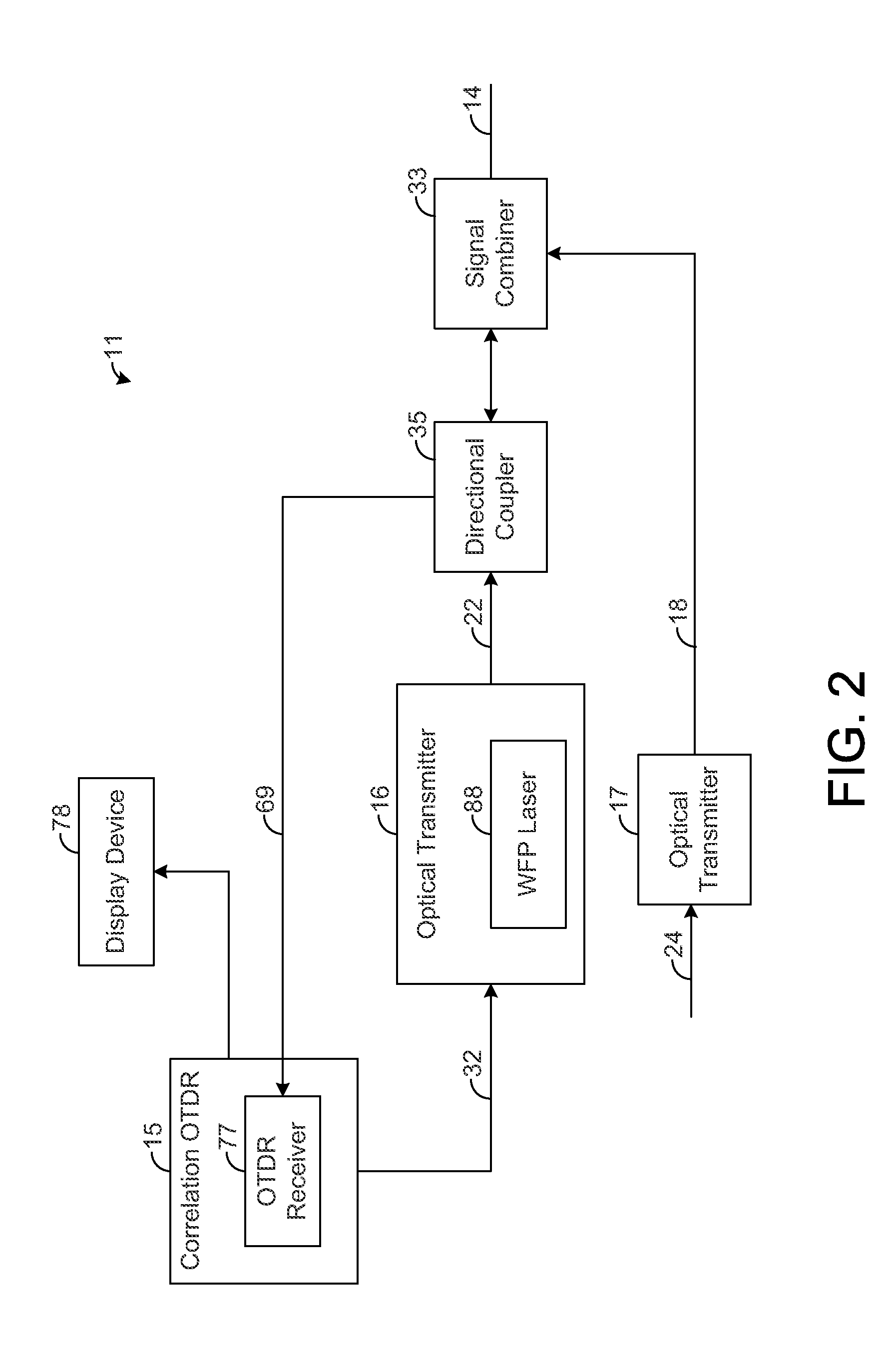
Optical time domain reflectometer systems and methods using wideband optical signals for suppressing beat noise
ActiveUS20140003821A1Distortion/dispersion eliminationReflectometers detecting back-scattered light in time-domainTime domainOptical time-domain reflectometer
A correlation optical time domain reflectometer (OTDR) provides a correlation sequence that is continuously transmitted along a fiber for testing the fiber for anomalies. Such continuous transmission can result in beat noise that degrades the quality of the measured returns. In this regard, each sample is composed of backscatter returns from many points along the fiber that arrive at the OTDR at the same time. When a subset of these returns have frequency differences that appear in the passband of the OTDR receiver, the constructive and destructive interference of these returns at the OTDR receiver can cause significant low-frequency beat noise in the OTDR signal. An optical transmitter is configured to transmit the correlation sequence through the fiber using a wideband optical signal such that the beat noise is suppressed within the passband of the OTDR receiver, thereby improving the quality of the returns measured by the OTDR.
Owner:ADTRAN
Method of setting colorless optical network unit uplink optical wavelength based on beat noise
ActiveCN104883226AFunction increaseImprove reliabilityWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsOptical network unitOptical transmitter
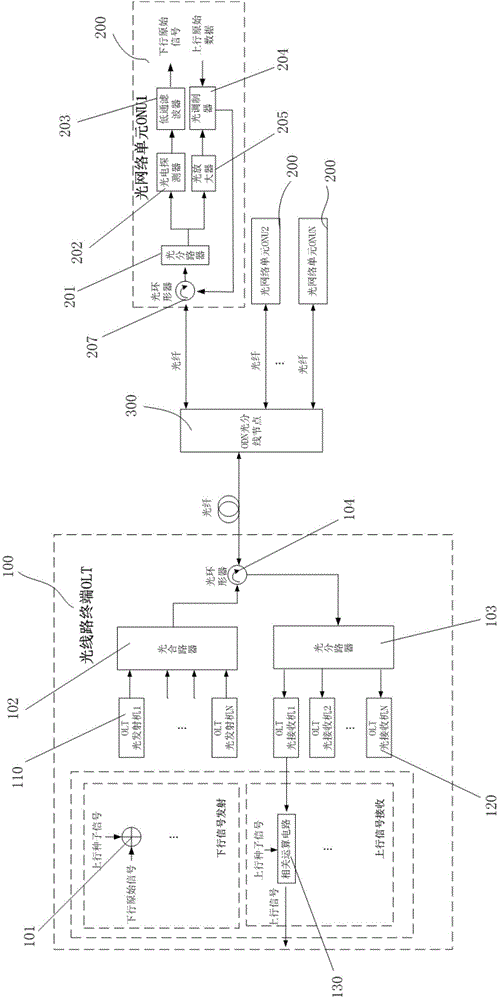
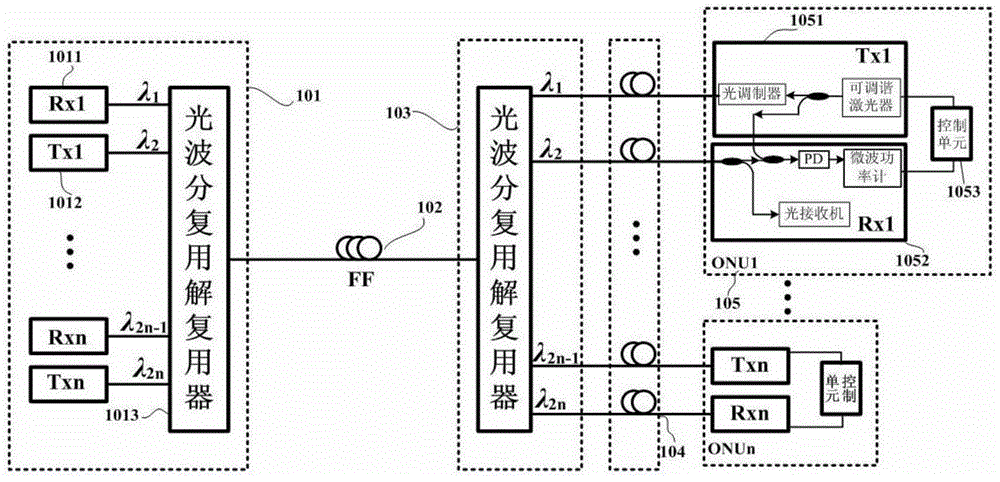
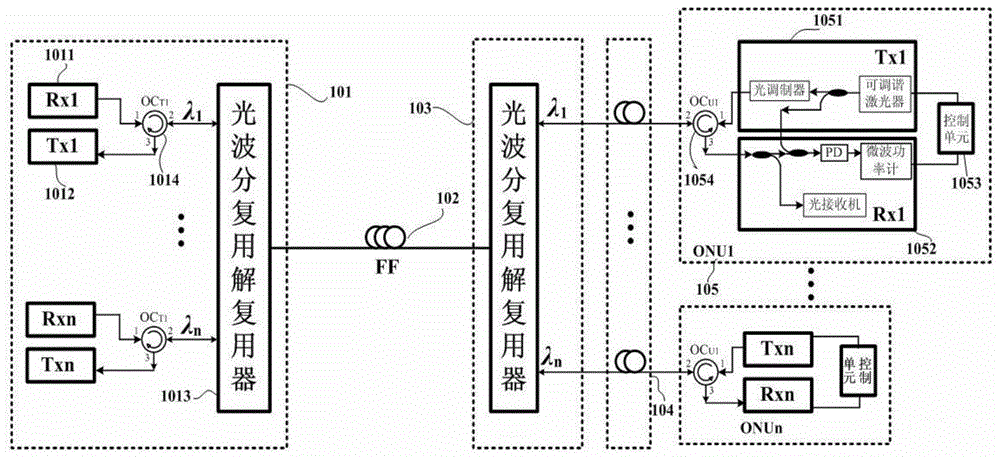
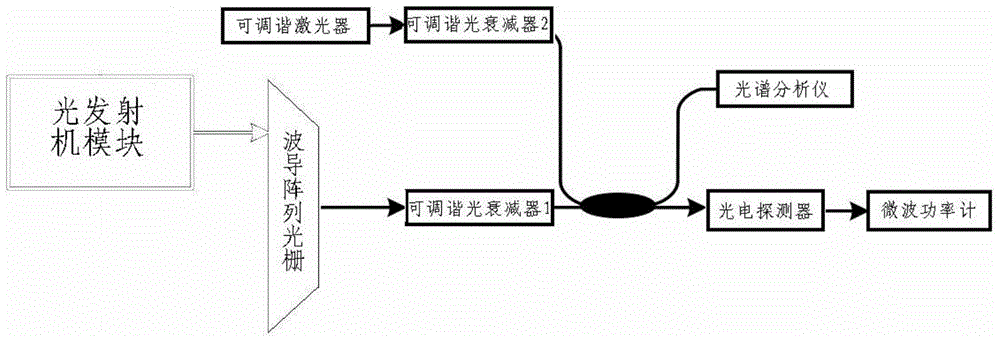
The invention relates to a method of setting a colorless optical network unit uplink optical wavelength based on beat noise. In a colorless ONU (105), a low bandwidth photoelectric detector used for generating beat noise is accessed; a microwave power meter transmits detected beat noise power to a control unit (1053) in real time; the control unit (1053) determines whether a current output optical wavelength of a tunable laser or a tunable optical transmitter is consistent with the wavelength of a downlink optical signal, and if yes, the operating wavelength of the tunable laser or the tunable optical transmitter is set as a current optical wavelength or a specified optical wavelength, otherwise the control unit (1053) controls the tunable laser or the tunable optical transmitter to continuously perform optical wavelength polling. According to the method, a colorless ONU based on a tunable laser or a tunable optical transmitter can independently set an upward optical wavelength by no means of an OLT, and thereby the method can be widely applied to the wavelength division multiplexing passive optical network technical field.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com