Patents
Literature
579results about "Reflectometers detecting back-scattered light in time-domain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
De-embedment of optical component characteristics and calibration of optical receivers using rayleigh backscatter
InactiveUS6947147B2Accurate analysisIncrease the number ofPhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansRayleigh scatteringFiber
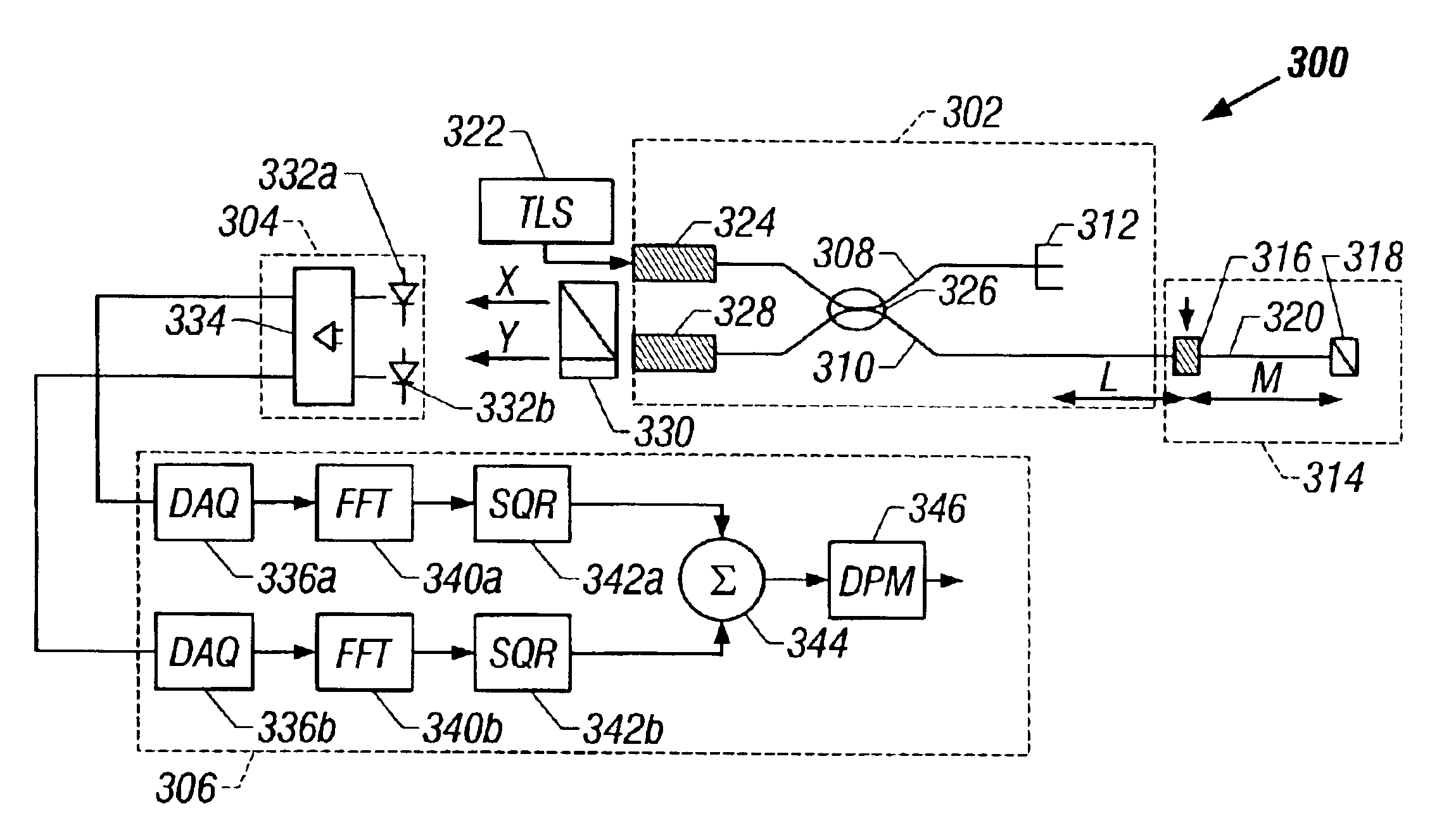
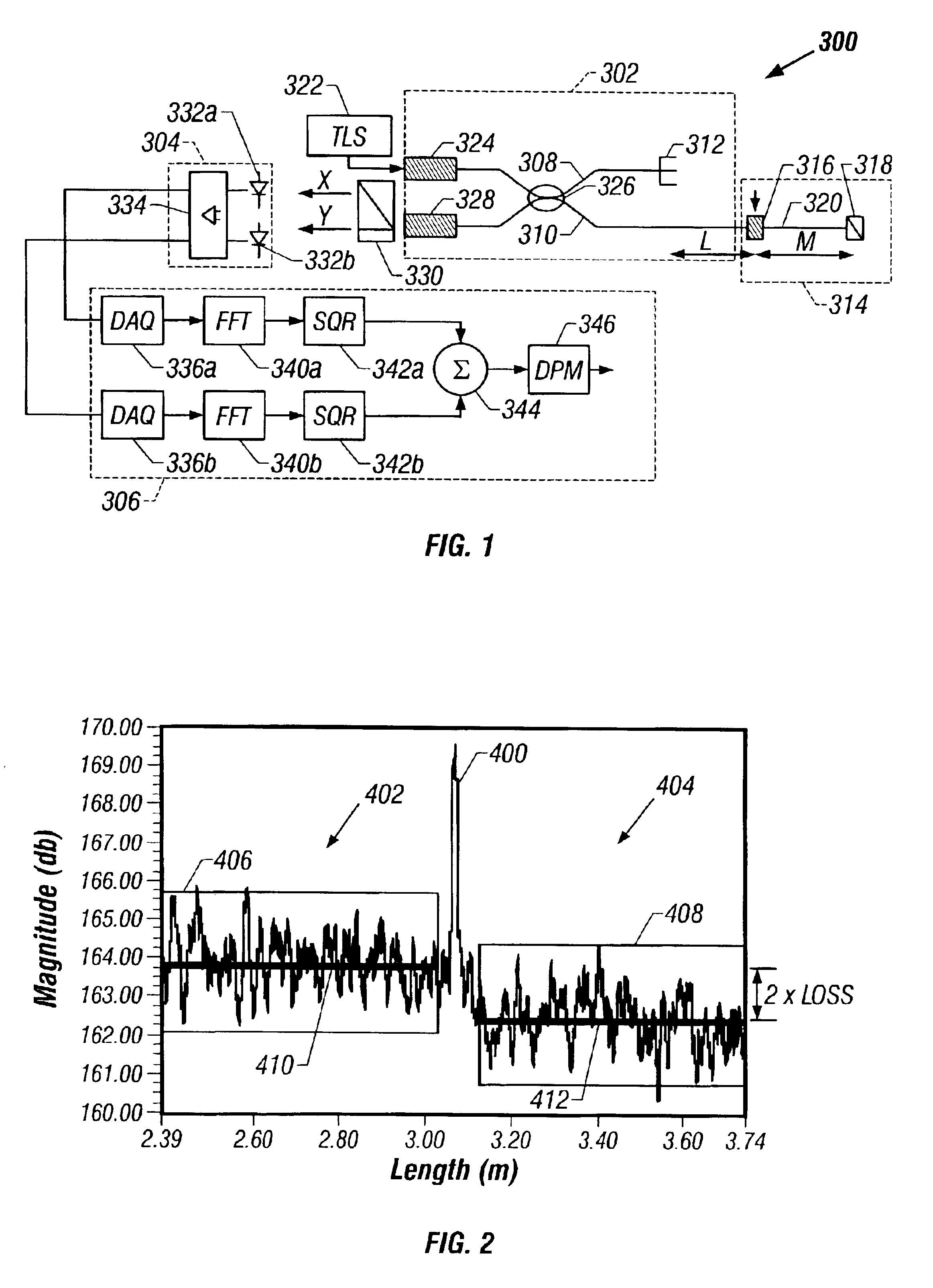
Method and system are disclosed for de-embedding optical component characteristics from optical device measurements. In particular, the invention uses frequency domain averaging of the RBS on both sides of an optical component to determine one or more of its optical characteristics. Where the RBS has a slope (e.g., as in the case of a lossy fiber), a frequency domain least square fit can be used to determine the optical component characteristics. In addition, the invention uses a reference DUT to correct for variations in the frequency response of the photoreceiver. A reference interferometer is used in the invention to correct for sweep non-linearity of the TLS. The optical component characteristics are then de-embedded from optical device measurements to provide a more precise analysis of the optical device.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
System and method to determine chromatic dispersion in short lengths of waveguides using a common path interferometer
InactiveUS7787127B2Material analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansReflected wavesIncident wave
The present invention relates to a system and method to determine chromatic dispersion in short lengths of waveguides using a two wave interference pattern and a common path interferometer. Specifically the invention comprises a radiation source operable to emit radiation connected to a means for separating incident and reflected waves; the means for separating incident and reflected waves possessing an output arm adjacent to a first end of the waveguide; and the means for separating incident and reflected waves further connected to an optical detector operable to record an interference pattern generated by a reflected test emission from the radiation source. The interference pattern consists of two waves: one reflected from a first facet of a waveguide and the second reflected from a second facet of the same waveguide.
Owner:GALLE MICHAEL +2
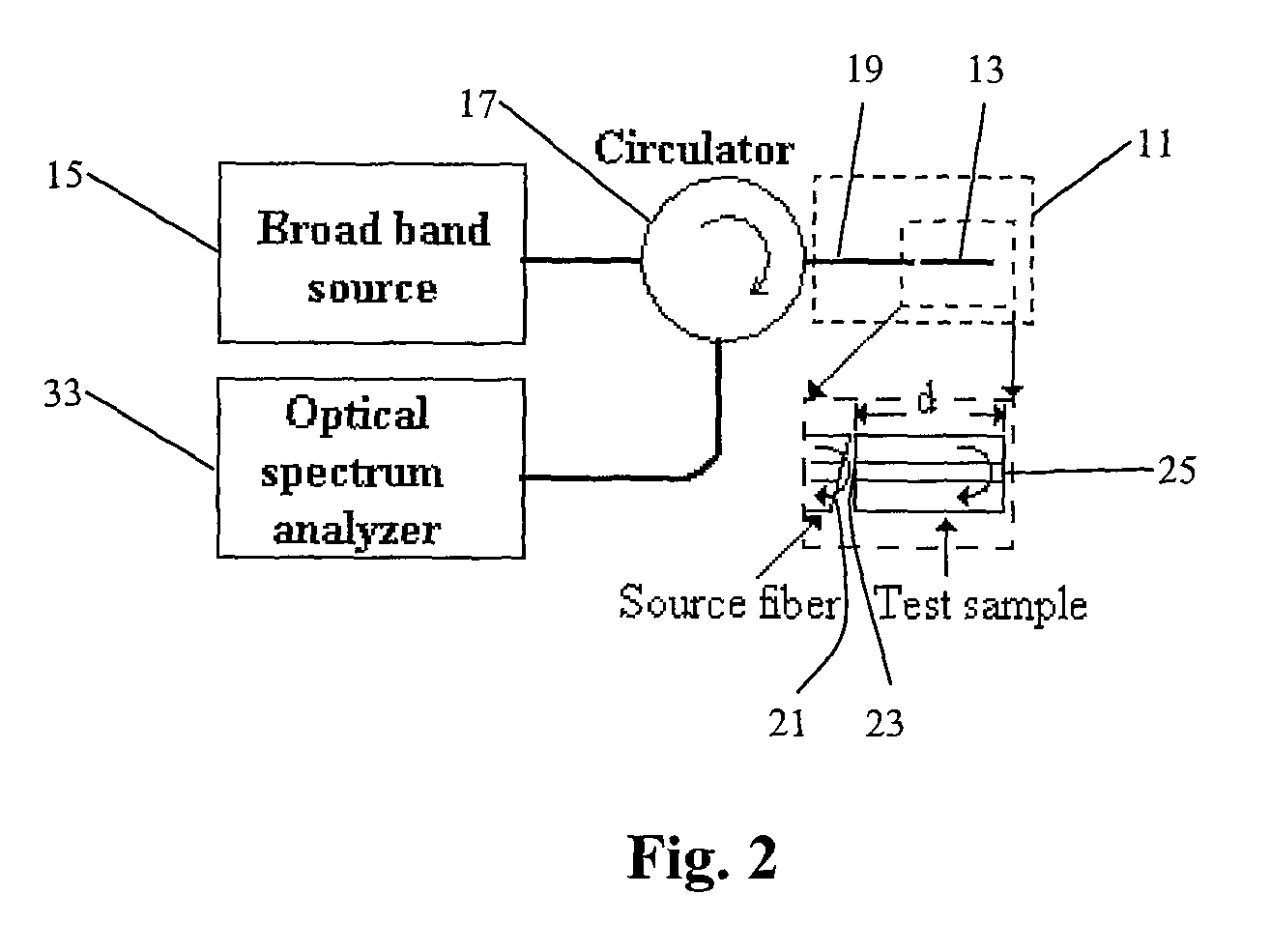
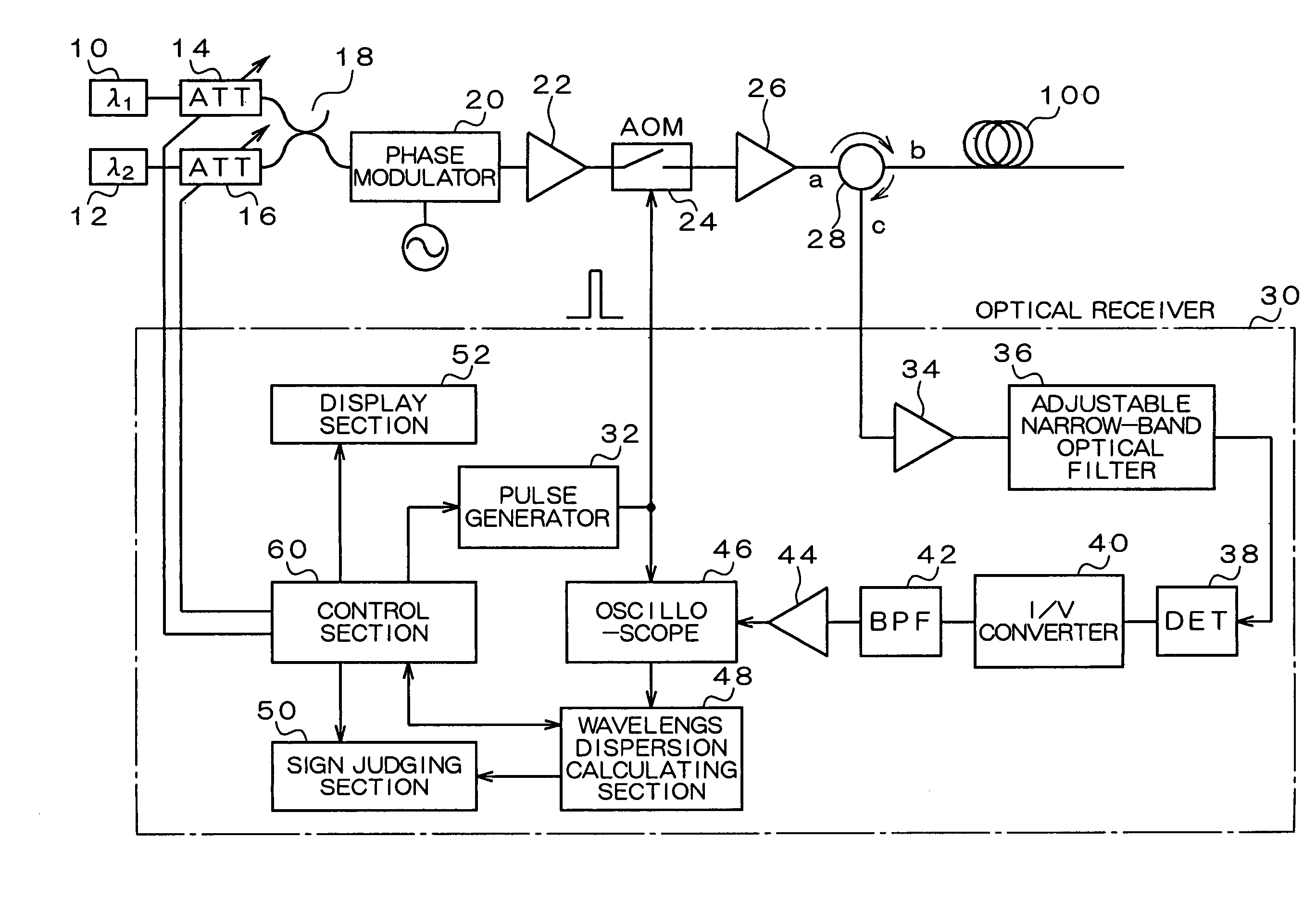
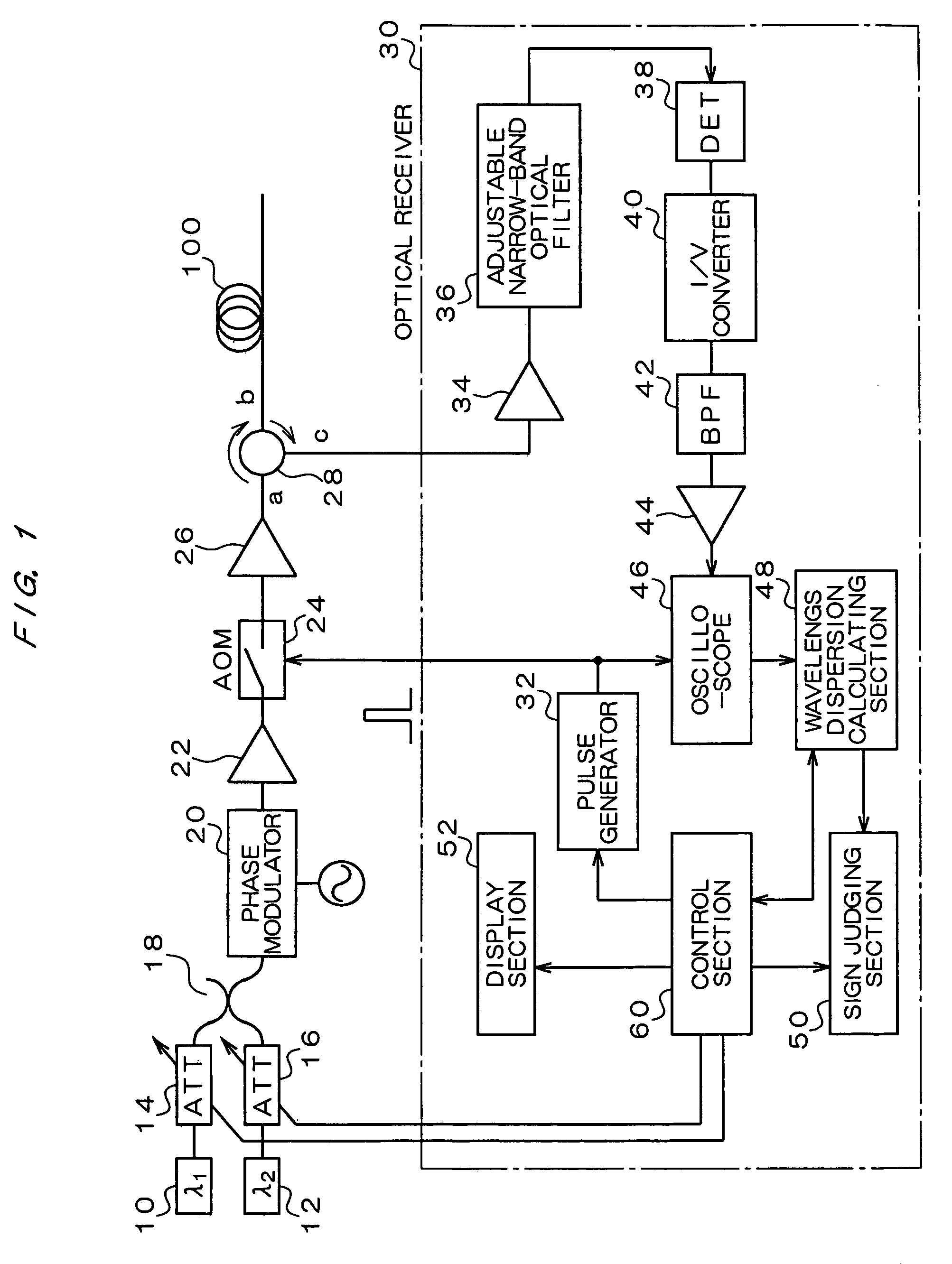
Wavelength dispersion probing system
InactiveUS7020360B2Time and troubleMaterial analysis by optical meansCoupling light guidesMultiplexingMultiplexer
A wavelength dispersion probing system for determining a value of wavelength dispersion and its sign and reducing the trouble and time required for this determination. This wavelength dispersion probing system comprises light sources 10, 12, light attenuators 14, 16, optical multiplexer 18, phase modulator 20, optical amplifiers 22, 26, acoustooptical modulator 24, optical receiver 30. The intensity ratio of two wavelengths is set at 1 to 2 to detect Stokes light or anti-Stokes light included in the return light of an optical fiber 100 by the optical receiver 30, so that wavelength dispersion is probed. The wavelength dispersion is probed by changing the intensity ratio of the two wavelengths to observe the state of the change of the wavelength dispersion, so that the sign of wavelength dispersion is determined by the optical receiver 30.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
Passive optical network (PON) in-band optical time domain reflectometer (OTDR)
ActiveUS20110013904A1Material analysis by optical meansTransmission monitoringSignal onNetwork Communication Protocols
An in-band OTDR uses a network's communication protocols to perform OTDR testing on a link. Because the OTDR signal (probe pulse) is handled like a data signal, the time required for OTDR testing is typically about the same as the time required for other global network events, and is not considered an interruption of service to users. A network equipment includes an optical time domain reflectometry (OTDR) transmitter and receiver, each operationally connected to a link to transmit and receive, respectively, an OTDR signal. When an OTDR is to be performed, a network device operationally connected to the link actuates the OTDR transmitter to transmit the OTDR signal on the link during a determined test time based on a communications protocol of the link, during which data signals are not transmitted to the network equipment. A processing system processes the OTDR signal to provide OTDR test results.
Owner:MICROSEMI ISRAEL STORAGE SOLUTIONS LTD
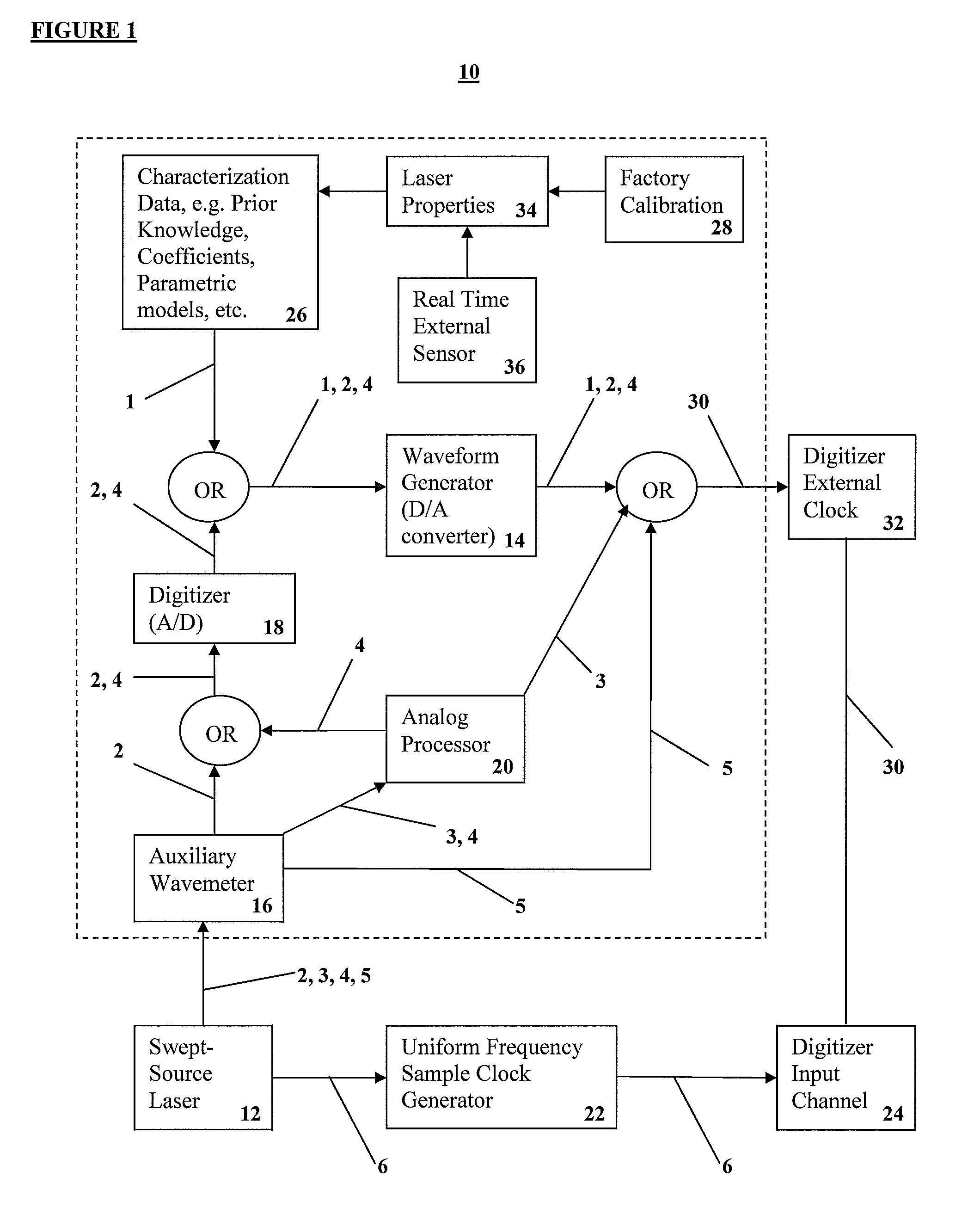
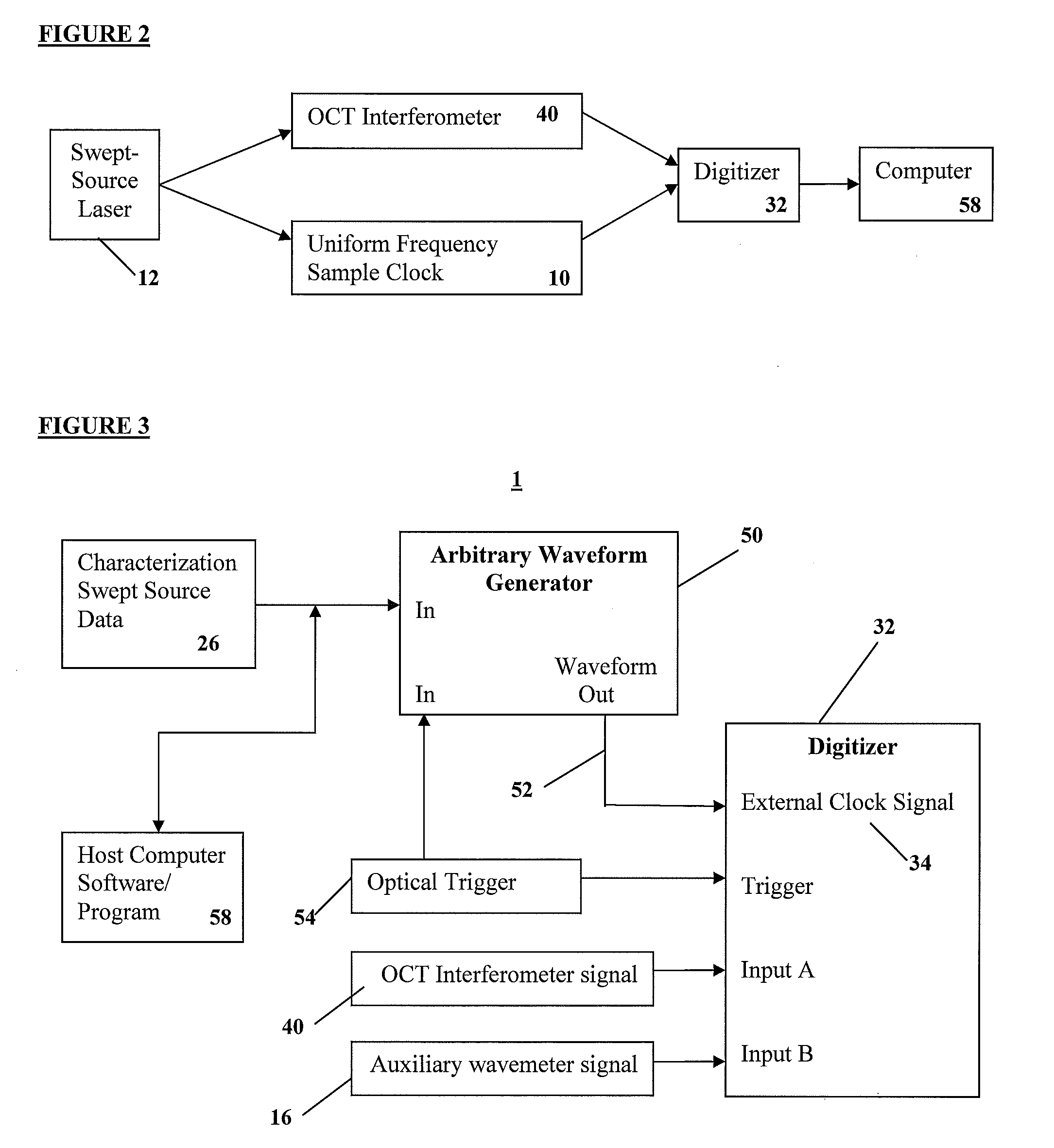
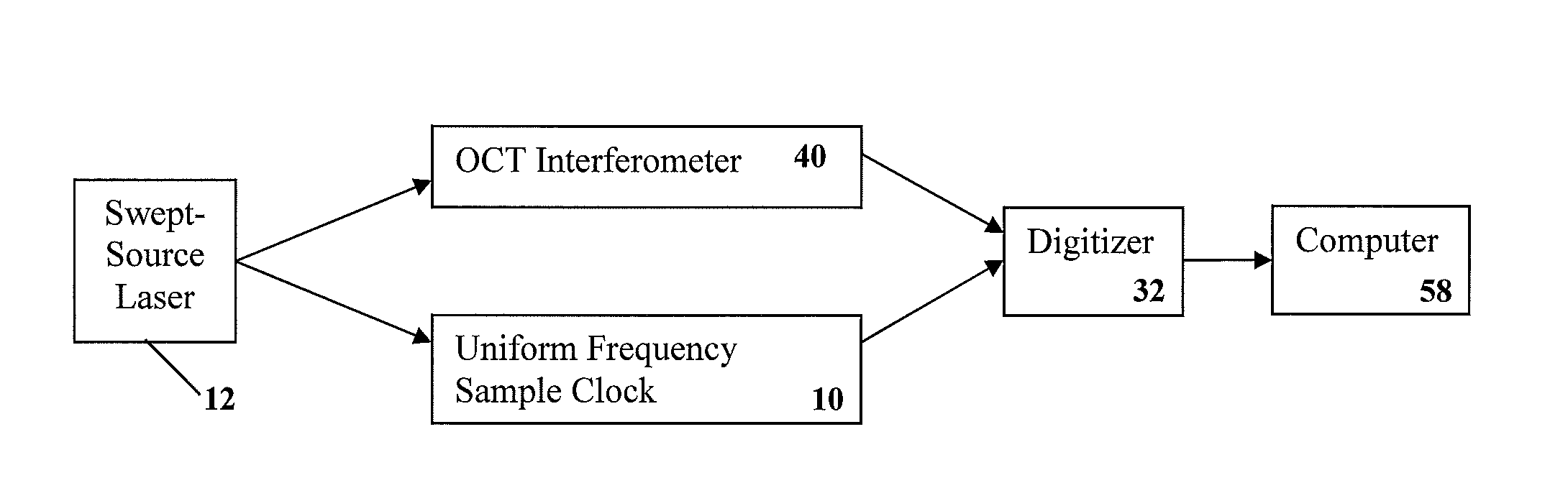
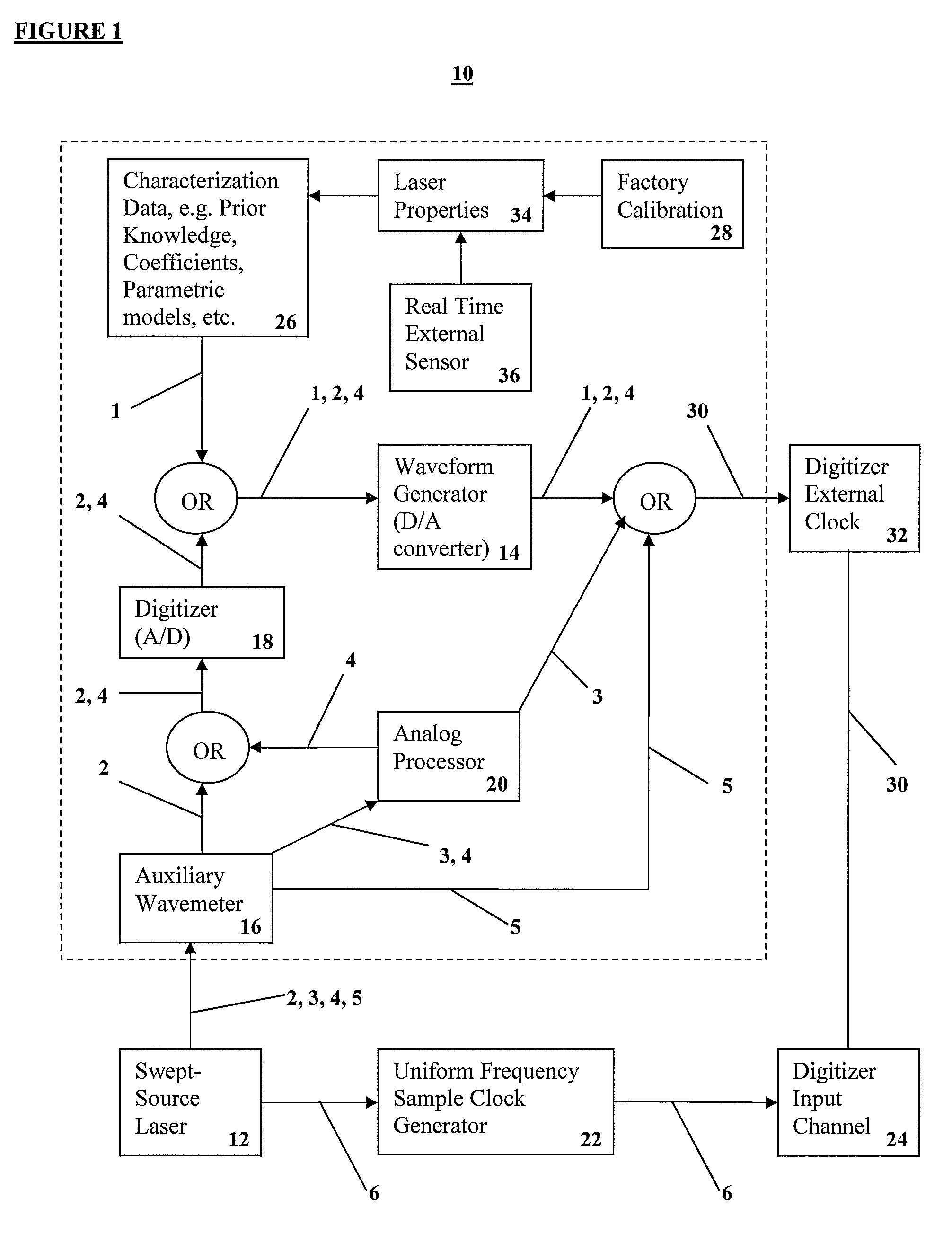
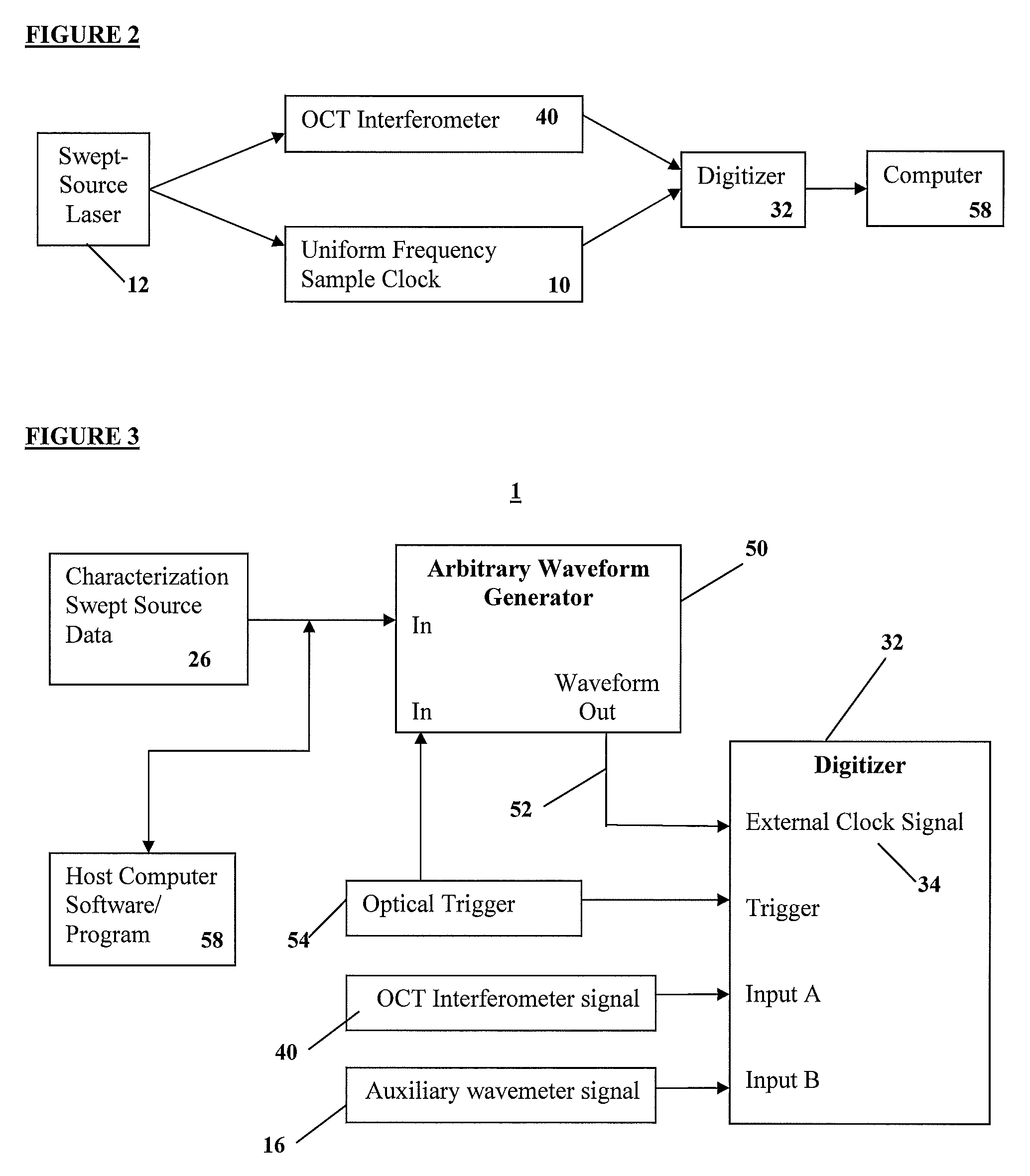
Apparatus and methods for uniform frequency sample clocking
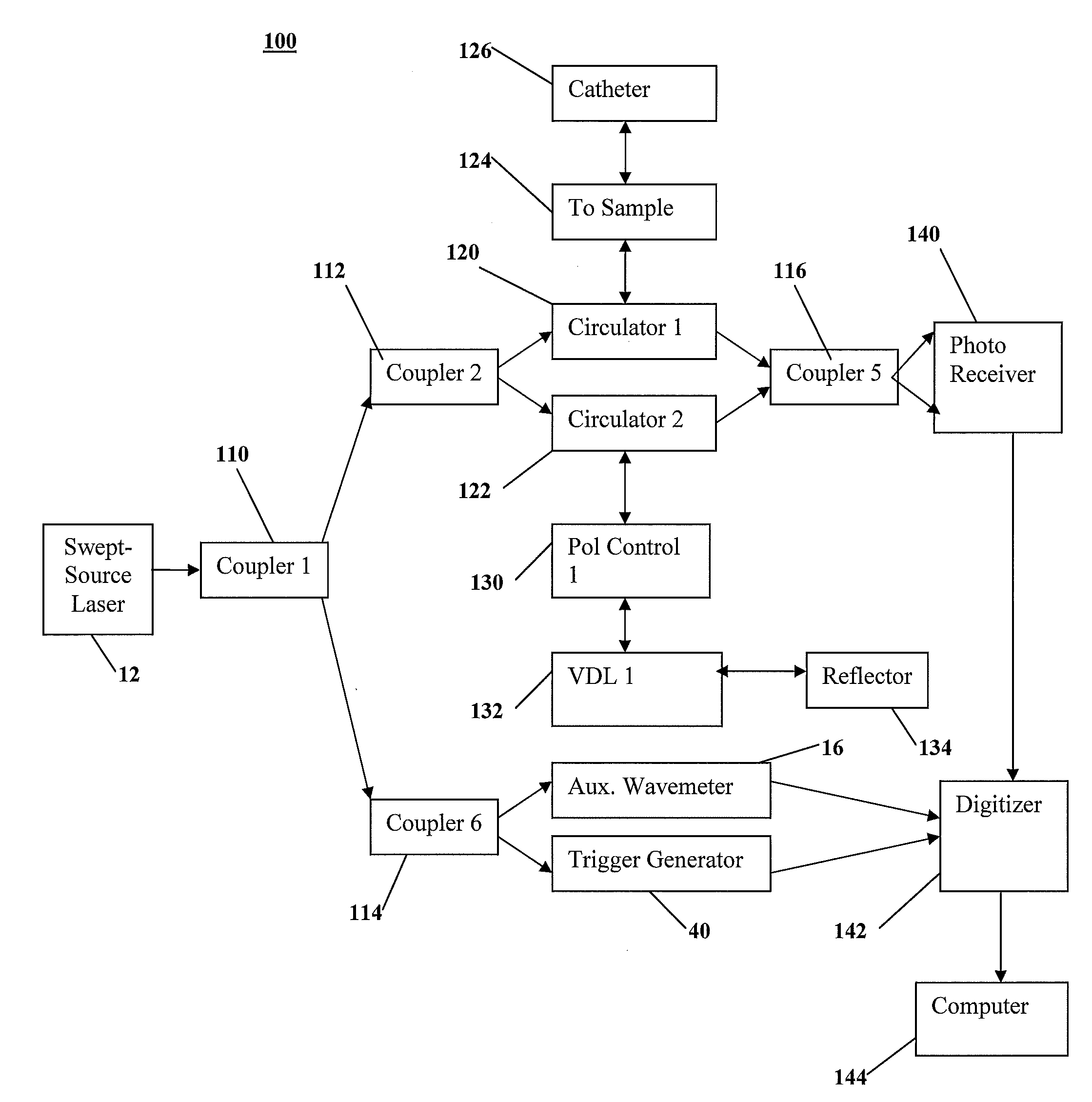
A method and a system for Uniform Frequency Sample Clocking to directly sample the OCT signal with a temporally-non-linear sampling clock derived from a k-space wavemeter on the external sample clock input port of a digitizer. The Uniform Frequency Sample Clocking comprises at least one Pathway, which includes characterizing the swept light source, creating a digital representation of the waveform based from the characterization data, and generating a clock signal using a waveform generator to output the clock signal to a digitizer external clock.
Owner:VOLCANO CORP
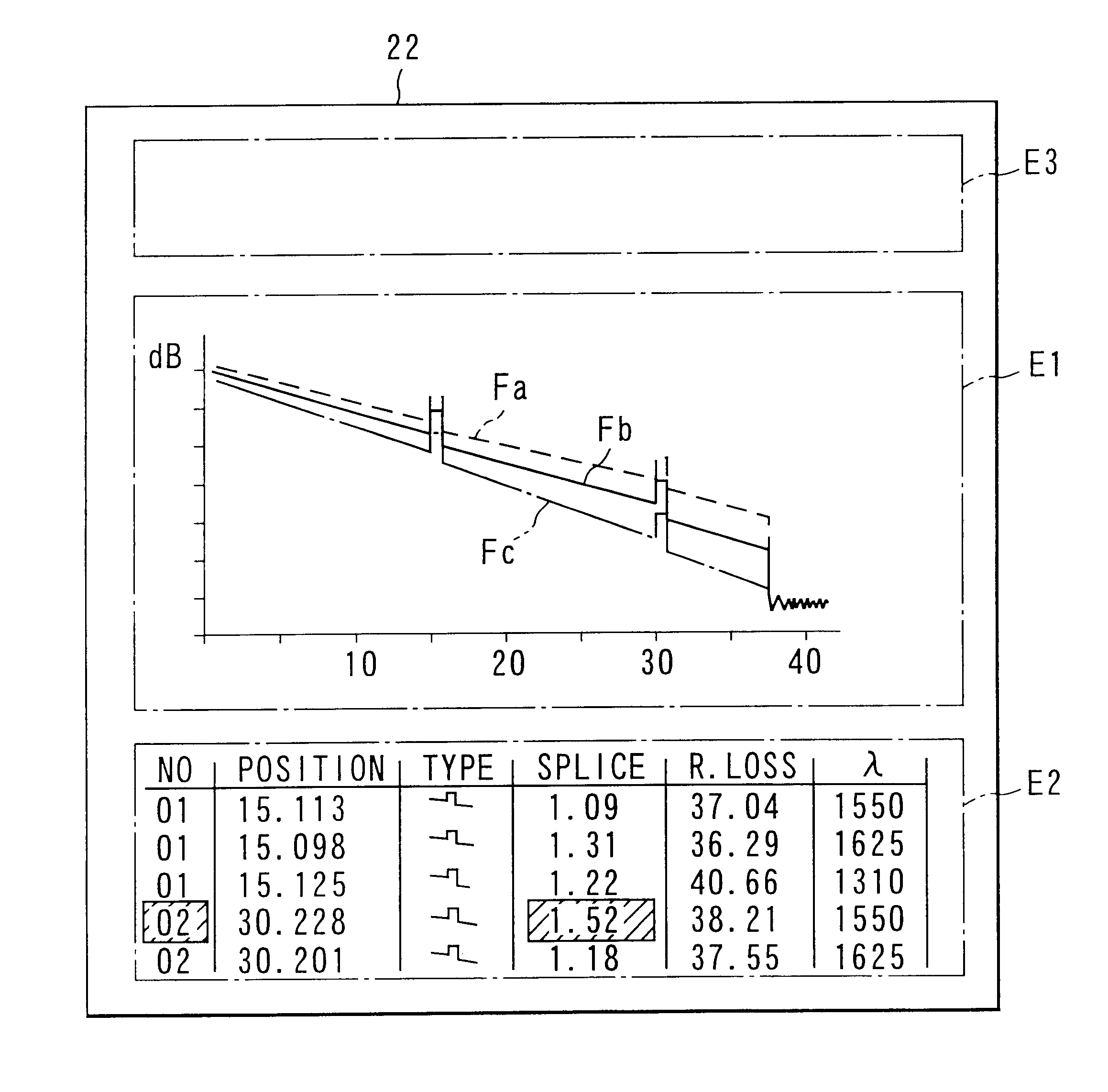
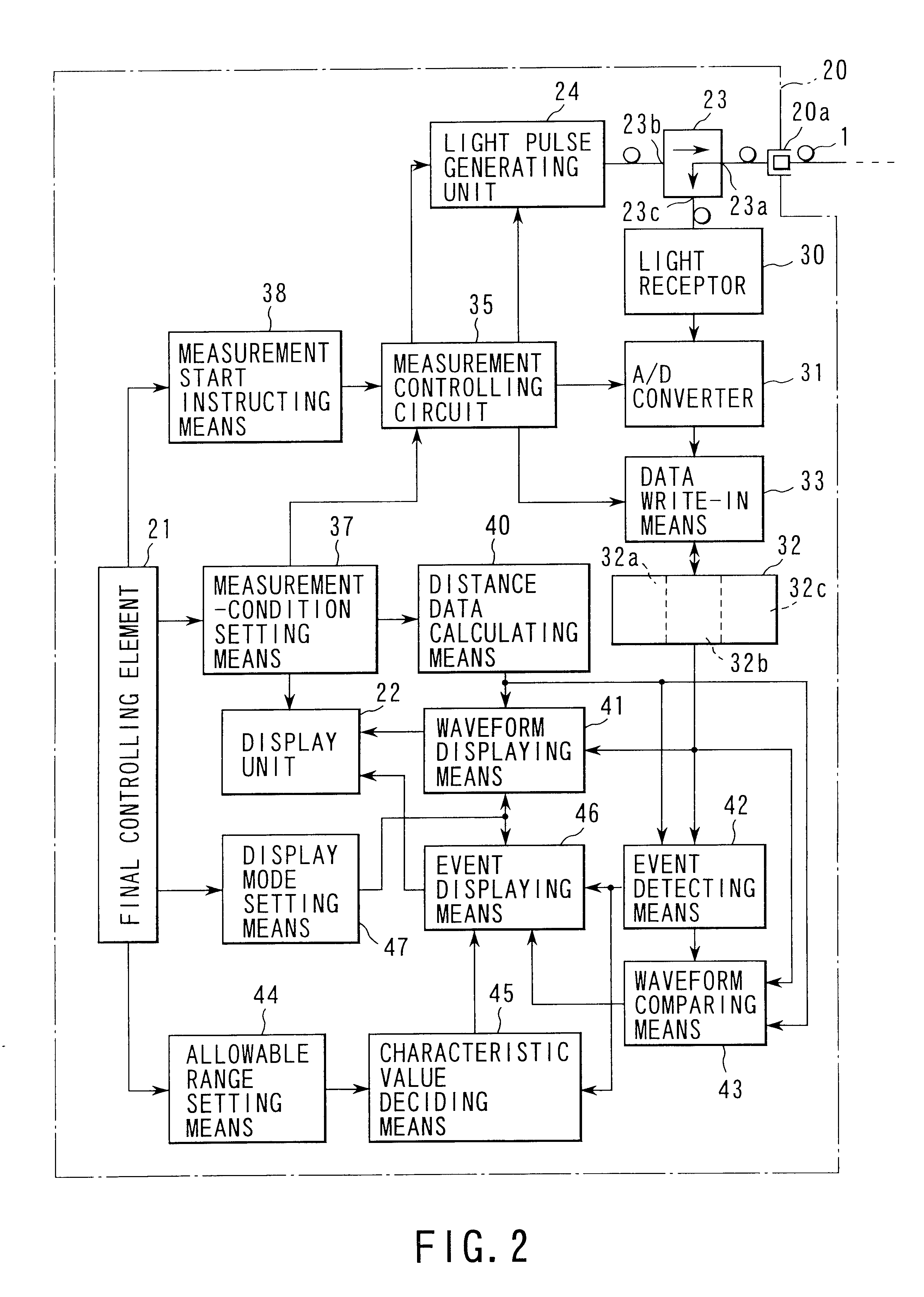
Optical time domain reflectometer which measures an optical fiber with different wavelengths according to an order and collectively displays waveform data and a list of events for each waveform in the same screen
InactiveUS6611322B1Easy to operateEasy to masterVehicle testingMaterial analysis by optical meansTime domainPhotodetector
A light pulse generator is connected with one end of an optical fiber which selectively emits light pulses of a plurality of wavelengths to the optical fiber. A photodetector outputs a signal corresponding to the strength of the light reflected from the optical fiber. A storage unit stores the signal output from the photodetector for each wavelength. A processor determines the position and characteristic of an event based on the waveform data for each wavelength stored in the storage device. A display device has first and second display areas. A display controller allows the first display area to display the waveform data for each wavelength stored in the storage unit in a discriminable manner, and allows the second display area to display a list of positions and characteristics of events for each wavelength determined by the processor.
Owner:ANRITSU CORP
Bidirectional optical module and optical time domain reflectometer
ActiveUS7853104B2Increase optical powerHigh sensitivityReflectometers dealing with polarizationMaterial analysis by optical meansTime domainOptical Module
A bidirectional optical module according to the present invention emits light to an optical fiber and allows returning light from the optical fiber to enter and includes a plurality of light emitting elements that emit light to enter the optical fiber, a light receiving element that receives light having exited the optical fiber, and a non-reciprocal unit for making an optical path in a forward direction from the light emitting element to the optical fiber and an optical path in a backward direction from the optical fiber to the light emitting element different. Then, polarization planes of light incident on the optical fiber after being emitted from the plurality of light emitting elements are mutually orthogonal, and the non-reciprocal unit emits returning light of light emitted from the plurality of light emitting elements from the optical fiber toward the light receiving element to one light receiving element.
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP +1
Natural fiber span reflectometer providing a virtual phase signal sensing array capability
ActiveUS20060028636A1Low costMaterial analysis by optical meansBurglar alarmRayleigh scatteringFrequency spectrum
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Method and apparatus for optical time domain reflectometry (OTDR) analysis
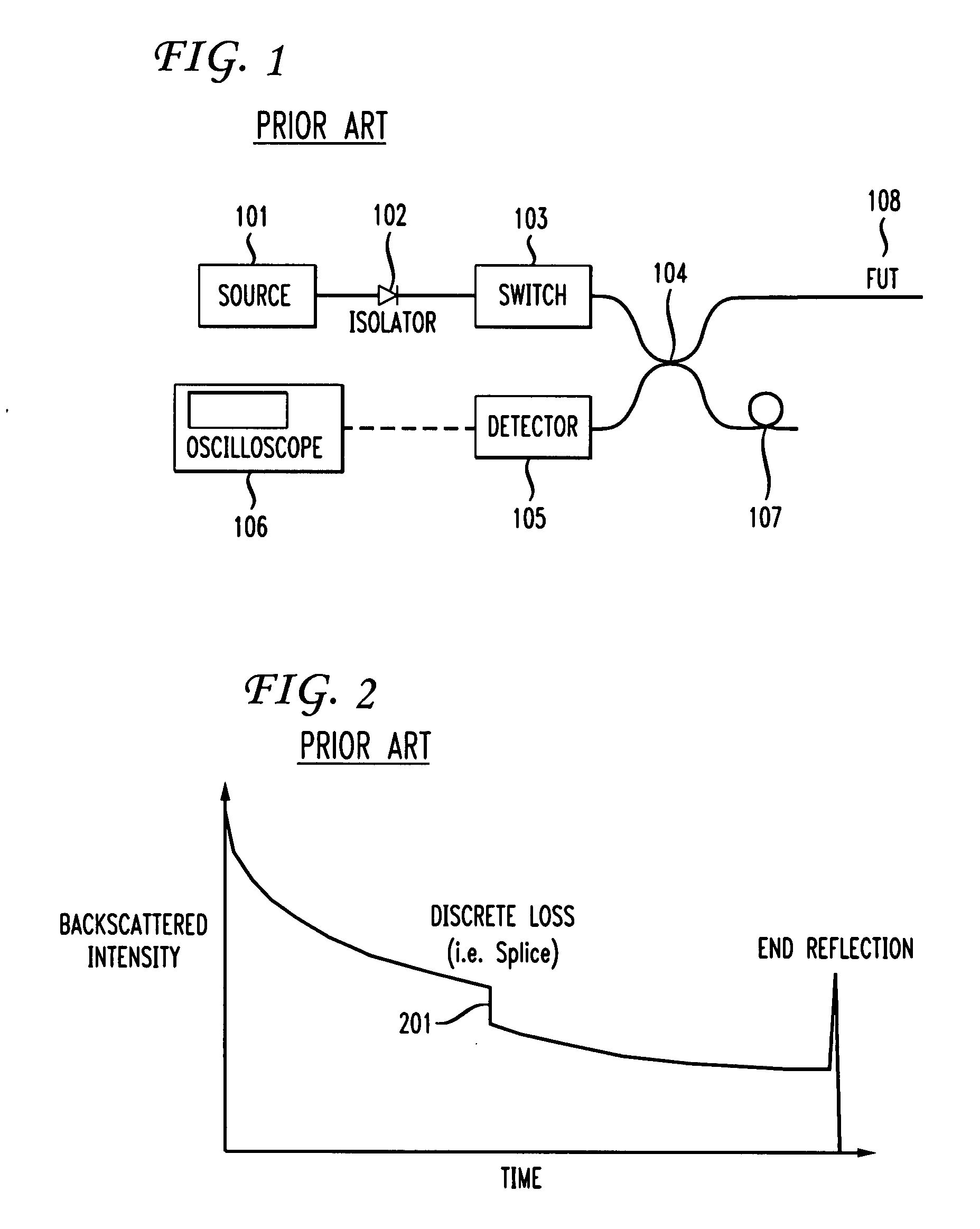
InactiveUS6674518B1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsFiberTime domain
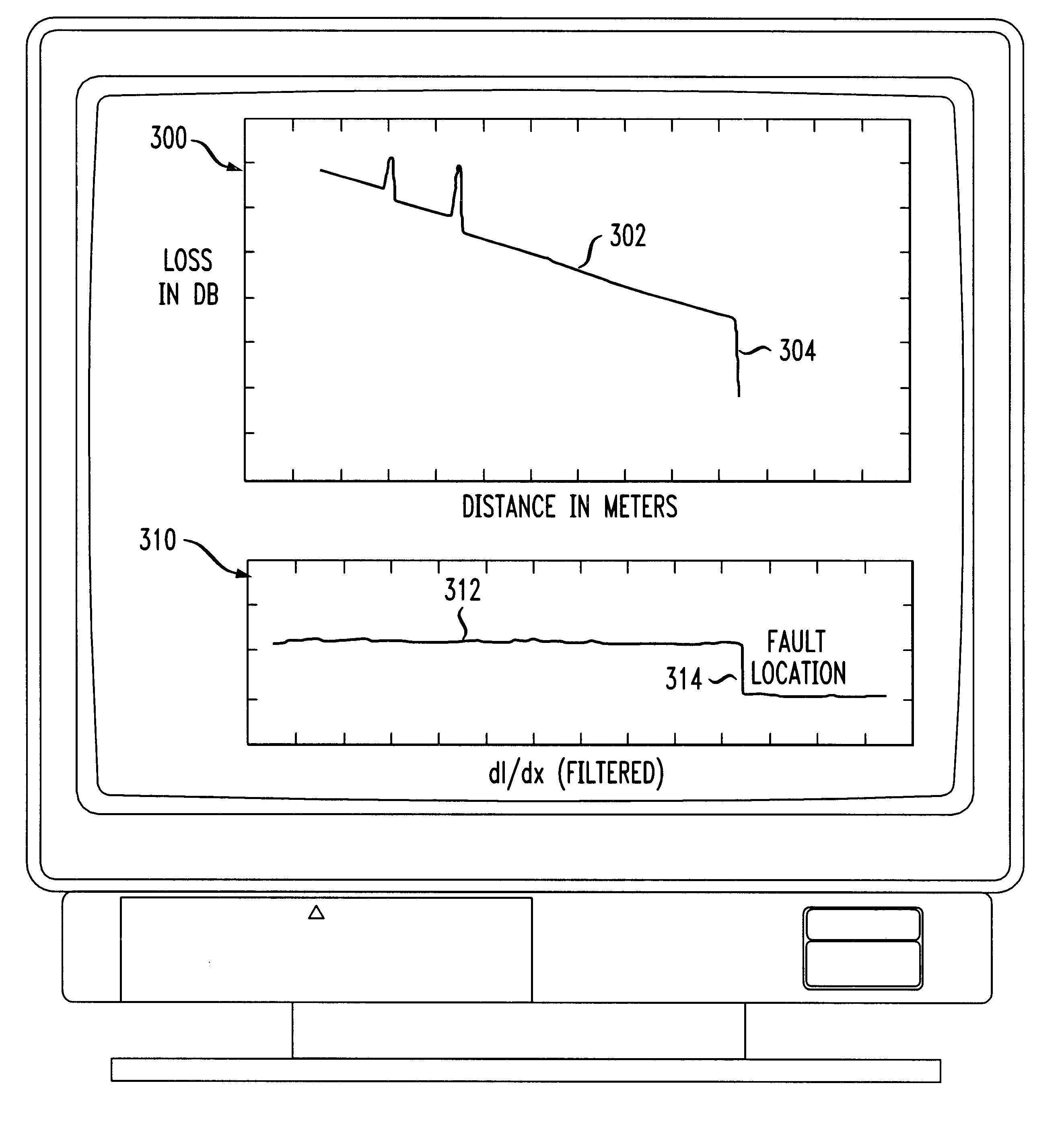
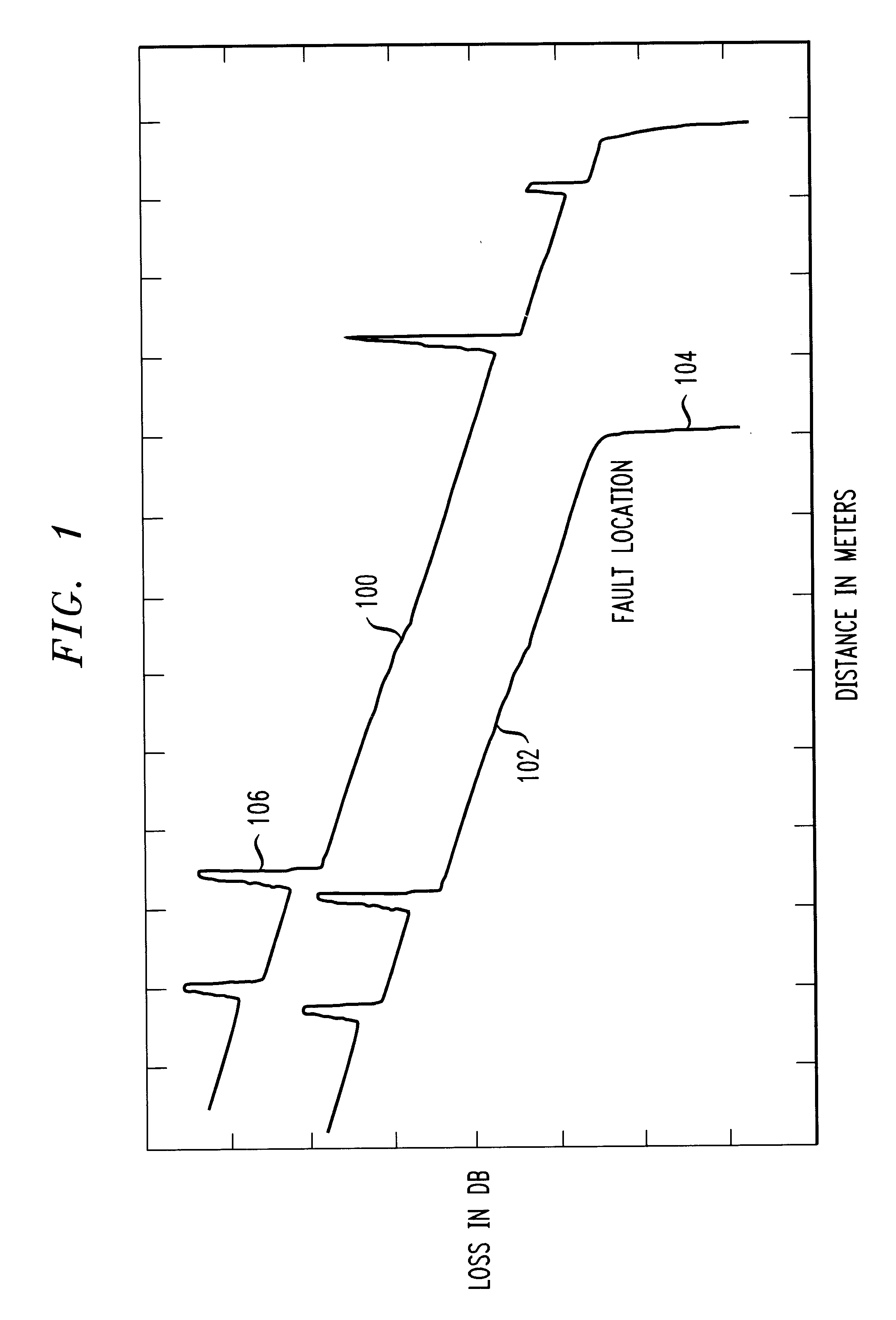
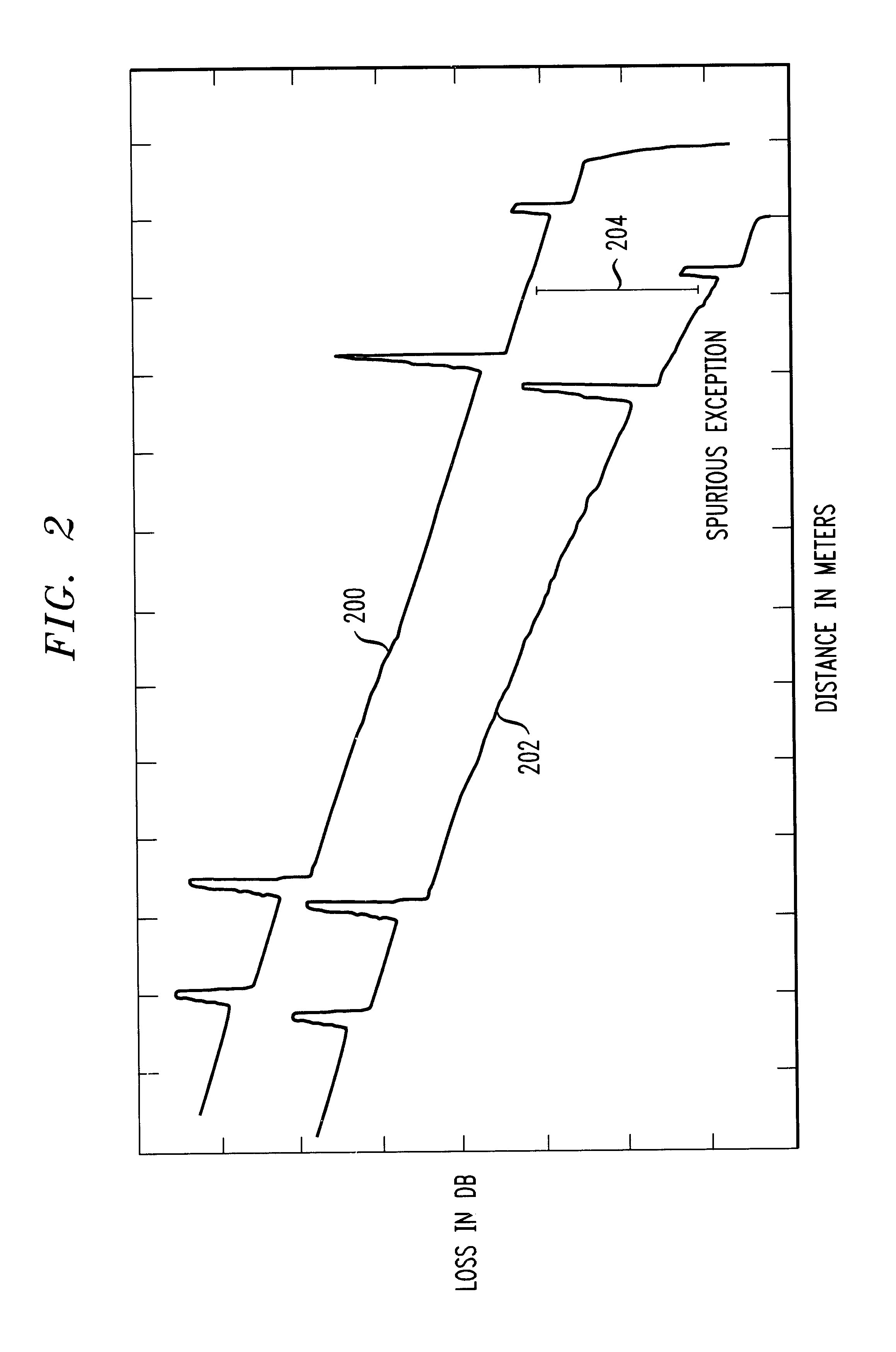
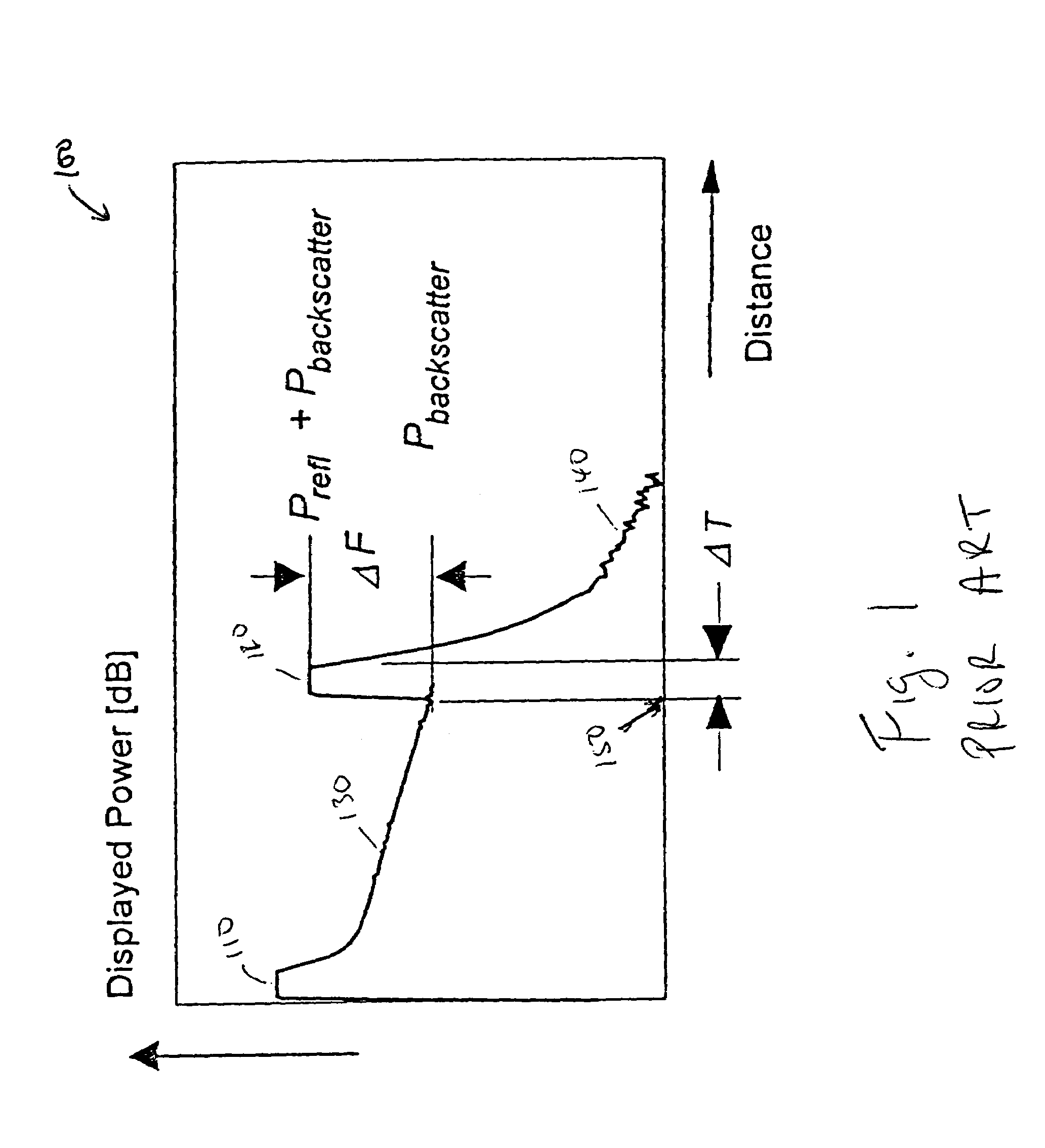
The present invention is directed to a method and apparatus for testing a fiber-optic cable. An Optical Time Domain Reflectometer (OTDR) is presented. Test signals are generated from the OTDR and received by the OTDR for processing. The received test signals are sampled and analyzed. The received test signals include reflectance spikes and a slope. A first-order derivative is taken of the received signal. The first-order derivative is then filtered to remove the reflectance spikes and the slope. Discontinuities in the filtered first-order derivative denote a fault in the fiber-optic cable.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Distributed Fibre Optic Sensing for Event Detection
ActiveUS20110216996A1Minimize couplingReflectometers dealing with polarizationOptical light guidesFiberSpeckle pattern
A fibre optic sensing method and apparatus for determining location and direction information of disturbances occurring in the environment of a sensor optical fibre are provided. The method comprises launching optical pulses into at least one polarisation eigenmode of a polarisation maintaining fibre as the sensor optical fibre, detecting temporal speckle patterns of light backscattered from the at least one polarisation eigenmode of the fibre, comparing the temporal speckle patterns to determine the location and direction information of a disturbance in the environment of the sensor optical fibre. The location information may be a distance along the fibre, and the direction information may be a direction radially from the axis of the fibre. The apparatus or instrument may be used to detect disturbance over long distances such as pipes, pipelines, or wells. Other applications include detecting intruders entering a controlled area.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Testing of Optical Cable Using Optical Time Domain Reflectometry
ActiveUS20120176607A1Material analysis by optical meansReflectometers detecting back-scattered light in time-domainTime domainEngineering
Methods for testing optical equipment are disclosed. One method includes connecting an optical time domain reflectometer to optical equipment to be tested, the optical equipment including at least one optical connector. The method includes injecting an optical signal onto the optical equipment from the optical time domain reflectometer, and observing an amount of reflected light at the connector. Based on the observed reflected light, an amount of loss attributable to the optical equipment is determined.
Owner:BISON PATENT LICENSING LLC
Real-time fiber optic interferometry controller
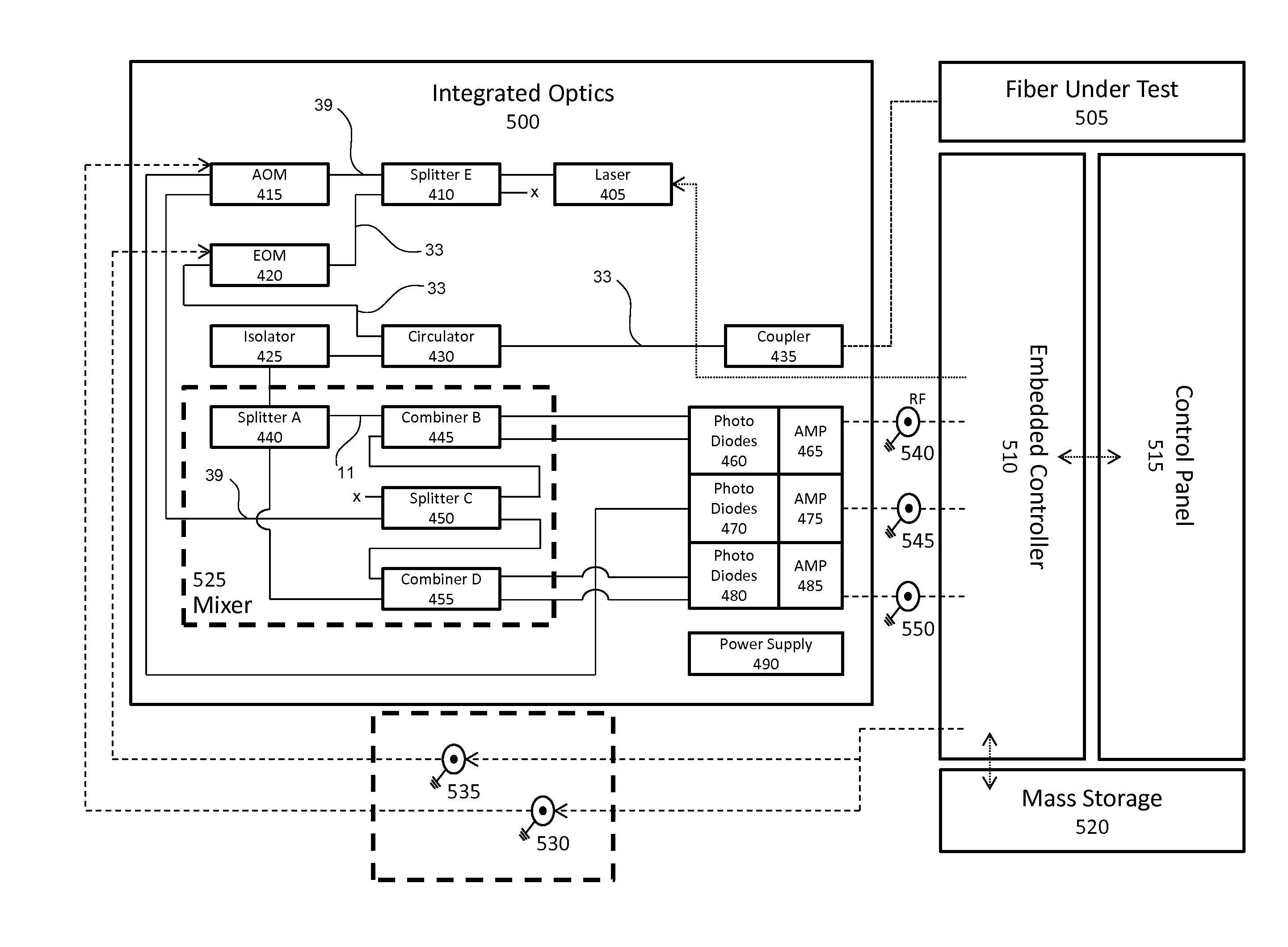
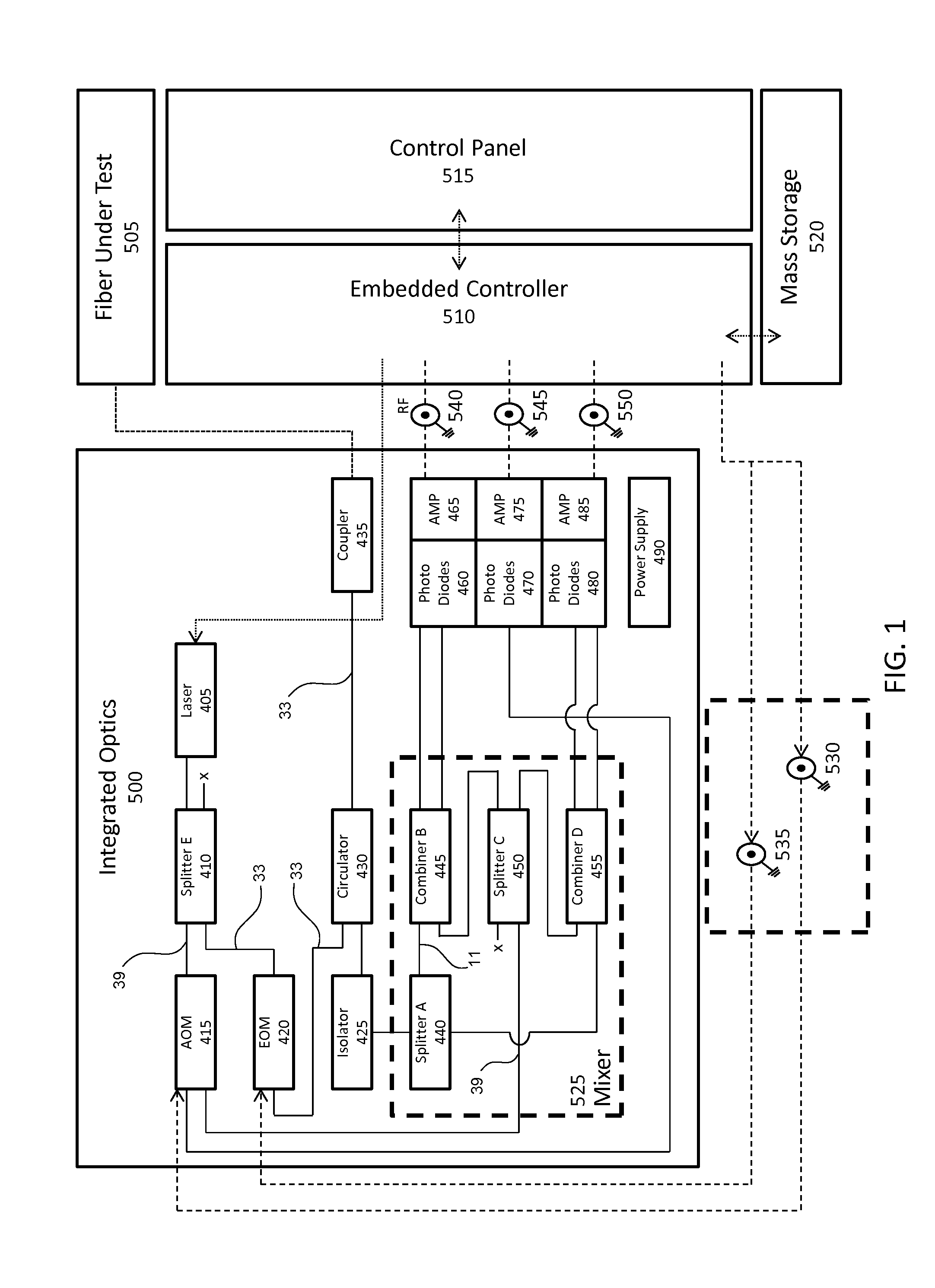
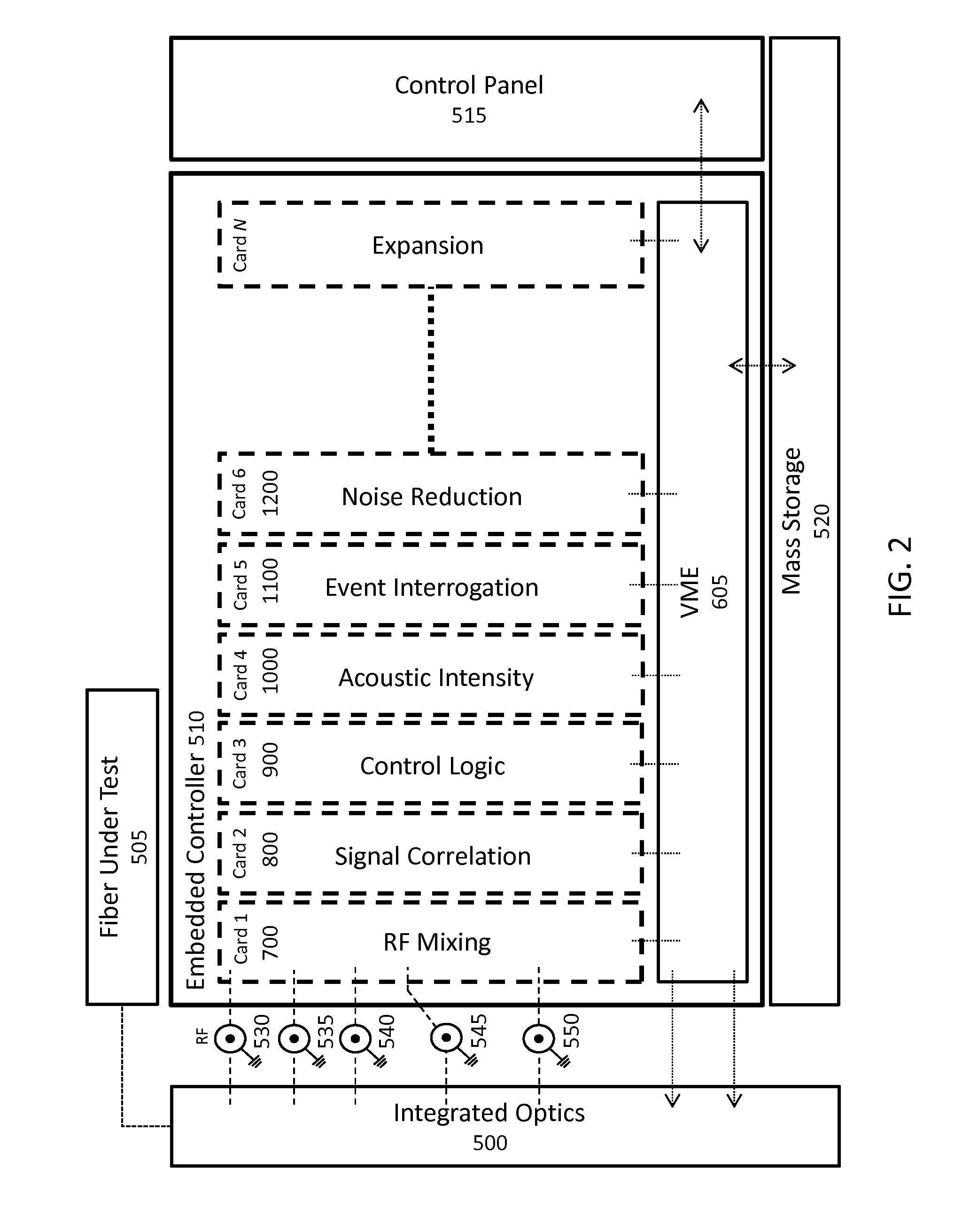
ActiveUS20160191163A1Increase flexibilityImprove utilizationReflectometers using simulated back-scatterSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementFiberMultiplexing
A modular fiber optic interferometry control system and method for extracting information from superimposed waves is disclosed. The system comprises a first module for converting a radio frequency input to a multiplexed binary data stream, a second module for correlating a pseudo random number (PRN) reference with a received PRN code modulated backscattered signal, and a third module comprising control logic. In some embodiments the system further comprises one or more of a fourth module for generating a power stream, a fifth module for event interrogation, and a sixth module for noise reduction.
Owner:ADELOS INC
Apparatus and method for monitoring a structure using a counter-propagating signal method for locating events
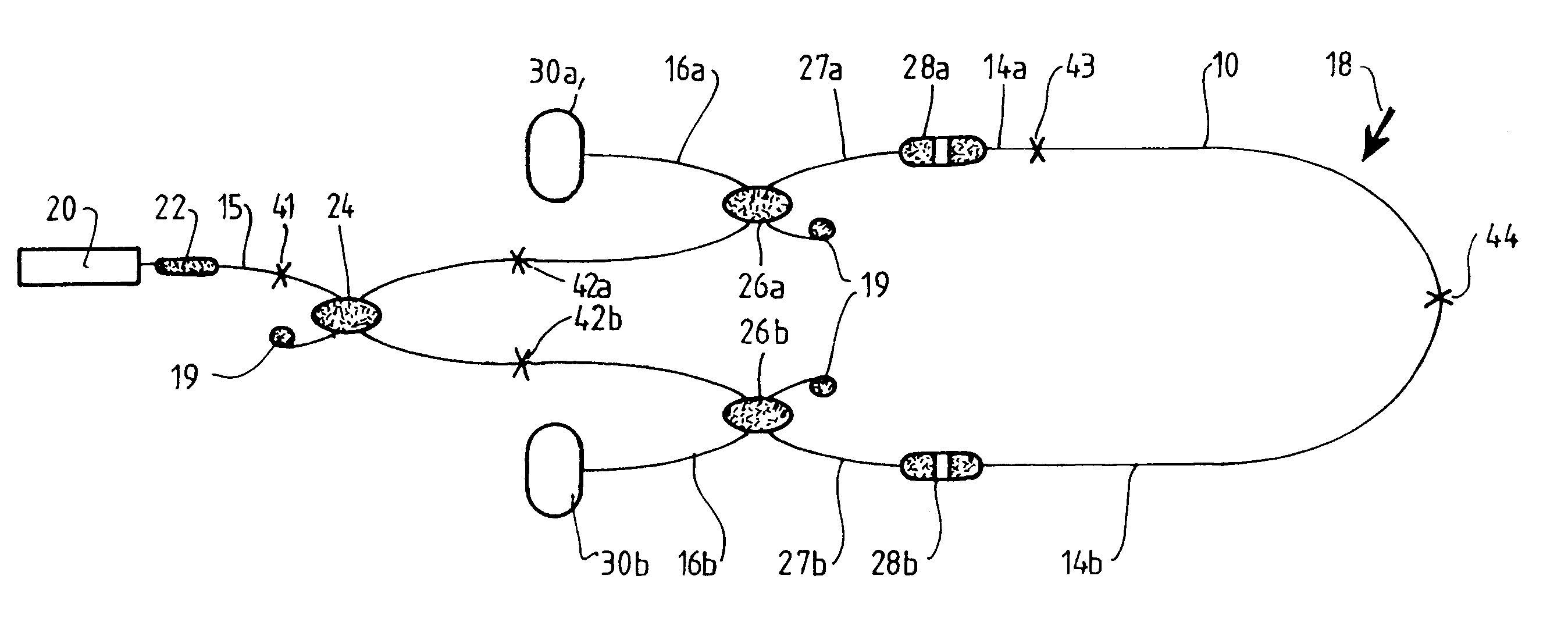
InactiveUS6621947B1Increase delayIncrease the number ofRadiation pyrometryAnalysis by material excitationWaveguideLight source
A method and apparatus for monitoring a structure and for locating the position of an event including a light source, a waveguide, and a detector means. The waveguide receives light from the light source so that the light is caused to propagate in counter-propagating optical signals in the waveguide. The waveguide includes the counter-propagating optical signals or some characteristic of the signals modified or effected by an external parameter caused by or indicative of the event to provide modified counter-propagating optical signals. The detector means detects the modified counter-propagating optical signals effected by the parameter and determines the time delay or difference between the modified counter-propagating optical signals in order to determine the location of the event.
Owner:FUTURE FIBRE TECH PTY LTD
Optical waveguide monitoring
InactiveUS6879386B2Cladded optical fibreMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotonic crystalEngineering
Owner:OMNIGUIDE
Testing fiber arrangement in multi-fiber cables
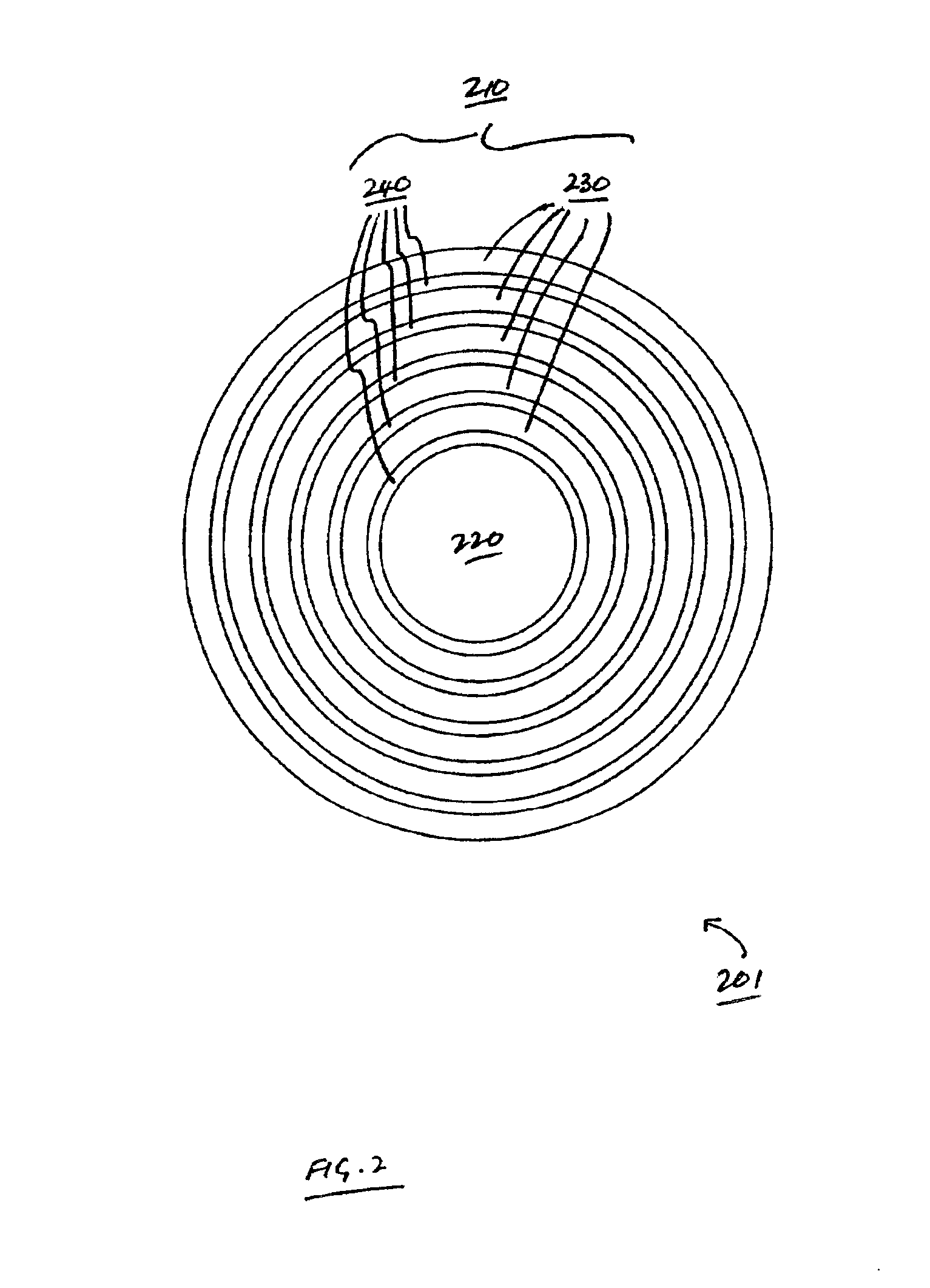
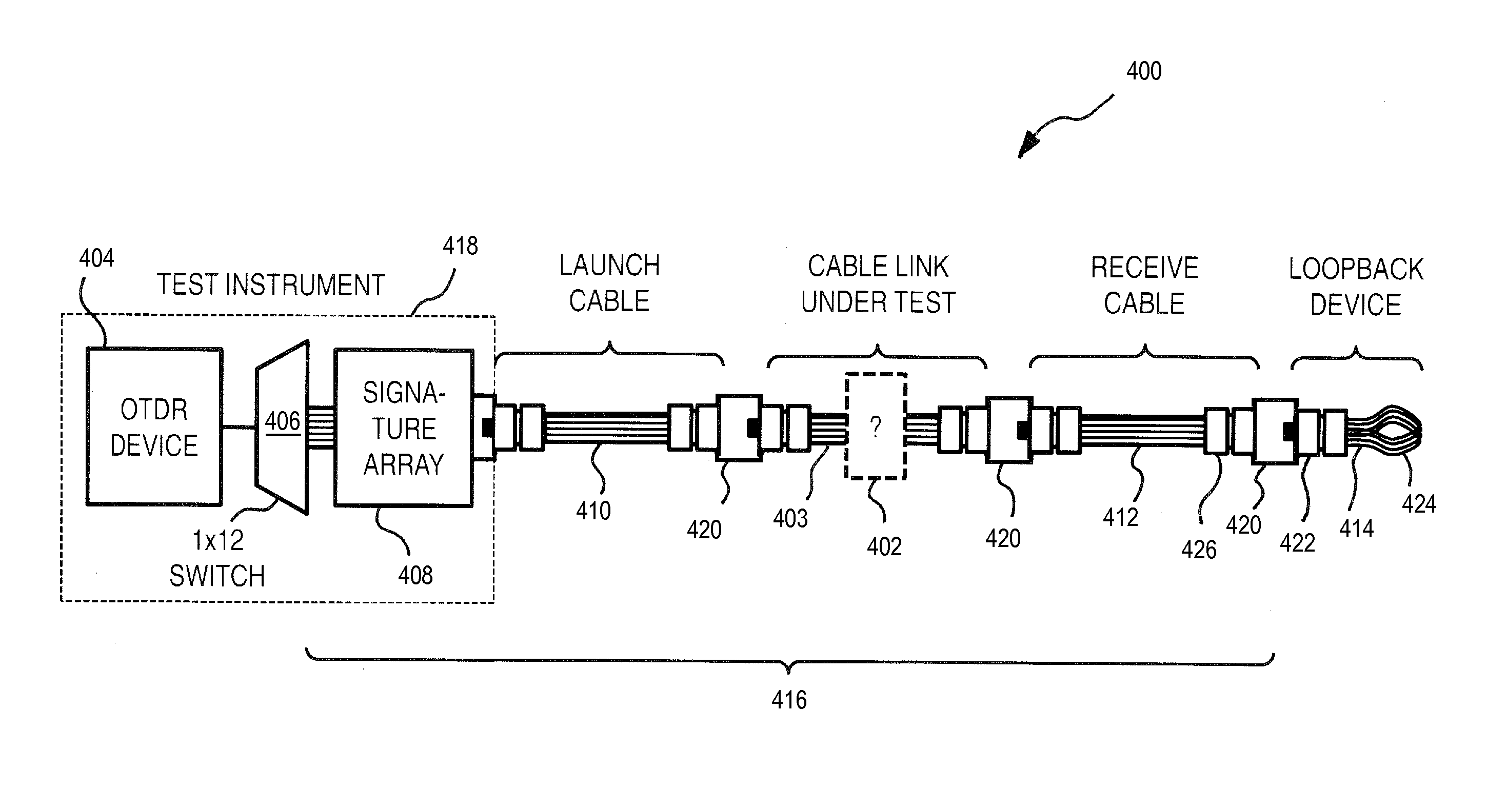
ActiveUS20160041065A1Risk minimizationWear minimizationMaterial analysis by optical meansElectromagnetic transmissionFiberFiber array
There is provided a method and a system for identifying or verifying the fiber arrangement and / or the cable type of multi-fiber array cables (such as MPO cables) which employs an OTDR acquisition device at the near end of the MPO cable, a loopback device at the far end and an array of signatures detectable by the OTDR, either at the far or the near end. The loopback device allows performing bidirectional OTDR measurements with a single OTDR acquisition device (without moving it from one end to the other) and the signature array provides fiber arrangement / cable type identification or verification.
Owner:EXFO
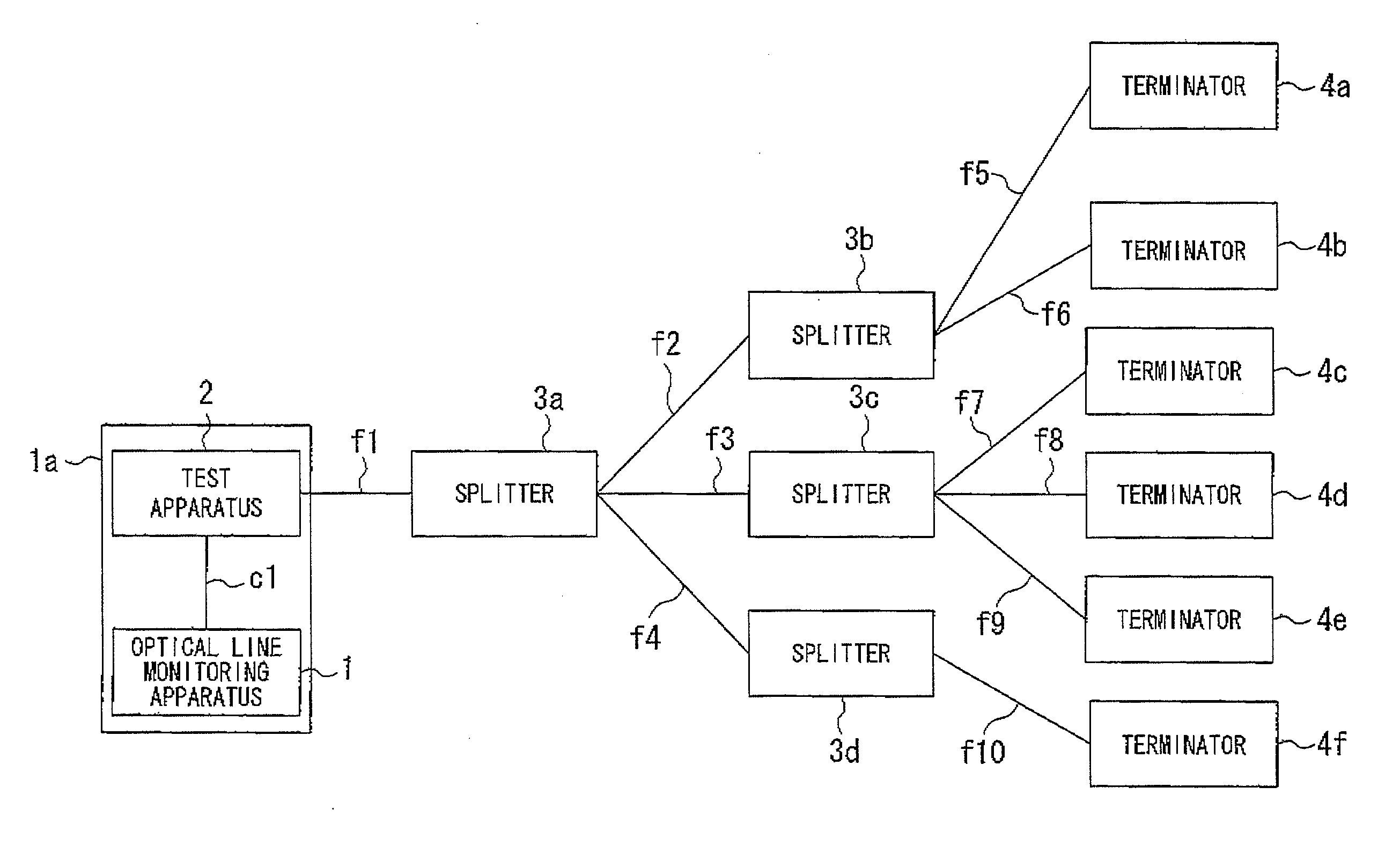
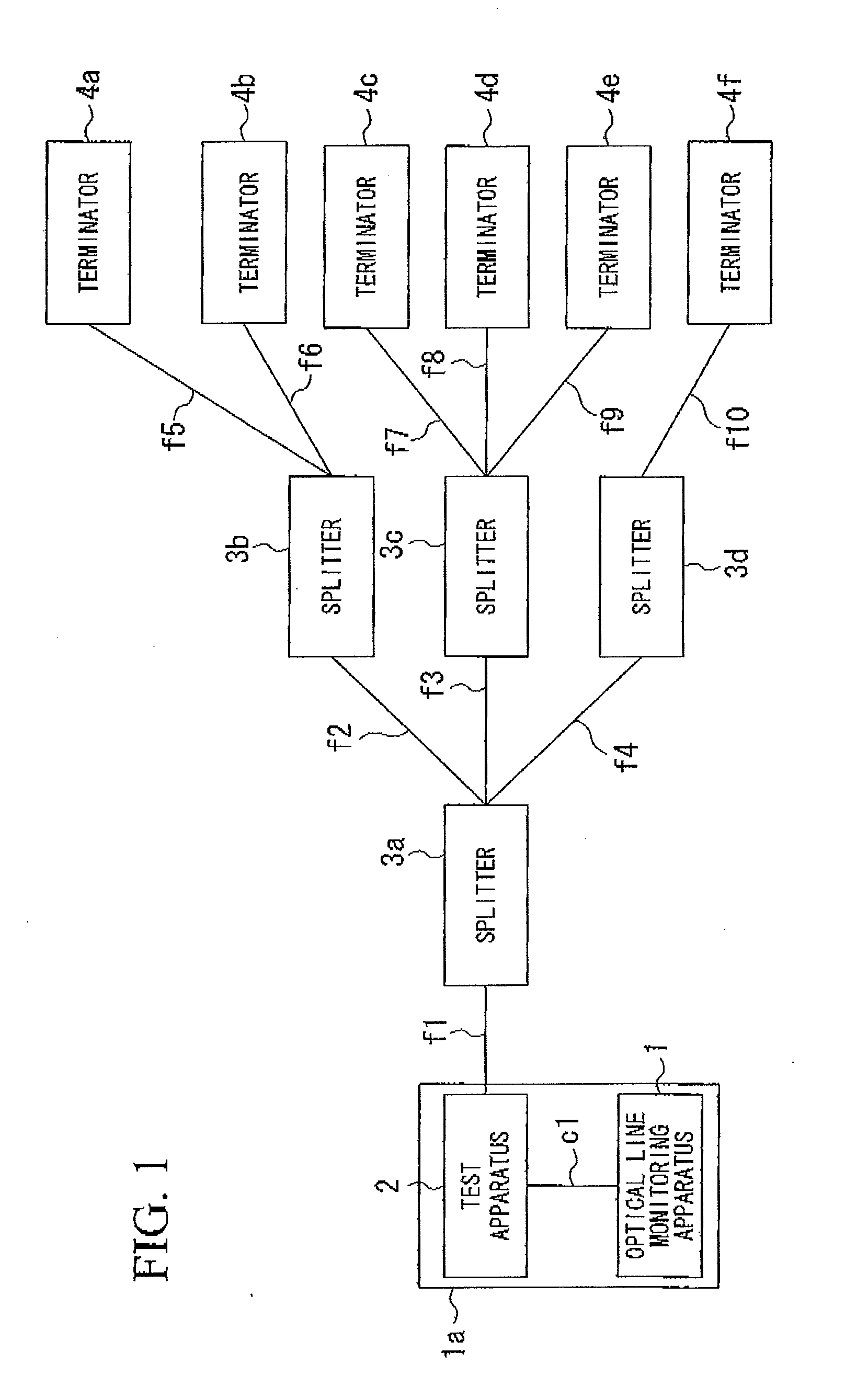
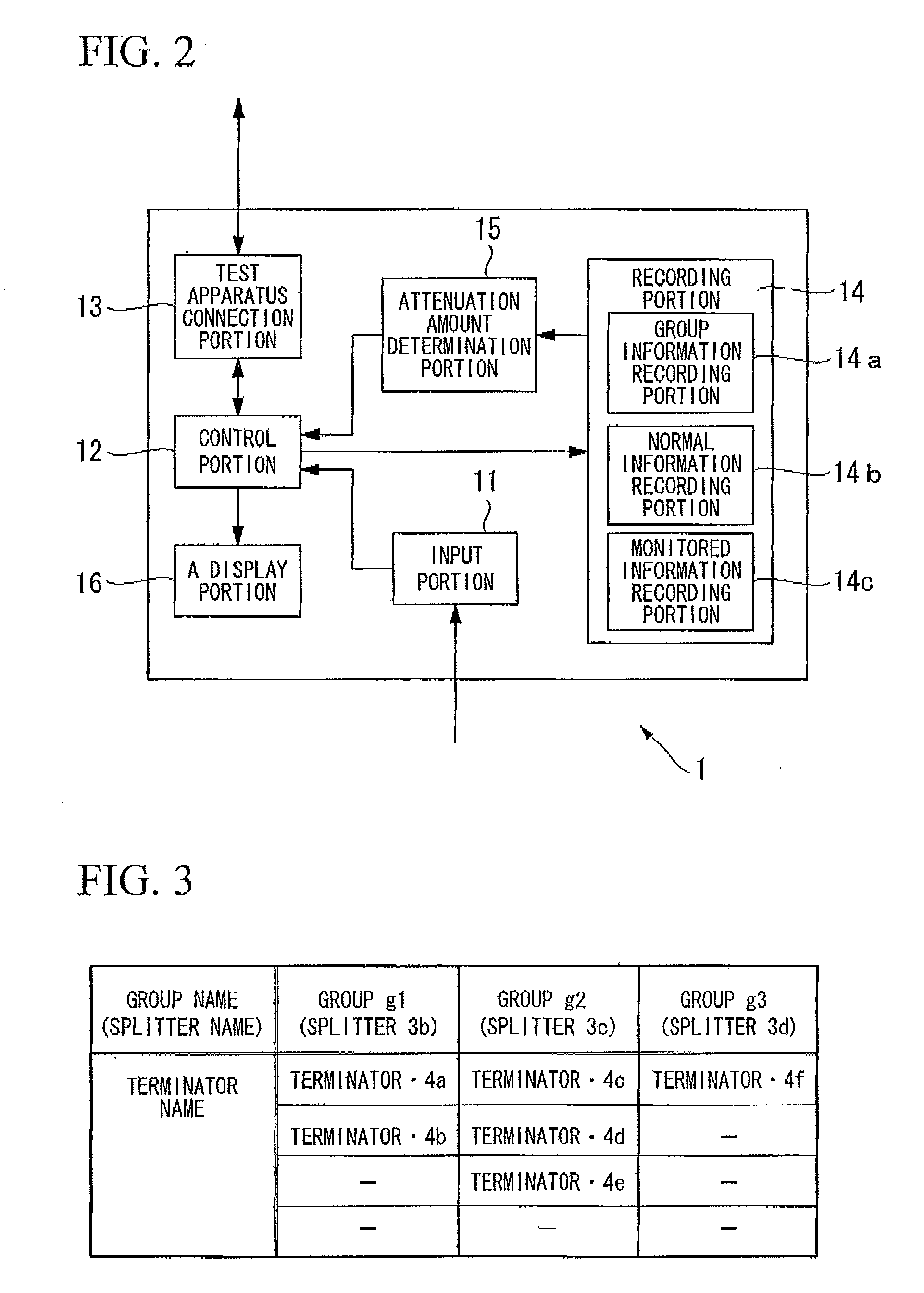
Optical line monitoring apparatus and optical line monitoring method
InactiveUS20090190921A1Low costAutomatically calculatingTransmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsUltrasound attenuationEmbedded system
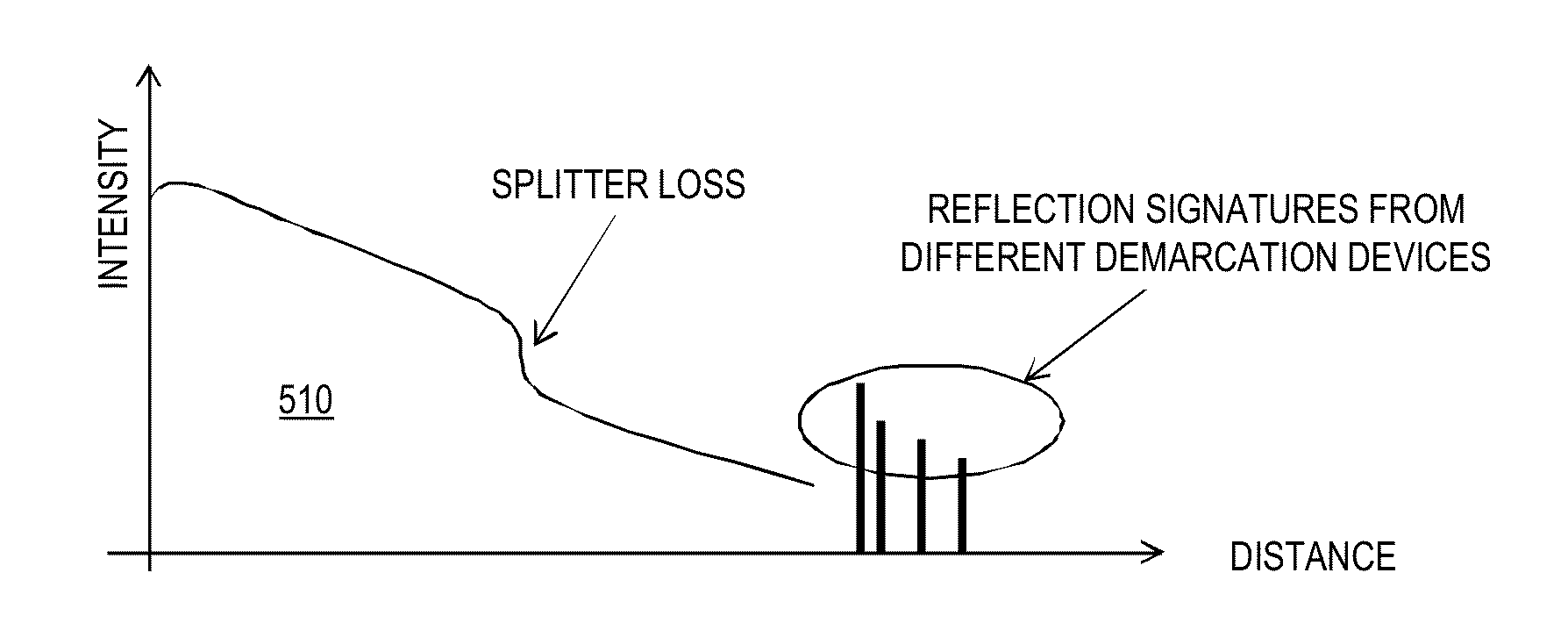
An optical line monitoring apparatus, including: a group information recording portion which records group information about to which splitter respective terminators are connected; a normal information recording portion which records intensities of reflected lights from a plurality of terminators in a state in which a failure is not occurring in optical lines; a monitored information recording portion which records intensities of reflected lights from the plurality of terminators in failure monitoring time; an attenuation amount determination portion which determines a terminator the reflected light intensity of which is attenuated compared with the corresponding reflected light intensity in normal information; and a control portion which determines, if the intensities of the reflected lights of all the terminators connected to the same splitter are attenuated by the same value, that a failure has occurred between the test apparatus and the splitter to which all the terminators are connected.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
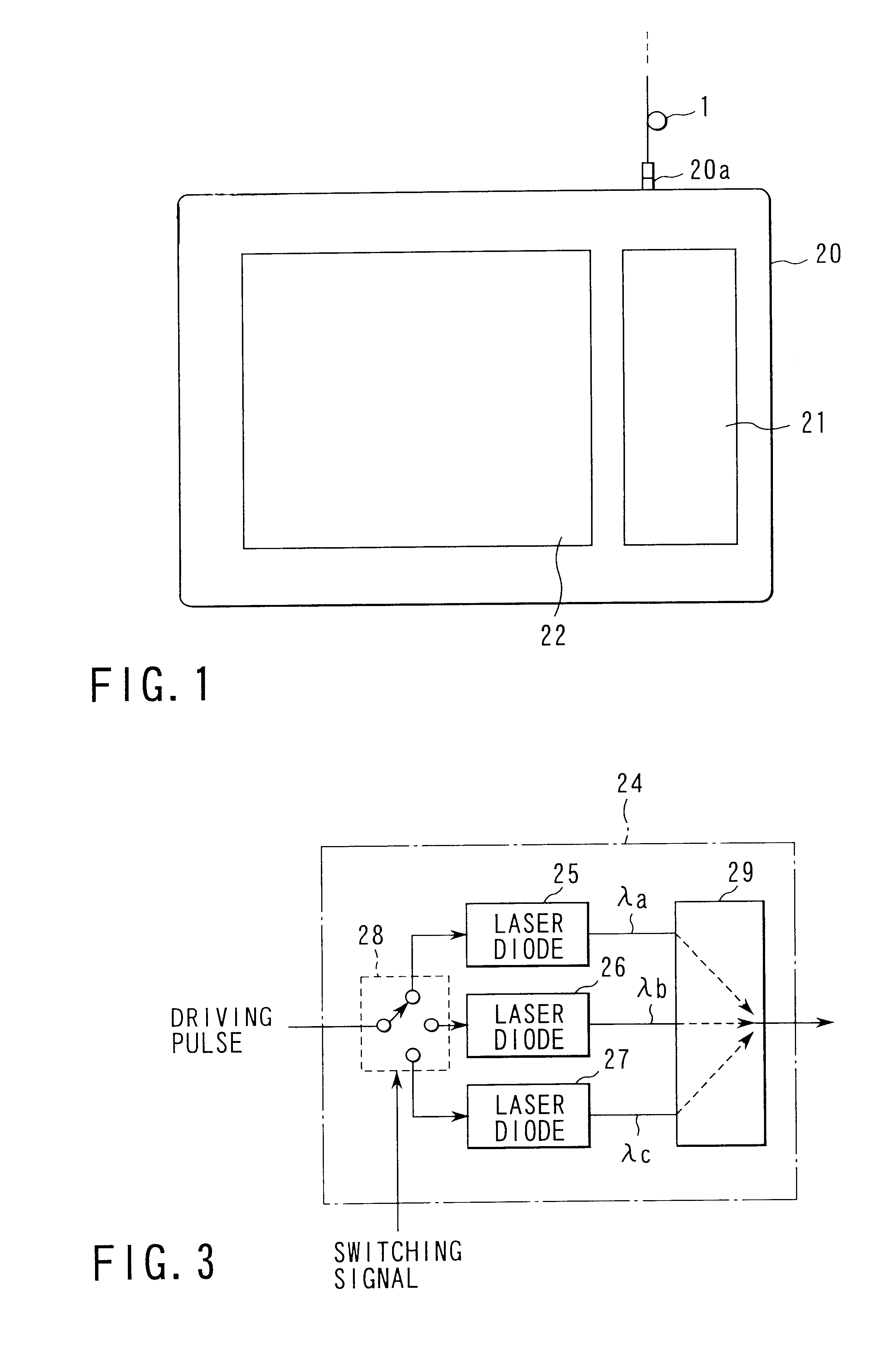
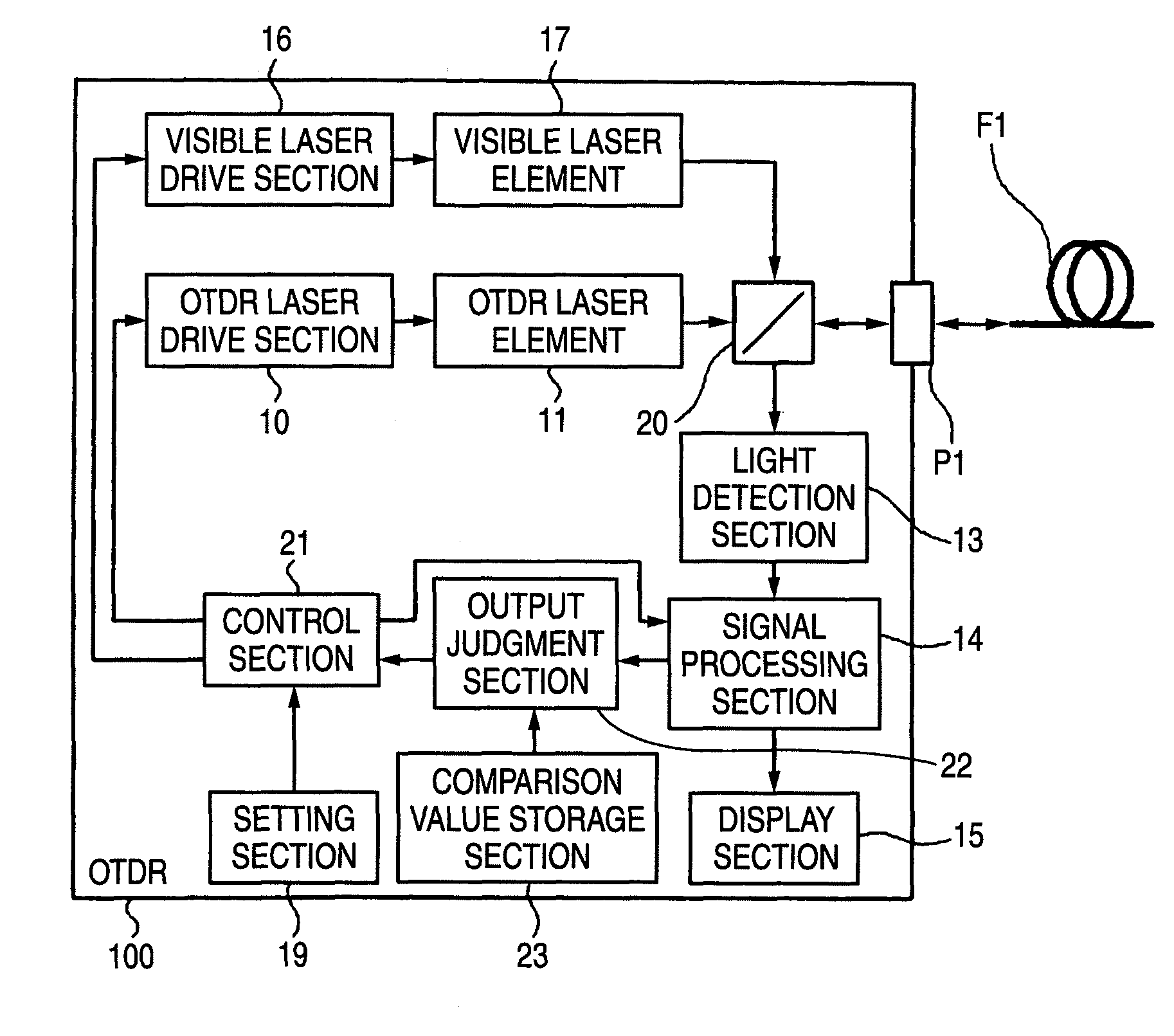
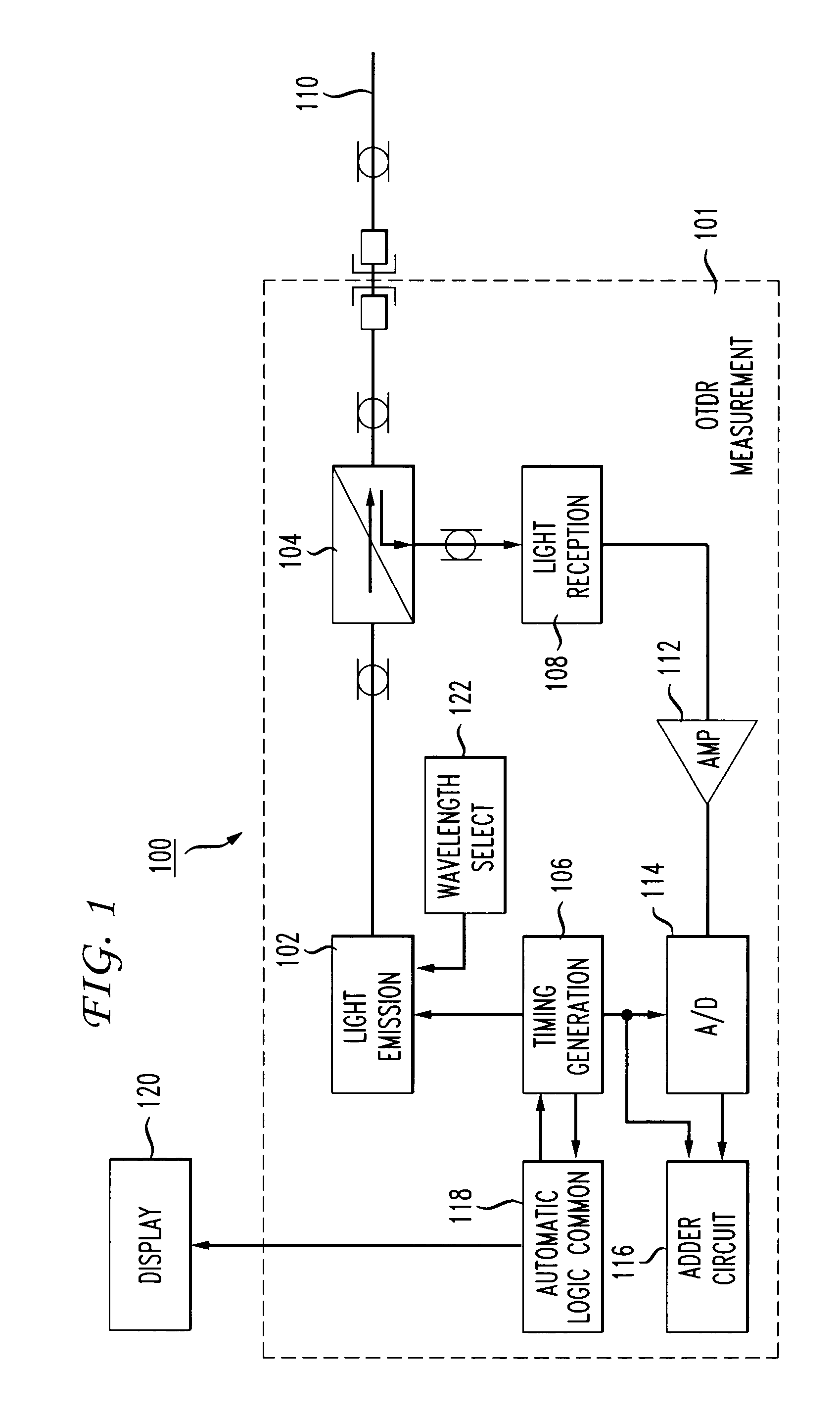
Optical time domain reflectometer
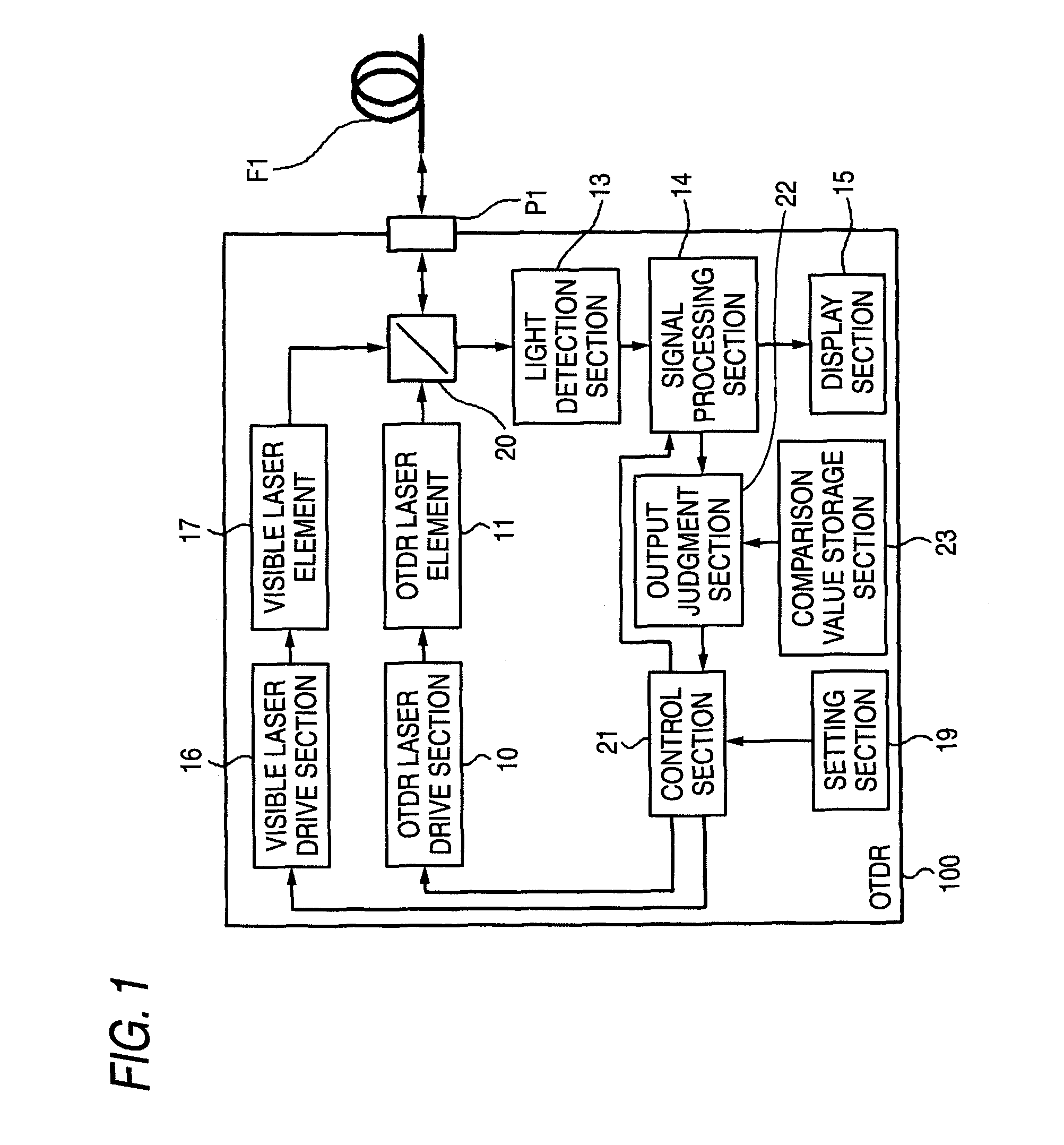
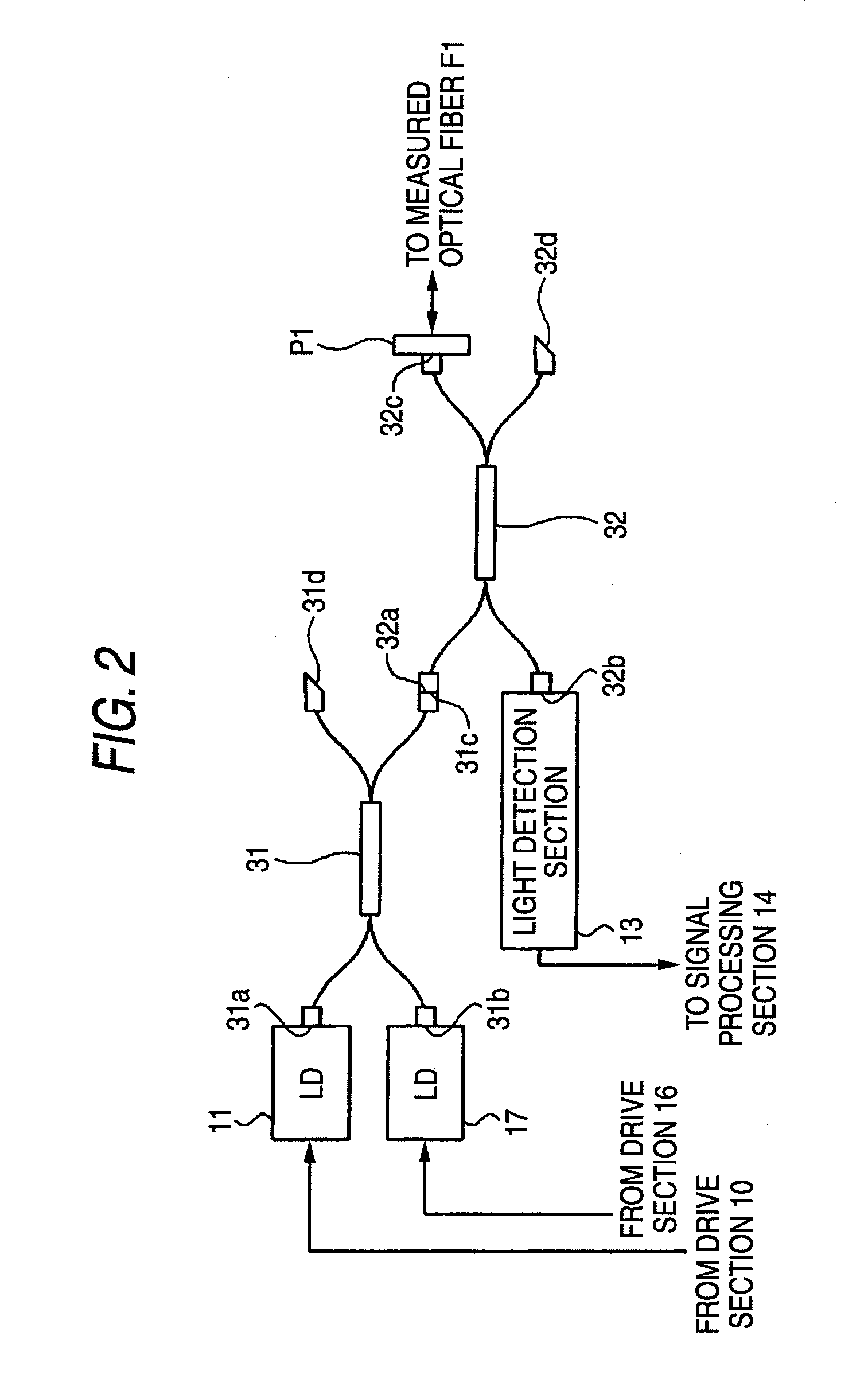
ActiveUS7880868B2Material analysis by optical meansReflectometers detecting back-scattered light in time-domainTime domainOptical time-domain reflectometer
An improvement is added to an optical time domain reflectometer for emitting pulsed light of invisible light to a measured optical fiber, receiving return light of the pulsed light by a light detection section, measuring the measured optical fiber, and emitting visible light for visible inspection of a fault point of the measured optical fiber to the measured optical fiber. The optical time domain reflectometer includes an incidence-emission port for emitting the invisible light and the visible light to the measured optical fiber and an output judgment section for judging that a communication light exists in the measured optical fiber based on the light power of the light detection section receiving light incident through the incidence-emission port in a state in which the pulsed light of the invisible light is not emitted.
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP
Distributed Optical Fibre Sensor
ActiveUS20130222811A1Improve the detection rateImprove dynamic rangeSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementFluid pressure measurementRelative phaseLength wave
There is described a distributed optical fibre sensor for detecting one or more physical parameters indicative of an environmental influence on a sensor optical fibre, as a function of position along the sensor fibre. The sensor uses probe light pulses of different wavelengths. At least some of the probe light pulses may also be of different pulse lengths. The relative phase bias between interferometric signals in backscattered probe light of different wavelength pulses may also be controlled.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Fiber diagnosis system for point-to-point optical access networks
ActiveUS8655167B1Efficient identification and positioningMultiplex system selection arrangementsTransmission monitoringTime domainAccess network
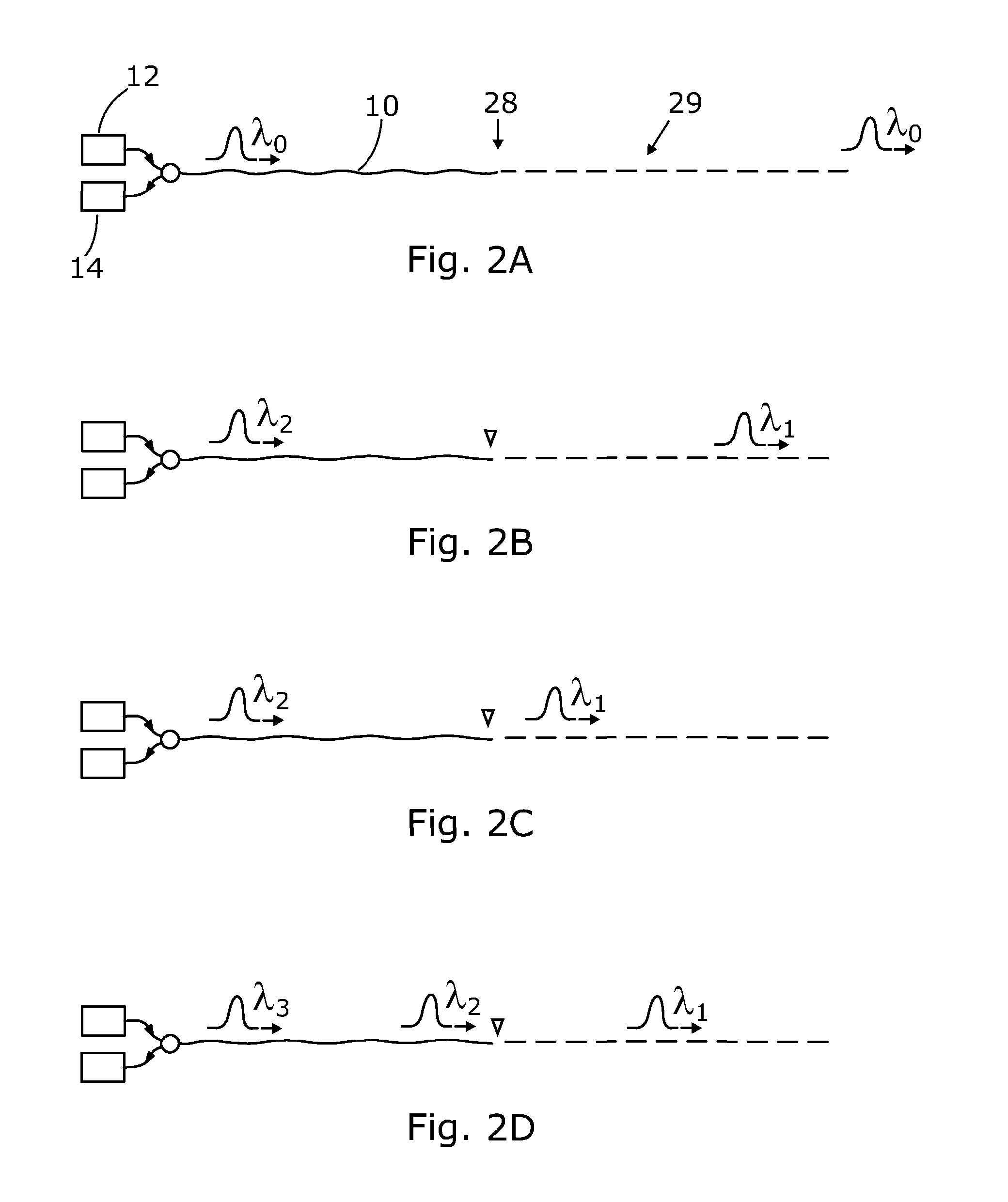
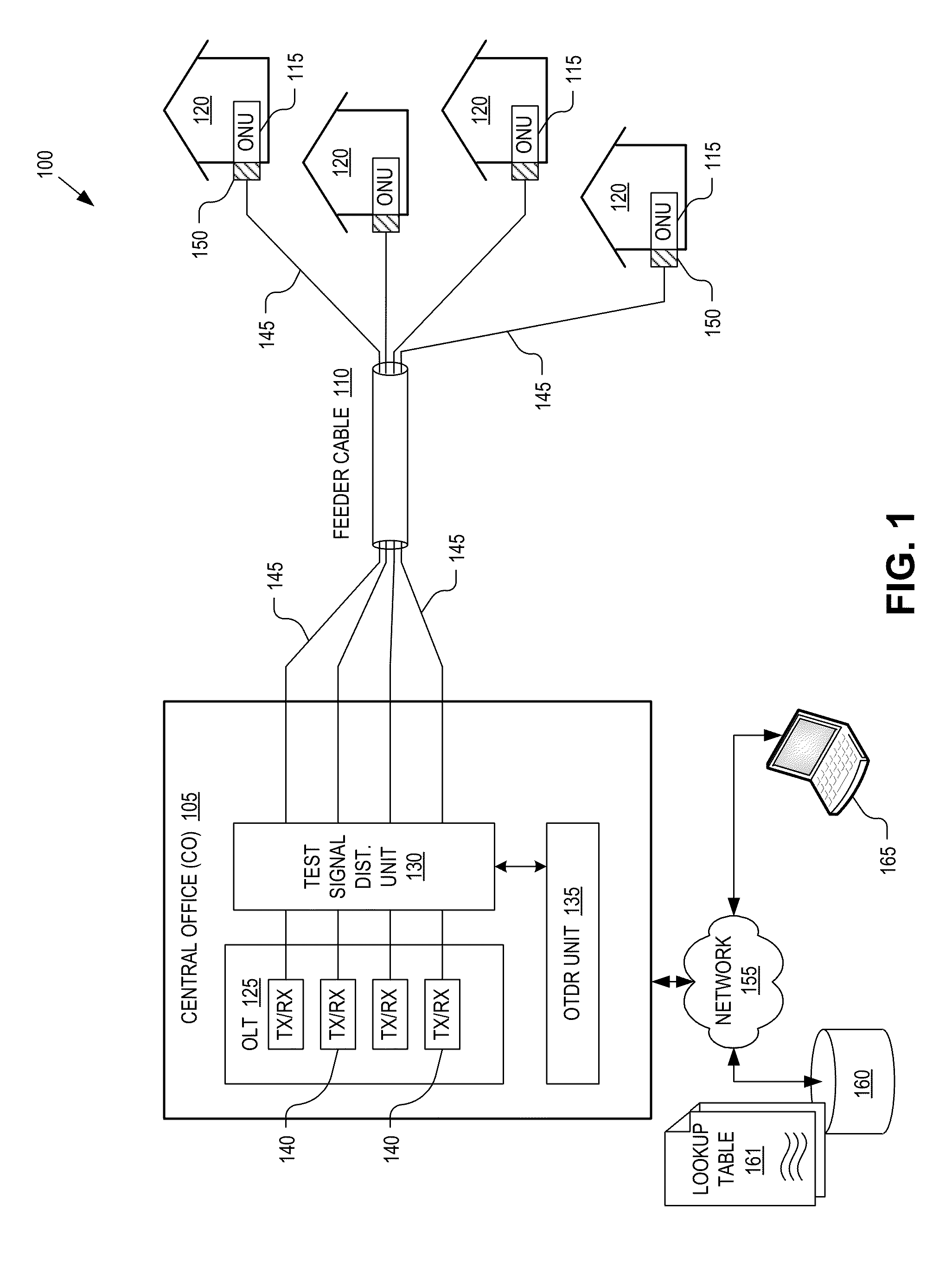
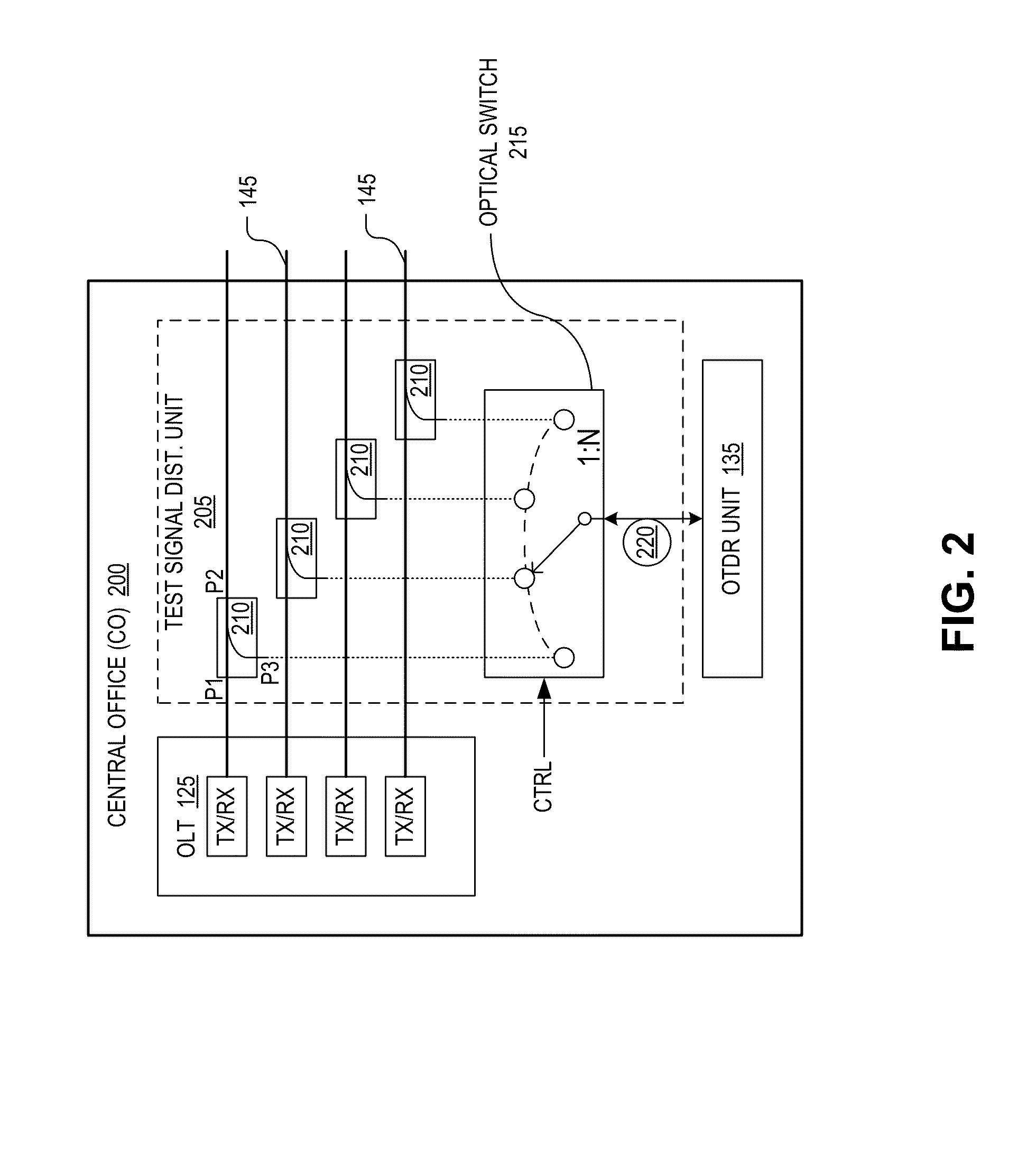
Implementations of techniques and systems are disclosed for detecting a fiber fault in a point-to-point optical access network based on optical time domain reflectometry (“OTDR”) measurements. The techniques include identifying loss of service between a central office (“CO”) and a given optical network unit (“ONU”) of a plurality of ONUs. In response to the identifying the loss of service, configuring a test signal distribution unit to optically couple an OTDR unit to a selected subset of the point-to-point fiber links which includes the given ONU. An optical test signal is launched from the OTDR unit into the selected subset of the point-to-point fiber links via the test signal distribution unit. Test signal reflections are received from each of the point-to-point fiber links within the selected subset as a reflection signature, which is analyzed to identify a location of the fiber fault.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
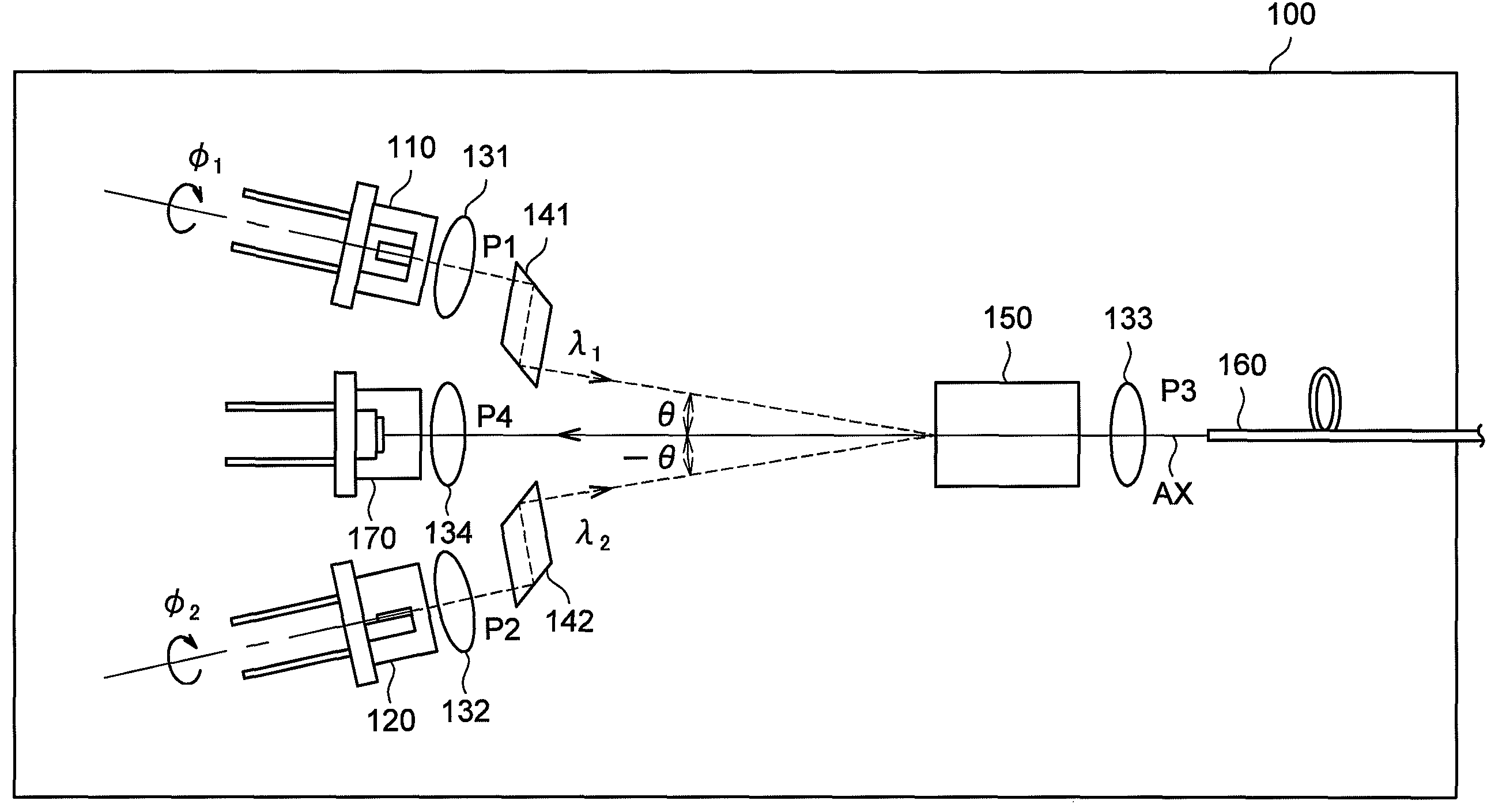
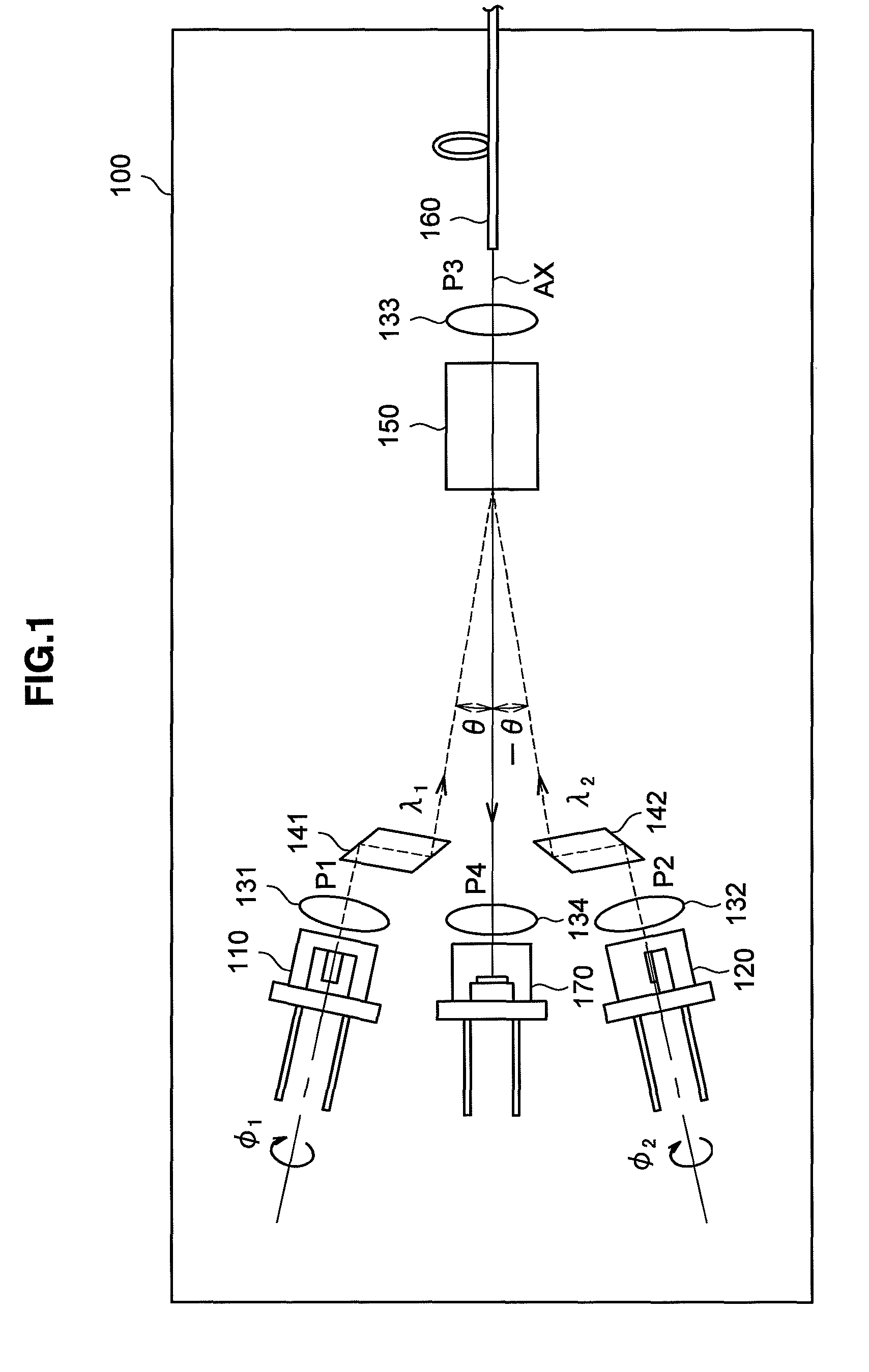
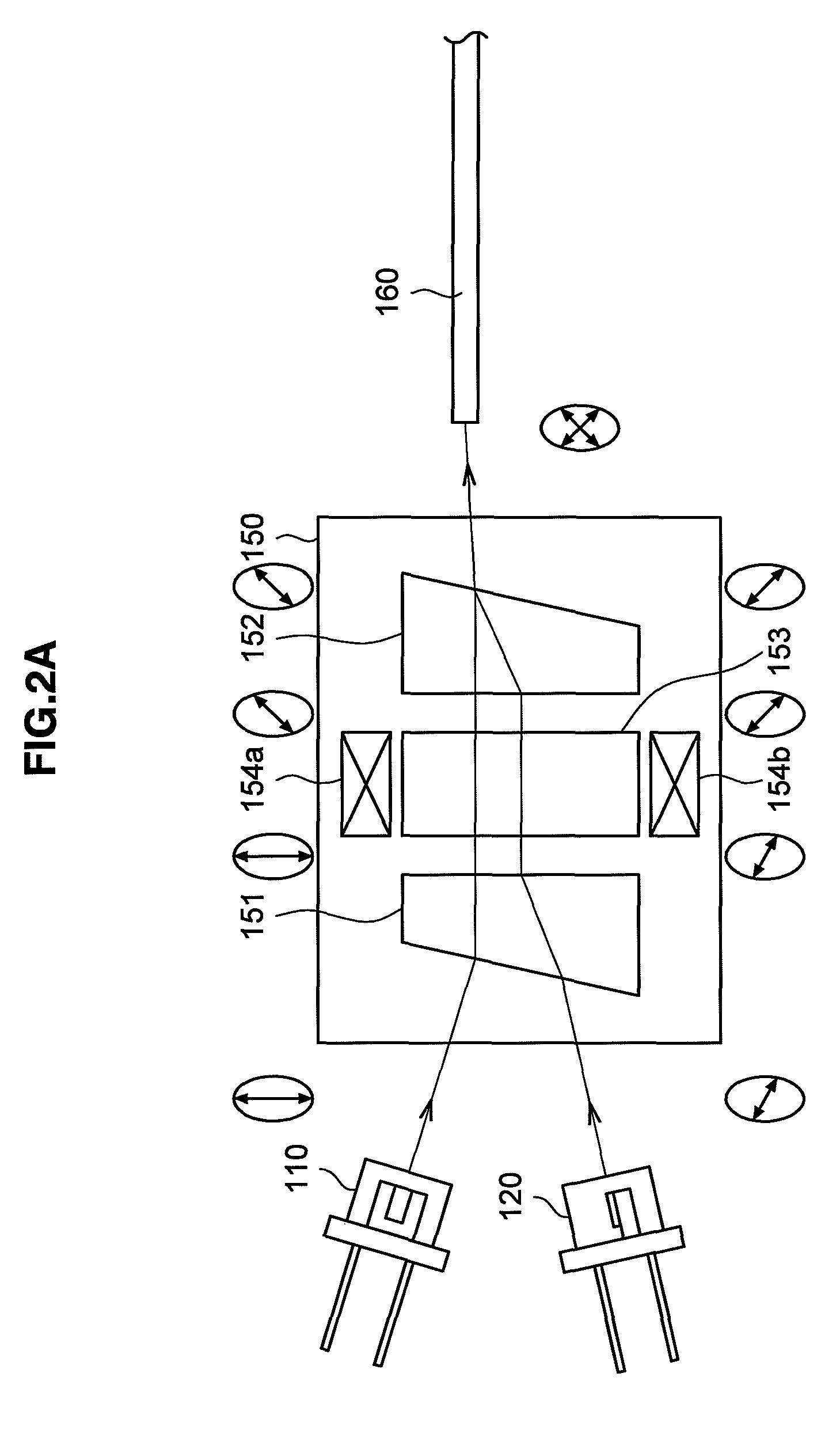
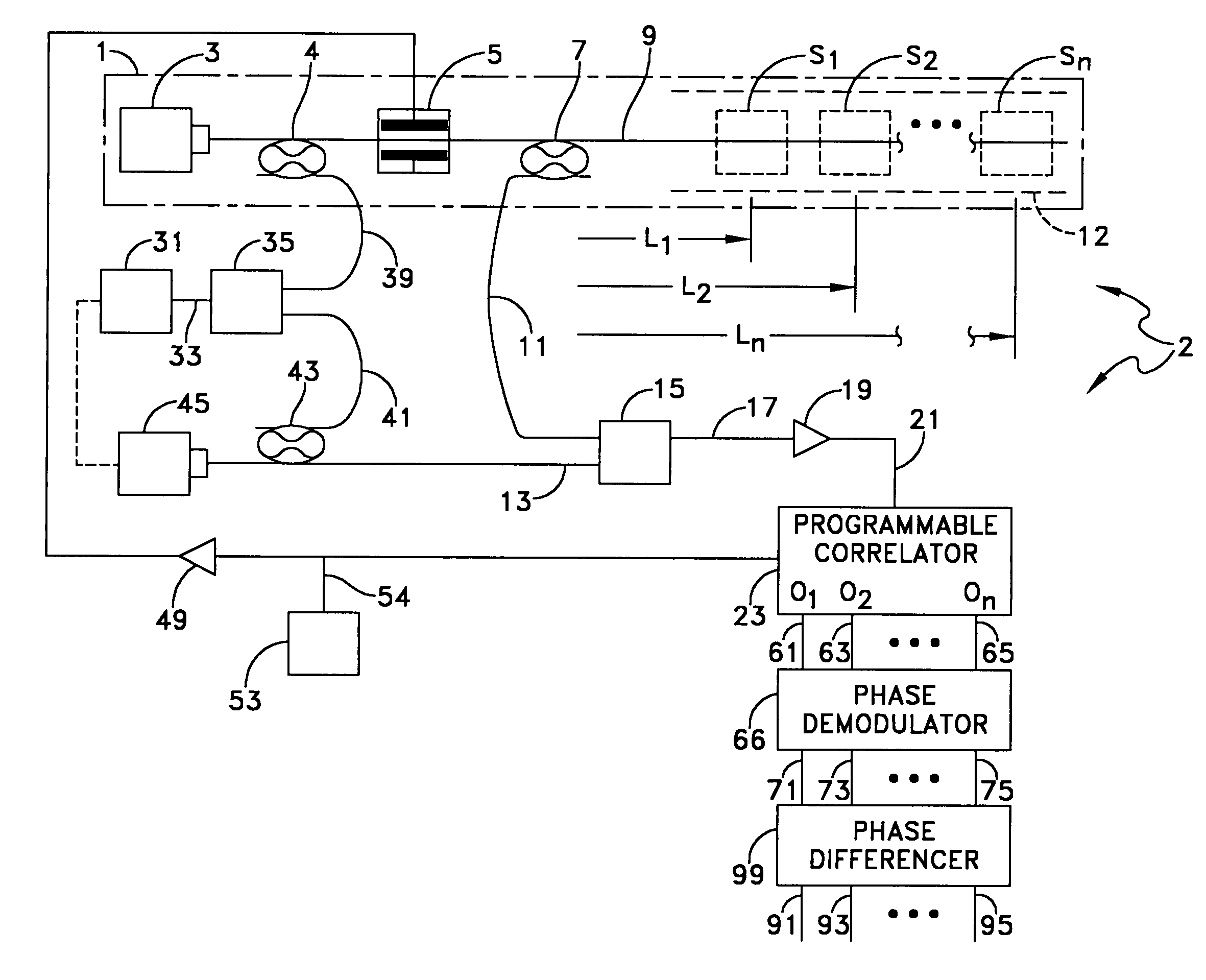
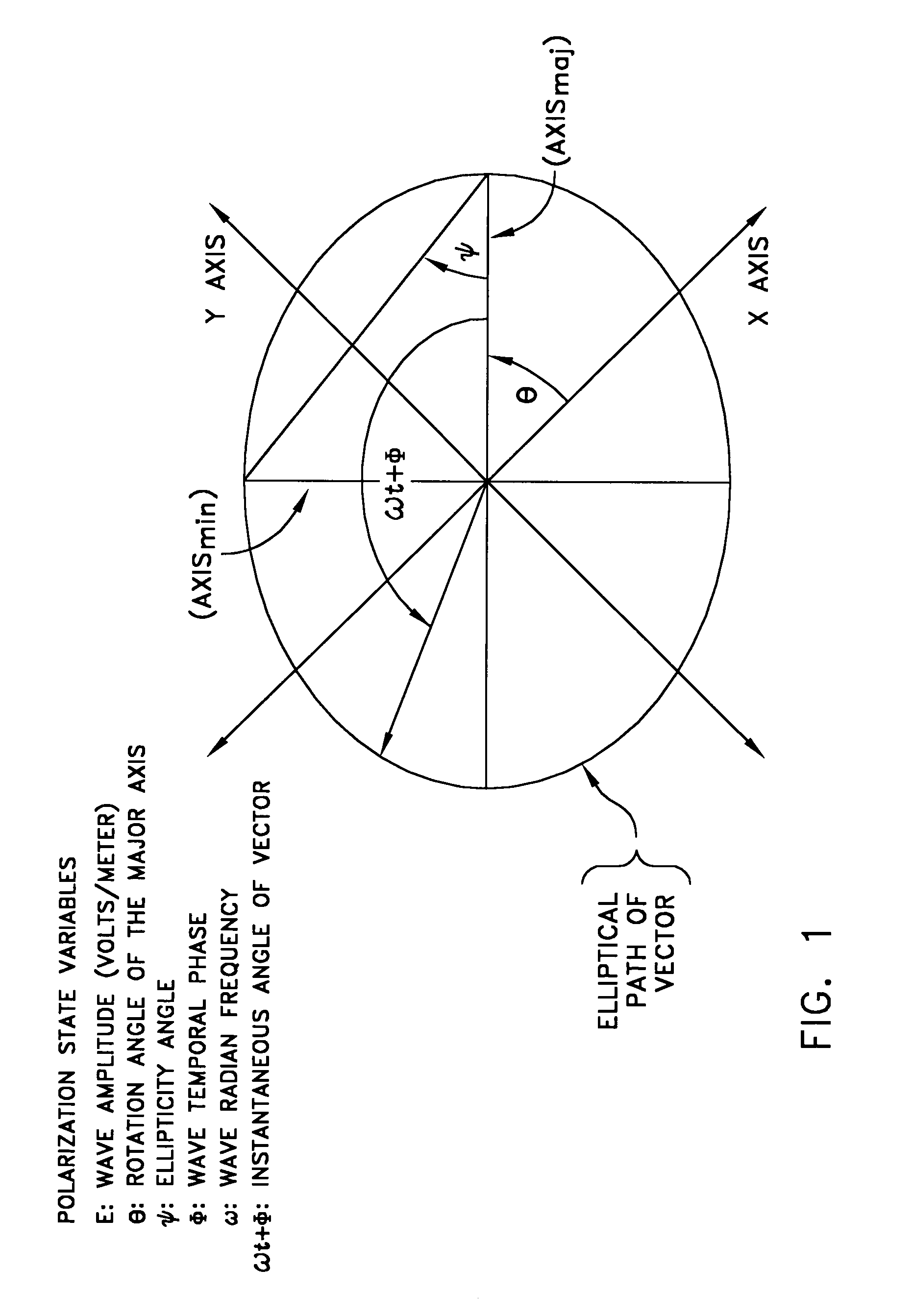
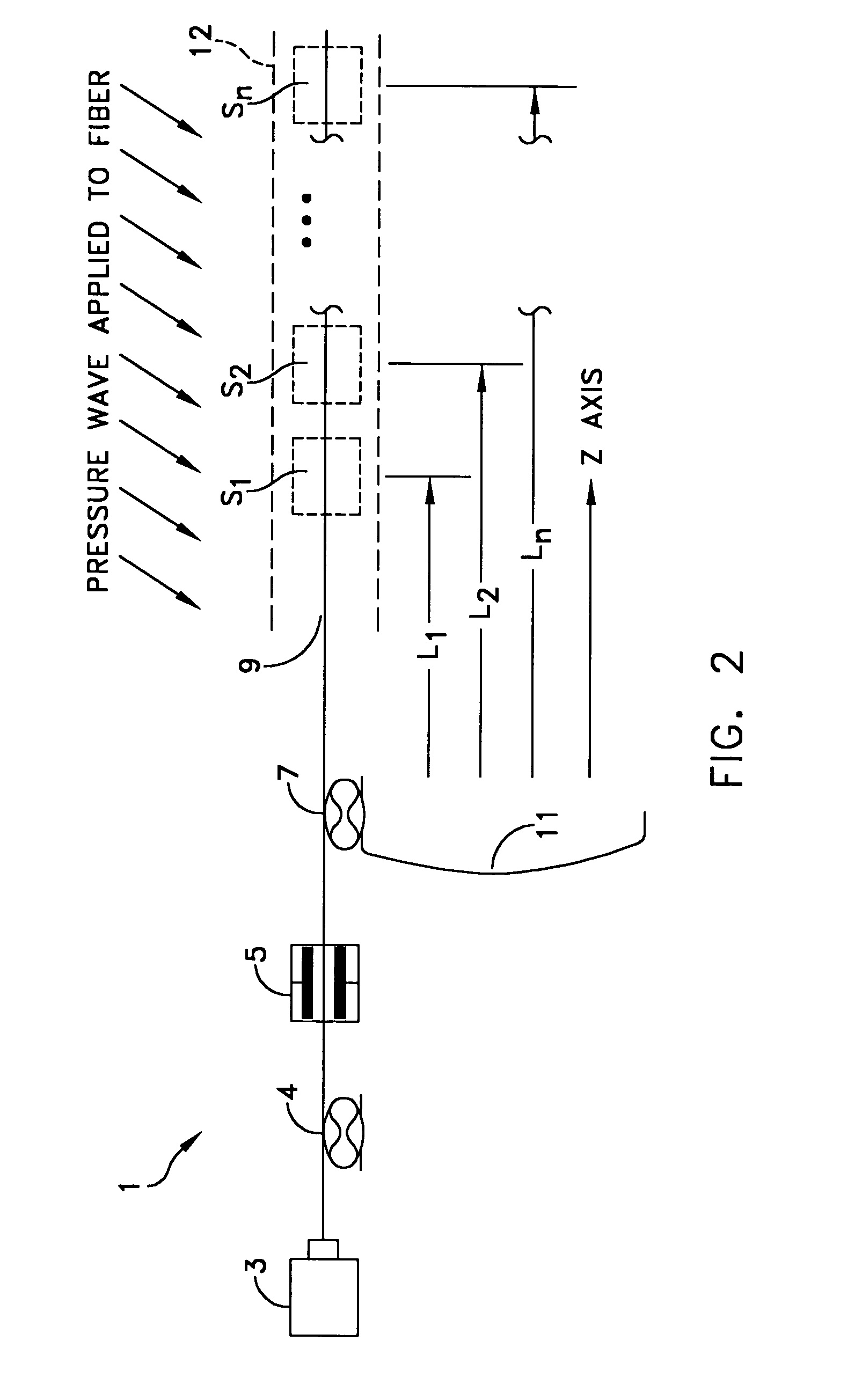
Detecting a Disturbance in the Propagation of Light in an Optical Waveguide
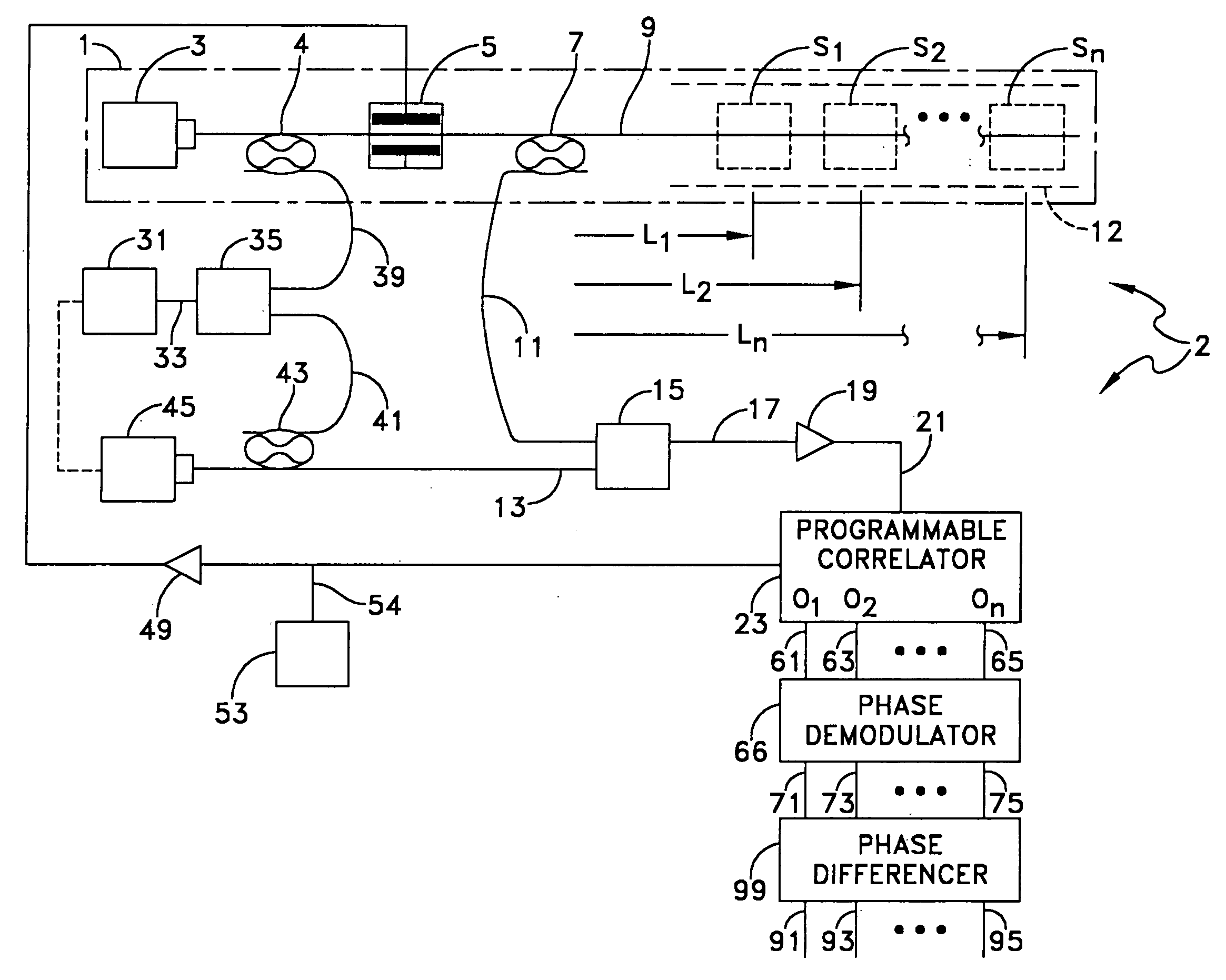
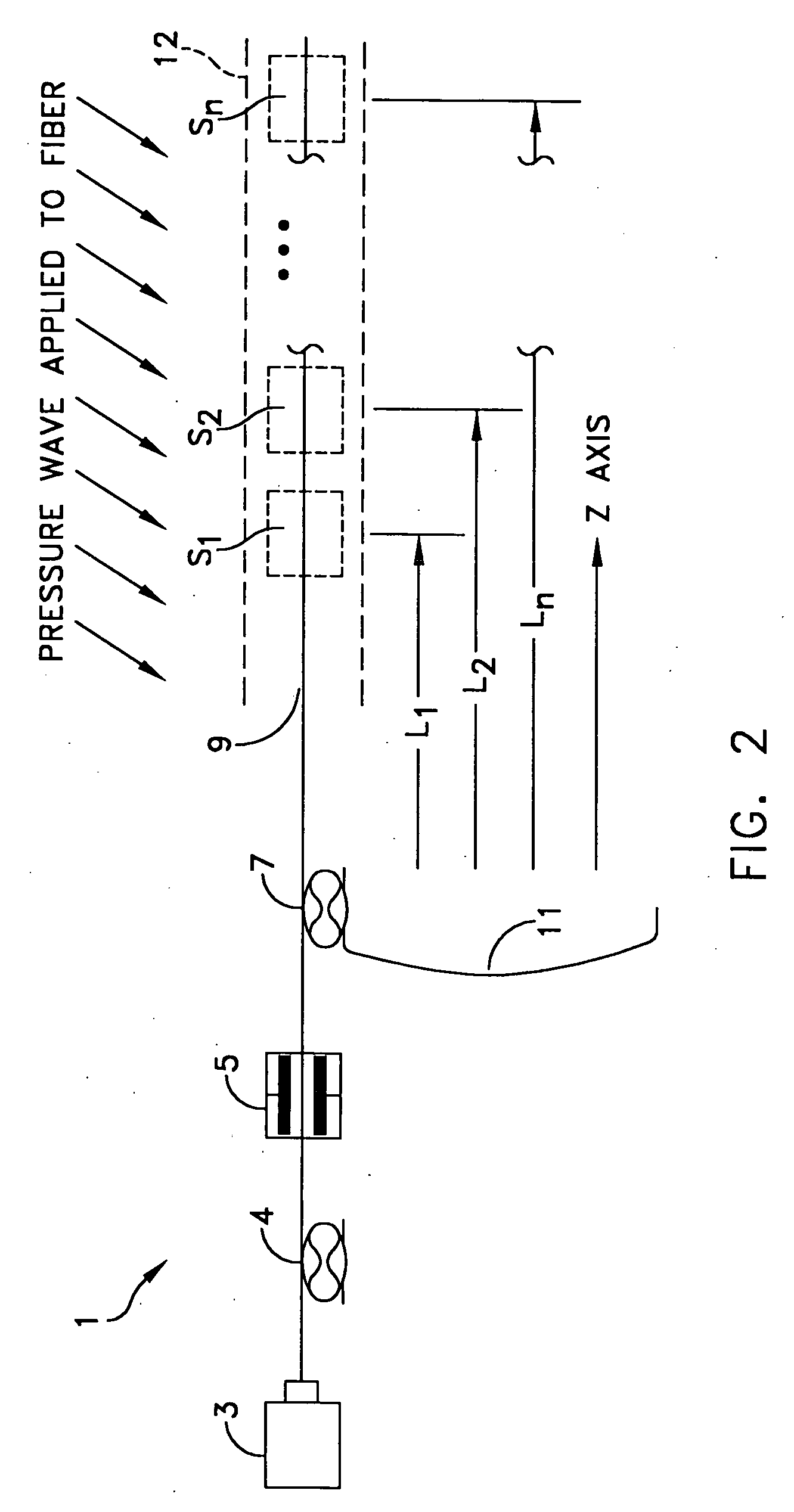
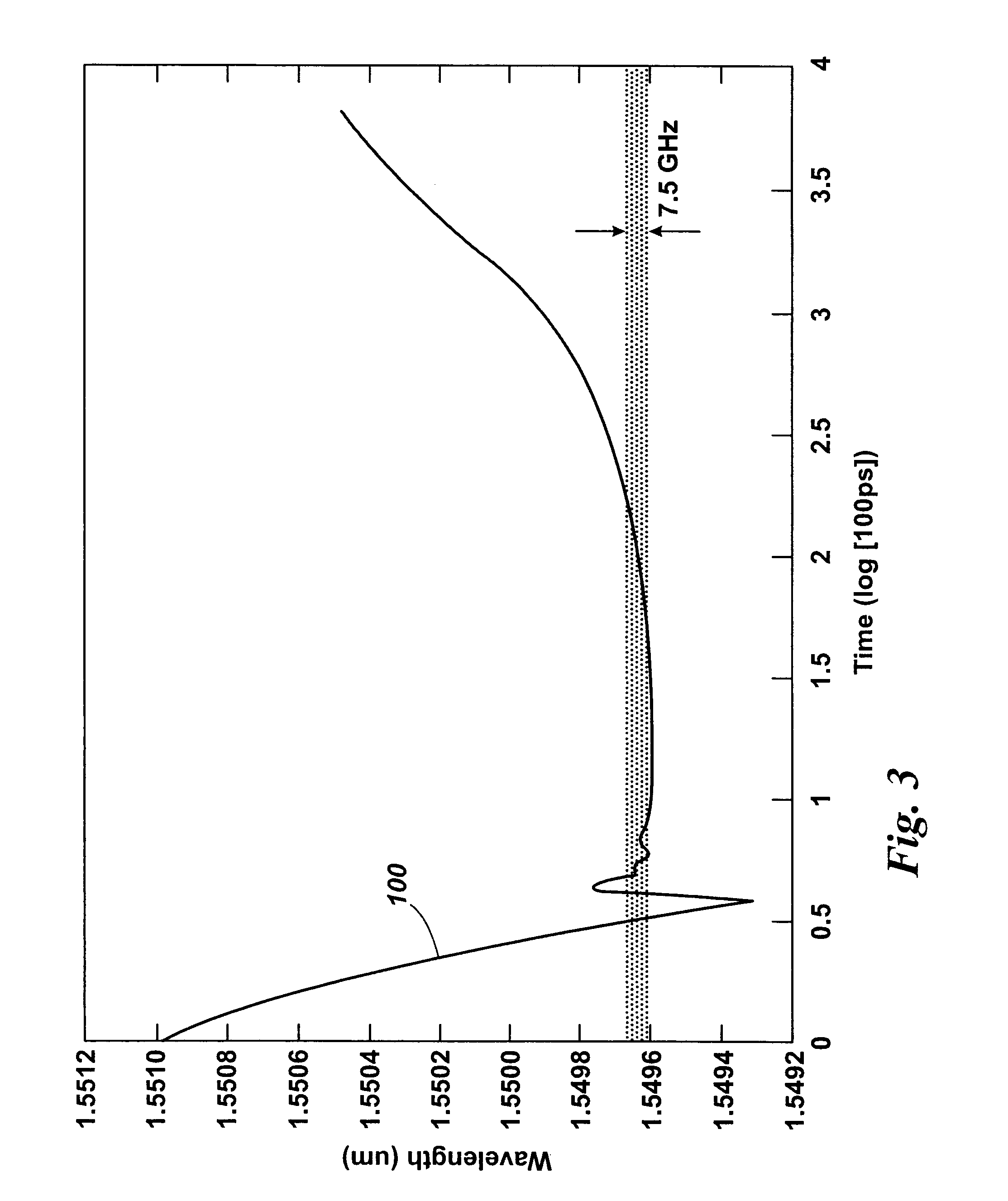
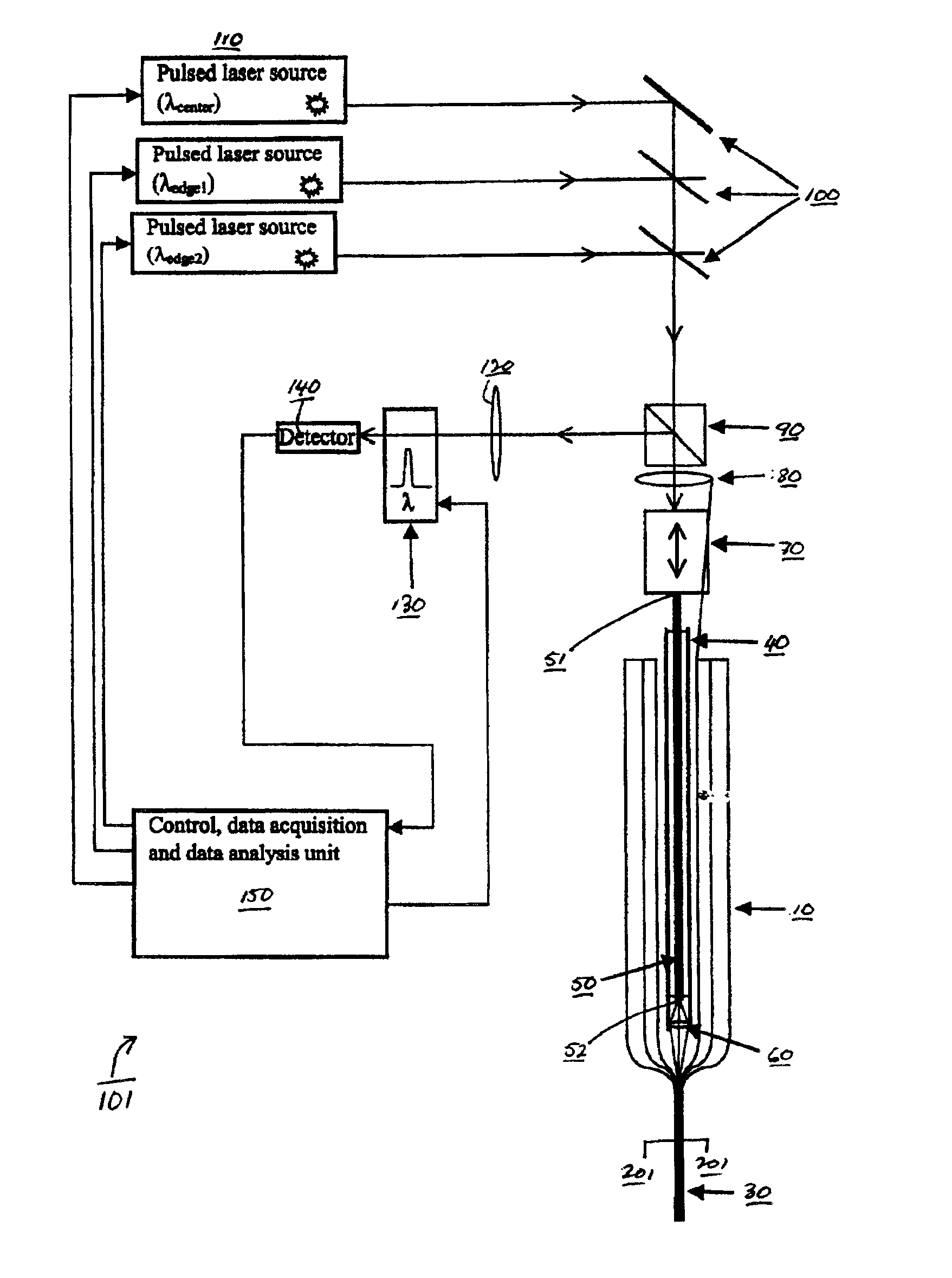
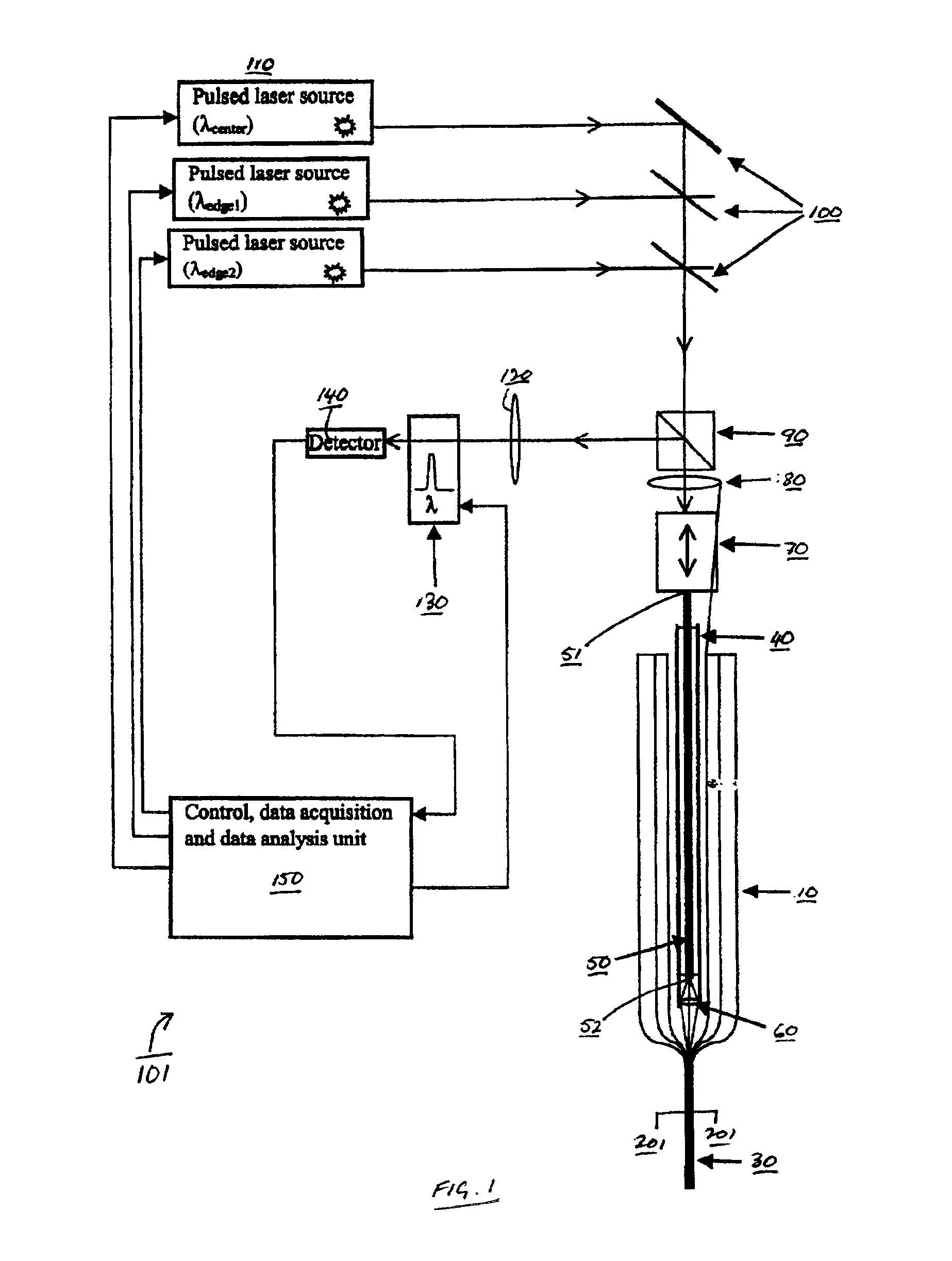
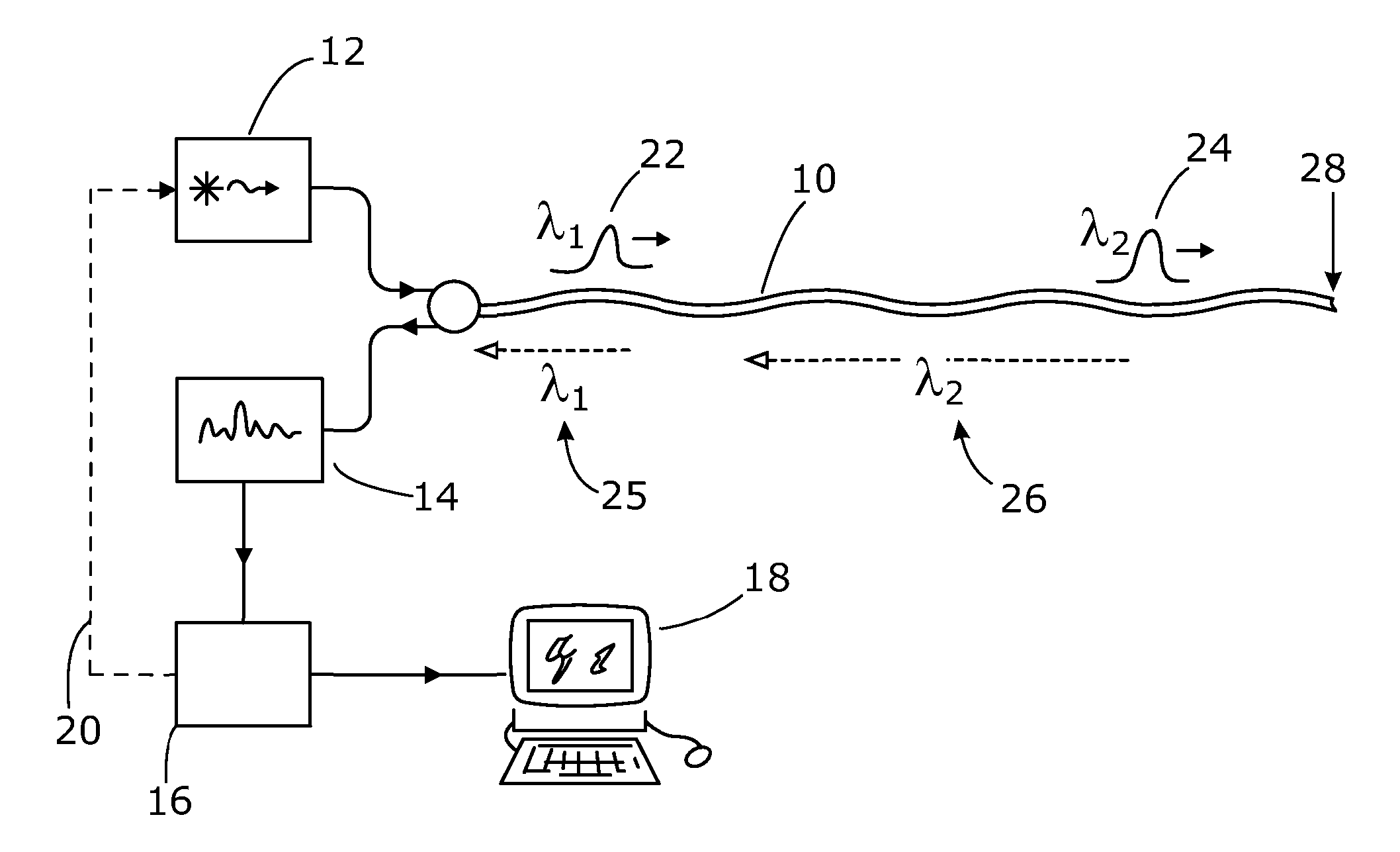
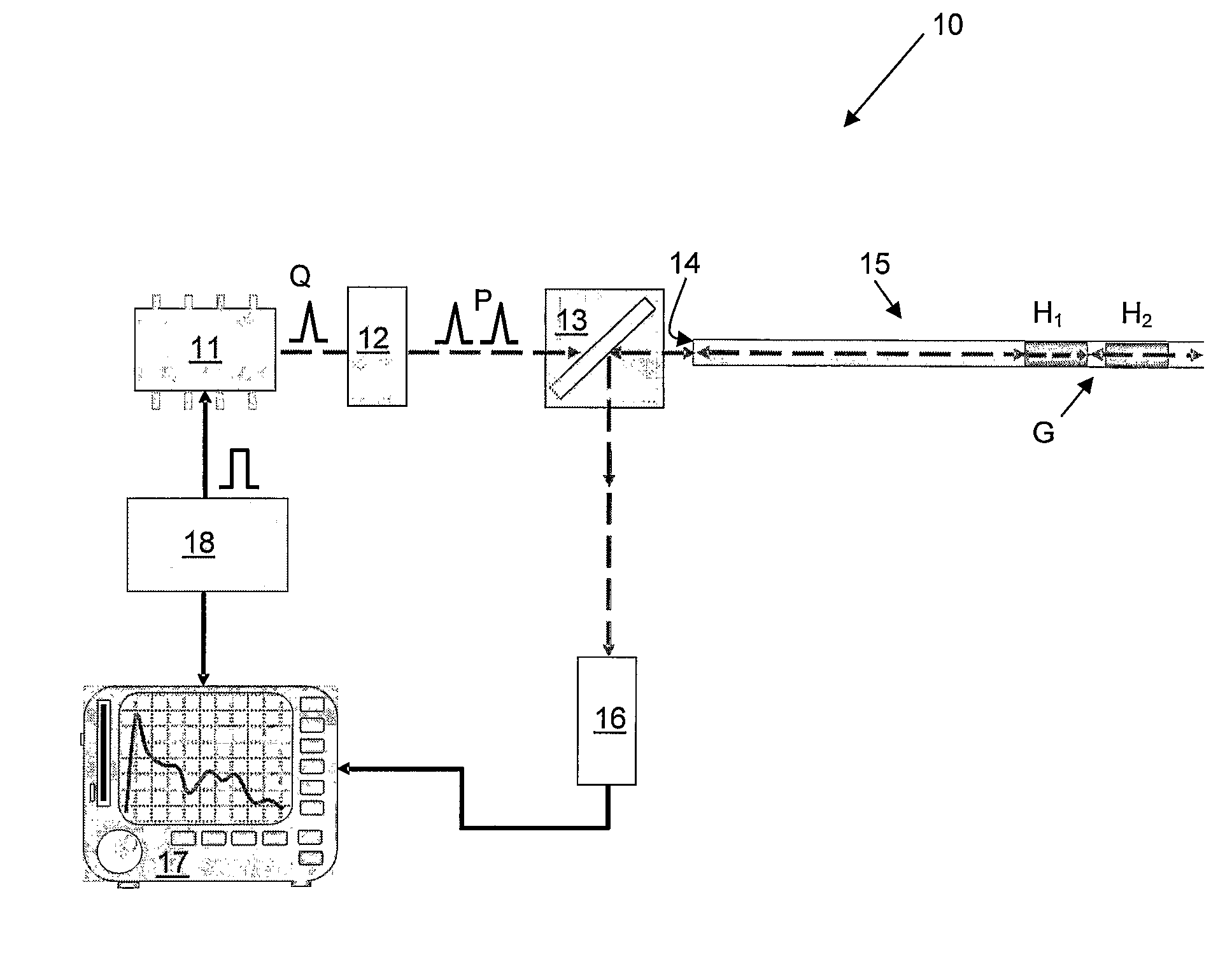
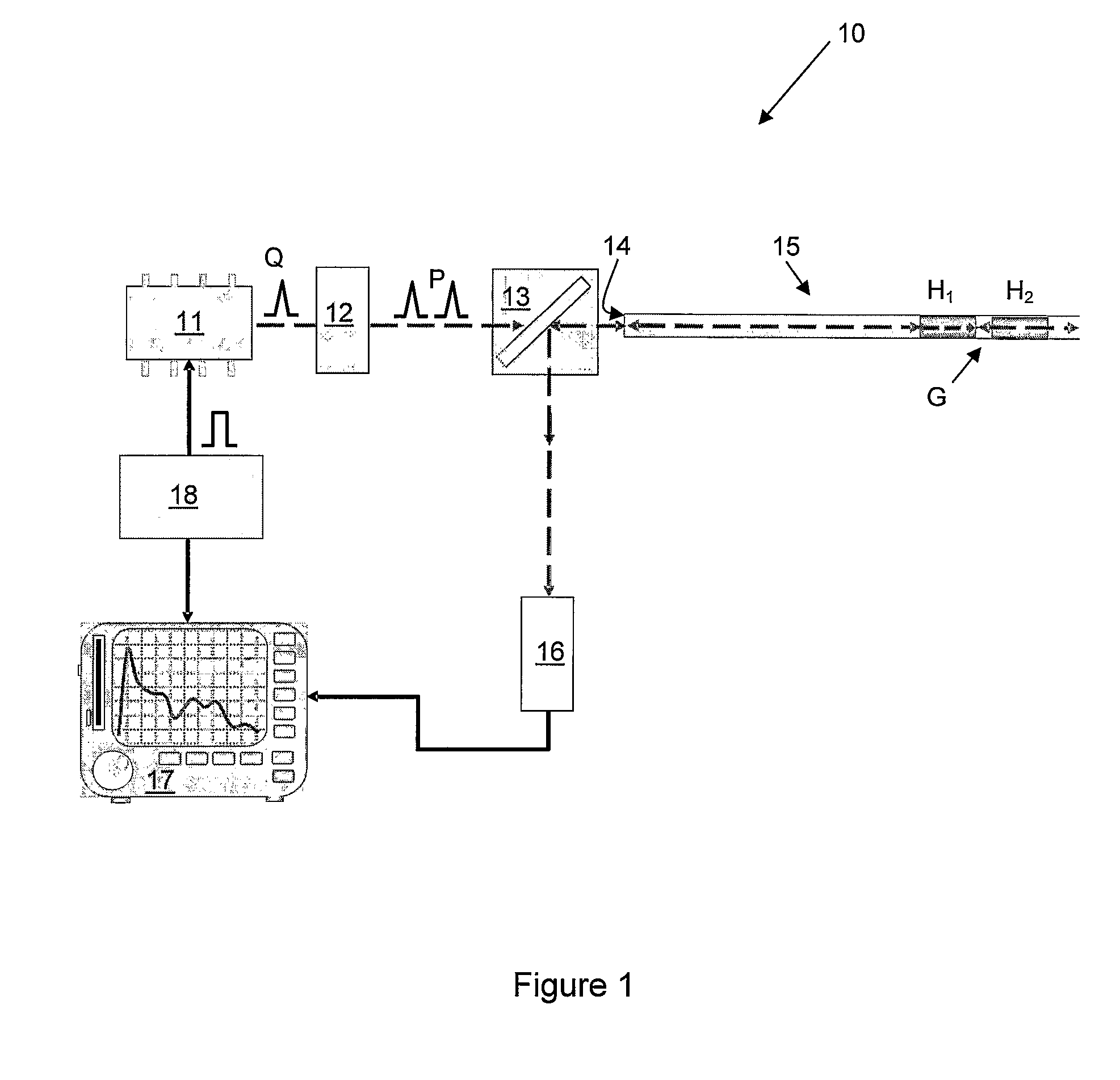
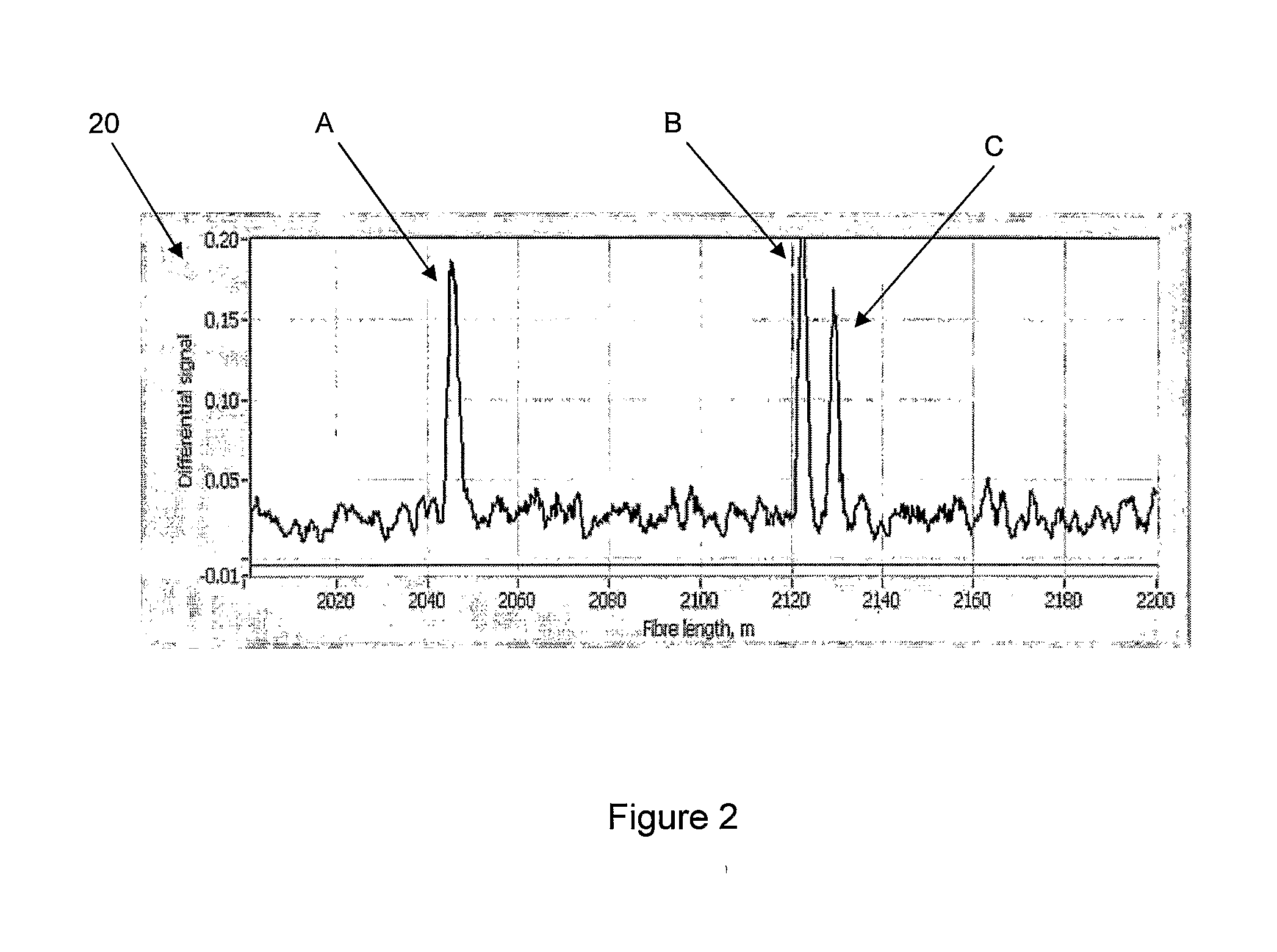
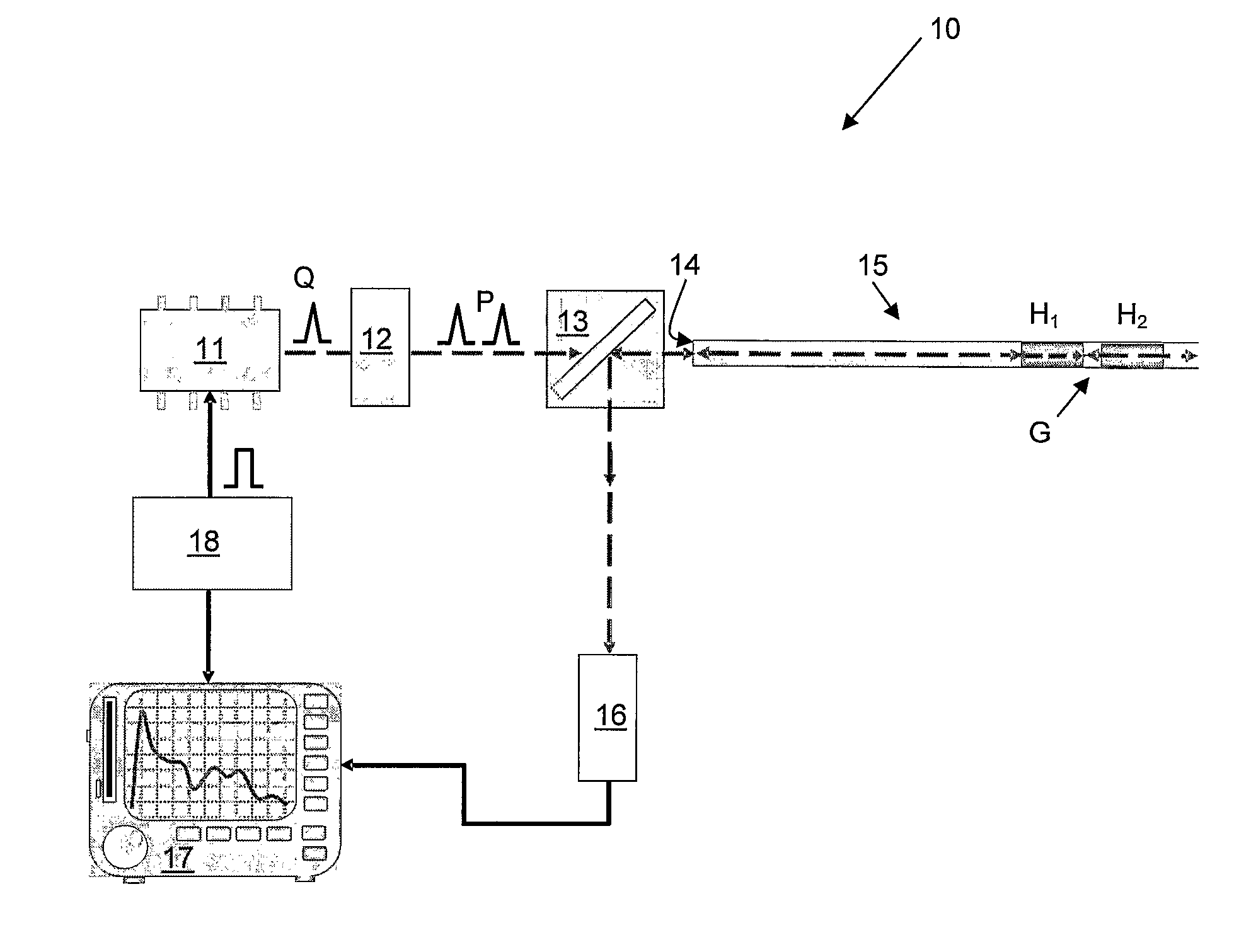
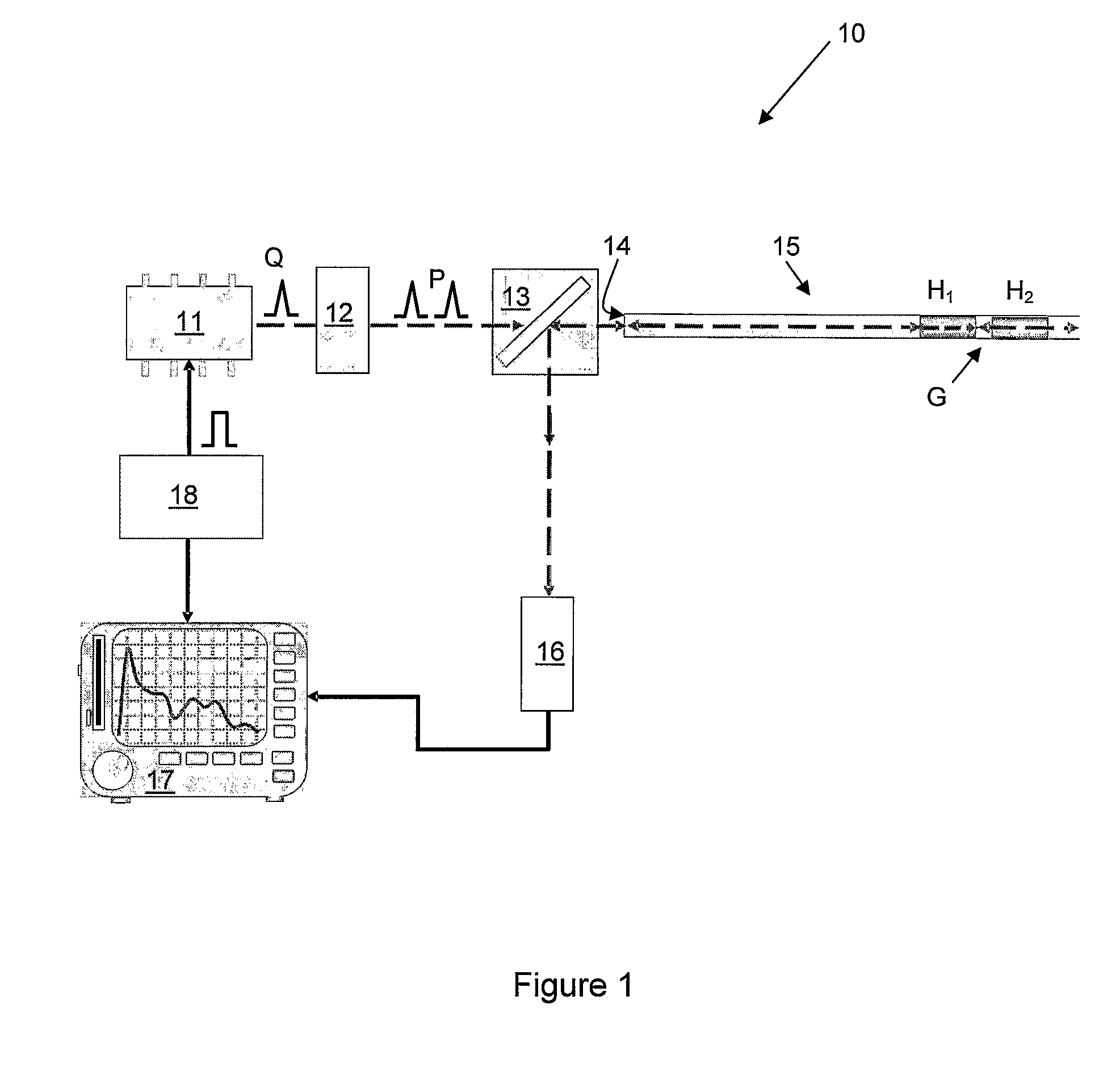
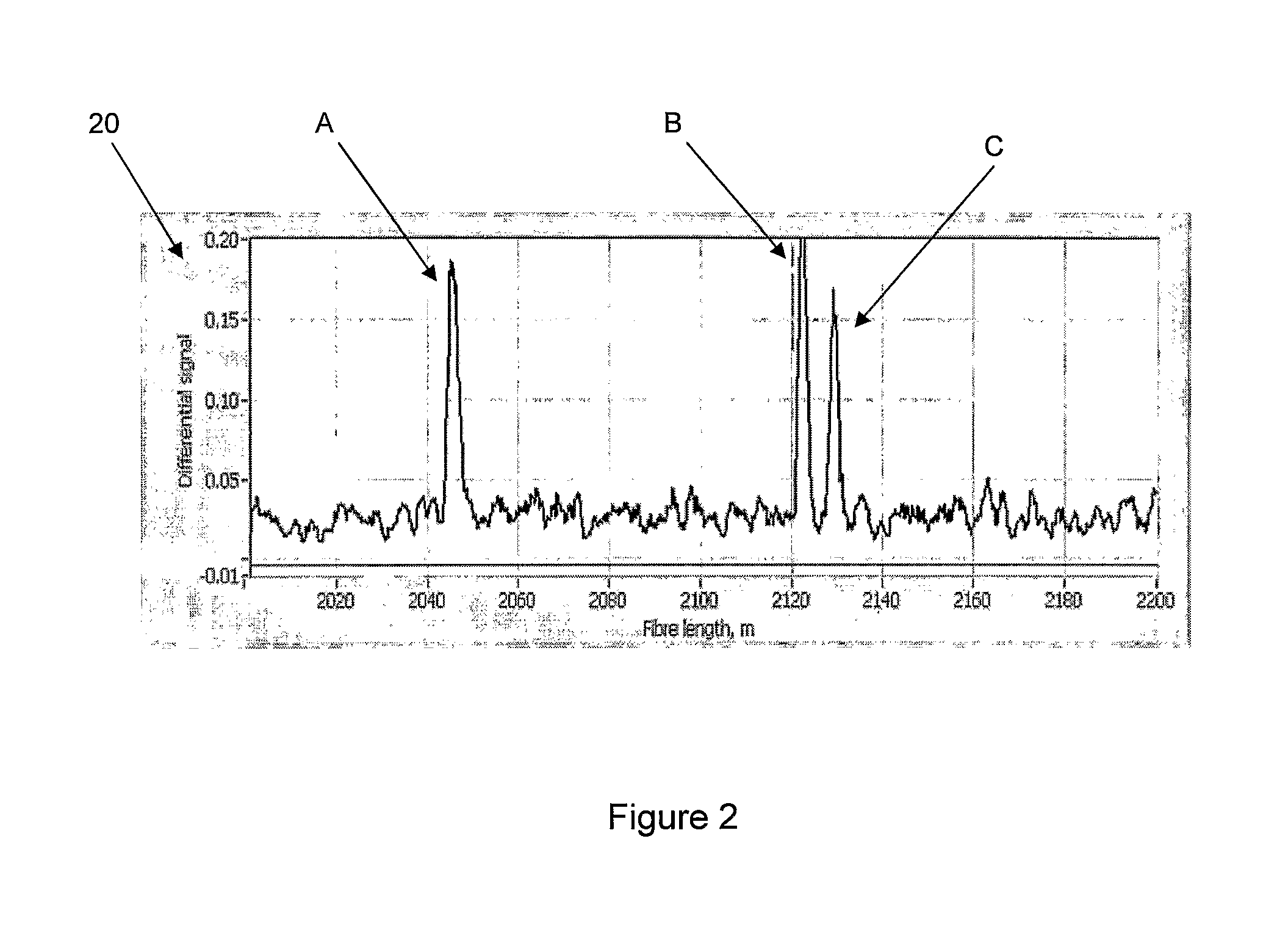
ActiveUS20080297772A1Efficient detectionAccurate detectionMaterial analysis by optical meansReflectometers detecting back-scattered light in time-domainPhotodetectorWaveguide
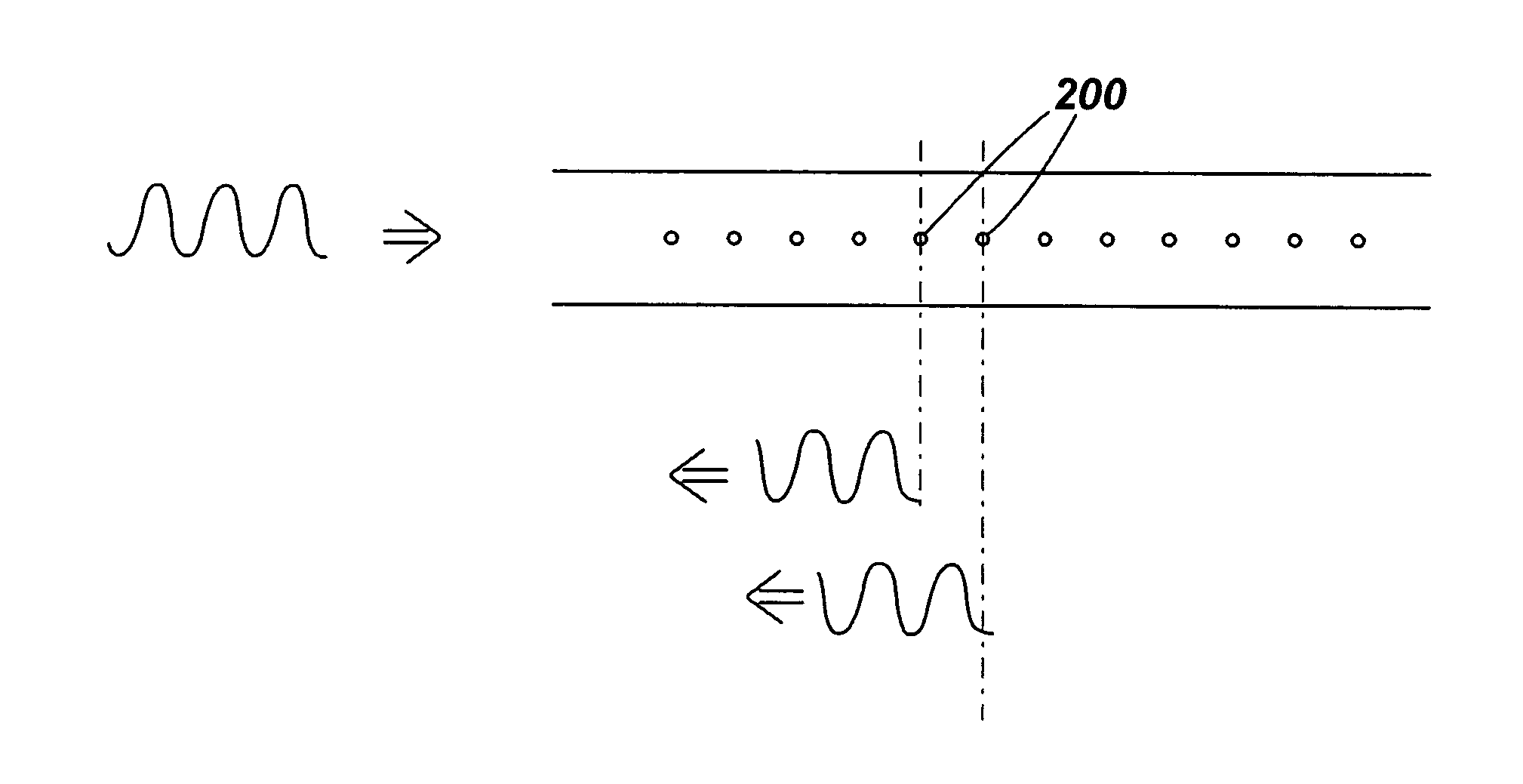
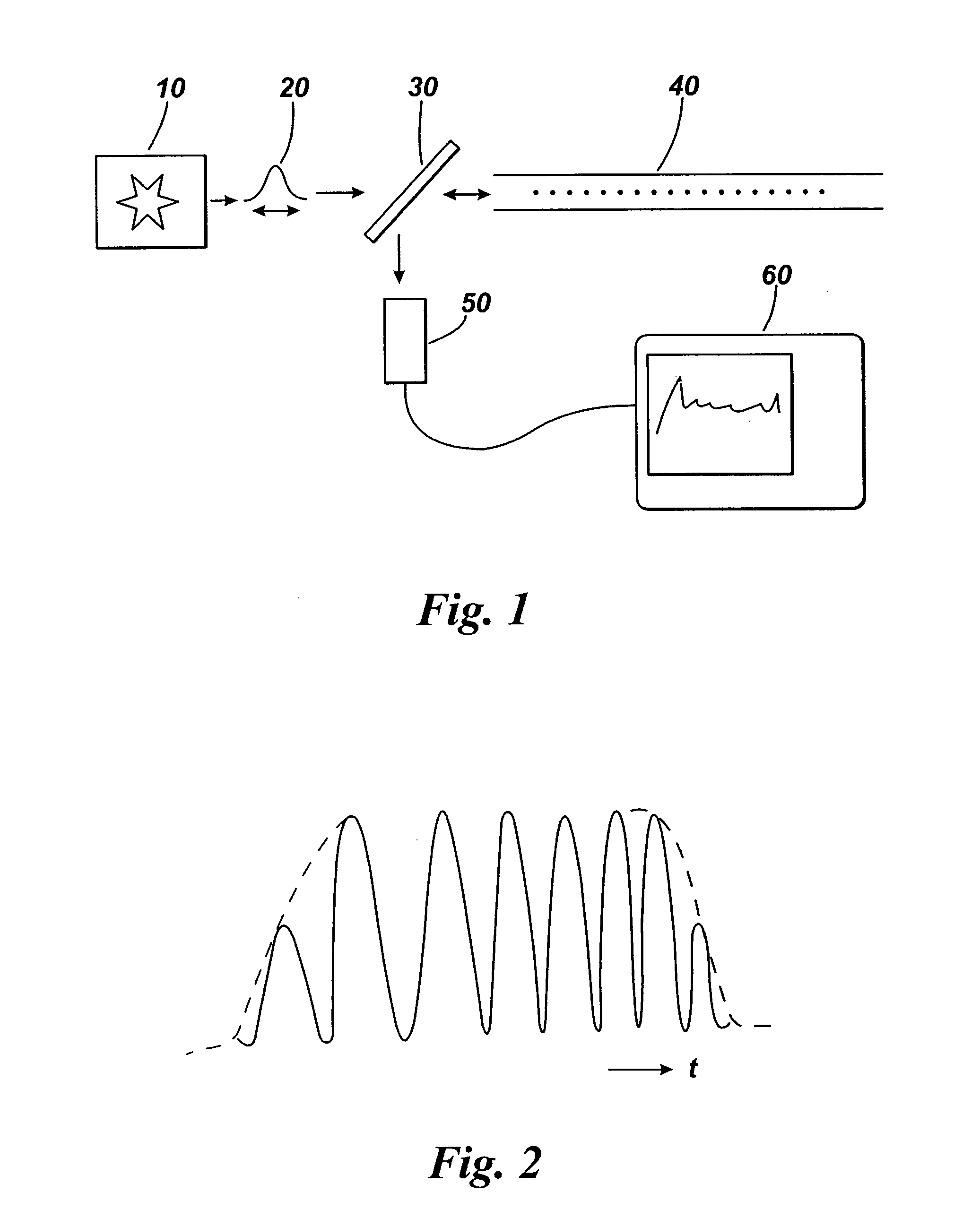
An optical time domain reflectometry apparatus has a laser and light modulator for producing coherent light pulses, each having two sections of higher intensity separated by a gap of lower or substantially zero intensity. As the light pulses propagate along the optical fibre, light is continuously Rayleigh backscattered by inhomogeneities of the optical fibre. A photodetector generates backscatter signals representing the intensity of light Rayleigh backscattered in the optical fibre as each light pulse travels along the optical fibre. The PC uses these backscatter signals to derive a difference signal representing a change dI in intensity between signals generated from two successive pulses. The PC then calculates the Root Mean Square (RMS) of the difference signal averaged over the interval between the two sections of the light pulses. Next, the PC averages the backscatter signal generated from the first of the pulses over the same interval and normalises the RMS difference signal using the averaged signal to obtain a compensated difference signal that depends only on differences in the rate of change of phase of light of the light pulses as they travelled along the waveguide. This is repeated at different wavelengths to allow the compensated difference signal to be adjusted to represent the magnitude of the differences.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
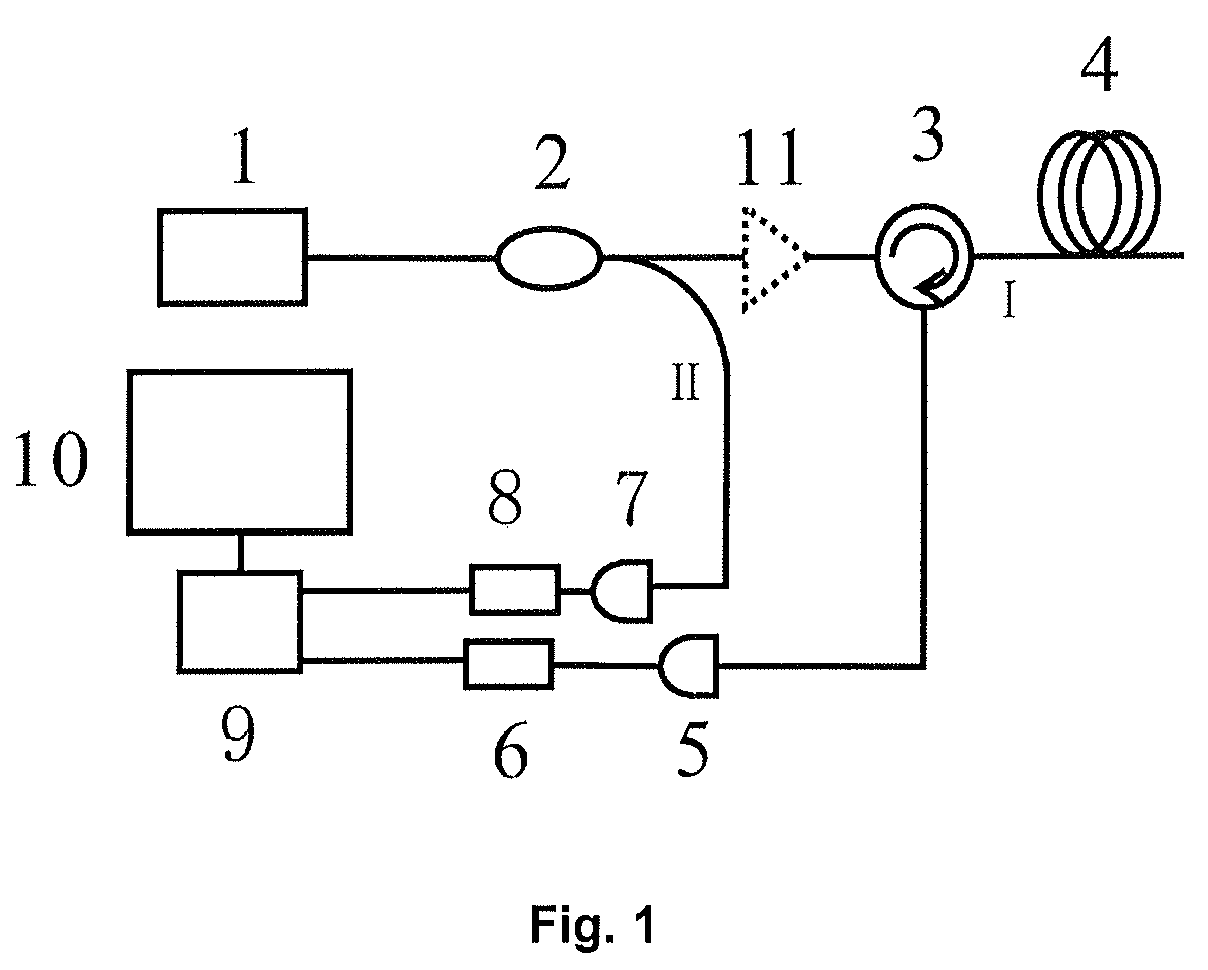
Chaotic optical time domain reflectometer method and apparatus
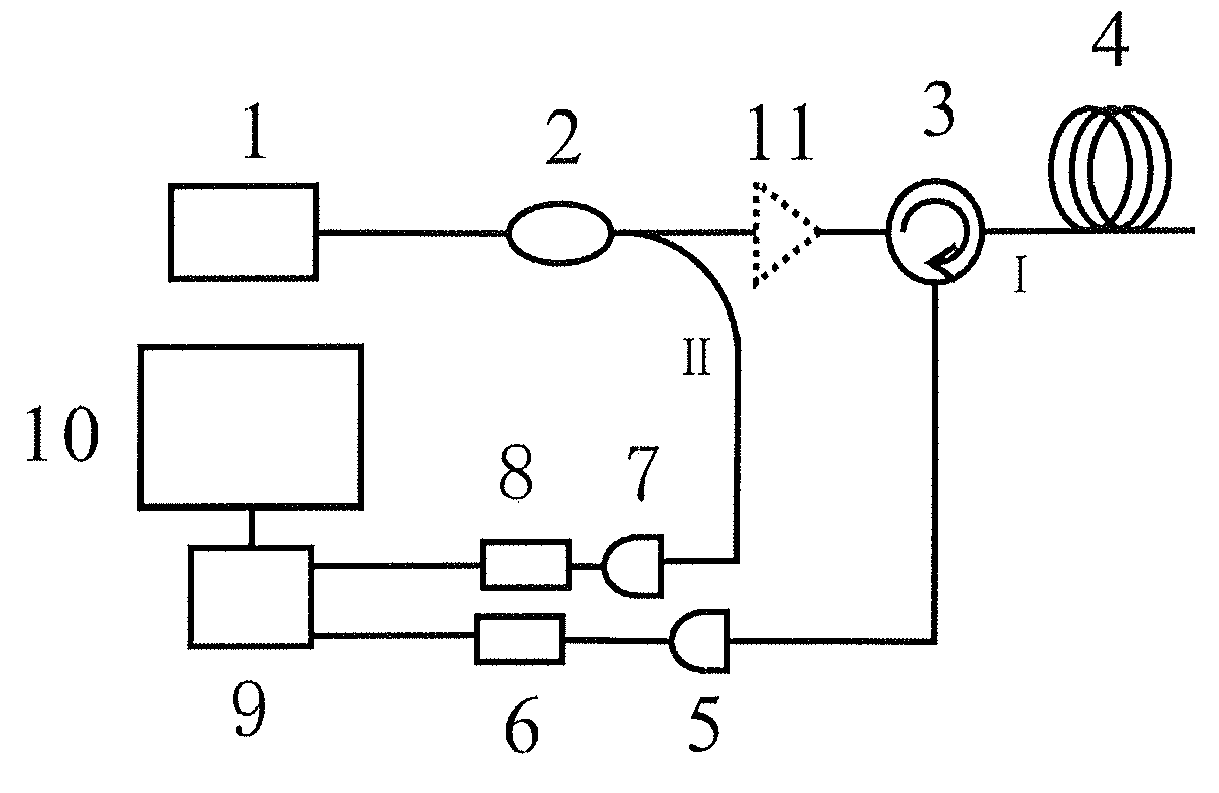
ActiveUS20100290035A1Avoid disadvantagesHigh resolutionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsFiberFiber coupler
In a method and a corresponding apparatus for performing chaotic optical time domain reflectometer, the chaotic laser signal, generated by the chaotic laser transmitter, is split into probe signal I and reference signal II by a fiber coupler. Through an optical circulator, the probe signal I is launched into the test fiber and the echo light is converted into electrical signal by a photodetector and digitalized by an A / D converter. The reference signal II is converted into electrical signal by a photodetector and digitalized by another A / D converter. Two digital signals received from two A / D converters are correlated in a signal processing device to locate the exact position of faults in fibers. The result output is then displayed on a display device. This invention was developed to overcome the tradeoff between resolution and dynamic range of the pulse-based OTDR. This method can improve the dynamic range and spatial resolution significantly; enhance the anti-jamming capability and noise tolerance. Also it has merits of simple structure and lower cost.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
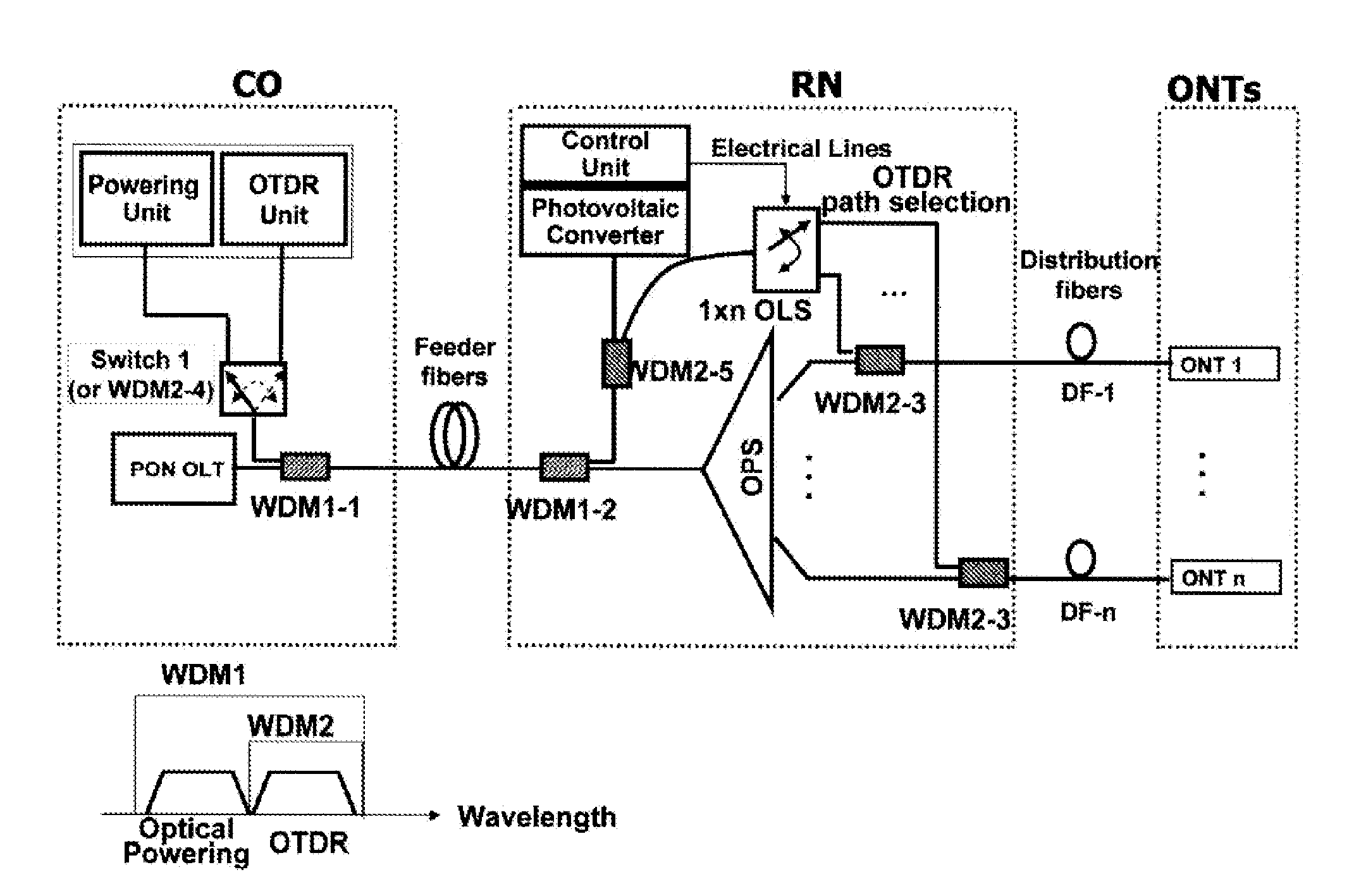
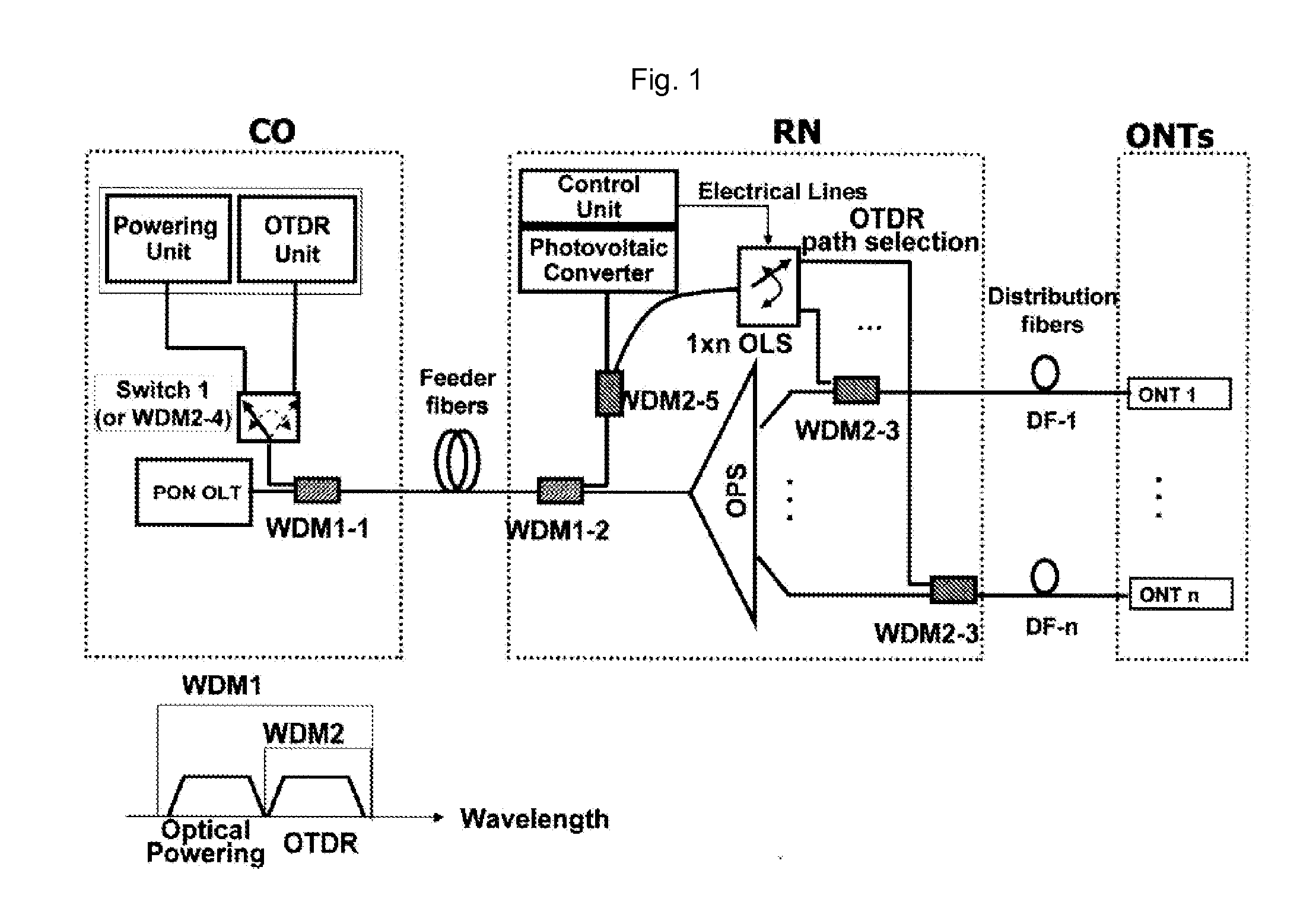
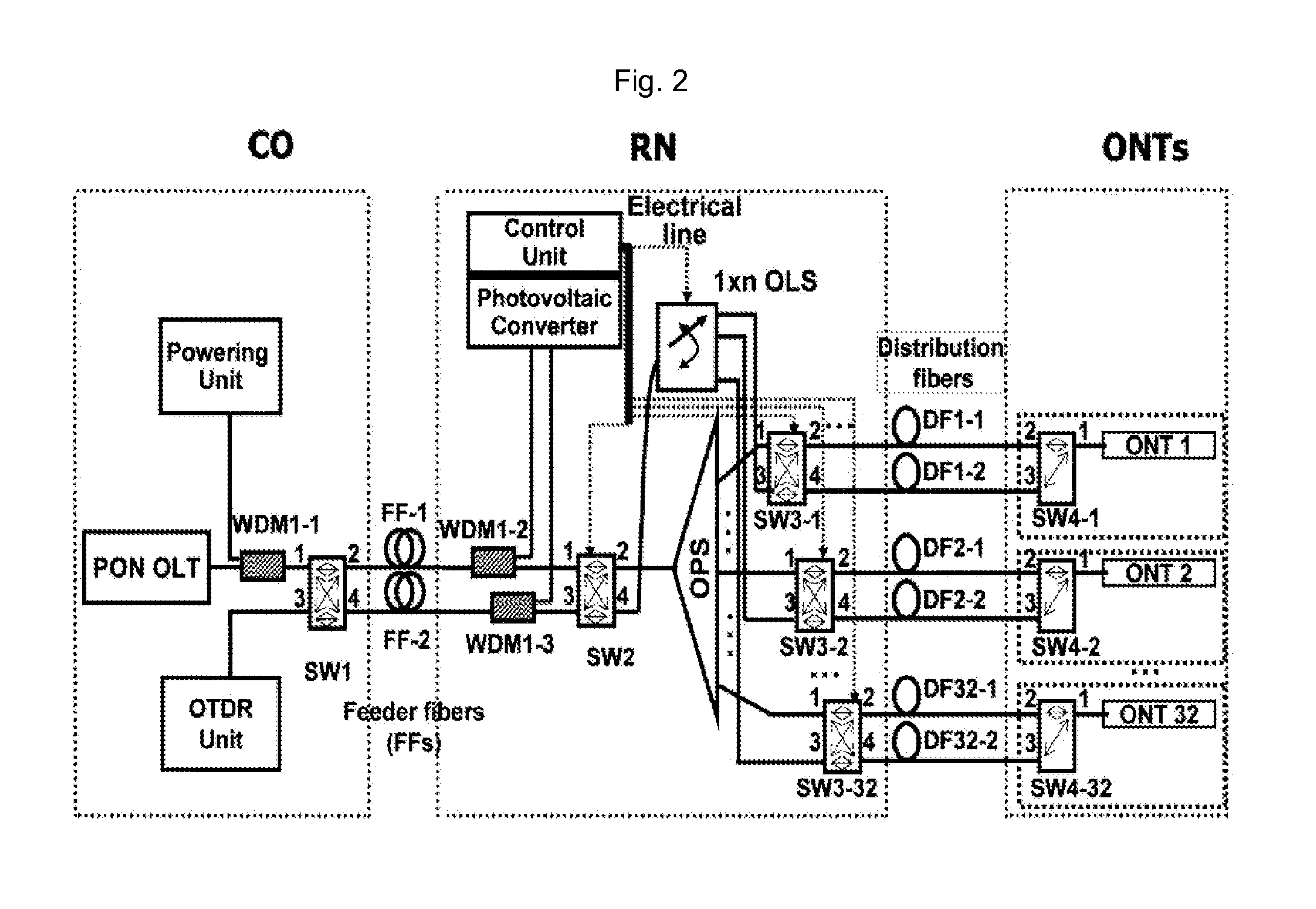
Fault localization method and a fault localization apparatus in a passive optical network and a passive optical network having the same
InactiveUS20110255860A1Detect fault positionImprove reliabilityTransmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsPassive networksEngineering
The present invention discloses a fault localization method and a fault localization apparatus in a Passive Optical Network (PON) and a passive optical network having the same.A fault localization method in PON according to the present invention comprises a) configuring an optical path of a remote node (RN) selectively by electric power being fed temporarily only when necessary, while the PON is regularly being operated as a passive network; and b) detecting a fault occurring on the selectively configured optical path by inserting a monitoring signal of an OTDR unit, which is positioned in a central office (CO), through the selectively configured optical path.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Natural fiber span reflectometer providing a virtual signal sensing array capability
ActiveUS7030971B1To offer comfortLow costForce measurement by measuring optical property variationMaterial analysis by optical meansRayleigh scatteringTime delays
A CW lightwave modulated by a continuously reiterated binary pseudorandom code sequence is launched into an end of a span of ordinary optical fiber cable. Portions of the launched lightwave back propagate to the launch end from a continuum of locations along the span because of innate fiber properties including Rayleigh scattering. This is picked off the launch end and heterodyned to produce a r.f. beat signal. The r.f. beat signal is processed by a plurality (which can be thousands) of correlator type binary pseudonoise code sequence demodulators respectively operated in different delay time relationships to the timing base of the reiterated modulation sequences. The outputs of the demodulators provide r.f. time-domain reflectometry outputs representative of signals (e.g., acoustic pressure waves) incident to virtual sensors along the fiber at positions corresponding to the various time delay relationships.
Owner:US REPRESENTED BY THE OFFICE OF NAVAL RES
Accuracy automated optical time domain reflectometry optical return loss measurements using a "Smart" Test Fiber Module
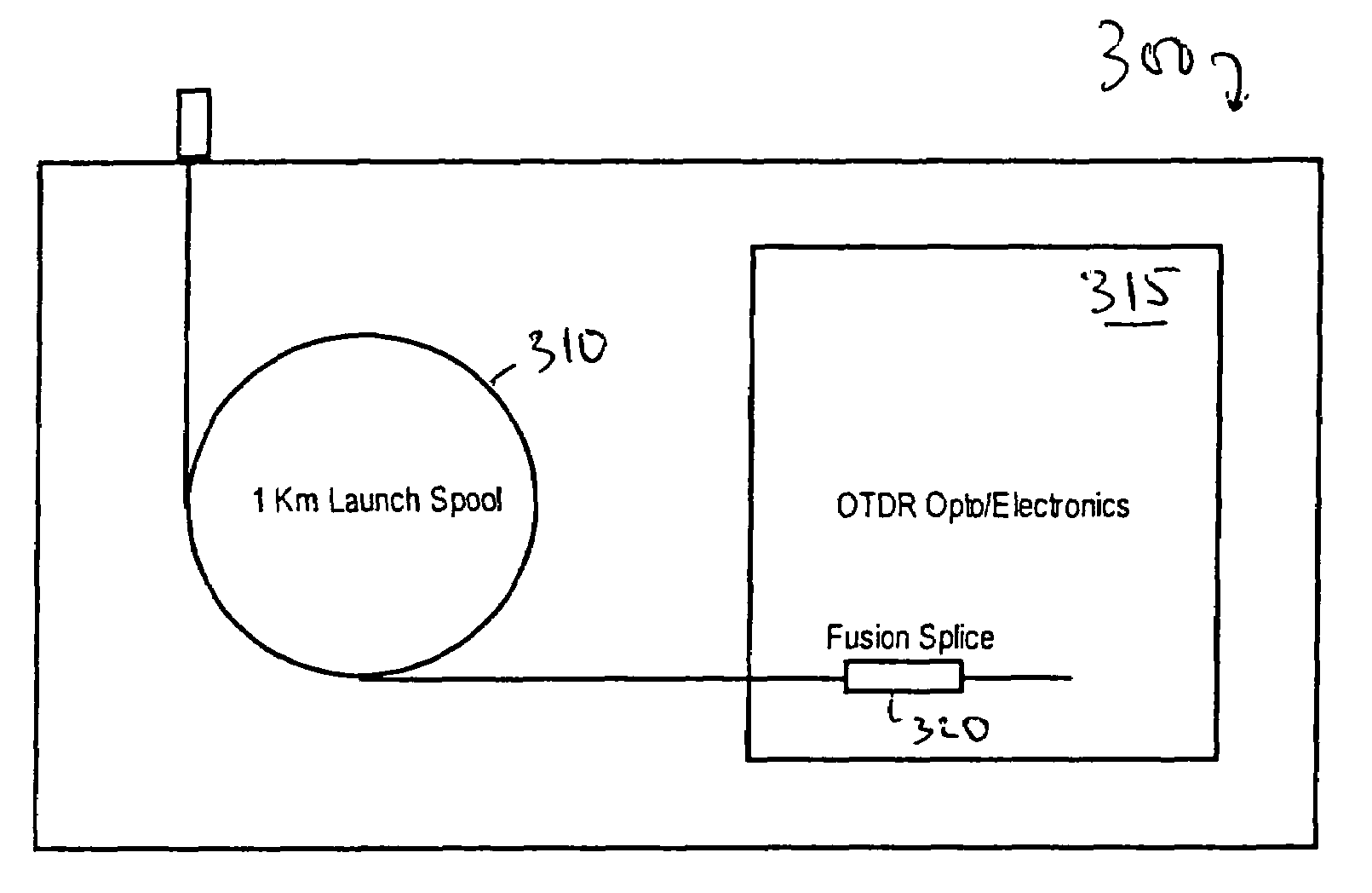
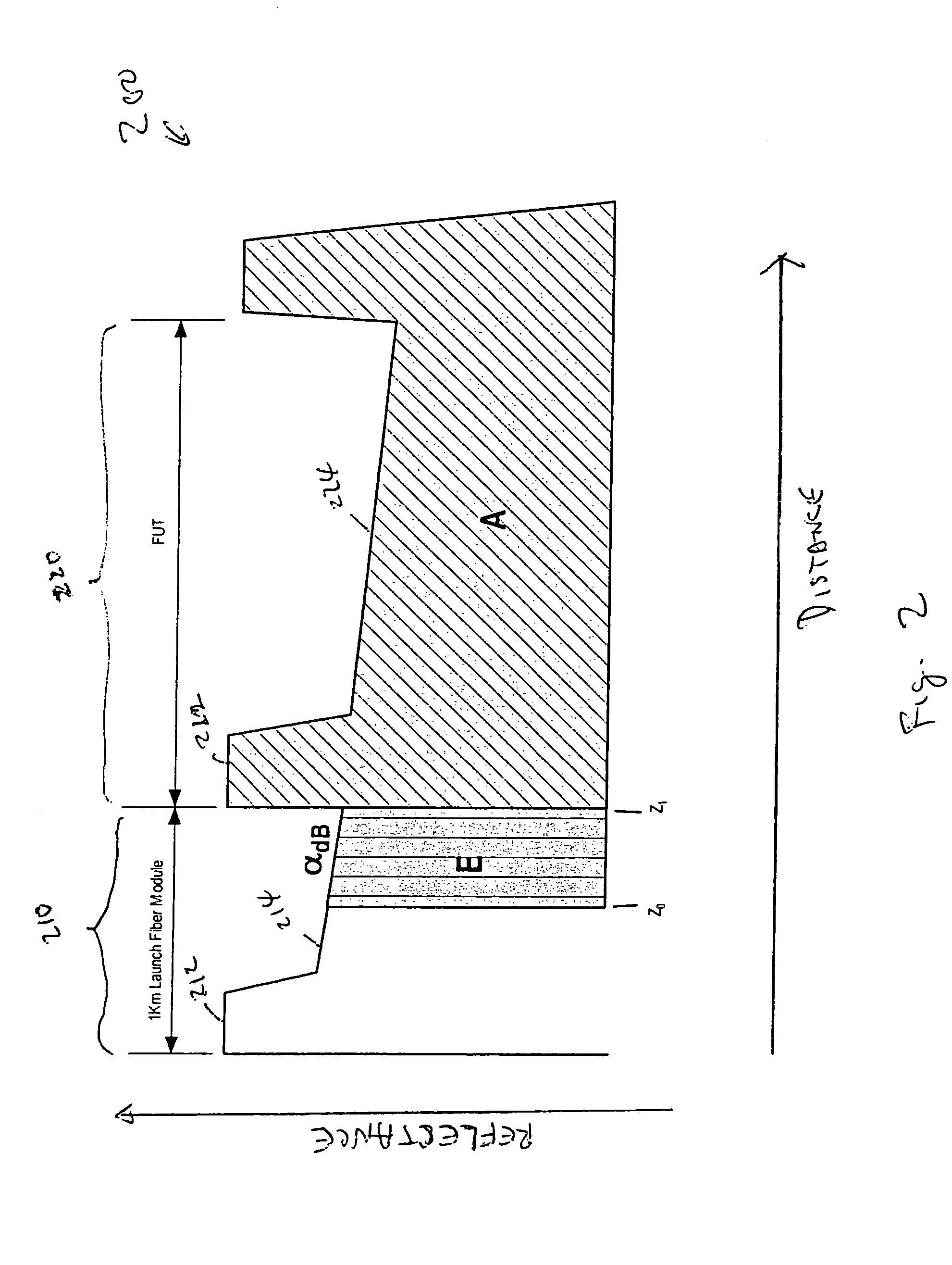
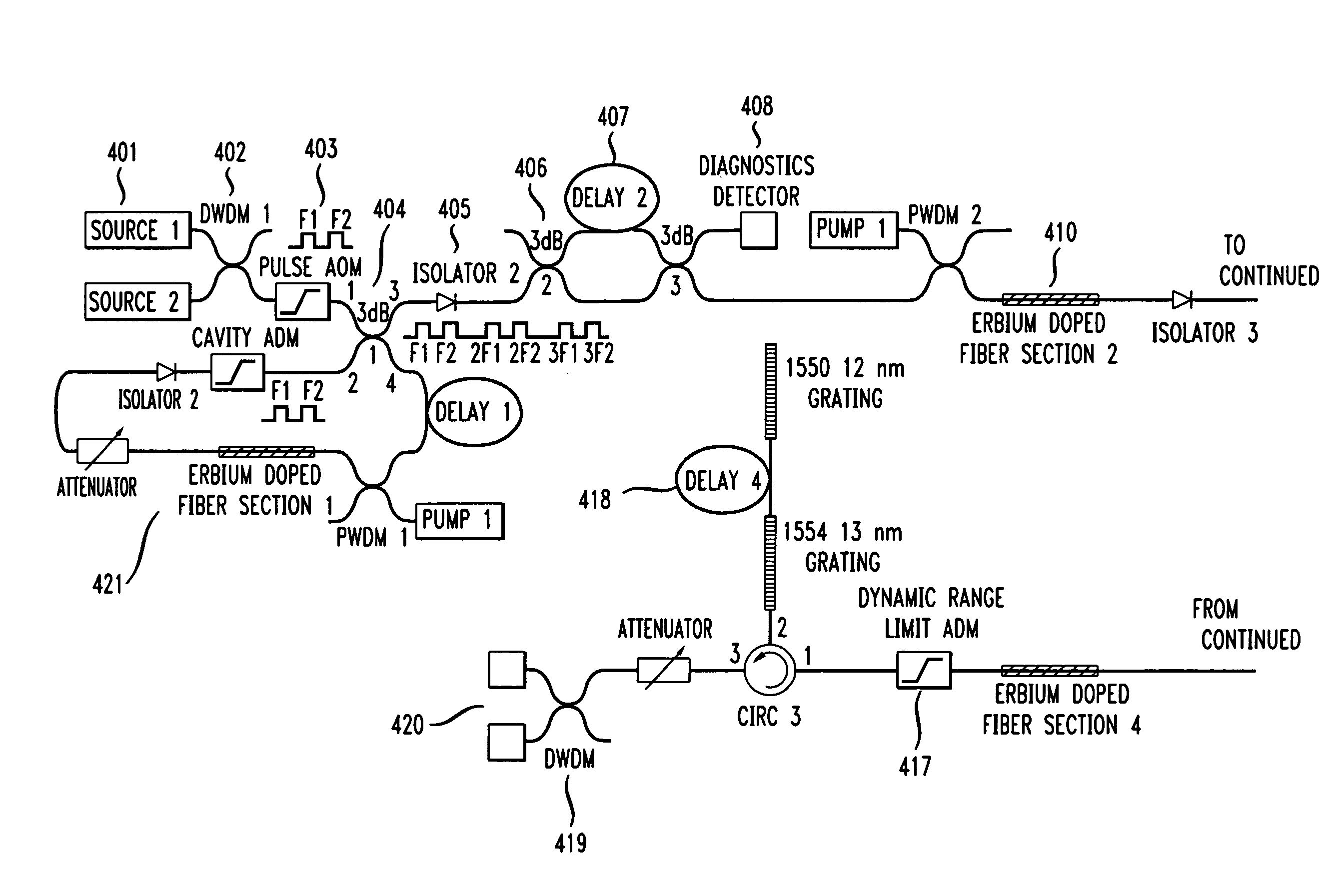
InactiveUS7016024B2Eliminate conditionSuitable signal-to-noise ratioMaterial analysis by optical meansReflectometers detecting back-scattered light in time-domainFiberTime domain
The invention provides automated systems and methods for measuring ORL of fibers under test. A computer-based test instrument using OTDR tests fibers with the help of a STFM having predefined characteristics that are recorded in a machine-readable memory. The information recorded in the memory is accessible to the computer-based instrument and is used to calibrate a power level of an illumination source in real time using the reflectance response of the STFM. The calibrated illumination power allows the instrument to automatically determine the ORL of the fiber being tested with precision, and without requiring the intervention of an operator. The instrument also has the capability to automatically sense the presence of a test fiber, and to automatically attenuate the reflectance signal to remove a saturation condition by controlling at least one of the illumination, the detector gain, an amplifier gain, and an optional in-line optical attenuator.
Owner:NETTEST NEW YORK
Detecting a disturbance in the propagation of light in an optical waveguide
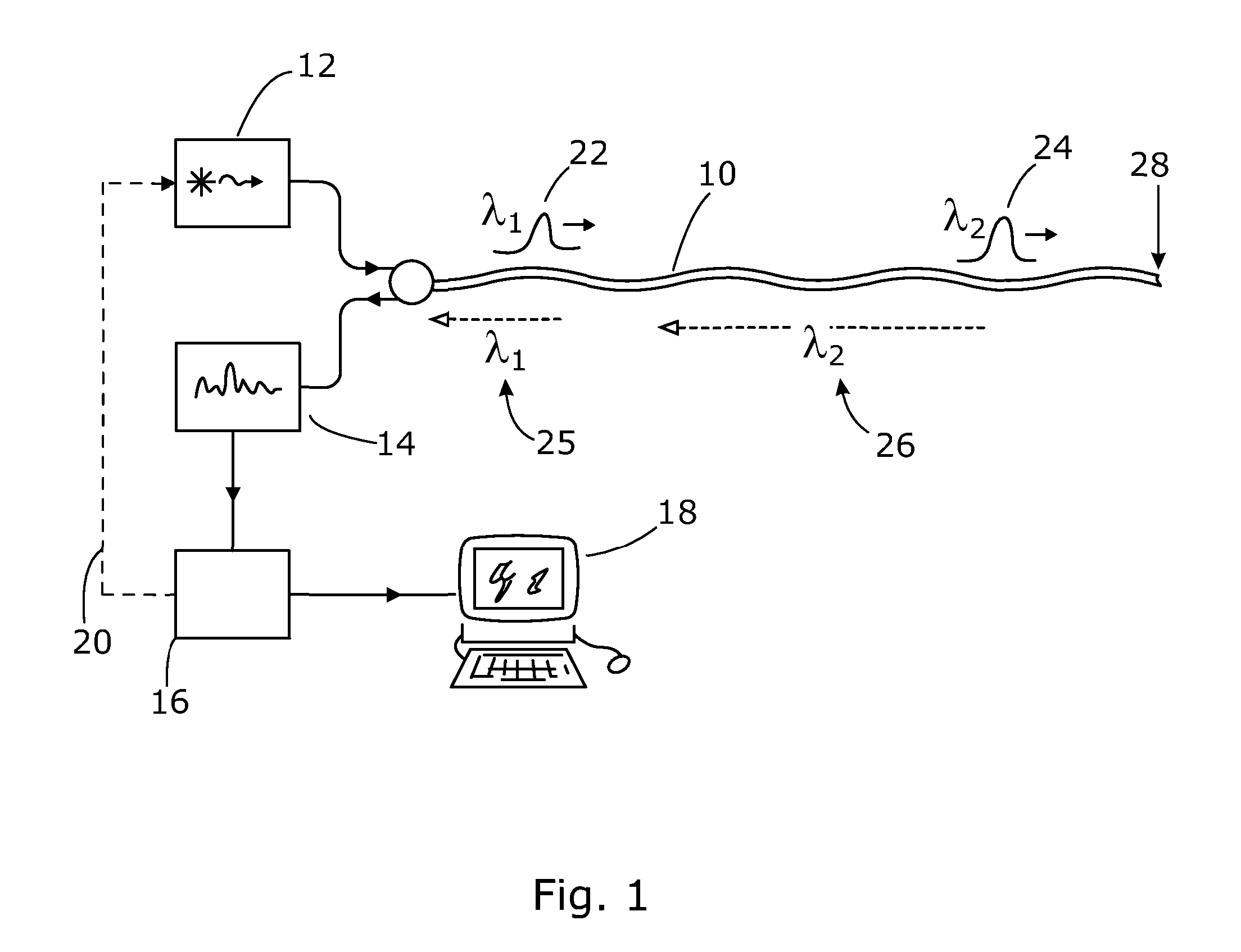
ActiveUS7872736B2Efficient detectionAccurate detectionMaterial analysis by optical meansReflectometers detecting back-scattered light in time-domainTime domainPhotovoltaic detectors
An optical time domain reflectometry apparatus has a laser and light modulator for producing coherent light pulses, each having two sections of higher intensity separated by a gap of lower or substantially zero intensity. As the light pulses propagate along the optical fibre, light is continuously Rayleigh backscattered by inhomogeneities of the optical fibre. A photodetector generates backscatter signals representing the intensity of light Rayleigh backscattered in the optical fibre as each light pulse travels along the optical fibre. The PC uses these backscatter signals to derive a difference signal representing a change dI in intensity between signals generated from two successive pulses. The PC then calculates the Root Mean Square (RMS) of the difference signal averaged over the interval between the two sections of the light pulses. Next, the PC averages the backscatter signal generated from the first of the pulses over the same interval and normalises the RMS difference signal using the averaged signal to obtain a compensated difference signal that depends only on differences in the rate of change of phase of light of the light pulses as they travelled along the waveguide. This is repeated at different wavelengths to allow the compensated difference signal to be adjusted to represent the magnitude of the differences.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Method and apparatus for acoustic sensing using multiple optical pulses
ActiveUS20080144016A1Detect presenceSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansFiberAcoustic wave
An improved technique for acoustic sensing involves, in one embodiment, launching into a medium, a plurality of groups of pulse-modulated electromagnetic-waves. The frequency of electromagnetic waves in a pulse within a group differs from the frequency of the electromagnetic waves in another pulse within the group. The energy scattered by the medium is detected and, in one embodiment, the beat signal may be used to determine a characteristic of the environment of the medium. For example, if the medium is a buried optical fiber into which light pulses have been launched in accordance with the invention, the presence of acoustic waves within the region of the buried fiber can be detected
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
System and method of an integrated fiber optic inspection and cleaning apparatus
ActiveUS20130229650A1Rapid positioningHigh resolutionOptically investigating flaws/contaminationFlexible article cleaningFiberWide field
This disclosure concerns a cleaning and inspection system for fiber optics that is rapid, reliable and useful for various types of fiber optics. In an embodiment, the system includes a wide field of view (FOV) camera to image the ferrule and rapidly locate the fiber ends and a narrow FOV camera to provide detailed inspection of fiber ends. A cleaning module with a cleaning tip and a cleaning media that is drawn through the tip is used to clean the fiber ends. Images captured by the dual cameras are automatically enhanced and analyzed to determine the effectiveness of the cleaning process and to identify the types and quantity of defects present. In another embodiment, a single higher resolution camera is provided with a lens that can image an entire fiber array and yet enable defects to be detected by analysis of sub-images of each fiber in the fiber array.
Owner:FIBERQA
Device, method and device for positioning the optical fiber failure
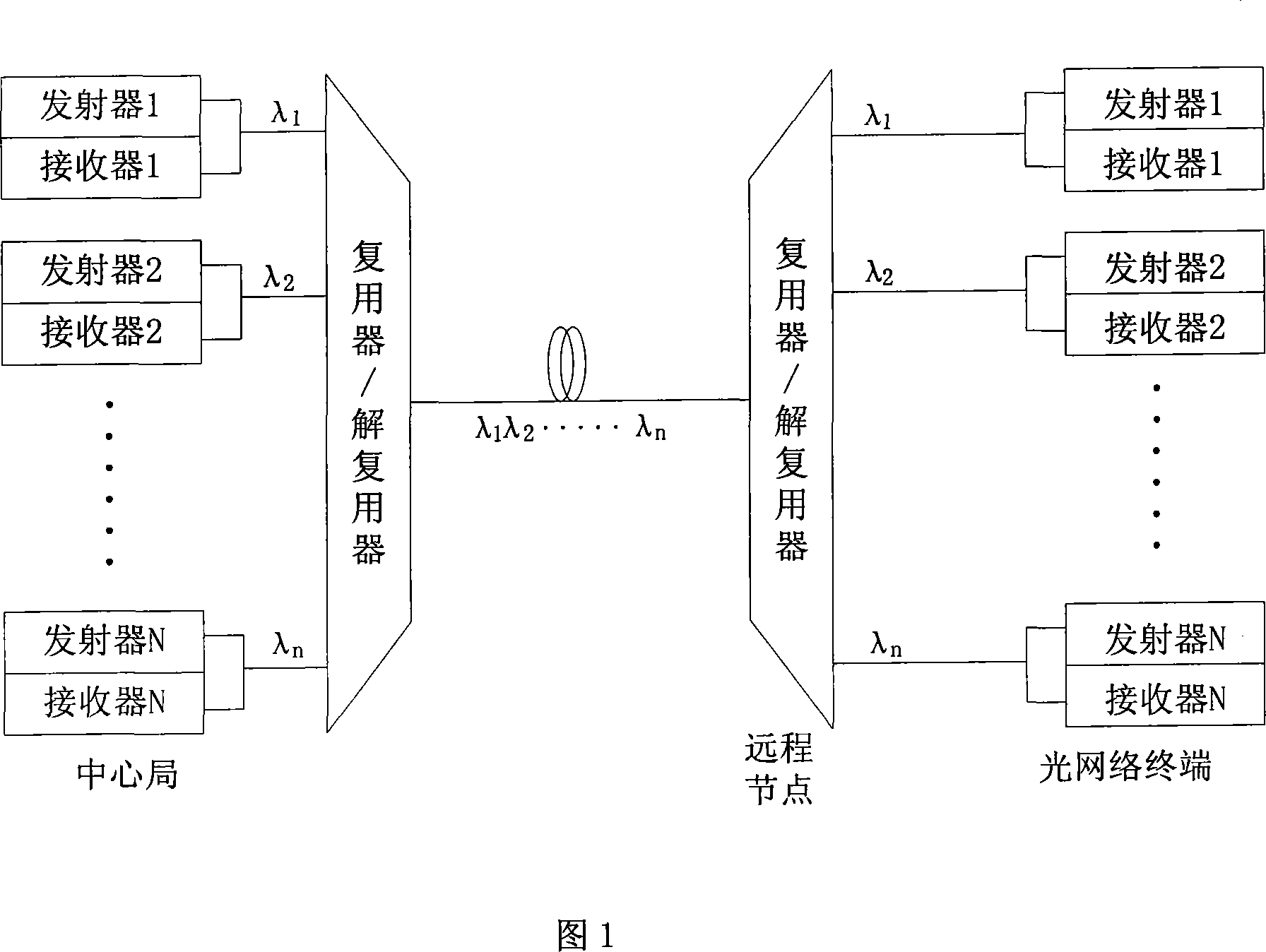
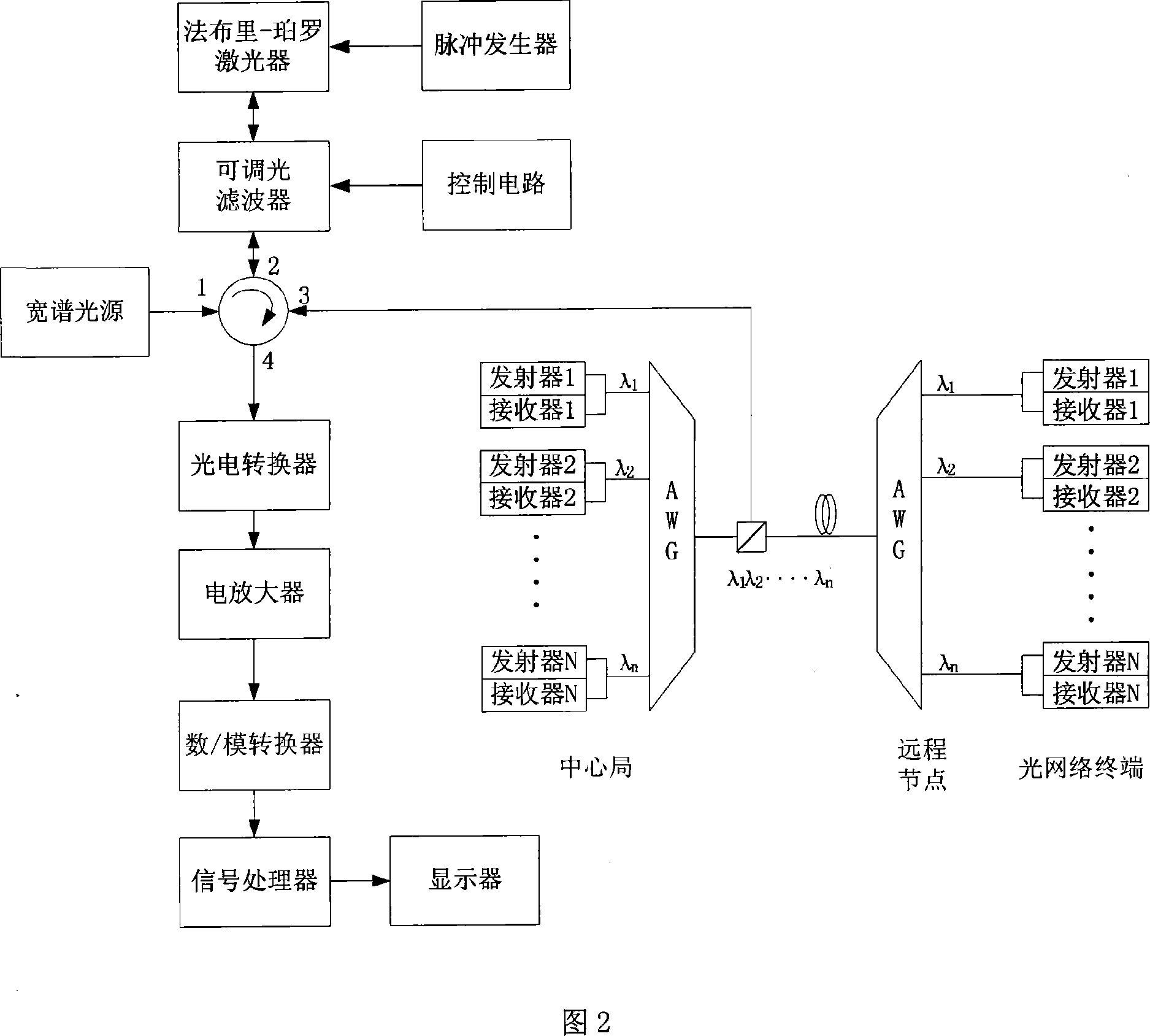
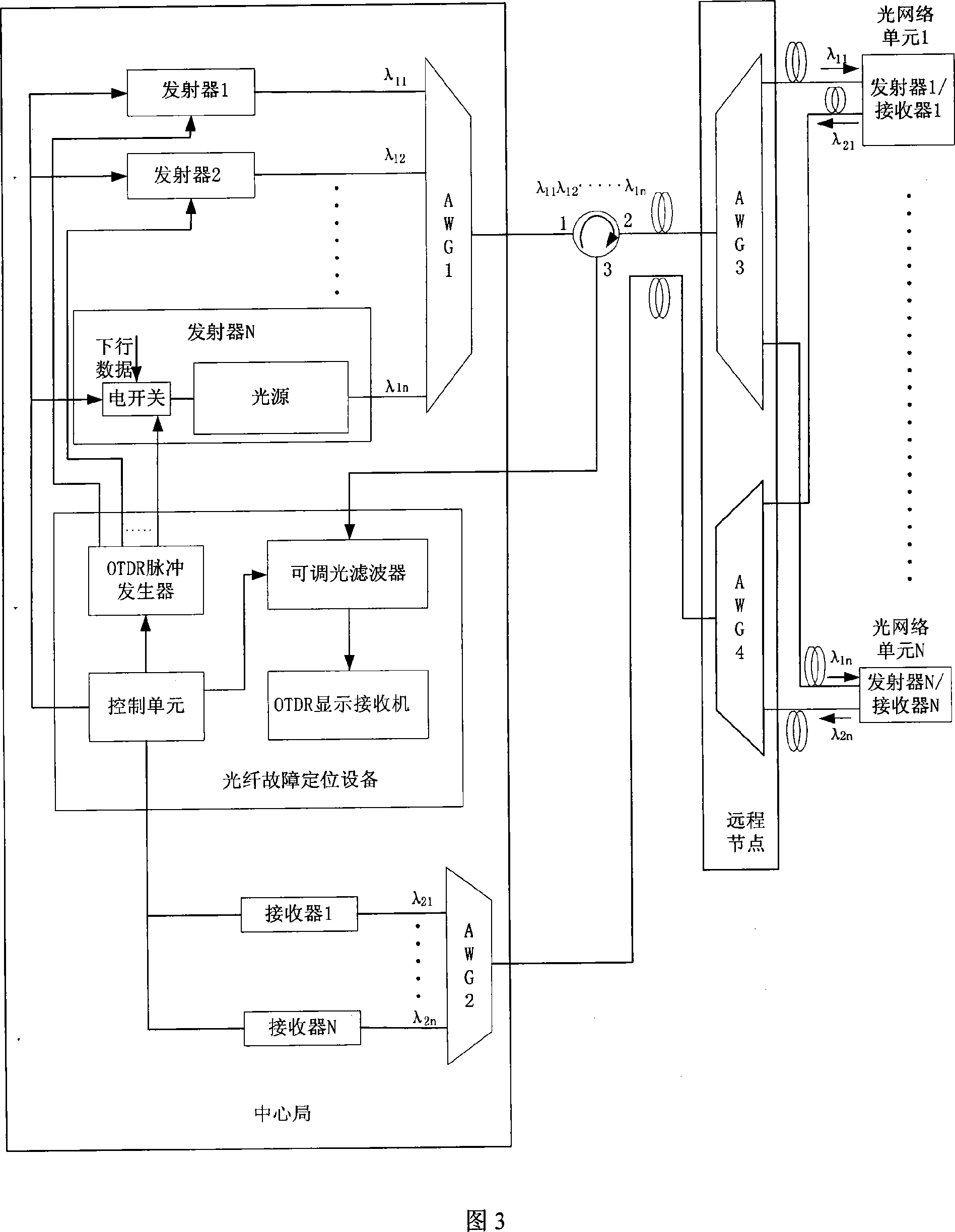
ActiveCN101079668AReduce the difficulty of operationLow input costOptical multiplexTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsFiberTime domain
The invention discloses a fiber fault location equipment, method and device in the optical receiving network field. The optical time-domain echo wave length selecting module of the equipment comprises the following parts: an optical switch and an array waveguide raster. The method comprises the following steps: detecting the fault of the turn-up channel by the fiber fault location equipment; informing the optical line ending equipment corresponding with the upgoing channel to break the sending of the downgoing data; producing the line diagnostic signal; proceeding with the downgoing sending of the light source modulating the optical line ending equipment; receiving selectively and analyzing the reflected line diagnostic signal by the fiber fault location equipment; reporting the concrete position of the fiber fault to the network administrator according to the analyzed result. The device comprises the following parts: a control module, a modulating module, a sending module and a fiber fault position module. The invention reduces the cost of the fiber fault position system.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
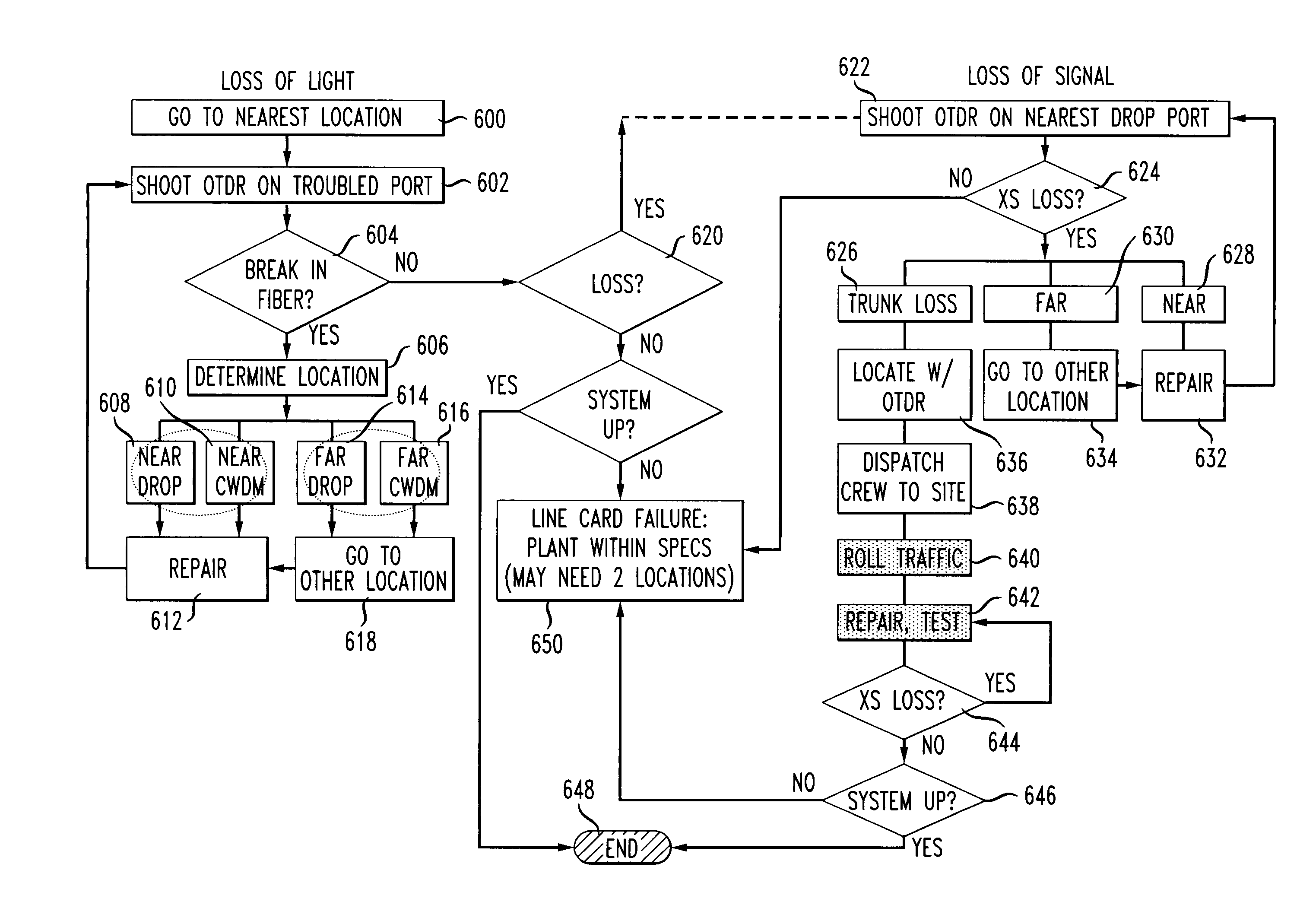
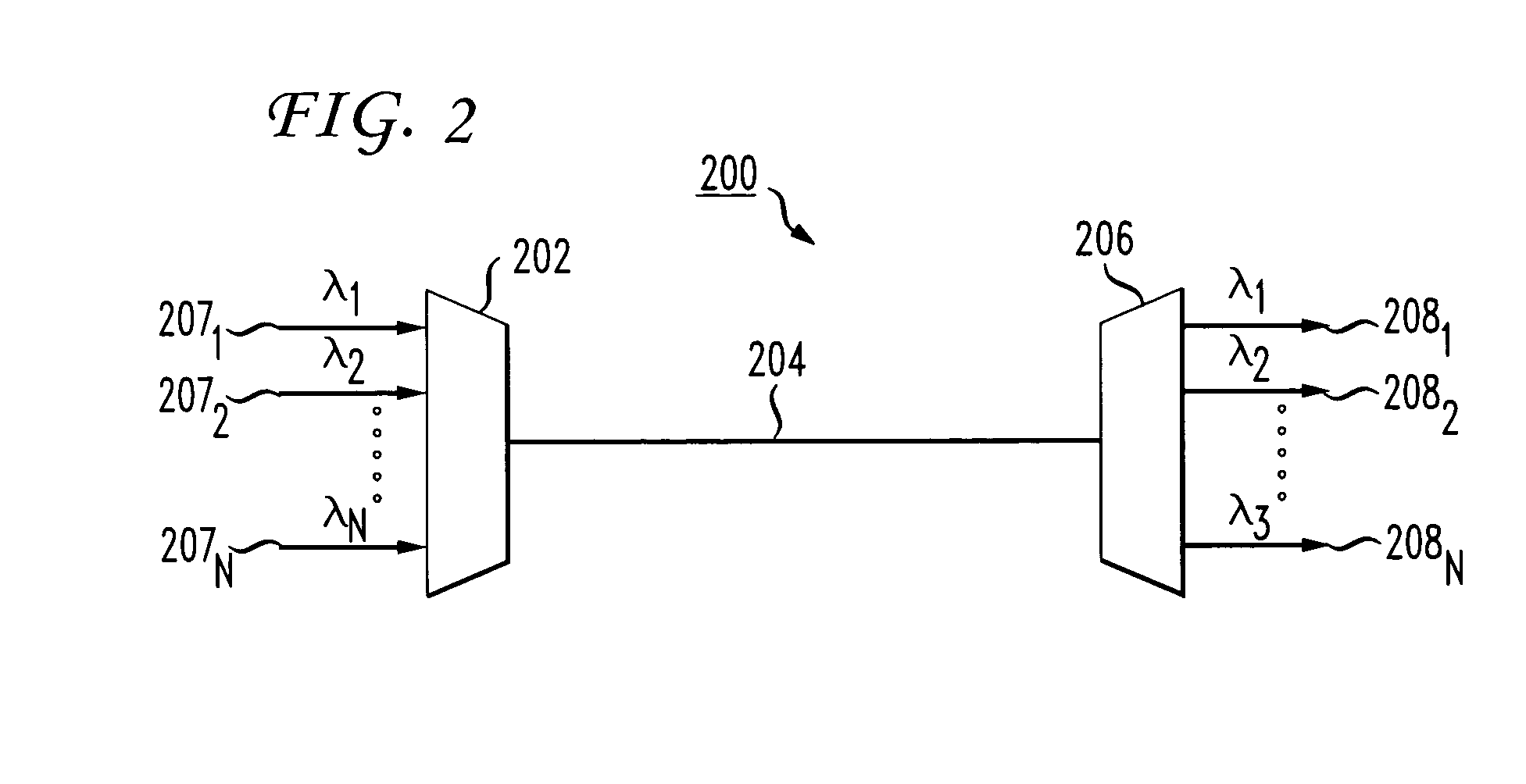
Fault location apparatus and procedures in CWDM business applications using wavelength selective OTDR
ActiveUS7042559B1Material analysis by optical meansReflectometers detecting back-scattered light in time-domainTime domainFiber
A method for verifying fiber connections and diagnosing loss of light or loss of signal conditions in a WDM optical system. The method utilizes an optical time domain reflectometer (OTDR) having user-selectable wavelengths to shoot OTDR traces at a specified wavelength corresponding to an optical data-bearing channel into a selected one of a plurality of optical fiber transmission lines that are connected to a multiplexer that respectively multiplexes a data bearing channel carried on each of the plurality of optical fiber transmission lines onto a trunk, or a demultiplexer that demultiplexes multiplexed data bearing channels from the trunk. The OTDR receives backscattered light from the selected optical fiber transmission line and generates a trace of the backscattered light, thereby enabling a fault location in the WDM optical system to be determined from the trace.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com