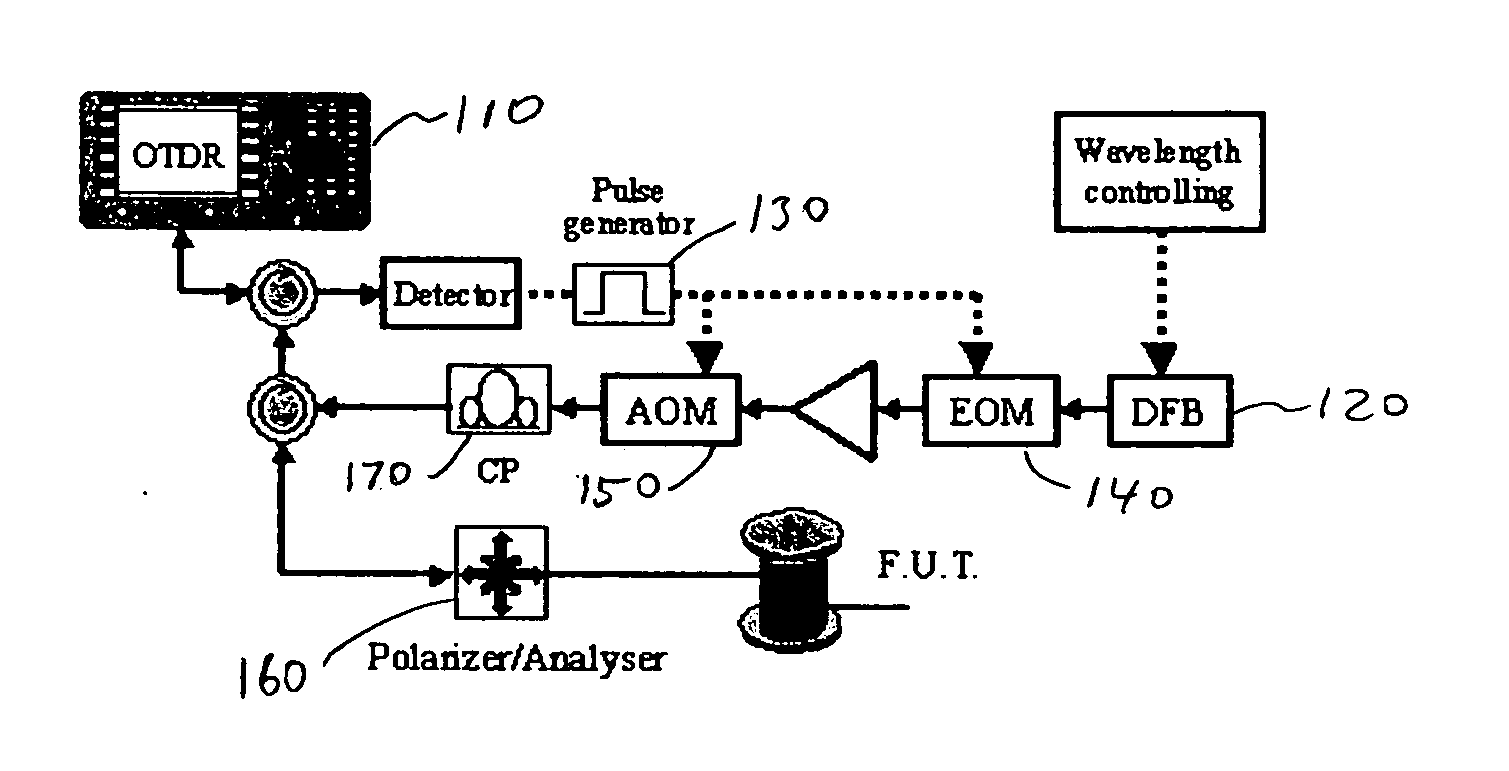
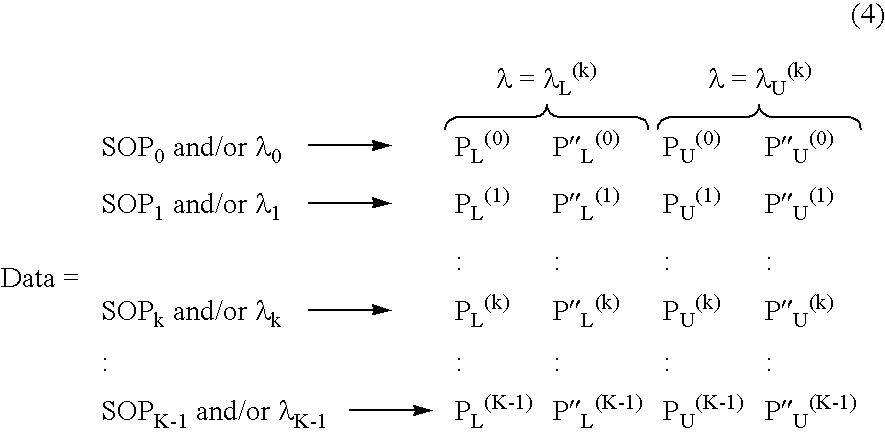Patents
Literature
111results about "Reflectometers dealing with polarization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
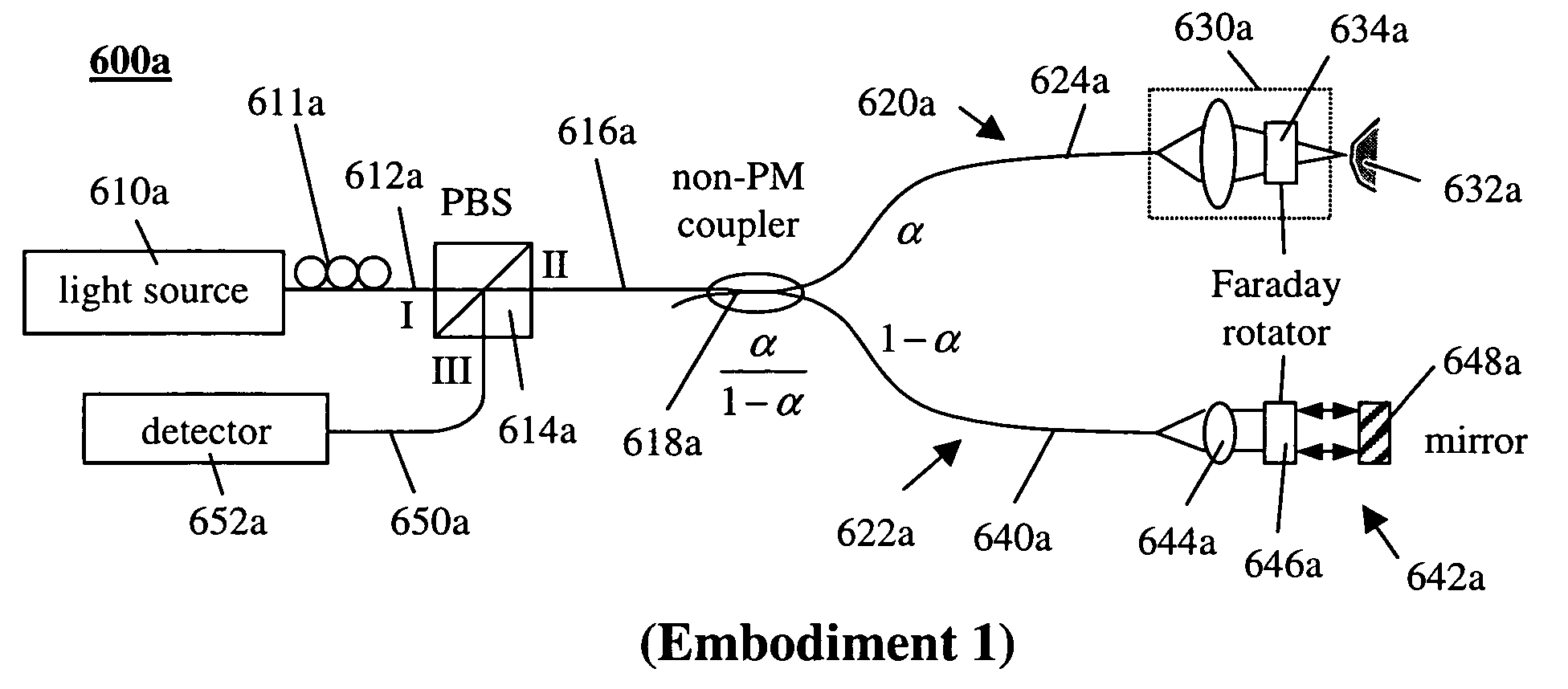
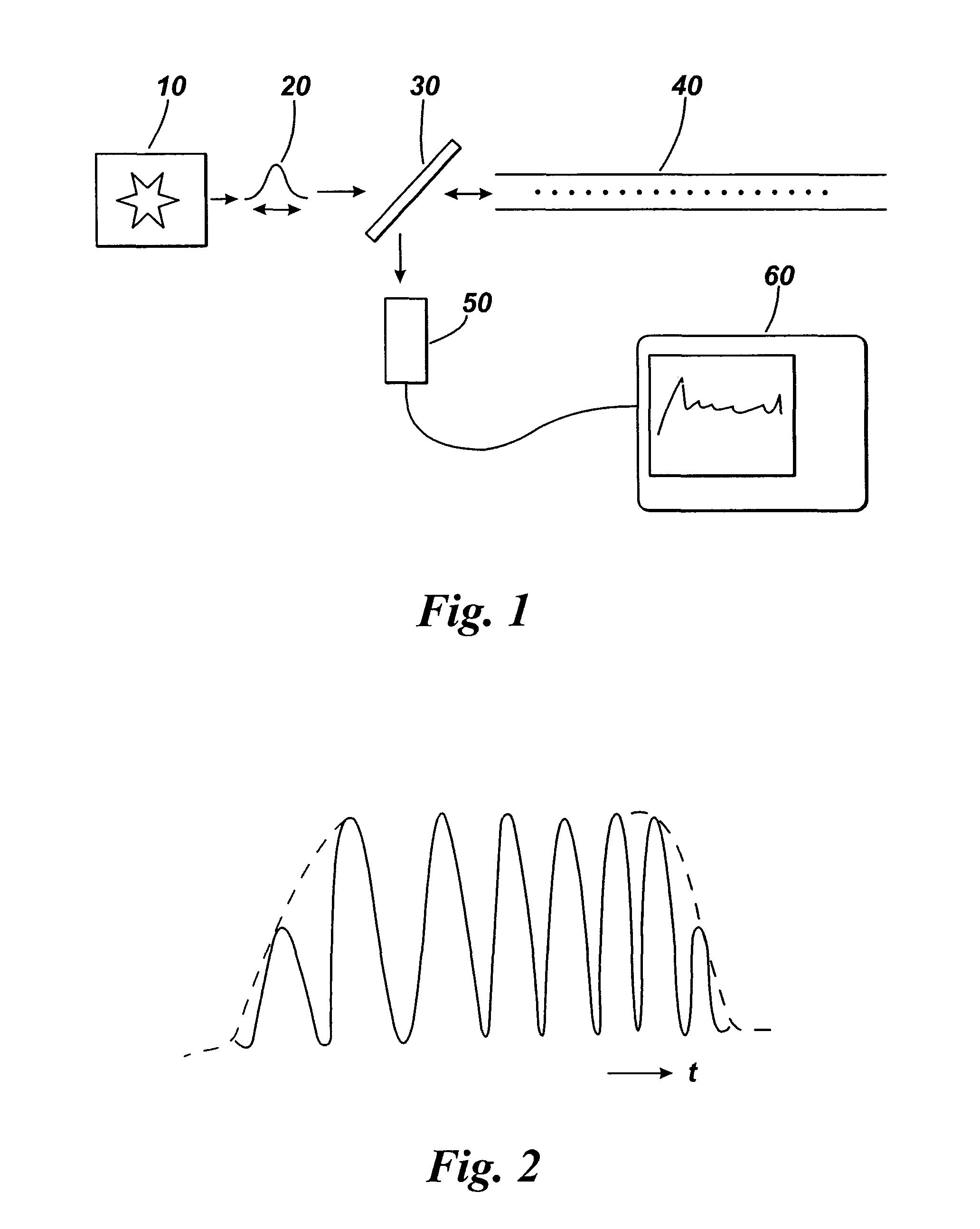
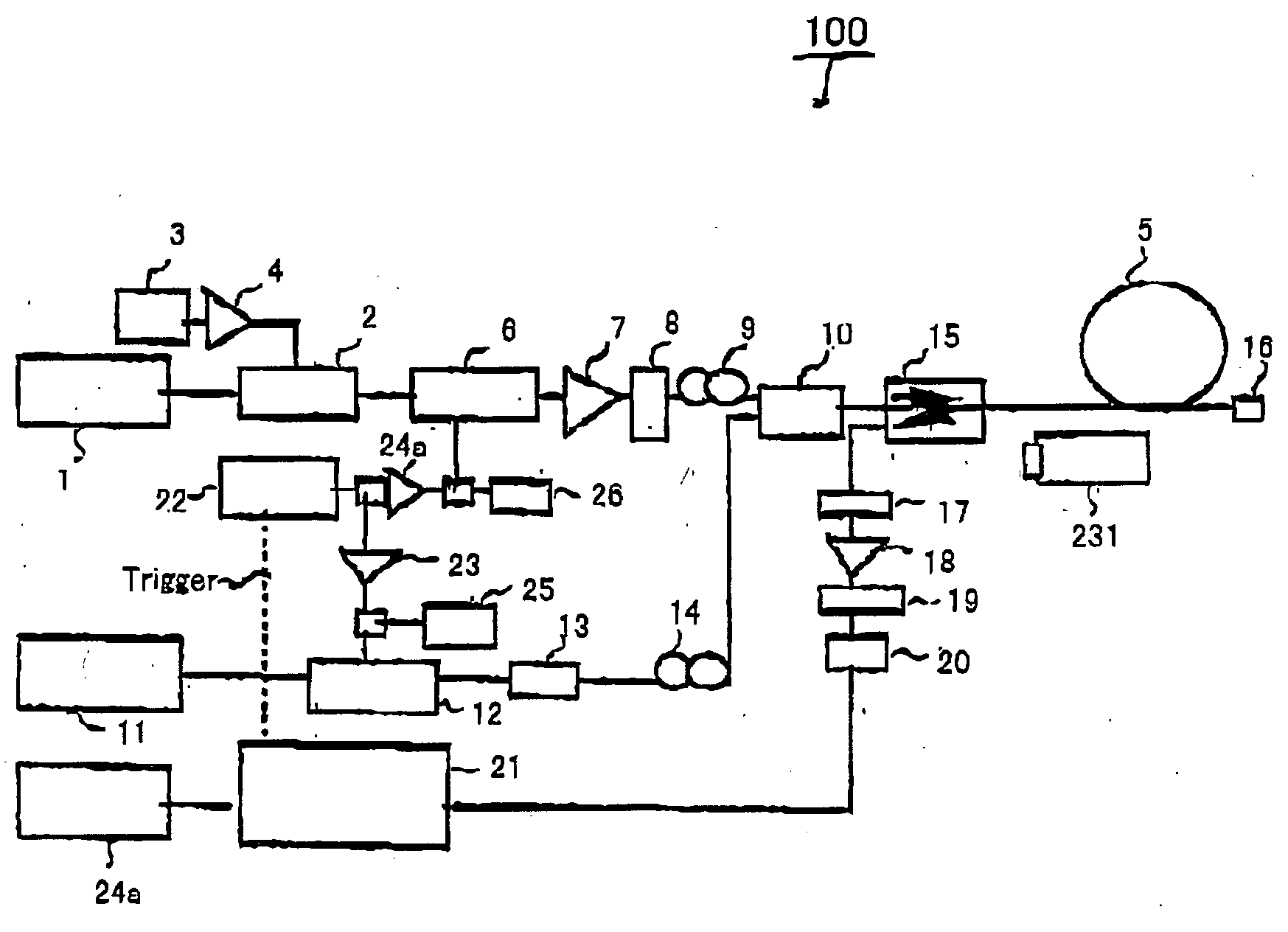
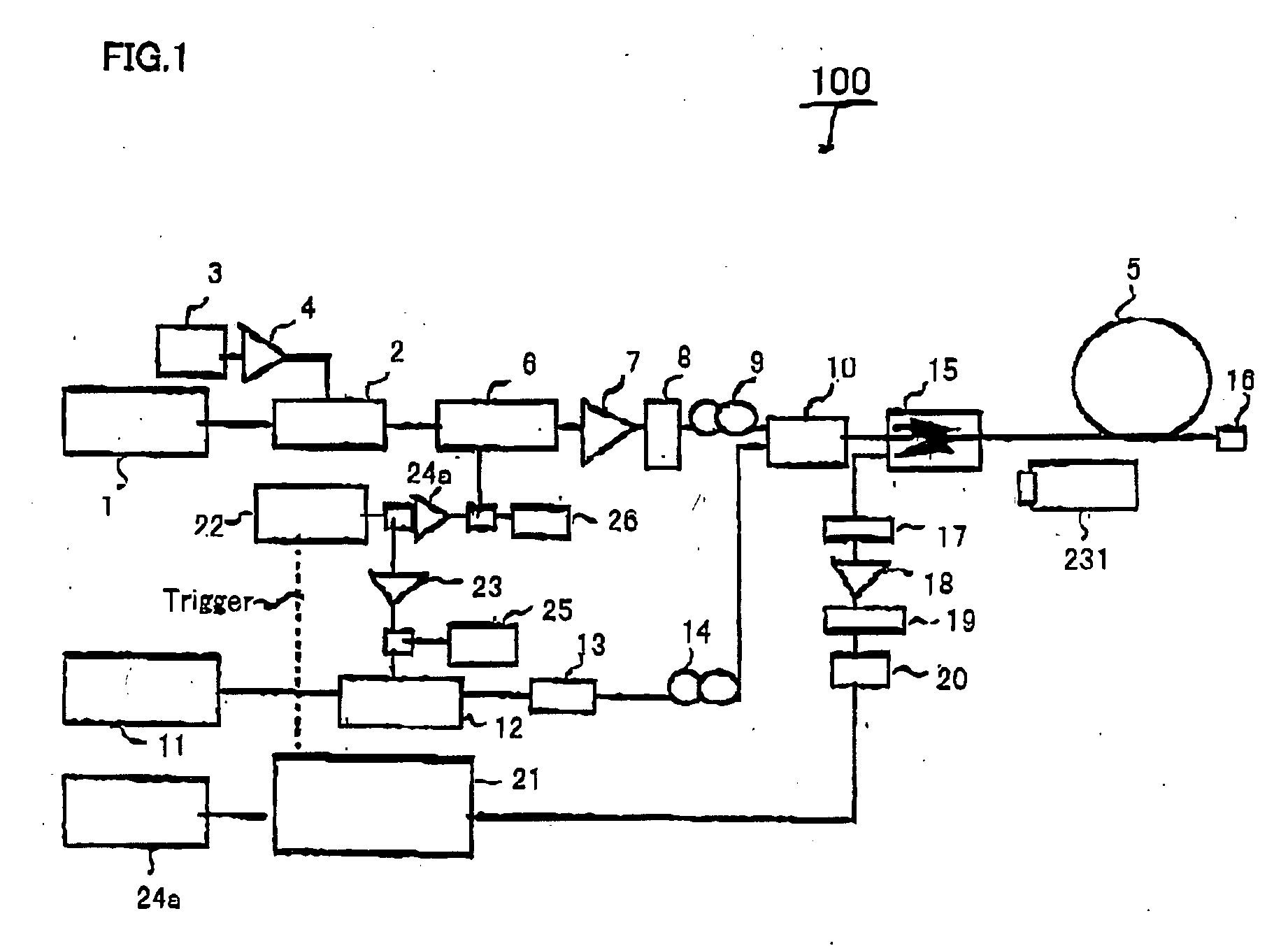
Simple high efficiency optical coherence domain reflectometer design
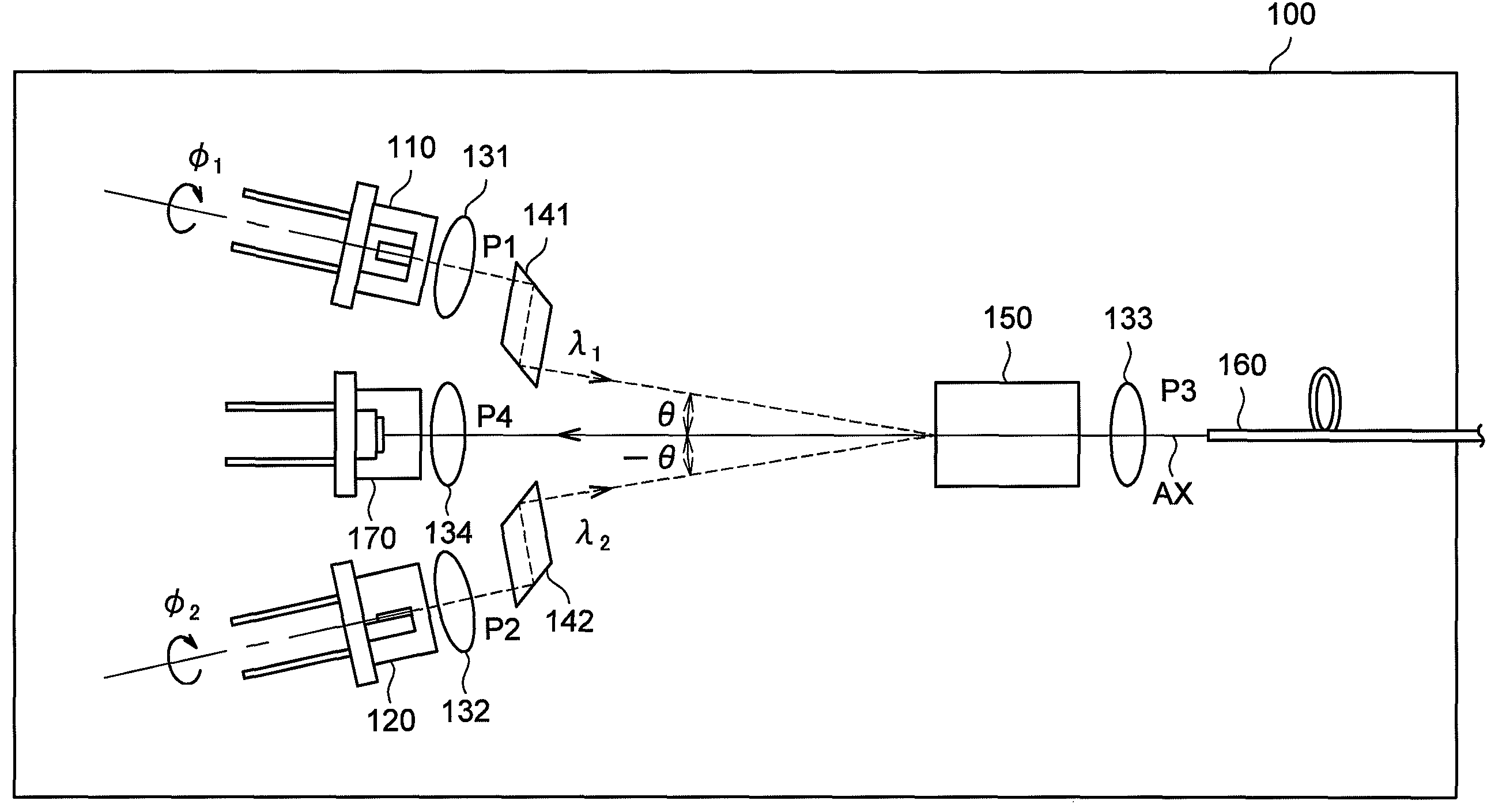
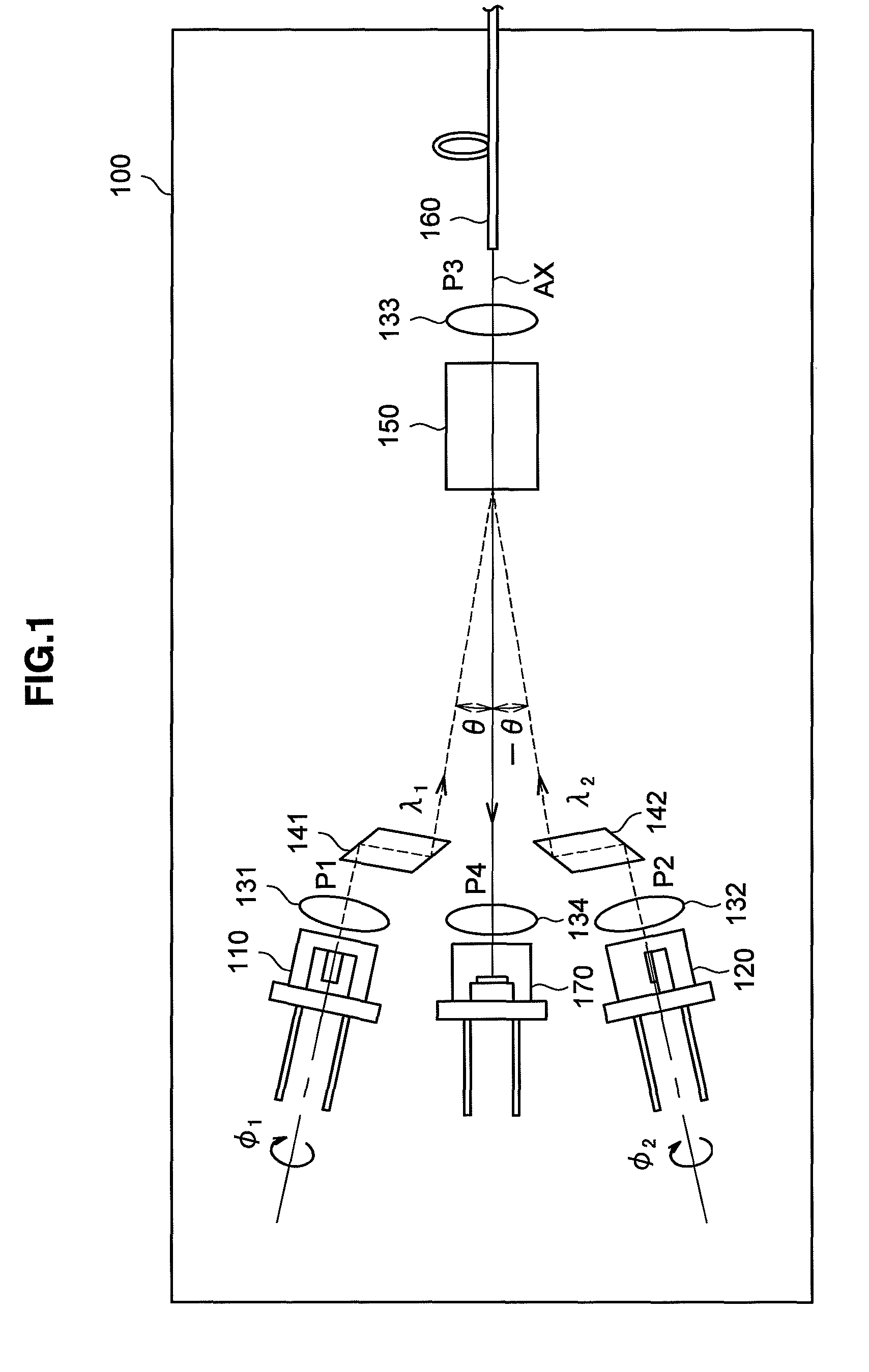
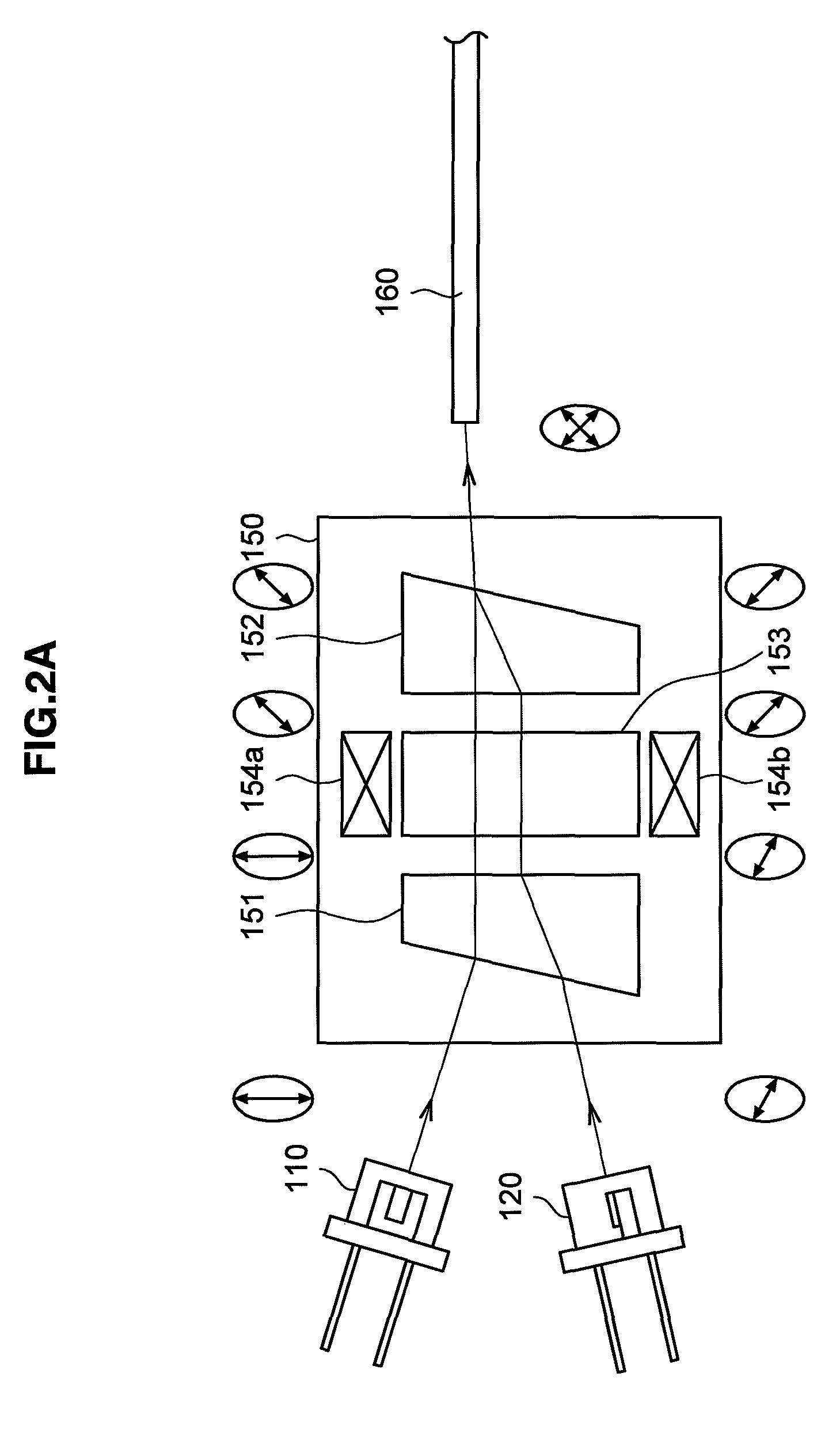
ActiveUS20050213103A1Reduce system costLow costReflectometers dealing with polarizationInterferometersBeam splitterDetector array
The present invention discloses simple and yet highly efficient configurations of optical coherence domain reflectometry systems. The combined use of a polarizing beam splitter with one or two polarization manipulator(s) that rotate the returned light wave polarization to an orthogonal direction, enables one to achieve high optical power delivery efficiency as well as fixed or predetermined output polarization state of the interfering light waves reaching a detector or detector array, which is especially beneficial for spectral domain optical coherence tomography. In addition, the system can be made insensitive to polarization fading resulting from the birefringence change in the sample and reference arms. Dispersion matching can also be easily achieved between the sample and the reference arm for high resolution longitudinal scanning.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
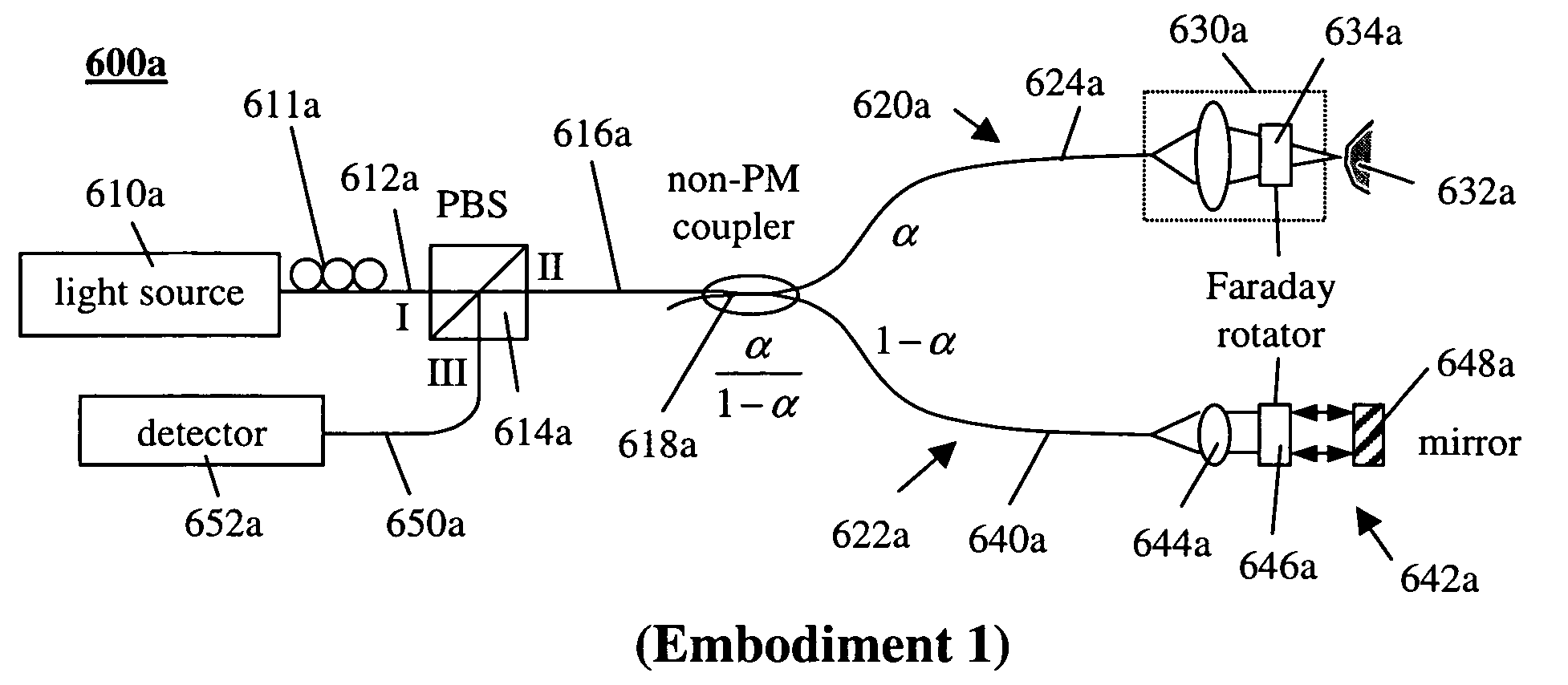
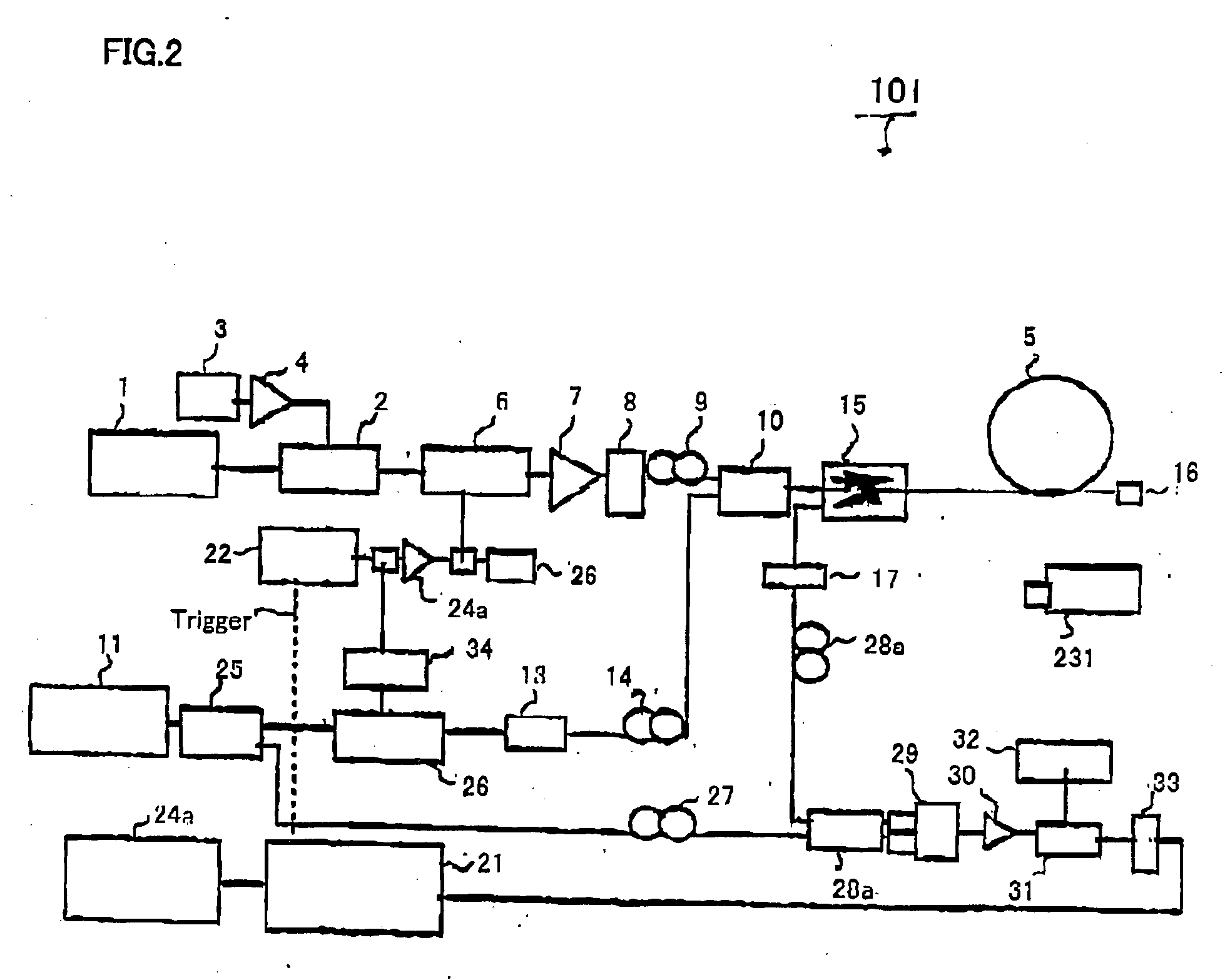
Simple high efficiency optical coherence domain reflectometer design
ActiveUS7126693B2Improve efficiencySimple configurationReflectometers dealing with polarizationInterferometersBeam splitterDetector array
The present invention discloses simple and yet highly efficient configurations of optical coherence domain reflectometry systems. The combined use of a polarizing beam splitter with one or two polarization manipulator(s) that rotate the returned light wave polarization to an orthogonal direction, enables one to achieve high optical power delivery efficiency as well as fixed or predetermined output polarization state of the interfering light waves reaching a detector or detector array, which is especially beneficial for spectral domain optical coherence tomography. In addition, the system can be made insensitive to polarization fading resulting from the birefringence change in the sample and reference arms. Dispersion matching can also be easily achieved between the sample and the reference arm for high resolution longitudinal scanning.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
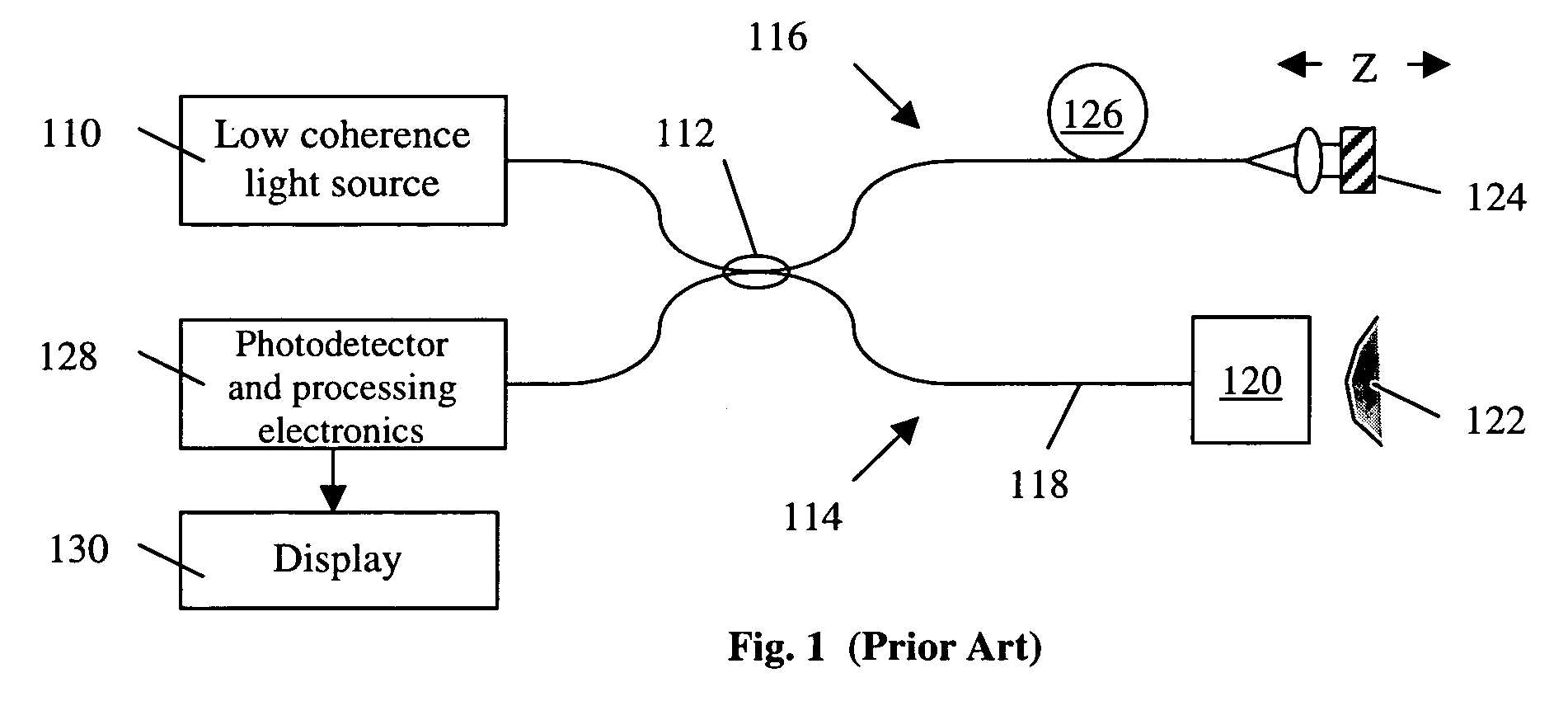
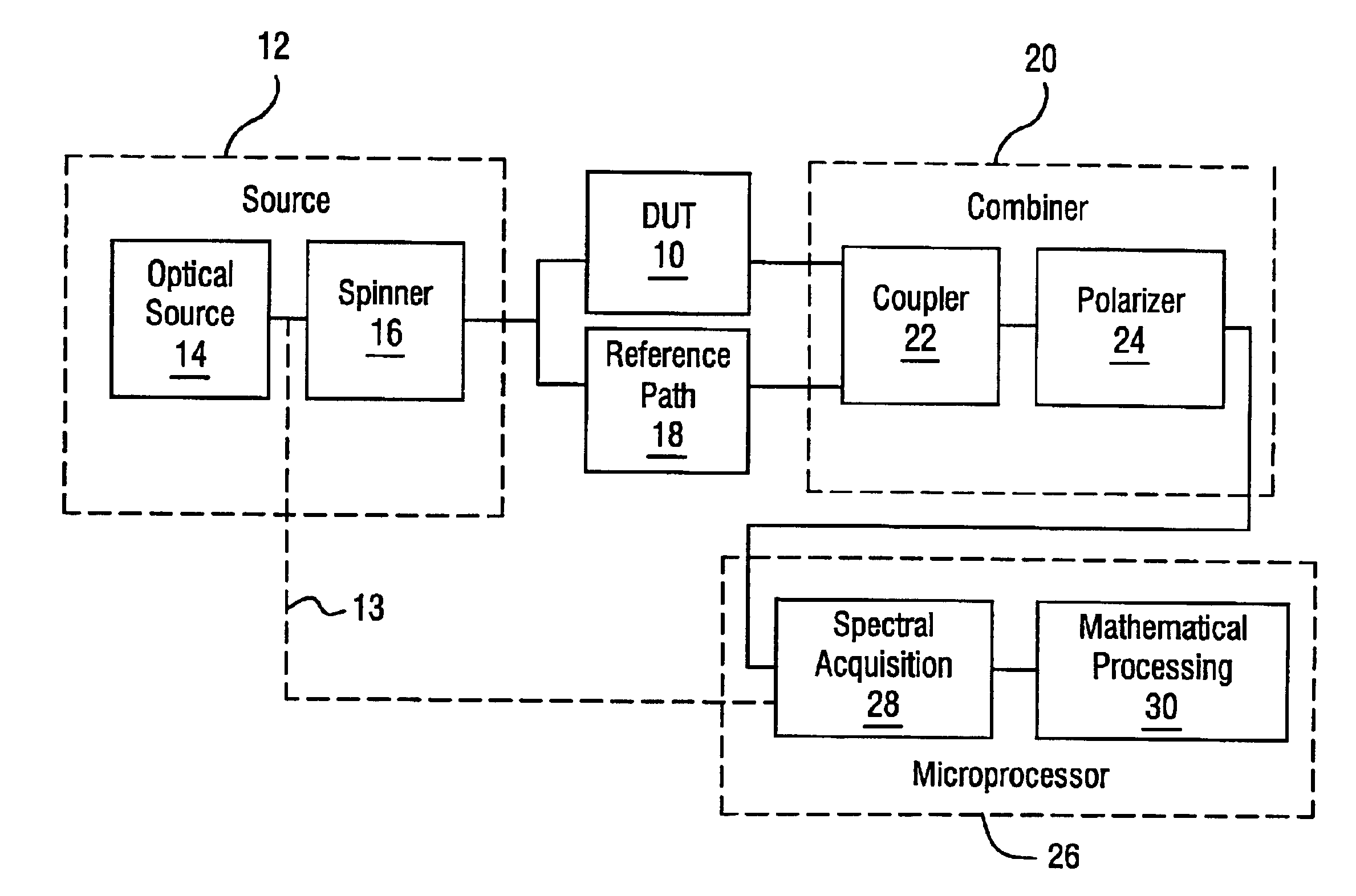
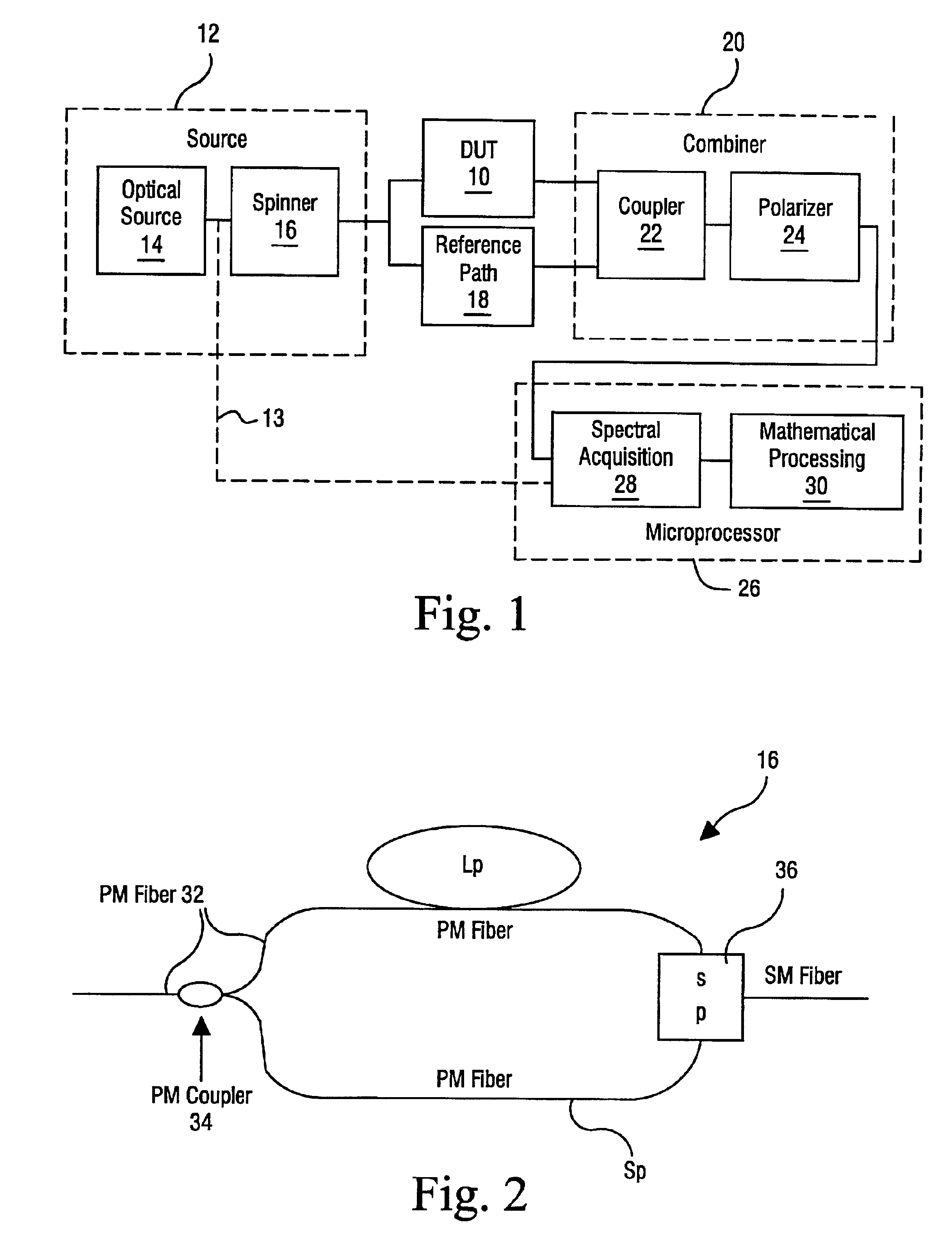
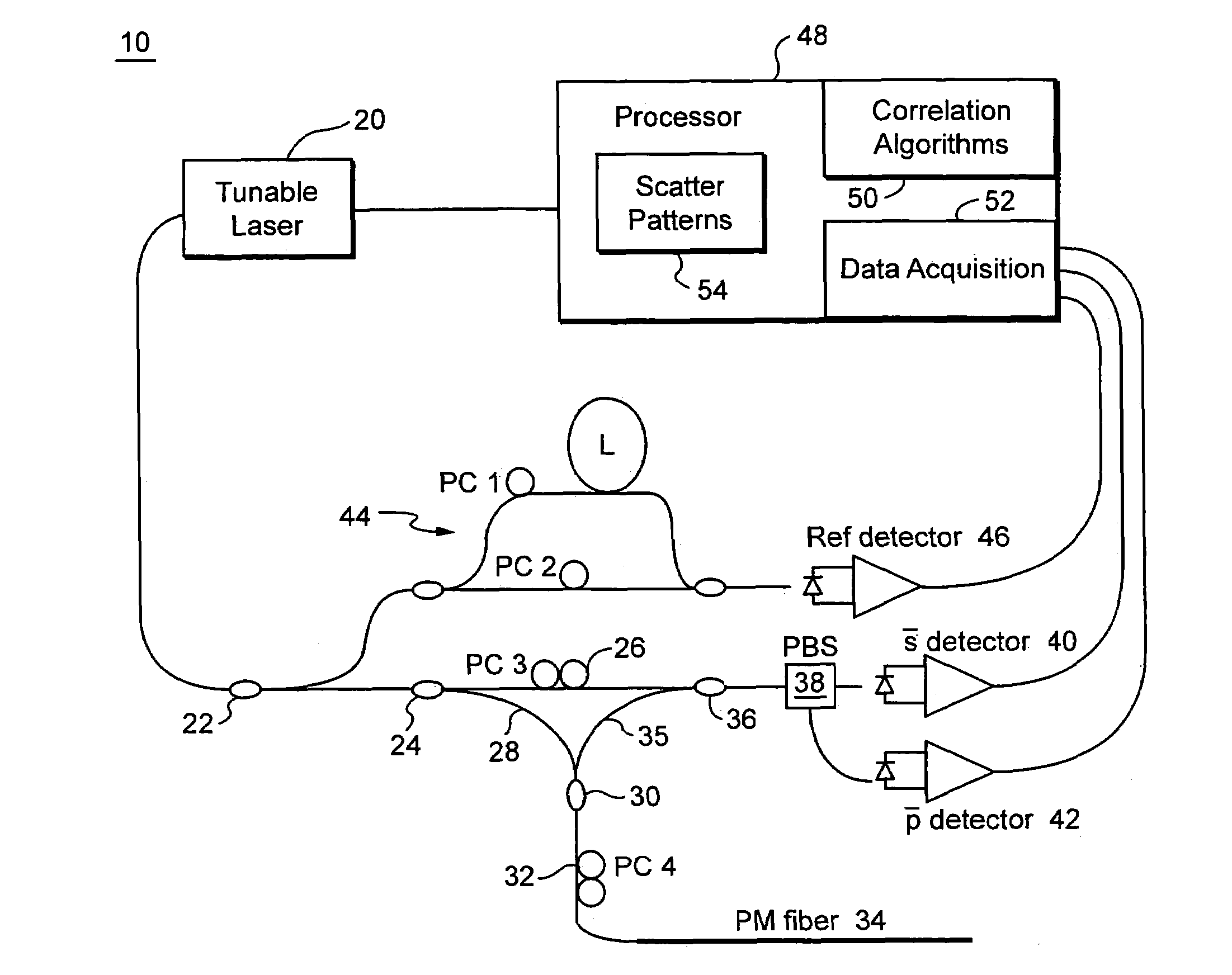
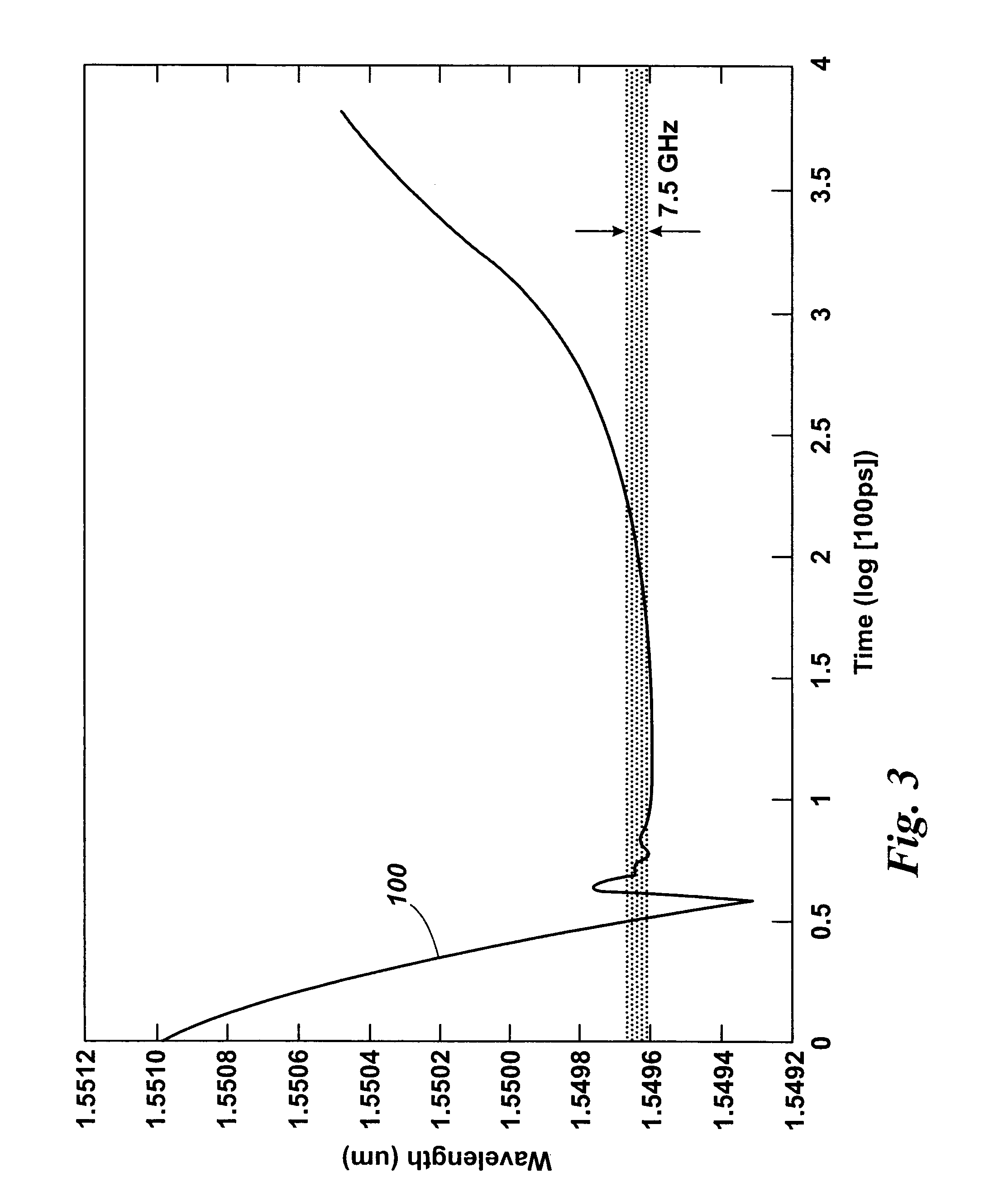
Apparatus and method for the complete characterization of optical devices including loss, birefringence and dispersion effects
InactiveUS6856400B1Reflectometers dealing with polarizationMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical frequenciesCurve fitting
In order to characterize the optical characteristics of a device, a source of light having a variable frequency with a polarization state which varies linearly with frequency is provided as an input to the device under test. The input light is also passed through a known reference path and is added to the light output from the device under test in a beam combiner. The combined light for the frequencies of interest is split into two orthogonal polarizations which are then detected in a spectral acquisition apparatus and supplied to a microprocessor. The spectral measurements are digitized and curve-fitted to provide optical power versus optical frequency curves. Fourier transforms of each of the curves are calculated by the microprocessor. From the Fourier transforms, the four arrays of constants are calculated for the Jones matrix characterizing the device under test.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
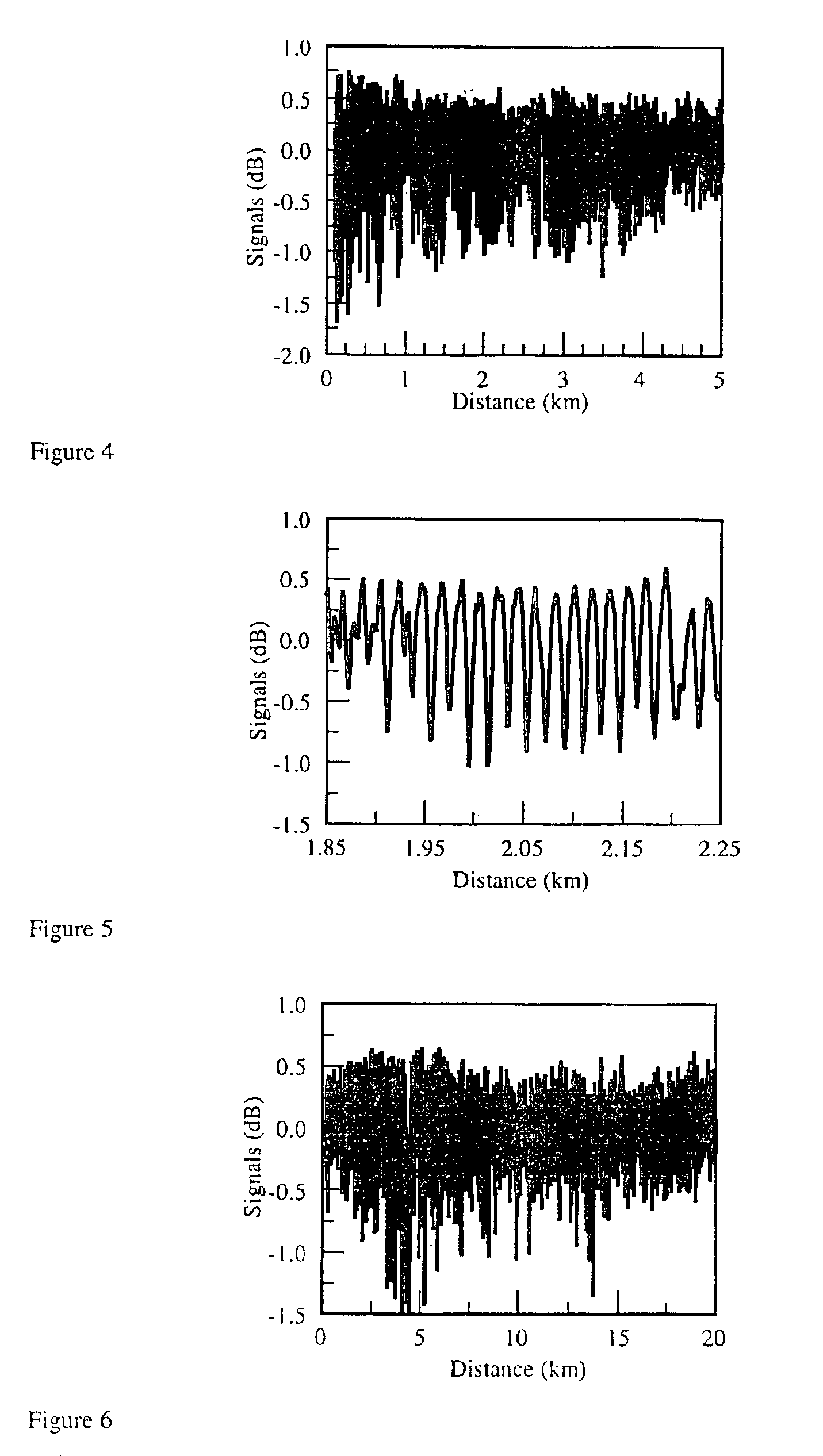
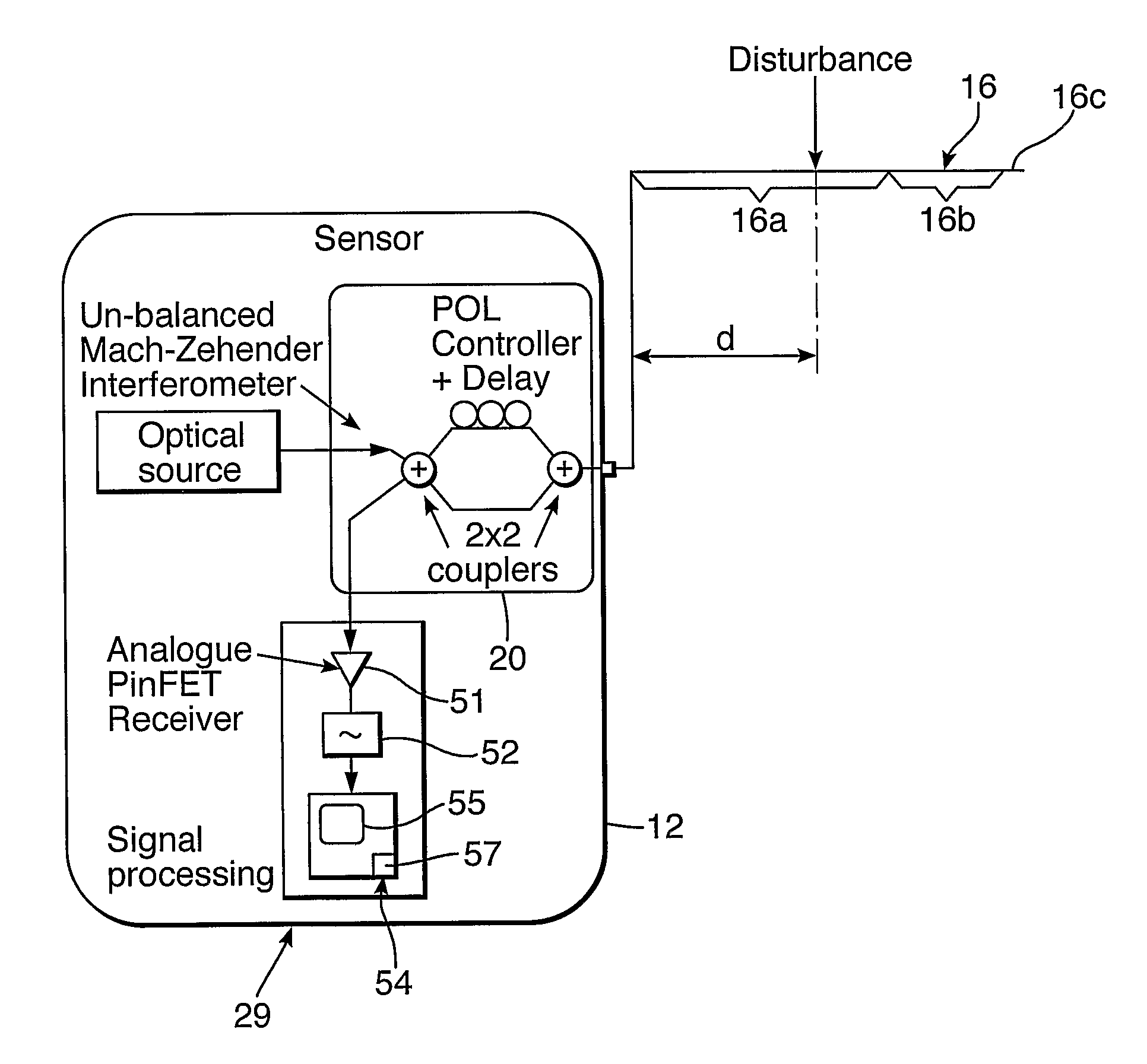
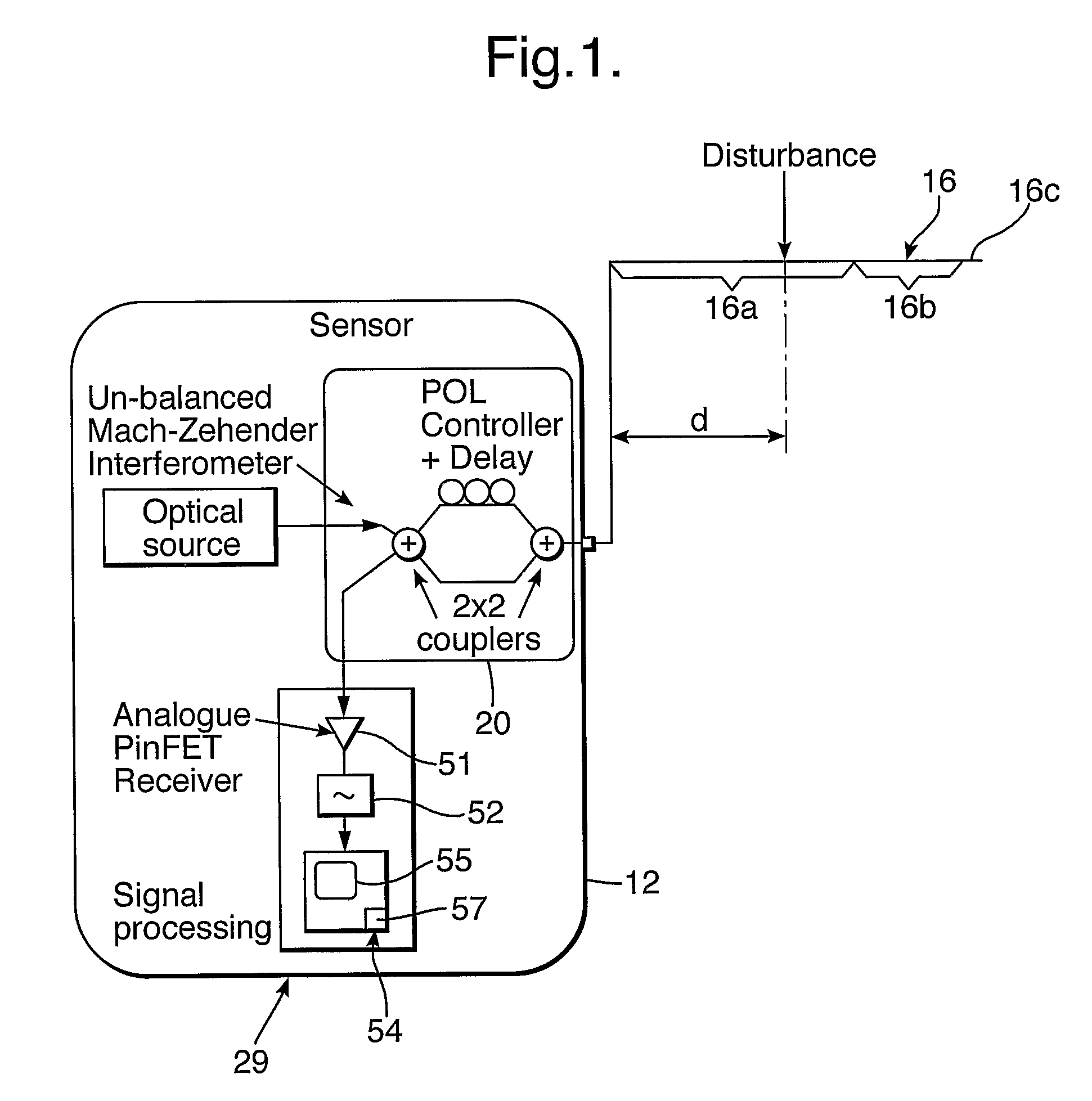
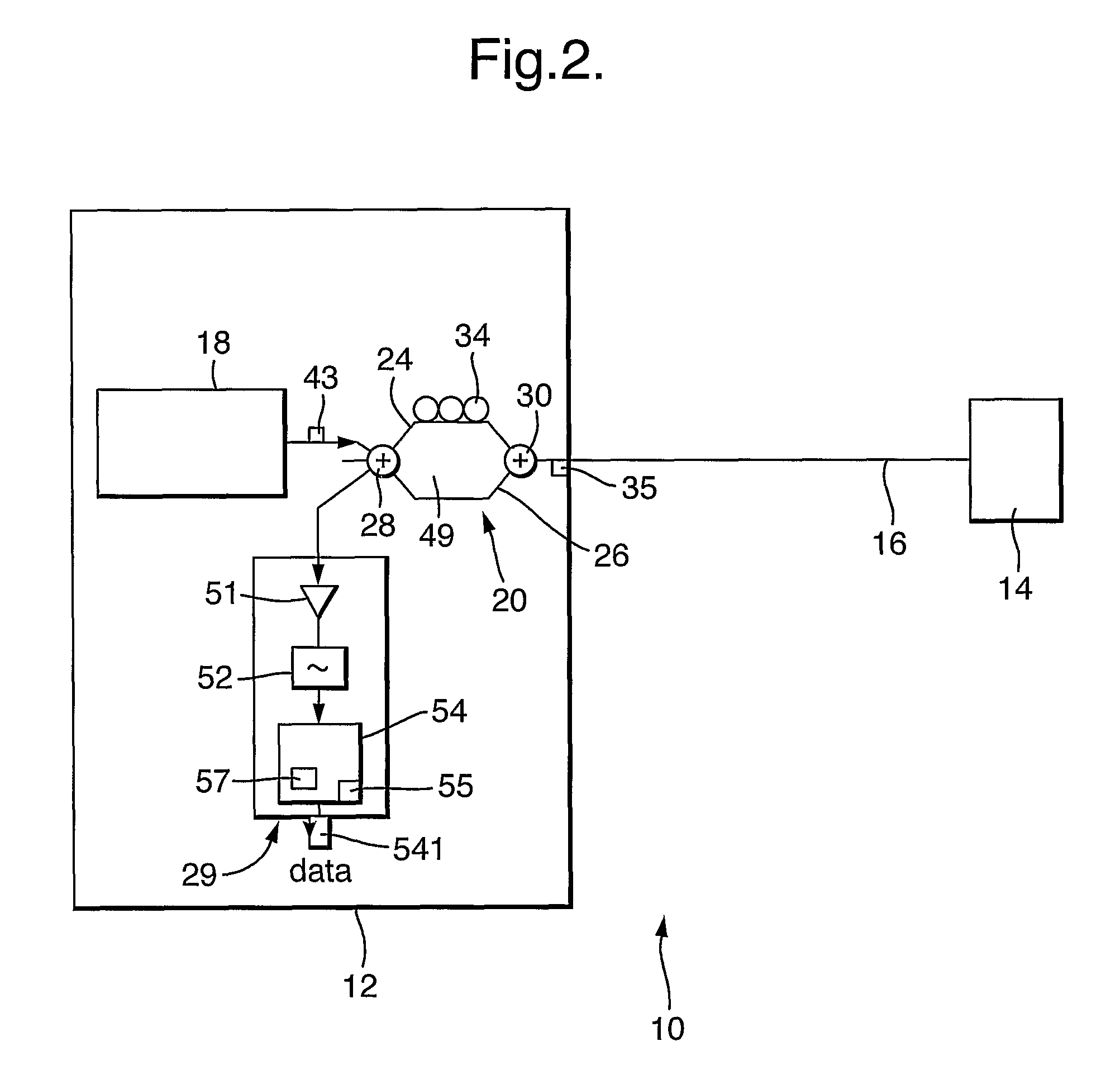
Distributed disturbance sensing device and the related demodulation method based on polarization sensitive optical frequency domain reflectometry
ActiveUS20140176937A1Long test distanceImprove spatial resolutionReflectometers dealing with polarizationSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementInformation analysisS-matrix
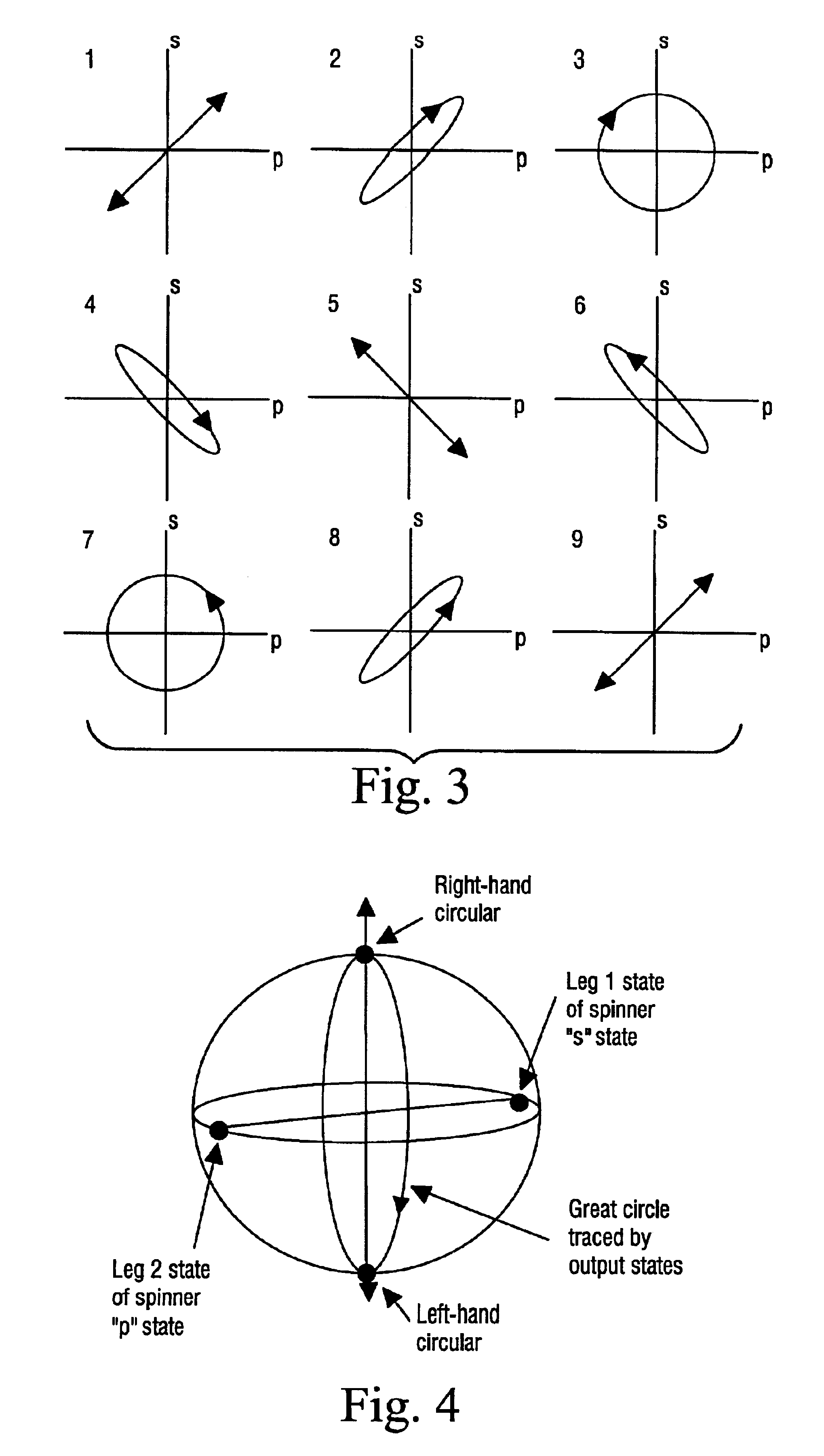
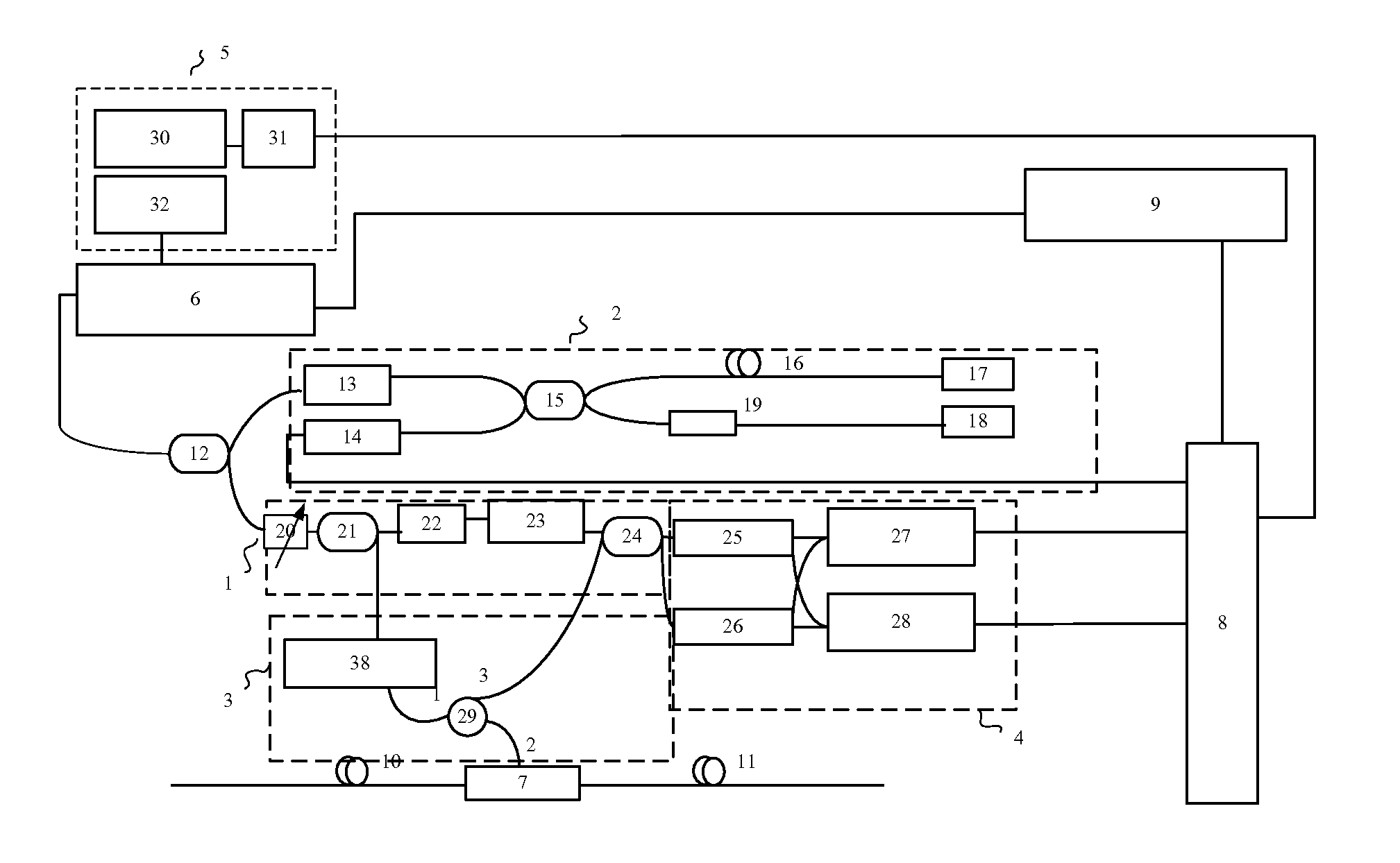
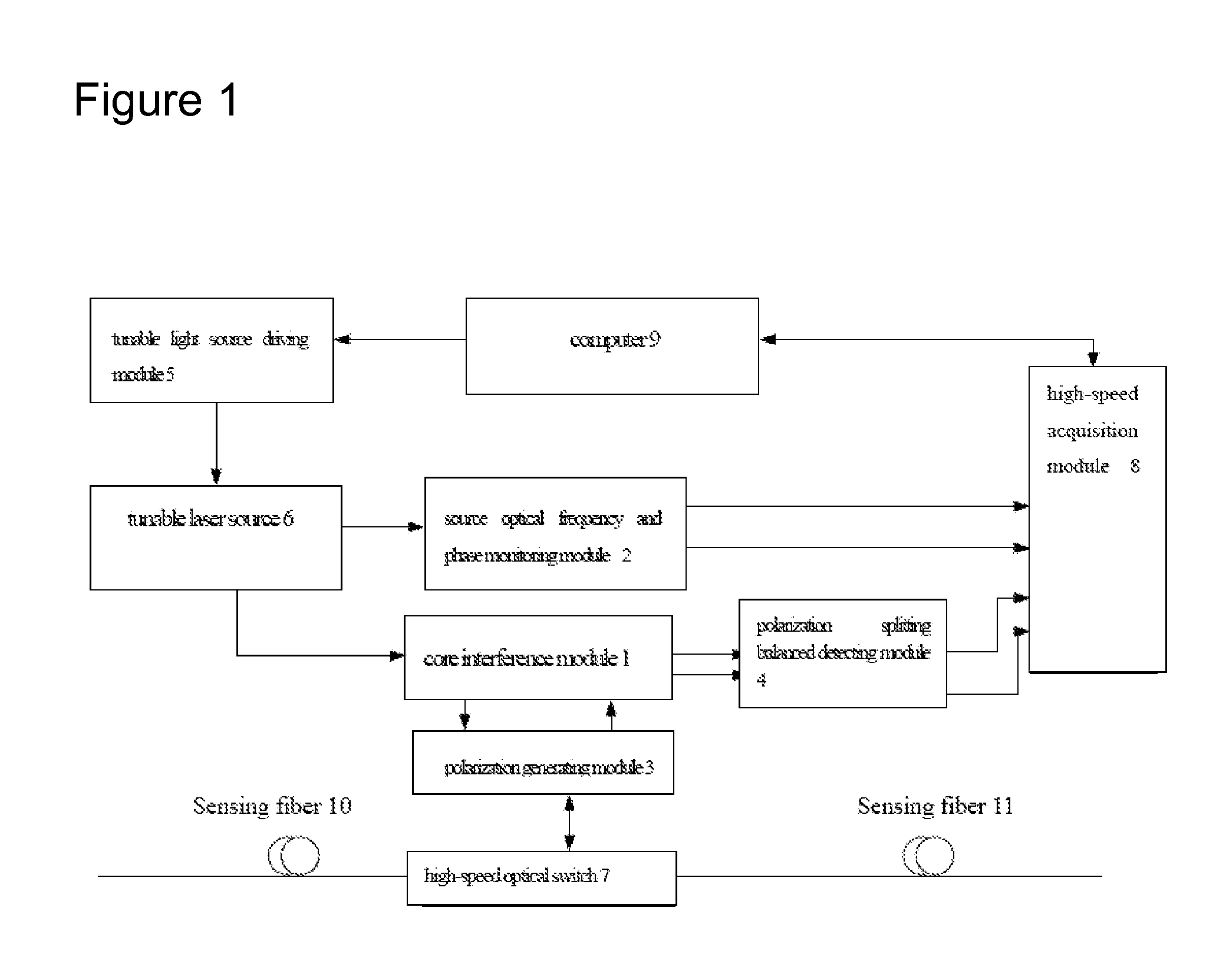
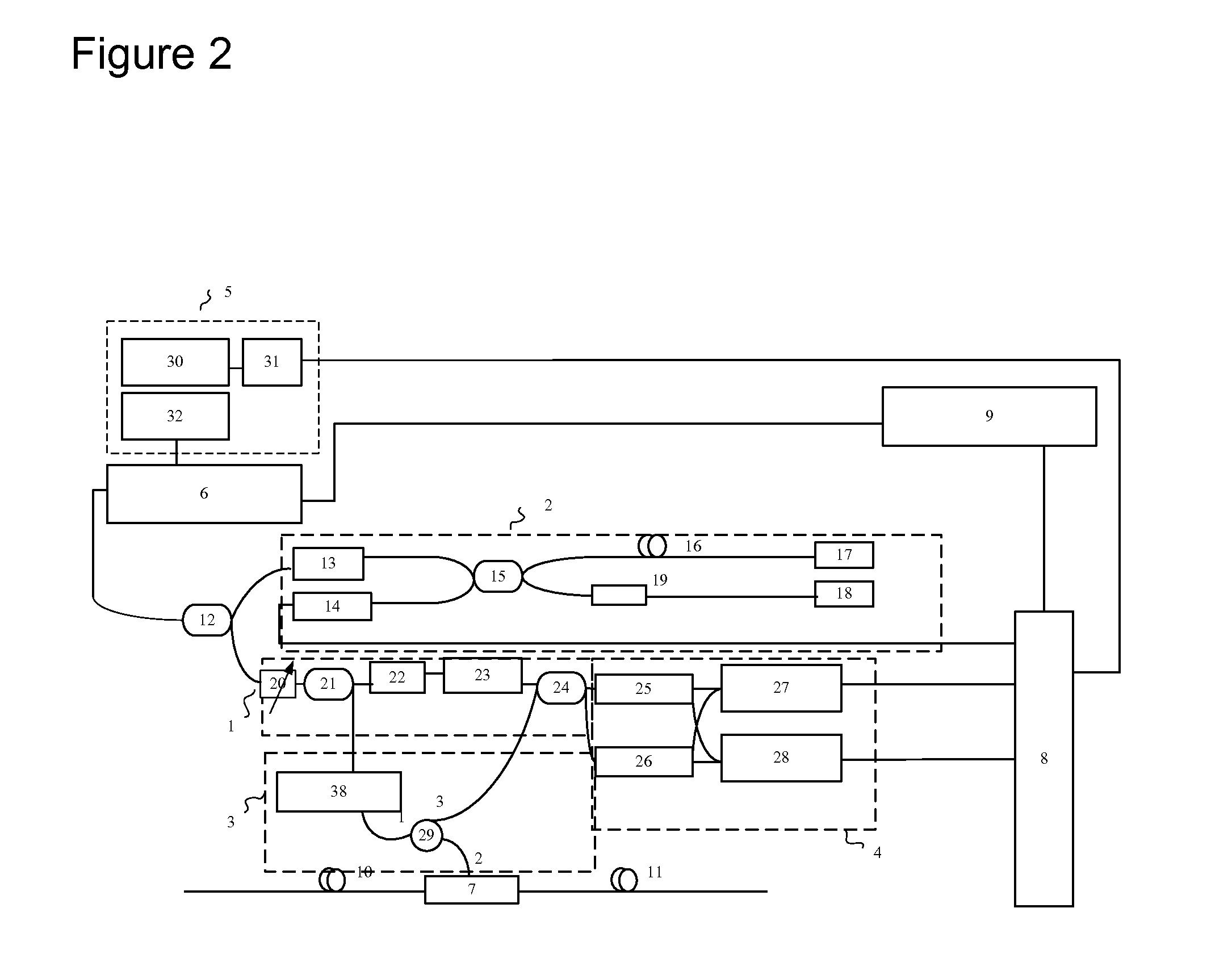
This invention relates to a distributed disturbance sensing device based on polarization sensitive optical frequency domain reflectometry (OFDR) and the related demodulation thereof. The device, adopting OFDR, polarization controlling and analysis techniques, consists of a ultra-narrow linewidth tunable laser source module, polarization generating and polarization splitting balanced detecting module, laser source optical frequency and phase monitoring module, high-speed optical switch and so on to establish a large-scale and long-distance optical sensing network. The demodulation method consists of analysis the polarization information from sensing optical fiber, the method of suppressing and compensating of the non-linear optical frequency and the laser phase noise, super-resolution analyzing, advanced denoising method and the polarization information analysis method based on Jones and Mueller's matrices using distributed wave plate model of optical fiber.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Bidirectional optical module and optical time domain reflectometer
ActiveUS7853104B2Increase optical powerHigh sensitivityReflectometers dealing with polarizationMaterial analysis by optical meansTime domainOptical Module
A bidirectional optical module according to the present invention emits light to an optical fiber and allows returning light from the optical fiber to enter and includes a plurality of light emitting elements that emit light to enter the optical fiber, a light receiving element that receives light having exited the optical fiber, and a non-reciprocal unit for making an optical path in a forward direction from the light emitting element to the optical fiber and an optical path in a backward direction from the optical fiber to the light emitting element different. Then, polarization planes of light incident on the optical fiber after being emitted from the plurality of light emitting elements are mutually orthogonal, and the non-reciprocal unit emits returning light of light emitted from the plurality of light emitting elements from the optical fiber toward the light receiving element to one light receiving element.
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP +1
Calculation of birefringence in a waveguide based on Rayleigh scatter
ActiveUS7330245B2Reflectometers dealing with polarizationCladded optical fibreRayleigh scatteringSpectral response
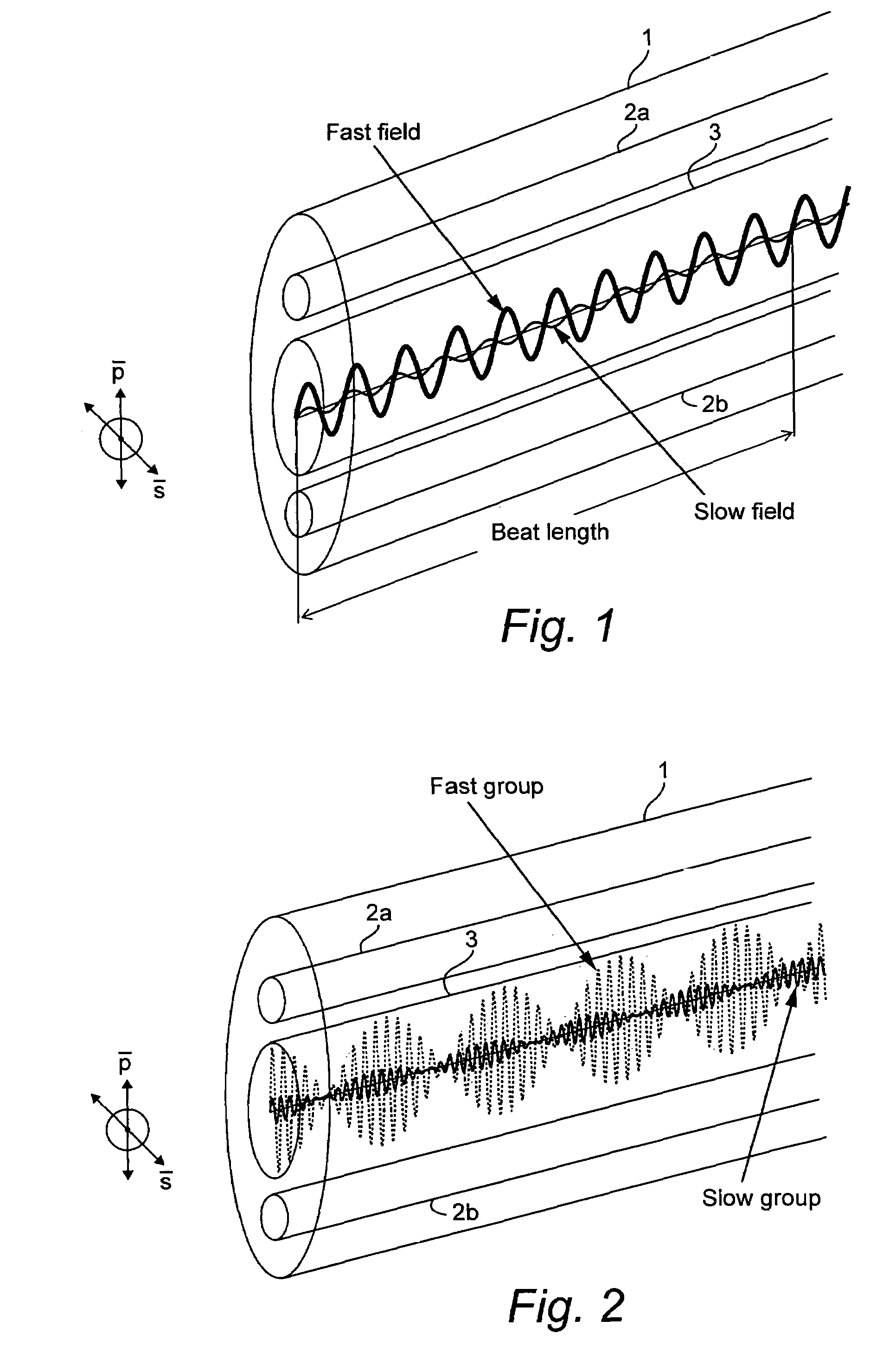
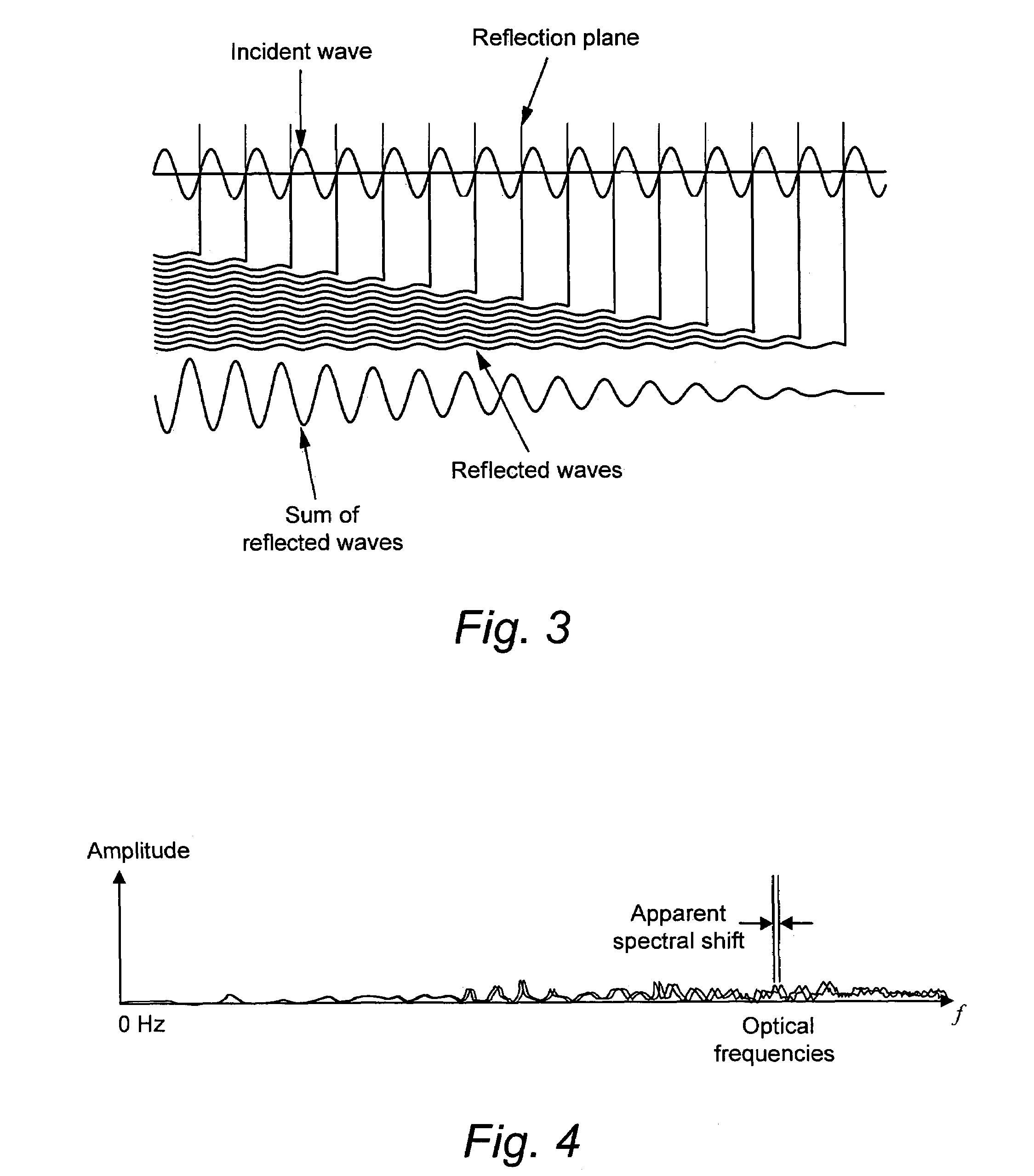
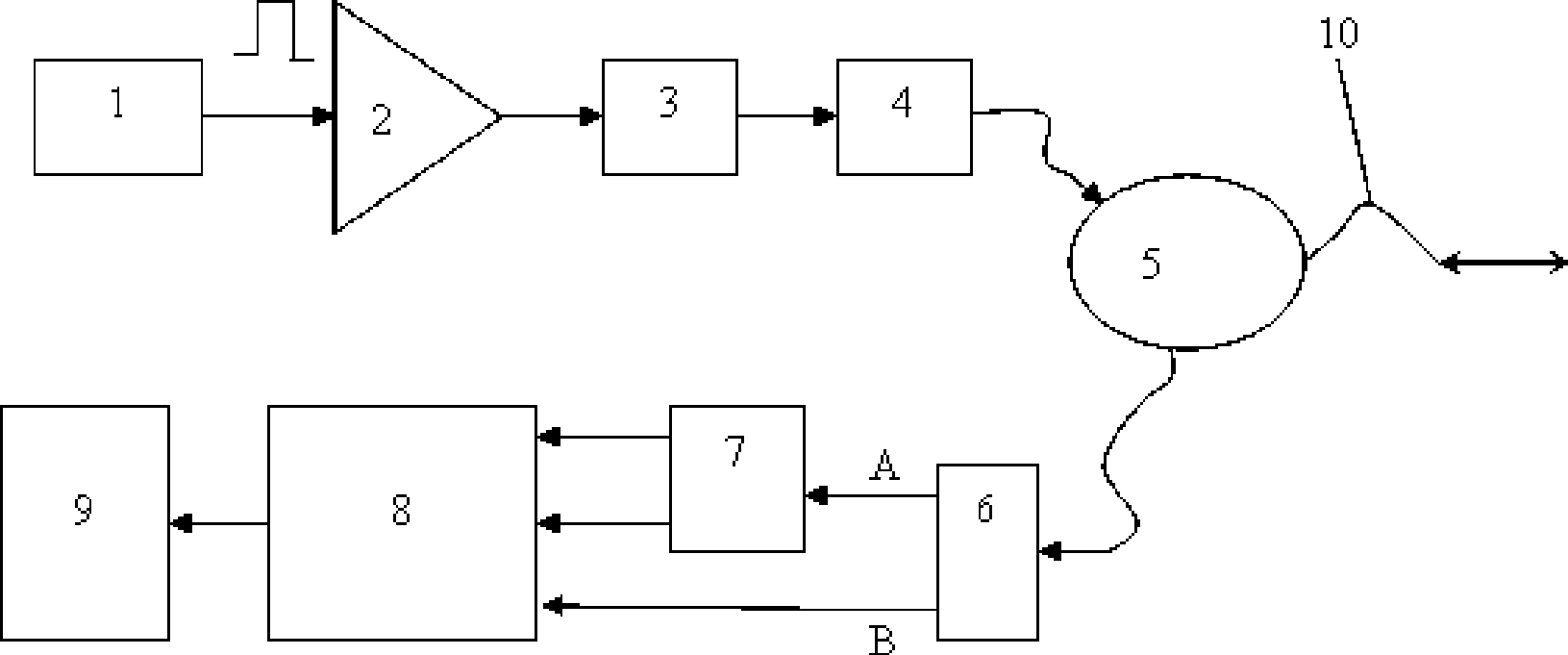
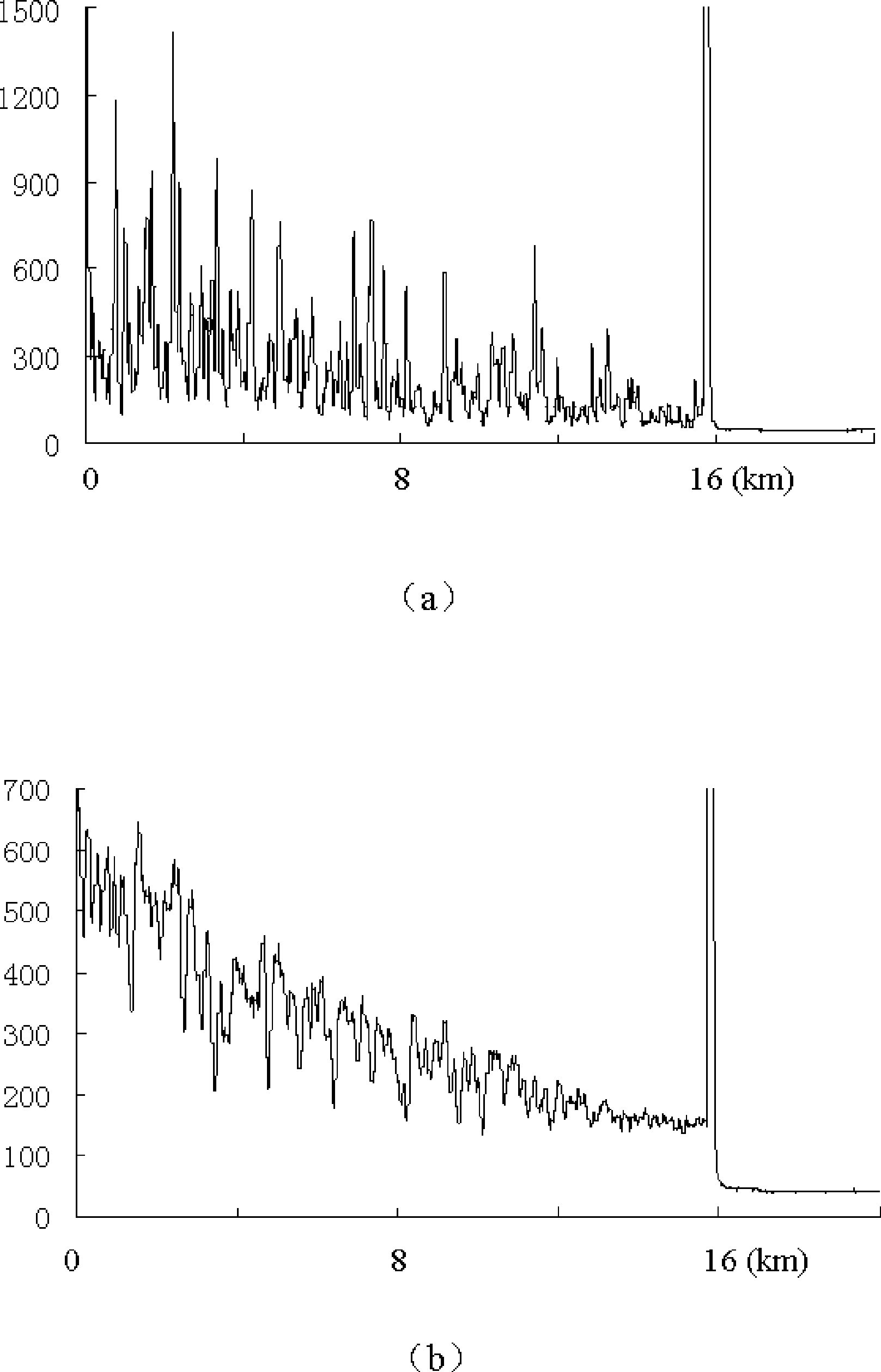
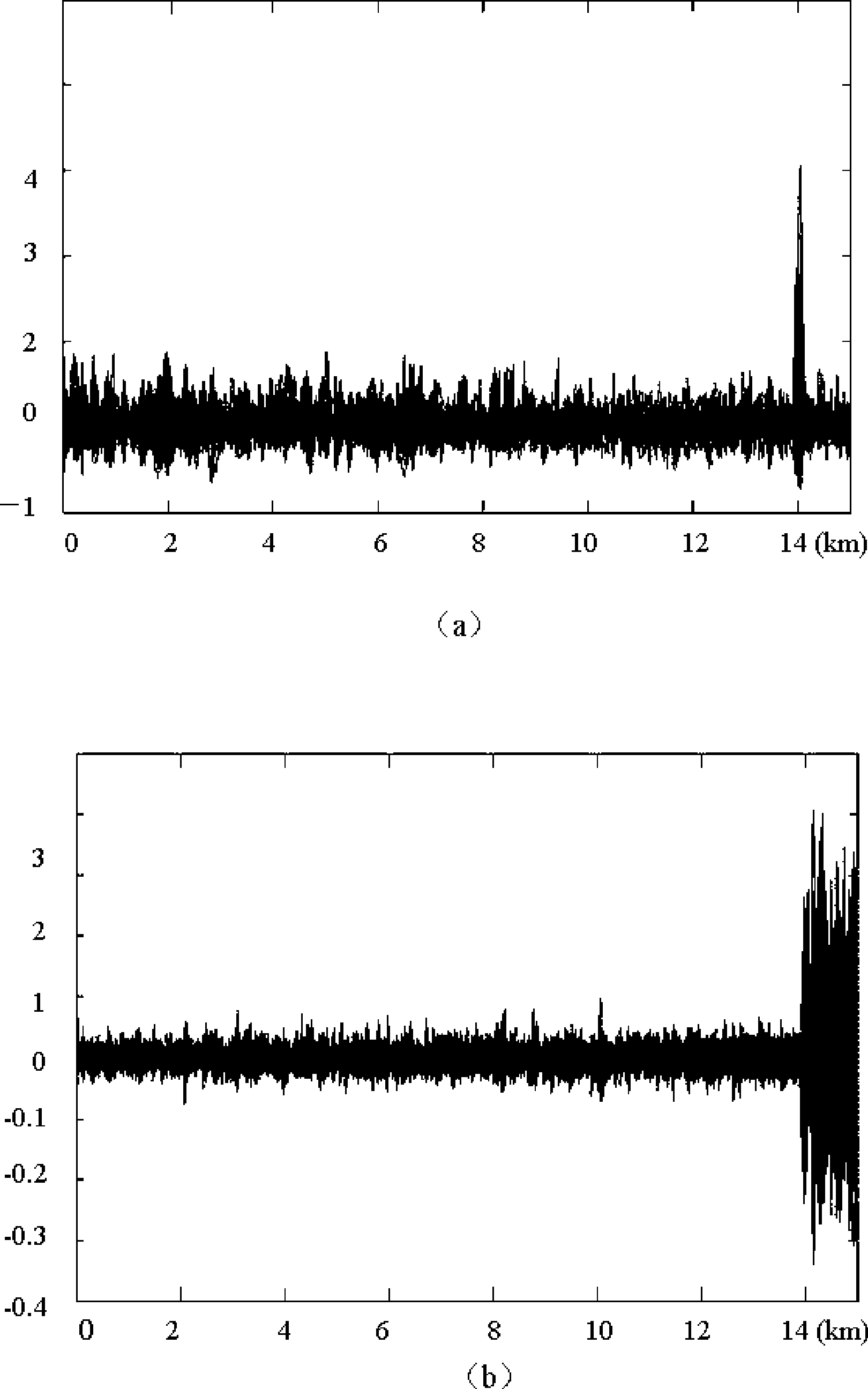
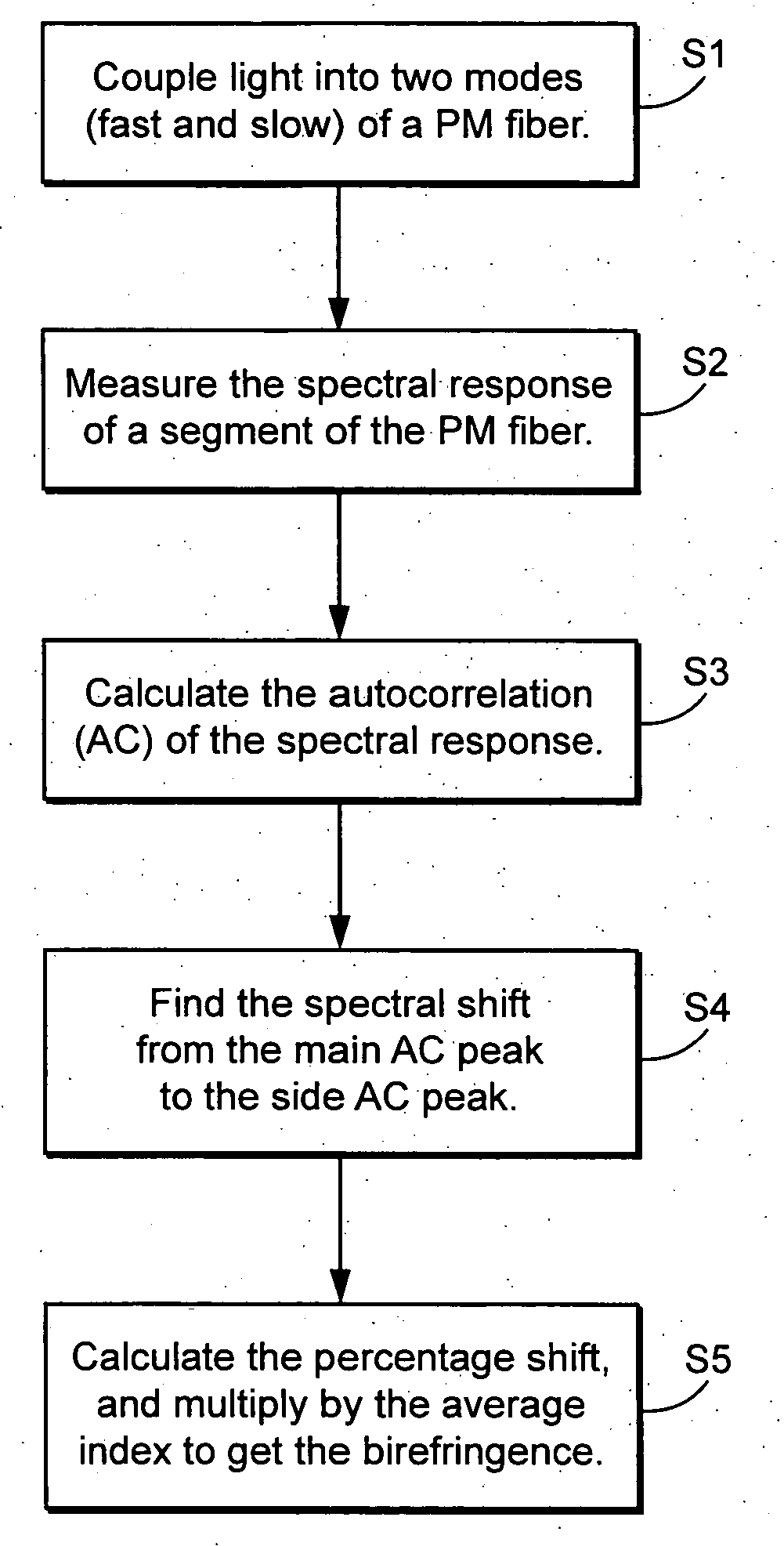
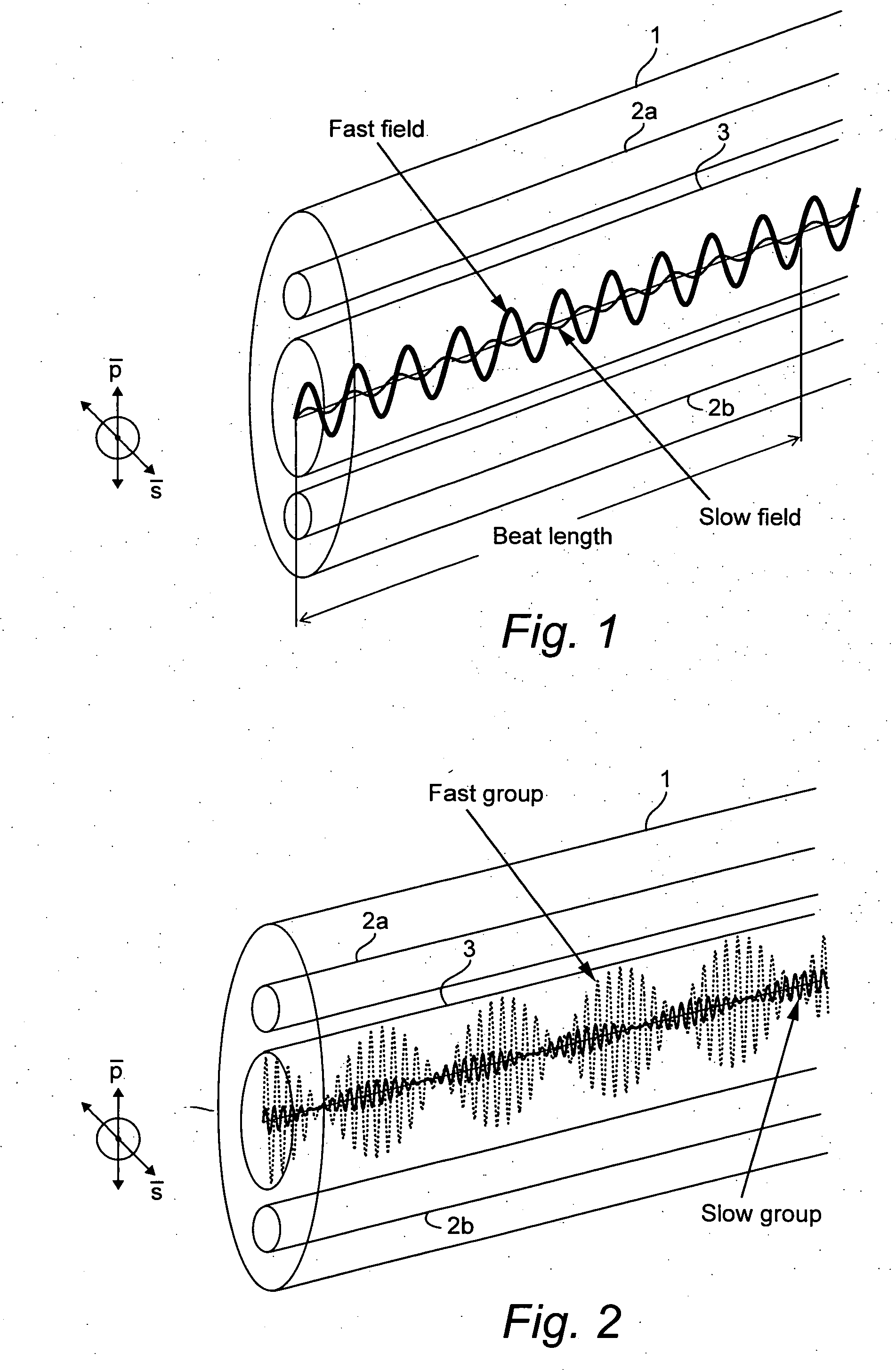
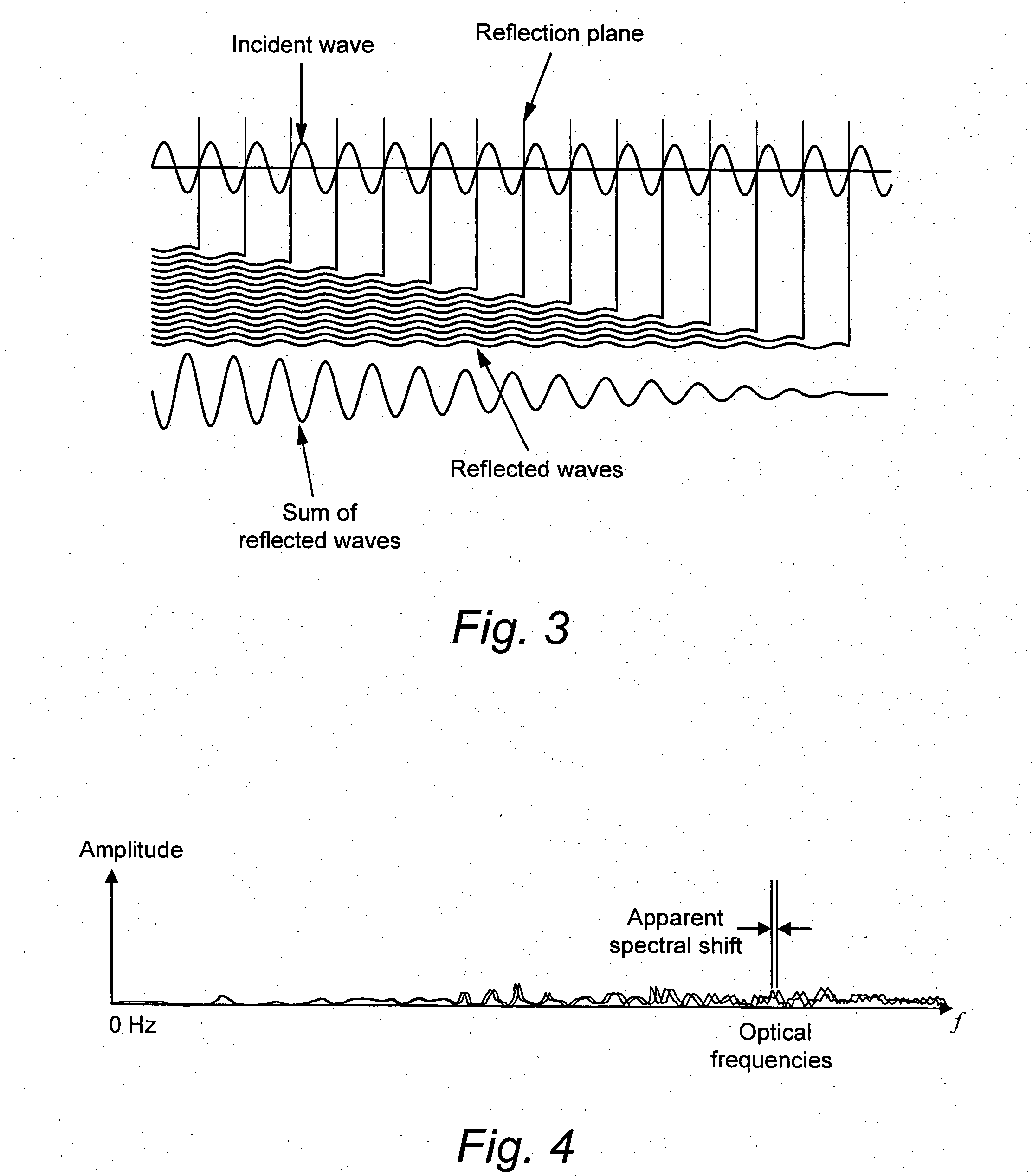
Light is coupled into two polarization modes of a waveguide, e.g., an optical fiber. The spectral response of Rayleigh backscatter in the waveguide segment for the two polarization modes is measured, e.g., using OFDR, OTDR, OLCR, etc. The autocorrelation of the spectral response is calculated. The spectral (wavelength) shift from a main autocorrelation peak to a side autocorrelation peak, corresponding to one of the two polarization modes of the waveguide segment, is determined. The spectral shift, corresponding to a beat length of the waveguide segment, is multiplied by an average index of refraction to determine a birefringence of the waveguide segment.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
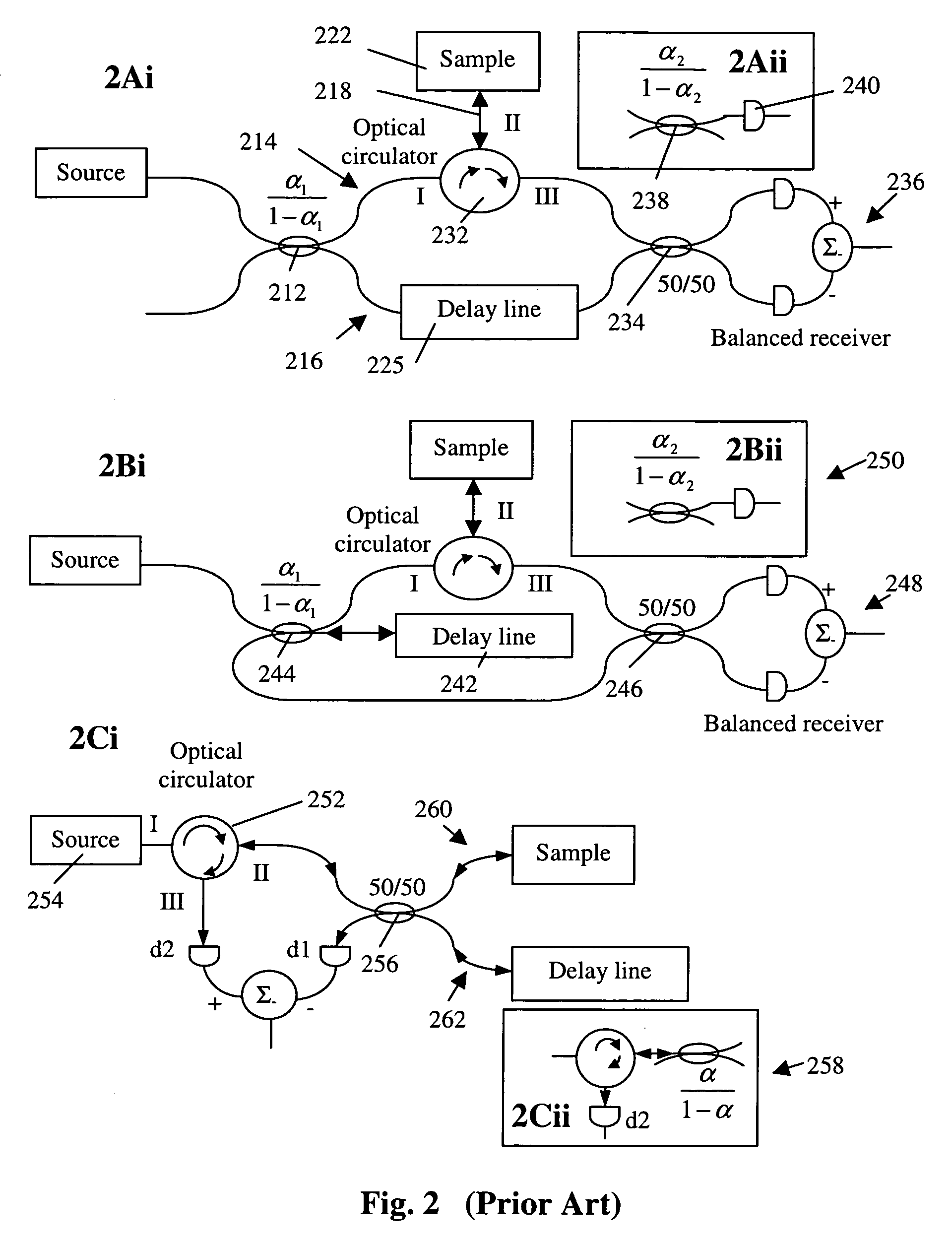
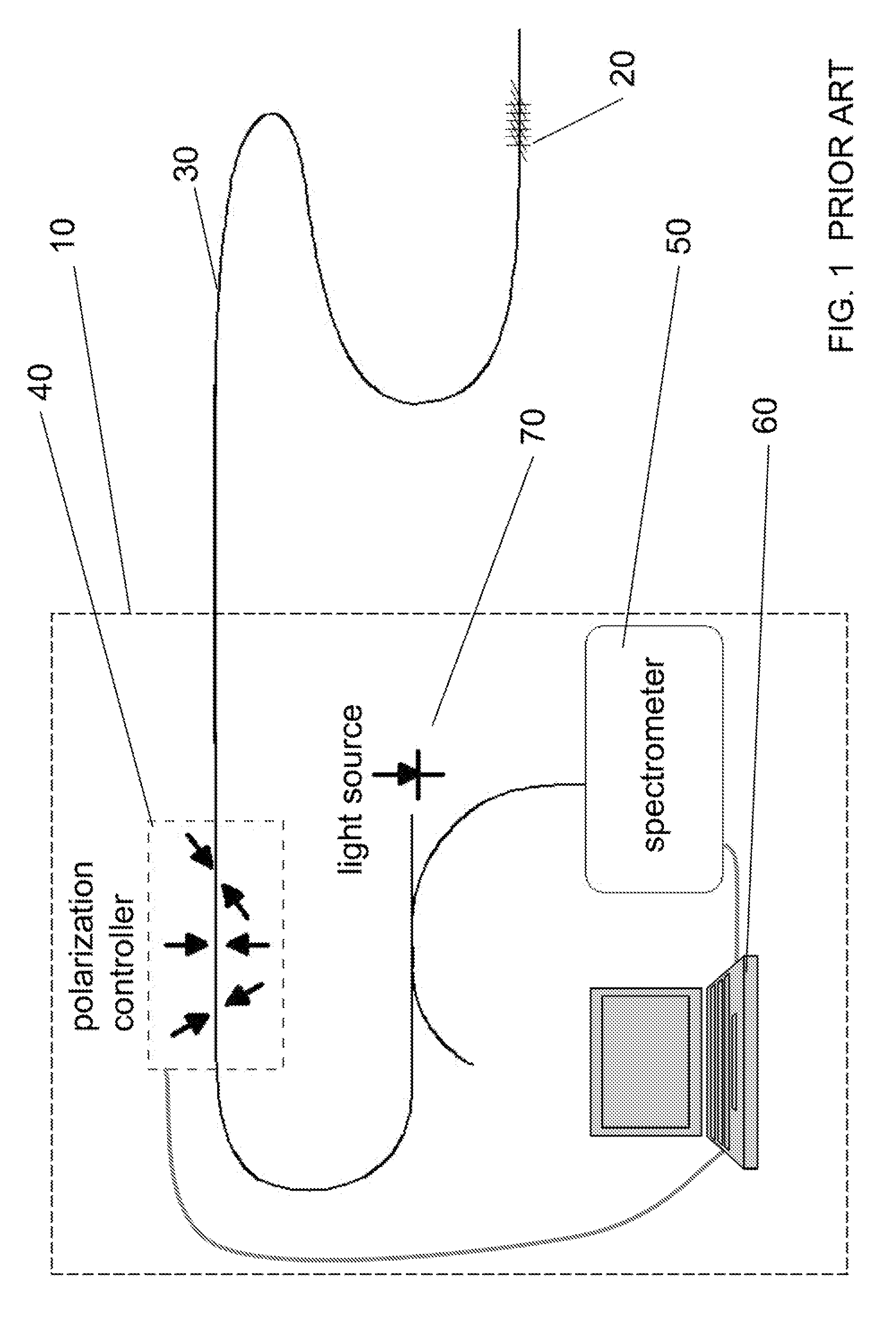
Polarization-OTDR for measuring characteristics of optical fibers
InactiveUS6724469B2Reflectometers dealing with polarizationMaterial analysis by optical meansStatistical analysisOptical time-domain reflectometer
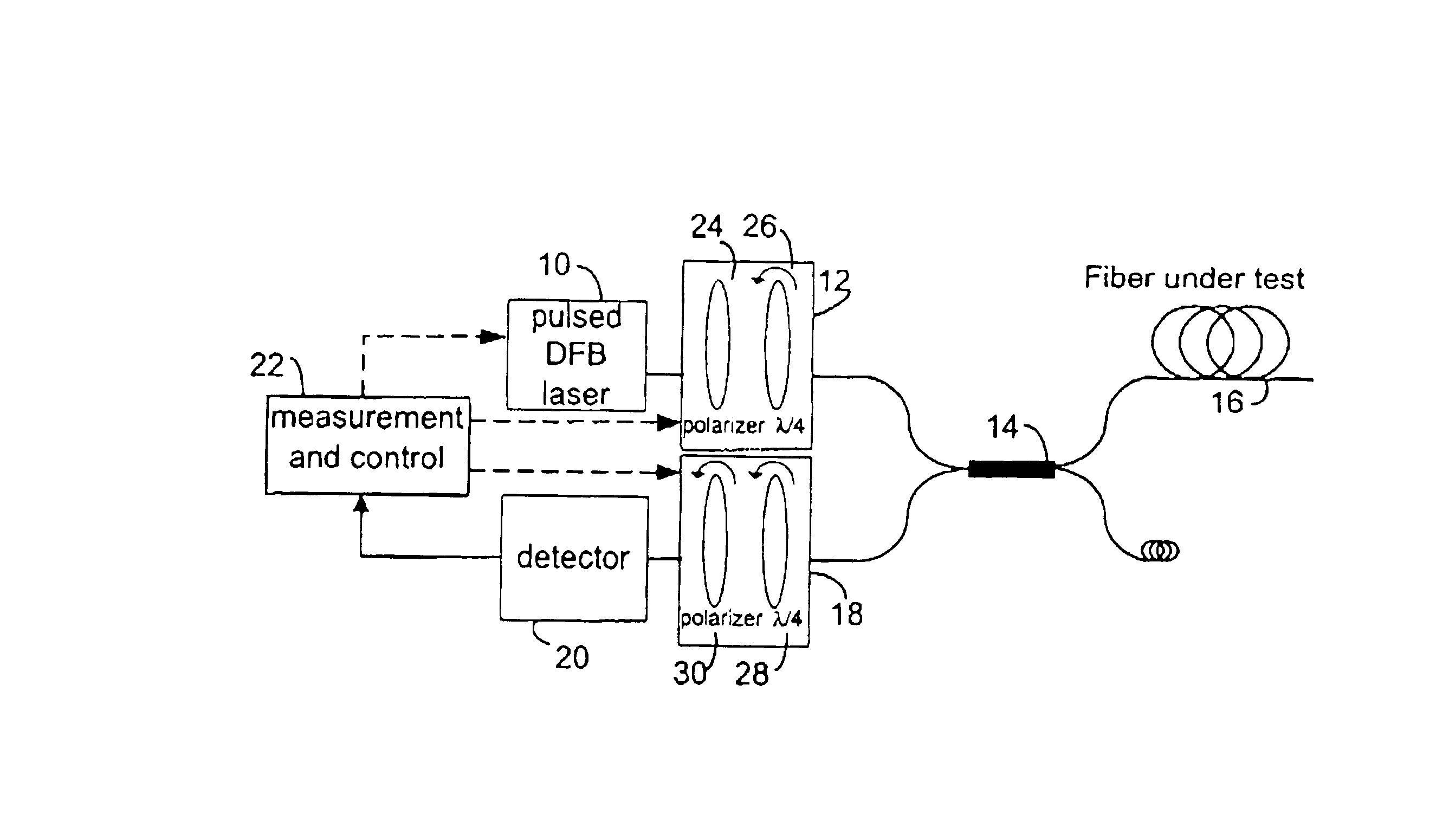
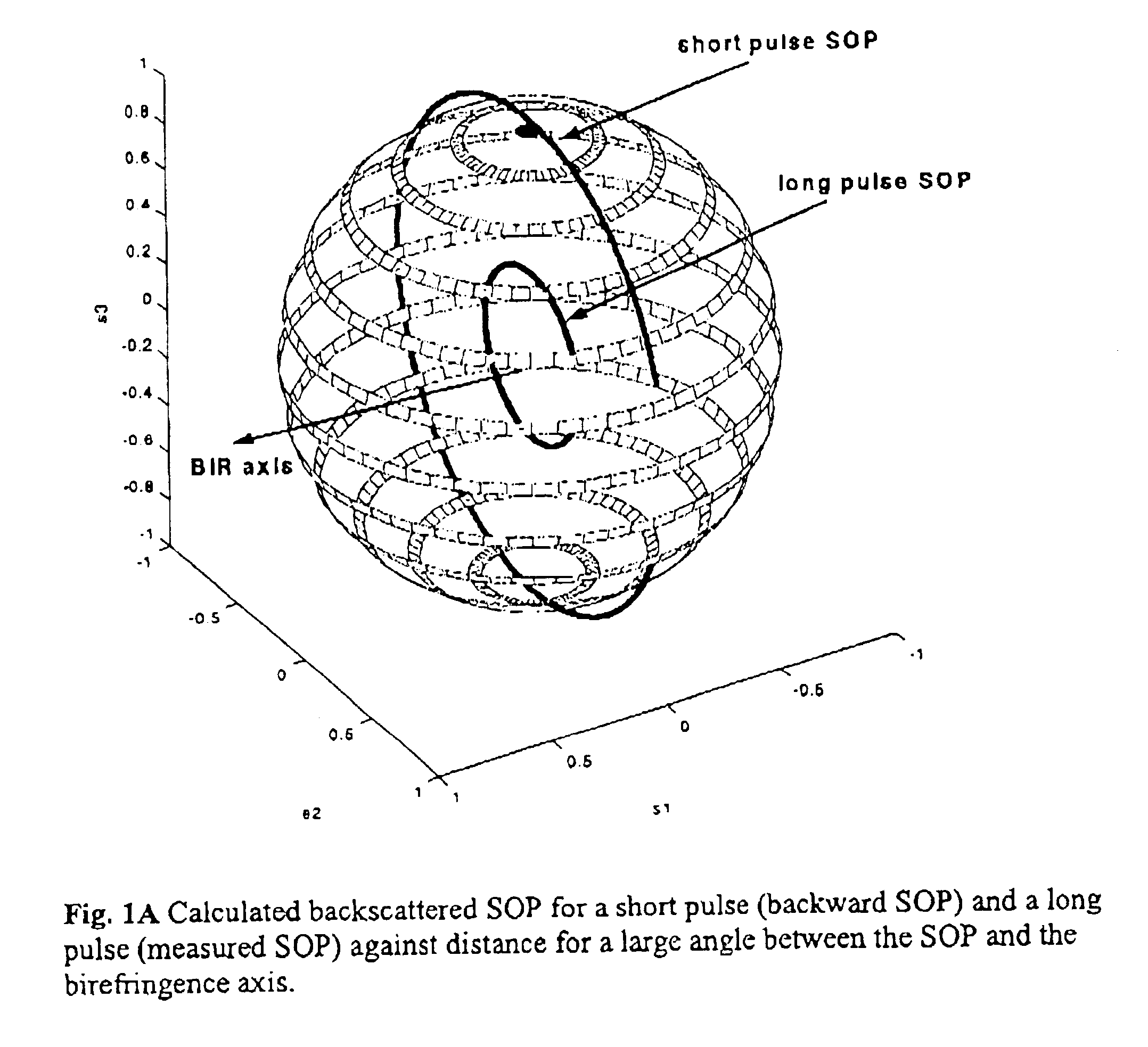
In a method of polarization optical time-domain reflectometer (P-OTDR) for measuring a parameter of an optical transmission path, for example an optical fiber, by transmitting pulses of light into the path and measuring the state of polarization of backscattered light against distance, statistical analysis of the degree of polarization (DOP) of the backscattered signal is used to detect sections of an optical transmission path for which mode-coupling behaviour (long h) leads to high PMD. Preferably, successive DOP measurement are taken with different state of polarization, SOP, for the P-OTDR light source.
Owner:EXFO ELECTRO OPTICAL ENG
Distributed Fibre Optic Sensing for Event Detection
ActiveUS20110216996A1Minimize couplingReflectometers dealing with polarizationOptical light guidesFiberSpeckle pattern
A fibre optic sensing method and apparatus for determining location and direction information of disturbances occurring in the environment of a sensor optical fibre are provided. The method comprises launching optical pulses into at least one polarisation eigenmode of a polarisation maintaining fibre as the sensor optical fibre, detecting temporal speckle patterns of light backscattered from the at least one polarisation eigenmode of the fibre, comparing the temporal speckle patterns to determine the location and direction information of a disturbance in the environment of the sensor optical fibre. The location information may be a distance along the fibre, and the direction information may be a direction radially from the axis of the fibre. The apparatus or instrument may be used to detect disturbance over long distances such as pipes, pipelines, or wells. Other applications include detecting intruders entering a controlled area.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Fully distributed optical fiber strain and vibration sensing method and sensor
InactiveCN102147236AOvercome the shortcoming of single functionExtended functional scopeReflectometers dealing with polarizationSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementContinuous lightGrating
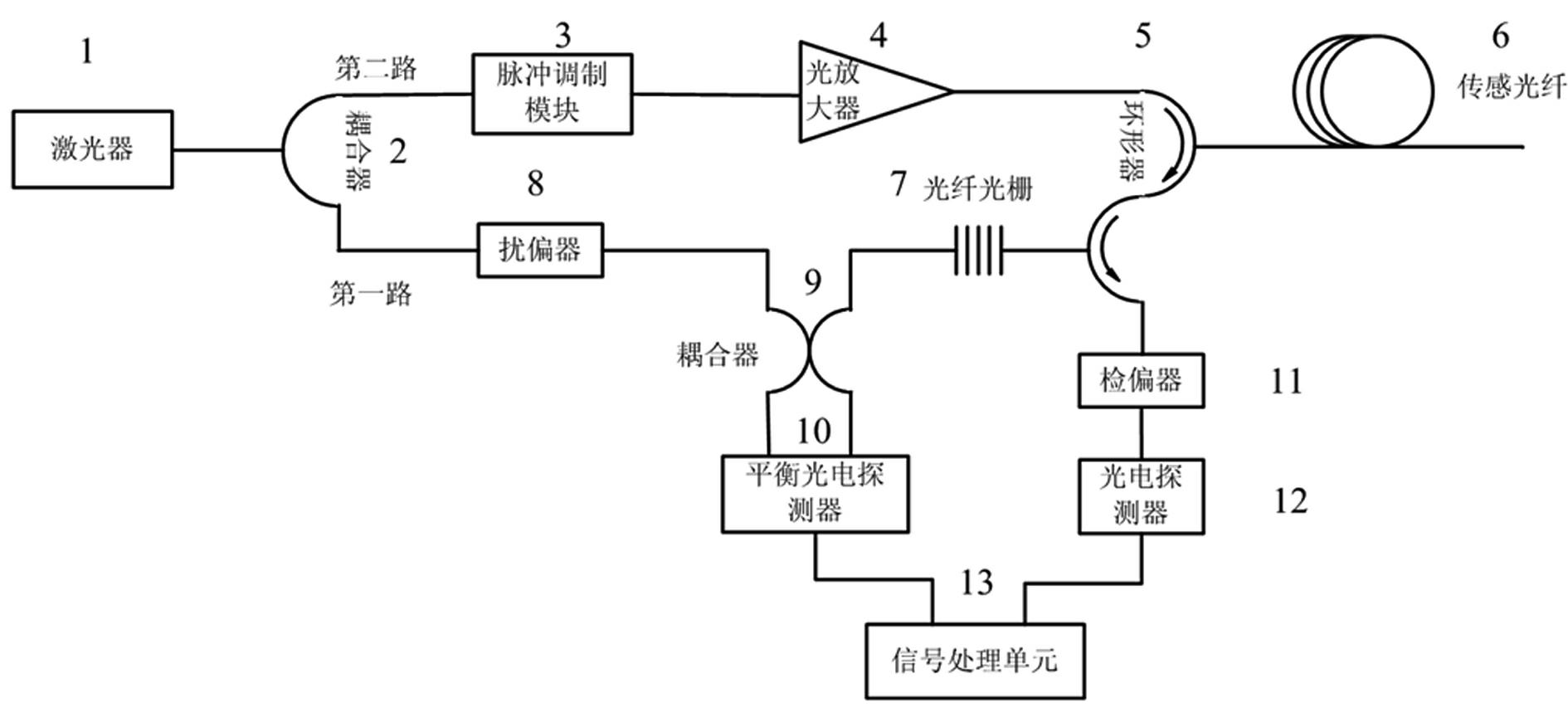
The invention discloses a fully distributed optical fiber strain and vibration sensor comprising a laser (1), a first coupler (2), a pulse modulation module (3), an optical amplifier (4), a circulator (5), a sensing optical fiber (6), a fiber bragg grating (7), a polarization scrambler, a second coupler, a balance photoelectric detector, an analyzer, a photoelectric detector (12) and a signal processing unit. Continuous light output by the laser (1) is split into two paths through the first coupler (2), wherein one path is used as reference light and is accessed to a first input end of the second coupler (9) through the polarization scrambler (8); and the second path is processed by the pulse modulation module (3) and the optical amplifier (4) and then used as detection pulse light to be injected into a first port of the circulator (5). In the invention, Brillouin optical time domain reflectometry (BOTDR) and polarization optical time domain reflectometry (POTDR) are simultaneously utilized for respectively and correspondingly carrying out fully distributed measurement on strain and vibration on a signal optical fiber, the defects of a system with single BOTDR or POTDR are overcome, and the false alarm rate or missed report rate of the system is decreased.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Polarization-OTDR for measuring characteristics of optical fibers
InactiveUS20030174312A1Reflectometers dealing with polarizationMaterial analysis by optical meansStatistical analysisOptical time-domain reflectometer
In a method of polarization optical time-domain reflectometer (P-OTDR) for measuring a parameter of an optical transmission path, for example an optical fiber, by transmitting pulses of light into the path and measuring the state of polarization of backscattered light against distance, statistical analysis of the degree of polarization (DOP) of the backscattered signal is used to detect sections of an optical transmission path for which mode-coupling behaviour (long h) leads to high PMD. Preferably, successive DOP measurement are taken with different state of polarization, SOP, for the P-OTDR light source.
Owner:EXFO ELECTRO OPTICAL ENG
Determining a polarization-related characteristic of an optical link
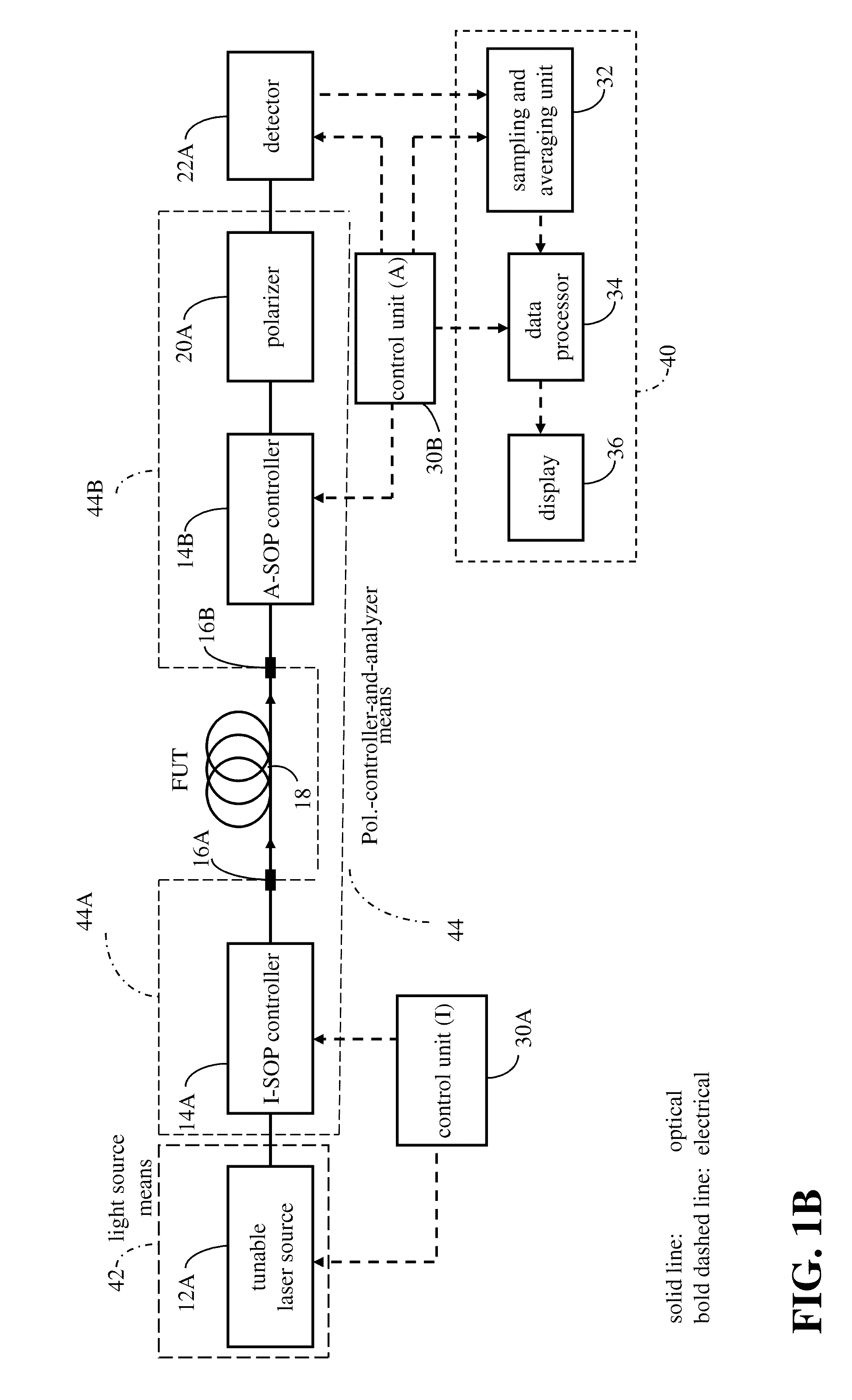
ActiveUS20140071436A1Eliminate disadvantagesReflectometers dealing with polarizationPolarisation-affecting propertiesMean squareOptical frequencies
A polarization-related characteristic of an optical path is determined from a predetermined function of the mean-square of a plurality of differences between polarization-analyzed optical power parameters corresponding to pairs of wavelengths mutually spaced about a midpoint wavelength by a small optical frequency difference. At least some of the said differences correspond to wavelength pairs measured under conditions where at least one of midpoint wavelength, input state of polarization (I-SOP) or analyzed state of polarization (A-SOP) of a pair is different.
Owner:EXFO
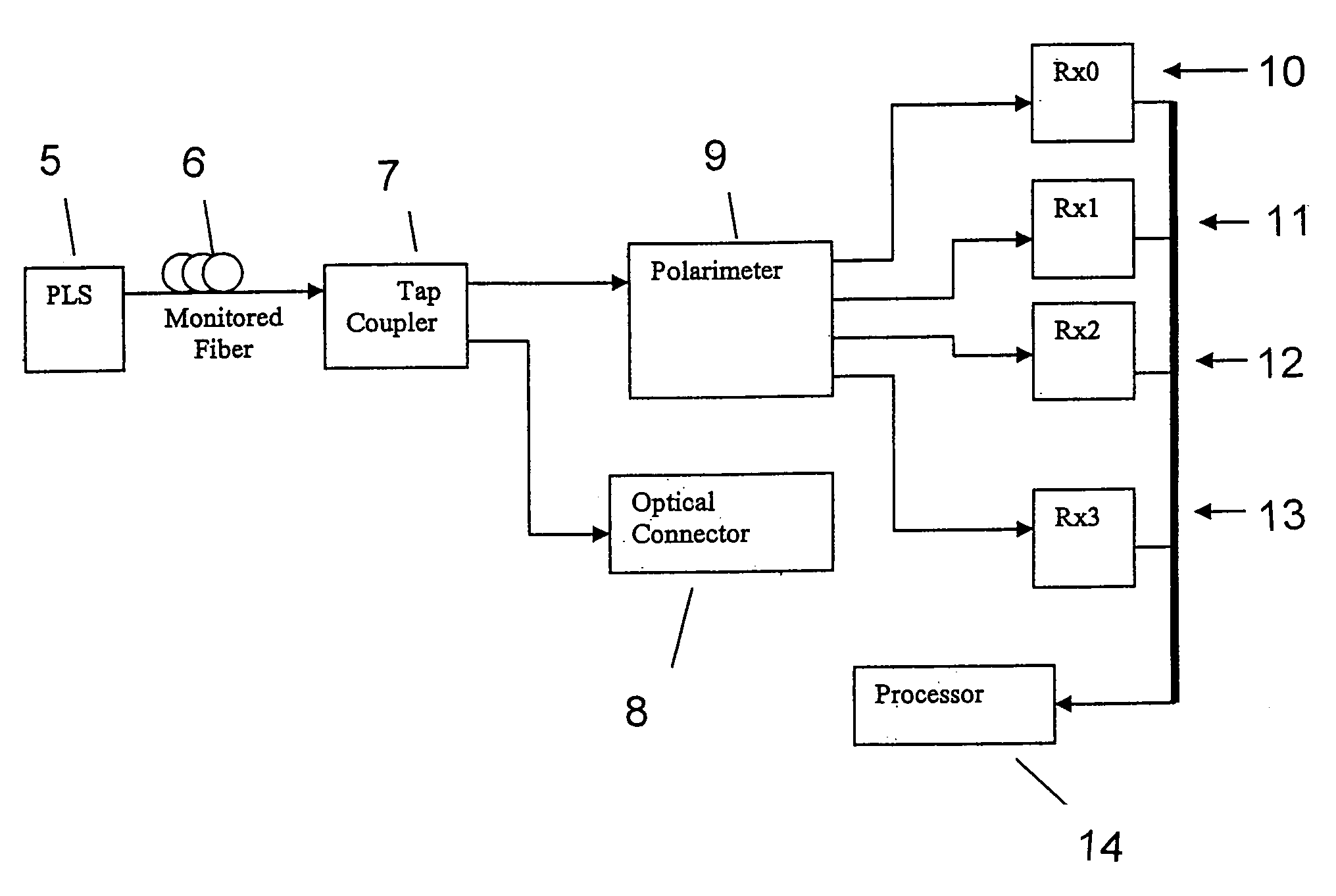
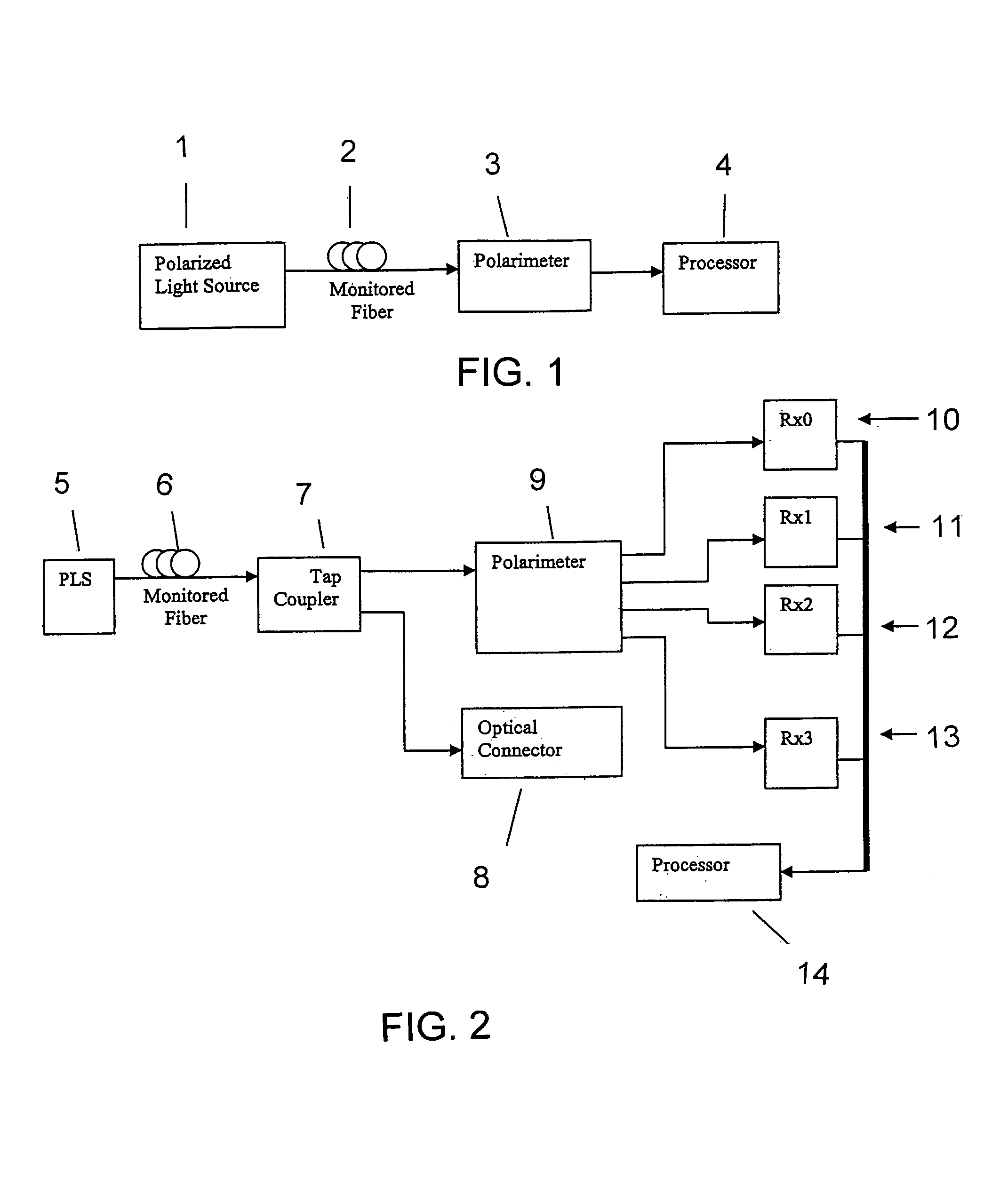
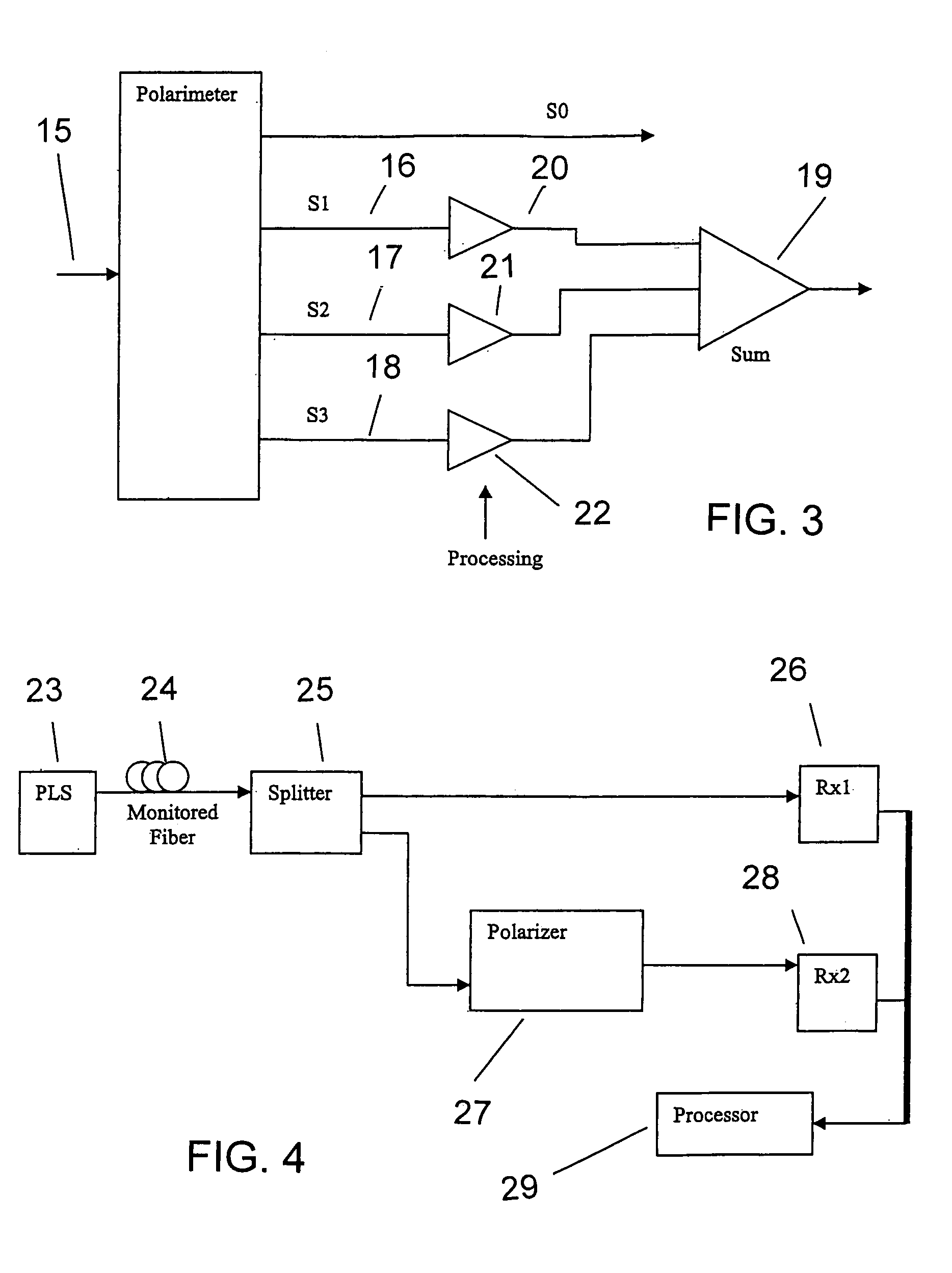
Intrusion detection system for use on single mode optical fiber using a storage register for data
ActiveUS7142737B1Overcome limitationsMaximum sensitivityReflectometers dealing with polarizationCoupling light guidesProcessor registerPolarimeter
A telecommunications optical fiber is secured against intrusion by detecting manipulation of the optical fiber prior to an intrusion event. This can be used in a non-locating system where the detection end is opposite the transmit end or in a locating system which uses Fresnel reflections and Rayleigh backscattering to the transmit end to detect and then locate the motion. The Rayleigh backscattering time sliced data can be stored in a register until an intrusion event is detected. The detection is carried out by a polarization detection system which includes an optical splitter which is manufactured in simplified form for economic construction. This uses a non-calibrated splitter and less than all four of the Stokes parameters. It can use a polarimeter type function limited to linear and circular polarization or two linear polarizers at 90 degrees.
Owner:NETWORK INTEGRITY SYST
Optical fiber disturbance detection method and apparatus
ActiveCN101488805AImprove accuracyHigh sensitivityReflectometers dealing with polarizationSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementRayleigh scatteringTime domain
The invention relates to an optical fiber sensor. The invention discloses an optical fiber destabilization detecting method combining based on a phase sensitivity light time domain reflection and a polarization sensitivity light time domain reflection method and distributed optical fiber sensing system thereof to improve the detecting accuracy and reliability of the optical fiber destabilization. The method comprises: a. injecting an optical signal with determined polarization state into the optical fiber; b. receiving the back rayleigh scattering light in the optical fiber; c. diving the rayleigh scattering light into two bundles to perform the Phi-OTDR data acquisition and the POTDR data acquisition; d. determining the destabilization and position thereof based on the distortion points of the Phi-OTDR data and the POTDR data. The invention also discloses an optical fiber destabilization detecting device. The technical scheme of the invention is used for monitoring and protecting the optical cable lines, thereby greatly improving the precision and the sensitivity of the monitoring system and reducing the erroneous judgment rate and the missing report rate.
Owner:OPTICAL SCI & TECH (CHENGDU) LTD
Calculation of birefringence in a waveguide based on Rayleigh scatter
ActiveUS20060204165A1Low costIntegrity be compromisedReflectometers dealing with polarizationCladded optical fibreRayleigh scatteringSpectral response
Light is coupled into two polarization modes of a waveguide, e.g., an optical fiber. The spectral response of Rayleigh backscatter in the waveguide segment for the two polarization modes is measured, e.g., using OFDR, OTDR, OLCR, etc. The autocorrelation of the spectral response is calculated. The spectral (wavelength) shift from a main autocorrelation peak to a side autocorrelation peak, corresponding to one of the two polarization modes of the waveguide segment, is determined. The spectral shift, corresponding to a beat length of the waveguide segment, is multiplied by an average index of refraction to determine a birefringence of the waveguide segment.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Method of evaluating fiber PMD using polarization optical time domain reflectometry
InactiveUS6946646B2Easy to identifyReflectometers dealing with polarizationRadiation pyrometryTime domainFiber
A method for screening fiber polarization mode dispersion using a polarization optical time domain reflectometer. A pulse radiation is emitted into the fiber under test, and the backscattered radiation is measured by the POTDR and used to obtain a POTDR trace. The POTDR trace is then analyzed to compare the variation of signals along the length of the fiber, the variation in signals relating to the level of PMD along the length of the fiber. Because high levels of PMD correspond to localized levels of low variability, by setting the variability of signal threshold sufficiently low, fibers having unacceptably high localized PMD can be identified and removed.
Owner:CORNING INC
Distributed backscattering
ActiveUS7995197B2Advantage in useReflectometers dealing with polarizationMaterial analysis by optical meansTelecommunications linkEngineering
The present invention relates to a method for detecting or inferring a physical disturbances on a communications link, in particular by using distributed backscattering. The method includes the steps of: transmitting test signals onto a link; receiving test signals returned from a remote portion of the link; performing a function on the returned test signals; and in dependence on at least one characteristic of the combination signal, inferring the presence of a disturbance. The test signal are returned by a process Rayleigh backscattering along the fibre, so existing fibre installations can be used without requiring a mirror to be specifically introduced.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
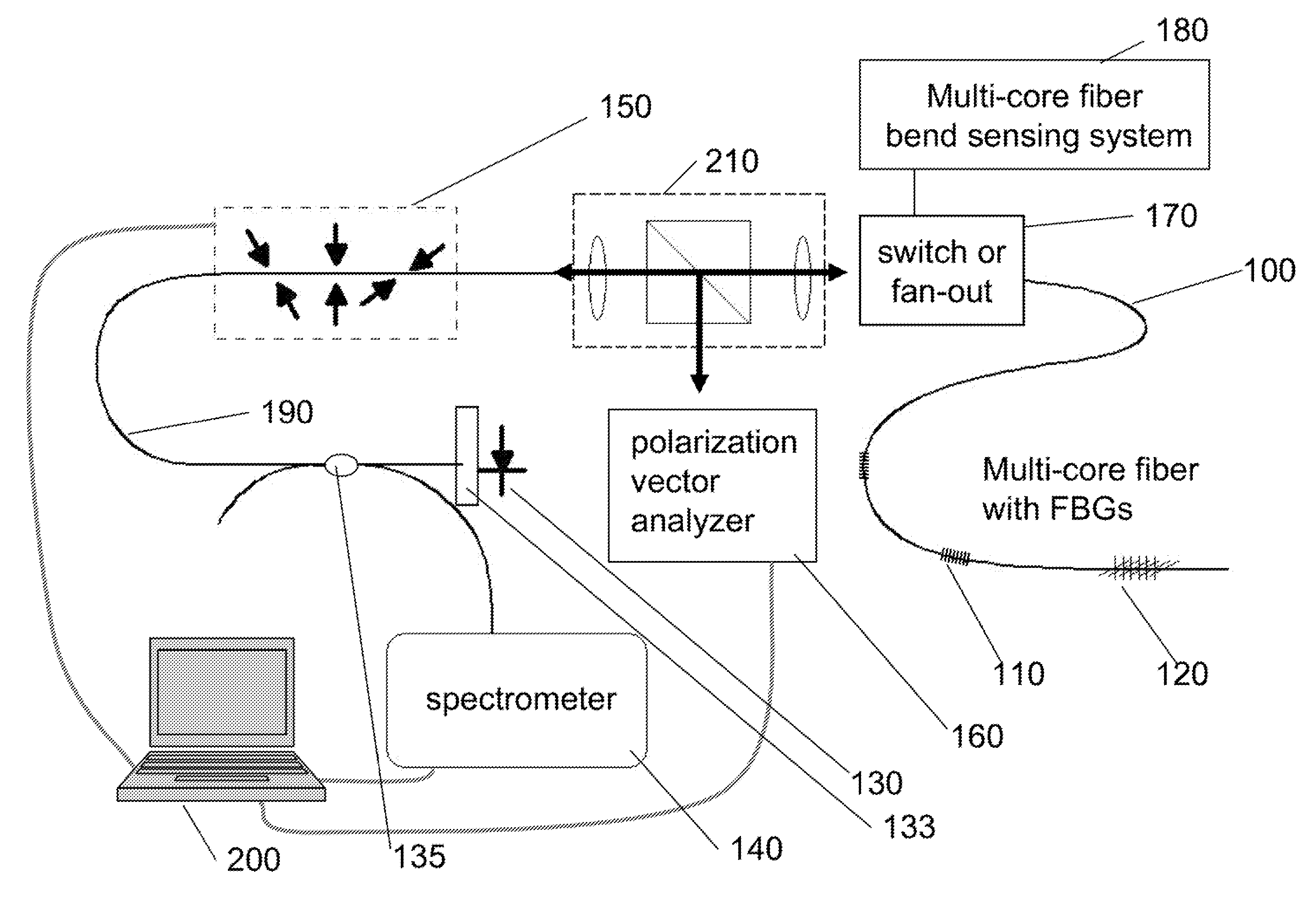
Optical position and/or shape sensing
ActiveCN102695938APhase-affecting property measurementsForce measurementOptical pathlengthMulti core fiber
An accurate measurement method and apparatus are disclosed for shape sensing with a multi-core fiber. A change in optical length is detected in ones of the cores in the multi-core fiber up to a point on the multi-core fiber. A location and / or a pointing direction are / is determined at the point on the multi-core fiber based on the detected changes in optical length. The accuracy of the determination is better than 0.5% of the optical length of the multi-core fiber up to the point on the multi-core fiber. In a preferred example embodiment, the determining includes determining a shape of at least a portion of the multi-core fiber based on the detected changes in optical length.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Method For Characterizing An Optical Fiber Link
InactiveUS20070201786A1Reflectometers dealing with polarizationMaterial analysis by optical meansPolarizerPolarization mode dispersion
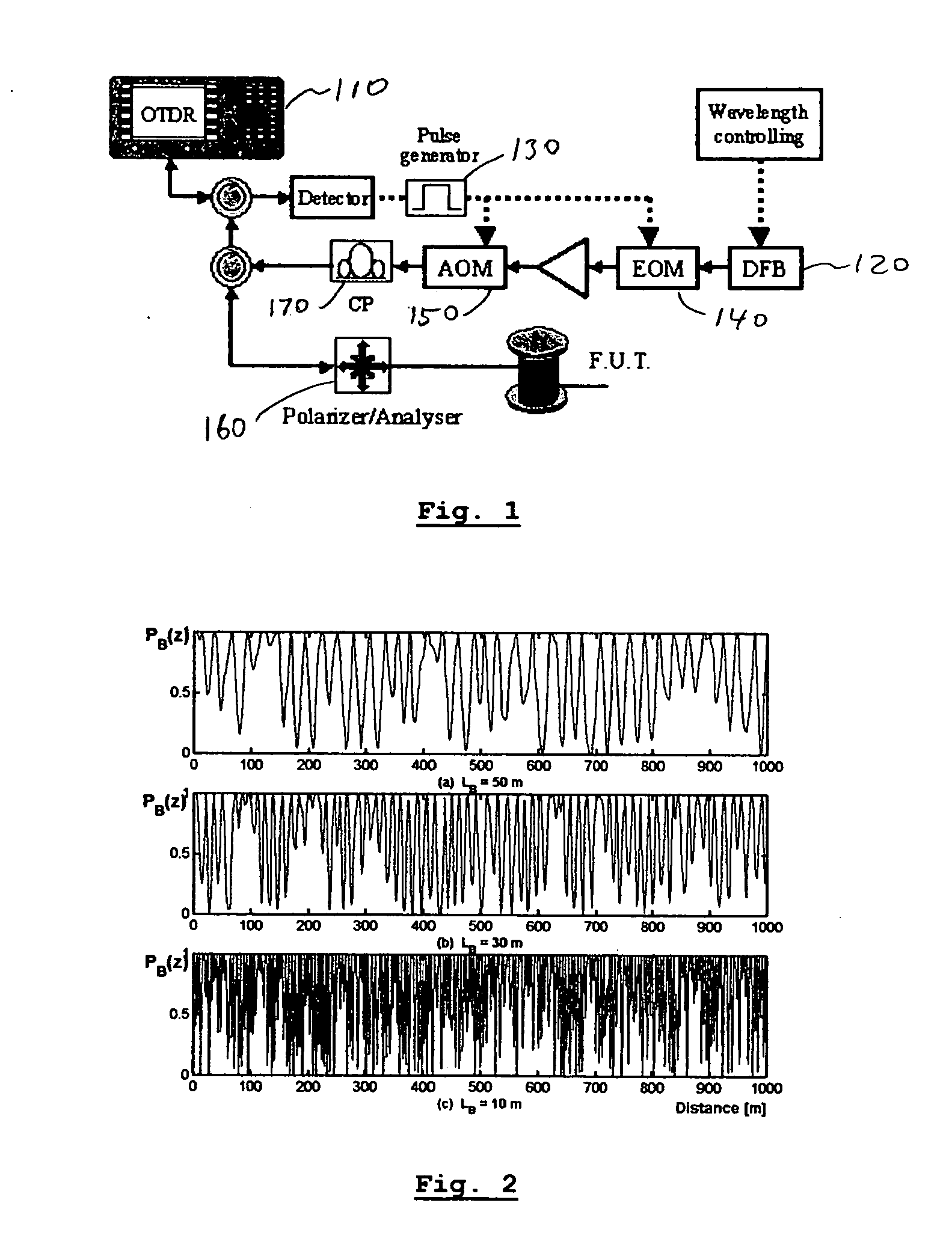
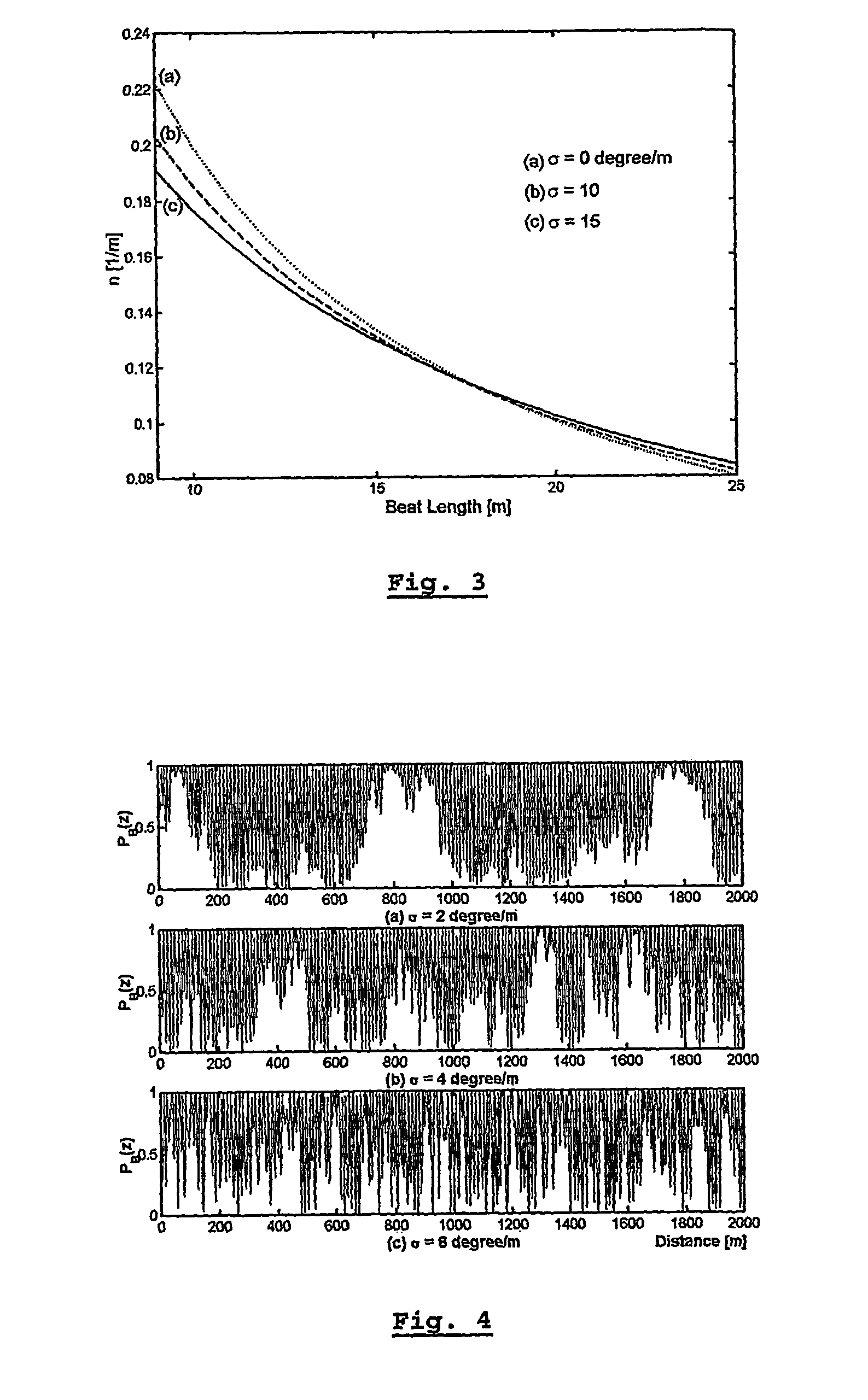
A method for characterizing an optical link by its beat length, coupling length and polarization mode dispersion is disclosed. A pulsed signal is sent along said optical fiber link and the backscattered signal (being a POTDR signal) is measured after passing through a polarizer. The length of said optical fiber, the average power difference between two successive minima of said backscattered signal and the number of maxima per unit length are derived. In an iterative way a beat length interval and an interval for the polarization mode coupling parameter are determined until the length of said intervals is below a predetermined value, yielding a value for the beat length and the coupling length, and the polarization mode dispersion is calculated.
Owner:FACULTE POLYTECHN DE MONS
Method and apparatus for measuring fiber twist by polarization tracking
ActiveUS20120281205A1Reflectometers dealing with polarizationMaterial analysis by optical meansFiberLength wave
A method of measuring fiber twist in a multi-core optical fiber bearing an FBG with polarization dependent reflectivity. The state of polarization of the launched light is adjusted until the reflected FBG wavelength is maximal, indicating that light reaching the FBG is linearly polarized, and the polarization axis of the light reaching the FBG is aligned with the slow birefringent axis of the FBG; the SOP of launched light is now measured. Bending experienced by the fiber is measured conventionally, and birefringence produced by bending of the multi-core optical fiber is calculated. A candidate amount of twist between the launch location and the FBG is proposed, and the corresponding twist-induced birefringence is calculated. When calculations show that light with the launched SOP becomes linearly polarized and aligned with the FBG after traversing a fiber section with the calculated birefringences and proposed rotation, the amount of twist has been properly identified.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Optical-fiber-characteristic measuring device and optical-fiber-characteristic measuring method
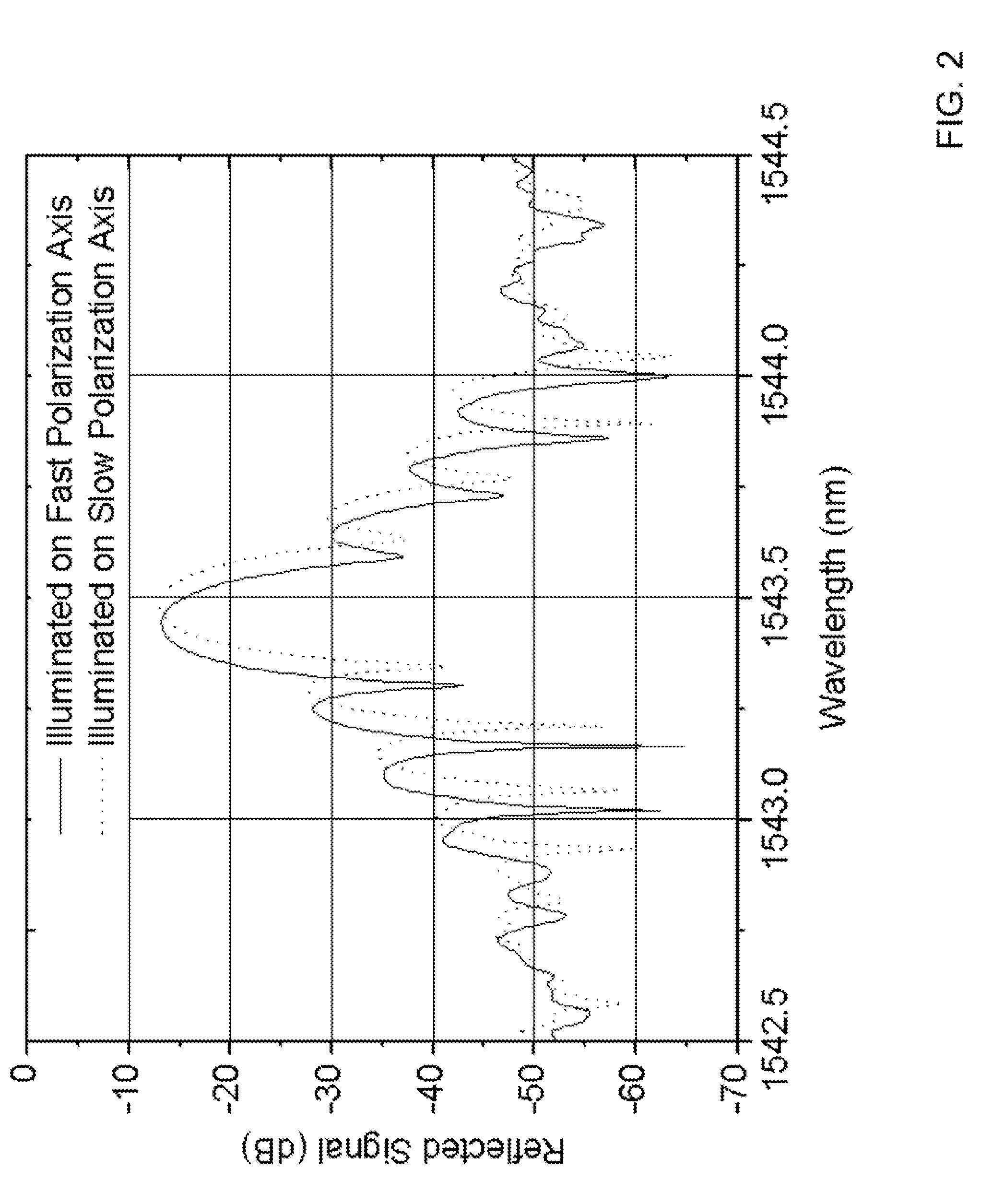
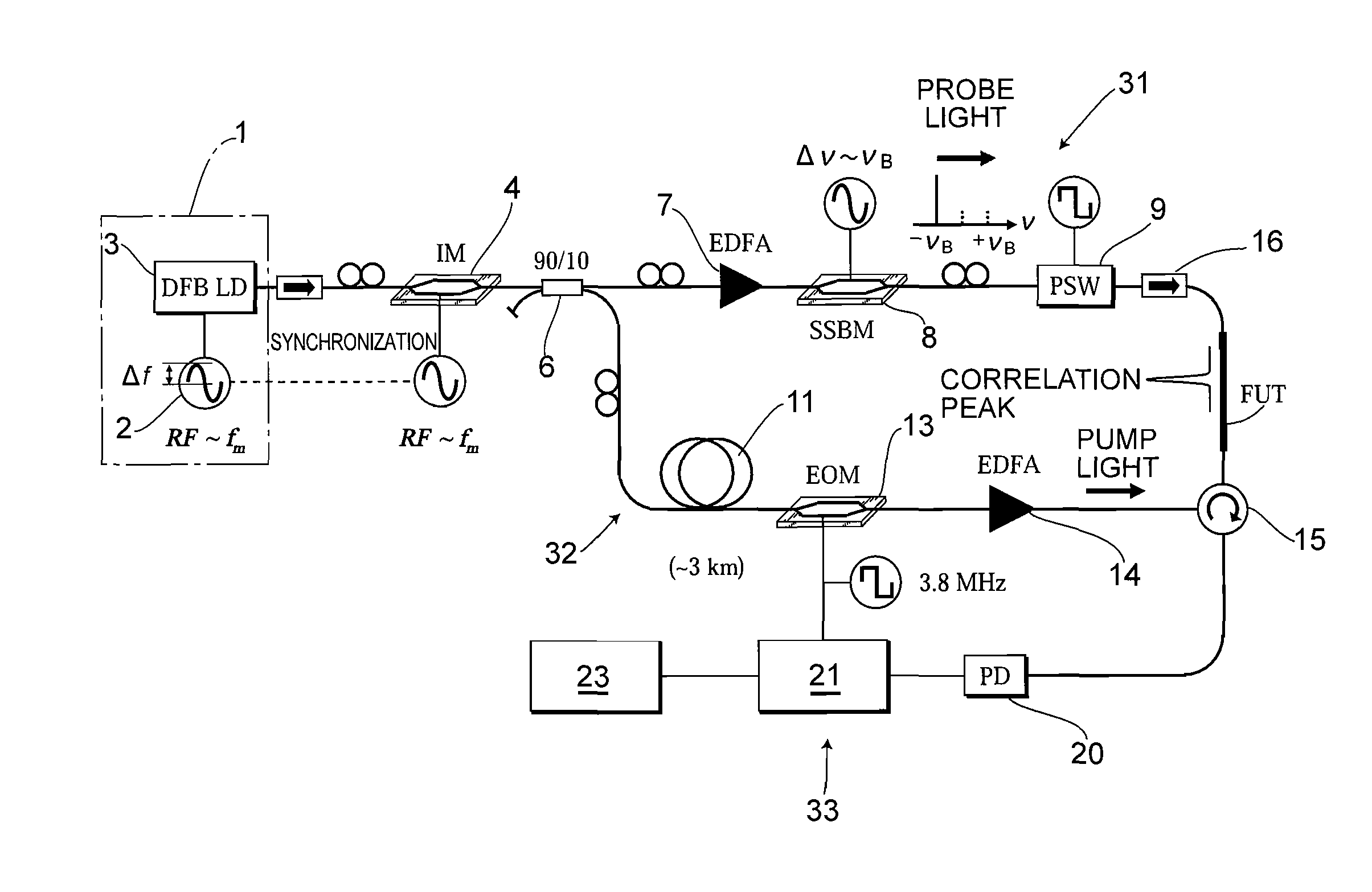
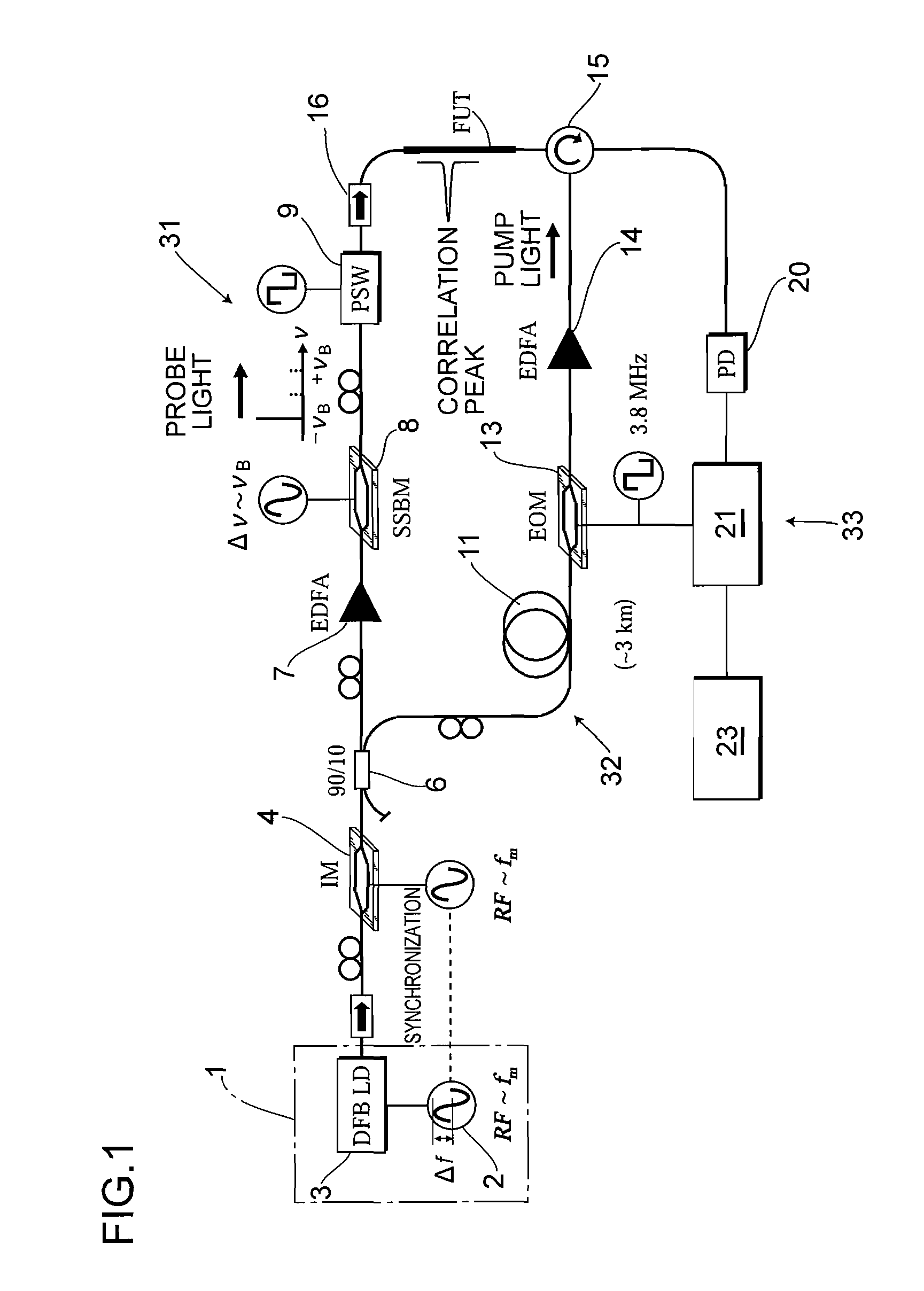
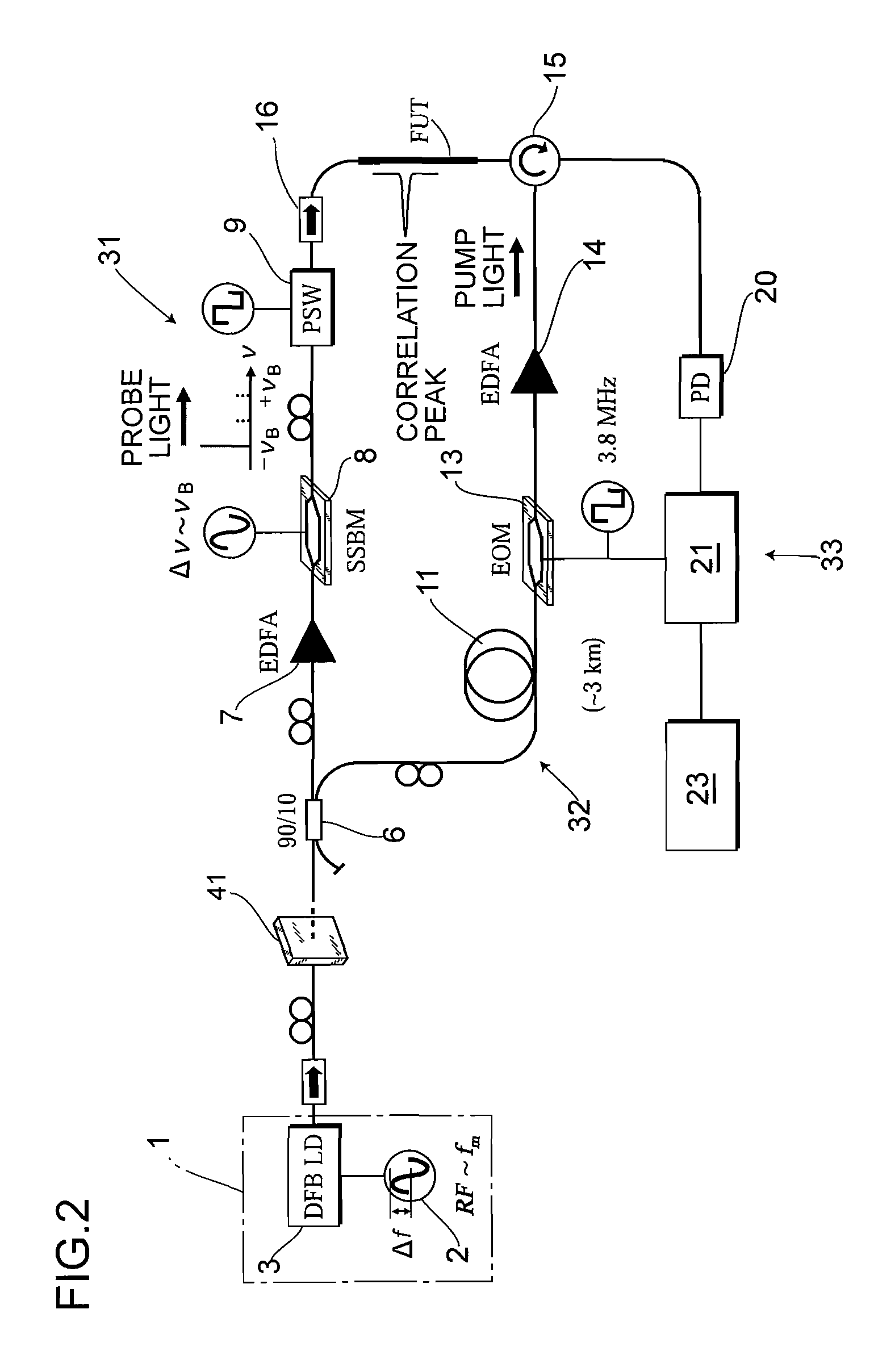
ActiveUS20100225900A1Intensity of output light can be increased and reducedExpand the measurement rangeReflectometers dealing with polarizationForce measurementMeasurement deviceFrequency spectrum
A measurement precision is improved and a measurement range is extended by efficiently suppressing a noise level of integrated unnecessary components from non-correlation positions. Measuring means 33 detects the Brillouin gain of a probe light output from a measurement-target optical fiber FUT while sweeping a frequency difference between the pump light and the probe light, and measures the distribution of strains of the measurement-target optical fiber FUT. An optical intensity modulator 4 performs intensity modulation on output light in synchronization with frequency modulation performed on a light source 1. Accordingly, the spectrum distribution with respect to the frequency of light from the light source 1 can be adjusted arbitrarily, and a noise spectrum shape generated at a position other than a correlation peak position and spreading over a frequency axis can be adjusted, and the peak frequency of a Lorentz spectrum generated at the correlation peak position can be measured precisely. Moreover, a measurement range dm can be extended.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO +1
Distributed multi-channel coherent optical fiber sensing system
ActiveUS20160202142A1Reflectometers dealing with polarizationMaterial analysis by optical meansMultiplexingFiber
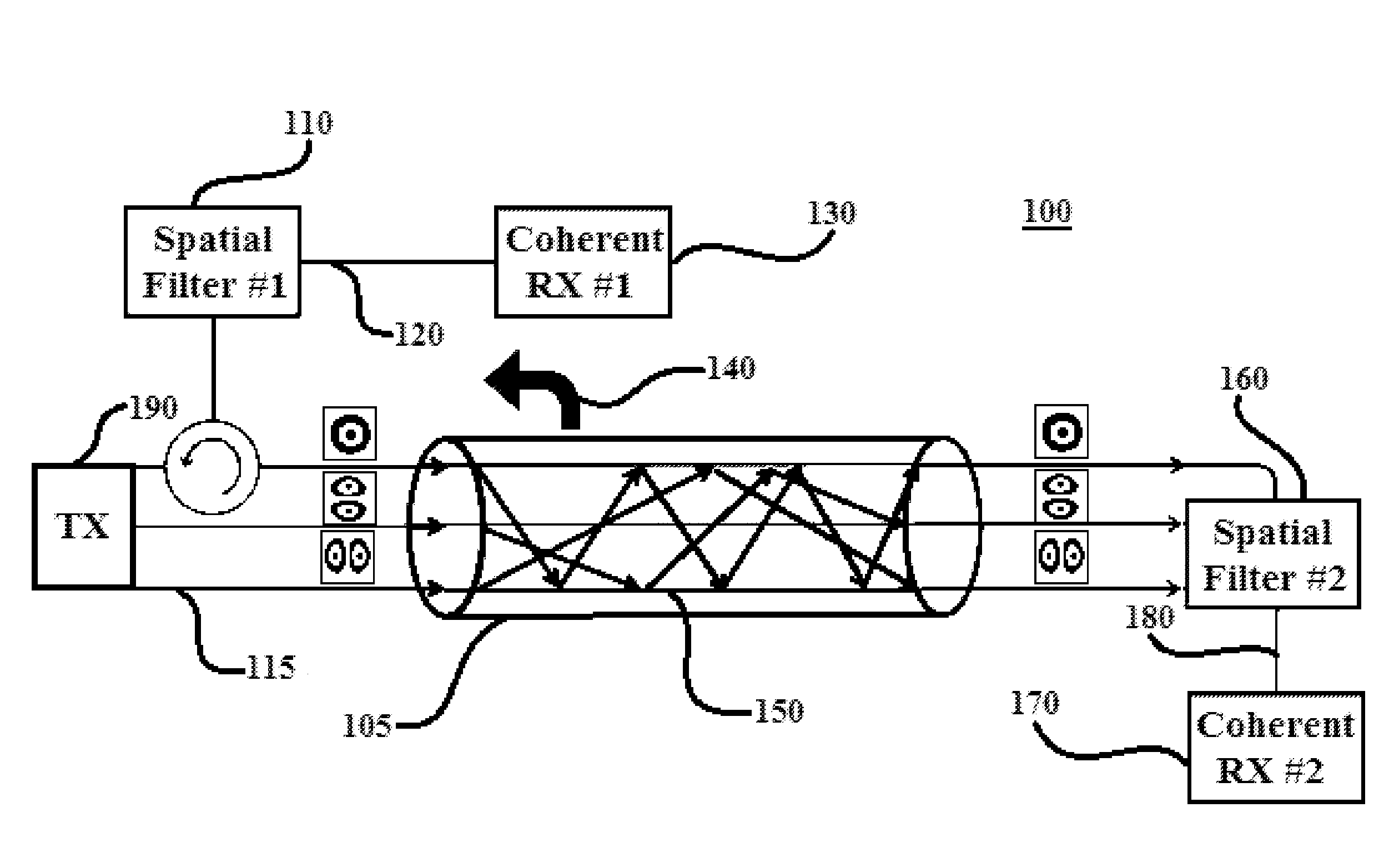
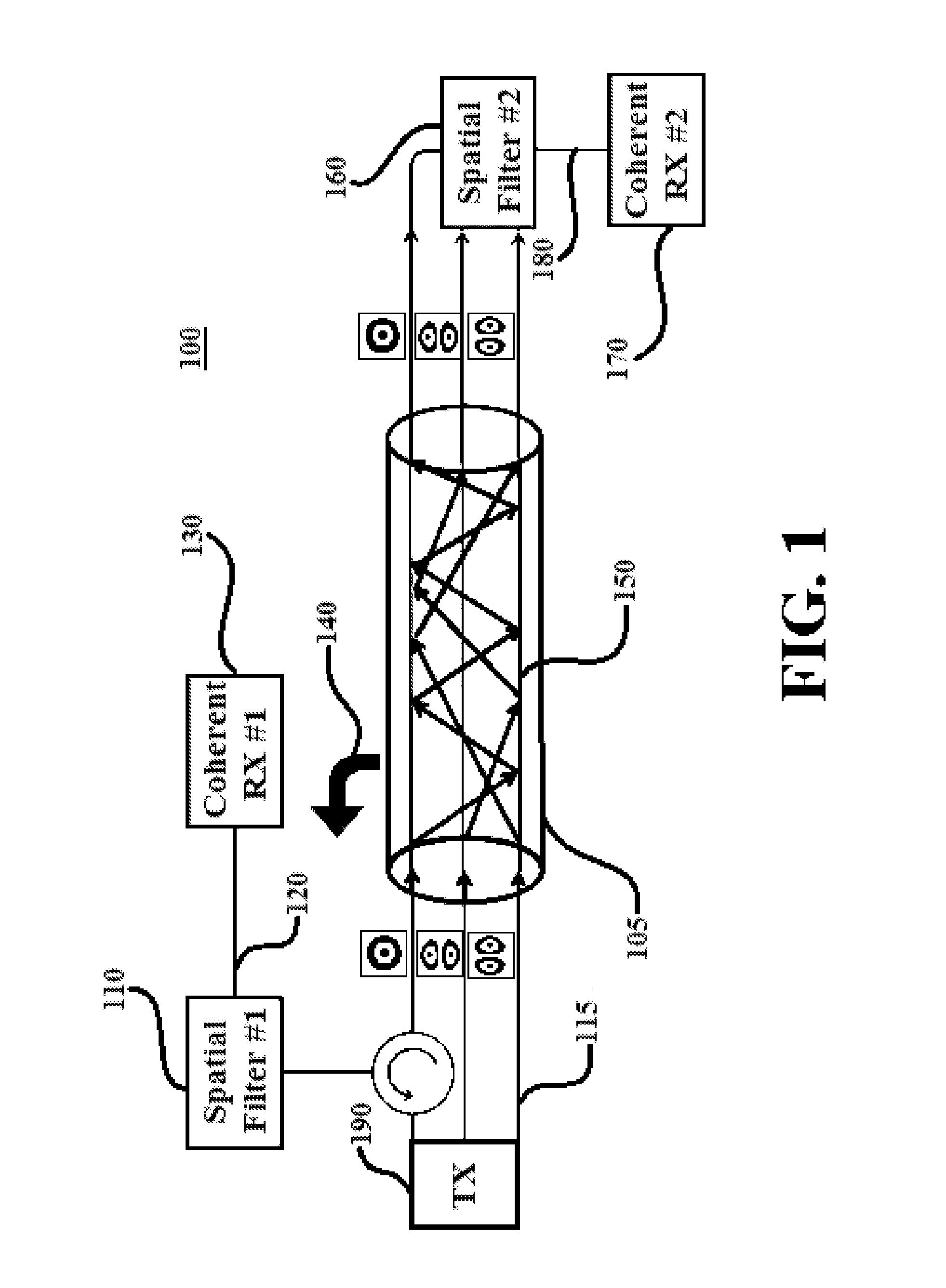
A method and system are provided. The method includes converting, using a spatial mode converter, an input signal into a plurality of spatial modes and performing polarization multiplexing and mode multiplexing, using a polarization multiplexer and a mode multiplexer, respectively, on the input signal. The method further includes injecting the input signal into a fiber optic medium. The method additionally includes applying, using at least one spatial filter in each of a forward and a backward direction within the fiber optic medium, the plurality of spatial modes within the fiber optic medium to transmit the input signal and perform distributed fault sensing on the input signal simultaneously
Owner:NEC CORP
Distributed fibre optic sensing for event detection
ActiveUS9002149B2Minimize couplingReflectometers dealing with polarizationOptical light guidesFiberSpeckle pattern
A fiber optic sensing method and apparatus for determining location and direction information of disturbances occurring in the environment of a sensor optical fiber are provided. The method comprises launching optical pulses into at least one polarisation eigenmode of a polarisation maintaining fiber as the sensor optical fiber, detecting temporal speckle patterns of light backscattered from the at least one polarisation eigenmode of the fiber, comparing the temporal speckle patterns to determine the location and direction information of a disturbance in the environment of the sensor optical fiber. The location information may be a distance along the fiber, and the direction information may be a direction radially from the axis of the fiber. The apparatus or instrument may be used to detect disturbance over long distances such as pipes, pipelines, or wells. Other applications include detecting intruders entering a controlled area.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Polarized lightwave reflectometry method (POTDR)
ActiveUS7126678B2Improve accuracyImprove compromiseReflectometers dealing with polarizationMaterial analysis by optical meansReflectometryLight signal
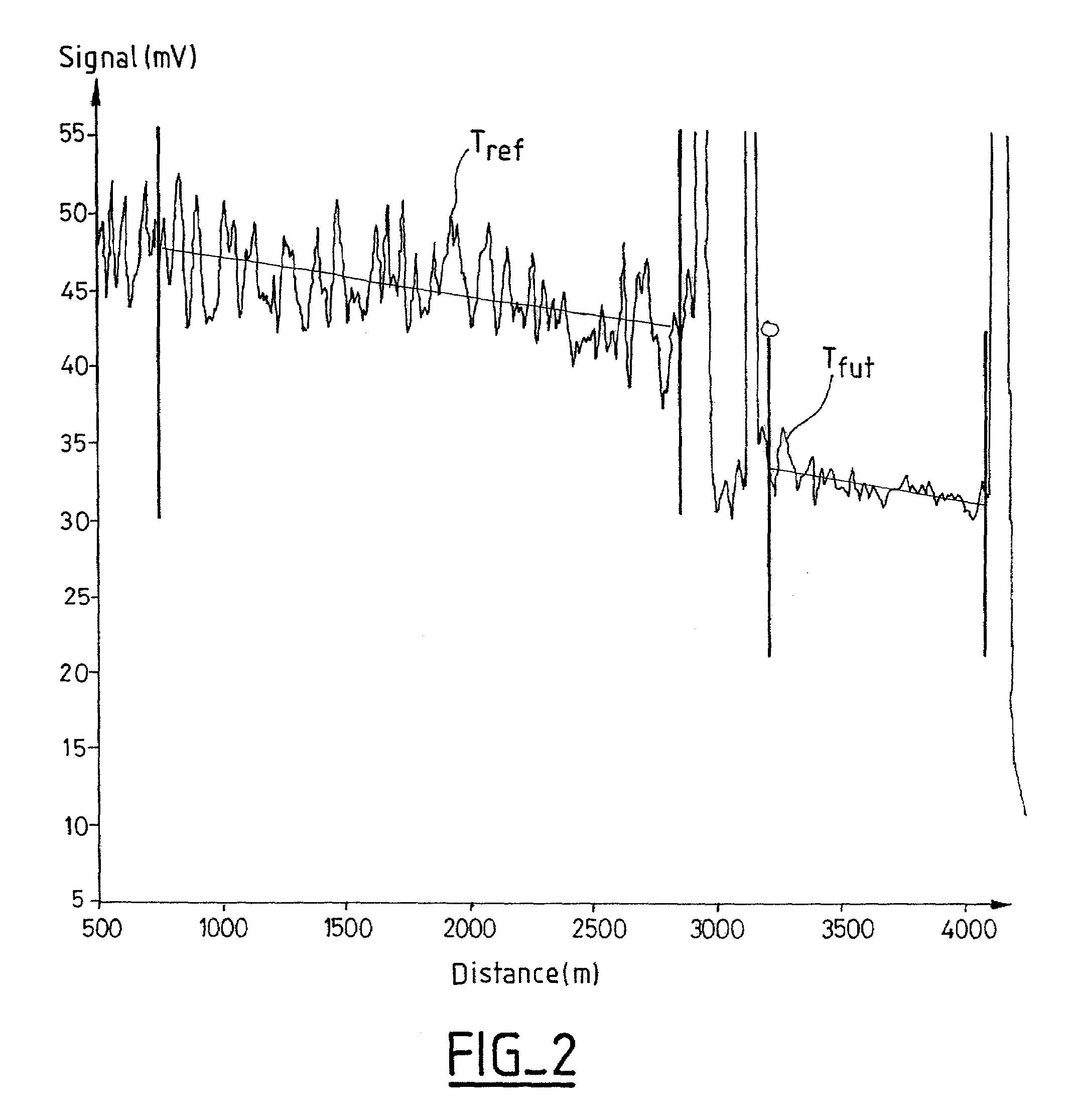
A polarized lightwave reflectometry method including the steps of sending at least two polarized light signals into the optical fiber to be tested, the signals presenting a determined angular offset relative to each other so that the polarization mode dispersion coefficient remains independent of any rotation of polarization in the optical fiber under test; extracting a scalar parameter of the relative noise type for each trace obtained by back-scattering of the light signal; and estimating the polarization mode dispersion coefficient by a function having a single scalar input, which function is of the type based on exponentials and has the form exp (a+bP+cP−1).
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Optical frequency domain reflectometer with optical wave frequency shift modulation
ActiveCN107515017AAchieving Simultaneous DetectionIncrease the lengthReflectometers dealing with polarizationTesting optical propertiesFrequency spectrumLine width
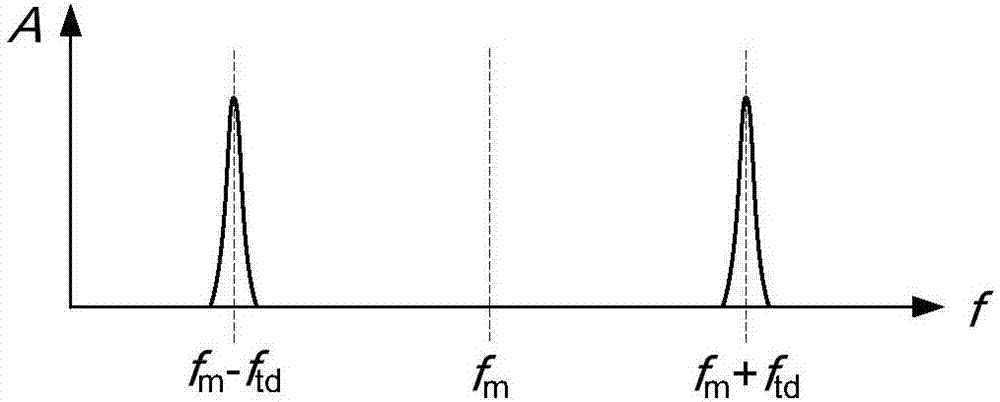
The invention discloses an optical frequency domain reflectometer with optical wave frequency shift modulation, which comprises a narrow linewidth scanning laser, a first optical fiber coupler, an optical circulator, a to-be-measured optical fiber, an optical wave frequency shifter, a second optical fiber coupler, a first polarization beam splitter, a second polarization beam splitter, a first balanced photodetector, a second balanced photodetector, a third optical fiber coupler, a first Faraday rotating mirror, a second Faraday rotating mirror, a reference optical fiber interferometer, a photodetector and a signal acquisition and processing unit. Through frequency shift modulation on measurement light and reference light, interference signals produced by superposition of scattering signal light of the to-be-measured optical fiber which is symmetrical about zero delay and local oscillation light are separated on the spectrum. According to the optical frequency domain reflectometer with optical wave frequency shift modulation, mutual interference among the interference signals of the to-be-measured optical fiber scattering signal light which is symmetrical about zero delay can be suppressed, measurement of the scattering signal light which is symmetrical about zero delay can be realized, and the maximum optical fiber measurement length can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF AEROSPACE CONTROL DEVICES
Apparatus and method for measuring characteristics of iptical fibers
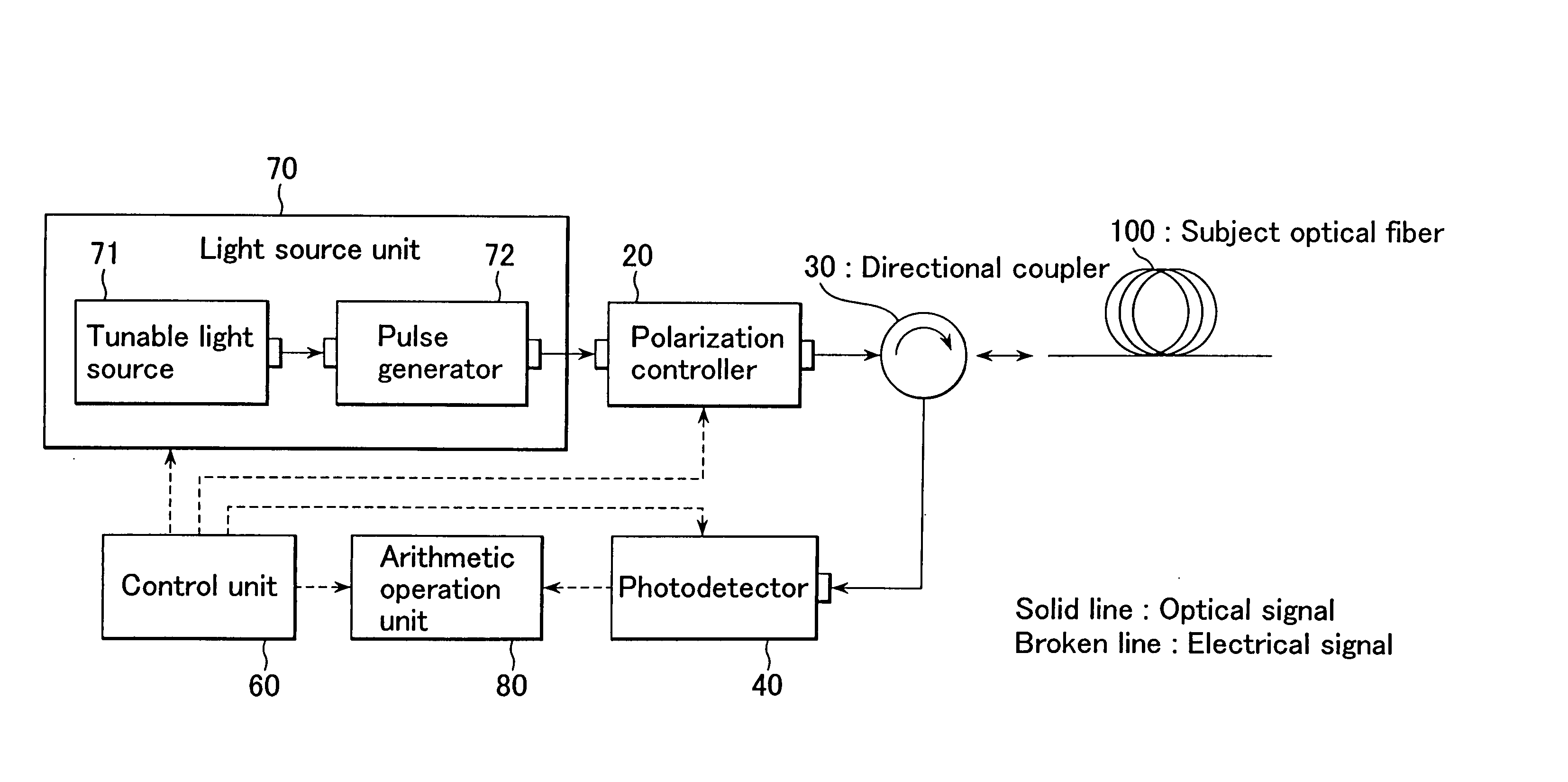
ActiveUS20050018174A1Accurate measurementReflectometers dealing with polarizationMaterial analysis by optical meansFiberPhotodetector
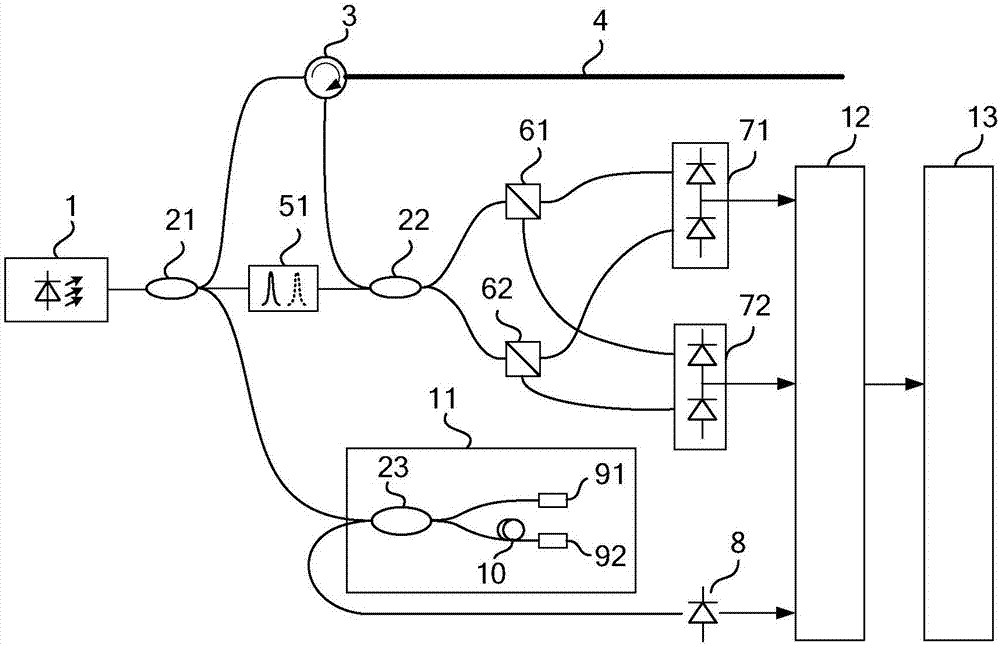
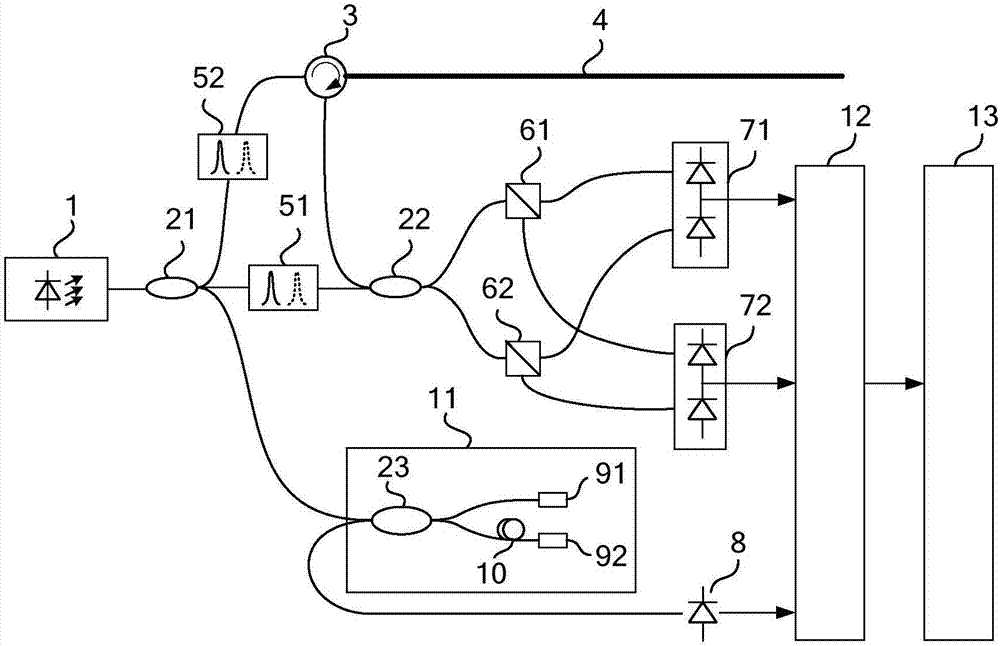
An apparatus and method for measuring characteristics of optical fibers that enable accurate measurement of characteristics of optical fibers (distribution of polarization mode dispersion and distribution of magnitude of birefringence) are to be realized. This invention is an improvement of an optical fiber characteristics measuring apparatus in which pulse light is inputted to a subject optical fiber, back scattered light of the pulse light from the subject optical fiber is detected by a photodetector to find a Stokes vector, and polarization mode dispersion in a longitudinal direction is measured. The apparatus comprises a light source unit for outputting the pulse light having at least three different angular frequencies, and an arithmetic operation unit for calculating the magnitude of linear polarization components and the magnitude of a circular polarization component of a polarization dispersion vector on the basis of the Stokes vector and thus calculating polarization mode dispersion.
Owner:ANDO ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
Polarization diversity detection without a polarizing beam splitter
InactiveUS7379168B2Reflectometers dealing with polarizationMaterial analysis by optical meansFiberMeasurement device
A fiber optic measurement device including an optical frequency domain reflectometer (OFDR) performs polarization diversity detection without using a polarizing beam splitter.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Polarization Optical Time Domain Reflectometer and Method of Determining PMD
InactiveUS20090244522A1Eliminate disadvantagesConvenient and accurateReflectometers dealing with polarizationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceTime-domain reflectometerFiber
In a method of measuring cumulative polarization mode dispersion (PMD) along the length of a fiber-under-test (FUT), a polarization-sensitive optical time domain reflectometer (POTDR) is used to inject into the FUT plural series of light pulses arranged in several groups. Each group comprises at least two series of light pulses having different but closely-spaced wavelengths and the same state of polarization (SOP). At least two, and preferably a large number of such groups, are injected and corresponding OTDR traces obtained for each series of light pulses by averaging the impulse-response signals of the several series of light pulses in the group. The process is repeated for a large number of groups having different wavelengths and / or SOPs. The PMD then is obtained by normalizing the OTDR traces of all of the groups, then computing the difference between each normalized OTDR trace in one group and the corresponding normalized OTDR trace in another group, followed by the mean-square value of the differences. Finally, the PMD is computed as a predetermined function of the mean-square difference. The function may, for example, be a differential formula, an arcsine formula, and so on.
Owner:EXFO ELECTRO OPTICAL ENG
Method and system for measuring the wavelength dispersion and nonlinear coefficient of an optical fiber, method of manufacturing optical fibers, method of measuring wavelength-dispersion distribution, method of compensating for measurement errors, and method of specifying conditions of measurement
ActiveUS20050058417A1Reflectometers dealing with polarizationReflectometers using simulated back-scatterLength waveAstigmatism
A method of simultaneously specifying the wavelength dispersion and nonlinear coefficient of an optical fiber. Pulsed probe light and pulsed pump light are first caused to enter an optical fiber to be measured. Then, the power oscillation of the back-scattered light of the probe light or idler light generated within the optical fiber is measured. Next, the instantaneous frequency of the measured power oscillation is obtained, and the dependency of the instantaneous frequency relative to the power oscillation of the pump light in a longitudinal direction of the optical fiber is obtained. Thereafter, a rate of change in the longitudinal direction between phase-mismatching conditions and nonlinear coefficient of the optical fiber is obtained from the dependency of the instantaneous frequency. And based on the rate of change, the longitudinal wavelength-dispersion distribution and longitudinal nonlinear-coefficient distribution of thee optical fiber are simultaneously specified.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Intrusion detection system for use on single mode optical fiber using a storage register for data
ActiveUS20060291795A1Overcome limitationsMaximum sensitivityReflectometers dealing with polarizationOptical light guidesPolarimeterPolarizer
A telecommunications optical fiber is secured against intrusion by detecting manipulation of the optical fiber prior to an intrusion event. This can be used in a non-locating system where the detection end is opposite the transmit end or in a locating system which uses Fresnel reflections and Rayleigh backscattering to the transmit end to detect and then locate the motion. The Rayleigh backscattering time sliced data can be stored in a register until an intrusion event is detected. The detection is carried out by a polarization detection system which includes an optical splitter which is manufactured in simplified form for economic construction. This uses a non-calibrated splitter and less than all four of the Stokes parameters. It can use a polarimeter type function limited to linear and circular polarization or two linear polarizers at 90 degrees.
Owner:NETWORK INTEGRITY SYST
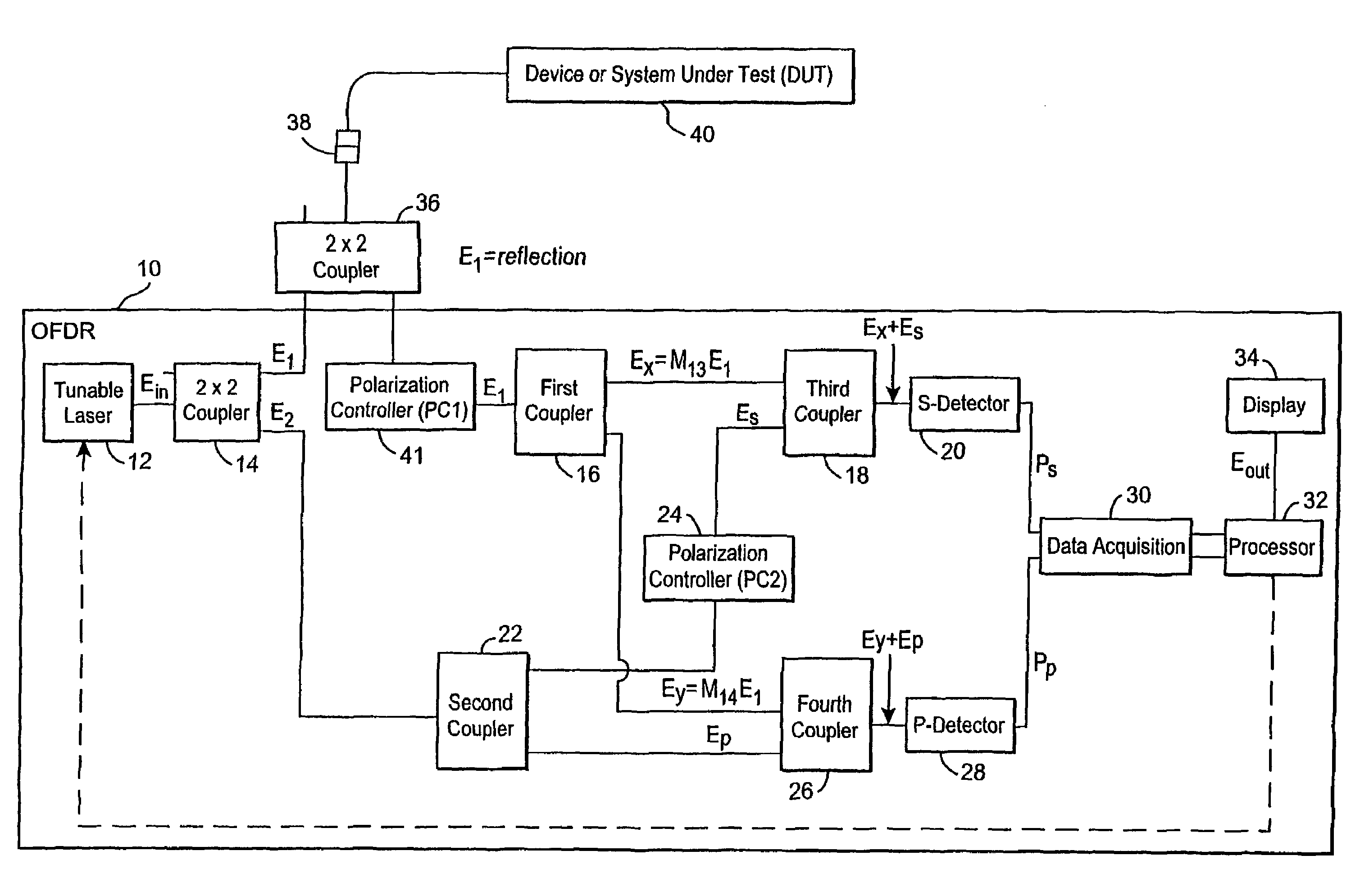
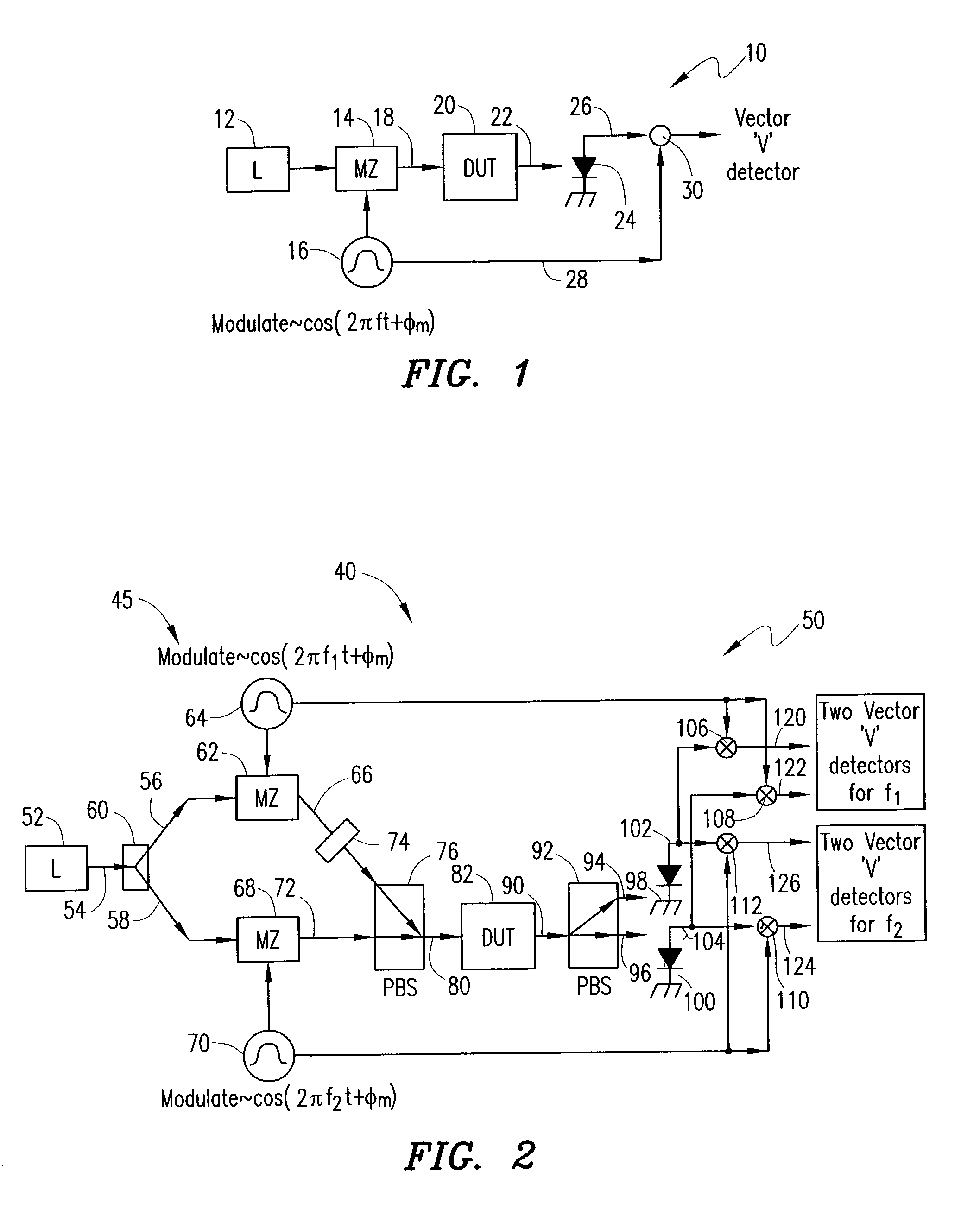
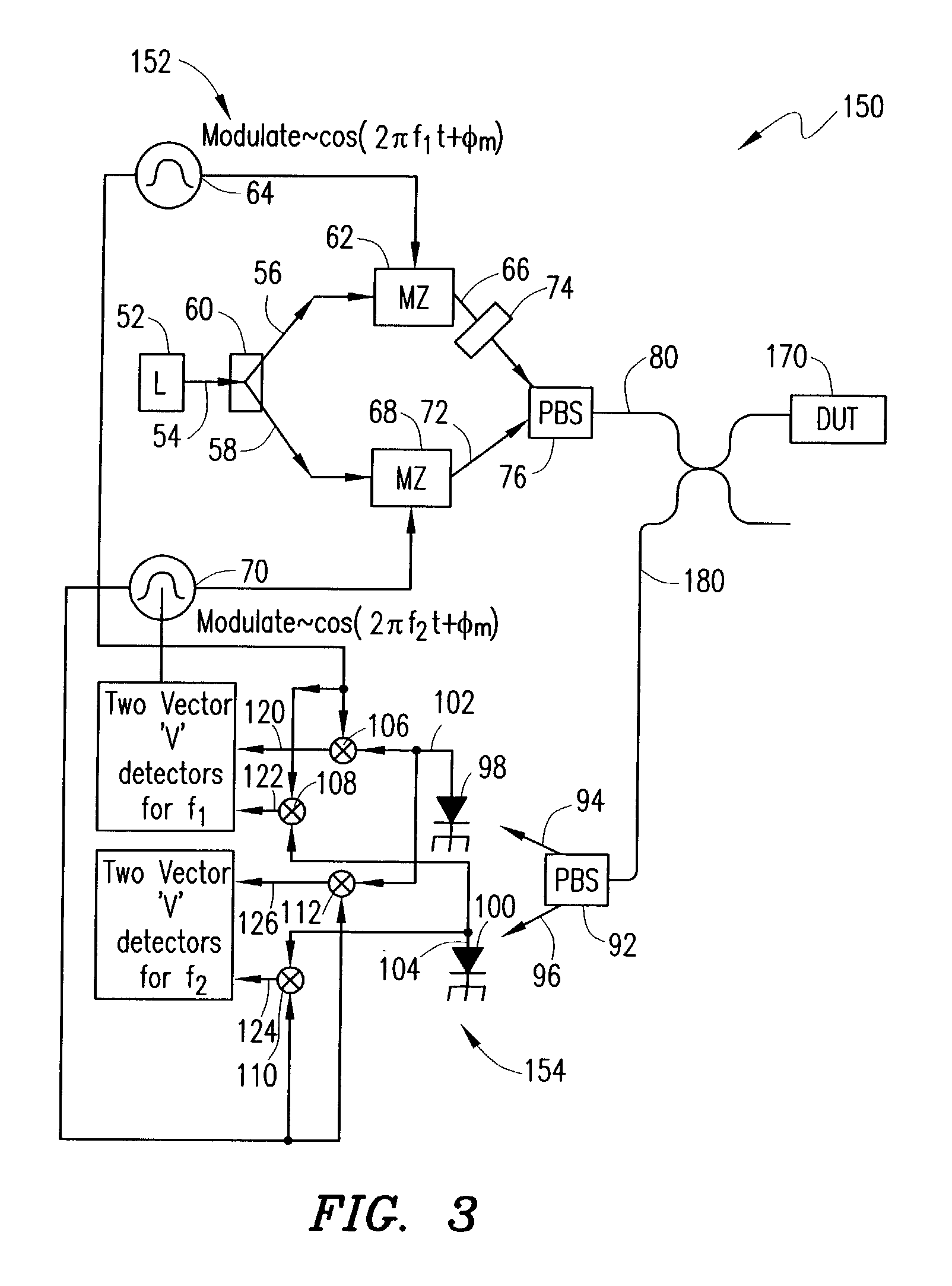
Single sweep phase shift method and apparatus for measuring chromatic and polarization dependent dispersion
InactiveUS20040021864A1Minimize chromatic dispersionNegatively influences the quality of an optical signal carriedReflectometers dealing with polarizationMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical propertyPhase shifted
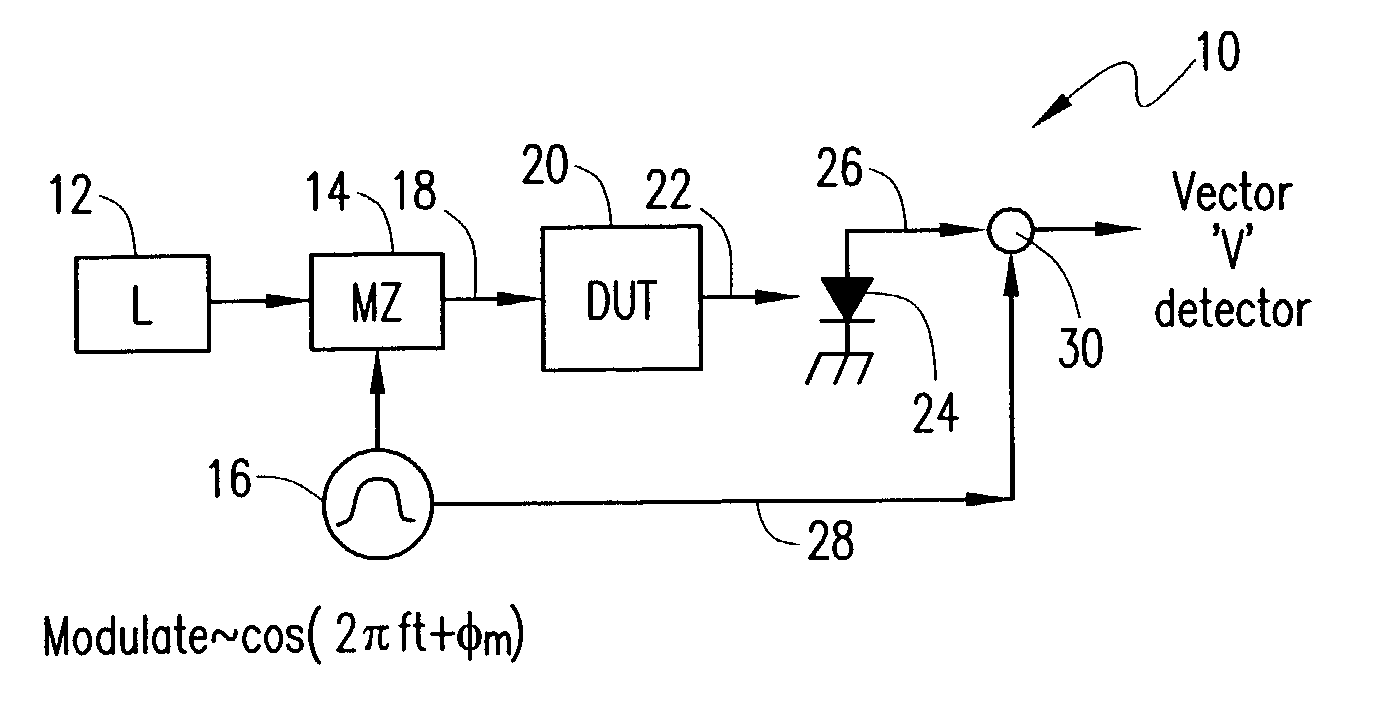
A method for determining at least one optical property of an optical device comprises providing an optical input signal that includes first and second signal components that are modulated at first and second frequencies, respectively, and that have first and second polarization states, respectively. The optical input signal is passed to an optical device. An optical output signal from the optical device is separated into first and second output signals that have third and fourth polarization states, respectively. The first and second output signals are each compared with reference signals at the first and second frequencies to provide four phase shift and amplitude measurements that can be used to determine the at least one optical property of the optical device as a function of wavelength.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Popular searches
Scattering properties measurements Catheter Diagnostic recording/measuring Sensors Using optical means Light polarisation measurement Using wave/particle radiation means Converting sensor output Reflectometers detecting back-scattered light in frequency-domain Reflectometers detecting back-scattered light in time-domain
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com