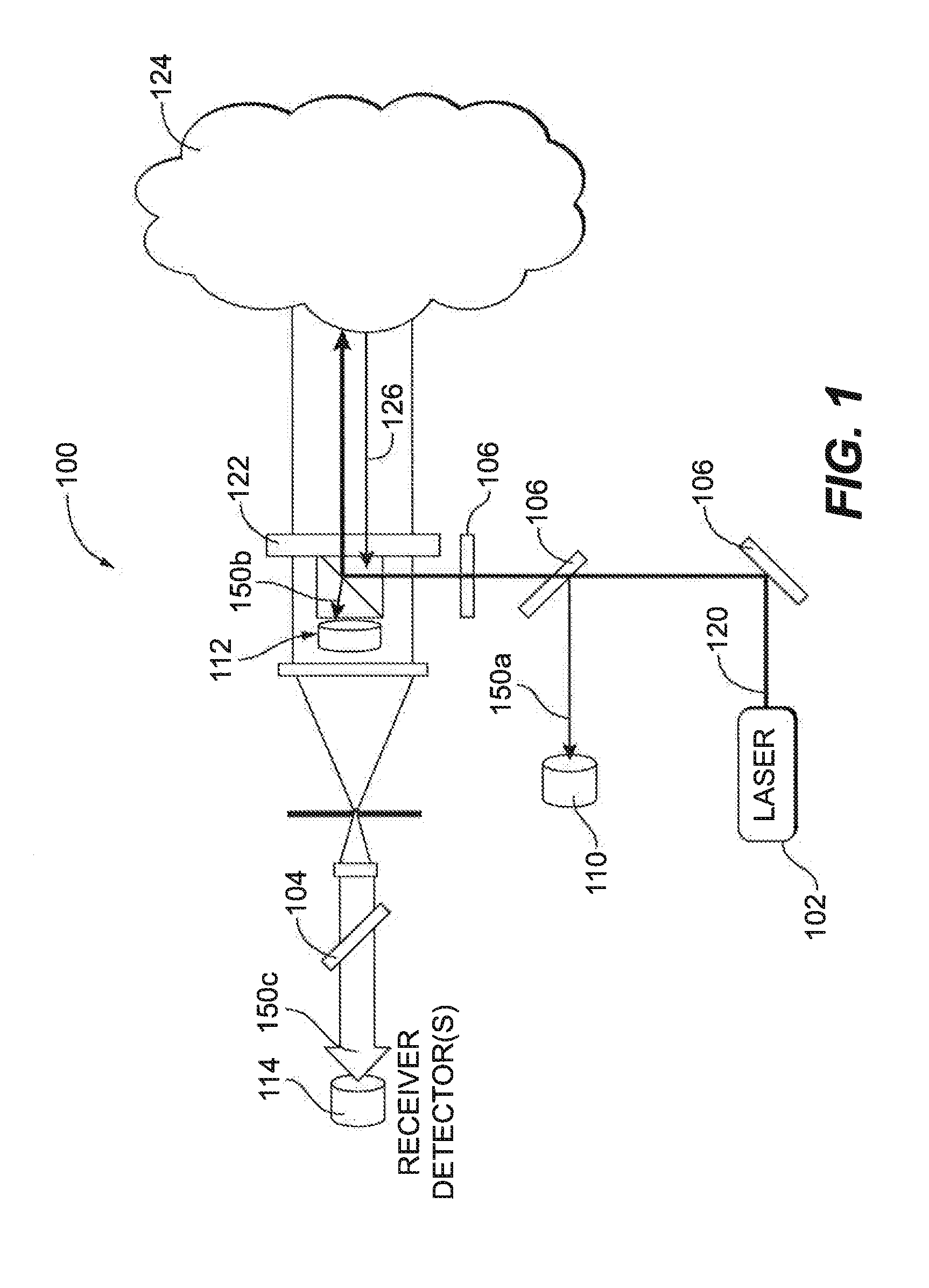
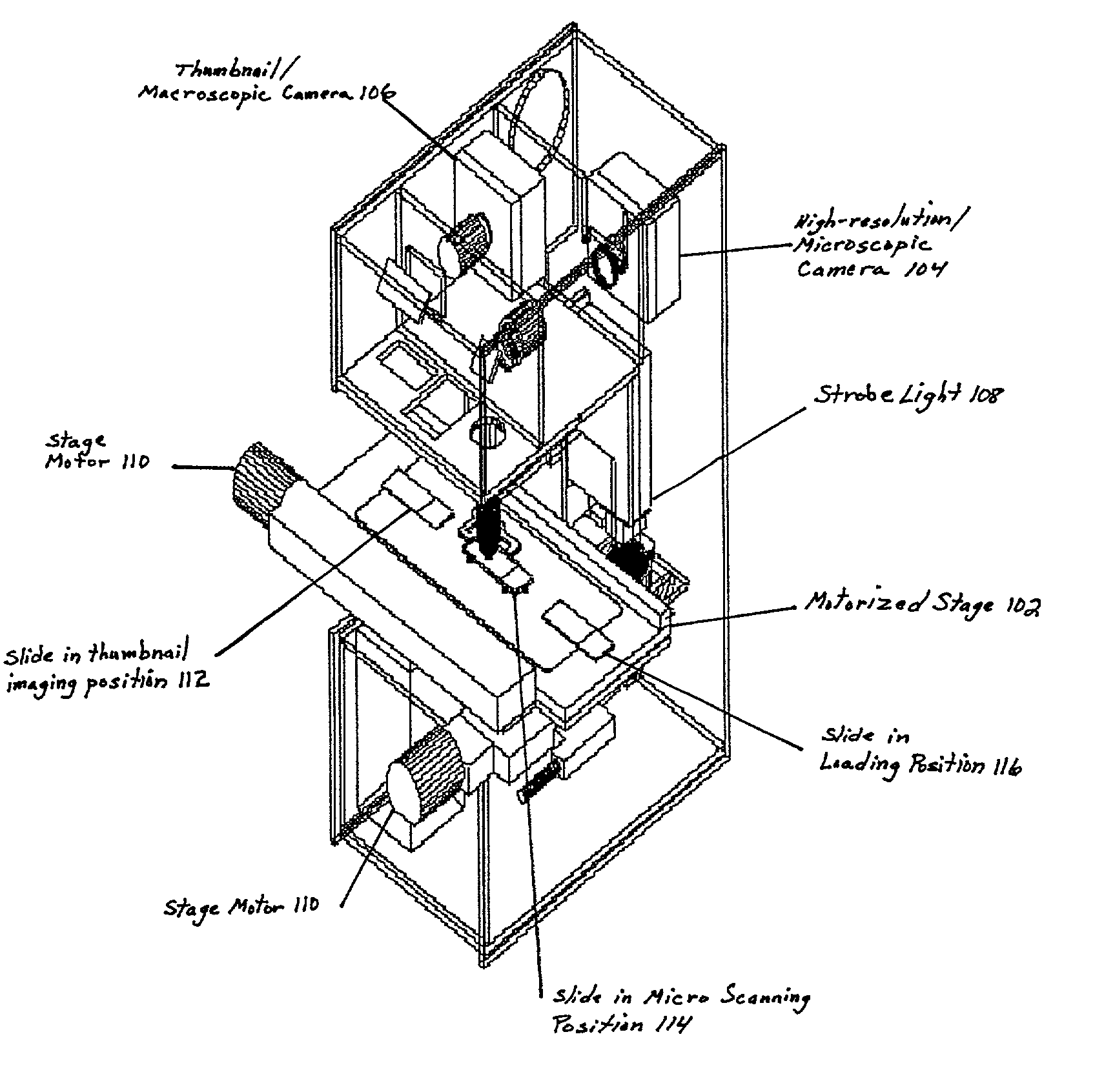
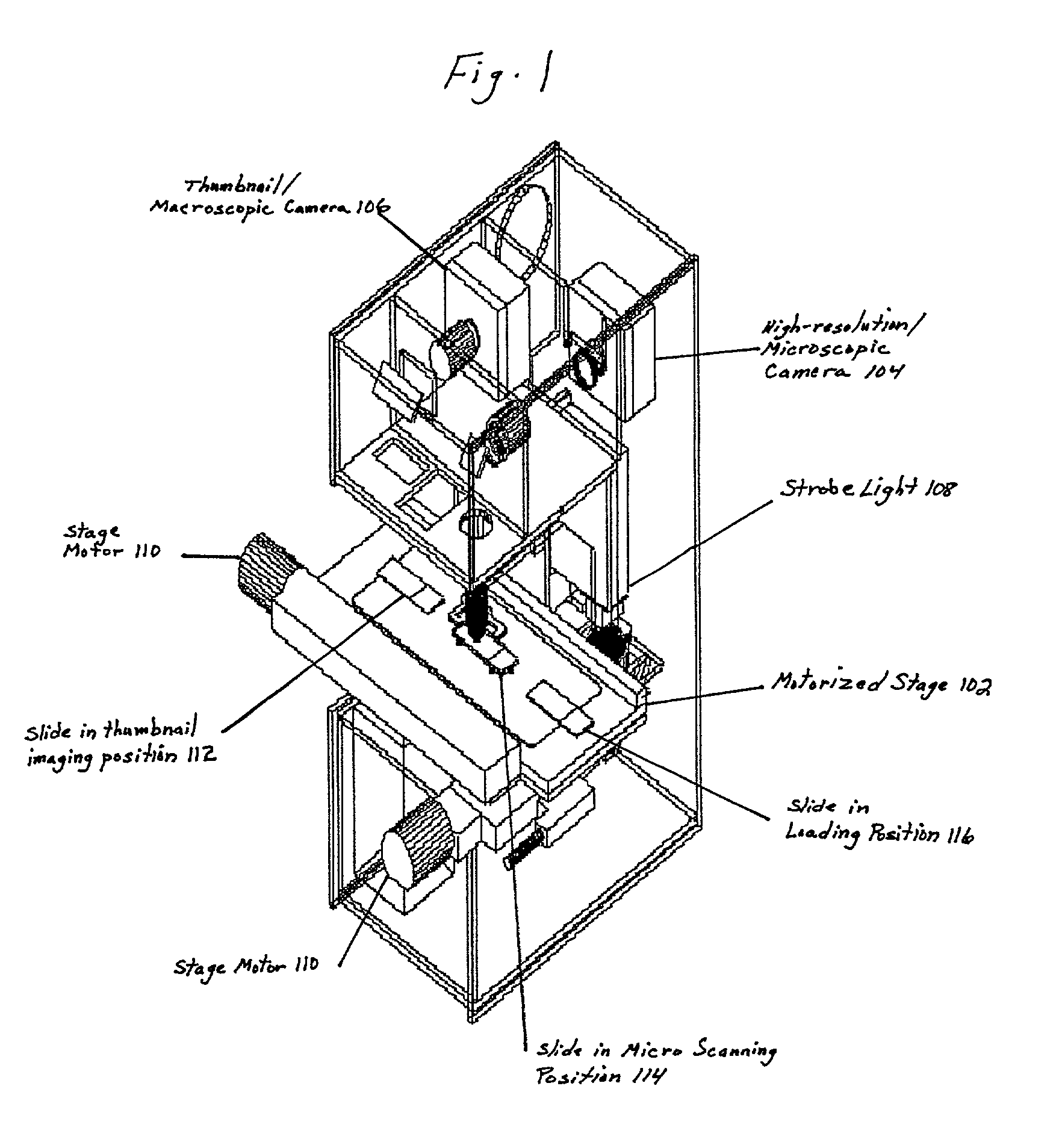
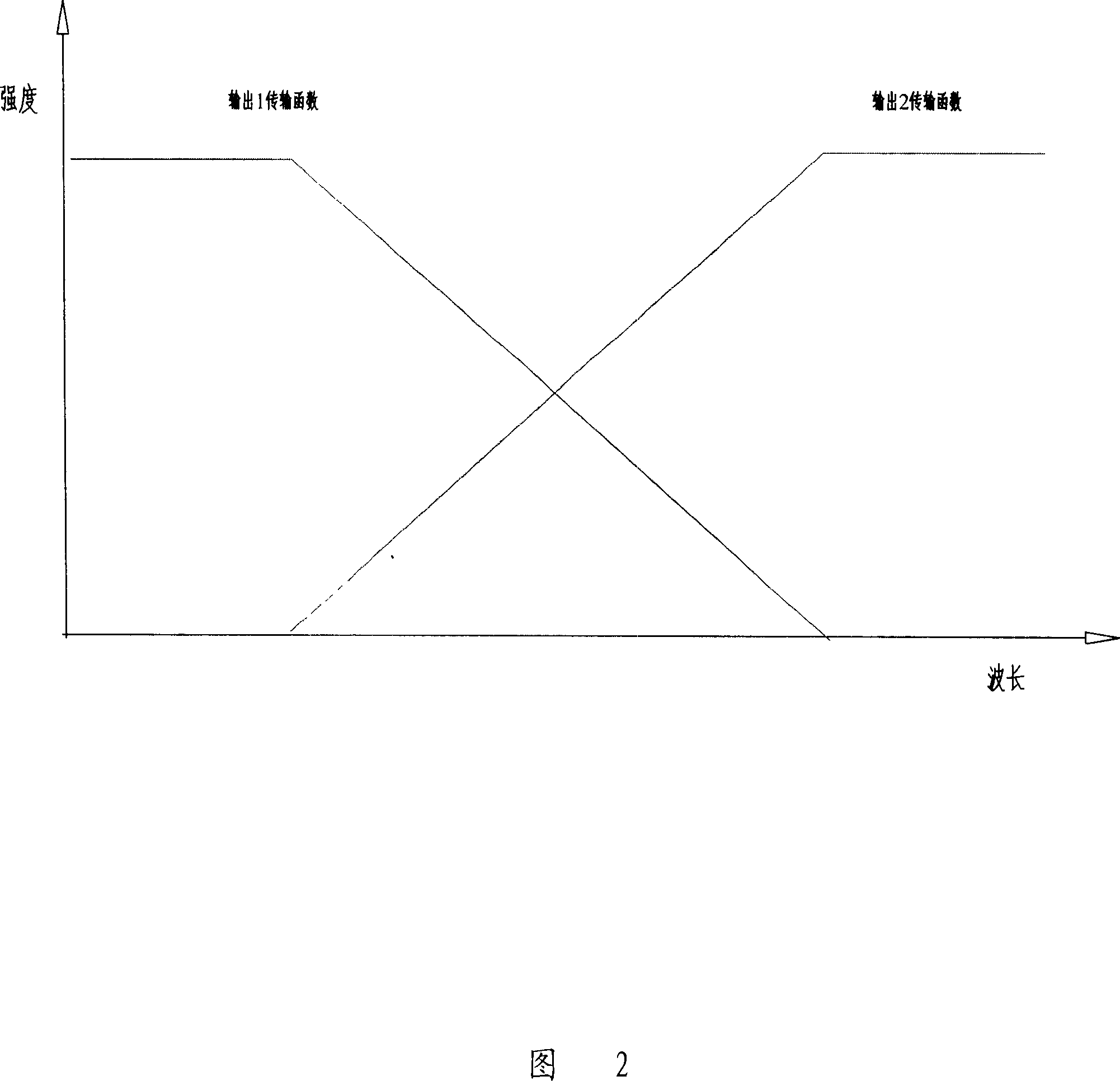
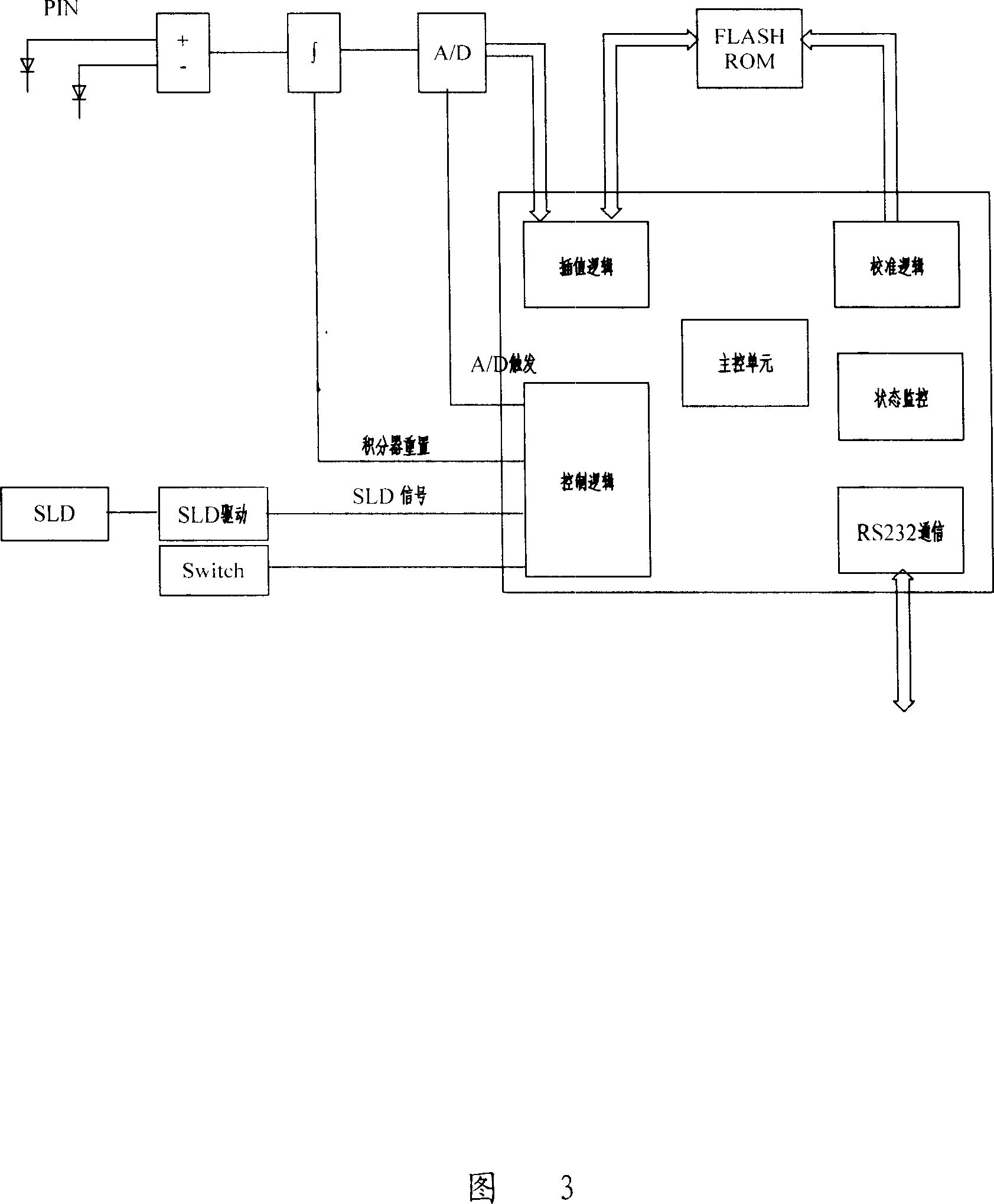
Patents
Literature
2362 results about "Pulse light" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
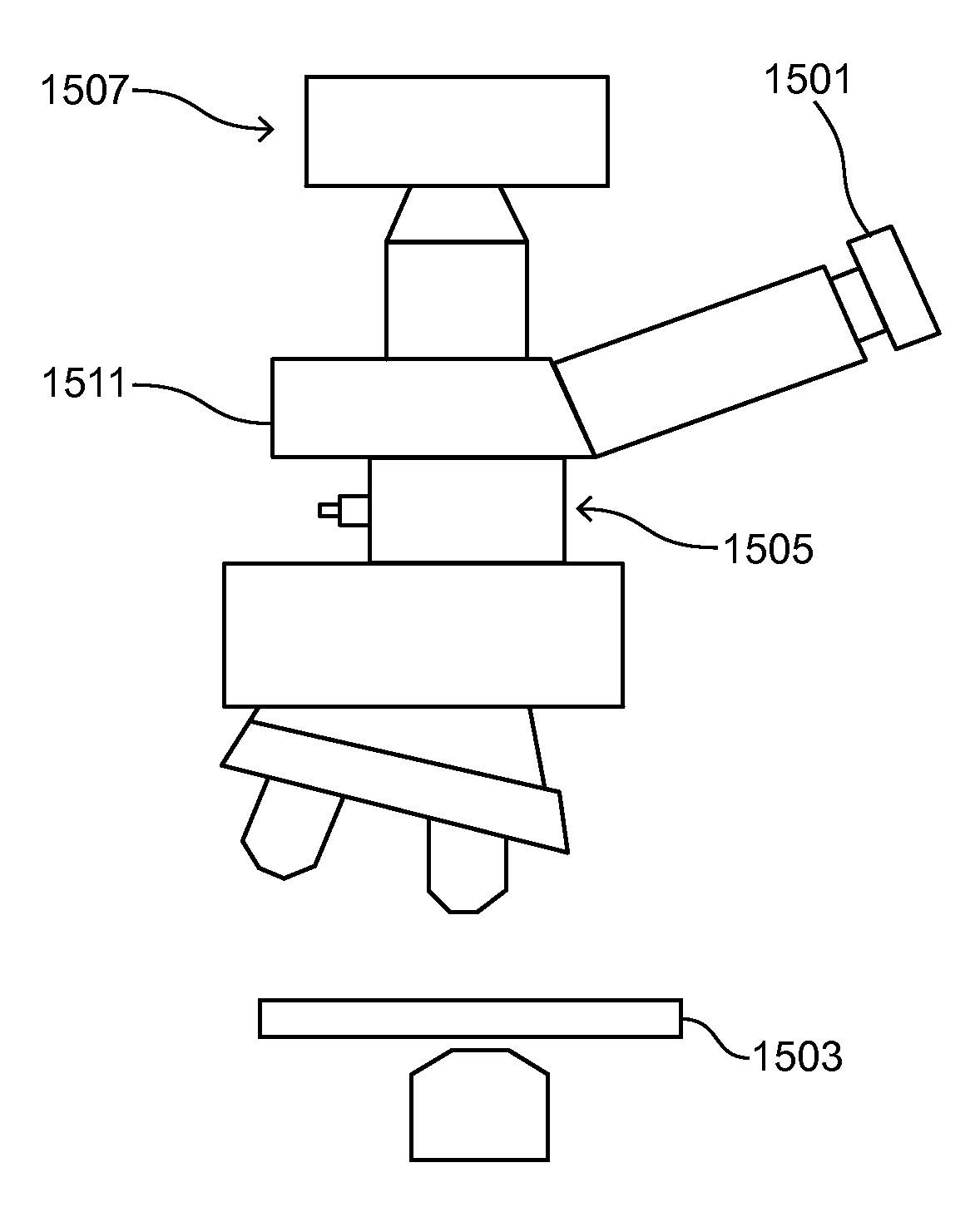
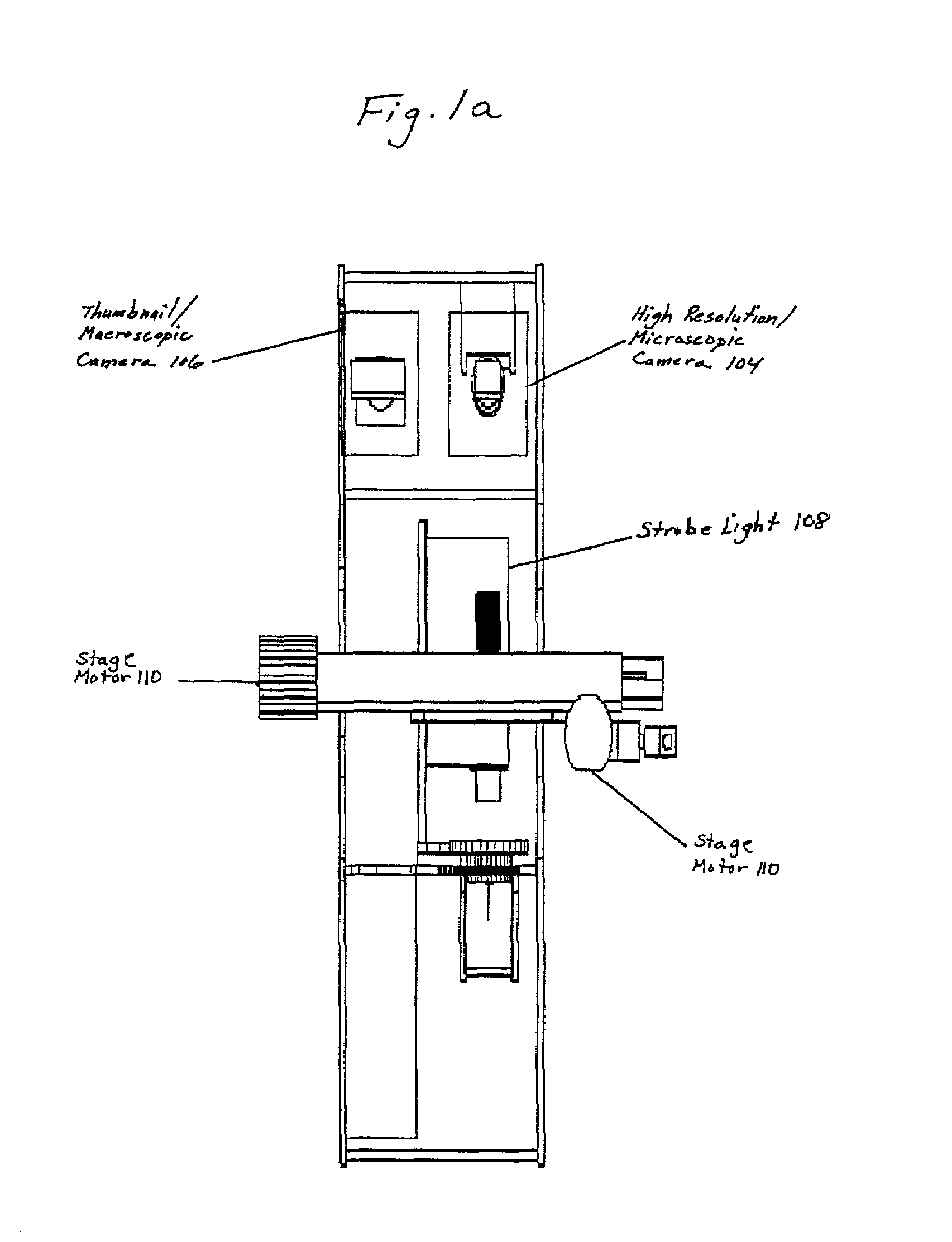
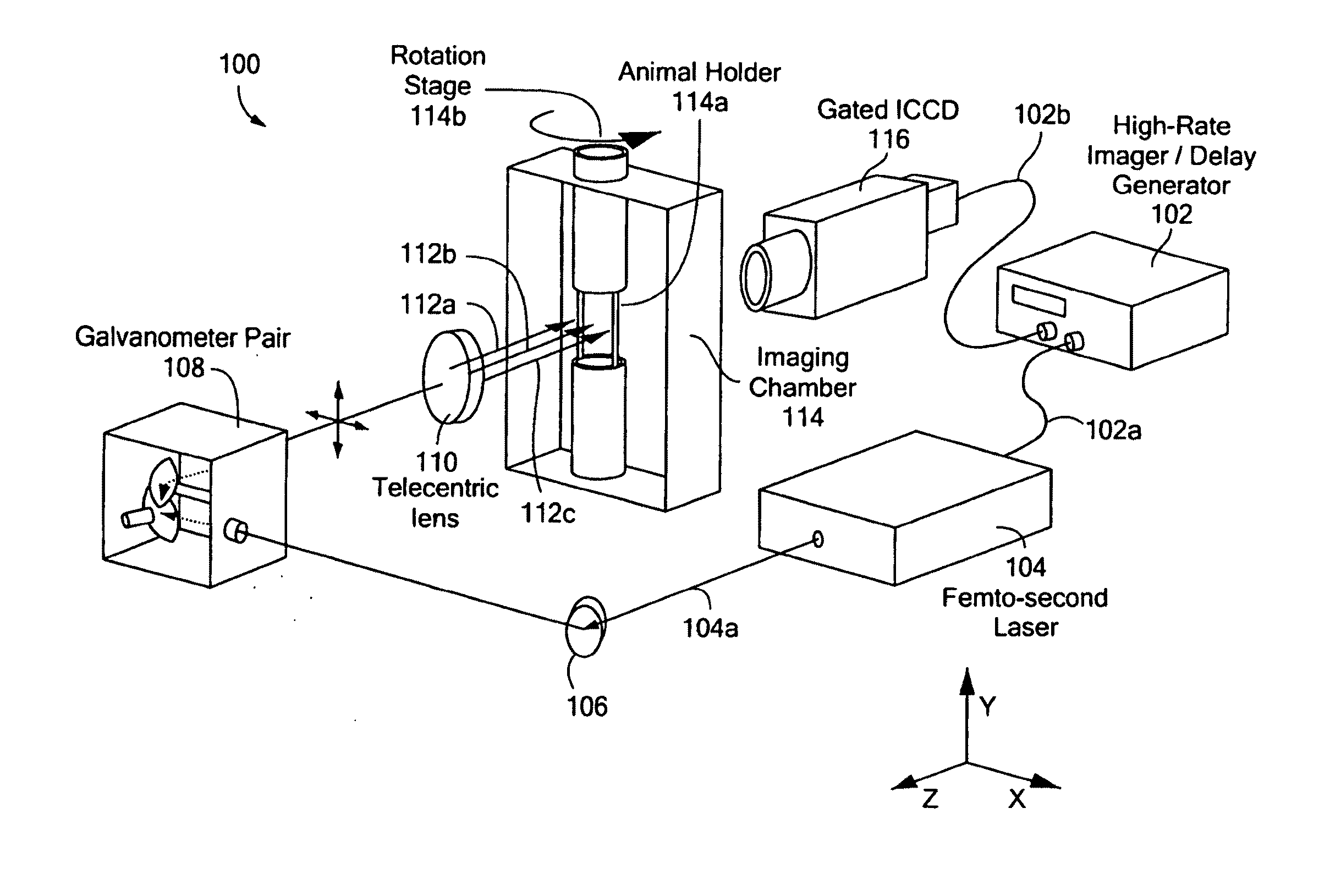
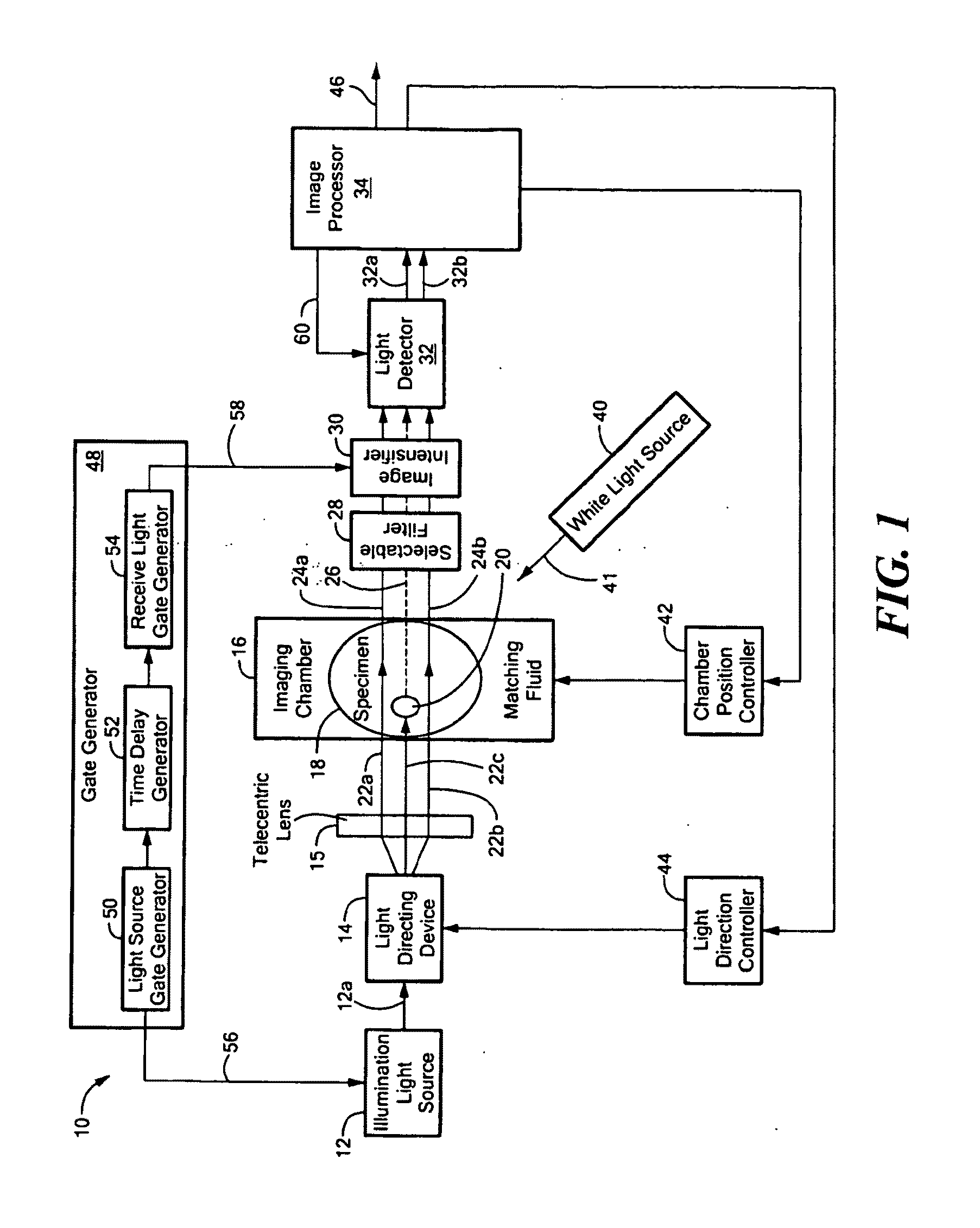
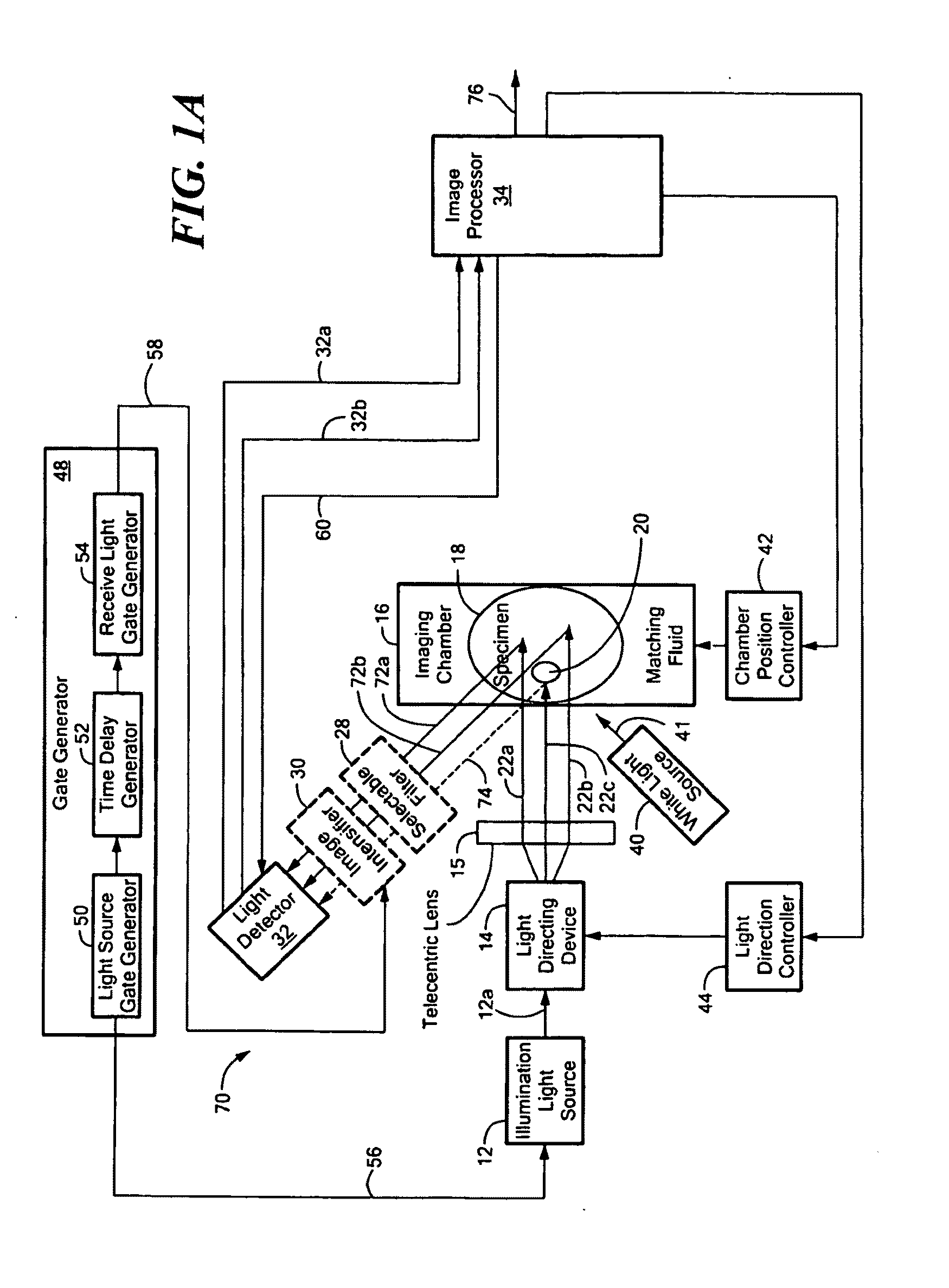
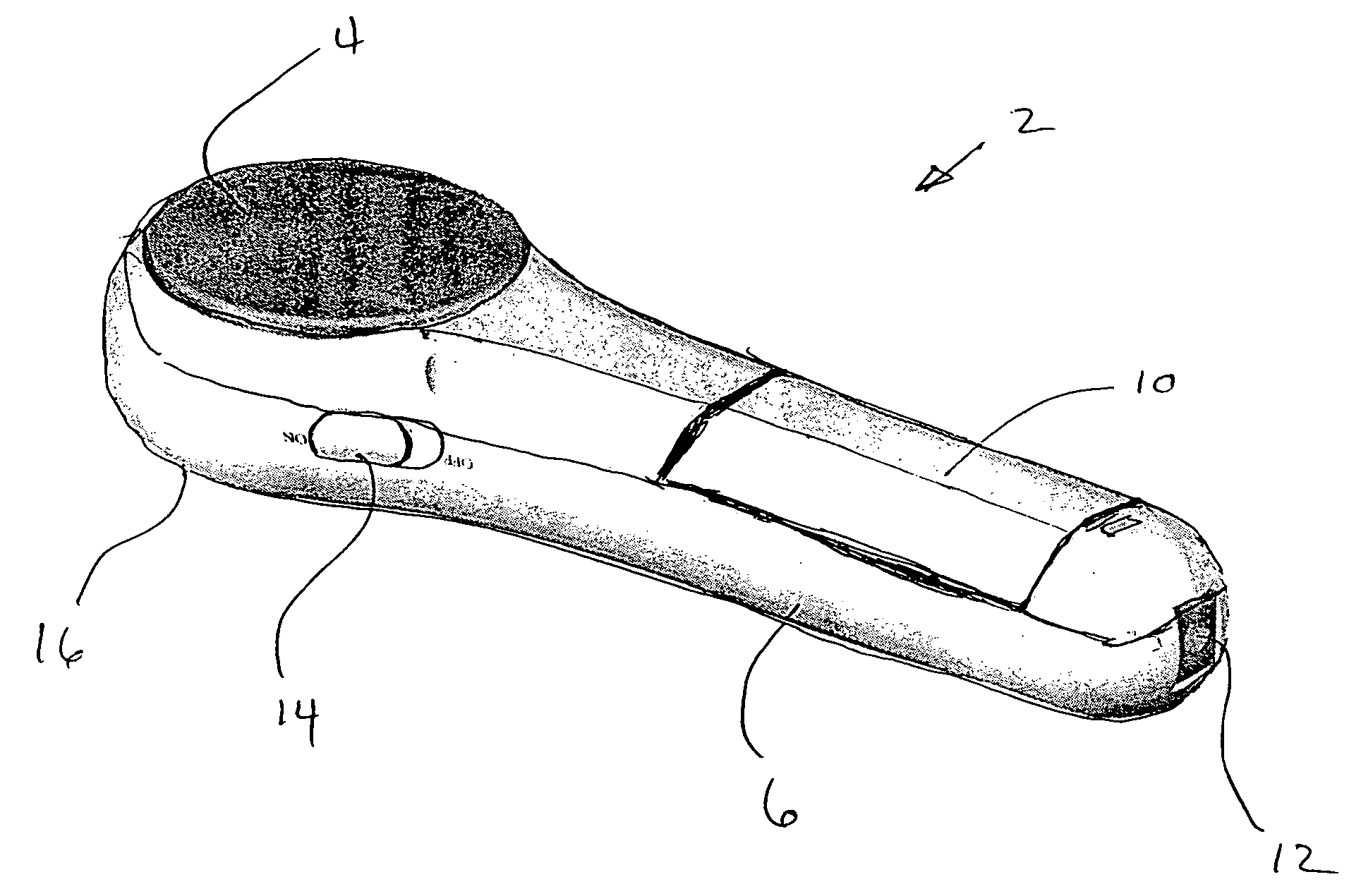
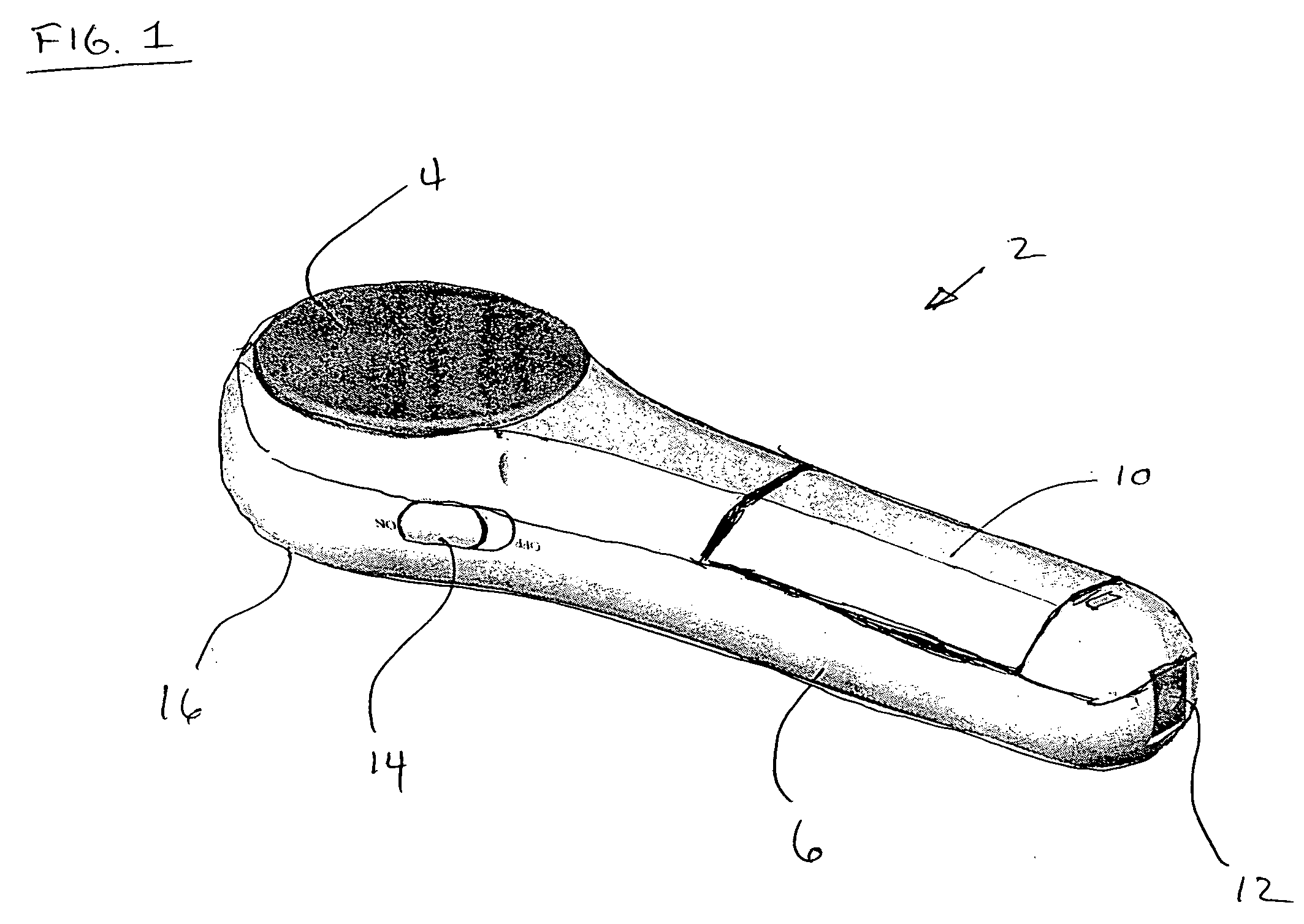
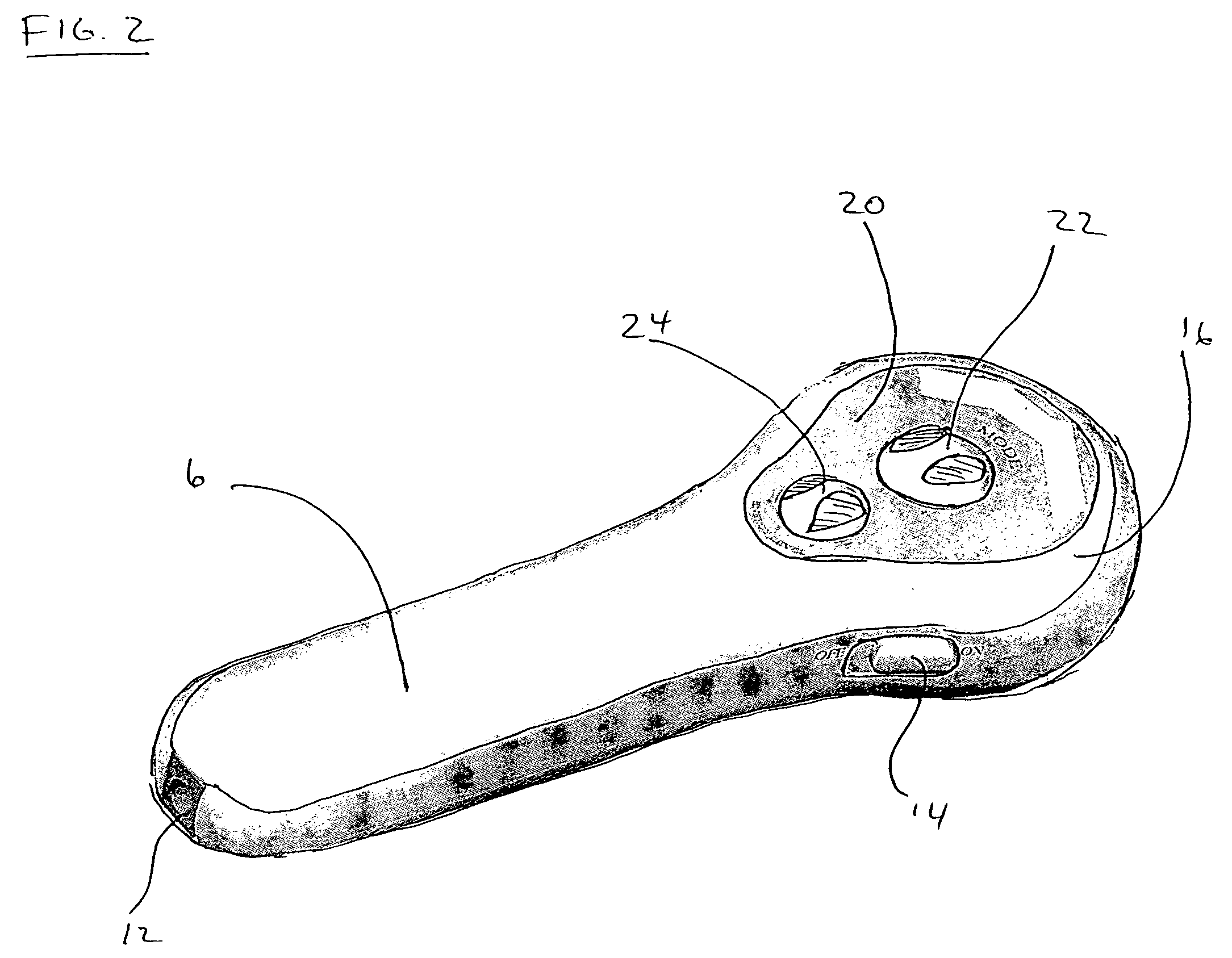
Microscope with tunable acoustic gradient index of refraction lens enabling multiple focal plan imaging
An apparatus, system and method for microscopy. The apparatus, system and method includes a stage configured to receive an item; a tunable acoustic gradient index of refraction (TAG) lens having a first aspect positioned to image the received item, wherein the first aspect of the TAG lens is configured to have an optical power profile in accordance with an operational frequency of the TAG lens; one or more lenses configured to magnify an image of the received item at a viewing point; and at least one pulsed light source configured to illuminate the received item and to pulse at one or more points within the optical power profile of the TAG lens.
Owner:MITUTOYO OPTICS MFG AMERICA CORP +1
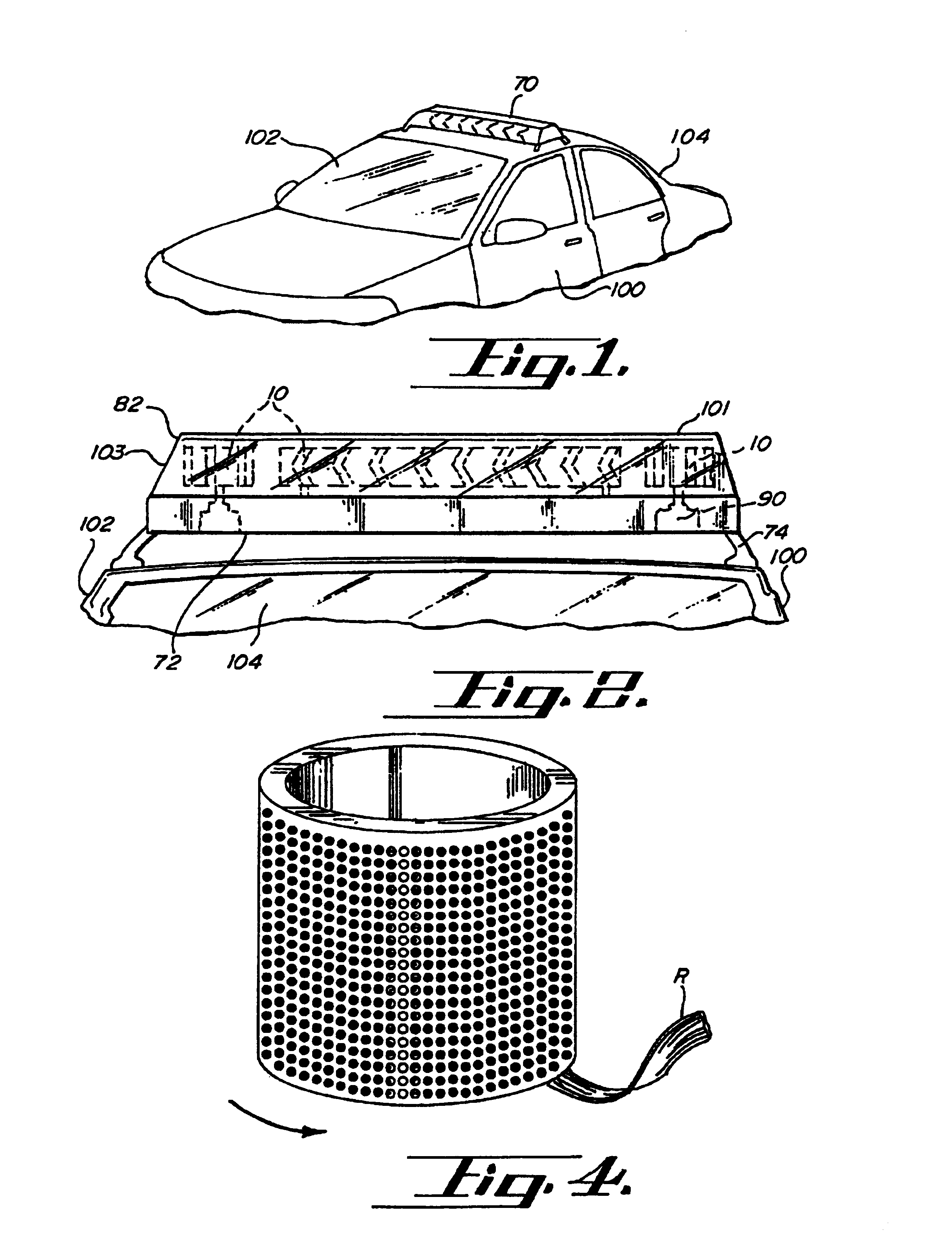
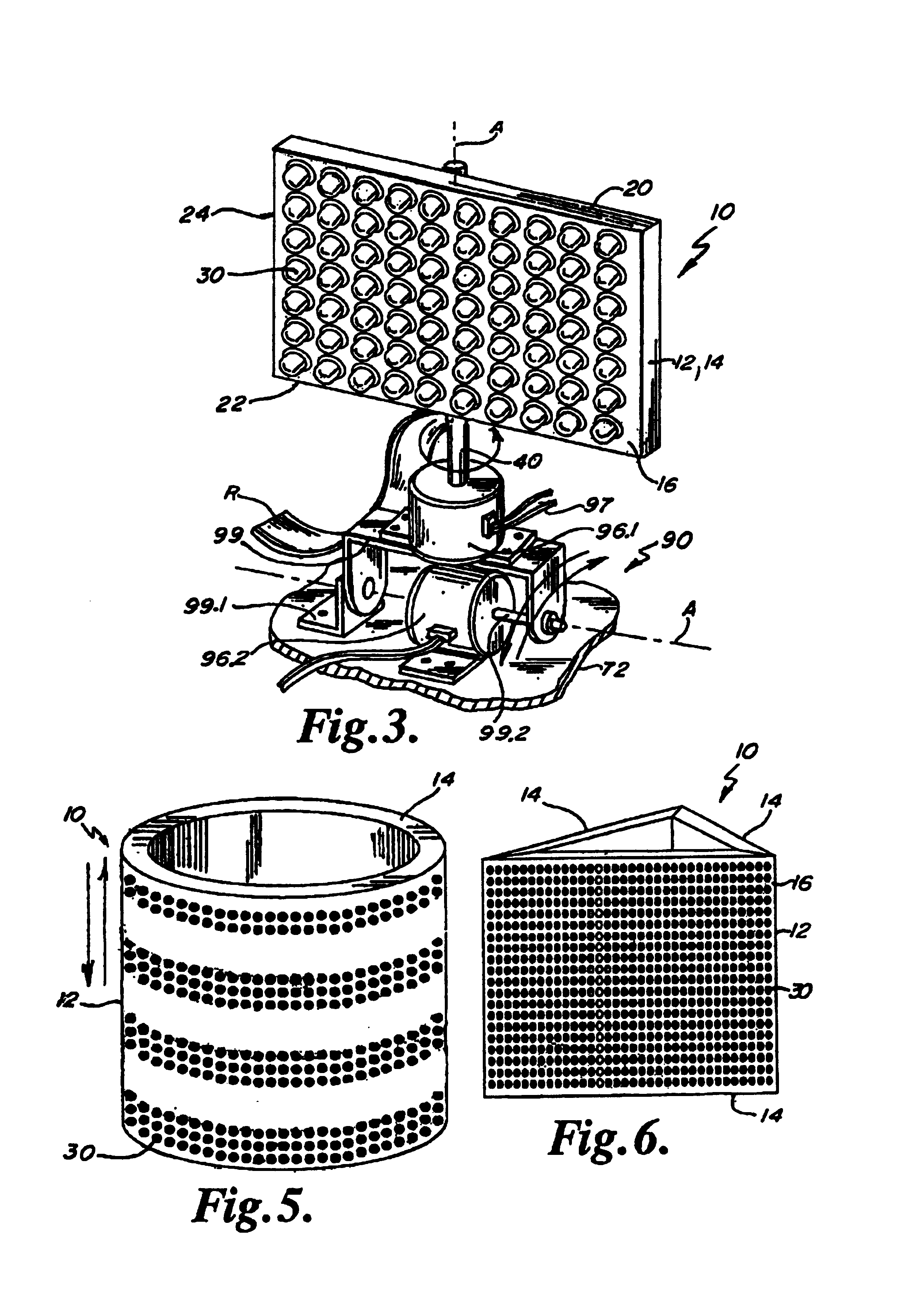
LED warning light and communication system
A light emitting diode (LED) warning signal light and communication device comprising a controller for generating a first observable light signal and a second non-observable light signal within said first light signal. The second light signal is formed of packets of individual pulsed light which may be processed for comparison to data stored in memory integral to a controller for communication of information to an individual through the use of pulsed light signals.
Owner:FEDERAL LAW ENFORCEMENT DEV SERVICES
Acoustic-optical therapeutical devices and methods
InactiveUS20050137656A1Effective and specific body therapyUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyMicrometerMedicine
Acoustic-optical therapy devices and methods for therapeutical purposes are disclosed in this invention. The devices provide a combination of ultrasound energy and optical pulsed energy exposed to human and animal body at frequencies of ultrasound and optical pulses within the range of 1 Hz to 1 GHz and at wavelengths from 0.2 micrometer to 20 micrometers. Both ultrasound energy and pulsed light radiation are delivered in effective combinations to maximize the therapy. Because of different interaction nature of ultrasound and light with body, the new invented devices will provide much more effective and specific body treatment.
Owner:UNITED LAB & MFG
Pulsed source scanning interferometer
InactiveUS6556305B1Improve signal utilizationChange is minimalUsing optical meansPhase shiftedCombined use
A pulsed light source in used conjunction with a ramping scanning mechanism for phase-shift and vertical-scanning interferometry. The pulse length and the scanning velocity are selected such that a minimal change in OPD occurs during the pulse. As long as the duration of the pulse is shorter than the detector's integration time, the effective integration time and the corresponding phase shift are determined by the length of the pulse, rather than the detector's characteristics. The resulting minimal phase shift produces negligible loss of fringe modulation, thereby greatly improving signal utilization during phase-shifting and vertical-scanning interferometry.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
3-D imaging multiple target laser radar
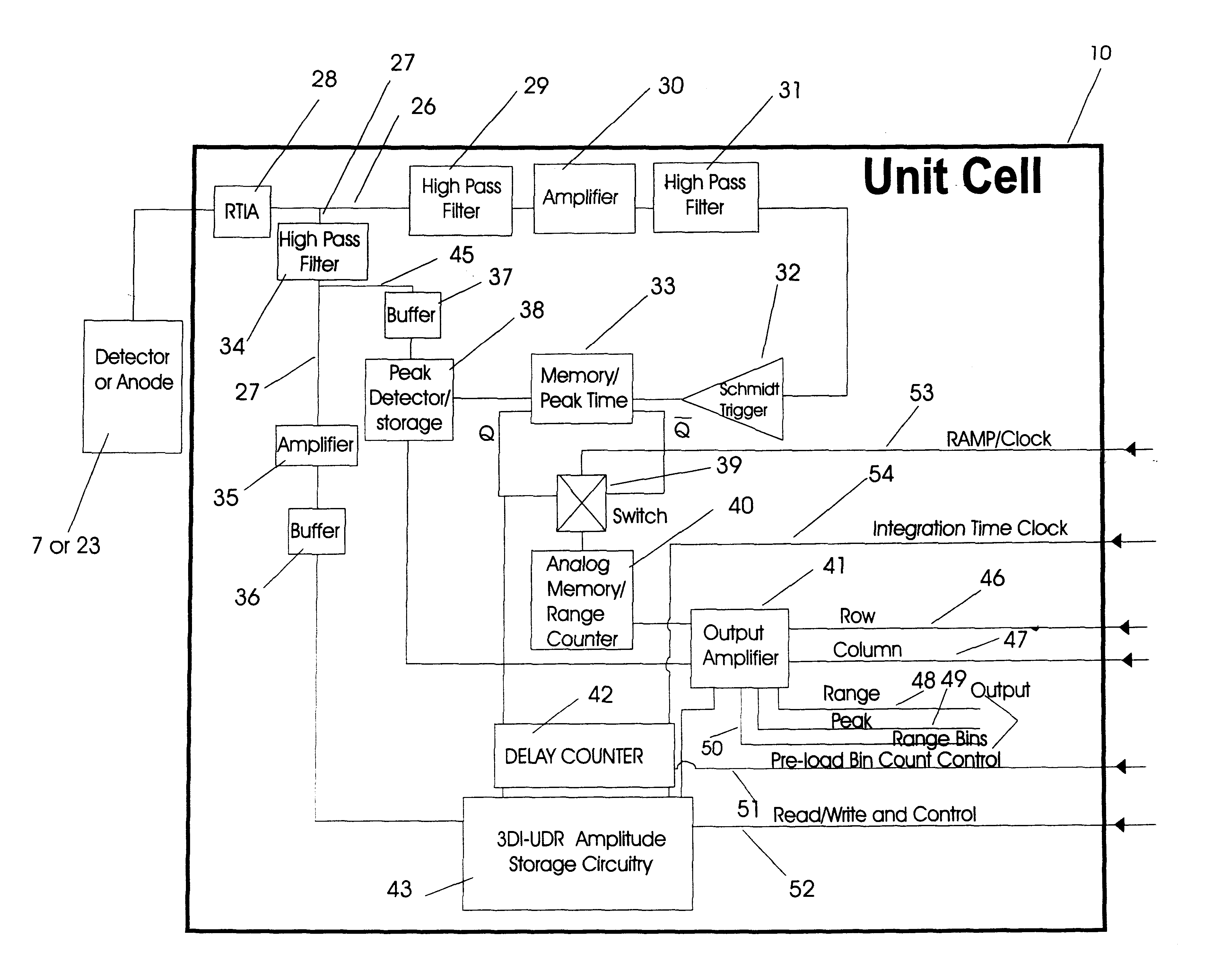
InactiveUS6414746B1Accurately determineOptical rangefindersSolid-state devicesElectronIntegrated circuit
A three dimensional imaging device is presented which uses a single pulse from a pulsed light source to detect objects which are obscured by camouflage, fog or smoke but otherwise enveloped by a light-transmitting medium. The device simultaneously operates in two modes, light reflected from the nearest object is processed to form a three-dimensional image by an array of pixels. This first image is based upon the light-pulse transit time recorded in each pixel. Each pixel also contains a high-speed analog memory that sequentially stores reflected signals at a repeated time interval. The first reflection acts as a time base that controls when the analog memory begins or ends the storage sequence. The first return could be from a camouflage net and the amplitudes of the return signals, after the first return, would then be from objects behind the net. Computer processing these amplitudes reveals the three-dimensional nature of the obscured objects.The device consists of the pulsed light source, optics for collecting the reflected light, a sensor for detecting the light and converting it to electrical data, drive and output electronics for timing and signal conditioning of data generated by the sensors and a computer for processing the sensor data and converting it to a three dimensional image. The sensor collects and processes the light data in a unique manner, first converting it to electricity by a number of alternate detector technologies and then using integrated circuit chips which consist of a two dimensional array of electronic pixels also called unit cells. The two dimensional array defines two dimensions of the image. Stored within each unit cells is data associated with the third dimension, ranges of targets, and amplitudes of target reflections. This data is read out of the integrated circuit chip in the time interval between laser pulses to a processing computer. The processing computer corrects the data and, by means of computer algorithms specific to the device, converts the data to a three-dimensional image of one or more targets. This image may be viewed or processed electronically to isolate targets.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTONOMOUS MOBILITY US LLC
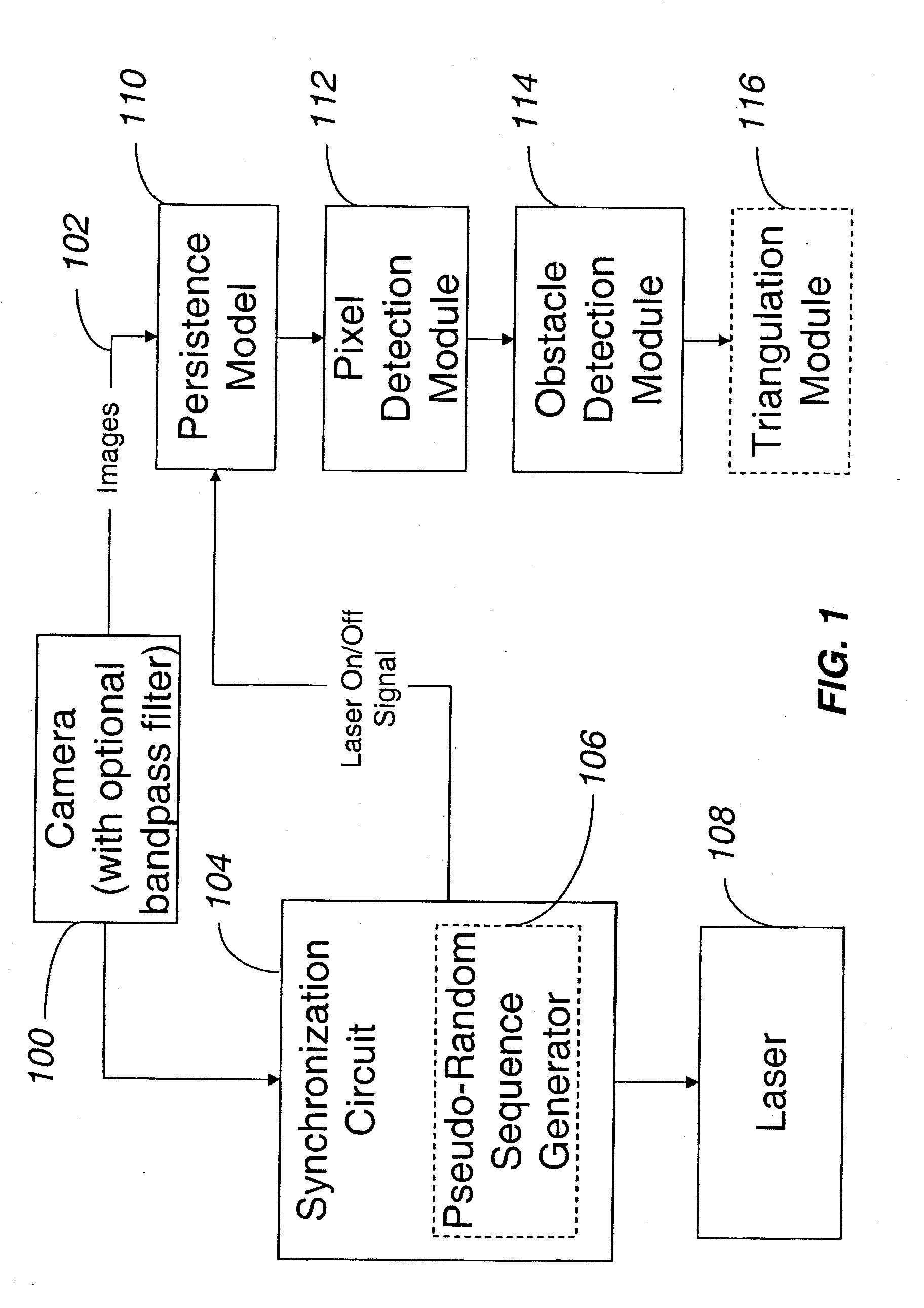
Methods and systems for obstacle detection using structured light
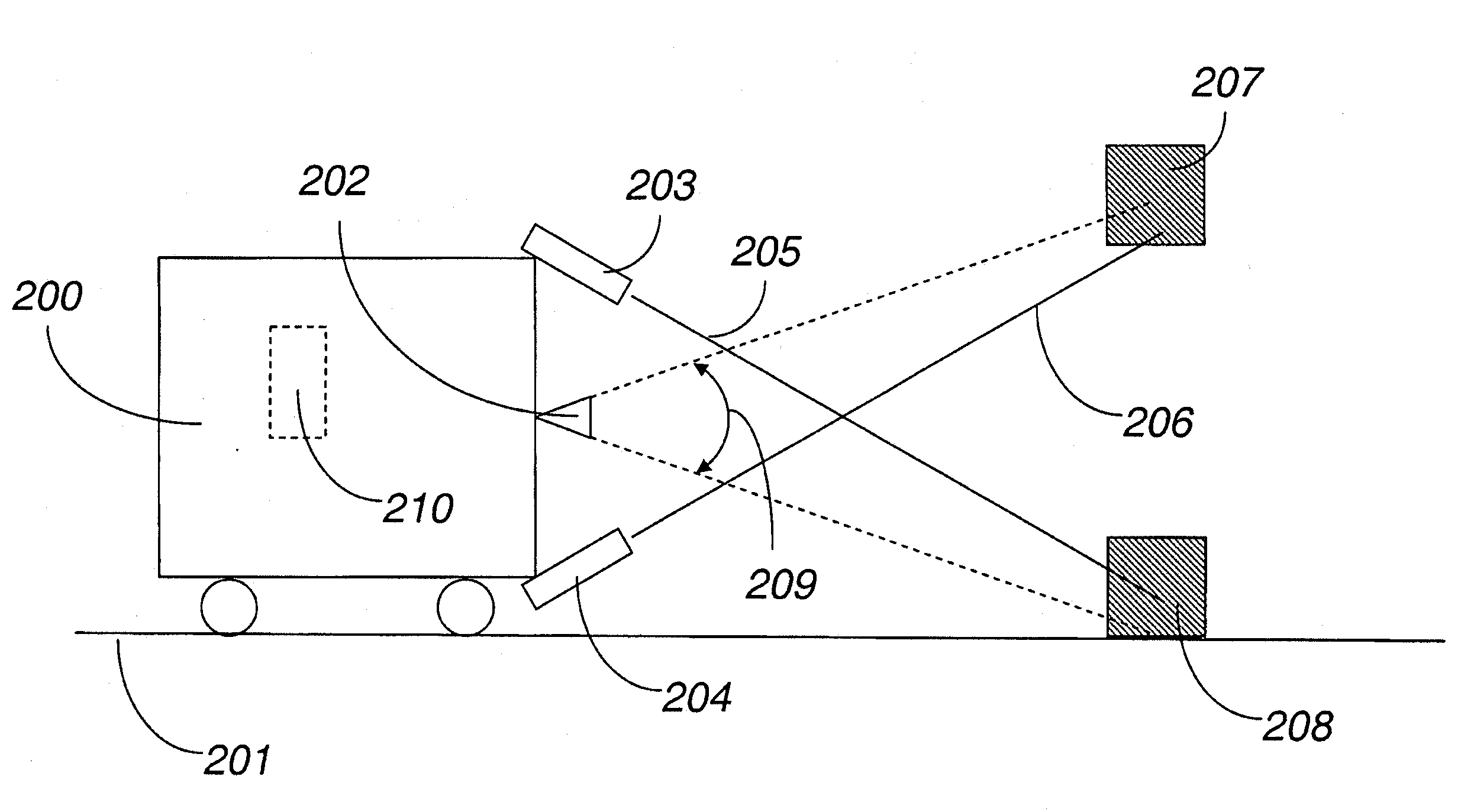
ActiveUS20150168954A1Robust detectionImprove accuracyProgramme controlComputer controlProcessing elementVision sensor
An obstacle detector for a mobile robot while the robot is in motion is disclosed. The detector preferably includes at least one light source configured to project pulsed light in the path of the robot; a visual sensor for capturing a plurality of images of light reflected from the path of the robot; a processing unit configured to extract the reflections from the images; and an obstacle detection unit configured to detect an obstacle in the path of the robot based on the extracted reflections. In the preferred embodiment, the reflections of the projected light are extracted by subtracting pairs of images in which each pair includes a first image captured with the at least one light source on and a second image captured with the at least one light source off, and then combining images of two or more extracted reflections to suppress the background.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
Method and apparatus for irradiating a surface with pulsed light
A method and apparatus irradiates a surface with at least one pulsed light beam emitted from an emission surface of an optical element. The at least one pulsed light beam comprises a plurality of pulses having a temporal pulsewidth in a range between about 0.1 millisecond and about 150 seconds. The at least one pulsed light beam has a beam cross-sectional area at the emission surface greater than about 2 cm2 and a time-averaged irradiance in a range between about 1 mW / cm2 and about 100 W / cm2.
Owner:PHOTOTHERA IP HLDG
Led-based illumination module on-board diagnostics
ActiveUS20110254554A1Light source combinationsElectrical apparatusLight-emitting diodeOperant conditioning
A light emitting diode (LED) based illumination module performs on-board diagnostics. For example, diagnostics may include estimating elapsed lifetime, degradation of phosphor, thermal failure, failure of LEDs, or LED current adjustment based on measured flux or temperature. The elapsed lifetime may be estimated by scaling accumulated elapsed time of operation by an acceleration factor derived from actual operating conditions, such as temperature, current and relative humidity. The degradation of phosphor may be estimated based on a measured response of the phosphor to pulsed light from the LEDs. A thermal failure may be diagnosed using a transient response of the module from a start up condition. The failure of LEDs may be diagnosed based on measured forward voltage. The current for LEDs may adjusted using measured flux values and current values and a desired ratio of flux values. Additionally, the LED current may be scaled based on a measured temperature.
Owner:SBC XICATO CORP
Photoacoustic analyzer of region of interest in a human body
InactiveUS7515948B1Improve signal-to-noise ratioSafer light energyAuscultation instrumentsDiagnostic recording/measuringAuditory radiationHuman body
A method and apparatus are presented for non-invasively monitoring at least one characteristic of a region of interest in a body. The body is illuminated by pulsed light to induce a photoacoustic effect. Acoustic radiation is detected, and measured data indicative thereof is generated. The photoacoustic effect is controlled by carrying out at least one of the following: providing the pulsed light of at least two different wavelength, analyzing the measured data to determine time variations of at least one predetermined parameter of a time dependent acoustic signal for each of wavelength, and determining oxygen saturation level in the region of interest; and operating a plurality of acoustic elements configured for detection of the acoustic radiation, to thereby define a focal volume for acoustic radiation detection to match dimensions of the region of interest.
Owner:ORNIM
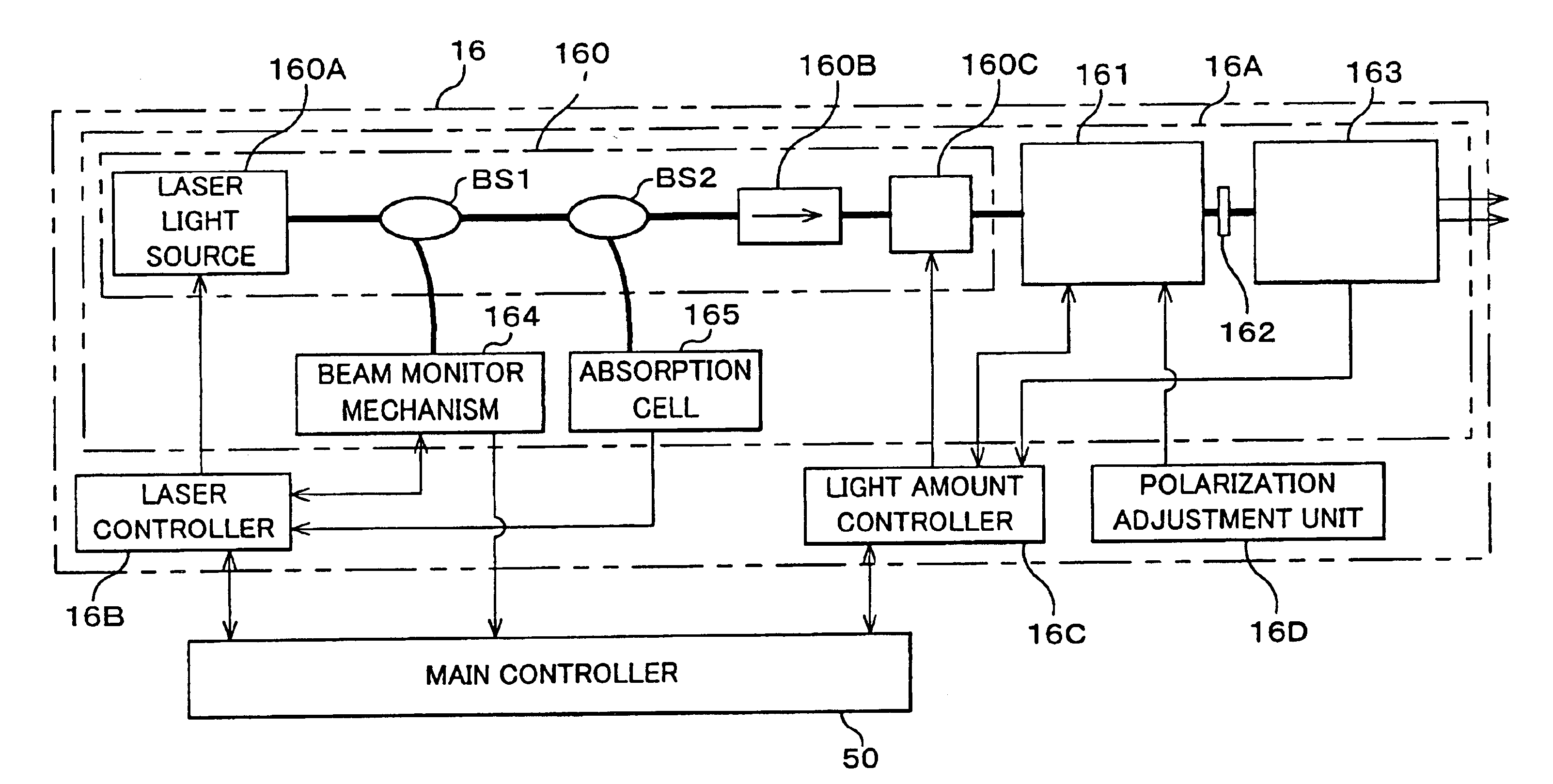
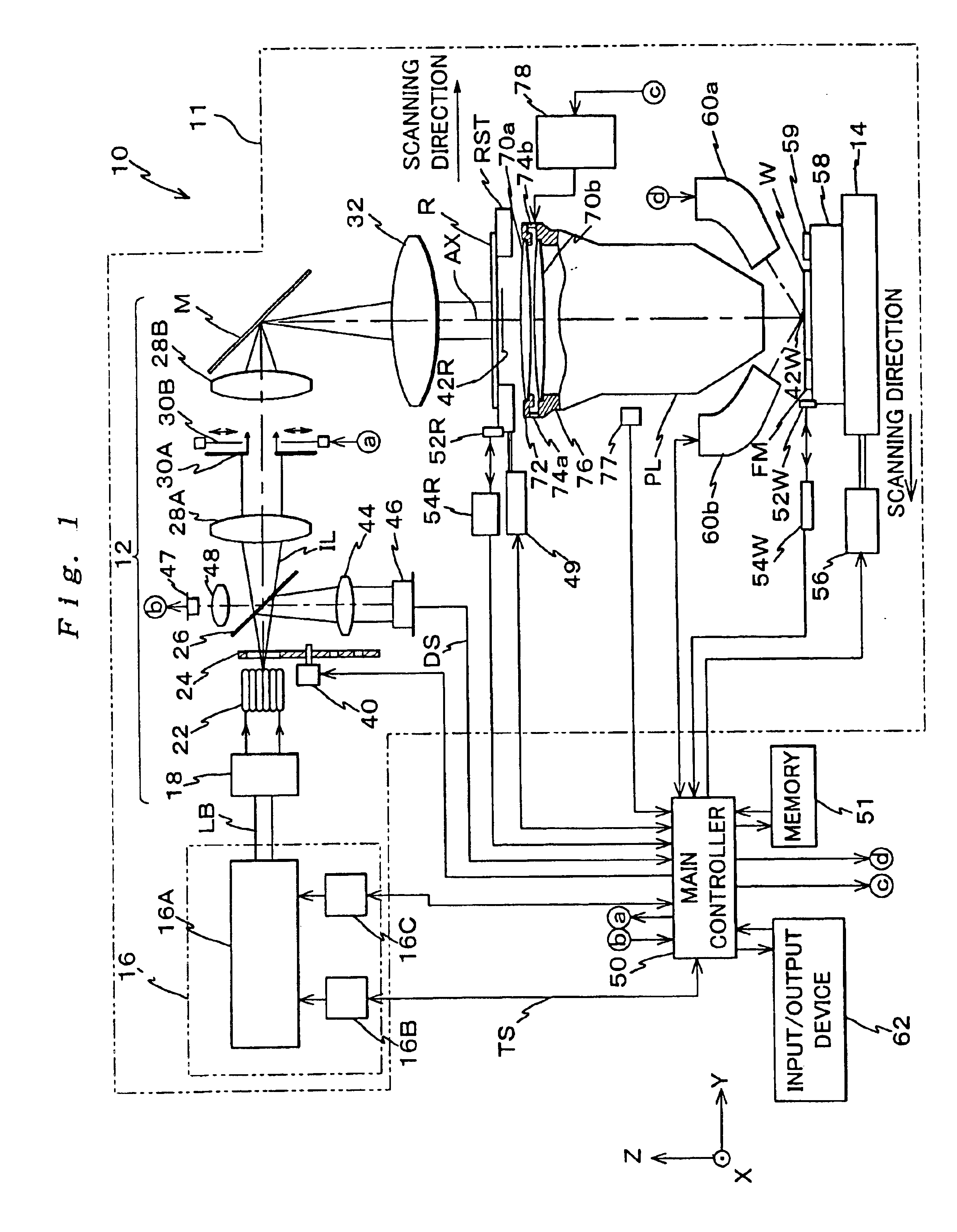
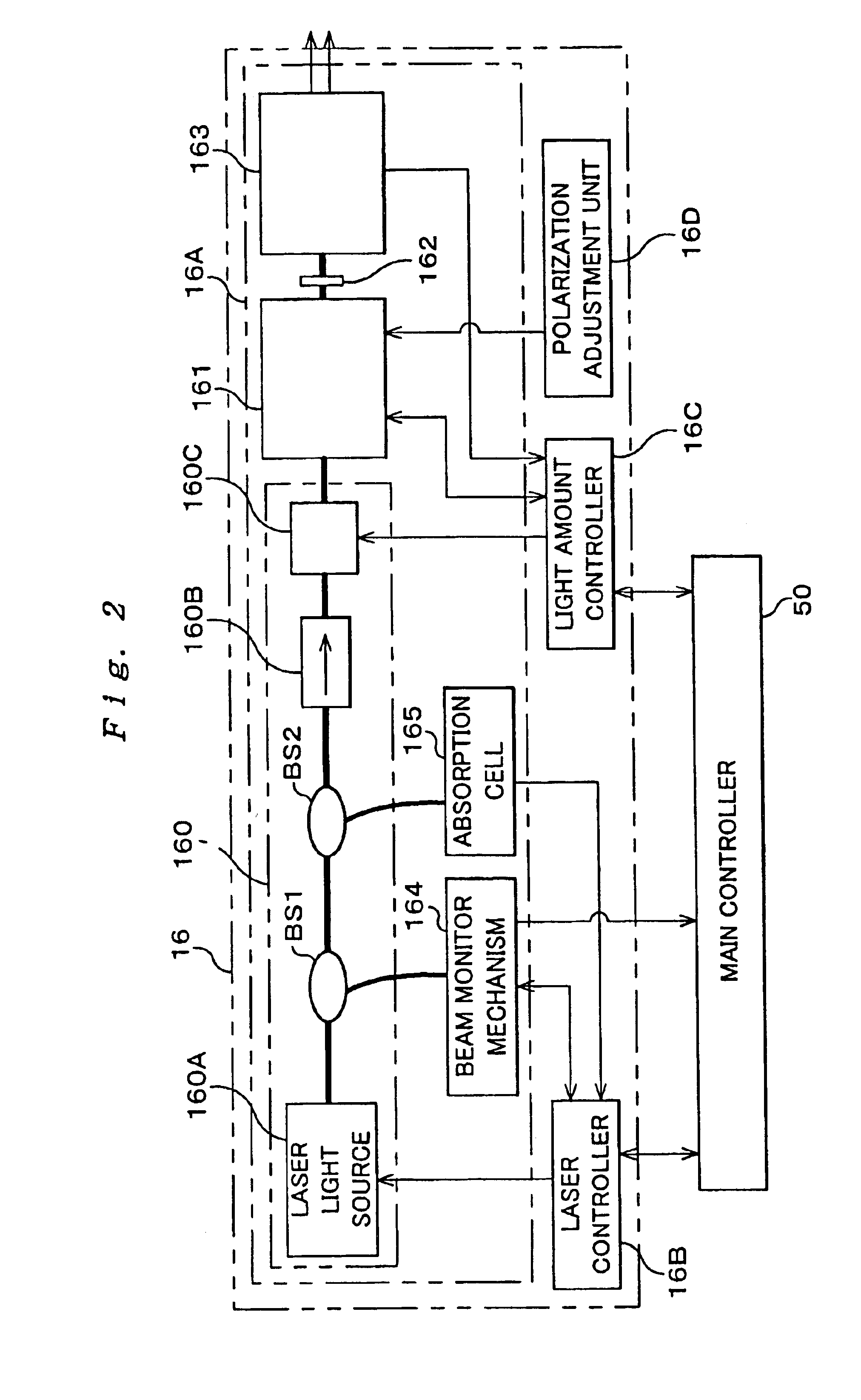
Light source unit and wavelength stabilizing control method, exposure apparatus and exposure method, method of making exposure apparatus, and device manufacturing method and device
InactiveUS7098992B2Accurate and reliable light amount controlDegree of linearityLaser arrangementsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusFiberPeak value
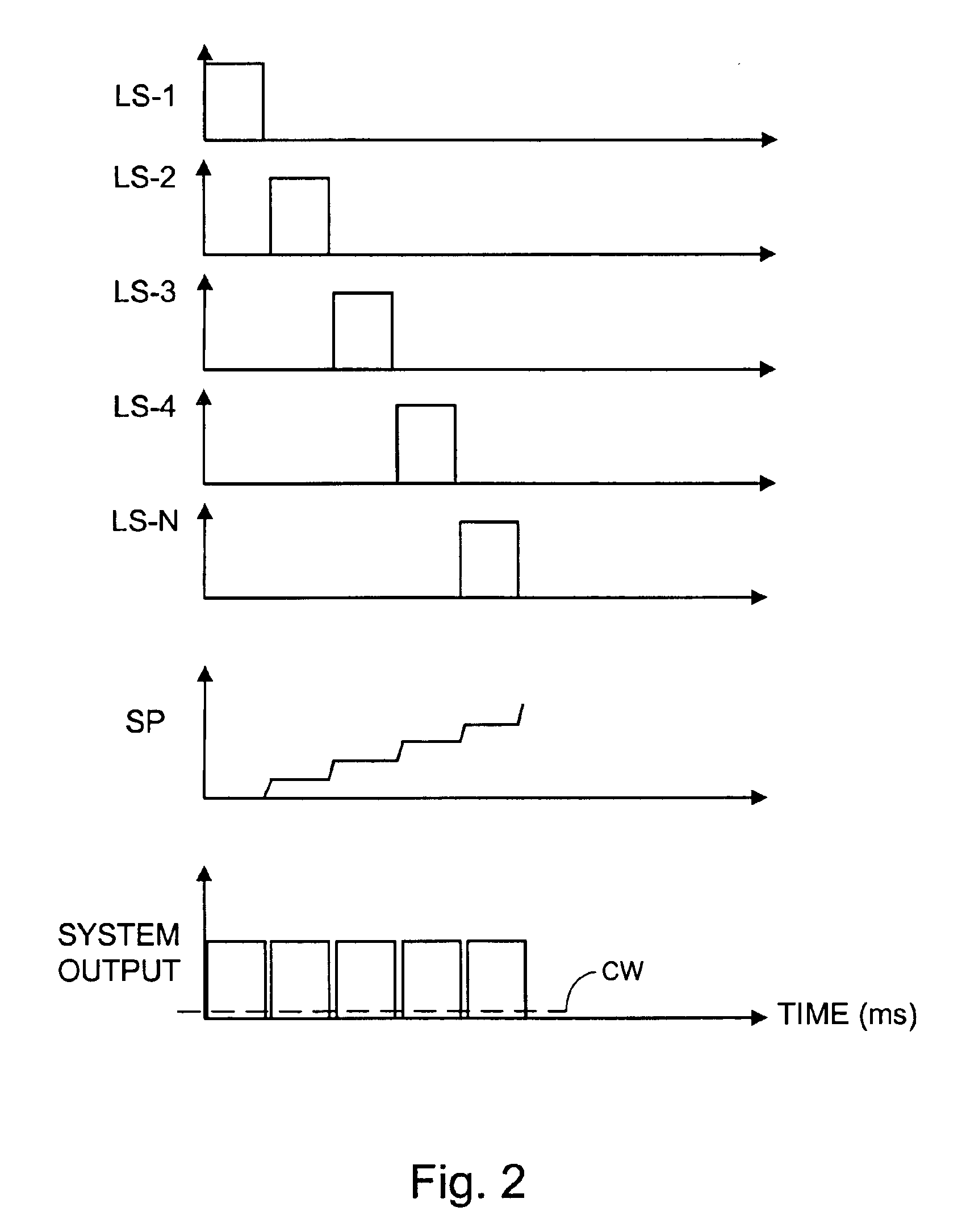
The light source unit includes a single wavelength oscillation light source, a light generating portion which has an optical modulator converting and emitting light from the light source into a pulse light, a light amplifying portion made up of an optical fiber group in which each fiber has a fiber amplifier to amplify the pulse light from the optical modulator, and a light amount controller. The light amount controller performs a step-by-step light amount control by individually turning on / off the light output of each fiber making up the optical fiber group, and a light amount control of controlling at least either of the frequency or the peak power of the emitted pulse light of the optical modulator. Accordingly, in addition to the step-by-step light amount control, fine adjustment of the light amount in between the steps becomes possible due to the control of at least either the frequency or the peak power of the pulse light, and if the set light amount is within a predetermined range, the light amount can be made to coincide with the set light amount.
Owner:NIKON CORP
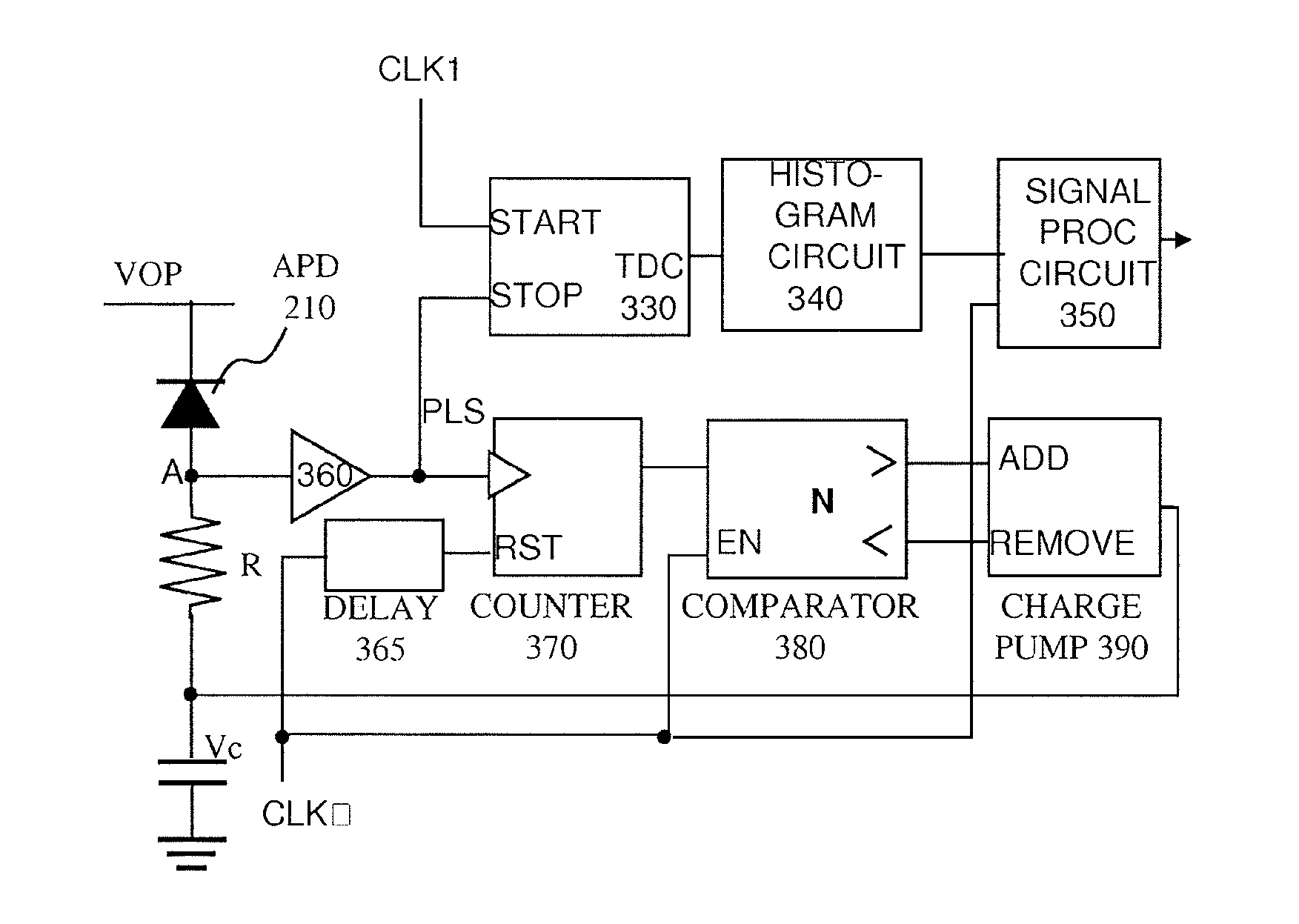
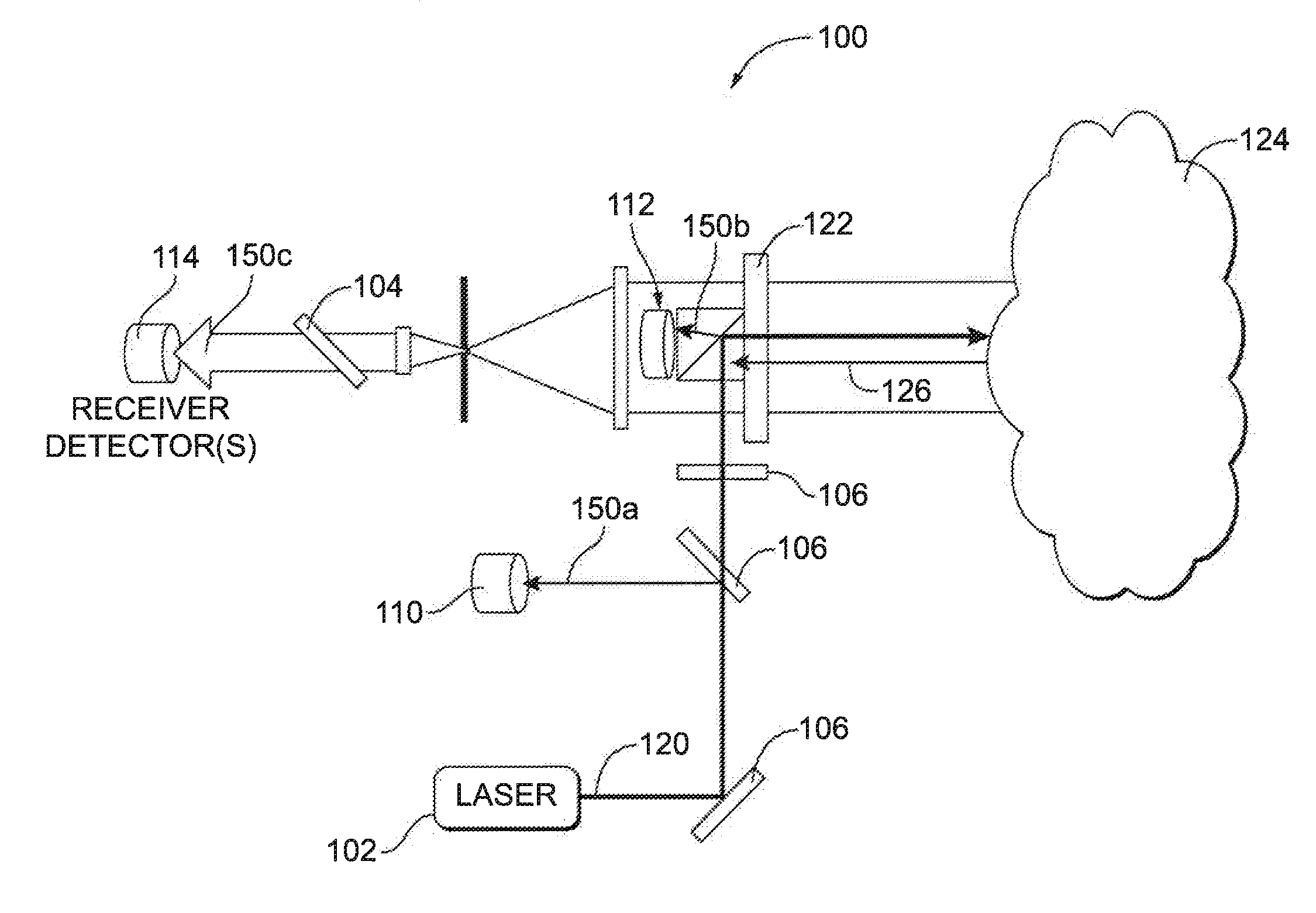
Pulsed light optical rangefinder
ActiveUS20120075615A1Improve dynamic rangeAvoid saturationOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationPhoton detectionTime of flight
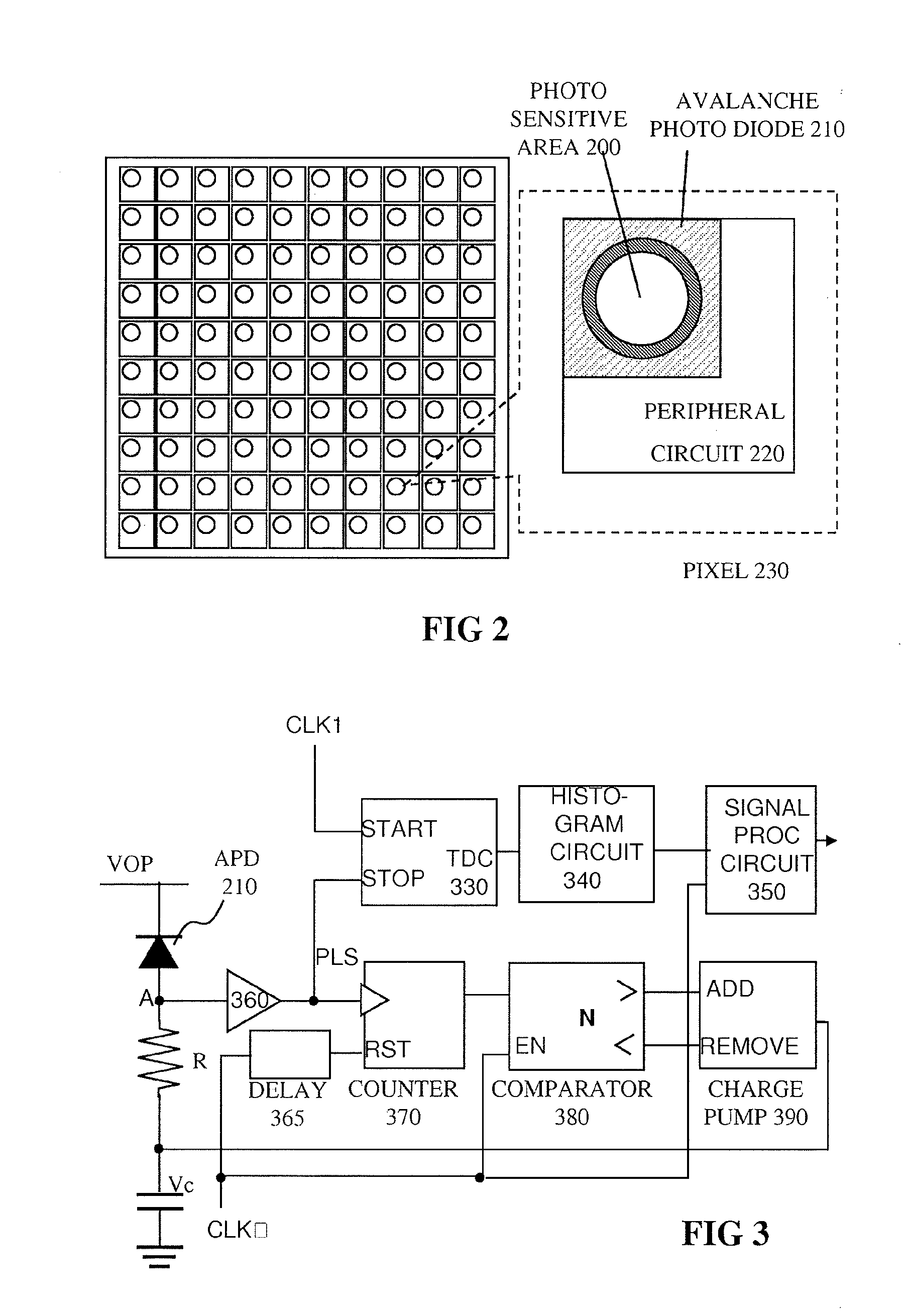
An optical rangefinder based on time-of-flight measurement, radiates pulsed light toward an object (70), and receives reflected light from the object, the receiver operating in a photon counting mode, so as to generate a pulse for a detected photon. There is a variable probability of a photon detection on the receiver, and a controller (370, 380, 390; 365, 470, 475, 380, 390; 570, 580, 590, 390) controls the photon detection probability of the receiver, based on a light level. By controlling the detection probability according to a light level, the receiver can have an increased dynamic range, and without the expense of using optical components. This can apply even while detecting very weak signals since the receiver can still be in a photon counting mode while the detection probability is controlled. The light level can be indicated by an output of the receiver itself, or by another detector external to the receiver.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Multispectral therapeutic light source
ActiveUS20140288351A1High cost-effectiveHigh quantum-efficiencyElectrotherapySurgeryUltravioletPeak value
A light source apparatus including light spectrum-converting materials that emit light primarily over large portions of the 360 nm-480 nm and the 590-860 nm spectral range is provided. This apparatus provides a cooled, high-luminance, high-efficiency light source that can provide a broader spectrum of light within these spectral ranges than has been cost-practical by using many different dominant peak emission LEDs. Up to 15% of the output radiant power may be in the spectral range 350-480 nm in one embodiment of this device, unless a specific separate source and lamp operating mode is provided for the violet and UV. Control methods for light exposure dose based on monitoring and controlling reflected or backscattered light from the illuminated surface and new heat management methods are also provided. This flexible or rigid light source may be designed into a wide range of sizes or shapes that can be adjusted to fit over or around portions of the bodies of humans or animals being treated, or mounted in such a way as to provide the special spectrum light to other materials or biological processes. This new light source can be designed to provide a cost-effective therapeutic light source for photodynamic therapy, intense pulsed light, for low light level therapy, diagnostics, medical and other biological applications as well as certain non-organic applications.
Owner:JONES GARY W
Parametric control in pulsed light sterilization
InactiveUS6566659B1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesControl systemFlash light
An approach for sterilizing microorganisms at a target object employs a flashlamp system including means for generating pulses of light, and for deactivating microorganisms within the target object by illuminating the target object with the pulses of light having been generated; a photo-sensitive detector positioned so as to receive a portion of each of the pulses of light as a measure of an amount of light illuminating the target object, for generating an output signal in response thereto; and a control system, coupled to the flashlamp system and the photo-sensitive detector, for determining, in response to the output signal, whether the pulses of light are sufficient to effect a prescribed level of deactivation of microorganisms at the target object. In accordance with this approach sterilizing microorganisms involves steps of generating a pulse of light; deactivating microorganisms at the target object by directing the pulse of light having been generated at the target object; receiving a portion of the pulse of light as a measure of an amount of the pulse of light illuminating the target object; generating an output signal in response to the receiving of the portion of the pulse of light; and determining, in response to the generating of the output signal, whether the pulse of light is sufficient to effect a prescribed level of deactivation of microorganisms at the target object.
Owner:TESLA INC +1
System and method for monitoring optical subsystem performance in cloud lidar systems
ActiveUS20160025842A1Optical apparatus testingElectromagnetic wave reradiationCloud systemsRadar systems
A method of detecting optical subsystem failures includes emitting a pulsed light beam from a laser through a window. A reflection signal indicative of a portion of the beam reflected by the window is compared to an expected signal to monitor for degradation of an optical component.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT AEROSPACE
System for creating microscopic digital montage images
InactiveUS7155049B2Precise alignmentDecreasing expense and precisionImage analysisElectric/magnetic position measurementsImage conversionImaging equipment
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
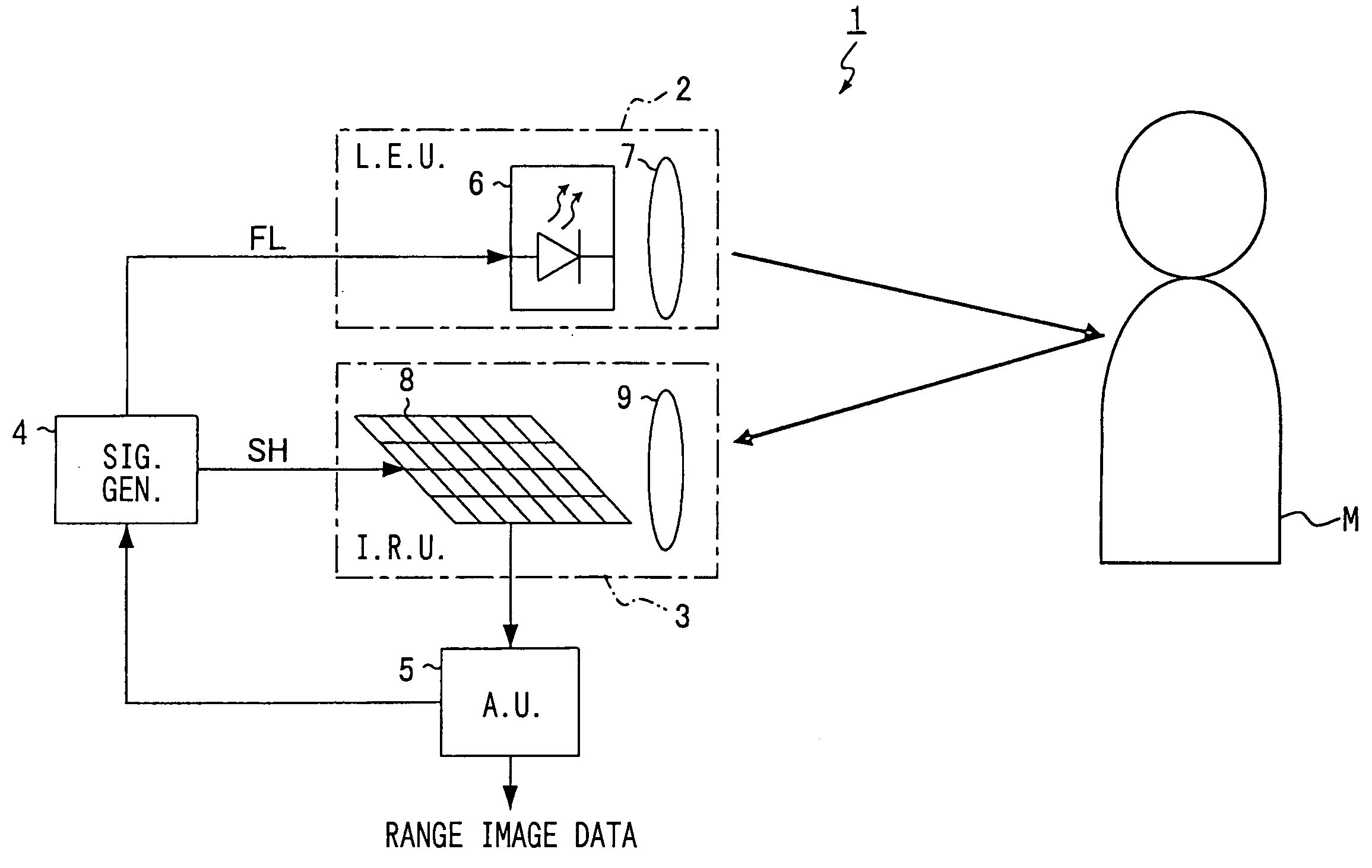
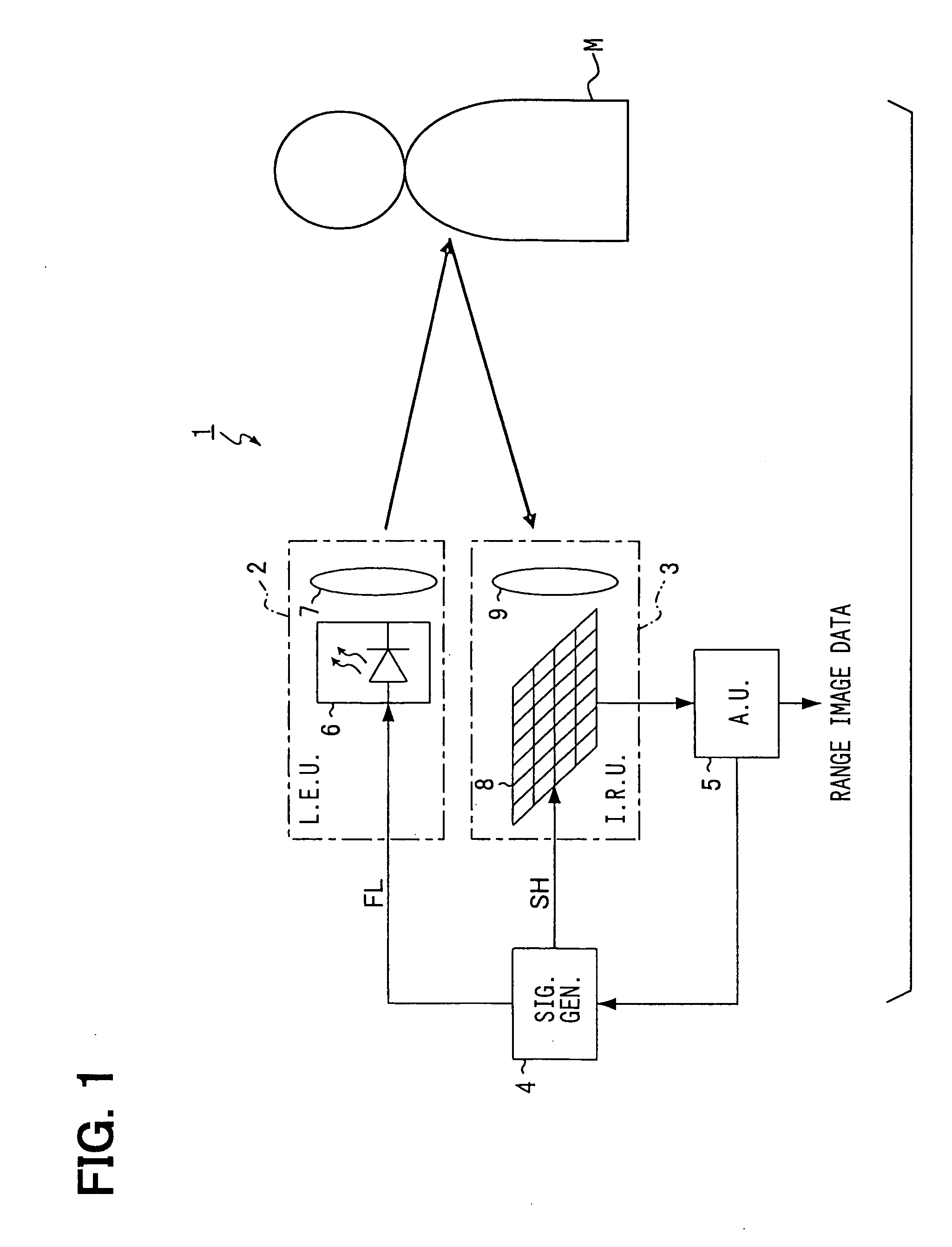
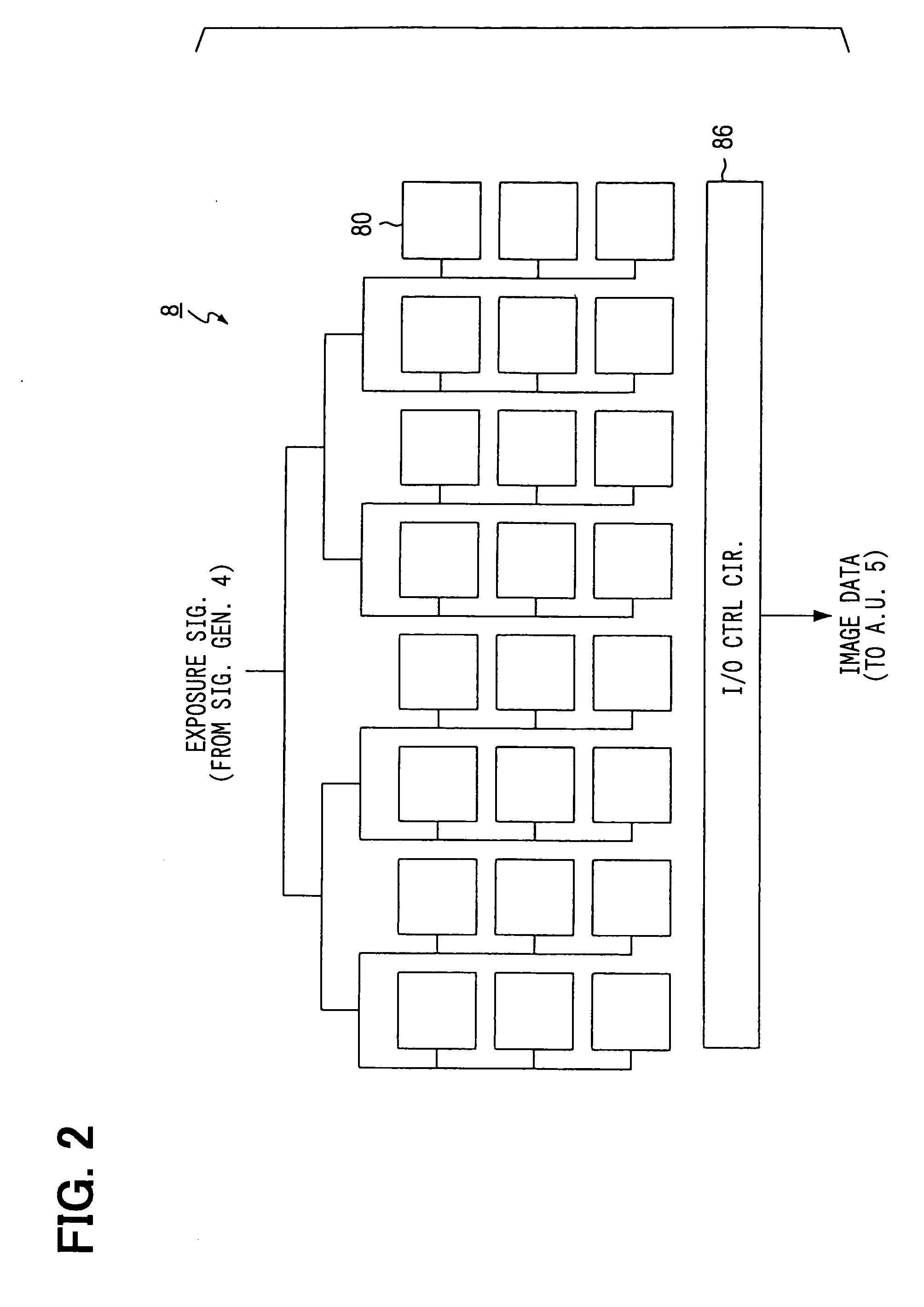
Apparatus, method, and program for generating range-image-data
ActiveUS20050162638A1Reduce distanceHigh reception levelOptical rangefindersSolid-state devicesExposure periodLight emission
First image data including a first pixel value according to the intensity of background light is obtained by means of only exposure. Second image data including a second pixel value according to the intensity of the light reflected or scattered by an object is obtained by so controlling light emission and exposure as to receive part of the reflected or scattered light over the whole exposure period. The part of the reflected or scattered light corresponds to the flat period of emitted pulsed light. Third image data including a third pixel value according to the distance to the object is obtained by so controlling light emission and exposure as to receive the part of the reflected or scattered light for a time according to the distance. The first pixel value is subtracted from each of the second and third pixel values so that the influence of the background light can be excluded. The ratio between the subtraction results is calculated so that the influences of factors that vary the intensity of the reflected or scattered light can be cancelled.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Scanning light source system
InactiveUS6856436B2High strengthIncrease brightnessNon-electric lightingLaser detailsOptoelectronicsPulse light
A scanning light source system combines the outputs from multiple, spatially separated, sequentially pulsed light sources for travel in rapid succession along one or more common delivery paths to provide one or more collective outputs that are comparatively higher than would otherwise be possible with the light sources operating singly.
Owner:INNOVATIONS & OPTICS
Systems and Methods for Optical Imaging Using Early Arriving Photons
Optical imaging systems and methods use early photons in order to generate processed fluorescent light images of fluorescent material on or within a tissue. The early photons are generated in accordance with a pulsed light source and an early-photon light receiver. The processed fluorescent light images tend to have improved resolution and imaging accuracy compared with fluorescent light images generated with photons beyond the early photons portions.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
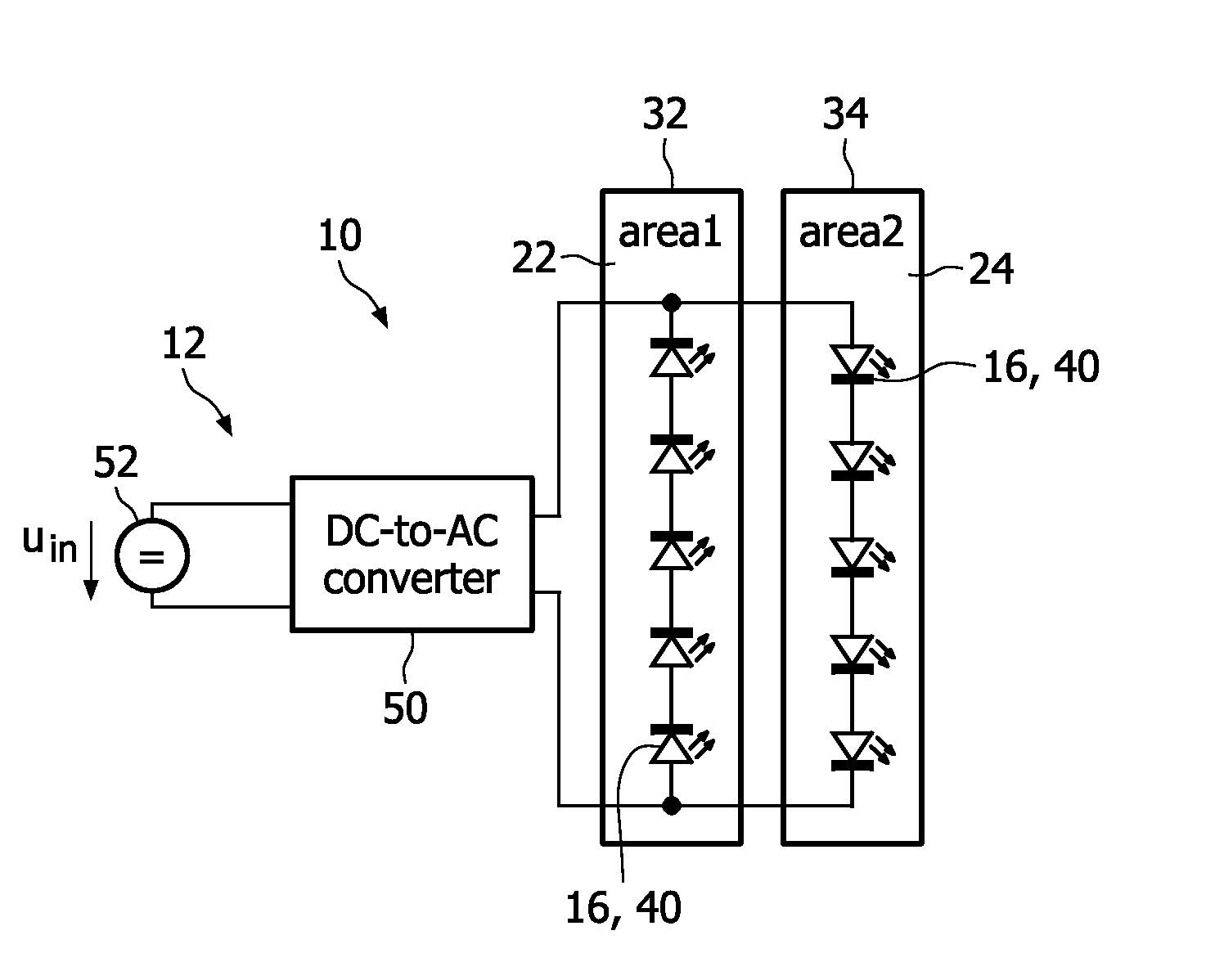
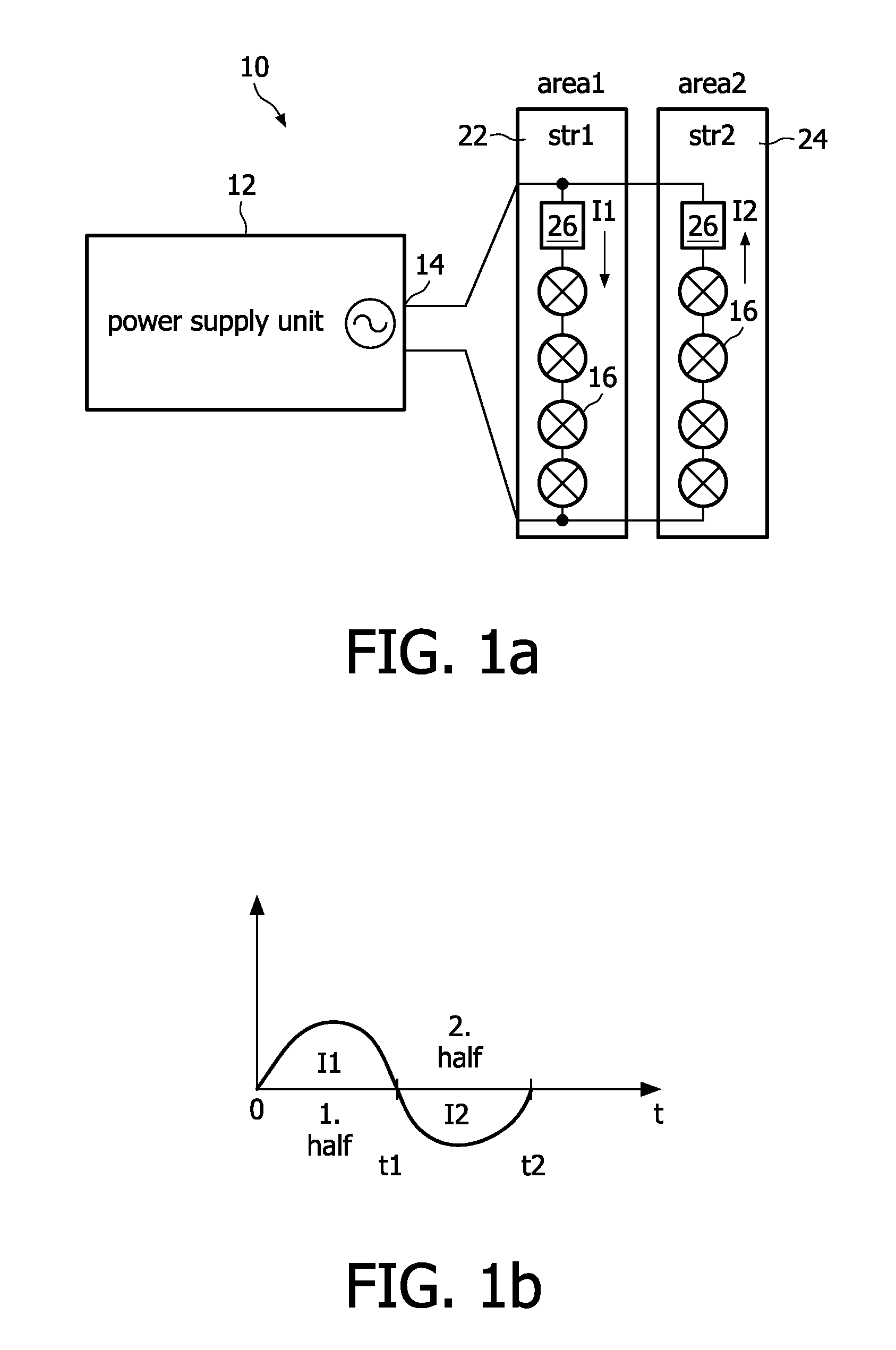
Lighting system for horticultural applications
InactiveUS20100244724A1Low costOvercome deficienciesElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesBiological bodyElectricity
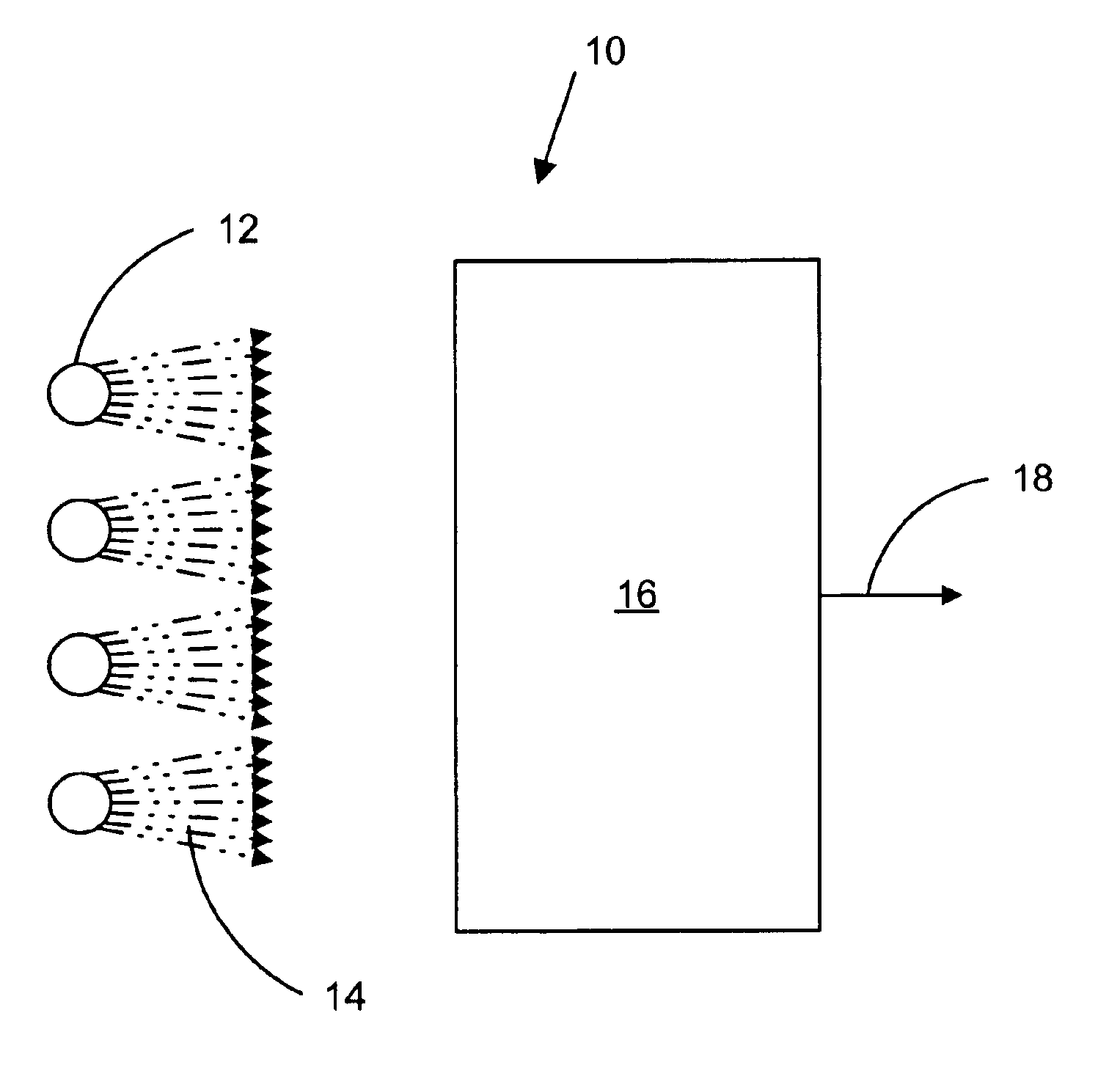
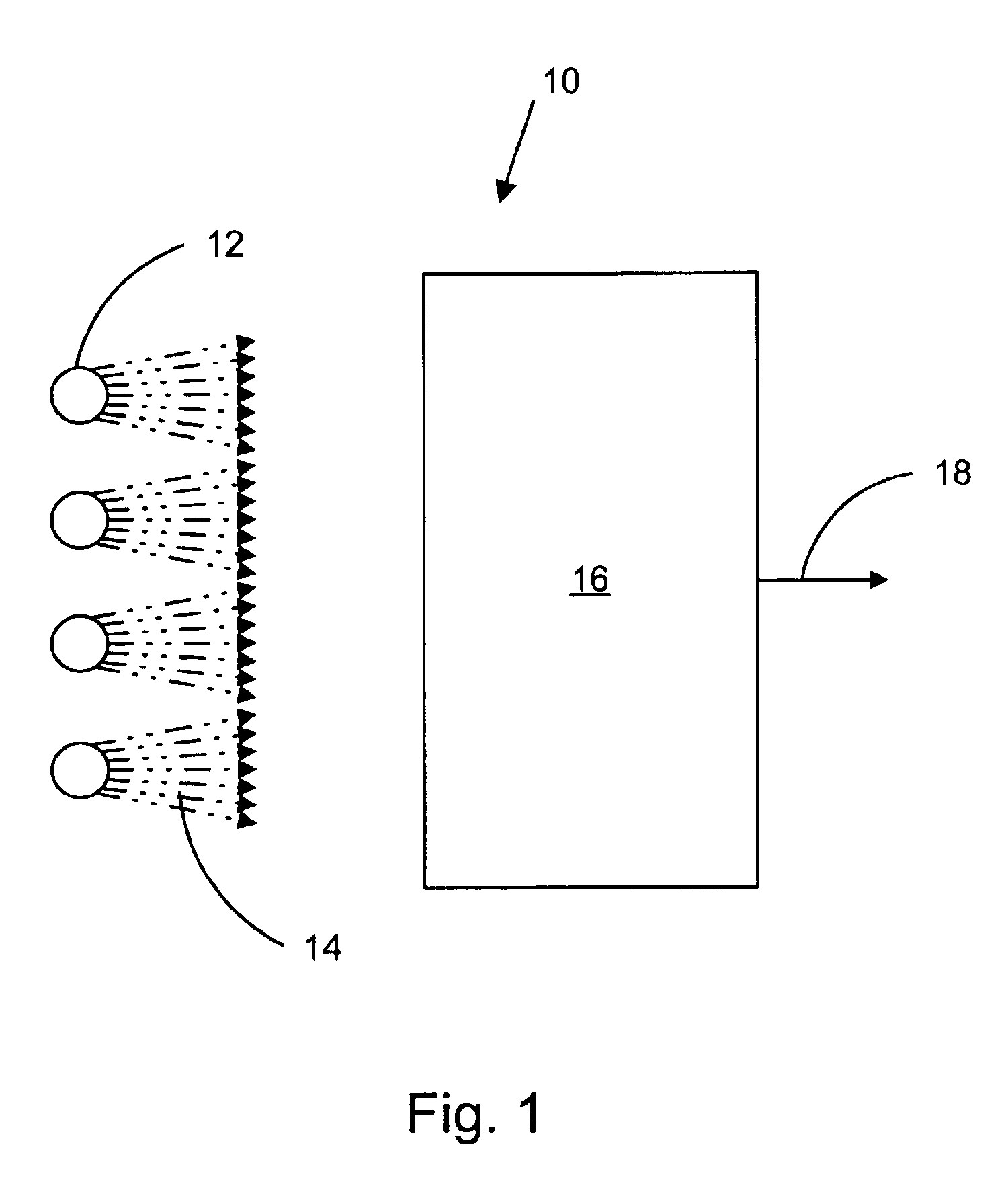
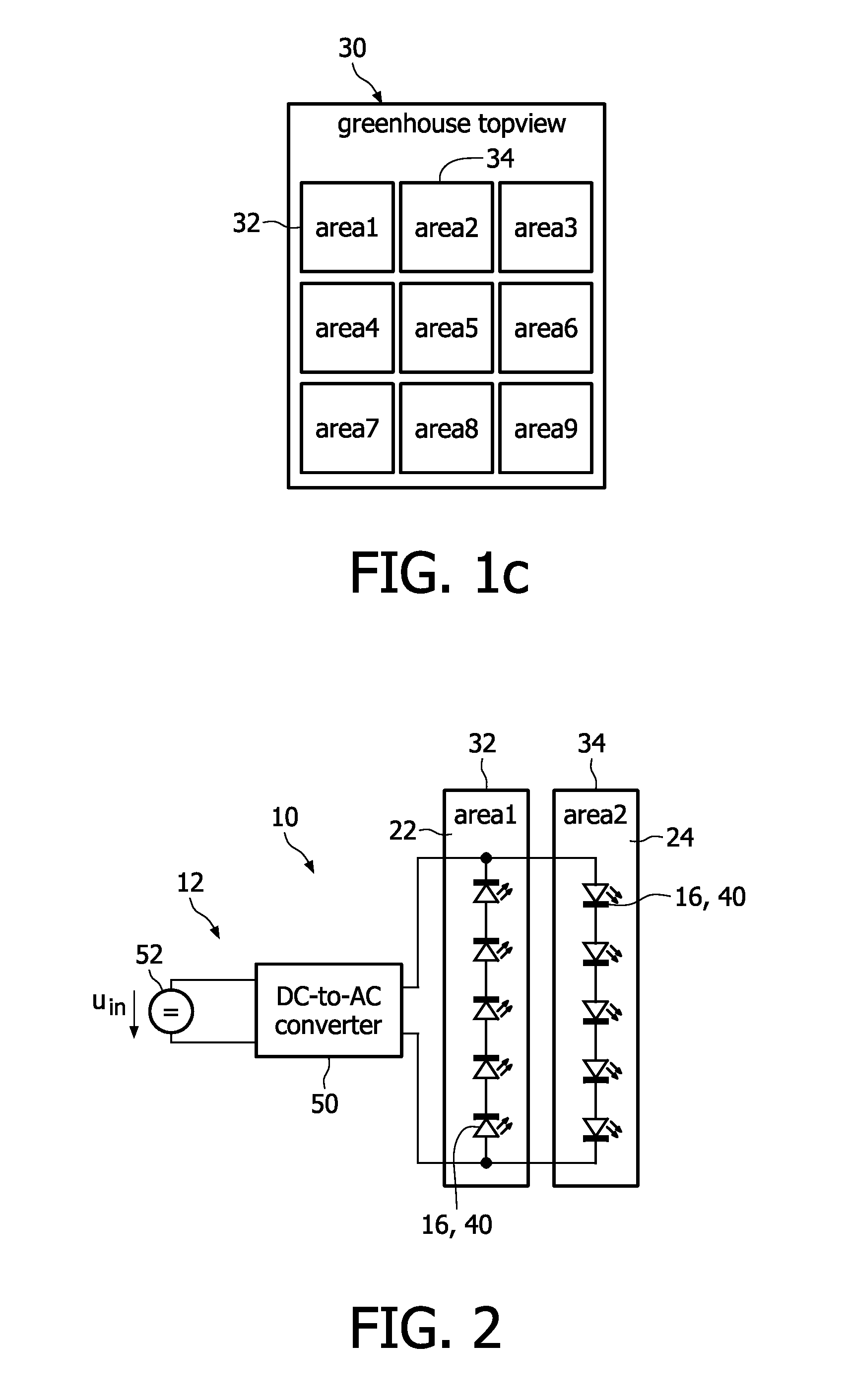
Horticultural lighting system comprising a first string (22) of at least one light element (16, 40), a second string (24) of at least one light element (16, 40), both strings being electrically connected in parallel with each other, a power supply unit (12, 50, 60, 70) providing an AC current / voltage to the parallel circuit of the strings, and means for energizing (26, 42) the first string during a first half period of the AC voltage and the second string during a second half period of the AC voltage, so that each string radiates pulsed light, said first string and said second string being arranged such that different areas (32, 34) are irradiated. The lighting system is also to be used in an environment where living organisms are irradiated with light, or a greenhouse for exposing plants to pulsed light. A corresponding method is also claimed.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Electromagnetic field near-field imaging system and method based on pulsed light detection magnetic resonance
InactiveCN107356820ASimple structureLow costAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceElectromagentic field characteristicsHigh resolution imagingSingle crystal
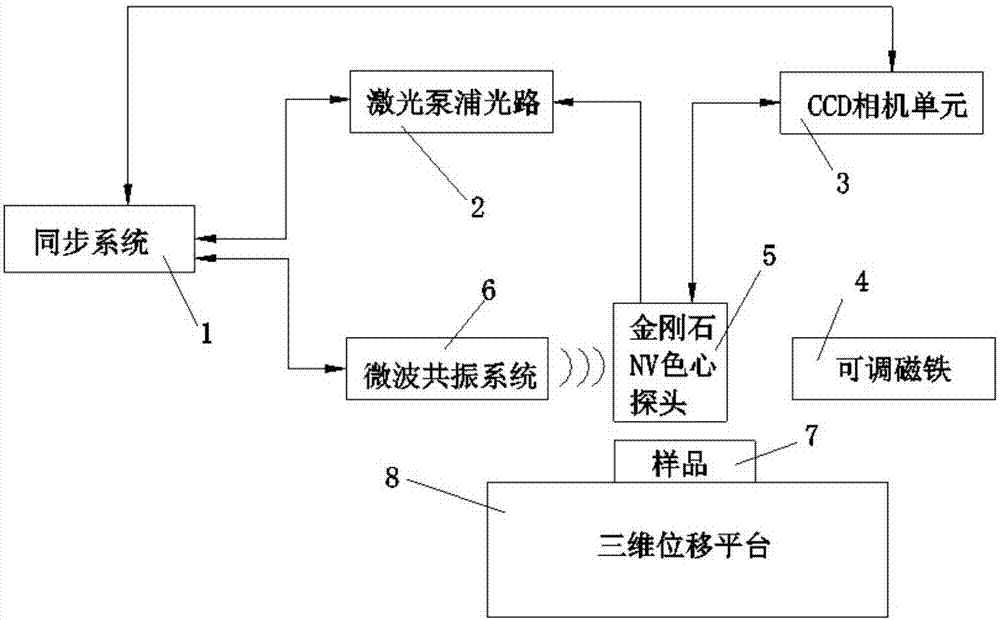
The invention discloses an electromagnetic field near-field imaging system and method based on pulsed light detection magnetic resonance. The system consists of a laser pump optical path, a microwave source, a diamond NV color-center probe, a CCD camera unit, a synchronization system, a displacement scanning platform, control software and a data analysis imaging system. In the system, a large diamond single crystal containing the NV color-center is used as a detection unit, a static magnetic field is used to split a magnetic resonance peak of the diamond NV color-center into eight peaks, the eight resonance peaks correspond to four crystal axis directions <111>, <1-11>, <-111>, <11-1> of a diamond lattice structure, by measuring the Rabi frequency of each resonance peak, the strength of a circularly polarized microwave field perpendicular to the corresponding crystal axis direction is obtained, and through comprehensive calculation of the microwave field strengths in the four directions, the strength and direction of a microwave vector are then reconstructed. Through the microwave near-field high-resolution imaging of a local region of a microwave chip under measurement, the quantitative data can be provided for the failure analysis of the chip.
Owner:南京昆腾科技有限公司
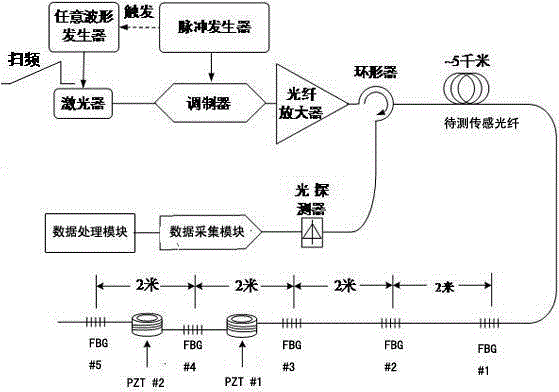
Fully distributed optical fiber strain and vibration sensing method and sensor
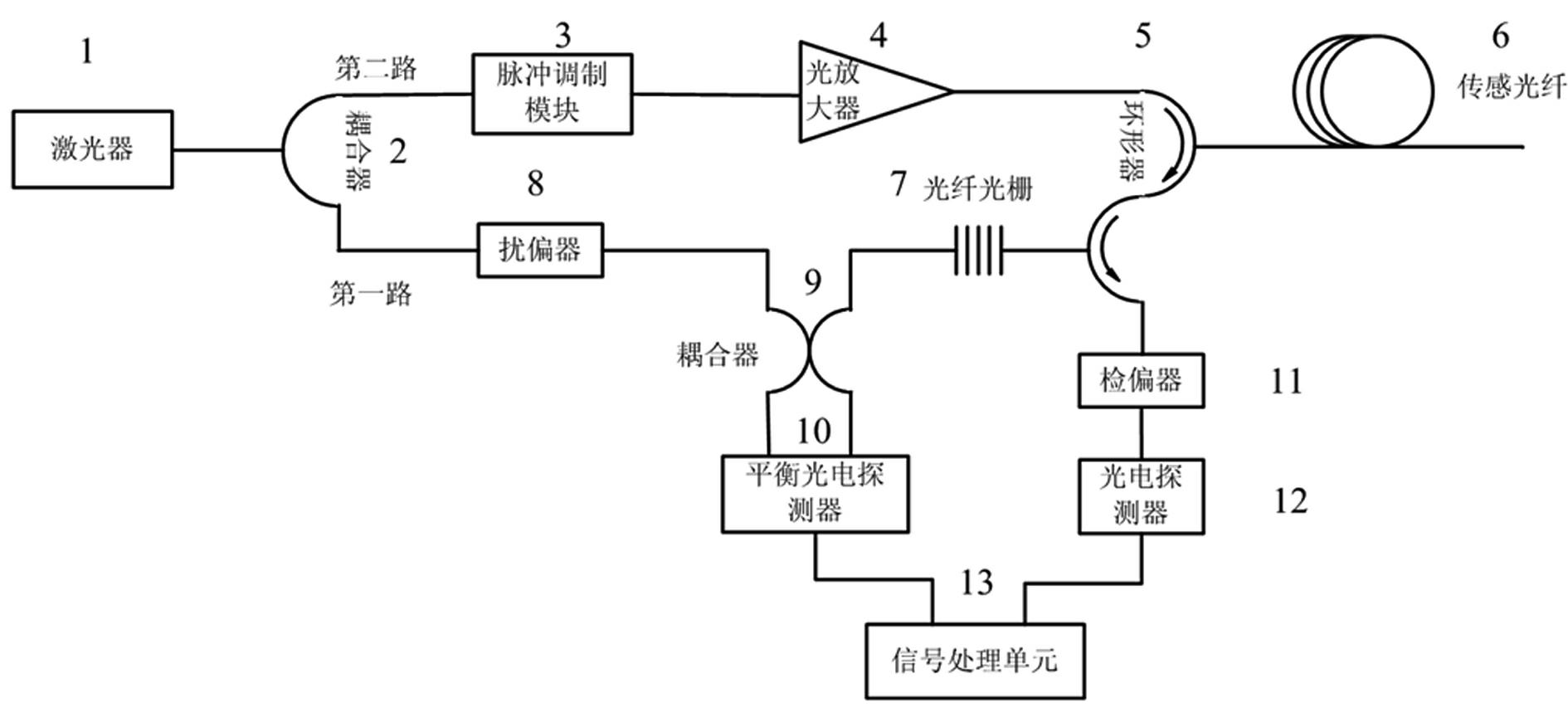
InactiveCN102147236AOvercome the shortcoming of single functionExtended functional scopeReflectometers dealing with polarizationSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementContinuous lightGrating
The invention discloses a fully distributed optical fiber strain and vibration sensor comprising a laser (1), a first coupler (2), a pulse modulation module (3), an optical amplifier (4), a circulator (5), a sensing optical fiber (6), a fiber bragg grating (7), a polarization scrambler, a second coupler, a balance photoelectric detector, an analyzer, a photoelectric detector (12) and a signal processing unit. Continuous light output by the laser (1) is split into two paths through the first coupler (2), wherein one path is used as reference light and is accessed to a first input end of the second coupler (9) through the polarization scrambler (8); and the second path is processed by the pulse modulation module (3) and the optical amplifier (4) and then used as detection pulse light to be injected into a first port of the circulator (5). In the invention, Brillouin optical time domain reflectometry (BOTDR) and polarization optical time domain reflectometry (POTDR) are simultaneously utilized for respectively and correspondingly carrying out fully distributed measurement on strain and vibration on a signal optical fiber, the defects of a system with single BOTDR or POTDR are overcome, and the false alarm rate or missed report rate of the system is decreased.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
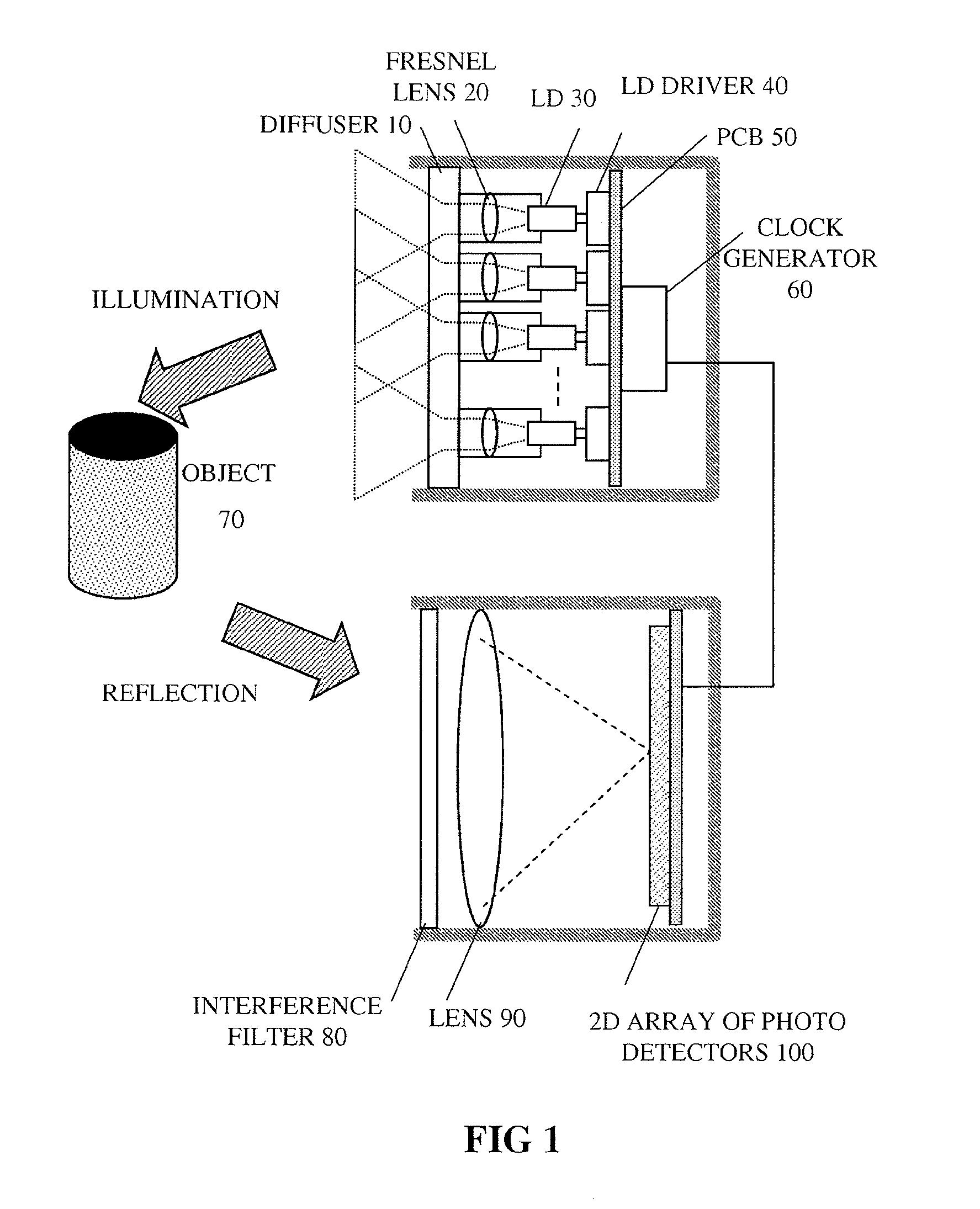
Method and apparatus for inspecting defects of patterns
InactiveUS20050110988A1Reducing amount-of-light unevennessDamage on the wafer caused by the illumination light can be reducedOptically investigating flaws/contaminationVisual field lossLight beam
Disclosed is a method and apparatus for inspecting defects of patterns of a sample at high speed and with high sensitivity while damage of the sample arising from high-power pulsed light is reduced. Light emitted from a pulsed laser light source is transmitted through a pseudo continuous-wave forming optical system having an optical system capable of reducing energy per pulse and yet maintaining the entire amount of light of the pulsed light, a beam formation optical system, and a coherence reduction optical system, and a beam deflected by a deformation illumination optical system is made to reflect on a PBS to be irradiated on a wafer. The apparatus is configured so that the diffracted light from the wafer is focused by an objective lens, transmitted through light modulation units, focused to form a plurality of images on a plurality of image sensors in a visual-field divided parallel detection unit 12, and then defects are detected by a signal processing unit.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Intravascular Diagnostic or Therapeutic Apparatus Using High-Intensity Pulsed Light
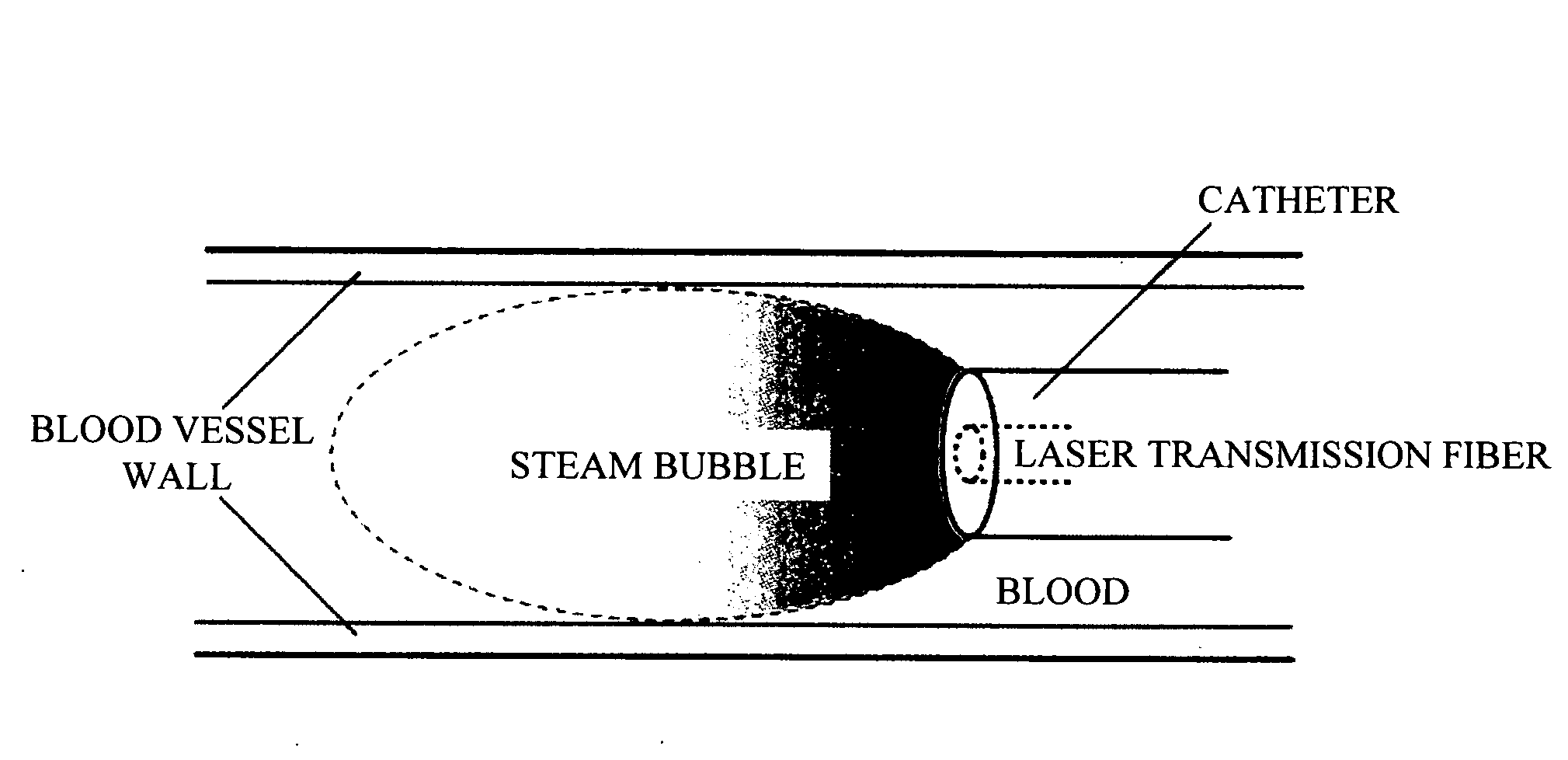
InactiveUS20080221560A1Method is invasiveMinimally invasiveEndoscopesLaproscopesVapor bubbleRemove blood
An intravascular diagnostic or therapeutic apparatus capable of removing blood in an intravascular lumen to be observed using a minimally invasive method is provided. The apparatus includes high-intensity pulsed light generating means and high-intensity pulsed light transmitting means for transmitting high-intensity pulsed light, capable of irradiating the interior of a blood vessel with high-intensity pulsed light, producing water-vapor bubbles and temporarily removing the blood in the blood vessel.
Owner:KEIO UNIV
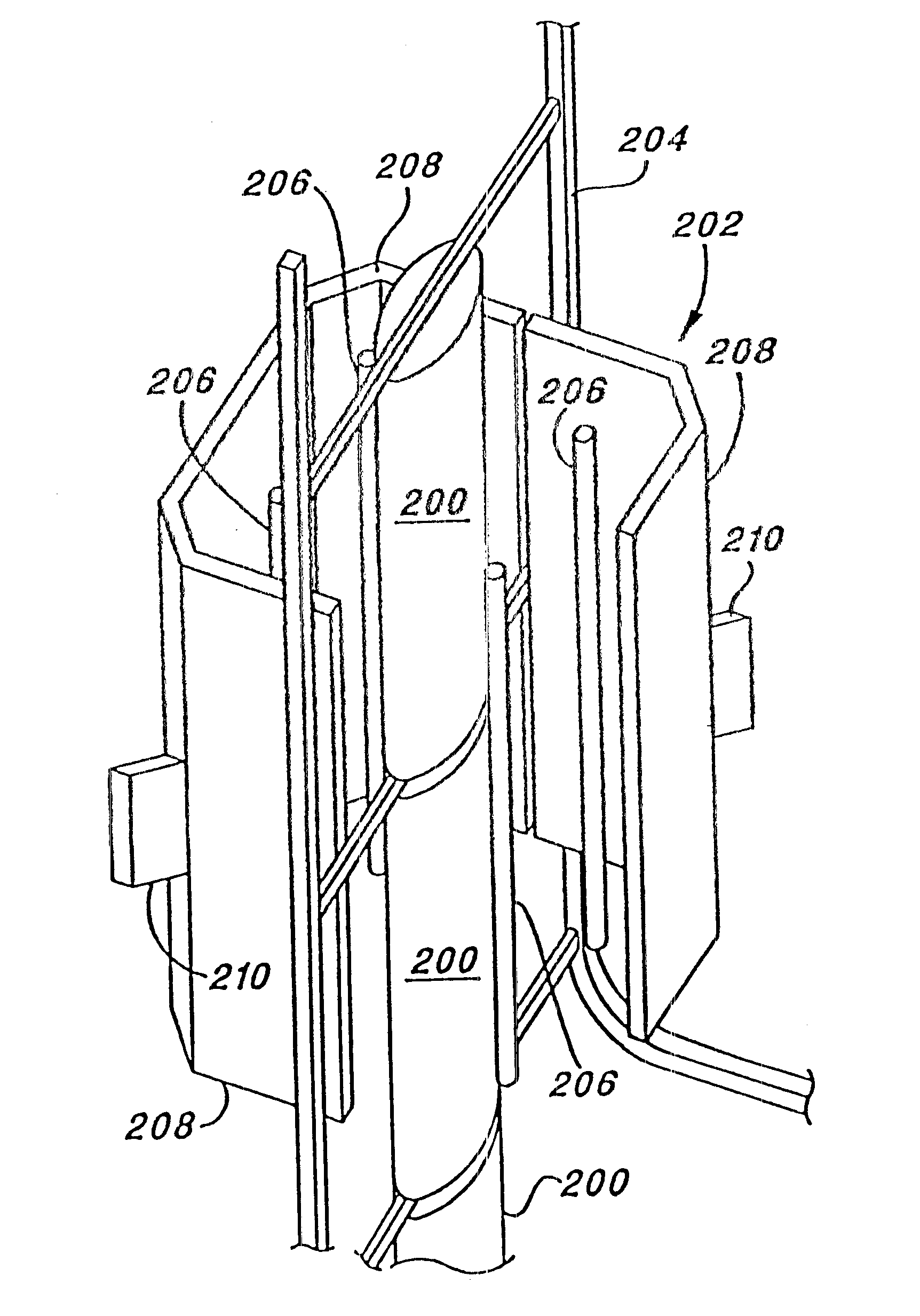
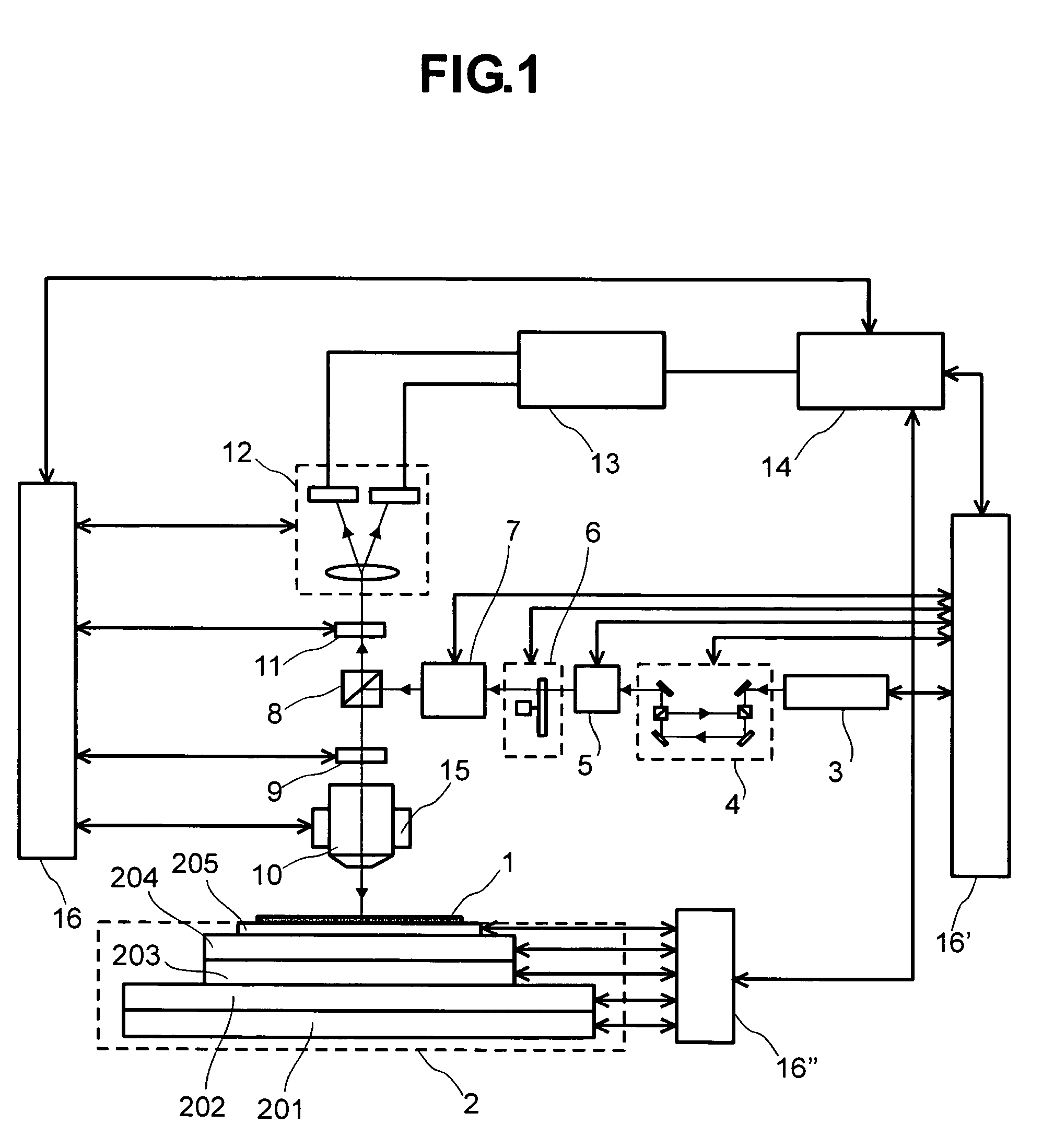
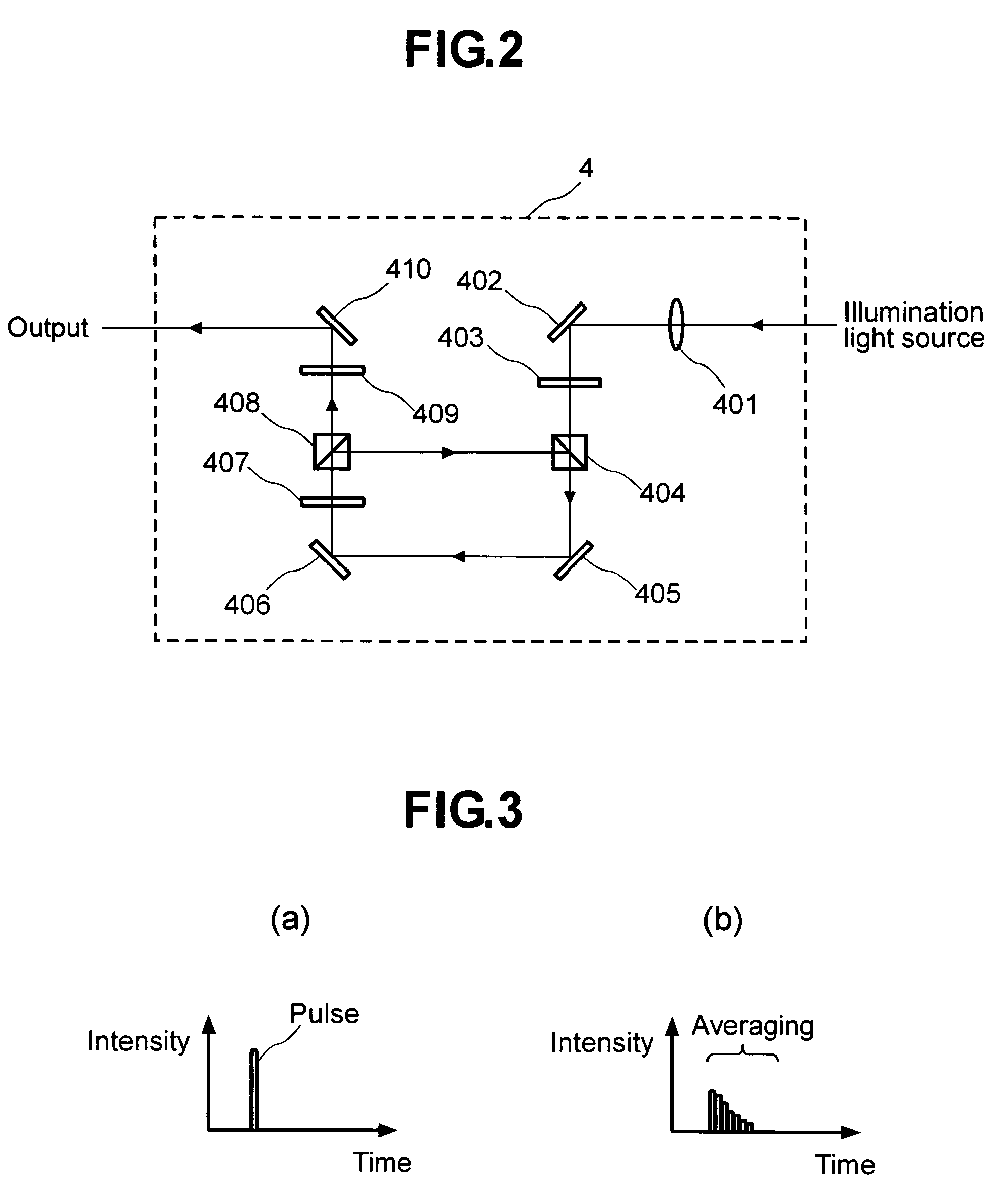
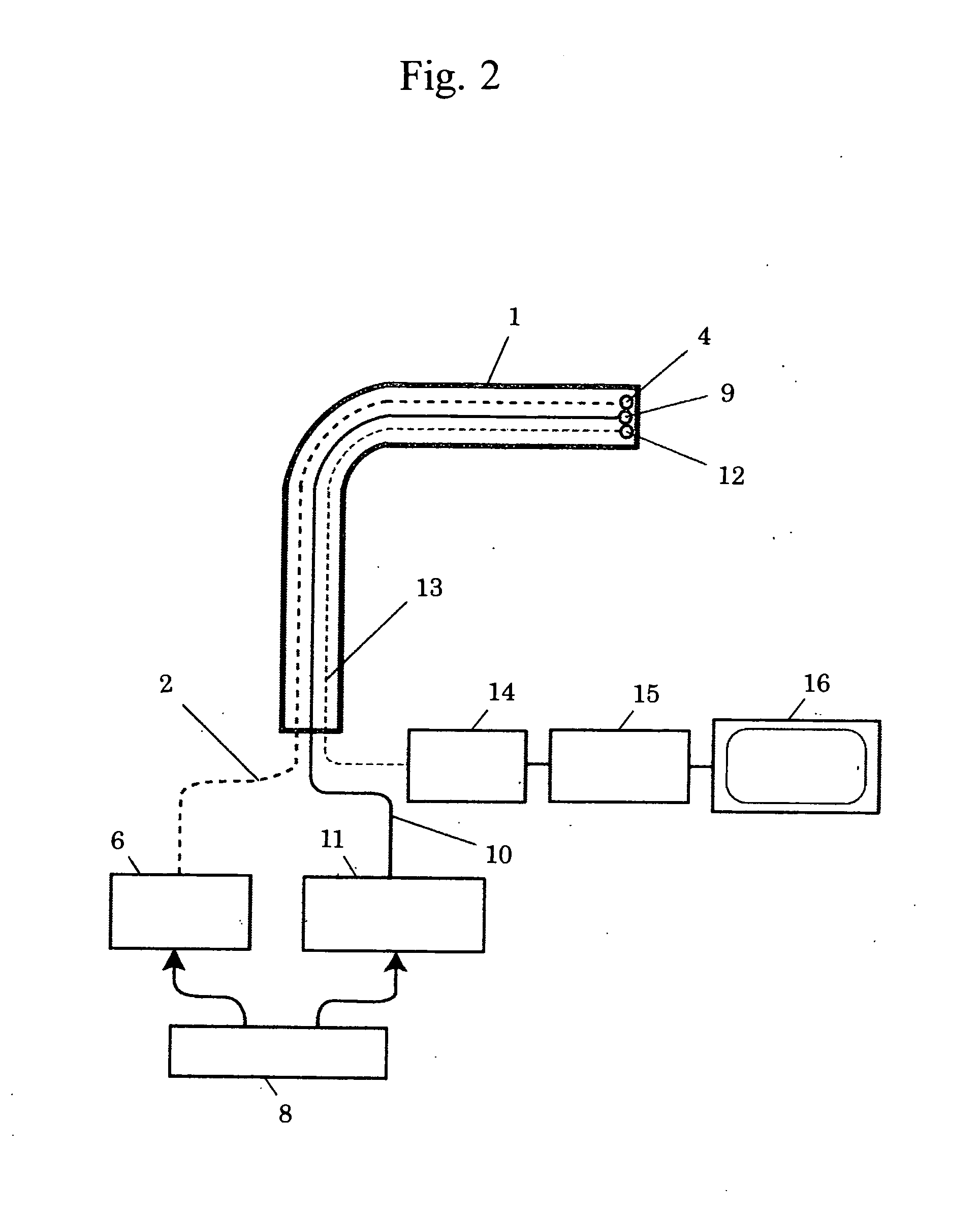
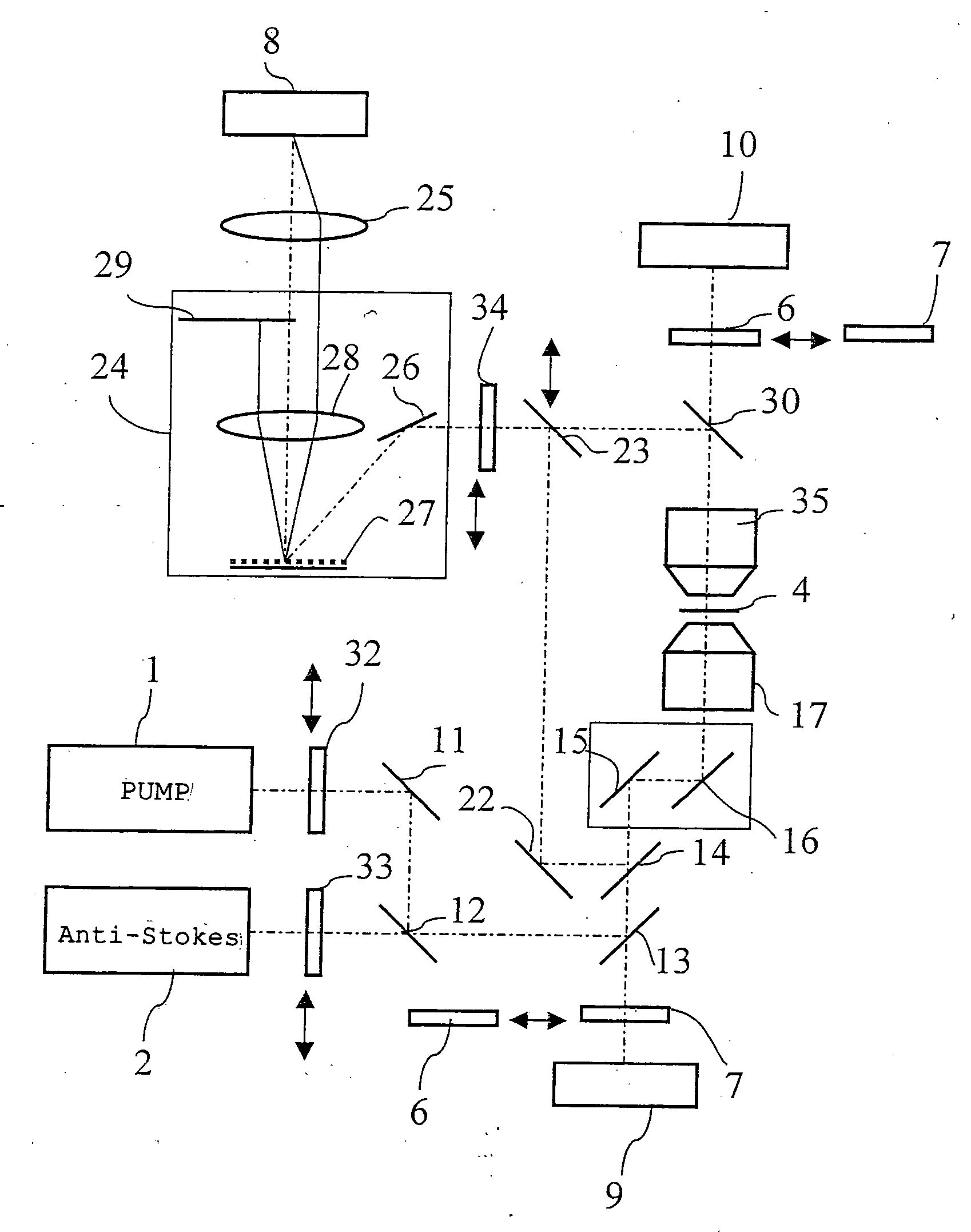
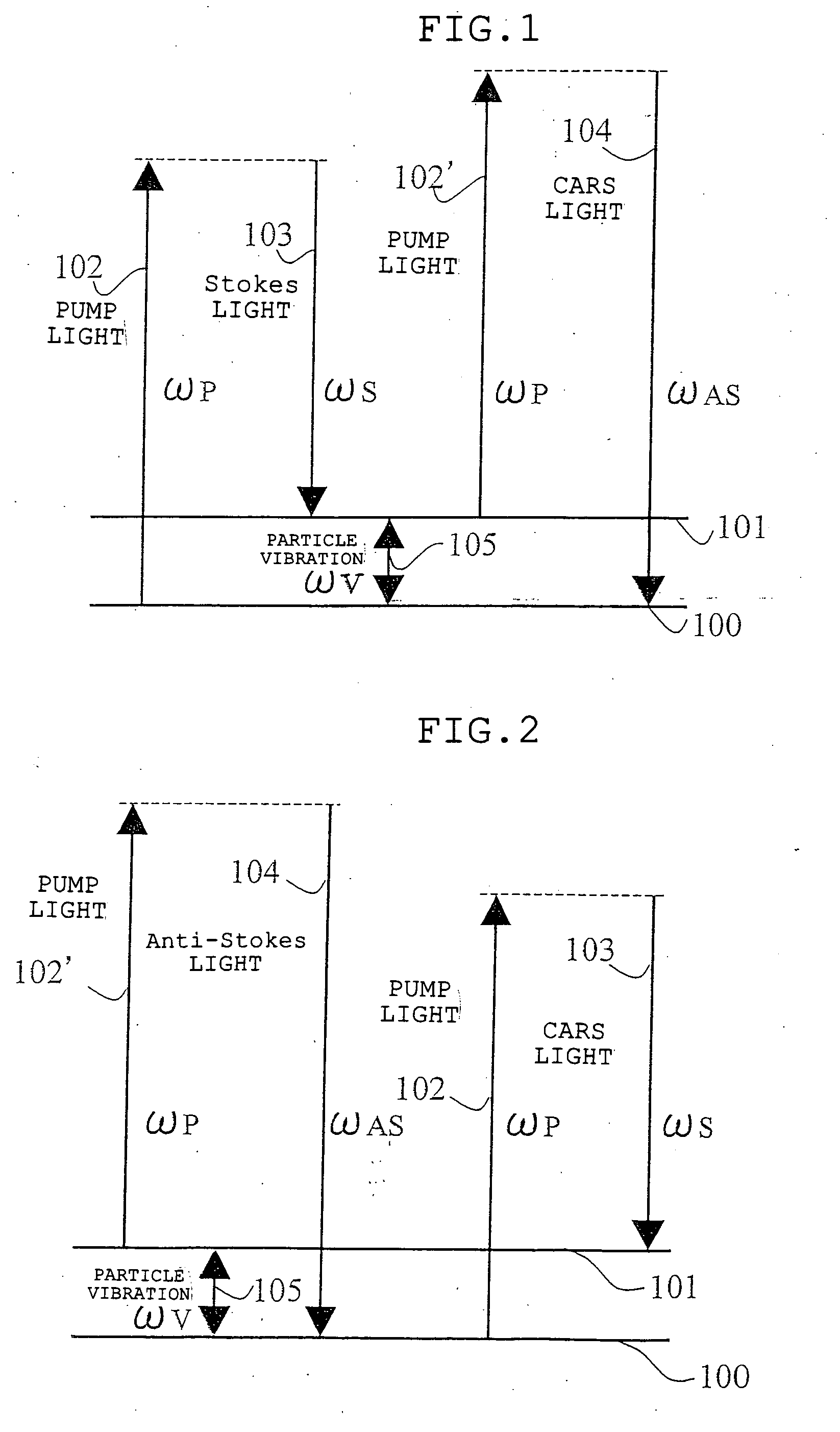
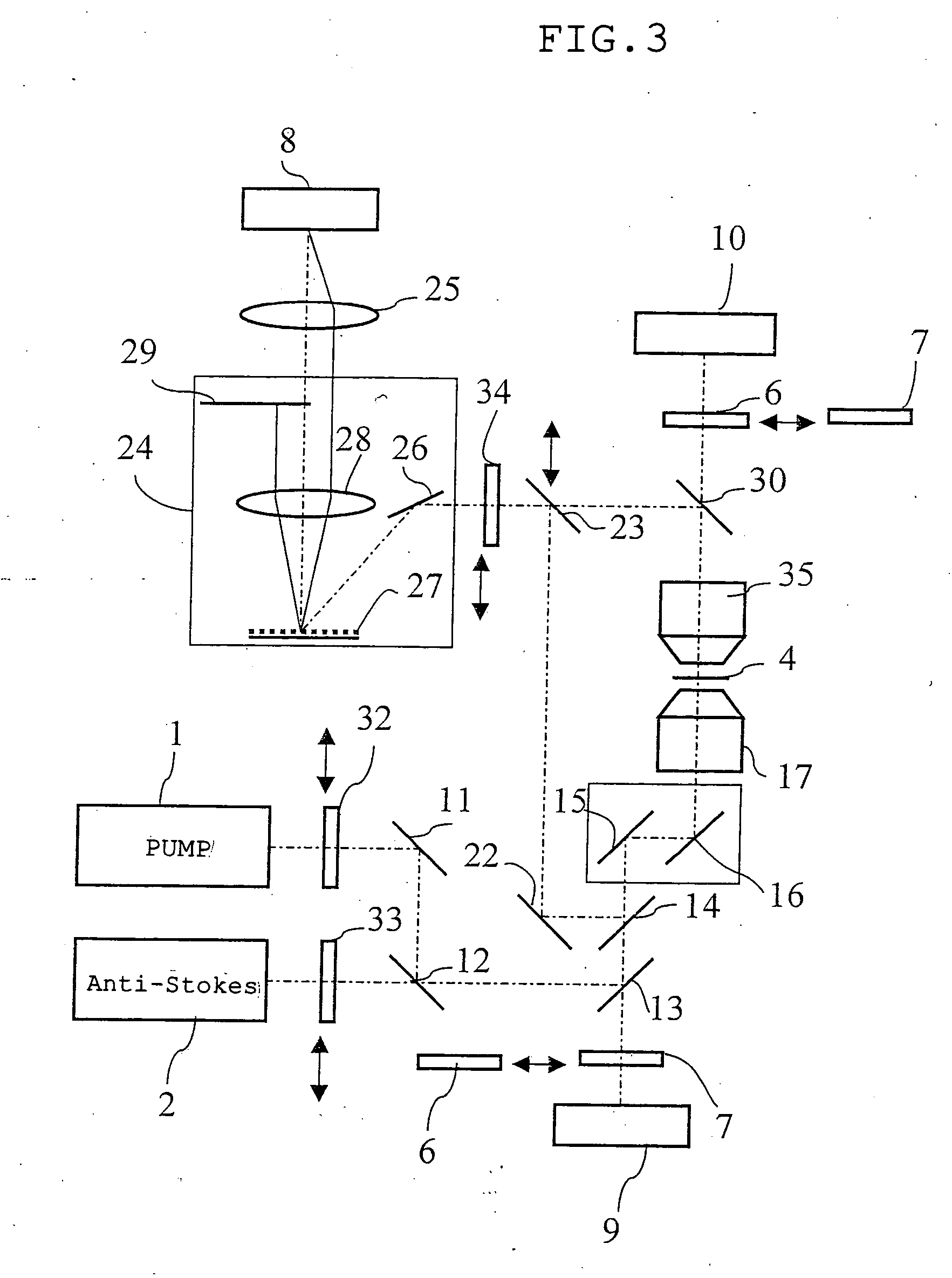
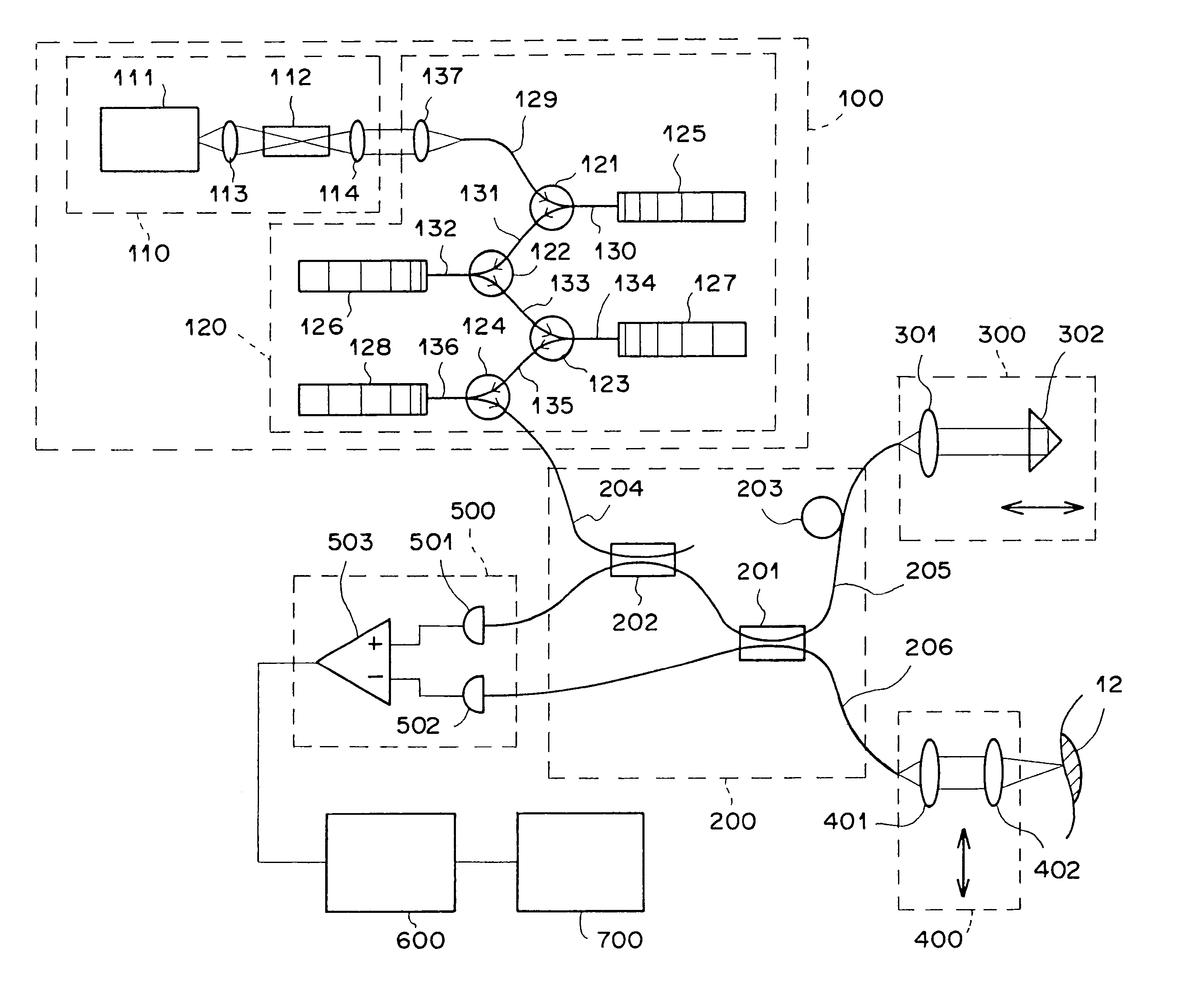
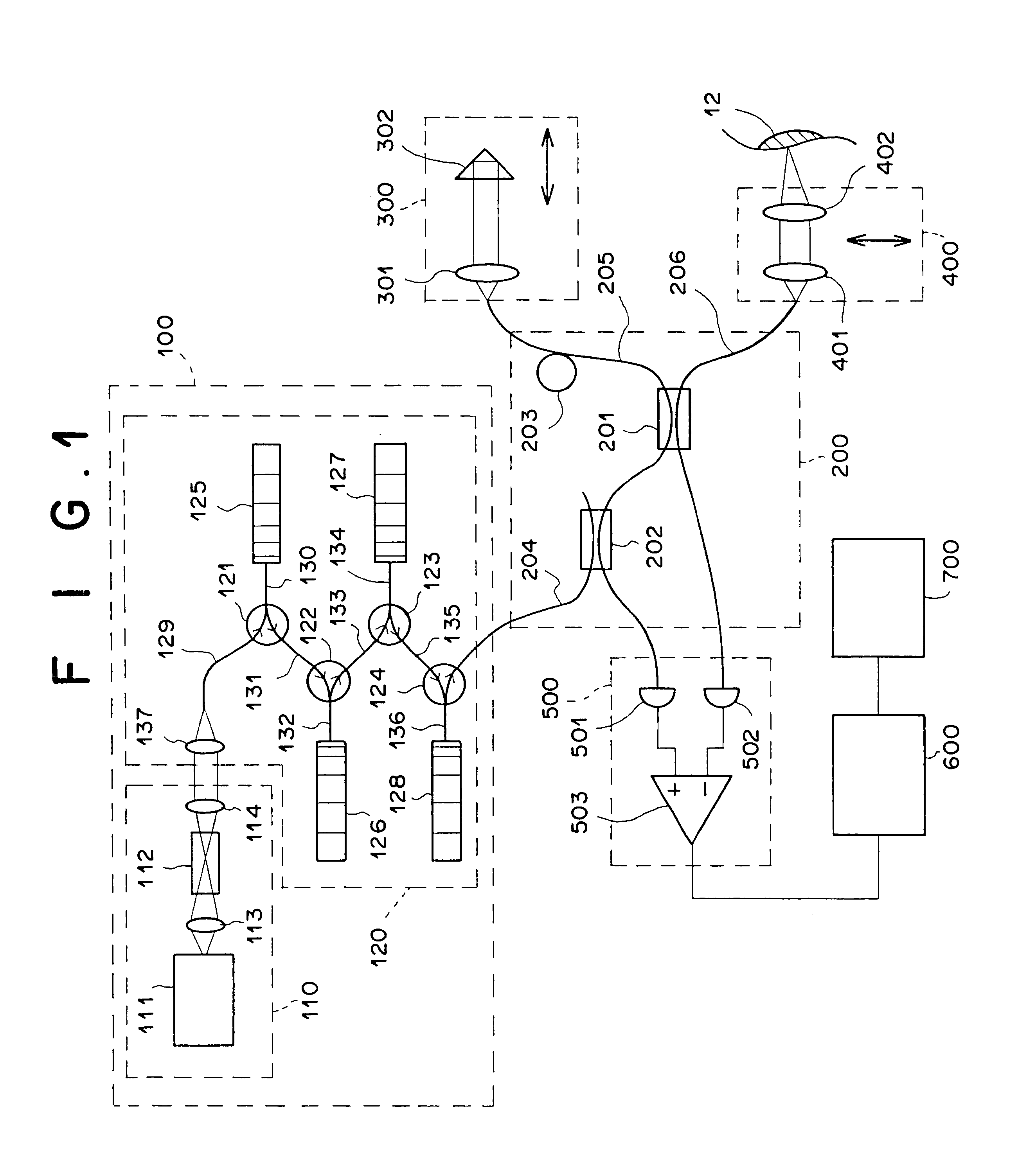
Microscope
The microscope has a first pulsed laser generating means, a second pulsed laser generating means, an irradiation means to irradiate to a specimen by composing the first pulse light and the second pulse light, a coherent Raman scattering light extraction means for extracting only the coherent Raman scattering light from light emanated from the specimen irradiated, an extraction means for extracting only the multiphoton excitation fluorescence, an extraction means for extracting only the second harmonic wave, a detection means for detecting the extracted coherent Raman scattering light, and a detection means for detecting the extracted fluorescence, and a detection means for detecting the second harmonic wave via the extraction means 7. To single specimen, responding to purposes, observations of the two-photon excitation fluorescence observation, the second harmonic wave observation, and the coherent Raman scattering light observations can be carried out in parallel, or selectively.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
Light wand for healing tissue
InactiveUS20050015121A1Easy to useAvoid contactSurgical instrument detailsLight therapyMedicineLight energy
A light wand includes light emitting diodes that transmit monochromatic light for a therapeutic response. The monochromatic light provides healing and relieves pain from such conditions as, for example, abrasions, cuts, wounds, acne, and other skin conditions. Pulsed light and / or a constant light stream are emitted from the wand under the user's control. Intensity of the light energy is also controlled by the user through a control pad on the light wand. The light wand is portable and dimensioned for consumer use.
Owner:AZNA HEALTH & WELLNESS
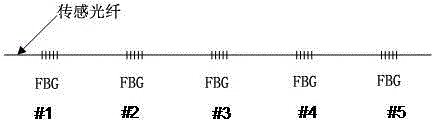
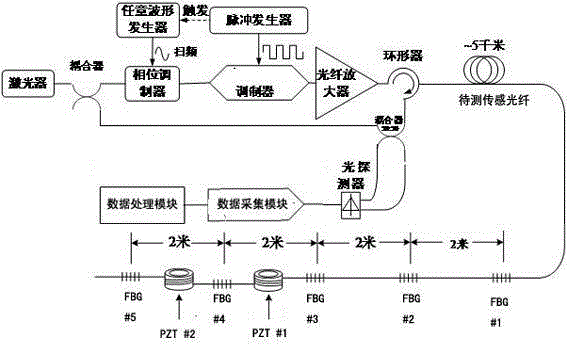
Fiber bragg grating array-based phase-sensitive optical time domain reflection device and method
ActiveCN104990620AEasy to measureRealize quantitative detection of strainSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansContinuous lightFiber
The invention discloses a fiber bragg grating array-based phase-sensitive optical time domain reflection device and method. The device includes a light source, a laser frequency adjustment module, a modulator, an optical fiber amplifier, a circulator, a sensing optical fiber, a light detector, a data acquisition module and a data processing module; the sensing optical fiber is provided with an optical fiber array formed by a plurality of FBGs (fiber bragg grating) which are arranged equidistantly; the laser frequency adjustment module is used for frequency adjustment of continuous light emitted by the light source; the continuous light is modulated by the modulator so as to form pulsed light; the optical fiber amplifier performs power amplification on the pulsed light; the sensing optical fiber is used for receiving and transmitting the pulsed light which has been subjected to power amplification; the light detector receives scattered light and reflected light; the scattered light and reflected light are acquired by the data acquisition module; and the data processing module generates interference signal frequency response spectrum and obtains the length variation quantity of the sensing optical fiber between two adjacent FBGs through processing. With the fiber bragg grating array-based phase-sensitive optical time domain reflection device and method of the invention adopted, strain quantitative detection can be realized, and high-spatial resolution measurement can be realized based on quantitative analysis.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
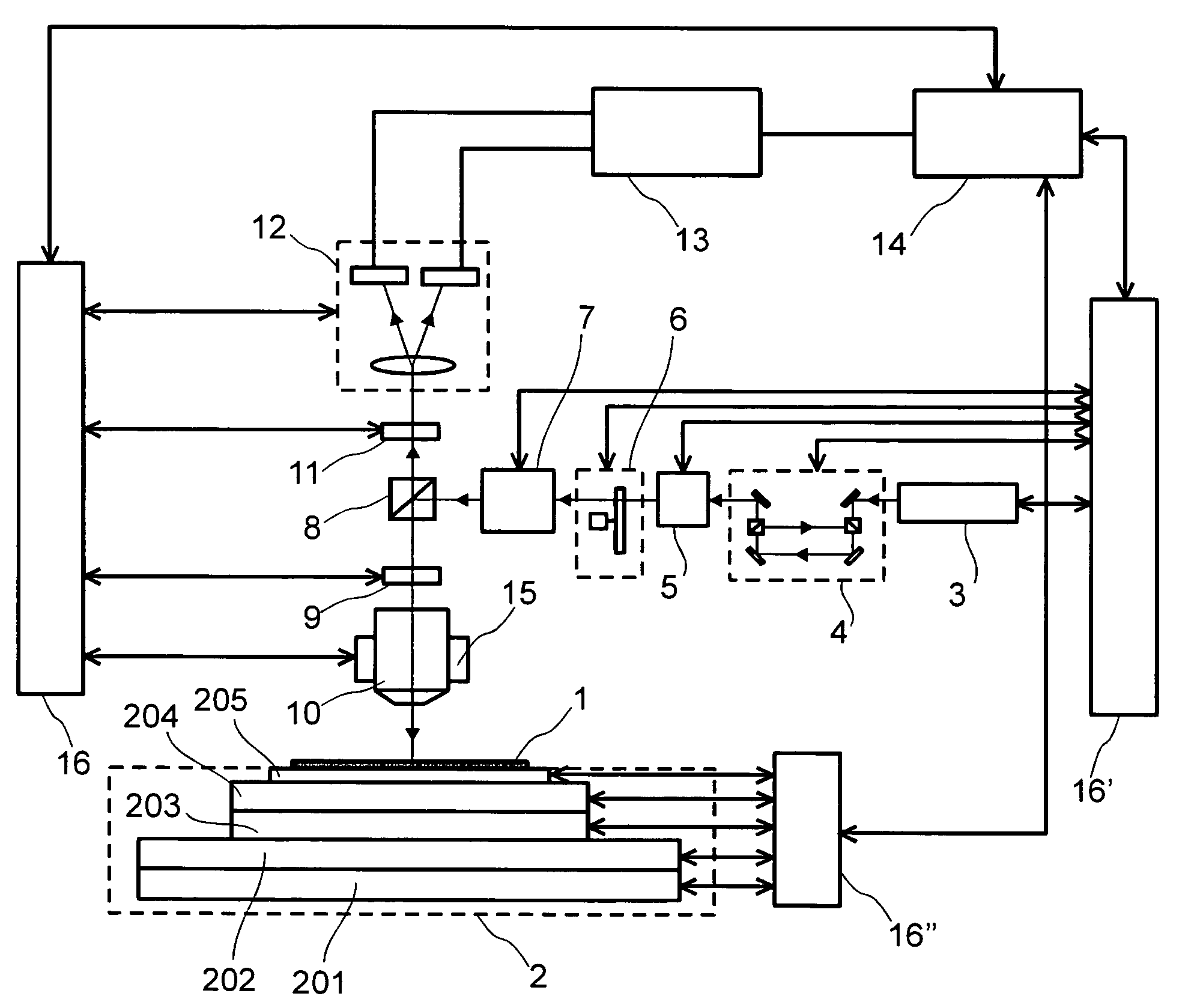
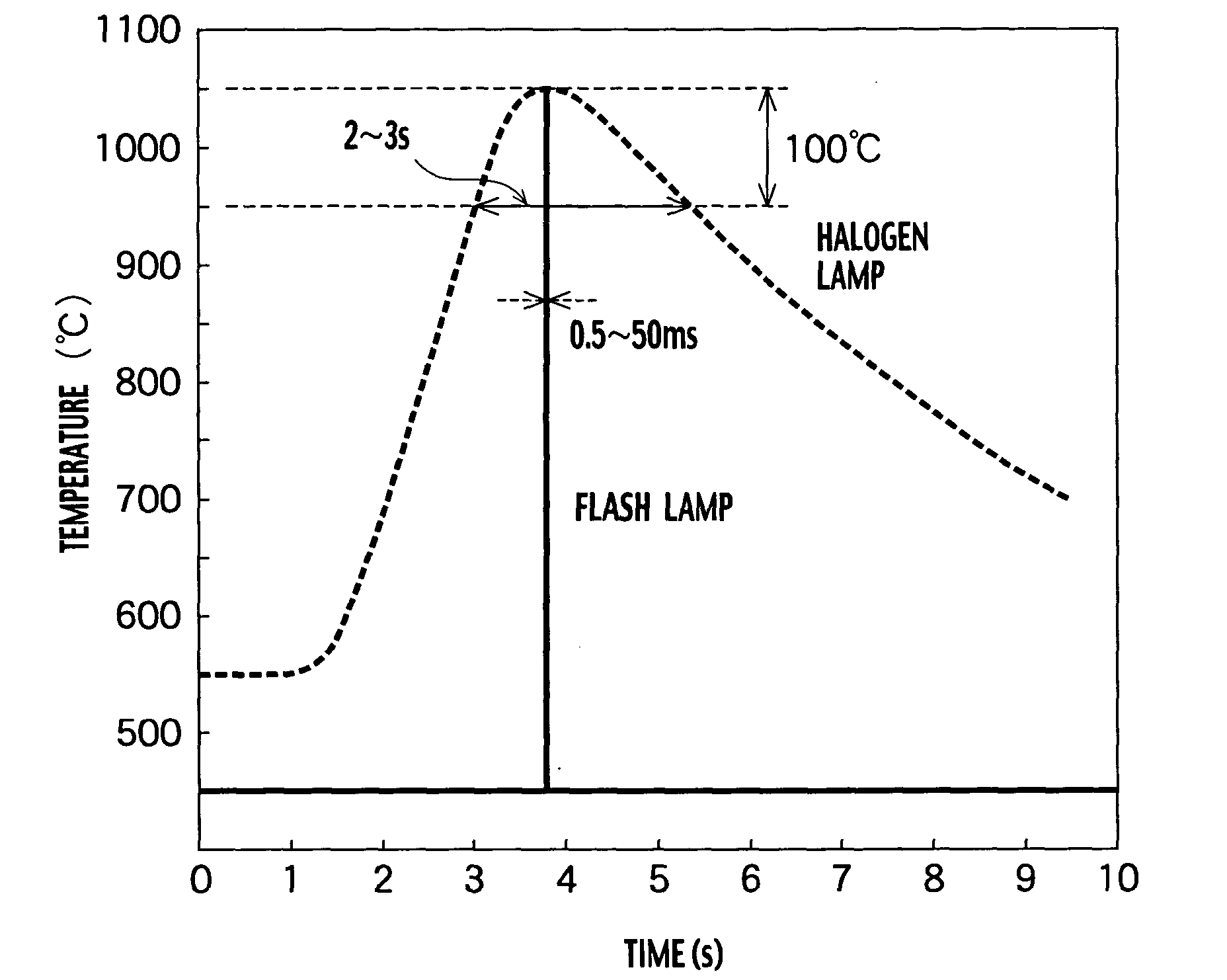
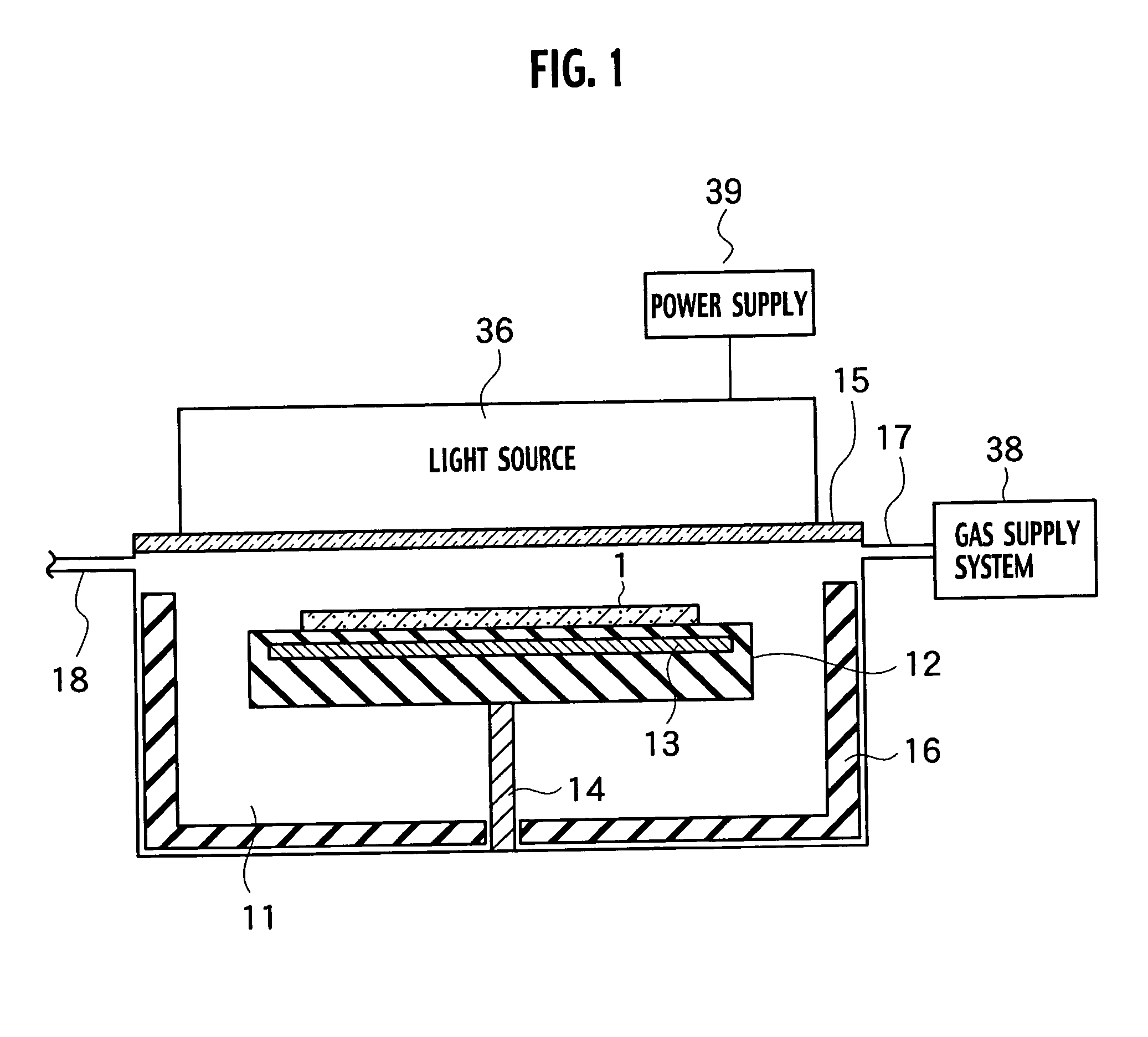
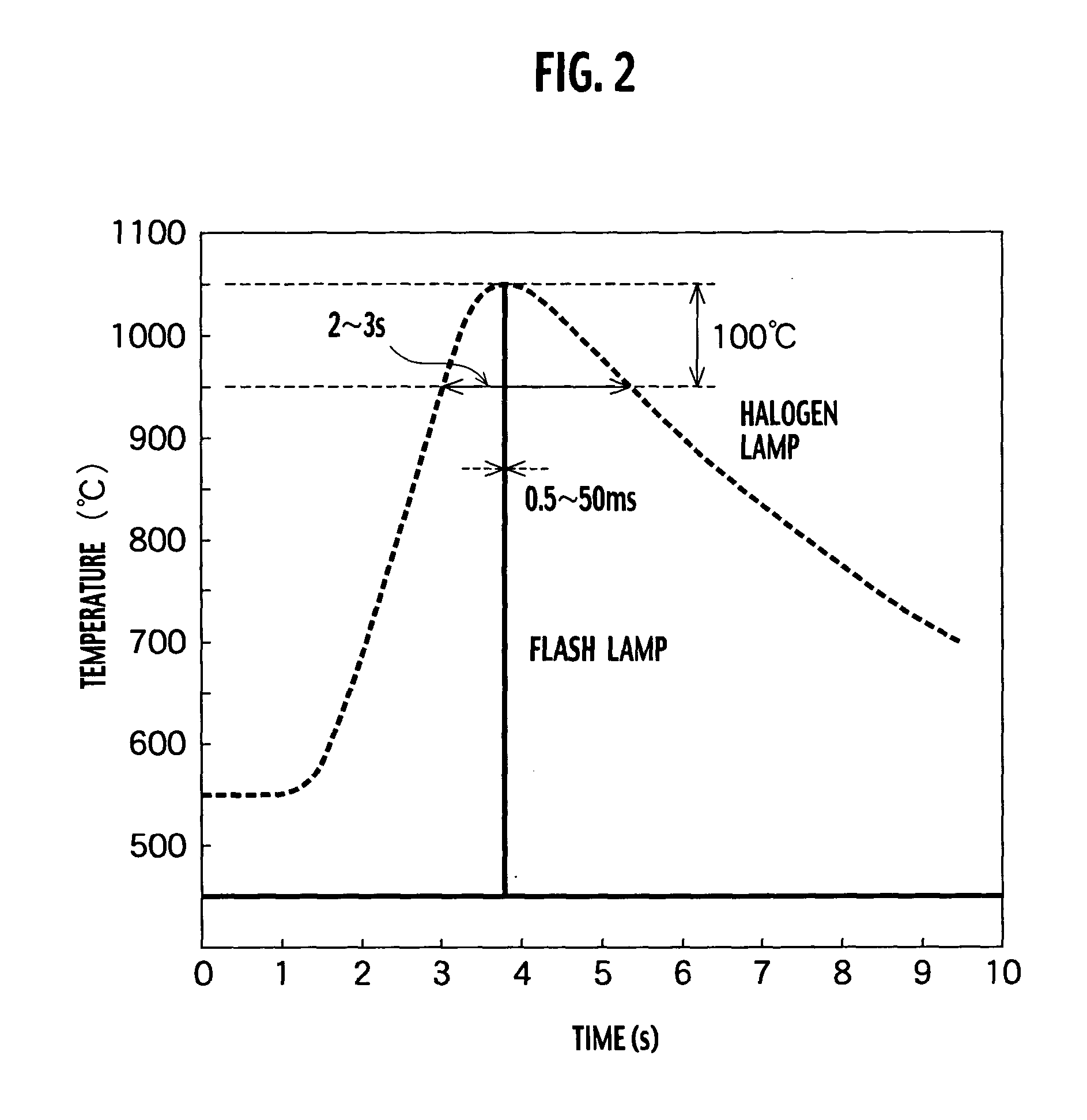
Annealing furnace, manufacturing apparatus, annealing method and manufacturing method of electronic device
InactiveUS20040266214A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSusceptorManufactured apparatus
An annealing furnace, includes a processing chamber configured to store a substrate; a susceptor located in the processing chamber so as to load the substrate and having an auxiliary heater for heating the substrate at 650° C. or less, the susceptor having a surface being made of quartz; a gas supply system configured to supply a gas required for a thermal processing on the substrate in parallel to a surface of the substrate; a transparent window located on an upper part of the processing chamber facing the susceptor; and a main heater configured to irradiate a pulsed light on the surface of the substrate to heat the substrate from the transparent window, the pulsed light having a pulse duration of approximately 0.1 ms to 200 ms and having a plurality of emission wavelengths.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Optical coherence tomography apparatus using optical-waveguide structure which reduces pulse width of low-coherence light
InactiveUS6618152B2Pulse widthBroaden the spectral widthScattering properties measurementsDiagnostics using tomographyOptical scannersSignal light
In an optical coherence tomography apparatus: low-coherence light from a light source is split into signal light and reference light; at least one of the frequencies of the signal light and the reference light is shifted so as to produce a predetermined frequency difference between the frequencies; the reference light and a portion of the signal light reflected from the object are optically multiplexed so as to produce interference light; and the optical intensity of the interference light is detected in order to obtain a tomographic image of the object. In the light source, the pulse width of pulsed light emitted from a pulsed light source unit is reduced by an optical-waveguide structure. The optical-waveguide structure is made of a material having a normal dispersion characteristic, and includes a structure which realizes an anomalous dispersion characteristic so as to reduce the pulse width of the pulsed light.
Owner:KK TOPCON +1
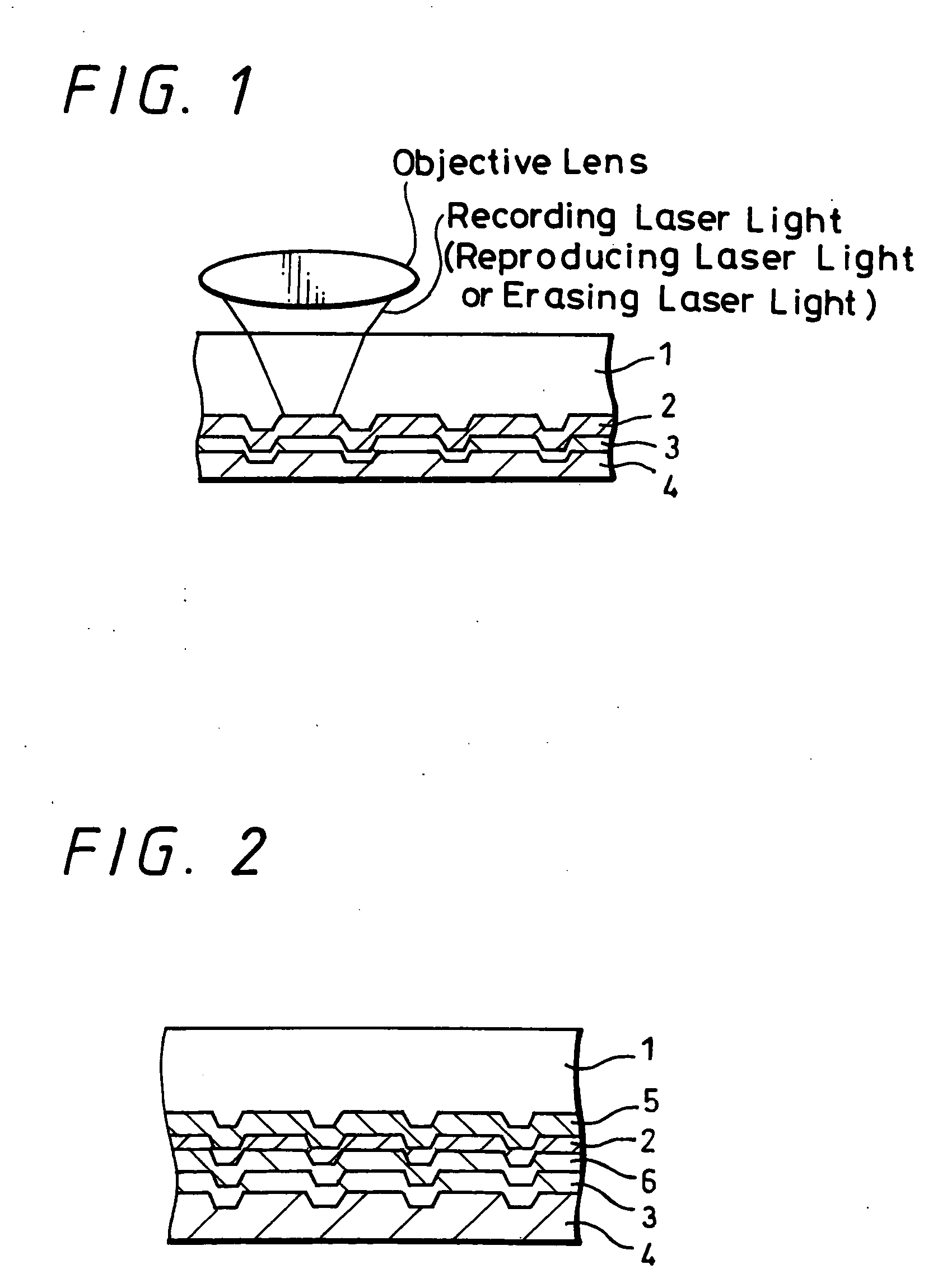
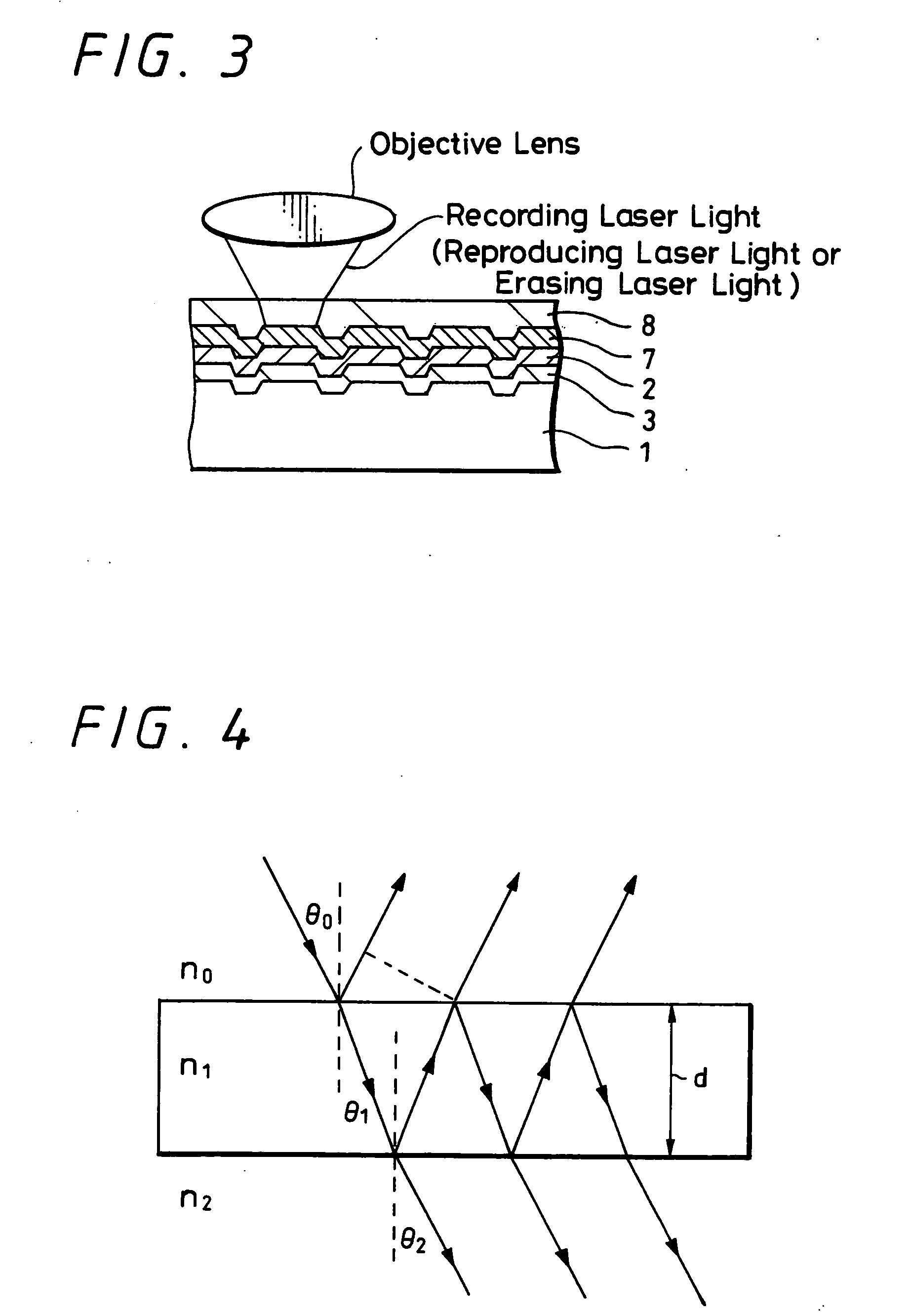
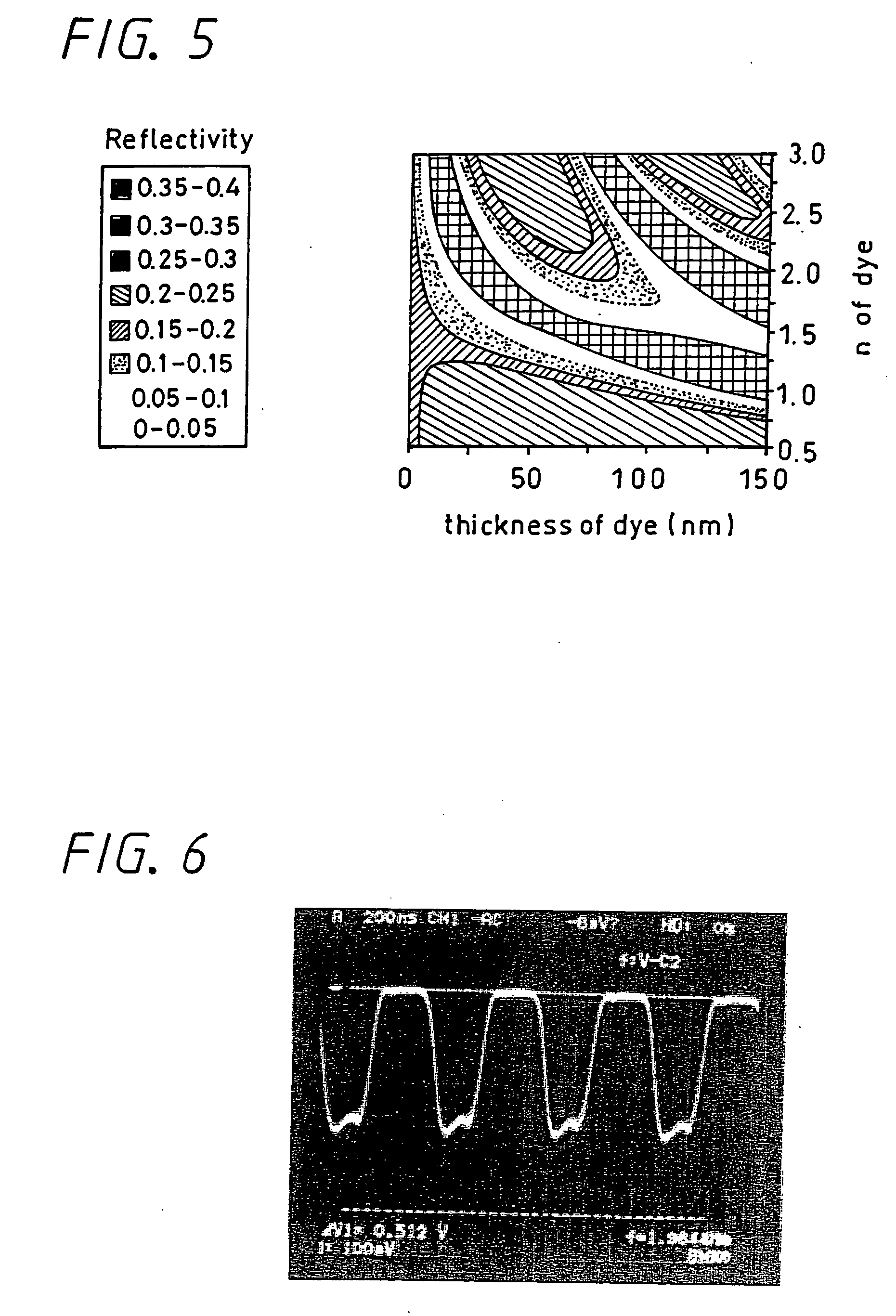
Rewritable optical information recording medium, recording and reproducing methods, as well as recording and reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS20060088786A1More powerLess powerOrganic chemistryReactive dyesContinuous lightOrganic dye
A rewritable optical information recording medium including a recording layer composed of an organic dye film is provided, in which recording and erasing information can be performed reversibly by laser light irradiation. A rewritable optical information recording medium including at least one organic dye film which is substantially made of only at least one kind of organic dye compounds as a recording film is provided. The recording and erasure of information are performed by a reversible physical change of the organic dye film substance caused by laser light irradiation. Specifically, data recording is performed by a physical change locally caused by the irradiation of recording laser light, data reproduction is performed by detecting change in intensity of returned light of reproducing laser light having less power than the recording laser light, and data erasure is performed by applying at least once continuous light or pulse light having laser power more than the reproducing laser light and less than the recording laser light. The physical change is a change in shape.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Parallel distribution optical fibre raster temp. sensing method and its system
InactiveCN101000267ADeployment restrictionsImprove consistencyThermometers using physical/chemical changesConverting sensor output opticallySensor arrayFiber coupler
The invention relates to full parallel distributing type optical fiber grating temperature sensing method and its system. The method includes the following steps: processing high speed modulation for the wide band light source to form pulse sequence with certain width and duty ratio; adopting parallel connection for the sensor each of which is corresponding with different time delay optical fiber; making the pulse light source signal enter into the sensor array by splitter; making each reflected light signal of the sensor enter into photo-electricity detecting unit by one and the same fiber coupler or optical circulator; receiving a series of pulsing signals in one light source modulating cycle each of which is corresponding with one sensor; gaining light signal center wavelength information by a special filter; detecting each of them to gain corresponding sensor temperature information.
Owner:福建迅捷光电科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com