Patents
Literature
1854 results about "Synchronization system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
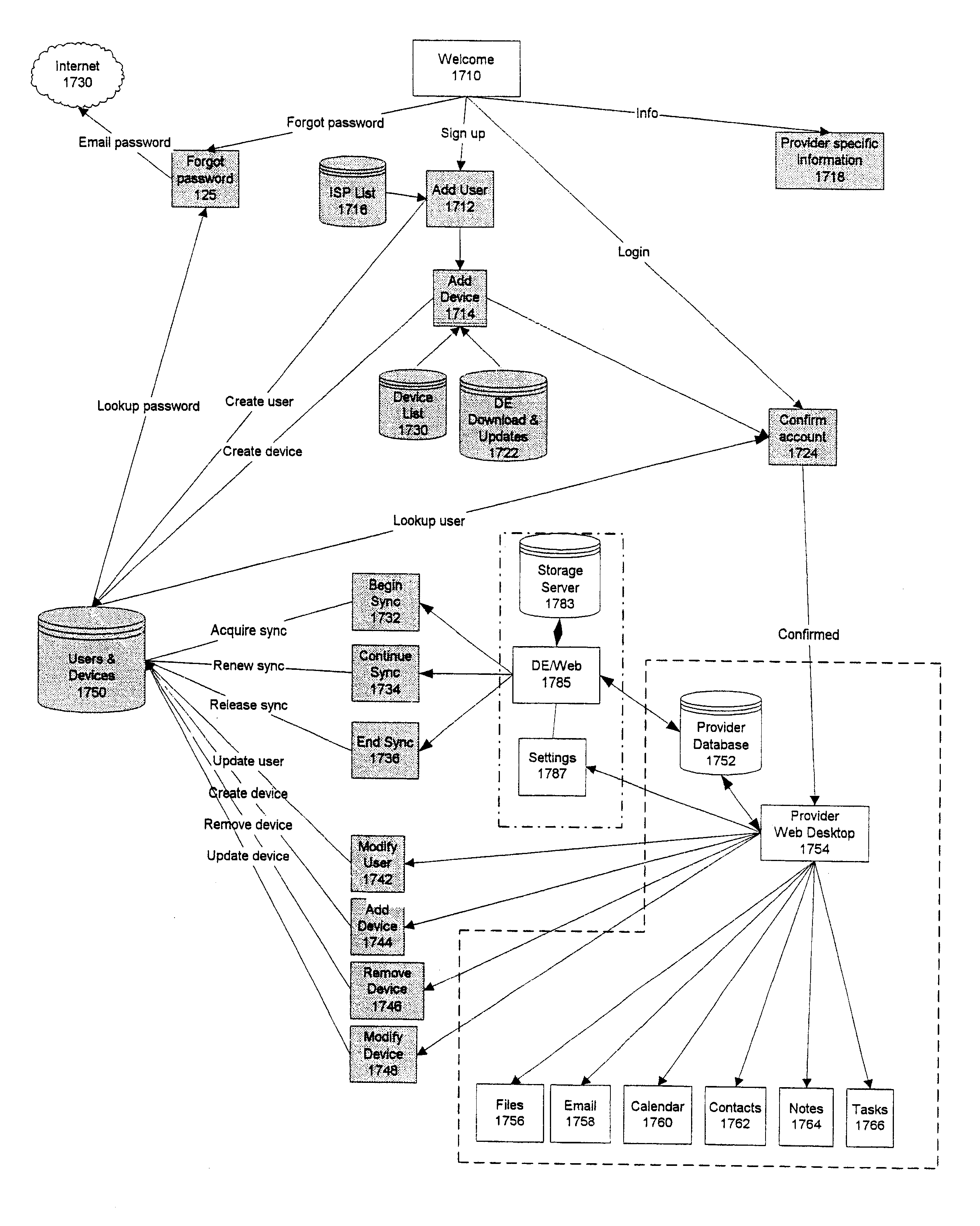
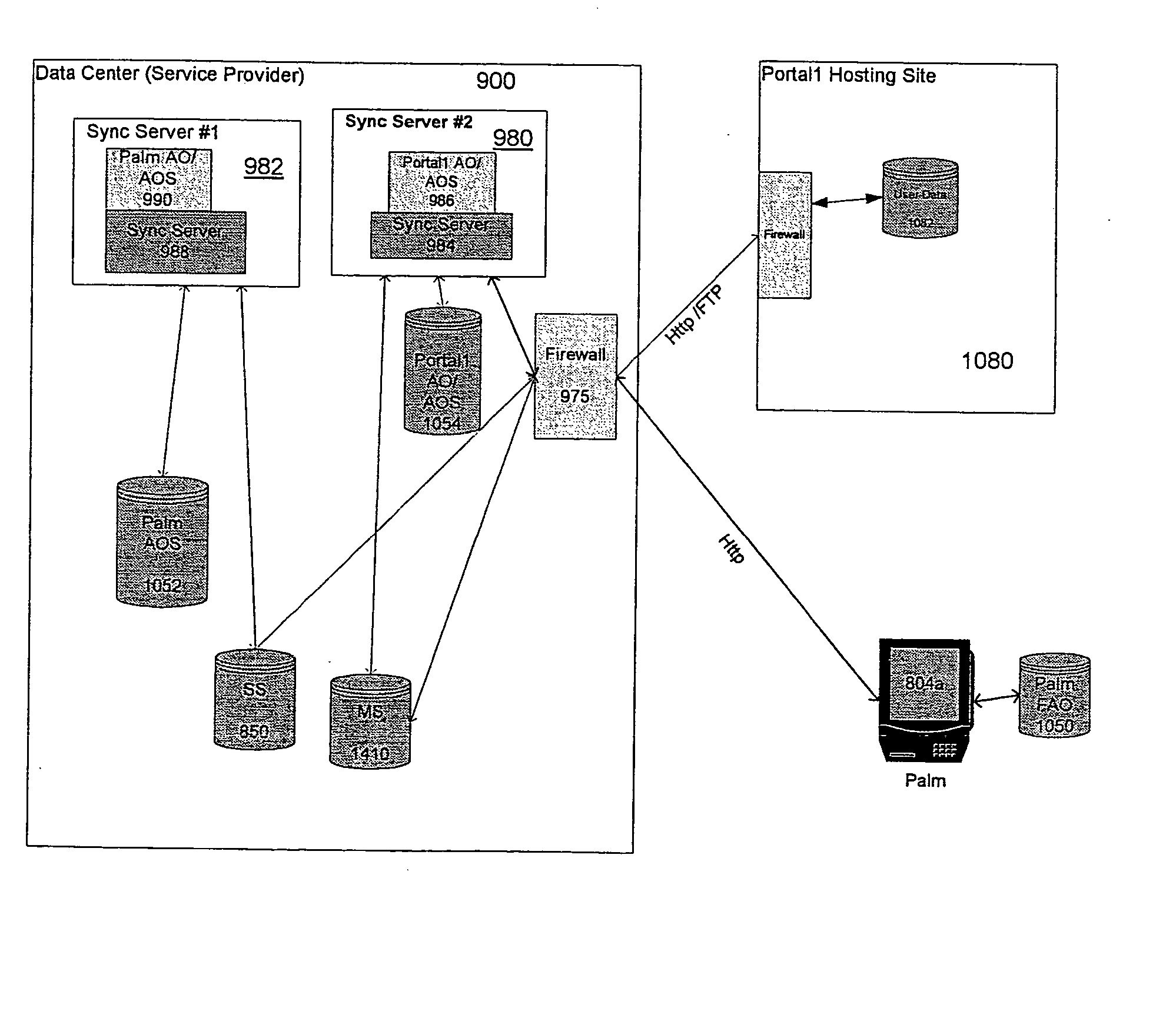
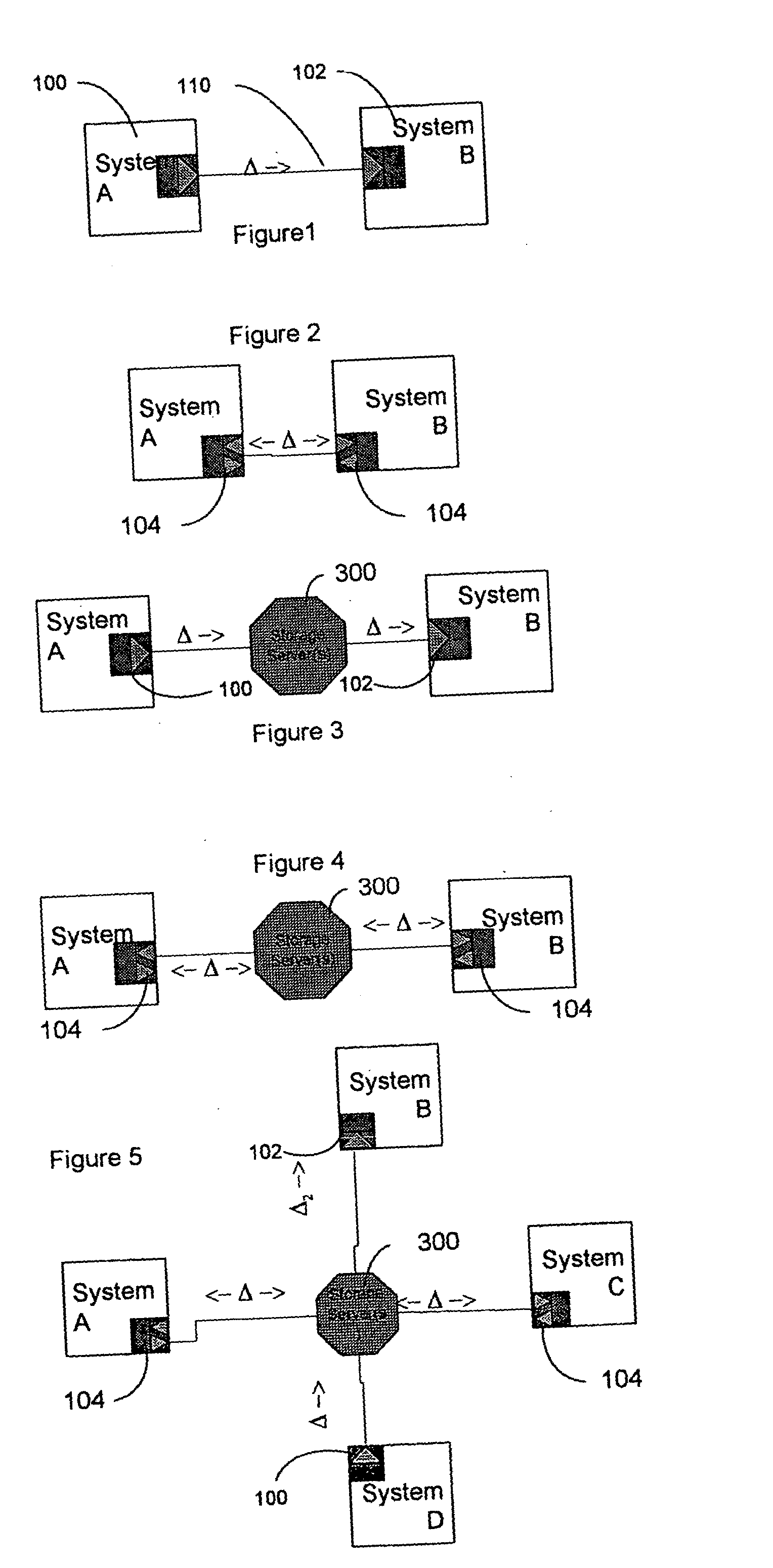
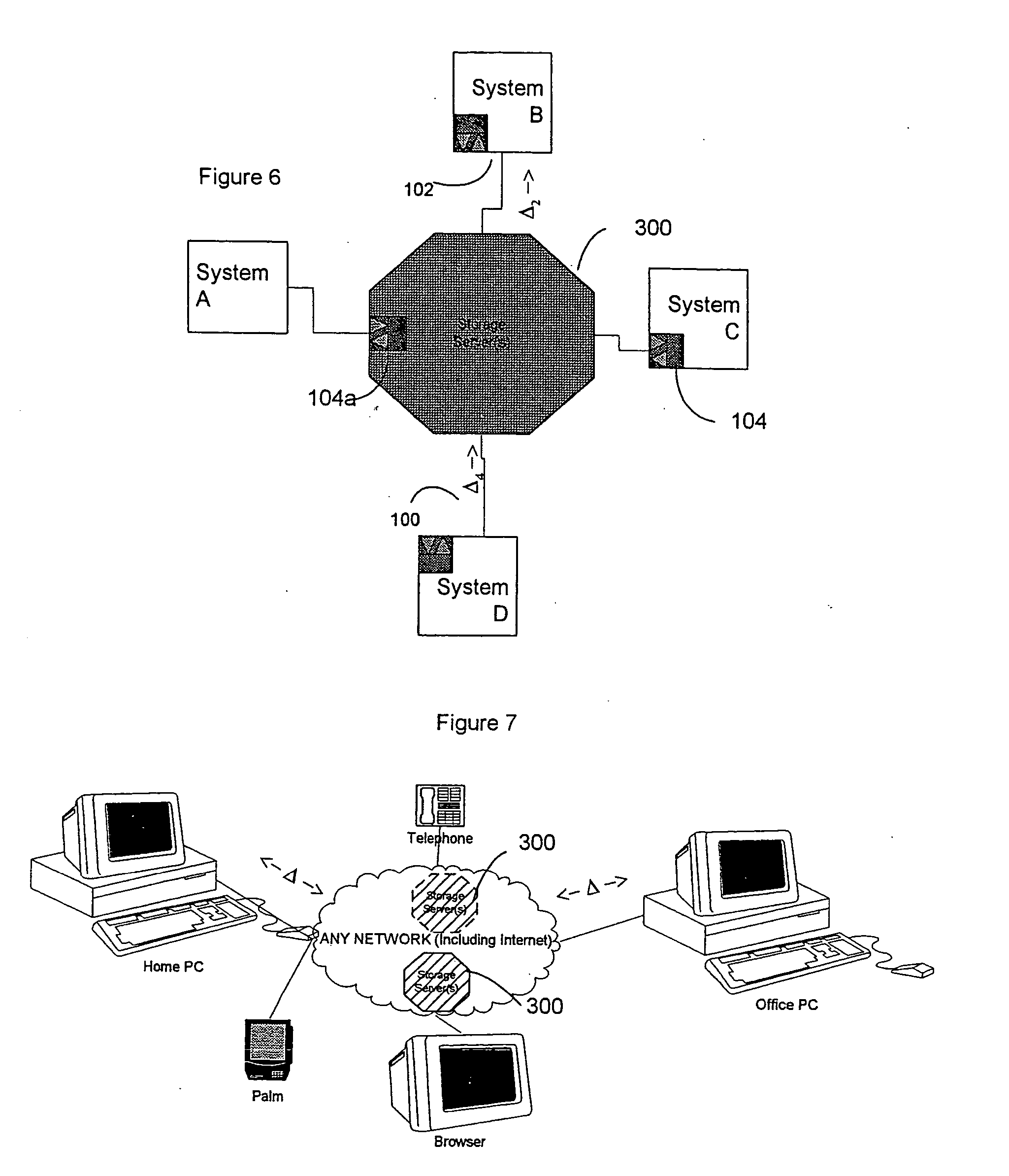
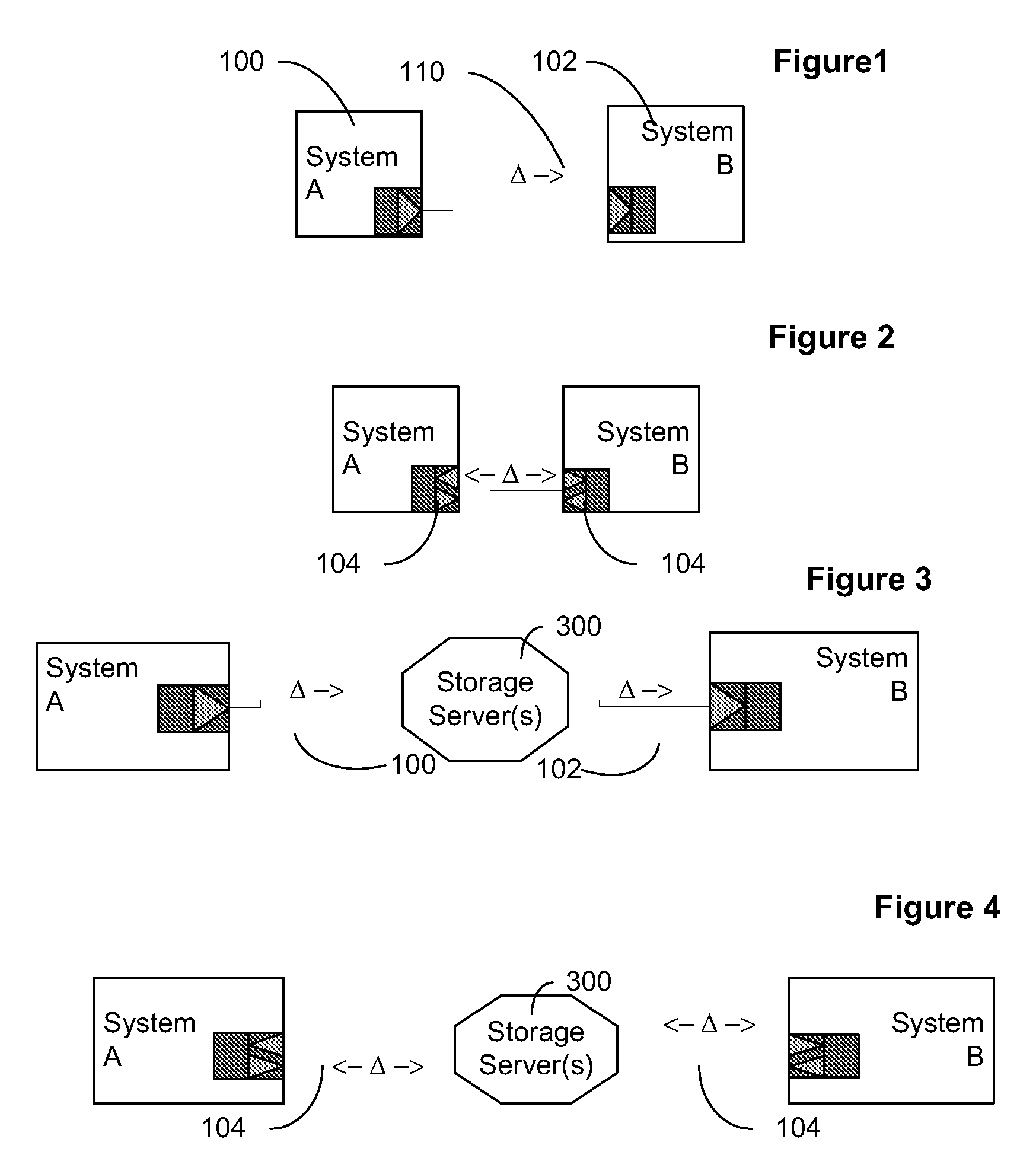
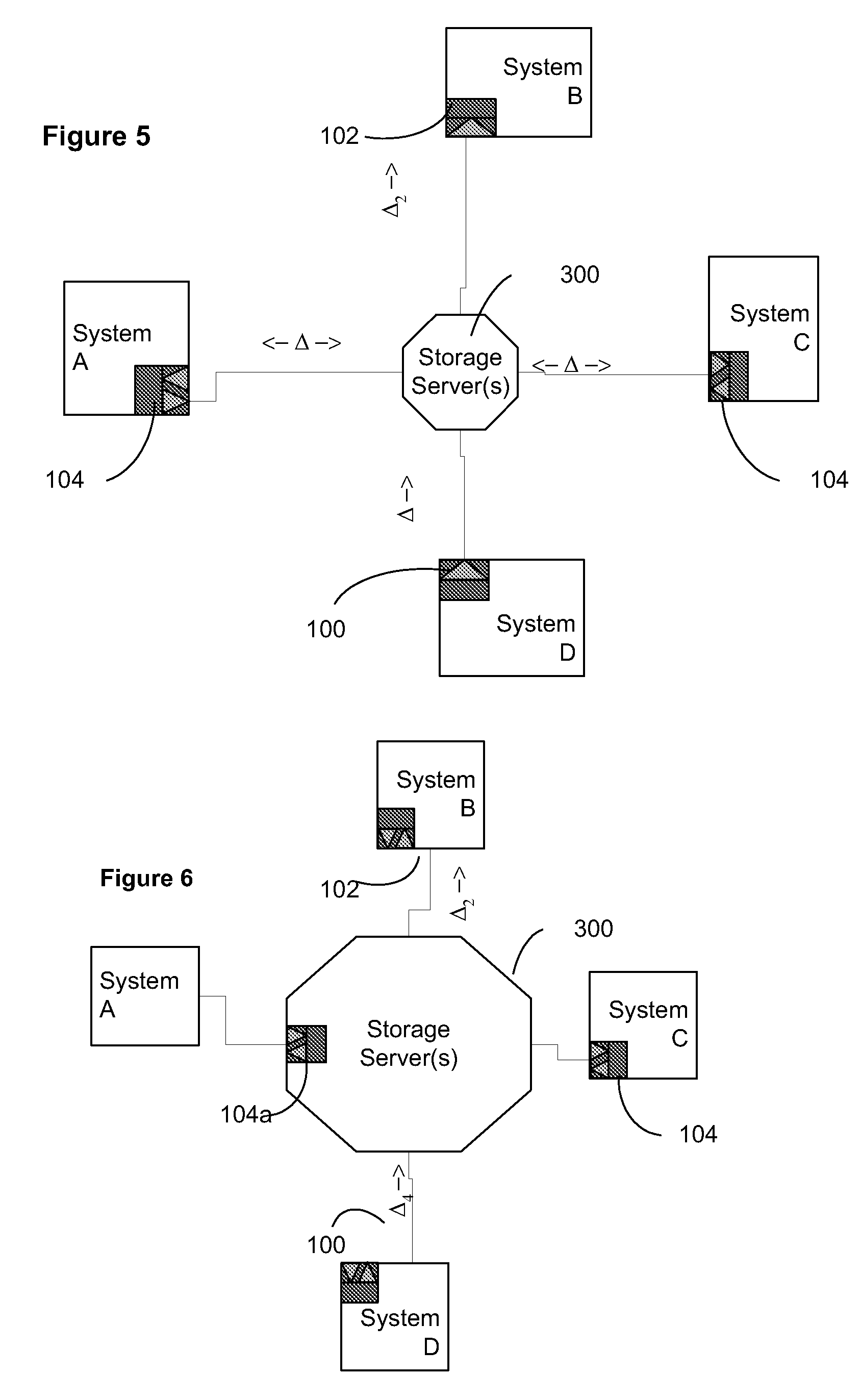
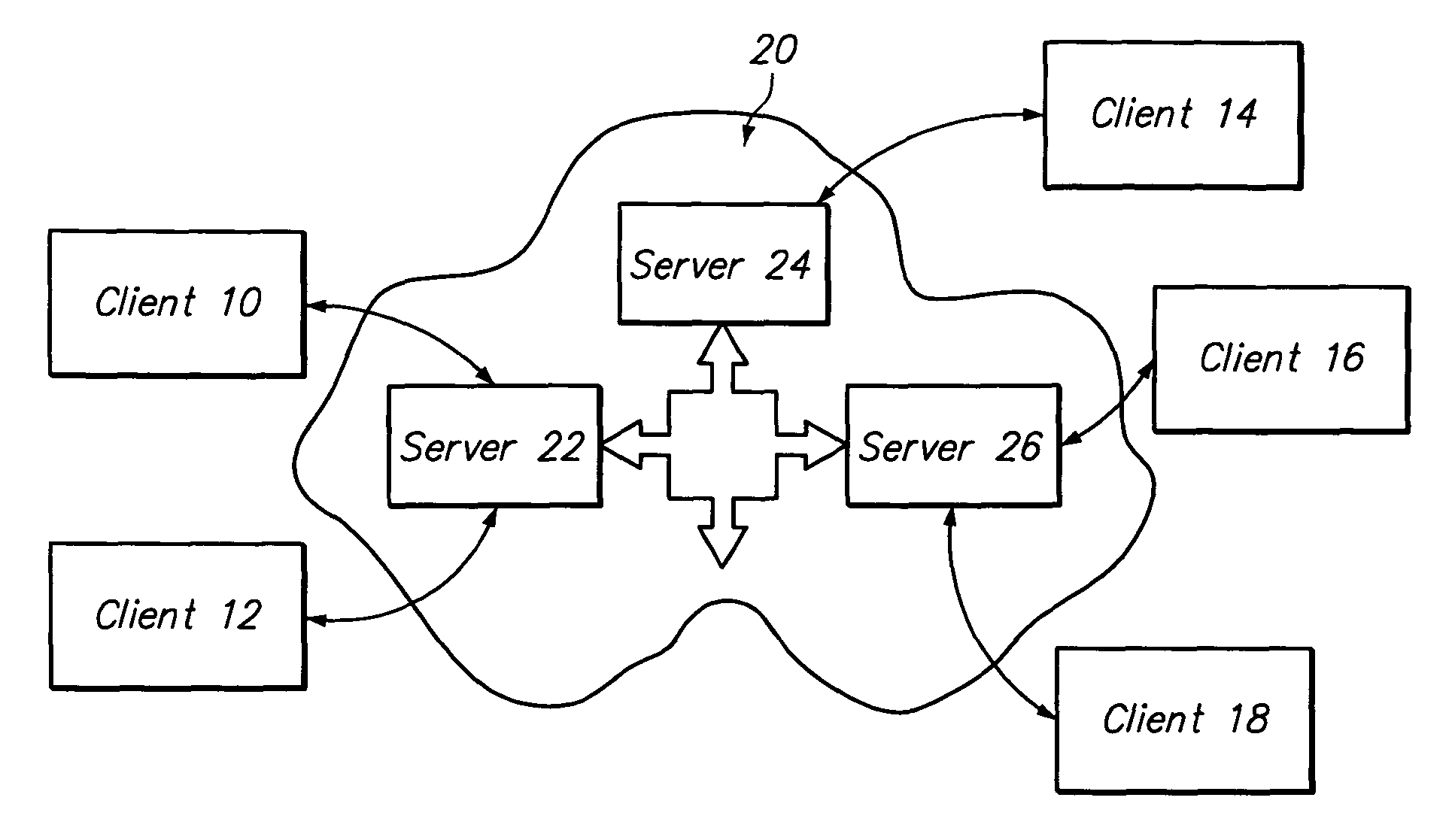
Data transfer and synchronization system
InactiveUS6671757B1Data processing applicationsUnauthorized memory use protectionThe InternetData memory
A system and method for synchronizing devices which can couple to the Internet, or any network. The system includes a first sync engine on the first system interfacing with data on the first system to provide difference information. A data store is coupled to the network and in communication with the first and second systems. A second sync engine is provided on the second system coupled to receive the difference information from the data store via the network, and interface with data on the second system to update said data on the second system with said difference information. Difference information is transmitted to the data store by the first sync engine and received from the data store from the second sync engine.
Owner:SYNCHRONOSS TECH
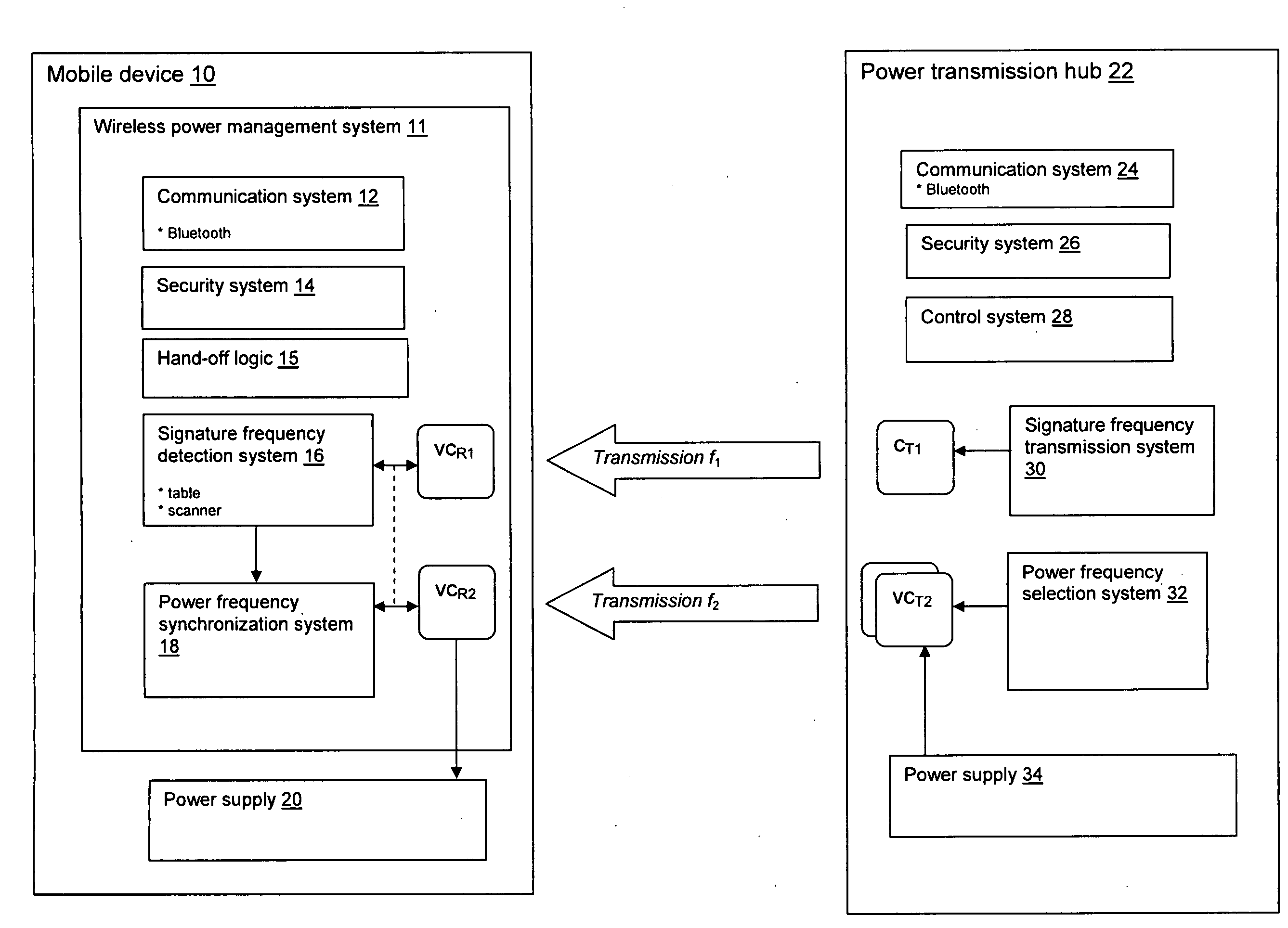
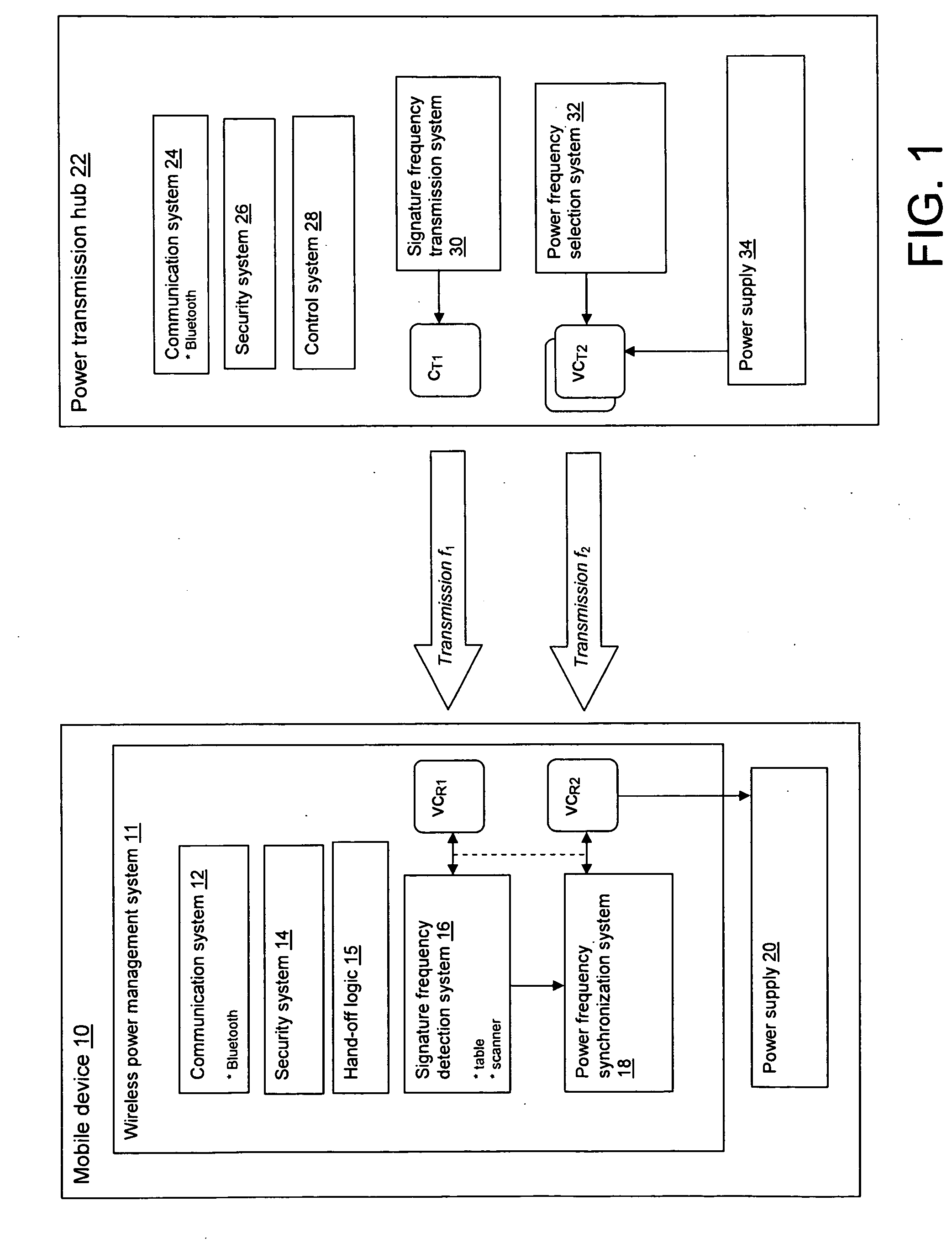
Wireless power infrastructure
ActiveUS20100256831A1Mechanical power/torque controlLevel controlElectric power transmissionElectricity infrastructure
A wireless power infrastructure for delivering wireless power from a wireless network to mobile devices. The infrastructure includes a plurality of power transmission hubs, each hub having: a first capacitor for transmitting a signature frequency for a defined range; and a set of second capacitors, each for transmitting resonant wireless power within the defined range at a selectable frequency. A mobile device for obtaining wireless resonant the plurality of power transmission hubs is also described, and includes: a first variable capacitor for detecting a signature frequency associated with a proximately located power transmission hub; a second variable capacitor for receiving wireless resonant capacitor from the proximately located power transmission hub; and a synchronization system for setting the second variable capacitor to a frequency that is synchronized with a wireless resonant power transmission of the proximately located power transmission hub.
Owner:IBM CORP
Collaborative agent interaction control and synchronization system
A system for supporting a coordinated distributed design process and which allows individuals to hold meetings over the internet and work together in a coordinated fashion on shared design problems is described.
Owner:INST OF TECHNOLOG MASSACHUSETTS
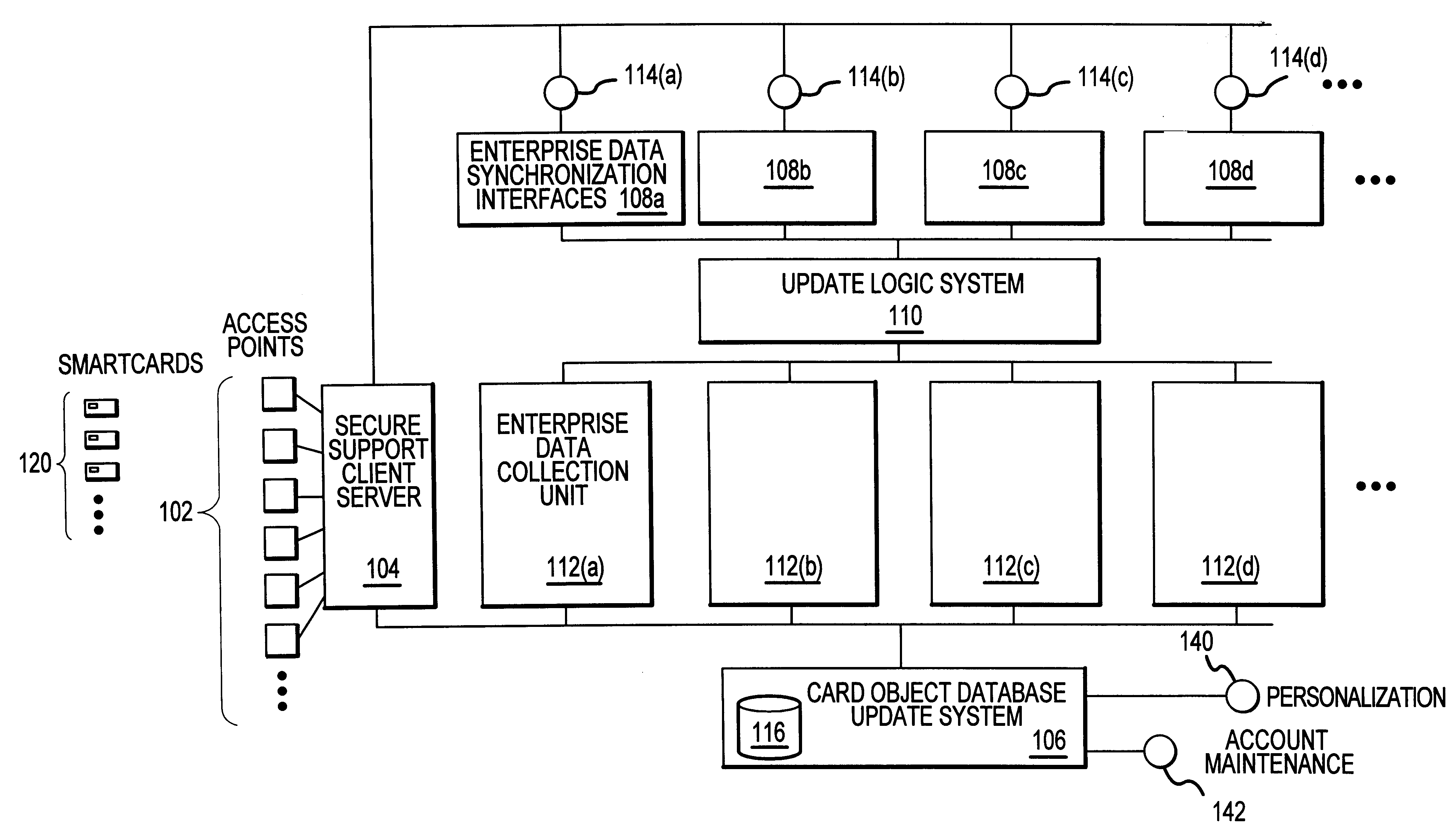
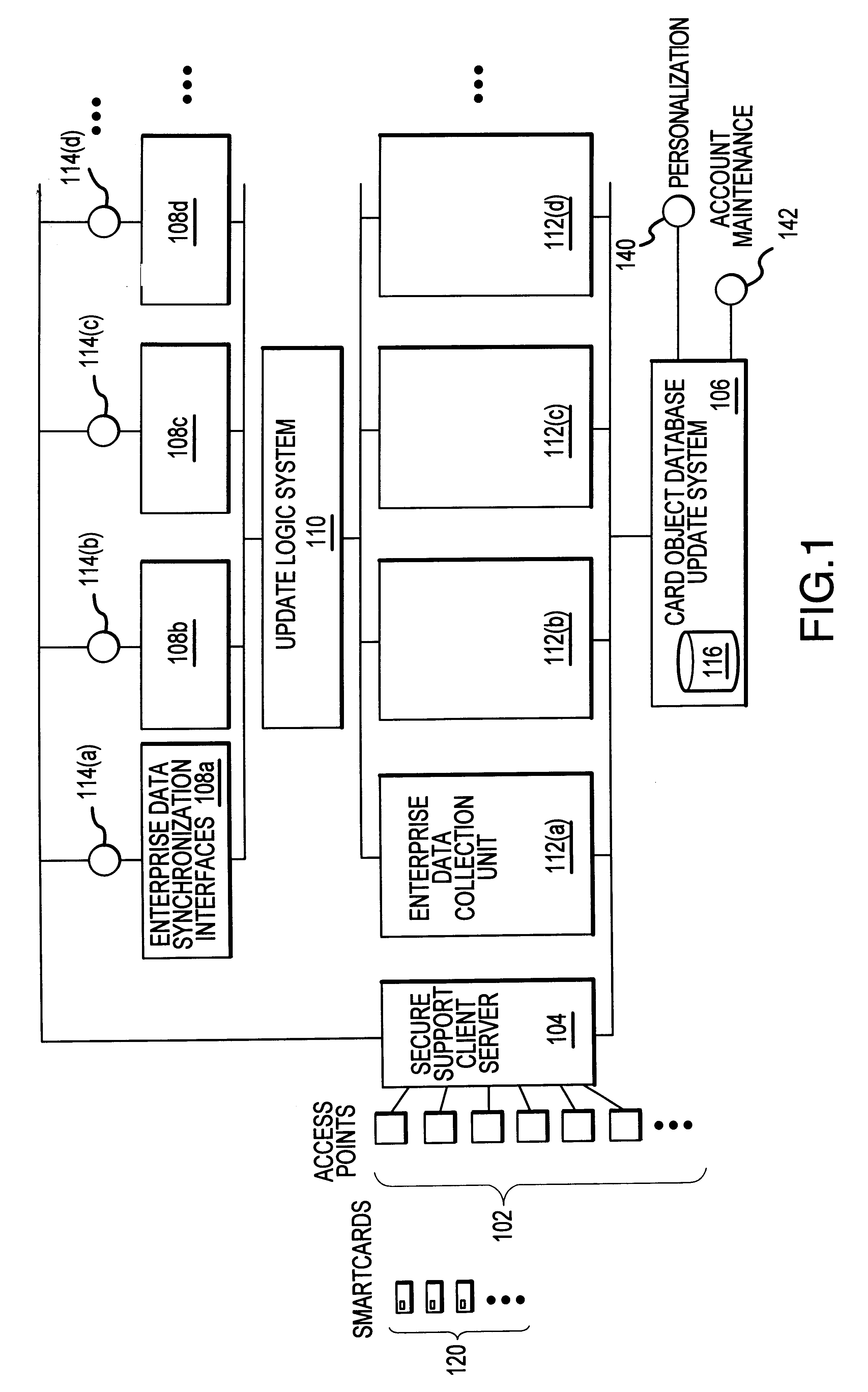
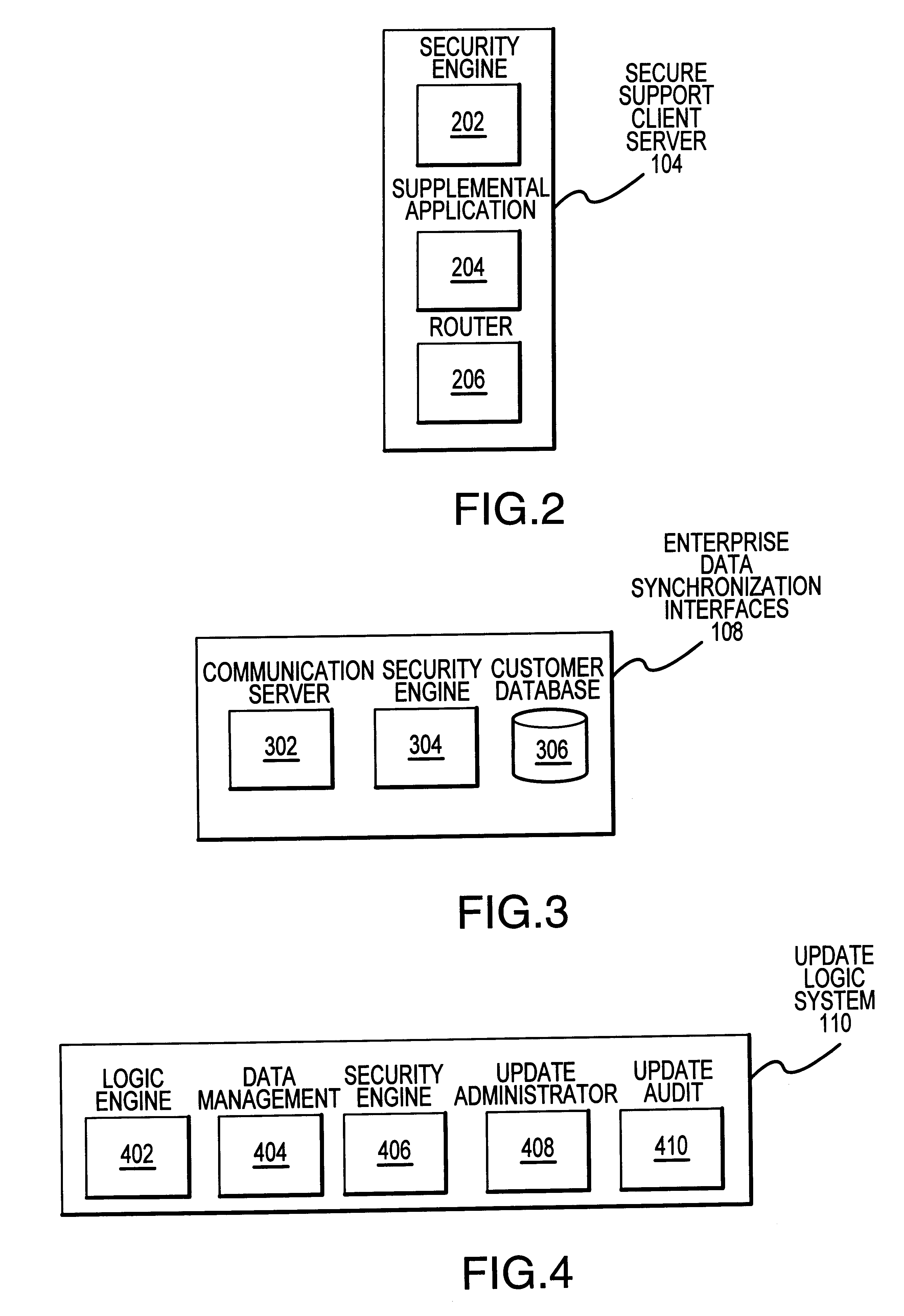
Methods and apparatus for dynamic smartcard synchronization and personalization
InactiveUS6199762B1Sensing by mechanical meansCo-operative working arrangementsPersonalizationData synchronization
A system generally for personalizing and synchronizing smartcard data in the context of a distributed transaction system is disclosed. A dynamic smartcard synchronization system comprises access points configured to initiate a transaction in conjunction with a smartcard, an enterprise data collection unit, and a card object database update system. An exemplary dynamic synchronization system (DSS) preferably comprises various smartcard access points, a secure support client server, a card object database update system (CODUS), one or more enterprise data synchronization interfaces (EDSI), an update logic system, one or more enterprise data collection units (EDCUs), and one or more smartcard access points configured to interoperably accept and interface with smartcards. In an exemplary embodiment, DSS comprises a personalization system and an account maintenance system configured to communicate with CODUS. Personalization of multi-function smartcards is accomplished using a security server configured to generate and / or retrieve cryptographic key information from multiple enterprise key systems during the final phase of the smartcard issuance process.
Owner:LIBERTY PEAK VENTURES LLC
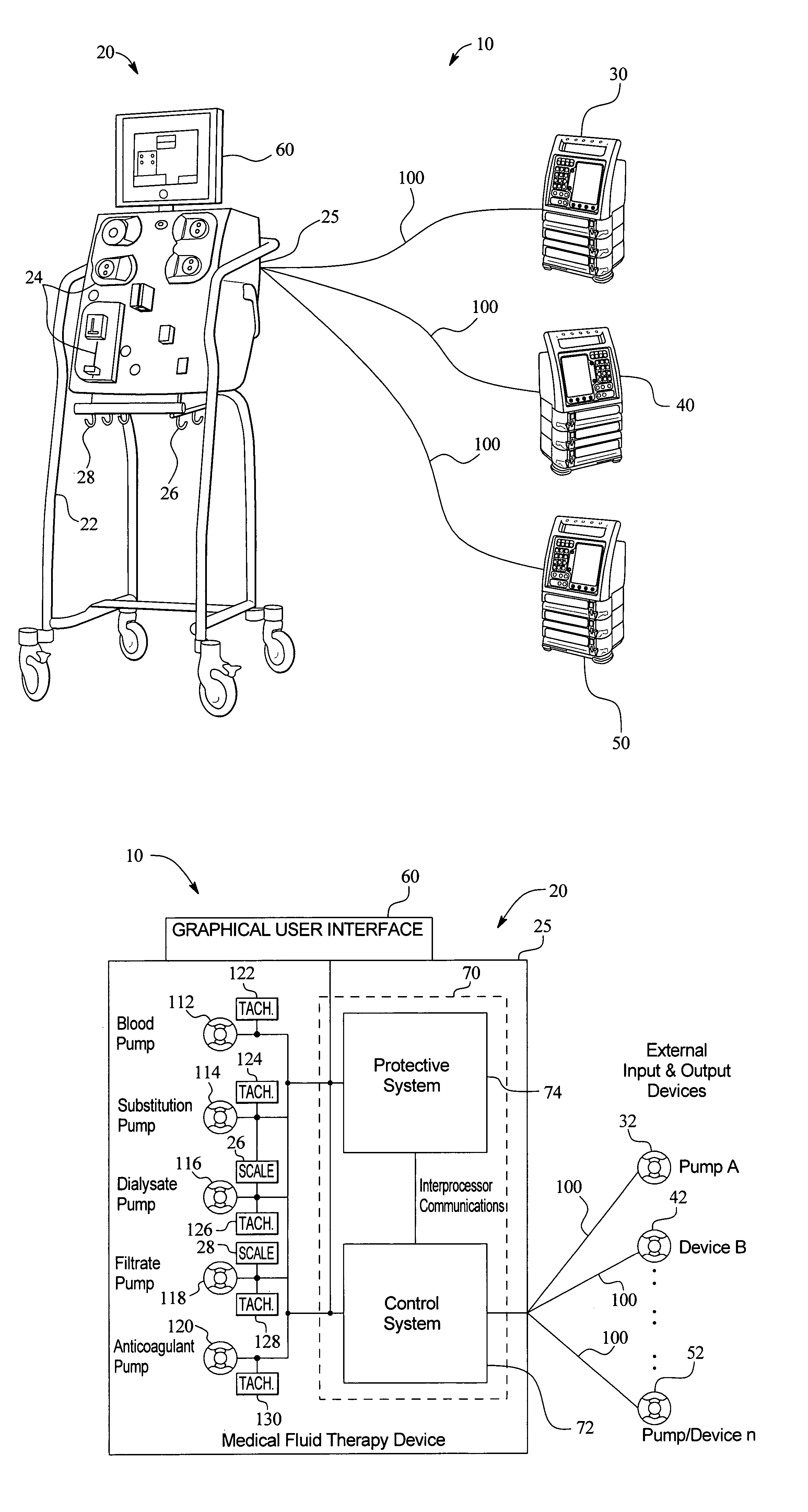
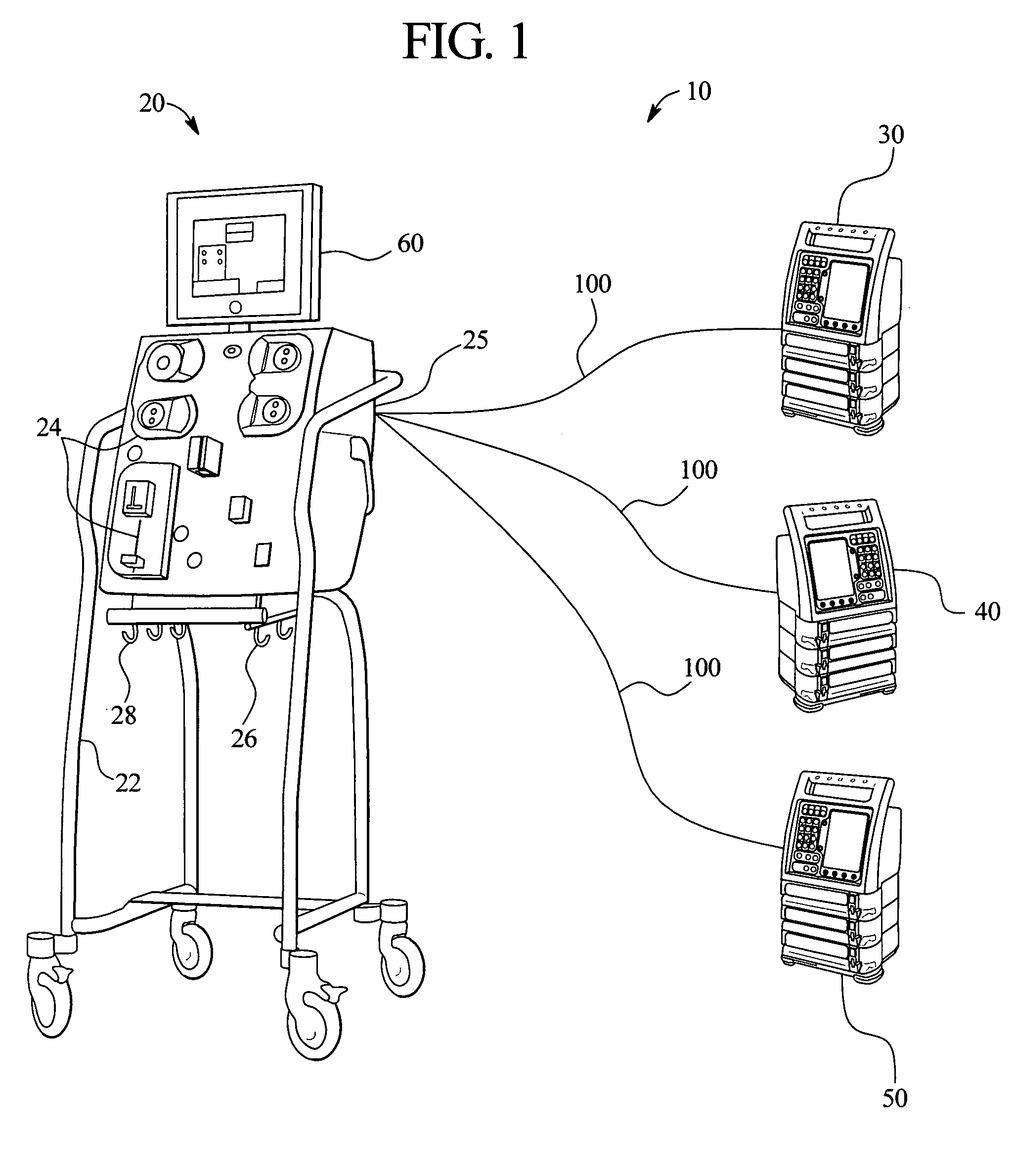
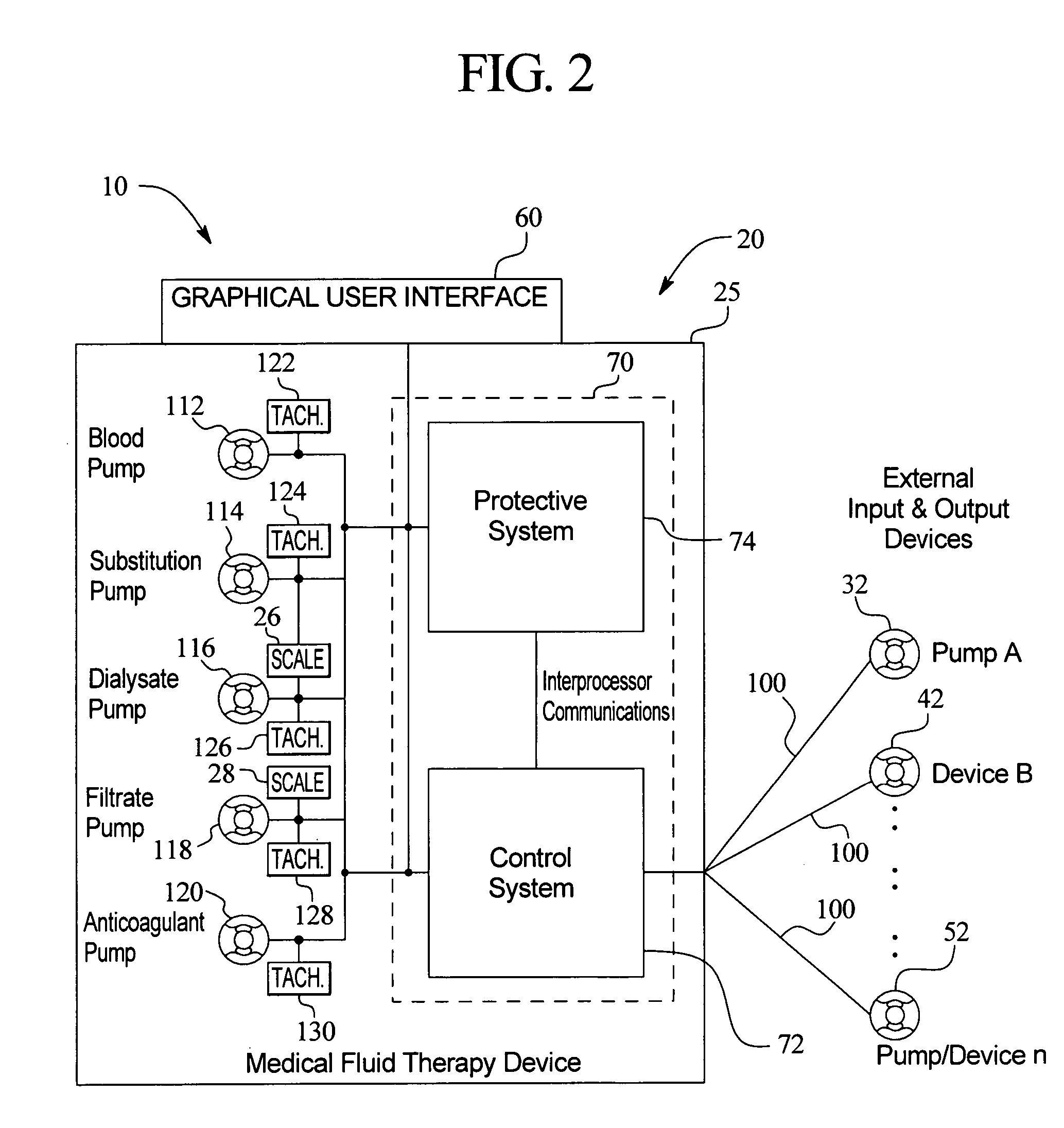
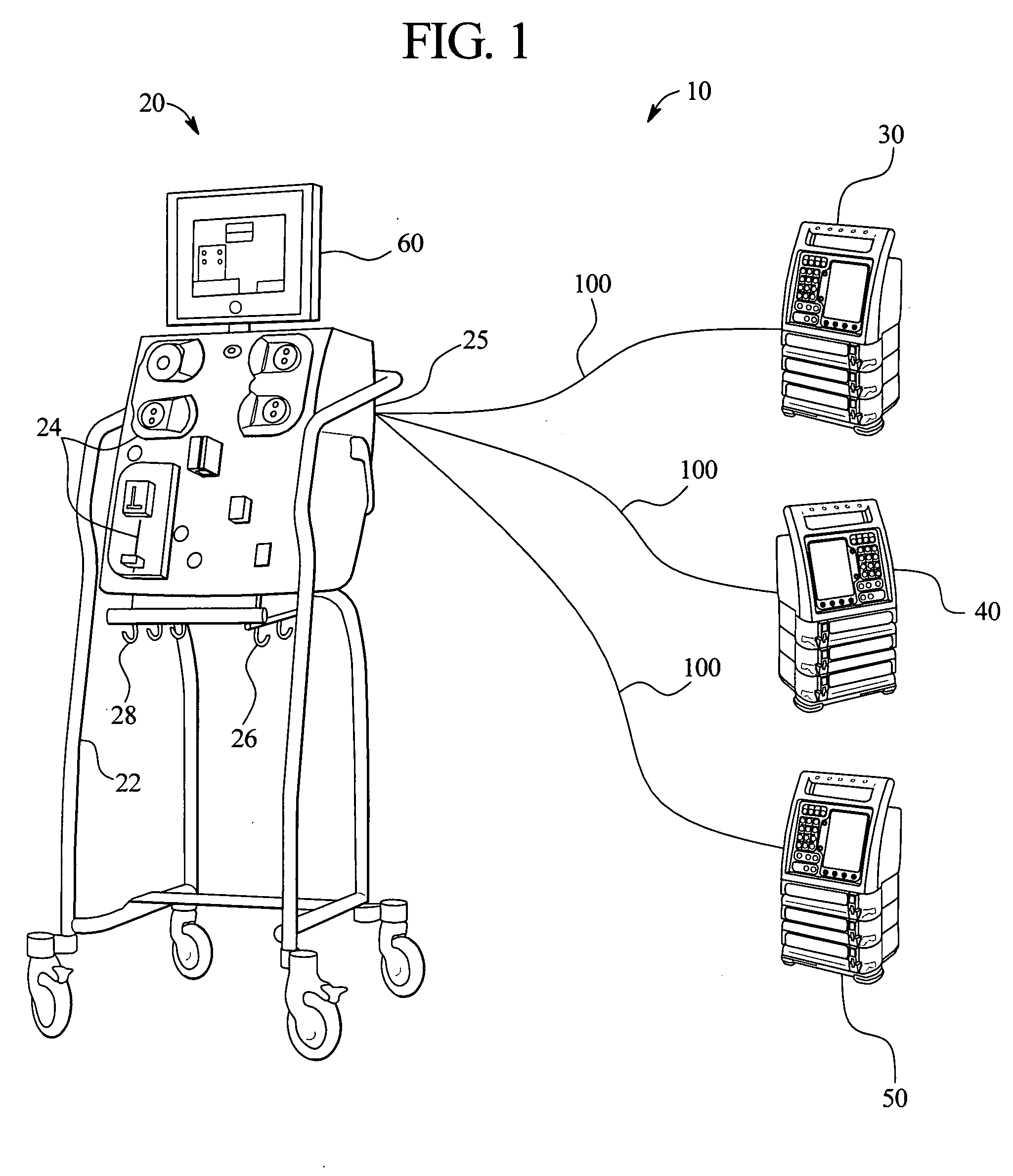
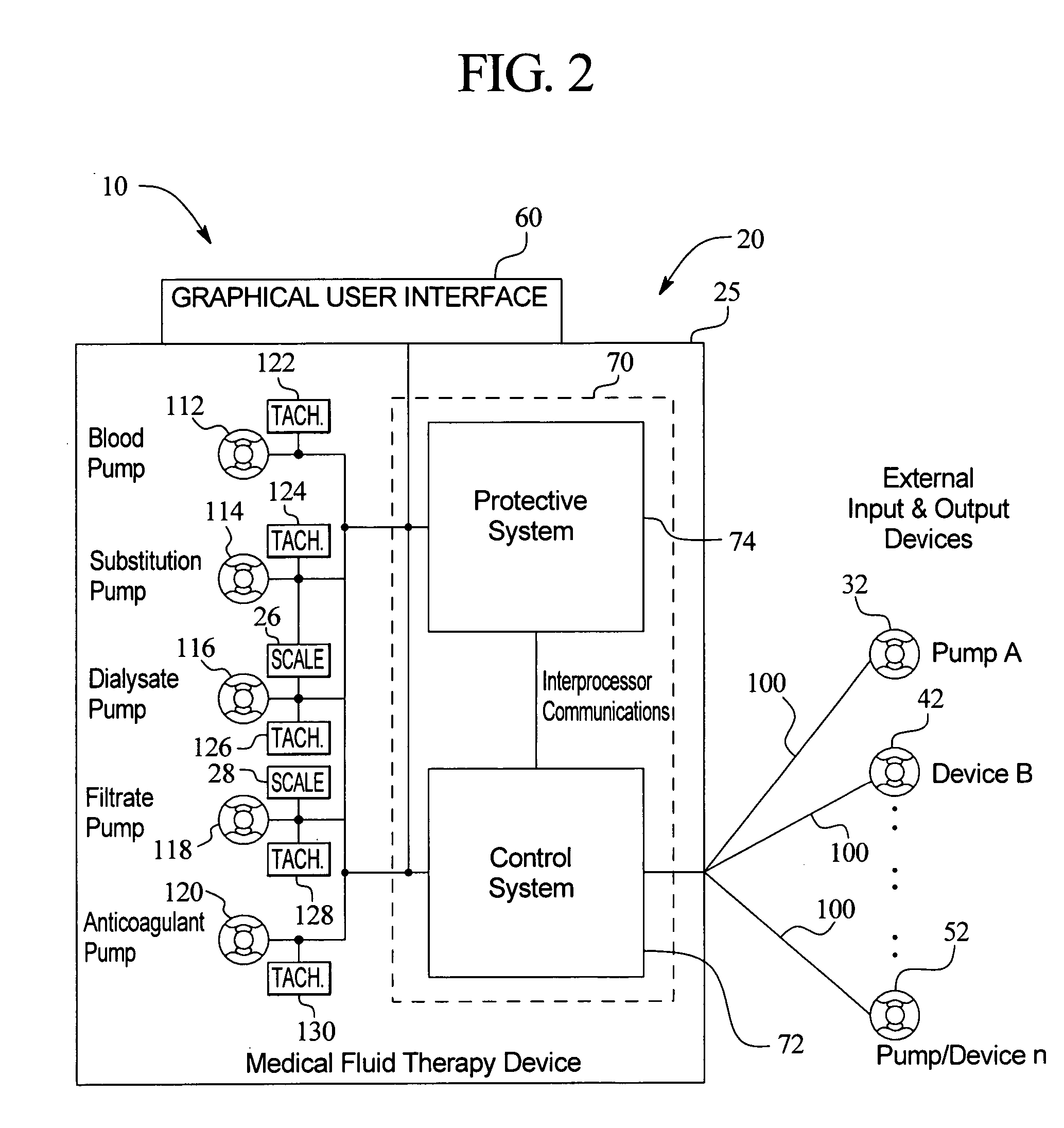
Medical fluid therapy flow balancing and synchronization system
InactiveUS7029456B2Simplify the startup processEasy maintenanceHaemofiltrationDrug and medicationsFluid therapyBiomedical engineering
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
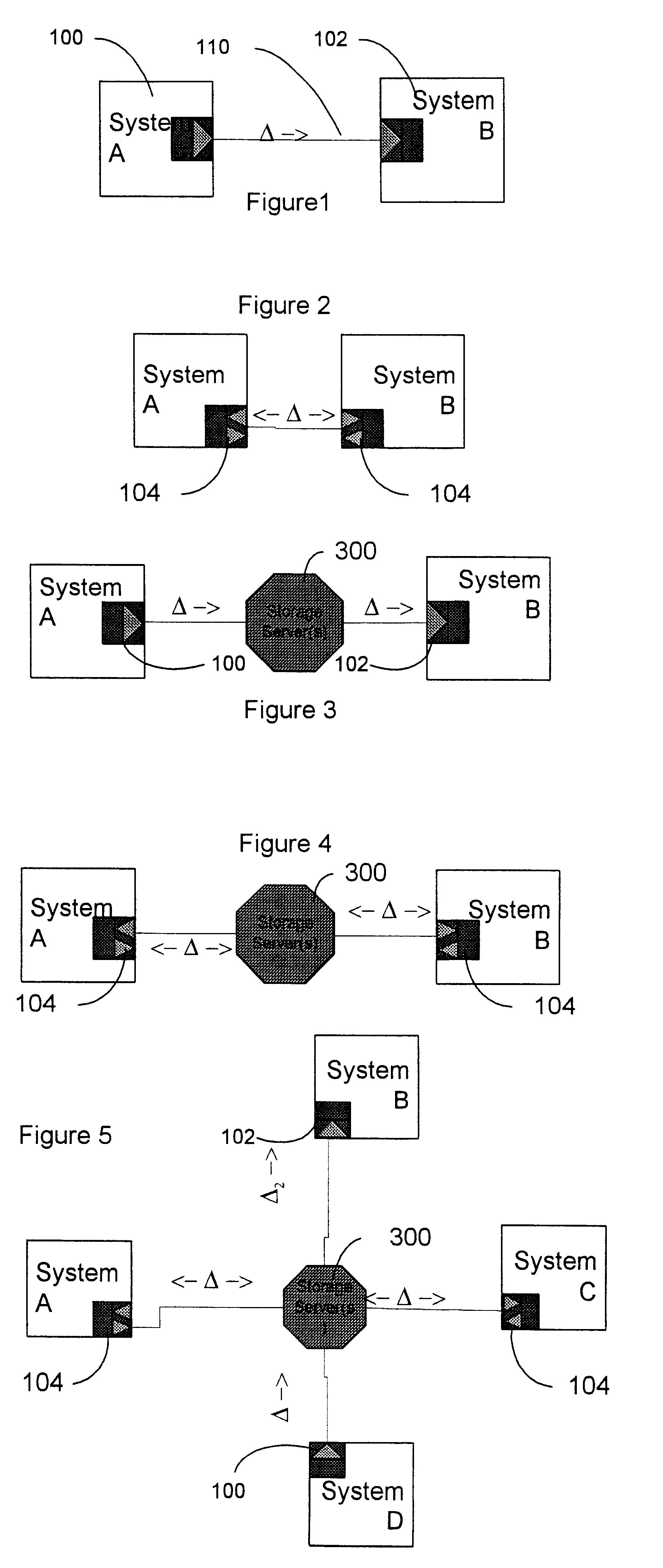
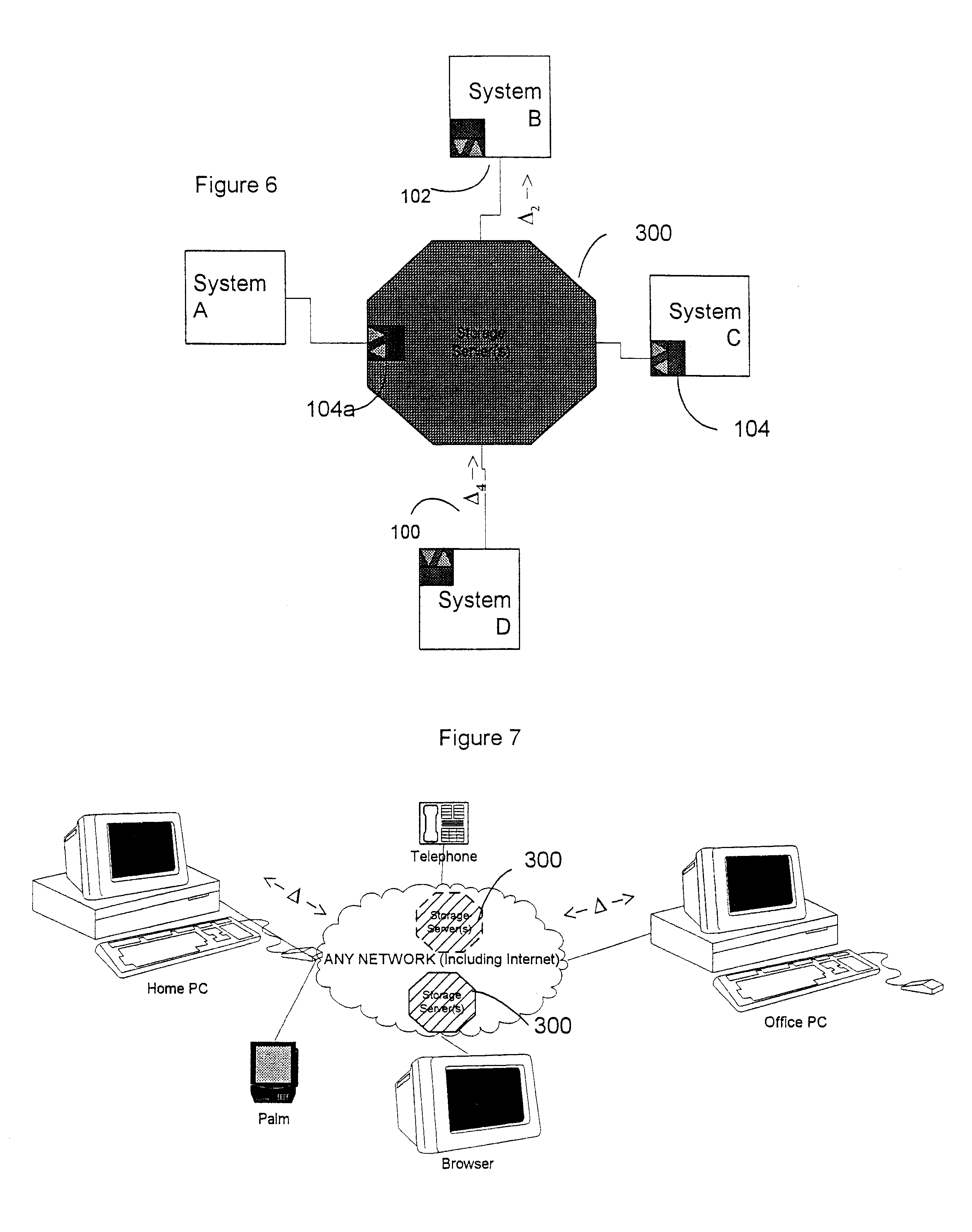
Data transfer and synchronization system
InactiveUS20040054711A1Data processing applicationsMultiple digital computer combinationsFile synchronizationData information
A system and method for synchronizing devices which can couple to the Internet, or any network. In one aspect a system for synchronizing data between a first system and a second system is provided. The system includes a first sync engine on the first system interfacing with data on the first system to provide difference information. A data store is coupled to network and in communication with the first and second systems. A second sync engine is provided on the second system coupled to receive the difference information from the data store via the network, and interfacing with data on the second system to update said data on the second system with said difference information. Difference information is transmitted to the data store by the first sync engine and received from the data store from the second sync engine. The system may include a management server coupled to the network and in communication with the first sync engine, the second sync engine and the data store. The system may include a plurality of sync engines on a respective plurality of systems, each of said plurality of engines being coupled to receive difference information from each of said first, second and plurality of sync engines from the data store via the network. Each said engine interfaces with data on the system on which it resides to update said data on said system on which it resides with said difference information, and interfaces with data on said system on which it resides to provide difference data information from the system on which it resides to the data store. In a further embodiment, the invention comprises a method for synchronizing at least a first file and a second file resident on a first and a second systems, respectively, coupled to the Internet, respectively. The method includes the steps of: determining difference data resulting from changes to the first file on the first system; transmitting the difference data to a server via the Internet; querying the server from a second system to determine whether difference data exists for files on the second system; retrieving the difference data to the second system; and updating the second file on the second system with the difference data.
Owner:SYNCHRONOSS TECH
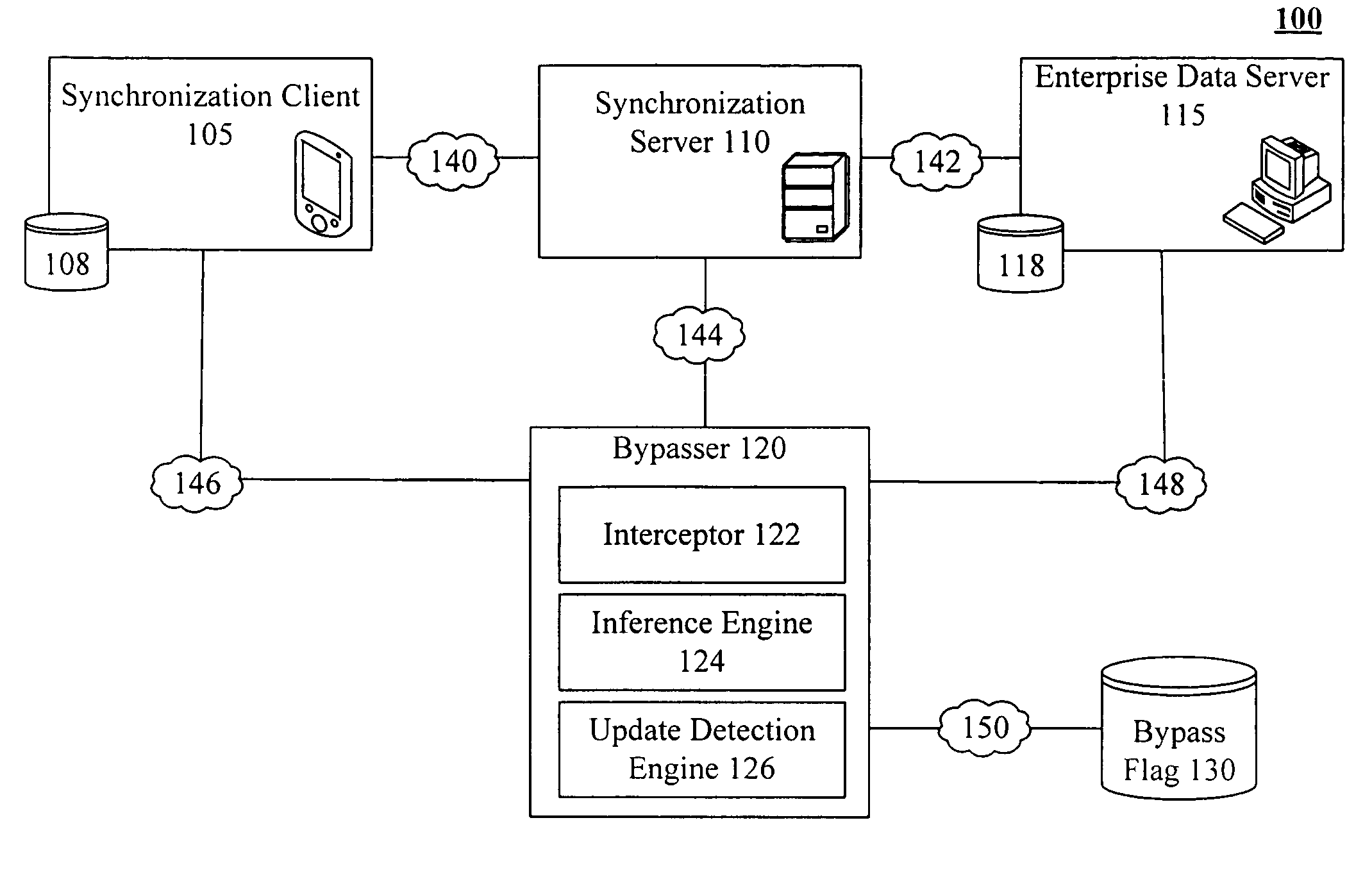
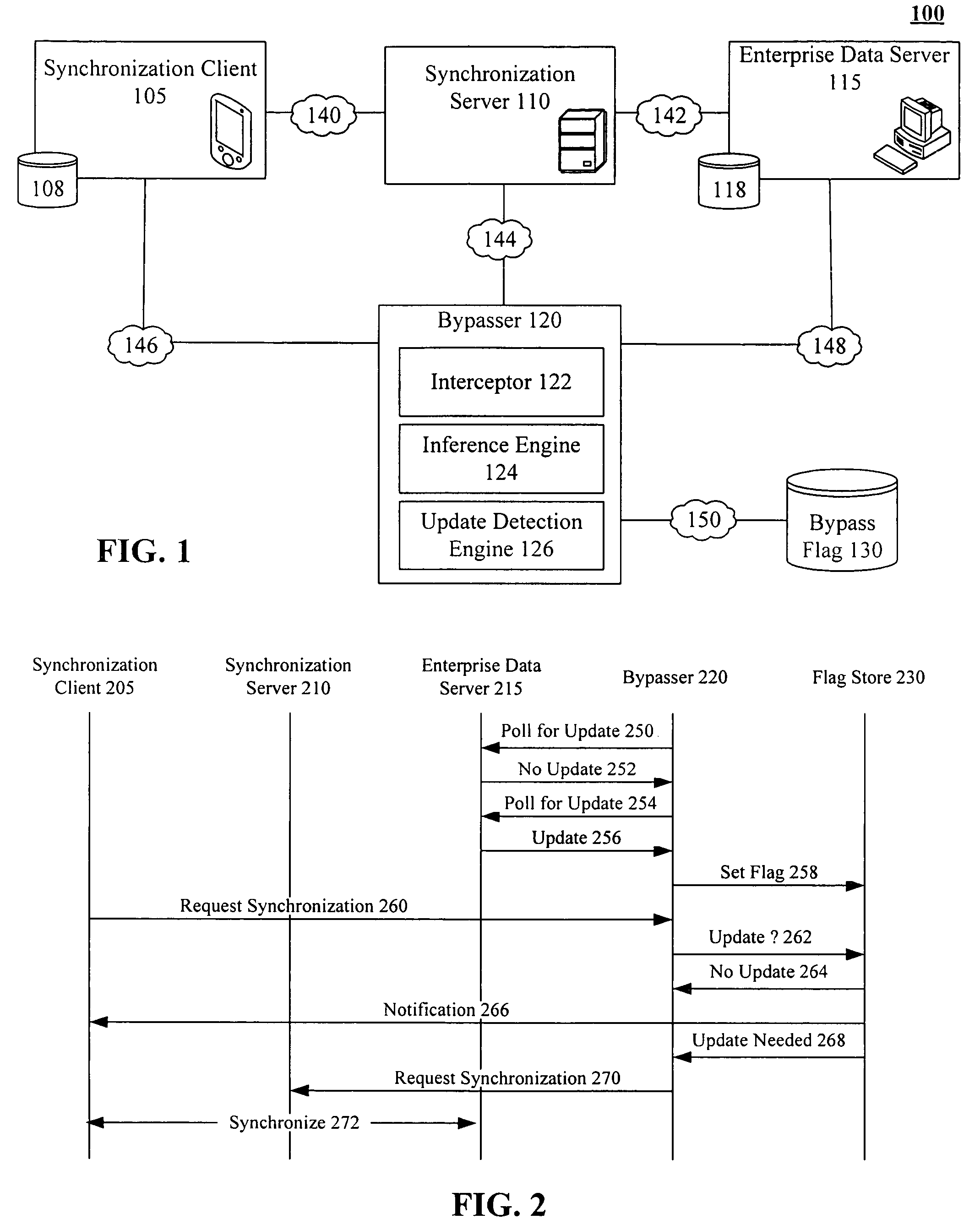
Bypassing an intermediate synchronization server of a three tiered synchronization system
InactiveUS7634519B2Data processing applicationsDatabase distribution/replicationData storeSynchronization system
A bypasser configured to operate within a three tiered synchronization system. The bypasser can include an interceptor and an inference engine. The interceptor can intercept synchronization requests before a synchronization event involving a synchronization server is initiated. The inference engine can determine if the data store and the another data store are to be synchronized and can selectively initiate the synchronization event based on the determination of the inference engine. For example, when the inference engine determines that synchronization is not to occur, the bypasser can convey a notification that no update is needed to the source of an intercepted synchronization request without requiring the synchronization server to process the synchronization request. When the inference engine determines that synchronization is to occur, the bypasser can convey an intercepted synchronization request to the intermediate synchronization server for processing.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Systems and methods for providing conflict handling for peer-to-peer synchronization of units of information manageable by a hardware/software interface system
InactiveUS20050044187A1Efficient application developmentFacilitate data sharingDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsThree stageUsability
Various embodiments of the present invention are directed to conflict handling for conflicts that occur in a peer-to-peer synchronization system, where the ability to correctly and efficiently handle conflicts minimizes data loss while retaining good usability and reduces the need for user intervention during synchronization. Conflict handling in the synchronization service is divided into three stages: (1) conflict detection; (2) automatic conflict resolution and logging; and (3) conflict inspection and resolution. Certain embodiments are directed to a conflict handling schema comprising one or more of the follow conflict handling elements: (a) schematized representation of conflicts; (b) detection of conflicts; (c) logging of conflicts into a durable store; (d) automatic resolution of conflicts according to a flexible and configurable azqsxqxwdconflict resolution policy; (e) composable and extensible conflict handlers to filter and resolve conflicts; (f) automatic detection and removal of obsolete conflicts; and (g) programmatic conflict resolutions.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Medical fluid therapy flow balancing and synchronization system
ActiveUS20050085760A1Simplify the startup processSimplify fluid flow maintenanceSemi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionFluid therapyBiomedical engineering
Systems, apparatus and methods that allow external infusion, IV or administration pumps to be synchronized with the internal pumps for a medical fluid therapy machine are provided. The system reduces the time and effort needed to calculate, set-up, enter and maintain flowrates of various fluids, maintained internally or externally with respect to the medical fluid therapy machine. The system also automatically follows therapy requirements, for example, a requirement that one pump / fluid be running / flowing for another pump / fluid to be enabled to run / flow. The system further automatically adjusts for variations in flowrate of one fluid with respect to another. In short, the system provides a more “hands-off”, safe and effective method and apparatus for medical fluid therapy fluid delivery.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
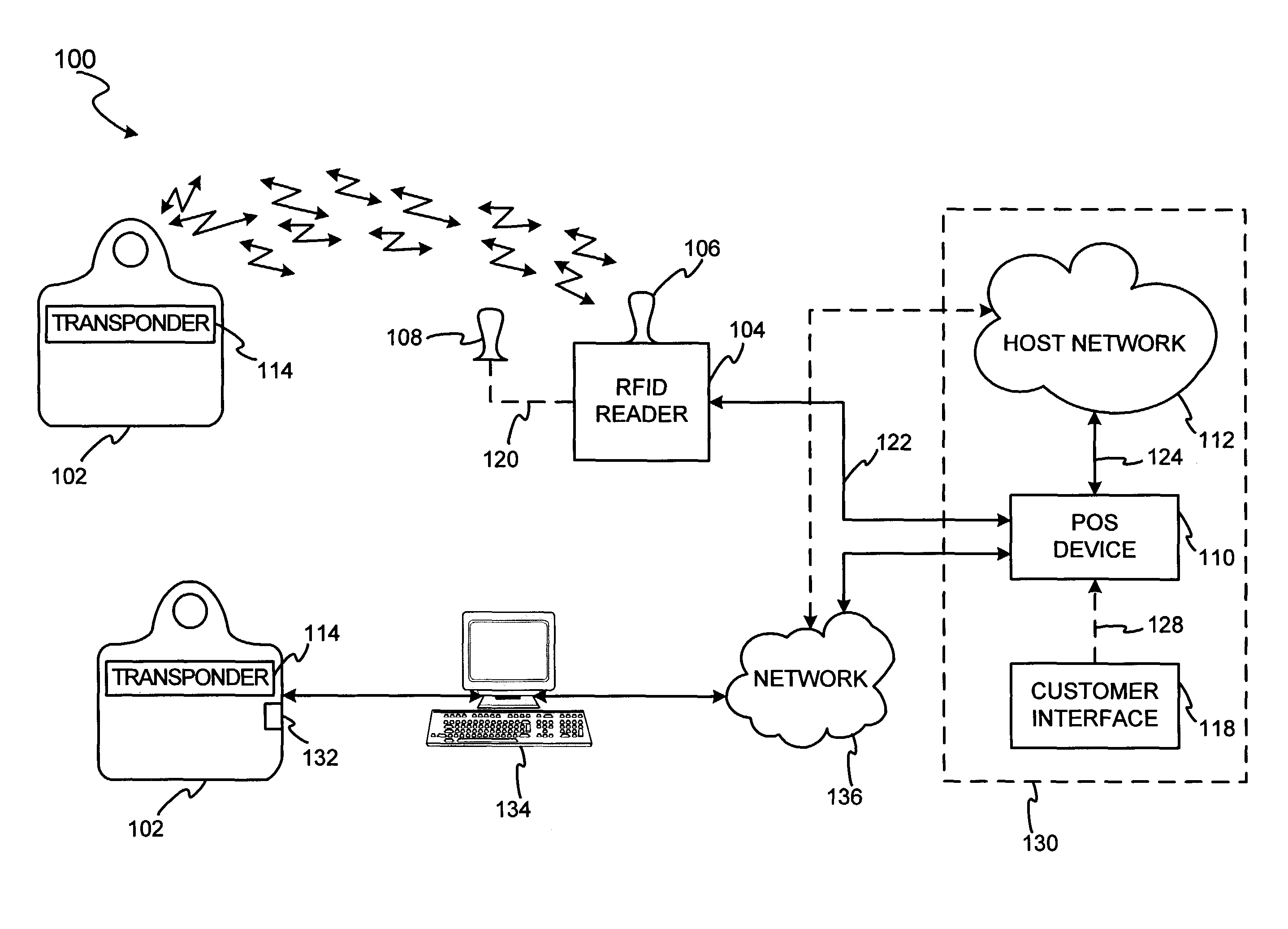
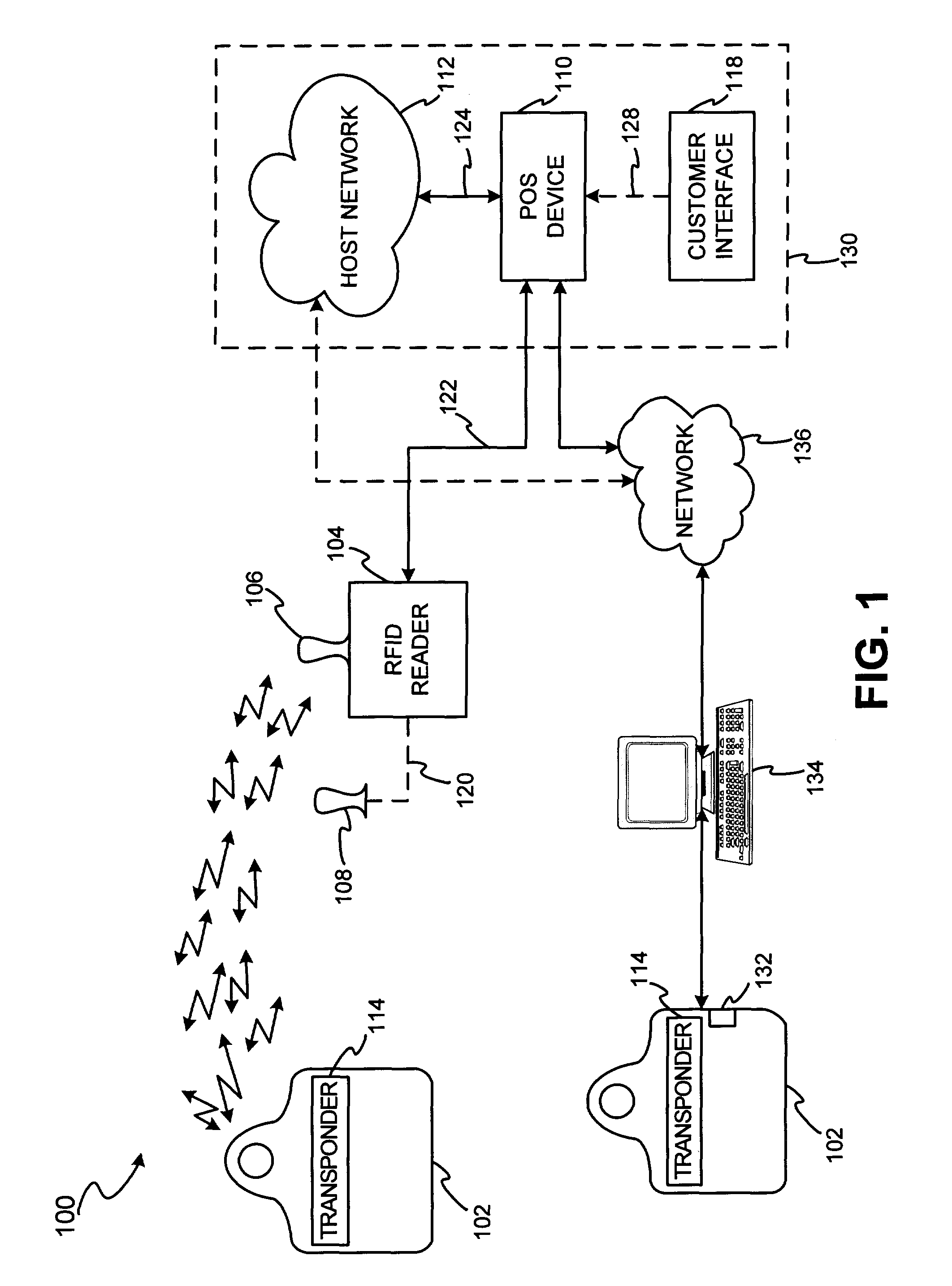
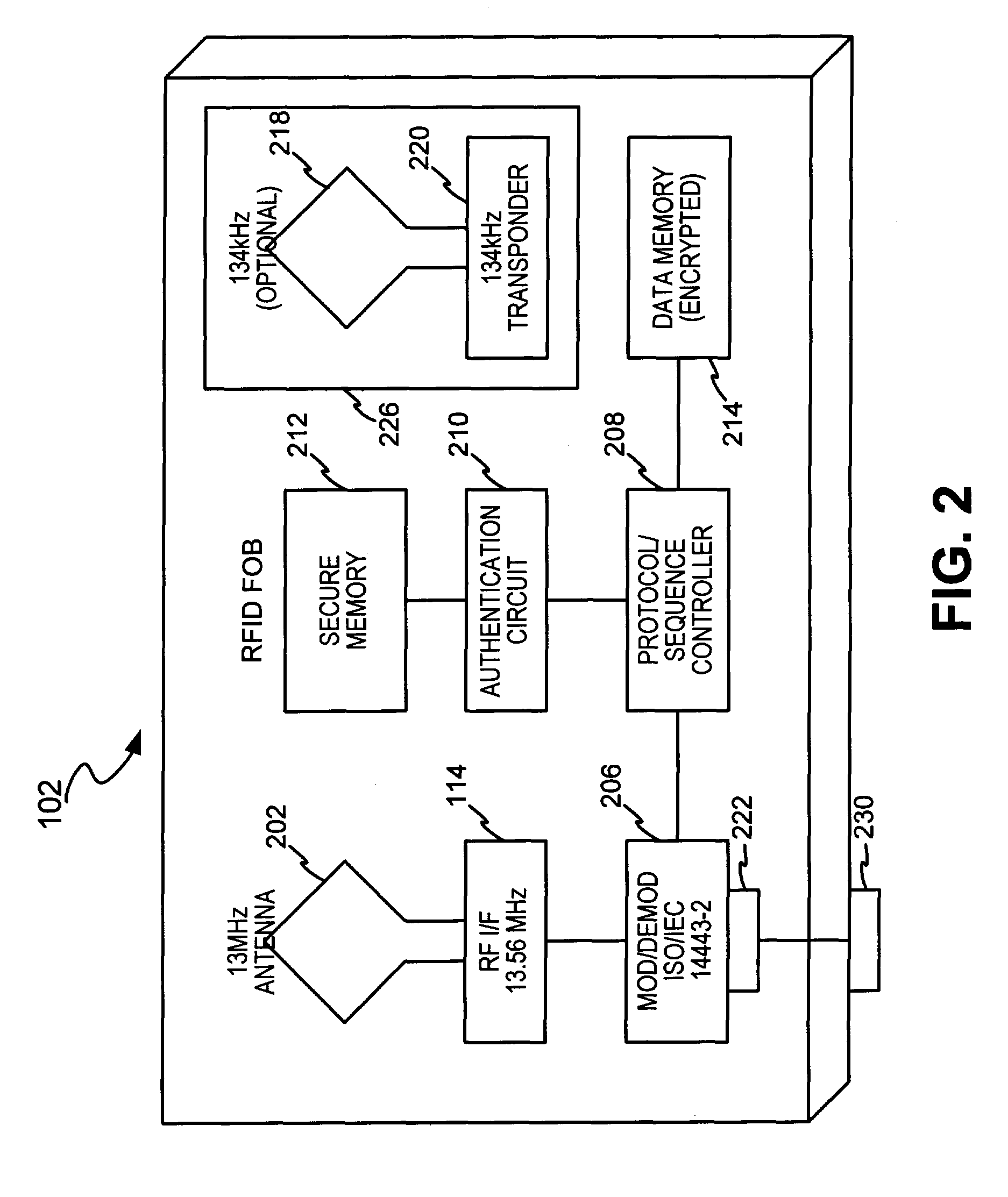
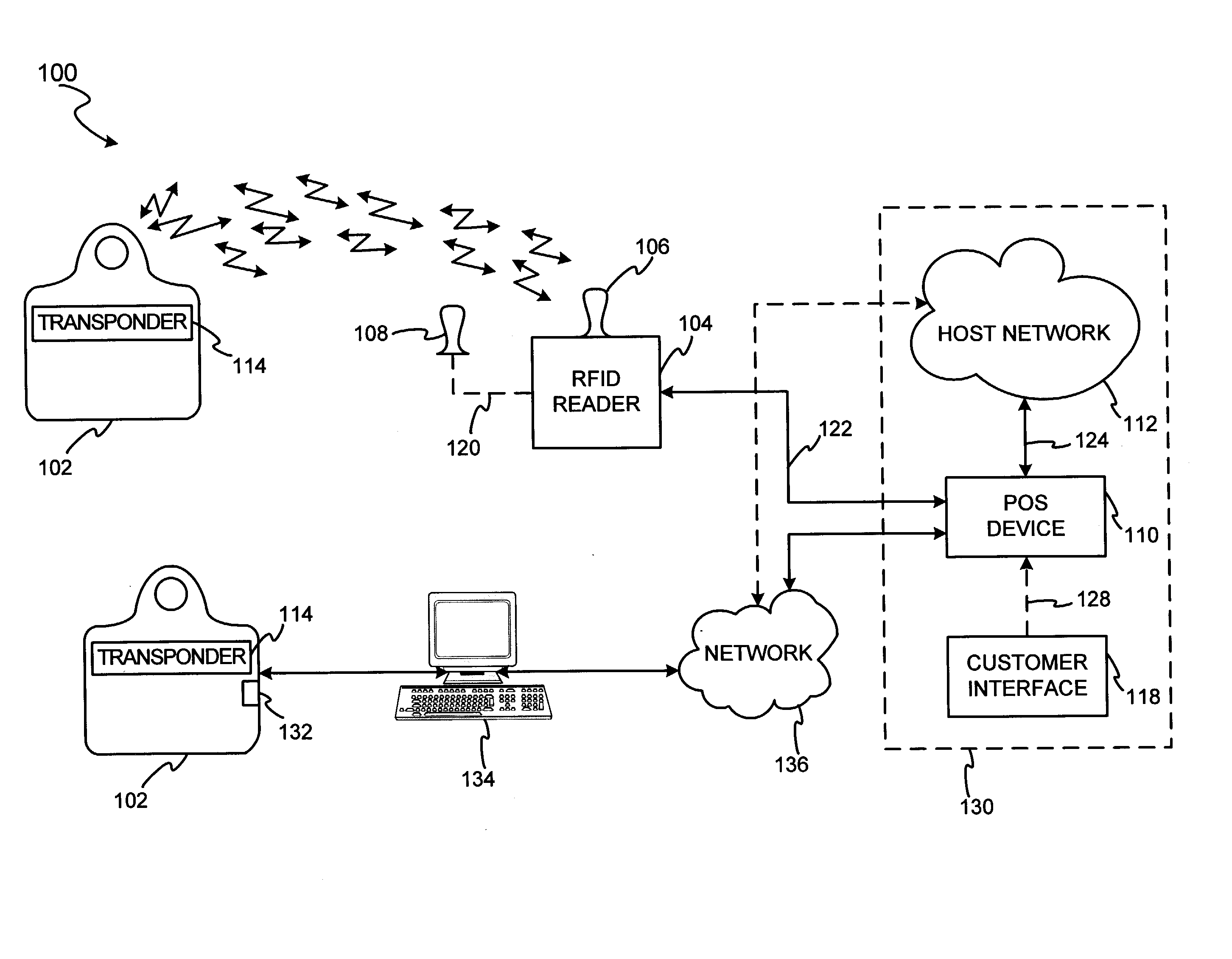
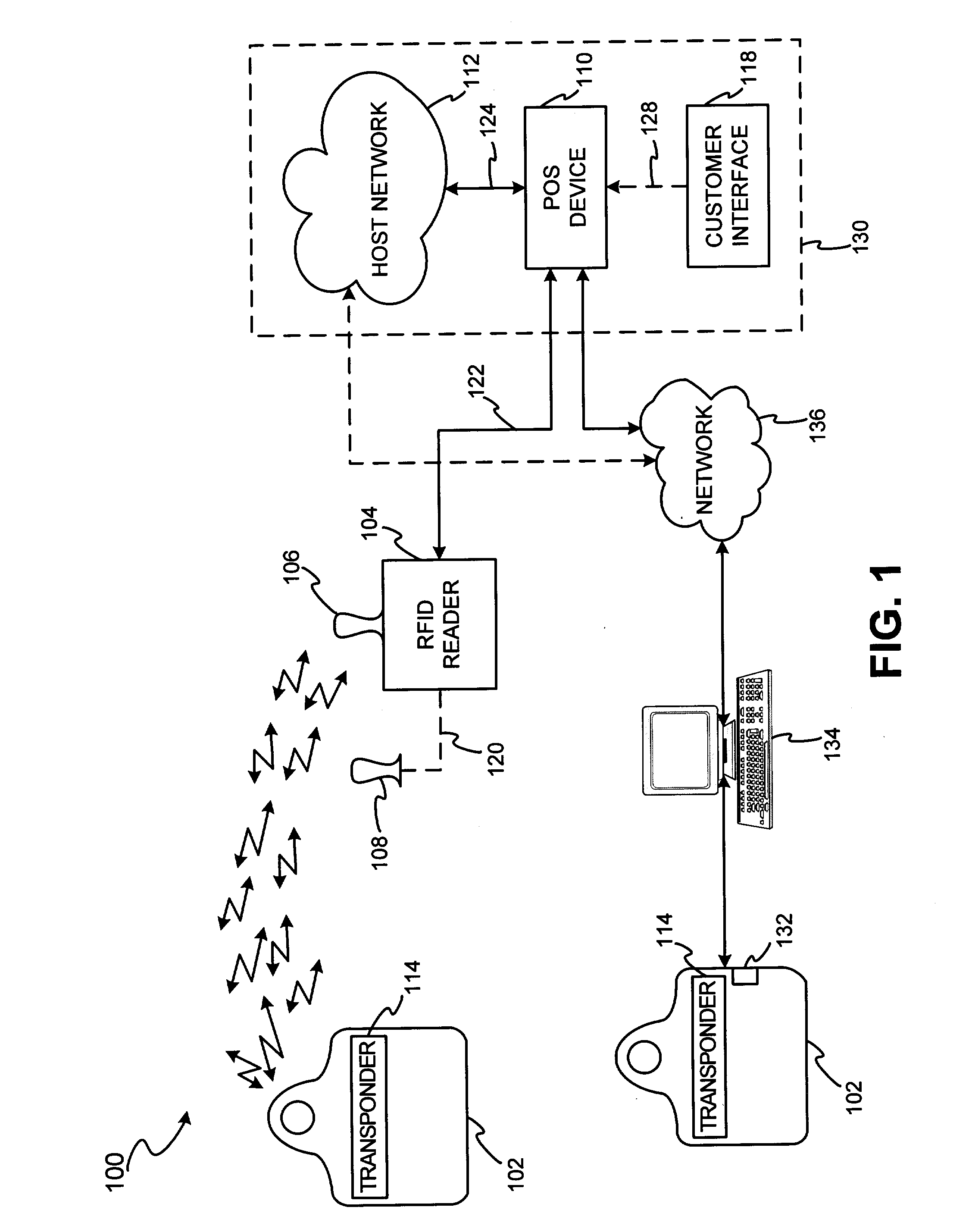
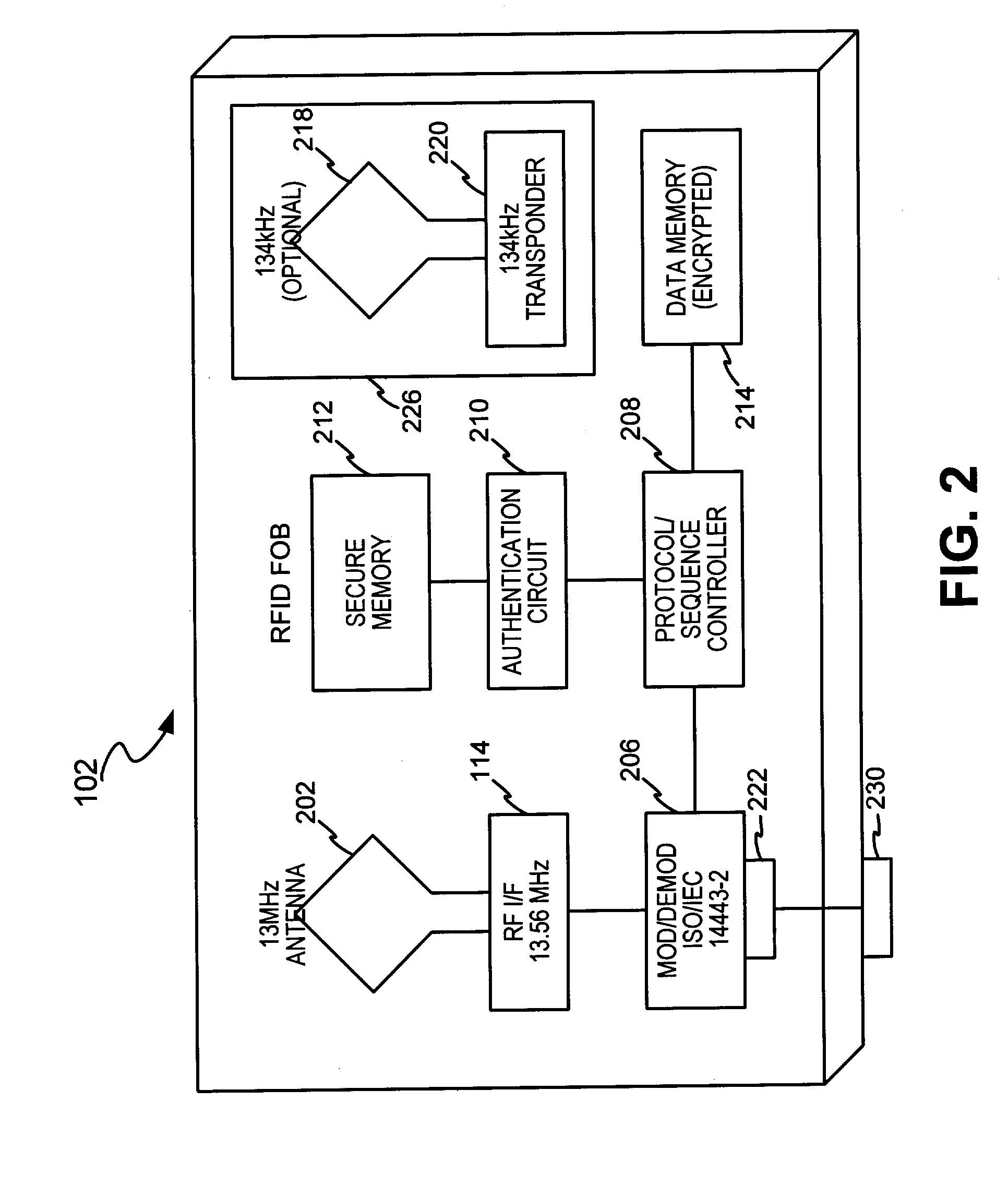
System and method for dynamic fob synchronization and personalization
A system generally for personalizing and synchronizing fob data in the context of a distributed transaction system is disclosed. A dynamic fob synchronization system may comprise point of service (POS) devices configured with transponder-readers to initiate a transaction in conjunction with a fob, an enterprise data collection unit, and a fob object database update system. An exemplary dynamic synchronization system (DSS) may comprise various fob POS devices, a secure support client server, a fob object database update system (FODUS), one or more enterprise data synchronization interfaces (EDSI), an update logic system, one or more enterprise data collection units (EDCUs), and one or more fob POS devices configured to interoperably accept and interface with fobs. In an exemplary embodiment, DSS may comprise a personalization system and an account maintenance system configured to communicate with FODUS. Personalization of multi-function fobs may be accomplished using a security server configured to generate and / or retrieve cryptographic key information from multiple enterprise key systems during the final phase of the fob issuance process.
Owner:LIBERTY PEAK VENTURES LLC
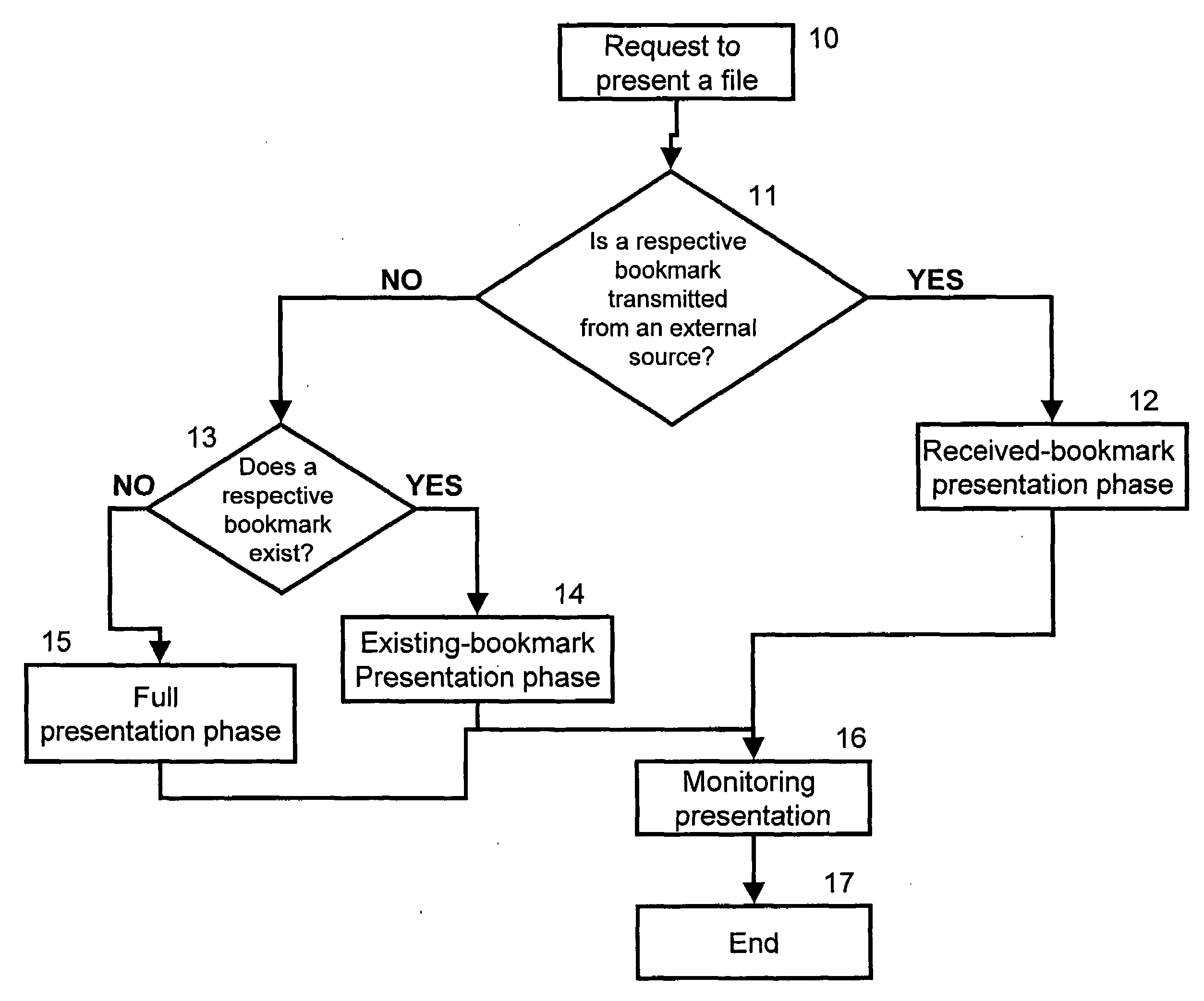
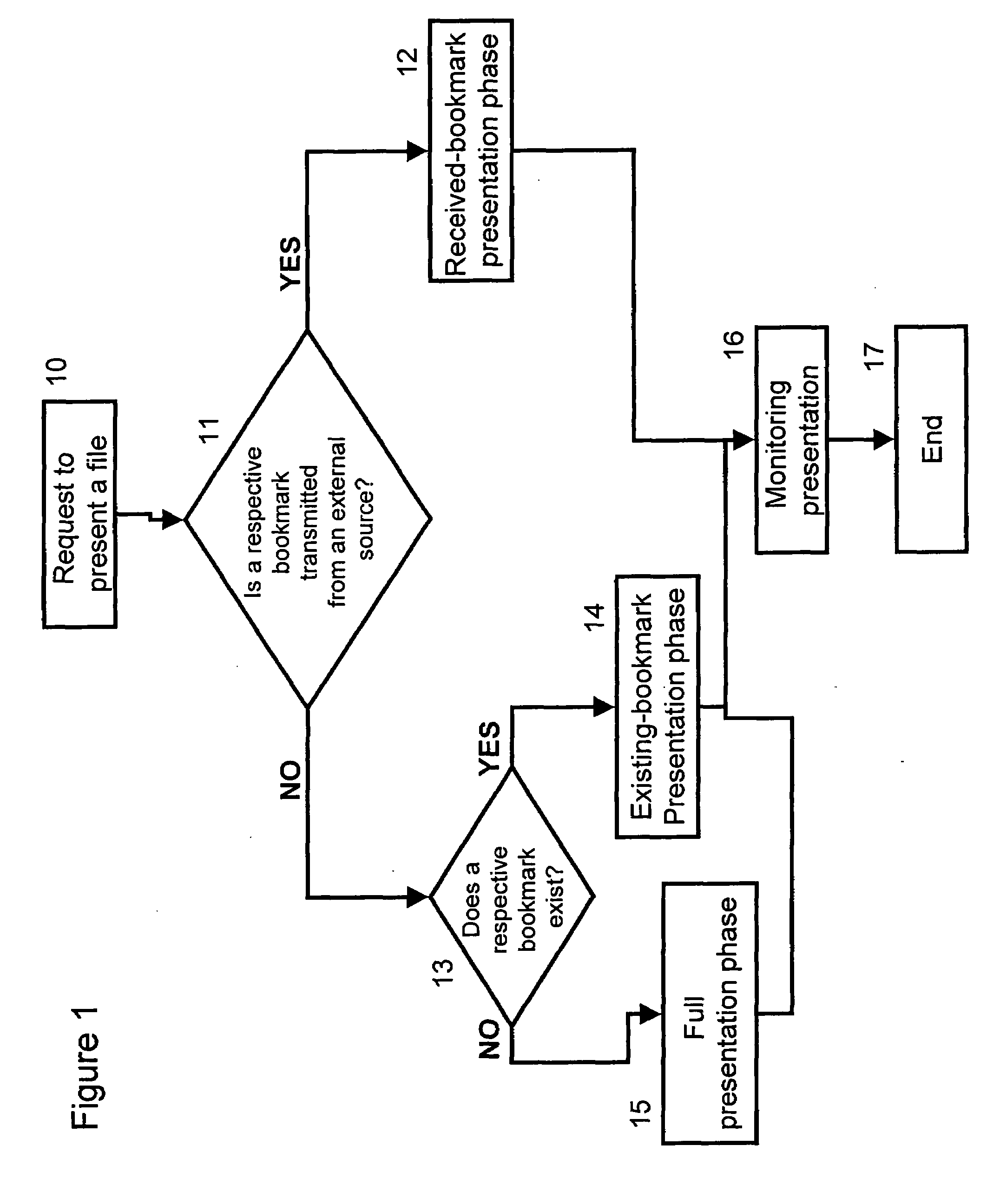
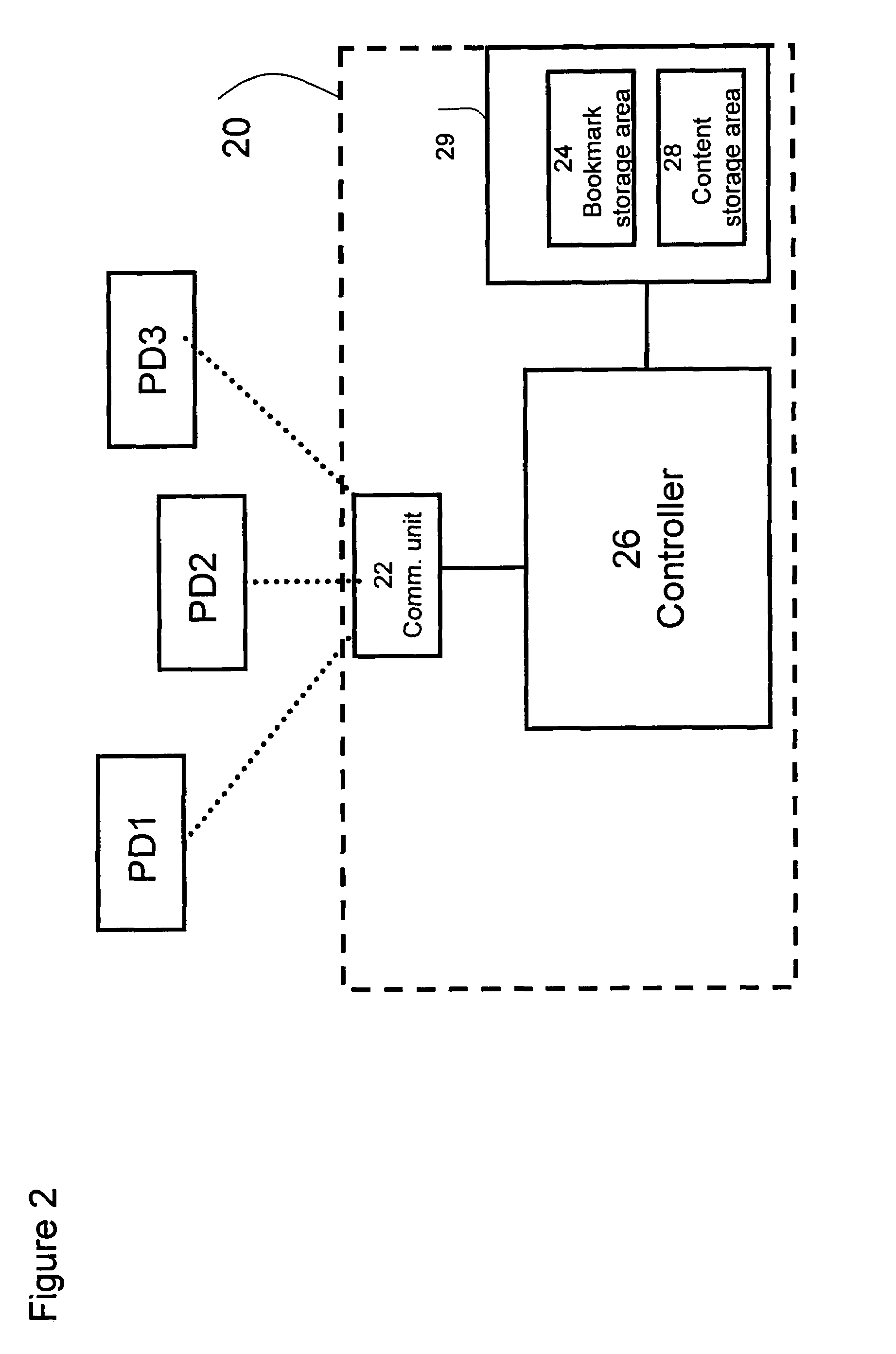
Bookmarked synchronization of files
ActiveUS20070203955A1Digital data processing detailsMultimedia data retrievalFile synchronizationBookmarking
A file synchronization system that includes a non-volatile memory for storing at least one bookmark respective to a file; a telecommunication mechanism for receiving a new bookmark value respective to this file; and a controller operative to update the respective bookmark according to the new bookmark value; and to control presentation of the file in accordance with the updated bookmark value. A plurality of bookmarks that associate to a single file are stored in the file synchronization system, each such bookmark respective to a different user.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL ISRAEL LTD
Network timing synchronization systems
ActiveUS20100118895A1Decreasing upgrade cost and upgrade timeInexpensive and ubiquitous precision timing synchronizationTime-division multiplexSynchronisationData setComputer science
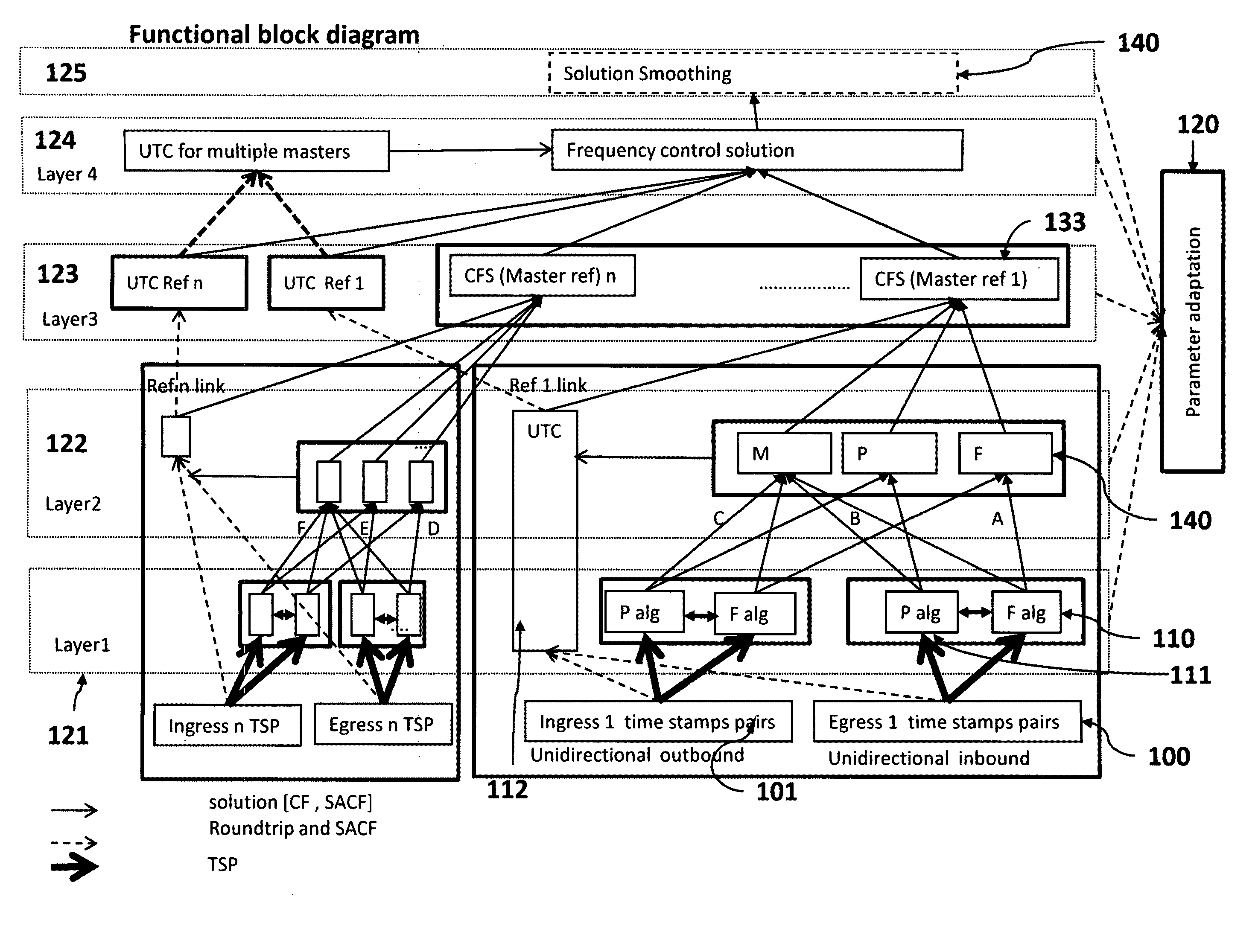
A method and means synchronize timing of a follower system to a reference system. A Hierarchical CFF function (“HCFF”) is applied to a set of Correction Factor Functions types (“CFFs”) or a set of other HCFF. Each CFF type uses the same input data set specific to that type and generates at least one Correction Factor Solution (“CFS”) for each of the CFF, wherein the CFS consists of only CF or the CFS consists of both i) CF and ii) a SACF. The HCFF takes as input a set of CFS and generates at least one CFS, wherein the CFS consist of only the CF, or the CFS consists of both the i) CF and ii) a SACF.
Owner:RADULESCU CODRUT RADU
Data transfer and synchronization system
InactiveUS20080201362A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData packTransfer system
A data transmission system is disclosed which optimizes transfer and updates of information between systems by providing difference information between the systems. The system transmits data packages having instructions for manipulating user data. The data packages include a header identifying the respective packages, as well as transaction objects for effecting a change to user data on a device having object instructions.
Owner:SYNCHRONOSS TECH
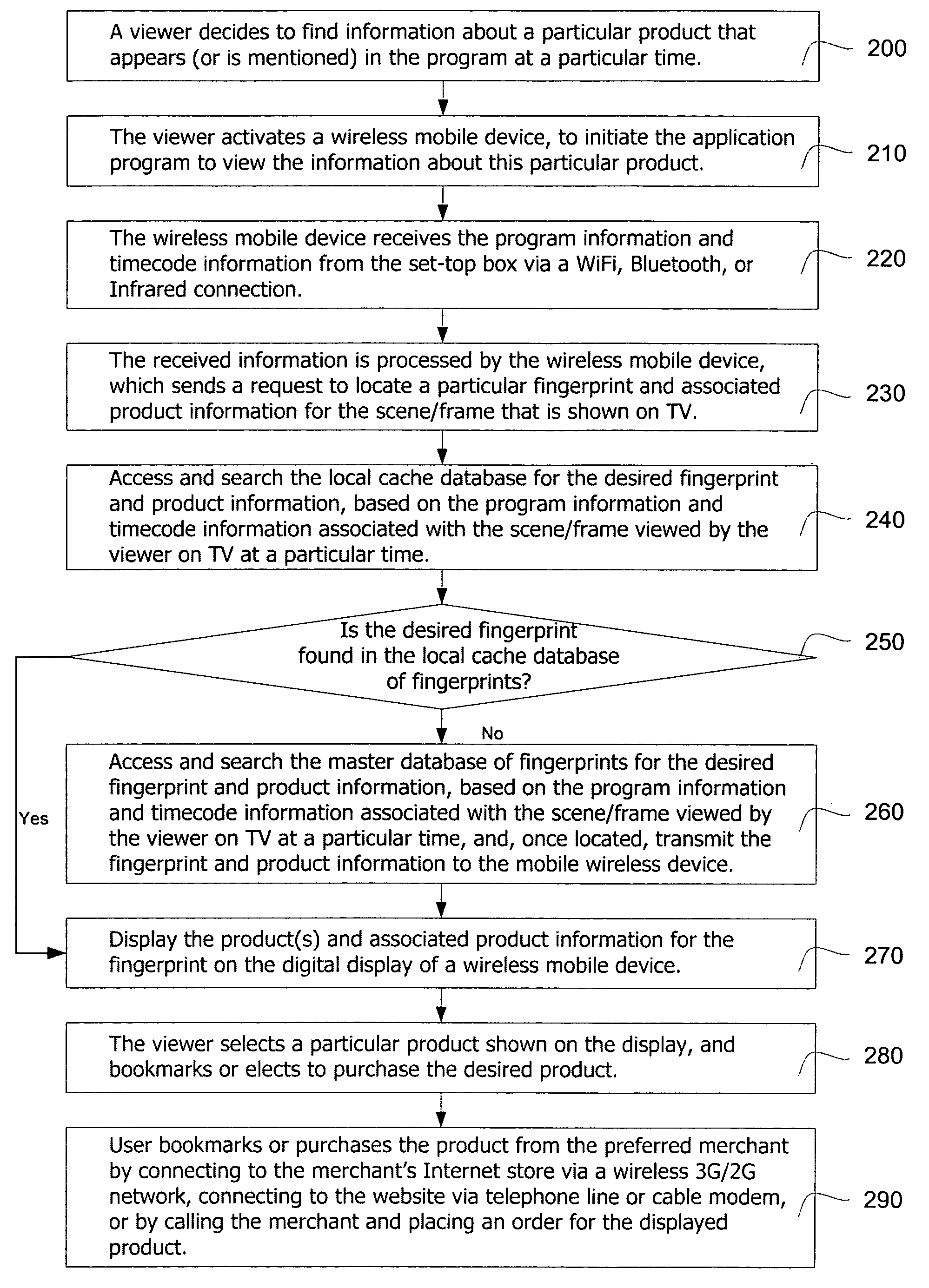
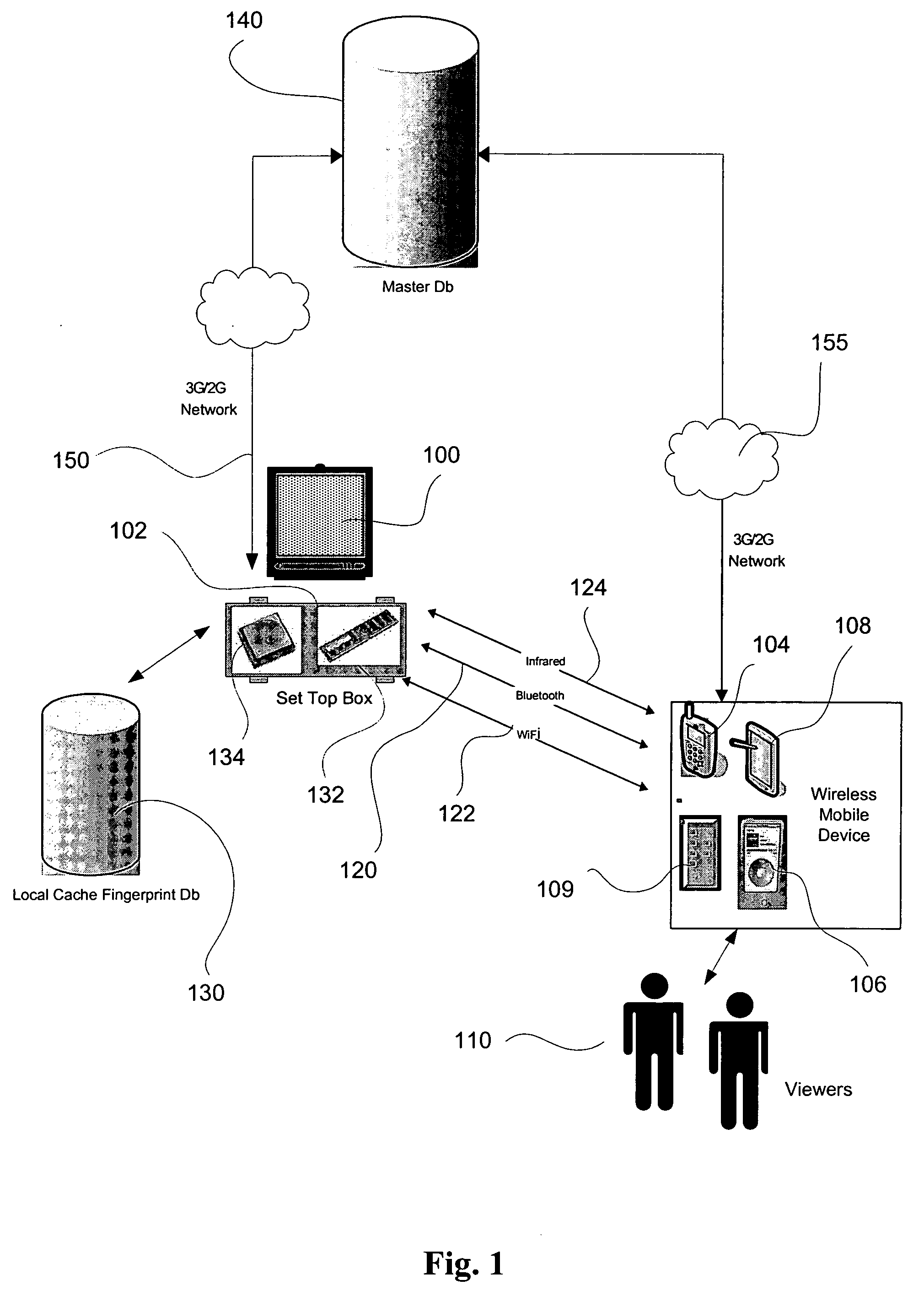
Interactive TV data track synchronization system and method
InactiveUS20080089551A1Easy to buyCharacter and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsThe InternetMobile device
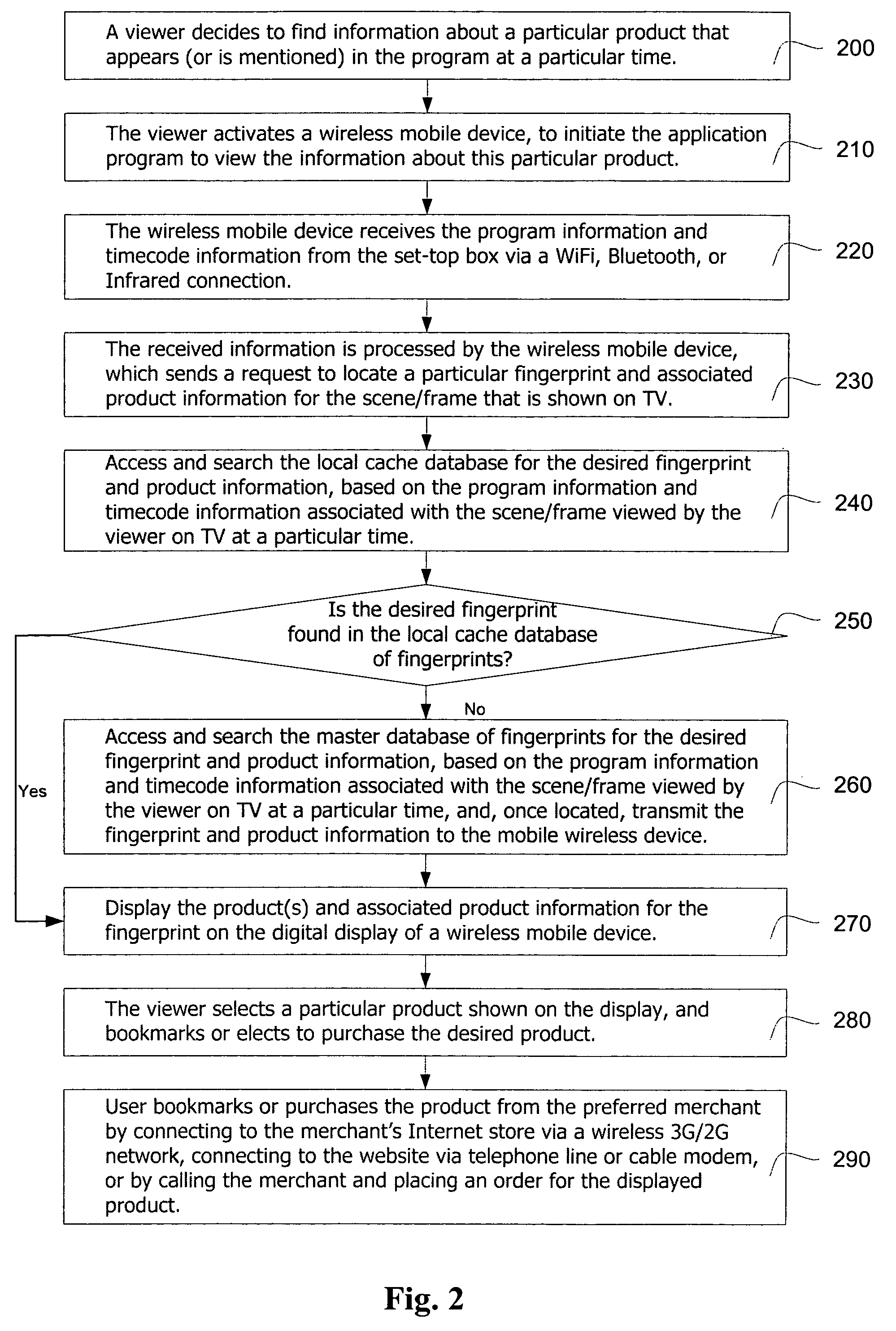
The present invention provides a system and method to allow product placement, i.e. showcasing products broadcast over TV, cable or similar media and to enable viewers to view, bookmark and purchase products placed within the program as they appear on the TV screen at a particular time. The present invention further provides a method and system for creating and identifying a digital fingerprint, which consists of a record of one or more frames in a program and associating information about products that appear in these frames to the digital fingerprint. The fingerprints are stored in a database of digital fingerprints, accessible via a wireless network and the Internet from the viewer's mobile wireless device. The mobile device submits a request to identify and locate the fingerprints corresponding to the program frame(s) being viewed, and it receives and displays the associated product information in order to facilitate the purchase of the featured products.
Owner:ENTERTAINMENT MEDIA WORKS
System and method for synchronizing of information without data duplication
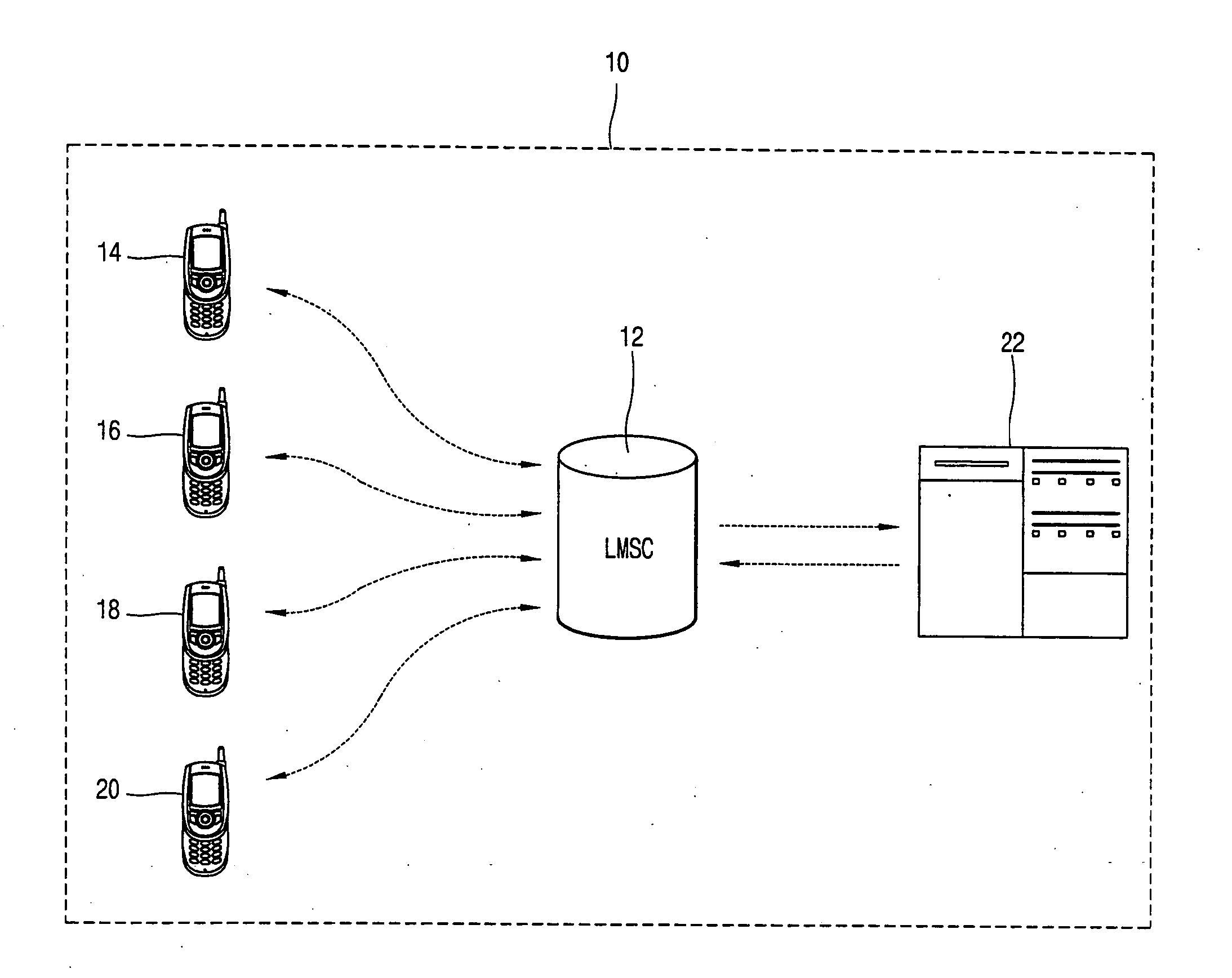
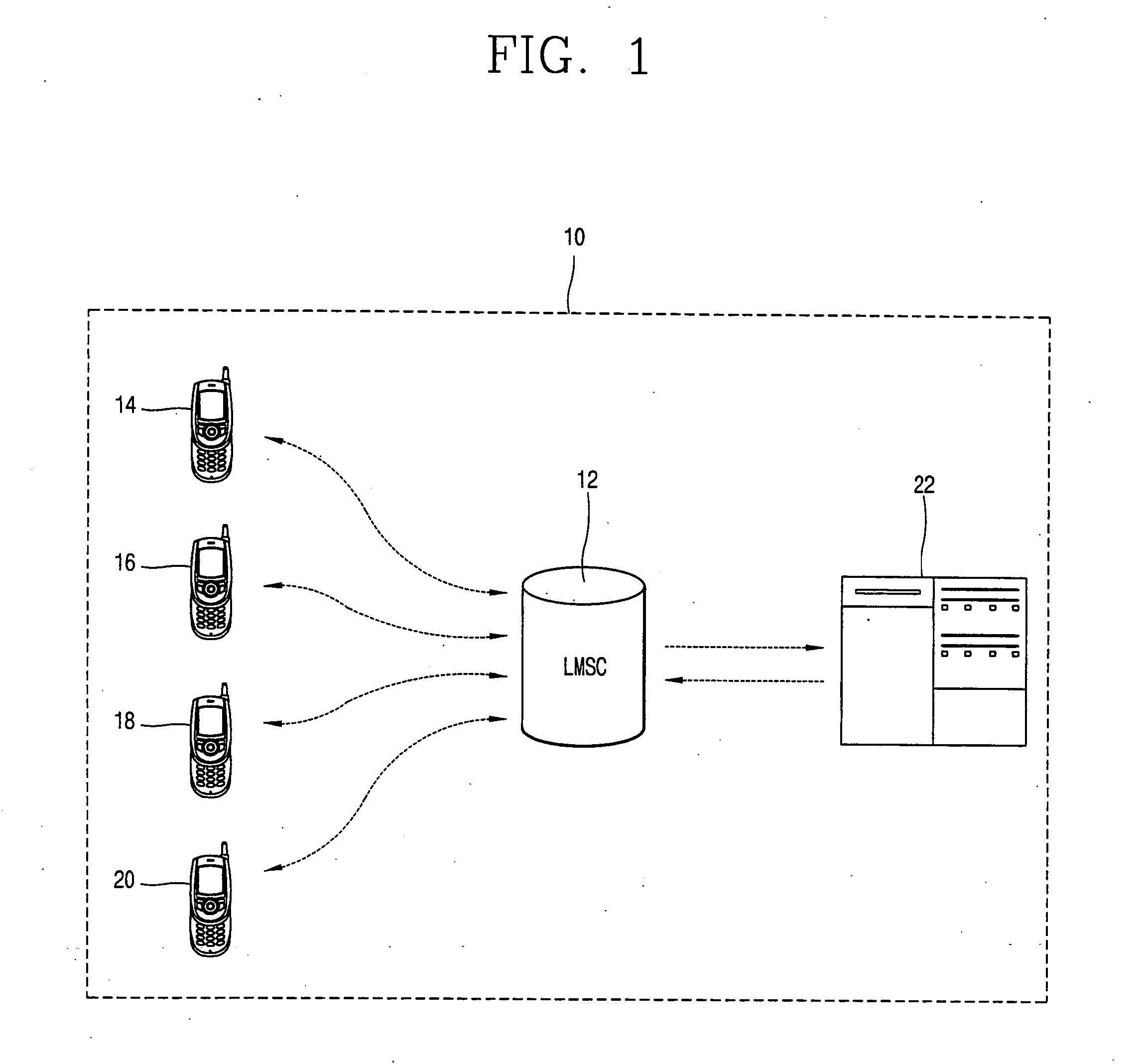
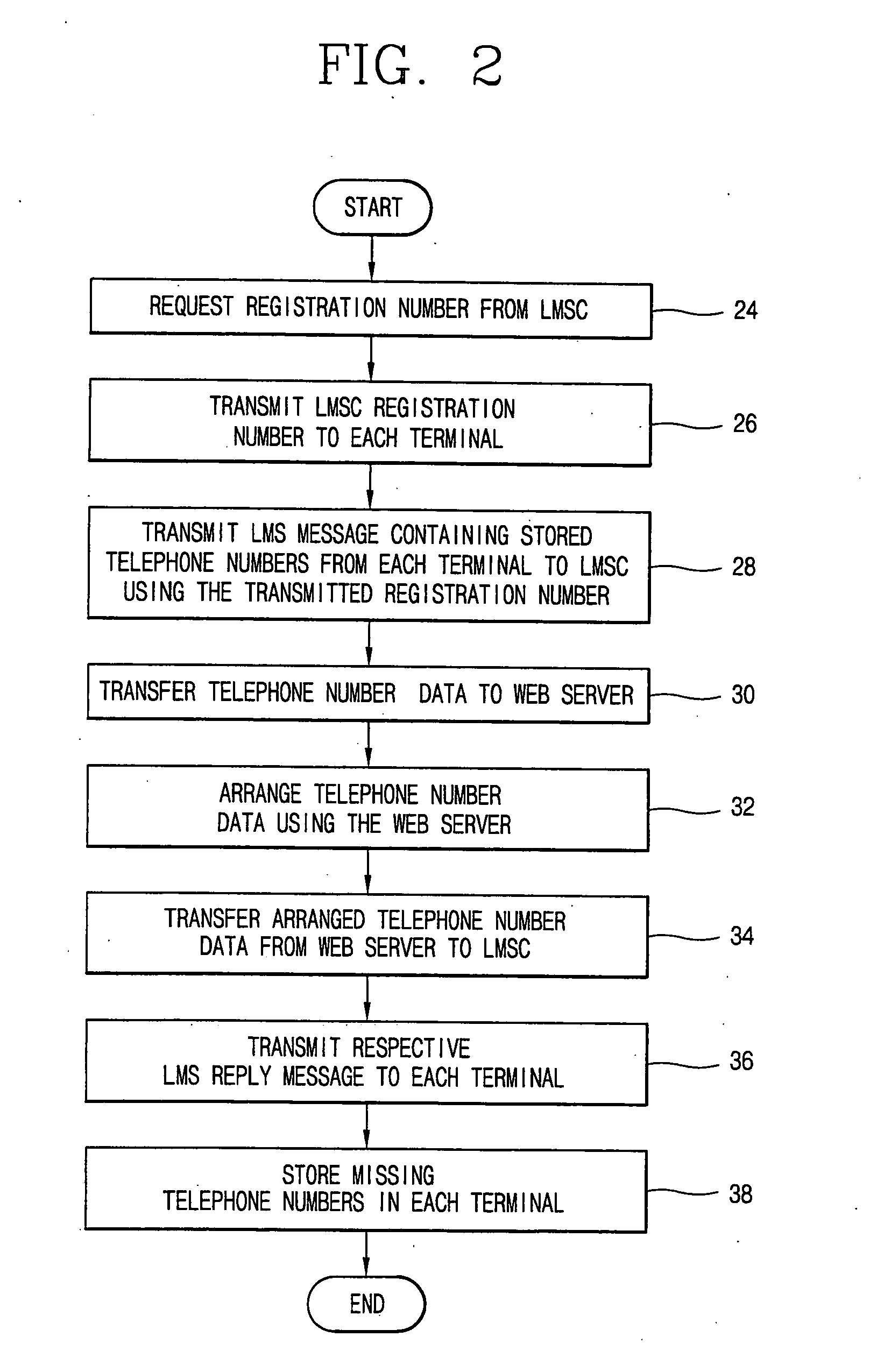
InactiveUS20050117606A1Digital data processing detailsSpecial service for subscribersMobile serviceCommunication device
A system for synchronizing information comprises a plurality of mobile communication devices storing individually incomplete user information, and at least one mobile service interface adapted to receive and transmit the stored user information for processing. The information synchronization system also comprises at least one processor adapted to arrange the transmitted user information to allow each mobile communication device to complete its user information without data duplication. The processor transmits the arranged user information to each mobile communication device via the mobile service interface for storage therein.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
A system and method for dynamic fob synchronization and personalization
InactiveUS20050033689A1Digital data processing detailsPayment architecturePersonalizationData synchronization
A system generally for personalizing and synchronizing fob data in the context of a distributed transaction system is disclosed. A dynamic fob synchronization system may comprise point of service (POS) devices configured with transponder-readers to initiate a transaction in conjunction with a fob, an enterprise data collection unit, and a fob object database update system. An exemplary dynamic synchronization system (DSS) may comprise various fob POS devices, a secure support client server, a fob object database update system (FODUS), one or more enterprise data synchronization interfaces (EDSI), an update logic system, one or more enterprise data collection units (EDCUs), and one or more fob POS devices configured to interoperably accept and interface with fobs. In an exemplary embodiment, DSS may comprise a personalization system and an account maintenance system configured to communicate with FODUS. Personalization of multi-function fobs may be accomplished using a security server configured to generate and / or retrieve cryptographic key information from multiple enterprise key systems during the final phase of the fob issuance process.
Owner:LIBERTY PEAK VENTURES LLC
Ethernet network synchronization systems and methods
ActiveUS20110200051A1Reduce in quantityImprove stabilityTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationSynchronization systemSynchronous Ethernet
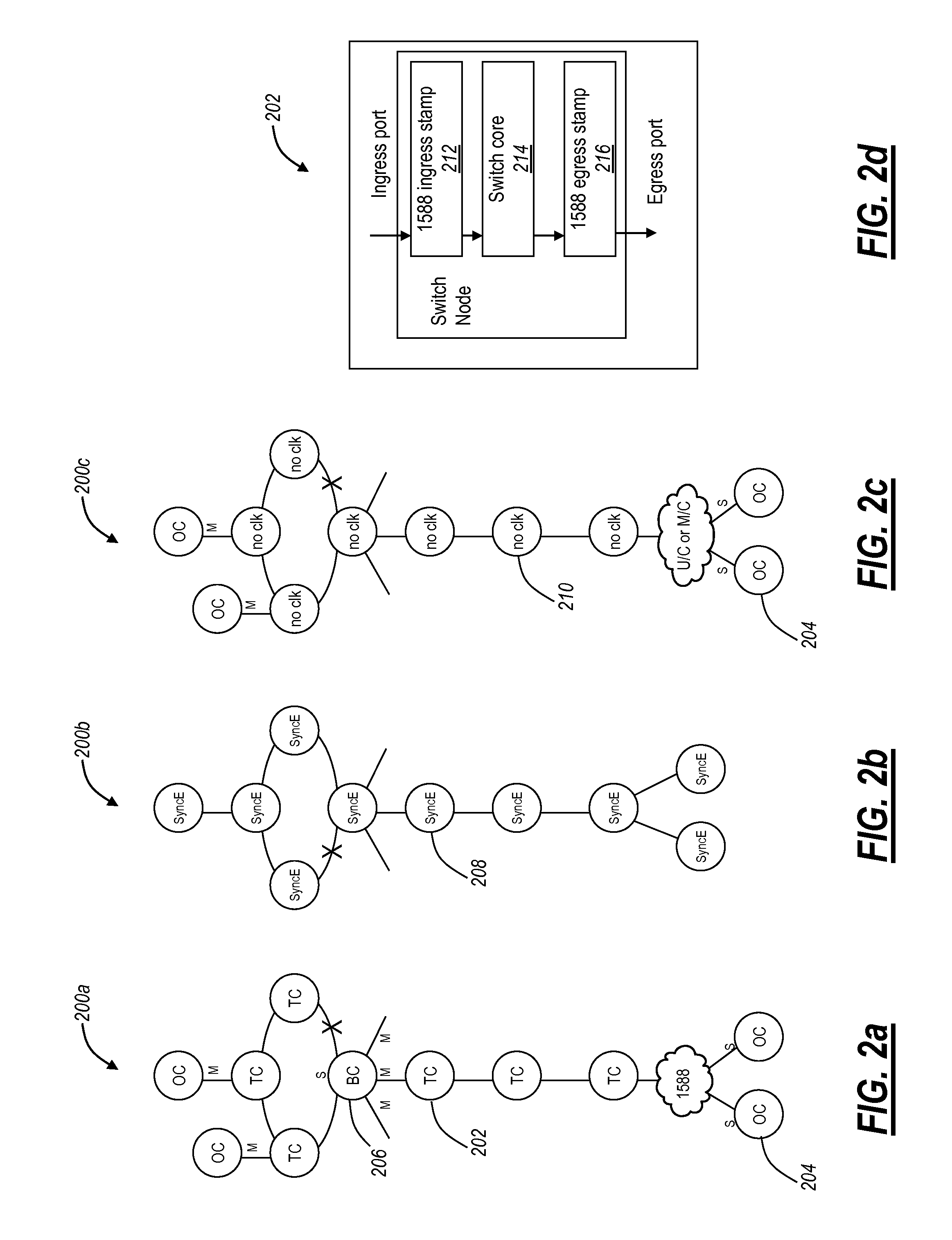
The present disclosure relates to Ethernet synchronization systems and methods that combines Synchronous Ethernet (Sync-E) and Precision Time Protocol (PTP) IEEE 1588 algorithms. The present invention includes systems and methods for Ethernet networks and node configurations that include a set of rules on node placement, such as Boundary Clock (BC) nodes and Sync-E nodes, a clock selection algorithm, a holdover algorithm, and the like. Advantageously, the present invention provides an architecture that allows practical and real-world useful clock propagation through placement of BCs and Sync-E nodes for best performance. Practical experience and theoretical design are embodied in the present invention to define a very specific set of rules on how to build a network capable of providing accurate and reliable synchronization. The present invention includes clock selection that unifies Sync-E and 1588 algorithms.
Owner:CIENA
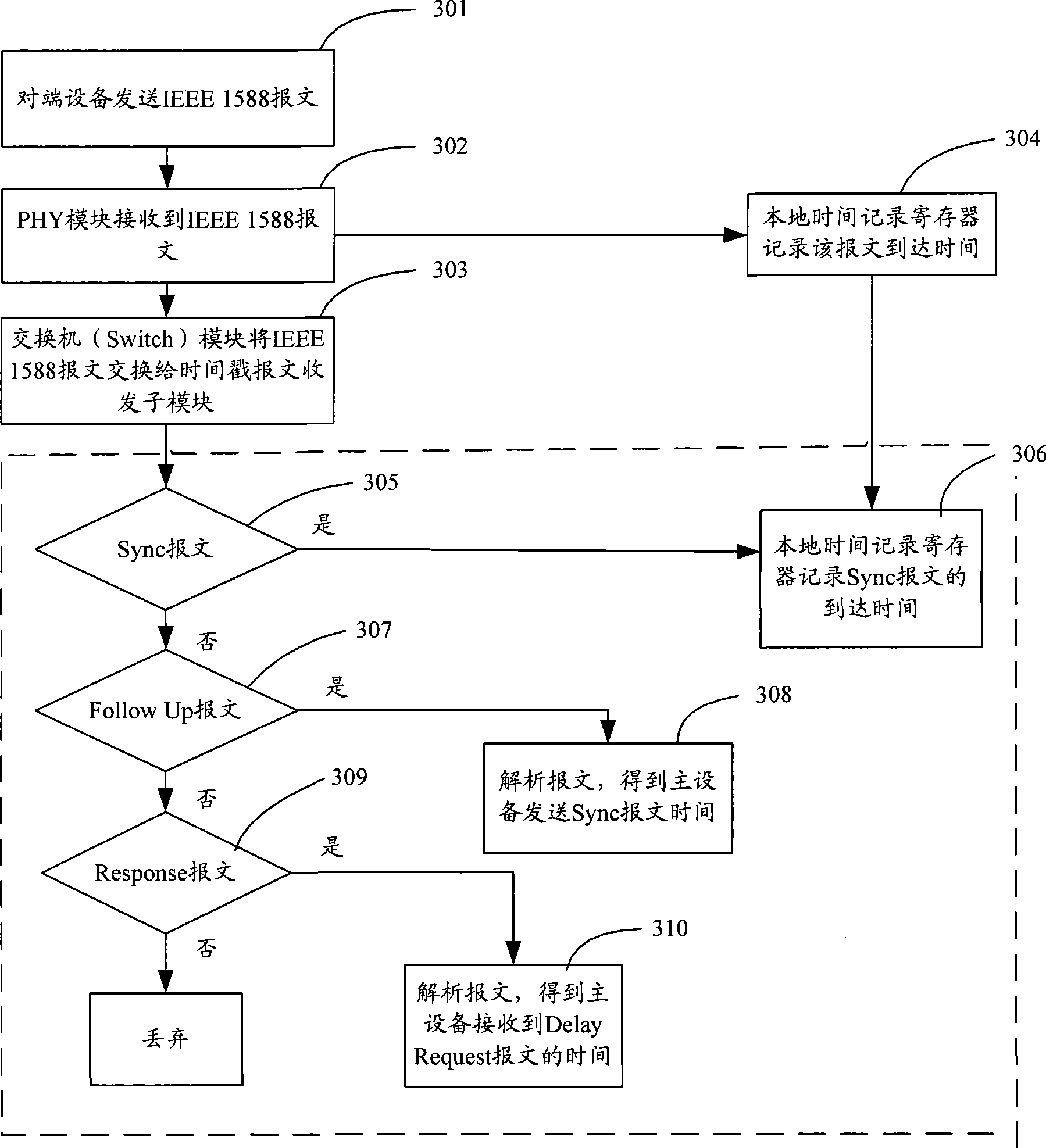
IEEE 1588 time synchronization system and implementation method thereof
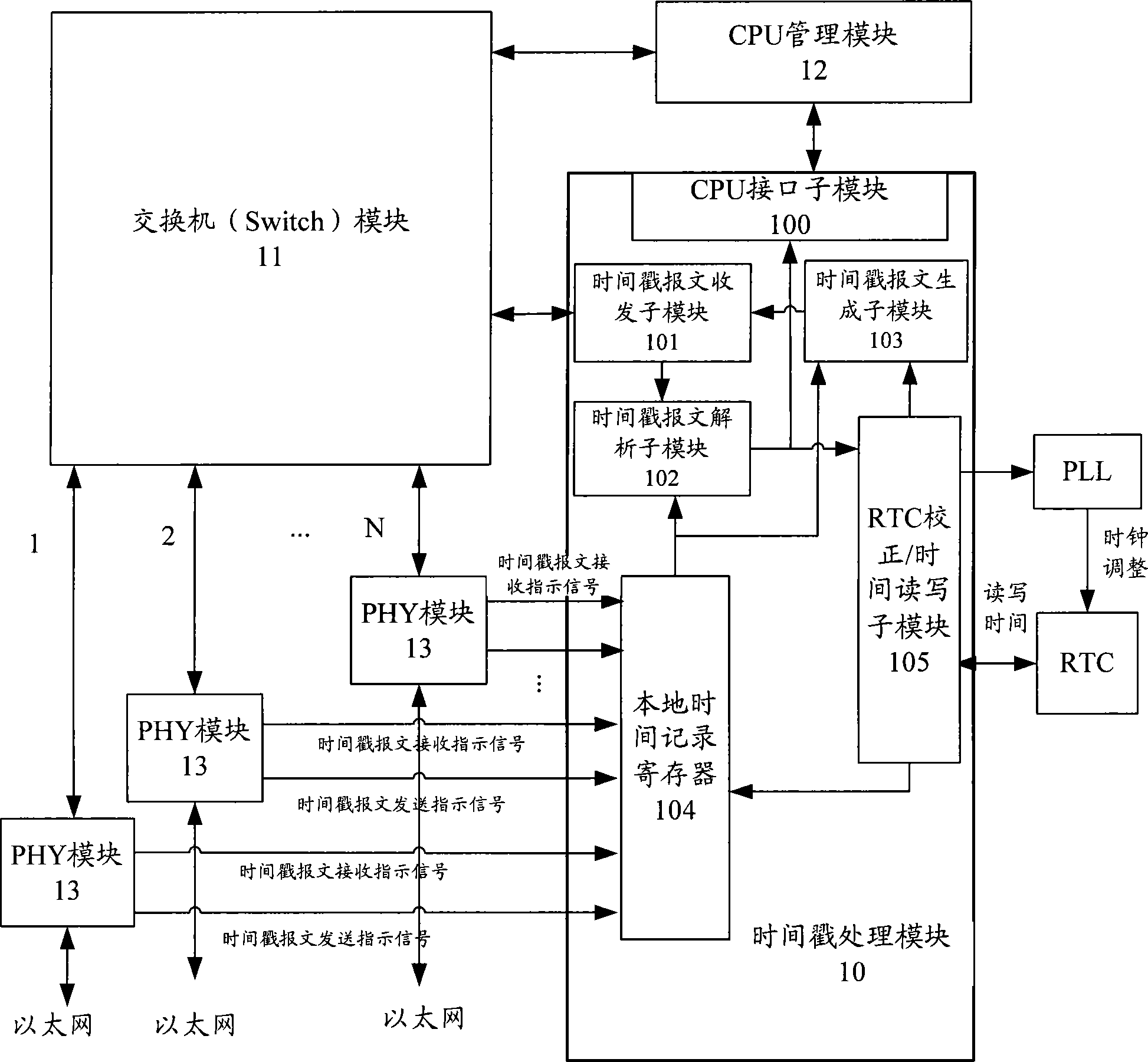
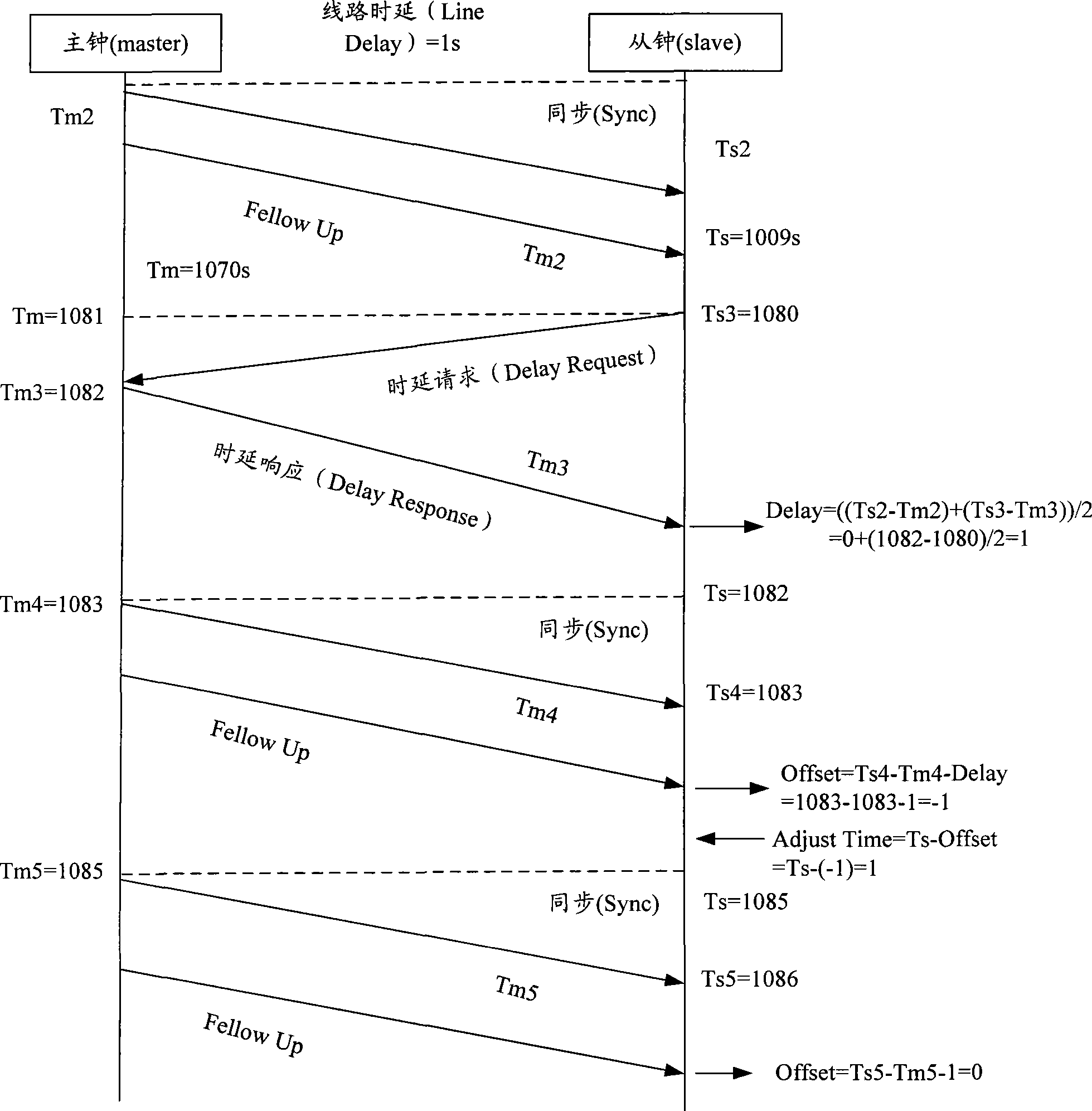
ActiveCN101447861ASynchronized High Precision TimeGuaranteed real-timeTime-division multiplexSynchronising arrangementTime informationPHY
The invention discloses an IEEE 1588 time synchronization system. By adding a time-stamp processing module, a time-stamp message transceiving sub module, a time-stamp message resolving sub module, a time-stamp message generating sub module, a local time recording register, and an RTC correction / time read-write module in the module are used for combining peripheral components such as a switch module, a PHY and a real-time clock (RTC) module to form a hardware system. When in use, the high precision time synchronization requested by an IEEE 1588v2 protocol can be implemented by using the modes of one-to-one or one-to-many of master-slave synchronization. The invention also discloses a method for implementing the IEEE 1588 time synchronization, which can implement the function of the time synchronization system by processing the time information of master-slave devices in real time. The invention plays an active role in promoting Ethernet construction.
Owner:ZTE CORP
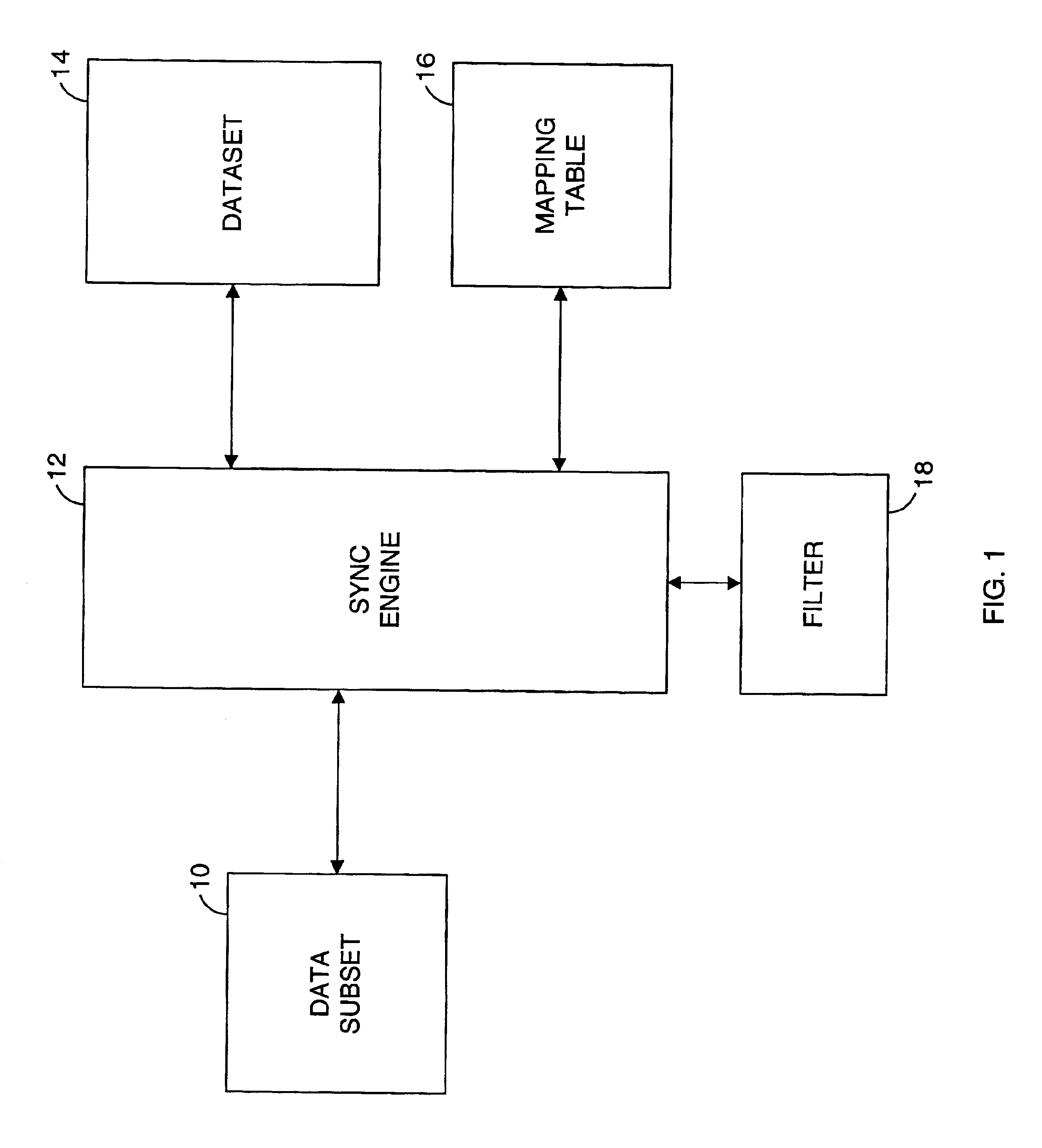
Method and system for implementing a filter in a data synchronization system
InactiveUS7024430B1Data processing applicationsDatabase distribution/replicationData synchronizationData set
A method and system for synchronizing data between a dataset and a data subset, in which filter criteria determine which data records in the dataset are excluded from the data subset. However, the filter is not applied to every record of the dataset during each synchronization. Instead, during a synchronization, the filter is applied to incoming changes received from the data subset and to outgoing changes that are intended to be sent to the data subset. Appropriate actions are taken on these changes to implement the filter parameters. When a filter is changed or newly activated, a method is performed which prepares the synchronization system so that, when the next synchronization is performed, the dataset and the data subset will automatically be synchronized according to the new filter, due to the standard application of the filter parameters during a standard synchronization.
Owner:INTELLISYNC CORP
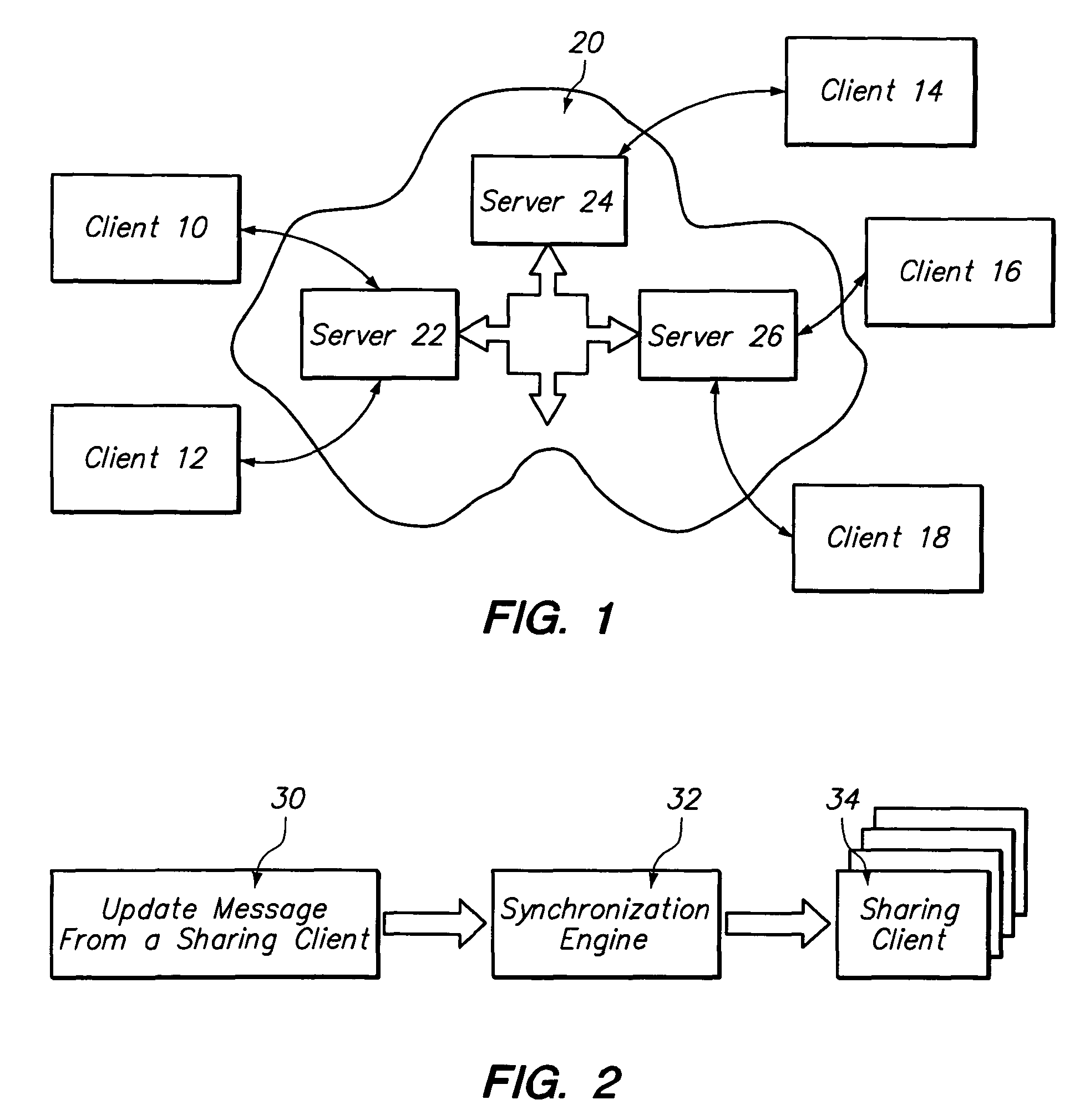
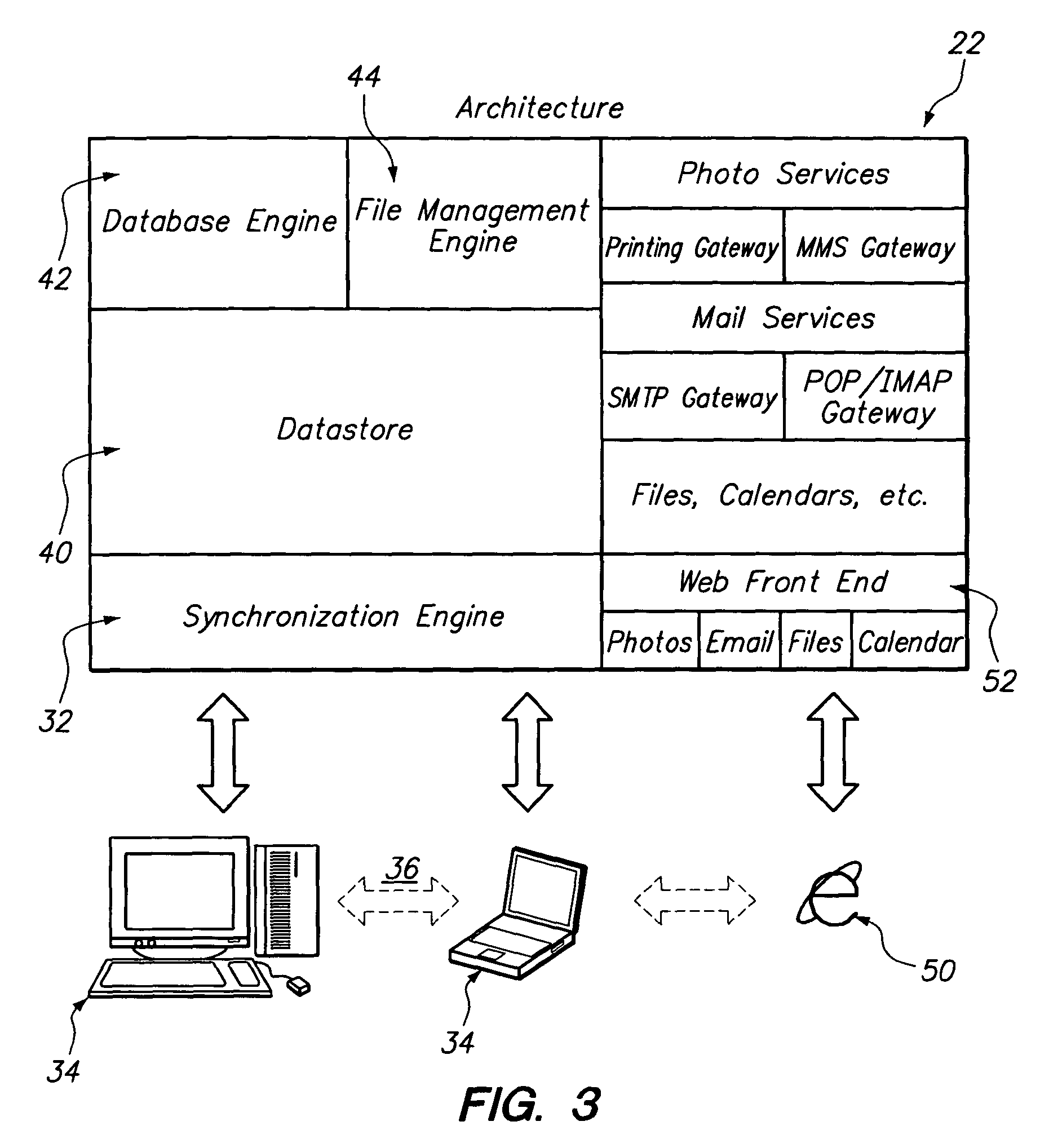
Method and apparatus for a file sharing and synchronization system
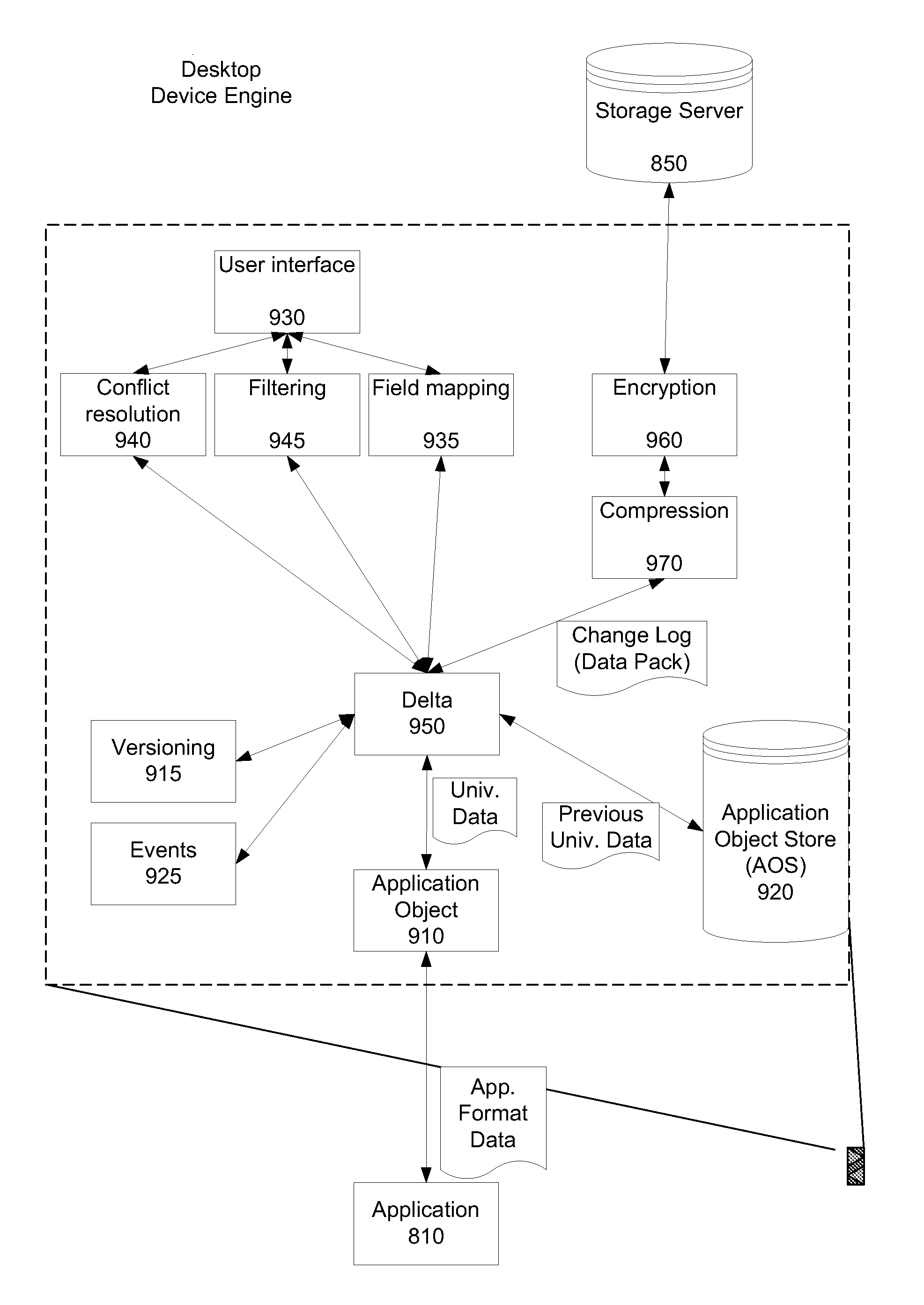
ActiveUS7885925B1Easy to shareDigital data processing detailsMetadata multimedia retrievalWeb browserClient-side
A computer-implemented method is provided for managing and sharing picture files. In one embodiment of the present invention, the method comprises providing a server platform and providing a datastore on the server platform for maintaining full resolution copies of the files shared between a plurality of sharing clients. A synchronization engine is provided on the server platform and is configured to send real-time updates to a plurality of sharing clients when at least one of the sharing clients updates or changes one of said files. A web interface may also be provided that allows a user to access files in the datastore through the use of a web browser.
Owner:DROPBOX
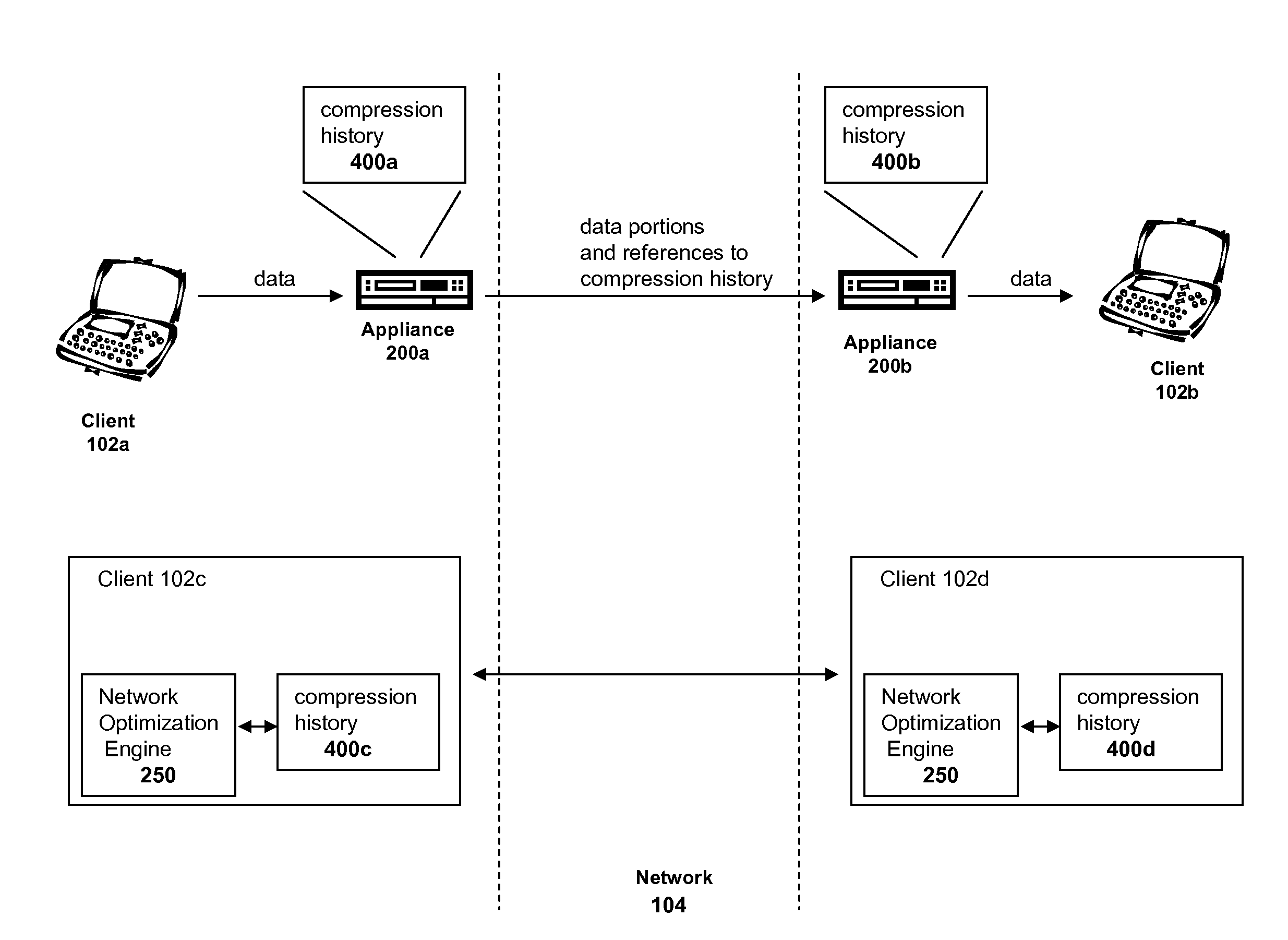
Systems and methods of compression history expiration and synchronization
ActiveUS20080229137A1Reduce bandwidth usageAccelerate future communicationMultiple digital computer combinationsGenerating/distributing signalsTraffic capacityApplication software
Systems and methods of storing previously transmitted data and using it to reduce bandwidth usage and accelerate future communications are described. By using algorithms to identify long compression history matches, a network device may improve compression efficiently and speed. A network device may also use application specific parsing to improve the length and number of compression history matches. Further, by sharing compression histories, compression history indexes and caches across multiple devices, devices can utilize data previously transmitted to other devices to compress network traffic. Any combination of the systems and methods may be used to efficiently find long matches to stored data, synchronize the storage of previously sent data, and share previously sent data among one or more other devices.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
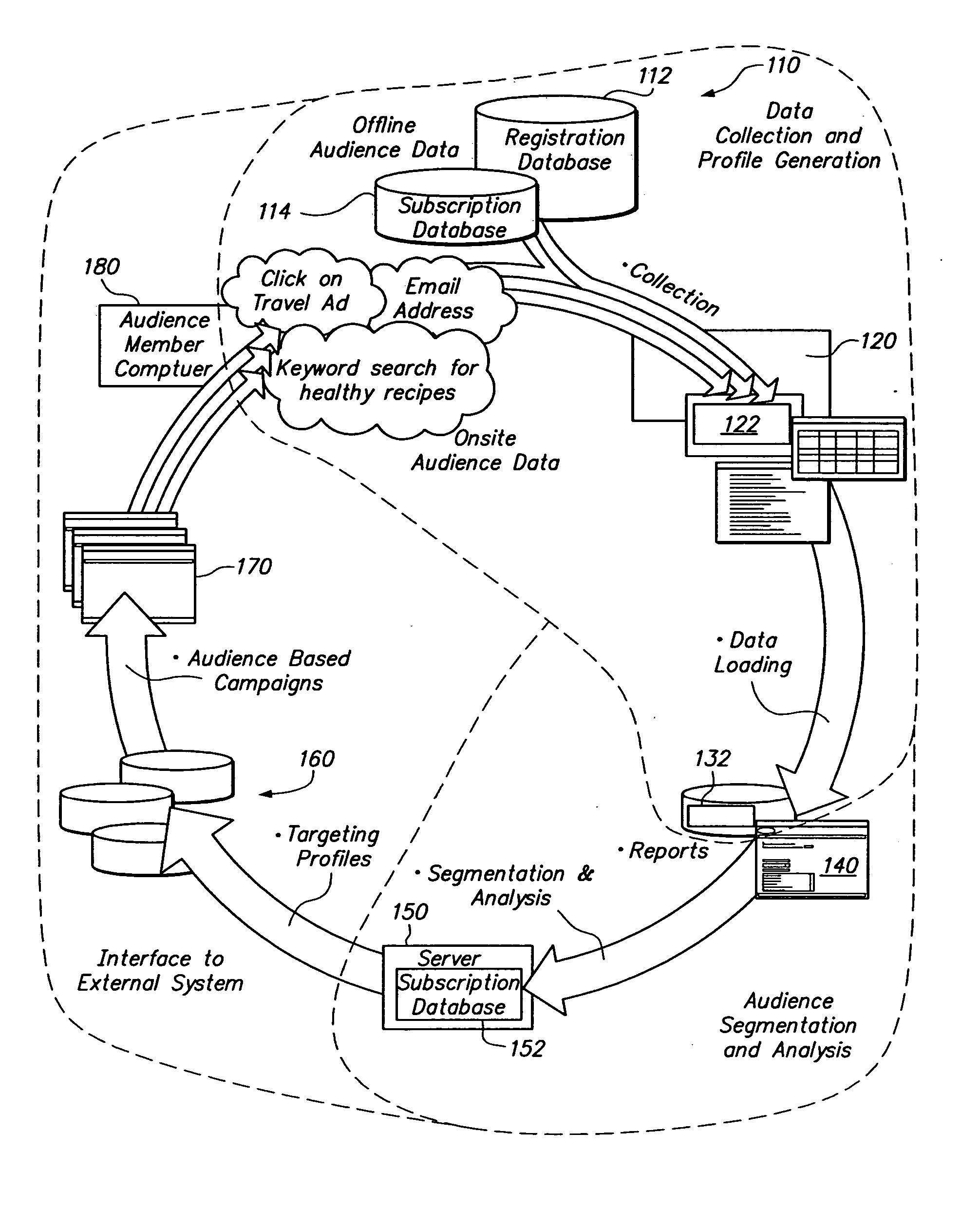
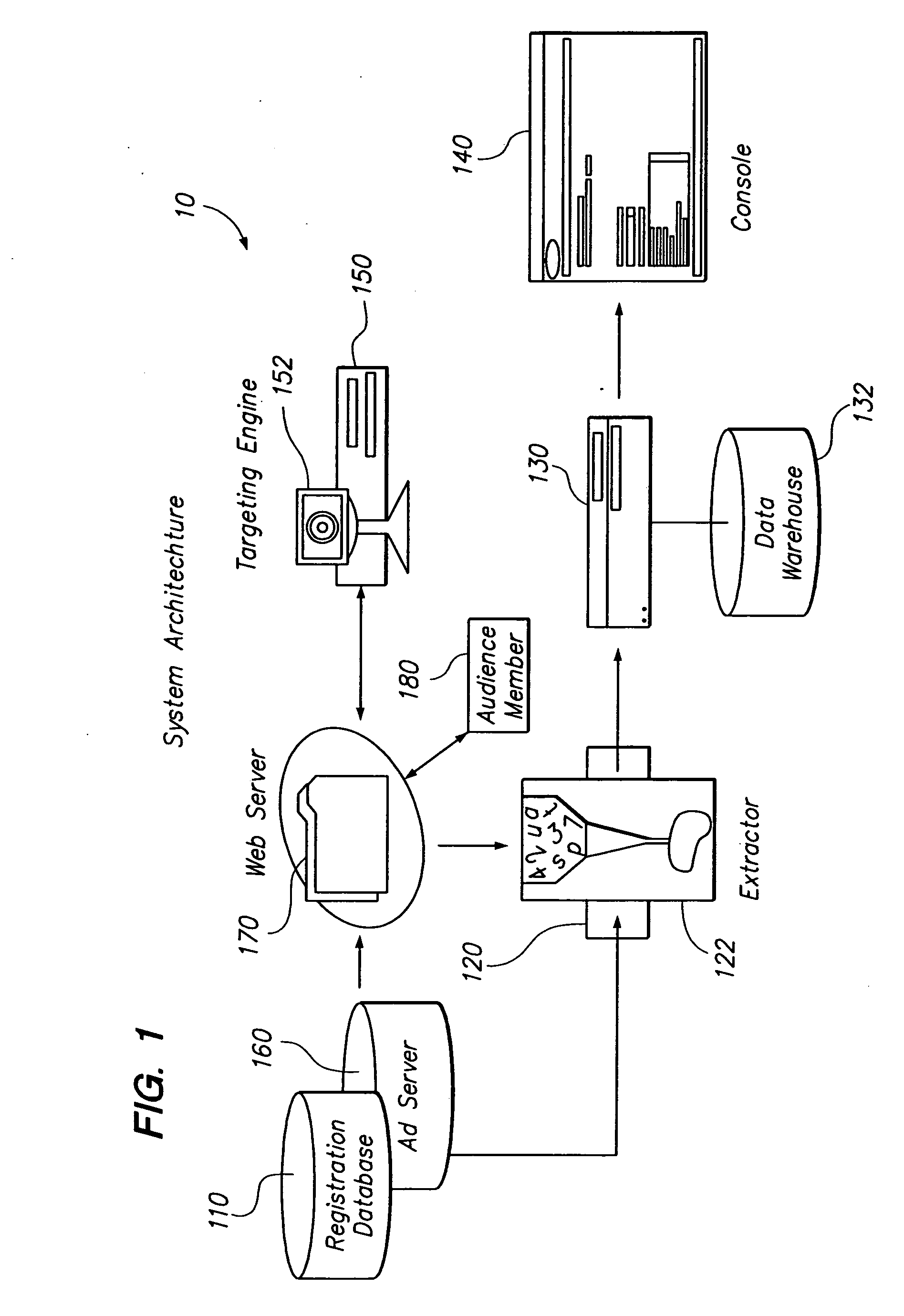
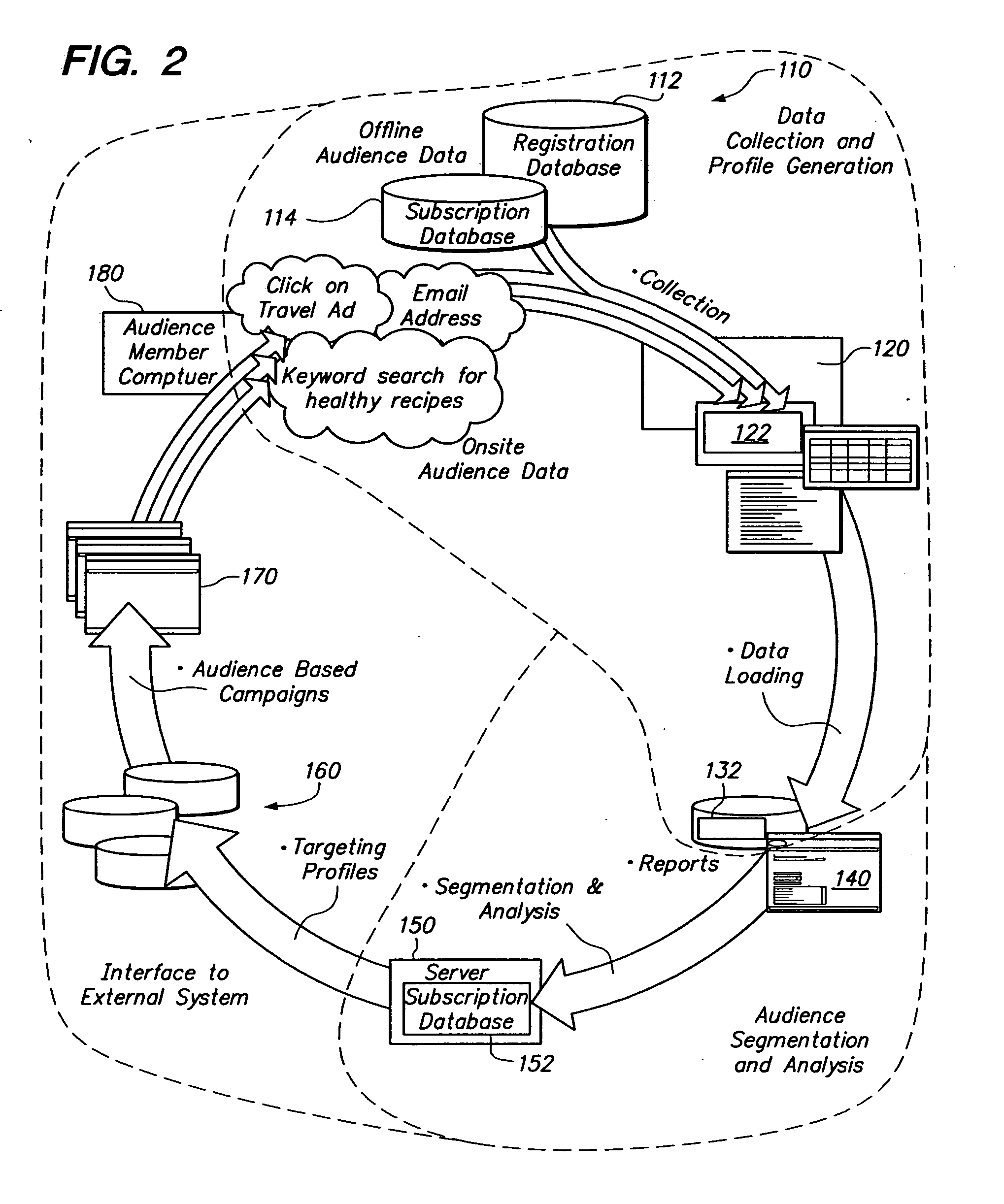
Audience targeting system with profile synchronization
InactiveUS20050125290A1Facilitates efficient calculationMarketingSpecial data processing applicationsData miningSystems approaches
Systems, methods and apparatus for delivering content to an audience member over a computer network. A console allows a user to define audience segments that are organized in hierarchical fashion. The segments are then calculated by collecting profile data for audience members and determining whether members have attributes that a defined by the audience segments. The hierarchical definition of segments allows audience segments to be logically combined and facilitates efficient recalculation of audience segments. Profile synchronization provides an authoritative identifier that is used to reconcile the potential issuance of multiple identifiers for a given audience member.
Owner:VERIZON MEDIA INC
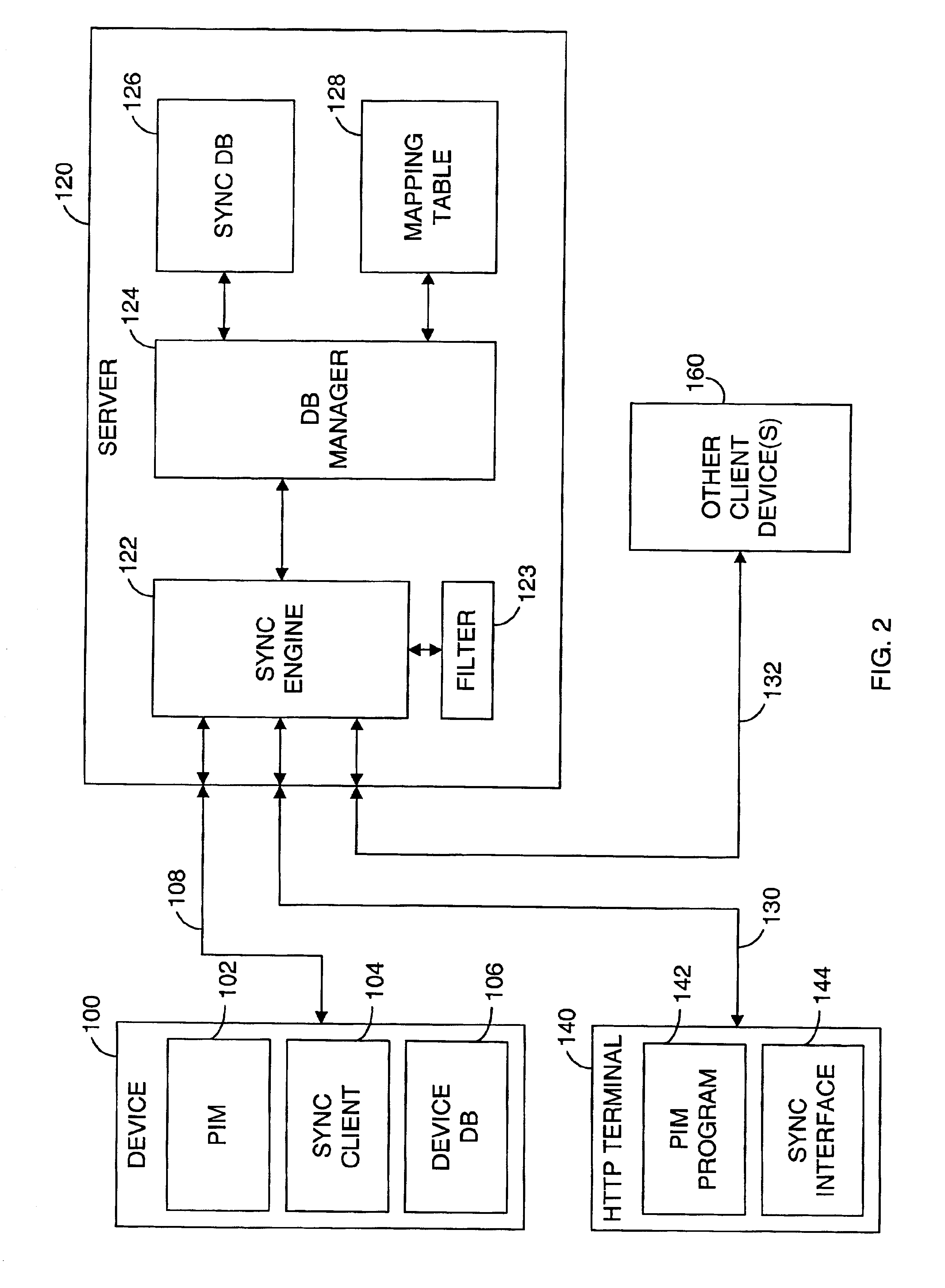
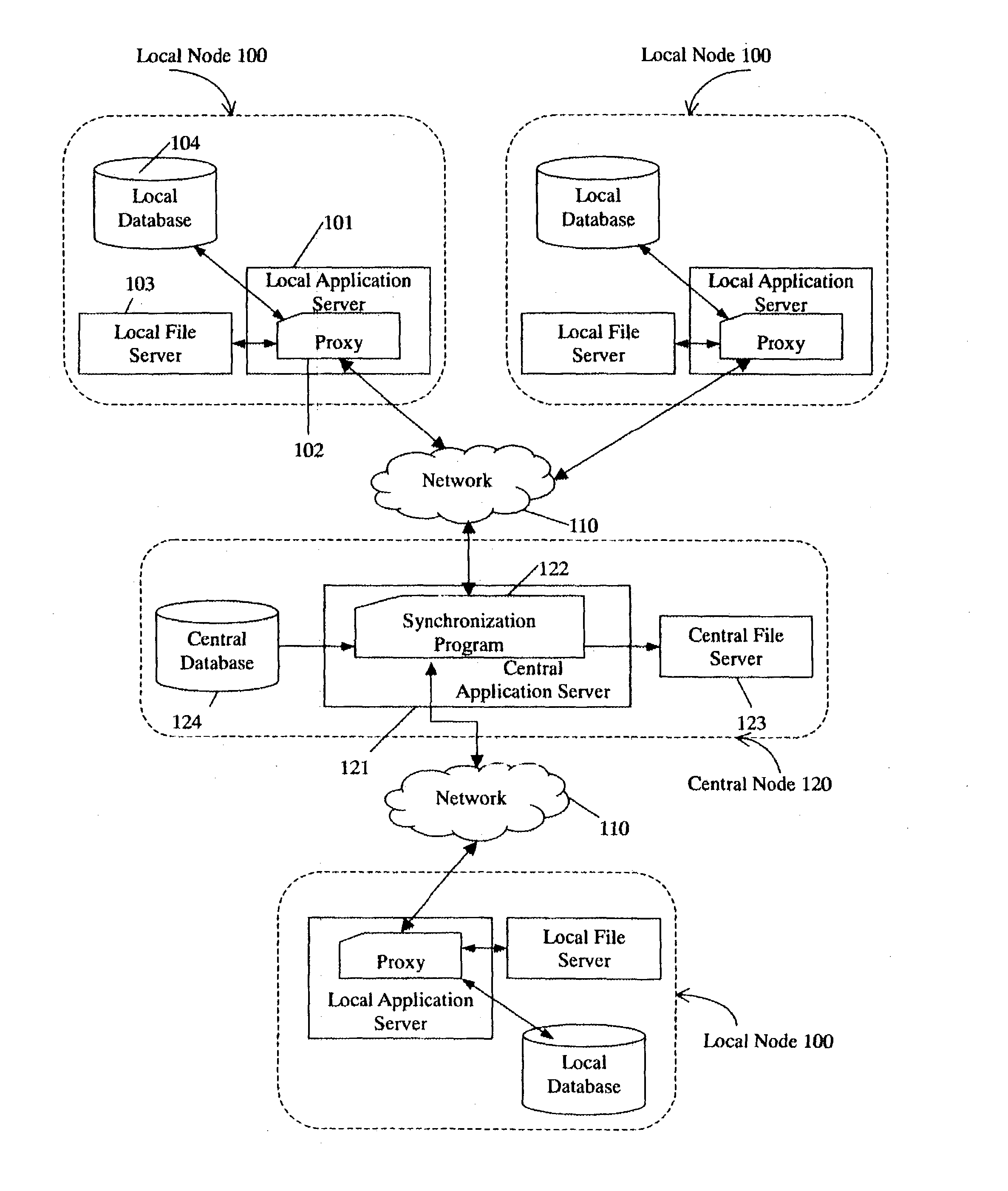
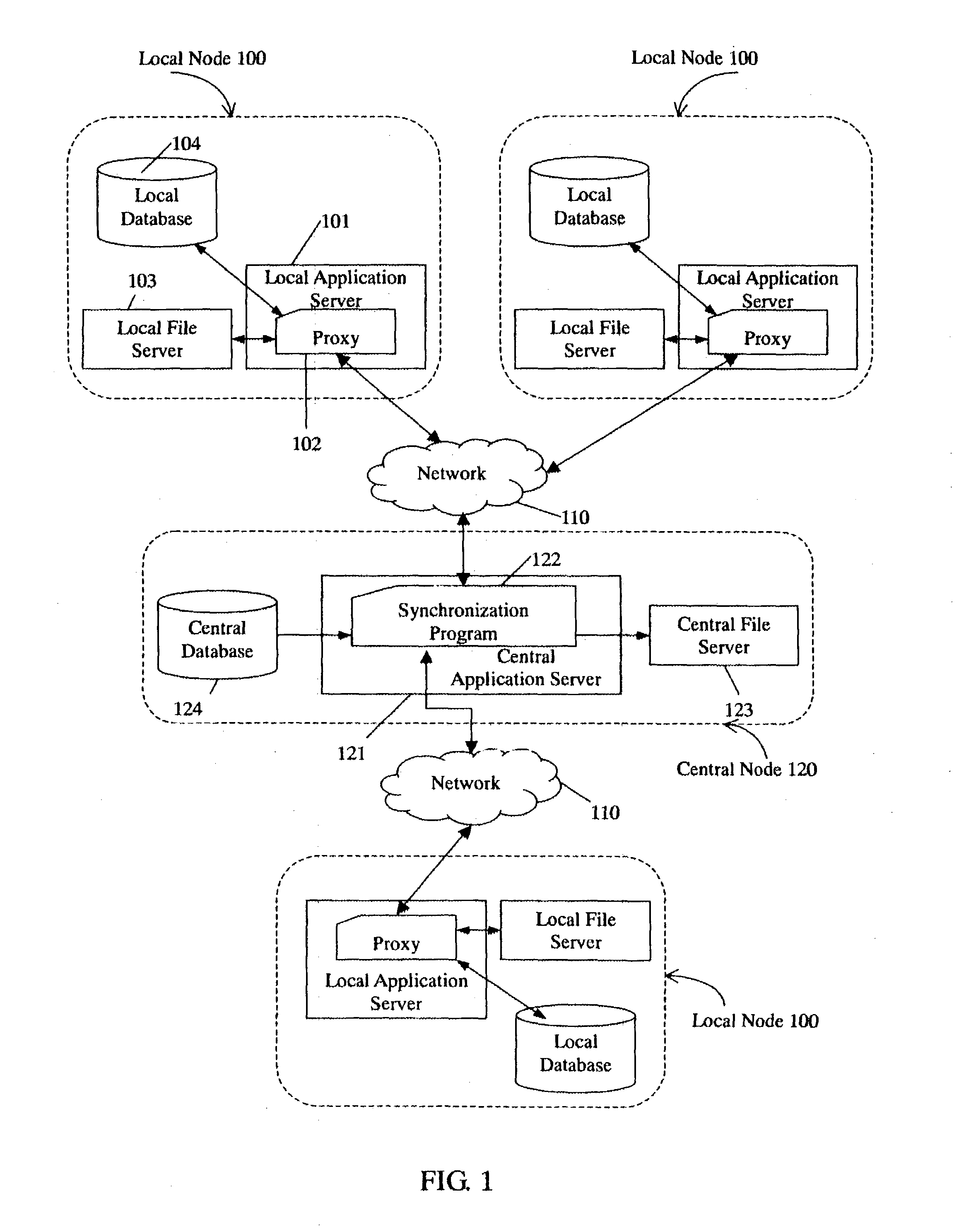
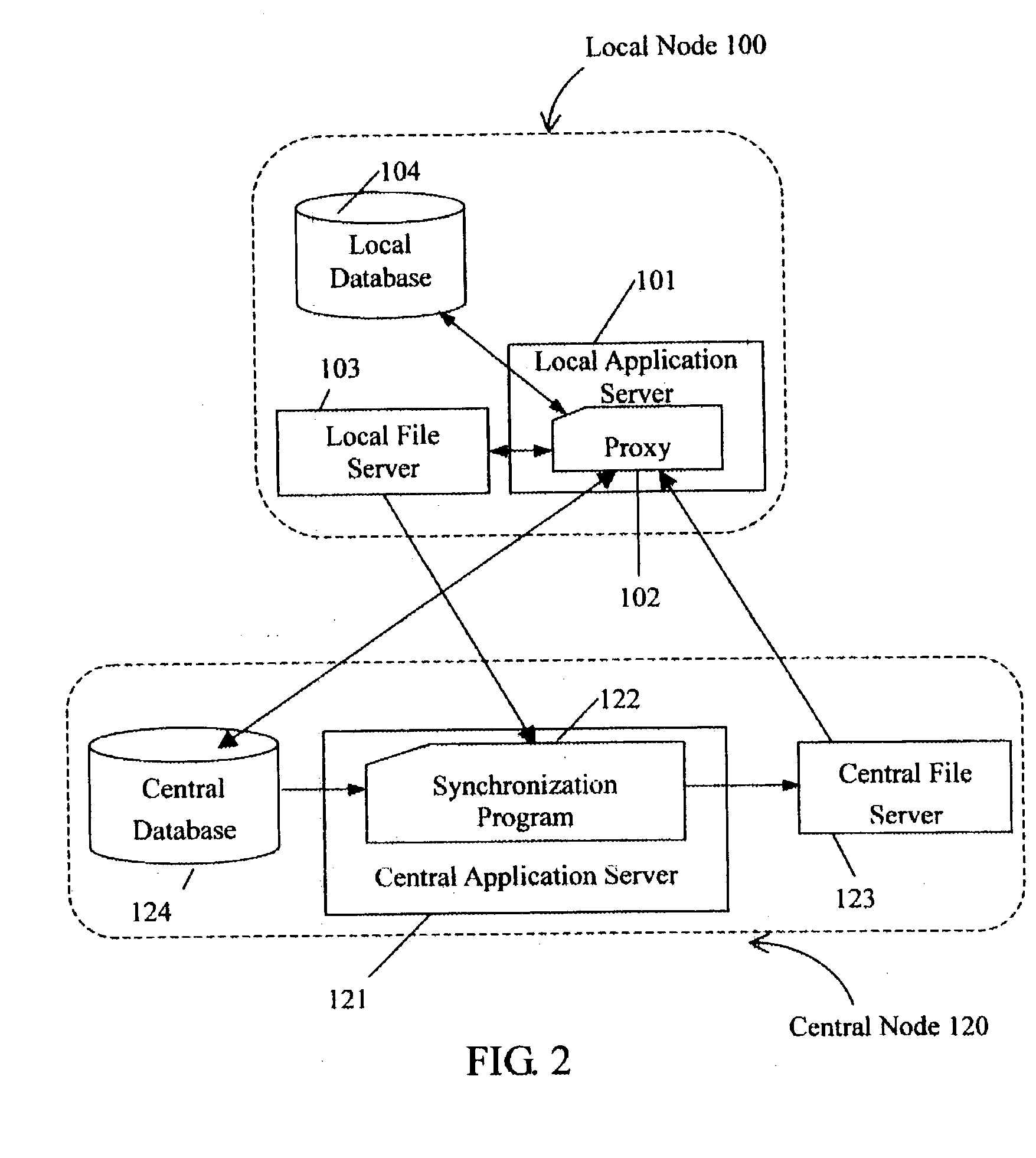
System and method for synchronizing files in multiple nodes
ActiveUS20040068516A1Excessively large network communication traffic is avoidedDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsFile synchronizationApplication server
A system and method for performing file synchronization in multiple nodes. The system includes a central node (120), and a plurality of local nodes (100) connected with the central node by a common communications network (110). Each local node includes a local application server (101), a local file server (103), and a local database (104). The central node includes a central application server (121), a central file server (123), and a central database (124). A synchronization program (122) running on the central application server downloads updated copies of files from the local file servers, and uploads the updated copies of files to the central file server as latest editions of the files. A proxy (102) running on each local application server updates copies of files in its respective local file server, and downloads latest editions of files from the central node.
Owner:DATACLOUD TECH LLC
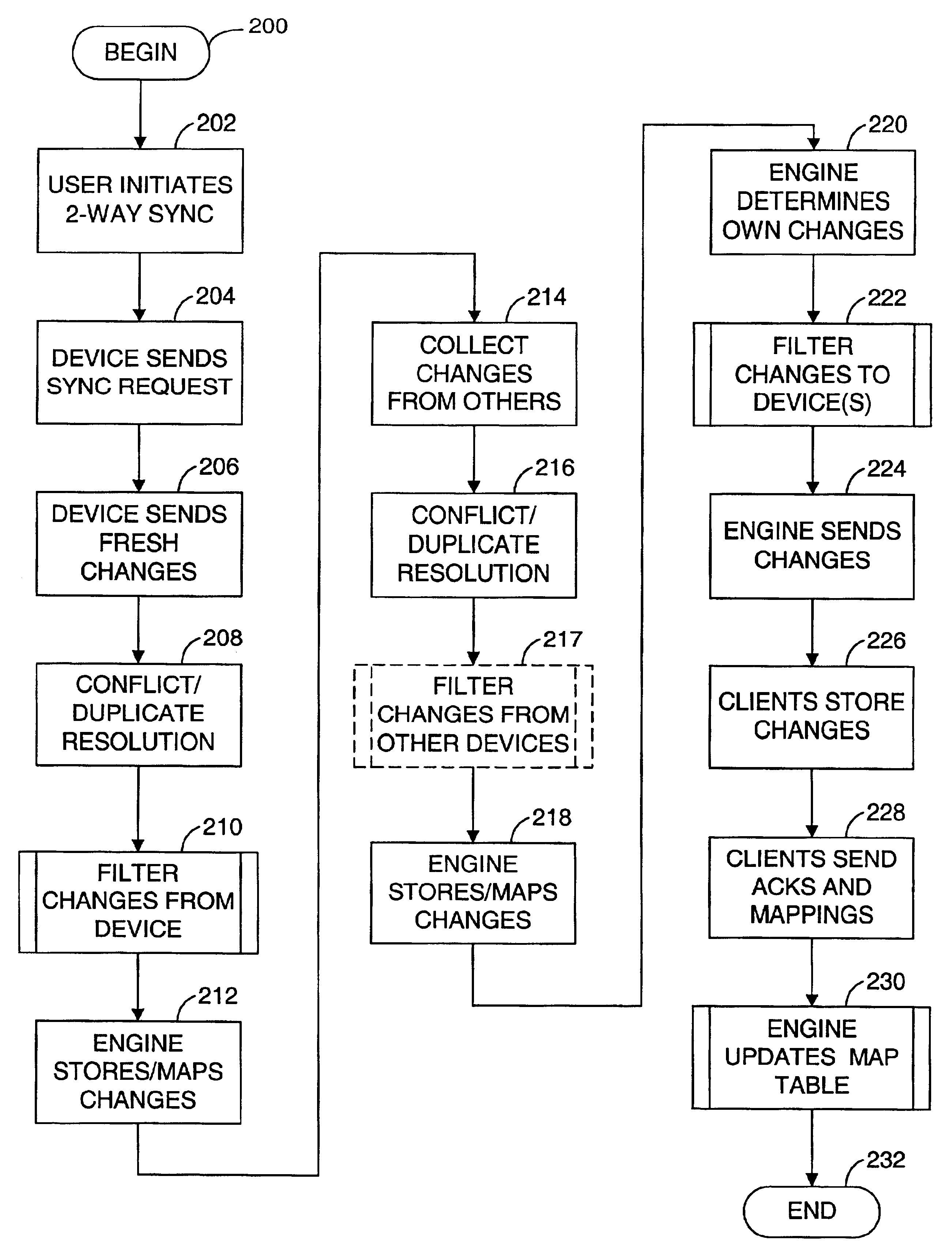
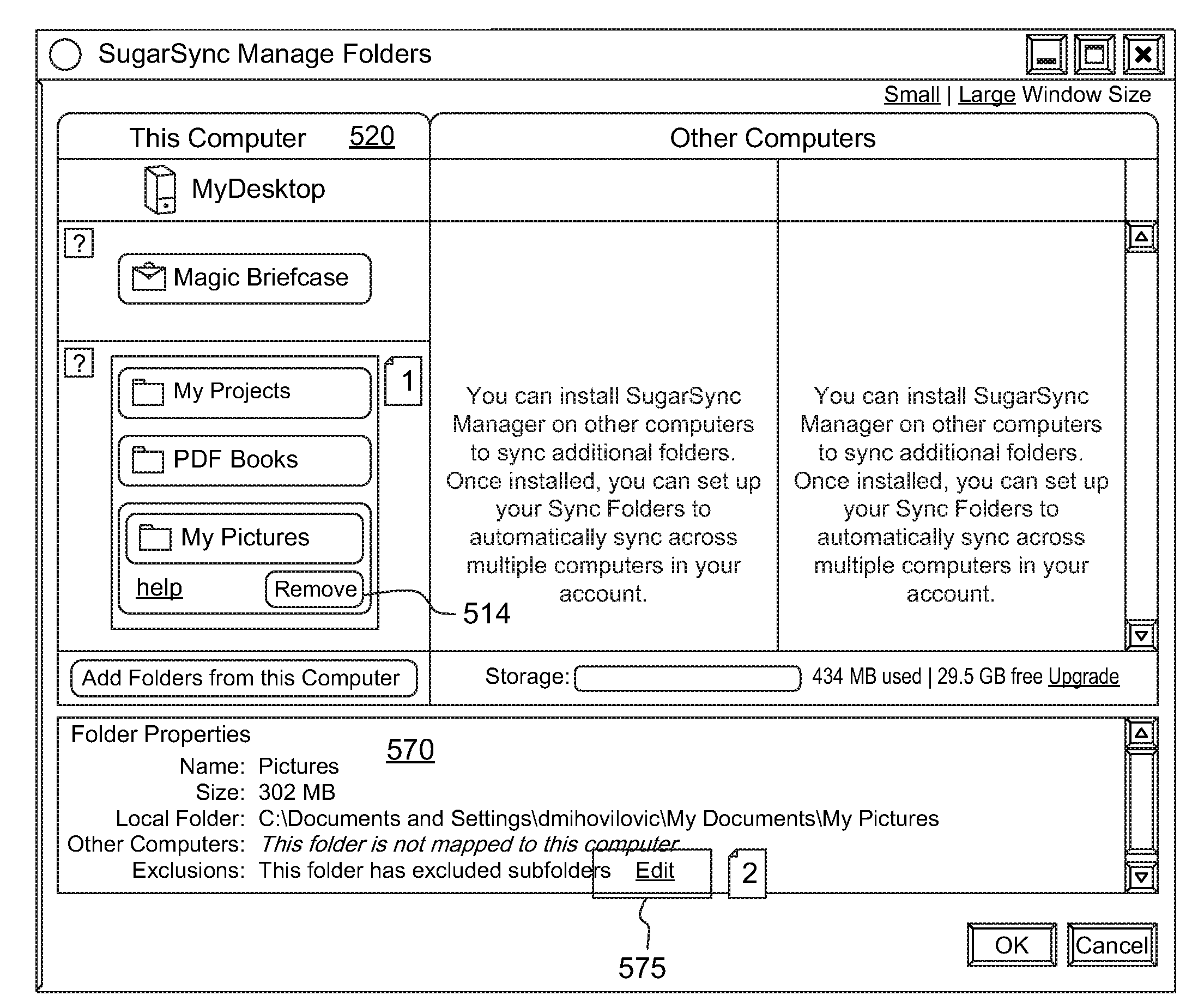
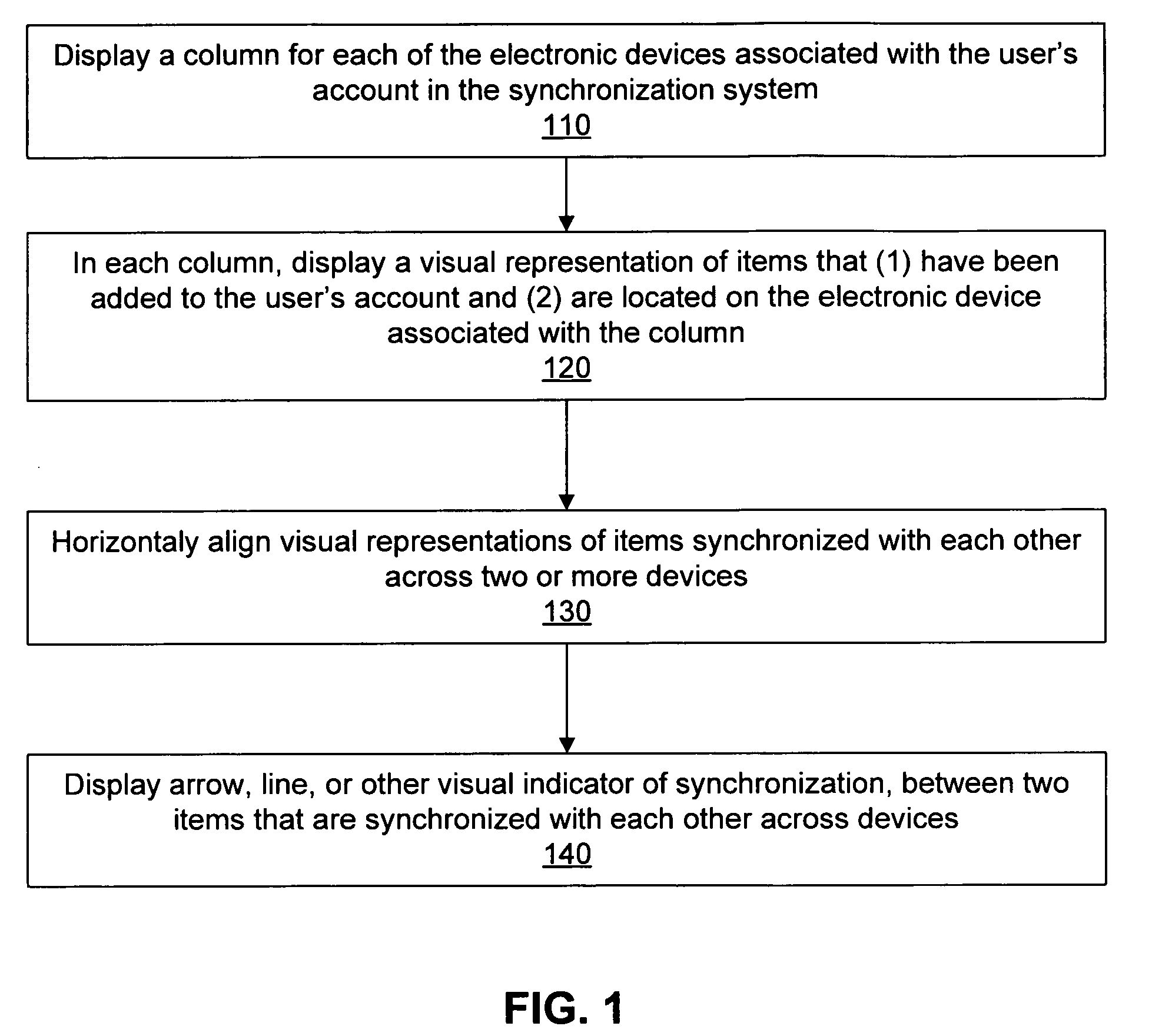
User interface for managing and viewing synchronization settings in a synchronization system
ActiveUS8650498B1Input/output to record carriersDigital data processing detailsHuman–computer interactionSynchronization system
In a synchronization system, the present invention provides an improved user interface through which a user can view and manage settings associated with the user's account in the synchronization system. In the preferred embodiment, a column is displayed for each electronic device associated with the user's account in the synchronization system. In each column is a visual representation of items (e.g., folders) that are (1) backed up, remotely accessible and / or synchronized in the synchronization system and (2) located on the electronic device associated with such column. For each item that is synchronized across multiple devices, all the visual representations of such item in the columns are aligned across a single row in the interface. In the preferred embodiment, there is an arrow, or other visual indicator, between the visual representations of such items to indicate that the items are synchronized.
Owner:DROPBOX
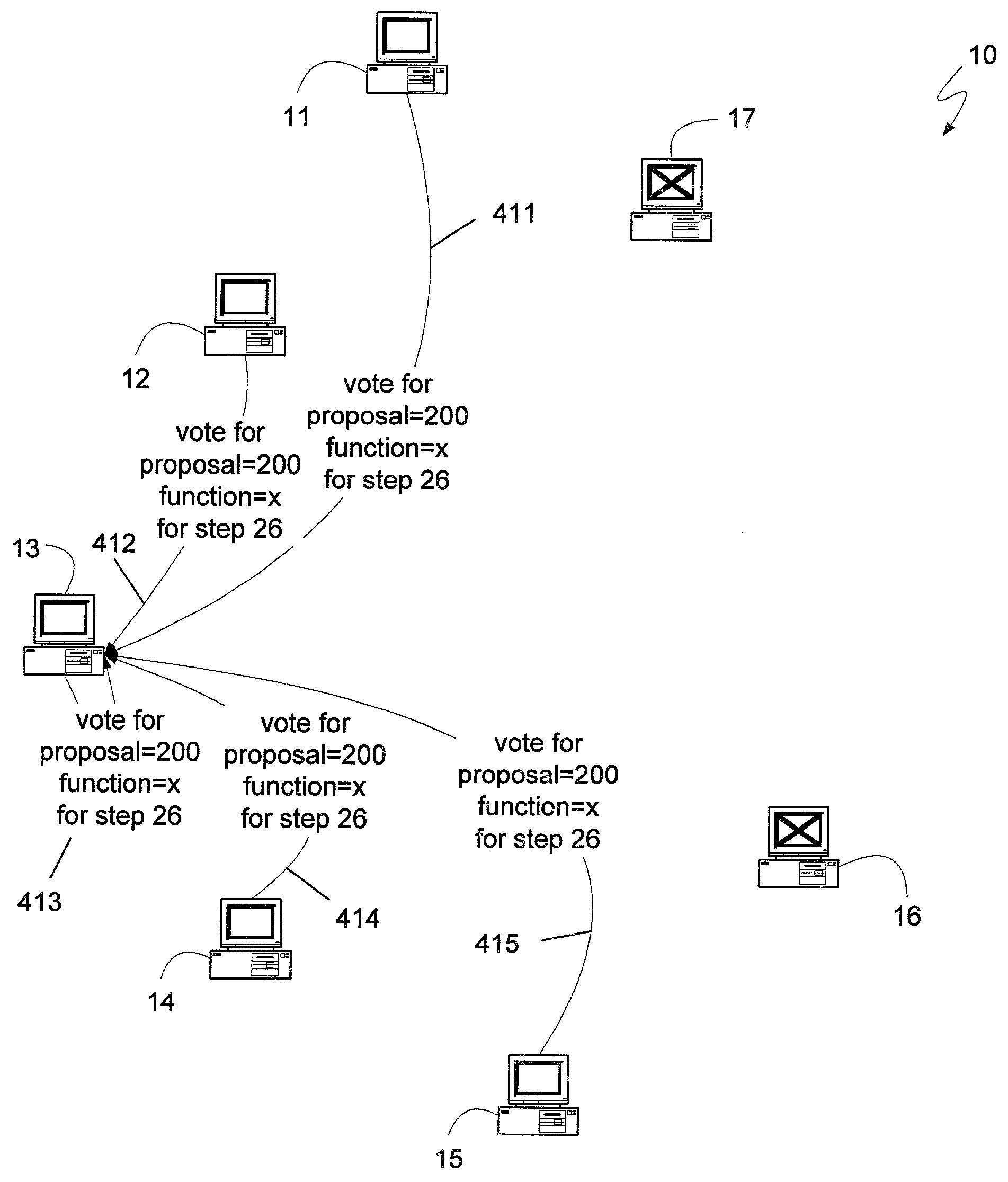
Fast transaction commit
InactiveUS7558883B1Few message delayMaintain consistencyError detection/correctionDatabase distribution/replicationClient-sideComputing systems
A distributed computing system, having a sufficient number of devices and requiring a sufficiently large number of devices to select any proposal, can maintain synchronization between its constituent devices and respond to client requests with as few as two message delays. A leader can synchronize the devices of the system and establish a safe proposal number for all current and future steps of the system. Devices can then receive client requests directly, treating the request as a proposal having the proposal number determined previously by the leader, and voting for the proposal. If the client receives an indication from a least a quorum of devices, where a quorum can be the minimum number of devices that can be operational at a given time, the client can know that the request was selected. If two or more clients attempt to request different functions at approximately the same time, the system may not select either request, in which case a leader can be requested to determine if any requests may have been selected, and to reestablish a safe proposal number. Systems with fewer devices can also implement the message-delay-reducing algorithm if they can also revert to the standard Paxos algorithm if an insufficient number of devices are operational. Such algorithms can be used to provide an efficient method for determining whether to commit or abort a client transaction.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
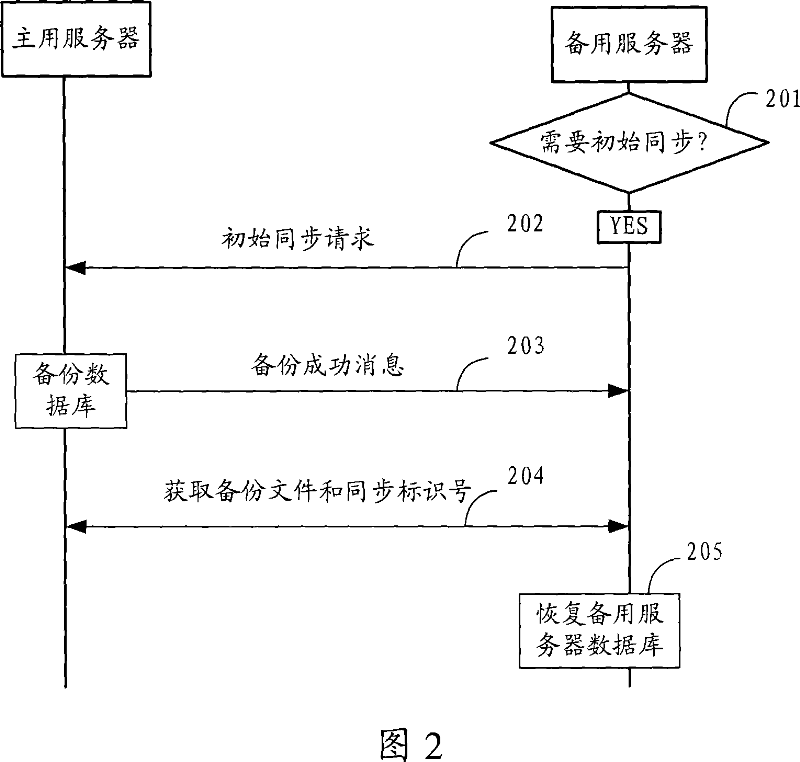
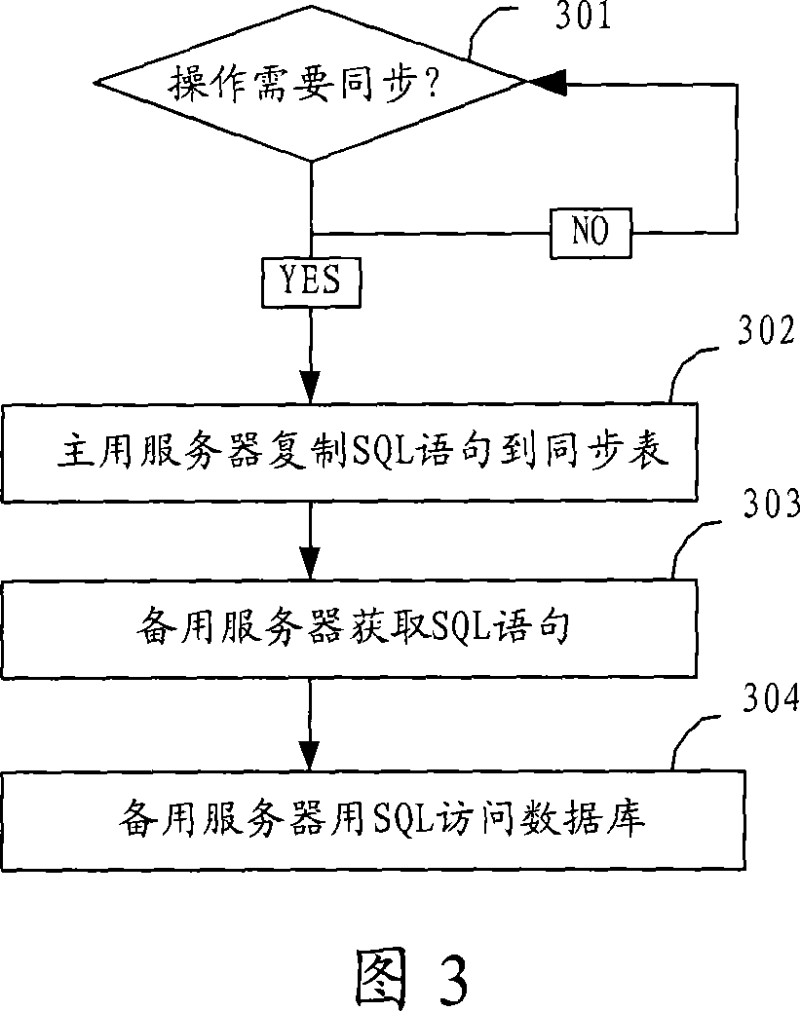
Method and system for synchronizing data base
ActiveCN101038591AEasy to modifyImprove synchronization efficiencyTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsData synchronizationOperational system
The invention discloses a database synchronization method, in which a synchronous table comprising a synchronous identification numbers and SQL statements is adopted to realize the data synchronization, a database synchronization system is disclosed also, which comprises a primary server having a backup unit, a synchronous table unit and a backup server having a request unit, an acquisition unit and a synchronization unit. The method and system realizes the synchronization of the database and simplifies the modification of the server configuration by use of a synchronous table, thereby the database can be implemented without the restriction of the operation system and the database system which results in an improved efficiency.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
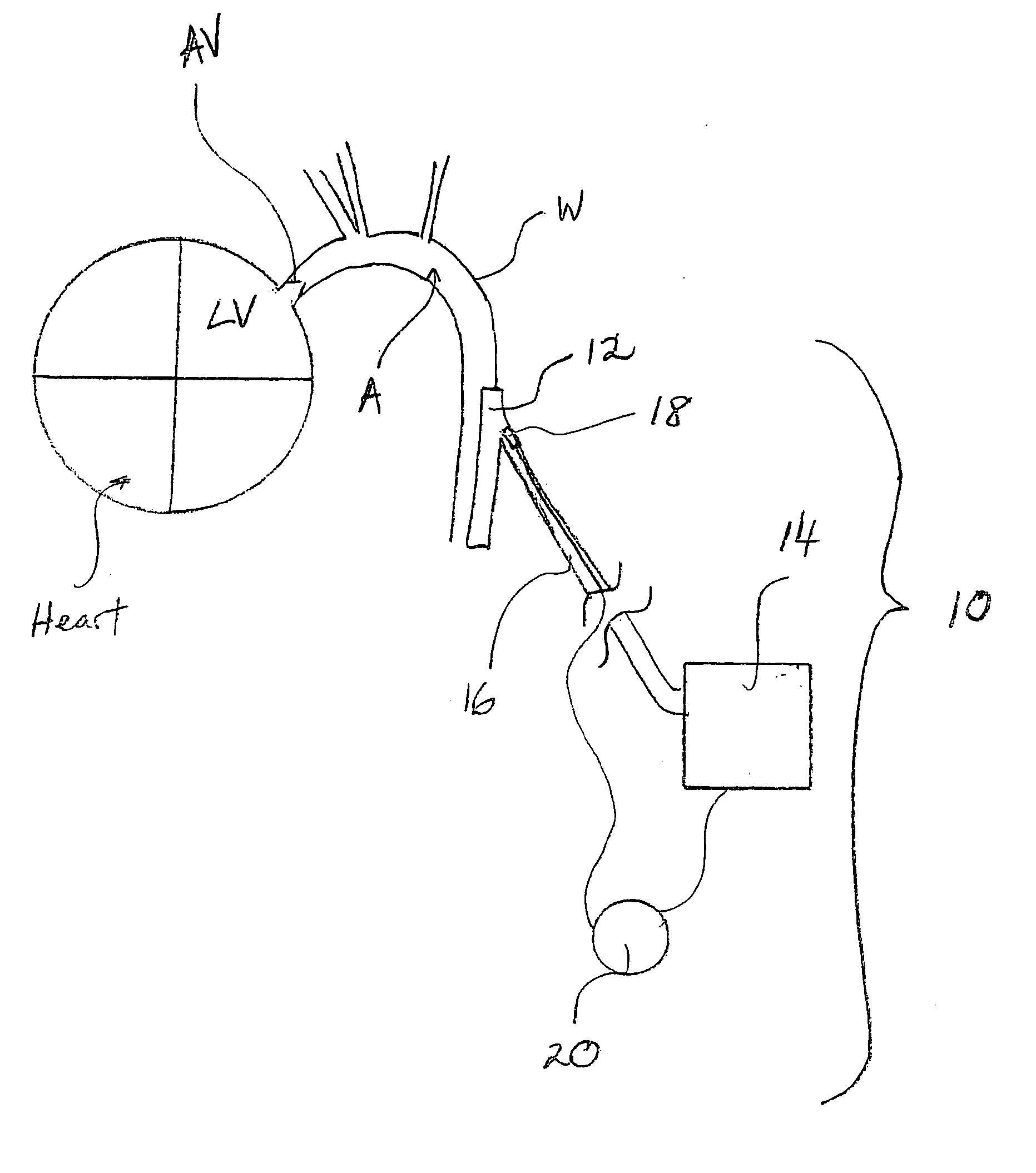
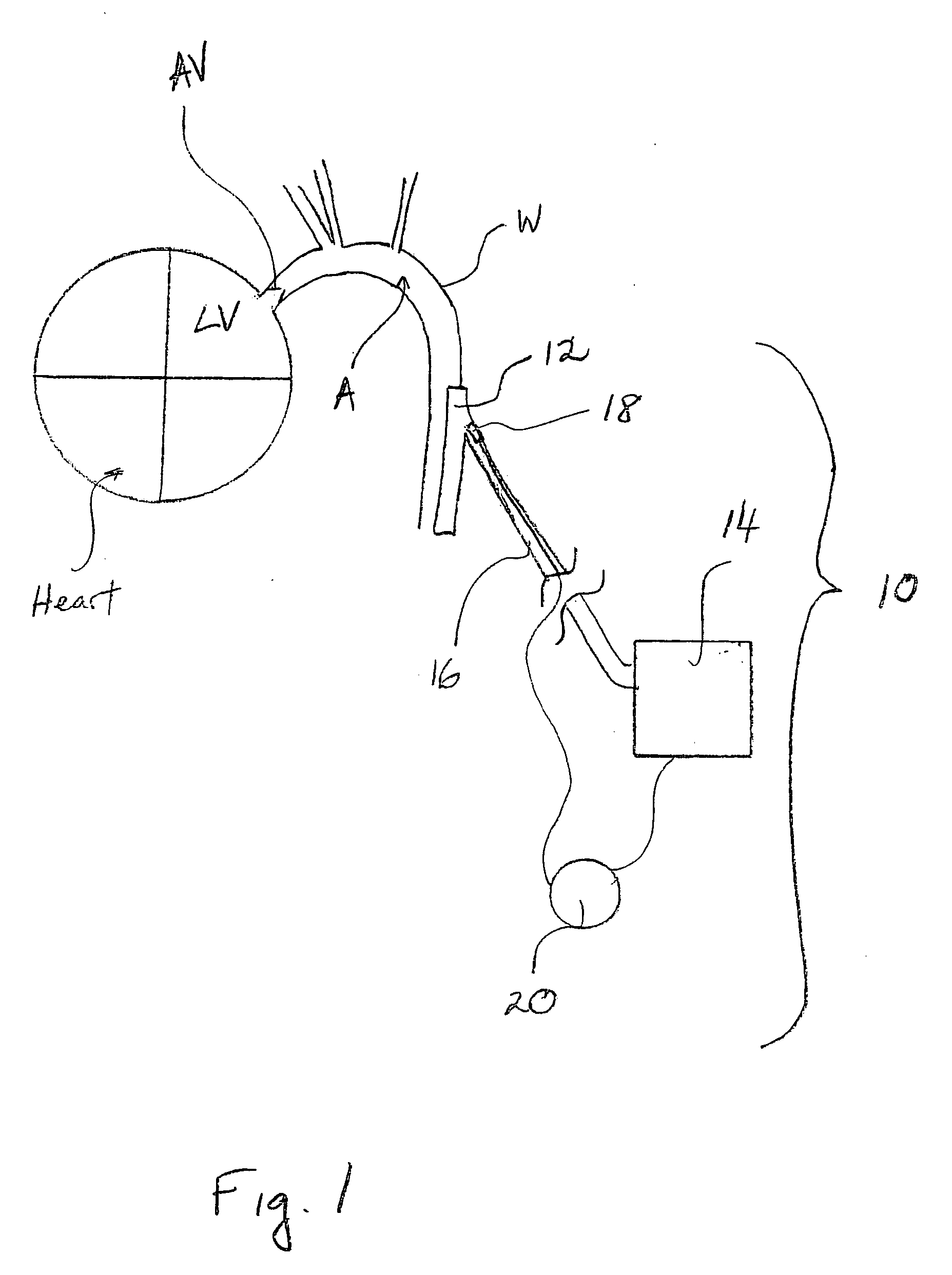
Synchronization system between aortic valve and cardiac assist device
ActiveUS20060030747A1Achieve synchronizationControl devicesMedical devicesAccelerometerThoracic cavity
A cardiac assist device synchronization system includes a cardiac assist device and an acoustic or accelerometer sensor that provides a signal input to the cardiac assist device indicative of aortic valve closure. The cardiac assist device is coupled to a mammalian aorta and includes an inflatable chamber and a fluid pump. A fluid conduit is in communication between the chamber and the pump to provide for selective inflation of the chamber. A pump controller triggers the pump in counter-pulsation to a mammalian heart upstream from the aorta. A process for synchronizing a cardiac assist device in counter-pulsation with a left ventricle includes locating an acoustic or accelerometer sensor within a thoracic cavity of a mammal having the assist device coupled to the aorta of the mammal. Through the measurement of an acoustic or acceleration property of an aortic valve of the mammal, and the transmission of aortic valve closure measurement through a controller for the cardiac assist device, counter-pulsatile synchronization for the cardiac assist device is achieved.
Owner:KANTROWITZ ALLEN B +1
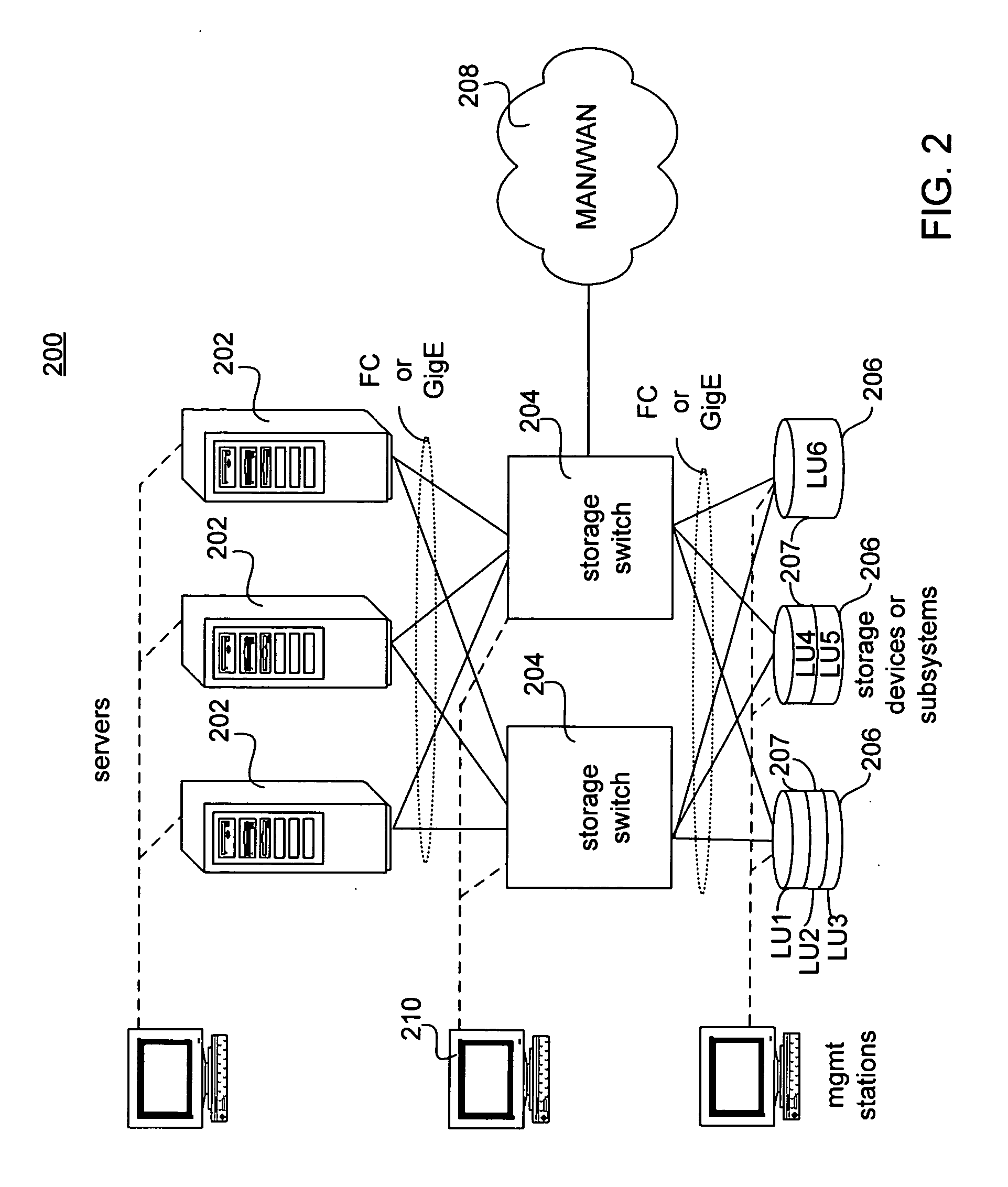
Storage switch task processing synchronization
ActiveUS20060036769A1Long timeoutInput/output to record carriersMultiple digital computer combinationsSynchronization systemOperating system
Systems and methods in accordance with various embodiments relate to a storage switch including task processing synchronization. In embodiments of the present invention, the packet processing units may generate and store Task Index and Generation Count information that prevents the processing of expired commands or responses. Additionally or alternatively, embodiments of the present invention may further employ timeout sequences to prevent previous instances of a stale task resource from disrupting the current use of the task resource.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
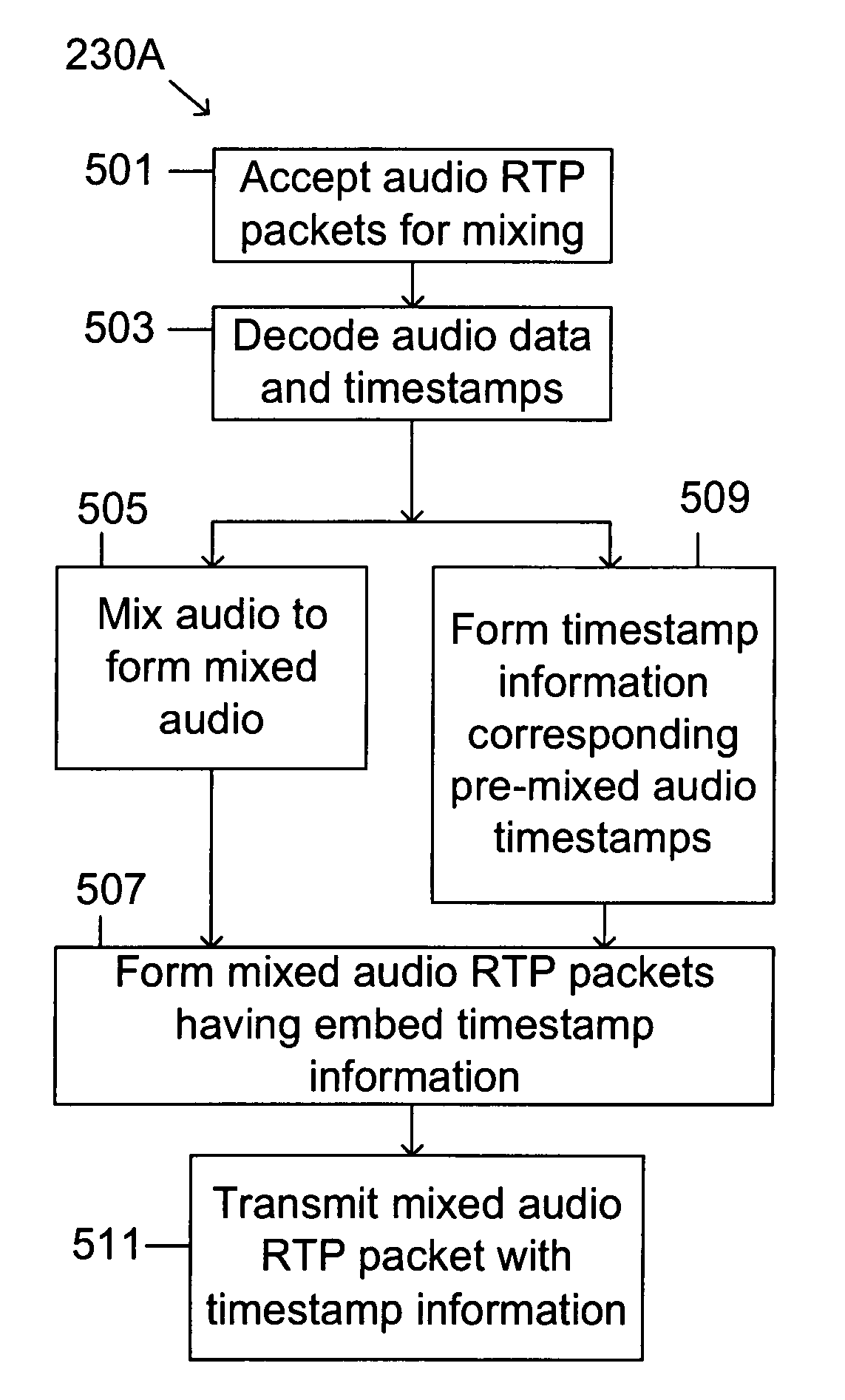
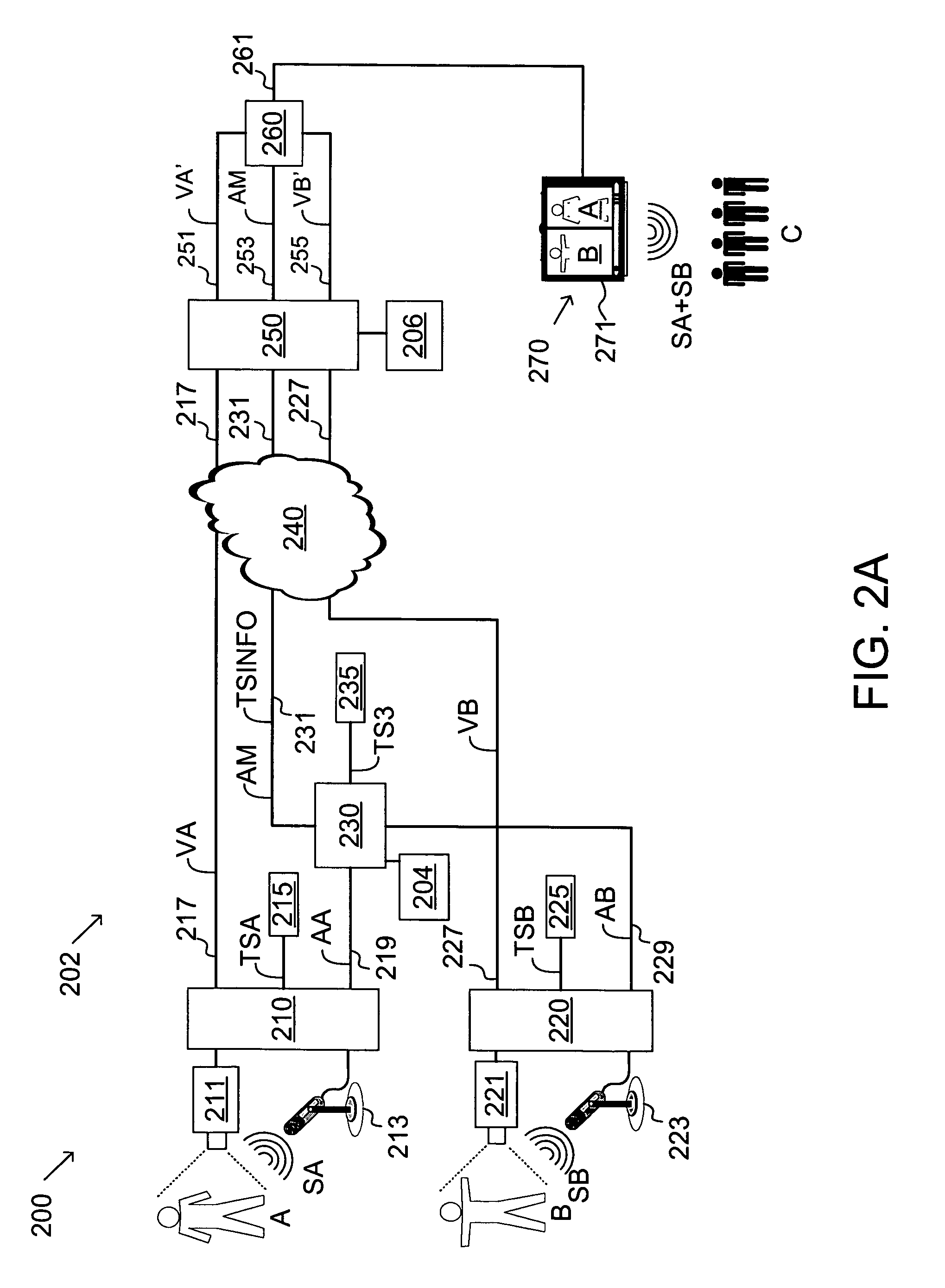
Audio-to-video synchronization system and method for packet-based network video conferencing
InactiveUS7664057B1Overcome disadvantagesReduce jitterMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationData synchronizationTimestamp
Synchronizing audio and video streams in packet-based networks requires synchronization of packet timestamps. The present invention provides such synchronization without resort to a network time standard. In one embodiment of the present invention, pairs of timestamp synchronized signals, such as audio and video signals, not having a common timestamp clock are mixed. One of the signals, for example, the audio signals, is mixed first while preserving the original audio timestamps. The preserved timestamp information is then used to synchronize the timestamps of the unmixed signals, in this example the video signals, to provide synchronization of all signals. In another embodiment, the present invention uses packets containing calibration of timestamps to reduce jitter. The present invention also includes specifications for a packet for transmitting timestamp information.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Distributed network synchronization system
InactiveUS6278718B1Effective absorptionOptimization rangeTime-division multiplexLoop networksAsynchronous communicationTelecommunications network
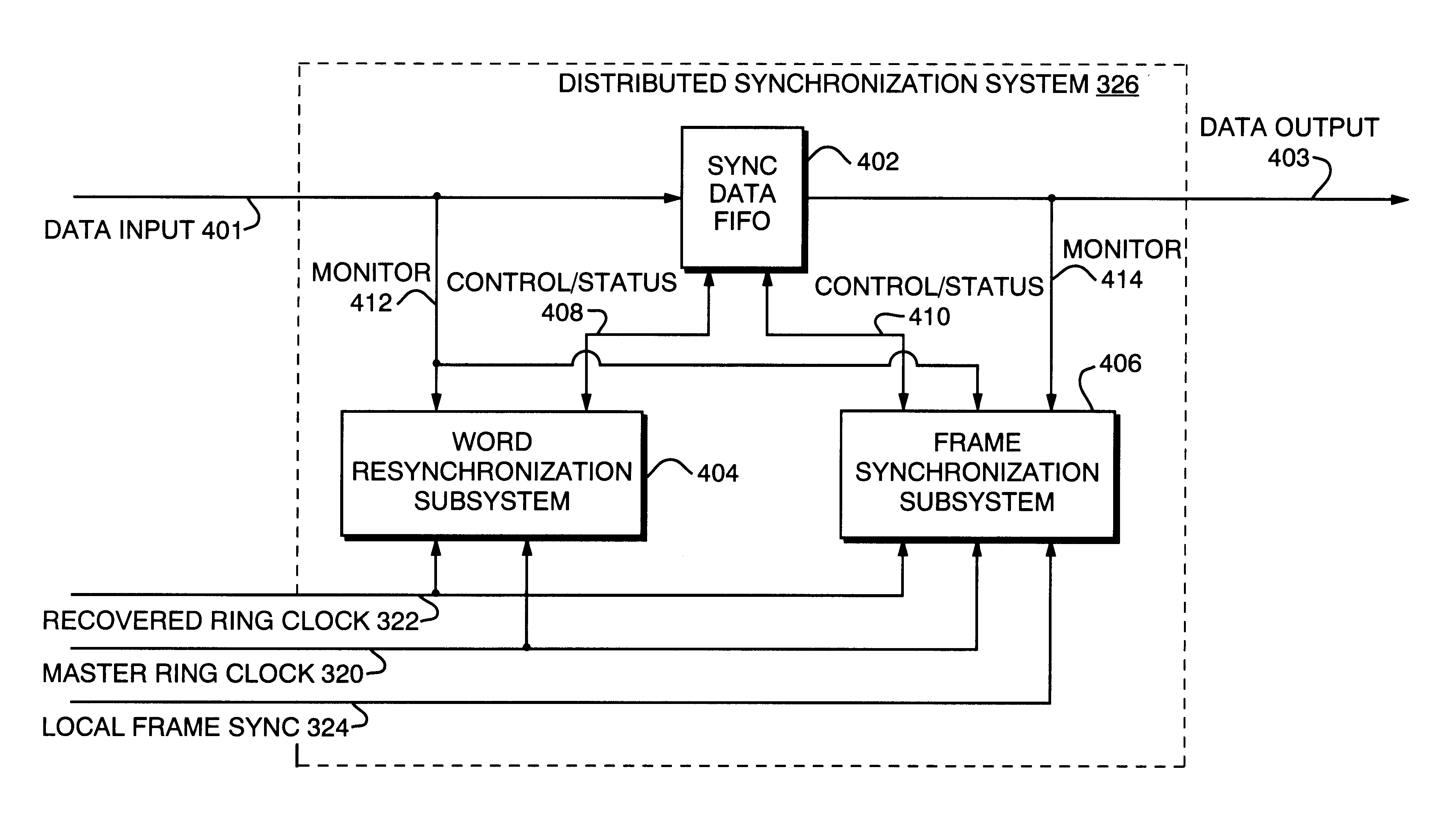
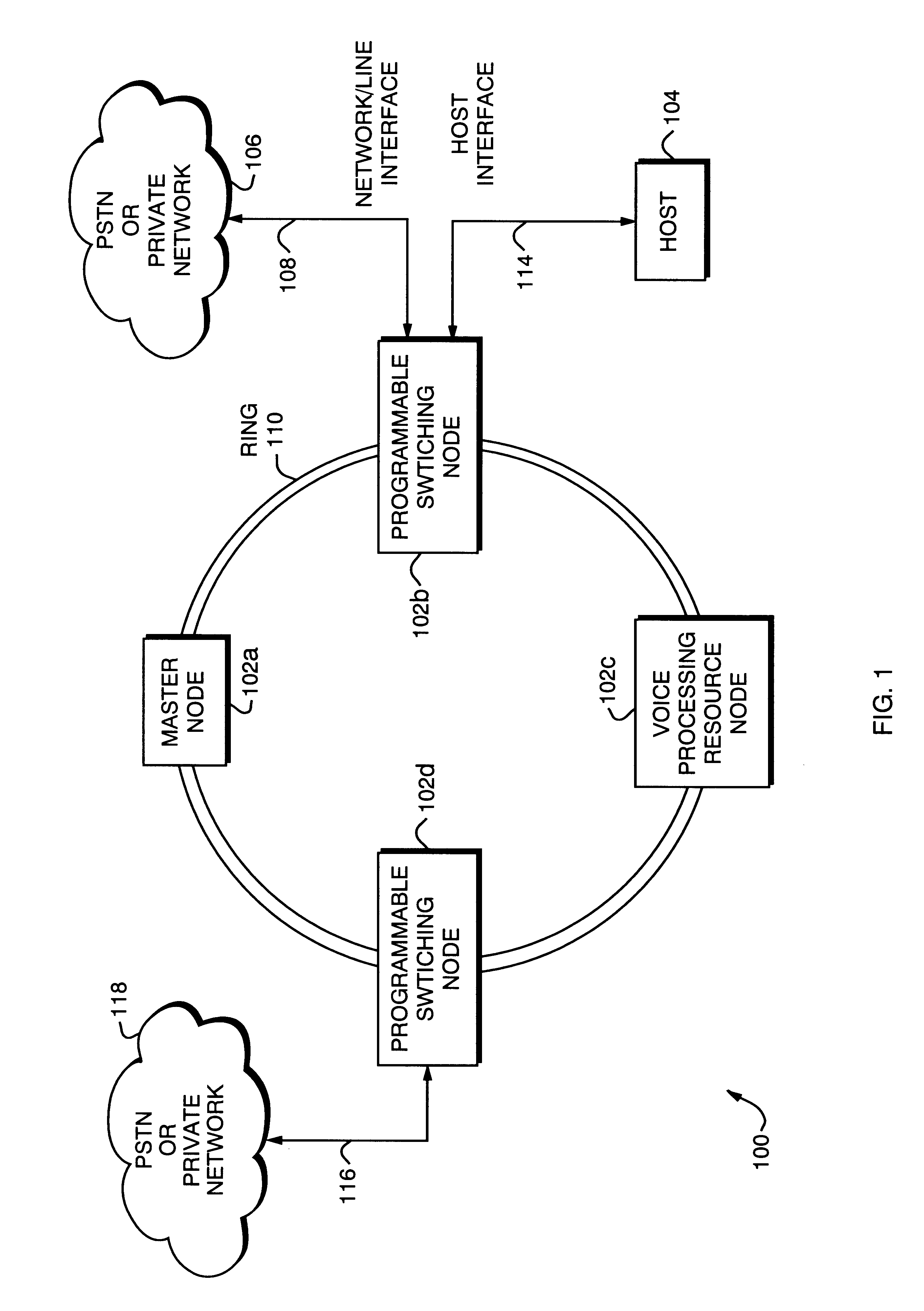
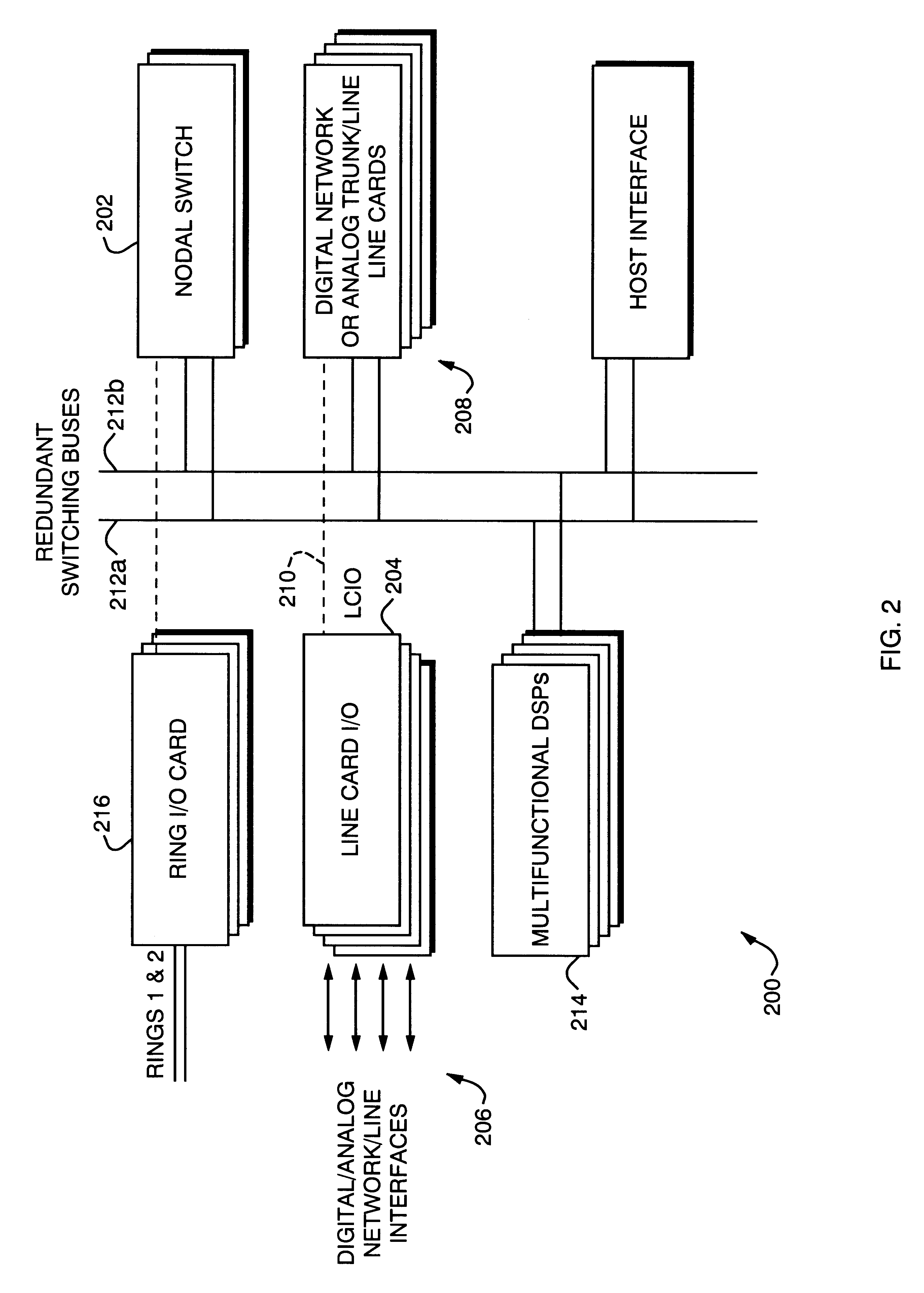
A distributed synchronization system for use in each node of a distributed asynchronous telecommunications network system that continually monitors and controls the flow of data through an implementing node to prevent dataflow errors due to phase and frequency differences in source and destination nodal clocks, and to control inter-nodal network latency so as to support the transmission of synchronous data. A synchronization data FIFO buffers predetermined fields or portions of fields of a unique frame packet received from a source node before retransmission to a destination node on the network. The frame packet includes a frame synchronization field indicating the beginning of a new frame packet; a payload field containing valid data; and a dead zone field providing bandwidth during which the present invention performs synchronization functions. A frame synchronization subsystem, implemented in a designated master node, guarantees that a frame is released at the beginning of an independently-determined frame regardless of network latency. A word resynchronization subsystem manages the flow of data through the data FIFO of each non-master node, receiving and storing data at the source node's clock rate and transmitting the data according to its own clock, thereby guaranteeing the efficient receipt and transmission of data between asynchronously-communicating nodes.
Owner:EXCEL SWITCHING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com