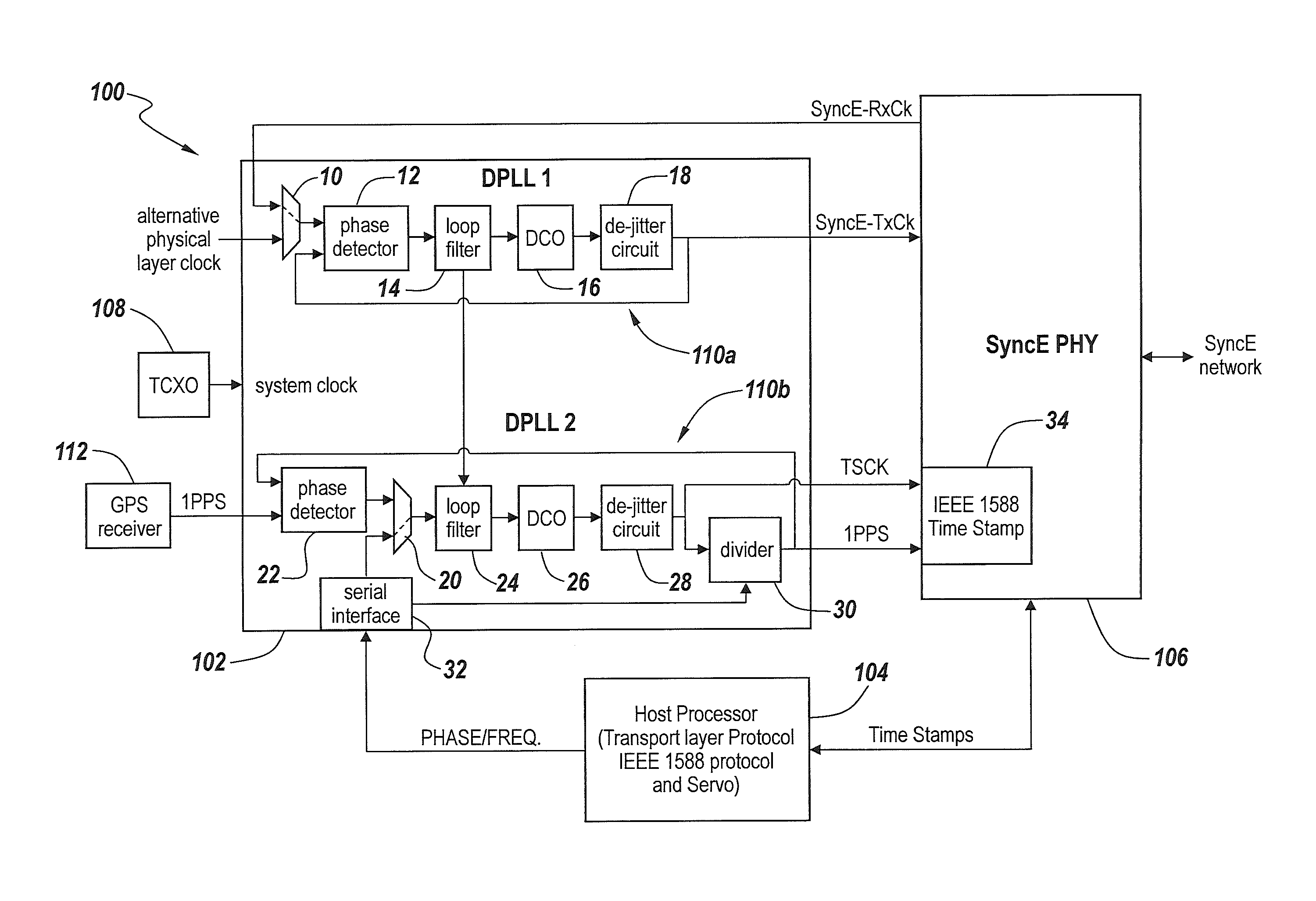
Patents
Literature
121 results about "Synchronous Ethernet" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
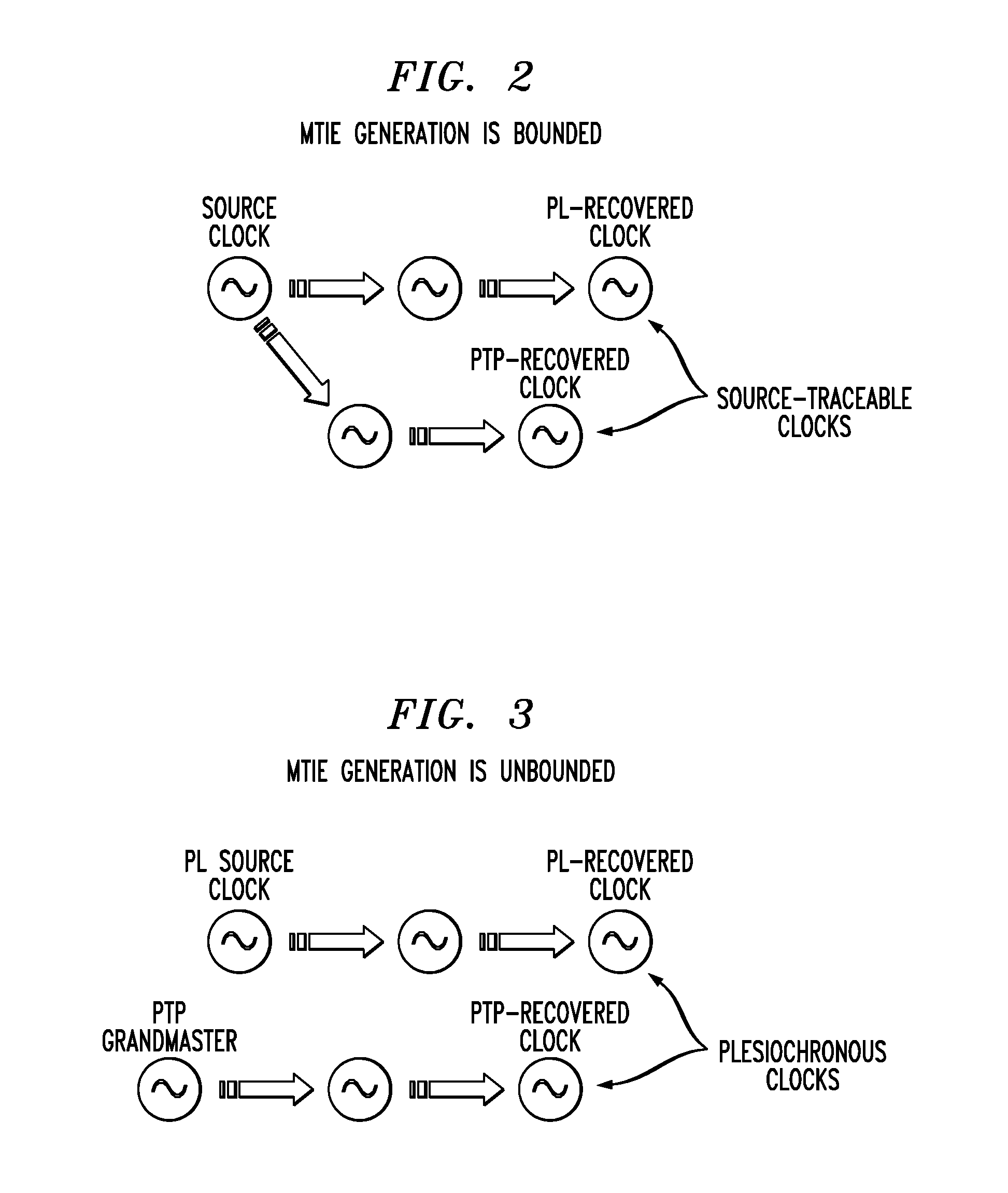
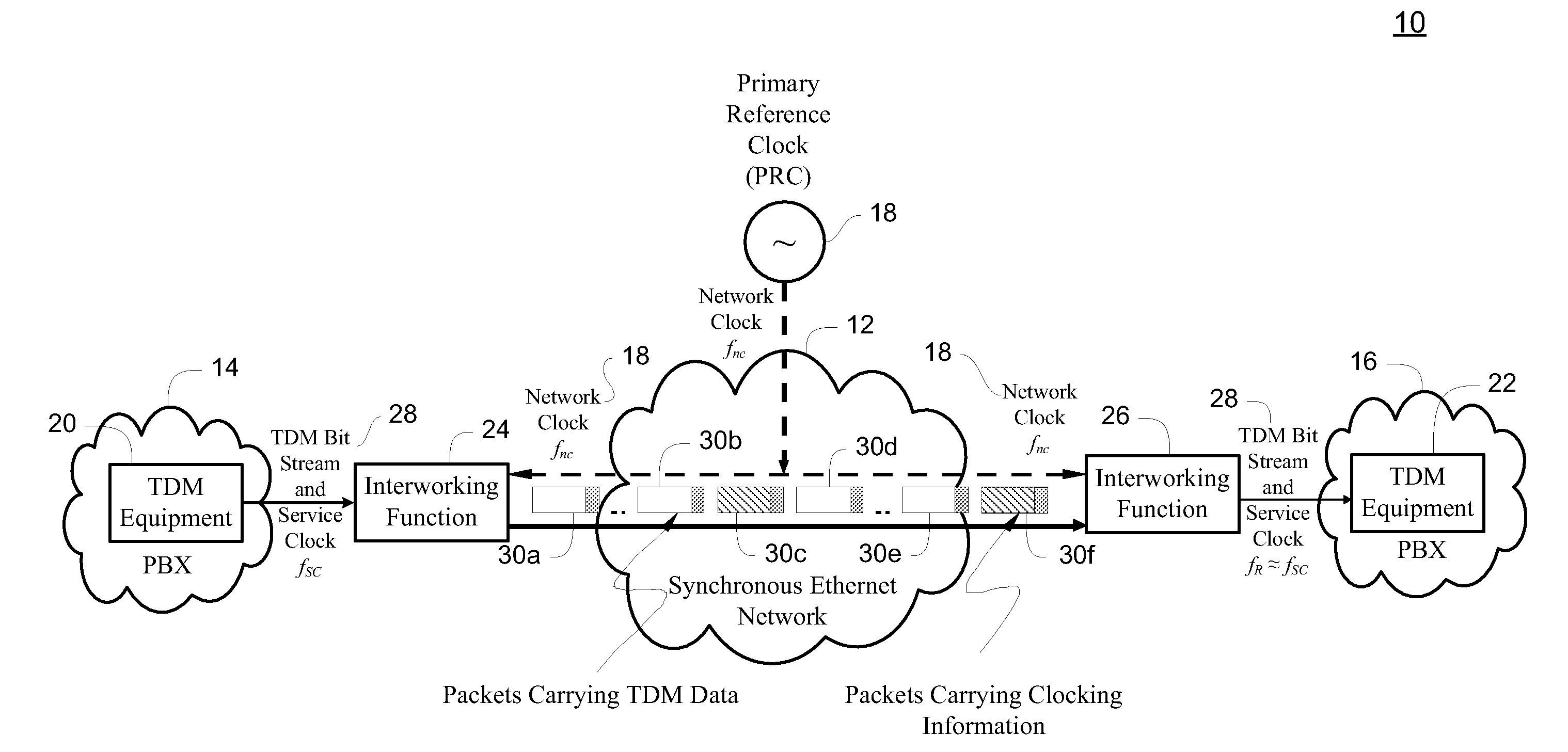
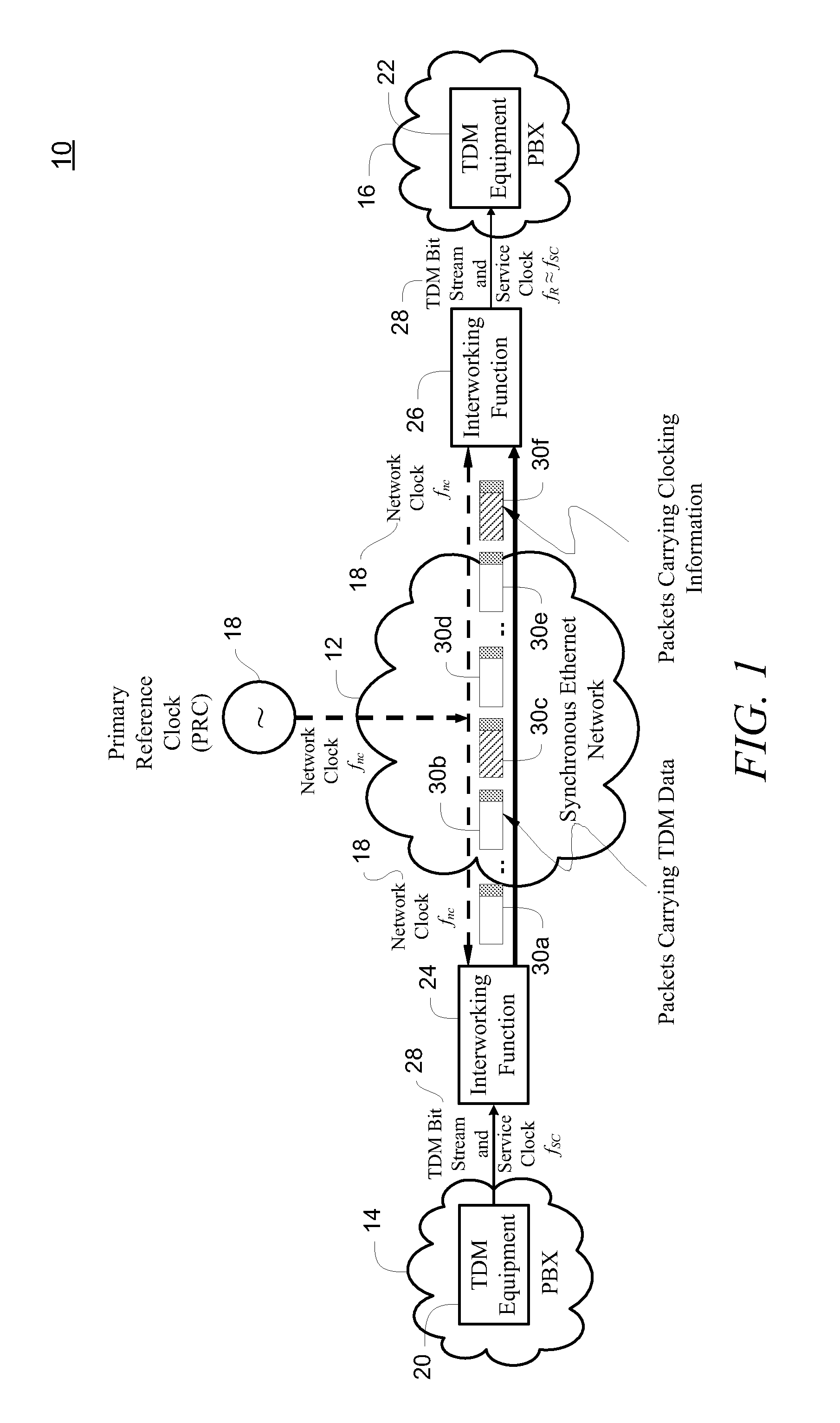
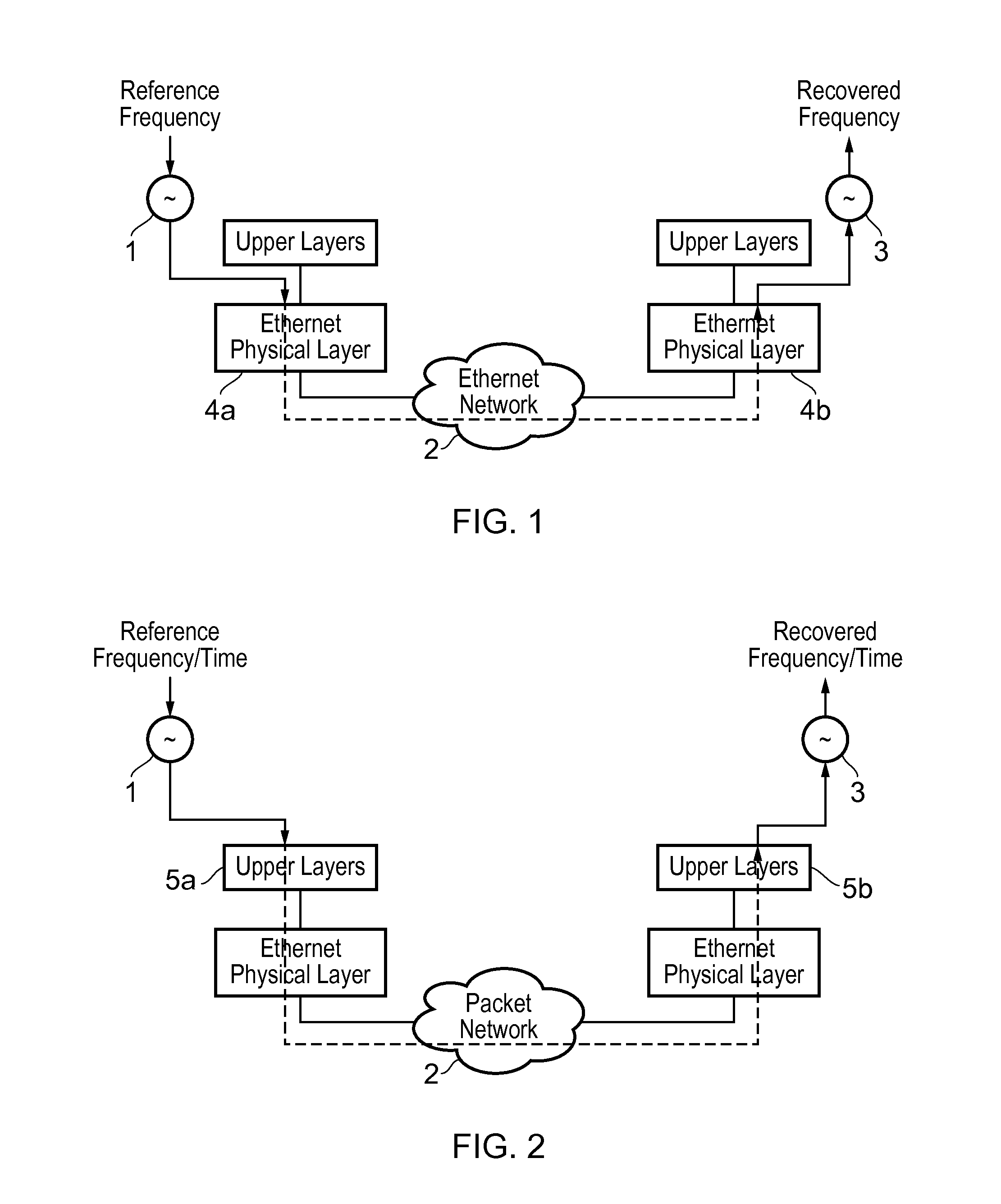
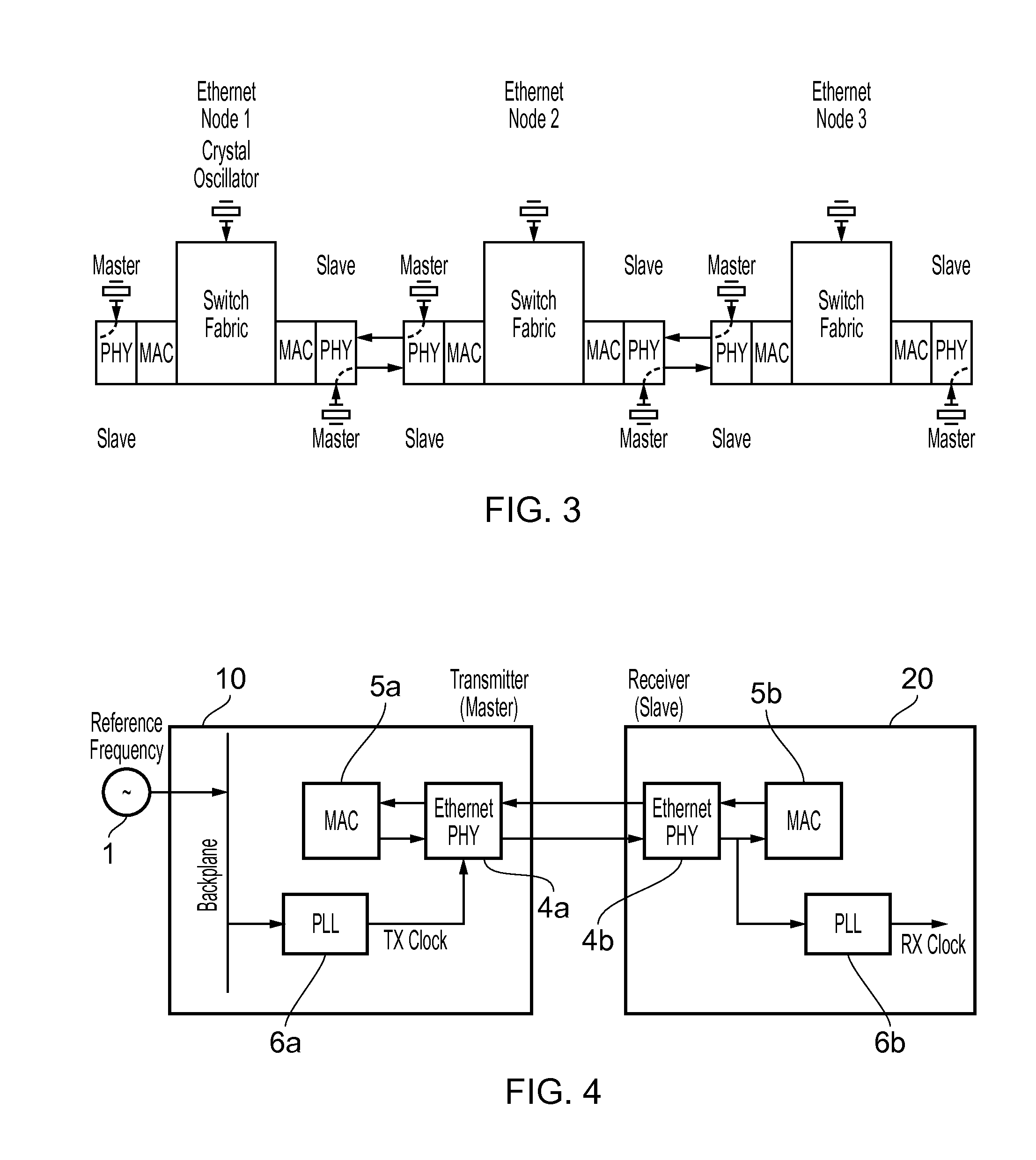
Synchronous Ethernet, also referred as SyncE, is an ITU-T standard for computer networking that facilitates the transference of clock signals over the Ethernet physical layer. This signal can then be made traceable to an external clock.
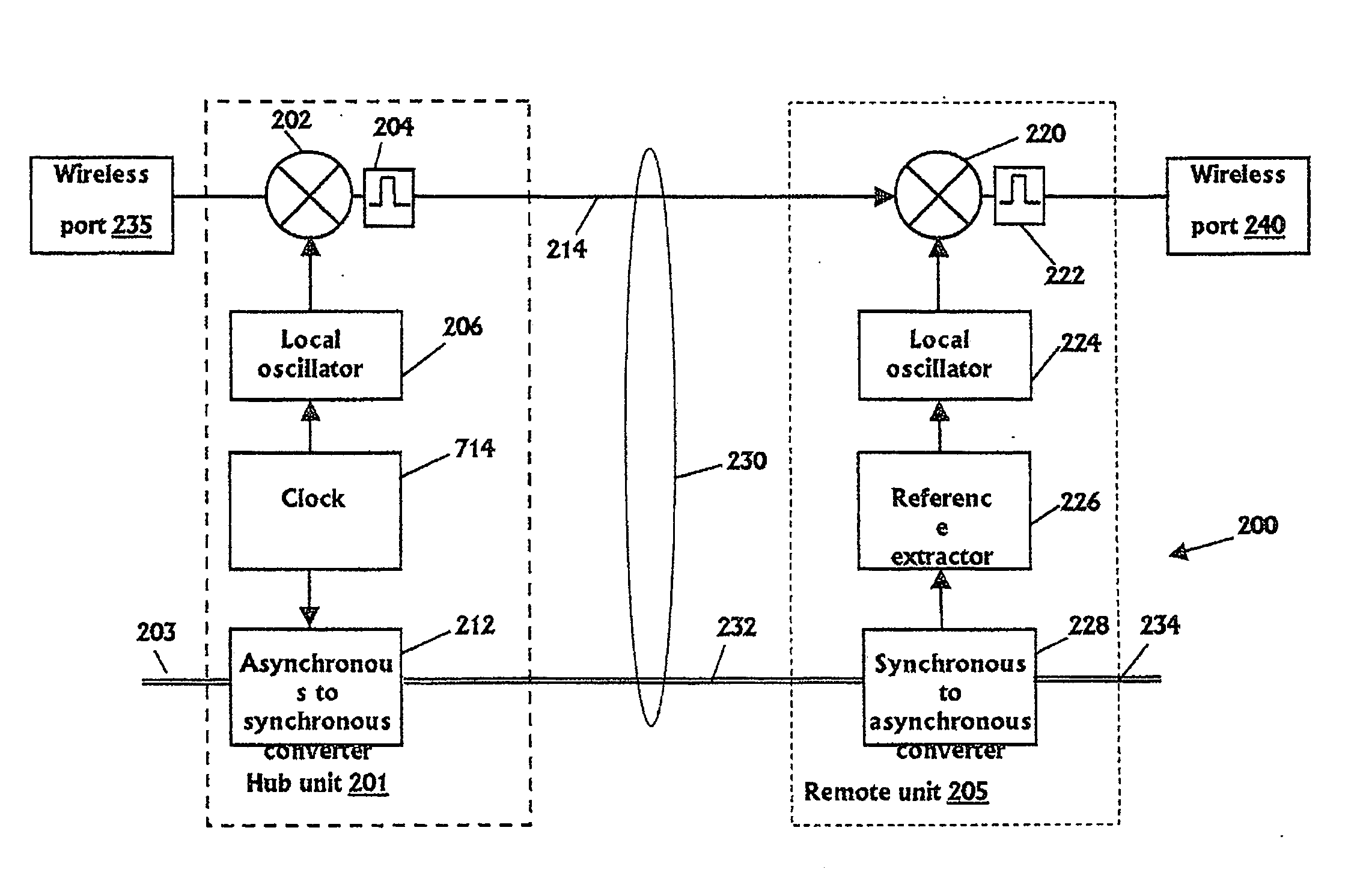
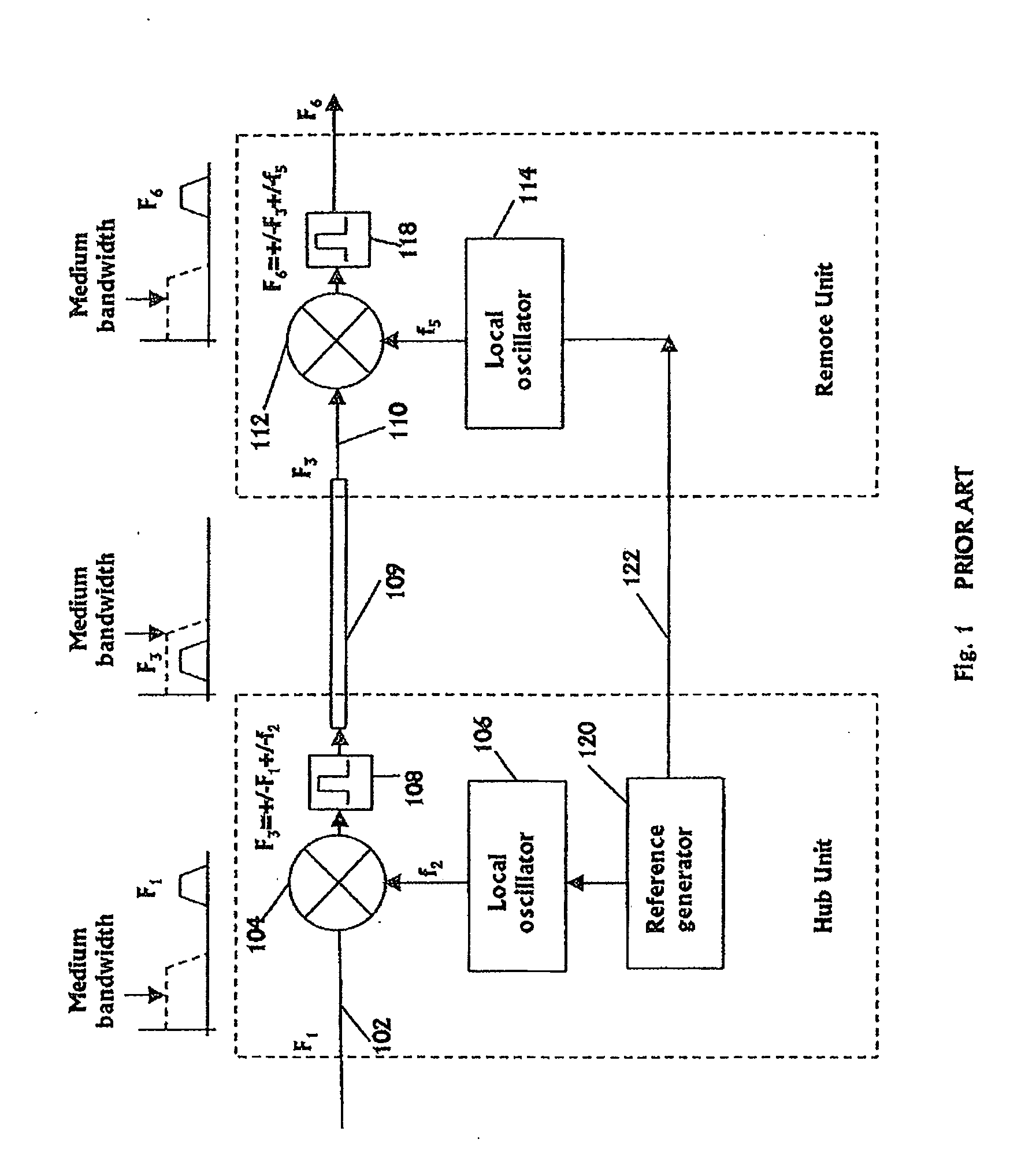
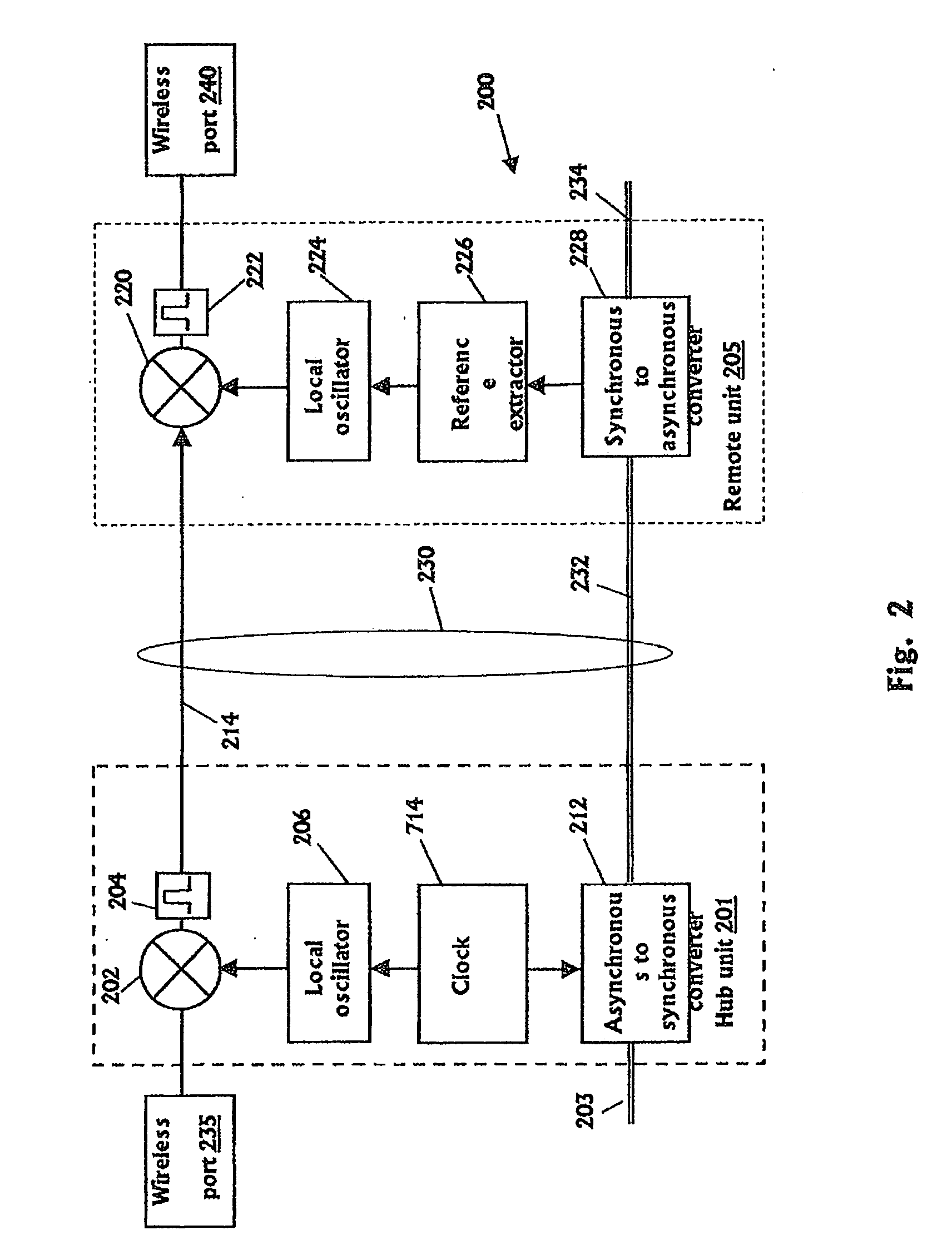
Communication system using cables carrying ethernet signals
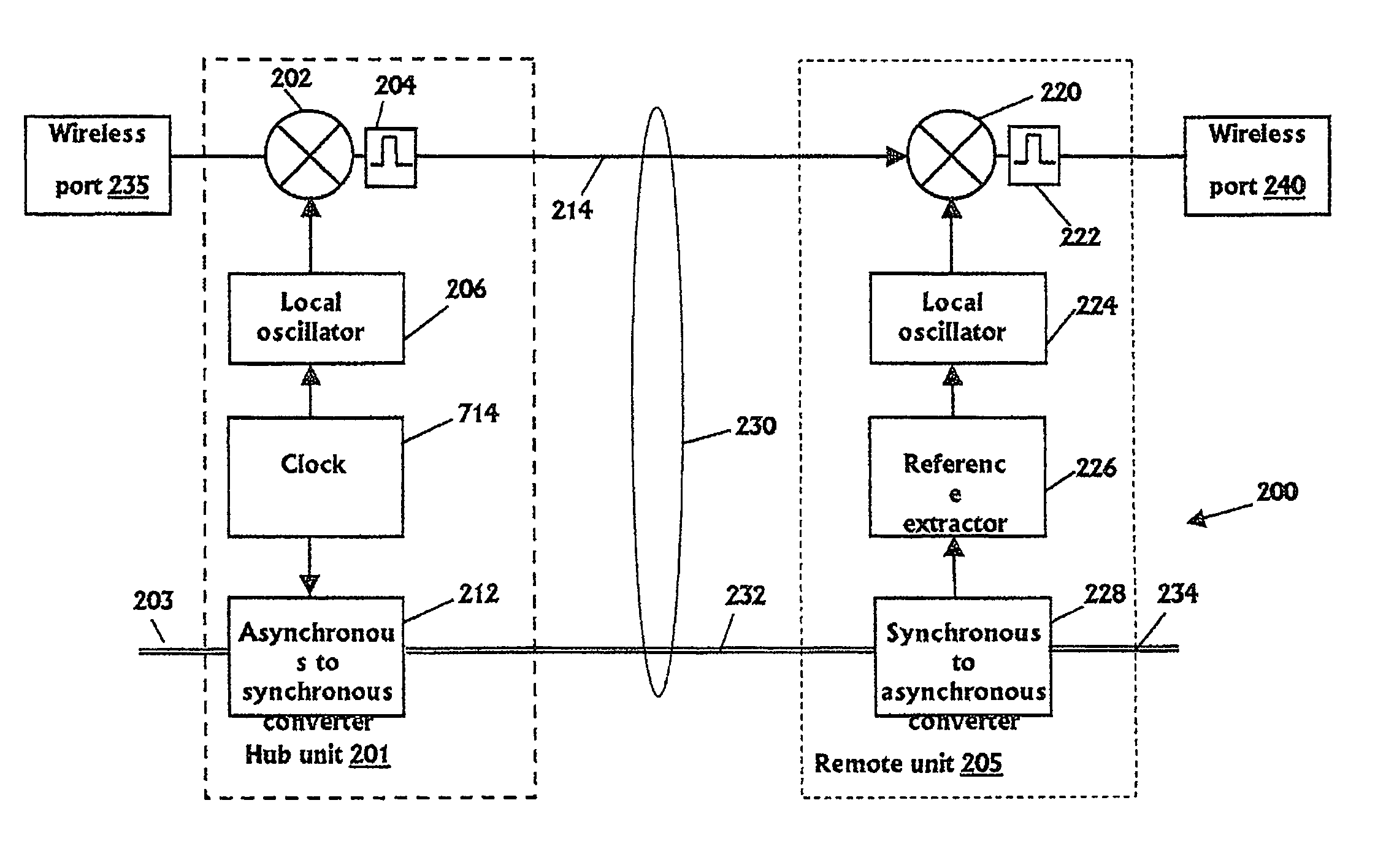
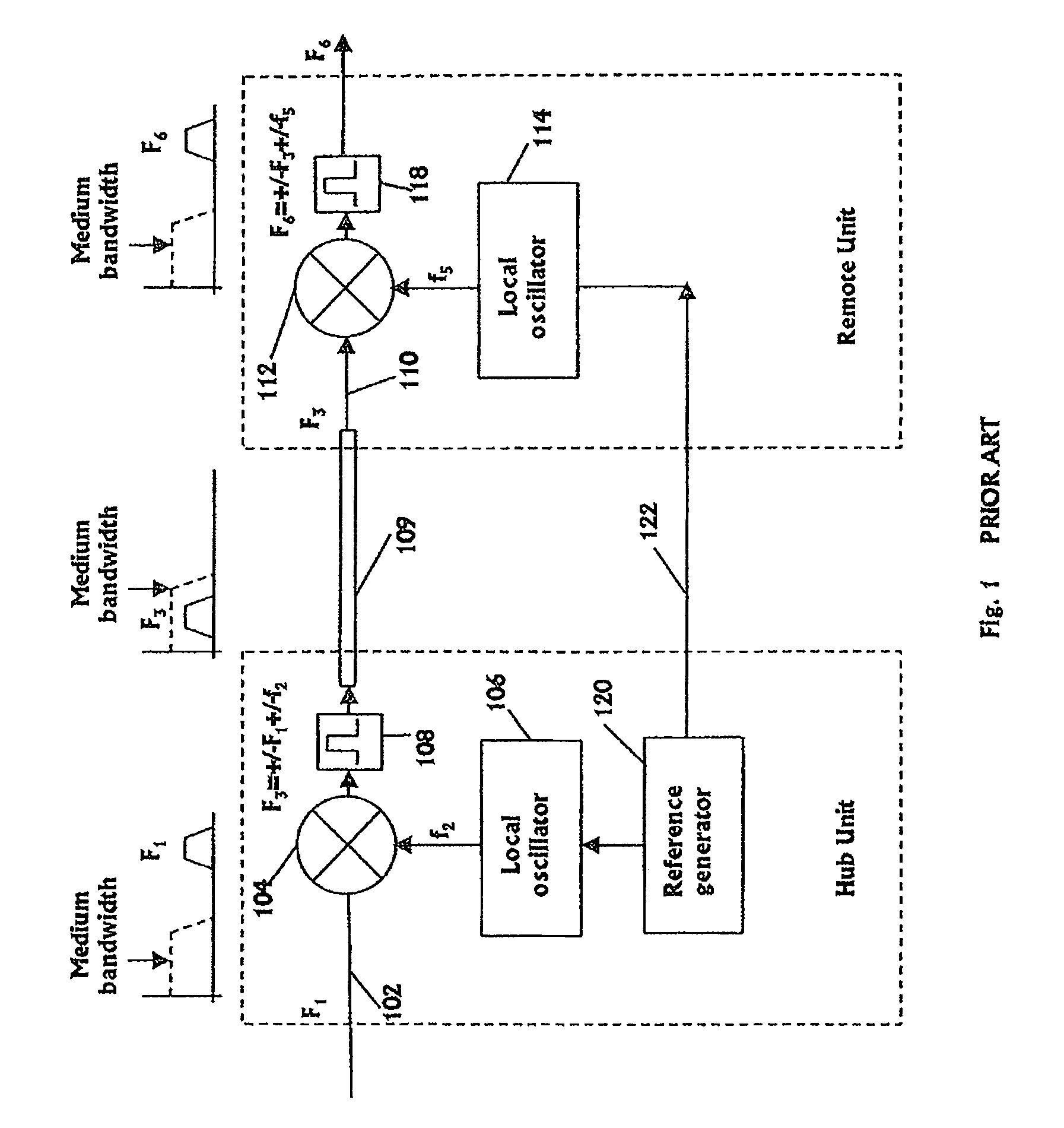
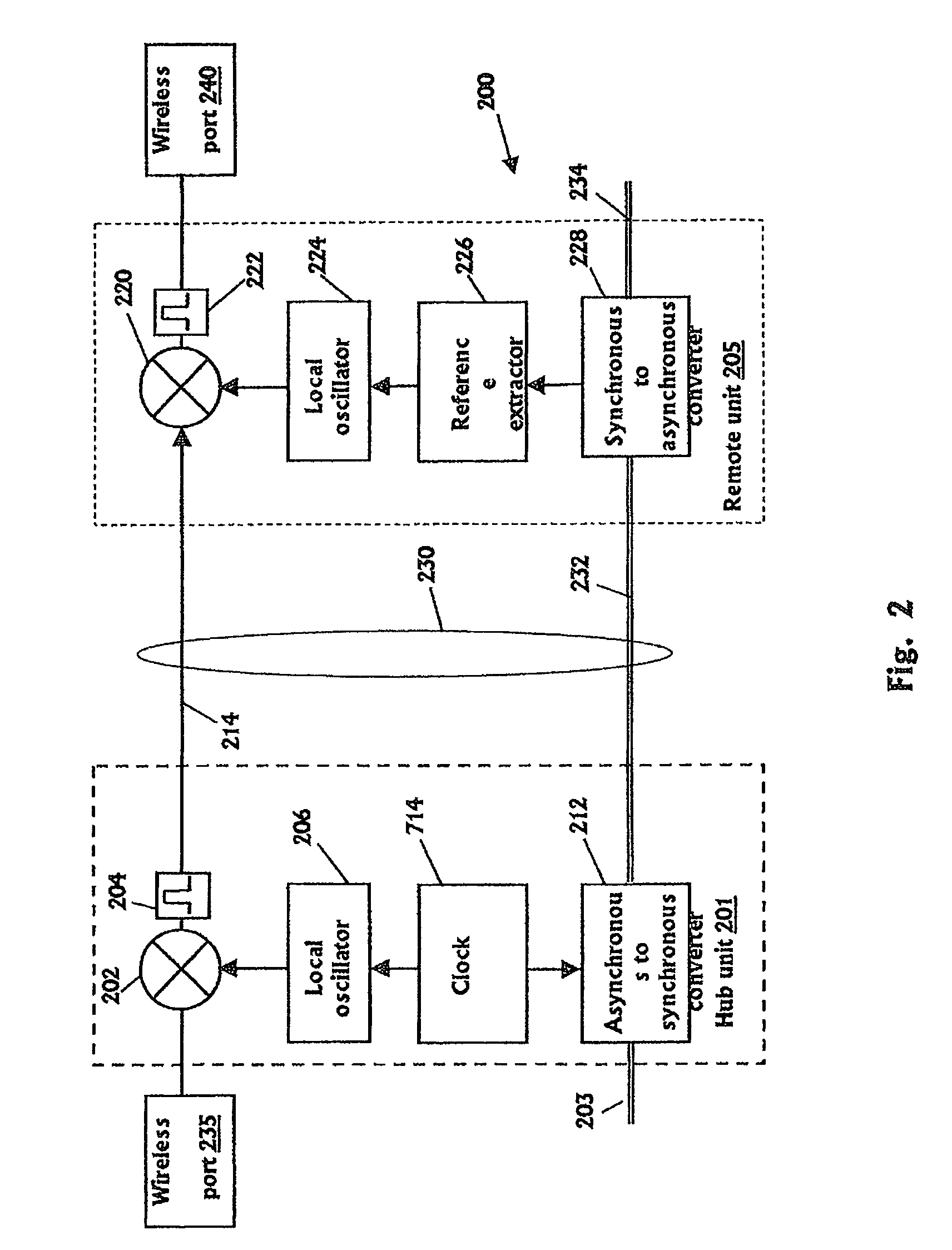
ActiveUS8897215B2Wireless commuication servicesData switching networksCommunications systemLocal oscillator
It is provided a method for transmitting a wireless signal on Ethernet wiring The wireless signal is received in a hub unit for delivery to a remote unit In the hub unit the wireless signal is down converted to a down-converted frequency band for propagation on the Ethernet wiring A reference signal associated with a local oscillator used for the down conversion is embedded on a synchronous Ethernet stream that may include Ethernet data received at hub unit The synchronous Ethernet stream and the down converted wireless signal are submitted through the Ethernet wiring to the remote unit. The synchronous Ethernet stream may include data for management of electronic circuits installed in the remote unit, as well as a synchronization signal used thereof A converted replica of the first signal may be included in digital form in frames of the synchronous Ethernet stream.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
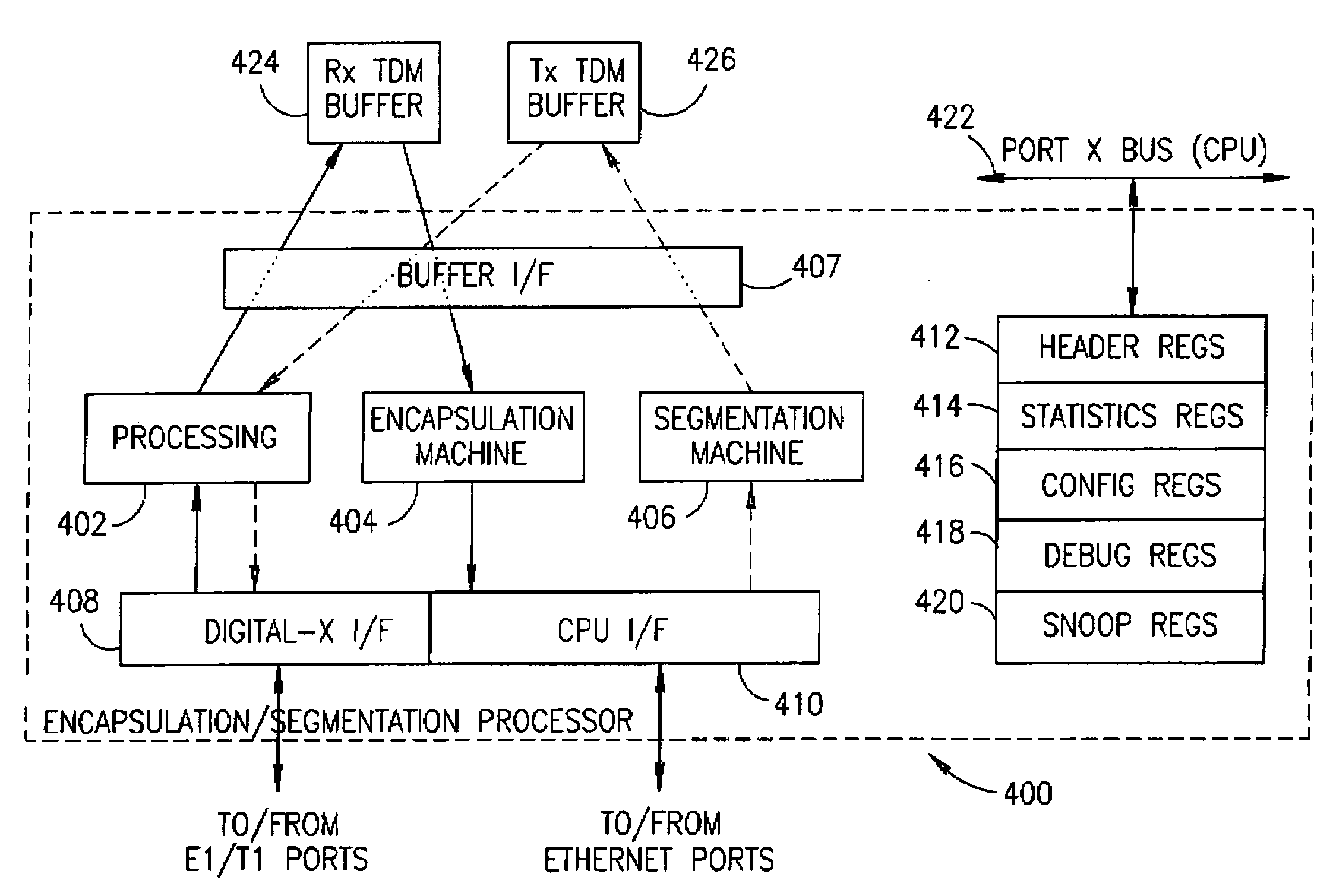
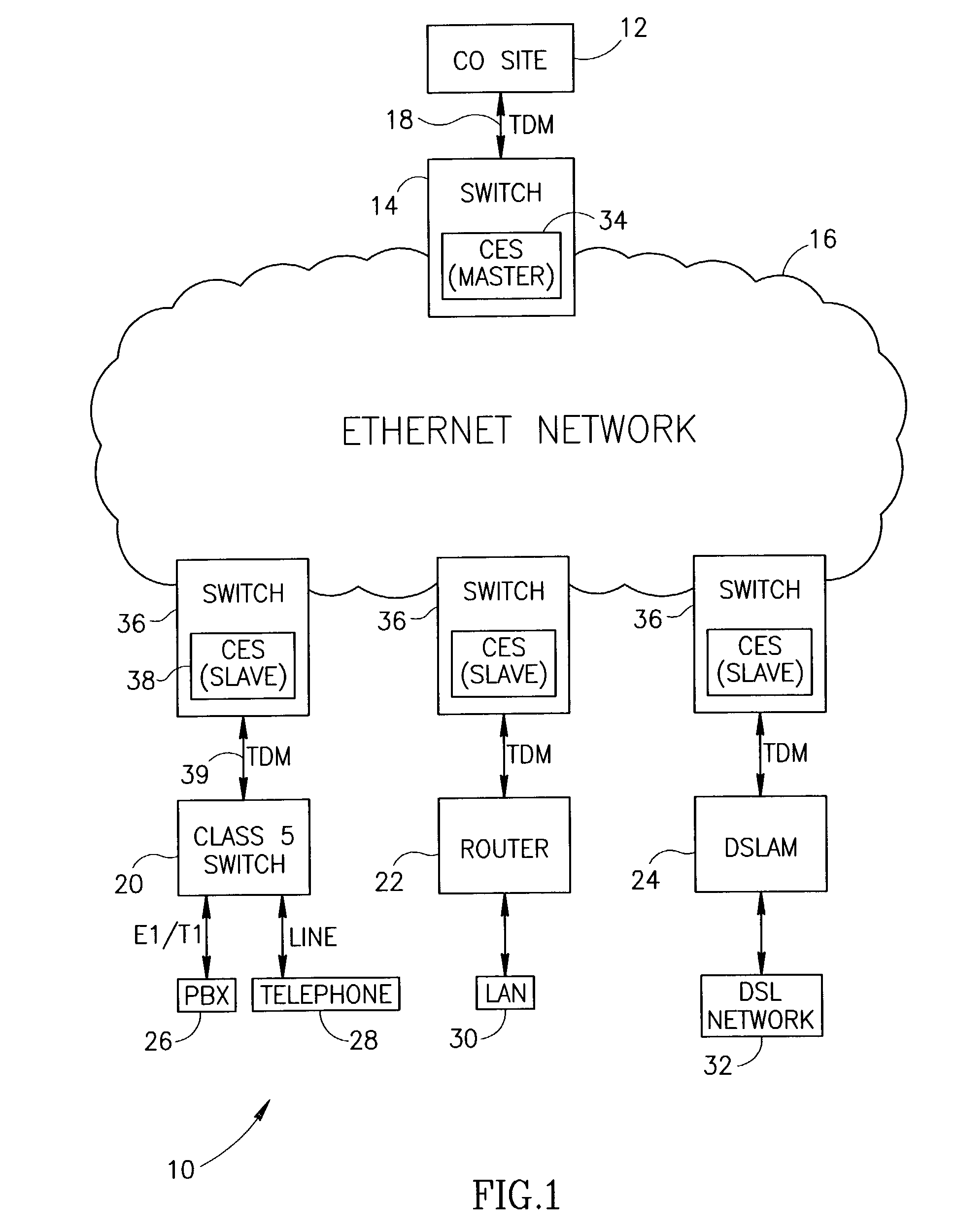
Facility for transporting TDM streams over an asynchronous ethernet network using internet protocol
InactiveUS6963561B1Low costTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationInternet protocol suiteSTM-1
A transport facility adapted to transport TDM bit streams using IP packets over an asynchronous Ethernet network. TDM bit streams such as E1, T1, E3, T3, OC-3, OC-12, STM-1, STM-4, etc. are received, buffered and encapsulated into Ethernet frames. The Circuit Emulation Device (CED) receives, buffers and assembles in real-time ingress data from TDM ports into Ethernet Frames and forwards them to an Ethernet interface. The TDM data is encapsulated within RTP, UDP and IP packets before being encapsulated within an Ethernet frame. In the egress direction, Ethernet frames enter the encapsulation / segmentation processor from the Ethernet port and the IP, UDP and RTP packets are extracted from the frame. TDM data is extracted and the bit streams are re-generated and forwarded to the TDM ports for transmission over legacy TDM facilities.
Owner:VENTURE LENDING & LEASING III
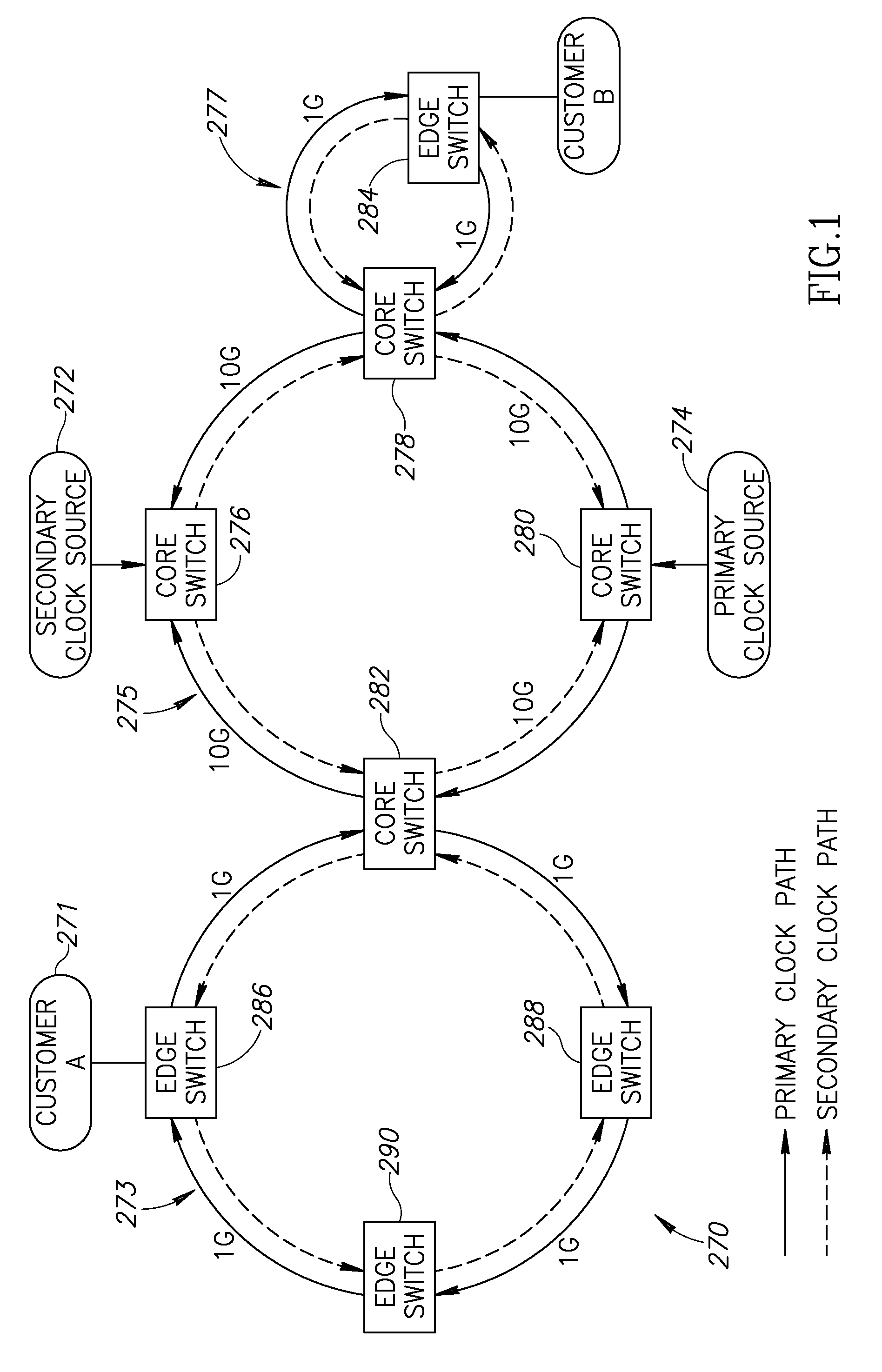
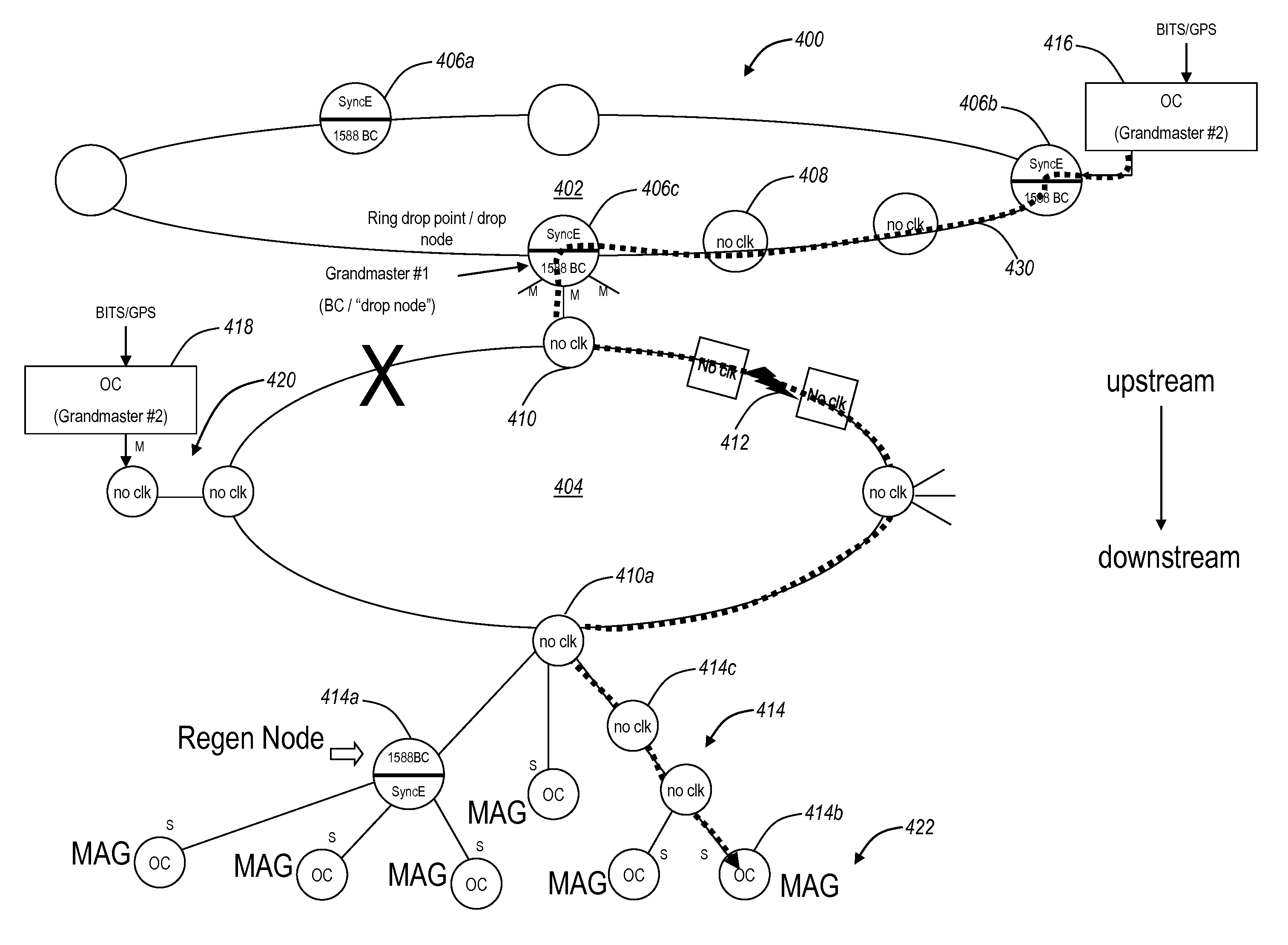
Ethernet network synchronization systems and methods
ActiveUS20110200051A1Reduce in quantityImprove stabilityTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationSynchronization systemSynchronous Ethernet
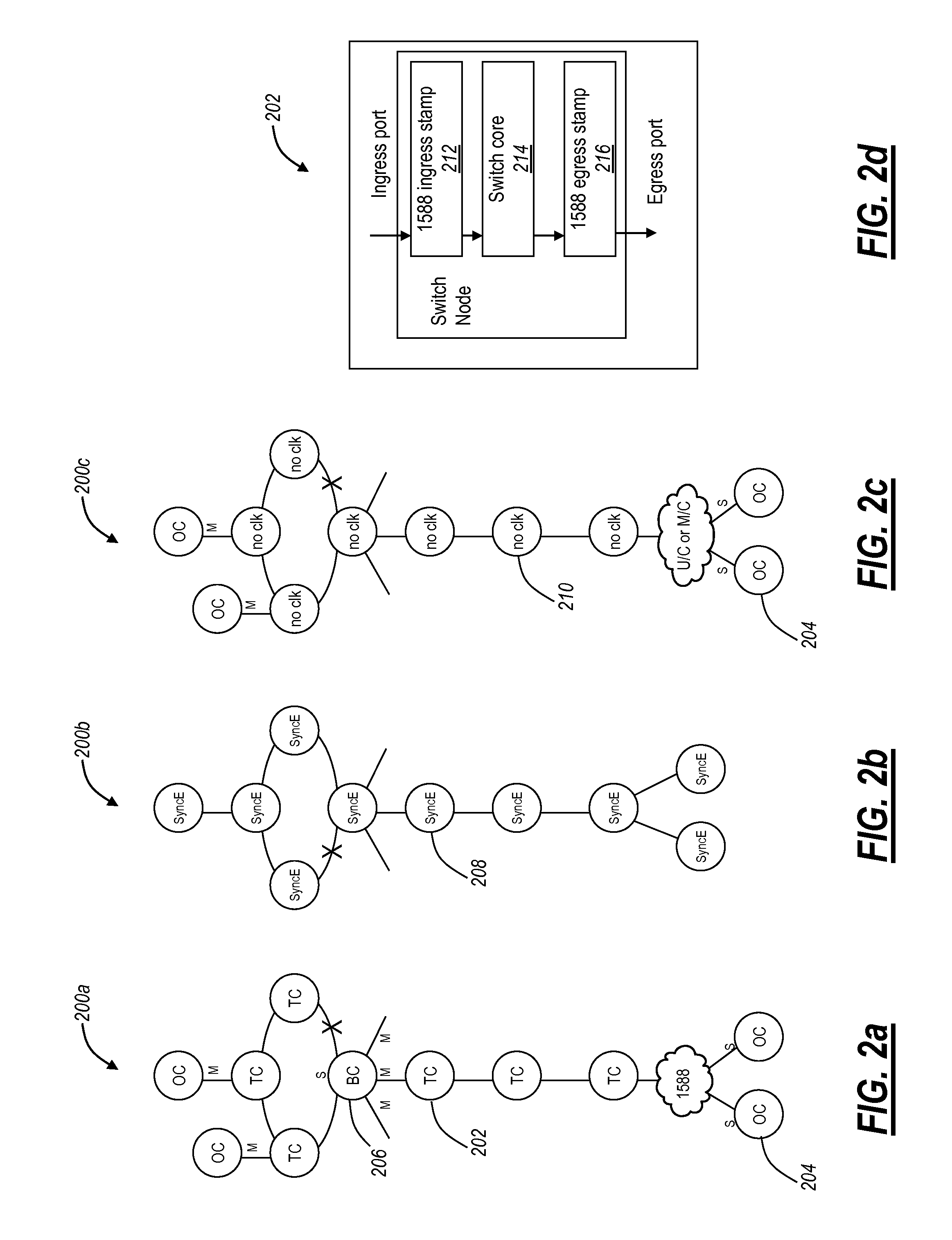
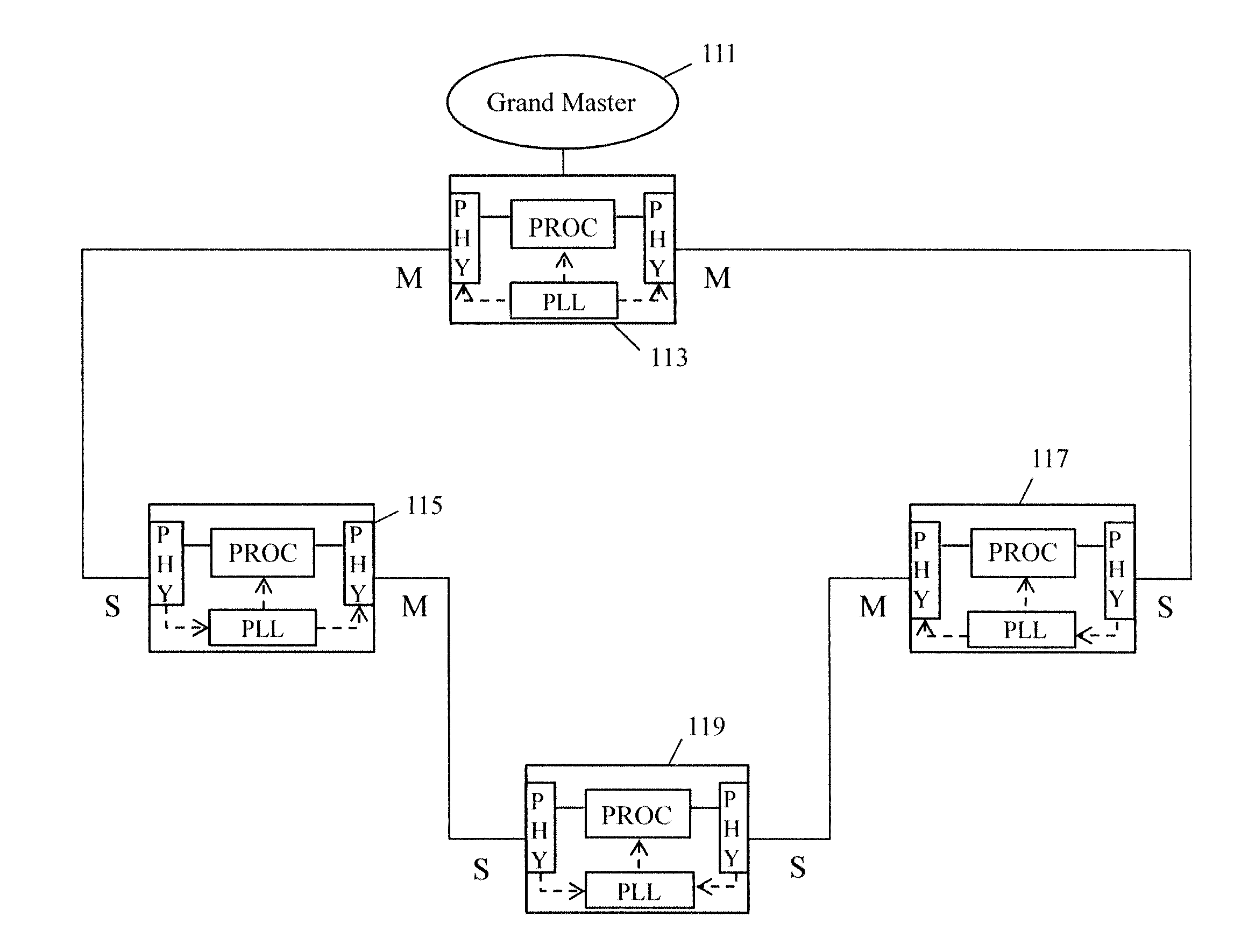
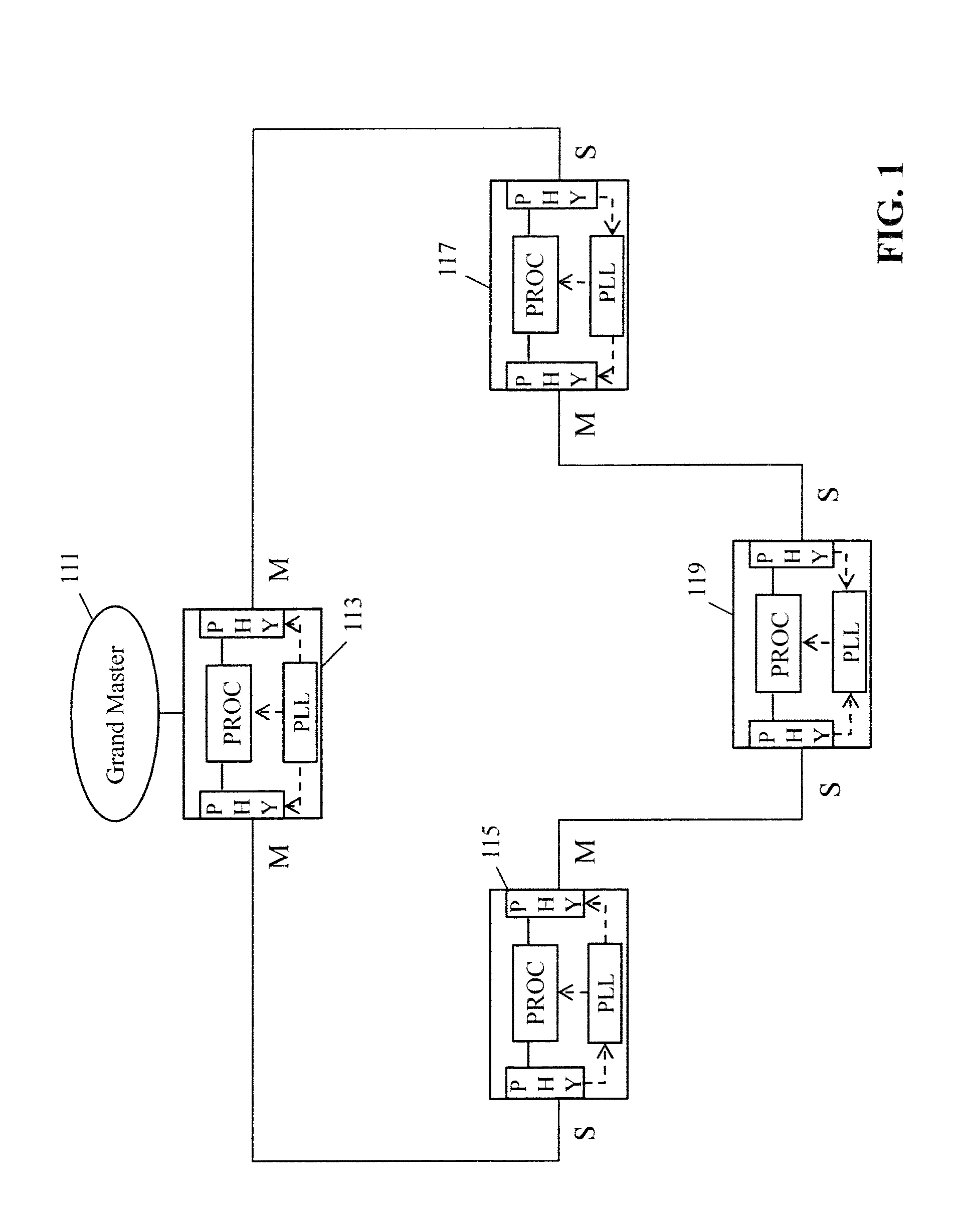
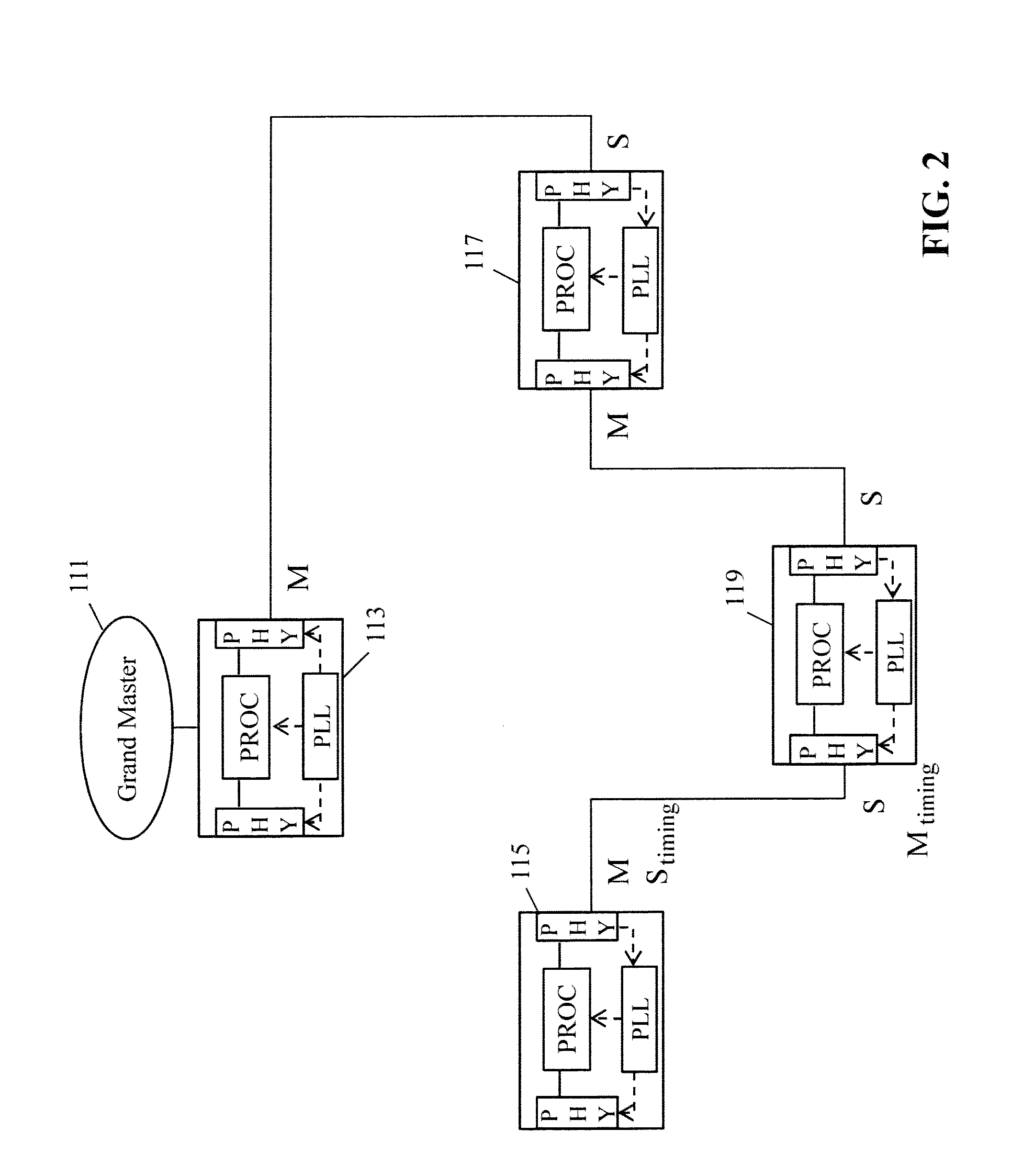
The present disclosure relates to Ethernet synchronization systems and methods that combines Synchronous Ethernet (Sync-E) and Precision Time Protocol (PTP) IEEE 1588 algorithms. The present invention includes systems and methods for Ethernet networks and node configurations that include a set of rules on node placement, such as Boundary Clock (BC) nodes and Sync-E nodes, a clock selection algorithm, a holdover algorithm, and the like. Advantageously, the present invention provides an architecture that allows practical and real-world useful clock propagation through placement of BCs and Sync-E nodes for best performance. Practical experience and theoretical design are embodied in the present invention to define a very specific set of rules on how to build a network capable of providing accurate and reliable synchronization. The present invention includes clock selection that unifies Sync-E and 1588 algorithms.
Owner:CIENA
Time Synchronization Using Packet-Layer and Physical-Layer Protocols
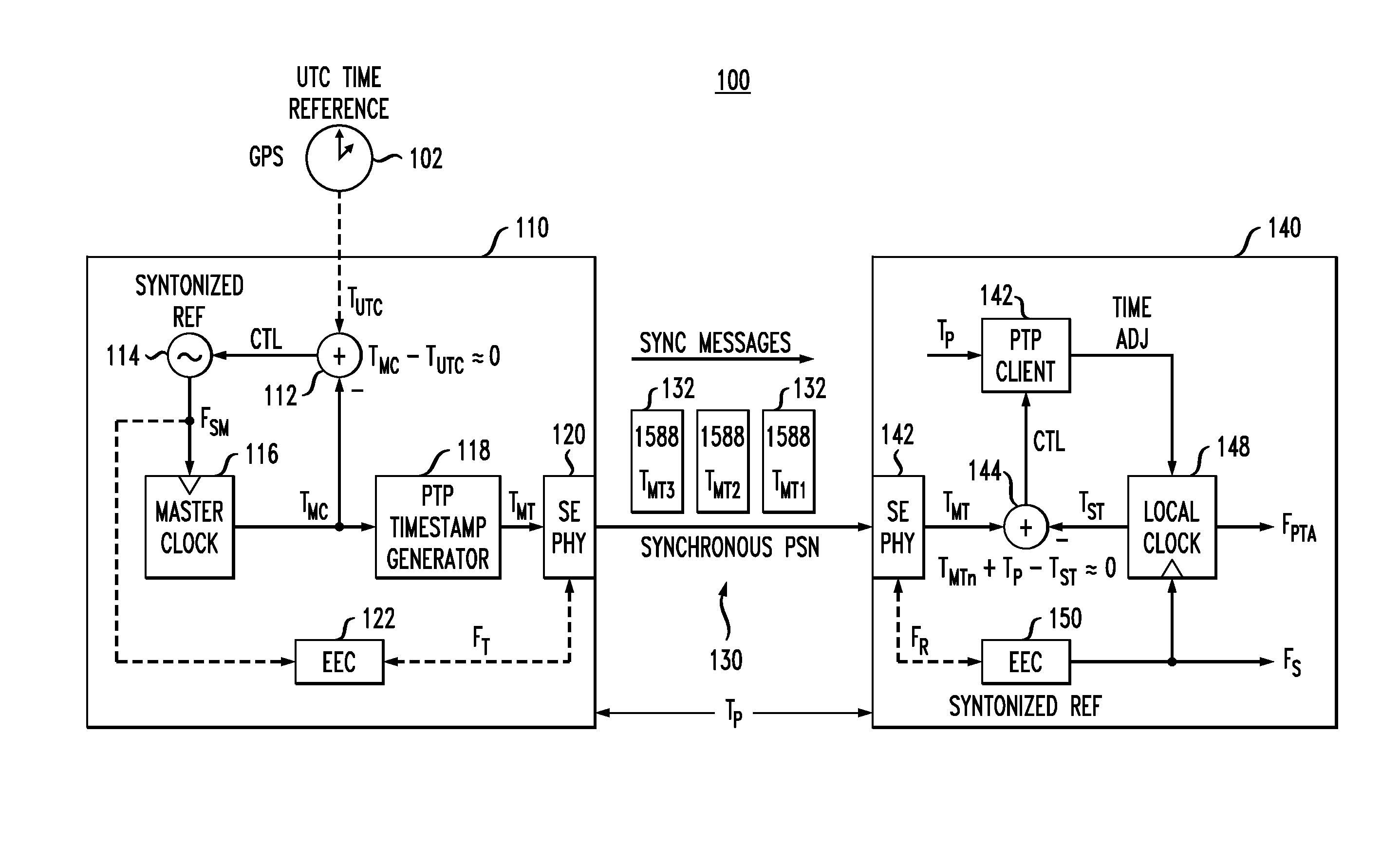
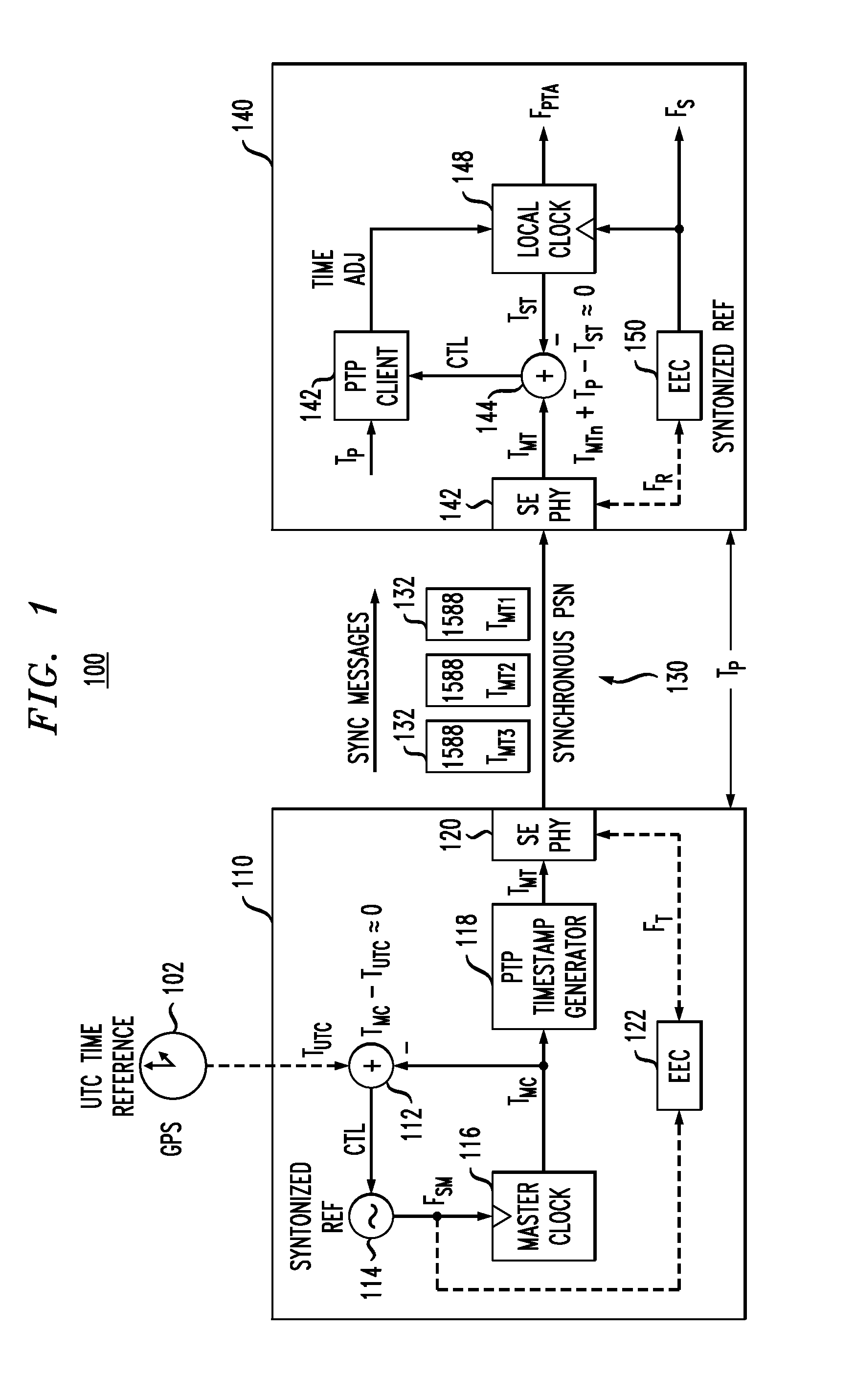
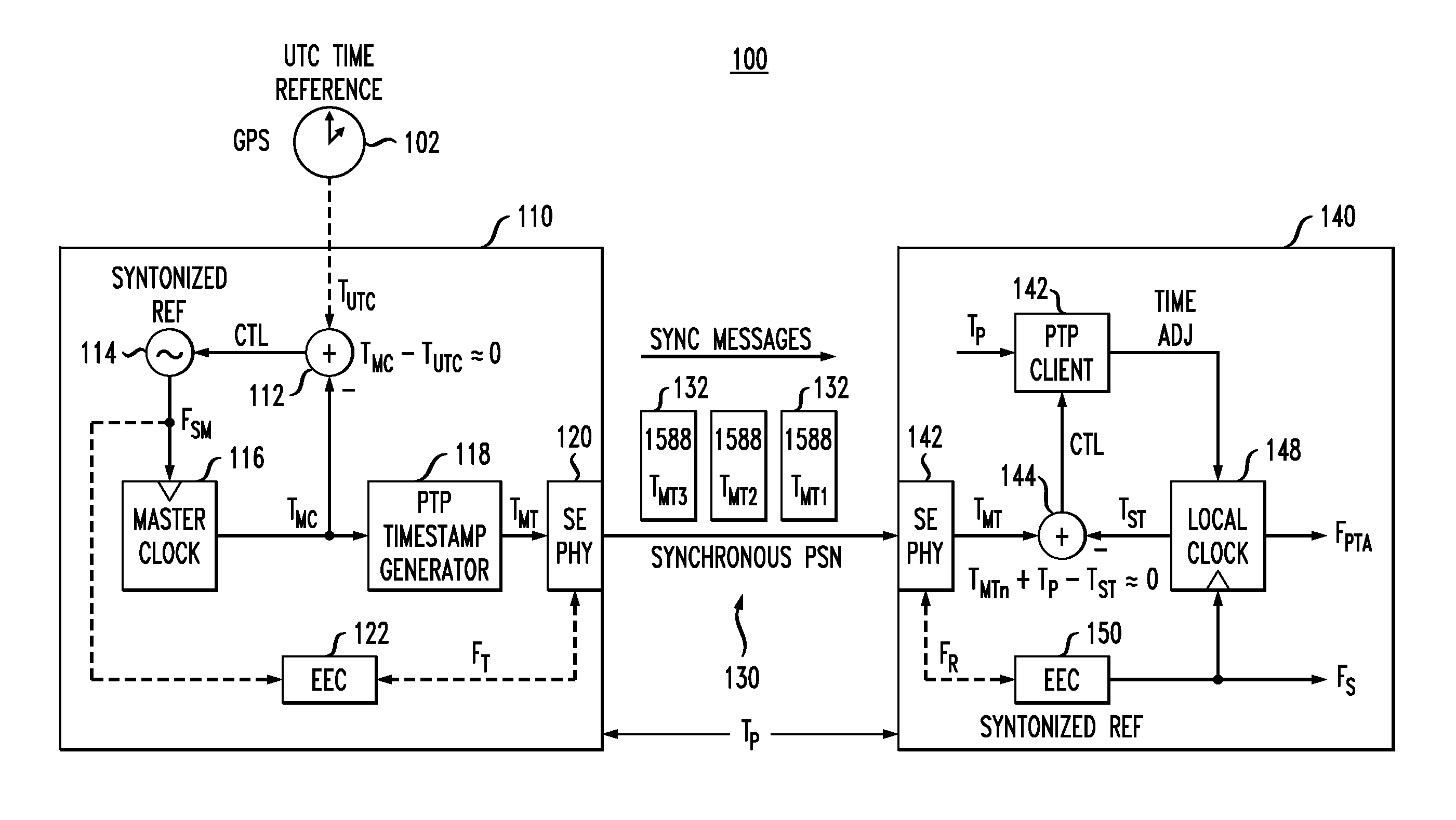
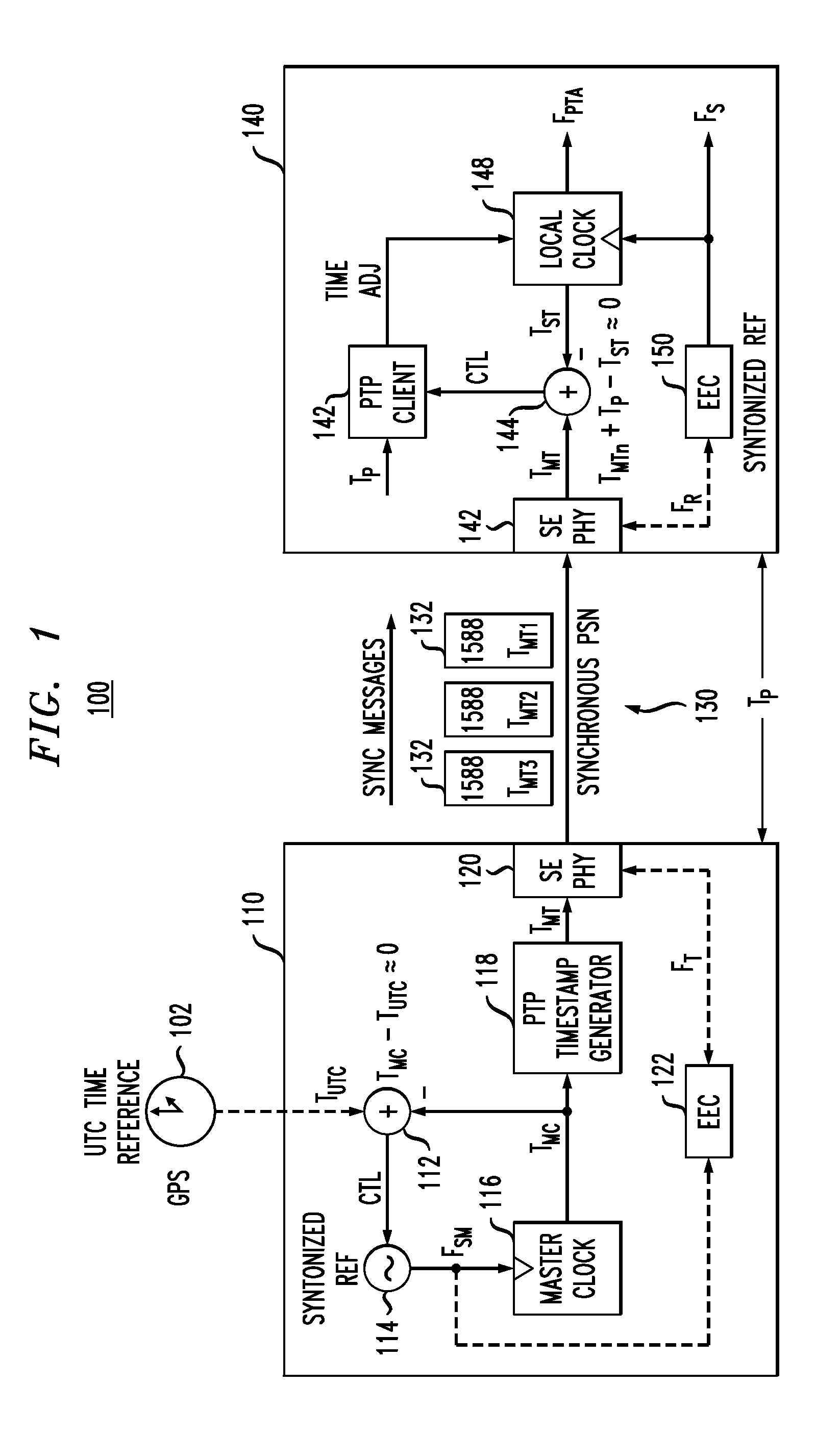
In certain embodiments, a slave node in a packet network achieves time synchronization with a master node by implementing a packet-layer synchronization procedure, such as the IEEE1588 precision timing protocol (PTP), to set the slave's local time based on the master's time. The slave's local time is then maintained by implementing a physical-layer syntonization procedure, such as synchronous Ethernet, without relying on the packet-layer synchronization procedure. The packet-layer synchronization procedure may be selectively employed to adjust the slave's local time (if needed) after significant periods of time (e.g., substantially greater than one second). Both the packet-layer synchronization procedure and the physical-layer syntonization procedure are traceable to a common reference timescale (e.g., UTC). Depending on the implementation, the packet-layer synchronization procedure can be, but does not have to be, terminated when not being employed to adjust the slave's local time.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Clock reconstruction for time division multiplexed traffic transported over asynchronous ethernet networks
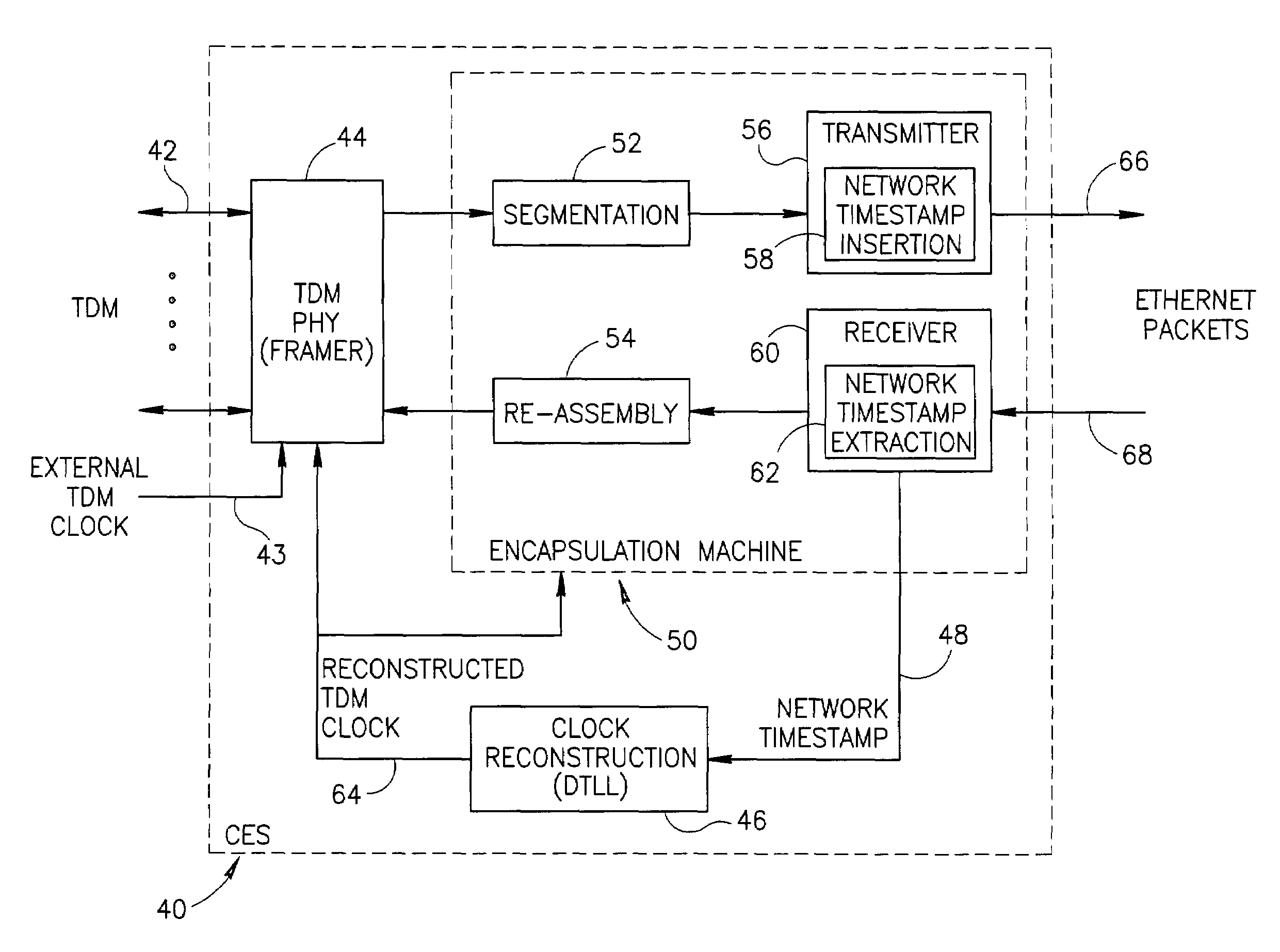
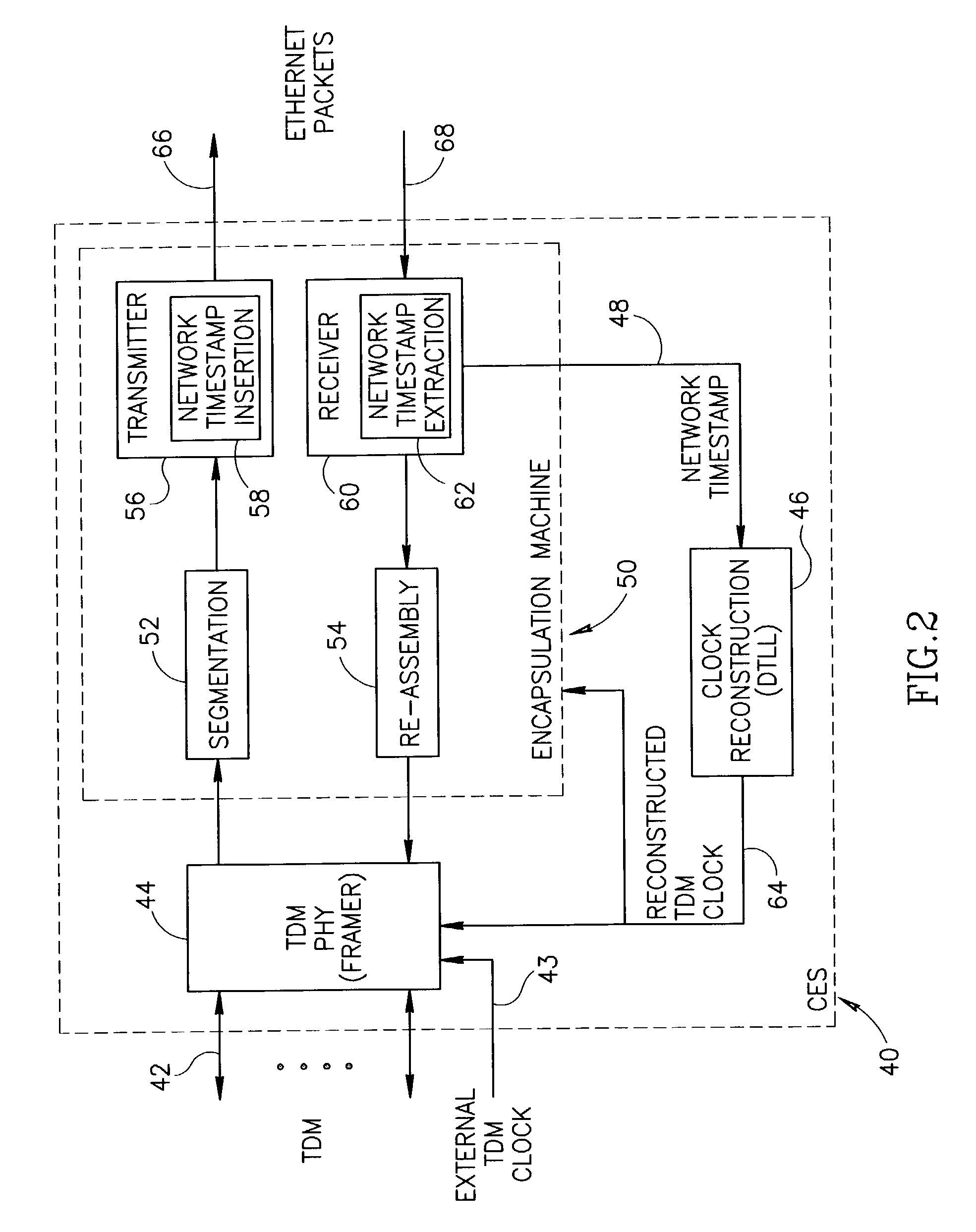
A clock reconstruction mechanism for synchronous TDM communications traffic transported over asynchronous networks such as Ethernet networks. The invention is applicable to edge switches in Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs) that transport legacy TDM traffic using a Circuit Emulation Services (CES) module whereby TDM traffic is encapsulated and transported across the Ethernet network where it is de-encapsulated and clocked out to the destination. The mechanism encapsulates the input TDM data stream into Ethernet packets and inserts a network timestamp within the packet. At the destination CES, a local timestamp is generated for each received packet as it is received. The network timestamp is extracted and input along with the local timestamp to a Digital Time Locked Loop (DTLL) which is operative to accurately reconstruct the original transmit TDM clock. The filter in the DTLL performs a Least Squares Regression (LSR) algorithm and Infinite Impulse Response (IIR) filter algorithm to generate a clock control signal for adjusting the clock generated.
Owner:VENTURE LENDING & LEASING III +1
Differential timing transfer over synchronous ethernet using digital frequency generators and control word signaling
InactiveUS20100118894A1Pulse automatic controlDigital data processing detailsReal-time computingBackplane
A method, system and master service interface transfer differential timing over a packet network. The transmitting service interface receives a service clock and is coupled to a receiving service interface through a network backplane. A primary reference clock is provided to time the network backplane. The primary reference clock and the service clock are used to synthesize a copy of the service clock connected to the transmitting service interface. A first control word containing an error differential between the service clock and the synthesized copy of the service clock is generated and transmitted through the network backplane via a packet. The first control word, together with the primary reference clock, is used to recreate the service clock for timing the receiving service interface.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
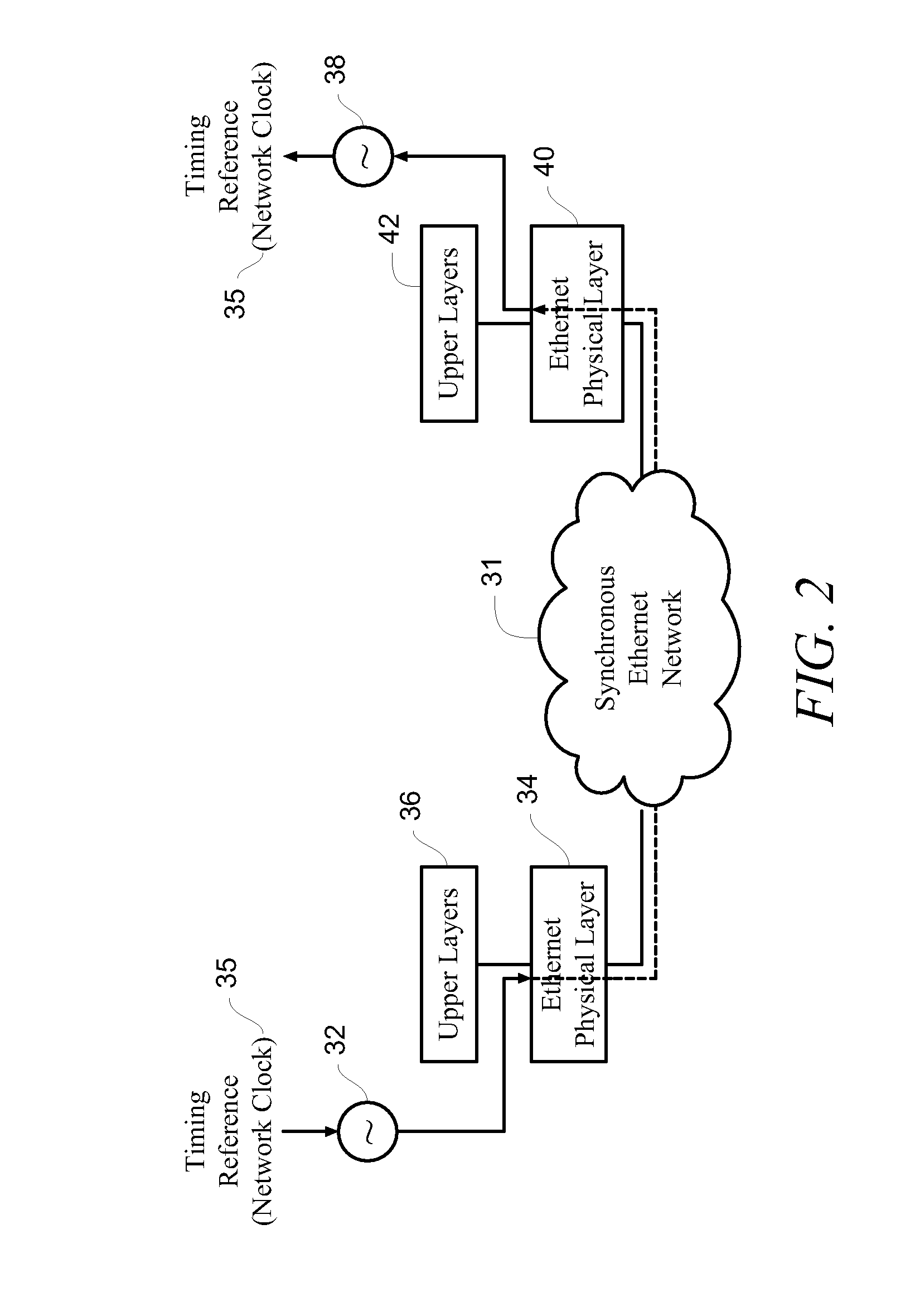
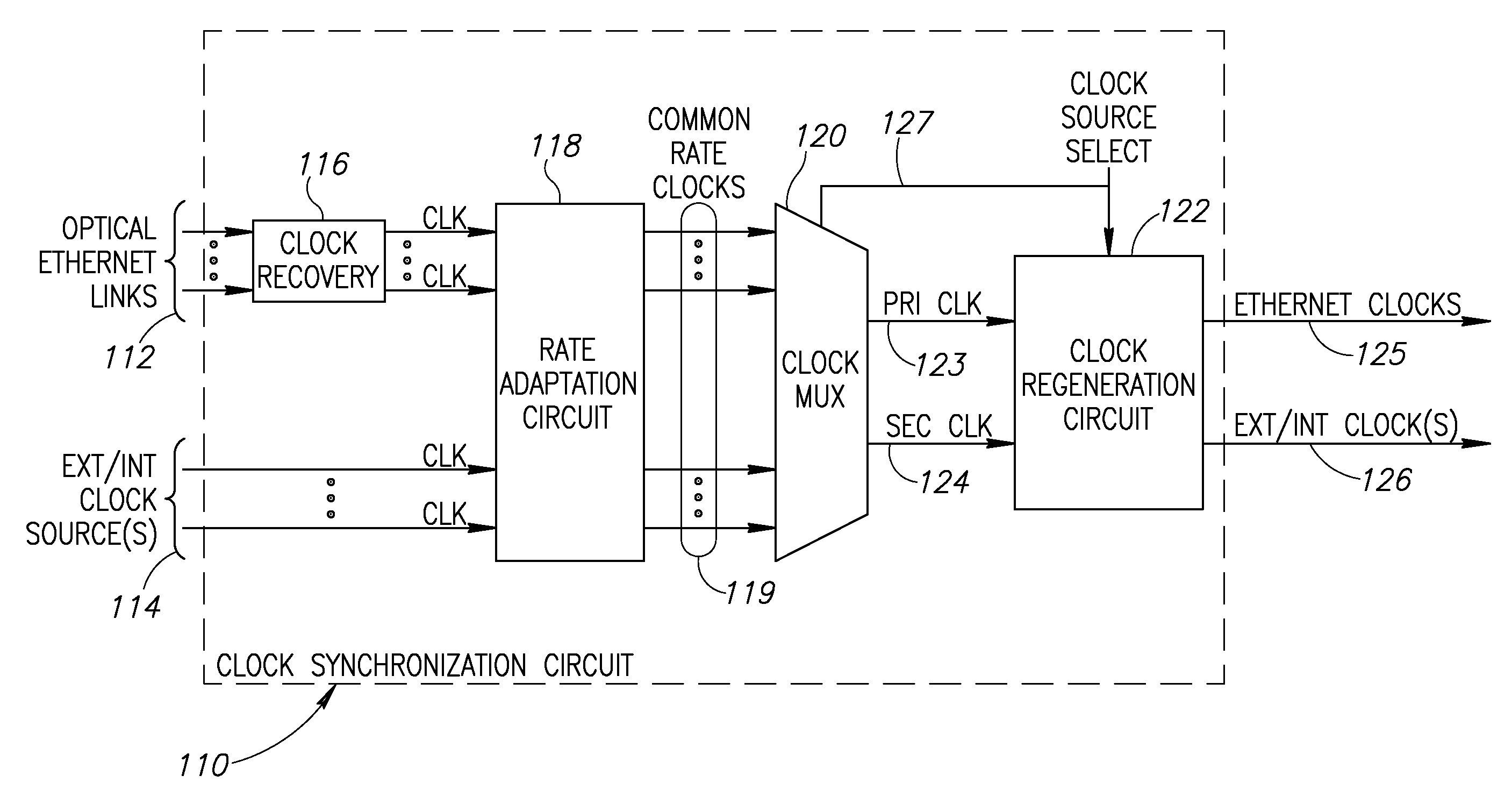
Clock synchronization and distribution over a legacy optical Ethernet network
InactiveUS7649910B1Time-division multiplexElectromagnetic transmissionData streamAsynchronous network
A novel clock method and synchronization mechanism for recovering and distributing a centralized clock source synchronously over legacy asynchronous network devices such as legacy optical Ethernet devices that do not support synchronous Ethernet. An external device functions transparently to provide legacy optical Ethernet devices a clock synchronization and distribution mechanism. The external devices implement a clock conversion scheme whereby multiple clocks having diverse rates are converted to clock signals all having a common rate. One of the converted clocks is selected and all downstream clock signals are then derived from this clock. A high quality clock source located anywhere on the network is distributed throughout the network thus turning an asynchronous Ethernet network into a synchronous Ethernet network. Synchronous TDM data streams can then be easily transported over the Ethernet network.
Owner:NOKIA SIEMENS NETWORKS ETHERNET SOLUTIONS +1
Method and devices for synchronization
ActiveUS20150092793A1Time-division multiplexSynchronising arrangementReal-time computingSynchronous Ethernet
This invention relates to methods and devices for time and frequency synchronization. The invention has particular application where time and frequency synchronization over packet networks using, for example, the IEEE 1588 Precision Time Protocol (PTP) is being carried out. The primary challenge in clock distribution over packet networks is the variable transit delays experienced by timing packets, packet delay variations (PDVs). Embodiments of the invention provide a method for time offset alignment with PDV compensation where a synchronized frequency signal is available at a slave device via Synchronous Ethernet and is used to determine the compensation parameters for the PDV.
Owner:KHALIFA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +2
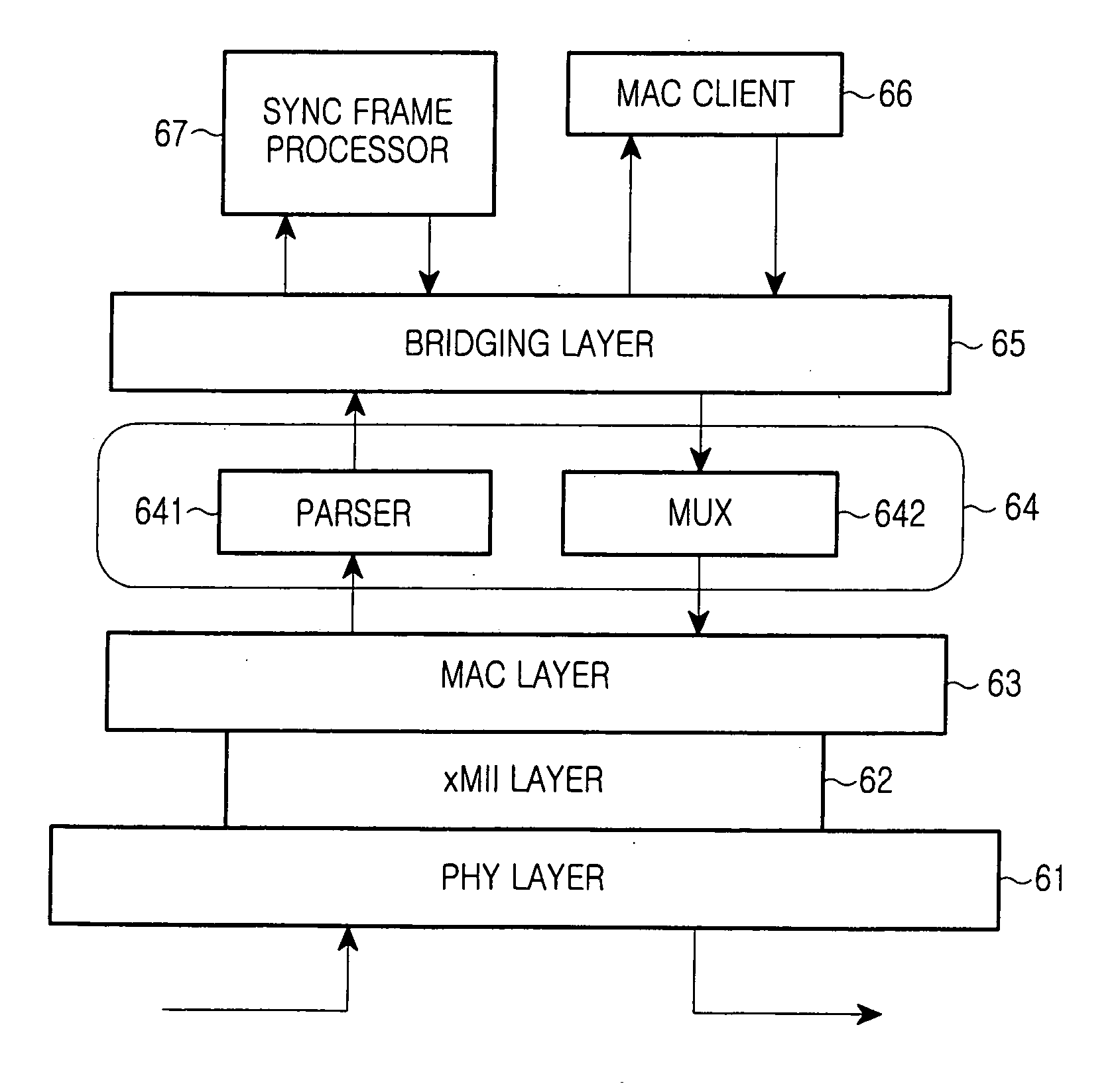
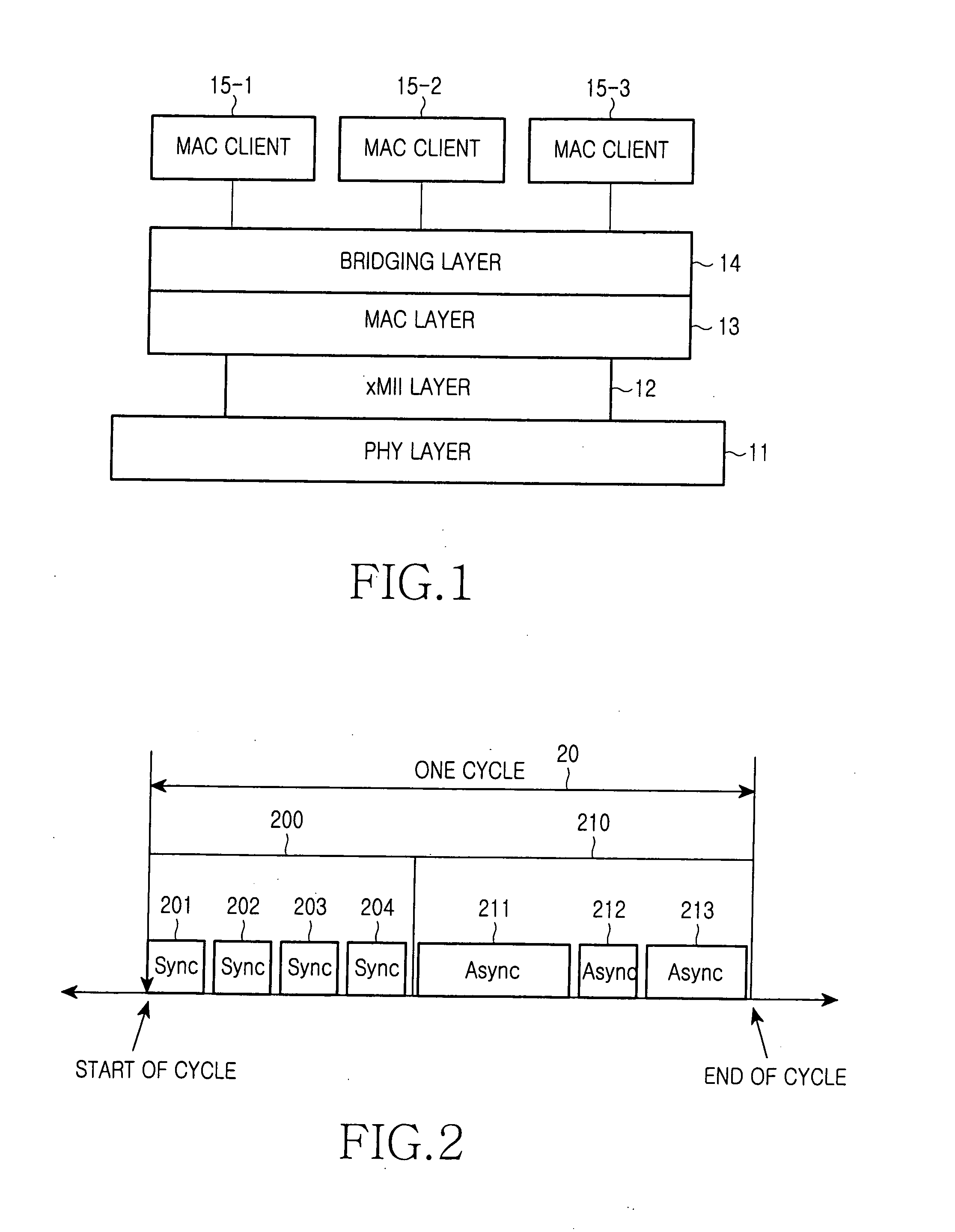
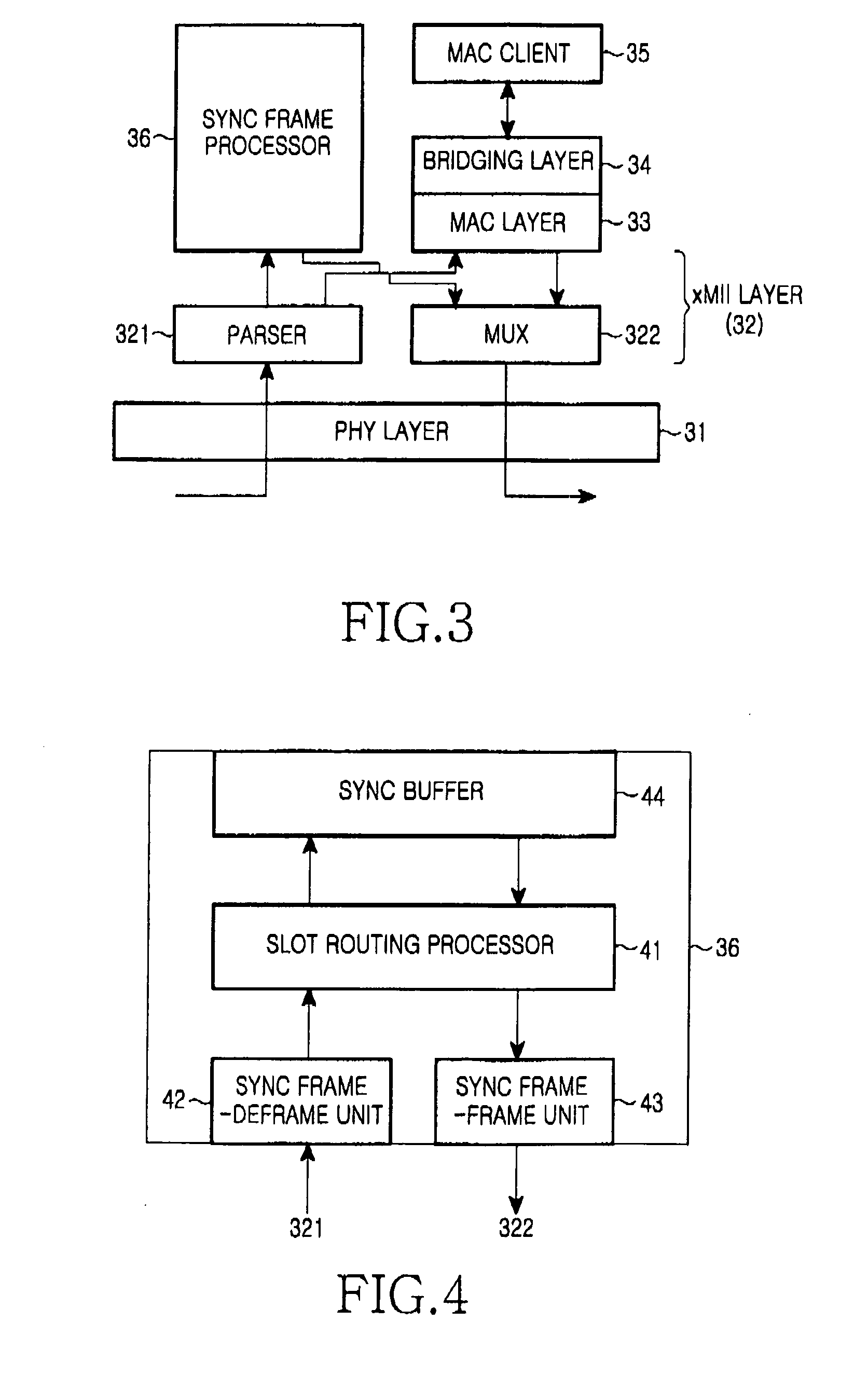
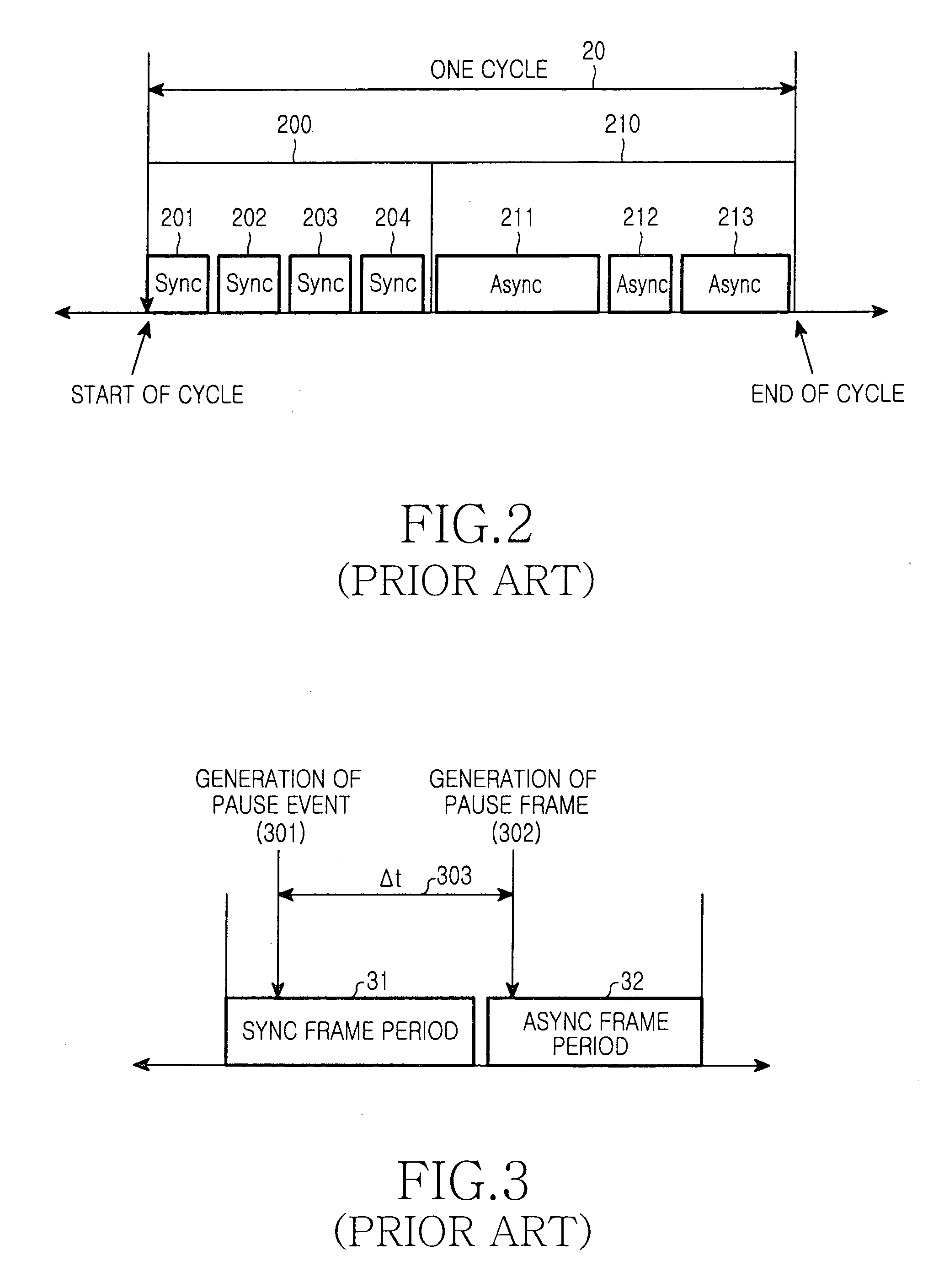
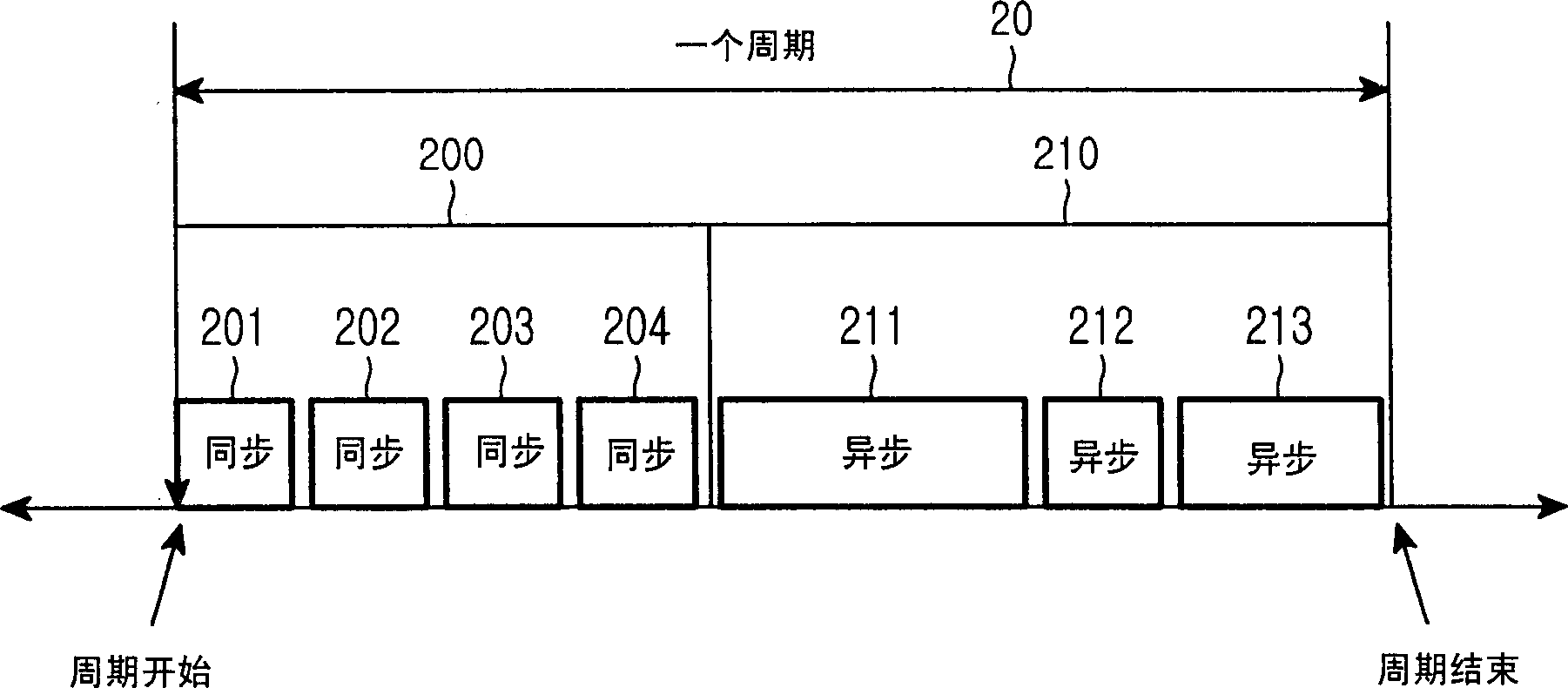
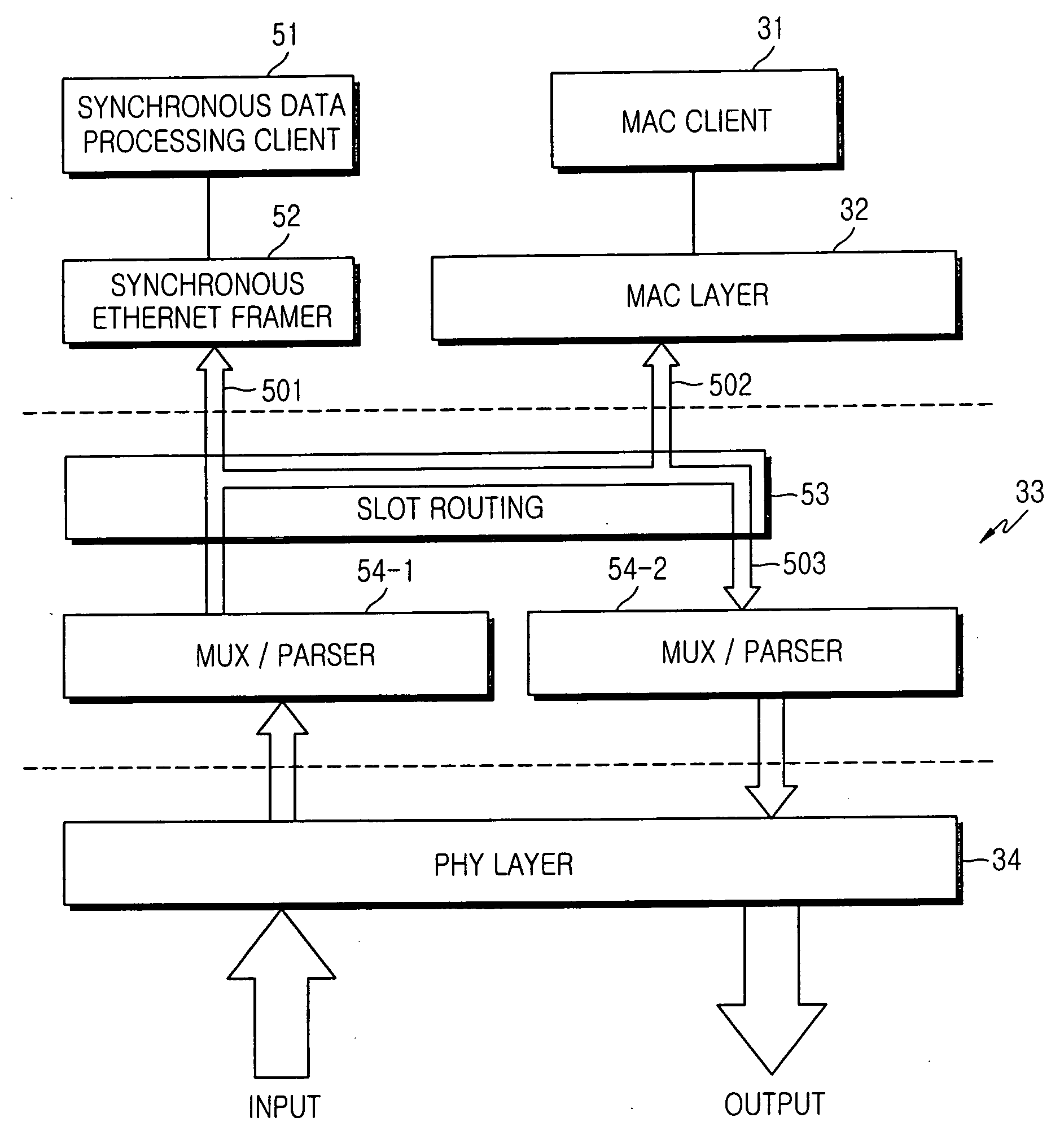
Method of configuring system layers for synchronous Ethernet
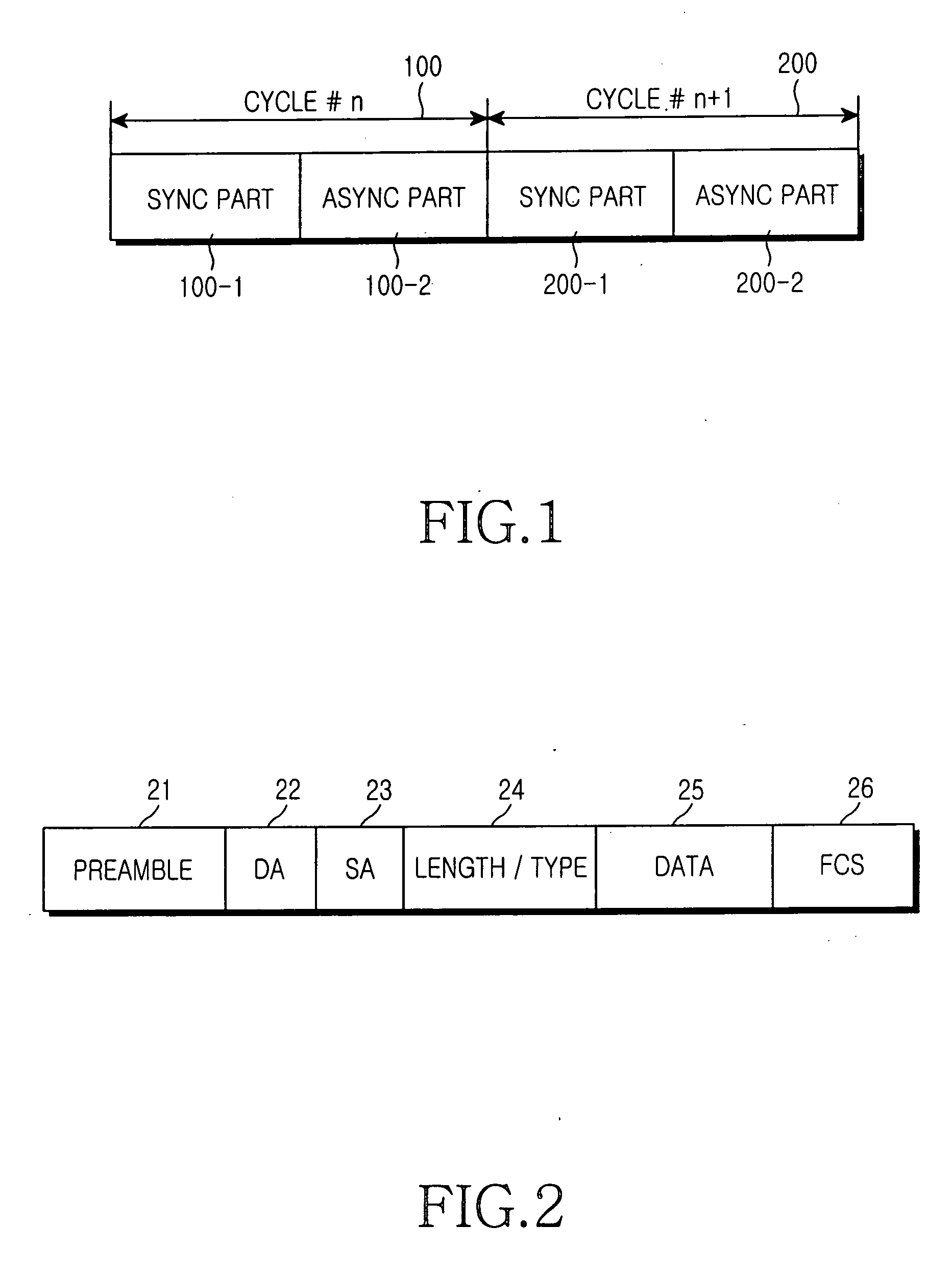
A method of configuring system layers for a synchronous Ethernet is provided. In the method, a physical layer takes charge of input and output of an Ethernet frame in direct relation to hardware, an xMII (x Media Independent Interface) layer connects the physical layer to a data link layer. The data link layer has a sync frame processor for processing a synchronous frame and an async frame processor for processing an asynchronous frame. A parser and multiplexer (MUX), included in the x MII layer, construct a super frame with a synchronous frame and an asynchronous frame, transmit the super frame through the physical layer, parse a received super frame into a synchronous frame and an asynchronous frame, and transmit the synchronous and asynchronous frames to the data link layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Time synchronization using packet-layer and physical-layer protocols
ActiveUS8446896B2Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationData synchronizationTime segment
In certain embodiments, a slave node in a packet network achieves time synchronization with a master node by implementing a packet-layer synchronization procedure, such as the IEEE1588 precision timing protocol (PTP), to set the slave's local time based on the master's time. The slave's local time is then maintained by implementing a physical-layer syntonization procedure, such as synchronous Ethernet, without relying on the packet-layer synchronization procedure. The packet-layer synchronization procedure may be selectively employed to adjust the slave's local time (if needed) after significant periods of time (e.g., substantially greater than one second). Both the packet-layer synchronization procedure and the physical-layer syntonization procedure are traceable to a common reference timescale (e.g., UTC). Depending on the implementation, the packet-layer synchronization procedure can be, but does not have to be, terminated when not being employed to adjust the slave's local time.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method of transmitting time-critical information in a synchronous ethernet system
InactiveUS20060092985A1Avoid lostTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationTime criticalControl signal
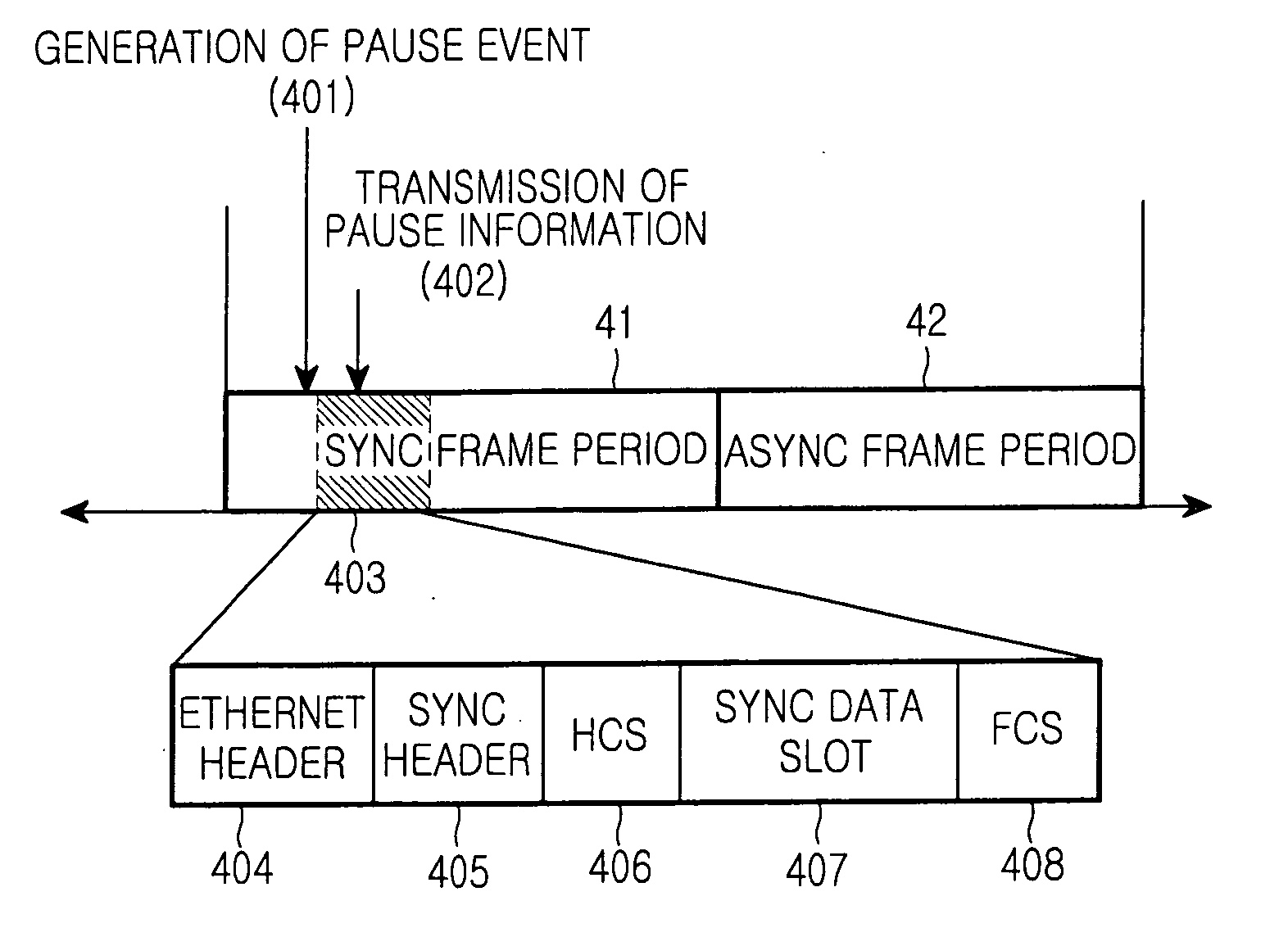
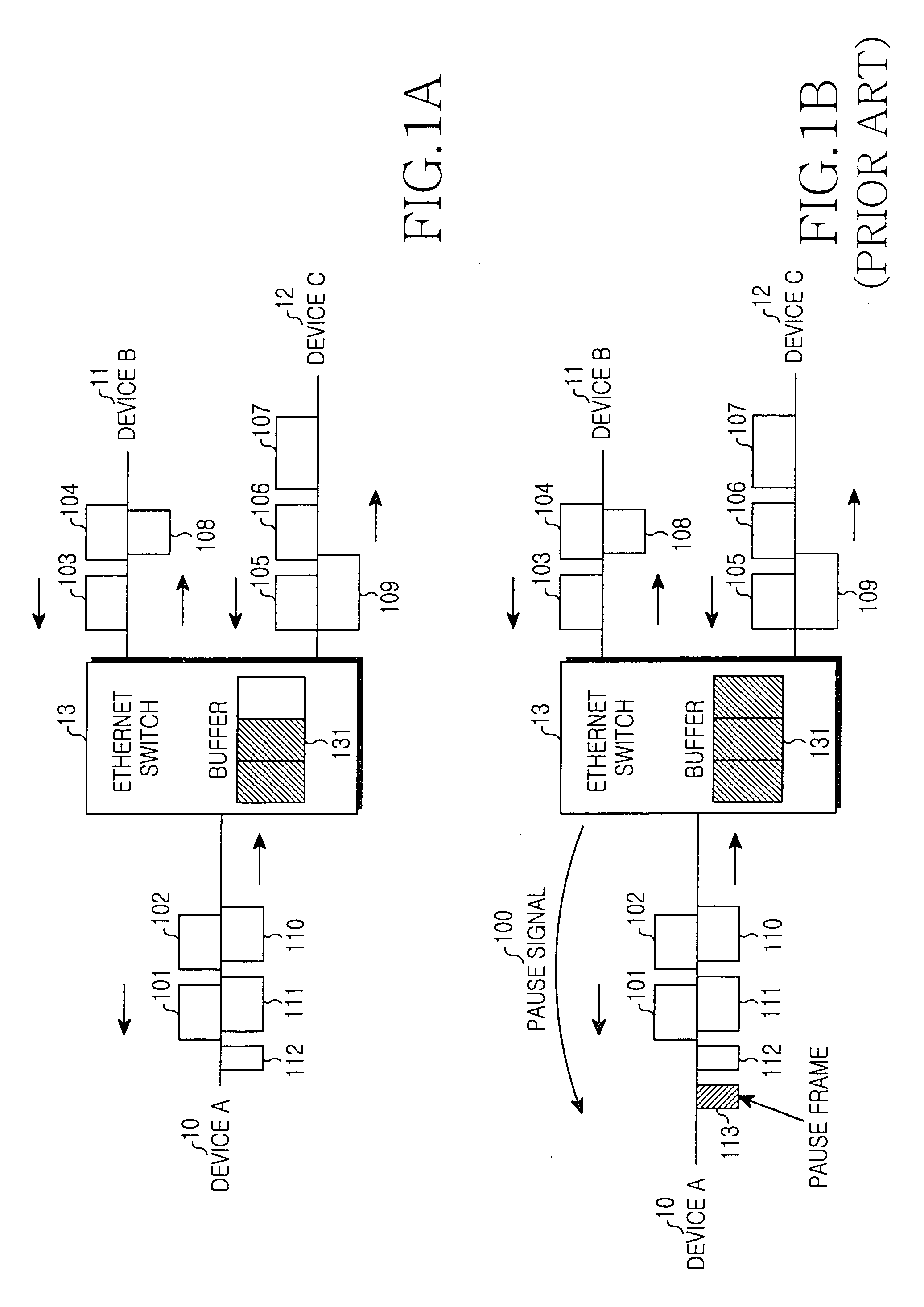
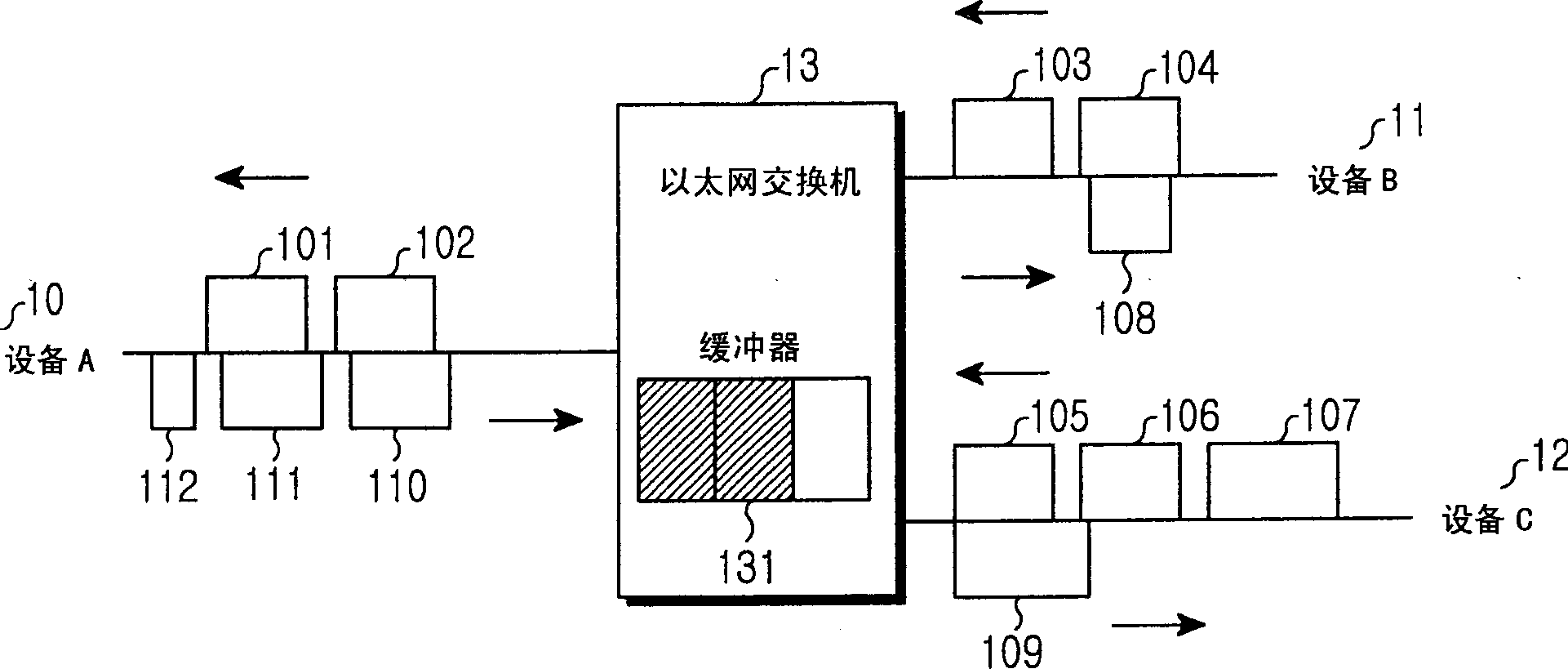
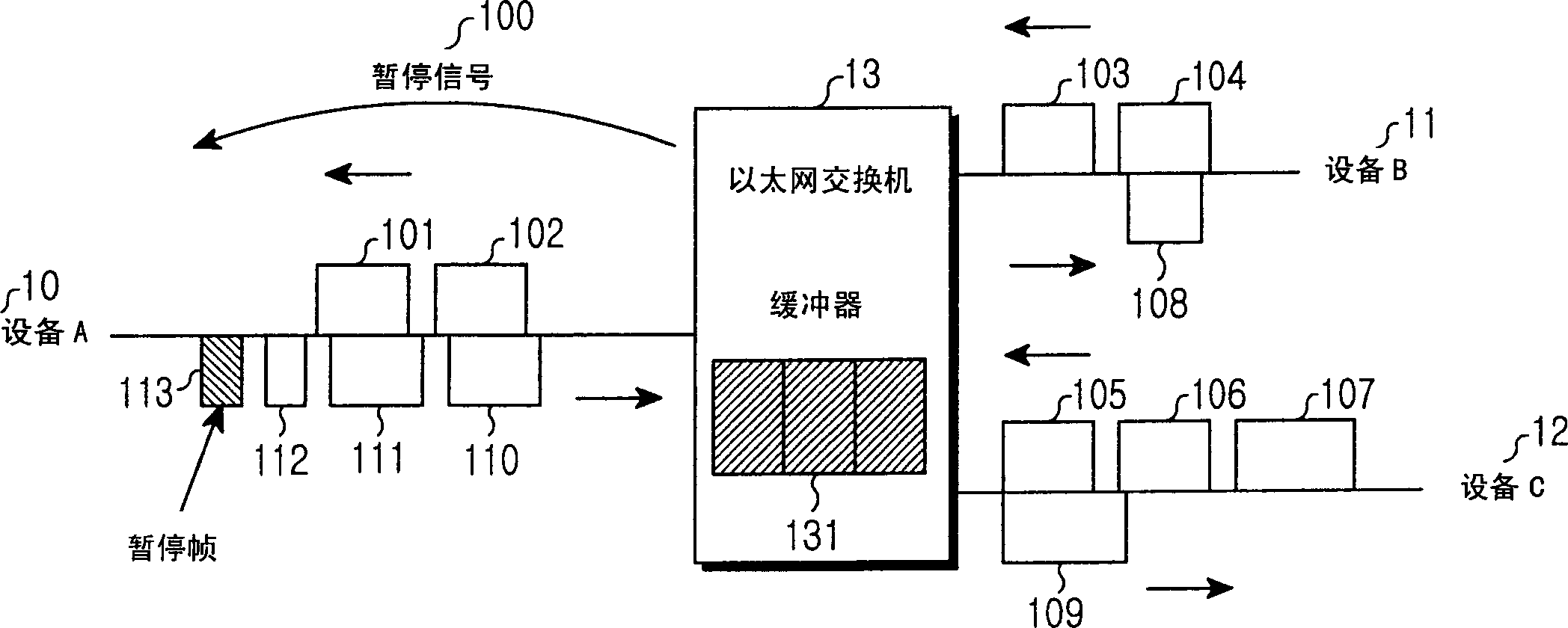
A method of enabling transmission of a time-critical control signal event in a sync frame period, such as a pause signal that is generated when the receive buffer of an Ethernet switch is filled with packets beyond a threshold due to congestion of uplink asynchronous data, is disclosed. To transmit time-critical information in a synchronous Ethernet system, a current transmission period is checked upon detection of a time-critical event. If the current transmission period is a sync frame period, time-critical control information is generated, inserted into the first sub-sync frame after the time-critical event, and transmitted. If the current transmission period is an async frame period, a control frame including the time-critical control information is generated and transmitted.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Clock synchronization method and system
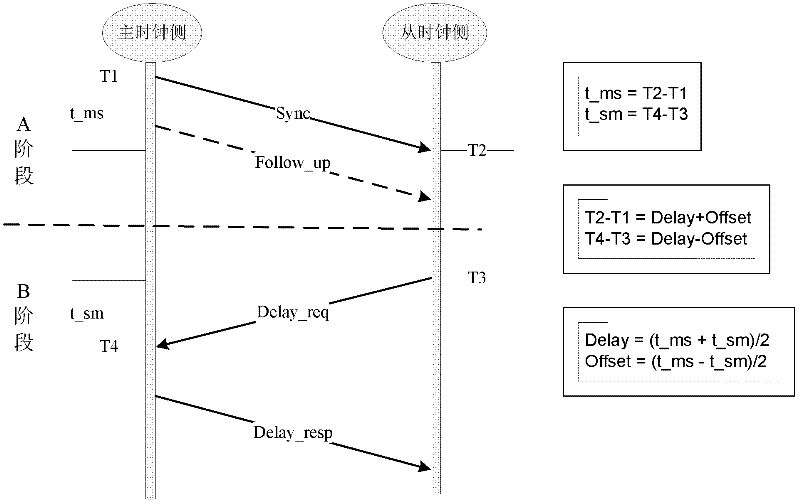
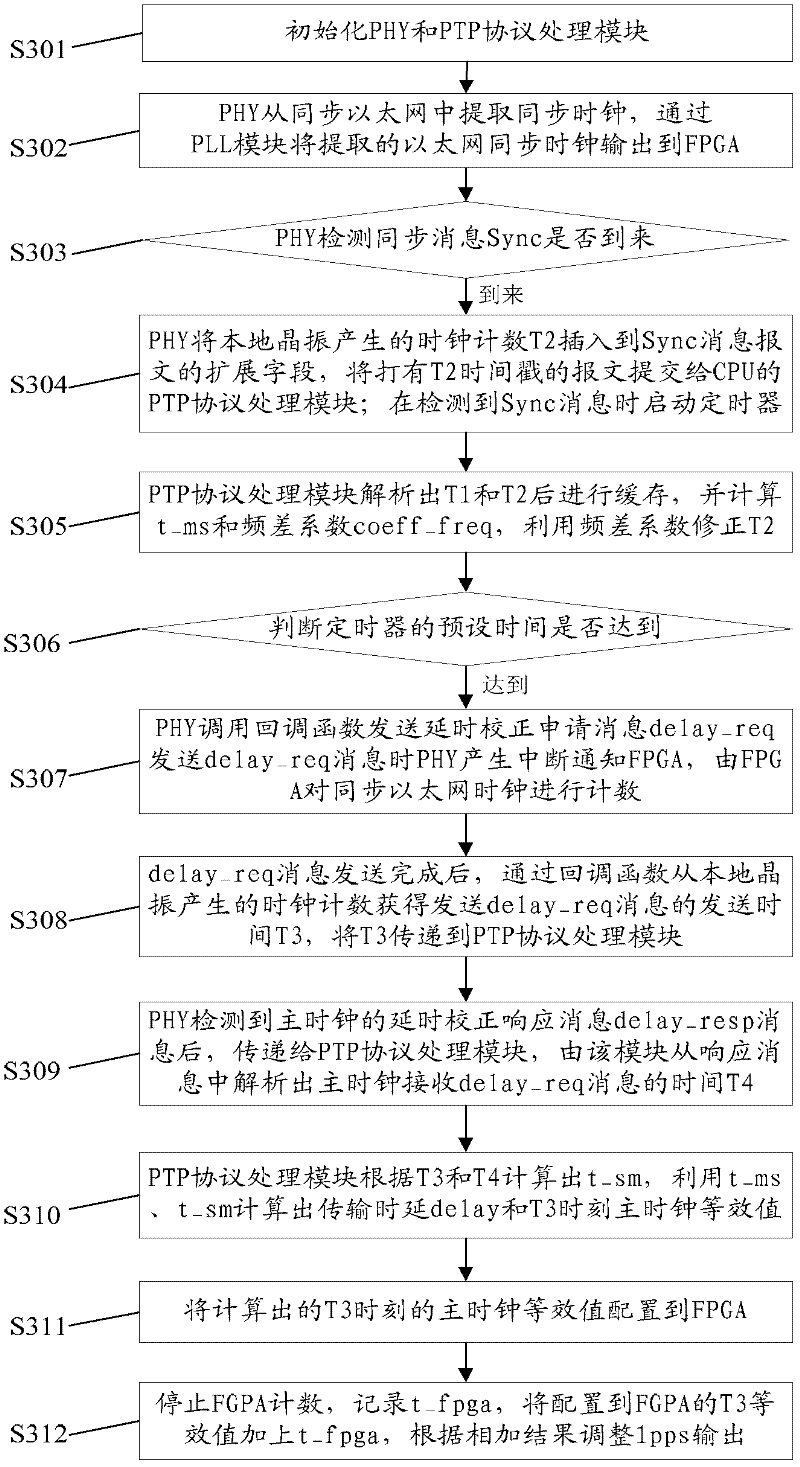
ActiveCN102546071AFast convergenceSave on deployment costsTime-division multiplexRate of convergenceCrystal oscillator
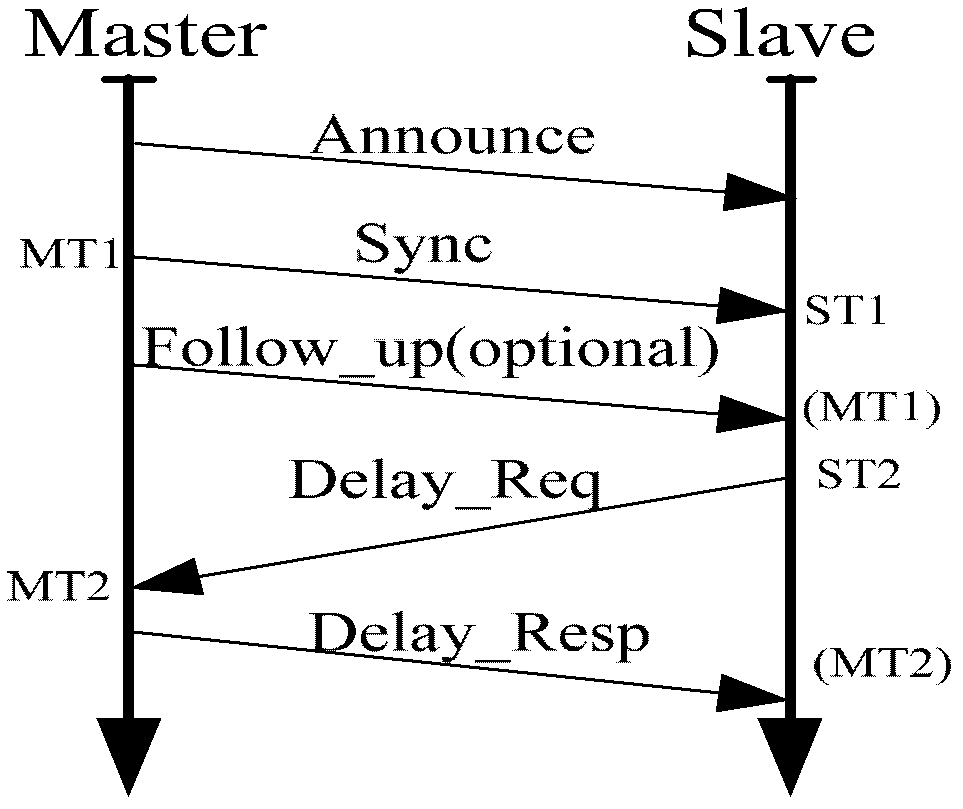
An embodiment of the invention provides a clock synchronization method, which includes of acquiring the transmission time T1 of synchronous messages after receiving the synchronous messages; recording the clock count T2 of a local crystal oscillator when the synchronous messages arrive; sending delay correction application messages, recording the clock count T3 of the local crystal oscillator when in sending of the delay correction application messages and starting counting of a synchronous Ethernet clock; receiving the time T4 for main clock equipment to receive the delay correction application messages after receiving delay correction application response messages; computing transmission delay according to the T1, the T2, the T3 and the T4, and computing the main clock equivalence of the T3 according to the T1, the T2, the T3 and the transmission delay; summing the main clock equivalence of the T3 and the current counting value of the synchronous Ethernet clock, and finally regulating clock output according to the summing results. The invention further provides a clock synchronization system. By the clock synchronization method and the clock synchronization system in the technical scheme, complexity of clock synchronization is reduced, convergence rate is increased and cost is saved.
Owner:WUHAN HONGXIN TELECOMM TECH CO LTD
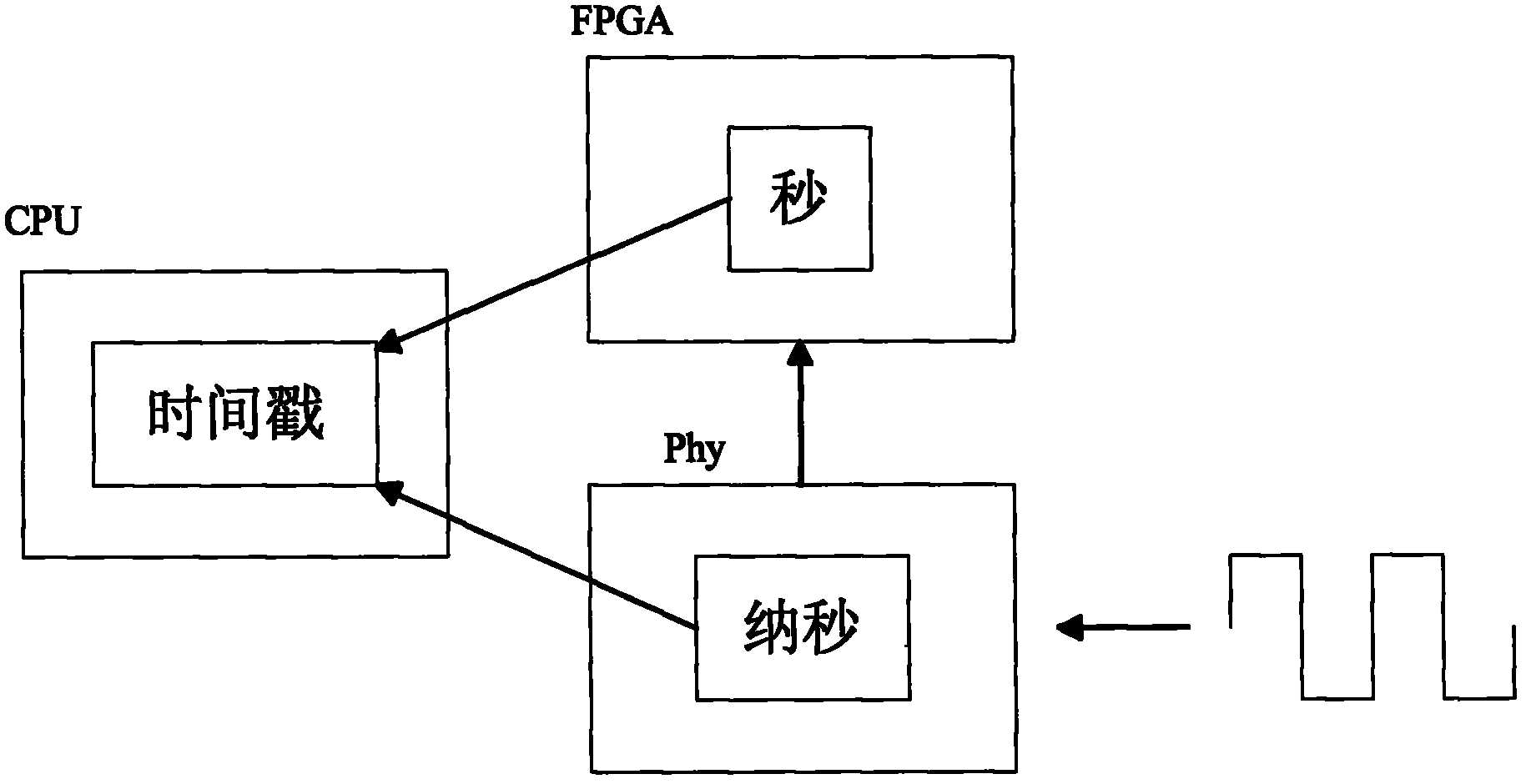
Method for realizing precision time protocol (PTP) with nanosecond-level precision
ActiveCN102195768AHigh precisionImprove accuracySynchronising arrangementCommunications systemTimestamp
The invention discloses a method for realizing a precision time protocol (PTP) with nanosecond-level precision. The method comprises the following steps of: identifying a PTP message and recording a leaving or arrival timestamp of the PTP message in a physical layer (PHY) chip; realizing frequency synchronization by using a synchronization Ethernet (SyncE) technology in a physical layer; and managing the timestamp in a way of combining the PHY chip and a field programmable gate array (FPGA), and ensuring the consistency of time in the PHY chip and FPGA maintenance time at the arrival of the PTP message by adopting a software processing method. By the technical scheme provided by the invention, the requirements of a communication system on time synchronization precision can be met, and the synchronization precision of the PTP reaches a nanosecond level.
Owner:北京神州数码云科信息技术有限公司
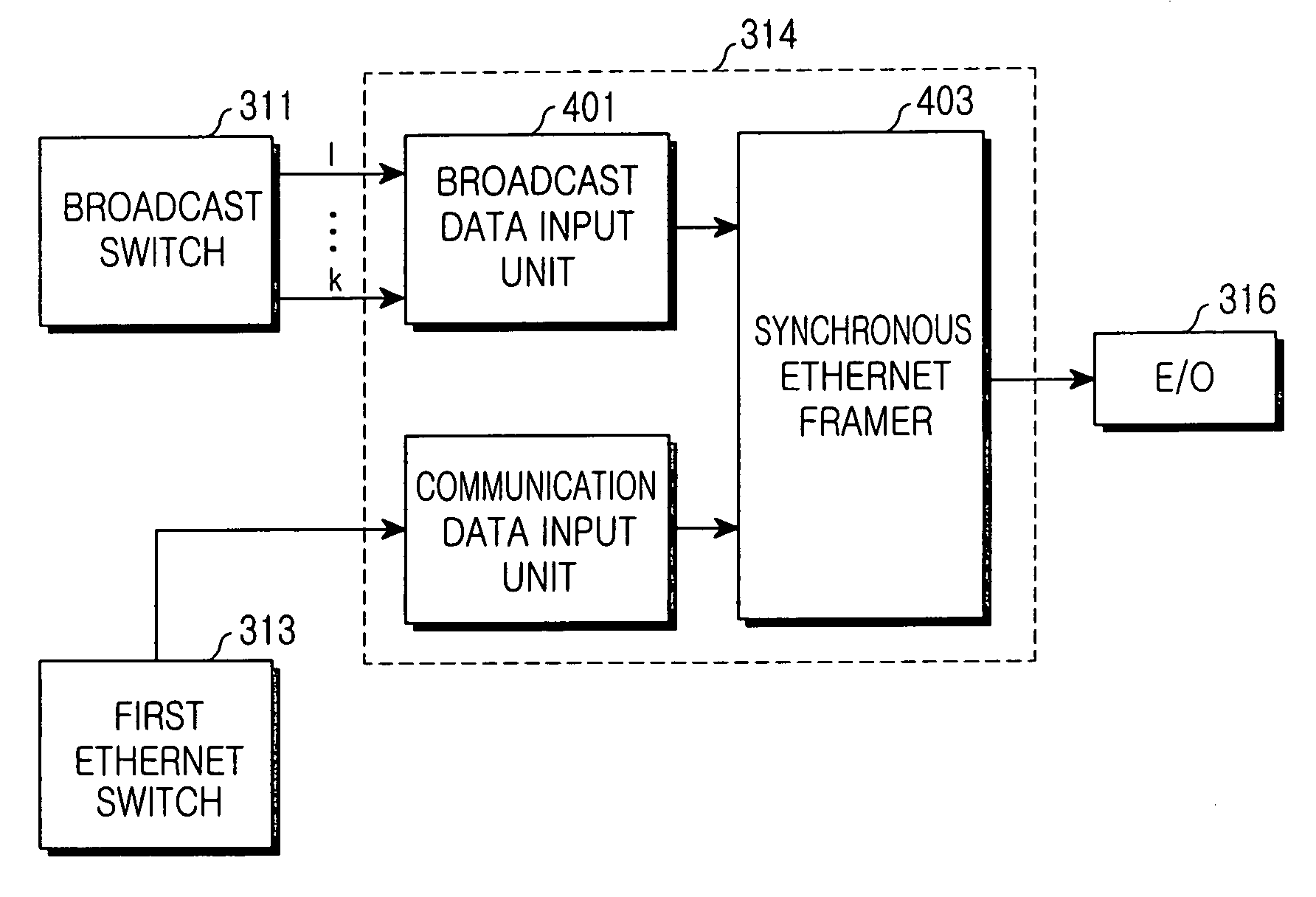
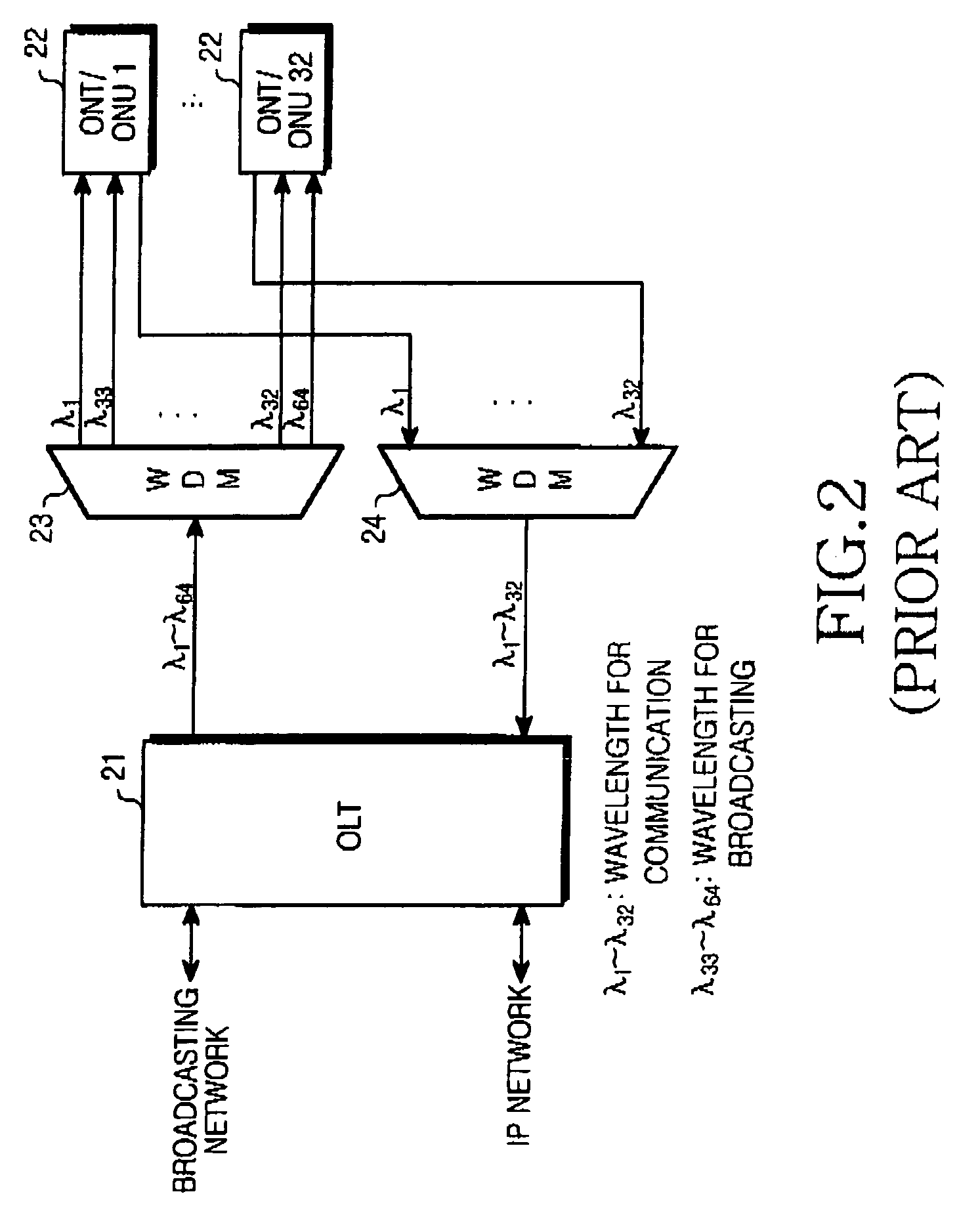
Communication/broadcast multiplexer and demultiplexer used in communication/broadcast-integrated system
InactiveUS20060018334A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsBroadband local area networksMultiplexerBroadcast data
A communication / broadcast multiplexer and demultiplexer for multiplexing and demultiplexing communication and broadcast signals using a specific transmission standard in an optical network system that integrates broadcast and communication services using a channel selection technique. The multiplexer comprises a broadcast data input unit, a communication data input unit, and a synchronous Ethernet framer. The broadcast data input unit receives broadcast data switched on a subscriber basis through a broadcast switch in an optical line terminal (OLT) in the system, and transfers it as a synchronous data frame to the synchronous Ethernet framer. The communication data input unit receives communication data on a subscriber basis through an Ethernet switch in the OLT and transfers it as an asynchronous data frame to the synchronous Ethernet framer. The synchronous Ethernet framer converts both the received synchronous and asynchronous data frames into a TDM synchronous Ethernet frame, and outputs the TDM synchronous Ethernet frame.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Clock synchronization method for synchronous Ethernets, as well as synchronous information sending/receiving method, device and apparatus
ActiveCN102208958AImprove protectionNo limitTime-division multiplexInformation transmissionMedia access control
The invention discloses a clock synchronization method for synchronous Ethernets, as well as a synchronous information sending / receiving method, device and apparatus. The clock synchronization processing performed by a network element on a looped network comprises the following steps: determining the current available clock sources, wherein line clock sources with clock identifications identical to the MAC (media access control) address of the network element can not be used; selecting a currently-used clock source from the determined current available clock sources according to the quality grade and priority of the clock sources; and transmitting a clock within the looped network, and transmitting the clock identification and clock quality information of the clock by an ESMC message, if a line clock source transmitted from the inside of the looped network is used currently, taking the clock identification of the line clock source as the transmitted clock identification, and if a clock source accessed from the outside of the looped network is used currently, taking the MAC address of the network element as the transmitted clock identification. A clock synchronization control device in the network element comprises a clock source selection device and an information transmission device. In the invention, through taking the MAC address of the network element as the clock identification, the problem that clocks on the looped network are looped is solved, and an operation of manually configuring clock identifications is not required.
Owner:RAISECOM TECH
Dual-coupled phase-locked loops for clock and packet-based synchronization
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Communication system using cables carrying ethernet signals
ActiveUS20110170476A1Wireless commuication servicesData switching networksCommunications systemLocal oscillator
It is provided a method for transmitting a wireless signal on Ethernet wiring The wireless signal is received in a hub unit for delivery to a remote unit In the hub unit the wireless signal is down converted to a down-converted frequency band for propagation on the Ethernet wiring A reference signal associated with a local oscillator used for the down conversion is embedded on a synchronous Ethernet stream that may include Ethernet data received at hub unit The synchronous Ethernet stream and the down converted wireless signal are submitted through the Ethernet wiring to the remote unit. The synchronous Ethernet stream may include data for management of electronic circuits installed in the remote unit, as well as a synchronization signal used thereof A converted replica of the first signal may be included in digital form in frames of the synchronous Ethernet stream
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
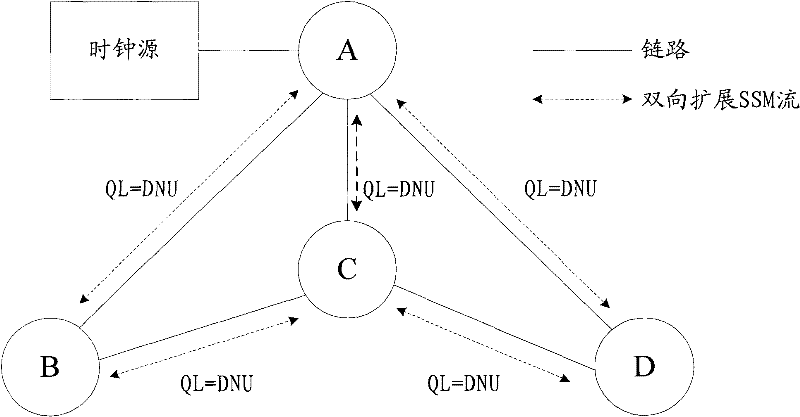
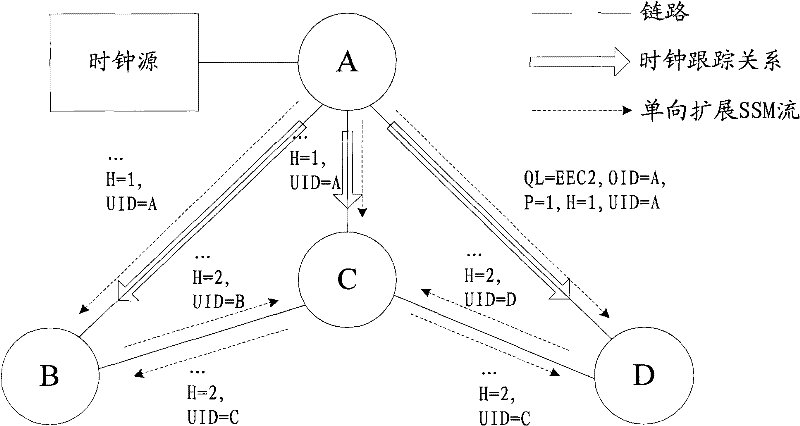
Method, equipment and system for synchronizing Ethernet clock tracking
ActiveCN102130766AAvoid manual configuration workReduce manual configuration workloadSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlWorkloadReal-time computing
The embodiment of the invention provides a method, equipment and system for synchronizing Ethernet clock tracking, which relate to the field of communications and can realize synchronization of automatic tracking of an Ethernet clock to lower the workload of manual configuration. According to the scheme of the invention, the method comprises the following steps of: acquiring at least one extension synchronization status message corresponding to at least one clock source from at least one message source node by using a network node, wherein the extension synchronization status message comprises the clock quality grade of a clock source and the hop between the network node and the clock source; determining an expansion synchronization status message corresponding to a usable clock source from the at least one expansion synchronization status message according to a preset rule, wherein the preset rule is as follows: selecting an expansion synchronization status message corresponding to a clock source which has a high clock quality grade and is small hop away from the network node; and selecting a message source node of the determined expansion synchronization status message for clock tracking. The embodiment of the invention is applied to synchronization of Ethernet clock tracking.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
OTN (Optical Transport Network) device and method for realizing time synchronous transmission
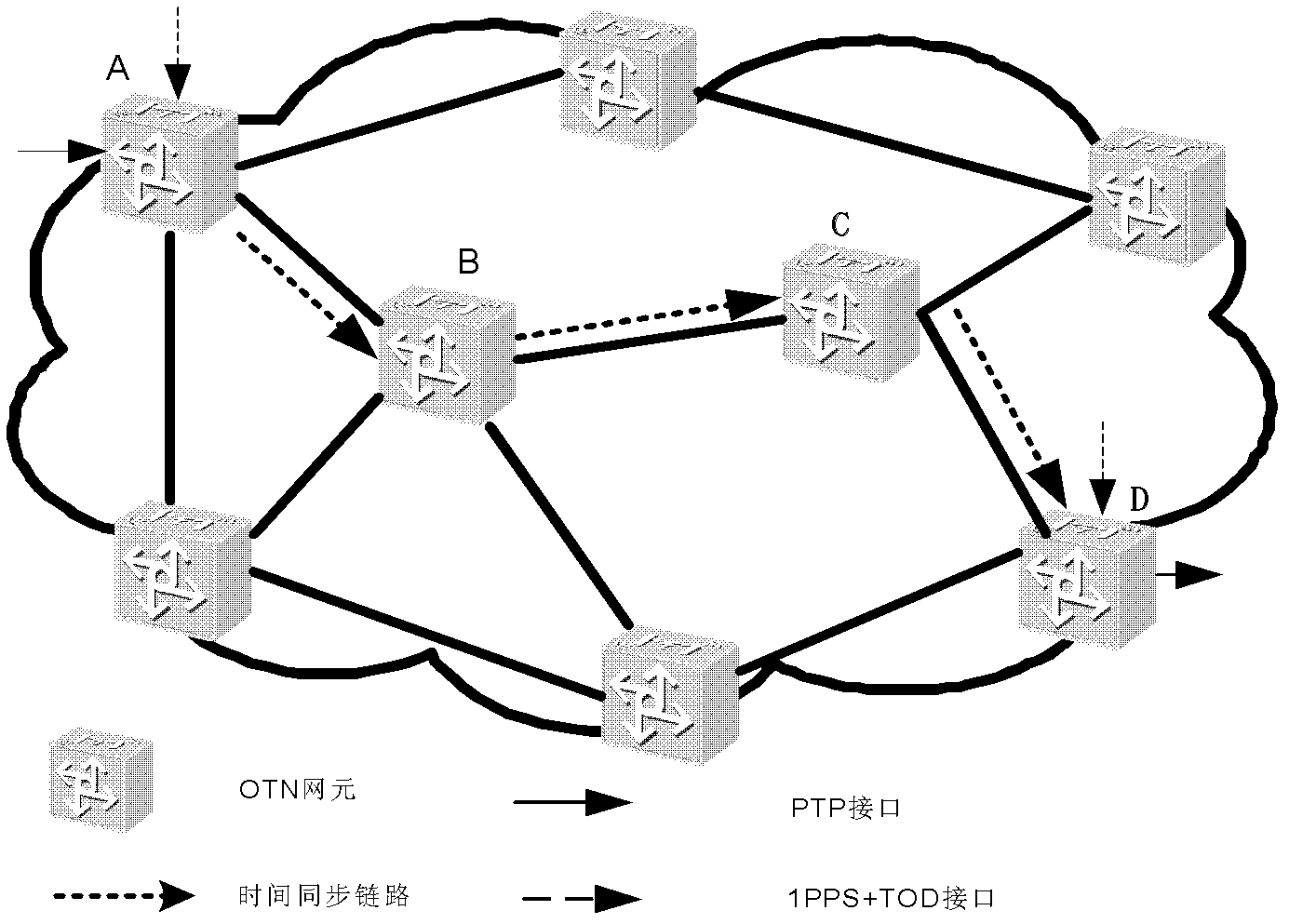
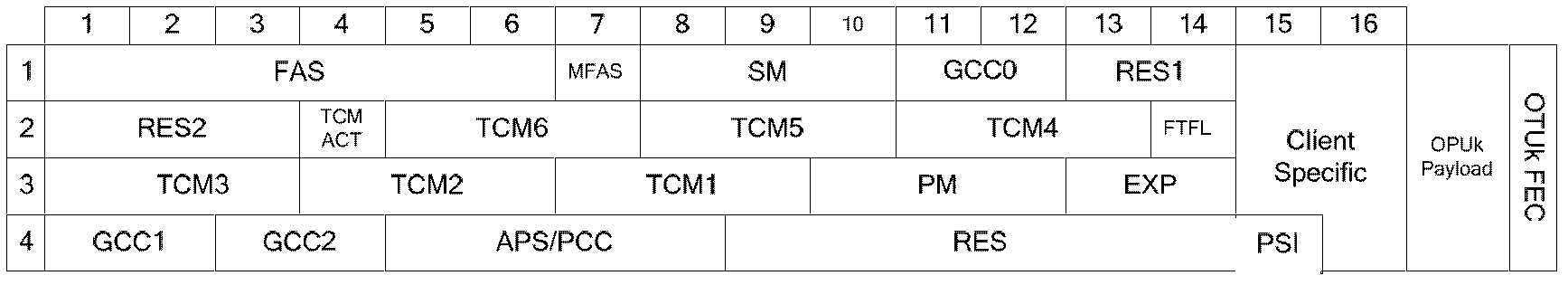
InactiveCN102843620AEasy constructionSimple technologyMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexComputer hardwareStructure of Management Information
The invention relates to the technical field of network communication, and provides an OTN (Optical Transport Network) device and a method for realizing the time synchronous transmission. According to the device and the method, provided by the invention, and on the basis of the synchronous message and the fundamental principle of IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineering) 1588v2 definition, the synchronous message package, the interactive process, the message processing mode, the clock regulation algorithm and the like which are suitable to be used in an OTN are provided, a corresponding device functional structure is also provided, the high-accuracy time synchronous transmission of the OTN which adopts a synchronous clock technology can be realized after compensation, and the high-accuracy synchronous transmission can be realized without on the basis that functions such as complicated synchronous Ethernet are added.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM +1
Method, terminal and system for measuring asymmetric time delay of transmission link
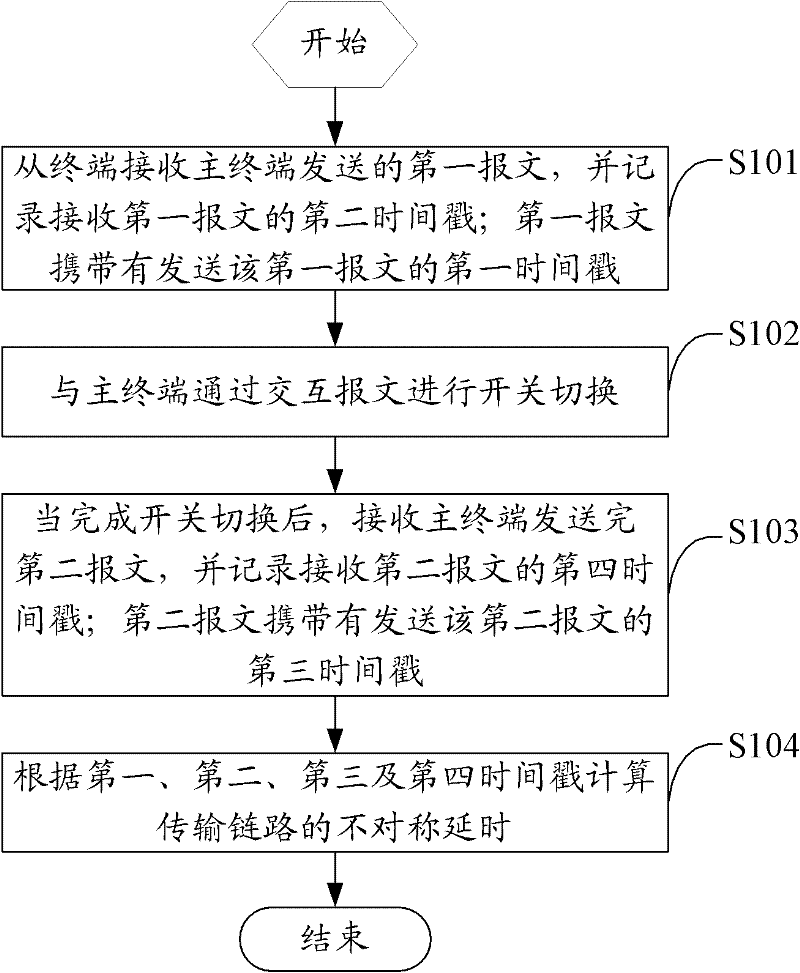
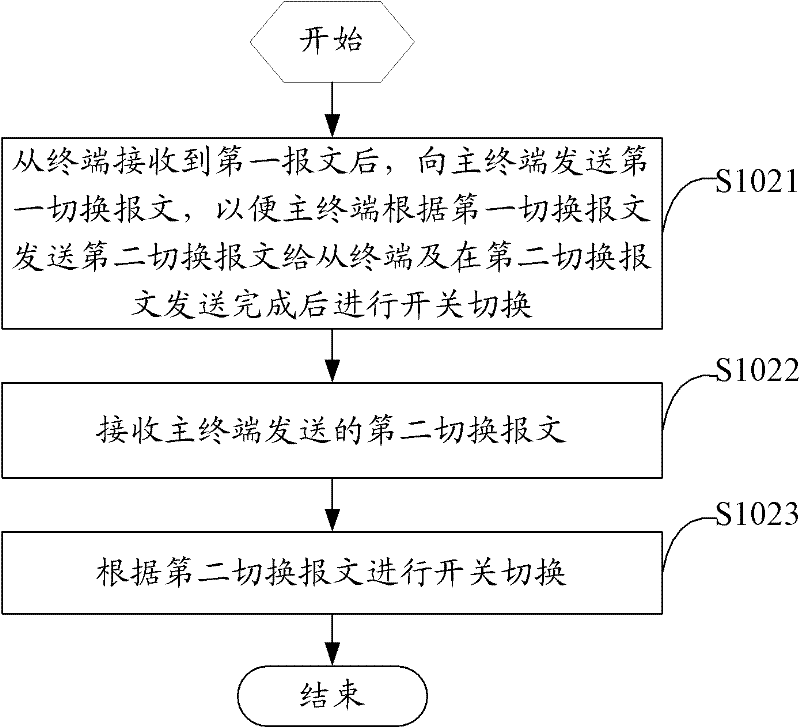
InactiveCN102201983AAvoid inconvenienceEliminate the testing processTime-division multiplexStore-and-forward switching systemsTimestampTime delays
The invention relates to a method, terminal and system for measuring the asymmetric time delay of a transmission line. The method comprises the following steps: a slave terminal receives a first message carrying a first timestamp sent by a master terminal, and records a second timestamp receiving the first message; the slave terminal and the master terminal perform switch changeover through message interaction; after that, the slave terminal receives a second message carrying a third timestamp sent by the master terminal, and records a fourth timestamp receiving the second message; and the slave terminal calculates the asymmetric time delay of the transmission line according to the first, second, third and fourth timestamps. According to the invention, the clocks of the master and slave terminals are synchronized by synchronizing Ethernet, the timestamps of receiving and sending messages of the master and slave terminals are recorded, and the optical fiber on the link is changed over in a changeover switch mode; after the changeover, the message is sent again and the timestamps of the message at the master and slave terminals are recorded, and the slave terminal can quickly calculate the asymmetric time delay of the transmission link according to the obtained four timestamps, wherein the precision can reach the nanosecond level; and the measurement process is simplified.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method of transmitting time-critical information in a synchronous Ethernet system
InactiveCN1767499AData switching by path configurationSynchronising arrangementControl signalFrame time
Disclosed is a method for enabling the transmission of time-critical control signals in a synchronous frame period, such as a pause signal generated when the receive buffer of an Ethernet switch is filled with packets exceeding a threshold due to congestion of uplink asynchronous data . In order to transfer time-critical information in Synchronous Ethernet systems, when a time-critical event is detected, the current transmission time period is checked. If the current transmission time period is a synchronization frame time period, time-critical control information is generated, inserted into the first sub-synchronization frame and transmitted after the time-critical event. If the current transmission time period is an asynchronous frame time period, a control frame including the time-critical control information is generated and transmitted.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for selecting timing master in synchronous ethernet system
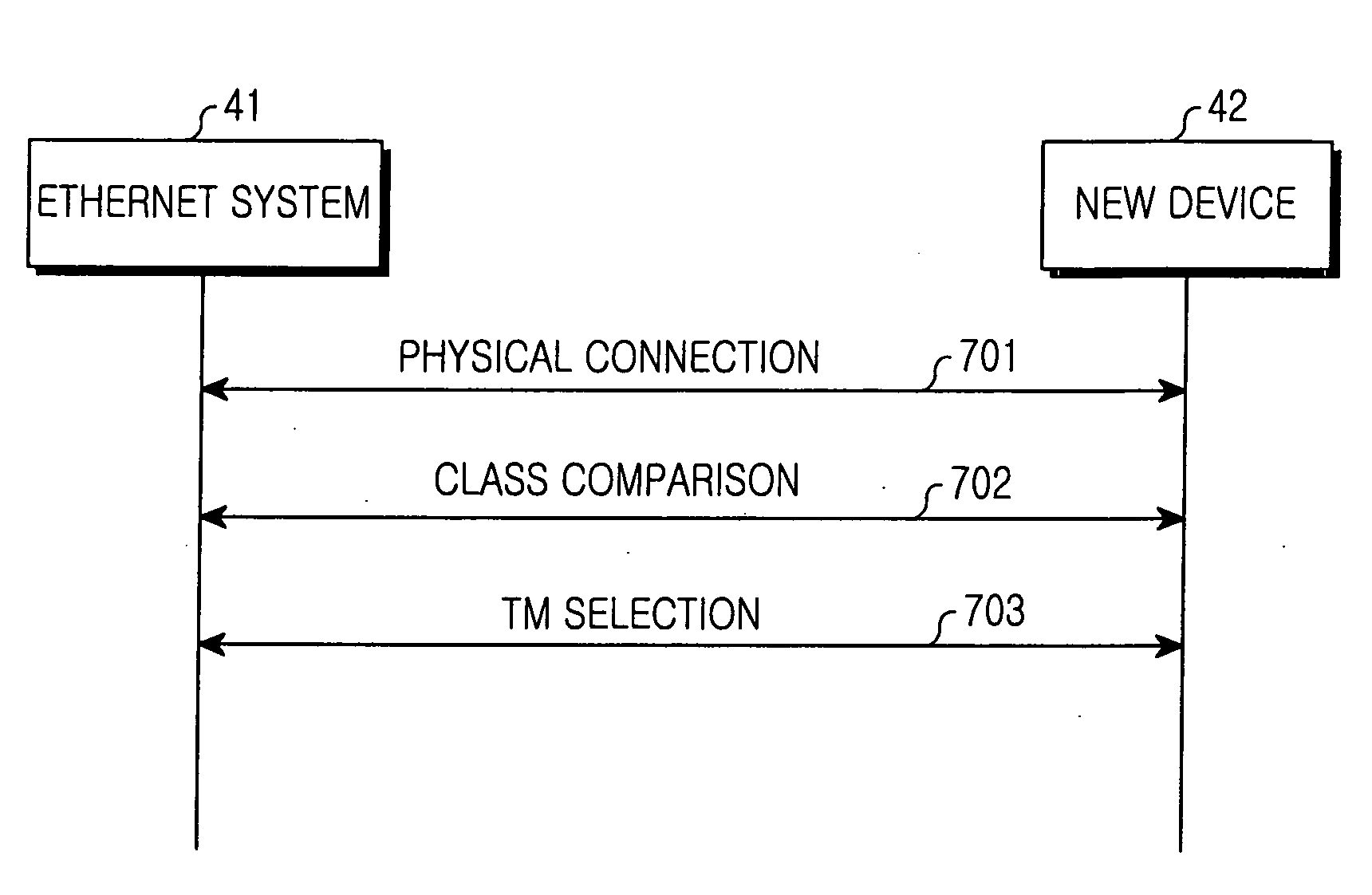
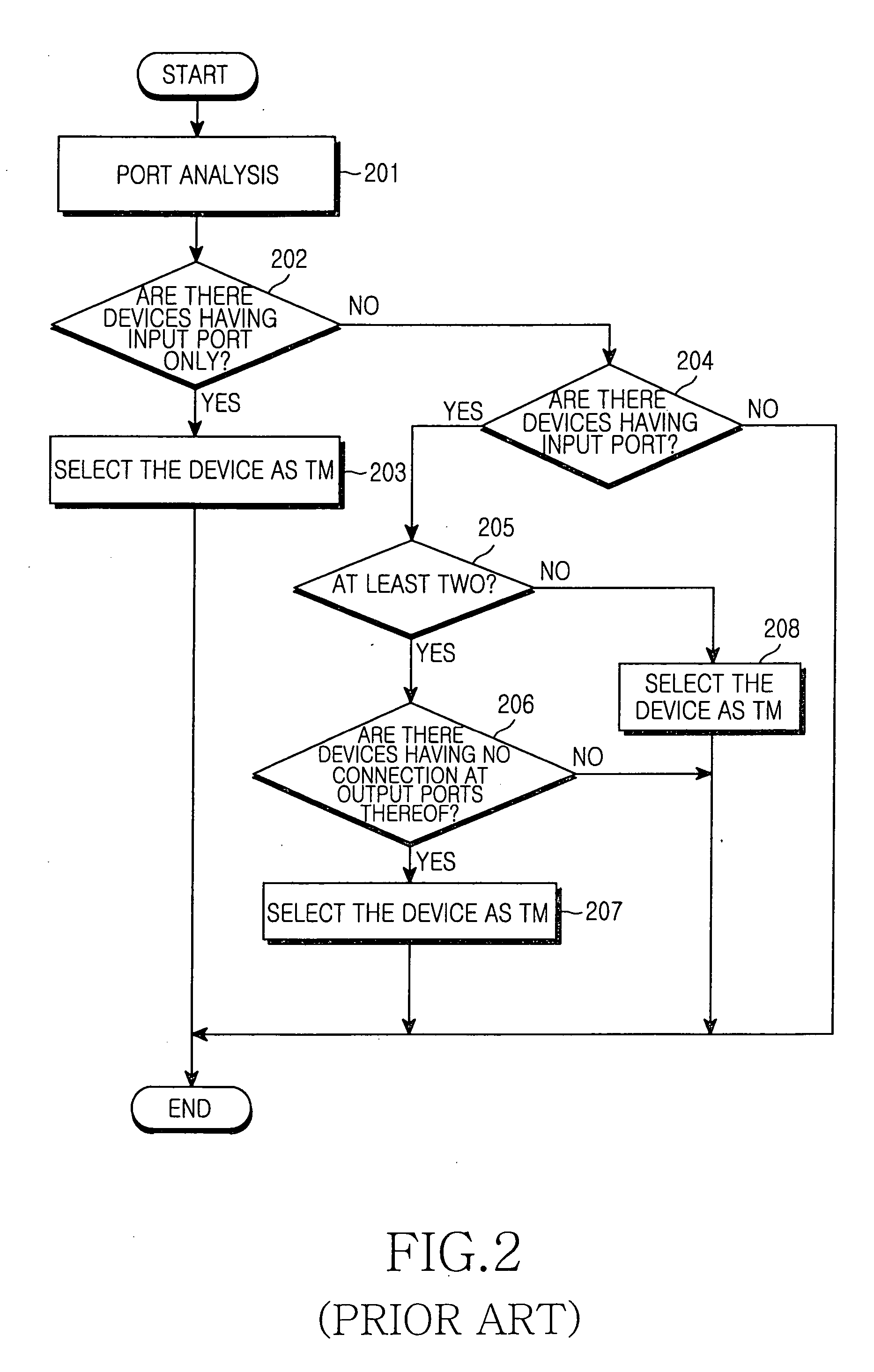
InactiveUS20060067367A1Stably and simply selectingTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationComputer scienceEmbedded system
Disclosed is a method for establishing a synchronization in a synchronous Ethernet system. Devices are classified according to the type of the devices, and a device having a highest class in the synchronous Ethernet system is detected, then it is determined if the device having the highest class is able to serve as the timing master. If so, the device having the highest class is able to serve as the timing master if only one such device is detected; otherwise, the timing master between devices having the highest class is selected through a collision algorithm.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
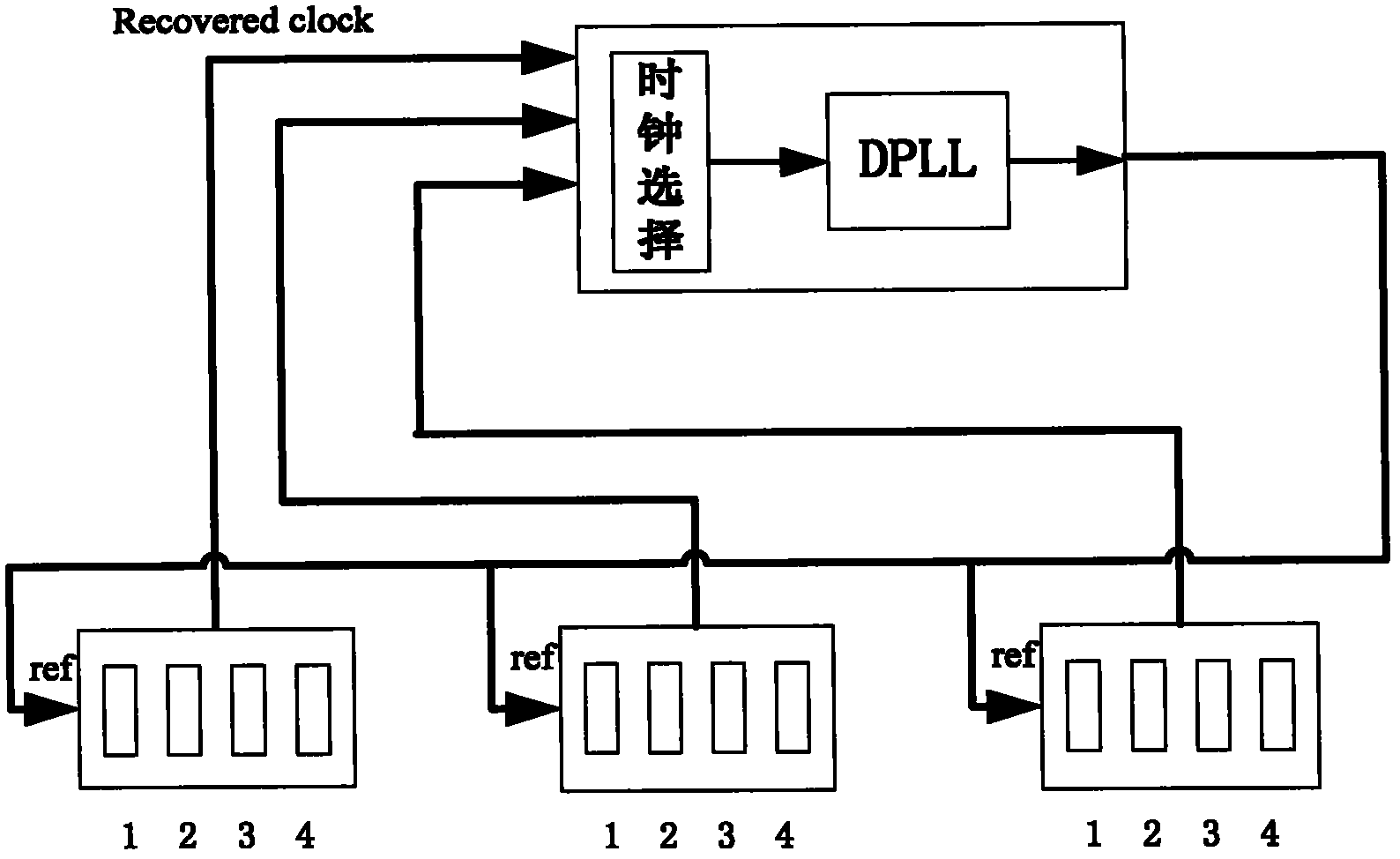
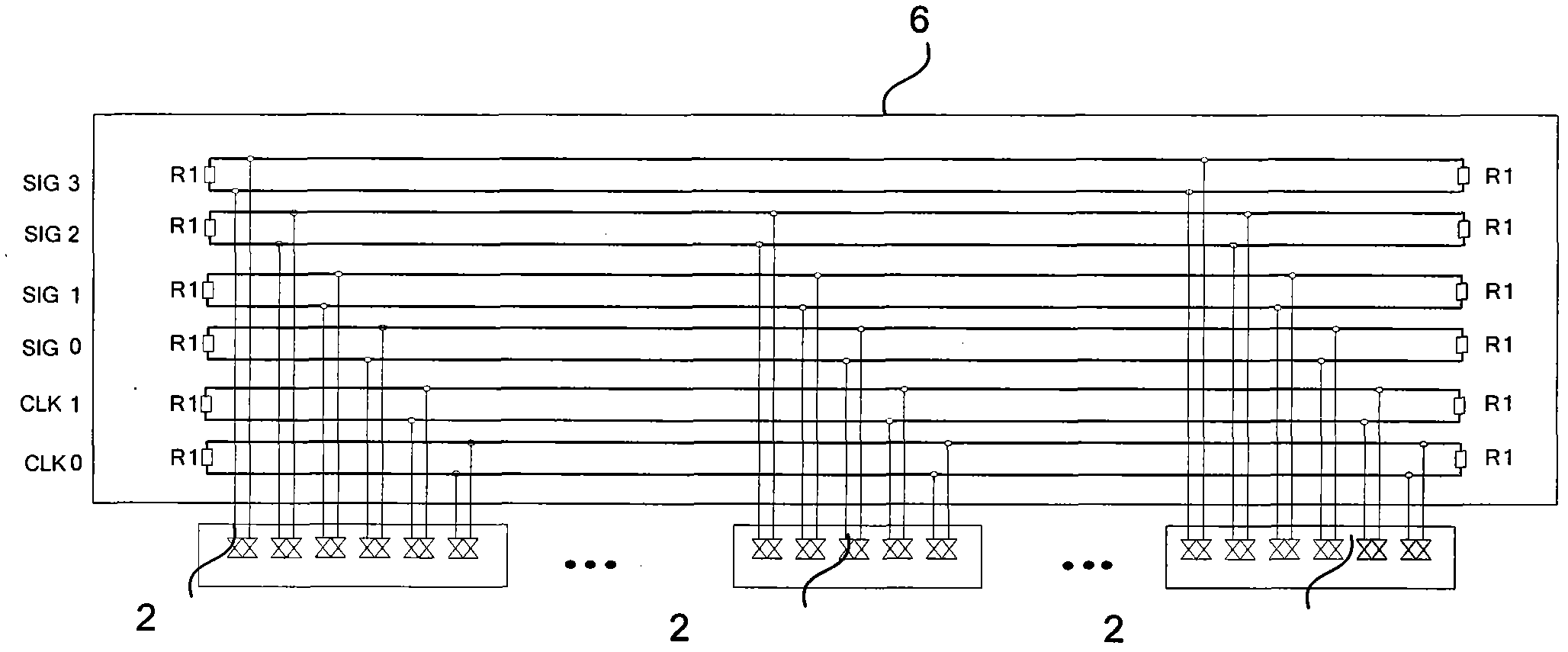
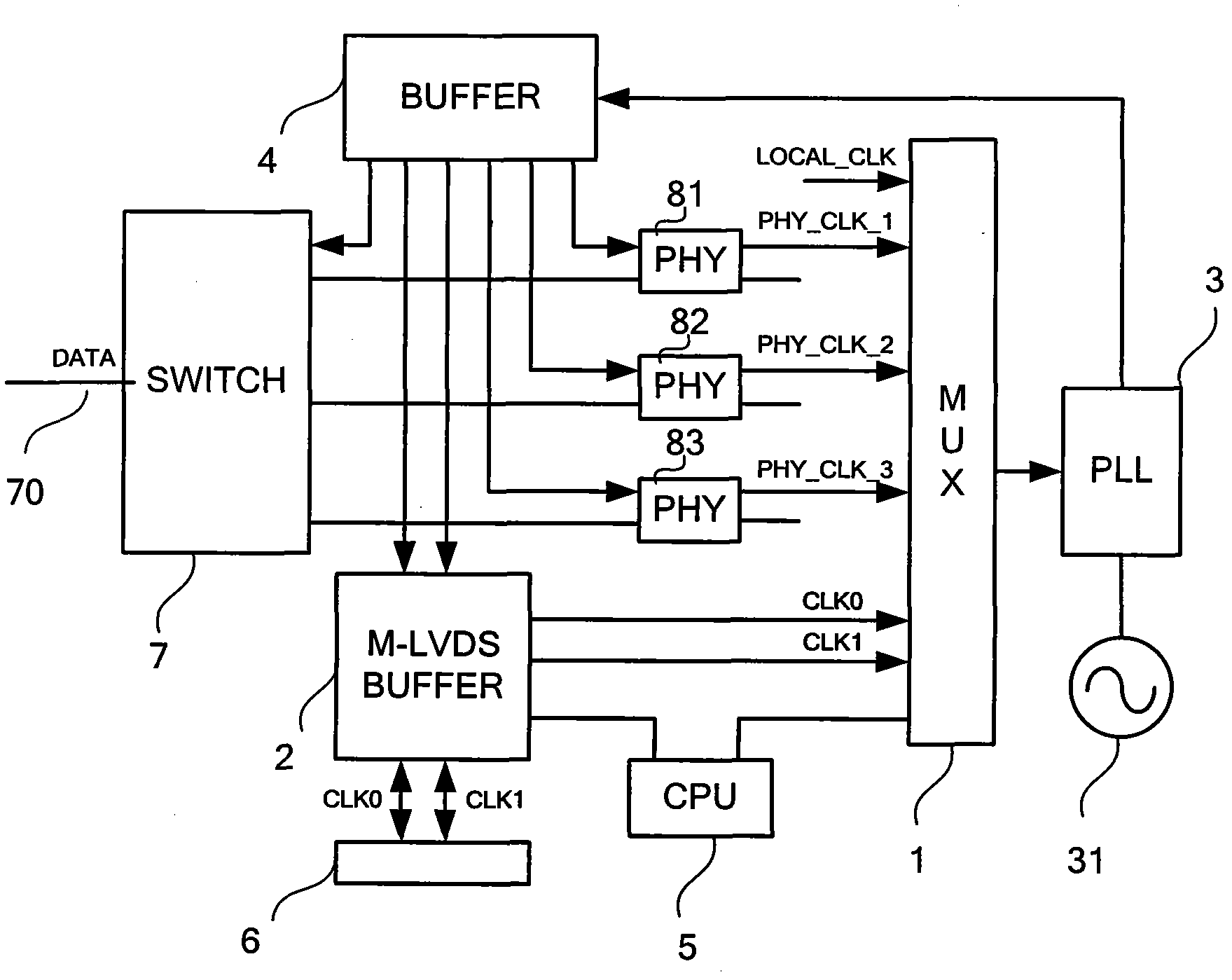
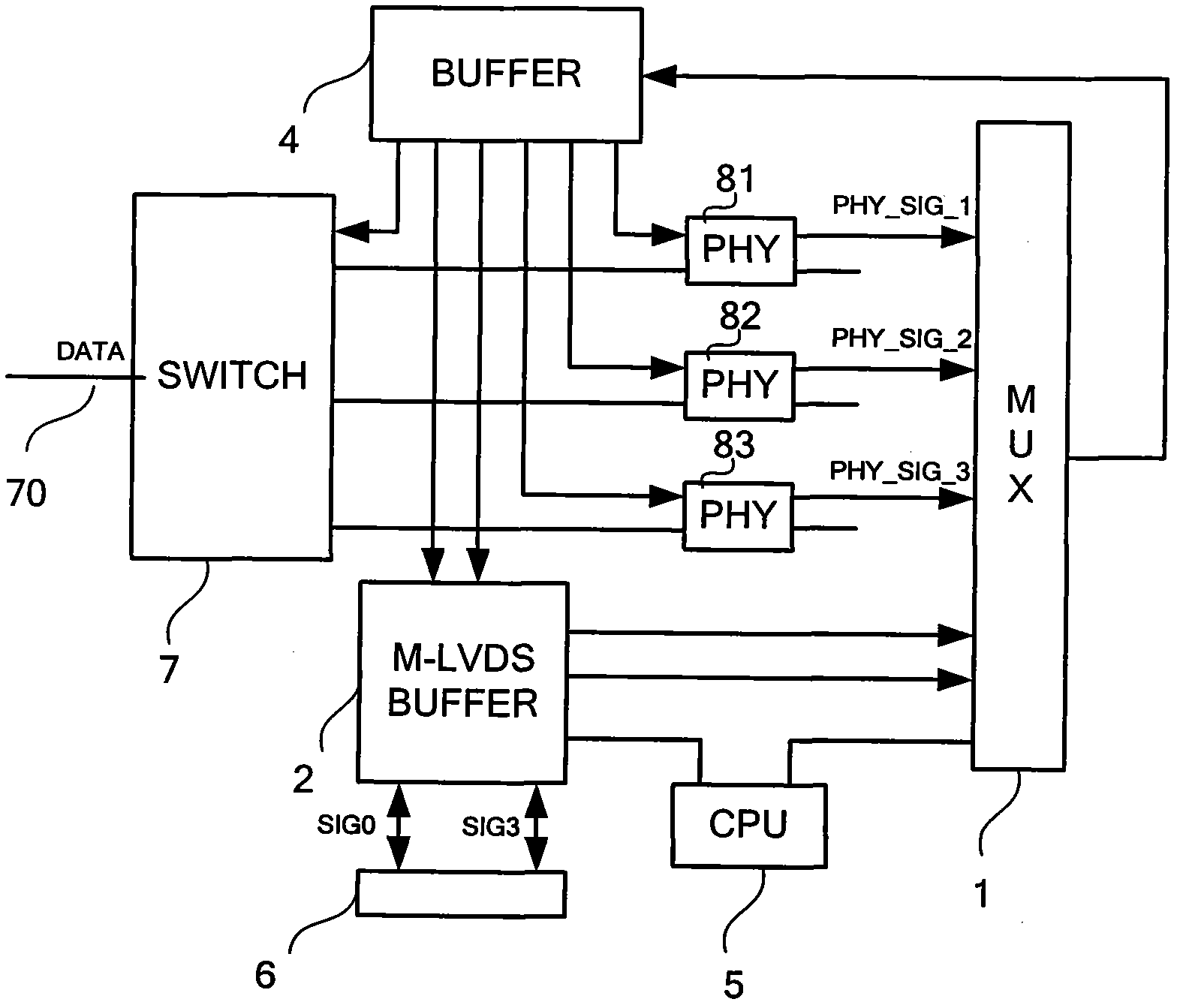
Rack-mount synchronous Ethernet architecture and clock synchronization control method
ActiveCN102045124AReliable Clock RecoveryReliable deliveryTime-division multiplexSynchronising arrangementMultiplexerClock recovery
The invention discloses a rack-mount synchronous Ethernet architecture and a clock synchronization control method. A back board topology structure is designed according to an M-LVDS (multiple low voltage differential signaling) scheme; each service board card selects a synchronous clock through a multiplexer, and a phase locked loop is used to process the synchronous clock, so that all service ports in the rack can serve as master ports of the synchronous Ethernet and also can serve as slave ports of the synchronous Ethernet. By using the rack-mount synchronous Ethernet architecture and the clock synchronization control method, a special block board card is eliminated for processing, and the equipment cost is reduced; and the flexibility of the clock source selection is improved, and reliable clock restoration, clock synchronization, clock degittering and the transmission of a synchronous time stamp are facilitated.
Owner:武汉神州数码云科网络技术有限公司
Ethernet network synchronization systems and methods
The present disclosure relates to Ethernet synchronization systems and methods that combines Synchronous Ethernet (Sync-E) and Precision Time Protocol (PTP) IEEE 1588 algorithms. The present invention includes systems and methods for Ethernet networks and node configurations that include a set of rules on node placement, such as Boundary Clock (BC) nodes and Sync-E nodes, a clock selection algorithm, a holdover algorithm, and the like. Advantageously, the present invention provides an architecture that allows practical and real-world useful clock propagation through placement of BCs and Sync-E nodes for best performance. Practical experience and theoretical design are embodied in the present invention to define a very specific set of rules on how to build a network capable of providing accurate and reliable synchronization. The present invention includes clock selection that unifies Sync-E and 1588 algorithms.
Owner:CIENA
Device and method for realizing time synchronization on Ethernet switch
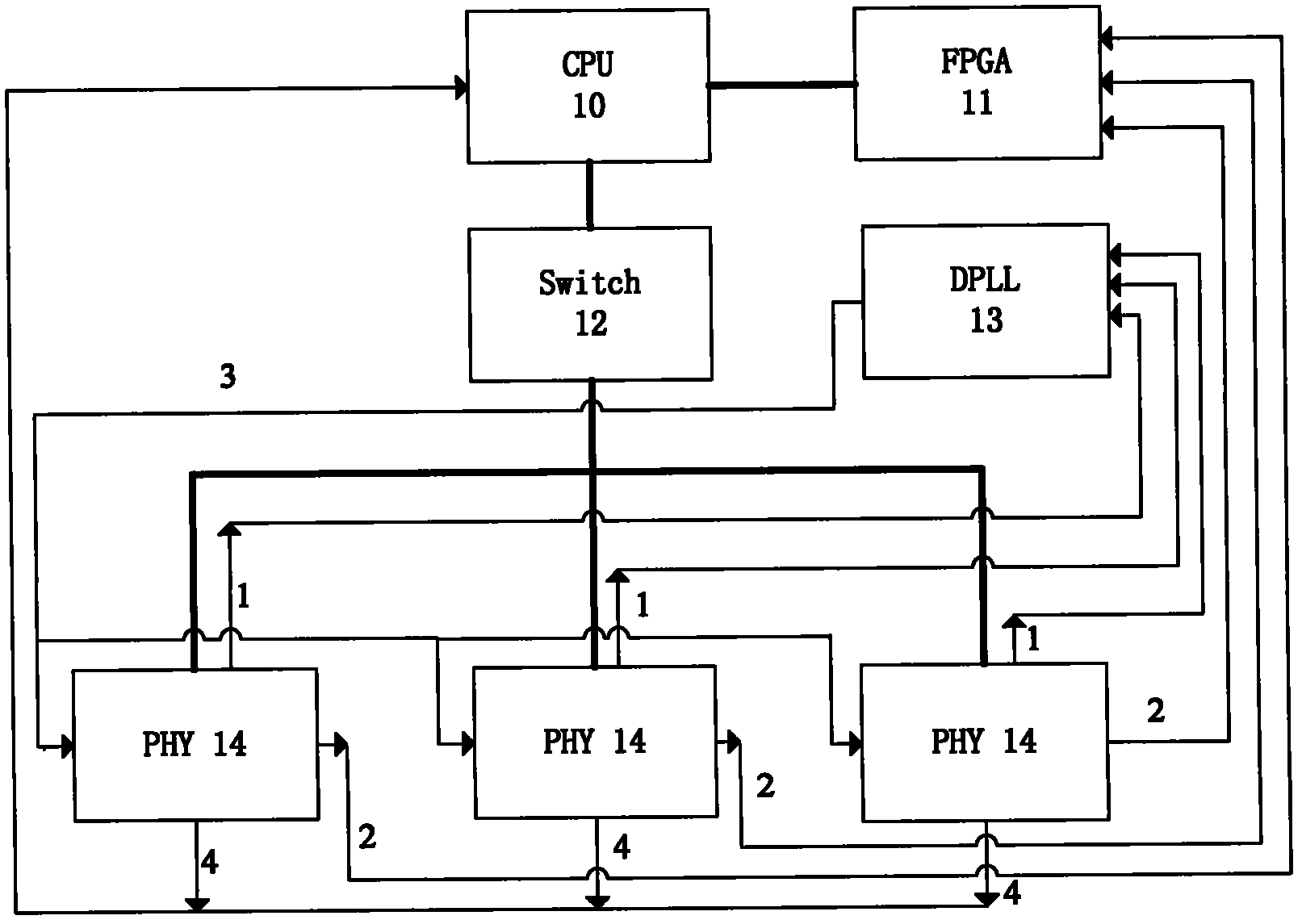
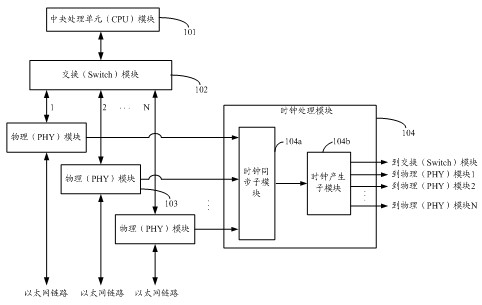
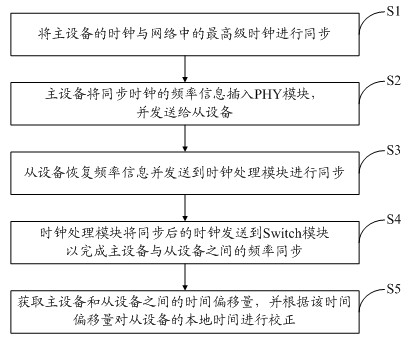
InactiveCN102404105AImprove time synchronization accuracyLow costData switching networksSynchronising arrangementData synchronizationTime delays
The invention discloses a method and a device for realizing time synchronization on an Ethernet switch. The device comprises a Switch module, a plurality of PHY (Physical layer) modules, a CPU module and a clock processing module, wherein the clock processing module comprises a clock synchronization sub-module and a clock production sub-module. The clock can be synchronized according to the clock provided by the PHY module through adopting the time delay measuring technology provided by the synchronic Ethernet (SyncE, SynchronousEthernet) protocol and the IEEE1588 protocol, then the reference input clock needed by the relative modules in the system can be produced, and the frequencies of the main device and the auxiliary device are synchronized. Because of adopting the PHY chip with SyncE function, the frequency synchronization precision is very high, which can reach nanosecond level.
Owner:SUZHOU CENTEC COMM CO LTD
Method for transmitting data without jitter in synchronous Ethernet
InactiveUS20060165172A1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningComputer hardwareAsynchronous data
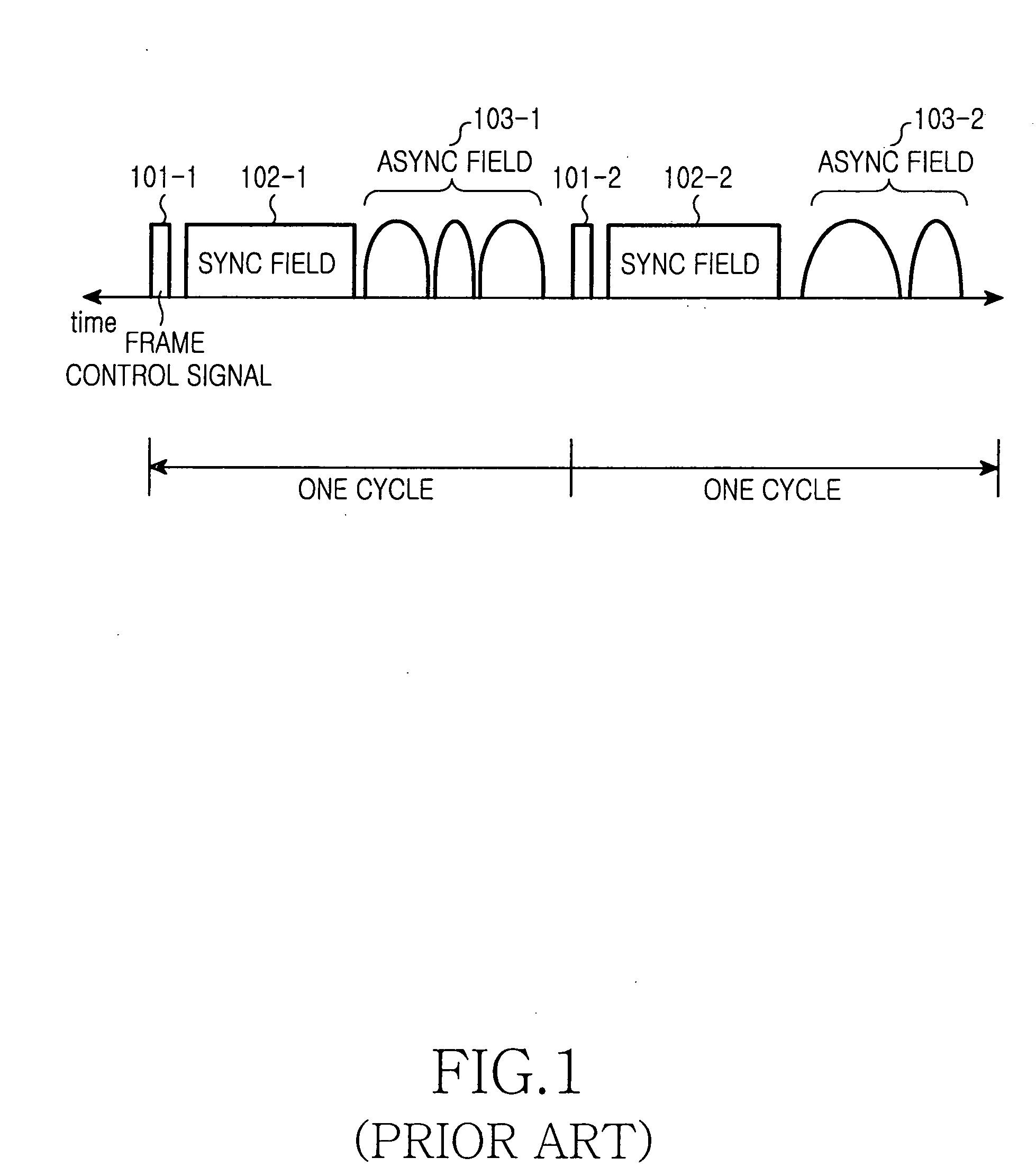
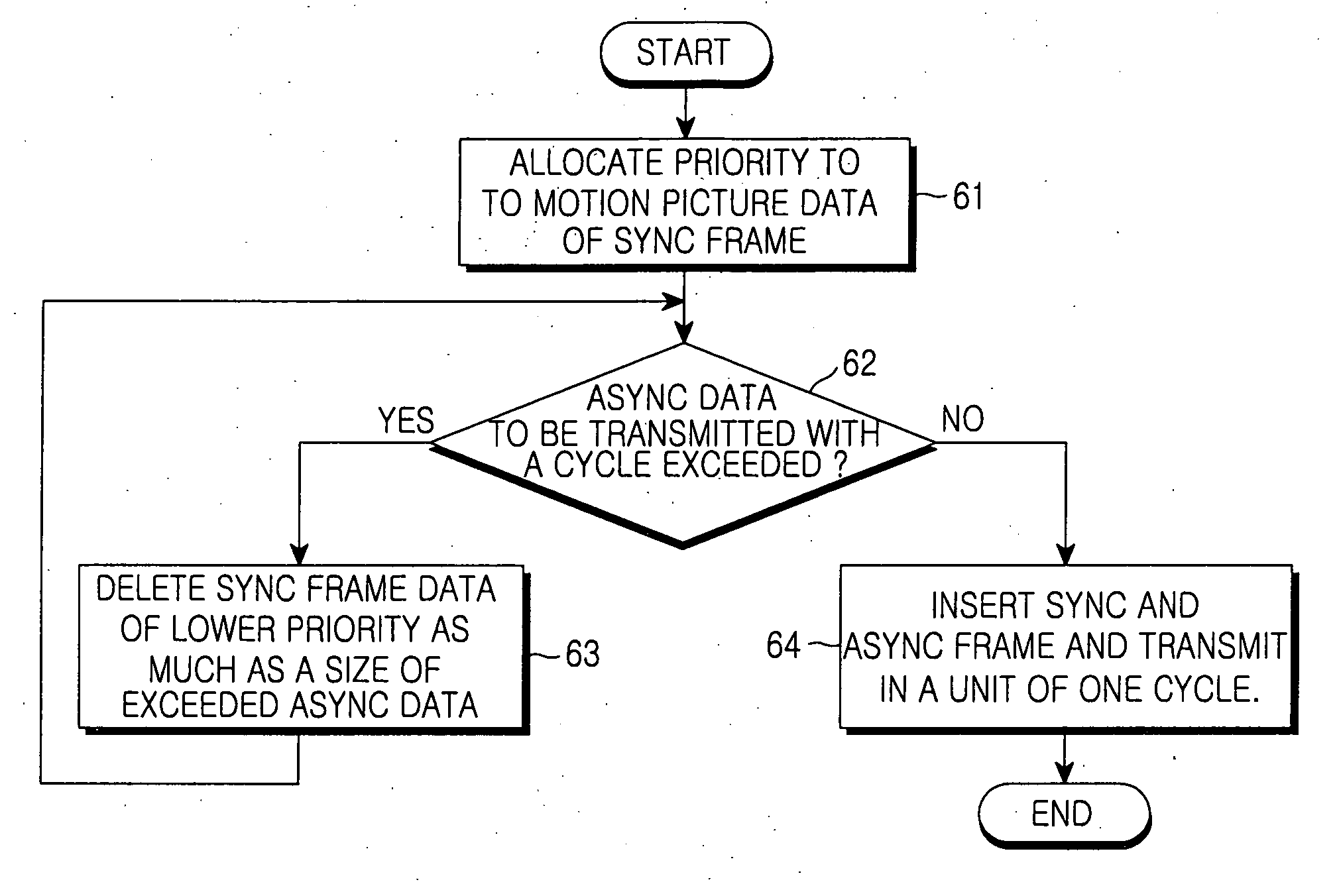
Disclosed is a method for transmitting asynchronous data in a synchronous Ethernet having a sync frame section and an async frame section. The method includes the steps of: a) allocating a priority to motion picture data for transmission through the sync frame section; b) determining if a size of the data of all frames for transmission in one cycle exceeds the predetermined length; c) dropping motion picture data having a lower priority (e.g. which corresponds to the size of the data exceeding the predetermined length); and d) transmitting the data in one cycle unit when the size of the data to be transmitted does not exceed the predetermined length.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Data frame construction method and data processing method according to data frame in synchronous Ethernet
InactiveUS20050265332A1Prevent transfer efficiencyUnnecessary overheadTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationSynchronous frameAsynchronous data
Disclosed is a method for constructing a frame of data for transmission by each Ethernet device in a synchronous Ethernet, which comprising the steps of receiving the data for transmission and confirming whether or not the data for transmission are synchronous data, when the received data are synchronous data, marking that the data are synchronous data in a preamble of the frame and constructing a synchronous frame by including the received data into a data portion of the frame which does not contain a MAC header and when the received data are asynchronous data, marking that the data are asynchronous data in the preamble of the frame and constructing an asynchronous frame by including the received data into a data portion of the frame containing a MAC header.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
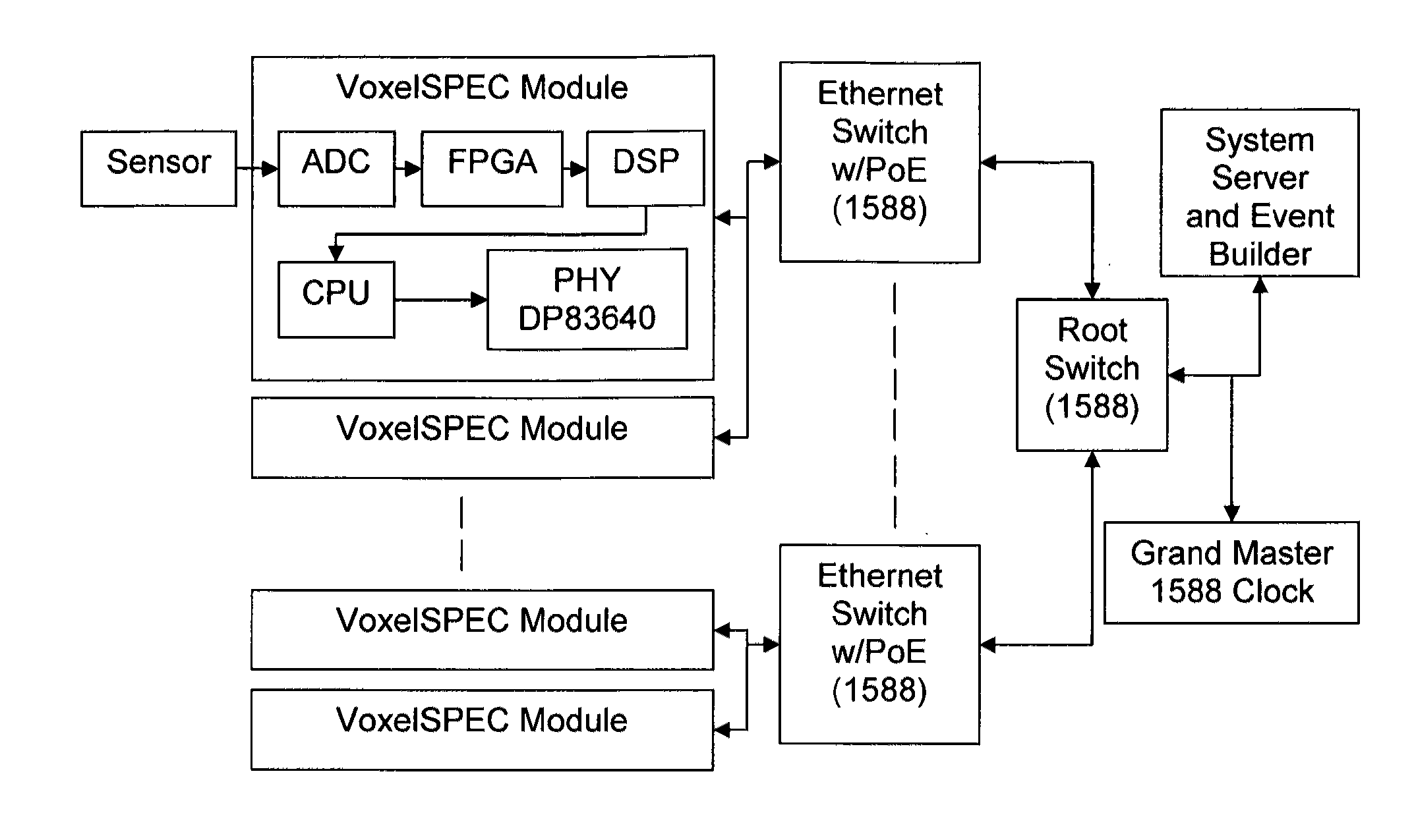
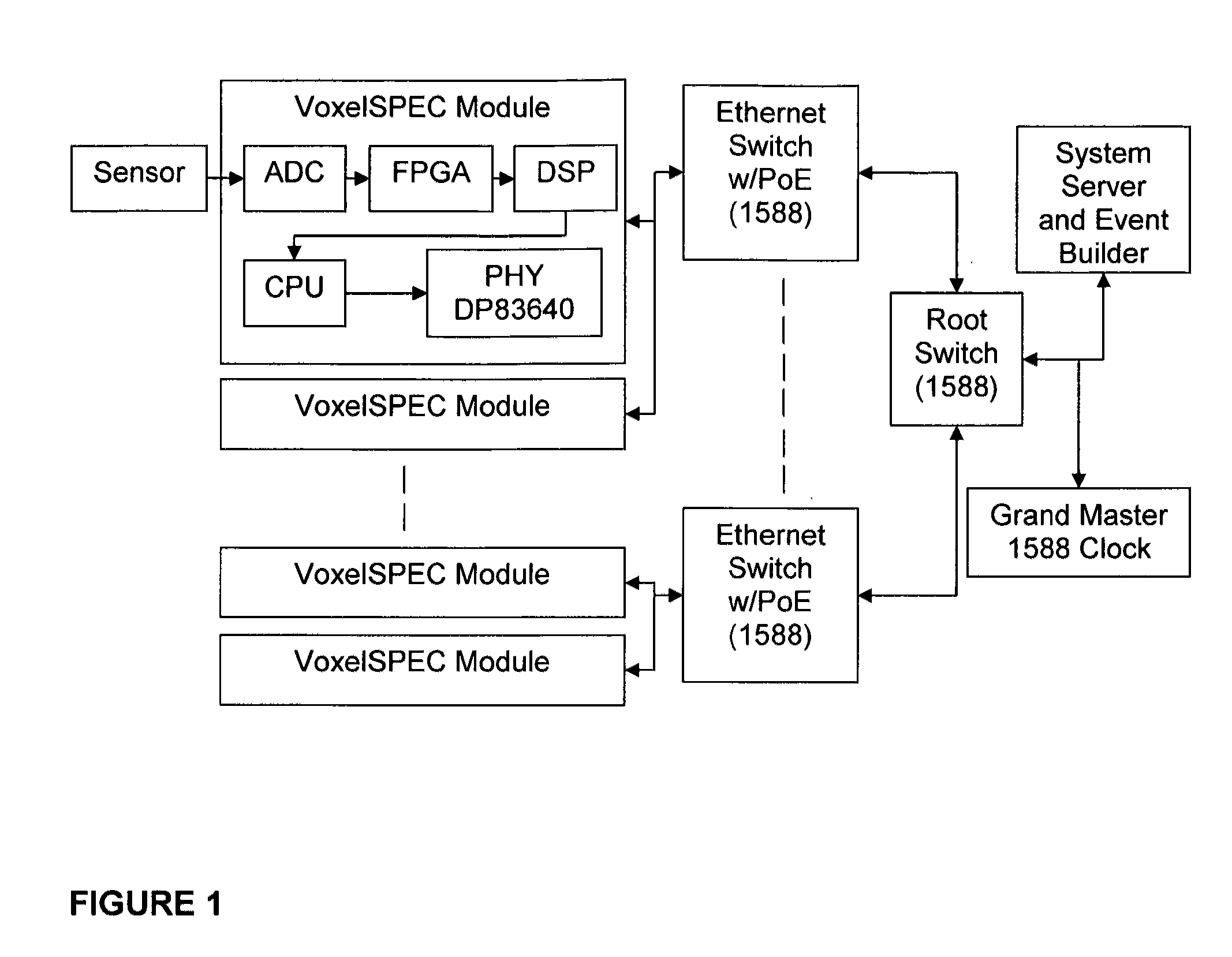
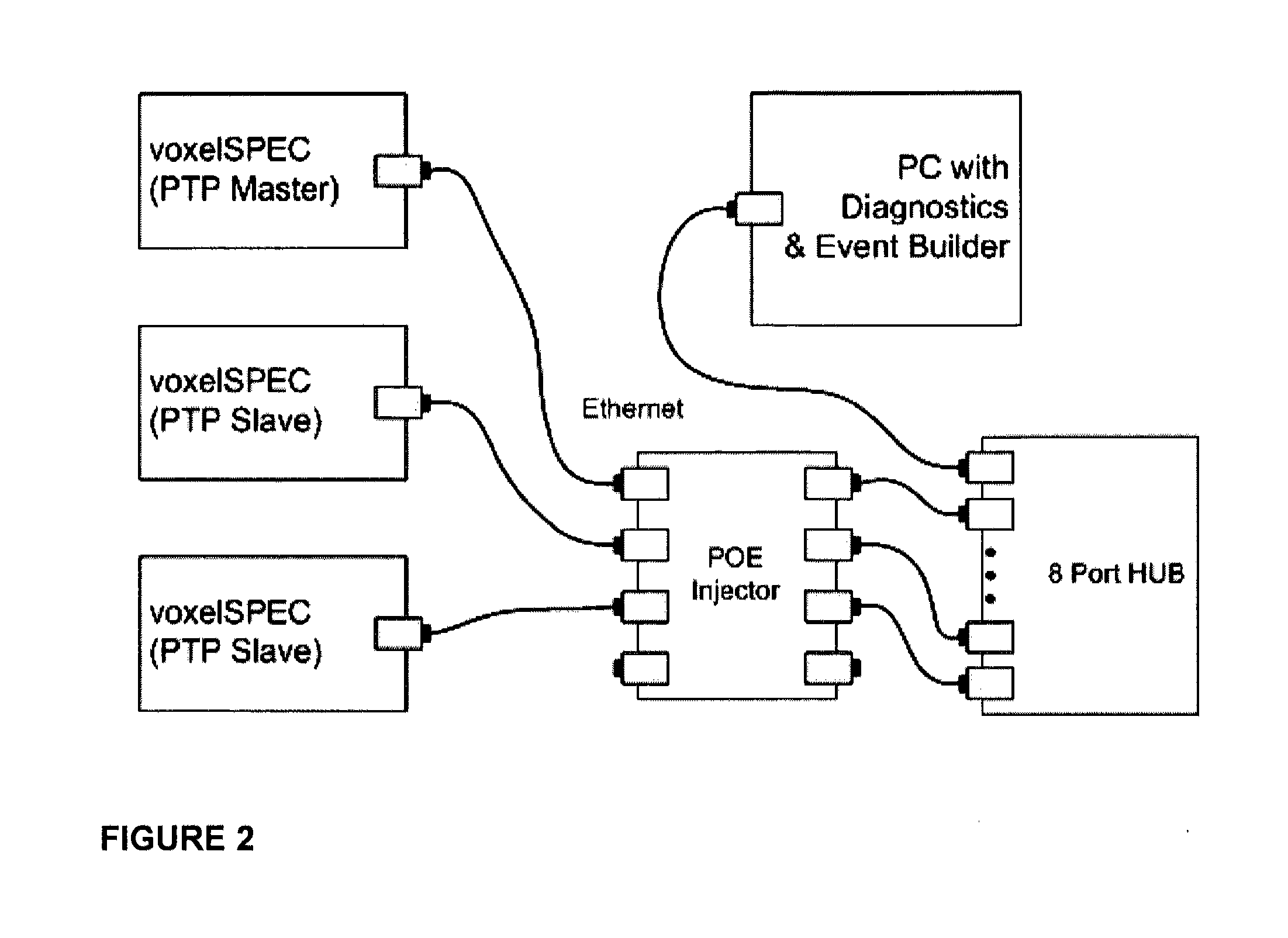
Radiation measurement using timing-over-Ethernet protocol
InactiveUS20120153166A1Reduce complexityAccurate time informationElectric discharge tubesSolid-state devicesEthernet protocolRadiation measurement
A highly scalable platform for radiation measurement data collection with high precision time stamping and time measurements between the elements in the detection array uses IEEE 1588 with or without Synchronous Ethernet (timing over Ethernet) to synchronize the measurements. At a minimum, the system includes at least two radiation detector units, an IEEE 1588 and SyncE enabled Ethernet switch, and a computer for processing. The addition of timing over Ethernet and power over Ethernet (PoE) allows a radiation measurement system to operate with a single Ethernet cable, simplifying deployment of detectors using standardized technology with a multitude of configuration possibilities. This eliminates the need for an additional hardware for the timing measurements which simplifies the detection system, reduces the cost of the deployment, reduces the power consumption of the detection system and reduces the overall size of the system.
Owner:FLIR DETECTION
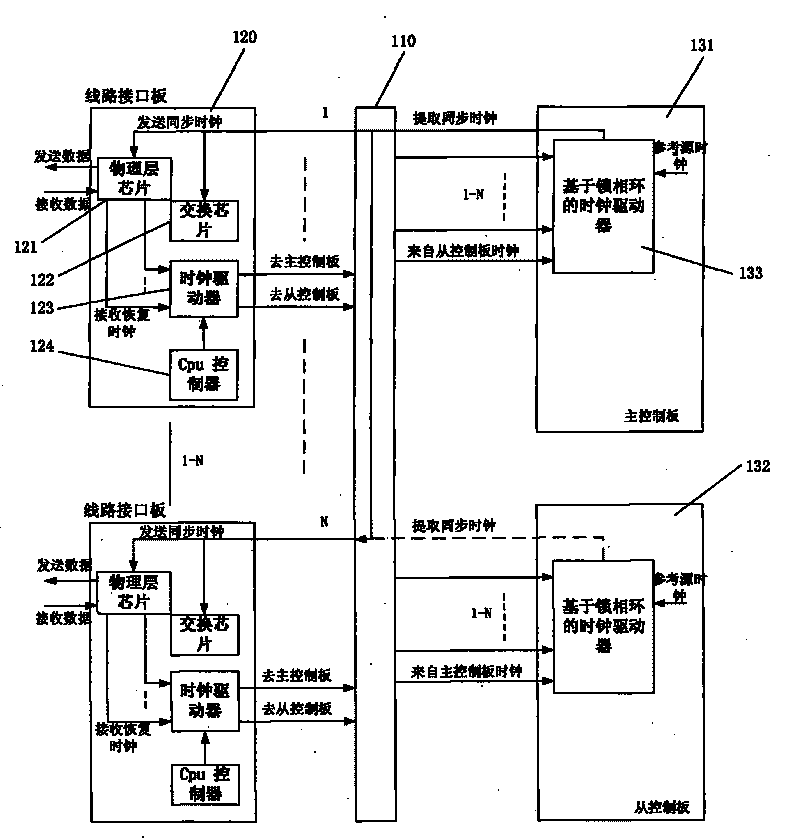
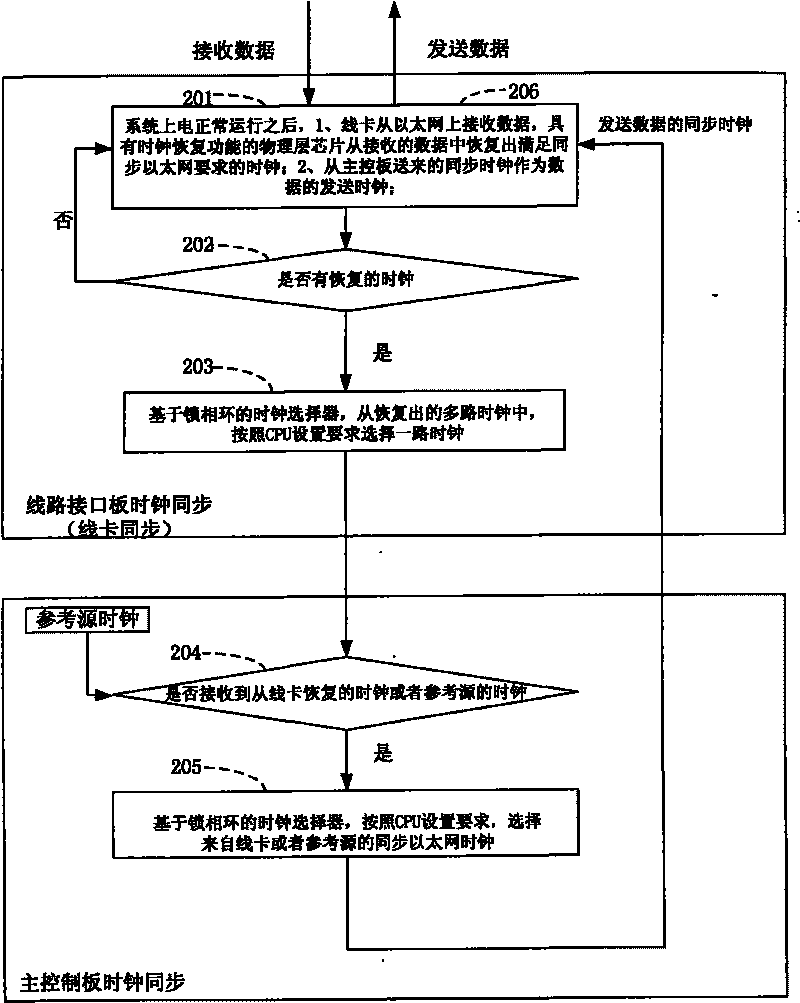
Method and system for implementing synchronous Ethernet based on clock recovery and public reference sources
InactiveCN101741539AGuaranteed clock synchronizationGood synchronizationData switching by path configurationSynchronising arrangementClock recoveryEmbedded system
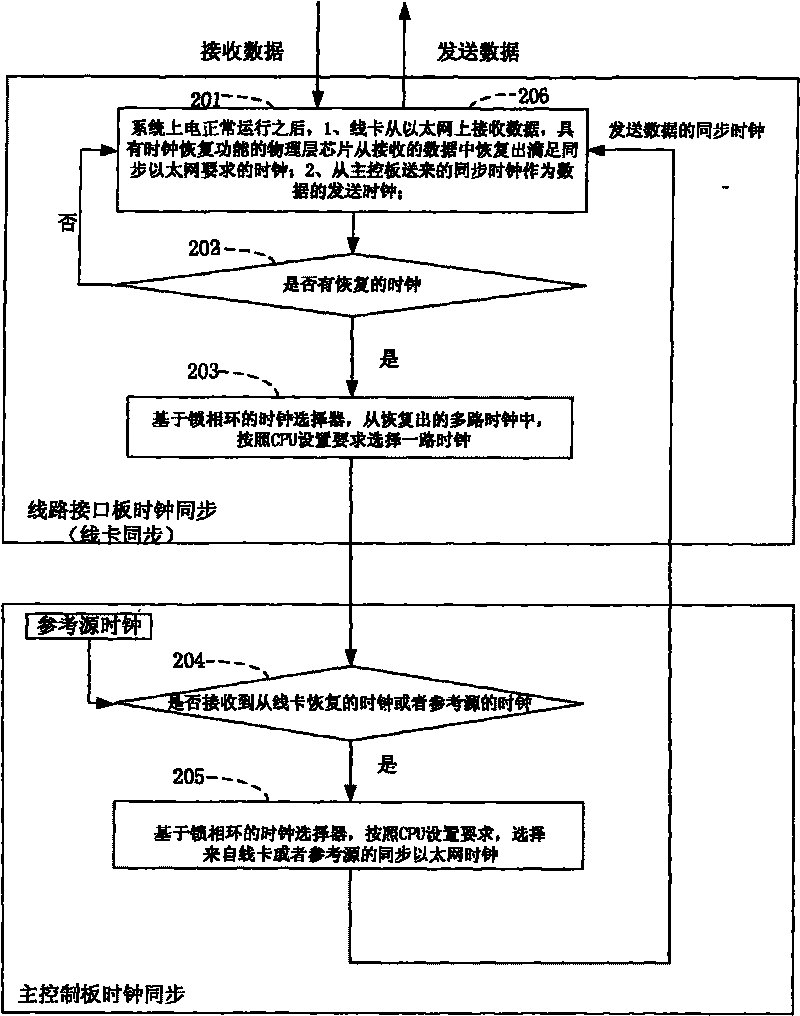
The invention discloses a method and a system for implementing a synchronous Ethernet based on clock recovery and public reference sources. The method comprises the following steps that: a plurality of line interface boards receive data from the Ethernet, recover clock signals meeting the requirement of the synchronous Ethernet through physical chips of the line interface boards, and send the clock signals to a main control board; the main control board selects a path of synchronous clock to be output to the line interface boards through a phase-locked loop-based clock driver according to a plurality of received recovered clock signals; and the line interface boards send the data according to the synchronous clock selected by the main control board. The method and the system for implementing the synchronous Ethernet based on the clock recovery and public reference sources ensure the clock synchronizing process of the synchronous Ethernet because the clock synchronizing operation and corresponding functional modules of the line interface boards and the main control board are adopted, and are convenient for the implementing process of each related service function.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method for switching master/slave timing in a 1000base-t link without traffic disruption
ActiveUS20110170645A1Fully comprehendedTime-division multiplexLoop networksMaster/slaveReal-time computing
A method switches master / slave timing in a communication network without traffic disruption. The method includes a master device informing a slave of timing loss. The master device additionally begins transmitting with timing from a local reference clock and begins receive timing recovery. The slave freezes its receive timing recovery and locks its transmit clock. The master device transitions its transmit timing to use the recovered receive clock. The slave gradually switches to transmitting using its local clock signal. The method may be used in synchronous Ethernet networks.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com