Patents
Literature
142 results about "Media Independent Interface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
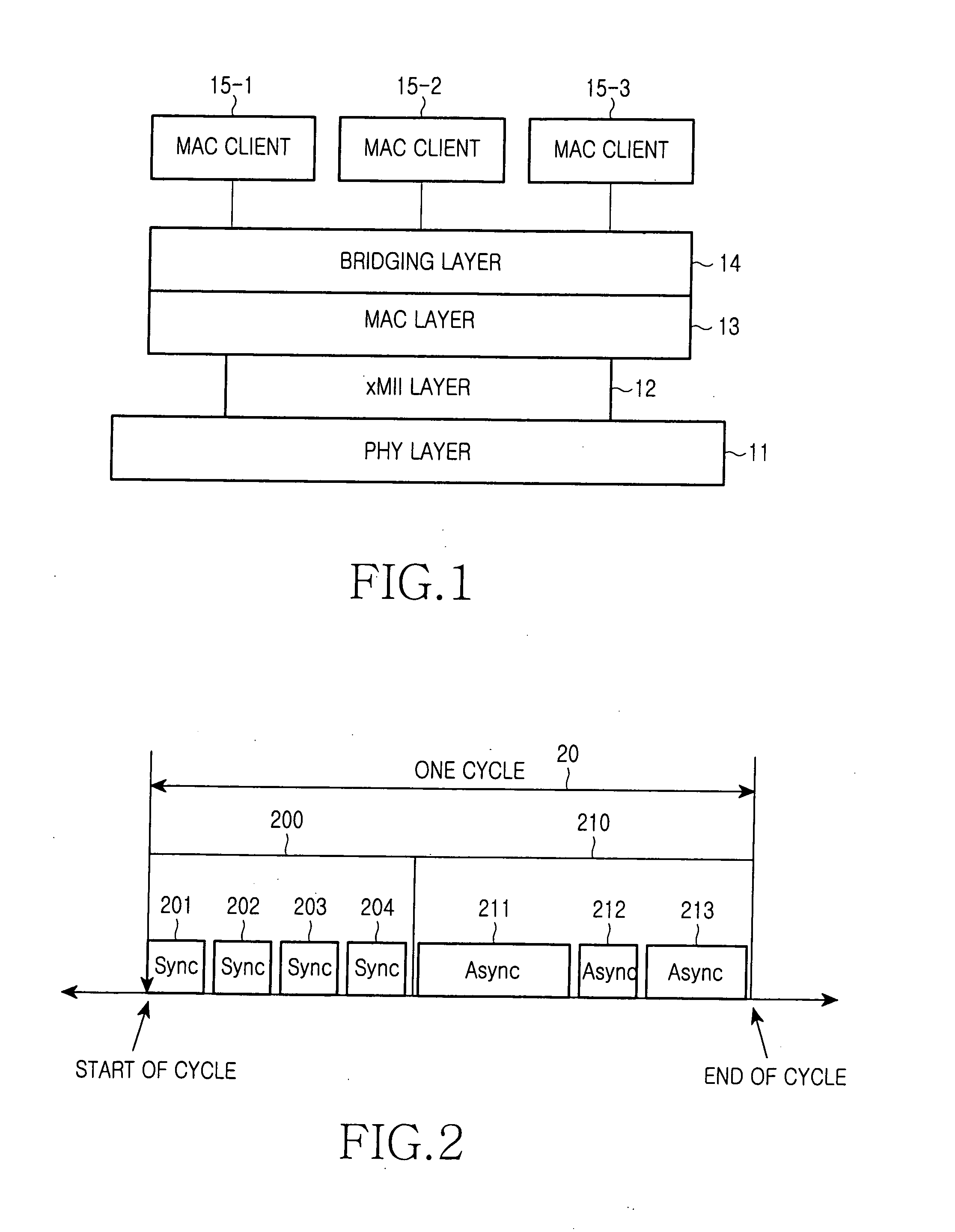
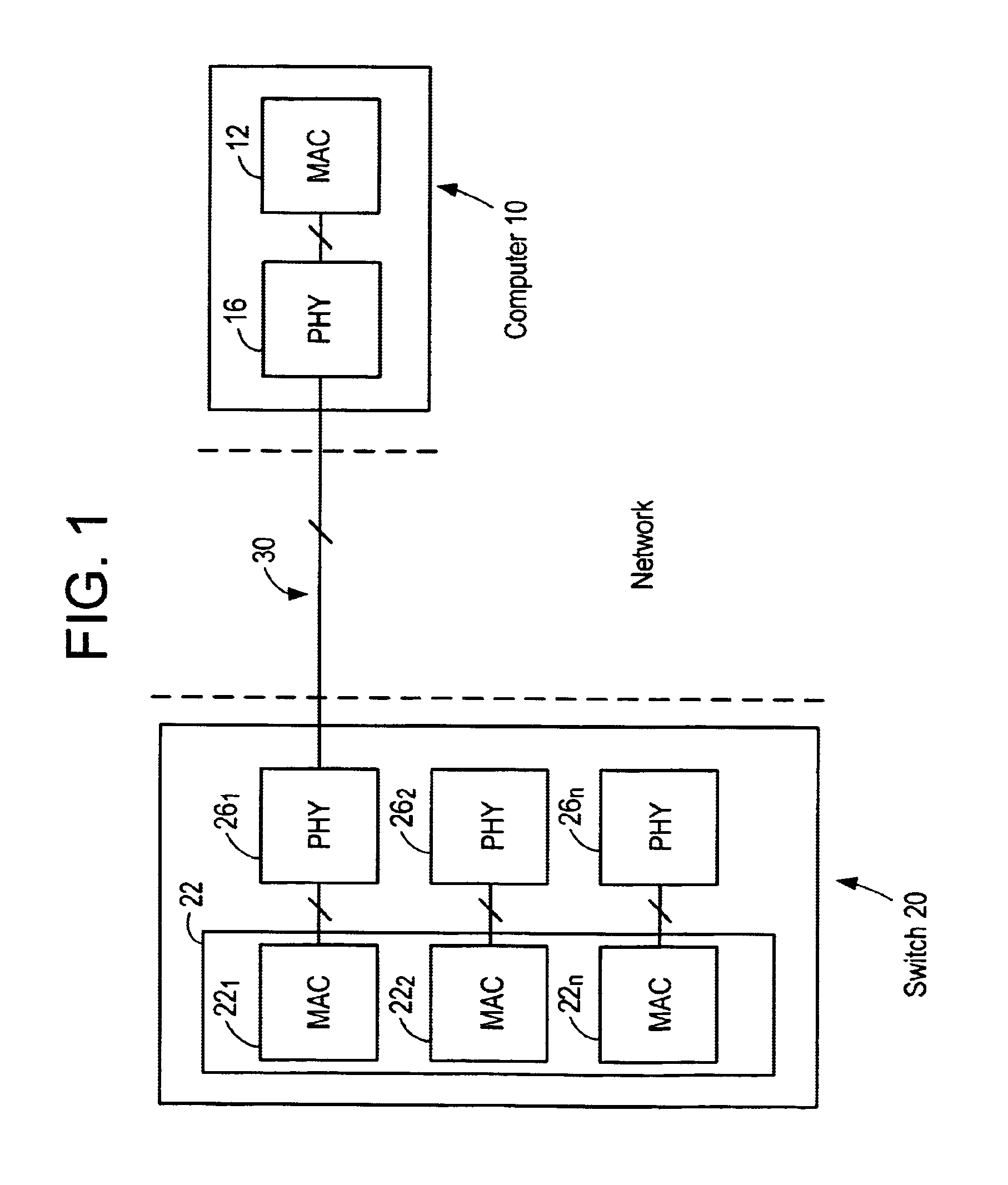
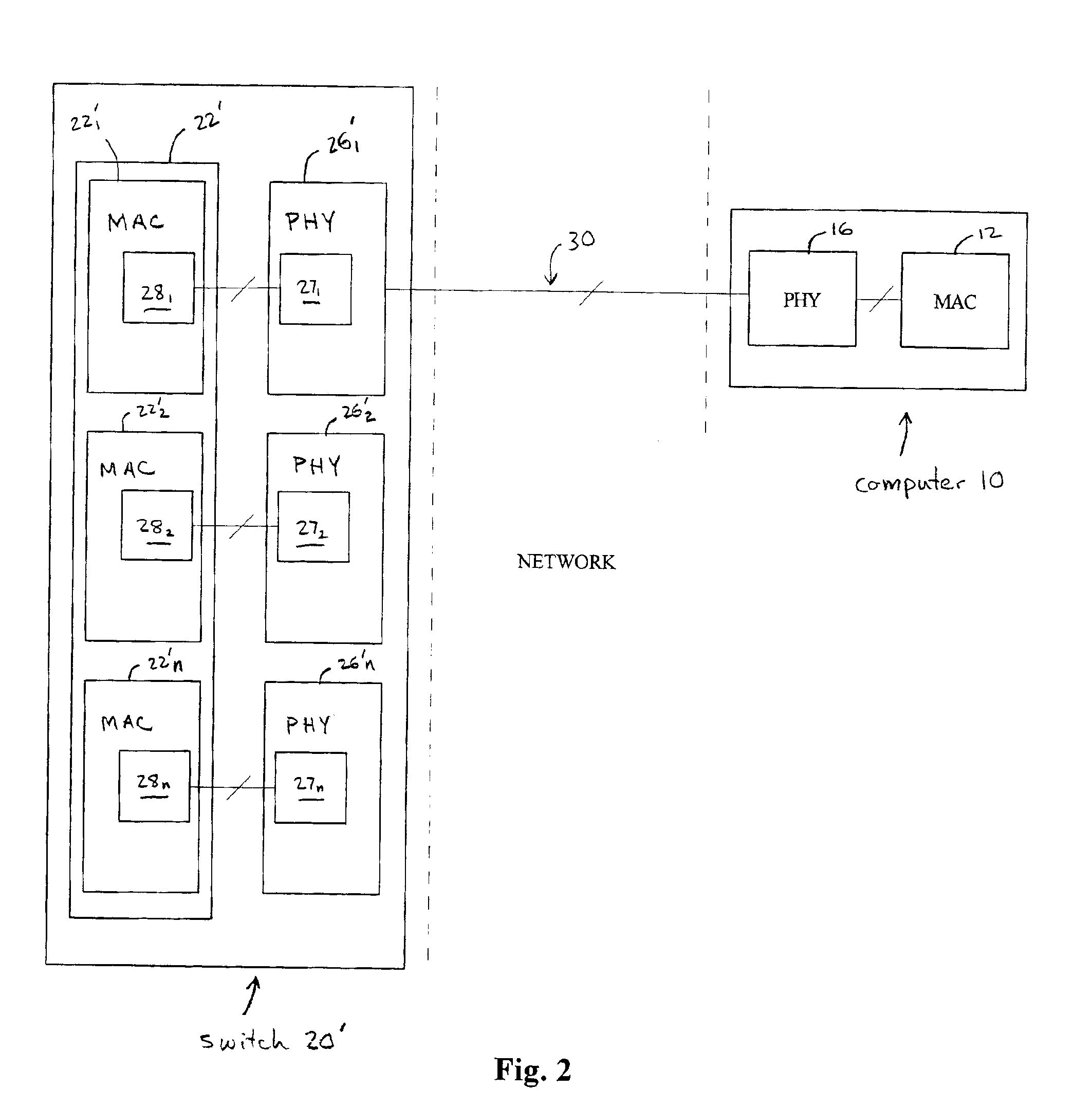
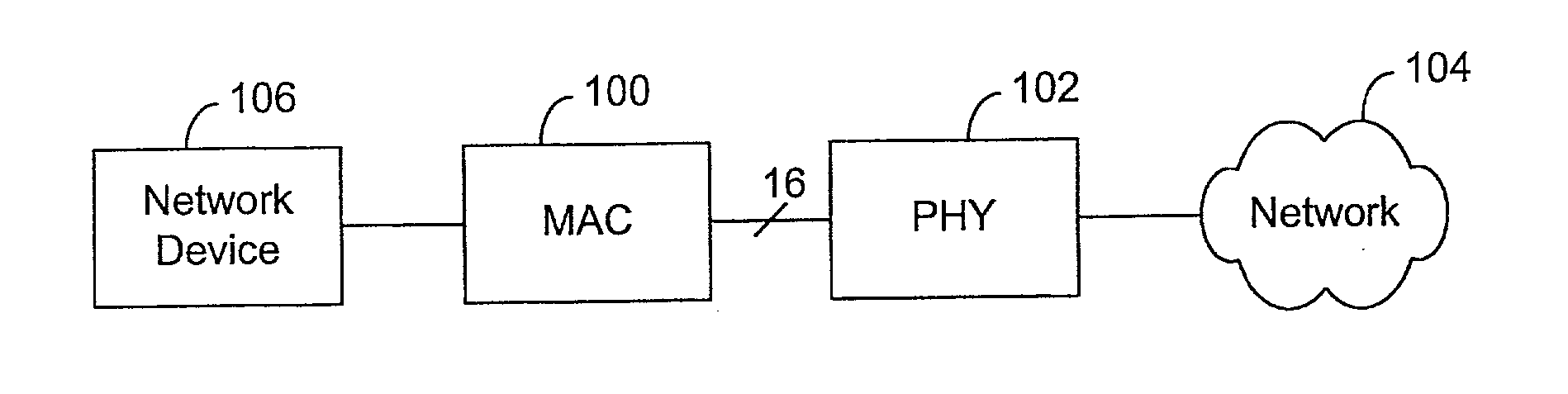
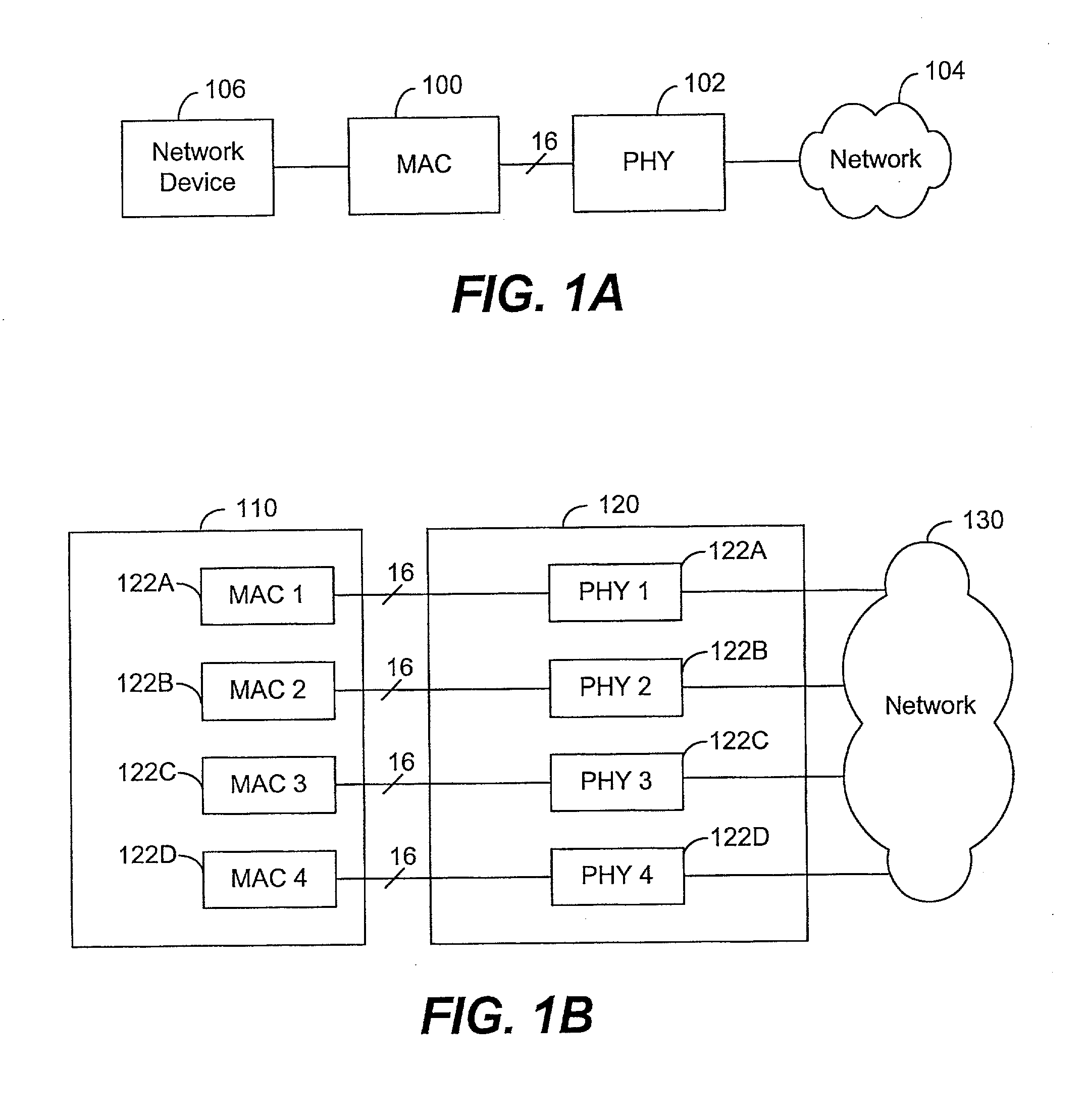
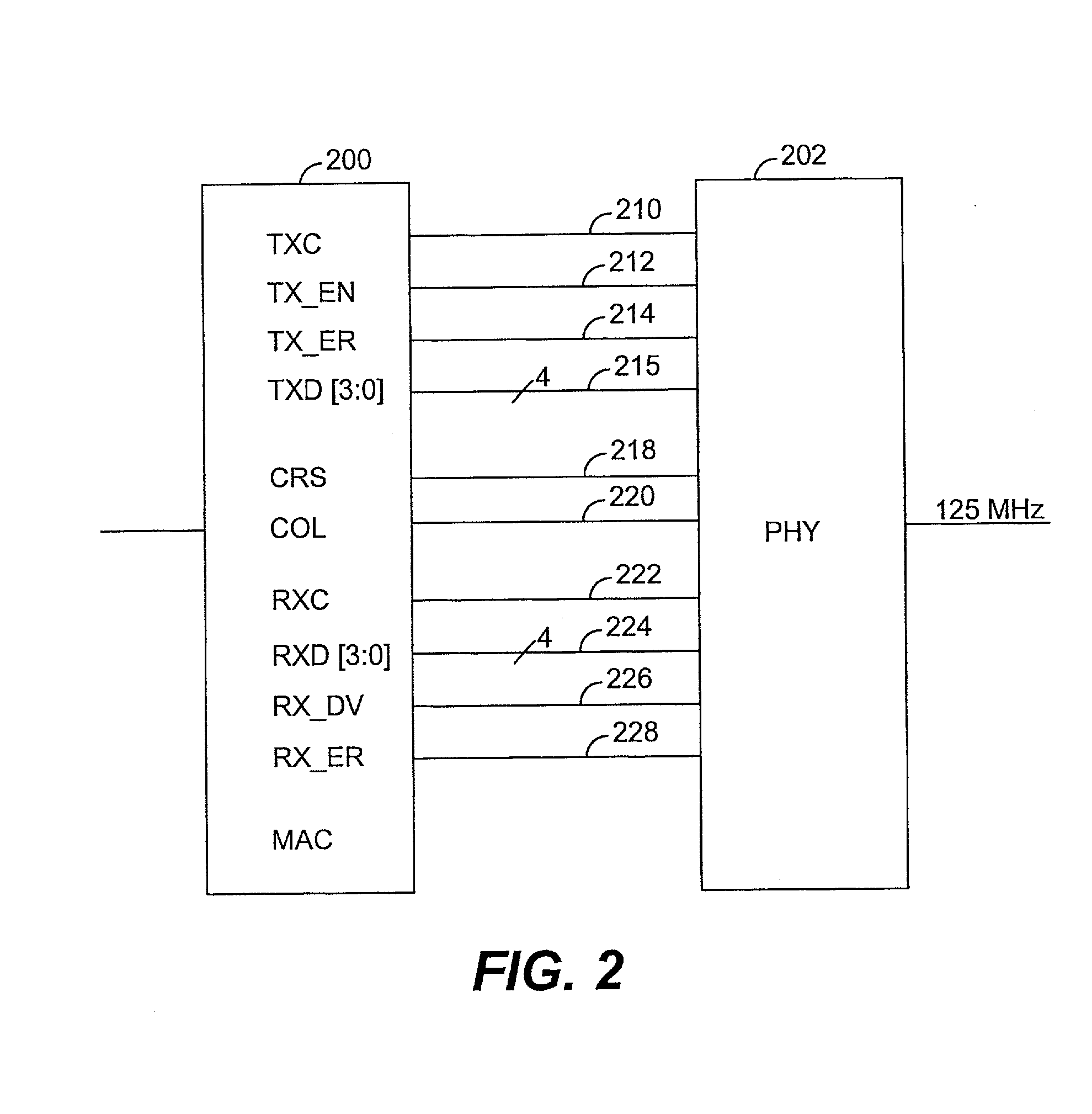
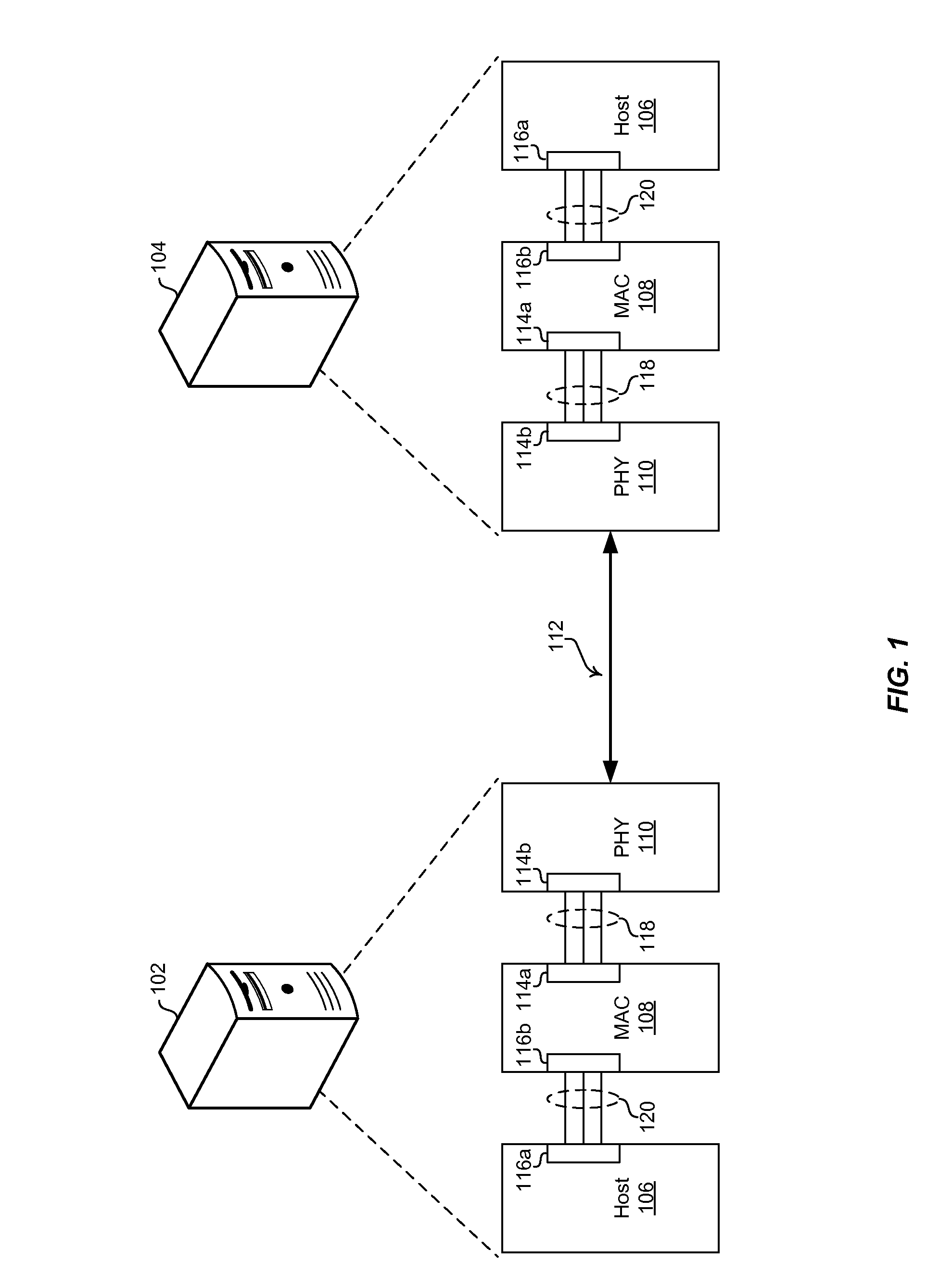
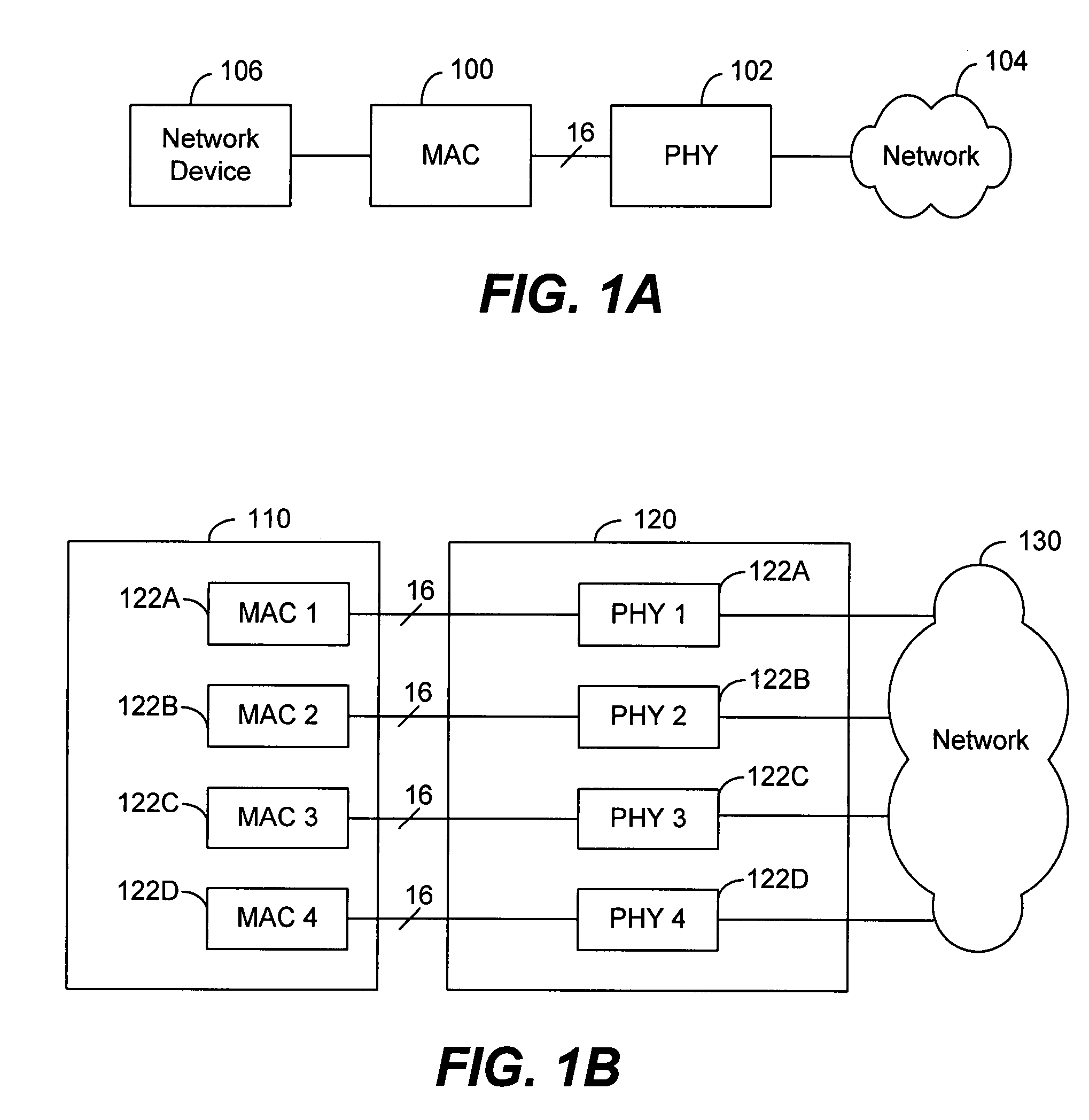
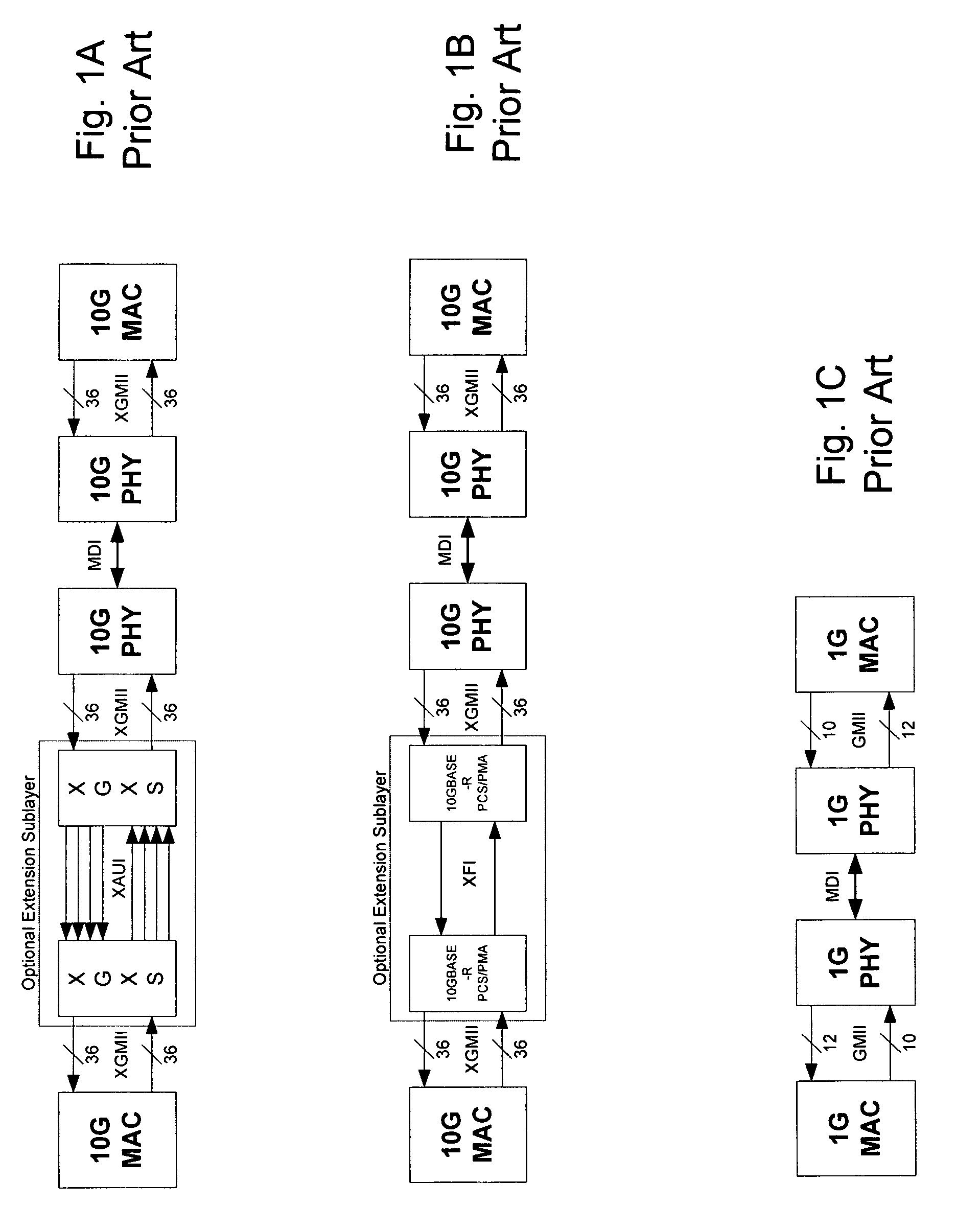
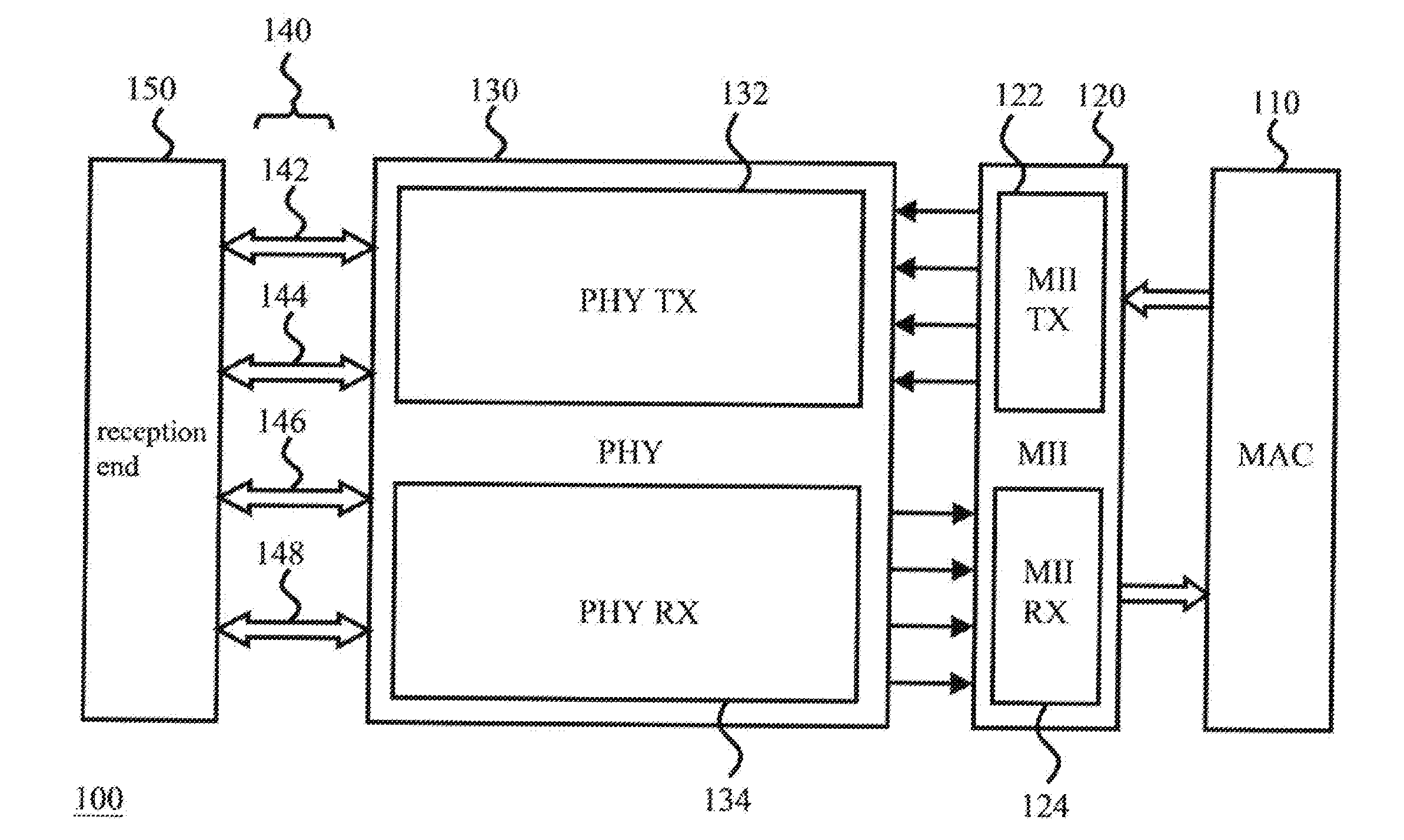
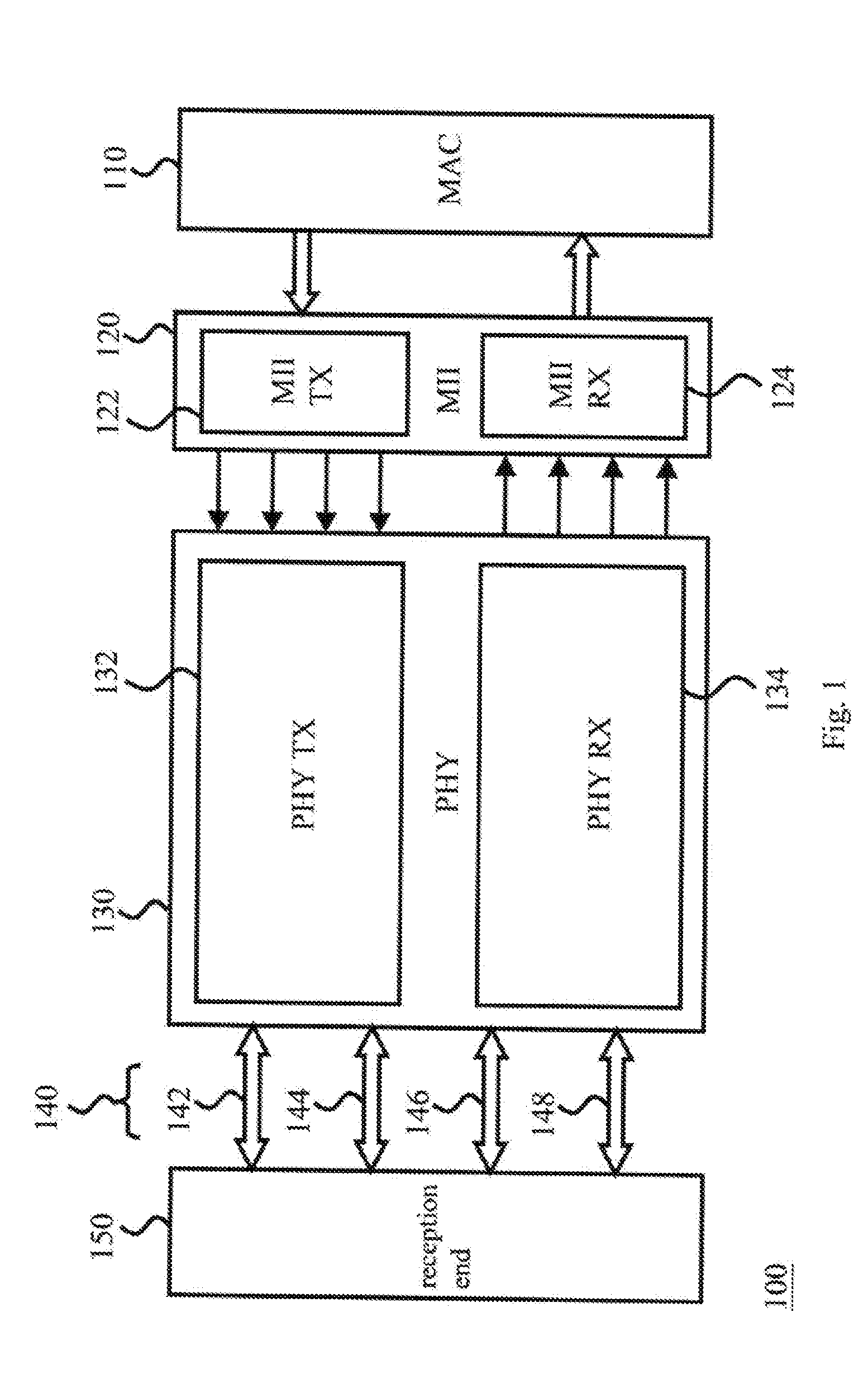
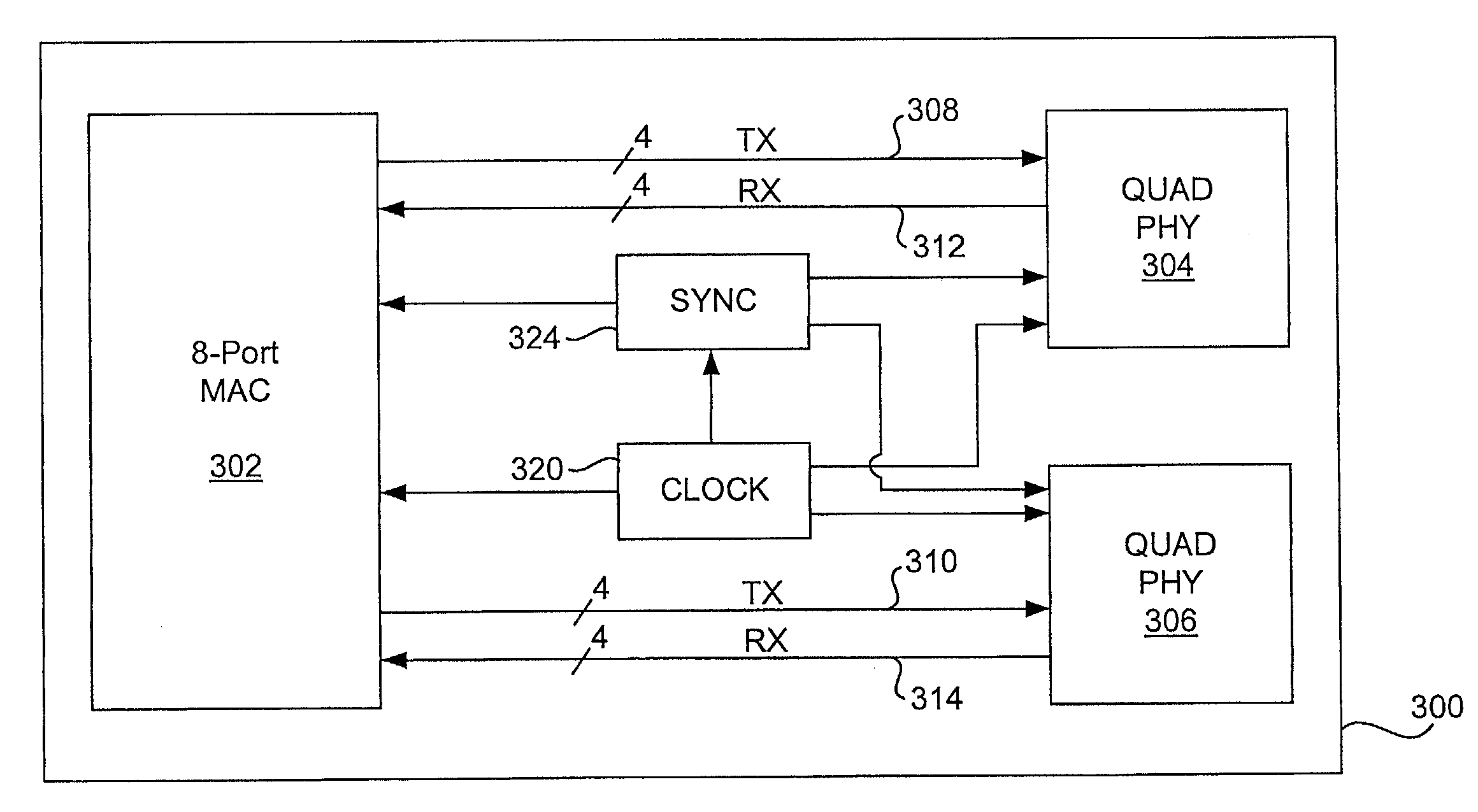
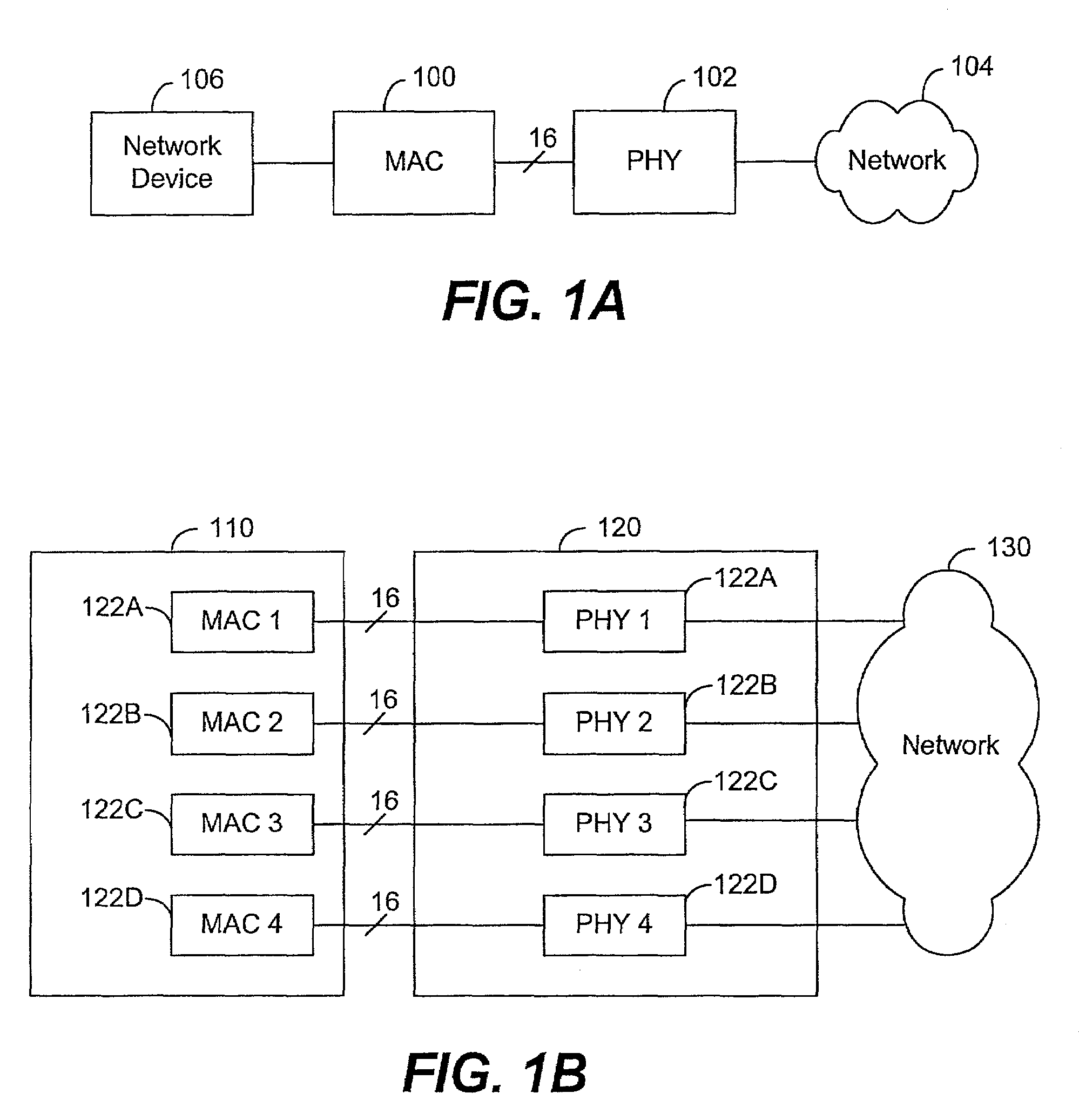
The media-independent interface (MII) was originally defined as a standard interface to connect a Fast Ethernet (i.e., 100 Mbit/s) media access control (MAC) block to a PHY chip. The MII is standardized by IEEE 802.3u and connects different types of PHYs to MACs. Being media independent means that different types of PHY devices for connecting to different media (i.e. twisted pair, fiber optic, etc.) can be used without redesigning or replacing the MAC hardware. Thus any MAC may be used with any PHY, independent of the network signal transmission media.
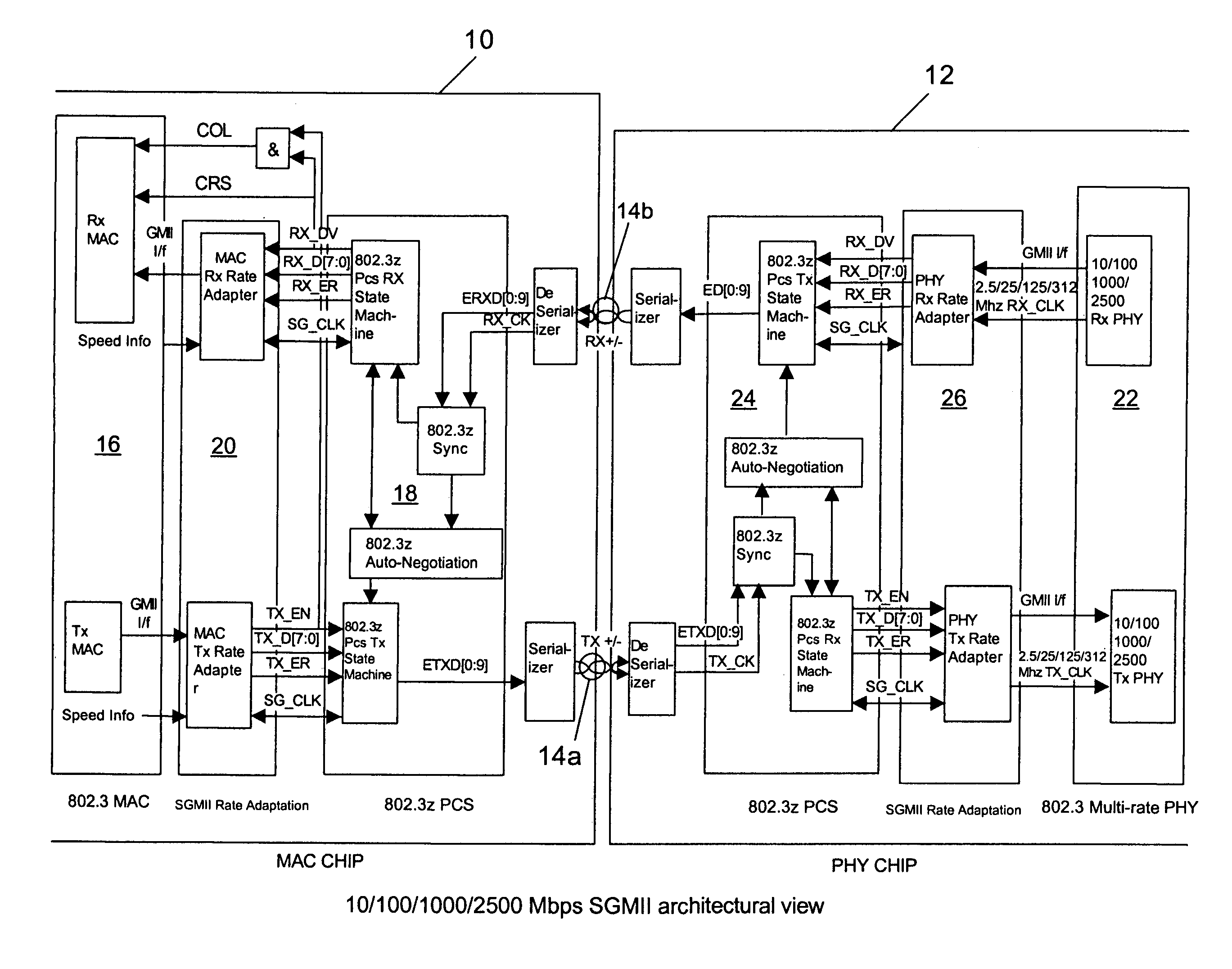
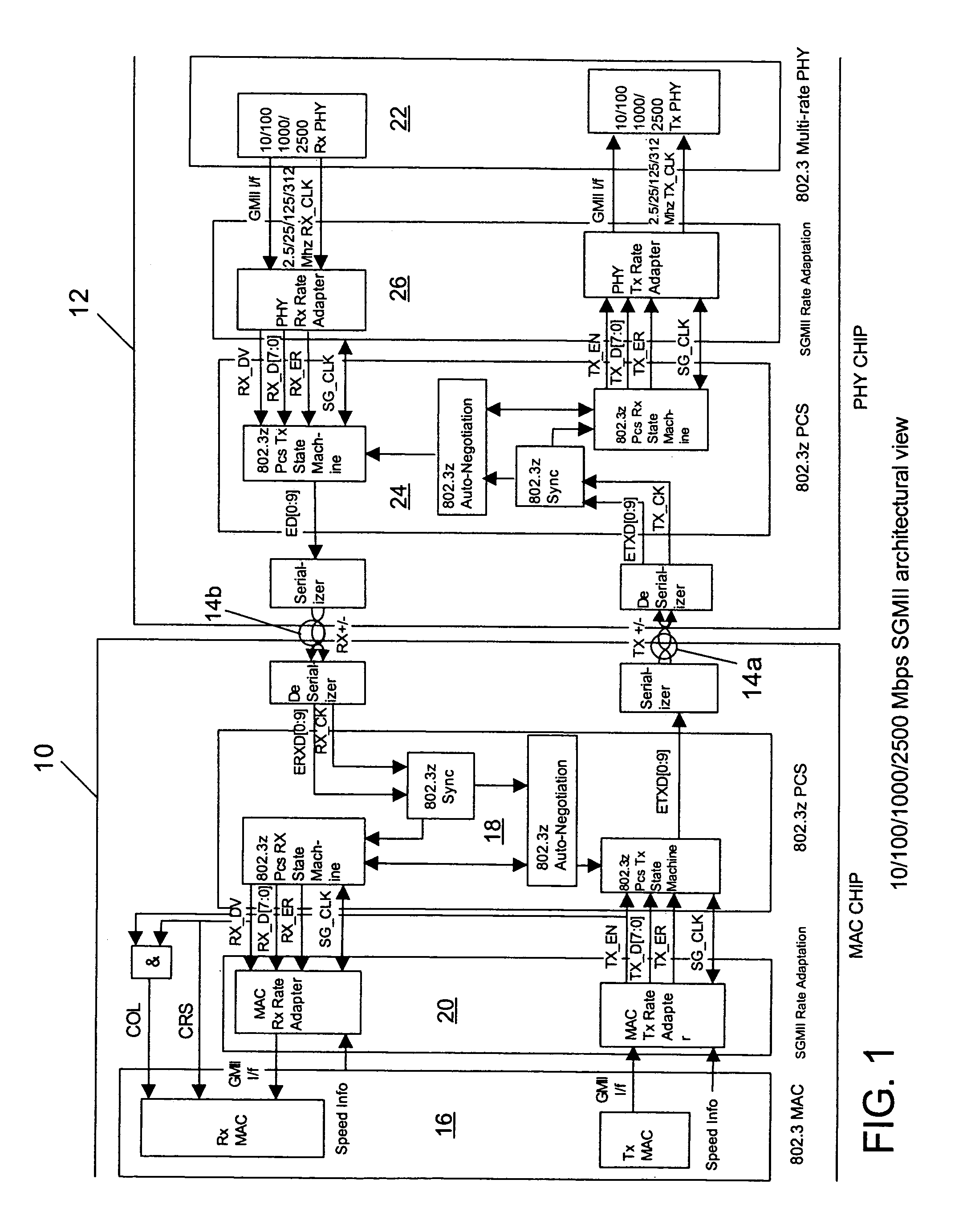
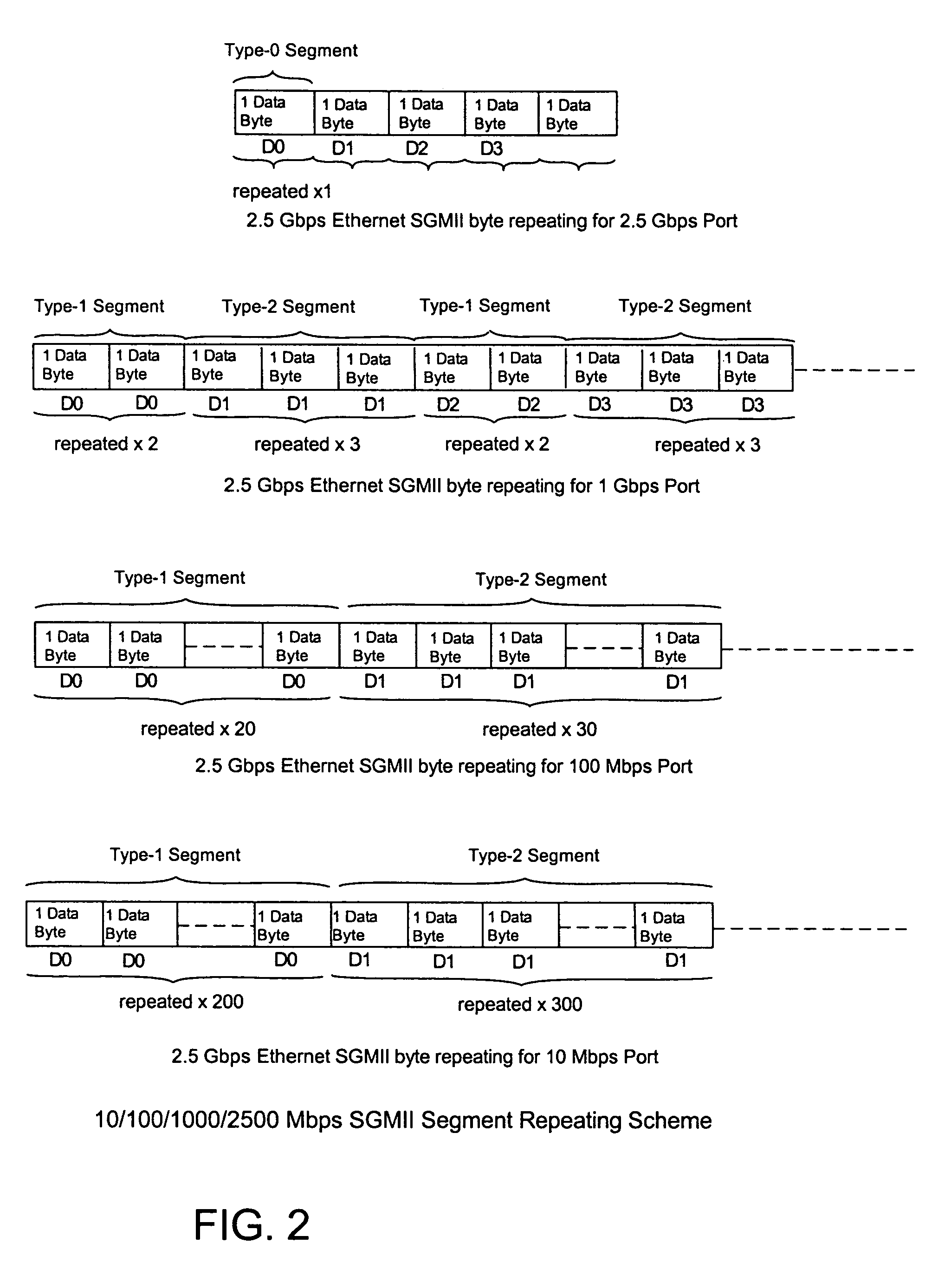
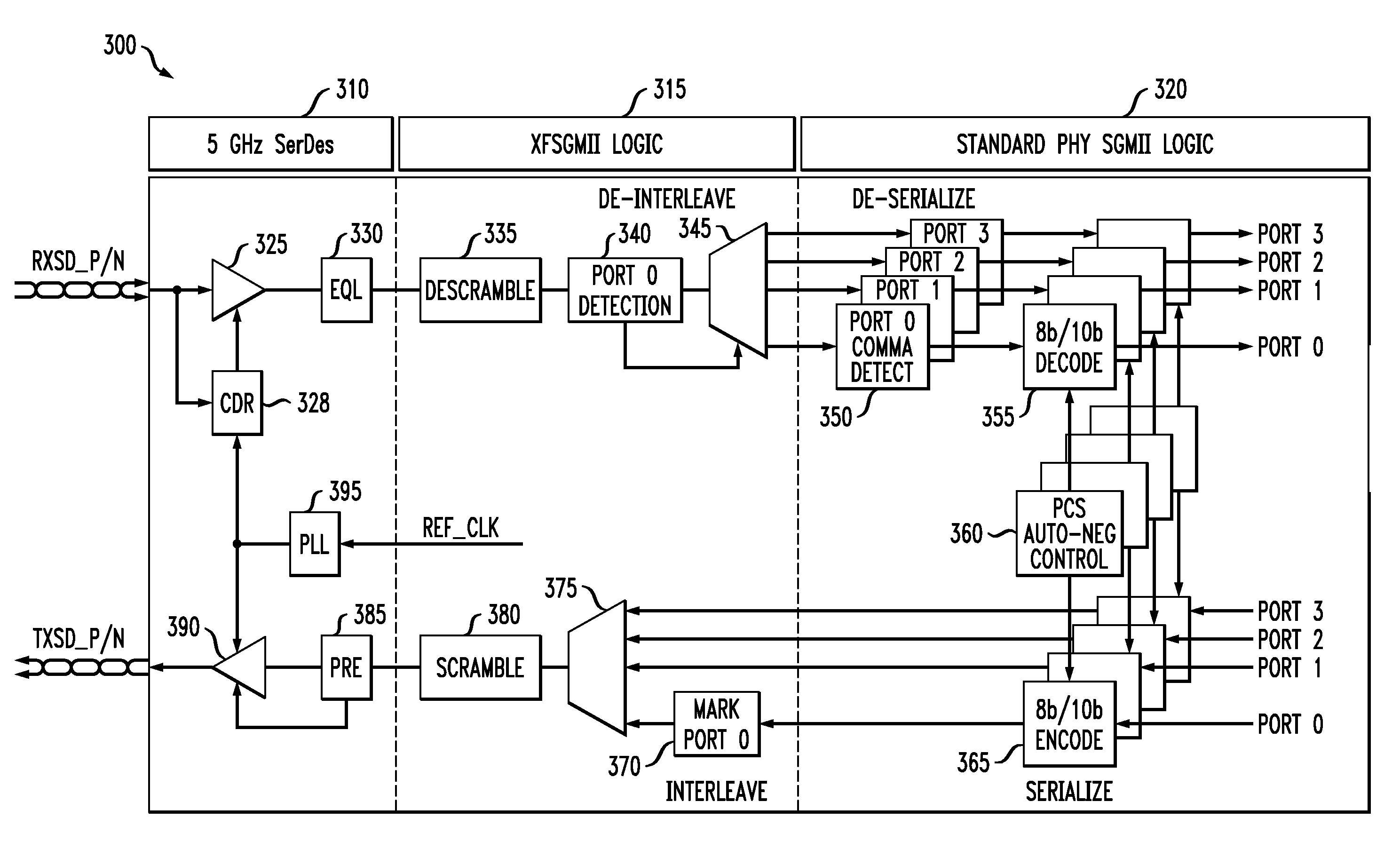
10/100/1000/2500 Mbps serial media independent interface (SGMII)
ActiveUS7356047B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationMedia Independent InterfaceByte
A SGMII that operates to transfer data between MAC and PHY chips at 2500 / 1000 / 100 / 10 Mbps utilizes a unique frame extending technique in one embodiment where frames having multiples of 2 and 3 data bytes are utilized to change the data transfer rate by multiples of 2.5. In another embodiment different clock signals are utilized.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
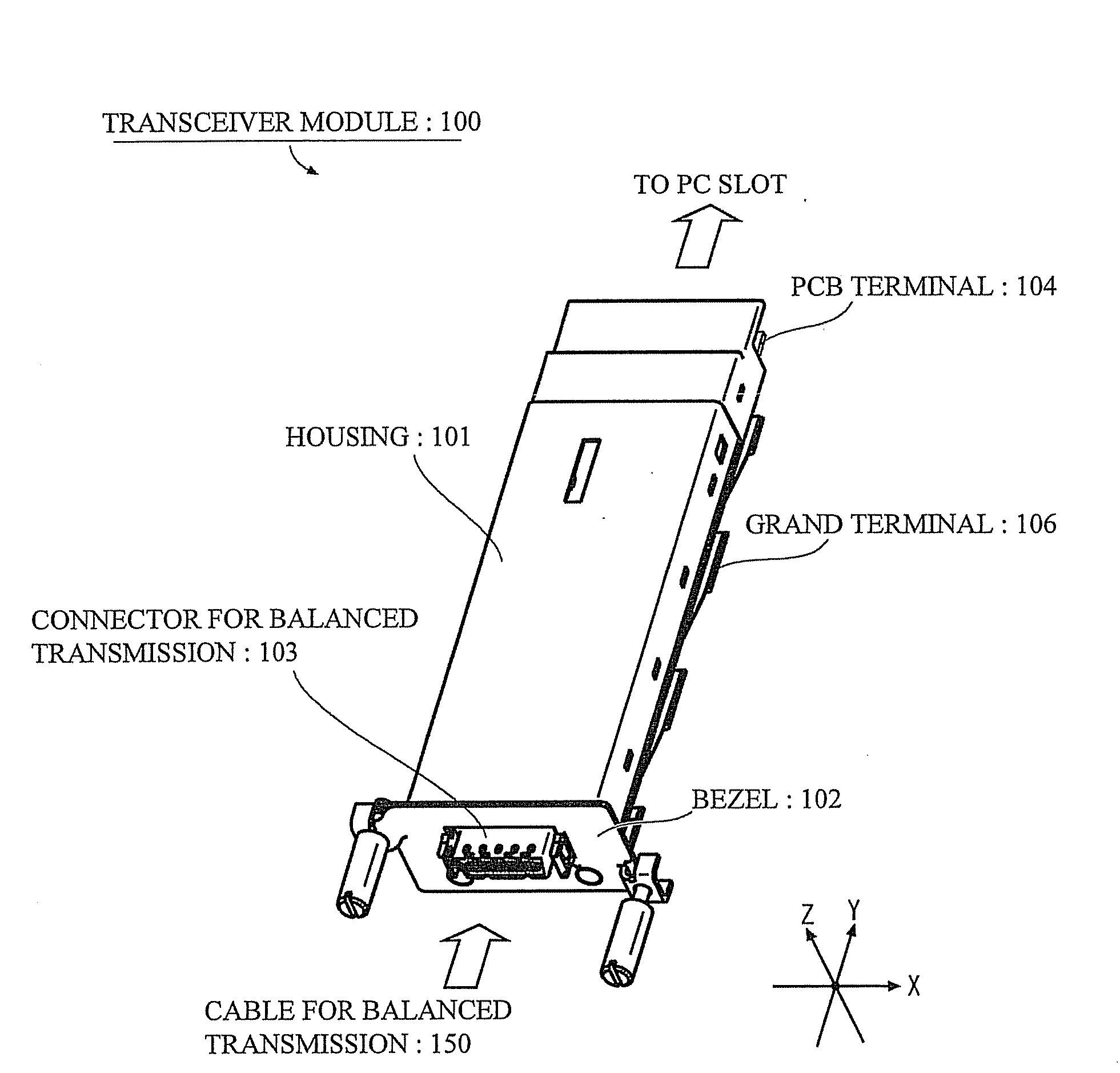
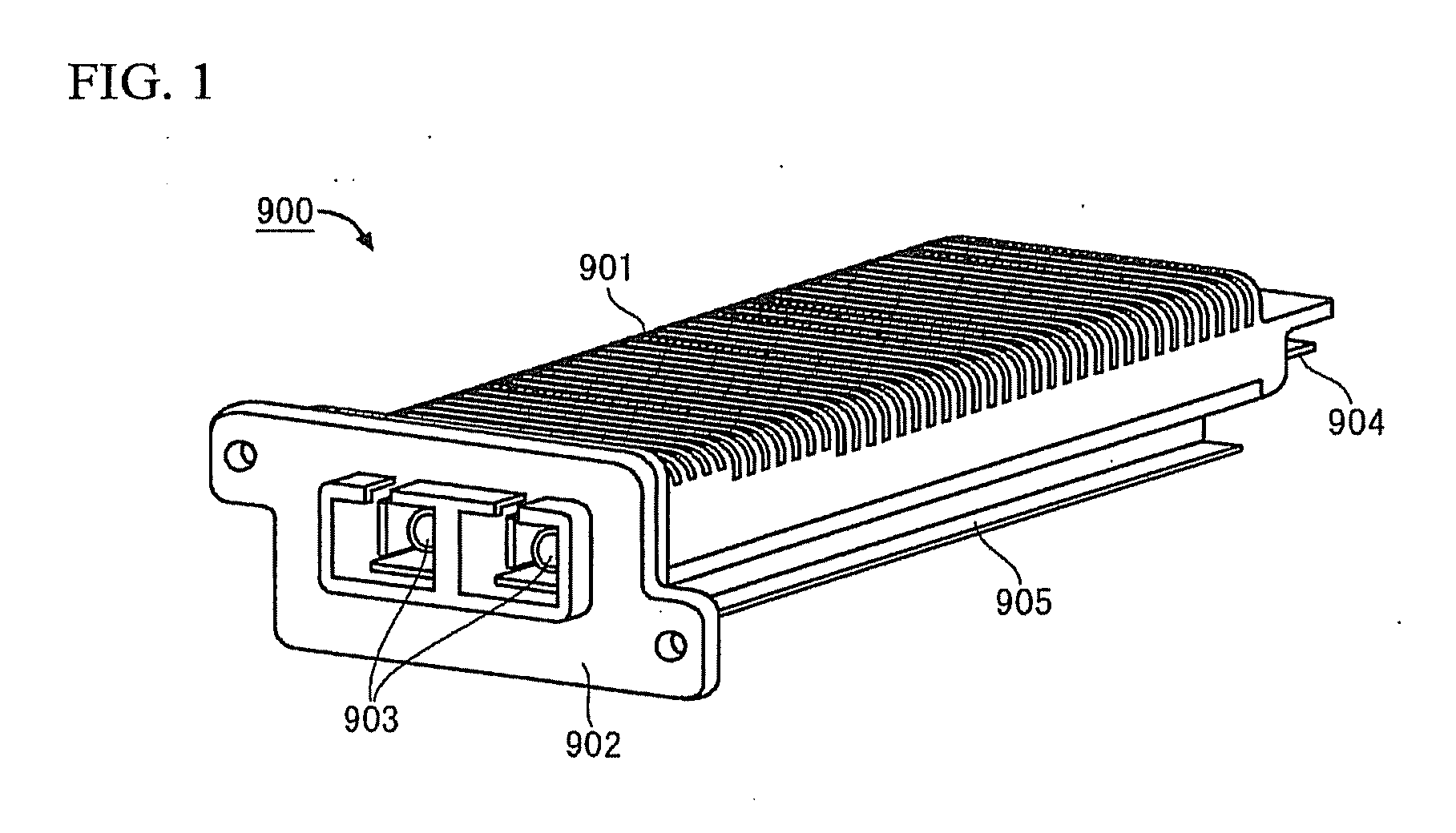
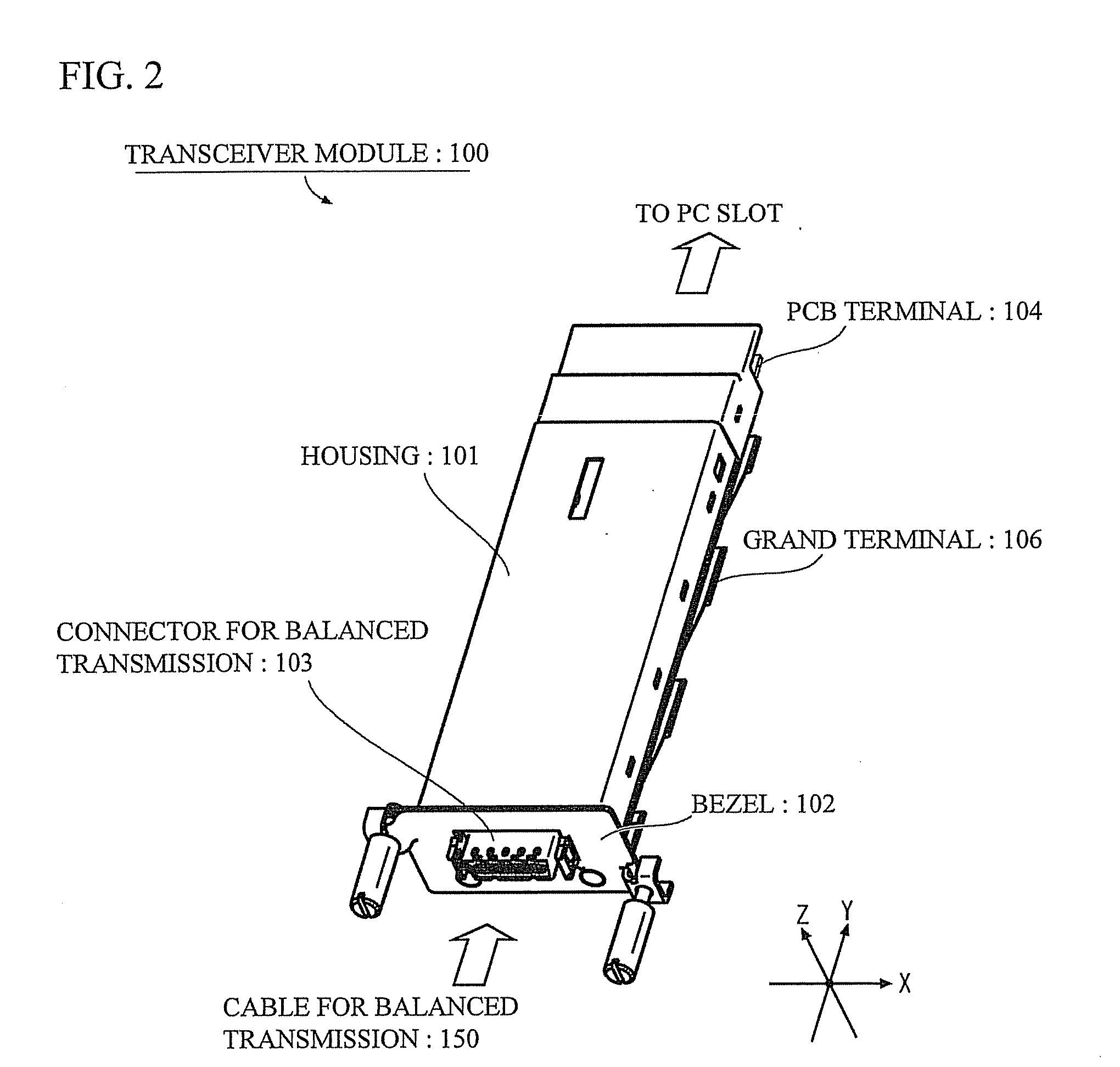
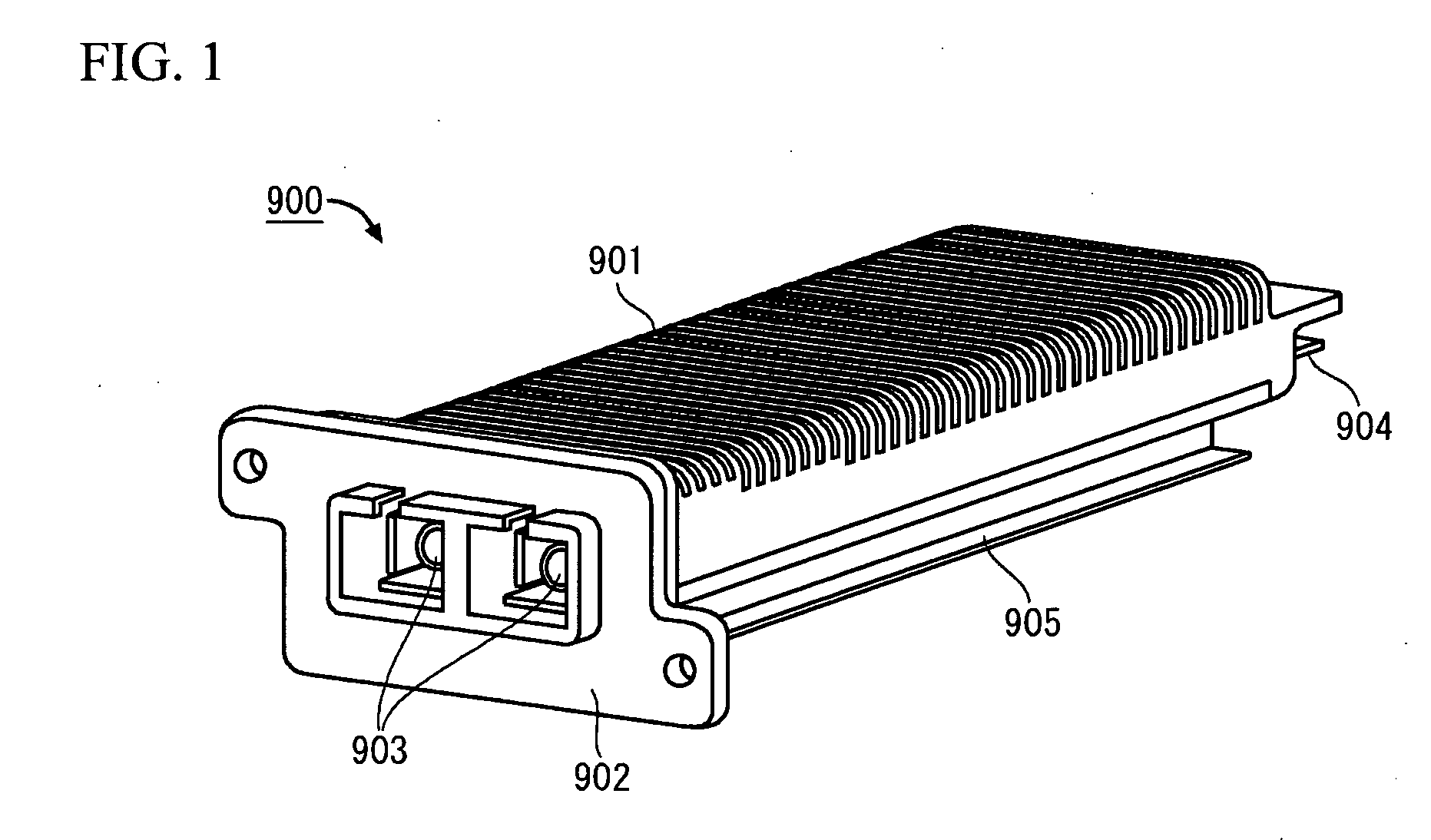
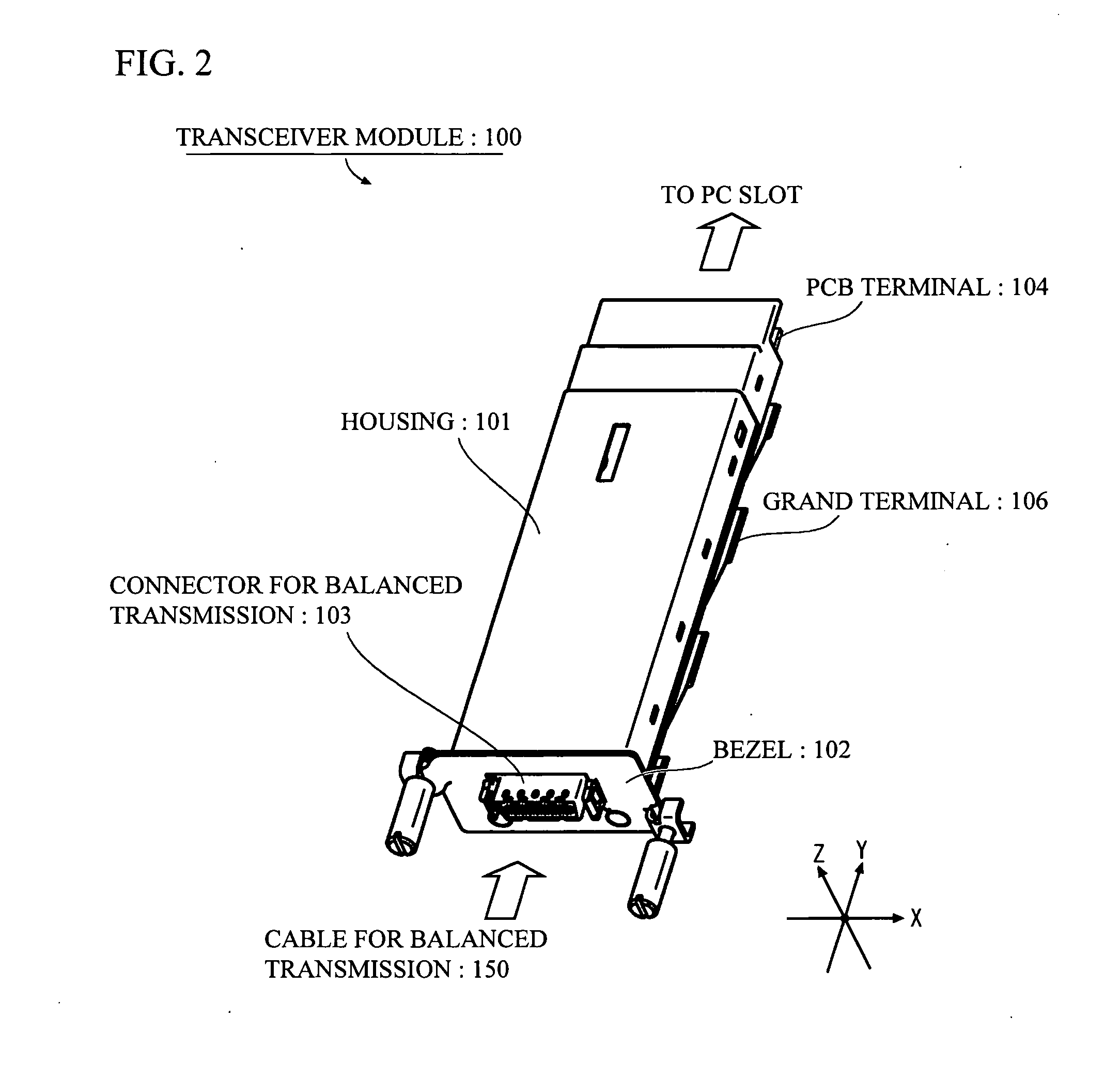
Transceiver module
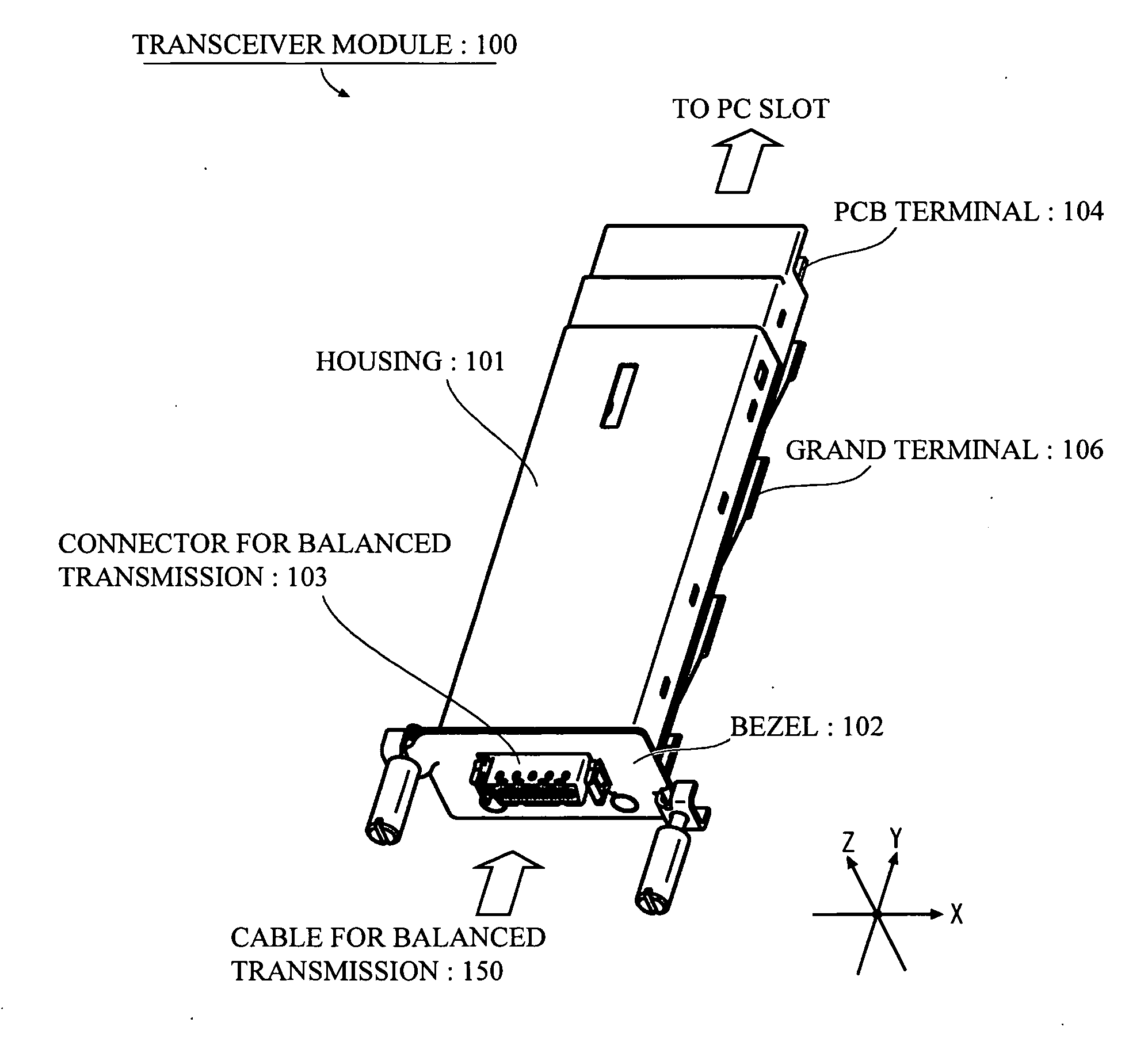
InactiveUS20080199133A1Meet needsLow costCoupling device connectionsCoupling light guidesHigh rateXAUI
The object is to provide a transceiver module that is capable of performing a high-rate communication, and satisfies the demand at a moderate cost in a case where short distance communication is enough for transmitting or receiving signals.The transceiver module has a Re-timer 11, a control portion 12, a reference clock generating portion 13, a power portion 14 and a CX4 interface 15. The Re-timer 11 is coupled to a transceiver portion (Tx / Rx) 21 through an XAUI (10 Gigabit Media Independent Interface) interface 22, and is coupled to other component that is coupled to one end of a cable 150 for balanced transmission through the CX4 (10GBASE-CX4) interface 15.
Owner:FUJITSU COMPONENENT LTD
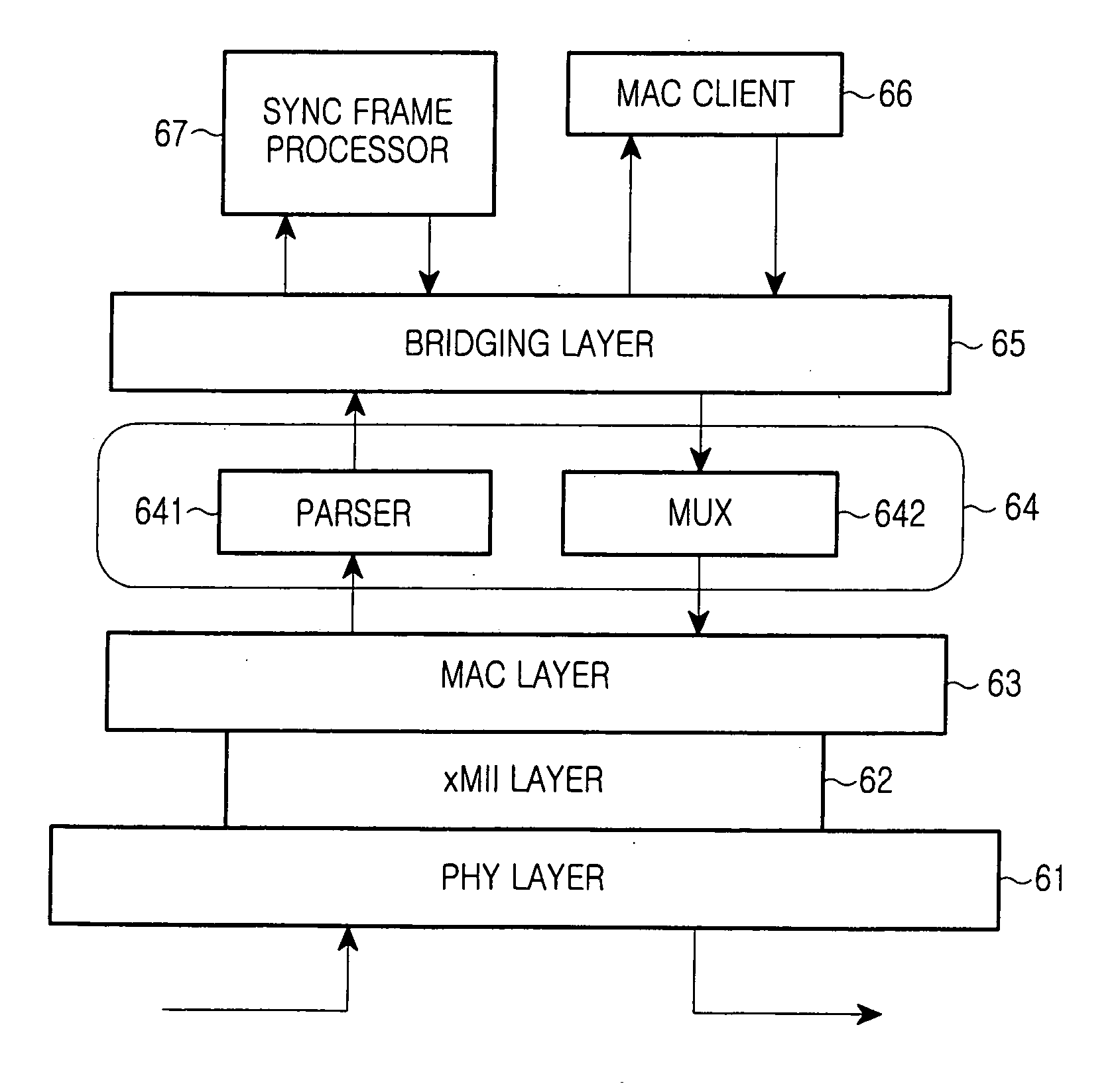
Method of configuring system layers for synchronous Ethernet
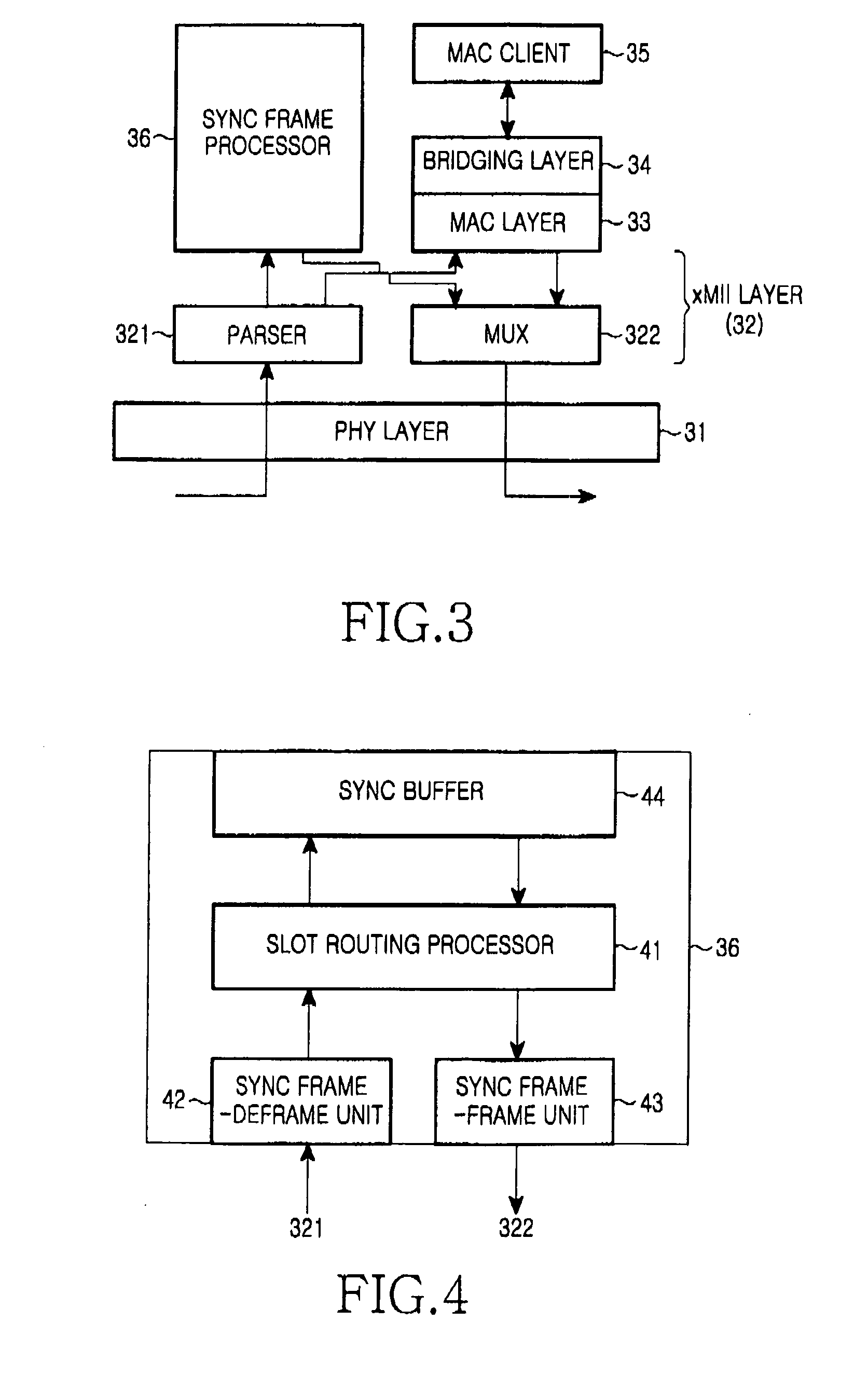
A method of configuring system layers for a synchronous Ethernet is provided. In the method, a physical layer takes charge of input and output of an Ethernet frame in direct relation to hardware, an xMII (x Media Independent Interface) layer connects the physical layer to a data link layer. The data link layer has a sync frame processor for processing a synchronous frame and an async frame processor for processing an asynchronous frame. A parser and multiplexer (MUX), included in the x MII layer, construct a super frame with a synchronous frame and an asynchronous frame, transmit the super frame through the physical layer, parse a received super frame into a synchronous frame and an asynchronous frame, and transmit the synchronous and asynchronous frames to the data link layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
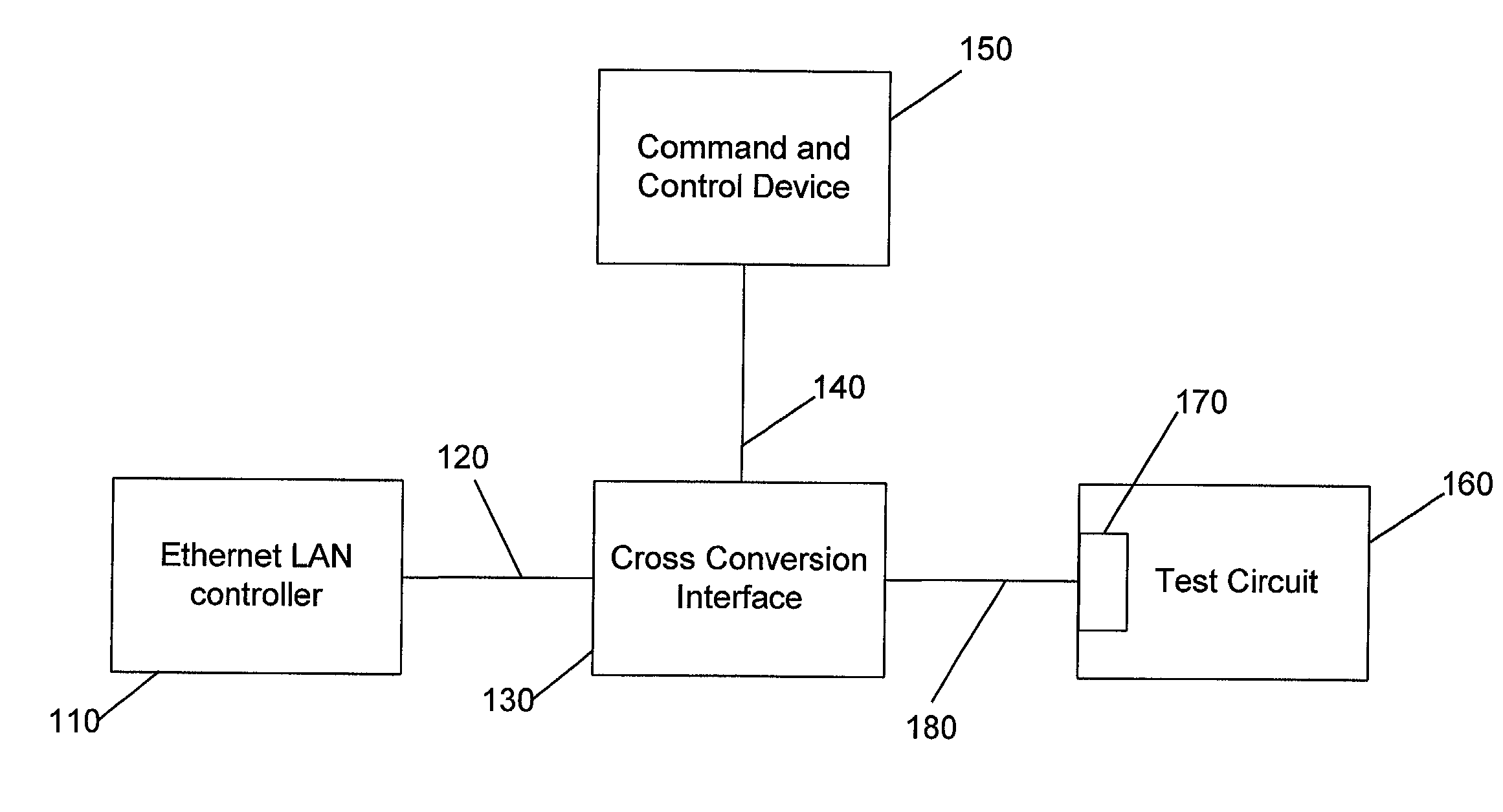
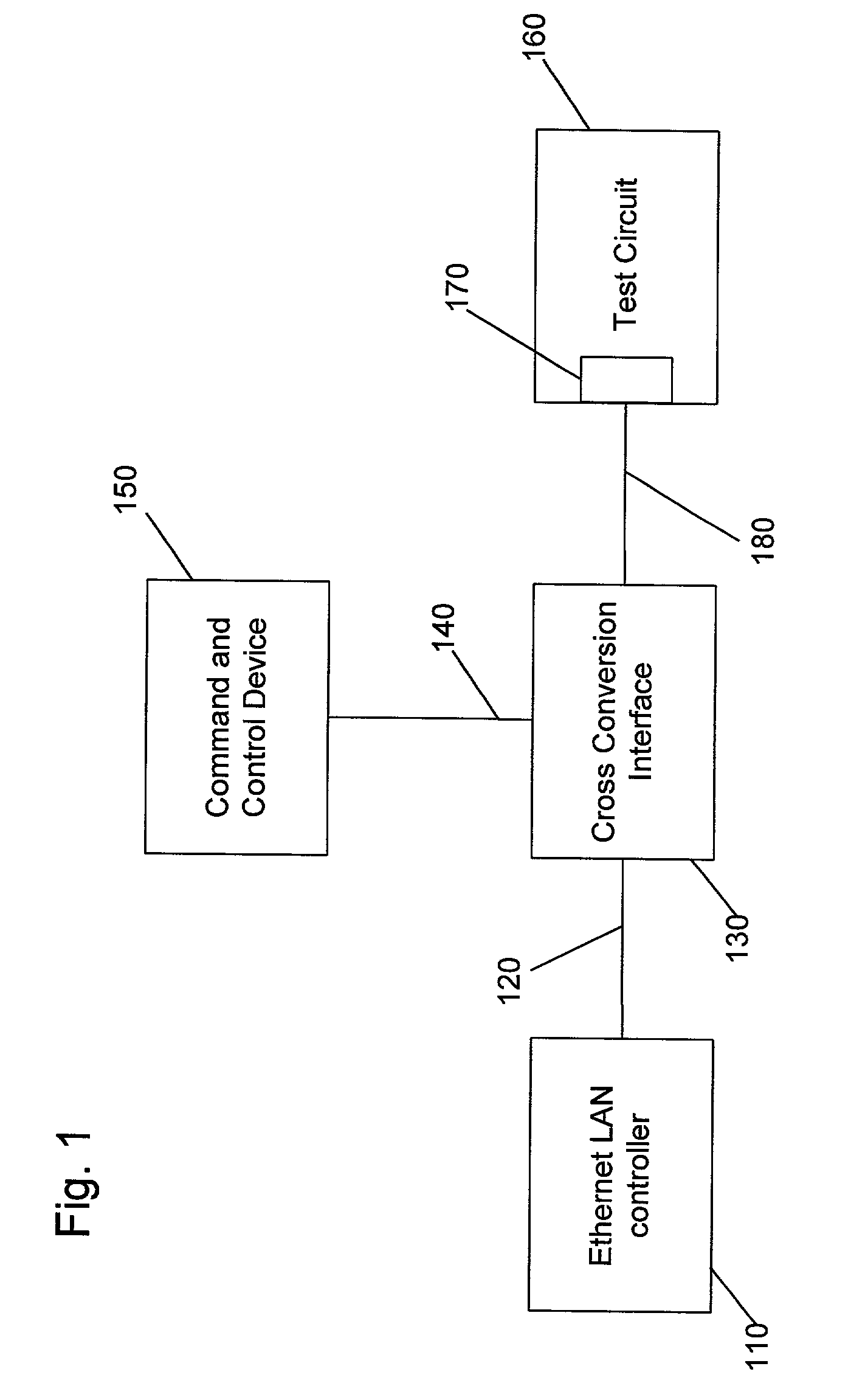
Media cross conversion interface
InactiveUS20030061341A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionMedia Independent InterfaceGigabit
A medium interface is revealed for connection between an Ethernet LAN controller without a physical (PHY) layer, and other network devices having different kinds of ports, including media independent interface (MII), serial media independent interface (SMII) and gigabit media independent interface (GMII). The interface makes possible a fast, efficient and inexpensive method to test, verify and emulate networks of integrated circuits before silicon is cast, that is, before an application specific integrated circuit (ASIC) is manufactured. The method also allows full test case coverage with high layer protocols.
Owner:INFINEON TECHNOLOGIES NORTH AMERICA CORPORATION
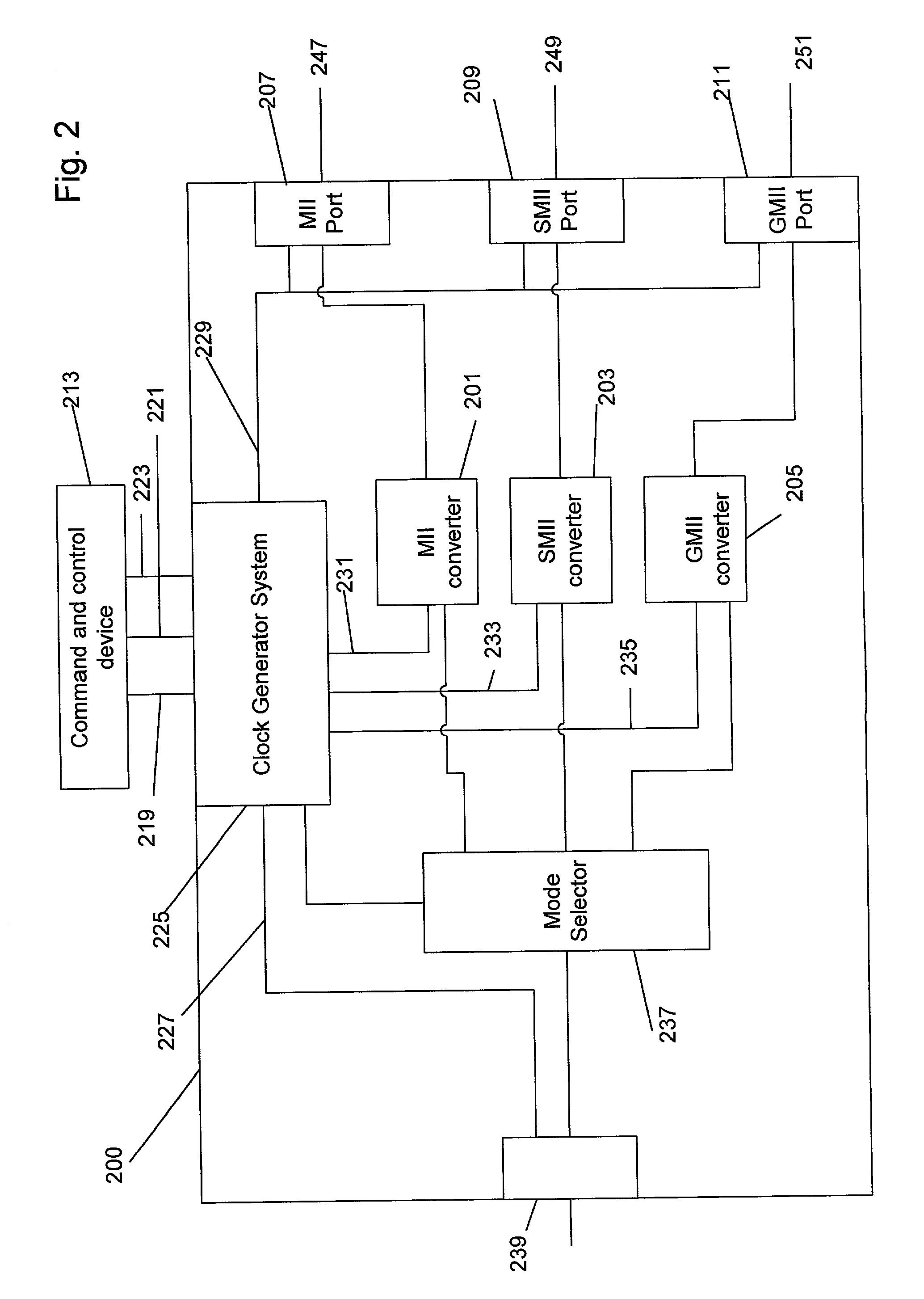
Method and system for a multi-rate gigabit media independent interface
ActiveUS20080049788A1Overcomes drawbackEnhanced advantageMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsTime-division multiplexGigabitMedia Independent Interface
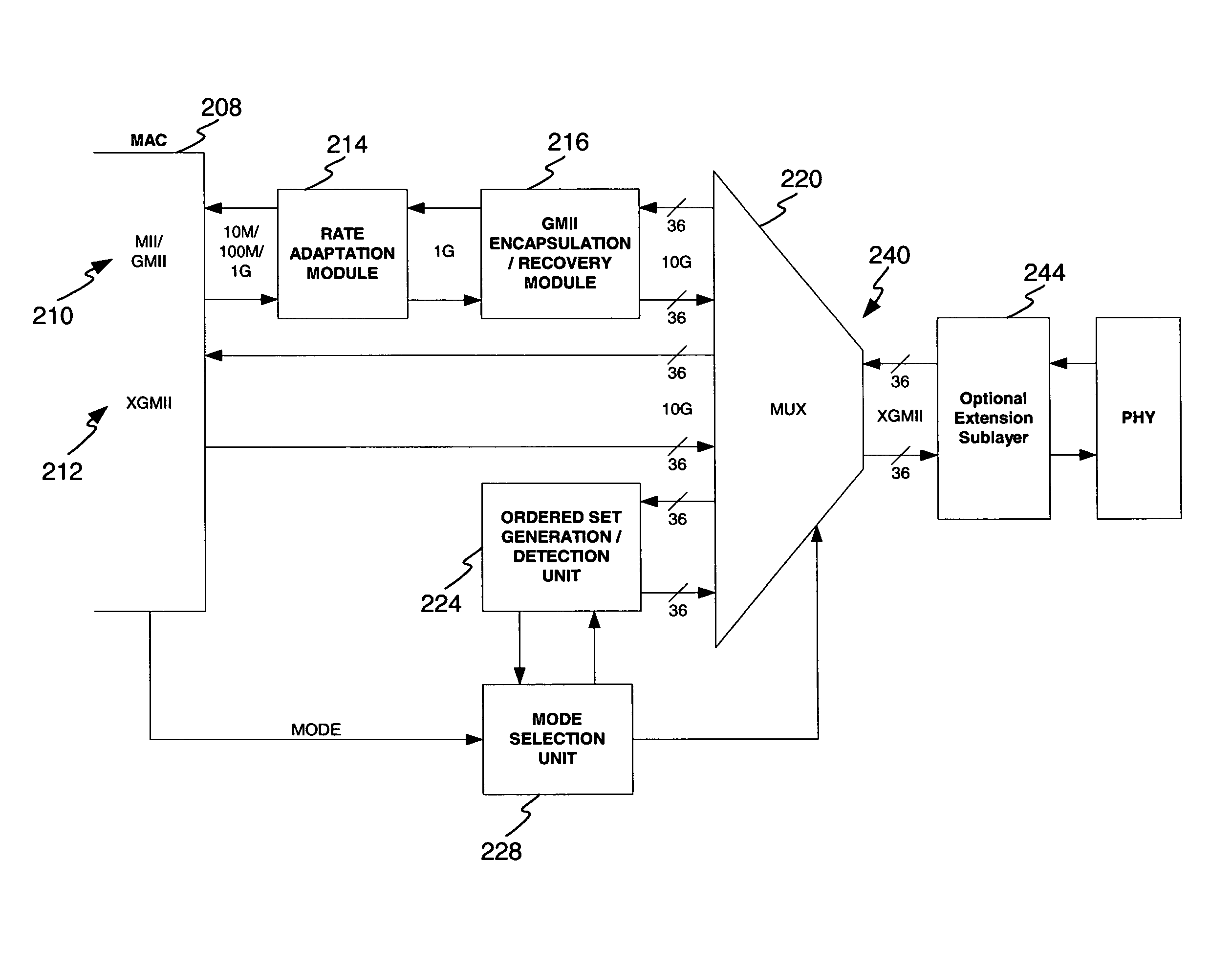
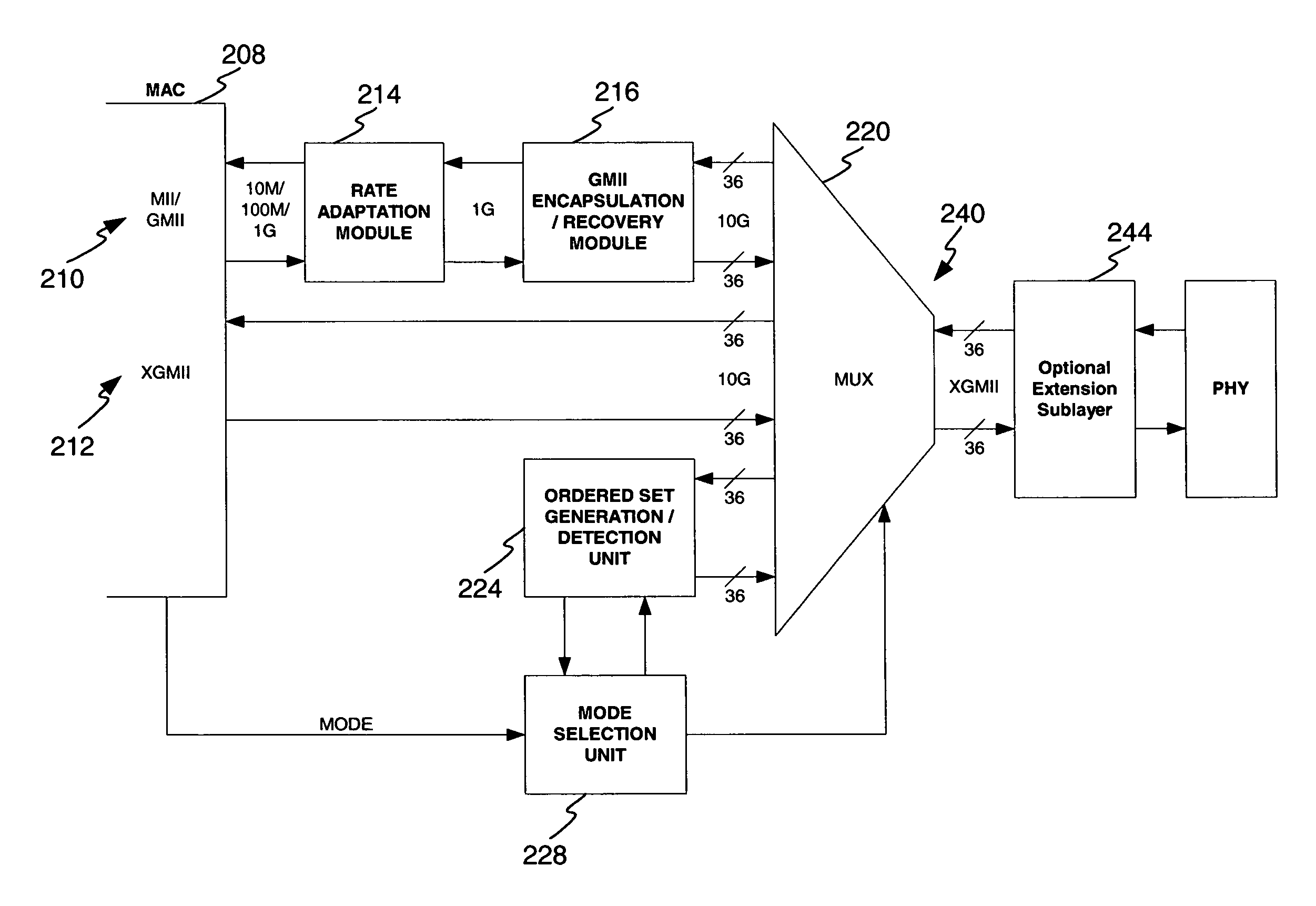
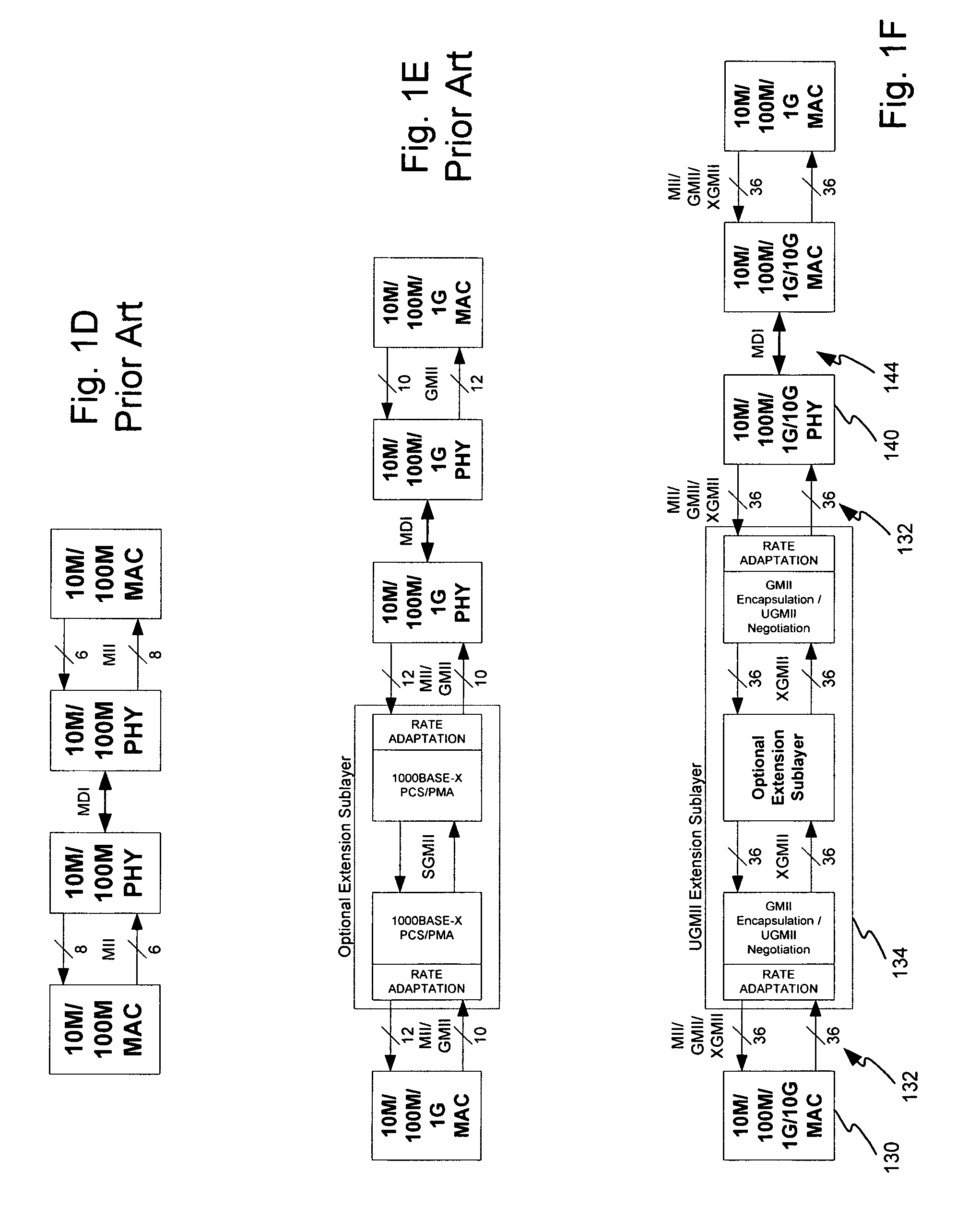
Disclosed is a UGMII system to interface multirate devices including 10 gigabit per second data exchange rates. Mode selection is enabled to provide for automatic detection and adaptation to any transmit rate including 10M, 100M, 1 G, and 10 G. Mode selection comprises the negotiation between the UGMII extension sublayers located at the MAC and PHY to select between one of several operational modes including: XGMII communication, GMII encapsulation, Clause 22 MDIO register management and Clause 45 MDIO register management. Selection of UGMII and XGMII operating modes are negotiated between the MAC and PHY using ordered sets to announce and acknowledgement a mode change. In one embodiment 802.3 Clause 46 defined ordered sets are utilized.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for distributing and receiving high-speed ethernet media independent interface blocks
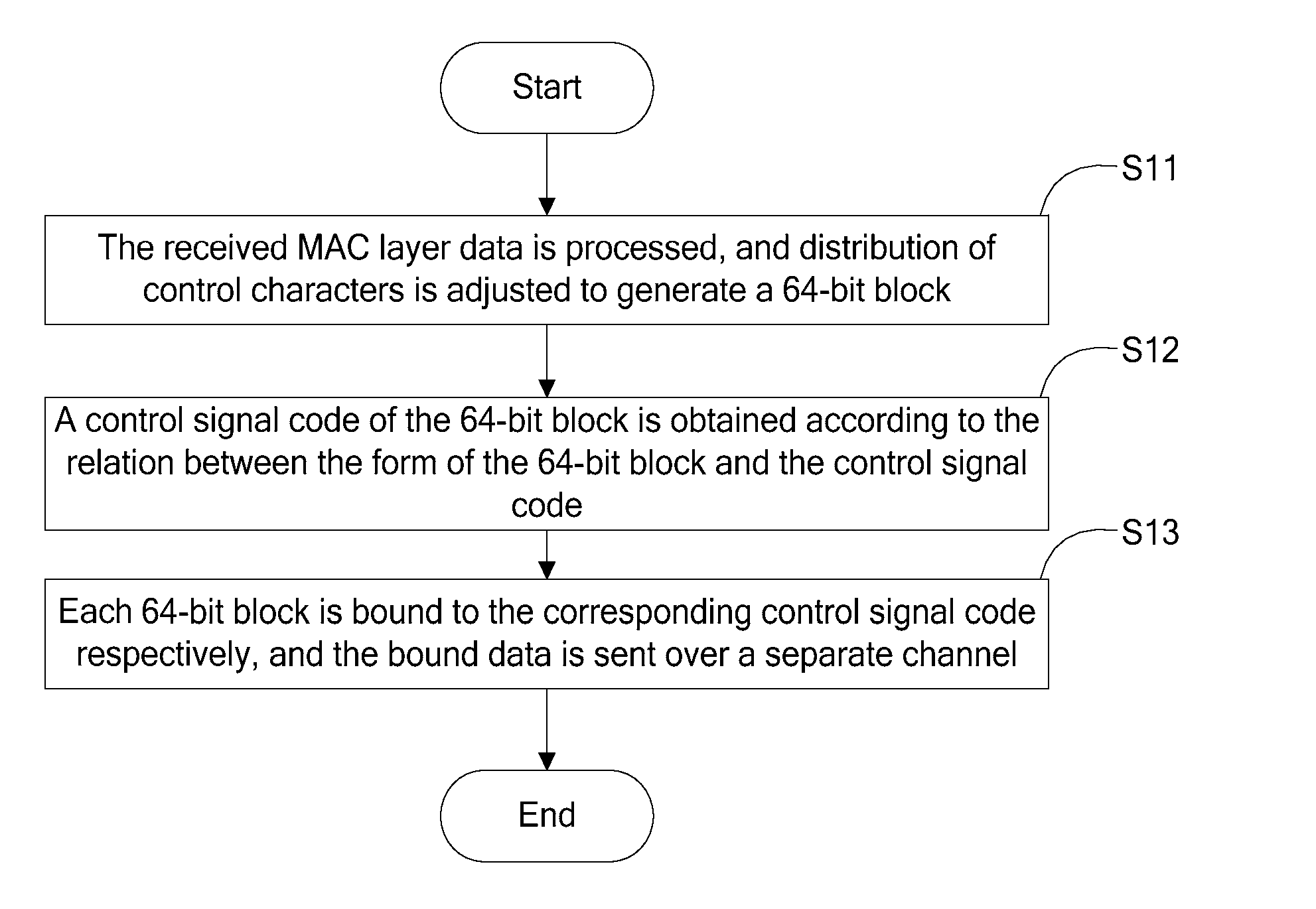
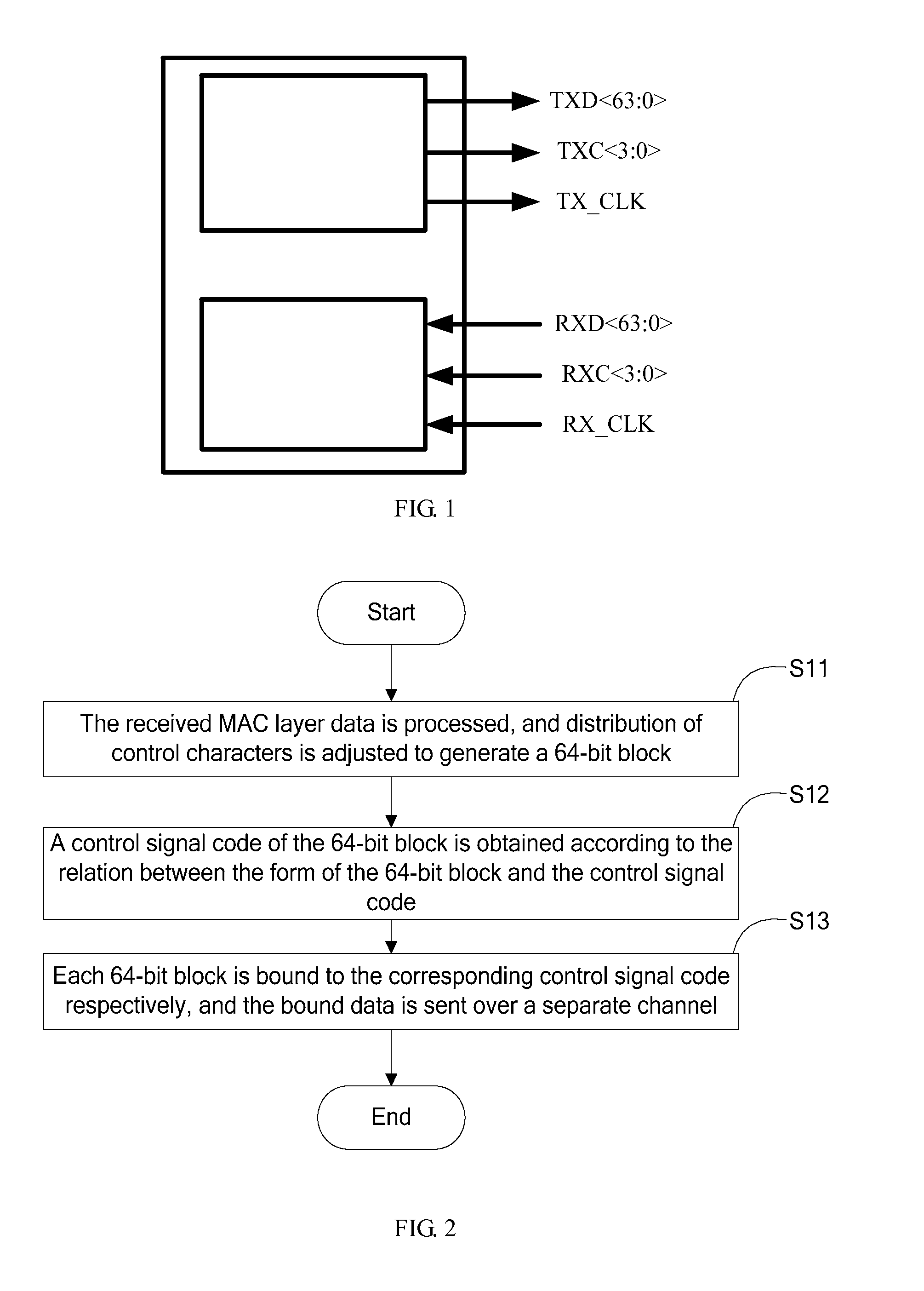
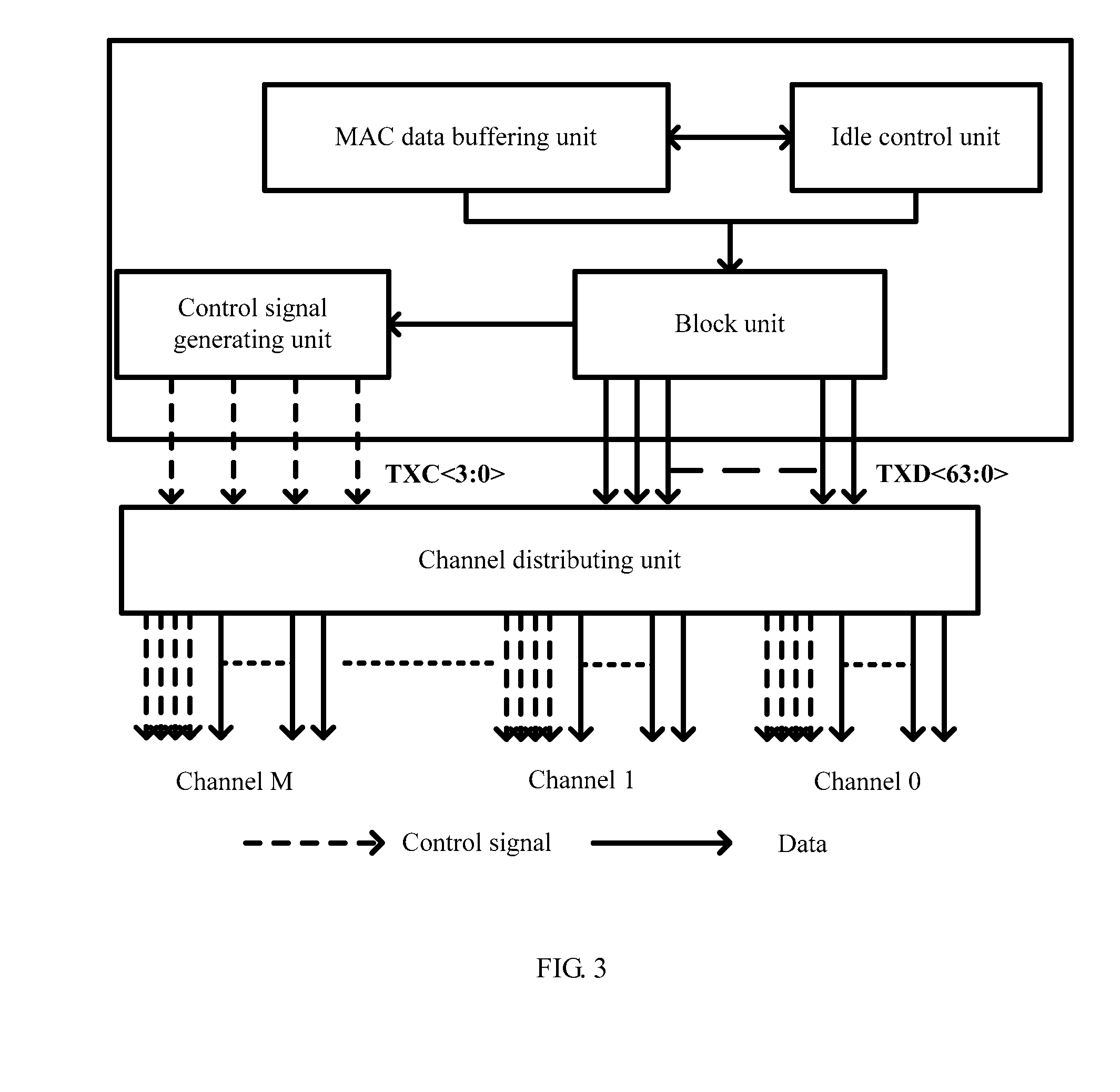
ActiveUS20090274172A1Increase bit widthControl information effectivelyError preventionTime-division multiplexControl signalControl character
A method and apparatus for distributing and receiving high-speed Ethernet Media Independent Interface (MII) blocks are provided to moderate the increase of control lines with the increase of the bit width and to simplify the block types in the coding process of the Physical Coding Sublayer (PCS). The technical solution disclosed herein includes: processing received Media Access Control (MAC) layer data, and adjusting distribution of control characters to generate a 64-bit block; obtaining a control signal code of the 64-bit block according to the relation between the form of the 64-bit block and the control signal code; and binding each 64-bit block to the corresponding control signal code respectively, and sending bound data over a separate channel.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Reduced pin gigabit media independent interface
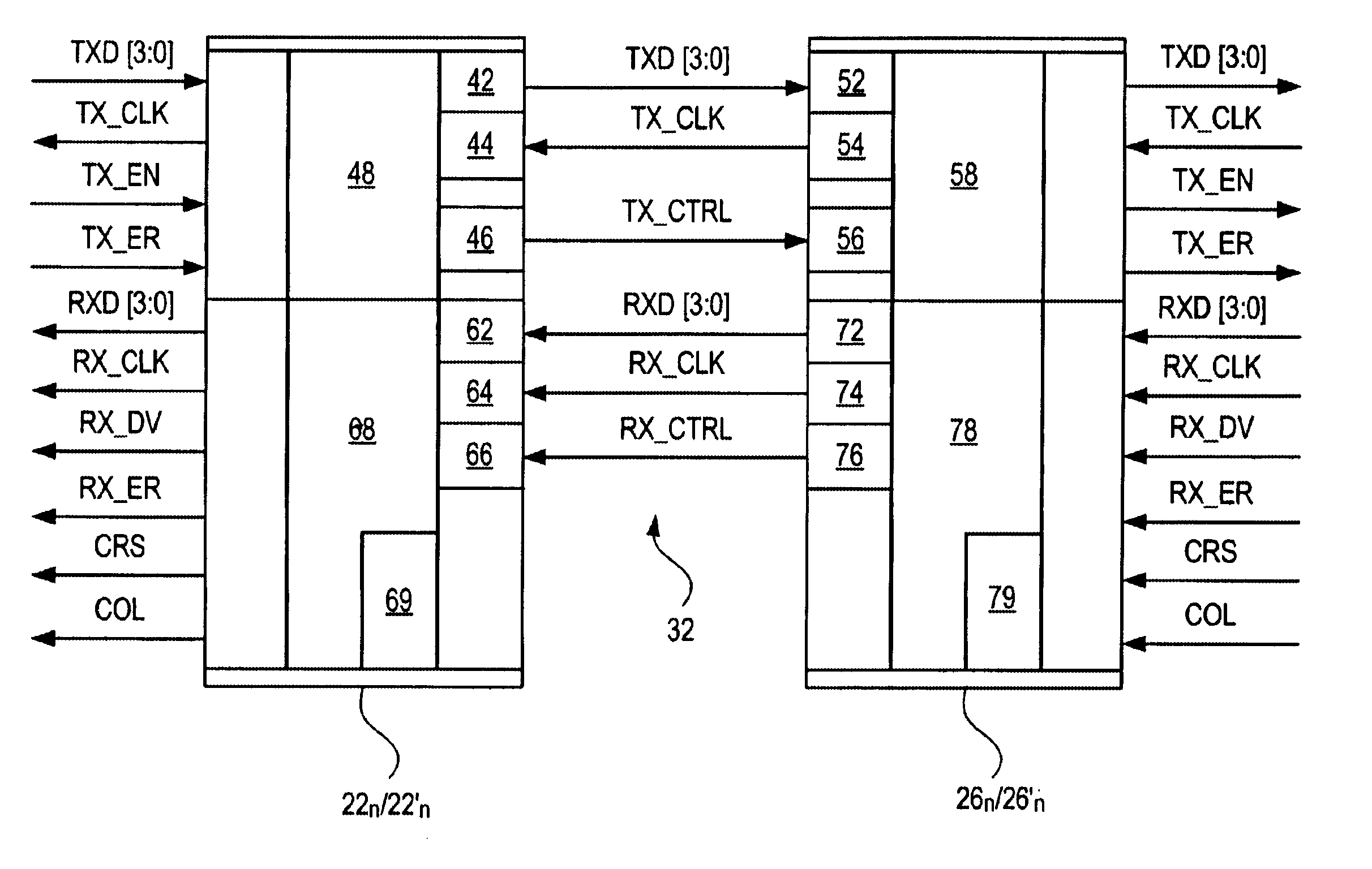
InactiveUS6920132B1Reduce in quantityMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexGigabitMedia Independent Interface
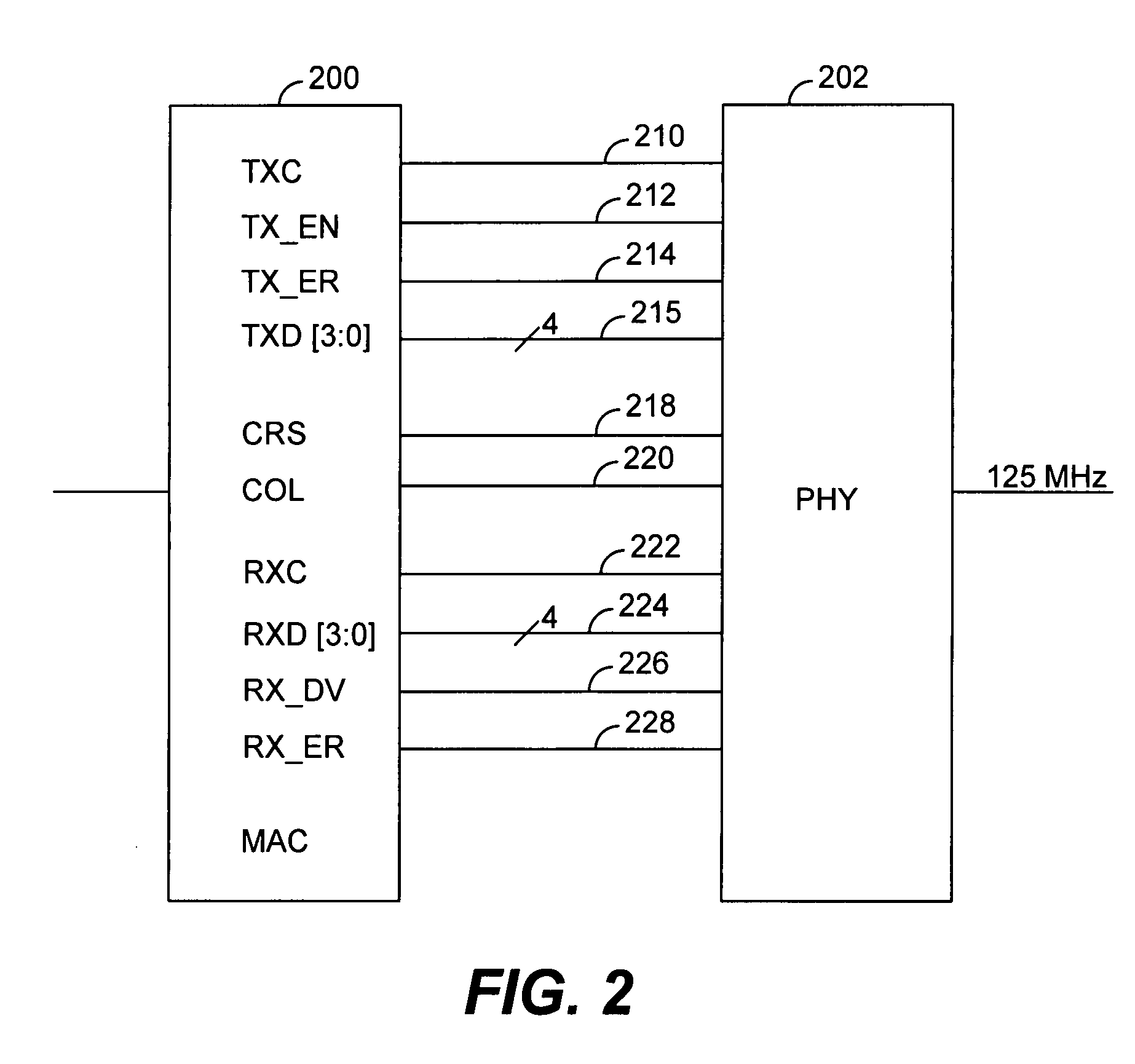
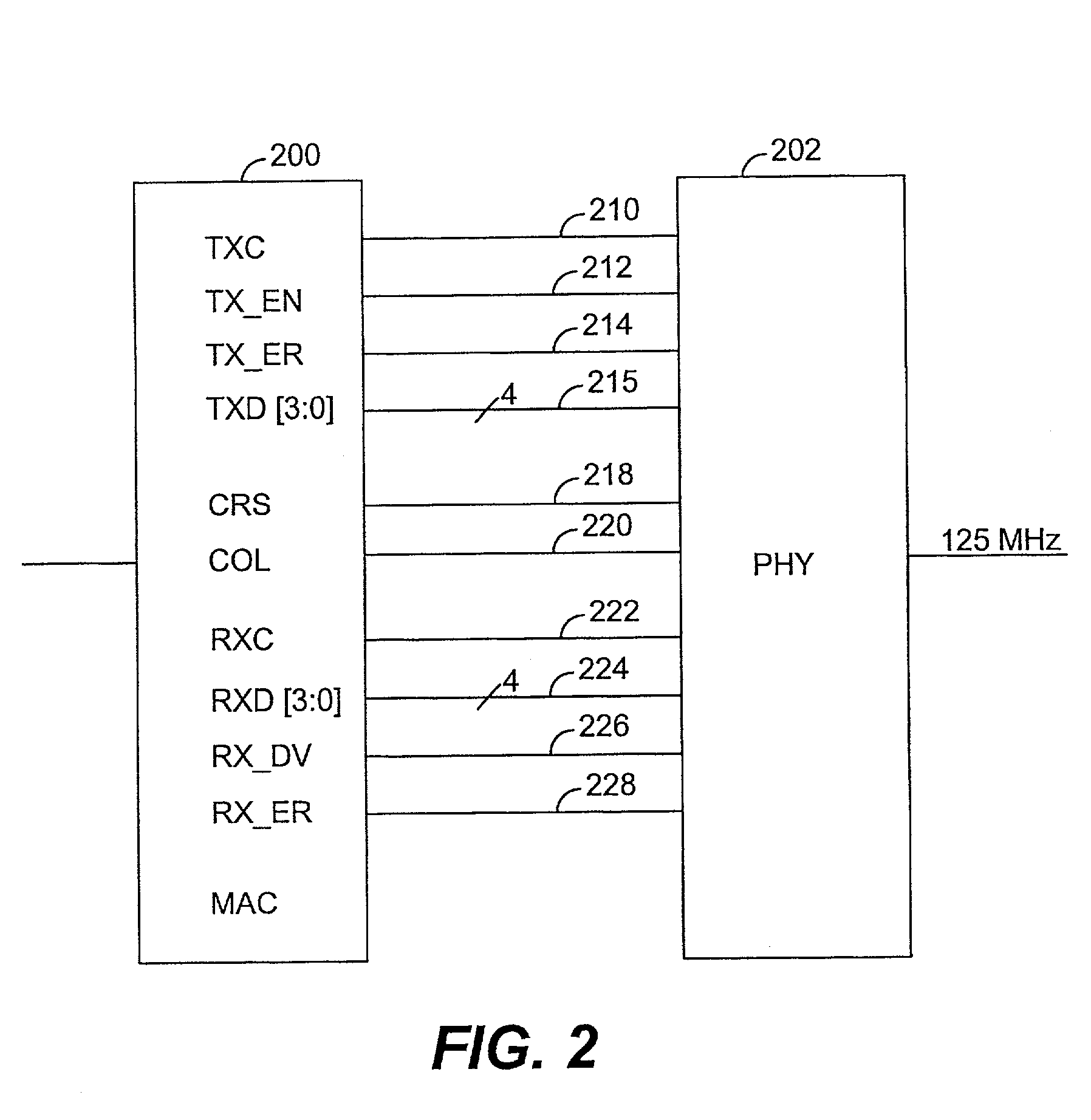
A network interface which reduces pin count in an MII or GMII system by logically combining certain signals to eliminate redundancies, thereby enabling one external connection or pin to perform the functions previously performed by multiple pins. In particular, the two connections previously used for TX_EN and TX_ER are reduced to a single TX_CTRL connection. Similarly, the three connections for RX_DV, CRS and RX_ER are reduced to a single RX_CTRL connection. The COL connection is also eliminated.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Serial media independent interface
InactiveUS20020126684A1Synchronisation information channelsTime-division multiplexTransceiverT interface
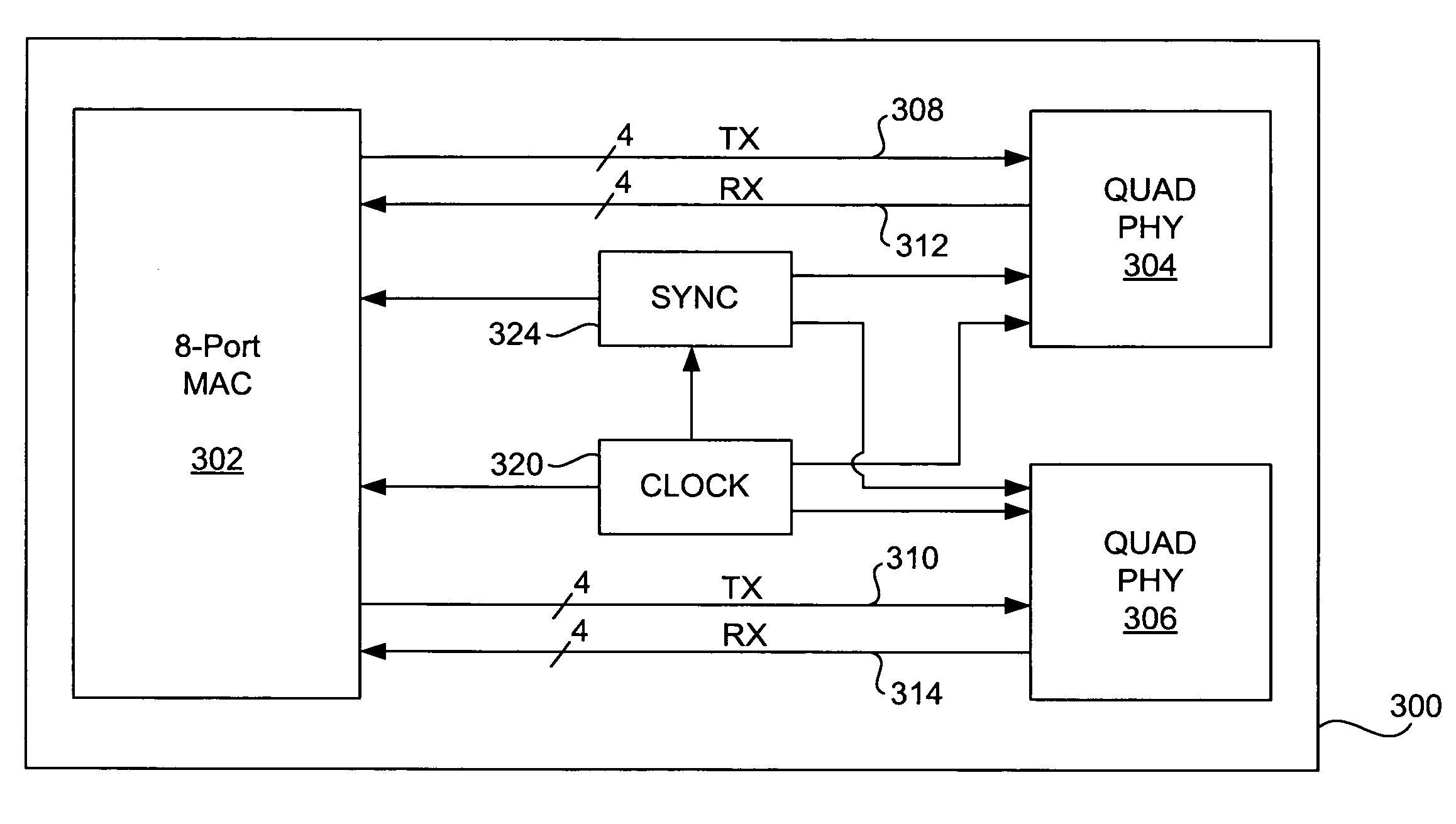
Provided is a 10 / 100Base-T MAC to PHY interface requiring only two wires (pins) per port, with two additional global wires: a clock wire (pin), and a synchronization wire (pin). This reduction in the number of pins associated with each port is achieved by time-division multiplexing wherein each time-division multiplexed wire combines a plurality of definitions from the conventional 100Base-T interface specified by IEEE 802.3u (clause 22). As a result, each port has its own pair of associated time-division multiplexed wires (pins) and the addition of each port simply requires two additional wires. According to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, information normally transferred on sixteen wires in a conventional 100Base-T interface at 25 MHz is time-division multiplexed onto two wires (corresponding to two pins) that transfer data at 125 MHz, five times the speed of conventional interfaces. Importantly, this multiplexing is done on a port by port basis. Therefore, the number of pins required for a MAC to transceiver interface is two times the number of ports plus two instead of sixteen times the number of ports, and the addition of each additional port requires only two more wires (pins).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Methods And Apparatus For Interfacing A Plurality Of Encoded Serial Data Streams To A Serializer/Deserializer Circuit
ActiveUS20080095218A1Data representation error detection/correctionParallel/series conversionData streamGigabit
Methods and apparatus are provided for interfacing a plurality of encoded serial data streams, such as Serial Gigabit Media Independent Interface streams, to a serializer / deserializer circuit. A plurality of encoded serial data streams are transmitted by receiving the plurality of encoded serial data streams that have been encoded using an encoding scheme that provides a substantially uniform distribution of a first code and a second code; marking at least one of the encoded serial data streams (such as changing a first code to a predefined code); and combining at least two of the plurality of encoded serial data streams into a single data stream. A plurality of encoded serial data streams are received by receiving a single data stream comprised of the plurality of encoded serial data streams; detecting a mark in the single data stream; demultiplexing the single data stream into the plurality of encoded serial data streams based on the mark; and providing the demultiplexed plurality of encoded serial data streams to a decoder that decodes the plurality of encoded serial data streams using a decoding scheme that provides a substantially uniform distribution of a first code and a second code.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and system for self-adapting dynamic power reduction mechanism for physical layer devices in packet data networks
InactiveUS20120188885A1Energy efficient ICTError preventionSufficient timeMedia Independent Interface
A physical layer (PHY) in a network device may provide self-adapting power reduction based on monitoring of activity associated with an interface between the PHY and remaining components of the network device. The power management operations of the PHY may then be configured and / or adjusted based on that monitoring. The PHY may comprise an Ethernet PHY, which may support energy efficient Ethernet (EEE) features. The monitored interface may comprise a Media Independent Interface (MII) based interface. In instances where the monitored activity comprises outbound traffic, outbound data received via the interface may be buffered when at least one subcomponent of the PHY that is operable to support transmission of the outbound traffic is unavailable due to the power management operations. The buffering may be configured to last to allow sufficient time to reactivate the at least one subcomponent.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Idle insertion for physical layer rate adaption and time-division duplexing
InactiveUS20140199069A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexMedia Independent InterfacePhysical layer
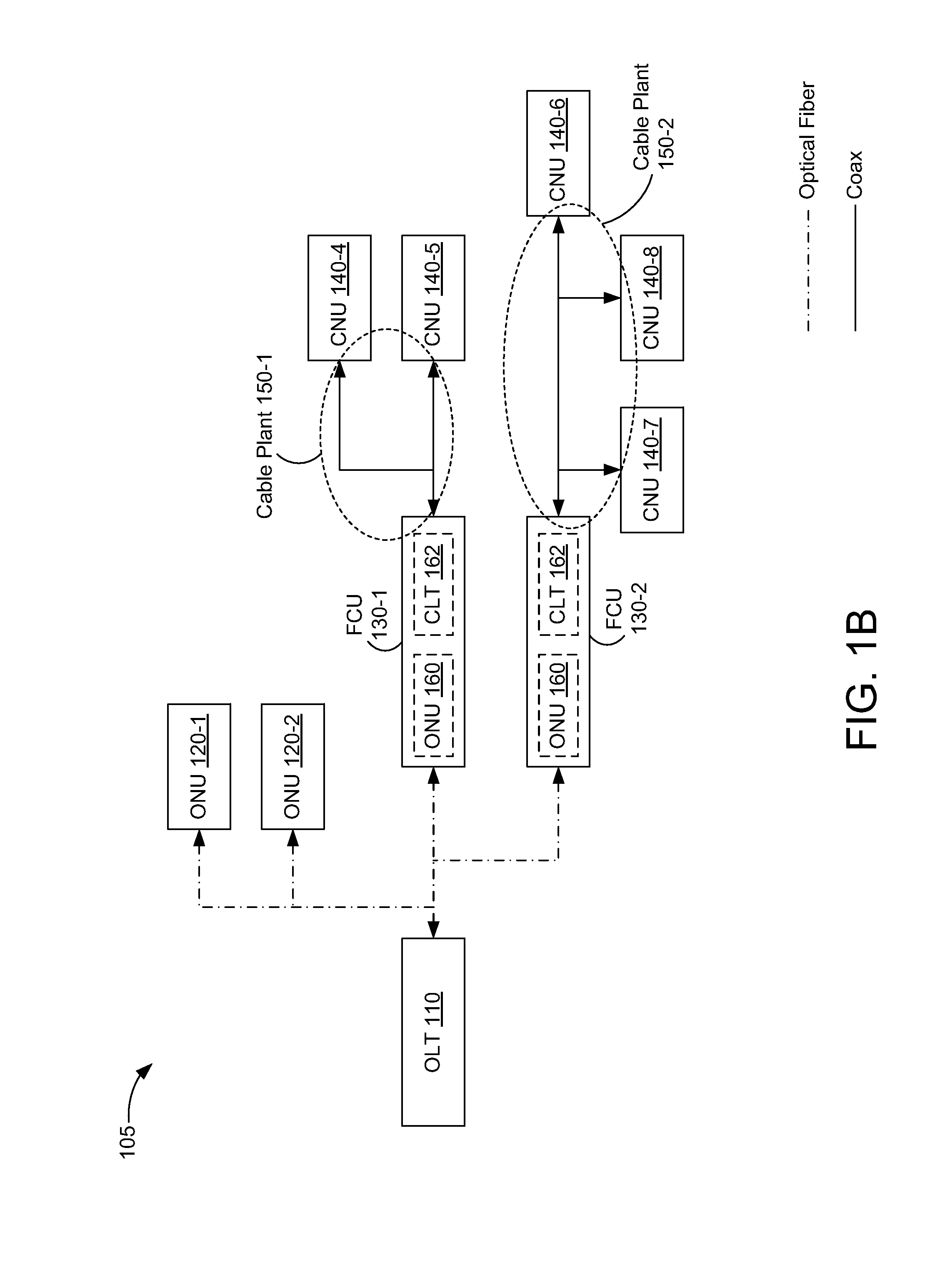
A method is performed in a communication device that includes one or more media access control (MAC) entities, a coax physical layer (PHY), and a media-independent interface coupling the one or more MAC entities with the coax PHY. In the method, a bitstream is generated that includes data frames and characters corresponding to time windows in which the coax PHY does not transmit signals. The bitstream is provided to the coax PHY through the media-independent interface. Signals corresponding to the data frames are transmitted from the coax PHY during a transmit mode. The coax PHY enters a receive mode when the bitstream contains the characters corresponding to the time windows.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Serial media independent interface
InactiveUS20070160087A1Synchronisation information channelsTime-division multiplexTransceiverT interface
A 10 / 100Base-T MAC to PHY interface requiring only two wires (pins) per port, with two additional global wires: a clock wire (pin), and a synchronization wire (pin) represents a reduction in the number of pins associated with each port and is achieved by time-division multiplexing wherein each time-division multiplexed wire combines a plurality of definitions from the conventional 100Base-T interface specified by IEEE 802.3u (clause 22). As a result, each port has its own pair of associated time-division multiplexed wires (pins) and the addition of each port simply requires two additional wires. According to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, information normally transferred on sixteen wires in a conventional 100Base-T interface at 25 MHz is time-division multiplexed onto two wires (corresponding to two pins) that transfer data at 125 MHz, five times the speed of conventional interfaces. Importantly, this multiplexing is done on a port by port basis. Therefore, the number of pins required for a MAC to transceiver interface is two times the number of ports plus two instead of sixteen times the number of ports, and the addition of each additional port requires only two more wires (pins).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
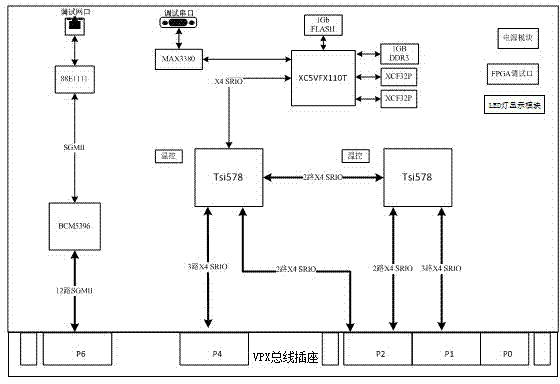
Network and SRIO (serial rapid input/output) data exchanging plate based on VPX bus and control method for network and SRIO data exchanging plate
InactiveCN104243174ASupport multicastSupport functionData switching detailsMedia Independent InterfaceGigabit
The invention relates to radar signal processing and relevant technical fields, in particular to a network and SRIO data exchanging plate based on a VPX bus and a control method for the network and SRIO data exchanging plate. The network and SRIO data exchanging plate based on the VPX bus comprises a power module, an FPGA (field programmable gate array) control module, a first SRIO exchanging module, a second SRIO exchanging module, a network exchanging module, a network interface module, an FLASH module, a debugging serial port module, an FPGA debugging port and an LED (light emitting diode) lamp display module. The problems that a data transmission mode of the existing signal processing system is inflexible, and the existing signal processing system does not have a system reconfigurable function are solved; an SRIO and network exchanging chip is adopted; a 12-channel SGMII (serial gigabit media independent interface) network and a 10-channel SRIO port can be exchanged; and the 10-channel SRIO port can be configured into an X4 or X1 SRIO exchanging port according to different application requirements. The data exchanging plate has the advantages that the data exchanging plate is high in integration level and real-time in exchanging and has abundant ports.
Owner:沈辉
Method and system for a multi-rate gigabit media independent interface
ActiveUS7720068B2Multiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsTime-division multiplexGigabitMedia Independent Interface
Disclosed is a UGMII system to interface multirate devices including 10 gigabit per second data exchange rates. Mode selection is enabled to provide for automatic detection and adaptation to any transmit rate including 10M, 100M, 1G, and 10G. Mode selection comprises the negotiation between the UGMII extension sublayers located at the MAC and PHY to select between one of several operational modes including: XGMII communication, GMII encapsulation, Clause 22 MDIO register management and Clause 45 MDIO register management. Selection of UGMII and XGMII operating modes are negotiated between the MAC and PHY using ordered sets to announce and acknowledgement a mode change. In one embodiment 802.3 Clause 46 defined ordered sets are utilized.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Scrambled block encoder
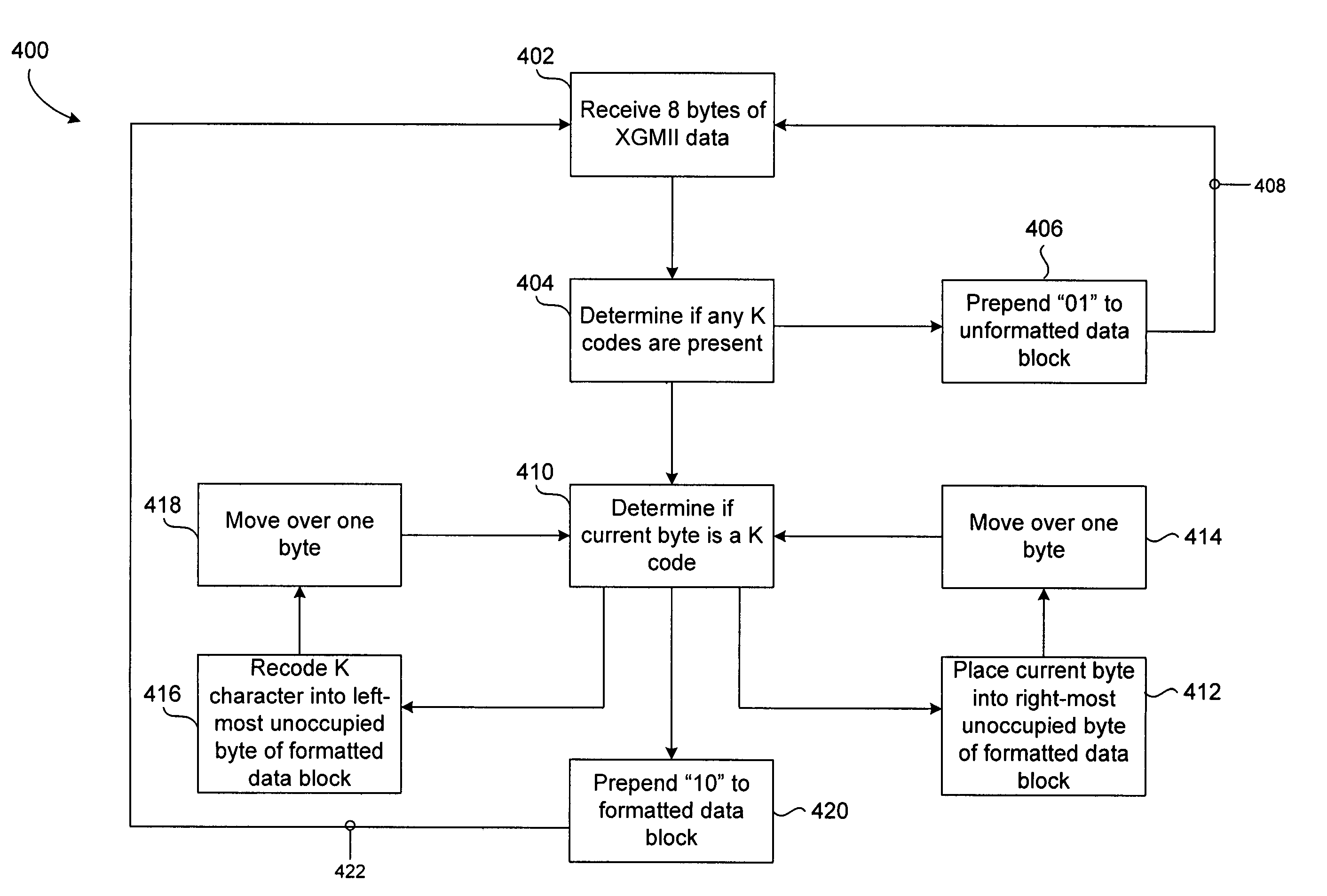
ActiveUS7274315B2Flexibly encode K codesInterference minimizationTime-division multiplexIndividual digits conversionComputer hardwareMedia Independent Interface
A block encoder flexibly encodes K codes to produce an encoded data block. The block encoder receives an unformatted block of 10 Gigabit Media Independent Interface (XGMII) data. The unformatted block of data includes data and / or K characters, both of which can be located in any position of the unformatted block. The block encoder inserts data characters into a first set of slots of the encoded data block. The block encoder encodes K characters to produce corresponding encoded K characters. Each encoded K character includes a link field, a position field and a recoded value field. The encoded K characters are inserted into a second set of slots of the encoded data block. A synchronization header is attached to the encoded data block to distinguish control blocks from pure data blocks. The header and encoded data block are subsequently scrambled in preparation for transmission.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Ethernet MAC (Media Access Control) sublayer controller applicable to WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network)
ActiveCN102065569AImprove general performanceImplement retransmissionNetwork topologiesWireless network protocolsProcessor registerControl data
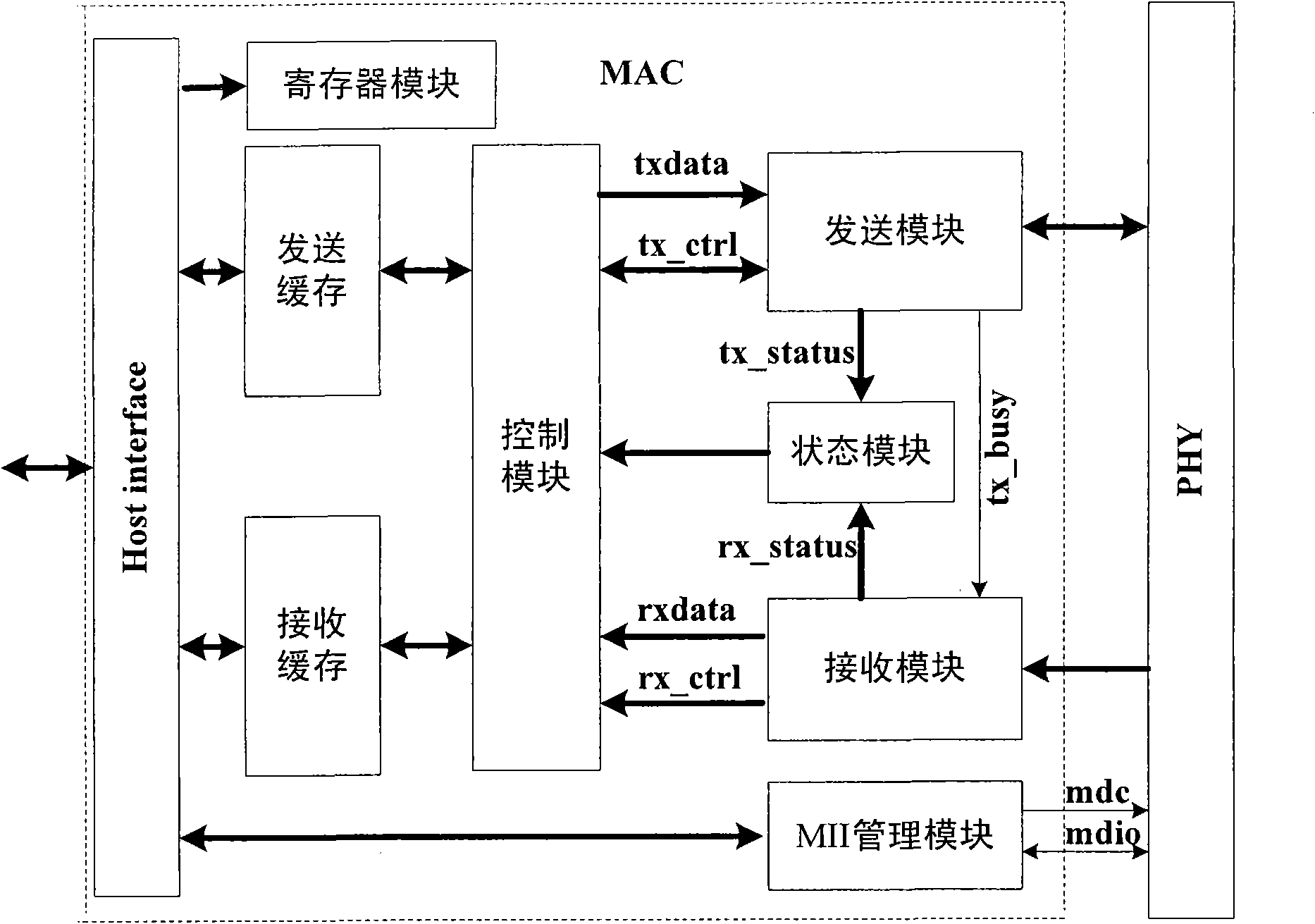
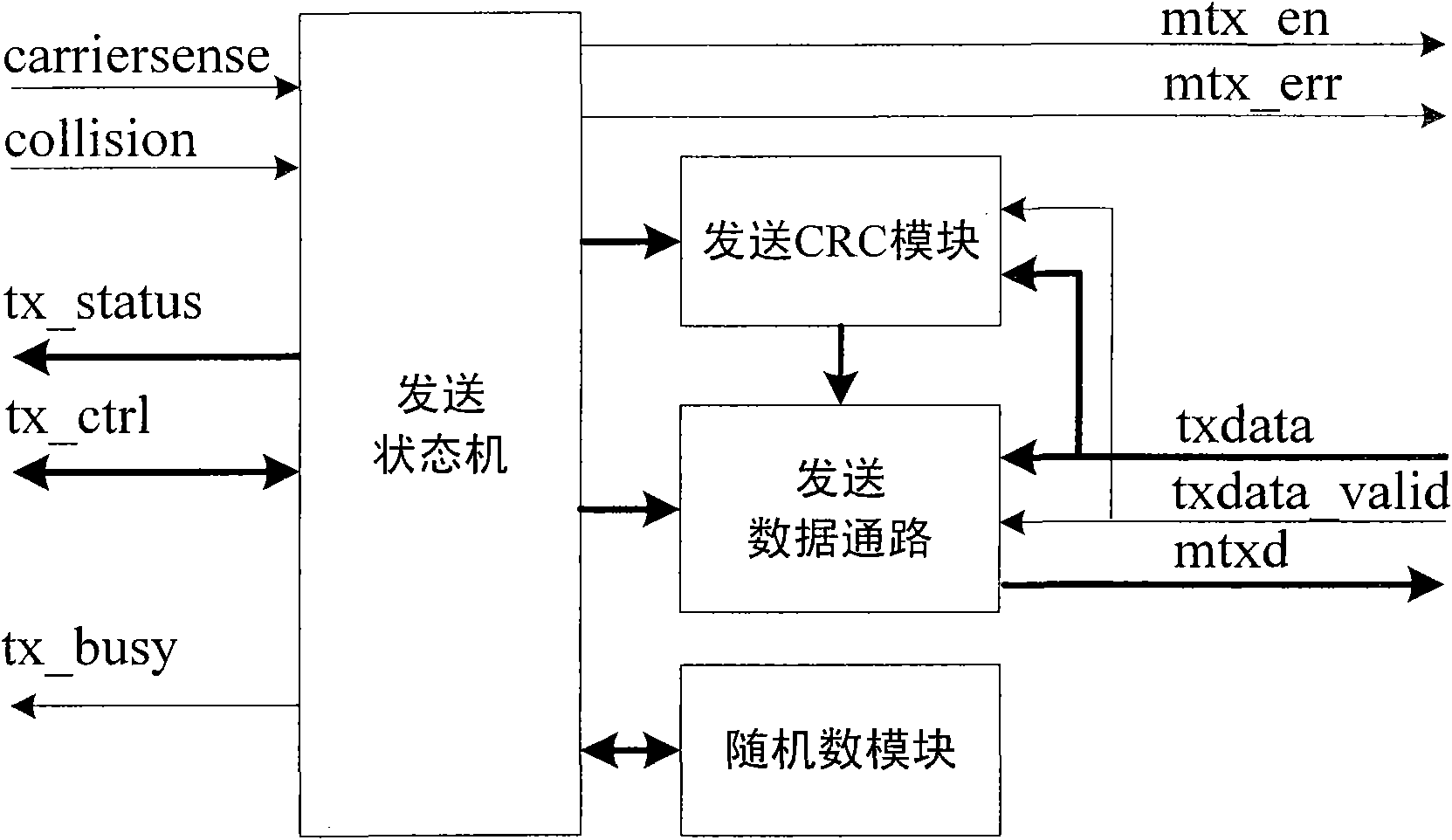
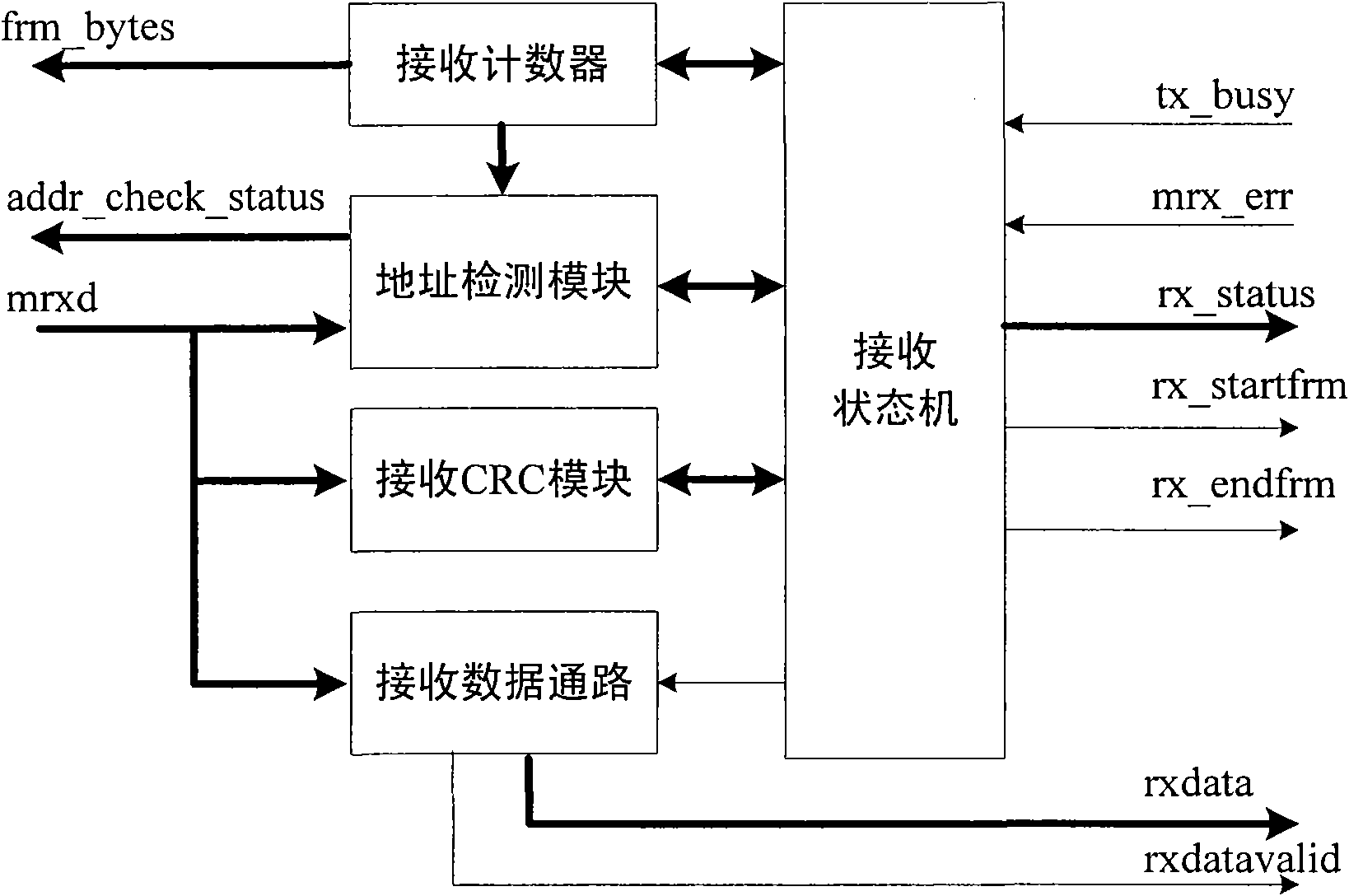
The invention discloses an Ethernet MAC (Media Access Control) sublayer controller applicable to WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network). The Ethernet MAC sublayer controller comprises a transmitter module, a receiver module, a state module, a control module, an MII (Media Independent Interface) management module, a transmission cache, a receiving cache and a register module, wherein the transmission cache and the receiving cache can realize storage, retransmission and discard of data frames by employing the asynchronous FIFO (First-in First-out) capable of loading read addresses, the information interaction of data frames between a host and the MAC sublayer controller is carried out through data frame cache descriptors which include transmitting cache descriptors and receiving cache descriptors, wherein the transmitting cache descriptors are used for controlling the transmitting process of the data frames, recording and returning a transmitting state; the receiving cache descriptors are used for controlling the reading of received data frames and returning a frame receiving state to the host. By the Ethernet MAC sublayer controller, the network access of embedded devices, the frame conflict retransmission and discard of bad frames are realized, and the utilization rate of cache in a chip is improved when short frames are received.
Owner:浙江科睿微电子技术有限公司
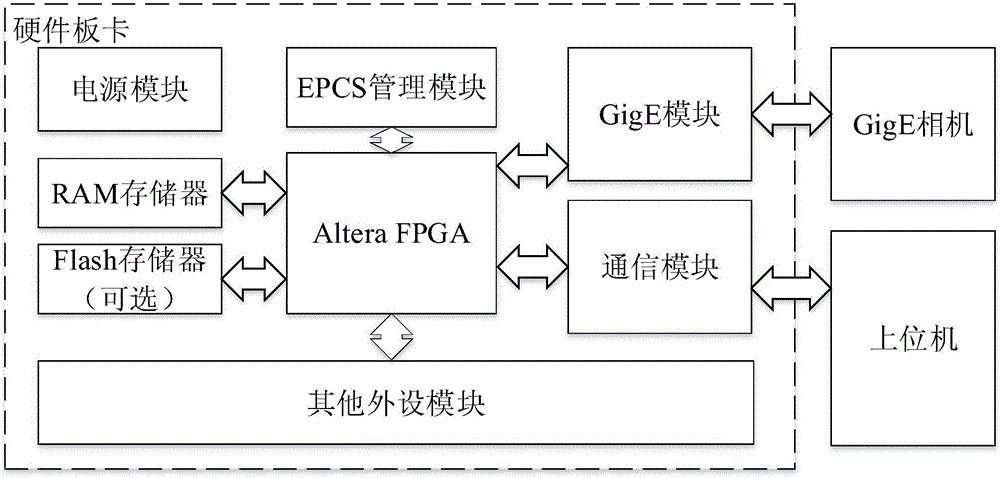
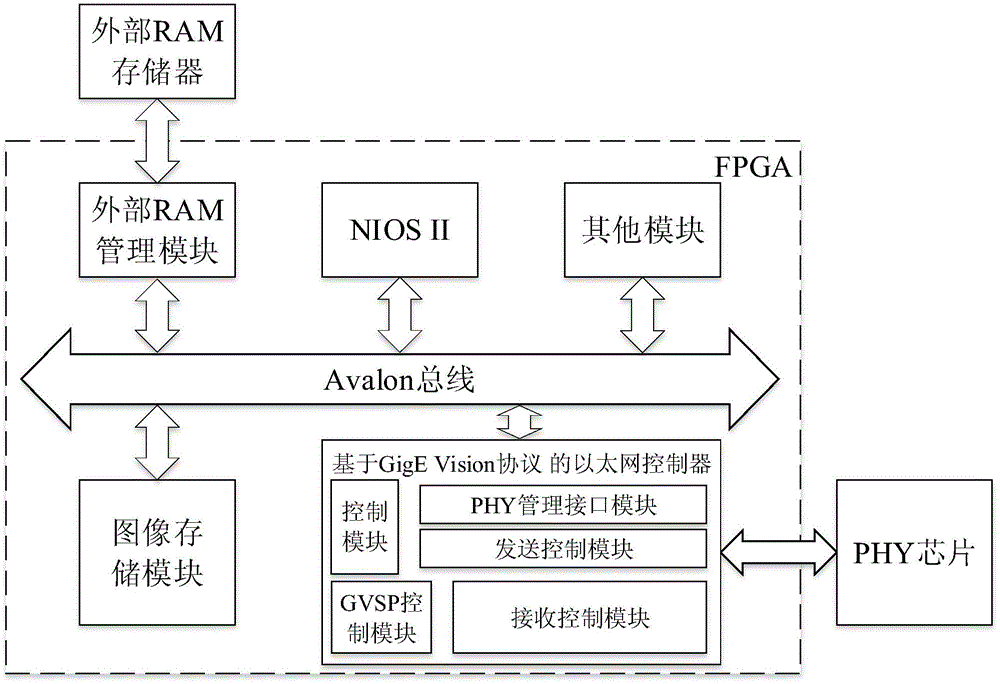
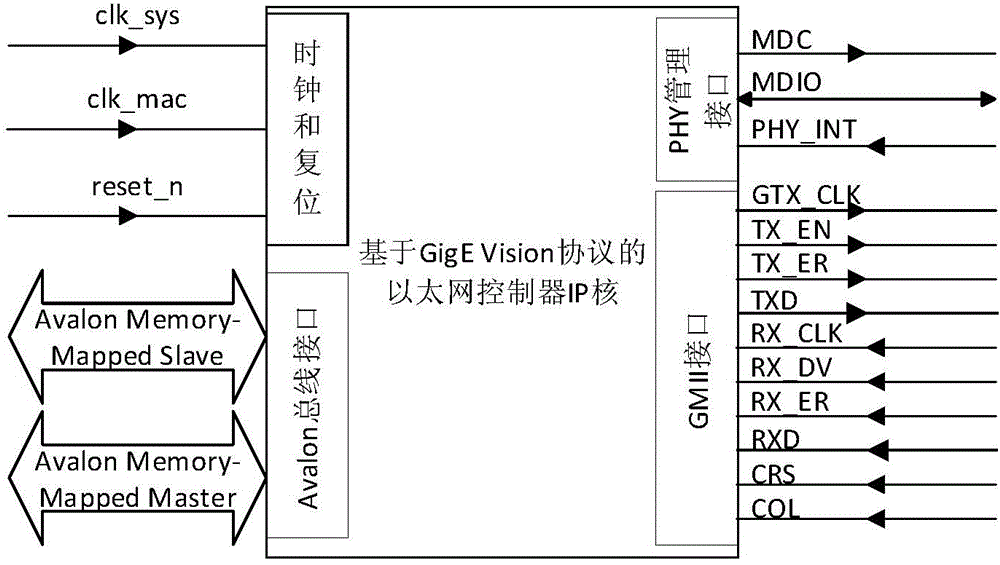
GigE (gigabit Ethernet) vision protocol-based Ethernet controller IP (Internet protocol) core and method
ActiveCN104572574AReduce complexityReduce consumptionArchitecture with single central processing unitData switching networksFpga implementationsMedia Independent Interface
The invention discloses a GigE vision protocol-based Ethernet controller IP core. The GigE vision protocol-based Ethernet controller IP core is composed of a control module, a PHY (physical layer) management interface module, a transmission control module, a flow control module and a receiving control module and implemented through FPGAs (field programmable gate array) and follows the Avalon Memory-Mapped interface specifications and the GMII (gigabit media independent interface) specifications. The GigE vision protocol-based Ethernet controller IP core is a special IP core designed according to the characteristics of the GigE Vision protocol and can achieve GigE camera image receiving and automatic storage; the GigE vision protocol-based Ethernet controller IP core achieves image collection and meanwhile overcomes the shortcomings of large resource occupation, high CPU (central processing unit) utilization rate, low image collecting efficiency and the like of traditional Ethernet controllers; by means of the characteristics of parallel processing of the FPGAs, the data receiving speed and the system timeliness can be improved. Under the same testing conditions, collecting images through the GigE vision protocol-based Ethernet controller IP core can reduce more than a half of FPGA resource consumption compared with a triple-speed Ethernet core of the Altera Company.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Physical-layer channel bonding
InactiveUS20140186041A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsPhysical layerMedia Independent Interface
A network device includes a plurality of physical-media entities (PMEs), each corresponding to a distinct channel, to generate transmit signals based on transmit packets received over a media-independent interface. The network device also includes a channel-bonding sublayer to direct the transmit packets from the media-independent interface to respective PMEs of the plurality of PMEs. The channel-bonding sublayer has a substantially fixed delay between the media-independent interface and the plurality of PMEs for the transmit packets.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
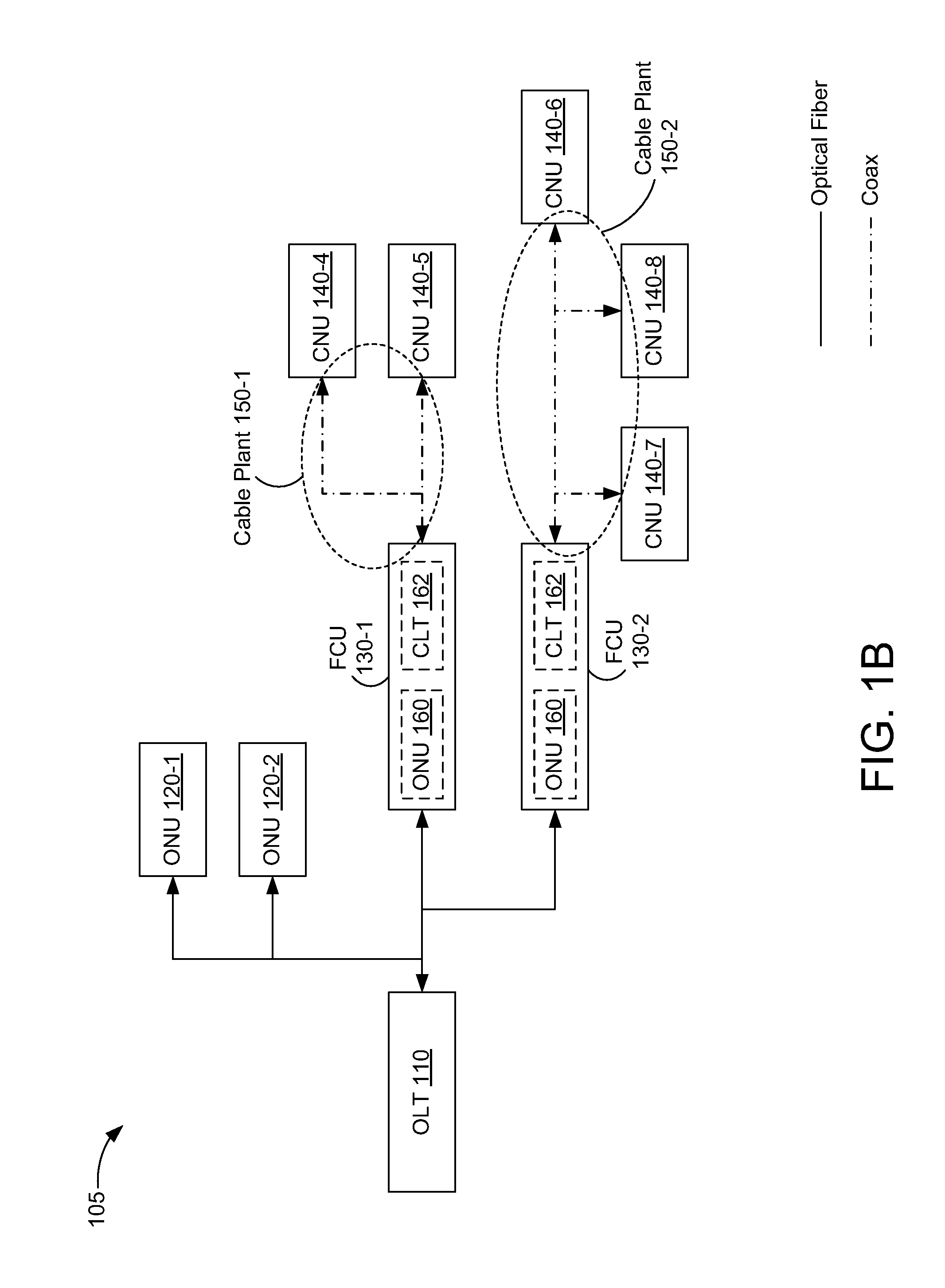
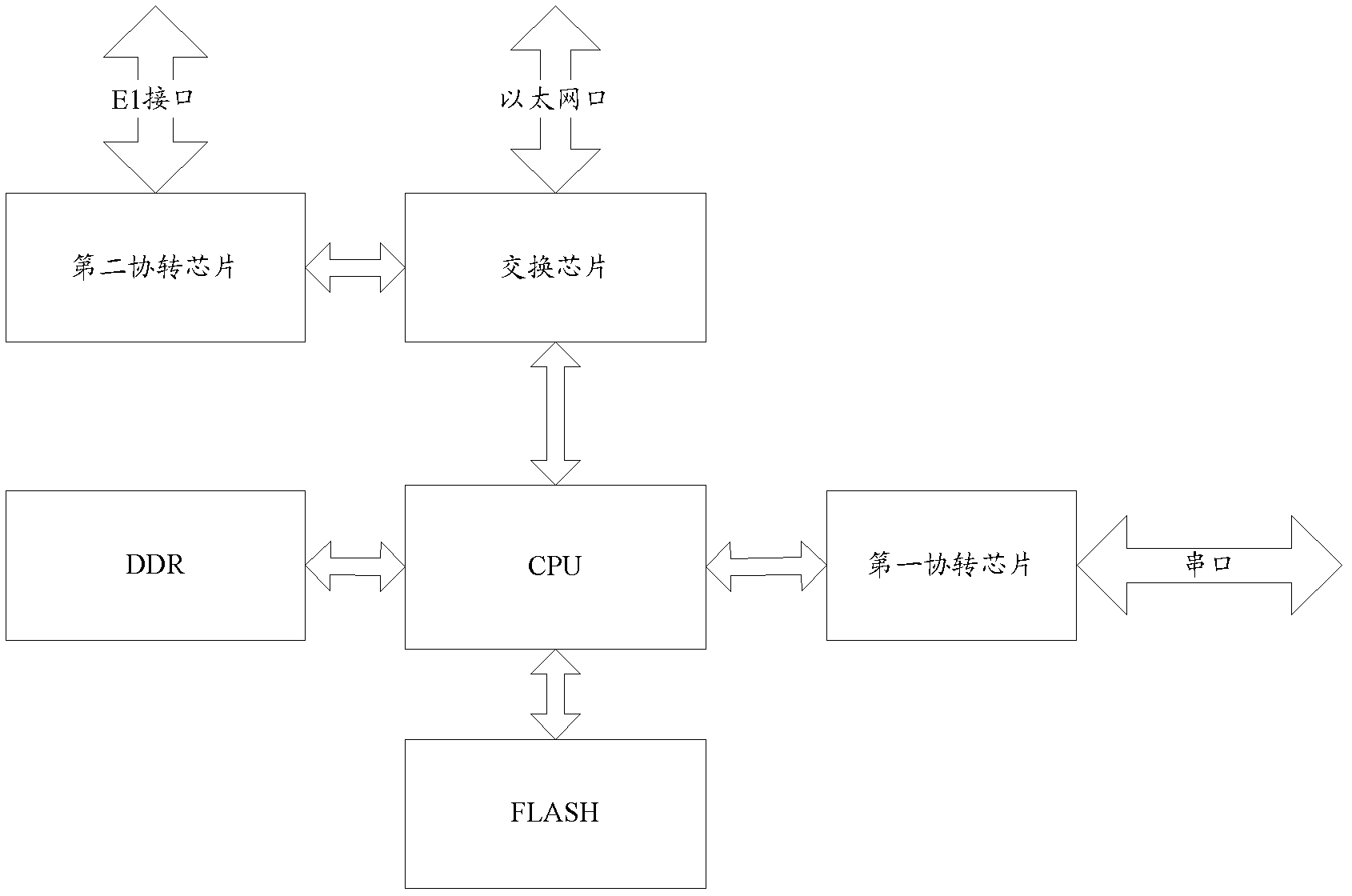
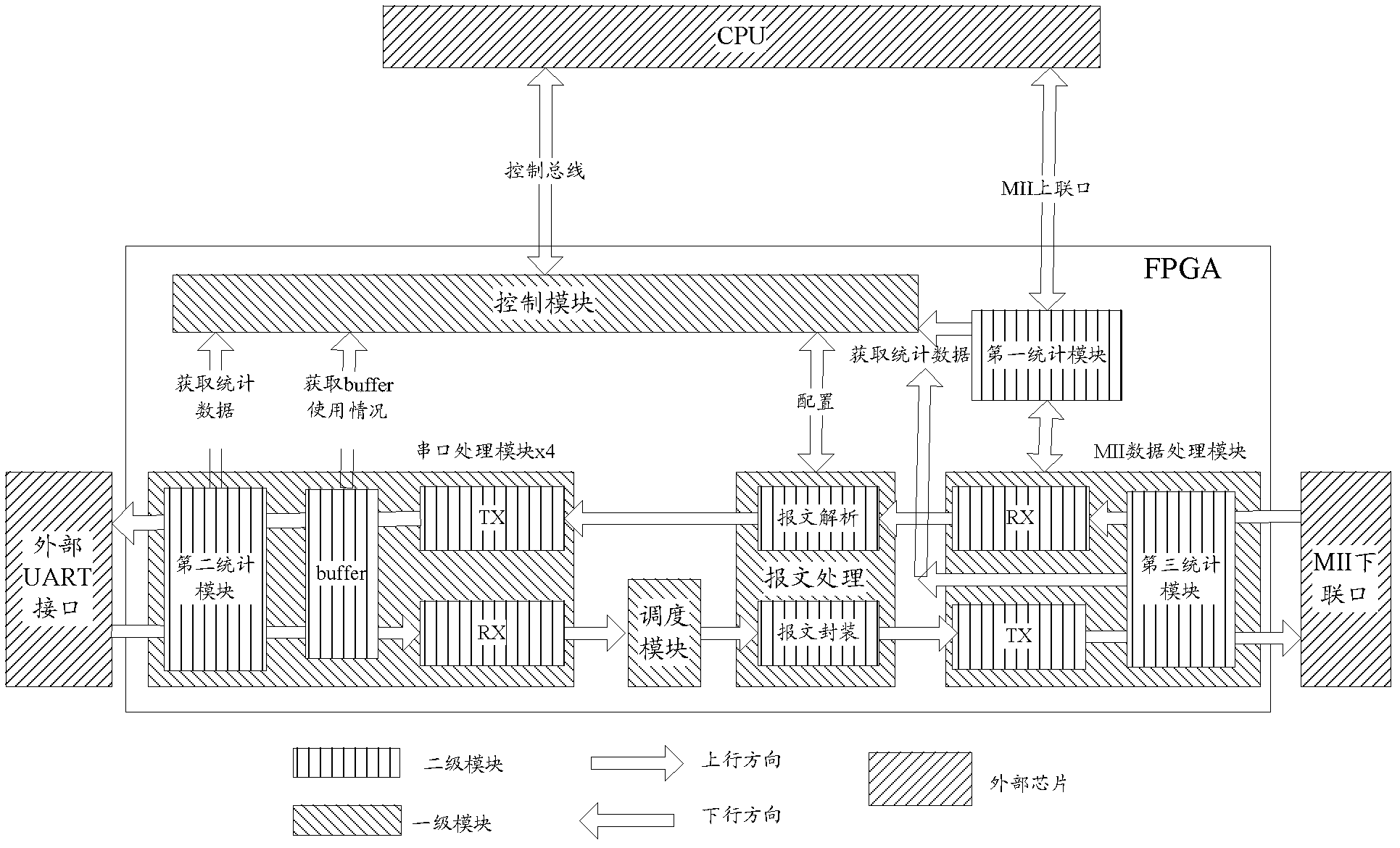
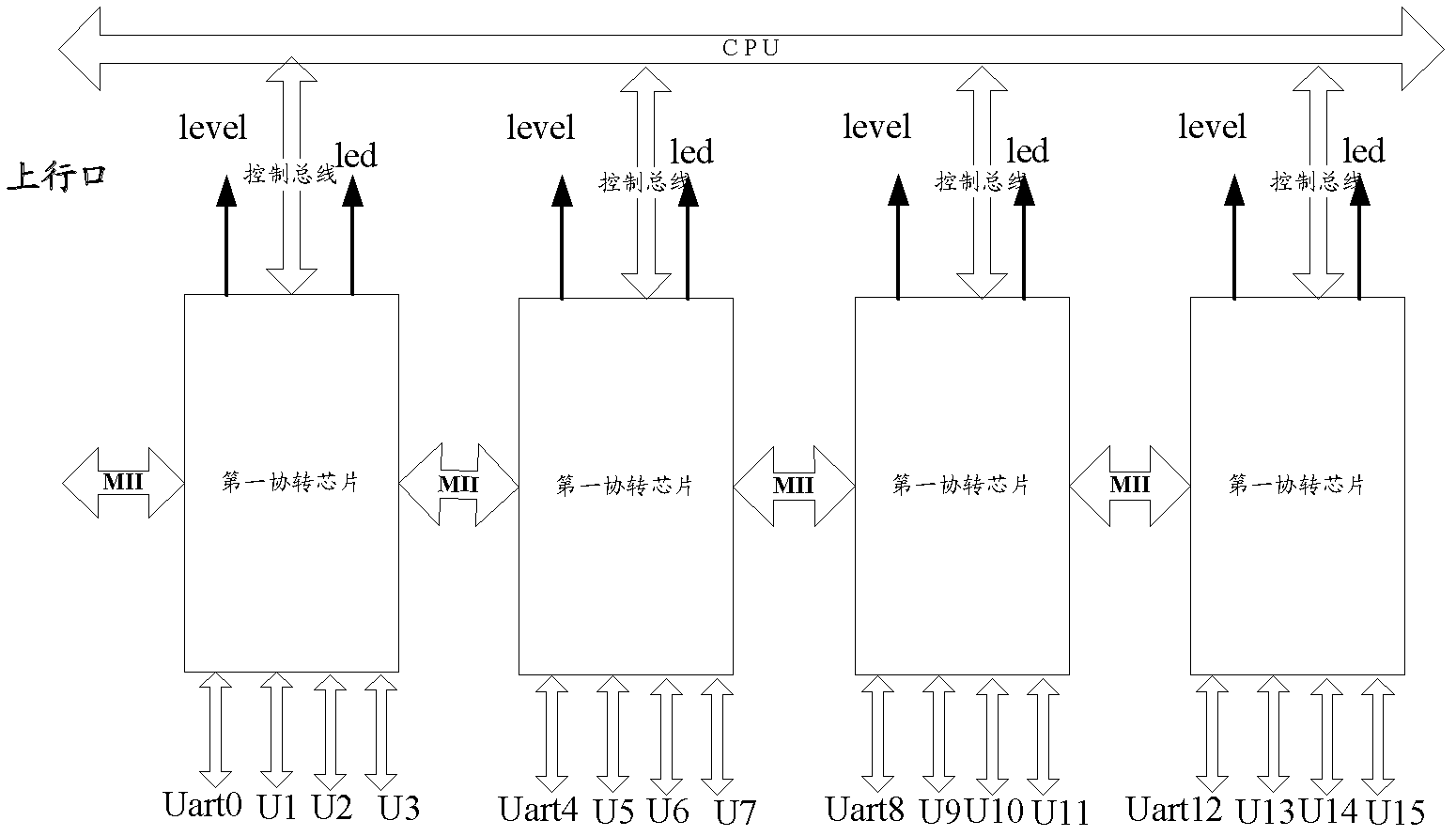
Serial port server, protocol conversion chip and data transmission method
The invention discloses a serial port server, a protocol conversion chip and a data transmission method, which are used for achieving the serial port server with a function for transforming media independent interface (MII) data and serial port data. The serial port server comprises at least one first protocol conversion chip. The first protocol conversion chip comprises an MII and a plurality of serial ports, is connected with a central processing unit (CPU) through the MII, and is used for receiving an Ethernet message from the CPU, analyzing out a media access control (MAC) address, determining the serial port corresponding to the MAC address, sending data in the Ethernet message from the serial port port, packaging the data received from the serial port into the Ethernet message, carrying the MAC address corresponding to the serial port port, and then sending the Ethernet message to the CPU. The CPU receives the Ethernet message from an exchange chip, sends the Ethernet message to the first protocol conversion chip, and sends the Ethernet message received from the first protocol conversion chip to the exchange chip.
Owner:RAISECOM TECH
System and method for automatic retry of transmit, independent of a host processor, after an underrun occurs in a LAN
InactiveUS6137804AImprove performanceData switching by path configurationLogic cellMedia Independent Interface
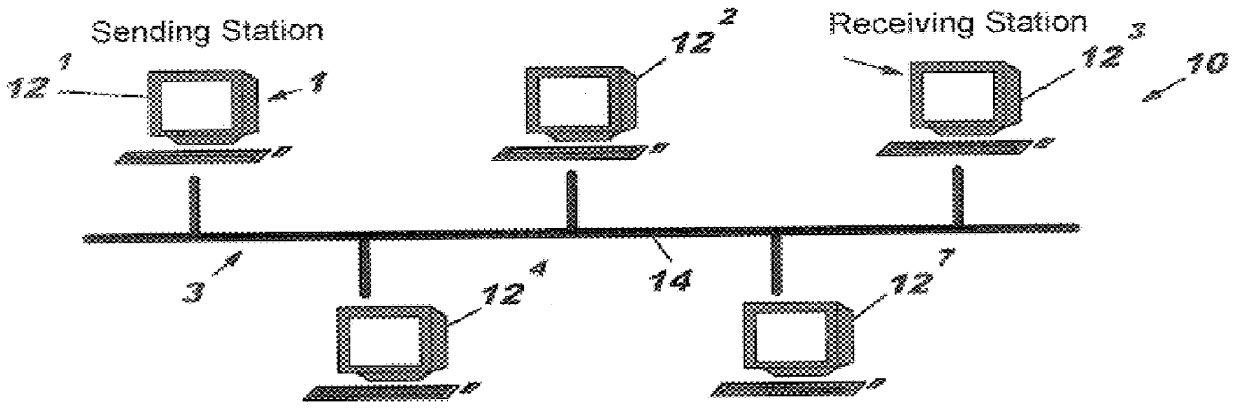
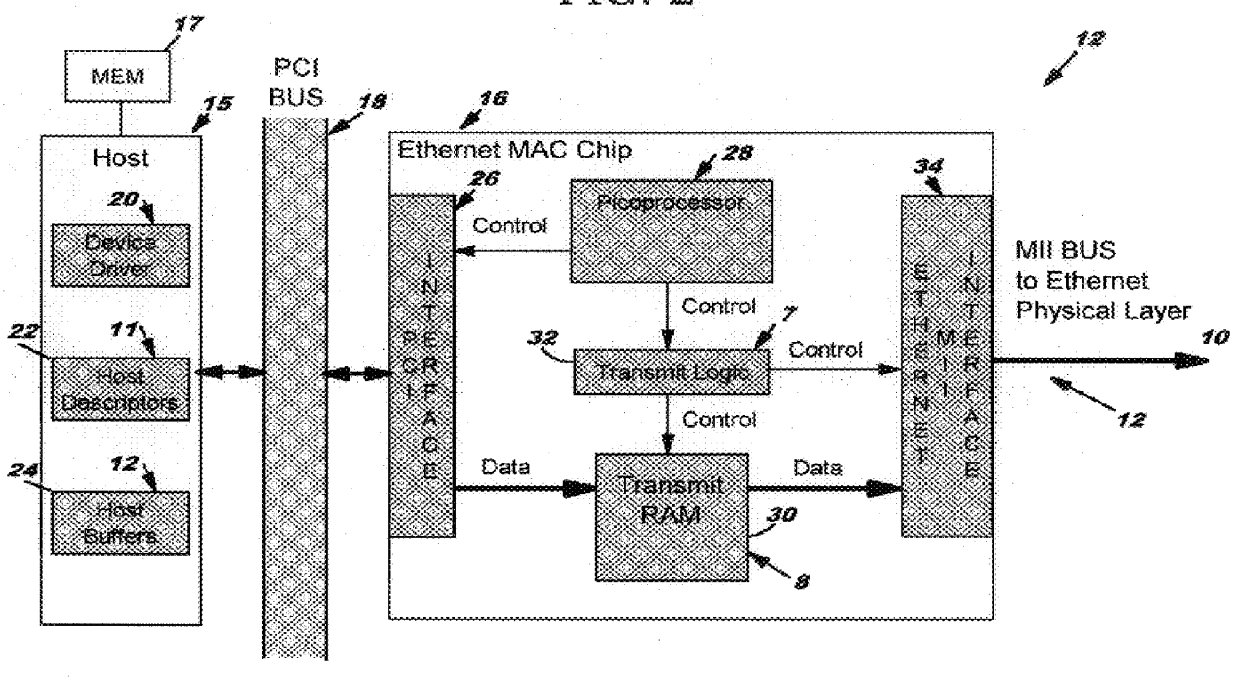
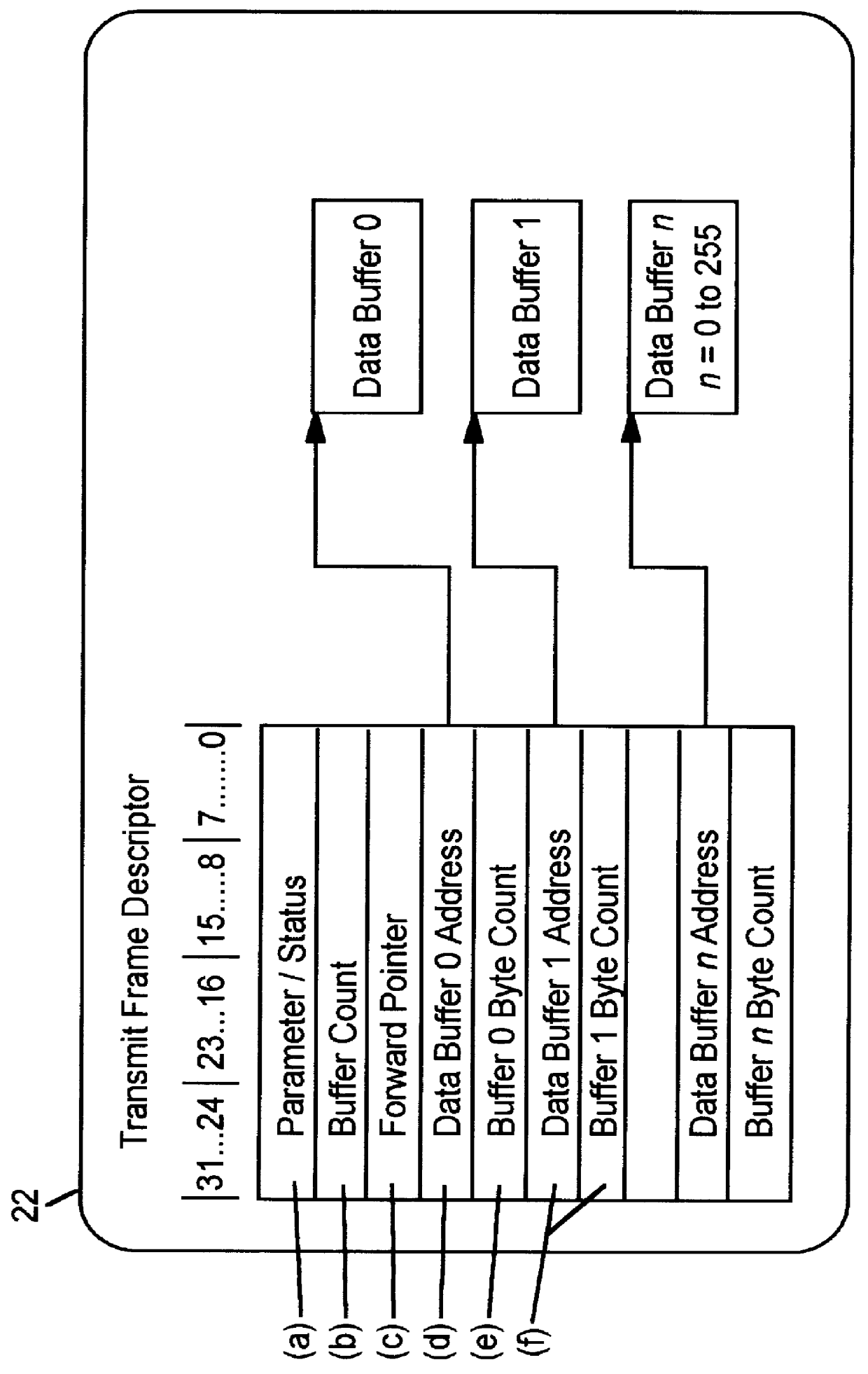
In a local area network, a system and a method to detect transmit underruns and retransmit frames between a sending station and a receiving station using a Media Access Control (MAC) device in lieu of a sending processor. The MAC device includes a MAC processor for transmitting data in blocks from a host buffer to a storage device, e.g., RAM for retransmission to the network via a Media Independent Interface (MII) unit. The MAC device includes a transmit logic unit which uses a control word set by the MAC processor to transmit data by frames from the storage device to the network. The transmit logic unit includes pointer control logic to identify the start address of the data and to track the data as read from the storage device to the network. When a transmit underrun occurs, the transmit logic recognizes the condition and resets the pointer logic to the start of the first frame for retransmission to the receiving station. During retransmission, the MAC processor continues to transfer data from the sending system to the storage device which eventually provides sufficient data to overcome the underrun condition. A frame is repeated if a underrun condition continues until the frame is transmitted without an underrun condition which eliminates the retransmission request of the receiving station to the sending station. The MAC device enables underruns to be transparent to the sending and receiving station.
Owner:IBM CORP
Transceiver module
InactiveUS20070086710A1Meet needsLow costCoupling device connectionsCoupling light guidesHigh rateXAUI
The object is to provide a transceiver module that is capable of performing a high-rate communication, and satisfies the demand at a moderate cost in a case where short distance communication is enough for transmitting or receiving signals. The transceiver module has a Re-timer 11, a control portion 12, a reference clock generating portion 13, a power portion 14 and a CX4 interface 15. The Re-timer 11 is coupled to a transceiver portion (Tx / Rx) 21 through an XAUI (10 Gigabit Media Independent Interface) interface 22, and is coupled to other component that is coupled to one end of a cable 150 for balanced transmission through the CX4 (10GBASE-CX4) interface 15.
Owner:FUJITSU COMPONENENT LTD
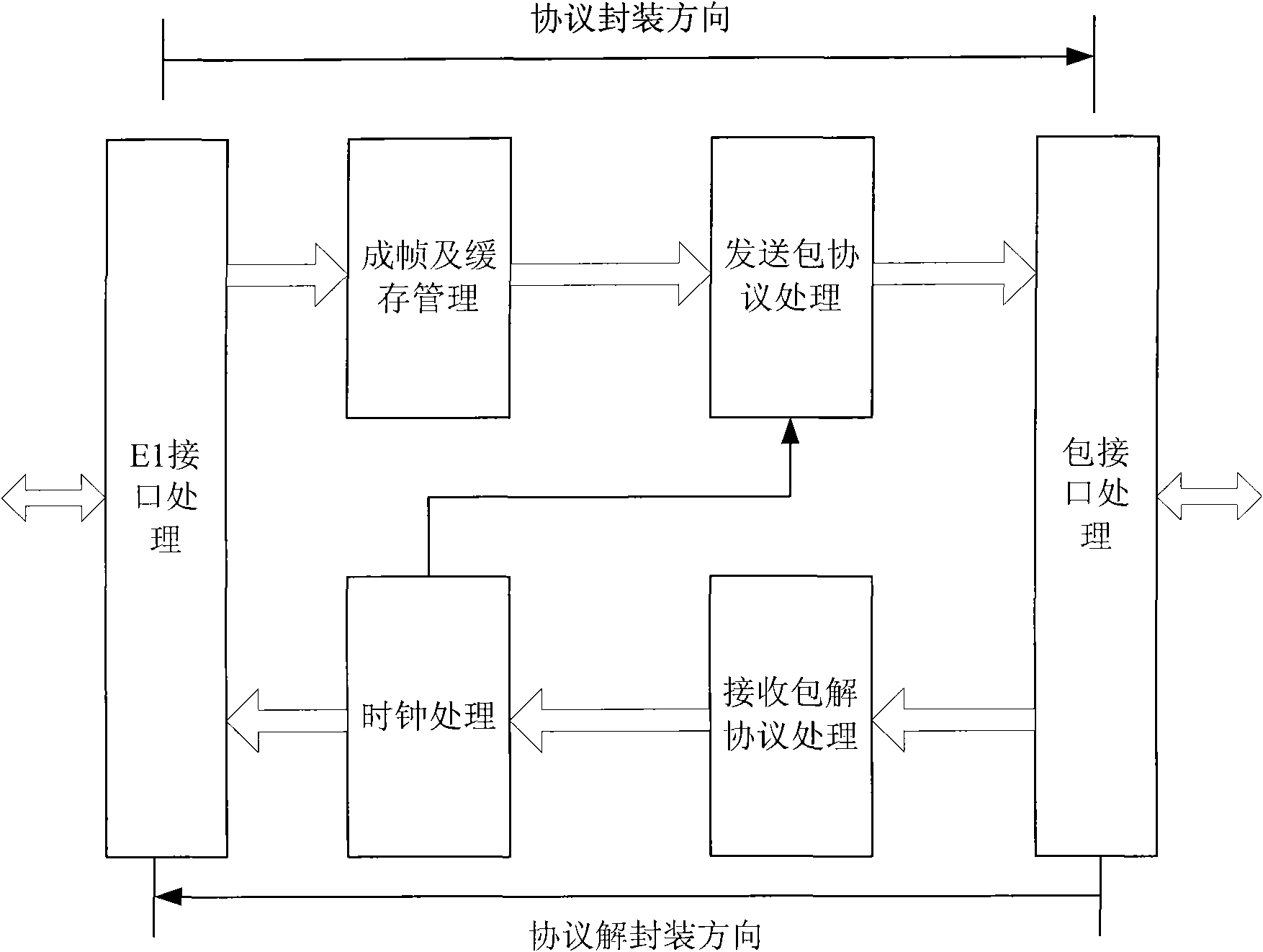
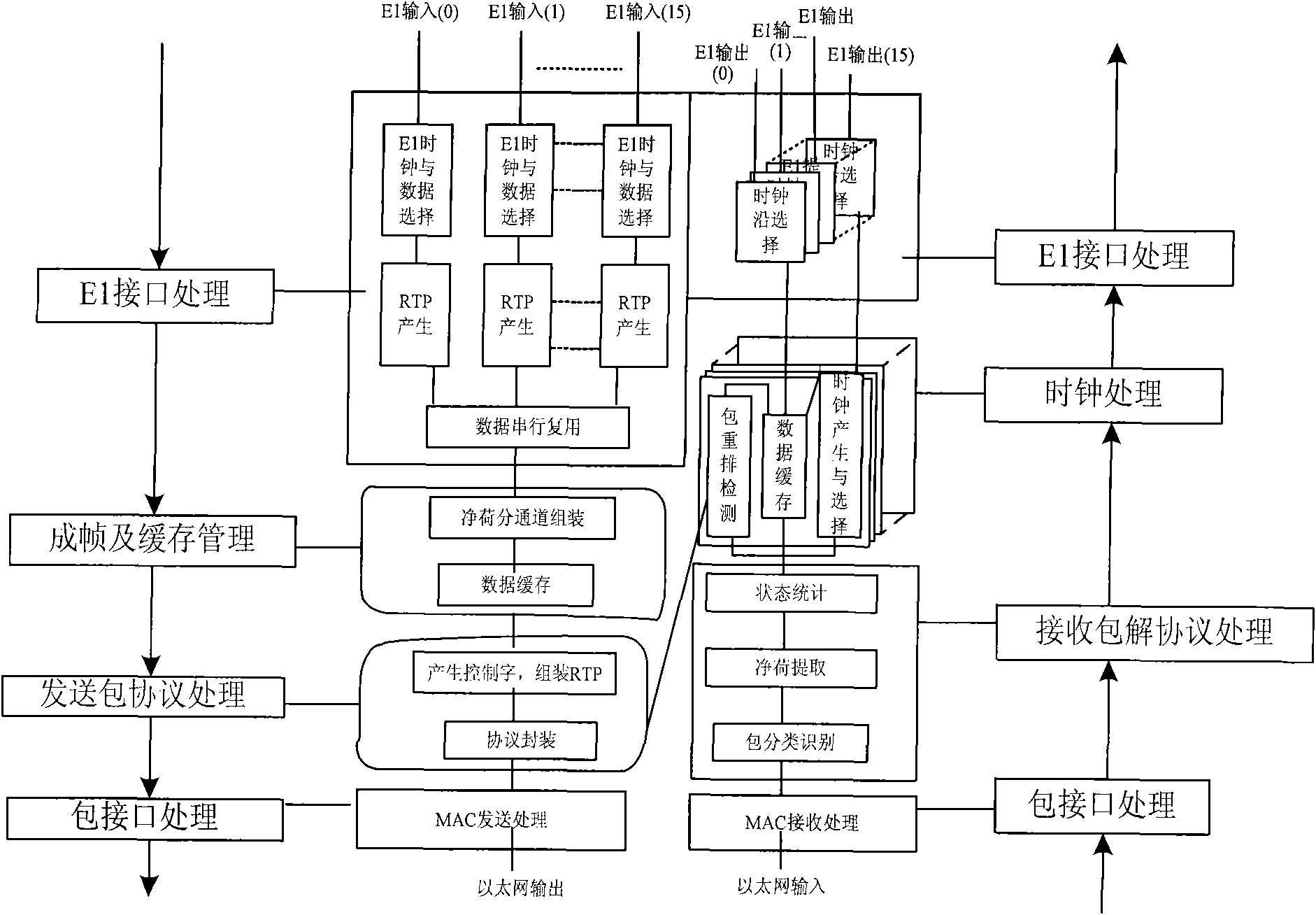
E1 emulation realization method
ActiveCN102148728ASimple methodReduced CPU performance requirementsData switching networksSynchronising arrangementMedia Independent InterfaceTime-division multiplexing
The invention discloses an E1 emulation realization method, which relates to the field of network simulation and comprises the following steps of: performing protocol encapsulation on a direction, and performing serialization processing on received data to generate a real-time transport protocol value; assembling a time division multiplexing (TDM) payload into a frame, forming cache data packets by using the processed data, and finishing a corresponding description table; attaching packet headers to the TDM payload, generating control word information and real-time transport protocol information according to configuration, and performing encapsulation according to a protocol; performing clock domain adaptation on the processed data, finishing Ethernet media access control (MAC) processing, and transmitting Ethernet data by using a media independent interface (MII); performing protocol decapsulation on the direction, receiving and caching the Ethernet data, and finishing MAC layer processing; classifying and identifying the Ethernet data packets, extracting the payload and related control bytes, and counting state information; and performing clock recovery on a processed TDM payload code stream, and externally transmitting the processed TDM payload code stream. The method is relatively lower in cost; updating can be performed; and requirements on the performance of a central processing unit (CPU) are reduced, and clock recovery performance is improved.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD +1
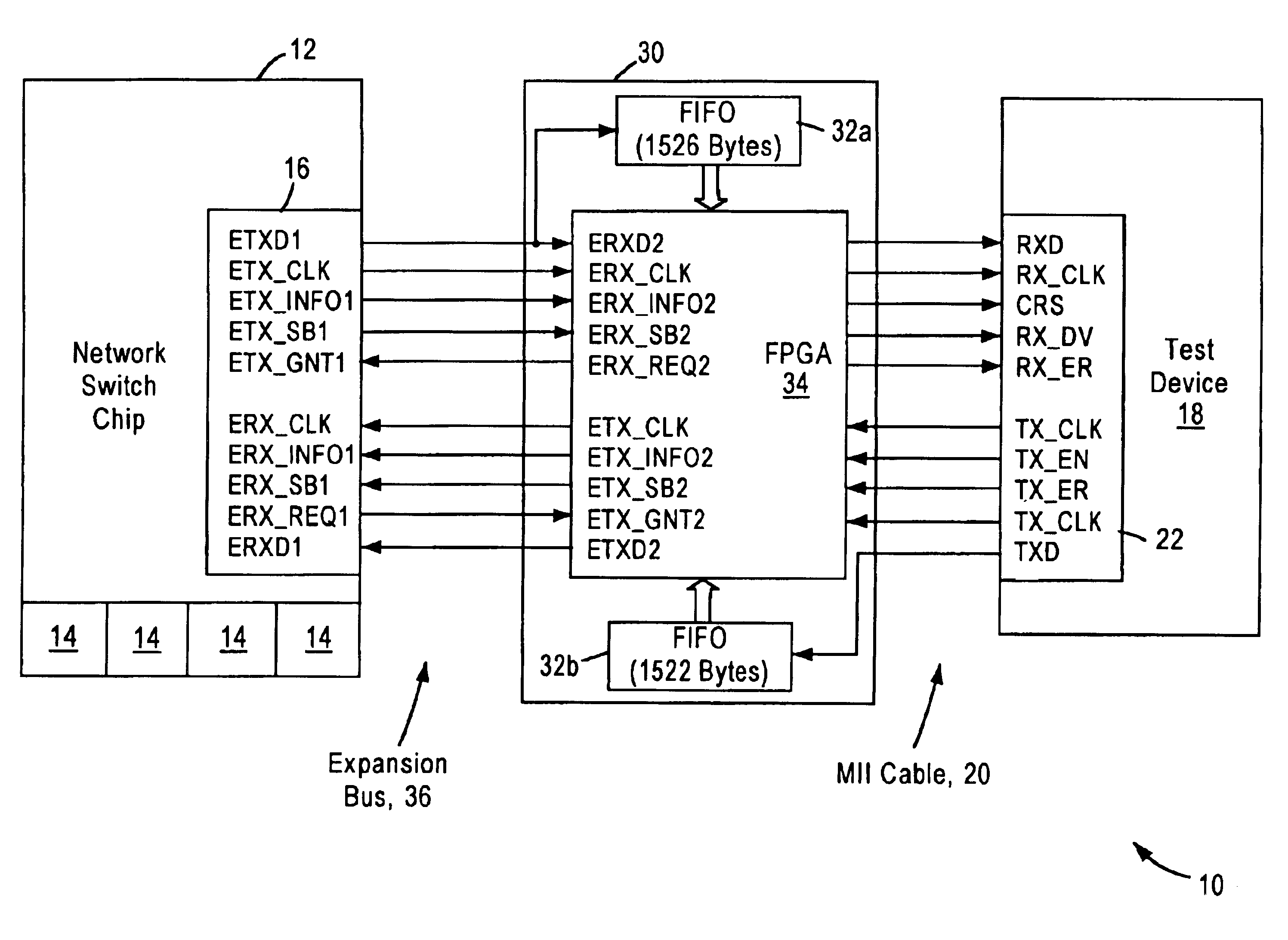
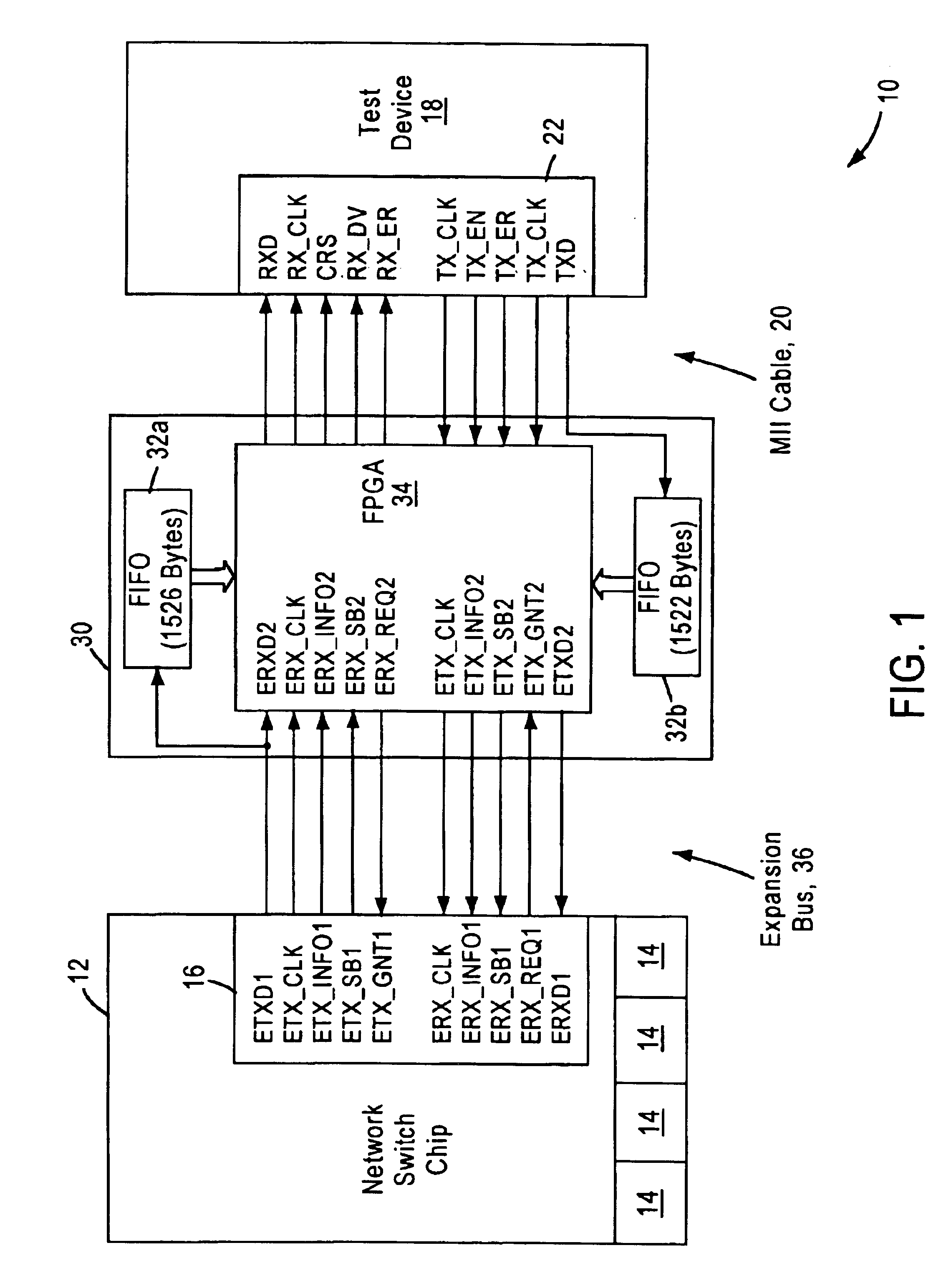
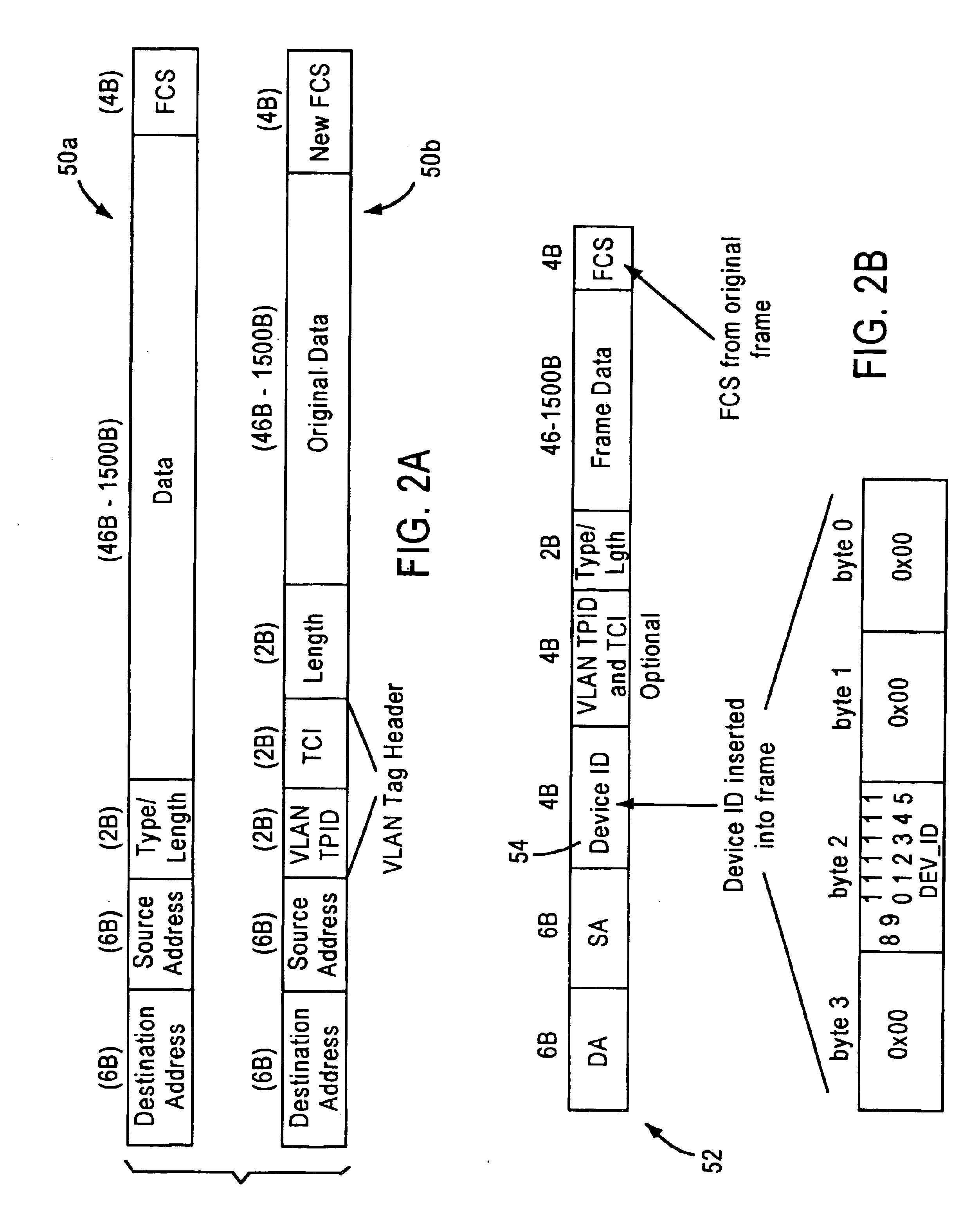
Arrangement for testing network switch expansion port data by converting to media independent interface format
InactiveUS6914892B1Enable useElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionComputer hardwareNetworking protocol
A method for testing a network switch chip having an expansion port configured for transferring data according to a prescribed expansion port protocol. The method includes outputting the expansion port frame data from the expansion port according to the prescribed expansion port protocol, converting the expansion port frame data from the prescribed expansion port protocol to a prescribed network protocol such as IEEE 802.3-based Media Independent Interface (MII) protocol, and outputting the converted data according to the prescribed MII protocol to a test device having an MII interface configured for receiving the data according to the prescribed MII protocol. The conversion of the data from the prescribed expansion port protocol to the prescribed MII protocol enables the use of the test device for validation of the expansion port, without the necessity of another network switch chip.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
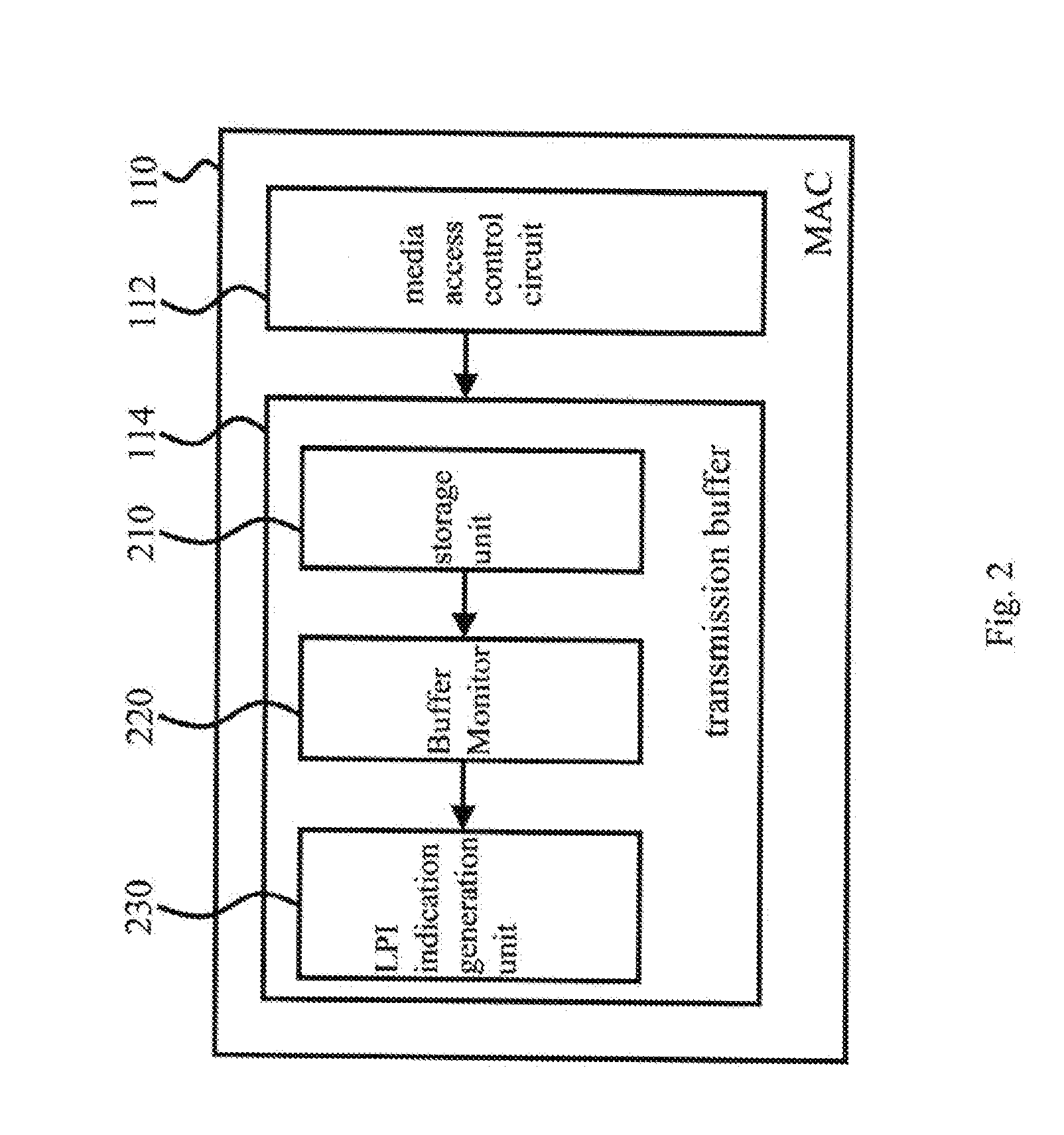
Energy efficient network communication device and method
ActiveUS20140126444A1Reduce power consumptionEnergy efficiencyPower managementTransmission systemsMedia Independent InterfaceNetwork communication
The present invention discloses an energy efficient network communication device comprising: a media-access-controller for outputting a transmission-end low power idle (LPI) indication and receiving a reception-end LPI indication; a media-independent-interface for generating a transmission-end LPI signal according to the transmission-end LPI indication, and generating the reception-end LPI indication according to a reception-end LPI signal; and a physical-layer-circuit, coupled to several pairs of transmission lines, for converting the transmission-end LPI signal into a transmission signal to send it to a reception end for requesting an LPI mode and receiving a reception signal from the reception end to convert it into the reception-end LPI signal. Said physical-layer-circuit uses some of the several pairs of transmission lines for transmission and reception when keeping the other pairs of transmission lines unused to save power; furthermore, the physical-layer-circuit can enter the LPI mode from an idle mode for additional power saving.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
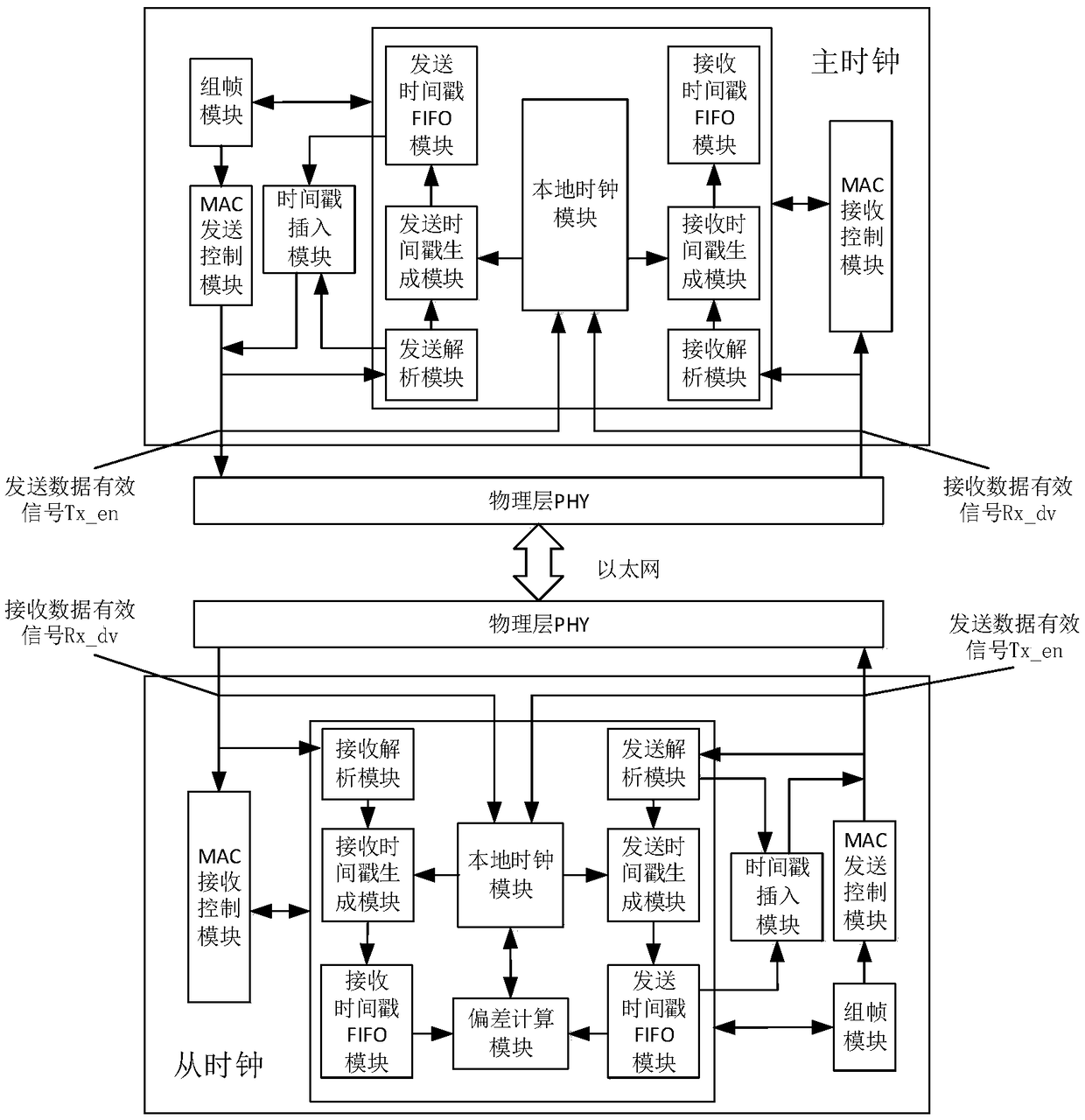
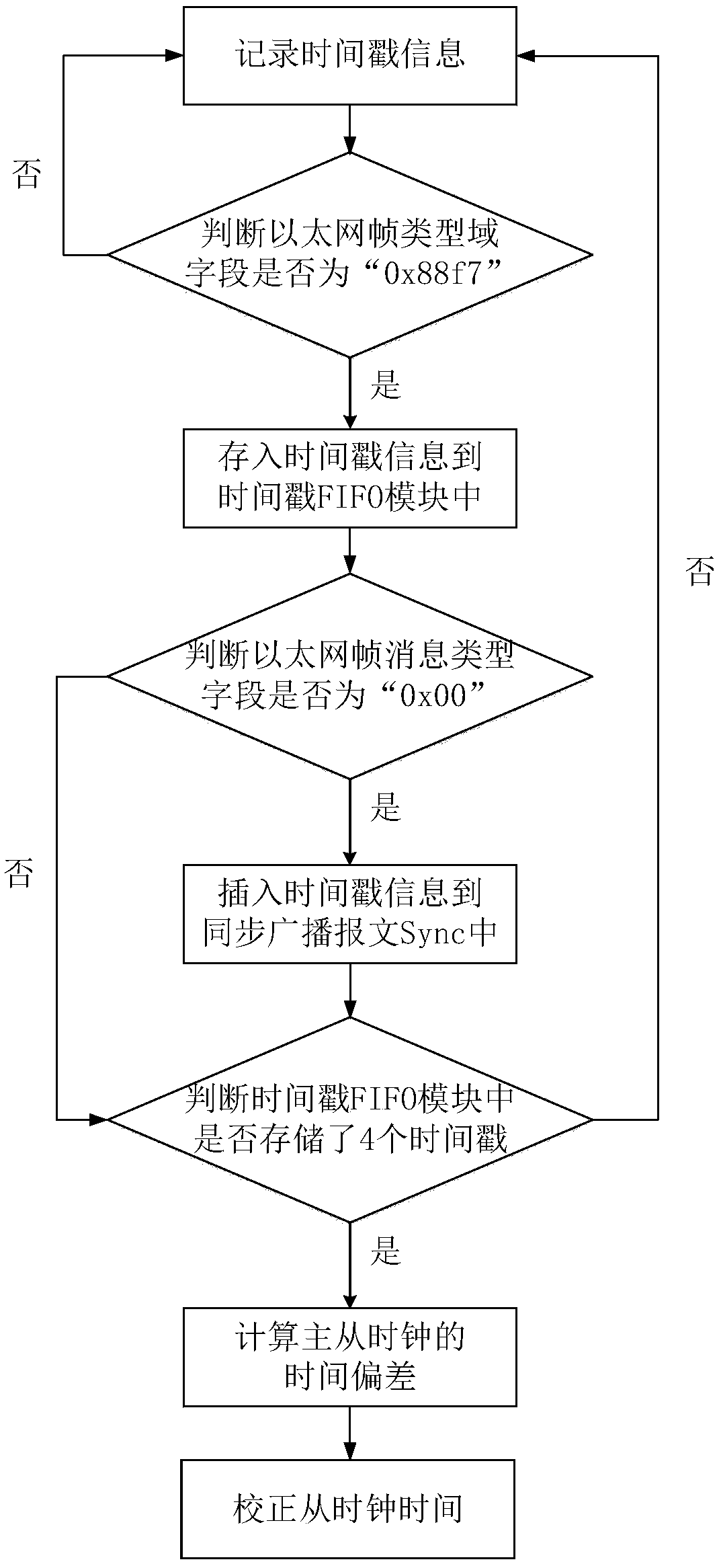
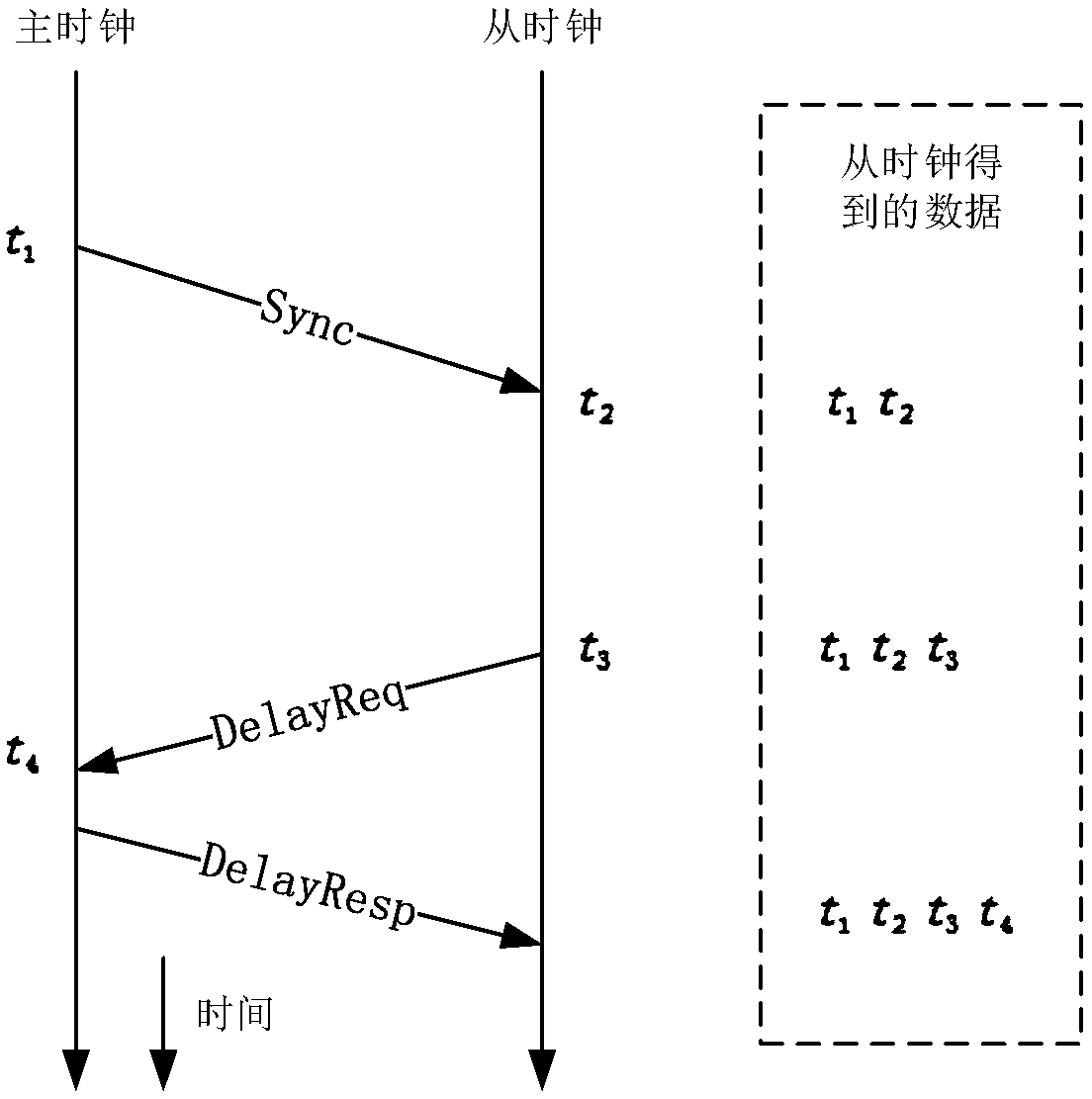
Universal full-hardware one-step 1588 clock synchronization device and method
ActiveCN108650051ALow hardware requirementsEliminate latency uncertaintyTime-division multiplexRecording durationTime deviation
The invention relates to a universal full-hardware one-step 1588 clock synchronization device and method. The device comprises a framing module, an MAC transmission control module, an MAC receiving control module, an analysis module, a timestamp generation module, a first-in first-out queue timestamp FIFO module, a local clock module, a deviation calculation module and a timestamp insertion module. The method of the invention includes the following steps: recording timestamp information, identifying synchronous messages, storing the timestamp information, identifying synchronous broadcast messages Sync, inserting the timestamp information, calculating the time deviation of master-slave clocks, and correcting the time of the slave clock. According to the scheme of the invention, a hardware-only one-step synchronization method is adopted, effective data signals ctrl at a reduced gigabit media independent interface (RGMII) between a data link layer MAC and a physical layer PHY are adoptedto collect accurate timestamp information, and thus the universality and synchronization accuracy of the system can be improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
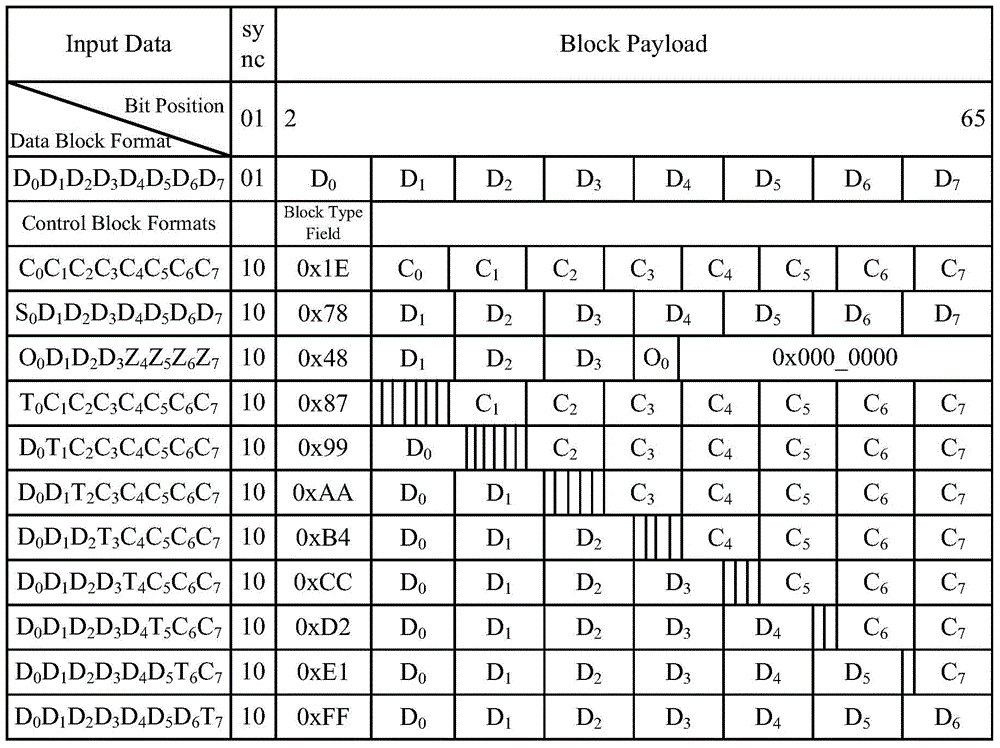
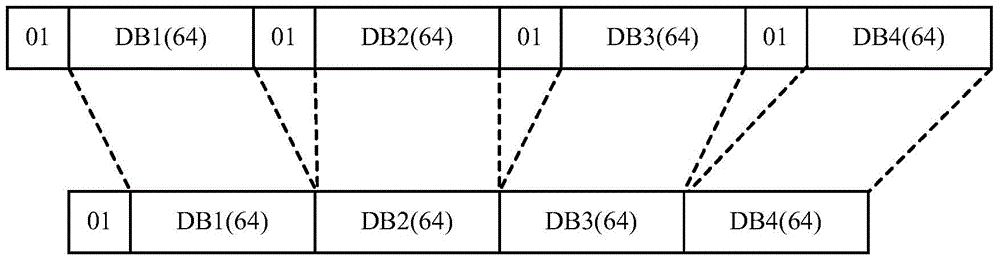
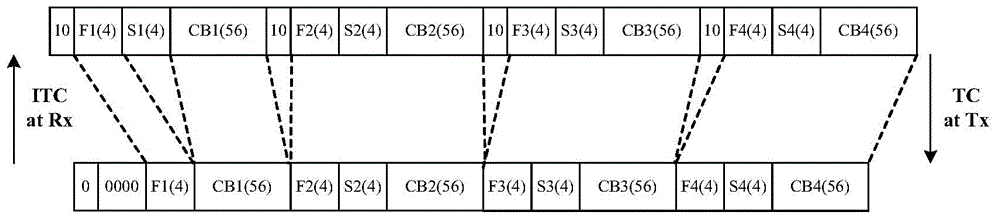
Physical layer coding and decoding methods and devices
Disclosed are a physical layer coding / decoding method and an apparatus thereof, comprising: receiving inputted MII (Media Independent Interface) control code blocks and first 256-bit to-be-coded code blocks; determining control code blocks in the first 256-bit to-be-coded code blocks according to the MII control code blocks, and compressing the determined control code blocks; determining physical layer coding format, sync field value, the hierarchy of Block Type Field and the value of Block Type Field according to the MII control code blocks; mapping the compressed to-be-coded code blocks into data in a format of physical layer data according to the determined physical layer coding format, adding sync field to the data, the value of the added sync field being the determined sync field value, adding Block Type Field into a space obtained by compression according to the hierarchy of Block Type Field in order to obtain a coding result, and the value of the added Block Type Field being the determined value of Block Type Field. The physical layer coding / decoding method can be used to meet the demands of RS-FEC (Reed-Solomon Forward Error Correction) algorithm.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Network time-setting system and method for secondary equipment of electric power system
ActiveCN104579623AHigh time accuracyLow costSynchronising arrangementHardware structureFpga implementations
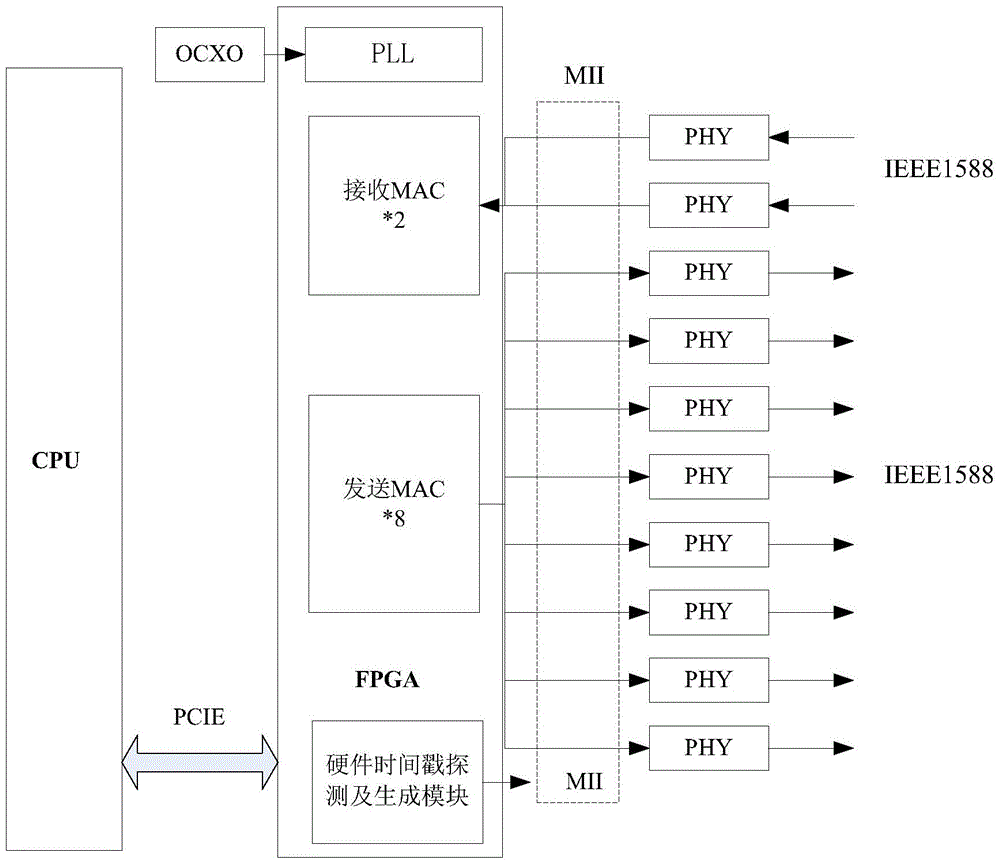
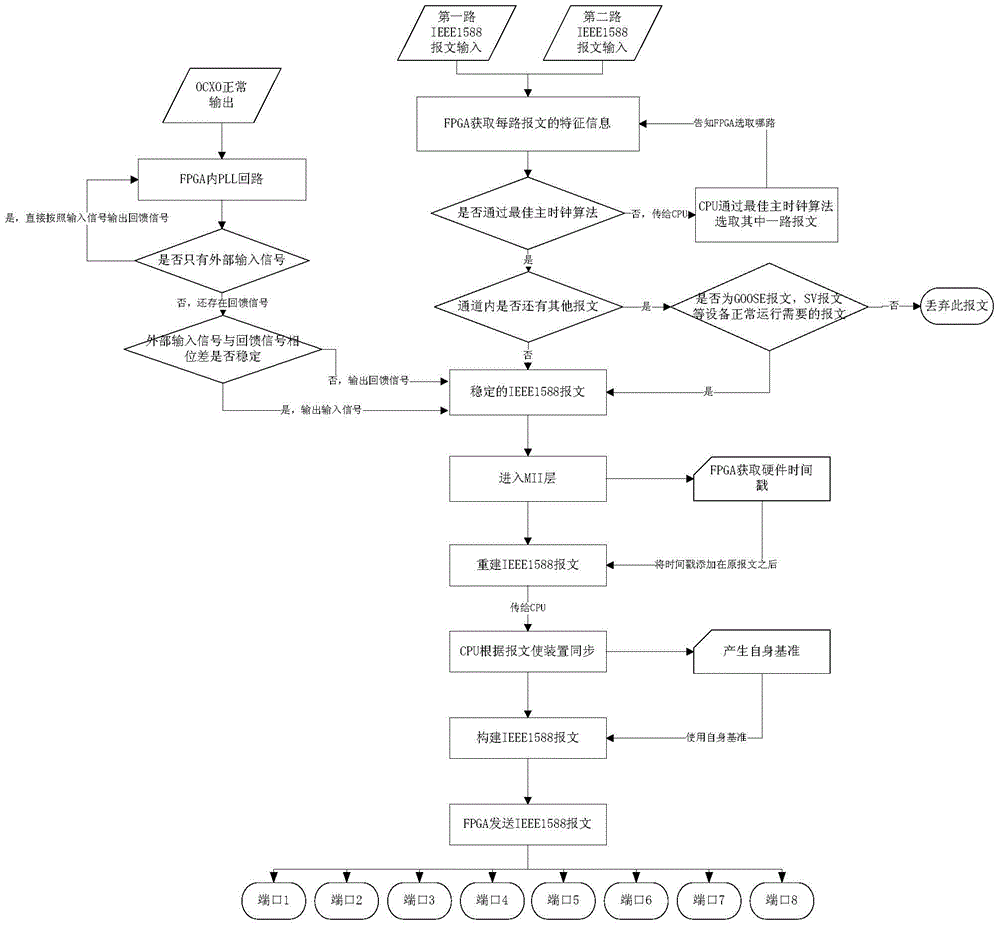
The invention discloses a network time-setting system and method for secondary equipment of an electric power system. The network time-setting system is characterized by comprising a CPU (central processing unit), an FPGA (field programmable gate array), a physical layer network card chip PHY and an oven controlled crystal oscillator OCXO, wherein the CPU is connected with the FPGA through a PCIE (peripheral component interface express) bus; the FPGA comprises Ethernet medium access controllers (MAC) which are realized through the FPGA, a hardware time stamp detecting and generating module and a phase locking loop (PLL). The time-setting method comprises the following steps: inputting setting time through a network, filtering messages, improving the time -setting synchronizing precision of the messages, adding hardware time stamps to the messages through the FPGA, synchronizing network setting-time, and outputting network setting-time. The network time-setting system disclosed by the invention uses the FPGA as a core, and under the condition that a hardware structure is not changed, multichannel high-precision network time setting can be realized at a relatively low cost; besides, through the phase locking loop (PLL) and a technique of additionally stamping the hardware time stamps on an MII (media independent interface) layer, the network time-setting precision can also be greatly improved, and the expansion performance is good.
Owner:NARI TECH CO LTD +1
Serial media independent interface
InactiveUS7227869B2Synchronisation information channelsTime-division multiplexTransceiverT interface
Provided is a 10 / 100Base-T MAC to PHY interface requiring only two wires (pins) per port, with two additional global wires: a clock wire (pin), and a synchronization wire (pin). This reduction in the number of pins associated with each port is achieved by time-division multiplexing wherein each time-division multiplexed wire combines a plurality of definitions from the conventional 100Base-T interface specified by IEEE 802.3u (clause 22). As a result, each port has its own pair of associated time-division multiplexed wires (pins) and the addition of each port simply requires two additional wires. According to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, information normally transferred on sixteen wires in a conventional 100Base-T interface at 25 MHz is time-division multiplexed onto two wires (corresponding to two pins) that transfer data at 125 MHz, five times the speed of conventional interfaces. Importantly, this multiplexing is done on a port by port basis. Therefore, the number of pins required for a MAC to transceiver interface is two times the number of ports plus two instead of sixteen times the number of ports, and the addition of each additional port requires only two more wires (pins).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Communication device, television receiver, and reproduction device
InactiveUS20110142022A1Easy to usePossible to connectTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionCommunication unitTelevision receivers
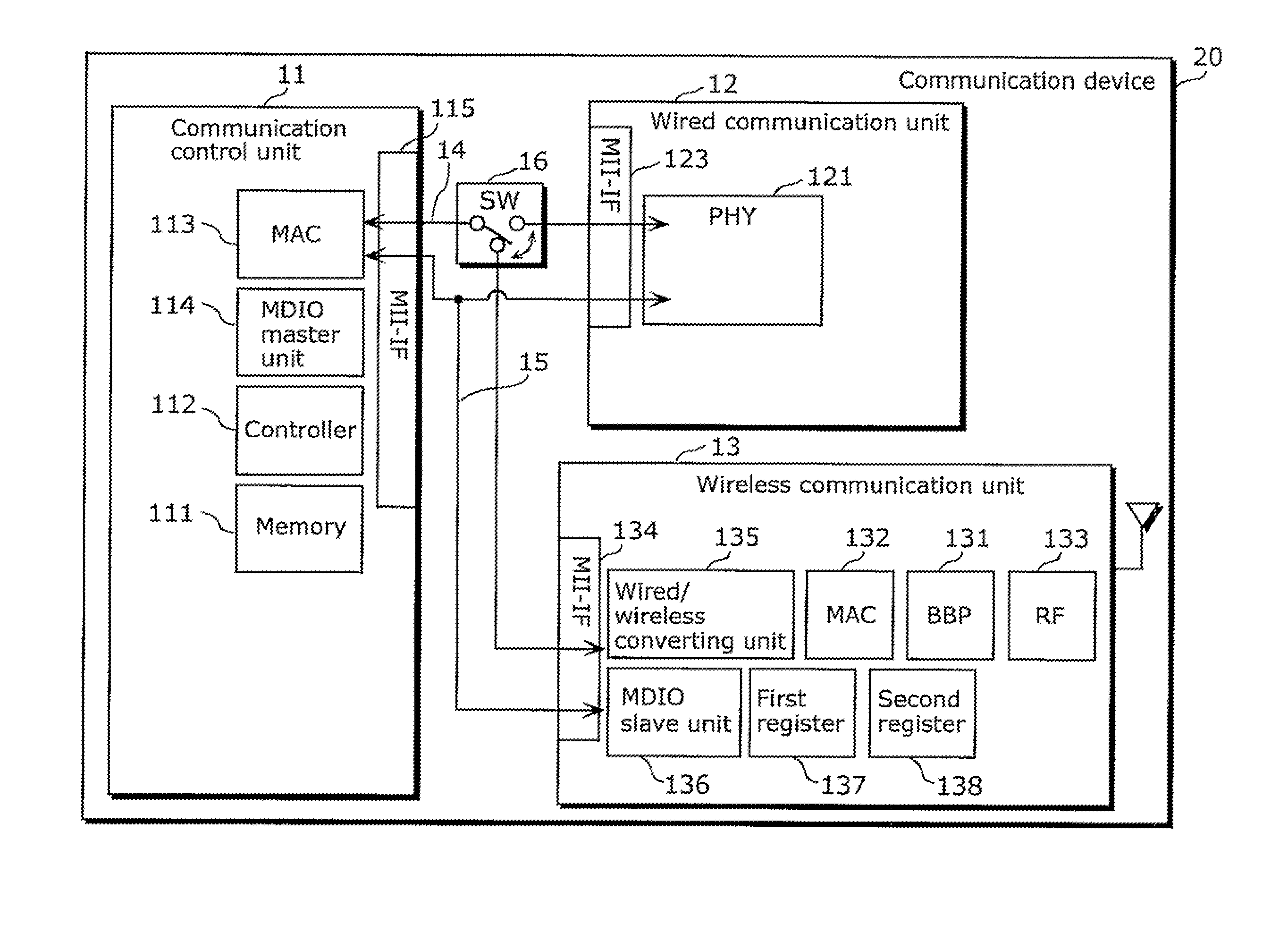
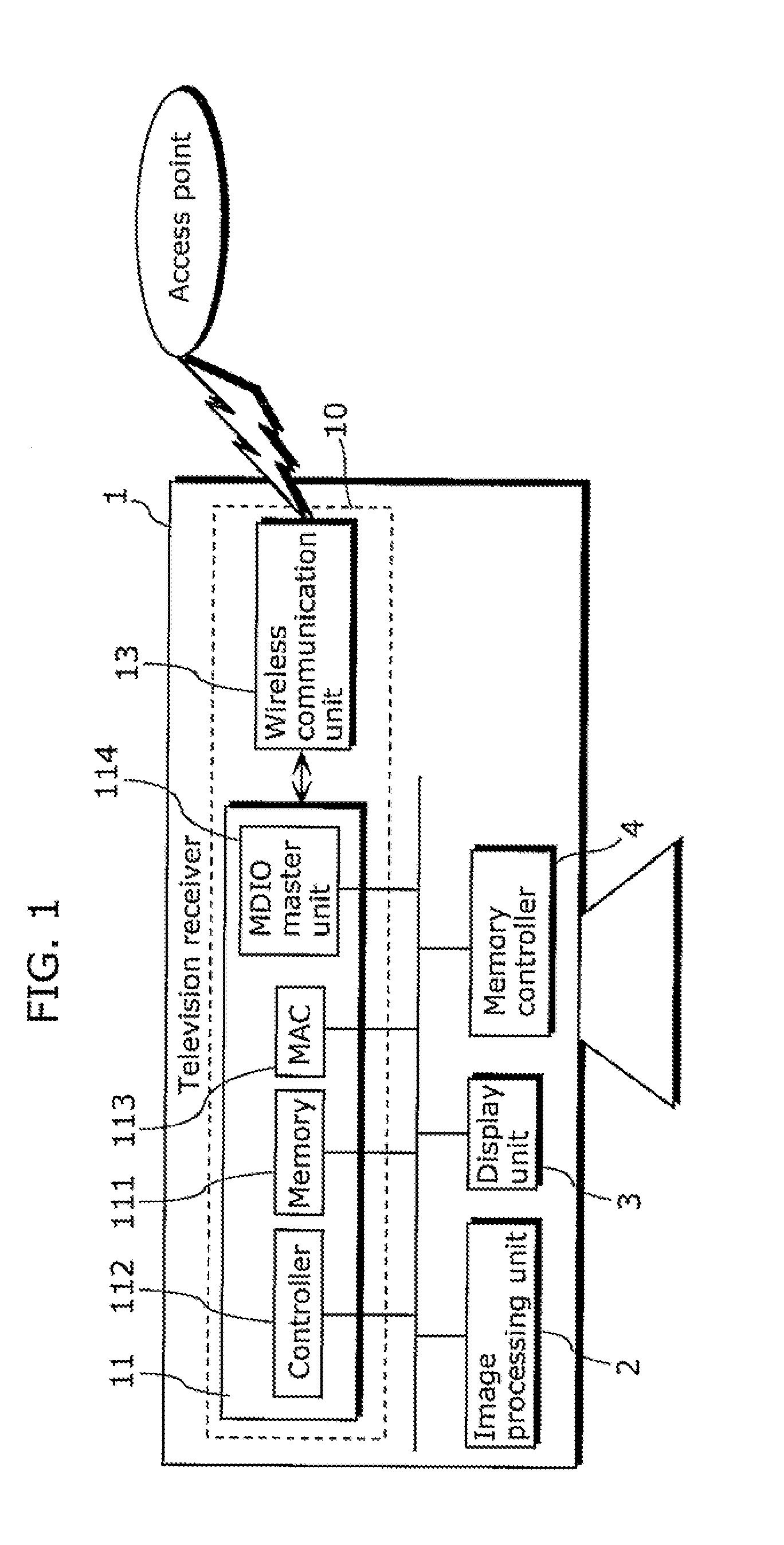
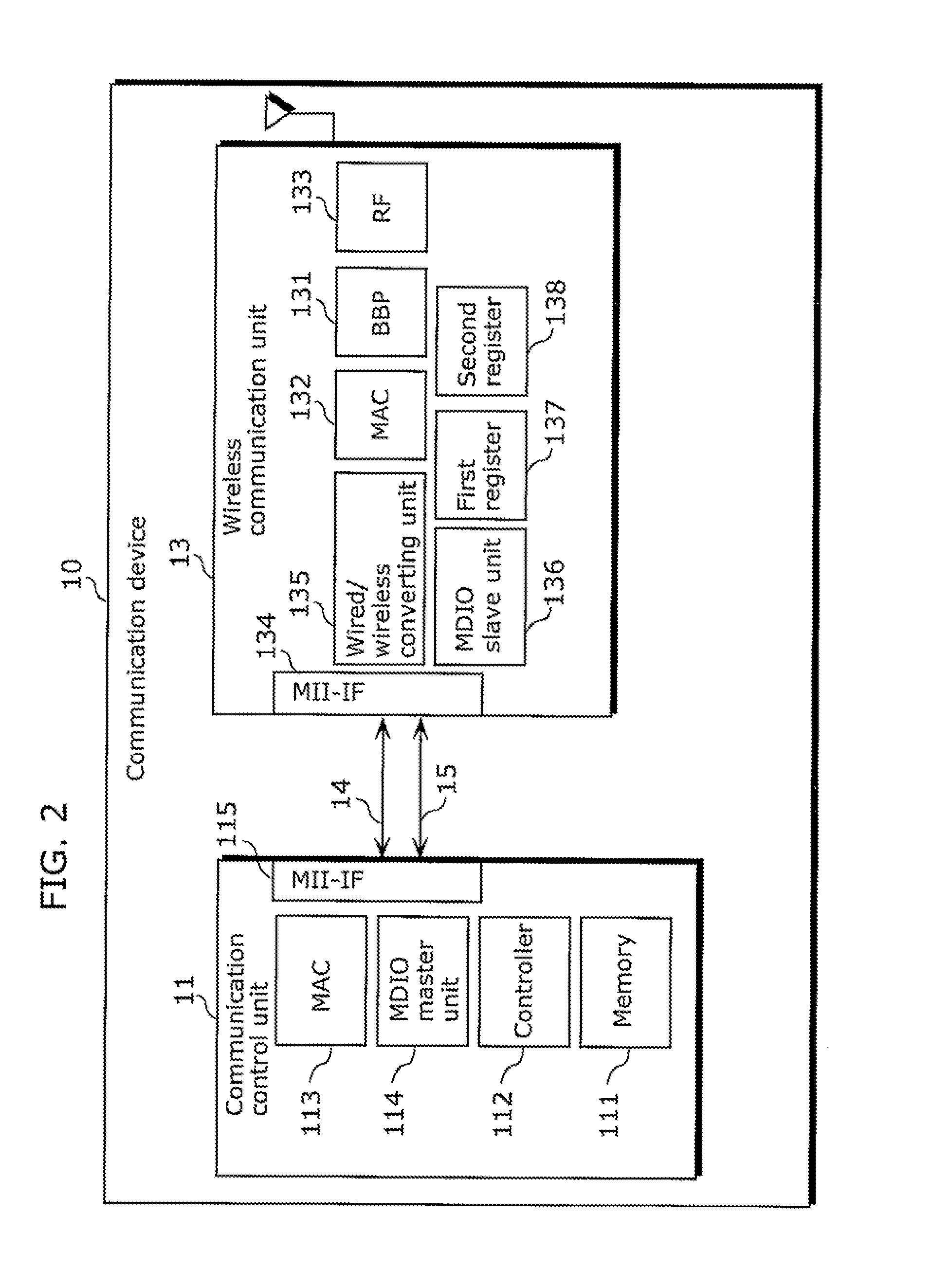
A communication device includes: a wireless communication unit configured to perform data transmission and receiving with another communication device via a wireless network; and a communication control unit electrically connected with the wireless communication unit via a media independent interface (MII) bus and configured to control the wireless communication unit using a management data input-output / management data clock (MDIO / MDC) included in the MII bus.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Special network switching method and equipment with synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH) network accurate clock synchronization function
ActiveCN102594683ATime synchronizationMeet the needs of real-time synchronous samplingTime-division multiplexData switching networksPrivate networkMedia Independent Interface
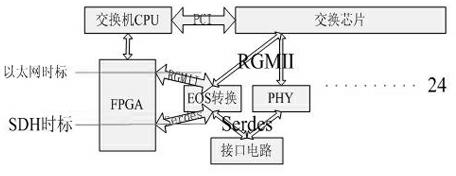
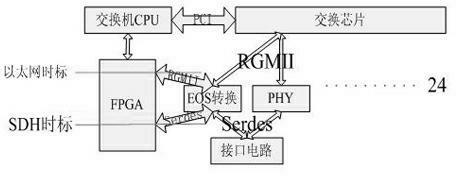
The invention discloses a special network switching method with a synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH) network accurate clock synchronization function. A master clock in a master substation of a power grid transmits a network clock synchronization message consistent with an institute of electrical and electronic engineers (IEEE)-1588 protocol, and the network clock synchronization message is transmitted to each satellite substation through an Ethernet over SDH (EOS) switch. In each satellite substation, an SDH over Ethernet switch converts the network clock synchronization message into a transmission message consistent with an Ethernet protocol, wherein the switch comprises an internal central processing unit (CPU) and a layer-3 network switching chip, and realizes the data exchange of the Ethernet, and the configuration (selection of adoption of an EOS chip) of each data exchange interface of the Ethernet realizes EOS switching. A data interface of the network switching chip is a reduced gigabit media independent interface (RGMII), and an output interface of the EOS chip is a serializer / deserializer (Serees) interface. A field programmable gate array (FPGA) receives data from the RGMII and the Serdes interface to realize the 1-microsecond accurate clock synchronization.
Owner:STATE GRID HEILONGJIANG ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com