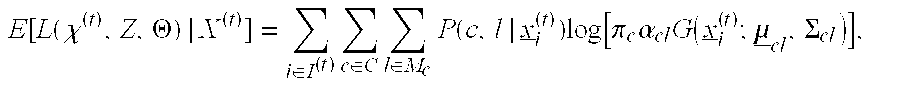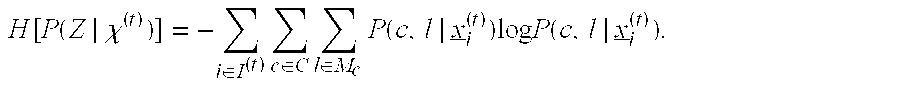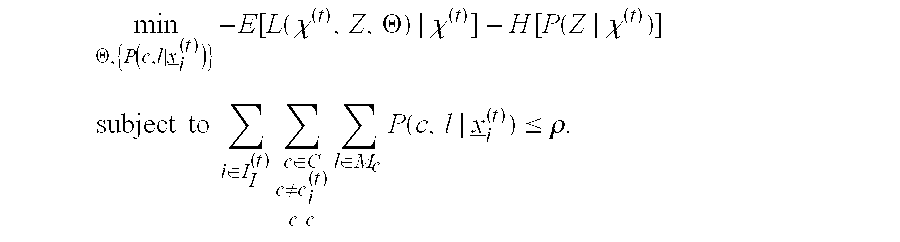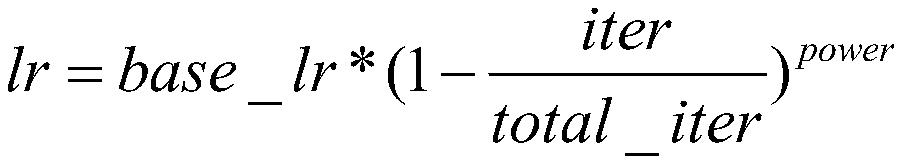Patents
Literature
454 results about "Domain adaptation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
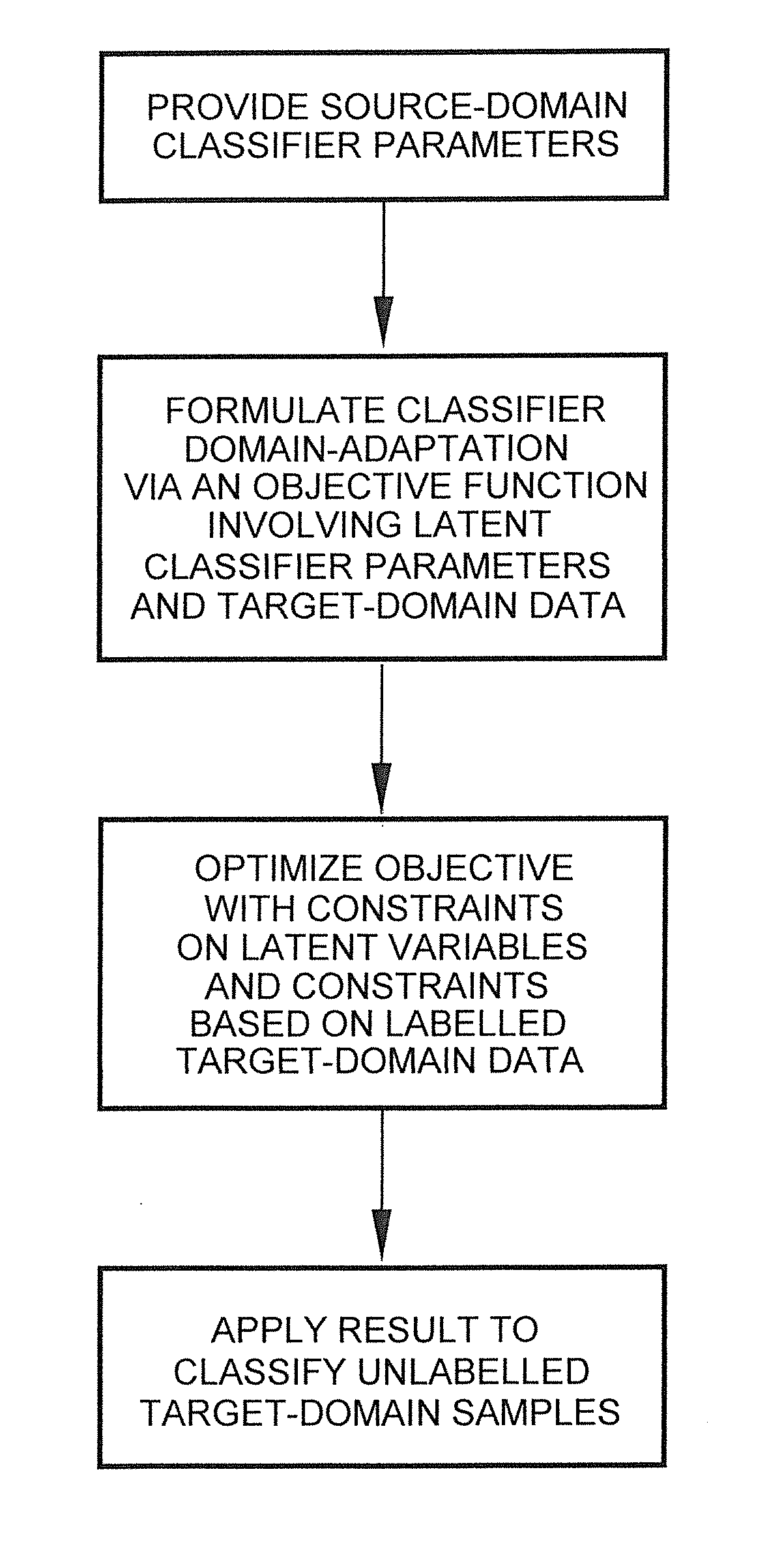
Domain adaptation is a field associated with machine learning and transfer learning. This scenario arises when we aim at learning from a source data distribution a well performing model on a different (but related) target data distribution. For instance, one of the tasks of the common spam filtering problem consists in adapting a model from one user (the source distribution) to a new one who receives significantly different emails (the target distribution). Domain adaptation has also been shown to be beneficial for learning unrelated sources. Note that, when more than one source distribution is available the problem is referred to as multi-source domain adaptation.
Robust anomaly detection and regularized domain adaptation of classifiers with application to internet packet-flows
InactiveUS20120284791A1Maximize aggregate statistical significanceMaximizesMathematical modelsMemory loss protectionCredit cardAlgorithm
Sound, robust methods identify the most suitable, parsimonious set of tests to use with respect to prioritized, sequential anomaly detection in a collected batch of sample data. While the focus is on detecting anomalies in network traffic flows and classifying network traffic flows into application types, the methods are also applicable to other anomaly detection and classification application settings, including detecting email spam, (e.g. credit card) fraud detection, detecting imposters, unusual event detection (for example, in images and video), host-based computer intrusion detection, detection of equipment or complex system failures, as well as of anomalous measurements in scientific experiments.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
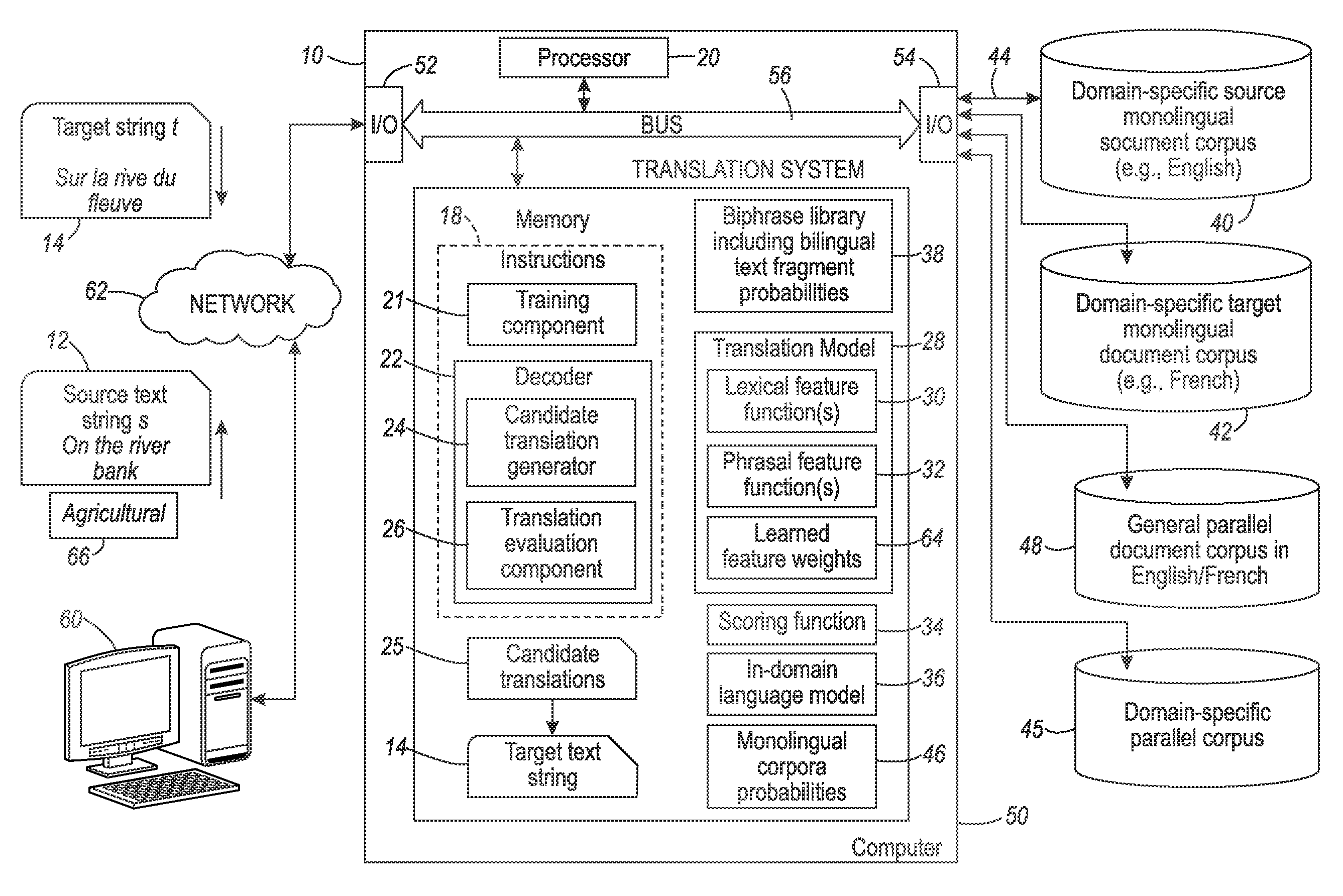
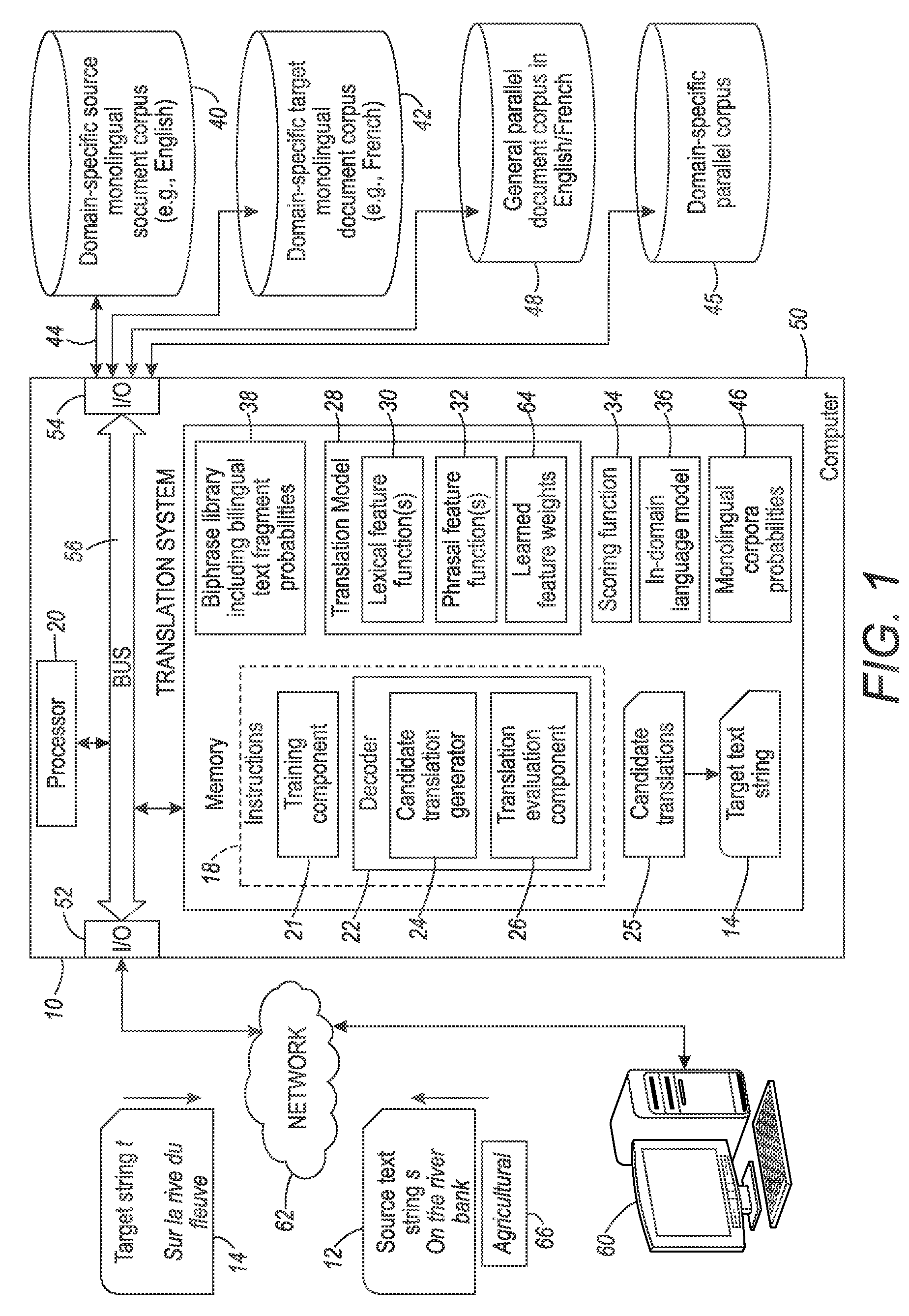
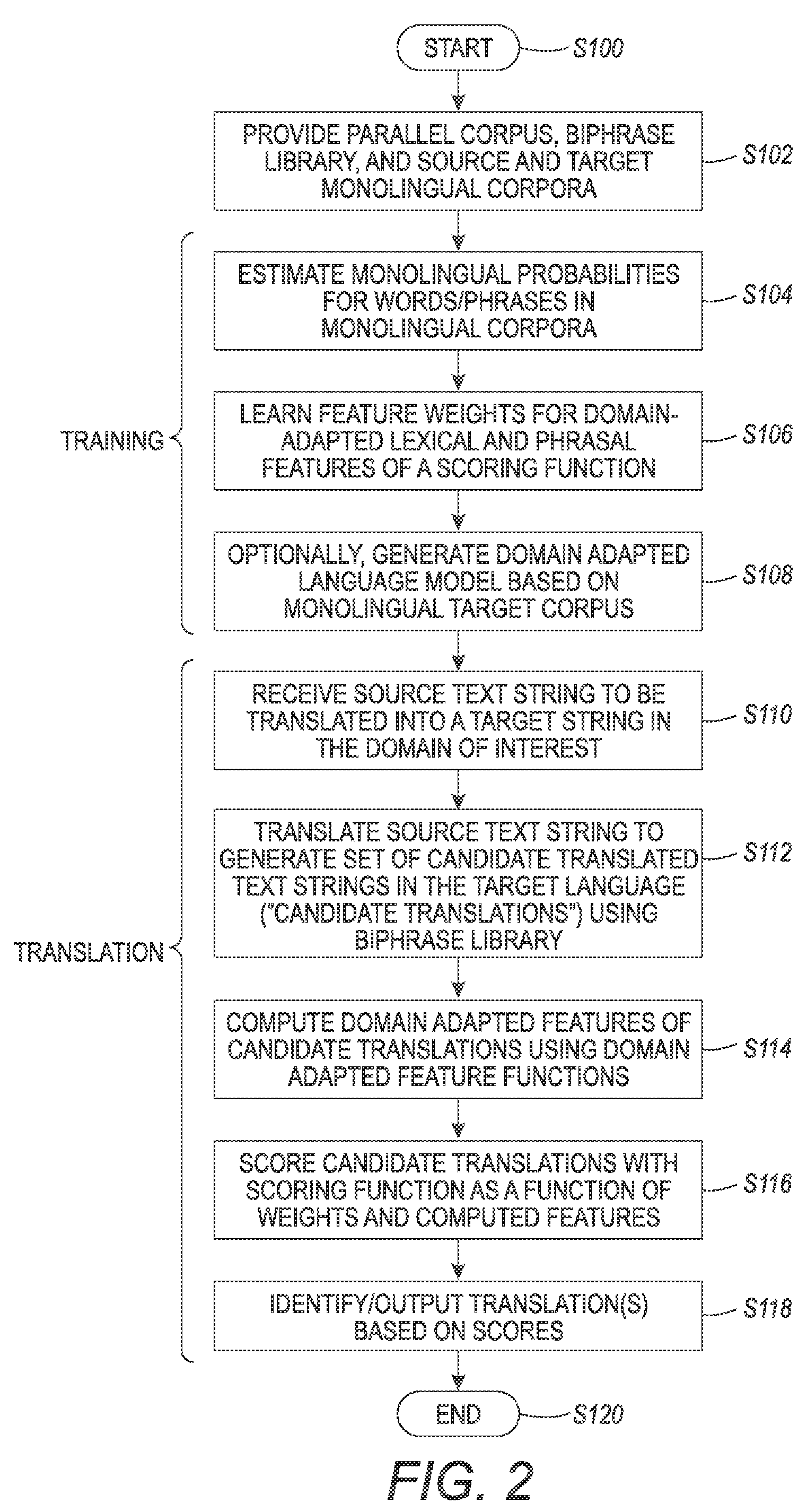
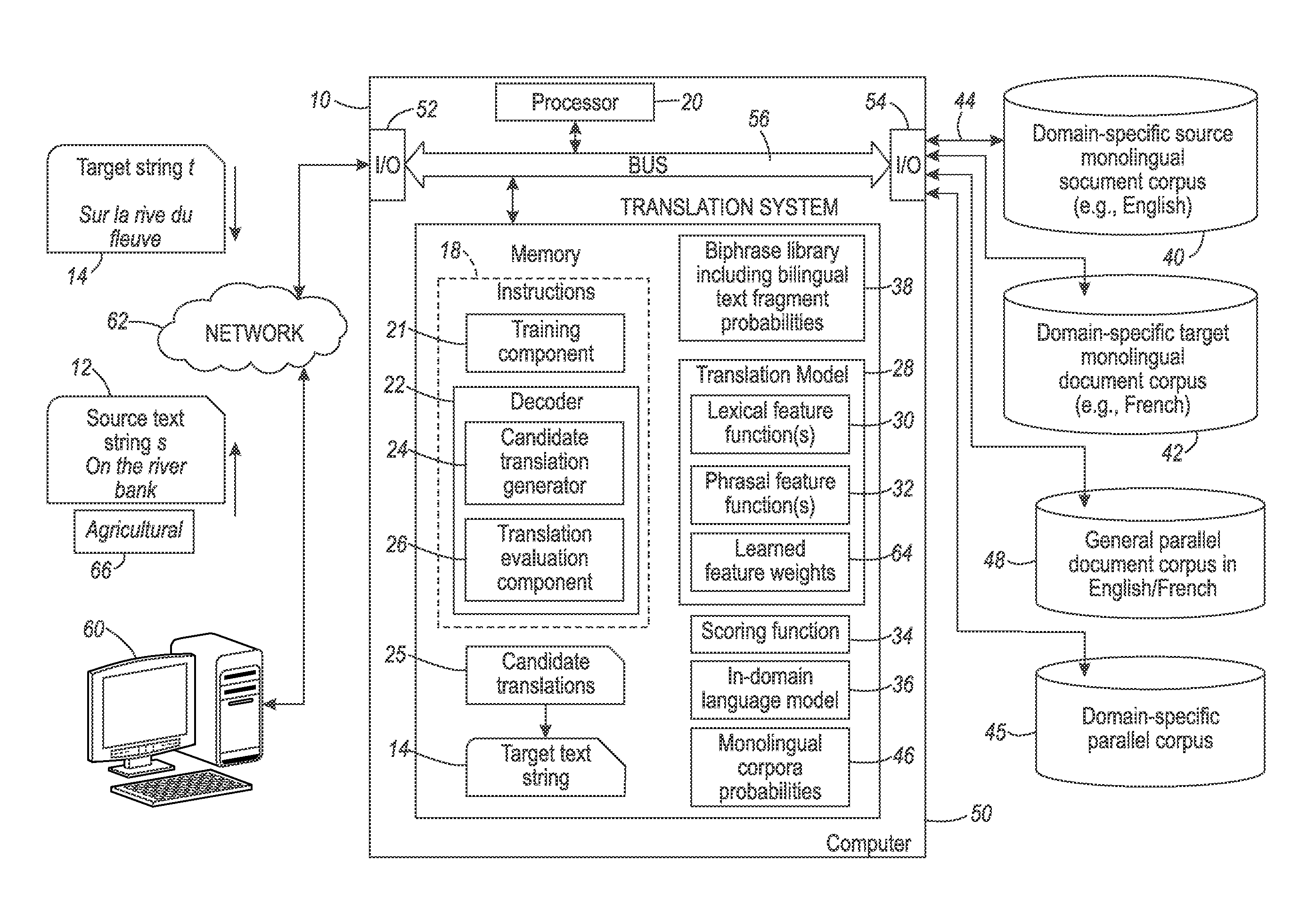
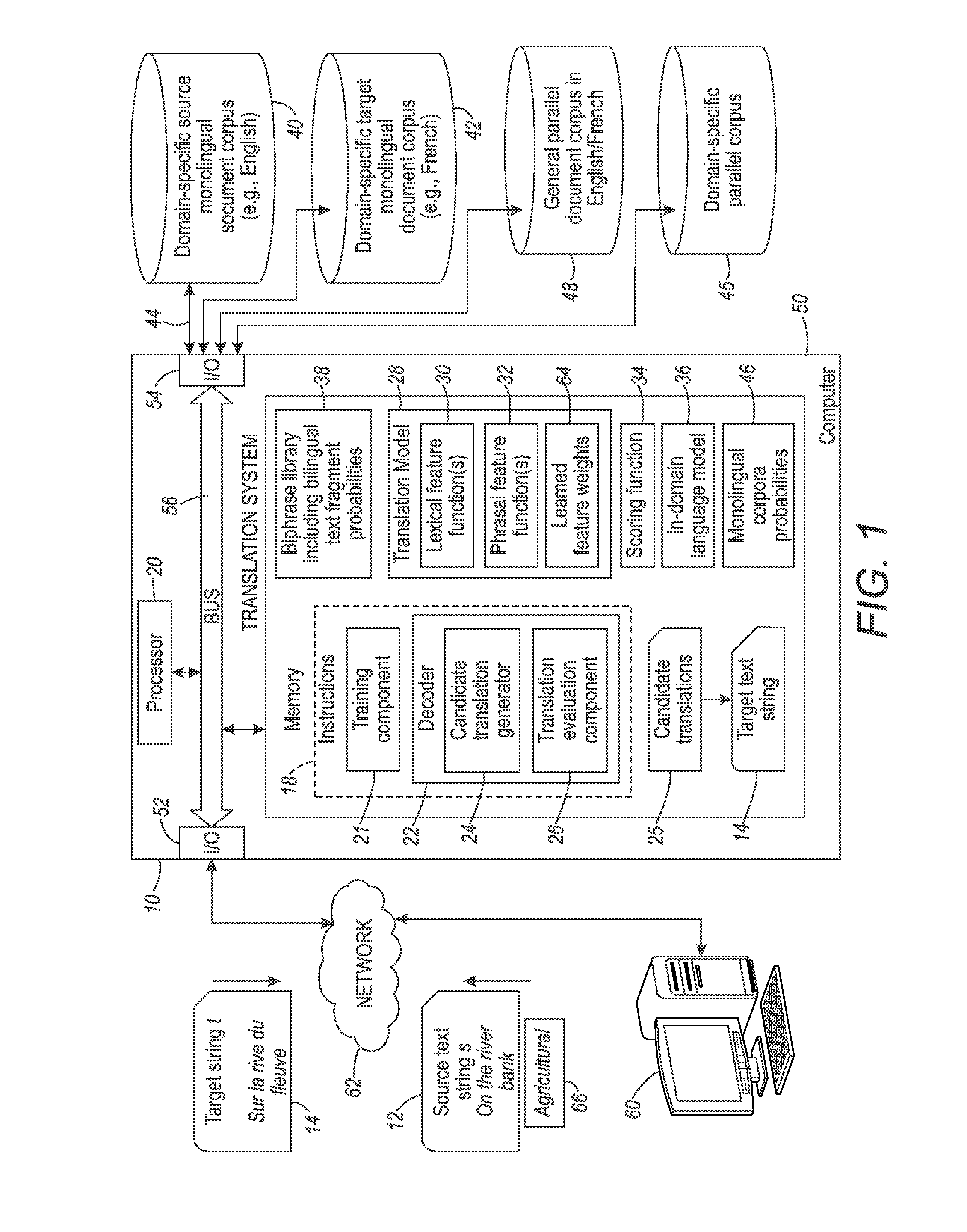
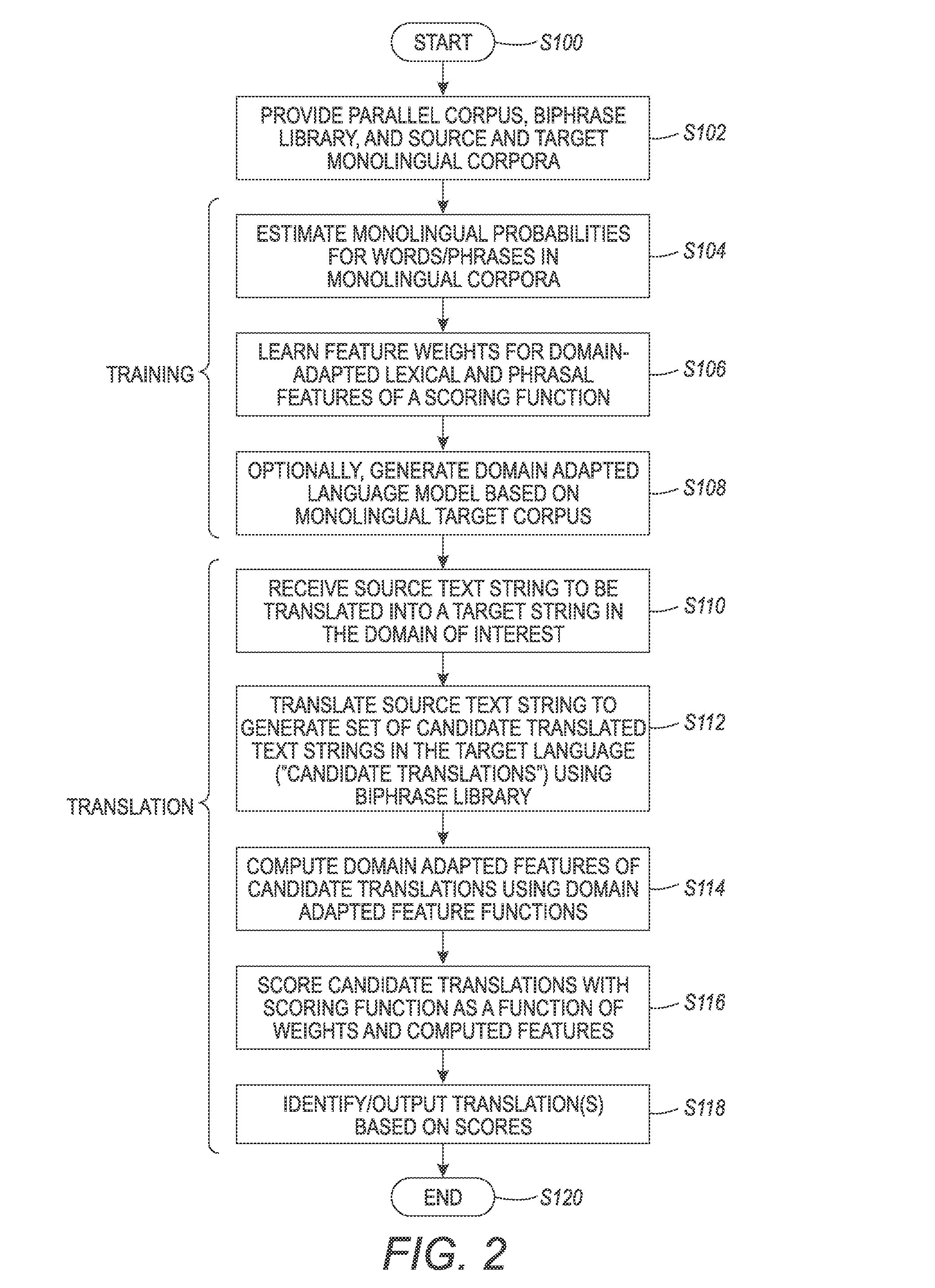
Lexical and phrasal feature domain adaptation in statistical machine translation
InactiveUS9026425B2Natural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsMachine translationA domain
A translation method is adapted to a domain of interest. The method includes receiving a source text string comprising a sequence of source words in a source language and generating a set of candidate translations of the source text string, each candidate translation comprising a sequence of target words in a target language. An optimal translation is identified from the set of candidate translations as a function of at least one domain-adapted feature computed based on bilingual probabilities and monolingual probabilities. Each bilingual probability is for a source text fragment and a target text fragment of the source text string and candidate translation respectively. The bilingual probabilities are estimated on an out-of-domain parallel corpus that includes source and target strings. The monolingual probabilities for text fragments of one of the source text string and candidate translation are estimated on an in-domain monolingual corpus.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Lexical and phrasal feature domain adaptation in statistical machine translation
InactiveUS20140067361A1Natural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsA domainMachine translation
A translation method is adapted to a domain of interest. The method includes receiving a source text string comprising a sequence of source words in a source language and generating a set of candidate translations of the source text string, each candidate translation comprising a sequence of target words in a target language. An optimal translation is identified from the set of candidate translations as a function of at least one domain-adapted feature computed based on bilingual probabilities and monolingual probabilities. Each bilingual probability is for a source text fragment and a target text fragment of the source text string and candidate translation respectively. The bilingual probabilities are estimated on an out-of-domain parallel corpus that includes source and target strings. The monolingual probabilities for text fragments of one of the source text string and candidate translation are estimated on an in-domain monolingual corpus.
Owner:XEROX CORP
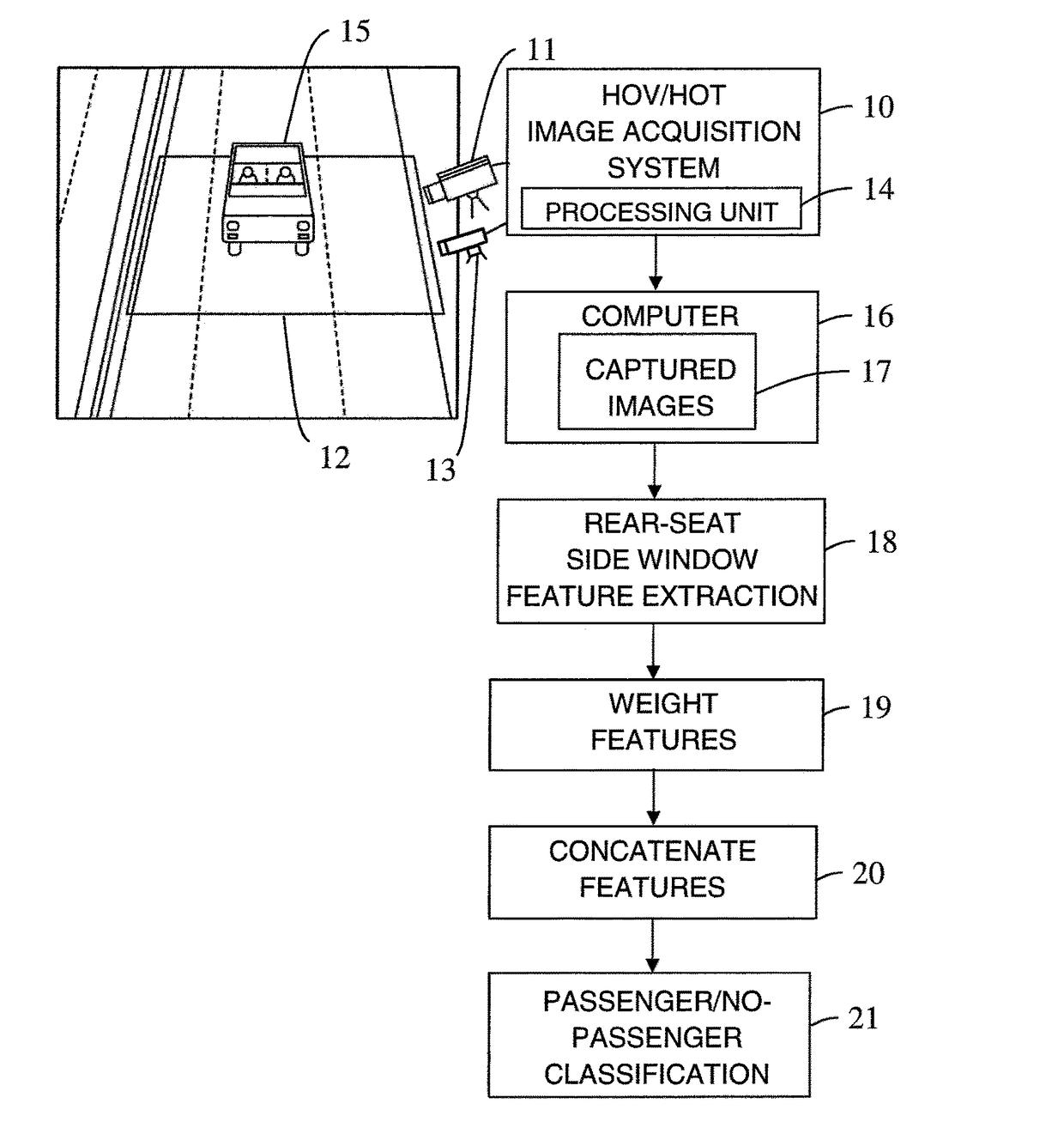
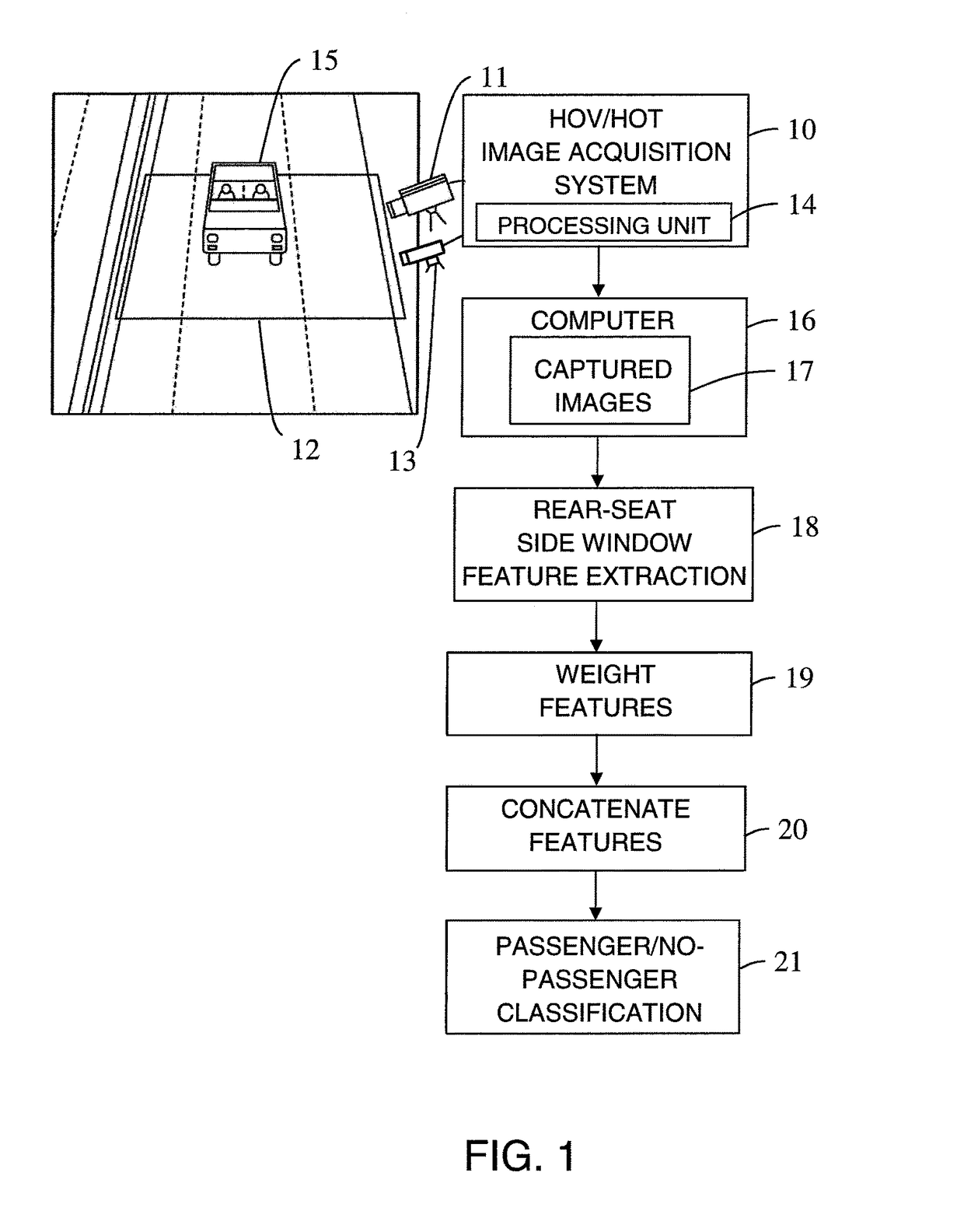
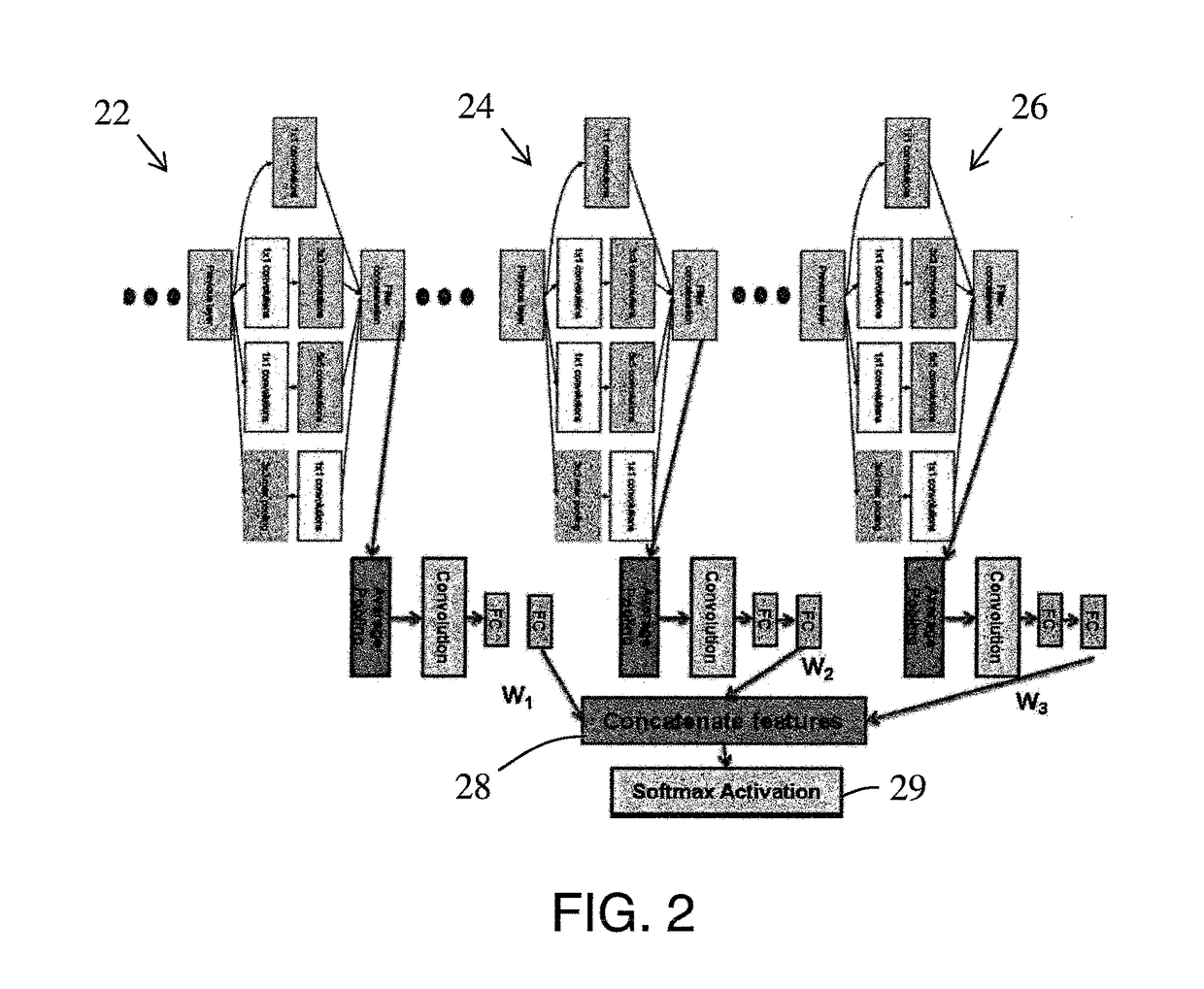
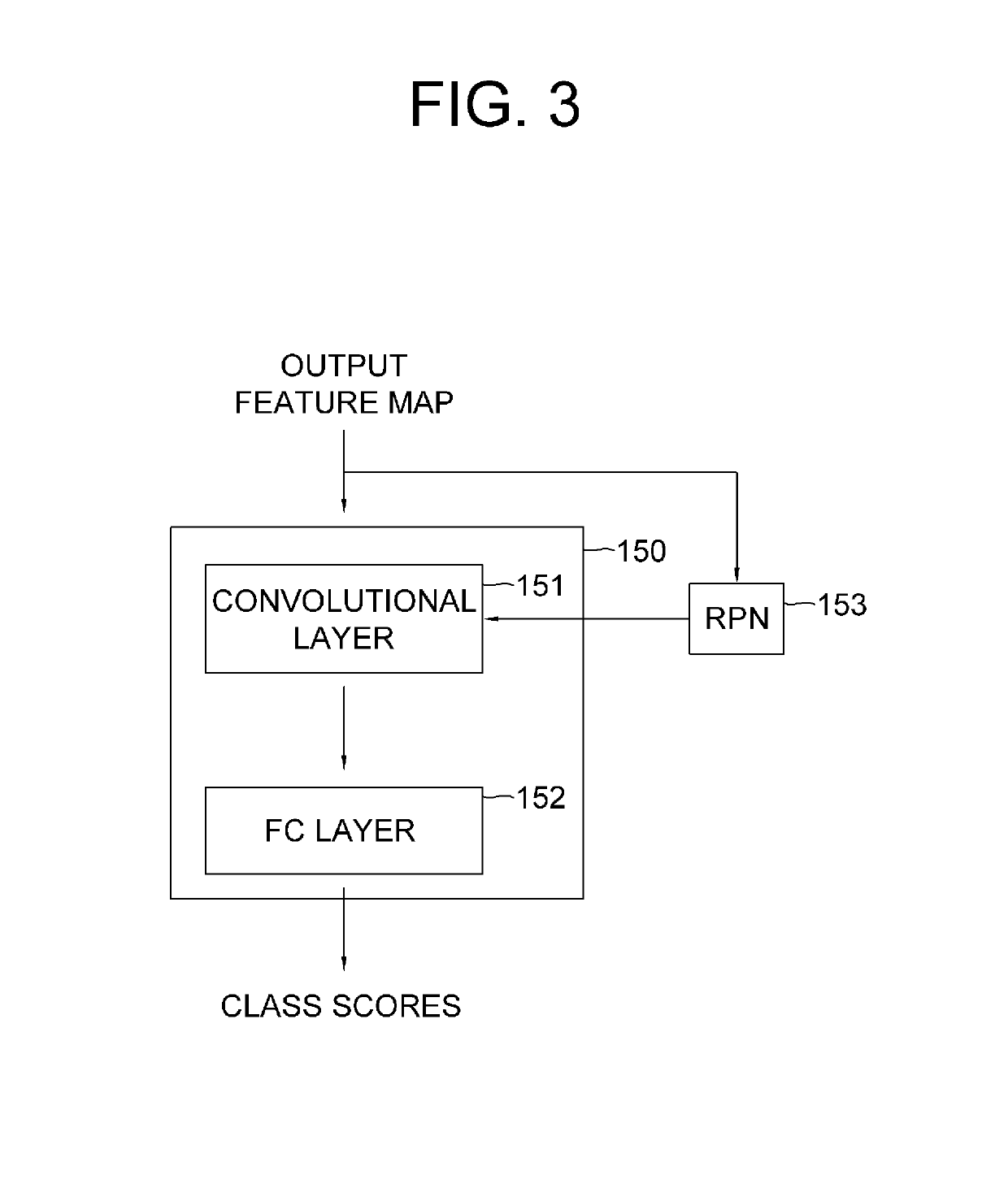
Multi-layer fusion in a convolutional neural network for image classification
ActiveUS20170140253A1Easy to adaptImprove classification accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsFeature extractionTwo step
A method and system for domain adaptation based on multi-layer fusion in a convolutional neural network architecture for feature extraction and a two-step training and fine-tuning scheme. The architecture concatenates features extracted at different depths of the network to form a fully connected layer before the classification step. First, the network is trained with a large set of images from a source domain as a feature extractor. Second, for each new domain (including the source domain), the classification step is fine-tuned with images collected from the corresponding site. The features from different depths are concatenated with and fine-tuned with weights adjusted for a specific task. The architecture is used for classifying high occupancy vehicle images.
Owner:CONDUENT BUSINESS SERVICES LLC
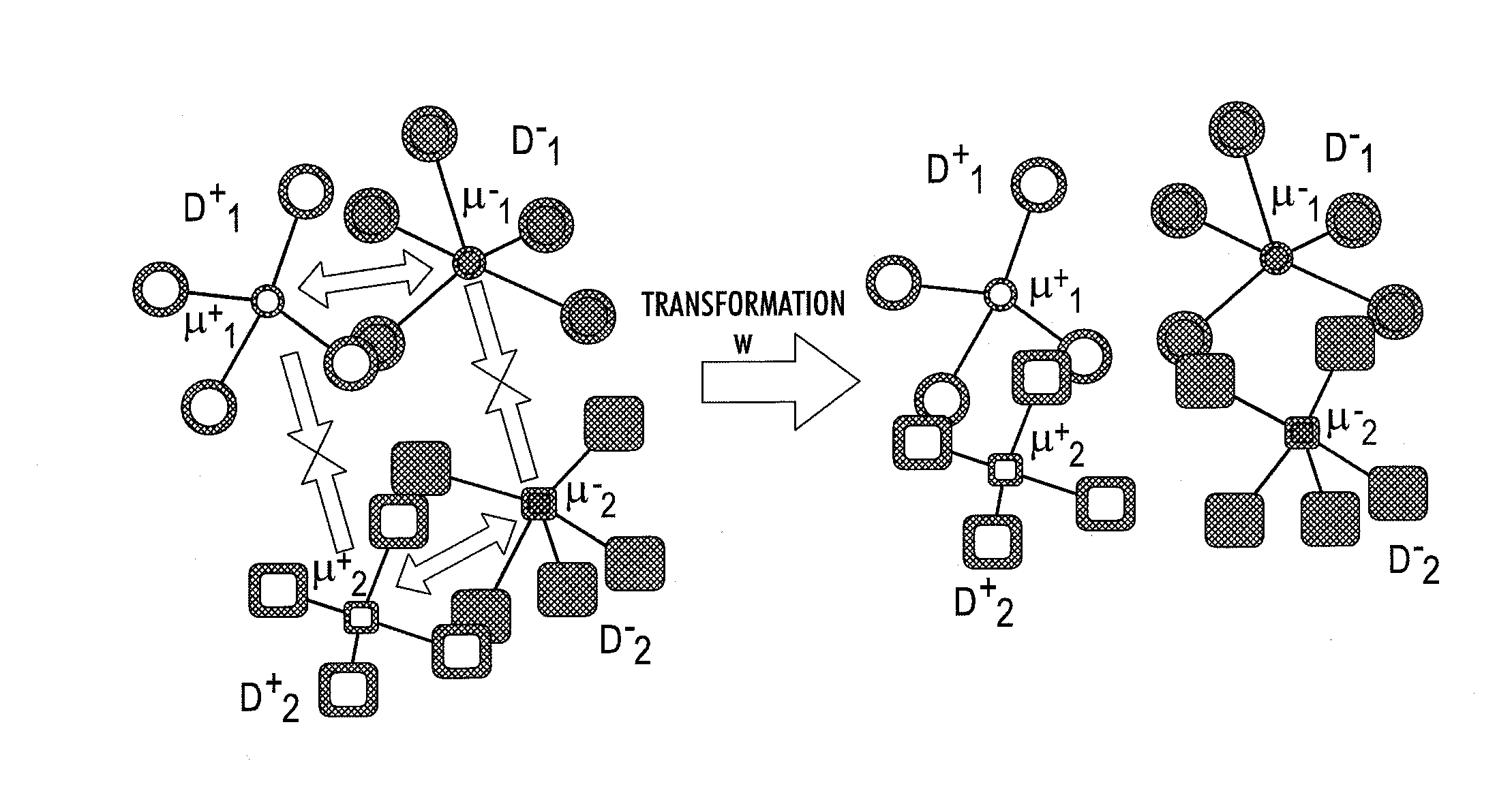
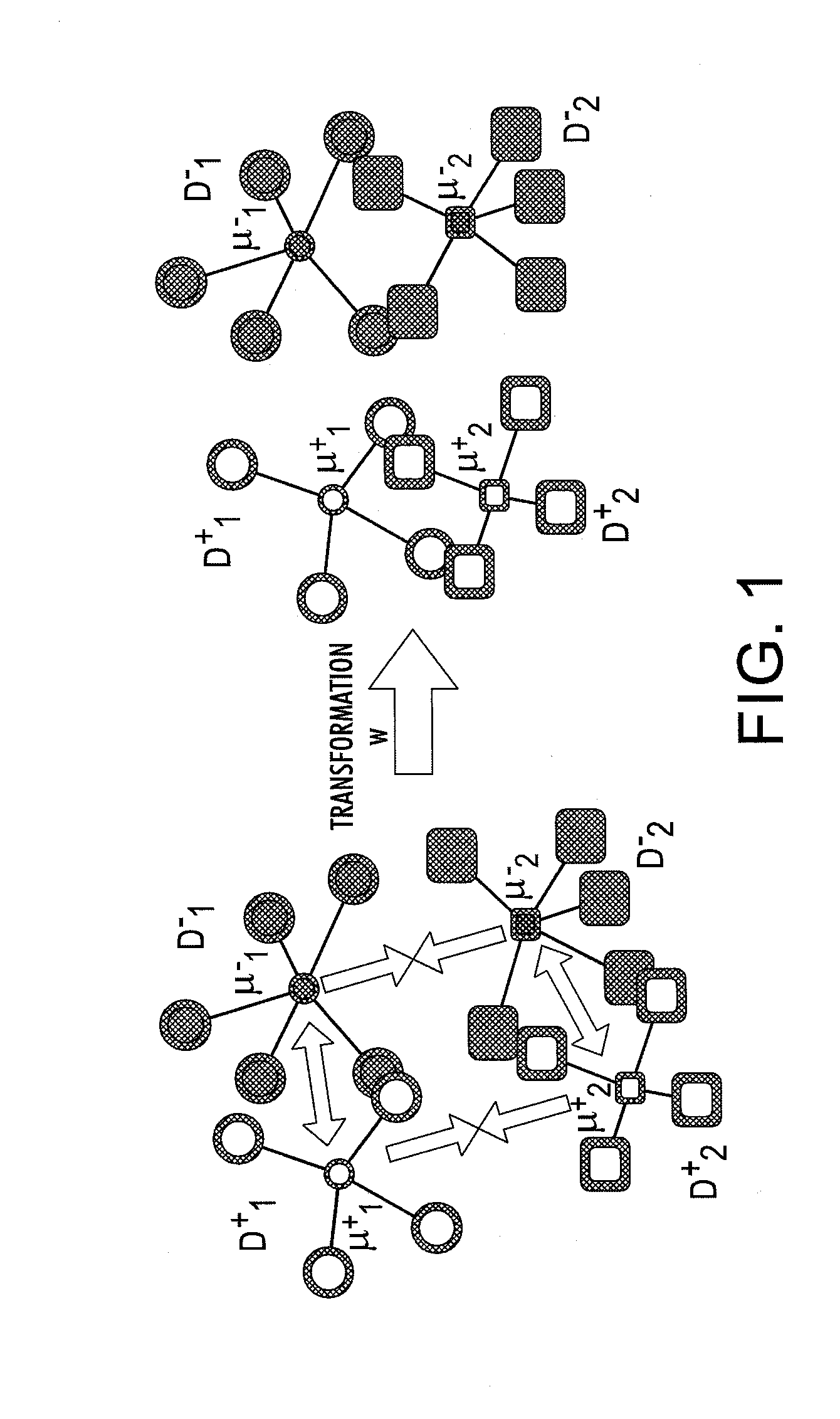
System for domain adaptation with a domain-specific class means classifier
A classification system includes memory which stores, for each of a set of classes, a classifier model for assigning a class probability to a test sample from a target domain. The classifier model has been learned with training samples from the target domain and from at least one source domain. Each classifier model models the respective class as a mixture of components, the component mixture including a component for each source domain and a component for the target domain. Each component is a function of a distance between the test sample and a domain-specific class representation which is derived from the training samples of the respective domain that are labeled with the class, each of the components in the mixture being weighted by a respective mixture weight. Instructions, implemented by a processor, are provided for labeling the test sample based on the class probabilities assigned by the classifier models.
Owner:XEROX CORP
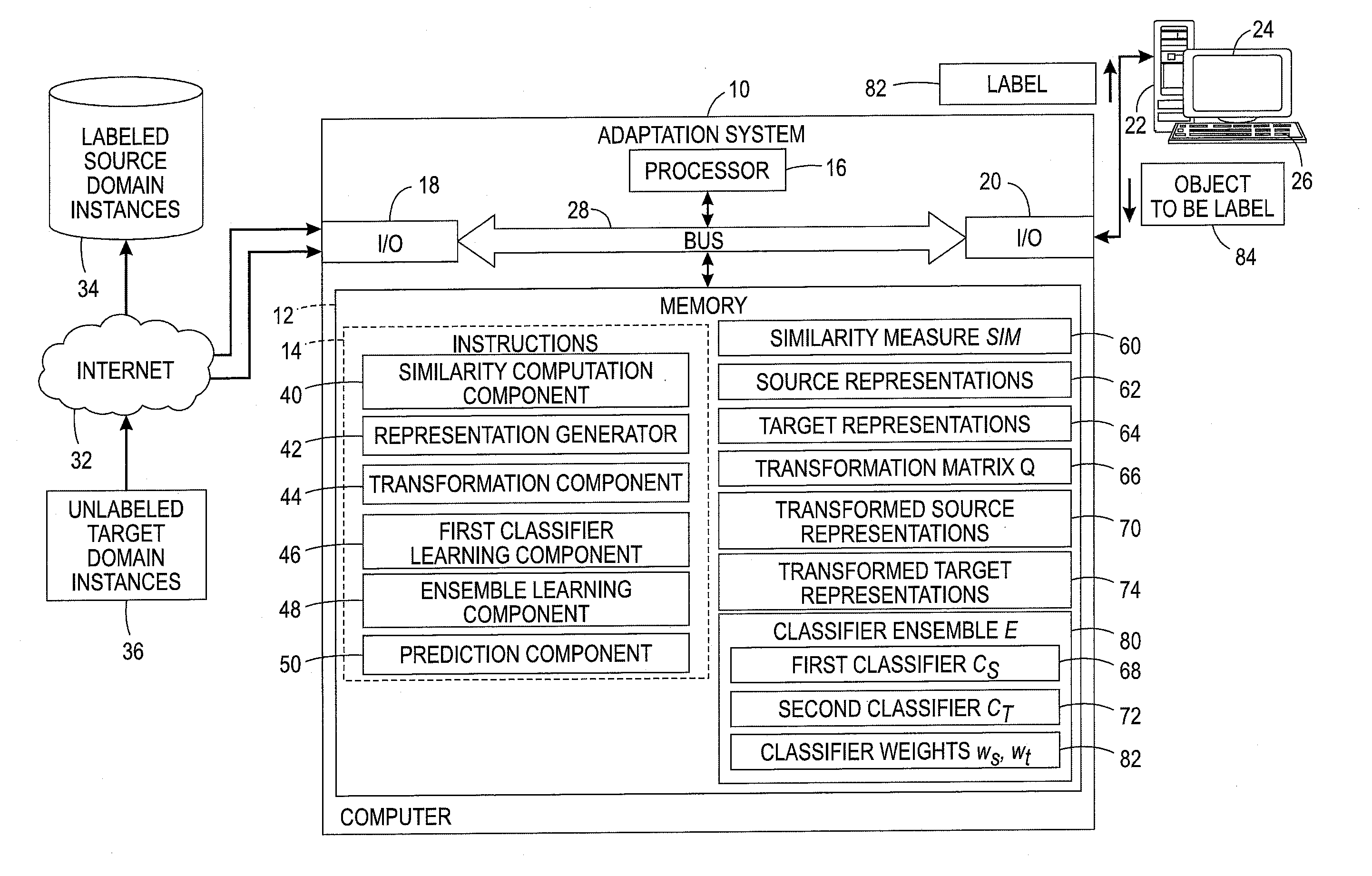
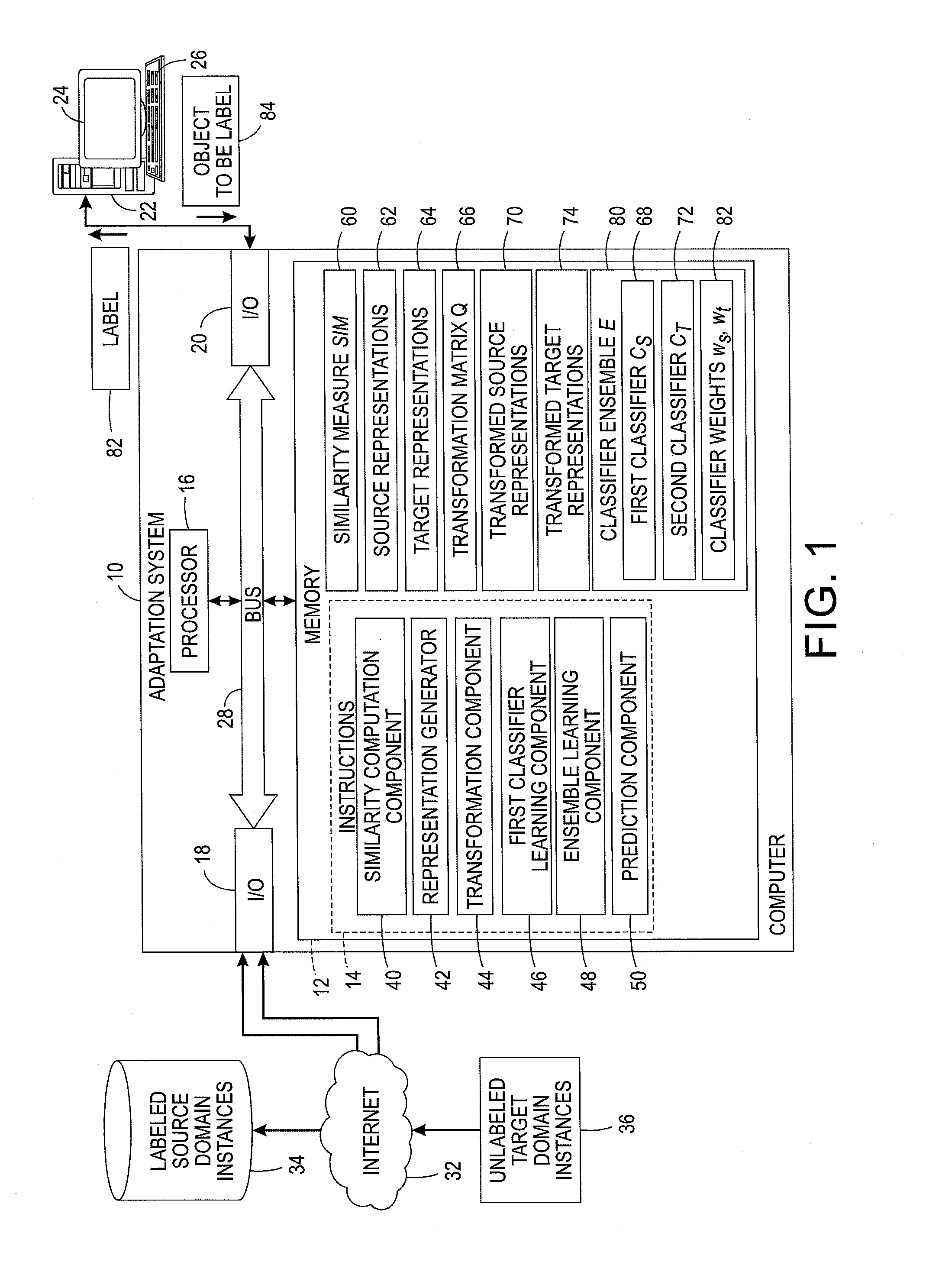
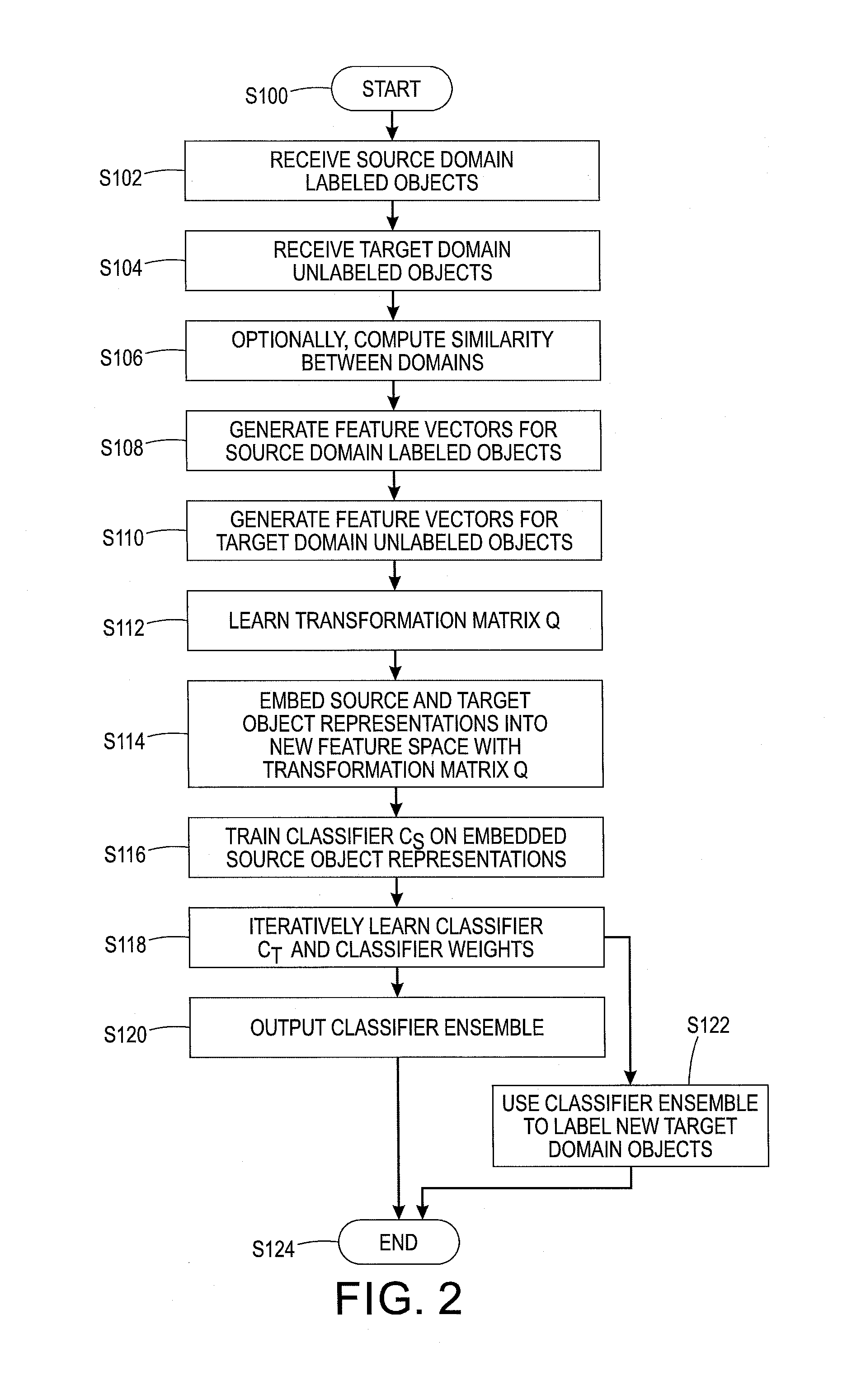
Content-aware domain adaptation for cross-domain classification
An adaptation method includes using a first classifier trained on projected representations of labeled objects from a first domain to predict pseudo-labels for unlabeled objects in a second domain, based on their projected representations. A classifier ensemble is iteratively learned. The ensemble includes a weighted combination of the first classifier and a second classifier. This includes training the second classifier on the original representations of the unlabeled objects for which a confidence for respective pseudo-labels exceeds a threshold. A classifier ensemble is constructed as a weighted combination of the first classifier and the second classifier. Pseudo-labels are predicted for the remaining original representations of the unlabeled objects with the classifier ensemble and weights of the first and second classifiers in the classifier ensemble are adjusted. As the iterations proceed, the unlabeled objects progressively receive pseudo-labels which can be used for retraining the second classifier.
Owner:XEROX CORP
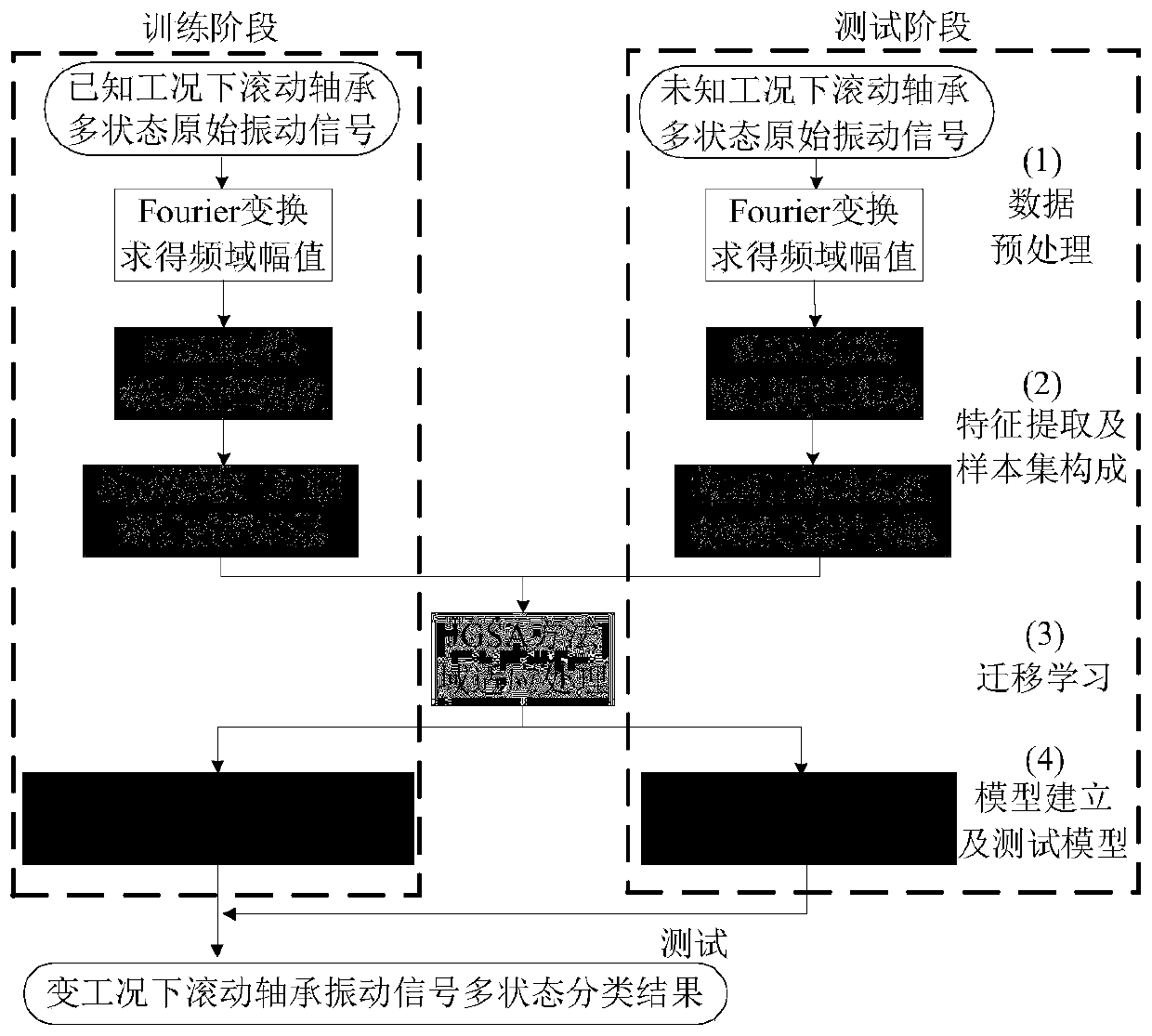
A rolling bearing fault diagnosis method under variable working conditions based on deep features and transfer learning
ActiveCN109902393AMitigate the effects of differences in the distribution of different vibration characteristicsSolve the problem of difficult multi-state deep feature extractionMachine bearings testingSpecial data processing applicationsLearning basedFeature extraction
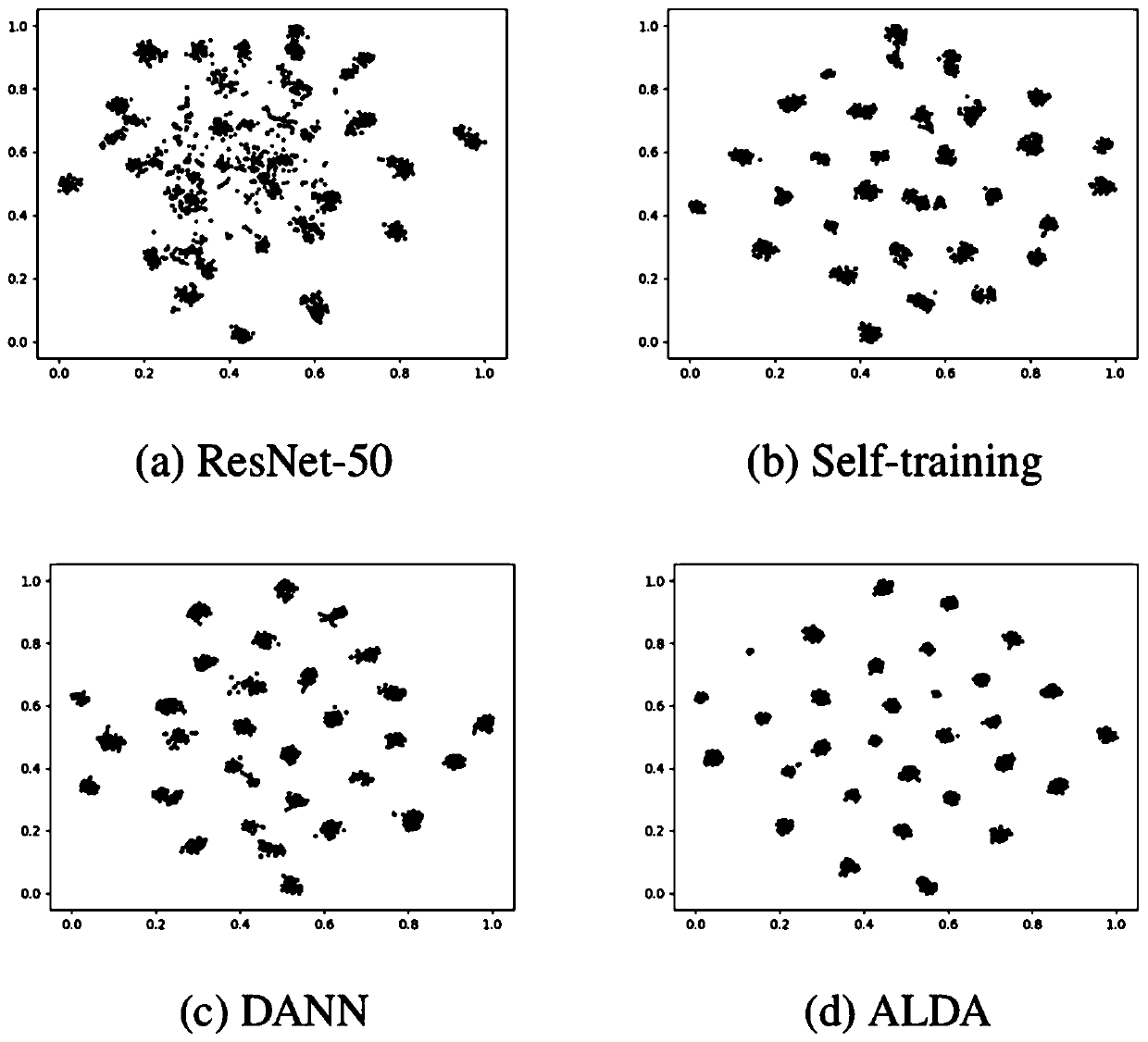
The invention discloses a deep feature and transfer learning-based rolling bearing fault diagnosis method under variable working conditions, relates to the technical field of fault diagnosis, and aimsto solve the problem of low state identification accuracy of different fault positions and different performance degradation degrees of a rolling bearing under the variable working conditions. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out feature extraction on the vibration signal frequency domain amplitude of the rolling bearing by adopting SDAE to obtain vibration signal deepfeatures, and forming a source domain feature sample set and a target domain feature sample set; then, adopting the JGSA to carry out domain adaptation processing on the source domain feature sample and the target domain feature sample, the purpose of reducing distribution offset and subspace transformation difference of feature samples between domains is achieved, and domain offset between different types of feature samples is reduced. And finally, completing rolling bearing multi-state classification under variable working conditions through a K nearest neighbor algorithm. Compared with other methods, the method disclosed by the invention shows better feature extraction capability under the variable working condition of the rolling bearing, the sample feature visualization effect of therolling bearing is optimal, and the fault diagnosis accuracy of the rolling bearing under the variable working condition is high.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
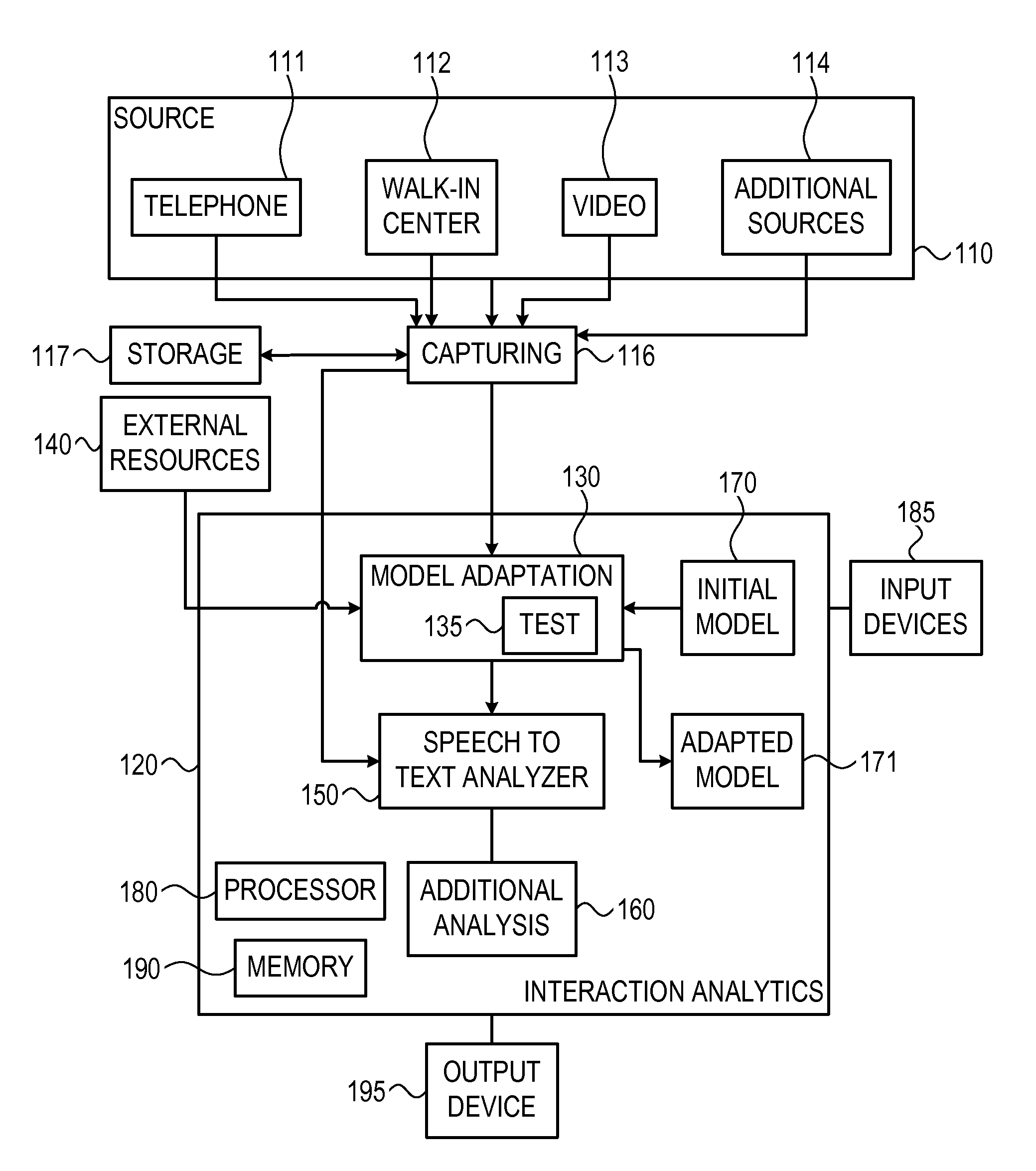
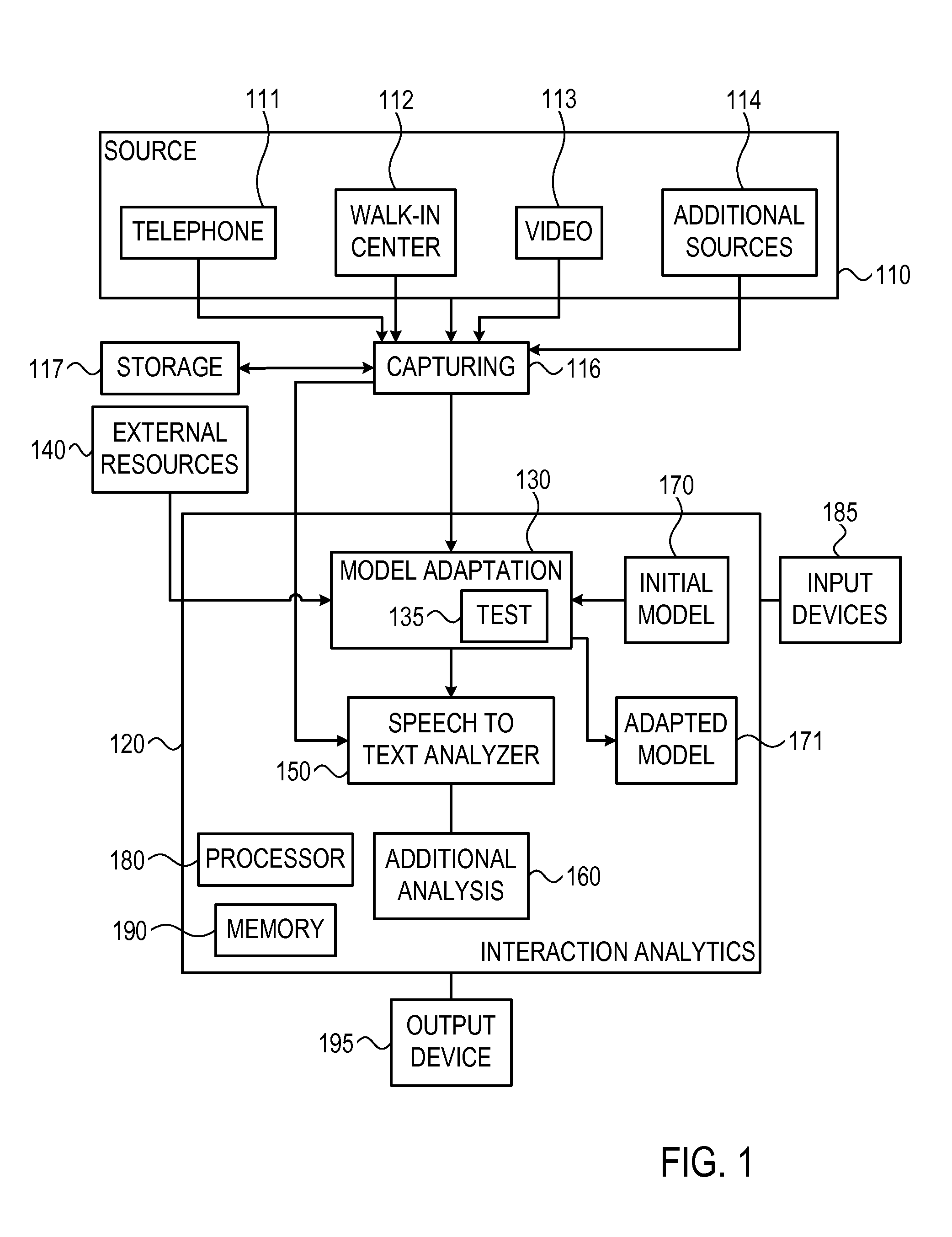
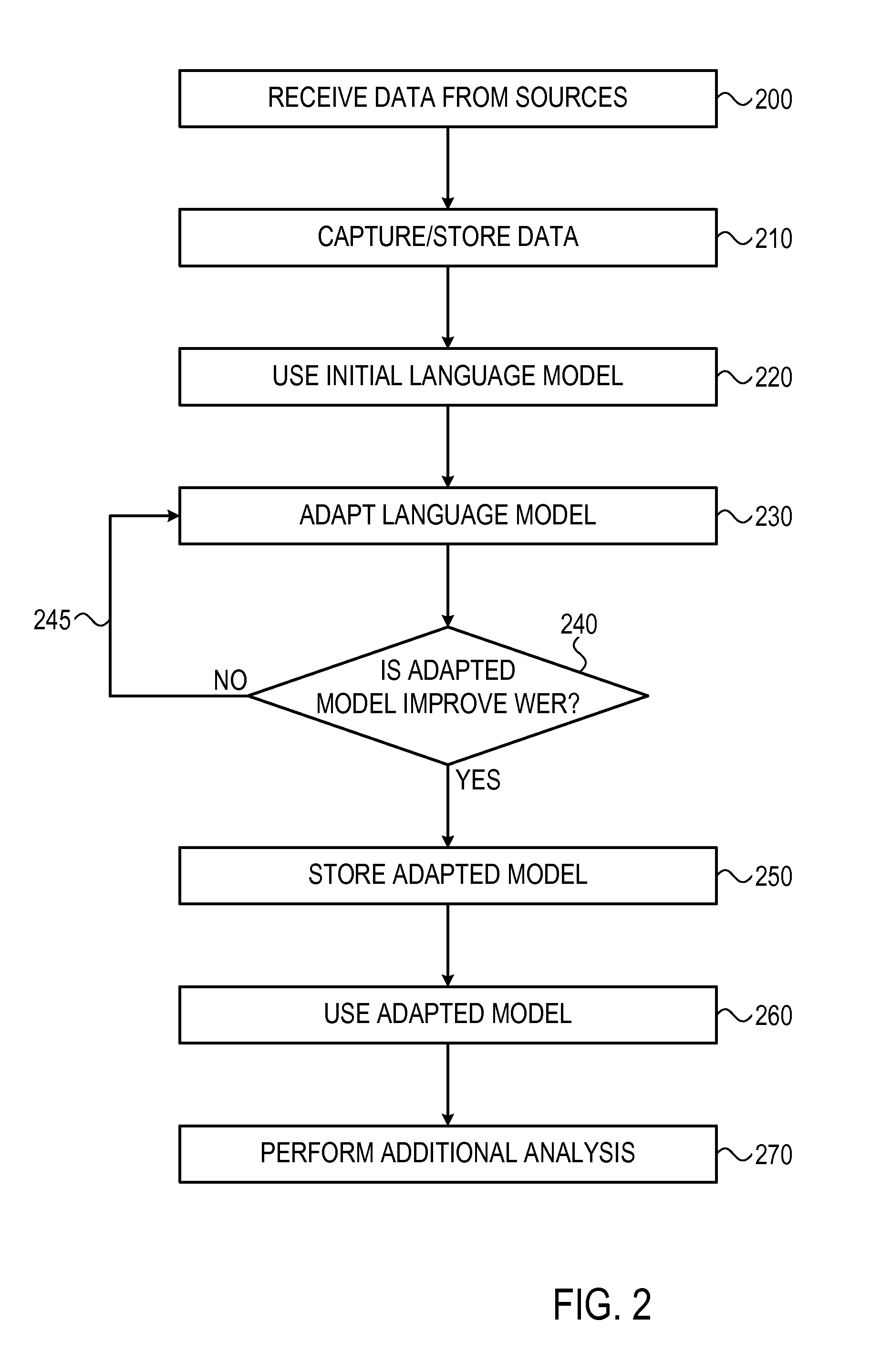
Method and system for automatic domain adaptation in speech recognition applications
A system and method for adapting a language model to a specific environment by receiving interactions captured the specific environment, generating a collection of documents from documents retrieved from external resources, detecting in the collection of documents terms related to the environment that are not included in an initial language model and adapting the initial language model to include the terms detected.
Owner:NICE LTD
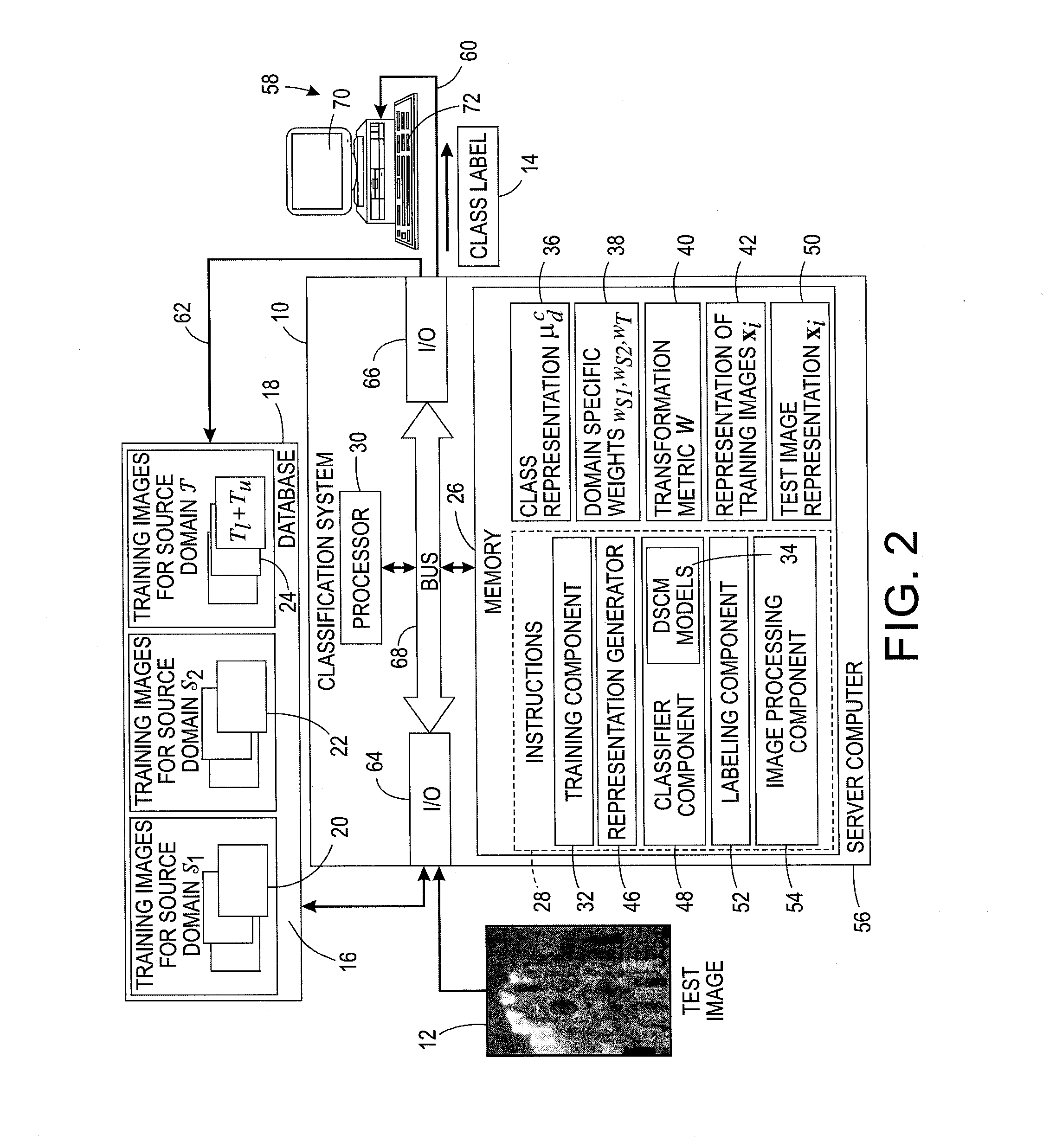
Domain adaptation for image classification with class priors
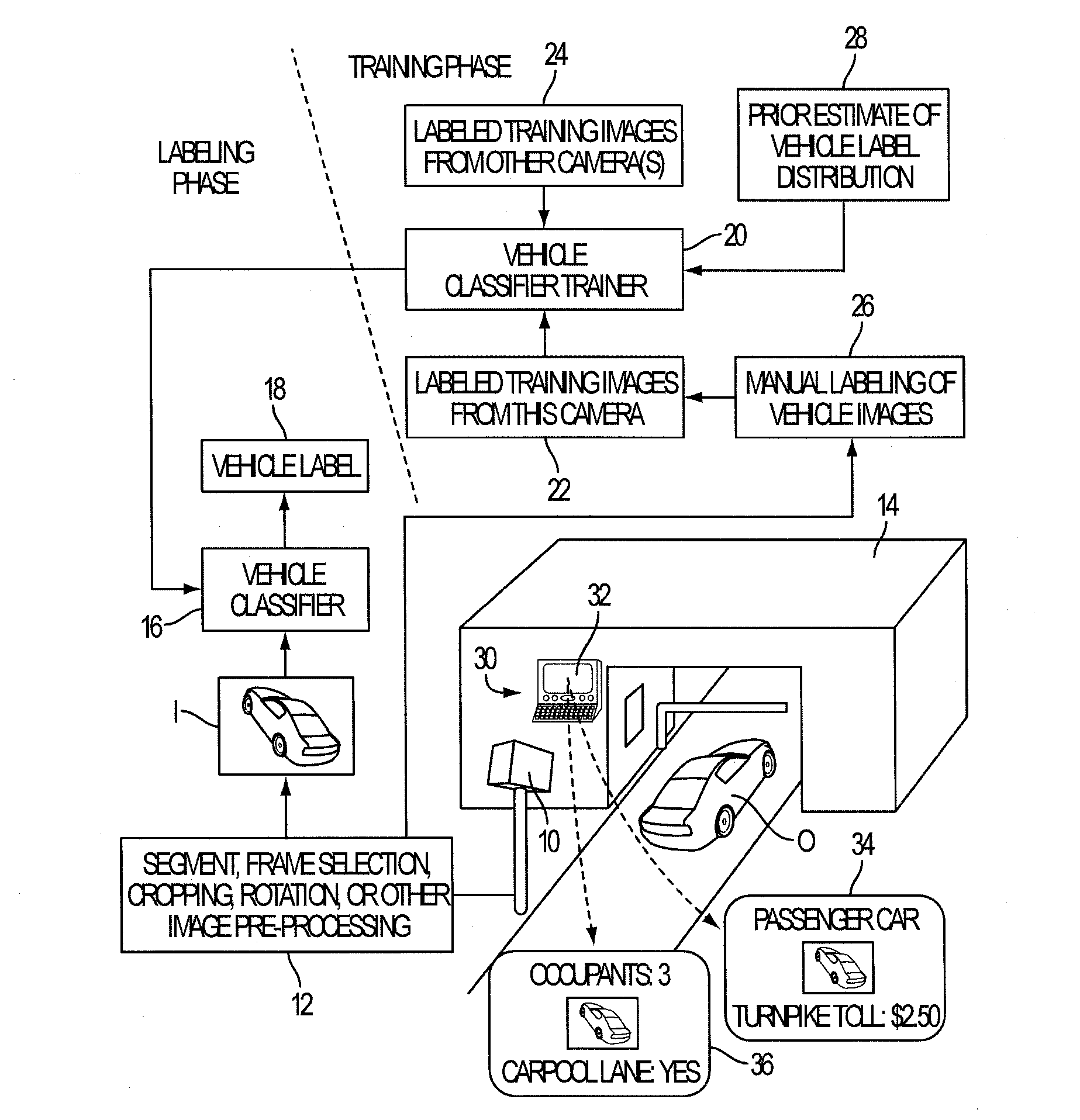
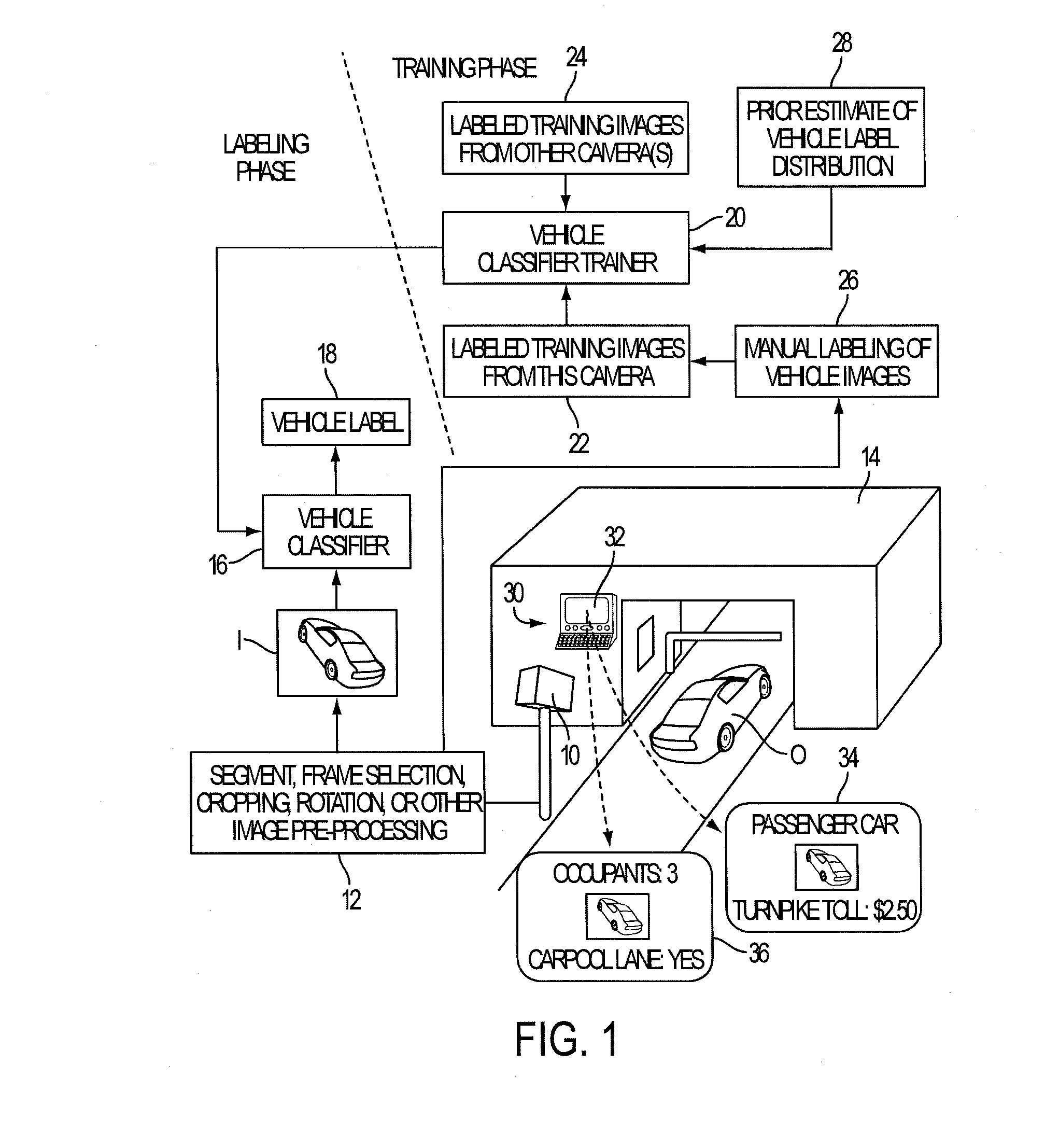
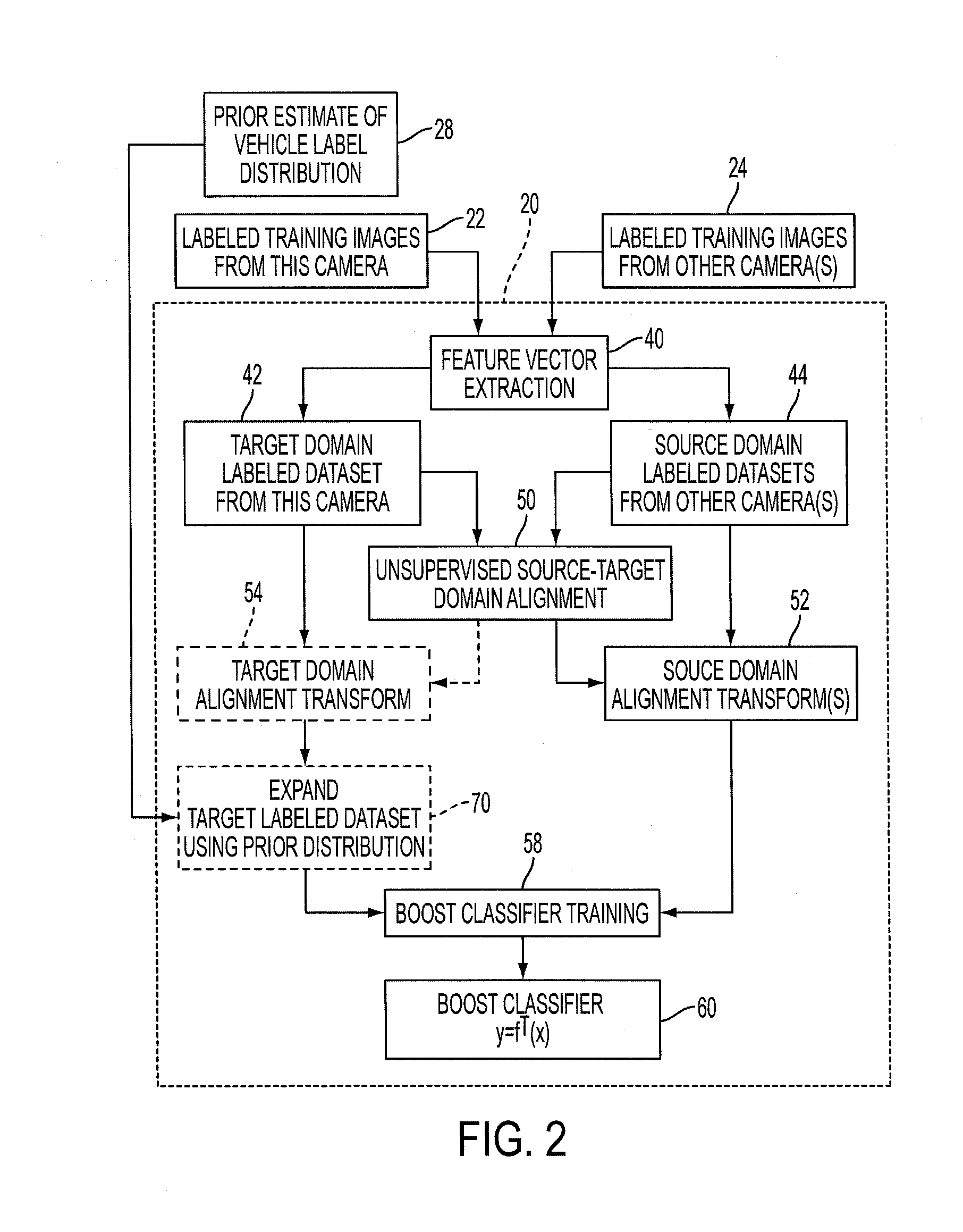
In camera-based object labeling, boost classifier ƒT(x)=Σr=1Mβrhr(x) is trained to classify an image represented by feature vector x using a target domain training set DT of labeled feature vectors representing images acquired by the same camera and a plurality of source domain training sets DS<sub2>1< / sub2>, . . . , DS<sub2>N < / sub2>acquired by other cameras. The training applies an adaptive boosting (AdaBoost) algorithm to generate base classifiers hr(x) and weights βr. The rth iteration of the AdaBoost algorithm trains candidate base classifiers hrk(x) each trained on a training set DT∪DS<sub2>k< / sub2>, and selects hr(x) from previously trained candidate base classifiers. The target domain training set DT may be expanded based on a prior estimate of the labels distribution for the target domain. The object labeling system may be a vehicle identification system, a machine vision article inspection system, or so forth.
Owner:XEROX CORP
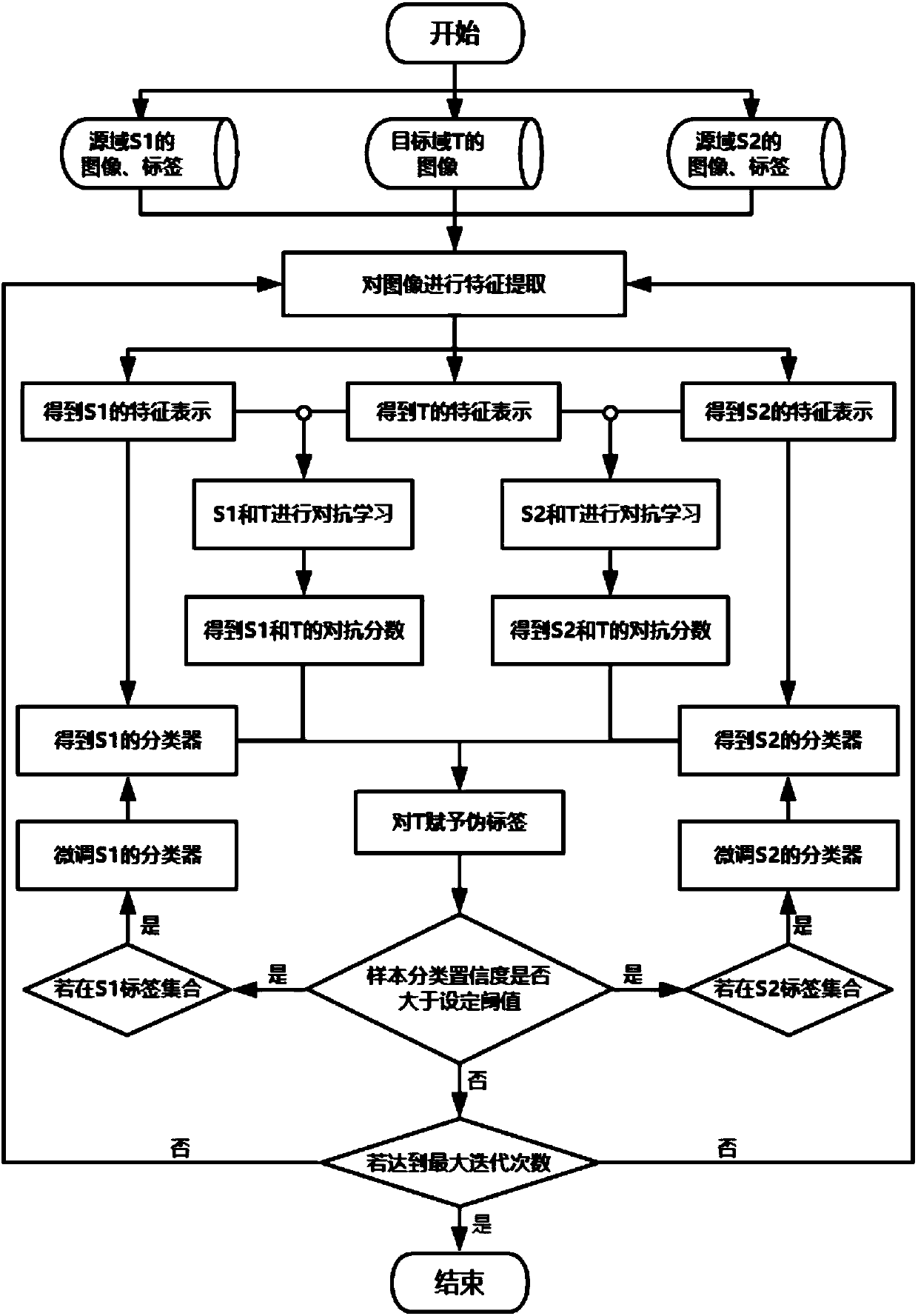
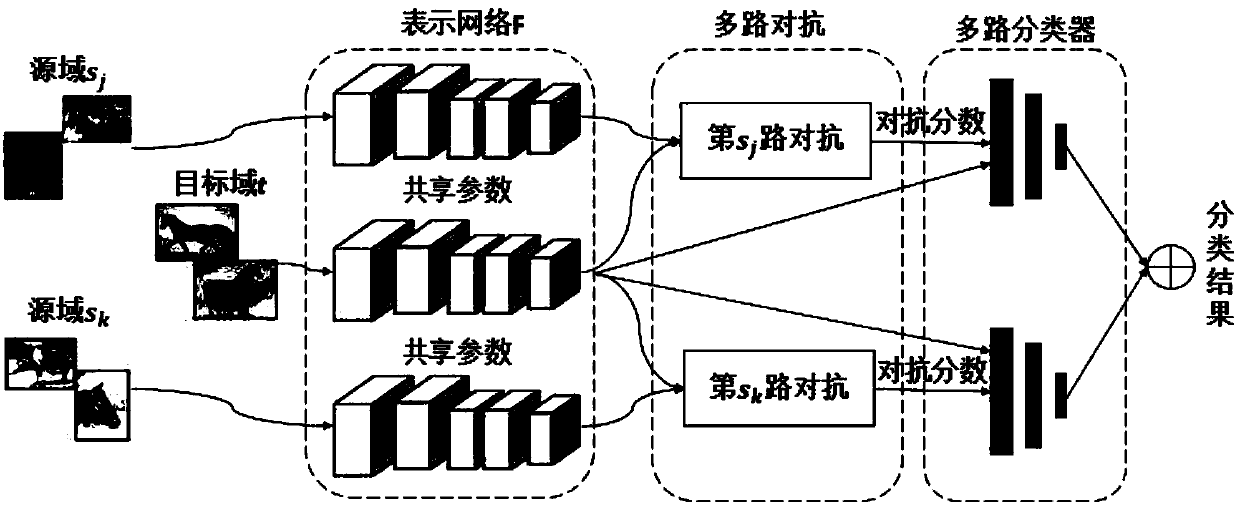
Adversarial-learning-based multi-source-domain adaptive migration method and system
ActiveCN108256561AImprove general performanceAvoid negative transferCharacter and pattern recognitionDomain adaptationObjective model
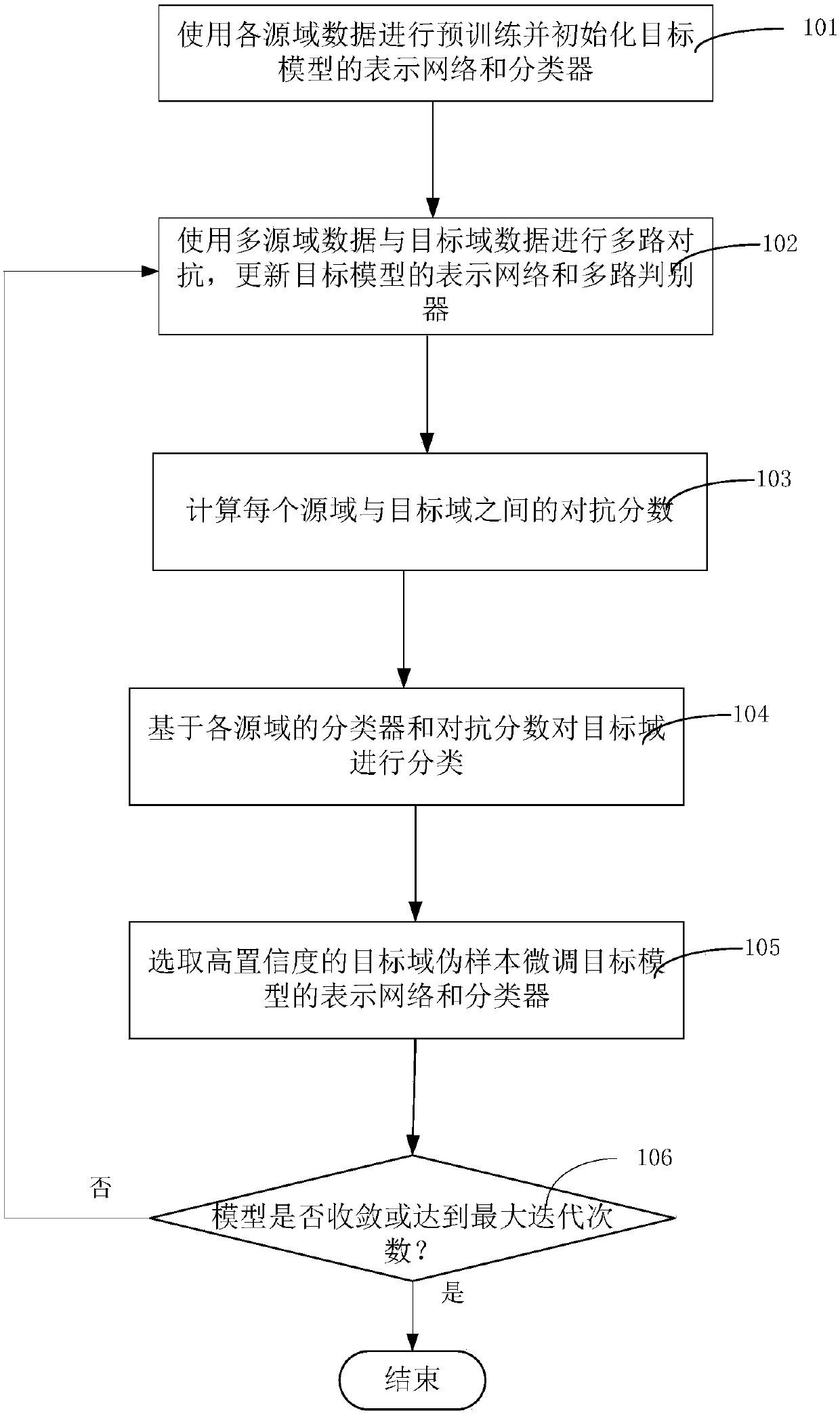
The invention discloses an adversarial-learning-based multi-source-domain adaptive migration method and system. The method comprises: step one, pre training is carried out by using all-source-domain data and a representation network and a classifier of a target model are initialized; step two, multi-path adversarial adversarial processing is carried out on multi-source-domain data and target-domain data and a representation network and a multi-path discriminator of the target model are updated; step three, adversarial scores between the source domains and the target domain are calculated; stepfour, target domain classification is carried out based on the classifiers and the adversarial scores of all source domains; step five, a target domain pseudo sample with a high confidence coefficient is selected for fine tuning of the representation network and the classifier of the target model; and step six, the steps from the step two to the step five are carried out again until model convergence is realized or a maximum iteration number of times is reached, and then training is stopped. According to the invention, reliance on the hypothesis of consistency of the single-source-domain tagset and the target domain is eliminated; and a negative migration phenomenon existing in the multi-source domain adaptation process is avoided effectively.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
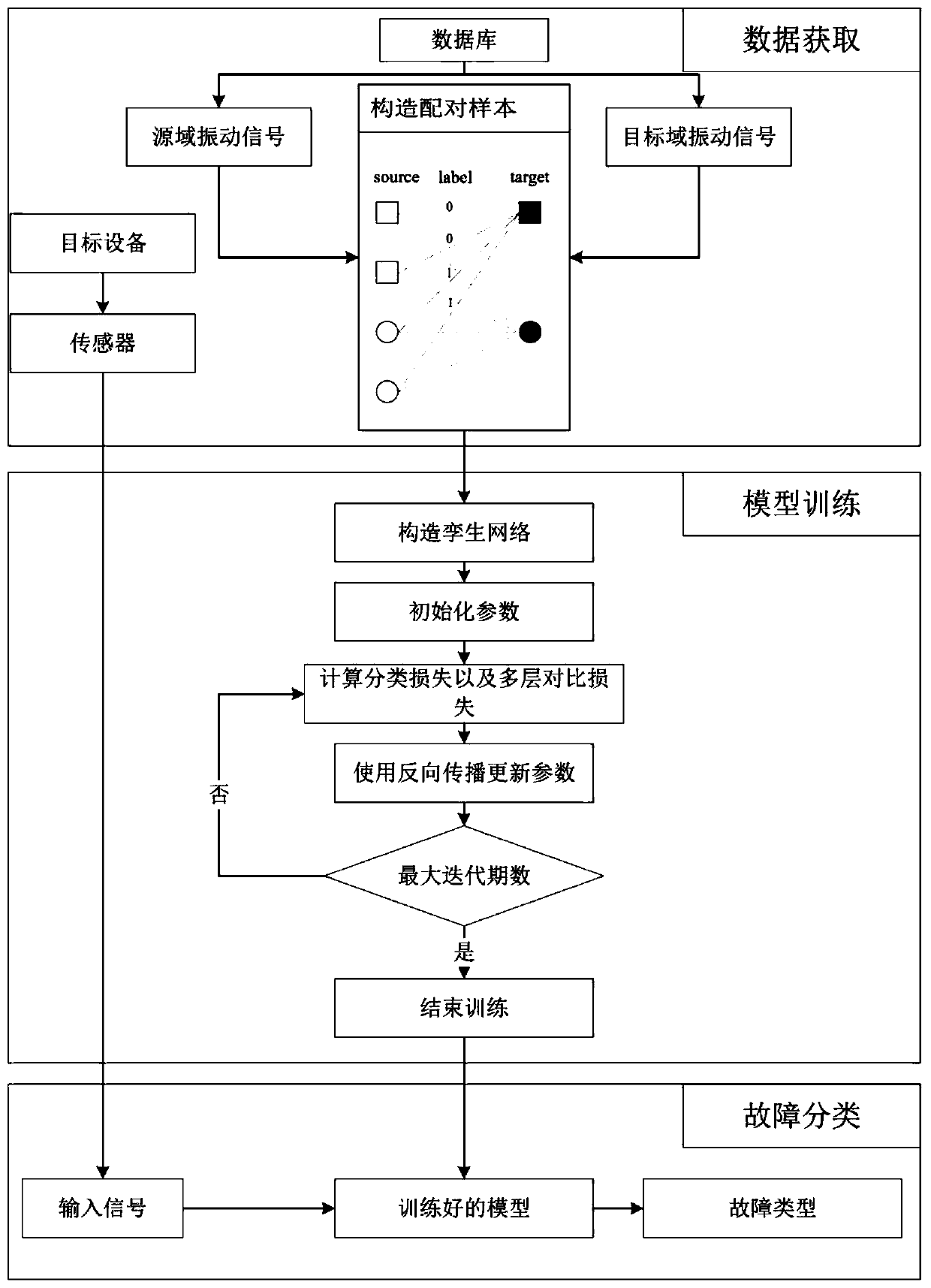
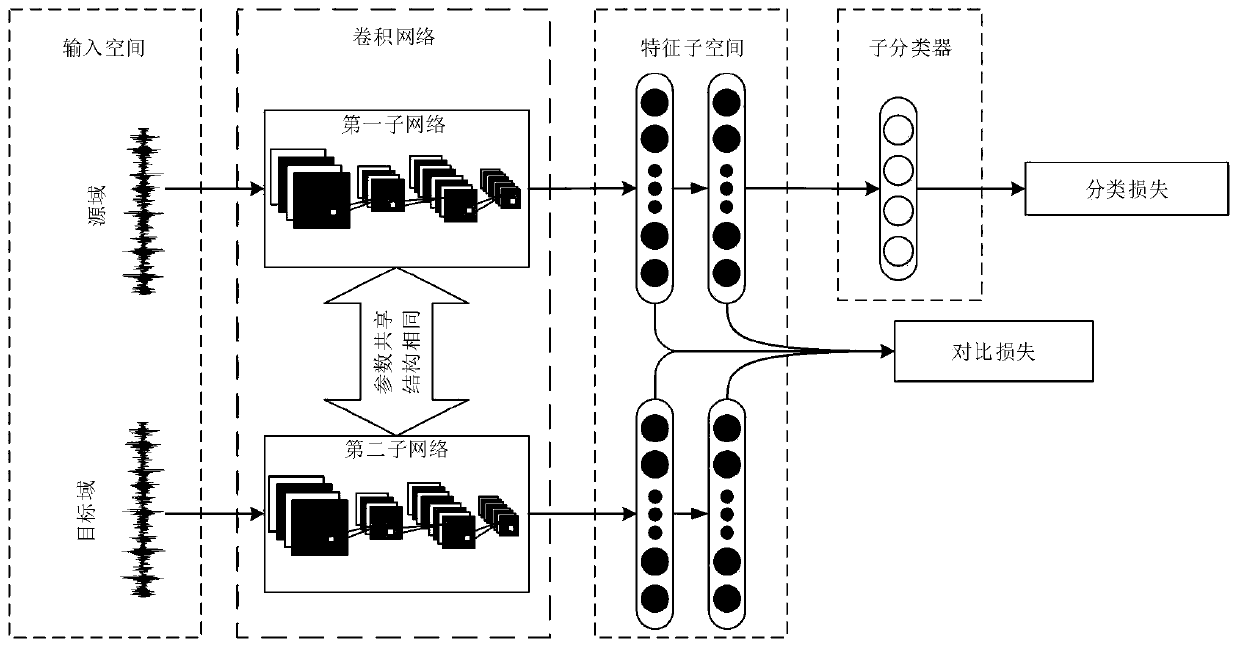
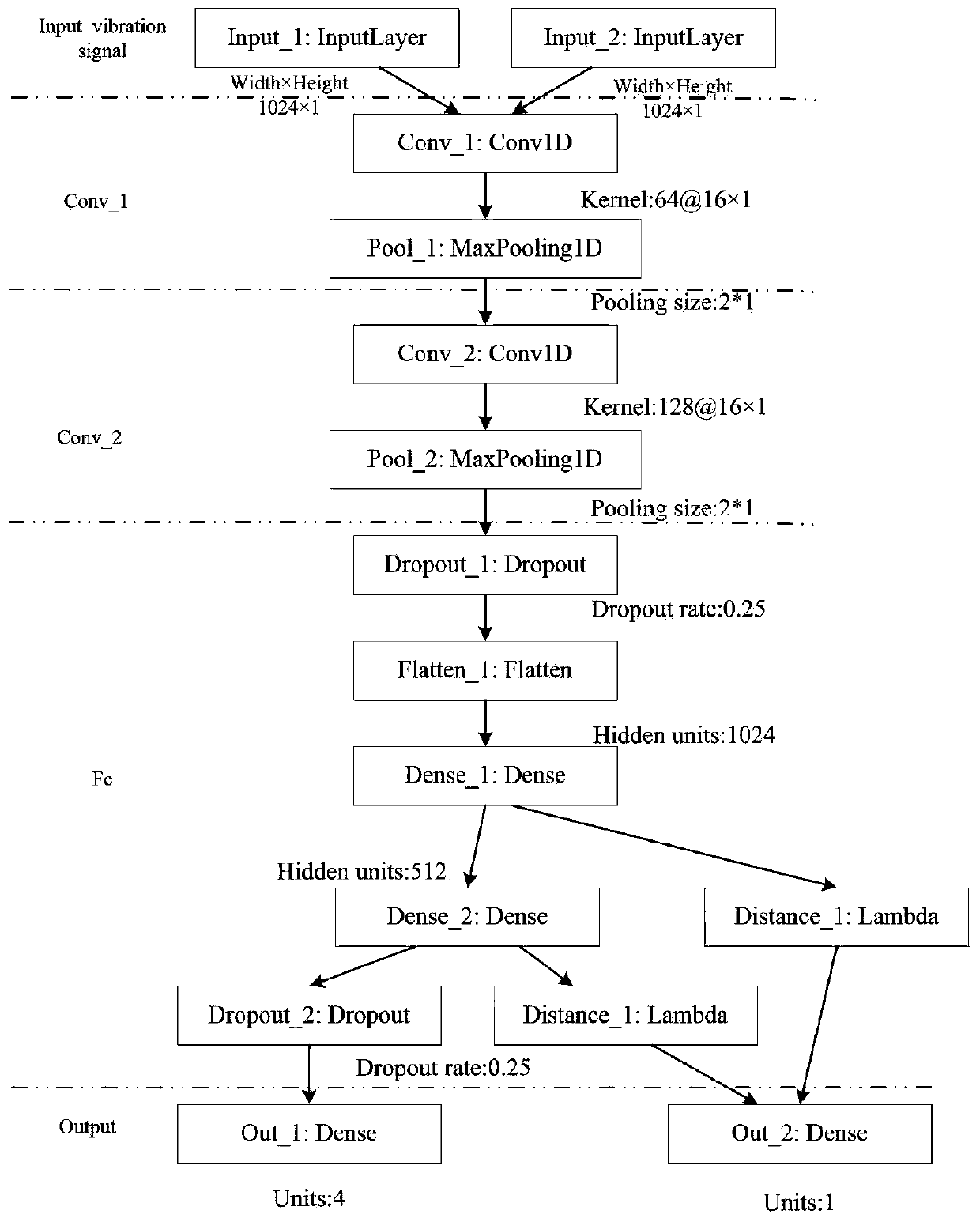
A vibration data fault classification method based on depth domain adaptation
ActiveCN109766921ASolve the problem of poor diagnosisImprove generalization abilityCharacter and pattern recognitionPaired samplesClassification methods
The invention discloses a vibration data fault classification method based on depth domain adaptation. The vibration data fault classification method comprises the steps of constructing a source domain containing a large amount of sample data and a target domain containing a small amount of sample data; constructing a classifier by using the sample data in the source domain; constructing paired samples according to the sample data in different domains in the source domain and the target domain; constructing a twin network, inputting the paired samples as training samples into the twin networkfor domain adaptation, and obtaining a final loss function of the paired samples; and optimizing the final loss function, and obtaining a trained fault classification model. According to the present invention, the problem that an existing deep network model is poor in diagnosis effect under the condition that fault sample data are insufficient is solved, a domain self-adaption method in deep learning and transfer learning is combined, the existing data are utilized to the maximum extent, the generalization capacity of the model is improved, and therefore better classification accuracy is obtained.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
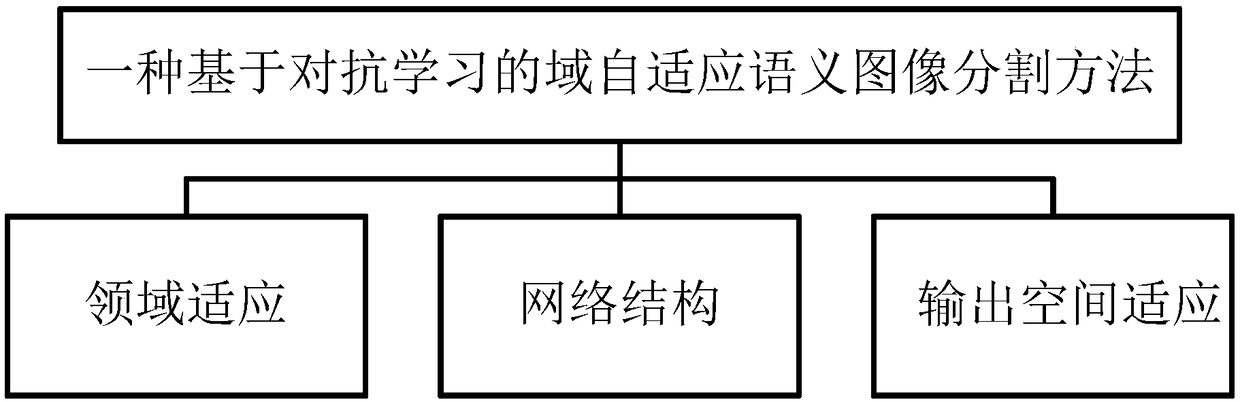
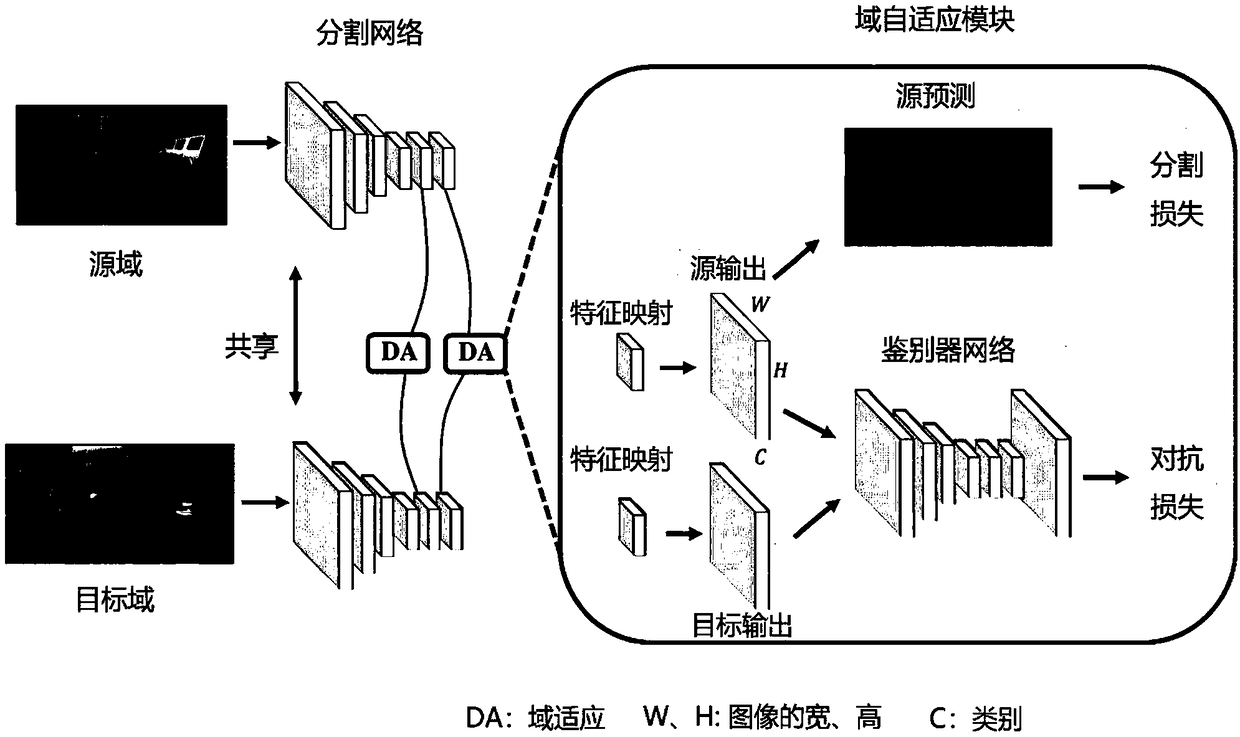
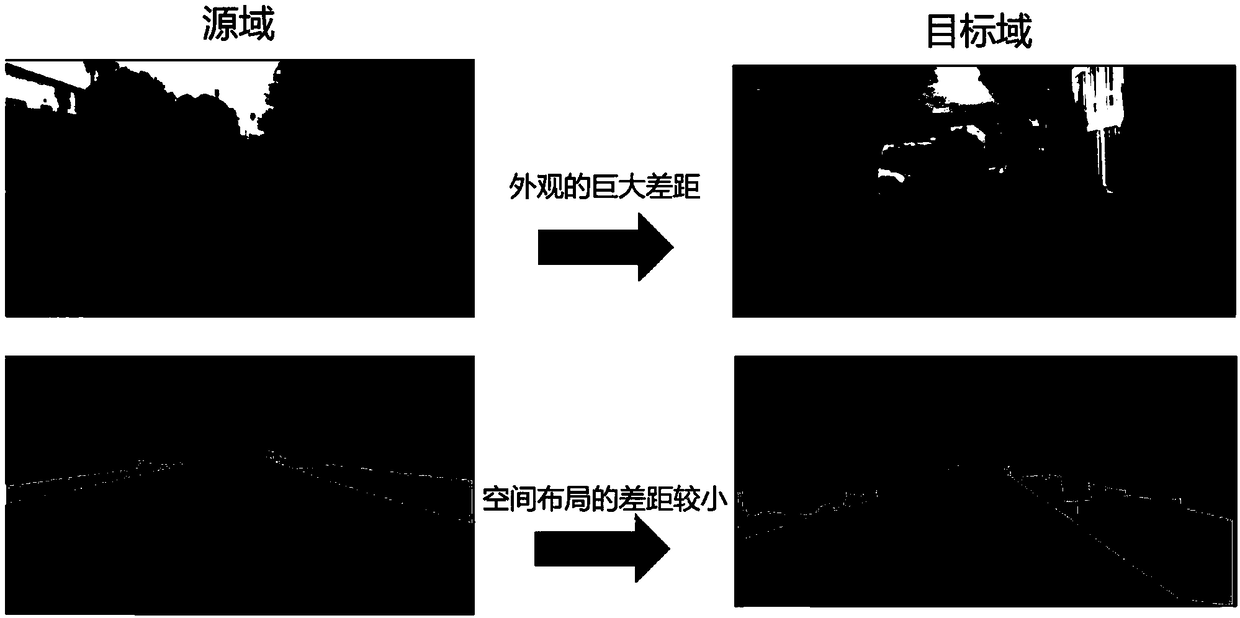
A domain adaptive image semantic segmentation method based on antagonistic learning
InactiveCN109190707ACharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesDiscriminatorNetwork structure
The invention provides a domain adaptive image semantic segmentation method based on antagonistic learning, which comprises the following main contents: domain adaptation, network structure and outputspace adaptation. The process comprises the following steps: firstly, inputting images of a source domain and a target domain to a segmentation network to predict the source domain and the target domain to obtain segmentation output; generating the segmentation loss of the source domain by the source prediction obtained from the source output. Then, two segmented outputs are used as the input ofthe discriminator to generate anti-loss, and then the anti-loss is transmitted to the segmented network. Finally, the pixel-level semantic image segmentation is achieved by minimizing the segmentationloss and maximizing the antagonistic loss. The invention develops a multi-level confrontation learning method, which can effectively align the scene layout and the local context between the source and the target images in the self-adaptation of the segmentation space. In addition, the invention is simple, convenient and easy to operate, and can well solve the influence of adapting to the complexity of the high-dimensional features.
Owner:SHENZHEN WEITESHI TECH
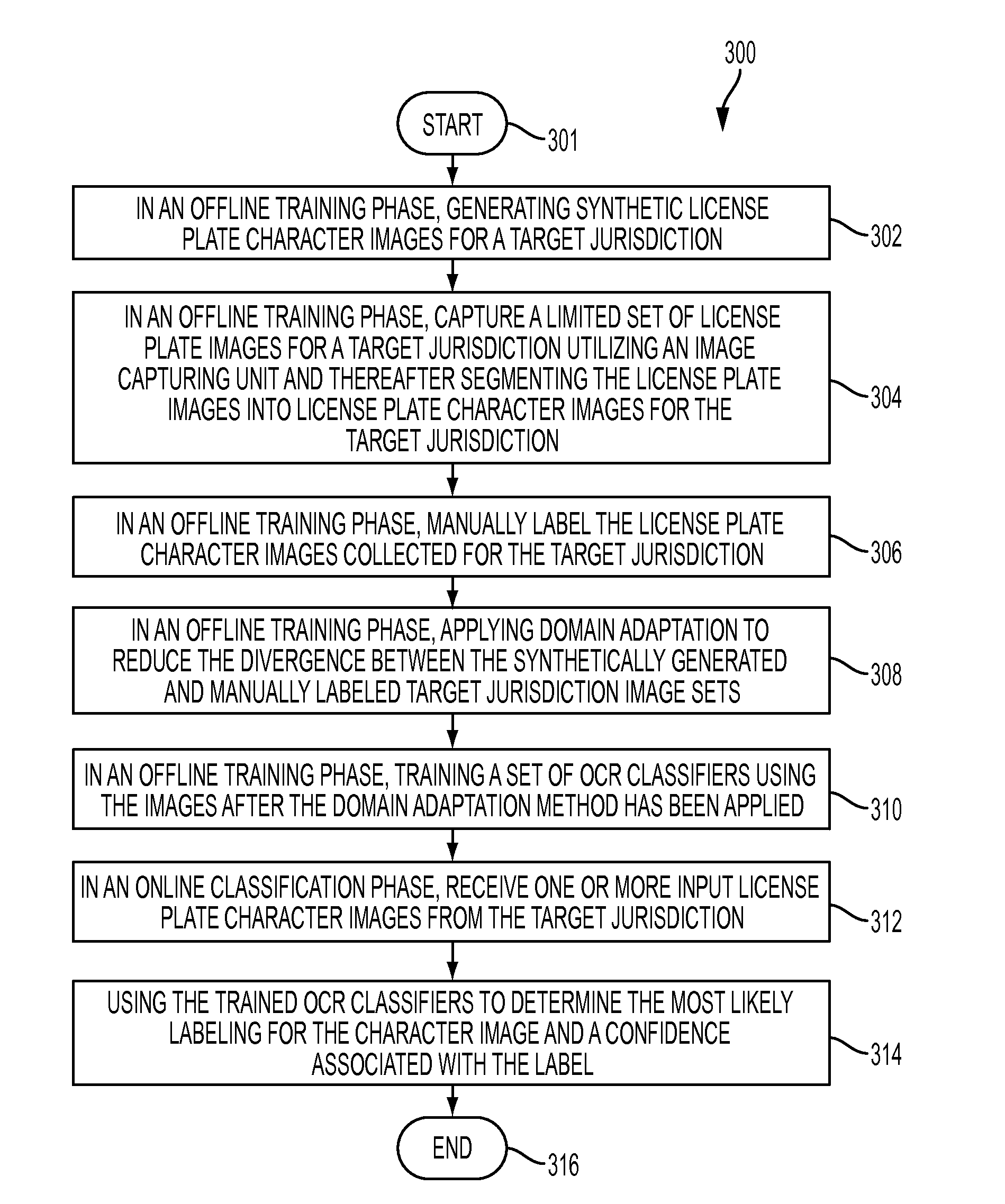
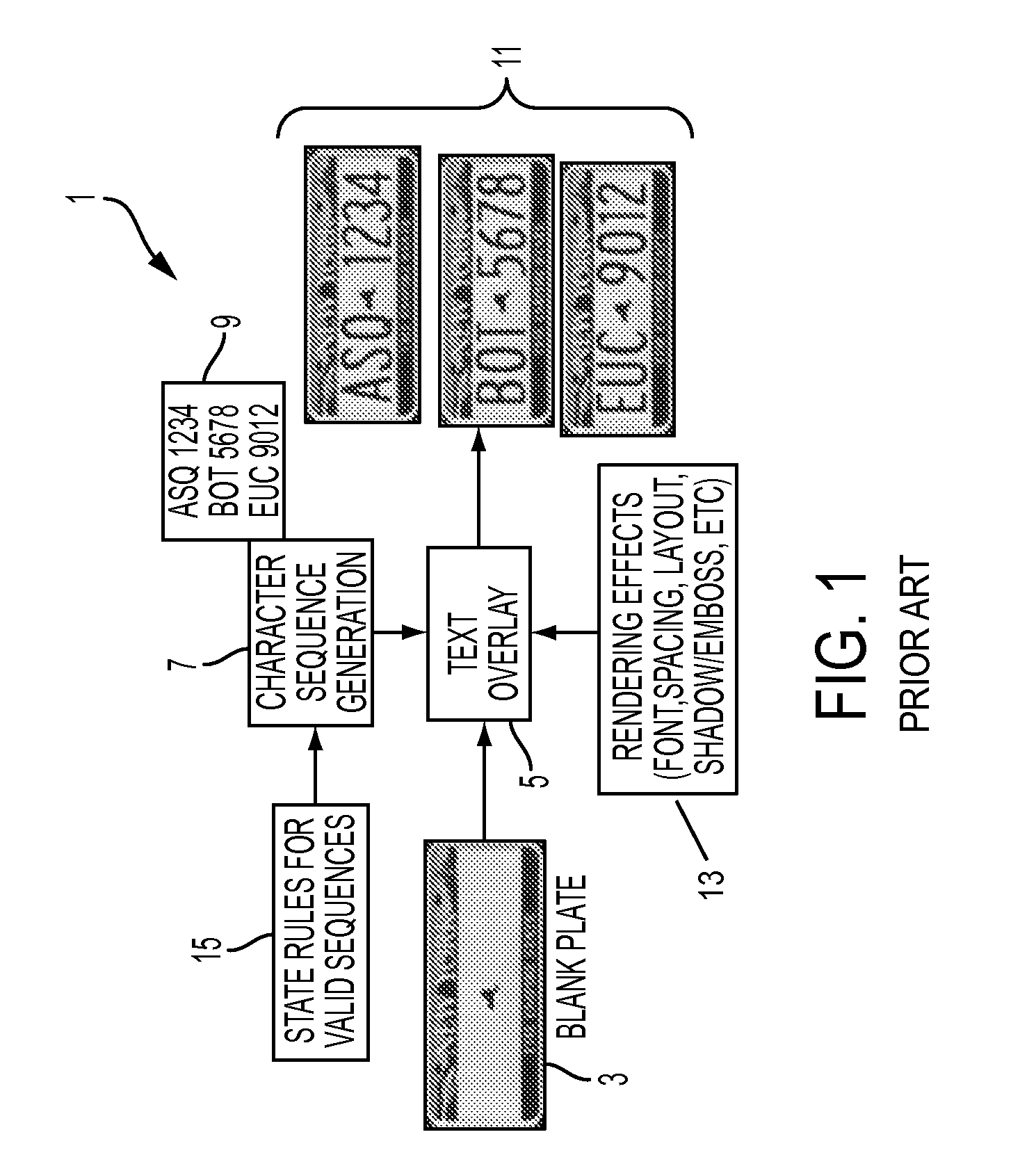
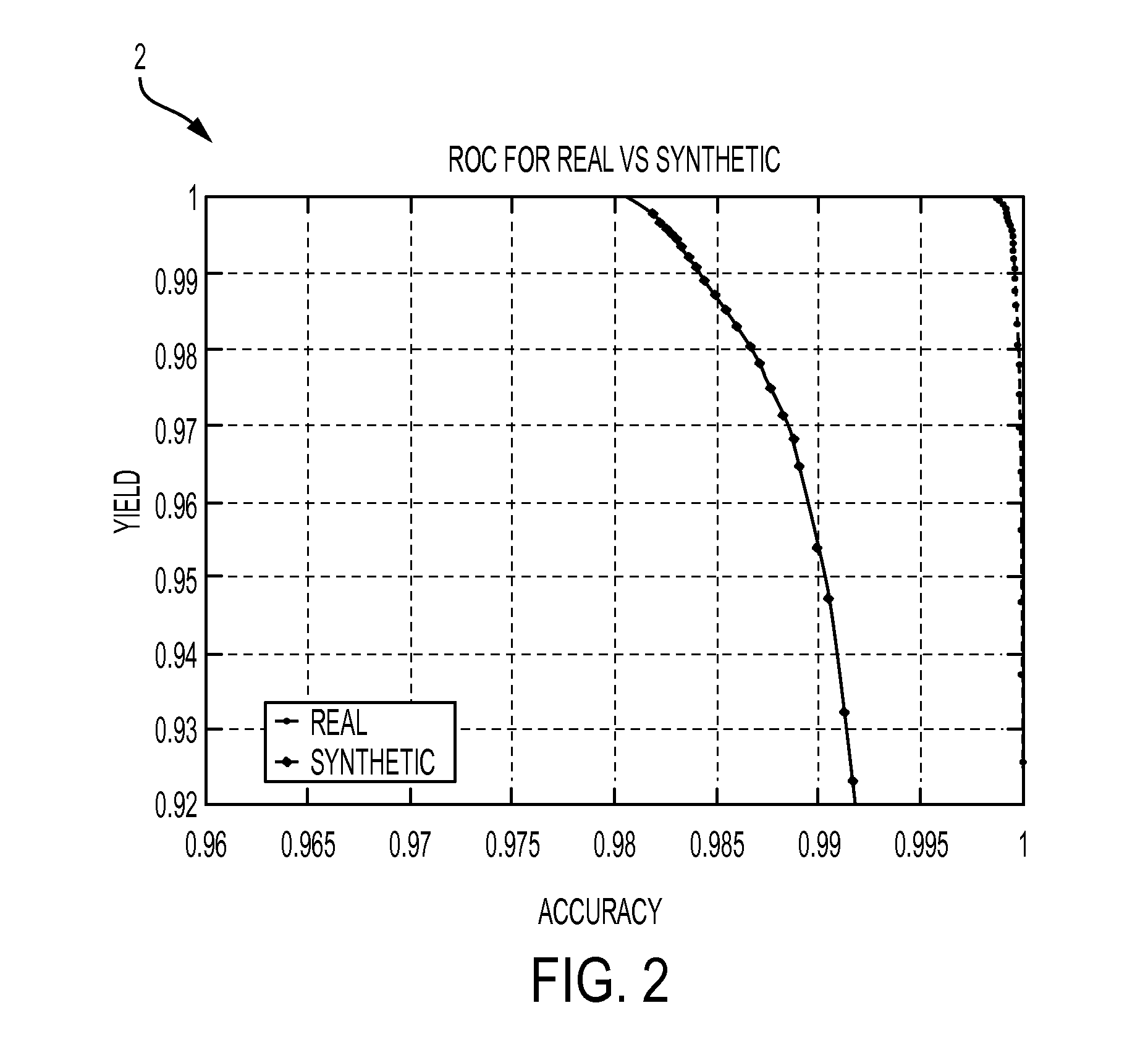
Annotation free license plate recognition method and system
ActiveUS20160203380A1Minimize manualDeterioration in OCR performanceImage analysisCharacter recognitionImage segmentationA domain
Methods and systems for recognizing a license plate character. Synthetic license plate character images are generated for a target jurisdiction. A limited set of license plate images can be captured for a target jurisdiction utilizing an image-capturing unit. The license plate images are then segmented into license plate character images for the target jurisdiction. The license plate character images collected for the target jurisdiction can be manually labeled. A domain adaptation technique can be utilized to reduce the divergence between synthetically generated and manually labeled target jurisdiction image sets. Additionally, OCR classifiers are trained utilizing the images after the domain adaptation method has been applied. One or more input license plate character images can then be received from the target jurisdiction. Finally, the trained OCR classifier can be employed to determine the most likely labeling for the character image and a confidence associated with the label.
Owner:CONDUENT BUSINESS SERVICES LLC
Efficient Online Domain Adaptation
ActiveUS20150106076A1Natural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsSentence pairTranslation memory
Systems and methods for efficient online domain adaptation are provided herein. Methods may include receiving a post-edited machine translated sentence pair, updating a machine translation model by adjusting translation weights for a translation memory and a language model while generating test machine translations of the machine translated sentence pair until one of the test machine translations approximately matches the post-edits for the machine translated sentence pair, and retranslating the remaining machine translation sentence pairs that have yet to be post-edited using the updated machine translation model.
Owner:SDL INK
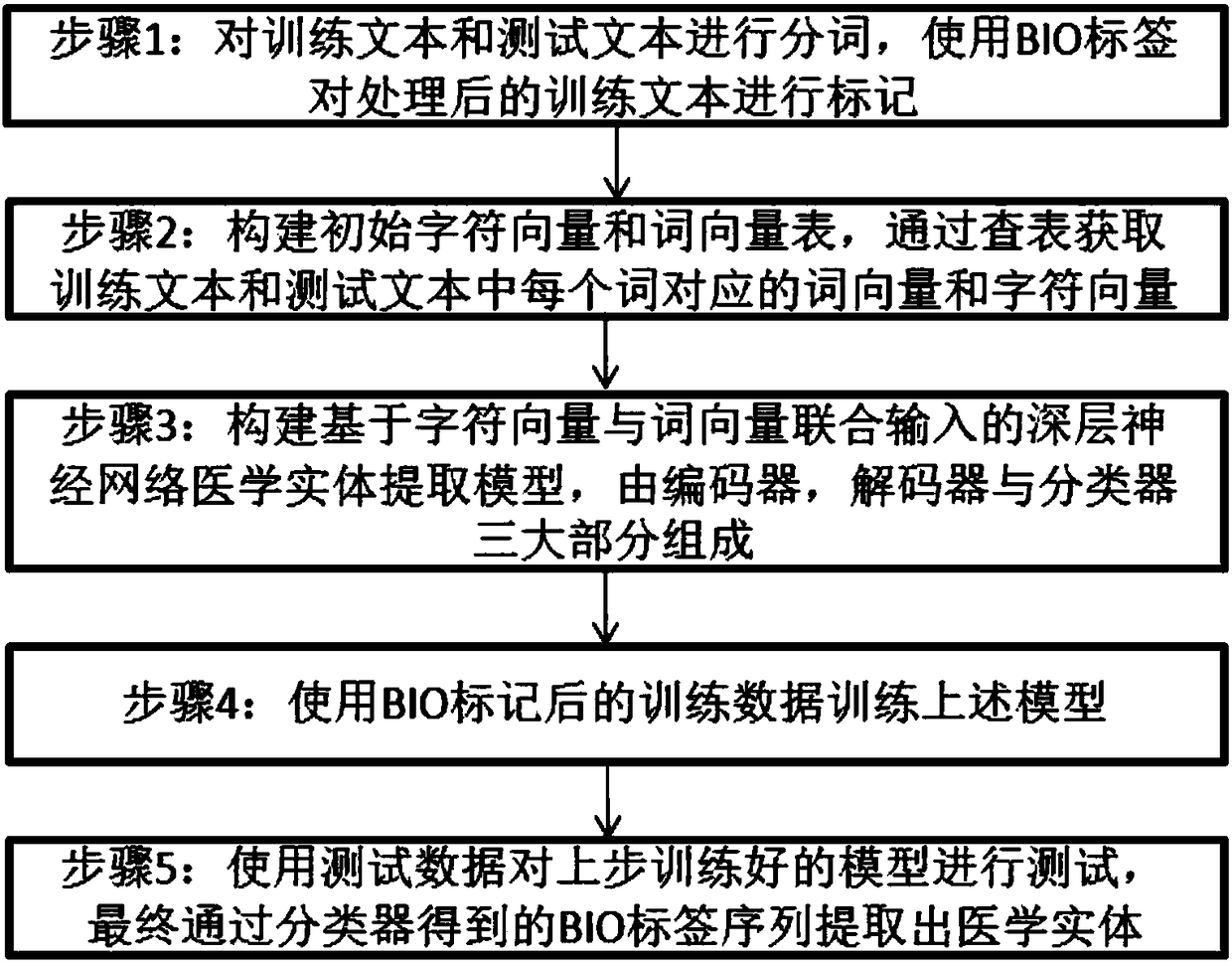
Method for extracting clinical medical information based on neural network
InactiveCN108182976AEasy to capturePromote resultsMedical data miningNatural language data processingData fieldTime expression
The invention discloses a method for extracting clinical medical information based on a neural network. Generally, a medical text has much professional vocabulary, uncommon vocabulary and time expressions composed of numbers and characters, but character vectors obtained by a convolutional neural network may contain the morphological information of words, so the problem can be solved very well. Further, a bidirectional LSTM can capture context information well. In addition, the method of using the neural network avoids a process of artificially designing features in machine learning, and can well solve domain adaptation. The method of the invention achieves good results in different data fields, and can extract information with practical values and research significance from massive medical data efficiently and accurately.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
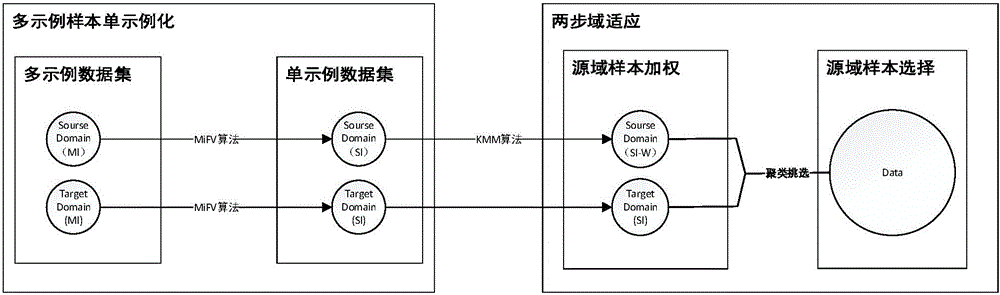
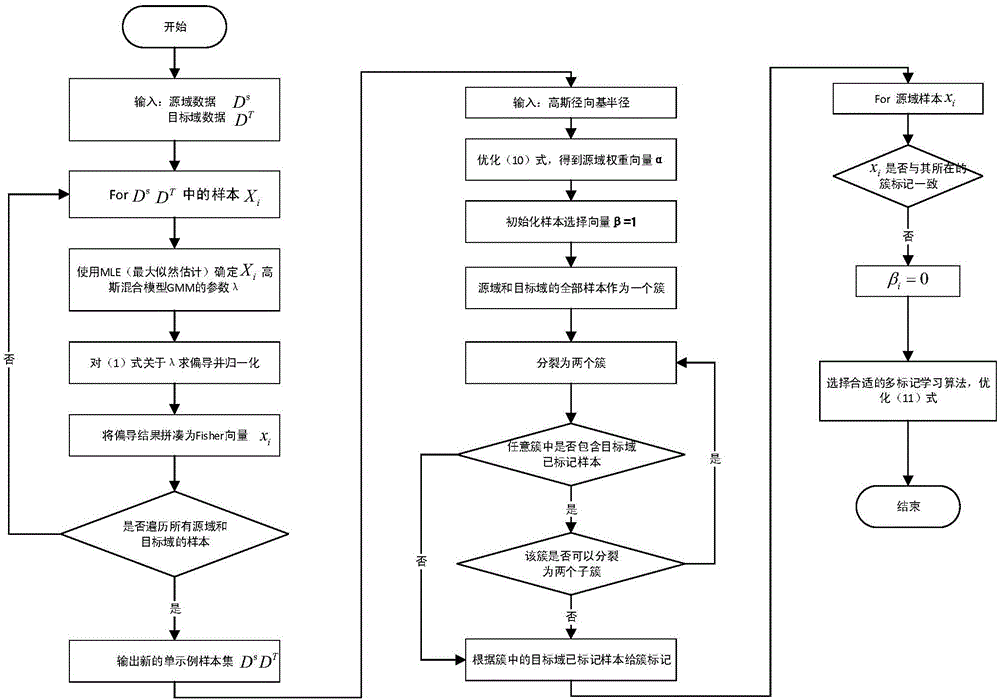
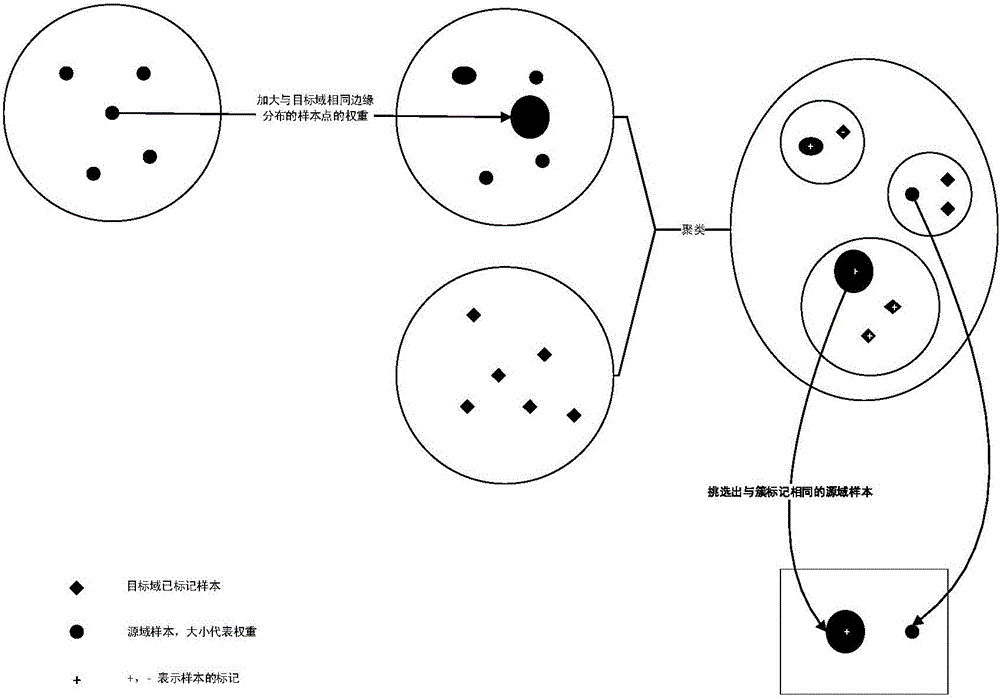
Transfer learning design method and system based on domain adaptation under multi-example multi-label framework
InactiveCN105787513AConsistent distributionSolve problemsCharacter and pattern recognitionData setSample selection
The invention discloses a transfer learning design method and system based on domain adaptation under a multi-example multi-label framework. According to the invention, multi-example multi-label learning and transfer learning are unified into one framework, source domain data samples and target domain data samples are effectively utilized for correlation statistics, and the source domain samples can be effectively used in the learning of target domain tasks; the characteristics of a source domain data sample set and a target domain data set in RKHS are utilized, a two-step domain adaptation process formed by sample weighting and a sample selection mechanism based on clustering is utilized, so that the learning of target tasks has enough training samples weighted and selected from the source domain set; and a miFV algorithm is utilized to convert multi-examples into a single example, and the calculation cost problem of domain adaptation is solved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
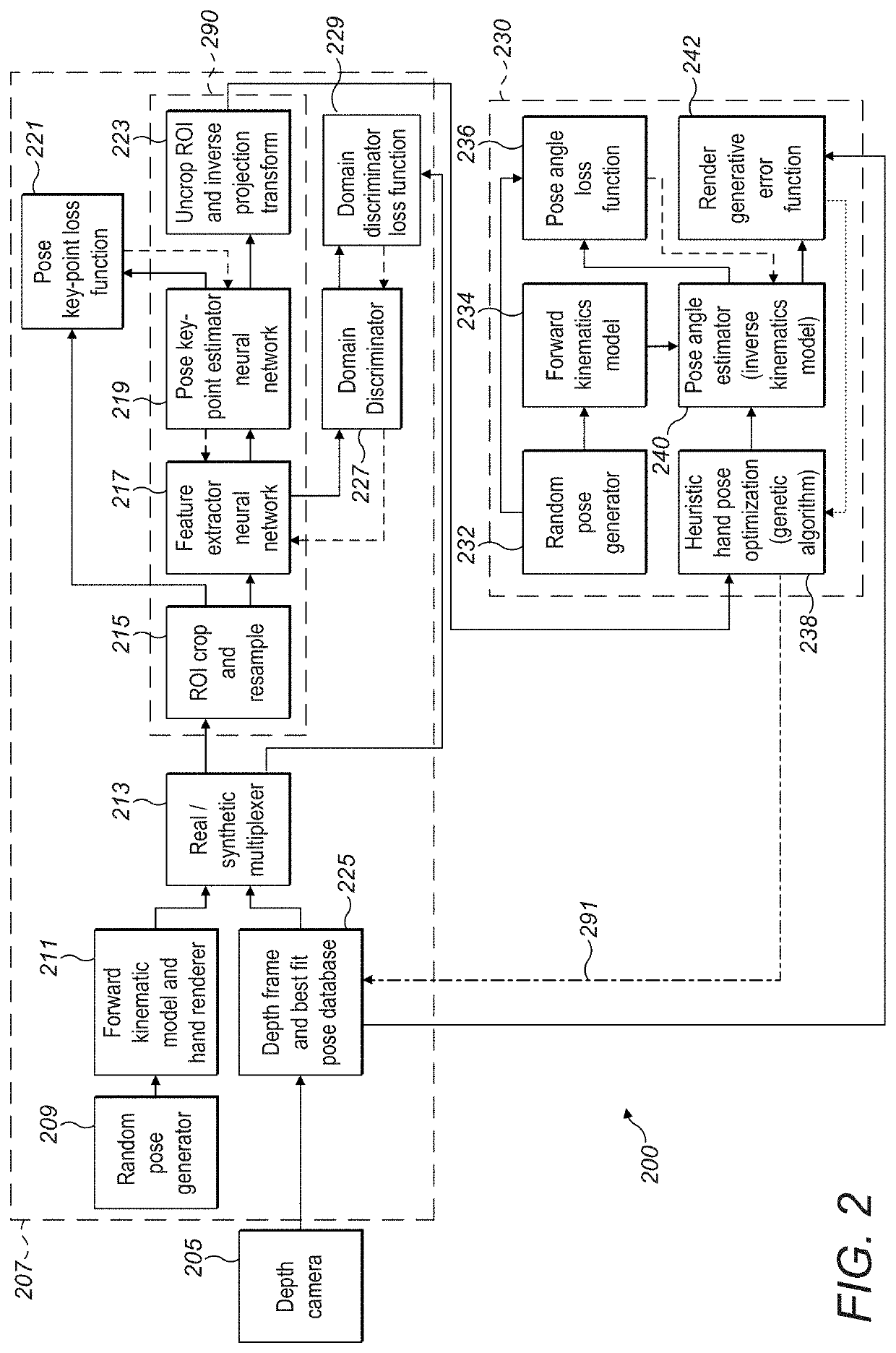
Using Iterative 3D-Model Fitting for Domain Adaptation of a Hand-Pose-Estimation Neural Network
PendingUS20200327418A1Improve accuracyAccurate labelingImage enhancementImage analysisData setA domain
Described is a solution for an unlabeled target domain dataset challenge using a domain adaptation technique to train a neural network using an iterative 3D model fitting algorithm to generate refined target domain labels. The neural network supports the convergence of the 3D model fitting algorithm and the 3D model fitting algorithm provides refined labels that are used for training of the neural network. During real-time inference, only the trained neural network is required. A convolutional neural network (CNN) is trained using labeled synthetic frames (source domain) with unlabeled real depth frames (target domain). The CNN initializes an offline iterative 3D model fitting algorithm capable of accurately labeling the hand pose in real depth frames. The labeled real depth frames are used to continue training the CNN thereby improving accuracy beyond that achievable by using only unlabeled real depth frames for domain adaptation.
Owner:ULTRAHAPTICS IP LTD
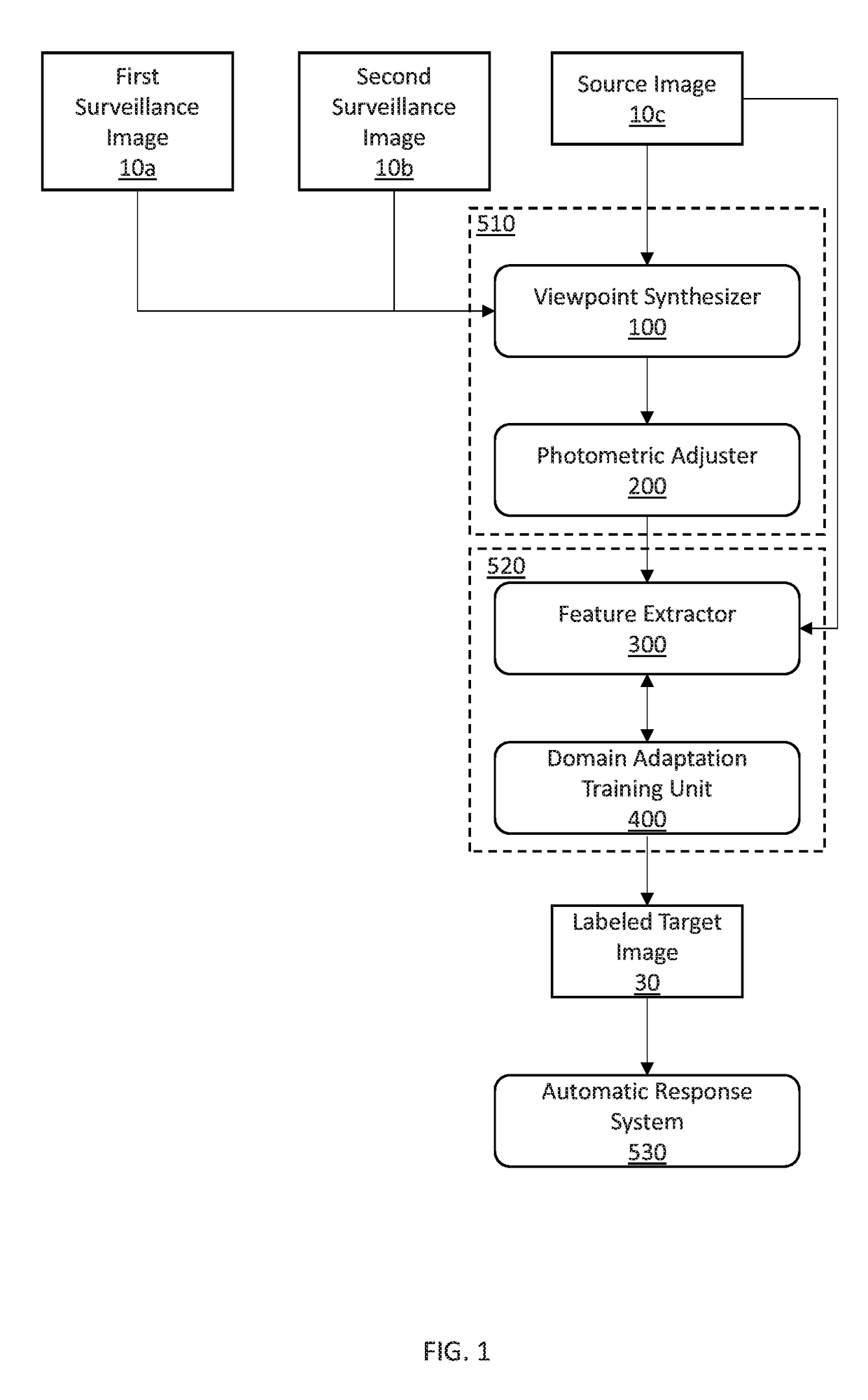
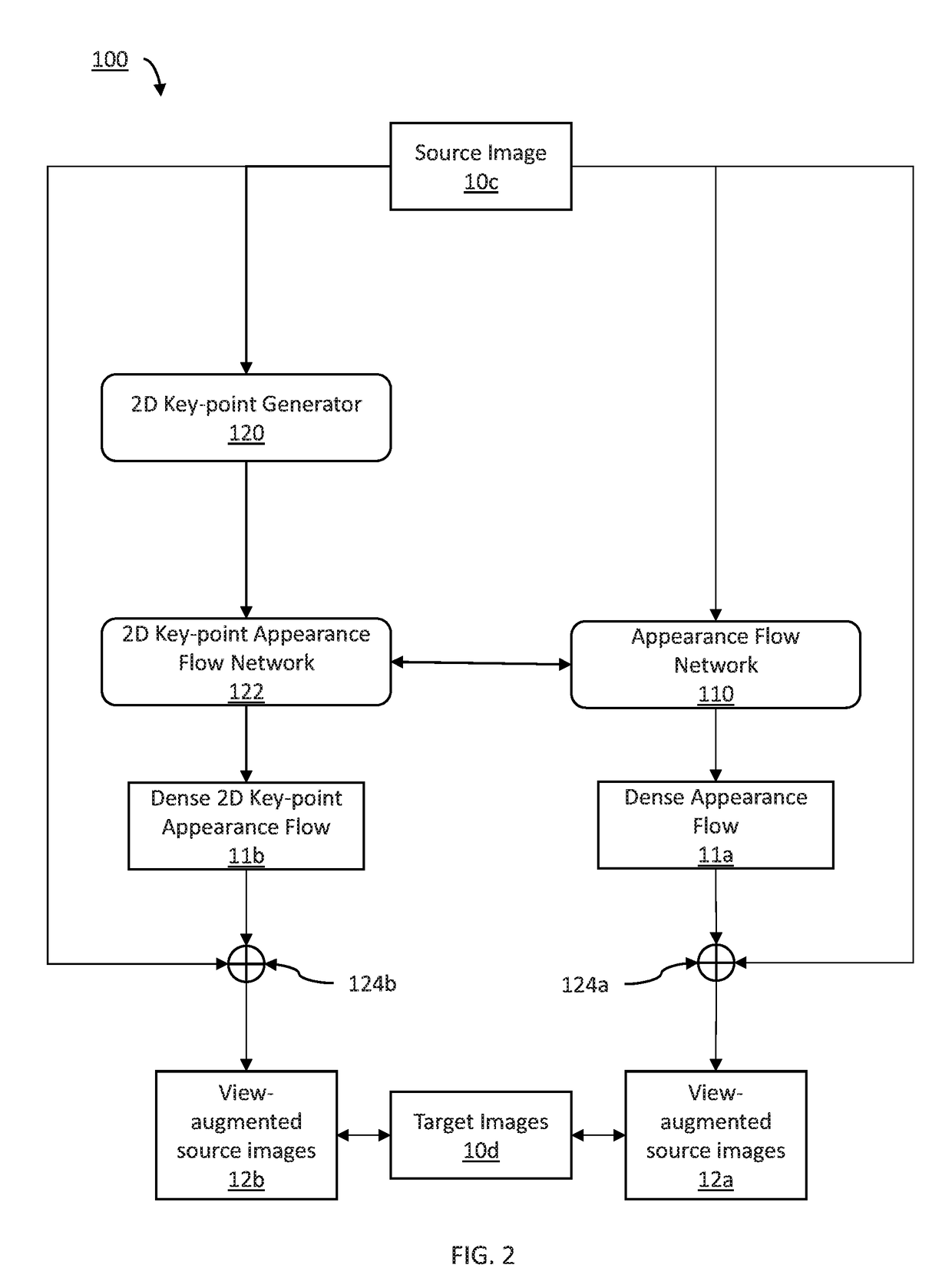
Viewpoint invariant object recognition by synthesization and domain adaptation
ActiveUS20190066493A1Detection of traffic movementCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature extractionViewpoints
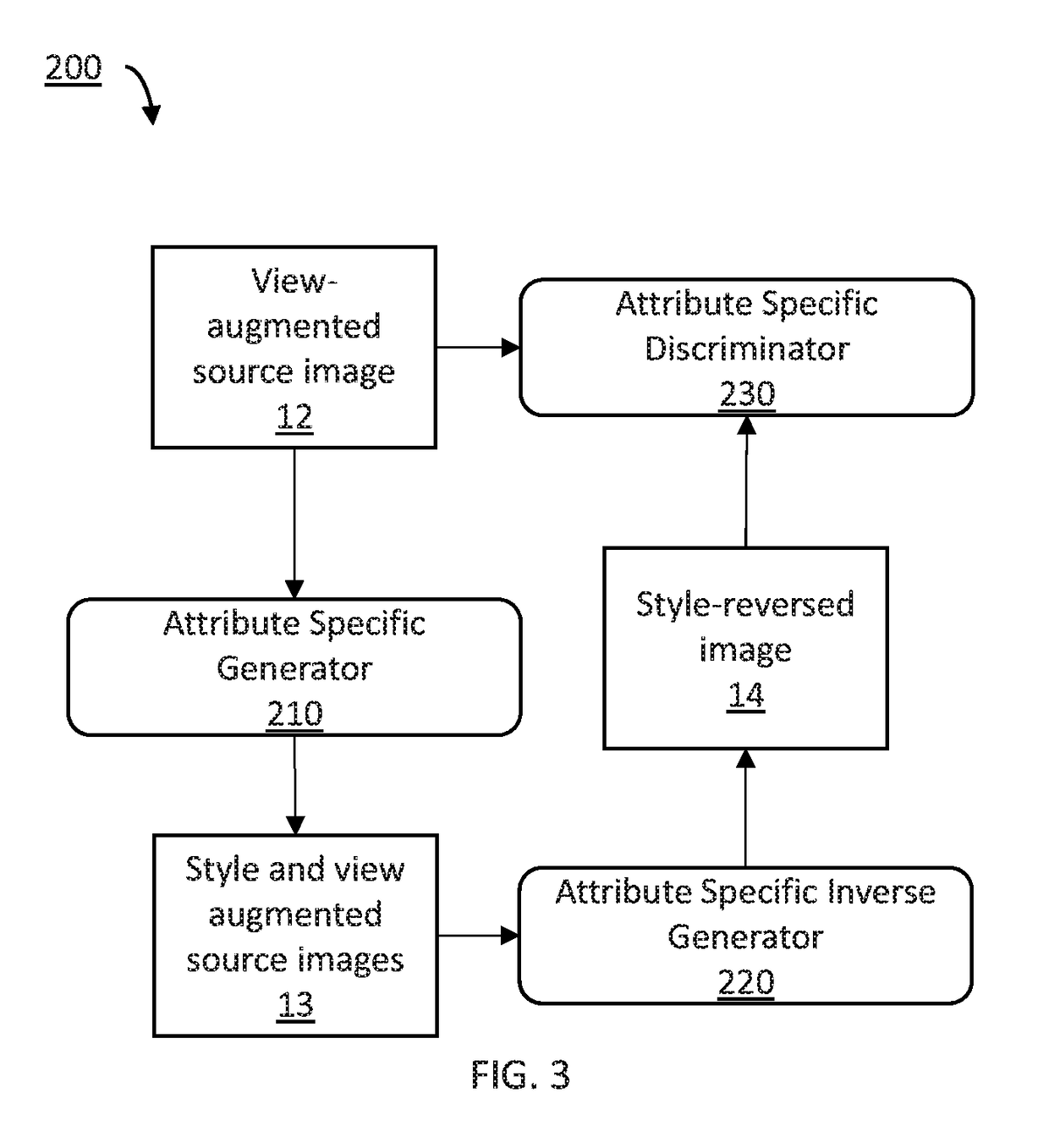
Systems and methods for performing domain adaptation include collecting a labeled source image having a view of an object. Viewpoints of the object in the source image are synthesized to generate view augmented source images. Photometrics of each of the viewpoints of the object are adjusted to generate lighting and view augmented source images. Features are extracted from each of the lighting and view augmented source images with a first feature extractor and from captured images captured by an image capture device with a second feature extractor. The extracted features are classified using domain adaptation with domain adversarial learning between extracted features of the captured images and extracted features of the lighting and view augmented source images. Labeled target images are displayed corresponding to each of the captured images including labels corresponding to classifications of the extracted features of the captured images.
Owner:NEC CORP
Picture classification method based on deep transfer learning
ActiveCN109523018ACharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesFeature extractionClassification methods
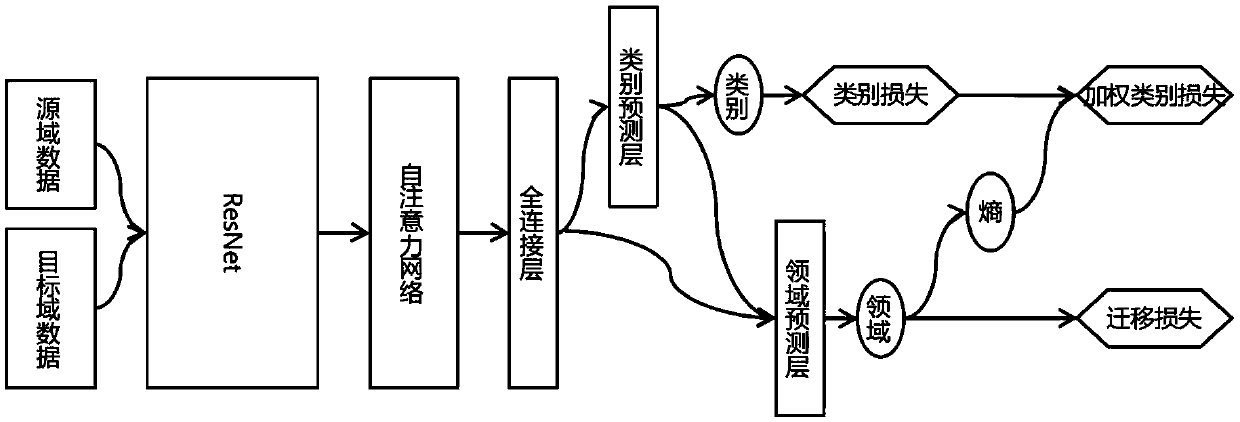
The invention requests to protect a picture classification method based on deep transfer learning. wherein the domain adaptation at least comprises data of two domains; wherein the domains are respectively a source domain and a target domain; wherein the source domain data is marked sample data, and the source domain data is marked sample data. The method comprises the following steps: 1) a data preparation stage: preparing source domain data and target domain data, The method comprises the steps of (1) establishing a target category set, (2) establishing a feature extraction model, (3) establishing a basic feature extraction model by using ResNet and a self-attention network, (4) establishing a domain confrontation model, and (5) predicting a sample category and a sample domain by using the domain confrontation model. Wherein domain marking is conducted on a source domain sample and a target domain sample, and a loss function based on the sample migration weight is set, and 5, prediction is conducted on target domain data, a category prediction result serves as a final result, the marking cost is reduced, and the purpose of knowledge migration is achieved.
Owner:深圳市快麦科技有限公司
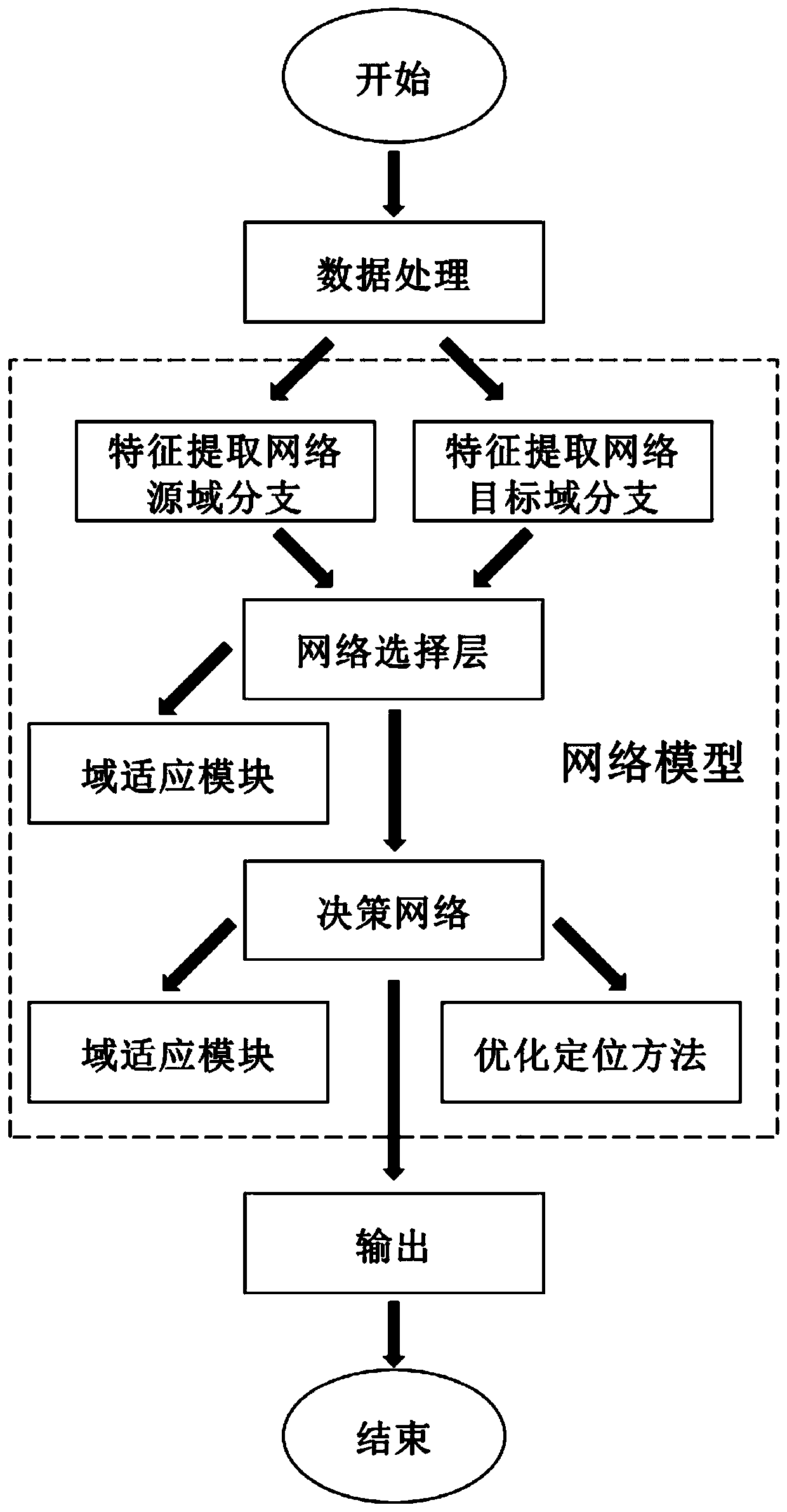
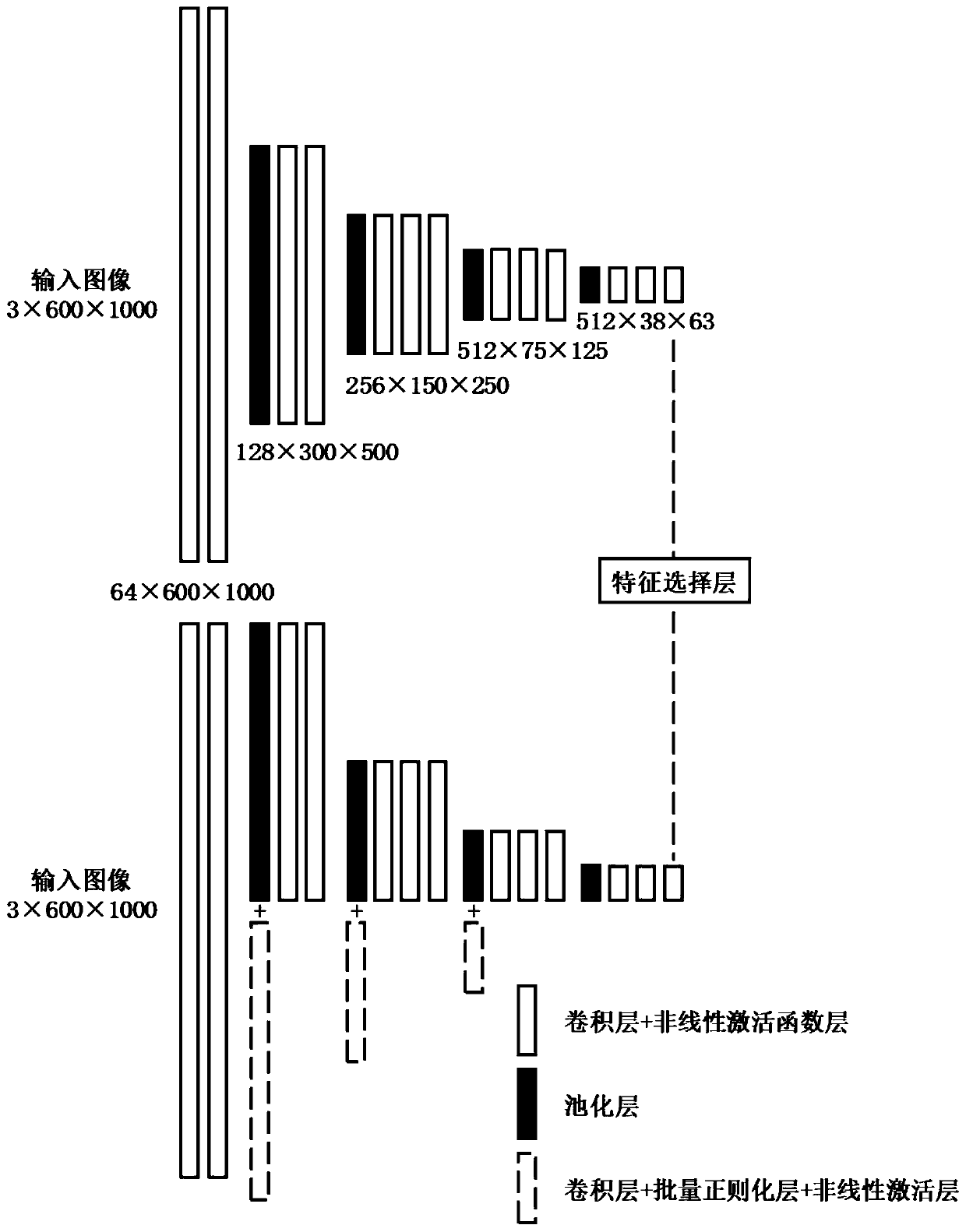
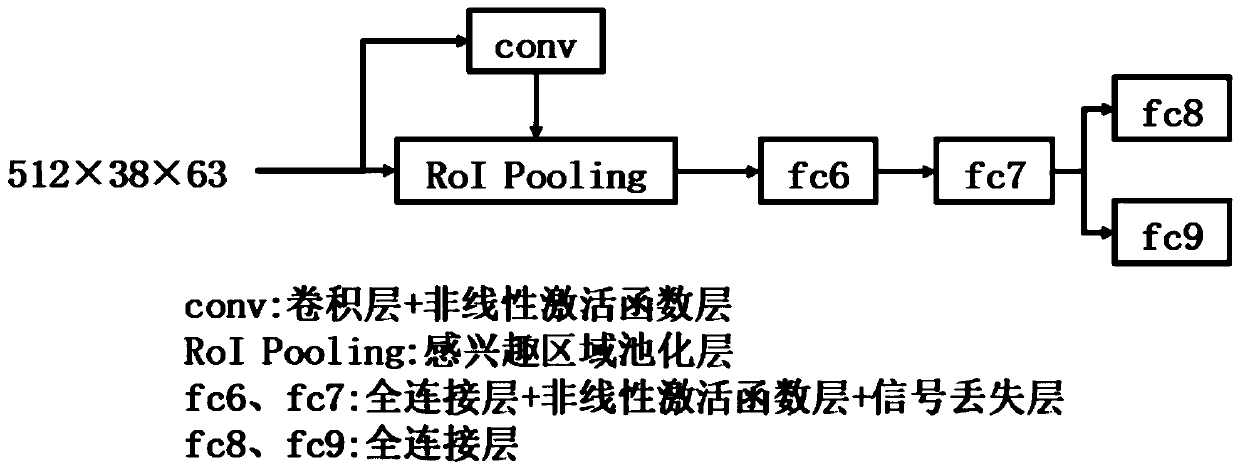
Target detection positioning optimization method based on unsupervised domain adaptation
ActiveCN109977918AImprove object detection performanceAvoid inaccuraciesInternal combustion piston enginesCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature extractionData set
The invention discloses a target detection positioning optimization method based on unsupervised domain adaptation, which aims to solve the technical problem that an existing domain adaptation targetdetection method is insufficient in positioning capability for the position of an object under the condition that the object migrates from a labeled data set to an unlabeled data set. The method comprises the steps of (1) processing the data, (2) constructing a model, (3) defining a loss function, (4) training the model and (5) verifying the model. The present invention provides a new feature extraction network model which is suitable for the unlabeled data set, the positioning is more optimized, and the representation effect of the object positioning is good.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
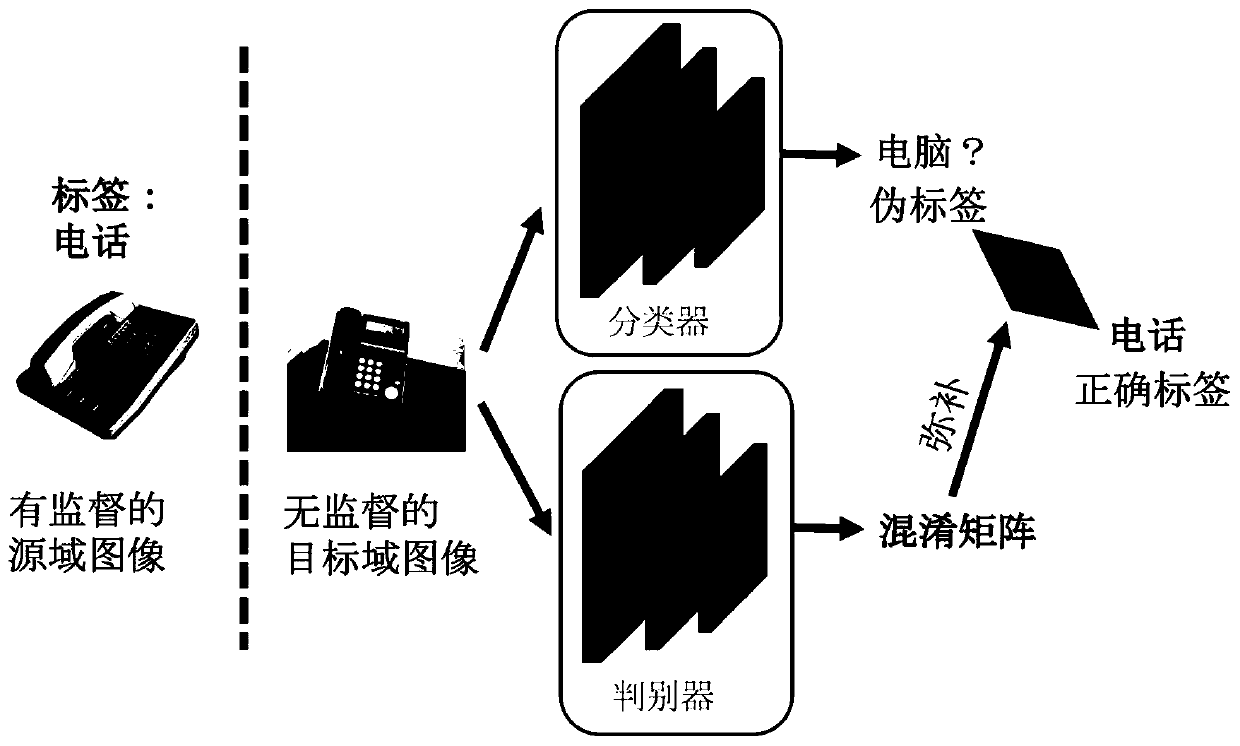
Unsupervised domain adaptation method based on adversarial learning loss function
ActiveCN110837850AEfficiently match feature distributionsMatch feature distributionCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature extractionA domain
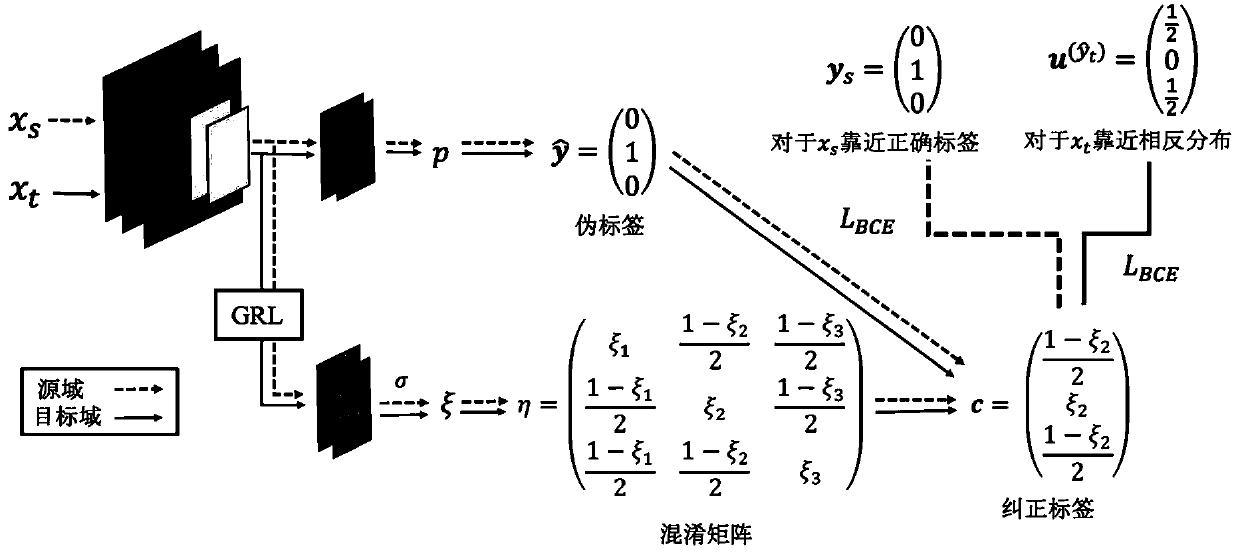
The invention discloses an unsupervised domain adaptation method based on an adversarial learning loss function, and the method comprises the steps: (1), generating a high-level feature of a source domain image through a feature extraction network G, carrying out the cross entropy loss with a real label through a classifier C, generating a confusion matrix through a domain discriminator D, and correcting a pseudo label into the real label; and (2) generating high-level features of the target domain image through a feature extraction network G, generating pseudo tags through a classifier C, generating a confusion matrix of the high-level features through a domain discriminator D, and correcting the pseudo tags to be in opposite distribution. (3) confronting and optimizing the loss functionby a feature generator and a discriminator. In addition, for the confusion matrix on the target domain, a correction label is generated and serves as a label of the target domain, and the classifier is optimized. By utilizing the method and the device, the noise of the pseudo tag can be corrected in unsupervised domain adaptation, and the distribution difference between the domains is matched, sothat the classification precision of the target domain is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
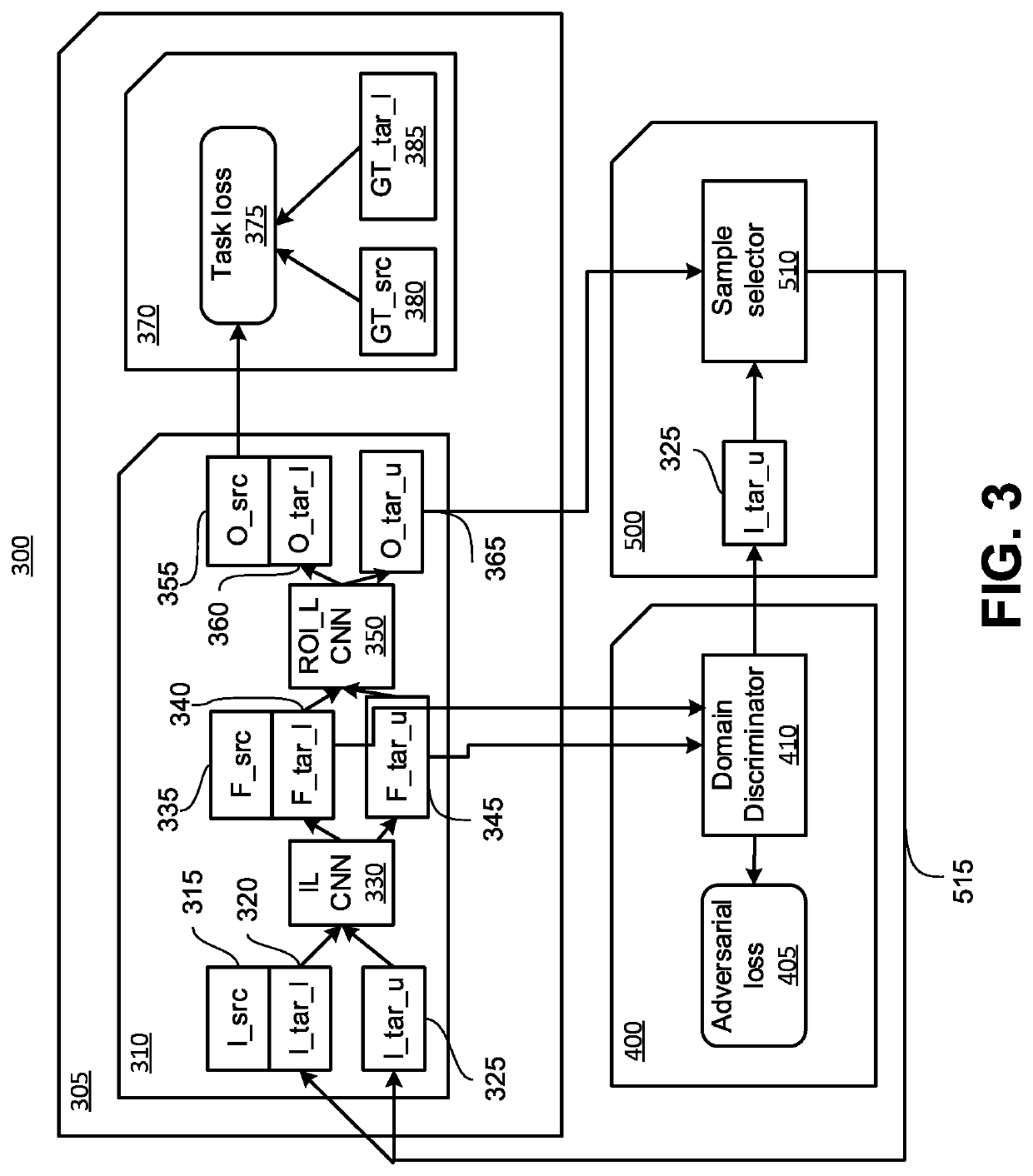
Domain adaptation for instance detection and segmentation
Systems and methods for domain adaptation are provided. The system aligns image level features between a source domain and a target domain based on an adversarial learning process while training a domain discriminator. The system selects, using the domain discriminator, unlabeled samples from the target domain that are far away from existing annotated samples from the target domain. The system selects, based on a prediction score of each of the unlabeled samples, samples with lower prediction scores. The system annotates the samples with the lower prediction scores.
Owner:NEC CORP
Domain adaptation via class-balanced self-training with spatial priors
InactiveUS20190130220A1Reducing target segmentation lossReduce segmentationImage enhancementImage analysisSelf trainingDomain adaptation
A vehicle, system and method of navigating a vehicle. The vehicle and system include a digital camera for capturing a target image of a target domain of the vehicle, and a processor. The processor is configured to: determine a target segmentation loss for training the neural network to perform semantic segmentation of a target image in a target domain, determine a value of a pseudo-label of the target image by reducing the target segmentation loss while providing aa supervision of the training over the target domain, perform semantic segmentation on the target image using the trained neural network to segment the target image and classify an object in the target image, and navigate the vehicle based on the classified object in the target image.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Robust anomaly detection and regularized domain adaptation of classifiers with application to internet packet-flows
InactiveUS9038172B2Maximize the aggregate statistical significance of “Area maximizationMathematical modelsMemory loss protectionCredit cardTraffic capacity
Sound, robust methods identify the most suitable, parsimonious set of tests to use with respect to prioritized, sequential anomaly detection in a collected batch of sample data. While the focus is on detecting anomalies in network traffic flows and classifying network traffic flows into application types, the methods are also applicable to other anomaly detection and classification application settings, including detecting email spam, (e.g. credit card) fraud detection, detecting imposters, unusual event detection (for example, in images and video), host-based computer intrusion detection, detection of equipment or complex system failures, as well as of anomalous measurements in scientific experiments.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
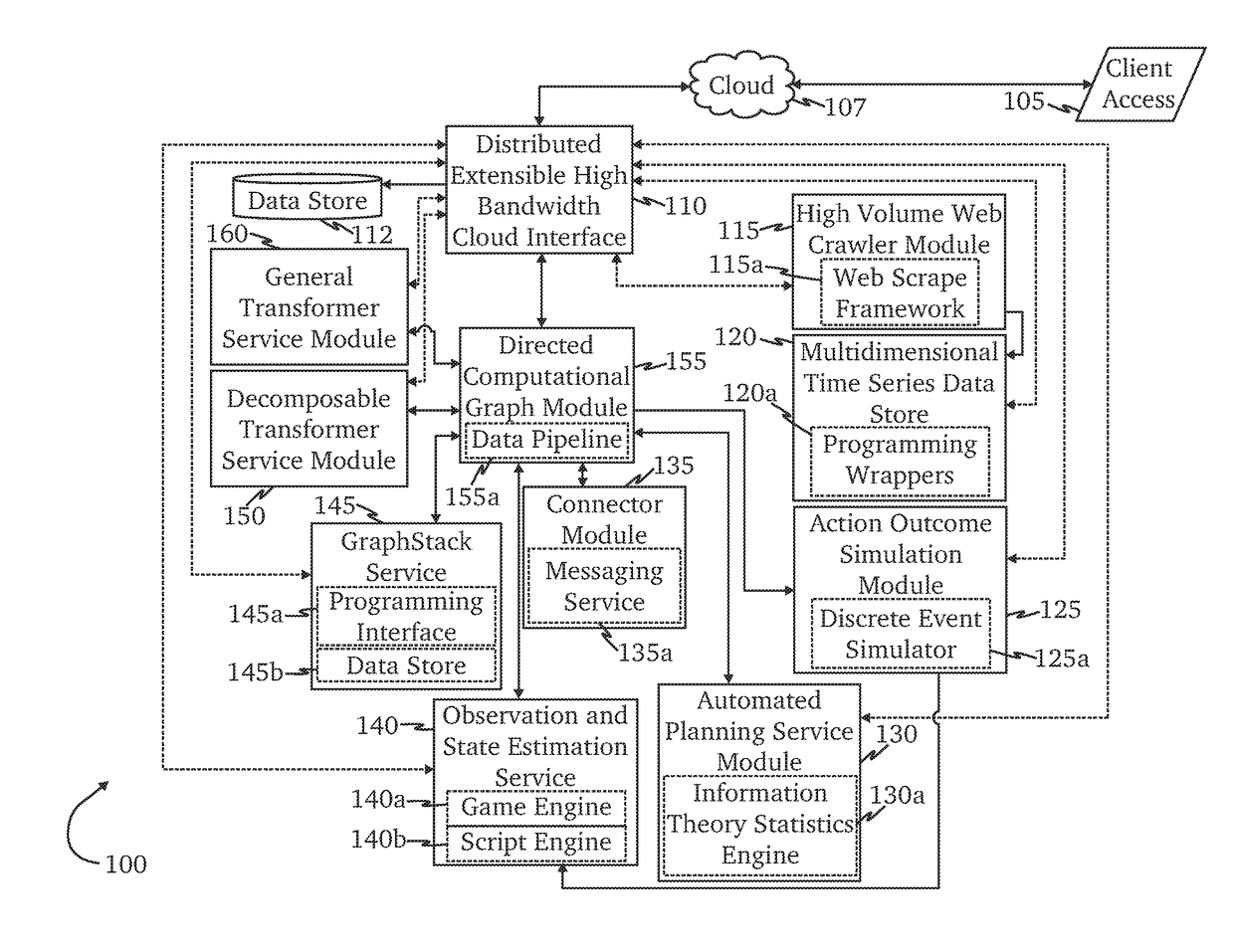
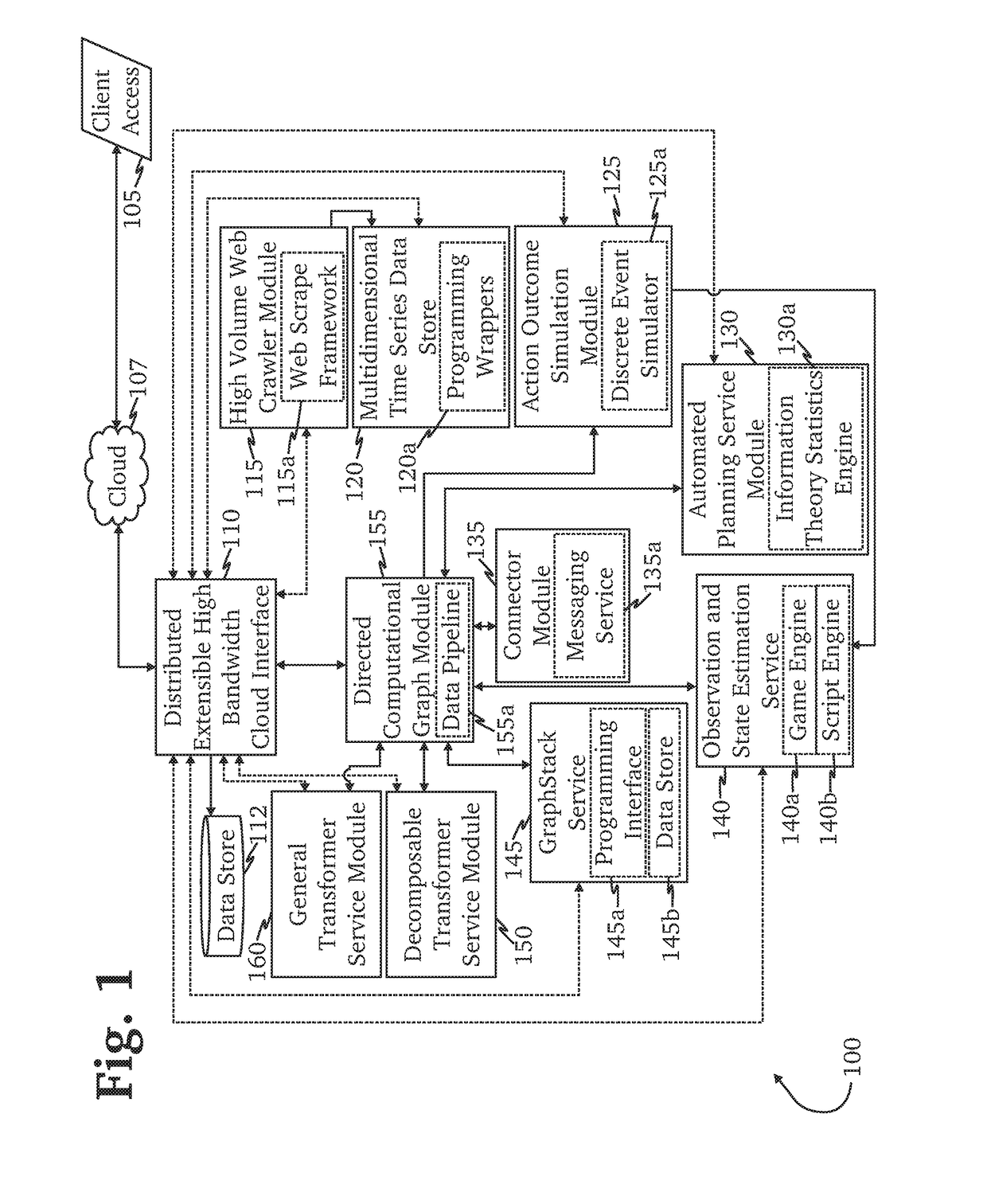
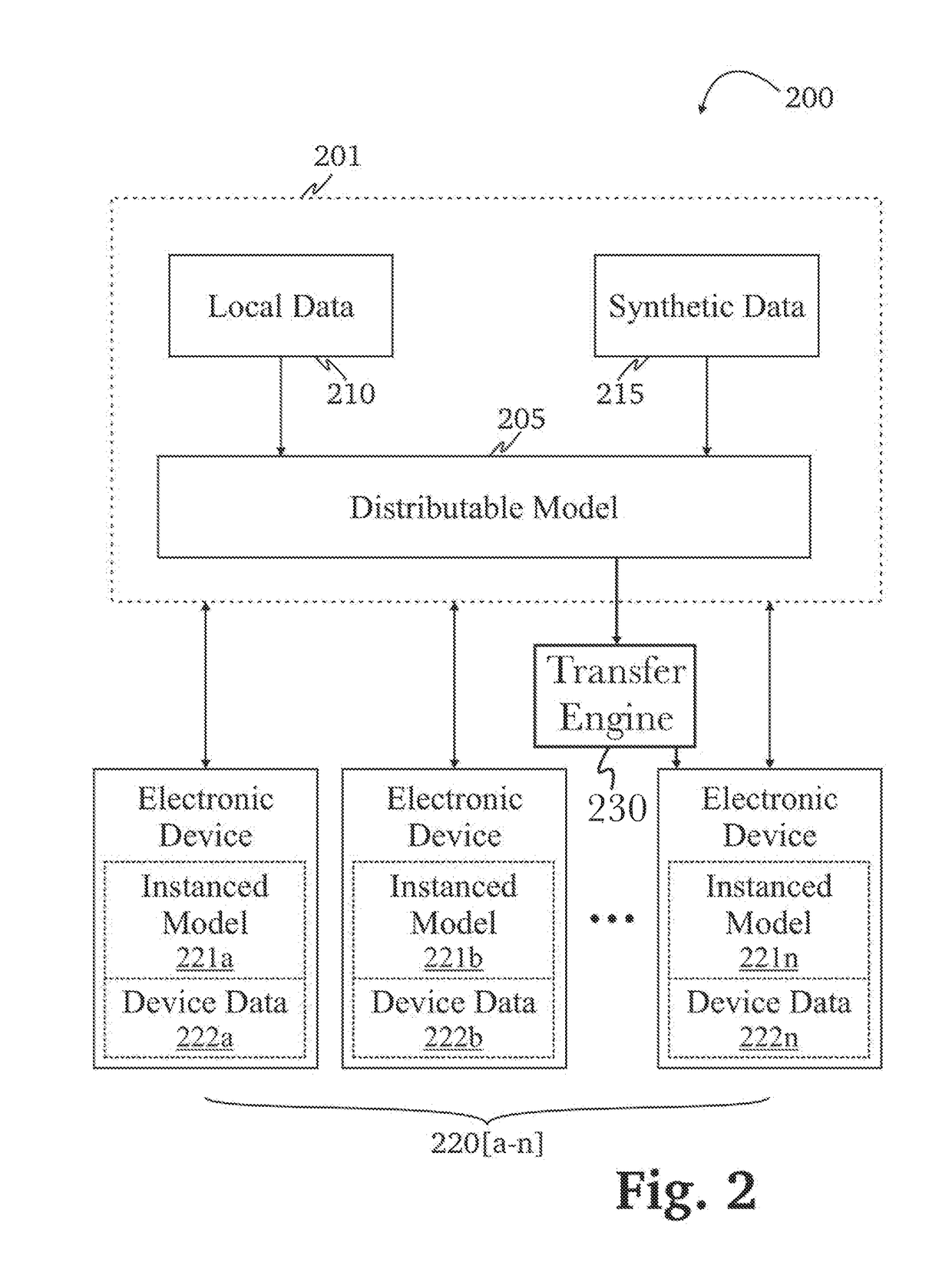
Transfer learning and domain adaptation using distributable data models
ActiveUS20180197111A1Increase heightImprove distributable modelDatabase distribution/replicationCharacter and pattern recognitionNetwork connectionTheoretical computer science
A system for transfer learning and domain adaptation using distributable data models is provided, comprising a network-connected distributable model configured to serve instances of a plurality of distributable models; and a directed computation graph module configured to receive at least an instance of at least one of the distributable models from the network-connected computing system, create a second dataset from machine learning performed by a transfer engine, train the instance of the distributable model with the second dataset, and generate an update report based at least in part by updates to the instance of the distributable model.
Owner:QPX LLC
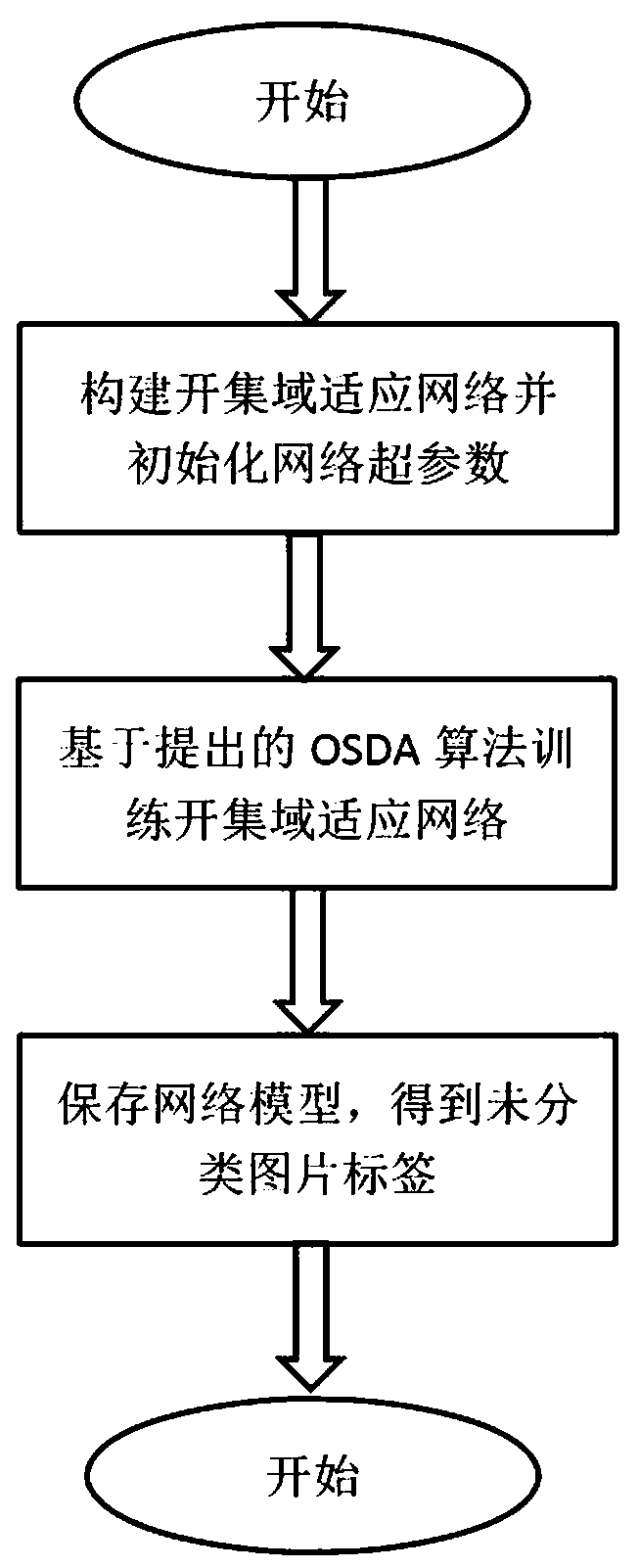
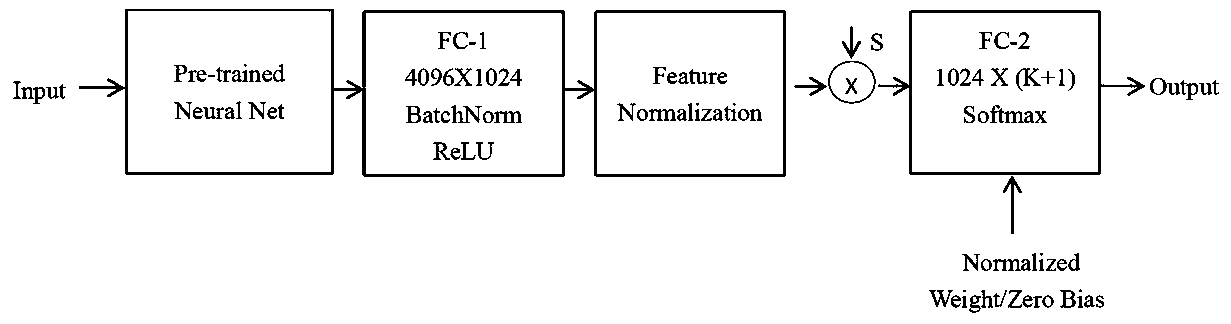
Open set domain adaptation method and system based on entropy minimization
InactiveCN110750665AImprove robustnessStable trainingCharacter and pattern recognitionStill image data clustering/classificationData setFeature extraction
The invention provides an open set domain adaptation method based on entropy minimization. The open set domain adaptation method comprises the steps of creating an open set domain adaptation network, and initializing network hyper-parameters; inputting a source domain picture and a target domain picture into an open set domain adaptive network, obtaining picture depth features through a networkfeature extraction layer, and then obtaining prediction probability vectors of various categories through a softmax layer according to a feature map; calculating an entropy loss function by using a known category prediction probability vector and a picture label so as to correctly identify a common category; on the basis, calculating binary cross entropy and a binary diversity loss function by using an unknown category prediction probability value so as to correctly classify unknown categories, updating network parameters by using a back propagation gradient until a loss function value is minimum, and stopping training the network; and storing the network model and the training result, and introducing the target domain data set into the network model to obtain a final target domain label.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
method, device, system and medium for text information extraction based on Domain adaptation
ActiveCN108664589AReduce the differenceImprove portabilityNatural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsDomain adaptationSpeech recognition
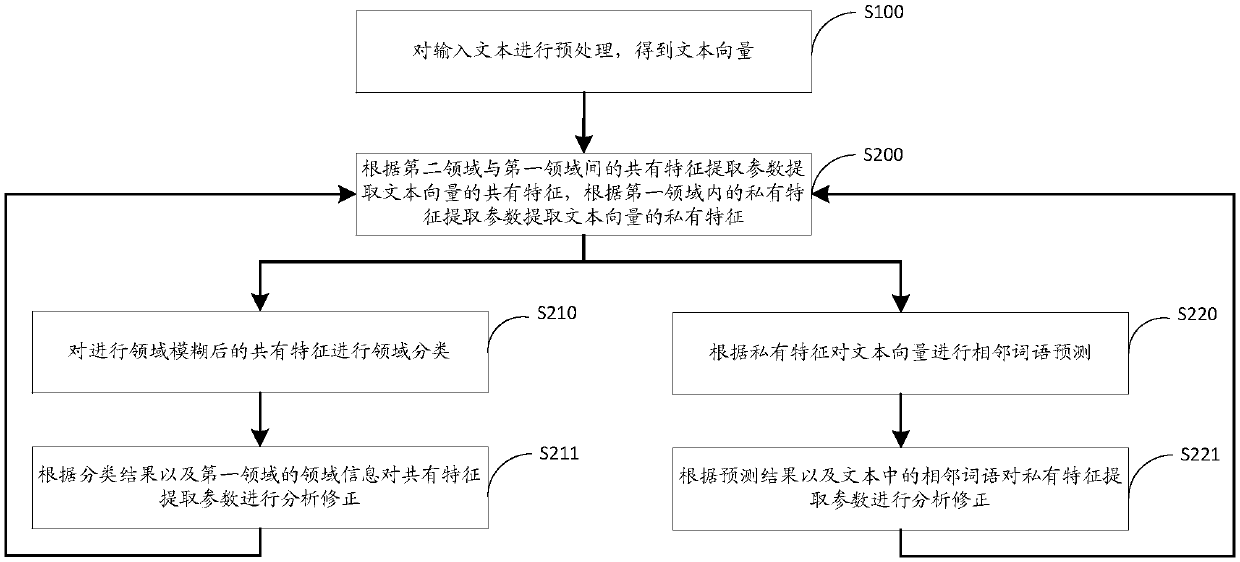
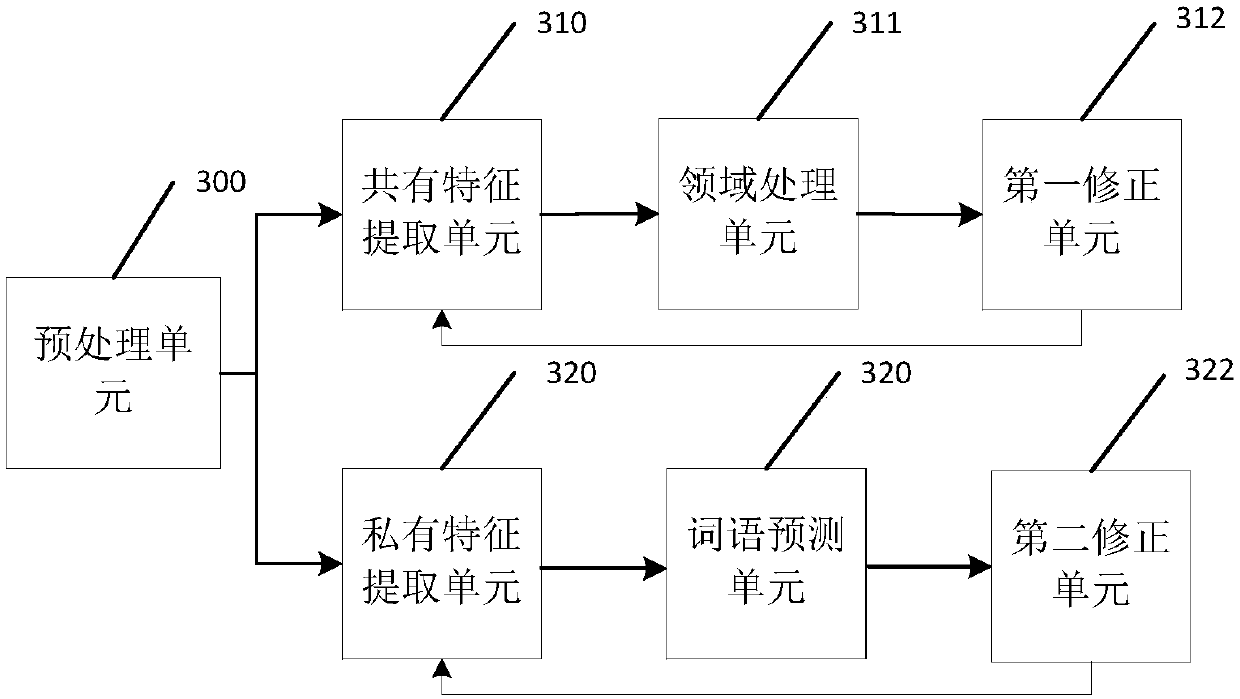
The invention discloses a text information extraction method based on the Domain adaptation, comprises the following steps of:preprocessing the input text to obtain a text vector; between the second domain and the first domain,extracting a common feature of a text vector according to a common feature extraction parameter,and in the first domain extracting a private feature of the text vector according to the private feature extraction parameter; carrying out field classification on common features after a field blurring is carried out; analyzing and correcting a common feature extraction parameters according to a classification result and a domain information of a first field; performing adjacent word prediction on the text vector according to a private feature; analyzing and correcting the private feature extraction parameters according to a prediction result and a adjacent words in the text. The method can improve text analysis and extraction capability in social media and other fields. The invention also discloses a text information extraction device and system based on a field adaptation and a readable storage medium, and a text information extraction device has the above beneficial effects.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Domain adaptive image semantic segmentation method based on GAN
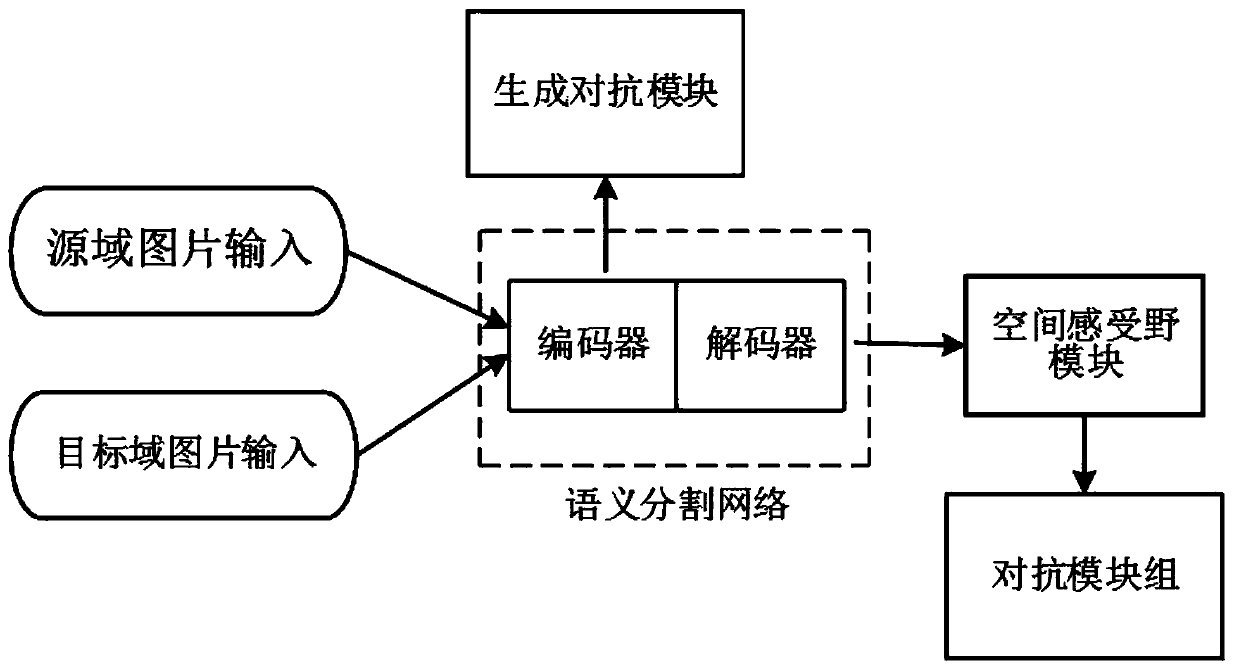
ActiveCN110533044AImprove accuracySemantic segmentation results are goodCharacter and pattern recognitionData setA domain
The invention relates to the technical field of image semantic segmentation, in particular to a domain adaptive image semantic segmentation method based on GAN. The method comprises a semantic segmentation network, a generative adversarial module, a spatial receptive field module and an adversarial module group. The target domain is a label-free data set, the source domain is a label data set, andthe task is to obtain a semantic segmentation label graph of the target domain. The inside of a classical image semantic segmentation network can be regarded as an encoder and a decoder, and an inputimage is encoded and decoded to obtain an output image with the same size. Corresponding adversarial training auxiliary modules are added to an encoder and a decoder respectively to reduce the domaindrift problem caused by domain adaptation. According to the invention, the problem of low accuracy of unsupervised image semantic segmentation in the prior art is solved.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Learning method and learning device for generation of virtual feature maps whose characteristics are same as or similar to those of real feature maps by using GAN capable of being applied to domain adaptation to be used in virtual driving environments
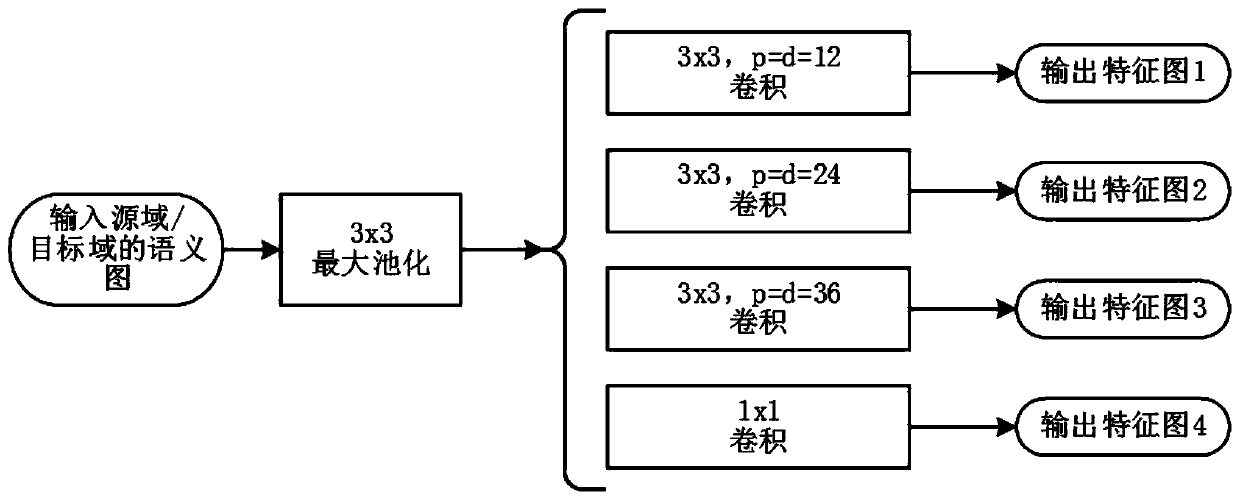
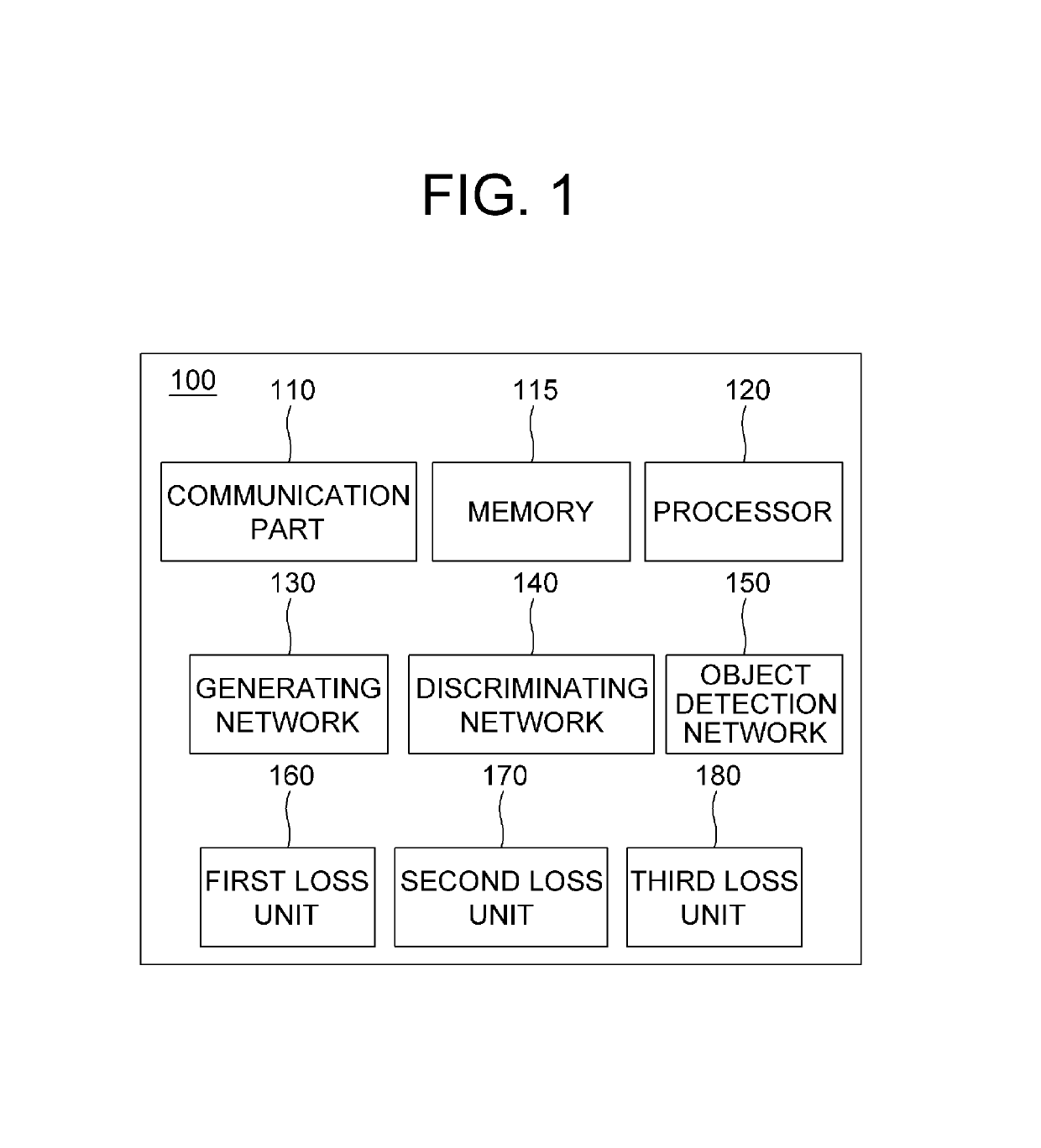
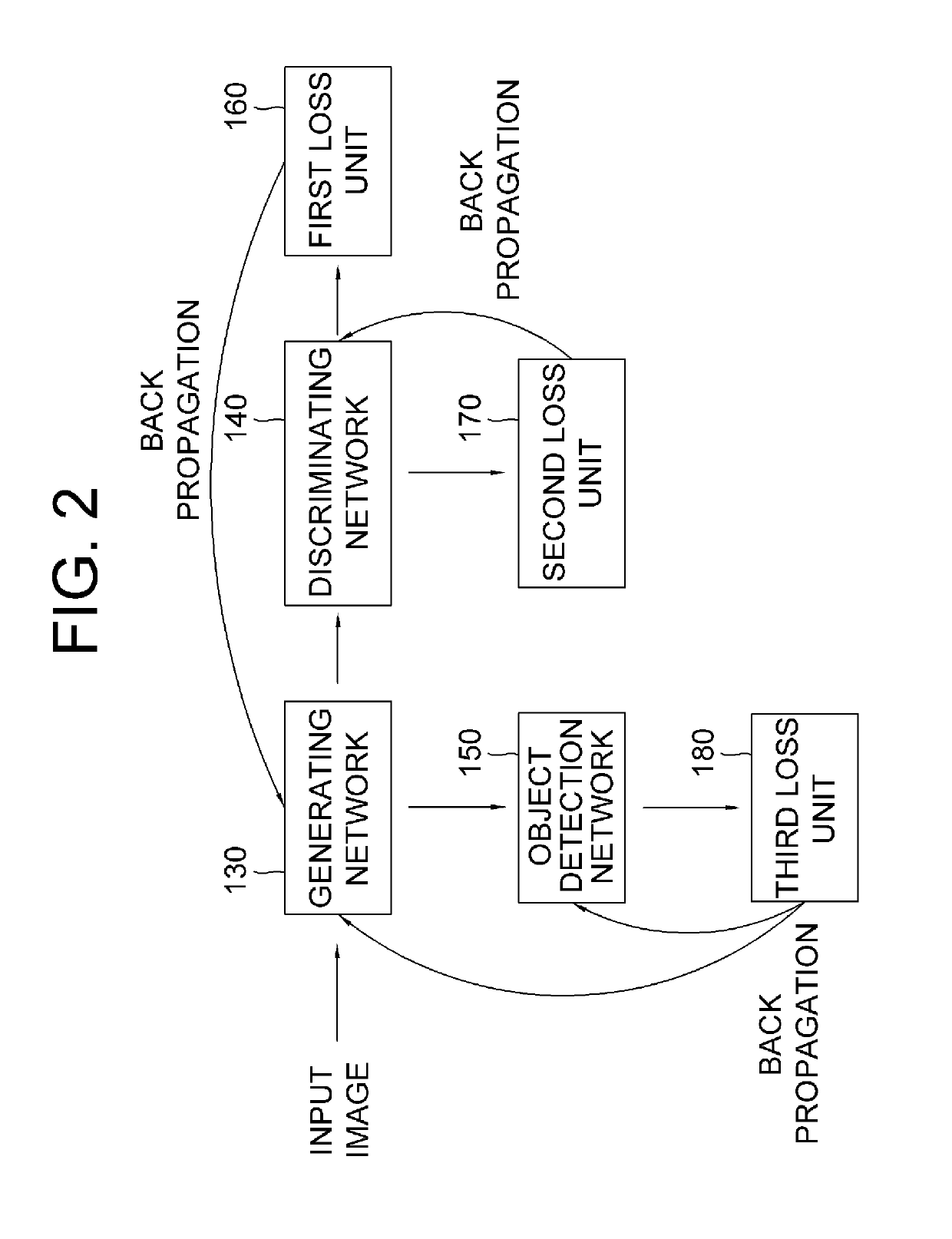
ActiveUS10373026B1Increase probability2D-image generationScene recognitionStudy methodsLearning methods
A method of learning for deriving virtual feature maps from virtual images, whose characteristics are same as or similar to those of real feature maps derived from real images, by using GAN including a generating network and a discriminating network capable of being applied to domain adaptation is provided to be used in virtual driving environments. The method includes steps of: (a) a learning device instructing the generating network to apply convolutional operations to an input image, to thereby generate a output feature map, whose characteristics are same as or similar to those of the real feature maps; and (b) instructing a loss unit to generate losses by referring to an evaluation score, corresponding to the output feature map, generated by the discriminating network. By the method using a runtime input transformation, a gap between virtuality and reality can be reduced, and annotation costs can be reduced.
Owner:STRADVISION
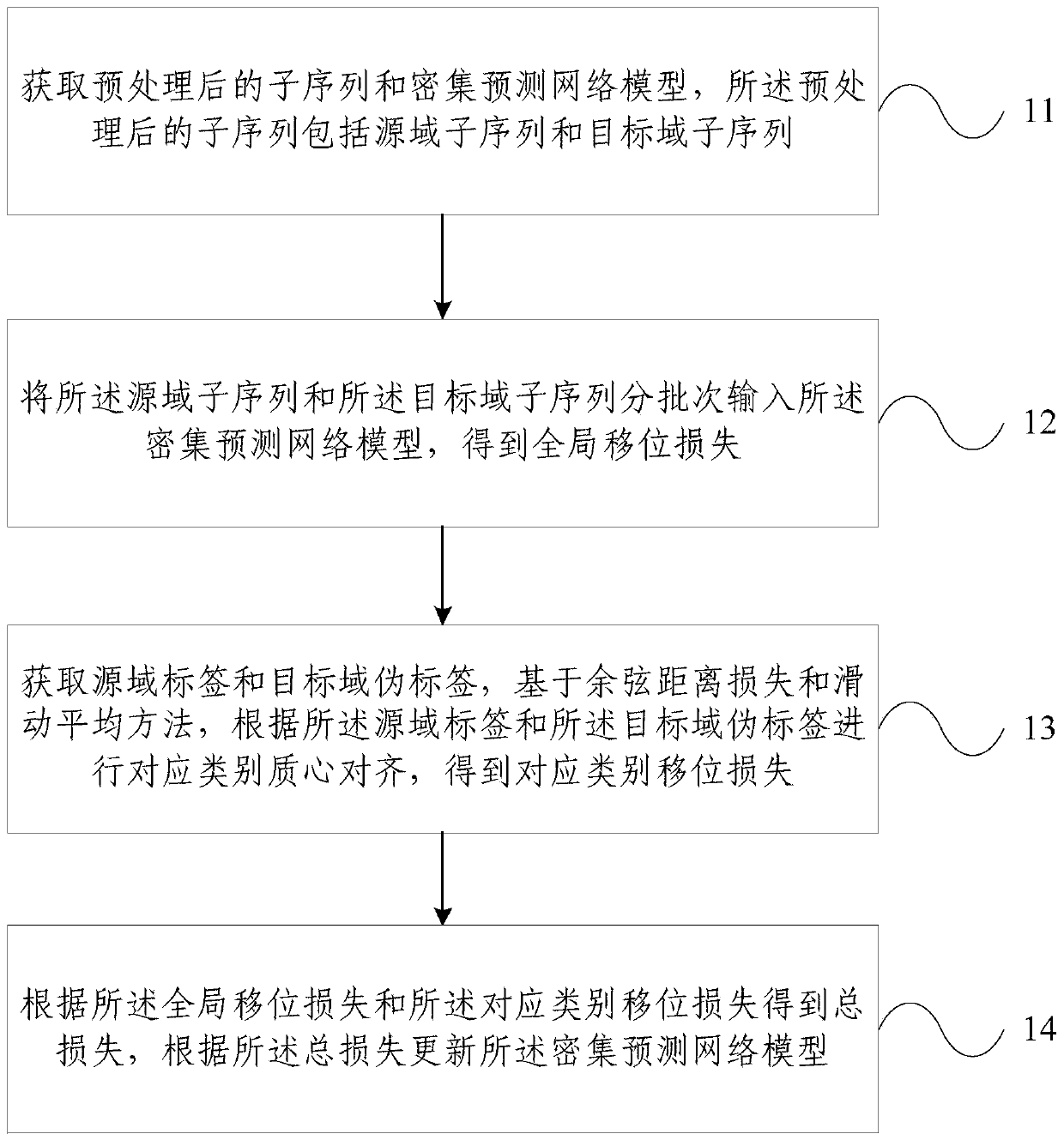
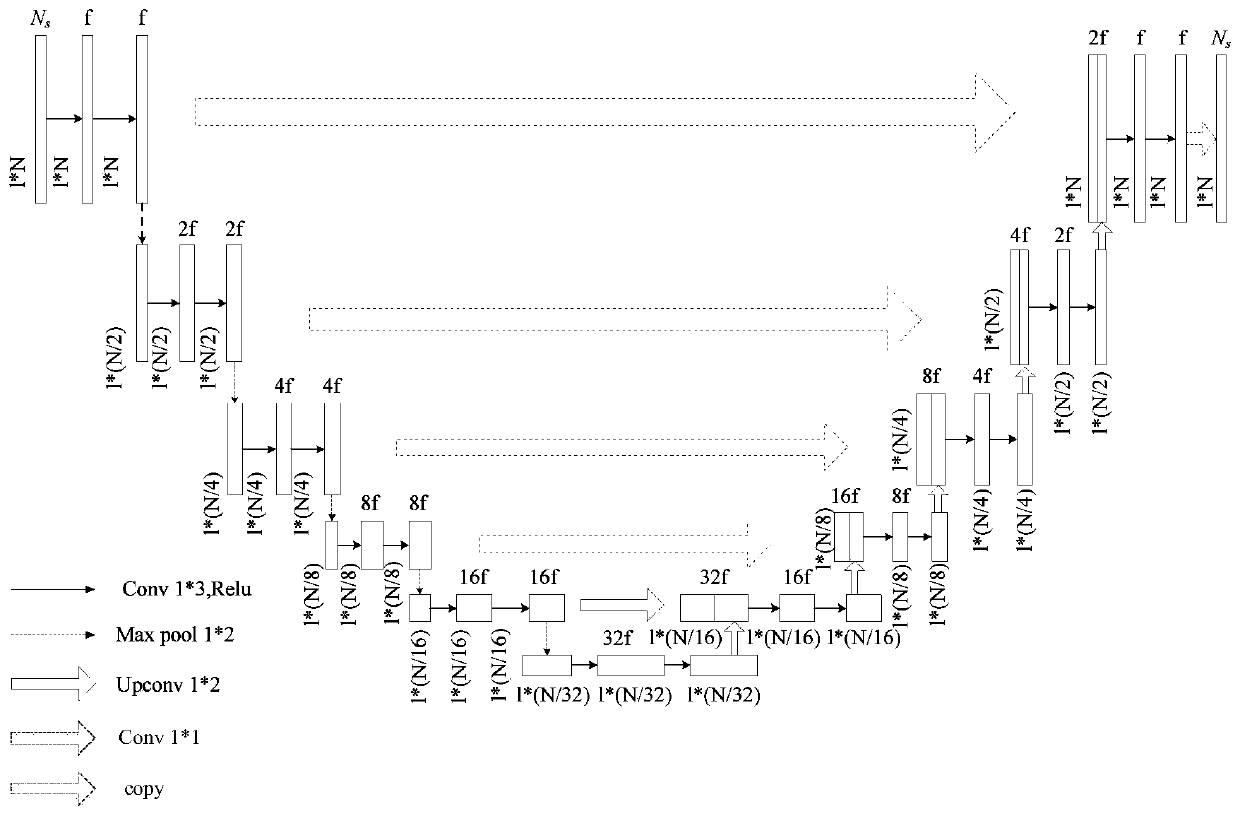
A transfer learning method and device
InactiveCN109948741AImprove performanceImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionMoving averageAlgorithm
The embodiment of the invention provides a transfer learning method and device, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a preprocessed sub-sequence and a dense prediction network model, whereinthe preprocessed sub-sequence comprises a source domain sub-sequence and a target domain sub-sequence; Inputting the source domain sub-sequence and the target domain sub-sequence into a dense prediction network model in batches to obtain global shift loss; Obtaining a source domain label and a target domain pseudo label, and performing corresponding category centroid alignment according to the source domain label and the target domain pseudo label on the basis of a cosine distance loss and moving average method to obtain corresponding category shift loss; And obtaining total loss according tothe global shift loss and the corresponding category shift loss, and updating the dense prediction network model according to the total loss. According to the migration learning method and device provided by the embodiment of the invention, a multi-level unsupervised domain adaptation method is provided, alignment of edge distribution and condition distribution is completed, migration of a time series data intensive prediction model is realized, and the performance is more superior.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com