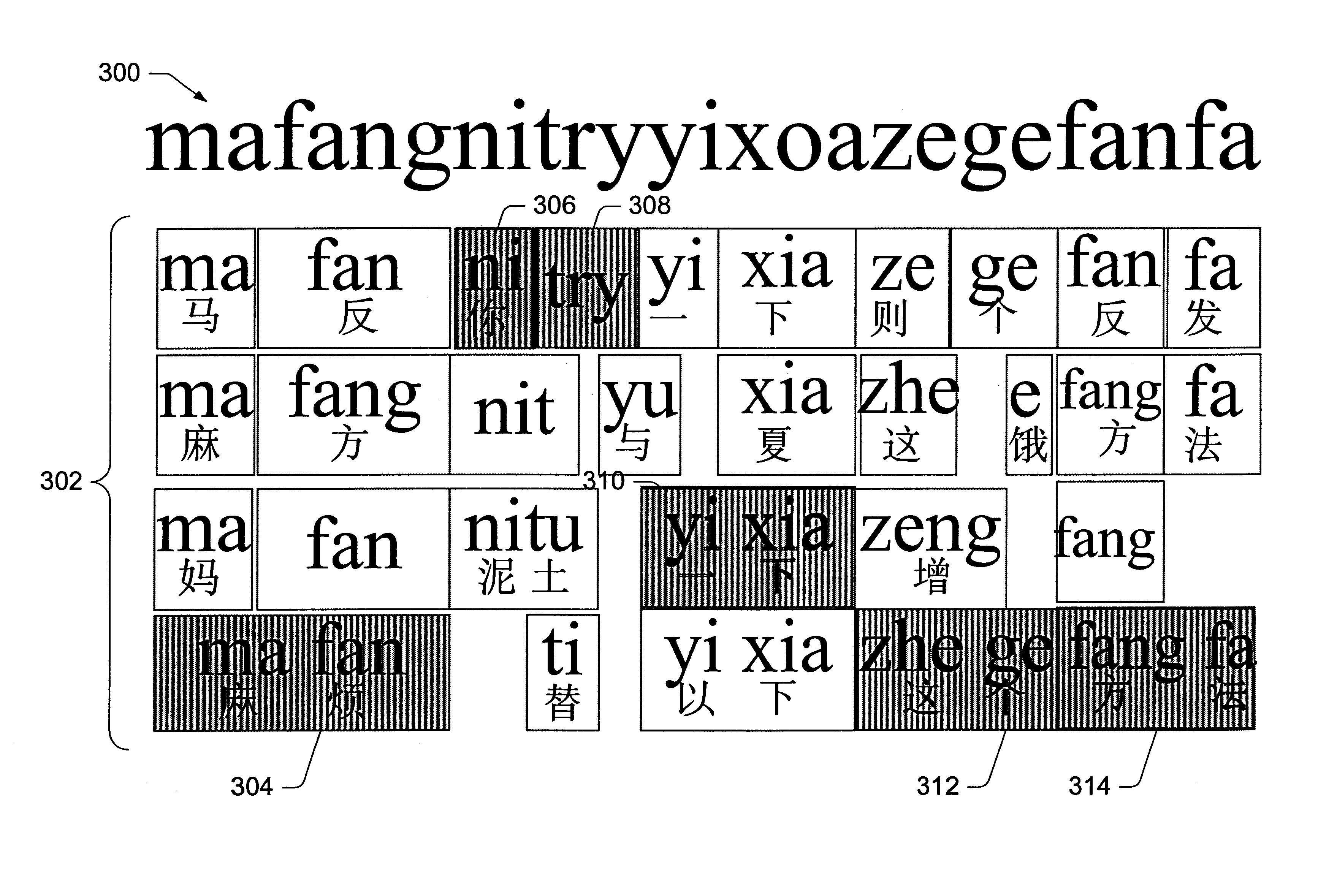Patents
Literature
1693 results about "Language model" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
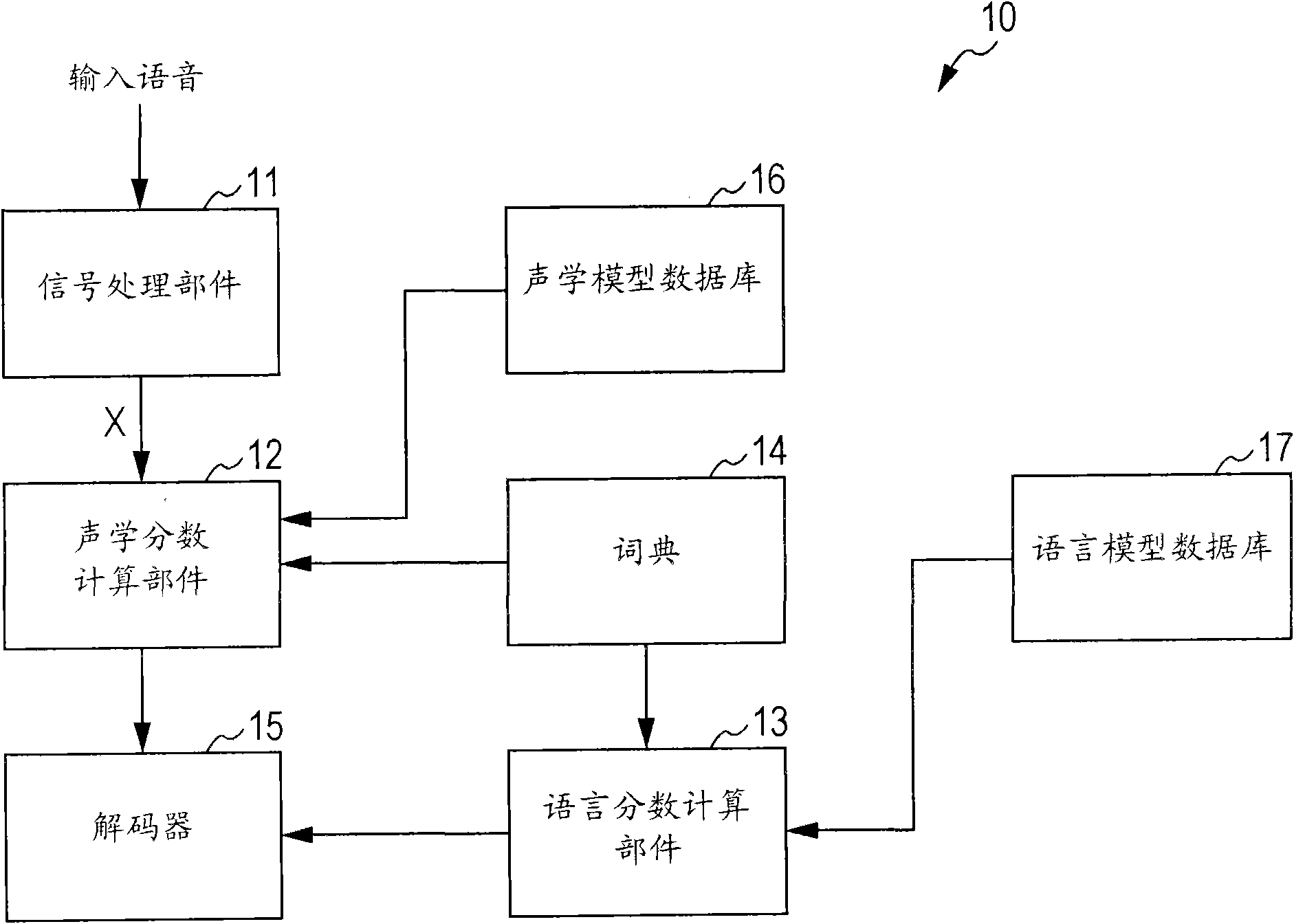
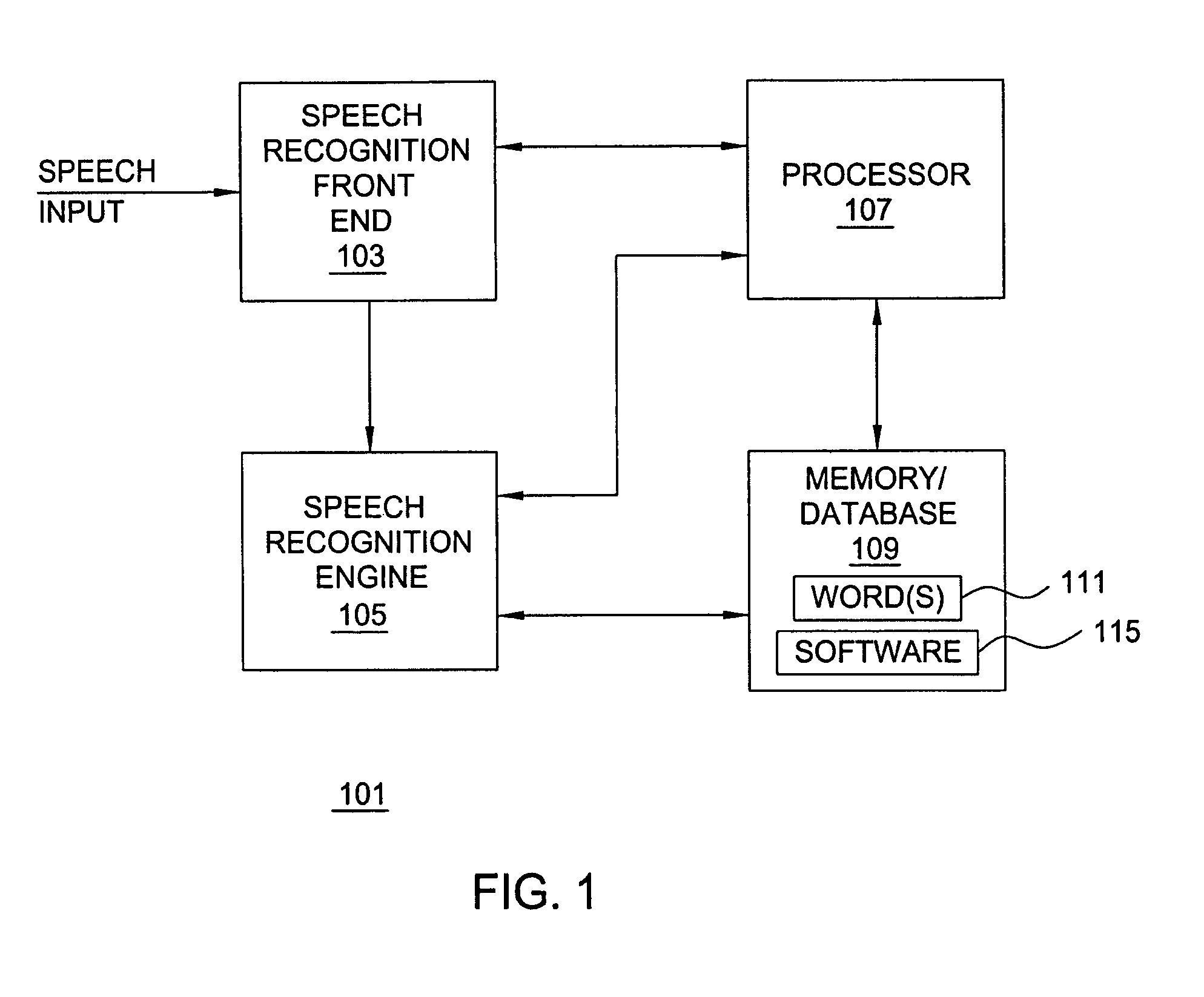
A statistical language model is a probability distribution over sequences of words. Given such a sequence, say of length m, it assigns a probability P(w₁,…,wₘ) to the whole sequence. The language model provides context to distinguish between words and phrases that sound similar. For example, in American English, the phrases "recognize speech" and "wreck a nice beach" sound similar, but mean different things.
Semantic object synchronous understanding implemented with speech application language tags
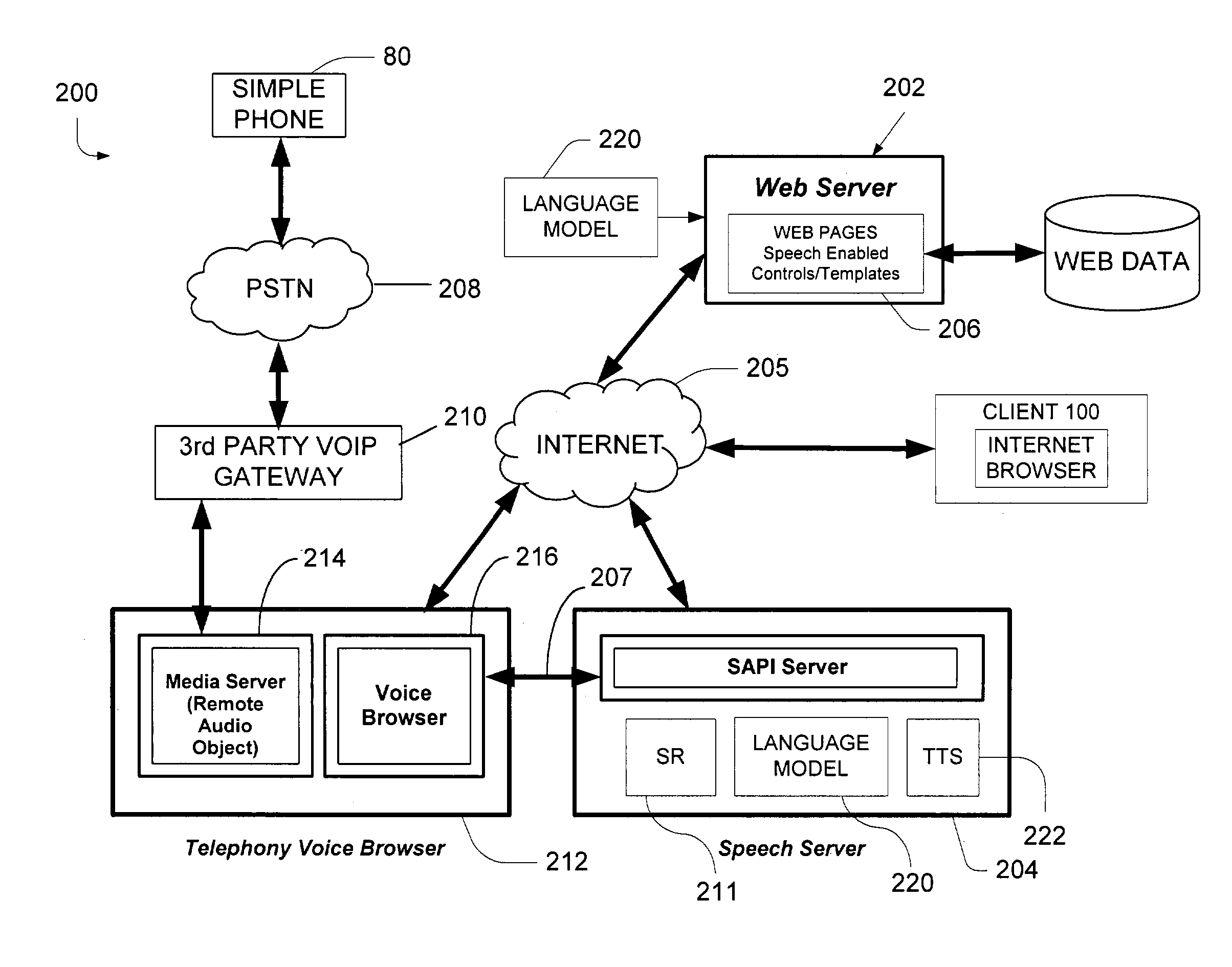
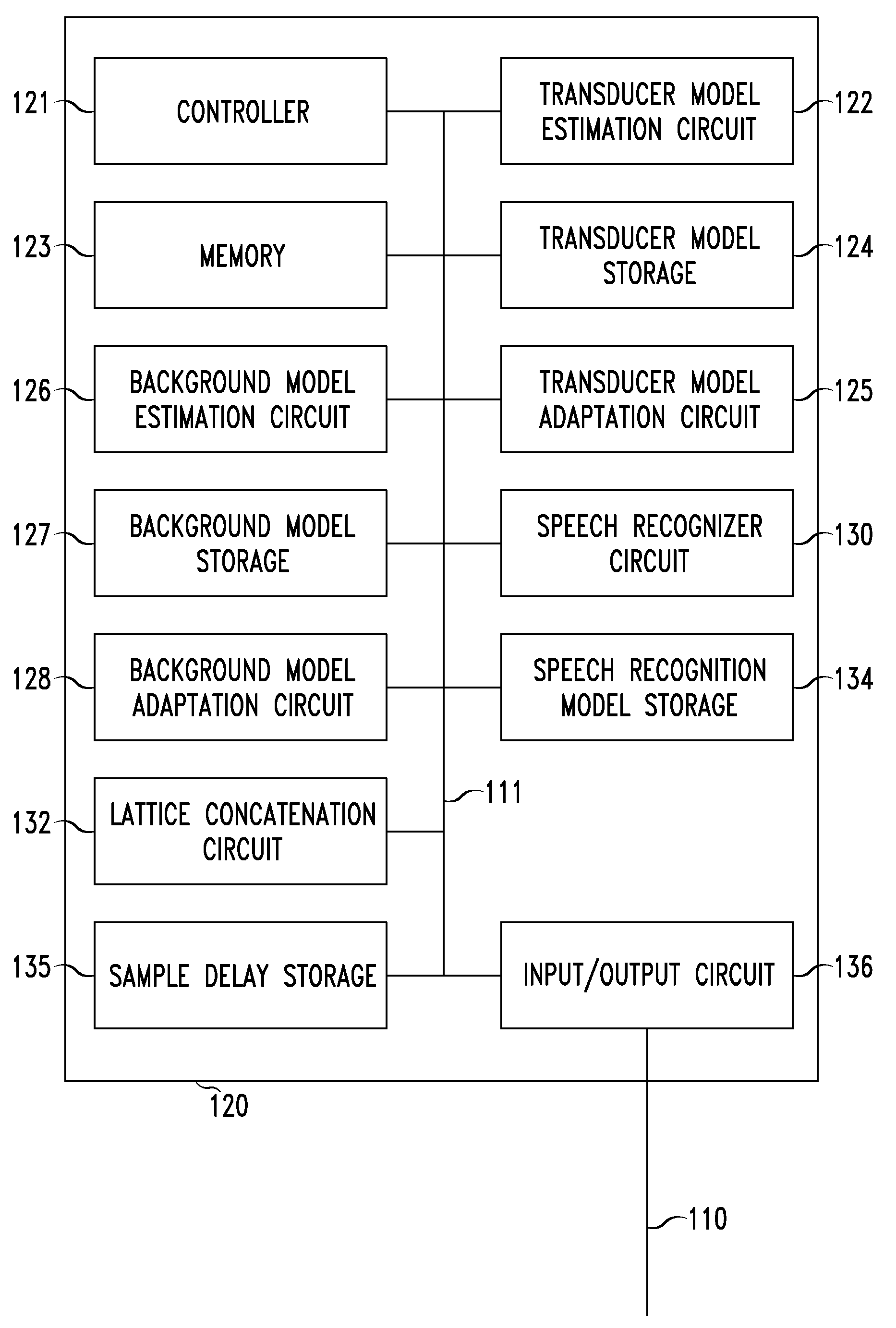
ActiveUS7200559B2Sound input/outputSpeech recognitionSpeech comprehensionApplication programming interface
A speech understanding system includes a language model comprising a combination of an N-gram language model and a context-free grammar language model. The language model stores information related to words and semantic information to be recognized. A module is adapted to receive input from a user and capture the input for processing. The module is further adapted to receive SALT application program interfaces pertaining to recognition of the input. The module is configured to process the SALT application program interfaces and the input to ascertain semantic information pertaining to a first portion of the input and output a semantic object comprising text and semantic information for the first portion by accessing the language model, wherein performing recognition and outputting the semantic object are performed while capturing continues for subsequent portions of the input.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
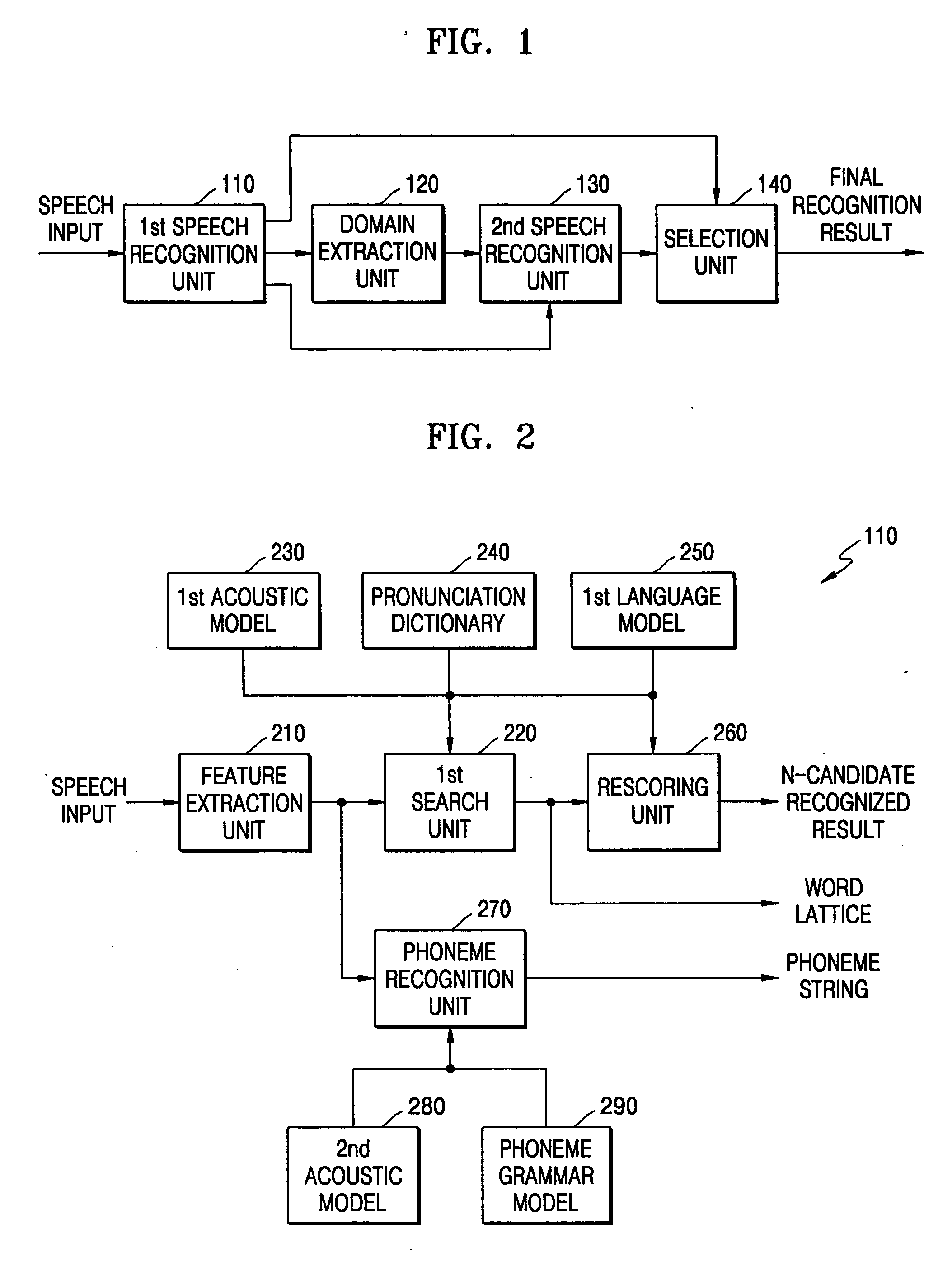
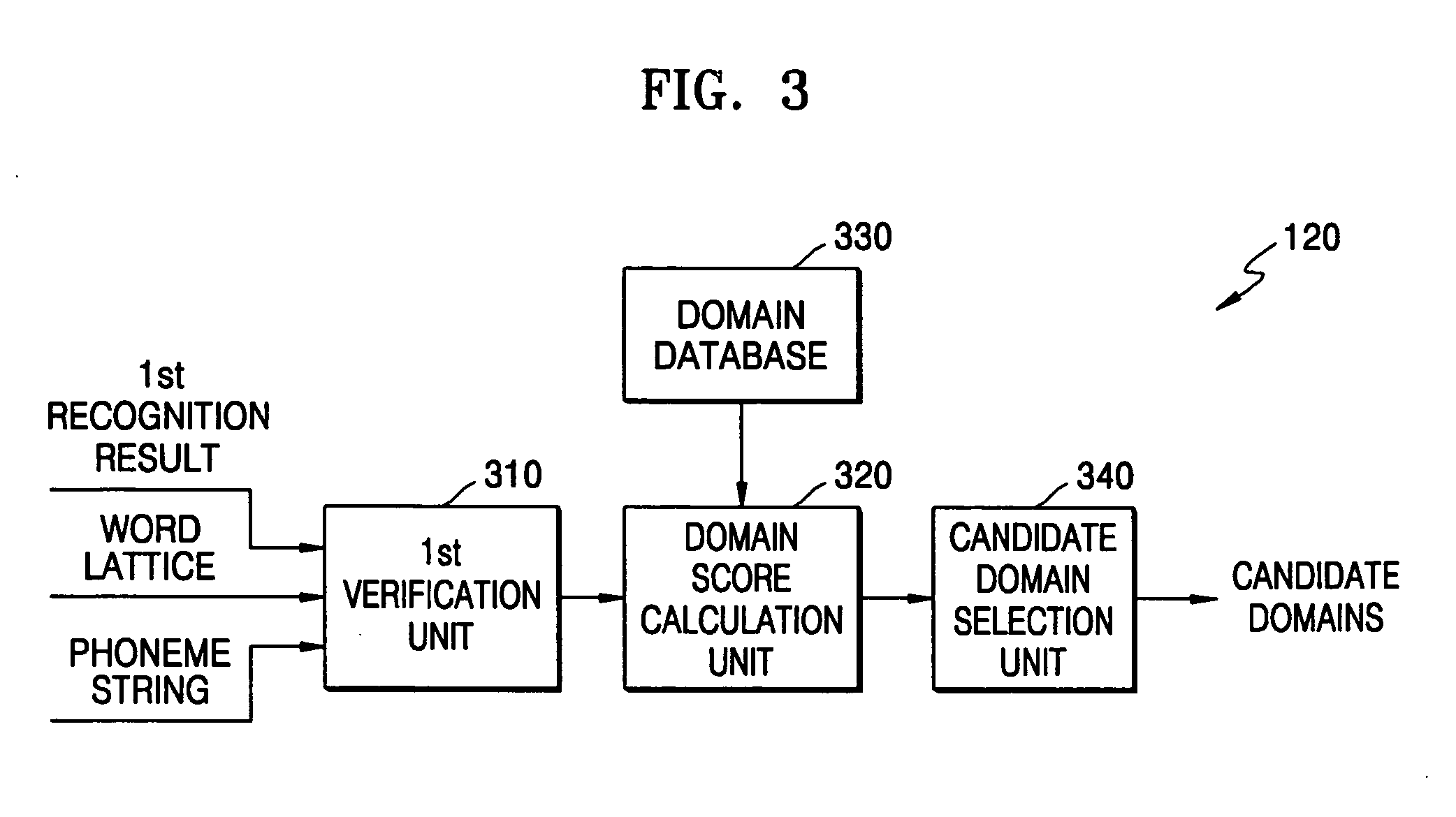
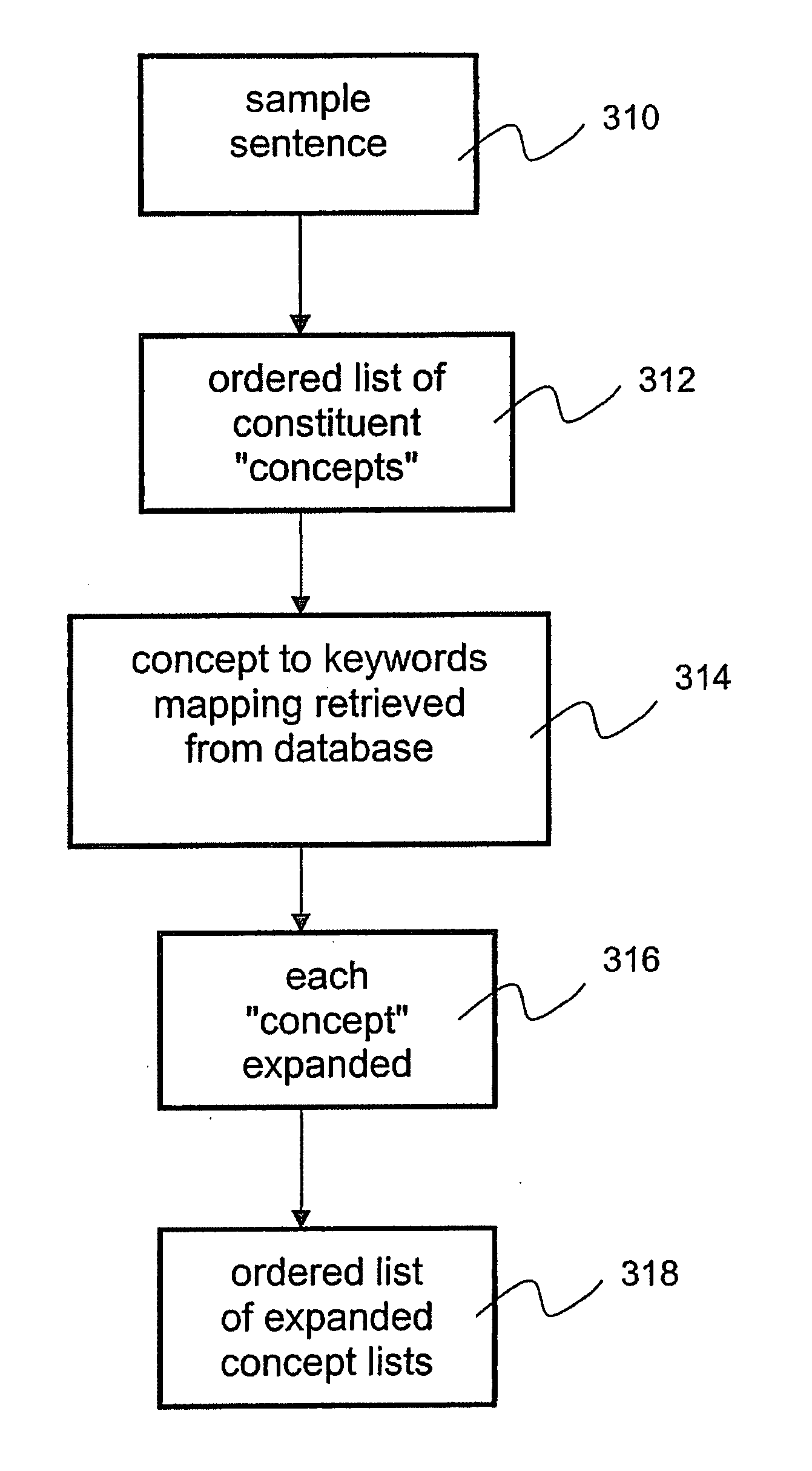
Domain-based dialog speech recognition method and apparatus
A domain-based speech recognition method and apparatus, the method including: performing speech recognition by using a first language model and generating a first recognition result including a plurality of first recognition sentences; selecting a plurality of candidate domains, by using a word included in each of the first recognition sentences and having a confidence score equal to or higher than a predetermined threshold, as a domain keyword; performing speech recognition with the first recognition result, by using an acoustic model specific to each of the candidate domains and a second language model and generating a plurality of second recognition sentences; and selecting at least one or more final recognition sentence from the first recognition sentences and the second recognition sentences. According to this method and apparatus, the effect of a domain extraction error by misrecognition of a word on selection of a final recognition result can be minimized.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
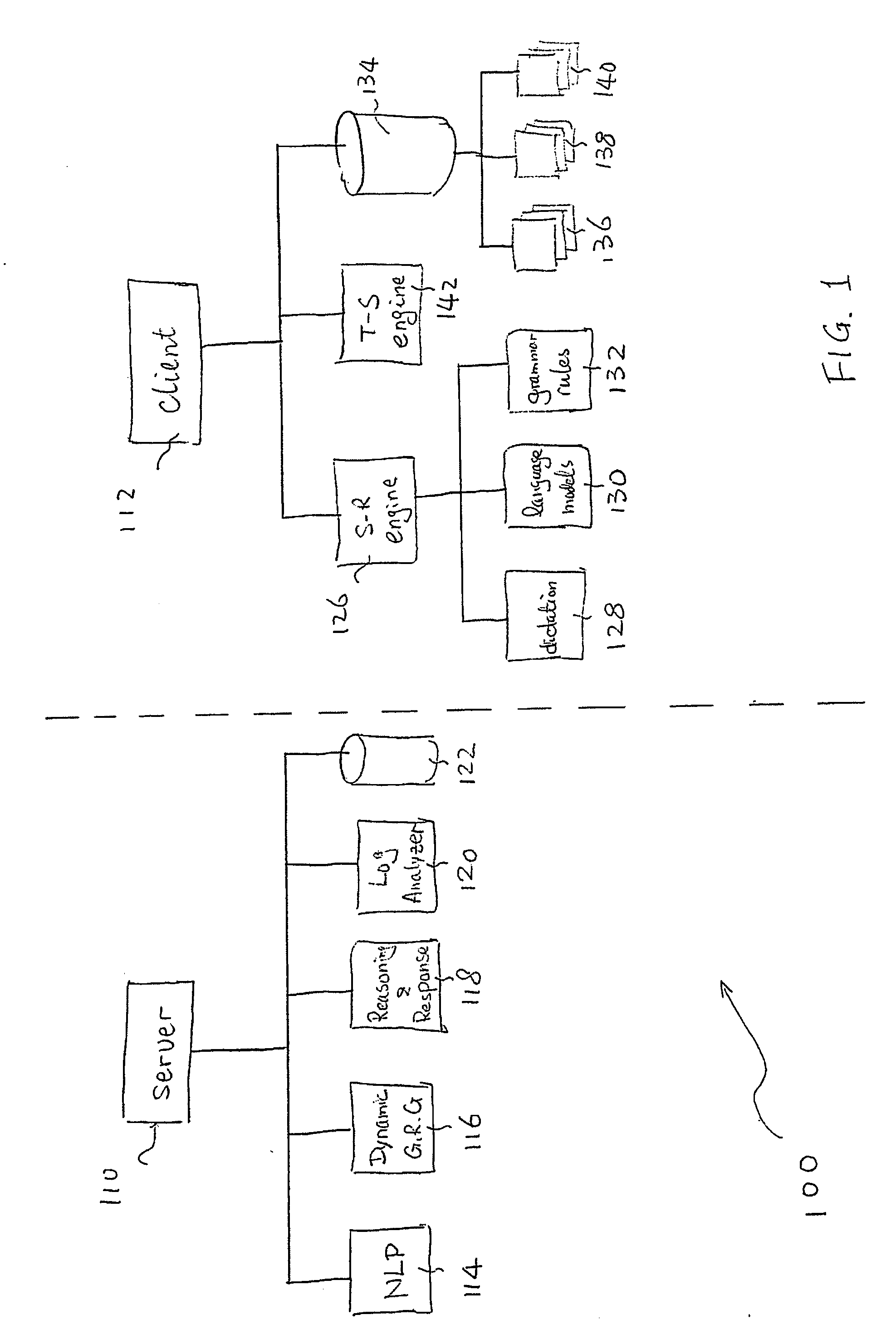
System and methods for improving accuracy of speech recognition
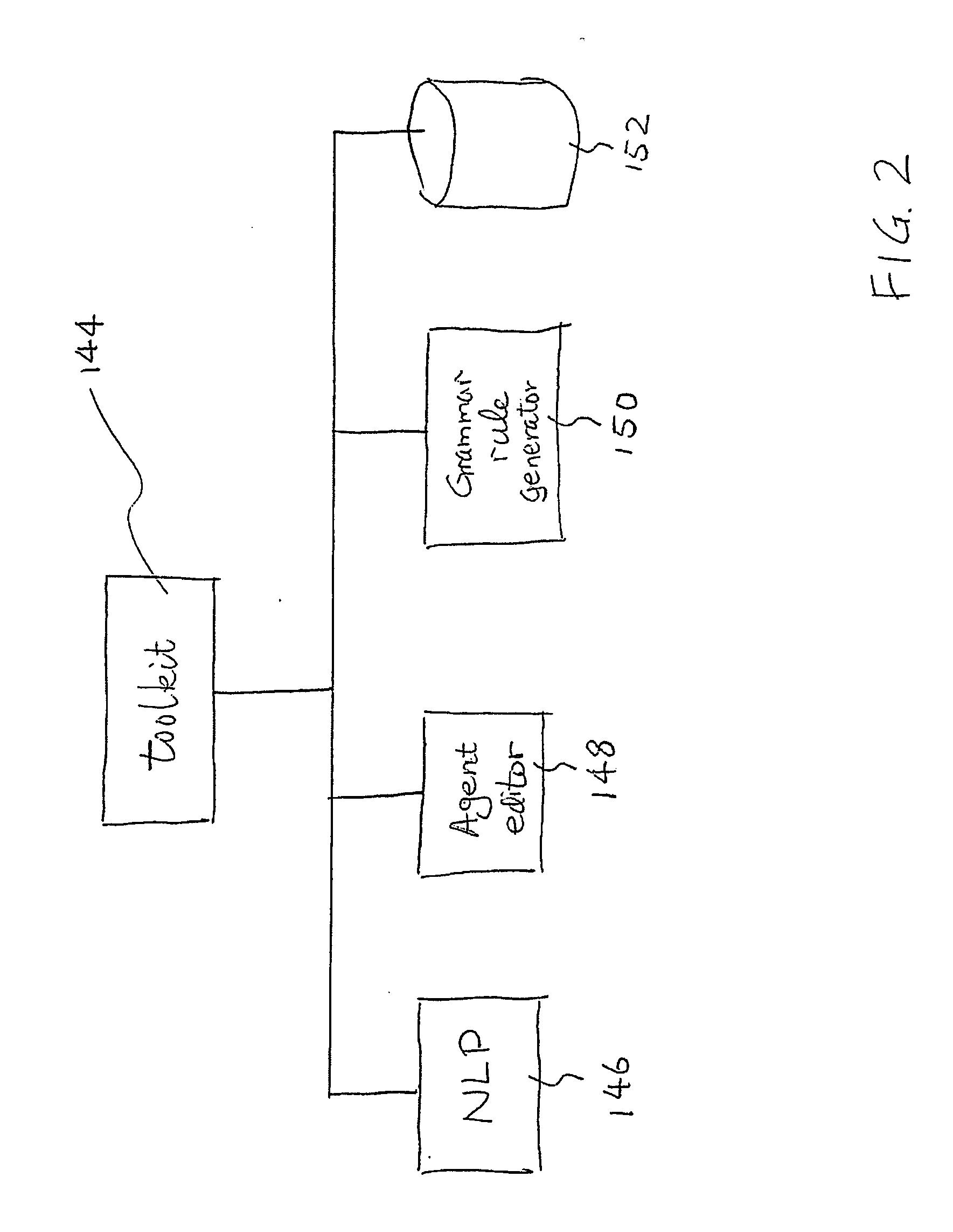
The invention provides a system and method for improving speech recognition. A computer software system is provided for implementing the system and method. A user of the computer software system may speak to the system directly and the system may respond, in spoken language, with an appropriate response. Grammar rules may be generated automatically from sample utterances when implementing the system for a particular application. Dynamic grammar rules may also be generated during interaction between the user and the system. In addition to arranging searching order of grammar files based on a predetermined hierarchy, a dynamically generated searching order based on history of contexts of a single conversation may be provided for further improved speech recognition. Dialogue between the system and the user of the system may be recorded and extracted for use by a speech recognition engine to refine or create language models so that accuracy of speech recognition relevant to a particular knowledge area may be improved.
Owner:INAGO CORP
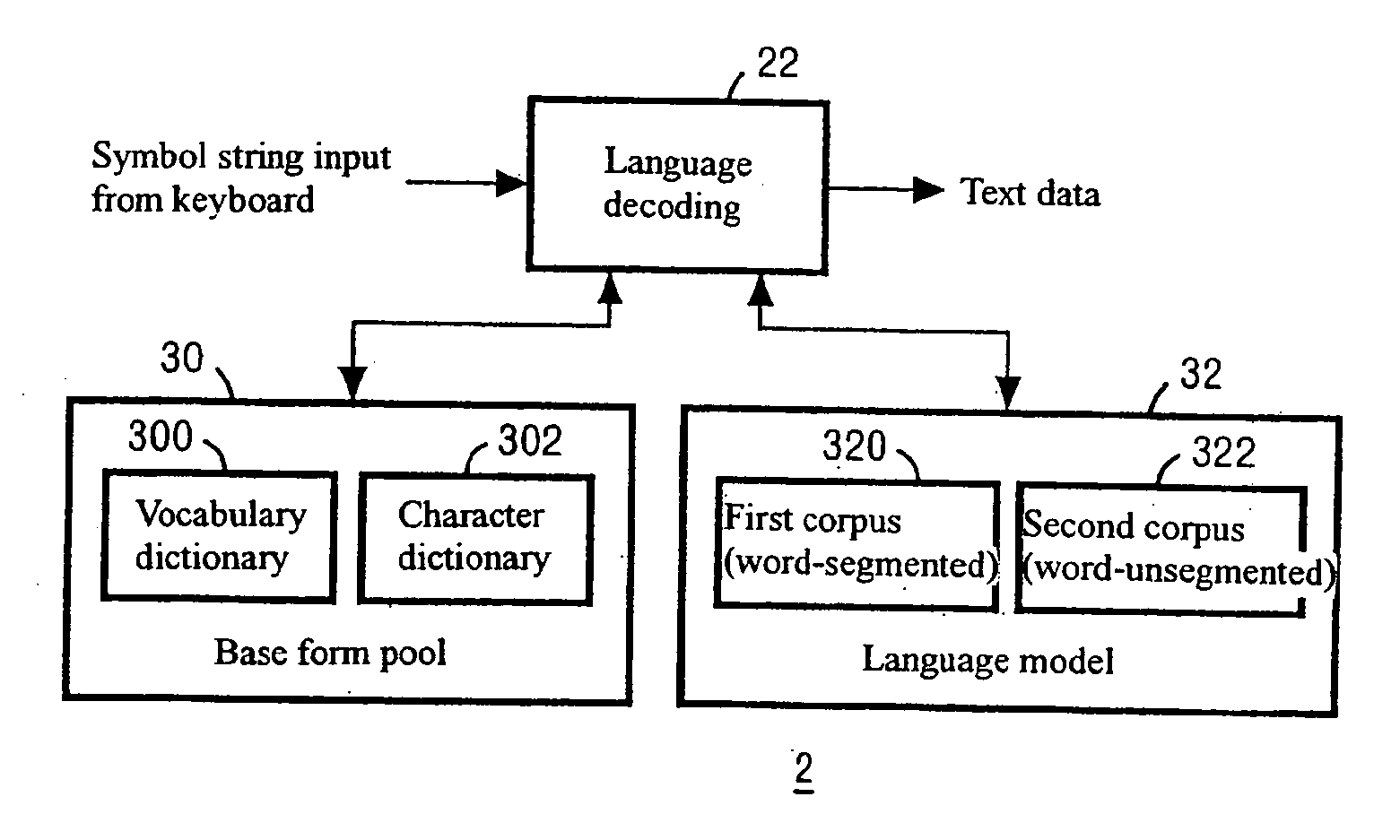
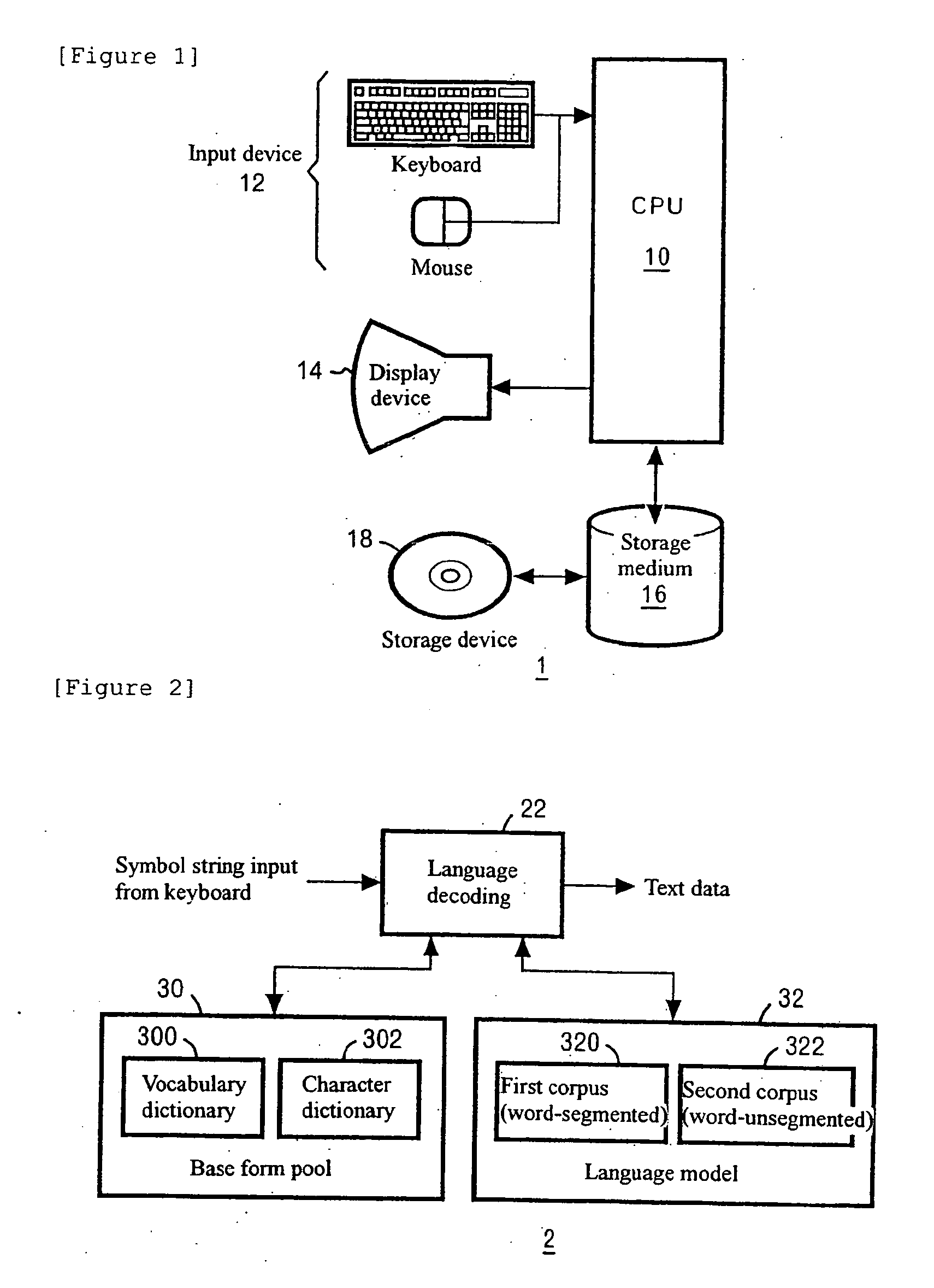
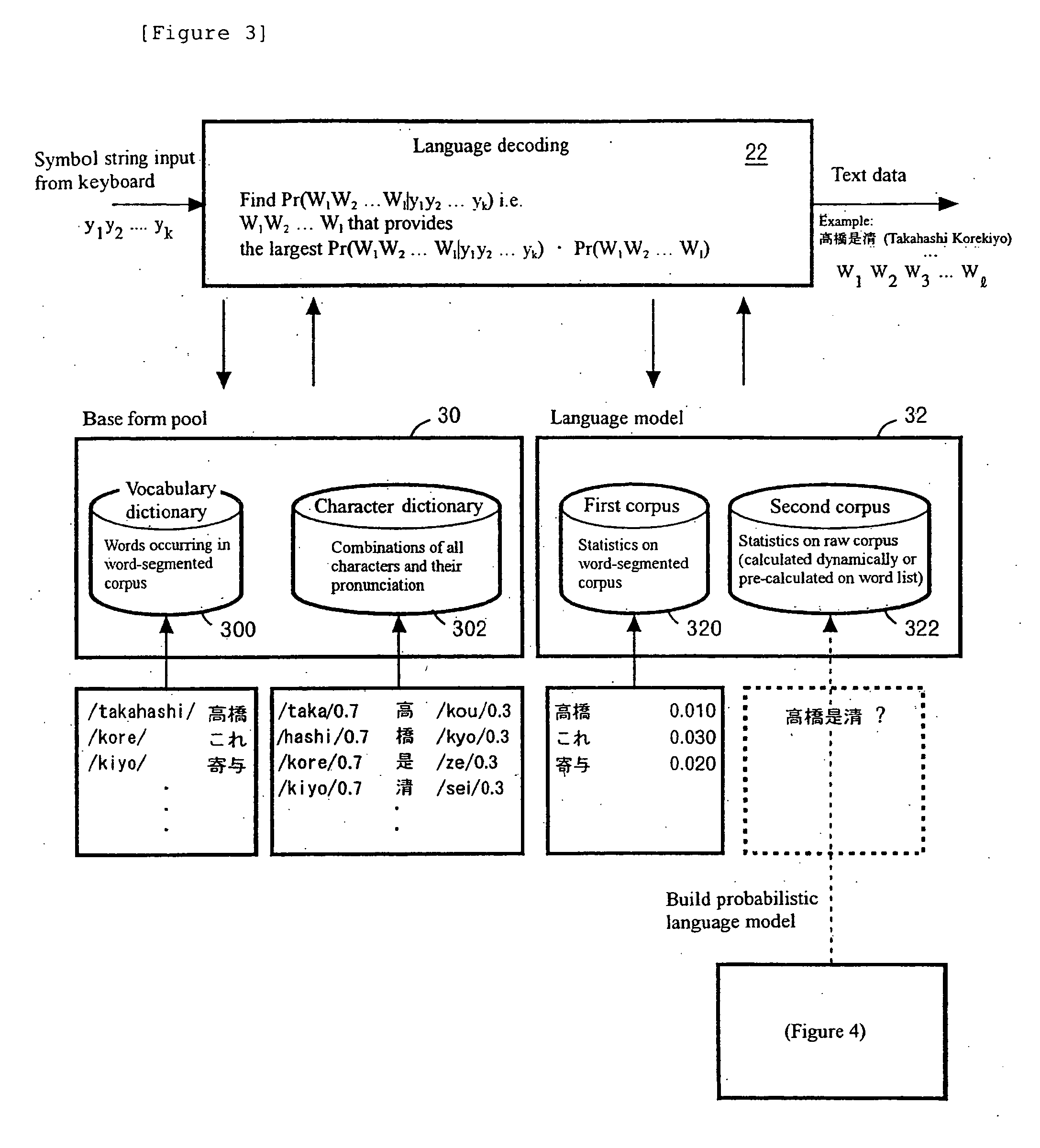
Pronunciation variation rule extraction apparatus, pronunciation variation rule extraction method, and pronunciation variation rule extraction program
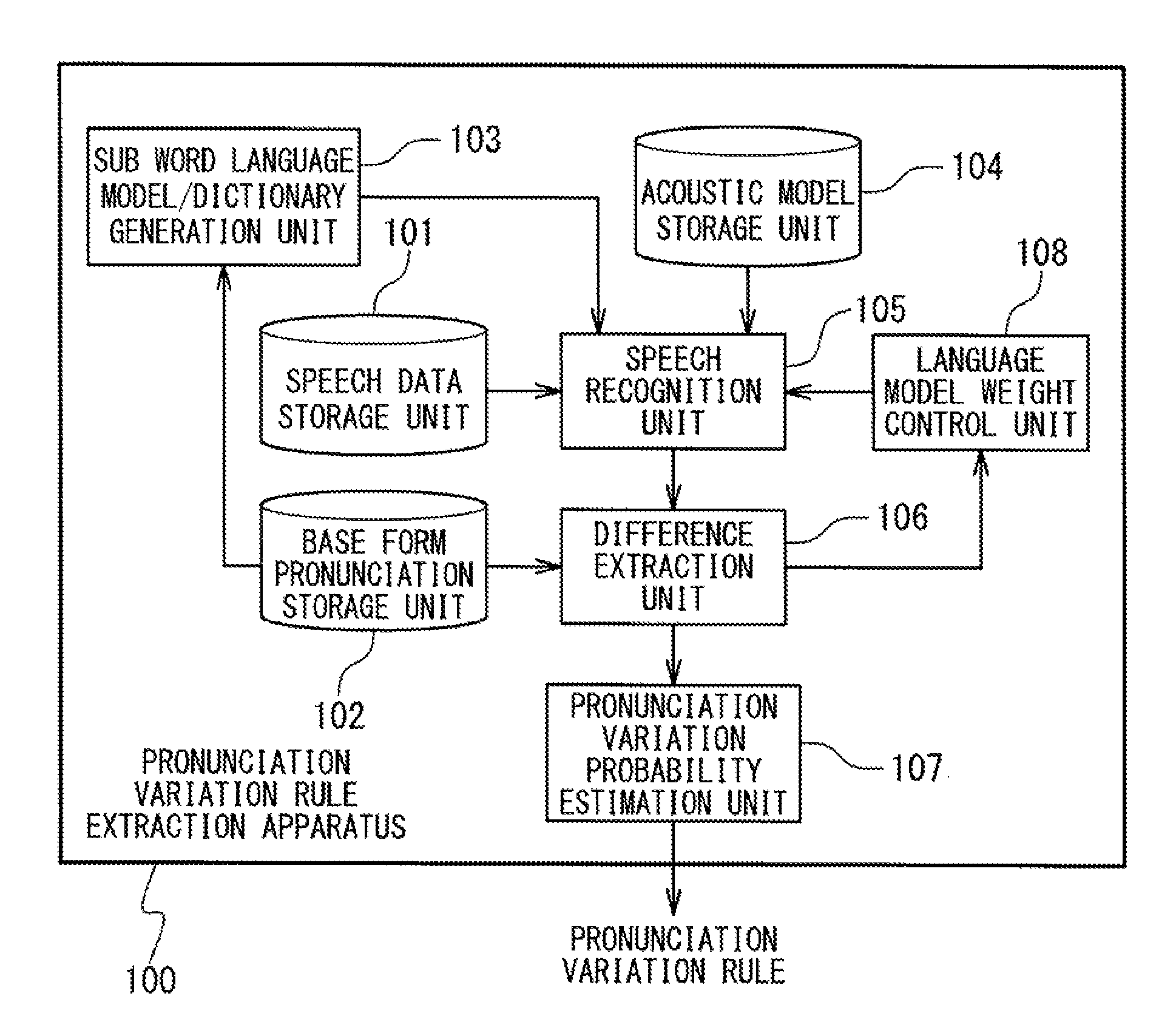
A problem to be solved is to robustly detect a pronunciation variation example and acquire a pronunciation variation rule having a high generalization property, with less effort. The problem can be solved by a pronunciation variation rule extraction apparatus including a speech data storage unit, a base form pronunciation storage unit, a sub word language model generation unit, a speech recognition unit, and a difference extraction unit. The speech data storage unit stores speech data. The base form pronunciation storage unit stores base form pronunciation data representing base form pronunciation of the speech data. The sub word language model generation unit generates a sub word language model from the base form pronunciation data. The speech recognition unit recognizes the speech data by using the sub word language model. The difference extraction unit extracts a difference between a recognition result outputted from the speech recognition unit and the base form pronunciation data by comparing the recognition result and the base form pronunciation data.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method for disambiguating multiple readings in language conversion
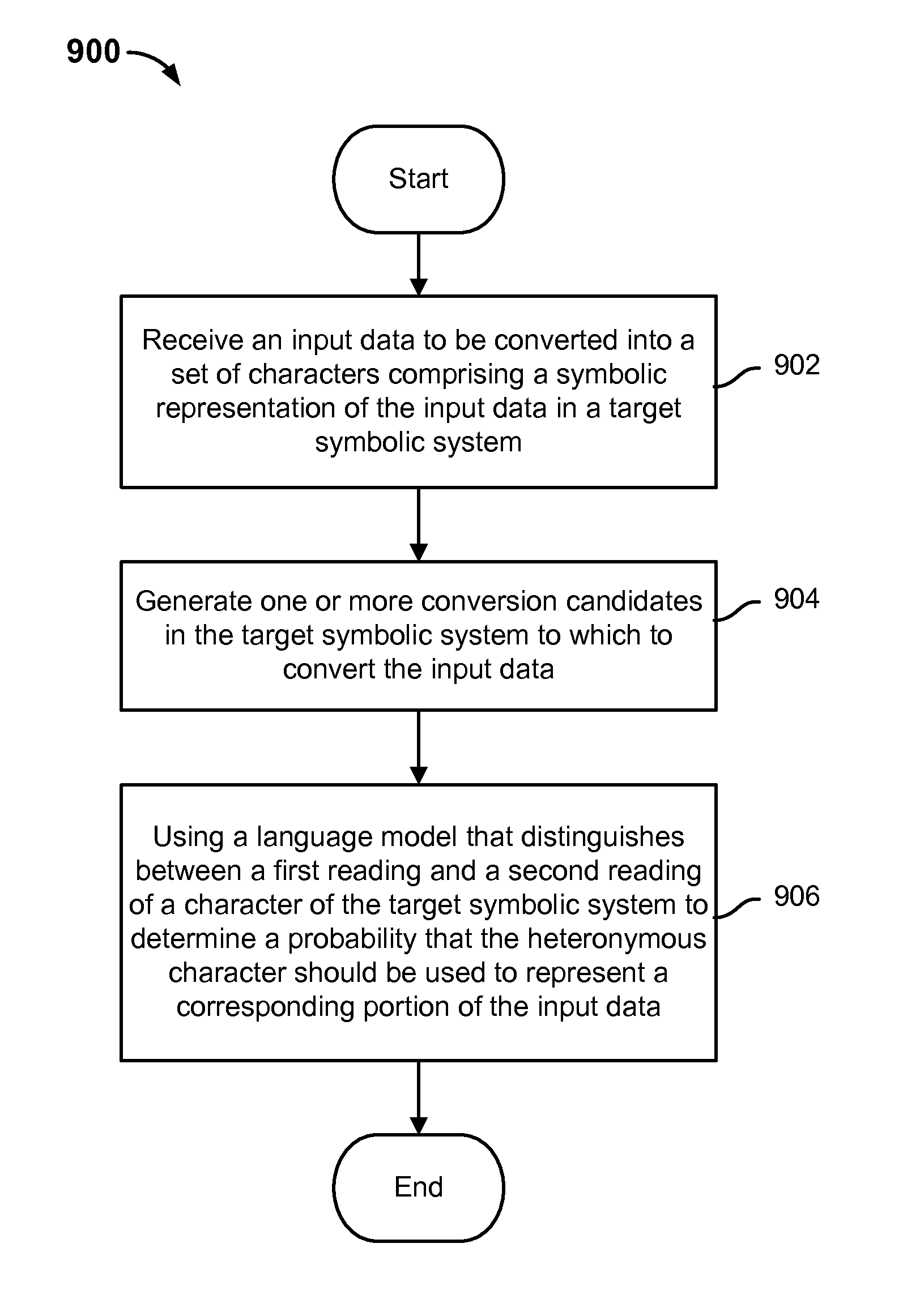
Disambiguating multiple readings in language conversion is disclosed, including: receiving an input data to be converted into a set of characters comprising a symbolic representation of the input data in a target symbolic system; and using a language model that distinguishes between a first reading and a second reading of a character of the target symbolic system to determine a probability that the heteronymous character should be used to represent a corresponding portion of the input data.
Owner:APPLE INC
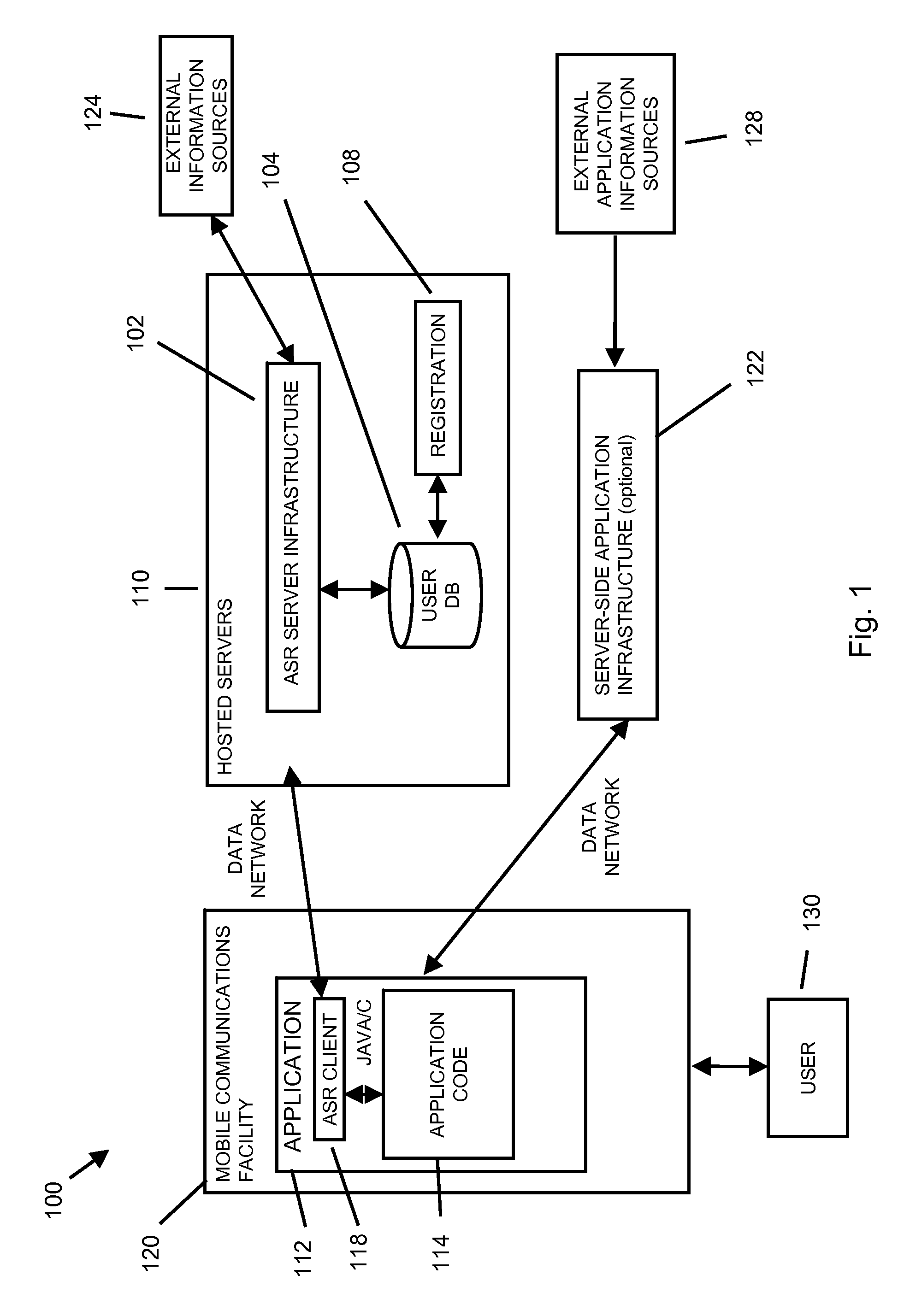
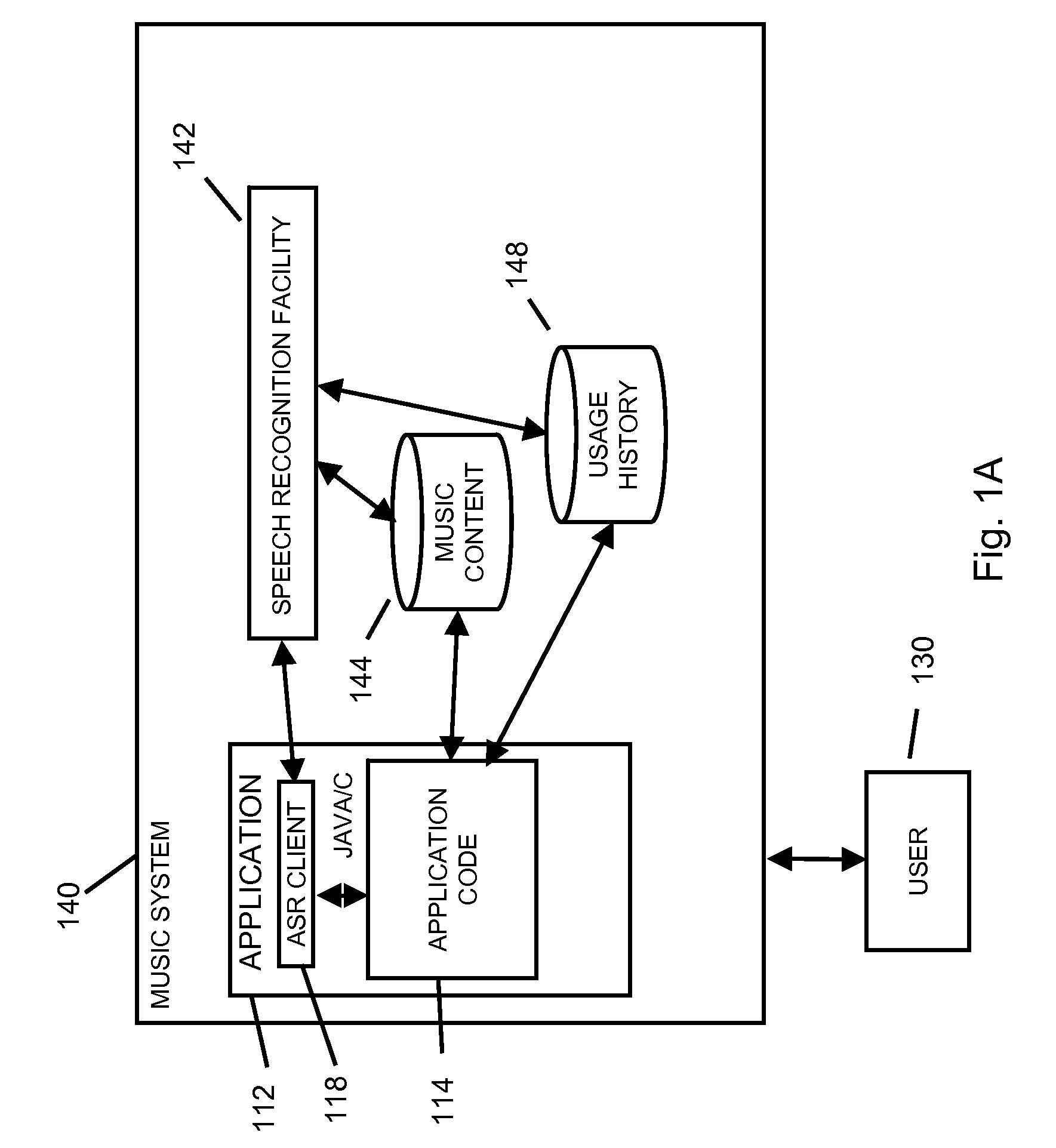
Using speech recognition results based on an unstructured language model in a mobile communication facility application
ActiveUS8886540B2Task to performImprove performanceDigital computer detailsDigital dataSpeech soundSubvocal recognition
A method and system for entering information into a software application resident on a mobile communication facility is provided. The method and system may include recording speech presented by a user using a mobile communication facility resident capture facility, transmitting the recording through a wireless communication facility to a speech recognition facility, transmitting information relating to the software application to the speech recognition facility, generating results utilizing the speech recognition facility using an unstructured language model based at least in part on the information relating to the software application and the recording, transmitting the results to the mobile communications facility, loading the results into the software application and simultaneously displaying the results as a set of words and as a set of application results based on those words.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC +1
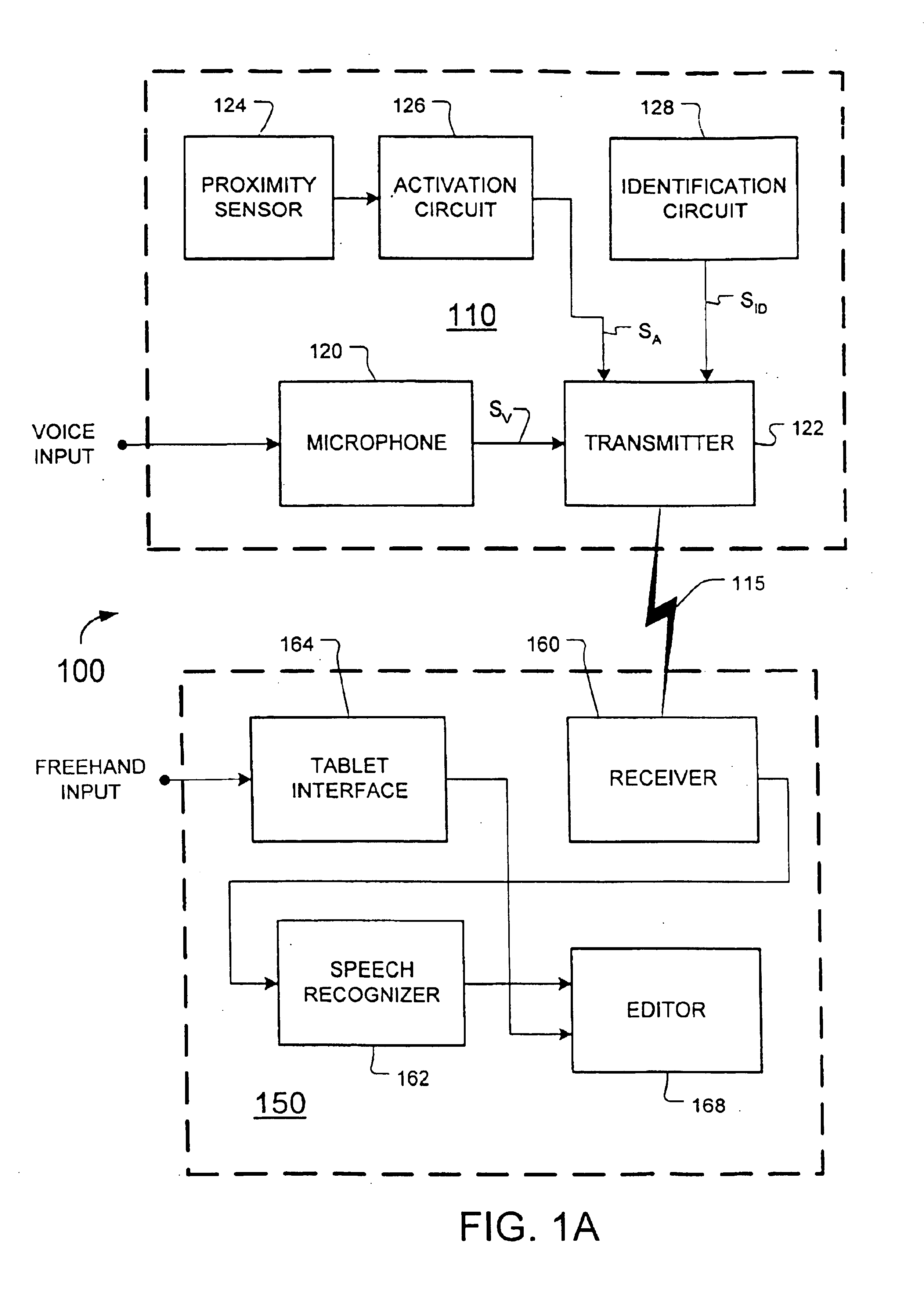
Message recognition using shared language model
InactiveUS6904405B2Speech recognitionInput/output processes for data processingHandwritingAcoustic model
Certain disclosed methods and systems perform multiple different types of message recognition using a shared language model. Message recognition of a first type is performed responsive to a first type of message input (e.g., speech), to provide text data in accordance with both the shared language model and a first model specific to the first type of message recognition (e.g., an acoustic model). Message recognition of a second type is performed responsive to a second type of message input (e.g., handwriting), to provide text data in accordance with both the shared language model and a second model specific to the second type of message recognition (e.g., a model that determines basic units of handwriting conveyed by freehand input). Accuracy of both such message recognizers can be improved by user correction of misrecognition by either one of them. Numerous other methods and systems are also disclosed.
Owner:BUFFALO PATENTS LLC
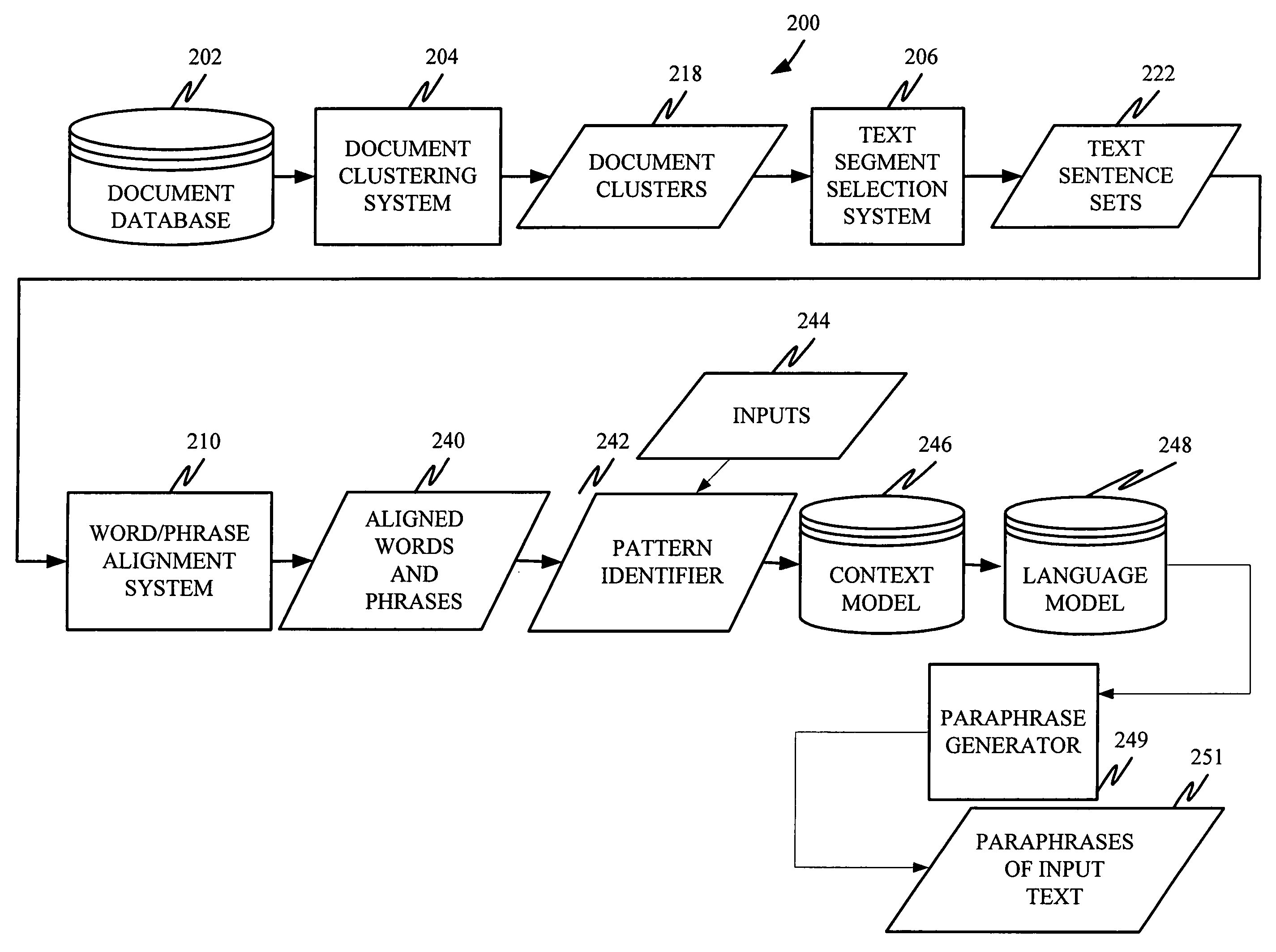
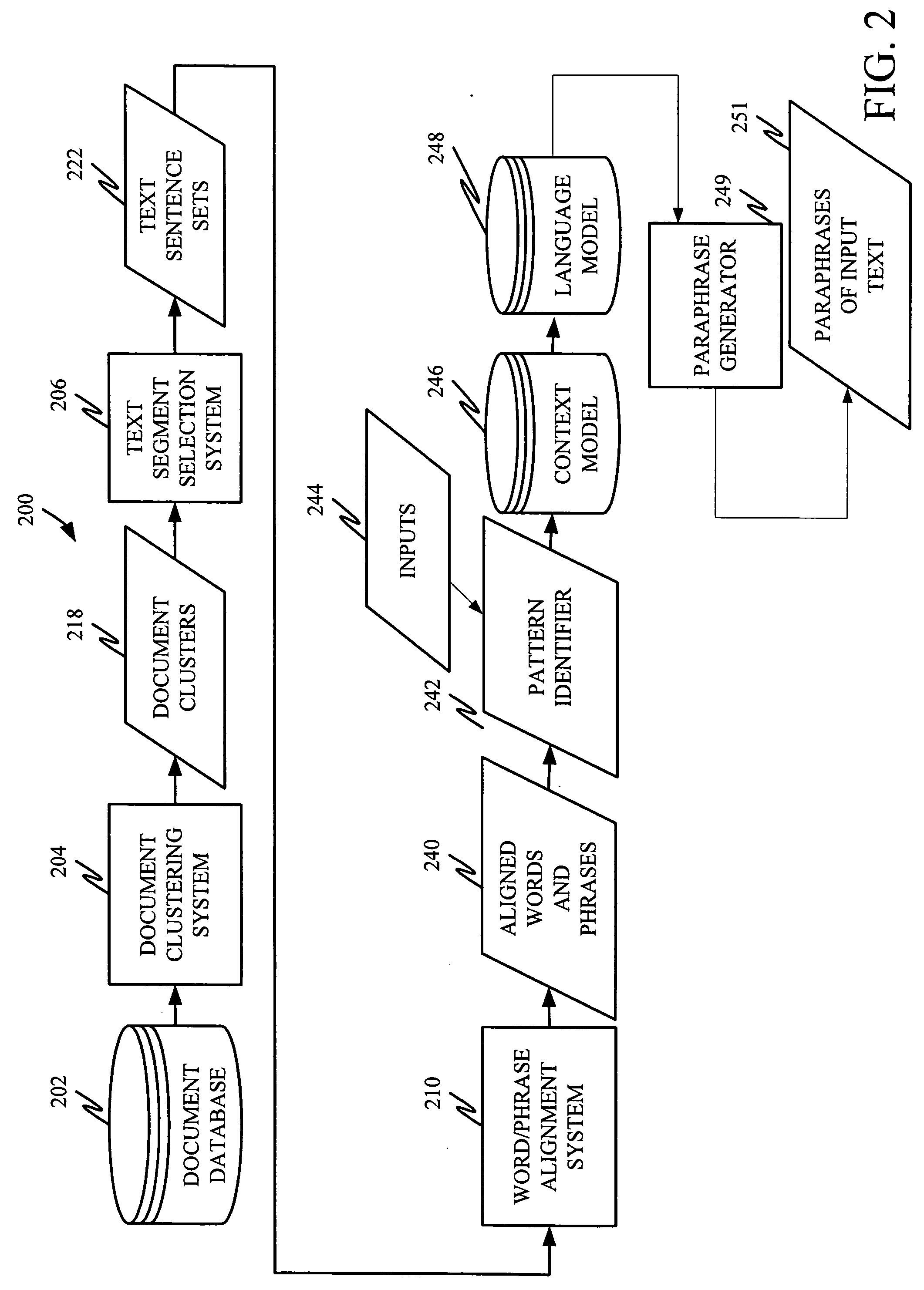
Unsupervised learning of paraphrase/translation alternations and selective application thereof
InactiveUS20060106595A1Without any changeNatural language translationSemantic analysisData setParaphrase
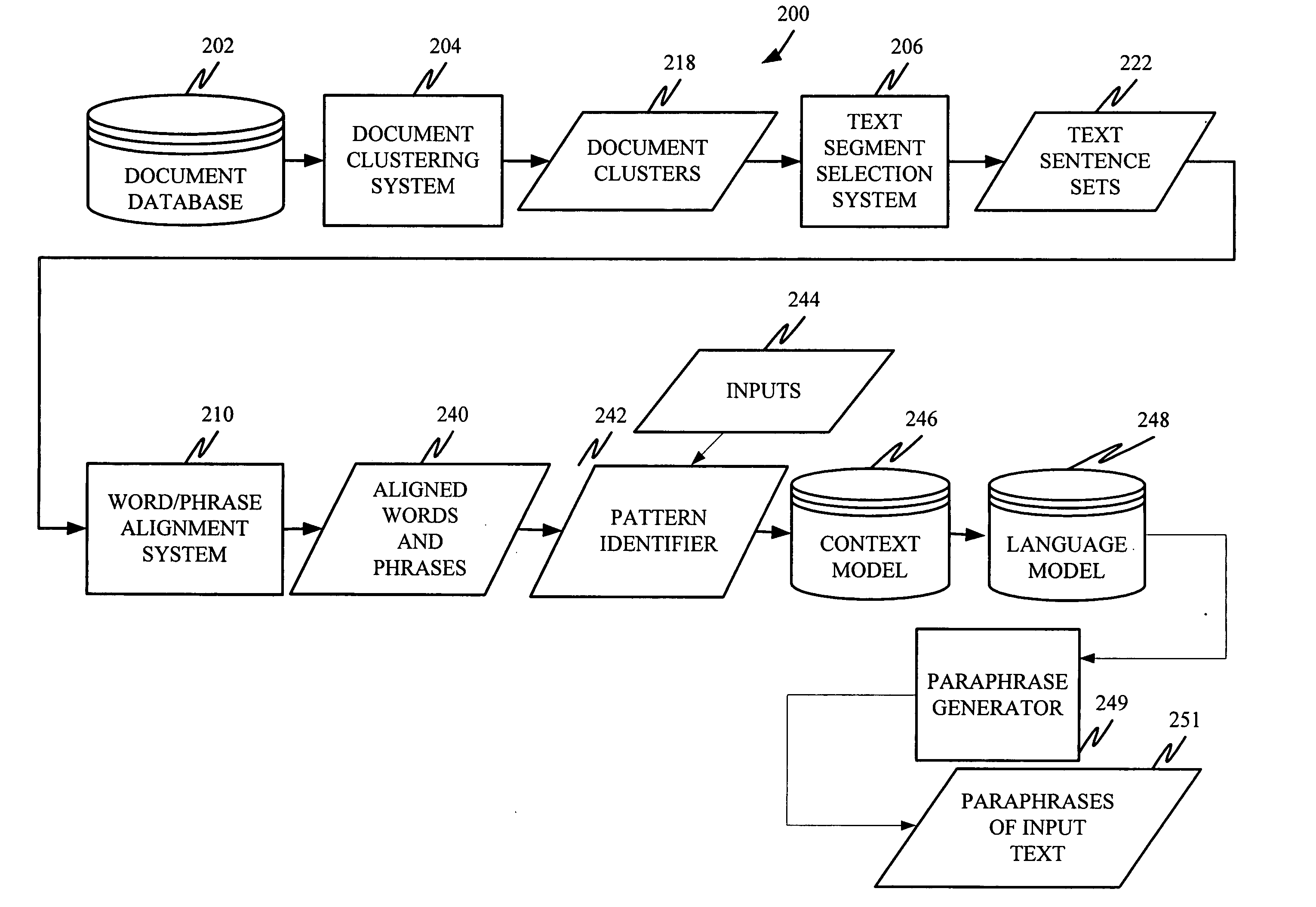
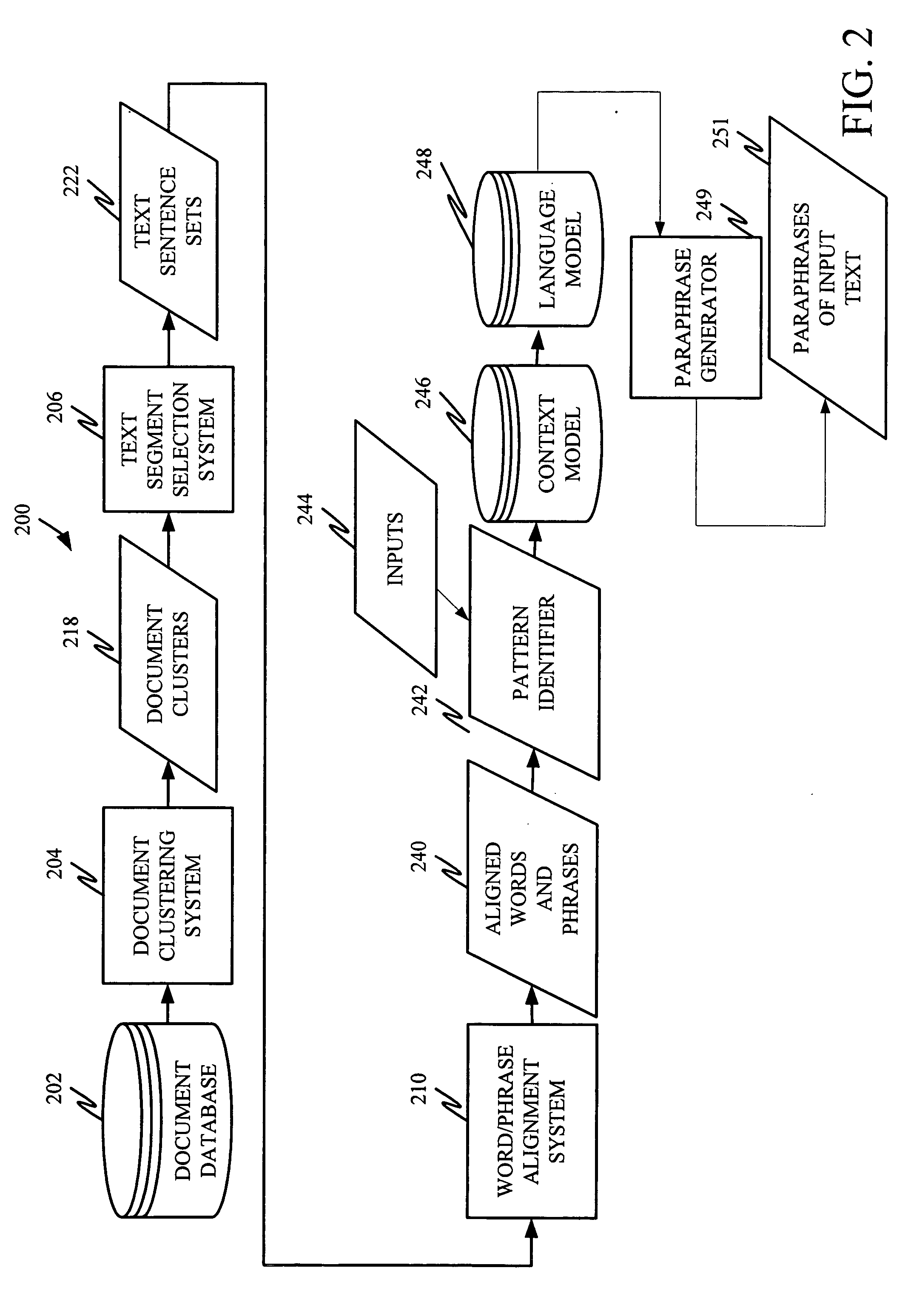
A system is disclosed for selectively applying a paraphrase alternation pattern to a textual input. The system includes a pattern identification component for processing a collection of data and identifying a plurality of potentially applicable paraphrase alternation patterns. A context model provides an objective frame of reference in which to compare one or more of the plurality of potentially applicable paraphrase alternation patterns to the textual input to determine whether the pattern can be applied without changing meaning. A language model provides a principled basis for determining the boundaries of the text segment to be modified.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
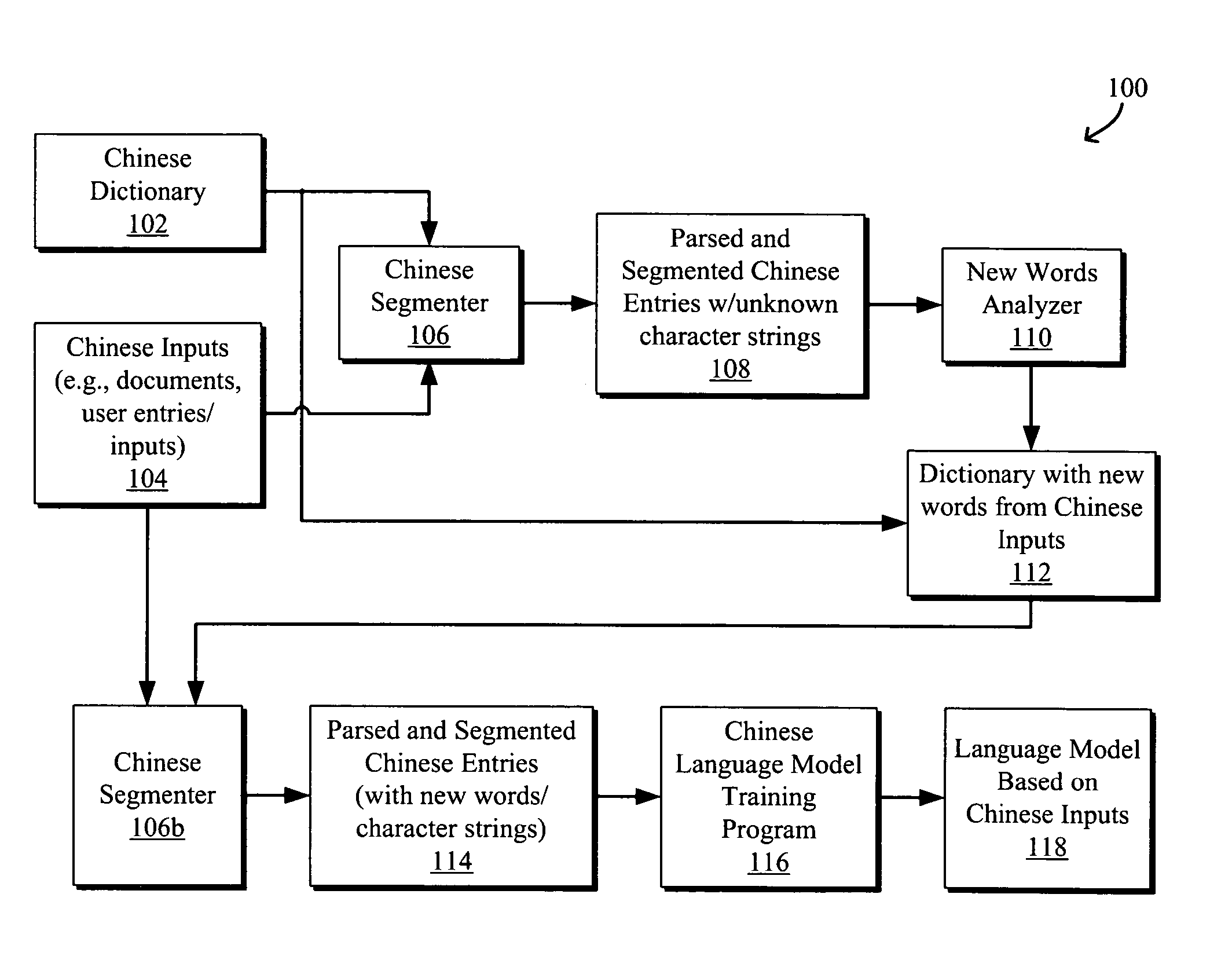
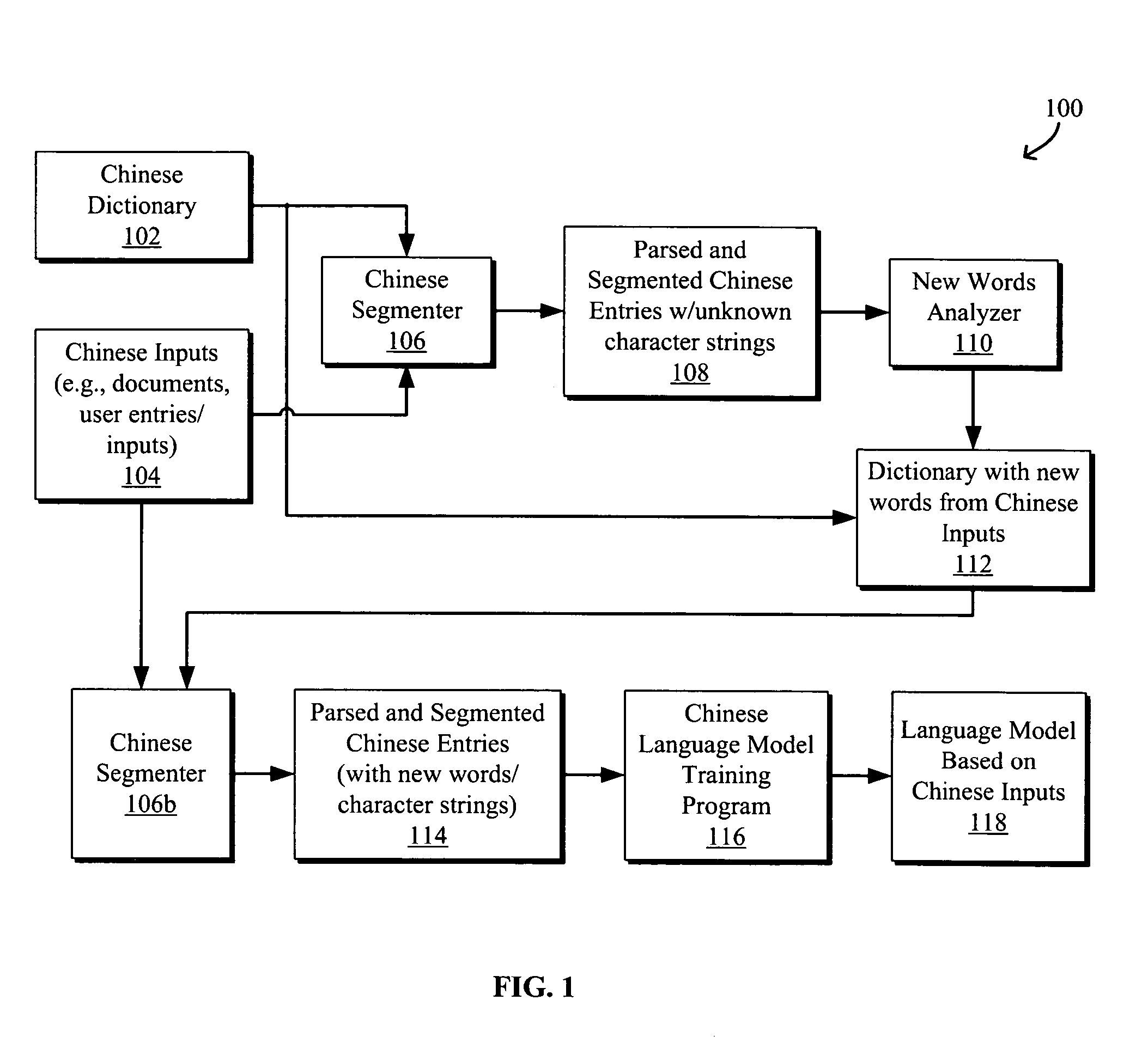
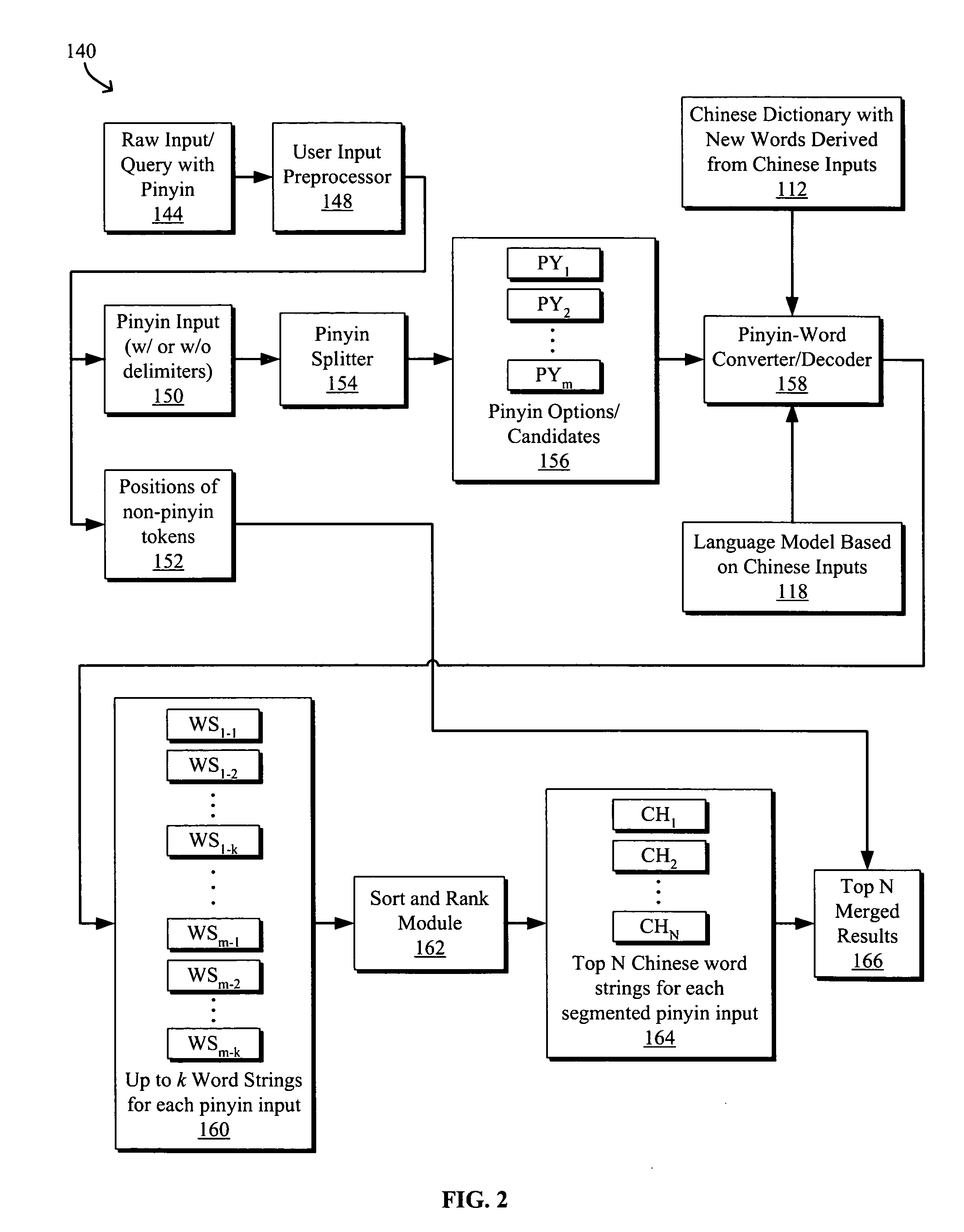
Systems and methods for translating chinese pinyin to chinese characters
ActiveUS20050209844A1Natural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsUser inputTransition matrices
Systems and methods to process and translate pinyin to Chinese characters and words are disclosed. A Chinese language model is trained by extracting unknown character strings from Chinese inputs, e.g., documents and / or user inputs / queries, determining valid words from the unknown character strings, and generating a transition matrix based on the Chinese inputs for predicting a word string given the context. A method for translating a pinyin input generally includes generating a set of Chinese character strings from the pinyin input using a Chinese dictionary including words derived from the Chinese inputs and a language model trained based on the Chinese inputs, each character string having a weight indicating the likelihood that the character string corresponds to the pinyin input. An ambiguous user input may be classified as non-pinyin or pinyin by identifying an ambiguous pinyin / non-pinyin ASCII word in the user input and analyzing the context to classify the user input.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
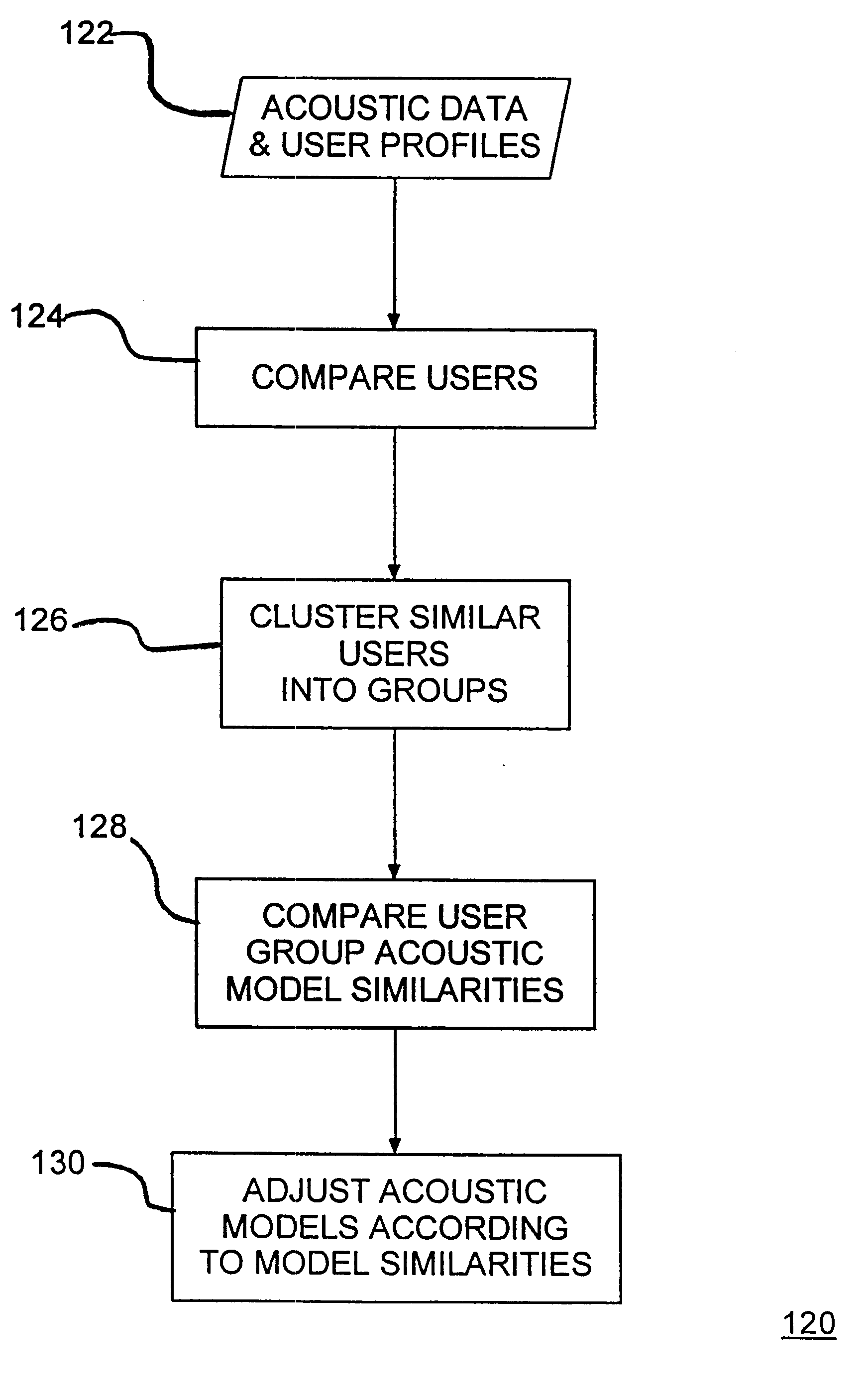
Speaker model adaptation via network of similar users
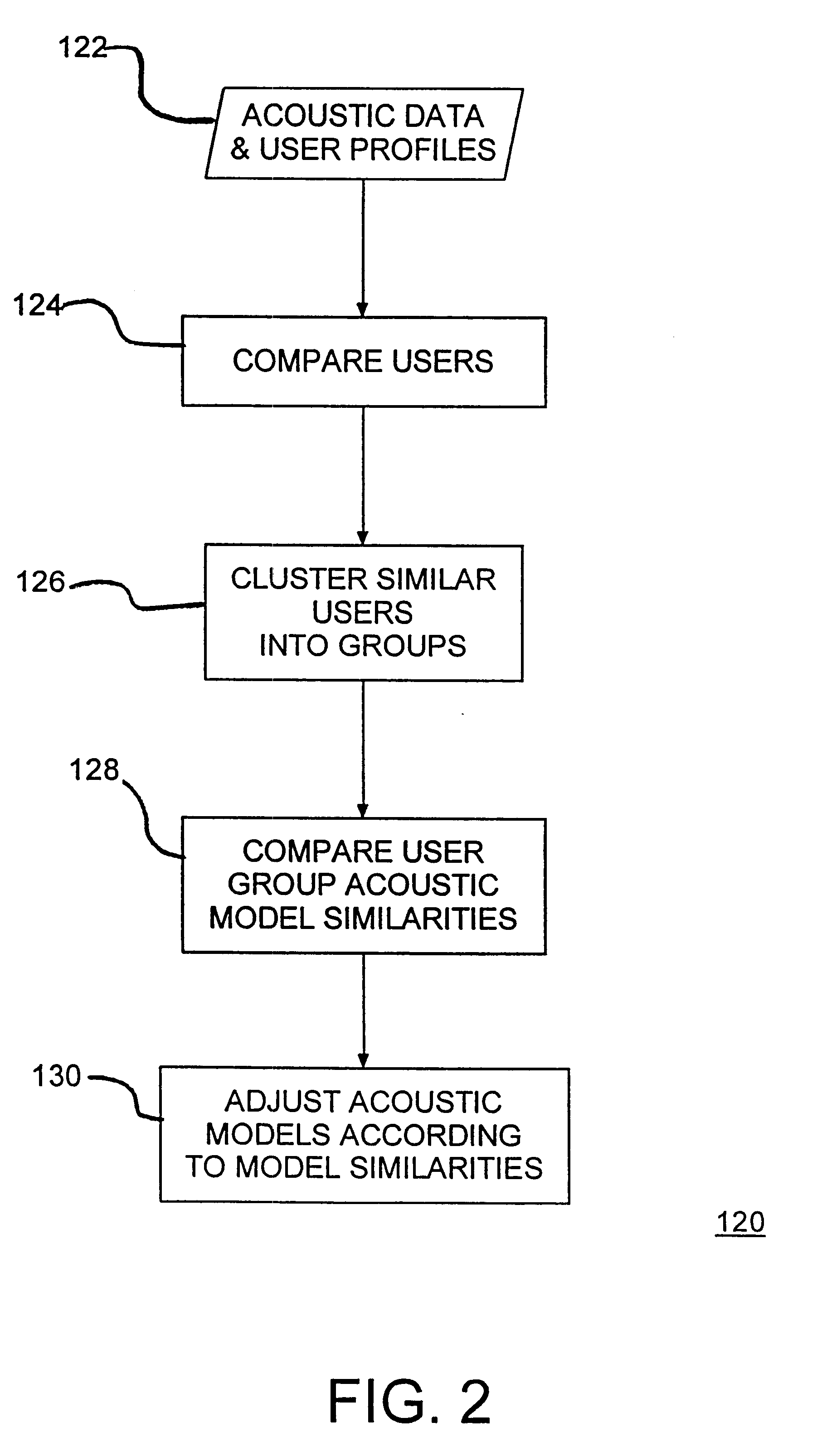
A speech recognition system, method and program product for recognizing speech input from computer users connected together over a network of computers. Speech recognition computer users on the network are clustered into classes of similar users according their similarities, including characteristics nationality, profession, sex, age, etc. Each computer in the speech recognition network includes at least one user based acoustic model trained for a particular user. The acoustic models include an acoustic model domain, with similar acoustic models being clustered according to an identified domain. User characteristics are collected from databases over the network and from users using the speech recognition system and then, distributed over the network during or after user activities. Existing acoustic models are modified in response to user production activities. As recognition progresses, similar language models among similar users are identified on the network. Update information, including information about user activities and user acoustic model data, is transmitted over the network and identified similar language models are updated. Acoustic models improve for users that are connected over the network as similar users use their respective speech recognition system.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
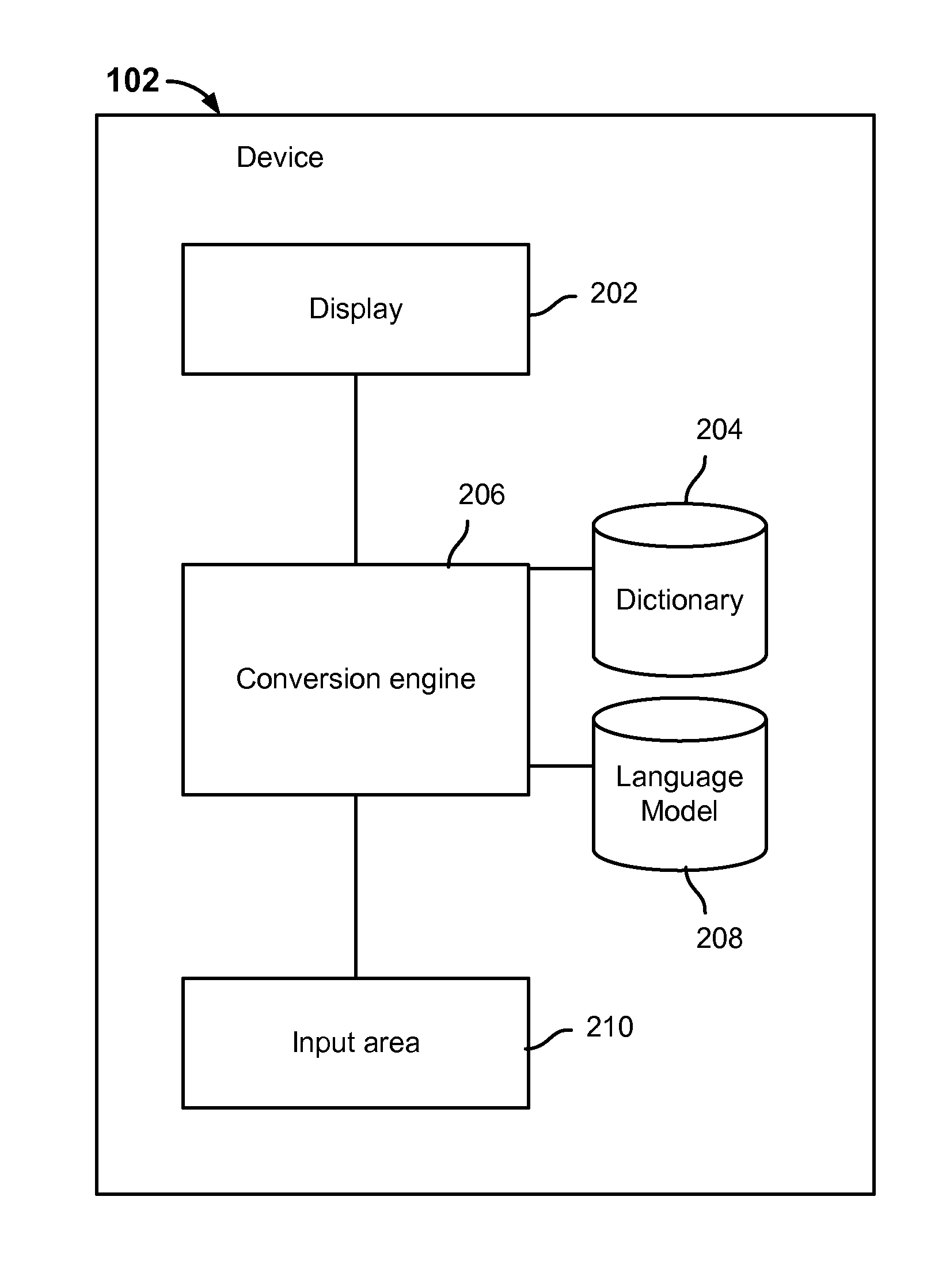
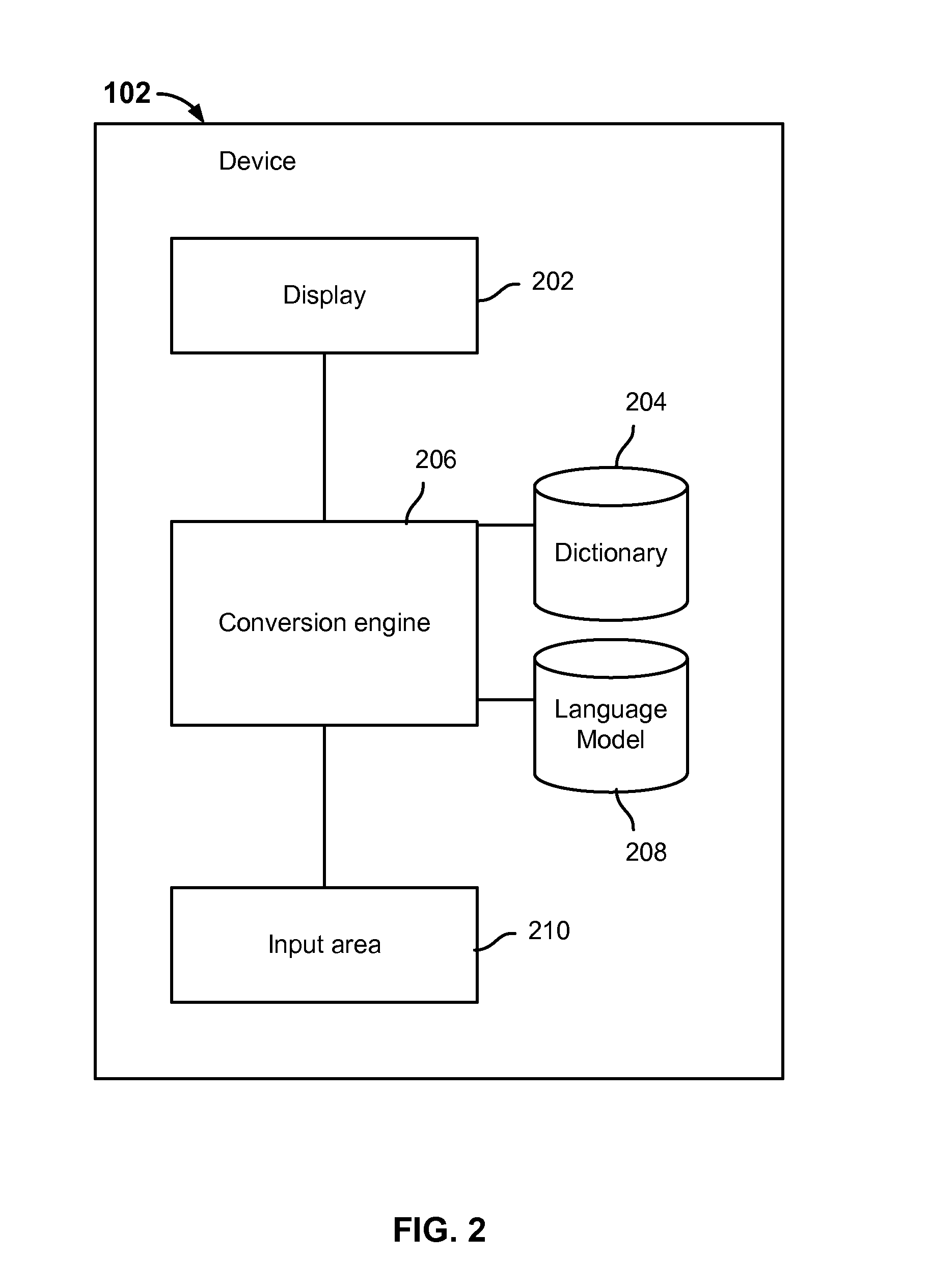
Language input architecture for converting one text form to another text form with tolerance to spelling, typographical, and conversion errors
InactiveUS6848080B1Error minimizationConvenience of userNatural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsTypingSpeech sound
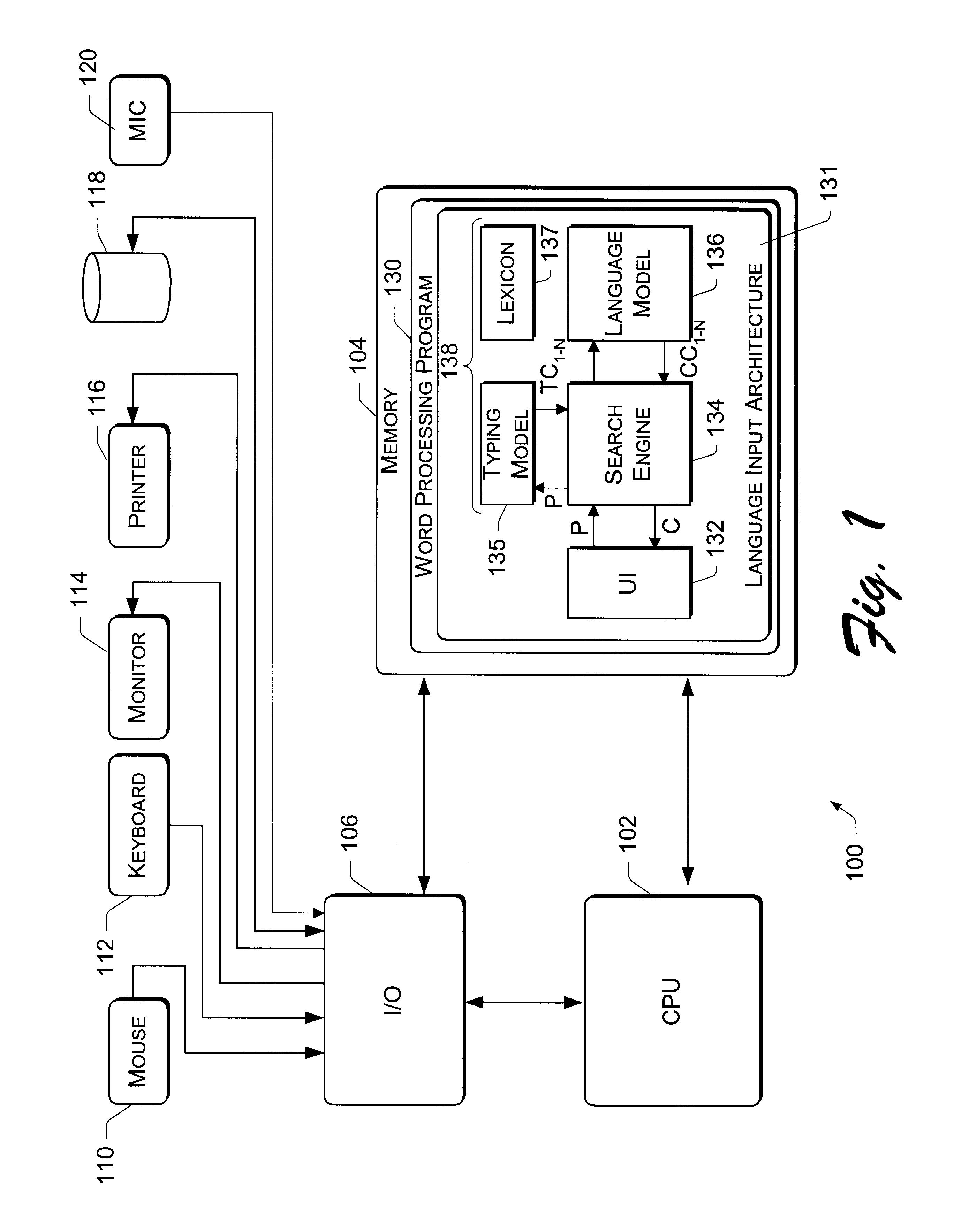
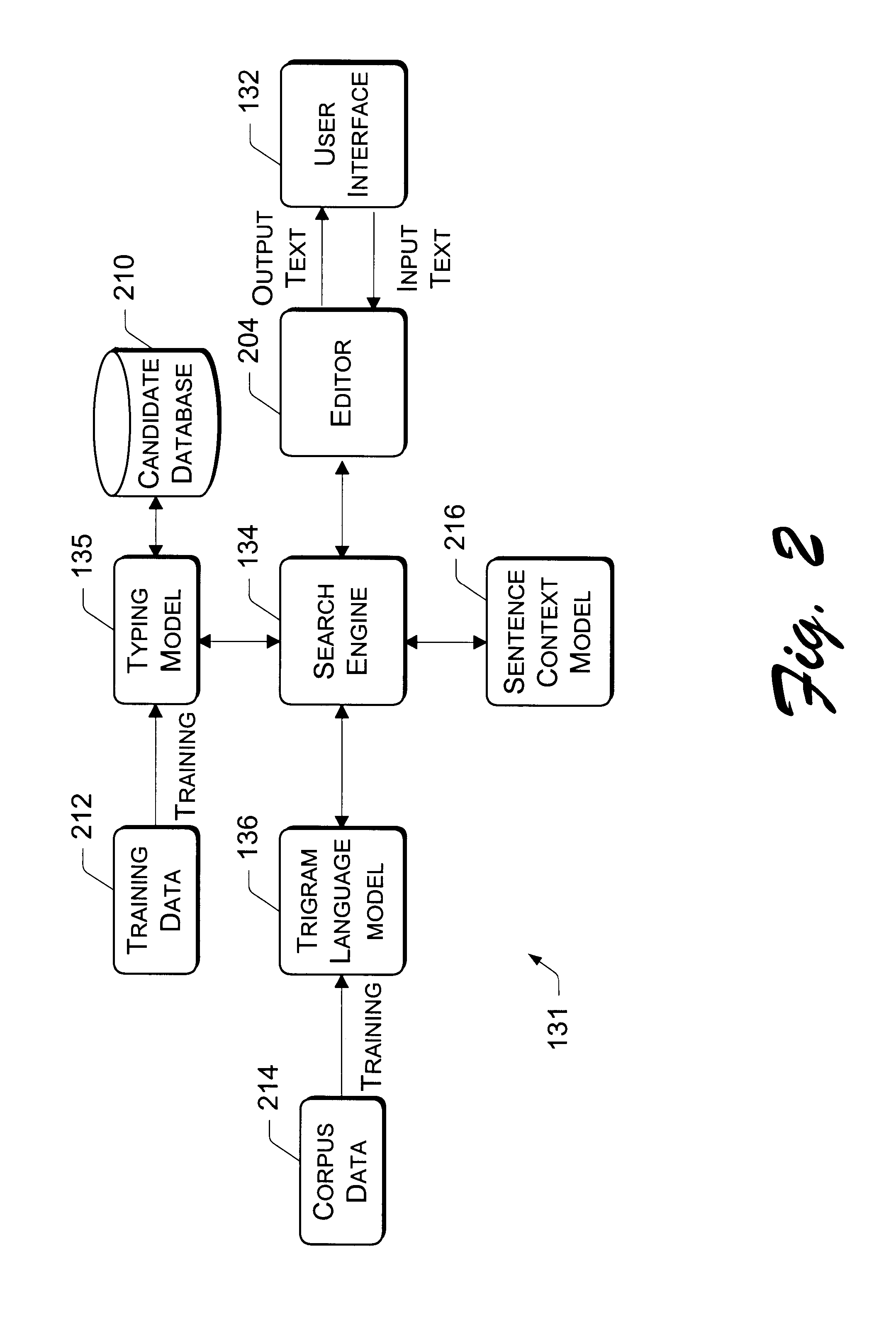
A language input architecture converts input strings of phonetic text to an output string of language text. The language input architecture has a search engine, one or more typing models, a language model, and one or more lexicons for different languages. The typing model is configured to generate a list of probable typing candidates that may be substituted for the input string based on probabilities of how likely each of the candidate strings was incorrectly entered as the input string. The language model provides probable conversion strings for each of the typing candidates based on probabilities of how likely a probable conversion output string represents the candidate string. The search engine combines the probabilities of the typing and language models to find the most probable conversion string that represents a converted form of the input string.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method for disambiguating multiple readings in language conversion
ActiveUS20130041647A1Natural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmAmbiguity
Disambiguating multiple readings in language conversion is disclosed, including: receiving an input data to be converted into a set of characters comprising a symbolic representation of the input data in a target symbolic system; and using a language model that distinguishes between a first reading and a second reading of a character of the target symbolic system to determine a probability that the heteronymous character should be used to represent a corresponding portion of the input data.
Owner:APPLE INC
Training a probabilistic spelling checker from structured data
InactiveUS8626681B1Increase the number ofDigital computer detailsNatural language data processingEntity typeAlgorithm
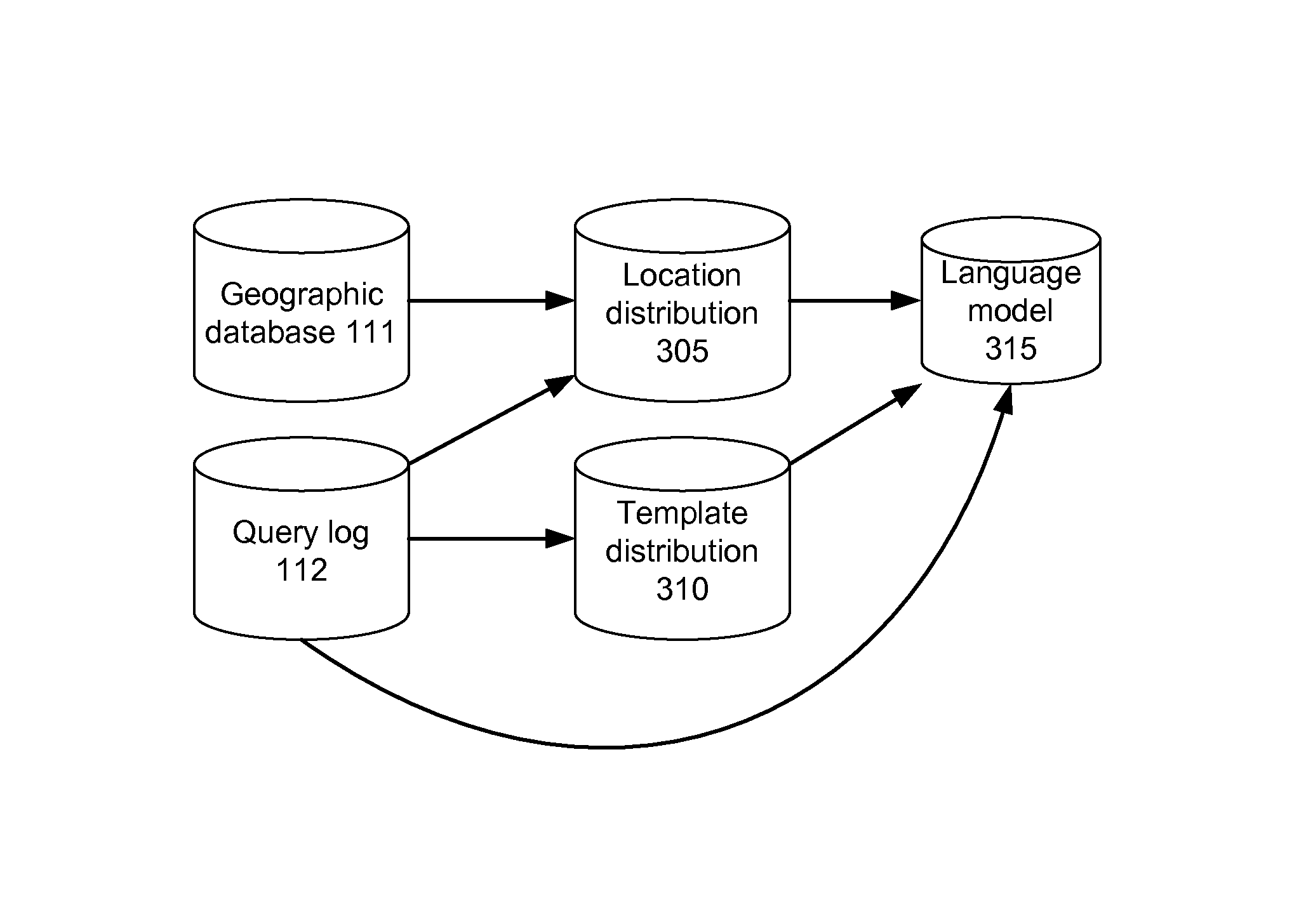
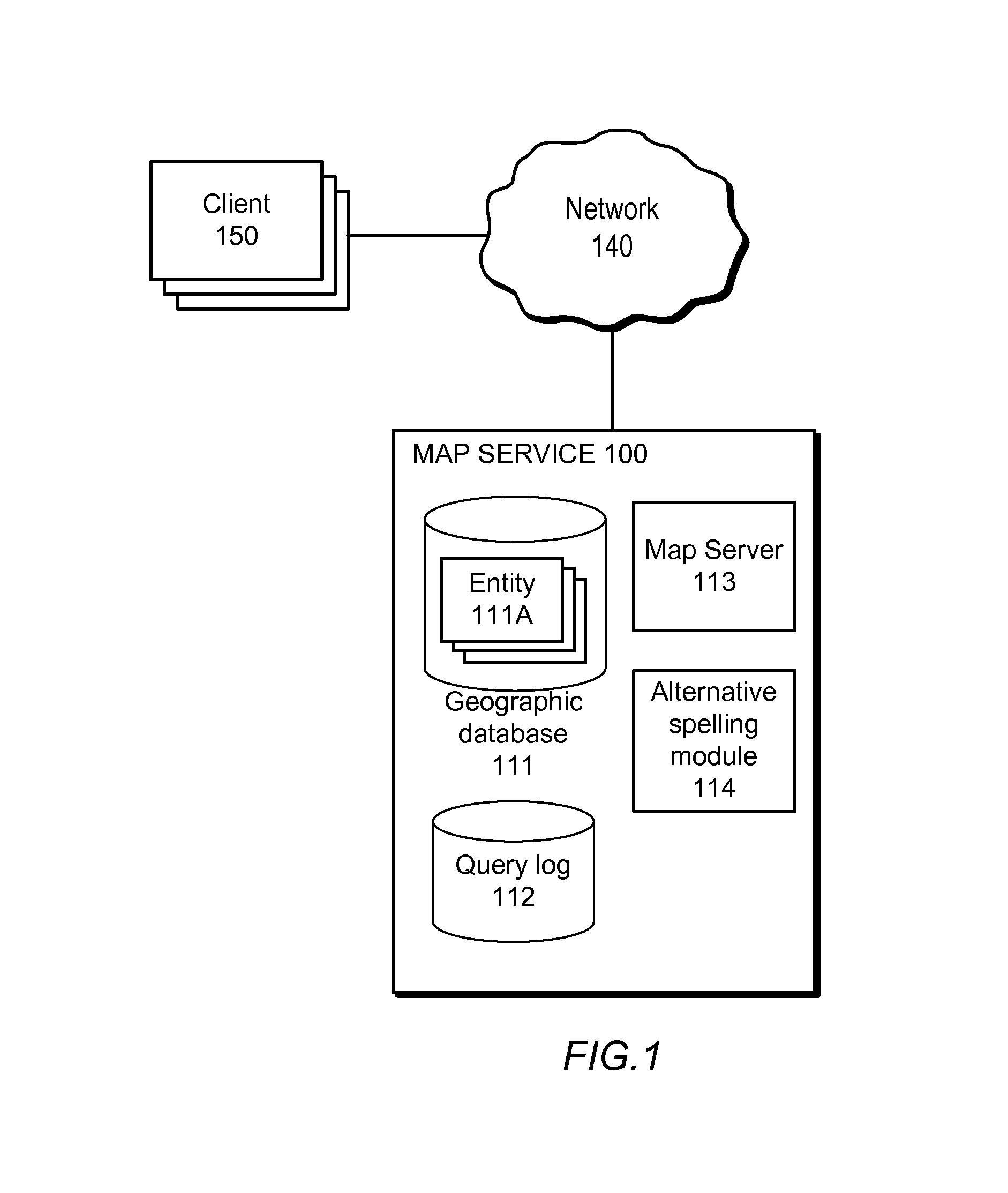
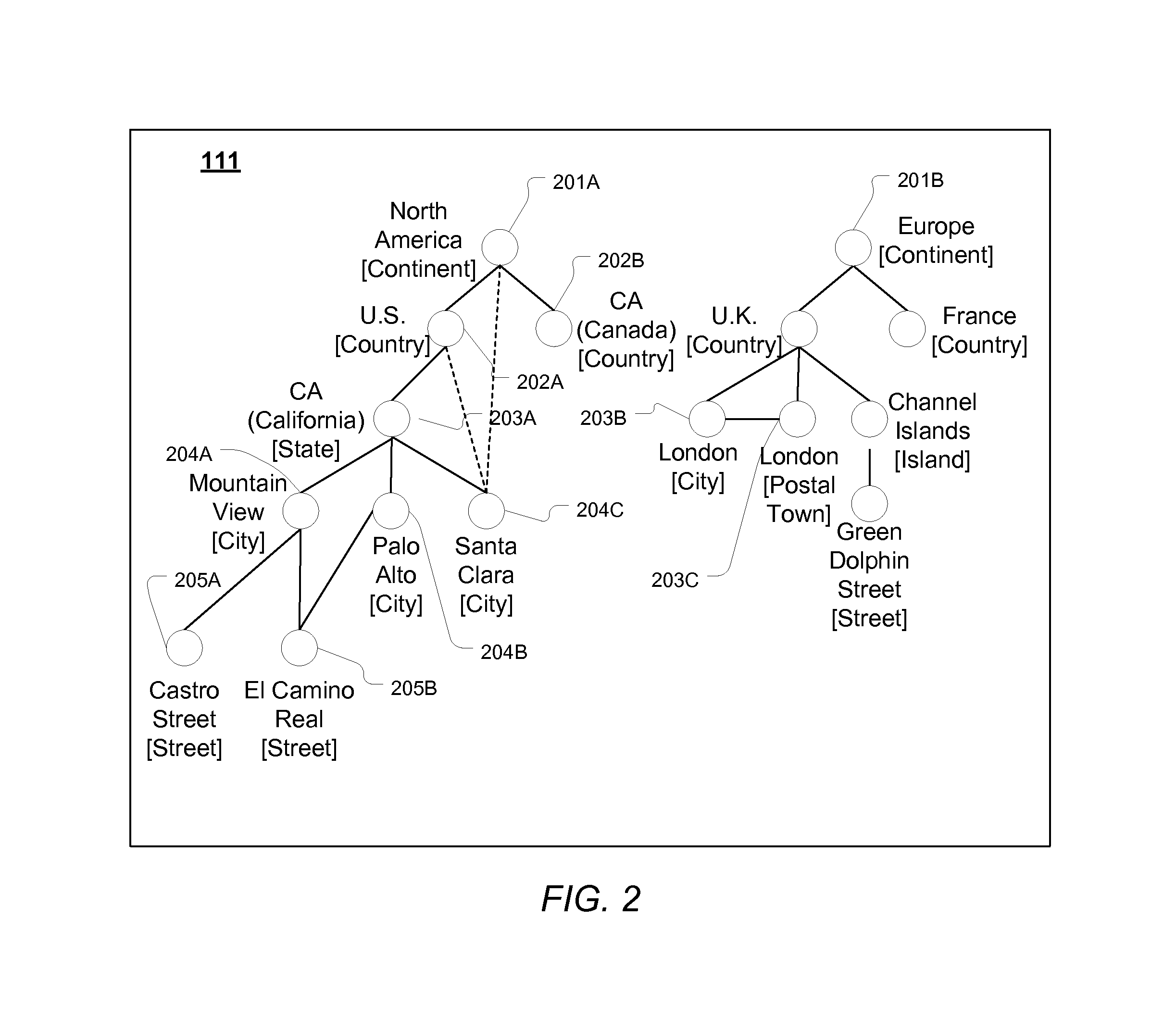
A spelling system derives a language model for a particular domain of structured data, the language model enabling determinations of alternative spellings of queries or other strings of text from that domain. More specifically, the spelling system calculates (a) probabilities that the various query entity types—such as STREET, CITY, or STATE for queries in the geographical domain—are arranged in each of the various possible orders, and (b) probabilities that an arbitrary query references given particular ones of the entities, such as the street “El Camino Real.” Based on the calculated probabilities, the spelling system generates a language model that has associated scores (e.g., probabilities) for each of a set of probable entity name orderings, where the total number of entity name orderings is substantially less than the number of all possible orderings. The language model can be applied to determine probabilities of arbitrary queries, and thus to suggest alternative queries more likely to represent what a user intended.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Apparatus and method for building domain-specific language models
InactiveUS6188976B1Satisfactory qualitySpeech recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsA domainMixture modeling
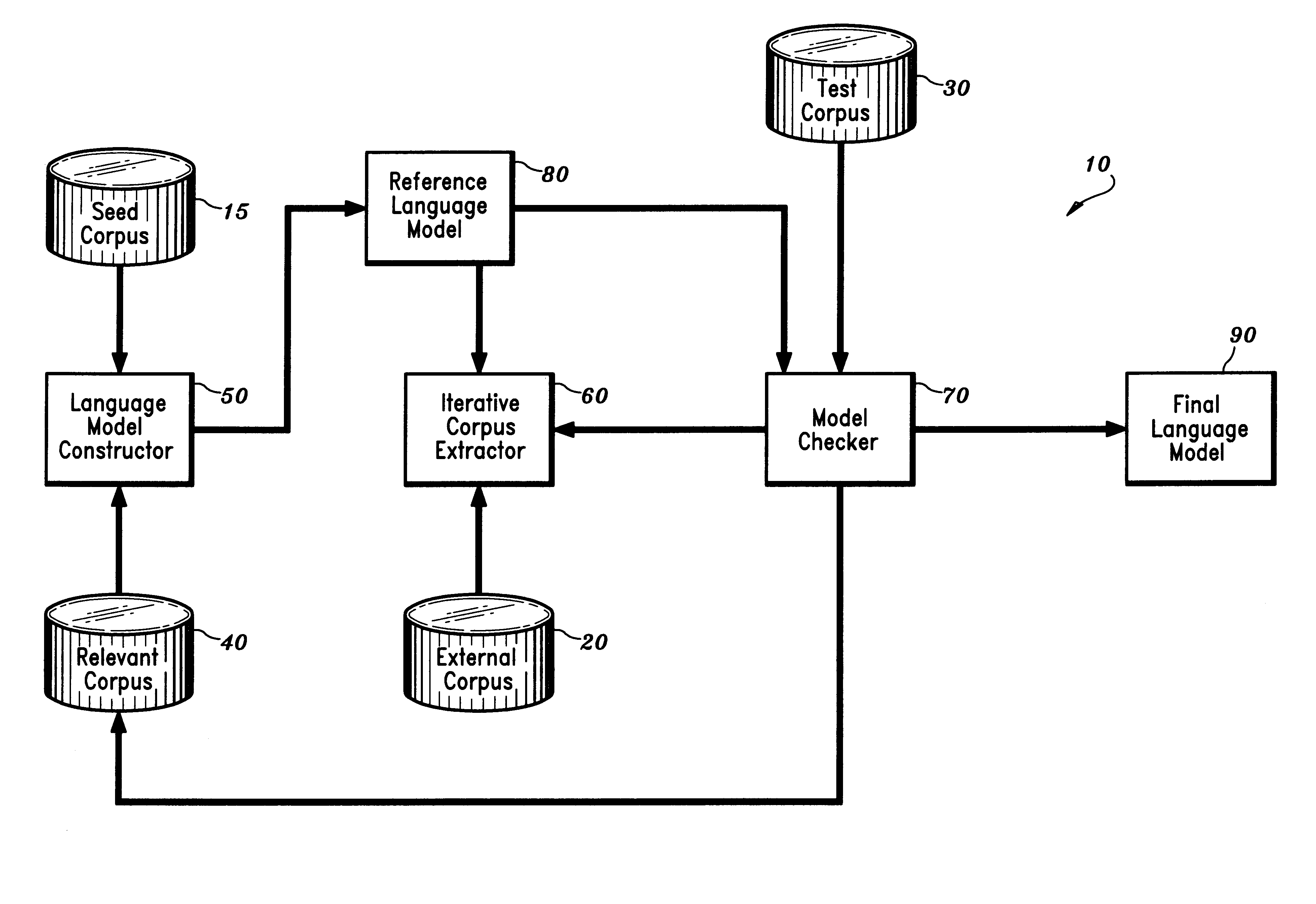
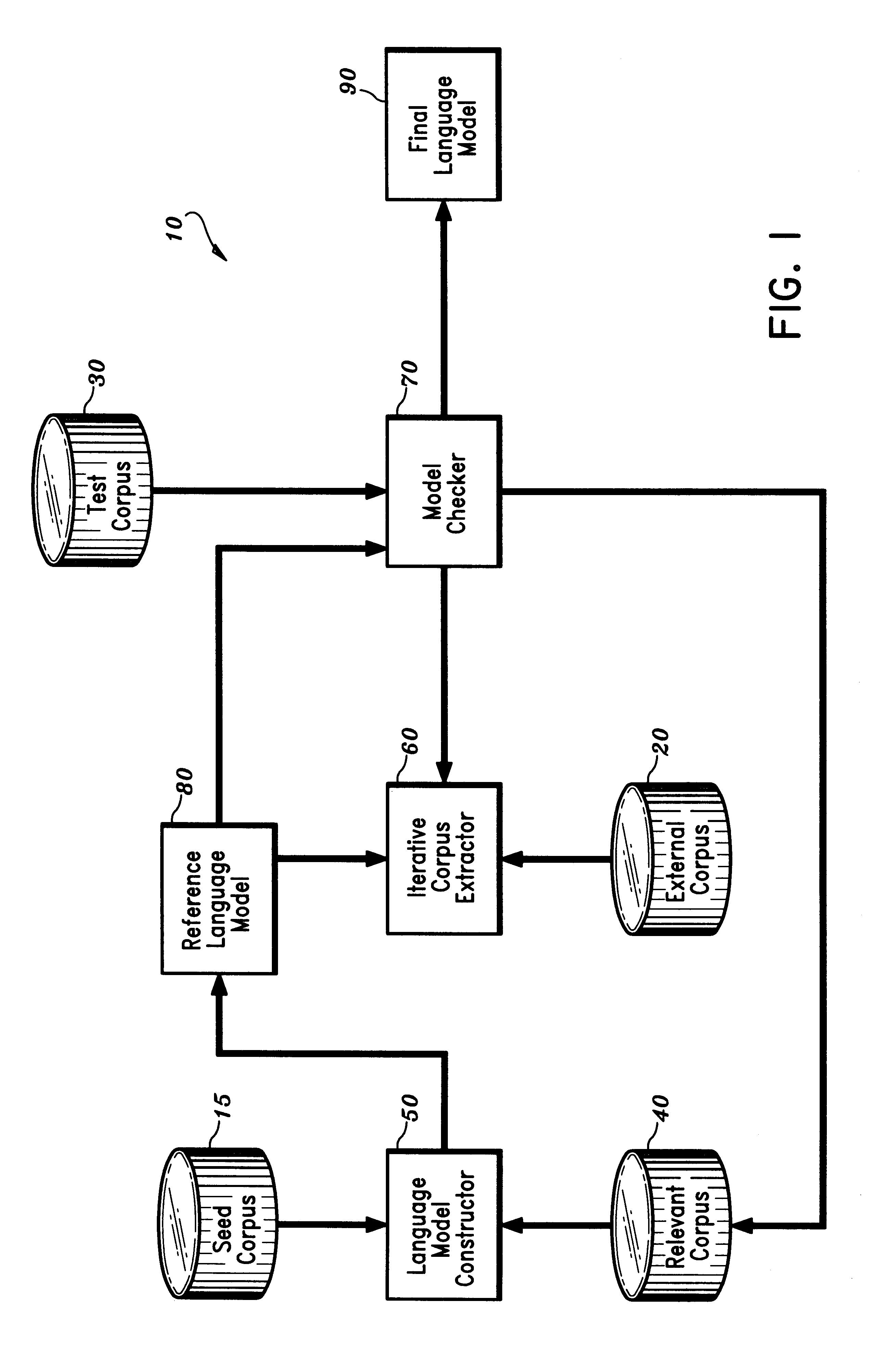
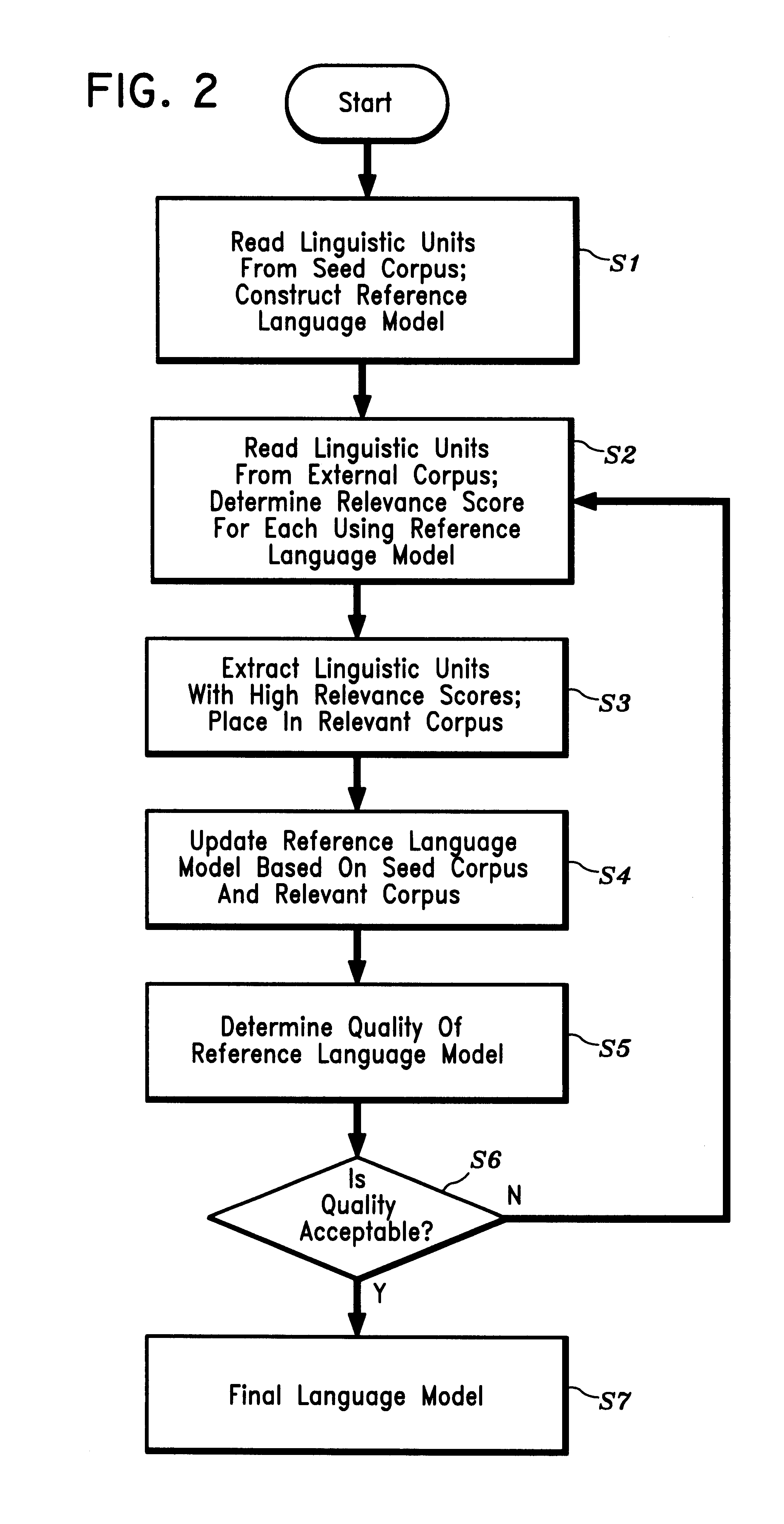
Disclosed is a method and apparatus for building a domain-specific language model for use in language processing applications, e.g., speech recognition. A reference language model is generated based on a relatively small seed corpus containing linguistic units relevant to the domain. An external corpus containing a large number of linguistic units is accessed. Using the reference language model, linguistic units which have a sufficient degree of relevance to the domain are extracted from the external corpus. The reference language model is then updated based on the seed corpus and the extracted linguistic units. The process may be repeated iteratively until the language model is of satisfactory quality. The language building technique may be further enhanced by combining it with mixture modeling or class-based modeling.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
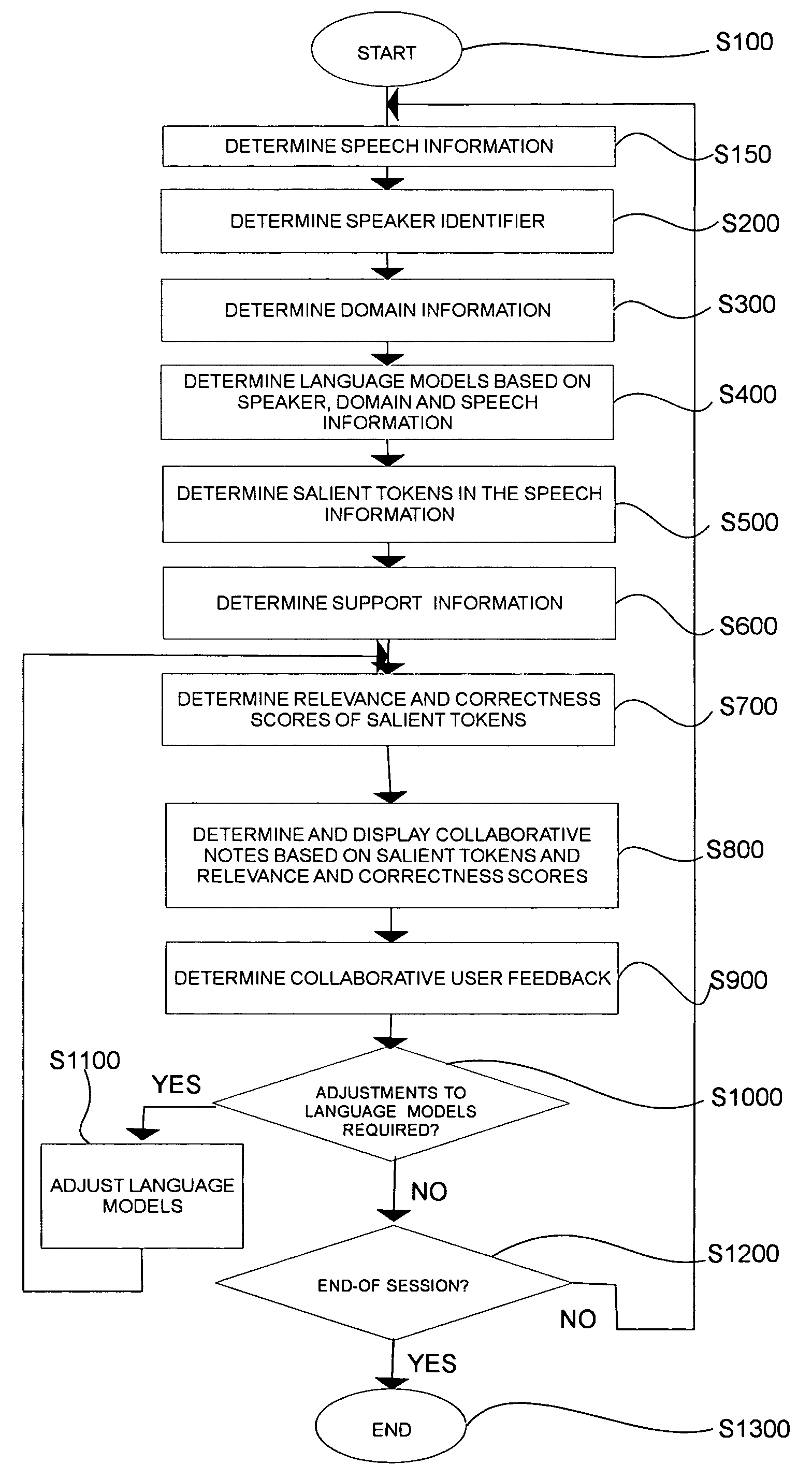
Dialog device with dialog support generated using a mixture of language models combined using a recurrent neural network
ActiveUS20170316775A1Digital data information retrievalNatural language data processingAlgorithmDisplay device
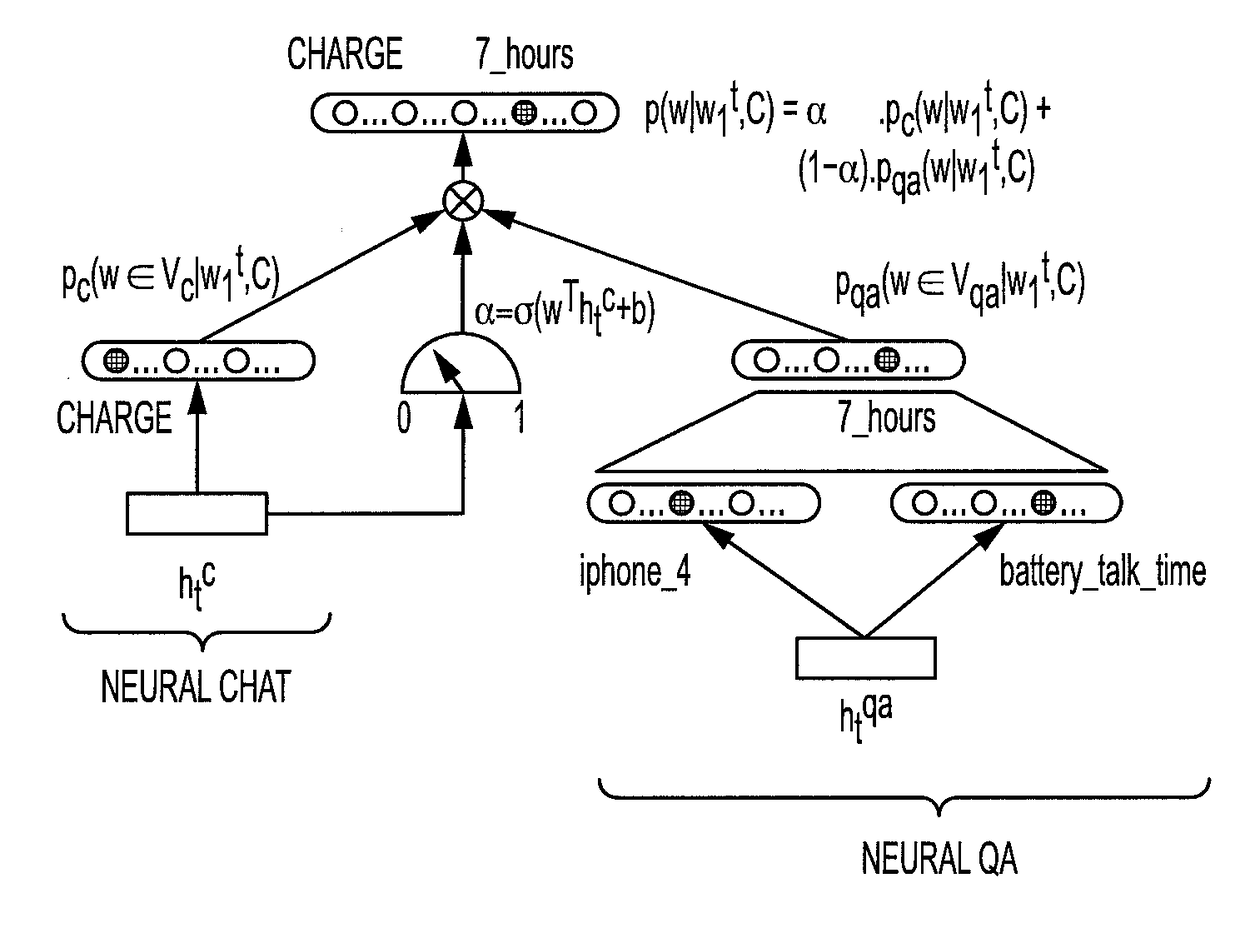
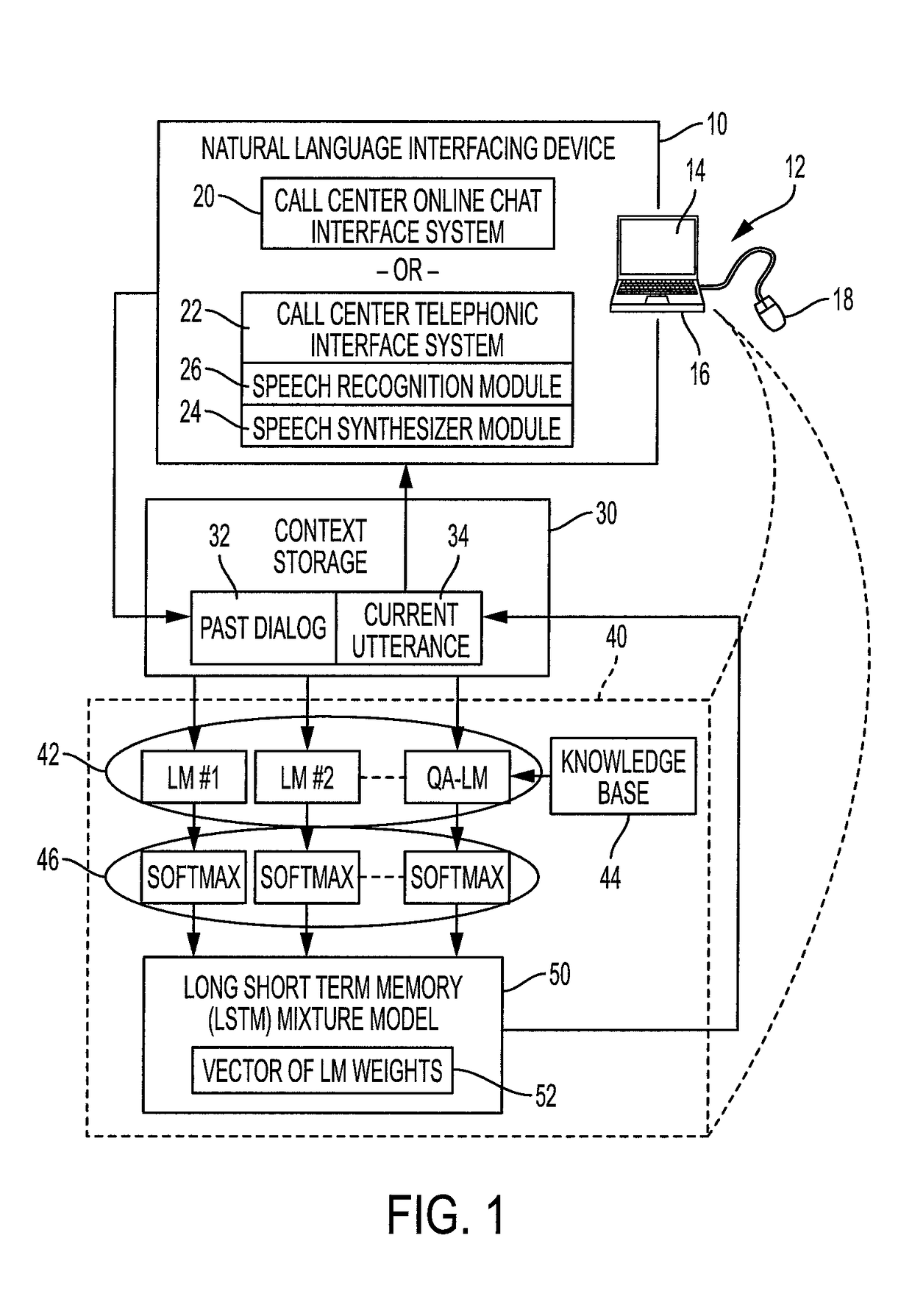
A dialog device comprises a natural language interfacing device (chat interface or a telephonic device), and a natural language output device (the chat interface, a display device, or a speech synthesizer outputting to the telephonic device). A computer stores natural language dialog conducted via the interfacing device and constructs a current utterance word-by-word. Each word is chosen by applying a plurality of language models to a context comprising concatenation of the stored dialog and the current utterance thus far. Each language model outputs a distribution over the words of a vocabulary. A recurrent neural network (RNN) is applied to the distributions to generate a mixture distribution. The next word is chosen using the mixture distribution. The output device outputs the current natural language utterance after it has been constructed by the computer.
Owner:CONDUENT BUSINESS SERVICES LLC
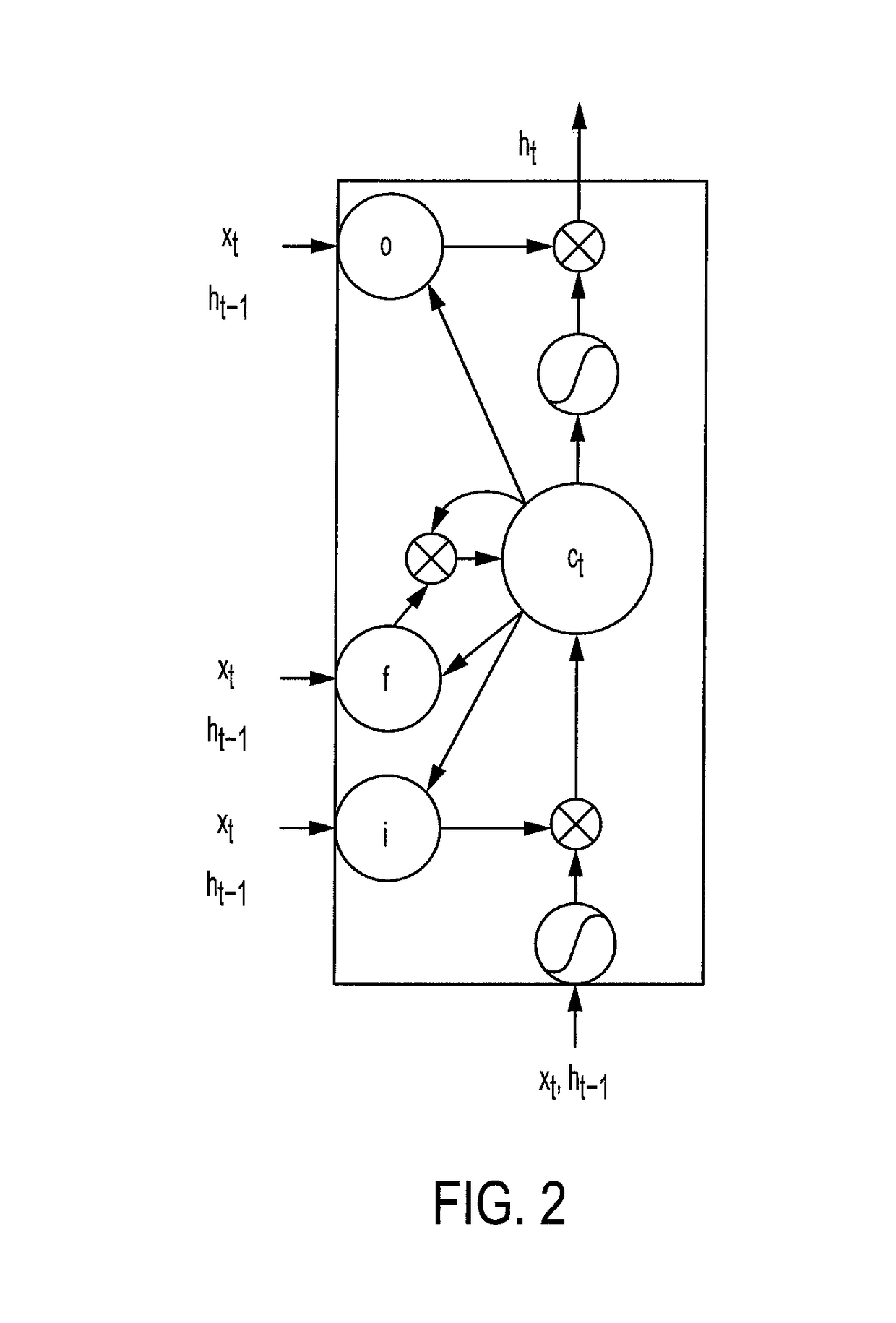
Word boundary probability estimating, probabilistic language model building, kana-kanji converting, and unknown word model building
InactiveUS20080228463A1Accuracy of recognitionImprove abilitiesNatural language translationSpeech recognitionCorpus restiformeWord model
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
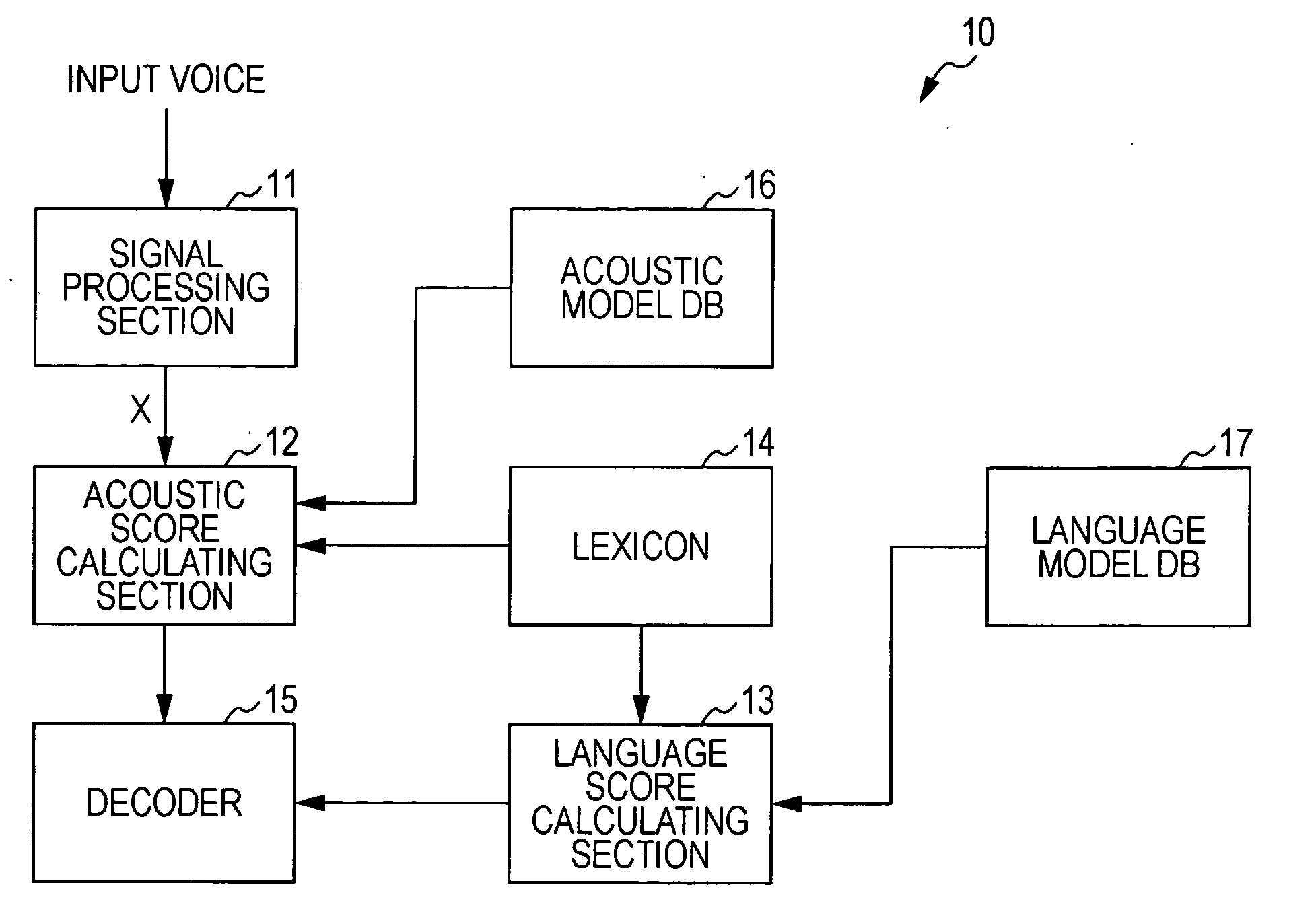
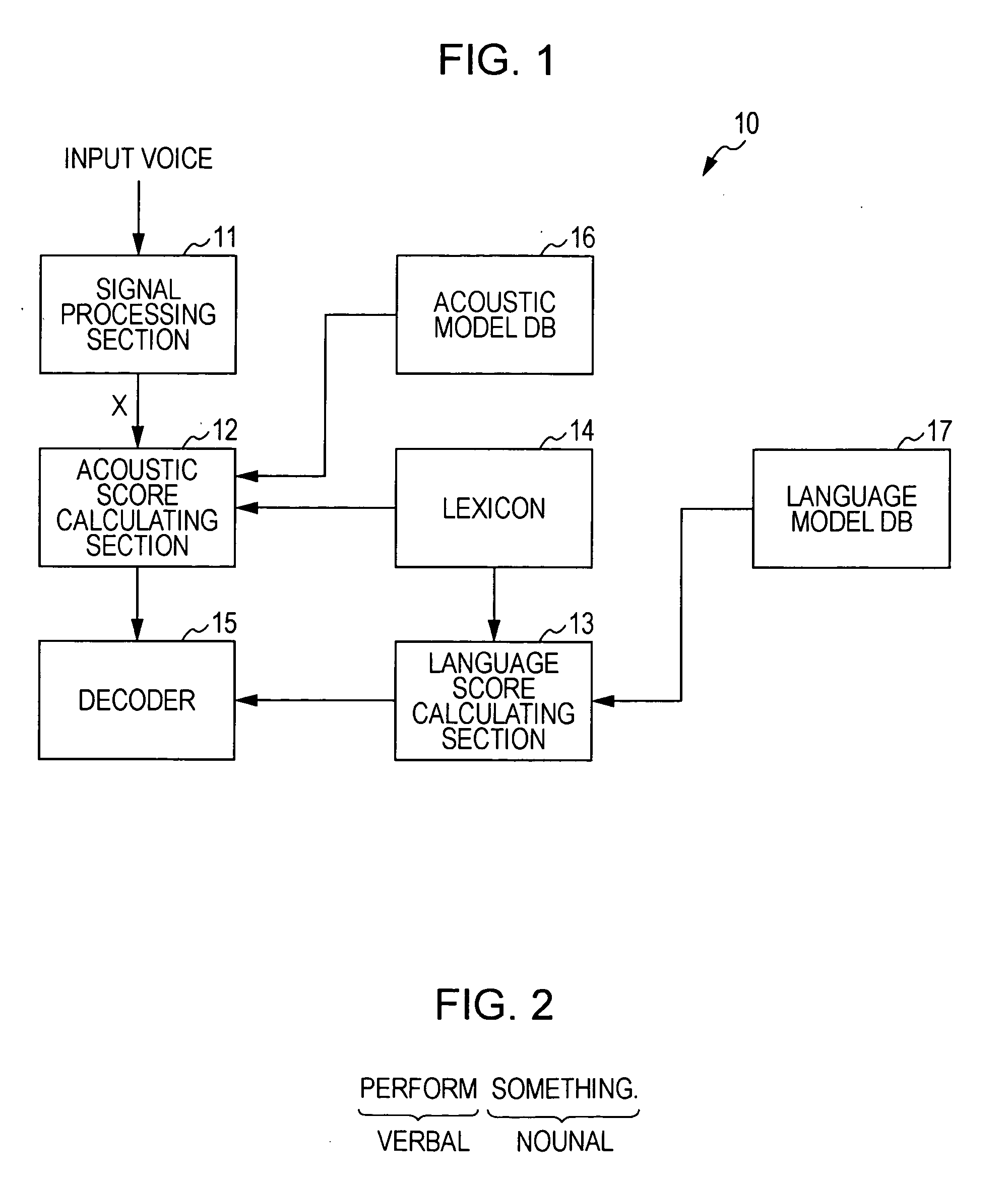
Voice recognition device and voice recognition method, language model generating device and language model generating method, and computer program
InactiveUS20100241418A1Speech recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsHuman languageComputer program
A speech recognition device includes one intention extracting language model and more in which an intention of a focused specific task is inherent, an absorbing language model in which any intention of the task is not inherent, a language score calculating section that calculates a language score indicating a linguistic similarity between each of the intention extracting language model and the absorbing language model, and the content of an utterance, and a decoder that estimates an intention in the content of an utterance based on a language score of each of the language models calculated by the language score calculating section.
Owner:SONY CORP
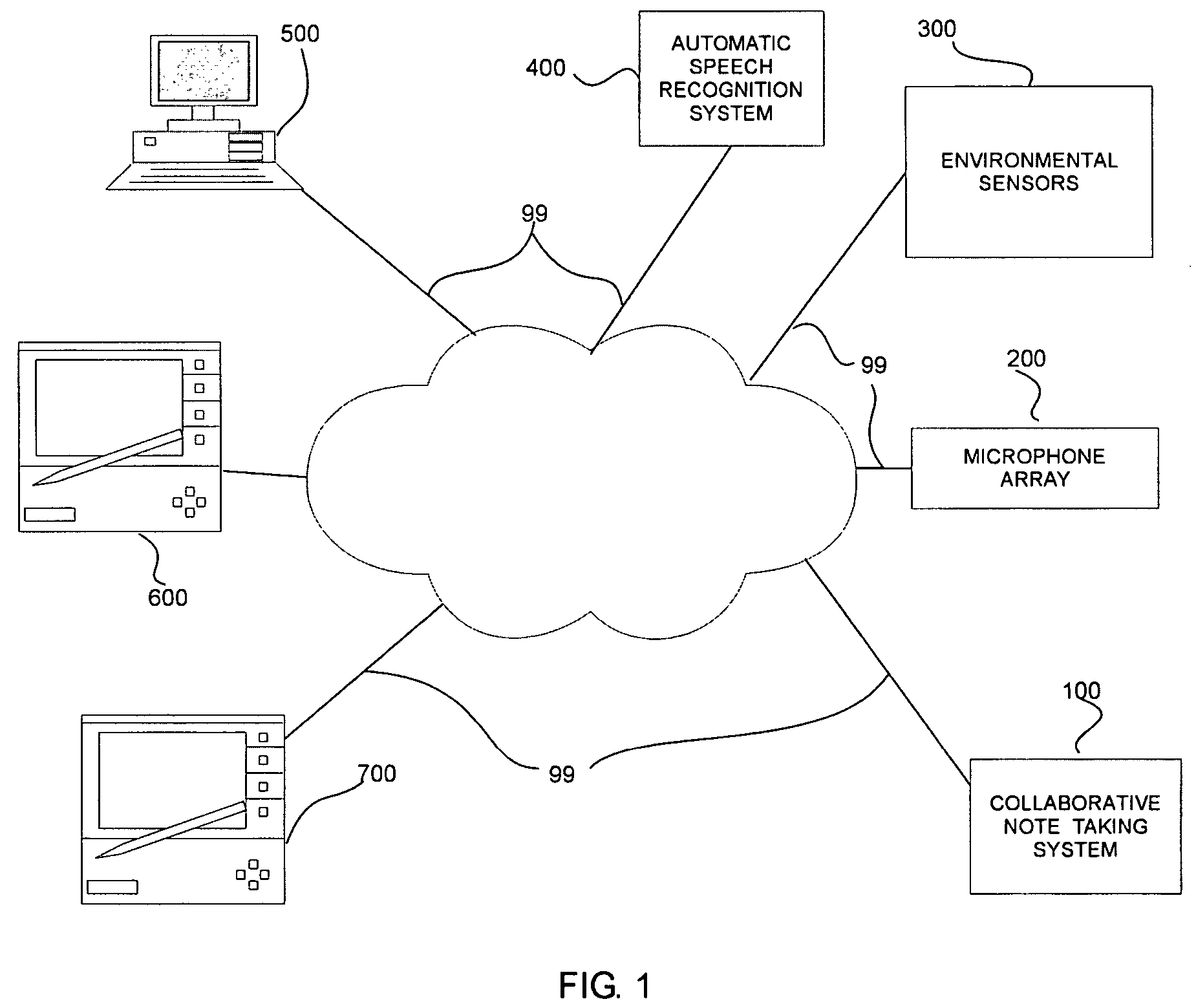
Systems and methods for collaborative note-taking
InactiveUS7542971B2Digital data processing detailsNatural language data processingHandwritingFunction word
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Unsupervised learning of paraphrase/translation alternations and selective application thereof
InactiveUS20060106594A1Natural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsParaphraseAlgorithm
A computer-implemented method is disclosed for applying a given paraphrase alternation pattern to an input string. The method includes generating a language model and applying the language model to determine how to apply the given paraphrase alternation pattern to the input string.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
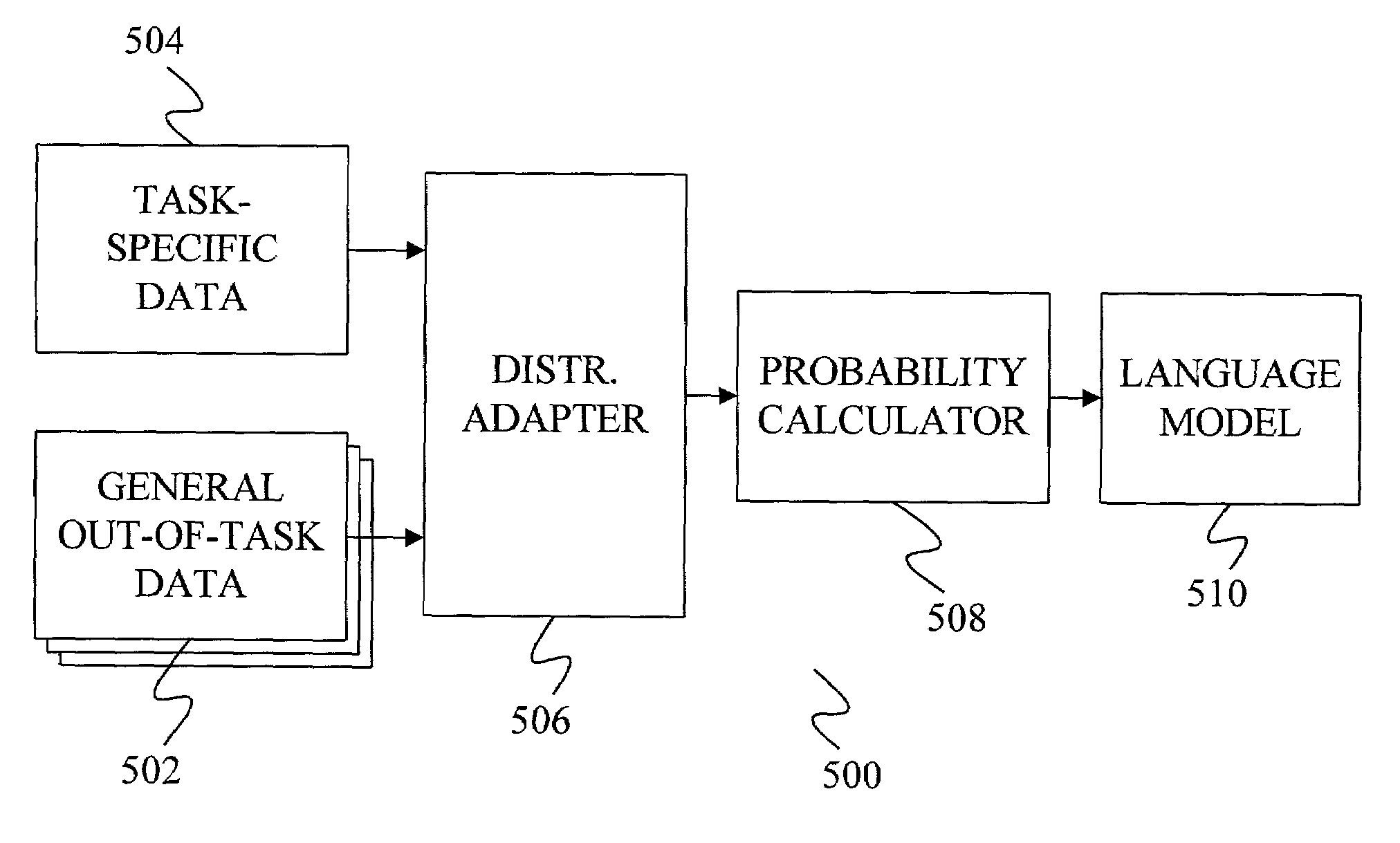
Method and apparatus for distribution-based language model adaptation
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method of performing speech recognition based on a user identifier
InactiveUS7451081B1Natural language data processingSpeech recognitionData fieldBackground information
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
Voice recognition device and voice recognition method, language model generating device and language model generating method, and computer program
InactiveCN101847405AImplement extractionImprove consistencySpeech recognitionSpeech identificationSpeech sound
The invention discloses a voice recognition device and a voice recognition method, a language model generating device and a language model generating method, and computer program. The speech recognition device includes one intention extracting language model and more in which an intention of a focused specific task is inherent, an absorbing language model in which any intention of the task is not inherent, a language score calculating section that calculates a language score indicating a linguistic similarity between each of the intention extracting language model and the absorbing language model, and the content of an utterance, and a decoder that estimates an intention in the content of an utterance based on a language score of each of the language models calculated by the language score calculating section.
Owner:SONY CORP
Encoding and Adaptive, Scalable Accessing of Distributed Models
ActiveUS20080262828A1Quality improvementImprove translation speedNatural language translationTransformation of program codeTheoretical computer scienceMachine translation
Systems, methods, and apparatus for accessing distributed models in automated machine processing, including using large language models in machine translation, speech recognition and other applications.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
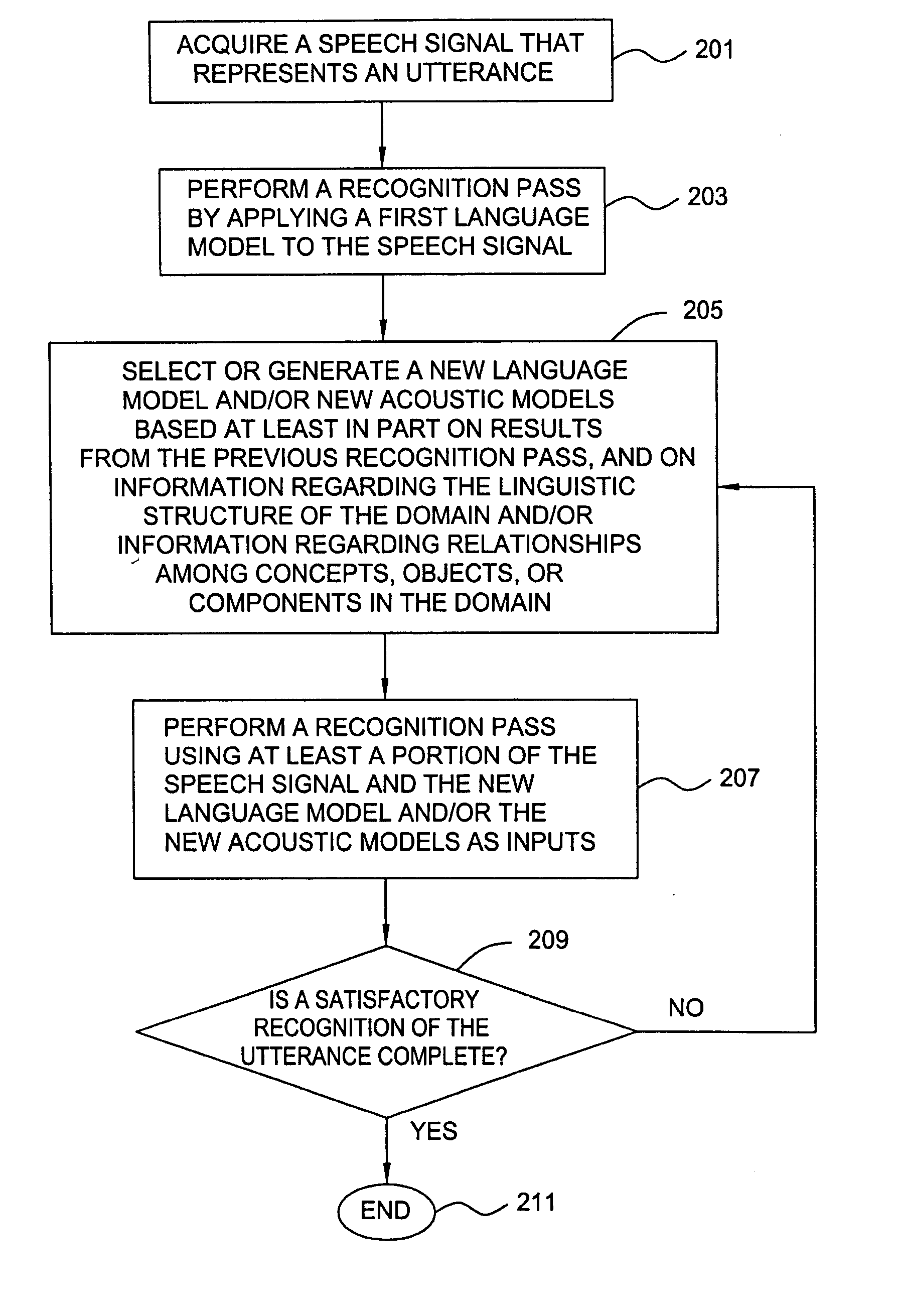
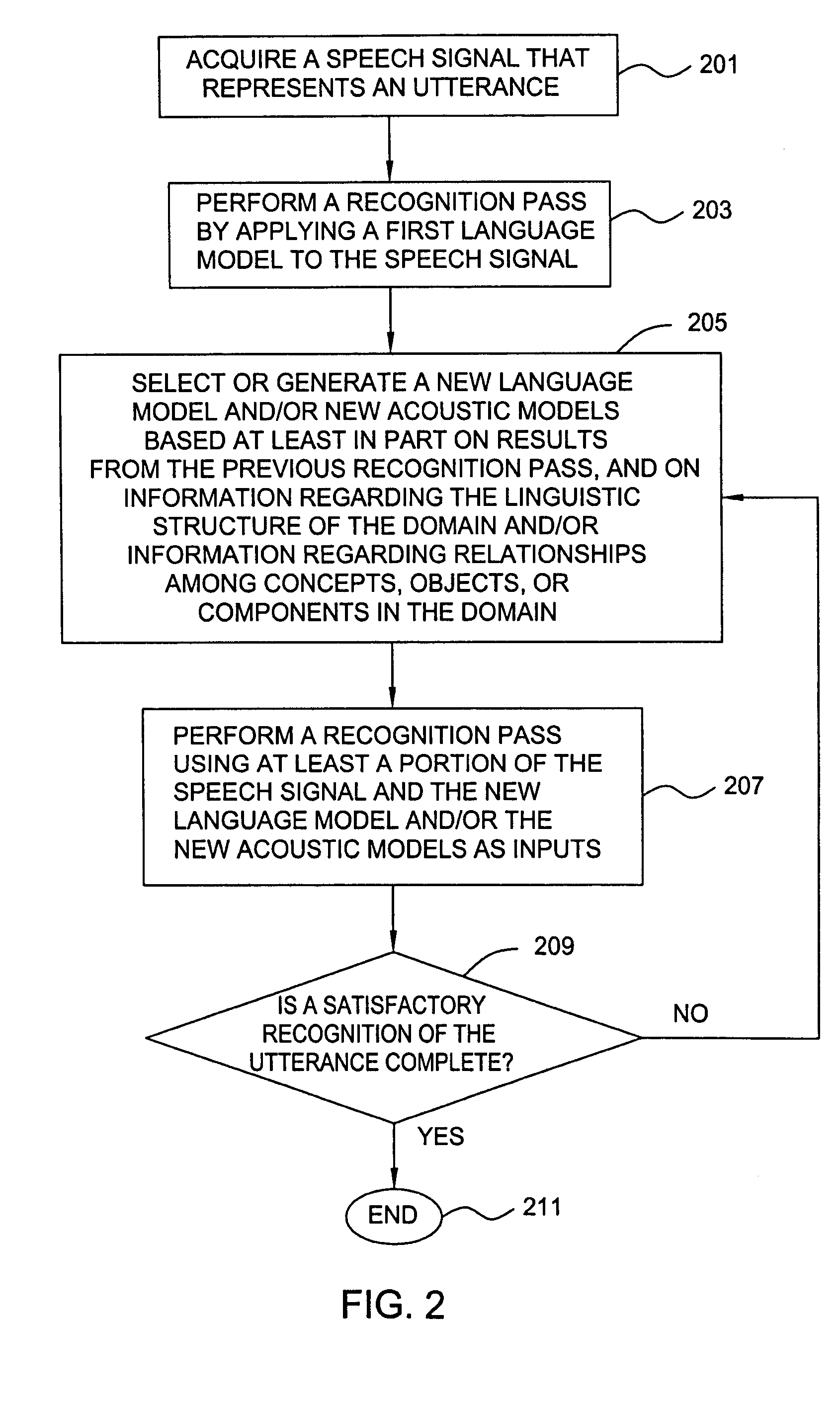
Method and apparatus for speech recognition using a dynamic vocabulary
A method and apparatus are provided for performing speech recognition using a dynamic vocabulary. Results from a preliminary speech recognition pass can be used to update or refine a language model in order to improve the accuracy of search results and to simplify subsequent recognition passes. This iterative process greatly reduces the number of alternative hypotheses produced during each speech recognition pass, as well as the time required to process subsequent passes, making the speech recognition process faster, more efficient and more accurate. The iterative process is characterized by the use of results from one or more data set queries, where the keys used to query the data set, as well as the queries themselves, are constructed in a manner that produces more effective language models for use in subsequent attempts at decoding a given speech signal.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
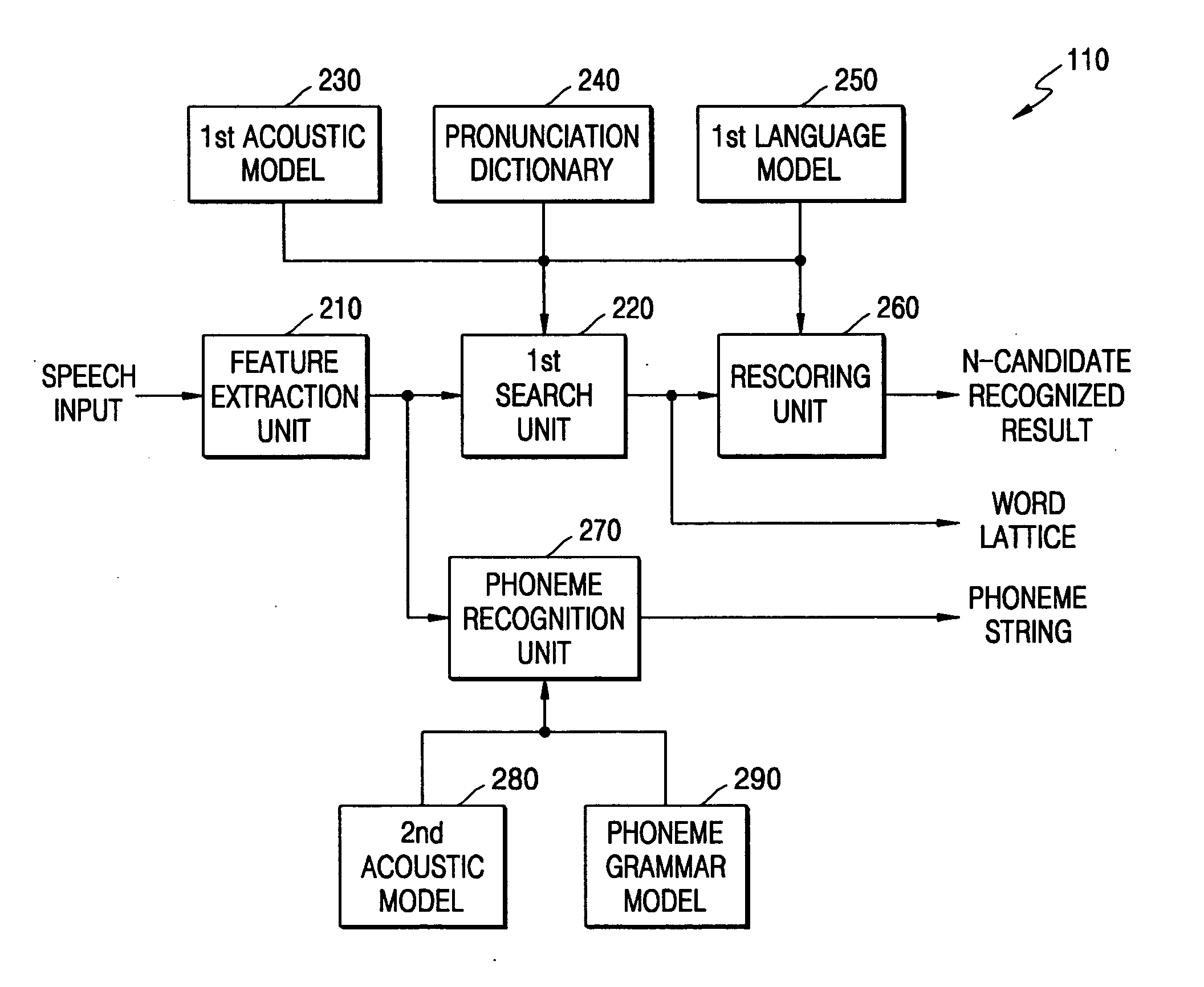
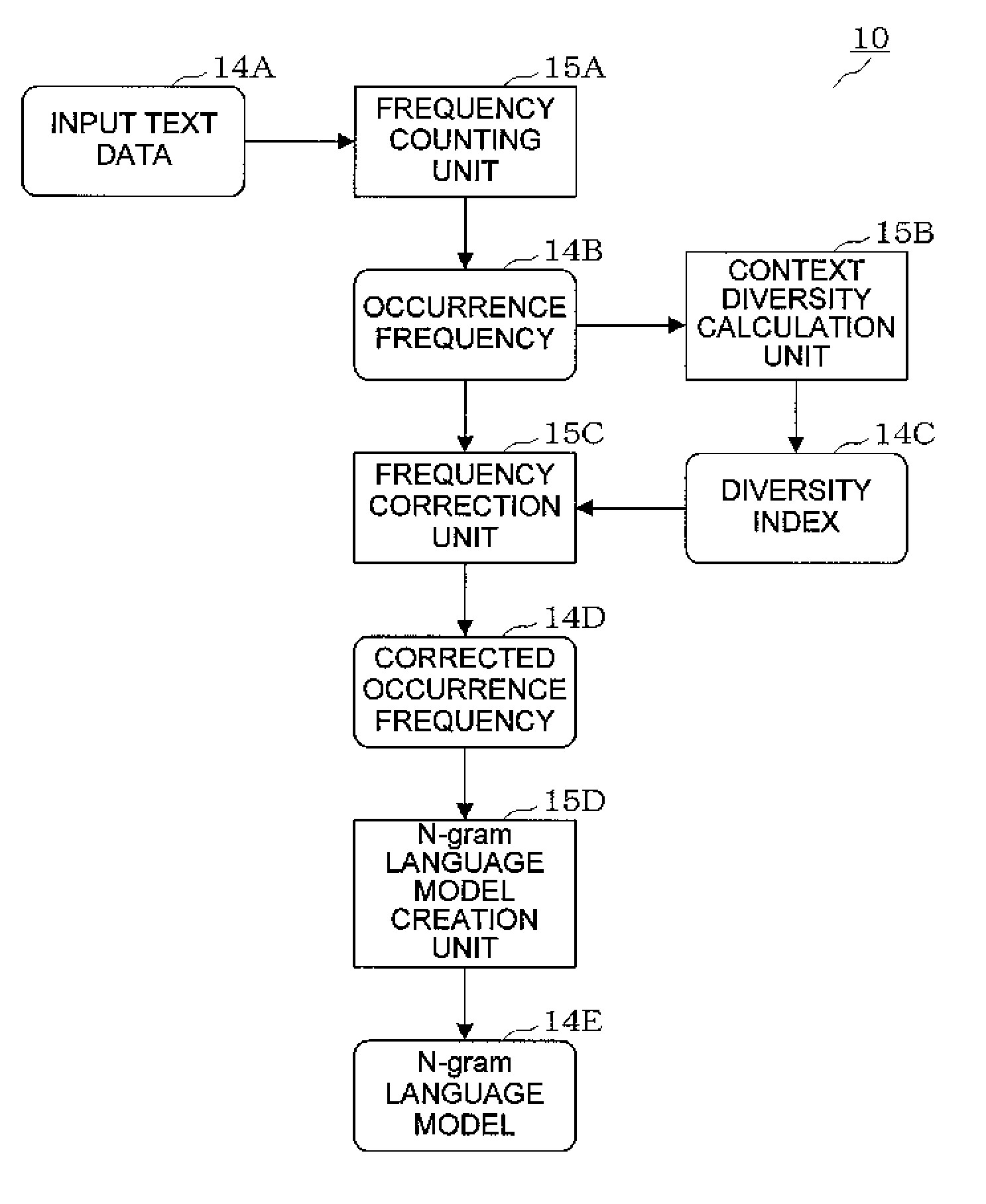
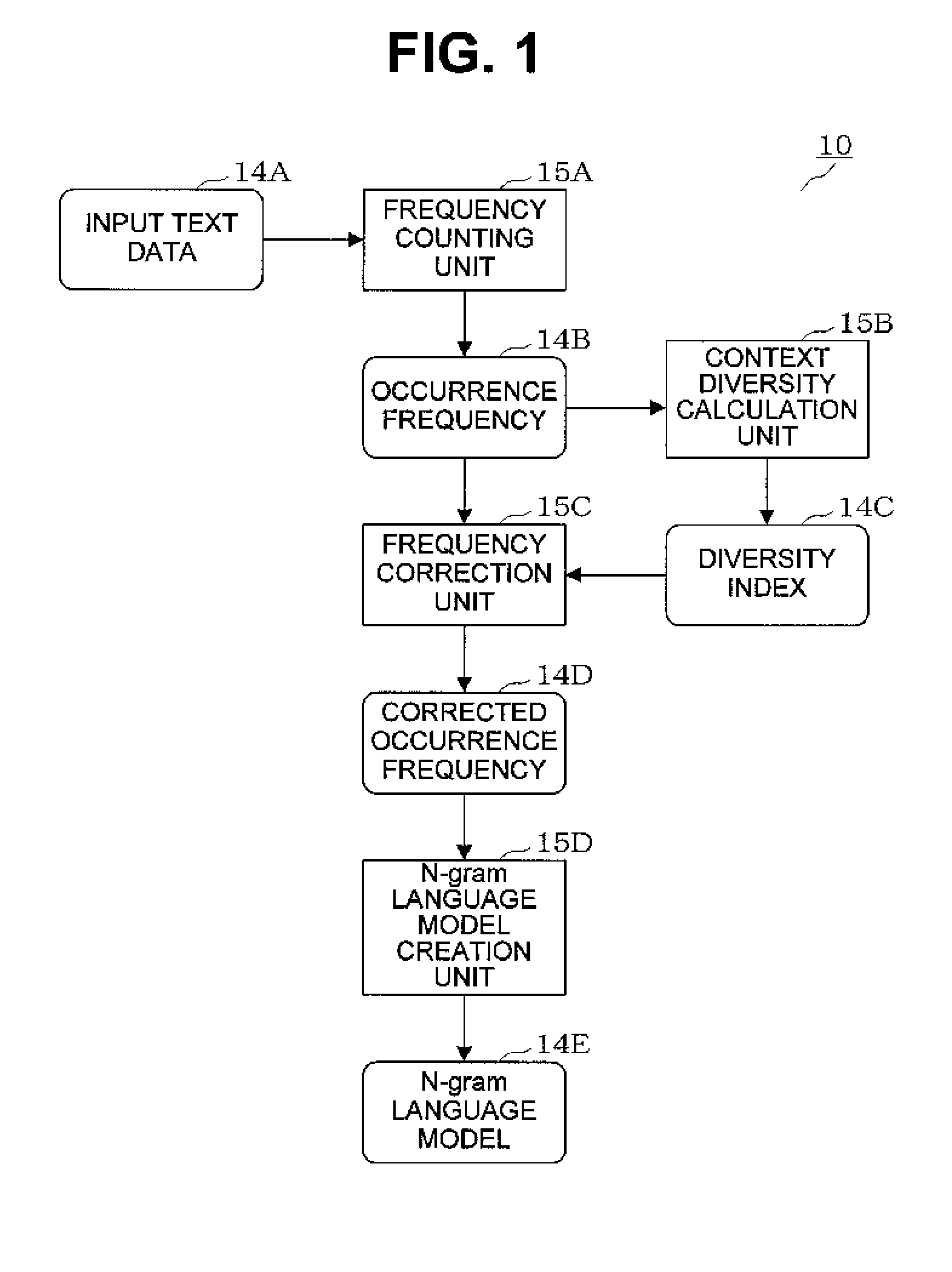
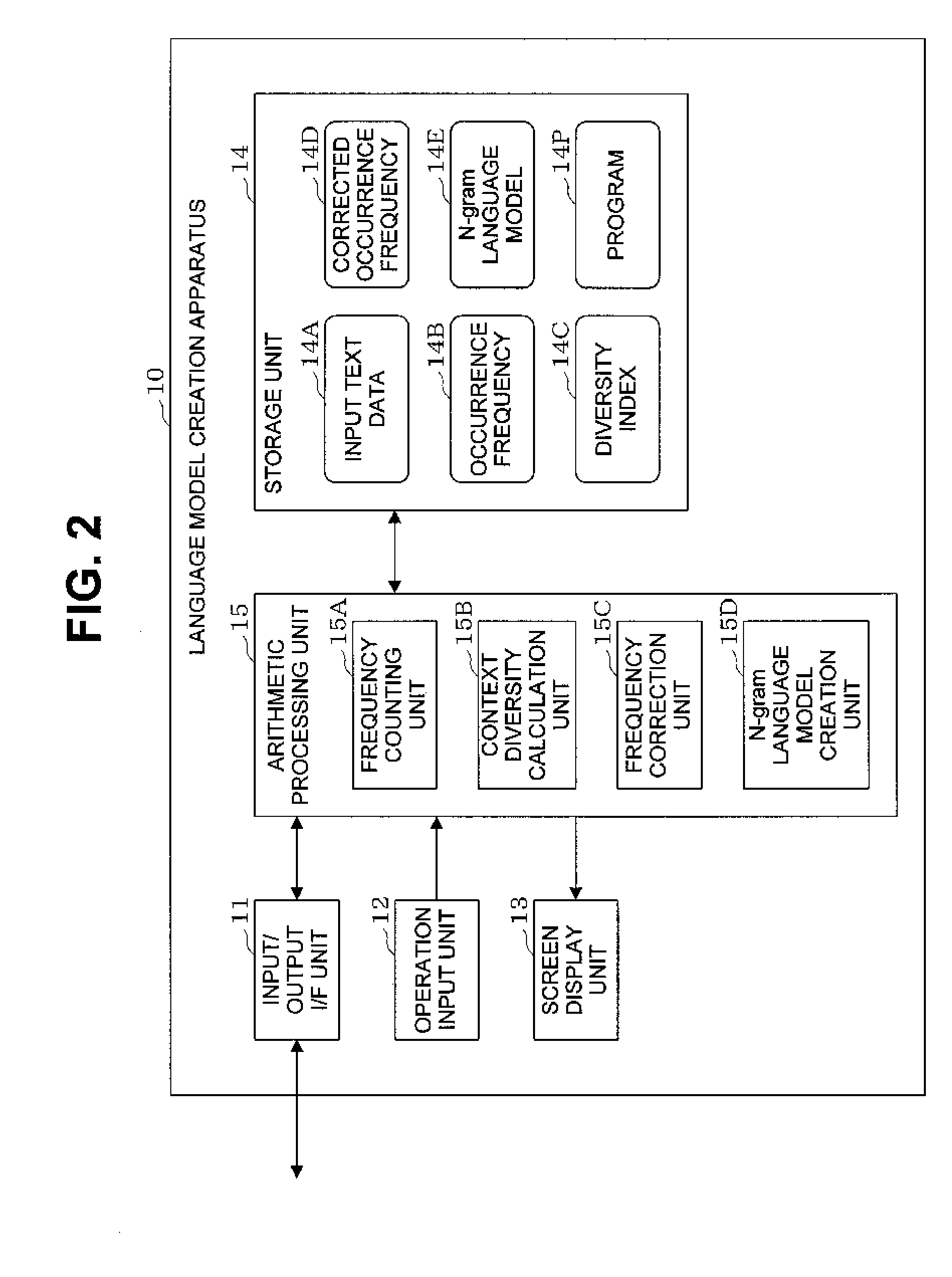
Language model creation apparatus, language model creation method, speech recognition apparatus, speech recognition method, and recording medium
InactiveUS20110161072A1Natural language translationSpeech recognitionDiversity indexContextual diversity
A frequency counting unit (15A) counts occurrence frequencies (14B) in input text data (14A) for respective words or word chains contained in the input text data (14A). A context diversity calculation unit (15B) calculates, for the respective words or word chains, diversity indices (14C) each indicating the context diversity of a word or word chain. A frequency correction unit (15C) corrects the occurrence frequencies (14B) of the respective words or word chains based on the diversity indices (14C) of the respective words or word chains. An N-gram language model creation unit (15D) creates an N-gram language model (14E) based on the corrected occurrence frequencies (14D) obtained for the respective words or word chains.
Owner:NEC CORP
Large Scale Distributed Syntactic, Semantic and Lexical Language Models
InactiveUS20130325436A1Semantic analysisSpeech recognitionExpectation–maximization algorithmModel parameters
A composite language model may include a composite word predictor. The composite word predictor may include a first language model and a second language model that are combined according to a directed Markov random field. The composite word predictor can predict a next word based upon a first set of contexts and a second set of contexts. The first language model may include a first word predictor that is dependent upon the first set of contexts. The second language model may include a second word predictor that is dependent upon the second set of contexts. Composite model parameters can be determined by multiple iterations of a convergent N-best list approximate Expectation-Maximization algorithm and a follow-up Expectation-Maximization algorithm applied in sequence, wherein the convergent N-best list approximate Expectation-Maximization algorithm and the follow-up Expectation-Maximization algorithm extracts the first set of contexts and the second set of contexts from a training corpus.
Owner:WRIGHT STATE UNIVERSITY
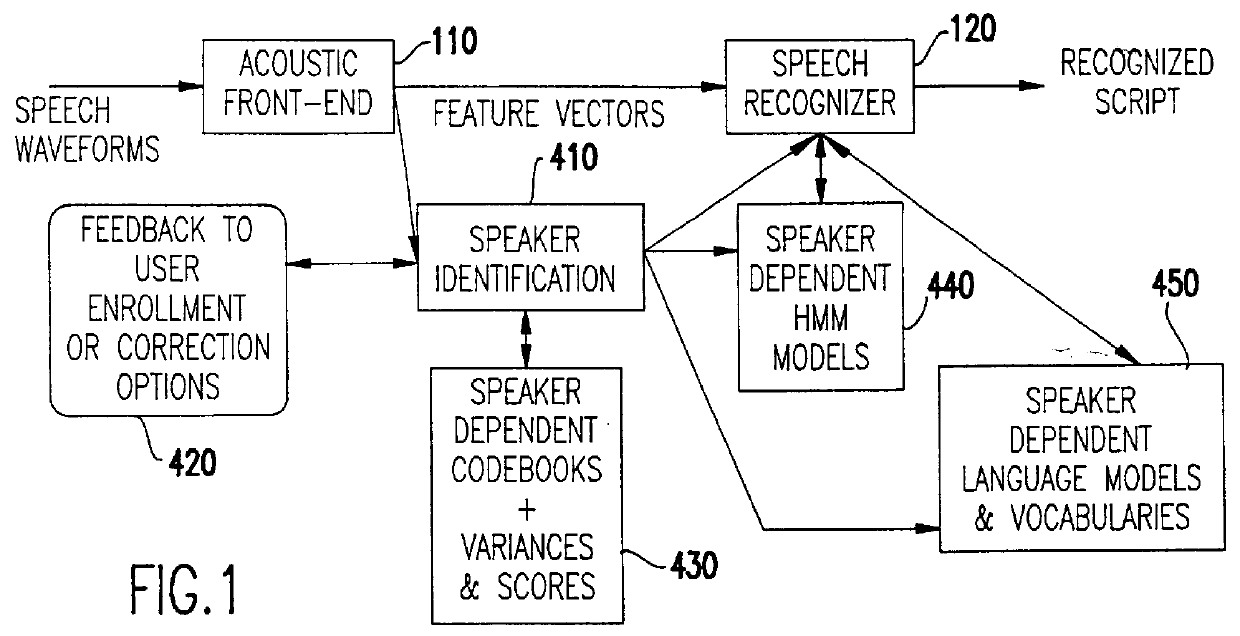
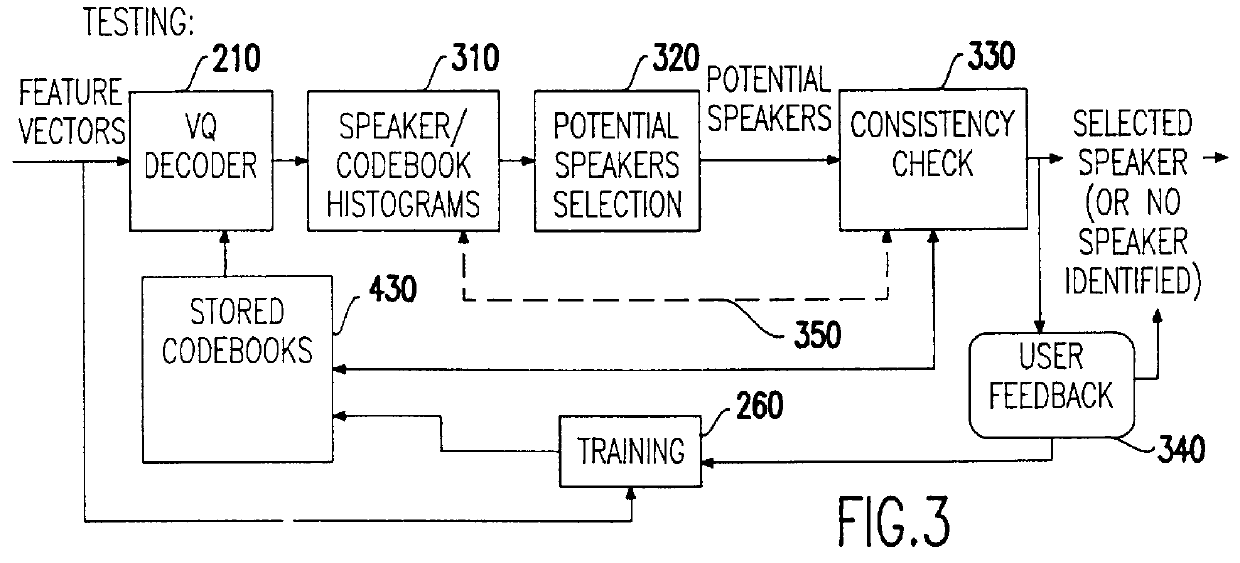
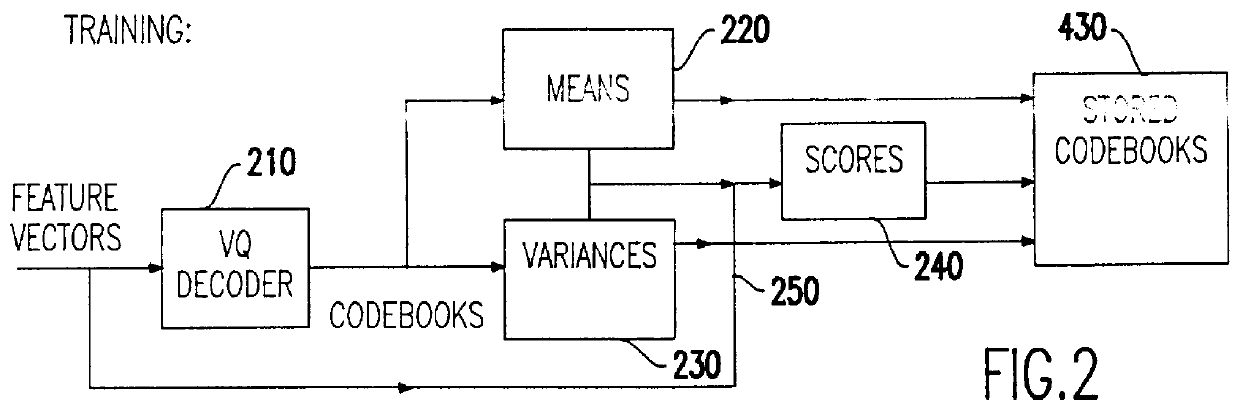
Speech recognition with attempted speaker recognition for speaker model prefetching or alternative speech modeling
Speaker recognition is attempted on input speech signals concurrently with provision of input speech signals to a speech recognition system. If a speaker is recognized, a speaker dependent model which has been trained on an enrolled speaker is supplied to the speech recognition system. If not recognized, then a speaker-independent recognition model is used or, alternatively, the new speaker is enrolled. Other speaker specific information such as a special language model, grammar, vocabulary, a dictionary, a list of names, a language and speaker dependent preferences can also be provided to improve the speech recognition function or even configure or customize the speech recognition system or the response of any system such as a computer or network controlled in response thereto. A consistency check in the form of a decision tree is preferably provided to accelerate the speaker recognition process and increase the accuracy thereof. Further training of a model and / or enrollment of additional speakers may be initiated upon completion of speaker recognition and / or adaptively upon each speaker utterance.
Owner:IBM CORP
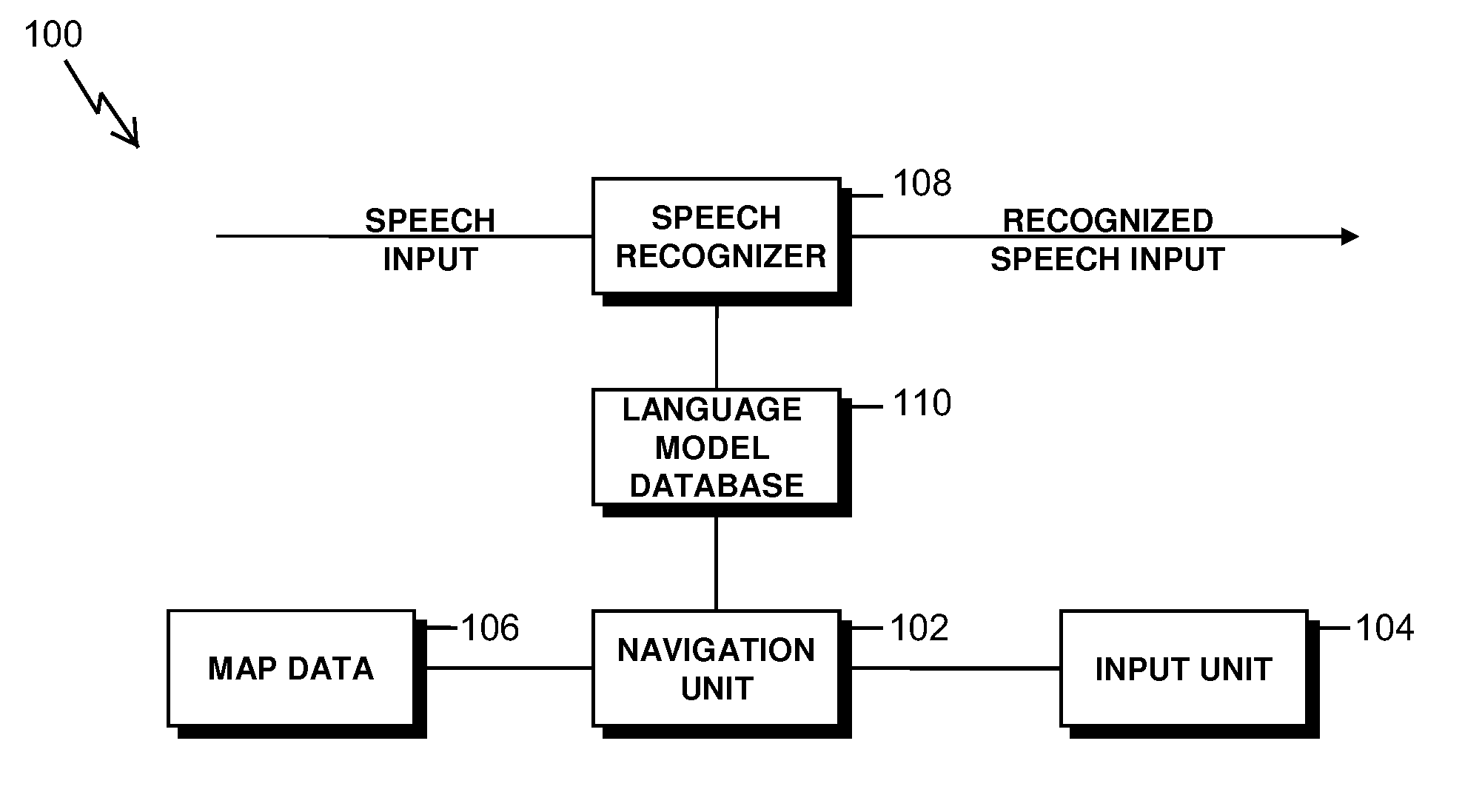
Text and speech recognition system using navigation information
ActiveUS20100191520A1Improve speech recognition accuracyRaise the possibilitySpeech recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsSpeech inputSpeech sound
A system and method are provided for recognizing a user's speech input. The method includes the steps for detecting the user's speech input, recognizing the user's speech input by comparing the speech input to a list of entries using language model statistics to determine the most likely entry matching the user's speech input, and detecting navigation information of a trip to a predetermined destination, where the most likely entry is determined by modifying the language model statistics taking into account the navigation information. A system and method is further provided that takes into account navigation trip information to determine the most likely entry using language model statistics for recognizing text input.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
Automated extraction of semantic content and generation of a structured document from speech
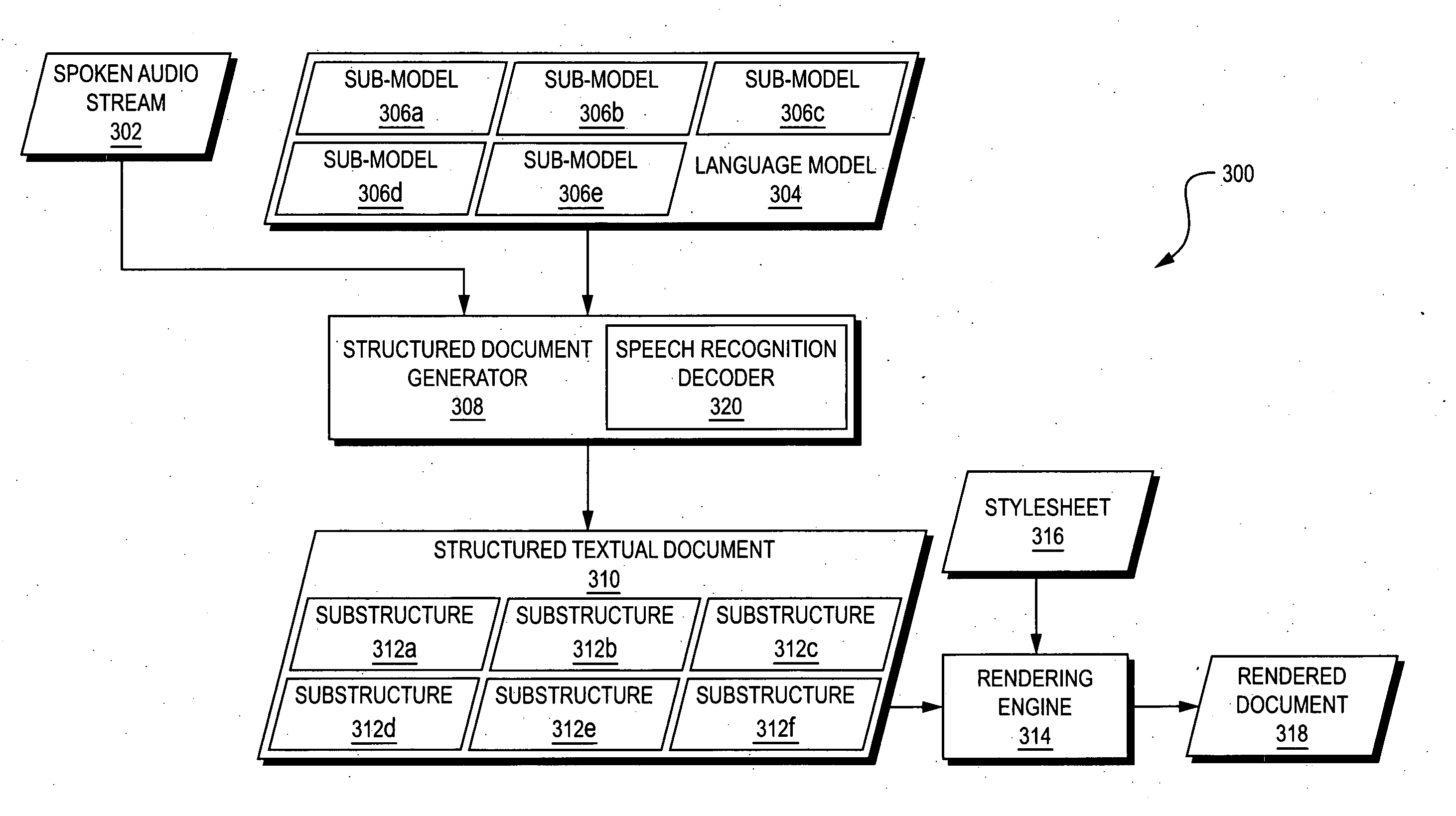
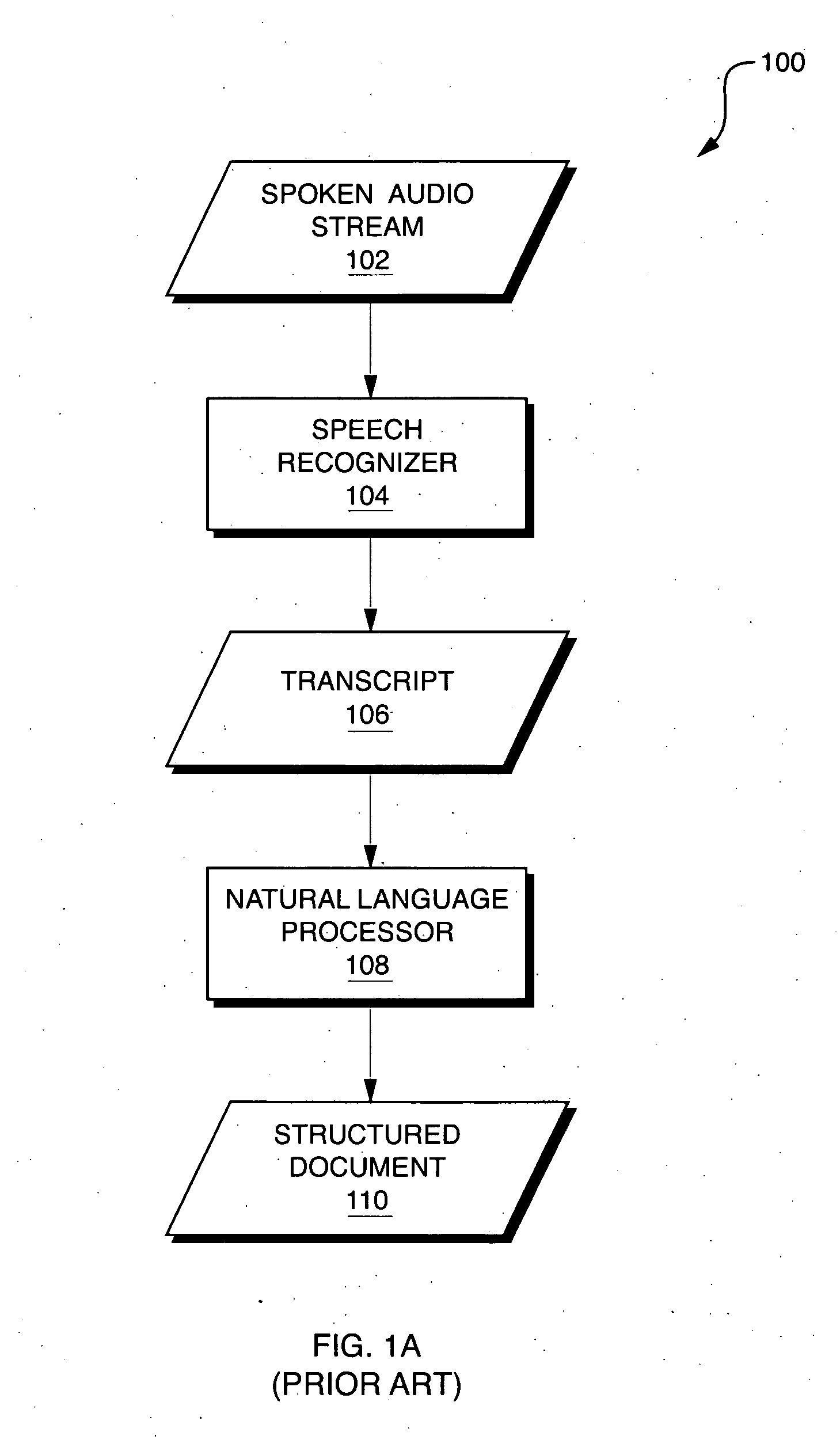
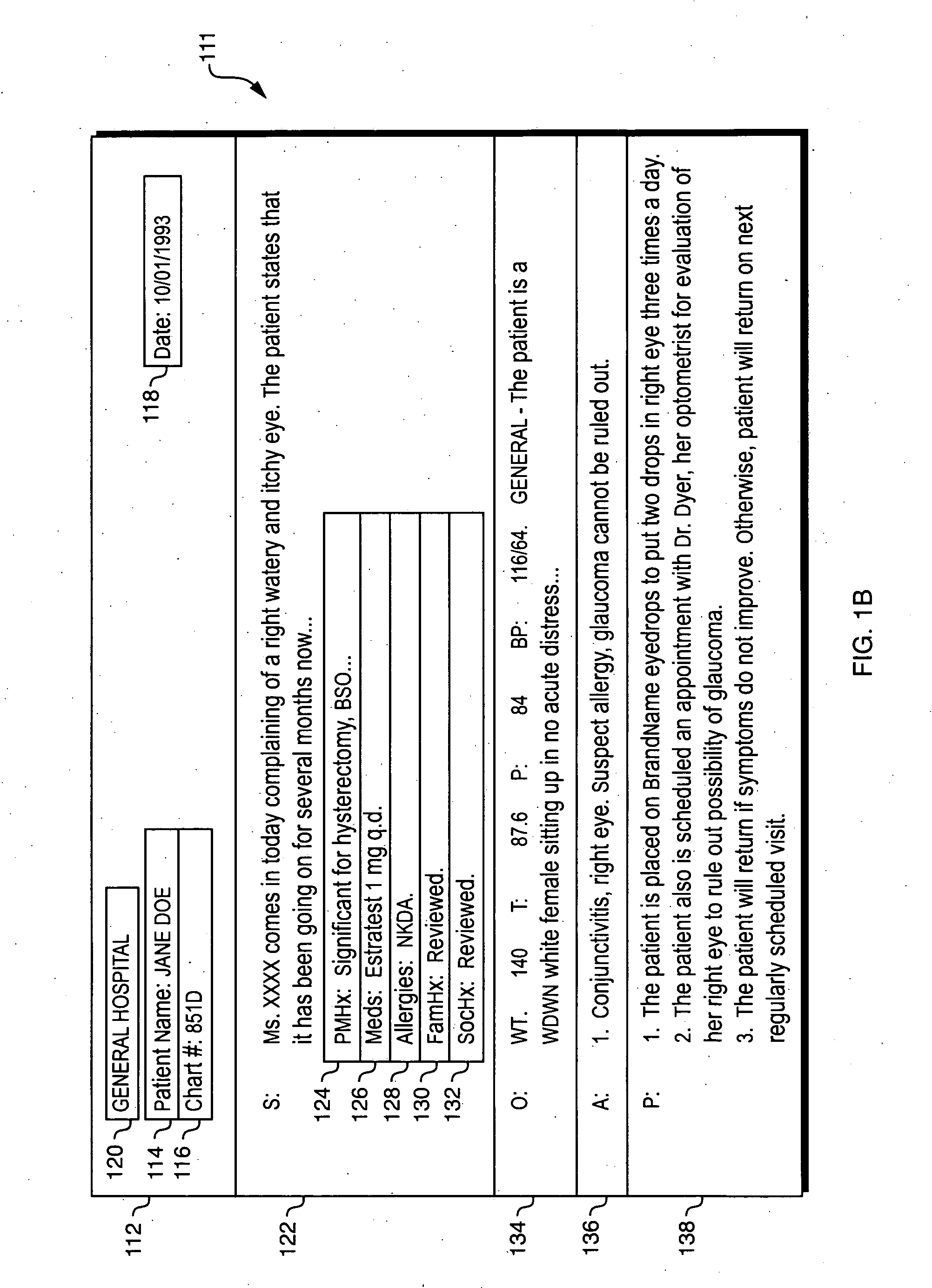
InactiveUS20060041428A1Simple technologyMedical report generationSpeech recognitionDocumentation procedureSpeech sound
Techniques are disclosed for automatically generating structured documents based on speech, including identification of relevant concepts and their interpretation. In one embodiment, a structured document generator uses an integrated process to generate a structured textual document (such as a structured textual medical report) based on a spoken audio stream. The spoken audio stream may be recognized using a language model which includes a plurality of sub-models arranged in a hierarchical structure. Each of the sub-models may correspond to a concept that is expected to appear in the spoken audio stream. Different portions of the spoken audio stream may be recognized using different sub-models. The resulting structured textual document may have a hierarchical structure that corresponds to the hierarchical structure of the language sub-models that were used to generate the structured textual document.
Owner:MULTIMODAL TECH INC
Creating a language model for a language processing system
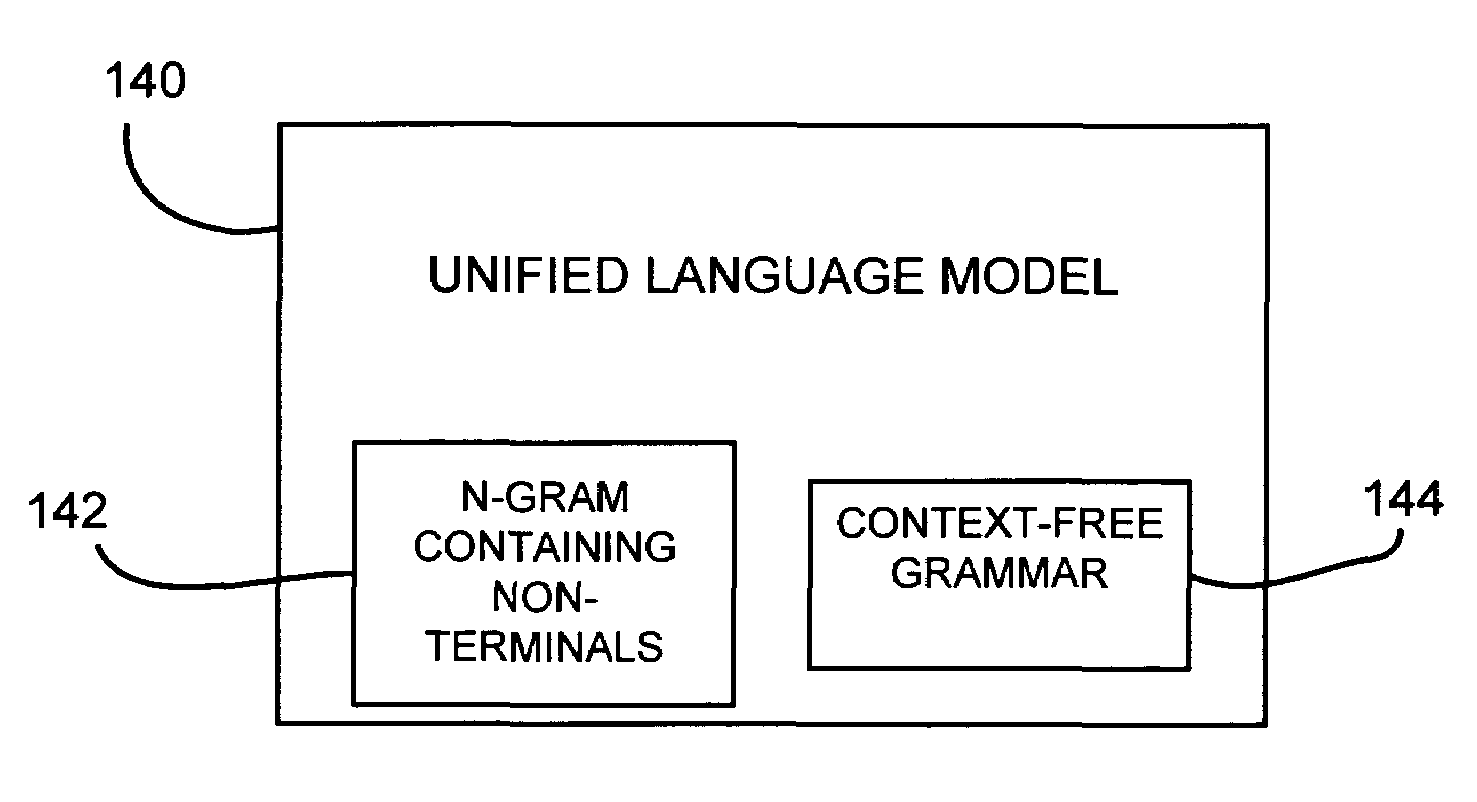
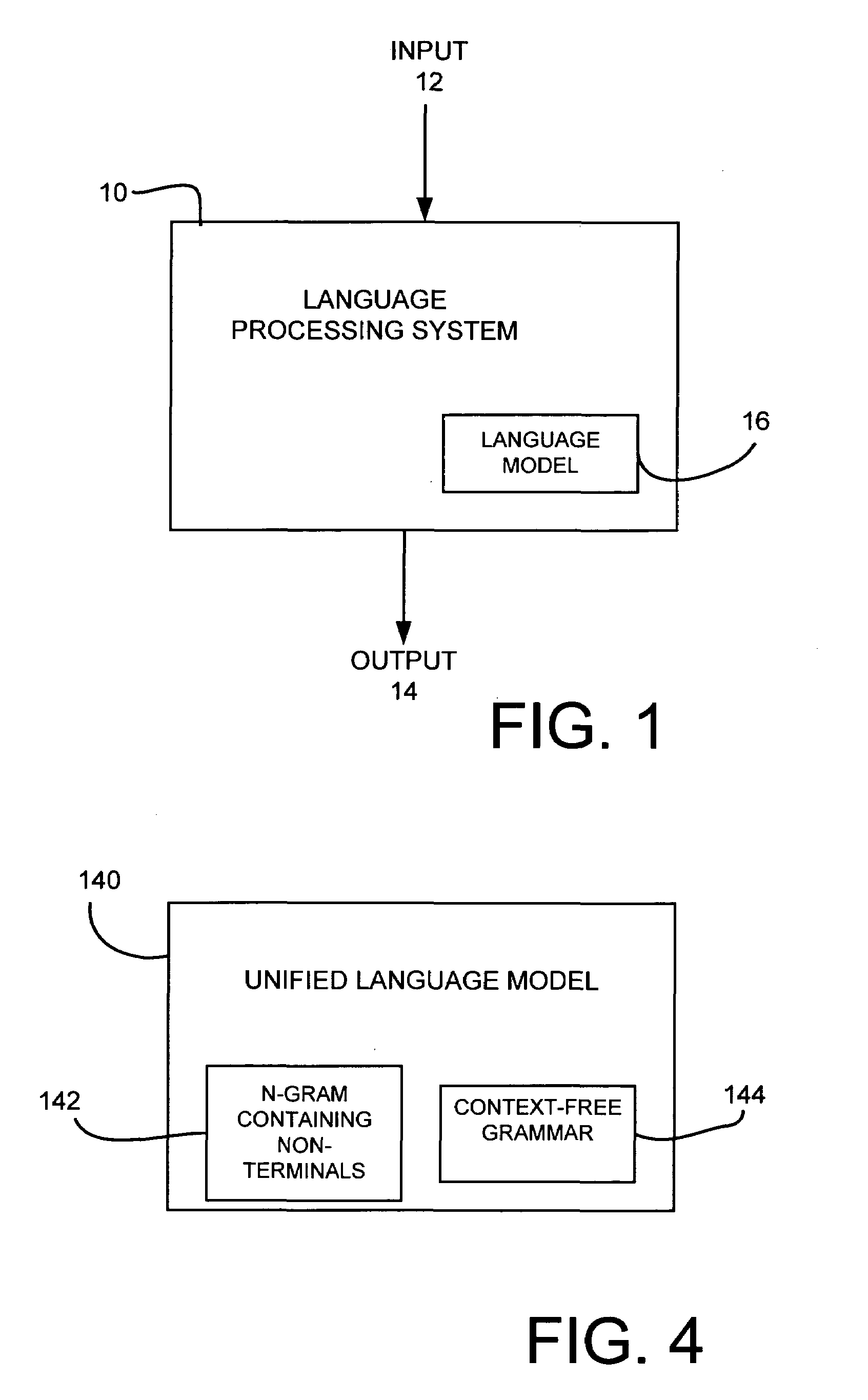
InactiveUS7031908B1Speech recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsHuman languageContext-free grammar
A method for creating a language model from a task-independent corpus is provided. In one embodiment, a task dependent unified language model is created. The unified language model includes a plurality of context-free grammars having non-terminals and a hybrid N-gram model having at least some of the same non-terminals embedded therein.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com