Patents
Literature
142 results about "Specific knowledge" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
By definition, specific knowledge is knowledge that is costly to transfer amongst individuals and general knowledge as knowledge that is inexpensive to transmit. For example, general knowledge is knowledge that can be researched through general information found in today’s media such as the internet, books, television, or radio broadcast.
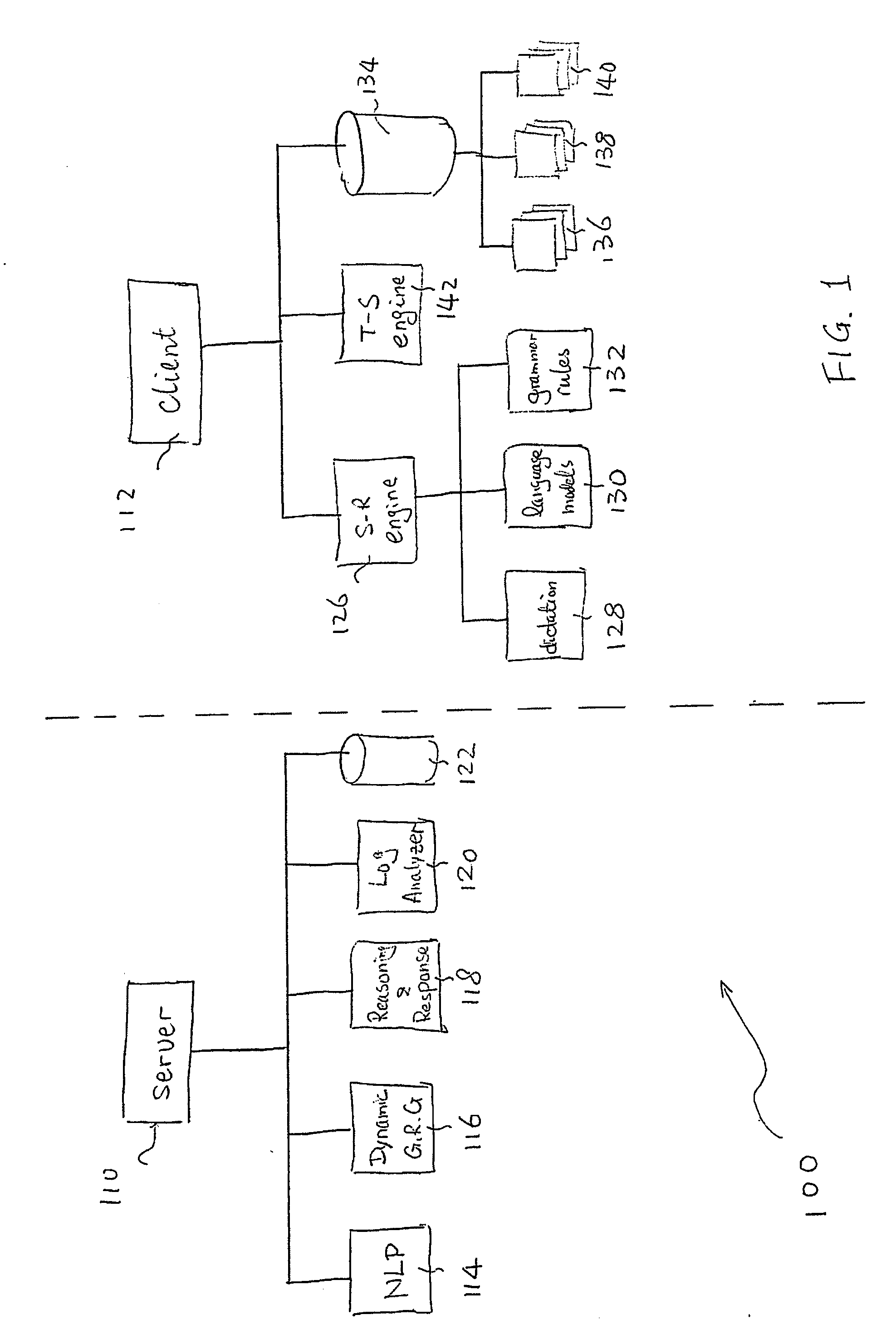
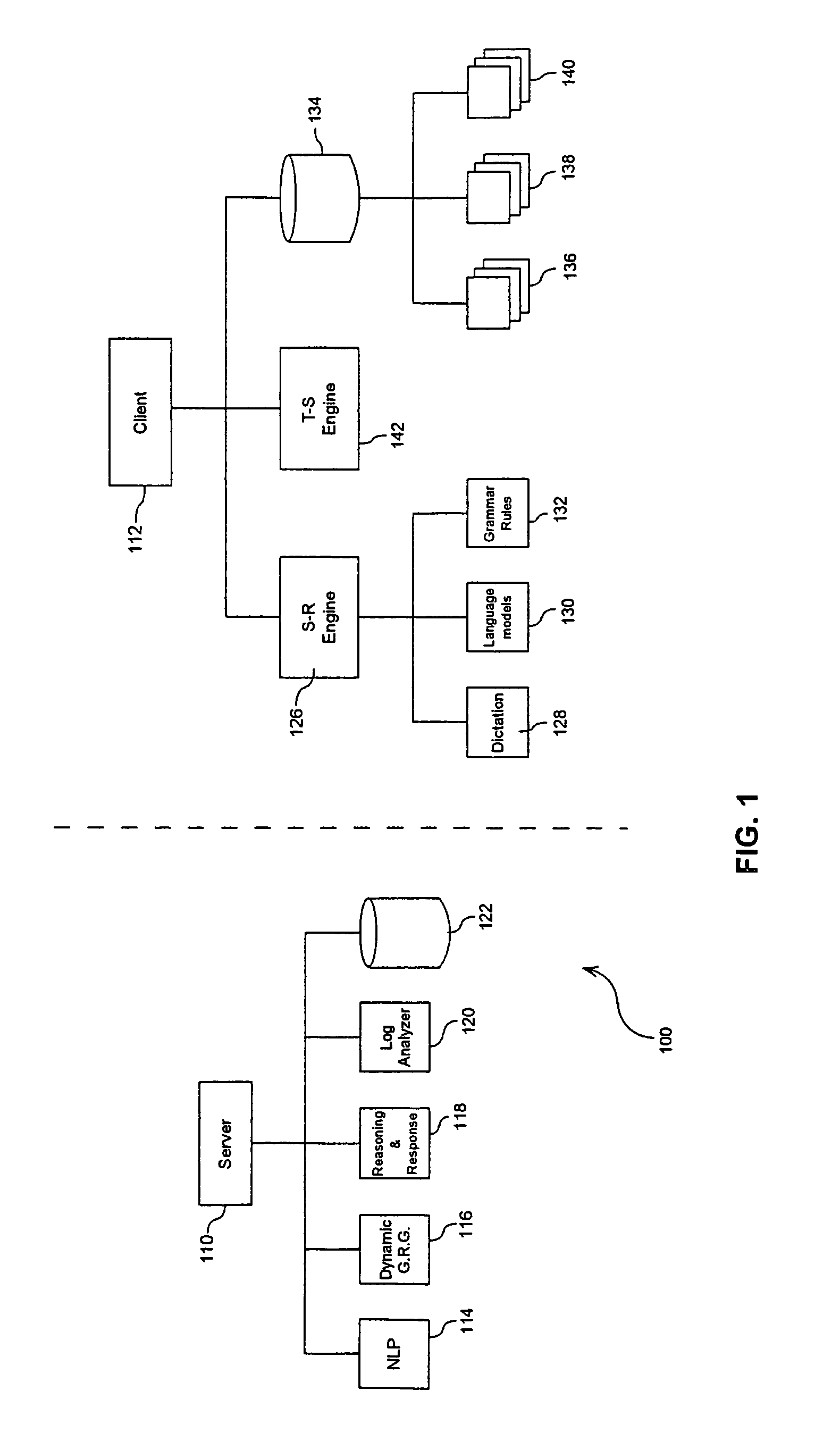
System and methods for improving accuracy of speech recognition
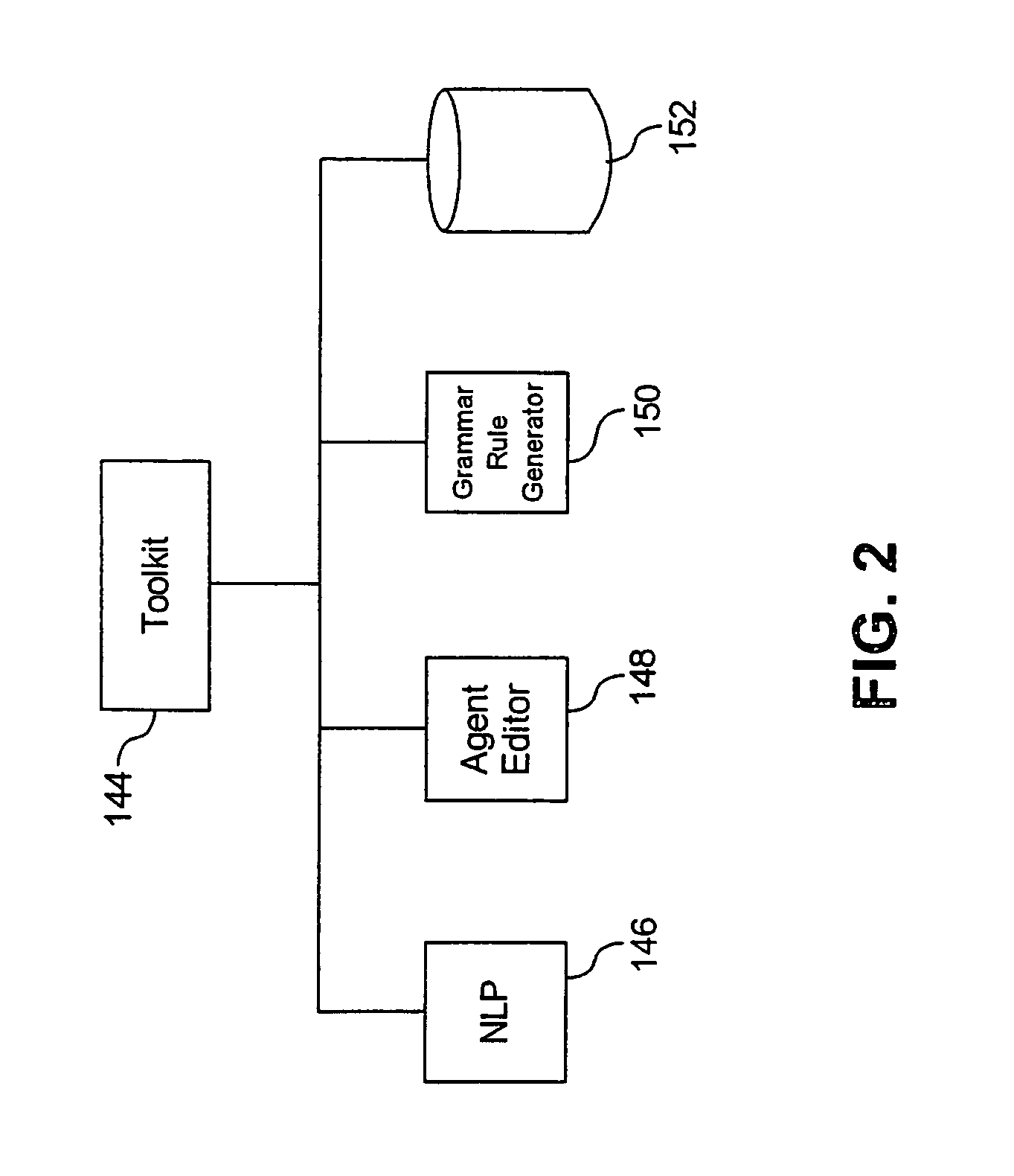
The invention provides a system and method for improving speech recognition. A computer software system is provided for implementing the system and method. A user of the computer software system may speak to the system directly and the system may respond, in spoken language, with an appropriate response. Grammar rules may be generated automatically from sample utterances when implementing the system for a particular application. Dynamic grammar rules may also be generated during interaction between the user and the system. In addition to arranging searching order of grammar files based on a predetermined hierarchy, a dynamically generated searching order based on history of contexts of a single conversation may be provided for further improved speech recognition. Dialogue between the system and the user of the system may be recorded and extracted for use by a speech recognition engine to refine or create language models so that accuracy of speech recognition relevant to a particular knowledge area may be improved.
Owner:INAGO CORP
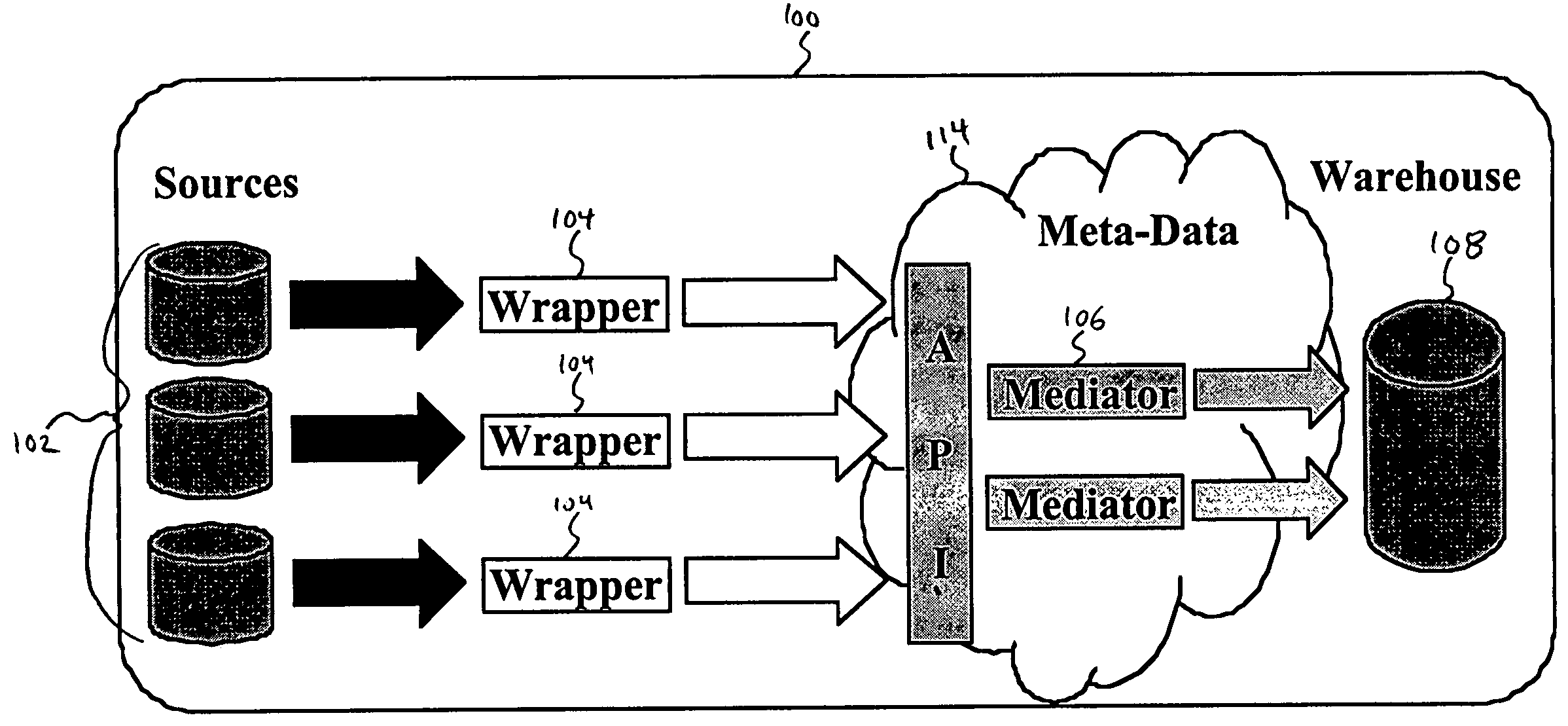
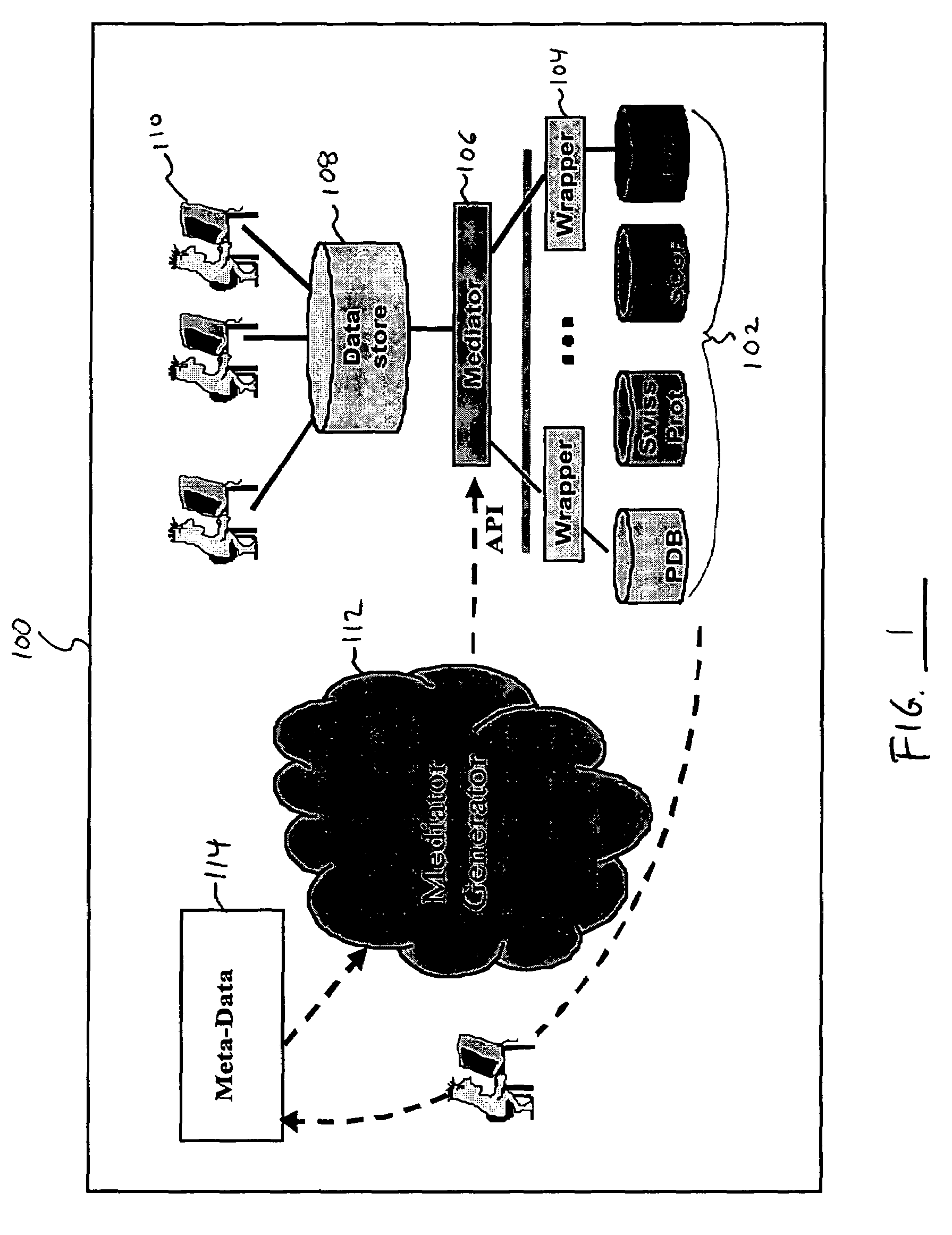
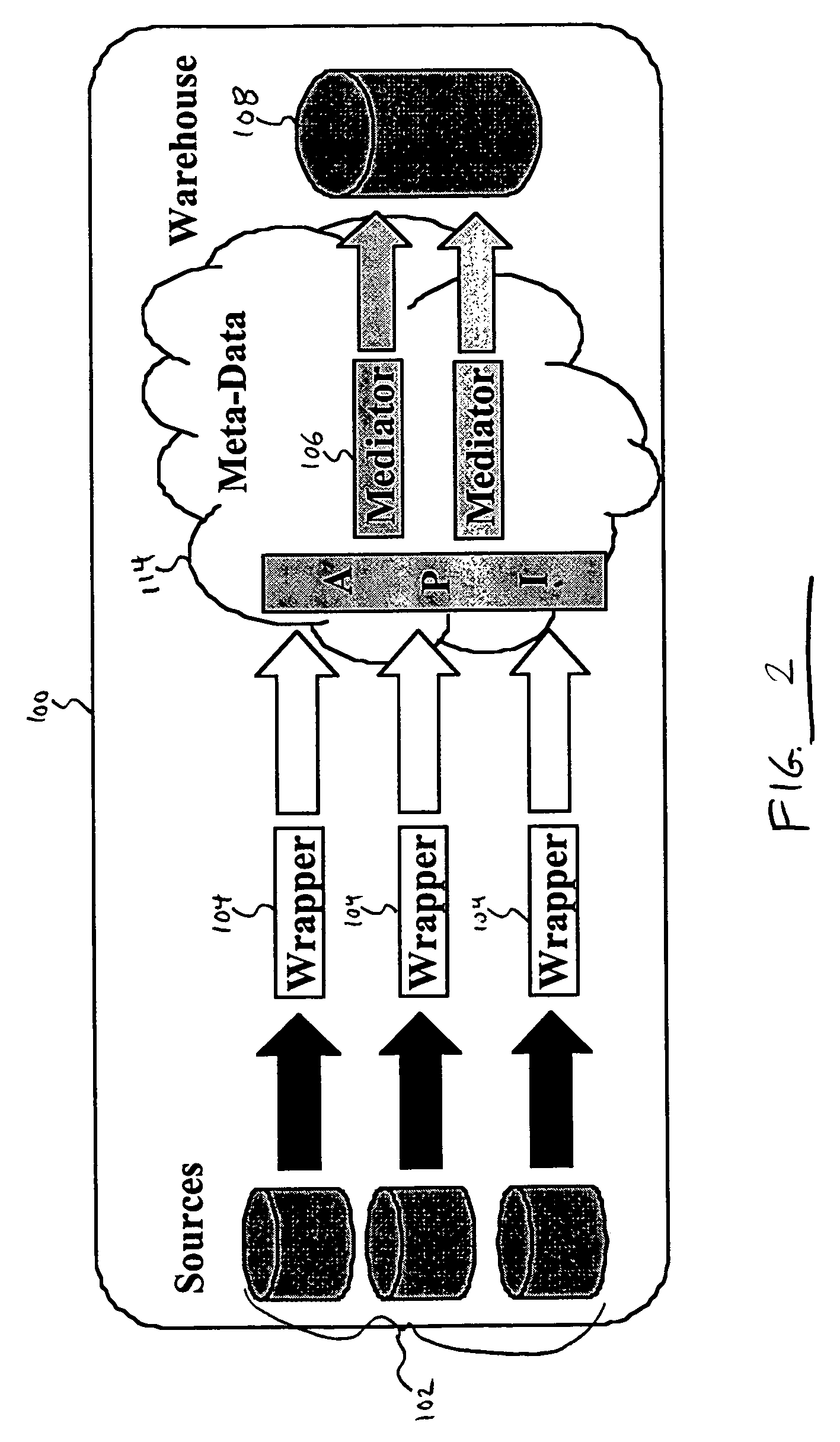
System and method for integrating and accessing multiple data sources within a data warehouse architecture
InactiveUS7152070B1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalPresent methodAnalysis data
A system and method is disclosed for integrating and accessing multiple data sources within a data warehouse architecture. The metadata formed by the present method provide a way to declaratively present domain specific knowledge, obtained by analyzing data sources, in a consistent and useable way. Four types of information are represented by the metadata: abstract concepts, databases, transformations and mappings. A mediator generator automatically generates data management computer code based on the metadata. The resulting code defines a translation library and a mediator class. The translation library provides a data representation for domain specific knowledge represented in a data warehouse, including “get” and “set” methods for attributes that call transformation methods and derive a value of an attribute if it is missing. The mediator class defines methods that take “distinguished” high-level objects as input and traverse their data structures and enter information into the data warehouse.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
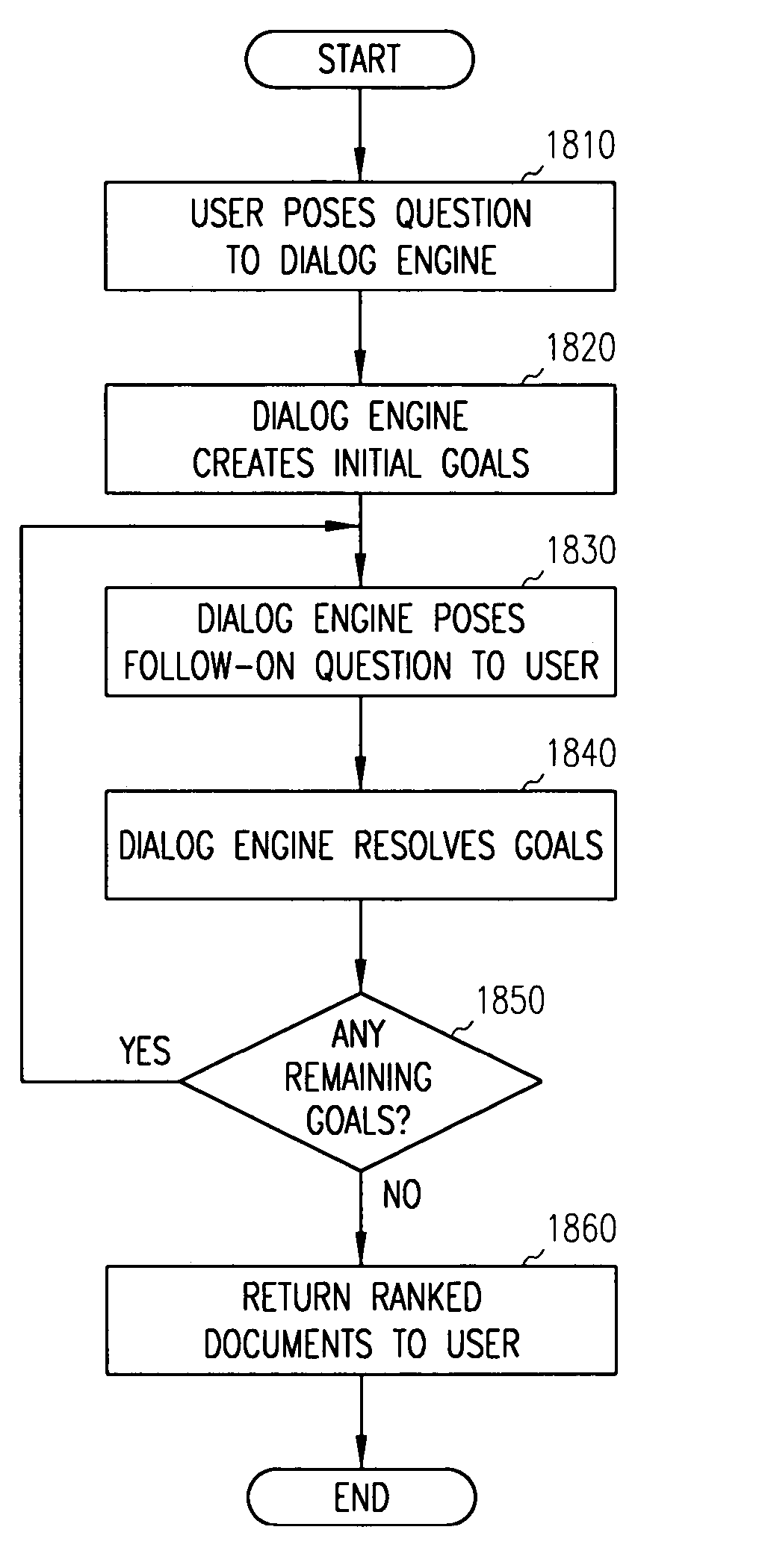
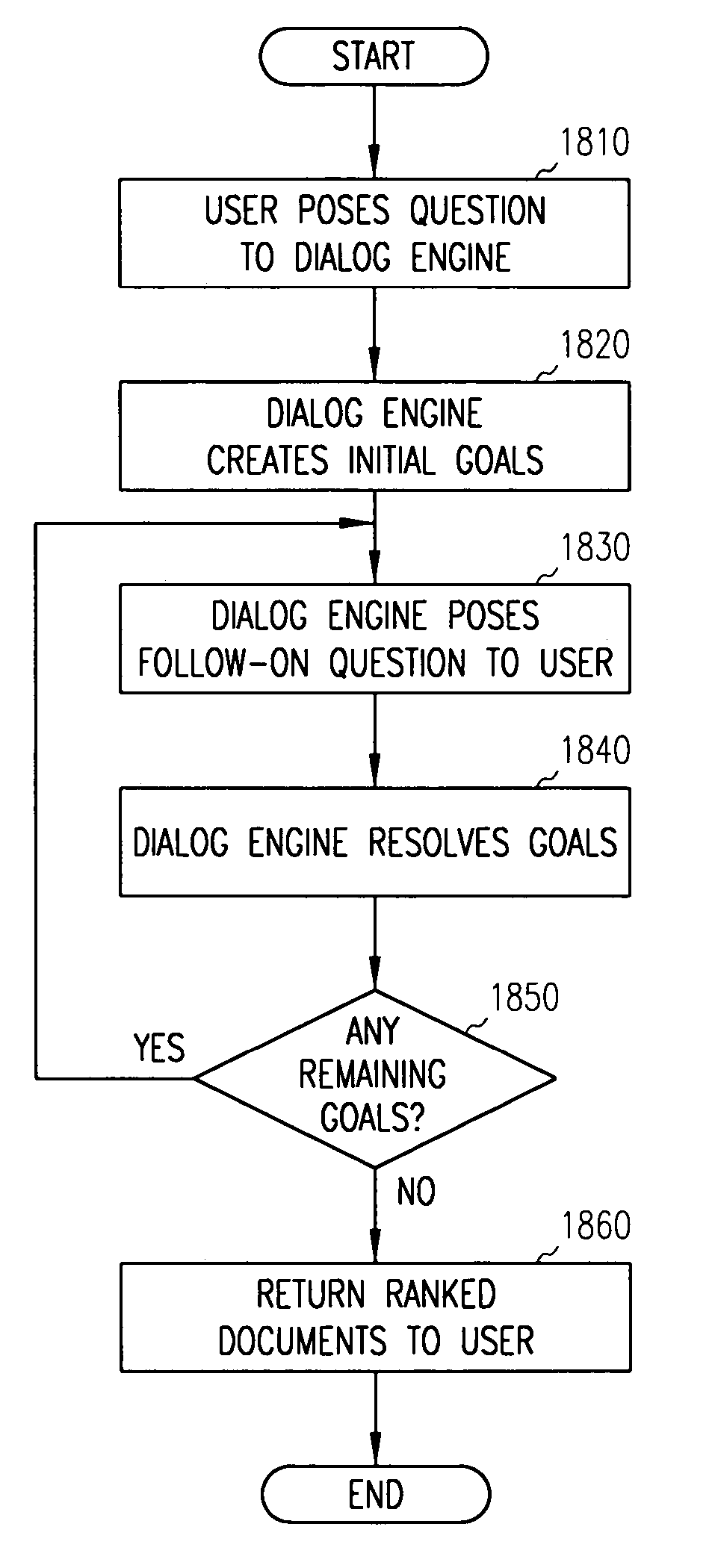
System and method for providing an intelligent multi-step dialog with a user
InactiveUS20050055321A1Efficient retrievalEasy to set upData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsClient-sideSpecific knowledge
A method and system are disclosed for retrieving information through the use of a multi-stage interaction with a client to identify particular knowledge content associated with a knowledge map.
Owner:AVOLIN LLC
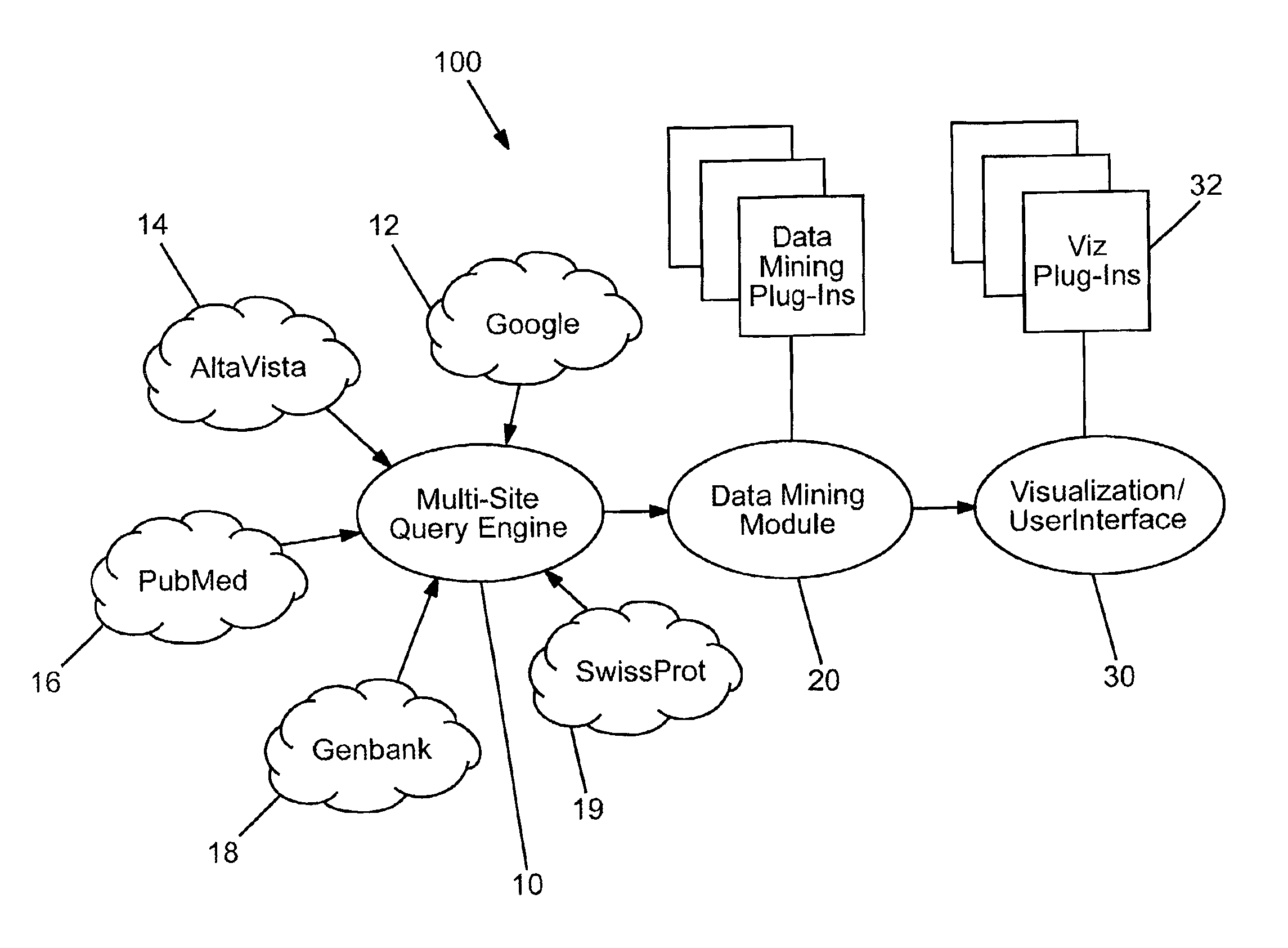
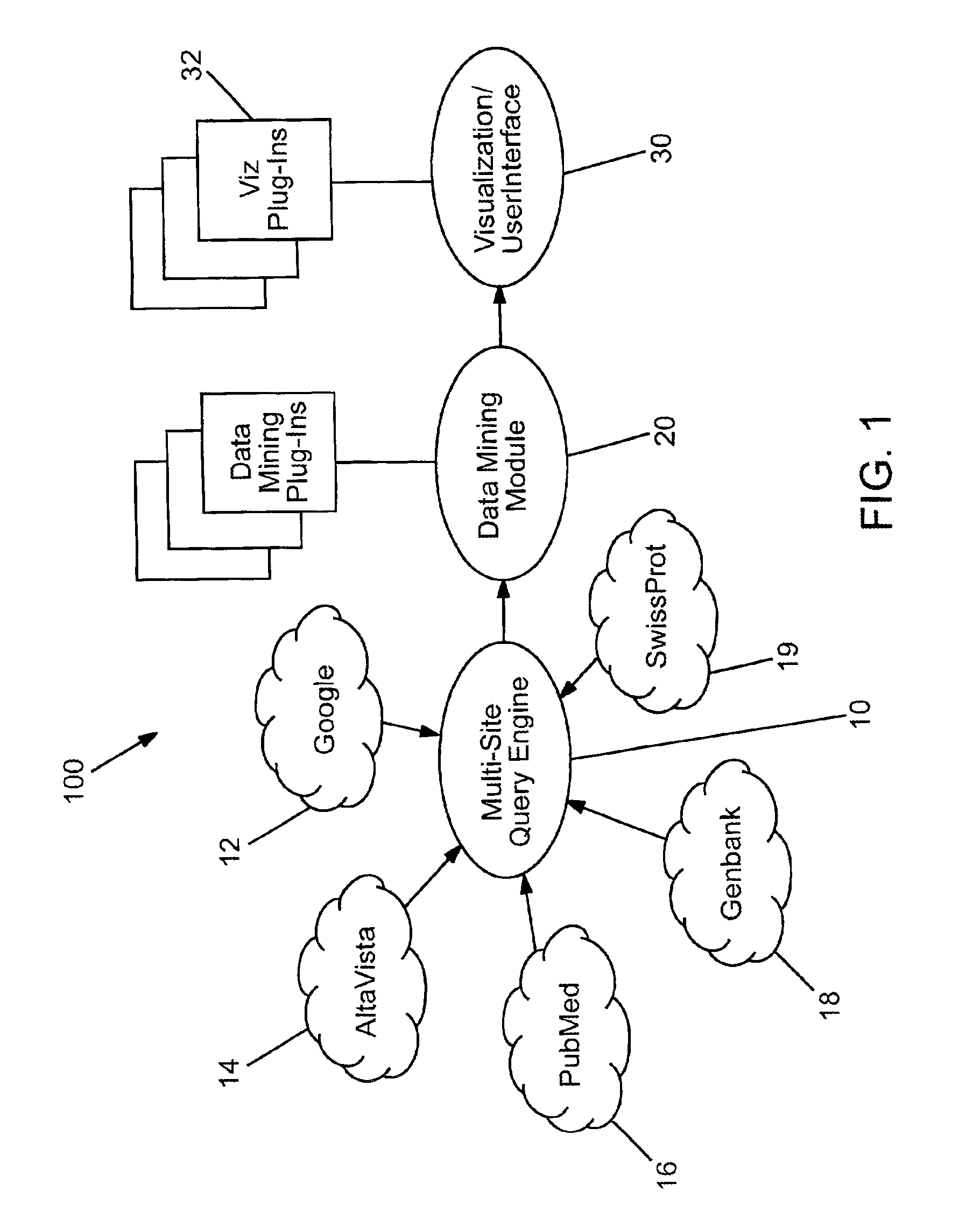
Domain specific knowledge-based metasearch system and methods of using
InactiveUS6920448B2Remove the burdenData processing applicationsWeb data indexingSequence databaseDocument preparation
A system and method for performing domain-specific knowledge based metasearches. A metasearch engine is provided for accessing a searching text-based documents using generic search engines while simultaneously being able to access publication based databases and sequence databases as well as in-house proprietary databases and any database capable of being interfaced with a web interface so as to produce search results in text format. A data mining module is also provided for organizing raw data obtained by unsupervised clustering, simple relevance ranking, and categorization, all of which are done independently of one another. The system is capable of storing previous search data for use in query refinement or subsequent searches based upon the stored data. A search results collection browser may be provided for analyzing current browsing patterns of the user for developing weighting factors to be used in ordering the results of future searches.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
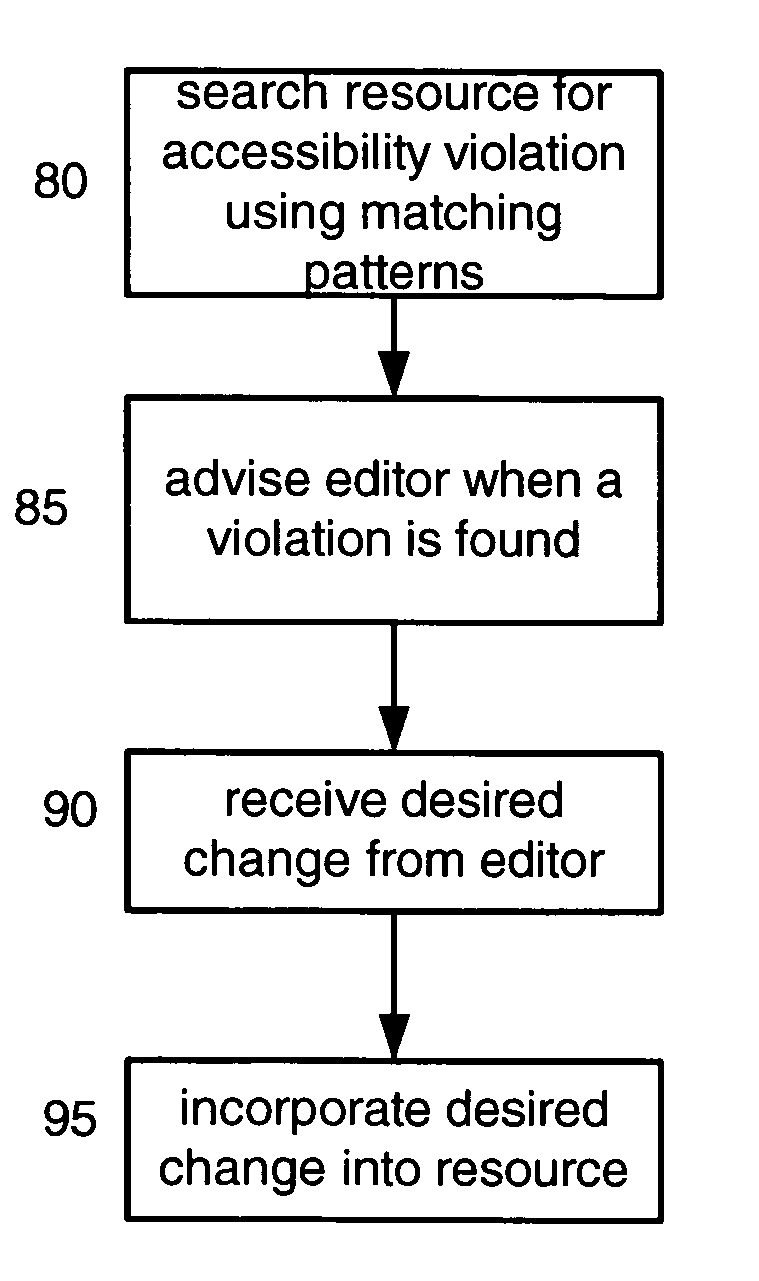
System and method for enhancing resource accessibility
InactiveUS20050160065A1Digital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsAmbiguityPaper document
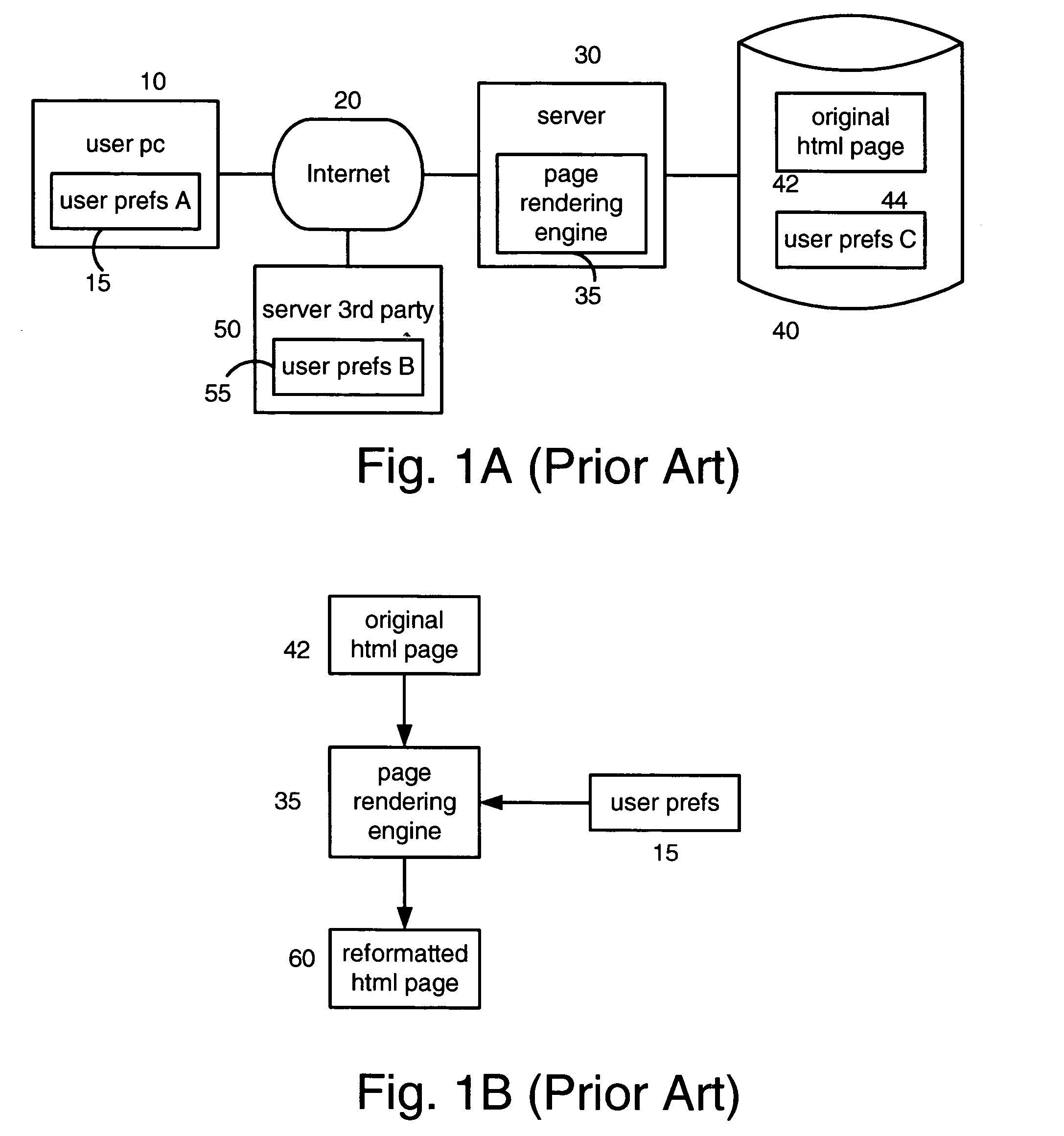
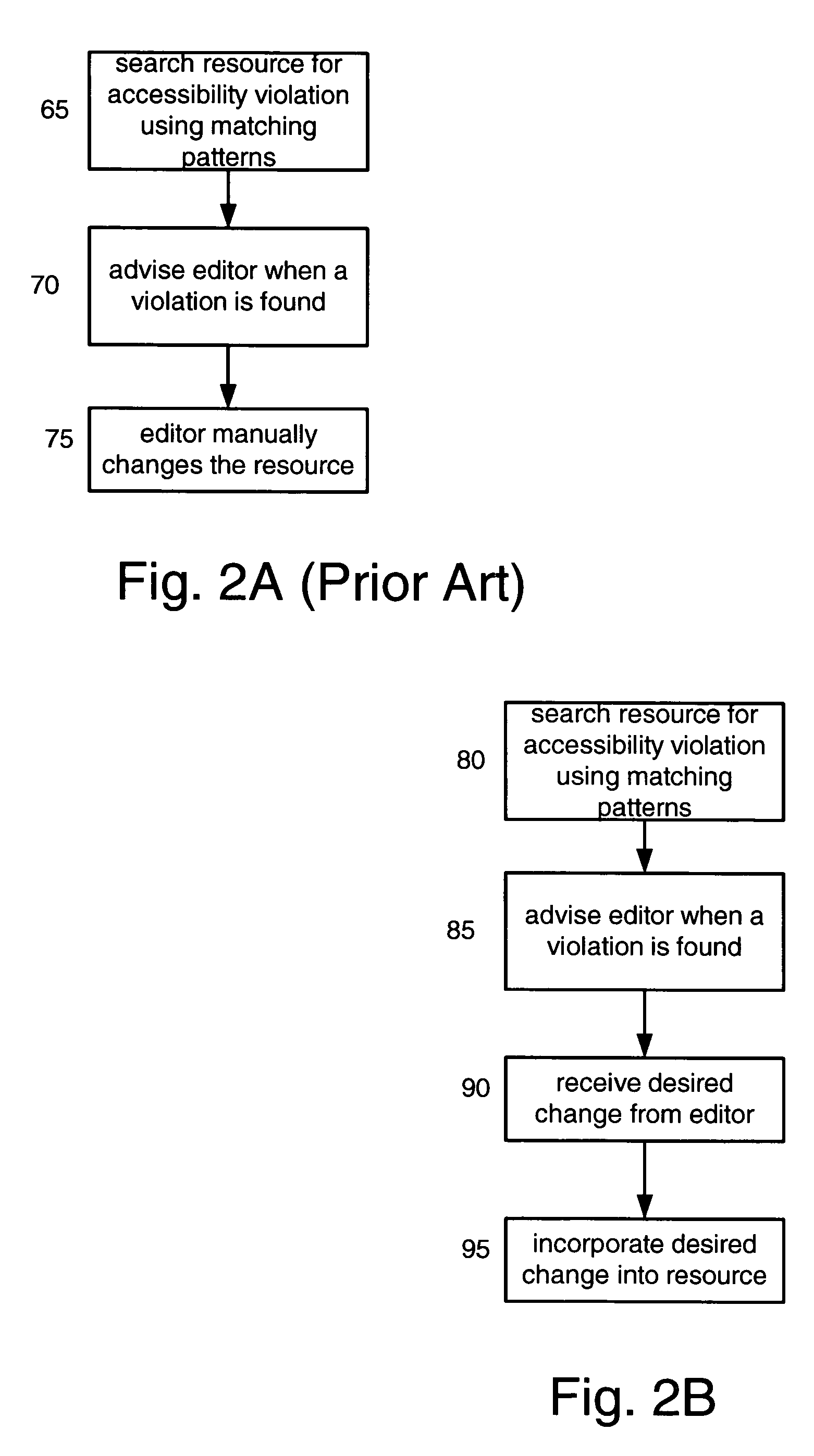
A resource accessibility engine according to the present invention uses a resource-specific knowledge base and user preferences to convert a resource into an improved accessibility resource. Examples of a resource include a website, document, webpage image file, multimedia file, auditory file or any other text and / or non-text record. The resource-specific knowledge includes content and formatting information that reduces ambiguities, translates implied information into explicit information and improves the accessibility of the resource content. The user preferences represent the physical capabilities of the user's access device, and the user's semantic and personal preferences for how content should be displayed. An editor uses an annotation wizard to create the resource-specific knowledge base based on the original resource.
Owner:UNBOUNDED ACCESS
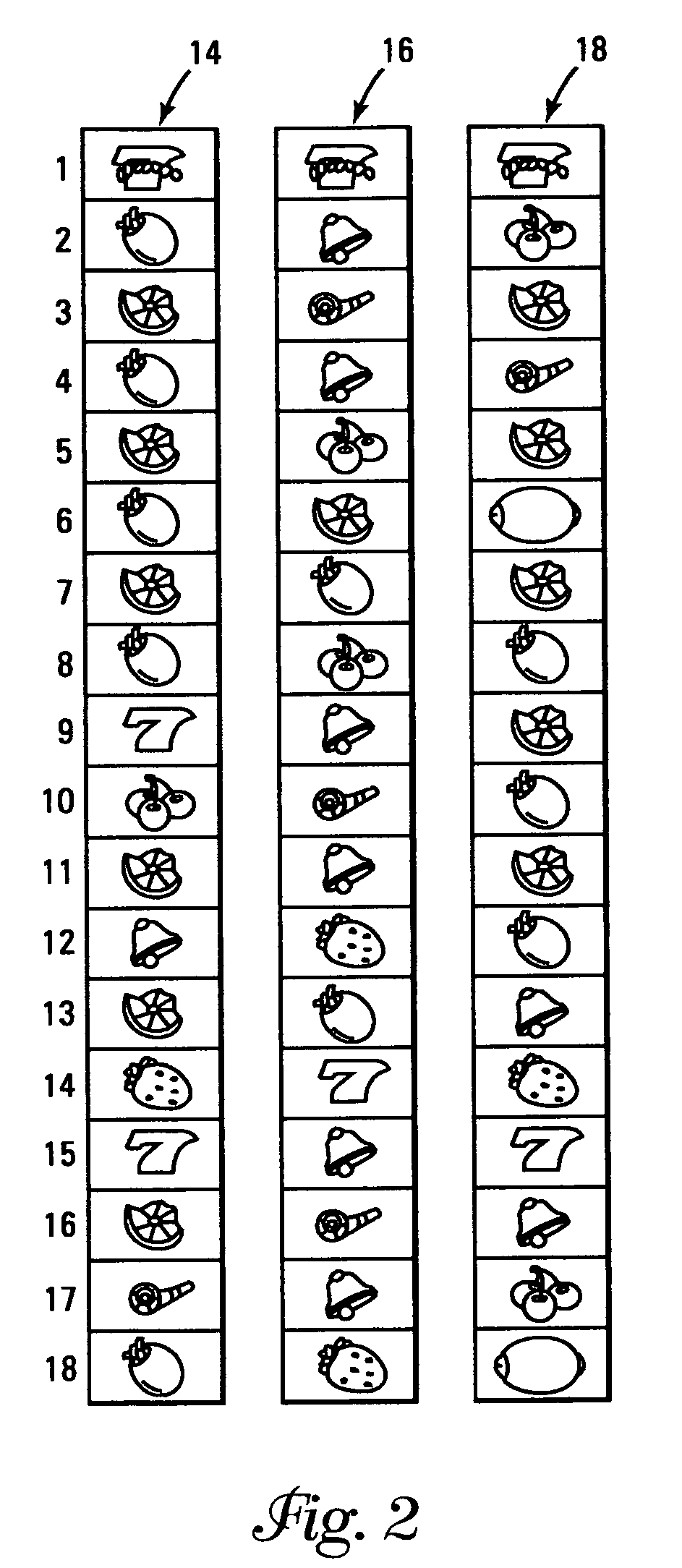
Reveal-hide-pick-reveal video wagering game feature
A game feature, and especially a bonus event game feature for video wagering apparatus has a unique method of displaying at least some of the potential individual rewards or other bonus event results, hiding those potential individual awards or other bonus event results ‘beneath’ a symbol or region, rearranging a location of the awards, allowing the player to select a symbol or region according to game play methods, and revealing at least the awards or other bonus event results that were underneath selected symbols or areas. Excitement is promoted by having a player anticipate the availability of specific bonus game awards and events during the selection process, as opposed to making selections without any specific knowledge of at least some of the specific bonuses or events that are potentially available in the bonus event.
Owner:IGT
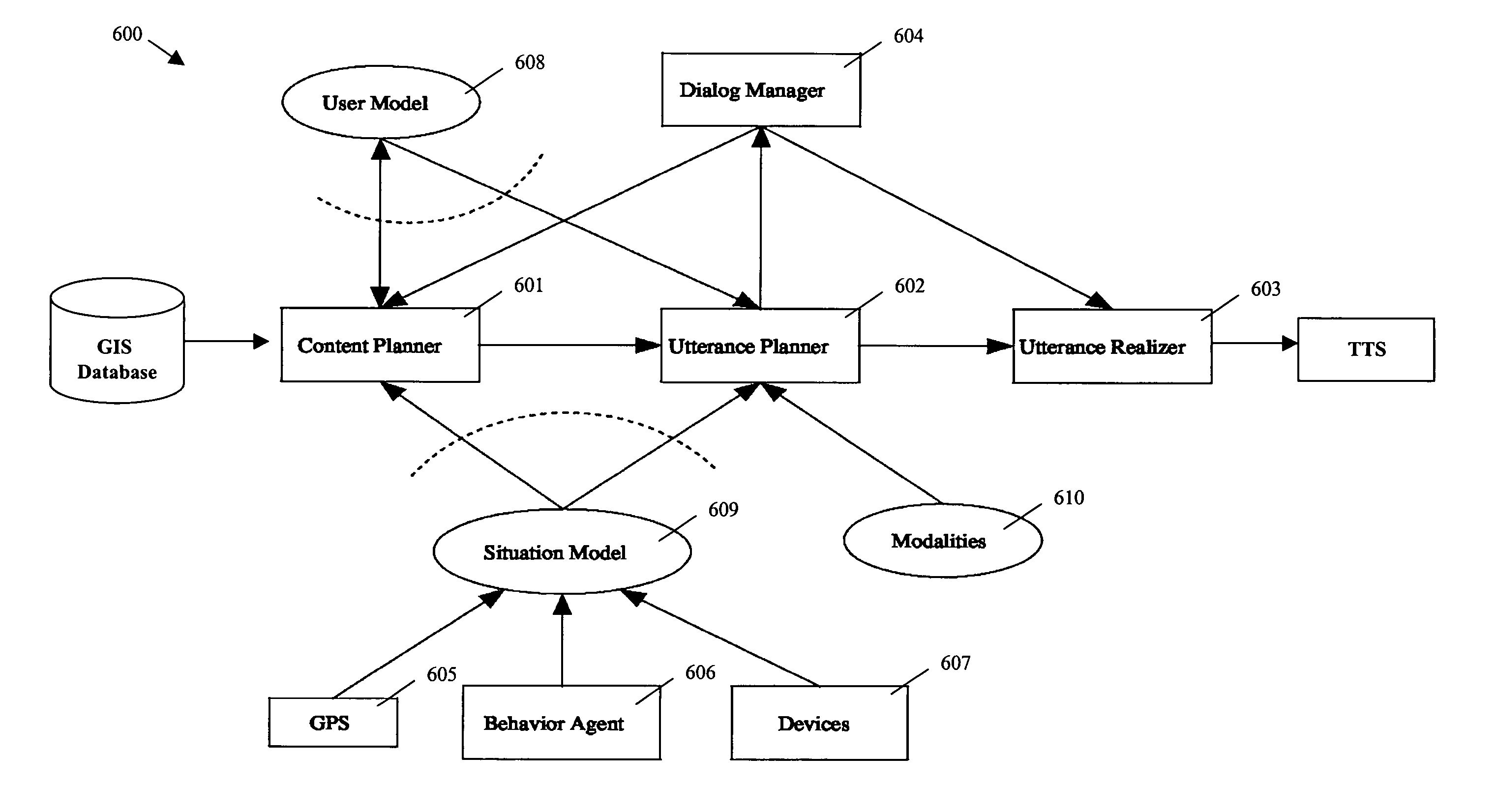
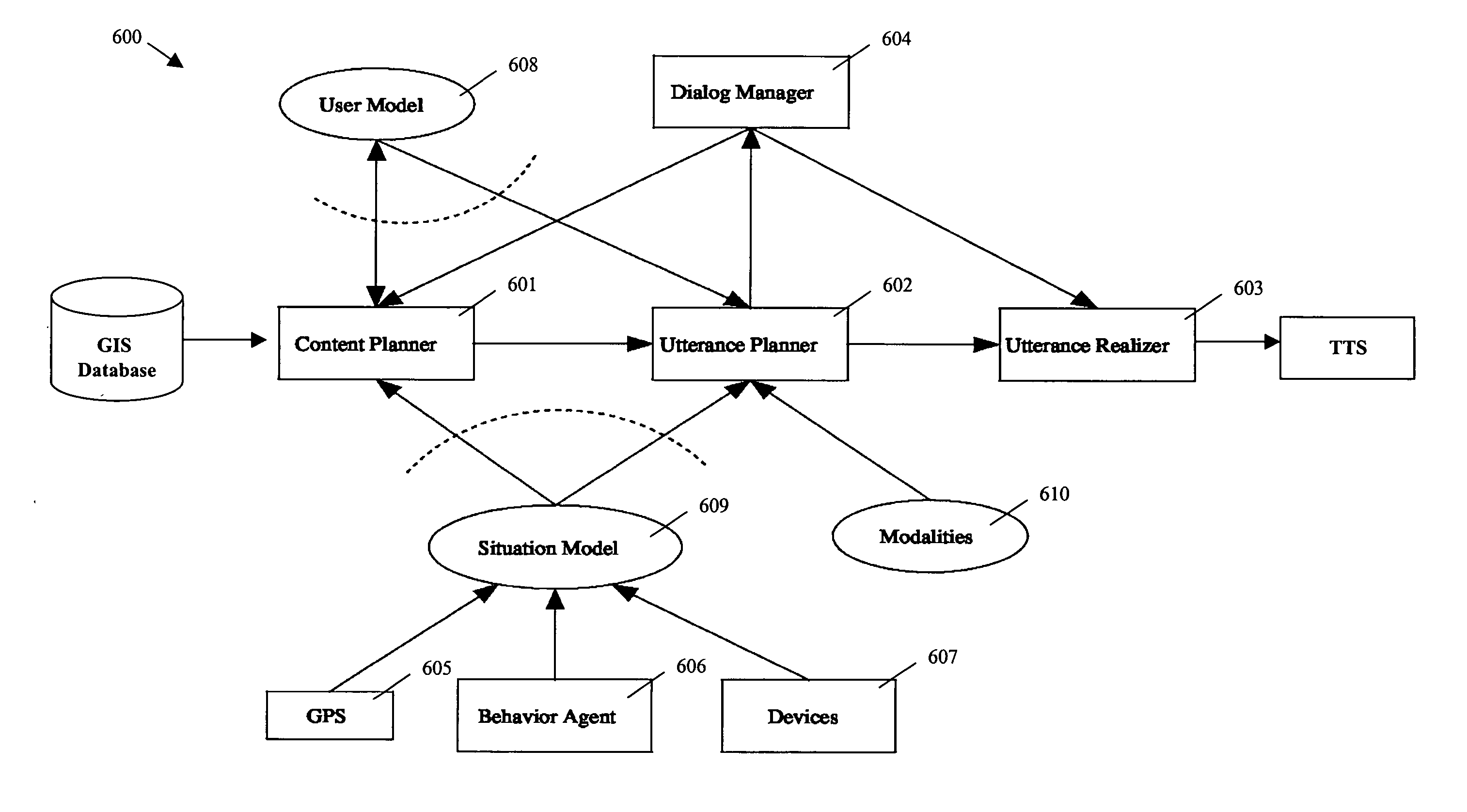
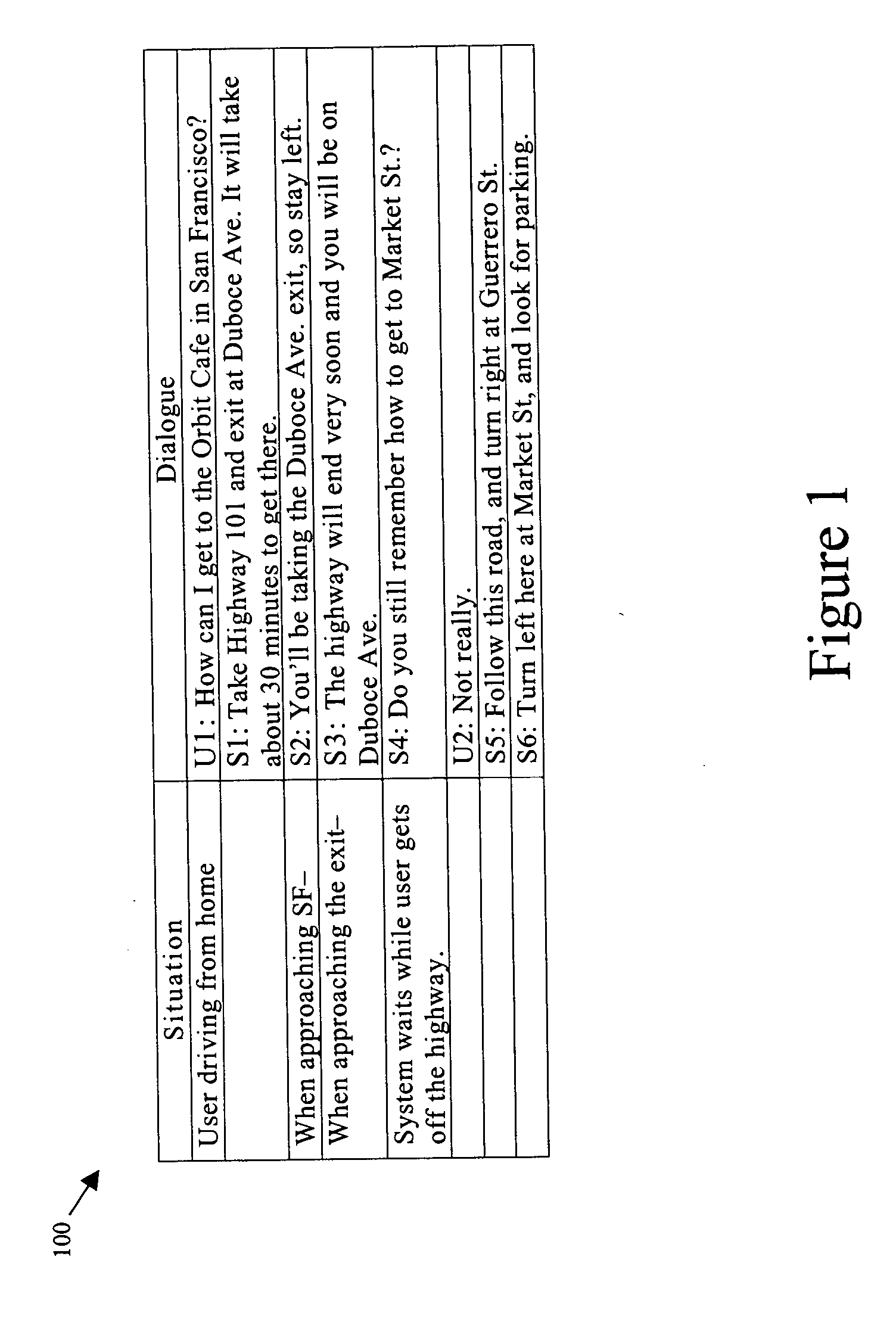
Method and system for adaptive navigation using a driver's route knowledge
ActiveUS7424363B2Minimal cognitive loadReduce cognitive loadInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlDriver/operatorHuman–computer interaction
A method and system are described to adapt instructions for performing a task by a user, which includes receiving generalized instructions for the task, selecting a content of the generalized instructions based on user-specific knowledge regarding the task, constructing utterances using the selected content, and conveying the utterances to the user.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH CORP
Method and system for adaptive navigation using a driver's route knowledge
ActiveUS20060041378A1Minimal cognitive loadReduce cognitive loadInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlDriver/operatorSelf adaptive
A method and system are described to adapt instructions for performing a task by a user, which includes receiving generalized instructions for the task, selecting a content of the generalized instructions based on user-specific knowledge regarding the task, constructing utterances using the selected content, and conveying the utterances to the user.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH CORP
System and method for providing an intelligent multi-step dialog with a user
InactiveUS7337158B2Efficient retrievalEasy to set upData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsKnowledge contentClient-side
A method and system are disclosed for retrieving information through the use of a multi-stage interaction with a client to identify particular knowledge content associated with a knowledge map.
Owner:AVOLIN LLC
Information system using healthcare ontology
InactiveUS20070005621A1Digital data processing detailsMedical report generationMedical treatmentInformation system
An information system using a healthcare ontology to provide a standardized representation for healthcare data is disclosed. One embodiment of the information system comprises a digital logic platform storing and using the healthcare ontology. The healthcare ontology describes concepts and relationships between the concepts derived from the corpus of domain specific knowledge and linking with standardized terminological systems.
Owner:WISPER TECH
Knowledge graph generating method and device
ActiveCN106156365AImprove interactive experienceMeet the needs of intelligent interactionSemantic analysisSpecial data processing applicationsStructural representationKnowledge graph
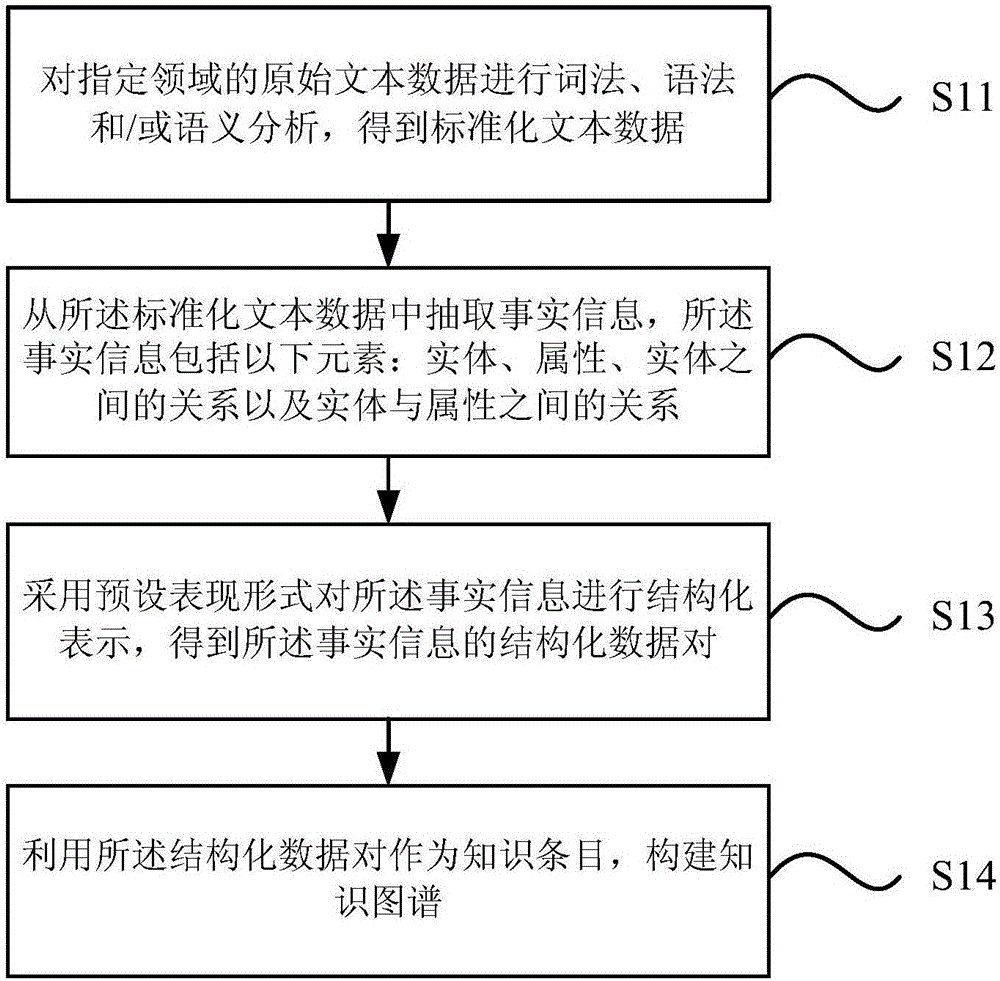
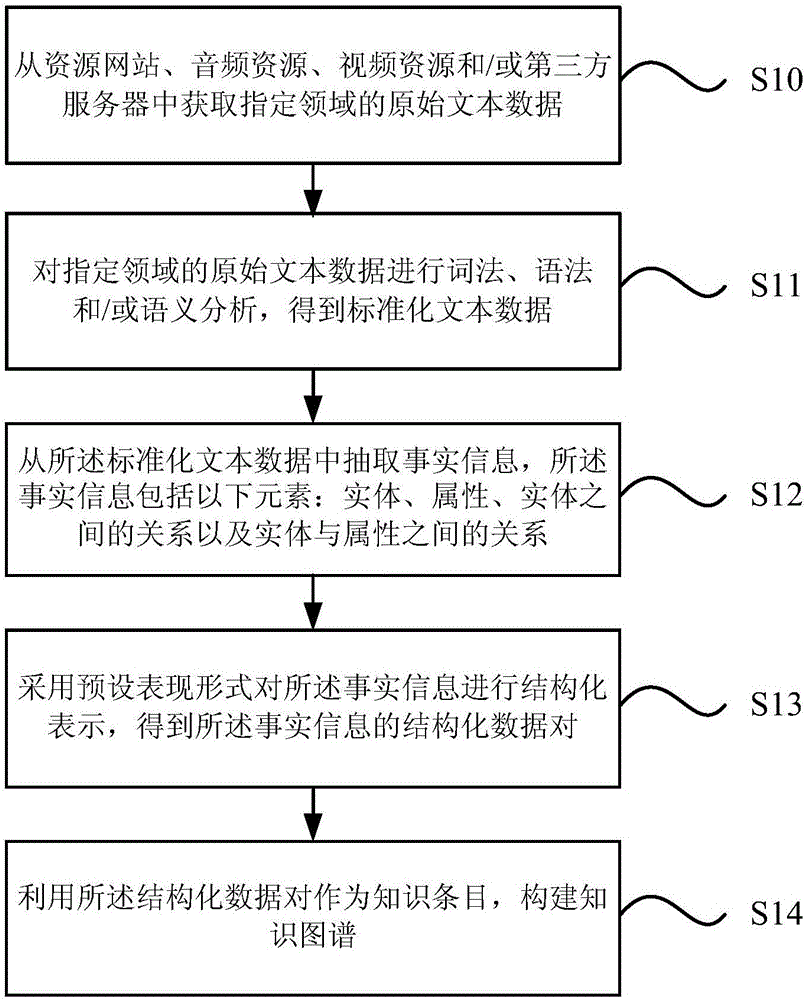
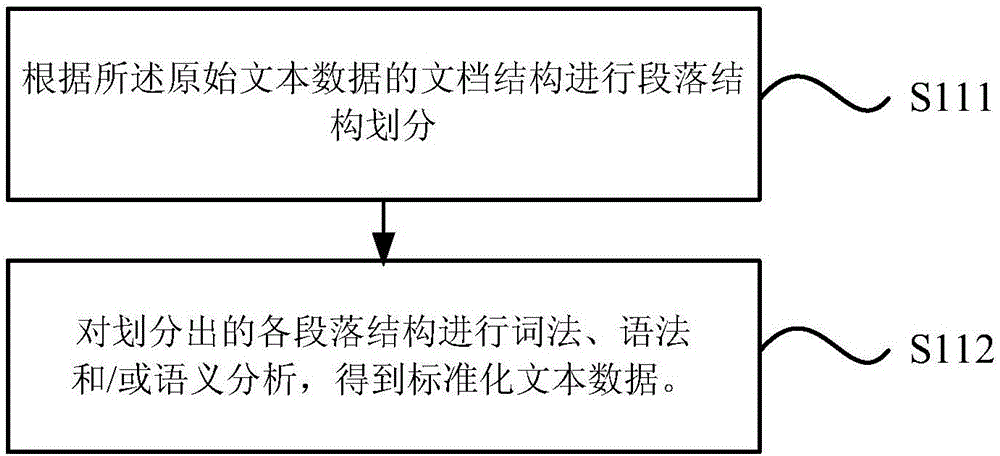
The invention provides a knowledge graph generating method and device. The method comprises the steps as follows: original text data in a designated field are subjected to morphological, semantic analysis and / or semantic analysis, and standard text data are obtained; factual information is extracted from the standard text data and comprises the following elements: the relation among entities, attributes and entities as well as the relation between the entities and the attributes; structural representation is performed on the factual information in a preset representation form, and structured data pairs of the factual information are obtained; the structured data pairs are adopted as knowledge entries for establishing of a knowledge graph. With the adoption of the knowledge graph generating method, the specific knowledge graph can be established, the intelligent interaction requirement in the specific field such as the children's filed is met, and the interactive experience of users with different requirements is improved.
Owner:北京如布科技有限公司
Detecting duplicate records
ActiveUS20100005048A1Digital data processing detailsKnowledge representationData miningComputer science
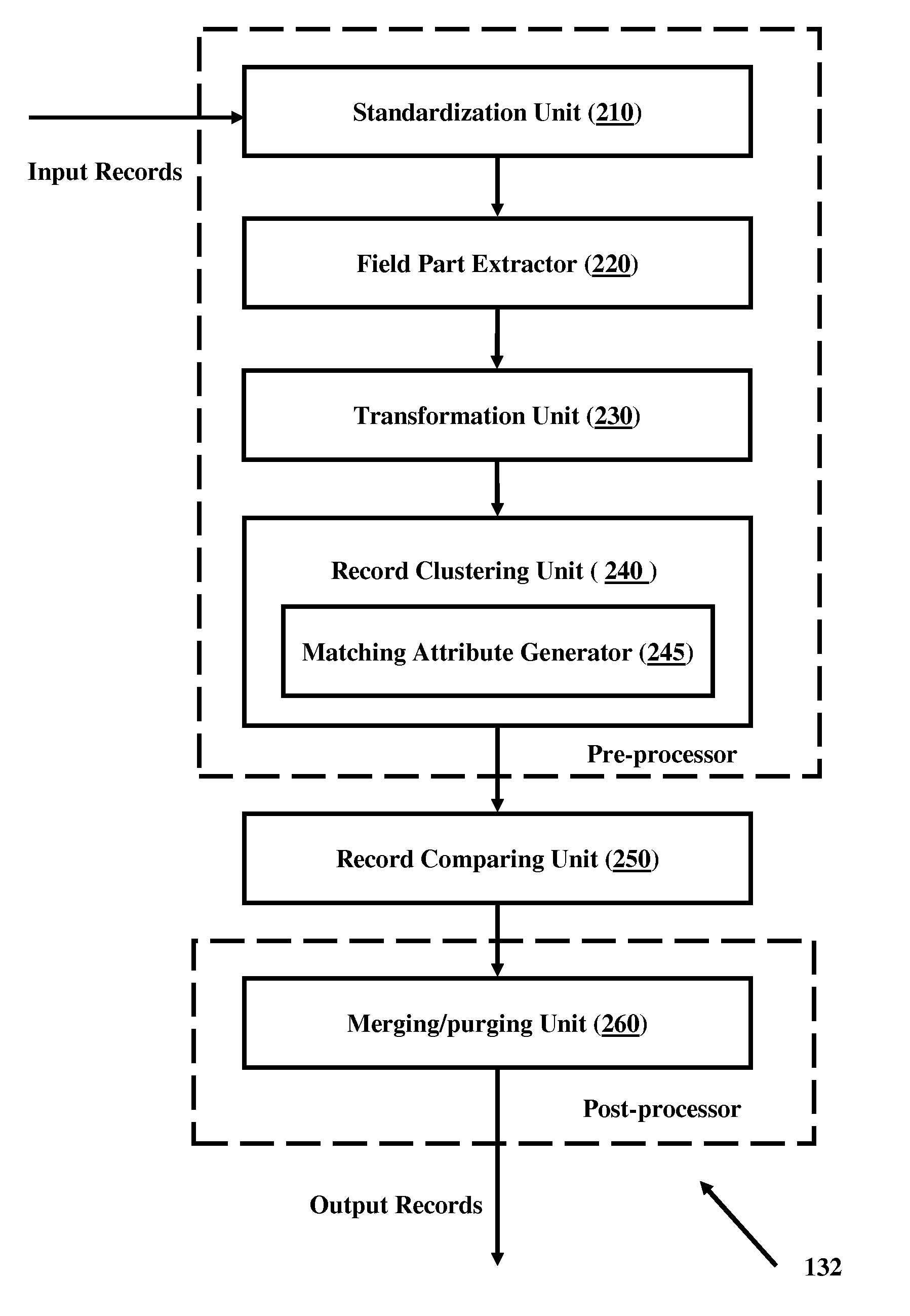
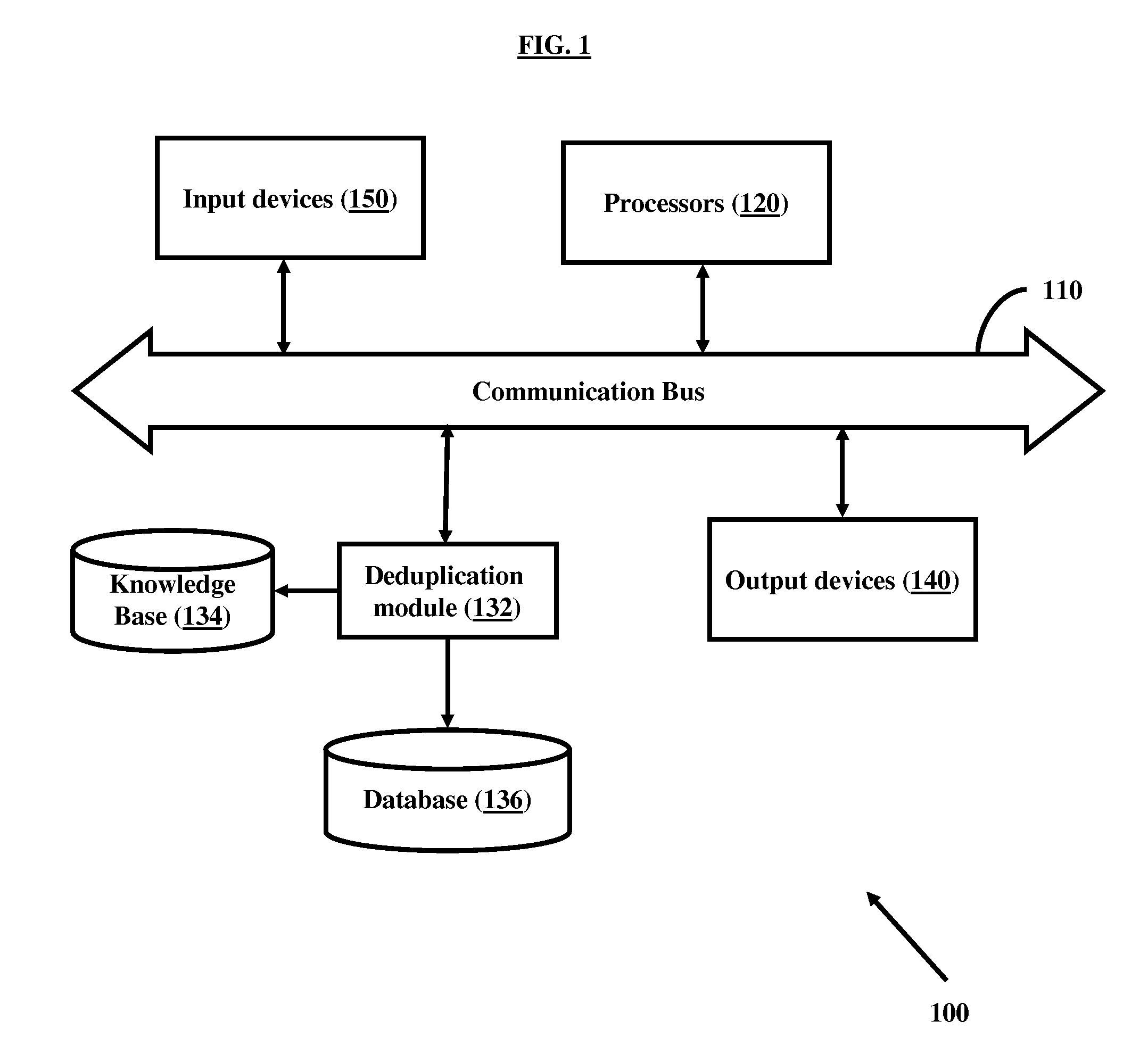
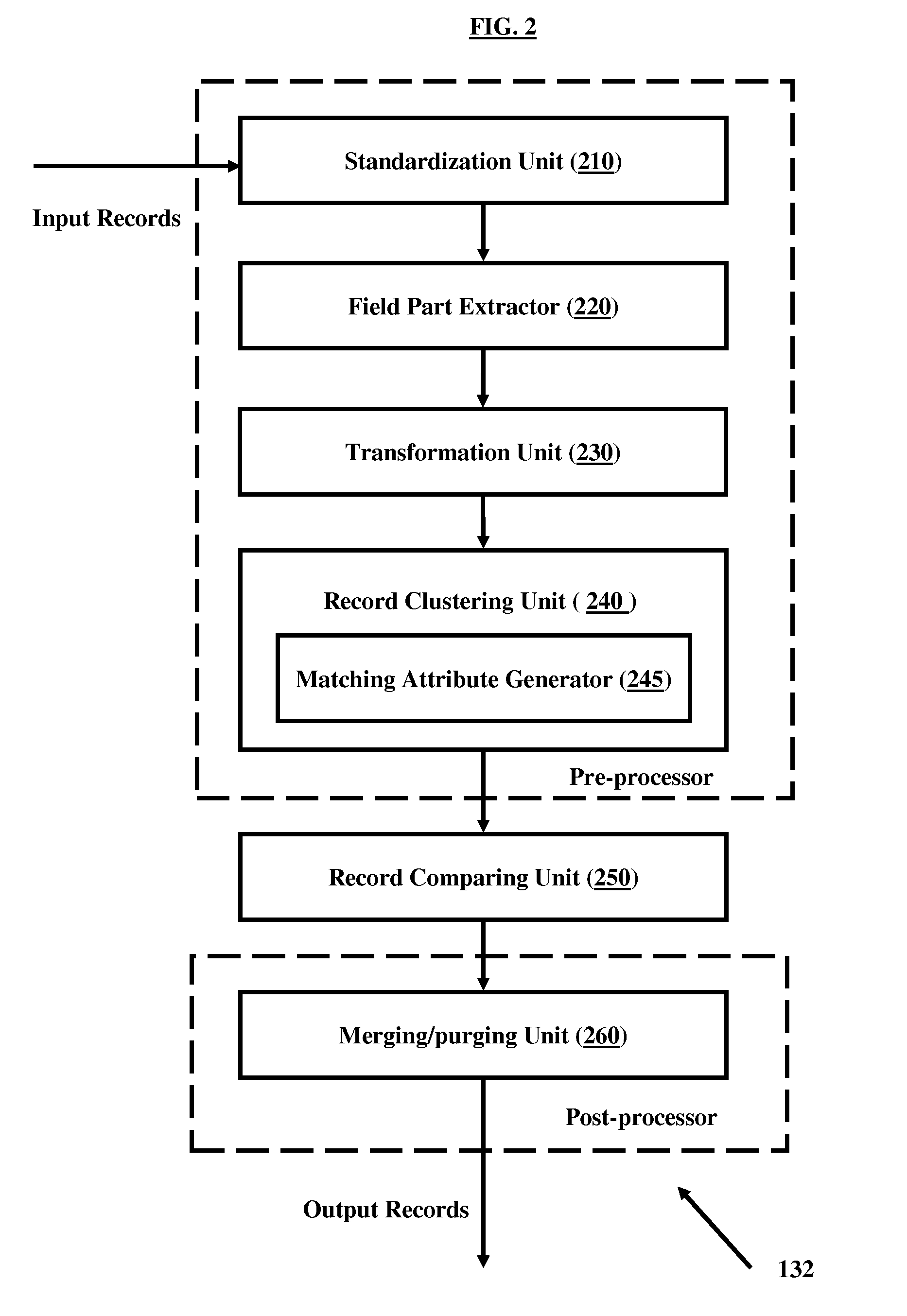
A method for finding duplicates by matching group of fields in records is disclosed. The method comprises standardizing data using field specific knowledge base; extracting at least part of one or more related fields of records; applying a matching attribute function to generate keys on the “comparable” field part extracted data; generating record level keys using generated field level keys; clustering the records based on generated record level keys; identifying reference record for each cluster identified; and calculating matching percentage for each record in a cluster with respect to reference record of the cluster. Devices and systems are disclosed that enable the method for finding duplicates.
Owner:EGRABBER
Identity verification via selection of sensible output from recorded digital data
ActiveUS20090328175A1Robust visual memory featIncrease probabilityDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsDigital dataData stream
Owner:SHUSTER GARY STEPHEN
Self-optimization with interactions
A method for computer-generating interaction-specific knowledge base for rapidly improving or optimizing a performance of an object comprises performing, according to computer-designed test matrices, at least several automatic experimental cycles on selected control variables. In at least one of the automatic experimental cycles after the first the computer plans a new test matrix designed to minimize or remove at least one expected two-variable interaction from a main effect of a designated control variable. A machine operating according to the method is also available.
Owner:LI FAMILY HLDG
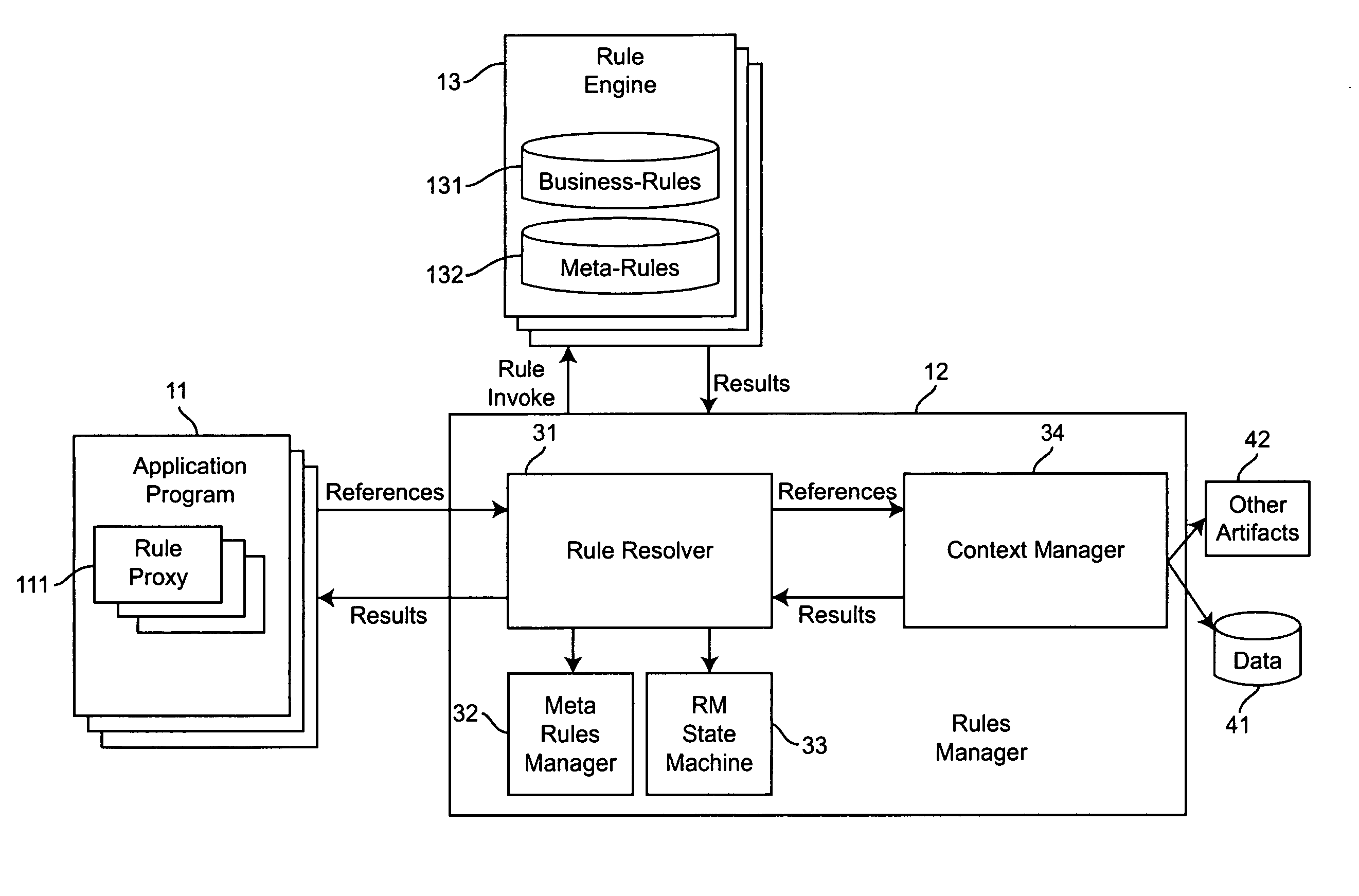
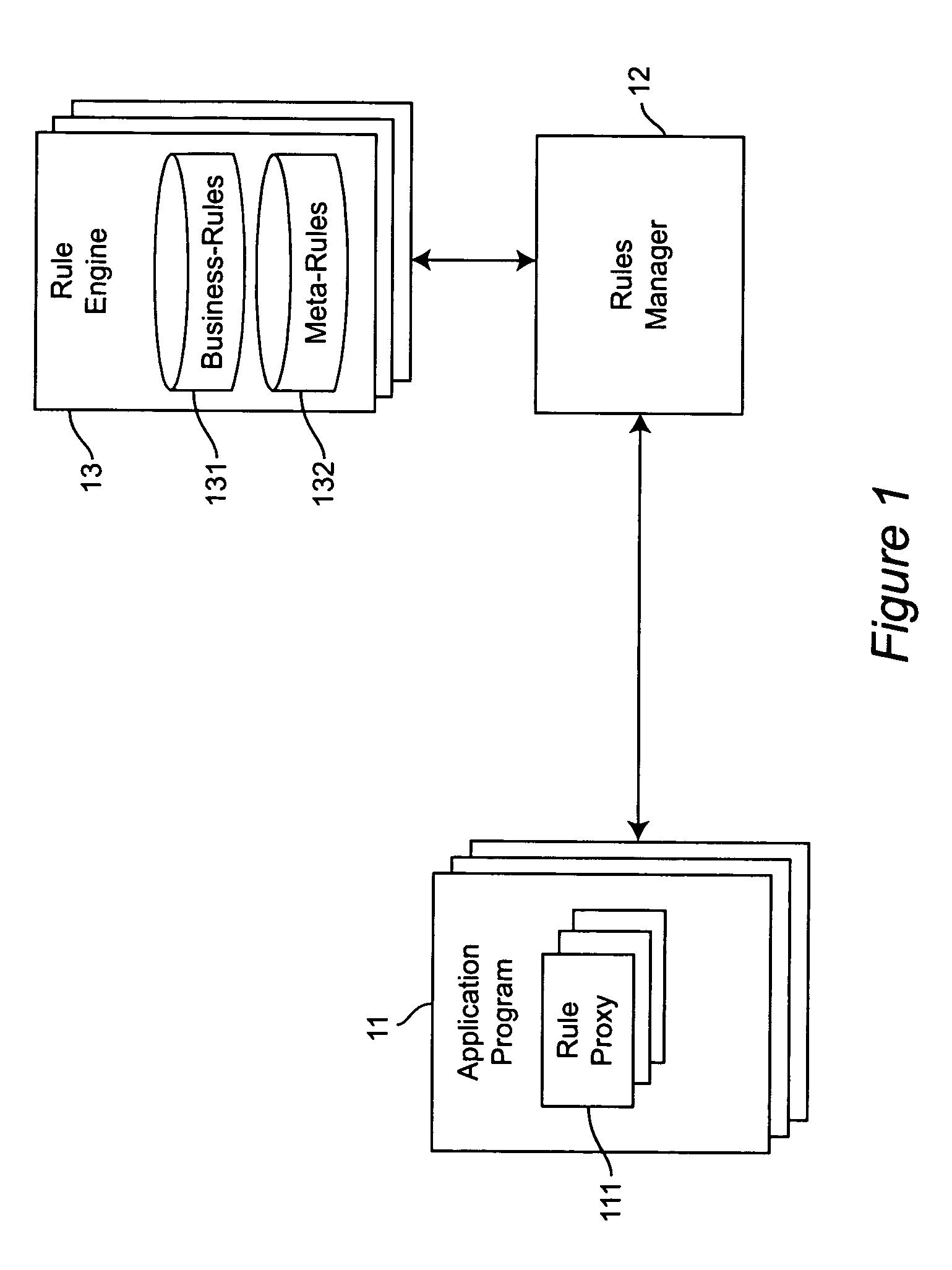
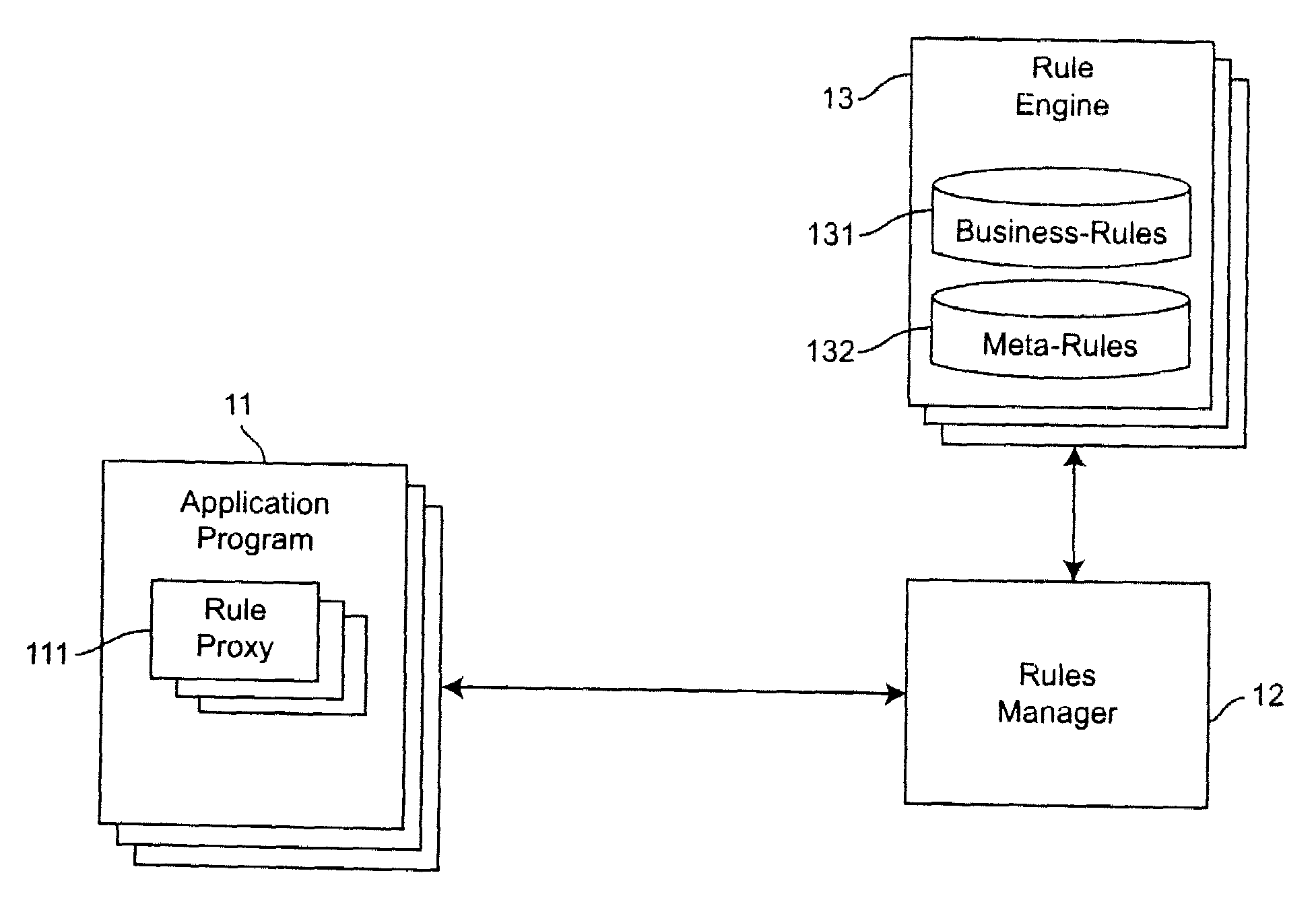
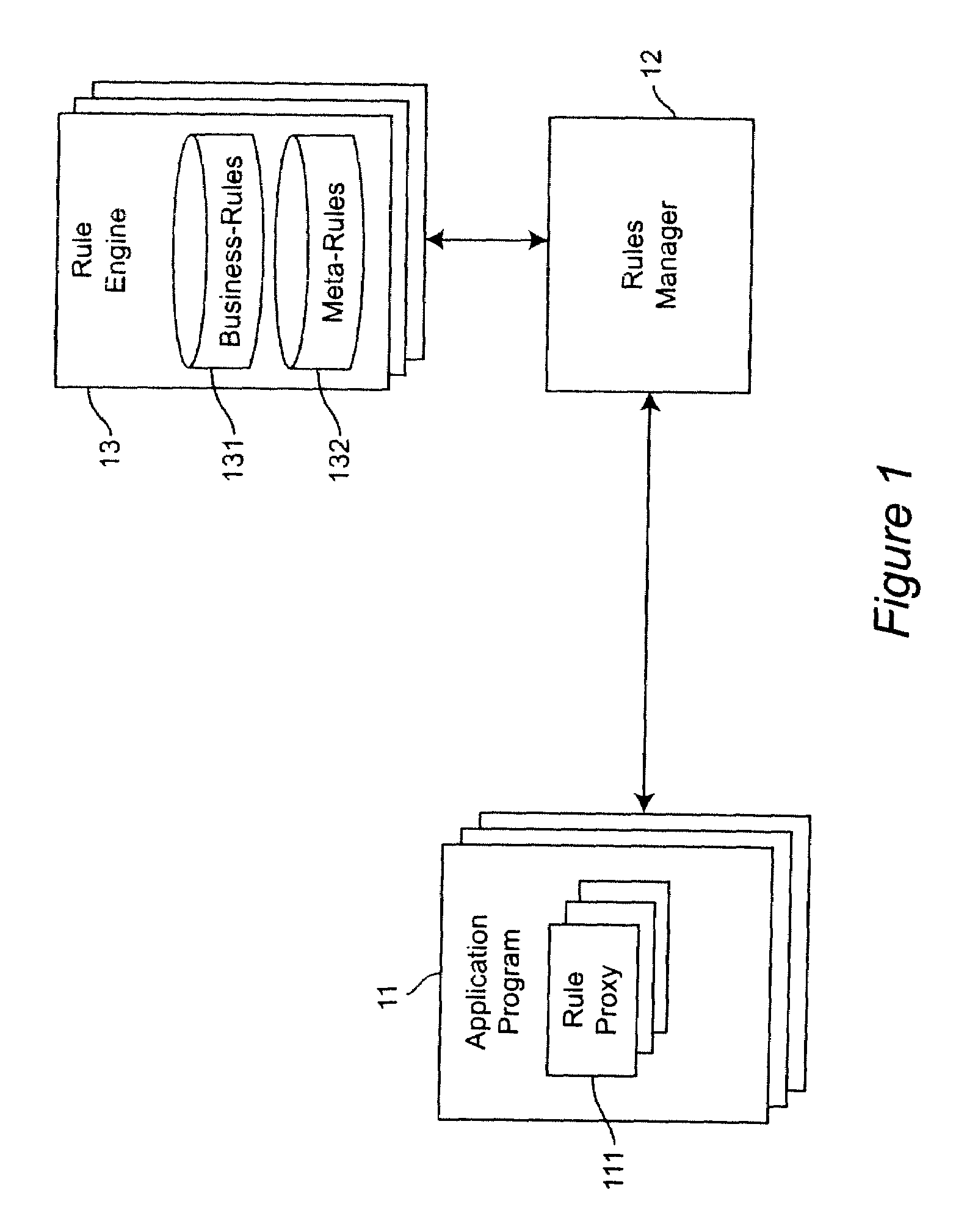
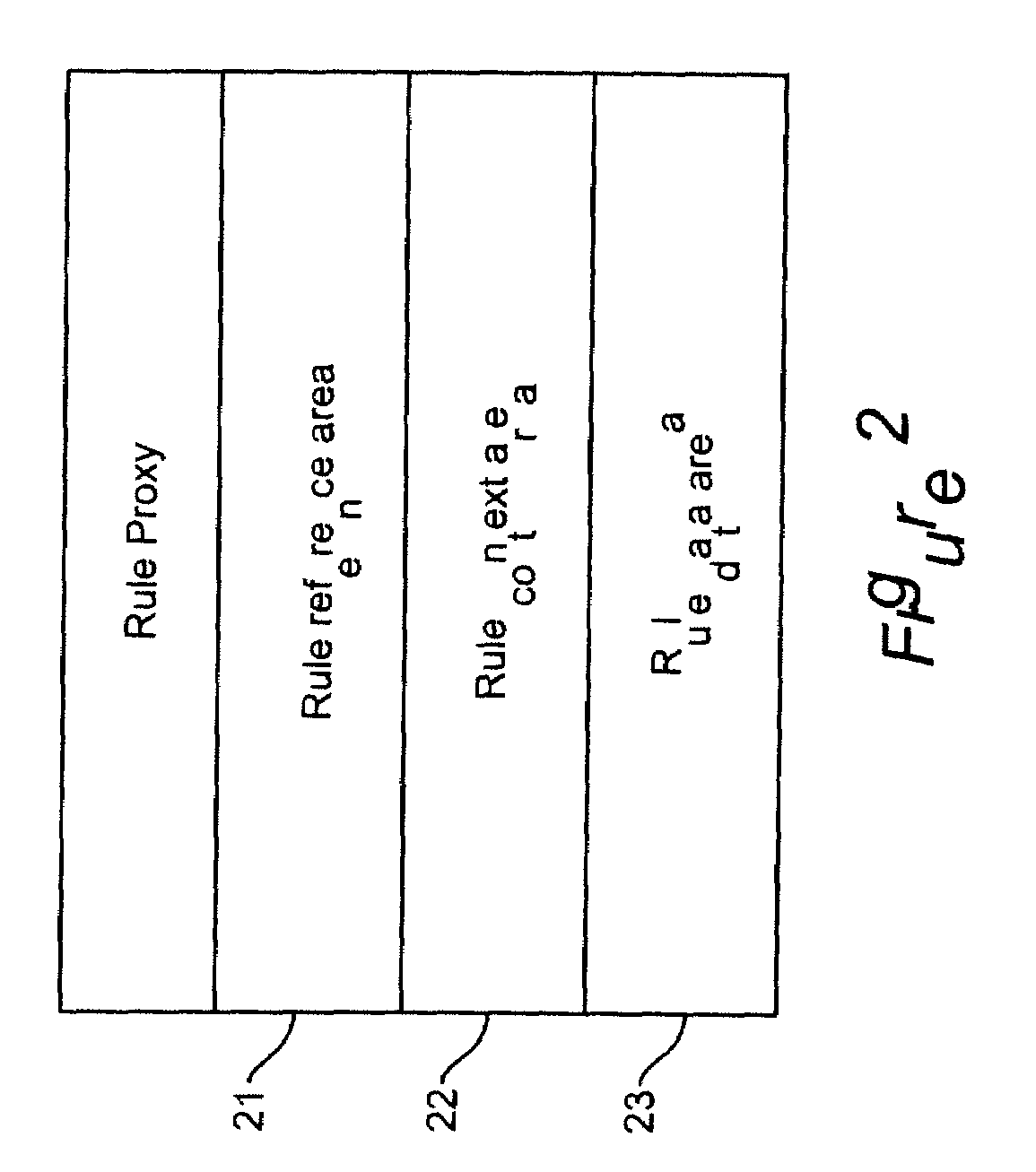
Method and apparatus for using meta-rules to support dynamic rule-based business systems
InactiveUS20060009991A1Insufficient flexibilityKnowledge representationCommerceApplication softwareBusiness policies
Meta-Rules are a special set of business rules whose purpose is to enable business rules selection and subsequent rule invocation by a business rules manager. Contained within a Meta-Rule are business policy and other information that enables the selection of a business rule used by a business application. Meta-rules allow the system to dynamically select and identify specific business rules to be executed within a given business application. By enabling a higher level of abstraction, and relying on rules to resolve specific business rule selection and invocations, Meta-rules further separate the binding of business knowledge and practice from application programming logic. The application programmer is freed from having specific knowledge of the business rule; all that is required is an assertion that a rule is to be used.
Owner:IBM CORP
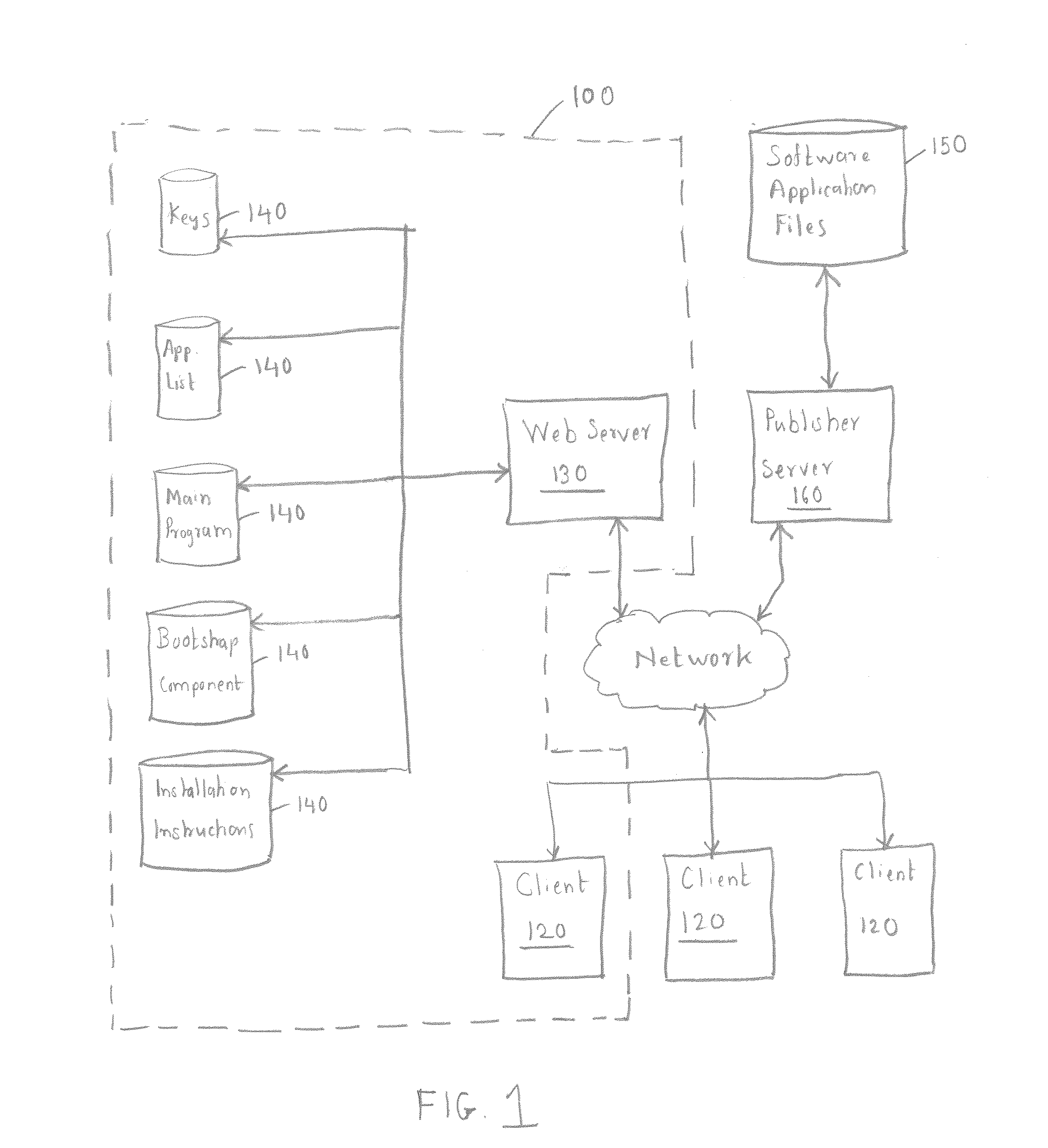
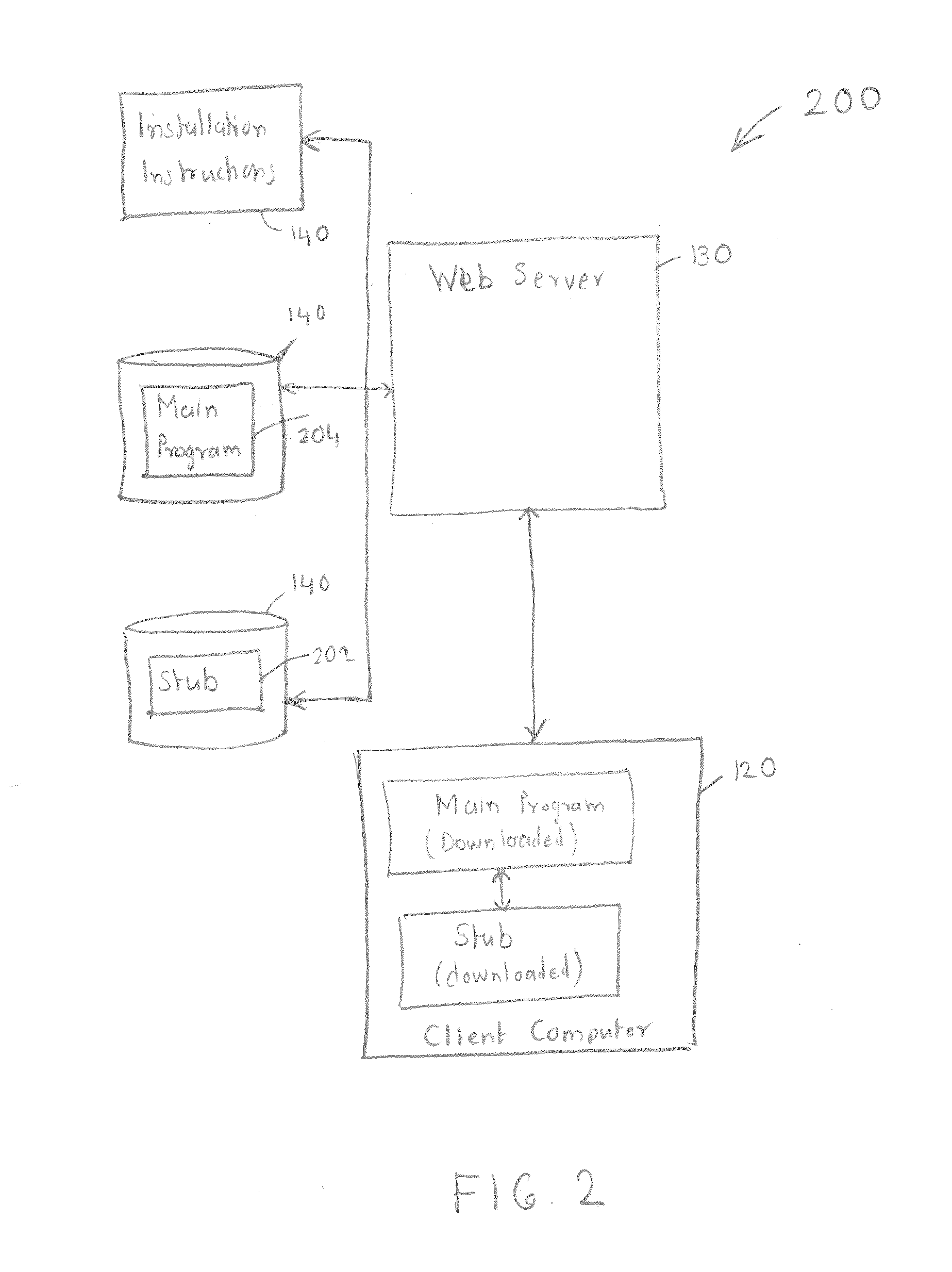
System and Method for Automating Installation and Updating of Third Party Software
InactiveUS20120246630A1Broaden applicationEasy to installProgram loading/initiatingMemory systemsThird partyUser input
A software application installation system facilitates automatic installation and / or updating of software applications without requiring a user to have any specific knowledge of the configuration of the computer system upon which the software application is to be installed and / or updated. The software applications to be installed may be supplied by third party providers. The installation is based on automatically derived knowledge of the computer system on which the software applications are to be installed. The software applications may be installed automatically using a standardized user interface (UI), and / or without requiring substantial user input.
Owner:SECURE BY DESIGN
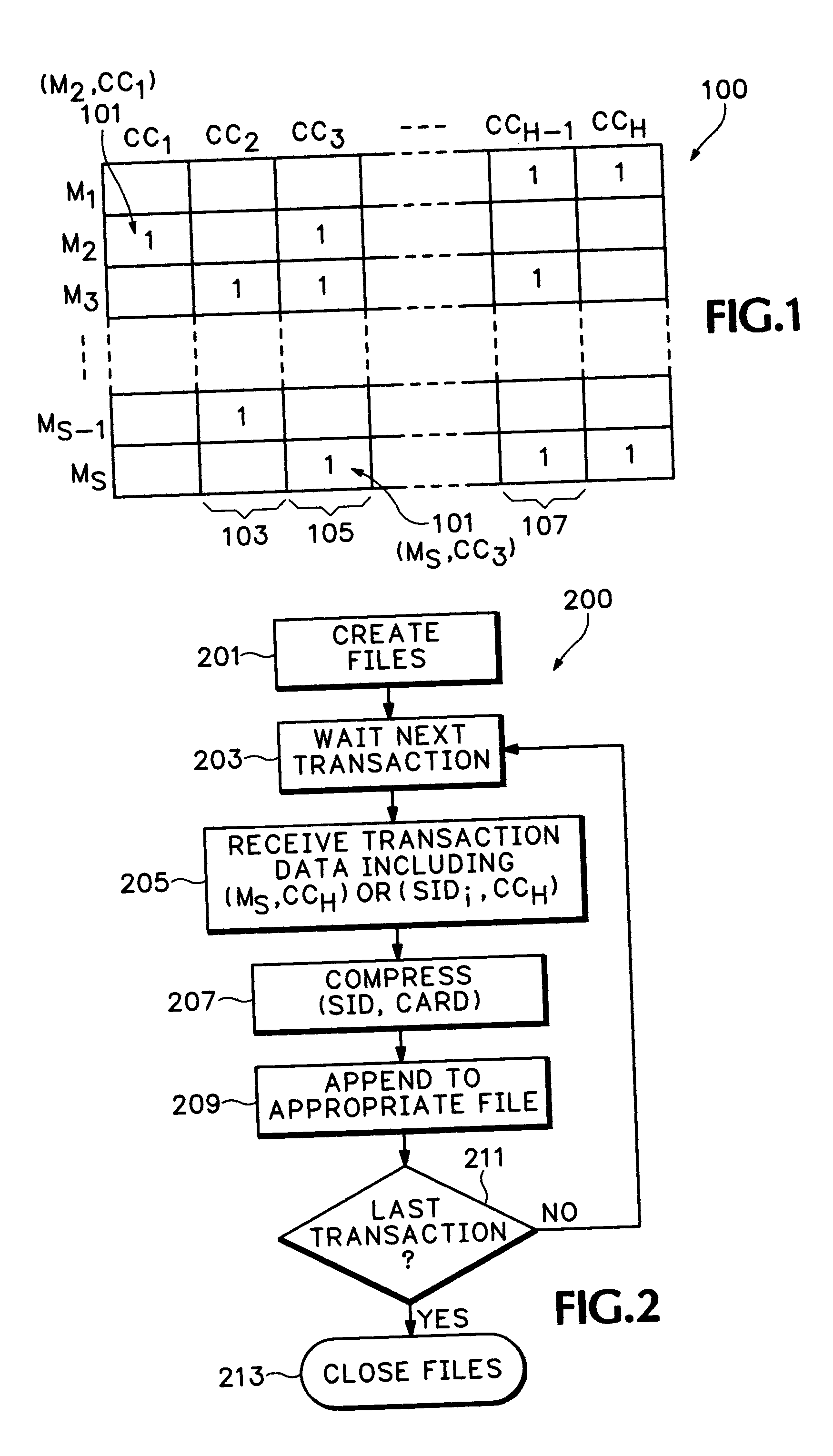
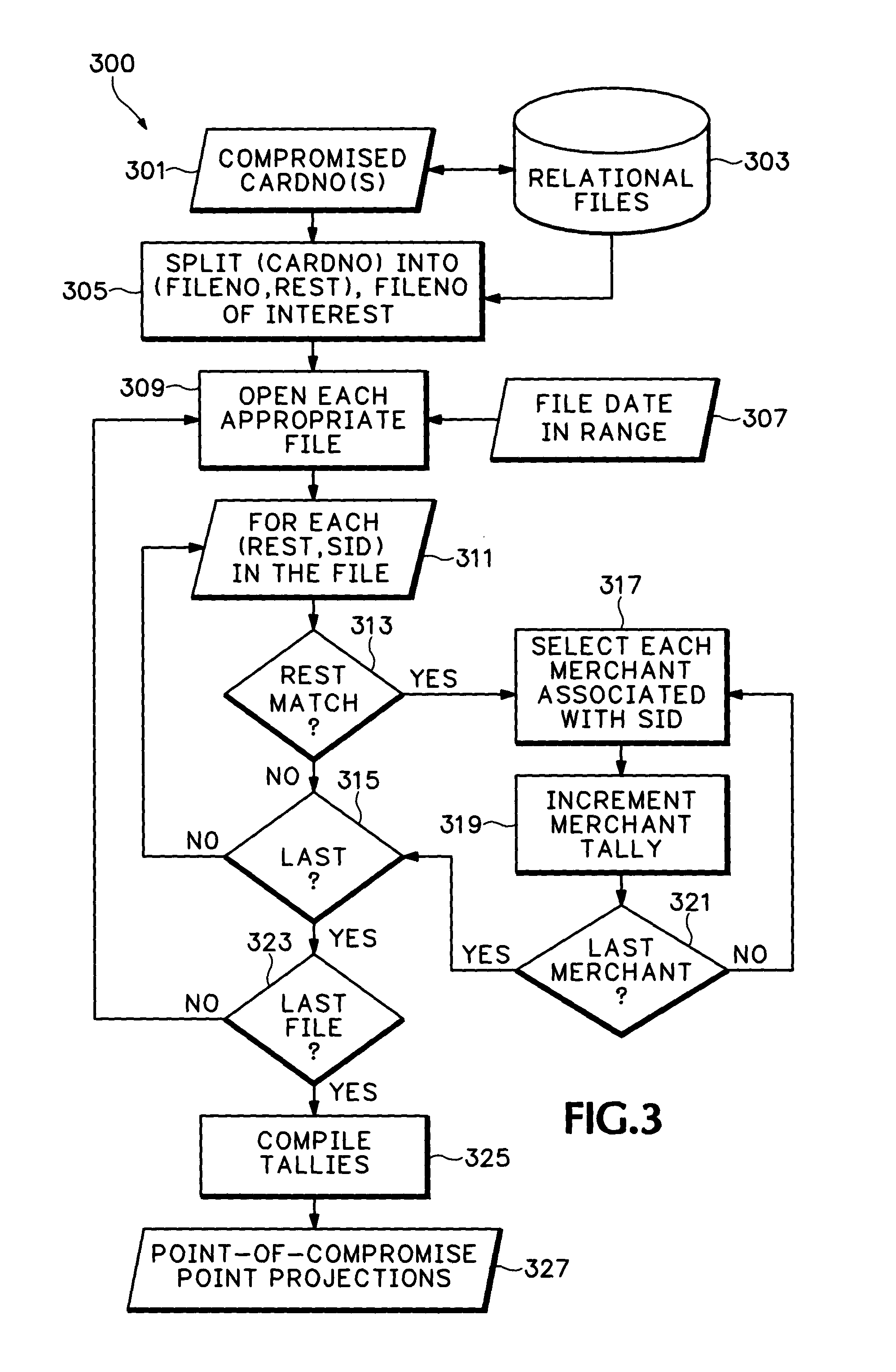
Determining point-of-compromise
A data mining and knowledge discovery method and system. A data base is established in a virtual matrix form for each transaction of large scale transactional events. Data is filed and logged in a manner for rapid sorting such that given a set of identifiers for comprised transactions, a limited subset of the matrix only need be accessed for specific knowledge discovery in the nature of point-of-compromise. For each potential point-of-compromise, a tally is compiled. Potential points-of-compromise are sorted according to tally score. Score is indicative of increasing likelihood of a source point-of-compromise.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
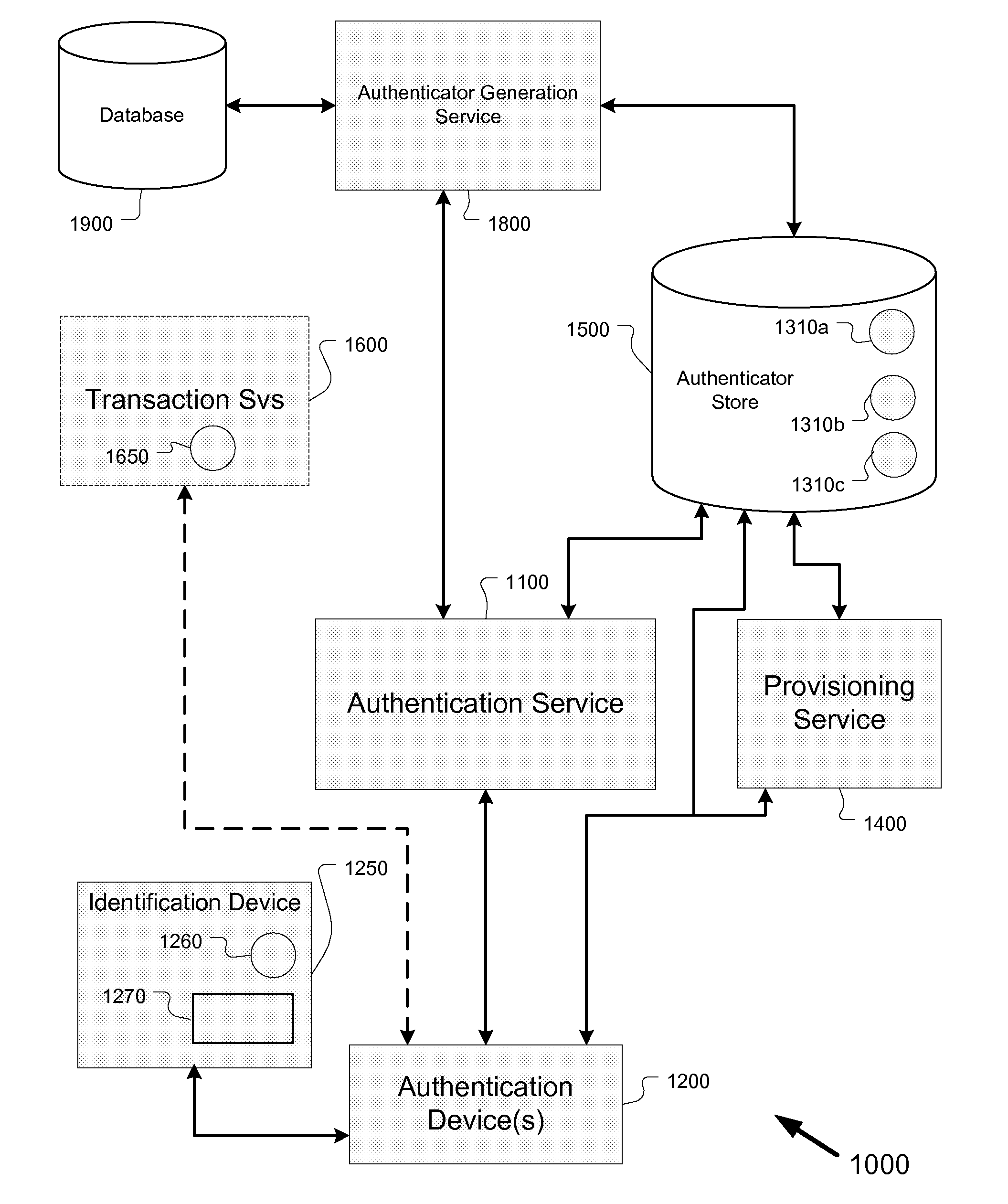
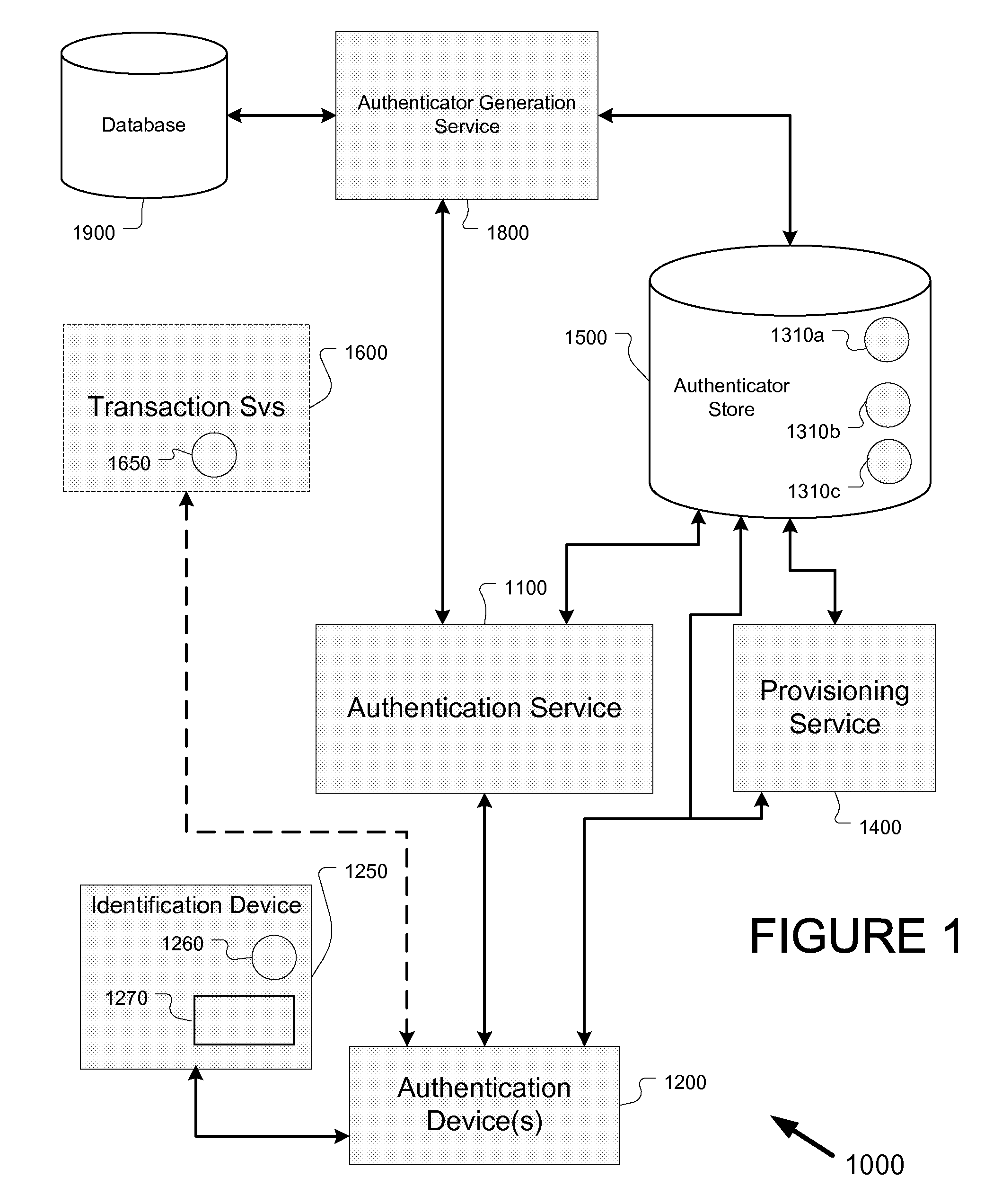
Systems, methods, and apparatus for secure transactions in trusted systems
InactiveUS20080216172A1Accurate authenticationDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionTrusted systemChallenge response
Systems, methods, and software for protecting the identities of individuals, groups, and organizations are provided. In one embodiment, the systems, methods, and software provided by the present invention include a challenge-response architecture based upon entity-specific knowledge for verification of identity. In one aspect, a method for authenticating a first entity to at least one other entity includes creating an authenticator effective to authenticate said first entity to said at least one other entity; providing said authenticator or a substantially secure derivative thereof to an intermediary authentication service configured to interrogate said first entity; receiving a response to an identity interrogation from said first entity at said intermediary; and comparing at said intermediary the content of said response, or a derivative of said content, to said authenticator or said substantially secure derivative thereof to generate an estimation as to whether said first entity is authentic at said intermediary.
Owner:DIALSAFE
Self-optimizing method and machine
A method for computer-generating interaction-specific knowledge base for rapidly improving or optimizing a performance of an object comprises performing, according to computer-designed test matrices, at least several automatic experimental cycles on selected control variables. In at least one of the automatic experimental cycles after the first the computer plans a new test matrix designed to minimize or remove at least one expected two-variable interaction from a main effect of a designated control variable. A machine operating according to the method is also available.
Owner:LI FAMILY HLDG
Method and Apparatus for Using Meta-Rules to Support Dynamic Rule-Based Business Systems
ActiveUS20080177689A1Insufficient flexibilityKnowledge representationCommerceApplication softwareBusiness knowledge
Meta-Rules are a special set of business rules whose purpose is to enable business rules selection and subsequent rule invocation by a business rules manager. Contained within a Meta-Rule are business policy and other information that enables the selection of a business rule used by a business application. Meta-rules allow the system to dynamically select and identify specific business rules to be executed within a given business application. By enabling a higher level of abstraction, and relying on rules to resolve specific business rule selection and invocations, Meta-rules further separate the binding of business knowledge and practice from application programming logic. The application programmer is freed from having specific knowledge of the business rule; all that is required is an assertion that a rule is to be used.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
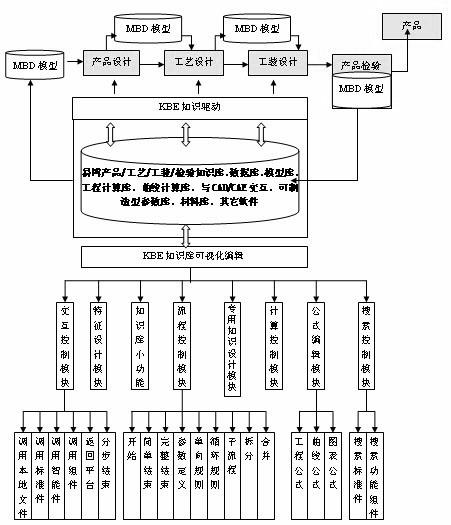
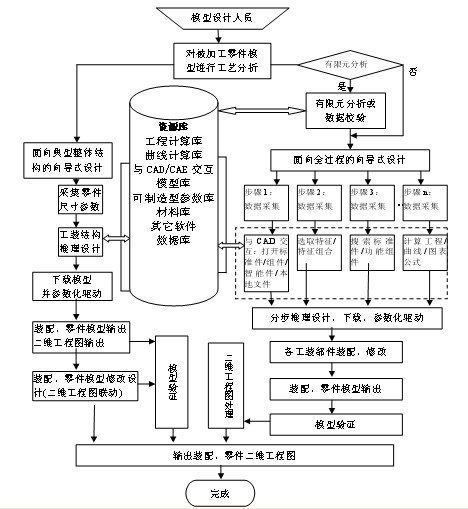
Full three-dimensional digital knowledge base system and application method of knowledge base
ActiveCN102324072AImprove general performanceDo not disclose design experienceData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsData acquisitionDigitization
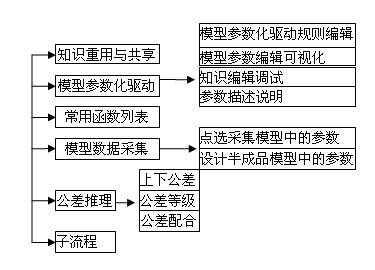
The invention discloses a full three-dimensional digital knowledge base system and an application method of a knowledge base. The knowledge base system comprises a flow control module, a specific knowledge design module, an interaction control module, an equation editing module, a search control module, a computing control module and a knowledge base small functional module and is an independent knowledge driving system capable of being hung on different CAD (Computer-Aided Design). The application method of the knowledge base can be applied to various fields such as products, processes, tool design, product inspection and the like in the mechanism manufacture industry. A designer expresses knowledge such as purposes, industry design specifications, standard manuals, design experience, computational formulas and the like through an open programming-free visual knowledge editing function and stores the knowledge into the knowledge base, a database and a model base for reusing; and wizard design is realized through parameter passing, data acquisition and interaction and platform interaction. The system has the advantages of strong generality, convenience and rapidness, no leakage of enterprise core technology experience knowledge and the like and provides means for technical innovation and knowledge and experience accumulation.
Owner:西安易博软件有限责任公司
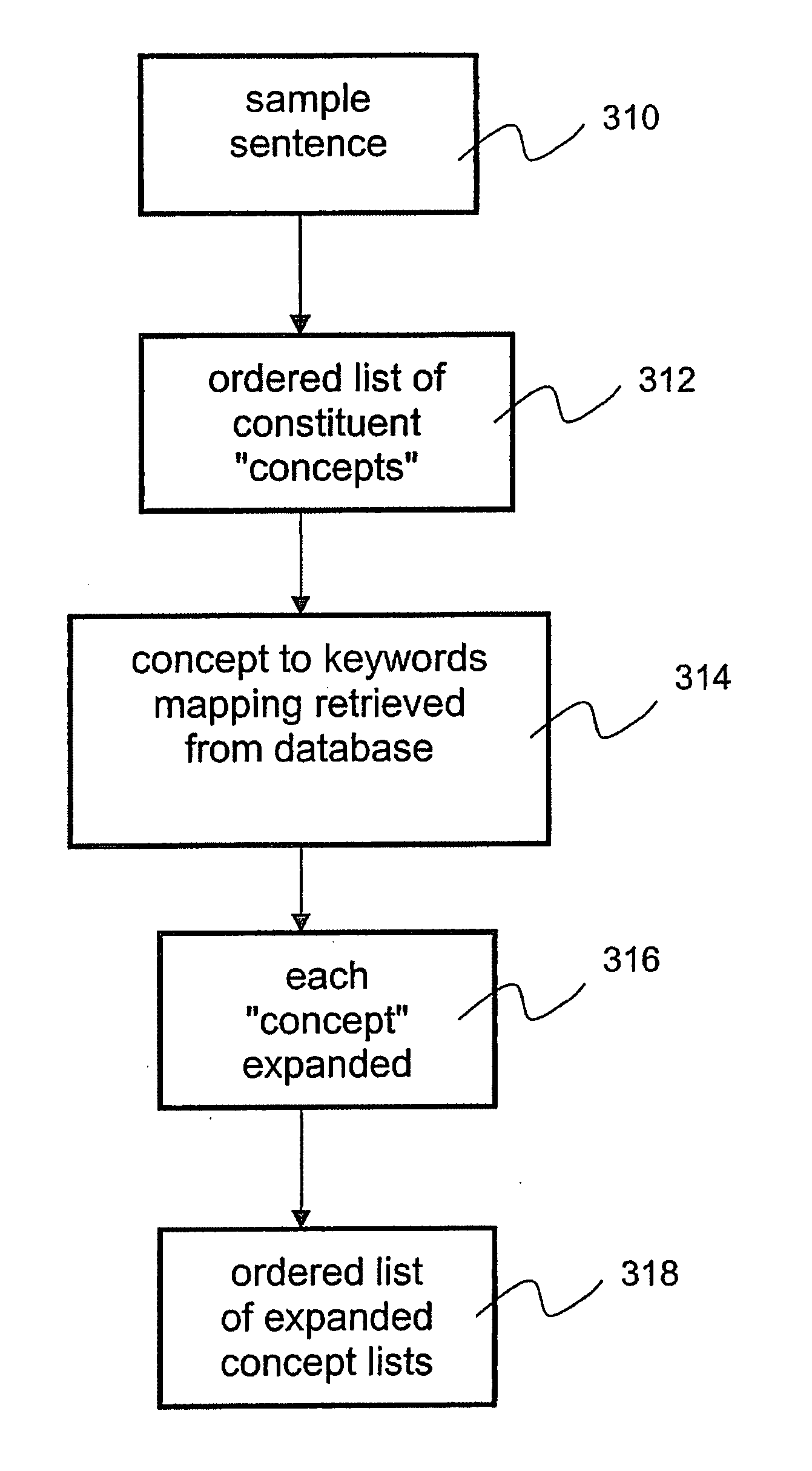
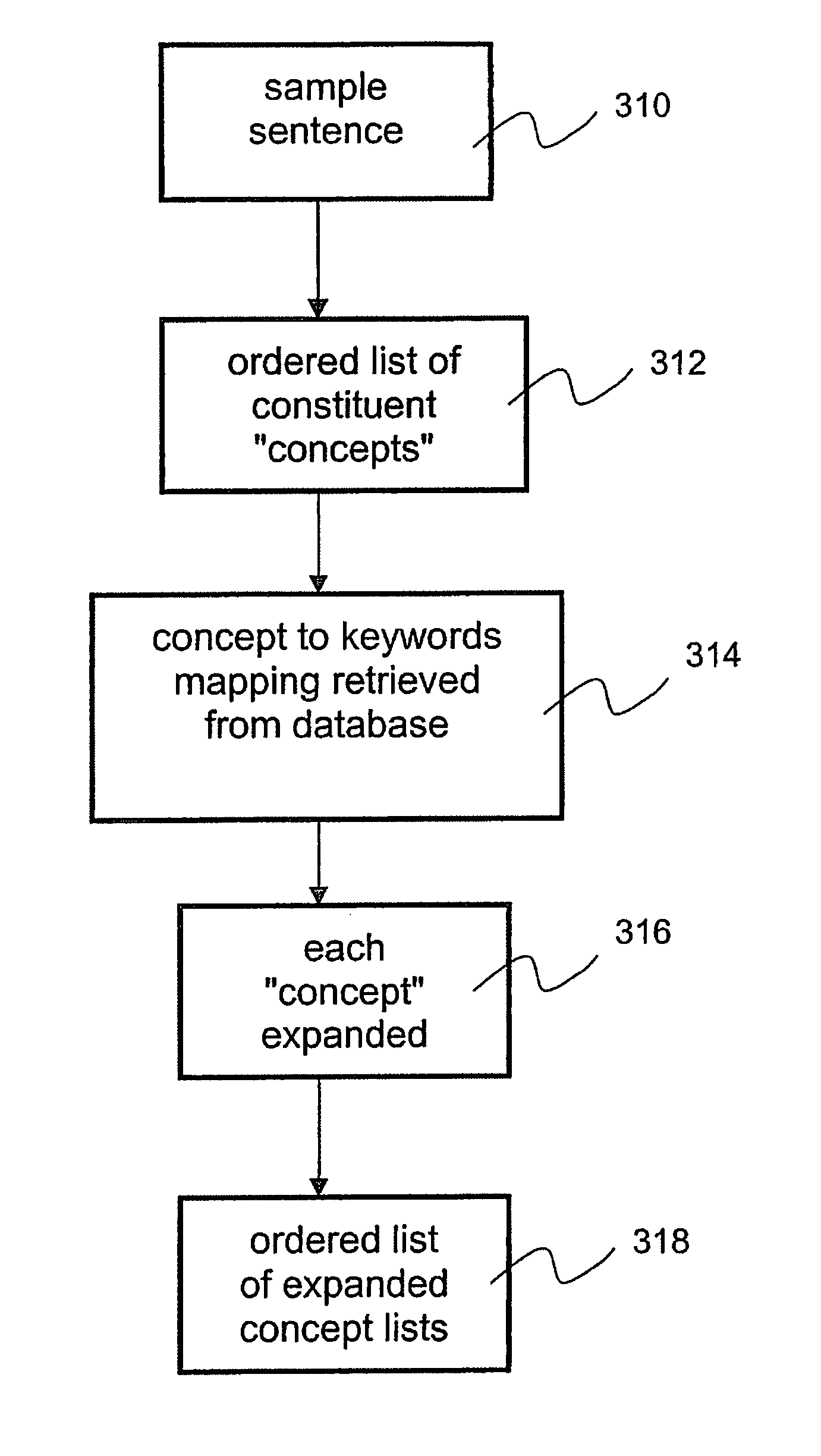
Speech recognition accuracy via concept to keyword mapping
The invention provides a system and method for improving speech recognition. A computer software system is provided for implementing the system and method. A user of the computer software system may speak to the system directly and the system may respond, in spoken language, with an appropriate response. Grammar rules may be generated automatically from sample utterances when implementing the system for a particular application. Dynamic grammar rules may also be generated during interaction between the user and the system. In addition to arranging searching order of grammar files based on a predetermined hierarchy, a dynamically generated searching order based on history of contexts of a single conversation may be provided for further improved speech recognition. Dialogue between the system and the user of the system may be recorded and extracted for use by a speech recognition engine to refine or create language models so that accuracy of speech recognition relevant to a particular knowledge area may be improved.
Owner:INAGO CORP
Method and apparatus for graphical device management using a virtual console
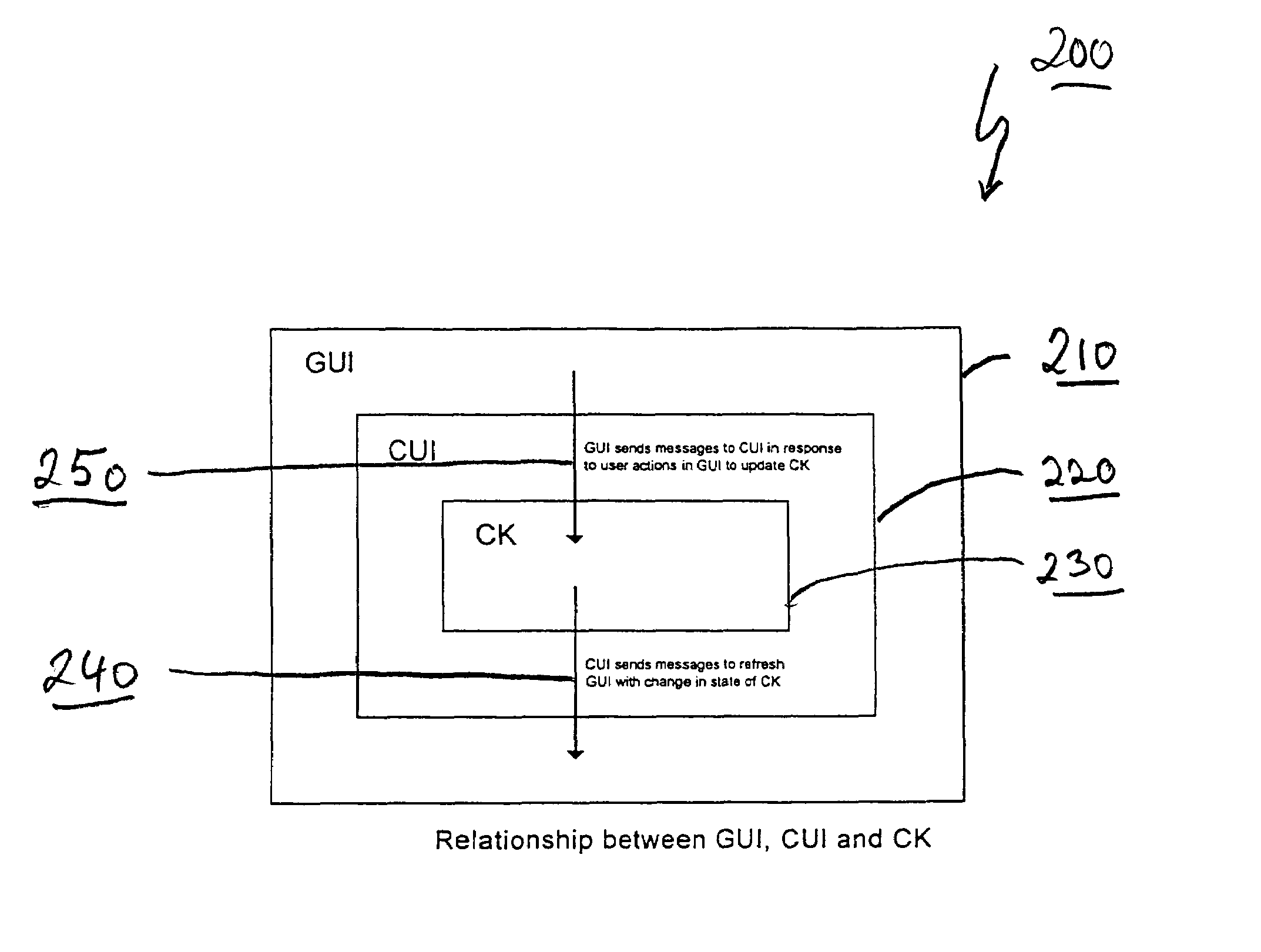
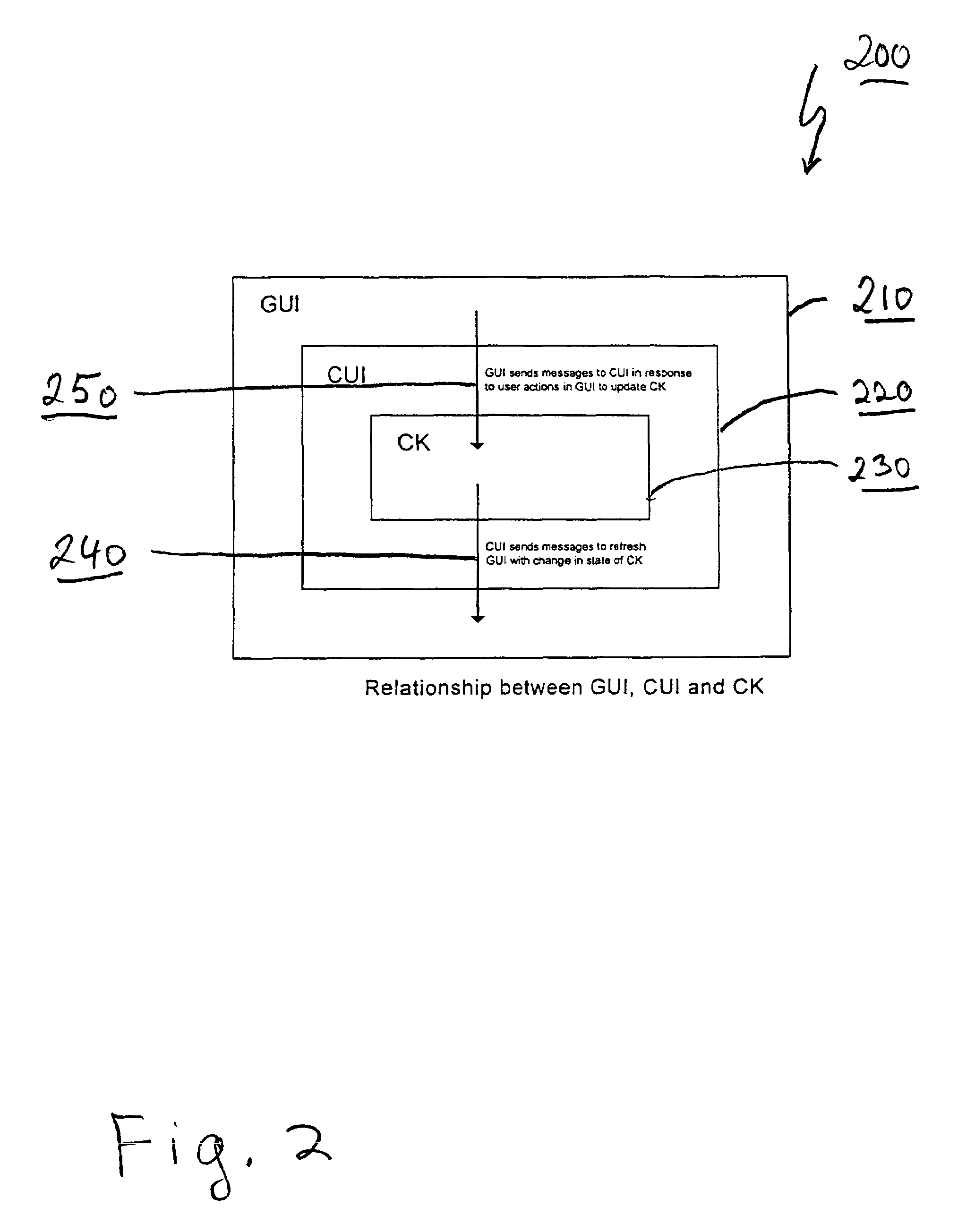
A method and apparatus is provided for remote device management using a virtual console. The method and apparatus implements a normalized scheme for developing a graphical user interface (GUI) for remotely managing any computer or networking device that has a console user interface (CUI) for updating a device configuration using a set of predefined configuration commands, and an underlying configuration kernel (CK) for maintaining the state of the device configuration (e.g. user names, passwords, timeout values, etc.). By re-using the CUI and underlying CK code, the scheme requires minimal specific knowledge of the configuration command set implementing the CUI and CK configuration functionality, thereby eliminating the necessity for creating redundant command set aware code in the GUI. In one embodiment, the method and apparatus employs a set of object-oriented classes and macros which interact with the CUI in a standardized manner to associate GUI components with the corresponding configuration command set. The standardized manner of interacting includes refreshing the state of the GUI in response to messages sent from the CUI, and sending messages to the CUI in response to user actions in the GUI. As a result, the GUI functions as a user-friendly interface that encapsulates the functionality of the CUI and underlying CK, and the CUI functions as a virtual console for the remote device.
Owner:INTEL CORP
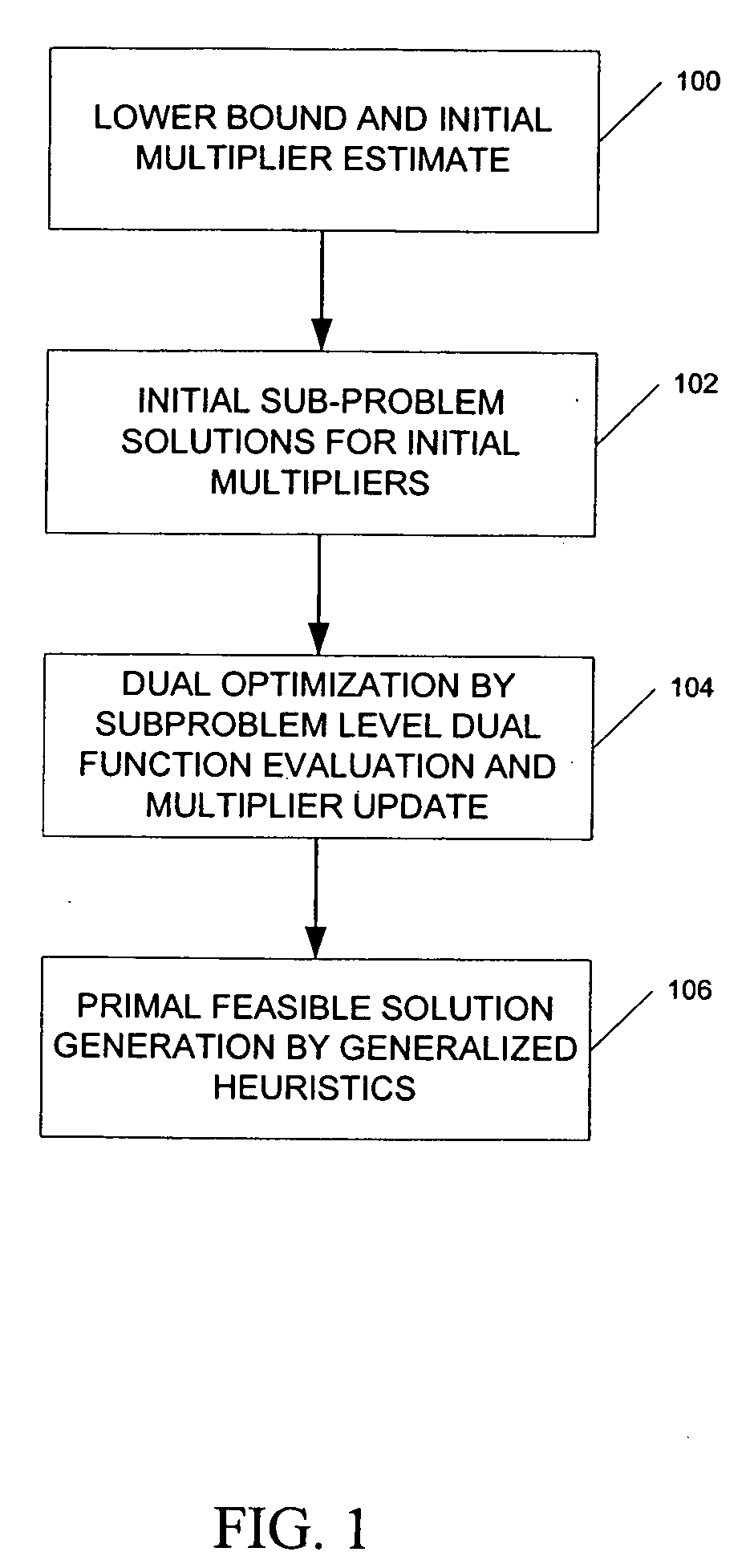
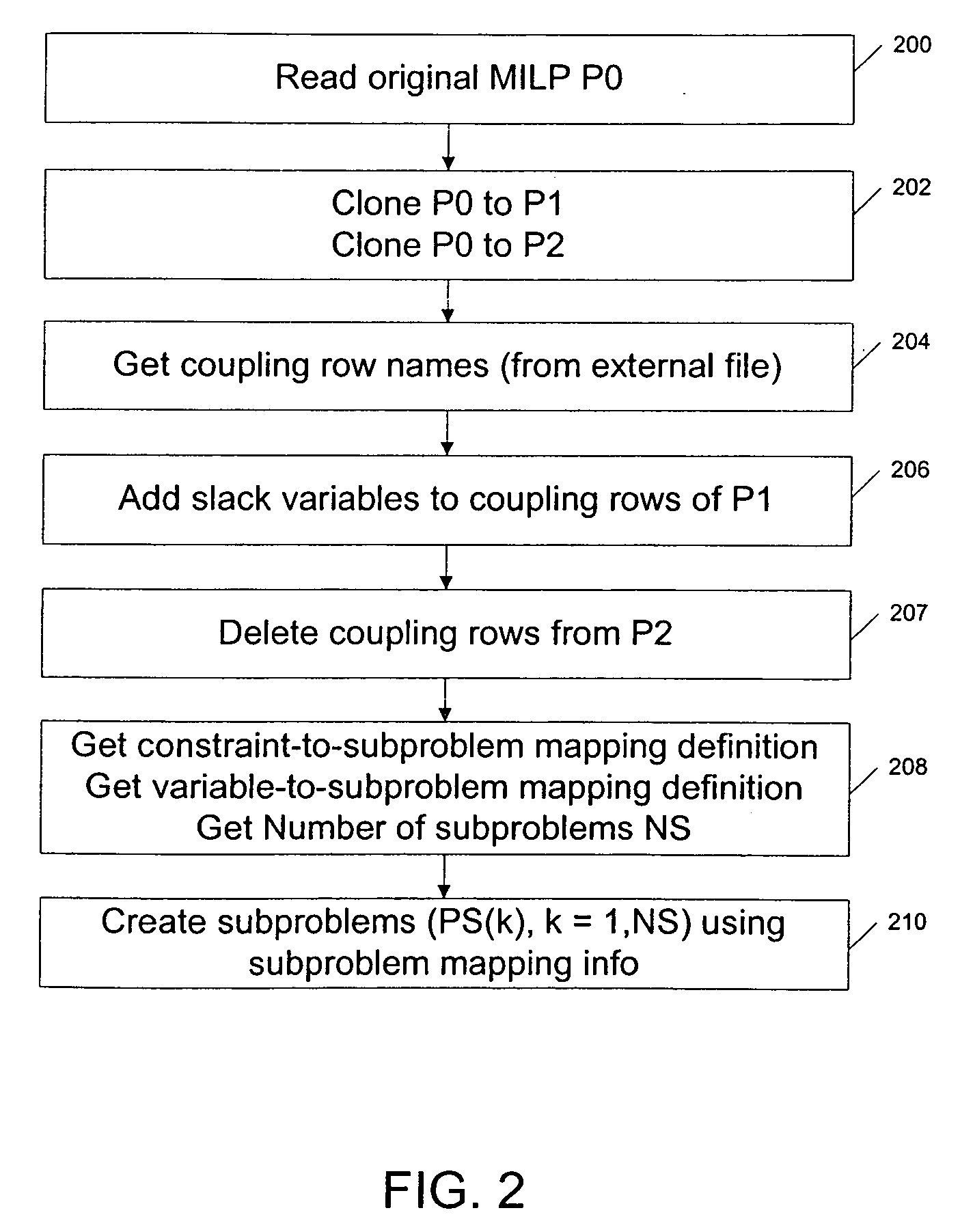
Formal sequential lagrangian algorithm for large scale resource scheduling optimization
ActiveUS20060089864A1Reduce operating costsFast dual optimization—obtainingDigital computer detailsForecastingProblem domainAlgorithm
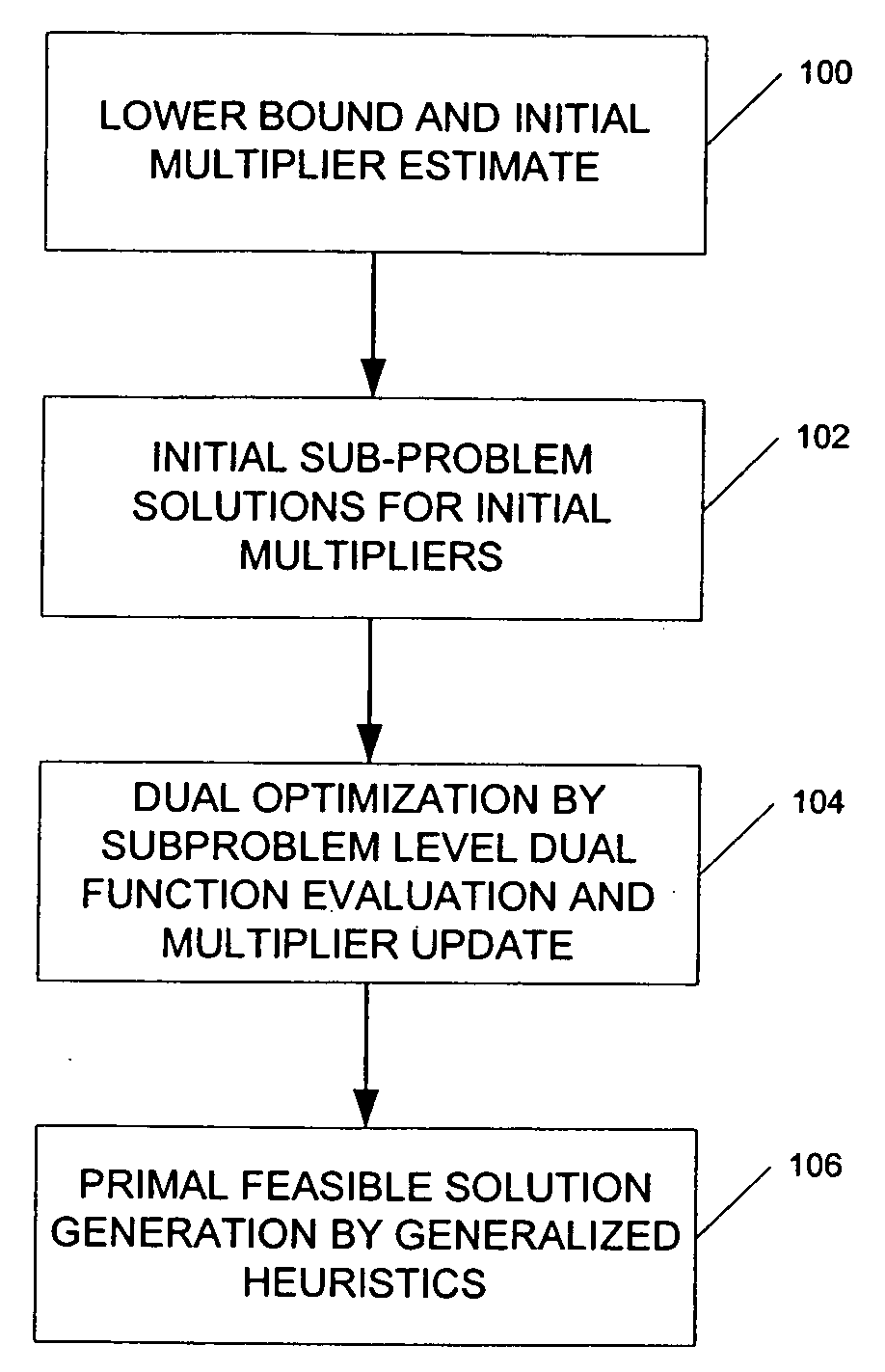
A method and computer program product for optimization of large scale resource scheduling problems. Large scale resource scheduling problems are computationally very hard and extremely time consuming to solve. This invention provides a Lagrangian relaxation based solution method. The method has two distinct characteristics. First, the method is formal. It is completely structure-based and does not use any problem domain specific knowledge in the solution process, either in the dual optimization or the primal feasibility enforcement process. Second, updating the Lagrangian multipliers after solution of every sub-problem without using penalty factors results in fast and smooth convergence in the dual optimization. The combination of high quality dual solution and the structure-based primal feasibility enforcement produces a high quality primal solution with very small solution gap. An optimal solution is first found to the dual of the resource scheduling problem by sequentially finding a solution to a plurality of sub-problems and updating a set of values used in the dual problem formulation after each sub-problem solution is obtained. Coupling constraint violations are systematically reduced and the set of values are updated until a feasible solution to the primal resource scheduling problem is obtained. An initial set of multiplier values is further determined by solving a relaxed version of the primal problem where most of the local constraints except the variable bounds are relaxed.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY SWITZERLAND AG
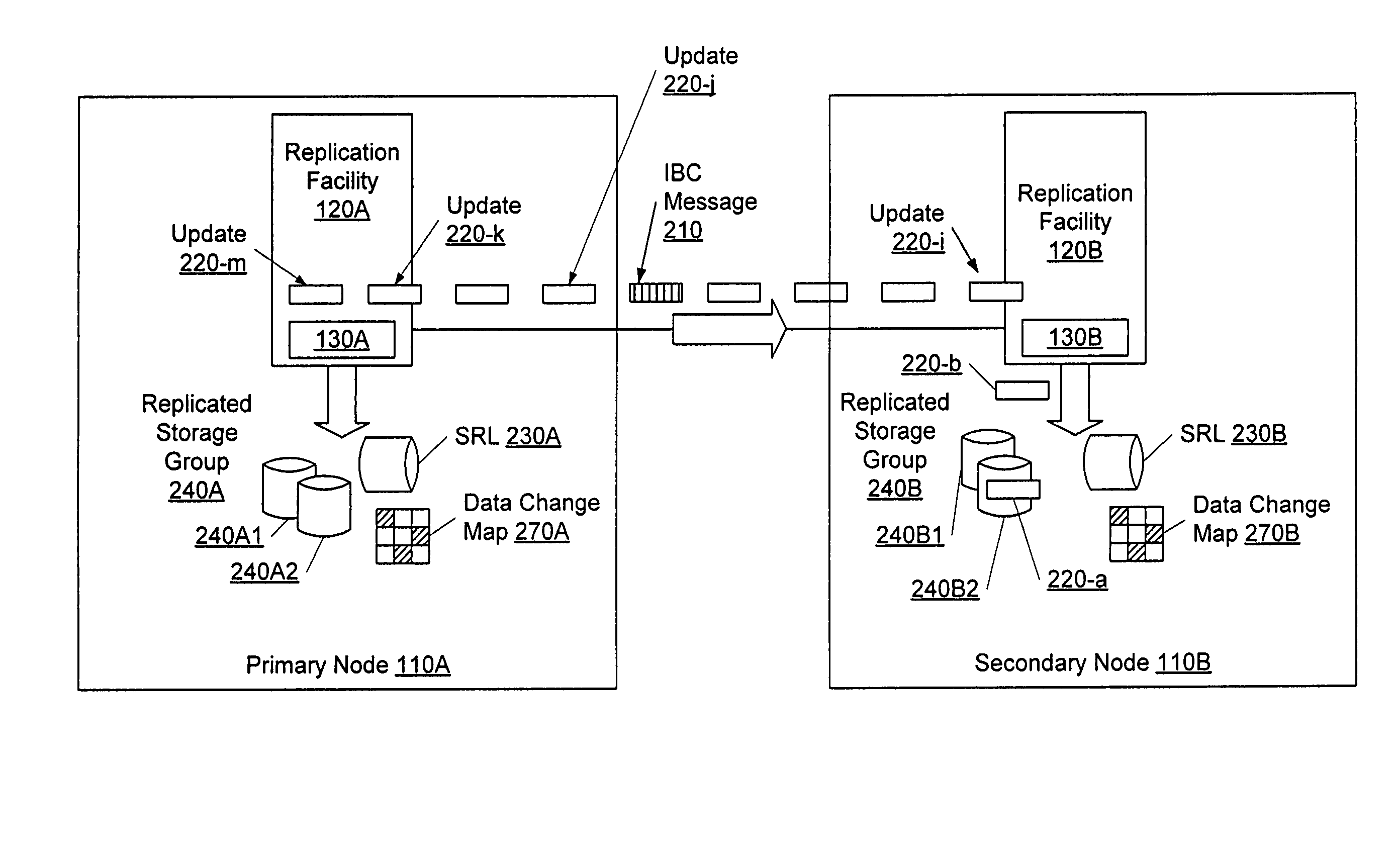
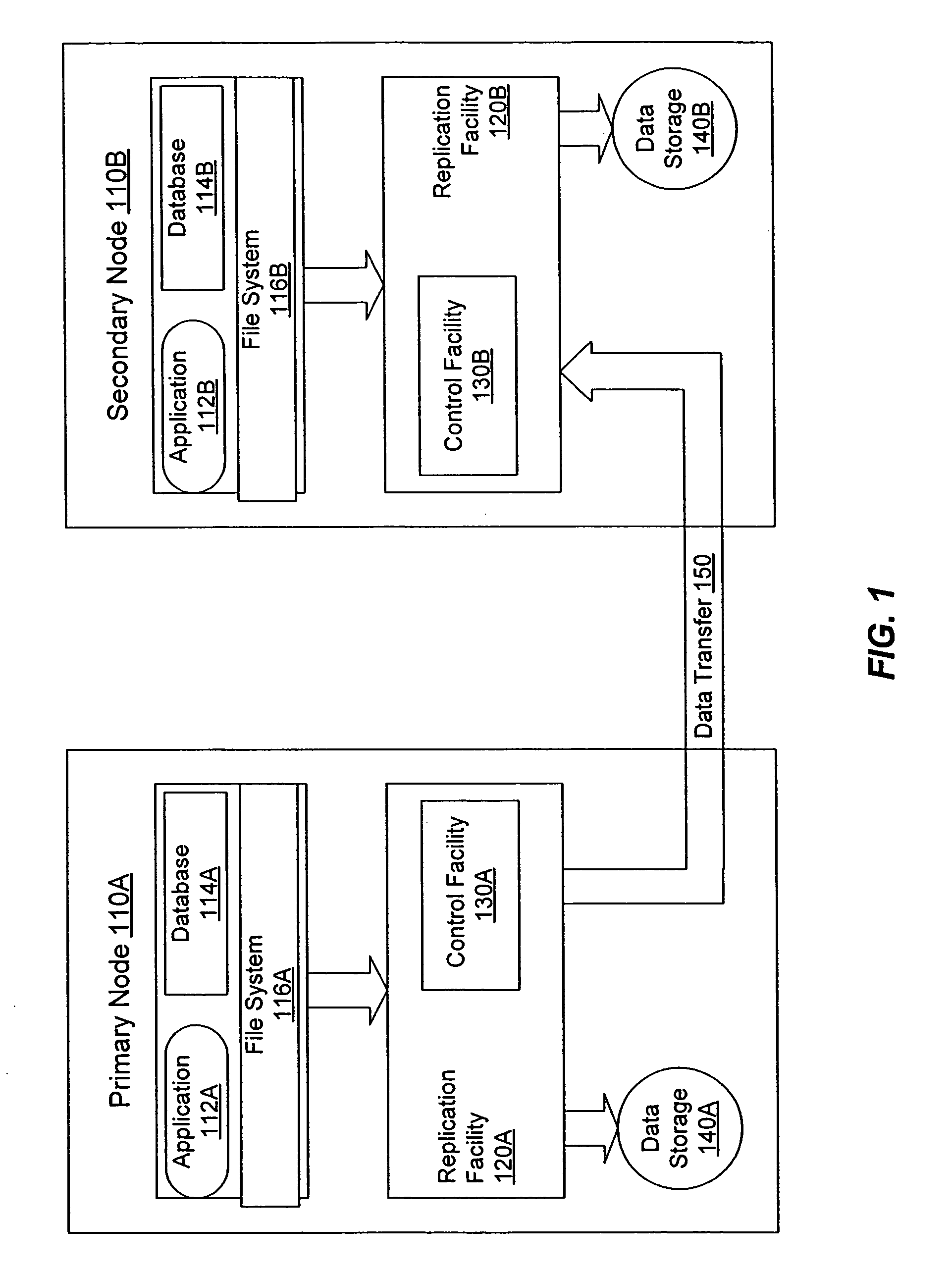
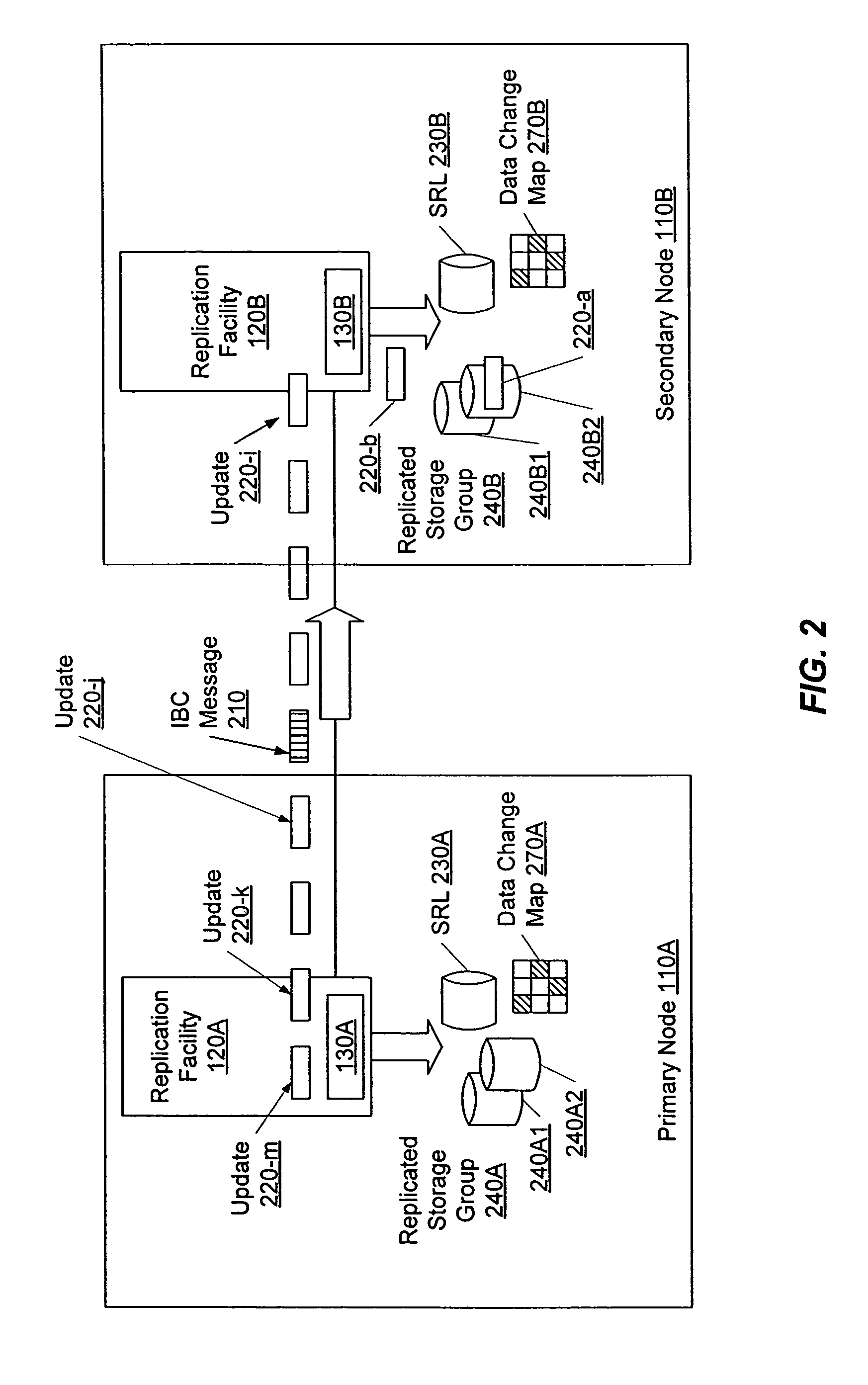
Control facility for processing in-band control messages during data replication
InactiveUS7373468B1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalExecution controlApplication software
A control facility that allows a non-programmer to use and manipulate replicated data without disrupting replication of the data itself. The control facility can be used and customized for a variety of software applications and storage platforms. These customized control facilities can enable a system administrator without application- or storage system-specific knowledge to perform off-host processing of the replicated data, such as taking snapshots of the data and running Decision Support System reports.In response to a single user command during replication of data from a primary node to a secondary node, the following steps are performed: obtaining a control message from the primary node, wherein the control message is associated with a control command for execution on the secondary node; and automatically executing the control command on the secondary node.
Owner:VERITAS TECH
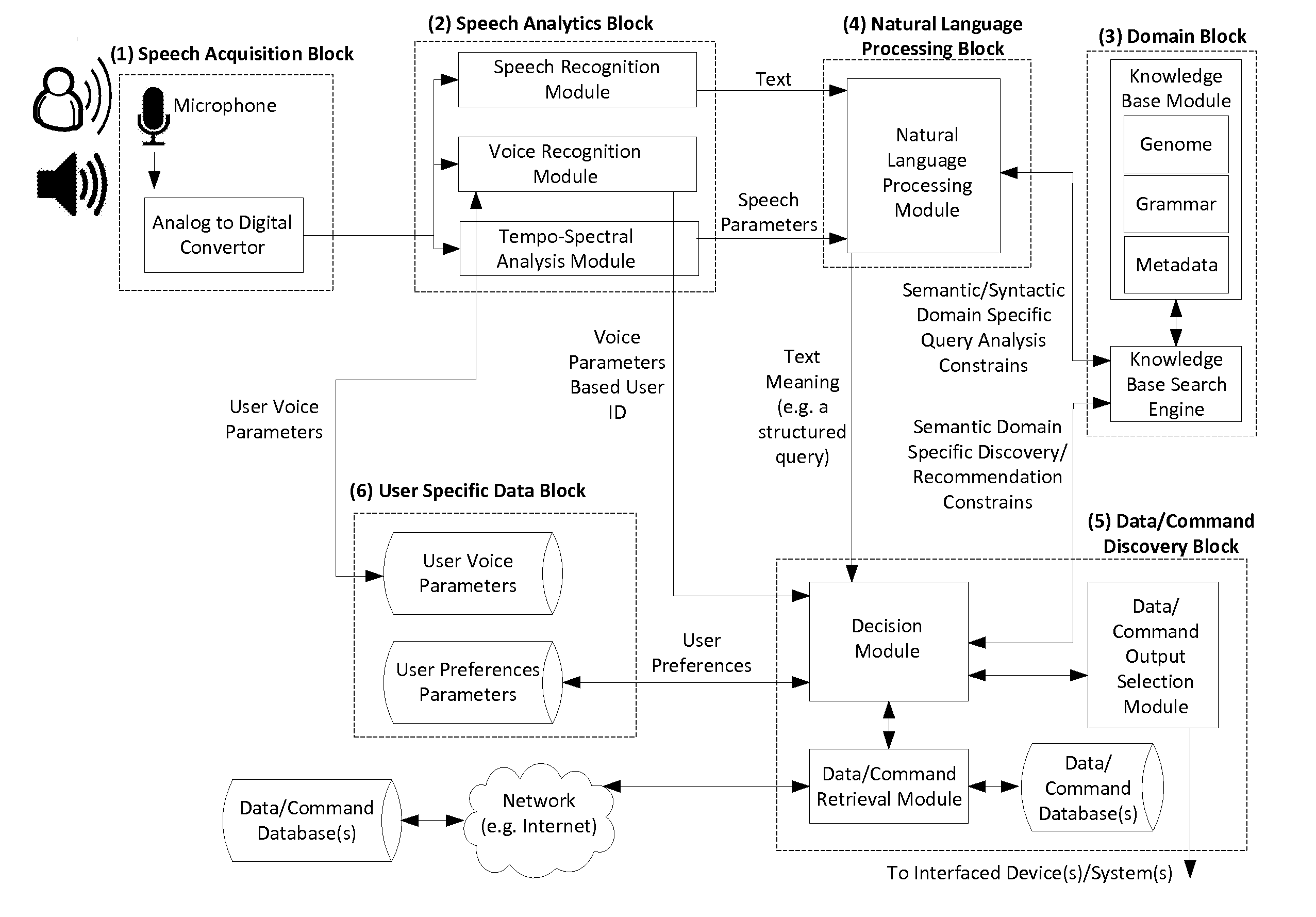
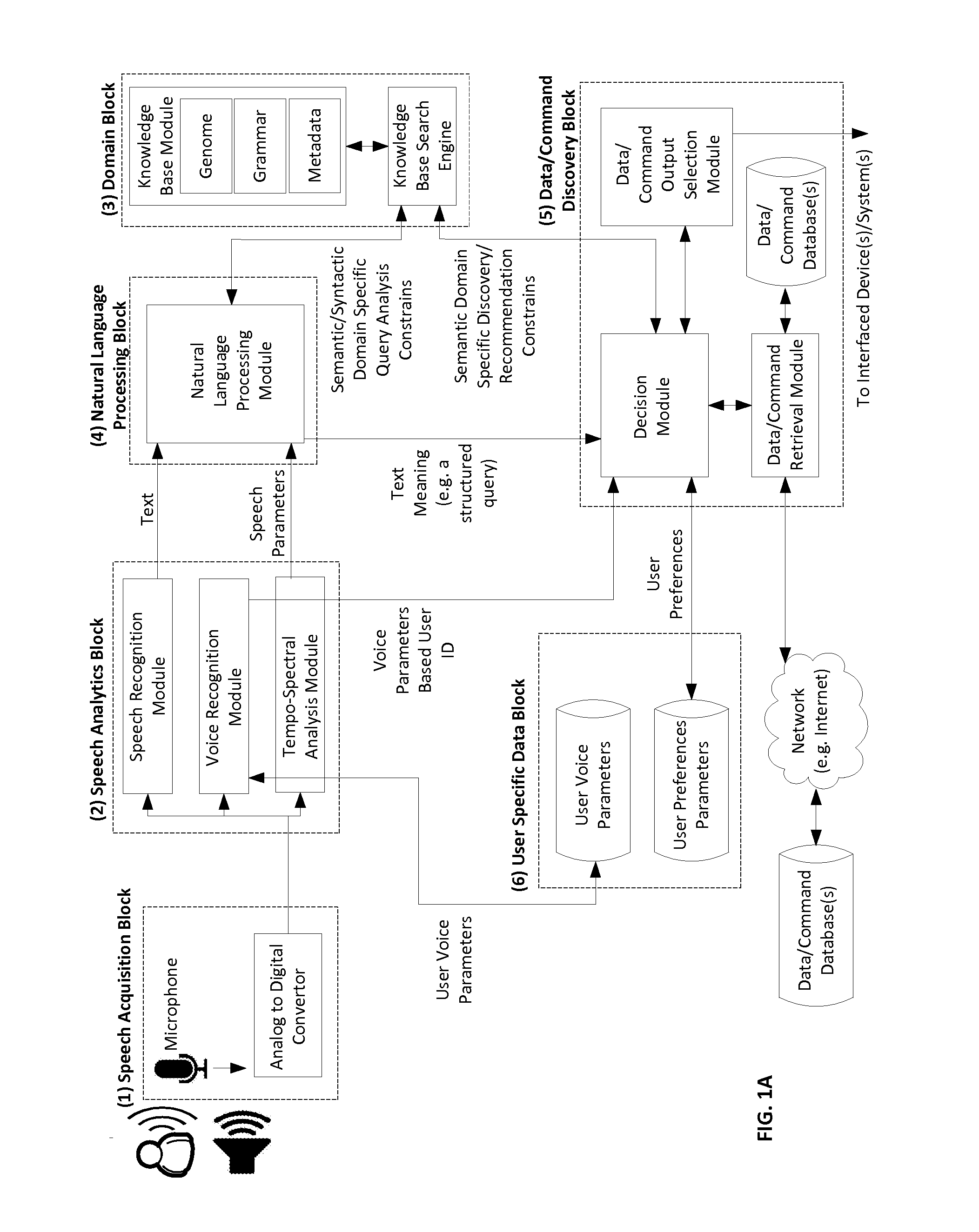
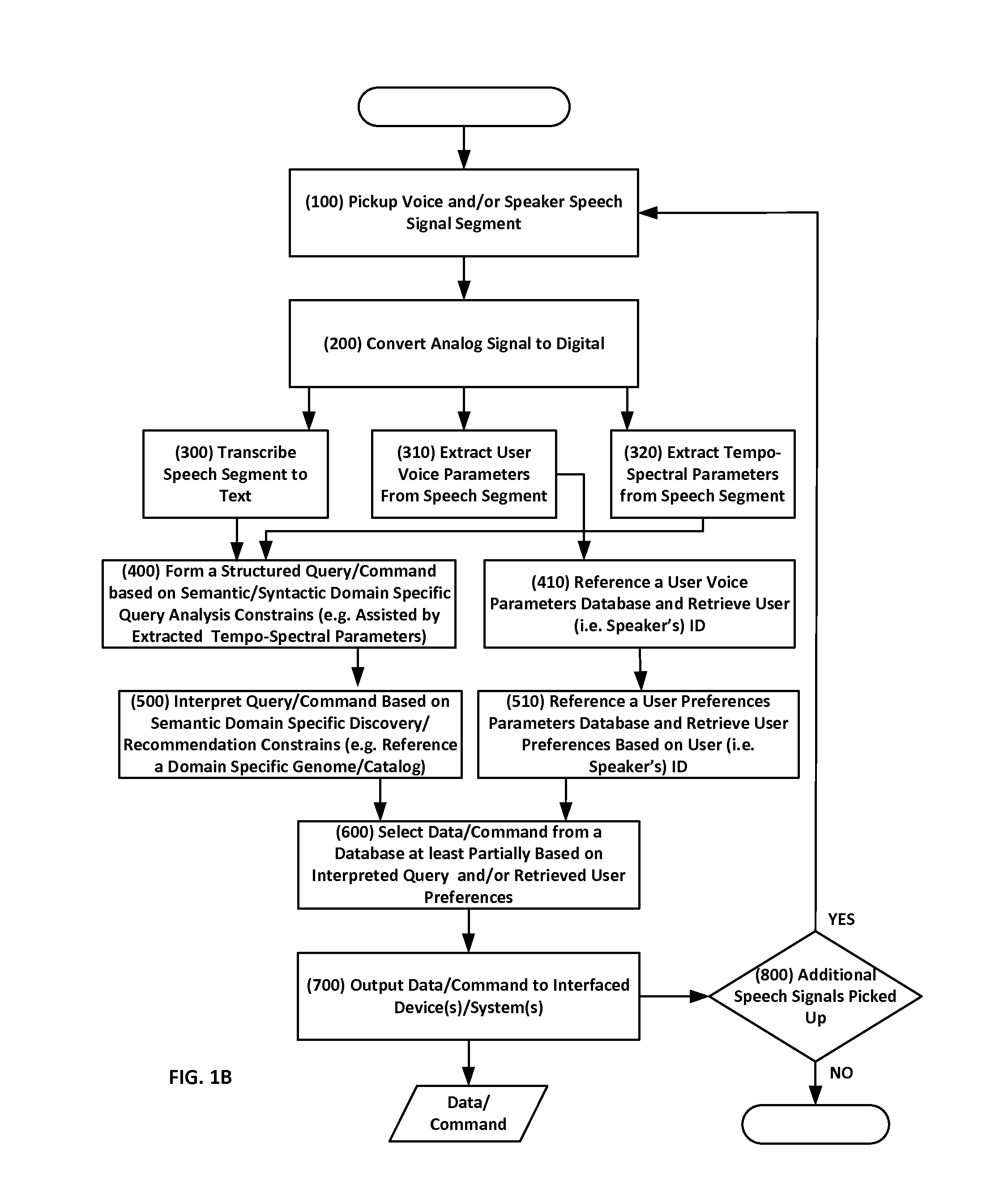
System Apparatus Circuit Method and Associated Computer Executable Code for Natural Language Understanding and Semantic Content Discovery
ActiveUS20140236572A1Inflated body pressure measurementSemantic analysisNatural language processingNatural language understanding
Disclosed are systems, apparatuses, circuits and methods for extrapolating meaning from vocalized speech or otherwise obtained text. Speech of a speaking user is sampled and digitized, the digitized speech is converted into a text stream, the text stream derived from speech or otherwise obtained is analyzed syntactically and semantically, a knowledgebase in the specific context domain of the text stream is utilized to construct one or more semantic / syntactic domain specific query analysis constrains / rule-sets, and a “Domain Specific Knowledgebase Query” (DSKQ) or set of queries is built at least partially based on the domain specific query analysis constrains / rule-sets.
Owner:JINNI MEDIA
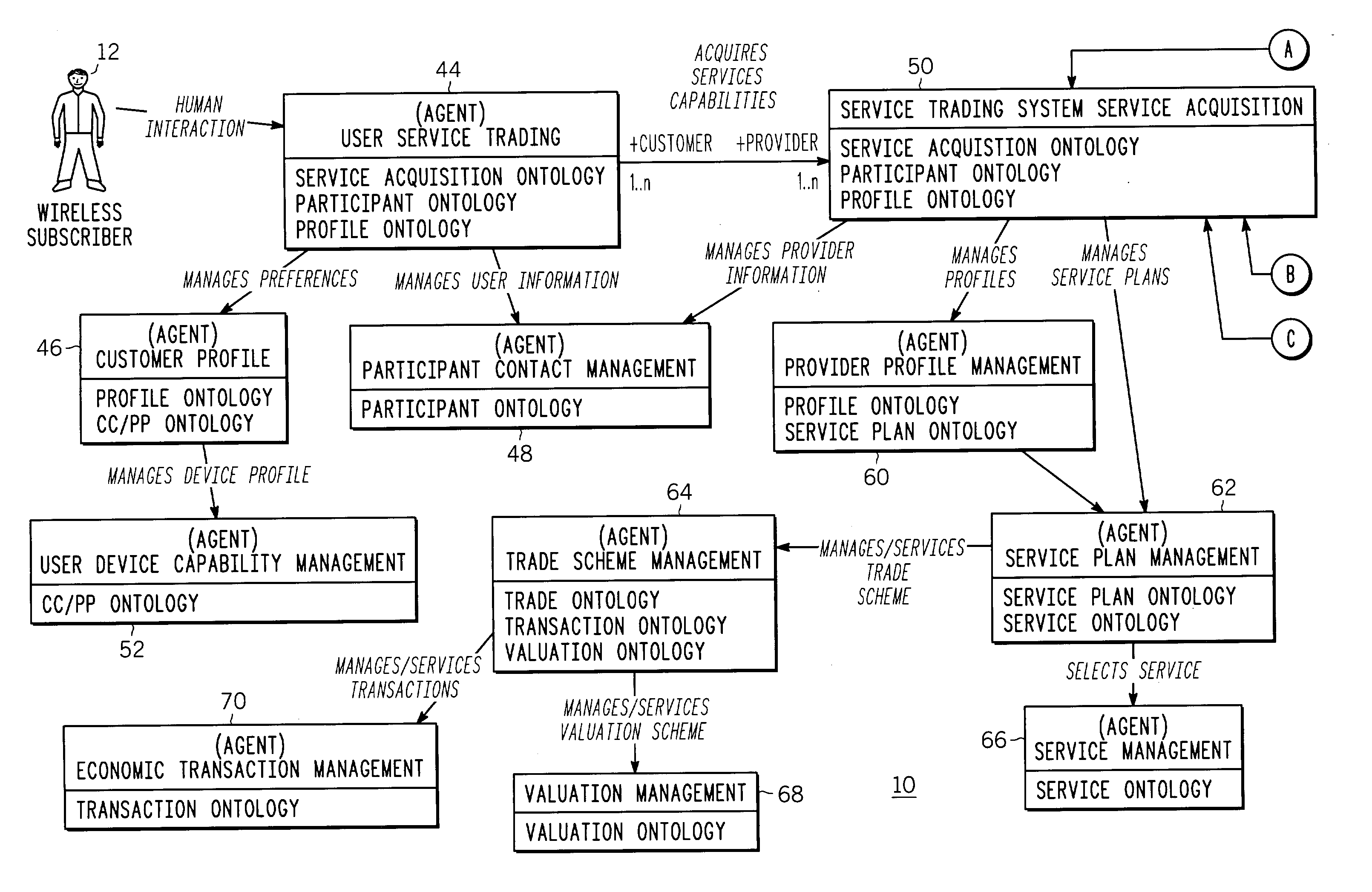
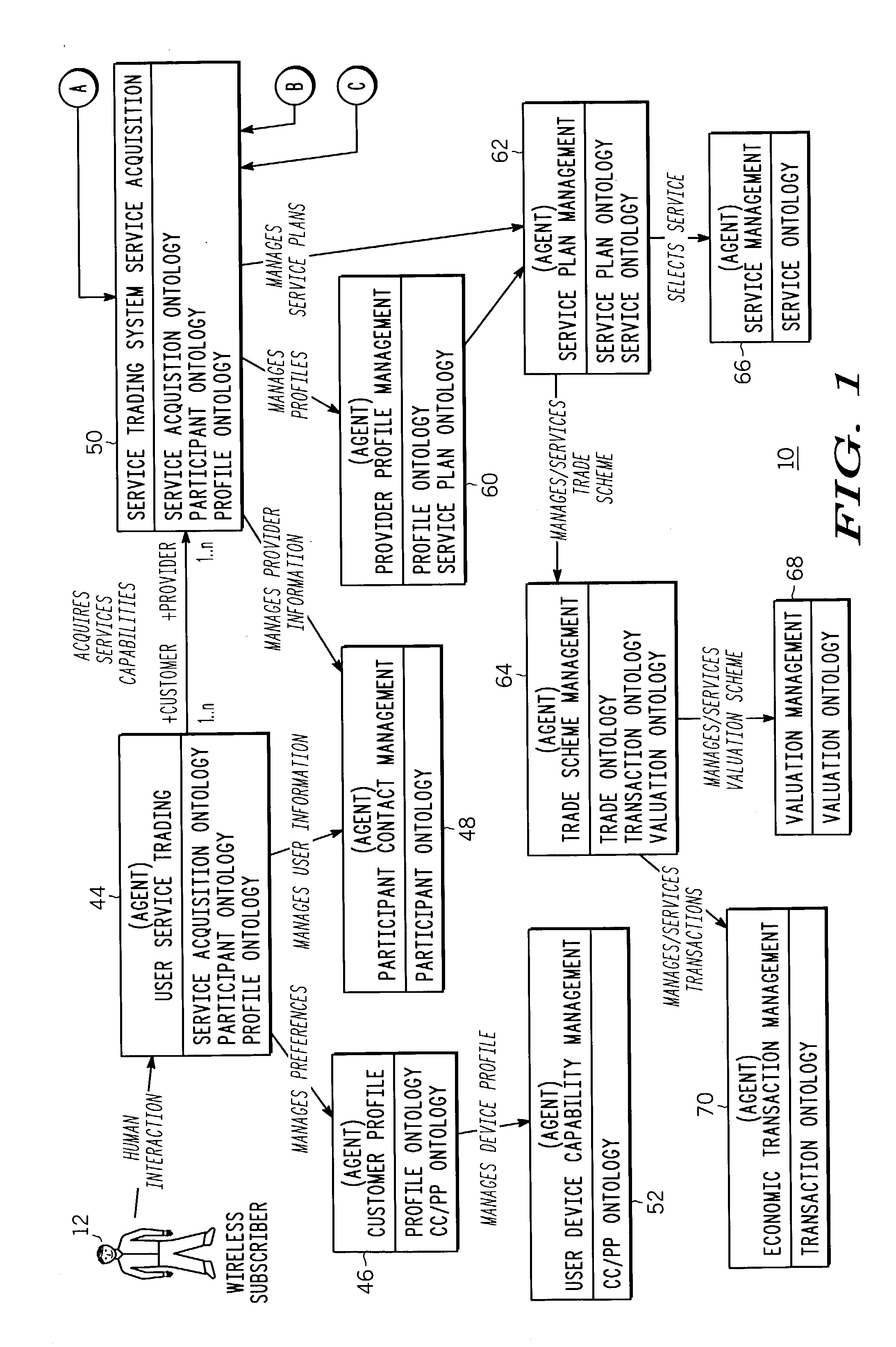
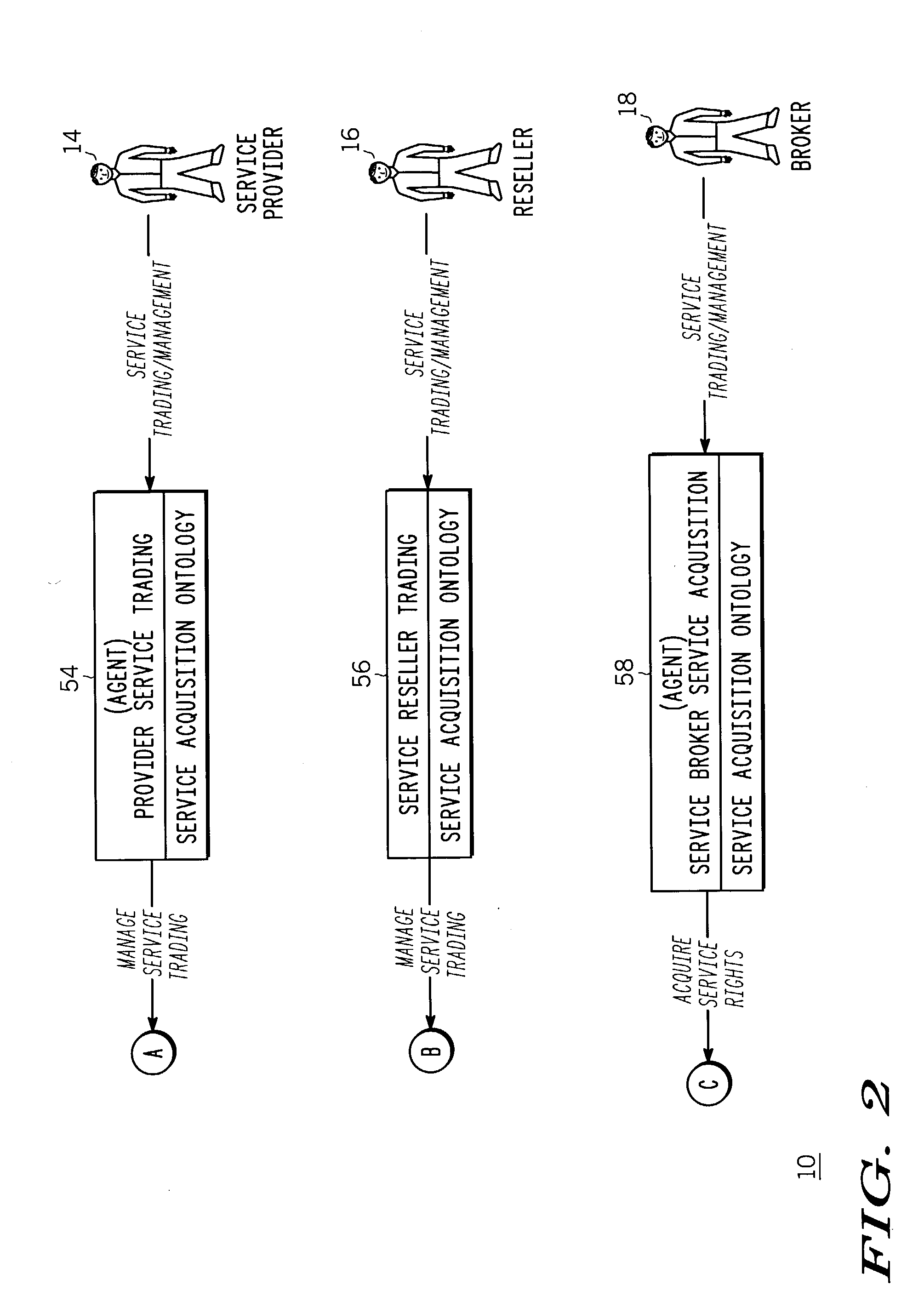
Open adaptive service trading system and method thereof
An open service trading system (10) and method therein enables the reselling of services among brokers (18), resellers (16) and service providers (14) to service subscribers (12). The service trading system (10) comprises domain specific knowledge bases (22a-40a) constrained by respective ontology domains (22b-40b), where the ontology domains (22b-40b) together define a service trading ontology structure. In addition, rational agents (42-70) are each committed to one or more of the domain specific knowledge bases (22a-40a) to enable interaction with others of the rational agents to achieve associated participant trading goals as defined within the service trading ontology structure.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
Compressing database workloads
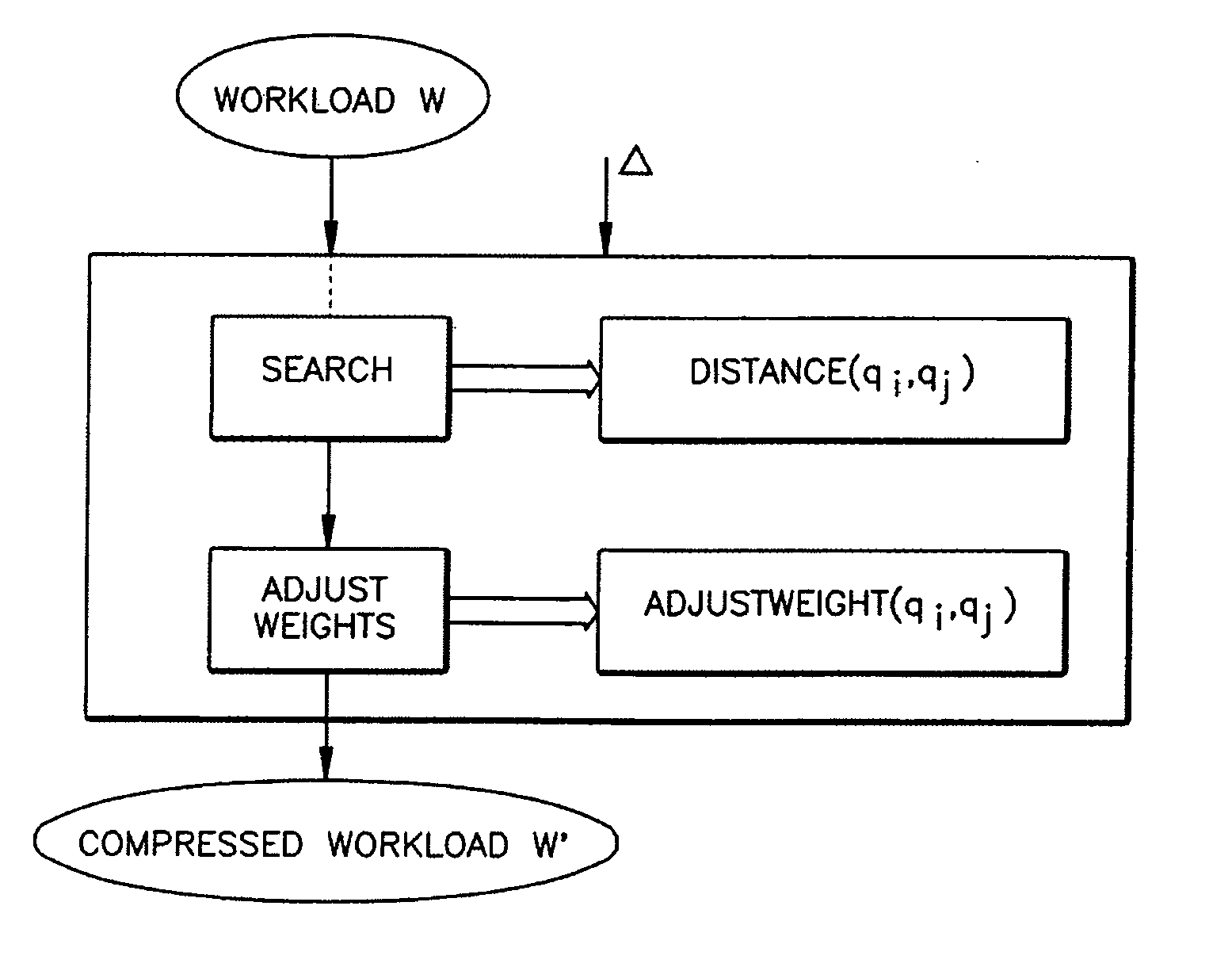
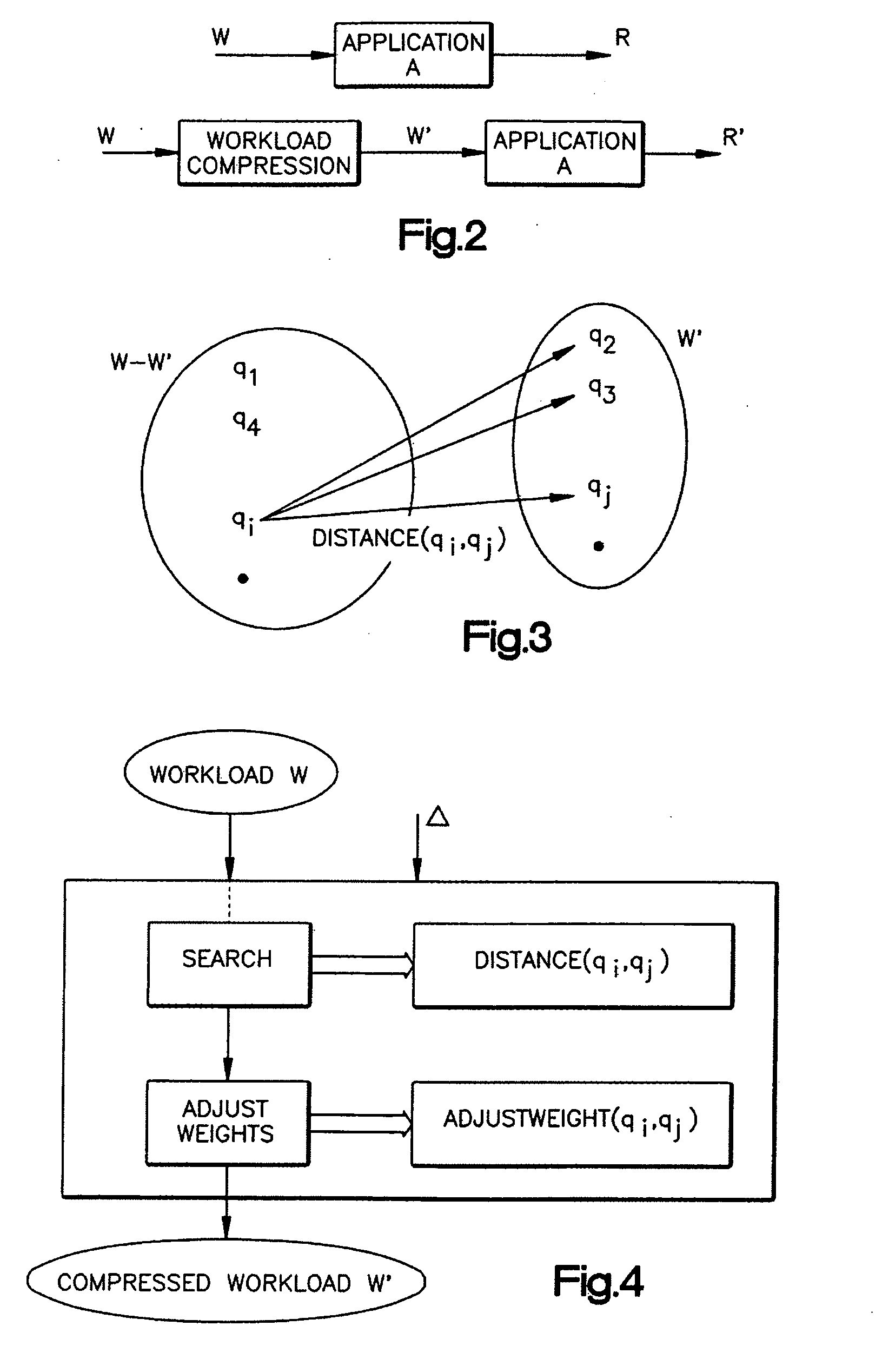
InactiveUS20050102305A1Quality lossData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsRelational databaseApplication specific
Relational database applications such as index selection, histogram tuning, approximate query processing, and statistics selection have recognized the importance of leveraging workloads. Often these applications are presented with large workloads, i.e., a set of SQL DML statements, as input. A key factor affecting the scalability of such applications is the size of the workload. The invention concerns workload compression which helps improve the scalability of such applications. The exemplary embodiment is broadly applicable to a variety of workload-driven applications, while allowing for incorporation of application specific knowledge. The process is described in detail in the context of two workload-driven applications: index selection and approximate query processing.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Natural language question expansion and extraction
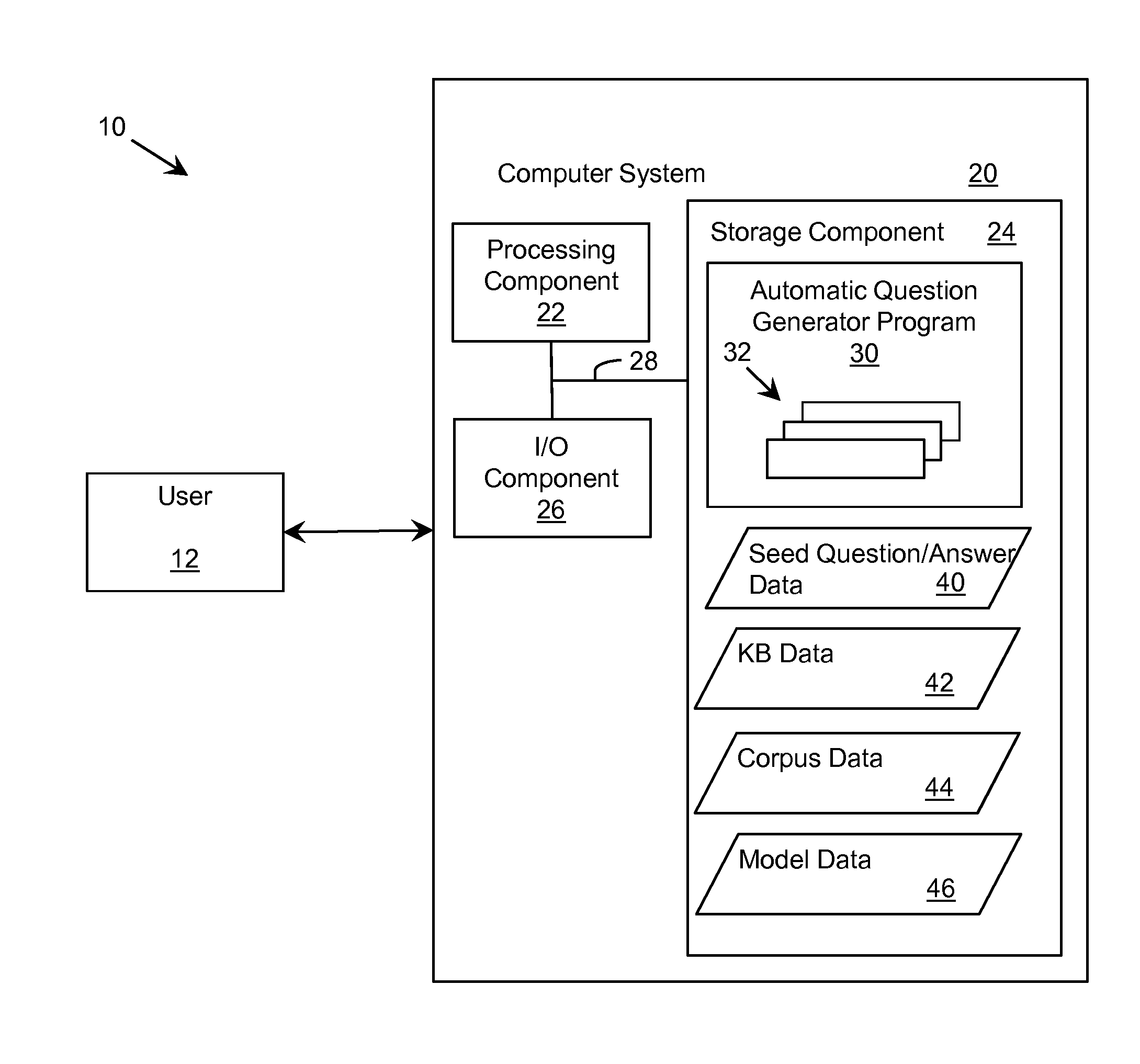
InactiveUS20140222743A1Natural language data processingKnowledge representationQuestions and answersHuman language
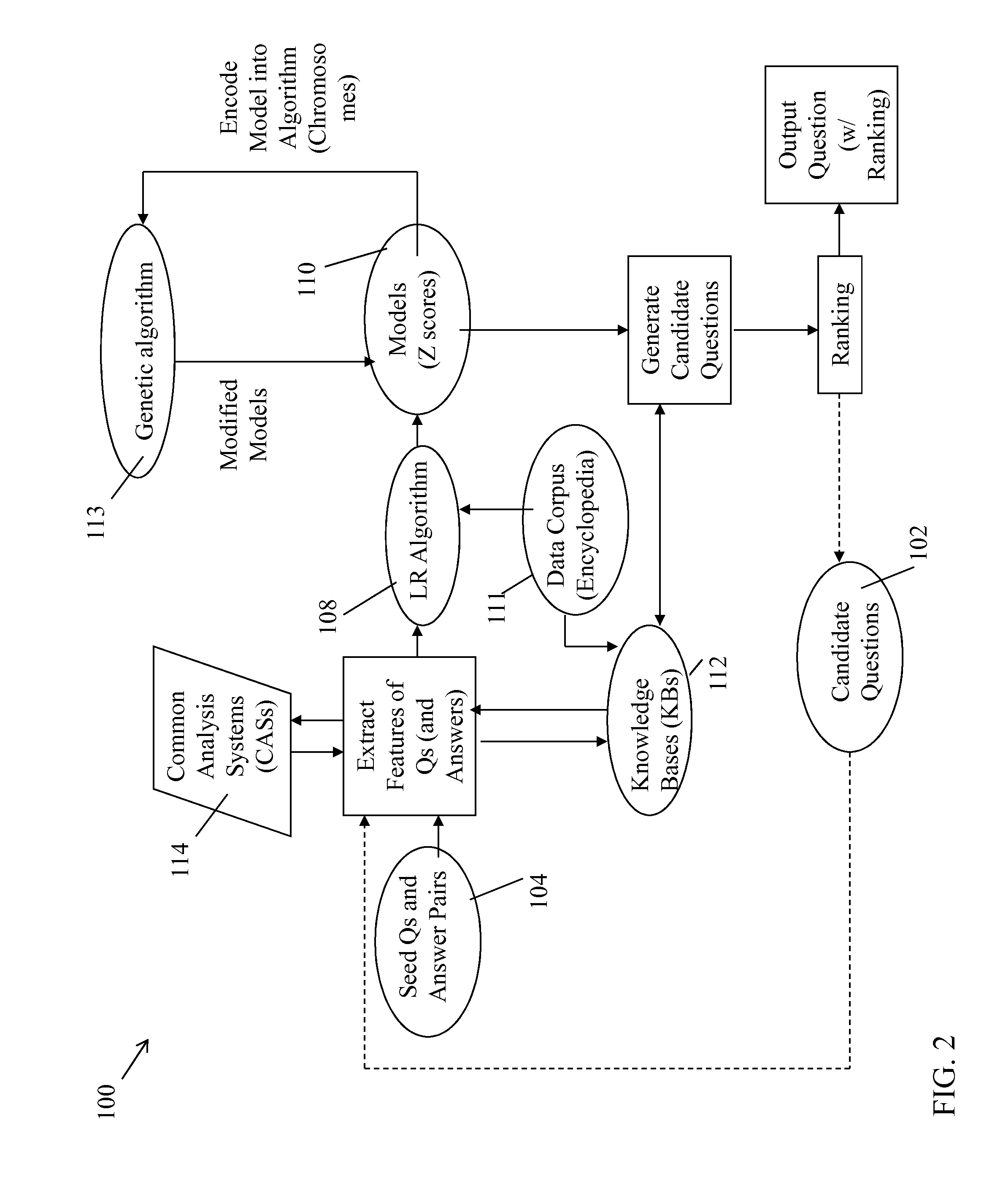
Methods, computer program products and systems for generating at least one factual question from a set of seed questions and answer pairs. One method includes: obtaining at least one seed question and answer pair from the set of seed question and answer pairs; extracting a set of features associated with the at least one seed question and answer pair using at least one common analysis system (CAS) in a set of CASs and a specific knowledge base; generating a set of candidate questions from the extracted set of features using a logistic regression algorithm and the specific knowledge base, wherein each candidate question includes an expansion of each of the extracted set of features; and ranking each candidate question relative to a remainder of candidate questions in the set of candidate questions based on the extracted set of features and the at least one seed question and answer pair.
Owner:IBM CORP
Systems and methods for semantic reasoning
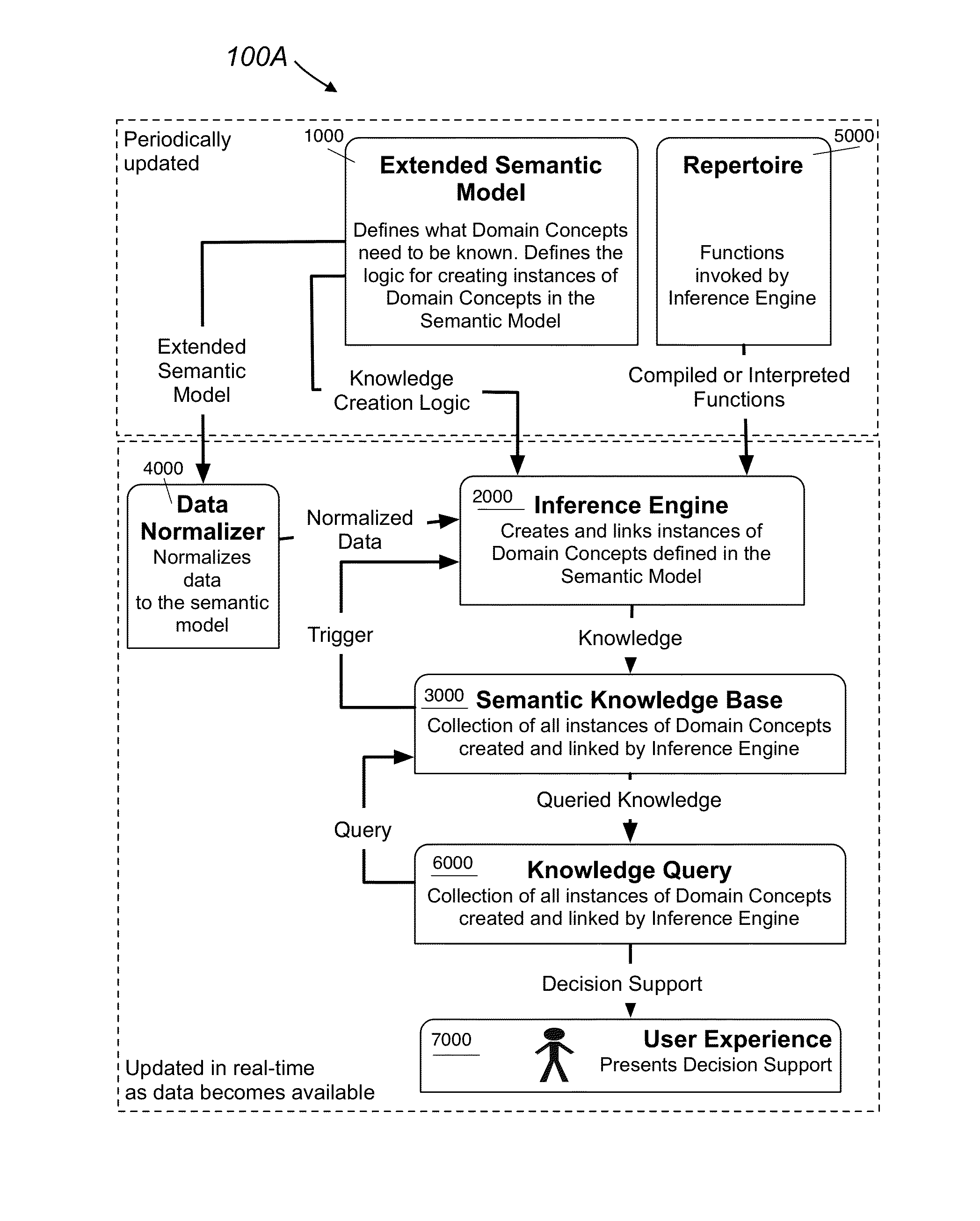
ActiveUS20150019462A1Increase situational understandingAutomate processingSemantic analysisMedical automated diagnosisData miningInference engine
A system for providing semantic reasoning includes an extended semantic model, a semantic knowledge database, and an inference engine. The extended semantic model includes existing concepts for a specific knowledge domain, existing relationships among the existing concepts, and logic including conditions and processes that cause a new concept or a new relationship to be inferred from an existing concept or an existing relationship, respectively. The semantic knowledge database includes existing nodes and existing links and the existing nodes represent instances of the existing concepts, and the existing links represent instances of the existing relationships. The inference engine is configured to add new nodes and new links to the semantic knowledge database by following the logic of the extended semantic model.
Owner:SENSCIO SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com