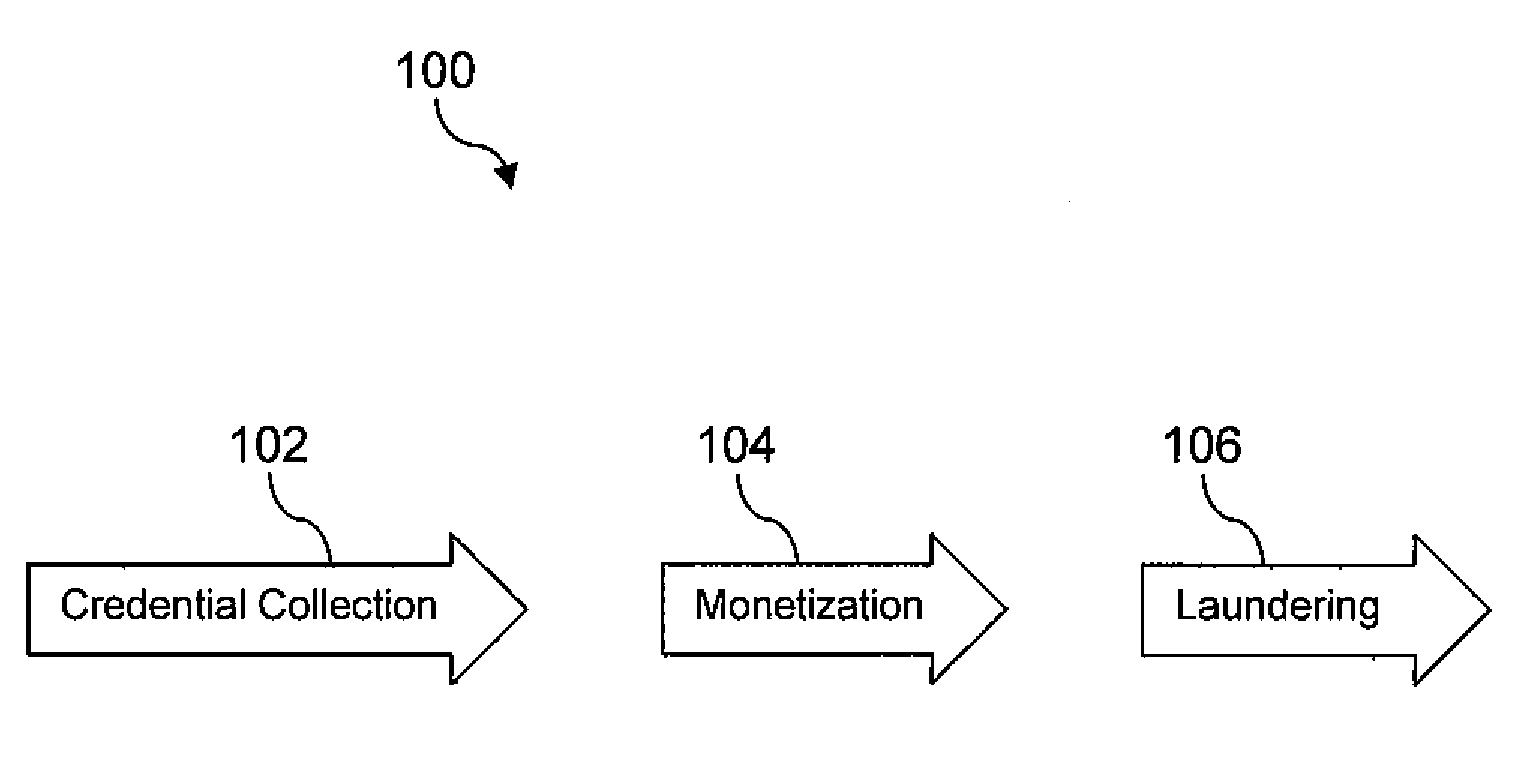
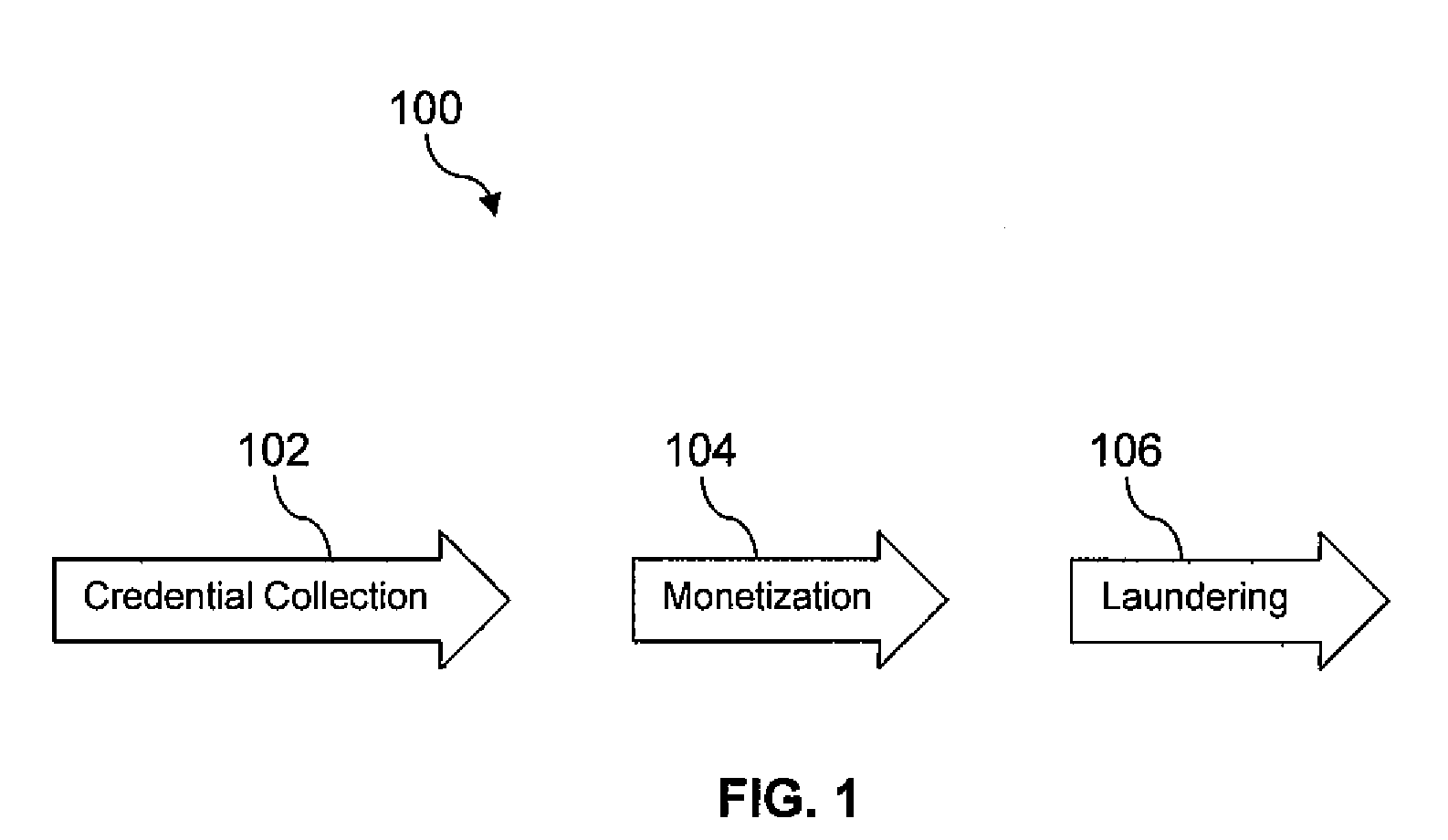
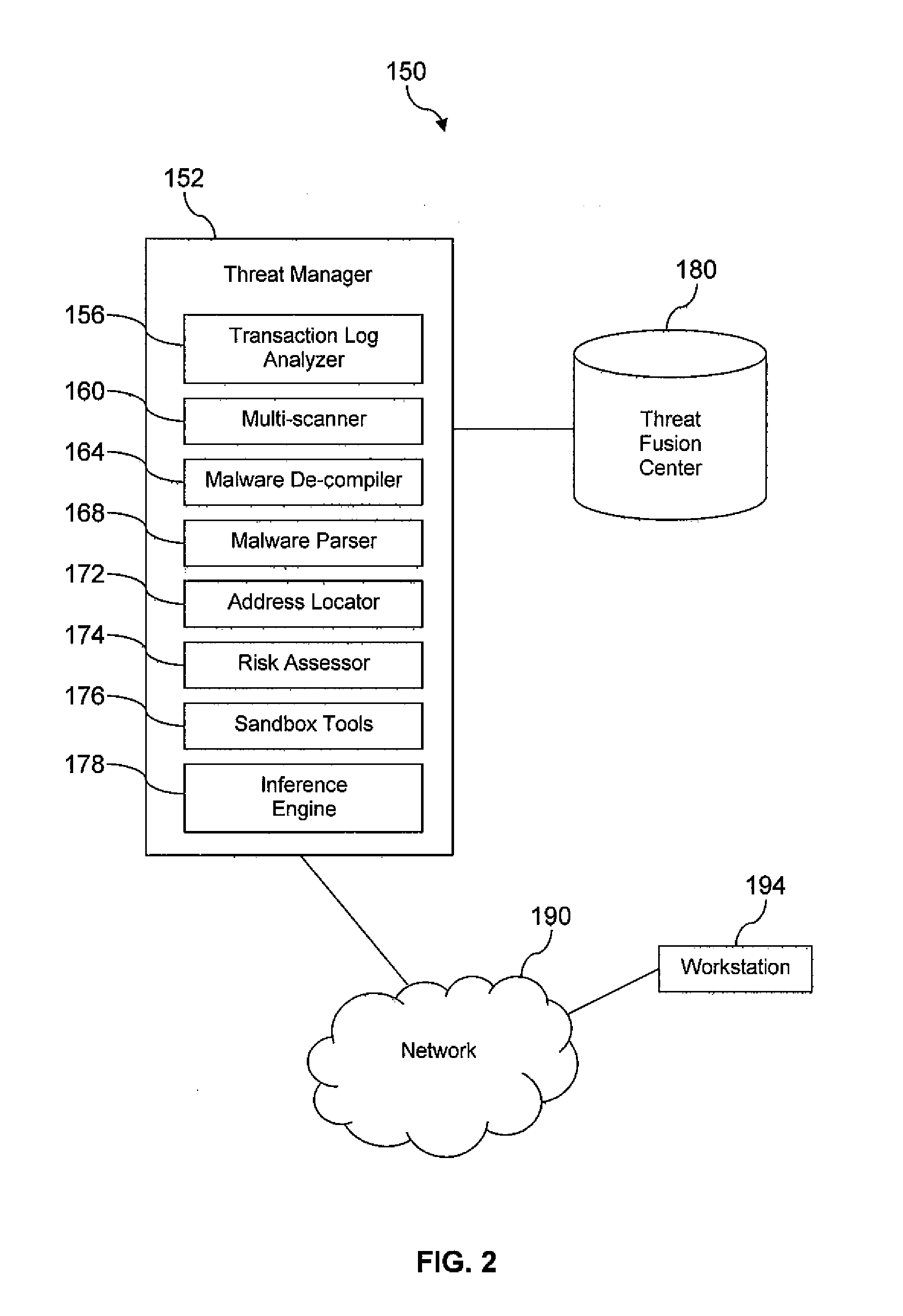
Patents
Literature
589 results about "Inference engine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In the field of Artificial Intelligence, inference engine is a component of the system that applies logical rules to the knowledge base to deduce new information. The first inference engines were components of expert systems. The typical expert system consisted of a knowledge base and an inference engine. The knowledge base stored facts about the world. The inference engine applies logical rules to the knowledge base and deduced new knowledge. This process would iterate as each new fact in the knowledge base could trigger additional rules in the inference engine. Inference engines work primarily in one of two modes either special rule or facts: forward chaining and backward chaining. Forward chaining starts with the known facts and asserts new facts. Backward chaining starts with goals, and works backward to determine what facts must be asserted so that the goals can be achieved.
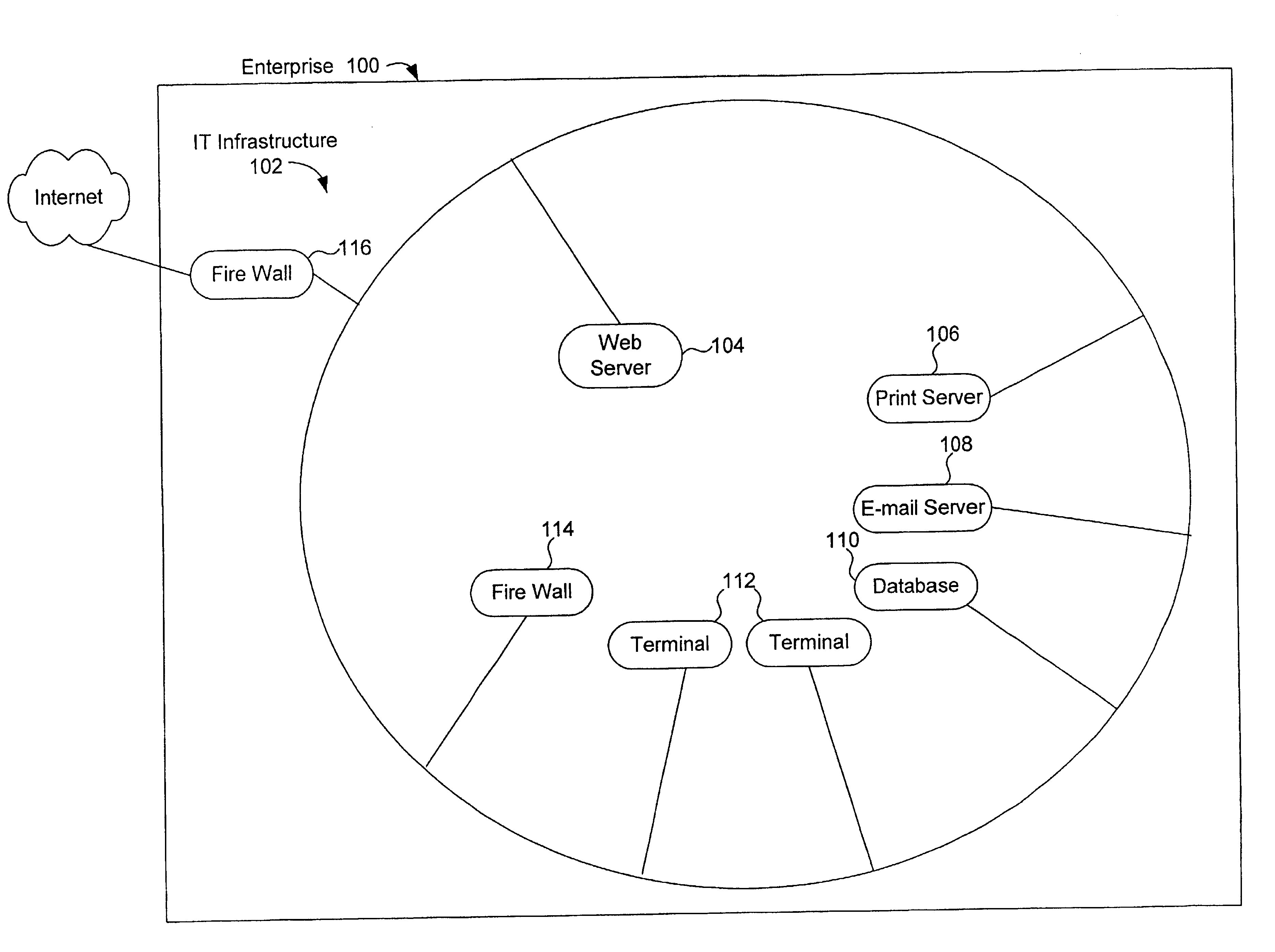
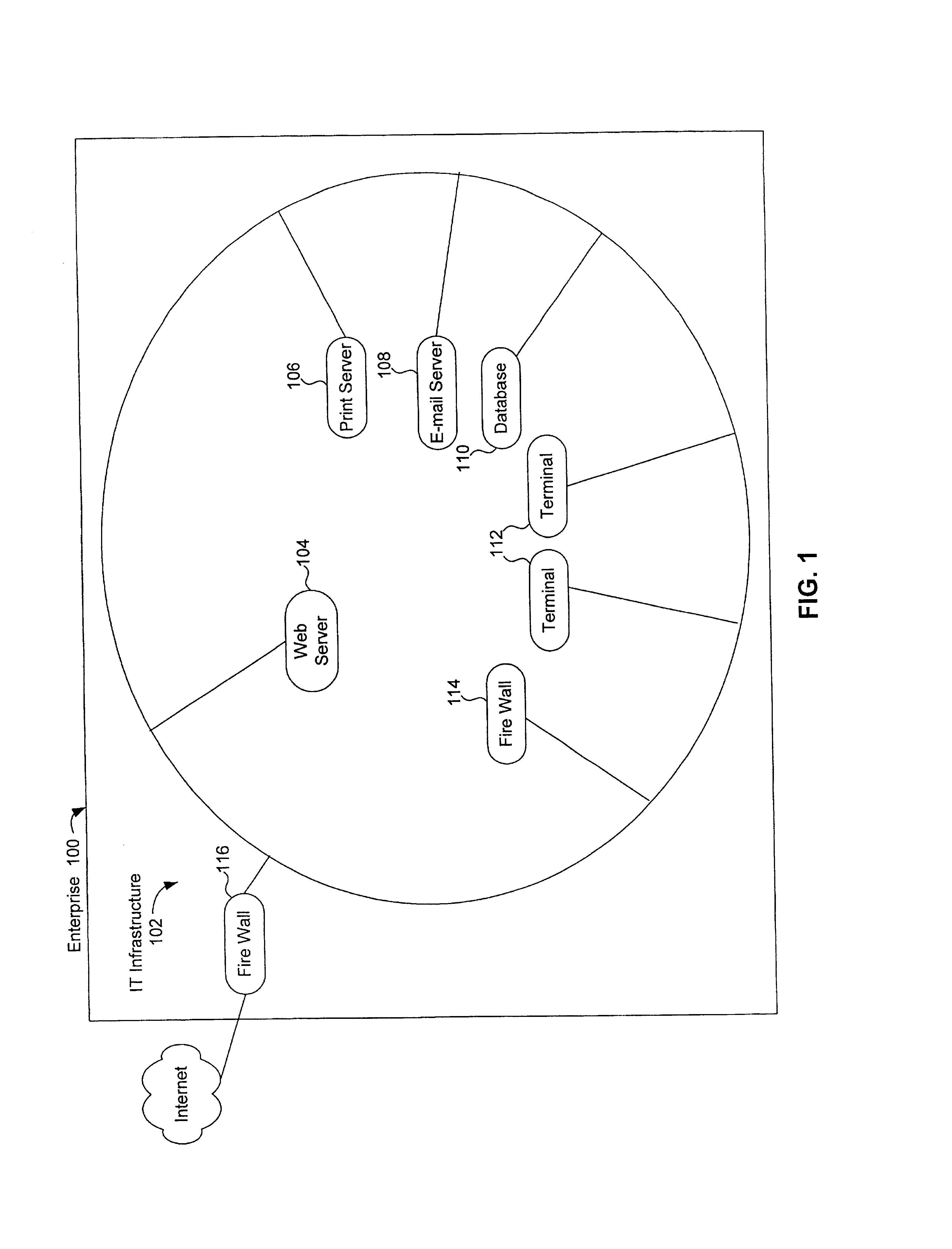
Method, system and computer program product for assessing information security
A method, system and computer program product for assessing information security interviews users regarding technical and non-technical issues. In an embodiment, users are interviewed based on areas of expertise. In an embodiment, information security assessments are performed on domains within an enterprise, the results of which are rolled-up to perform an information security assessment across the enterprise. The invention optionally includes application specific questions and vulnerabilities and / or industry specific questions and vulnerabilities. The invention optionally permits users to query a repository of expert knowledge. The invention optionally provides users with working aids. The invention optionally permits users to execute third party testing / diagnostic applications. The invention, optionally combines results of executed third party testing / diagnostic applications with user responses to interview questions, to assess information security. A system in accordance with the invention includes an inference engine, which may include a logic based inference engine, a knowledge based inference engine, and / or an artificial intelligence inference engine. In an embodiment, the invention includes an application specific tailoring tool that allows a user to tailor the system to assess security of information handled by a third party application program.
Owner:SAFEOPERATIONS
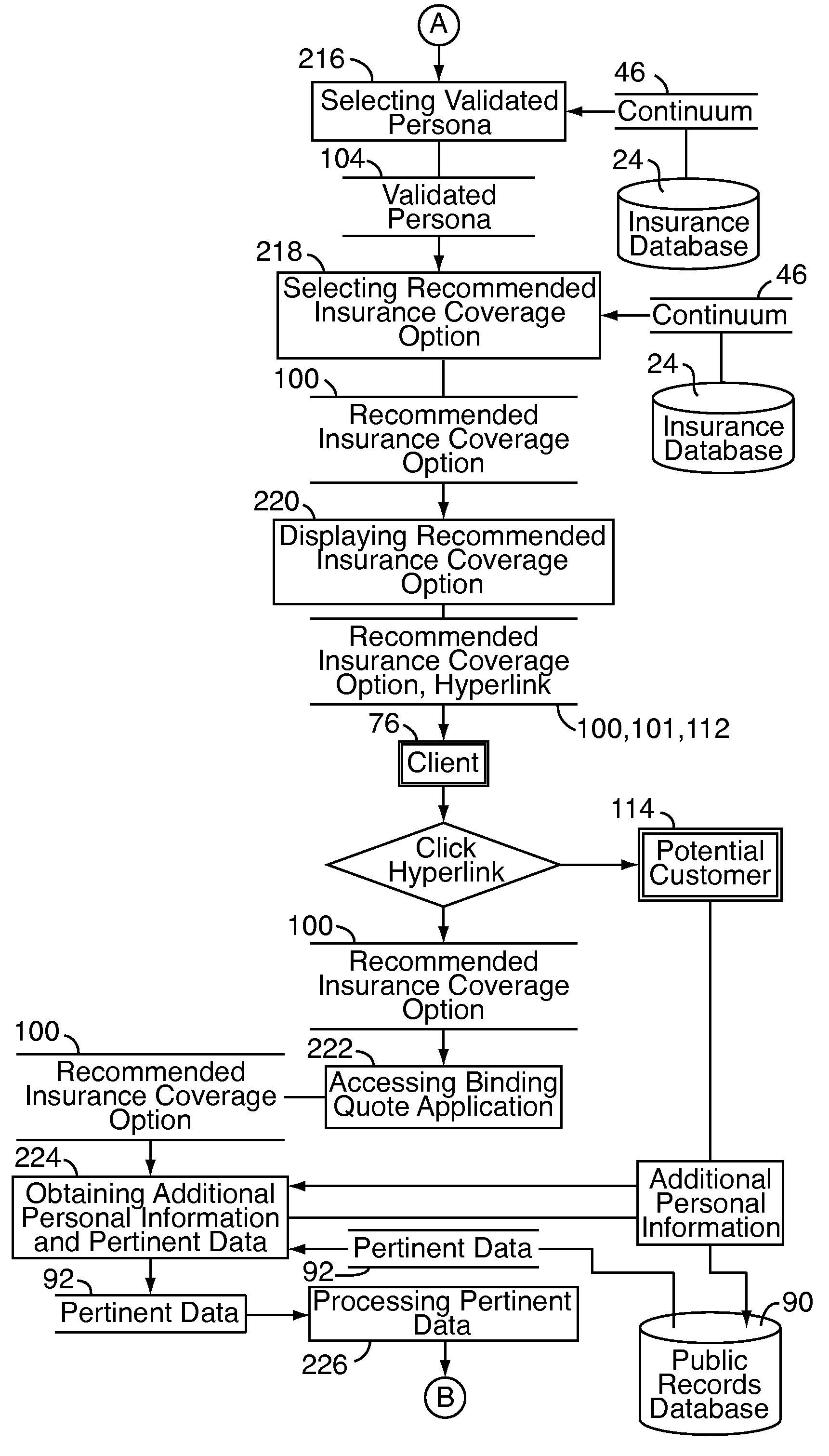
Social network interface
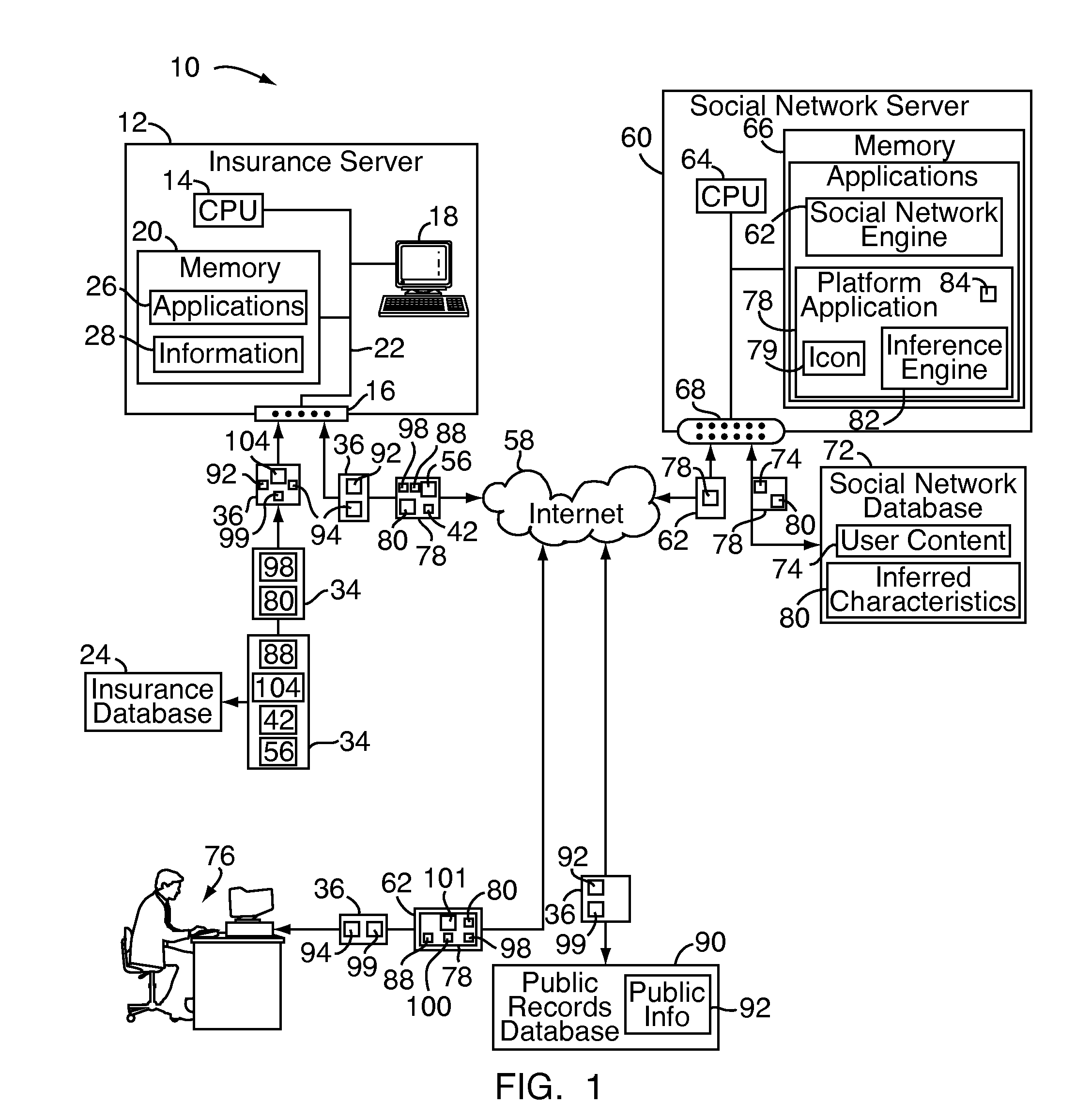
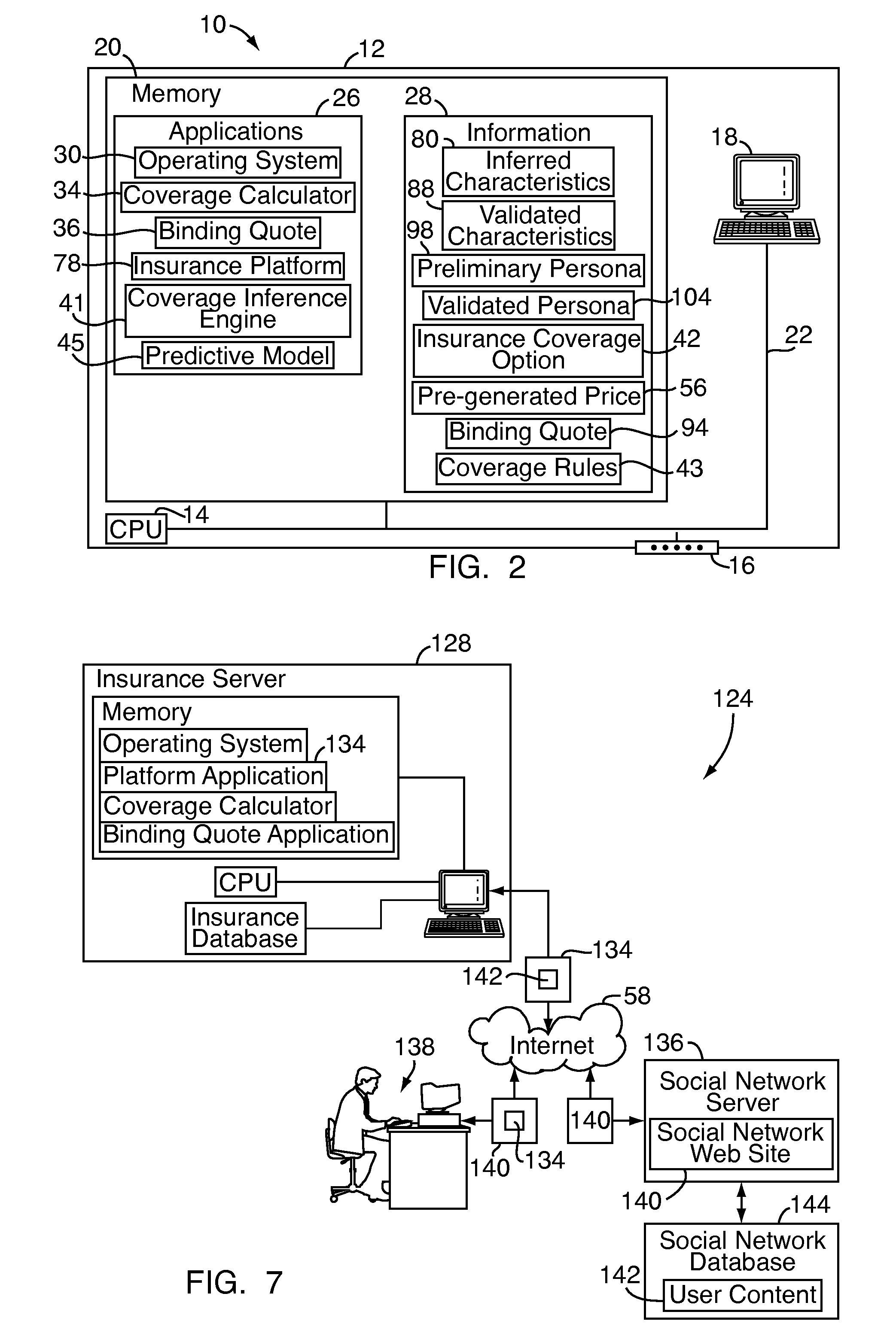
A system and method for providing online insurance quotes to a client on a social network web site includes an insurance server adapted to execute a coverage calculator application and an insurance database in communication with the insurance server for storing a plurality of personas, a plurality of insurance coverage options associated with each persona, and a price quote associated with each insurance coverage option. The system is in communication with a platform application on the social network web site. The platform application is in communication with a social network database for storing user content of the social network client. In one embodiment, the platform application uses an inference engine to query the user content of the social network client and return a set of inferred characteristics. The coverage calculator application selects a persona in response to the set of inferred characteristics and selects one of the insurance coverage options in response to the selected persona.
Owner:HARTFORD FIRE INSURANCE
Multimedia conceptual search system and associated search method
InactiveUS20070130112A1High returnLess sensitive to lighting conditionMultimedia data indexingSpecial data processing applicationsPattern perceptionWeb crawler
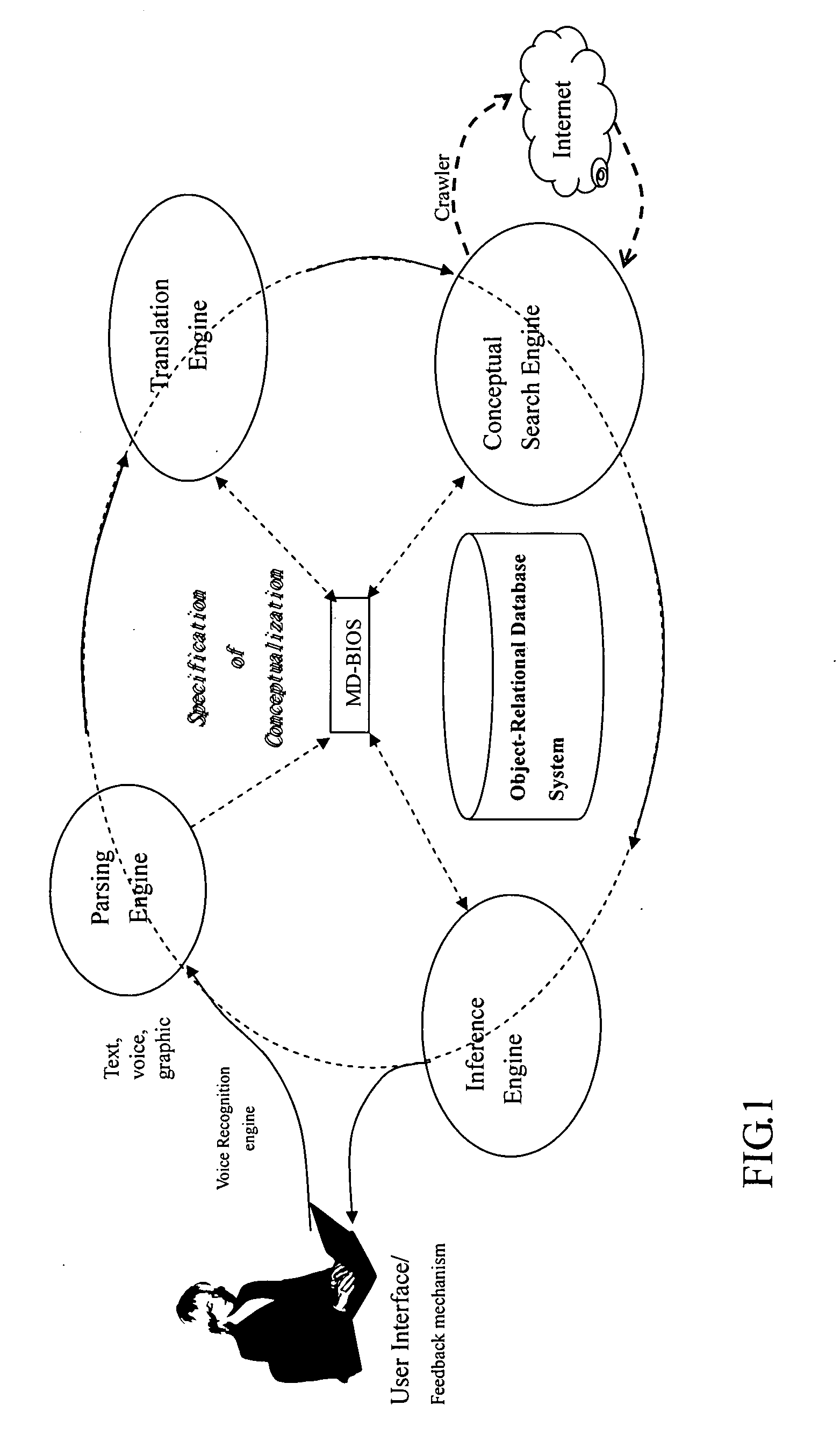
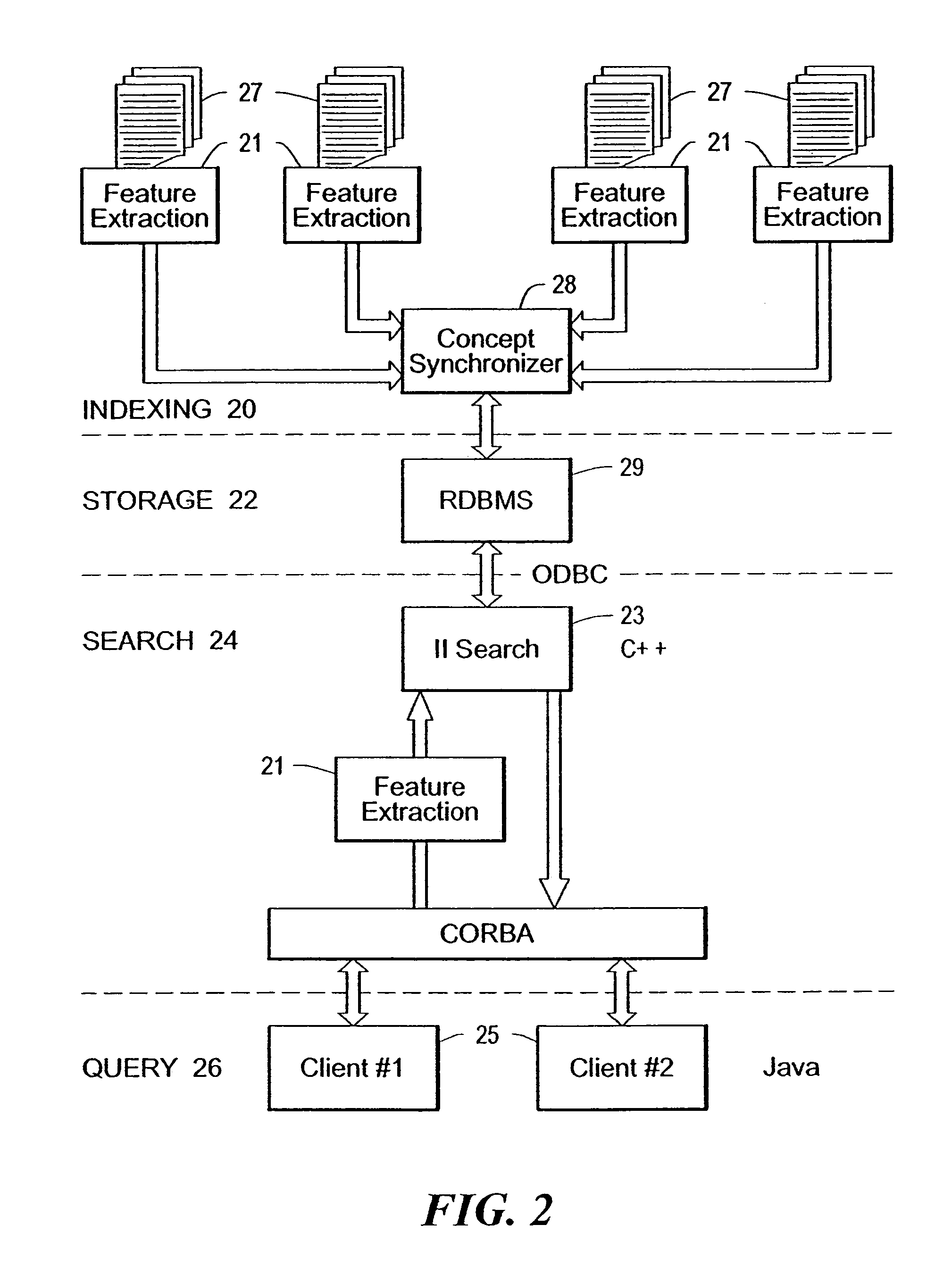
The current disclosure uses the disciplines of Ontology and Epistemology to implement a context / content-based “multimedia conceptual search and planning”, in which the formation of conceptualization is supported by embedding multimedia sensation and perception into a hybrid database. The disclosed system comprises: 1) A hybrid database model to host concept setup. 2) A graphic user interface to let user freely issue searching request in text and graphic mode. 3) A parsing engine conducting the best match between user query and dictionaries, analyzing queried images, detecting and presenting shape and chroma, extracting features / texture of an object. (4) A translation engine built for search engine and inference engine in text and graphic mode. 5) A search engine using partitioned, parallel, hashed indexes from web crawler result, conducting search in formal / natural language in text and graphic mode. 6) A logic interference engine working in text and graphic mode, and 7) A learning / feedback interface.
Owner:INTELLIGENTEK CORP
System for timely delivery of personalized aggregations of, including currently-generated, knowledge
InactiveUS20040059705A1Shorten the timeEffectively and efficiently aggregate and delivers personalized informationDigital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsPersonalizationDatasheet
A multidimensional method and apparatus for adaptively characterizing and aggregating data through a secure automated means of database modification, a prioritization and weighting system, a third party enhanced metadata entry and classification mechanism, adaptive and time varying individual personality and preference characterization, and an aggregation and delivery capability which allows for multiple data formats and mediums. Individual characterization incorporates an inference engine which formulates client composite images which vary with time. Asynchronous data interchanges enabled through the use of XML allow for more efficient and effective resource utilization and time. The knowledge system of this invention A) effectively integrates information from diverse sources, B) verifies, adds to or enhances source metadata (product data sheet; article title), and C) searches, queries, retrieves, and aggregates information. Selected product information can be obtained by e-mail without exposure to spamming by using e-mail address translation.
Owner:MINDAGENT
Apparatus and methods for developing conversational applications
InactiveUS20040083092A1Improve speech recognition performanceQuick fixSemantic analysisSpeech recognitionState switchingApplication software
Owner:GYRUS LOGIC INC
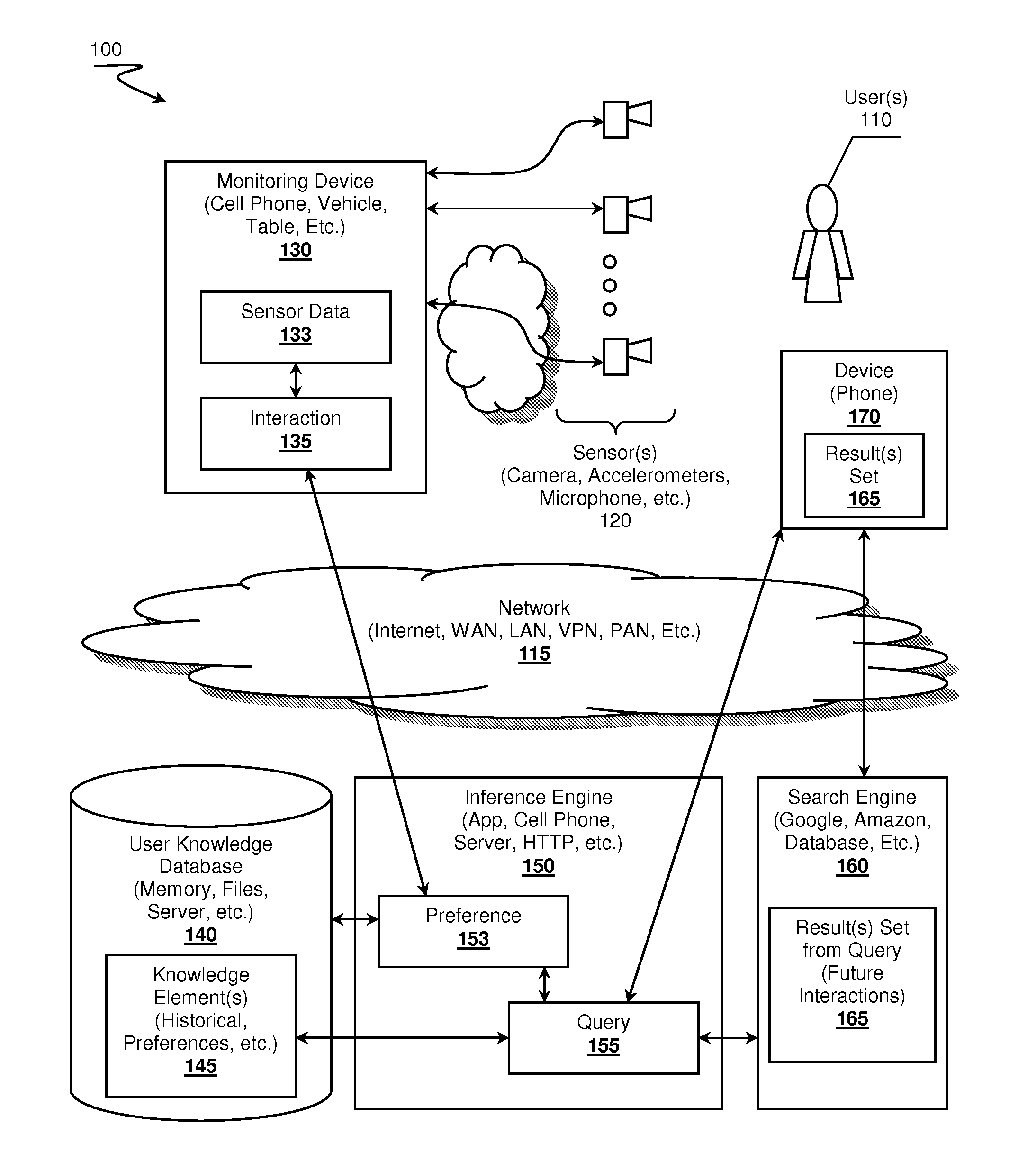
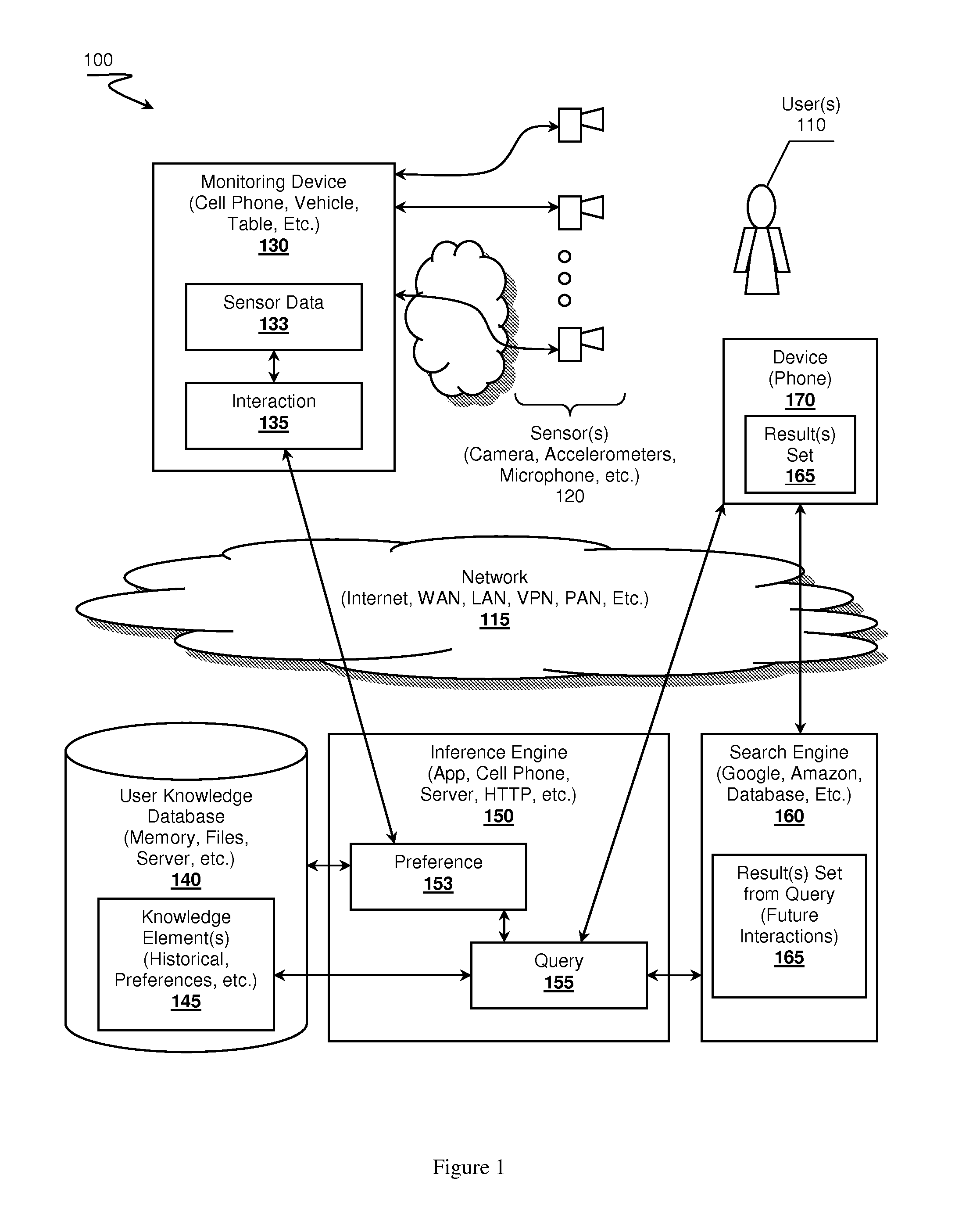
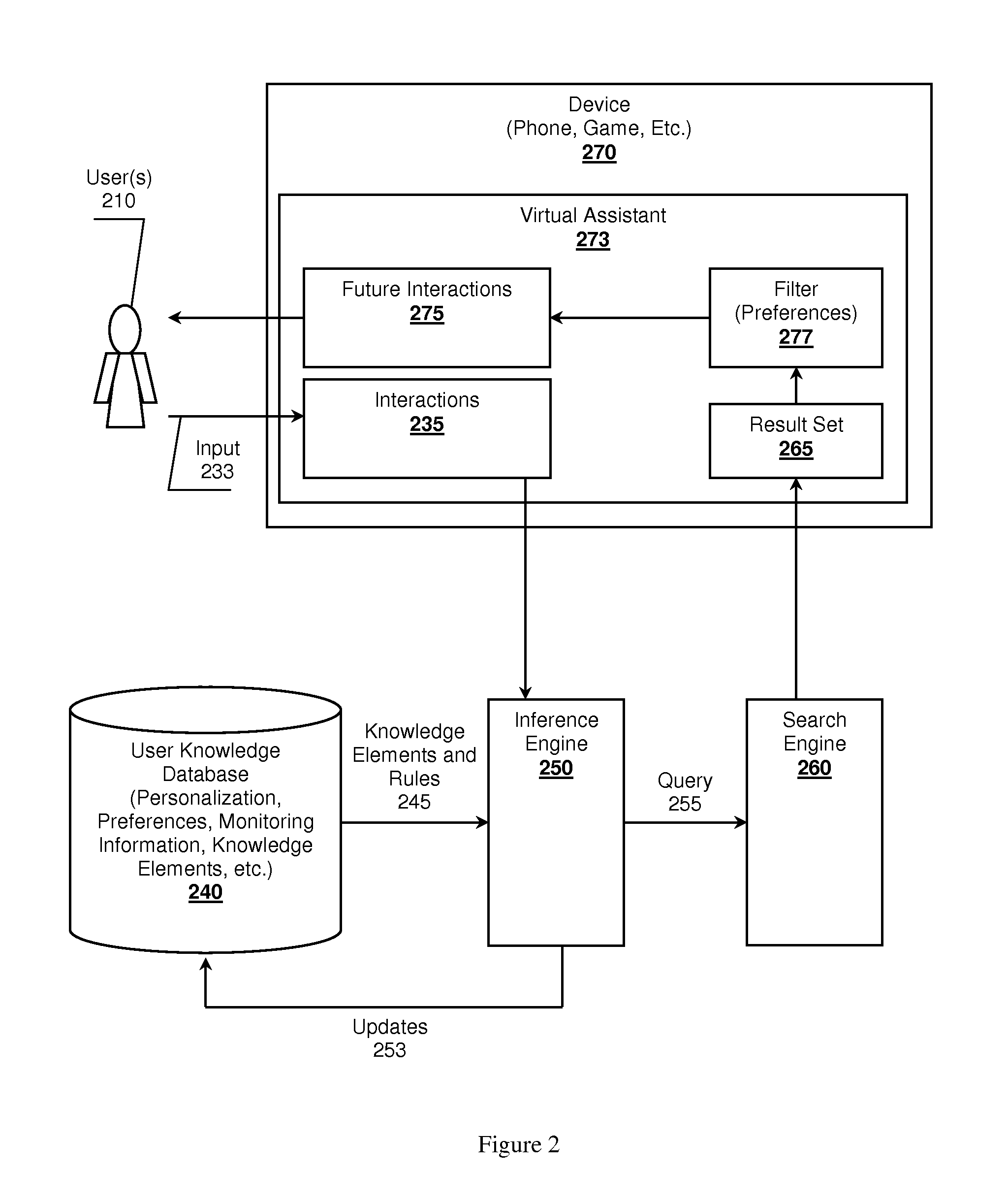
Self-learning, context aware virtual assistants, systems and methods
A virtual assistant learning system is presented. A monitoring device, a cell phone for example, observes user interactions with an environment by acquiring sensor data. The monitoring device uses the sensor data to identify the interactions, which in turn is provided to an inference engine. The inference engine leverages the interaction data and previously stored knowledge elements about the user to determine if the interaction exhibits one or more user preferences. The inference engine can use the preferences and interactions to construct queries targeting search engines to seek out possible future interactions that might be of interest to the user.
Owner:NANT HLDG IP LLC
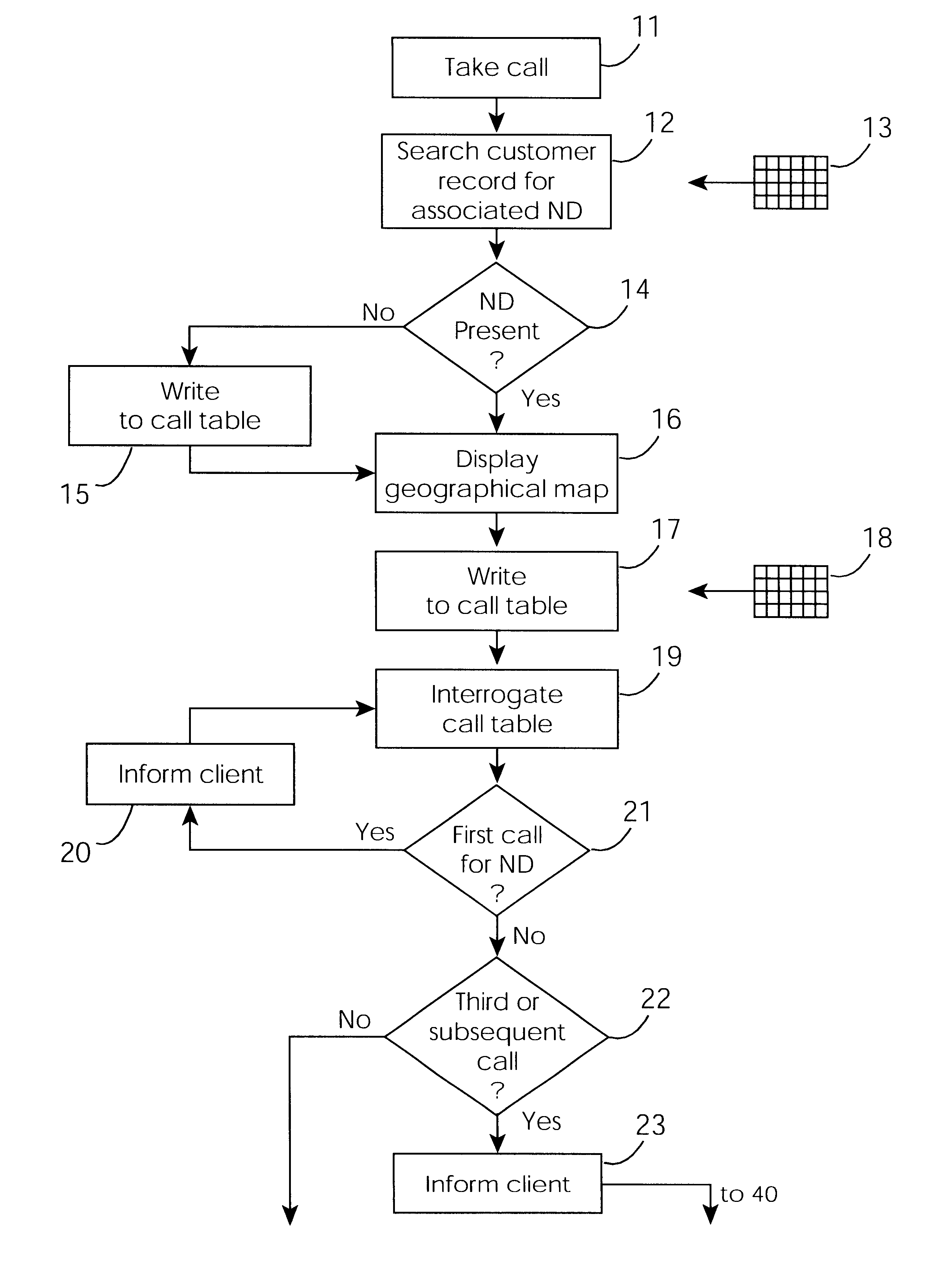
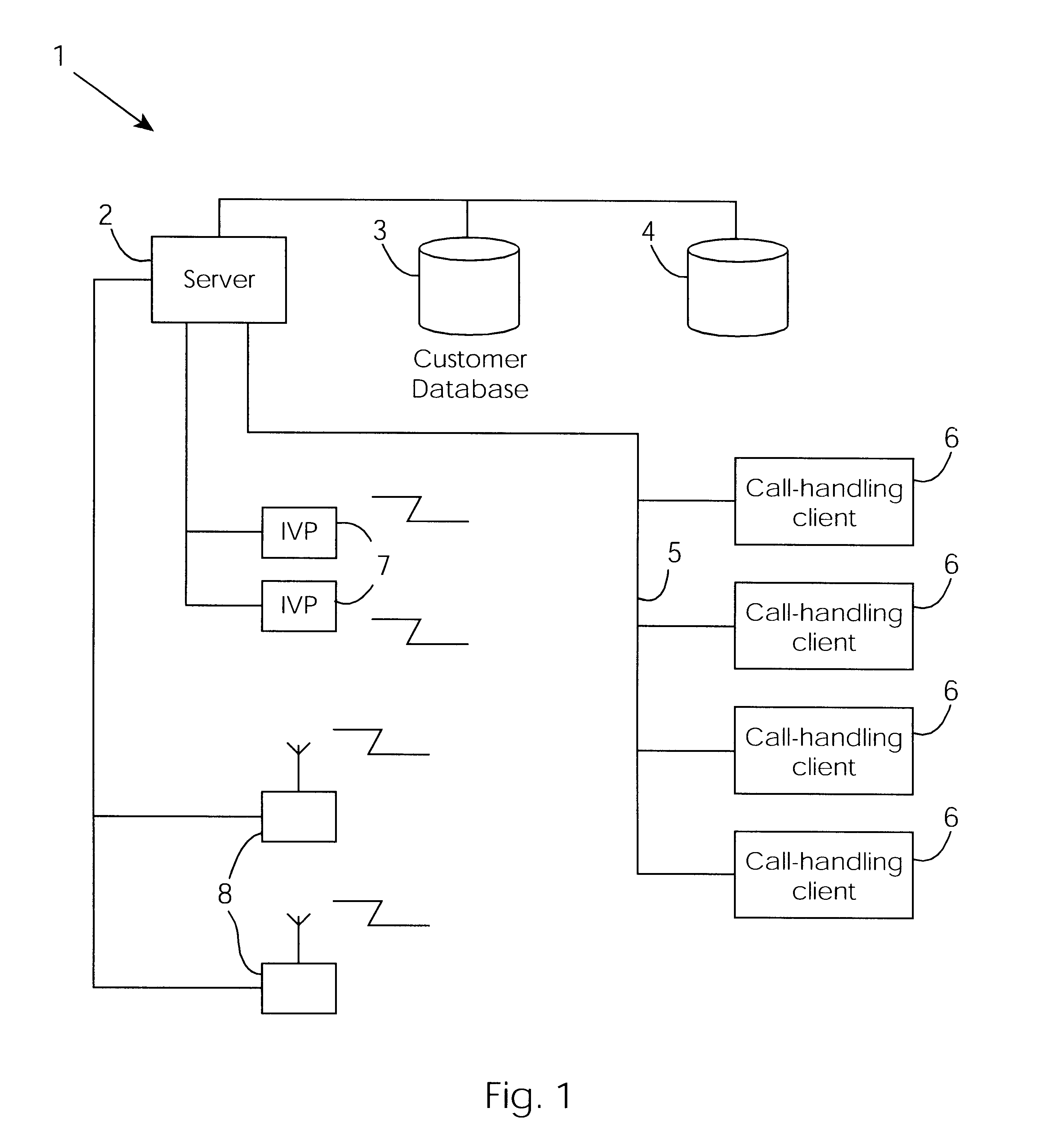
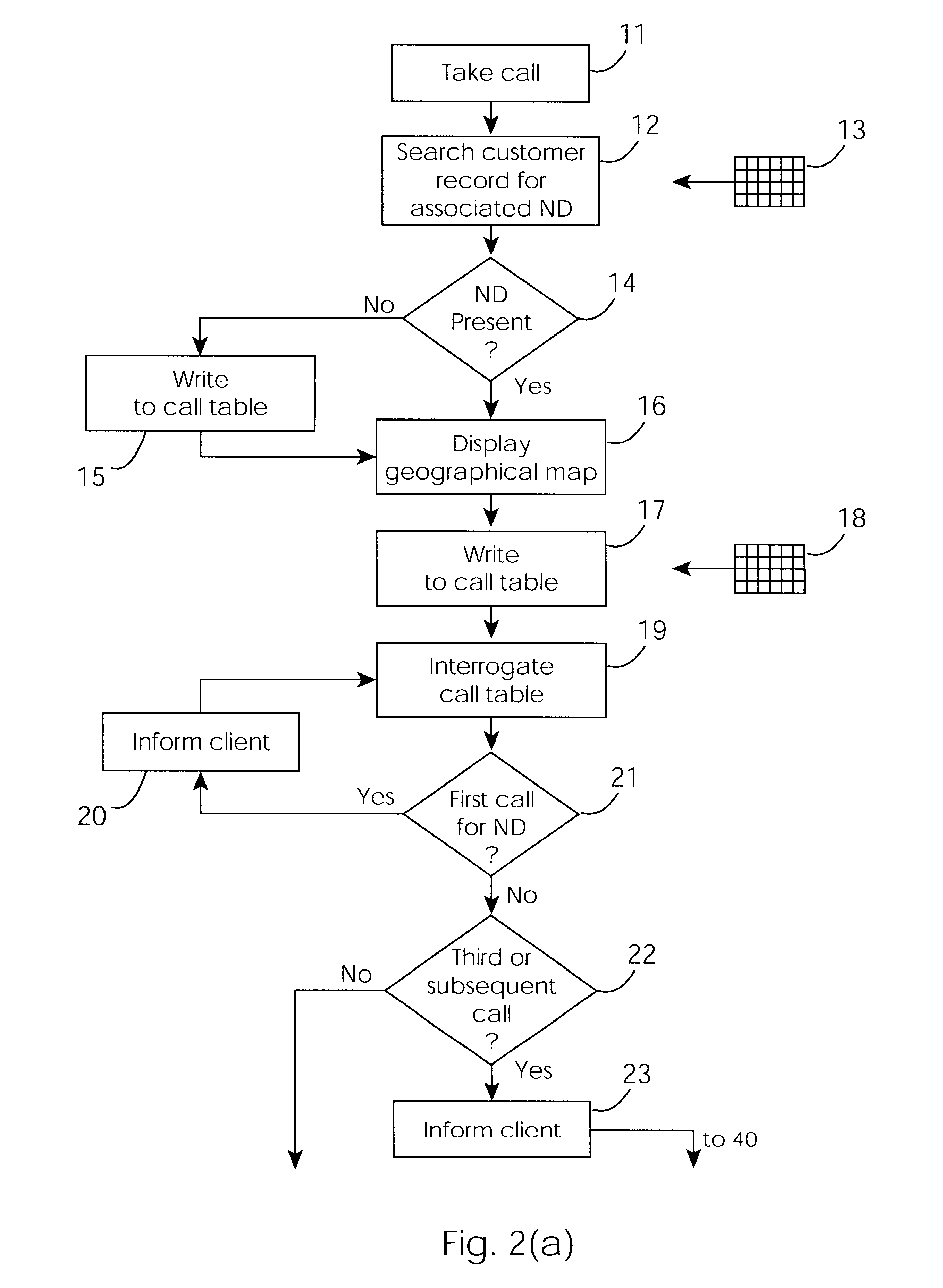
Cable network repair control system
InactiveUS6671824B1Shorten the timeSupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsSubstation equipmentControl systemEngineering
A cable network repair control system including a server communicating with multiple call-handling clients in a trouble call center. The databases are used to automatically determine an associated network device for the customer who makes a trouble call. When a second call is received for a particular network device, an inferencing engine automatically operates to identify potential repairs crews and to control communication with them to ensure that optimum use of the repair crew time and quick repair. Various tables are generated dynamically and are used to update management status tables for reviewing of network repair status.
Owner:LAKEFIELD ETECH GROUP
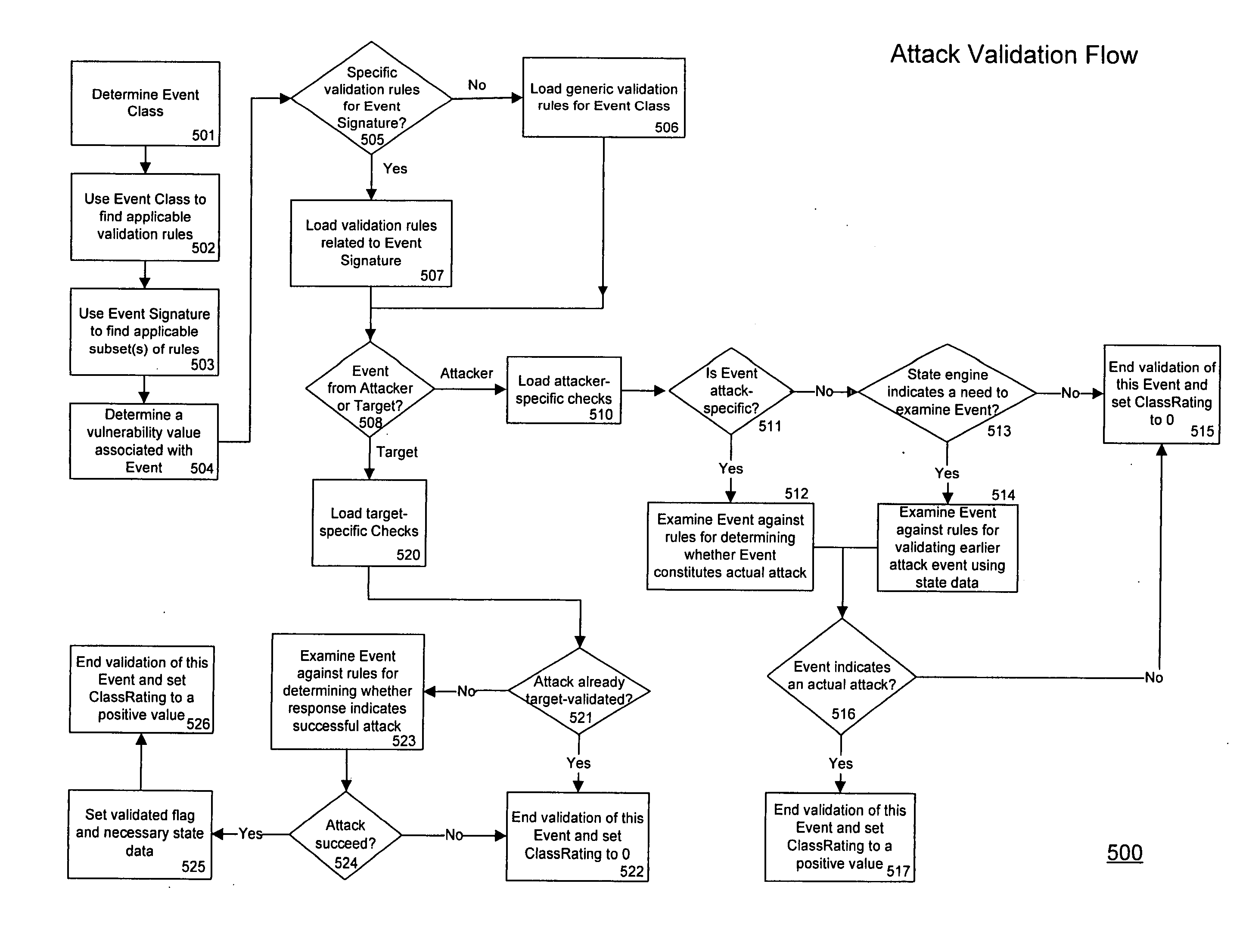
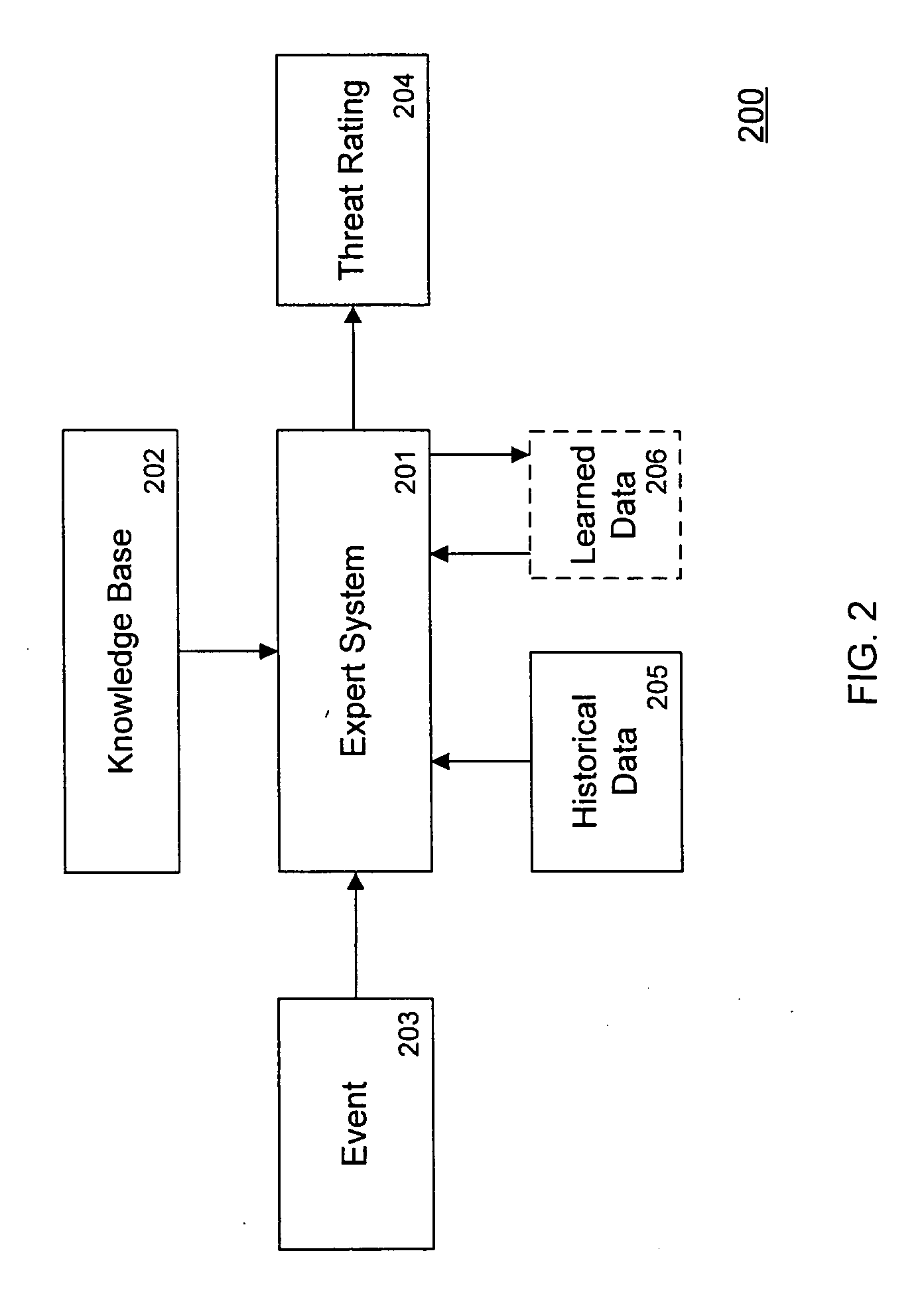
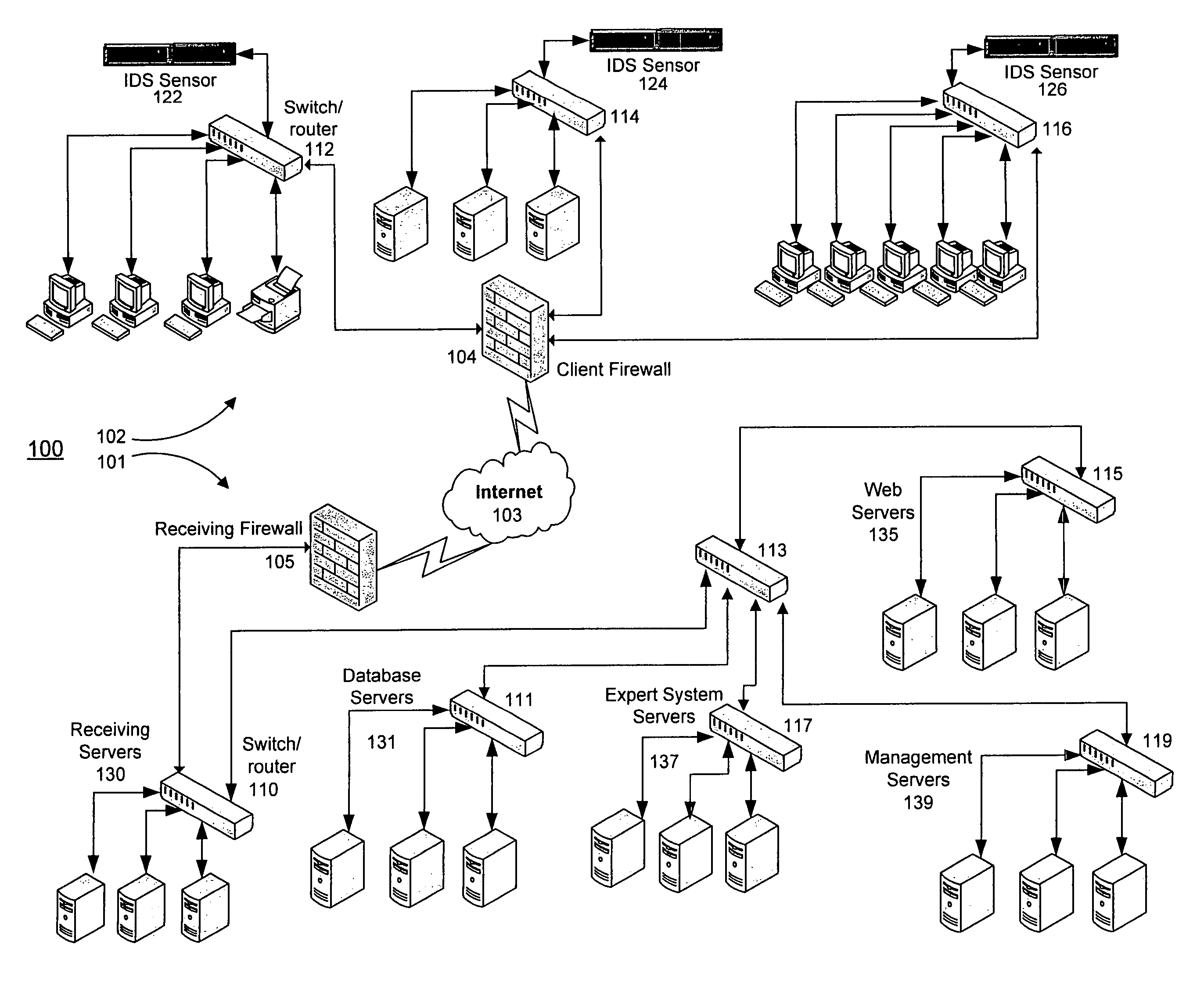
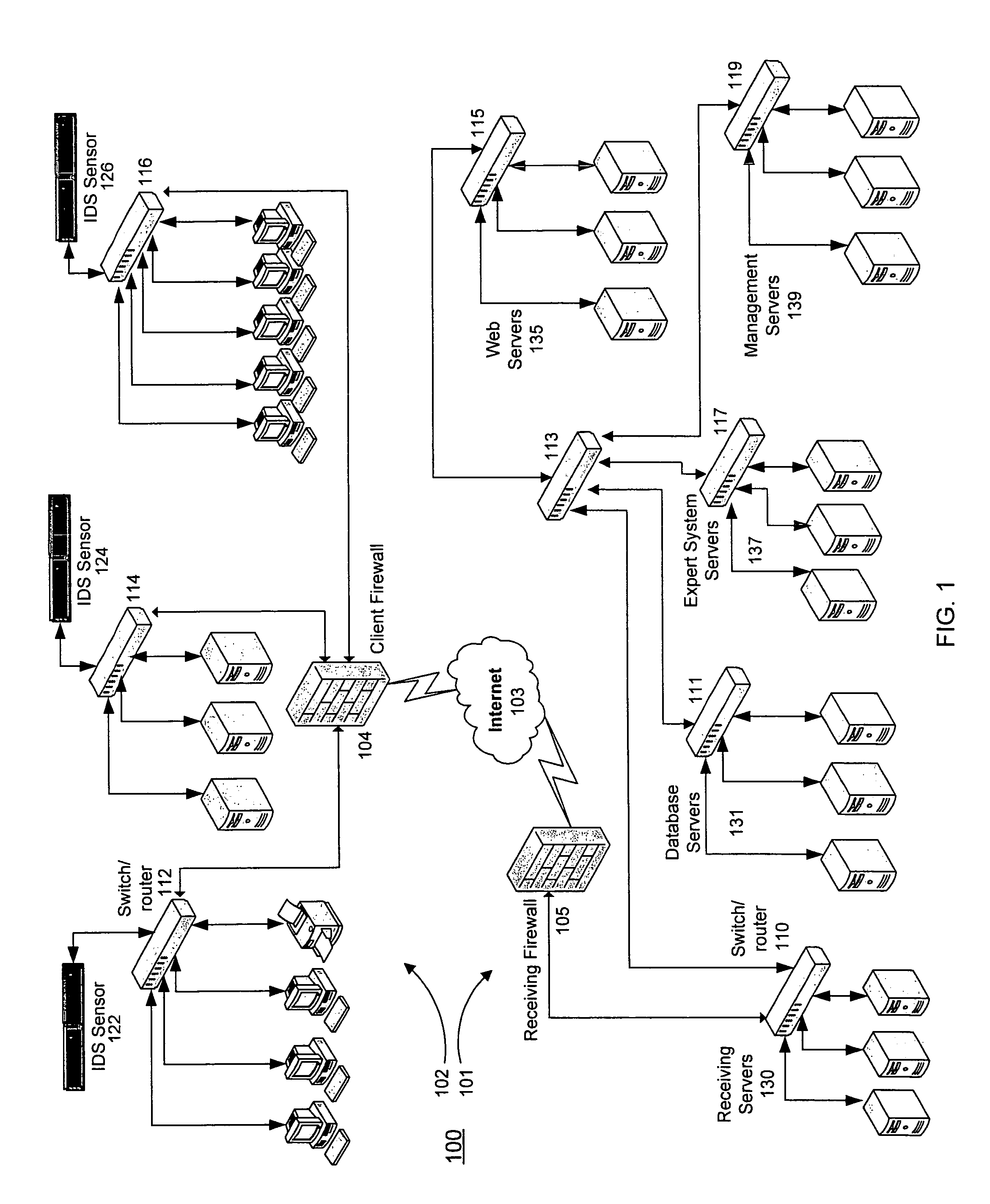
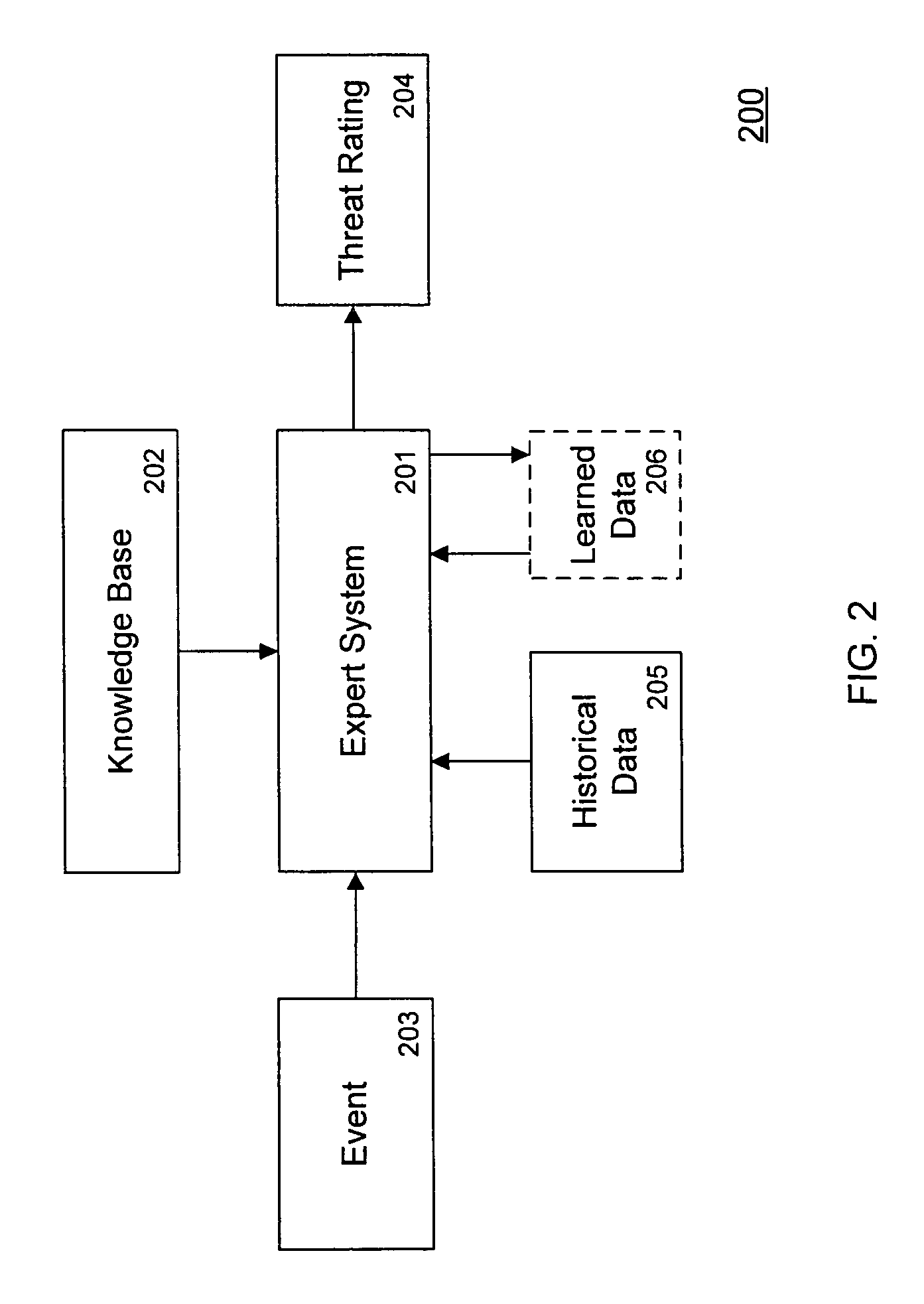
Threat scoring system and method for intrusion detection security networks
ActiveUS20070169194A1Rapid deploymentAutomate quicklyMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionTriage CodeSecurity expert
Embodiments of the invention provide a security expert system (SES) that automates intrusion detection analysis and threat discovery that can use fuzzy logic and forward-chaining inference engines to approximate human reasoning process. Embodiments of the SES can analyze incoming security events and generate a threat rating that indicates the likelihood of an event or a series of events being a threat. In one embodiment, the threat rating is determined based on an attacker rating, a target rating, a valid rating, and, optionally, a negative rating. In one embodiment, the threat rating may be affected by a validation flag. The SES can analyze the criticality of assets and calibrate / recalibrate the severity of an attack accordingly to allow for triage. The asset criticality can have a user-defined value. This ability allows the SES to protect and defend critical network resources in a discriminating and selective manner if necessary (e.g., many attacks).
Owner:ALERT LOGIC
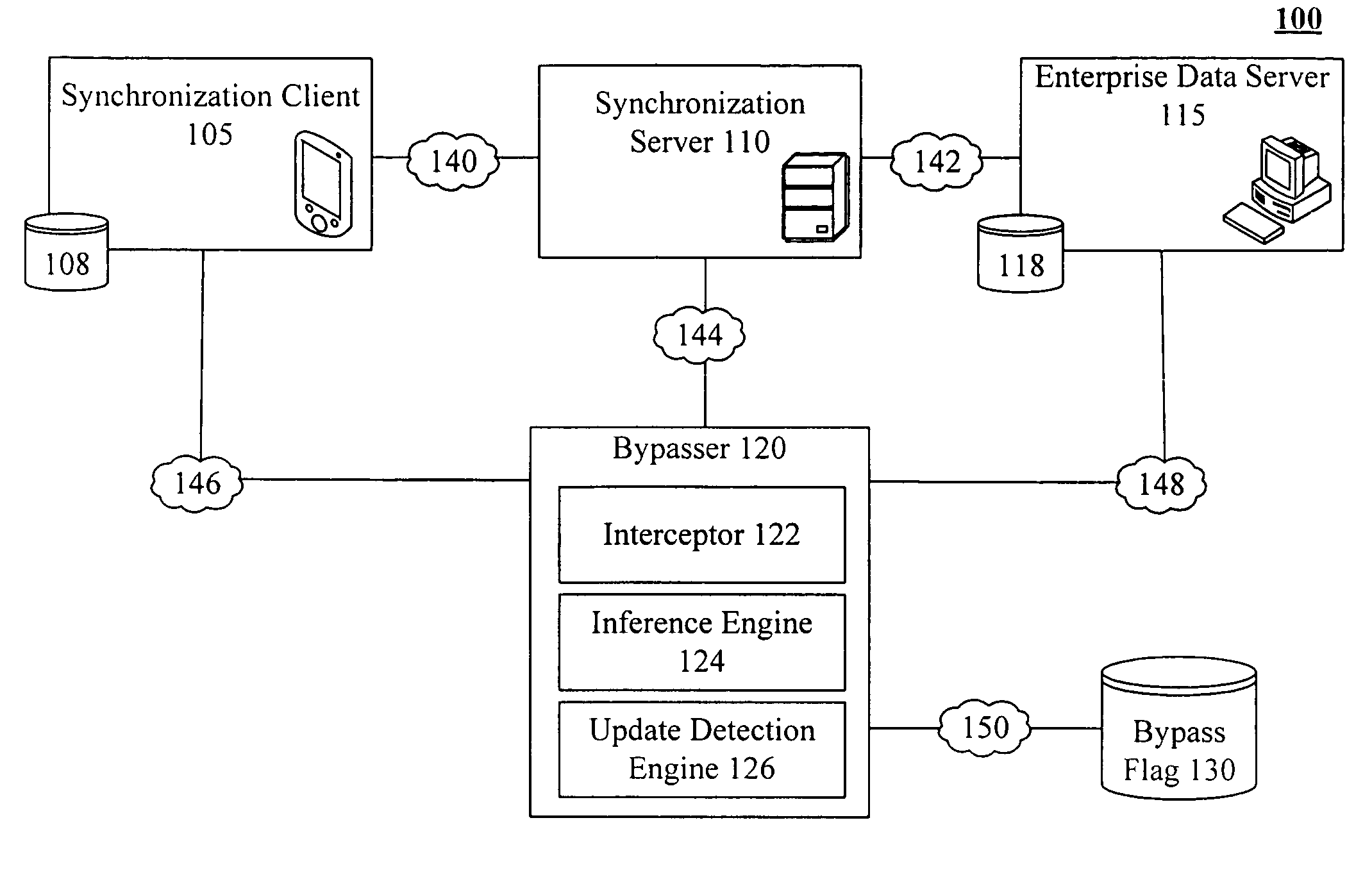
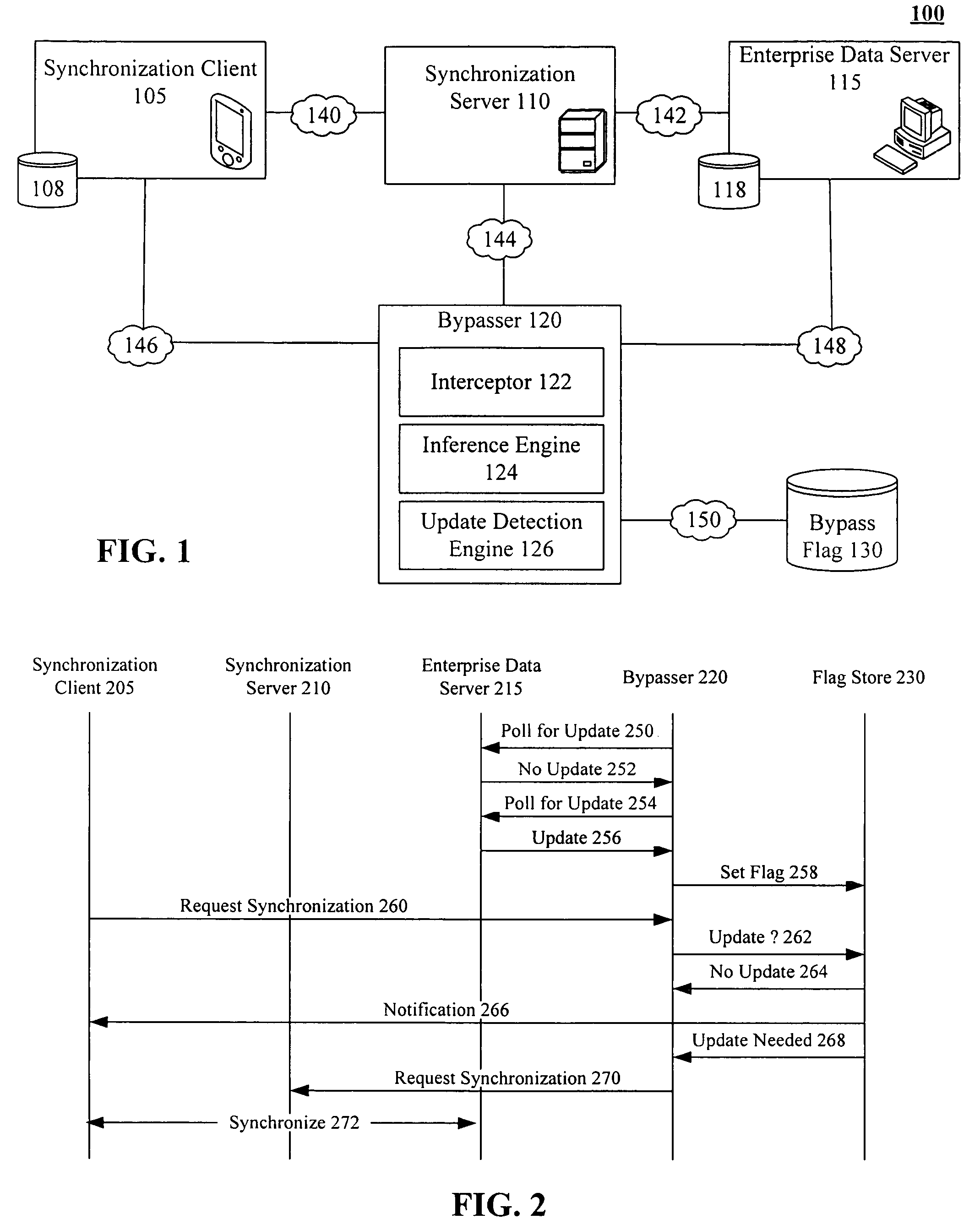
Bypassing an intermediate synchronization server of a three tiered synchronization system
InactiveUS7634519B2Data processing applicationsDatabase distribution/replicationData storeSynchronization system
A bypasser configured to operate within a three tiered synchronization system. The bypasser can include an interceptor and an inference engine. The interceptor can intercept synchronization requests before a synchronization event involving a synchronization server is initiated. The inference engine can determine if the data store and the another data store are to be synchronized and can selectively initiate the synchronization event based on the determination of the inference engine. For example, when the inference engine determines that synchronization is not to occur, the bypasser can convey a notification that no update is needed to the source of an intercepted synchronization request without requiring the synchronization server to process the synchronization request. When the inference engine determines that synchronization is to occur, the bypasser can convey an intercepted synchronization request to the intermediate synchronization server for processing.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Virtual sales person for electronic catalog
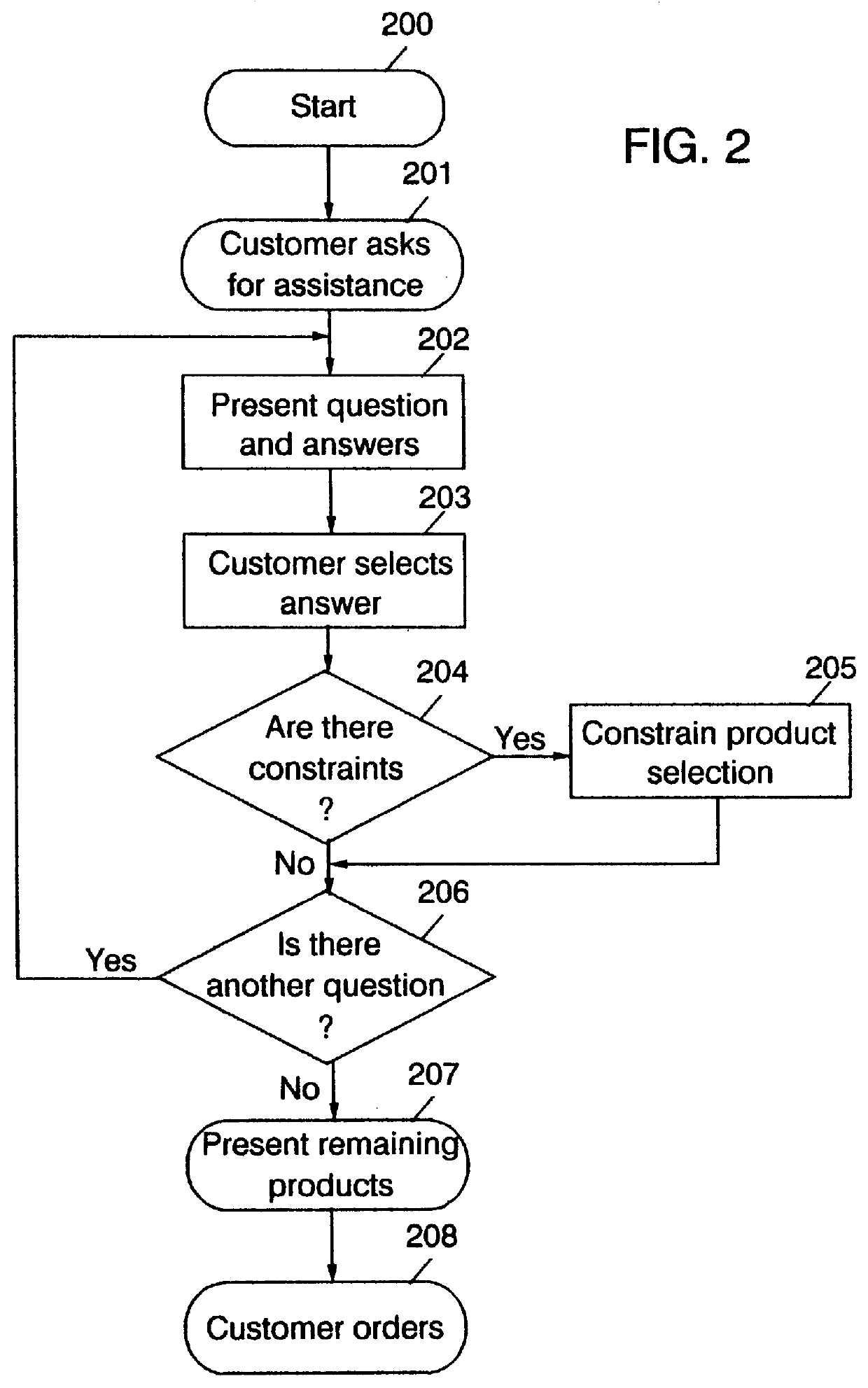
InactiveUS6035283AMarket predictionsBuying/selling/leasing transactionsQuestions and answersElectronic catalog
This invention involves an electronic catalog system which employs the knowledge and experience of a "Sales Agent", which is provided to a computer data base, and used with an inference engine to assist and guide actual customers to products that they will most likely be interested in purchasing. This system is employs hypothetical questions and answers, based on the sales agents experience with generic customers, as well as criteria and constraints provided by both the Sales Agent and the electronic catalog content.
Owner:PAYPAL INC
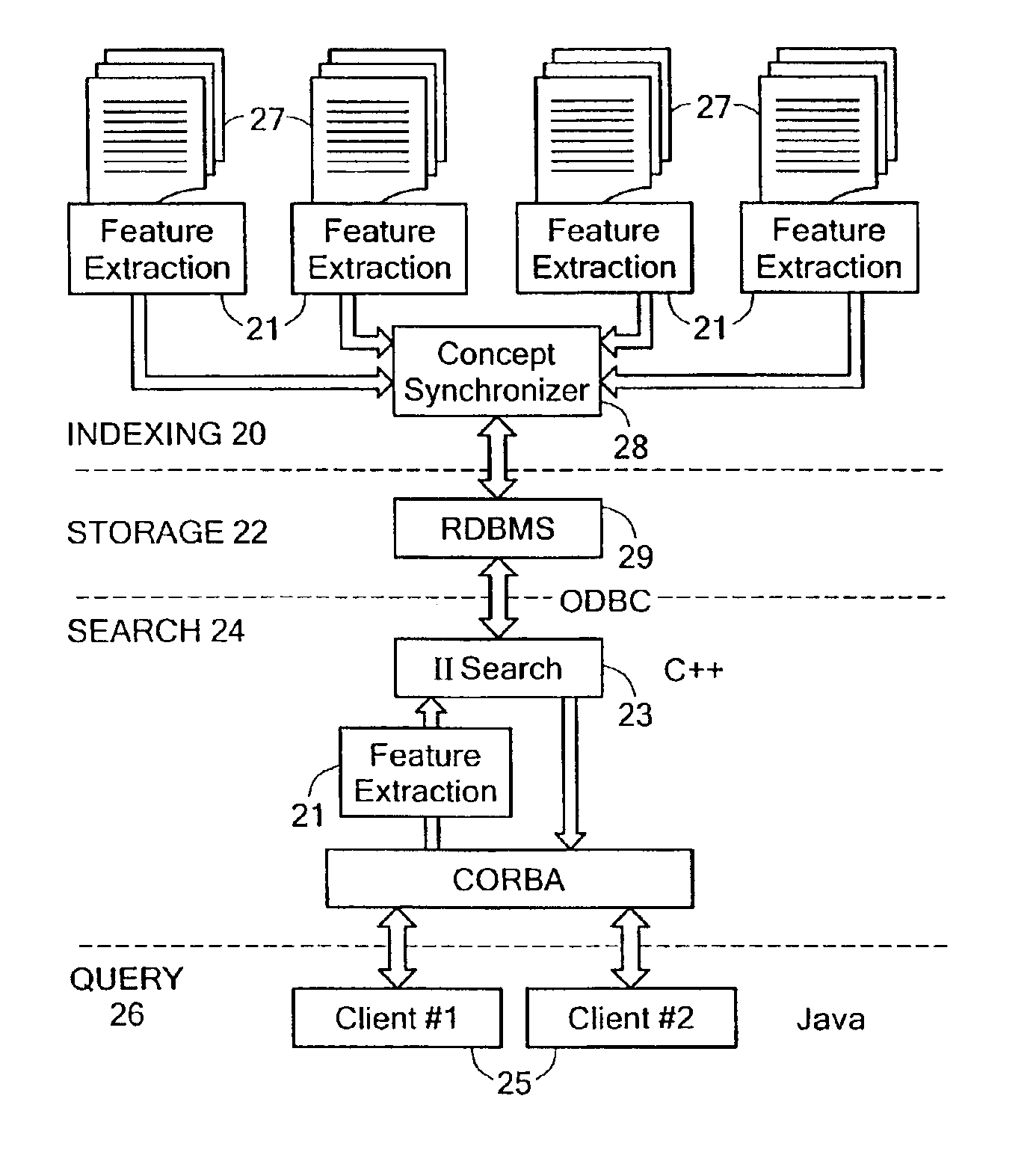
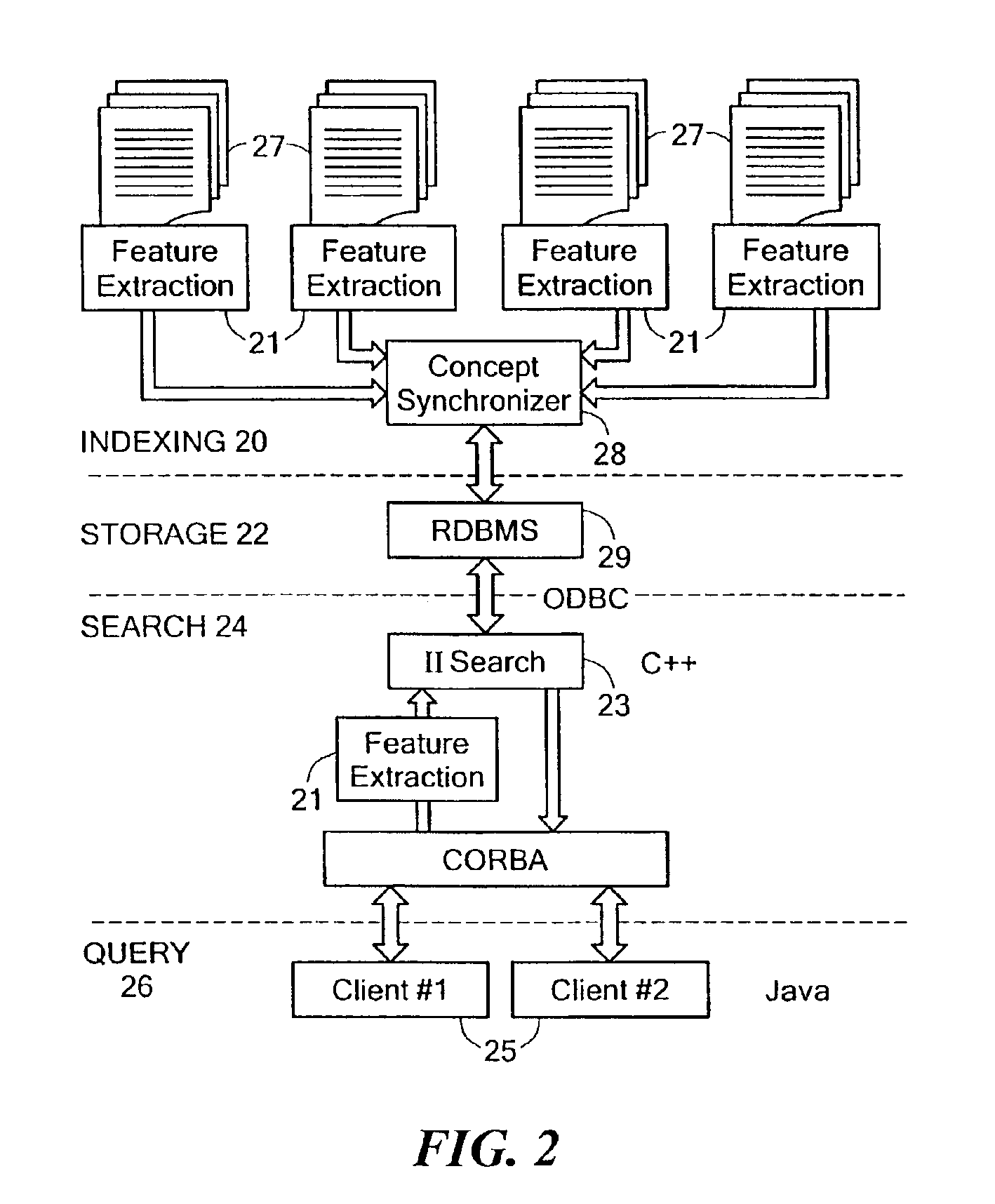
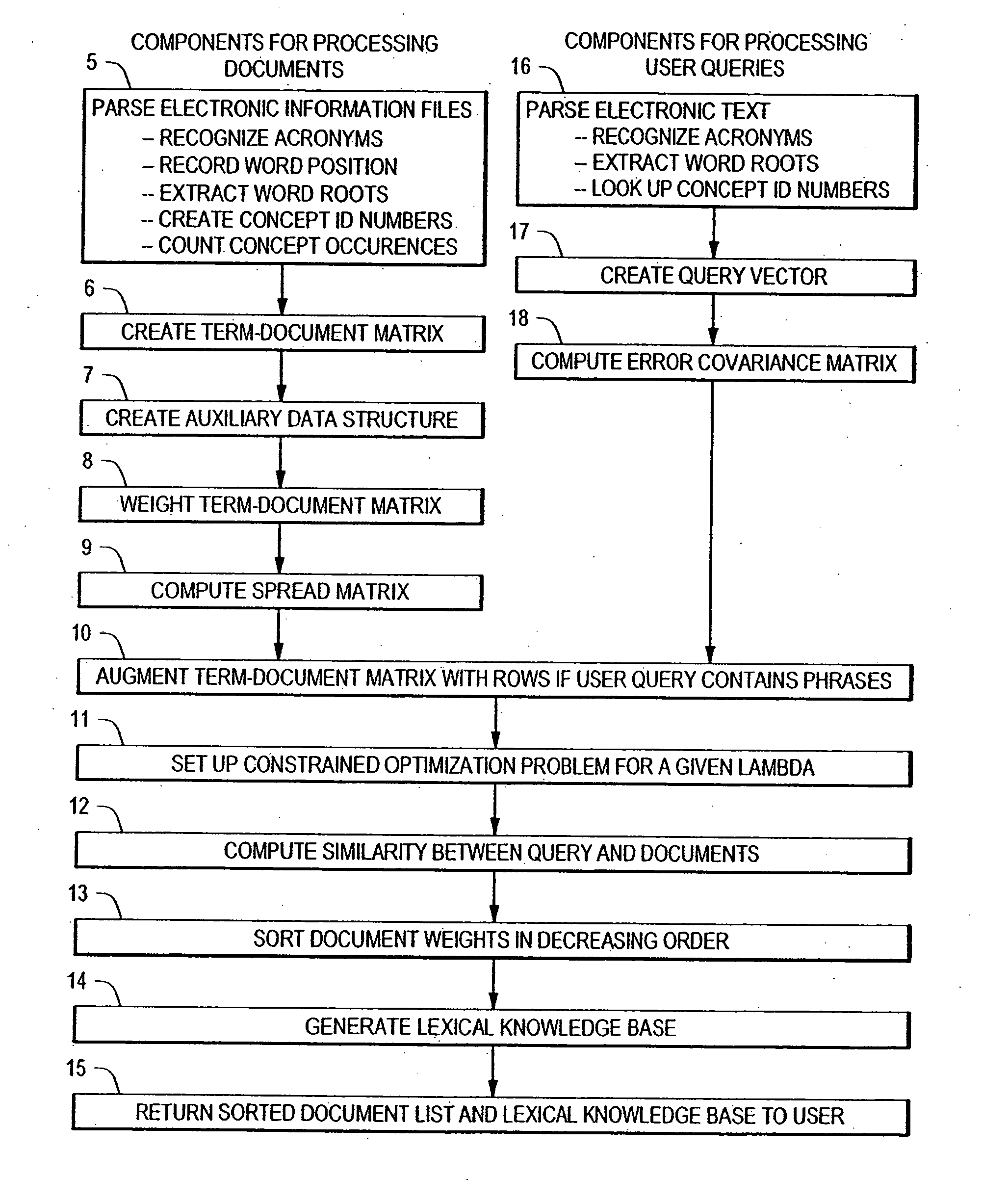
Inverse inference engine for high performance web search
InactiveUS7051017B2Eliminate needIncrease computing speedData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsDecompositionOrthogonal basis
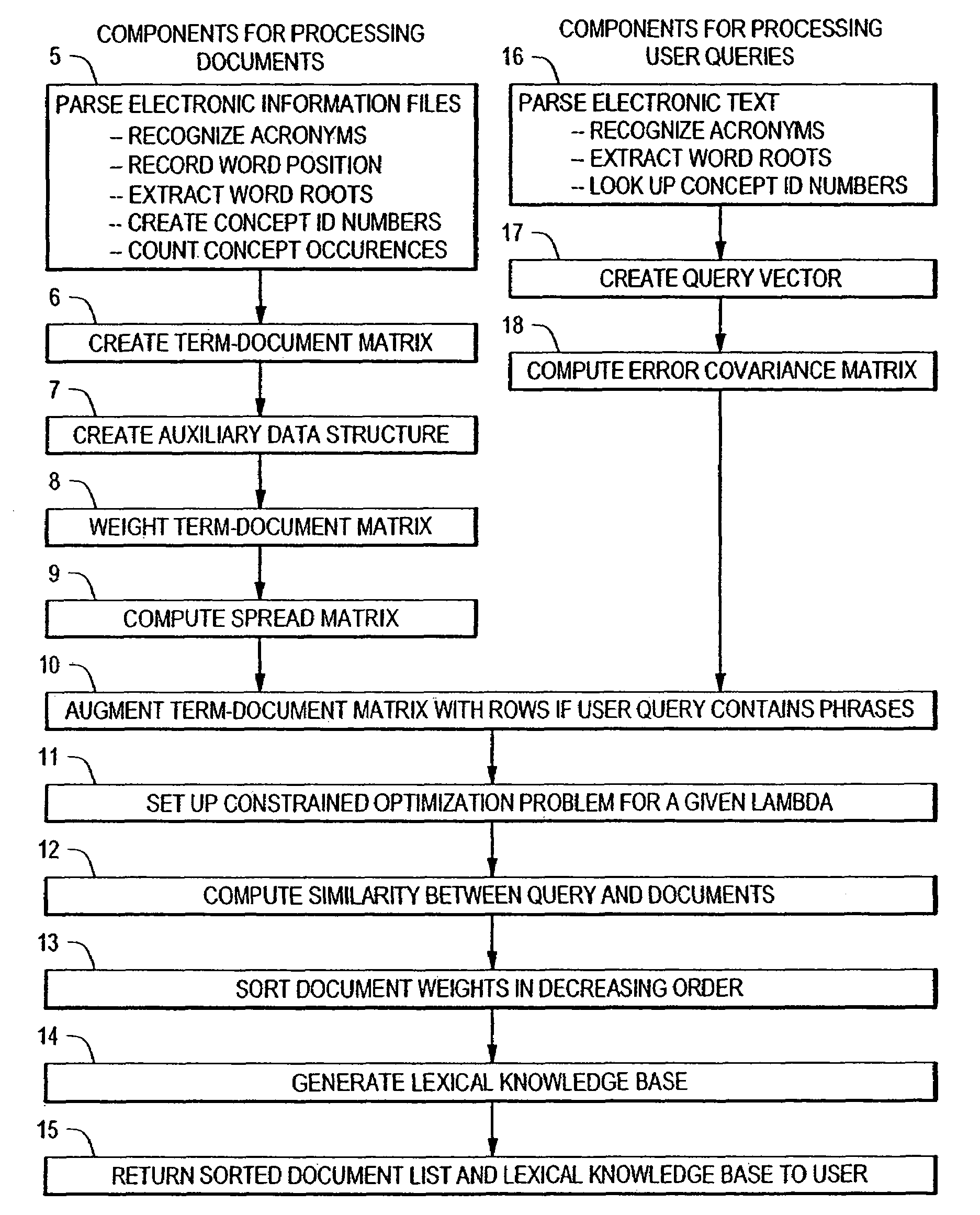
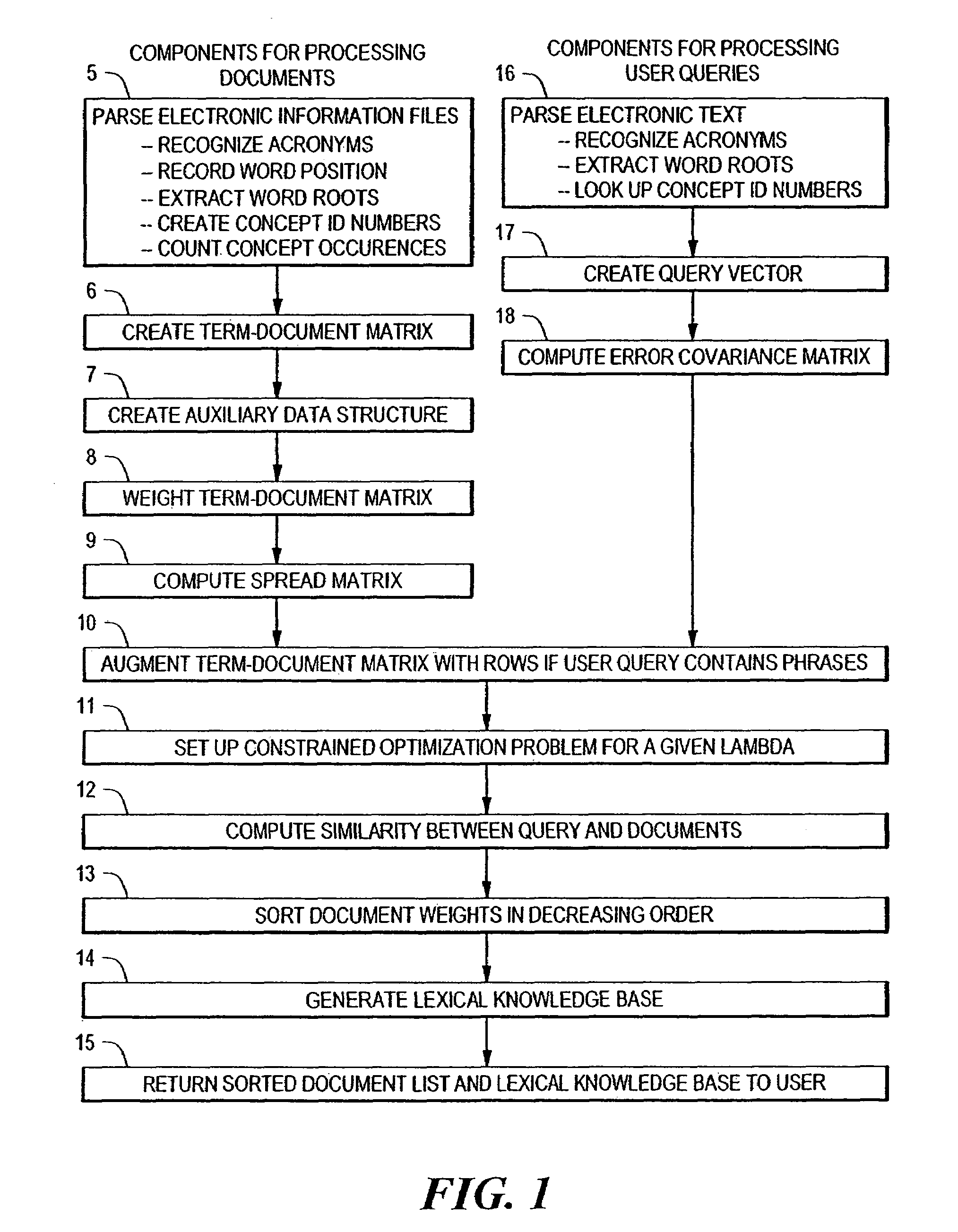
An information retrieval system that deals with the problems of synonymy, polysemy, and retrieval by concept by allowing for a wide margin of uncertainty in the initial choice of keywords in a query. For each input query vector and an information matrix, the disclosed system solves an optimization problem which maximizes the stability of a solution at a given level of misfit. The disclosed system may include a decomposition of the information matrix in terms of orthogonal basis functions. Each basis encodes groups of conceptually related keywords. The bases are arranged in order of decreasing statistical relevance to a query. The disclosed search engine approximates the input query with a weighted sum of the first few bases. Other commercial applications than the disclosed search engine can also be built on the disclosed techniques.
Owner:FIVER LLC
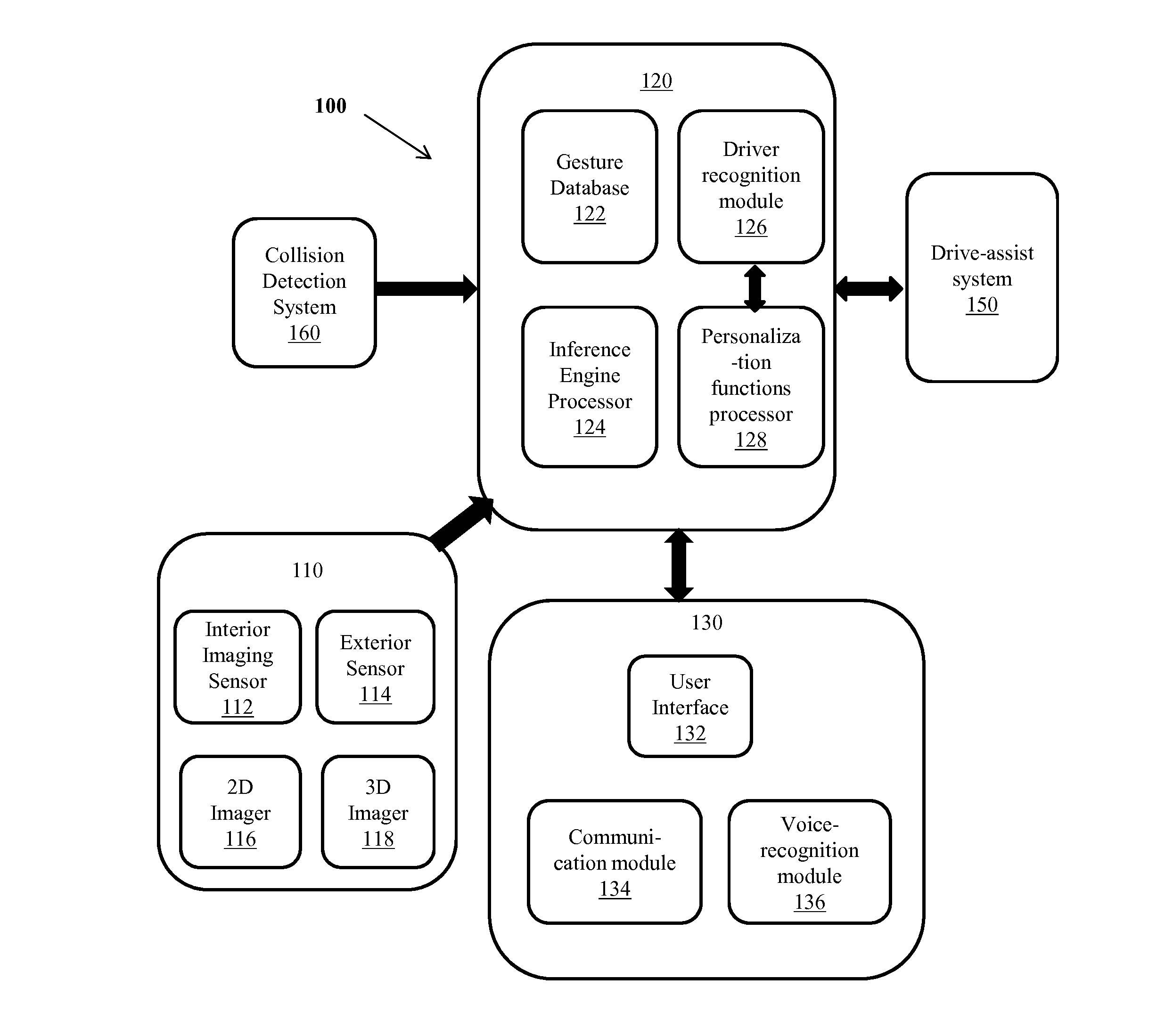
Interacting with vehicle controls through gesture recognition
InactiveUS20130204457A1Digital data processing detailsInstrument arrangements/adaptationsPersonalizationDriver/operator
A gesture-based recognition system obtains a vehicle occupant's desired command inputs through recognition and interpretation of his gestures. An image of the vehicle's interior section is captured and the occupant's image is separated from the background, in the captured image. The separated image is analyzed and a gesture recognition processor interprets the occupant's gesture from the image. A command actuator renders the interpreted desired command to the occupant along with a confirmation message, before actuating the command. When the occupant confirms, the command actuator actuates the interpreted command. Further, an inference engine processor assesses the occupant's state of attentiveness and conveys signals to a drive assist system if the occupant in inattentive. The drive-assist system provides warning signals to the inattentive occupant if any potential threats are identified. Further, a driver recognition module readjusts a set of vehicle's personalization functions to pre-stored settings, on recognizing the driver.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
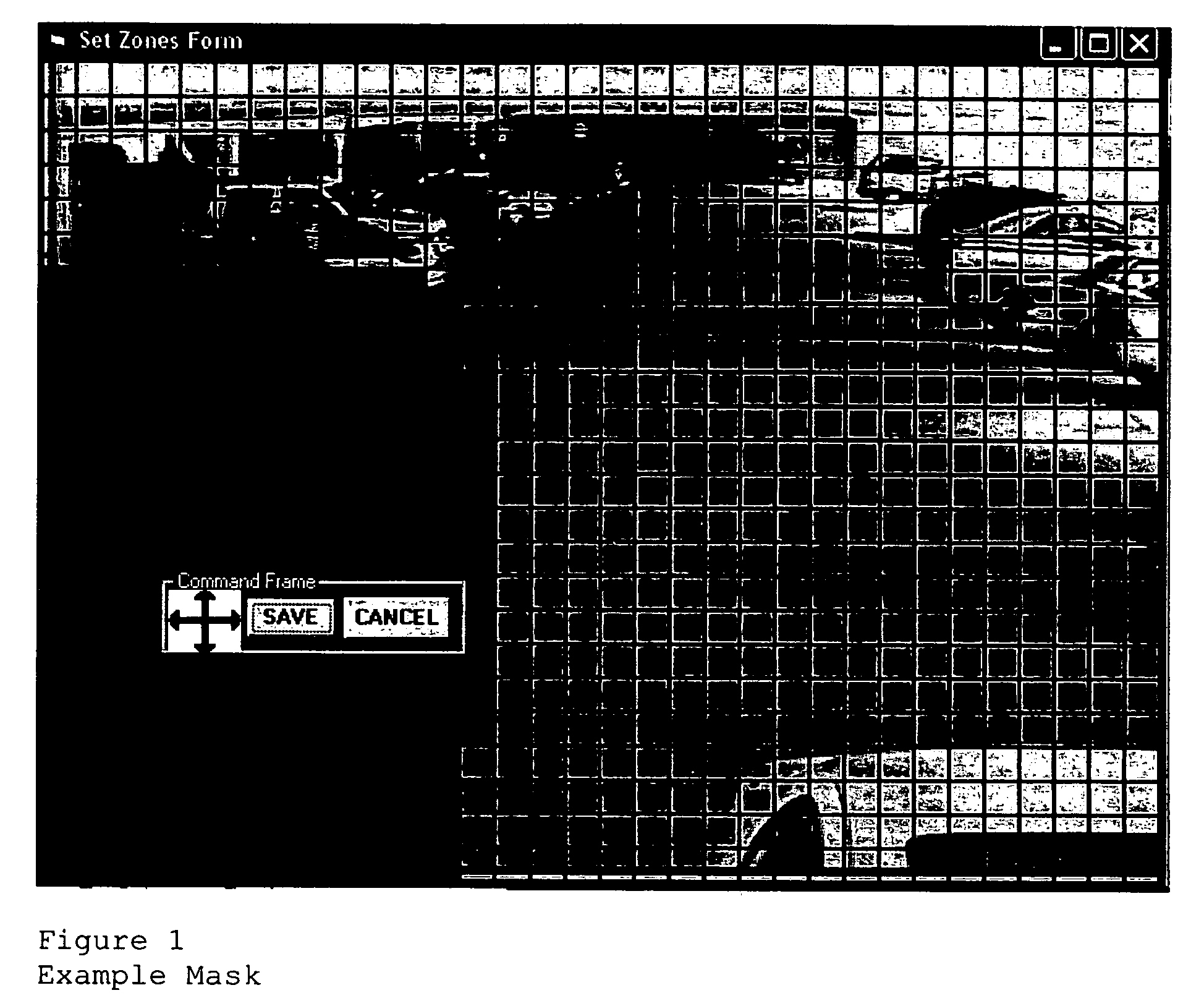
Intelligent video behavior recognition with multiple masks and configurable logic inference module
InactiveUS20060222206A1Character and pattern recognitionClosed circuit television systemsMulti eventSystem usage
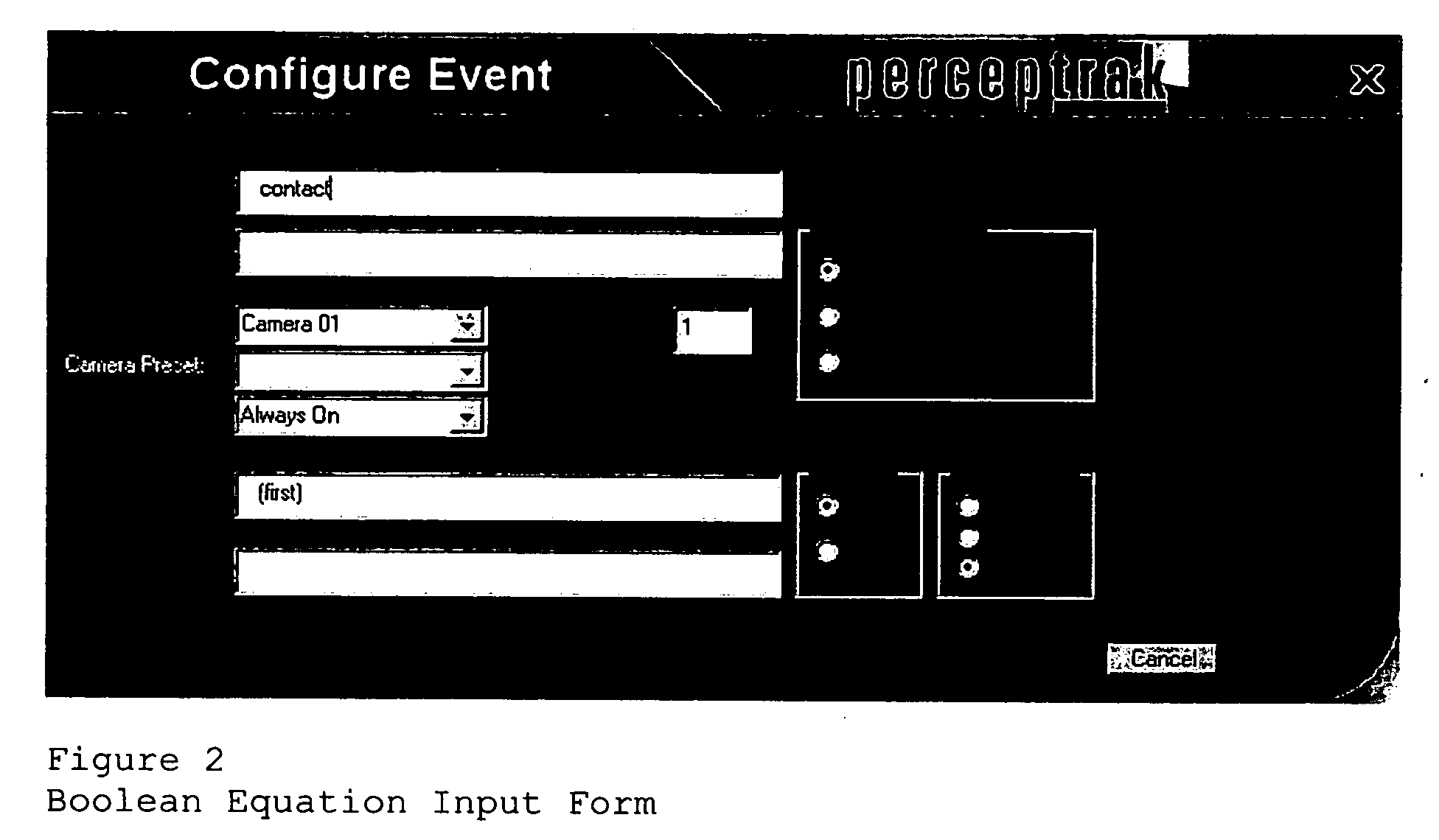
Methodology of implementing complex behavior recognition in an intelligent video system includes multiple event detection defining activity in different areas of the scene (“What”), multiple masks defining areas of a scene (“Where”), configurable time parameters (“When”), and a configurable logic inference engine to allow Boolean logic analysis based on any combination of logic-defined events and masks. Events are detected in a video scene that consists of one or more camera views termed a “virtual view”. The logic-defined event is a behavioral event connoting behavior, activities, characteristics, attributes, locations and / or patterns of a target subject of interest. A user interface allows a system user to select behavioral events for logic definition by the Boolean equation in accordance with a perceived advantage, need or purpose arising from context of system use.
Owner:CERNIUM
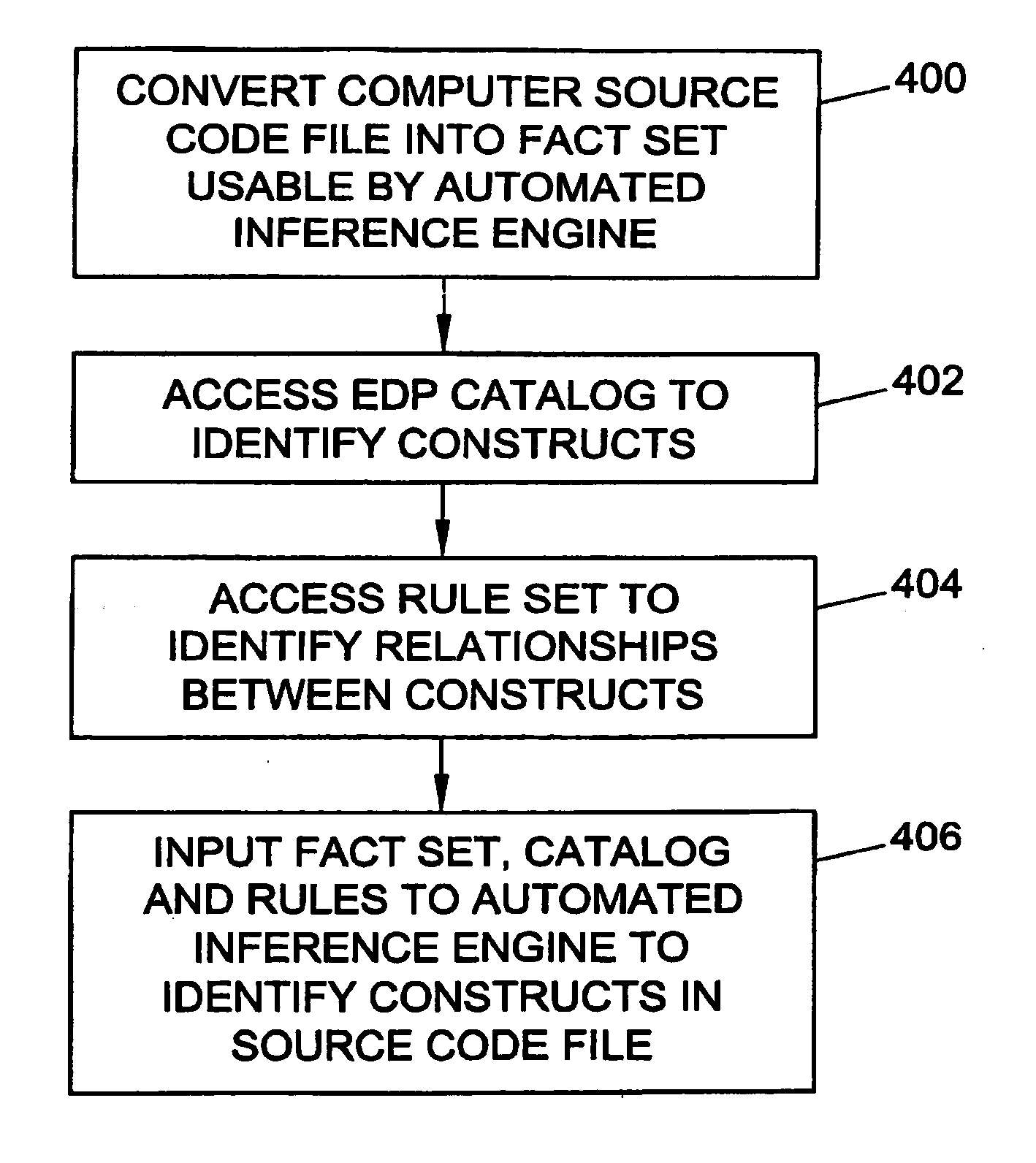
Methods, systems, and computer program products for identifying computer program source code constructs
Methods, systems, and computer program products for identifying computer source code constructs are disclosed. According to one method, computer source code is converted to a format suitable for an automated inference engine. The automated inference engine receives as inputs the converted source code, a set of elemental design patterns defining patterns to be identified, and a set of rules defining relationships between patterns. The automated inference engine outputs proofs indicative of patterns present in the source code. The proofs may be converted to a source code pattern report.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
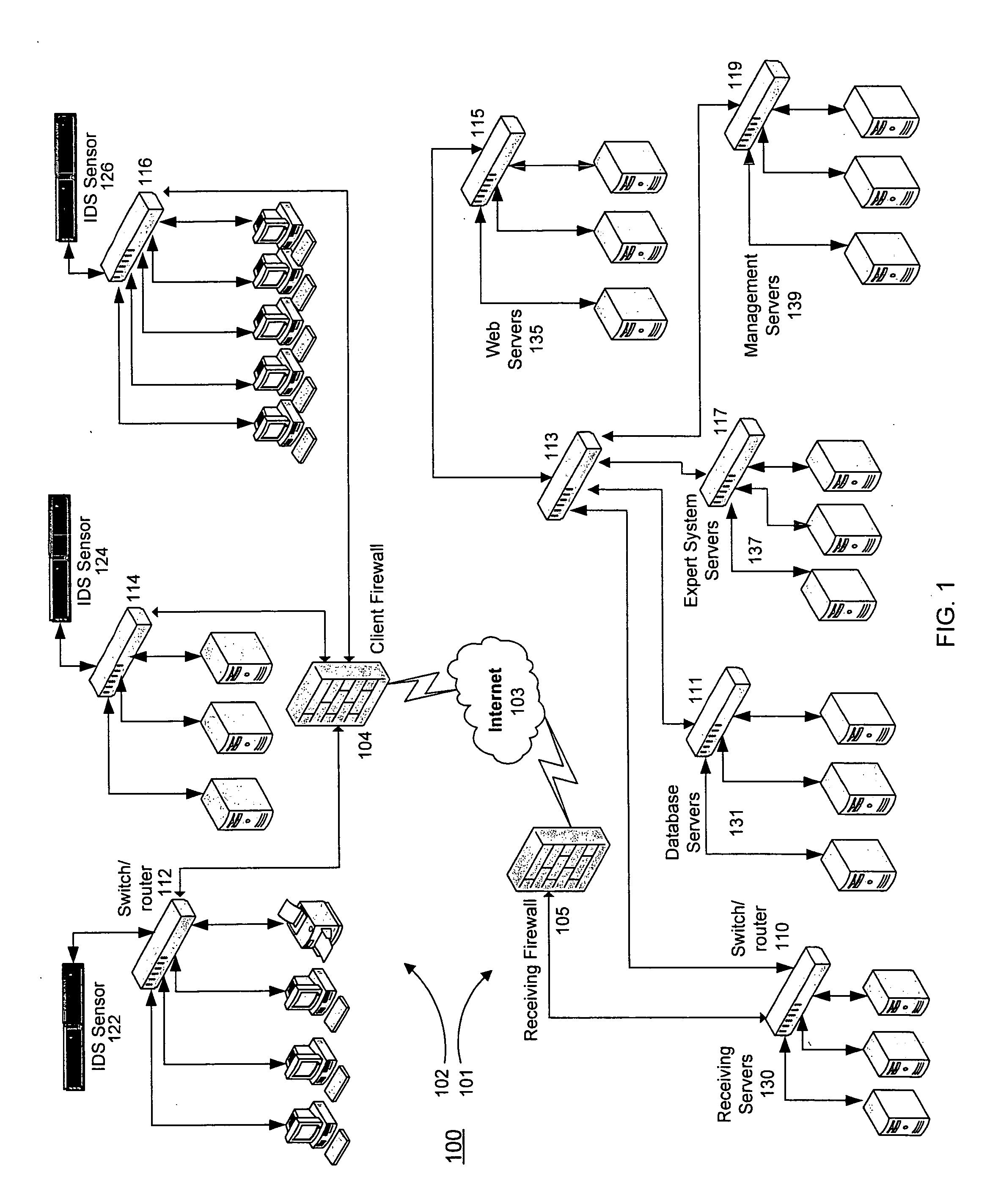
IP network vulnerability and policy compliance assessment by IP device analysis
InactiveUS20080172716A1Reduce vulnerabilityImprove network securityTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsNetwork security policyCompliance problem
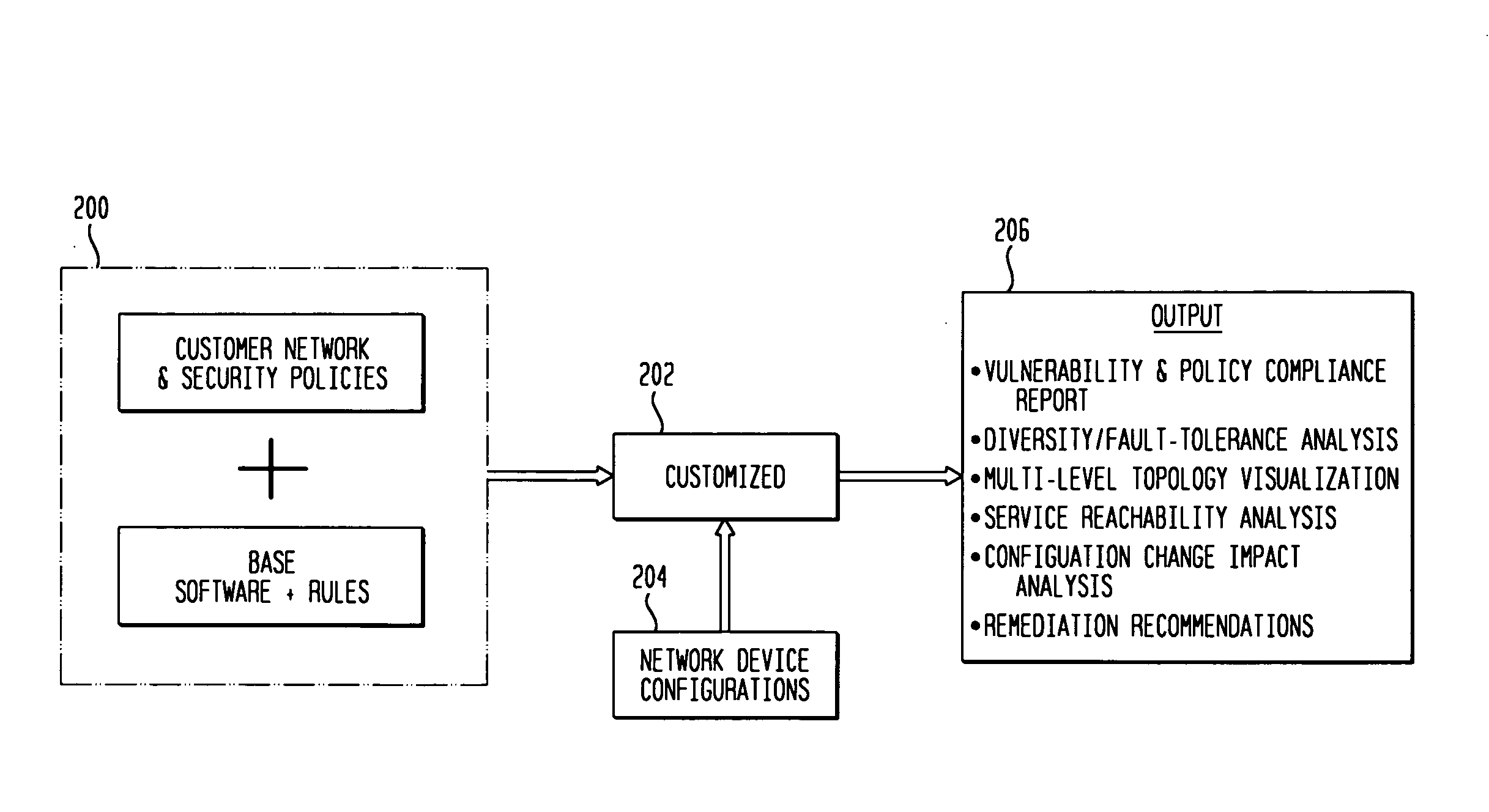
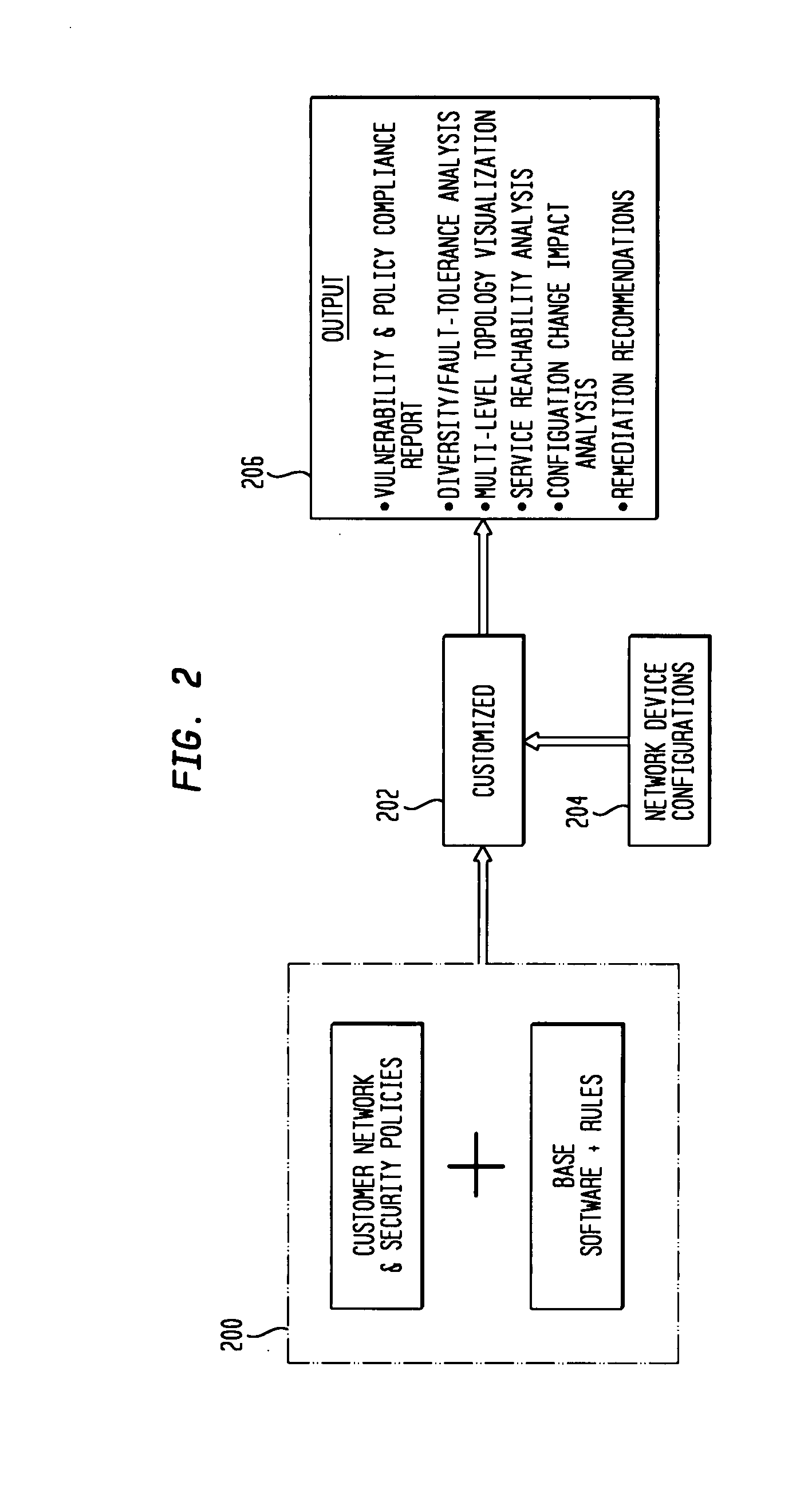
Customizable software provides assurances about the ability of an IP network to satisfy security, regulatory and availability requirements by comprehensive vulnerability and compliance assessment of IP networks through automated analysis of configurations of devices such as routers, switches, and firewalls. The solution comprises three main approaches for testing of IP device configurations to eliminate errors that result in vulnerabilities or requirements compliance issues. The first two fall in to the “static constraint validation” category since they do not change significantly for each IP network, while the last approach involves incorporation of each specific IP network's policies / requirements. These approaches are complementary, and may be used together to satisfy all the properties described above. The first approach involves checking the configurations of devices for conformance to Best-Current-Practices provided by vendors (e.g. Cisco Network Security Policy) and organizations such as the NIST, NSA or CERT. Also this includes checks of compliance with regulations such as FISMA, SOX, HIPPA, PCI, etc. The second approach is where as one reads device configurations, one collects beliefs about network administrator intent. As each belief is collected, an inference engine checks whether the new belief is inconsistent with previously accumulated beliefs. The third approach addresses the multiple device / protocol issue by including an understanding of high-level service and security requirements about the specific IP network under test from the network administrators.
Owner:TT GOVERNMENT SOLUTIONS
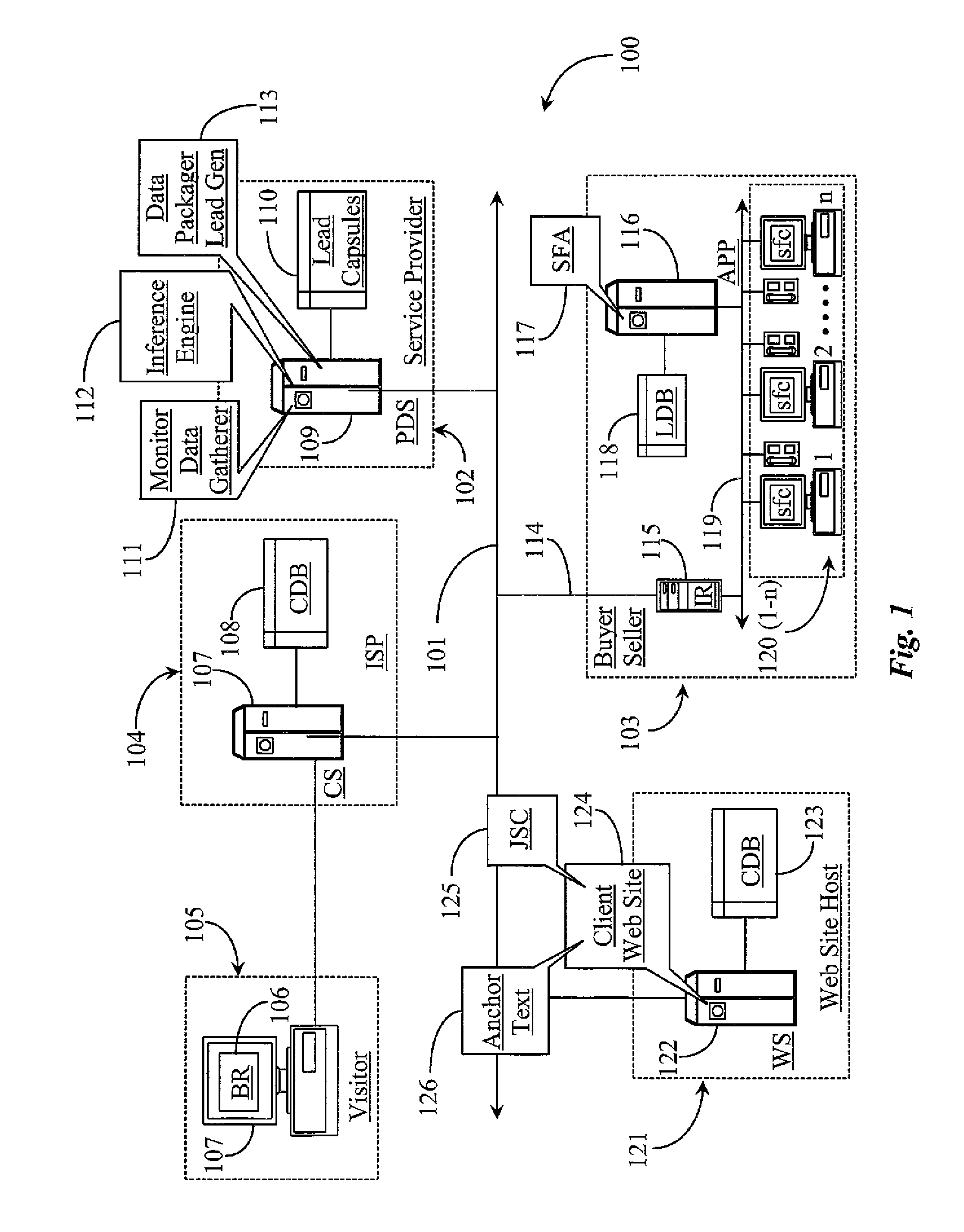
System and methods for inferring intent of website visitors and generating and packaging visitor information for distribution as sales leads or market intelligence
ActiveUS20100131835A1Without ambiguityInterprogram communicationCommerceWeb siteBehavioral analytics
A system for inferring intent of visitors to a Website has a visitor-tracking application executing from a digital medium coupled to a server hosting the Website, the server connected to a repository adapted to store data about visitor behavior, and an inference engine for processing the data to infer the intent of visitors. Visitor behavior relative to links is tracked, and intent of a visitor is inferred from one or both, or a combination of analysis of the behavior and deducing meaning for anchor text of links selected.
Owner:CALLIDUS SOFTWARE
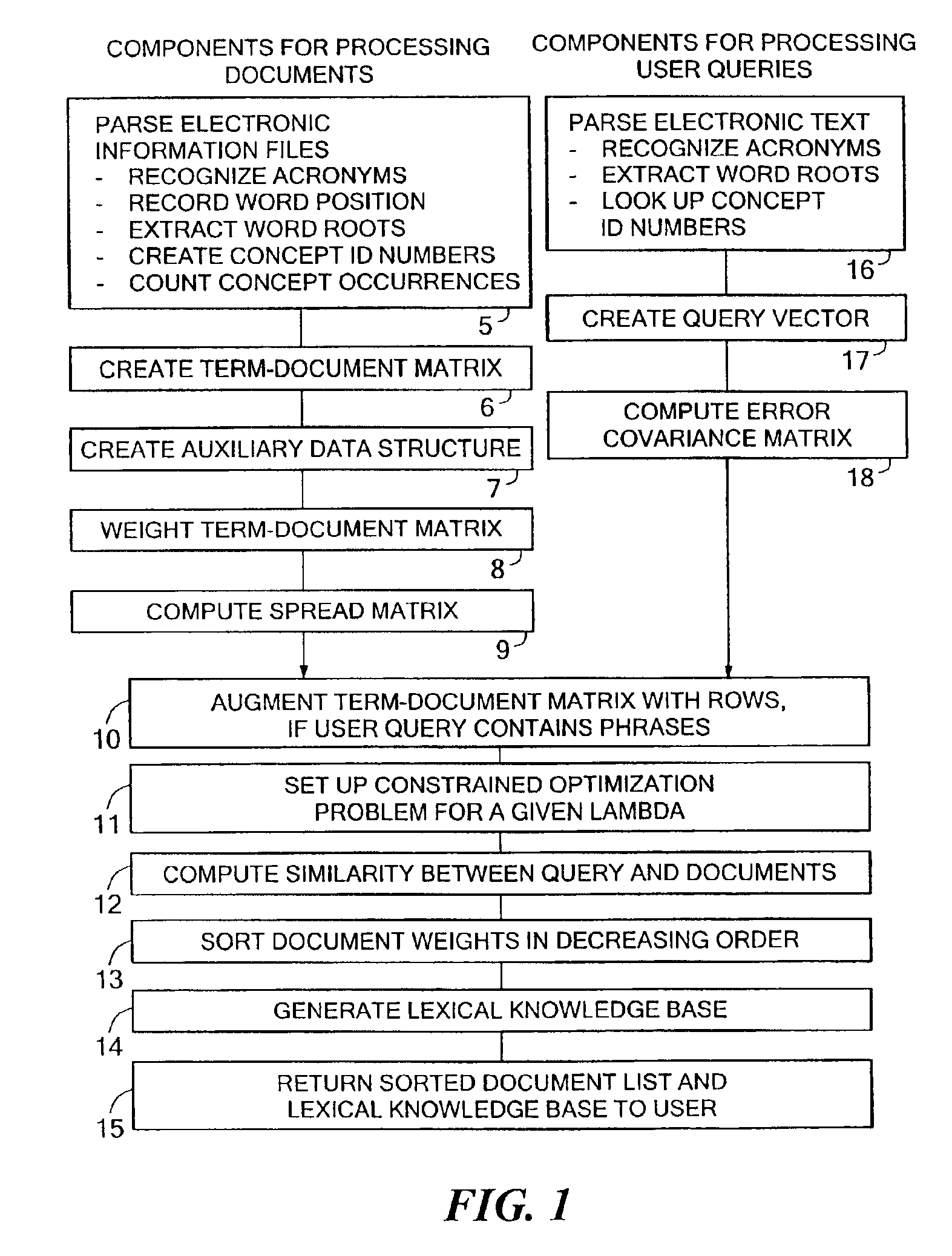
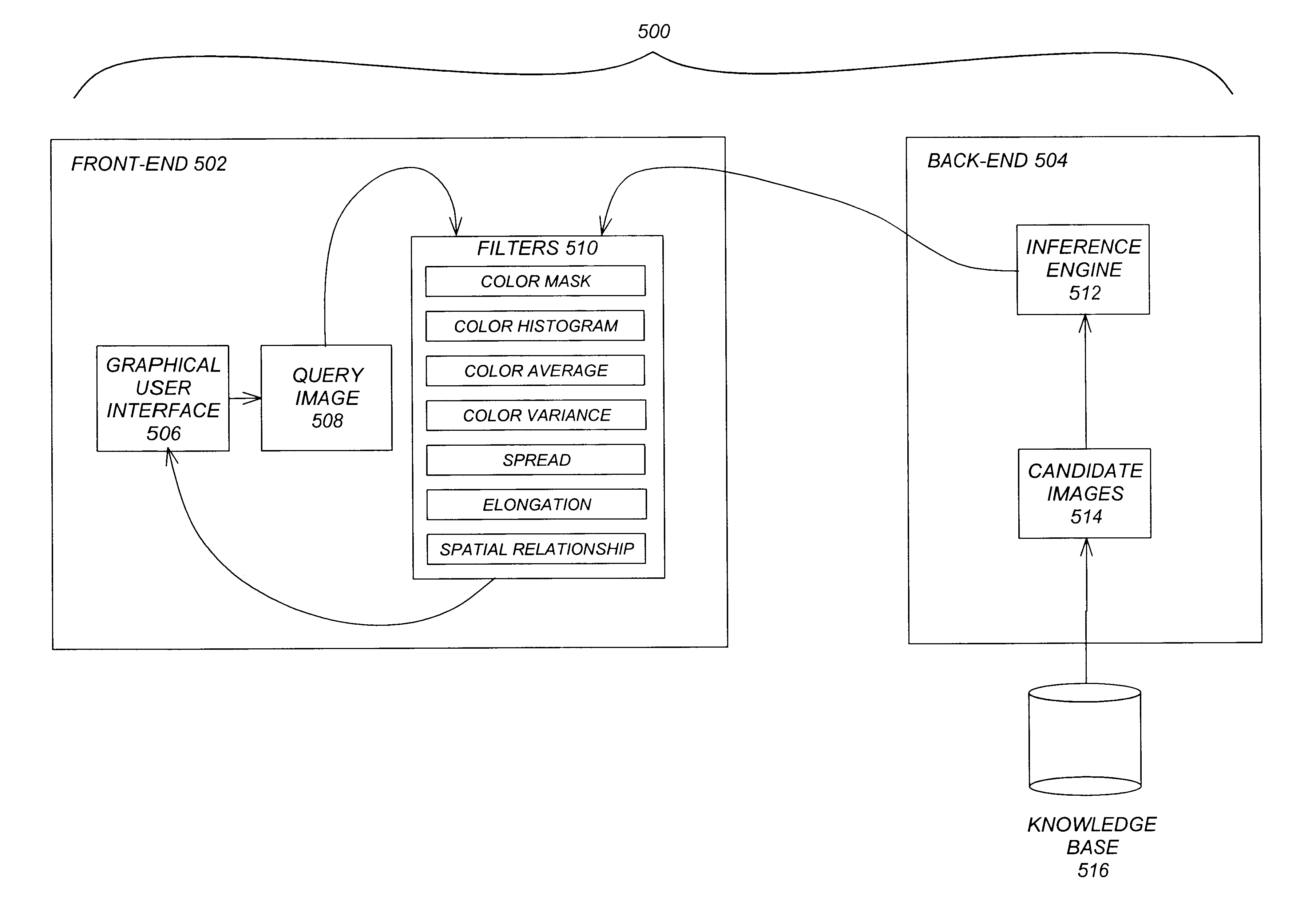
Perception-based image retrieval
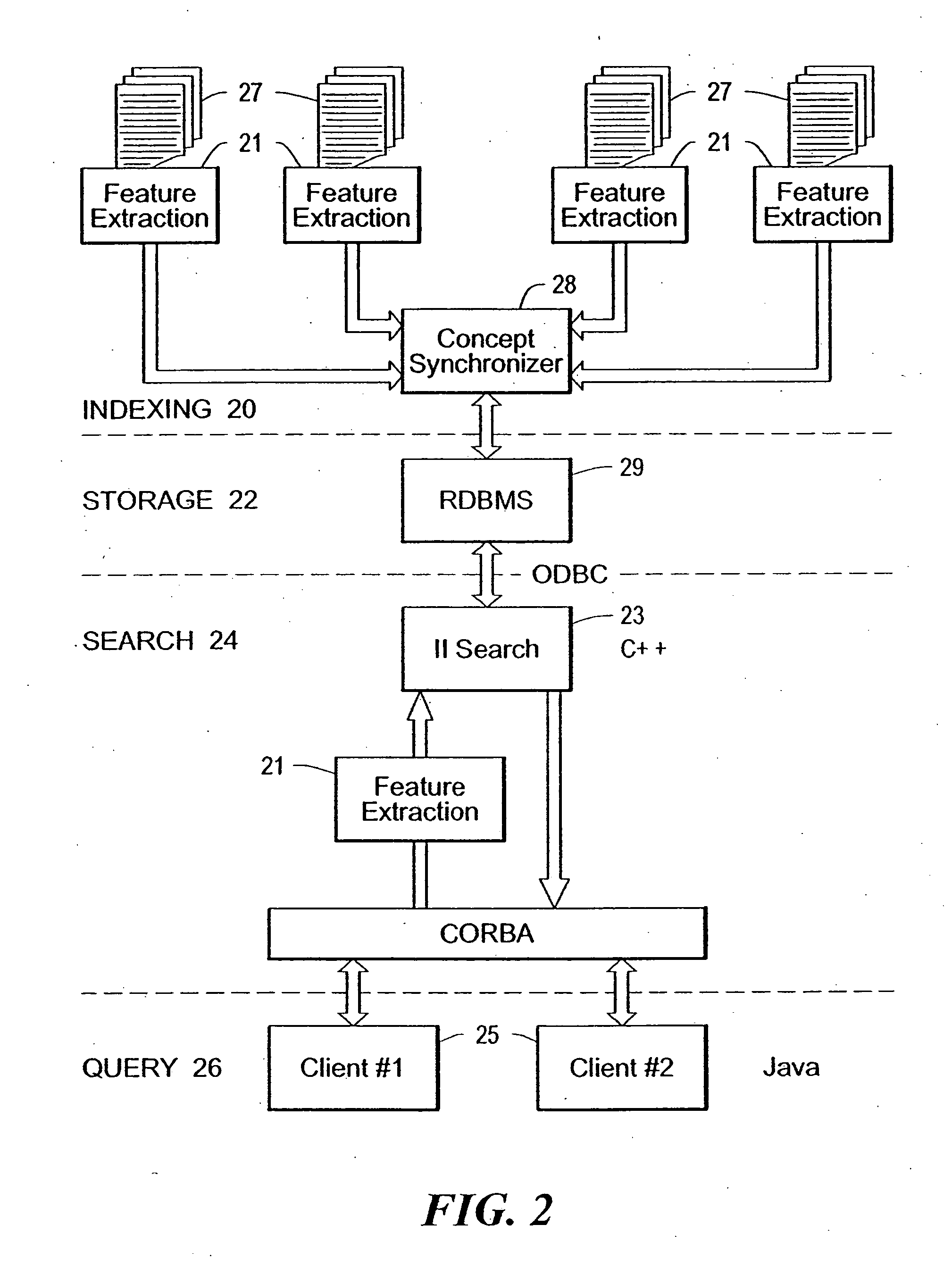
InactiveUS6865302B2Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalAverage filterPattern perception
A content-based image retrieval (CBIR) system has a front-end that includes a pipeline of one or more dynamically-constructed filters for measuring perceptual similarities between a query image and one or more candidate images retrieved from a back-end comprised of a knowledge base accessed by an inference engine. The images include at least one color set having a set of properties including a number of pixels each having at least one color, a culture color associated with the color set, a mean and variance of the color set, a moment invariant, and a centroid. The filters analyze and compare the set of properties of the query image to the set of properties of the candidate images. Various filters are used, including: a Color Mask filter that identifies identical culture colors in the images, a Color Histogram filter that identifies a distribution of colors in the images, a Color Average filter that performs a similarity comparison on the average of the color sets of the images, a Color Variance filter that performs a similarity comparison on the variances of the color sets of the images, a Spread filter that identifies a spatial concentration of a color in the images, an Elongation filter that identifies a shape of a color in the images, and a Spatial Relationship filter that identifies a spatial relationship between the color sets in the images.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Electronic Crime Detection and Tracking
A system for electronic crime reduction is provided, comprising a computer system, a database, a malware de-compiler, a malware parser, and an inference engine. The database contains information that associates electronic crime attack signature data with at least one of an individual, a group, and a location. The malware de-compiler, when executed on the computer system, translates a first malware executable to an assembly language version. The first malware is associated with an electronic crime that has been committed. The malware parser, when executed on the computer system, analyzes the assembly language version to identify distinctive coding preferences used to develop the first malware. The inference engine, when executed on the computer system, analyzes the distinctive coding preferences identified by the malware parser application in combination with searching the database to identify one of an individual, a group, and a location associated with the electronic crime.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Extended functionality for an inverse inference engine based web search
InactiveUS20050021517A1Improve efficiencyFast and scalableNatural language translationData processing applicationsMain diagonalAlgorithm
An extension of an inverse inference search engine is disclosed which provides cross language document retrieval, in which the information matrix used as input to the inverse inference engine is organized into rows of blocks corresponding to languages within a predetermined set of natural languages. The information matrix is further organized into two column-wise partitions. The first partition consists of blocks of entries representing fully translated documents, while the second partition is a matrix of blocks of entries representing documents for which translations are not available in all of the predetermined languages. Further in the second partition, entries in blocks outside the main diagonal of blocks are zero. Another disclosed extension to the inverse inference retrieval document retrieval system supports automatic, knowledge based training. This approach applies the idea of using a training set to the problem of searching databases where information that is diluted or not reliable enough to allow the creation of robust semantic links. To address this situation, the disclosed system loads the left-hand partition of the input matrix for the inverse inference engine with information from reliable sources.
Owner:FIVER LLC
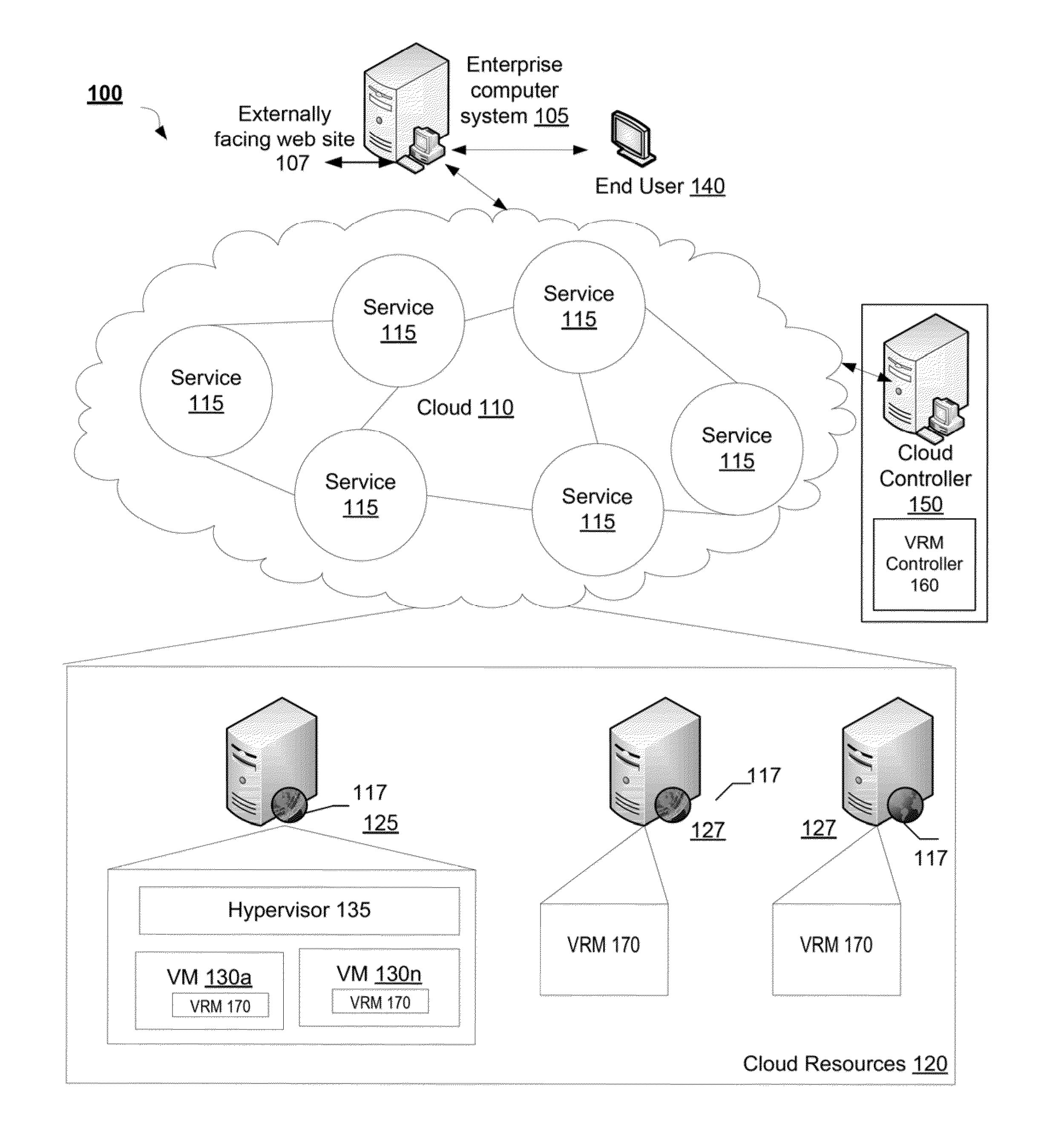
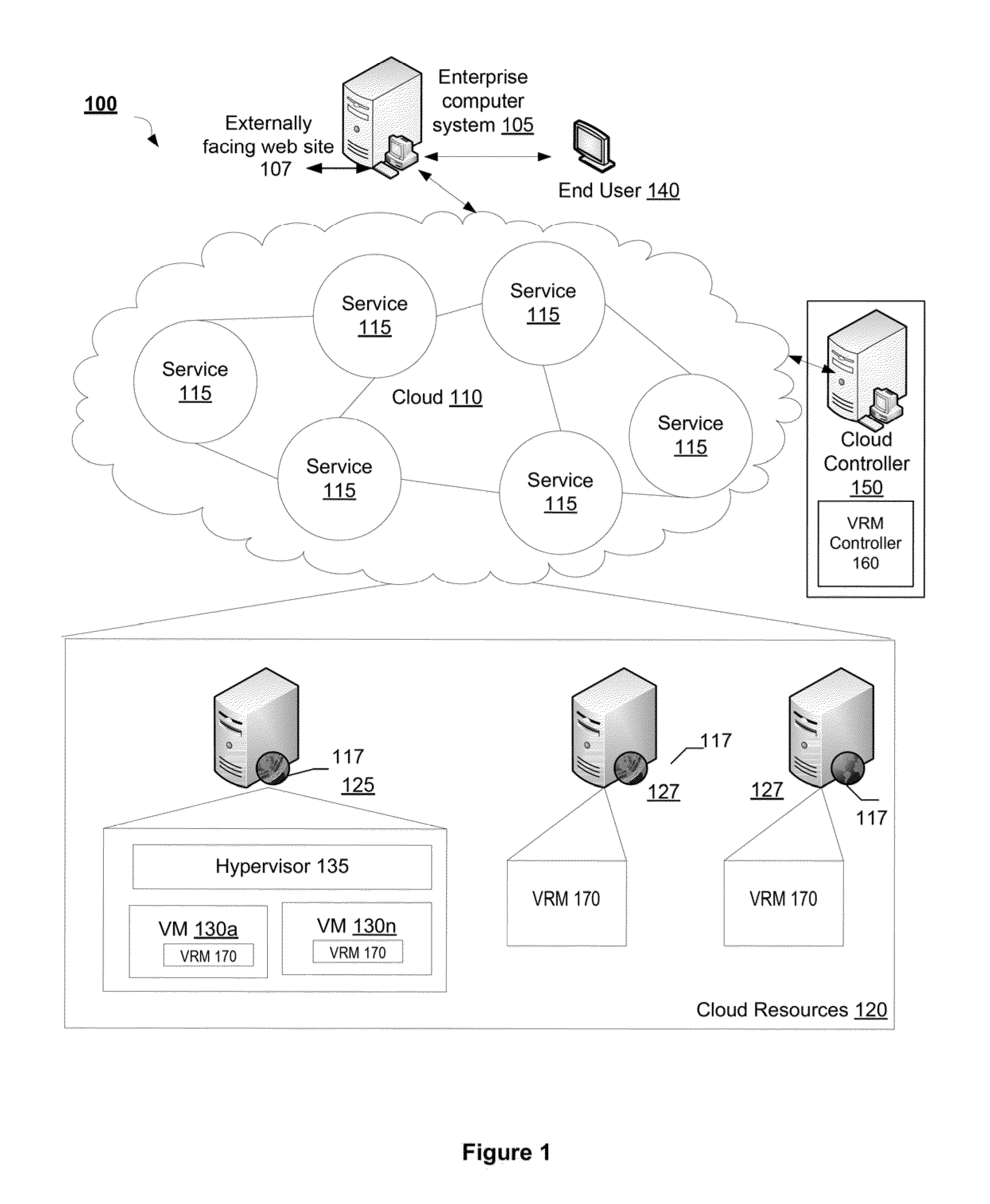
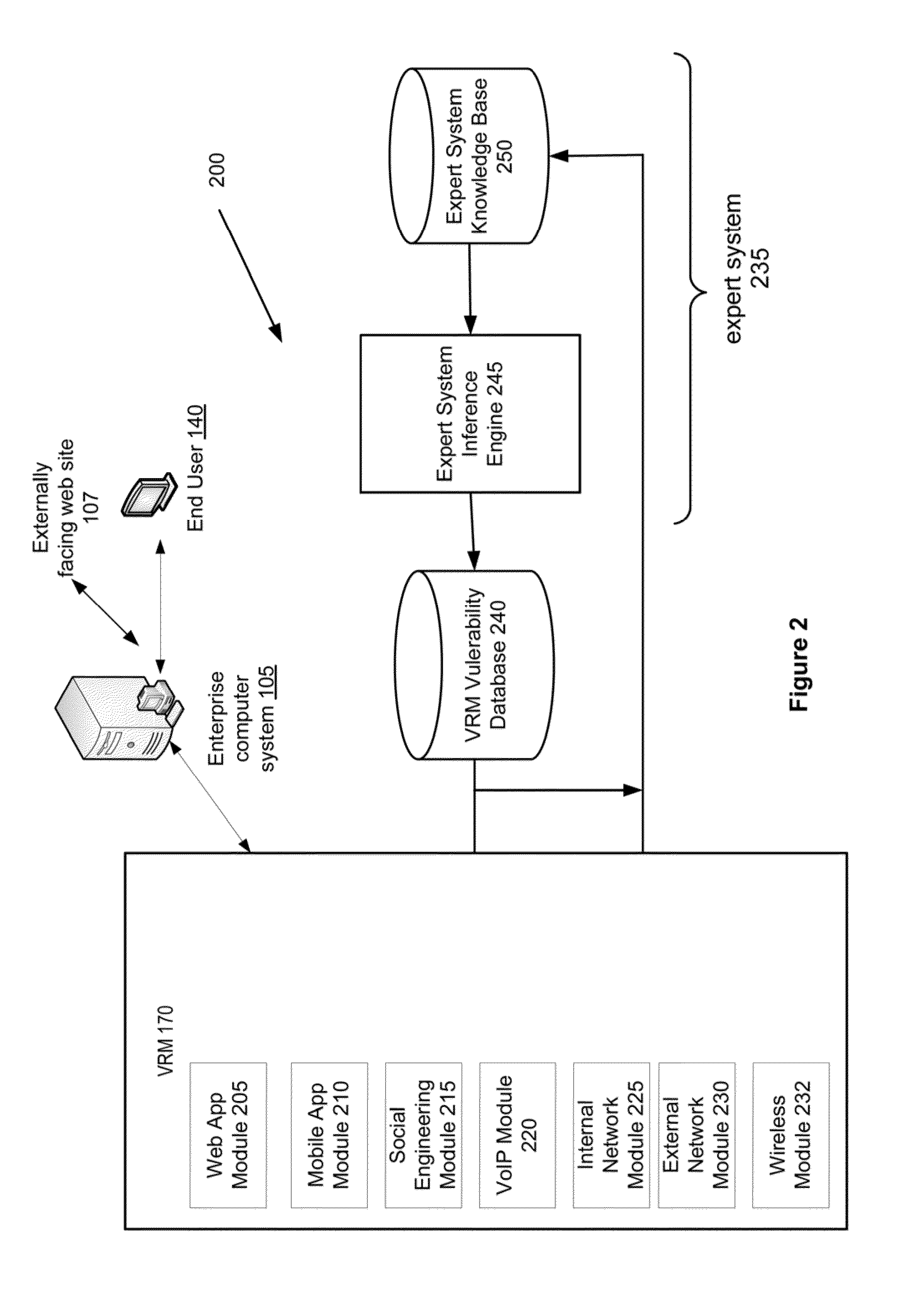
Method and System for Managing Computer System Vulnerabilities
A vulnerability risk management (VRM) module receives an indication of a VRM service to be provided from the end user. The VRM module extracts from the indication either external IP addresses or the web application URL and a list of assets of the enterprise computer system to be tested. The VRM module discovers the assets of the enterprise computer system. The VRM module receives a request for a vulnerability scan using a predefined scan configuration based on preferences of the end user and a specified date and time to conduct the scan. The VRM module reports and stores a preliminary list of potential vulnerabilities in the VRM vulnerability database. The preliminary list is fed to an expert system, which applies specific rule sets using an inference engine and a knowledge base to refine results stored in the VRM vulnerability database by removing extraneous information and false positives.
Owner:NOPSEC
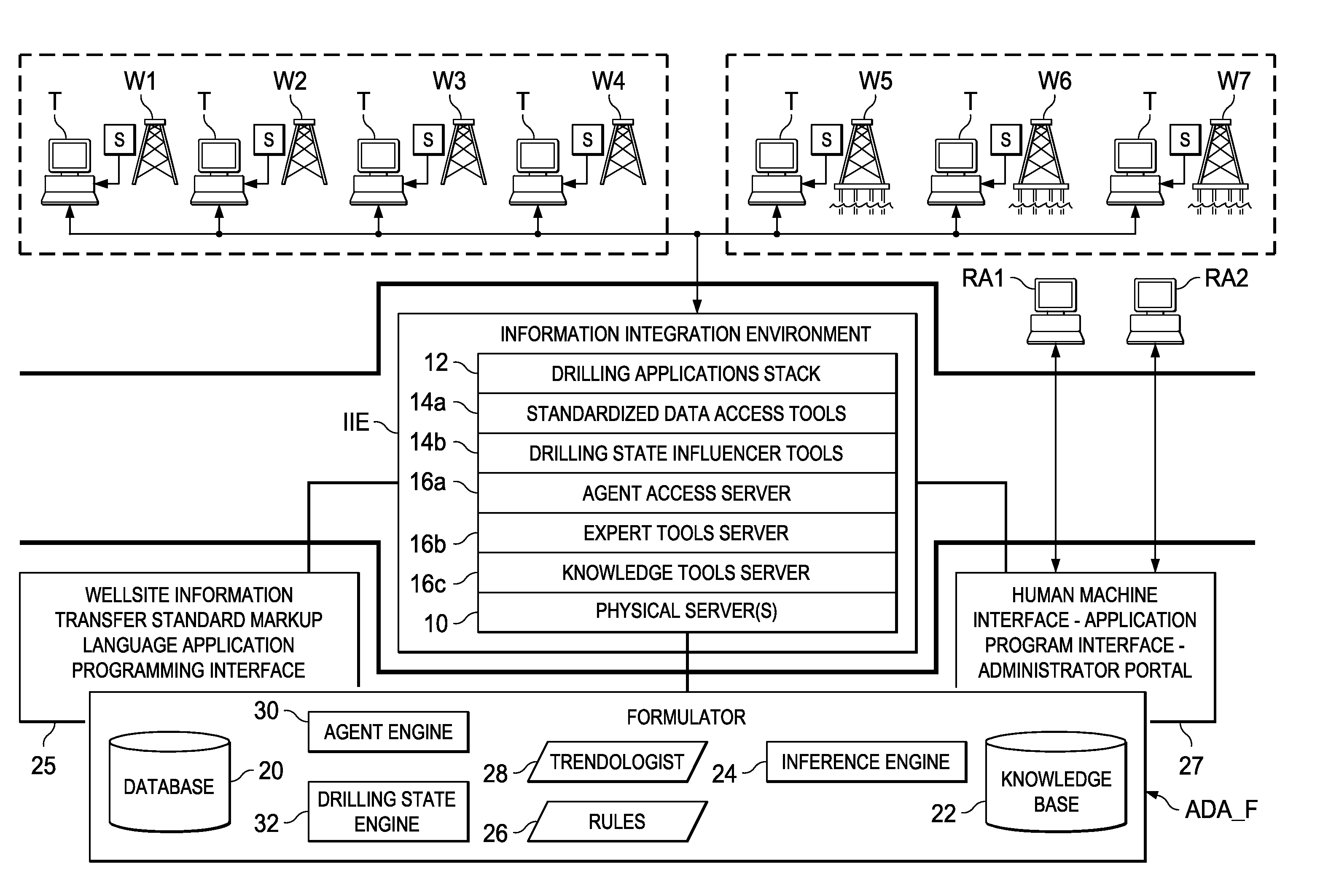
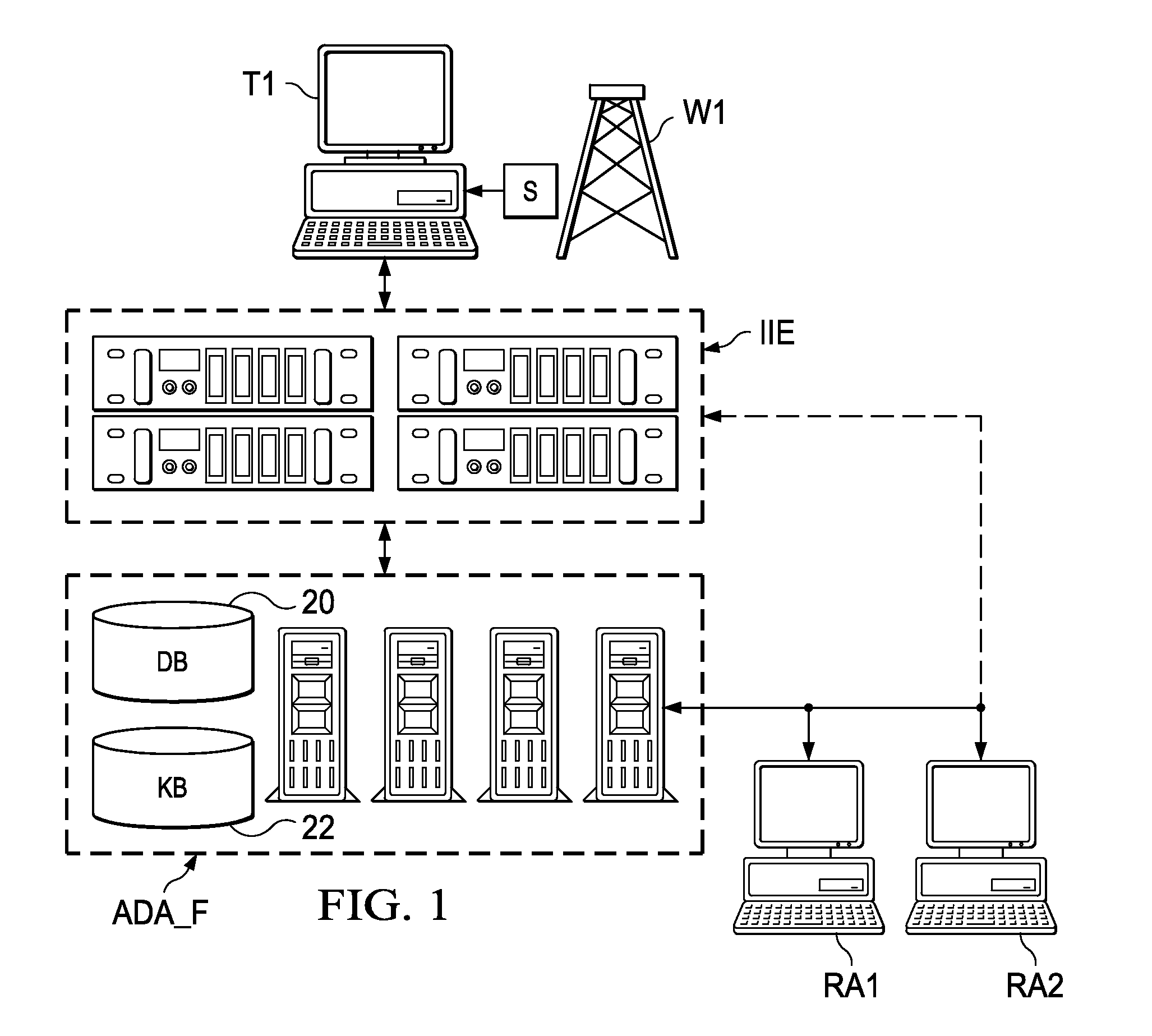
Intelligent drilling advisor
ActiveUS8121971B2Easy to operateElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingKnowledge representationHeuristicInformation integration
An information integration environment identifies the current drilling sites, and drilling equipment and processes at those current drilling sites. Based upon that identification, and upon data received from the drilling sites, servers access and configure software agents that are sent to a host client system at the drilling site; these software agents operate at the host client system to acquire data from sensors at the drilling site, to transmit that data to the information integration environment, and to derive the drilling state and drilling recommendations for the driller at the drilling site. These software agents include one or more rules, heuristics, or calibrations derived by the inference engine, and called by the information integration environment. In addition, the software agents sent from the information integration environment to the host client system operate to display values, trends, and reliability estimates for various drilling parameters, whether measured or calculated.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Extended functionality for an inverse inference engine based web search
InactiveUS7269598B2Improve efficiencyFast and scalableNatural language translationData processing applicationsMain diagonalAlgorithm
An extension of an inverse inference search engine is disclosed which provides cross language document retrieval, in which the information matrix used as input to the inverse inference engine is organized into rows of blocks corresponding to languages within a predetermined set of natural languages. The information matrix is further organized into two column-wise partitions. The first partition consists of blocks of entries representing fully translated documents, while the second partition is a matrix of blocks of entries representing documents for which translations are not available in all of the predetermined languages. Further in the second partition, entries in blocks outside the main diagonal of blocks are zero. Another disclosed extension to the inverse inference retrieval document retrieval system supports automatic, knowledge based training. This approach applies the idea of using a training set to the problem of searching databases where information that is diluted or not reliable enough to allow the creation of robust semantic links. To address this situation, the disclosed system loads the left-hand partition of the input matrix for the inverse inference engine with information from reliable sources.
Owner:FIVER LLC
Threat scoring system and method for intrusion detection security networks
ActiveUS7594270B2Rapid deploymentAutomate quicklyMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionTriageSecurity expert
Owner:ALERT LOGIC
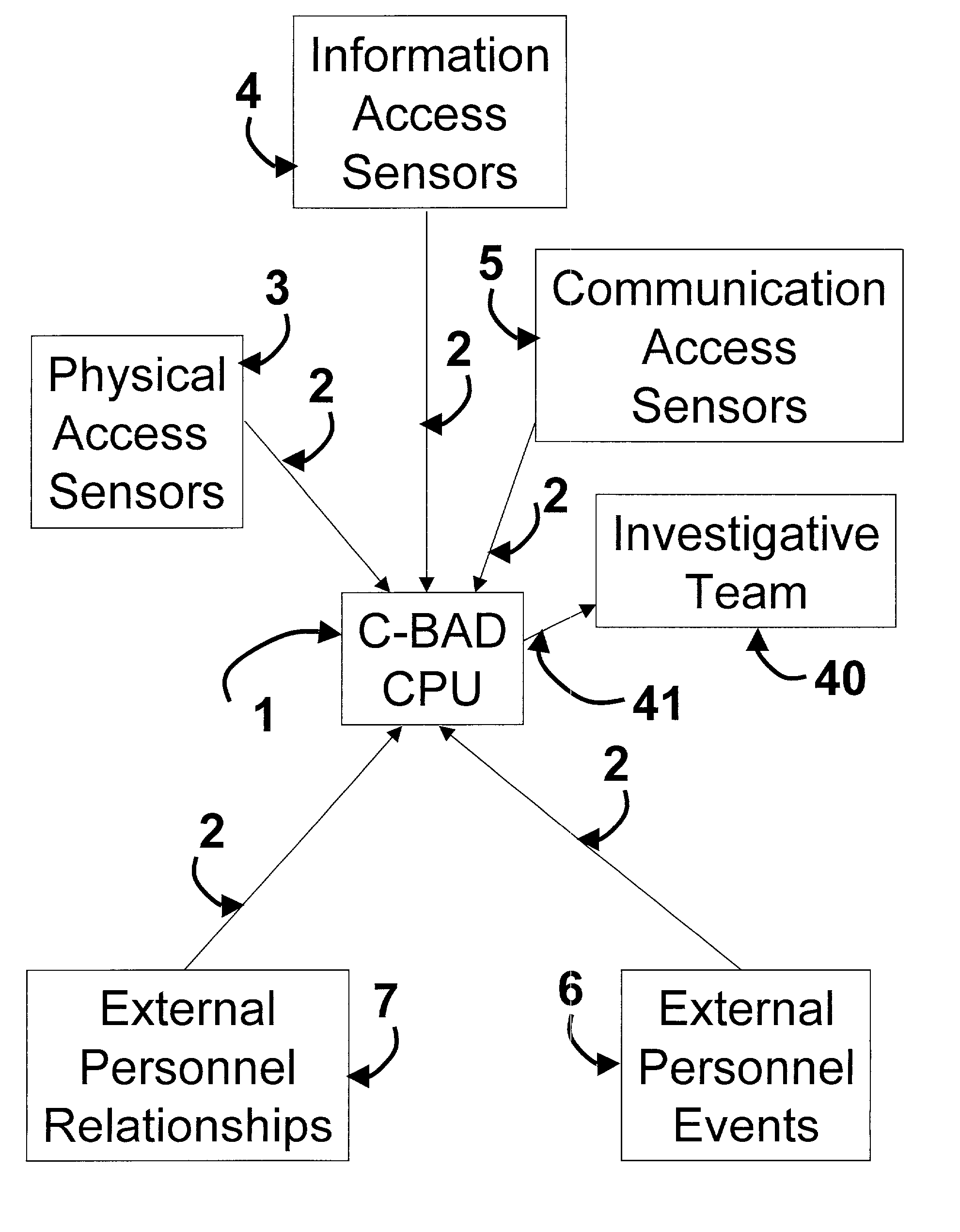
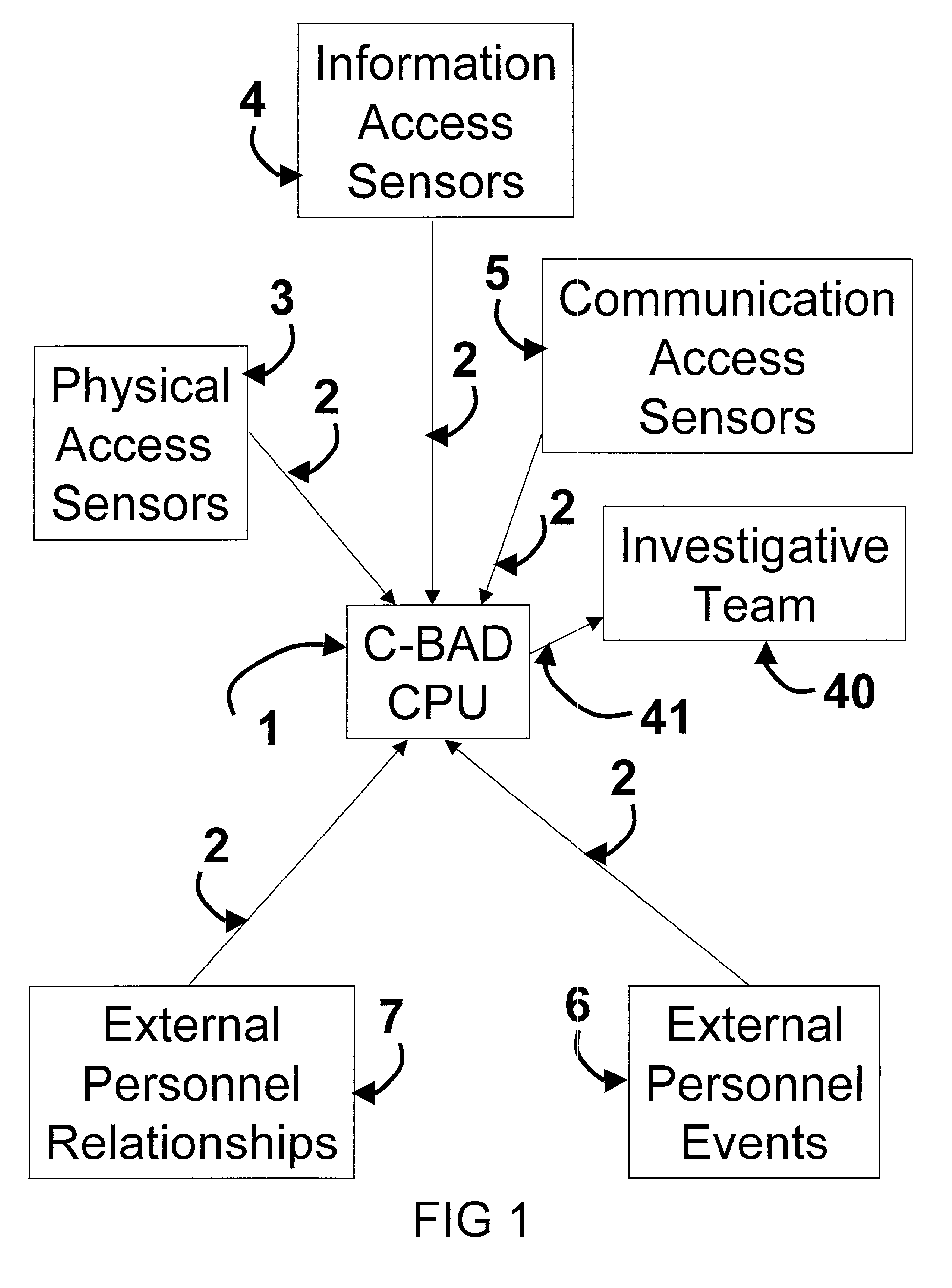
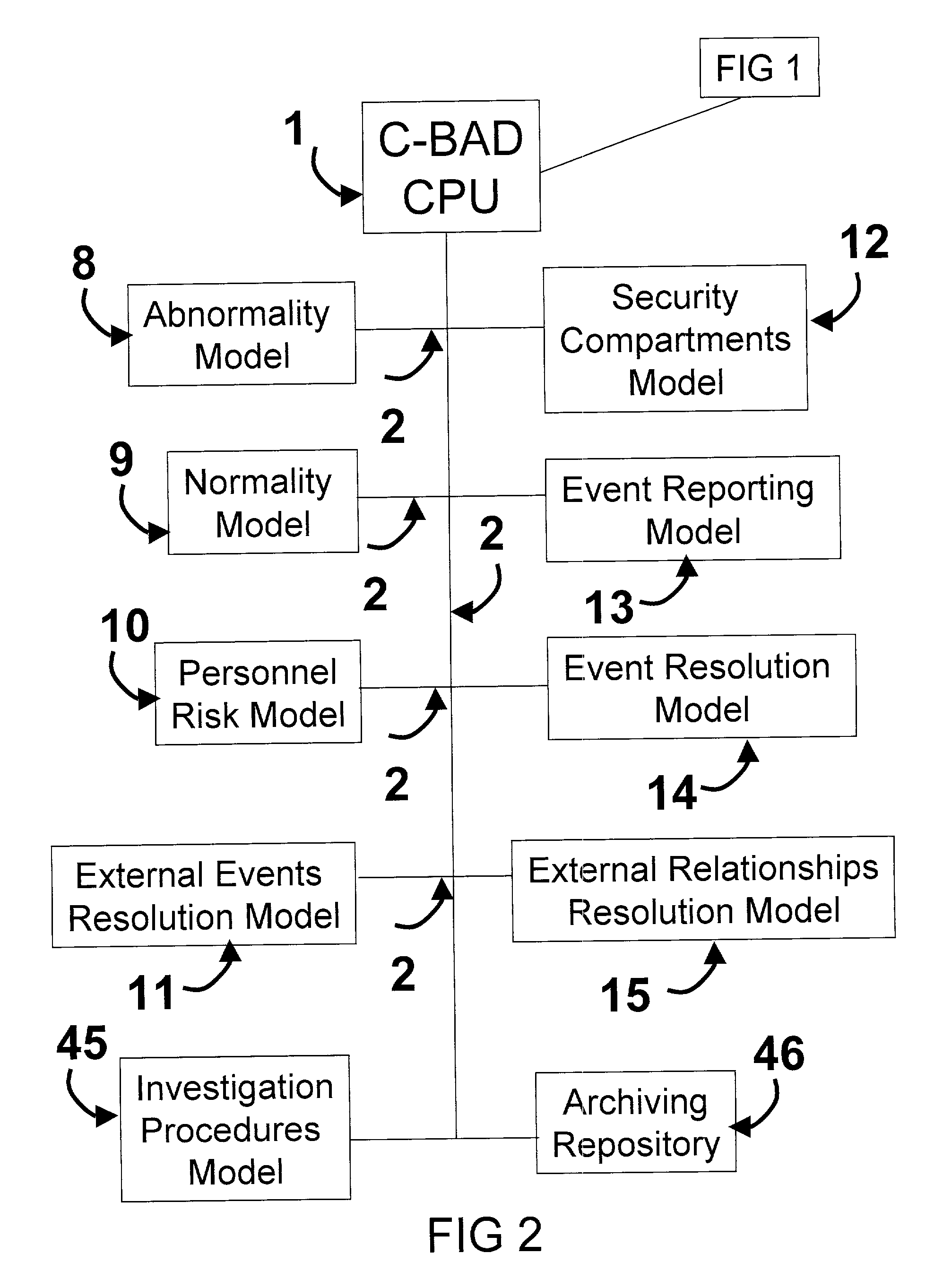
Cooperative biometrics abnormality detection system (C-BAD)
ActiveUS20030217024A1Increase the difficultyElectric signal transmission systemsMultiple keys/algorithms usagePaper documentSmart card
The Cooperative Biometrics Abnormality Detection (C-BAD) system is a network of sensors that track personnel throughout physical locations, communications, and computer systems. These systems are then linked to a central computer that contains detailed information on the individual, and rule-based risk, relationship, and abnormality models that will deter, detect, and document possible insiders. It is only at this point that C-BAD will then objectively report suspicious activities to a supervisory team for further investigation. (C-BAD) This System replaces previous current labor-intensive, subjective analysis, which has proven to be a weak deterrent and fraught with human error. C-BAD uses a full spectrum of sensors that identify personnel through the use of contact, contactless, biometrics, smart cards, or a combination of any one of these. The C-BAD central monitoring computer contains an inference engine based on artificial intelligence or a rule-based system, which reviews databases and furnished information.
Owner:THE RIGHT PROBLEM
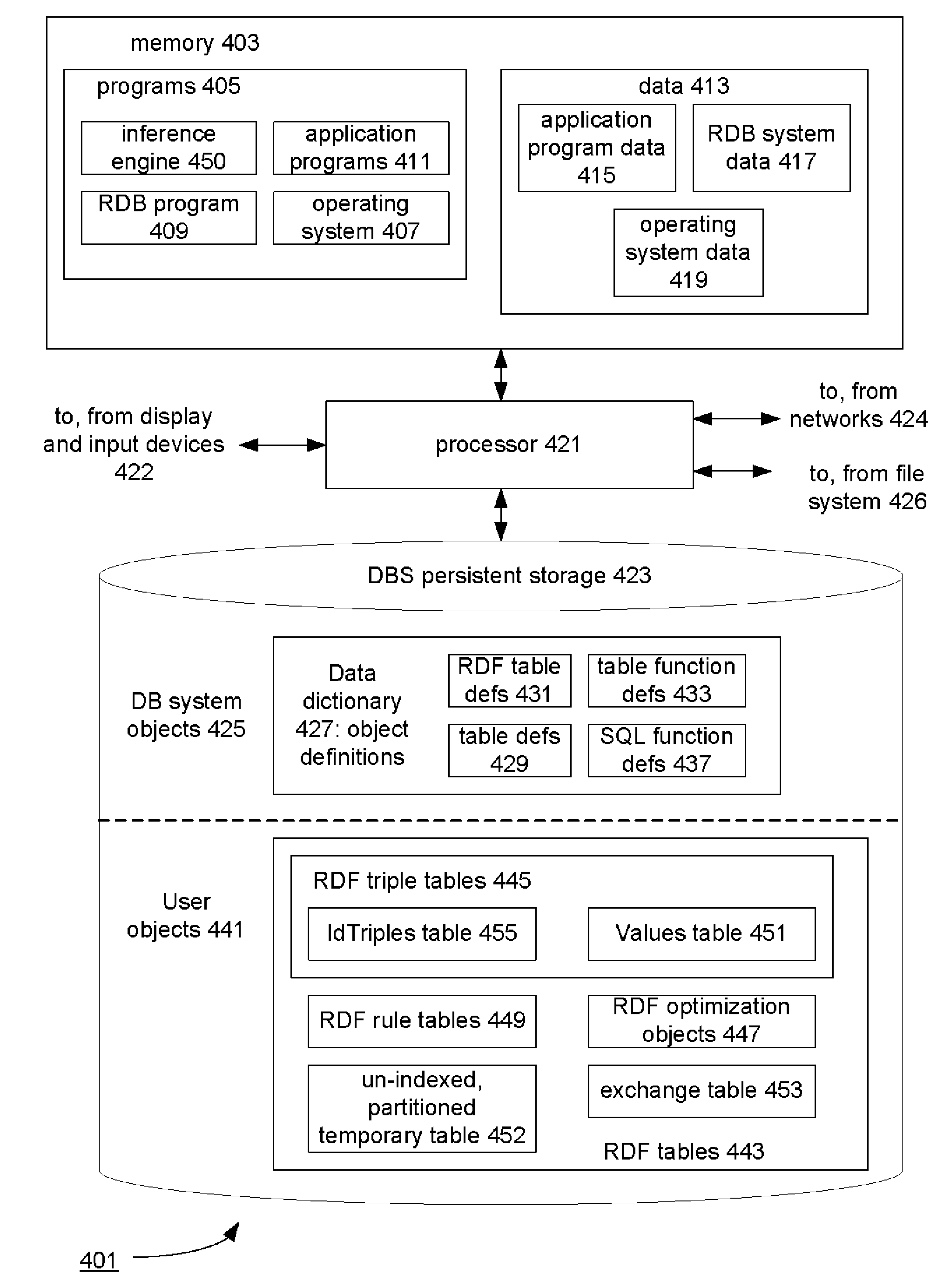
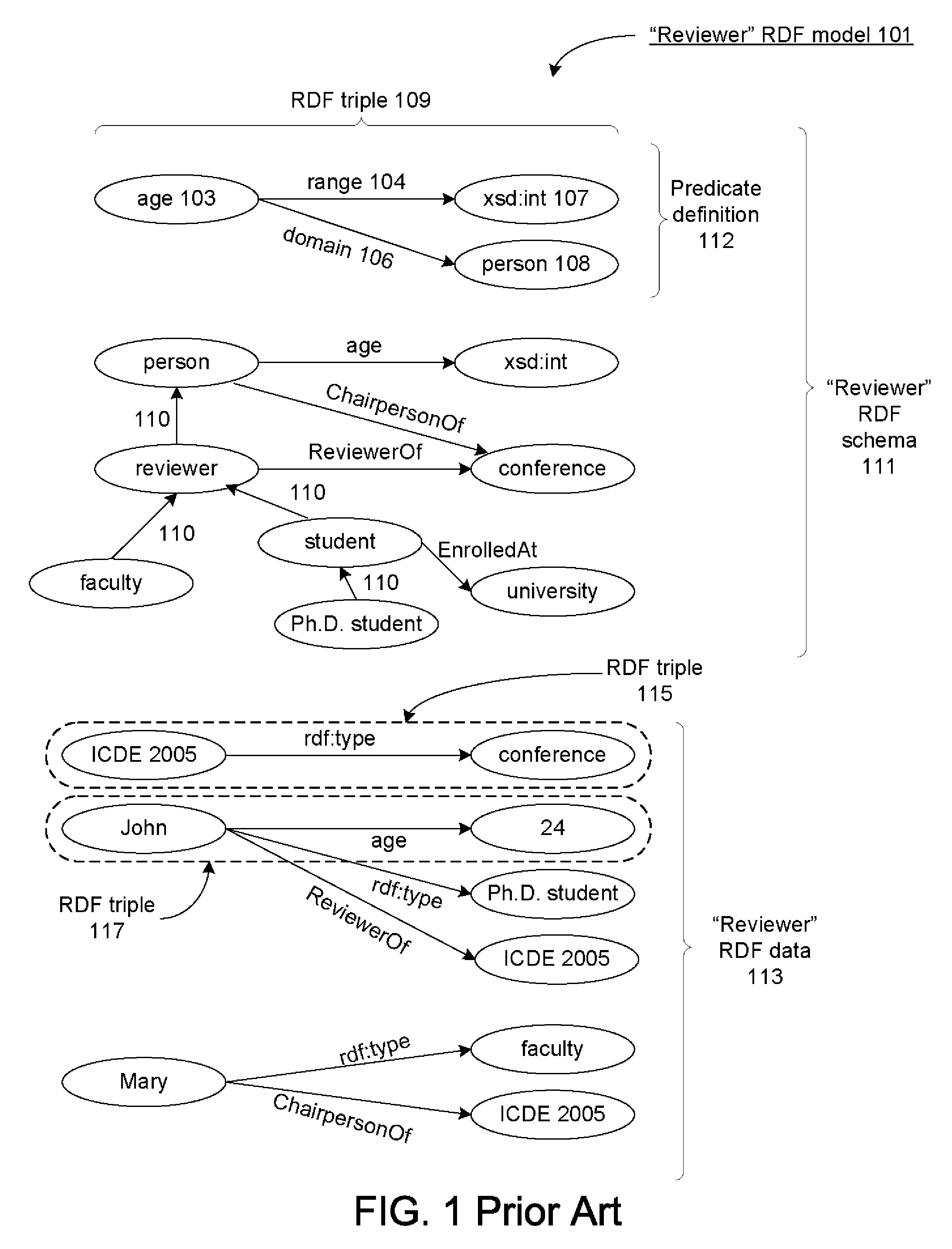
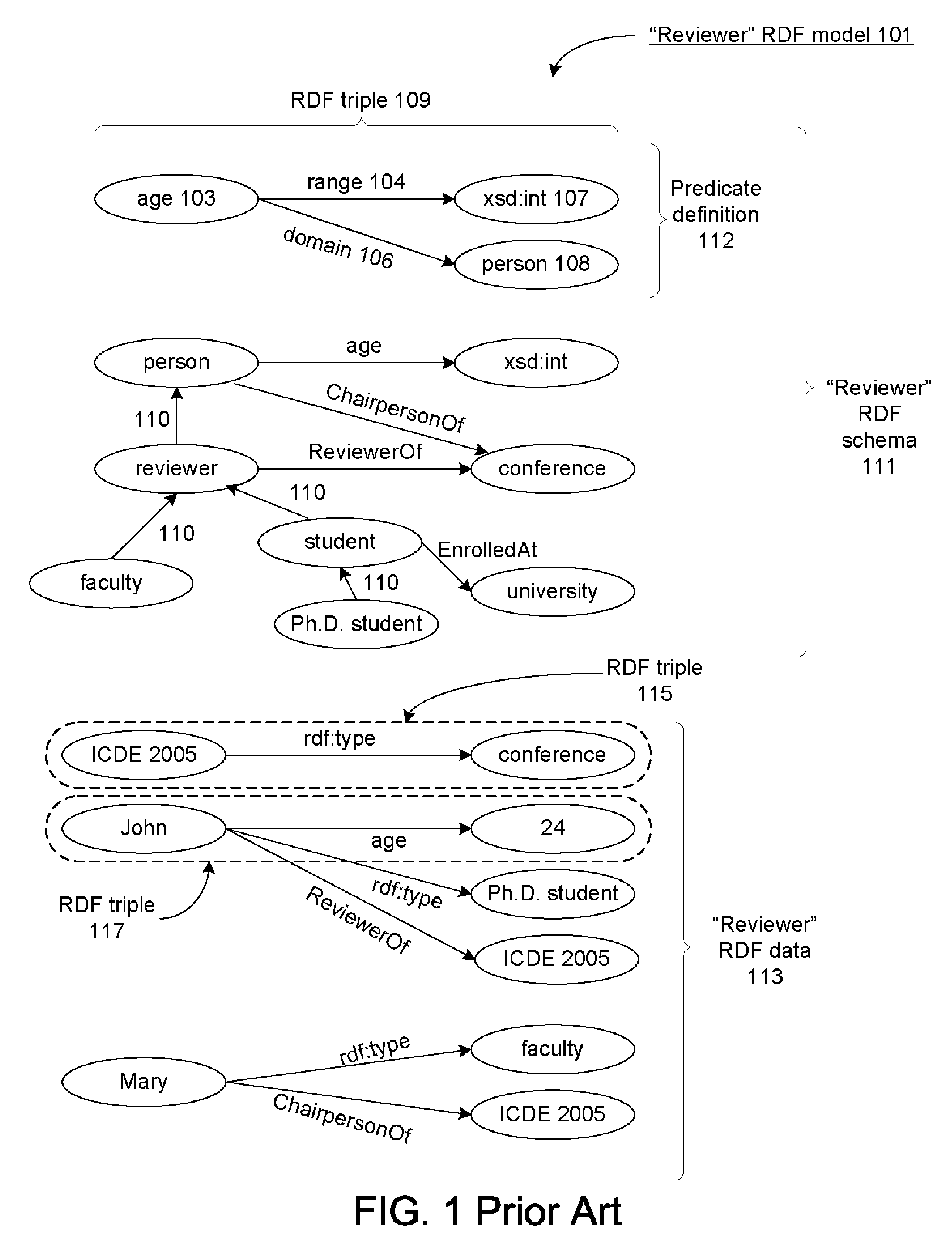
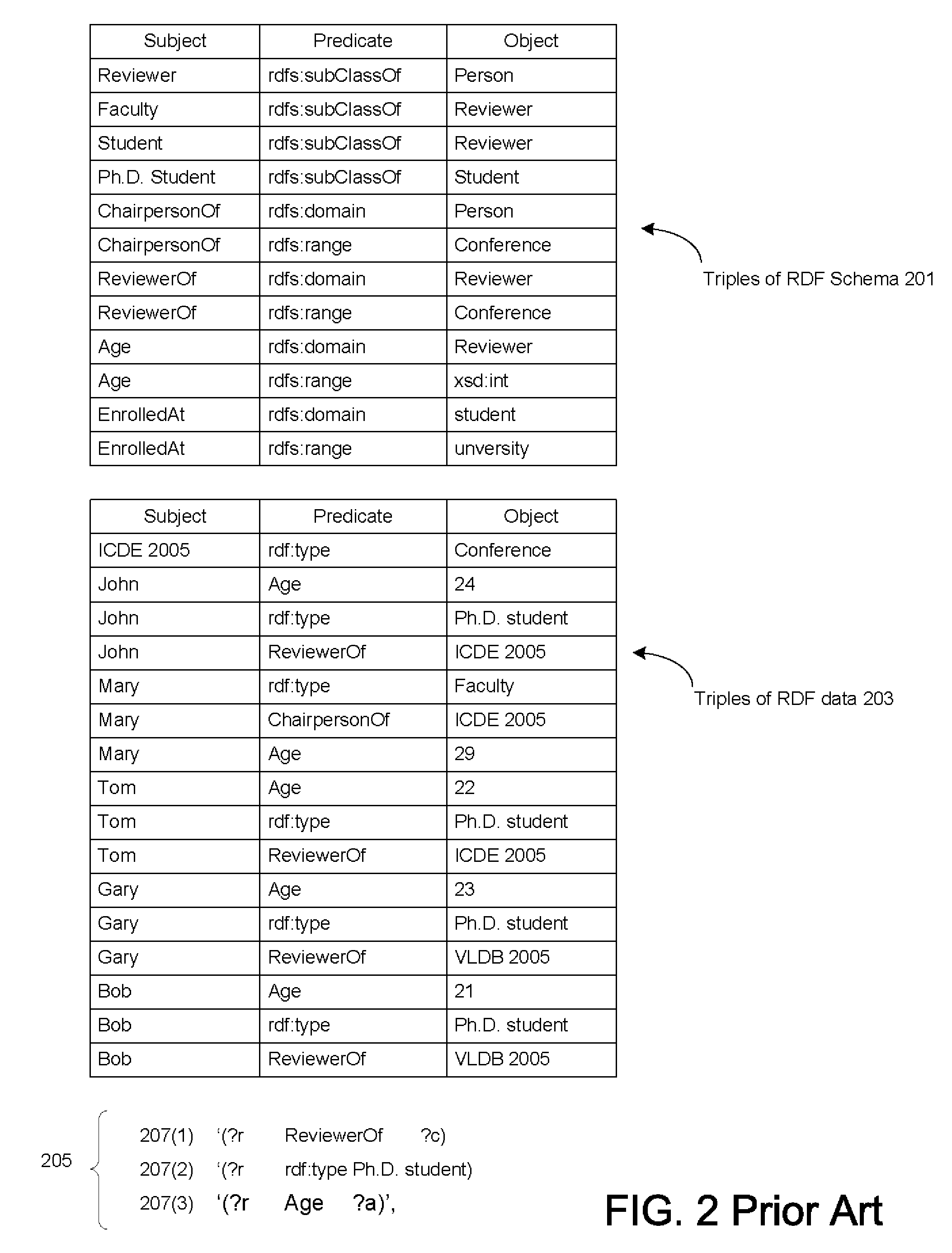
Database-based inference engine for RDFS/OWL constructs
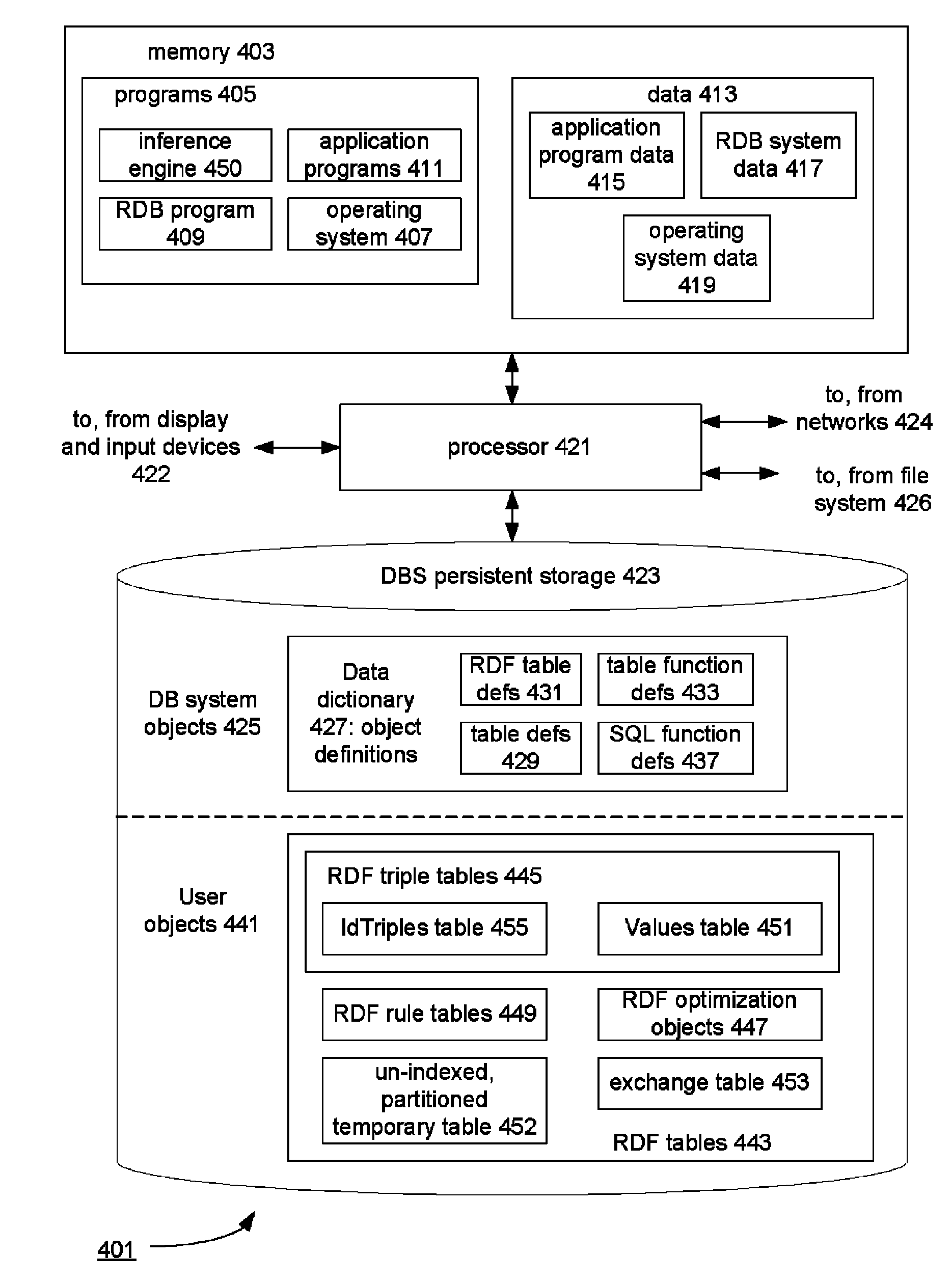
ActiveUS20100036788A1Improve efficiencyAvoid overheadDigital data processing detailsKnowledge representationIncremental maintenanceRelational database
An un-indexed, partitioned temporary table and an exchange table are used in the inferencing of semantic data in a relational database system. The exchange table has the same structure as a semantic data table storing the semantic data. In the inferencing process, a new partition is created in the semantic data table. Inference rules are executed on the semantic data table, and any newly inferred semantic data generated is added to the temporary table. Once no new data is generated, the inferred semantic data is copied from the temporary table into the exchange table. Indexes that are the same as indexes for the semantic data table are built for the exchange table. The indexed data in the exchange table is then exchanged into the new partition in the semantic data table. By use of the un-indexed, partitioned temporary table, incremental maintenance of indexes is avoided, thus allowing for greater efficiency.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
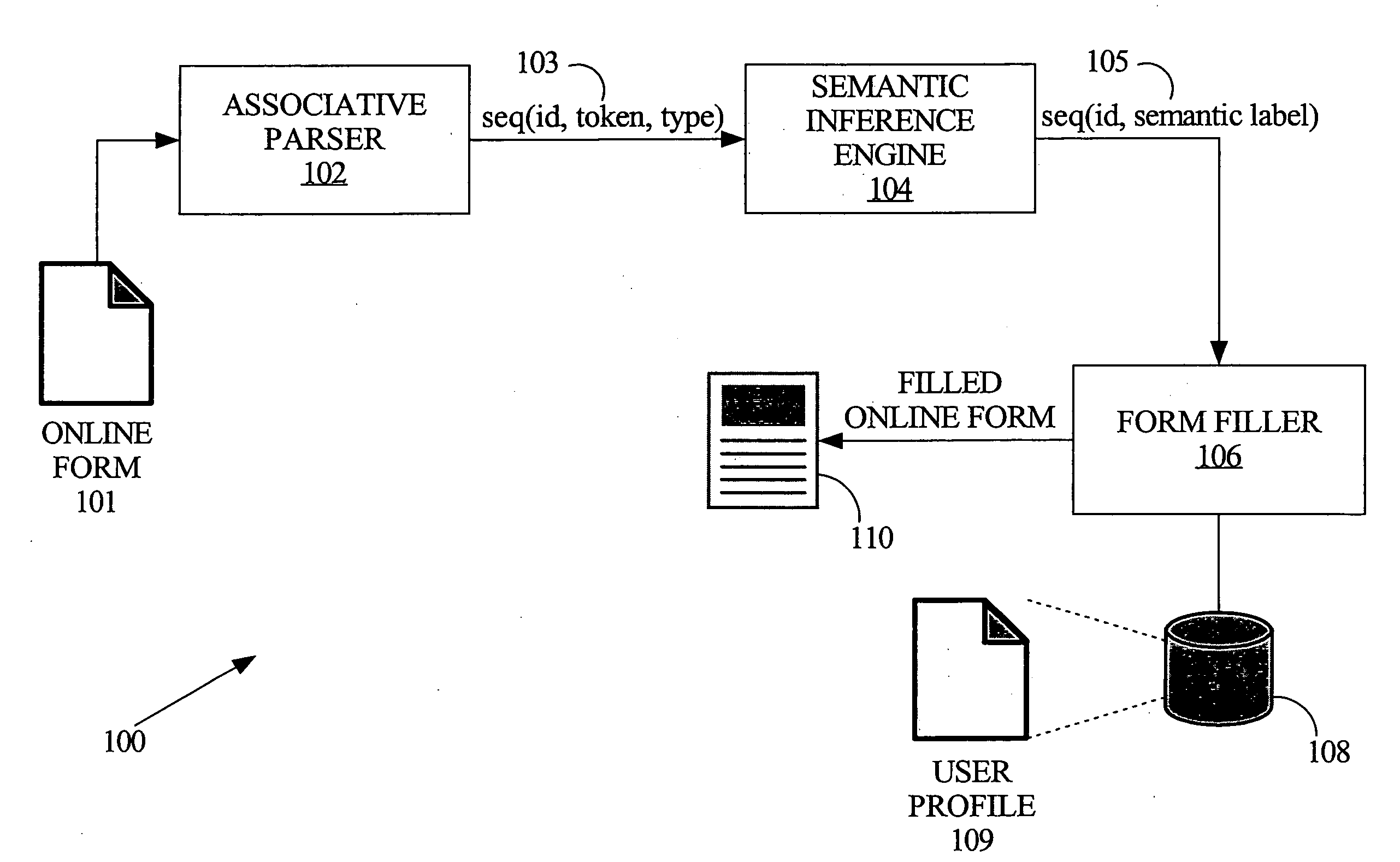
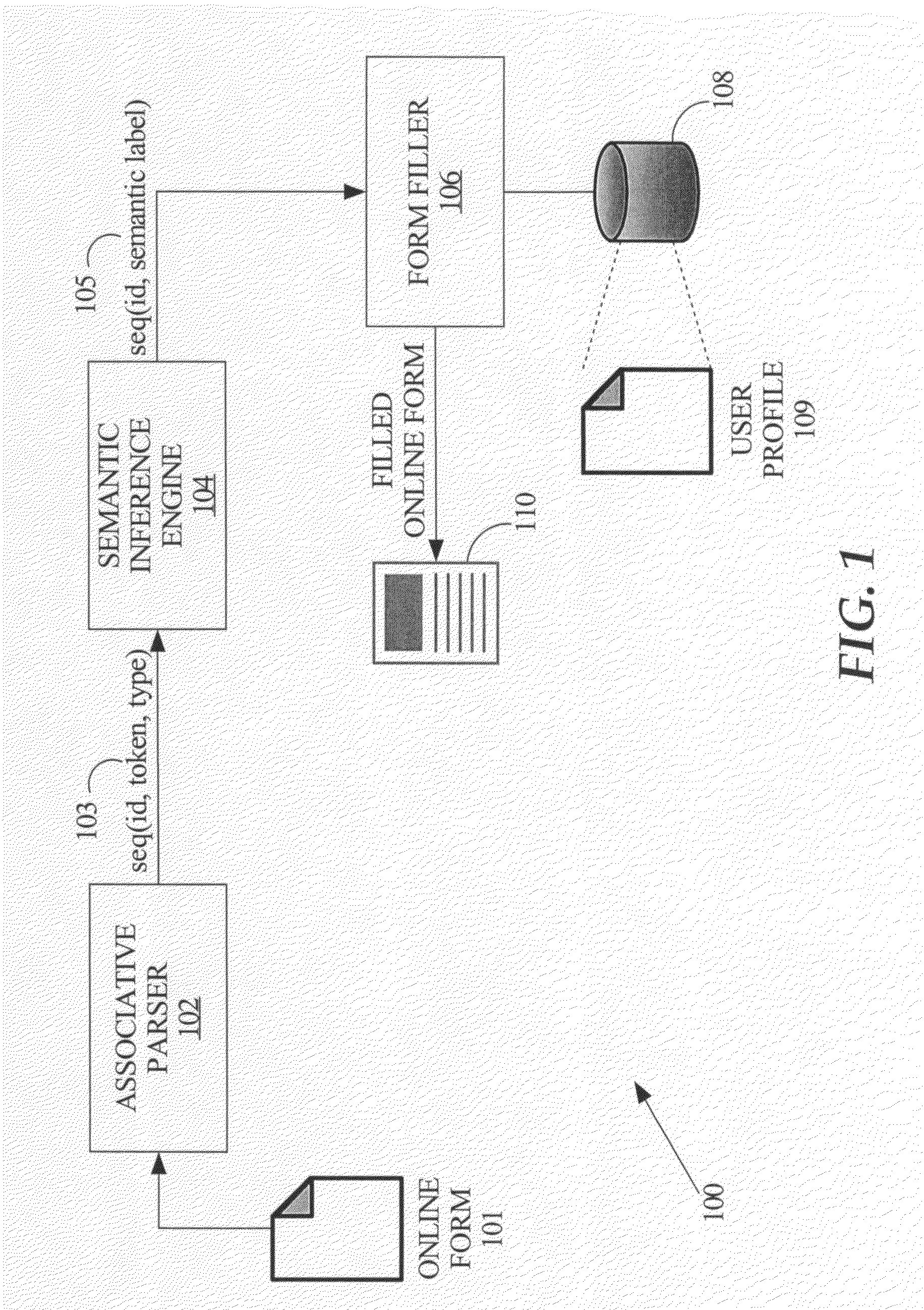
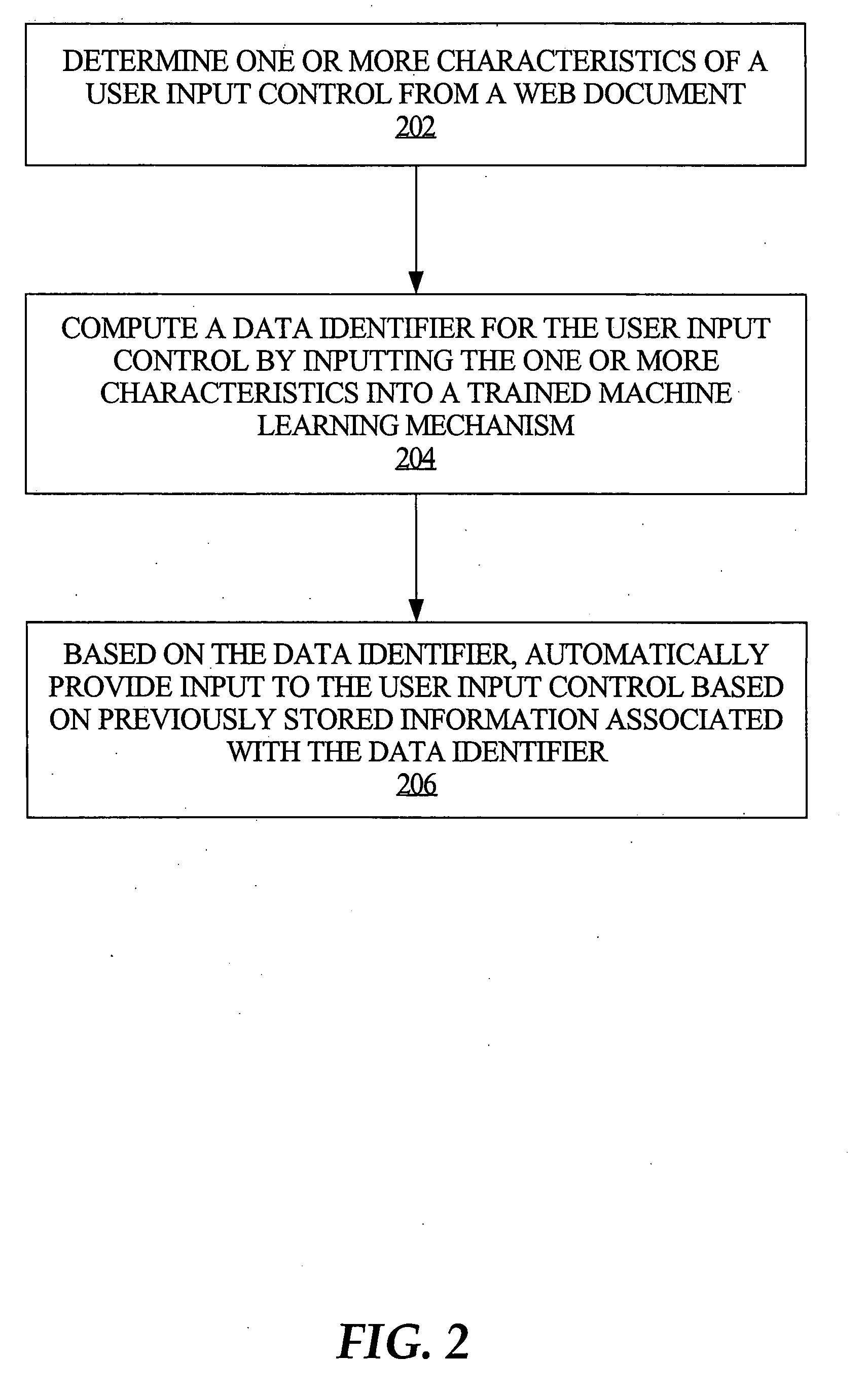
Automatic online form filling using semantic inference
InactiveUS20080120257A1Digital computer detailsNatural language data processingInformation typeLearning based
A machine learning based automated online form-filling technique provides for automatically completing user input controls based on previously stored information. An associative parser is used to identify and associate characteristics related to form controls with the corresponding form controls. The characteristics of the user input controls are input into a machine learning based semantic inference engine that was trained for the purpose of identifying the type of information that is supposed to be input into various user input controls. The semantic inference engine operates to label the controls in a manner that describes the meaning of the control, i.e., the type of information that should be automatically input into the corresponding controls. Consequently, the user input controls can be automatically filled in with previously stored user profile information associated with the corresponding labels.
Owner:OATH INC
System and method facilitating network diagnostics and self-healing
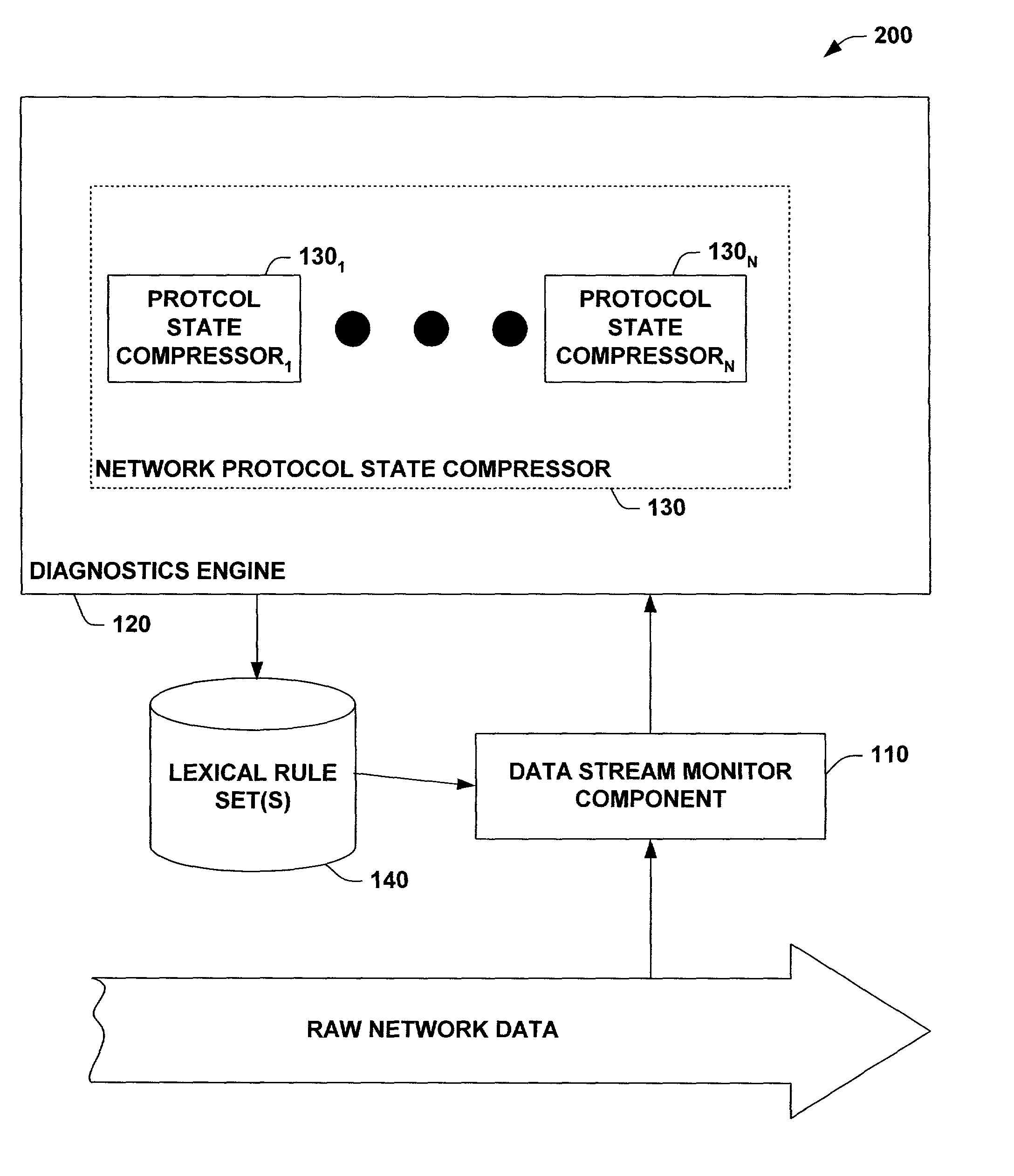
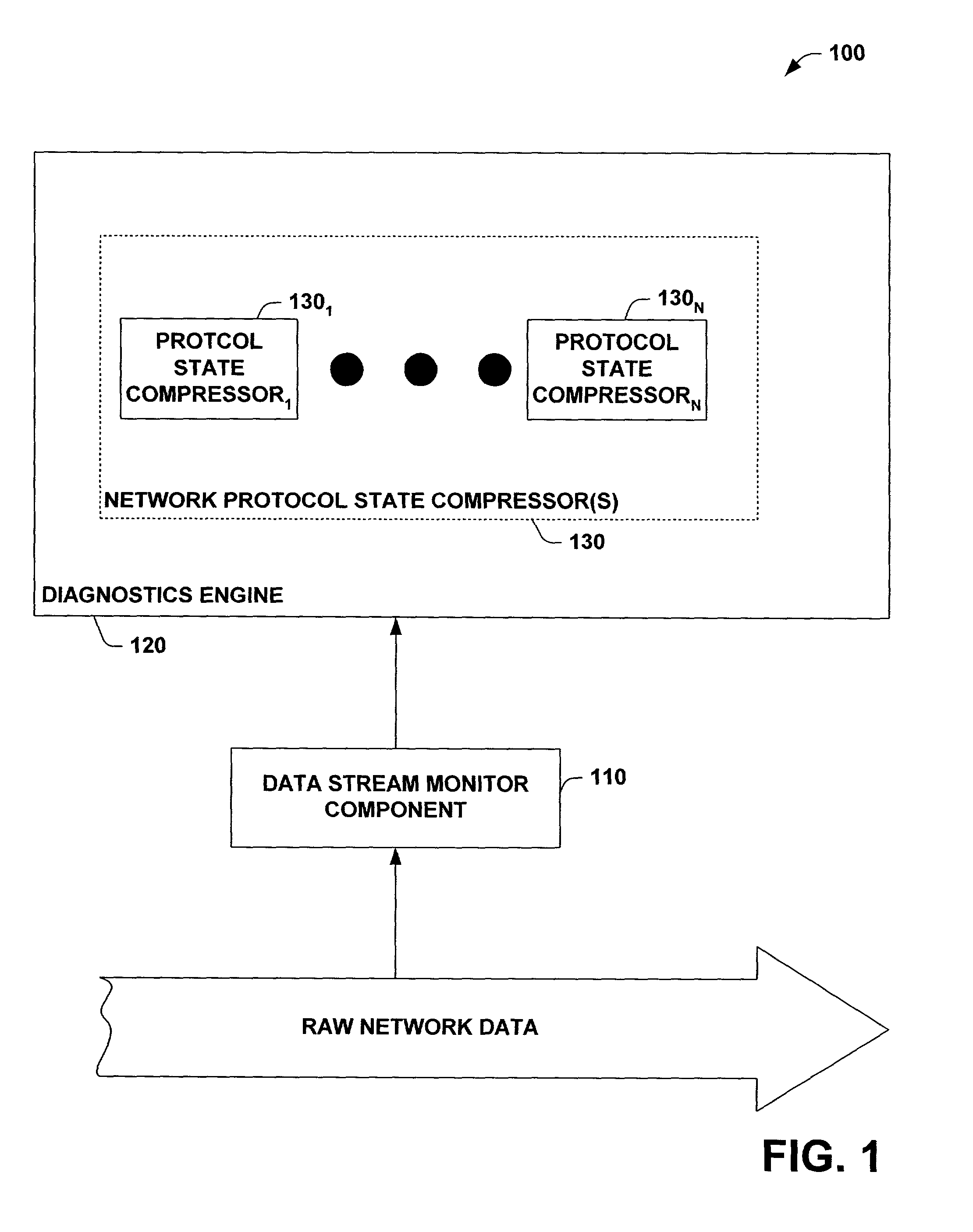
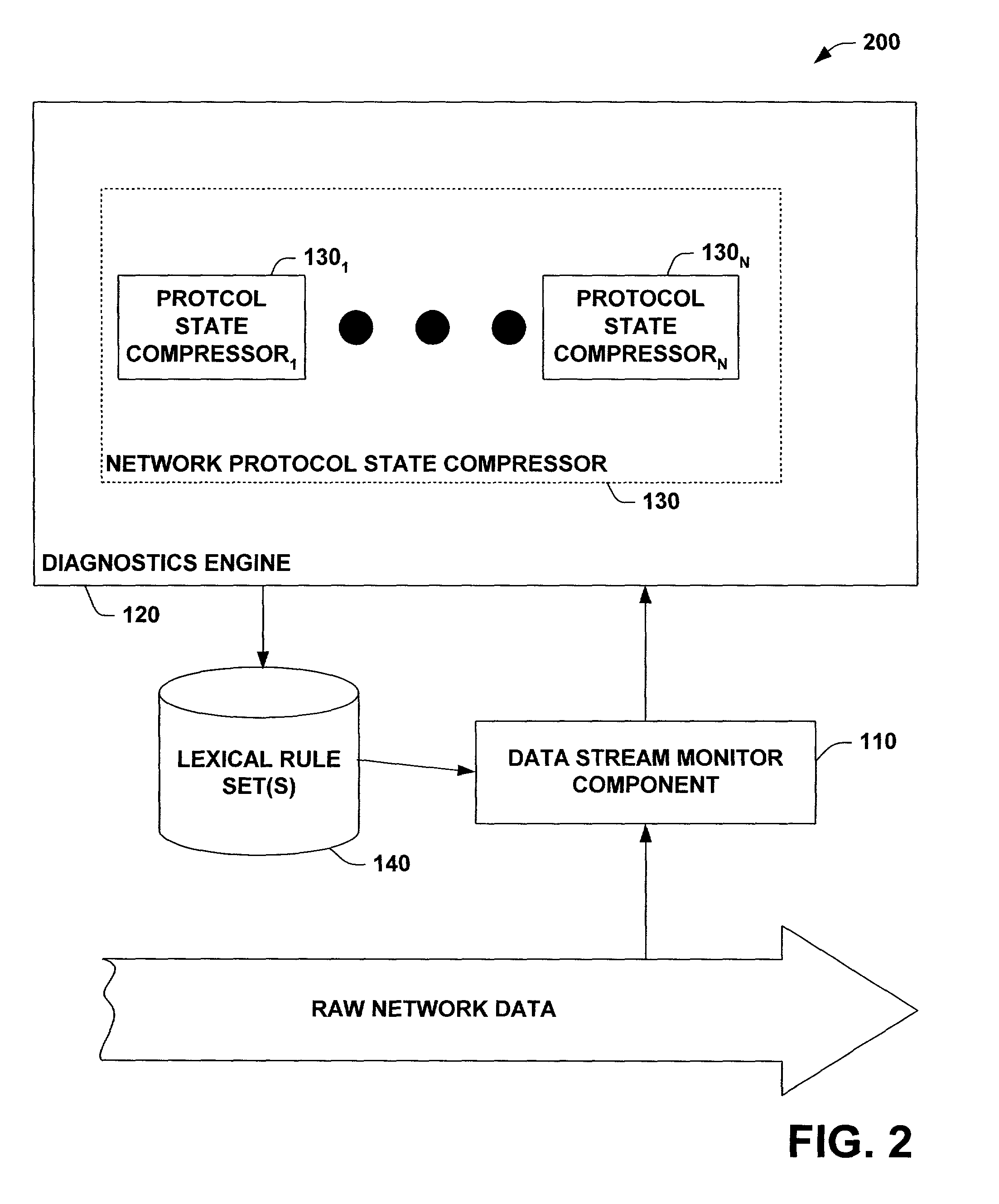
InactiveUS7313613B1Facilitates network diagnosticsFacilitates self-healingDigital computer detailsTransmissionSelf-healingData stream
A system and method facilitating network diagnostics and self-healing is provided. The invention includes a data stream monitor component adapted to selectively copy protocol specific subset(s) of raw network data and provide the subset(s) of data to a diagnostics engine. The invention further includes a diagnostic engine adapted to facilitate network diagnostics and / or self-healing.The invention further provides for protocol state compressor(s) to analyze the protocol specific subset(s) of data to abstract and / or analyze relevant information about the specific protocol without having to strictly process the protocol or preserve protocol state variable(s) in order to analyze the state of the specific protocol. Based upon this analysis, the protocol state compressor(s) can generate event(s) for undesirable state(s) (e.g., error(s) and / or failure(s)) and / or congested state(s) for use by the event correlator / inference engine. Additionally, the protocol state compressor(s) can provide information to the event correlator / inference engine regarding the state of the specific protocol (e.g., success(es)).
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Database-based inference engine for RDFS/OWL constructs
ActiveUS8401991B2Improve efficiencyAvoid overheadDigital data processing detailsKnowledge representationIncremental maintenanceRelational database
An un-indexed, partitioned temporary table and an exchange table are used in the inferencing of semantic data in a relational database system. The exchange table has the same structure as a semantic data table storing the semantic data. In the inferencing process, a new partition is created in the semantic data table. Inference rules are executed on the semantic data table, and any newly inferred semantic data generated is added to the temporary table. Once no new data is generated, the inferred semantic data is copied from the temporary table into the exchange table. Indexes that are the same as indexes for the semantic data table are built for the exchange table. The indexed data in the exchange table is then exchanged into the new partition in the semantic data table. By use of the un-indexed, partitioned temporary table, incremental maintenance of indexes is avoided, thus allowing for greater efficiency.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Recommending personally interested contents by text mining, filtering, and interfaces
ActiveUS20130254217A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsPersonalizationData stream
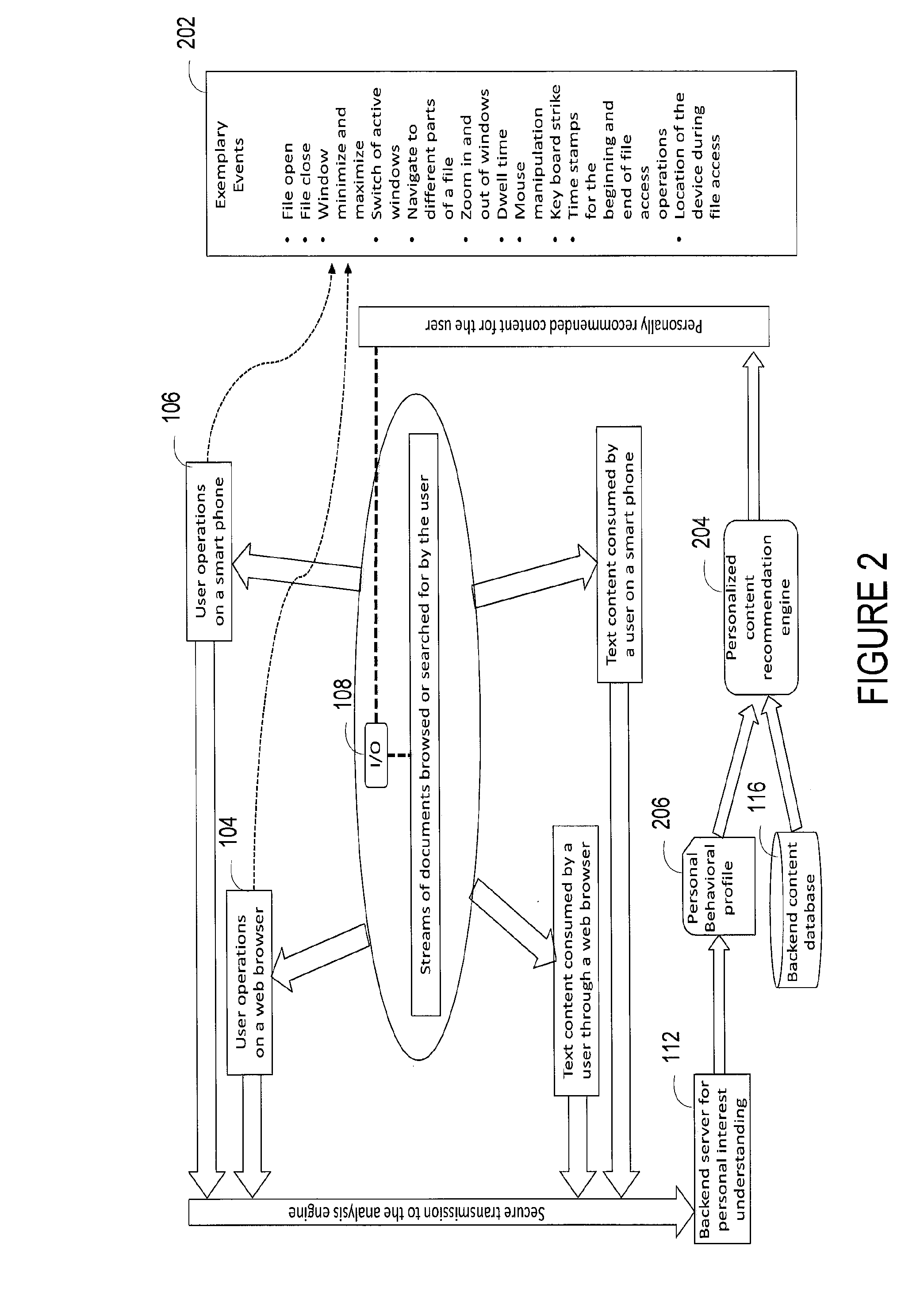
A personalized content recommendation system includes a client interface device configured to monitor a user's information data stream. A collaborative filter remote from the client interface device generates automated predictions about the interests of the user. A database server stores personal behavioral profiles and user's preferences based on a plurality of monitored past behaviors and an output of the collaborative user personal interest inference engine. A programmed personal content recommendation server filters items in an incoming information stream with the personal behavioral profile and identifies only those items of the incoming information stream that substantially matches the personal behavioral profile. The identified personally relevant content is then recommended to the user following some priority that may consider the similarity between the personal interest matches, the context of the user information consumption behaviors that may be shown by the user's content consumption mode.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
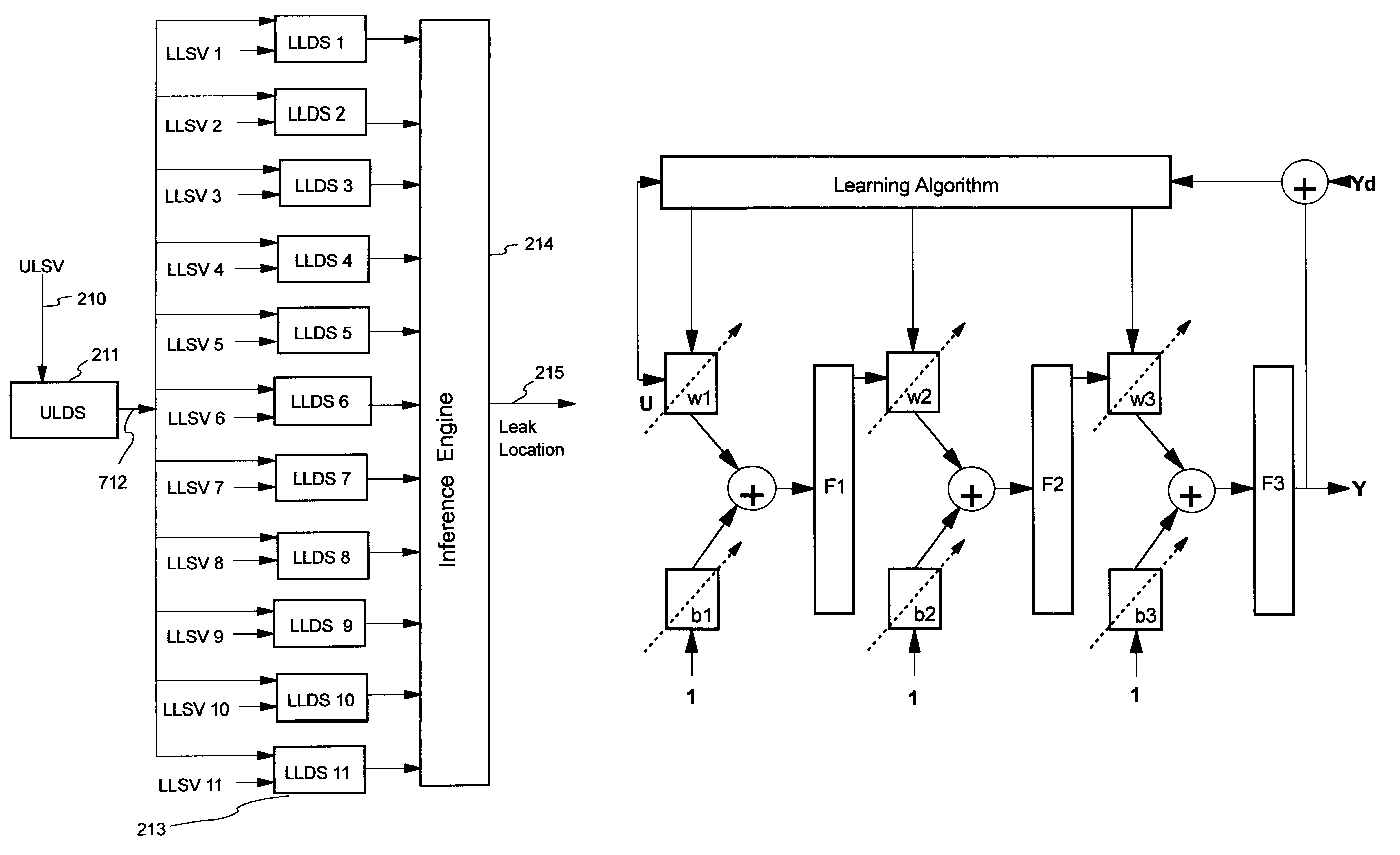
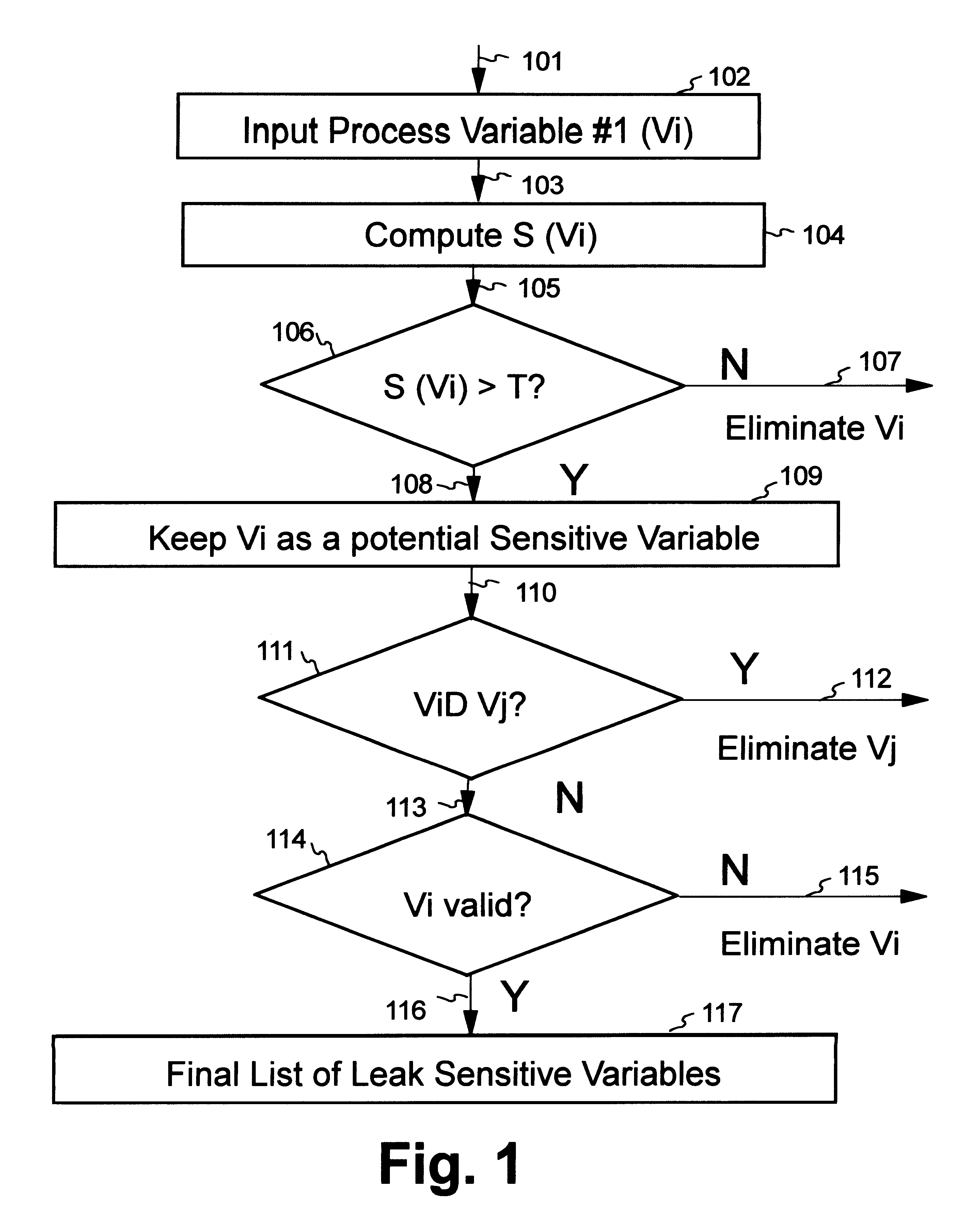
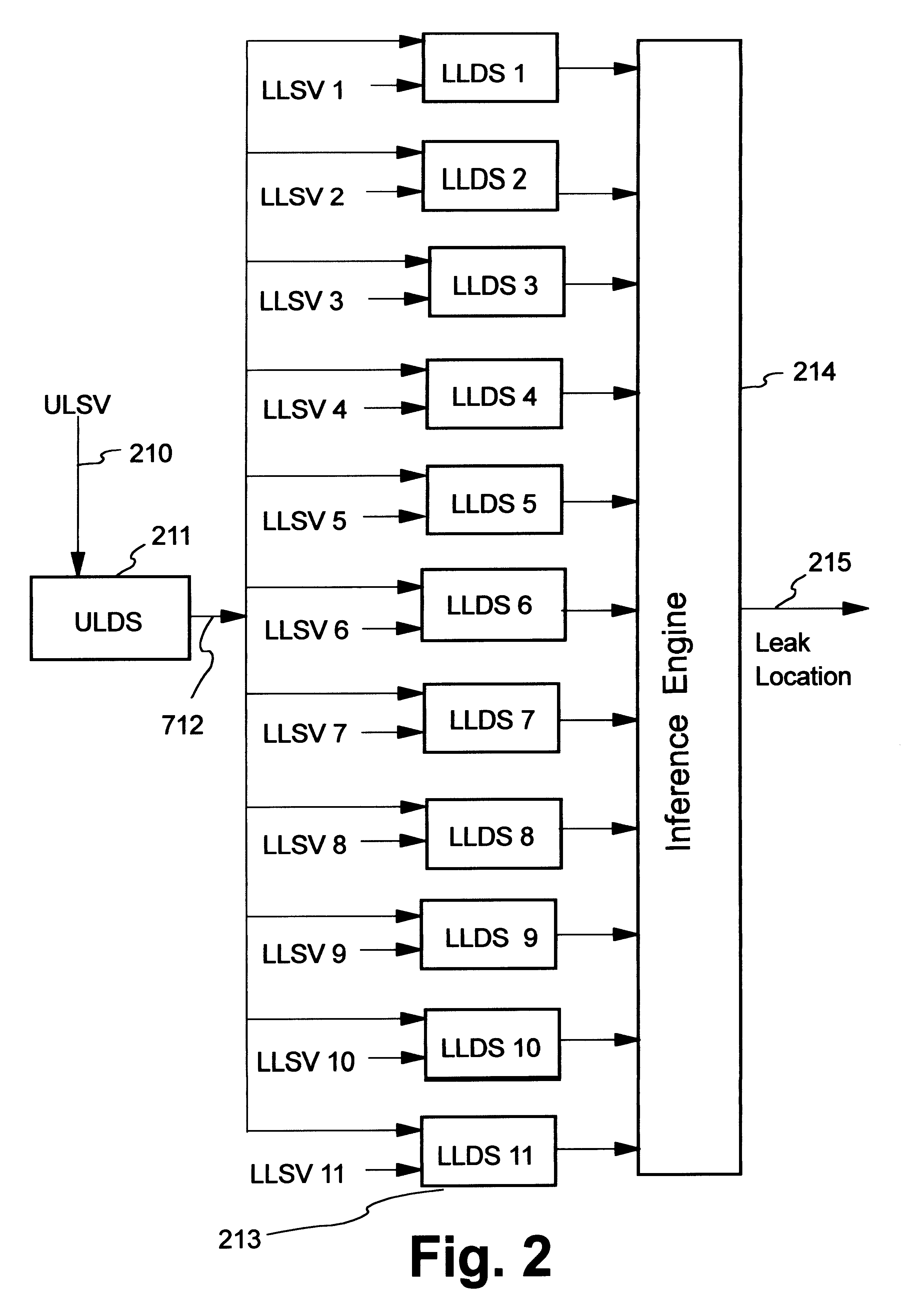
Artificial neural network and fuzzy logic based boiler tube leak detection systems
Power industry boiler tube failures are a major cause of utility forced outages in the United States, with approximately 41,000 tube failures occurring every year at a cost of $5 billion a year. Accordingly, early tube leak detection and isolation is highly desirable. Early detection allows scheduling of a repair rather than suffering a forced outage, and significantly increases the chance of preventing damage to adjacent tubes. The instant detection scheme starts with identification of boiler tube leak process variables which are divided into universal sensitive variables, local leak sensitive variables, group leak sensitive variables, and subgroup leak sensitive variables, and which may be automatically be obtained using a data driven approach and a leak sensitivity function. One embodiment uses artificial neural networks (ANN) to learn the map between appropriate leak sensitive variables and the leak behavior. The second design philosophy integrates ANNs with approximate reasoning using fuzzy logic and fuzzy sets. In the second design, ANNs are used for learning, while approximate reasoning and inference engines are used for decision making. Advantages include use of already monitored process variables, no additional hardware and / or maintenance requirements, systematic processing does not require an expert system and / or a skilled operator, and the systems are portable and can be easily tailored for use on a variety of different boilers.
Owner:TENNESSEE VALLEY AUTHORITY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com