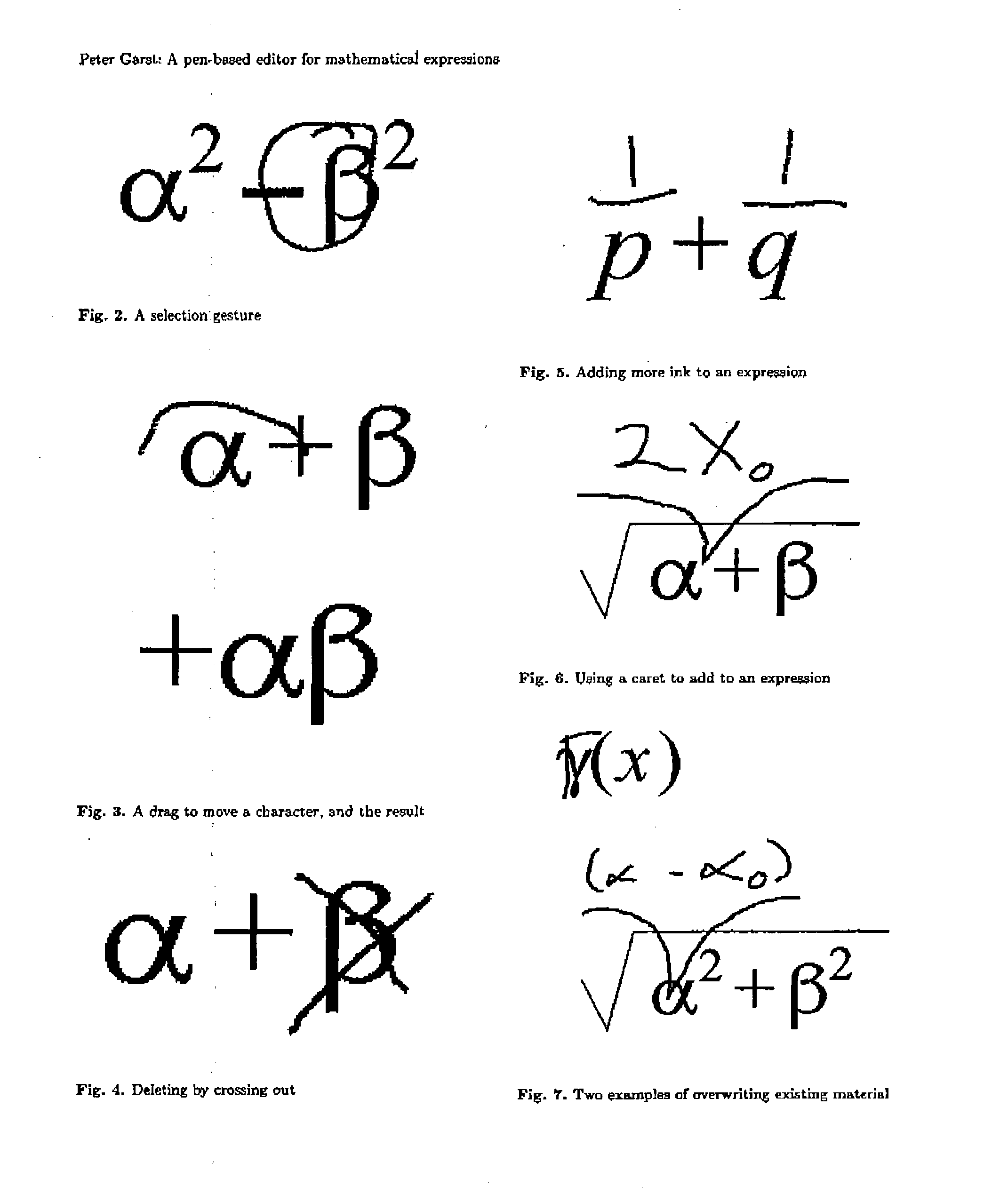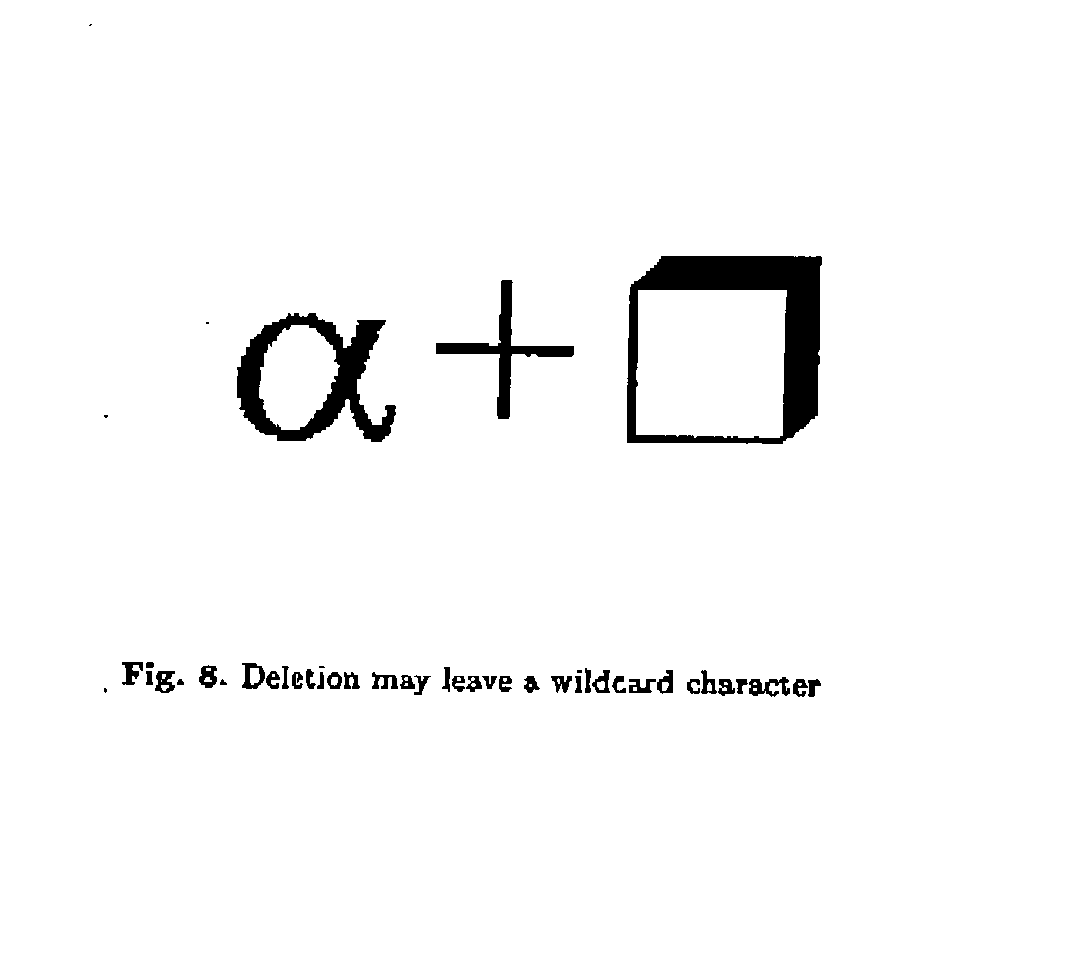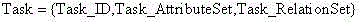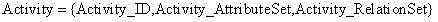Patents
Literature
68 results about "Problem domain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A problem domain is the area of expertise or application that needs to be examined to solve a problem. Focusing on a problem domain is simply looking at only the topics of an individual's interest, and excluding everything else. For example, when developing a system to measure good practice in medicine, carpet drawings at hospitals would not be included in the problem domain. In this example, the domain refers to relevant topics solely within the delimited area of interest: medicine.
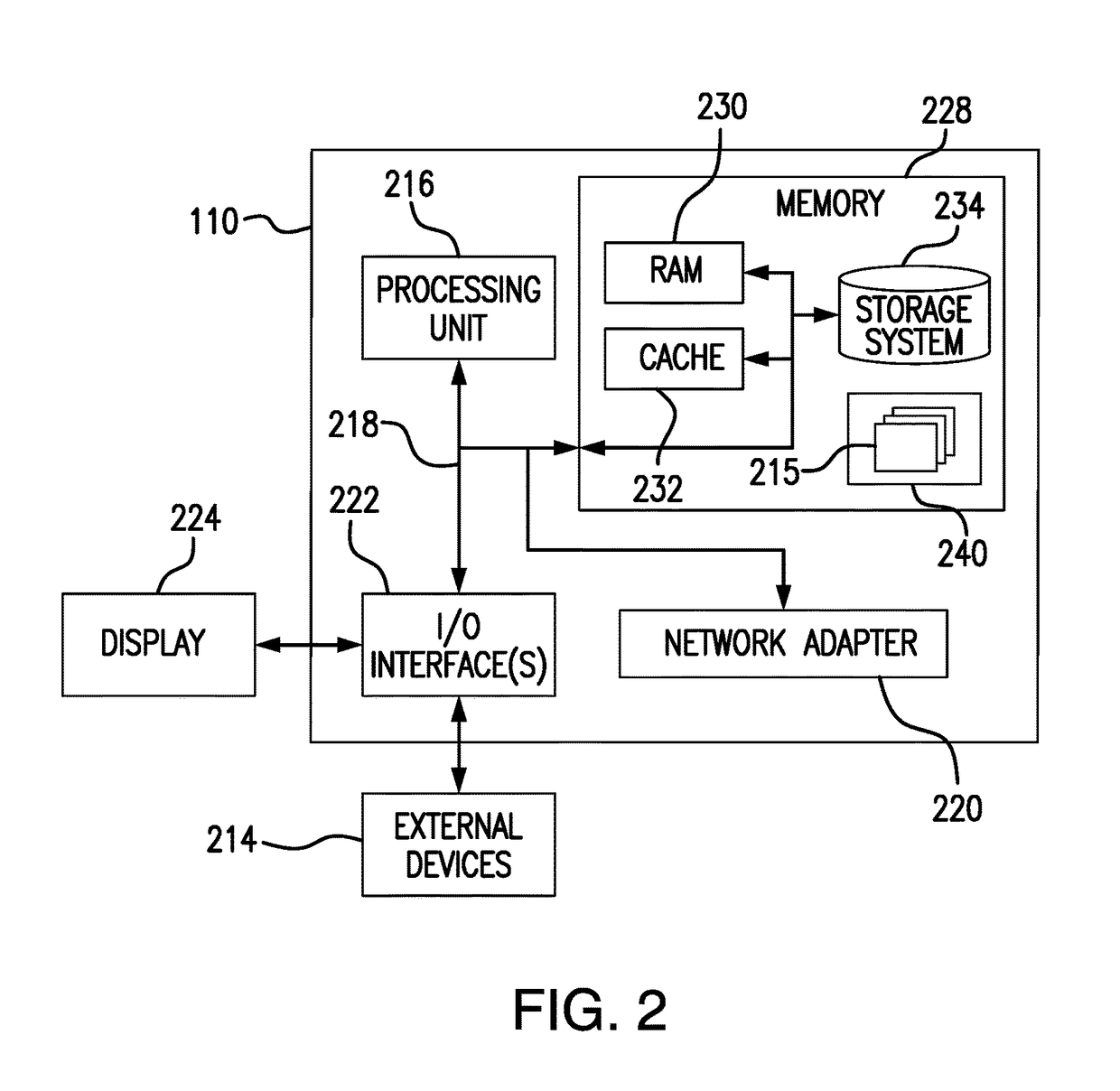
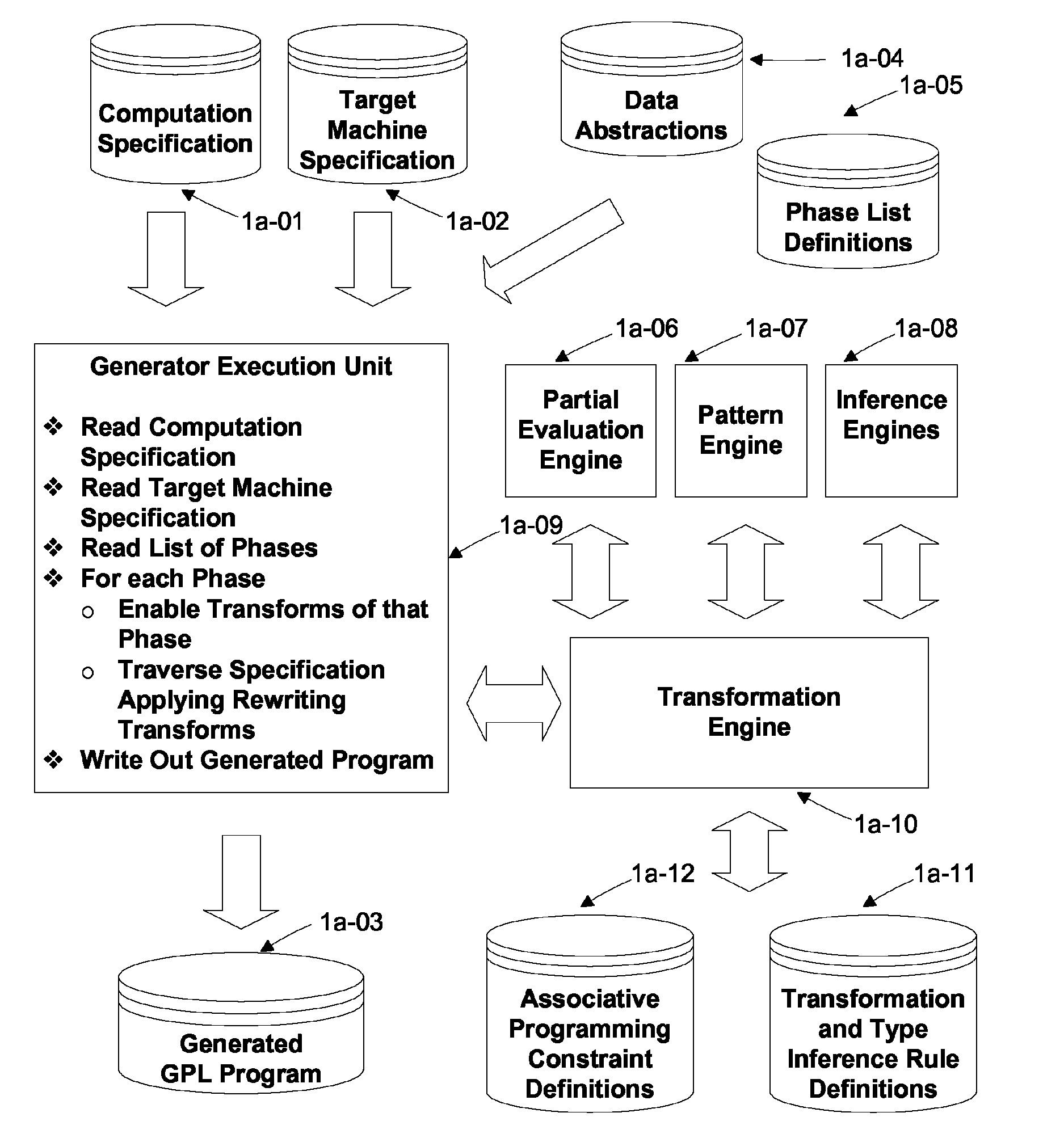
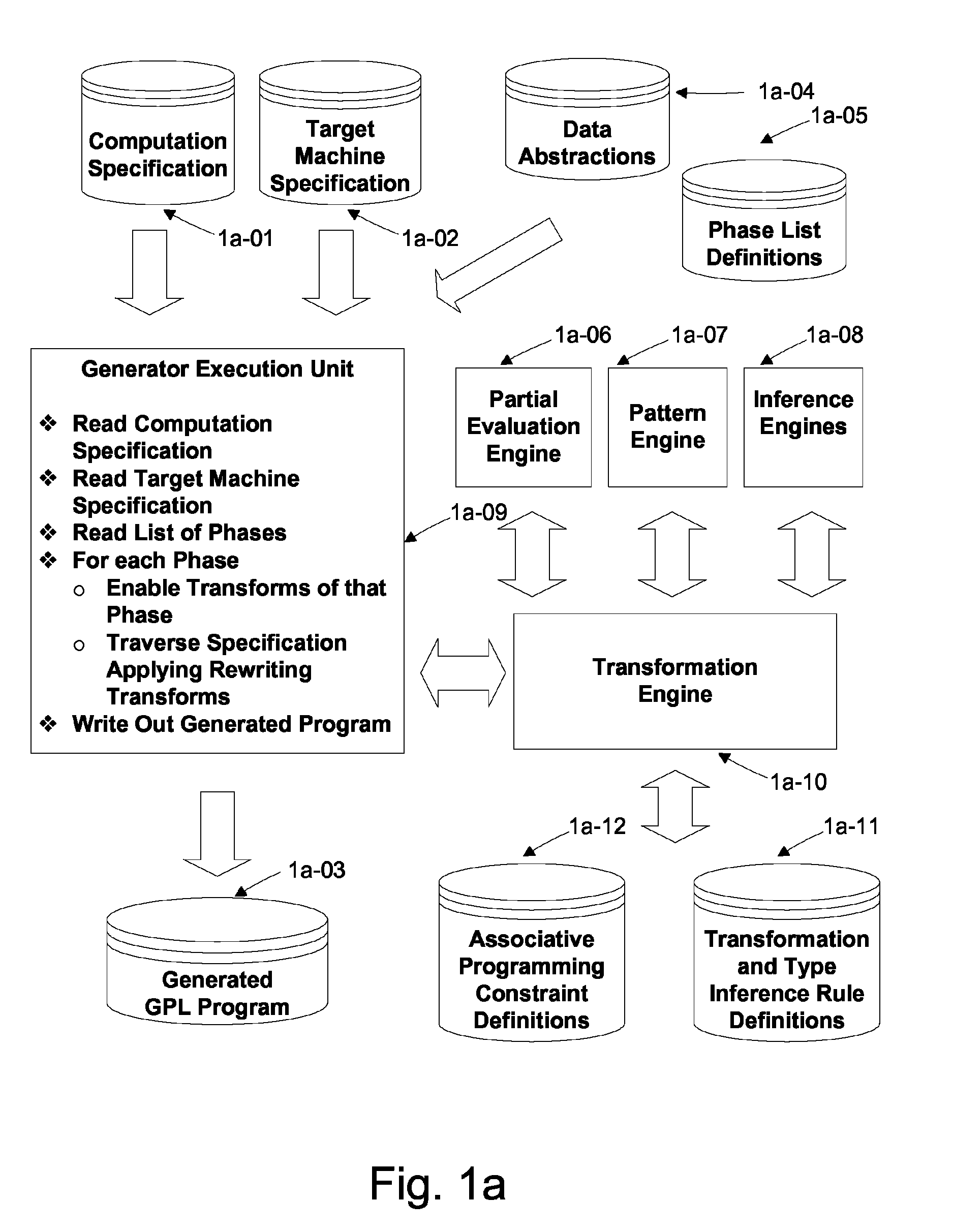
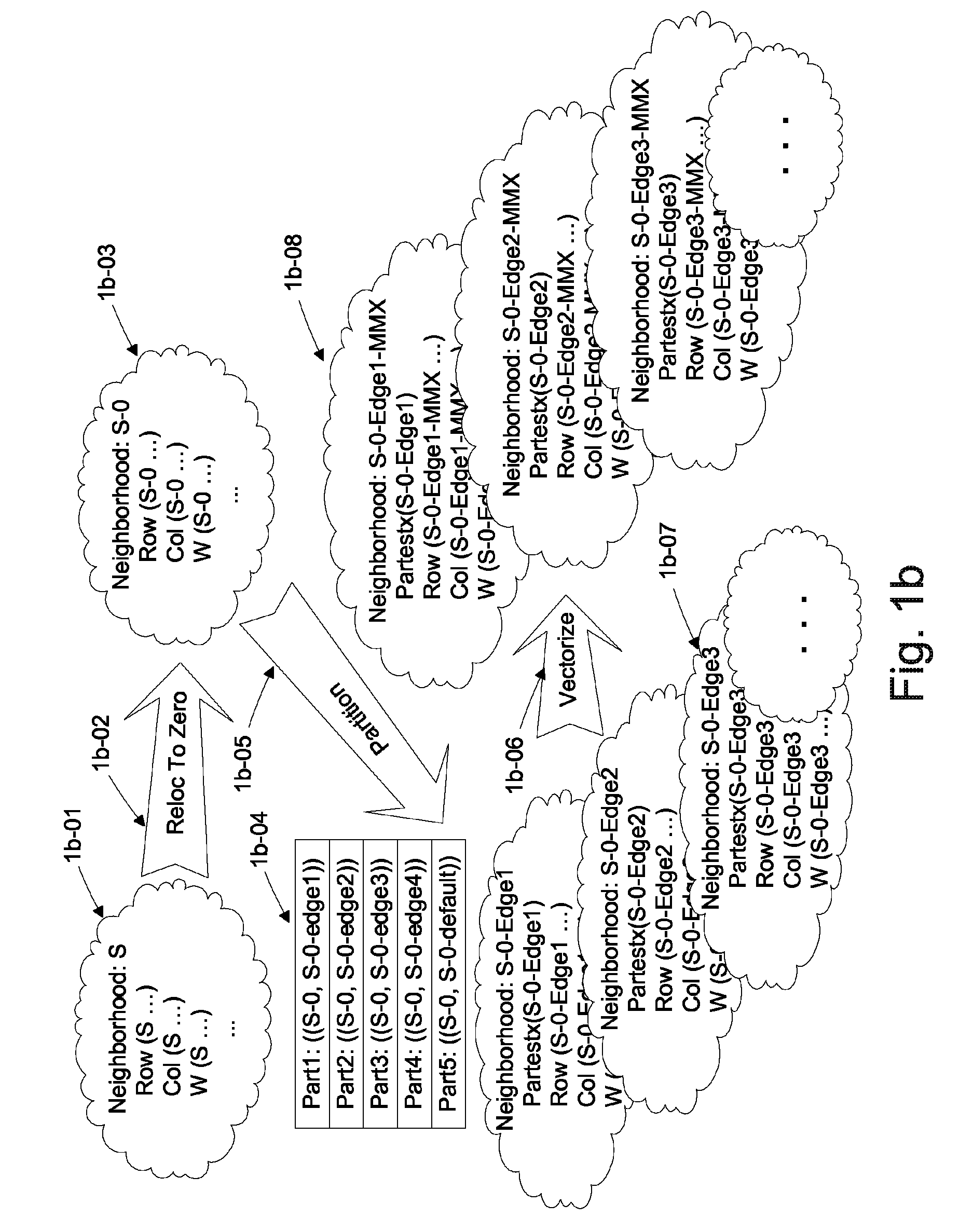
Automated Partitioning of a Computation for Parallel or Other High Capability Architecture
ActiveUS20100199257A1Program code adaptionSpecific program execution arrangementsProblem domainComputer science
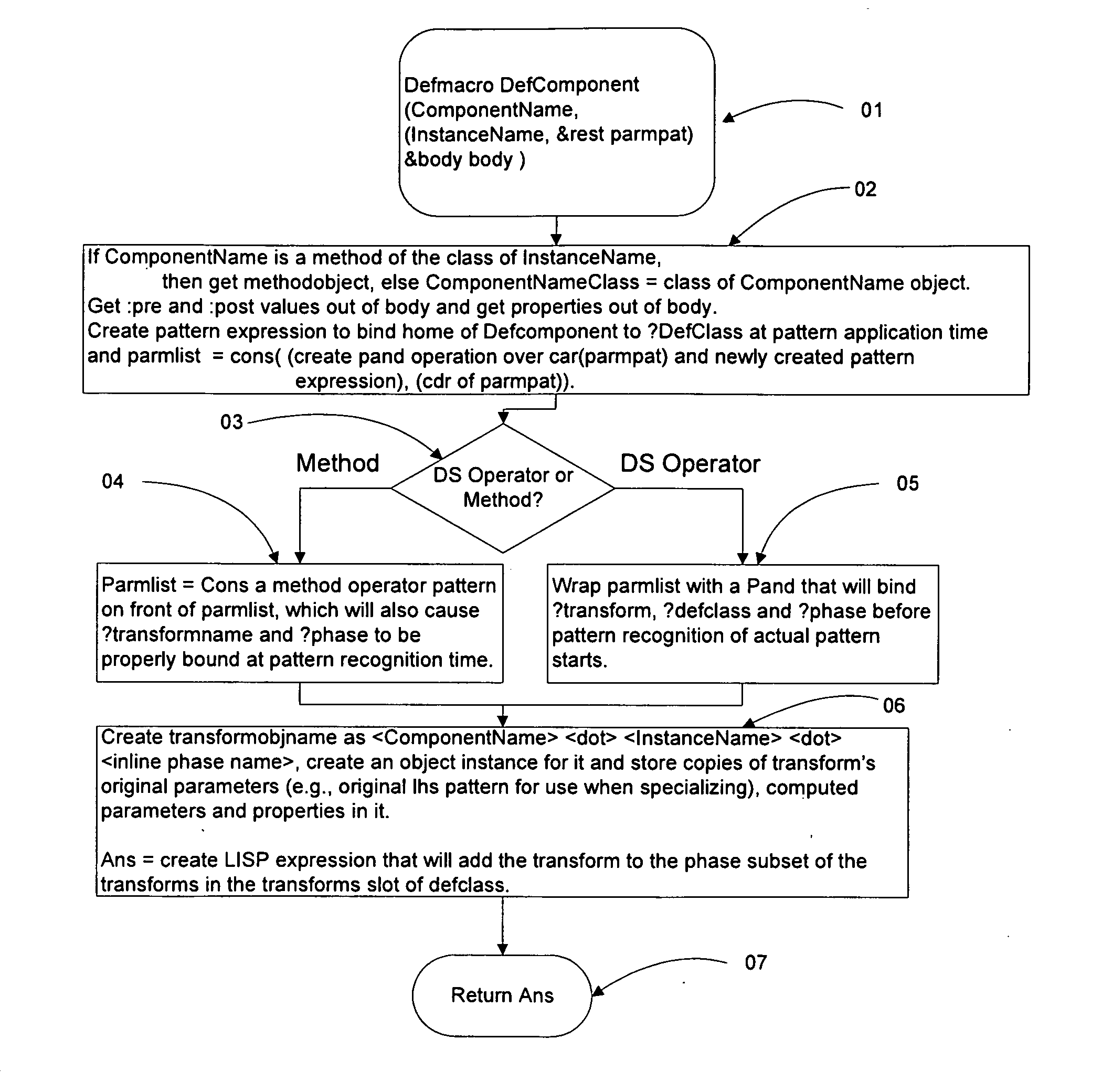
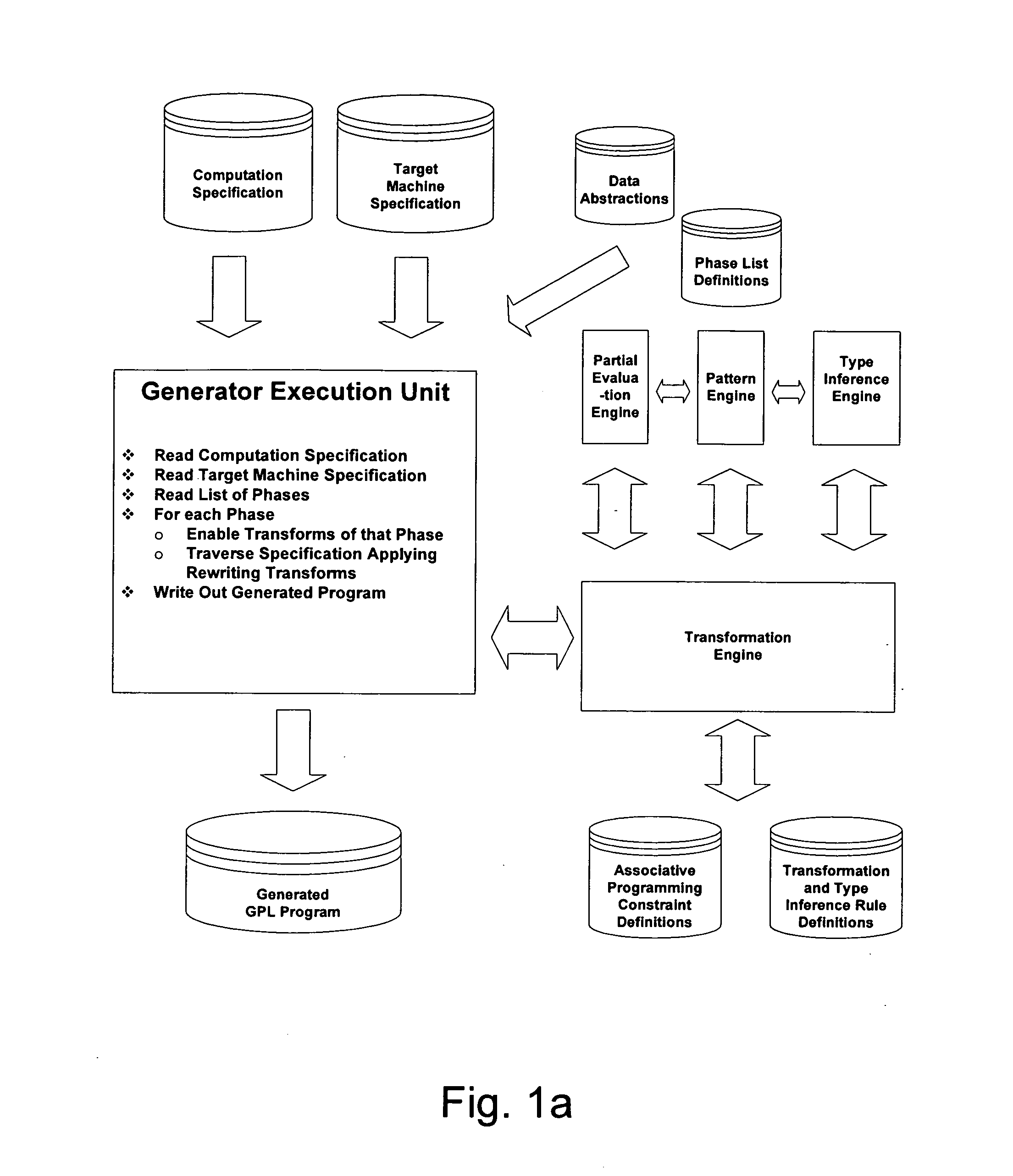
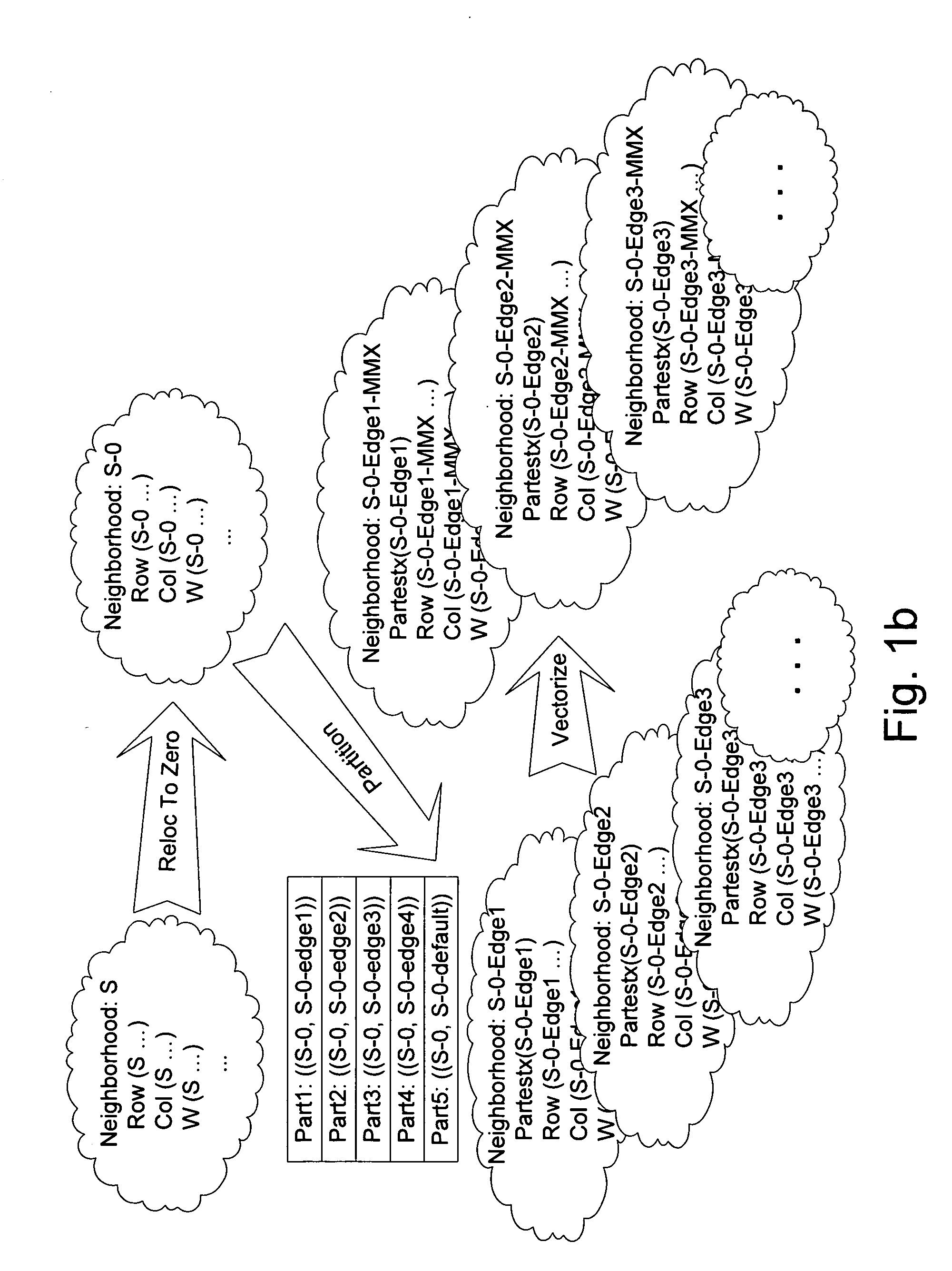
A method and a system for transformation-based program generation using two separate specifications as input: An implementation neutral specification of the desired computation and a specification of the execution platform. The generated implementation incorporates execution platform opportunities such as parallelism. Operationally, the invention has two broad stages. First, it designs the abstract implementation in the problem domain in terms of an Intermediate Language (IL) that is unfettered by programming language restrictions and requirements. Concurrently, the design is evolved by specializing the IL to encapsulate a plurality of desired design features in the implementation such as partitioning for multicore and / or instruction level parallelism. Concurrently, constraints that stand in for implied implementation structures are added to the design and coordinated with other constraints. Second, the IL is refined into implementation code. With this invention, porting an implementation neutral computation to an arbitrary architecture can be automated.
Owner:BIGGERSTAFF TED J
Modeless gesture driven editor for handwritten mathematical expressions
InactiveUS20040054701A1Method is smallAccurate identificationDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsProblem domainTheoretical computer science
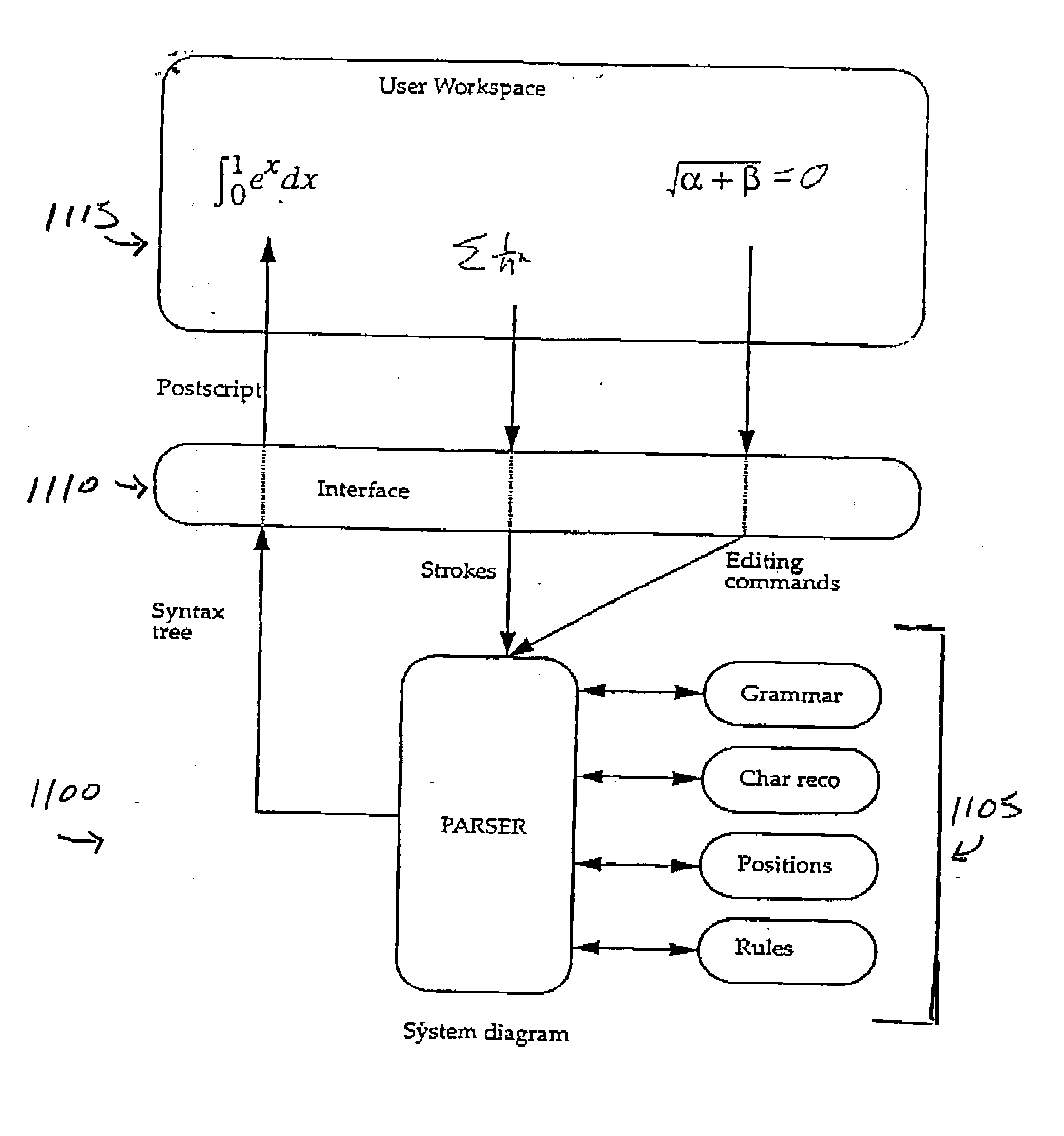
Provided herein is a pen-based editing system for manipulating mathematical expressions. Through a largely gesture based, directly manipulative interface, the system allows a user to make conventional changes to expressions, such as copy and move, and also to work with the expressions in ways peculiar to the problem domain, including, for example, handling ambiguity, expression fragments and alternate recognitions. The system is a generalization of an online recognizer for mathematical expressions. The system uses the same basic recognition techniques as the online recognizer, however the input information available to the editor is more varied, including mixtures of known and unknown characters and positional relations.
Owner:PARAMETRIC TECH CORP
N-tiered eurt breakdown graph for problem domain isolation
A method for visual representation of end user response time (EURT) in a multi-tiered network application is provided. Search criteria for searching a repository of client statistics records is received. The search criteria specifies identification information pertaining to a user of a multi-tiered network application experiencing application performance problems and a time period associated with the application performance problems. The identification information identifies an IP address of user's computing device. A plurality of client statistics records matching the search criteria is retrieved from the repository. The retrieved plurality of client statistics records is sorted based on measurements of performance parameters. A graph representing relevant topology hierarchy of the multi-tiered network application is presented to a user based on the sorted client statistics records. The graph visually identifies connections between nodes of the multi-tiered application. The identified connections include potential root-causes of the specified application performance problems.
Owner:NETSCOUT SYSTEMS
Automated partitioning of a computation for parallel or other high capability architecture
ActiveUS8060857B2Program code adaptionSpecific program execution arrangementsProblem domainComputer science
A method and a system for transformation-based program generation using two separate specifications as input: An implementation neutral specification of the desired computation and a specification of the execution platform. The generated implementation incorporates execution platform opportunities such as parallelism. Operationally, the invention has two broad stages. First, it designs the abstract implementation in the problem domain in terms of an Intermediate Language (IL) that is unfettered by programming language restrictions and requirements. Concurrently, the design is evolved by specializing the IL to encapsulate a plurality of desired design features in the implementation such as partitioning for multicore and / or instruction level parallelism. Concurrently, constraints that stand in for implied implementation structures are added to the design and coordinated with other constraints. Second, the IL is refined into implementation code. With this invention, porting an implementation neutral computation to an arbitrary architecture can be automated.
Owner:BIGGERSTAFF TED J
Method for domain specific test design automation
InactiveUS7392509B2Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsTest designSpecific test
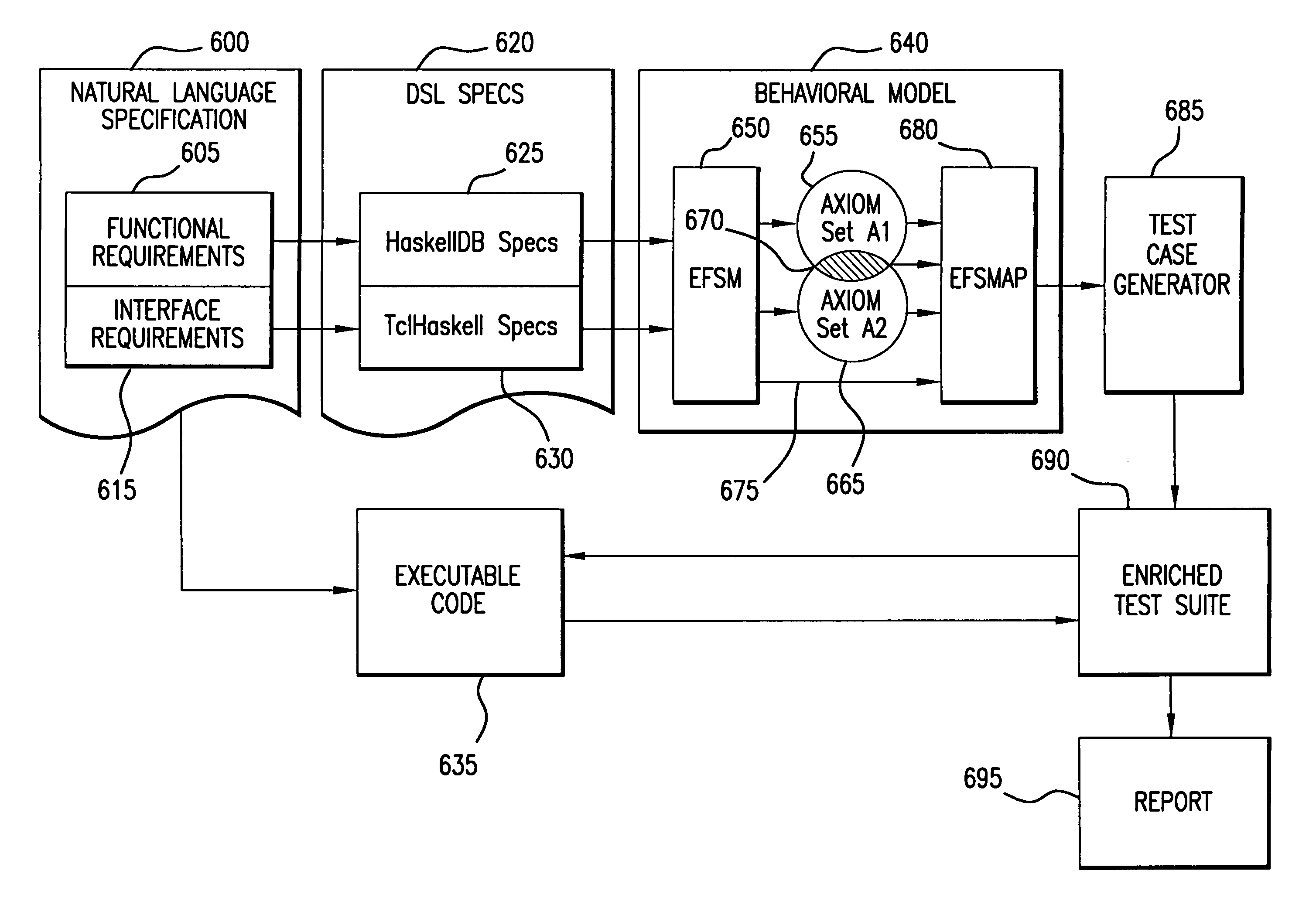
A method for automatically generating test cases from a domain specific description language specification makes use of the properties of the language to derive domain specific axioms and language specific predicates. These properties are embedded into an extended finite state machine which is in turn supplied to the input of a test case generator. The enhanced extended finite state machine, referred herein as an extended finite state machine accounting for axioms and predicates (EFSMAP) contains states and transitions associated with information on implied behavior of the specified system within a particular problem domain. The implicit behavior, defined by the axiomatic properties of the operators of the domain specific language, provide test capability of the associated system that was not explicitly set forth in the formal specification, but nevertheless should be tested to increase confidence in the reliability of the finished product.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF +1
Formal sequential lagrangian algorithm for large scale resource scheduling optimization
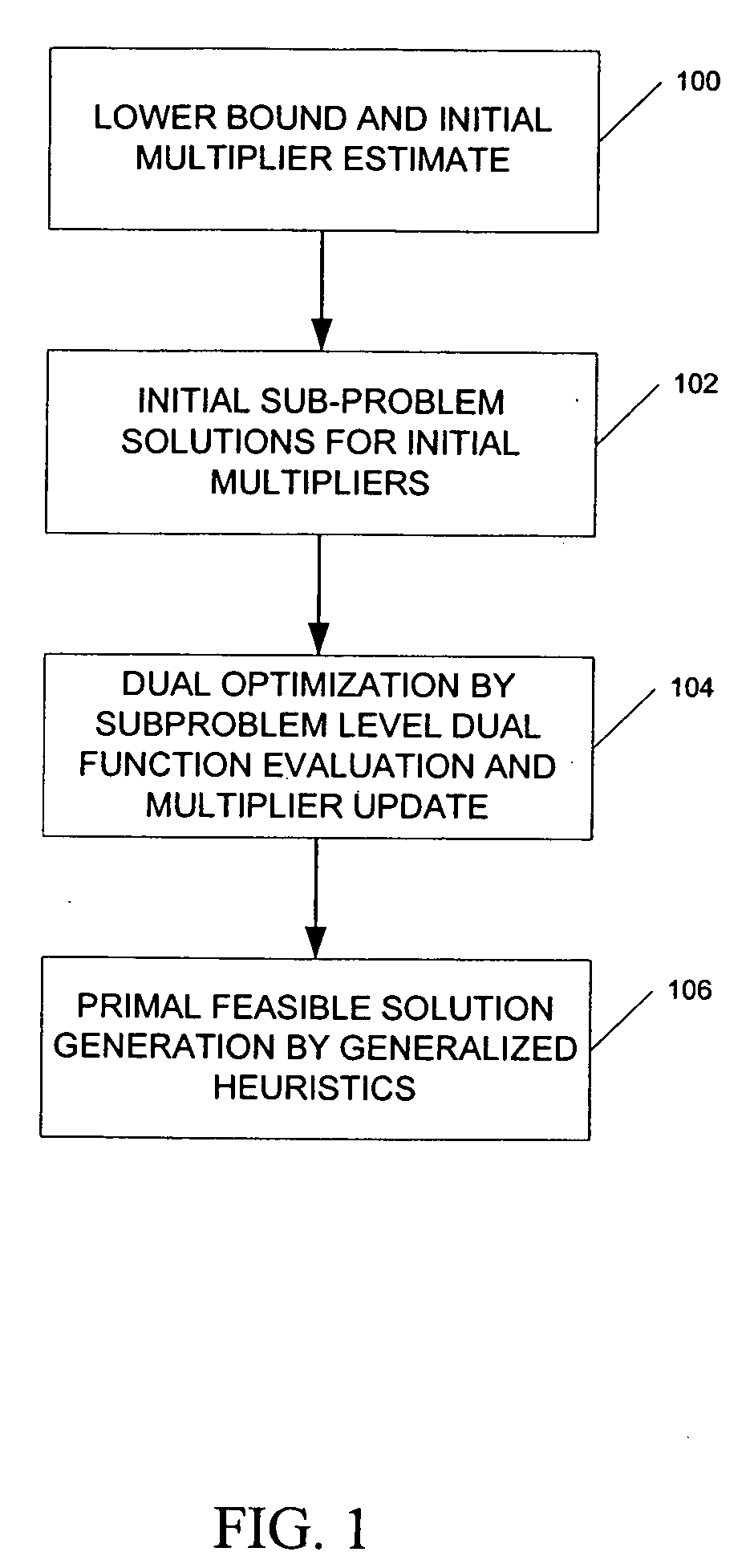
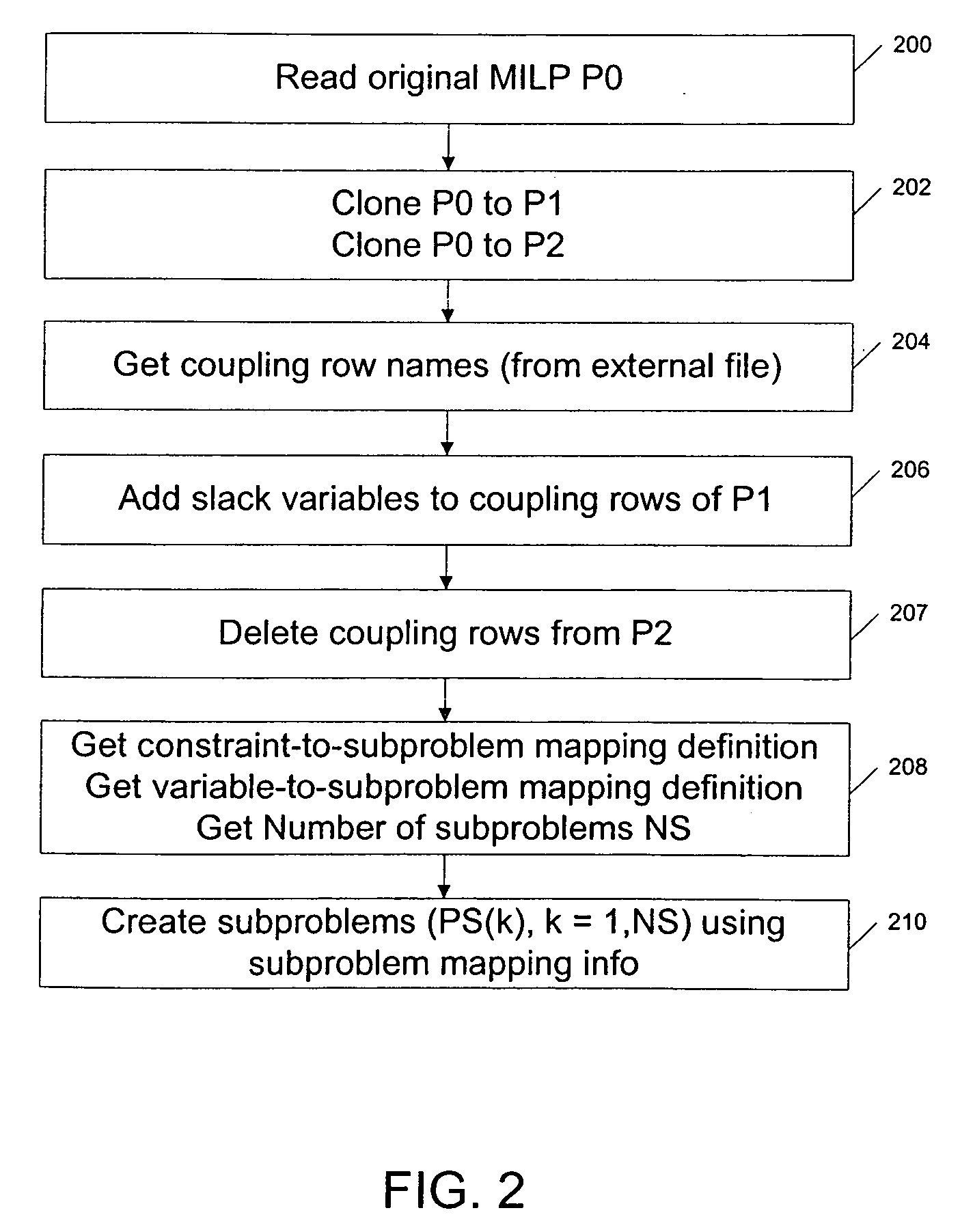
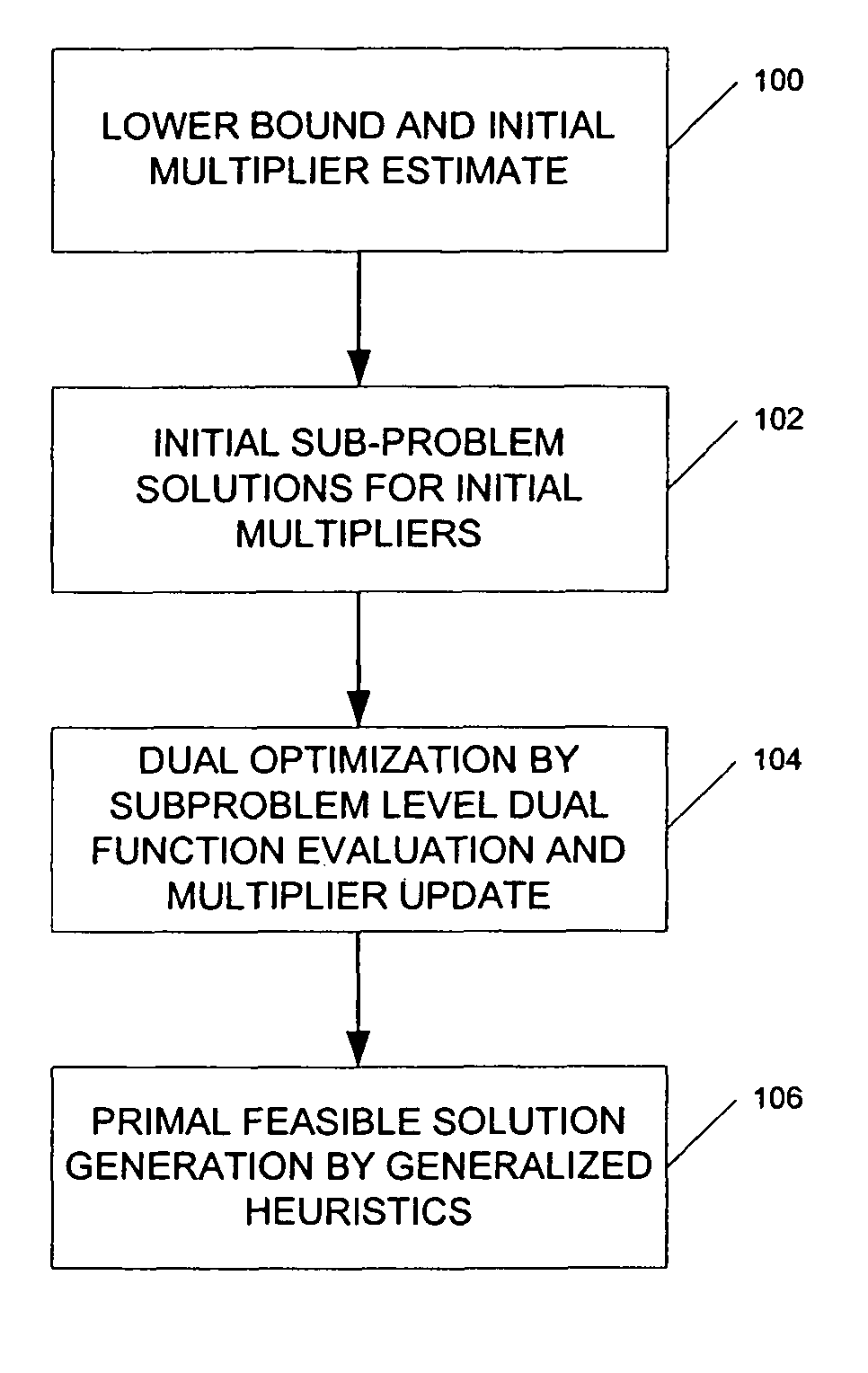
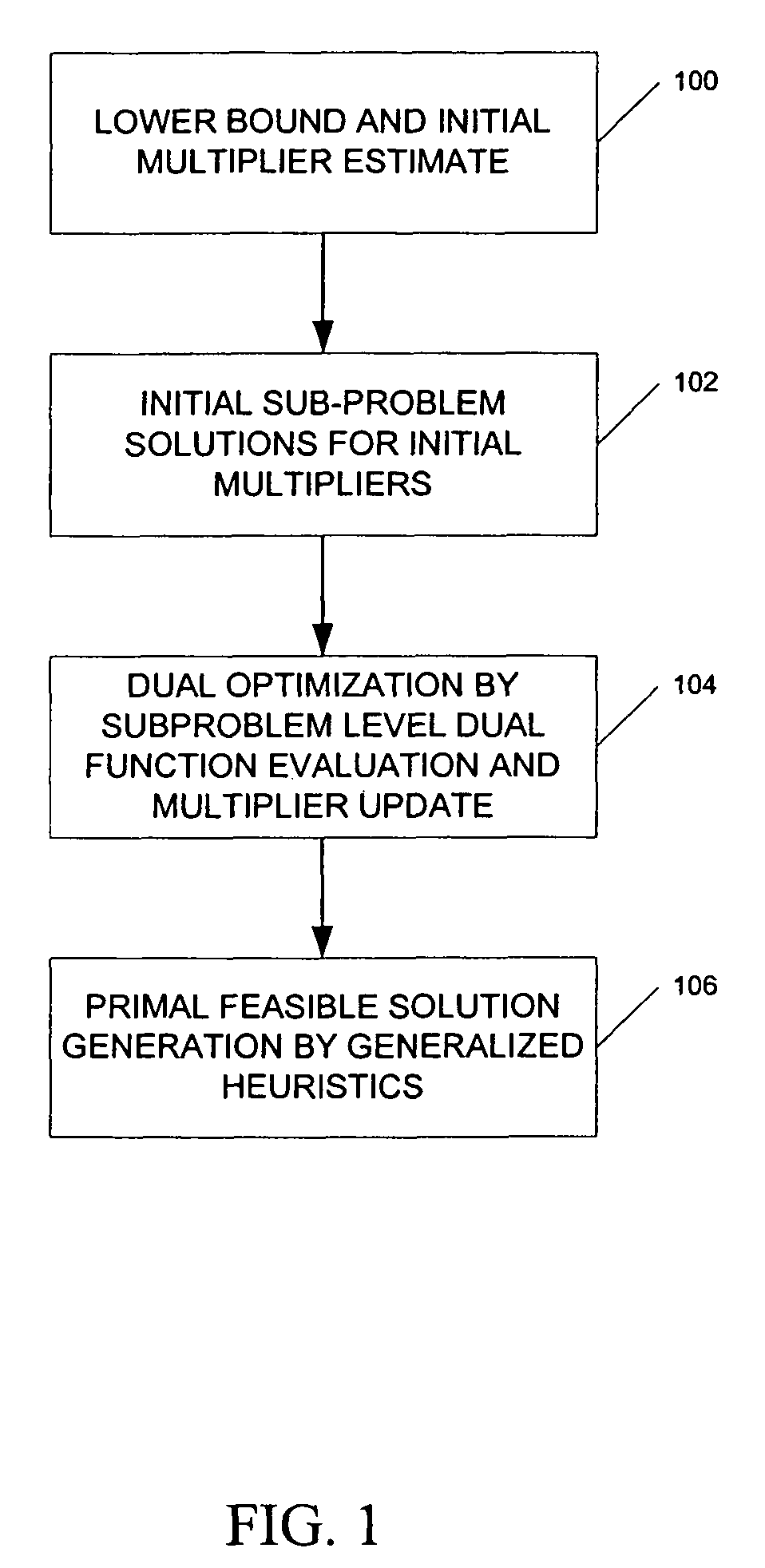
ActiveUS20060089864A1Reduce operating costsFast dual optimization—obtainingDigital computer detailsForecastingProblem domainAlgorithm
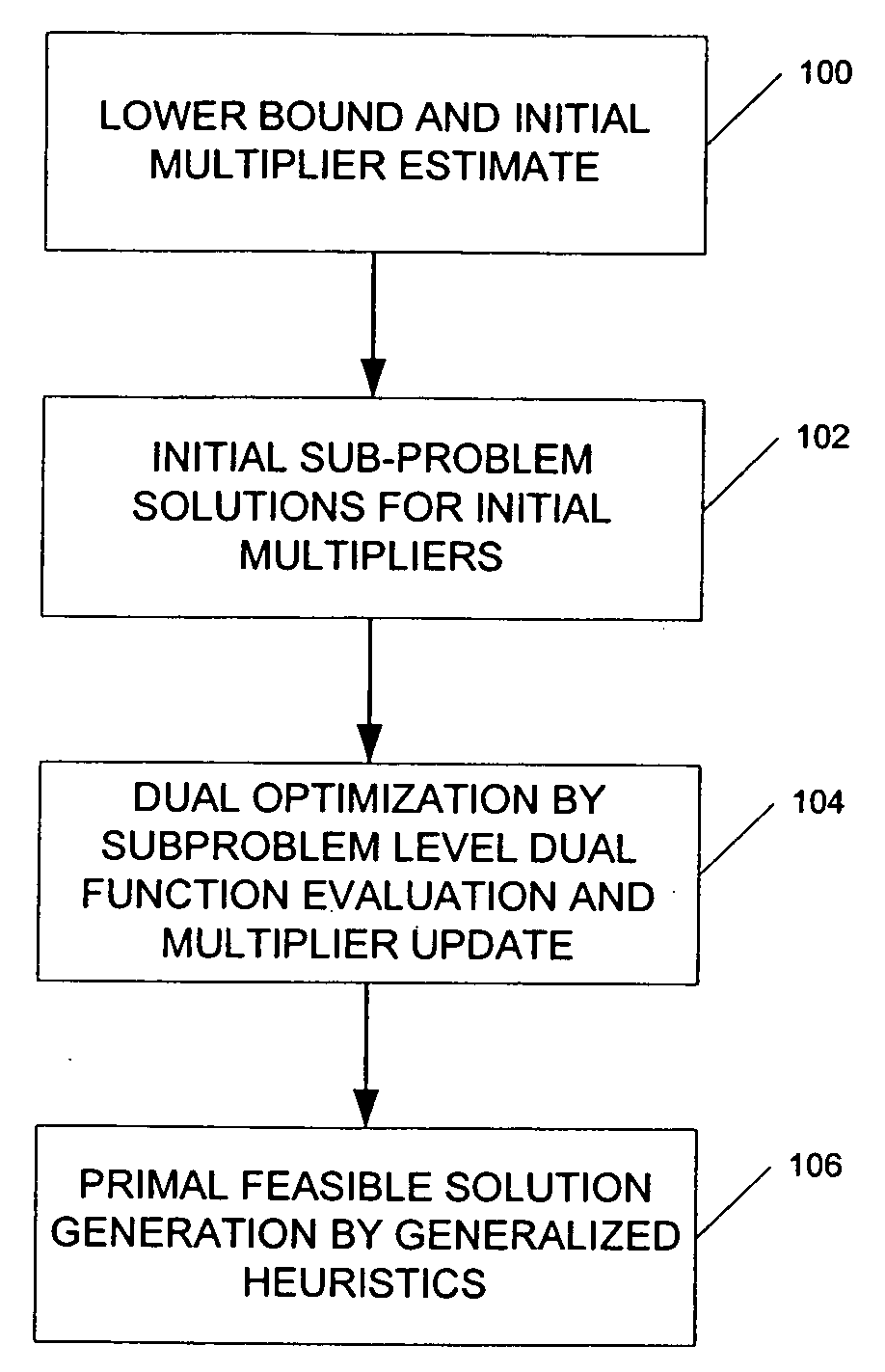
A method and computer program product for optimization of large scale resource scheduling problems. Large scale resource scheduling problems are computationally very hard and extremely time consuming to solve. This invention provides a Lagrangian relaxation based solution method. The method has two distinct characteristics. First, the method is formal. It is completely structure-based and does not use any problem domain specific knowledge in the solution process, either in the dual optimization or the primal feasibility enforcement process. Second, updating the Lagrangian multipliers after solution of every sub-problem without using penalty factors results in fast and smooth convergence in the dual optimization. The combination of high quality dual solution and the structure-based primal feasibility enforcement produces a high quality primal solution with very small solution gap. An optimal solution is first found to the dual of the resource scheduling problem by sequentially finding a solution to a plurality of sub-problems and updating a set of values used in the dual problem formulation after each sub-problem solution is obtained. Coupling constraint violations are systematically reduced and the set of values are updated until a feasible solution to the primal resource scheduling problem is obtained. An initial set of multiplier values is further determined by solving a relaxed version of the primal problem where most of the local constraints except the variable bounds are relaxed.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY SWITZERLAND AG
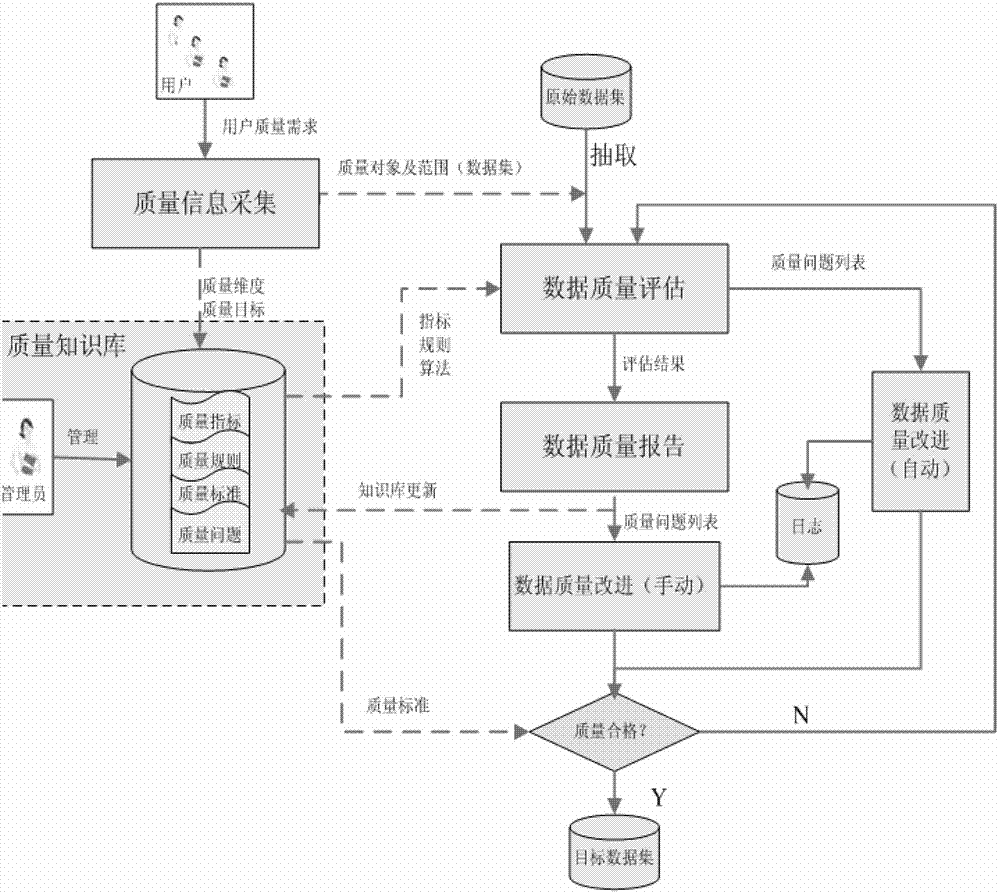
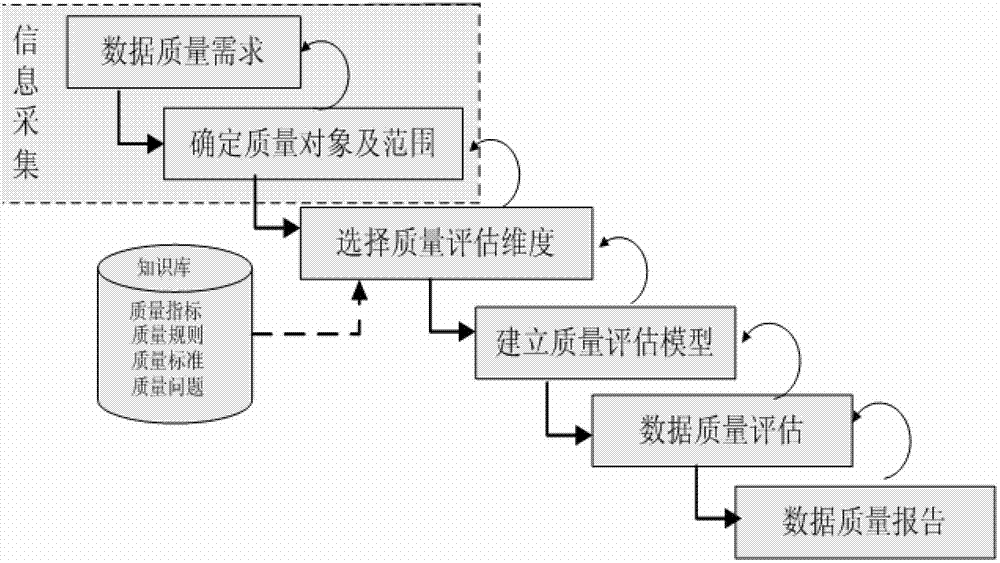
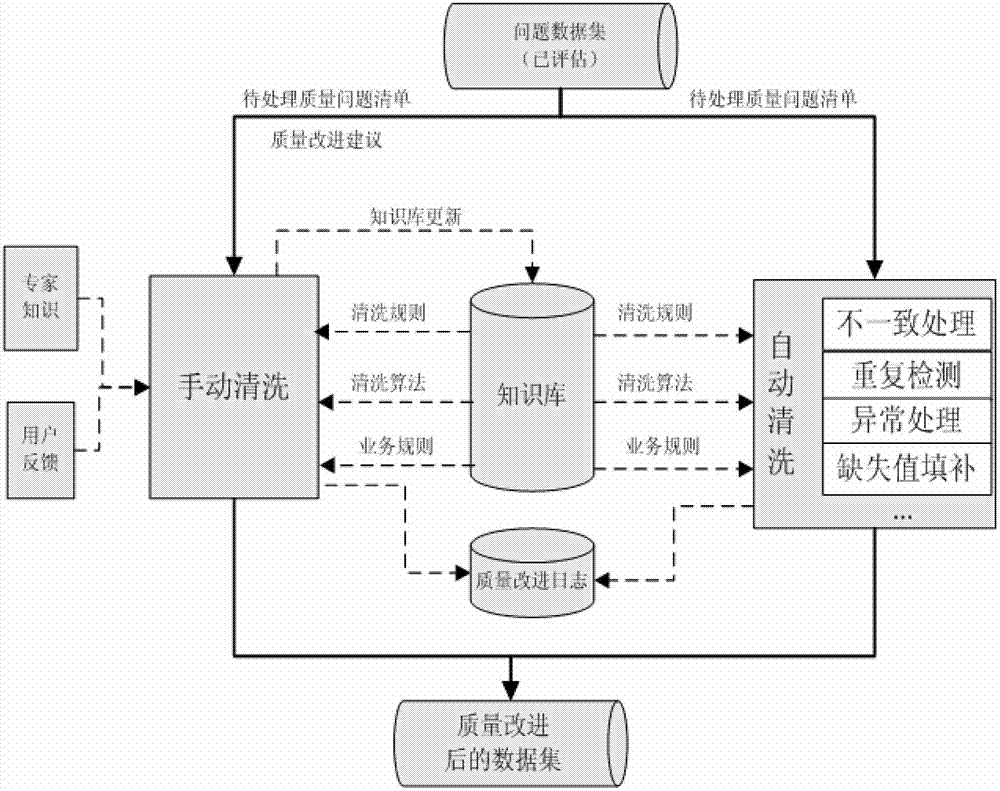
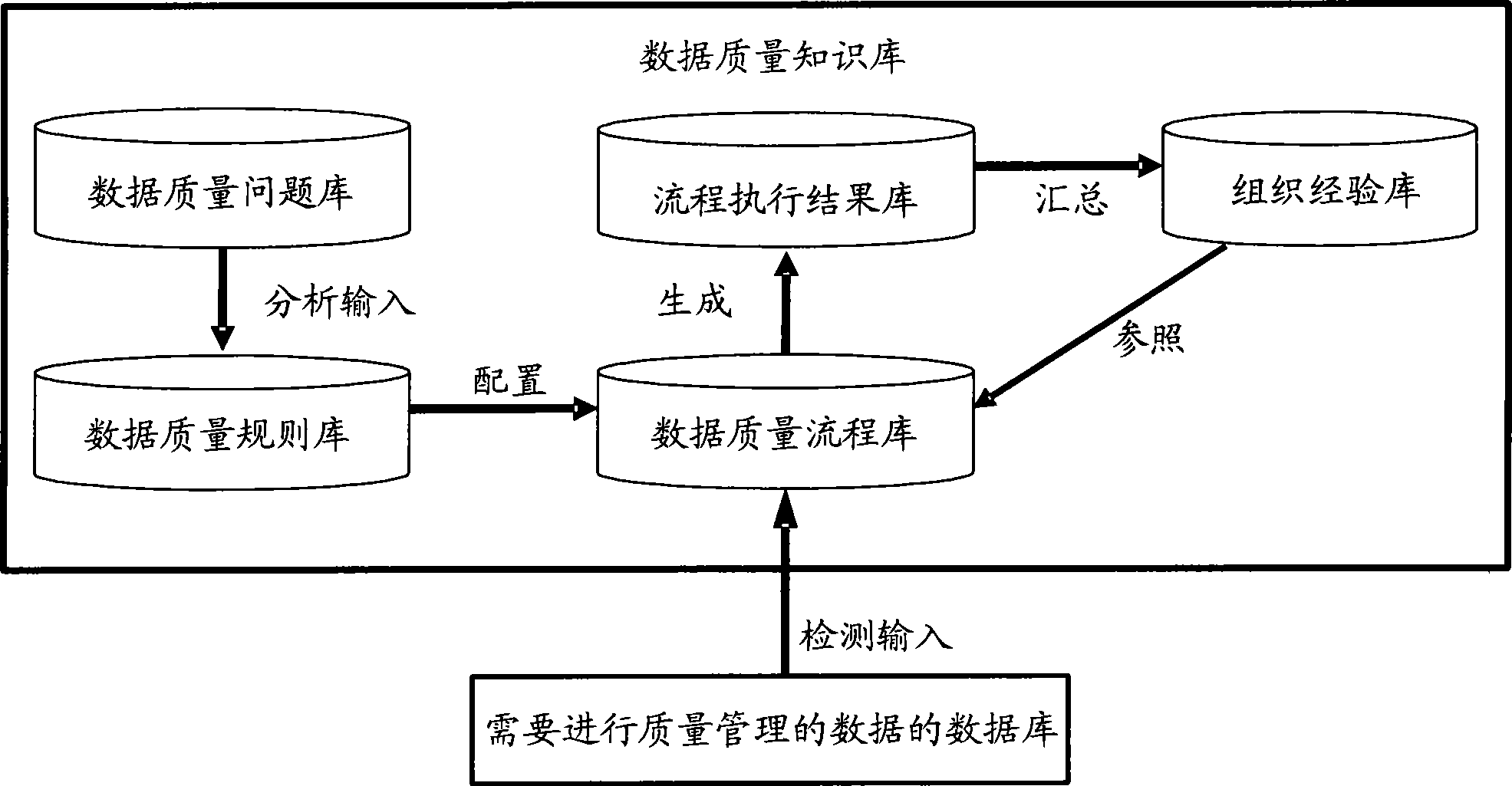
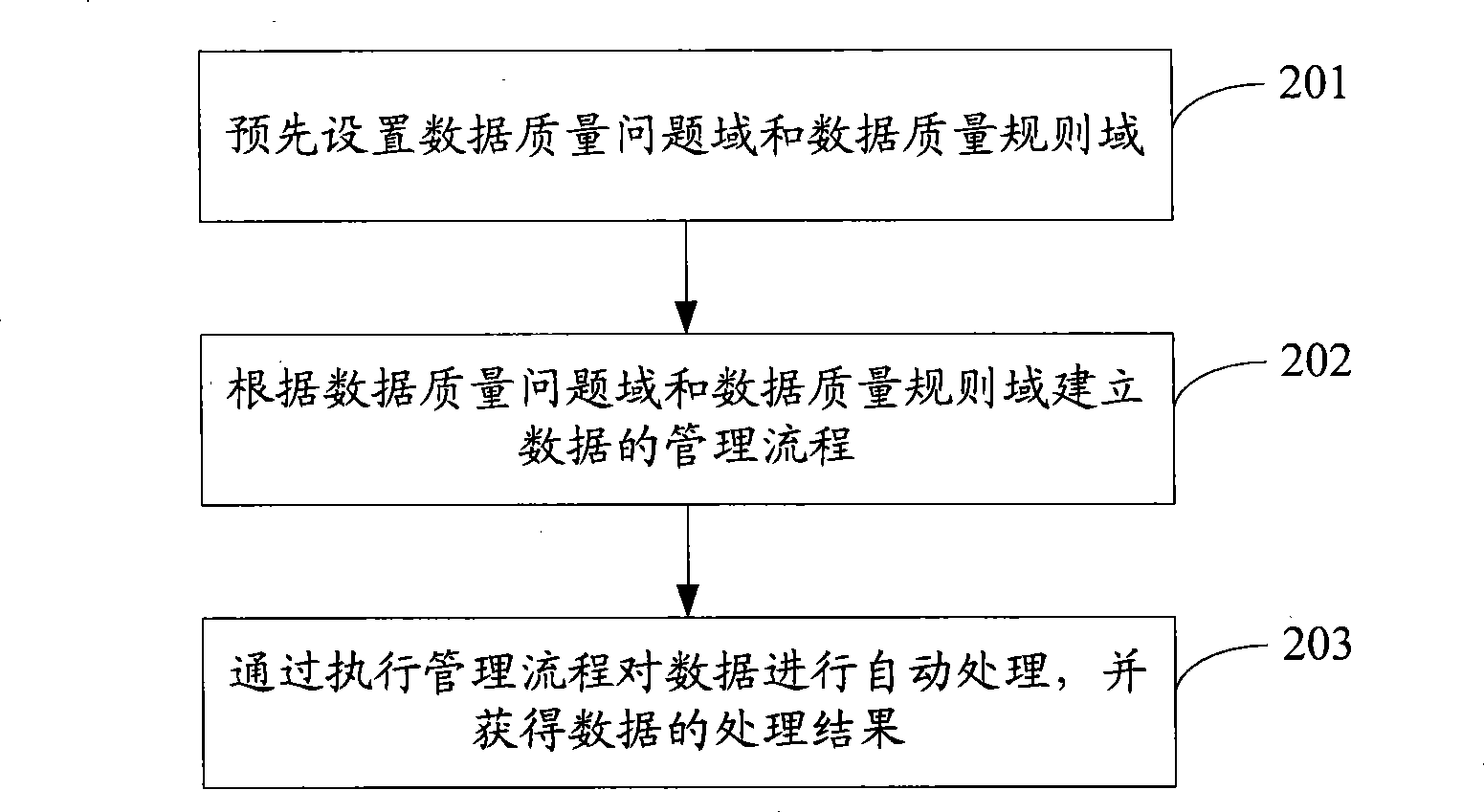
Data quality management method and system
The invention discloses a data quality management method and a data quality management system. The data quality management method comprises the following steps: managing a quality knowledge library; analyzing the data quality characteristics, and presetting a quality problem domain, a quality dimension domain, a quality rule domain and a quality standard domain; collecting quality information: selecting the quality dimension and the quality rules required by a user from the quality knowledge library, and extracting a data set meeting the user requirements from the original data sets; evaluating the data quality: evaluating the data quality according to the collected quality information, and generating and submitting a data quality report to the user or a quality manager according to the quality problem domain and the quality standard domain in the quality knowledge library; and improving the data quality: correcting the data quality problem detected in the evaluation of the data quality for improvement. The data quality management method and the data quality management system are applied to monitoring, evaluating and continuously improving the data quality in the whole hydrology industry based on the whole data processing procedure of the hydrology industry.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Method and system for automated modeling
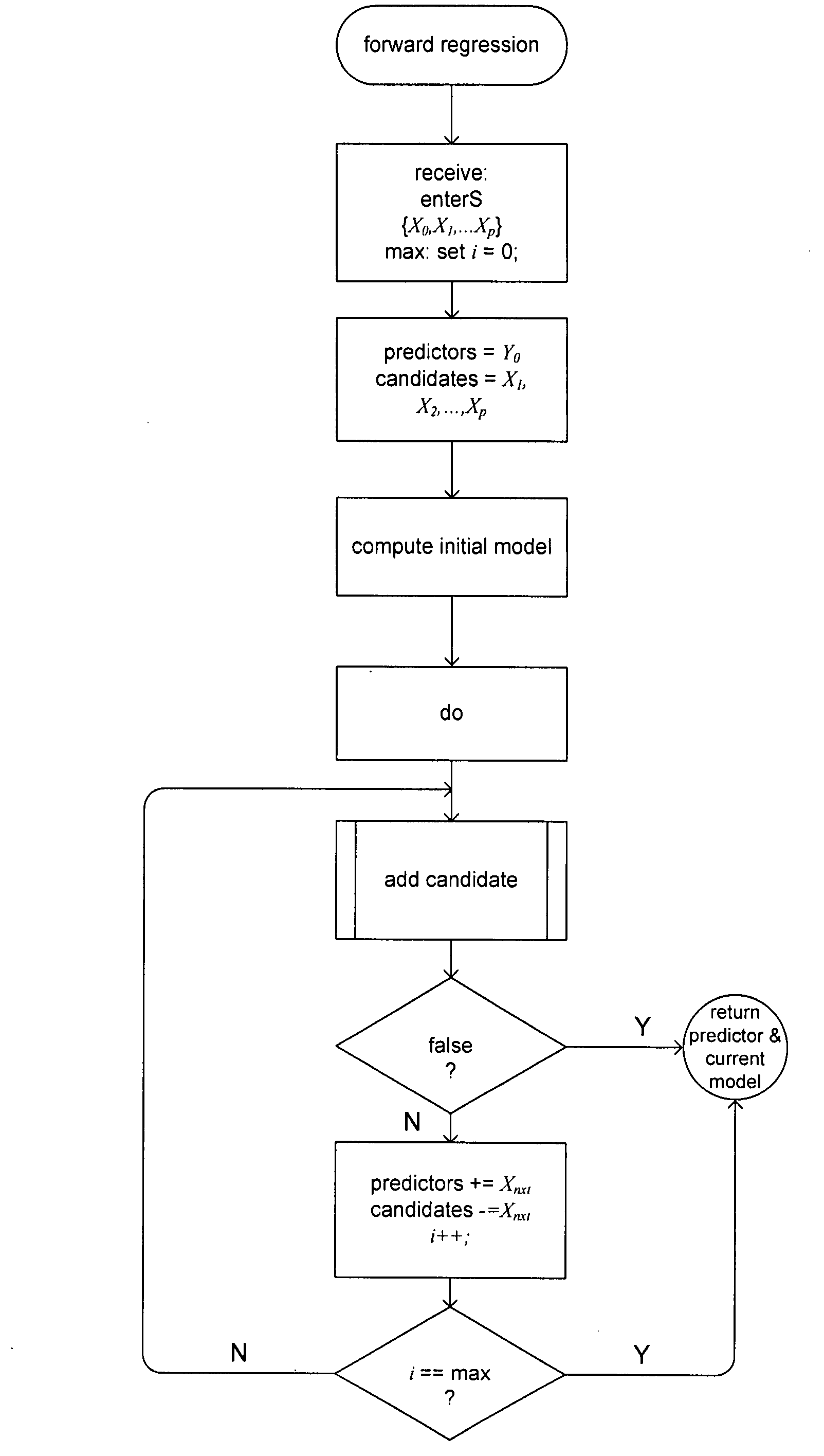
Embodiments of the present invention include automated methods and systems for statistical modeling in high-dimensional problem domains. The automated statistical-analysis methods and systems of the present invention employ computationally efficient methods for preparing large amounts of high-dimensional data for analysis, computationally efficient methods for selecting and transforming predictors, and, based on these methods, computationally efficient model-building methods to generate effective prediction models. Embodiments of the present invention are especially useful when the high-dimensional nature of a problem domain exceeds that of problem domains that can be analyzed by human statisticians, or by human-guided automated systems, within reasonable time and budget constraints.
Owner:CASSILL WILLIAM
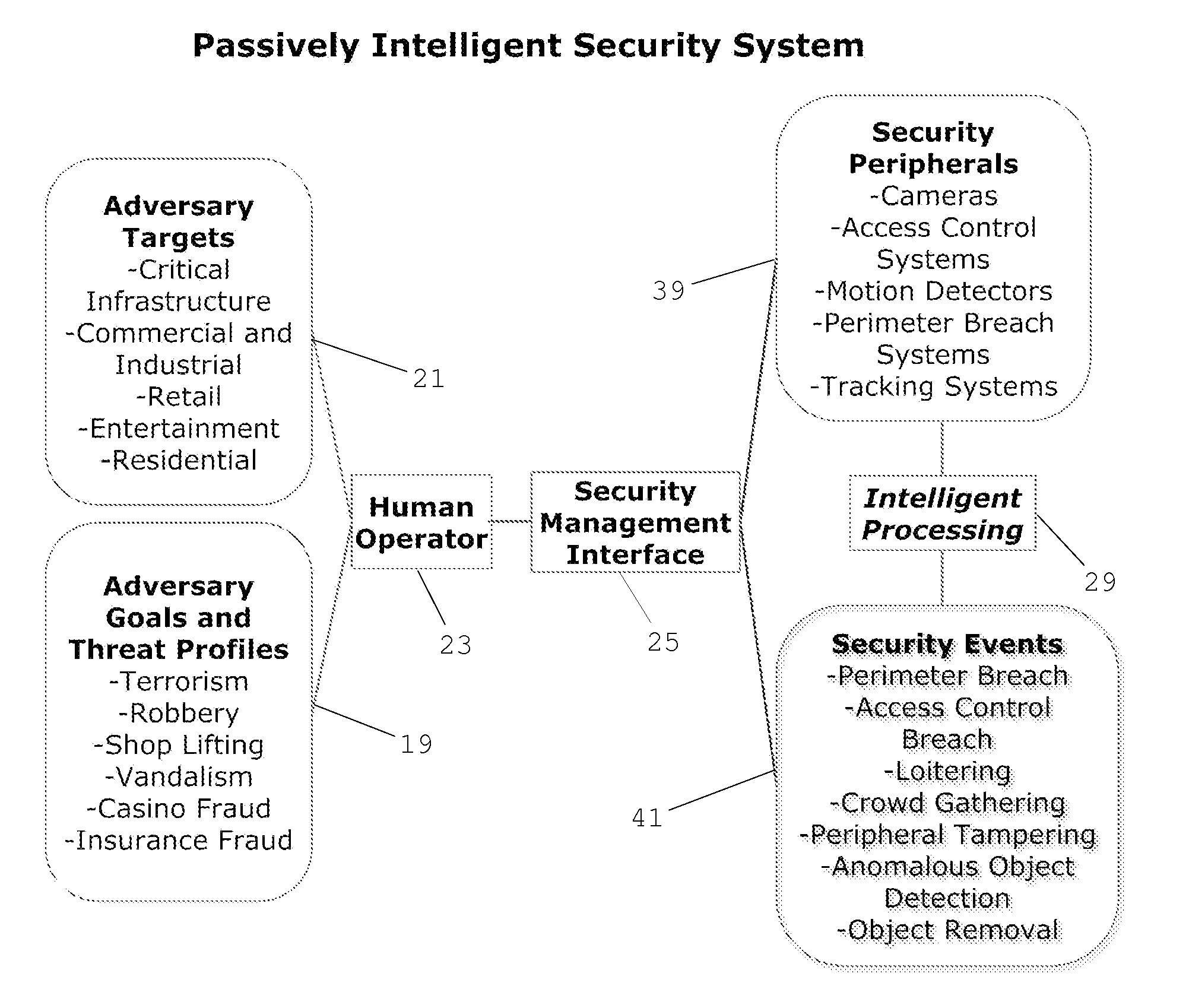
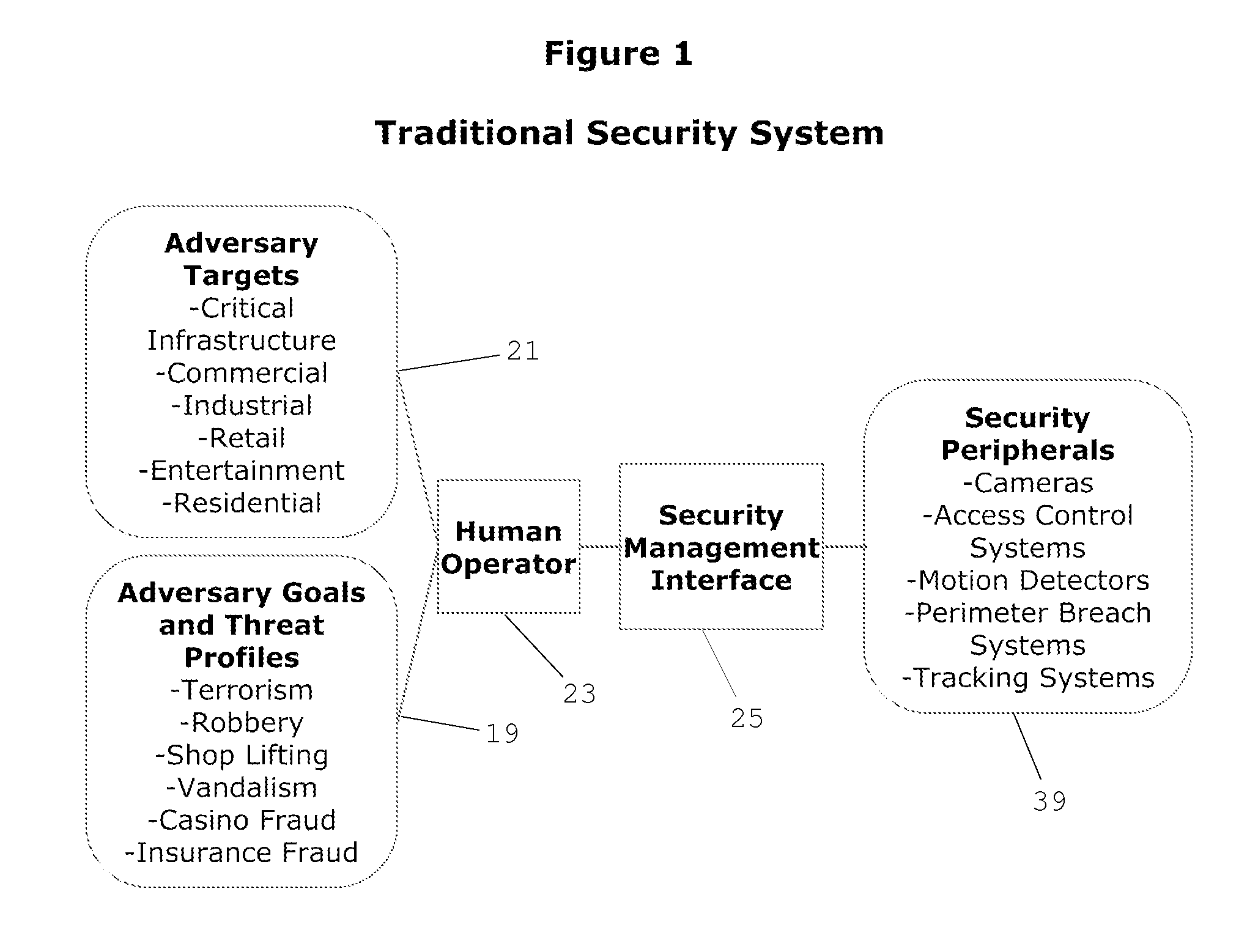
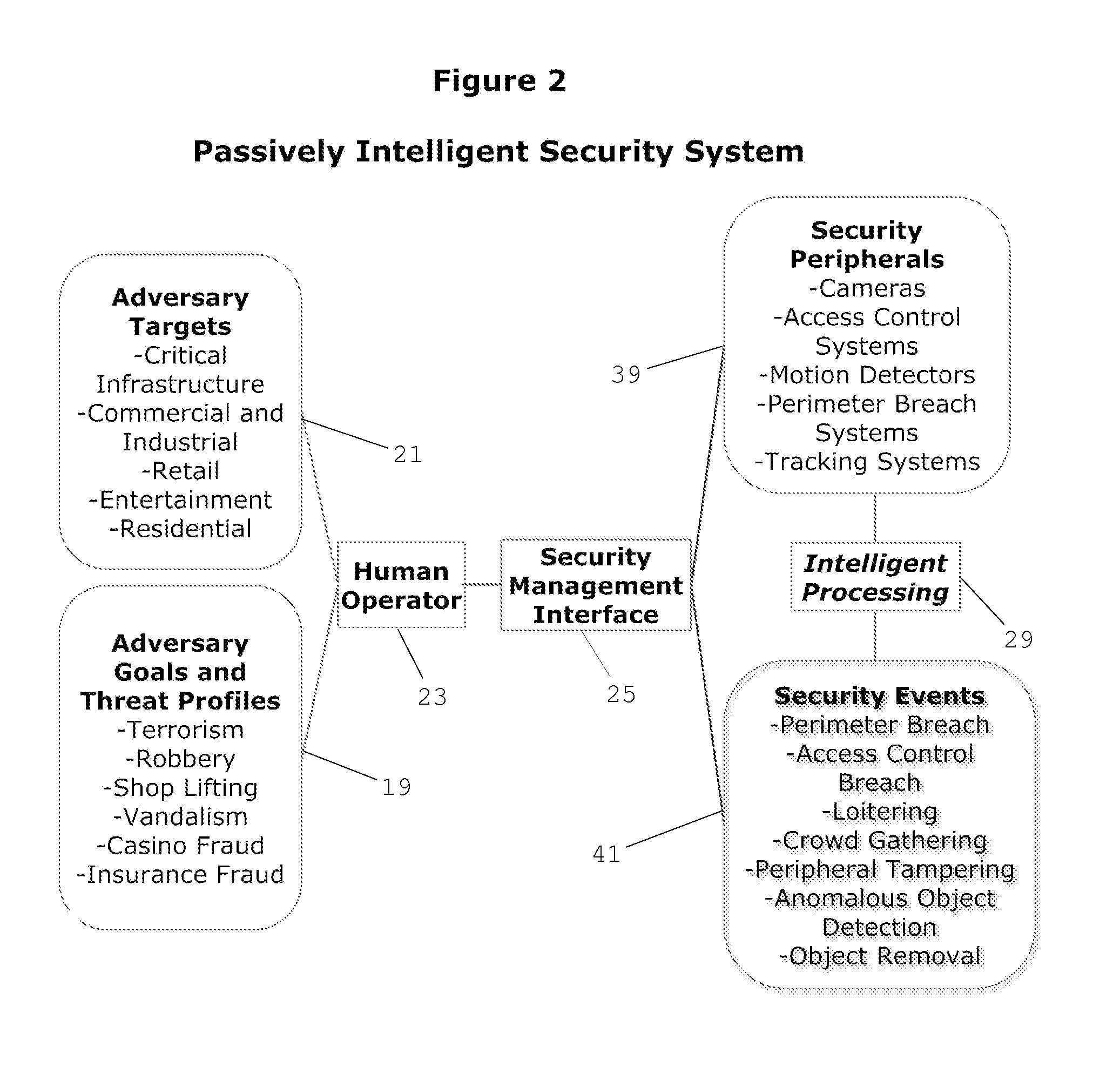
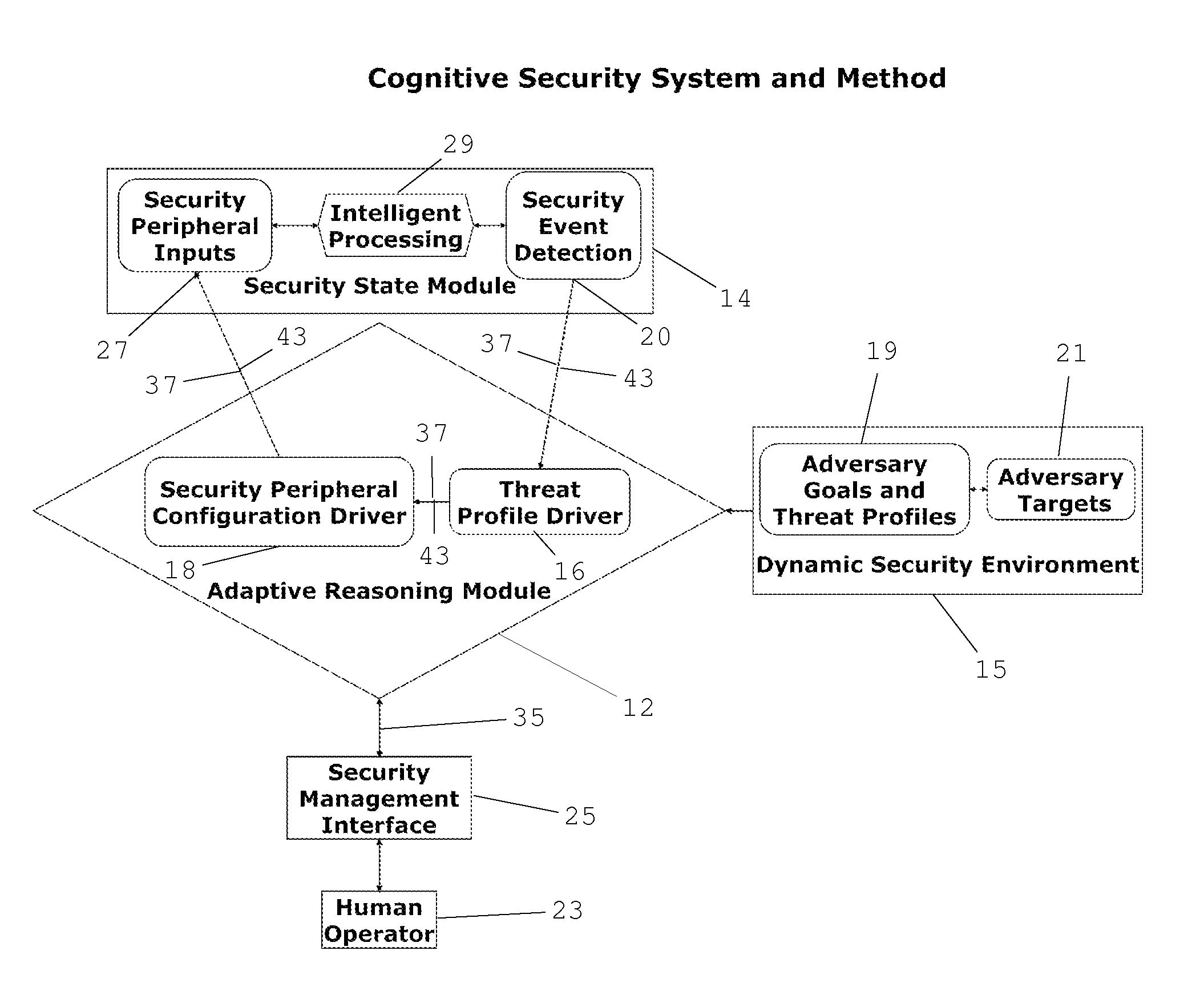
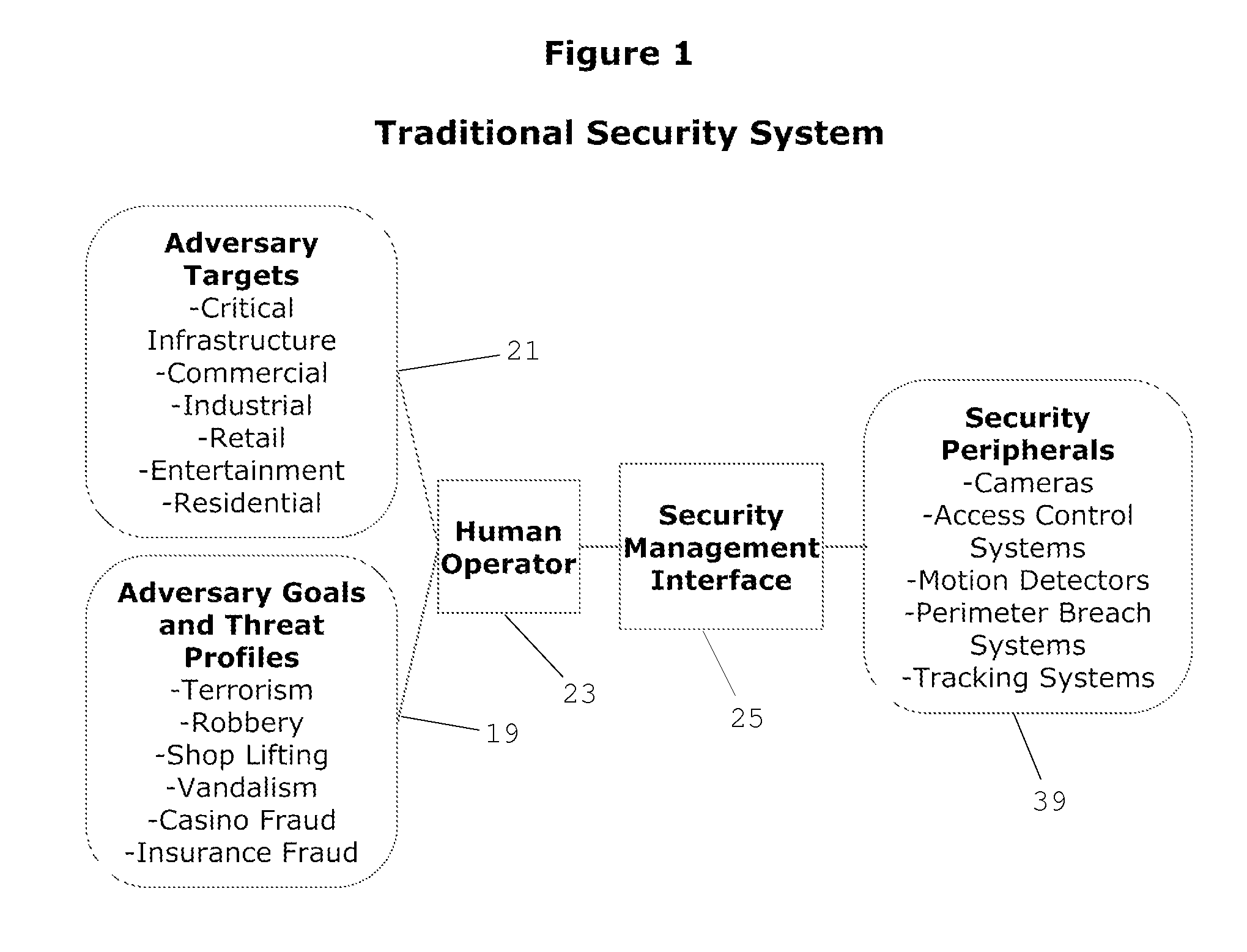
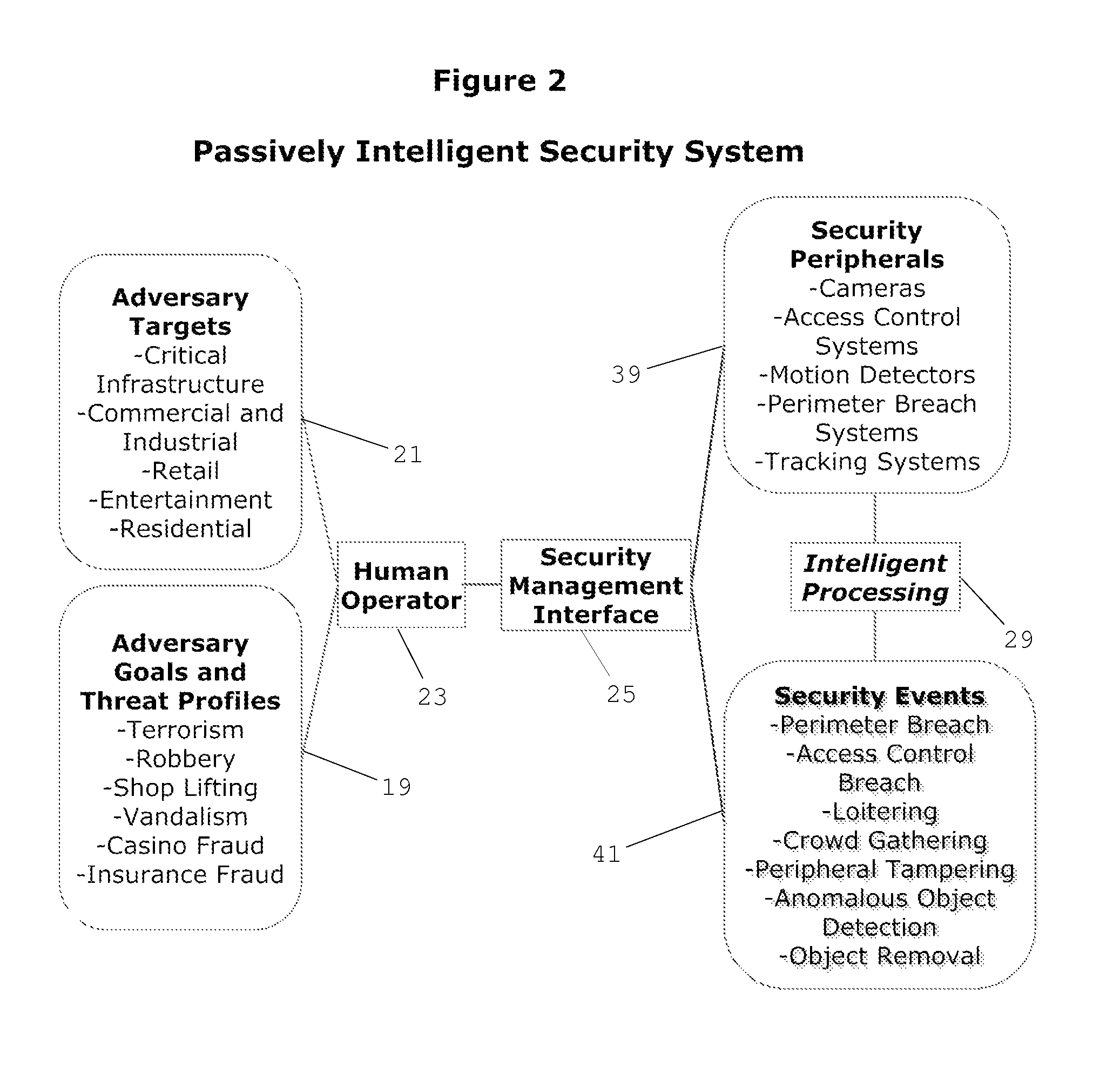
Cognitive Security System and Method
ActiveUS20140070947A1Well formedMinimize “suspicion”Burglar alarmSpecial data processing applicationsProblem domainReal-time data
A cognitive system and method for predicting and detecting security breaches is provided which yields cognitive inputs to a security management interface accessible by a human operator. The system utilizes symbolic cognitive architectures and inference processing algebras allowing the system to respond to open, incomplete, and / or unknown problem domains, offering flexibility in the case of unexpected changes in the security environment. The system is also capable of intelligently, and in real-time, adapting security peripheral configurations to further probe and analyze the real-time security environment, provided real-time data that can be processed with symbolic cognitive architectures and inference process algebras enabling the identification of new and emerging threat profiles leading to the prediction and detection of security breaches.
Owner:JANSSEN LAW PROFESSIONAL CORP IN TRUST
Geodesic Massively Parallel Computer.
InactiveUS20120331269A1Shorten the interconnection distanceCommunication latencySingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsDigital data processing detailsSystems designProblem domain
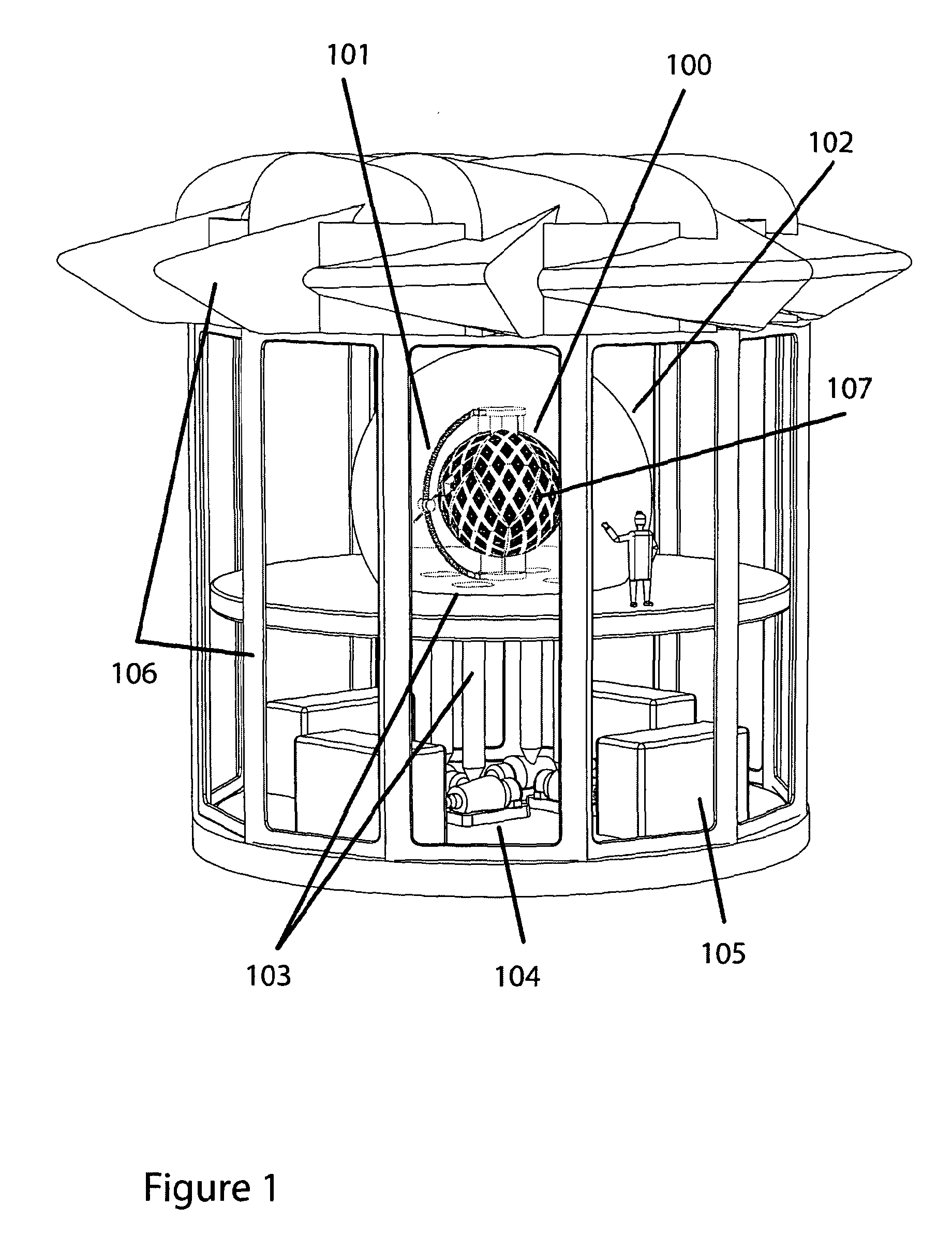
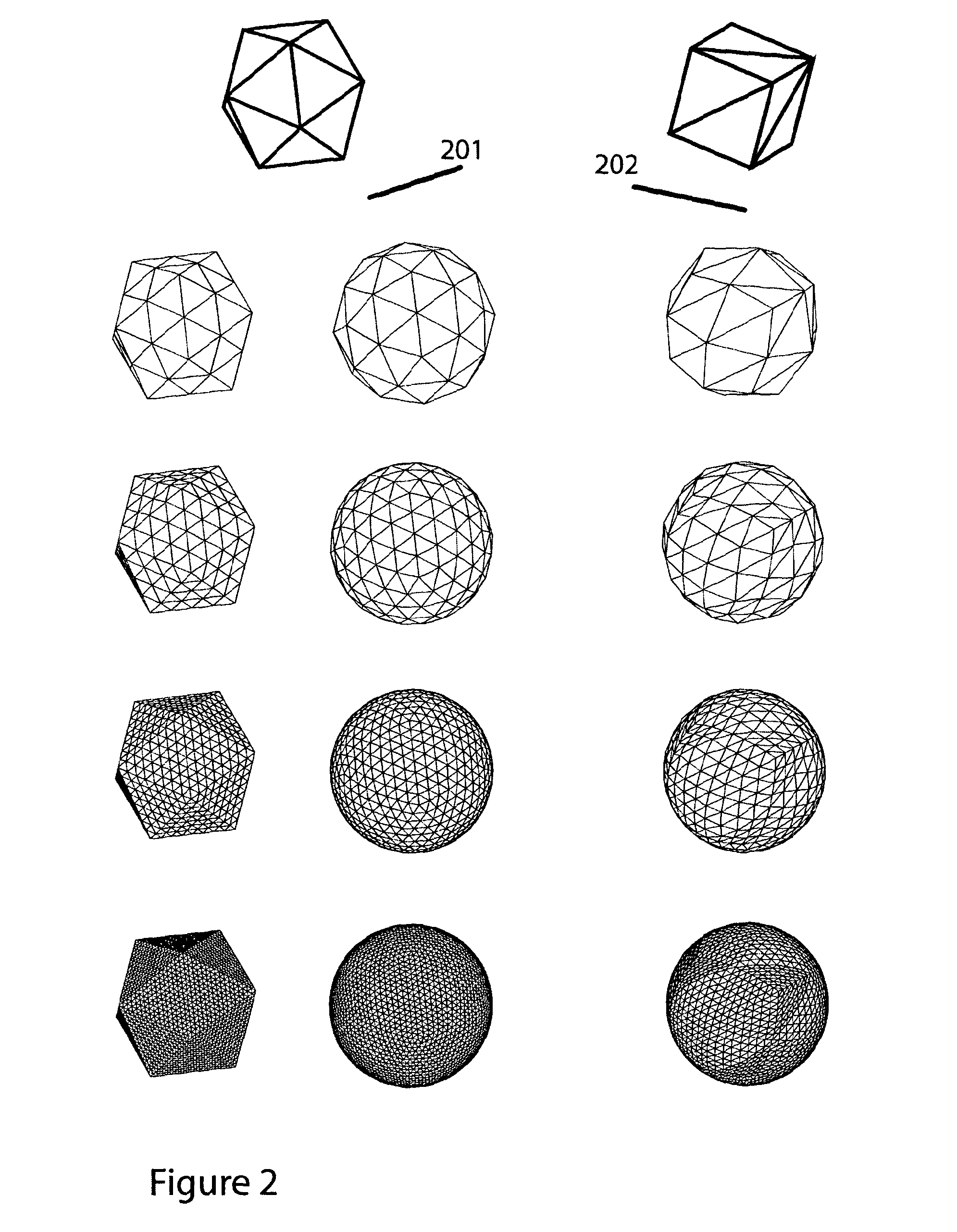
Communication latency, now a dominant factor in computer performance, makes physical size, density, and interconnect proximity crucial system design considerations. The present invention addresses consequential supercomputing hardware challenges: spatial packing, communication topology, and thermal management. A massively-parallel computer with dense, spherically framed, geodesic processor arrangement is described. As a mimic of the problem domain, it is particularly apt for climate modelling. However, the invention's methods scale well, are largely independent of processor technology, and apply to a wide range of computing tasks. The computer's interconnect features globally short, highly regular, and tightly matched distances. Communication modes supported include neighbour-to-neighbour messaging on a spherical-shell lattice, and a radial network for system-synchronous clocking, broadcast, packet-switched networking, and IO. A near-isothermal cooling system, physically divorcing heat source and sink, enables extraordinarily compact geodes with lower temperature operation, higher speed, and lower power consumption.
Owner:ARAS RICHARD JOHN EDWARD
Domain specific language design
InactiveUS20130031529A1Programming languages/paradigmsSpecific program execution arrangementsProblem domainHuman language
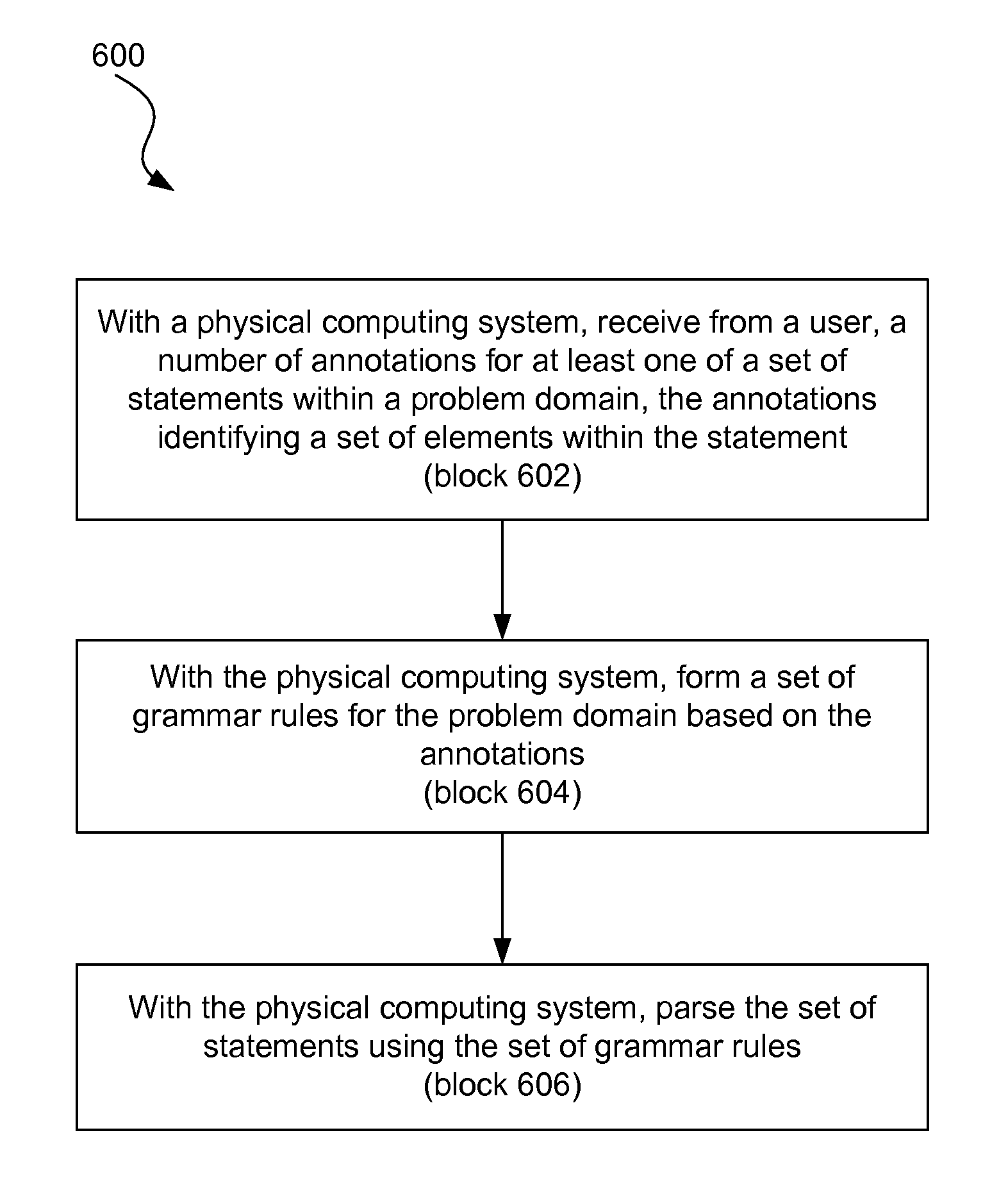
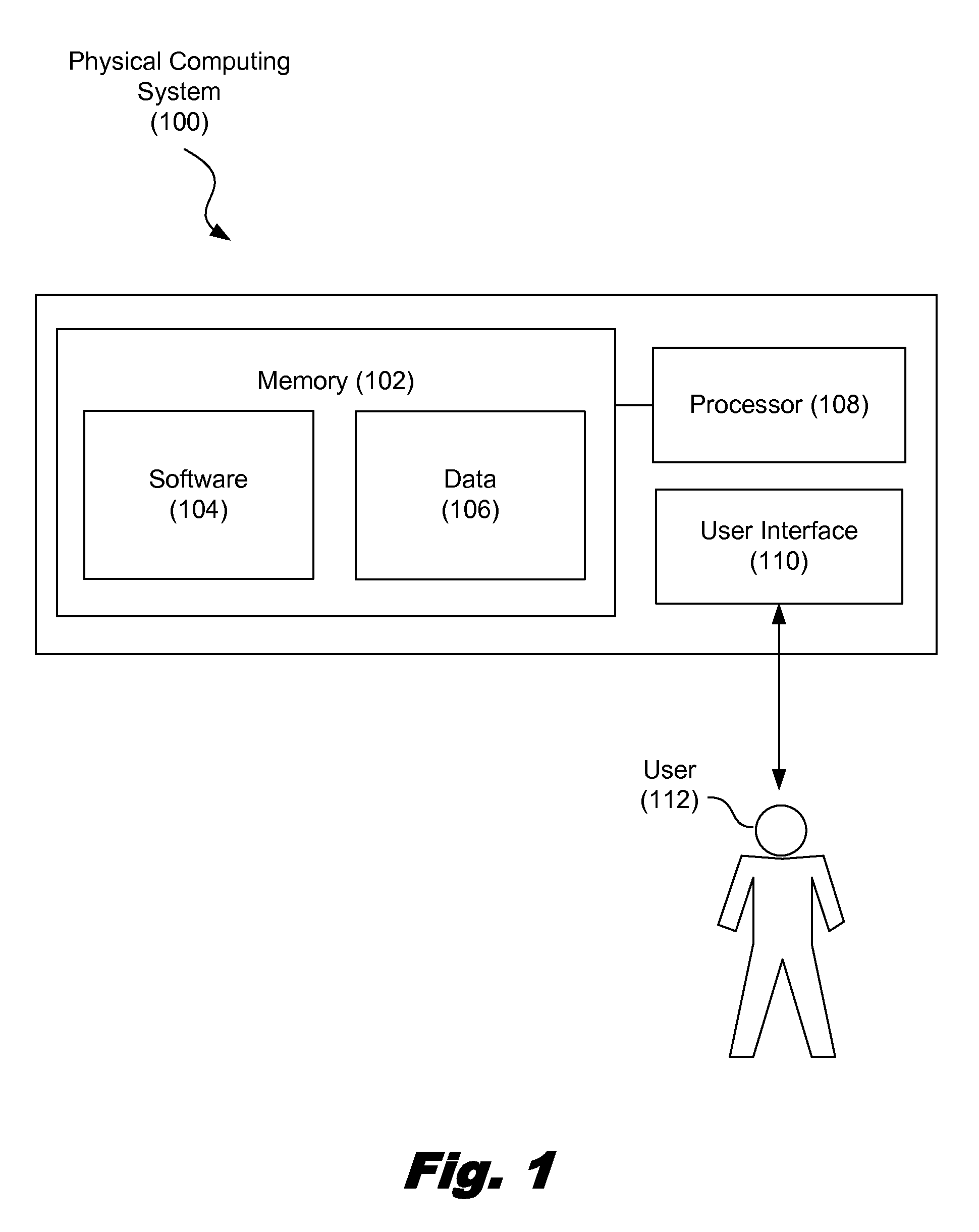
A method for domain specific language design includes, with a physical computing system, receiving from a user, a number of annotations for at least one of a set of statements within a problem domain, the annotations identifying a set of elements within the statement. The method further includes forming a set of grammar rules for the problem domain based on the annotations, and parsing the set of statements using the set of grammar rules.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for domain specific test design automation
InactiveUS20050240794A1Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsSpecific testProblem domain
A method for automatically generating test cases from a domain specific description language specification makes use of the properties of the language to derive domain specific axioms and language specific predicates. These properties are embedded into an extended finite state machine which is in turn supplied to the input of a test case generator. The enhanced extended finite state machine, referred herein as an extended finite state machine accounting for axioms and predicates (EFSMAP) contains states and transitions associated with information on implied behavior of the specified system within a particular problem domain. The implicit behavior, defined by the axiomatic properties of the operators of the domain specific language, provide test capability of the associated system that was not explicitly set forth in the formal specification, but nevertheless should be tested to increase confidence in the reliability of the finished product.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF +1
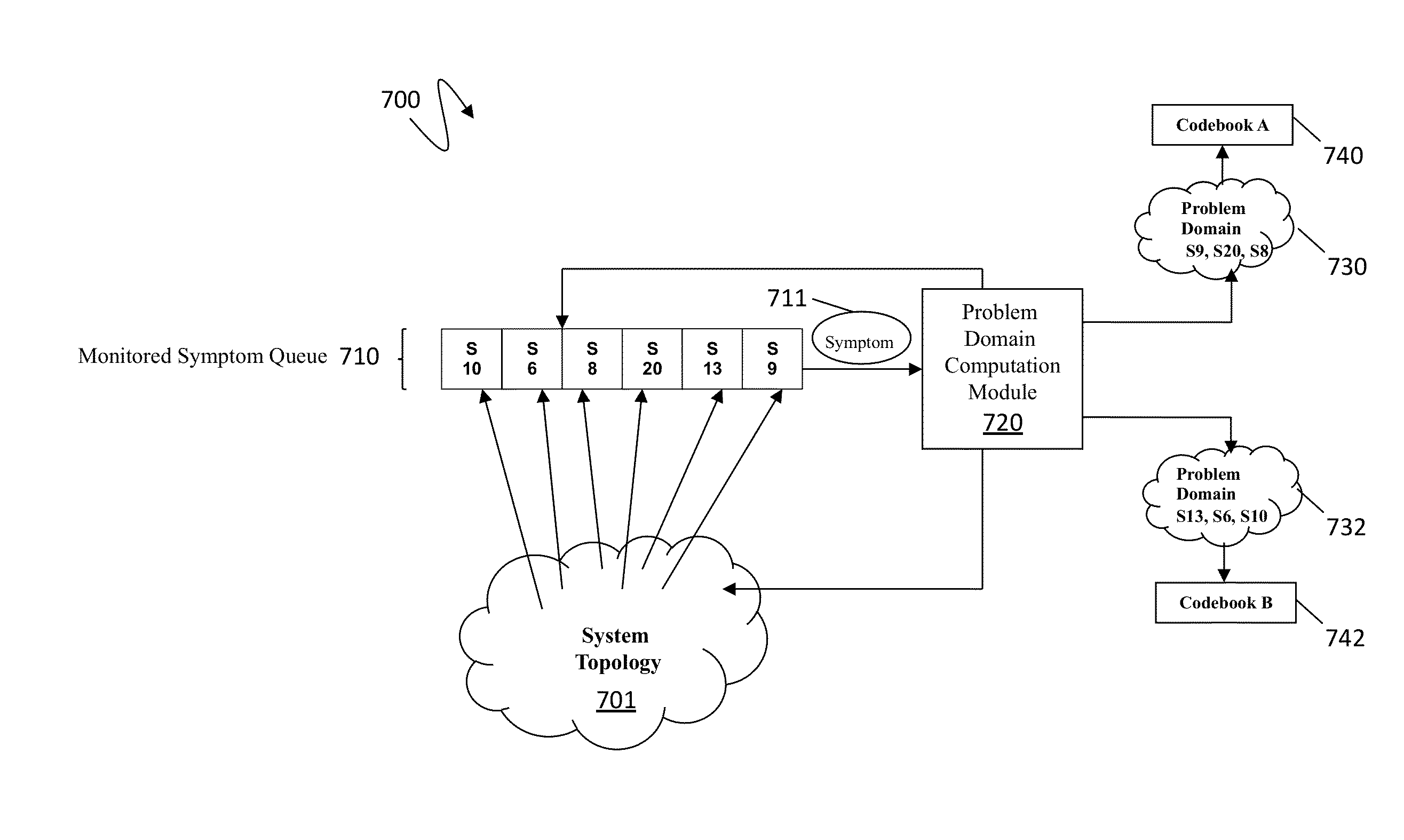
Scalable codebook correlation for cloud scale topology
ActiveUS8832498B1Eliminating duplicate symptomMultimedia data retrievalHardware monitoringProblem domainObject store
A system and algorithm to map alerts to a problem domain is provided so that the size of a codebook for the problem domain may be reduced and correlated independently of the general system and / or other problem domains in the system topology. When one or more symptoms of a fault appear in the system topology, the problem domain is discovered dynamically and the codebook for the problem domain generated dynamically. The system described herein provides for computation of a problem domain that has a reduced object repository for a set of objects which are directly or indirectly impacted by monitored symptoms. Multiple problem domains may be independently computed in order to build one or more codebooks. Each problem domain may be smaller compared to a system topology resulting in scale and performance improvements for codebook computation and correlation.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Valuation-based learning system
The present invention relates to a valuation-based learning system. The system is configured to receive a plurality of inputs, each input being input evidence corresponding to a variable in a Dempster-Shafer Reasoning System. The Dempster-Shafer Reasoning System is a network of interconnected nodes, with each node representing a variable that is representative of a characteristic of a problem domain. A discount weight is then optimized for assigning to each of the inputs. A basic probability assignment (bpa) is generated using the Dempster-Shafer Reasoning System, and where the bpa is an output for use in determining a solution of the problem domain. Finally, a solution to the problem domain is determined using the bpa.
Owner:HRL LAB
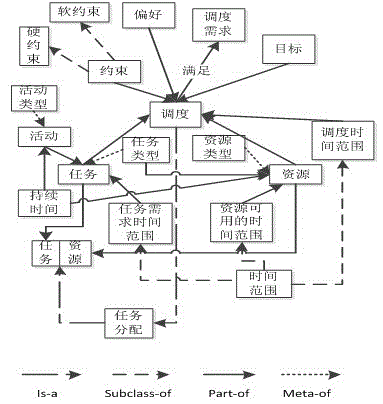
Imaging satellite scheduling problem model building method based on body
The invention discloses an imaging satellite scheduling problem model building method based on a body. The method comprises the following specific steps of (1) treating tasks, resources, a scheduling time range, restraints, goals, preferences and scheduling demands as related items of an imaging satellite scheduling problem, (2) combining the related items of the tasks, the resources, the scheduling time range, the restraints, the goals, the preferences and the scheduling demands with specific application knowledge to carry out instantiation on the mutual relation, and generating a specific application model, and (3) building the specific application model by the utilization of a body tool, and describing the body of the specific application model through a standard format. According to the imaging satellite scheduling problem model building method based on the body, a problem domain is confirmed by building the goals, the restraints and problem parameters, and accordingly the imaging satellite scheduling problem can be described generally.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Schema-based machine generated programming models
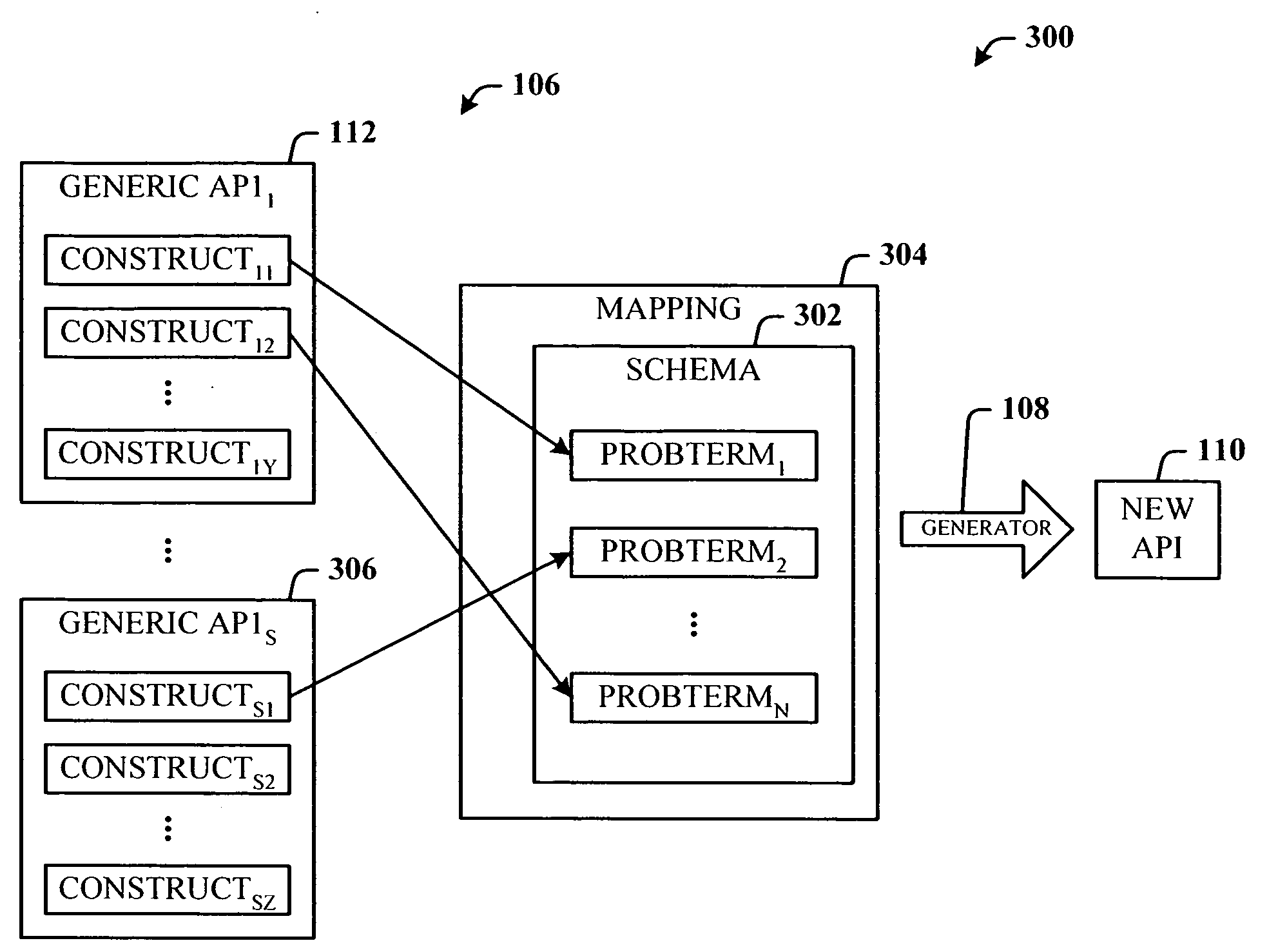
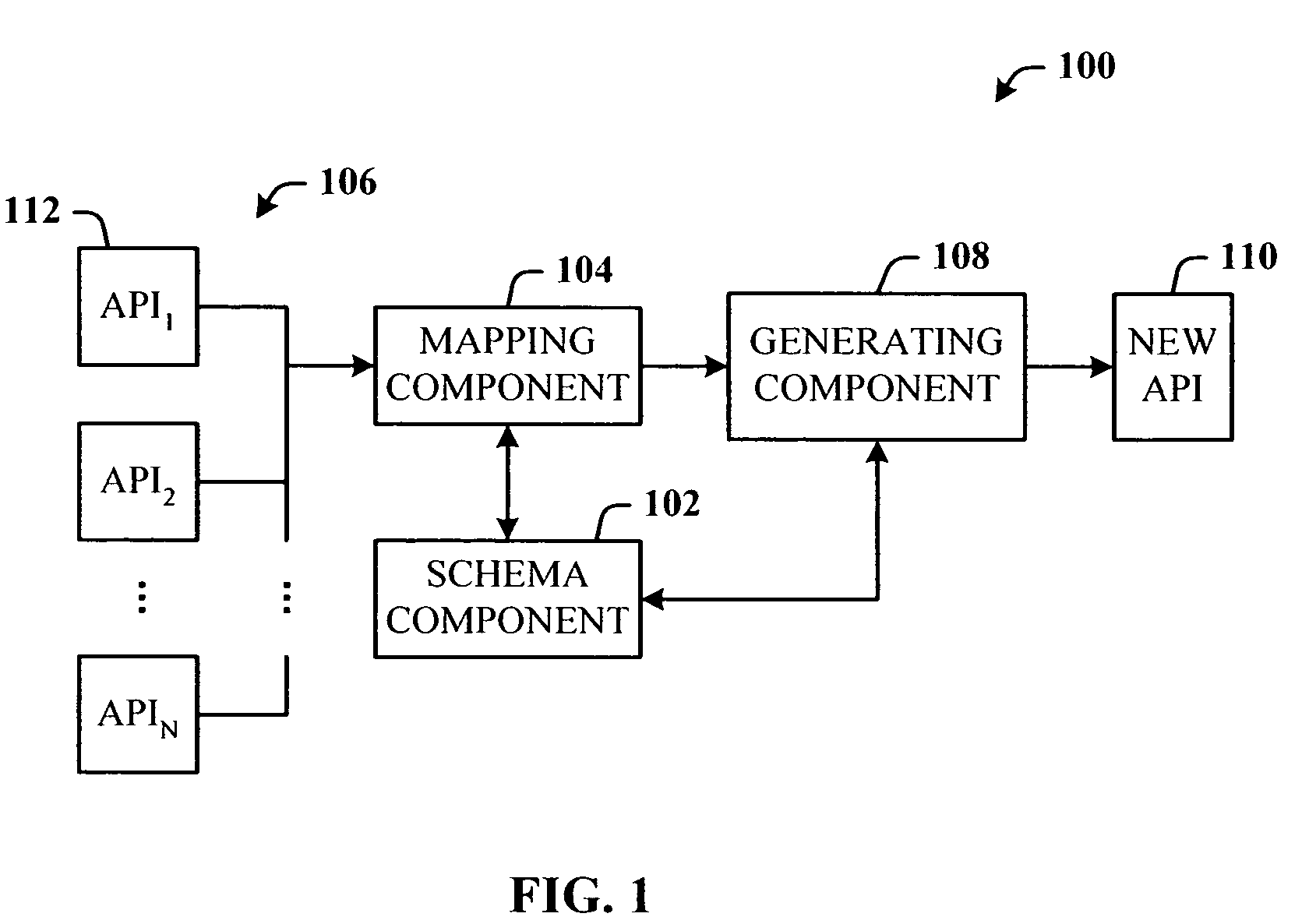
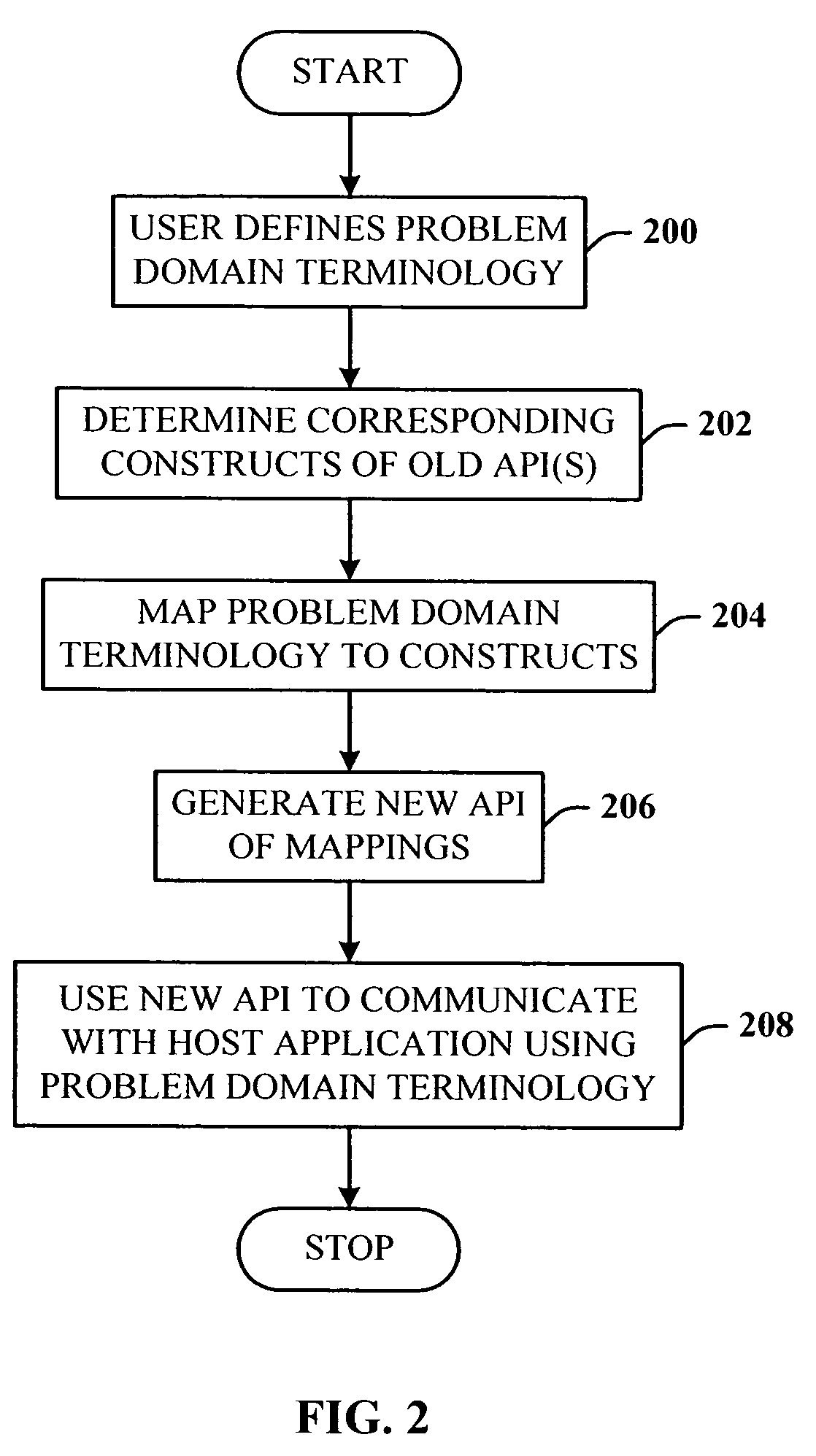
A programming model that takes general purpose APIs and machine-generates new programming models based on user defined schemas that provide the developer with data and view separation, and a way to communicate to the host application using the domain of the problem being solved. The system comprises a schema component that the developer uses to define a schema that includes one or more domain terms related to the problem to be solved, and a mapping component that uses the schema to search and map selected constructs from one or more generic host application APIs to the corresponding problem domain terms. Once the mapping is completed, a generating component generates a new API that is used by a host application to facilitate developing an application document using terms related to the domain of the problem to be solved.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Building and delivering highly adaptive and configurable tutoring systems
Owner:SCANDURA JOSEPH M
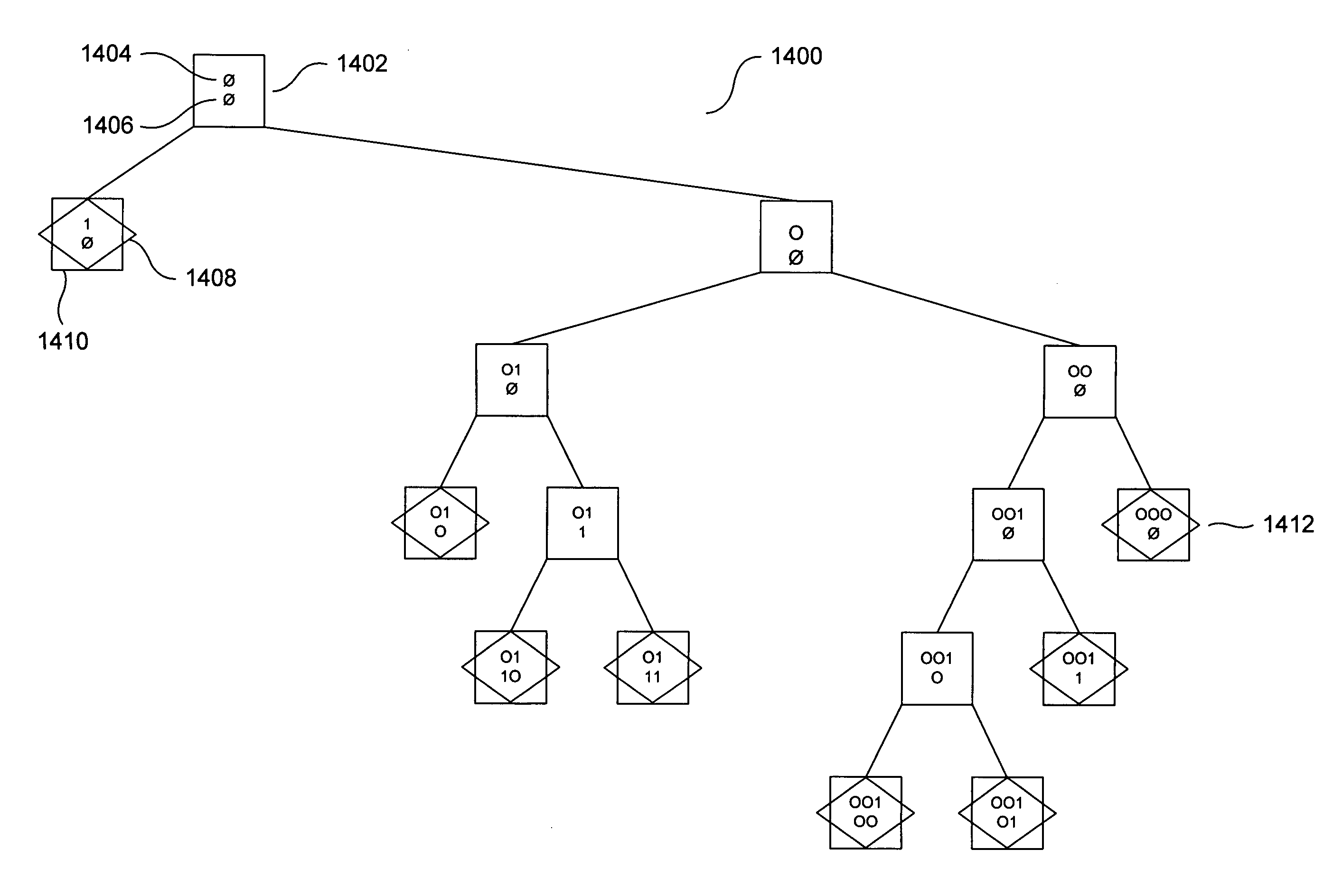
Method and system for determining an optimal or near optimal set of contexts by constructing a multi-directional context tree
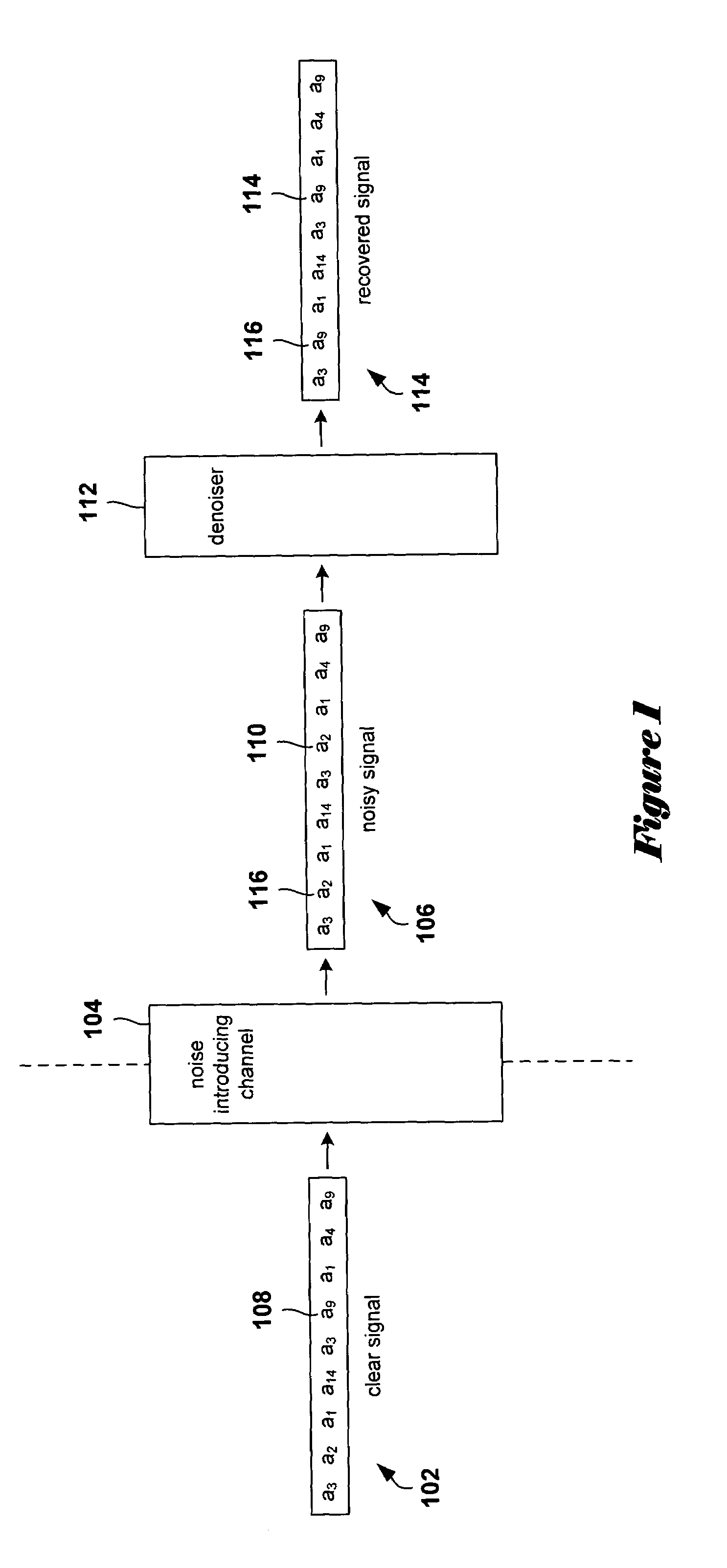
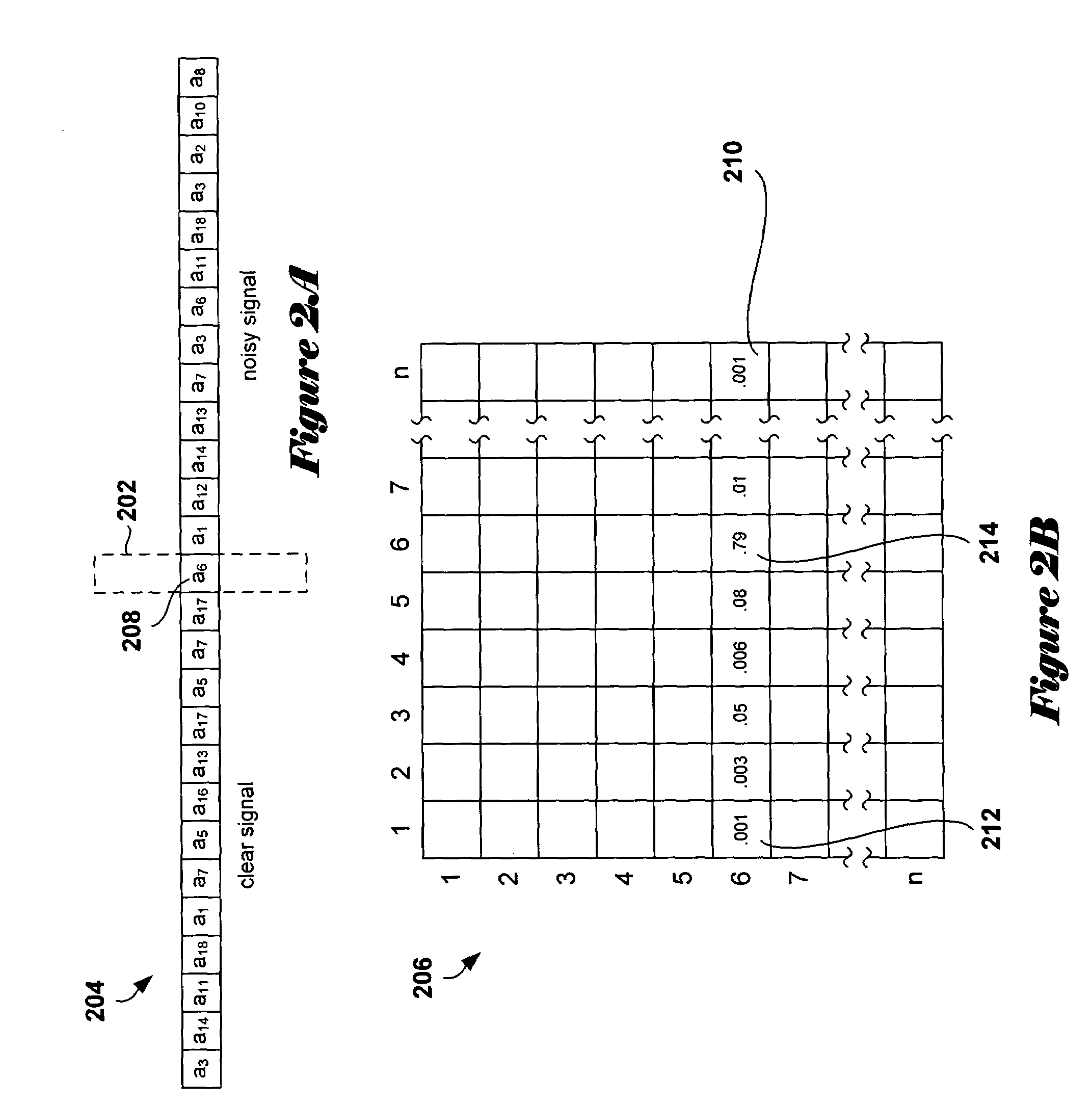
In various embodiments of the present invention, optimal or near-optimal multidirectional context sets for a particular data-and / or-signal analysis or processing task are determined by selecting a maximum context size, generating a set of leaf nodes corresponding to those maximally sized contexts that occur in the data or signal to be processed or analyzed, and then building up and concurrently pruning, level by level, a multidirectional optimal context tree constructing one of potentially many optimal or near-optimal context trees in which leaf nodes represent the context of a near-optimal or optimal context set that may contain contexts of different sizes and geometries. Pruning is carried out using a problem-domain-related weighting function applicable to nodes and subtrees within the context tree. In one described embodiment, a bi-directional context tree suitable for a signal denoising application is constructed using, as the weighting function, an estimated loss function.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
Method for establishing software requirement model
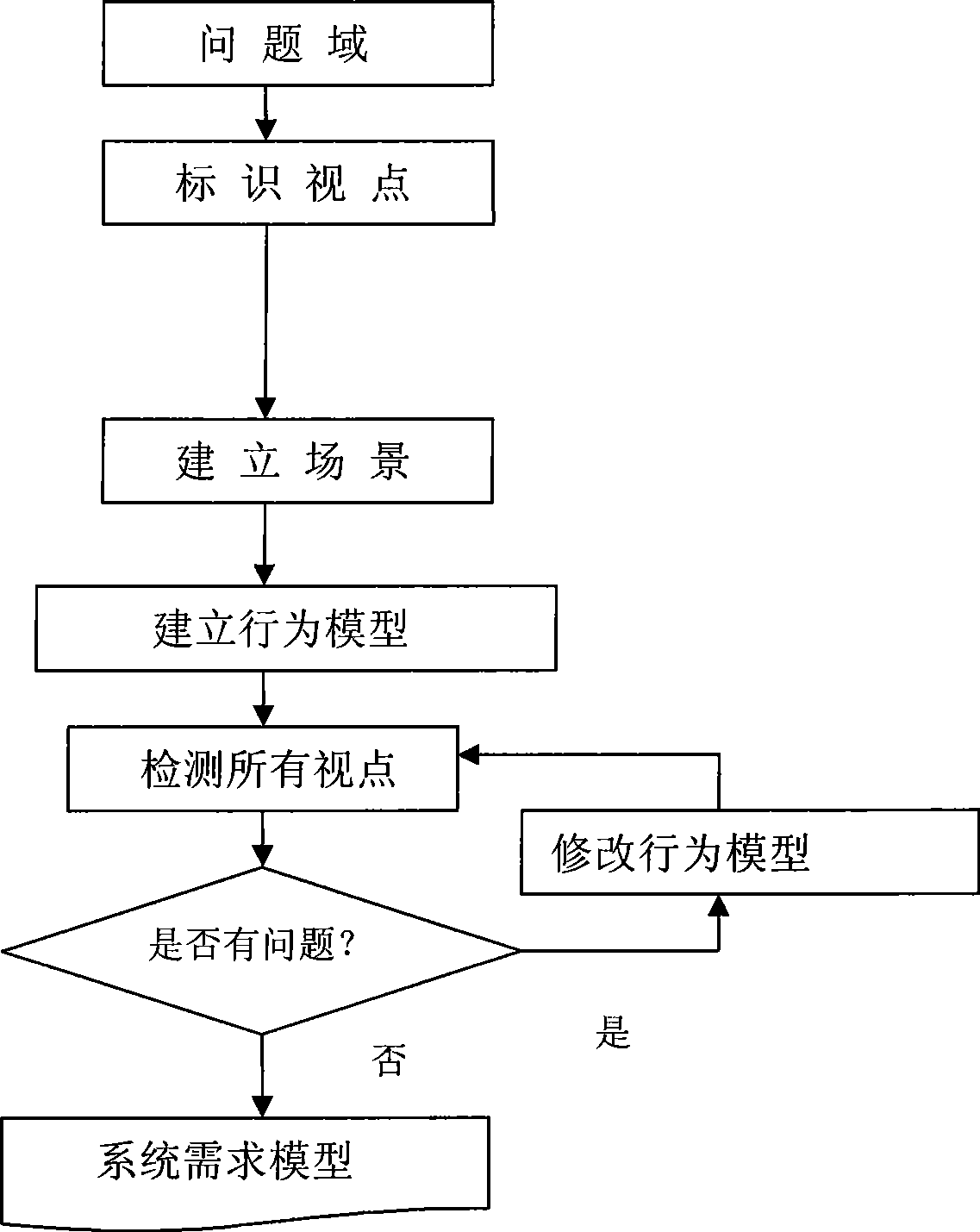
InactiveCN101464796AReduce the difficulty of requirement modelingExtensiveSpecific program execution arrangementsRequirements modelViewpoints
The invention discloses a method for establishing a software requirement model, which comprises the following steps: a problem domain is identified and a viewpoint is defined; a scene is established for each viewpoint relevant to a software system to be developed; a system requirement model is established in an action description language; all the viewpoints are tested; if the testing result is problem finding, the corresponding scene action model or the viewpoint action model is required to be modified and returned to be detected again until the testing result of every viewpoint passes; and if the testing result passes, all the viewpoint action models are synthesized to get and output a final system requirement model. By adopting the technologies of scene and viewpoint, a good foundation is laid by the method of the invention for establishing the high quality requirement model for a complex software system and automatically detecting whether a software system is correct and complete; moreover, the invention is compatible with other modeling methods and technologies and has good universality and utility.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Formal structure-based algorithms for large scale resource scheduling optimization
ActiveUS8412551B2Fast dual optimization—obtainingQuality improvementDigital computer detailsForecastingProblem domainAlgorithm
A method and computer program product for optimization of large scale resource scheduling problems. Large scale resource scheduling problems are computationally very hard and extremely time consuming to solve. This invention provides a Lagrangian relaxation based solution method. The method has two distinct characteristics. First, the method is formal. It is completely structure-based and does not use any problem domain specific knowledge in the solution process, either in the dual optimization or the primal feasibility enforcement process. Second, updating the Lagrangian multipliers after solution of every sub-problem without using penalty factors results in fast and smooth convergence in the dual optimization. The combination of high quality dual solution and the structure-based primal feasibility enforcement produces a high quality primal solution with very small solution gap. An optimal solution is first found to the dual of the resource scheduling problem by sequentially finding a solution to a plurality of sub-problems and updating a set of values used in the dual problem formulation after each sub-problem solution is obtained. Coupling constraint violations are systematically reduced and the set of values are updated until a feasible solution to the primal resource scheduling problem is obtained. An initial set of multiplier values is further determined by solving a relaxed version of the primal problem where most of the local constraints except the variable bounds are relaxed.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY LTD
Enhancing performance of a constraint solver across individual processes
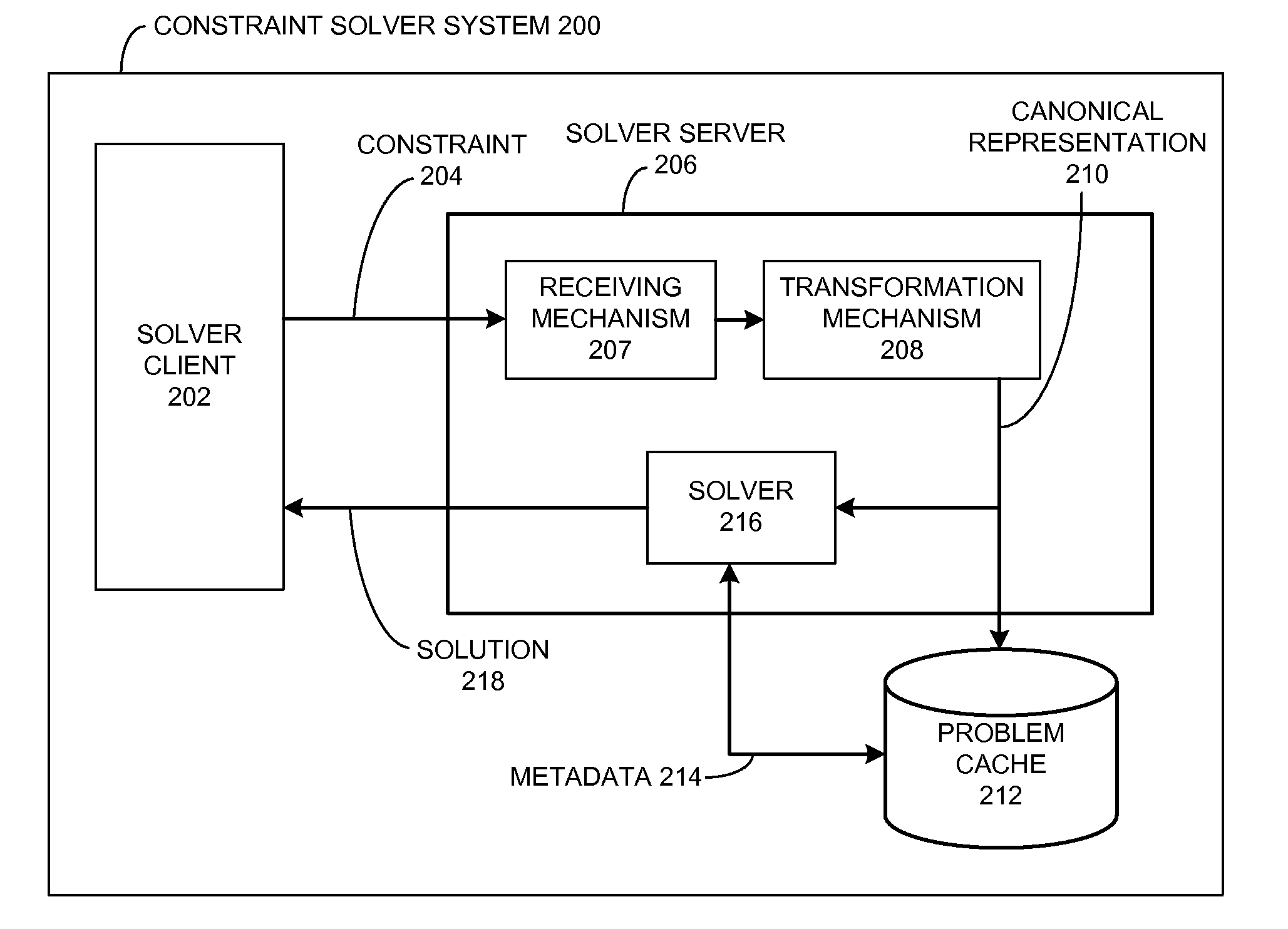
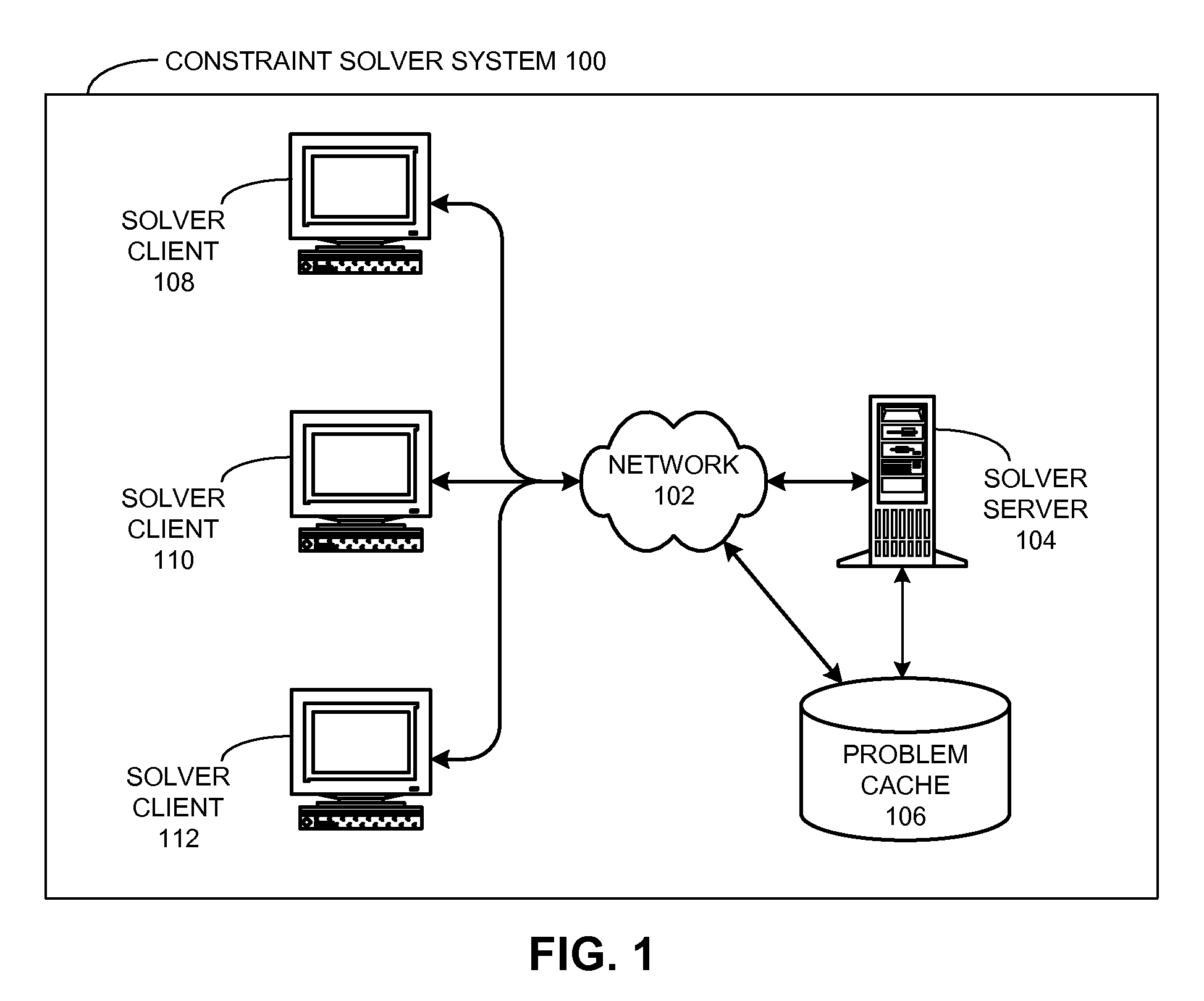
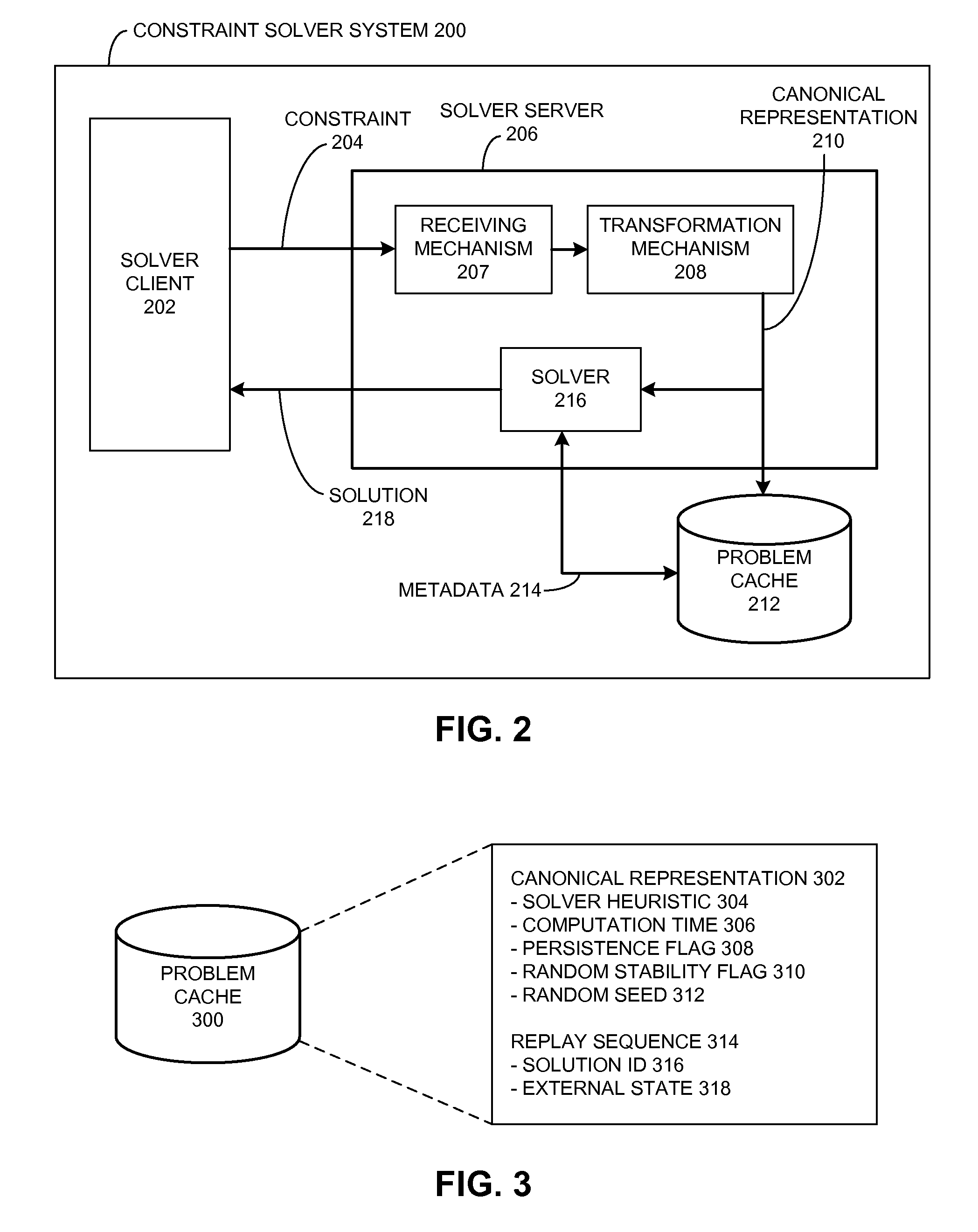
ActiveUS20100017352A1Provide stabilityKnowledge representationInference methodsProblem domainAlgorithm
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that reuses information associated with a constraint solving operation for a problem domain. This system begins by receiving a constraint problem from the problem domain. Then, the system searches through a problem cache for an entry which corresponds to the canonical representation. If a corresponding entry does not exist in the problem cache, the system produces an entry in the problem cache for the canonical representation. Otherwise, if a corresponding entry already exists in the problem cache, the system generates a solution to the canonical representation by reusing the solver heuristic associated with the corresponding entry in the problem cache.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Layering collocation method of land utilization
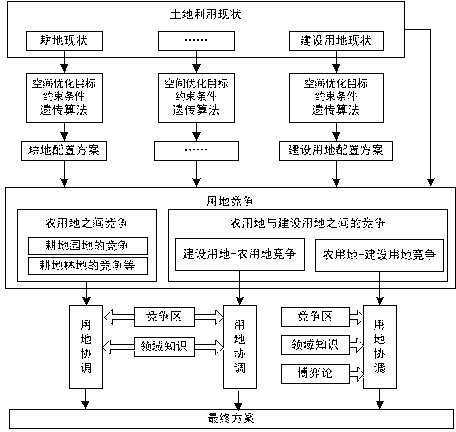
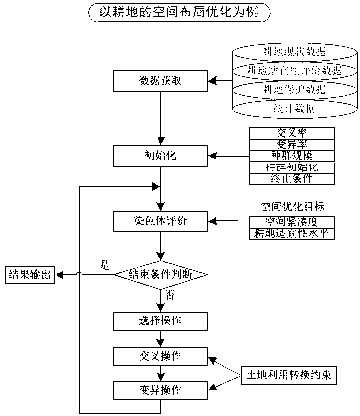
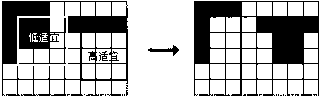
ActiveCN103136707AImprove rationalityCoordinate competitionData processing applicationsCollocationProblem domain
The invention relates to a layering collocation method of land utilization. According to the layering collocation method of the land utilization, basic data of the land utilization are firstly obtained and collected by a land utilization layering collocation model, land needing to be optimized in spatial arrangement is suitability evaluated, a specific genetic algorithm chromosome and a genetic evolution operator are constructed aiming at optimization problems of the land utilization spatial arrangement, mapping from a problem domain to the algorithm domain is accomplished and the spatial arrangement of various kinds of land is optimized by using the genetic algorithm under the guidance of a space optimization objective, and then land utilization competition between the optimized spatial arrangement of the various kinds of land and the land utilization in an existing state is solved by combining knowledge in the land planning field and the game theory. The layering collocation method of the land utilization is capable of well optimizing the spatial arrangement of the various kinds of land and good at coordinating the land utilization. The knowledge in the land planning field ensures that a land utilization coordination result is reasonable and the game theory is capable of solving the land utilization competition by introducing benefit factors, and feasibility of the land utilization coordination result is well guaranteed.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
A software security requirement acquisition method based on formal modeling
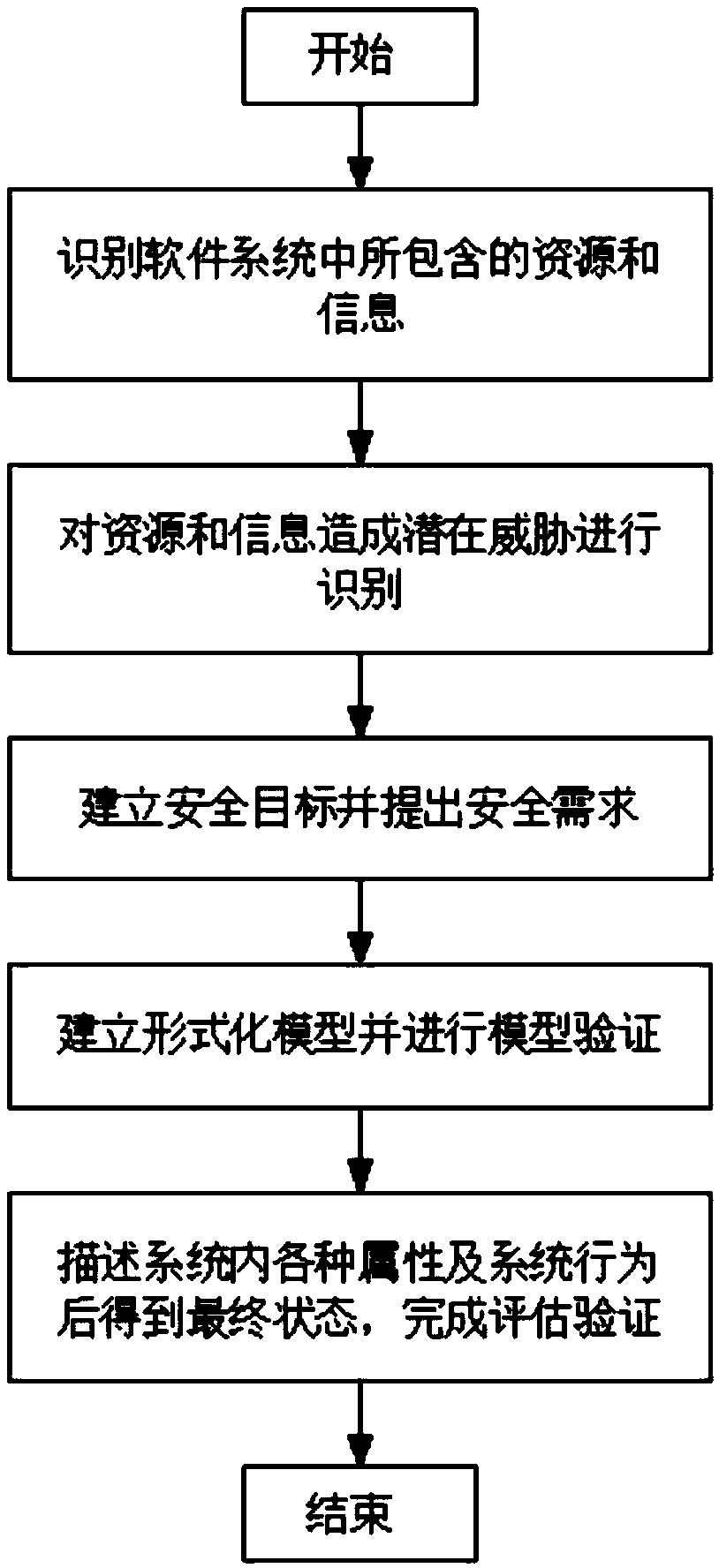
InactiveCN109388377ASecurity Requirements CaptureImprove securitySoftware testing/debuggingRequirement analysisProblem domainRequirements elicitation
The invention discloses a software security requirement acquisition method based on formal modeling in the technical field of software security. The specific steps of the method are as follows: S1, identifying resources and information contained in a software system; S2: identifying potential threat behaviors caused by resources and information; S3: establishing security objectives and proposing security requirements, and verifying the security requirements; 4, establishing a formal model and verifying that model; 5, describing various attributes and system behavior in that system to obtain afinal state, to realize the interpretation, evaluation and verification of the software system. The invention firstly identifies information in a software system, acquire the description of information security threat, determines whether the phenomenon description of problem domain meets the condition of security threat, establishes formal model and verifying, which makes up for the shortcomings of traditional security requirements analysis methods, and enables the requirements analysts to further capture the security requirements of software systems.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV FOR NATITIES
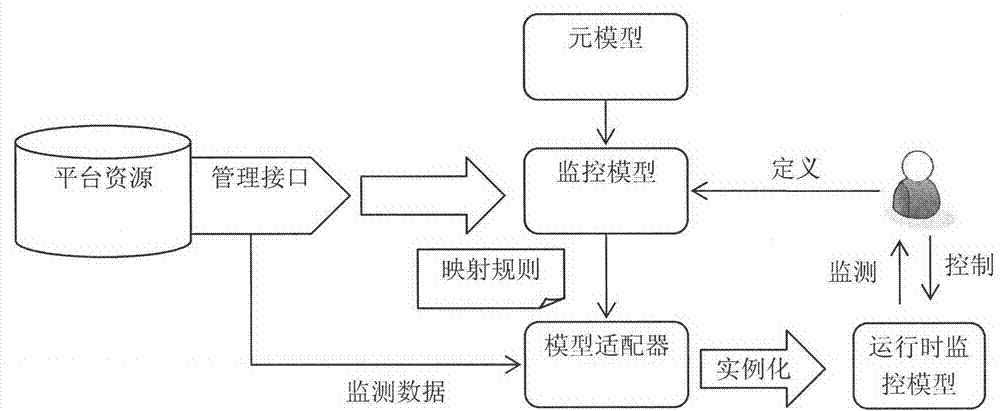
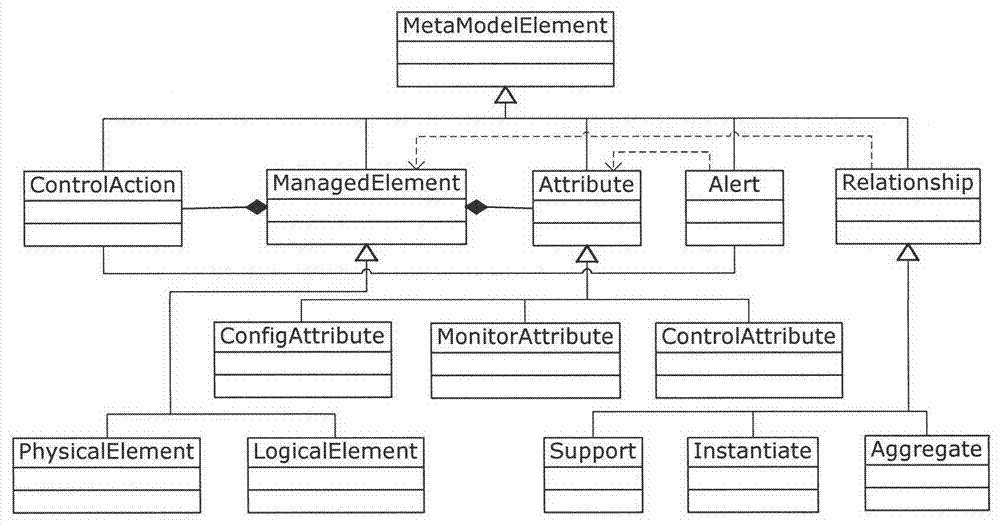
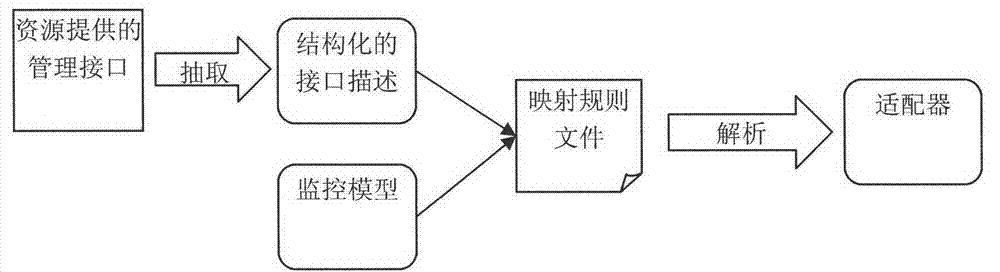
Service platform monitoring model capable of supporting user visible user-definition
The invention discloses a service platform monitoring model capable of supporting user visible user-definition. According to the model, a method for management is provided for a software service operation platform in the cloud environment in the process of operation, wherein the method starts from a problem domain and is high in level of abstraction. The service platform monitoring model capable of supporting user visible user-definition is mainly characterized in that a set of visual monitoring modeling elements supporting user-definition are provided, wherein the modeling elements comprise the characteristics and the relationships of various monitored objects contained in management when the software service platform is operated; a monitoring model generating method based on a mapping rule in the process of operation is provided. Based on the management requirement and the mapping rule in the process of operation which are obtained through modeling by a platform manager, corresponding adaptors can be automatically generated according to different resource types. In the process of operation, real-time monitoring data obtained by a bottom-level management API are automatically instantiated to corresponding monitoring models in the process of operation by the adaptors and are analyzed to graphical model representation.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
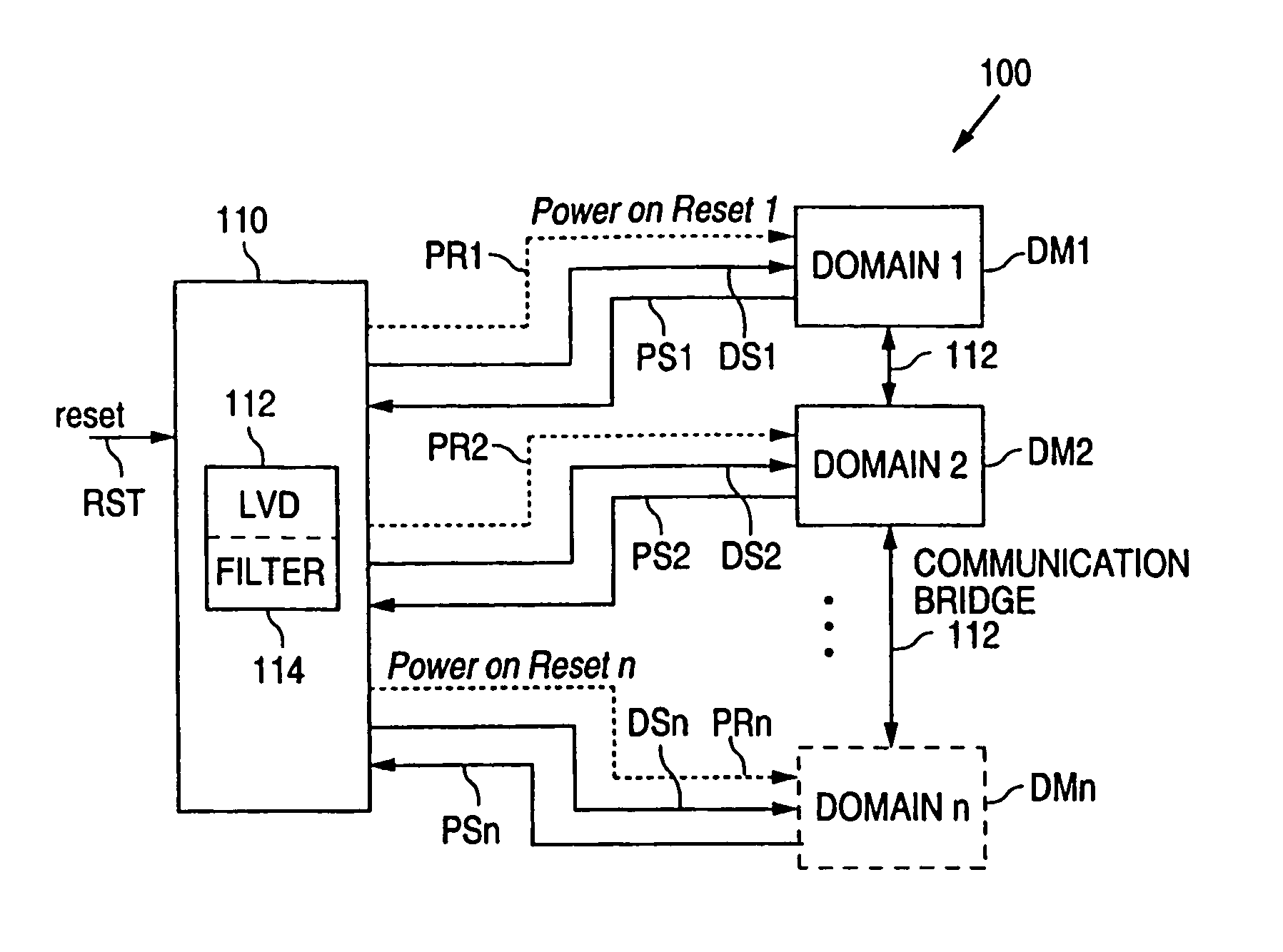
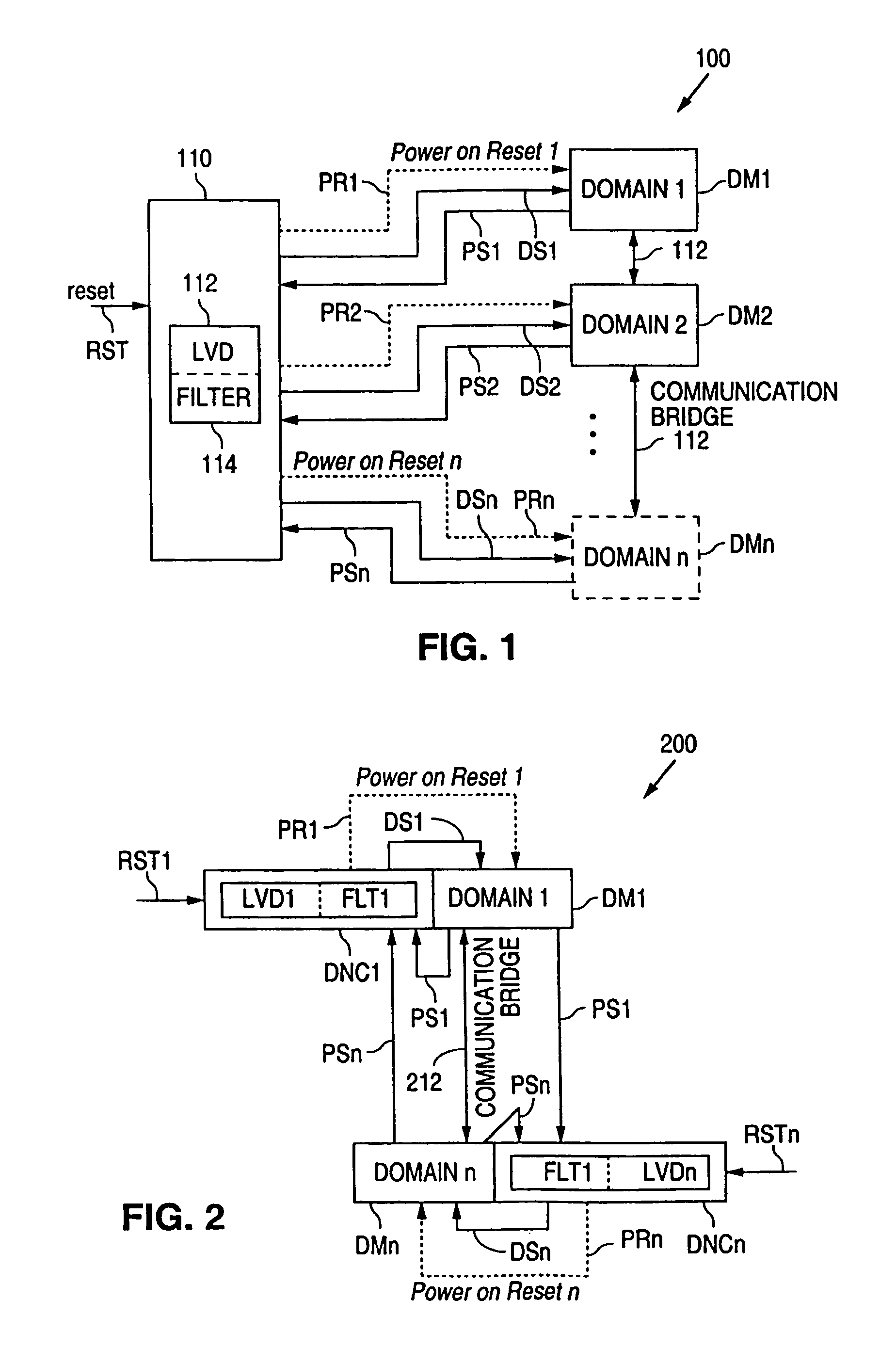
System and method for domain power monitoring and notification
A domain power notification system detects when a power domain experiences a power condition, such as lost power and low-voltage power, and communicates that information to the domains that communicate with the problem domain. As a result, the effected domains stop communicating with the problem domain without passing erroneous information.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Pattern-based construction and extension of enterprise applications in a cloud computing environment
Methods, software programs and systems for extending and modifying software functionality, and, more particularly, for using one or more patterns for an enterprise software object to express desired functionality and configuration, and to generate the enterprise software object using the patterns, in an enterprise environment are disclosed. A method according to certain of these embodiments includes selecting one or more patterns from a number of patterns, where the one or more patterns are for an enterprise software object. The enterprise software object can then be generated. The enterprise software object is generated using the one or more patterns. Each of the patterns is configured to describe a solution within a corresponding one of a number of problem domains.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
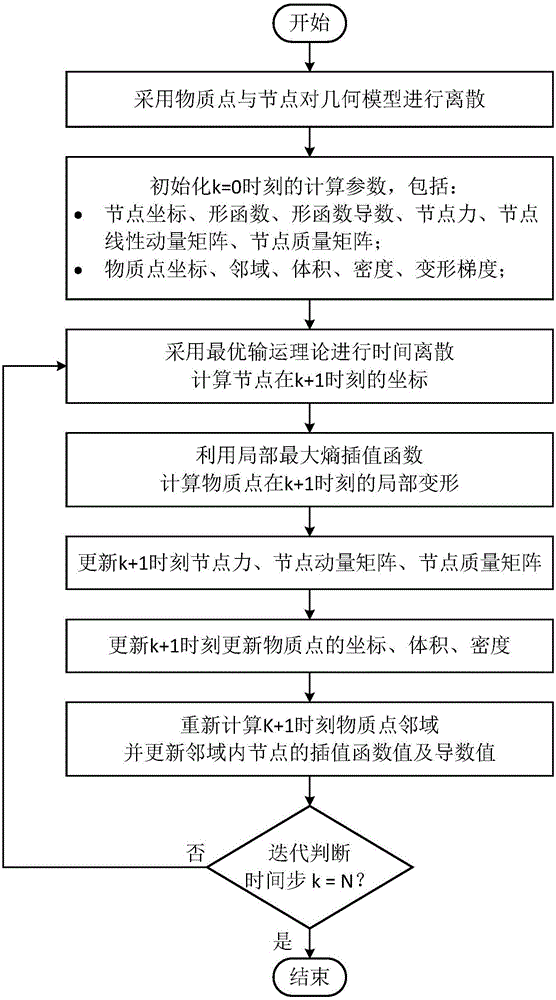
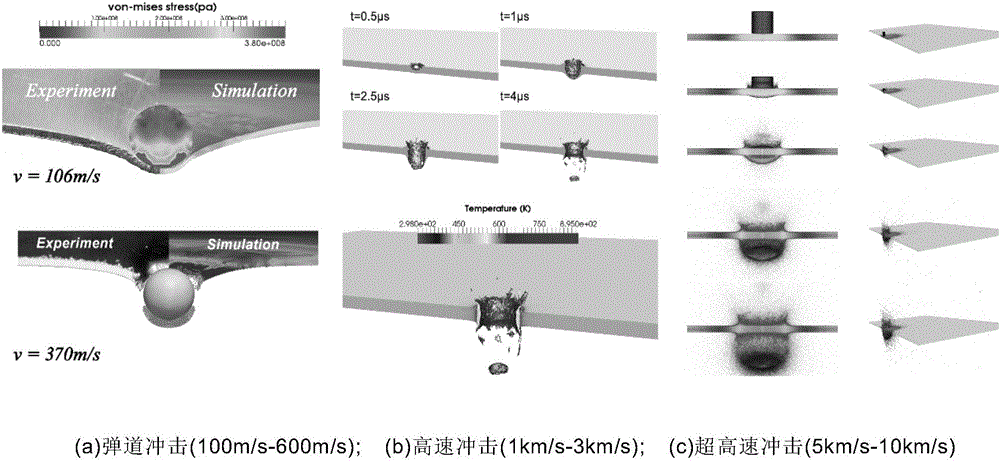
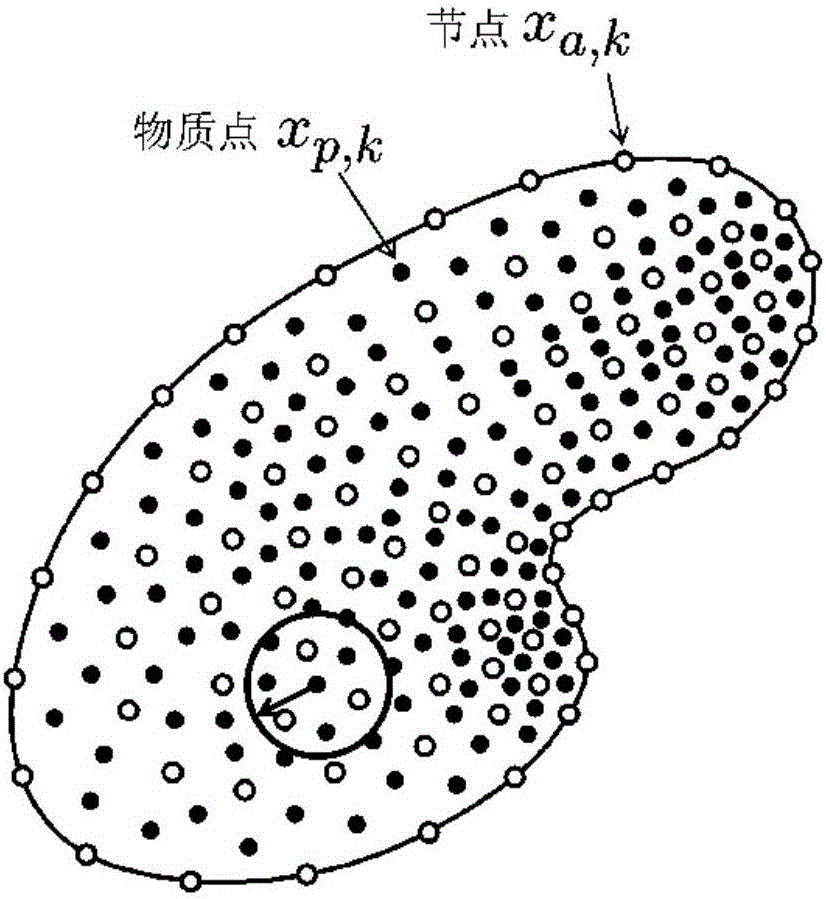
Optimal transportation meshless method for solving large deformation of material
ActiveCN106446432AResolving Tensile Stress InstabilityAvoid high computationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsProblem domainMetallic materials
The invention relates to an optimal transportation meshless (OTM) method for solving large deformation of a material and aims at solving the problems of effective and stable solving of maximum deformation, high-speed impact and geometric distortion, metal material molding, multiphase coupling and the like. The OTM method adopts a material point and node pair original problem domain to perform discretion and adopts a local maximum entropy interpolation function to construct a continuous movement function, and the problem that mesh distortion caused in maximum deformation processed by adopting a finite element method, the problem that a Dirichlet boundary condition cannot be directly added for a meshless method, calculating misconvergence and the like are avoided. In addition, due to the fact that interpolation and integration are performed at different discrete points, an effective meshless numerical integration mode is provided, and the problem of tensile stress instability is solved. The OTM method serves as an incremental updating Lagrangian method to make mass conservation automatically achieved without solving. Time discretion is performed by adopting an optimal transportation theory, the momentum conservation and symplectic conservation of a discrete system are ensured, and the operation efficiency and precision are greatly improved.
Owner:云翼超算(北京)软件科技有限公司
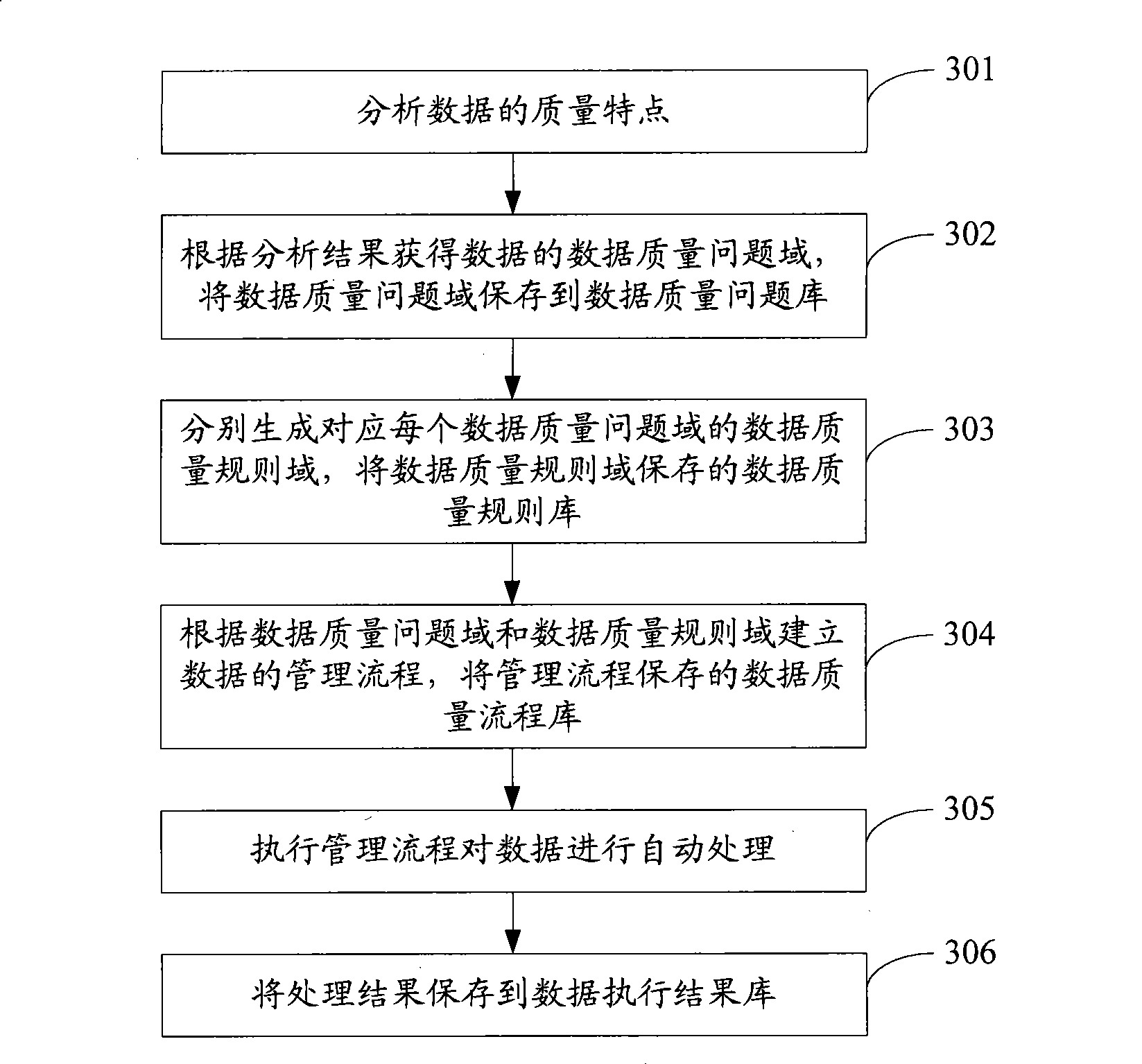
Processing method and system for data quality
InactiveCN101477653AImprove stabilityQuality improvementSpecial data processing applicationsData processing systemComplete data
The invention discloses a method for processing data quality and a system, wherein, the method comprises the following steps: establishing the management process of data according to the pre-set data quality problem domain and the pre-set data quality planning domain; automatically processing the data by implementing the management process so as to obtain the processing result of the data. As an integral data processing process is established according to the characteristic of the data, and all the problems are managed in a unified manner, the invention has the advantage that the root of an occurred problem can be found in the data processing process according to the problem, thereby improving the stability and the quality of a data production process; and, as both the data processing processes based on the data quality problem domain and the data quality planning domain can be executed automatically, the invention further has the advantages that the automaticity of the data management is higher; the accuracy and the practicability of the analysis are enhanced; and the basis of the following analysis management is provided.
Owner:DATANG SOFTWARE TECH
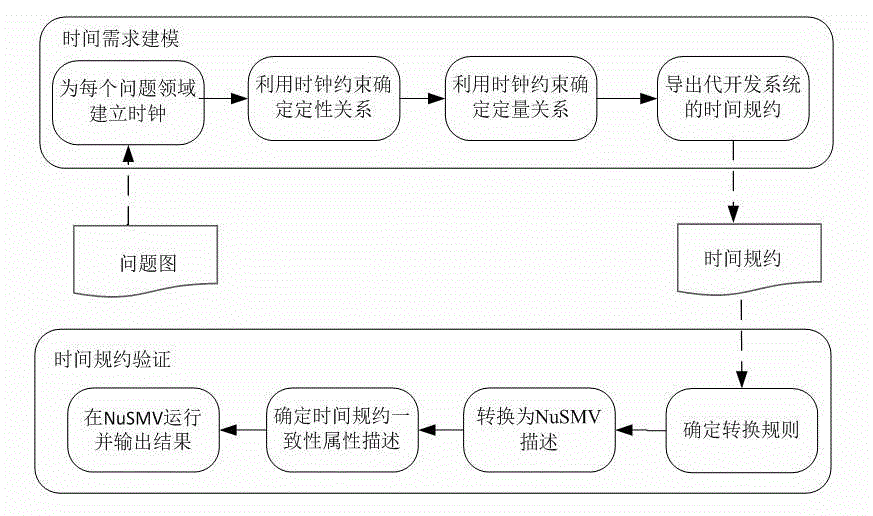
Time requirement modeling and verification method based on problem frame method
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Cognitive security system and method
ActiveUS8856057B2Minimize “suspicion”Maximize “curiosity”Burglar alarmSpecial data processing applicationsProblem domainReal-time data
A cognitive system and method for predicting and detecting security breaches is provided which yields cognitive inputs to a security management interface accessible by a human operator. The system utilizes symbolic cognitive architectures and inference processing algebras allowing the system to respond to open, incomplete, and / or unknown problem domains, offering flexibility in the case of unexpected changes in the security environment. The system is also capable of intelligently, and in real-time, adapting security peripheral configurations to further probe and analyze the real-time security environment, provided real-time data that can be processed with symbolic cognitive architectures and inference process algebras enabling the identification of new and emerging threat profiles leading to the prediction and detection of security breaches.
Owner:JANSSEN LAW PROFESSIONAL CORP IN TRUST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com