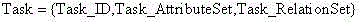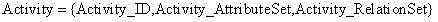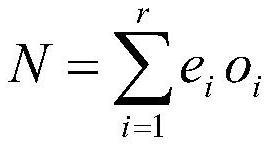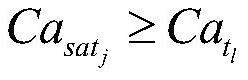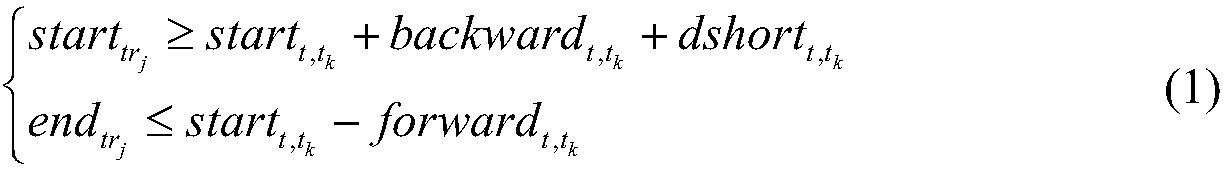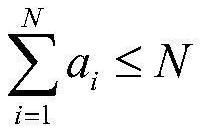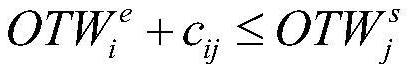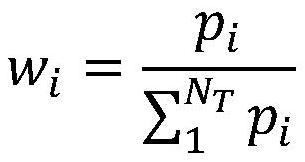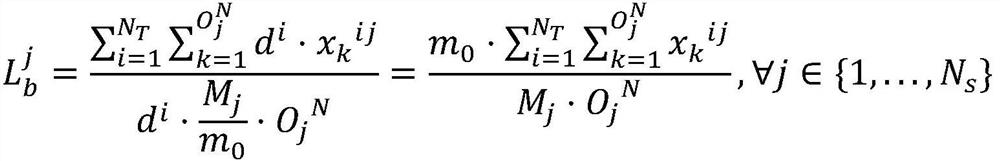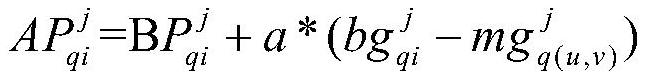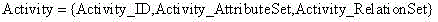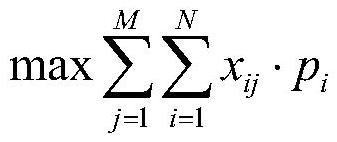Patents
Literature
49 results about "Satellite scheduling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Innovative satellite scheduling method based on genetic algorithms and simulated annealing and related mission planner
ActiveUS20180341894A1Maximal diversityCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsSimulation basedGenetic algorithm
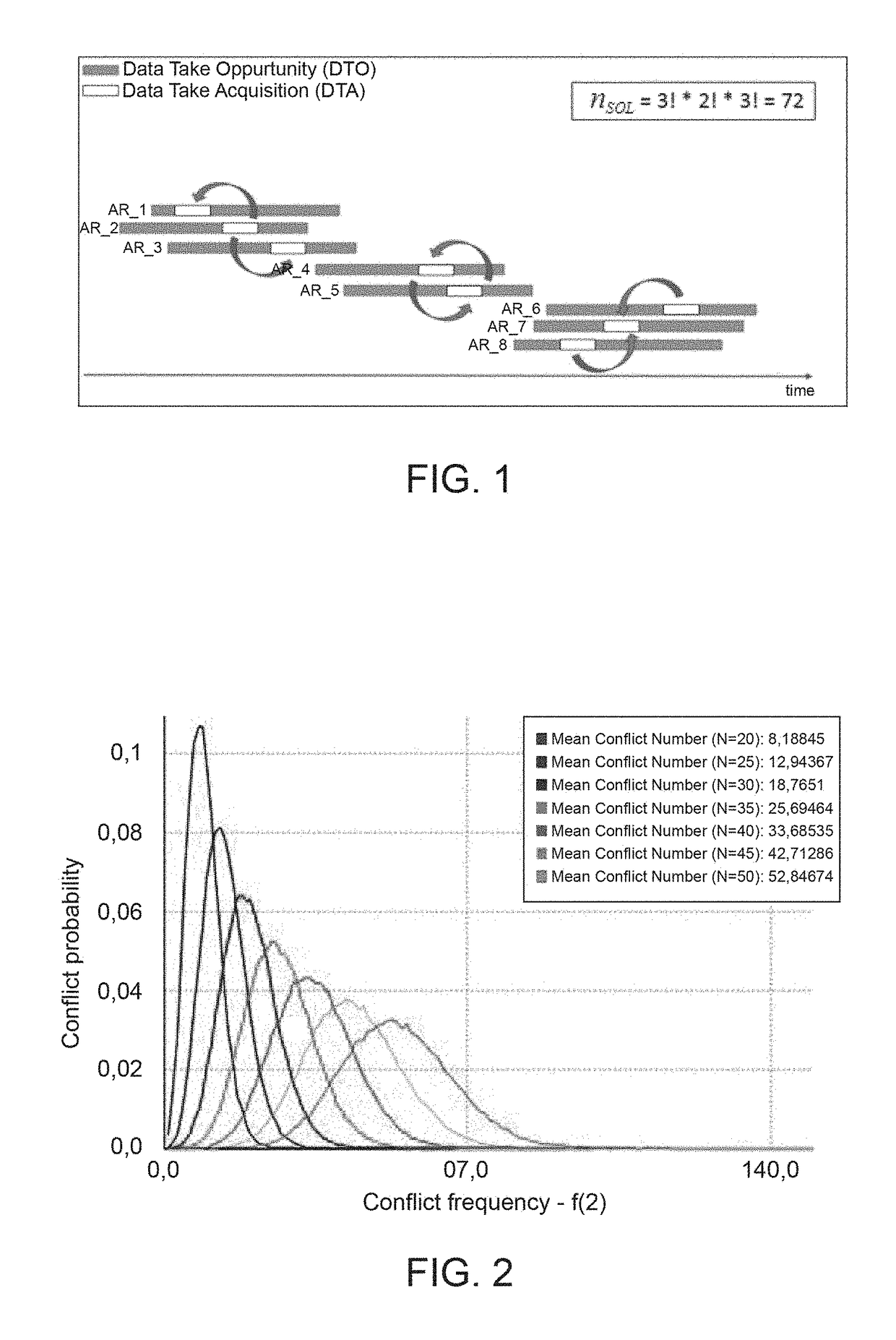
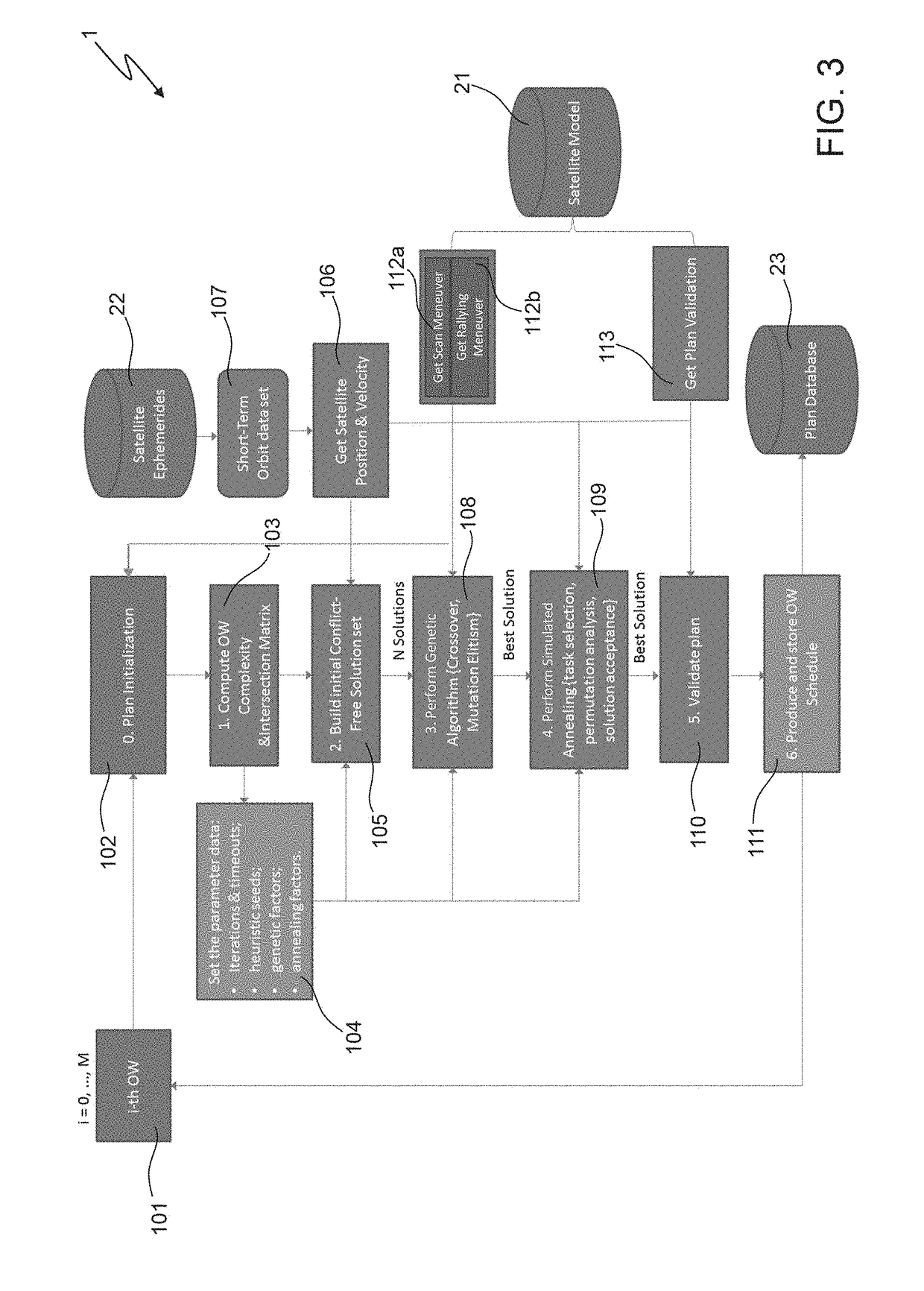
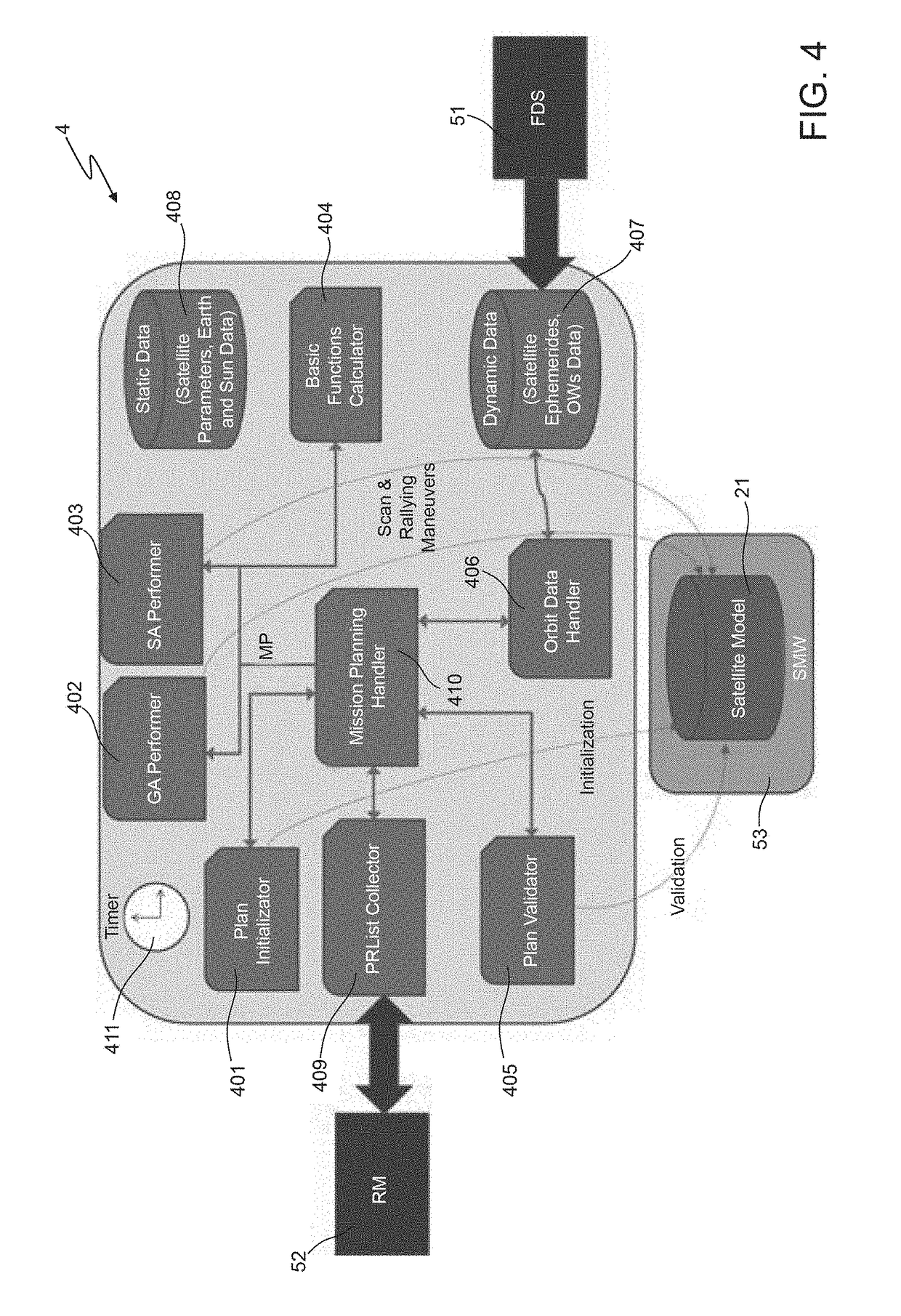
A method includes: a) producing initial scheduling plans based on requests related to tasks to be performed within a time period by a remote sensing satellite; wherein each initial scheduling plan schedules respective tasks, which do not conflict with each other in time and in using satellite resources; and each task is scheduled in at least one of the initial scheduling plans; b) applying a genetic-algorithm-based processing to the initial scheduling plans to produce a genetic-algorithm-based scheduling plan which is for mission objectives, and complies with constraints related to the satellite resources, to the tasks, and to the time period; and c) applying a simulated-annealing-based processing to the genetic-algorithm-based scheduling plan to produce a simulated-annealing-based scheduling plan that fits the mission objectives, complies with the constraints, and in which a larger number of tasks is scheduled than in the genetic-algorithm-based scheduling plan.
Owner:TELESPAZIO SPA
Algorithm for imaging satellite-oriented time-dependent scheduling problem
InactiveCN104063748AExcellent solutionImprove image qualityForecastingSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmImaging quality
The invention relates to an algorithm for solving the imaging satellite-oriented time-dependent scheduling problem. The imaging satellite-oriented time-dependent scheduling problem is the extension of the traditional satellite scheduling problem. According to the invention, modeling is performed for the problem for the time-dependent relationship between the task earnings and the imaging time, and a heuristic algorithm for solving the problem is provided. According to the invention, the time dependence is taken into account in the traditional satellite scheduling problem, so the imaging quality can be improved, the possibility for generating useless products can be reduced, and the solving effect of the provided heuristic algorithm is superior to the constrained programming algorithm engine ILOG CP Optimizer of the IBM company.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Global positioning system satellite searching and scheduling method
ActiveCN101493511AImprove the odds of successImprove usabilityBeacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationUrban forestSelf adaptive
The invention relates to the field of global satellite positioning and navigation, in particular to a satellite searching and dispatching method for a global positioning system (GPS); the method comprises three parts: a classifying satellite possibility dispatching method which comprises the steps as follows: the state of the satellite is judged by the obtained satellite information; each satellite is classified by the satellite state, thus presuming the searching scene further; according to the satellite classes and the searching scenes, different searching weights are arranged for each satellite so as to carry out the searching; a maintaining re-catching method for continuously searching the blocked satellites and a self-adaptive sensitiveness catching method which uses the catching methods of different sensitiveness by aiming at the satellites of different signal-noise-ratio. When the three methods are smartly used, the successful possibility of searching satellite is greatly improved, the time used for searching the satellite is reduced, the starting and positioning speed and the re-catching positioning precision are greatly improved, the power dissipation is reduced, and the problems of robustness and reliability in the satellite dispatching arithmetic are solved, thus improving the feasibility of the receiving machines in the urban forests where the blocking is severe, and greatly improving the experience of the user.
Owner:北京中科微知识产权服务有限公司
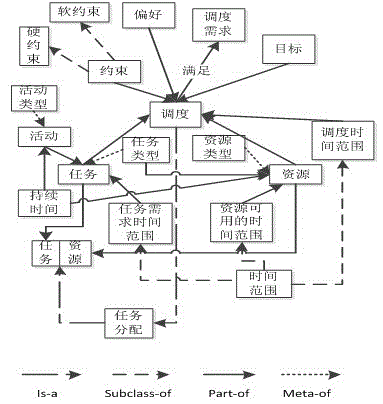
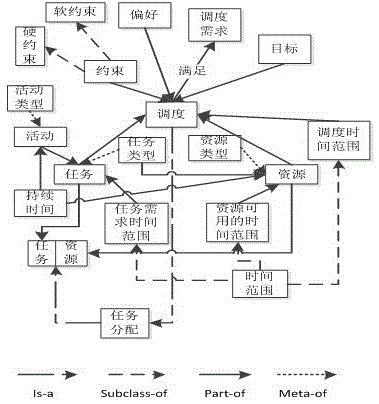
Imaging satellite scheduling problem model building method based on body
The invention discloses an imaging satellite scheduling problem model building method based on a body. The method comprises the following specific steps of (1) treating tasks, resources, a scheduling time range, restraints, goals, preferences and scheduling demands as related items of an imaging satellite scheduling problem, (2) combining the related items of the tasks, the resources, the scheduling time range, the restraints, the goals, the preferences and the scheduling demands with specific application knowledge to carry out instantiation on the mutual relation, and generating a specific application model, and (3) building the specific application model by the utilization of a body tool, and describing the body of the specific application model through a standard format. According to the imaging satellite scheduling problem model building method based on the body, a problem domain is confirmed by building the goals, the restraints and problem parameters, and accordingly the imaging satellite scheduling problem can be described generally.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
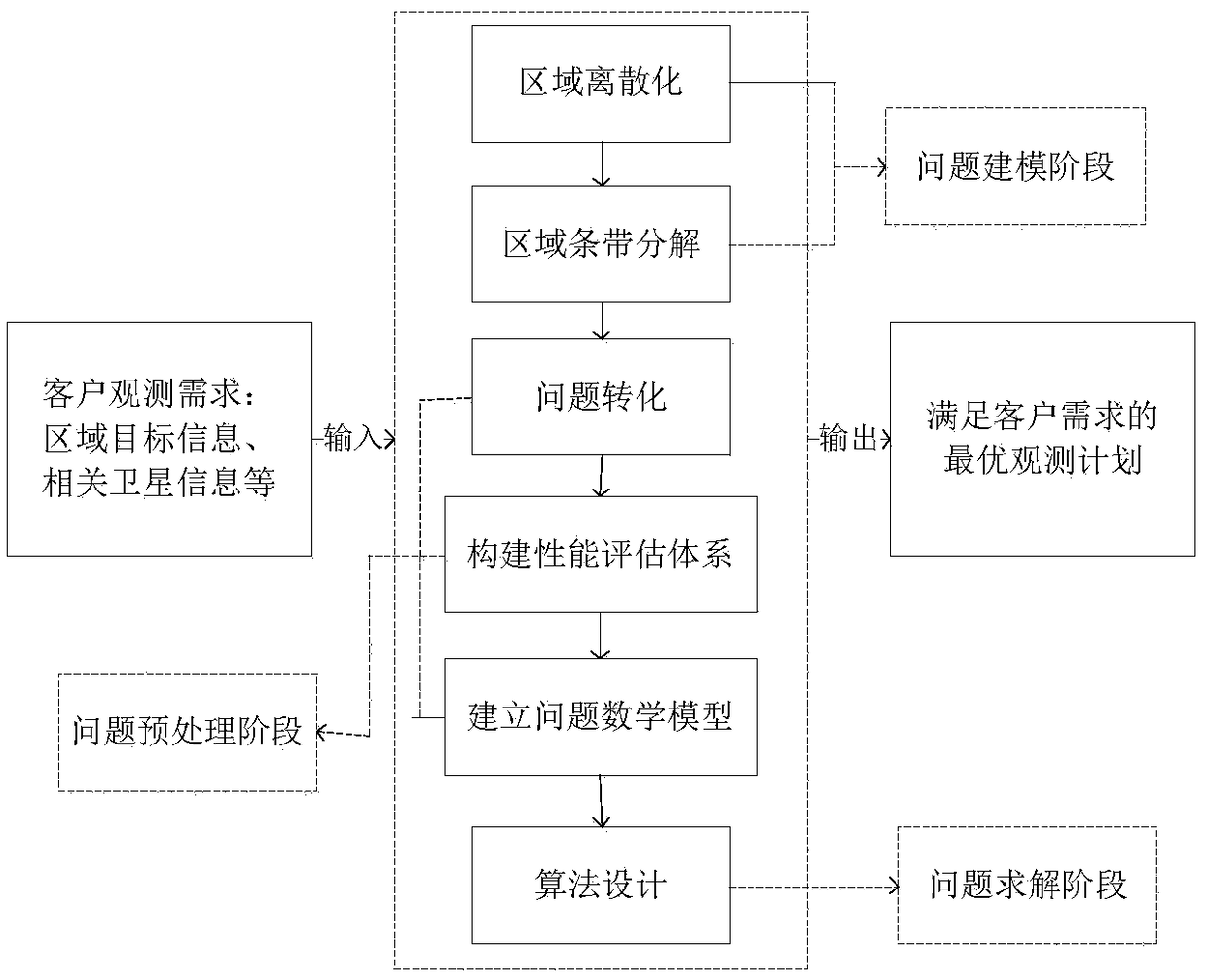
Multi-satellite scheduling method for large-area target observation
ActiveCN109165858ARealize generationSolve the phenomenon of missing coverageResourcesGenetic algorithmsUser needsMathematical model
The invention provides a multi-satellite scheduling method for large-area target observation. Firstly, according to the user's demand, the observation task is determined, that is to say, the target area T (i.e., the position and area of the known target area) to be observed is determined. A set of available satellites S and satellite parameter information for all available satellites in the set ofavailable satellites S are determined. Then the target region is discretized and the target region is decomposed into stripes. The method converts the multi-satellite scheduling problem oriented to large-area target observation into a set covering problem with a plurality of constraints, and establishes a mathematical model. Finally, the mathematical model established in S4 is solved by genetic algorithm, and the output is the observation plan obtained from the solution. The method solves the problem that the satellite image acquisition method related to the current environmental protection activities consumes long time and has the phenomenon of coverage omission, and the method of the invention can obtain a feasible observation scheme with higher target coverage rate for a specific observation area.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
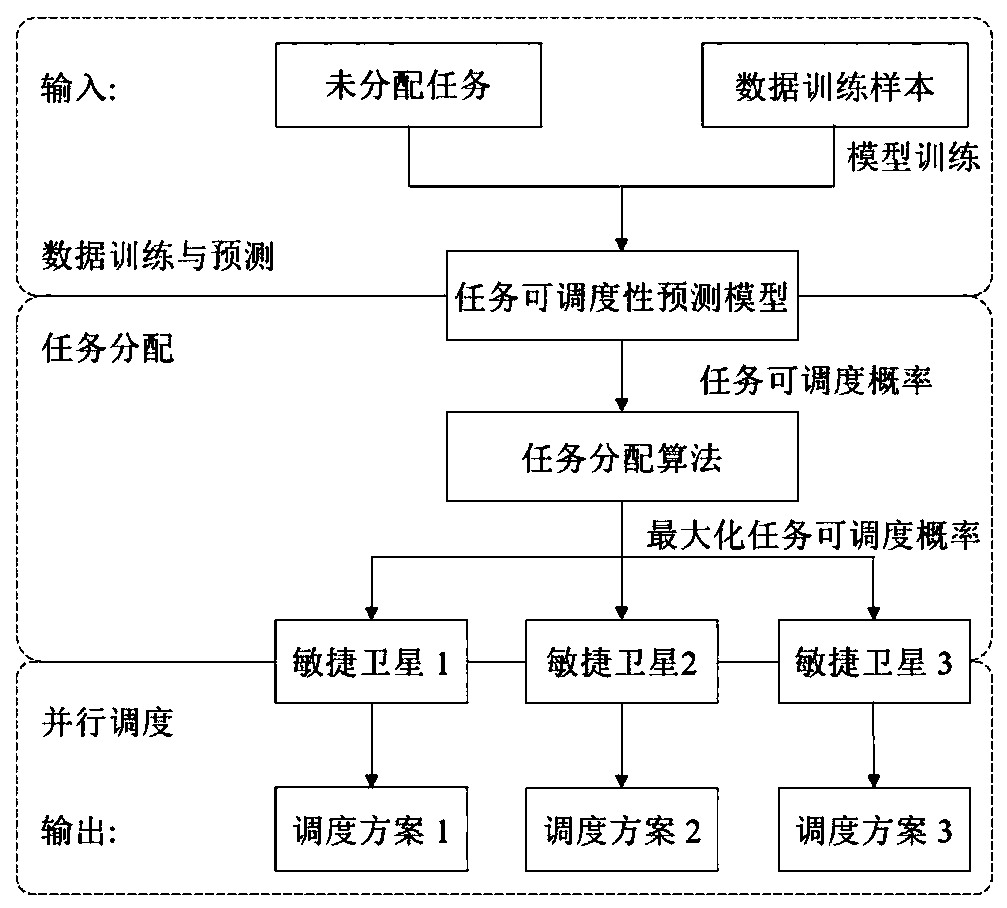
Agile satellite task parallel scheduling method based on data driving
ActiveCN109960544AImprove scheduling efficiencyReduce dispatch timeProgram initiation/switchingArtificial lifeData-drivenScaling agile
The invention discloses an agile satellite task parallel scheduling method based on data driving. The method comprises the steps of 1, obtaining agile imaging satellite historical task scheduling dataand a to-be-allocated task set; 2, training a task prediction model based on a deep learning algorithm, and predicting the scheduling probability of each to-be-allocated task; 3, according to a probability prediction result, allocating each task to the satellite with the maximum scheduling probability, and converting a large-scale satellite task scheduling problem into a plurality of parallel single-satellite scheduling problems; 4, solving; and 5, outputting the agile imaging satellite task scheduling sequence of each task to be distributed. The task scheduling probability prediction model is obtained through the machine learning algorithm, each task is allocated to the satellite with the maximum scheduling probability for execution, the complex problem is simplified, the task schedulingtime is shortened from the hour level to the minute level, and the scheduling efficiency of large-scale agile imaging satellite tasks is effectively improved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
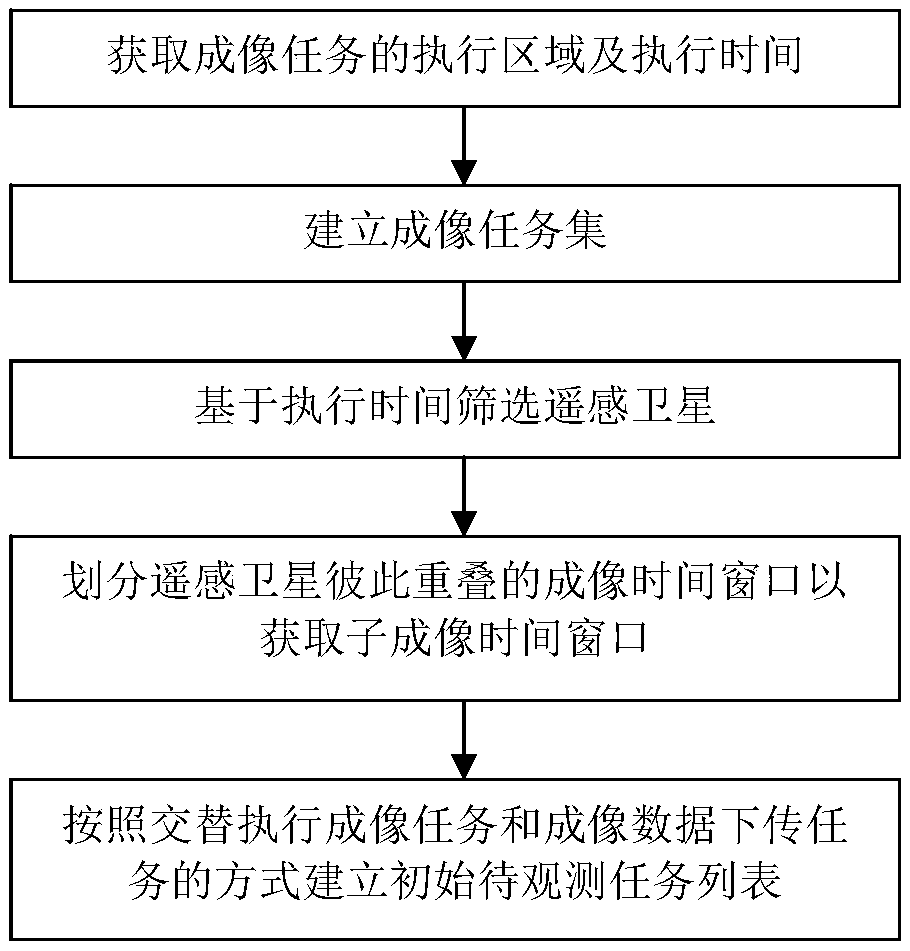
A satellite scheduling method based on an active observation task
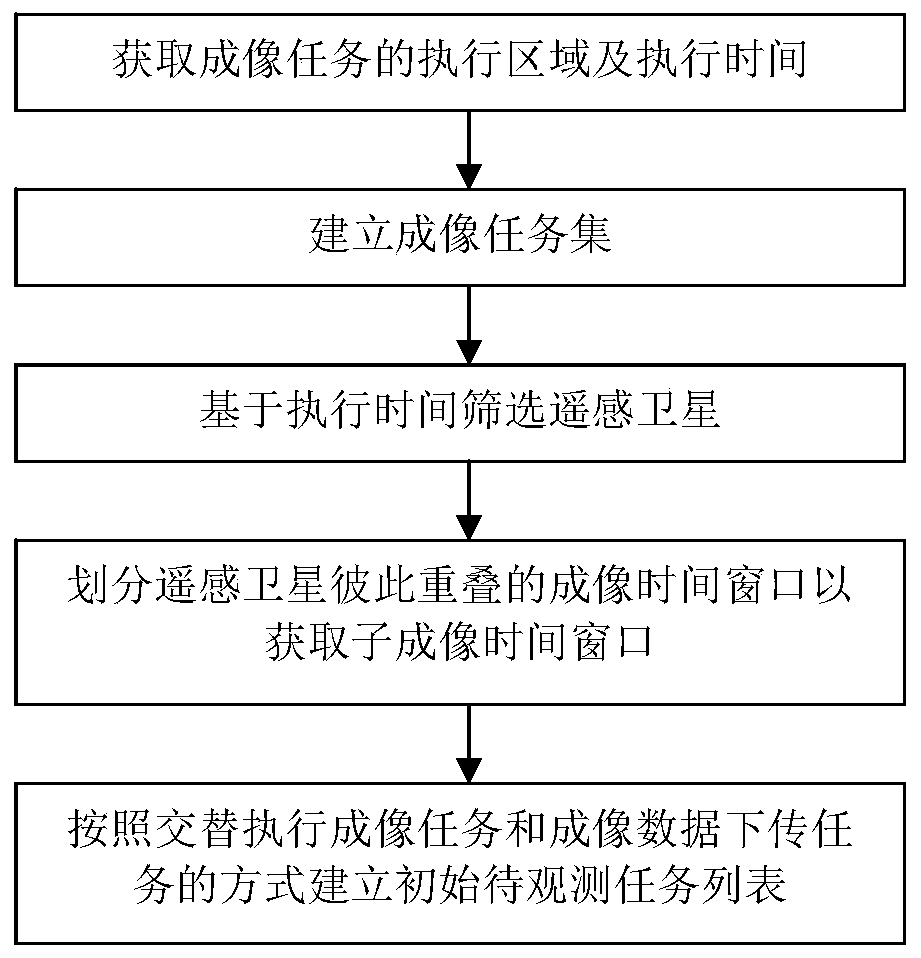
ActiveCN109684055AIncrease profitAvoid Duplicate ImagingProgram initiation/switchingStart timeComputer science
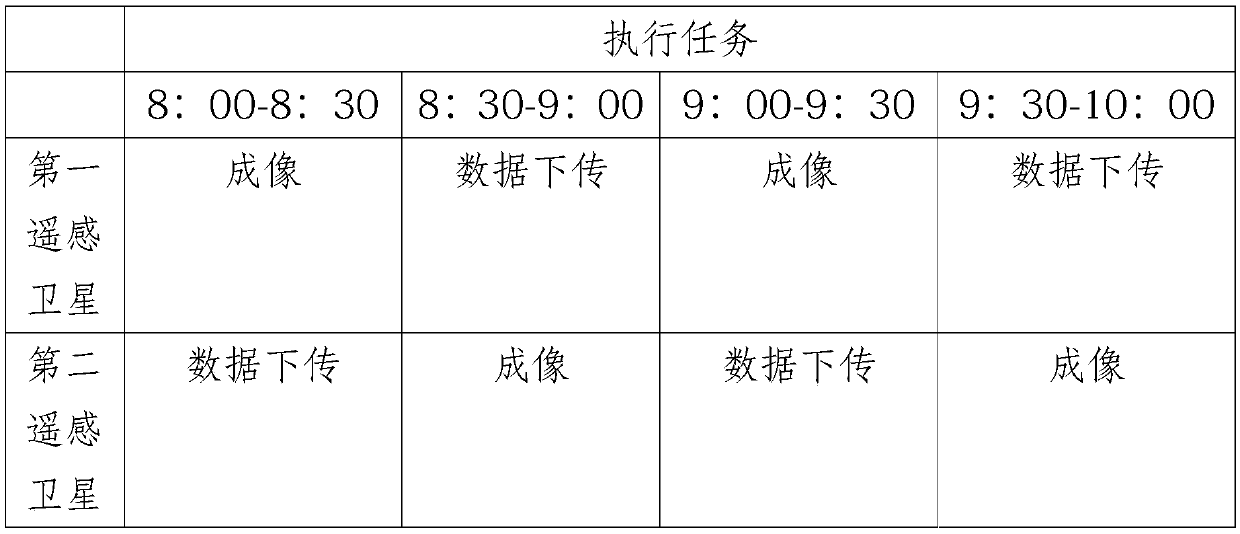
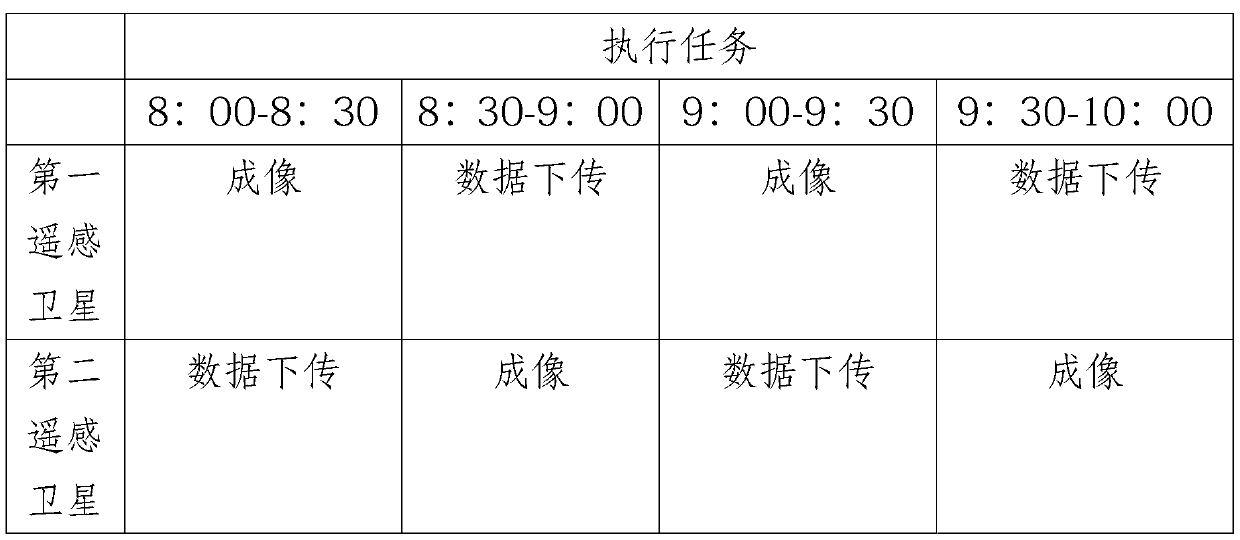
The invention discloses a satellite scheduling method based on an active observation task. At least an execution area and execution time of an imaging task are obtained based on real-time task demanddata; Classifying the imaging tasks based on parameters, execution areas and execution time of the remote sensing satellites to establish an imaging task set needing at least two remote sensing satellites to cooperatively complete; Screening out at least two remote sensing satellites respectively involved in each imaging task based on the execution starting time and the execution ending time of the execution time; dividing the overlapped imaging time windows of the remote sensing satellites into a plurality of sub-imaging time windows, wherein the remote sensing satellites establish an initialto-be-observed task list based on the sub-imaging time windows according to a mode of alternately executing an imaging task and an imaging data download task. The remote sensing satellites are set toexecute the imaging task and the data downloading task in an alternating mode, and dramatic increase of the storage capacity of the remote sensing satellites can be effectively reduced in the mode ofincreasing the data turnover speed.
Owner:SPACETY CO LTD (CHANGSHA)
Satellite scheduling method, processing system and software program product
The invention relates to a satellite scheduling method, processing system and software program product. The method includes: a) producing initial scheduling plans based on requests related to tasks tobe performed within a time period by a remote sensing satellite; b) applying a genetic-algorithm-based processing to the initial scheduling plans to produce a genetic-algorithm-based scheduling planwhich is for mission objectives, and complies with constraints related to the satellite resources, to the tasks, and to the time period; and c) applying a simulated-annealing-based processing to the genetic-algorithm-based scheduling plan to produce a simulated-annealing-based scheduling plan that fits the mission objectives, complies with the constraints, and in which a larger number of tasks isscheduled than in the genetic-algorithm-based scheduling plan.
Owner:TELEVISION BROADCASTS LTD
Imaging satellite scheduling method and system based on genetic algorithm
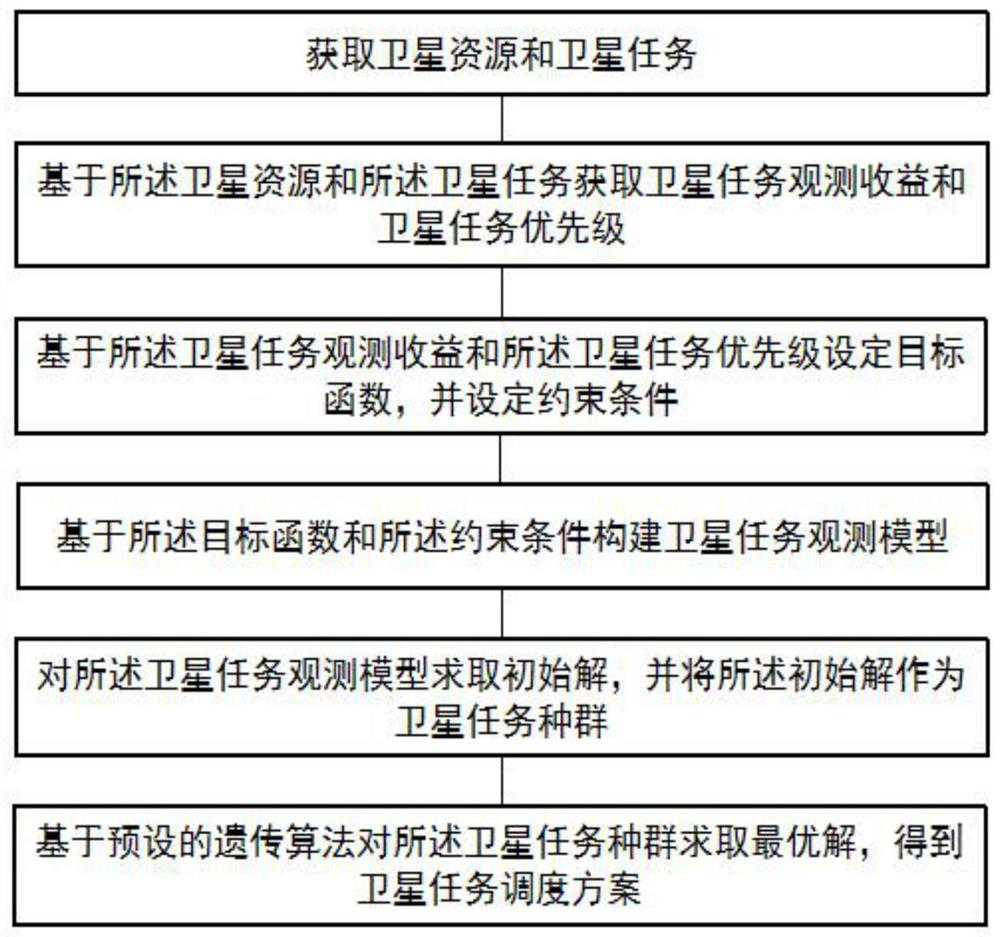
ActiveCN111913787AImprove efficiencyProgram initiation/switchingResourcesAlgorithmSatellite observation
The invention provides an imaging satellite scheduling method and system based on a genetic algorithm, and relates to the field of satellite observation. The method comprises the steps of obtaining satellite resources and satellite tasks; acquiring satellite task observation benefits and satellite task priorities based on the satellite resources and the satellite tasks; setting a target function based on the satellite task observation benefits and the satellite task priorities, and setting constraint conditions; constructing a satellite task observation model based on the target function and the constraint conditions; solving an initial solution of the satellite task observation model, and taking the initial solution as a satellite task population; and solving an optimal solution for the satellite task population based on a preset genetic algorithm to obtain a satellite task scheduling scheme. The method is high in satellite scheduling efficiency.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Task scheduling method and system for imaging satellite
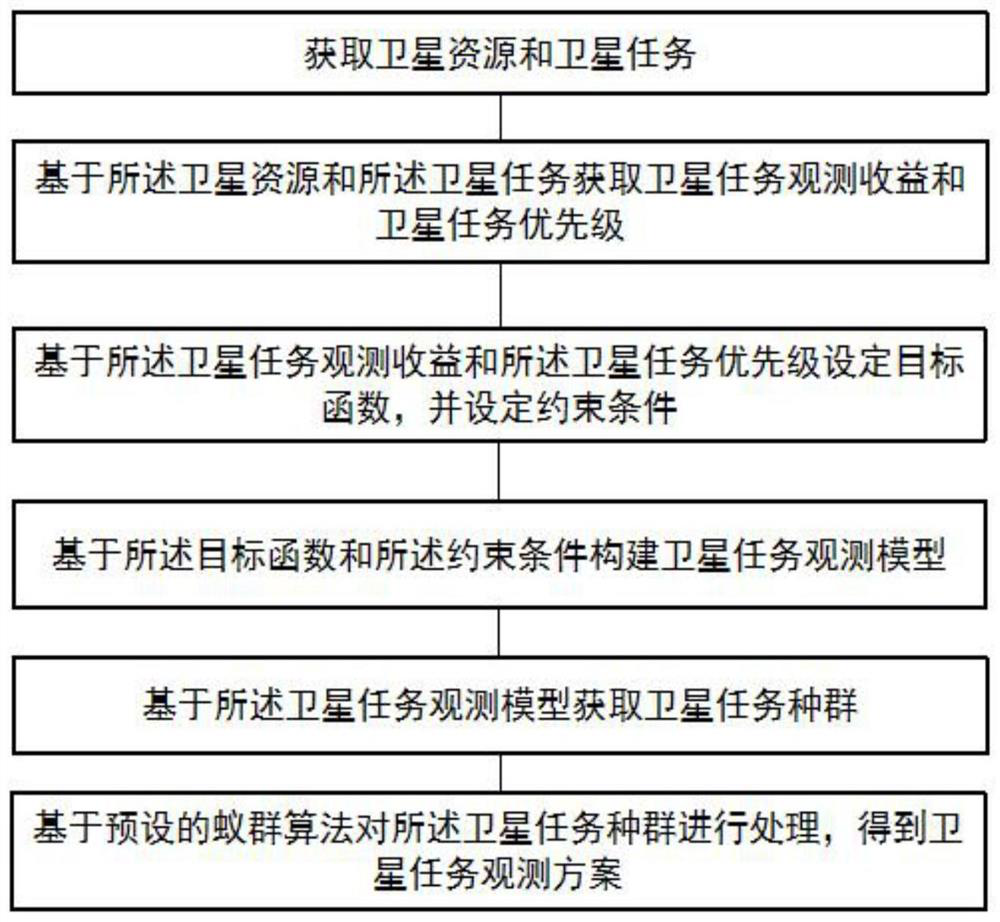
ActiveCN111913788AImprove efficiencyOptimizing Satellite Scheduling SchemeProgram initiation/switchingArtificial lifeTelecommunicationsSatellite observation
The invention provides a task scheduling method and system for an imaging satellite, and relates to the field of satellite observation. The method comprises the steps of obtaining satellite resourcesand satellite tasks; acquiring satellite task observation benefits and satellite task priorities based on the satellite resources and the satellite tasks; setting a target function based on the satellite task observation benefits and the satellite task priorities, and setting constraint conditions; constructing a satellite task observation model based on the target function and the constraint conditions; acquiring a satellite task population based on the satellite task observation model; and processing the satellite task population based on a preset ant colony algorithm to obtain a satellite task observation scheme. The method is high in satellite scheduling efficiency.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Random search method for relay satellite single-access antenna scheduling based on collision resolution
ActiveCN109039428AQuality improvementMethod is fastRadio transmissionStructure of Management InformationRandom subspace method
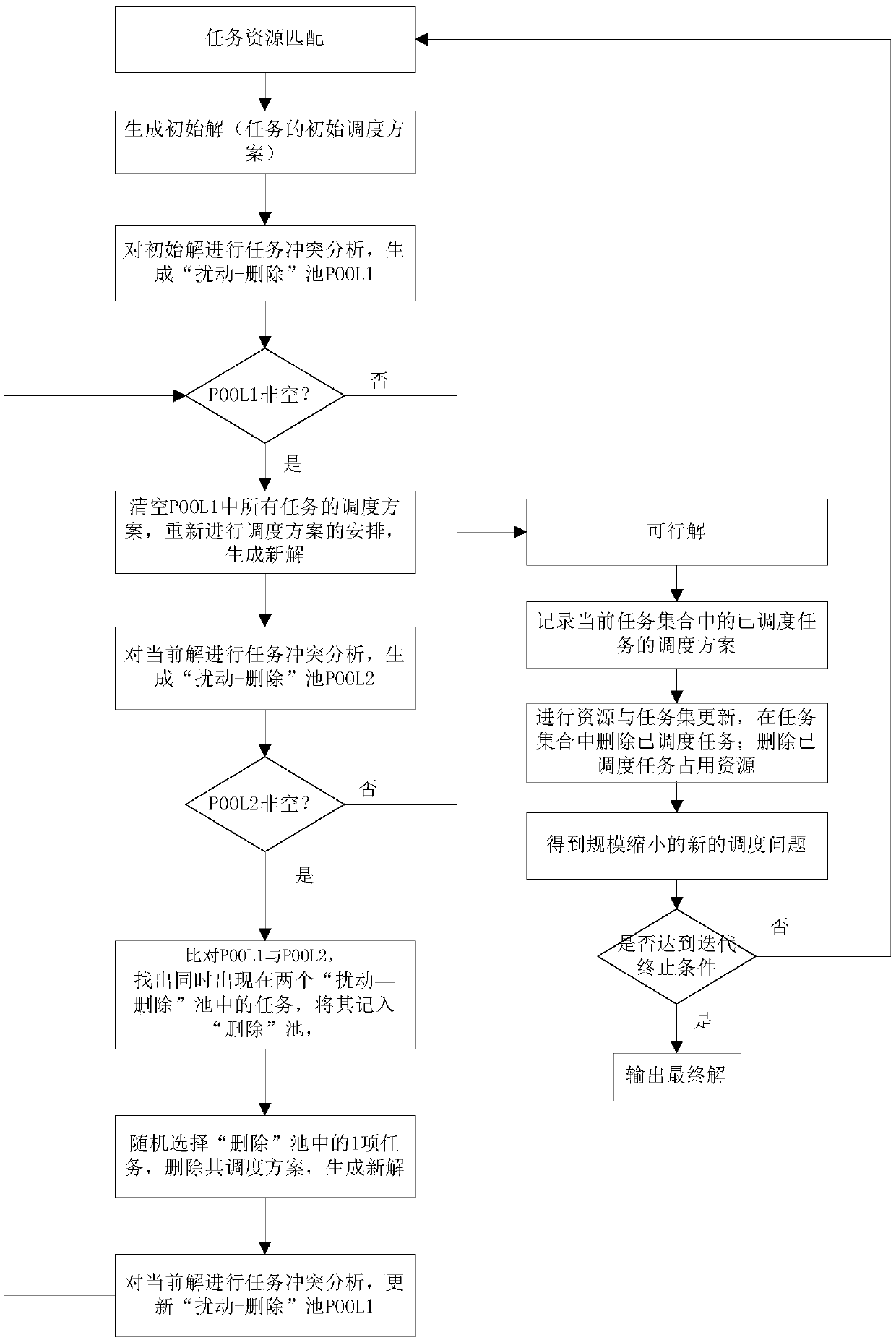
The invention belongs to the satellite scheduling field and relates to a relay satellite single-address antenna scheduling random search method based on conflict resolution. The method comprises the following steps: (S1) matching the relay satellite resources for the task according to the alternative service time window information submitted by the task; 12) generating an initial solution of a relay satellite single-access antenna scheduling random search accord to a task resource matching result; (3) evaluating the fitness of the current solution, finding out the key task causing the conflict, and generating a perturbation -deletion pool of the task; (4) randomly perturbing or deleting tasks in the perturbation-deletion pool, and gradually iteratively resolving task conflicts; (S5) updating resource and task sets: deleting the resource and task without conflict and updating the resource and task set. The method of the invention has high speed, is suitable for large-scale relay satellite dispatching scene, adopts double iterative structure, and generates a dispatching scheme with high quality.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
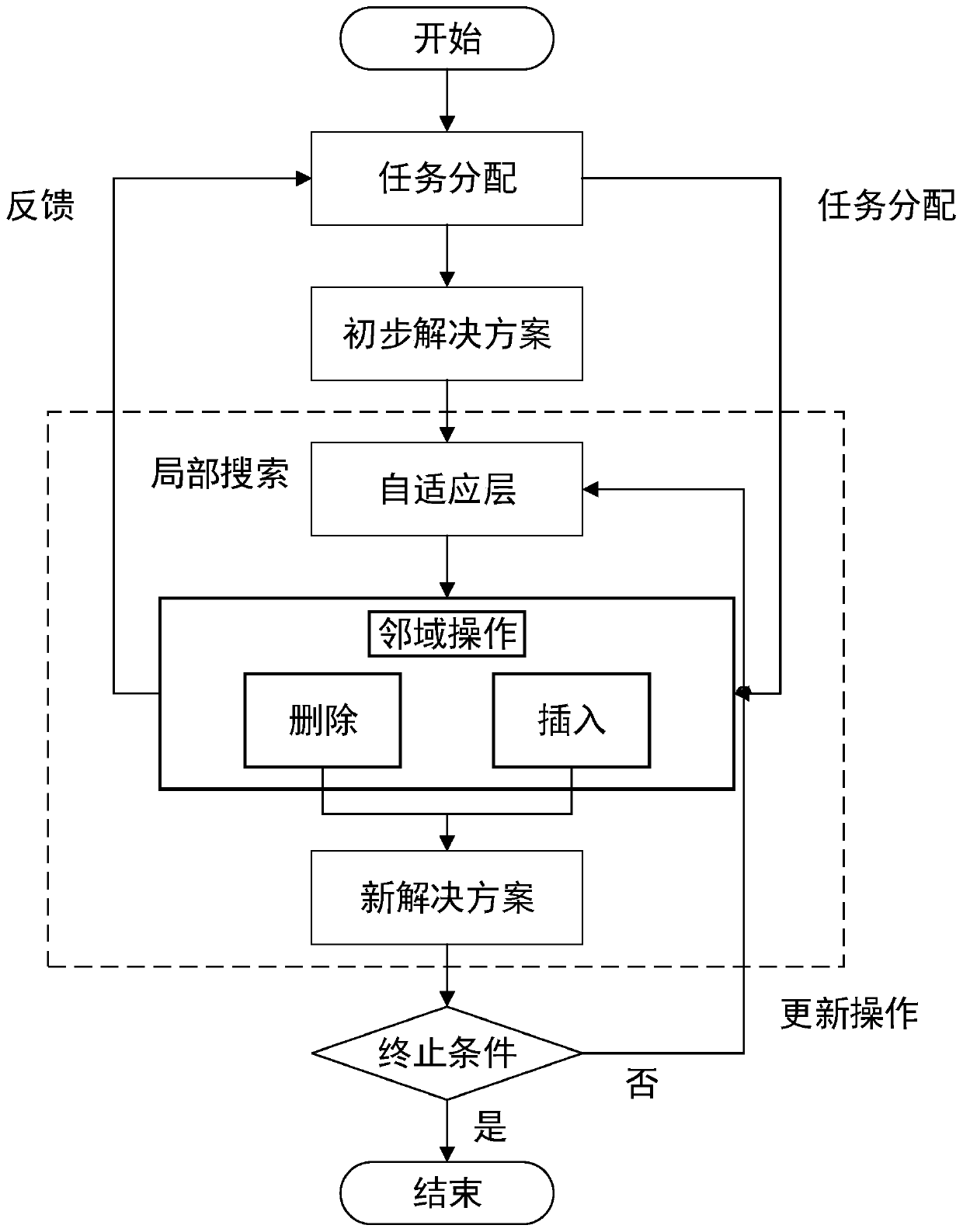
Multi-agile earth observation satellite task allocation method based on large neighborhood search algorithm
InactiveCN110458470AImprove efficiencyTake advantage ofResourcesLarge neighborhood searchSelf adaptive
The invention discloses a multi-agile earth observation satellite task allocation method based on a large neighborhood search algorithm. Self-adaptive large neighborhood search of a single satellite scheduling problem is expanded to a multi-satellite scheduling problem. By defining four allocation operations, an adaptive task allocation mechanism is introduced into a large neighborhood search framework. In large neighborhood search based on adaptive task allocation, a removal operation removes a task from a current solution, an insertion operation inserts the task into the removed solution, and an allocation operation reallocates the task to different satellites if the solution is still not improved after multiple iterations. According to the method, the task allocation problem of the agile earth observation satellite group of the dynamic tasks is optimized, so that the dynamic tasks can be processed at any time in the operation process of satellites.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
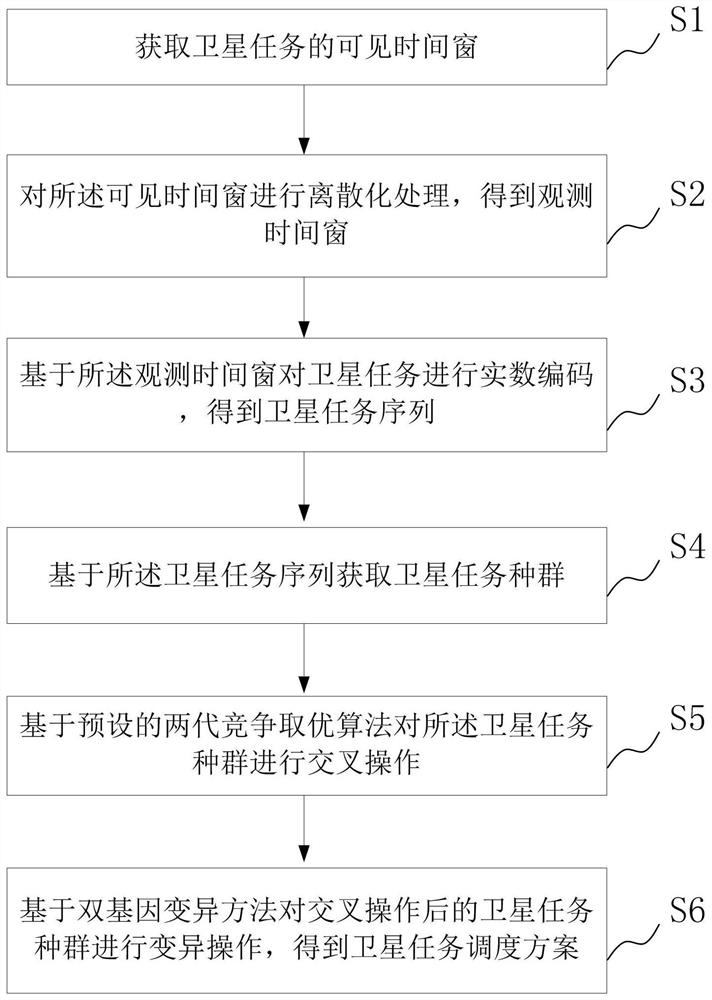
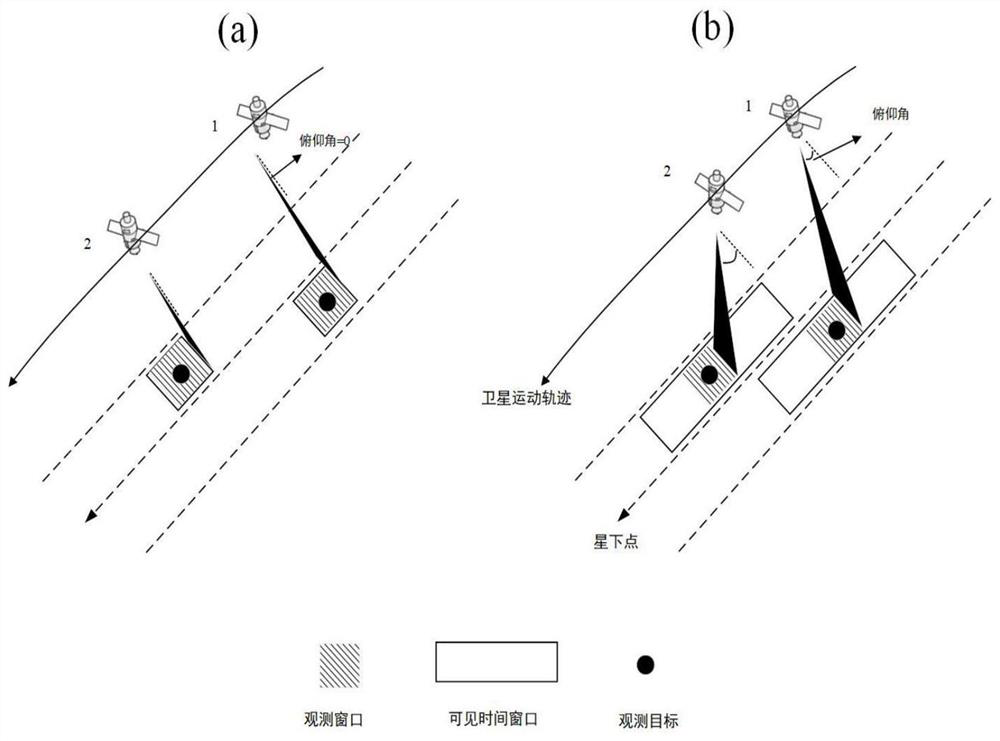
Satellite task scheduling method and system based on time window segmentation
ActiveCN111913786AImprove efficiencyExpand the solution spaceProgram initiation/switchingArtificial lifeSatellite observationEngineering
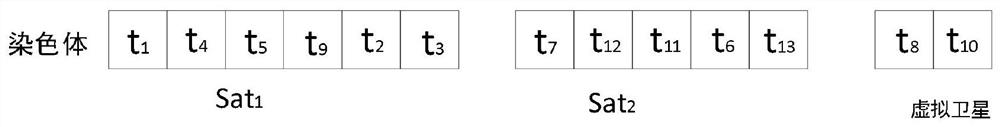
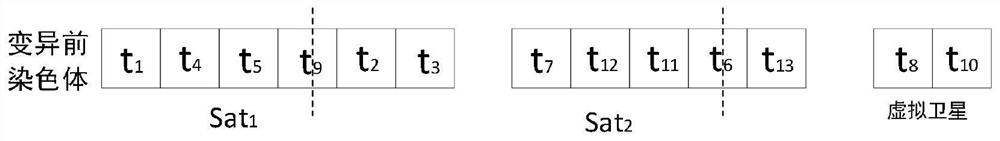
The invention provides a satellite task scheduling method and system based on time window segmentation, and relates to the field of satellite scheduling. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a visible time window of a satellite task; discretizing the visible time window to obtain an observation time window; performing real number encoding on the satellite task based on the observation time window to obtain a satellite task sequence; acquiring a satellite task population based on the satellite task sequence; performing crossover operation on the satellite task population based ona preset two-generation competitive optimization algorithm; and performing mutation operation on the satellite task population after the crossover operation based on a double-gene mutation method toobtain a satellite task scheduling scheme. According to the invention, the efficiency of satellite observation tasks is improved.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
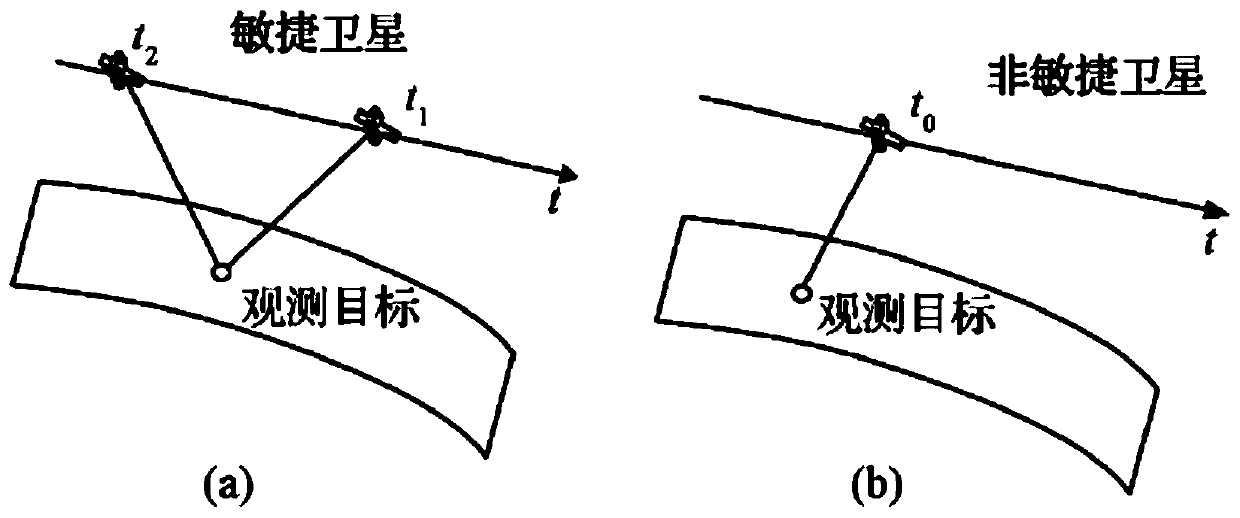
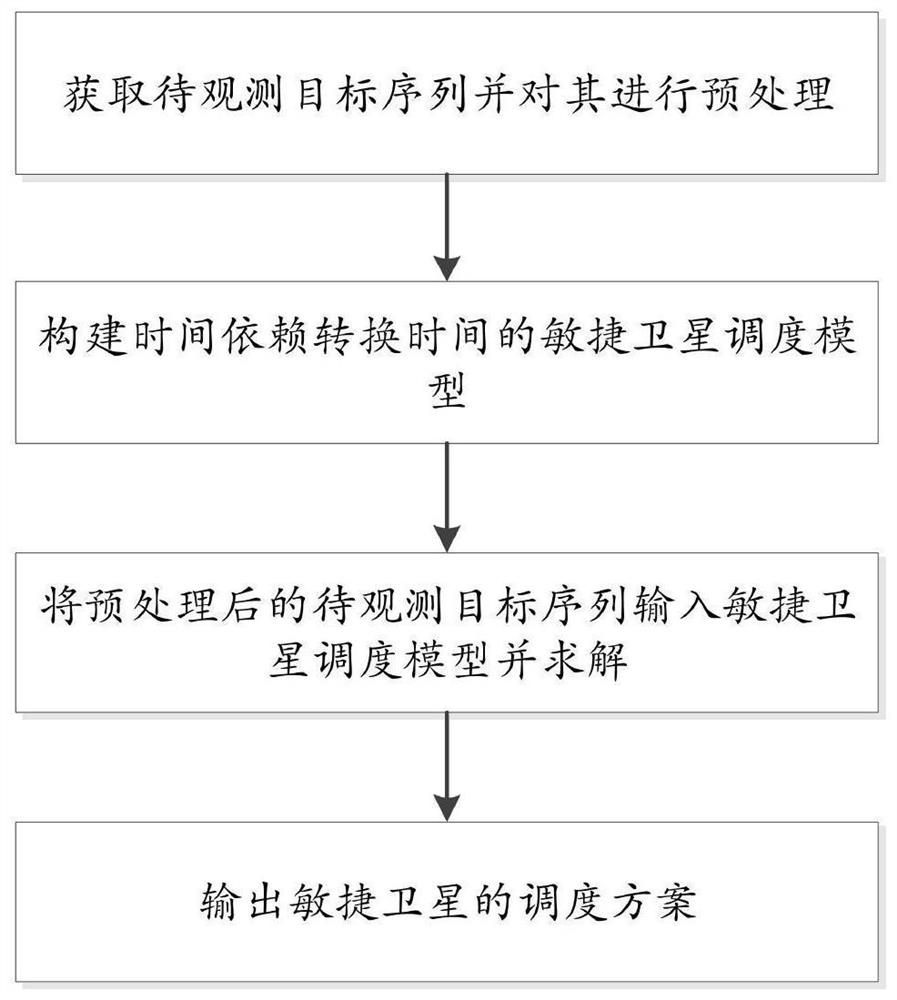
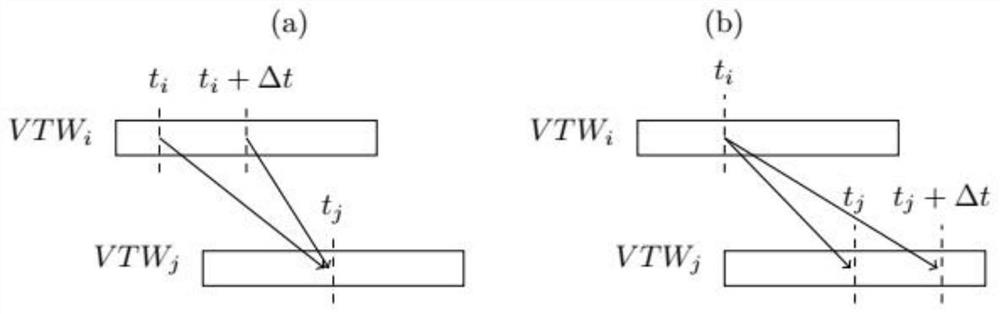
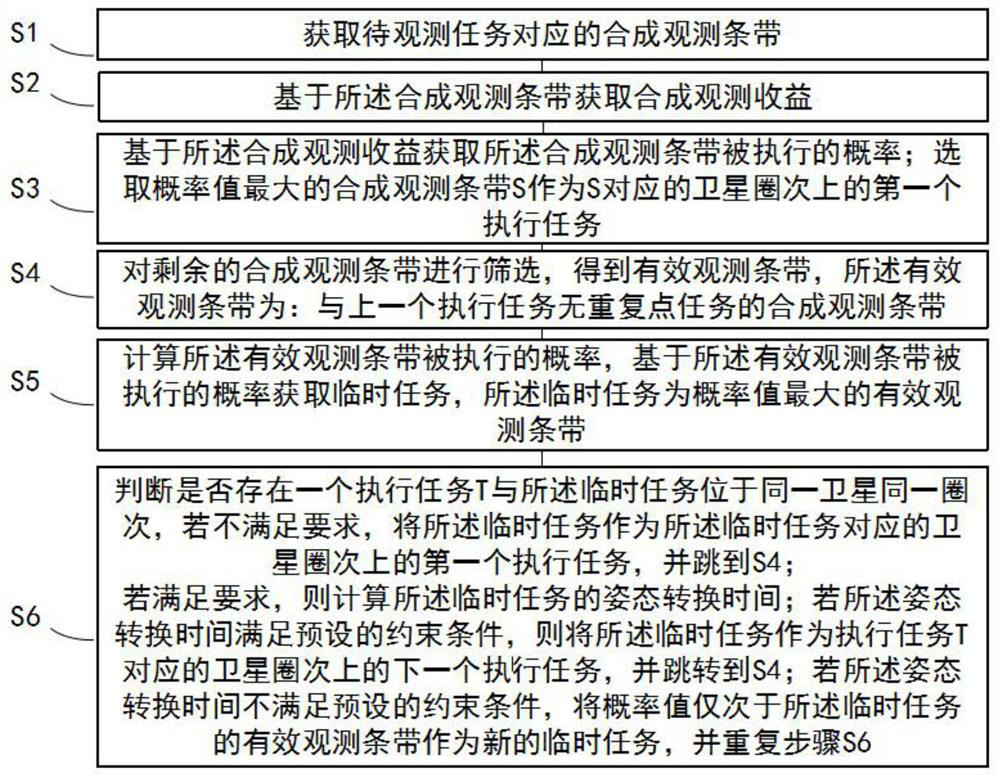
Agile satellite scheduling method considering time-dependent conversion time
PendingCN111651905AImprove scheduling efficiencyMeet scheduling needsDesign optimisation/simulationConstraint-based CADStart timePrecomputation
The invention discloses an agile satellite scheduling method considering time-dependent conversion time. The agile satellite scheduling method comprises the steps of obtaining a to-be-observed targetsequence and preprocessing the to-be-observed target sequence; constructing an agile satellite scheduling model of time-dependent conversion time; inputting the preprocessed to-be-observed target sequence into an agile satellite scheduling model, and solving the agile satellite scheduling model; and outputting a solving result in the step 3 to obtain a scheduling scheme of the agile satellite. Dueto the fact that the time dependence of the attitude conversion time between the continuous observation tasks is considered, the constructed agile satellite scheduling model can better meet the scheduling requirement, and the scheduling efficiency of the solved scheduling scheme is higher. In the solving process, the earliest and latest unreachable time of each time window and the earliest starting time and latest starting time between any pair of observation windows in the same circle are pre-calculated, so that repeated calculation is reduced when insertion operation is tried, the calculation time is shortened, and the scheduling efficiency is improved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
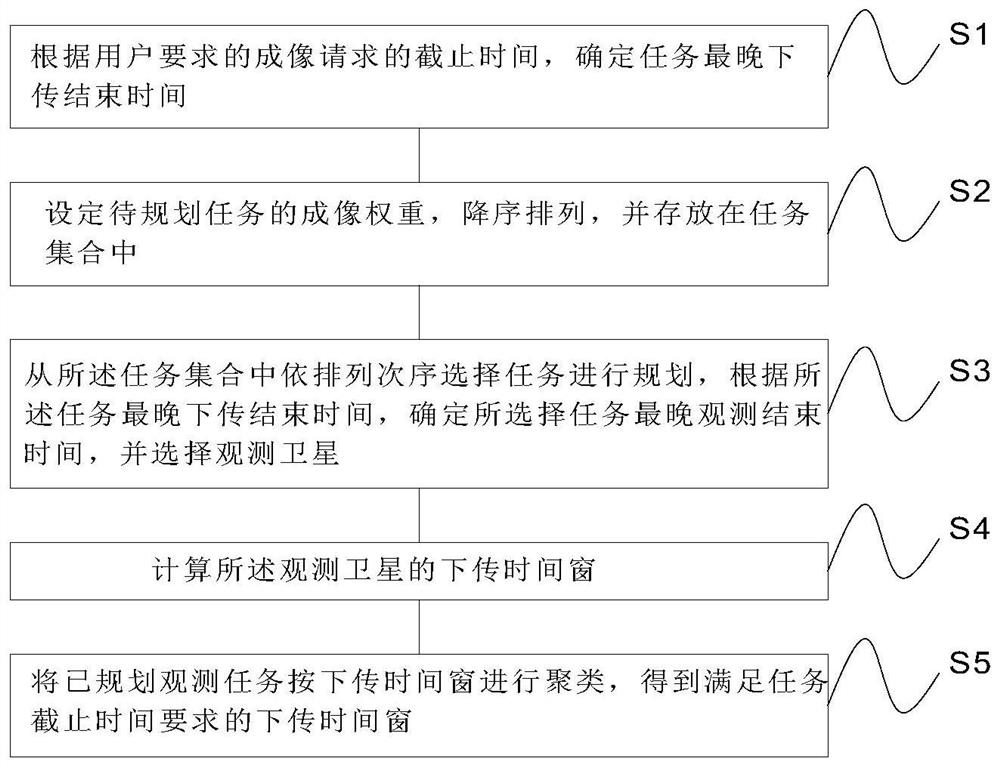
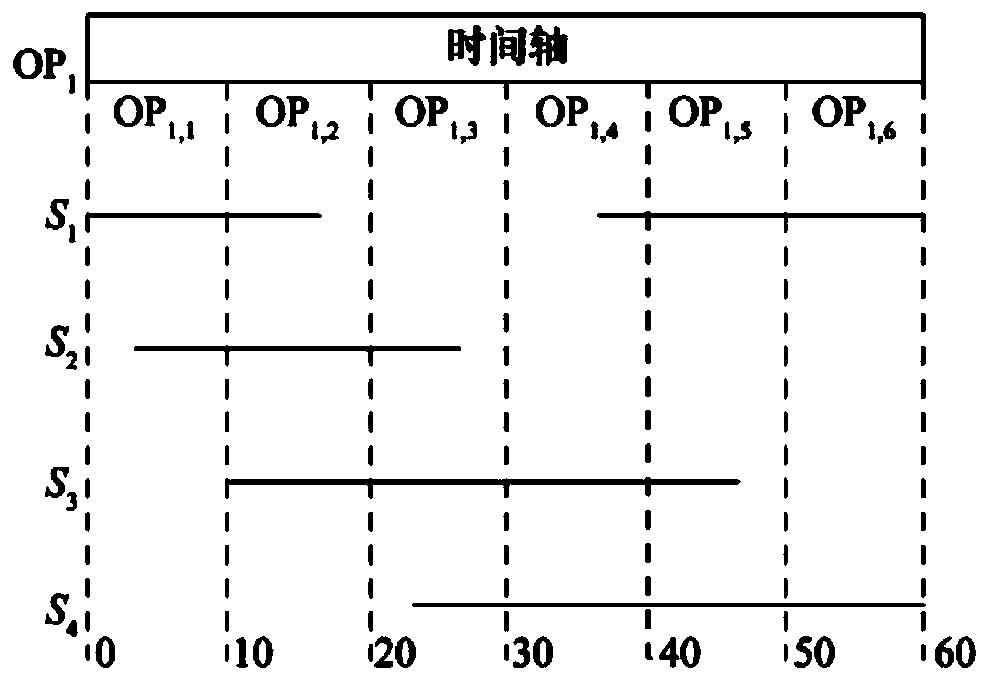
Multi-satellite multi-station data downloading scheduling method and system
ActiveCN112737660AReduce sensitivityImprove solution efficiencyRadio transmissionEngineeringGround station
The invention provides a multi-satellite multi-station data downloading scheduling method and system, and relates to the technical field of satellite scheduling. According to the imaging request deadline requirement required by a user, the latest task downloading end time is calculated, the task imaging weight is defined, clustering is carried out according to a satellite downloading time window, and an available ground station is selected for data downloading. Different from data downloading scheduling based on greedy rules and the like in previous research, a downloading scheduling strategy based on task deadline is provided, so that the downloading time sensitivity of a currently planned task is relatively low, and the solving efficiency and effect are improved.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Satellite task planning method based on greedy adaptive annealing contract net algorithm
PendingCN114841500ASolve the main goalSolving Consistency IssuesClimate change adaptationResourcesMathematical modelGlobal optimal
The invention provides a satellite task planning method and system based on a greedy adaptive annealing contract net algorithm, a storage medium and electronic equipment, and relates to the field of satellite scheduling. According to a preset slave satellite mathematical model, each slave satellite generates a corresponding current bidding scheme for a task sequence which is not arranged currently by adopting a greedy-based adaptive annealing contract net algorithm; according to a preset main satellite mathematical model, the main satellite performs bid evaluation by adopting a total observation income maximization bid evaluation strategy, and a bid winning scheme is selected from the bidding schemes; and finally, outputting a global optimal satellite task planning scheme. By establishing a double-layer decision mathematical model, the problem of inconsistency of a main target and a sub-target existing in distributed satellite task allocation and scheduling problems which are not considered by a traditional contract network is solved; and a scheme with higher quality is obtained through multiple rounds of bidding and bidding processes.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Cross-layer protocol communication method based on planet network MAC protocol
InactiveCN101242414BIncrease profitEnhanced ability to transfer dataRadio transmissionTelecommunicationsNetworking protocol
The invention is a cross-layer protocol communication method based on a satellite network MAC protocol, which relates to a MAC protocol applied to a satellite network, for solving the problem that focuses on MAC improvement, in no consideration of the effect of dynamic channel status to protocol performance in current MAC satellite network protocol. When receiving a free distributive timeslot, land terminals apply for resource to a satellite dispatcher in the next frame, otherwise the land terminals apply for resource to the satellite dispatcher; a uplink channel in deep fade state performs no reserved information sending, and the uplink channel in otherwise state performs reserved information sending; the satellite dispatcher transmits the land terminals in different channel states in corresponding modes, forwards data from the land terminals as the next line data, and dispatches channel resource, at the same time, dispatches the transmission mode of next frame for each terminal, andmoves the ID of a land terminal to the list tail after finishing the timeslot reservation of the land terminal.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Relay satellite mission scheduling method and system
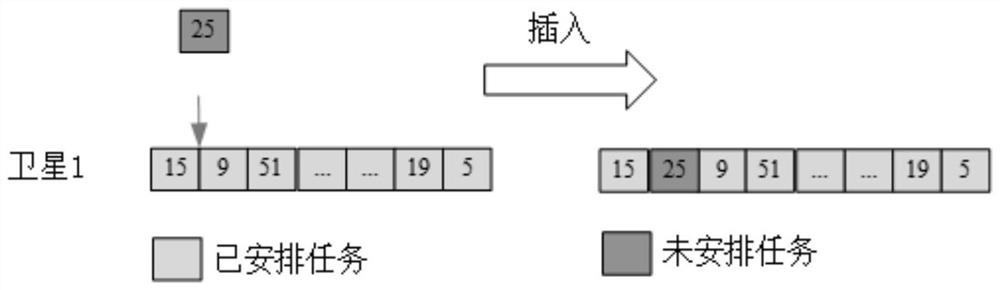
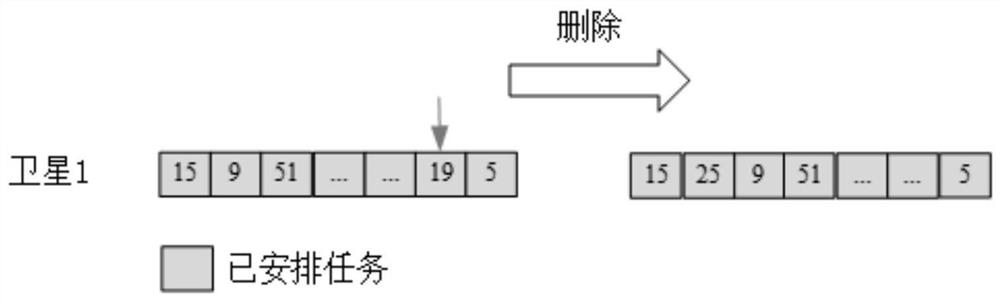
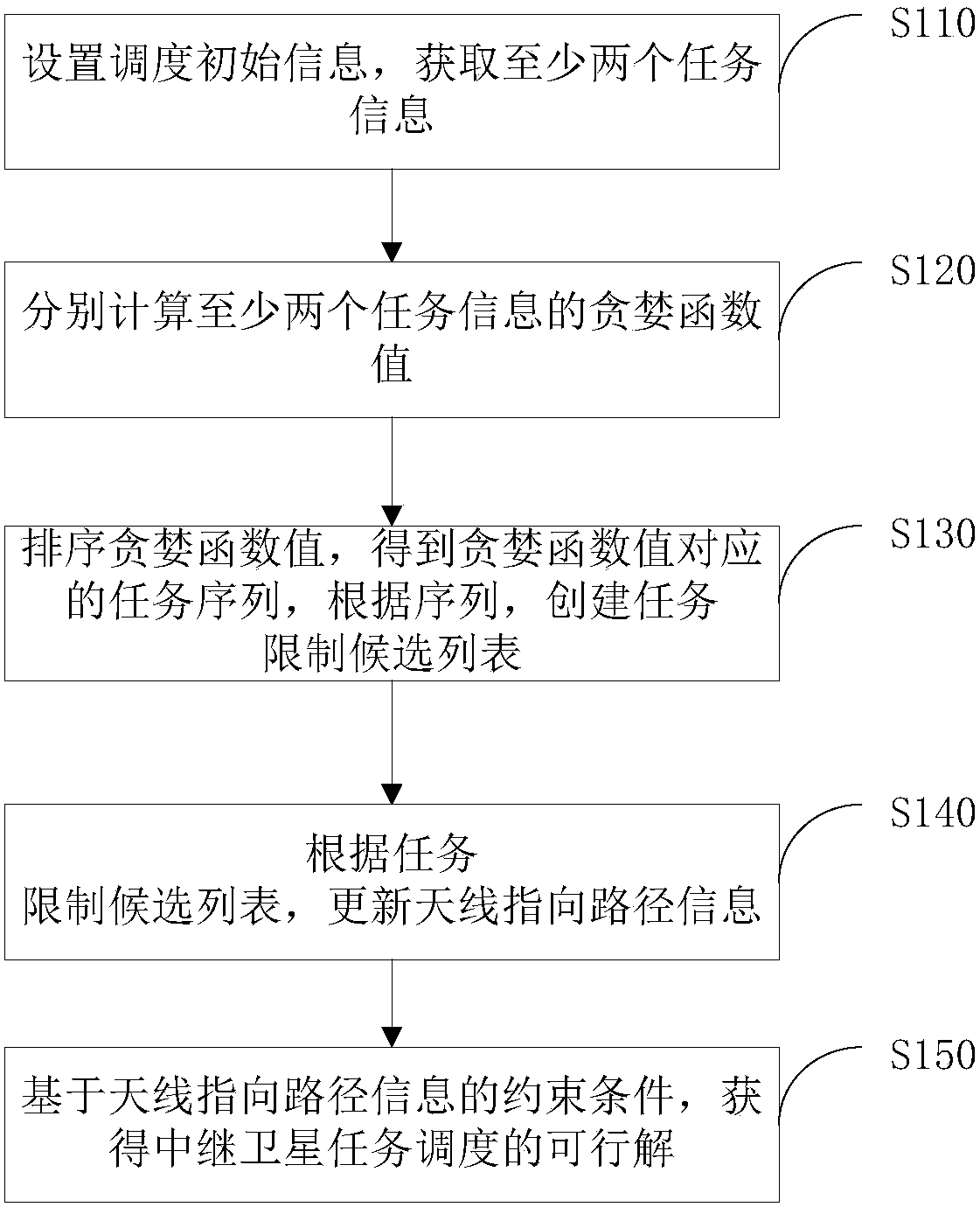
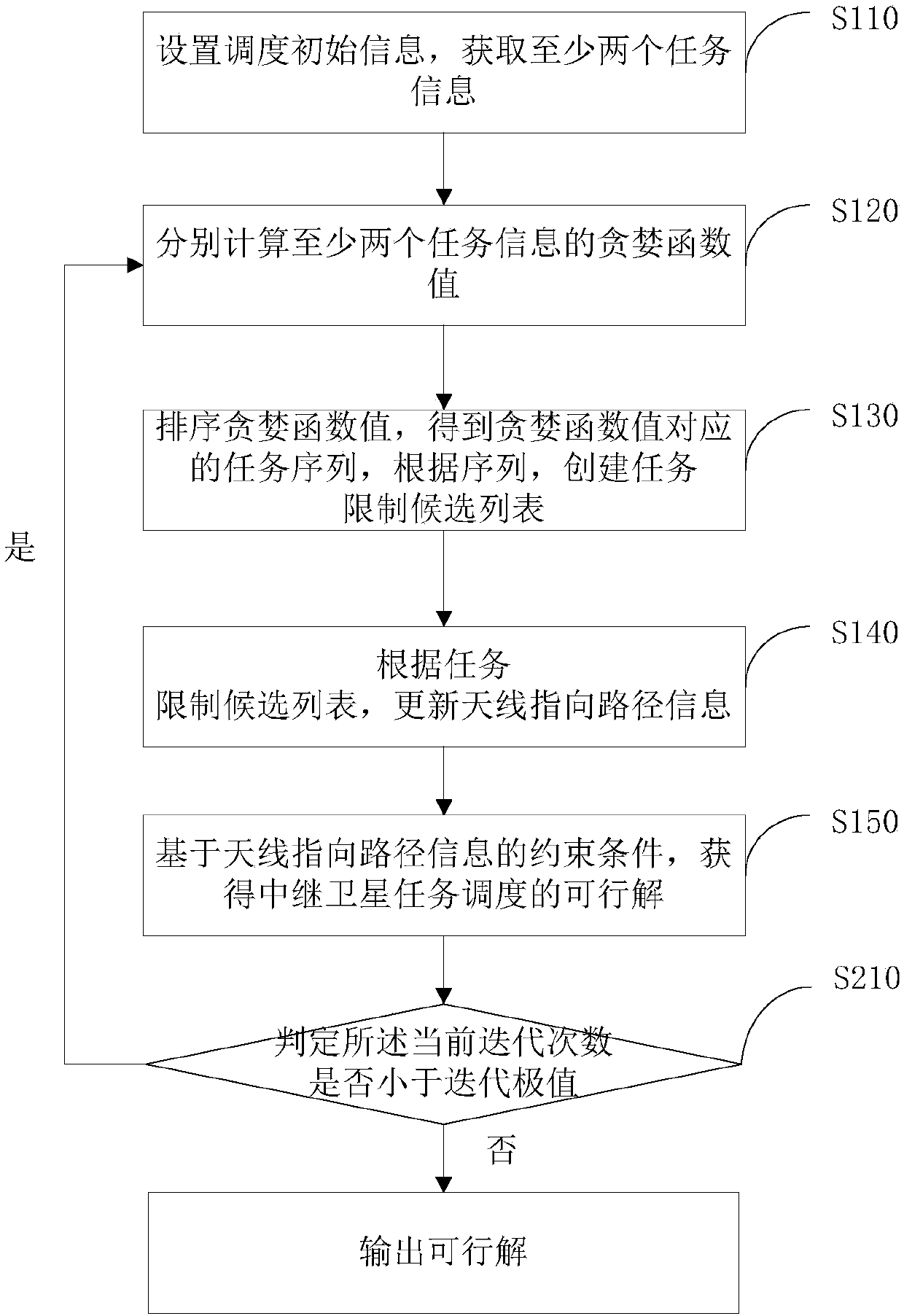
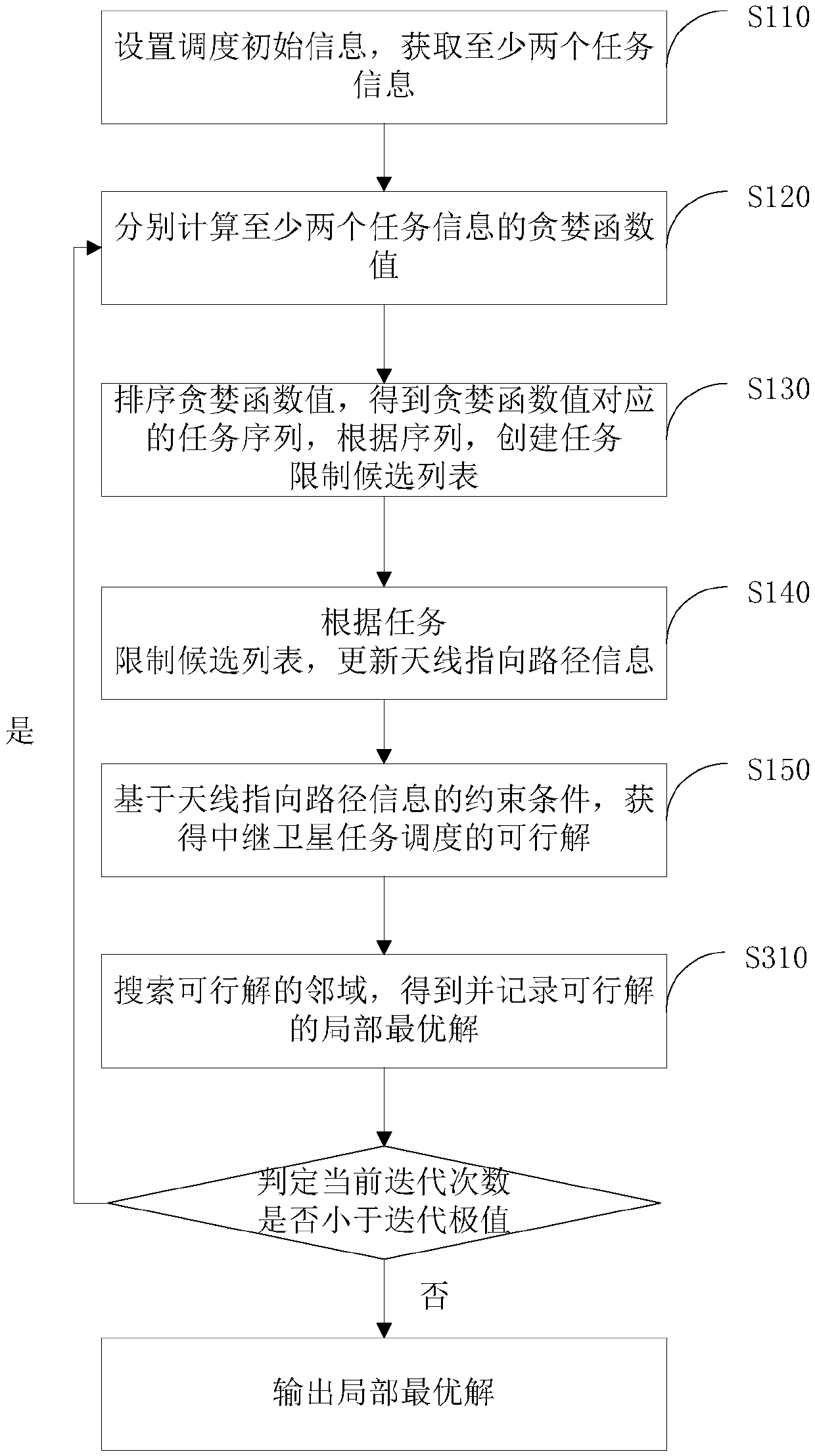
The invention provides a relay satellite mission scheduling method and system, and relates to the technical field of relay satellites. The method comprises the following steps: setting scheduling initial information, and acquiring at least two pieces of mission information; respectively calculating greedy function values of the at least two pieces of mission information; sequencing the greedy function values to obtain a mission sequence corresponding to the greedy function values, and establishing a mission constraint candidate list according to the sequence; updating antenna pointing path information according to the mission constraint candidate list; and acquiring a feasible solution for relay satellite mission scheduling based on a constraint condition of the antenna pointing path information. According to the relay satellite mission scheduling method provided by the invention, the technical problems of unreasonable preparation time distribution, waste of antenna time resources andinfluence on the relay service quality which are caused by the reason that the relay satellite scheduling system reserves the longest and same mission preparation time for all users are solved, and atechnical effect of optimizing the relay satellite mission scheduling is achieved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Relay satellite single-address antenna dynamic scheduling method for temporary task arrival
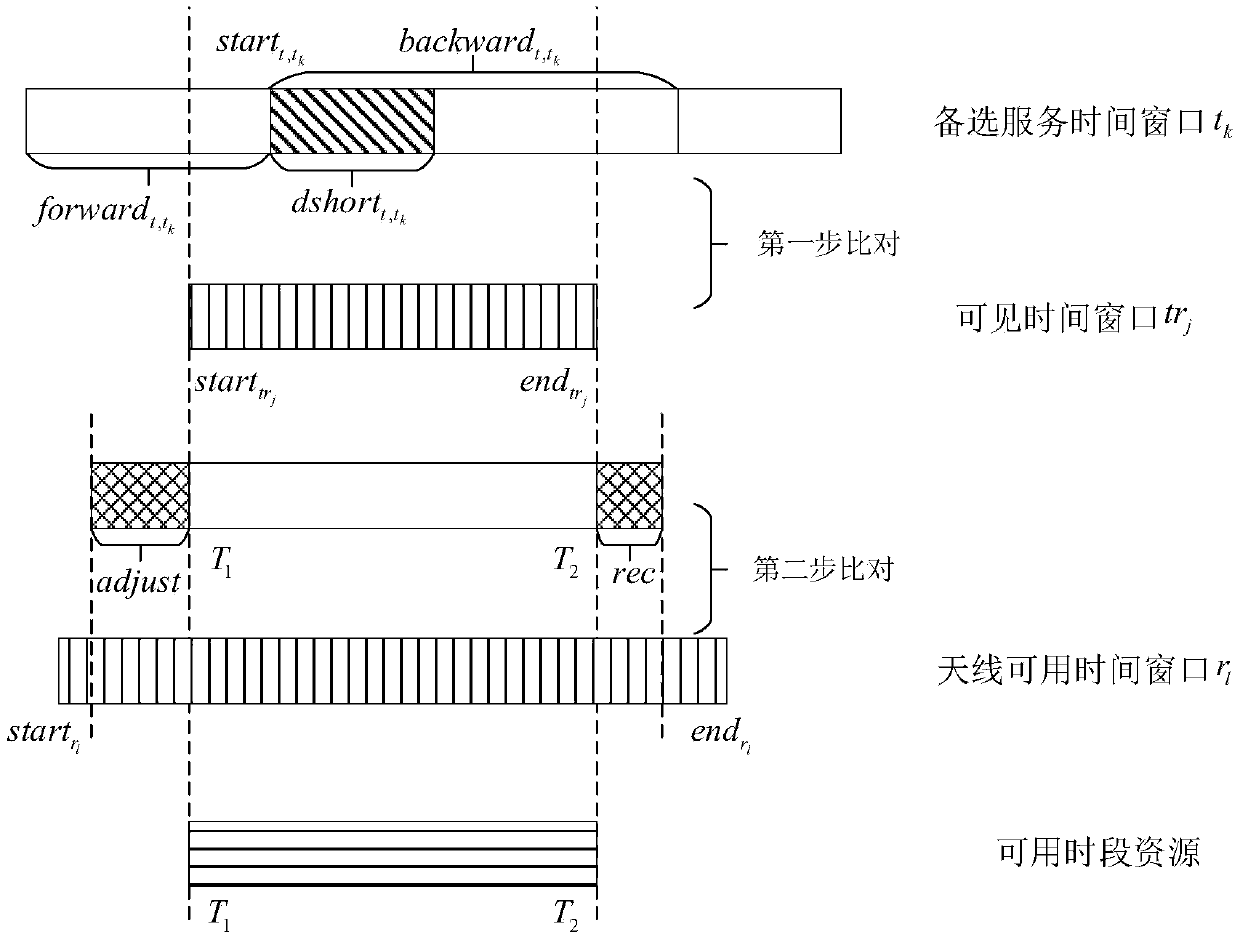
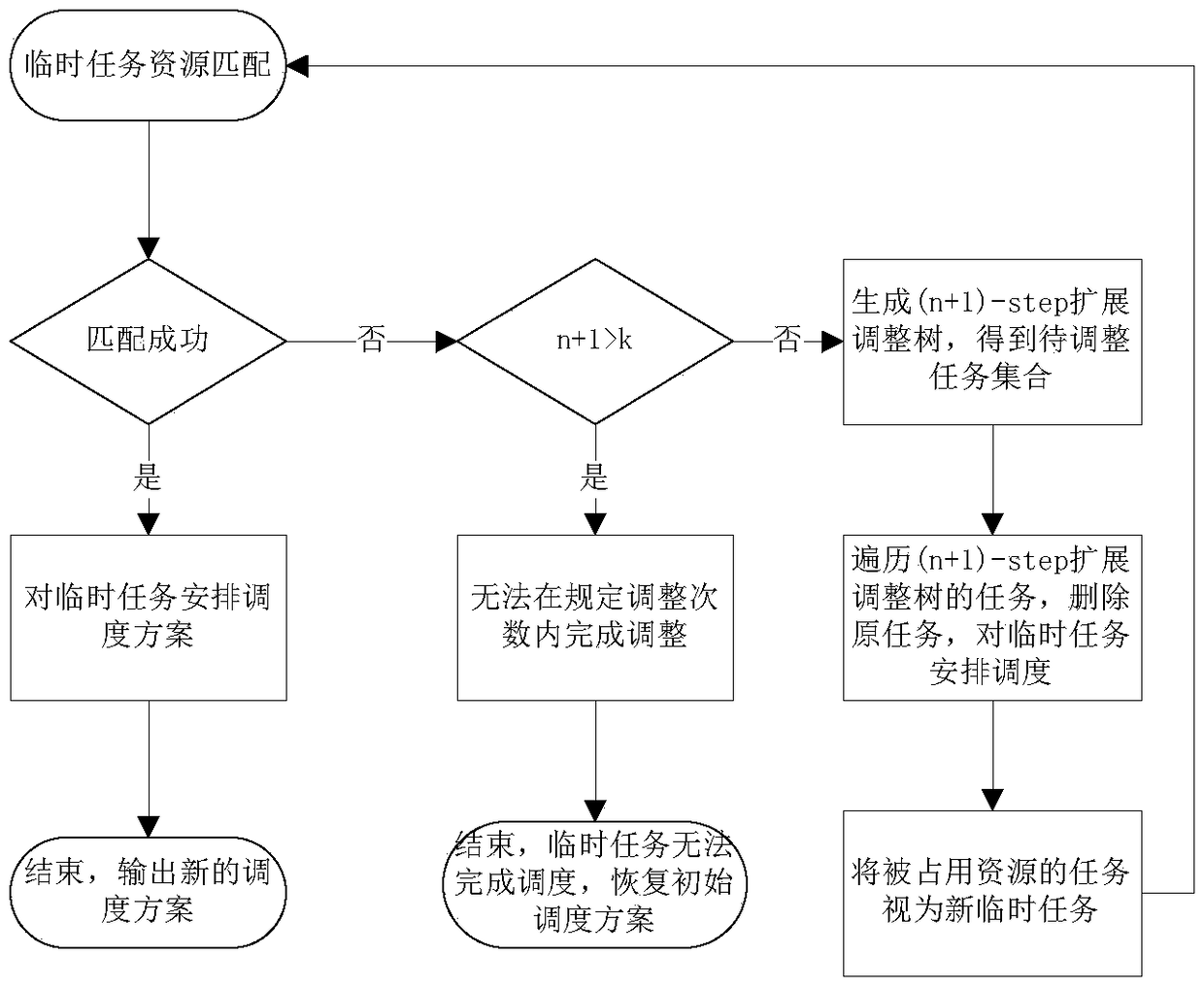
The invention belongs to the satellite scheduling field and relates to a relay satellite single-address antenna dynamic scheduling method for temporary task arrival. The method comprises the followingsteps: (1) according to the temporary task application information to be processed, matching the visible time window and the antenna available time window; if there are available time period resources, scheduling the temporary task; otherwise, proceeding to the next step; (2) analyzing the scheduled tasks that conflict with the temporary task requirements, and generating t set of tasks to be adjusted at the current layer; (3) trying to adjust the tasks to be adjusted, and if the scheduling is successful, putting an end to the scheduling process; otherwise proceeding to the next step; 4) deleting the resources occupied by the tasks to be adjusted in the current layer, and after scheduling the original temporary tasks, treating the tasks to be adjusted in the current layer as new temporarytasks respectively, so as to realize the expansion operation of the adjustment tree; if the conflicts are resolved within the set adjustment times, determining that the original temporary tasks are scheduled successfully, and outputting the adjusted scheduling scheme; otherwise, outputting the initial scheduling scheme.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
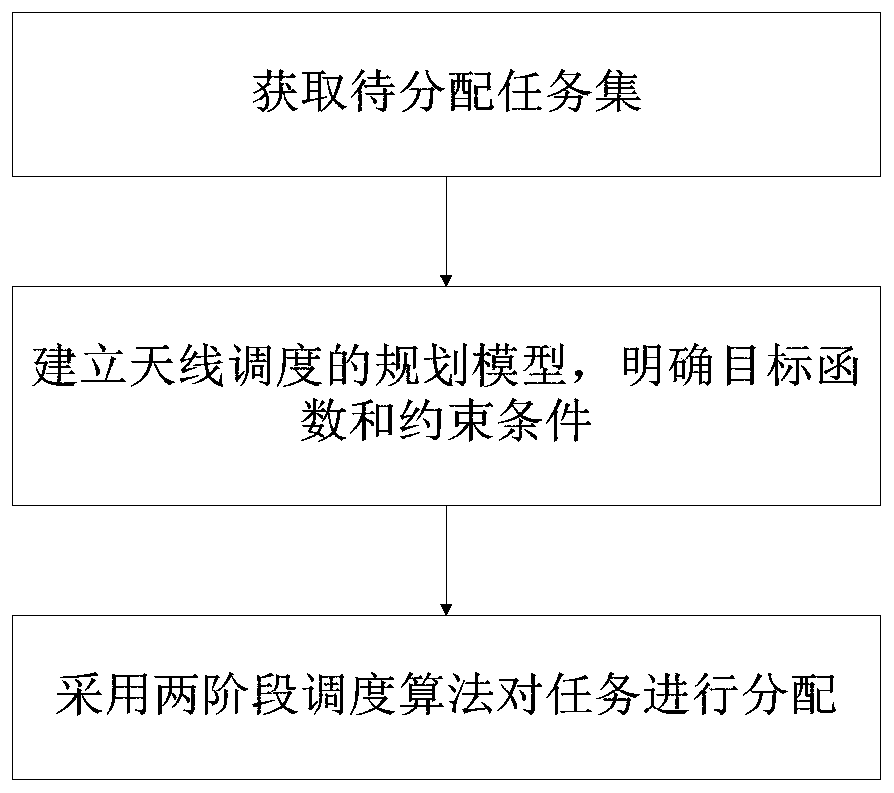
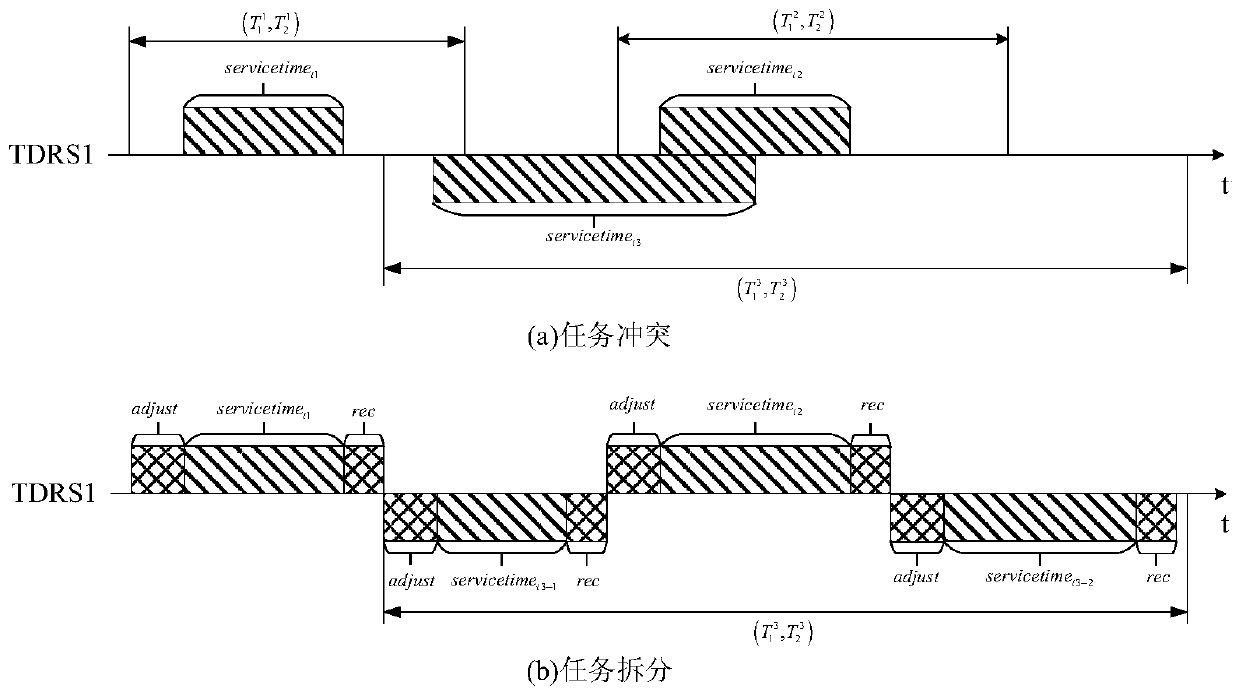
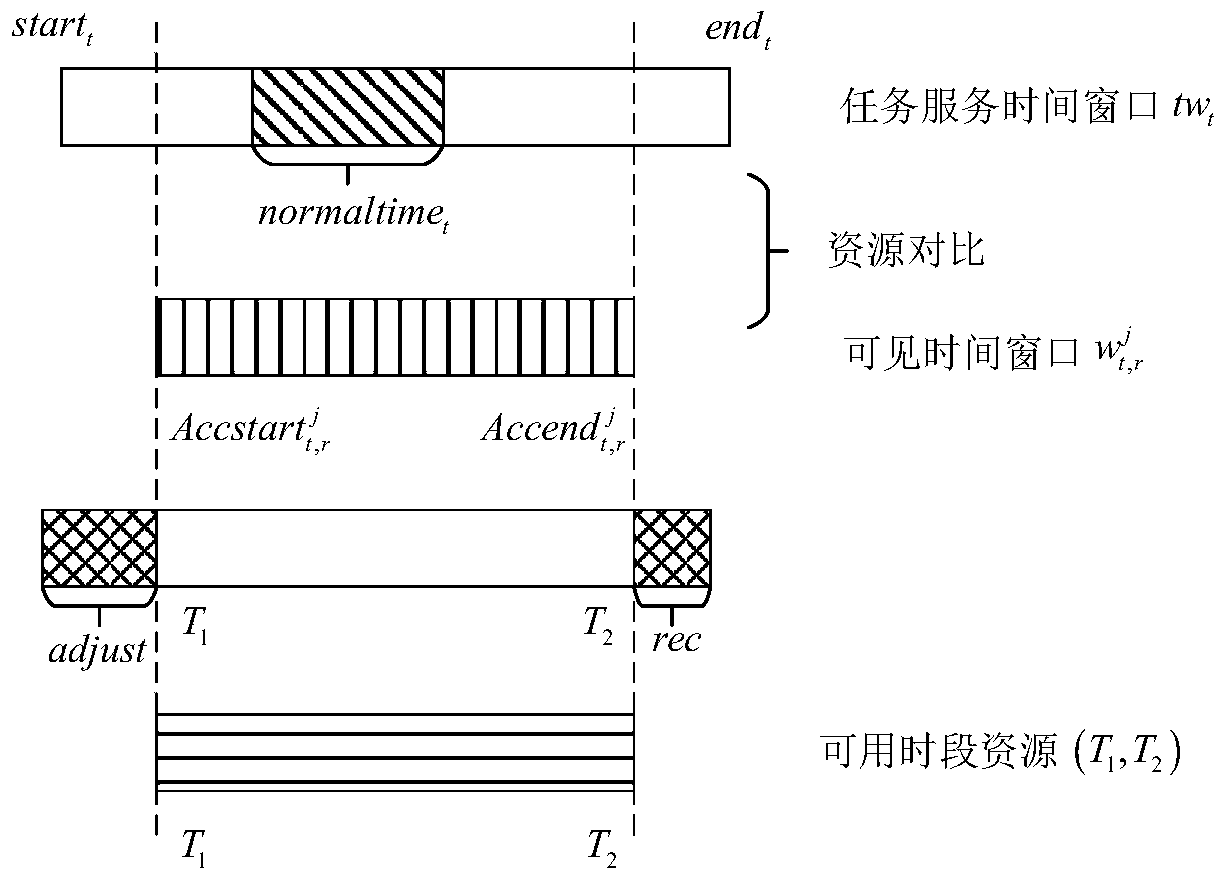
Relay satellite single-address antenna scheduling method suitable for breakpoint resumption
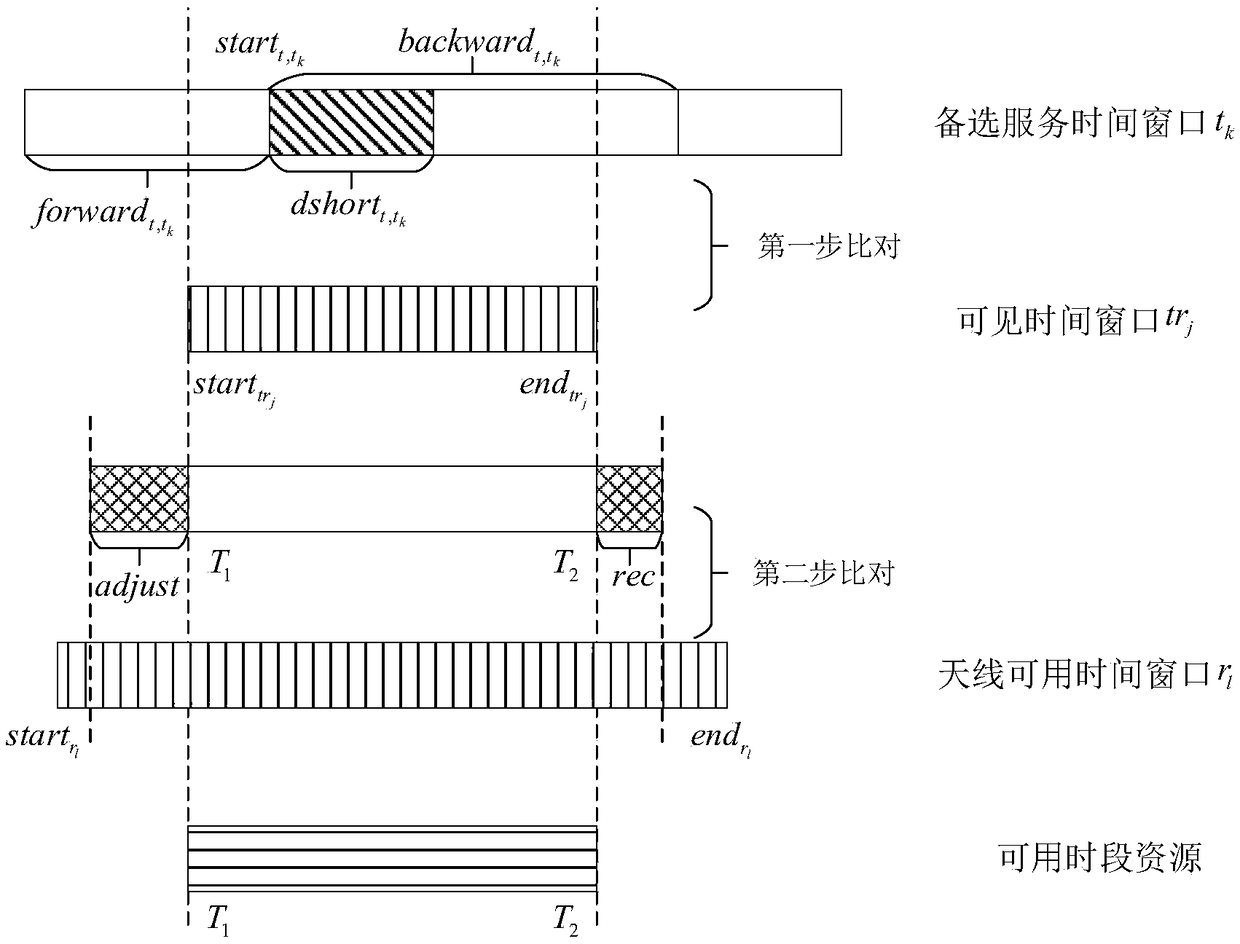
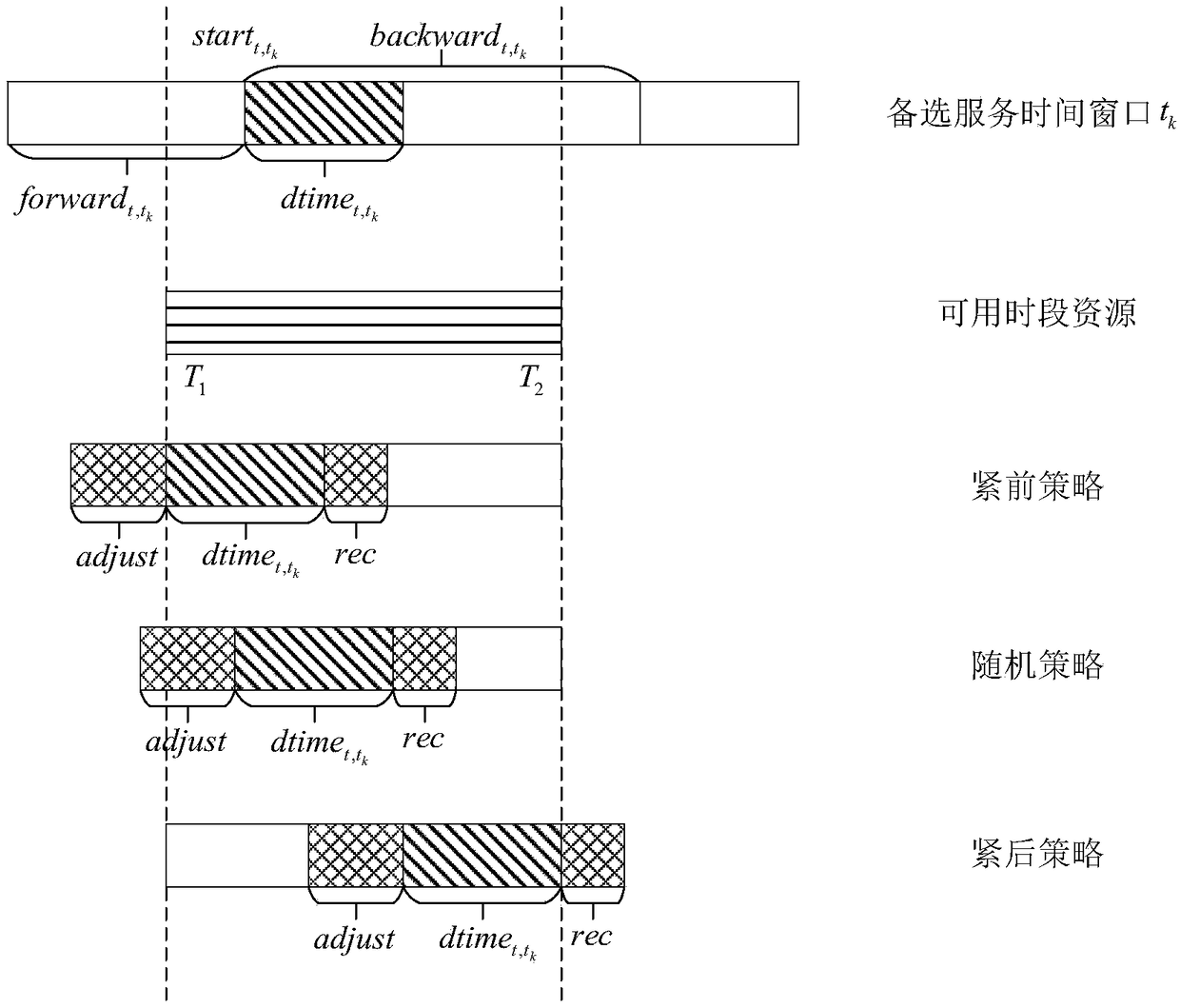
The invention discloses a relay satellite single-address antenna scheduling method suitable for breakpoint resumption. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a to-be-distributed task set; establishing a planning model of antenna scheduling, and defining an objective function and constraint conditions; allocating the tasks by adopting a two-stage scheduling algorithm, wherein the two-stage scheduling algorithm comprises a complete task distribution stage and a breakpoint resume task distribution stage, and the algorithm comprises the task resource matching, task available resource set generation, available time period conflict degree calculation, task insertion and operator updating by a task available resource set. The method of the invention aims to solve the problems of low task completion rate and low resource utilization rate caused by the difference of task requirements during the relay service process, considers the actual situation and the user requirements of the relay service at the same time and improves a traditional relay satellite application model, the algorithm can obtain a high-quality scheduling scheme within the shorter time, and is suitable for a relay satellite scheduling scene with higher requirements for scheduling time and has gains at the aspects of task completion rate, resource utilization rate and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Task satellite scheduling method for infrared LEO constellation
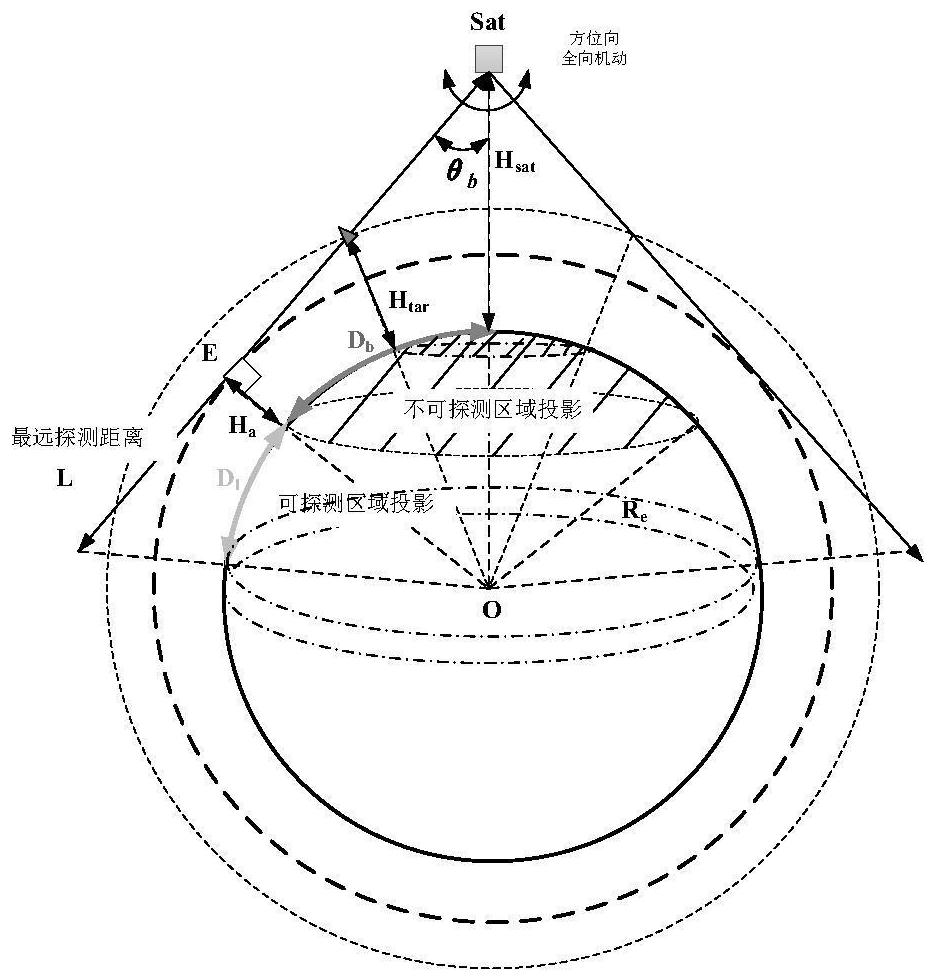
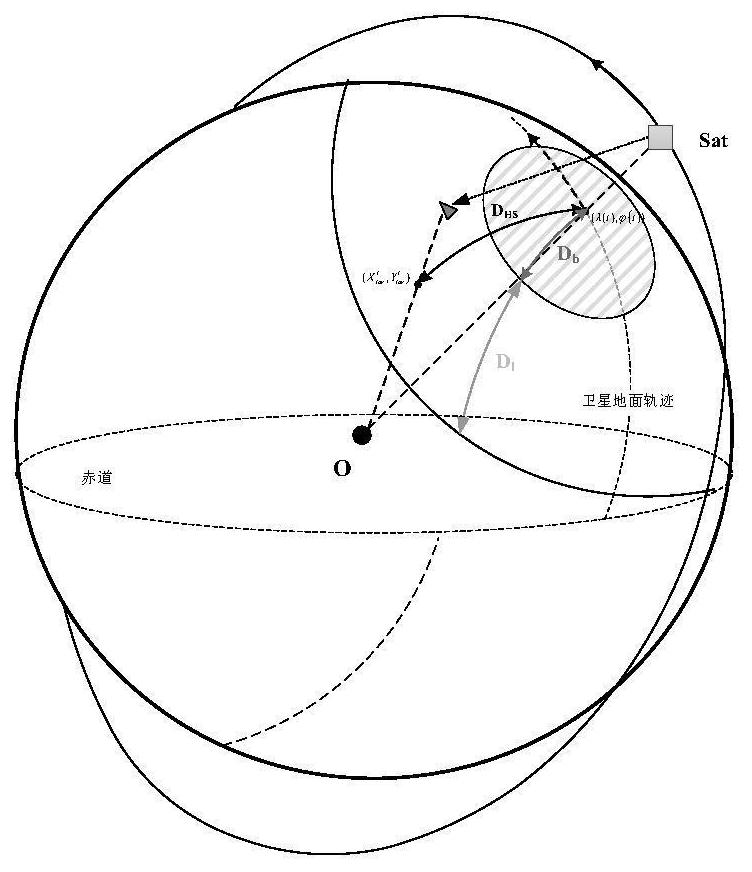
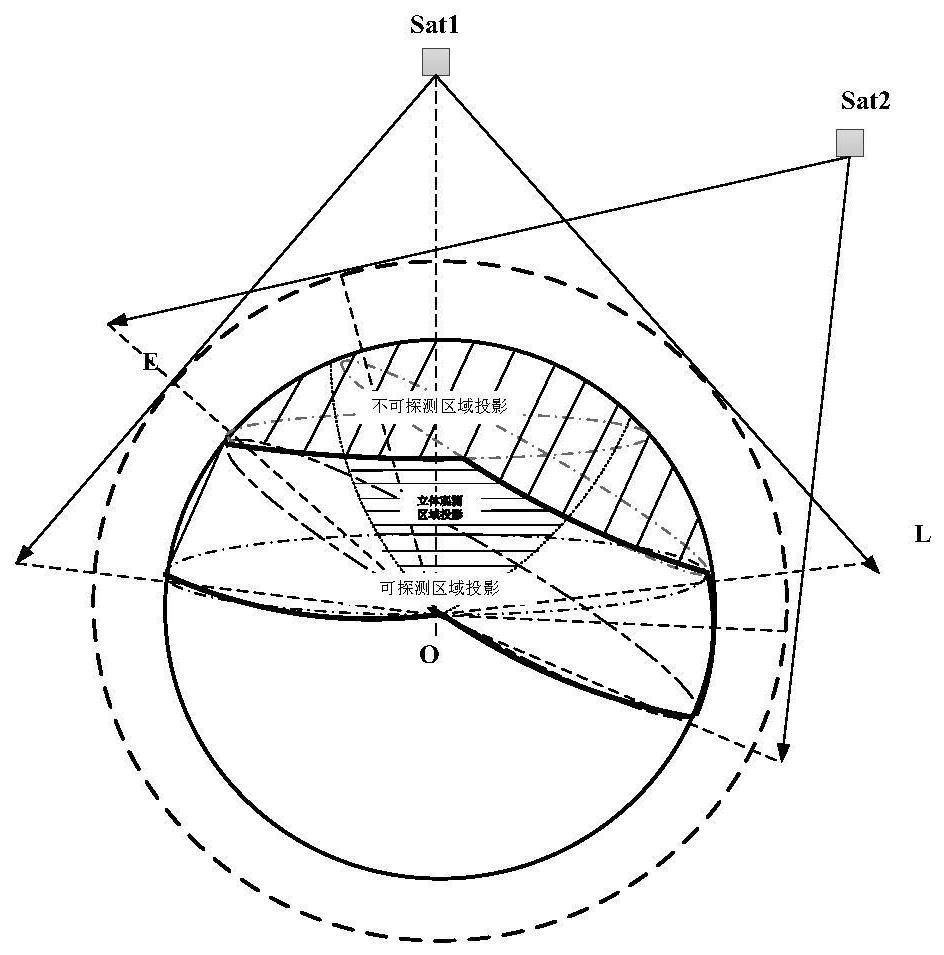
ActiveCN112874814AImprove preferenceImprove timelinessArtificial satellitesSpacecraft guiding apparatusOrbital planeLongitude
The invention relates to the technical field of aerospace, and provides a task satellite scheduling method for an infrared LEO constellation. The method comprises the following steps: projecting an invisible observation angle range of a satellite to a target to earth surface to obtain an undetectable range Db; projecting the maximum detection distance L of the satellite to the earth surface and removing the undetectable range Db to obtain a detectable range D1; projecting the target to the earth surface, and performing detectable analysis of the satellite and the target; screening orbital planes according to the longitude range of ascending nodes of the orbital planes and the geographic position of the target; and screening a task satellite from the screened orbital planes according to the relative motion relation between the satellite and the target and observable conditions. The problems that in the prior art, calculation is complex, on-satellite resource overhead is large and task planning timeliness is low in the task satellite scheduling process are at least partially solved, task satellite optimization efficiency and timeliness are improved, and the method has application value for task satellite scheduling of an infrared LEO constellation and design optimization of the constellation.
Owner:INNOVATION ACAD FOR MICROSATELLITES OF CAS +1
Satellite screening method and system based on task invitation
ActiveCN111027801AImprove efficiencyReduce complexityCharacter and pattern recognitionResourcesEngineeringRemote sensing
The invention provides a satellite screening method and system based on task invitation, and relates to the field of satellite scheduling. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring historical task data, wherein the historical task data comprise historical tasks and satellites corresponding to the historical tasks; acquiring a historical task demand vector based on the historical task; obtaining a to-be-observed task demand vector based on the to-be-observed task; obtaining the similarity between the historical task and the to-be-observed task based on the two demand vectors; obtaining a target historical task based on the similarity, and extracting a target satellite corresponding to the target historical task; inviting the target satellite based on the to-be-observed task; if the target satellite meets the energy constraint, the storage capacity constraint and the task time window constraint at the same time, enabling the target satellite to accept the invitation to obtain an invited satellite; if the number of the invited satellites is one, enabling the invited satellite to execute the task to be observed; and if the number of the inviting satellites is more than one, executing the task to be observed by the inviting satellite with the maximum income when the task to be observed is executed. The method and system are high in satellite screening efficiency.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
A Satellite Scheduling Method Based on Active Observation Tasks
ActiveCN109684055BIncrease profitAvoid Duplicate ImagingProgram initiation/switchingEngineeringRemote sensing
The invention discloses a satellite scheduling method based on an active observation task. At least an execution area and execution time of an imaging task are obtained based on real-time task demanddata; Classifying the imaging tasks based on parameters, execution areas and execution time of the remote sensing satellites to establish an imaging task set needing at least two remote sensing satellites to cooperatively complete; Screening out at least two remote sensing satellites respectively involved in each imaging task based on the execution starting time and the execution ending time of the execution time; dividing the overlapped imaging time windows of the remote sensing satellites into a plurality of sub-imaging time windows, wherein the remote sensing satellites establish an initialto-be-observed task list based on the sub-imaging time windows according to a mode of alternately executing an imaging task and an imaging data download task. The remote sensing satellites are set toexecute the imaging task and the data downloading task in an alternating mode, and dramatic increase of the storage capacity of the remote sensing satellites can be effectively reduced in the mode ofincreasing the data turnover speed.
Owner:SPACETY CO LTD (CHANGSHA)
Satellite scheduling method, device and equipment and computer storage medium
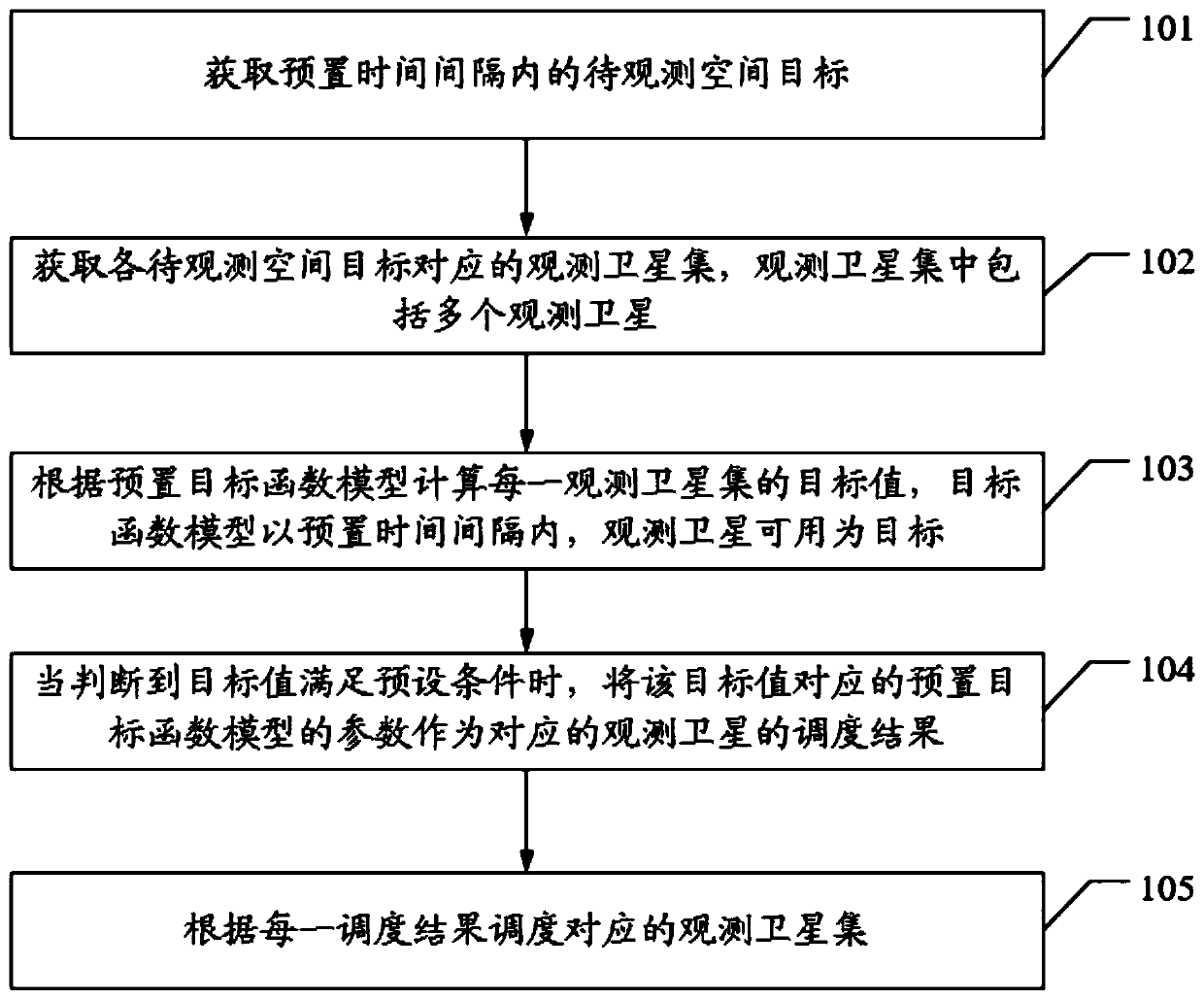
PendingCN110210788ASolve technical problems that prevent the implementation of observation tasksResourcesGenetic algorithmsSatelliteReal-time computing
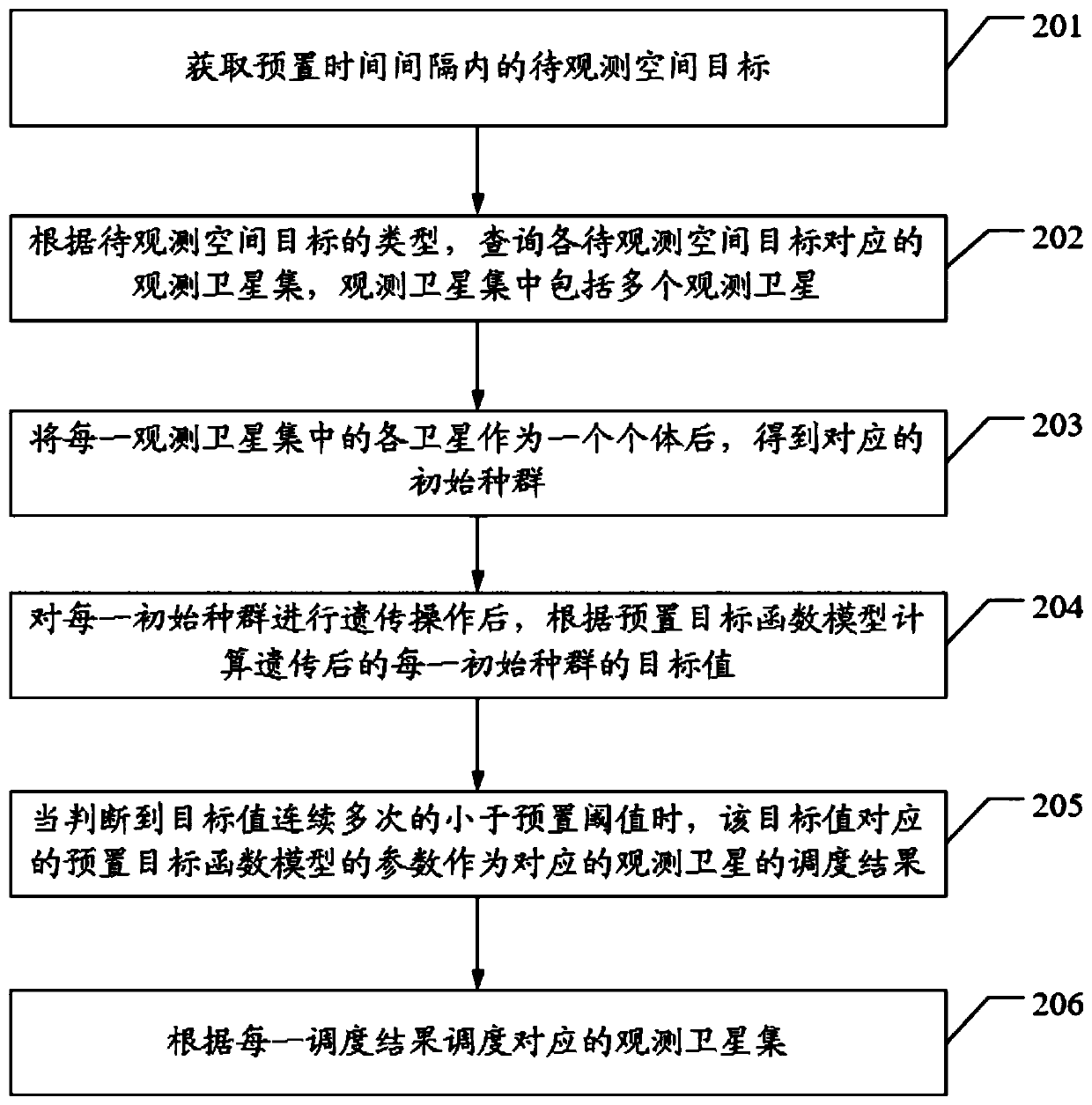
The invention discloses a satellite scheduling method, device and equipment and a computer storage medium. The method comprises the steps that a to-be-observed space target in a preset time interval is acquired; an observation satellite set corresponding to each to-be-observed space target is obtained, wherein each to-be-observed satellite set comprises a plurality of observation satellites; a target value of each observation satellite set is calculated according to a preset target function model, wherein the target function model takes the available observation satellite as a target within apreset time interval; when it is judged that the target value meets the preset condition, parameters of a preset objective function model corresponding to the target value serve as scheduling resultsof the corresponding observation satellites; and scheduling the corresponding observation satellite set according to each scheduling result, thereby solving the technical problem that an observation satellite cannot execute an observation task due to the fact that the observation satellite receives two observation tasks at the same time in an existing satellite scheduling method.
Owner:GUANGDONG POWER GRID CO LTD +1
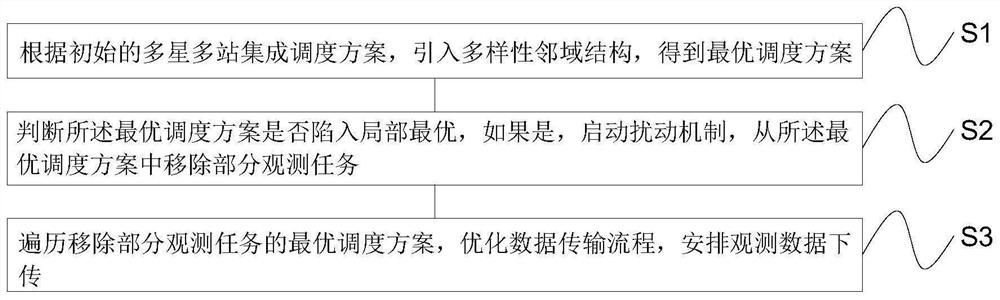
Multi-satellite multi-station integrated scheduling method and system
ActiveCN112613644AOptimize the transfer processForecastingComplex mathematical operationsLocal optimumOptimal scheduling
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
A task allocation method and system in a virtual constellation dynamic environment
The invention provides a task allocation method in a virtual constellation dynamic environment, and relates to the technical field of satellite scheduling. The method comprises the steps that when a virtual constellation management and control system receives a to-be-processed task, a meta-task set corresponding to the to-be-processed task is formed; the satellite platform searches an executable task set of each satellite in the management domain of the satellite platform and sends the executable task set of each satellite in the management domain of the satellite platform to the virtual constellation management and control system; a candidate meta-task subset formed by the executable meta-tasks of each satellite is determined in the management domain of the satellite platform; and the meta-task with the maximum expected revenue of each satellite in the candidate meta-task subset is used as the meta-task expected to bid by the satellite in the candidate meta-task subset; aiming at eachmeta-task in the meta-task set, the virtual constellation management and control system forms a candidate satellite set corresponding to the meta-task set; and an ordered satellite sequence corresponding to the meta-task is determined. According to the present invention, the task allocation efficiency can be improved.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Scheduling method and system for multi-satellite earth observation tasks
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
An Algorithm for Solving Time-Dependent Scheduling Problems for Imaging Satellites
InactiveCN104063748BExcellent solutionImprove image qualityForecastingSpecial data processing applicationsImaging qualityAlgorithm
The invention relates to an algorithm for solving the imaging satellite-oriented time-dependent scheduling problem. The imaging satellite-oriented time-dependent scheduling problem is the extension of the traditional satellite scheduling problem. According to the invention, modeling is performed for the problem for the time-dependent relationship between the task earnings and the imaging time, and a heuristic algorithm for solving the problem is provided. According to the invention, the time dependence is taken into account in the traditional satellite scheduling problem, so the imaging quality can be improved, the possibility for generating useless products can be reduced, and the solving effect of the provided heuristic algorithm is superior to the constrained programming algorithm engine ILOG CP Optimizer of the IBM company.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Ontology-based Modeling Method for Imaging Satellite Scheduling Problem
The invention discloses an imaging satellite scheduling problem model building method based on a body. The method comprises the following specific steps of (1) treating tasks, resources, a scheduling time range, restraints, goals, preferences and scheduling demands as related items of an imaging satellite scheduling problem, (2) combining the related items of the tasks, the resources, the scheduling time range, the restraints, the goals, the preferences and the scheduling demands with specific application knowledge to carry out instantiation on the mutual relation, and generating a specific application model, and (3) building the specific application model by the utilization of a body tool, and describing the body of the specific application model through a standard format. According to the imaging satellite scheduling problem model building method based on the body, a problem domain is confirmed by building the goals, the restraints and problem parameters, and accordingly the imaging satellite scheduling problem can be described generally.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
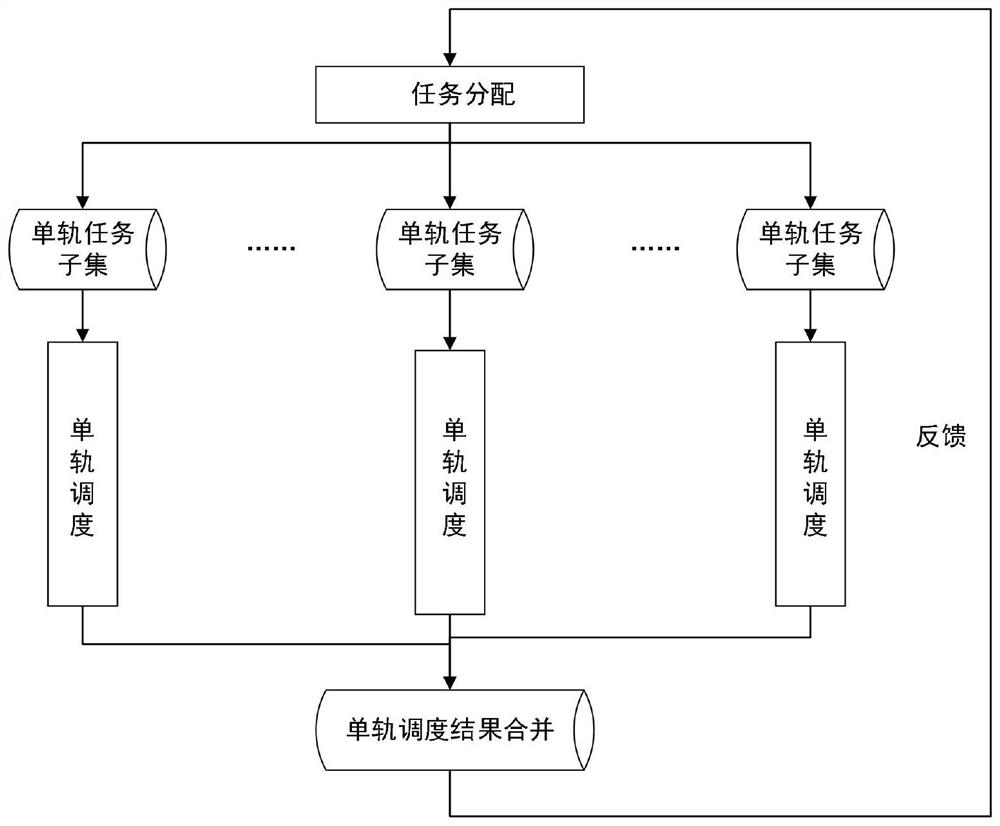
A hierarchical scheduling method and system for multi-satellite observation based on divide-and-conquer strategy
ActiveCN109087023BReduce complexityImprove performanceResourcesSatellite observationAllocation algorithm
The present invention provides a multi-satellite observation hierarchical scheduling method and system based on a divide-and-conquer strategy, which specifically includes the following steps: S1, using an allocation algorithm to assign tasks to each orbital cycle to form a task set for each orbital cycle; S2 .Use the approximate optimization algorithm to solve the scheduling sequence of the task set on each orbital circle; S3. The allocation algorithm re-updates the allocation scheme of the allocation algorithm according to the tasks that have not generated the scheduling sequence fed back by the scheduling sequence of each orbital circle, and then forms a new orbit. A new task set for the lap; S4. Repeat steps S1, S2, and S3 until the termination condition of multi-satellite observation hierarchical scheduling is reached. By effectively decomposing and simplifying a complex combinatorial optimization problem into a two-level programming, the complexity of problem solving is effectively reduced, and it shows excellent performance especially in solving large-scale multi-satellite observation scheduling problems. The invention is applied in the technical field of satellite scheduling.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com