Relay satellite mission scheduling method and system
A technology for task scheduling and relay satellites, applied in transmission systems, radio transmission systems, program startup/switching, etc., can solve problems such as unreasonable allocation of preparation time, waste of antenna time resources, and affecting the quality of relay services
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
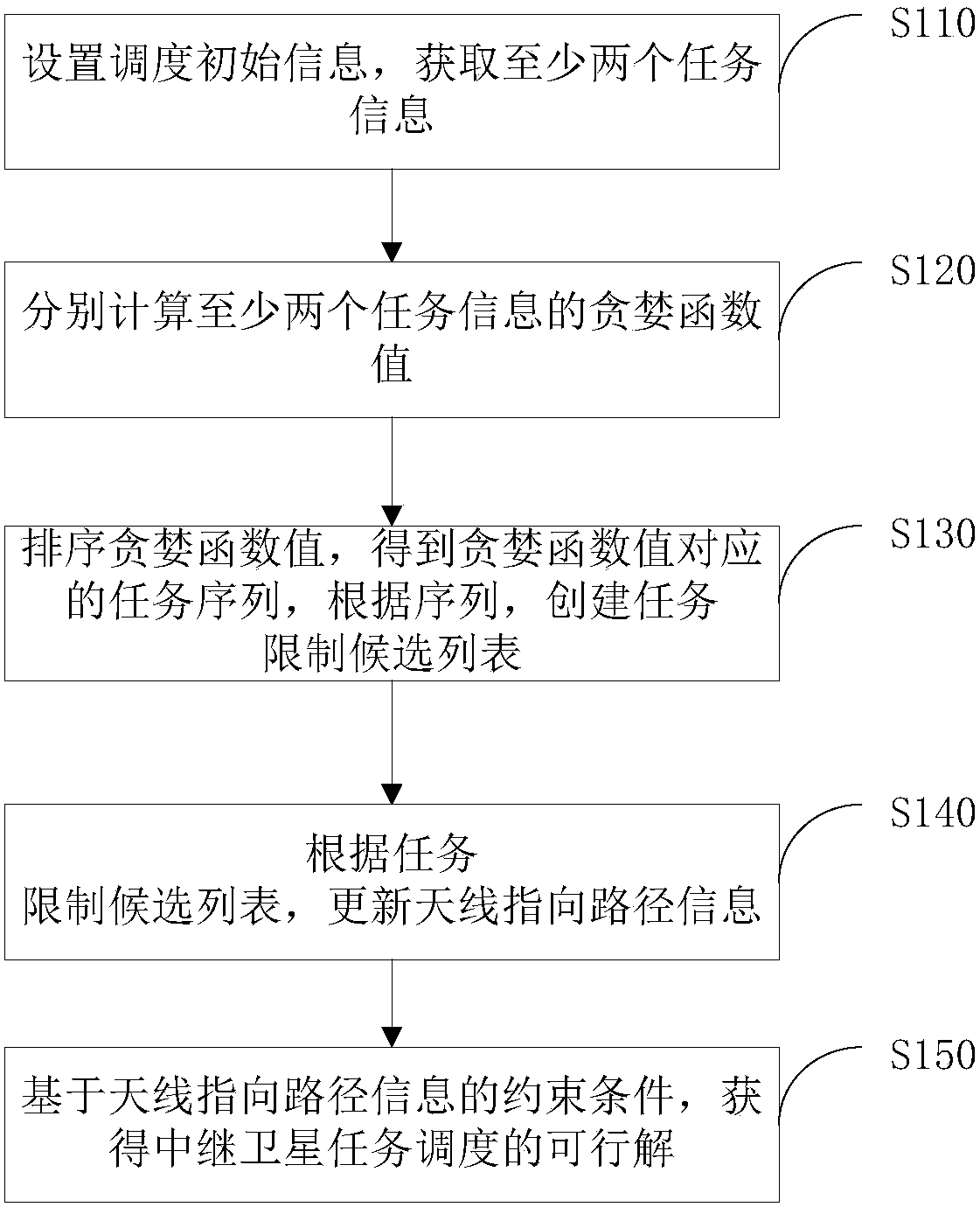
[0053]figure 1 A relay satellite task scheduling method provided by an embodiment of the present invention is shown, the method includes:
[0054] Step S110: Set initial scheduling information and obtain at least two task information;
[0055] Specifically, the foregoing initial scheduling information includes constraint conditions of iteration extremum and antenna pointing path information. The above-mentioned iteration extreme value refers to an upper limit number of iterative calculations performed by this method, which is used to obtain the optimal value of relay satellite task scheduling.
[0056] The constraint condition of the antenna pointing path information refers to the basis for judging when the relay satellite performs service insertion according to the current path. Only when the constraint condition is met can the service be inserted, otherwise it will not be allowed.
[0057] Step S120: Calculate greedy function values of at least two task information respec...
Embodiment 2
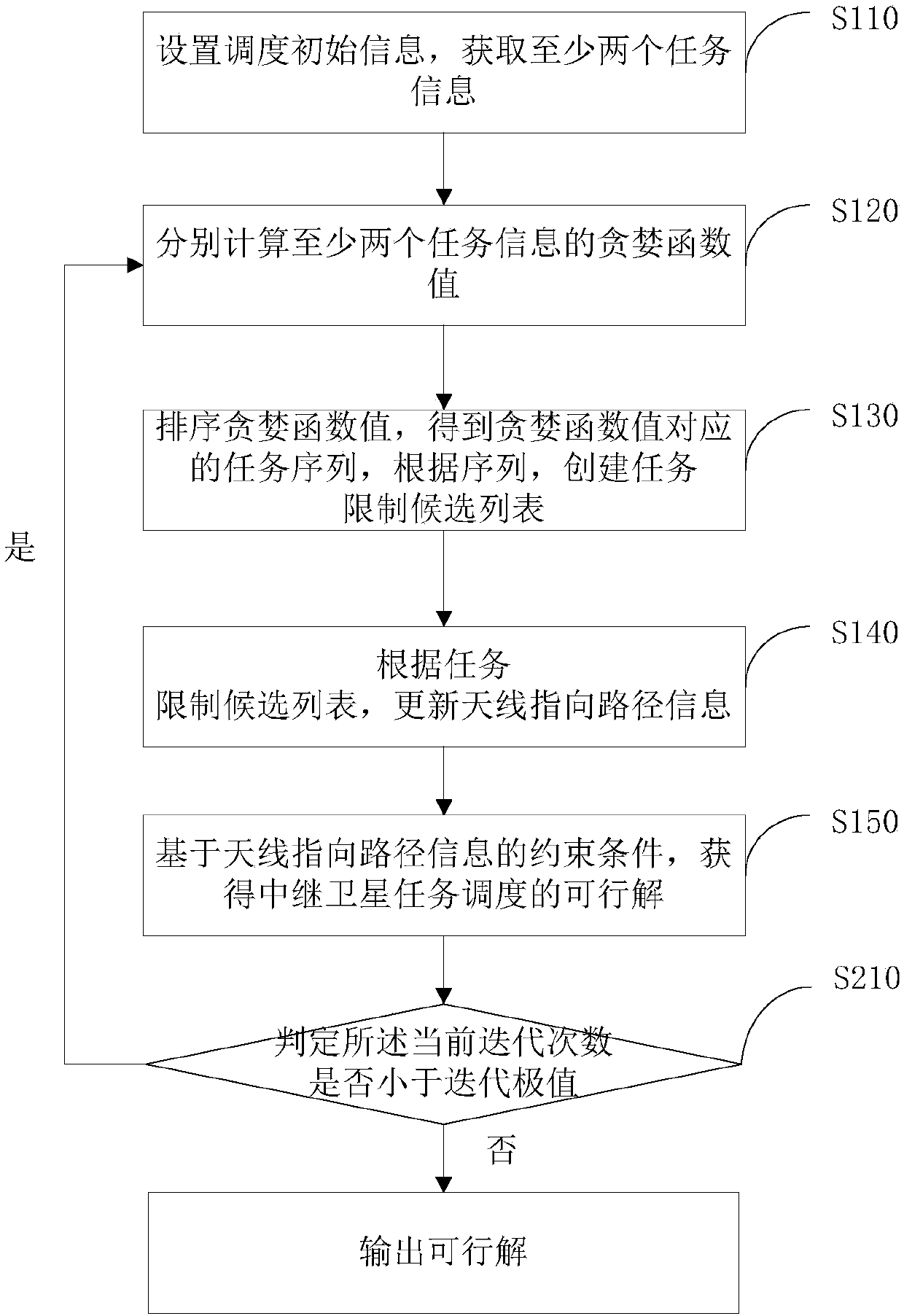
[0106] figure 2 It shows the second relay satellite task scheduling method provided by the embodiment of the present invention. The difference from Embodiment 1 is that, after obtaining the feasible solution of the relay satellite task scheduling, it also includes:
[0107] Step S210: Determine whether the current number of iterations is less than the iteration limit,
[0108] If so, return the steps of calculating the greedy function values of at least two task information respectively;
[0109] If not, output a feasible solution.
[0110] After obtaining the feasible solutions for the task scheduling of the relay satellite, the relay satellite repeats the above steps through iteration, so as to obtain the feasible solutions of the iteration extremum under the constraints of the iterative extremum, and select the satisfactory result for output.
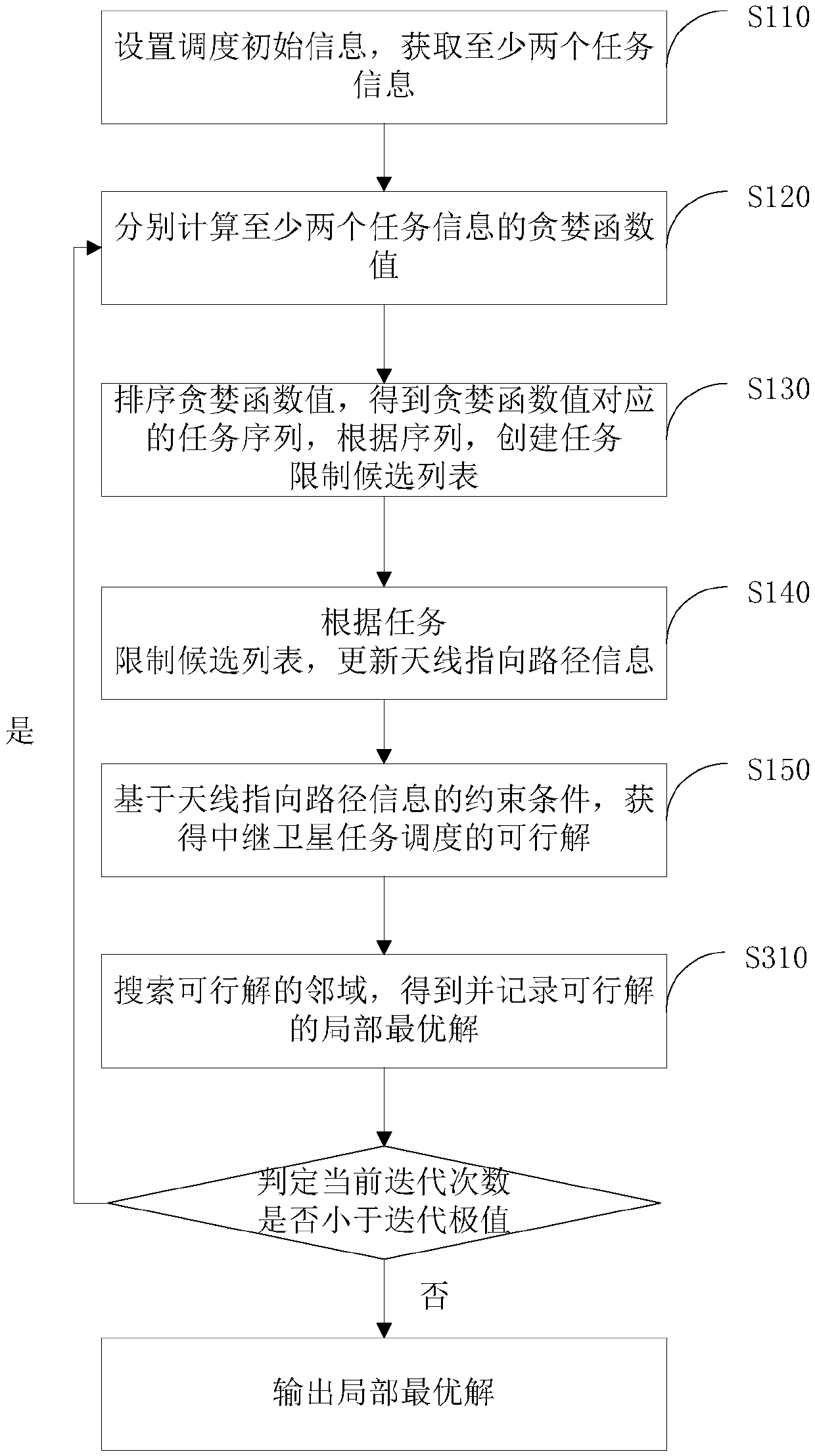
[0111] image 3 The third relay satellite task scheduling method provided by the embodiment of the present invention is shown...
Embodiment 3
[0126] Embodiment 3 lists an application example of the relay satellite task scheduling method, assuming that each relay satellite is equipped with 2 single-site antennas and 1 multiple-access antenna, and the single-site antenna can provide S and Ka two frequency band relays For services, phased array antennas provide S-band multiple access services, so the two relay satellites have a total of 6 antennas for resource allocation and task scheduling. The classic dual-satellite scheduling scenario considers a task scale of 400, and its total task duration is close to the maximum service duration that all antenna resources can provide.
[0127] In addition, this embodiment also calculates and analyzes that the business scale is 200 (the total task duration is about 50% of the maximum service duration that antenna resources can provide) and 600 (the total task duration is approximately 50% of the maximum service duration that antenna resources can provide). In the case of 150%), t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com