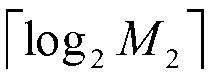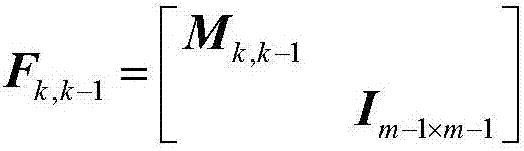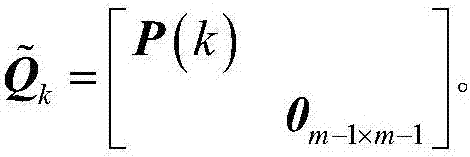Patents
Literature
858 results about "Satellite system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
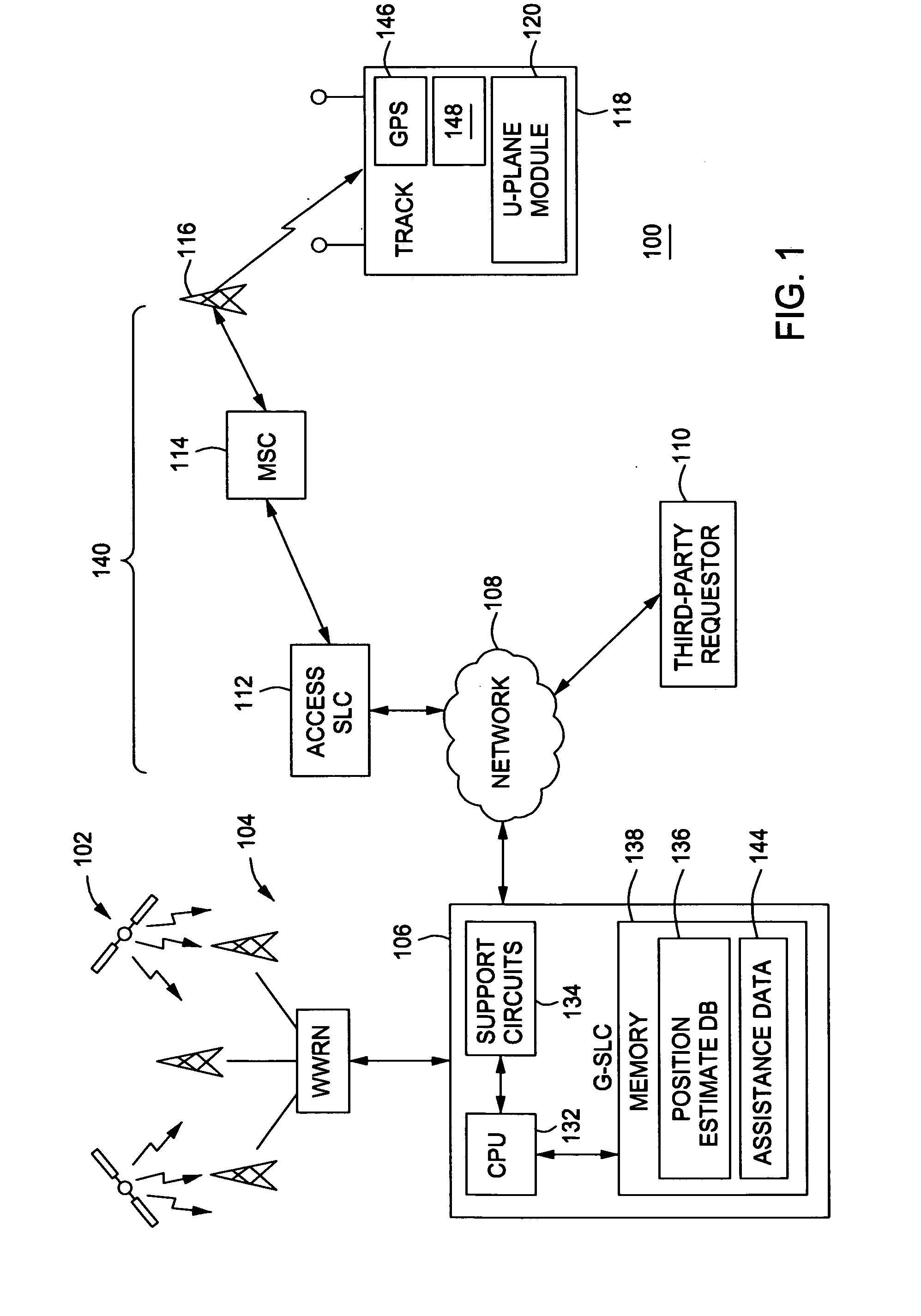
A satellite system is a set of gravitationally bound objects in orbit around a planetary mass object or minor planet. Generally speaking, it is a set of natural satellites (moons), although such systems may also consist of bodies such as circumplanetary disks, ring systems, moonlets, minor-planet moons and artificial satellites any of which may themselves have satellite systems of their own. Some bodies also possess quasi-satellites that have orbits gravitationally influenced by their primary, but are generally not considered to be part of a satellite system. Satellite systems can have complex interactions including magnetic, tidal, atmospheric and orbital interactions such as orbital resonances and libration. Individually major satellite objects are designated in Roman numerals. Satellite systems are referred to either by the possessive adjectives of their primary (e.g. "Jovian system"), or less commonly by the name of their primary (e.g. "Jupiter system"). Where only one satellite is known, or it is a binary orbiting a common centre of gravity, it may be referred to using the hyphenated names of the primary and major satellite (e.g. the "Earth-Moon system").
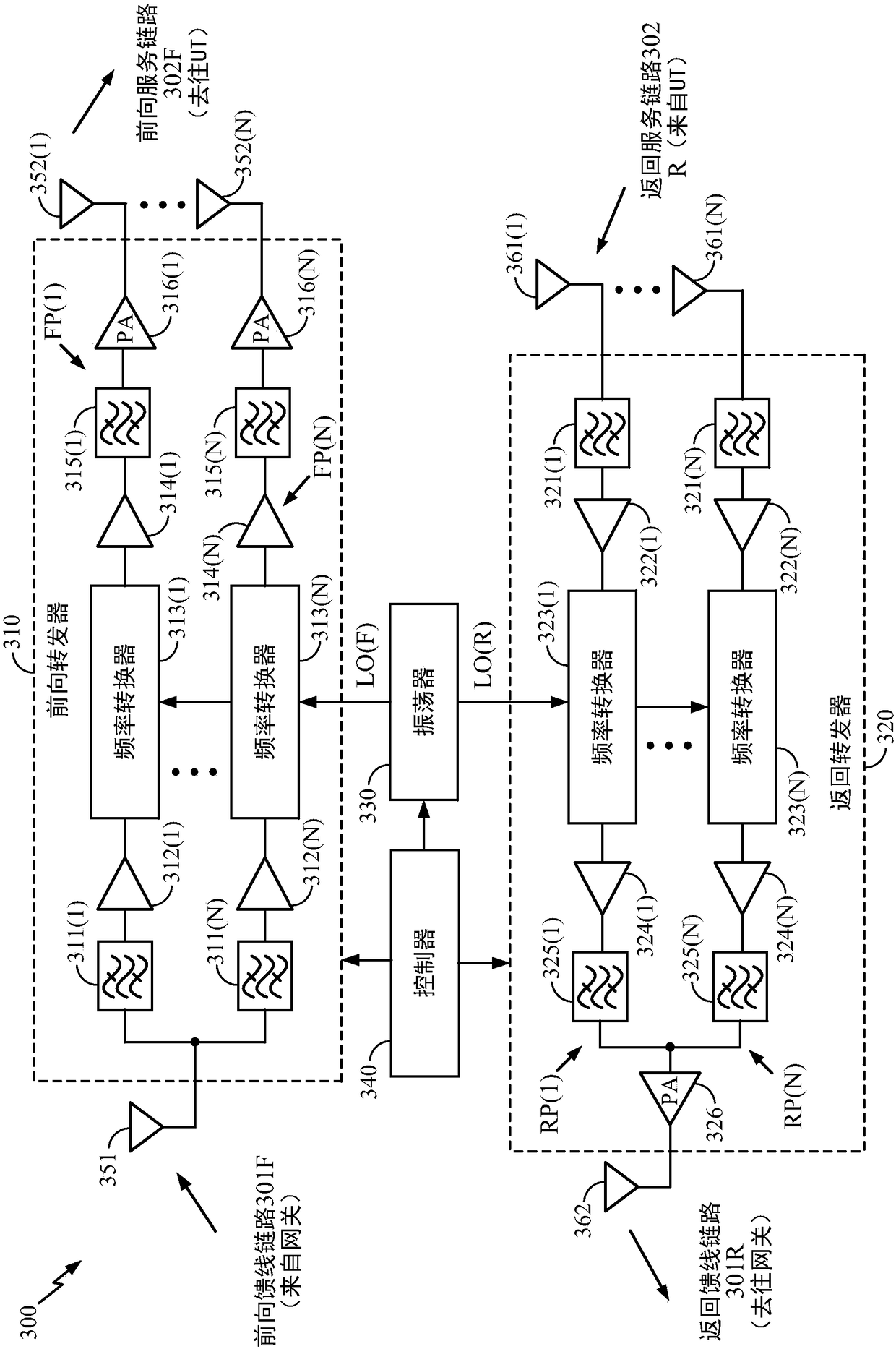
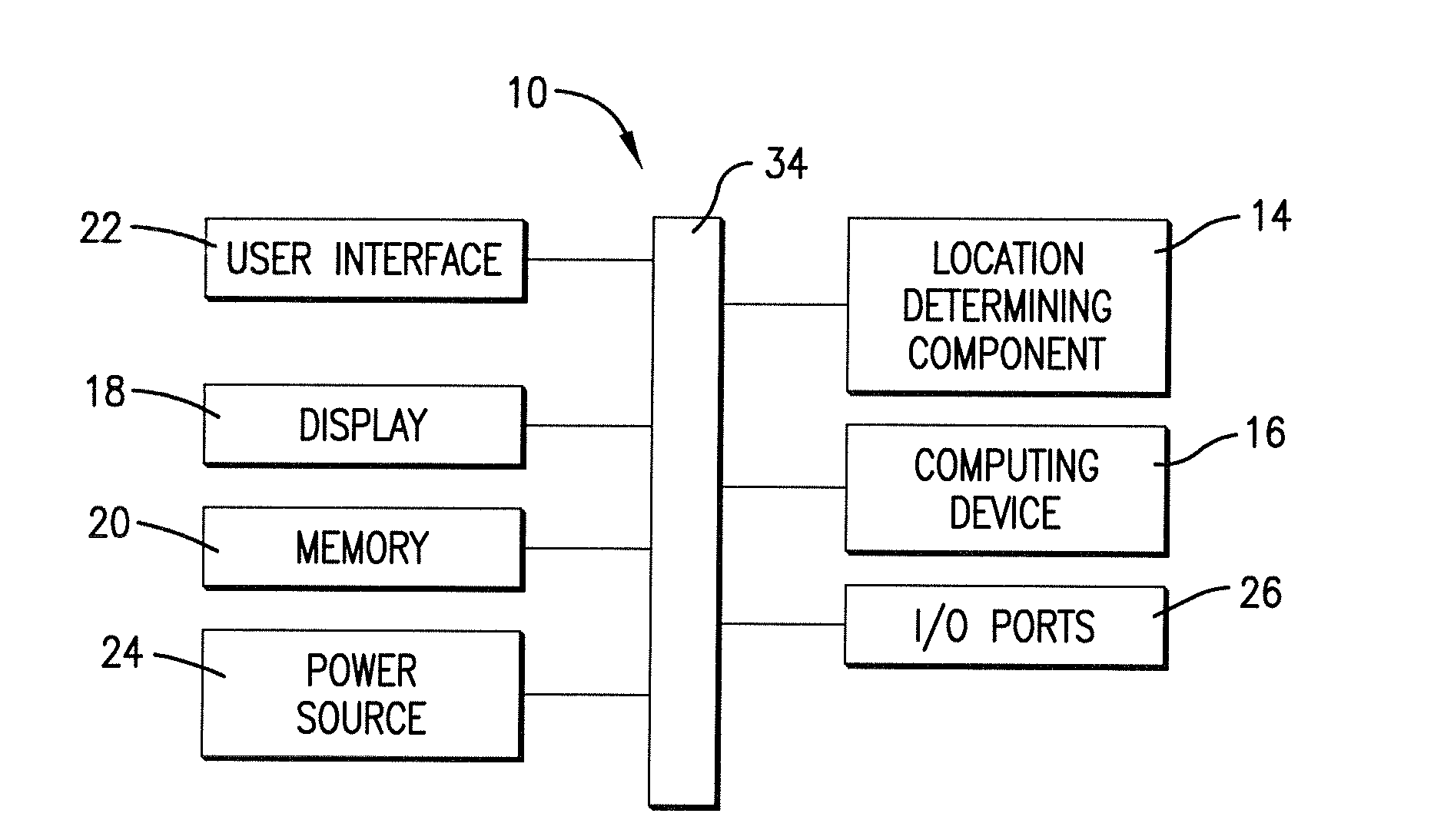
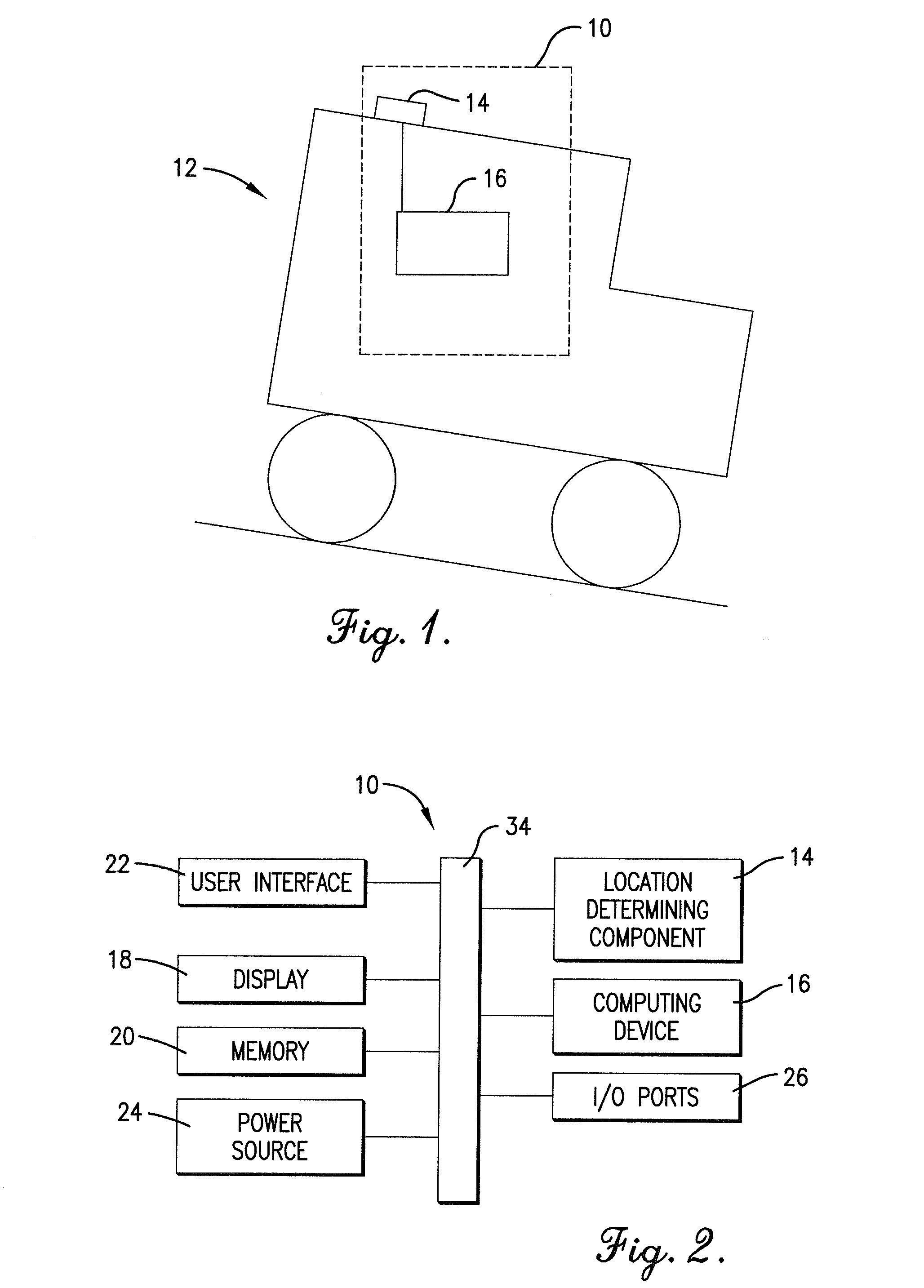
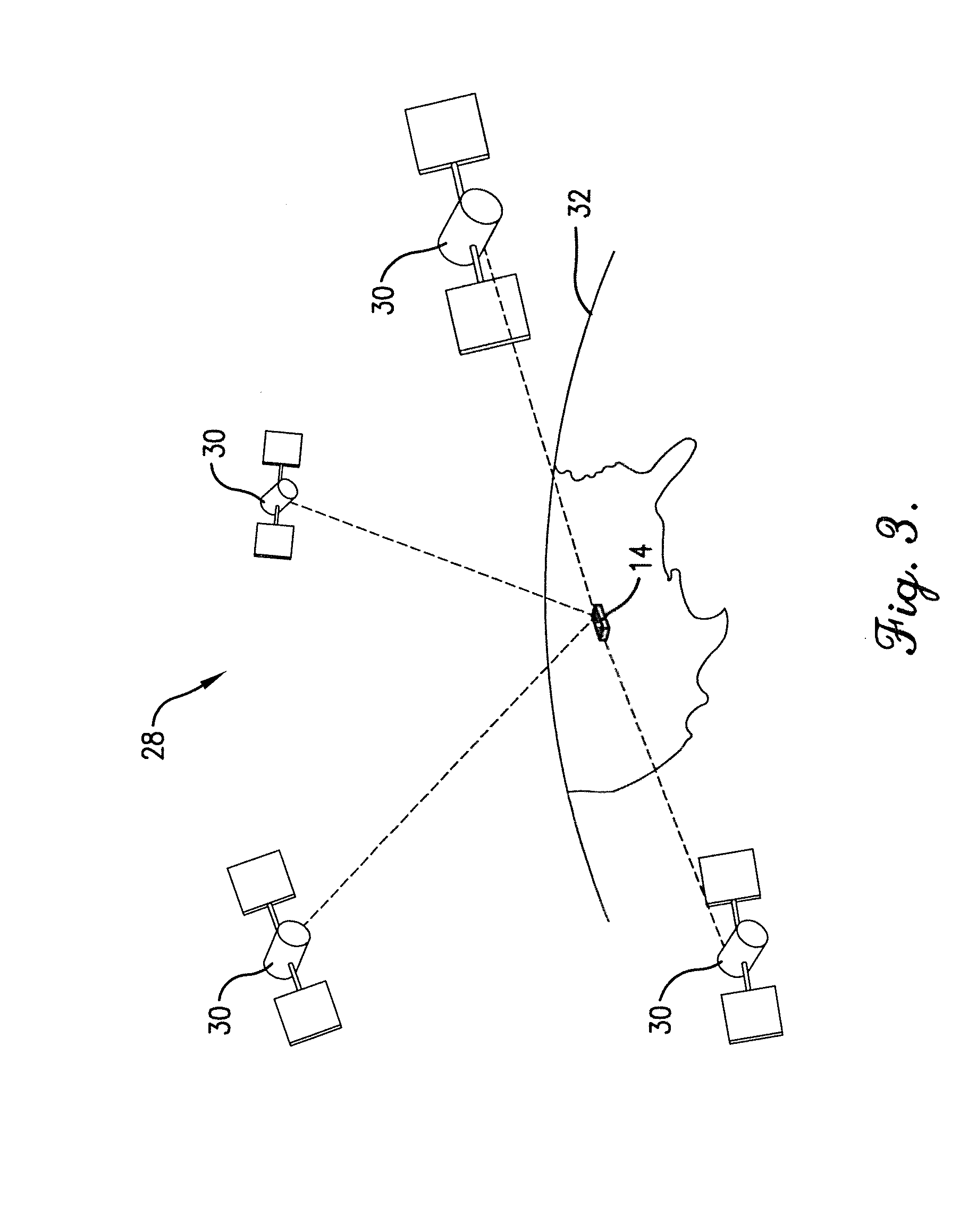
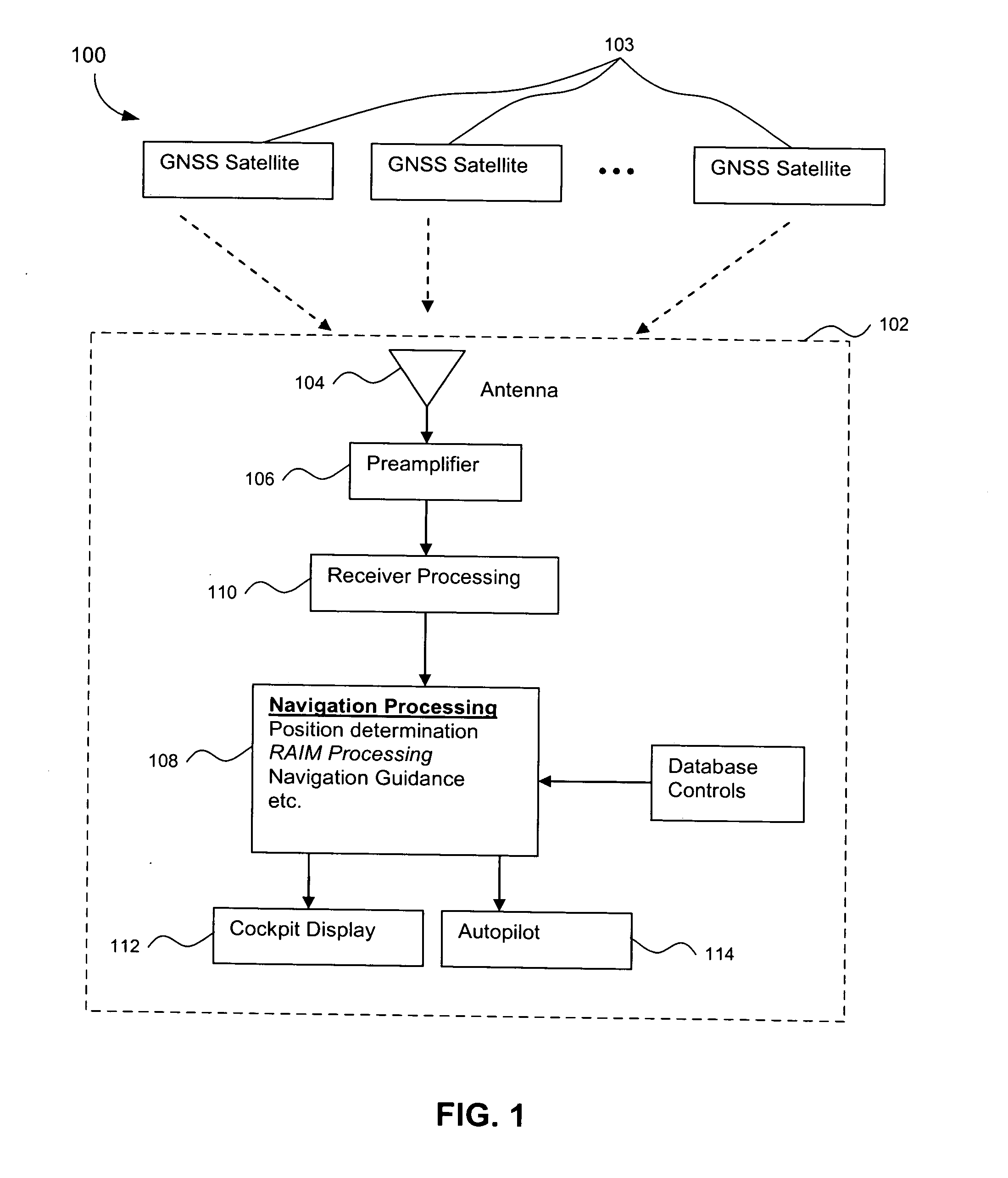
GNSS and optical guidance and machine control
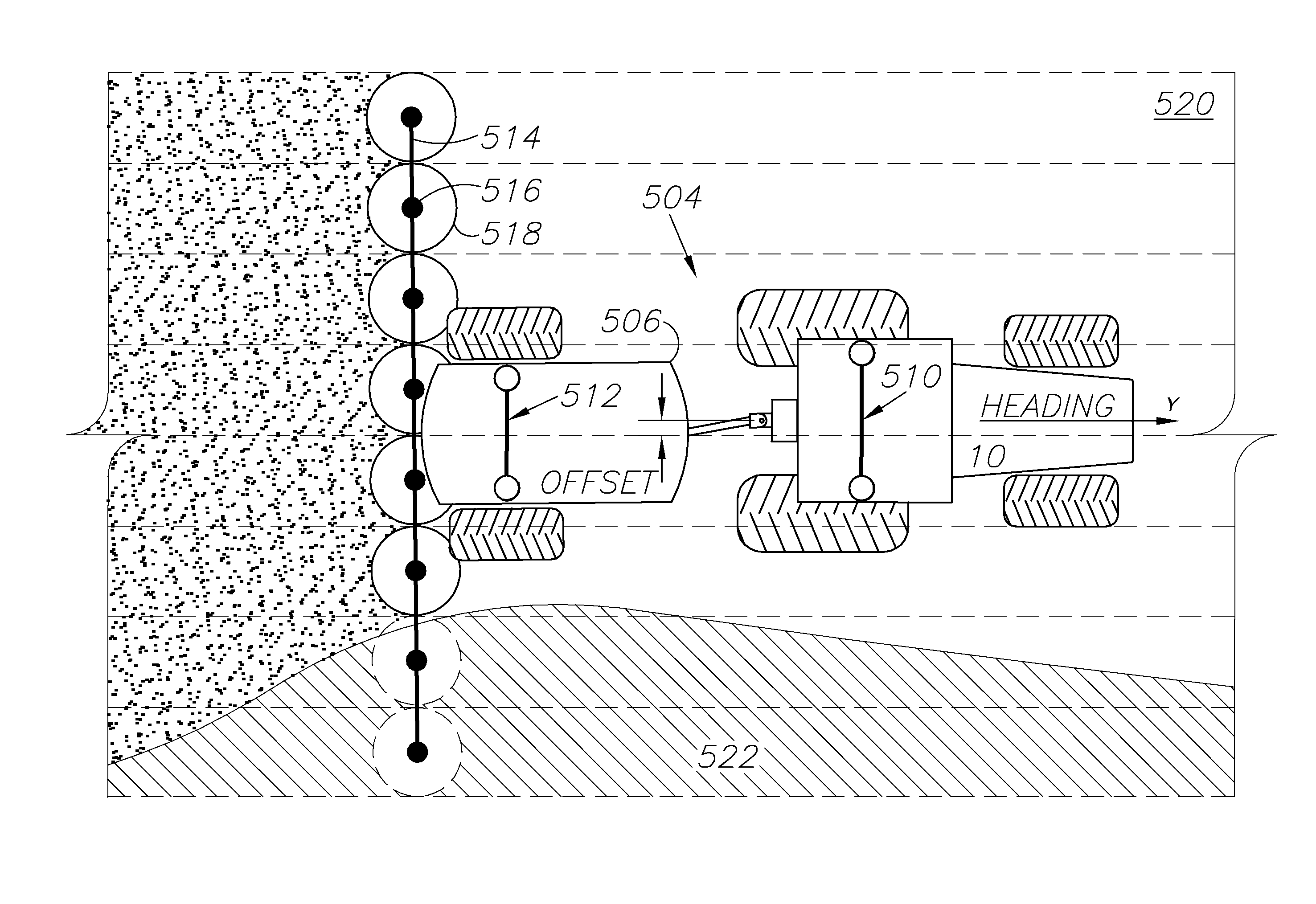
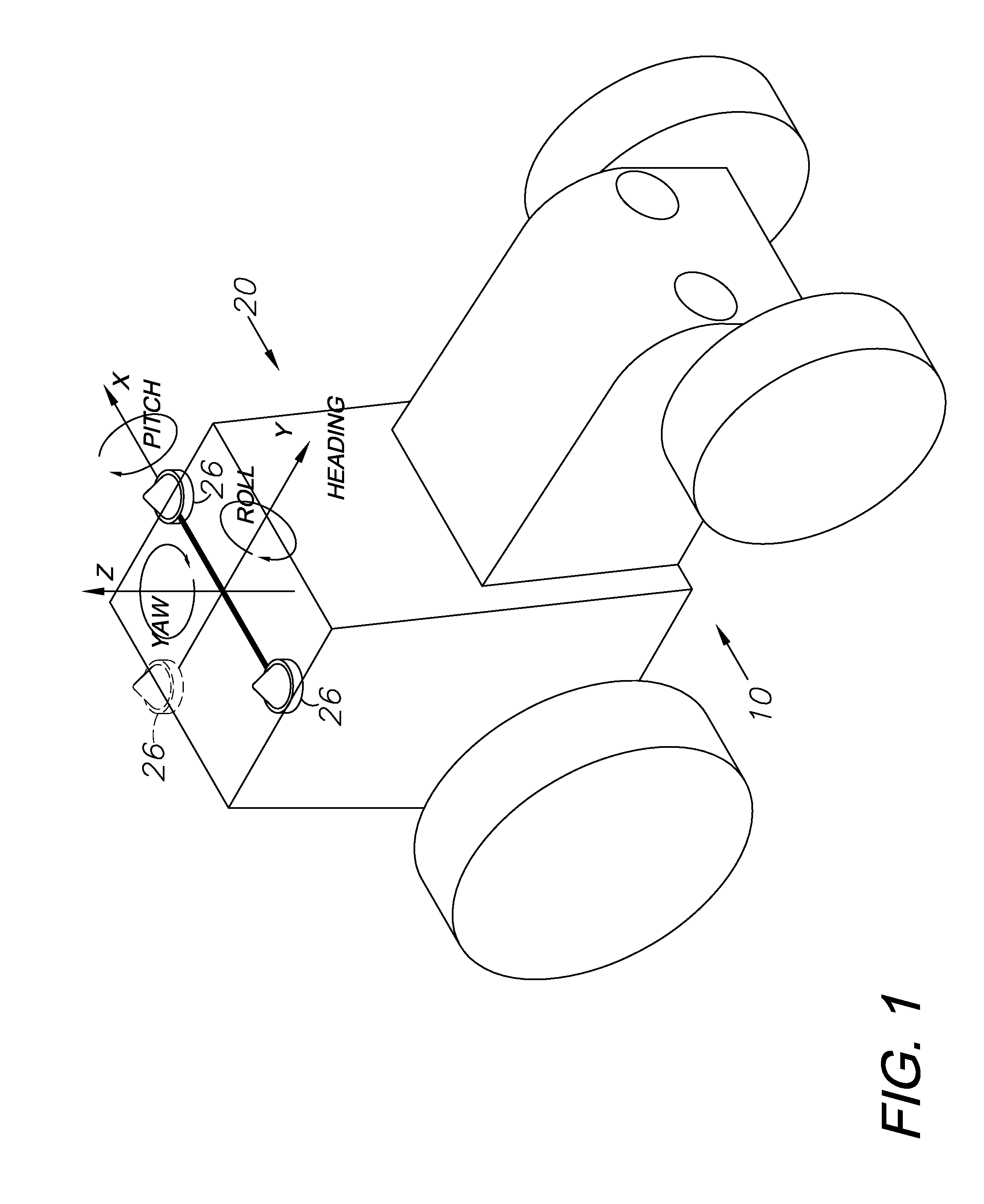
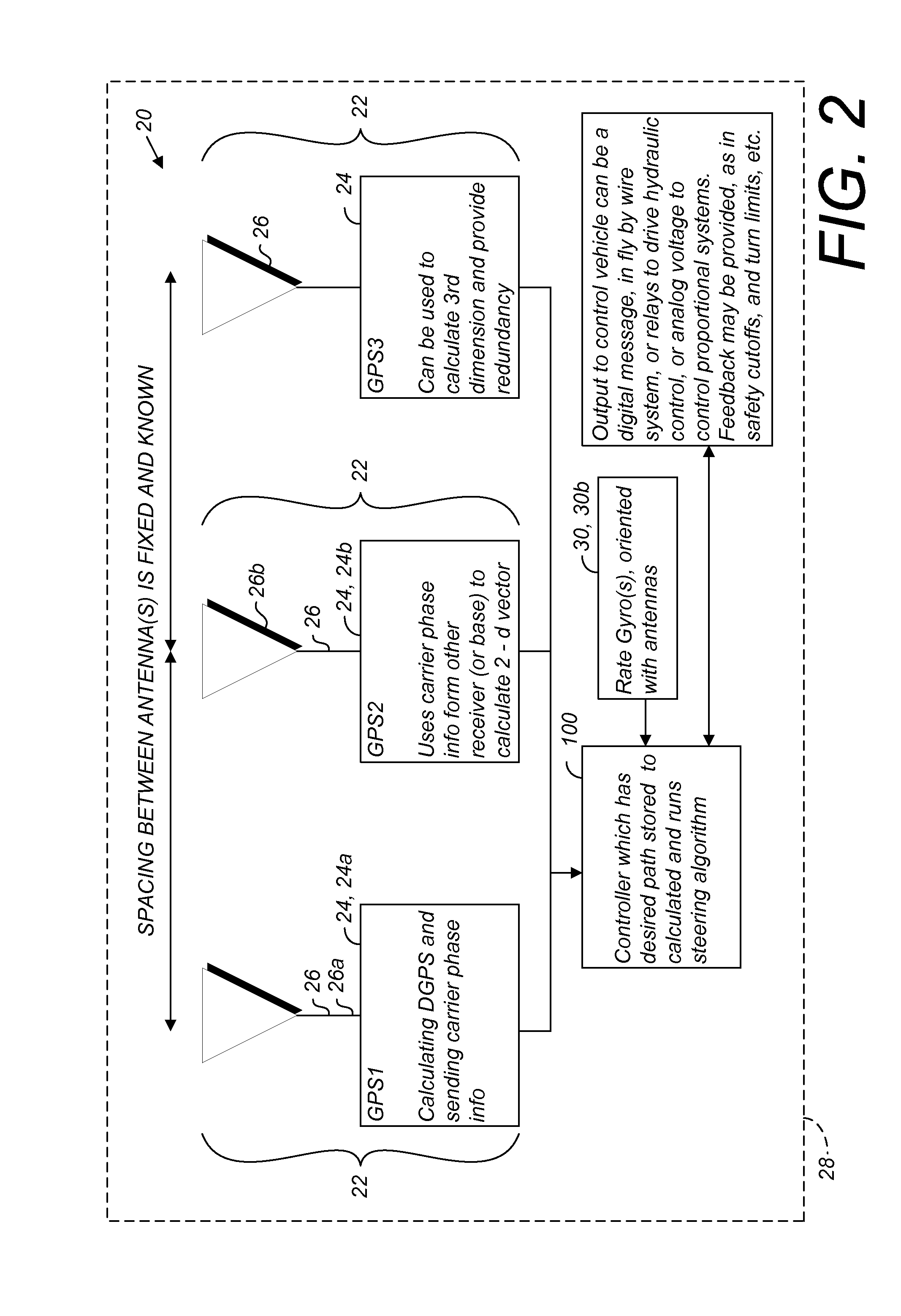
ActiveUS20140324291A1Accurate and economical preplannedEasy to correctDigital data processing detailsNavigation instrumentsCarrier signalSteering control
A global navigation satellite system (GNSS) and gyroscope control system for vehicle steering control comprising a GNSS receiver and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase position differences. The system also includes a control system configured to receive the vehicle position, heading, and at least one of roll and pitch, and configured to generate a steering command to a vehicle steering system. A vehicle control method includes the steps of computing a position and a heading for the vehicle using GNSS positioning and a rate gyro for determining vehicle attitude, which is used for generating a steering command. Relative orientations and attitudes between tractors and implements can be determined using optical sensors and cameras. Laser detectors and rangefinders can also be used.
Owner:AGJUNCTION
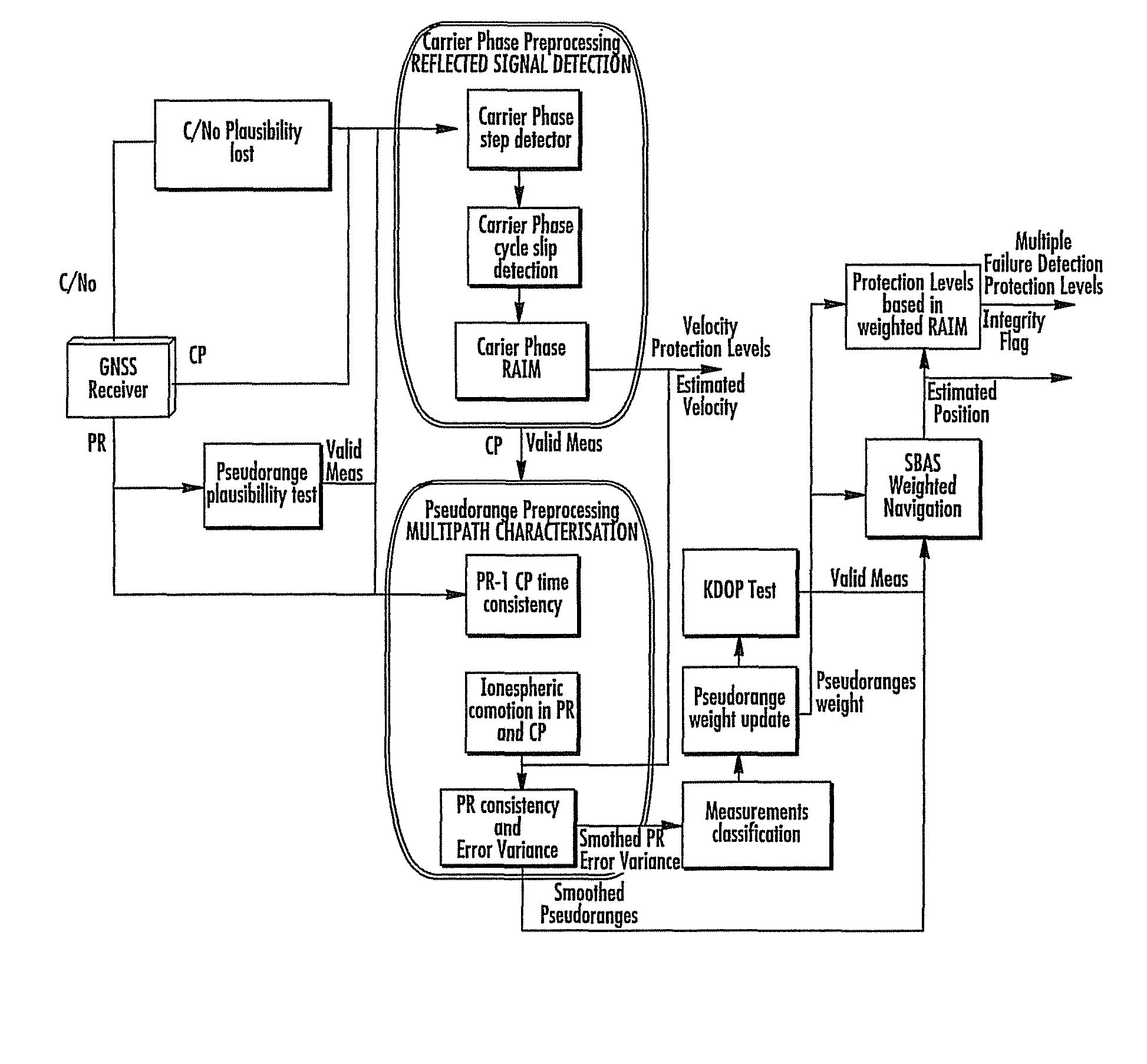
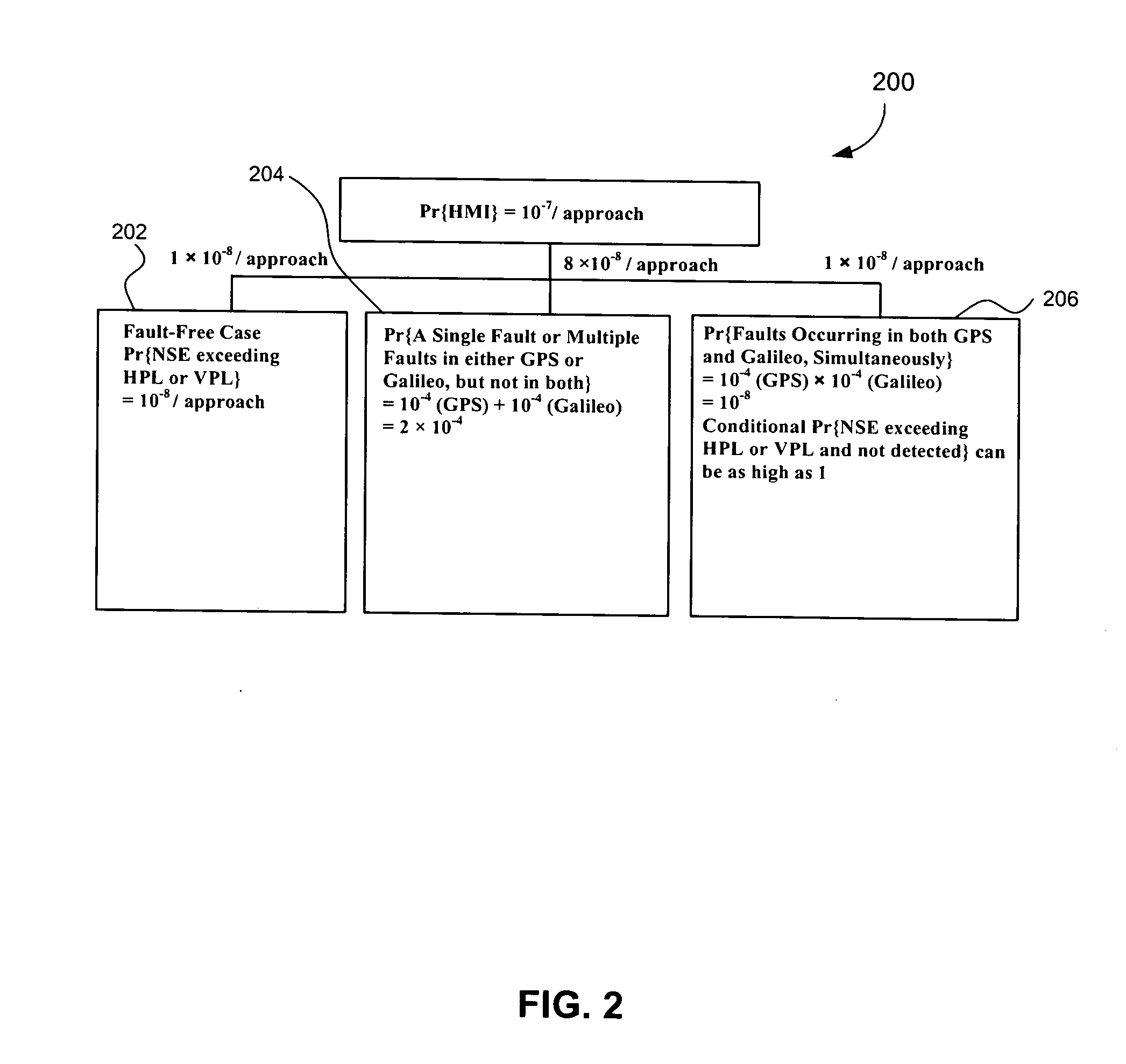
GNSS navigation solution integrity in non-controlled environments
ActiveUS20100033370A1Efficient methodImprove navigation accuracyPosition fixationNavigation instrumentsNoise levelMarine navigation
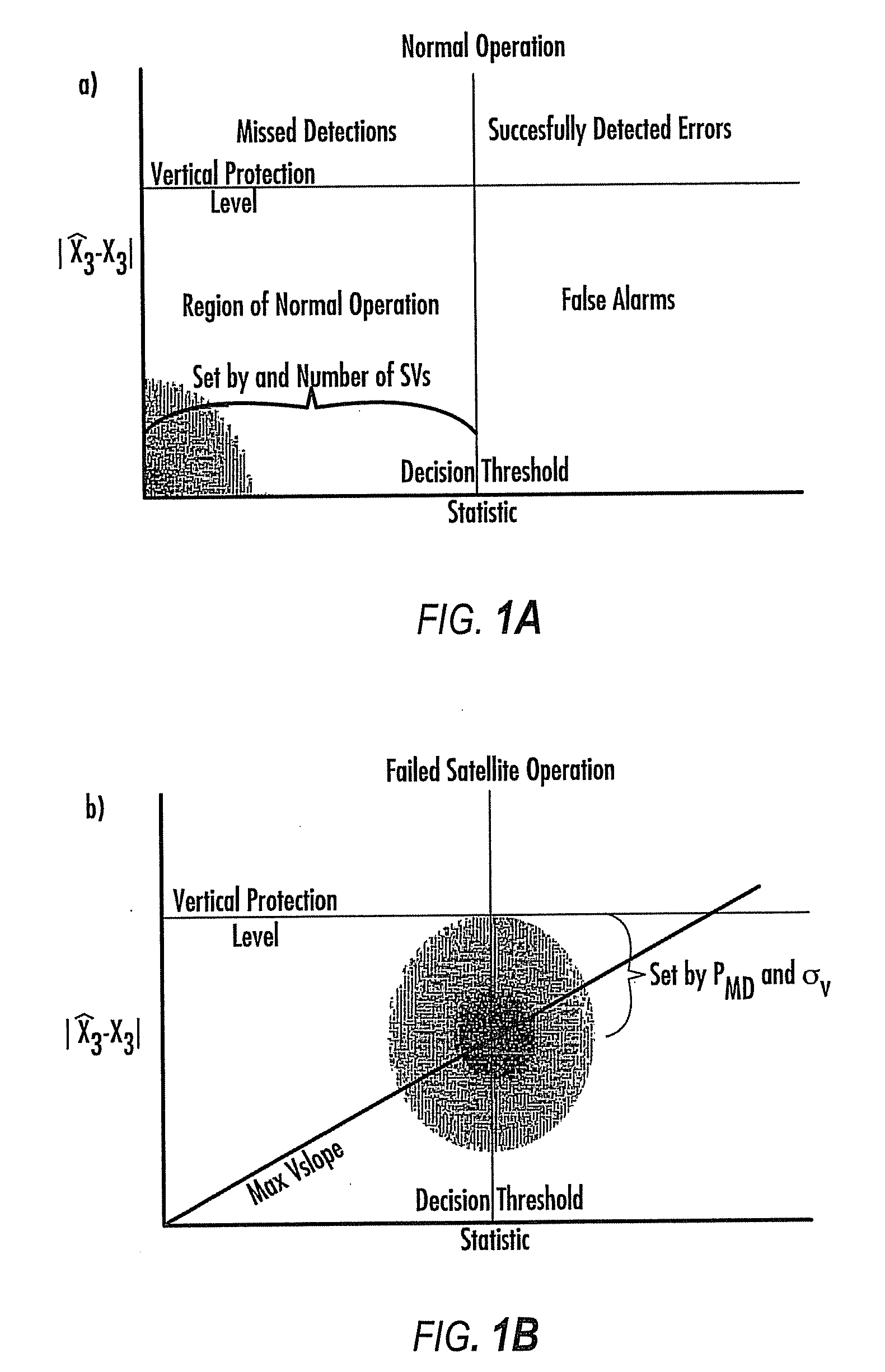
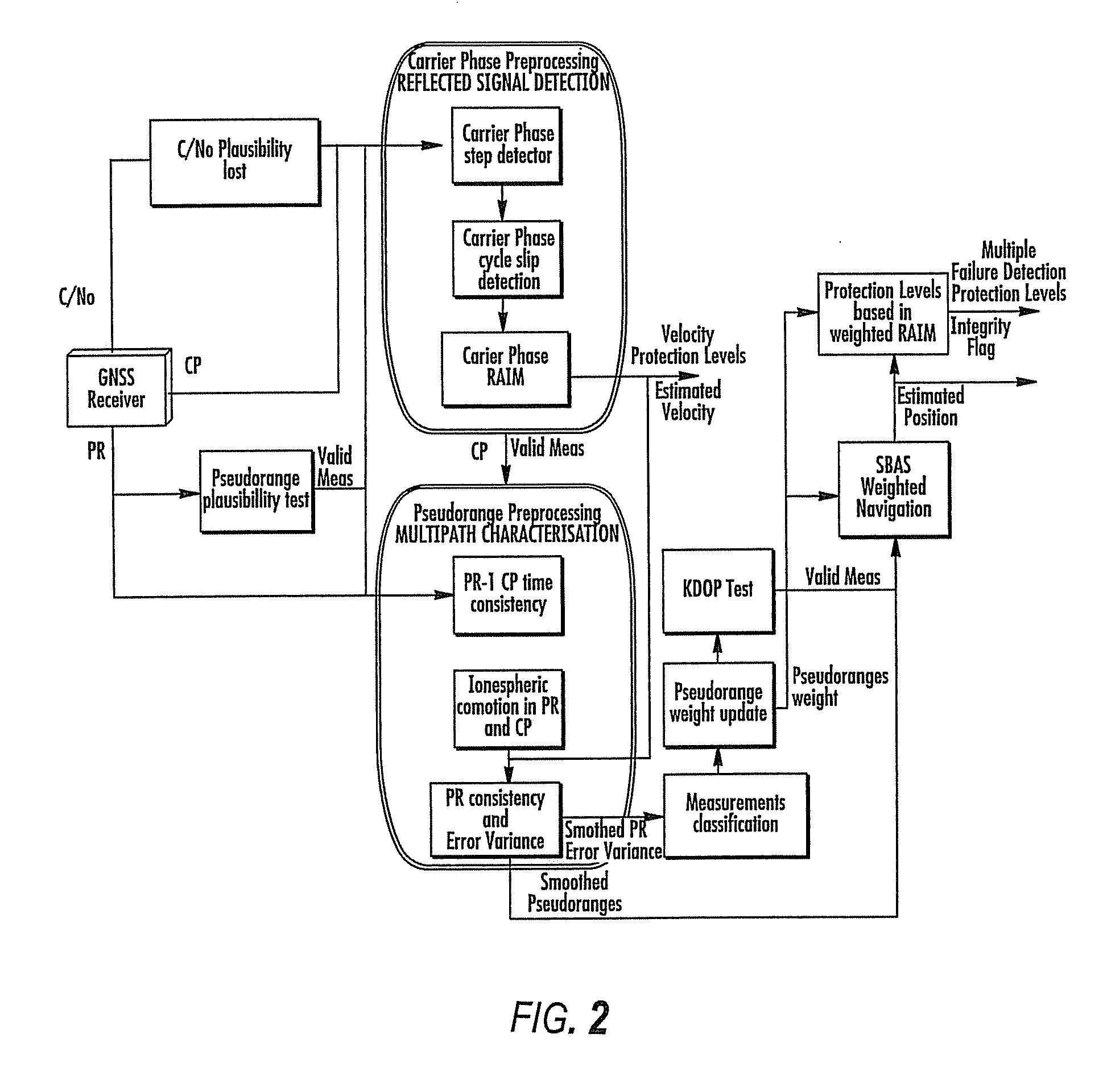
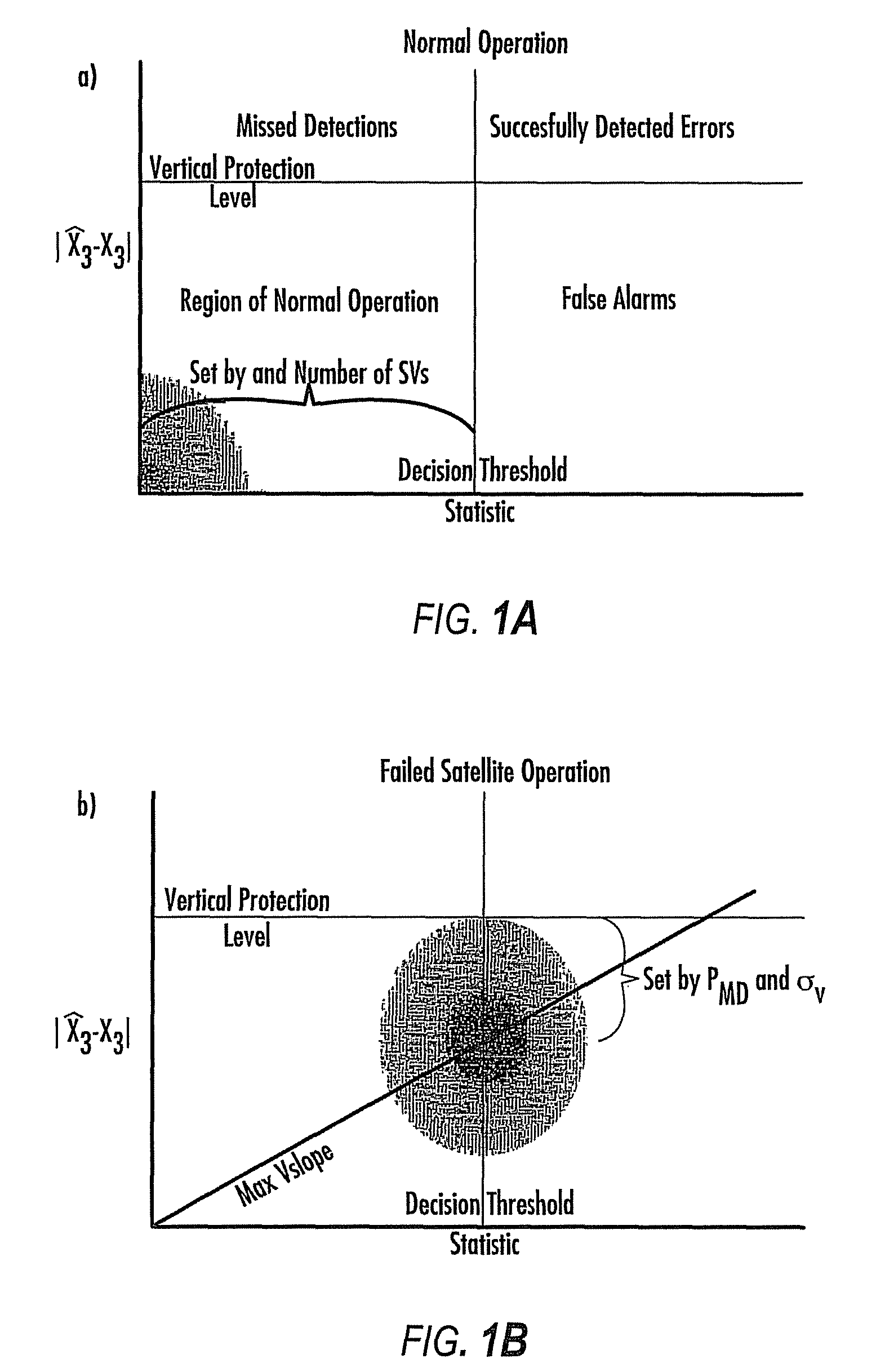
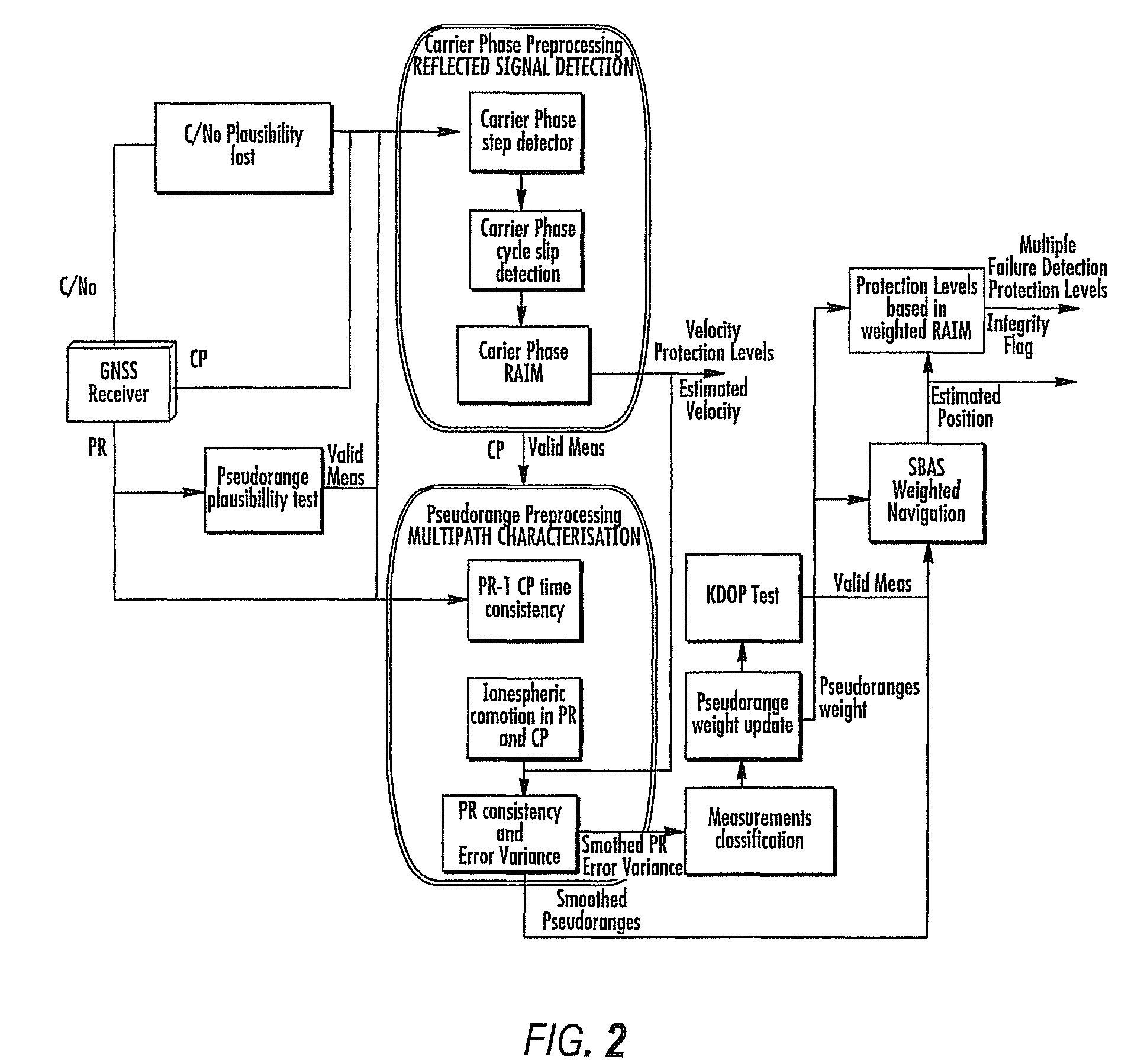
Disclosed is a method for providing a Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) navigation position solution with guaranteed integrity in non-controlled environments, the method including processing a (GNSS) signal including multiple satellites generating at least one signal to obtain carrier phase and pseudorange measurements; pre-processing the measurements to detect and characterize local errors in the measurements, wherein the local errors cannot be ascertained a priori, the characterization including providing error bounds estimated by measuring the carrier phase and pseudoranges measurements, thereby providing a set of measurements rejections when the characterization is not possible; and using the estimated error bounds, together with error bounds provided by the GNSS signal concerning satellite and ionospheric errors, to build in each measurement an estimated noise level in the measurements as input to a weighted Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring (RAIM) algorithm in order to compute position coordinates and associated protection levels in the non-controlled environments.
Owner:GMV AEROSPACE & DEFENCE
Monitoring and prewarning system and method for geological disasters
InactiveCN102354431AReal-time monitoring of displacementBandwidthSeismologyAlarmsVideo monitoringThird generation
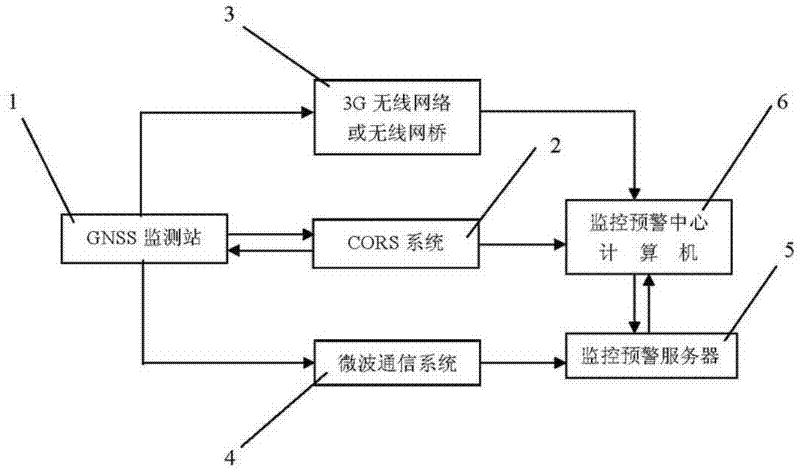
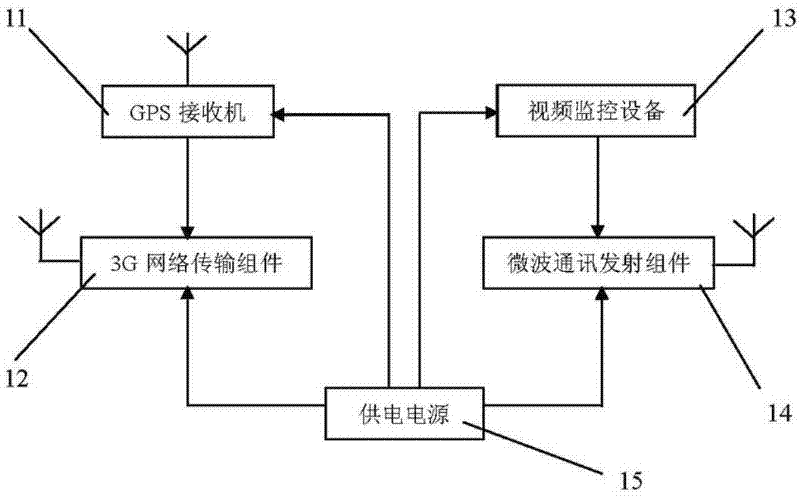
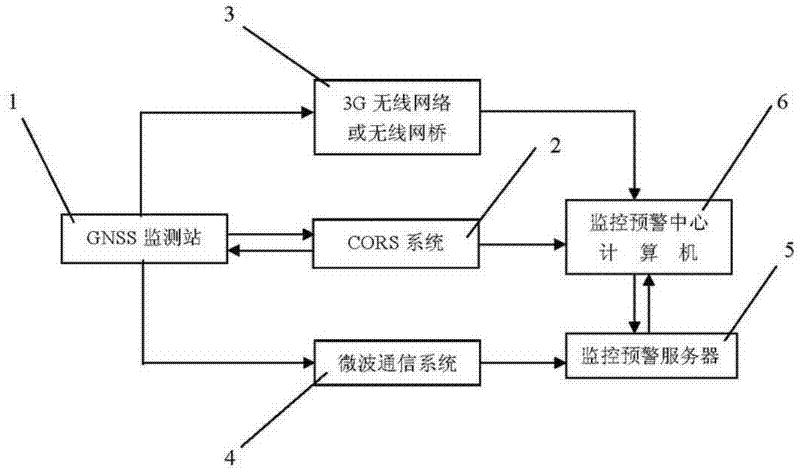
The invention relates to a monitoring and prewarning system and a monitoring and prewarning method for geological disasters. The monitoring and prewarning system for the geological disasters comprises a plurality of global navigation satellite system (GNSS) monitoring stations 1, a continuous operational reference system (CORS) 2, a 3rd-generation (3G) wireless network or wireless bridge 3, a microwave communication system 4, a monitoring and prewarning server 5, a monitoring and prewarning central computer 6 and the like which are arranged in a monitored area. Each GNSS monitoring station 1 comprises a global positioning system (GPS) receiver 11, a 3G network transmission component 12, video monitoring equipment 13, a microwave communication transmission component 14, a power supply 15 and the like. In the method, the aims of forecasting and prewarning possibly initiated geological disasters automatically in real time can be fulfilled by setting the GNSS monitoring stations in areas liable to the geological disasters, monitoring ground surface displacement in real time by the CORS, performing real-time ground surface displacement monitoring on the geological disasters, such as collapse, landslide, debris flow, surface collapse, subsidence, ground fissure and the like, which can be caused by ground surface displacement, combining remote video monitoring, performing data processing on monitoring information, and automatically issuing prewarning information.
Owner:河北省第一测绘院
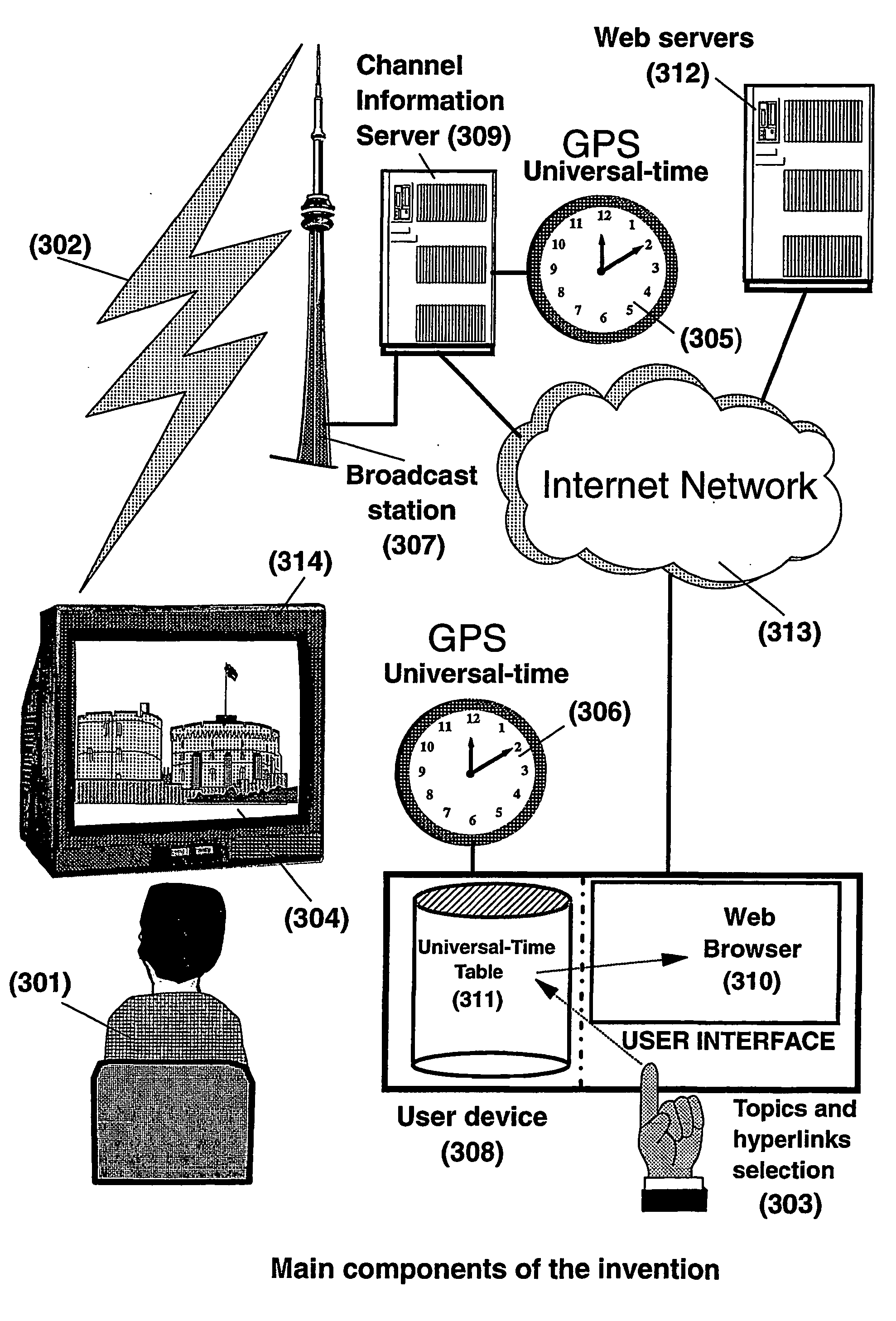
System and method for enhancing recorded radio or television programs with information on the world wide web
ActiveUS20040133919A1Enhanced informationEasy access to informationTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionHyperlinkBroadcasting
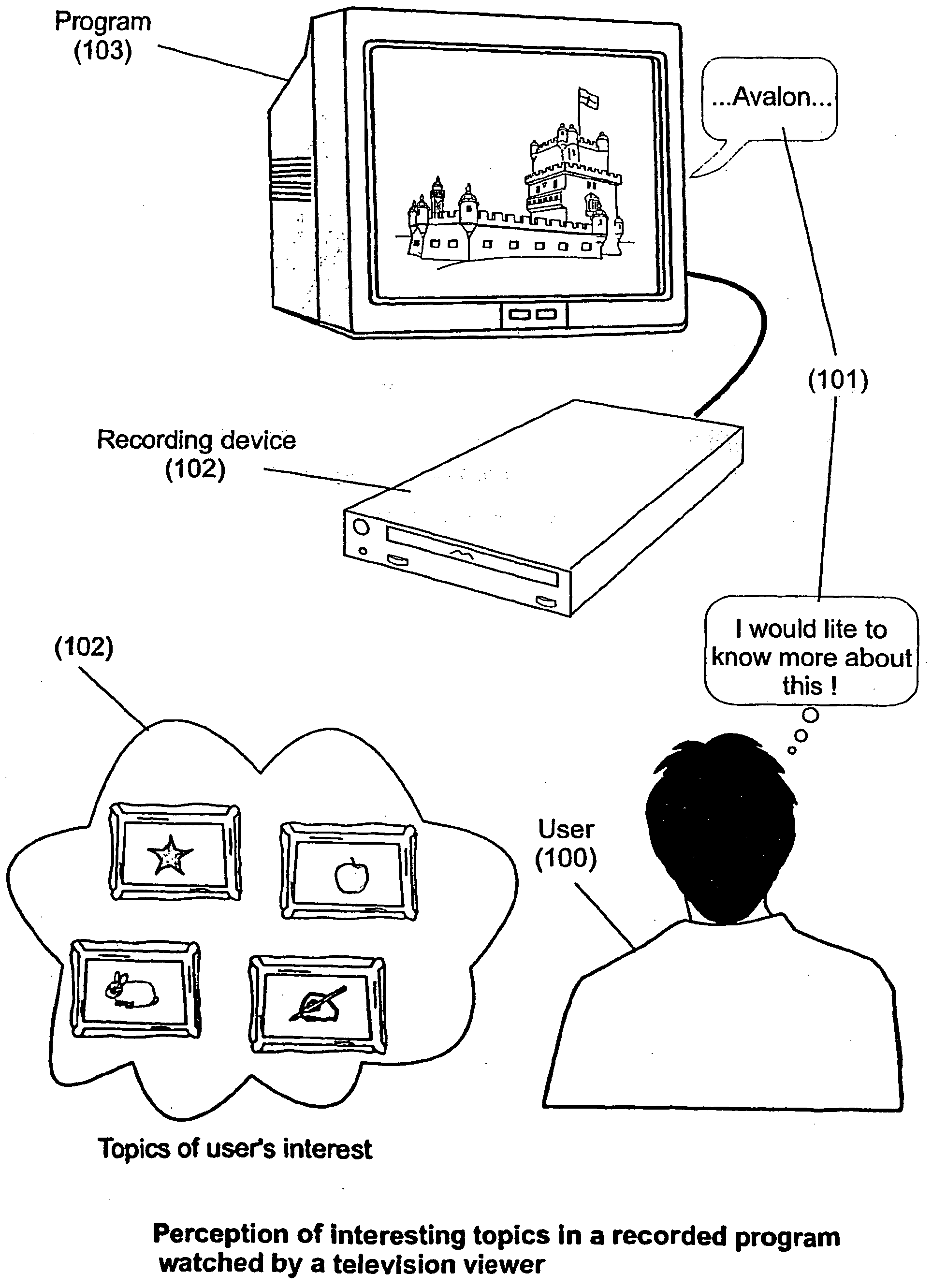
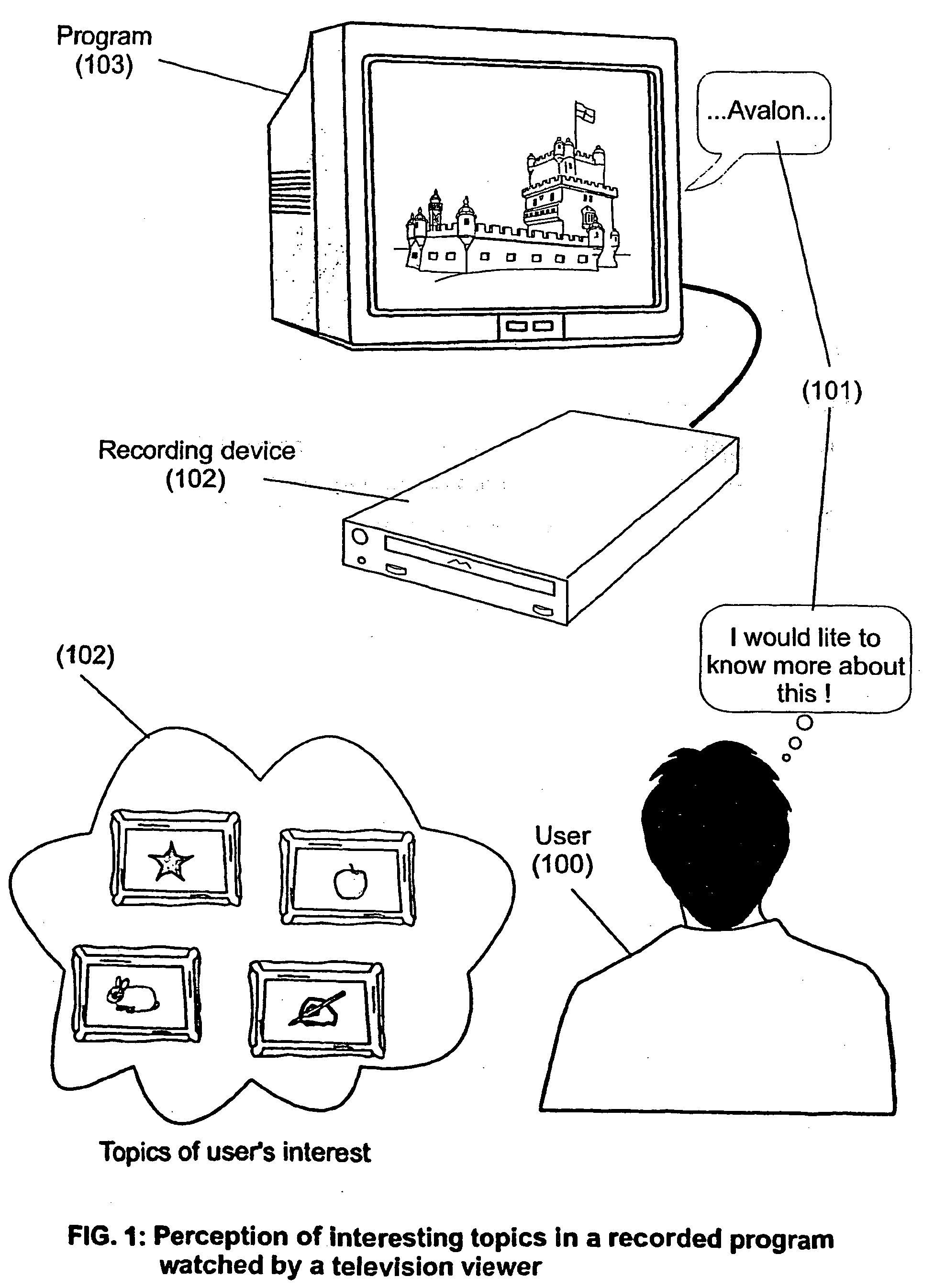
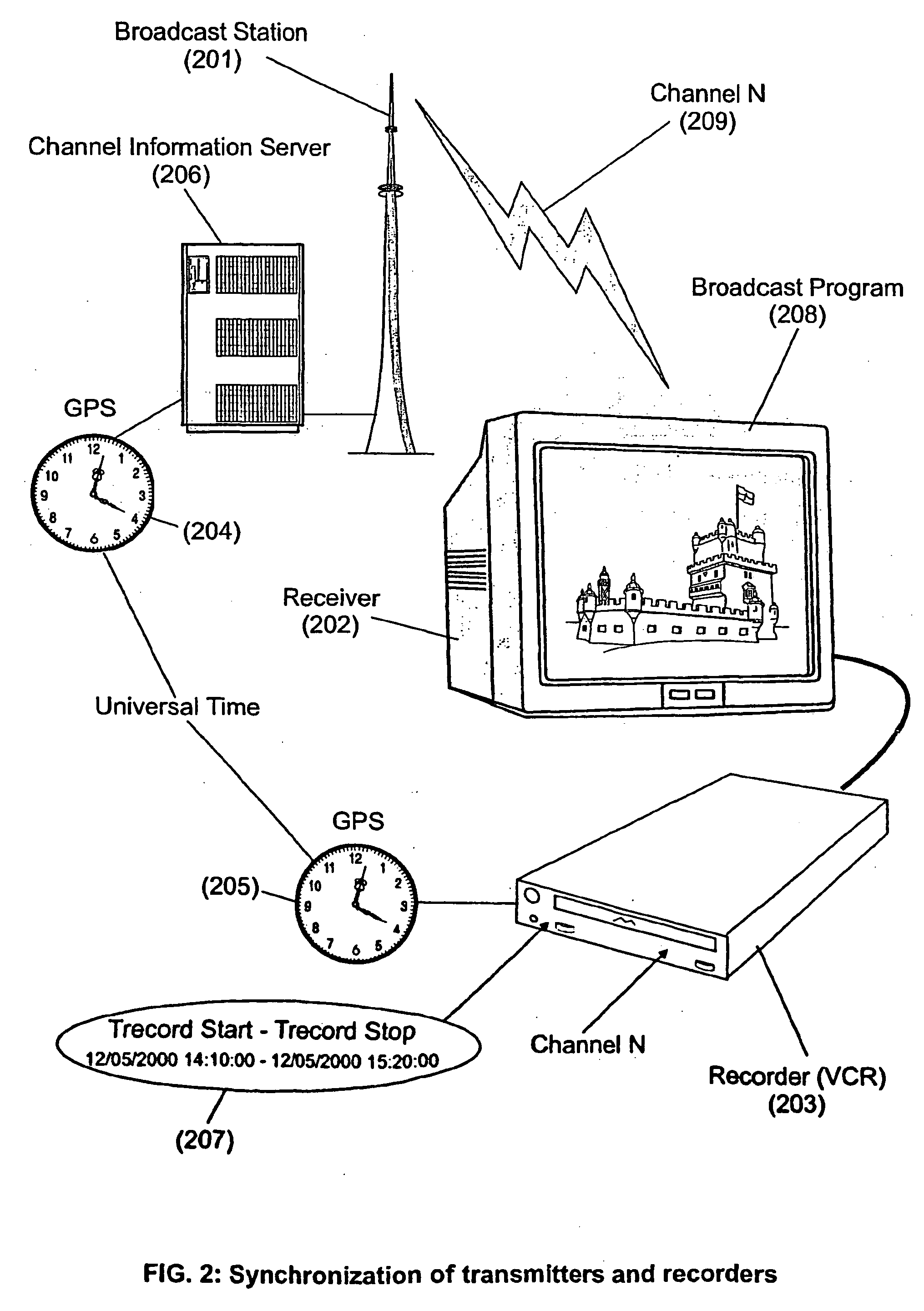
The present invention is directed to a system, method and computer program for enabling a user (100) (an auditor or a viewer) to access complementary information related to one or a plurality of sequences or topics of interest (102) in a recorded program (103) previously broadcast on the radio or television and played back on a device, such as an audio or video tape or disk recorder / player (104). The preferred embodiment of the invention relates to a system and method for enabling a person (100) listening to or watching a recorded program (103), to select one or a plurality of topics (101) (102) drawing his or her attention and for immediately receiving further information related to these topics from the World Wide Web. The system is based on the synchronization of local times (204) (205) of transmitters (201) and recorders (203). The flow of information transmitted, received and recorded is always synchronized, independently of the relative positions of recorders and transmitters. The synchronization is done referring to an absolute or universal time such as the Global Positioning System Time (GPS-time), the Global Orbiting Navigational Satellite System (GLONASS) time or another suitable universal time based on a satellite system. The GPS or GLONASS receivers are integrated or connected to the broadcasting stations. At the receiver side, GPS or GLONASS receivers may be integrated or connected to the audio or video recorders. The system is also based on a plurality of hyperlinks defined during the production and recording of the broadcast program, for given sequences corresponding to particular intervals of time synchronized with the universal (absolute) time. The hyperlinks are associated wit the information that is broadcast in the program. They can be selected by users during the playback of the recorded program during predefined intervals of time and activated to access additional information and services.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC +1
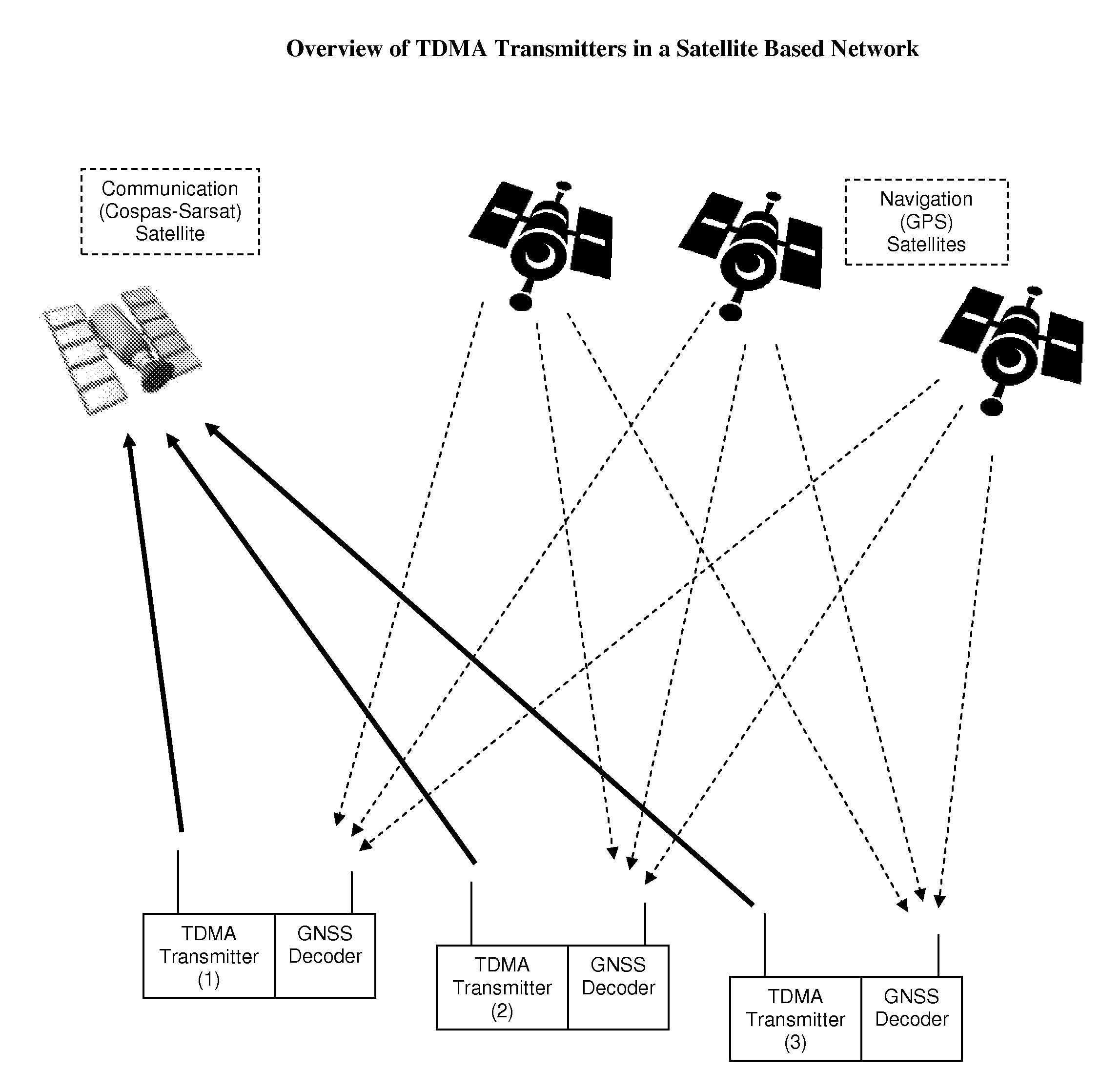
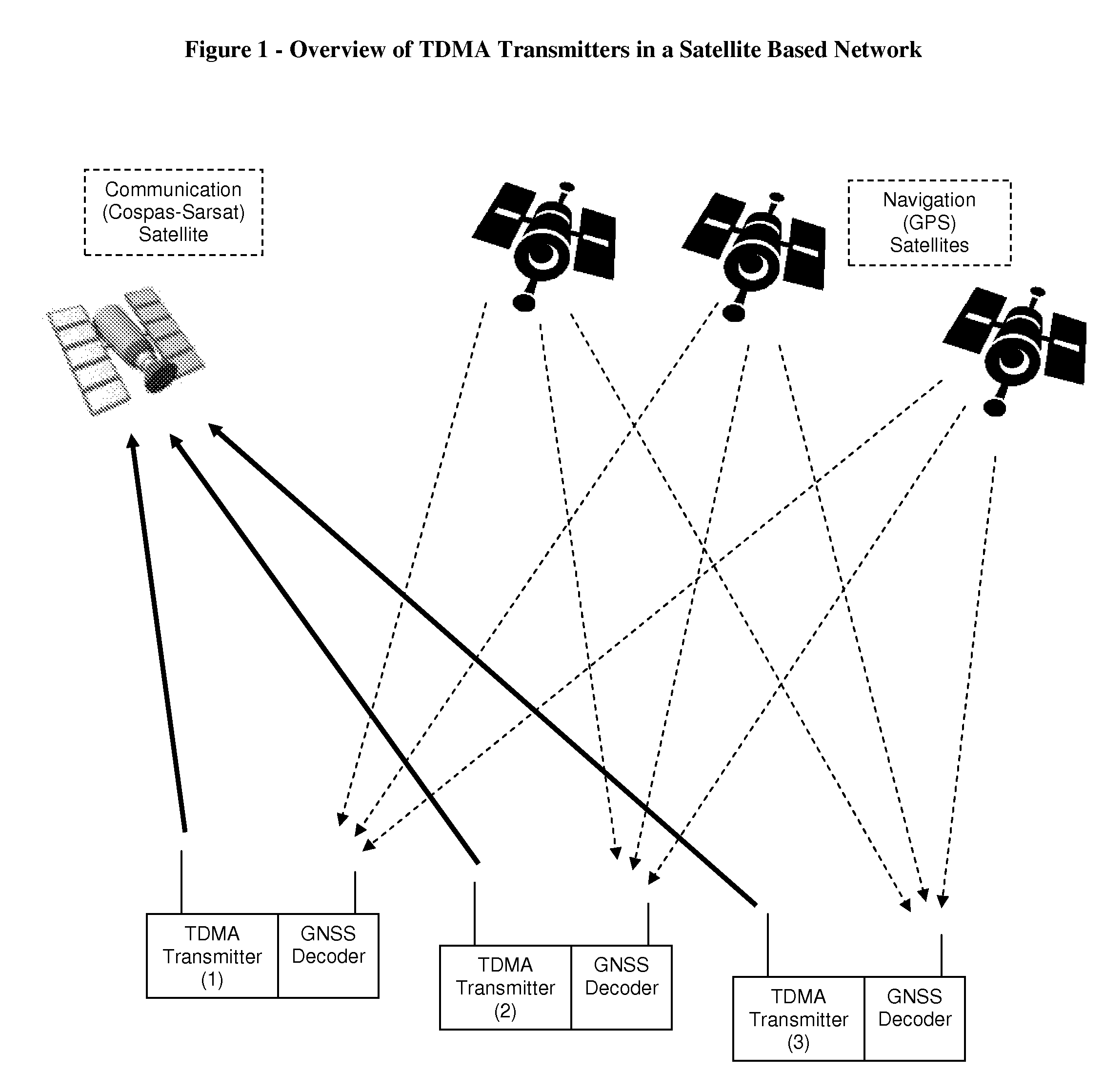
Increasing channel capacity of TDMA transmitters in satellite based networks
InactiveUS7440427B1Decrease transmission collision rateIncrease channel capacityTime-division multiplexLoop networksGeolocationEngineering
The present invention discloses a method for increasing the channel capacity of a communications network, comprising a plurality of one-way TDMA transmitters sharing said channel, and at least one compatible receiver, by reducing transmission collisions among said transmitters. This is achieved by coupling a Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) decoder, such as a GPS receiver, to each transmitter, and limiting transmissions to discrete time slots, determined by timing signals provided by said GNSS. Further, this basic set of time slots is divided into several sub sets, and each transmitter selects a sub set of time slots according to its geographic location, in order to enable reusing time slots in spaced apart areas, as frequencies are reused in cellular networks. Then, each transmitter selects its own transmission time slot, from said sub set, in a way that statistically minimizes collisions among nearby transmitters. The present invention does not intend to ensure collision-free communications, yet is projected to reduce the transmission collision rate among simplex in nature transmitters, which have no means to detect other transmissions, or discover if a transmission was successful. One embodiment of this invention is related to distress radio beacons in satellite based Search and Rescue (SAR) systems, such as Cospas-Sarsat.
Owner:MOBIT TELECOM
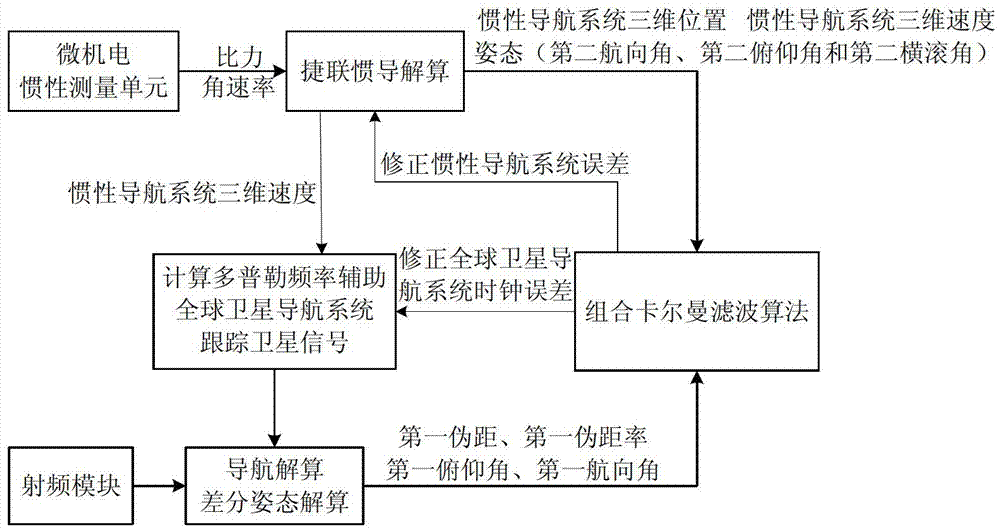
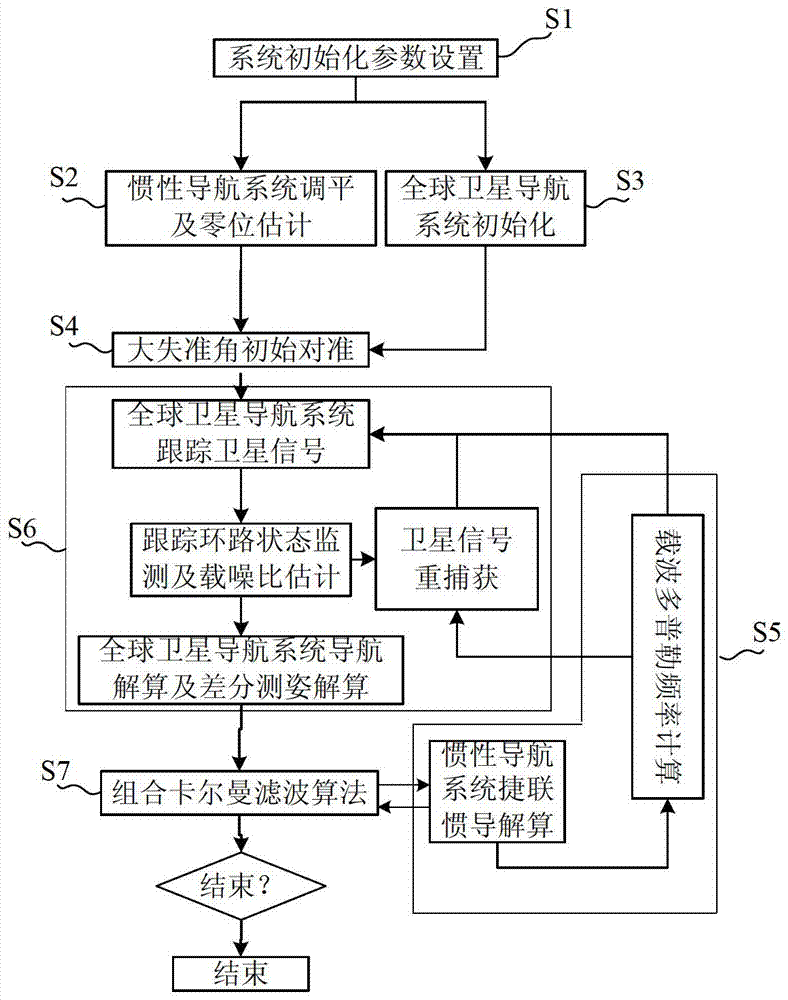
Double-antenna GNSS/INS deeply integrated navigation method and device
InactiveCN103245963AImprove robustnessCompressed ambiguity search spaceSatellite radio beaconingNavigation systemRadio frequency
The invention provides a double-antenna GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) / INS (Inertial Navigation System) deeply integrated navigation method and device. The device comprises a power supply module, an MEMS (Micro Electro Mechanical System) inertial measurement unit, a radio frequency module, an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) module, a DSP (Digital Signal Processor) module and at least two antennas. According to the device, with the assistance of an INS, the probability of cycle slip of the GNSS can be reduced effectively, the integer ambiguity searching space of the GNSS is reduced, attitude measurement information is guaranteed to be continuously outputted, and the tracking loop robustness of the GNSS is enhanced; and with the assistance of a double-antenna GNSS, quick initial alignment of the INS can be realized, the attitude observability of the INS is improved, and the attitude divergence of the INS is inhibited.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method and apparatus for position determination with hybrid sps orbit data
InactiveUS20100194634A1Improves accuracy in fixImprove clock accuracyBeacon systemsSatellite radio beaconingMobile stationSatellite orbit
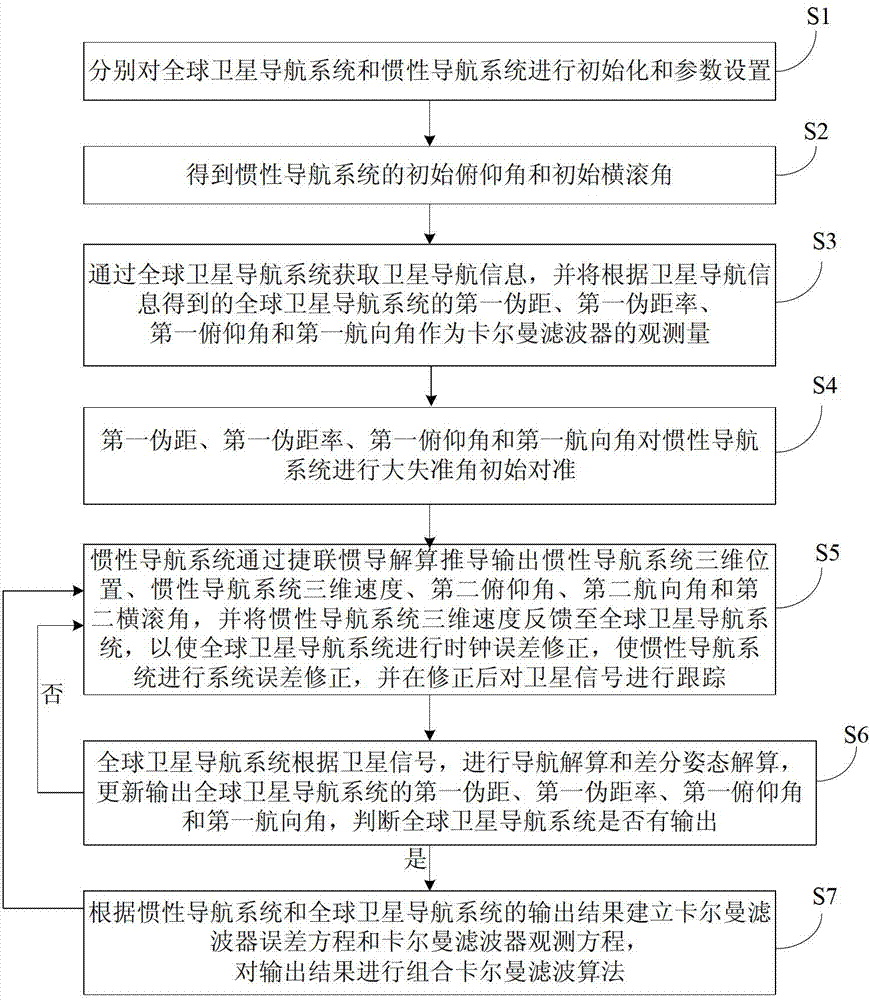
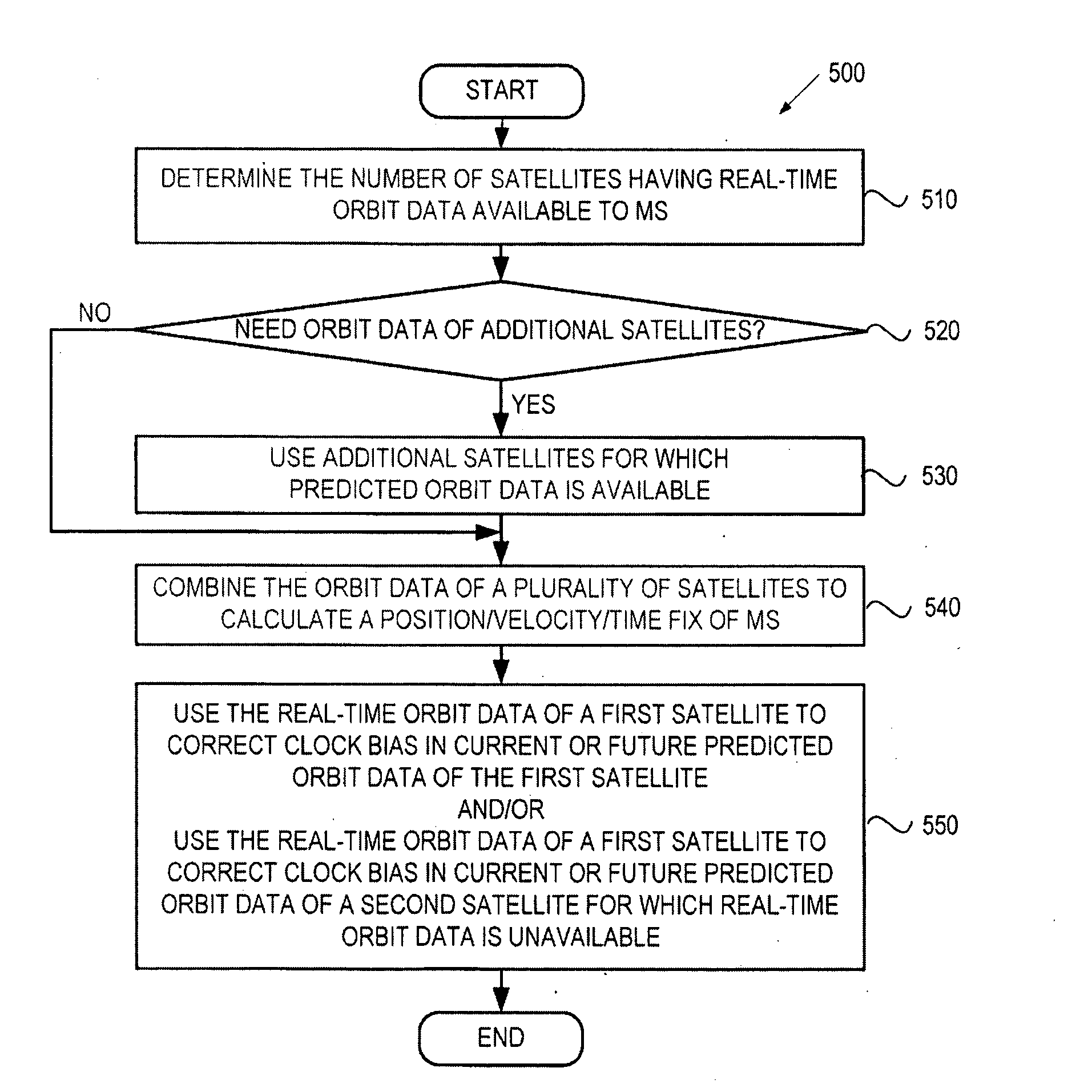
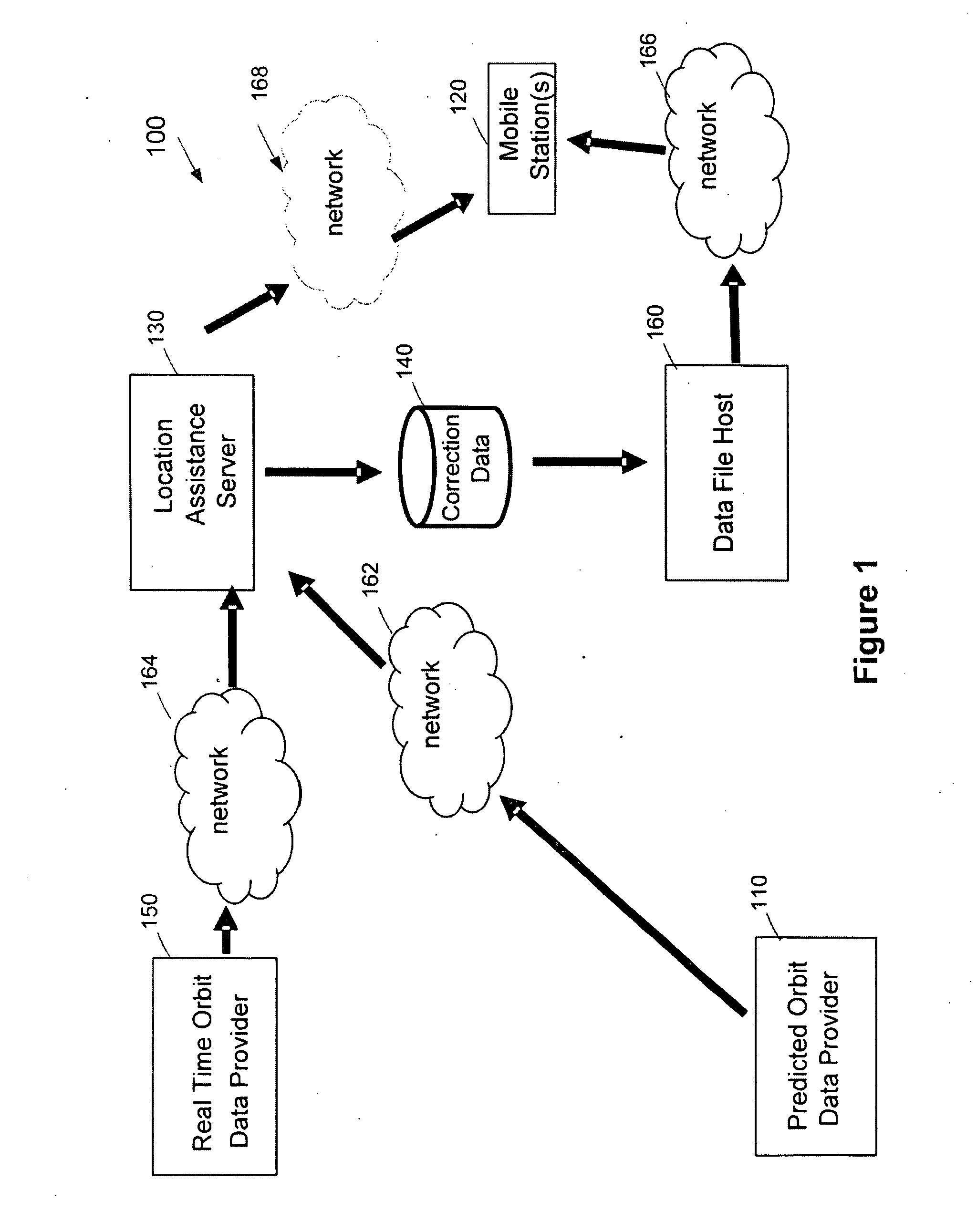
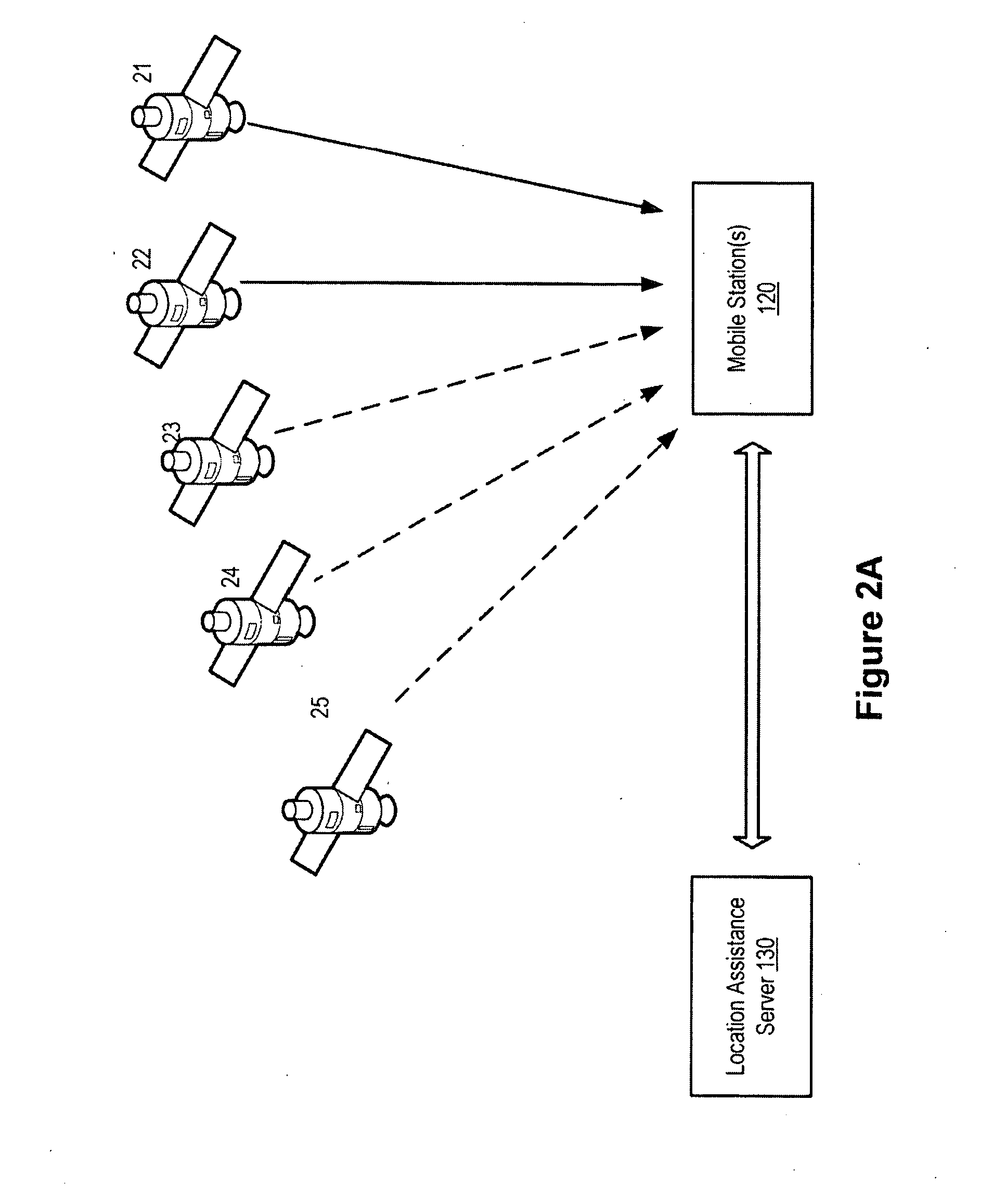
A method and system for a mobile station to determine its position (or velocity) and time using a hybrid combination of satellite orbit data. In one aspect, the mobile station combines predicted orbit data from one satellite and real-time orbit data from another satellite in the determination of a fix. The combination can be made to the satellites in the same or different satellite systems. The mobile station can use the real-time orbit data of a satellite at one time period and the predicted orbit data of the same satellite at another time period. In another aspect, the mobile station can use the real-time orbit data to correct the clock bias in the predicted orbit data. The correction to the clock bias can be made to the same satellite that provides the real-time orbit data, or to a different satellite in the same or in another satellite system.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
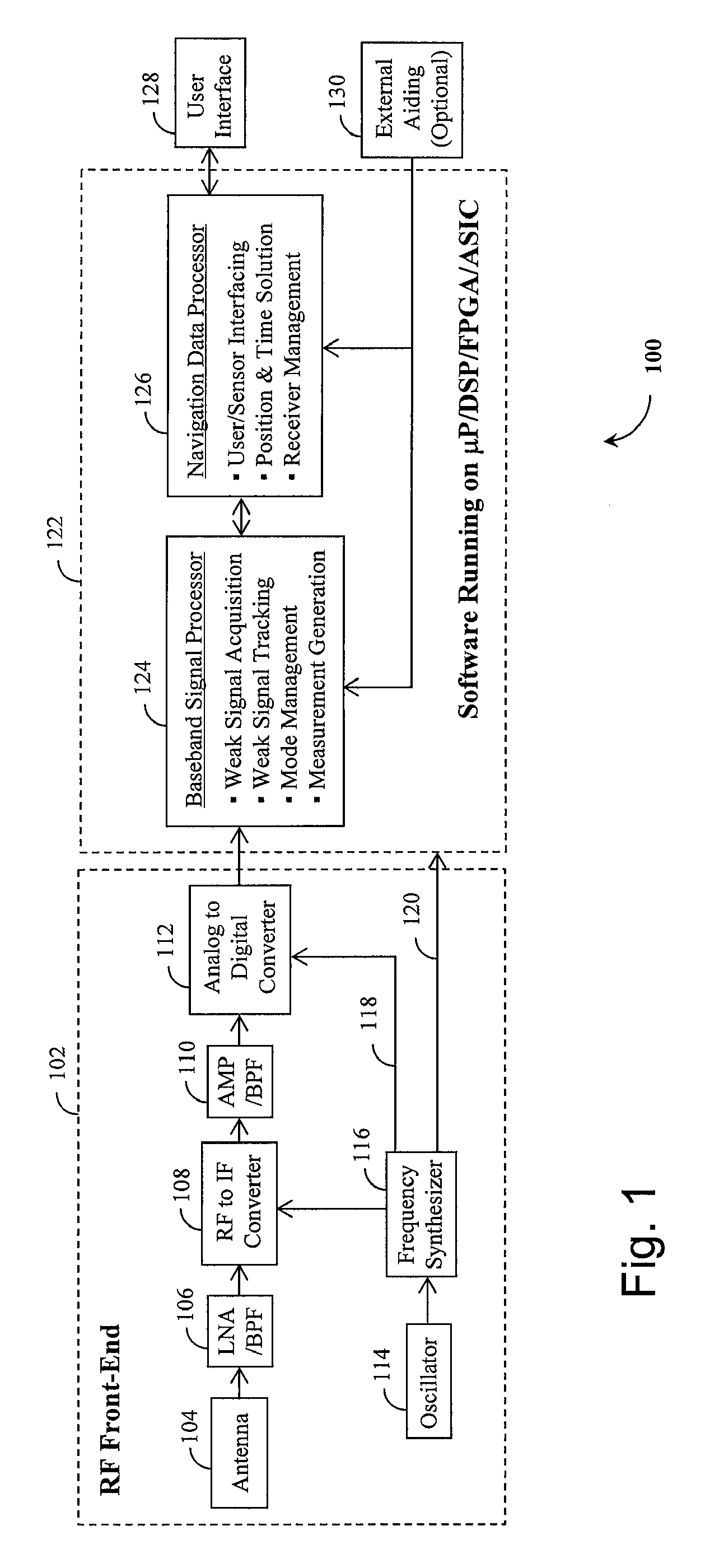
Method and device for acquiring weak global navigation satellite system (GNSS) signals
InactiveUS20070008217A1Reduces time and frequency uncertainty spaceWeak signalPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingBandpass filteringSignal tracking
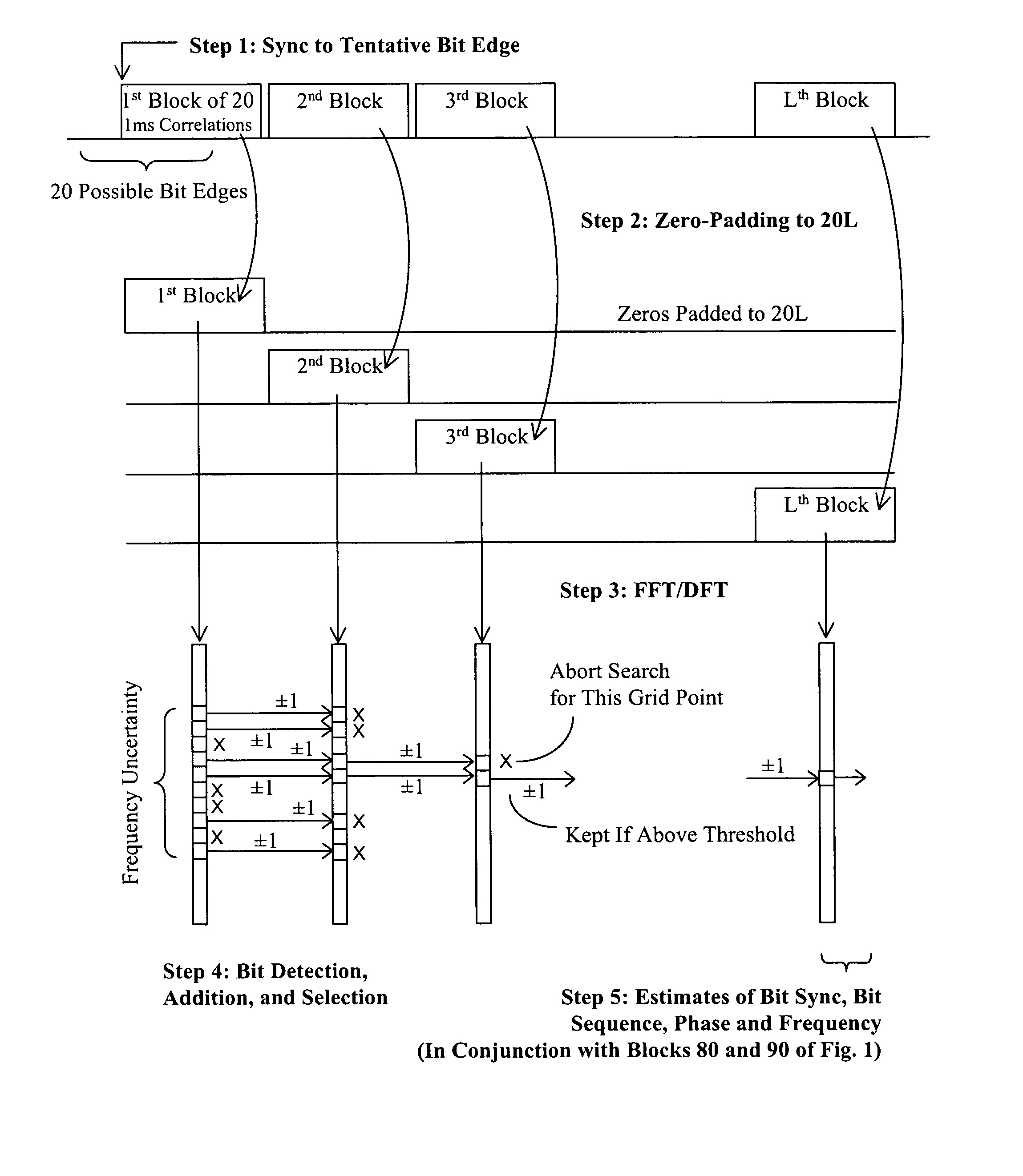
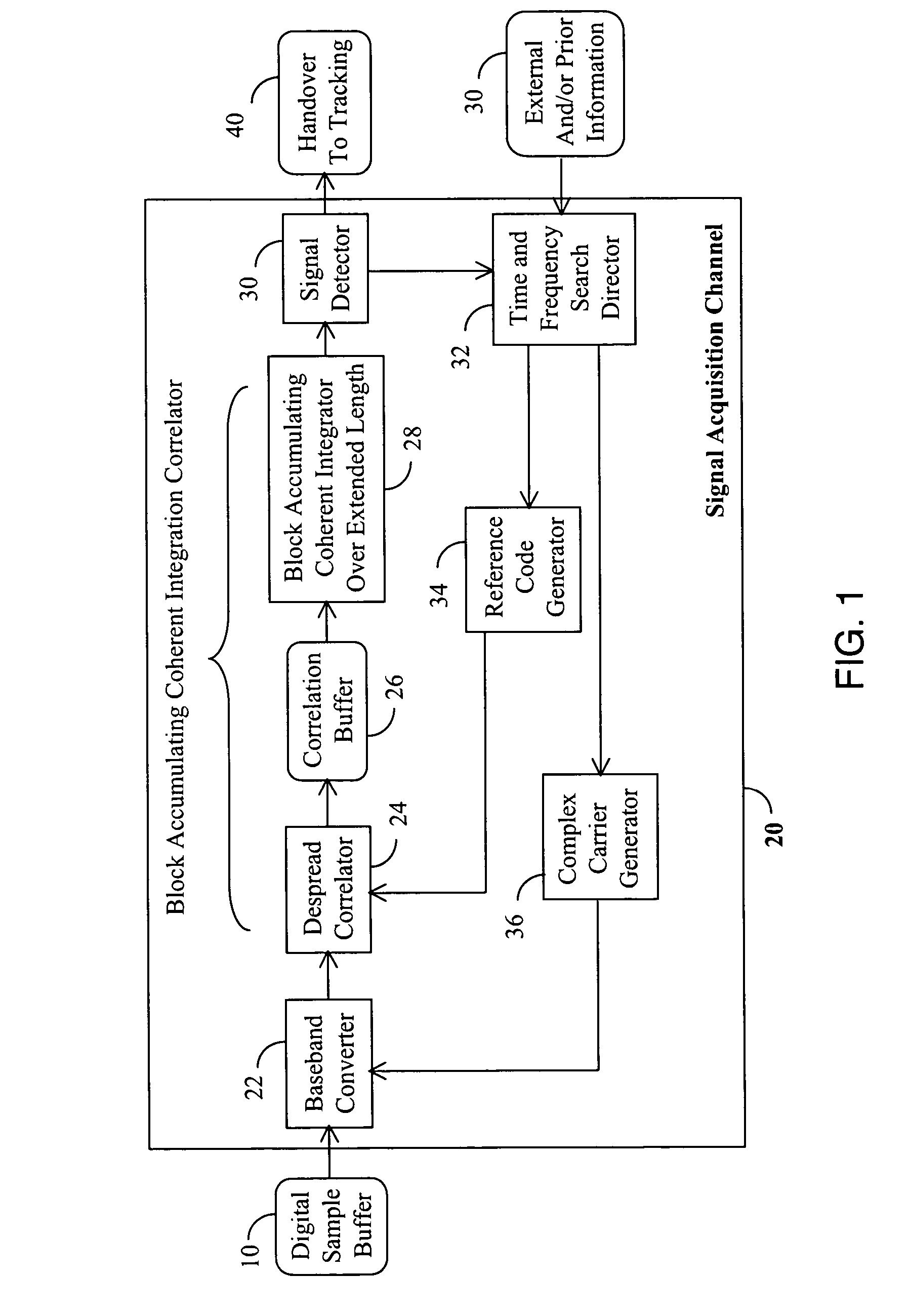
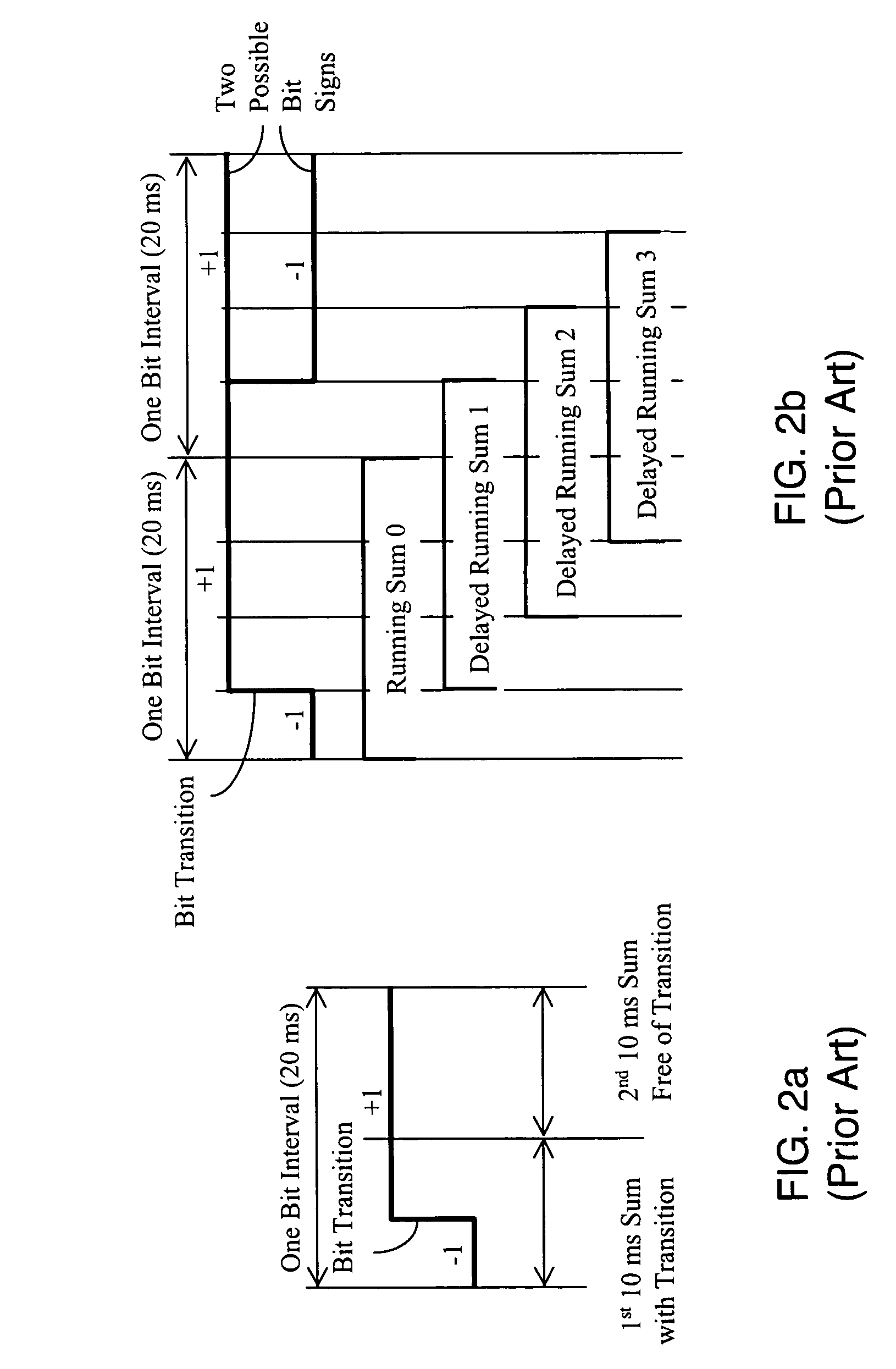
A Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receiver and associated method capable of acquiring weak GNSS signals from a plurality of GNSS satellites produces a GNSS signal's code time, carrier frequency, and data bit transition parameters for subsequent signal tracking and position fixing. The GNSS receiver includes a baseband signal processor with special functionalities for acquiring weak signals. In a preferred embodiment, the time and frequency uncertainty space is reduced using available information and then special techniques are used to rapidly search the remaining uncertainty space. Successive reversal of short-length correlations within a data bit interval (a block) enables data bit transition detection and data bit sign correction prior to coherent integration. Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) is applied as a bank of bandpass filters to coherently accumulate blocks of short-length correlations over extended coherent integration intervals to boost the signal power while averaging noise out despite unknown data bit transitions.
Owner:CSR TECH HLDG
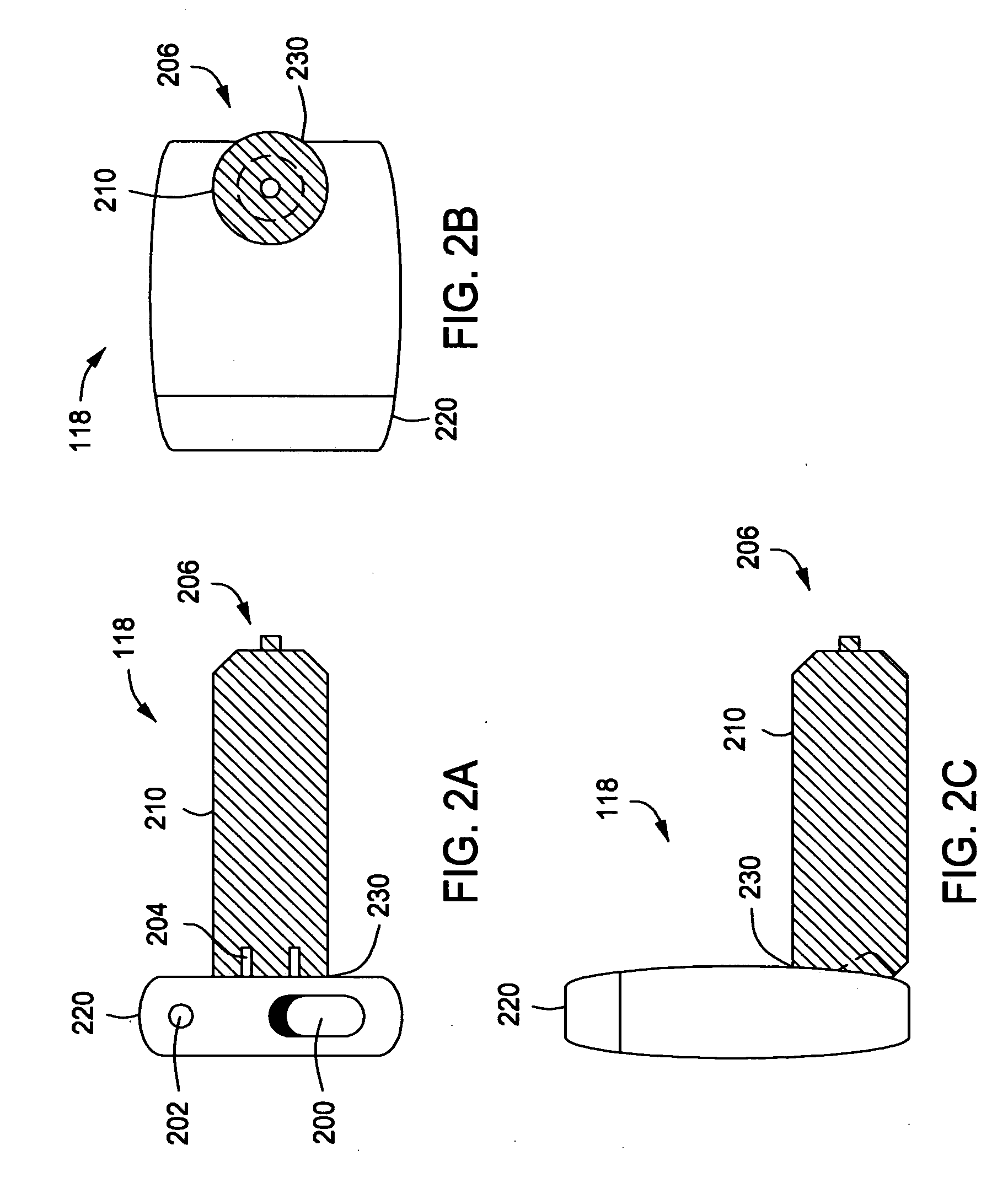
Satellite-positioning-system tracking device and method for determining a position of the same
ActiveUS20070182628A1Position fixationSatellite radio beaconingComputer scienceSatellite positioning
A global navigation satellite system-tracking (“GNSS-tracking”) device and method for determining one or more positions of the GNSS-tracking device utilizing a user-plane service is disclosed. The GNSS-tracking device may comprise: charging and tracking modules adapted to be disengagably coupled together, wherein the tracking module comprises (i) tracking circuitry for determining at least one position of the tracking module using the user-plane service in a satellite positioning system, and (ii) a chargeable source for supplying power to the tracking circuitry when disengaged from the charging module, and wherein the charging module is operable to charge the chargeable source when the charging module is coupled to the tracking module.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
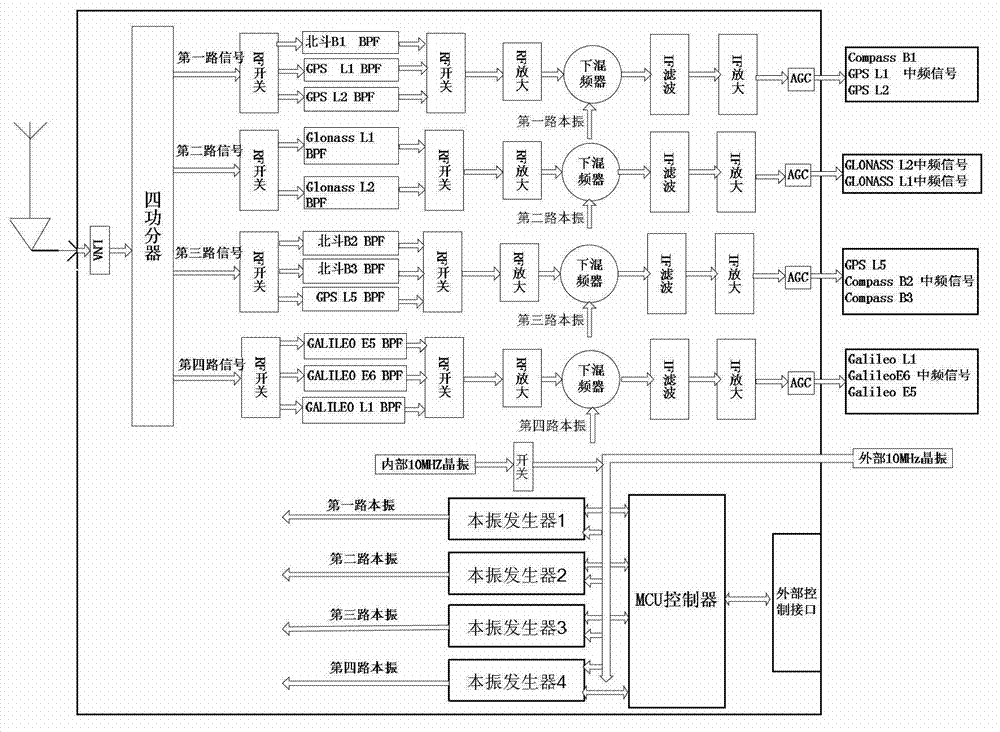
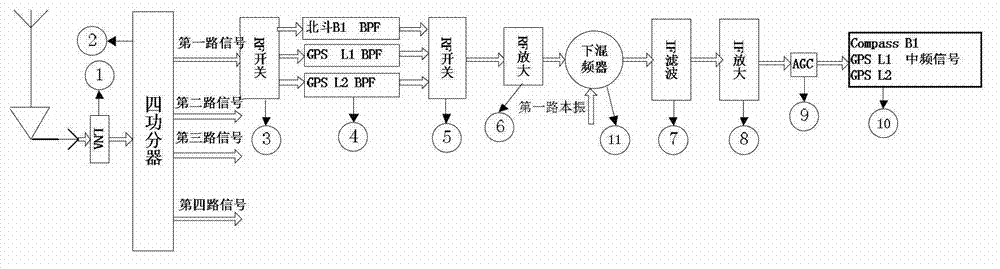
Multi-mode multi-frequency global navigational satellite system receiver radio frequency front end device
ActiveCN103117767AEasy to changeEasy to adjustSatellite radio beaconingTransmissionLow noiseSignal processing circuits
The invention discloses a multi-mode multi-frequency global navigational satellite system receiver radio frequency front end device. The device comprises a low-noise amplifier, a power divider, and multiple radio-frequency signal processing circuits, wherein the low-noise amplifier, the power divider, and the multiple radio-frequency signal processing circuits are connected in sequence. Each radio-frequency signal processing circuit comprises a first radio-frequency switch, a radio-frequency filter bank, a second radio-frequency switch, a radio-frequency amplifying module, a lower frequency mixing module, an intermediate frequency filter module, an intermediate frequency amplifying module, and an automatic gain control unit, wherein the first radio-frequency switch, the radio-frequency filter bank, the second radio-frequency switch, the radio-frequency amplifying module, the lower frequency mixing device, the intermediate frequency filter module, the intermediate frequency amplifying module, and the automatic gain control unit are connected in sequence. The lower frequency mixing module comprises a lower frequency mixing device and a local oscillating generating module which are connected with each other. A control unit is connected with the first radio-frequency switch and the second radio-frequency switch of each radio-frequency signal processing circuit and the local oscillating generating module of the lower frequency mixing module. The device can flexibly select intermediate frequency inputting from various combination frequency ranges of a quad-mode 11 frequency range, and therefore functions of collecting in the same module and processing navigation system intermediate frequency signals of four system satellites are realized, namely a global position system (GPS), Glonass, Galileo, and Big Dipper.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method of processing global navigation satellite system data
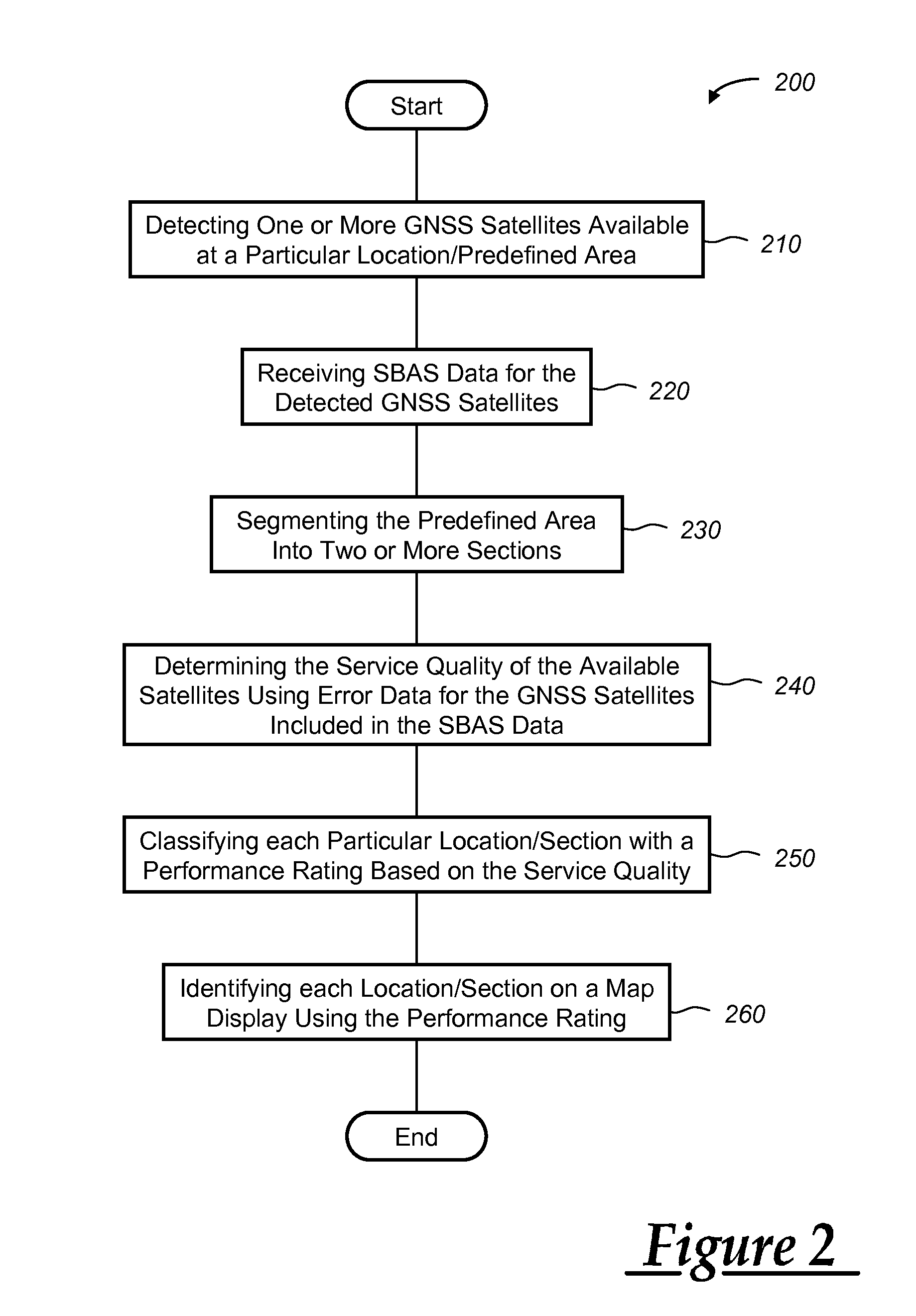
ActiveUS20110144911A1Instruments for road network navigationActuated automaticallyEngineeringSatellite system
A method of processing global navigation satellite system (GNSS) data includes identifying one or more GNSS satellites servicing a predefined area, receiving at least one of GNSS almanac data or space-based augmentation system (SBAS) data for the satellites servicing the predefined area, determining the performance of the GNSS satellites servicing the predefined area using the almanac data or SBAS data, and applying a performance rating to the predefined area based on the performance of the GNSS satellites.
Owner:GENERA MOTORS LLC +1
Optimal space situational awareness system
A satellite system for observing space objects includes two or more satellites positioned in an Earth orbit and configured to observe objects in various orbits including those viewed (i) against the Earth's background; (ii) against a sunlit Earth background; and (iii) against a space background. An electromagnetic sensor may be provided on at least one of the satellites that is responsive to electromagnetic radiation having a wavelength that discriminates against substantial reflection of electromagnetic radiation from the Earth's atmosphere to observe the space object. A method of observing a space object using a satellite system is also disclosed.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
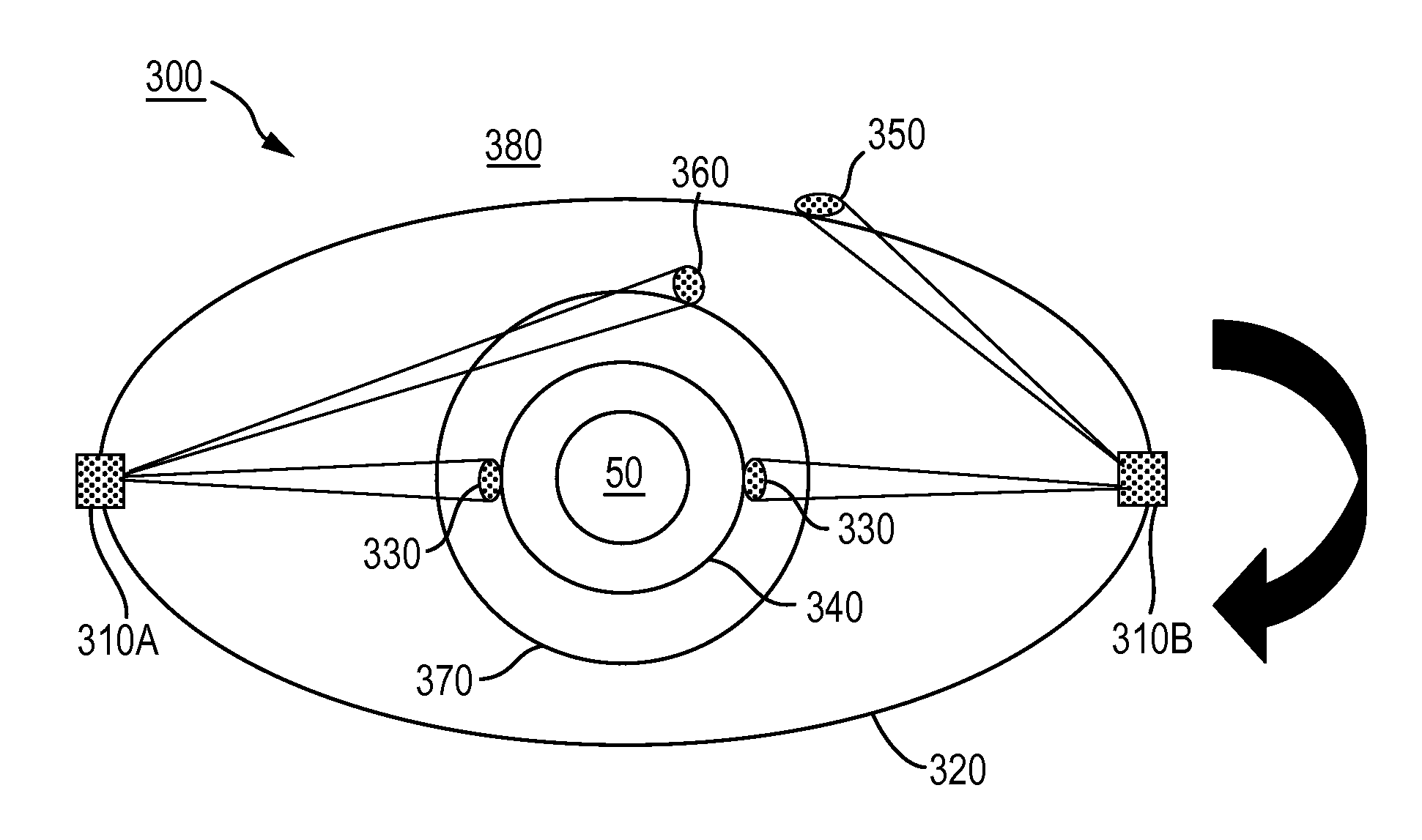
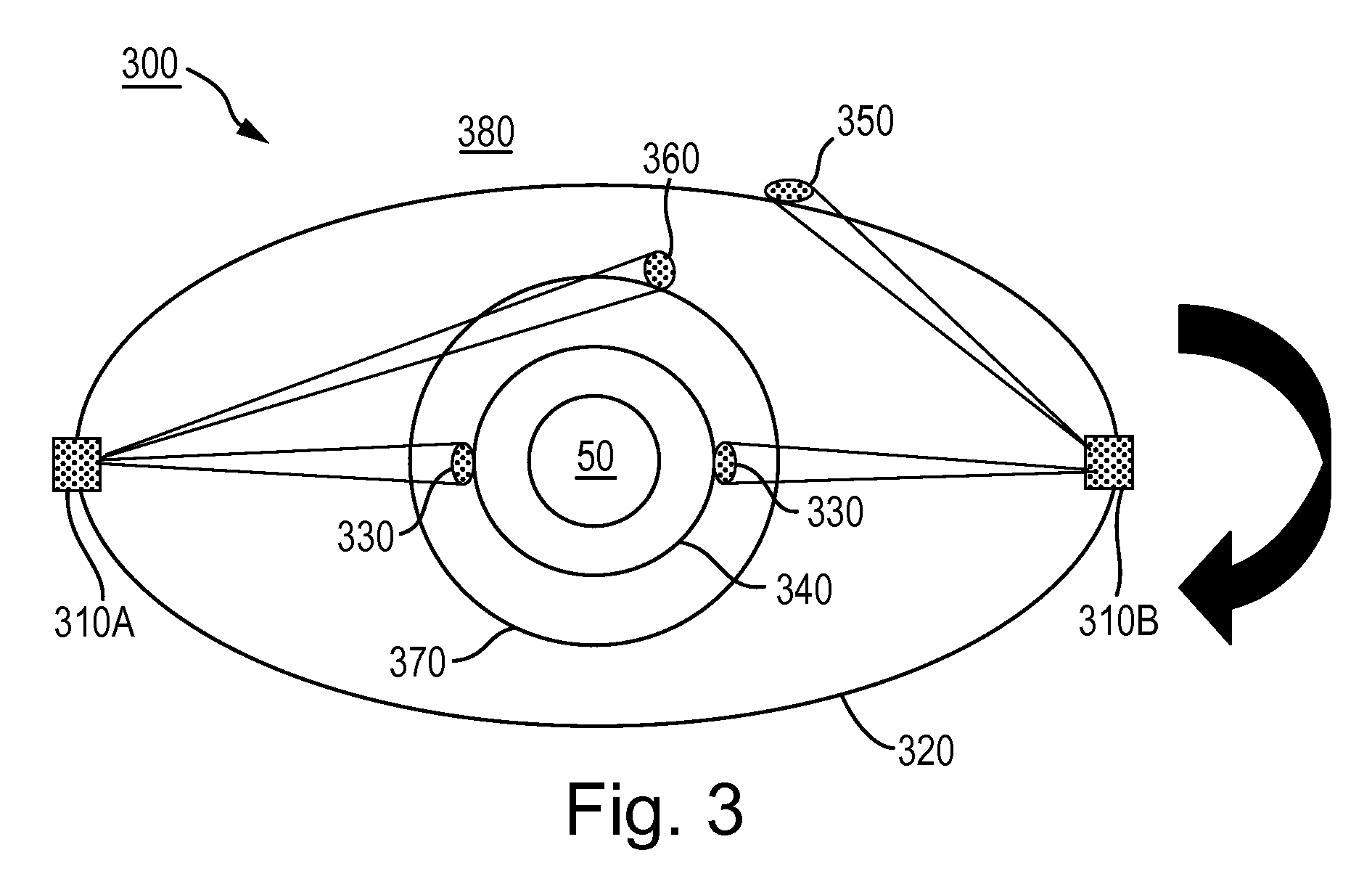
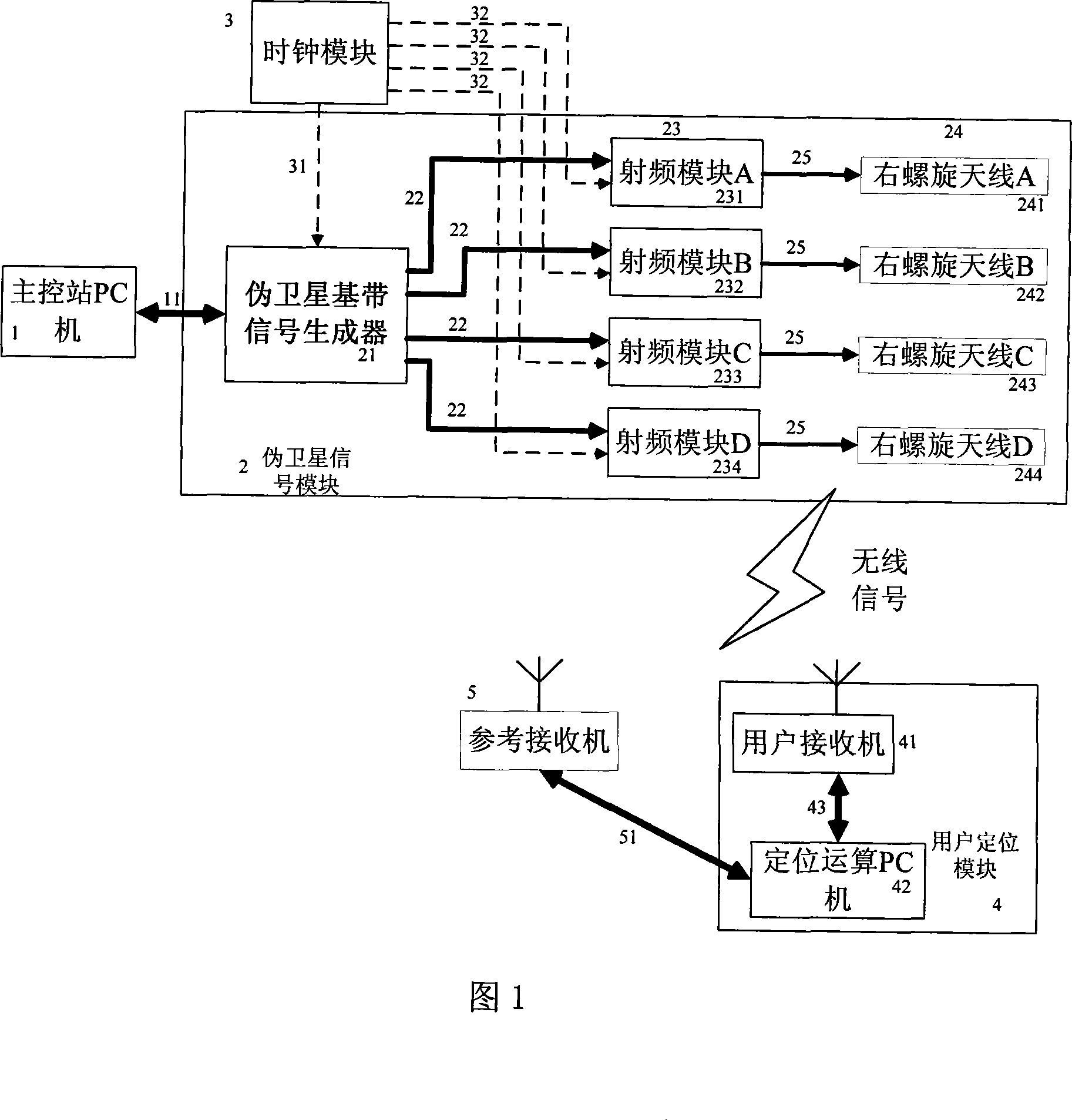
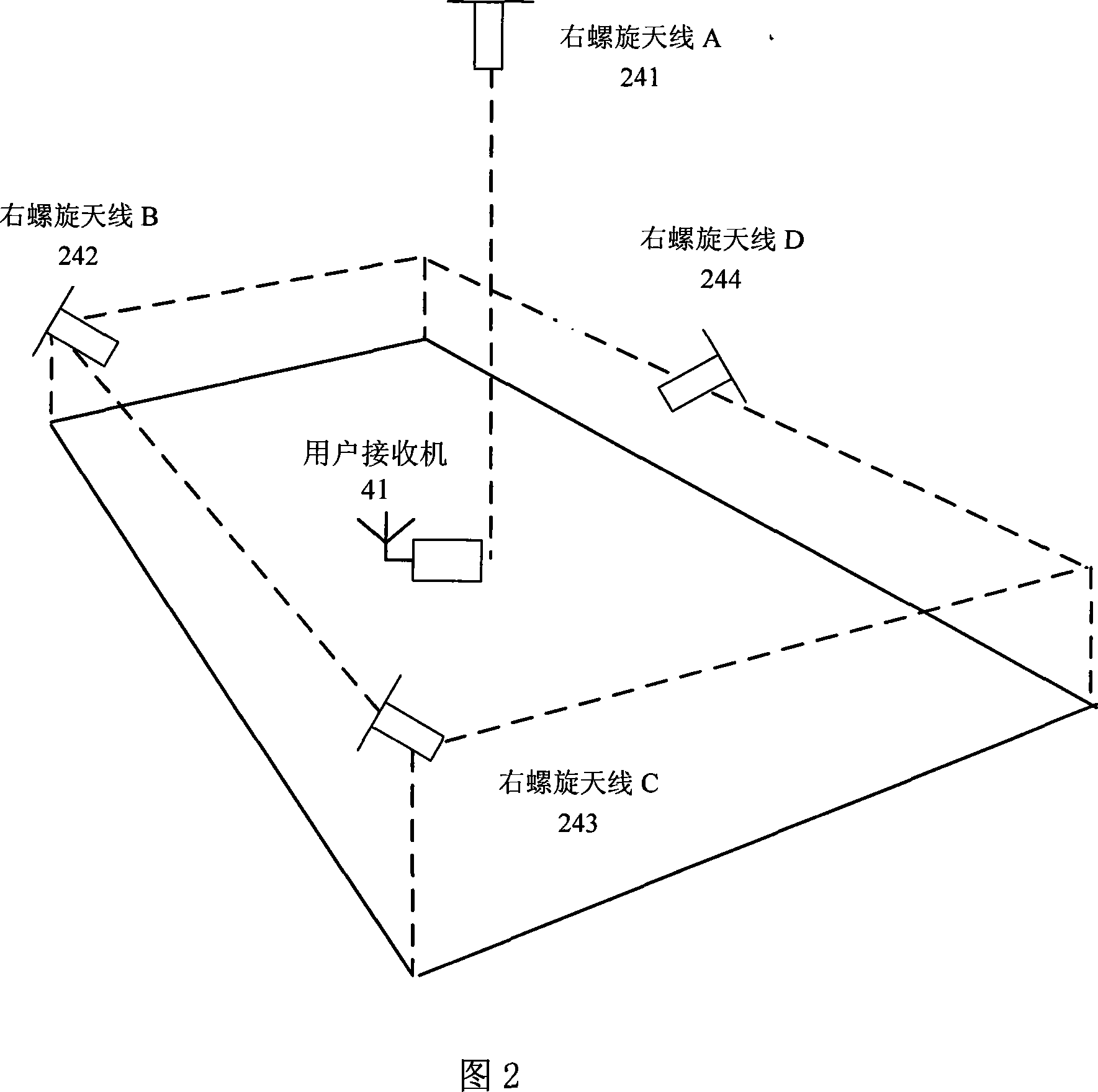
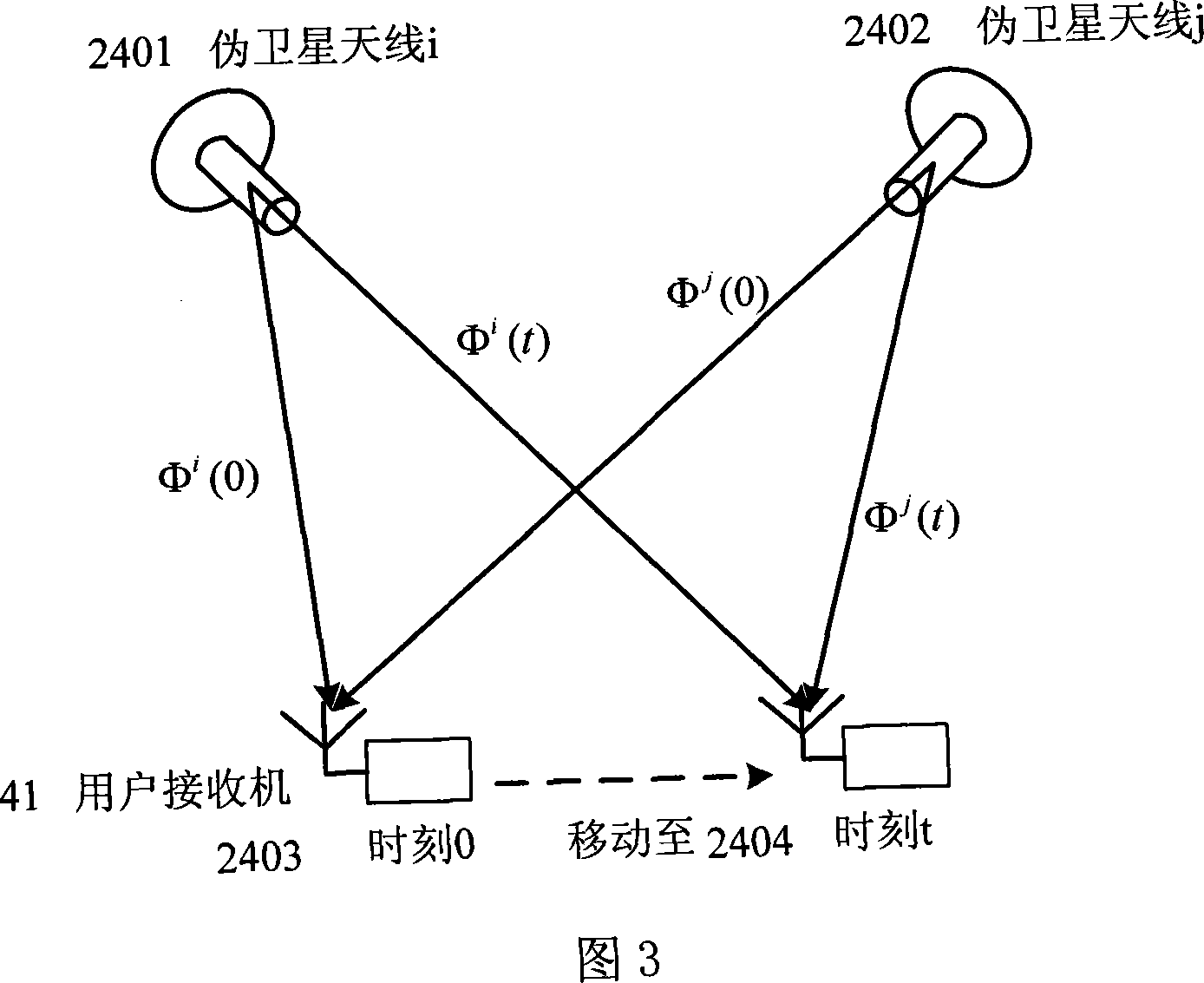
False satellite sub-decimeter level indoor position location system and carrier phase positioning method thereof
InactiveCN101158719ARealize autonomous navigationHigh positioning accuracyBeacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationSoftware designCarrier signal
The invention relates to an apparatus using GPS techniques of the global position satellite system and a carrier phase location method thereof, in particular to a hardware and software design techniques based on navigational satellite signal of the global position satellite system; the invention is applied in a pseudosateilite indoor position system with sub-decimeter level mainly of the situations in which GPS satellite signal of the global position satellite system cannot be received indoors, as well as a carrier phase location method thereof. The system at least comprises a personal computer of a master control station and a consultation receiver, etc, and the indoor position system that is integrated by all apparatuses. The method is realized by the way of carrier phase location, and mainly resolves the related technological problems of the hardware and software implementation of pseudosateilite and the layout of indoor pseudosateilite, etc. The invention has the advantages that the system and the method can achieve autonomous navigation in a closed region, which are suitable for the situations in which ethereal GPS satellite signal cannot be received indoors but the location result with higher precision is required and so on, and has the advantages of convenient use, simple and effective control, etc.
Owner:HERONAV BEIJING TECH DEV
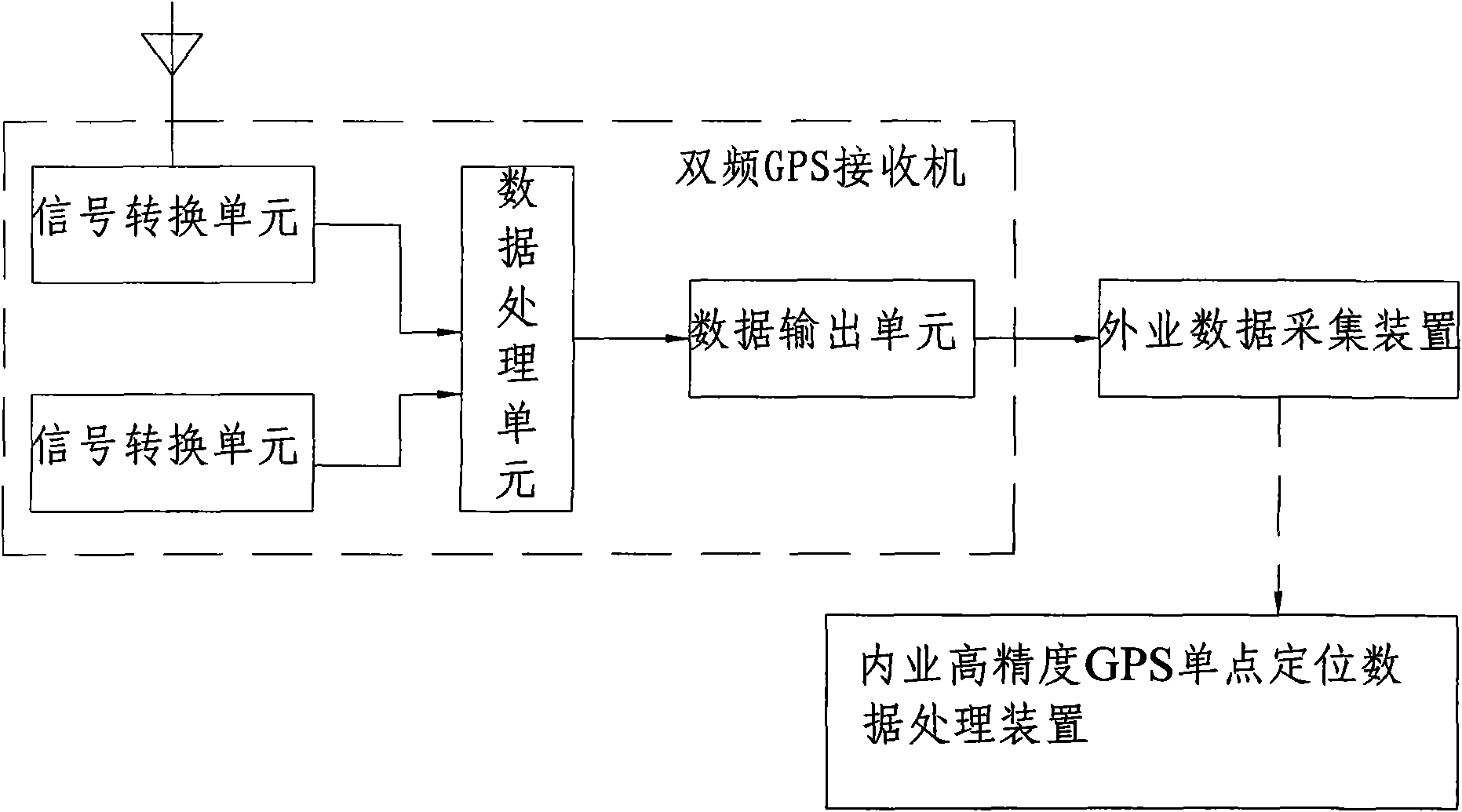
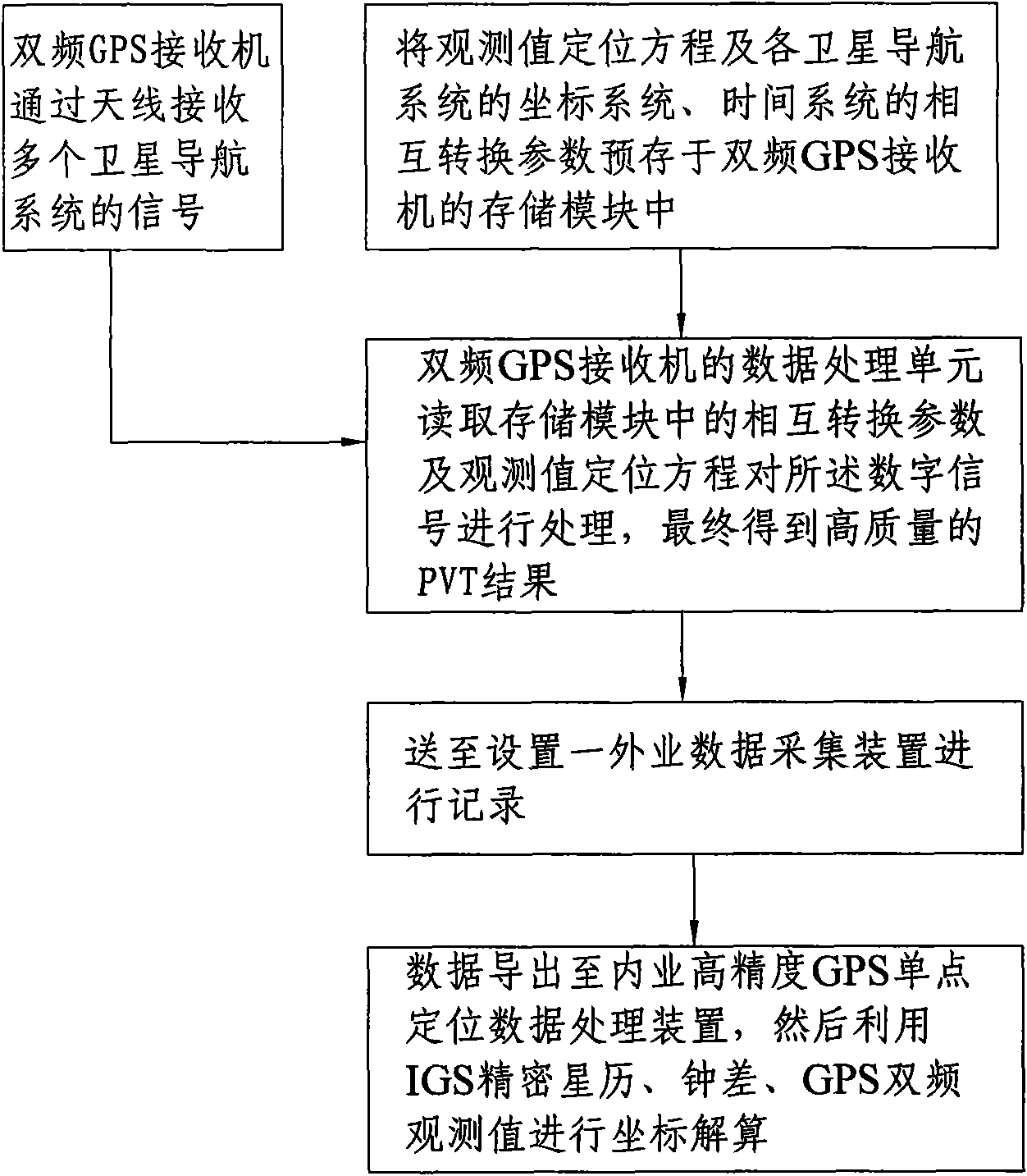
High-precision point positioning method and system for global navigation satellite system (GNSS)
InactiveCN101581774AQuality improvementPrecise 3D positionBeacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationData acquisitionGalilean moons
The invention provides a high-precision point positioning method and a high-precision point positioning system for a global navigation satellite system (GNSS). The method comprises the following steps: prestoring an observed value positioning equation with commonality for a compass navigation satellite system, a GPS, a GLONASS and a Galileo satellite navigation system, and interconvertible parameters of coordinate systems and time systems of the various satellite navigation systems into a storage module of a double-frequency GPS receiver; receiving signals of the various satellite navigation systems by the double-frequency GPS receiver through an antenna, and converting the signals into digital signals by a signal converting unit; reading the interconvertible parameters in the storage module and the observed value positioning equation by a data processing unit to process the digital signals; finally obtaining a high-quality PVT result; realizing the combination use of observed quantities and ephemerides of the various satellite navigation systems; and sending the PVT result to a field data acquisition device for recording. The method and the system realize the compatible high-precision point positioning based on the compass navigation satellite system / the GPS / the GLONASS / the Galileo satellite navigation system, and can provide point positioning position information with higher quality.
Owner:CHINA ZHENGYUAN GEOMATICS CO LTD
Multiple access using different codes lengths for global navigation satellite systems
InactiveUS20050129096A1Reduce impactEnhance the auto-correlation peaksCode division multiplexBeacon systemsParallel computingCorrelation function
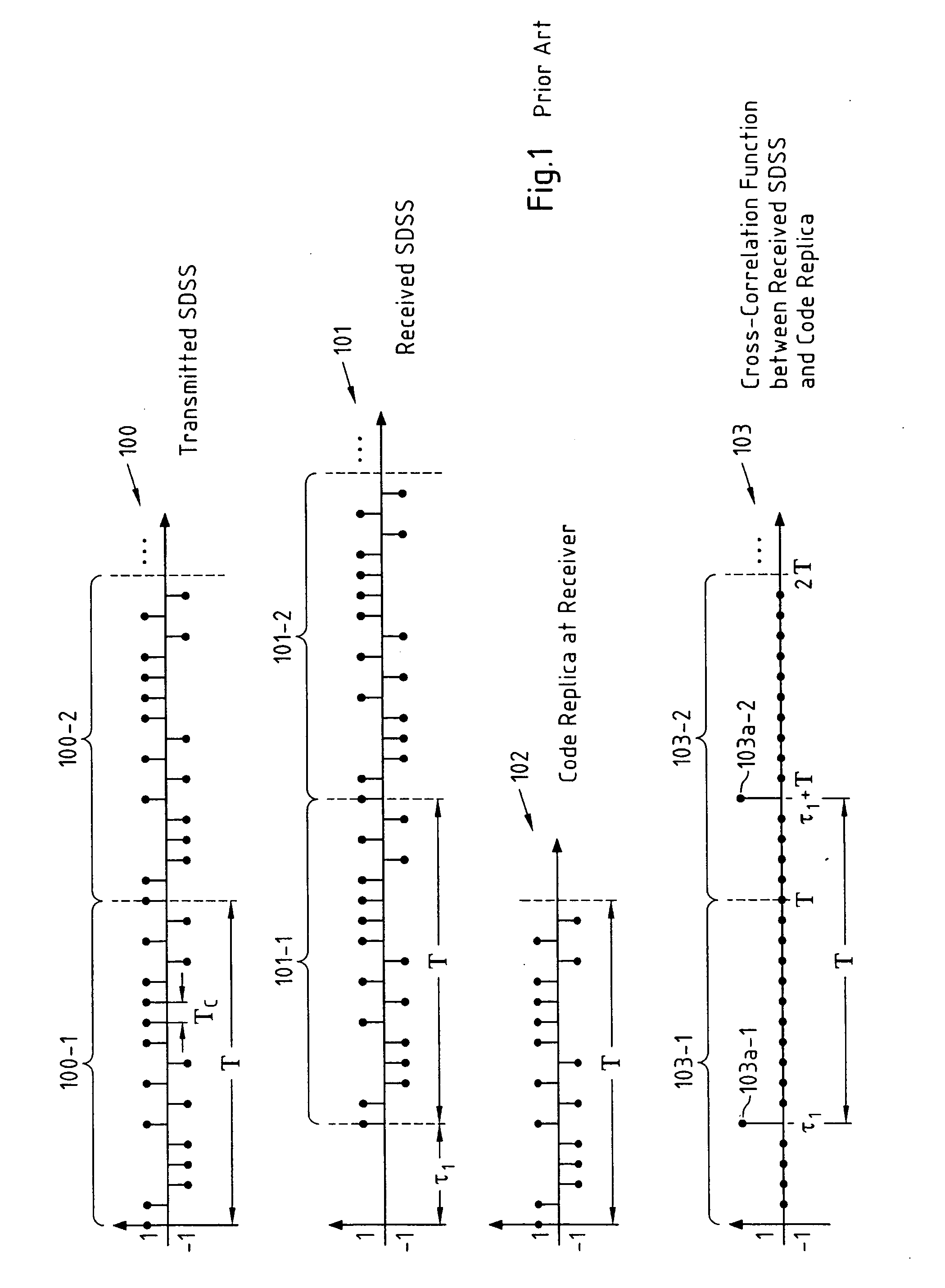
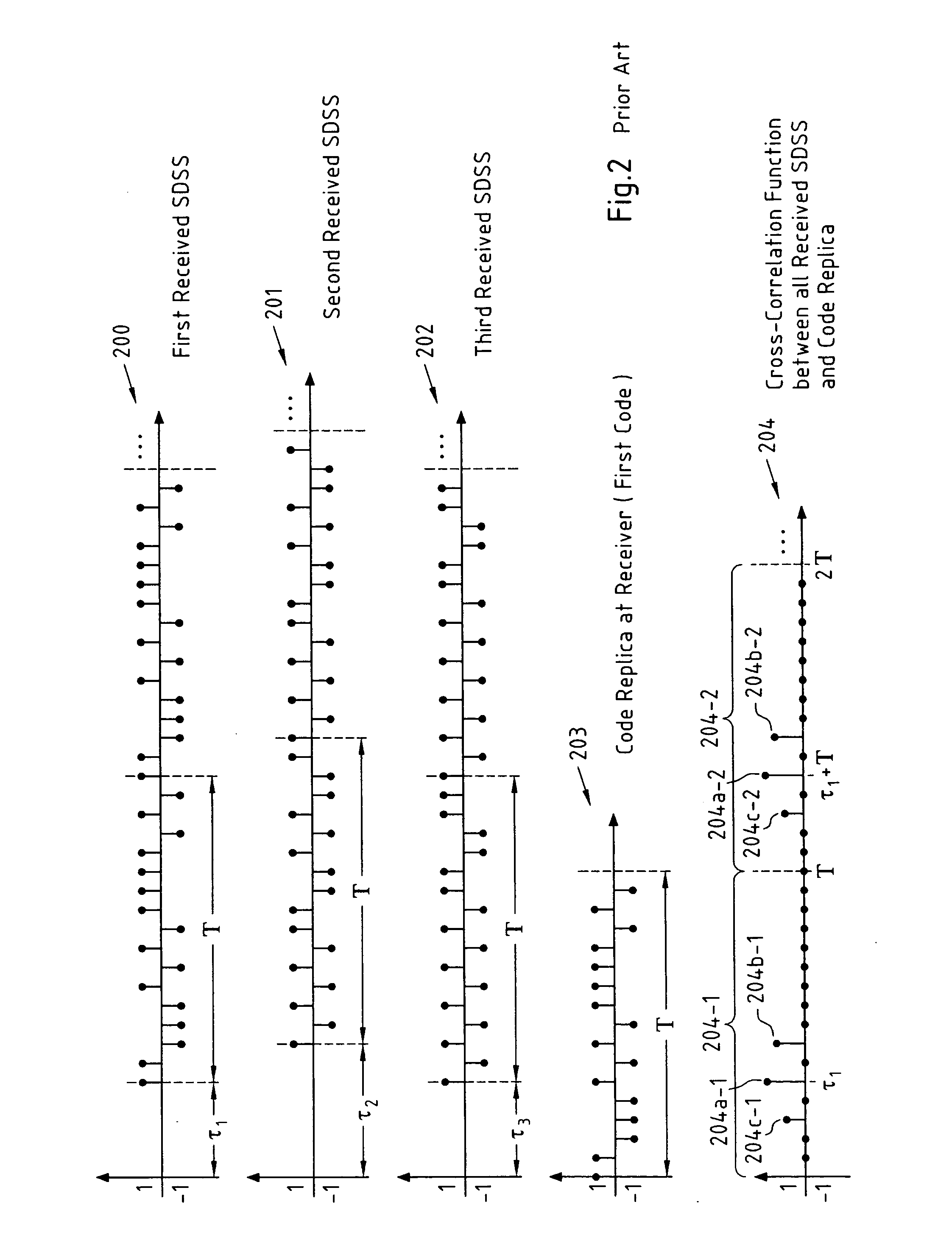
A method for determining a delay of a spread data symbol stream comprises the steps of at least partially correlating a signal, which comprises at least first and second spread data symbol streams (300, 301) that are obtained by spreading at least a first and second data symbol stream with a respective first (302) and second code, with said first code (302) to obtain at least two portions (303-1, 303-2) of a Cross-Correlation Function CCF (303), and combining said at least two portions (303-1, 303-2) of said CCF (303) to obtain a combined CCF portion from which a first delay of said first spread data symbol stream is determined, wherein said first code (302) and said second code are composed of chips and wherein the number of chips of said first code (302) is different from the number of chips of said second code. The invention further relates to a computer program, a computer program product, a device and a system.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
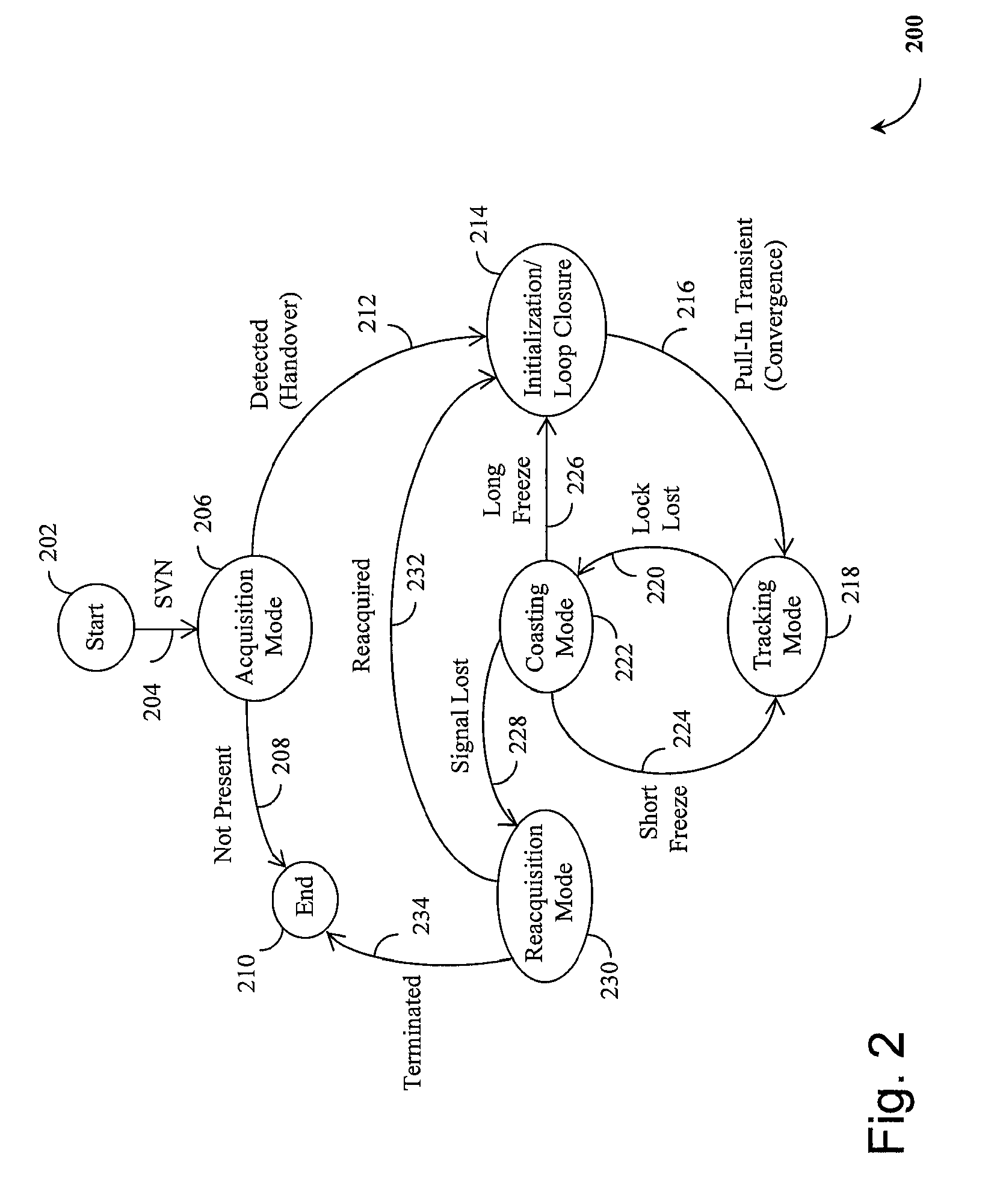
Method and device for tracking weak global navigation satellite system (GNSS) signals
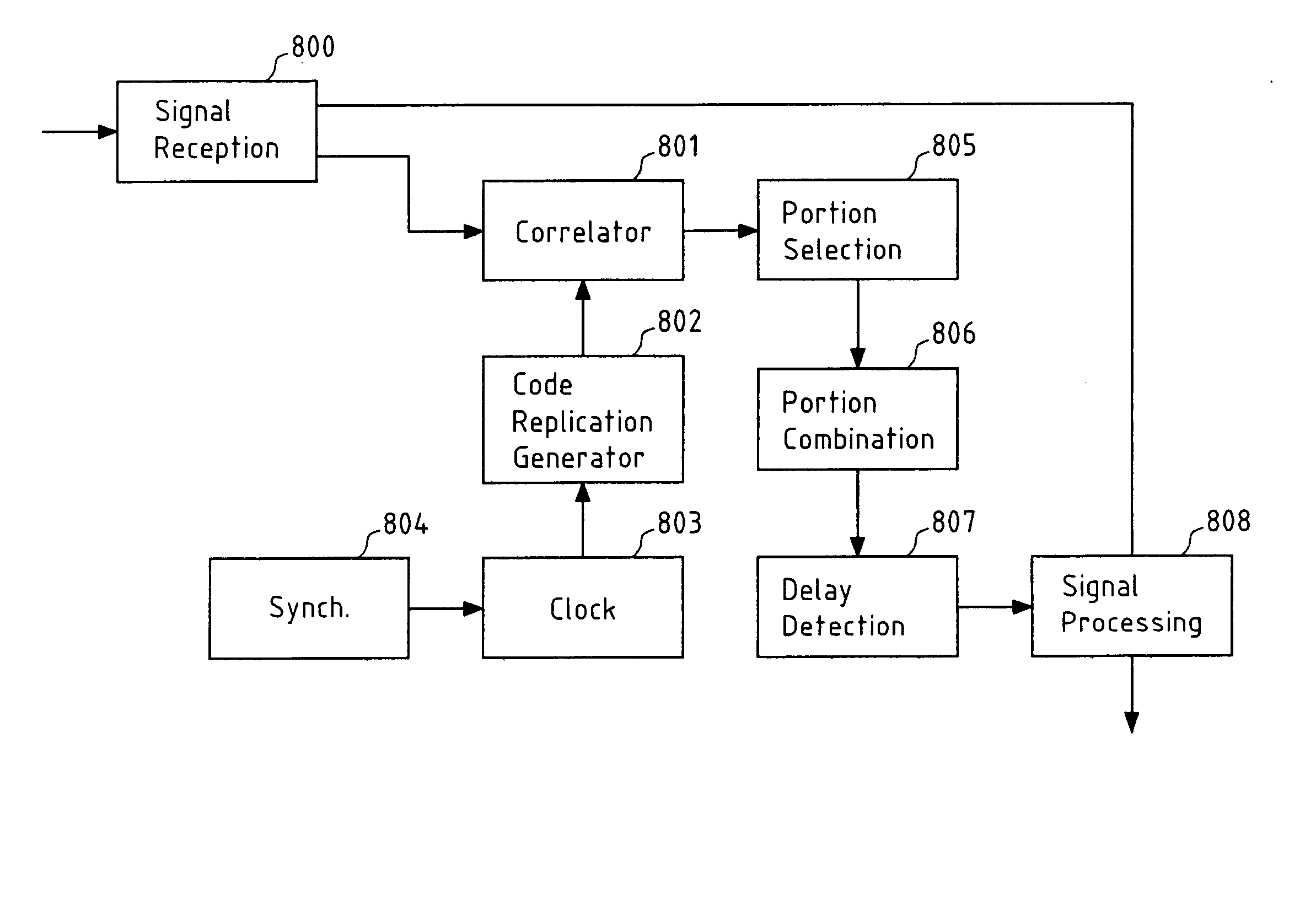
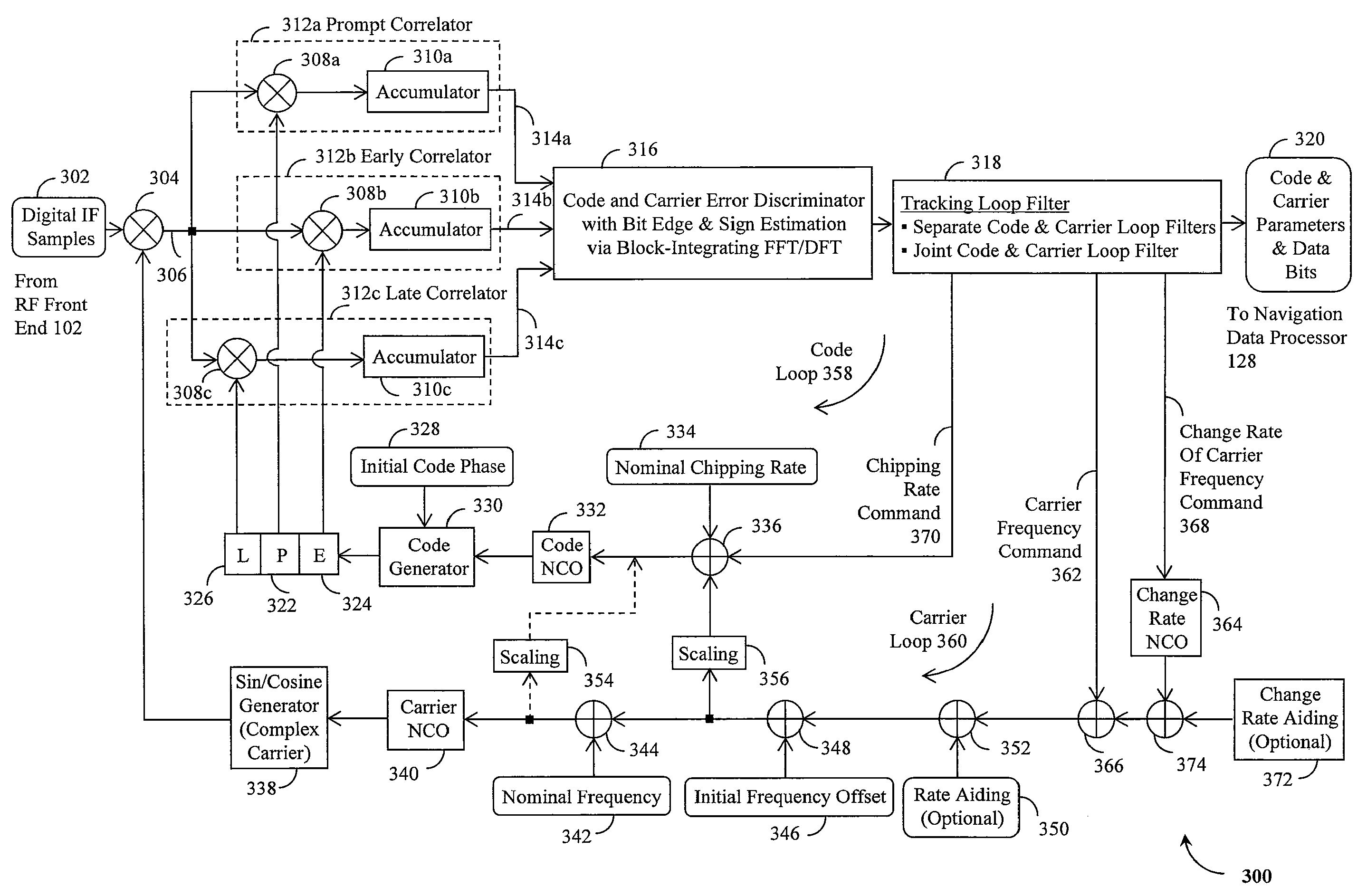
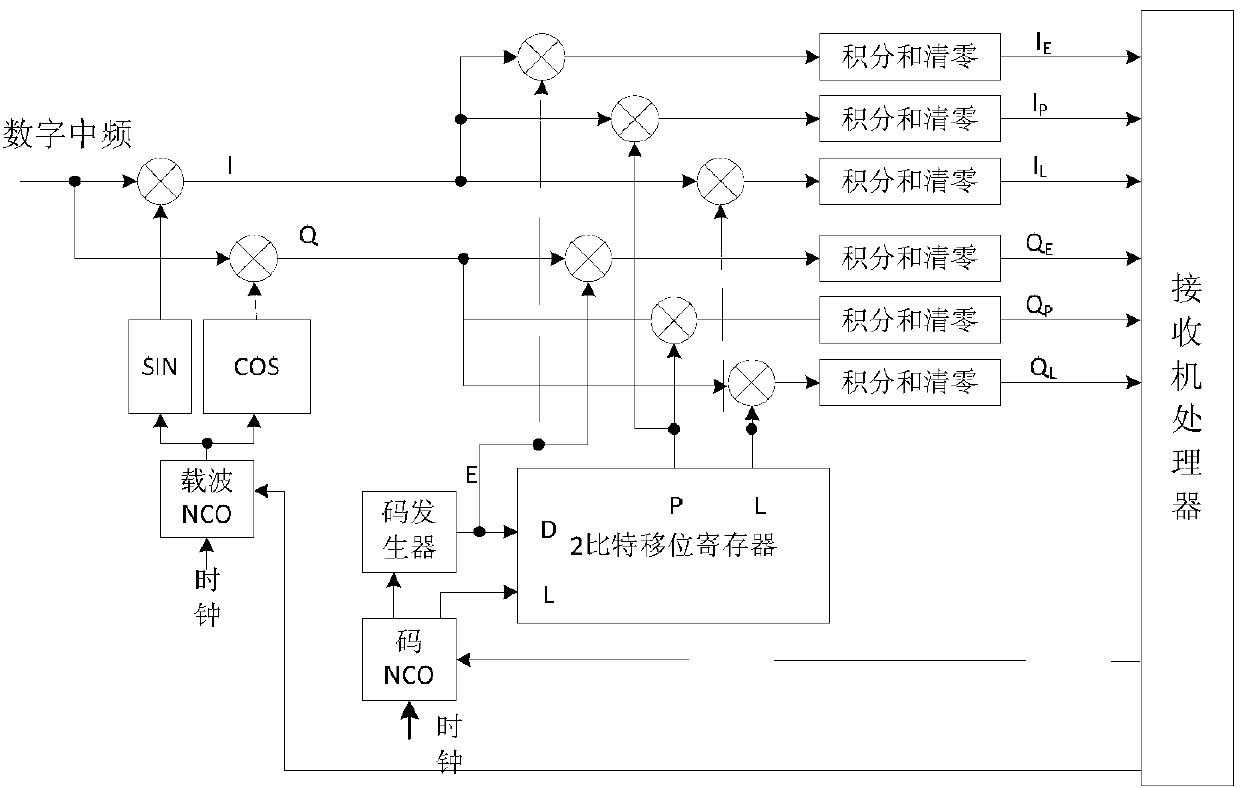
A Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receiver and associated method capable of tracking weak GNSS signals from a plurality of GNSS satellites. In a preferred embodiment, code and carrier tracking loops are initially closed around the code phase, carrier frequency, and data bit edge estimates handed over from an acquisition mode. In subsequent tracking, early, prompt, and late copies of the code replica are correlated with the incoming signal. The prompt correlations are coherently integrated over an extended updating interval for data bit edge and sign estimation as well as for carrier phase and frequency error discrimination whereas the early and late correlations are used for code error discrimination. Code delay and carrier phase and frequency errors are used to update the code and carrier tracking loop filters. Together with data bits, they form observables of a GNSS signal's time and frequency parameters for timing and position fixing.
Owner:CSR TECH HLDG
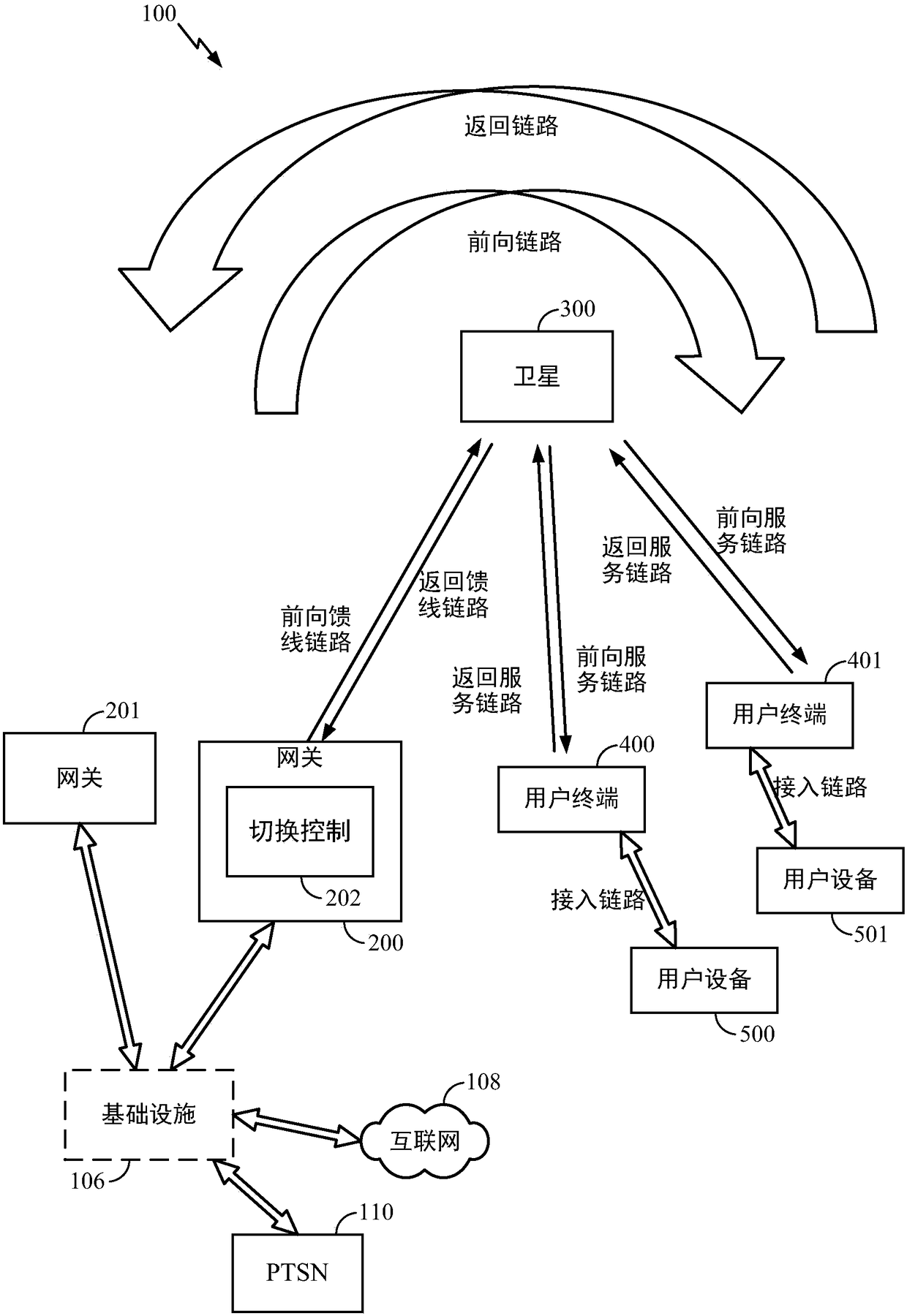
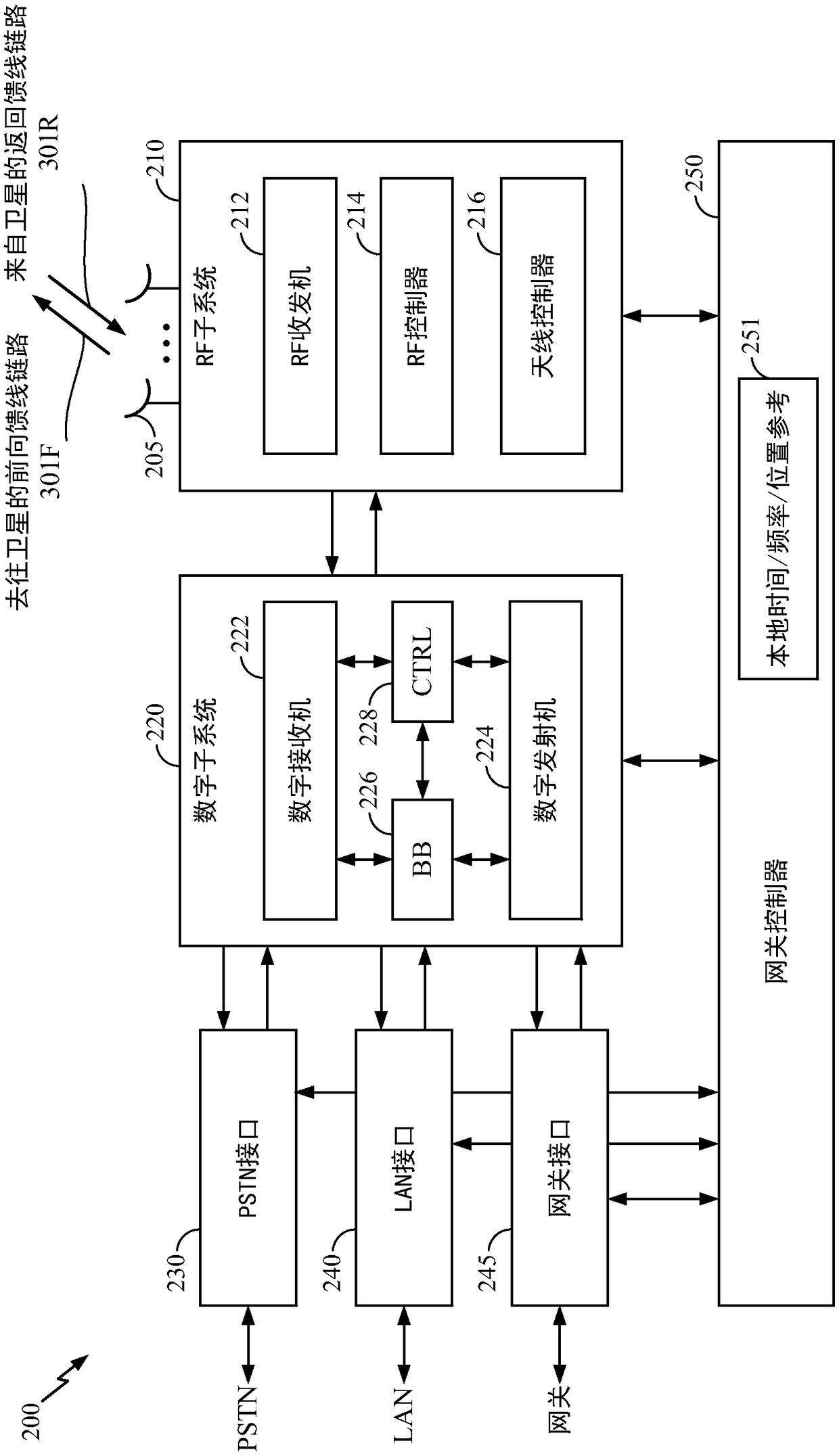
Method and apparatus for inter-satellite handovers in low-earth orbit (LEO) satellite systems
Methods and apparatuses for managing inter-satellite handovers are provided to allow a user terminal to reduce the frequency of handovers while maintaining a sufficiently high system capacity in a non-geosynchronous satellite communication system. The method and apparatus for managing inter-satellite handovers may be implemented in a gateway, in infrastructure connected to a gateway, in a user terminal, or in a satellite.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
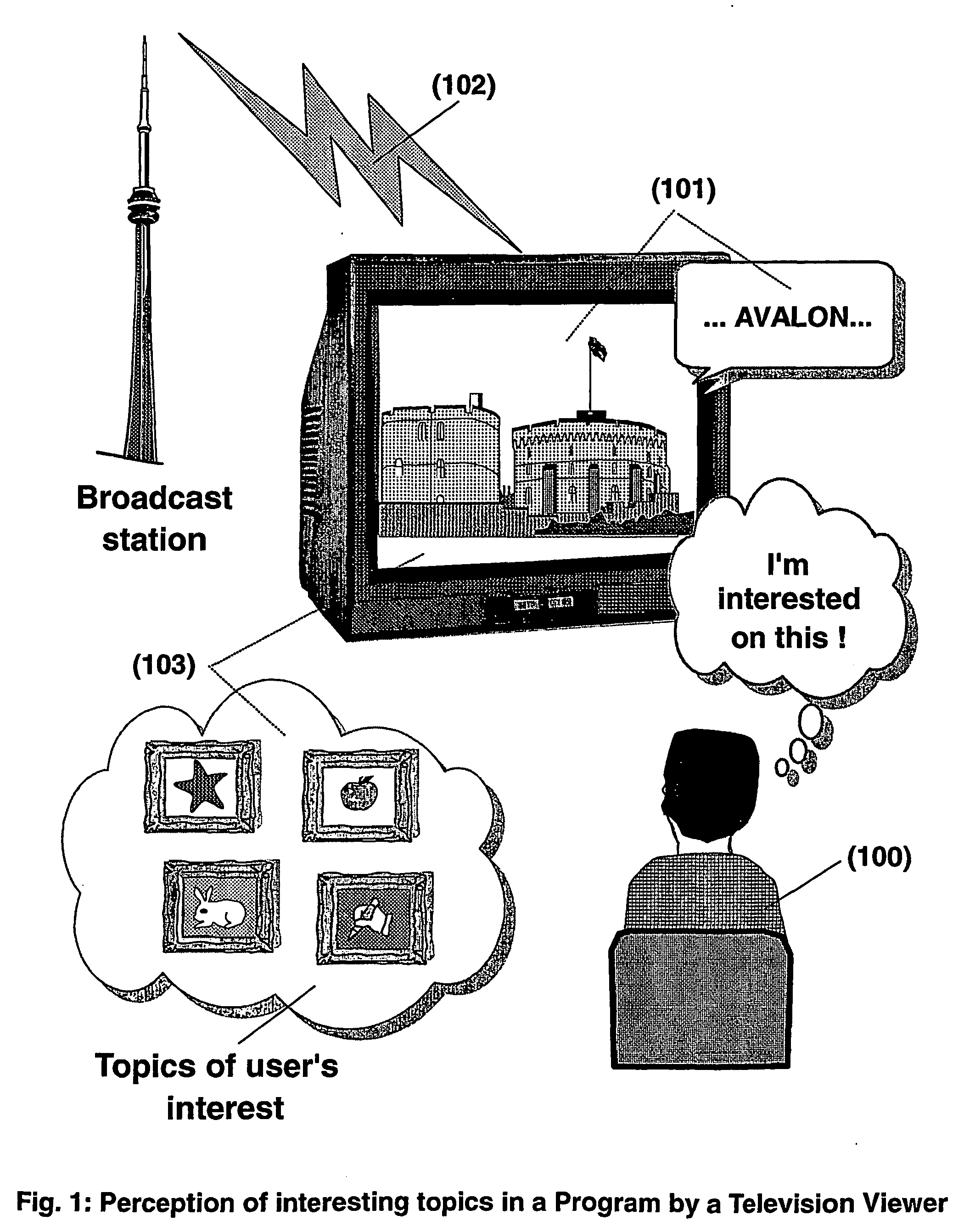
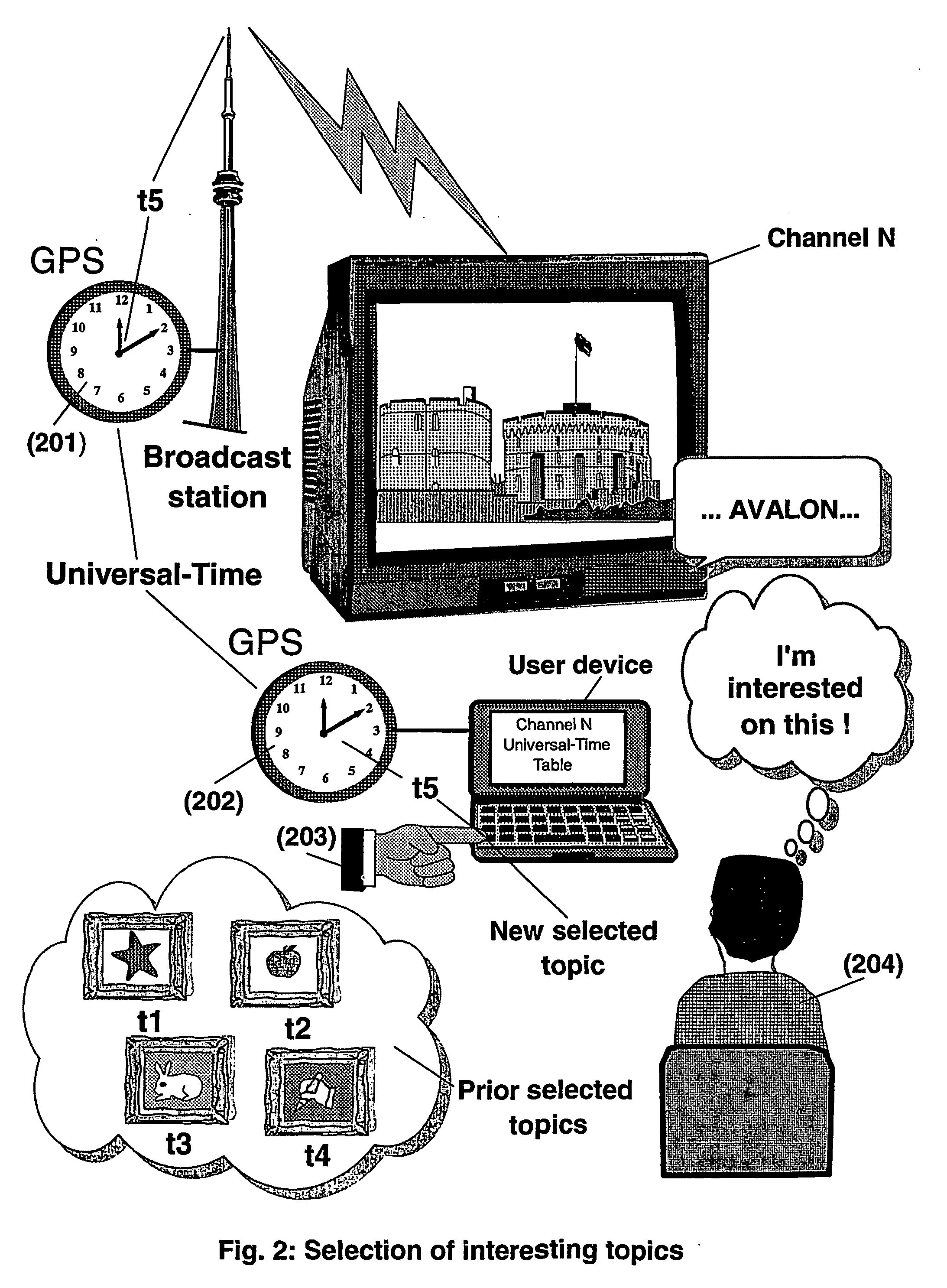
System and method for enhancing broadcast programs with information on the world wide web
ActiveUS20040139469A1Easy access to informationEasy accessTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionTelevision receiversBroadcasting
The present invention is directed to a system and method for enabling a radio auditor or a television viewer (100) to access complementary information (101) related to a broadcast program (102) received in real-time. The preferred embodiment of the invention relates to a system and method for enabling a person (100) receiving a broadcast program (102), to select a plurality of topics drawing his or her attention (101) (103) and for immediately, or at a later time, accessing additional information related to these topics from the Word Wide Web. The system is based on a synchronization of the local times of receivers and transmitters according to a same universal-time (201) (202), so that the flow of information transmitted and received is always synchronized, independently of the relative positions of receivers and transmitters. The synchronization is done referring to an universal time such as the Global Positioning System Time (GPS-time), the Global Orbiting Navigational Satellite System (GLONASS) time or another suitable universal time based on a satellite system. The GPS or GLONASS receivers are connected or integrated to the broadcasting stations. At the receiver side, GPS or GLONASS receivers may be integrated or connected to devices (e.g., Personal Computers, wearable computers, Personal Digital Assistants (PDAs), smart phones or onboard mobile computers) that may be independent or separate from the radio or television receivers. The system is also based on a plurality of hyperlinks defined for given universal-time intervals of retransmission. The hyperlinks are associated with the transmitted information. The hyperlinks can be retrieved, selected and activated by radio auditors or television viewers during the time intervals for which they have been defined.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
Methods and apparatus for using position/attitude information to enhance a vehicle guidance system
ActiveUS20090312948A1Increase robustnessLow costInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationTerrainGuidance system
An enhanced vehicle guidance system comprising a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) receiver and a data processor with a memory component and a computing device. The method of enhancing a vehicle's guidance system may comprise calculating the altitude, latitude, and longitude of a GNSS receiver for each of a plurality of positions; calculating the incline angle between adjacent points; and using the calculated incline angles to infer the attitude of the vehicle at any of the plurality of positions. The attitude may be used to calculated an inertial correction factor to compensate for GNSS position inaccuracies induced as a result of the vehicle rolling and pitching on uneven terrain. The altitude, latitude, longitude, and attitude of the plurality of positions may be stored in the memory such that the system may look-up the attitude for a given position without recalculating the attitude and without using an inertial sensor.
Owner:AGCO CORP
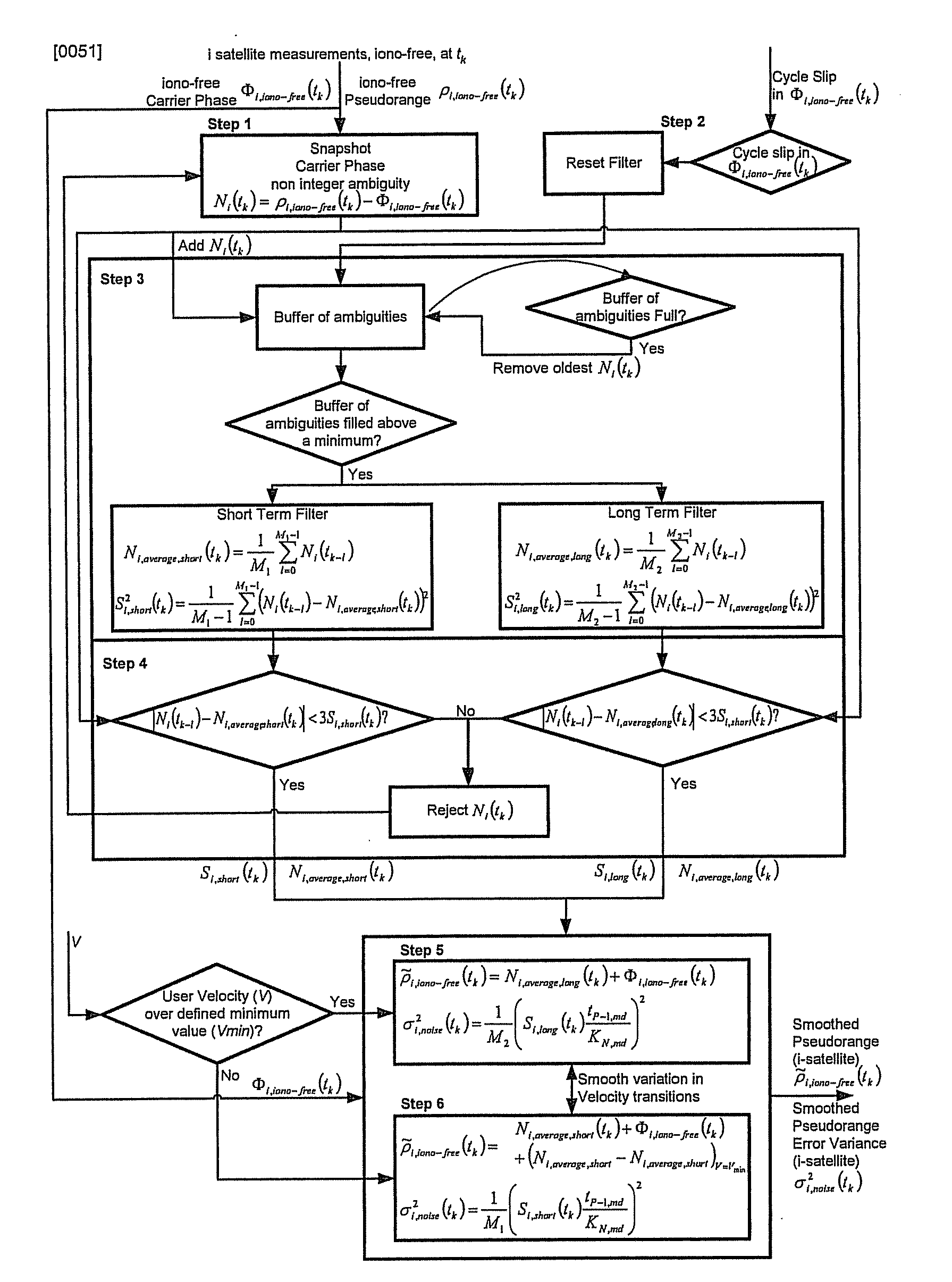
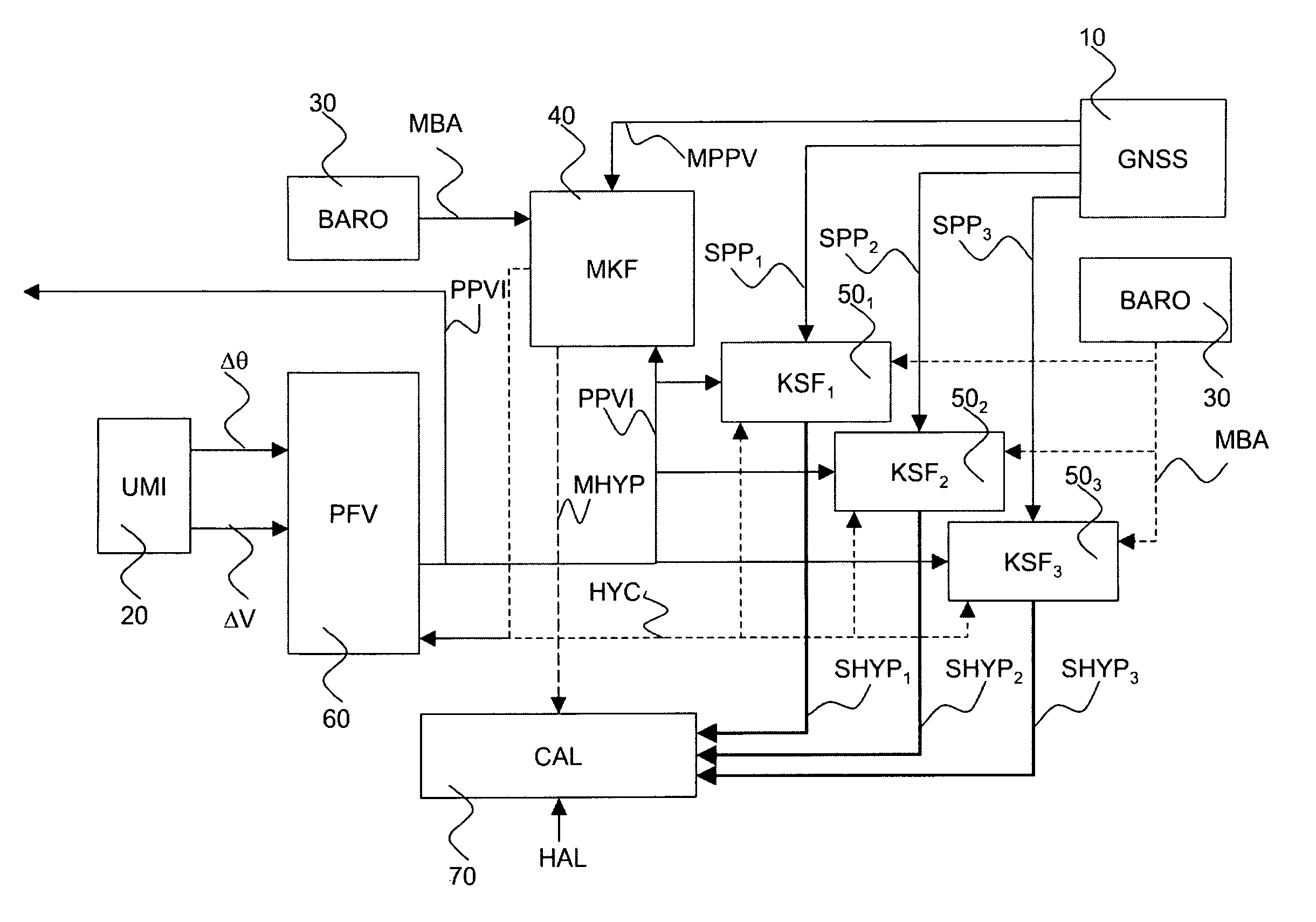
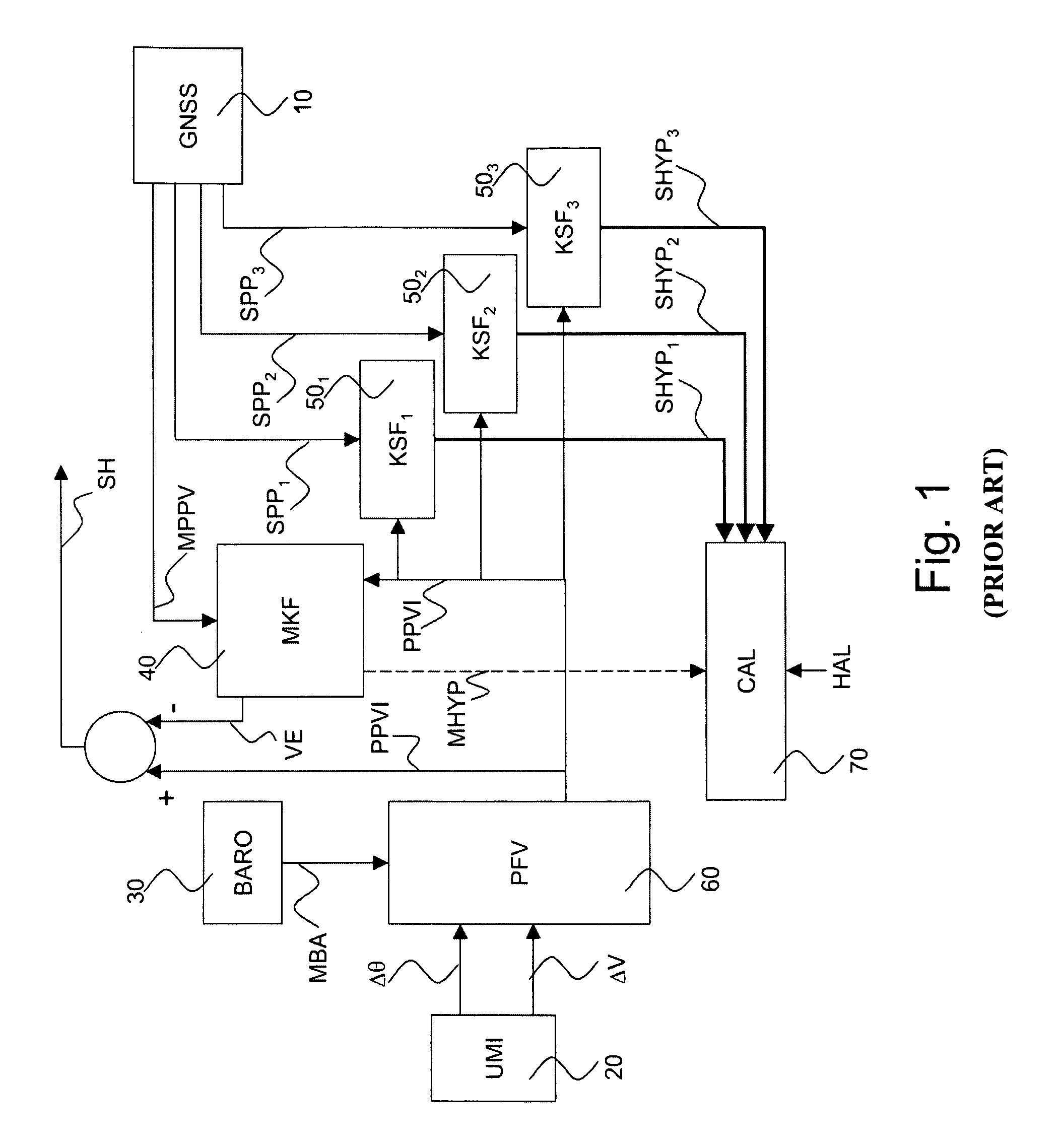
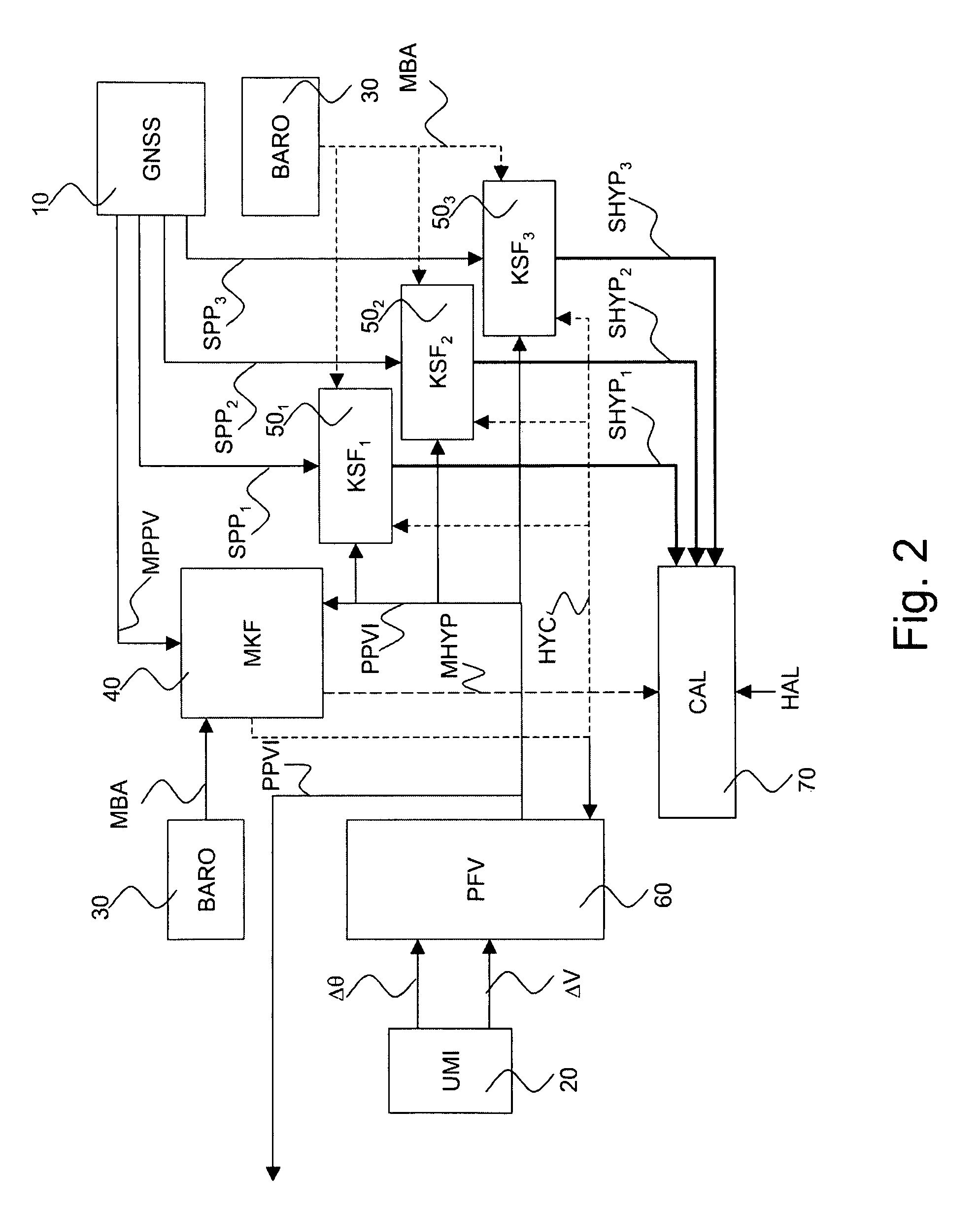
Advanced global navigation satellite systems (gnss) positioning using precise satellite information
A method is provided for estimating parameters useful to determine the position of a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) receiver or a change in the position thereof. The method includes the steps of: obtaining at least one GNSS signal received at the GNSS receiver from each of a plurality of GNSS satellites; obtaining, from at least one network node, precise satellite information on: (i) the orbit or position of at least one of the plurality of GNSS satellites, and (ii) a clock offset of at least one of the plurality of GNSS satellites; identifying, among the obtained GNSS signals, a subset of at least one GNSS signal possibly affected by a cycle slip, the identified subset being hereinafter referred to as cycle-slip affected subset; and estimating parameters useful to determine the position of the GNSS receiver or a change in the position of the GNSS receiver using at least some of the obtained GNSS signals which are not in the cycle-slip affected subset, and the precise satellite information.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
Hybrid ins/gnss system with integrity monitoring and method for integrity monitoring
ActiveUS20100026567A1High precisionPosition fixationNavigation instrumentsClosed loopInertial frame of reference
The invention pertains to the monitoring of the integrity of position and speed information arising from a hybridization between an inertial reference system and a satellite-based positioning receiver. The invention relates more precisely to a navigation apparatus known in the art by the name INS / GNSS system (for “Inertial Navigation System” and “Global Navigation Satellite System”) hybridized in closed loop.
Owner:THALES SA
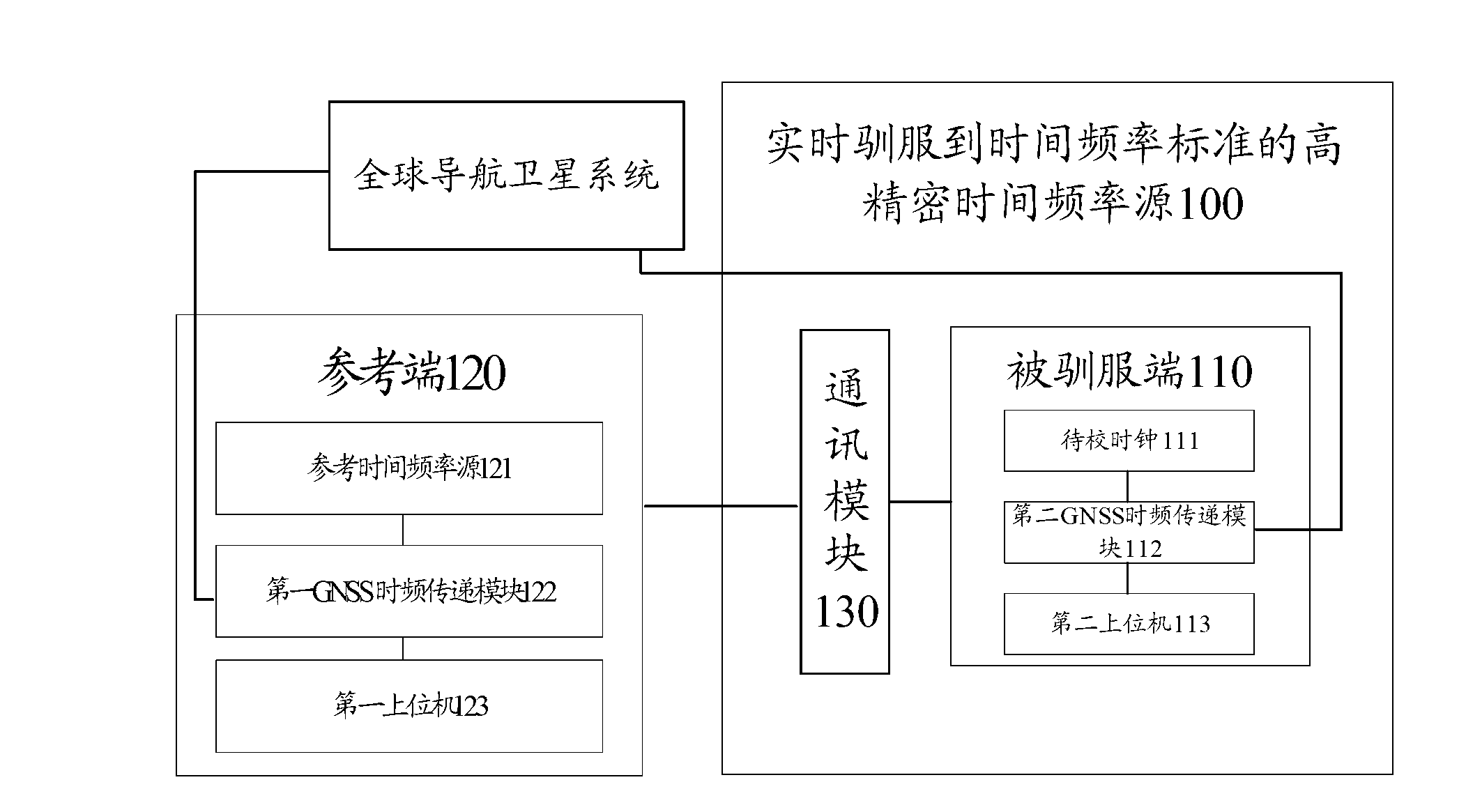
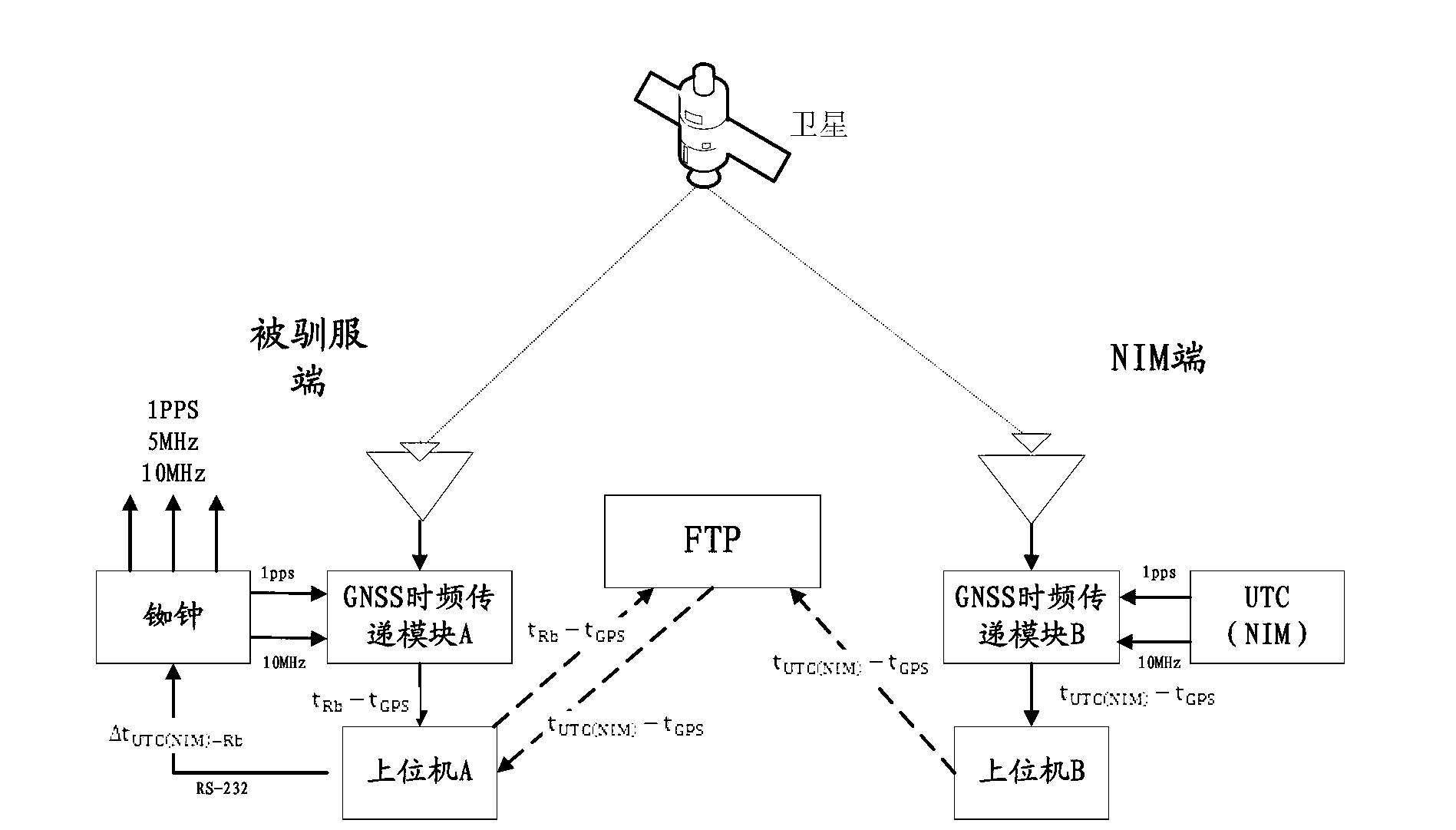
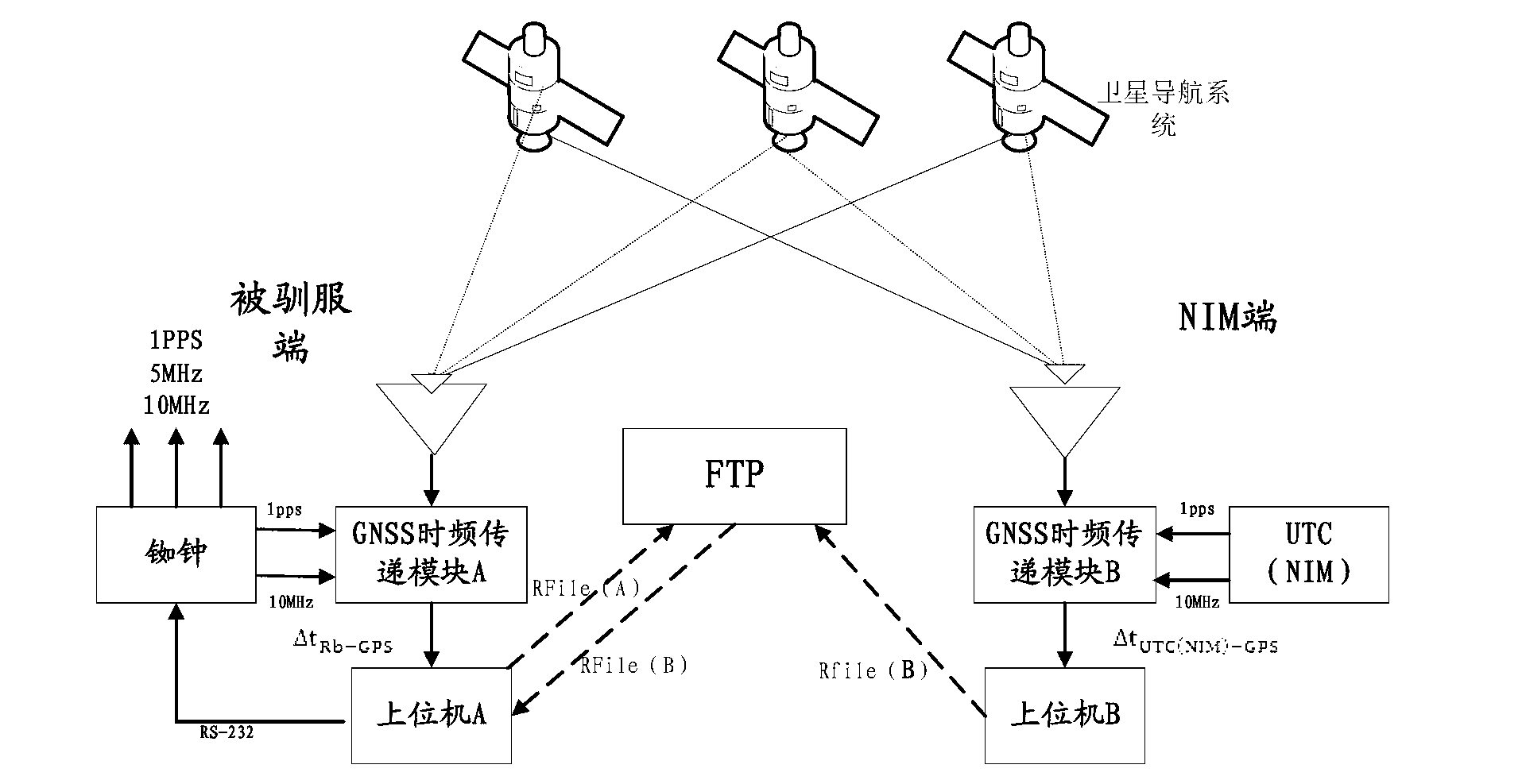
High-precision time-frequency source capable of being tamed to time-frequency standard in real time
InactiveCN103226324AHigh calibration time accuracyStrong reliabilityApparatus using atomic clocksRadio-controlled time-piecesTelecommunicationsSatellite system
The invention provides a high-precision time-frequency source capable of being tamed to a time-frequency standard in real time. The high-precision time-frequency source can obtain a first time-frequency clock difference sequence generated by a reference side and a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) remotely and in almost real time, and comprises a tamed side; the reference side generates N time-frequency signals of a to-be-calibrated clock; according to the N time-frequency signals and a satellite signal, a second time-frequency clock difference sequence is generated; according to the first time-frequency clock difference sequence and the second time-frequency clock difference sequence, a third time-frequency clock difference sequence between N time-frequency signals of a reference time-frequency source and the N time-frequency signals of the to-be-calibrated clock is obtained; according to the third time-frequency clock difference sequence, a relative frequency difference sequence is computed and acquired; and through the third time-frequency clock difference sequence and the corresponding relative frequency difference sequence, the to-be-calibrated clock is monitored and calibrated. The high-precision time-frequency source capable of being tamed to the time-frequency standard in real time can easily trace time performance and frequency performance of the reference time-frequency source (generally, the time-frequency standard, including a national time-frequency reference) in any laboratory, can trace the time and the frequency back to the International System of Units, and is relatively high in reliability, accuracy and stability.
Owner:NAT INST OF METROLOGY CHINA
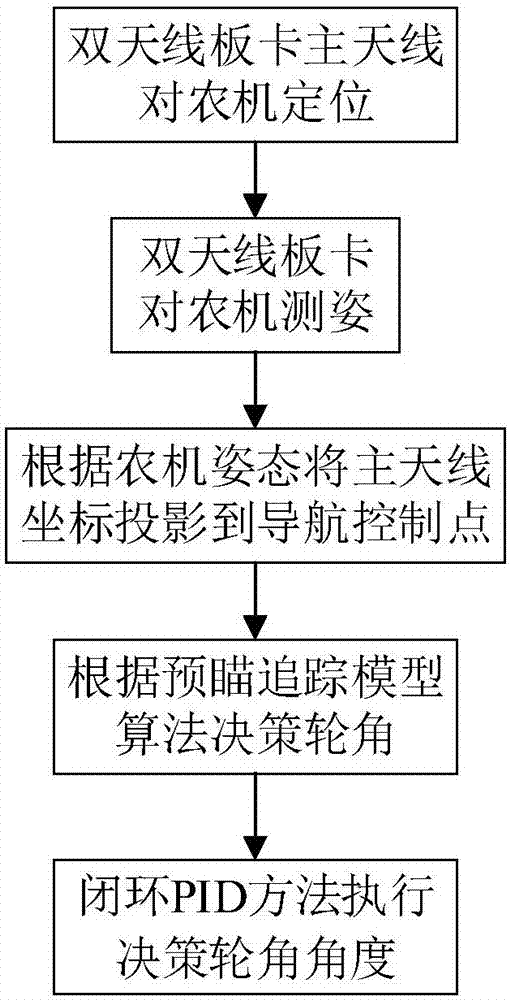
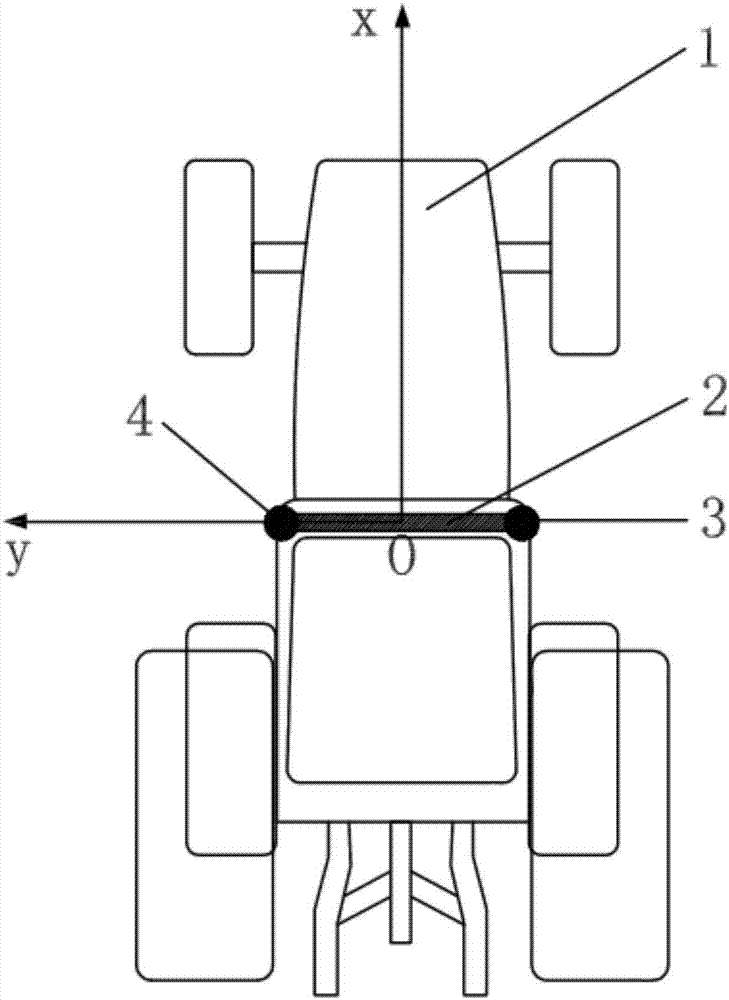
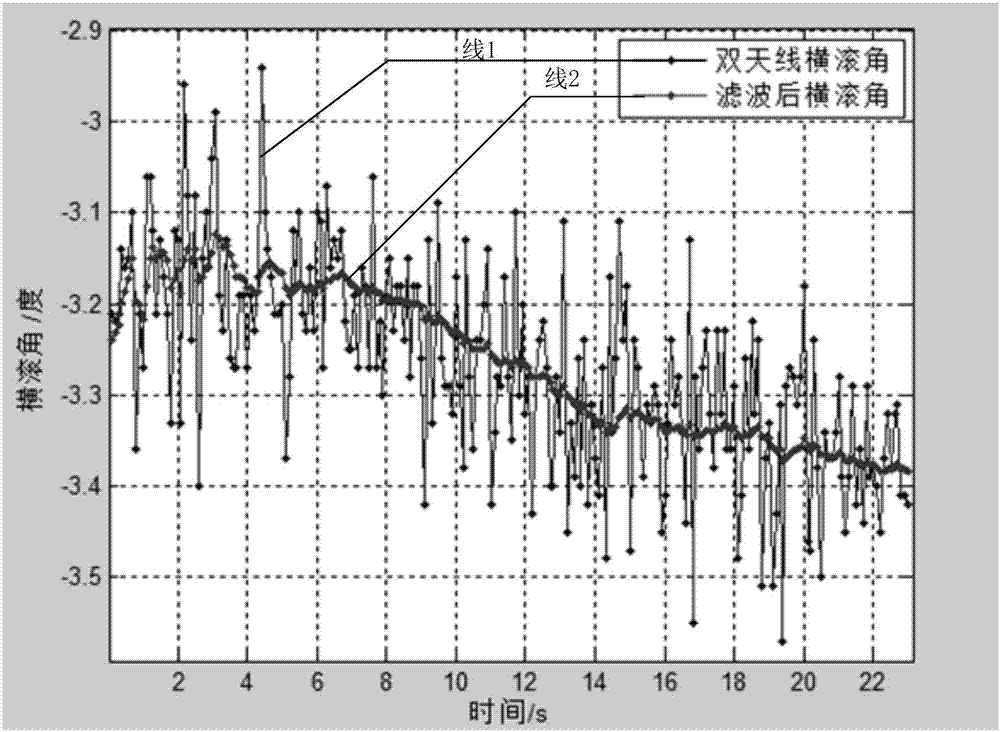
Agricultural machinery automatic navigation control method based on double-antenna GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) and preview tracking model
ActiveCN107315345AHigh precisionImprove stabilityAdaptive controlTracking modelAgricultural engineering
The present invention discloses an agricultural machinery automatic navigation control method based on a double-antenna GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) and a preview tracking model. According to the method, a clock-shared integrated dual-antenna GNSS receiver supporting multi-satellite system carrier phase difference technique is used for performing positioning and attitude measurement of agricultural machinery; and a piecewise adaptive foresight distance related to speed is adopted as a parameter in a preview tracking model, so that path tracking control can be performed on the agricultural machinery. A positioning board card supporting the multi-satellite system carrier phase difference technique can effectively increase the number of satellites participating in positioning calculation and improve the precision and stability of navigation and positioning; navigation satellite system-based inertial navigation attitude measurement can improve the accuracy and real-time performance of the attitude measurement of the agricultural machinery; the design and simulation of driving behaviors of a user by the preview tracking model algorithm have predictability, and therefore, a path tracking control effect is good, the quickness and stability of the launch of the agricultural machinery and the adaptability of the agricultural machinery to compacted field road conditions can be improved; and the foresight distance is related to speed, and therefore, the control accuracy and stability of an agricultural machinery automatic navigation system in relatively high-speed operation can be improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
GNSS navigation solution integrity in non-controlled environments
ActiveUS8131463B2Improve navigation accuracyPosition fixationNavigation instrumentsNoise levelErrors and residuals
Disclosed is a method for providing a Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) navigation position solution with guaranteed integrity in non-controlled environments, the method including processing a (GNSS) signal including multiple satellites generating at least one signal to obtain carrier phase and pseudorange measurements; pre-processing the measurements to detect and characterize local errors in the measurements, wherein the local errors cannot be ascertained a priori, the characterization including providing error bounds estimated by measuring the carrier phase and pseudoranges measurements, thereby providing a set of measurements rejections when the characterization is not possible; and using the estimated error bounds, together with error bounds provided by the GNSS signal concerning satellite and ionospheric errors, to build in each measurement an estimated noise level in the measurements as input to a weighted Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring (RAIM) algorithm in order to compute position coordinates and associated protection levels in the non-controlled environments.
Owner:GMV AEROSPACE & DEFENCE
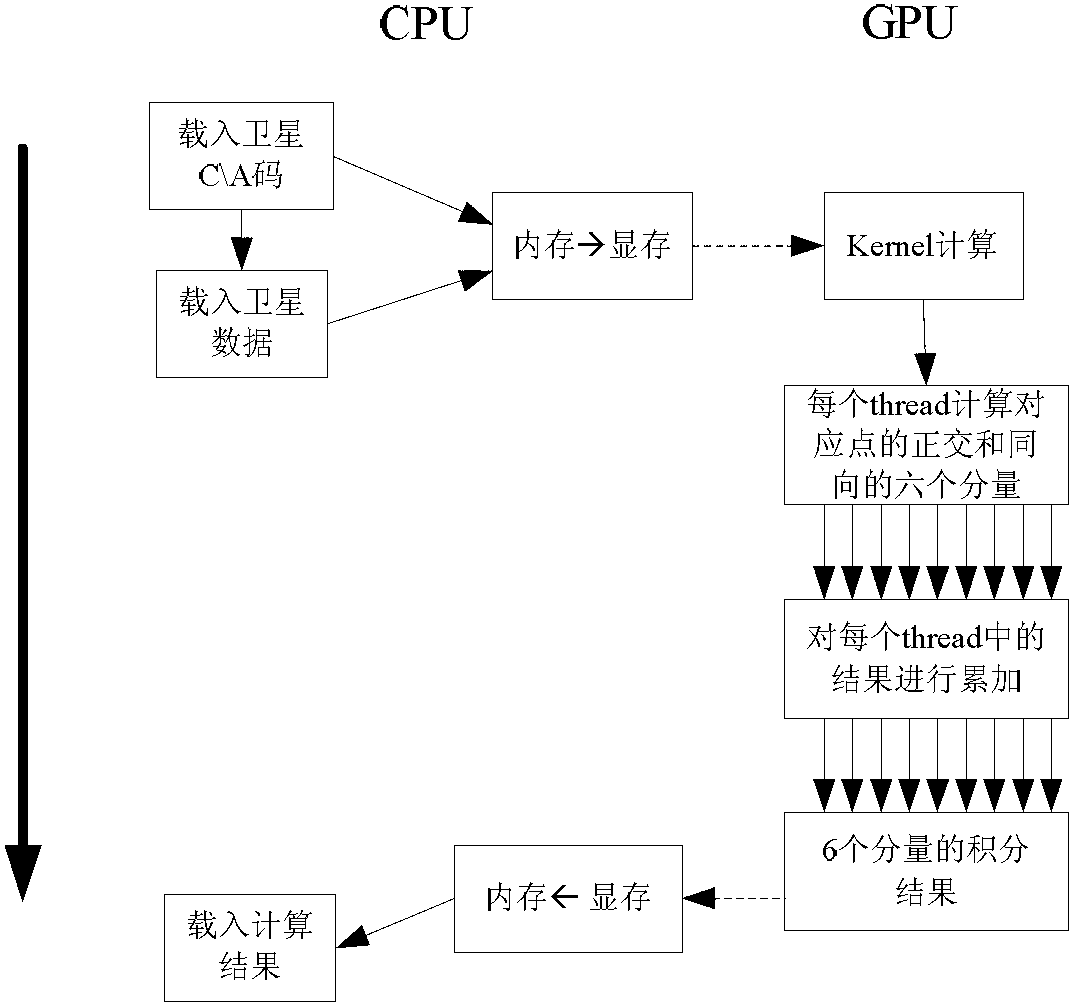
Parallel navigation satellite signal tracking method based on GPU (graphics processing unit) and system thereof
ActiveCN103278829APowerful floating-point parallel computing capabilityTake full advantage of hardware performanceSatellite radio beaconingCarrier signalEngineering
The invention discloses a parallel navigation satellite signal tracking method based on GPU (graphics processing unit) and a system thereof. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a multichannel carrier tracking loop and a pseudo code tracking loop on CPU(central processing unit)-GPU, wherein the CPU is in charge of data reading, loop phase discrimination and control functions and the like, and the GPU is in charge of the relevant calculation and integral summation functions of a great quantity of data sequences; after the GPU finishes the integral summation calculation, adopting a two-stage binary tree calculation structure; calculating an error by a carrier phase discriminator and a CA (certification authority) code phase discriminator on the CPU; and controlling a local carrier phase and a CA code phase to correct to realize the tracking. According to the invention, the defects of poor flexibility and black box operation of a hardware receiver system and the defect that various navigation satellite signal systems can not be supported are overcome. Meanwhile, the processing speed and precision of a software receiver can be enhanced, the cost of the software receiver is lowered, and a GNSS (global navigation satellite system) software receiver can track the multichannel navigation satellite signal in real time.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
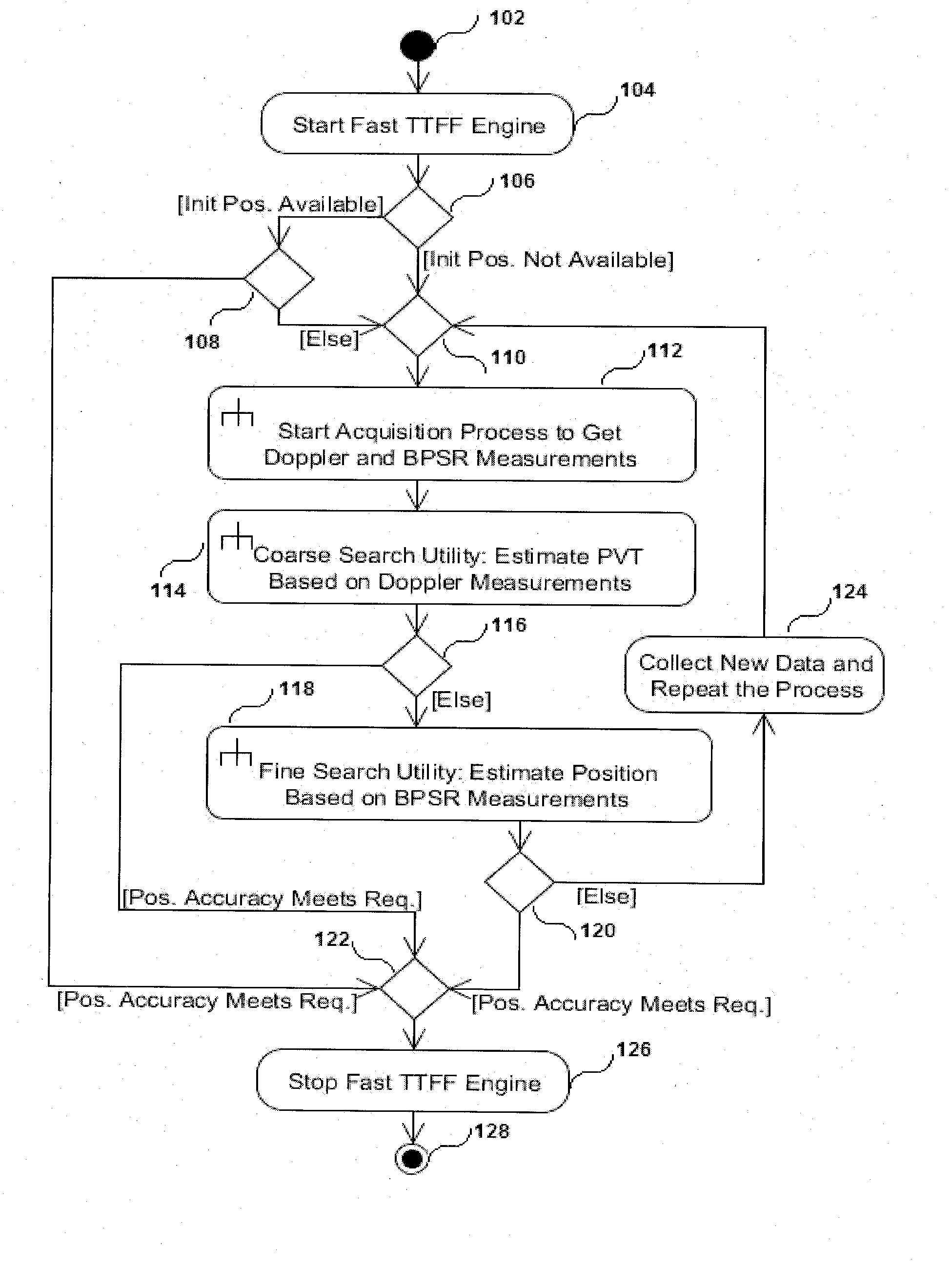
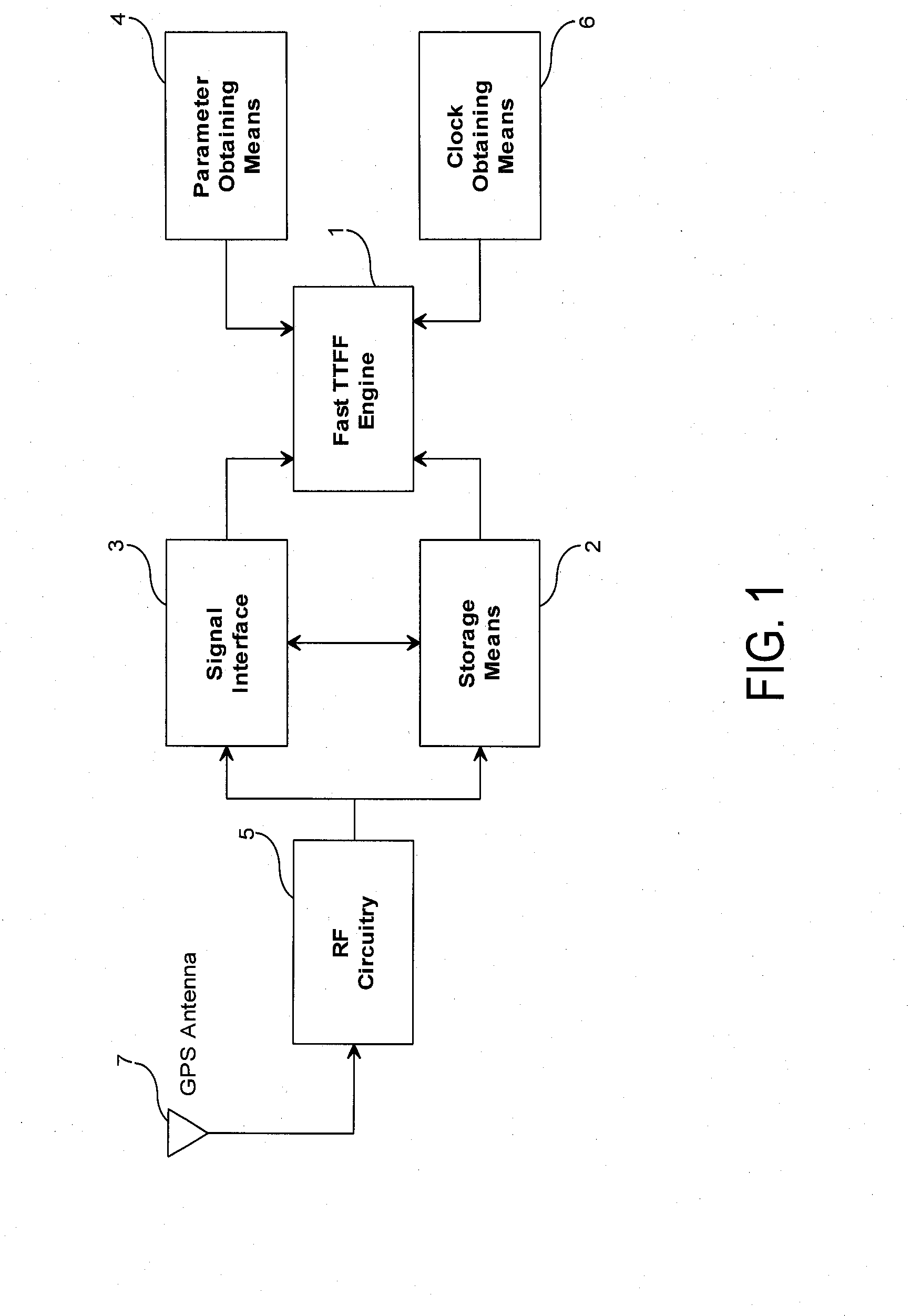
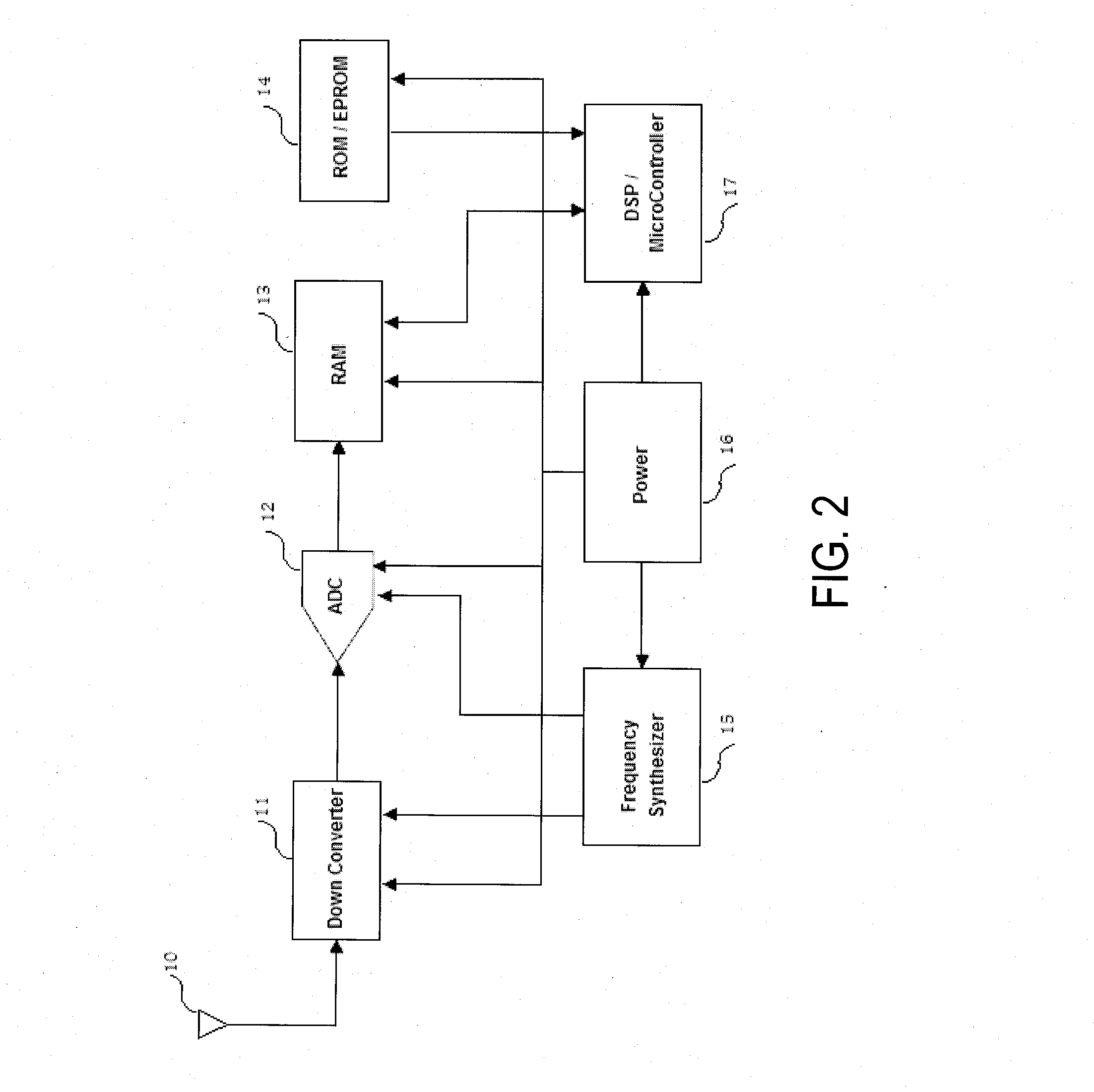
System, method and computer program for ultra fast time to first fix for a GNSS receiver
The present invention provides a system, method and computer program for a GNSS receiver that is operable to provide an ultra fast Time To First Fix (TTFF). The invention is implementable without requiring the decoding of a navigation message transmitted by GNSS satellite systems. The system of the present invention may comprise a parameter obtaining means, a clock obtaining means and a Fast TTFF engine. The parameter obtaining means may obtain satellite parameters of one or more GNSS satellites. The clock obtaining means may obtain a clock for estimating a GNSS time tag. The Fast TTFF engine may be linkable to a signal interface that is operable to provide I / Q samples from a GNSS antenna. The Fast TTFF engine may comprise a measurement generation utility, a coarse search utility and a fine search utility. The measurement generation utility may compute the Doppler frequency shift and the code phase of the one or more GNSS satellites based on the I / Q samples.
Owner:BASEBAND TECH
GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System)-based Kalman relative positioning method
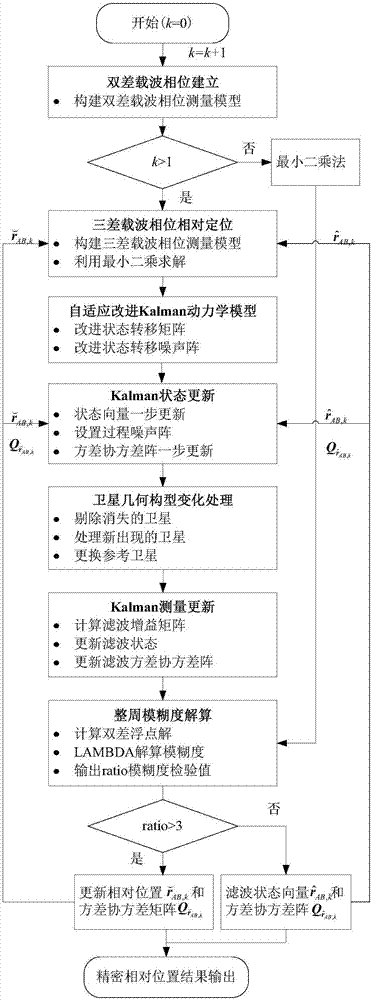
ActiveCN107193028AHigh precisionIncrease success rateSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceKalman filter
The invention discloses a GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System)-based Kalman relative positioning method. The method comprises steps: 1, a double difference carrier phase is built; 2, relative positioning of a triple difference carrier phase is carried out; 3, a Kalman filter dynamic model is improved adaptively; 4, the Kalman filter state is updated; 5, satellite geometrical configuration changes are processed; 6, Kalman filter measurement is updated; 7, integer ambiguity is solved; and 8, relative position information is outputted. The method is better adaptive to relative positioning of a variably accelerated motion carrier, the precision of ambiguity floating point solution and the integer ambiguity fixing success rate are improved, the initialization time of a relative positioning system is shortened, and the real-time performance and the reliability of relative positioning are enhanced.
Owner:CHINESE AERONAUTICAL RADIO ELECTRONICS RES INST
Methods and systems for mobile navigational applications using global navigation satellite systems
ActiveUS20080062041A1Improve usabilityPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingMobile navigationHigh availability
The present invention relates to providing navigation guidance for mobile users, using Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSSs) for applications where the user position needs to be determined in real time while meeting the navigation requirements, especially integrity requirement, for the given application. The present invention assists in providing guidance with a high availability of integrity function by trading accuracy for integrity for two different types of navigation applications. A first type of application requires a capability of detecting an occurrence of multiple satellite signal faults; the first embodiment of the invention provides this capability with a high availability of integrity, using two or more independent GNSSs. A second type of application requires a capability of detecting an occurrence of a single satellite signal fault; the second embodiment of the invention provides this capability with a high availability of integrity, using any one or a combination of GNSSs. The detecting and deriving of both methods are (i) in position domain and (ii) determinative of mobile user safety.
Owner:MITRE SPORTS INT LTD
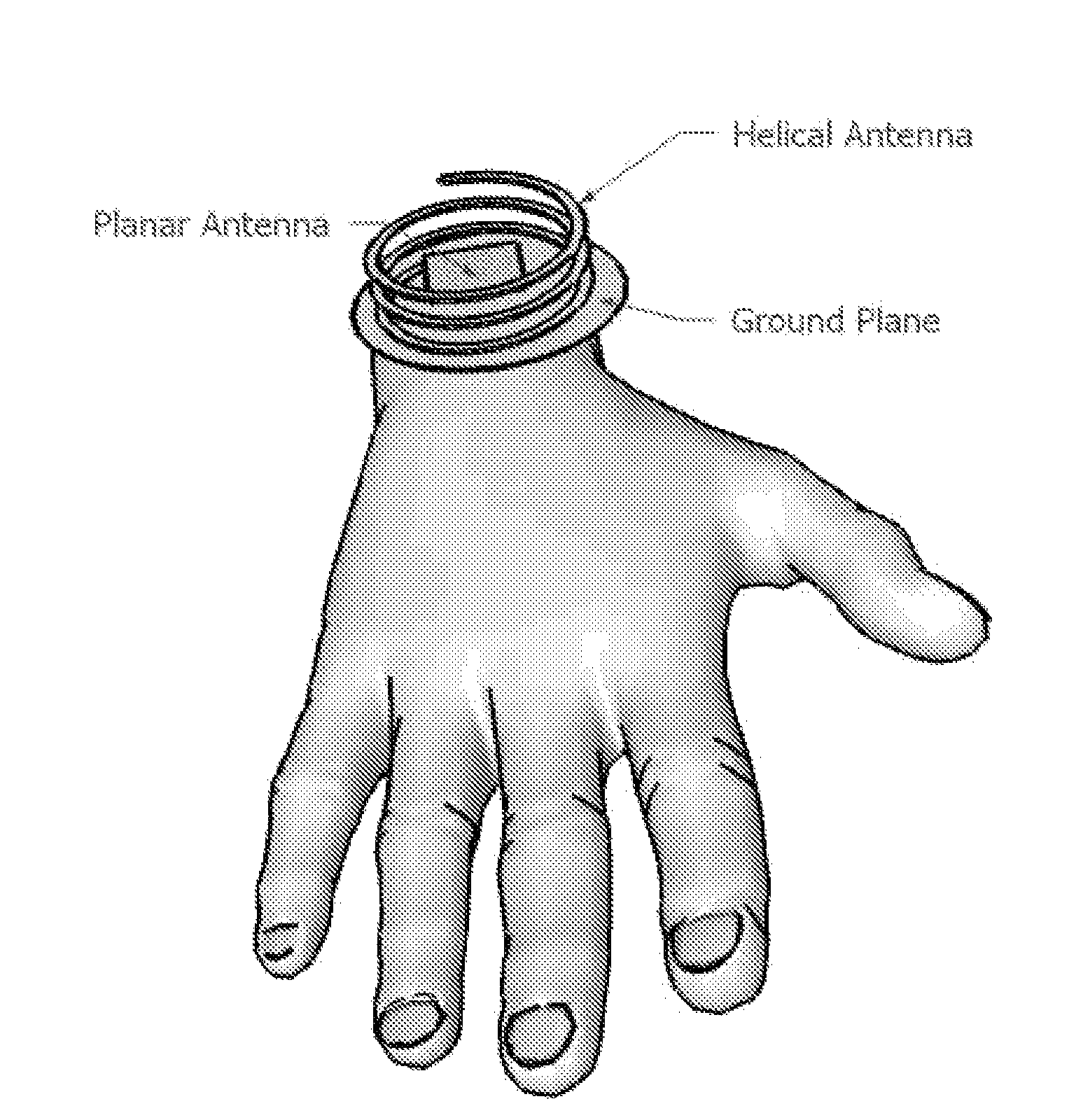
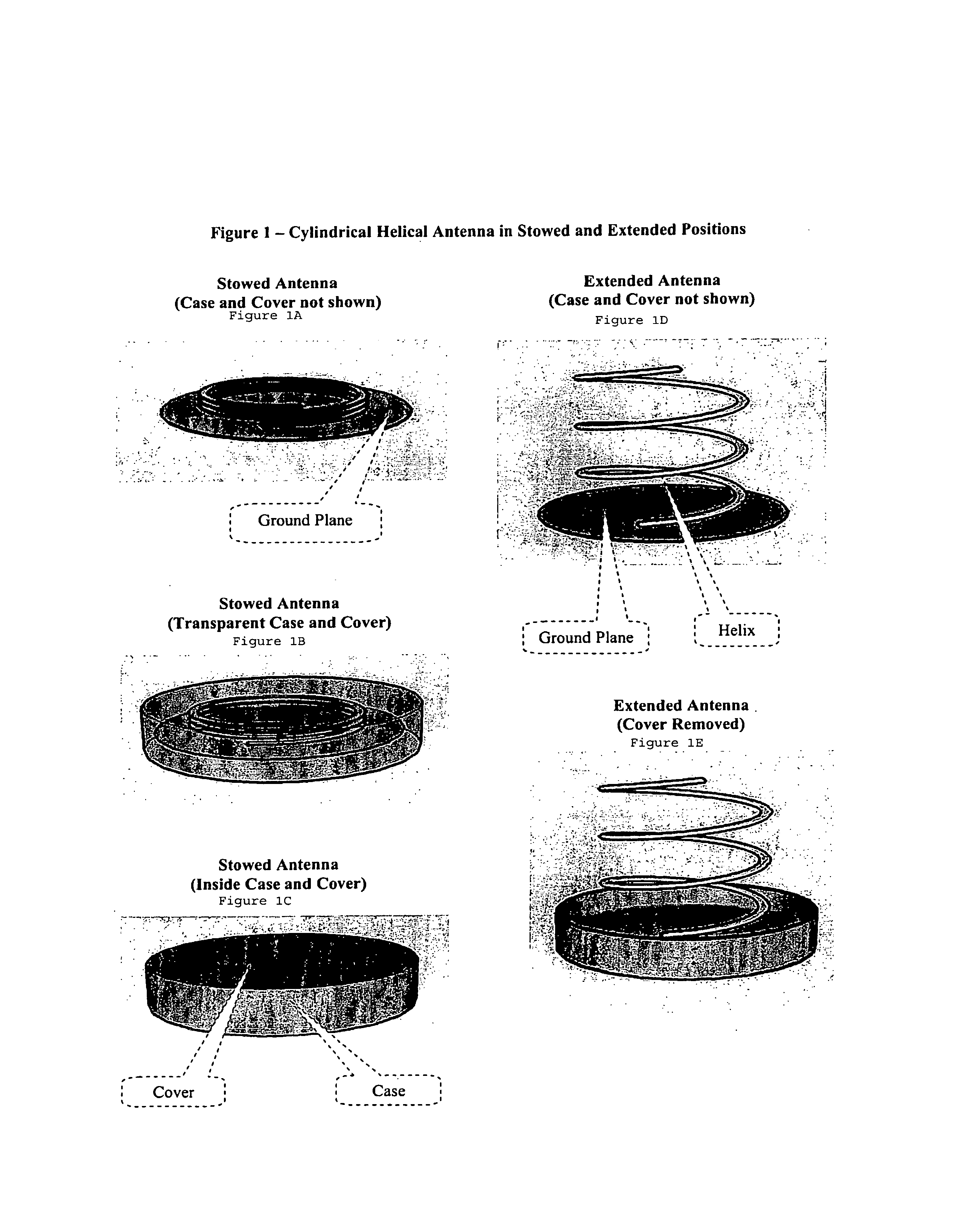
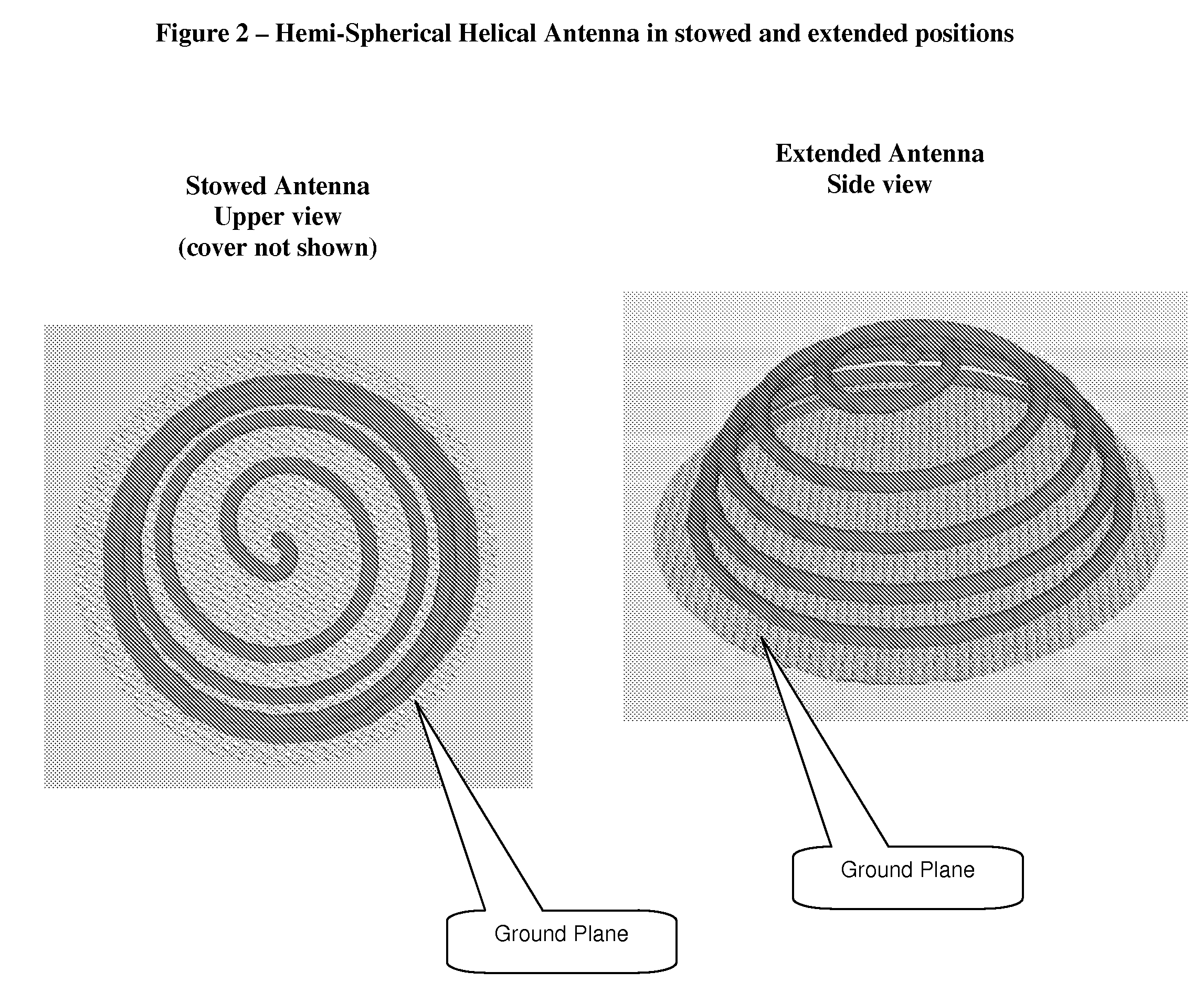
Extendable helical antenna for personal communication device
ActiveUS7586463B1Substantial electromagnetic decouplingOverall small sizeCollapsable antennas meansAntenna supports/mountingsGround planeHelical antenna
The present invention discloses a portable personal communication device with an extendable helical antenna. This helical antenna is made of an elastic conductive spring, configured to change its height over a ground plane and along the antenna axis, mainly having two positions: a stowed position where the antenna is pressed down between the ground plane and a rigid cover, achieving a low profile; and an operational position where the rigid cover is removed and the antenna is extended by its own spring force, to a higher height, improving antenna gain. Normally, a second planar antenna may be placed over the same ground plane, not exceeding the footprint of the helical antenna, thus utilizing a compactly small volume and yet achieving a considerable electromagnetic decoupling between the antennas, due to their different radiation patterns. According to one embodiment, these antennas are installed in a Personal Locator Beacon (PLB) for Search and Rescue (SAR) of people in distress, where the planar antenna is coupled to a Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS, such as GPS) receiver, and the helical antenna is coupled to a VHF / UHF radio.
Owner:MOBIT TELECOM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com