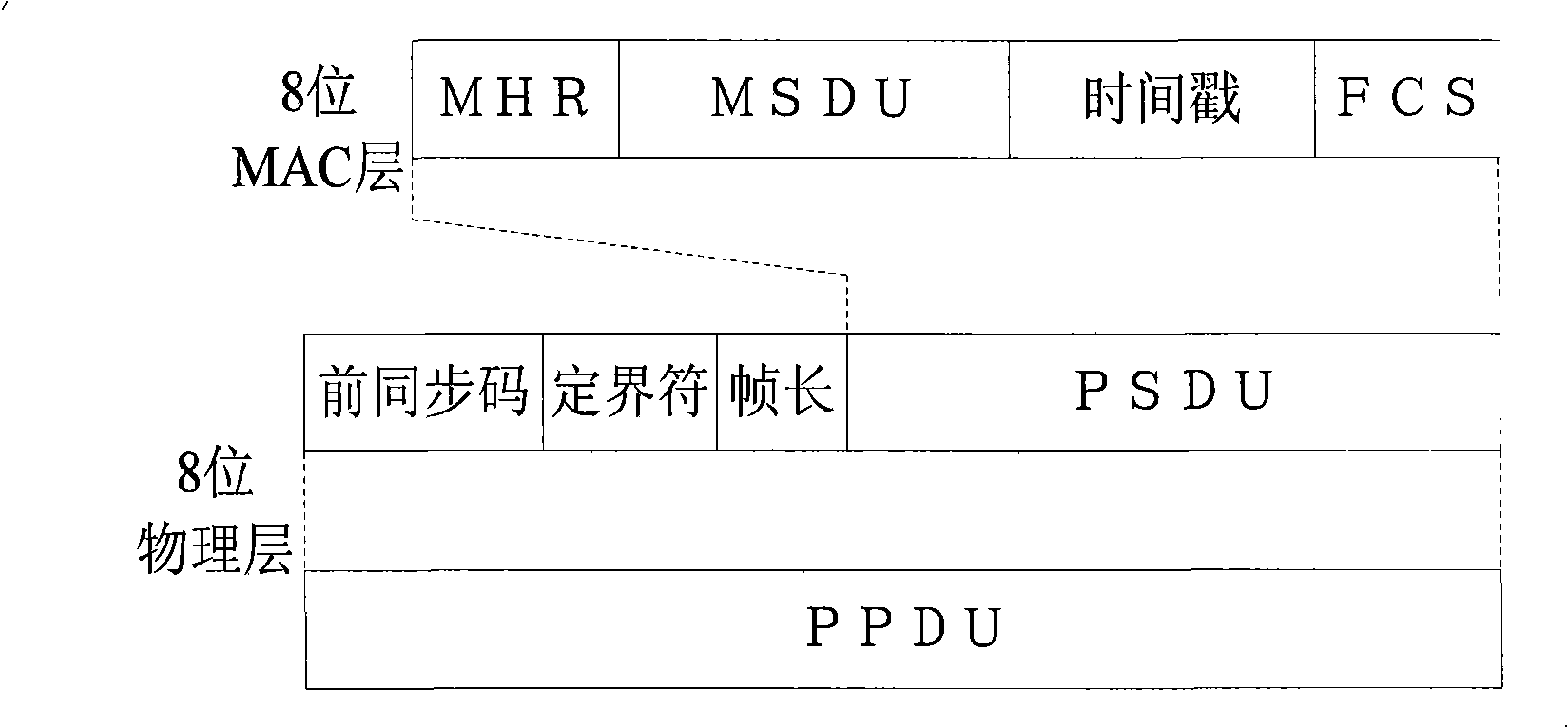
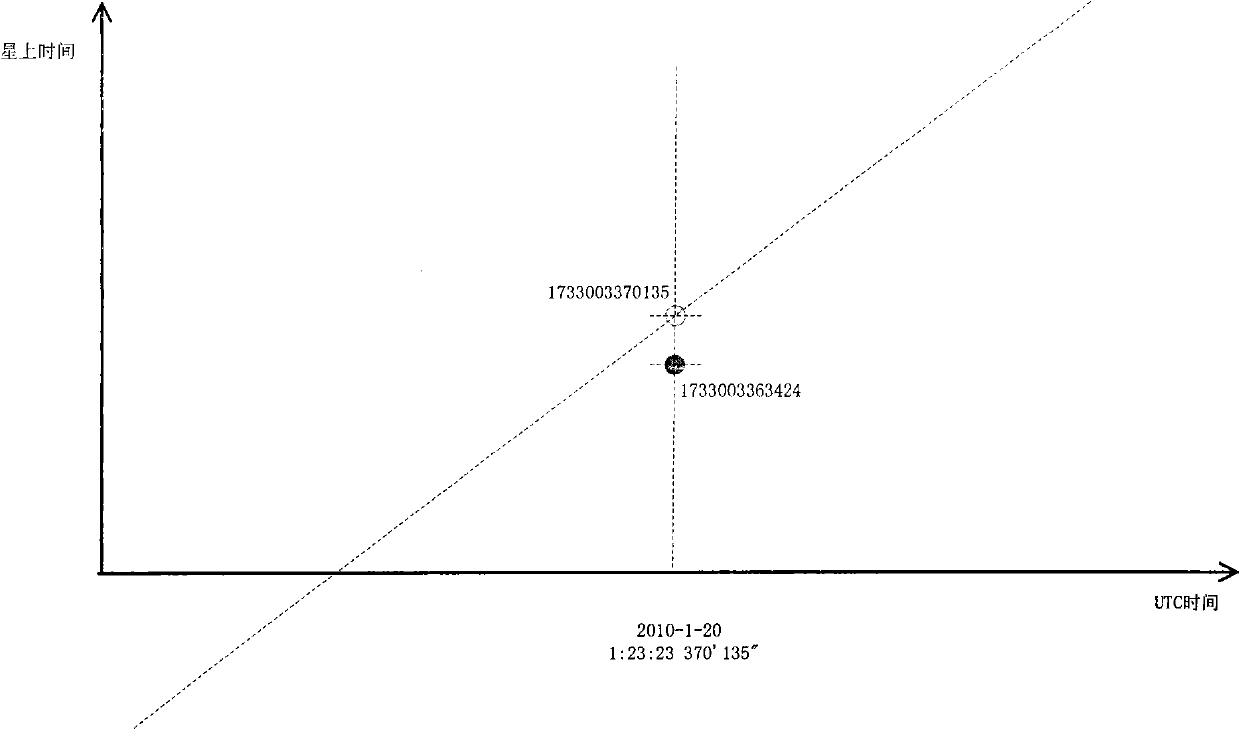
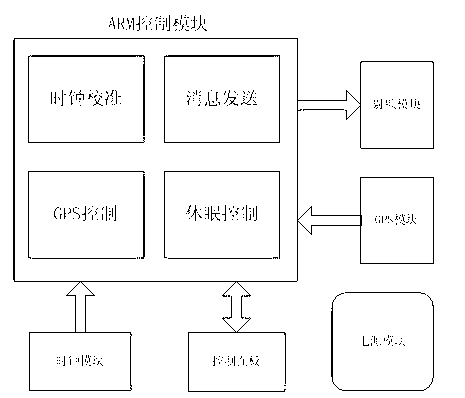
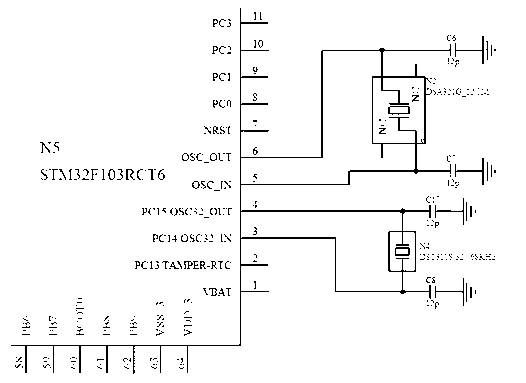
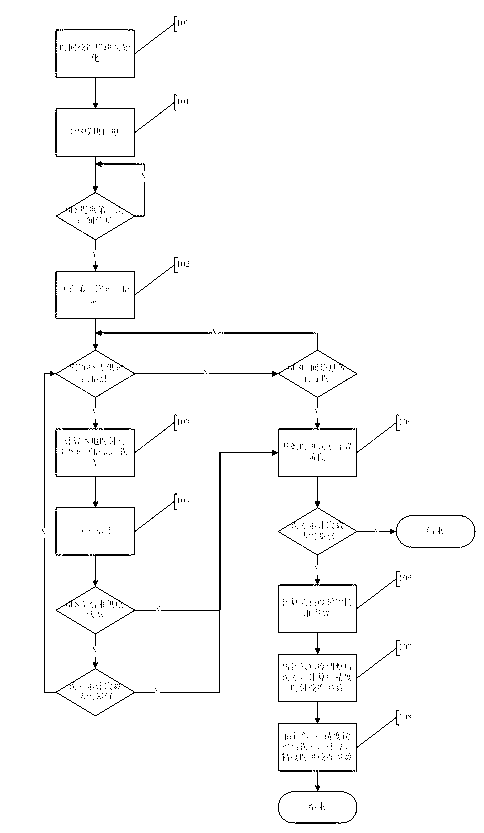
Patents
Literature
146 results about "Universal Time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Universal Time (UT) is a time standard based on Earth's rotation. It is a modern continuation of Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), i.e., the mean solar time on the Prime Meridian at Greenwich, England. In fact, the expression "Universal Time" is ambiguous (when accuracy of better than a few seconds is required), as there are several versions of it, the most commonly used being Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) and UT1 (see § Versions). All of these versions of UT, except for UTC, are based on Earth's rotation relative to distant celestial objects (stars and quasars), but with a scaling factor and other adjustments to make them closer to solar time. UTC is based on International Atomic Time, with leap seconds added to keep it within 0.9 second of UT1.
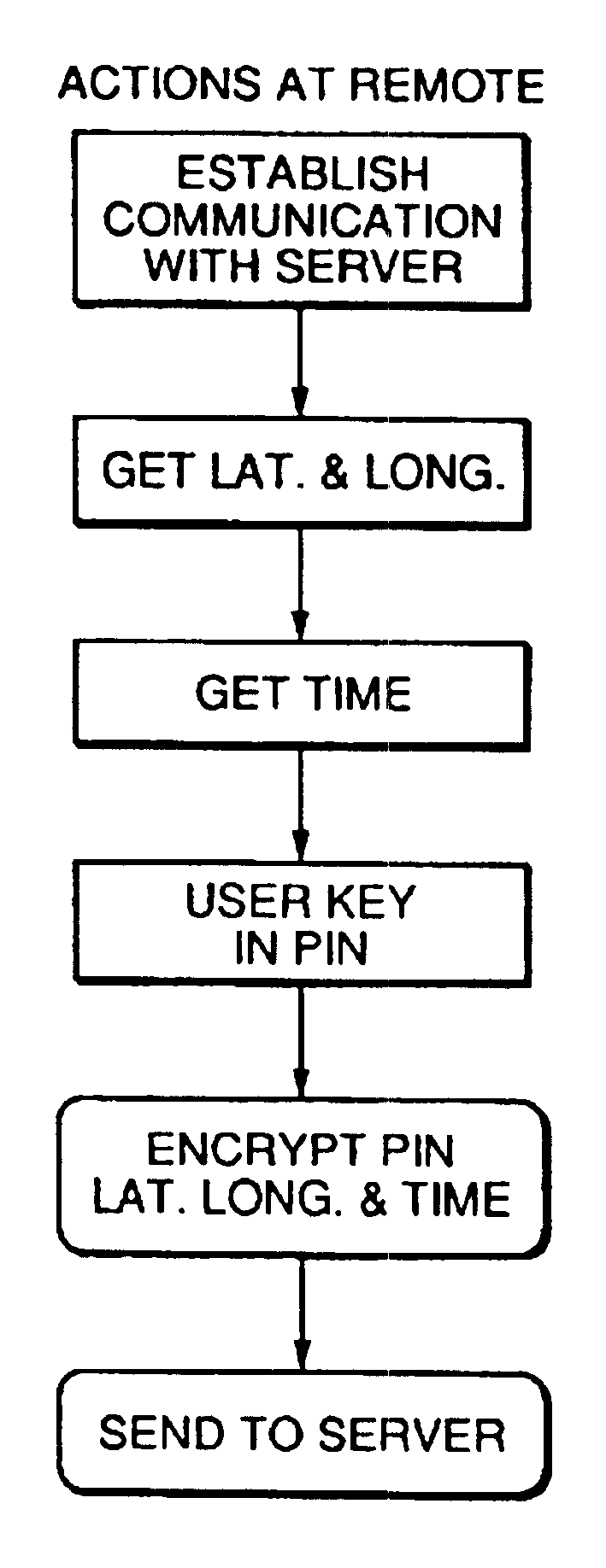
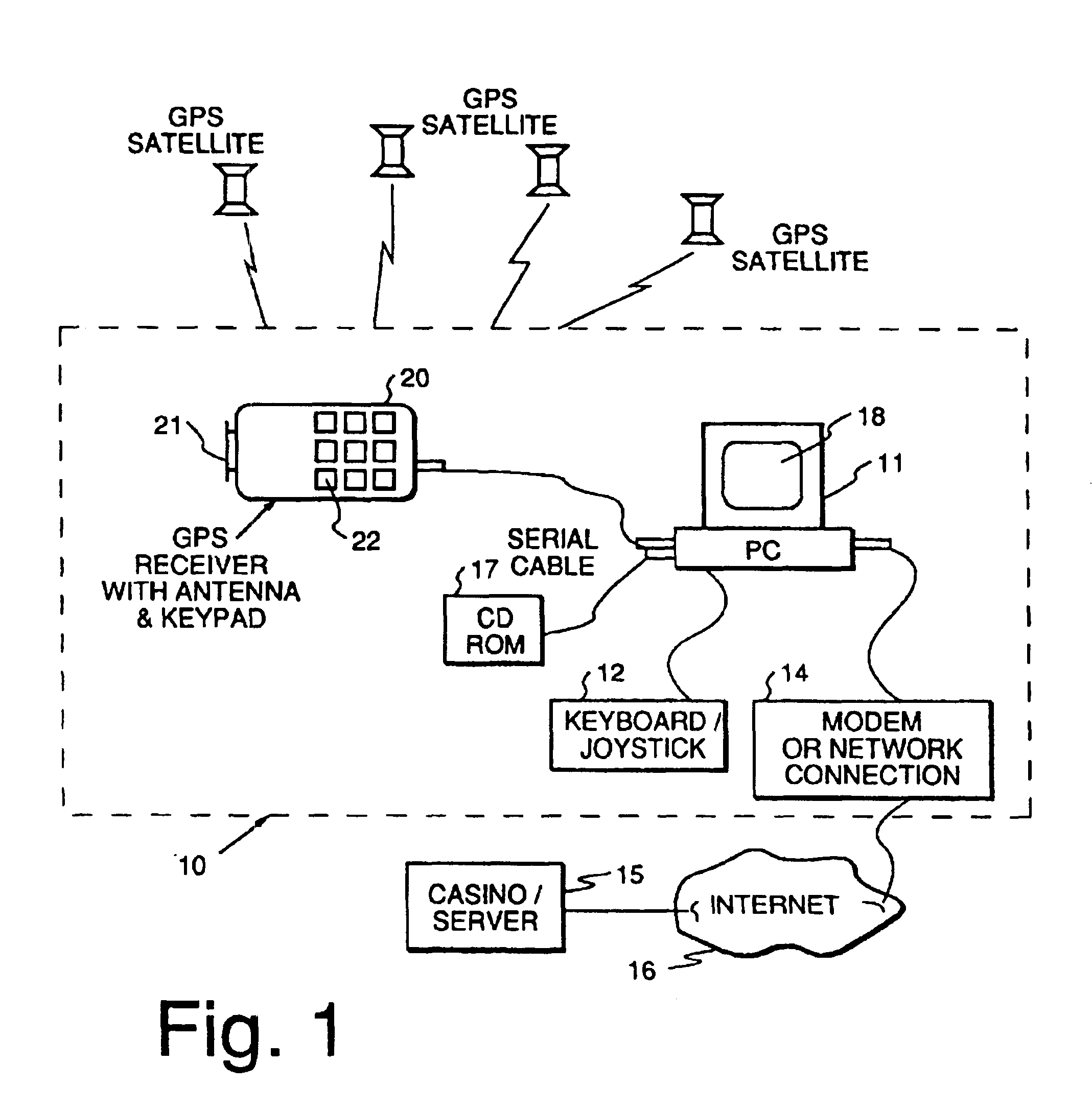
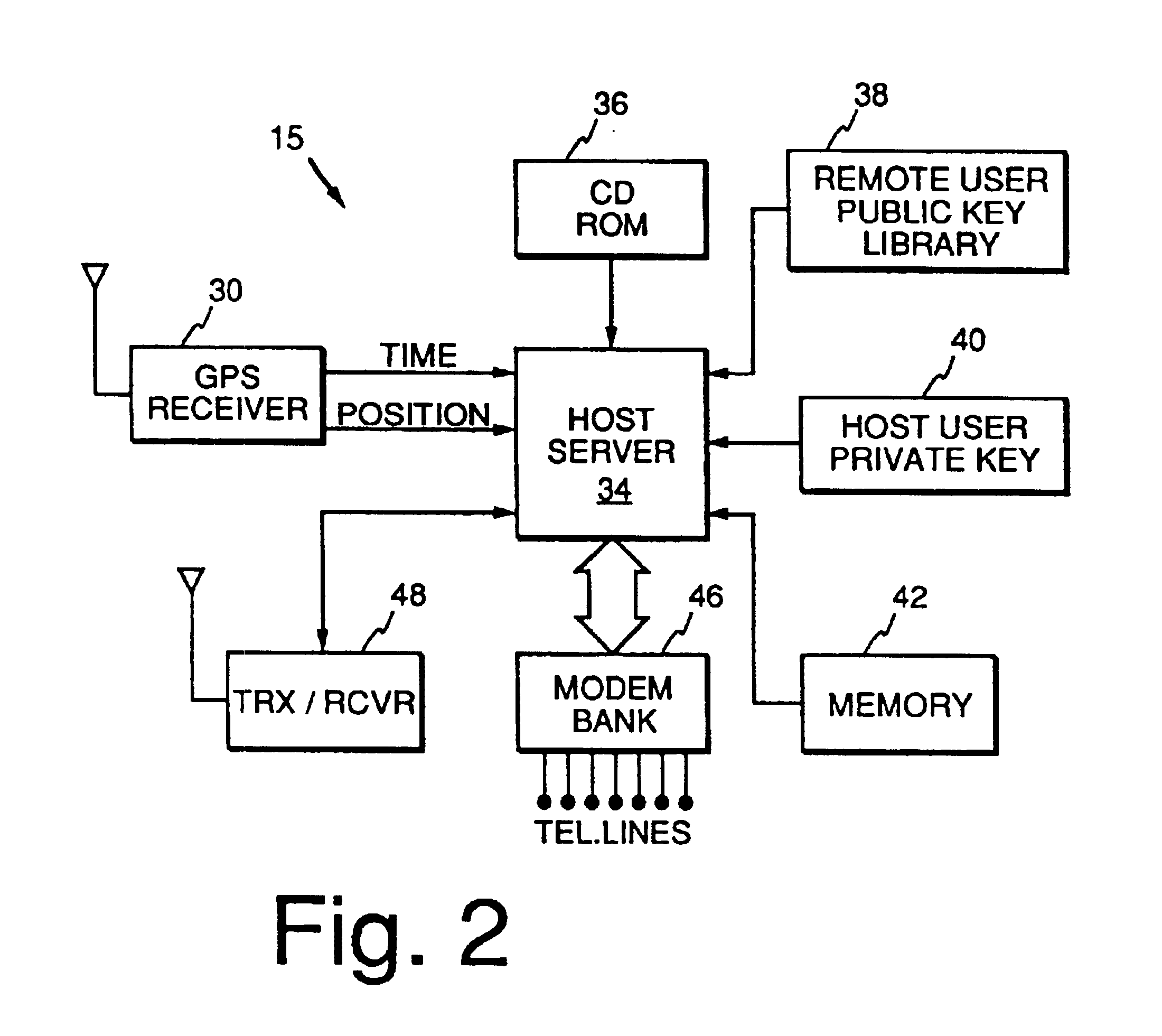
Method and apparatus using geographical position and universal time determination means to provide authenticated, secure, on-line communication between remote gaming locations
InactiveUSRE39644E1Facilitates denialAccurately determineSecret communicationApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingGeolocationThe Internet
Method and apparatus for providing authenticated, secure, on-line communication between remote locations including a user terminal adapted to enable a player in one location to remotely communicate via a communications medium such as the Internet with a gaming host in another location. Location of the remote user terminal, the host server and universal time are determined using means for accessing signals generated by geostationary navigational transmitters, such as in the global positioning satellite (GPS) system. Player authentication (identity verification) is determined by use of a personal identification number (PIN) and an electronic signature verification service. Security of communication is accomplished through use of a public-key / private-key encryption system. The remote user terminal may be comprised of one or more discreet components adapted to be used with a laptop or desktop personal computer (PC), or may be embodied in a stand alone or self-contained single unit that is portable and communicates via radio waves, telephone lines or the Internet to a host server.
Owner:IGT
Window flow control with common time reference
ActiveUS7307989B2Restrict levelData processing applicationsTime-division multiplexSlide windowData transmission
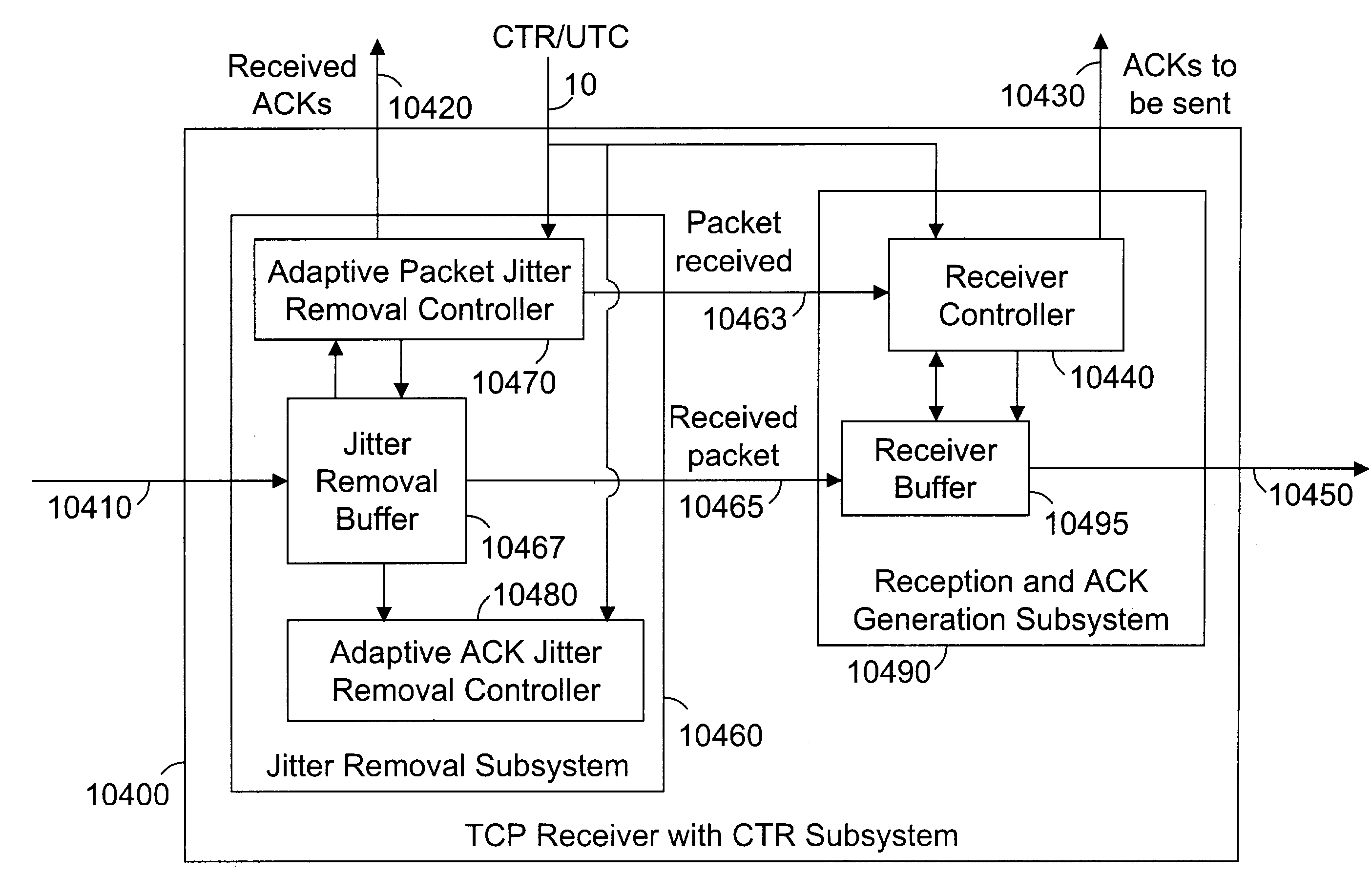
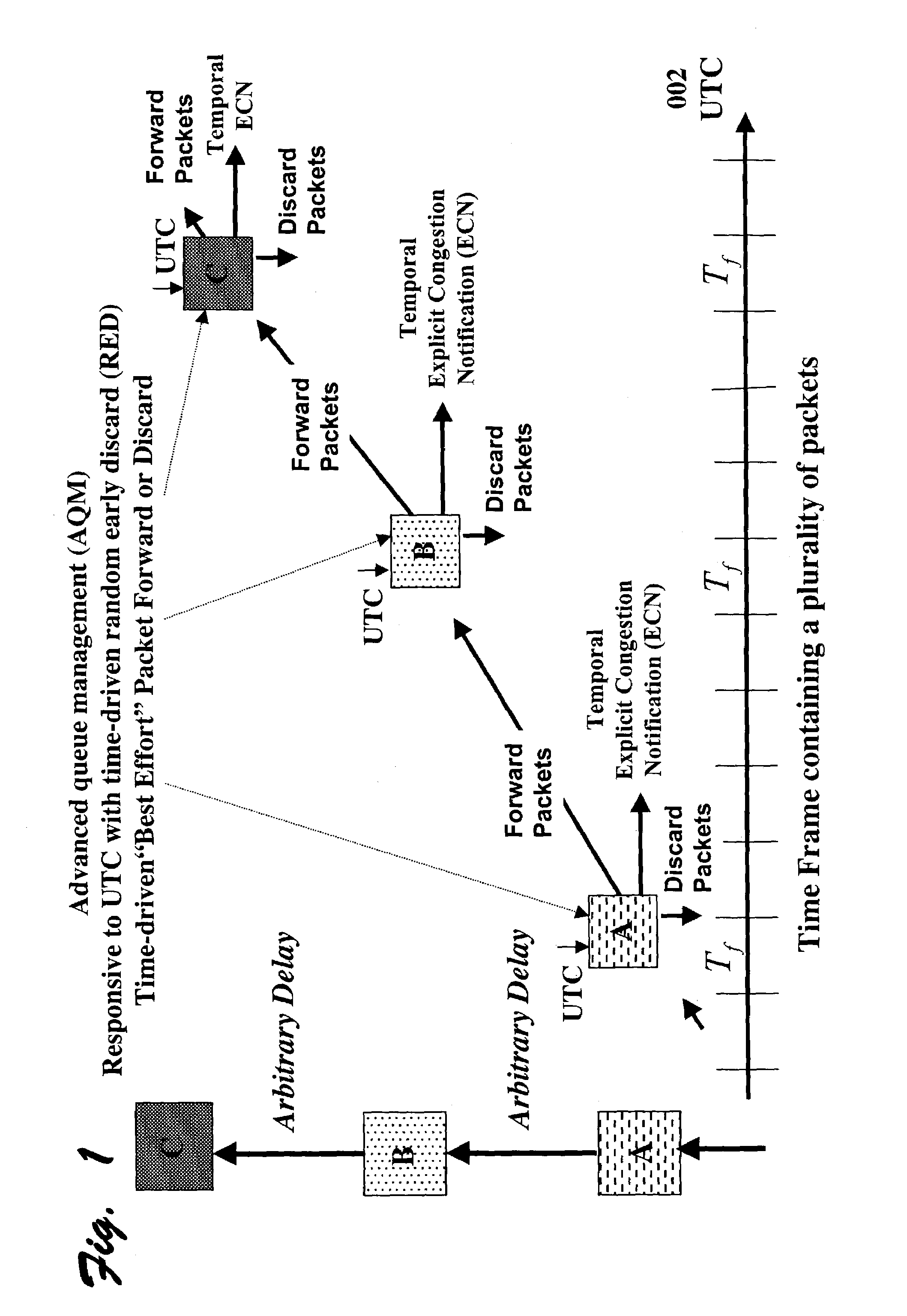
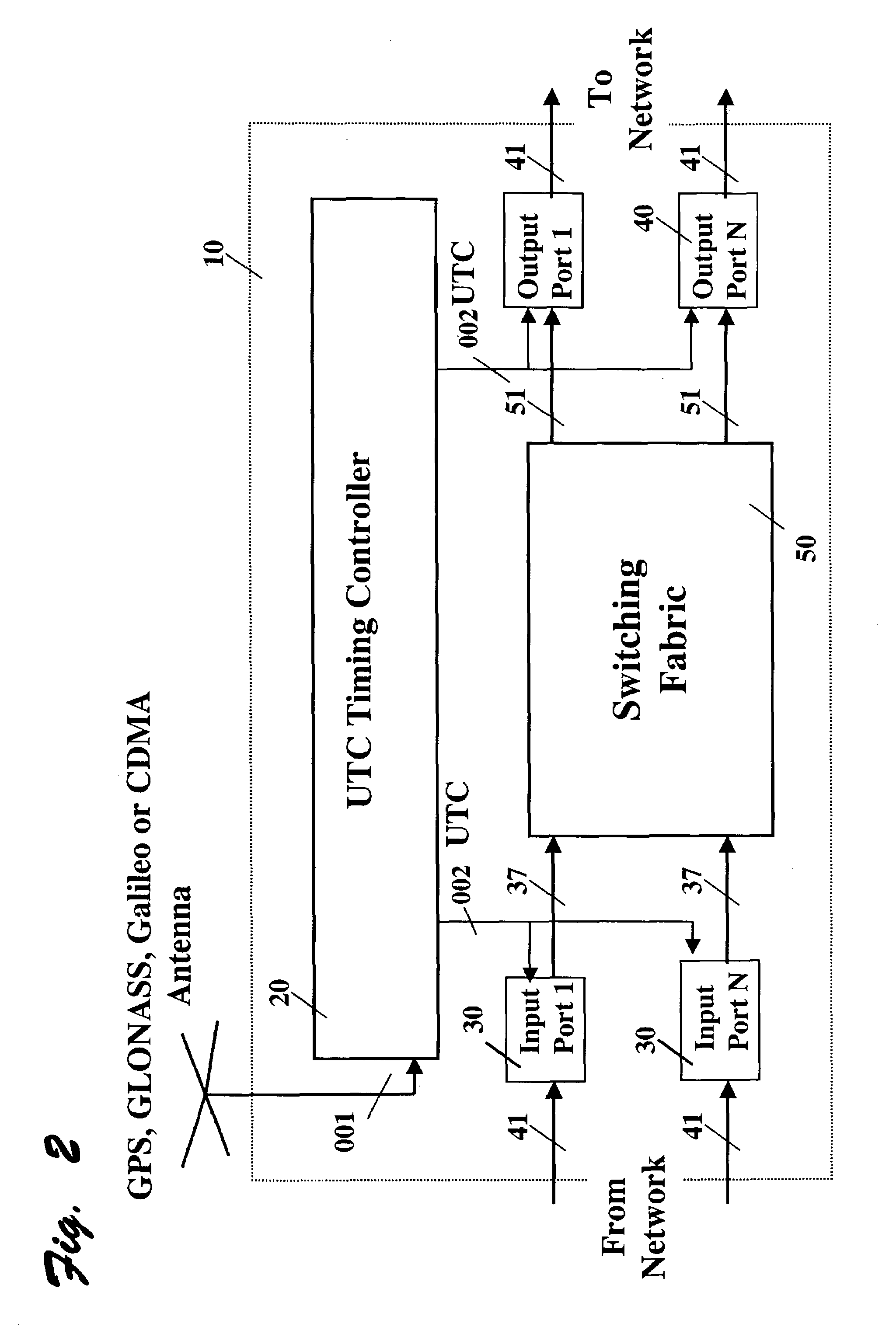
This invention relates generally to a method and apparatus for timely forwarding, discarding, and delivering data packets over the network and to their destination nodes and the optimization of data transfer throughput through the network. The timely forwarding and discarding are possible thanks to the standard global common time reference (CTR) that is known as UTC (Coordinated Universal Time). UTC is available from GPS (Global Positioning System), Galileo, and GLONASS (Global Navigation Satellite System). Data transfer throughput optimization is pursued by taking advantage of the timely forwarding and discarding properties to improve the data packets transfer flow control mechanisms, such as the sliding window re-sizing algorithm implemented by the widely deployed Transmission Control Protocol (TCP).
Owner:ATTESTWAVE LLC
System and method for enhancing recorded radio or television programs with information on the world wide web
ActiveUS20040133919A1Enhanced informationEasy access to informationTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionHyperlinkBroadcasting
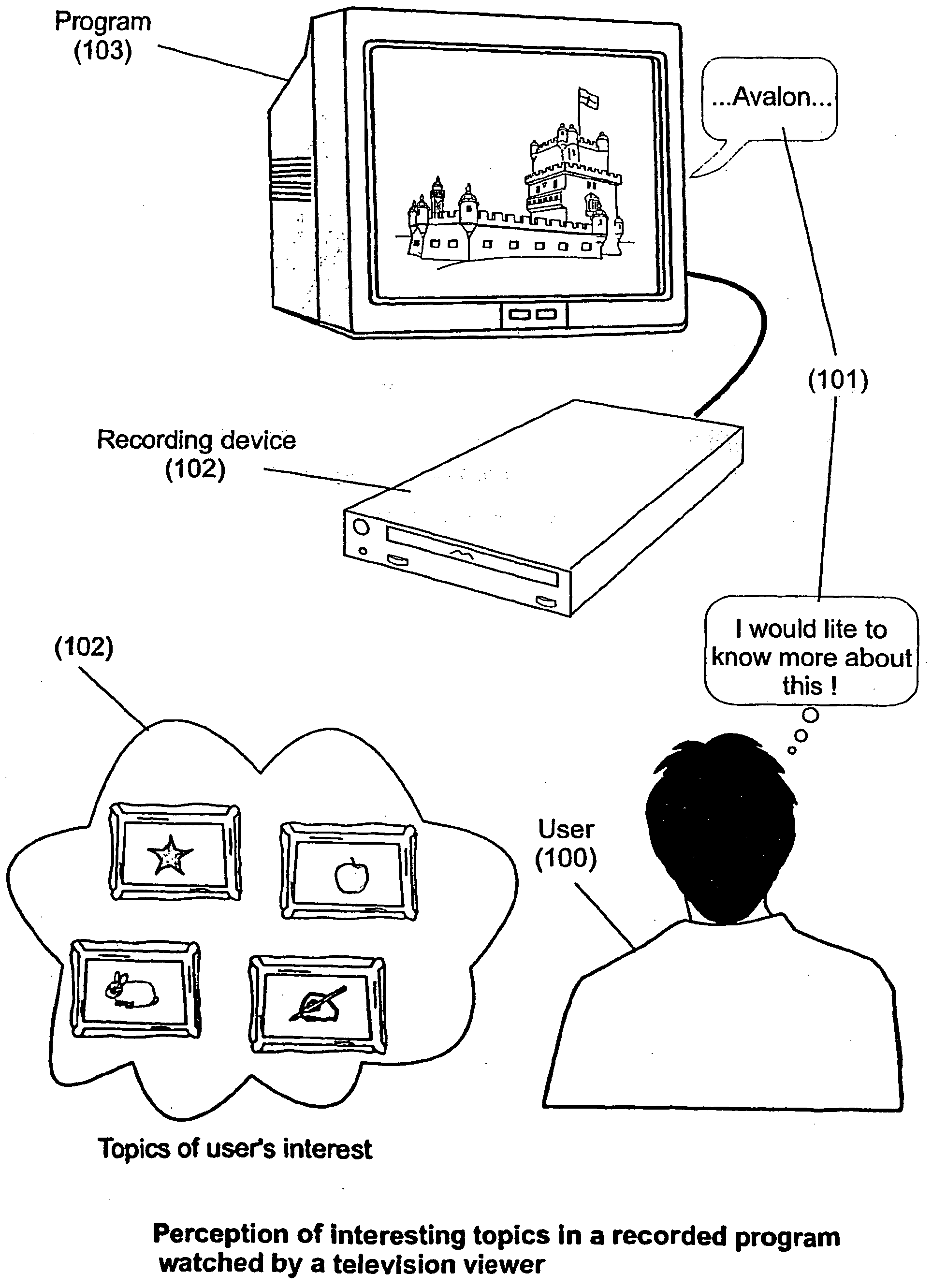
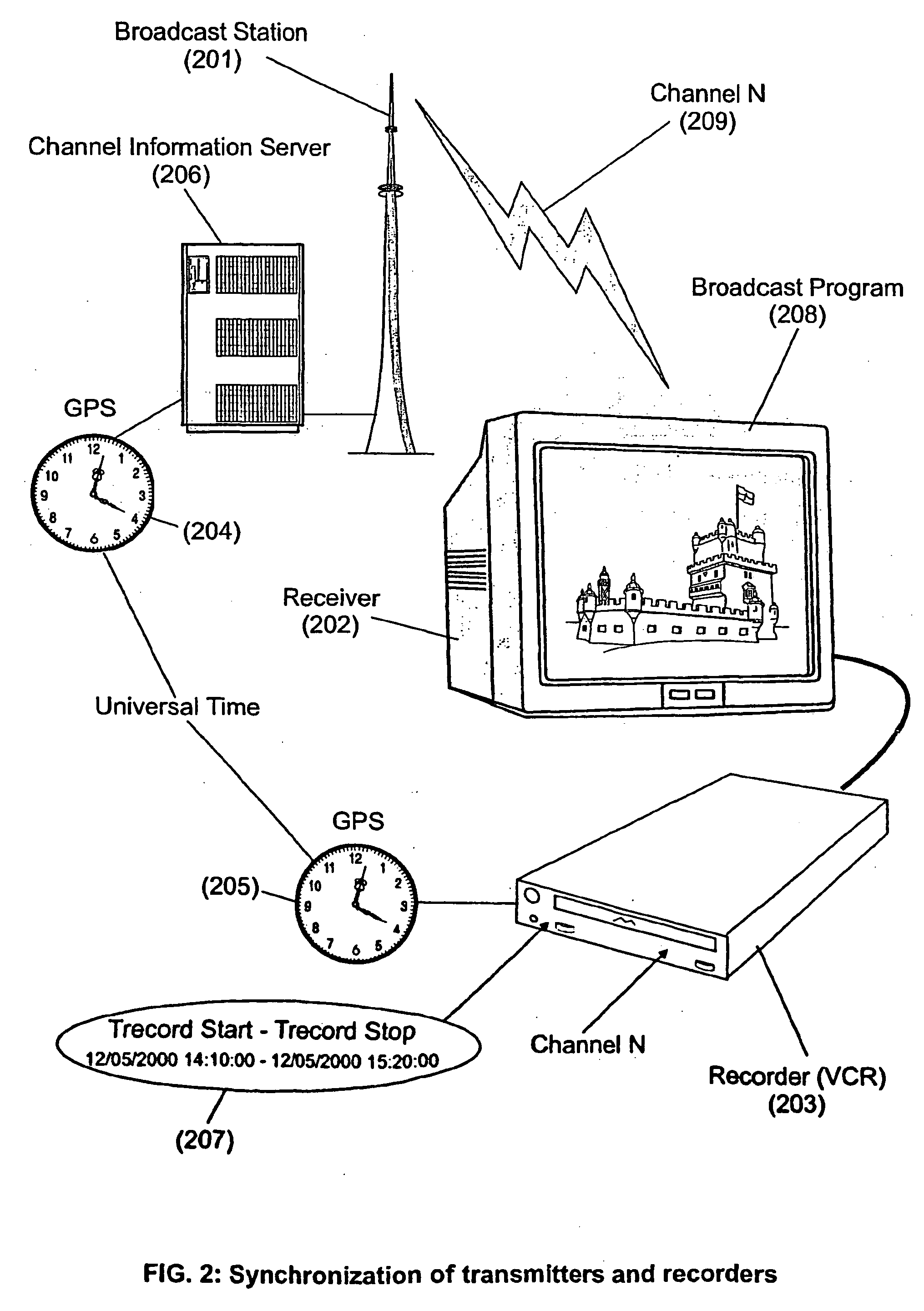
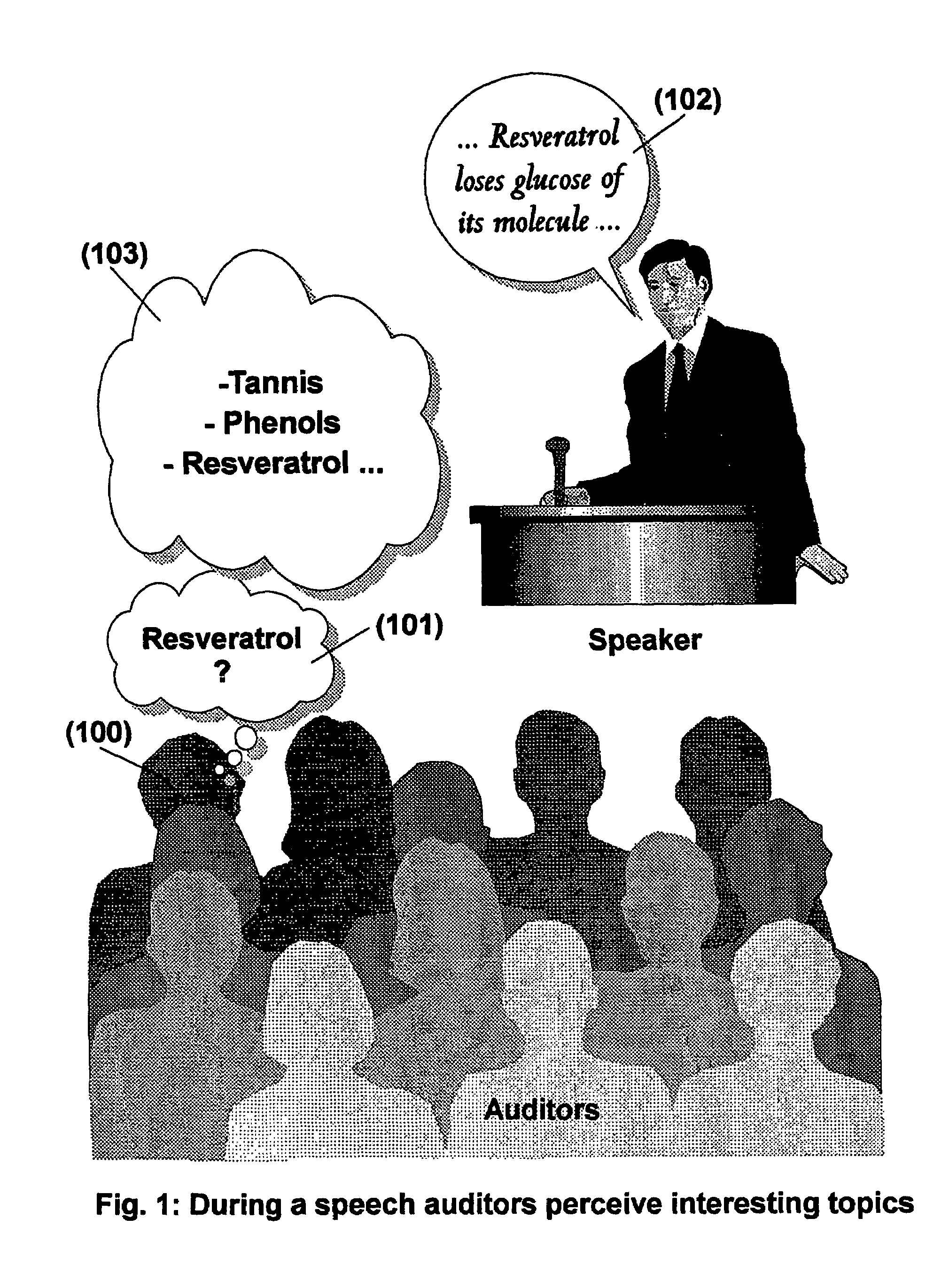
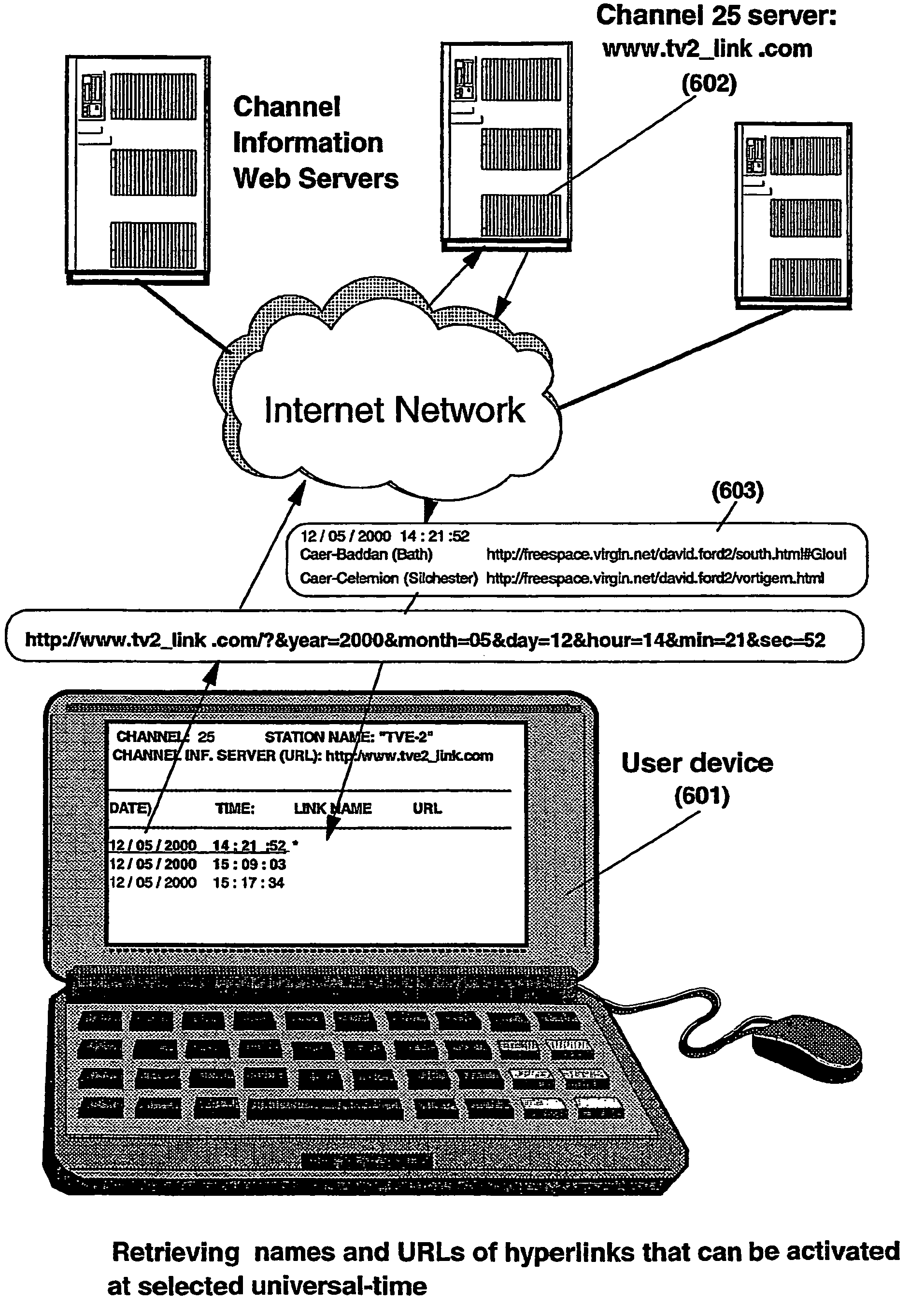
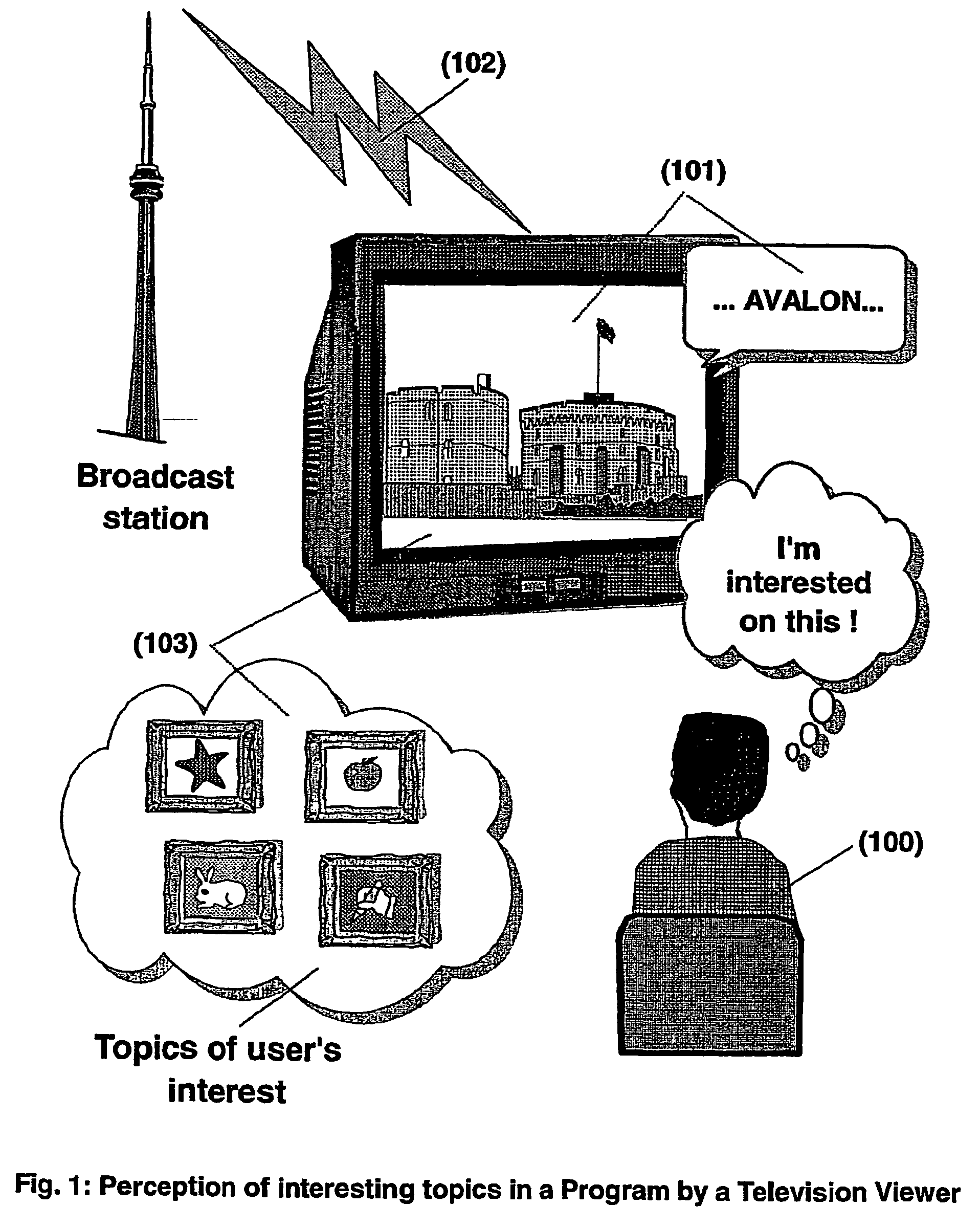
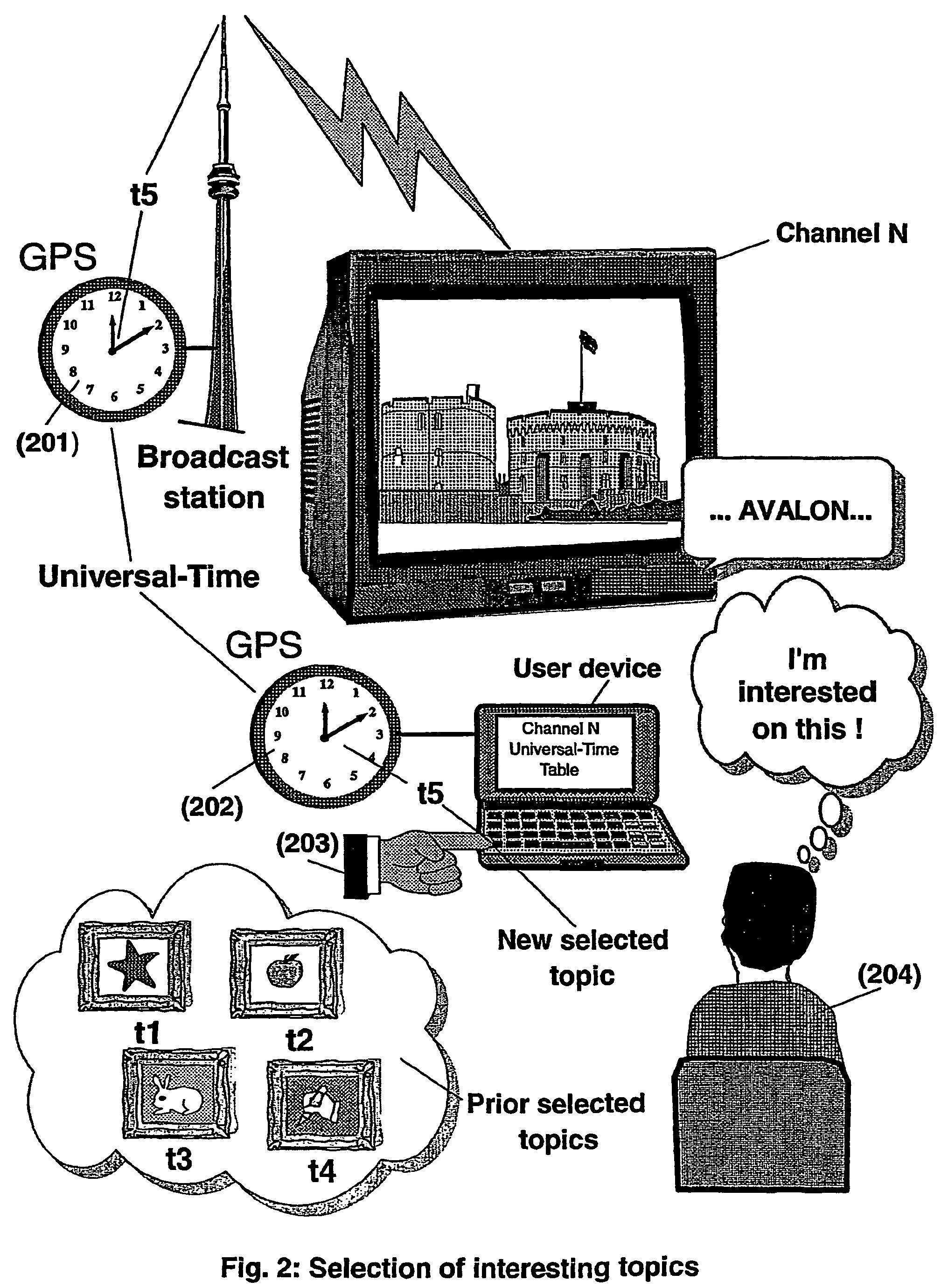
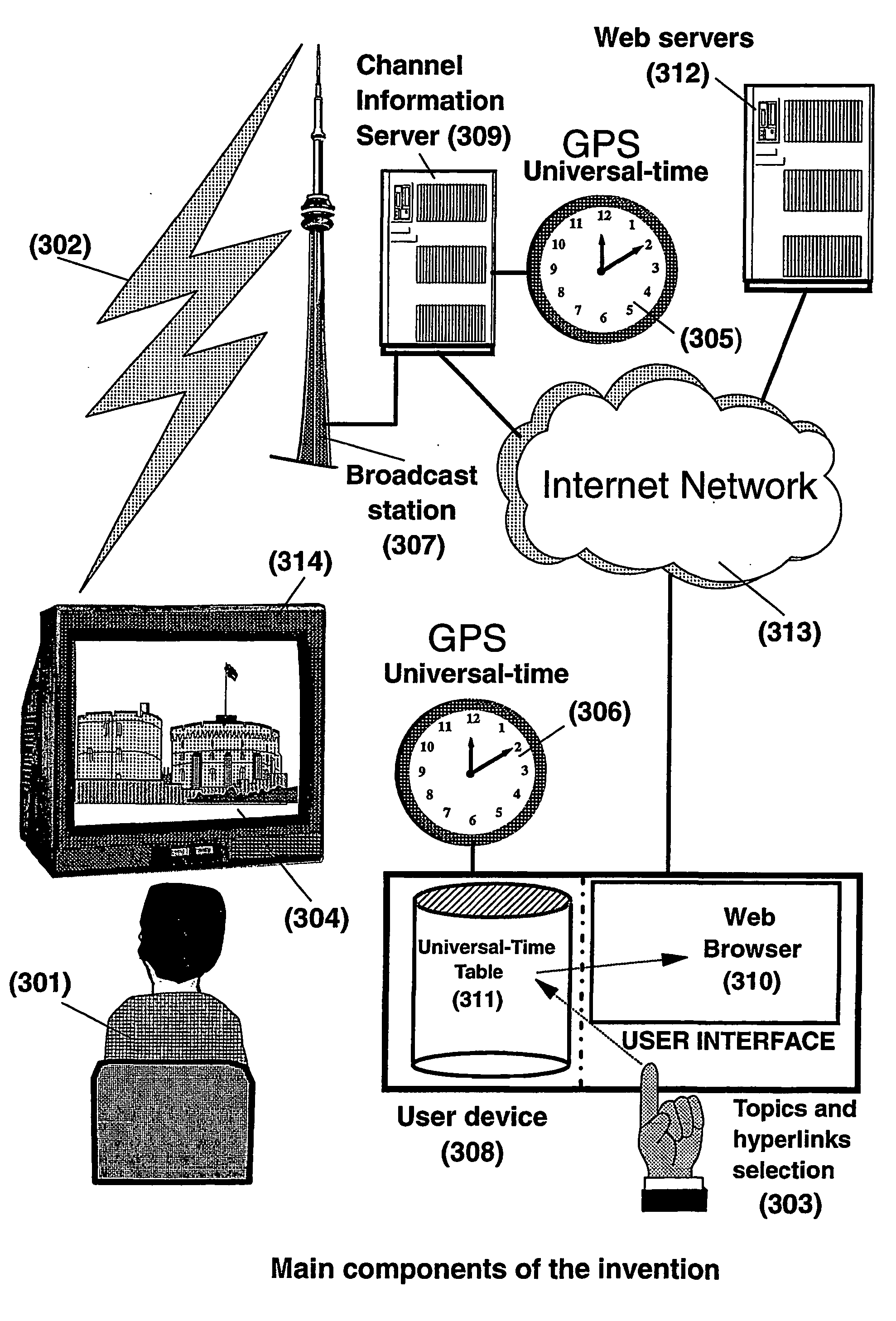
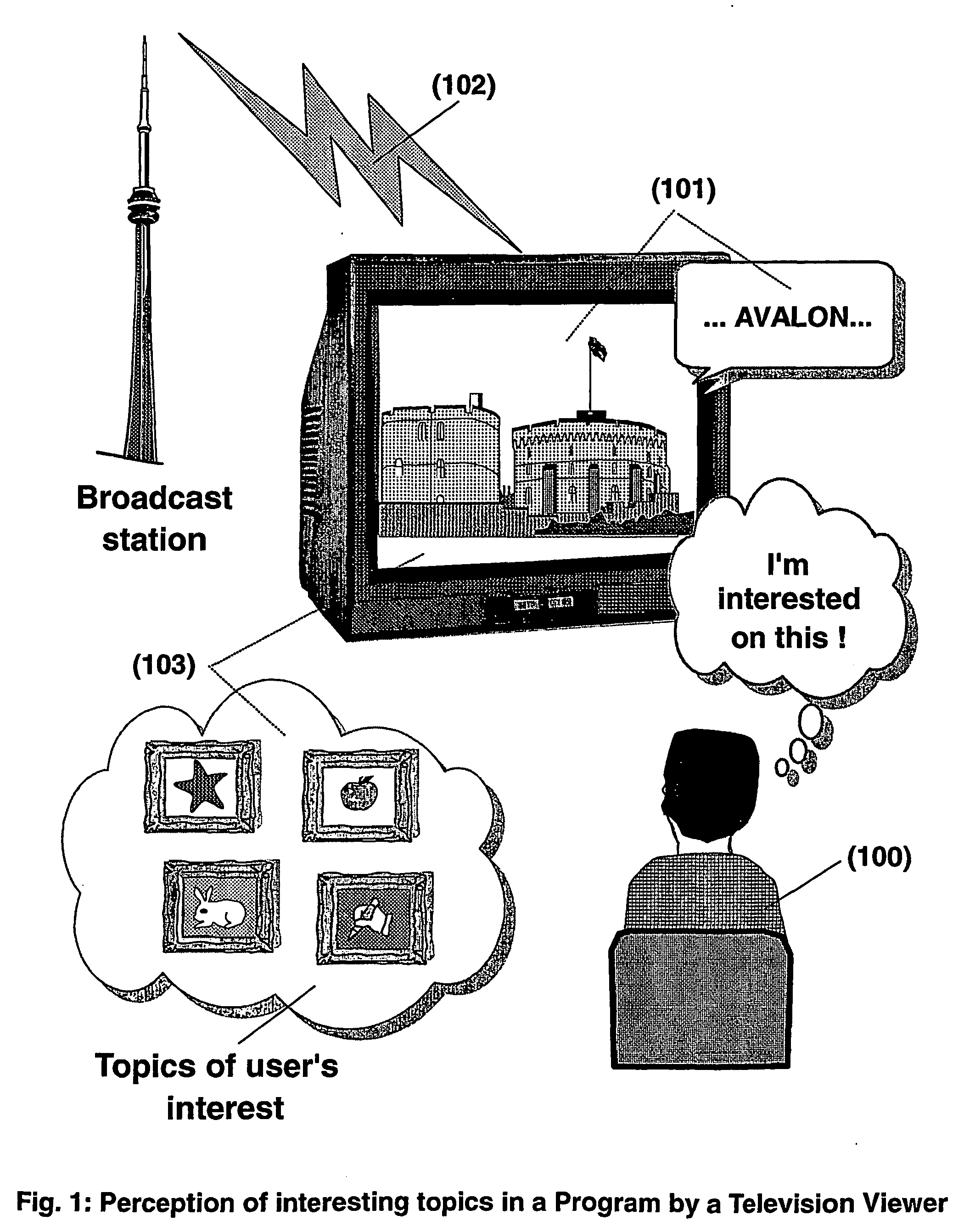
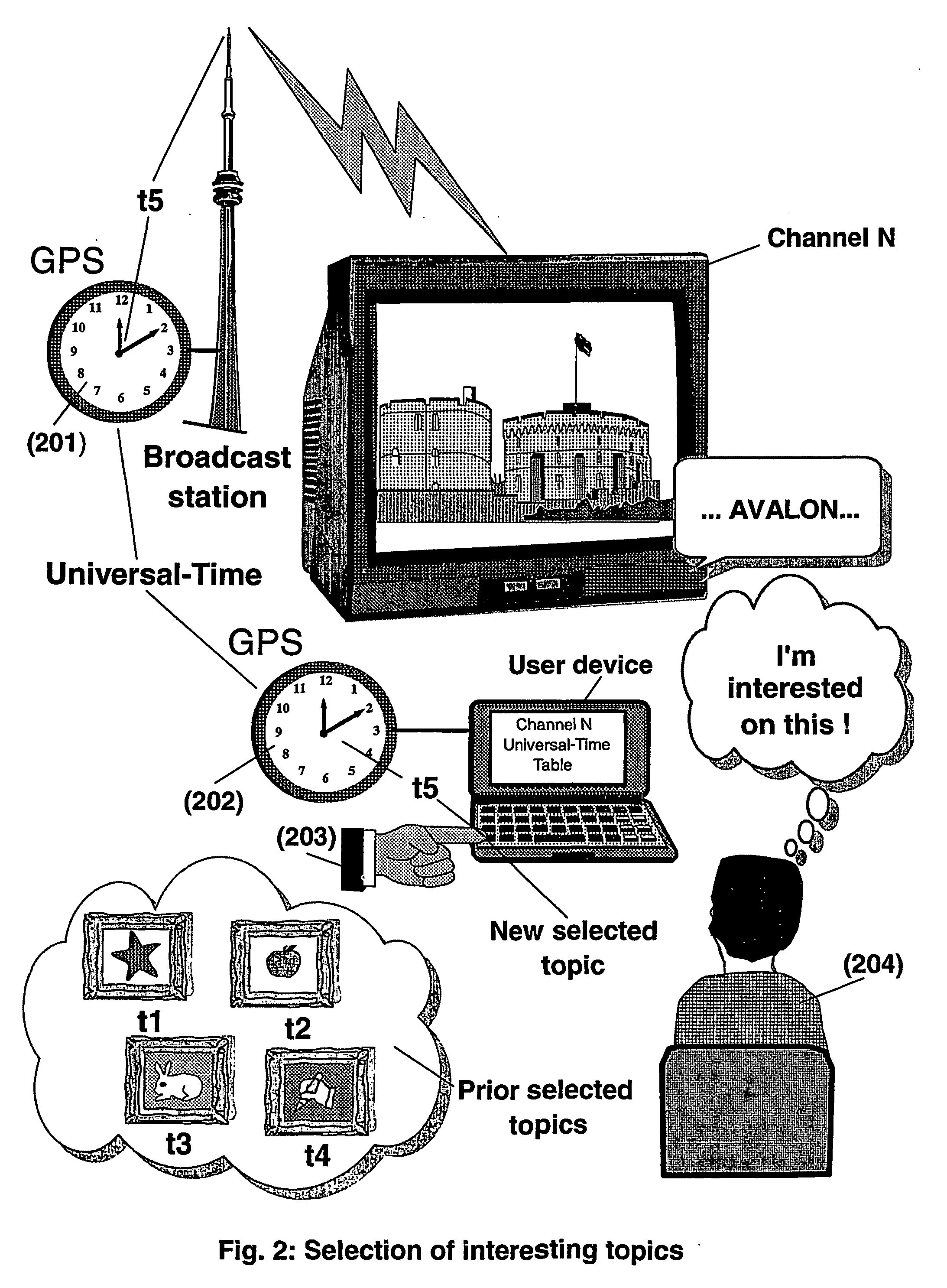
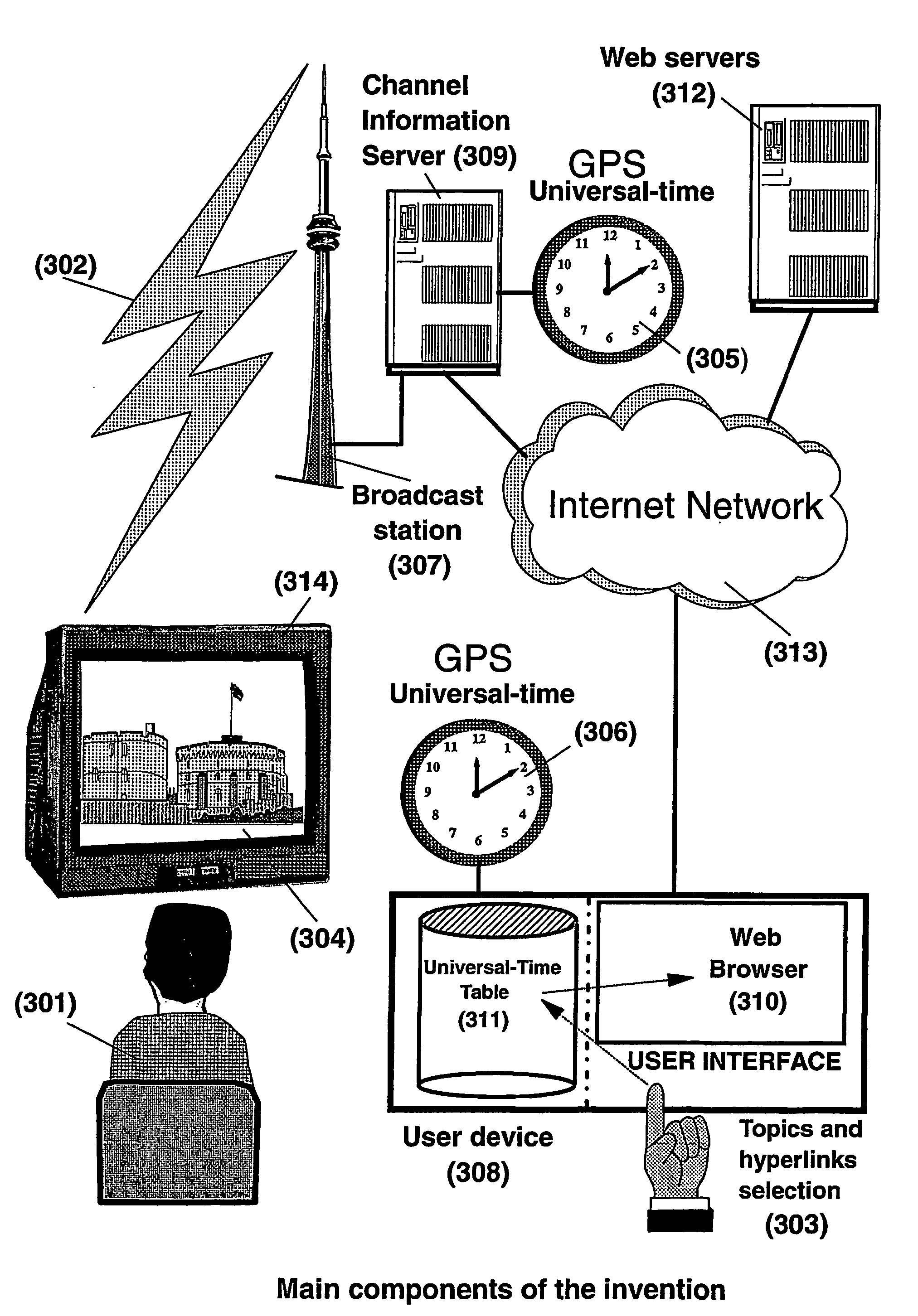
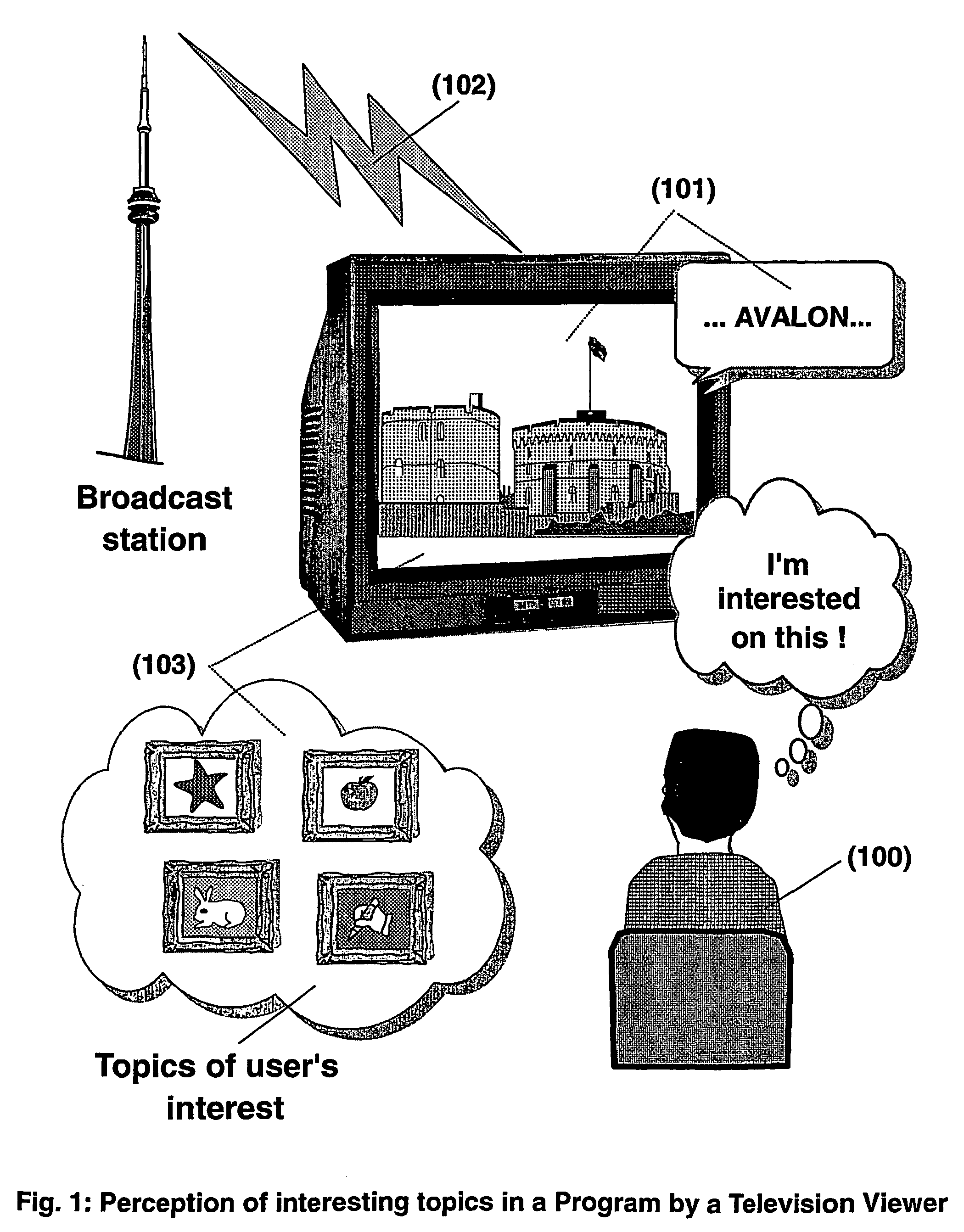
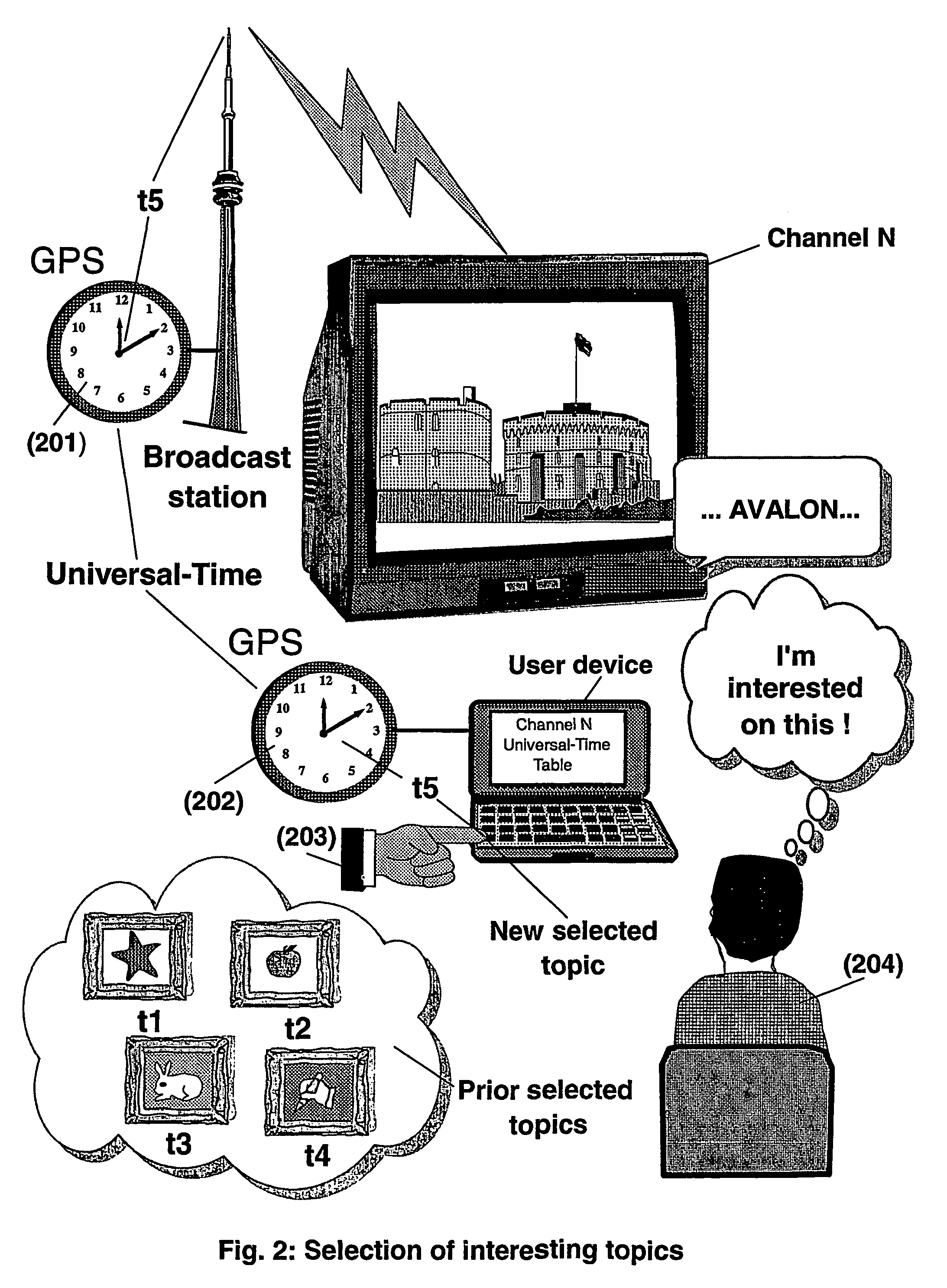
The present invention is directed to a system, method and computer program for enabling a user (100) (an auditor or a viewer) to access complementary information related to one or a plurality of sequences or topics of interest (102) in a recorded program (103) previously broadcast on the radio or television and played back on a device, such as an audio or video tape or disk recorder / player (104). The preferred embodiment of the invention relates to a system and method for enabling a person (100) listening to or watching a recorded program (103), to select one or a plurality of topics (101) (102) drawing his or her attention and for immediately receiving further information related to these topics from the World Wide Web. The system is based on the synchronization of local times (204) (205) of transmitters (201) and recorders (203). The flow of information transmitted, received and recorded is always synchronized, independently of the relative positions of recorders and transmitters. The synchronization is done referring to an absolute or universal time such as the Global Positioning System Time (GPS-time), the Global Orbiting Navigational Satellite System (GLONASS) time or another suitable universal time based on a satellite system. The GPS or GLONASS receivers are integrated or connected to the broadcasting stations. At the receiver side, GPS or GLONASS receivers may be integrated or connected to the audio or video recorders. The system is also based on a plurality of hyperlinks defined during the production and recording of the broadcast program, for given sequences corresponding to particular intervals of time synchronized with the universal (absolute) time. The hyperlinks are associated wit the information that is broadcast in the program. They can be selected by users during the playback of the recorded program during predefined intervals of time and activated to access additional information and services.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC +1
Satellite time synchronization system
ActiveCN102882586ATime uniform maintenanceRadio-controlled time-piecesRadio transmissionSensing dataTime information
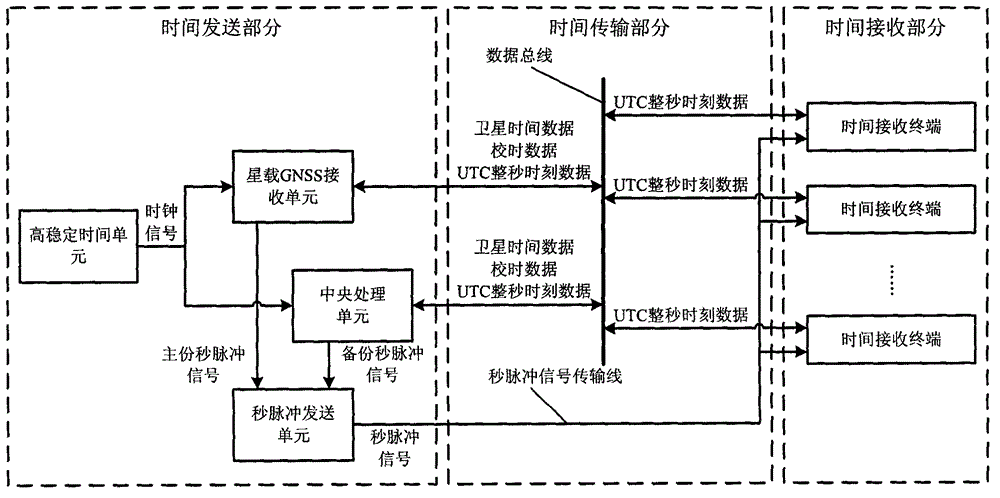
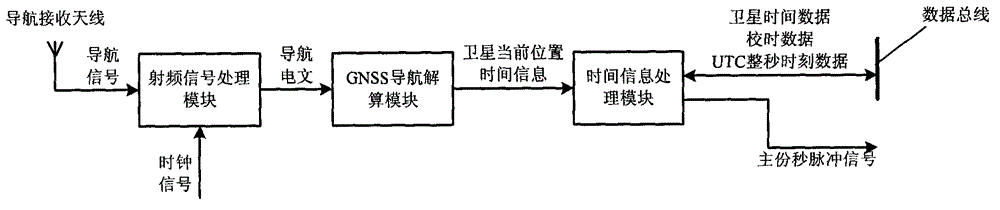
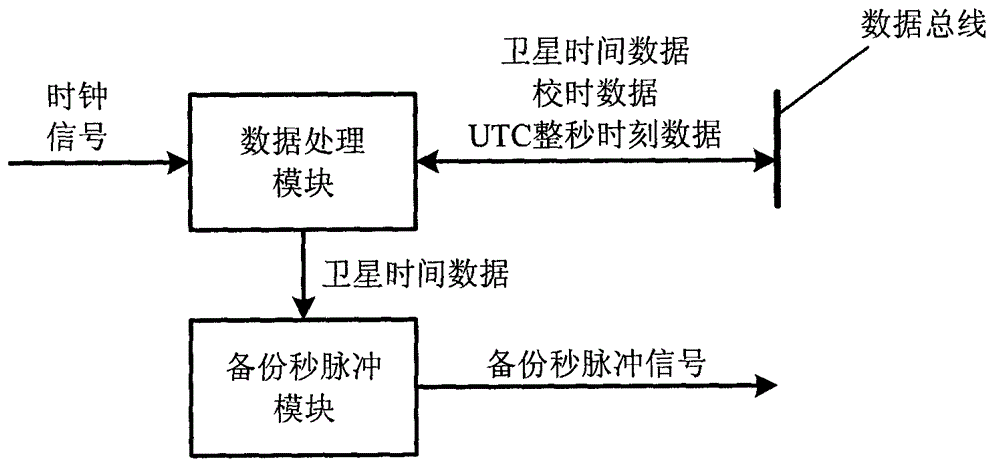
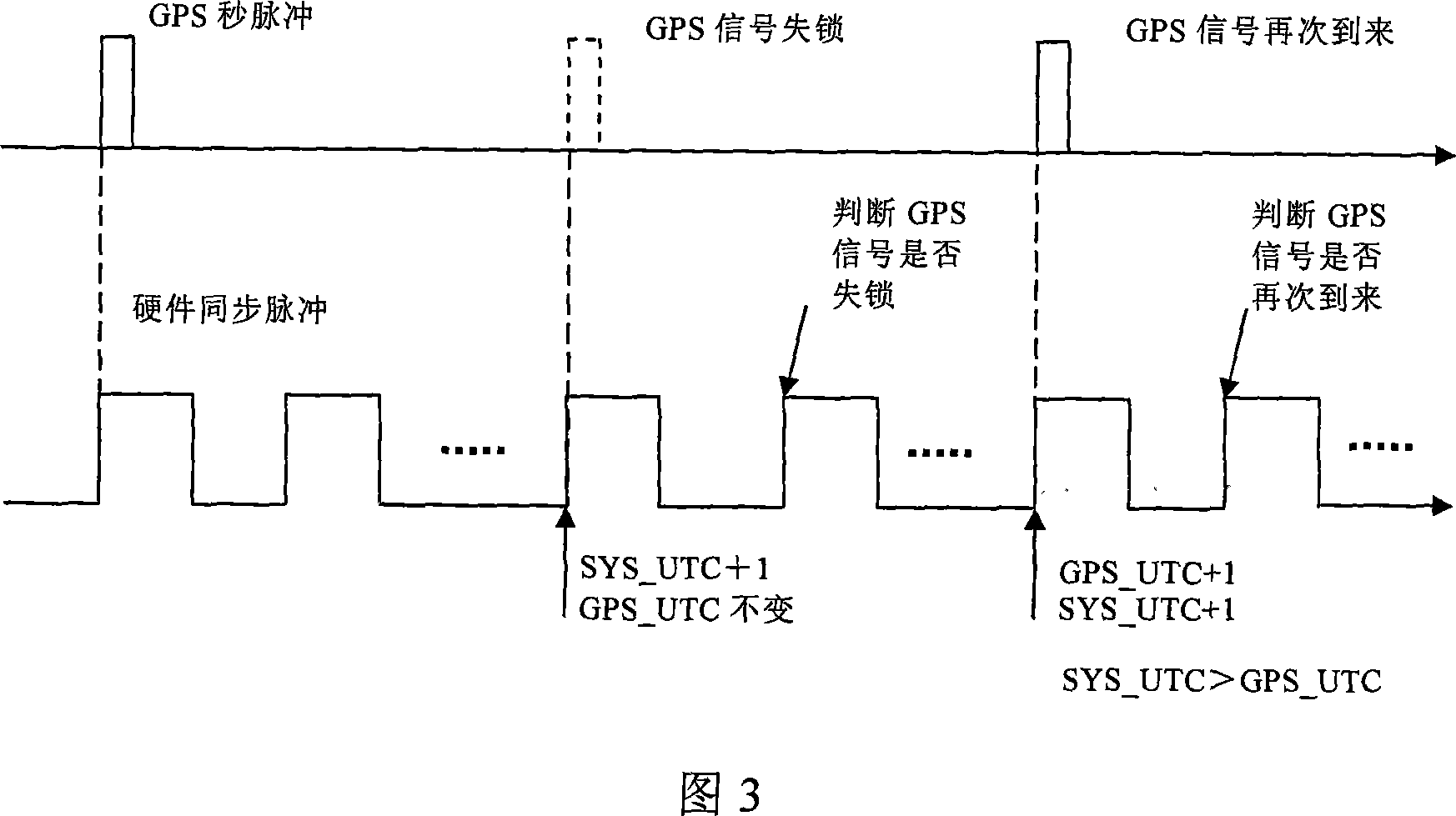
The invention discloses a satellite time synchronization system. The satellite time synchronization system comprises a time sending part, a time transmitting part and a time receiving part, wherein the time sending part generates accurate universal time coordinated (UTC) time by receiving a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) navigation signal, and sending out a pulse per second corresponding to a UTC whole second moment; the time transmitting part transmits the pulse per second and UTC whole second moment information corresponding to the pulse per second to the time receiving part; the time receiving part receives the pulse per second and the UTC whole second moment information corresponding to the pulse per second, pulse per second serves as a trigger point, and a local clock counts to obtain accurate current time. By adopting a high-precision satellite time synchronization system provided by the invention, each piece of measurement equipment for the satellite can work on the same time reference; measured data can be accurately matched according to the time information when processed on the ground; and the measurement precision of remote sensing data or scientific detection data is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
Adaptive packet routing
InactiveUS20040146056A1Congested or slow links can be automatically avoidedLower latencyError preventionTransmission systemsUniversal TimeReal-time computing
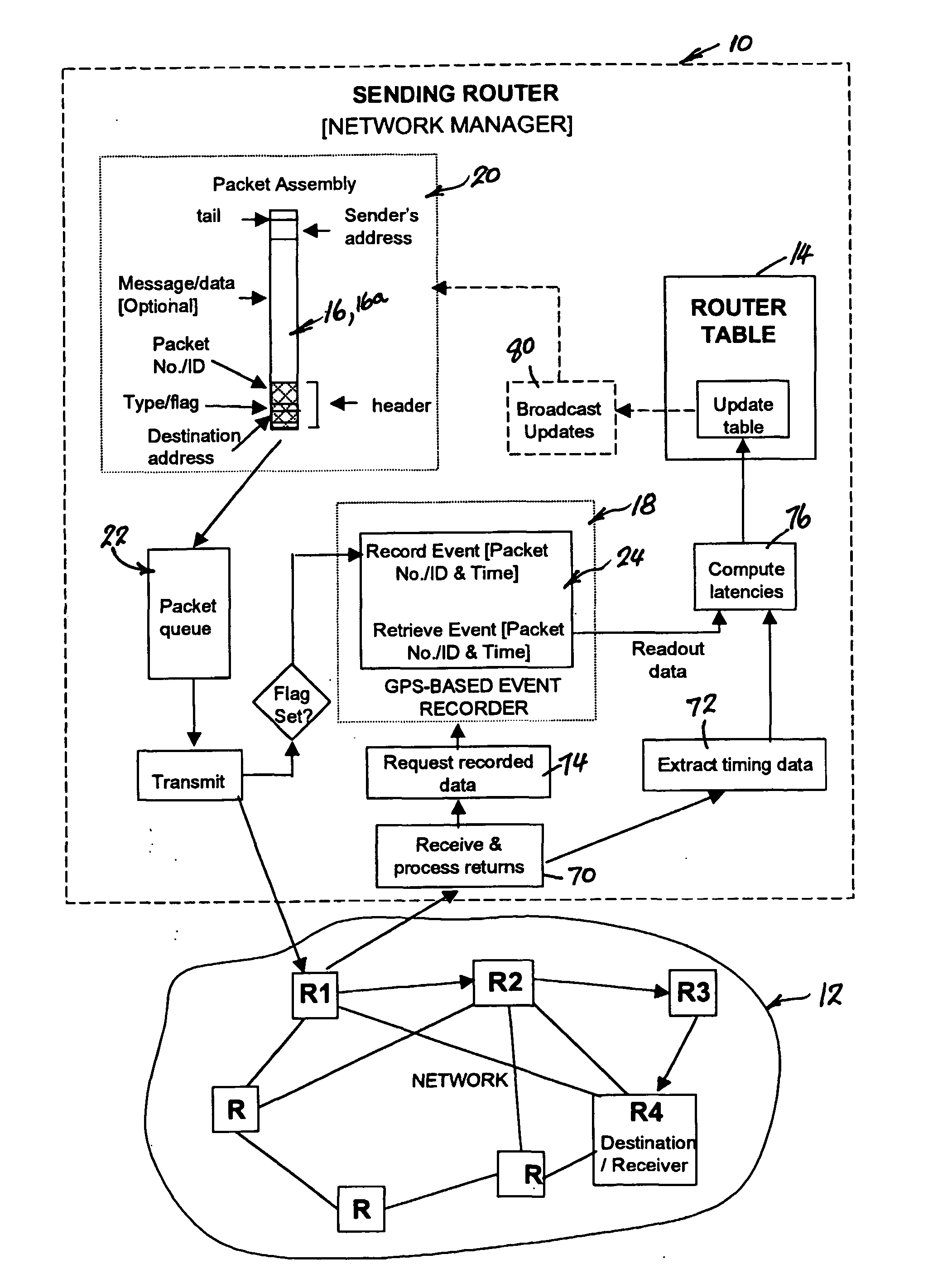
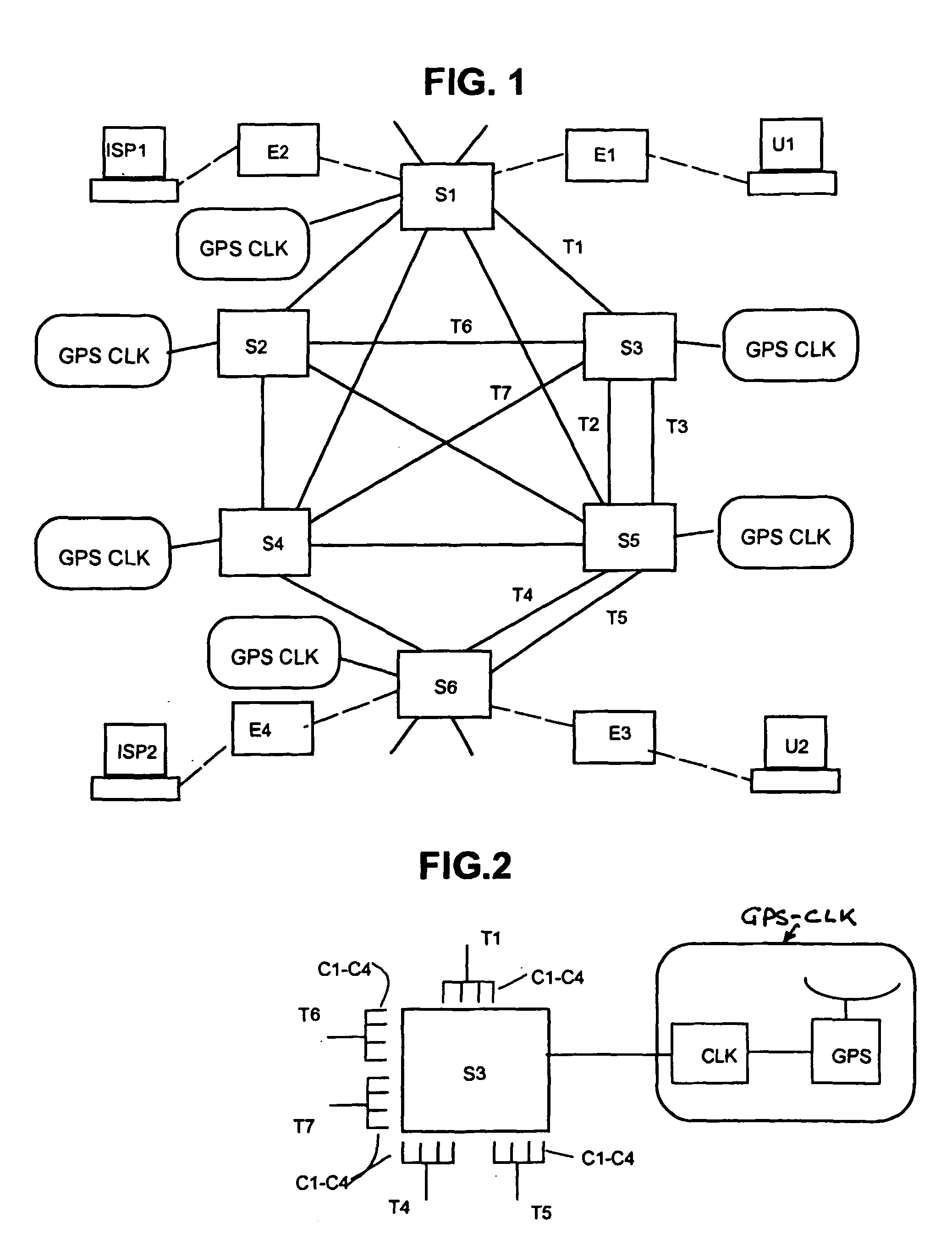
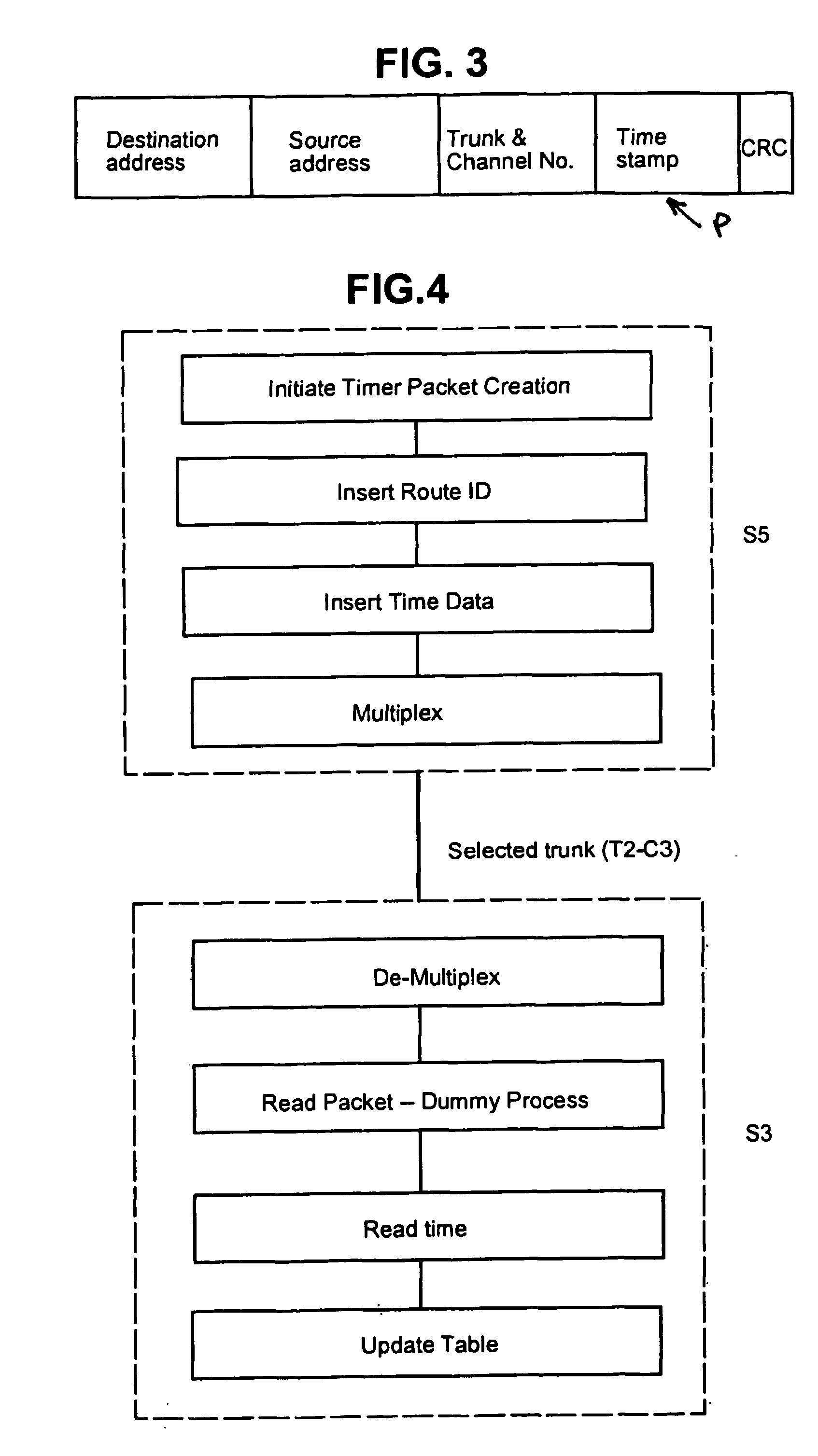
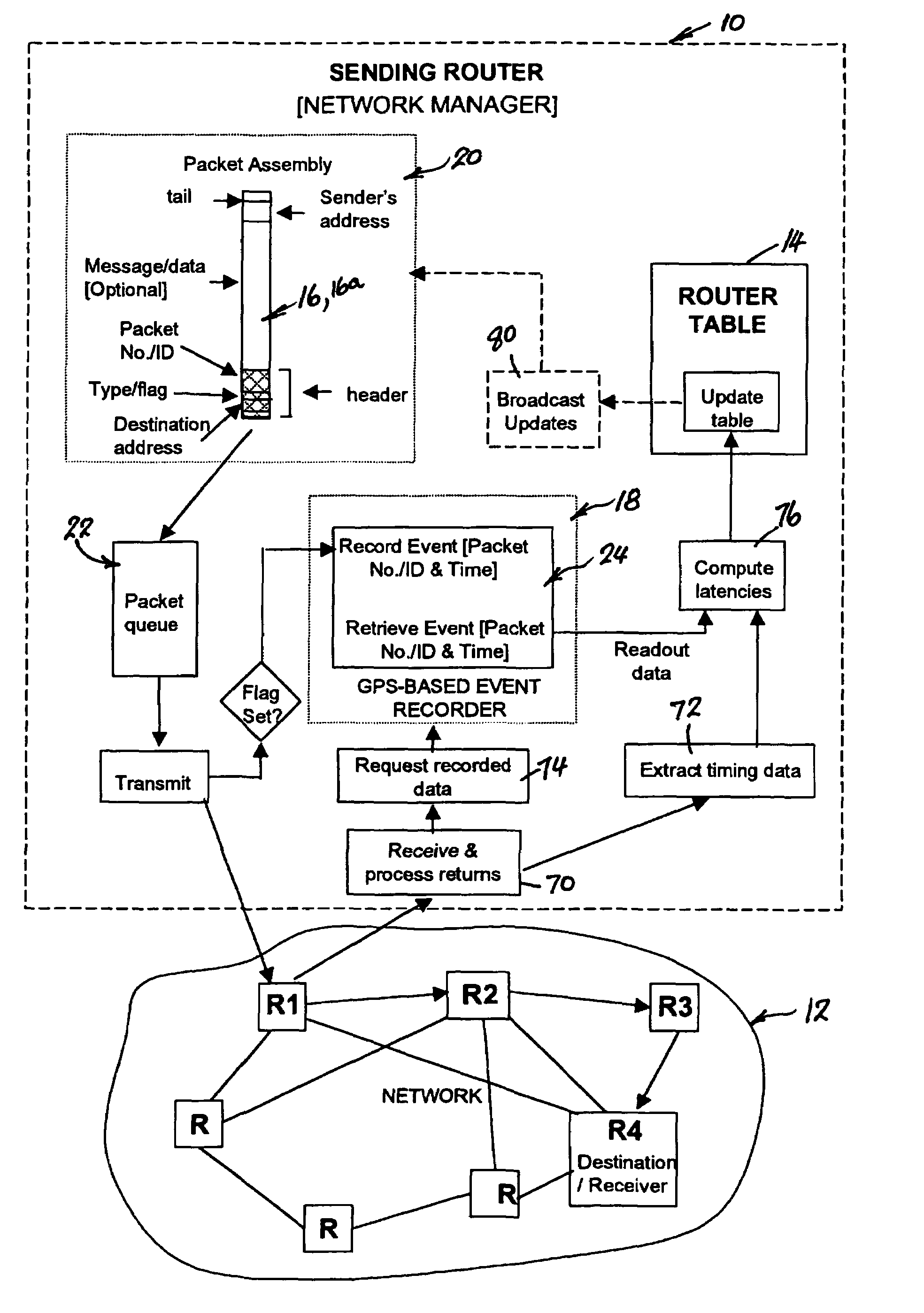
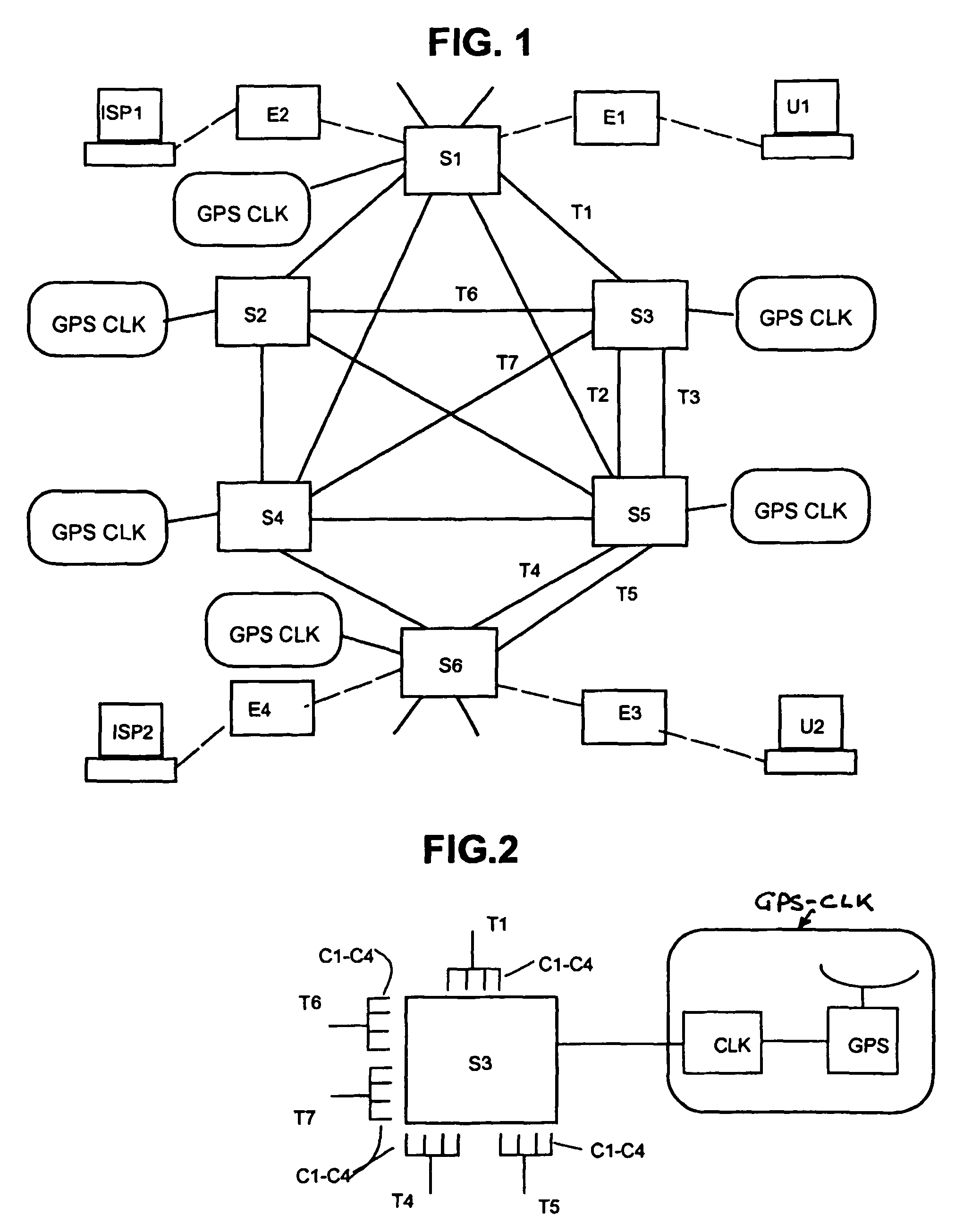
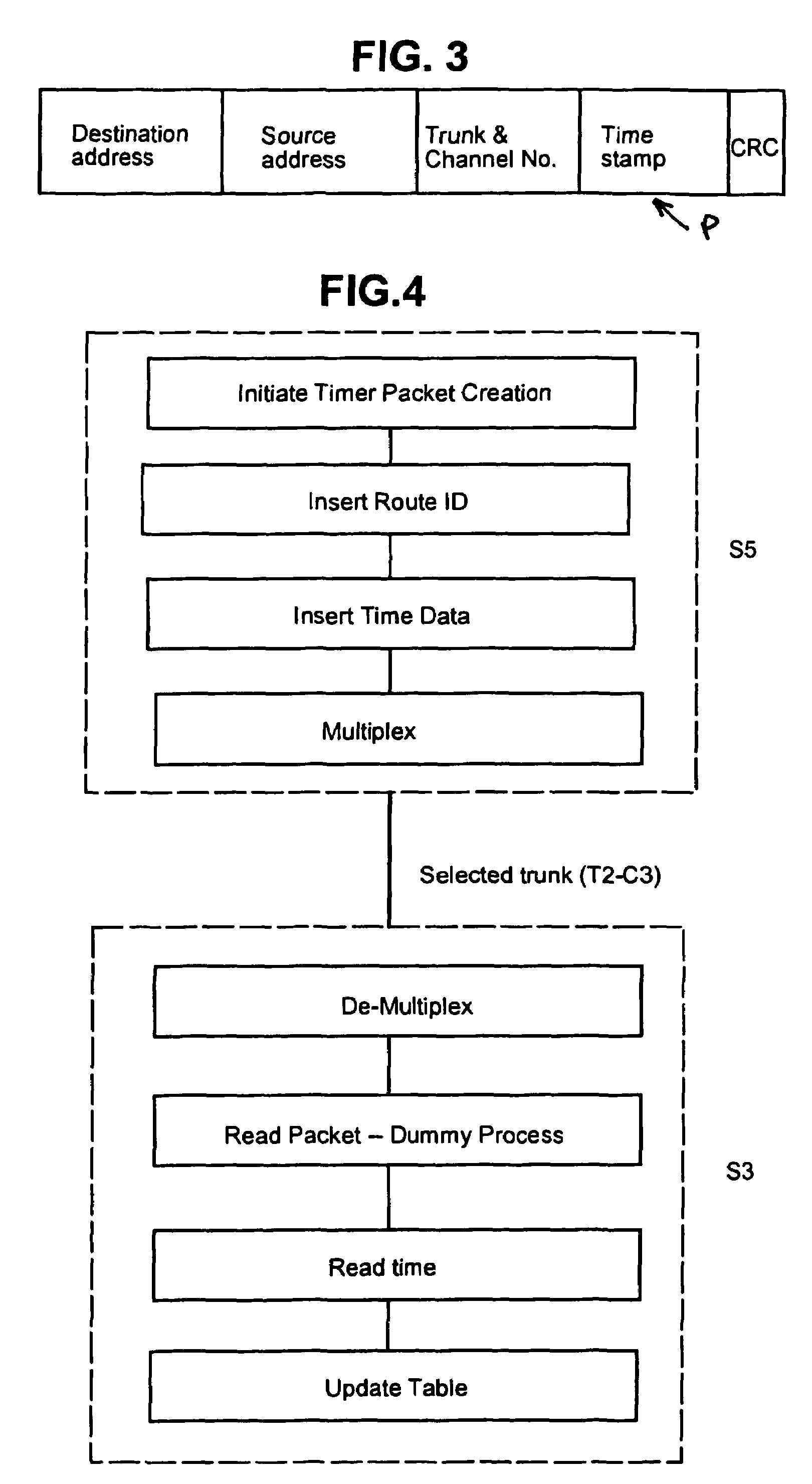
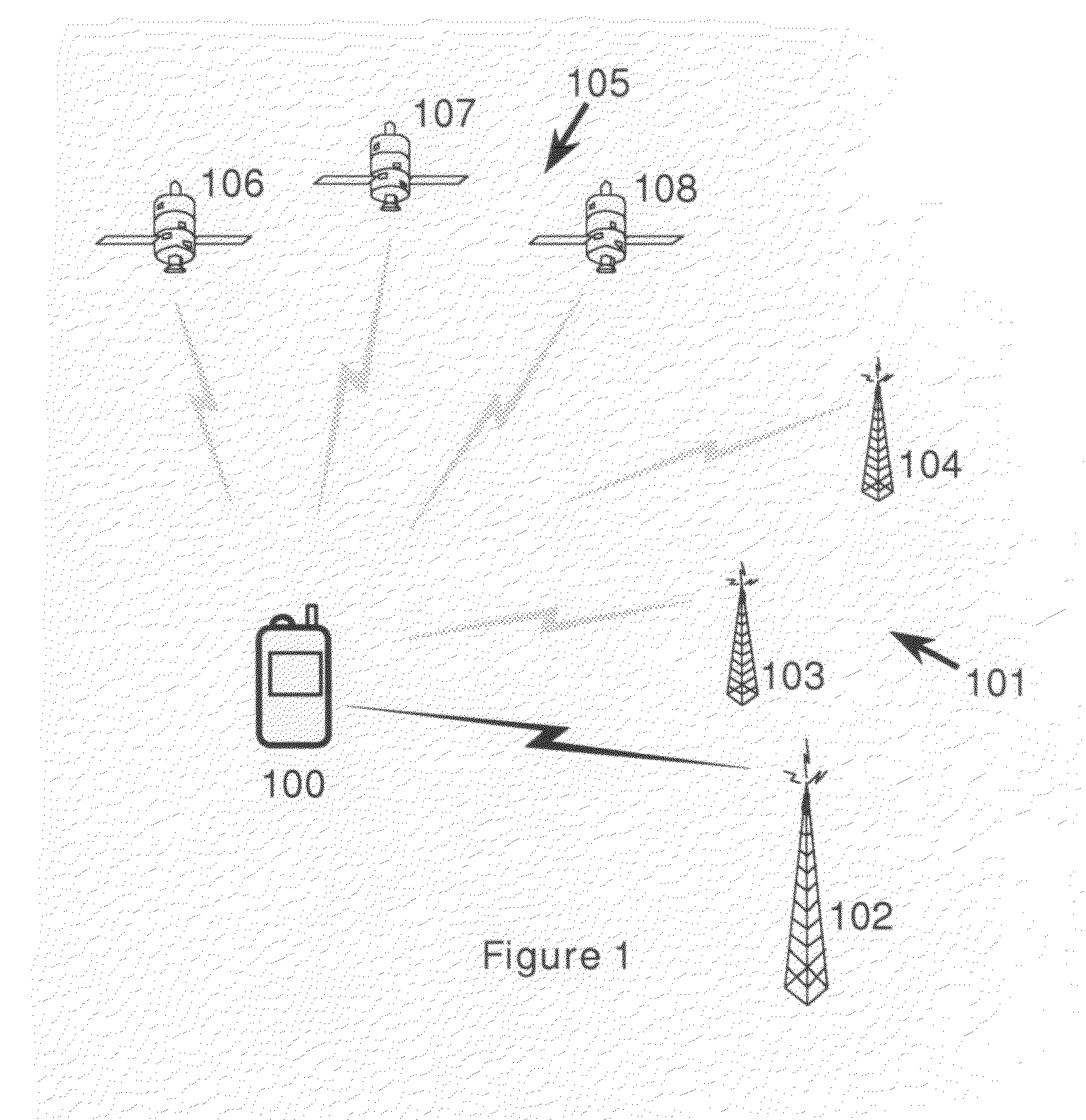
A method of determining the latency of a route in a packet-switched network, a packet switch for use in such a method and network and a packet-switched network are disclosed. Preferably, each switch maintains a routing table that records the latency of the routes accessible by that switch. Each switch also preferably has a GPS-based universal time clock which it employs to time the transmission and arrival of identifiable timing packets, these times being used to compute route latency and to up-date the routing tables. In one example (<cross-reference target="DRAWINGS">FIG. 1< / CROSS-REFERENCE>) a packet-switched network has a plurality of switches (S1-S6) interconnected by links or trunks (T1-T7). A local GPS-base clock (GPS CLK) is connected to each switch (S1-S6) to enable the accurate timing of transmission and reception of identifiable timing packets in accordance with a system-wide universal timing standard.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Accurate time synchronization method for industrial wireless network
InactiveCN101335587ACurb the free growth of synchronization errorsHigh precisionTime-division multiplexData synchronizationBeacon frame
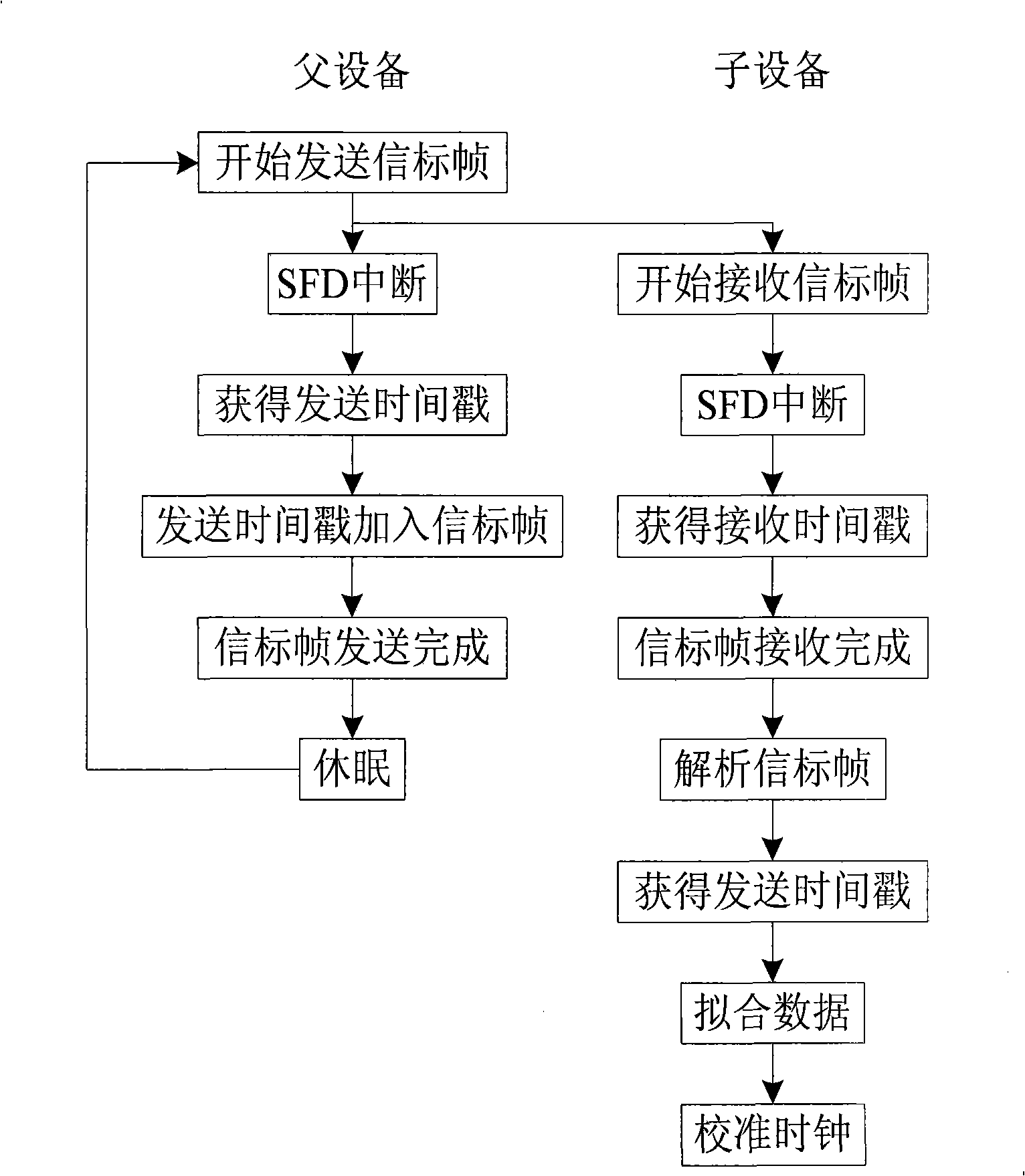
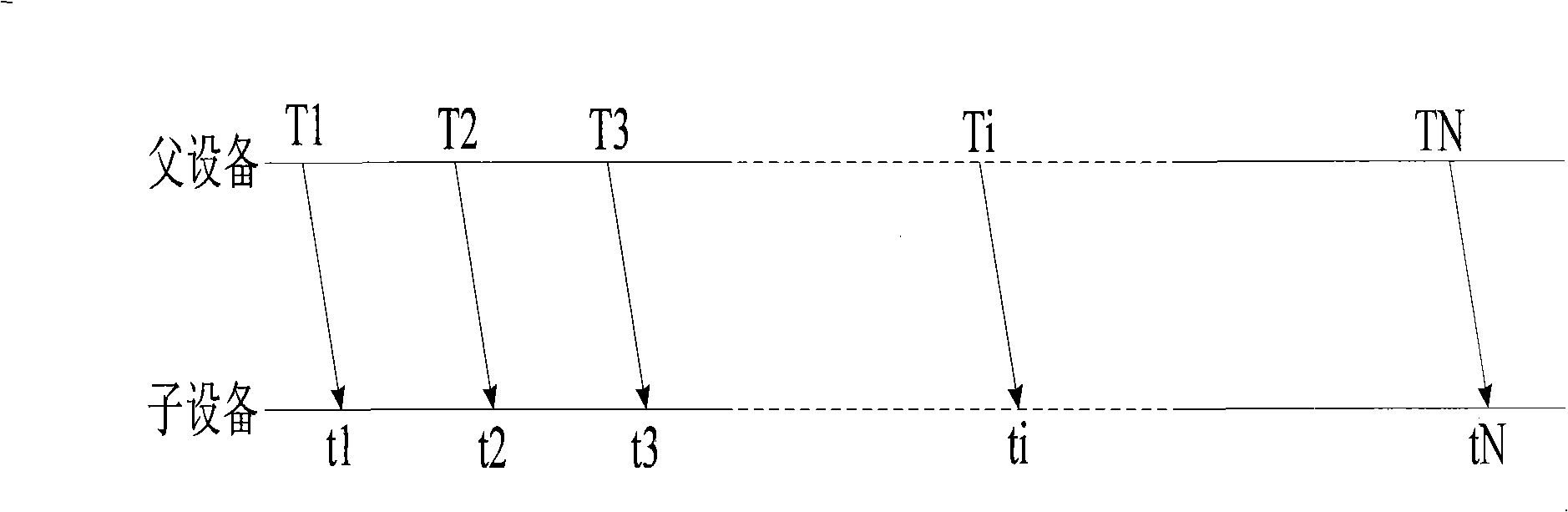
The invention provides a precise time synchronization method for an industrial wireless network, relating to the industrial wireless network communication technology. Aiming at the characteristics of the industrial wireless network, such as limited energy supply, dynamic and variable network environment, the openness of the wireless network media, and the like, the invention provides a unique precise time synchronization method, wherein, a layering and grading synchronization strategy is adopted to divide the industrial wireless network according to a hierarchical structure; an MAC layer of a parent device generates beacon frames, sends the beacon frames periodically, obtains a time stamp in the processes of sending and receiving beacon frames, obtains the frequency deviation and time deviation of the equipment clock and the universal time clock by fitting the time stamps sent and received in most recently N times, compensates the local clock, realizes the time clock synchronization of a child device and the parent device; time synchronization is carried out in a grade-wise manner and finally the time synchronization of the whole network is realized. On the premise of meeting the performance requirements on the industrial wireless network, the precise time synchronization method of the invention can ensure that the whole network runs within a uniform time scale and guarantee the normal operation of the system.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Position attitude system hardware time synchronizing method
InactiveCN101067656AHigh data time synchronization accuracyHigh synchronization accuracyPosition fixationFluid speed measurement using thermal variablesClock driftGps receiver
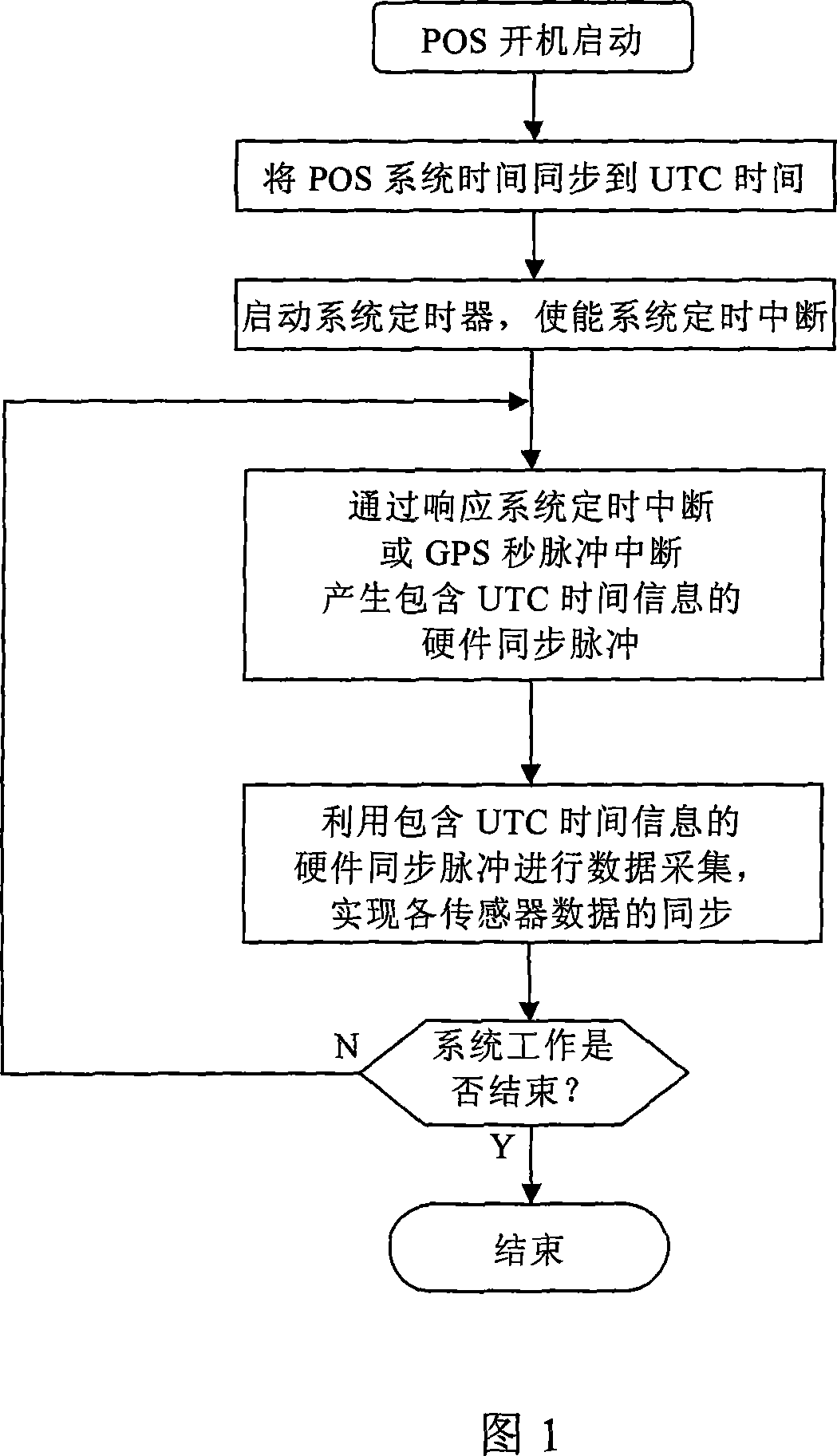
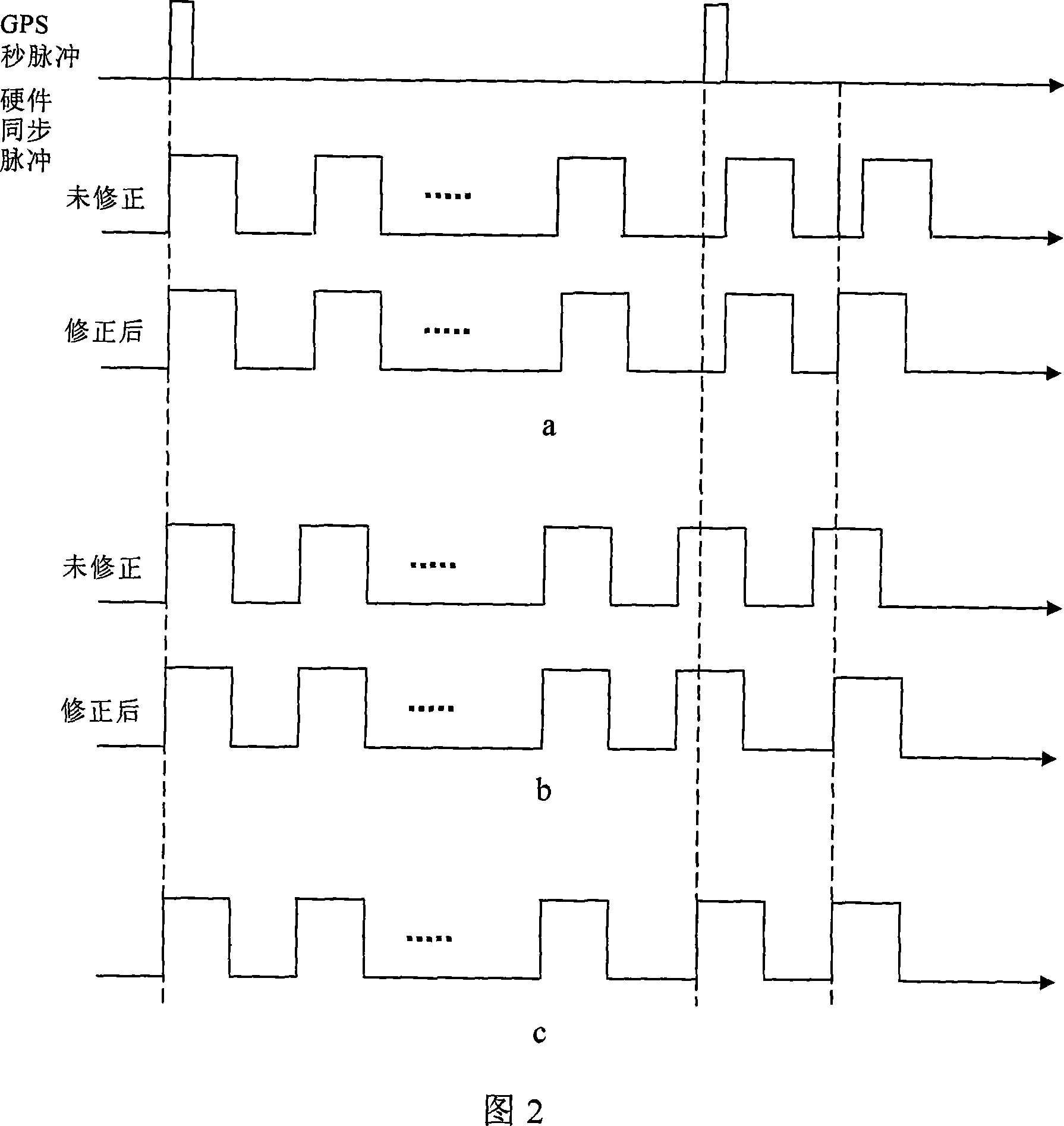
The invention is a hardware synchronizing method for position and orientation system (POS), relating to a method for synchronizing various sensor data in the POS, firstly using GPS receiver-outputted GPS second pulse signal accurately synchronous with UTC time (Coordinate Universal Time) to synchronize the system time of the POS with the UTC time, then generating UTC time-containing hardware synchronous pulse through system timer and collecting various sensor data, and then implementing synchronization of various sensor data in the POS. And the invention uses GPS second pulse to real-timely correct system clock drift and implements GPS signal monitoring and thus has features of high synchronizing accuracy, good adaptability and high reliability.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
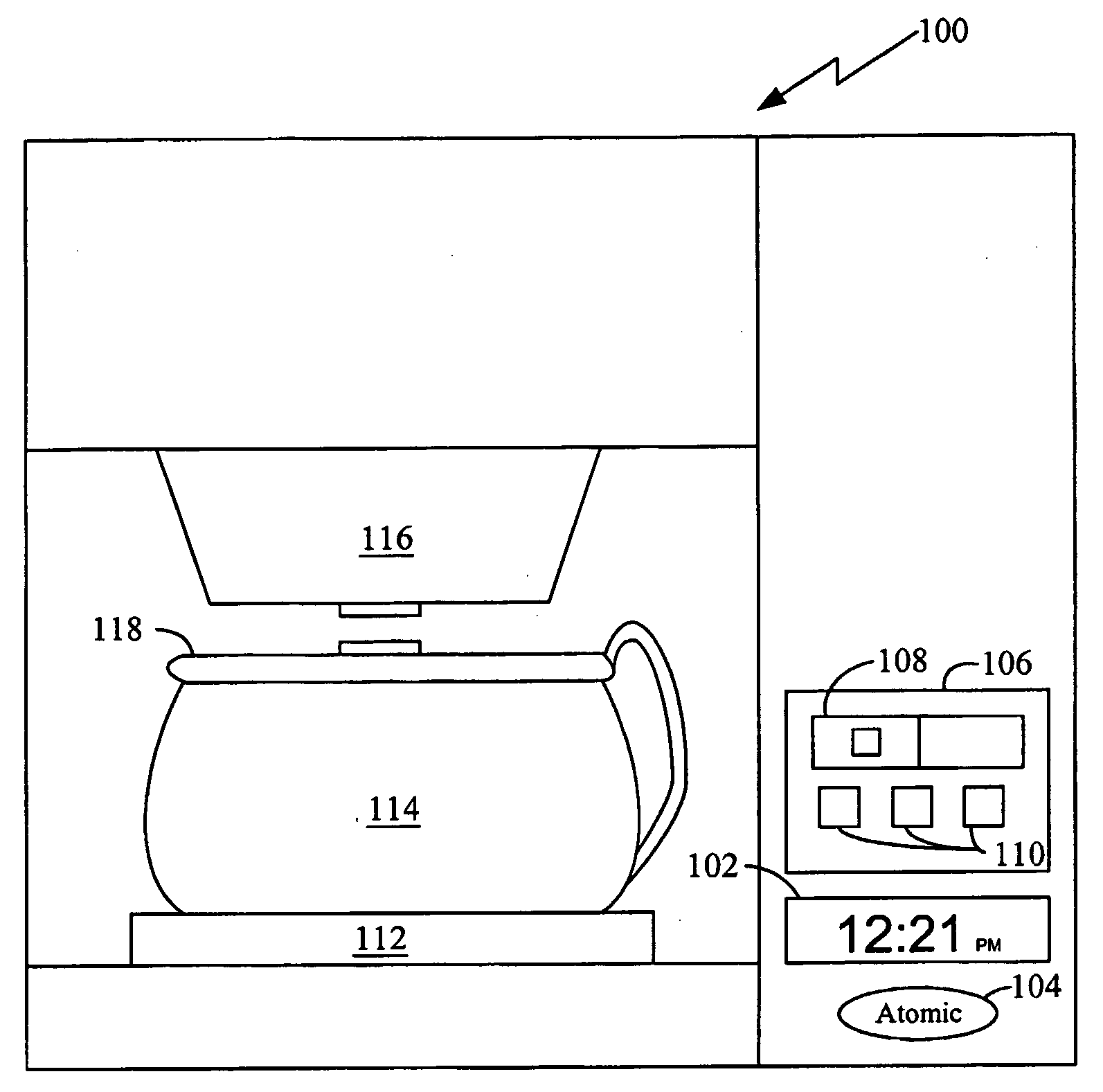
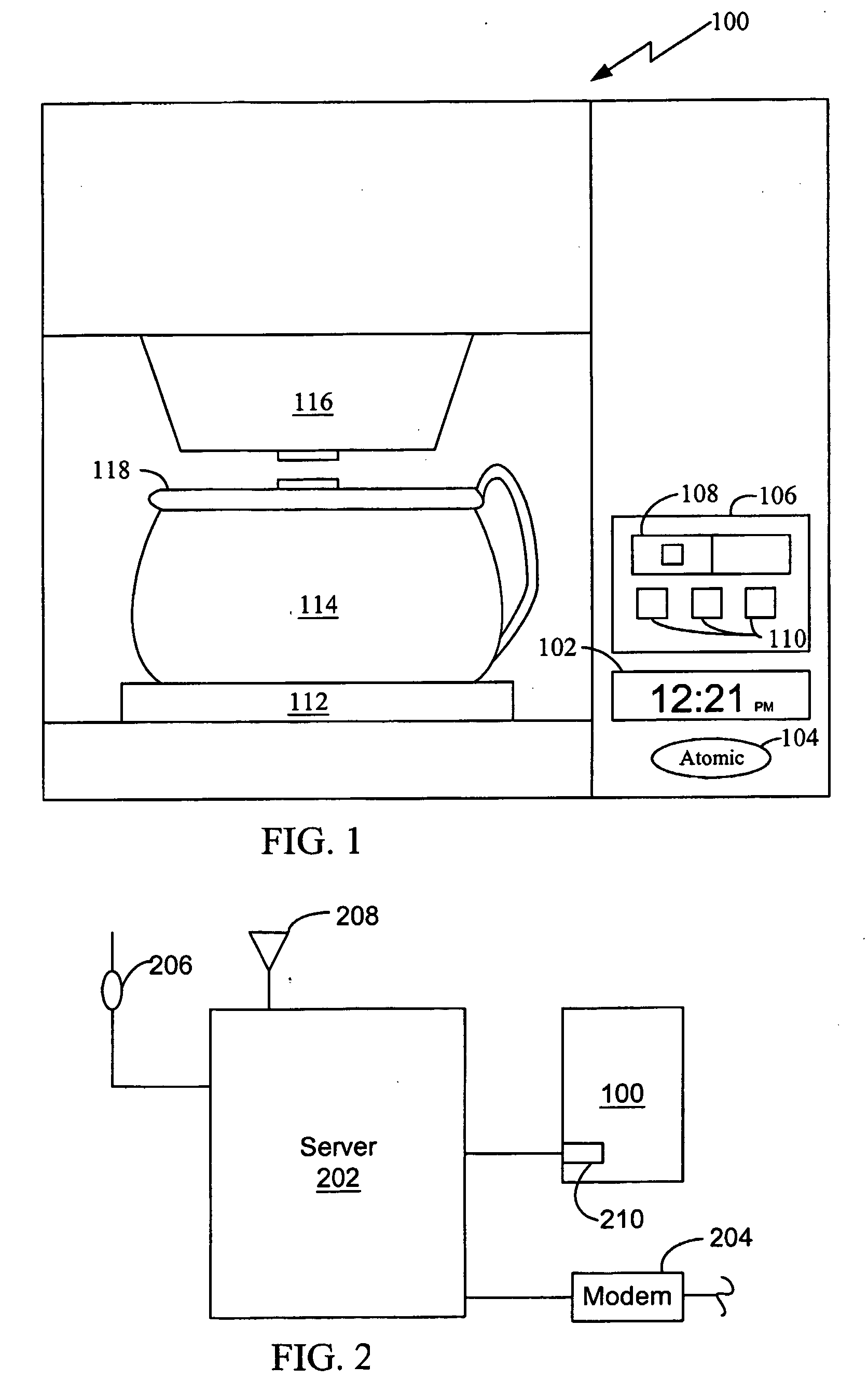
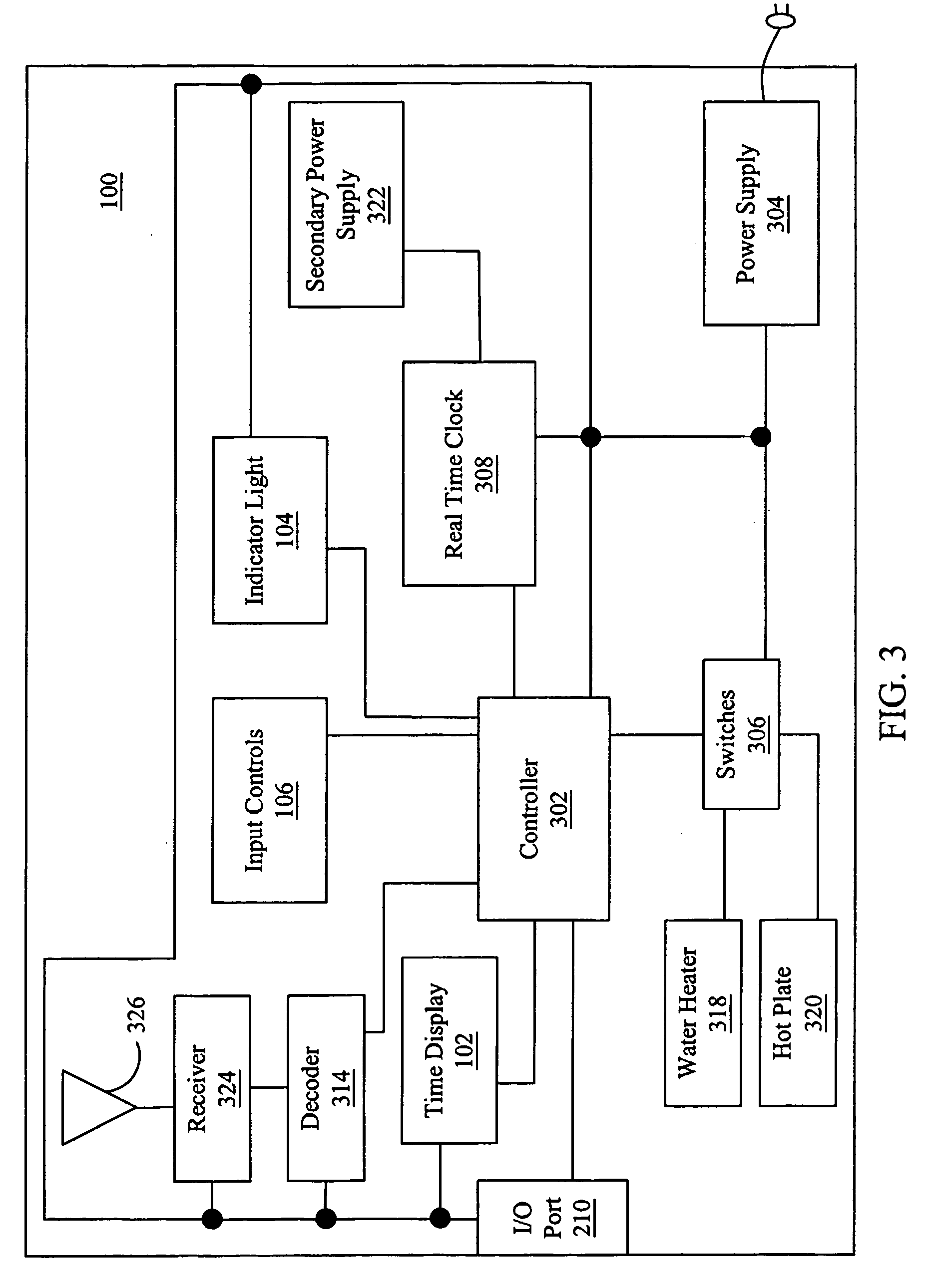
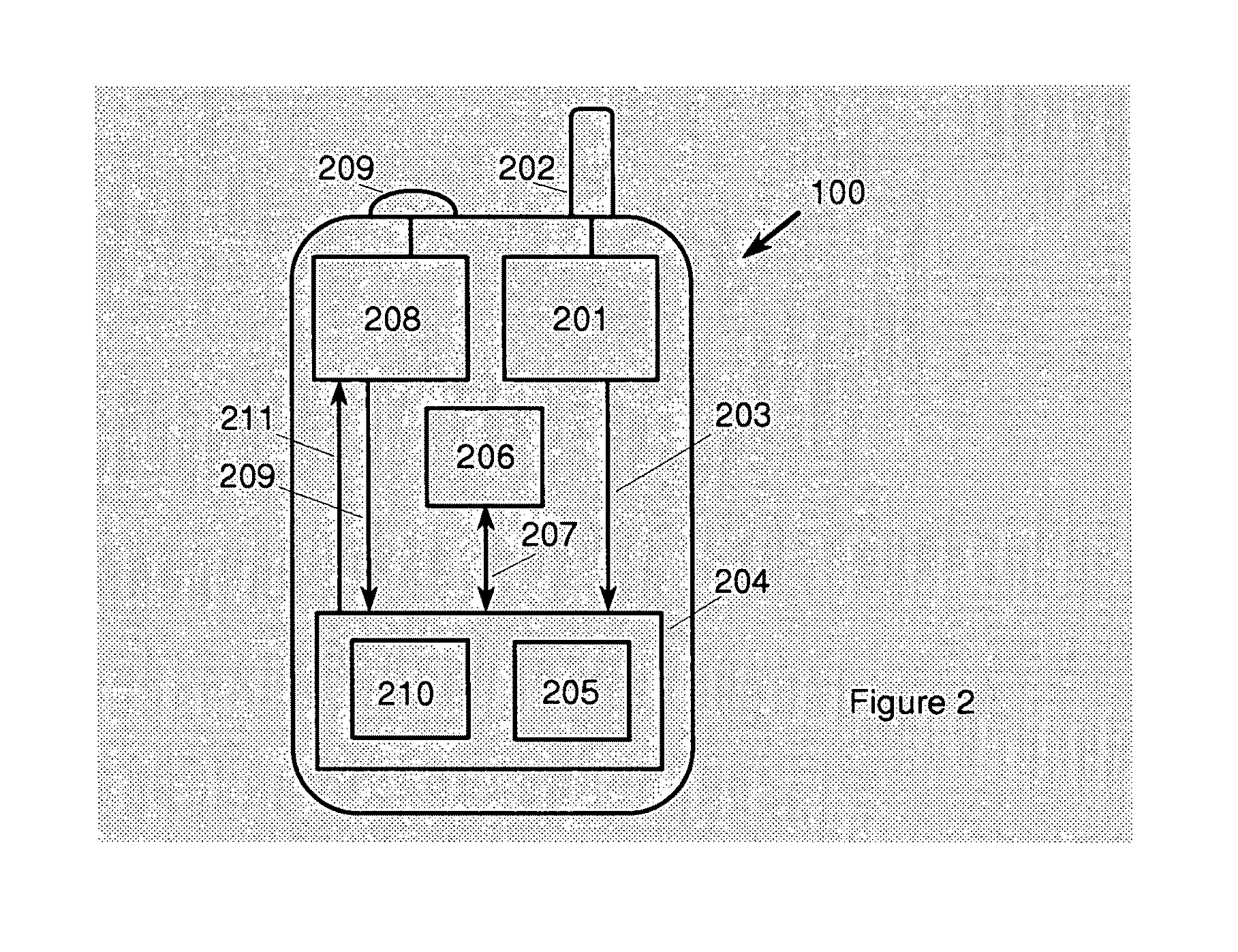
Appliance having a clock set to universal time
A appliance (100) having a receiver (324) capable of receiving and a decoder (314) capable of decoding a time signal (400) into a time value. A clock (308) in the appliance (100) is updated or set with the received time value and an indicator (104) is activated to notify consumers that time synchronization to a time signal has occurred. The decoder (314) from the decoded time signal (400) is able to identify leap years and changes to and from daylight savings time.
Owner:SALTON
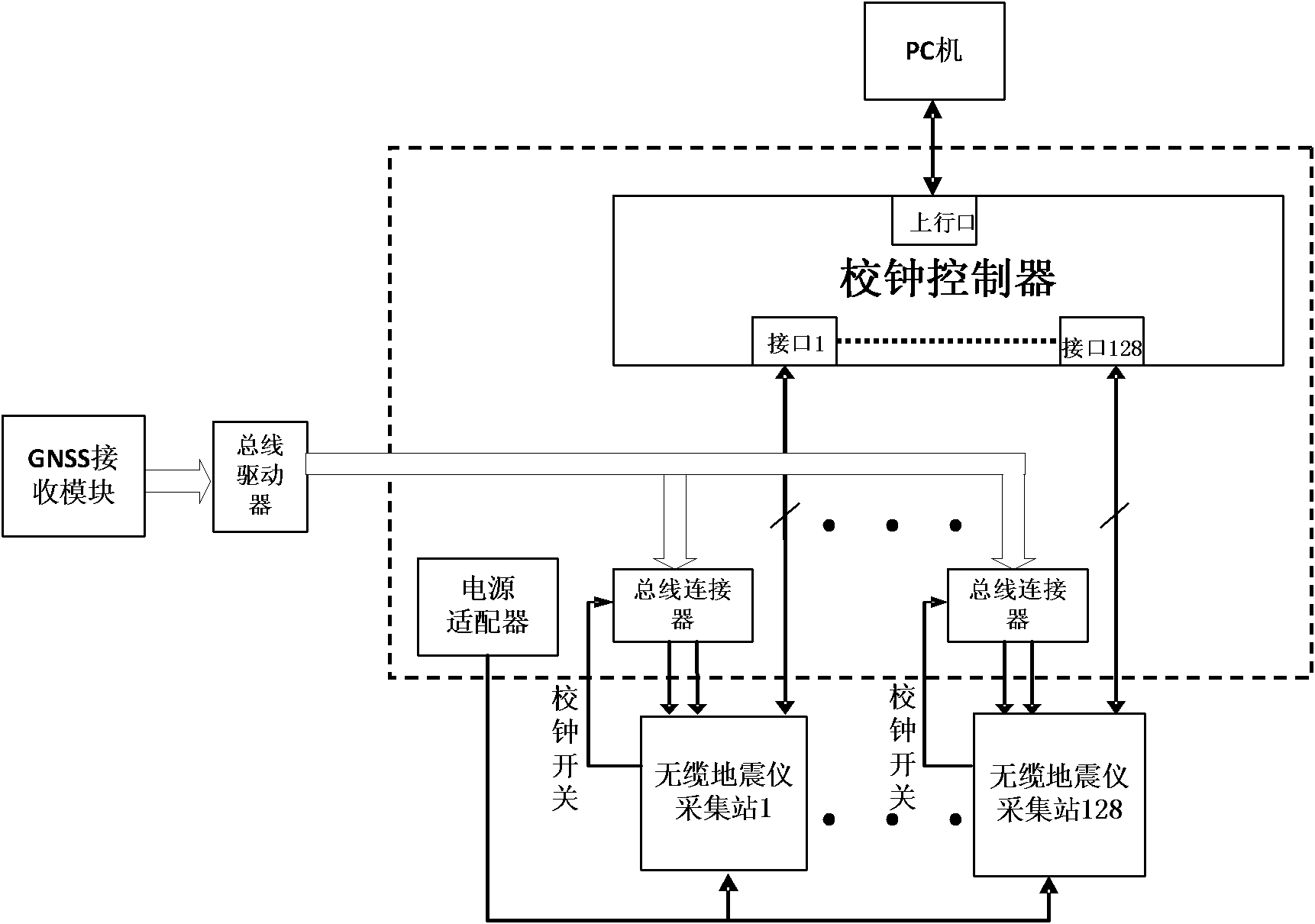
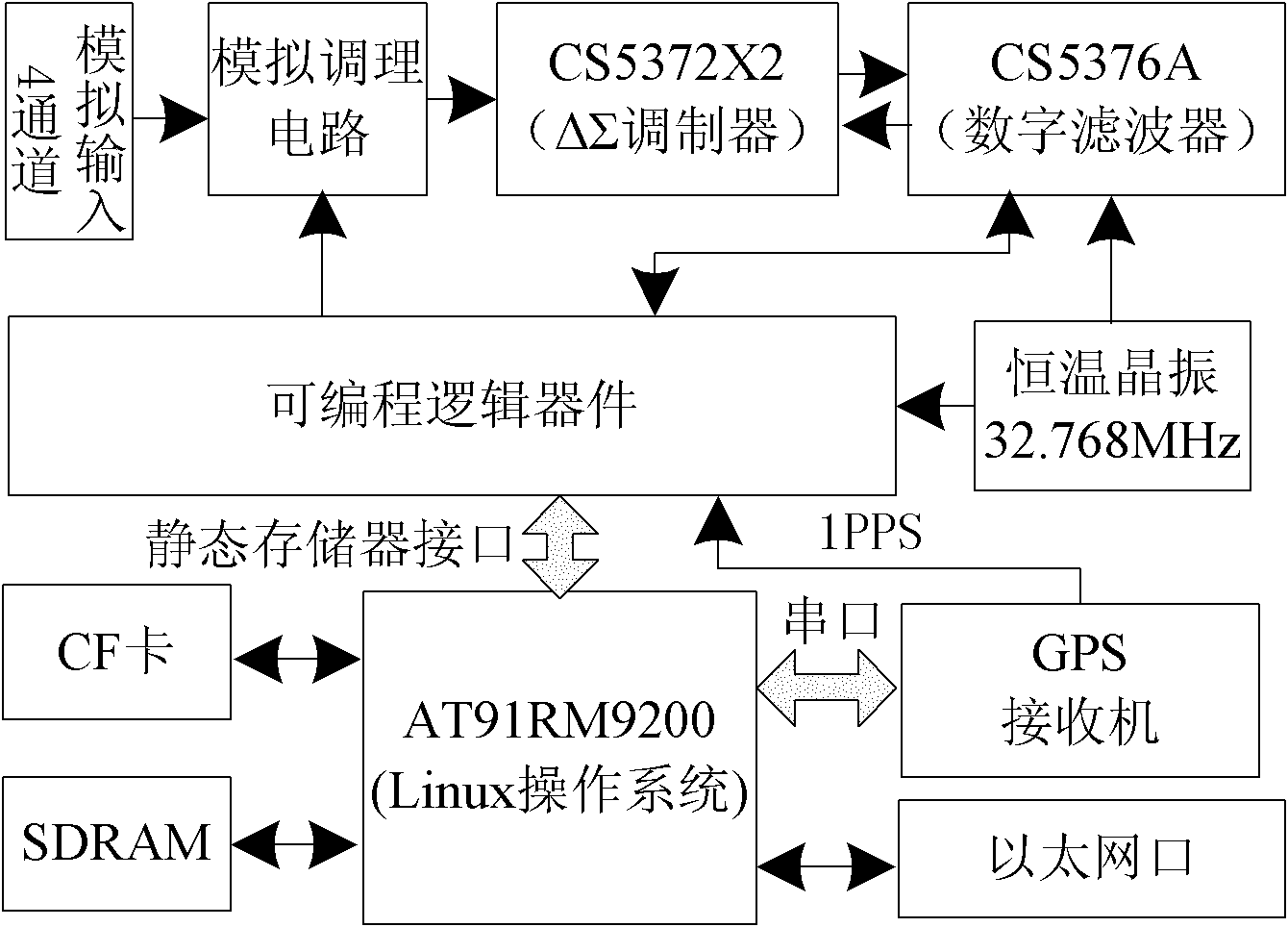
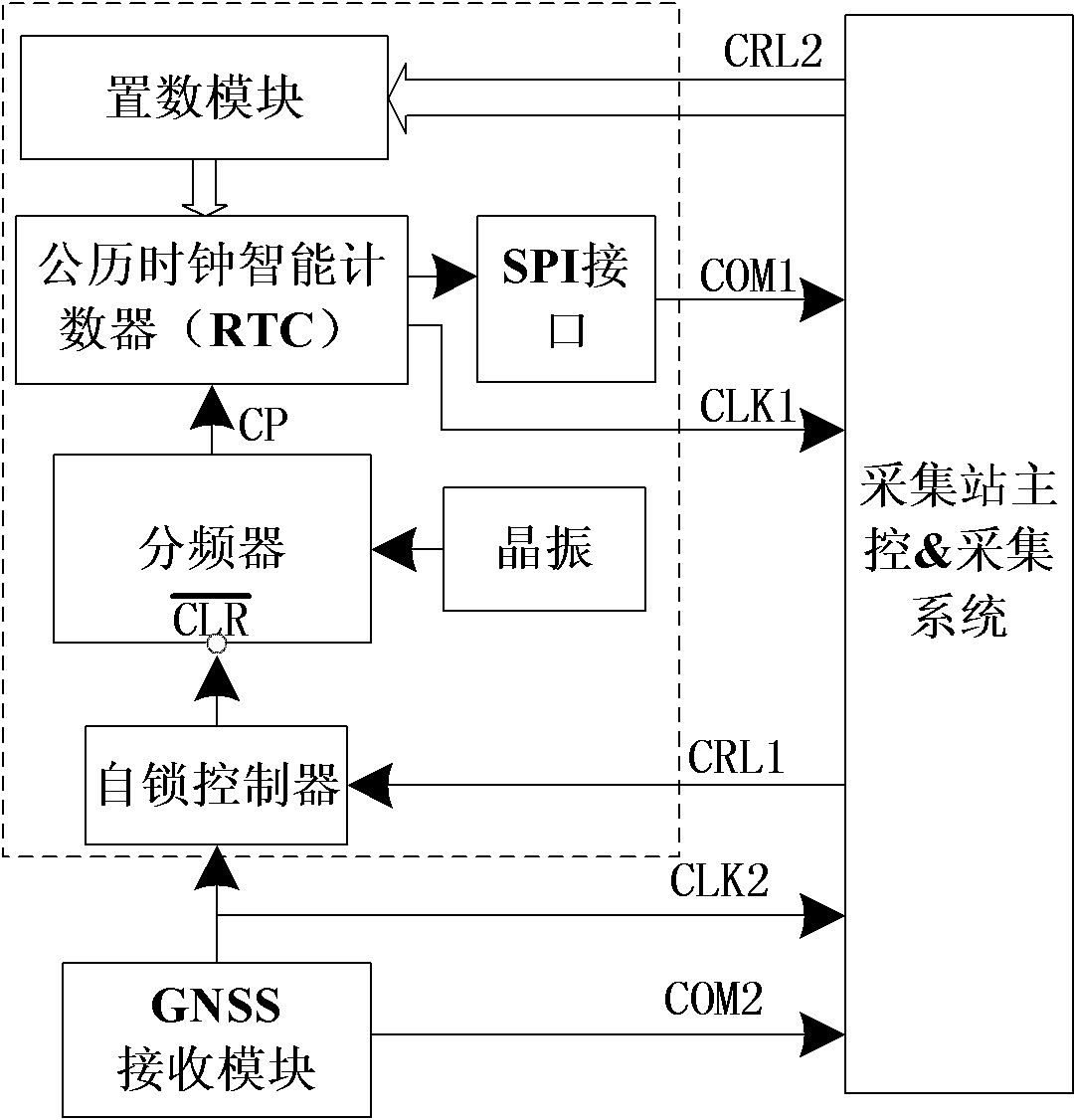
Multi-redundant synchronous data acquiring device and method of non-cable seismograph
InactiveCN102183785ASatisfy synchronization requirementsGood synchronization accuracySeismic signal receiversData acquisitionLocal memories
The invention discloses a multi-redundant synchronous data acquiring device and method of a non-cable seismograph. The method is a multi-redundant synchronous data acquiring method of a non-cable seismograph based on a UTC (universal time coordinated) time system, and comprises the following steps: through introducing a local auxiliary UTC time service system and combining a GNSS (global navigation satellite system) time service technology, constructing a multi-redundant TUC time service system so as to guarantee that a non-cable seismograph acquiring station can synchronize the data acquisition under the condition of loading a GNSS time service signal; before acquiring the seismic data, firstly timing the local UTC, selecting one of continuous record or UTC time interval or UTC time point to set a synchronous acquiring task so as to generate a synchronous data acquiring task list; and marking the UTC time scale information on the acquired seismic data according to the UTC time service information, storing in a local memory, and finally obtaining a complete synchronous single shot record. The synchronous seismic data can be acquired by the non-cable seismograph acquiring station under any severe satellite signal condition by using the acquiring device and the acquiring method; and the synchronous precision is superior to 4 microseconds, and the synchronous requirement of resource exploration is completed satisfied.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
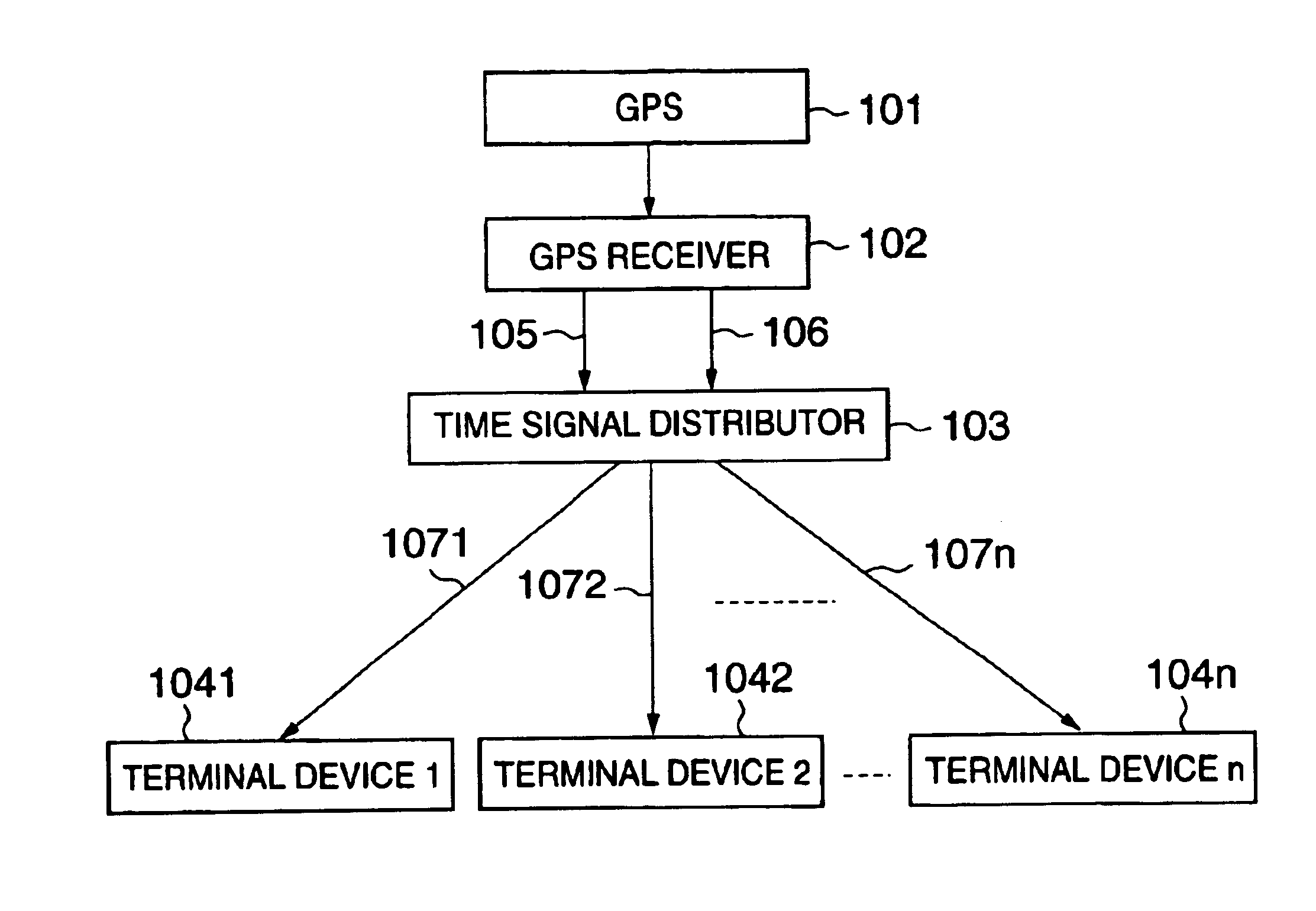
Time synchronizing system
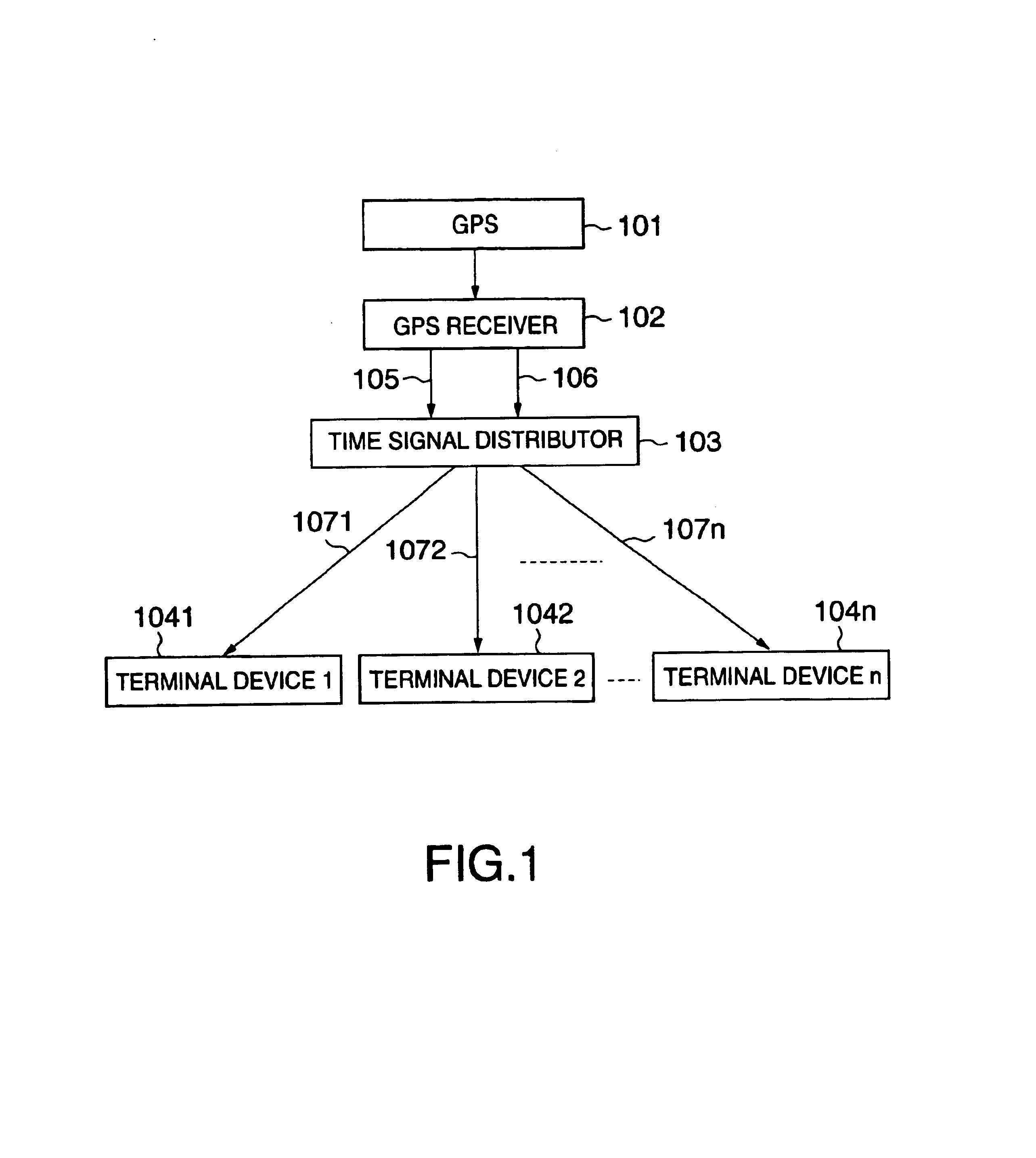
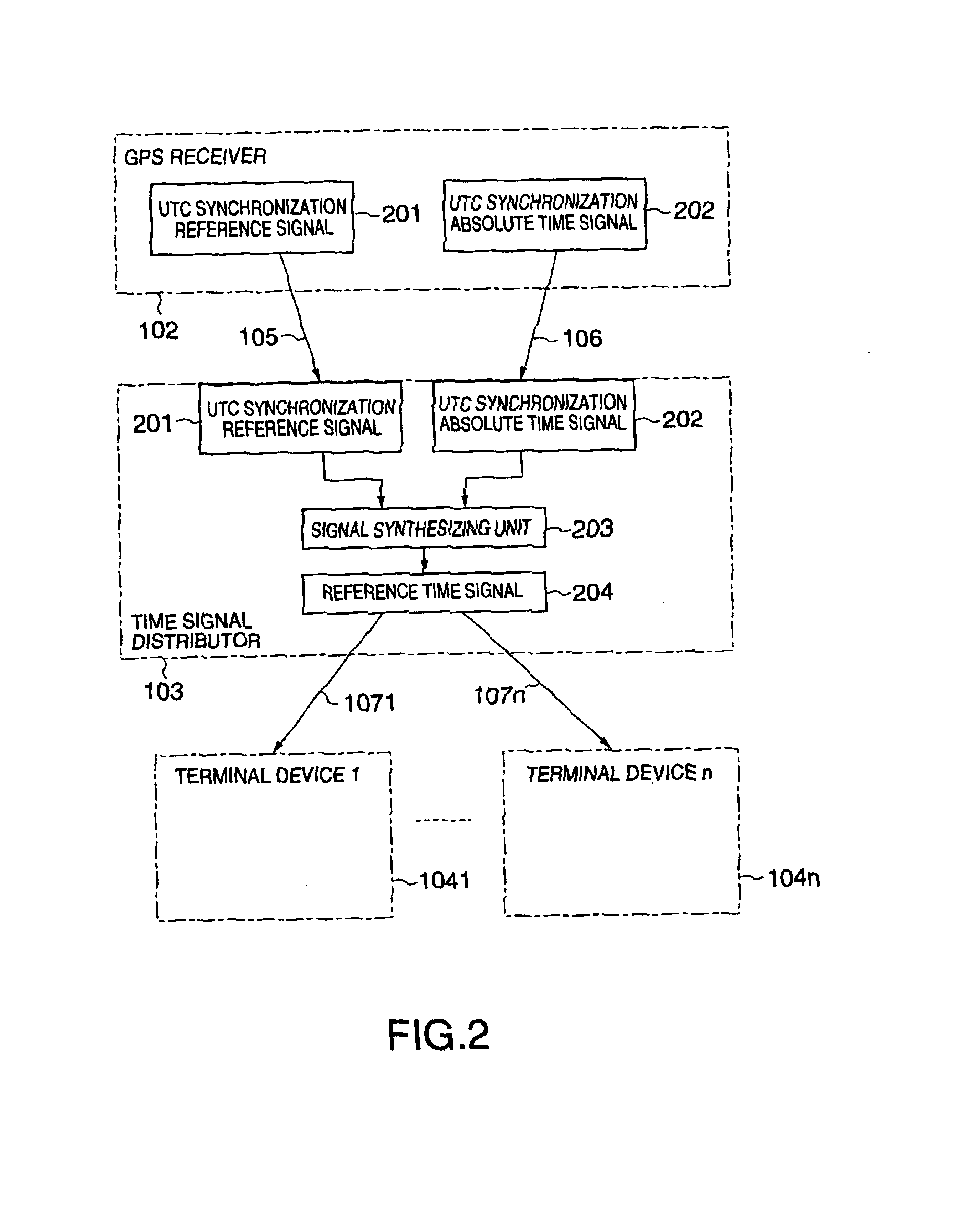
InactiveUS6847691B2Improve accuracyGood economical characteristicSynchronous motors for clocksSetting time indicationControl orientedData synchronization
A time synchronization system comprises a GPS (Global Positioning System) receiver for receiving a time signal from a Global Positioning System (GPS), and outputting a UTC (Universal Time Coordinated) synchronization reference signal synchronizing with UTC and a UTC synchronization absolute time signal, and a time signal distributor for generating a reference time signal synchronizing with UTC from the synchronization reference signal and the absolute time signal, and transmits this reference time signal in distribution to a plurality of distributed control oriented terminal devices. The time synchronization between the plurality of distributed control oriented terminal devices can be thereby taken.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Serial data real-time acquisition and time calibration method
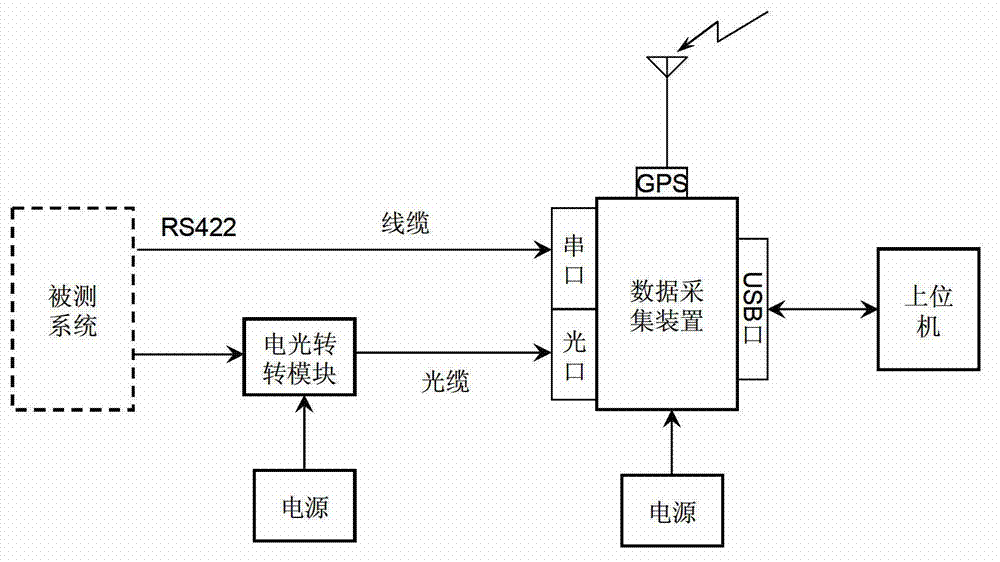
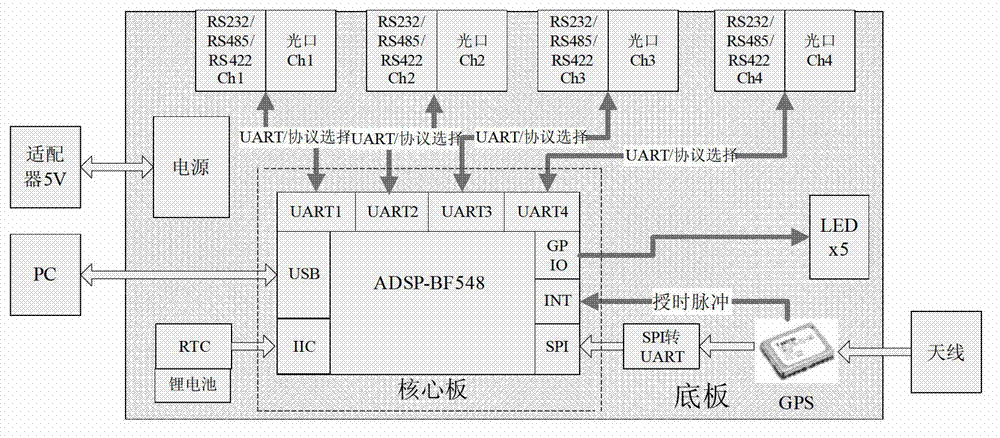
InactiveCN103207851AGuaranteed Time AccuracyElectric digital data processingDigital signal processingTime information
The invention belongs to the field of data acquisition and provides a serial data real-time acquisition and time calibration method. An acquisition device comprises a base plate composed of serial data acquisition circuits and a core plate composed of digital signal processing (DSP) chips, wherein a global position system (GPS) module is added in the circuits of the base plate. The system base plate finishes a serial signal acquisition task and transmits acquired signal to the core plate. The core plate finishes data acquisition, data storage and time calibration processing tasks and adopts an dominant type software design concept and sets the priority level of universal asynchronous receiver and transmitter (UART) data acquisition to be highest, and other tasks are interrupted and an UART data acquisition task is carried out when data arrives. An internal real-time clock adopted by the method provides accurate time for a system and is composed of universal time coordinated (UTC) time and a timer. Acquired data and data acquisition time information are packed together, are temporarily stored in a device cache and can be uploaded to a personal computer (PC) to be stored in real time, and the time calibration accuracy can reach to + / -0.2ms.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
SOPC (System on a Programmable Chip) networking based sub-microsecond level clock synchronizing method and system
ActiveCN105429725ASynchronous high precisionGuaranteed accuracy requirementsTime-division multiplexSlave clockNetwork switch
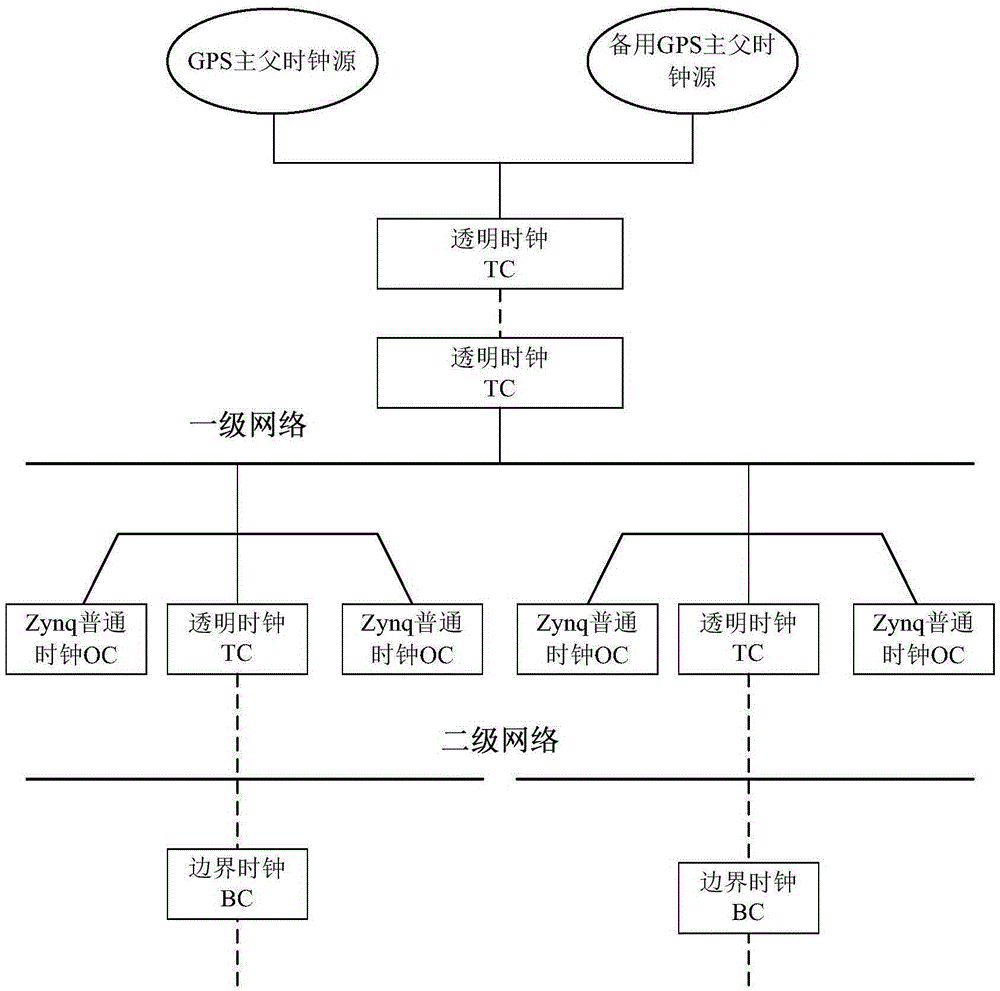
The invention provides an SOPC (System on a Programmable Chip) networking based sub-microsecond level clock synchronizing method. The clock synchronizing method comprises the steps of synchronizing UTC (Universal Time Coordinated) of a remote reference primary parent clock with UTC from an external GPS (Global Positioning System) clock or a Big Dipper system clock; synchronizing each node of a local first-level PTP (Precision Time Protocol) domain with the remote reference primary parent clock through a network switching device which supports a transparent clock function; receiving an optimal primary clock from a network at the same level by each Zynq platform based slave clock which supports IEEE158V2 protocol and gigabit Ethernet for time synchronization and frequency synchronization; when a PTP domain at the next level synchronizes with the primary parent clock through a border clock, performing clock synchronization by a primary clock at the upper level; and during the period that the PTP domain at the same level masters an independent clock synchronization control right, selecting the optimal primary clock as the primary clock of the network at the same level through an optimal primary clock algorithm. The invention also provides an SOPC networking based sub-microsecond level clock synchronizing system which adopts the clock synchronizing method.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
System and method for enhancing live speech with information accessed from the World Wide Web
ActiveUS7505907B2Minimum effort and involvementMinimize complexityTelevision system detailsDigital data information retrievalRecording durationInformation access
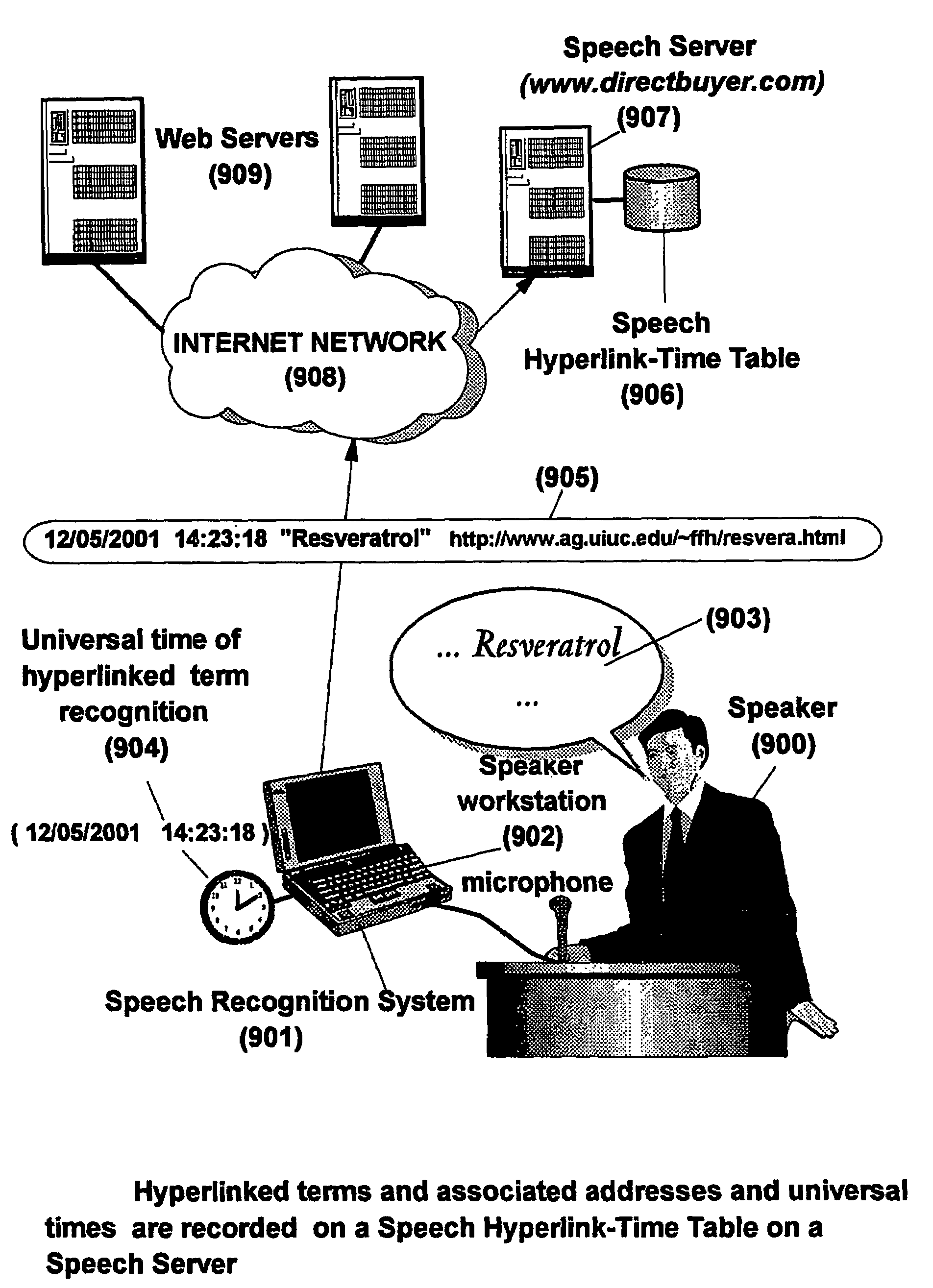
The present invention is directed to a system, method and computer program for enabling an auditor of a live speech to access immediately after or at a later time, complementary information related with terms pronounced during this speech. The system associates hyperlinks (i.e., URLs) with selected terms or words likely to be pronounced by the speaker in the course of the speech. A speech recognition system operating on a speaker device (i.e., a computing system a with a microphone connected to it) recognizes during the speech (i.e., word spotting) the pronunciation by the speaker of anyone of said hyperlinked terms, and records the time at which each recognized hyperlinked term has been pronounced. The system is also based on the synchronization of the speaker device with several auditors devices (e.g., workstations, portable computers, personal digital assistants—PDAs, smart phones, or any other type of handheld computing devices) according to a same universal time, so that the flow of information transmitted by the speaker and received by the auditors is always synchronized, independently of the relative positions of the speaker and auditors. Each time the auditor perceives an interesting topic during the speech, he immediately selects the topic simply by pressing a reserved key on the auditor's device. Universal times at which topics are selected by the auditor are stored in the auditor device.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
System and method for enhancing broadcast or recorded programs with information on the world wide web
ActiveUS7552193B2Easy access to informationEasy accessTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesVideo playerTelevision receivers
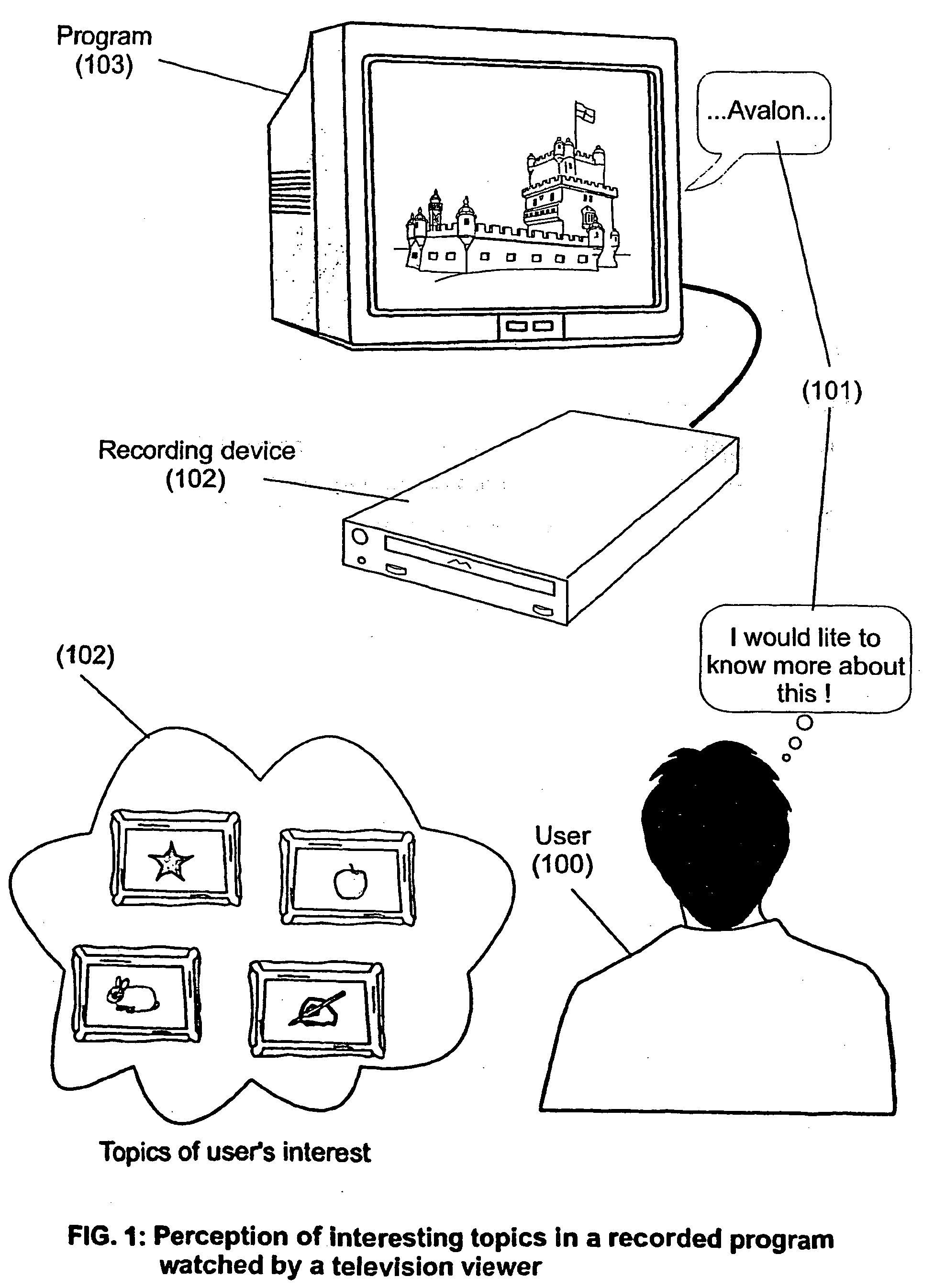
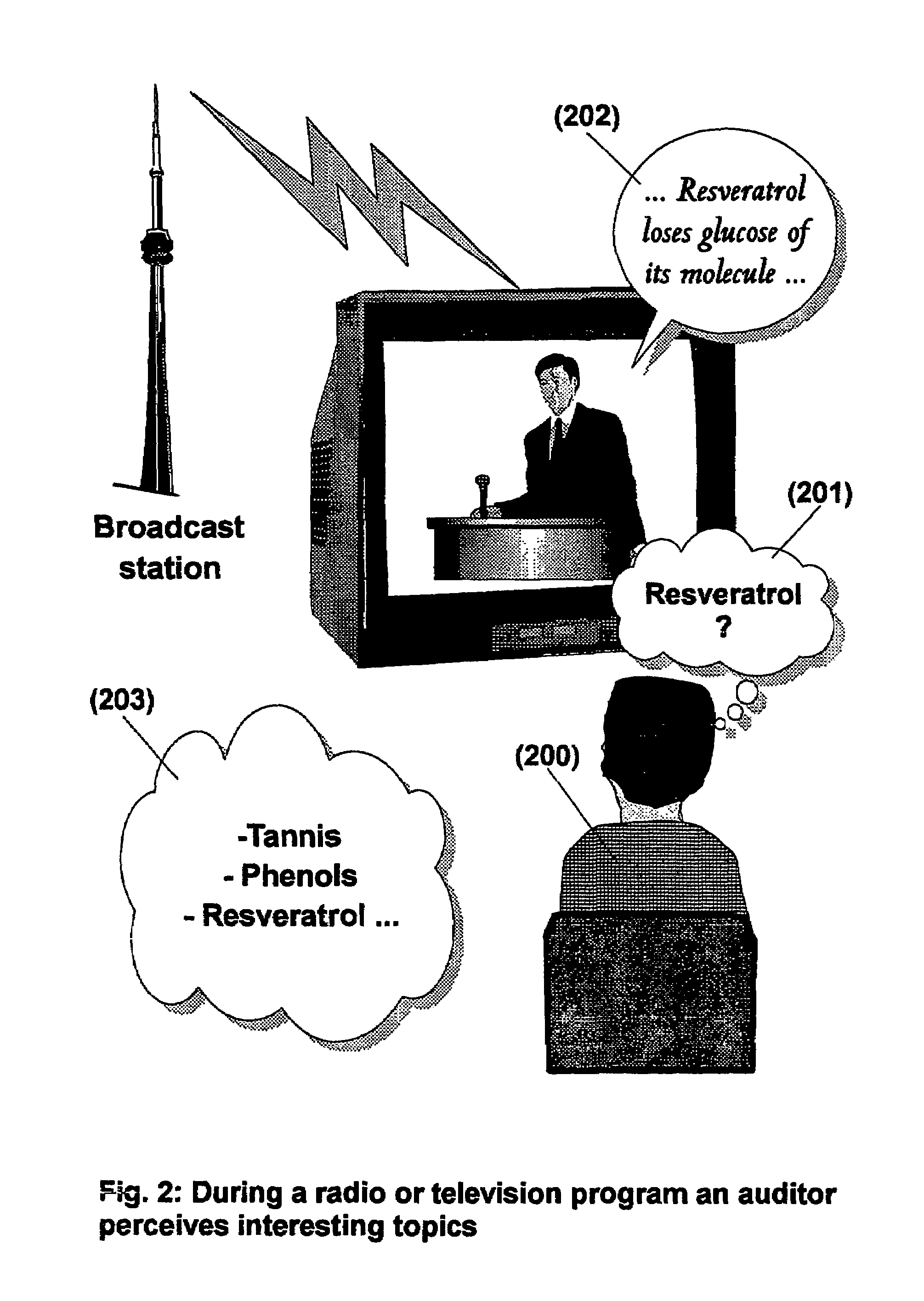
The present invention is directed to a system, method or computer program, for enabling a radio auditor or a television viewer (100) to access complementary information (101) related to a broadcast program (102) received in real-time (or to a recorded program previously broadcast and played back on an audio or video player / recorder). The preferred embodiment of the invention relates to a system and method for enabling a person (100) receiving a broadcast program (102), (or listening or watching a recorded program), to select a plurality of topics or sequences drawing his or her attention (101, 103) and for immediately, or later on, accessing additional information related to these topics or sequences from the Word Wide Web. The system is based on a synchronization of the local times of receivers (or recorders) and transmitters according to a same universal-time (201, 202), so that the flow of information transmitted and received (or recorded) is always synchronized, independently of the relative positions of receivers (or recorders) and transmitters. The synchronization is done referring to an universal time such as the Global Positioning System Time (GPS-time), the Global Orbiting Navigational Satellite System (GLONASS) time or another suitable universal time based on a satellite system. The GPS or GLONASS receivers are connected or integrated to the broadcasting stations. At the receiver side, GPS or GLONASS receivers may be integrated or connected to user devices e.g., Personal Computers, wearable computers, Personal Digital Assistants (PDAs), smart phones or onboard mobile computers (or to the audio or video recorders) that may be independent or separate from the radio or television receivers. The system is also based on a plurality of hyperlinks defined for given time intervals during the production of the broadcast program. These time intervals are synchronized with the universal Time. The hyperlinks are associated with the transmitted (and recorded) information. The hyperlinks can be retrieved, selected and activated by radio auditors or television viewers during the time intervals for which they have been defined, during the broadcast of the program (or during its playback).
Owner:IBM CORP +1
System and method for enhancing broadcast programs with information on the world wide web
ActiveUS20040139469A1Easy access to informationEasy accessTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionTelevision receiversBroadcasting
The present invention is directed to a system and method for enabling a radio auditor or a television viewer (100) to access complementary information (101) related to a broadcast program (102) received in real-time. The preferred embodiment of the invention relates to a system and method for enabling a person (100) receiving a broadcast program (102), to select a plurality of topics drawing his or her attention (101) (103) and for immediately, or at a later time, accessing additional information related to these topics from the Word Wide Web. The system is based on a synchronization of the local times of receivers and transmitters according to a same universal-time (201) (202), so that the flow of information transmitted and received is always synchronized, independently of the relative positions of receivers and transmitters. The synchronization is done referring to an universal time such as the Global Positioning System Time (GPS-time), the Global Orbiting Navigational Satellite System (GLONASS) time or another suitable universal time based on a satellite system. The GPS or GLONASS receivers are connected or integrated to the broadcasting stations. At the receiver side, GPS or GLONASS receivers may be integrated or connected to devices (e.g., Personal Computers, wearable computers, Personal Digital Assistants (PDAs), smart phones or onboard mobile computers) that may be independent or separate from the radio or television receivers. The system is also based on a plurality of hyperlinks defined for given universal-time intervals of retransmission. The hyperlinks are associated with the transmitted information. The hyperlinks can be retrieved, selected and activated by radio auditors or television viewers during the time intervals for which they have been defined.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
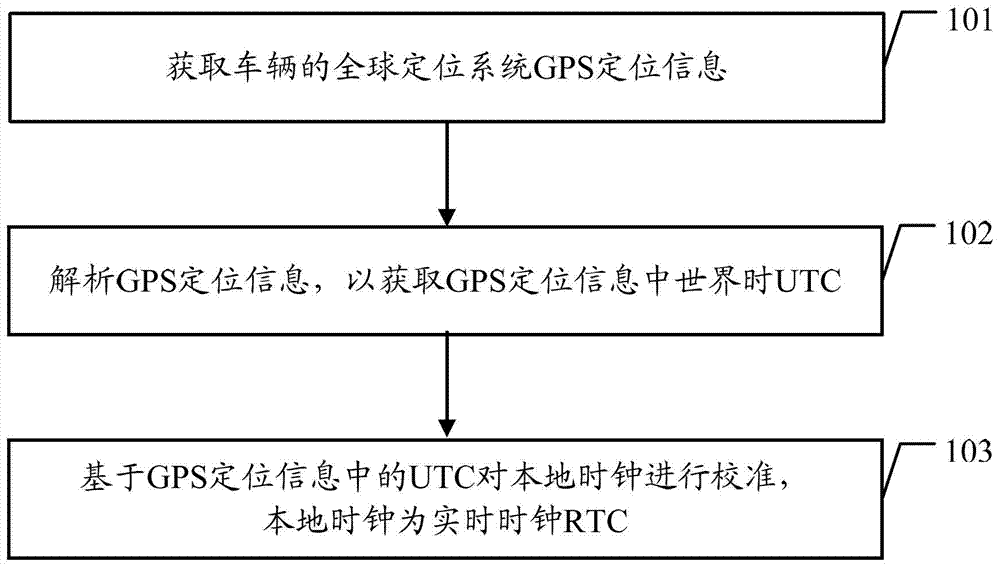
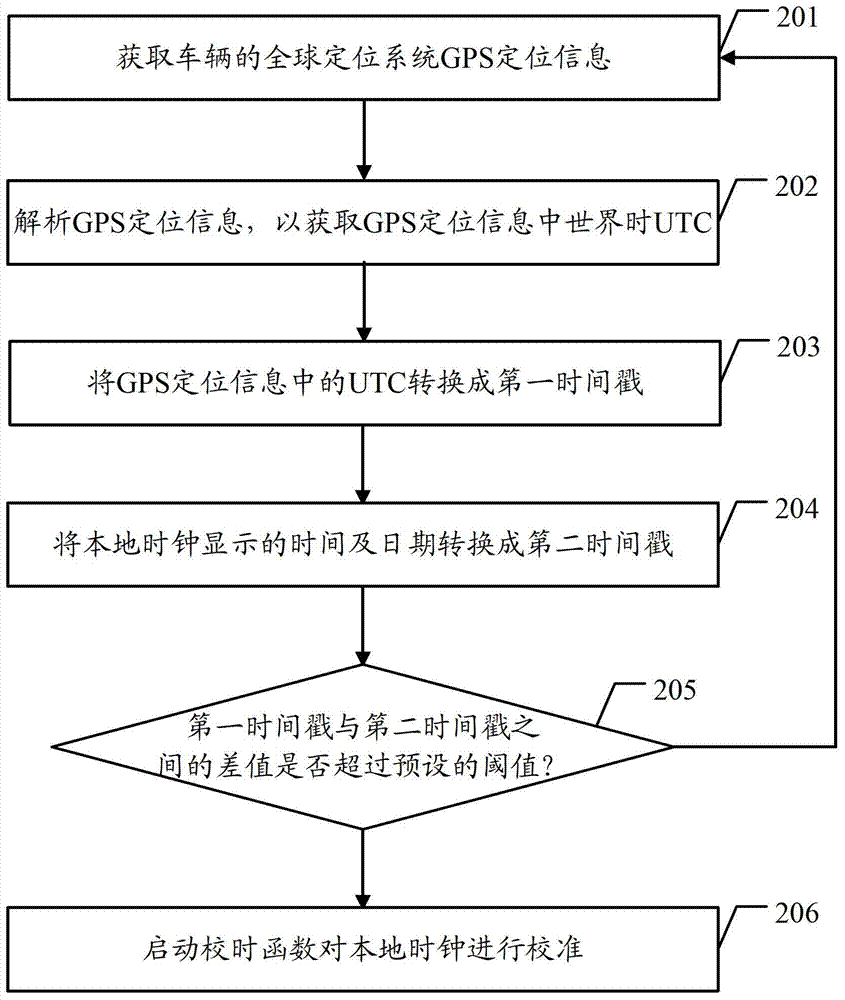
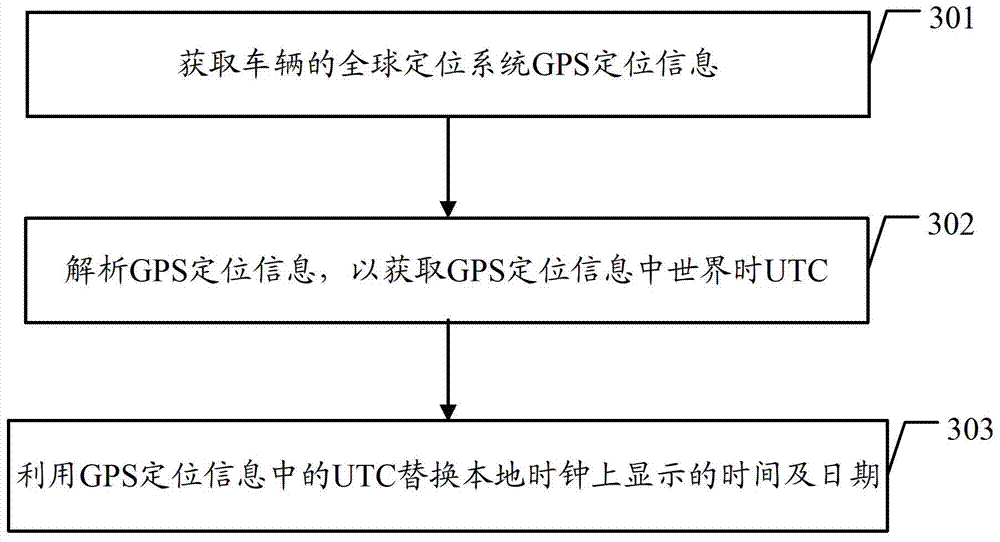
Local clock calibrating method and vehicle-mounted equipment
ActiveCN103399484AGuaranteed accuracyRadio-controlled time-piecesReal-time clockGlobal Positioning System
The embodiment of the invention discloses a local clock calibrating method and vehicle-mounted equipment. In the embodiment of the invention, the method comprises the following steps that the vehicle-mounted equipment acquires global positioning system (GPS) positioning information of a vehicle; the vehicle-mounted equipment resolves the GPS positioning information to obtain universal time coordinated (UTC) in the GPS positioning information; the vehicle-mounted equipment calibrates the local clock on the basis of the UTC in the GPS positioning information, wherein the local clock is a real-time clock (RTC). The embodiment of the invention further provides vehicle-mounted equipment. According to the embodiment of the invention, accurate time can be provided for the vehicle-mounted equipment.
Owner:LAUNCH TECH CO LTD
Adaptive packet routing
InactiveUS7372819B2Congested or slow links can be automatically avoidedLower latencyError preventionTransmission systemsRouting tableExchange network
A method of determining the latency of a route in a packet-switched network, a packet switch for use in such a method and network and a packet-switched network are disclosed. Preferably, each switch maintains a routing table that records the latency of the routes accessible by that switch. Each switch also preferably has a GPS-based universal time clock which it employs to time the transmission and arrival of identifiable timing packets, these times being used to compute route latency and to up-date the routing tables. In one example (FIG. 1) a packet-switched network has a plurality of switches (S1-S6) interconnected by links or trunks (T1-T7). A local GPS-base clock (GPS CLK) is connected to each switch (S1-S6) to enable the accurate timing of transmission and reception of identifiable timing packets in accordance with a system-wide universal timing standard.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
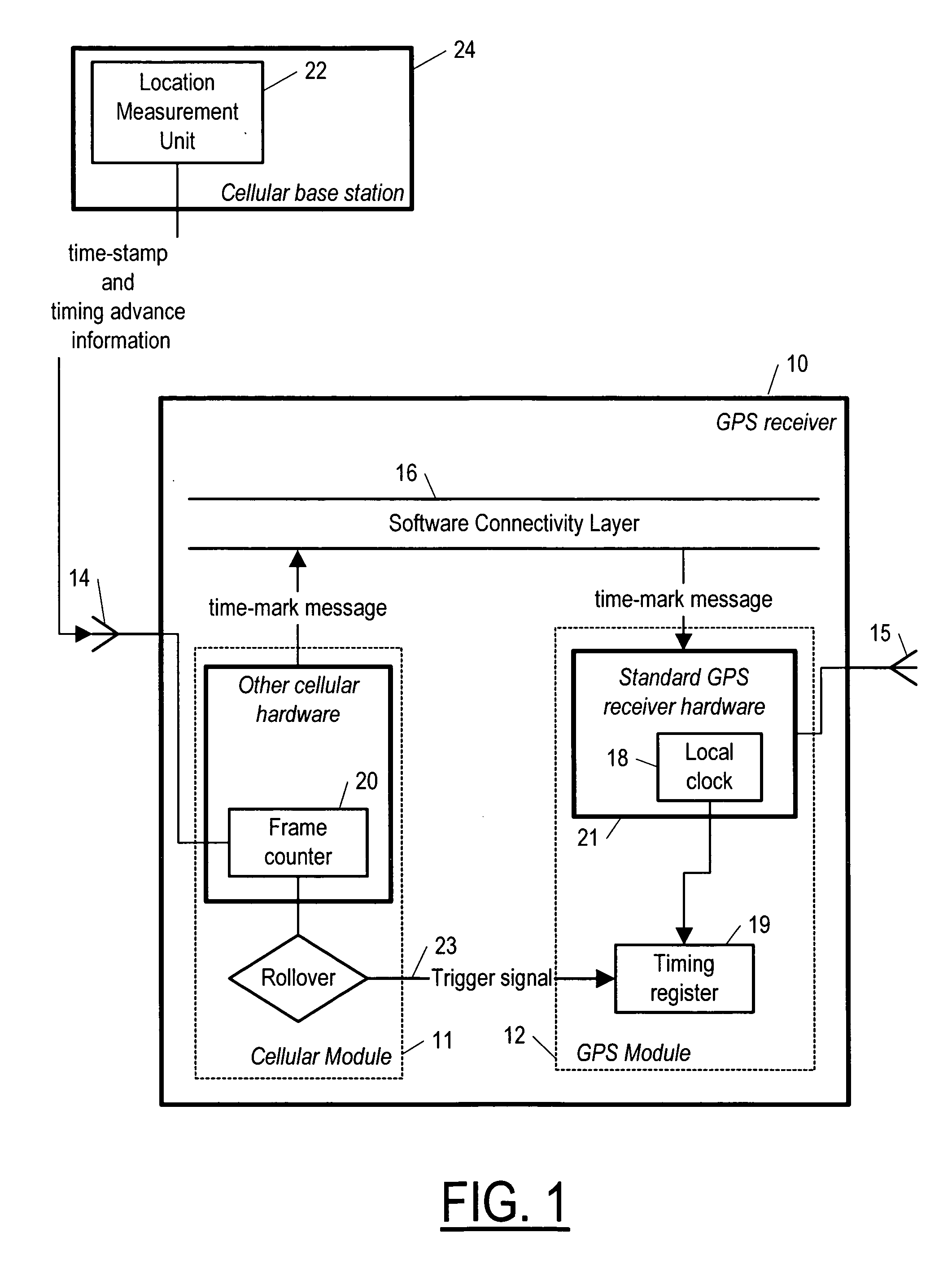
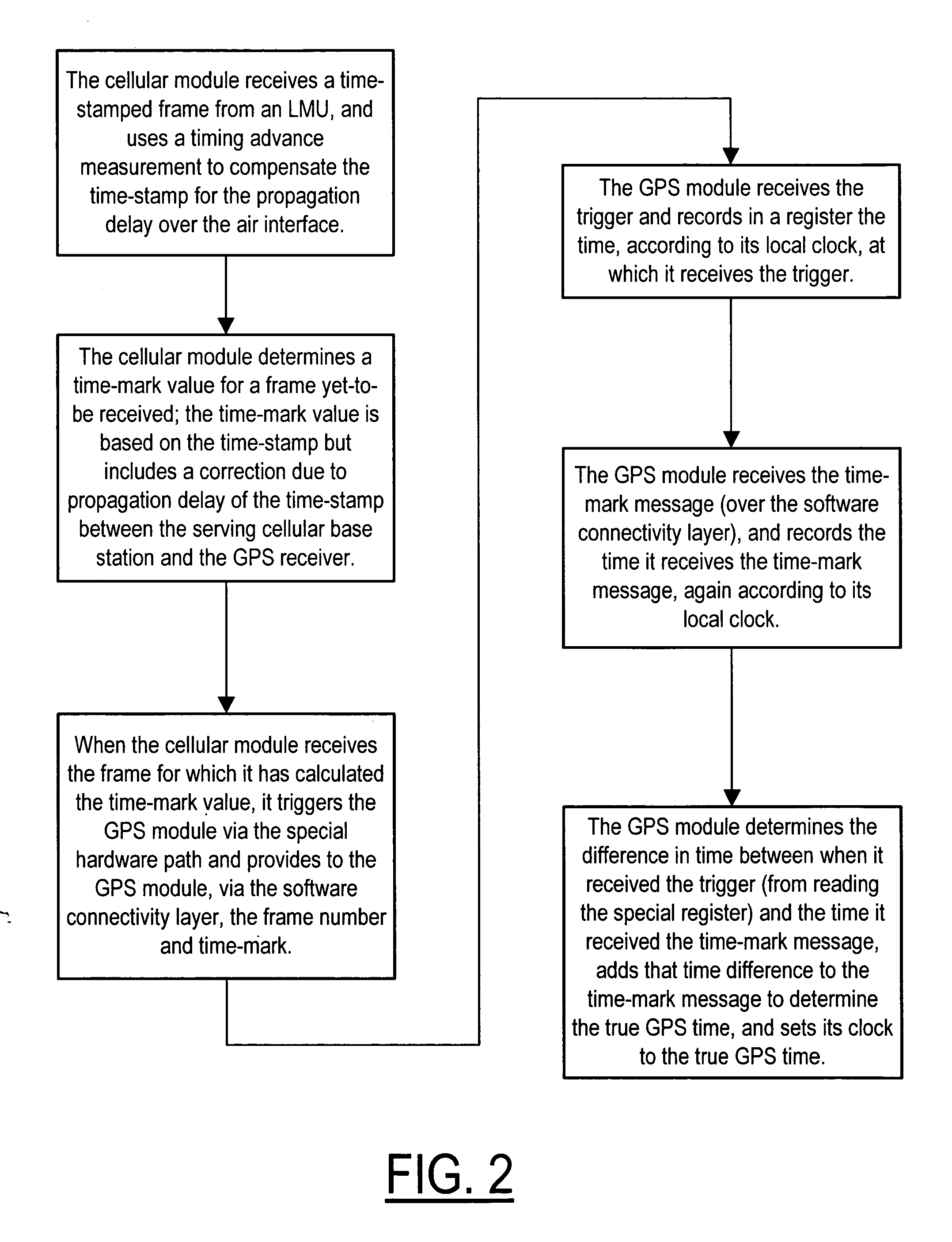
Method, apparatus and system for GPS time synchronization using cellular signal bursts
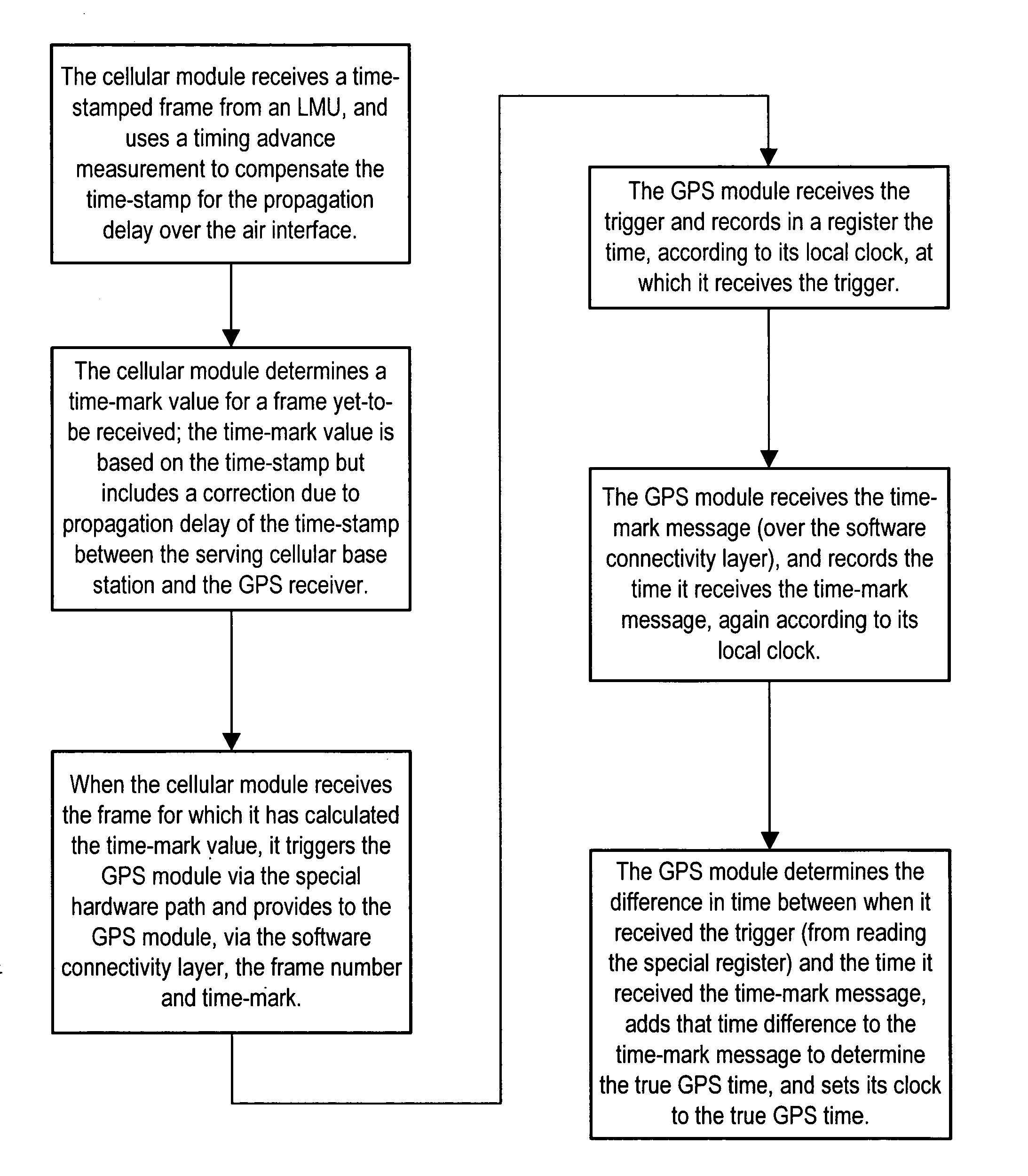
InactiveUS20060234724A1Avoid delayImprove accuracySynchronous motors for clocksSetting time indicationGlobal positioning system receiverReal-time computing
A system, apparatus and corresponding method by which to synchronize to a time reference a main module of a device—a main module such as global positioning system (GPS) receiver—using a cellular communication signal received by a cellular module also included in the device. To synchronize the main module to the reference time, the invention provides a method including the steps of: having the cellular module respond to the cellular communication signal by providing to a clock module of the main module a trigger pulse derived from the data component of the cellular communication signal, and also by providing to the main module information relating the trigger pulse to a universal time. The main module is then able to resolve a value for time based on the information relating the trigger pulse to a universal time and the trigger pulse.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY +1
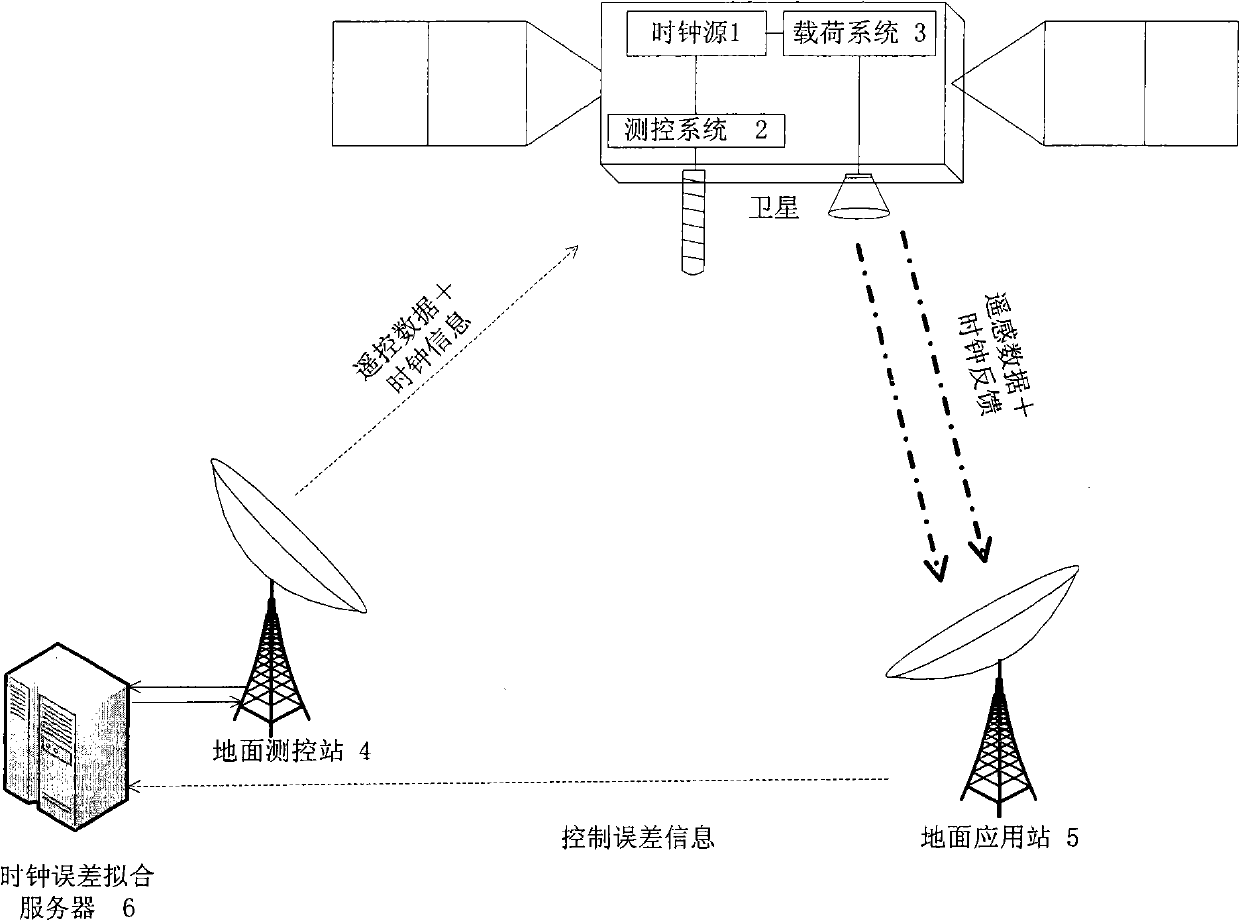
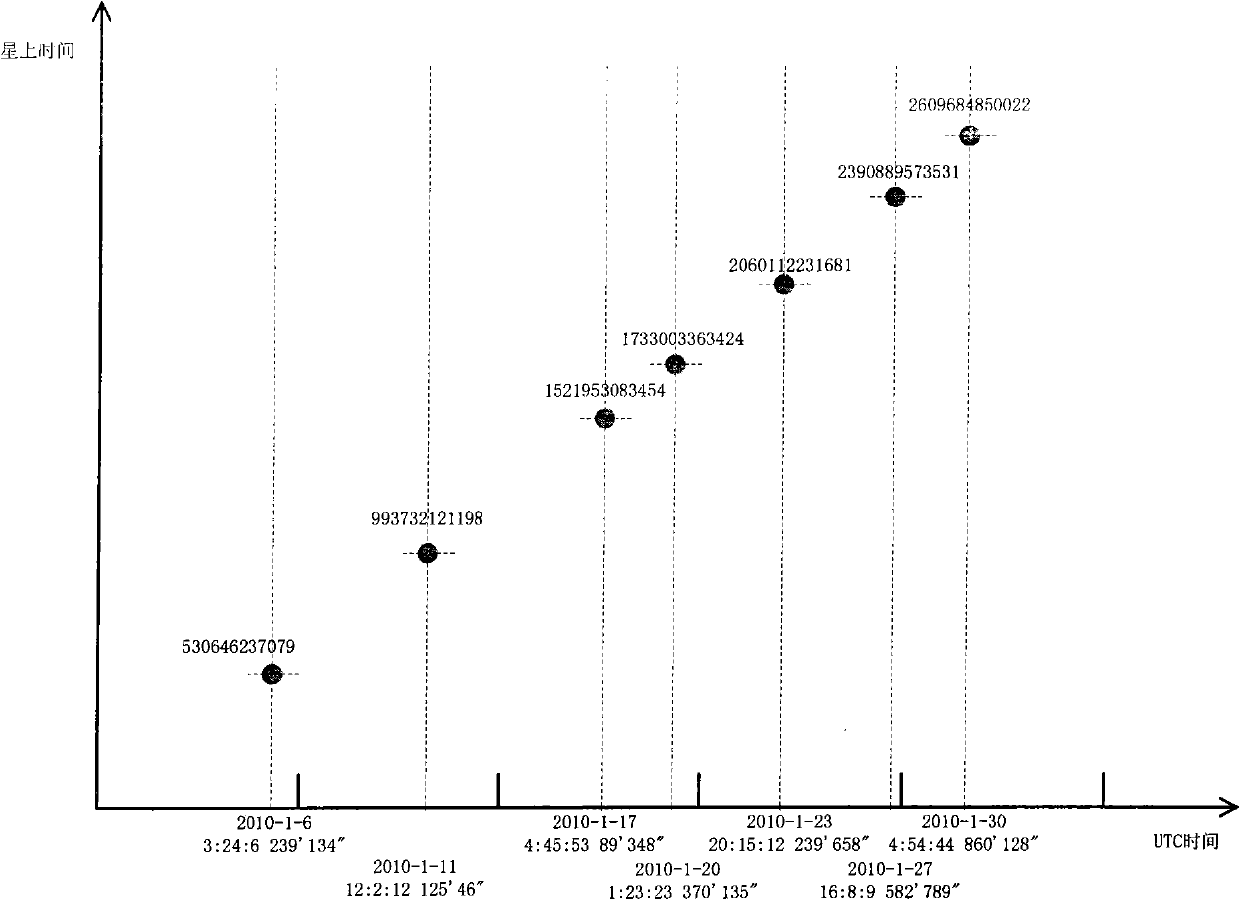
Calibration system for satellite clock and calibration method thereof
ActiveCN102566408AHigh precisionSetting time indicationRadio-controlled time-piecesControl systemClosed loop feedback
The invention relates to the calibration of a satellite clock, and discloses a calibration system for a satellite clock and a calibration method of the system. The calibration system comprises a satellite clock source, a satellite measuring and controlling system, a satellite load system, a ground measuring and controlling station, a ground application station and a clock error fitting server. The calibration method comprises the following steps: 1) compiling a satellite program control operation sheet and loading to a satellite; 2) executing program control operation; 3) generating load data; 4) downloading load data; 5) analyzing the load data to calculate current UTC (Coordinated Universal Time); and 6) carrying out clock data fitting, and giving a corresponding relation between satellite time and the UTC. According to the calibration system for a satellite clock and the calibration method, the current problem that only satellite clock source precision is blindly improved to cause the complicated design of the satellite clock system and a control system, but the improvement effect of the practical working precision is not obvious can be solved. The working precision of the satellite is economically and reliably improved with a large-system closed loop feedback method.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
Method for correcting clock of automatic ship identifying terminal equipment
ActiveCN102938220ATo achieve the purpose of clock calibrationIssues Affecting SendingSynchronous motors for clocksMarine craft traffic controlThree levelClock correction
The invention relates to a method for correcting a clock of automatic ship identifying terminal equipment. The method comprises the following steps that: a clock correcting module acquires a UTC (universal time coordinated) time through a GPS (global position system) module and calculates errors of a local time through the UTC time; the error of a local clock is calculated after the errors are accumulated for a period; three levels of clock adjusting parameters are calculated through the errors; a clock compensating module compensates the local time according to the three levels of clock adjusting parameters so as to control the error of the local clock within a relatively small range, then the purpose of clock correction is achieved. By utilizing the method, AIS (automatic identification system) ship automatic identification terminal equipment can correct the error caused by the inaccuracy of the local clock, ensure that the synchronous error between the local time and the UTC time is not larger than 0.1 time slot (2.6ms) within half an hour under the condition that the UTC time reference is lost, and ensure that the AIS time synchronization in broadcast messages is still met. Therefore, the problem that the message transmission of other equipment is influenced when the AIS ship automatic identifying terminal equipment transmits a message due to the fact that the equipment time is not synchronous with the UTC time is solved.
Owner:TIANJIN 712 COMM & BROADCASTING CO LTD
Automatic time-tick synchronization system of intelligent electronic equipment of transformer substation
InactiveCN101795020AHigh precisionAvoid complex structuresCircuit arrangementsInformation technology support systemTransformerNetwork structure
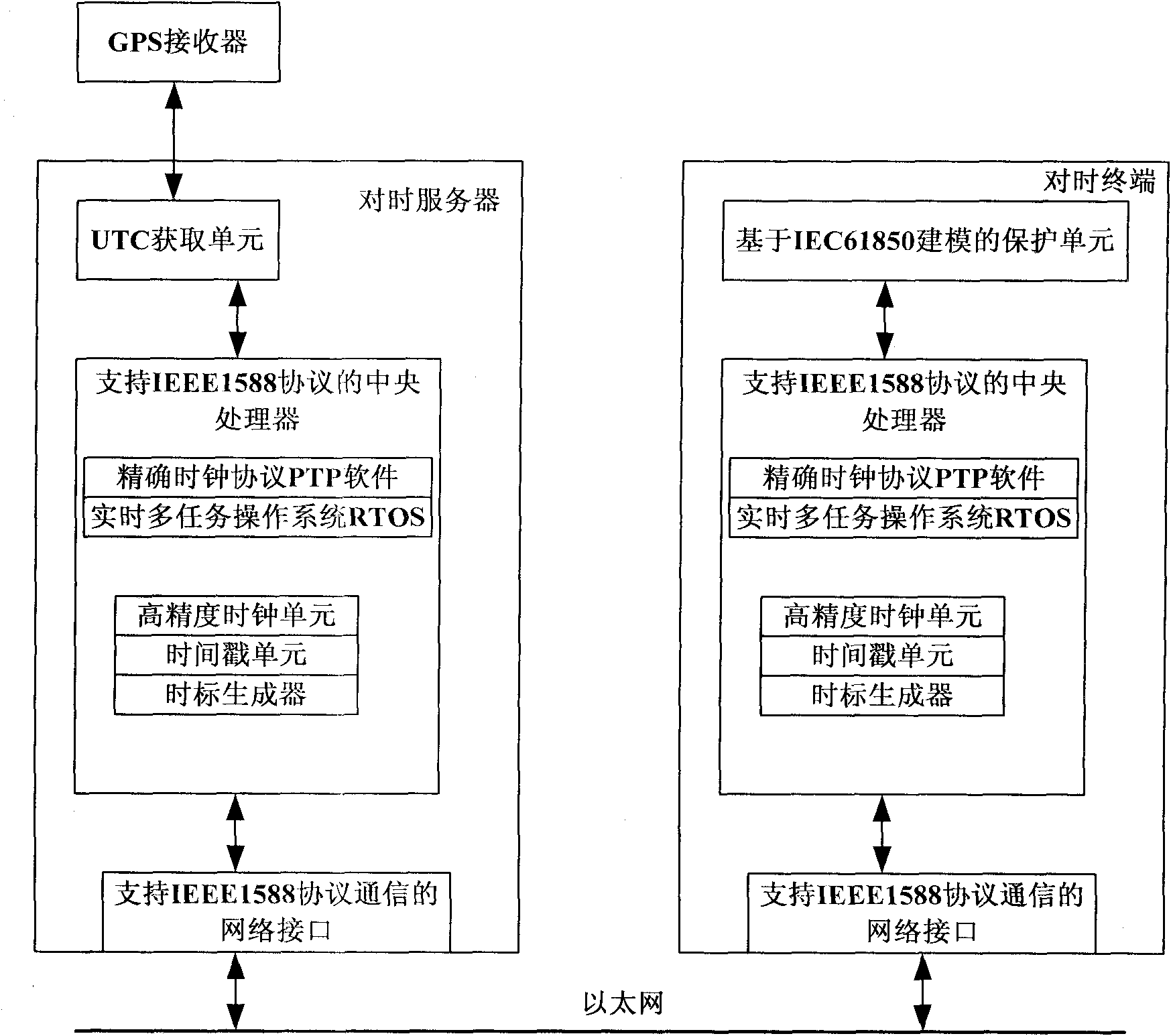
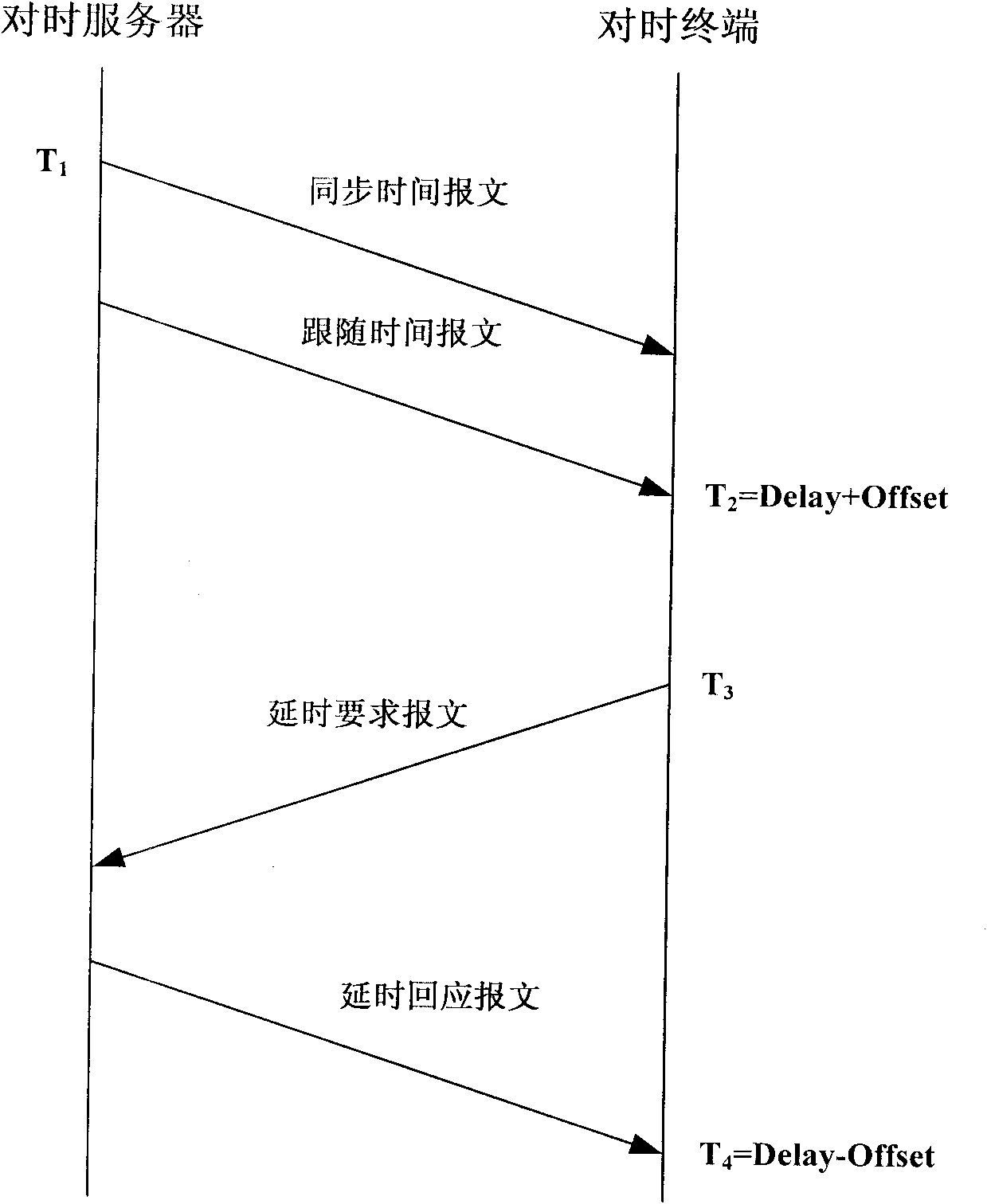
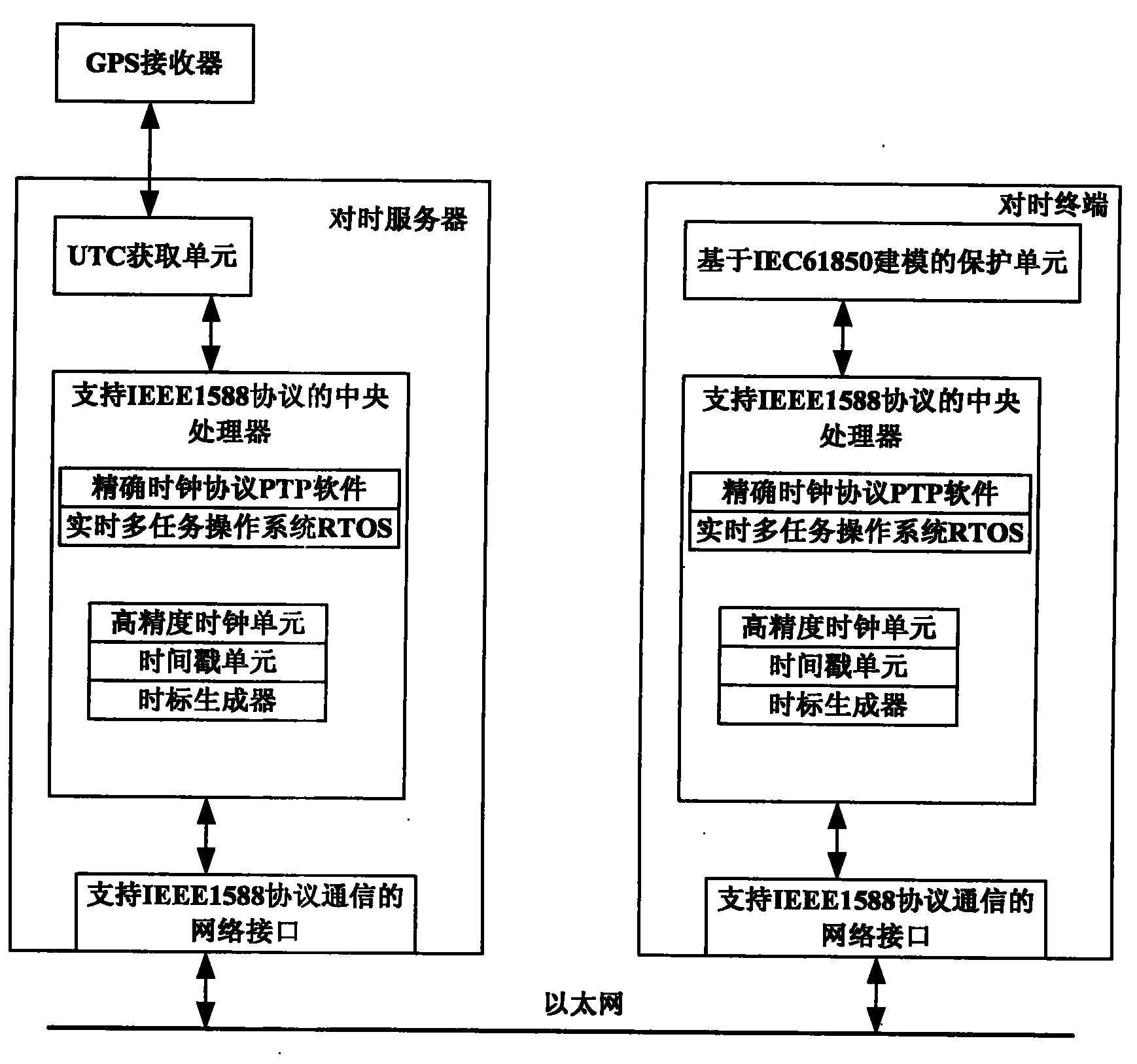
The invention discloses an automatic time-tick synchronization system of intelligent electronic equipment of a transformer substation in the technical filed of automatic time-tick of intelligent electronic equipment of a transformer substation in the power sector. The automatic time-tick synchronization system comprises a time-tick server and a time-tick terminal installed on the intelligent electronic equipment of the transformer substation. The time-tick server comprises a UTC (Universal Time Coordinated) acquisition unit, a central processing unit supporting an IEEE1588 protocol and a network interface supporting IEEE1588 protocol communication; the time-tick terminal comprises a protection unit based on IEC61850 modeling, a central processing unit supporting the IEEE1588 protocol and a network interface supporting IEEE1588 protocol communication; and the time-tick server and the time terminal are connected by the network interfaces supporting IEEE1588 protocol communication. The invention avoids the problems of complicated network structure and overhigh cost of the traditional time-tick system and improves the accuracy of clock synchronization.
Owner:四方华能电网控制系统有限公司
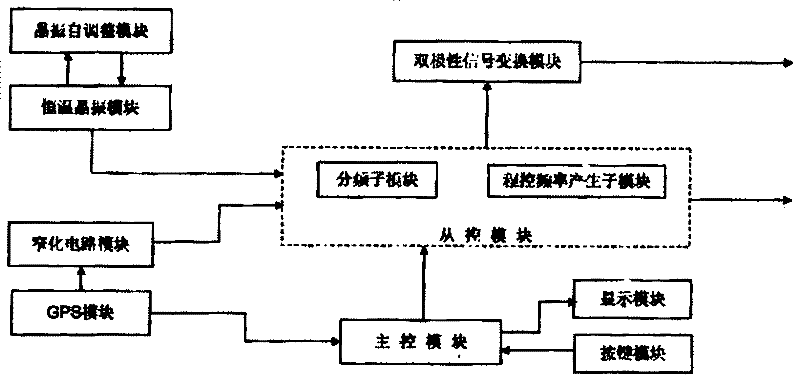
Clock source device based on GPS (global positioning system) and constant-temperature crystal oscillator and synchronous control method
InactiveCN102510320AEliminate cumulative errorsSolve the problem of short time failureTime-division multiplexSatellite radio beaconingPulse-per-second signalGlobal Positioning System
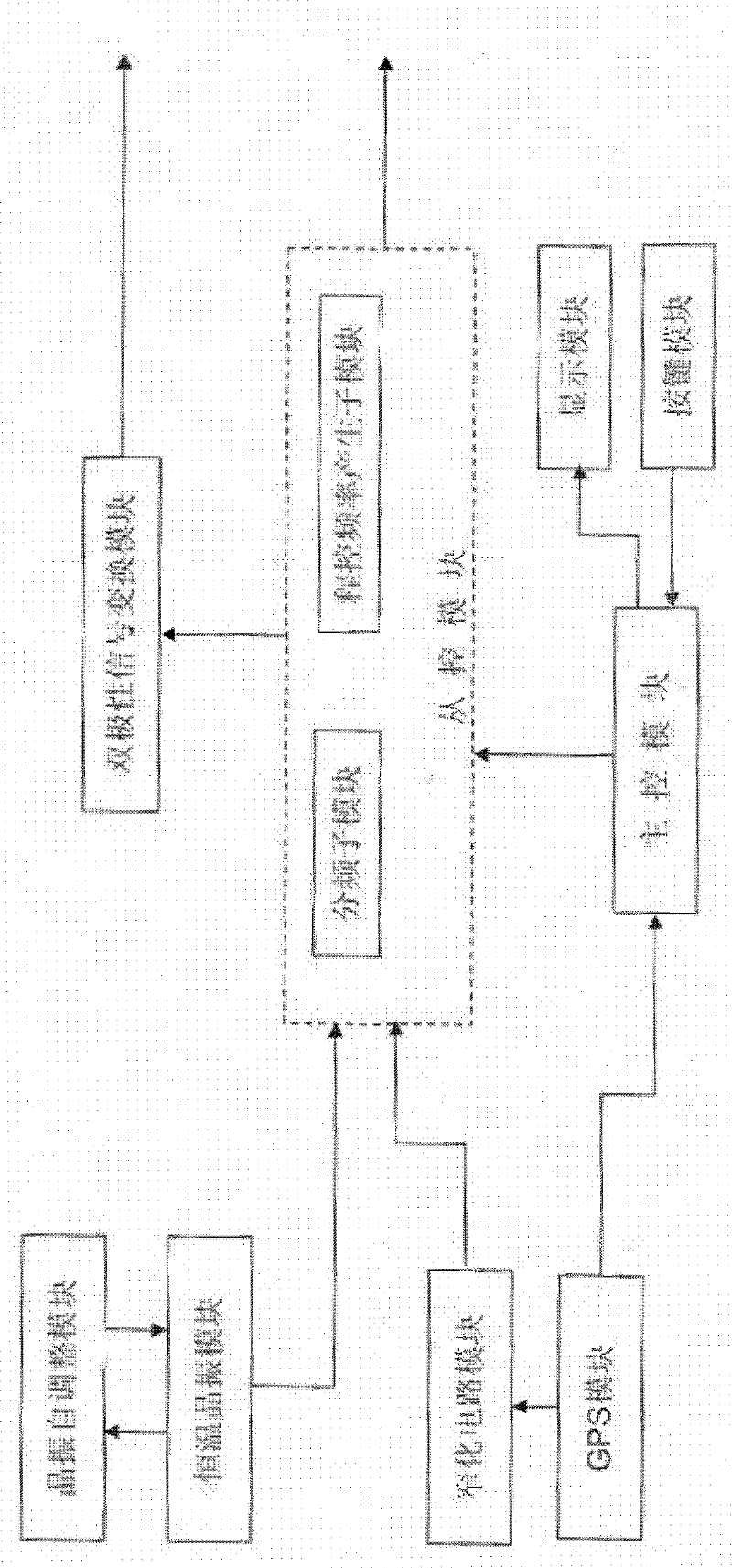
The invention relates to a clock source device based on a GPS (global positioning system) and a constant-temperature crystal oscillator and a synchronous control method. The clock source device comprises a constant-temperature crystal oscillator module, a master control module, a GPS module, a narrowing circuit module and an auxiliary control module and the like, wherein the constant-temperature crystal oscillator module is connected with the auxiliary control module, the GPS module receives satellite pulse-per-second signals, the auxiliary control module resets a fractional-frequency submodule therein at the regular time according to the satellite pulse-per-second signals and eliminates accumulated errors of the constant-temperature crystal oscillator. The synchronous control method includes calibrating crystal oscillator phase voltage; receiving satellite signals by the GPS module; inputting selected frequency signals to the main control module through a key module; sending the GPS pulse-per-second signals which are subjected to narrowing treatment into the auxiliary control module; sending clock frequency signals of the constant-temperature crystal oscillator module into the auxiliary control module; resetting the fractional-frequency submodule by the auxiliary control module at the regular time according to GPS signals; and selecting signal output frequency signals according to frequency. The frequency signals and UTC (universal time coordinated) are synchronous by the aid of the GPS combined with the constant-temperature crystal oscillator, and the phase error is smaller than 100ns.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
System and method for enhancing broadcast programs with information on the world wide web
ActiveUS7673316B2Enhanced informationEasy accessTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionTelevision receiversGlobal Positioning System
The present invention is directed to a system and method for viewer real-time access complementary information related to a broadcast program including selecting a plurality of topics drawing his or her attention and for accessing additional information related to these topics from the WWW. The system is based on a synchronization of the local times of receivers and transmitters according to a same universal-time. The synchronization uses a universal time such as the Global Positioning System Time, the Global Orbiting Navigational Satellite System time or others GPS or GLONASS receivers may be integrated or connected to devices independent or separate from the radio or television receivers. The system includes associated with the transmitted information and can be retrieved, selected and activated during the time intervals for which they have been defined.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP +1
Associating a Universal Time with Received Signal
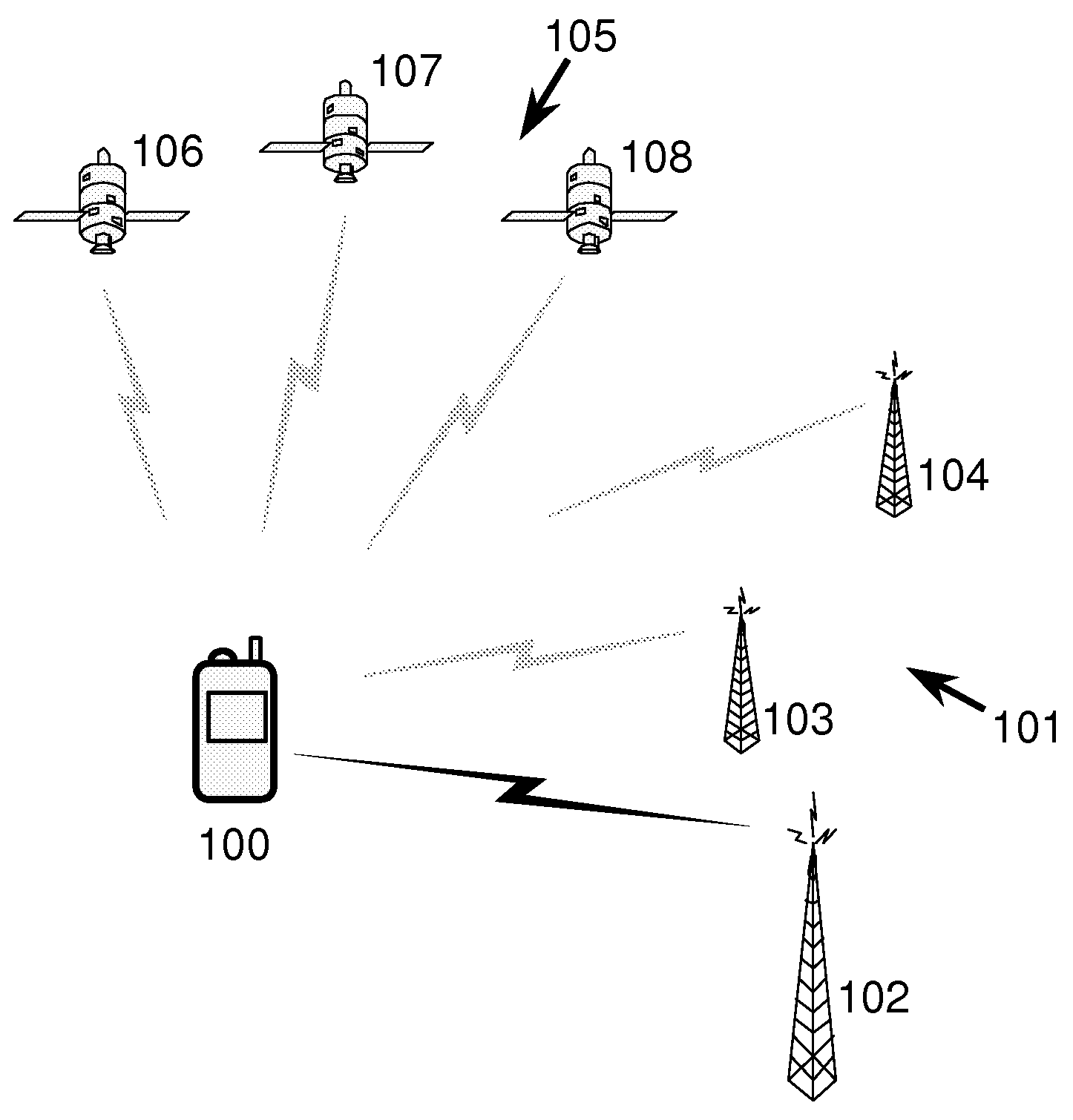
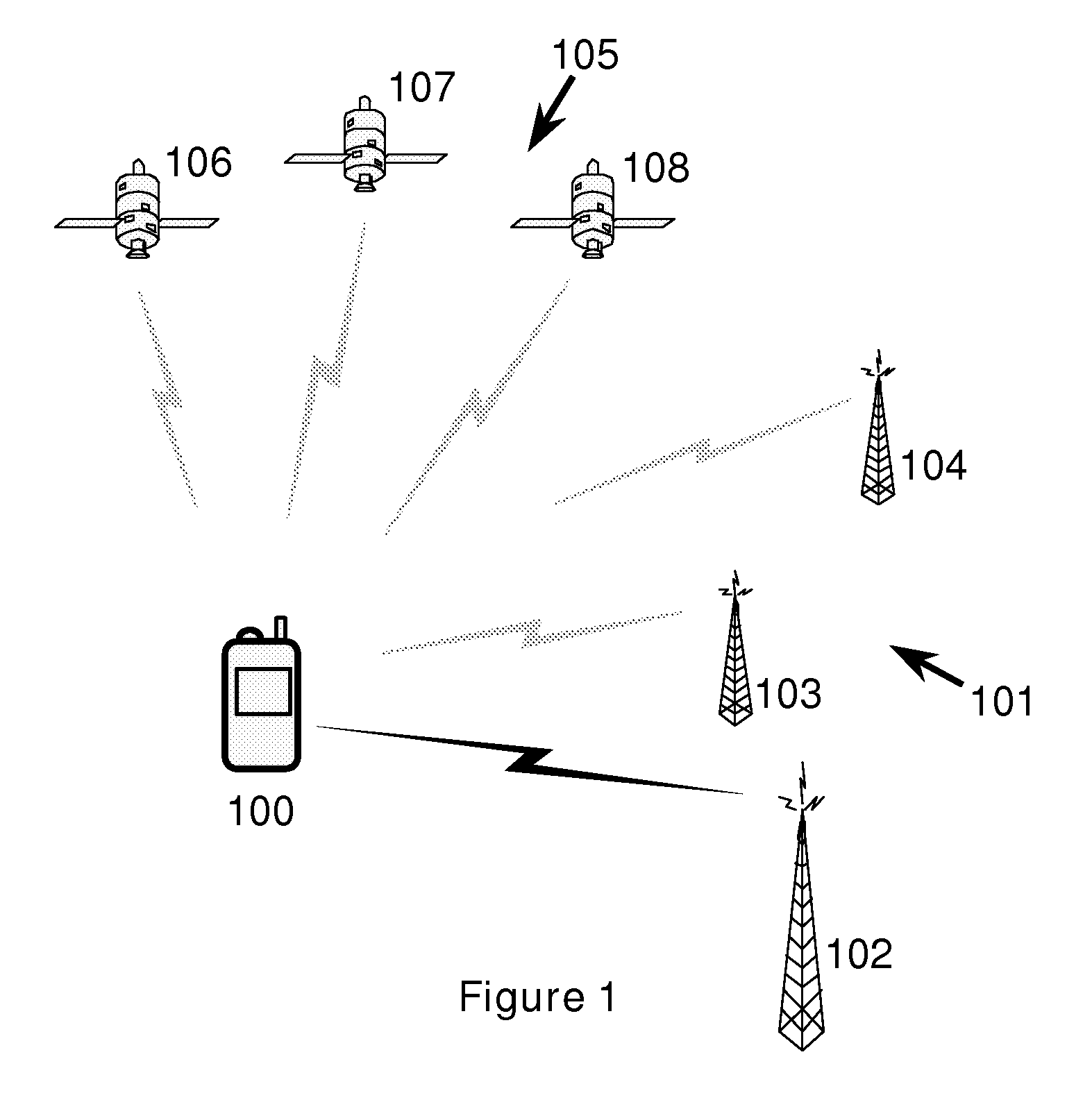
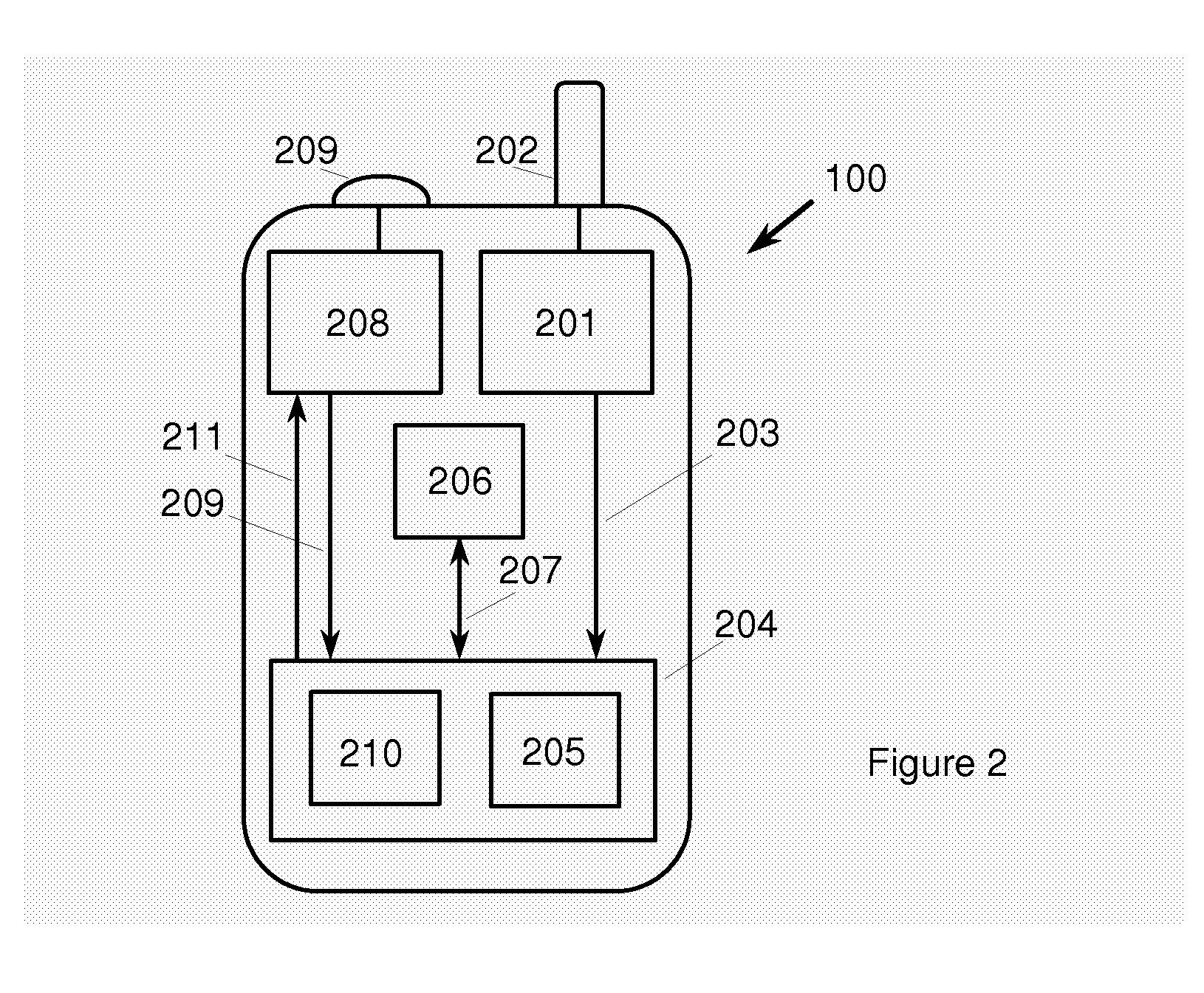
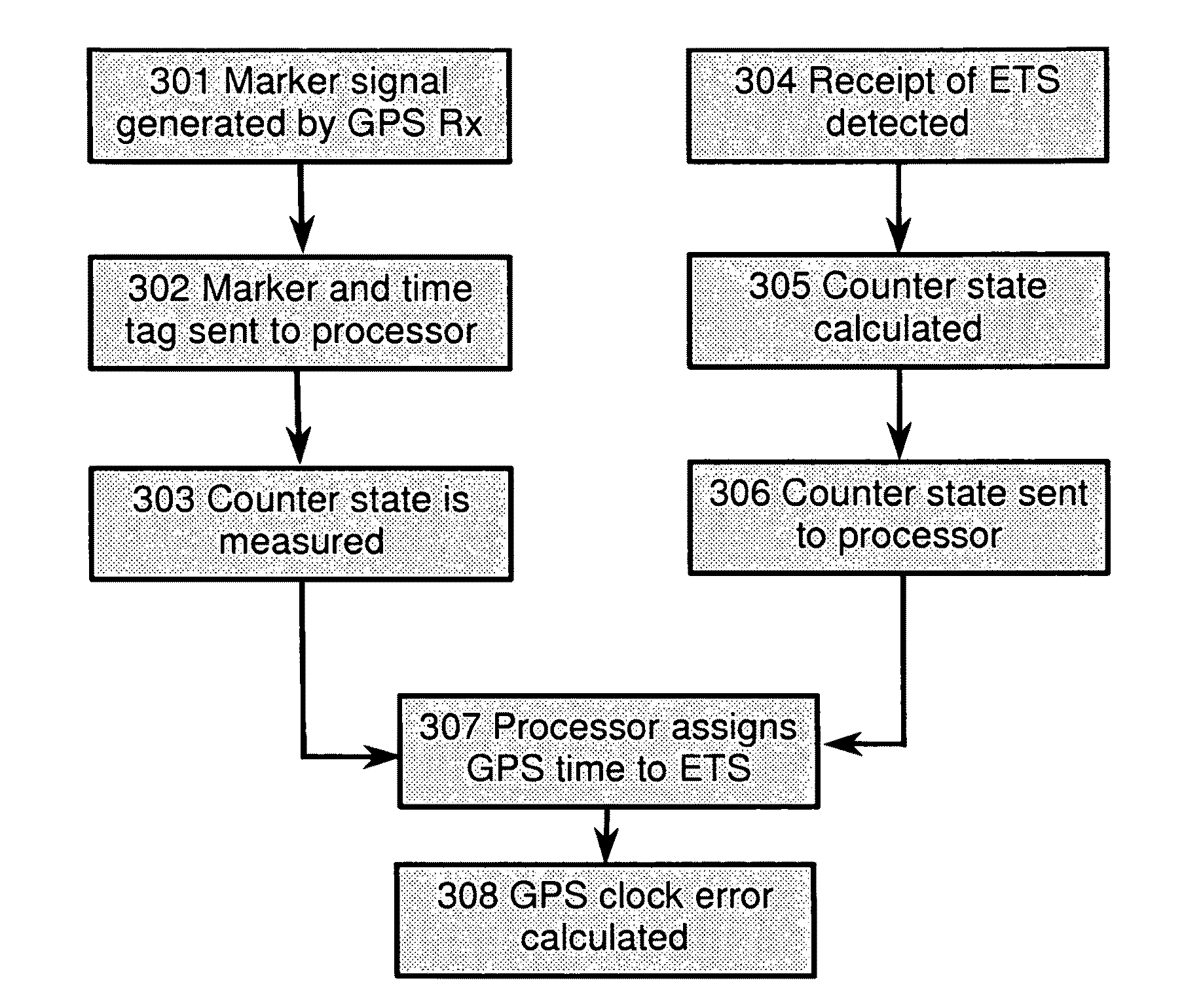
ActiveUS20090273518A1Uncertainty in arrival timeReducing range of timeBeacon systemsSatellite radio beaconingSignal correlationPositioning system
A method of associating a universal time with time of arrival information of an identified component of a signal at a terminal of a radio positioning system is disclosed. In the method a marker signal with an associated universal time tag is obtained from a timing device (or the marker signal is obtained from an independent oscillator and a universal time tag assigned to the marker signal), and the time or phase relationship between the marker signal (or between the time of arrival information of said identified component respectively) and the oscillator is measured. The time of arrival information of said identified component relative to the oscillator is determined and the universal time corresponding to the time of arrival information of said identified component is calculated from said universal time tag and said measured time or phase relationship, before the calculated universal time is associated with said time of arrival information.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE POSITIONING SYST LTD
Associating a universal time with received signal
A method of associating a universal time with time of arrival information of an identified component of a signal at a terminal of a radio positioning system is disclosed. In the method a marker signal with an associated universal time tag is obtained from a timing device (or the marker signal is obtained from an independent oscillator and a universal time tag assigned to the marker signal), and the time or phase relationship between the marker signal (or between the time of arrival information of said identified component respectively) and the oscillator is measured. The time of arrival information of said identified component relative to the oscillator is determined and the universal time corresponding to the time of arrival information of said identified component is calculated from said universal time tag and said measured time or phase relationship, before the calculated universal time is associated with said time of arrival information.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE POSITIONING SYST LTD
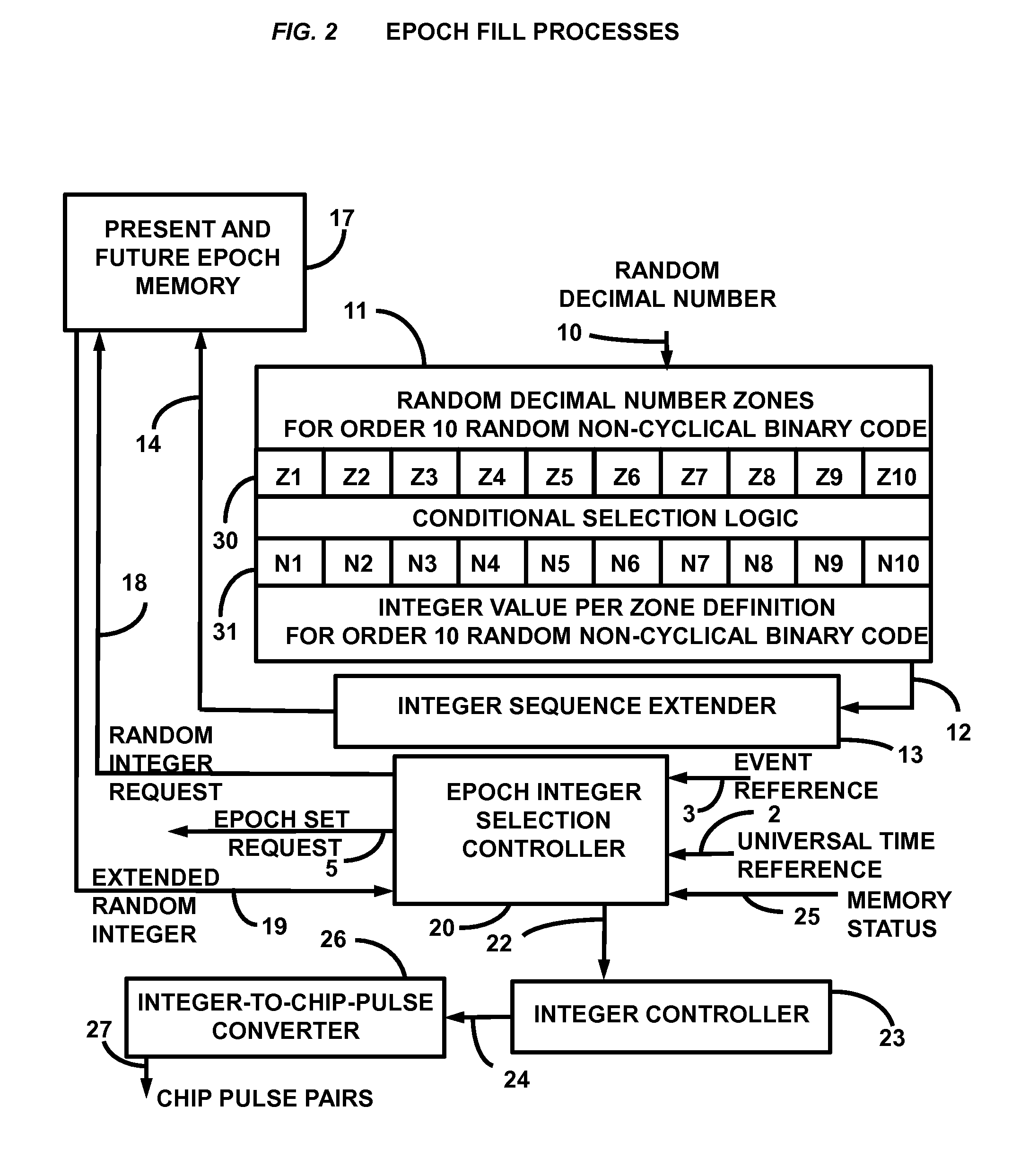
Random Non-Cyclical Binary Code Generator
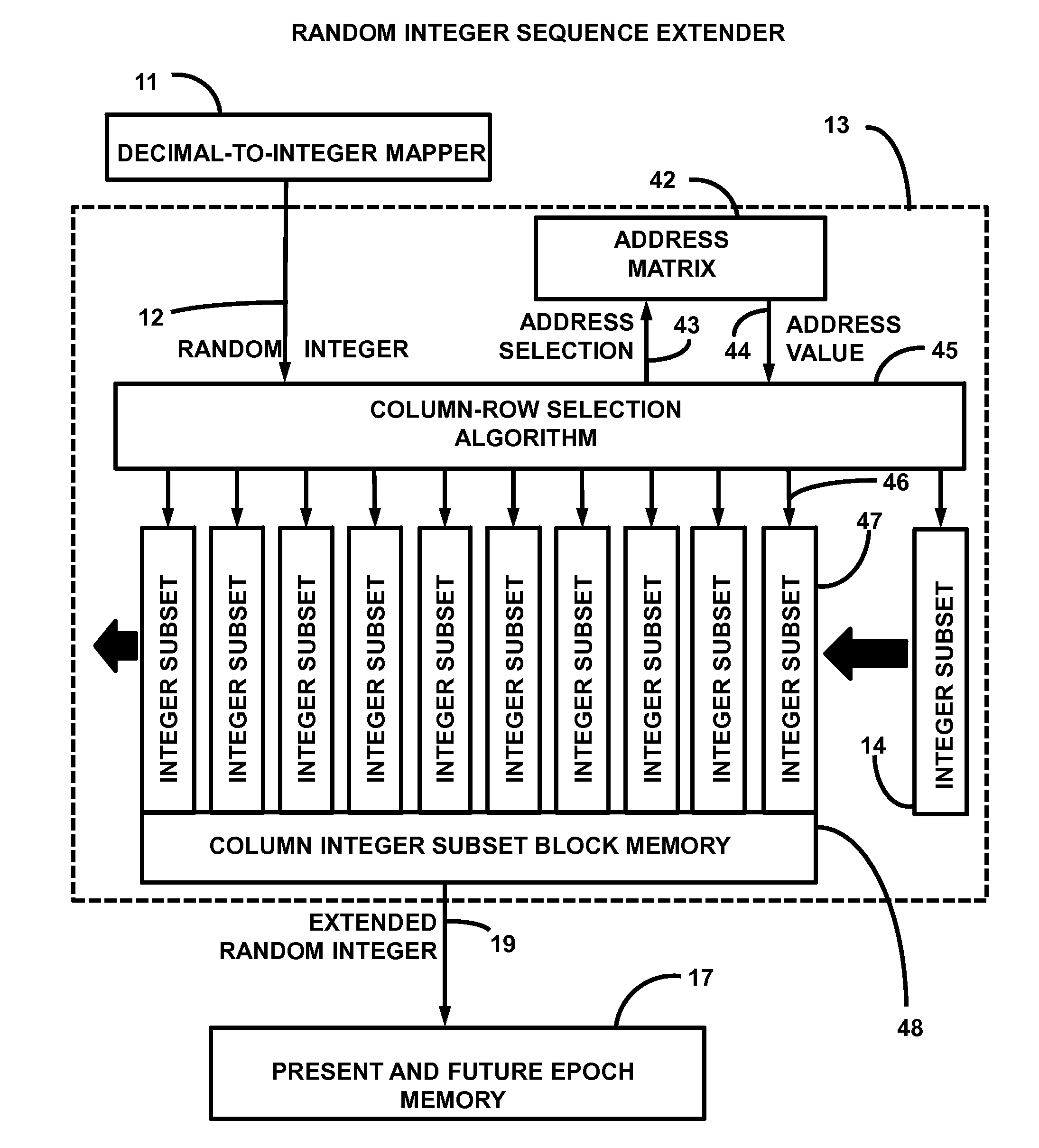
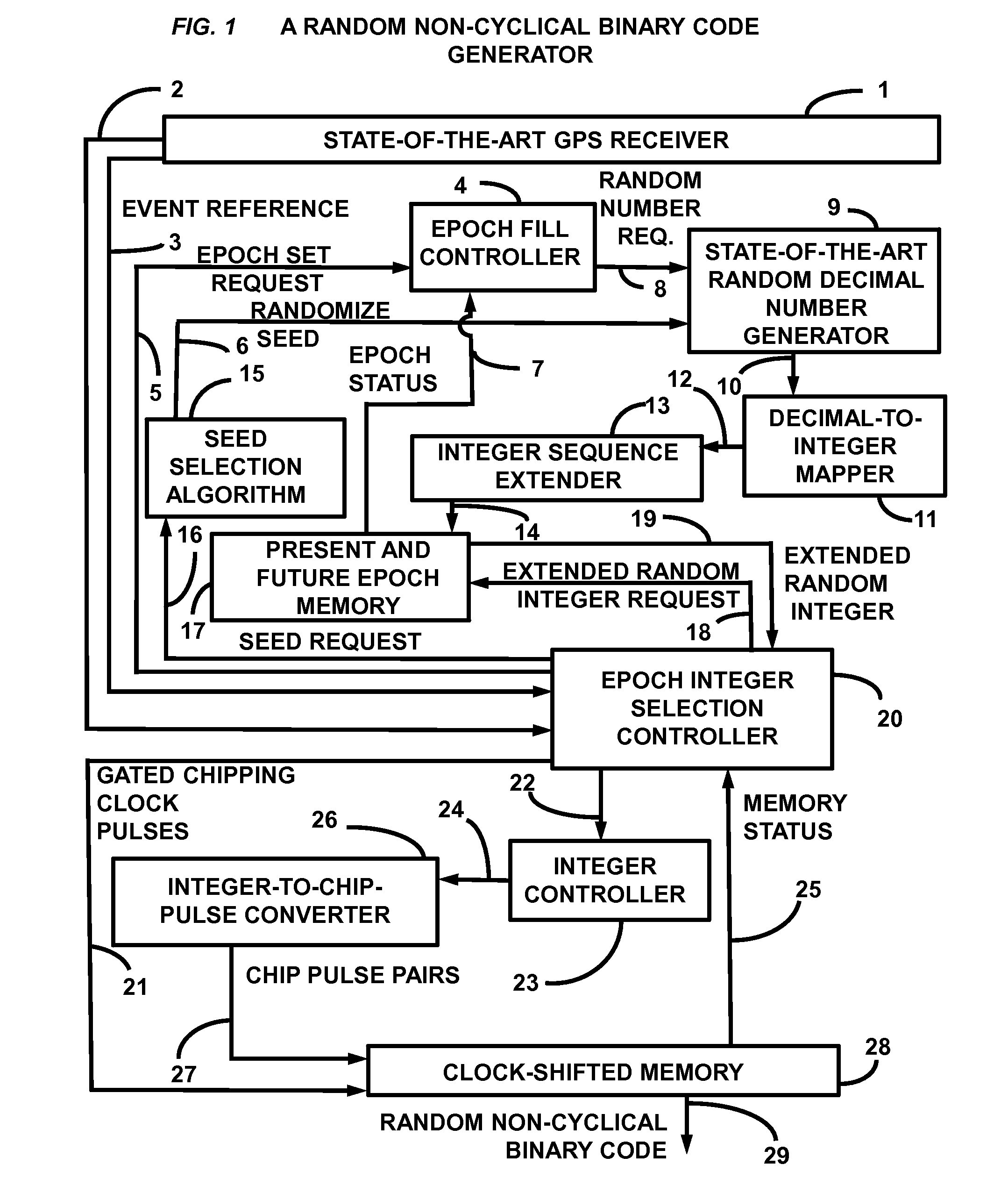
Presented is a random non-cyclical binary code generator for communications systems. A random non-cyclical sequence of integers from a random number generator is extended in length to form an extended integer sequence. This integer set is immediately loaded into a 10-minute epoch memory consistent with 10 minutes of chips. These integers are then synchronously retrieved from memory under GPS time-of-day control. Retrieved integers are immediately converted into pulse pairs of all ones followed by all zeros with each pulse width equal to the integer value in chips. The chips are immediately concatenated to a chipping clock shifting memory wherein each memory location is a unique phase source of the binary code. The memory length in chips is twice the range uncertainty for a 10 MHz chip rate, with the center chip of the shifting memory maintained as the source of universal time synchronized local binary code.
Owner:NEFF RUPERT THEODORE
Multiple star image and attitude associated star sensor internal parameter calibration method and device thereof
ActiveCN107449444ARealize splicing associationImprove calibration accuracyMeasurement devicesTime informationGyroscope
The invention discloses a multiple star image and attitude associated star sensor internal parameter calibration method and a device thereof. A GPS antenna 3, a gyroscope unit 1 and a to-be-calibrated star sensor 2 communicate with a GPS receiver 4 respectively, and a data processing computer 5 is connected with the gyroscope unit 1 and the to-be-calibrated star sensor 2 respectively; synchronous data acquisition of the gyroscope unit 1 and the star sensor 2 is realized by virtue of UTC (universal time coordinated) time information acquired by the GPS receiver 5, and calibration algorithm solution of the to-be-calibrated star sensor 2 is completed in the data processing computer 5. According to the method, the gyroscope unit is used for providing accurate rotating angle information to implement splicing association of a plurality of frames of star images, thereby increasing observed data samples for internal parameter calibration of the star sensor; the method can be used for calibration under a dynamic condition, no strict requirements are made to the motion state of the to-be-calibrated star sensor 2, the calibration accuracy and reliability are improved, a calibration flow is simplified, dynamic calibration of the to-be-calibrated star sensor 2 can be conveniently implemented, and the method and the device are also applied to calibration of an inertial / celestial combined navigation system.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Electronic resume recording device of unmanned aerial vehicle
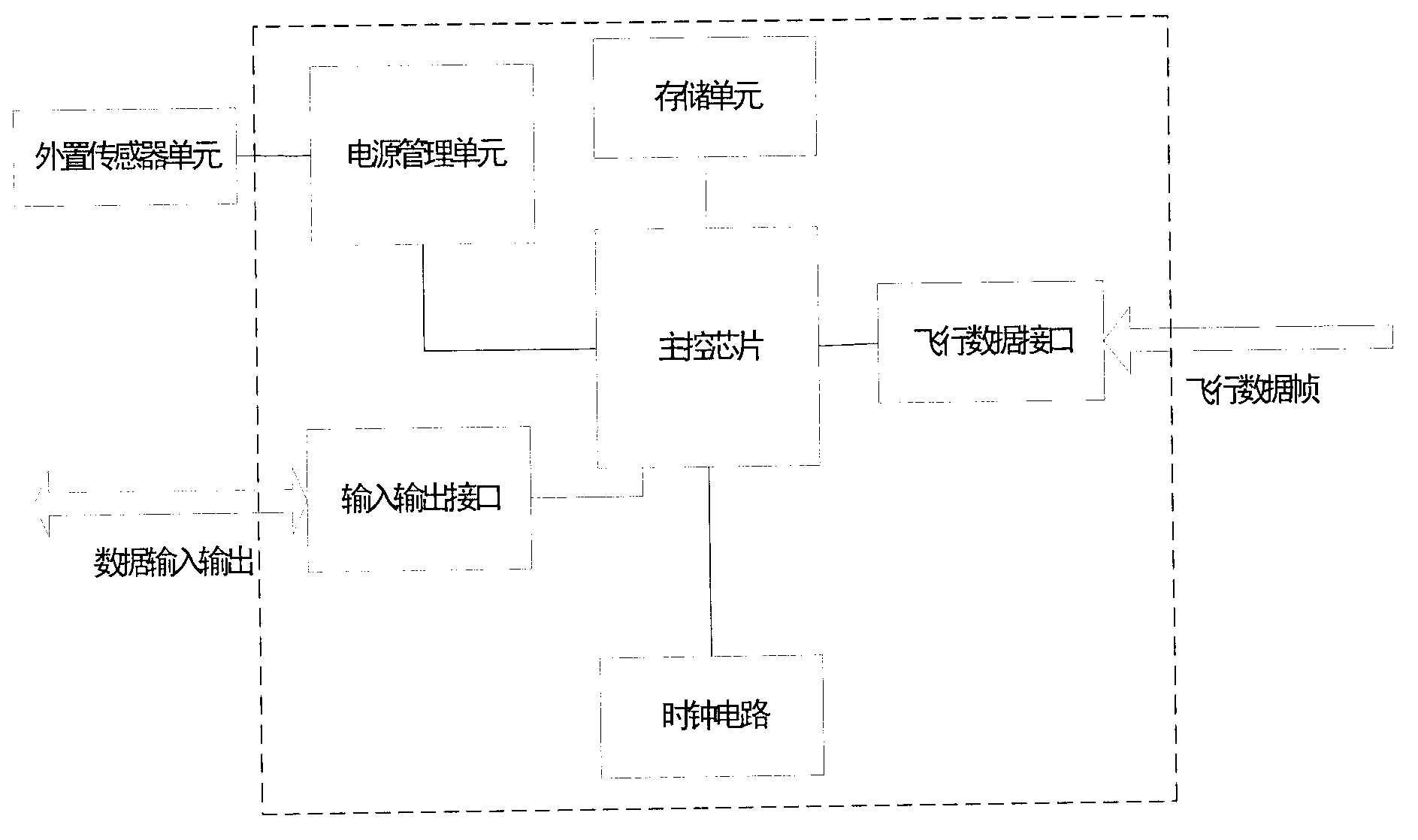
ActiveCN102915576ARealize simultaneous recordingAchieve finishingRegistering/indicating working of machinesUncrewed vehicleWork status
The invention discloses an electronic resume recording device of an unmanned aerial vehicle, which comprises a main control chip, a flight data receiving interface, a clock circuit, a storage unit and a power management chip, wherein the main control chip reads flight data frames through the flight data receiving interface, and extracts a status bit and UTC (universal time coordinated) time in the flight data frames; the flight data frames are added with time stamps output by the clock circuit and output to the flight data region in the storage unit; the status bit is output to the resume use region of the storage unit; the UTC time is output to the clock circuit to carry out time correction on the clock circuit; the status bit is used for identifying the flight operation condition of the unmanned aerial vehicle; and the main control chip periodically queries the power supplying state of the power management chip and outputs the power supplying state to the resume use region of the storage unit. The electronic records such as device working conditions, storage environment, mounted equipment configuration information, flight and task data of the unmanned aerial vehicle are recorded.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF AEROSPACE AERODYNAMICS
Distributed relay selection method and device
ActiveCN101790218AReduce complexityImprove performanceHigh level techniquesWireless communicationChannel state informationTimer
Owner:BEIJING STARPOINT TECH COMPANY
Simulation method for super speed aircraft conformal sub-grid electromagnetic scattering characteristic analysis
ActiveCN105653747AFit closelyImprove adaptabilitySpecial data processing applicationsFinite difference methodRadar cross-section
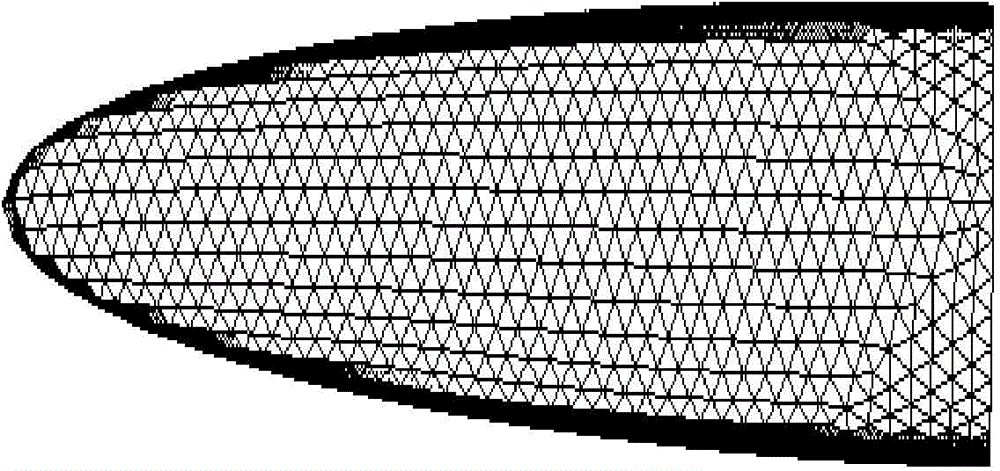
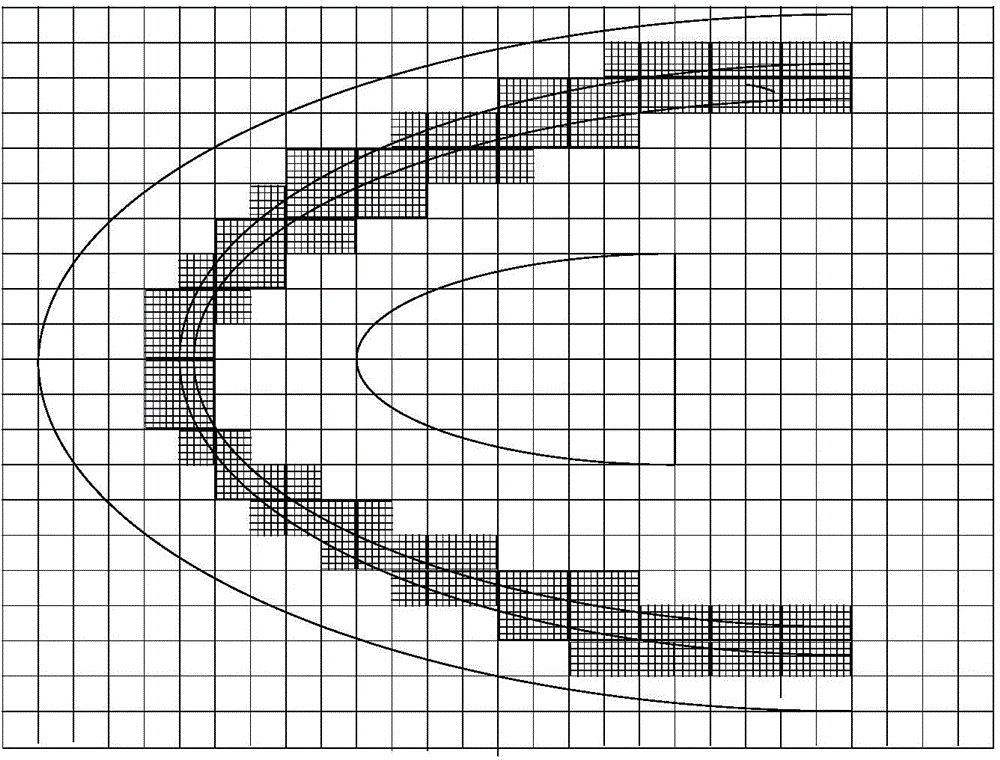
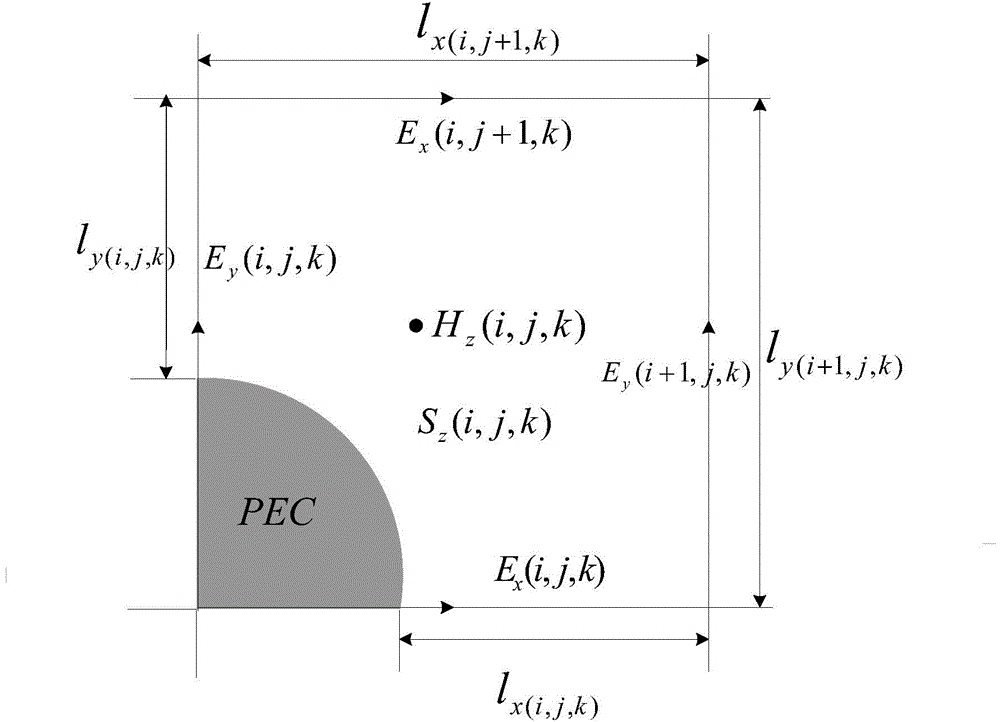
The invention discloses a simulation method for super speed aircraft conformal sub-grid electromagnetic scattering characteristic analysis. The simulation method includes the following steps: performing aerothermodynamics simulation according to an aerodynamic configuration, the flight speed and the flight height of an aircraft, and determining the plasma collision frequency and the plasma oscillation frequency of all parts through simulation information; performing subdivision on an aircraft model and a plasma sheath through a tetrahedron to obtain structure information of the aircraft model; mapping flow field point information to ridges of a finite difference time domain computing grid, and determining a zone with a relative dielectric constant more than 6 according to the collision frequency and the oscillation frequency on the ridges to perform sub-grid processing; processing junctions between the ridges of the finite difference time domain computing grid and a metal surface through a finite difference universal time domain method; and computing the plasma zone through an iterative formula of plasma to finally determine the radar cross section of the super speed aircraft. The simulation method has good adaptability and high computational efficiency.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com