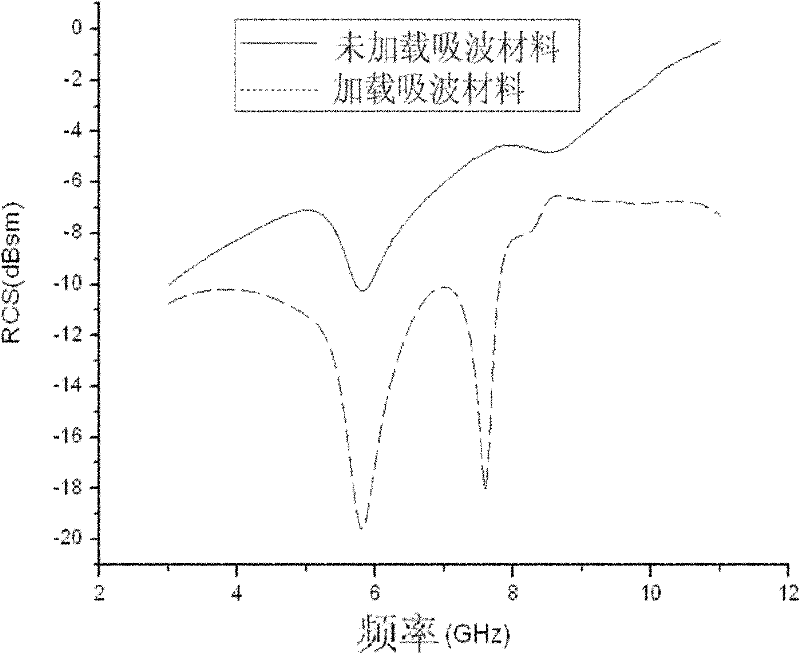
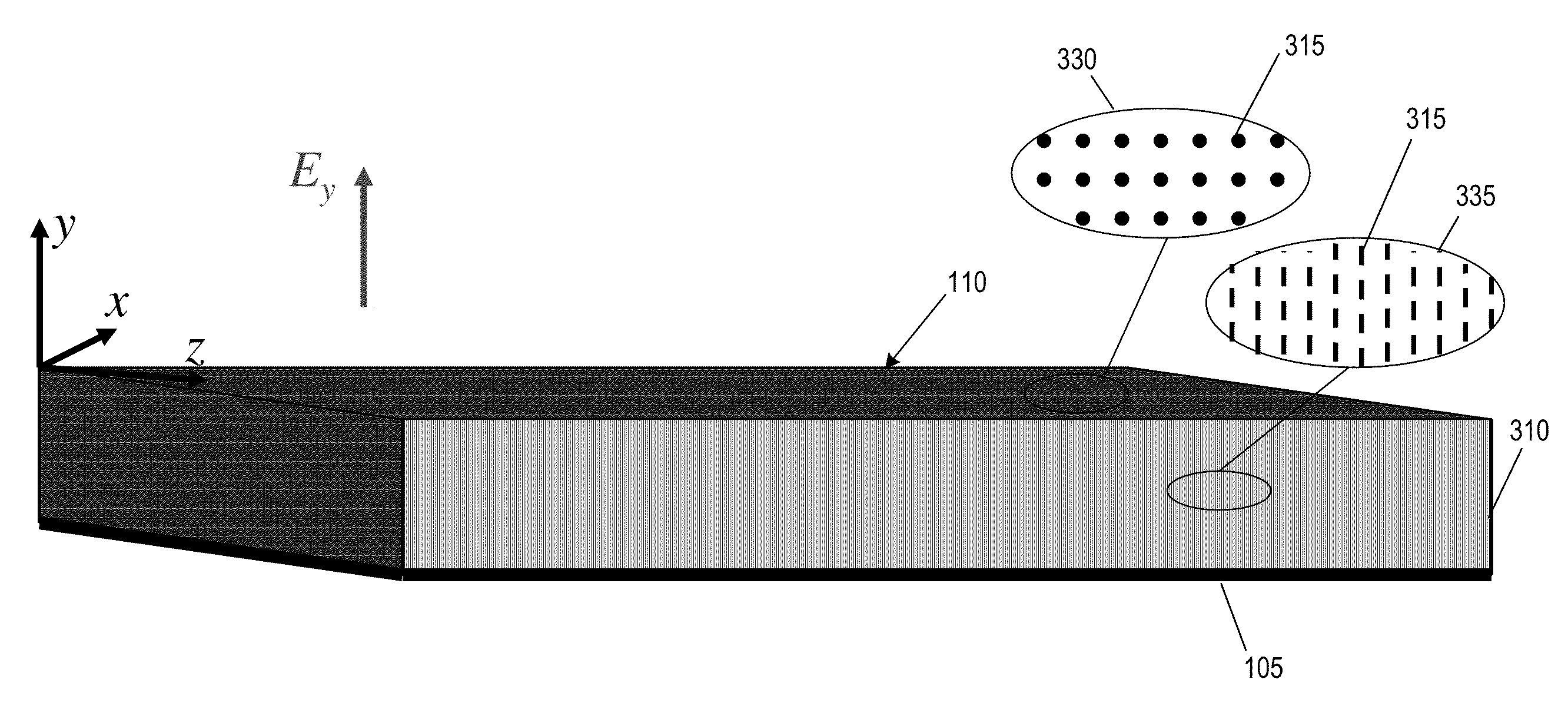
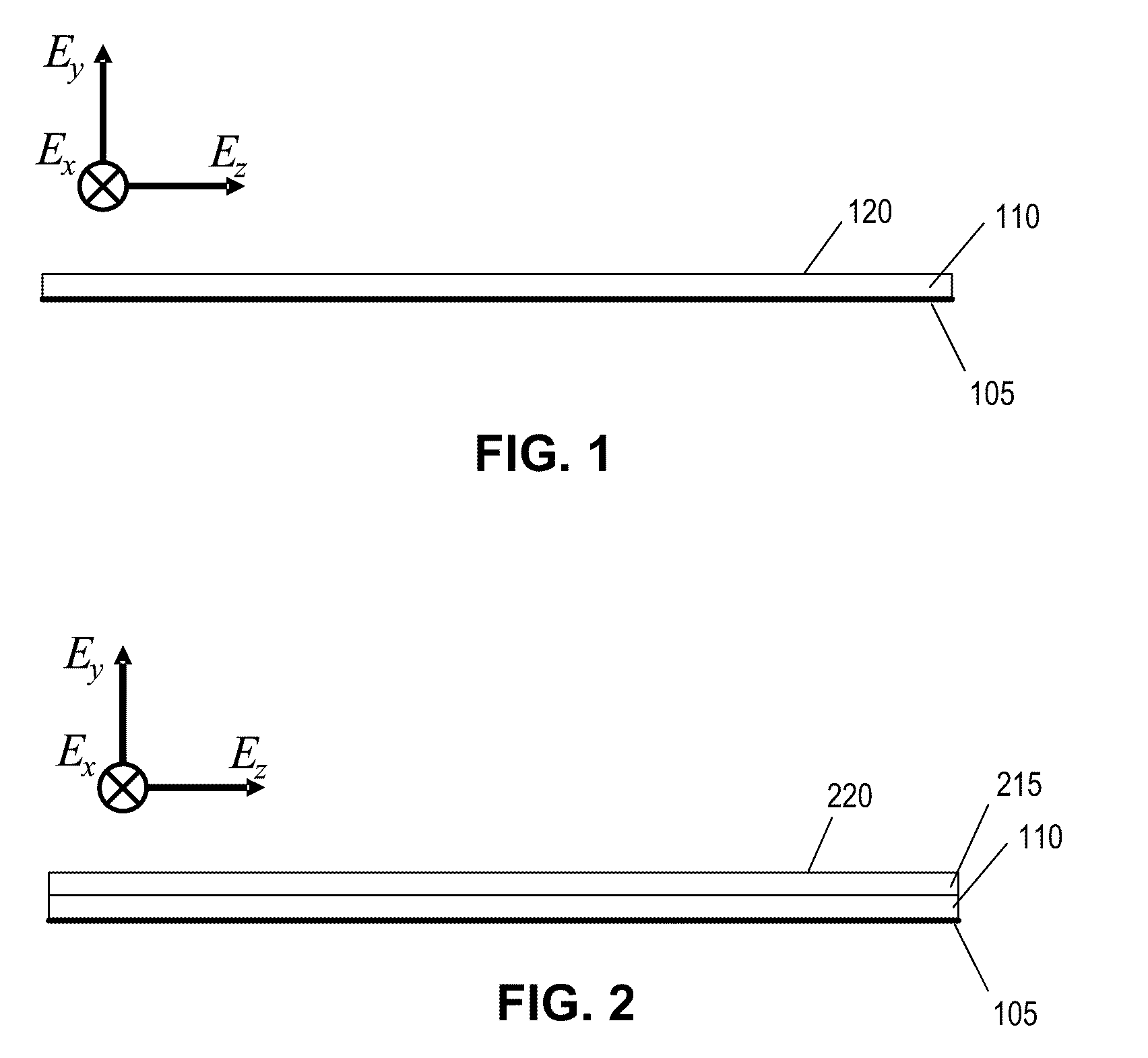
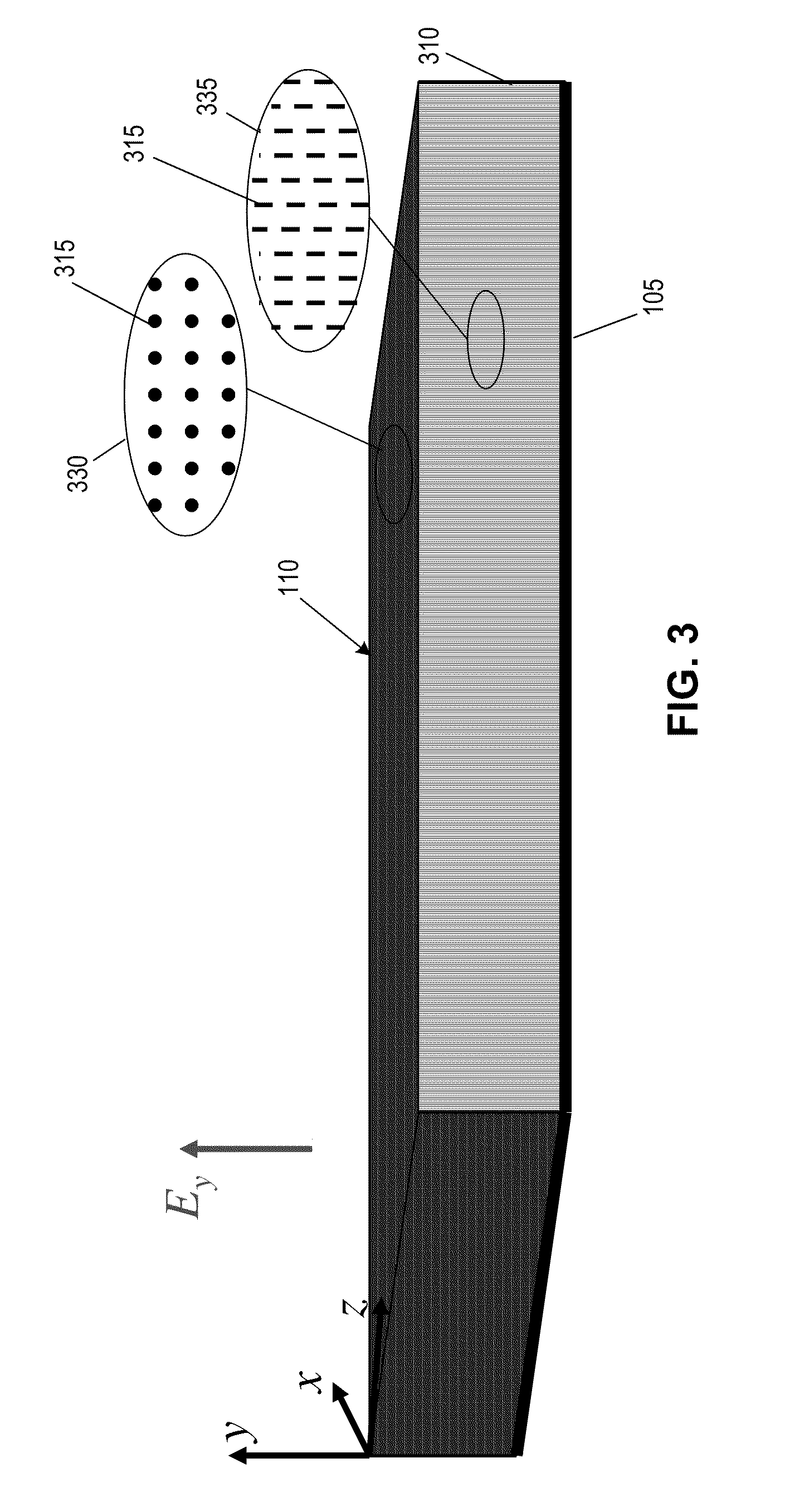
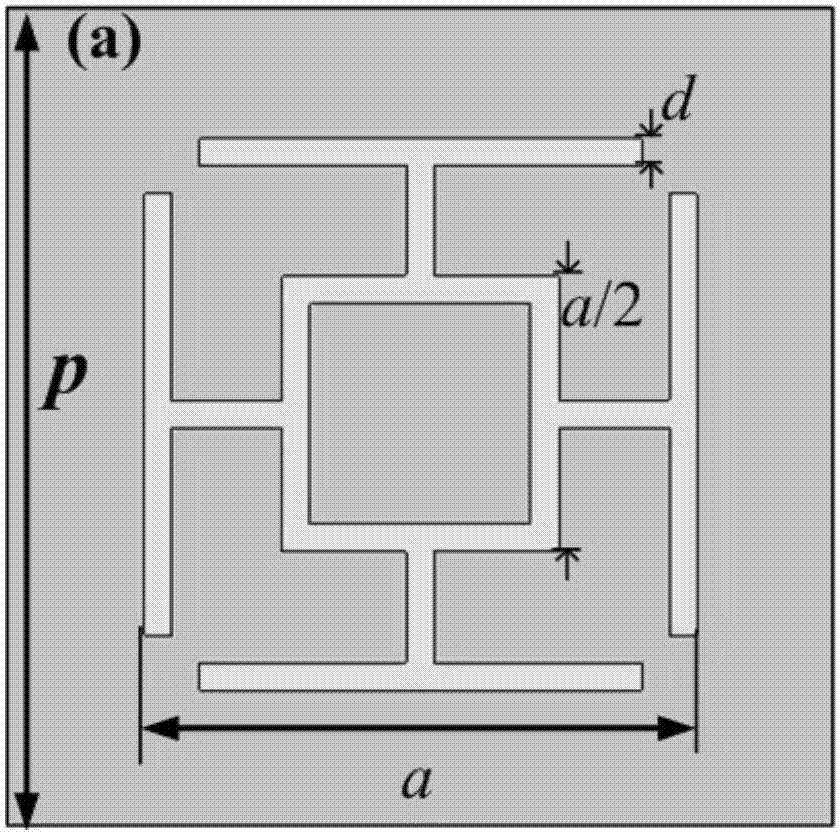
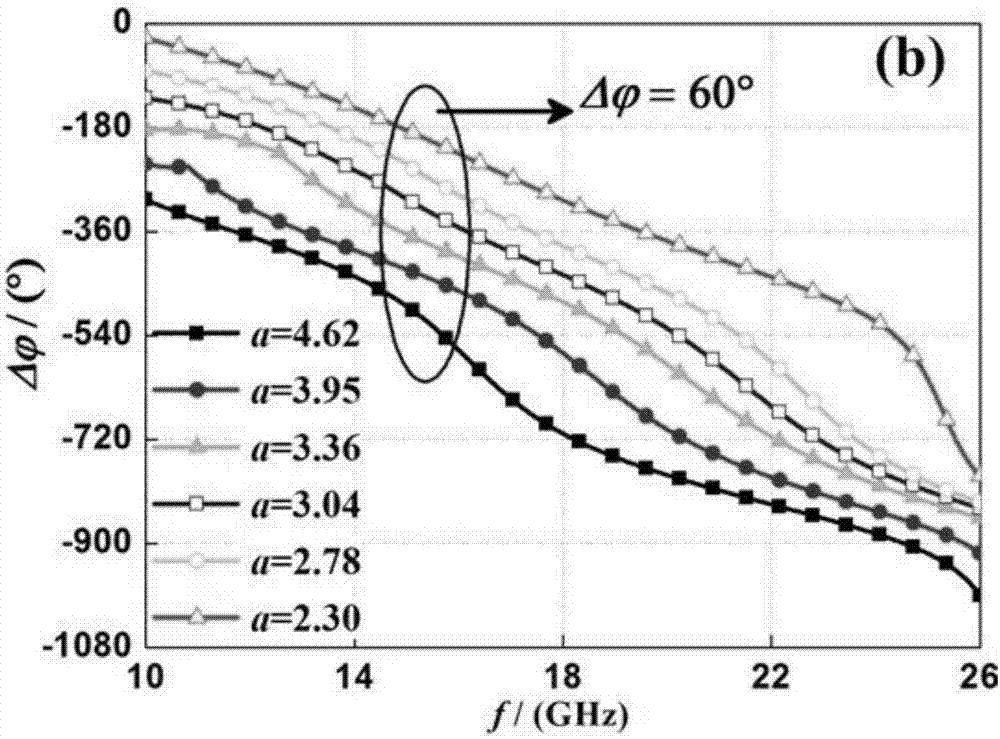
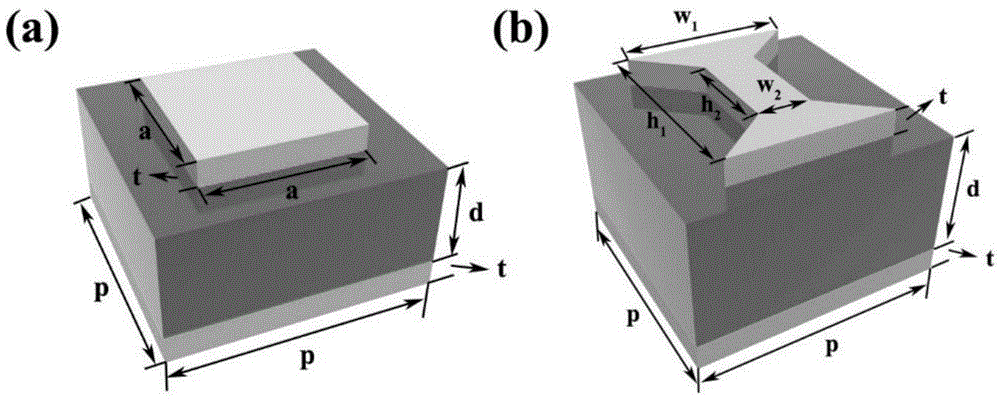
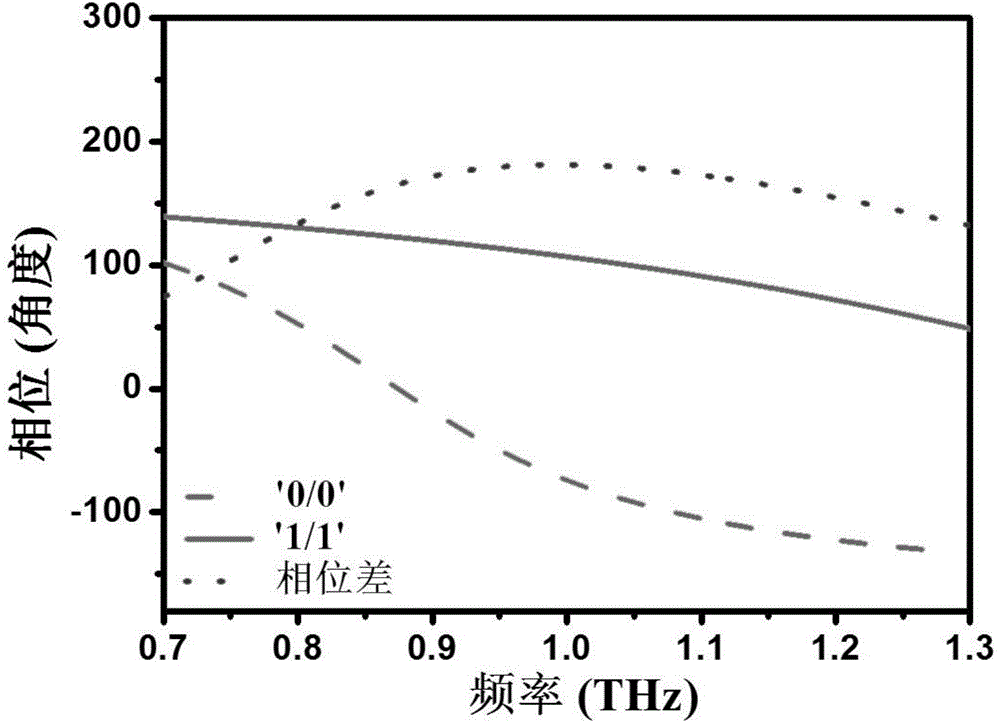
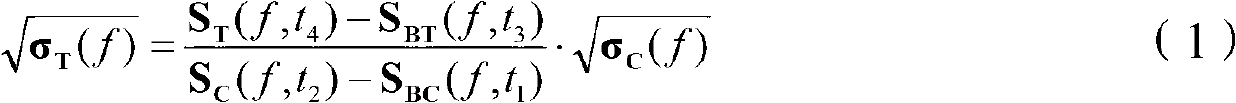Patents
Literature
579 results about "Radar cross-section" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
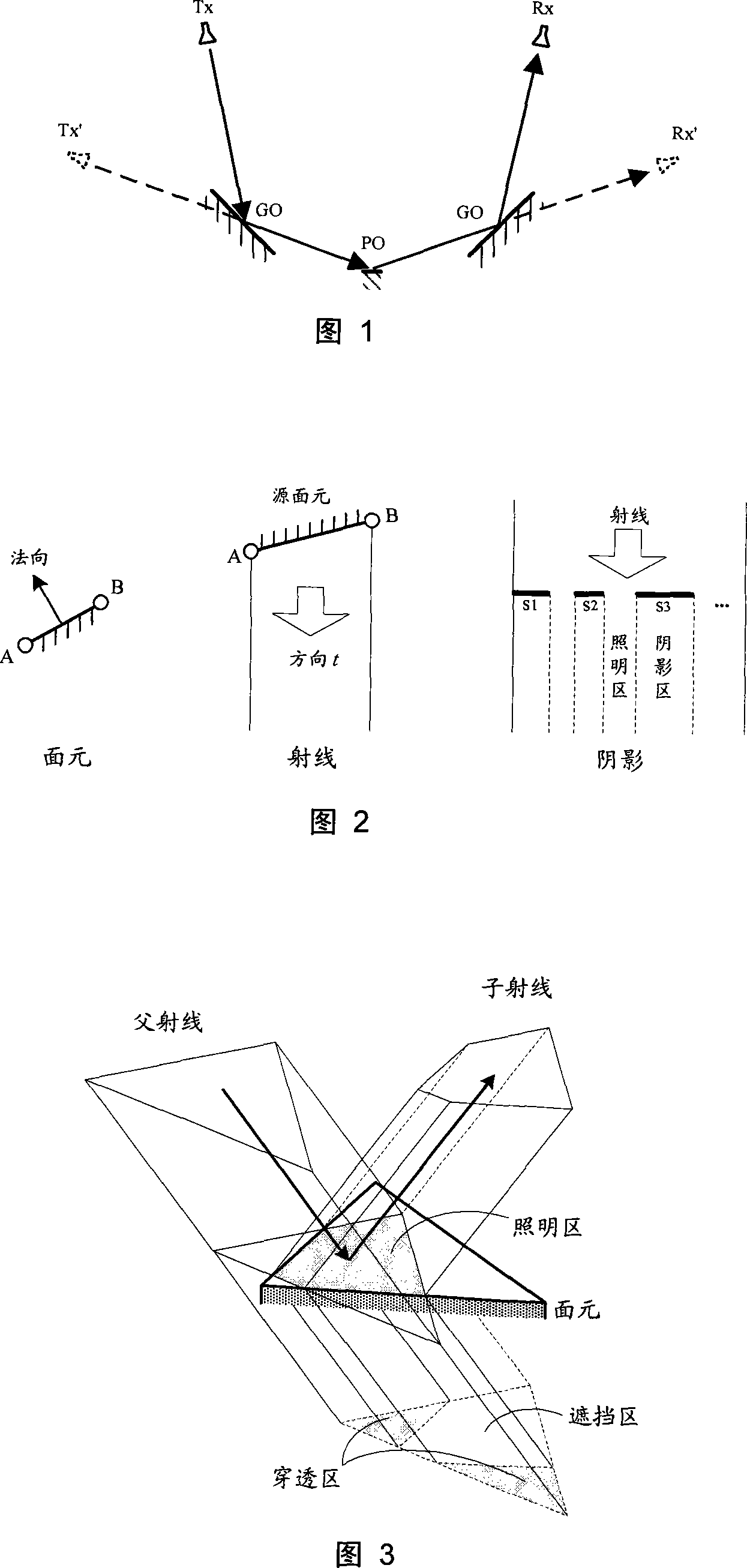
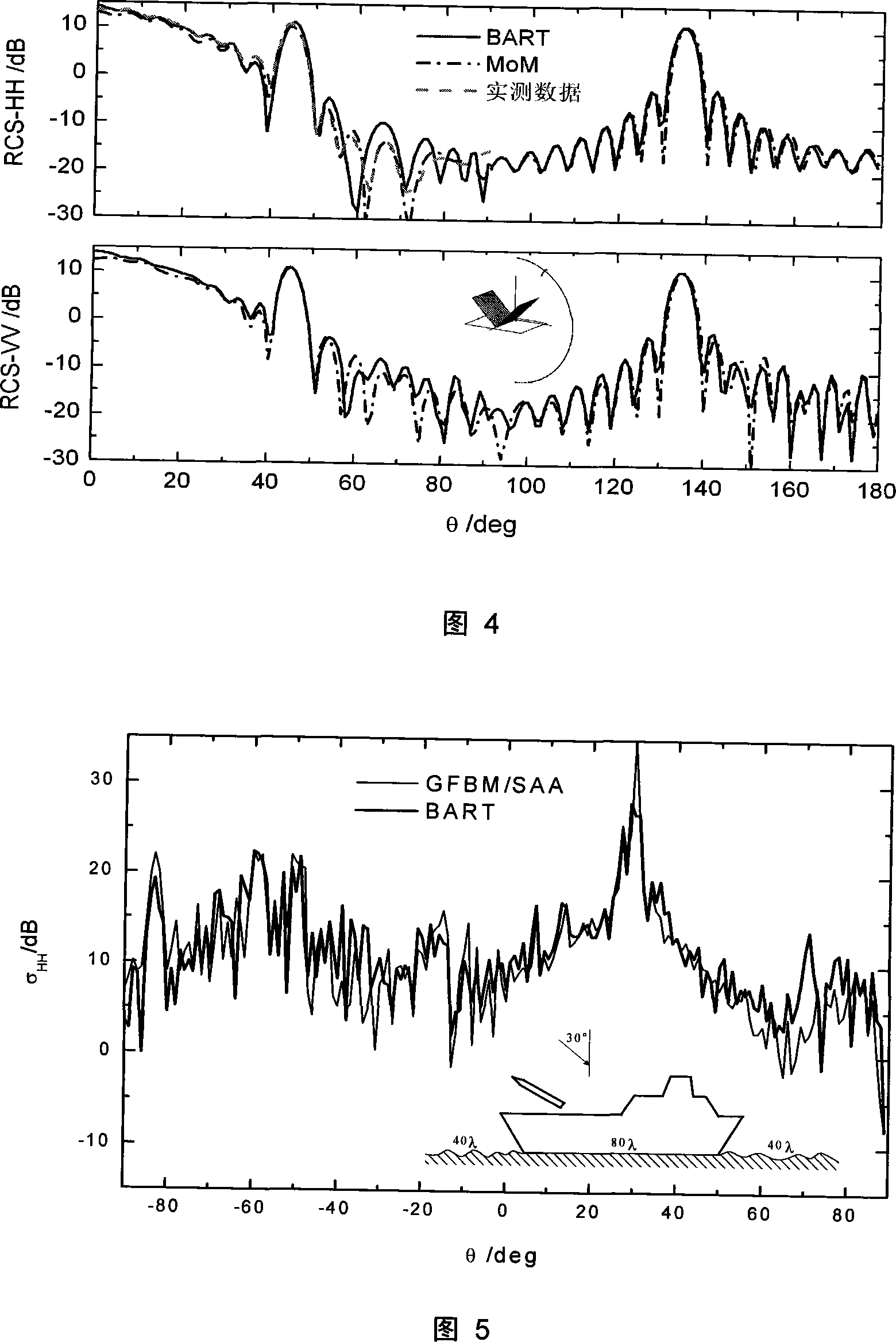
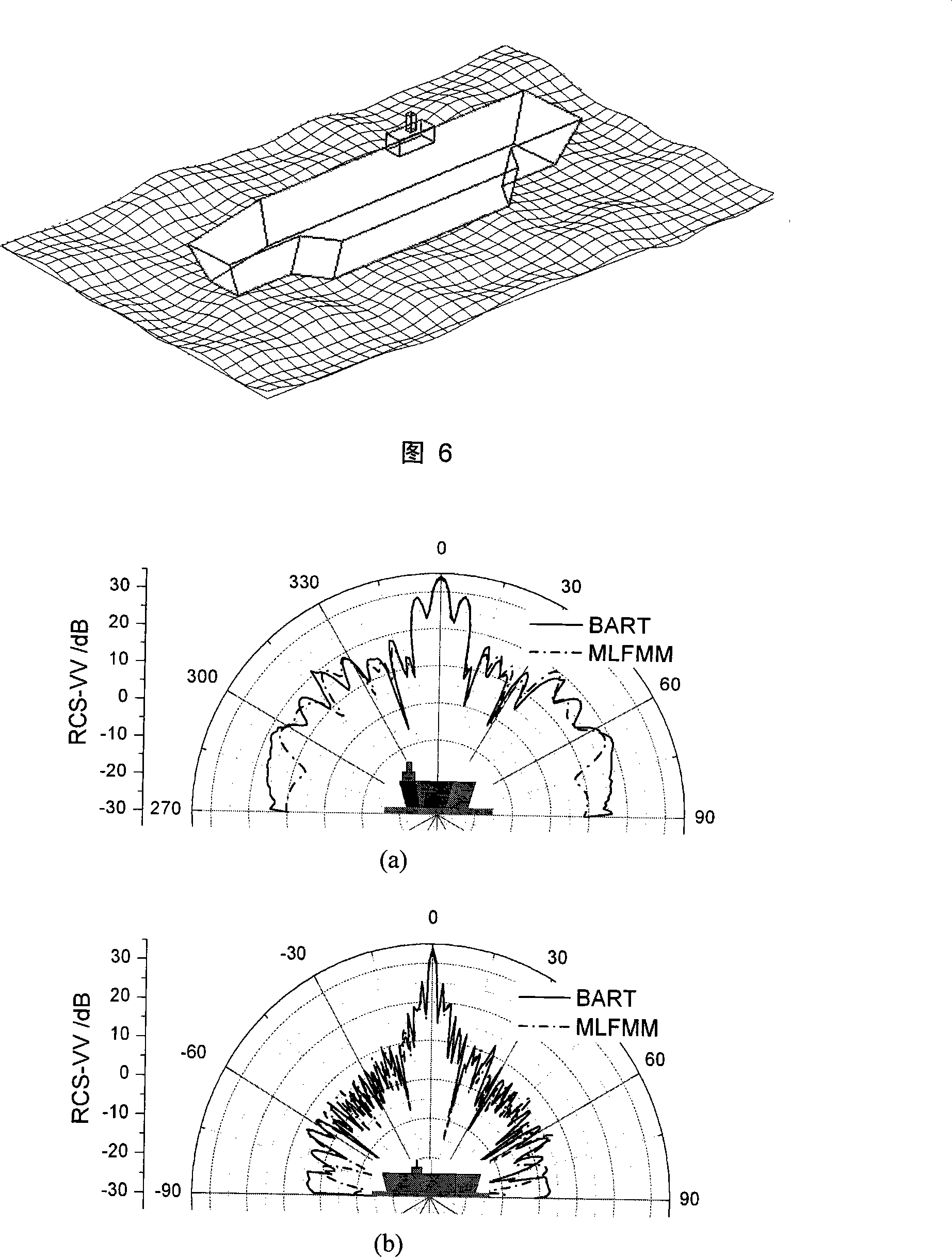
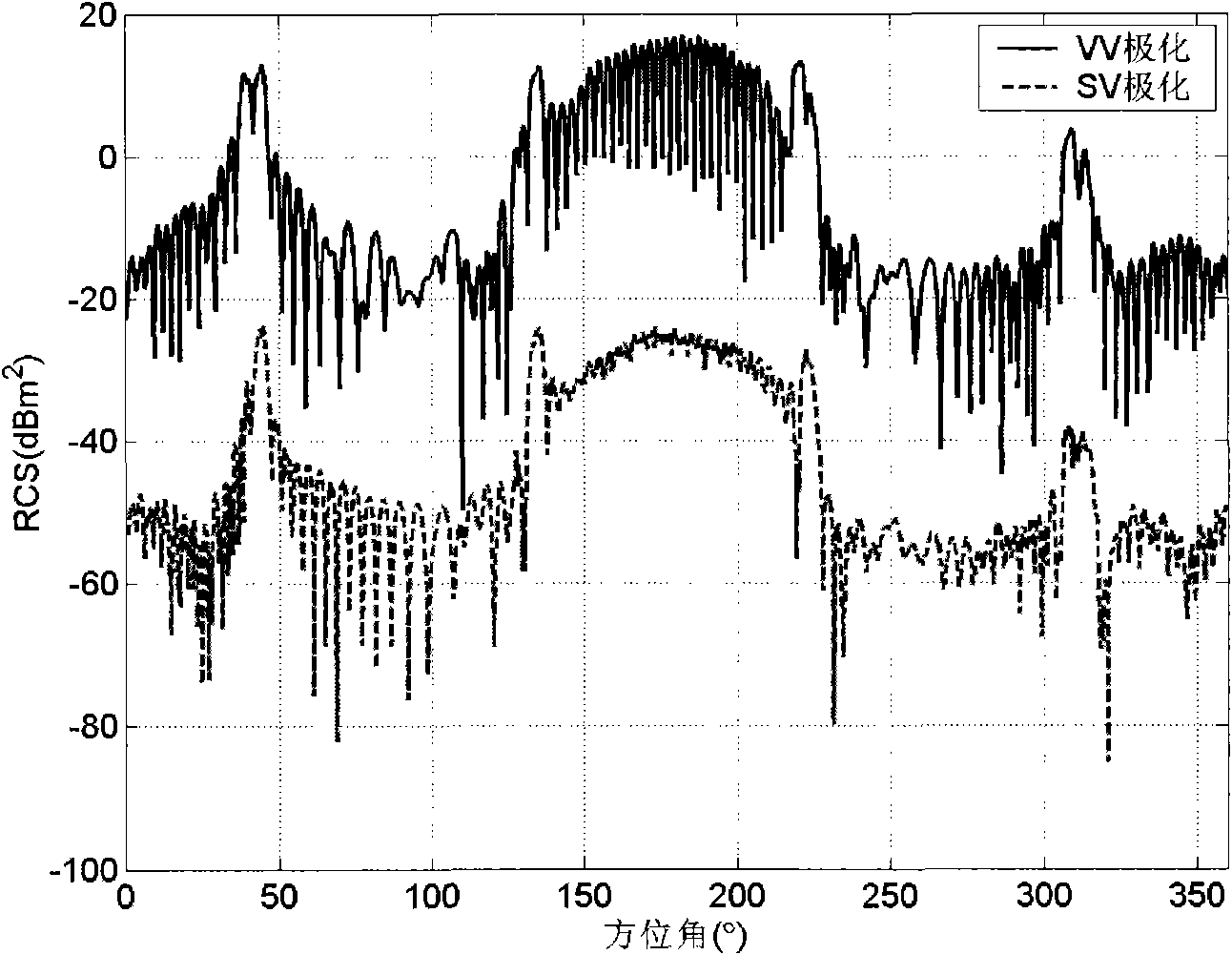
Radar cross-section (RCS) is a measure of how detectable an object is by radar. A larger RCS indicates that an object is more easily detected. An object reflects a limited amount of radar energy back to the source. The factors that influence this include: the material of which the target is made; the size of the target relative to the wavelength of the illuminating radar signal; the absolute size of the target; the incident angle (angle at which the radar beam hits a particular portion of the target, which depends upon the shape of the target and its orientation to the radar source); the reflected angle (angle at which the reflected beam leaves the part of the target hit; it depends upon incident angle); the polarization of the transmitted and the received radiation with respect to the orientation of the target.
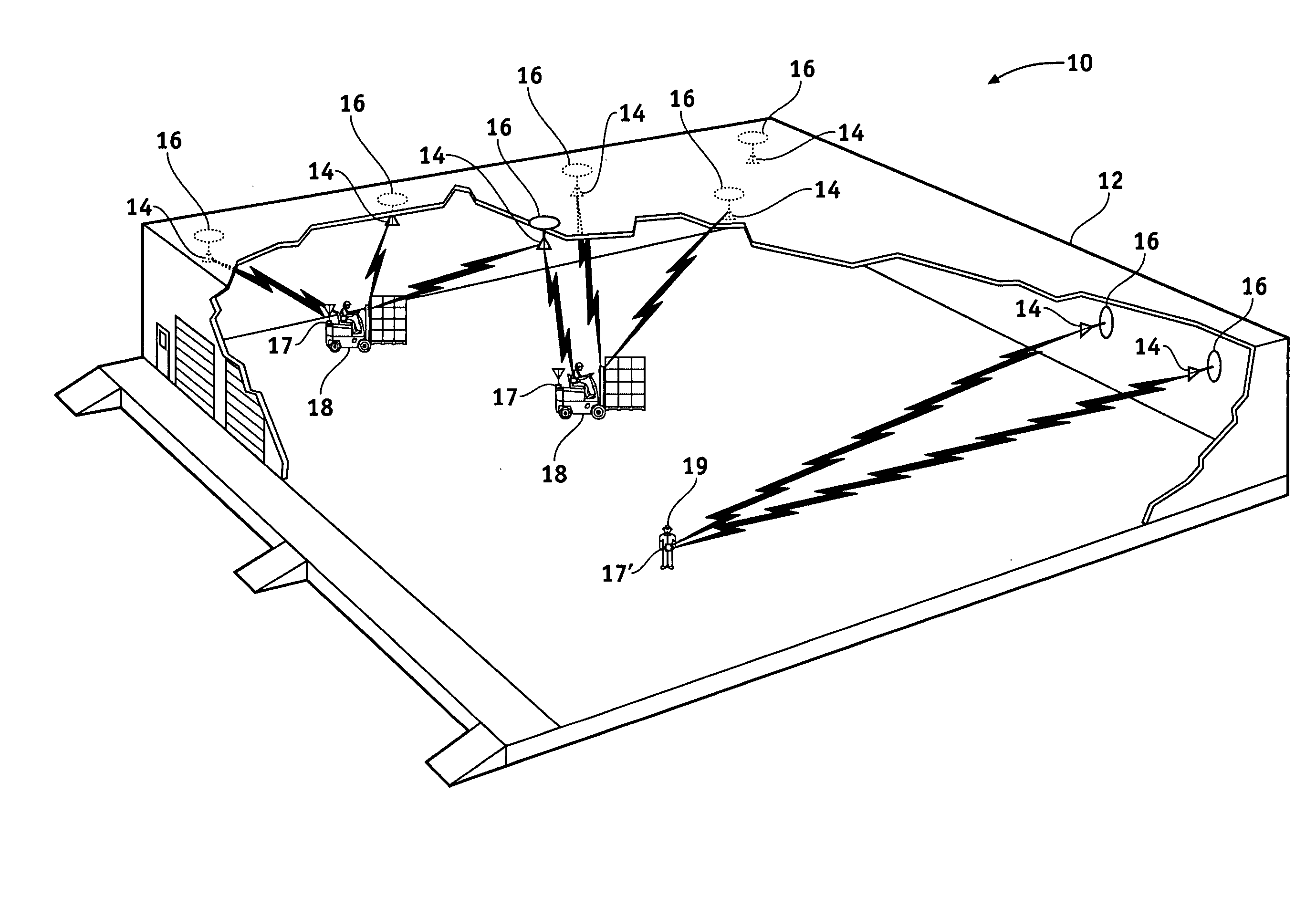
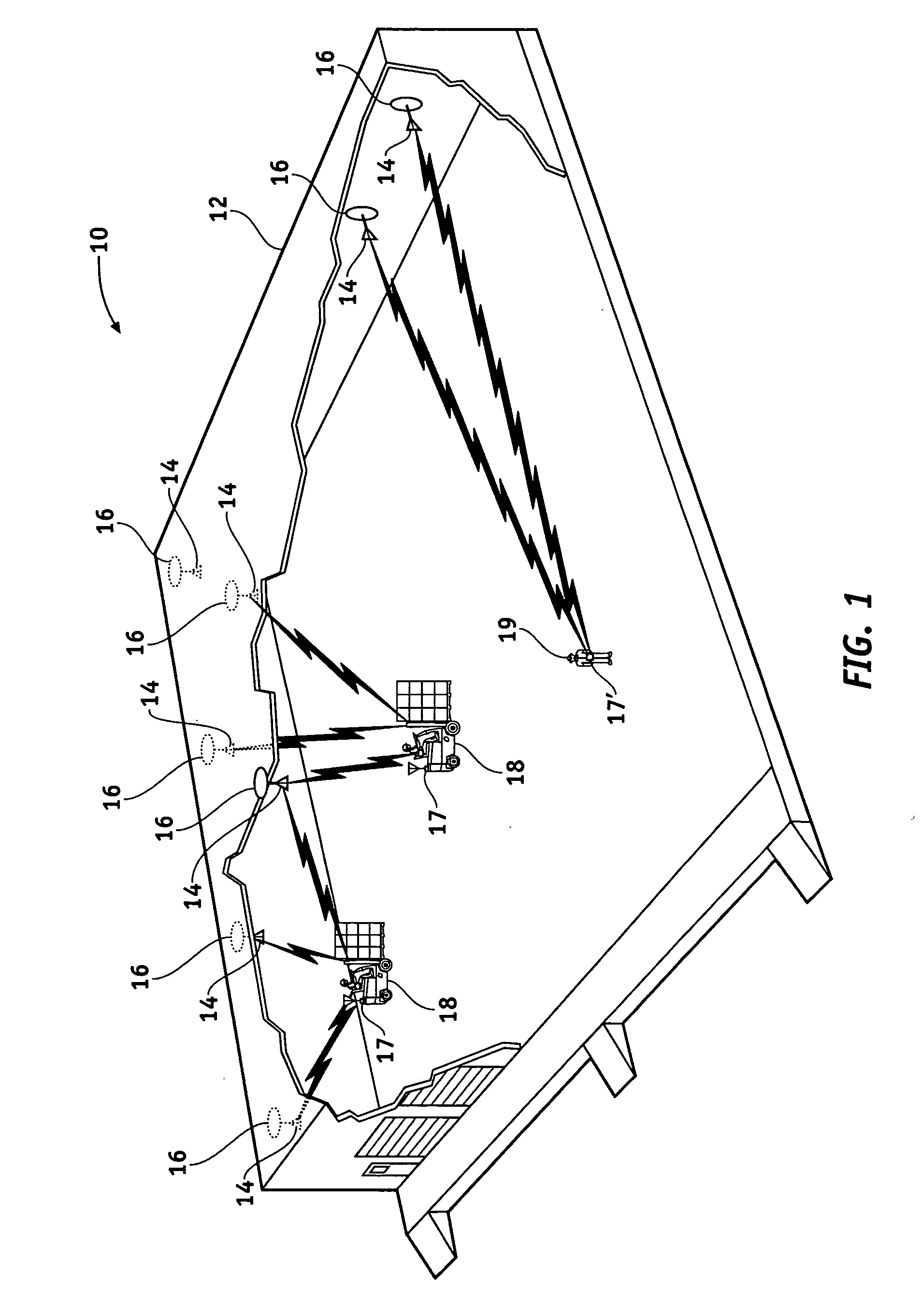
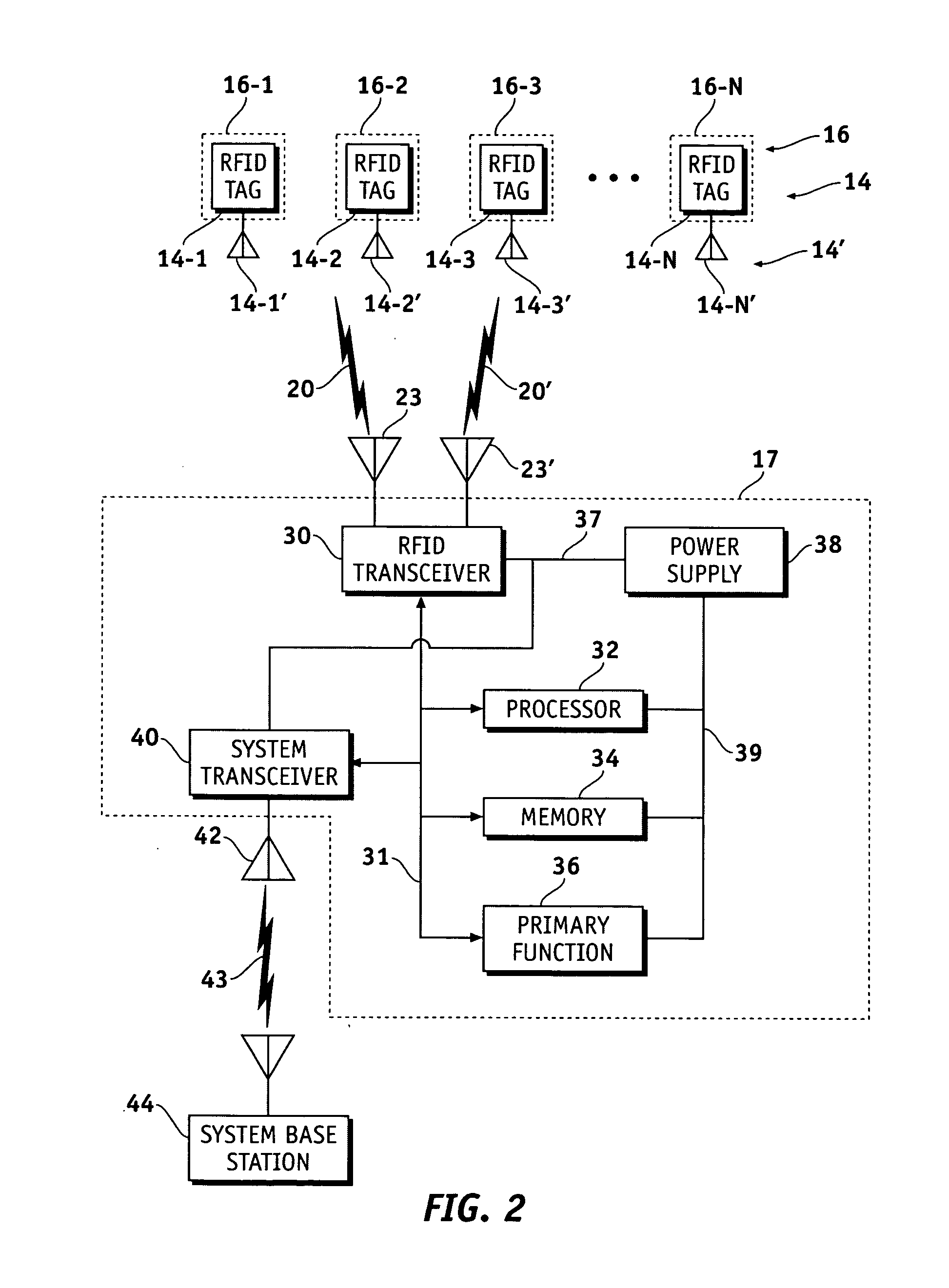
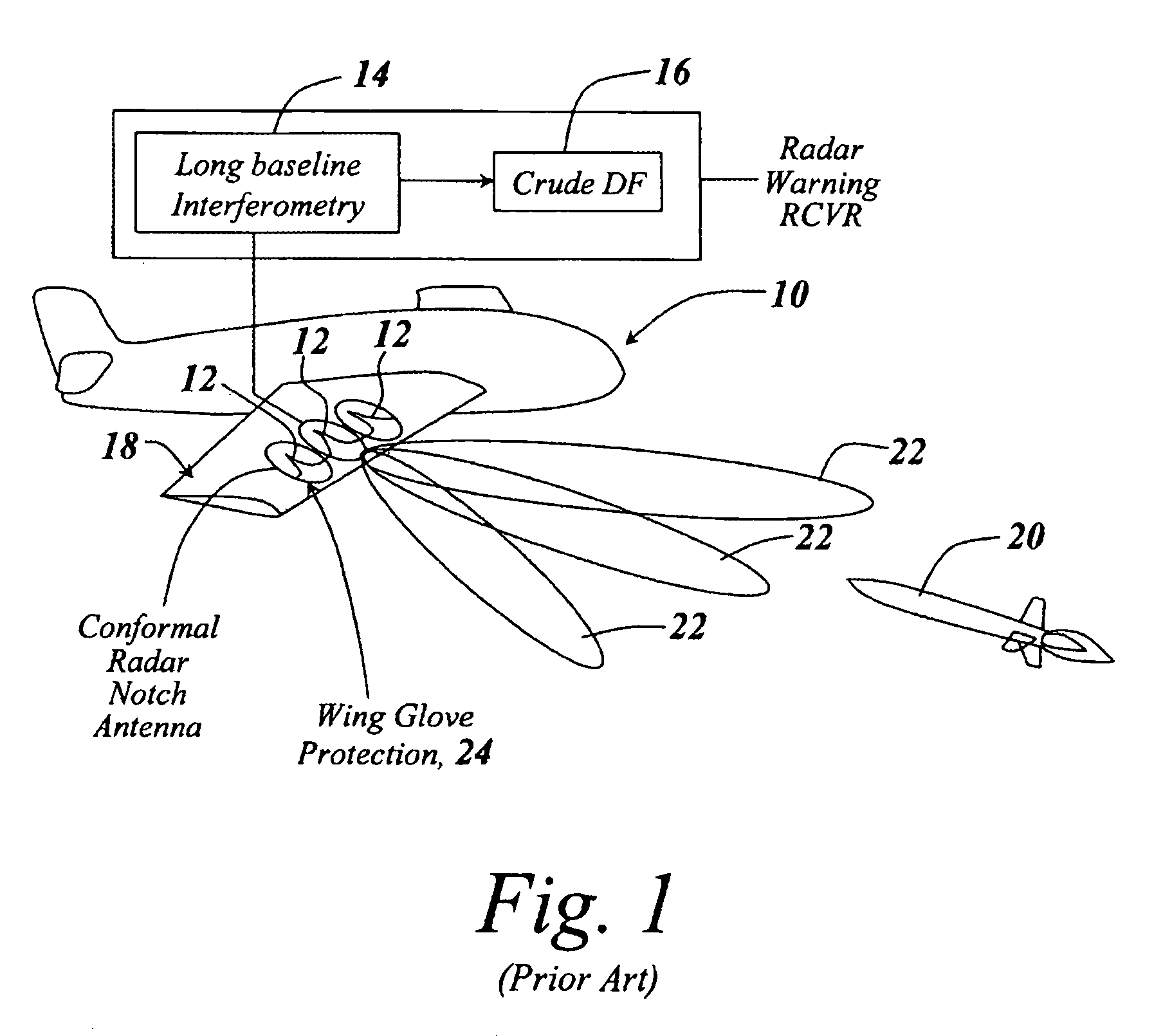
Reverse infrastructure location system and method
InactiveUS20060071790A1Good precisionVoting apparatusRoad vehicles traffic controlTransceiverTransmitted power
Methods and apparatus are provided to locate a terminal within a workspace. Radio frequency identification (RFID) tags are provided in known locations, preferably in, on or adjacent the light fixtures or other workspace infrastructure. The terminal comprises an RFID tag interrogation transceiver, processor and memory. The transceiver interrogates the tags which respond with information correlatable with their unique locations. The terminal determines its locations relative to the known locations of responding tags by, for example, varying its transmit power and / or receiver sensitivity and / or by trilateration using, for example, phase or time difference of arrival measurements on the tag response signals. Once it has determined its own location it may transmit or otherwise announce its location as desired by the user. In a preferred embodiment, the natural electromagnetic radiation and / or RADAR cross section backscatter from fluorescent type fixtures, modulated with their position information, acts as the RFID infrastructure beacon.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH INC
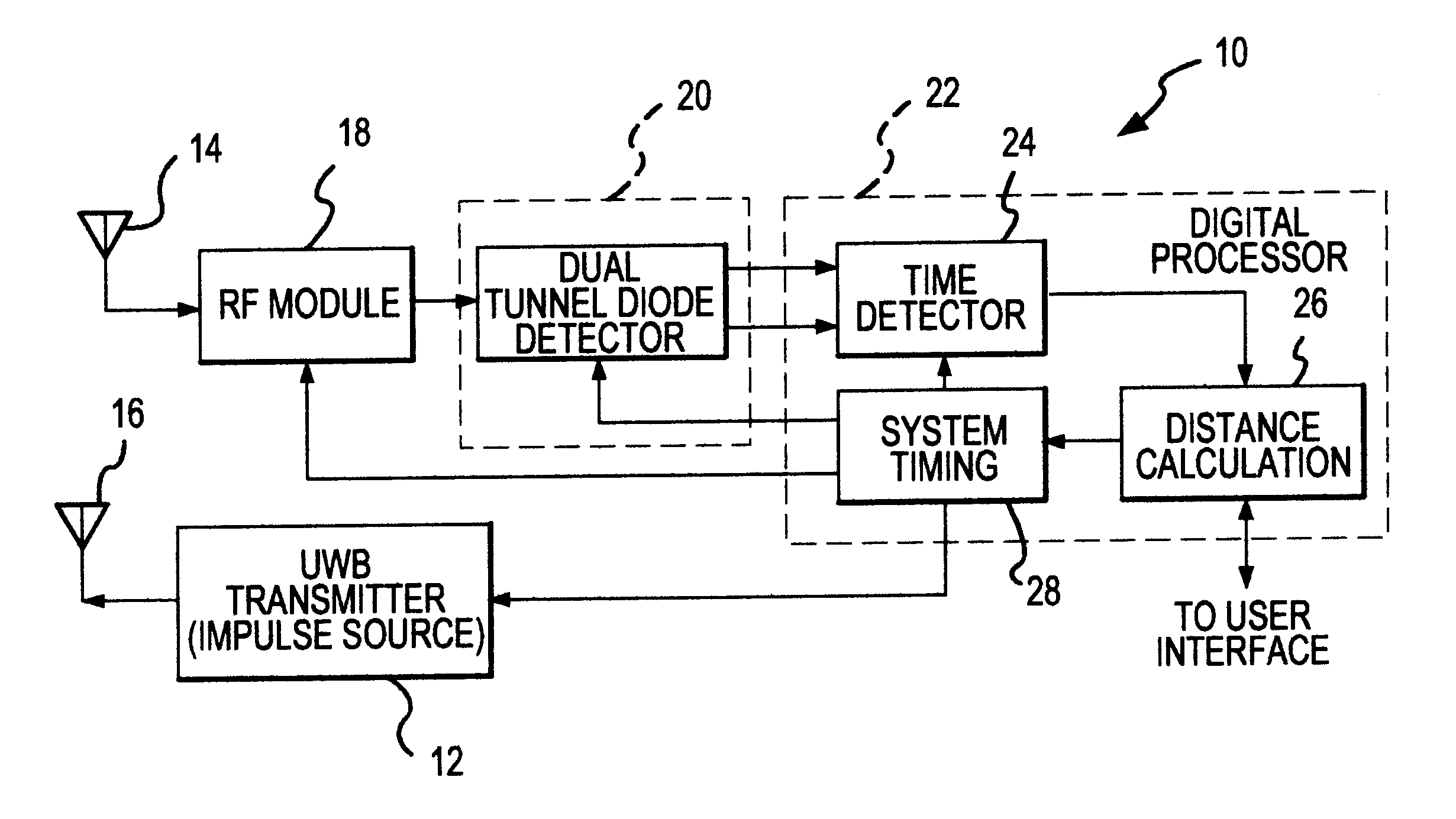
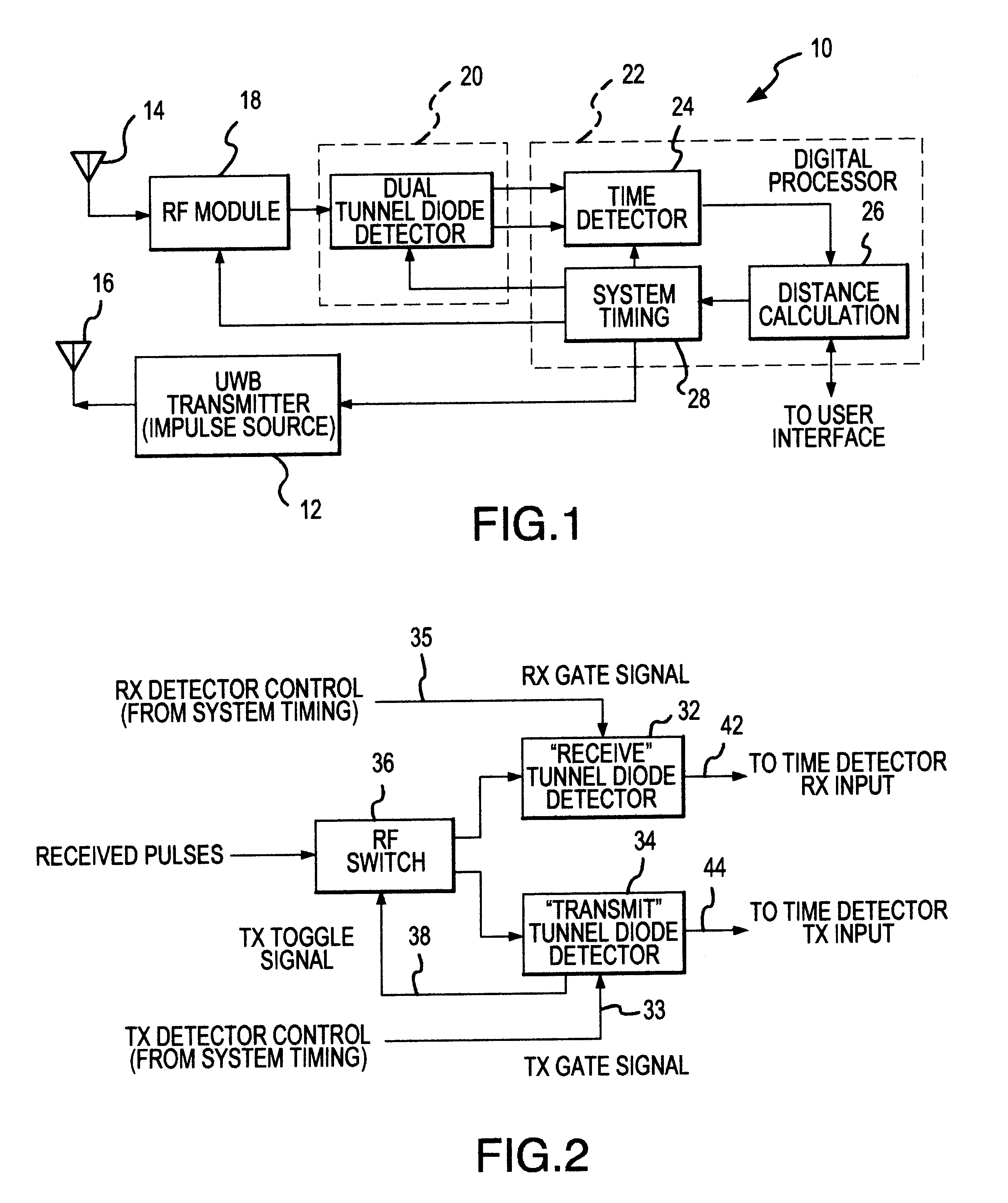
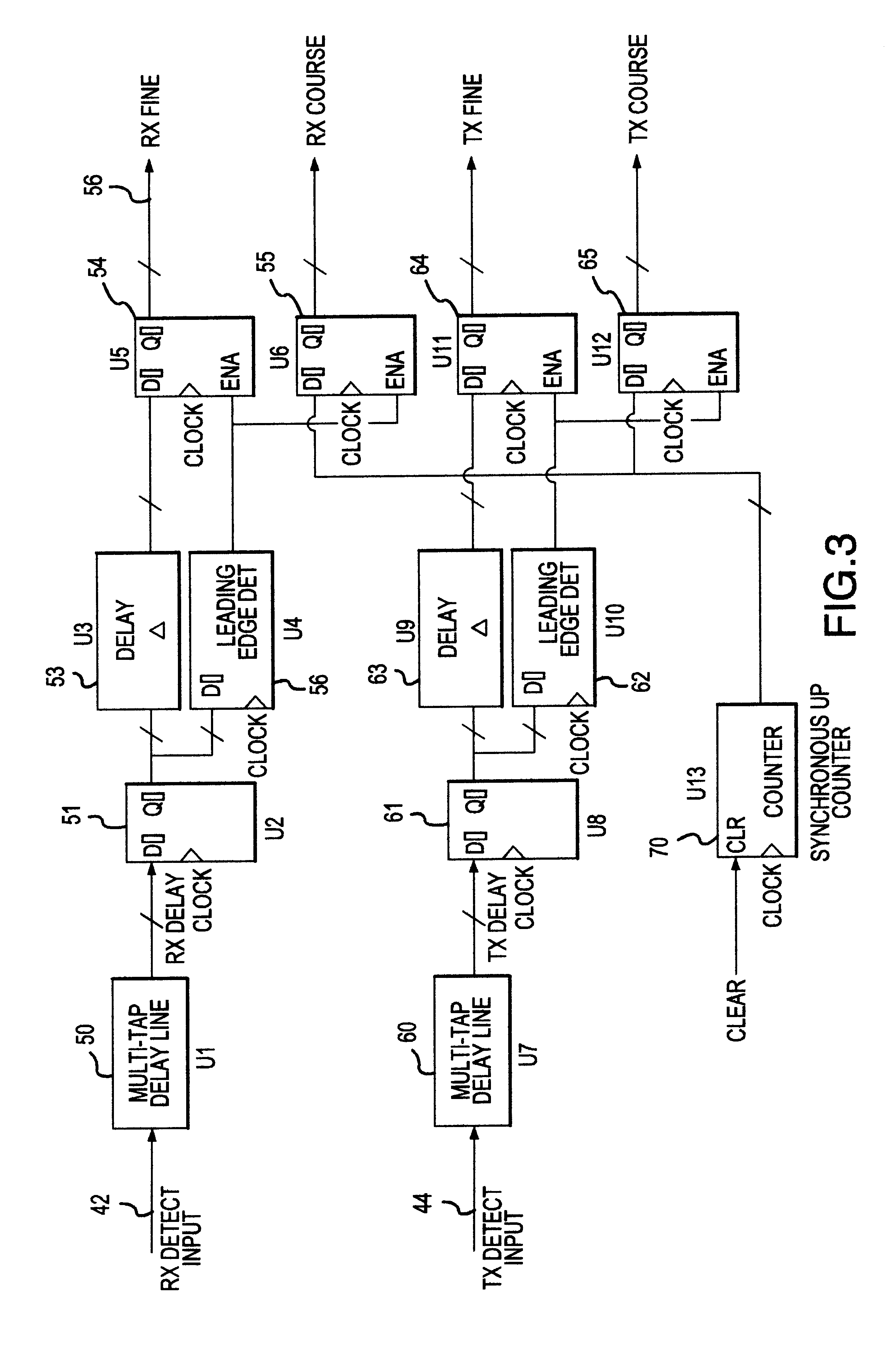
UWB dual tunnel diode detector for object detection, measurement, or avoidance
InactiveUS6239741B1Baseband system detailsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsUltra-widebandTunnel diode
A highly sensitive, high-speed dual tunnel diode detector is described for use in Ultra Wideband (UWB) object detection systems, such as a radar. The extended capability of the detector to both extremely short (sub-foot) and long distance (tens of thousands of feet) ranges is unique and permits the application of low power UWB radar to a wide variety of applications including high resolution radar altimetry at altitudes exceeding 10,000 feet and for autonomous on-deck landing operations (e.g., one-foot altitudes), the detection of extremely low radar cross section (RCS) targets for such applications as suspended wire detection for helicopters and other manned and unmanned craft, etc. High noise and interference immunity of the detector permits co-location of a UWB radar sensor with other active systems. The invention has immediate and significant application to all areas, both military and commercial, of precision distance measurement, intrusion detection, targeting, etc. over a wide range of distances.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
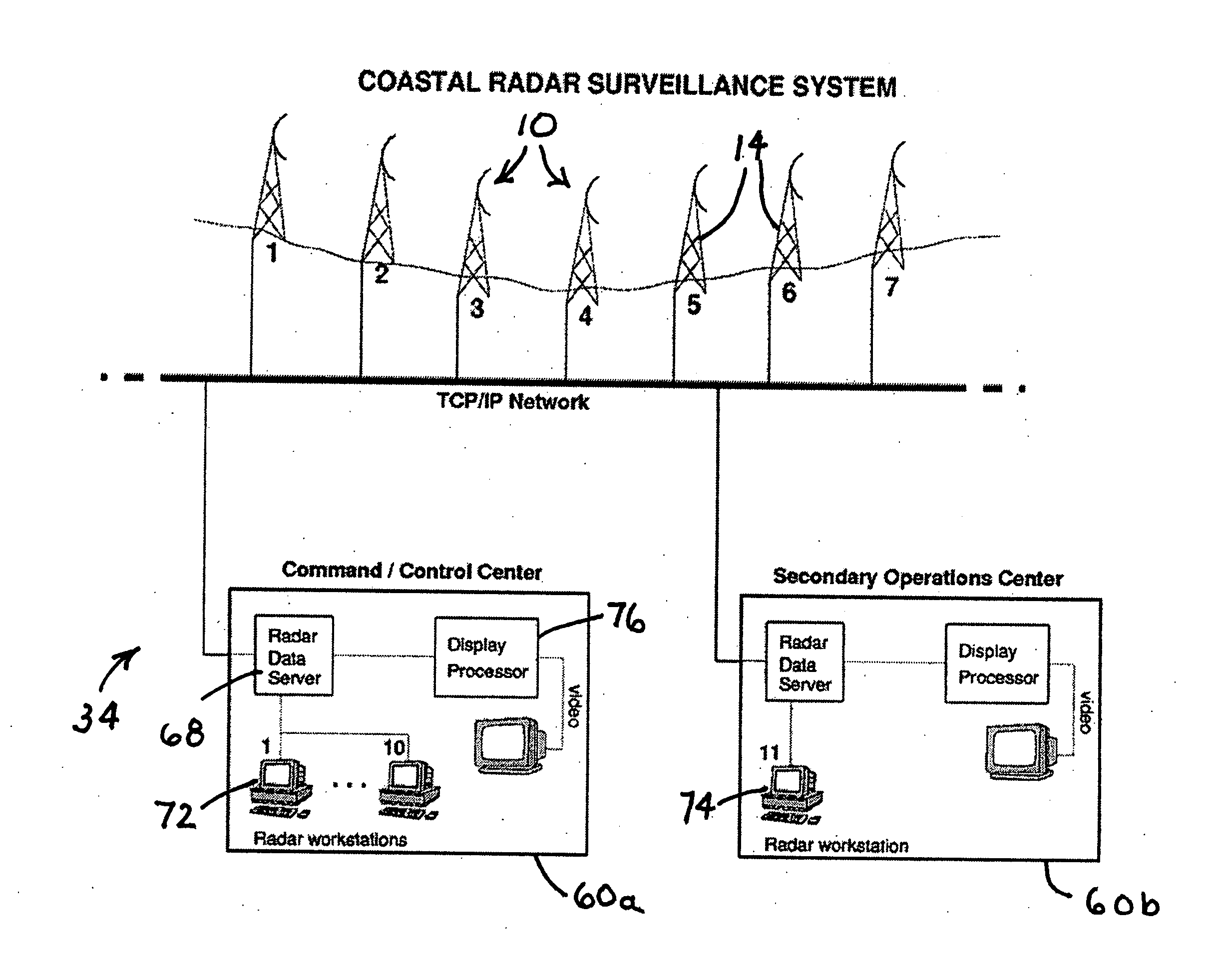
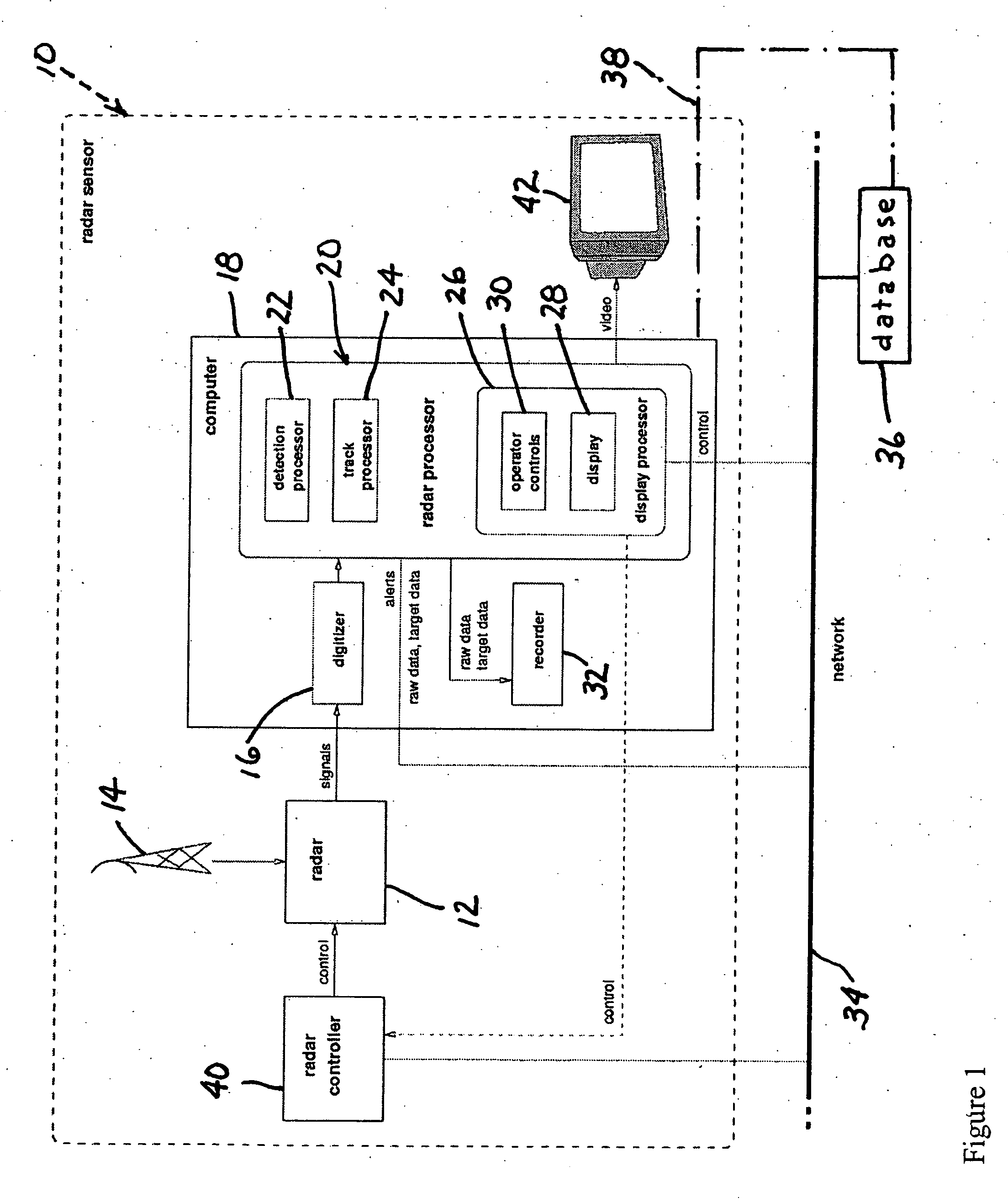
Low-cost, high-performance radar networks
ActiveUS20060238406A1Quality improvementImprove tracking performanceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionLand basedRadar network
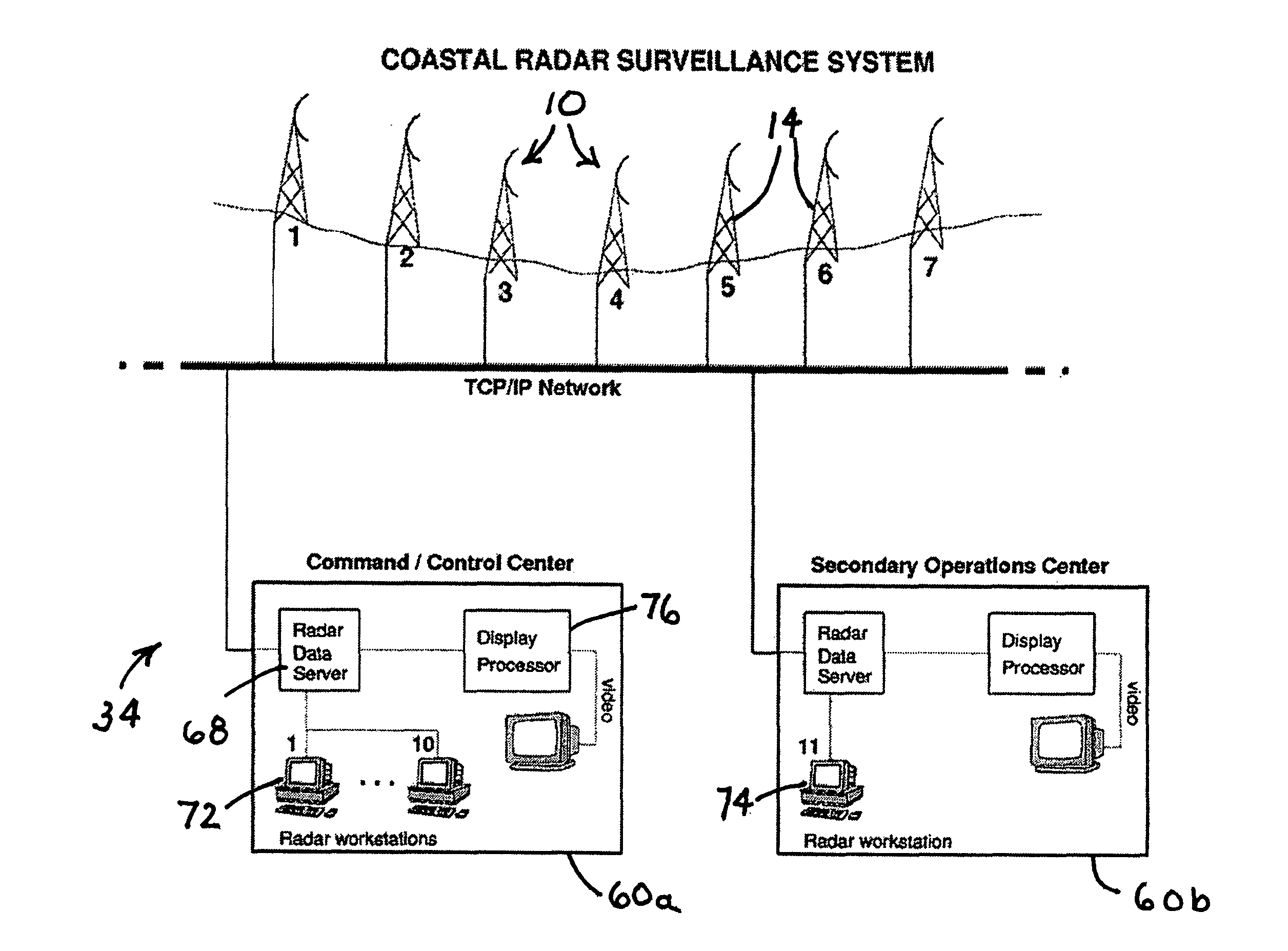
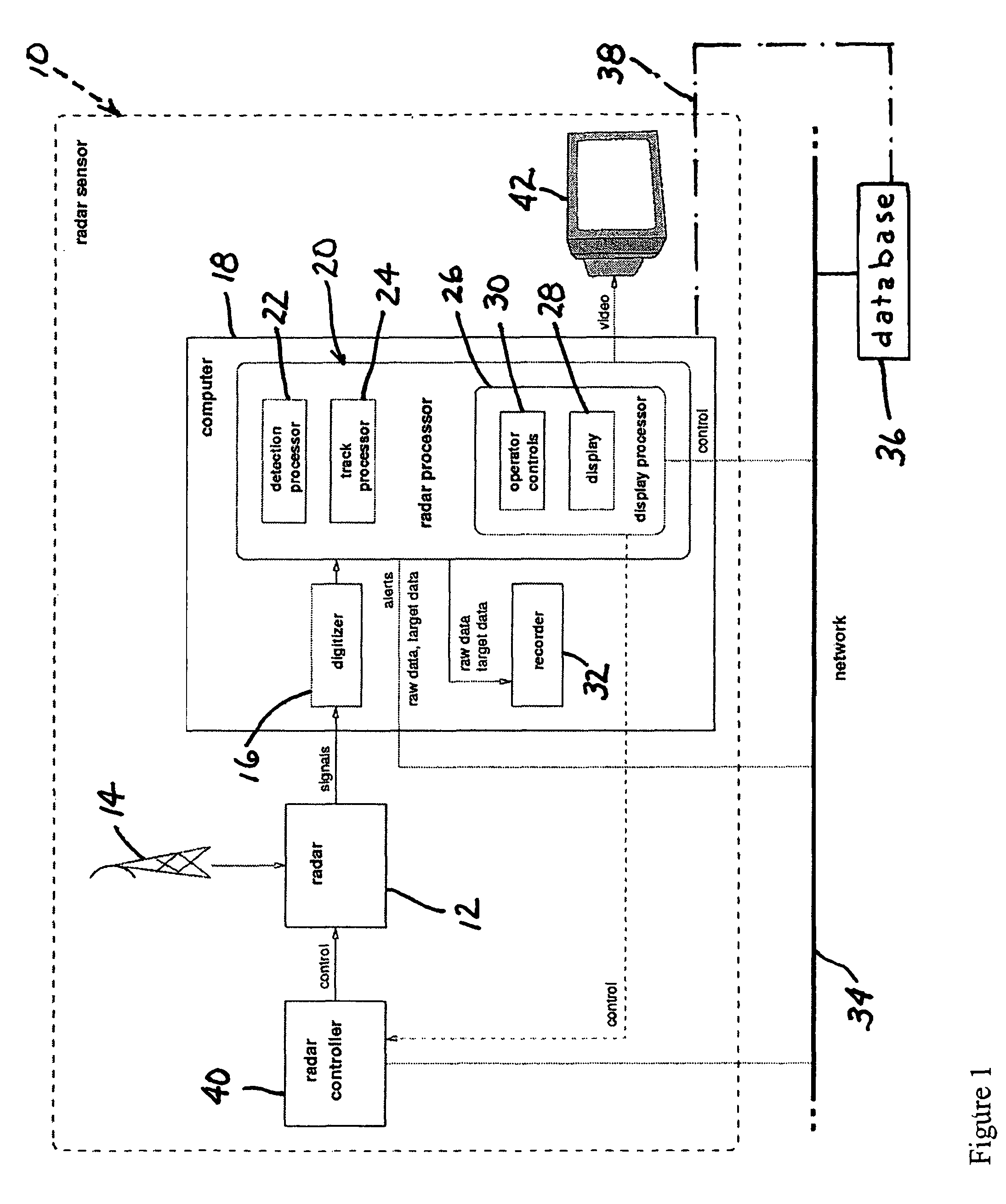
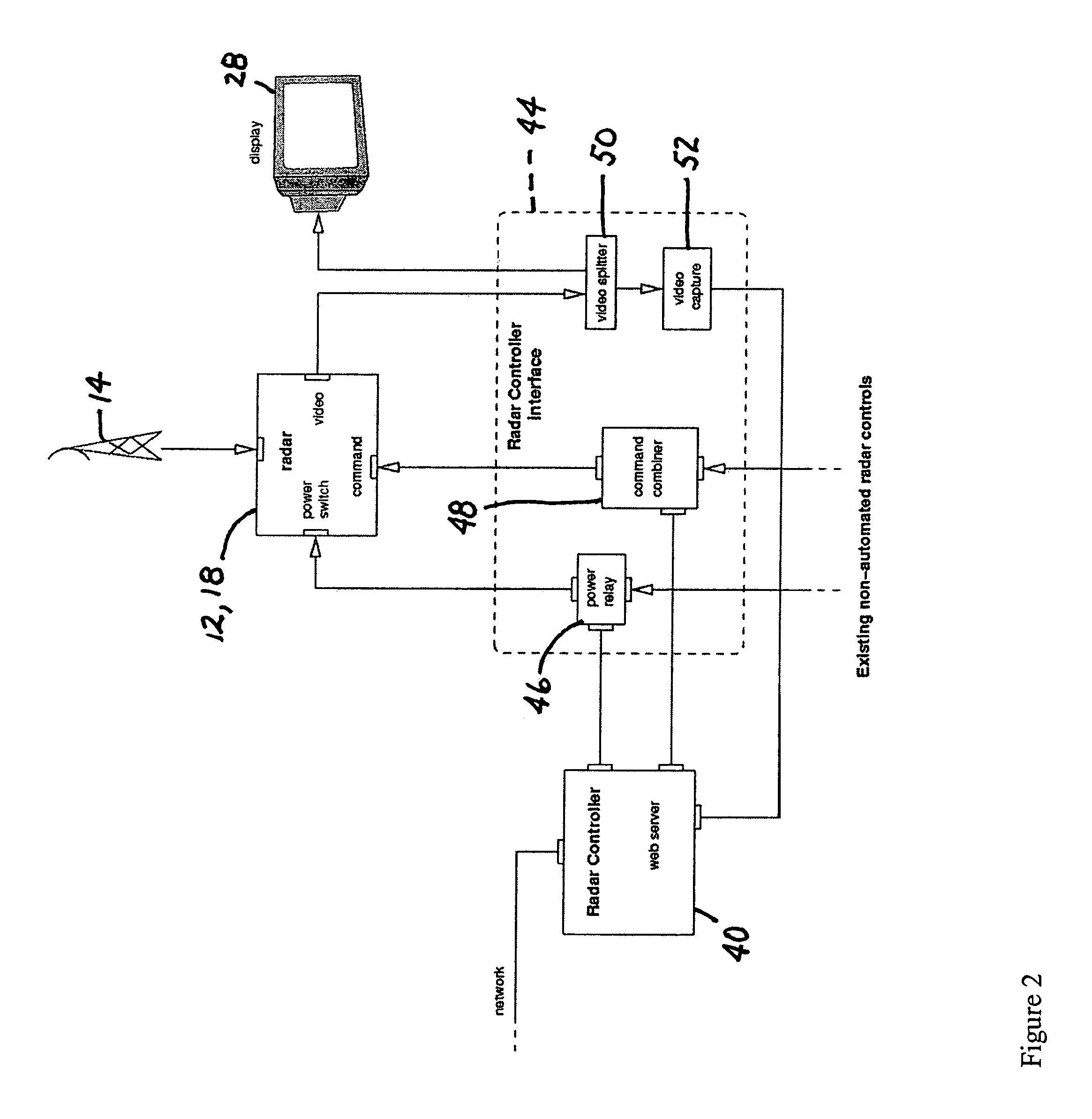
A real-time radar surveillance system comprises at least one land-based non-coherent radar sensor apparatus adapted for detecting maneuvering targets and targets of small or low radar cross-section. The radar sensor apparatus includes a marine radar device, a digitizer connected to the marine radar device for receiving therefrom samples of radar video echo signals, and computer programmed to implement a software-configurable radar processor generating target data including detection data and track data, the computer being connectable to a computer network including a database. The processor is figured to transmit at least a portion of the target data over the network to the database, the database being accessible via the network by at least one user application that receives target data from the database, the user application providing a user interface for at least one user of the system.
Owner:ACCIPITER RADAR TECH
General signal generator for radar target simulation
InactiveCN105403870AControllable distanceEasy to control speedWave based measurement systemsSequence controlRadar systems
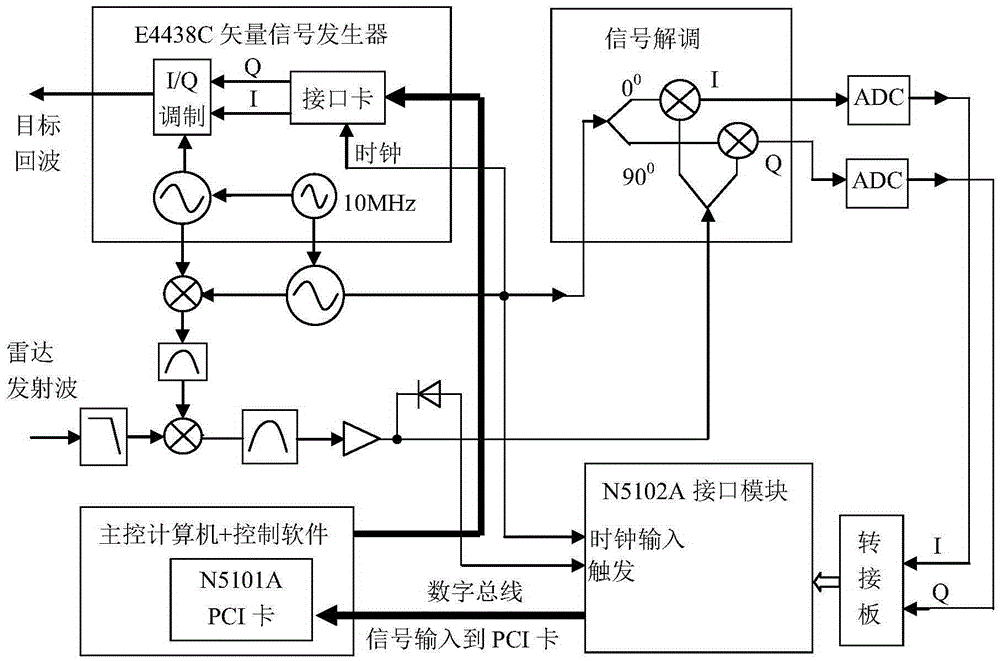
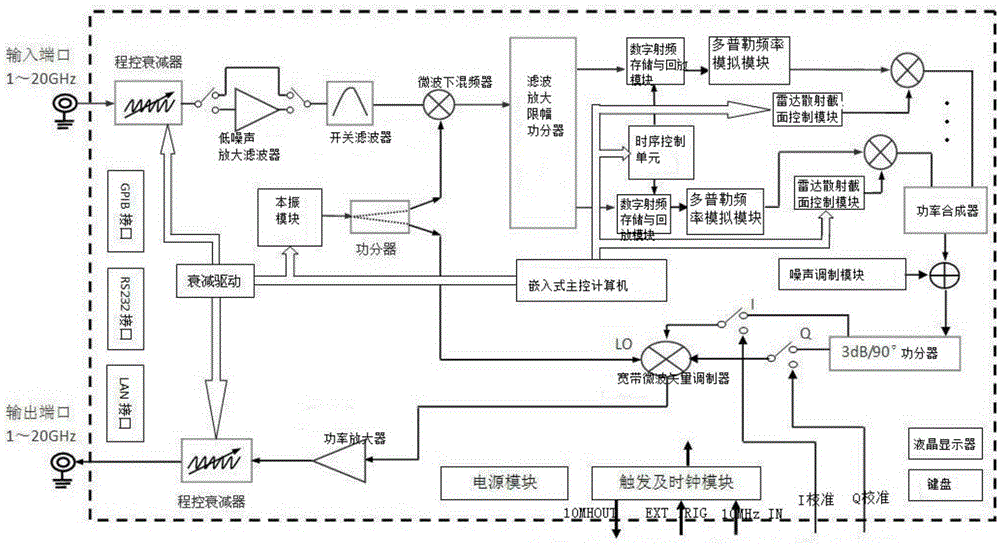
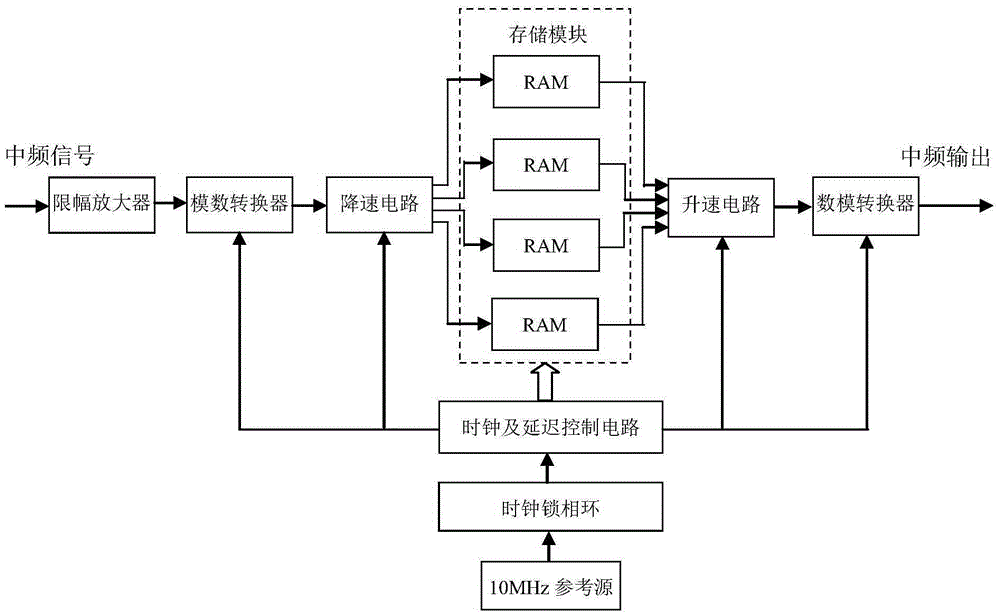
The invention, which relates to the technical field of the radar target simulation, discloses a general signal generator for radar target simulation. With the signal generator, a defect that the existing radar target signal generator is based on a special-purpose signal generator and only serve a radar system with a specific type in terms of frequency band coverage and function setting and thus the application range is limited can be solved. The signal generator comprises an embedded main control computer, a timing sequence control unit, an attenuation drive, a local oscillation module, a filtering, amplifying and limiting amplitude power divider, a plurality of digital radio frequency storage and playback modules, a plurality of Doppler frequency simulation modules, a radar cross section control module, a noise modulation module, a microwave down mixer, and IQ up mixing unit and the like. The output terminal of the microwave down mixer is connected with the filtering, amplifying and limiting amplitude power divider; the multiple digital radio frequency storage and playback modules are connected to the filtering, amplifying and limiting amplitude power divider; and the output terminal of each digital radio frequency storage and playback module is connected with one Doppler frequency simulation module.
Owner:THE 41ST INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
Low-cost, high-performance radar networks
ActiveUS7940206B2Improve performanceReduce labor costsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDigital converterRadar cross-section
A real-time radar surveillance system comprises at least one land-based non-coherent radar sensor apparatus adapted for detecting maneuvering targets and targets of small or low radar cross-section. The radar sensor apparatus includes a marine radar device, a digitizer connected to the marine radar device for receiving therefrom samples of radar video echo signals, and computer programmed to implement a software-configurable radar processor generating target data including detection data and track data, the computer being connectable to a computer network including a database. The processor is figured to transmit at least a portion of the target data over the network to the database, the database being accessible via the network by at least one user application that receives target data from the database, the user application providing a user interface for at least one user of the system.
Owner:ACCIPITER RADAR TECH
Electromagnetic scattering simulation method based on parallel moment method and physical optics mixing
InactiveCN103870654AImprove accuracyAvoid artificial reflexesSpecial data processing applicationsRough surfacePhysical optics
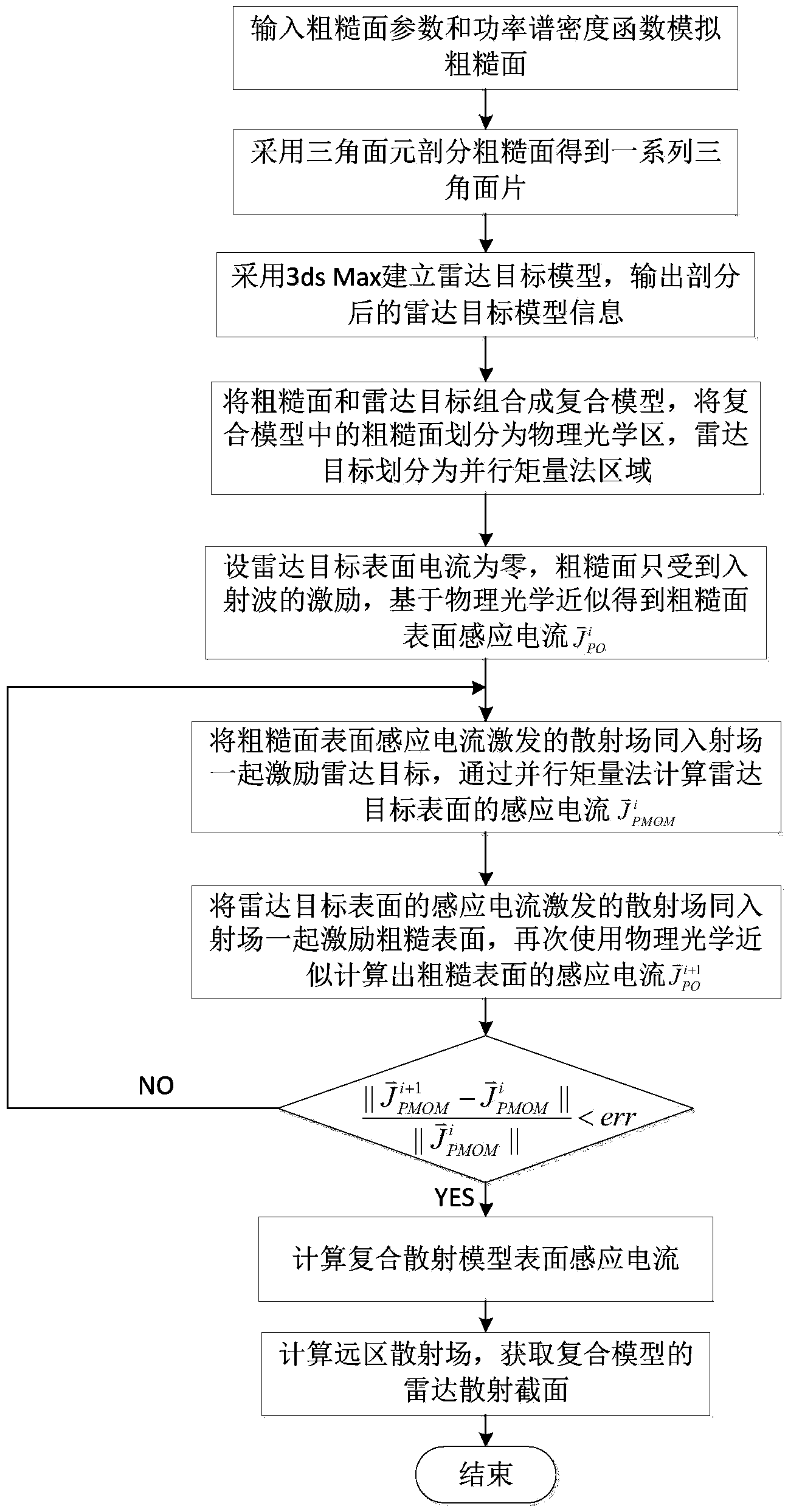
The invention discloses an electromagnetic scattering simulation method based on parallel moment method and physical optics mixing to mainly solve the problem that when electrically large models are processed in the prior art, the simulation efficiency of electromagnetic scattering and the precision are low. The electromagnetic scattering simulation method comprises the steps that a rough surface power spectrum and rough surface parameters are input, and a rough surface is simulated based on the Monte Carlo method; geometric modeling is carried out on a radar target through 3dsMax software, and the subdivided radar target is output; a combined model is formed by combining the rough surface and the radar target, the rough surface is divided into a physical optics area, and the radar target is divided into a parallel moment method area; induced currents on the rough surface and induced currents on the surface of the radar target are obtained; a far scattered field of the combined model is calculated based on the induced currents on the surface of the combined model, a radar cross section of the combined model is obtained, and simulation between the rough surface and the combined electromagnetic scattering of the radar target is achieved. According to the electromagnetic scattering simulation method, the memory consumption is little, the simulation efficiency is high, and the electromagnetic scattering simulation method can be used in the study on the rough surface and the radar target combined electromagnetic scattering character in the field of national defense and the civil using.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
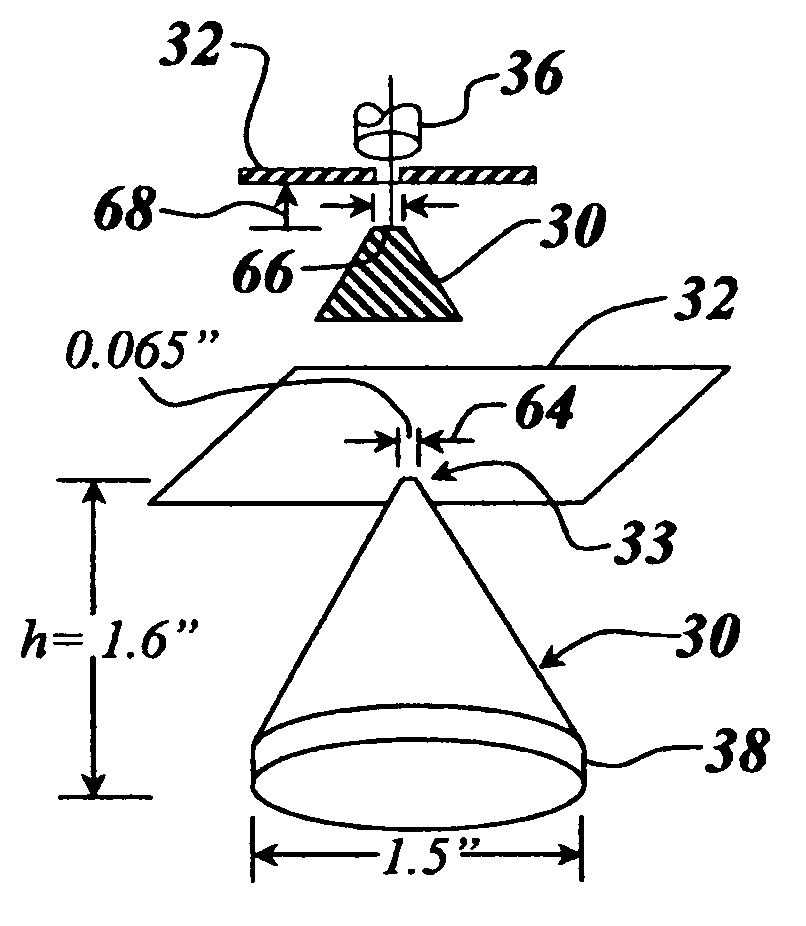
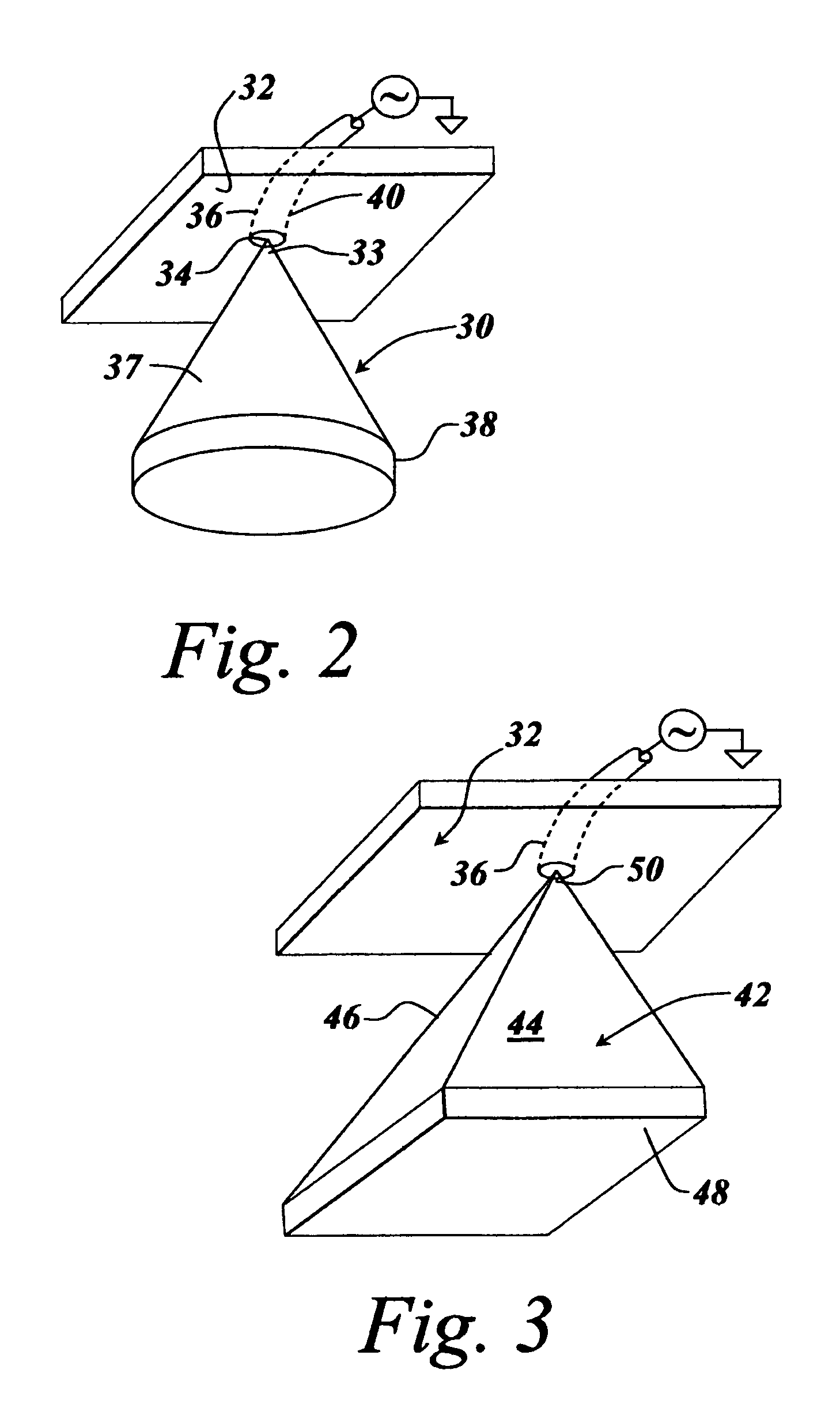
Compact low RCS ultra-wide bandwidth conical monopole antenna
InactiveUS7006047B2Low costHigh gainAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadiating elements structural formsRadar cross-sectionMonopole antenna
A low radar cross-section monocone antenna is provided with an ultra-wide bandwidth in the microwave region of the electromagnetic spectrum running from 1 gigahertz to 18 gigahertz by decreasing the low frequency cutoff through enlarging the overall dimensions of the cone while at the same time maintaining the base diameter of the apex of the cone to the initially-set dimension that establishes the high frequency cutoff of the antenna. The apex of this cone that serves as its feed point has a base diameter that results in the wide bandwidth, with the monocone antenna having a 5 dBi gain and omnidirectional coverage.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTEGRATION INC
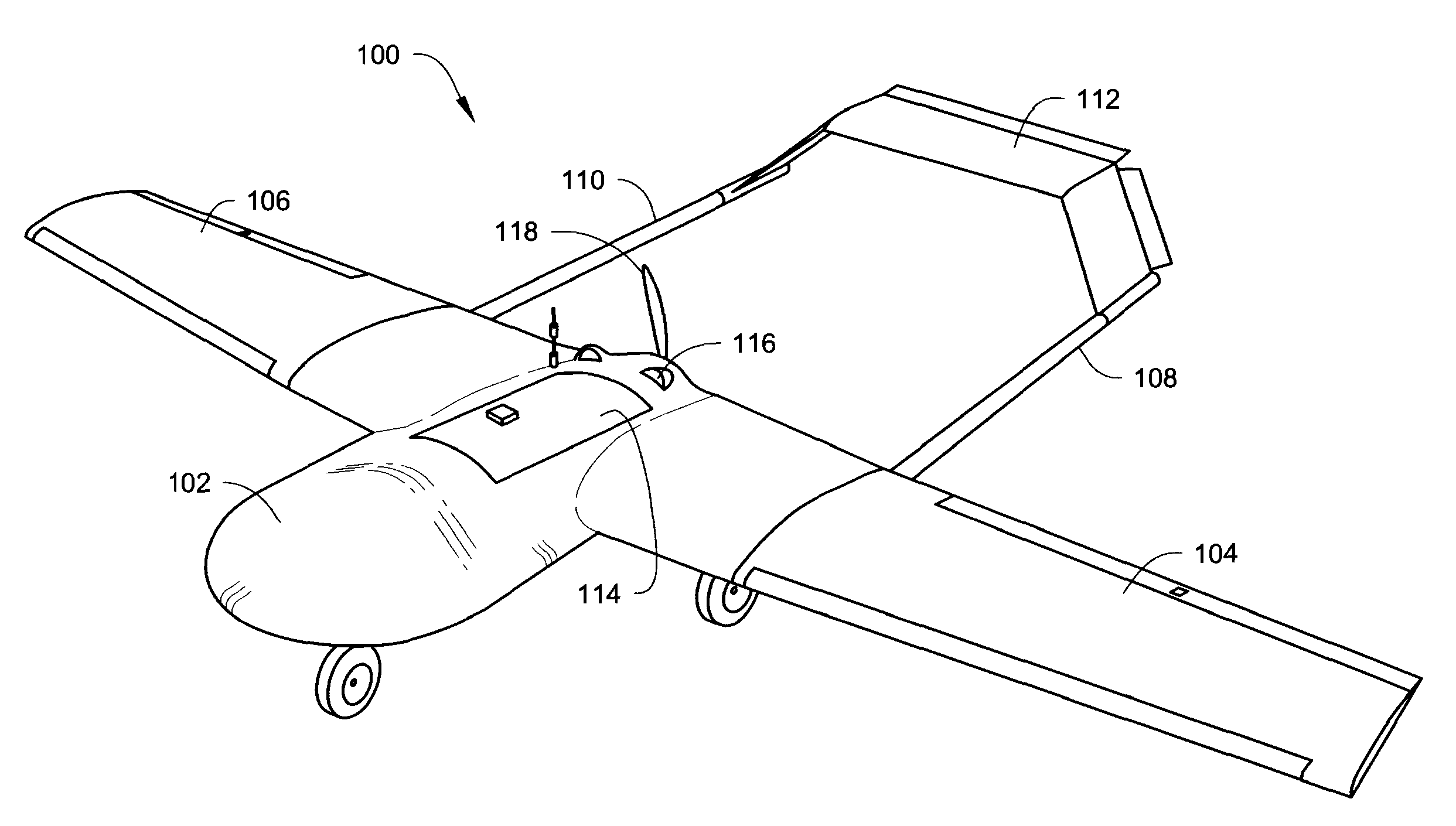
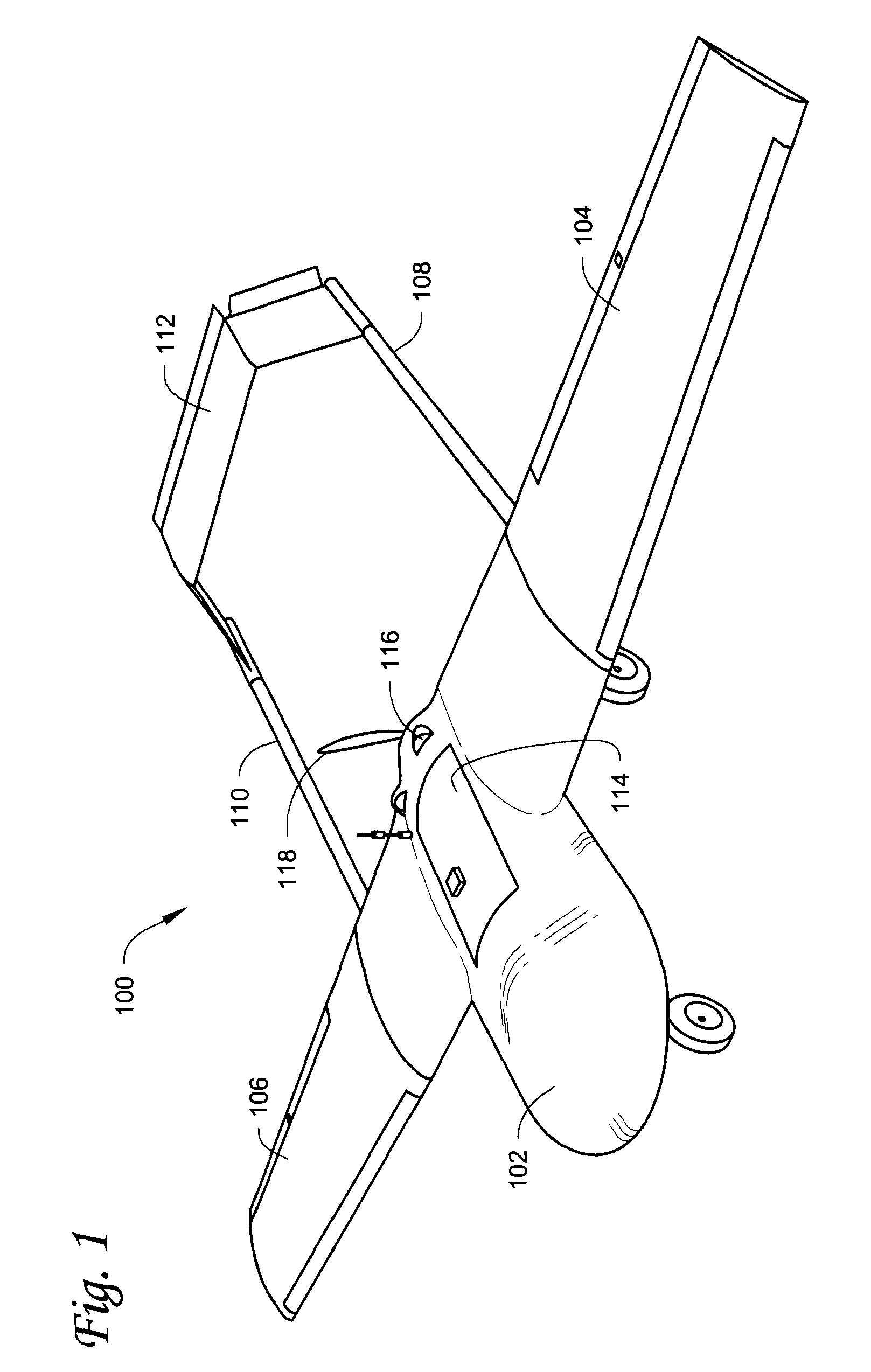
Small unmanned airborne vehicle airframe
InactiveUS7699261B2High strengthQuickly and easily assembled and dissembledUnmanned aerial vehiclesRemote controlled aircraftLow speedModularity
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) is designed for low-speed, low altitude, long endurance missions typical to UAVs of this size and class. The UAV structure is configured to be substantially impervious to small arms fire and to have a very small representative radar cross-section. The UAV is modular such that the main wings and tail wing assembly are quickly and easily, detached from the fuselage for ease of transport and to provide an airframe that is quickly and easily adapted to any particular mission.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Electrically Large complex target and rugged face background composite electromagnetic scattering numerical value emulation method
InactiveCN101216556AElectromagnetic wave reradiation3D modellingScattering cross-sectionClassical mechanics
The invention belongs to the technical field of radar target monitor, in particular to a numerical simulation method of composite electromagnetic scattering of electric-large complex body target and coarse land-sea surface background. The method comprises the following steps of : respectively dividing a body target and a surface target into polygonal planar elements; respectively tracing the front incident direction and the inverse scattering direction with rays and recording rays of each order irradiating the scattering elements; constructing the tracing path by an arbitrary pair of front and back rays meeting at the same planar element or edge to form a scattering item by adopting the resolution of body target scattering element, or the edge physic-optics scattering or physical diffracting as well as the coarse surface element scattering and through the surface-body target scattering and interaction described by scattering ray tracing; and accumulating the scattering items of all planar elements to obtain the composite electromagnetic scattering of the body target and the surface target. The method can numerically simulate composite electromagnetic scattering or radar scattering cross section of a coarse land-sea surface background with complex shape, electric-large size and a three-dimensional body target at high speed and high efficiency.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Symmetric polarization RCS (radar cross-section) testing method for targets at near fields
ActiveCN102401893ARealize measurementMake up for the incomplete measurementWave based measurement systemsRadar cross-sectionNon uniform illumination
The invention relates to technology for measuring electromagnetic scattering properties of targets, and aims to provide an effective and feasible symmetric polarization RCS (radar cross-section) testing method for targets at near fields. An observation antenna rotationally scans along a peripheral track, the position and the posture of the observation antenna are changed, simulative symmetric polarization non-uniform illumination fields are combined, multiple times of target scattering measurements are successively carried out and realize coherent combination, symmetric polarization RCS measurement for the targets at the near fields is realized, and the shortcoming that measurement of polarization electromagnetic scattering data of the targets at the near fields is incomplete is overcome.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
Anti-radar space-filling and/or multilevel chaff dispersers
InactiveUS6876320B2Small sizeLight weightWave based measurement systemsCommunication jammingGeometric designChaff
The present invention consists of the particular geometry of the reflectors or dispersers which constitute the anti-radar chaff cloud. Instead of using conventional rectilinear forms, in the present invention multilevel and space-filling forms are introduced. Due to this geometric design, the properties of the radar chaff clouds improve mainly in two aspects: radar cross-section (RCS) and mean time of suspension.
Owner:FRACTUS
Composite frequency-selective-surface invisible radome
InactiveCN102882002AReduce processing difficultyDoes not affect normal work scanningRadiating element housingsWaveguide type devicesScattering cross-sectionMicrowave
The invention discloses a composite frequency-selective-surface invisible radome and relates to the technical field of microwaves. The composite frequency-selective-surface invisible radome solves the problems that an existing radome is streamline in shape and cannot be spread to a plane, random preparation of an FFS (frequency selective surface) on the radome is difficult in process implementation, and FFS passband transmittance is low as incident angles of electromagnetic waves on the FFS are large. The composite frequency-selective-surface invisible radome is prepared by embedding an inner Y-ring-unit frequency-selective-surface conical cover into an outer radome by the aid of special laminating equipment. The composite frequency-selective-surface invisible radome has a band-pass filtering characteristic within a specific radar frequency range and good passband characteristics, is capable of efficiently transmitting through the working frequency range electromagnetic waves, reflects the out-of-band detection electromagnetic waves to a vast space according to the radome shape and reduces backward radar cross section so that invisibility of the radome is achieved. The composite frequency-selective-surface invisible radome can be used for invisibility of radomes of guided missiles and airplanes.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
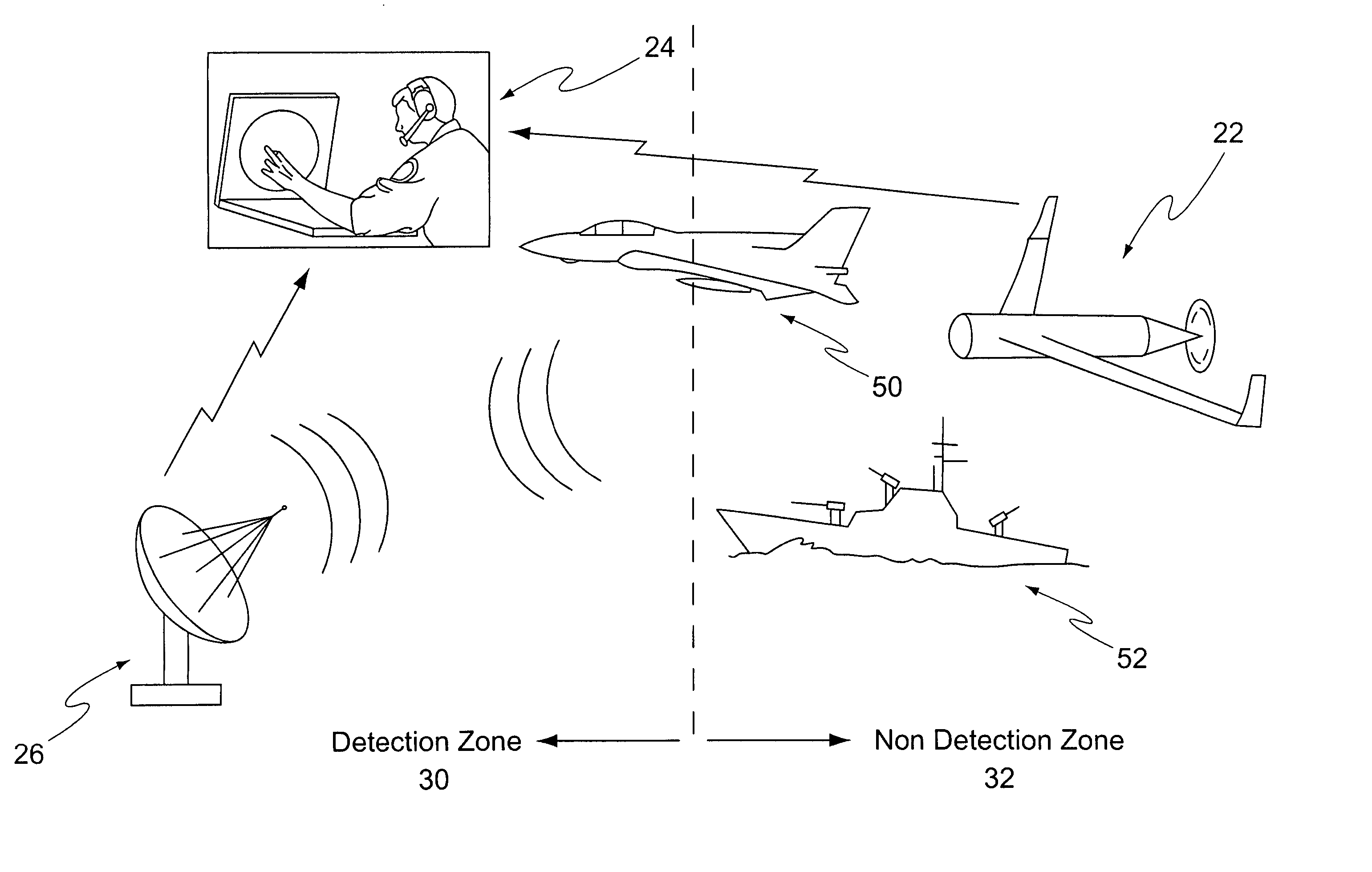
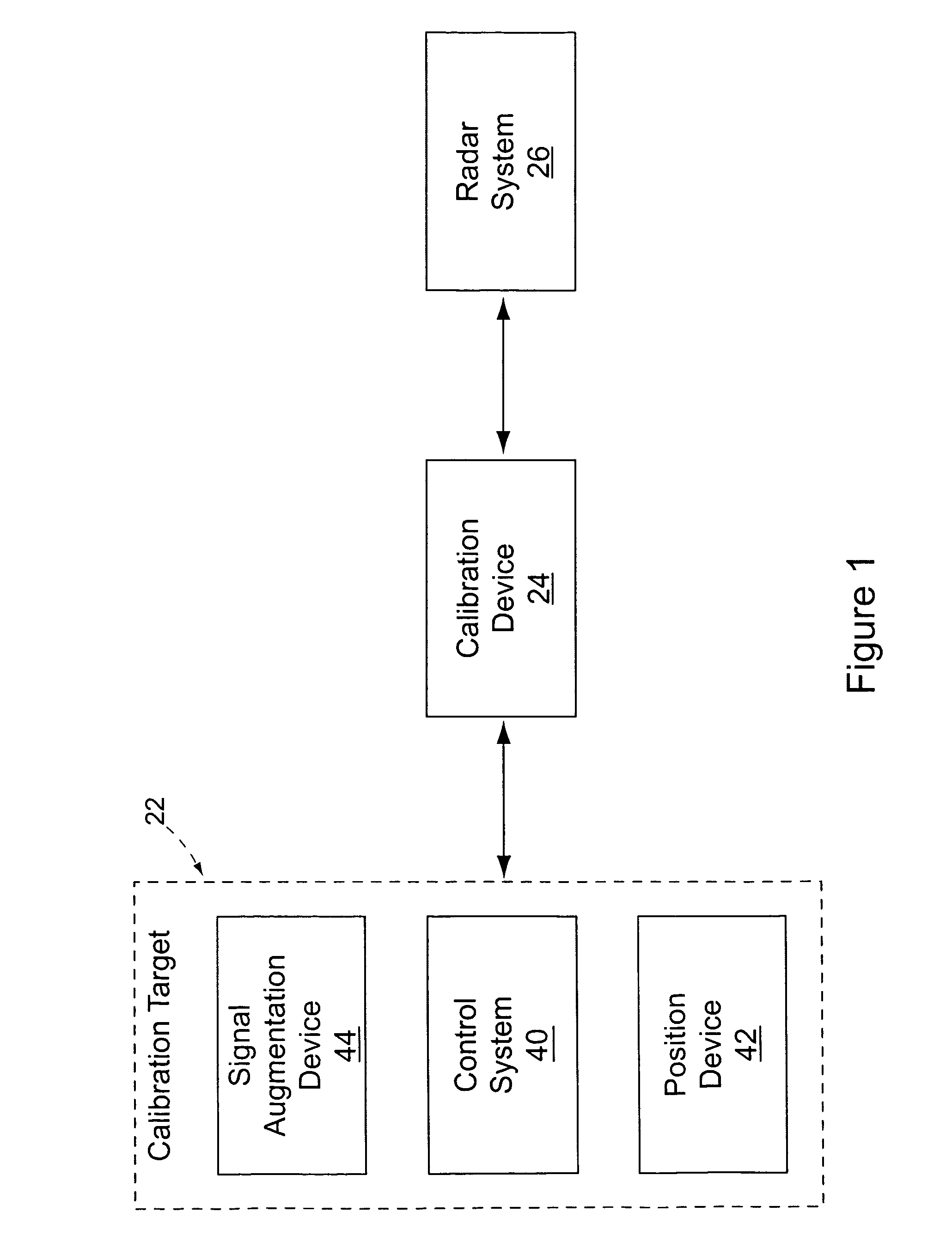
System and method for radar detection and calibration
A system and method for radar detection and calibration. By measuring the true range of a calibration target on entry to the radar's detection zone, the actual detection capability of the radar in current atmospheric conditions with the actual radar can be determined. The radar system is also adapted to determine a sensed position at a sensed time of a target in the radar's detection zone. A calibration target, preferably an unmanned air vehicle (UAV), includes a position device for determining the actual position of the calibration target. A calibration device communicates with the radar system and the calibration target and receives the sensed and actual positions of the calibration target. The calibration device calculates the error between the sensed position and the actual position and adjusts the radar system to minimize the error. The target may include a signal augmentation device to augment the radar cross-section of the target to replicate the radar cross-sections of targets of various types. In this manner the true detection range of the radar system can be determined for various types of targets under existing atmospheric conditions.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
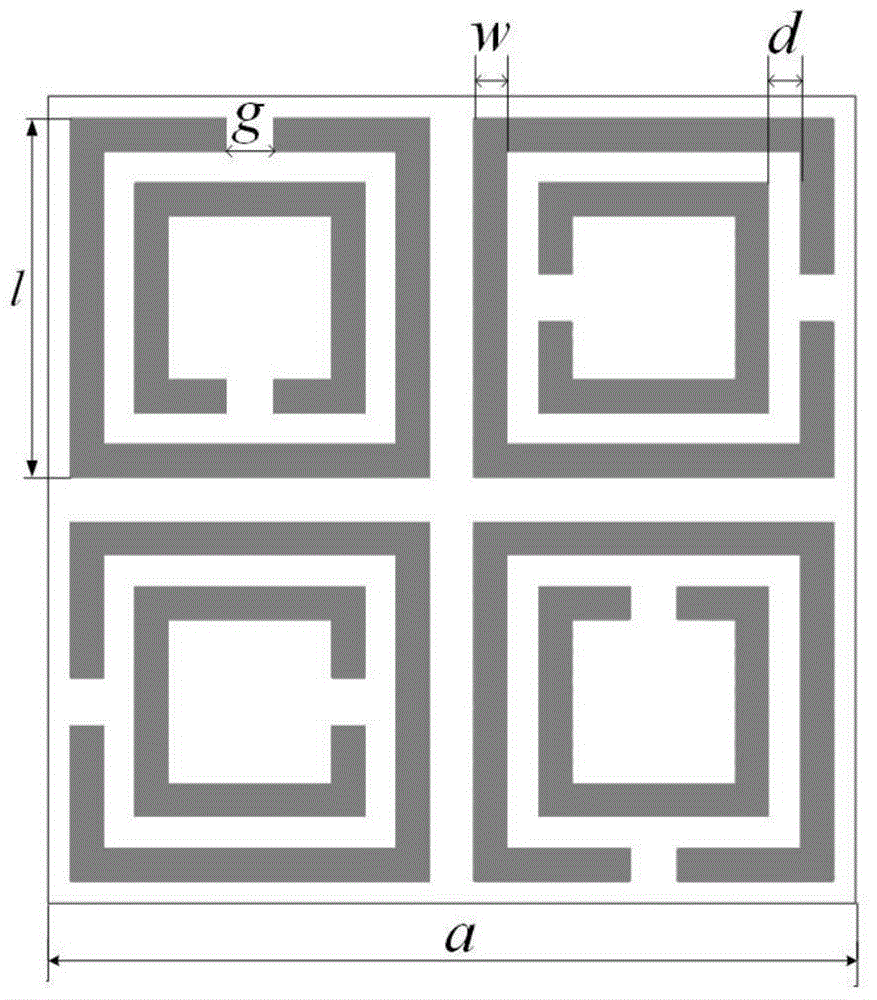
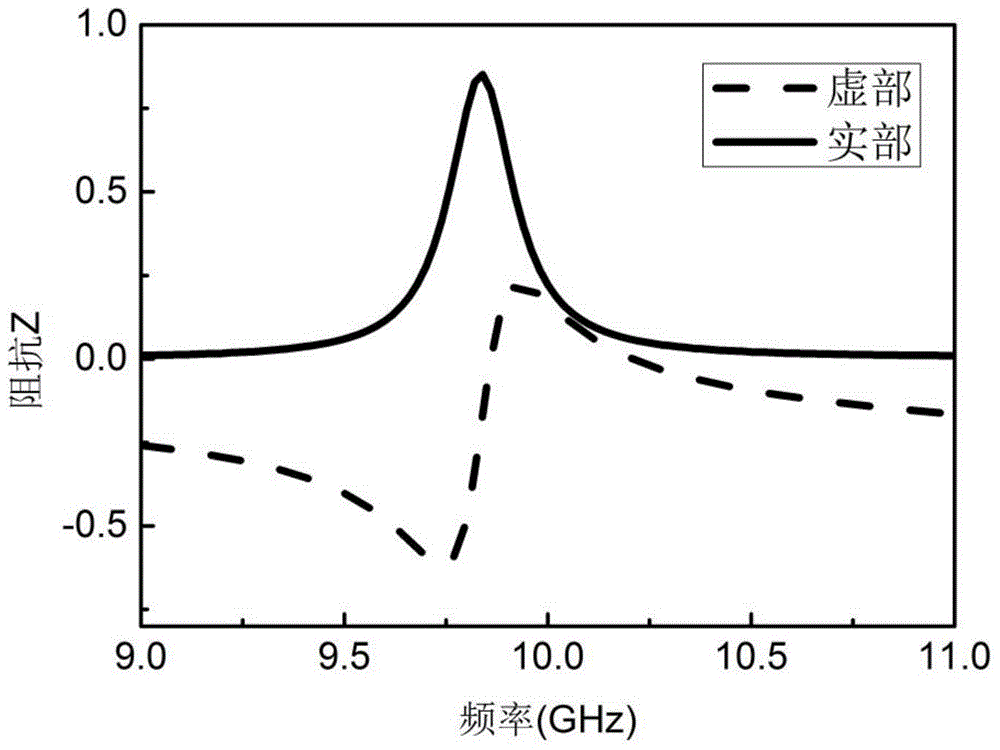
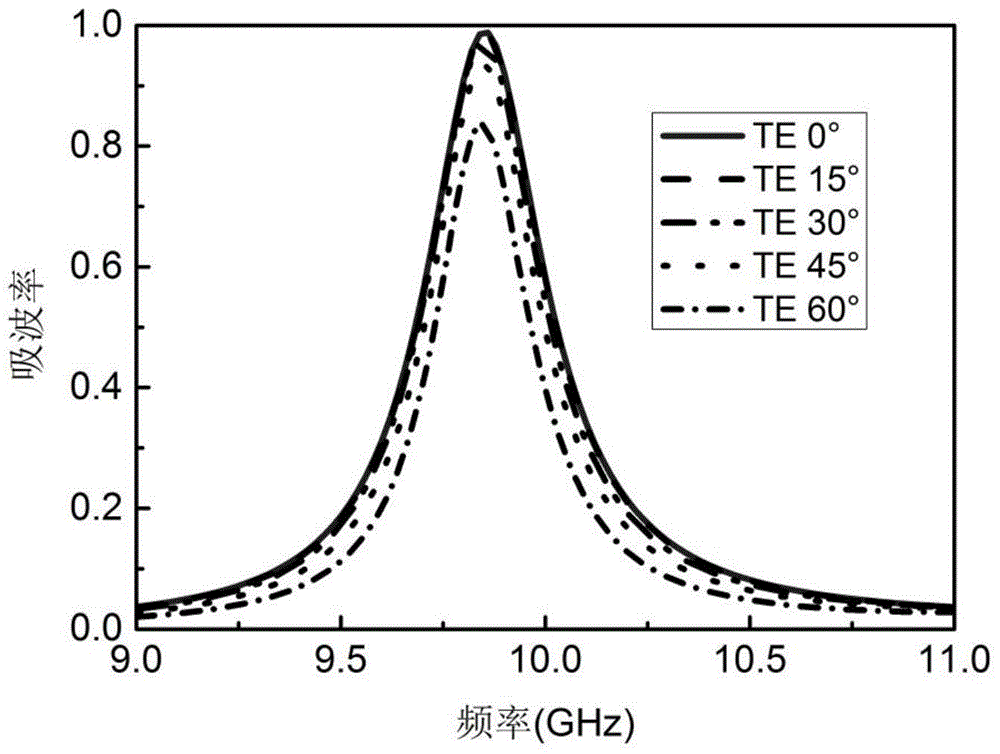
Wide-angle polarization-insensitive low RCS meta-material wave absorber
InactiveCN104682013AWith incident anglePolarization insensitiveAntennasIncident waveRadar cross-section
The invention relates to a wide-angle polarization-insensitive low RCS (Radar Cross Section) meta-material wave absorber. The wide-angle polarization-insensitive low RCS meta-material wave absorber is applied to great reduction of a target echo, thereby achieving the stealth characteristic of a target. A basic unit of the wave absorber consists of four double-opening resonant rings which are rotationally symmetric, the transmission number of a meta-material unit in a working band is 0, the minimum reflection coefficient is minus 18.75dB, the maximum wave absorption rate is 98.9 percent, and a perfect wave absorbing effect is achieved. The TE and TM polarization incident wave within a range of minus 60 degrees to 60 degrees can be absorbed, the maximum decrement of an RCS in the working band can reach 12.35dB, and the effective stealth of the radar target is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method and apparatus for discriminating a target objective, and related program
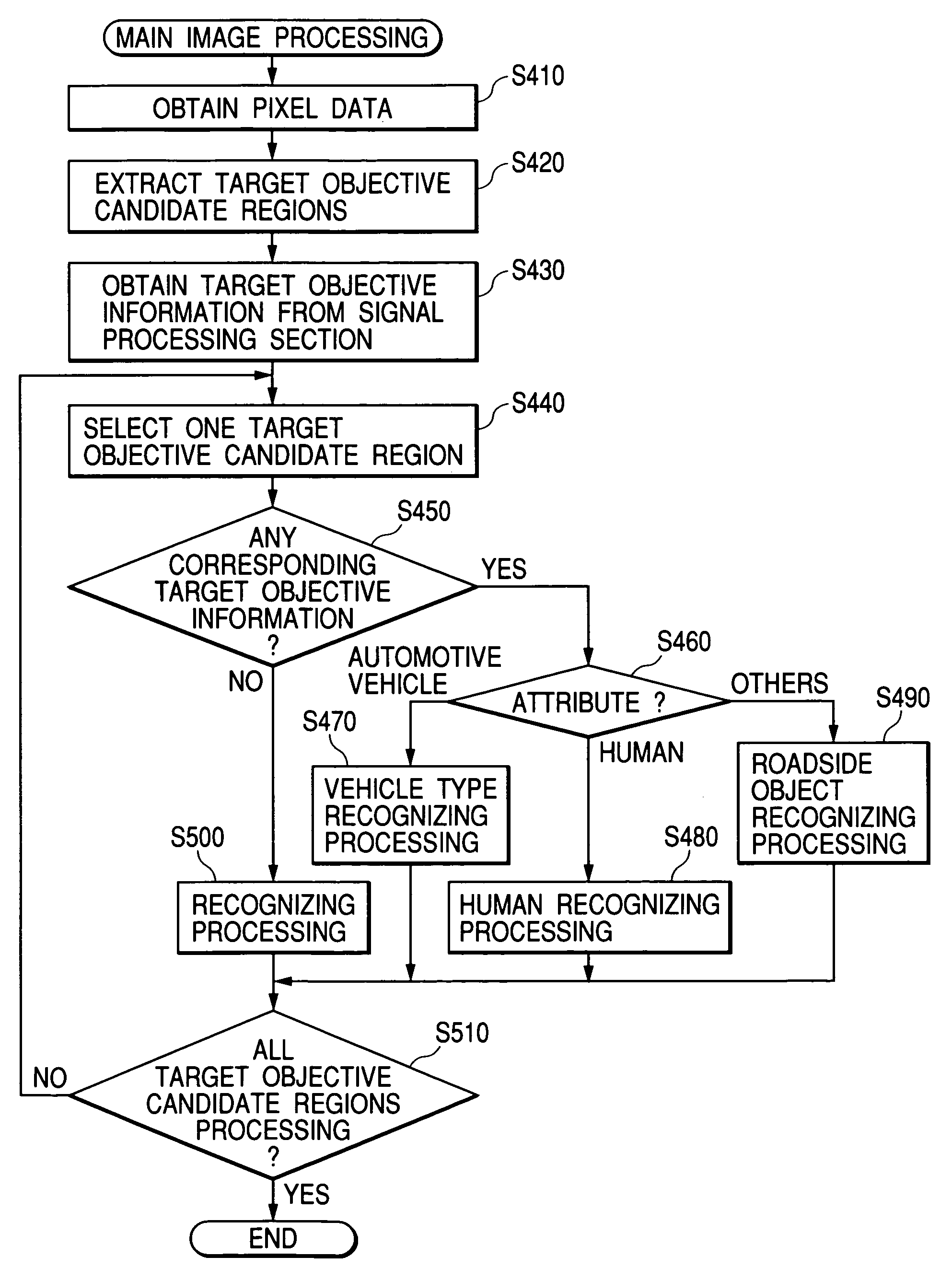
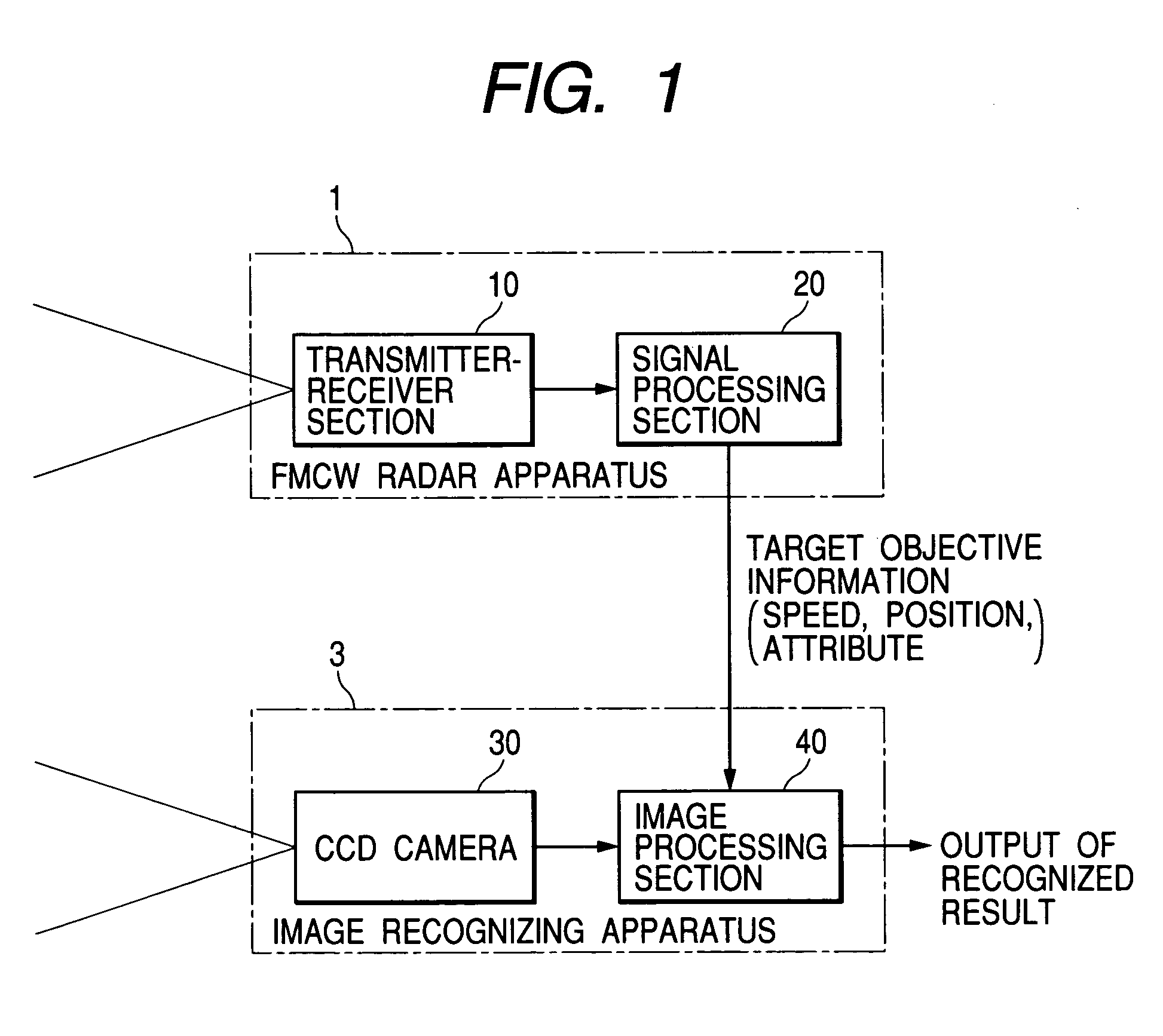
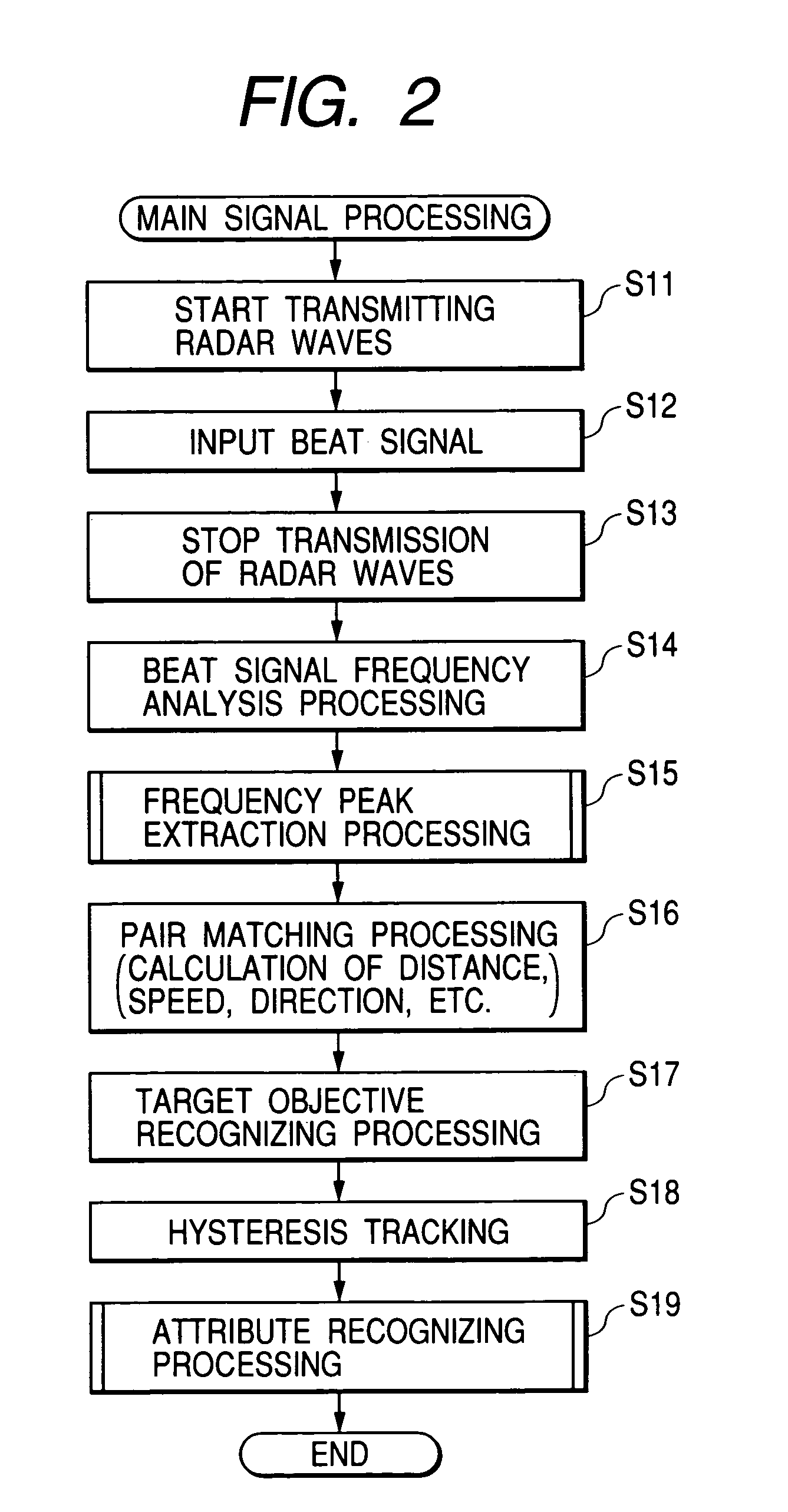
ActiveUS6999024B2Reduce the amount of processingPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementUsing optical meansMobile vehicleEngineering
An average power value of a peak pair corresponding to a subjective target objective is converted into a radar cross section, to calculate a normalized average power value NP and a standard deviation DP representing a temporal dispersion of a power difference between peak pairs. When the value NP is larger than an automotive vehicle discriminating threshold THnp, the attribute of the subjective target objective is set to “automotive vehicle.” When the value NP is not larger than the threshold THnp and the deviation DP is larger than a human objective discriminating threshold THdp, the attribute of the subjective target objective is set to “non-vehicle objective: human objective.” Furthermore, when the value NP is not larger than the threshold THnp and the deviation DP is not larger than the threshold THdp, the attribute of the subjective target objective is set to “non-vehicle objective: non-human.”
Owner:DENSO CORP
Antenna for reducing radar scattering cross section
InactiveCN102176537ASimple structureEasy to processRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsCapacitanceScattering cross-section
The invention discloses an antenna for reducing a radar scattering cross section, aiming to solve the problem of large radar scattering cross section of the traditional microstrip antenna. The antenna comprises a dielectric slab (1), a microstrip radiating unit (2) and an earth plate (3), wherein the microstrip radiating unit is arranged at the upper surface of the dielectric slab, and the earth plate is arranged at the lower surface of the dielectric slab; both sides of the microstrip radiating unit are provided with a high impedance surface array (4) respectively; each high impedance surface array is formed by arranging a plurality of metal chips into a rectangle, a gap is arranged between the adjacent metal chips to form a capacitor C; the center of each metal chip is provided with a metal via hole which penetrates through the dielectric slab; a current path connected by the via holes can form an inductor L, and the capacitor and the inductor form an LC resonant circuit; the frequency of the resonant circuit can be adjusted to be coincident with the working frequency of the antenna, thus realizing scattered field compensation of the high impedance surface array and the antenna. The invention has stable performance of reducing radar scattering cross section within and outside the frequency band of the antenna, and also has no effect on the size, weight and cost of the antenna.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Array antenna used for reducing radar scattering cross section
InactiveCN102227040ASimple structureEasy to processWave based measurement systemsAntenna arraysCapacitanceMicrostrip array antenna
The invention discloses an array antenna used for reducing radar scattering cross section, and mainly solves a problem of large scattering cross section of a present microstrip array antenna radar. The array antenna in the invention comprises a medium plate, a ground plate and n microstrip radiation units (2). The n microstrip radiation units (2) are on the upper surface of the medium plate (1). The ground plate (3) is on the lower surface of the medium plate (1). Structural type absorbing material arrays (4) are provided between each two adjacent microstrip radiation units, and N*M square metal pasters (5) are arranged as rectangular. The metal pasters (5) form inductances L. Connection resistors (7) connect adjacent metal pasters to form resistors R. Gap (6) between adjacent metal pasters (5) form capacitors C. The capacitors C, the inductances L and the resistors R form RLC resonance circuits. By adjusting resonance circuits frequency to superpose the resonance circuits frequency with antenna work frequency, absorption of vertical incident surface wave is realized. The array antenna used for reducing radar scattering cross section in the invention has the advantages of stable performance of reducing in-band and outband radar scattering cross sections of antenna and no influence on antenna volume, weight and cost.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Low index metamaterial
ActiveUS20100078203A1Facilitate propagationReduce applicationsWaveguide hornsPrinted circuitsElectrical conductorRefractive index
Various aspects of the disclosure provide low index metamaterials. The low index metamaterials may be used to form soft and / or hard electromagnetic (EM) boundaries to facilitate desired EM performance or propagation in applications including feed horns, spatial feed / combiners, isolation barriers between antennas or RF modules, and reduced radar cross-section applications. In one aspect, a low index metamaterial comprises a dielectric layer and a plurality of conductors on a surface of the dielectric layer, embedded in the dielectric layer or both, wherein the low index metamaterial appears as a medium having a dielectric constant less than one with respect to electromagnetic waves at predetermined frequencies and propagating at grazing angles with respect to a surface of the low index metamaterial.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Marine navigation radar signal simulation method
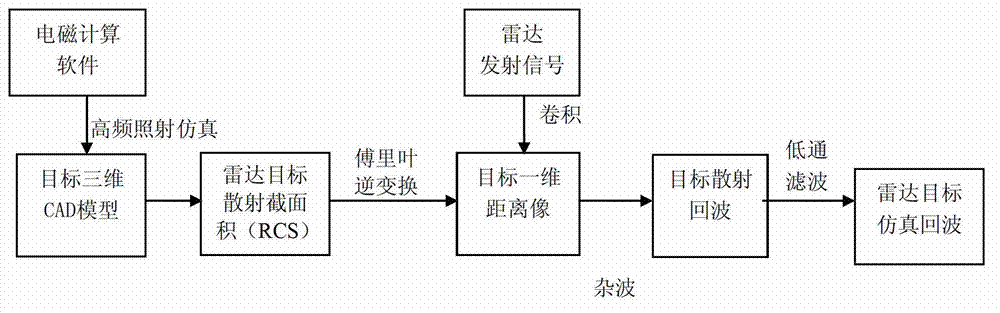
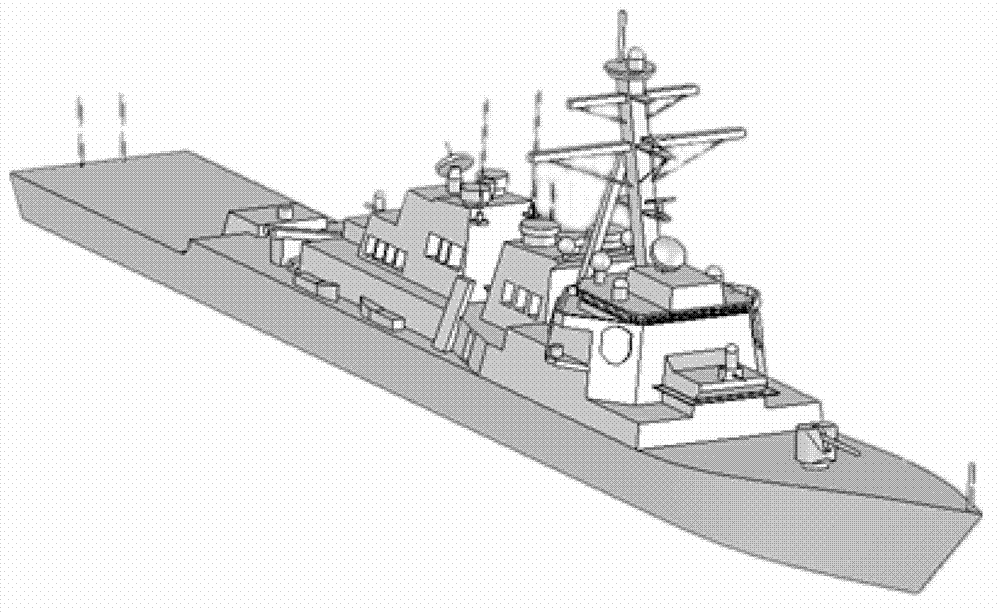
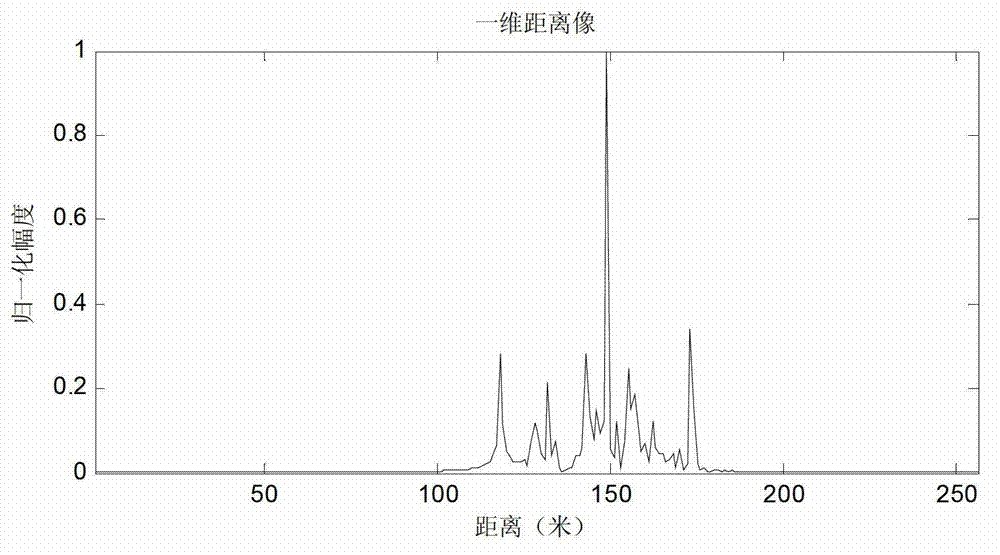
The invention belongs to the technical field of civil marine navigation, and relates to a marine navigation radar signal simulation method. A three-dimensional computer aided design (CAD) model of an offshore ship target is built by adopting computer aided design technology, predication is conducted to radar scattering sectional area of the target by high-frequency electromagnetic calculation software, the scattering area sectional area is processed so as to obtain a one-dimensional range image of the target, and convolution is conducted to radar transmitted wave form and the obtained one-dimensional range distance; Doppler frequency shift factors are introduced according to states of target motion; distance attenuation factors are introduced according to located position of the target; and low pass filtering is conducted so as to obtain marine navigation radar signal simulation echo through adding a sea clutter model. According to the marine navigation radar signal simulation method, a navigation radar ship target echo sample base which is high in similarity in various characteristic spaces with actual radar echo signals is provided, and radar echo signal sources are provided for teaching and training of navigation radars and seamen.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Full-polarization single-passband bilateral microwave absorbing band composite metamaterial and antenna housing
ActiveCN106207480ARealize the purpose of stealthGood radiation characteristicsRadiating element housingsMicrowaveDielectric substrate
The invention relates to a composite metamaterial which is characterized in displaying a wave transmitting band and two wave absorbing bands in different bands, belongs to the technical field of a material and an antenna housing, and solves the technical problem of providing the full-polarization composite metamaterial for the defect that the wave absorbing characteristic is only formed at a high frequency side out of the wave transmitting passband. The scheme is that periodic metamaterial structure layers, namely, a resistive film layer and a metal coil layer are respectively attached on the upper surface and the lower surface of a dielectric substrate made of a non-conductive material; the metamaterial is virtually divided into multiple square unit structures which are arranged periodically; and each square unit structure comprises the dielectric substrate and micro-unit structures on the upper surface and the lower surface of the dielectric substrate. The composite metamaterial and the antenna housing have the advantages that the bilateral wave absorbing characteristic appears in the metamaterial, an incoming wave from incidence to the antenna housing is absorbed well, the radar cross section of an antenna is reduced, and the antenna is hidden.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
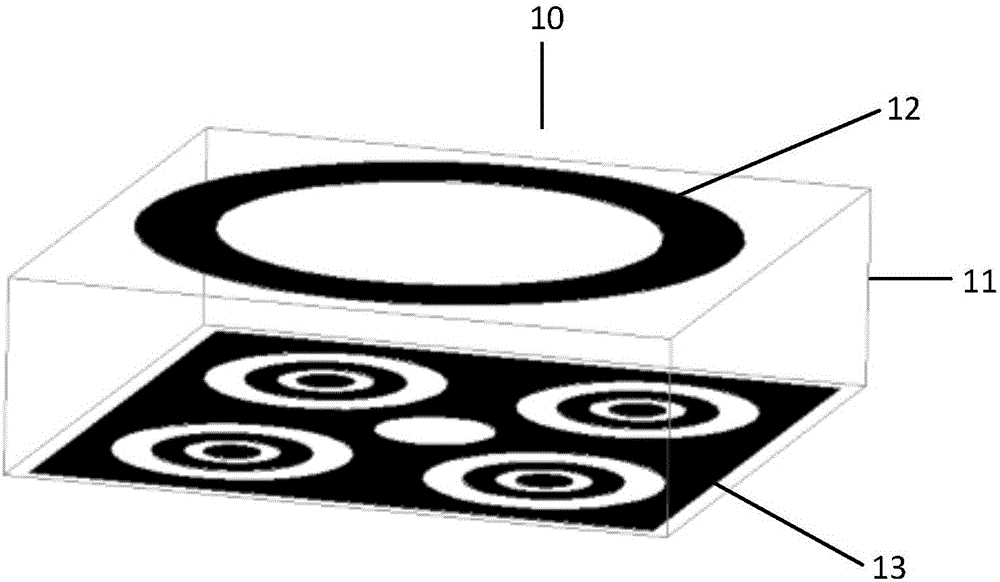
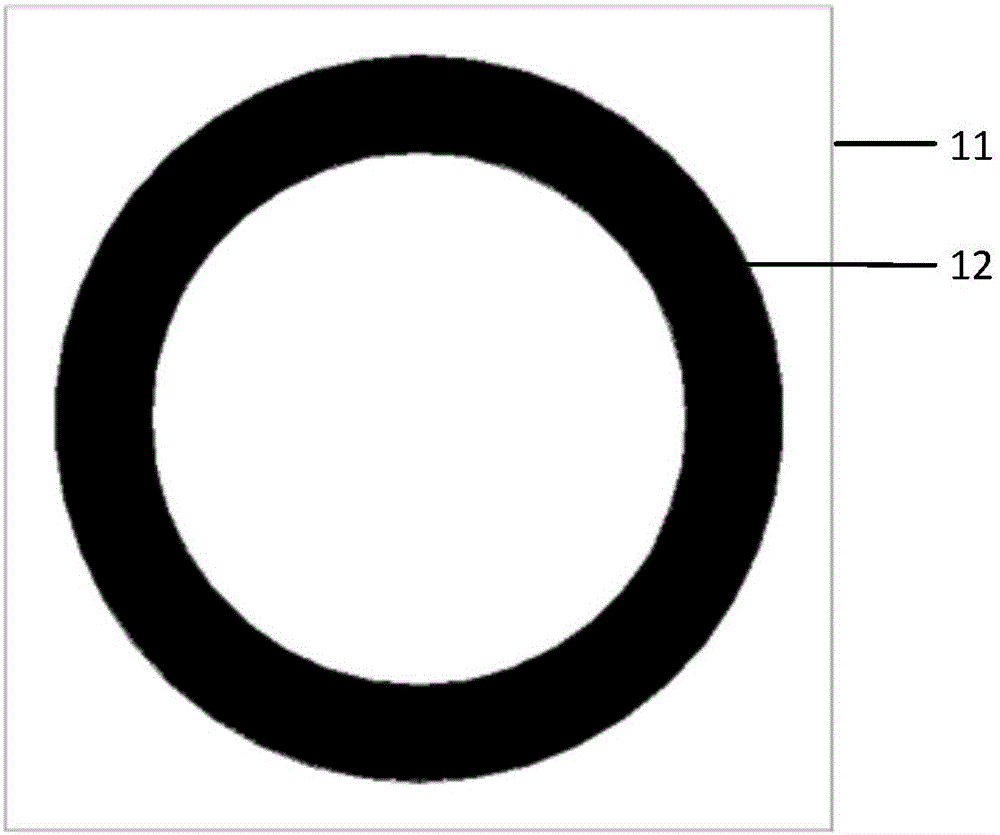
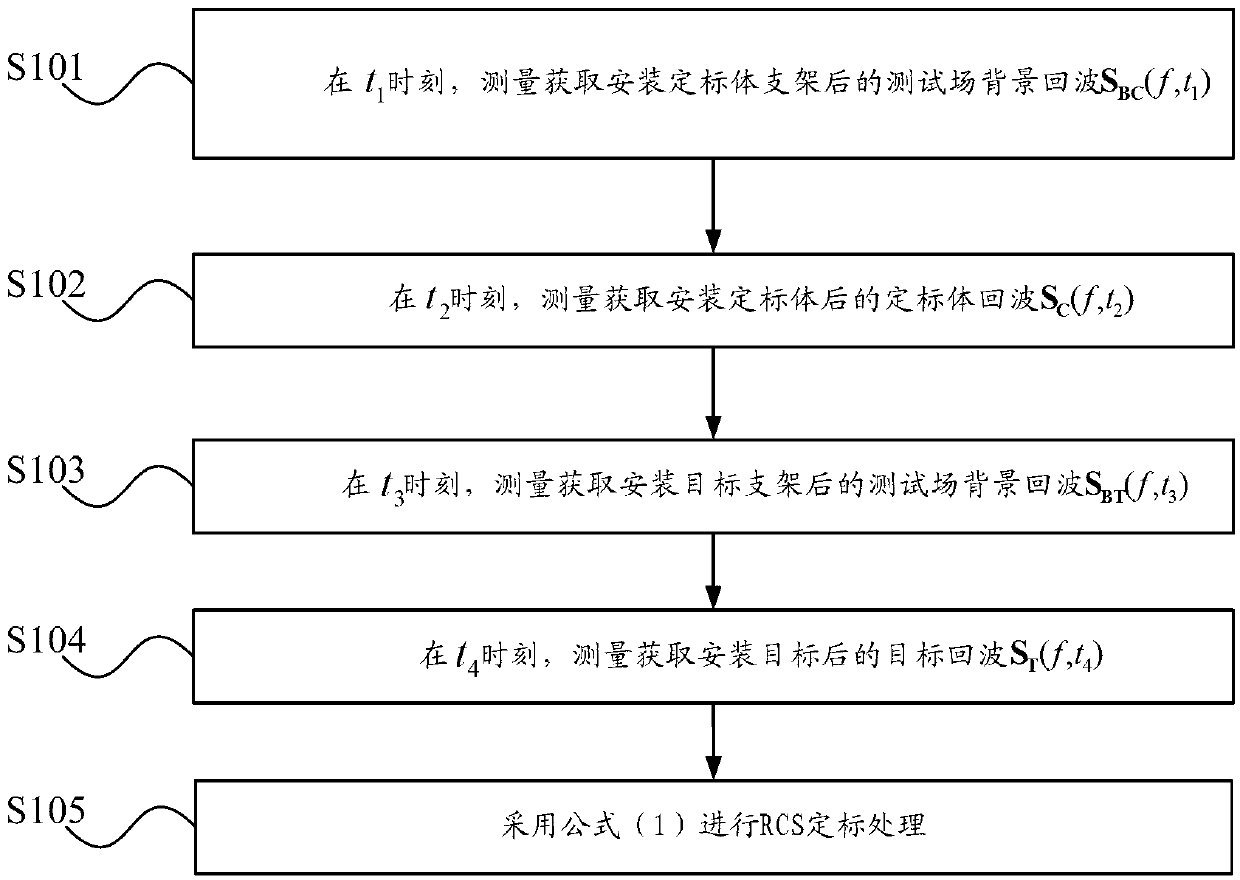
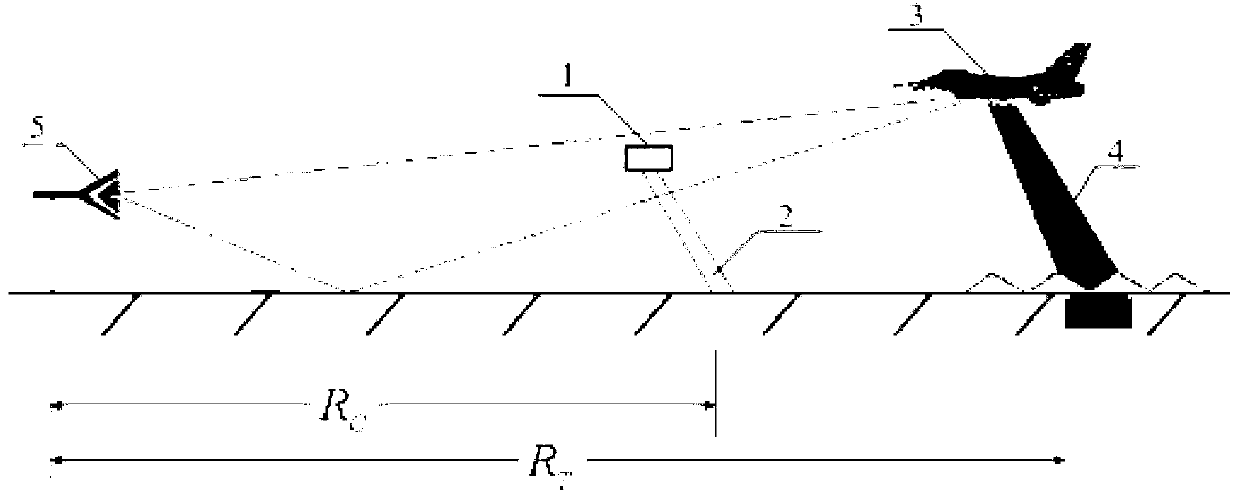
Target radar cross section measuring and calibrating processing method
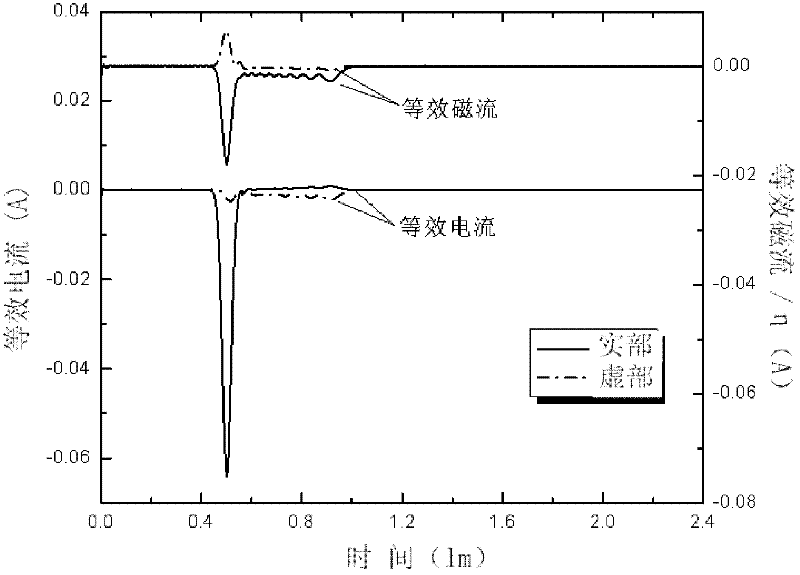
ActiveCN102998665ASolve the problem of large measurement calibration errorWave based measurement systemsPhysicsRadar cross-section
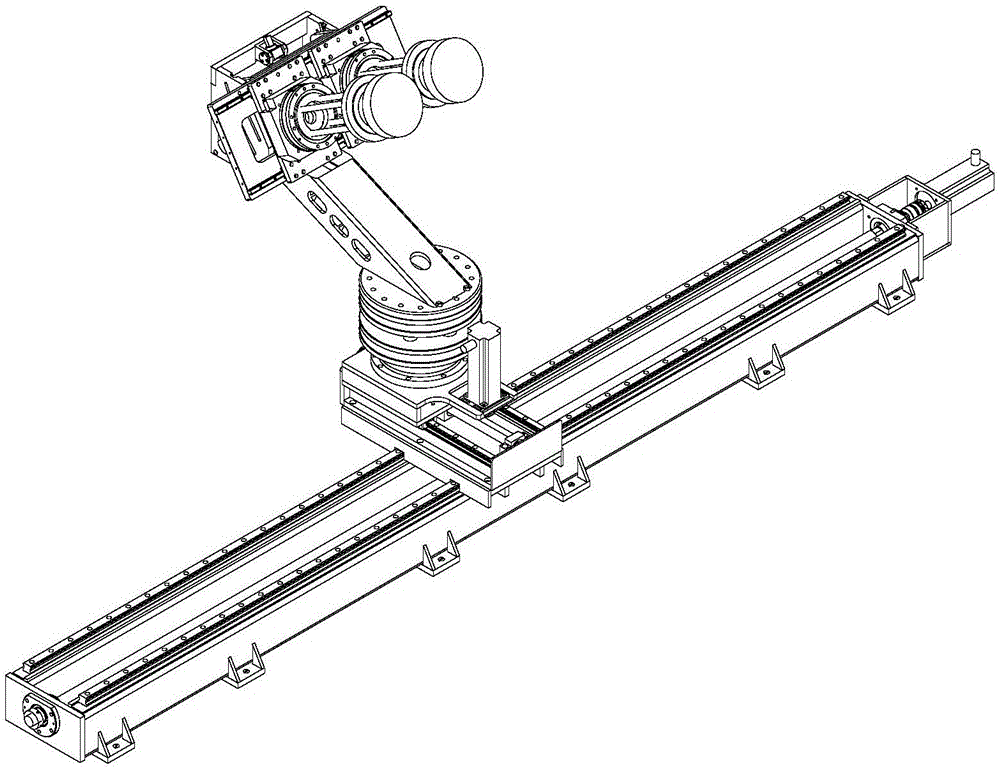
The invention provides a target radar cross section measuring and calibrating processing method. The method includes measuring and acquiring a test field background echo SBC (f,t1) at the moment of t1 after a calibration member support is installed, wherein SBC (f, t) is equal to HC(f, t1) * BC (f, t1); measuring and acquiring a calibration member echo SC (f, t2) at the moment of t2 after a calibration member is installed; measuring and acquiring a test field background echo SBT (f, t3) at the moment of t3 after a target support is installed, wherein SBT (f, t3) is equal to HT(f, t3) * BT (f, t3); and measuring and acquiring a target echo ST (f, t4) at the moment of t4 after a target is installed. The formula (1) is used for performing calibrating processing. By means of the target radar cross section measuring and calibrating processing method, the problem that measuring calibrating errors caused by many time varying factors in outfield testing are large can be solved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
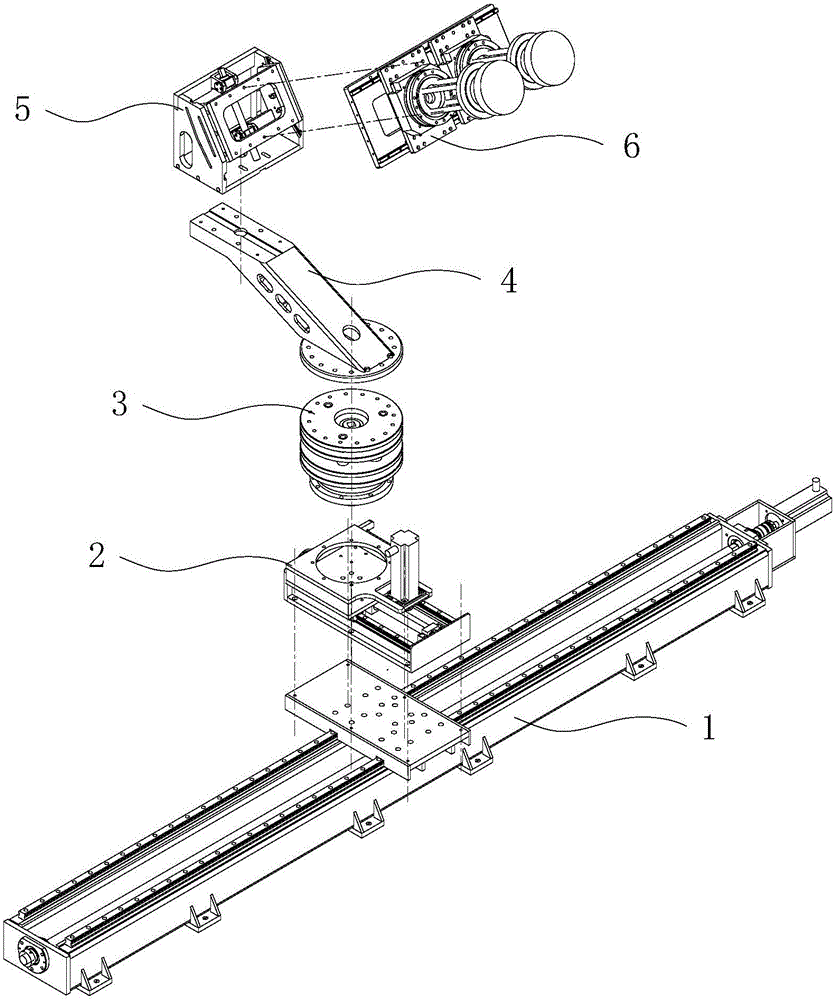
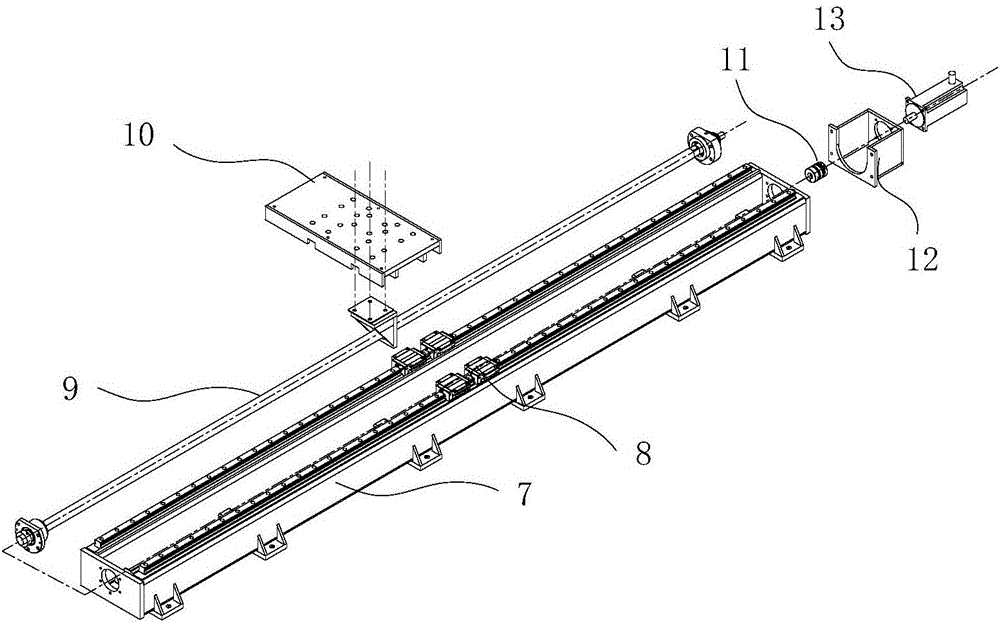
Feed source locating and focus offset device for compact range measurement
ActiveCN106356634AAchieve left and right translationHigh precisionWaveguide hornsAntennas earthing switches associationCompact rangeUniform rotation
The invention provides a feed source locating and focus offset device for compact range measurement. The device is used for precise location and focus offset motion of a feed horn in an electromagnetic measurement process of a compact range. The device mainly comprises left and right transverse movement along the X axis, front and back longitudinal movement along the Y axis, rotation and translation around the Z axis and pitching movement around the phase center of a feed source. Accurate locating and focus offset of the feed source are realized through movement of five freedom degrees, and focus offset measurement is completed. By means of servo control, polarization rotation and uniform rotation at a certain rotation speed of the feed horn can be realized, and RCS (radar cross-section) measurement or antenna measurement is completed. The device comprises an X-axial moving unit, a Y-axial compensation unit, a Z-axial rotating and height adjusting unit, an offset arm, a feed source pitching unit and a feed source polarization unit. Different from a fixed feed source locating device, the device can not only be used for precise location of the feed source during measurement of the compact range in a traditional manner, but also be used for measurement of new demand ways such as focus offset and the like; the device has the advantages of high measurement efficiency, high locating precision and simple and reliable control process.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
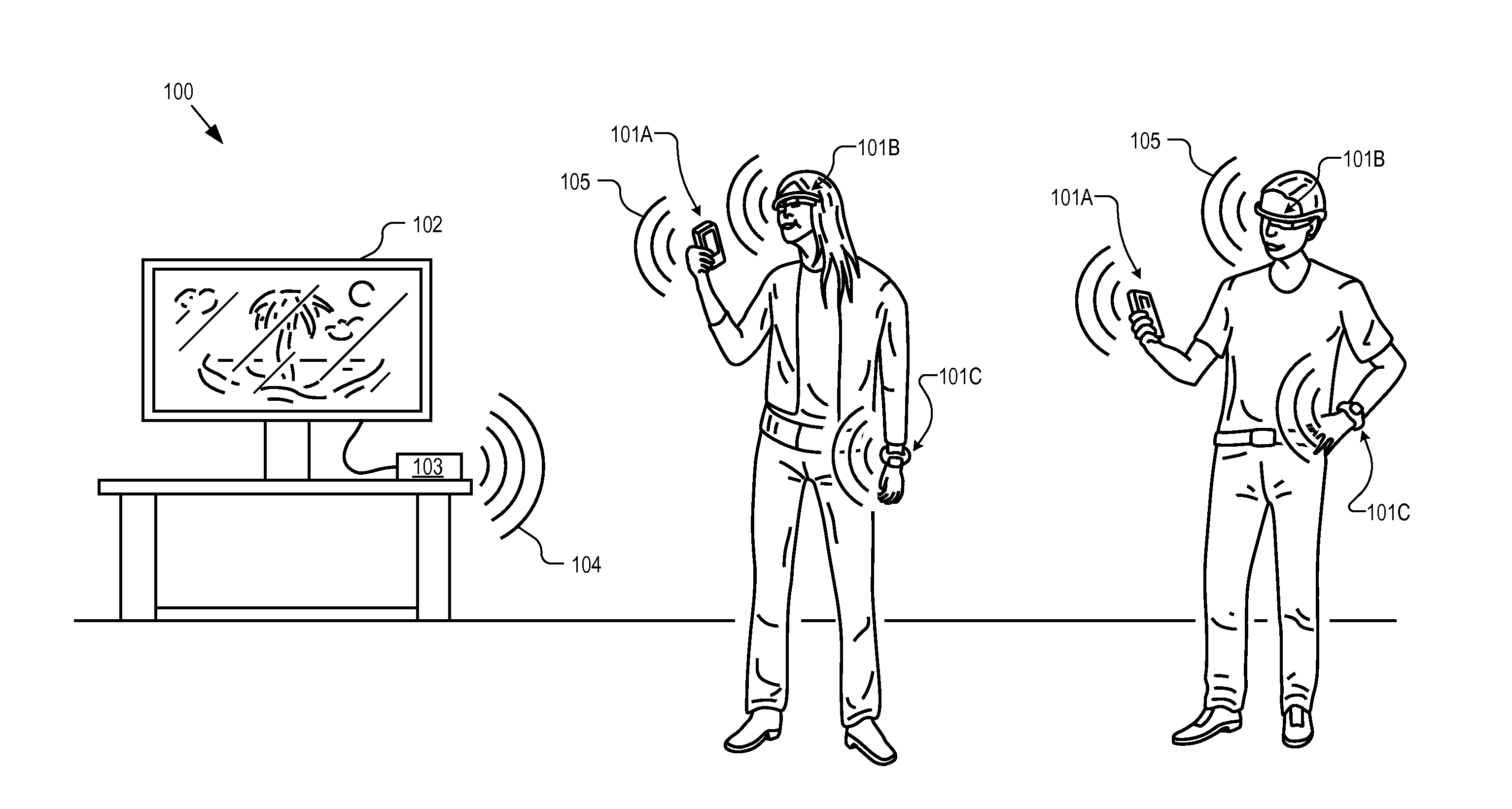
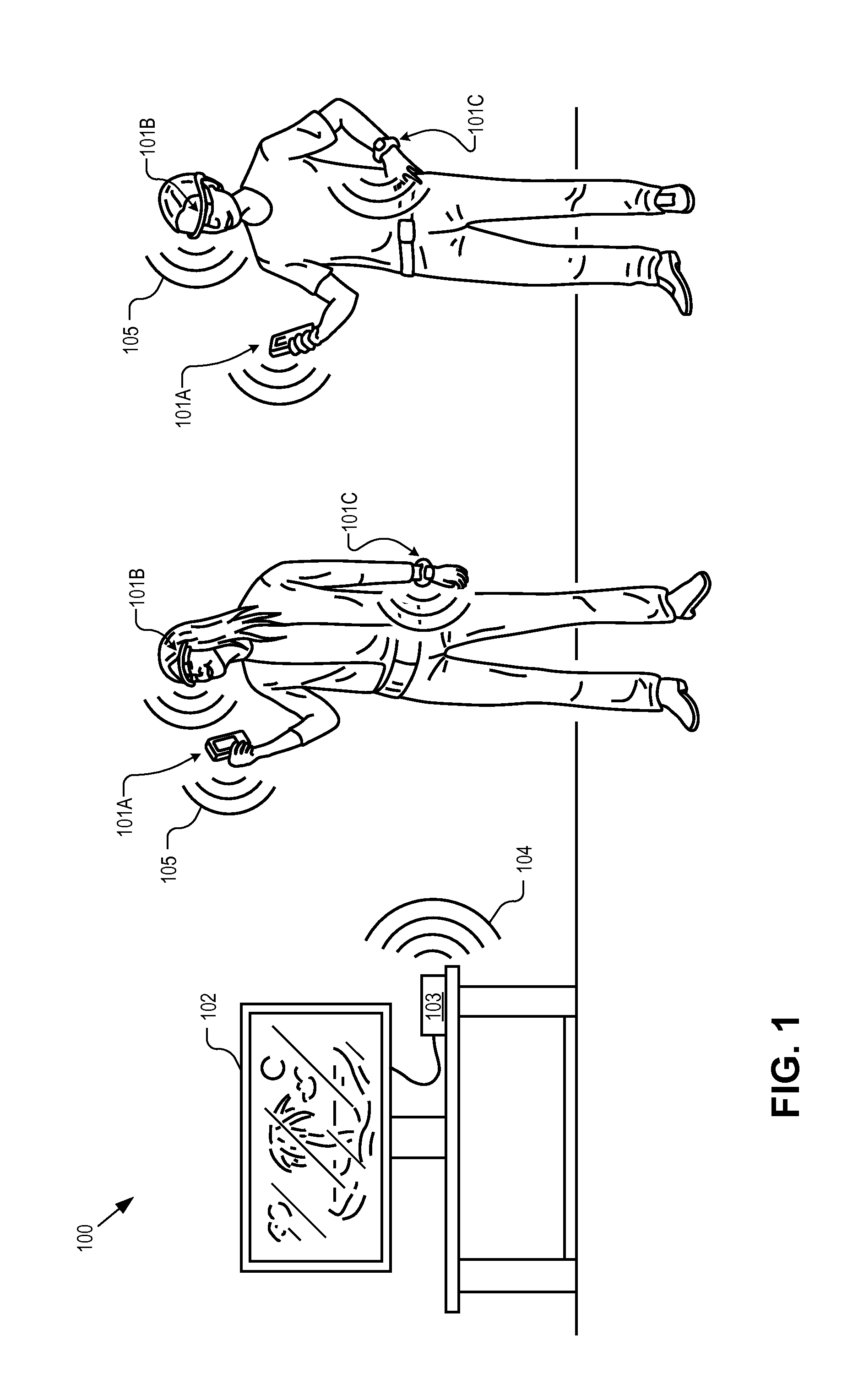
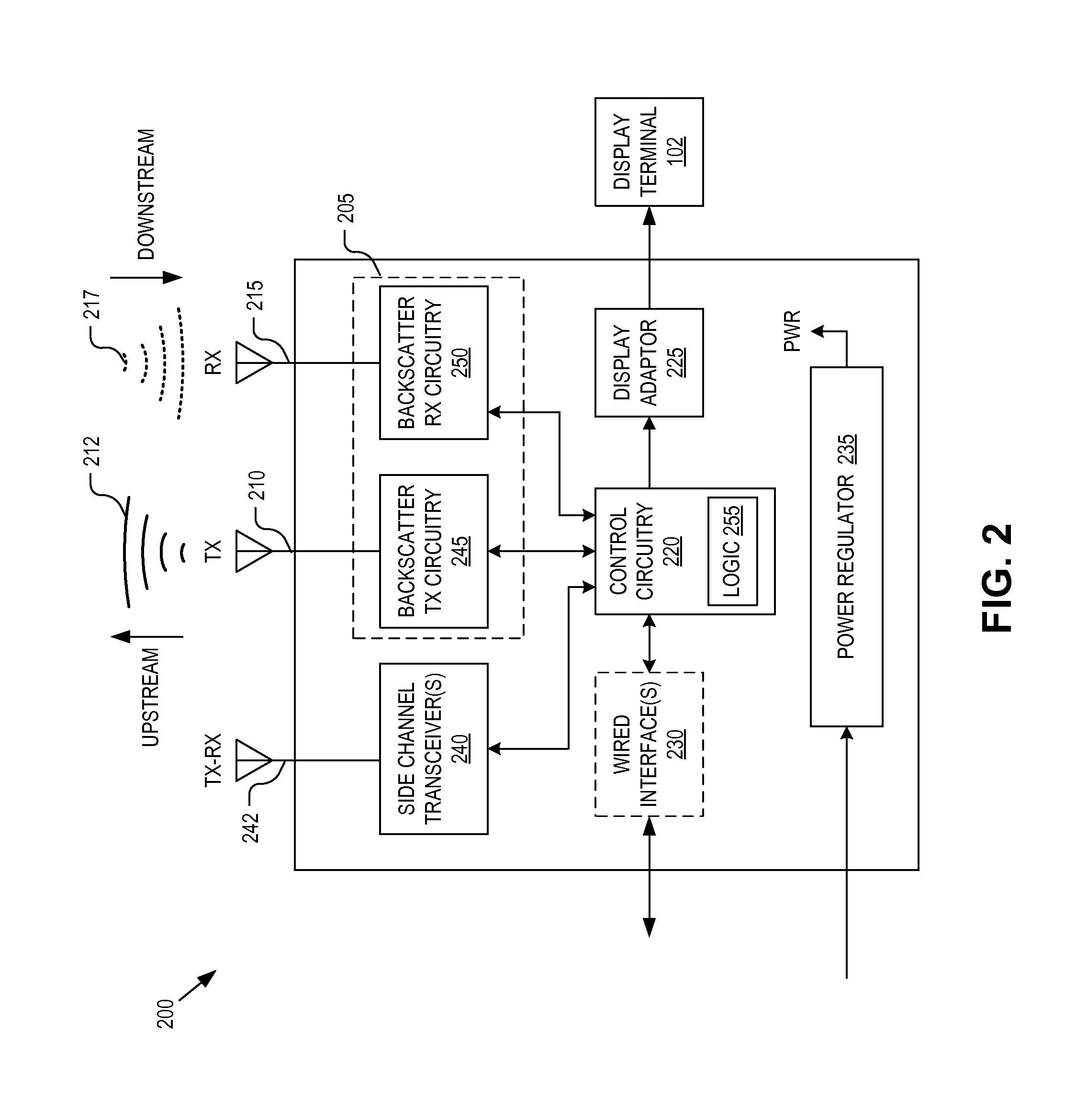
Streaming display data from a mobile device using backscatter communications
ActiveUS20150381269A1Scatter propogation systemsRadio transmission for post communicationMobile deviceRadar cross-section
A method of wirelessly communicating a screen image between a mobile device and a base station coupled to a display terminal includes establishing a wireless display session between the mobile device and the base station. Electromagnetic (“EM”) radiation emitted from the base station is incident upon an antenna of the mobile device. The screen image is transmitted to the base station for display on the display terminal by modulating a radar cross-section of the mobile device between two or more states to encode the screen image on a backscatter channel of the EM radiation.
Owner:X DEV LLC
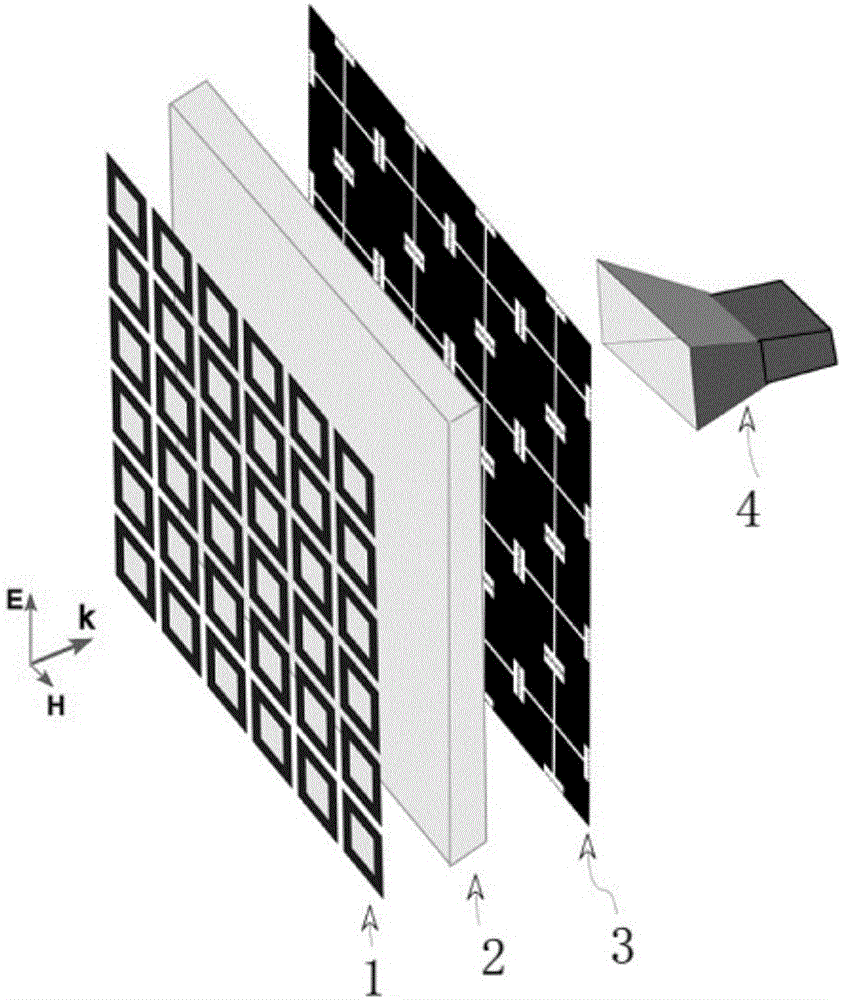
Wideband spirally-coding radar cross-section (RCS) reducing metasurface insensitive to polarization and design method thereof
ActiveCN107465000AEasy to processThe overall thickness is thinAntennasDielectric plateRadar cross-section
The invention belongs to the technical field of radar stealth, and particularly relates to a wideband spirally-coding radar cross-section (RCS) reducing metasurface insensitive to polarization and a design method thereof. The metasurface is of a two-dimensional limited size structure and is formed by arranging eight types of linear super-elements having different gradient directions in 8 by 8 according to a spiral sequence, the gradient directions of eight types of linear super-elements are respectively 0 degree, 45 degrees, 90 degrees, 135 degrees, 180 degrees, 225 degrees, 270 degrees and 315 degrees, each linear super-element is of a two-dimensional limited size structure and is formed by six types of artificial electromagnetic structure units having different sizes in 6 by 6 according to linear gradient, the six types of artificial electromagnetic structure units realize 360-degree coverage, the phase gradient is 60 degrees, the spiral sequence is a single spiral circulation arrangement mode from outside to inside, each artificial electromagnetic structure unit is of a rotary symmetric reflection structure and comprises an upper-layer internal closed ring, an external Jerusalem metal structure, an intermediate-layer dielectric plate and a bottom-layer metal copper plate. The RCS reducing metasurface has the excellent characteristics of thin thickness, good robustness, ultra-wideband working and the like and is easy to process.
Owner:AIR FORCE UNIV PLA
1-bit microwave anisotropic electromagnetic coding meta-material
The invention provides a 1-bit microwave anisotropic electromagnetic coding meta-material. A unit structure of the meta-material consists of an isotropic structure and an anisotropic structure. The design and optimization of geometric parameters of the unit structure can enable each unit to represent independent reflection phase 0 degree and 180 degrees during the irradiation of x-polarization and y-polarization vertically-incident electromagnetic waves, wherein the independent reflection phase 0 degree and 180 degrees are respectively corresponding to a digital state '0' and a digital state '1'. The digital units are arranged on a two-dimensional plane according to digital coding designed in advance, thereby forming the anisotropic electromagnetic coding meta-material. Because each unit is independent in response during x-polarization and y-polarization, the coded meta-material can make independent response during the irradiation of x-polarization and y-polarization vertically-incident electromagnetic waves, including abnormal beam separation and random surface scattering. The meta-material is simple in structure, is easy to machine, is wide in frequency band, can be used for the design of beam separation to generate a plurality of beams, or can be used for the design of an invisible surface, and effectively reduces the radar scattering section of a target.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
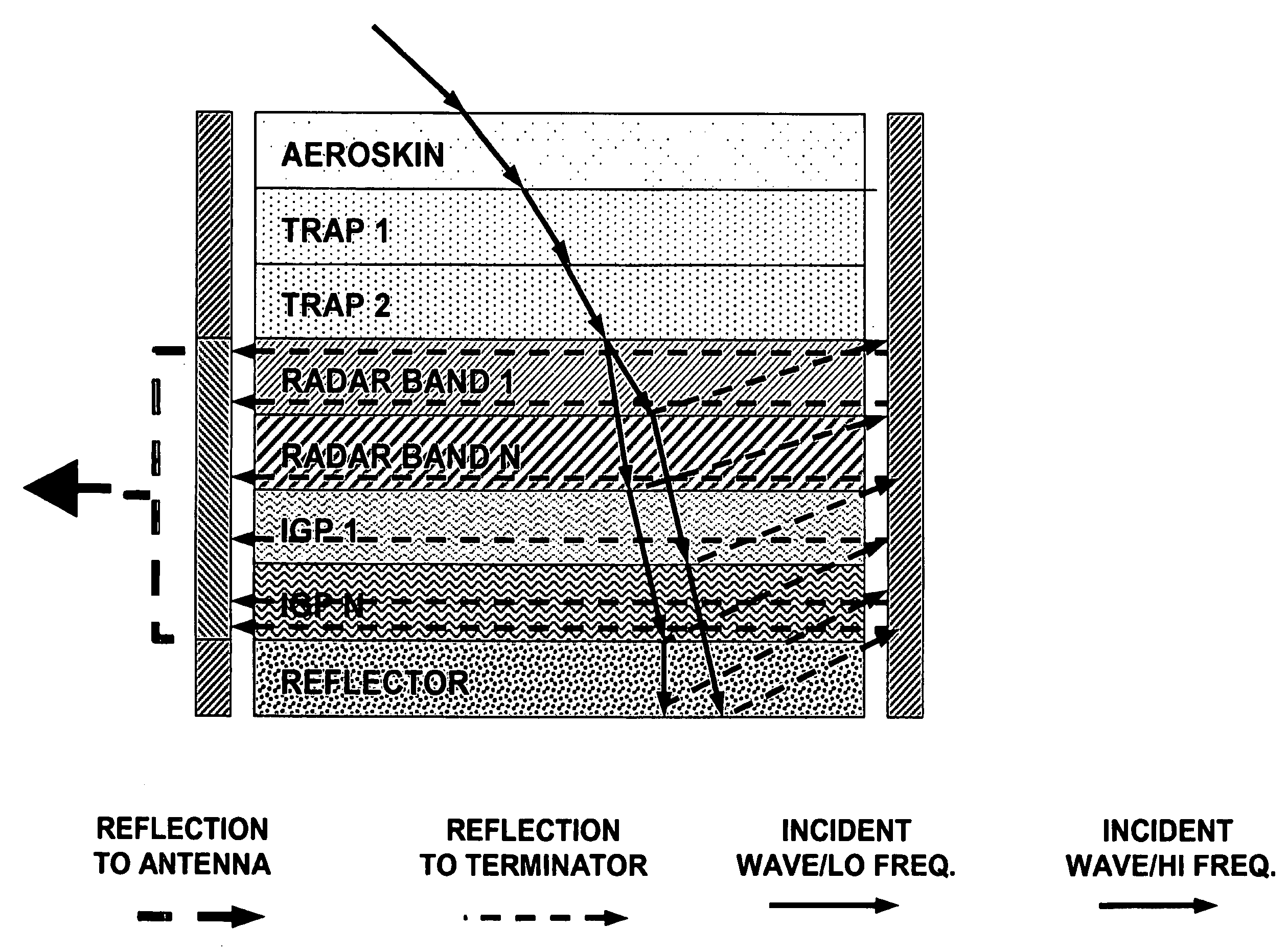
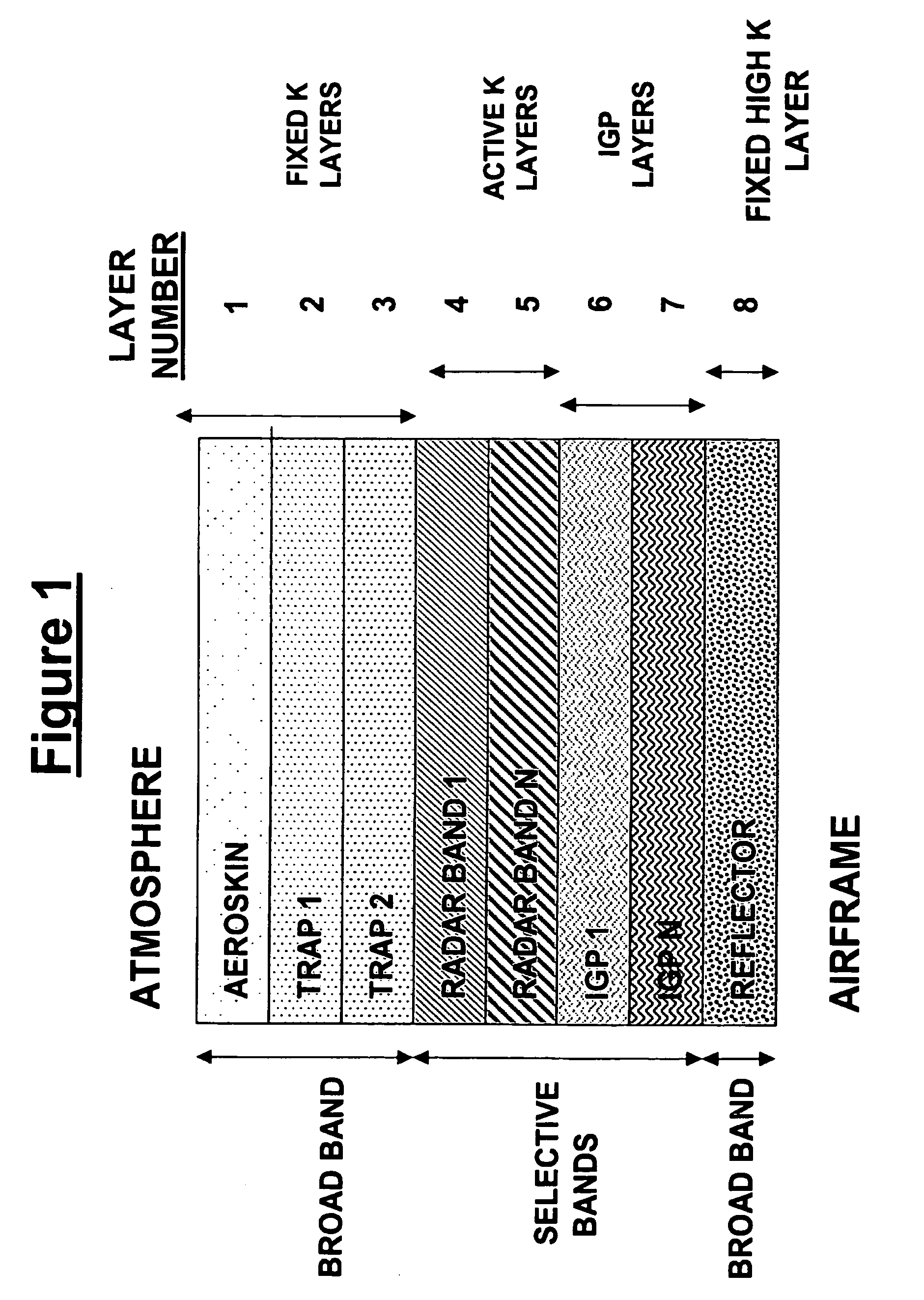
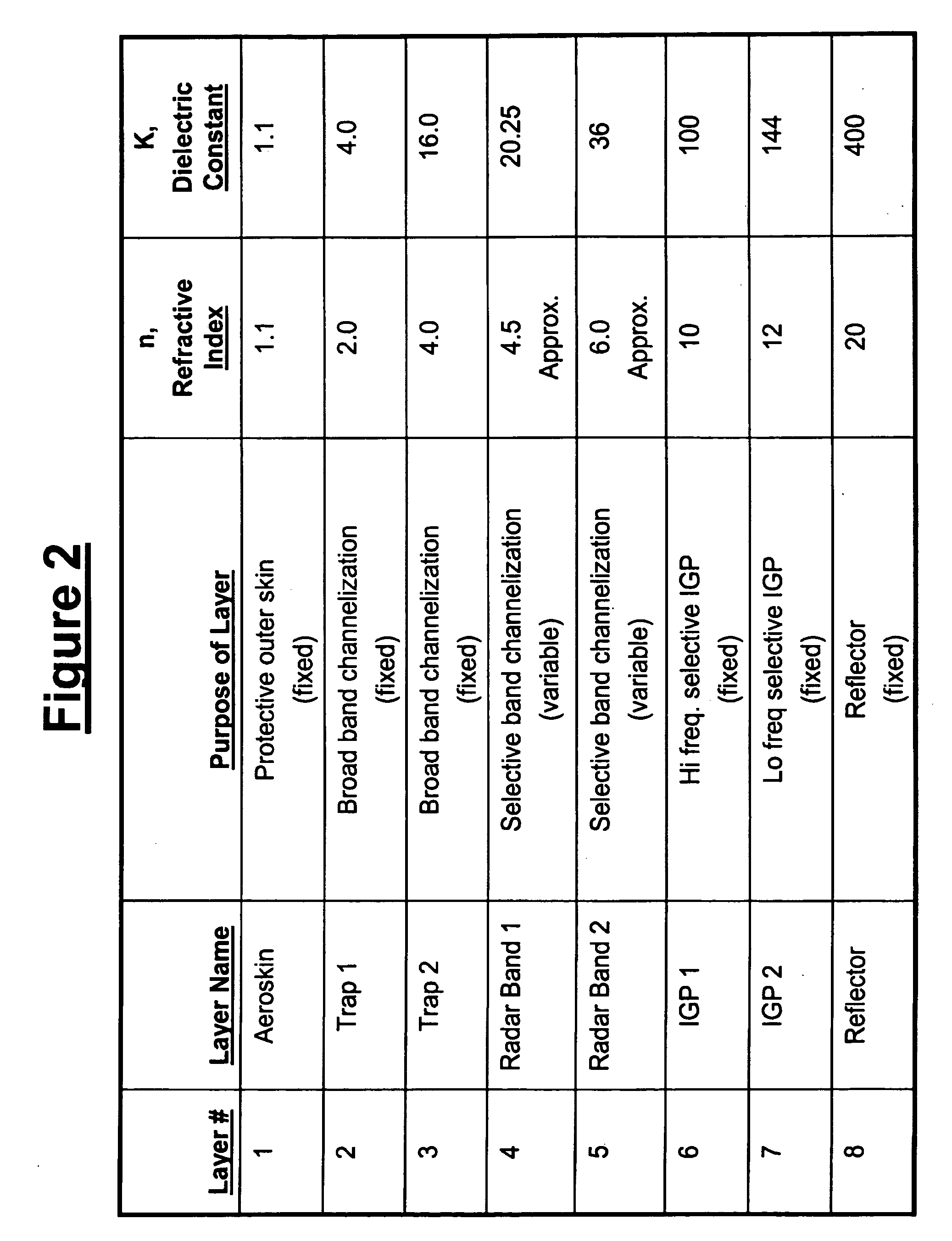
Method of agile reduction of radar cross section using electromagnetic channelization
A method for reducing radar cross section of an object that has conductive portions and that is expected to be scanned by radar, which includes providing the object with a multiple layer radar cross section reducing structure that reduces or entraps or dissipates radar waves therein so that the size or configuration of the object cannot be correctly detected by radar scanning. The invention also relates to the radar cross section reducing structure alone or associated with an object such as a vehicle that transports personnel or equipment. The structure can be provided on an object that previously has no stealth capability or it can be applied to an object that already has stealth capability for increasing its capability to prevent correct detection by radar scanning.
Owner:ALAN ROSS
Method for obtaining radar cross section (RCS) of homogeneous bi-isotropic medium object
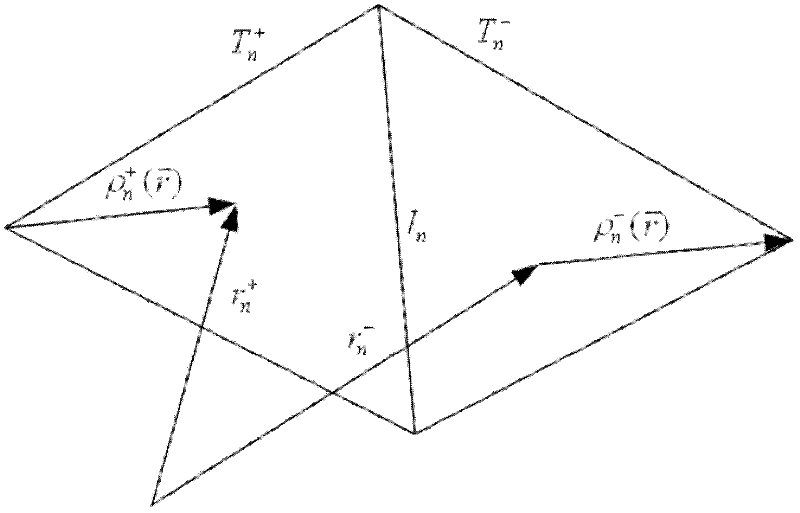
InactiveCN102508220AUniform Scattering Cross SectionScattered field stabilizationWave based measurement systemsMagnetic sourceRao wilton glisson
The invention relates to the field of electromagnetic wave and radar monitoring and provides a method for obtaining radar cross section (RCS) of a homogeneous bi-isotropic medium object. The method comprises the following steps of: building a geometrical model of the homogeneous bi-isotropic medium object and dividing the surface of the model into a plurality of triangular patches in seamless connection; introducing a planar power source vector function and a planar magnetic source vector function; applying a field decomposition method in the homogeneous bi-isotropic medium object; obtaining a boundary integral equation on the surface of a scatterer according to the boundary conditions; applying a moment method to carry out numerical solution on the boundary integral equation, including space test and time test; adopting RWG (Rao-Wilton-Glisson) basis functions as the spatial basis function and test function and adopting Laguerre functions with amplitude factors as the temporal basis function and test function; and obtaining electromagnetic scattering of an observation point according to the equivalence principle and then applying Fourier transform to obtain the RCS. The method has the following advantages that: the obtained scattered field of the homogeneous bi-isotropic medium object is stable; and the RCS with wide frequency range can be obtained.
Owner:郑州微纳科技有限公司
Broadband bionic yagi antenna with low radar cross section
InactiveCN102931481AEasy to hideAchieve stealthRadiating elements structural formsBroadbandWide band
The invention discloses a broadband bionic yagi antenna with a low radar cross section and mainly solves the problems of high radar cross section and relatively narrow band width in the traditional yagi antenna. The antenna simulates an opposite phyllotaxis plant leaf structure and comprises a director (2), a radiating element (3), a parallel strip line (4), a reflector (5) and a coaxial conversion joint (6). The radiating element (3) is of an oval structure, the director (2) simulates a feather-shaped leaf structure, and the reflector (4) is a rectangle patch with a tooth-shaped structure. The radiating element (3) is printed on a top layer and a bottom layer of a double-layer medium material plate (1) and respectively connected with an inner core and an outer core of the coaxial conversion joint (6) by the parallel strip line (4); the director (2) is printed on the top layer of the double-layer medium material plate (1); and the reflector (4) is printed between two layers of the double-layer medium material plate (1). The broadband bionic yagi antenna with the low radar cross section has the advantages of wide frequency band and good invisibility performance and can be used on an invisible target carrier.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
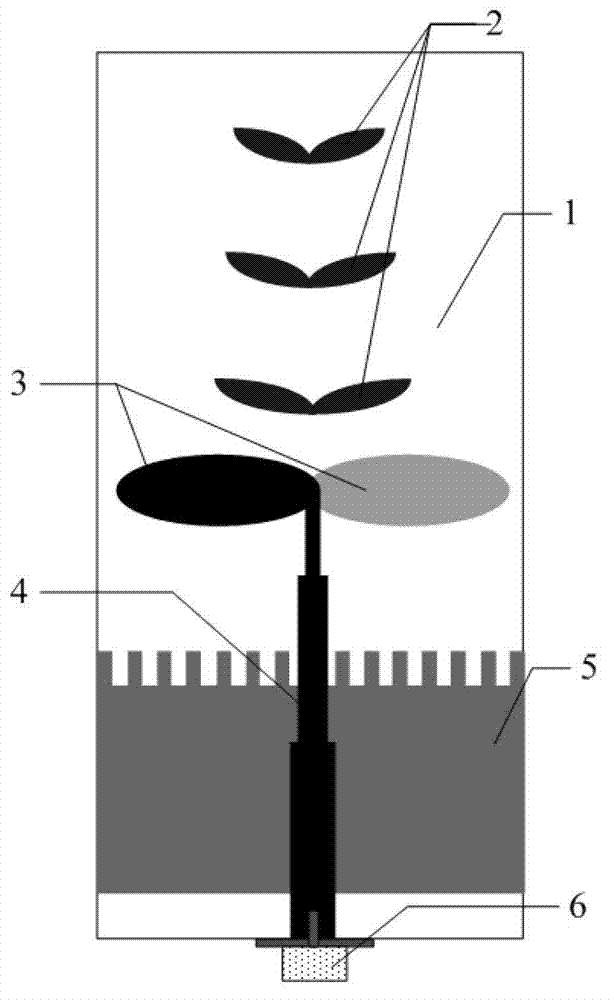
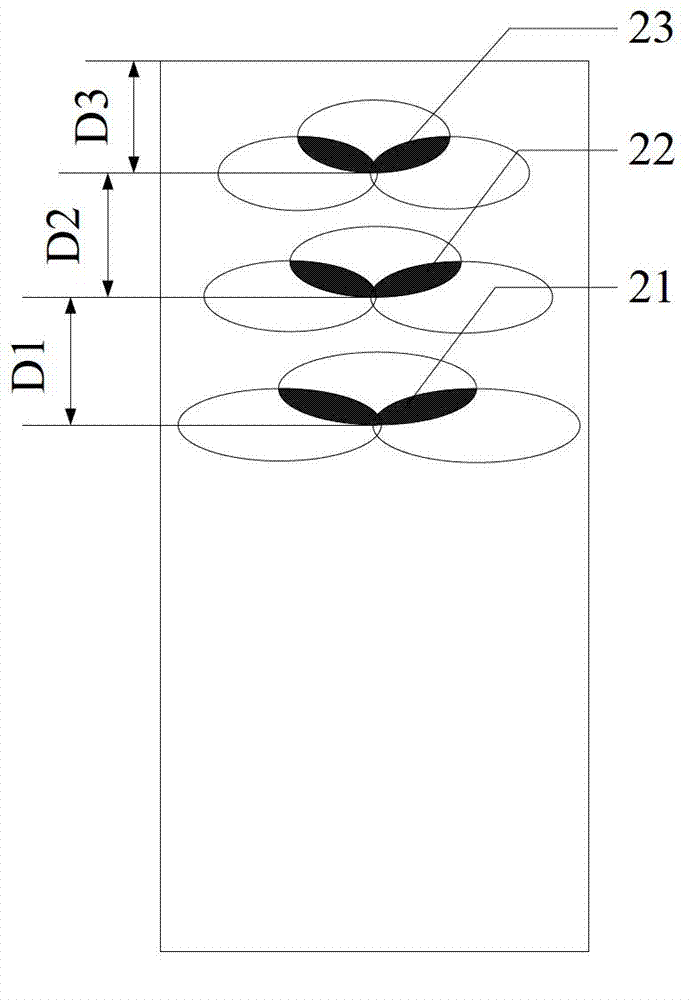
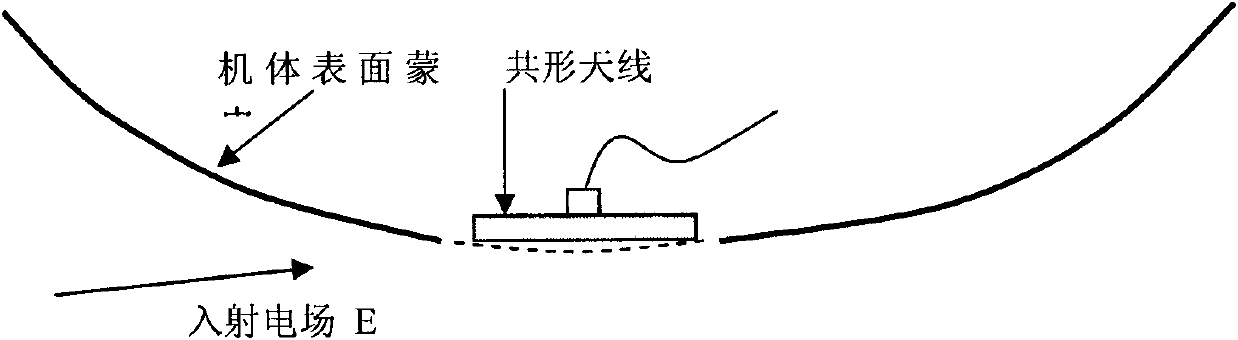
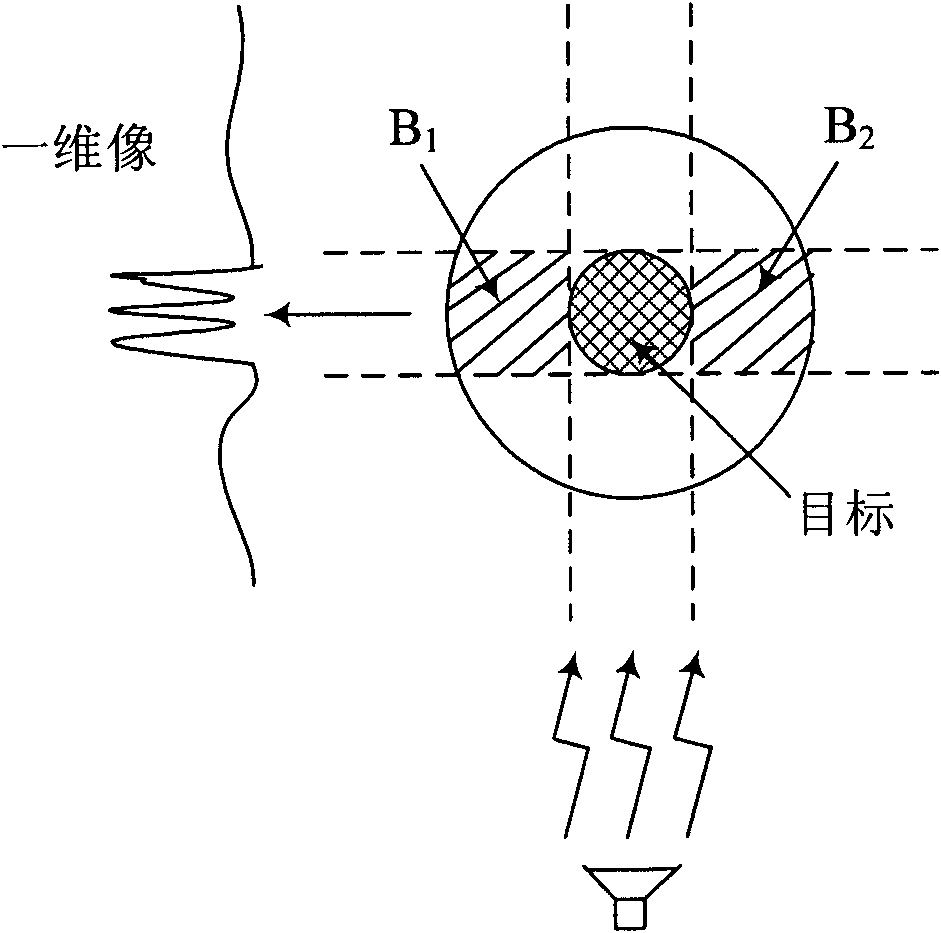
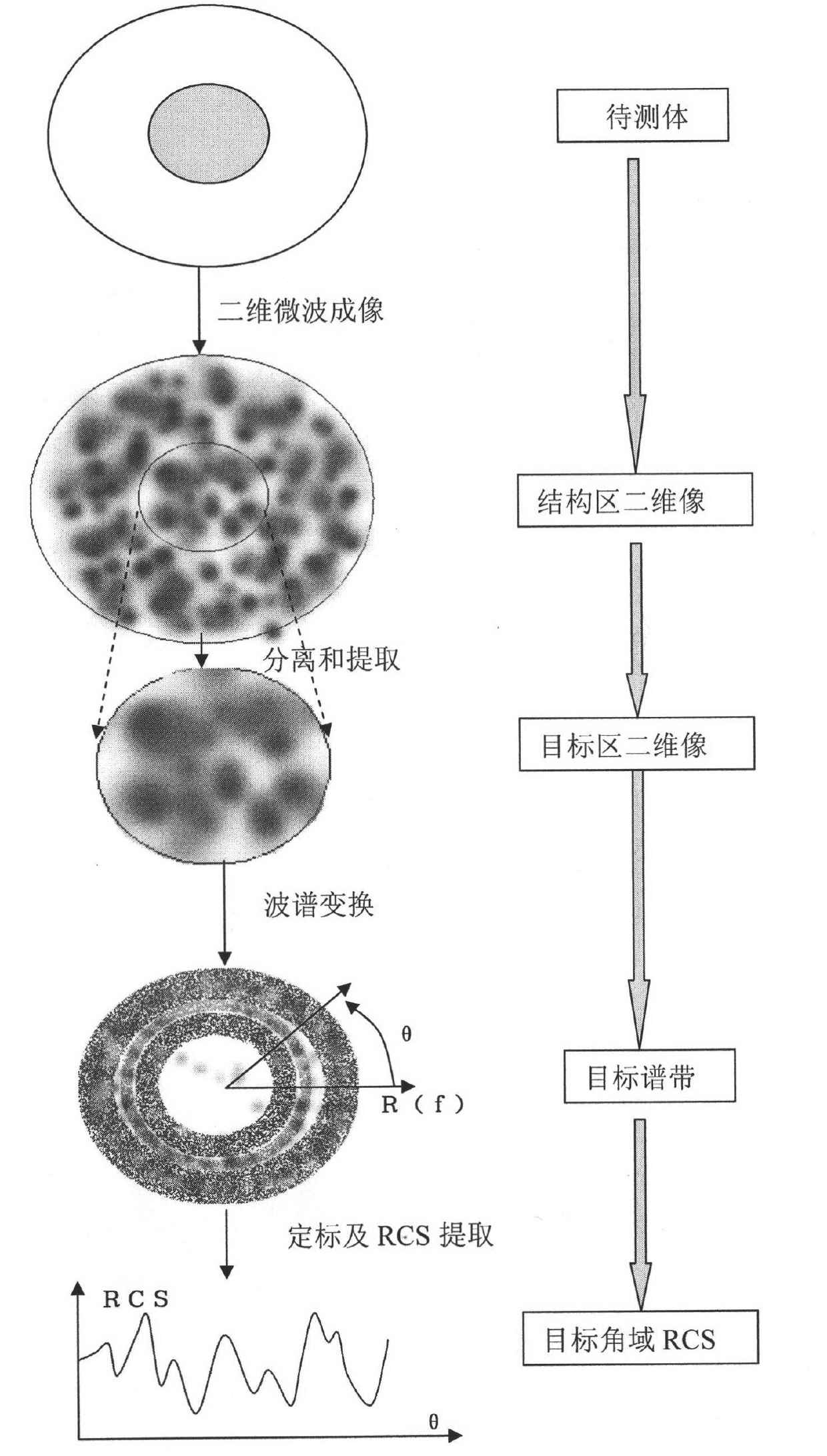
Method for testing RCS (radar cross section) of low-scattering conformal antenna based on two-dimensional microwave imaging
InactiveCN102253376AGood effectPromotion value of large projectsWave based measurement systemsSpectral domainFourier transform on finite groups
The invention relates to a method for testing an RCS (radar cross section) of a low-scattering conformal antenna based on two-dimensional microwave imaging, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: carrying out an RCS test on a metal envelope and a low-scattering conformal antenna in an installed state so as to obtain a two-dimensional microwave image; carrying out two-dimensional Fourier transform on the obtained new two-dimensional microwave image so as to obtain the data of a target spectral domain; carrying out an RCS test on a metal ball (the RCS of the metal ball is known) so as to obtain a two-dimensional microwave image, then carrying out two-dimensional Fourier transform on the obtained two-dimensional microwave image so as to obtain the data G0 (f, theta) of a scattered field of the metal ball, wherein the data of the scattered field varies with frequency and angle; and finally, obtaining the RCS of the conformal antenna, wherein the RCS of the conformal antenna meets the following formula: RCS= G1 (f, theta) (of the conformal antenna) - G0 (f, theta) (of the metal ball) + RCS (of the metal ball). The method provided by the invention is a method for testing an RCS (radar cross section) of a low-scattering conformal antenna in an installed state based on the two-dimensional microwave imaging technology, and after practicing, the obtained effect is good, therefore, the method provided by the invention has great engineering popularization value.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
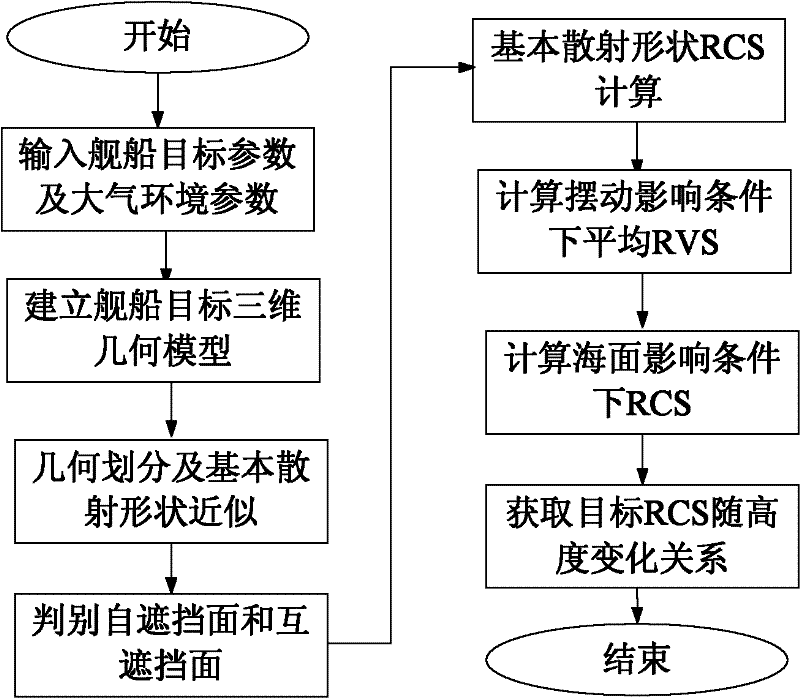
Radar cross-section layered calculation method of ship target within atmospheric duct range
InactiveCN102226840ALower requirementSmall amount of calculationWave based measurement systemsHorizonScattering cross-section
The invention discloses a radar cross-section (RCS) layered calculation method of a ship target within an atmospheric duct range. According to the invention, after partition of a three-dimensional geometric model of a ship target, most similar basic geometrical shapes of the all partitioned parts of the three-dimensional geometric model are selected and are approximated as basic scatterers; geometric information of all basic scatterers are extracted and RCSs of the all basic scatterers are calculated; Change relations of RCS values of all parts of the ship target at different heights are calculated by combining heights of all parts of the ship target; and scattering power intensity of the ship target is calculated according to a transmission factor of an electromagnetic wave of an atmospheric duct. According to the RCS calculation method of the ship target within the atmospheric duct range provided in the invention, computational complexity and requirements for computing equipment canbe substantially reduced and real-time calculation is allowed. Besides, an influence of up-and-down sea surface on transmission of an electromagnetic wave is fully considered, and a calculation result is more reasonable and effective. The method provided in the invention has important military significances for technological development, equipment update, and operational application of microwave beyond-the-horizon radar.
Owner:NAVAL UNIV OF ENG PLA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com